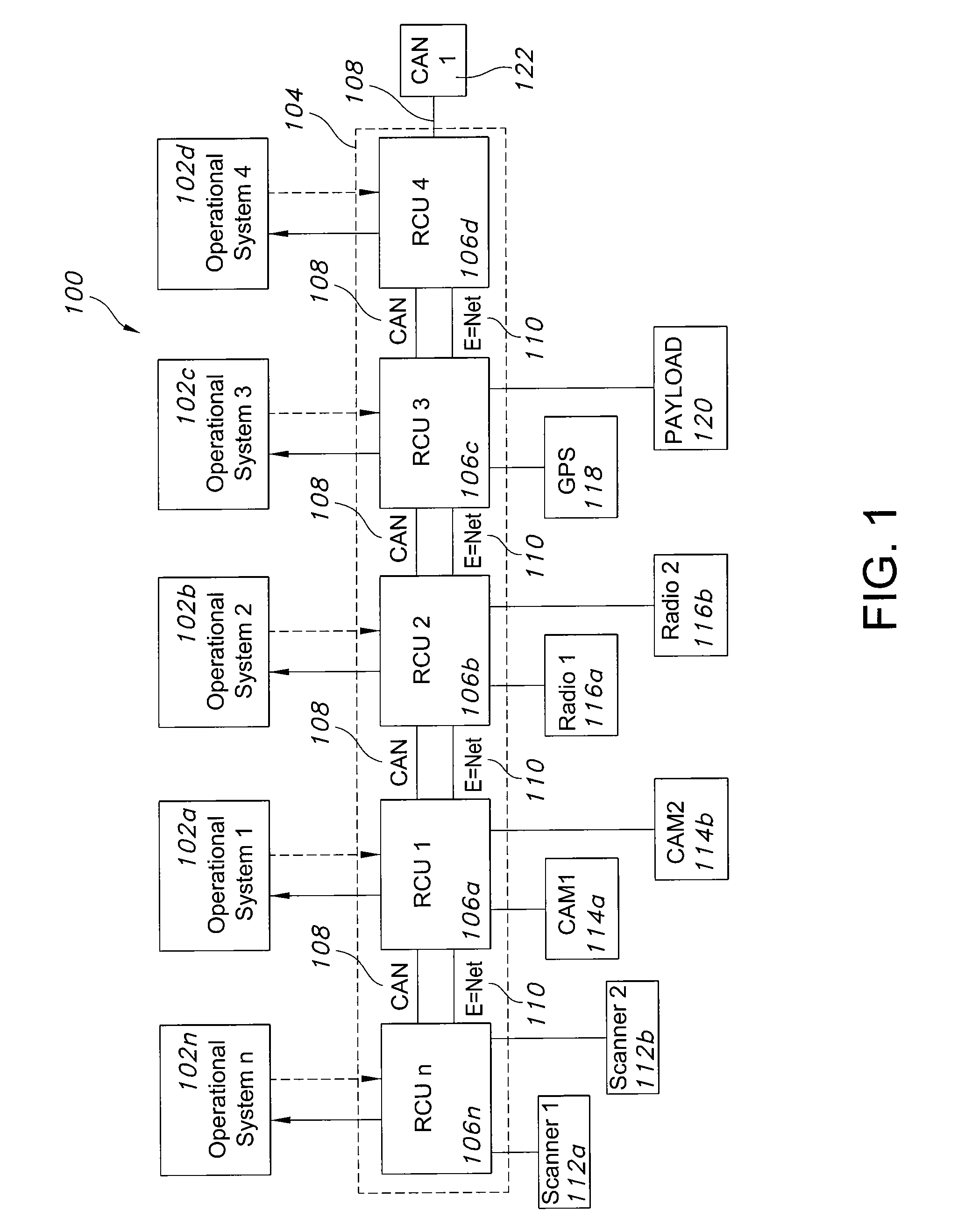
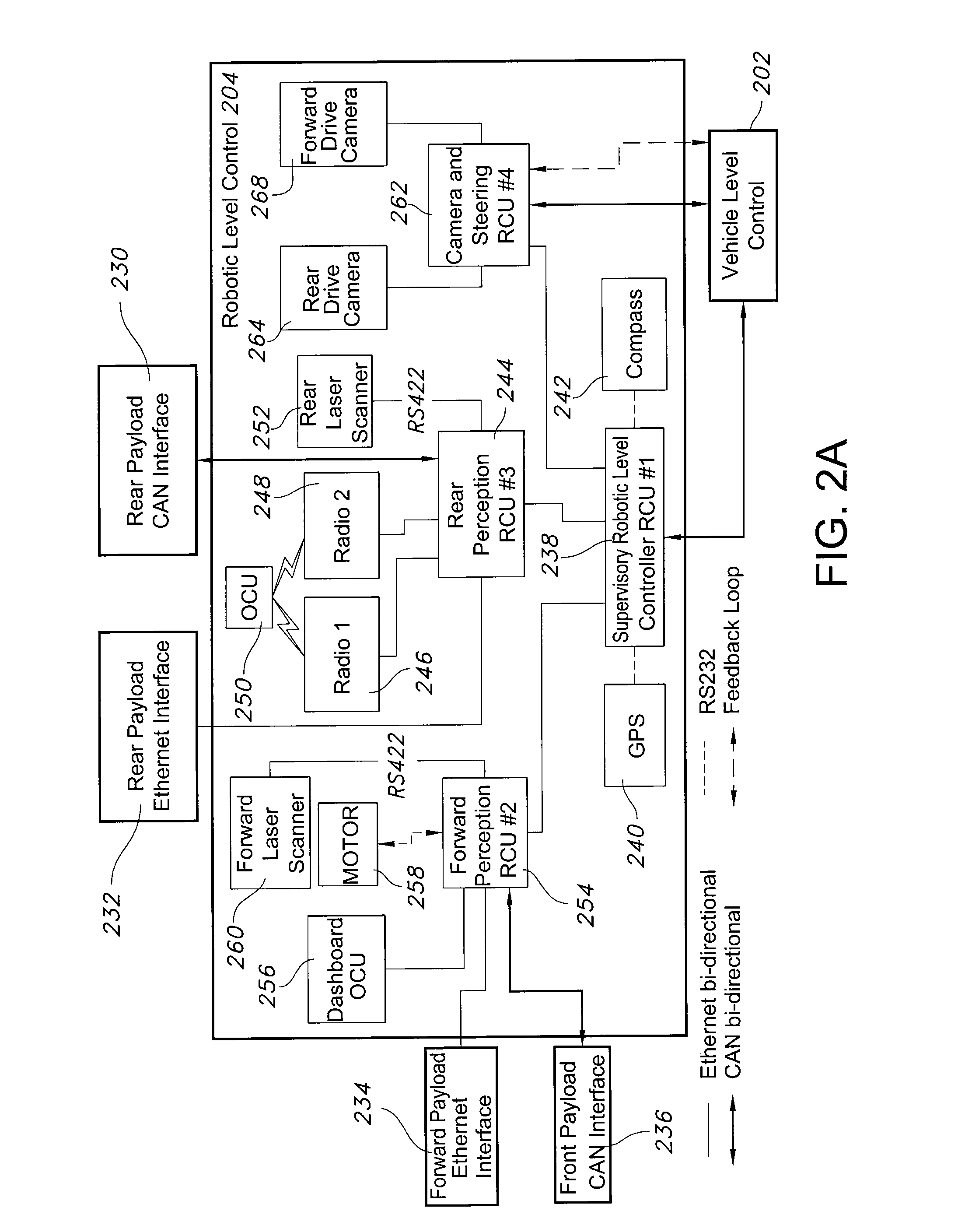
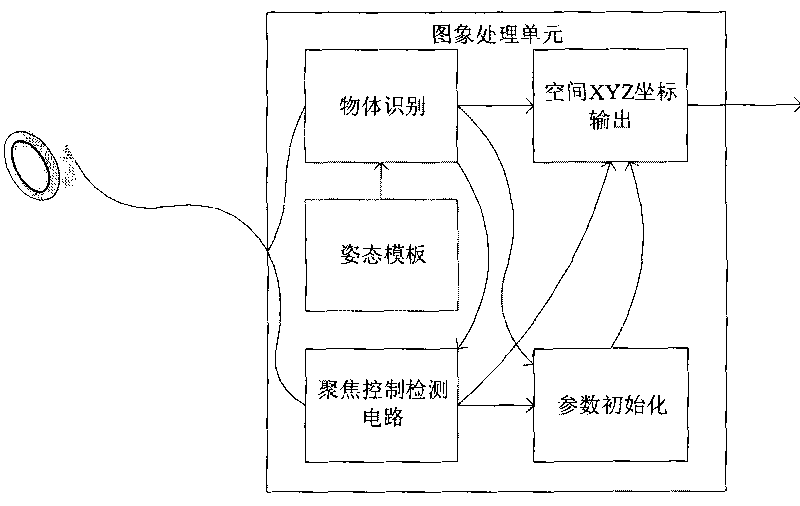
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1531 results about "Teleoperation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
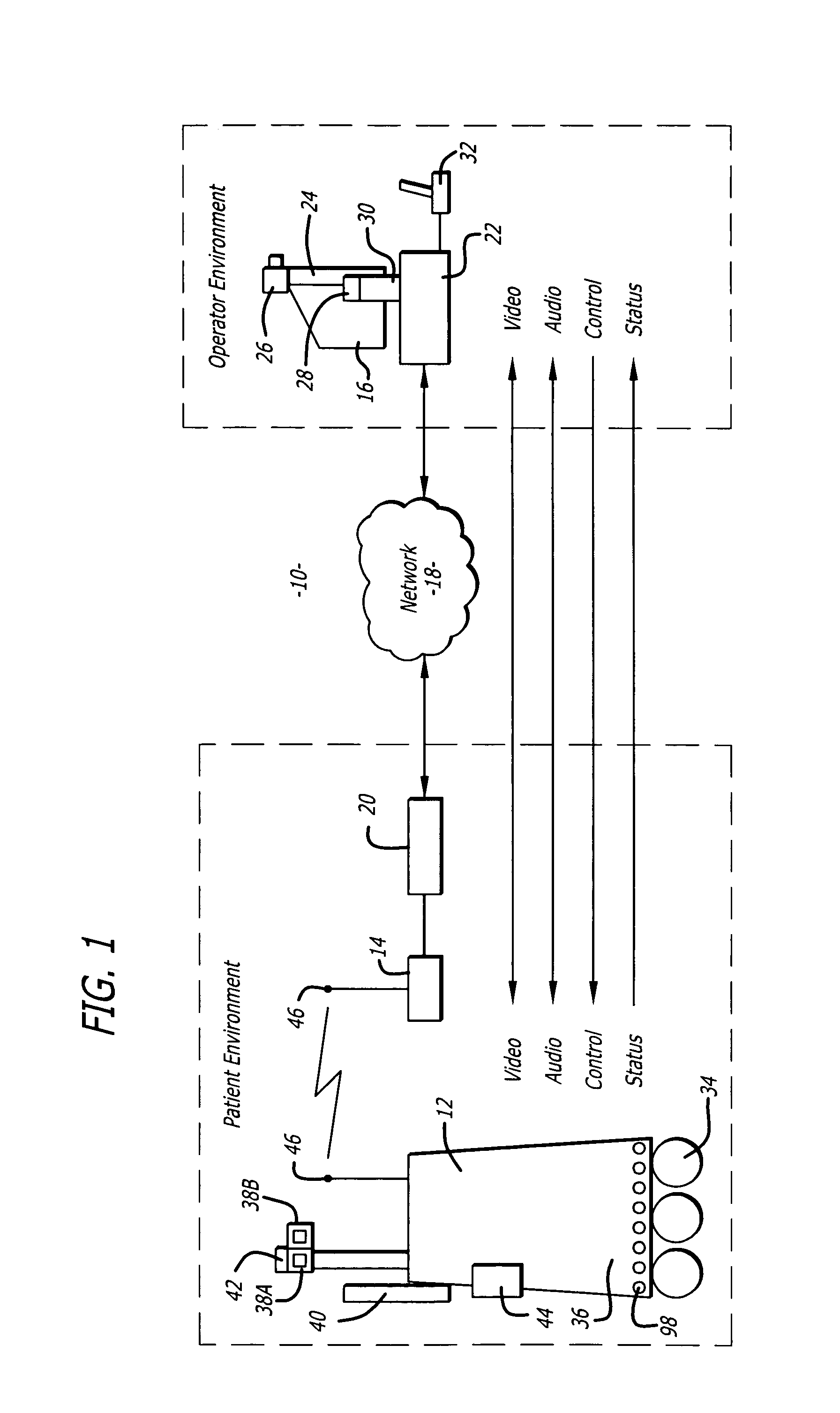
Teleoperation (or remote operation) indicates operation of a system or machine at a distance. It is similar in meaning to the phrase "remote control" but is usually encountered in research, academic and technical environments. It is most commonly associated with robotics and mobile robots but can be applied to a whole range of circumstances in which a device or machine is operated by a person from a distance.
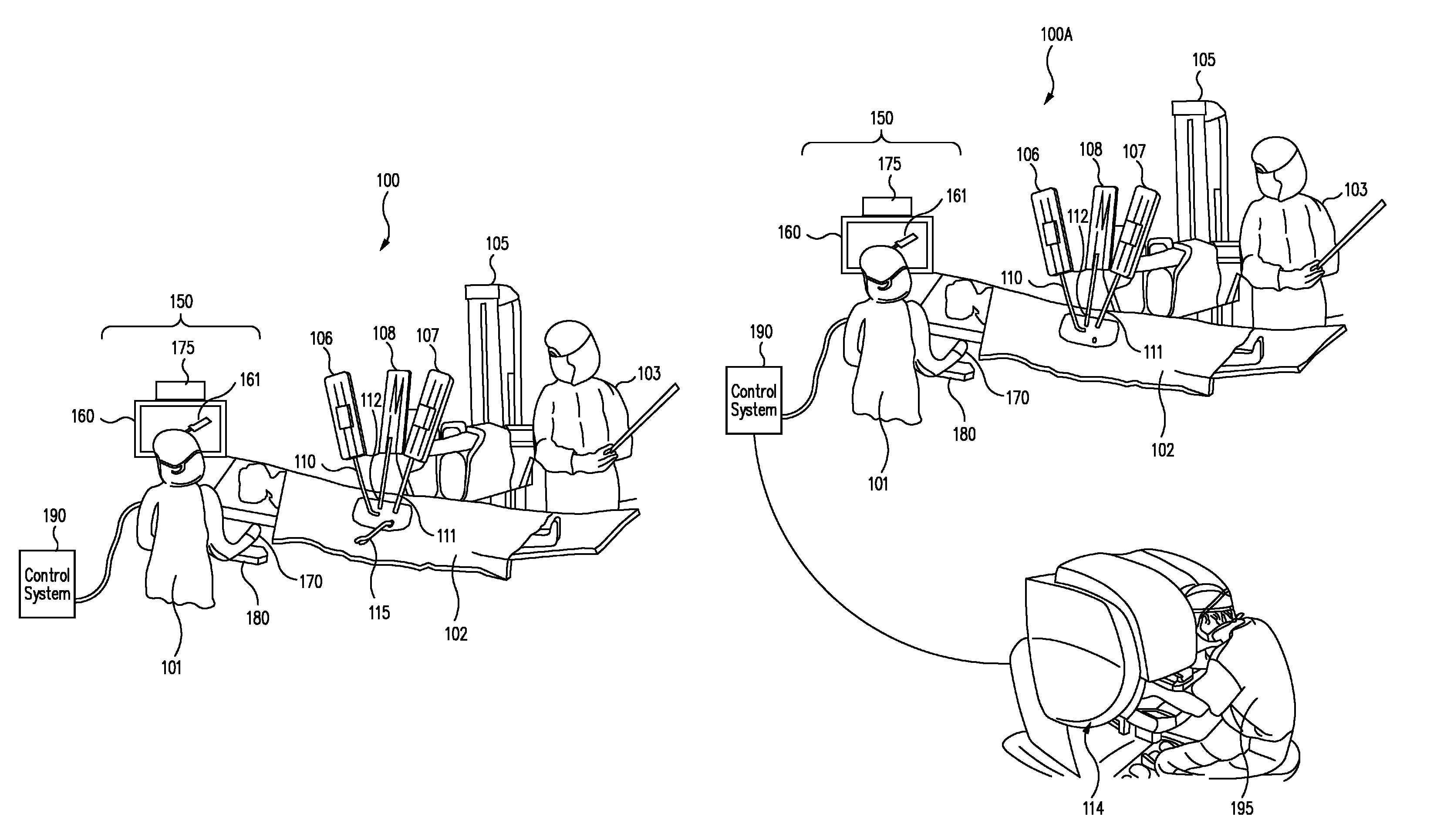
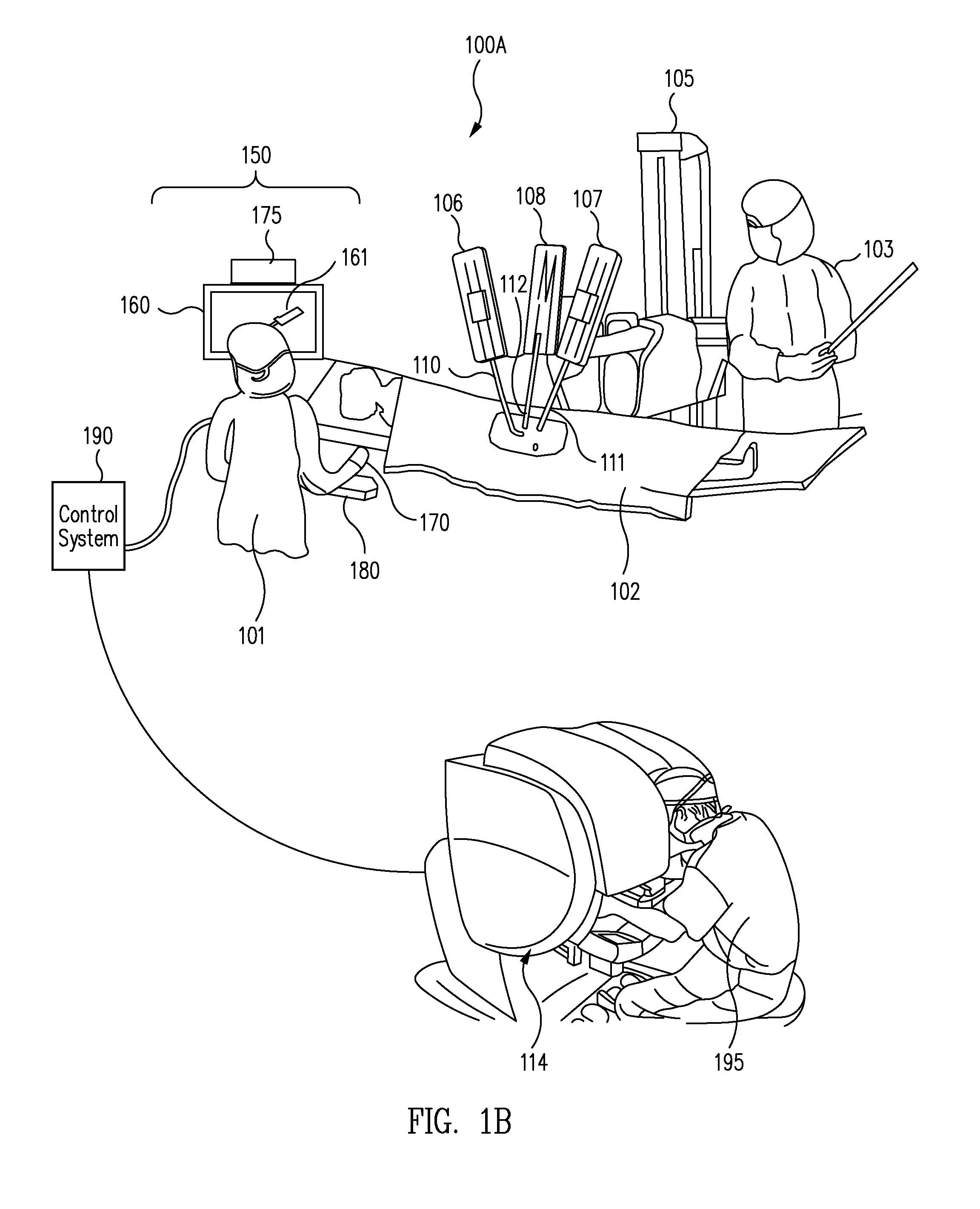
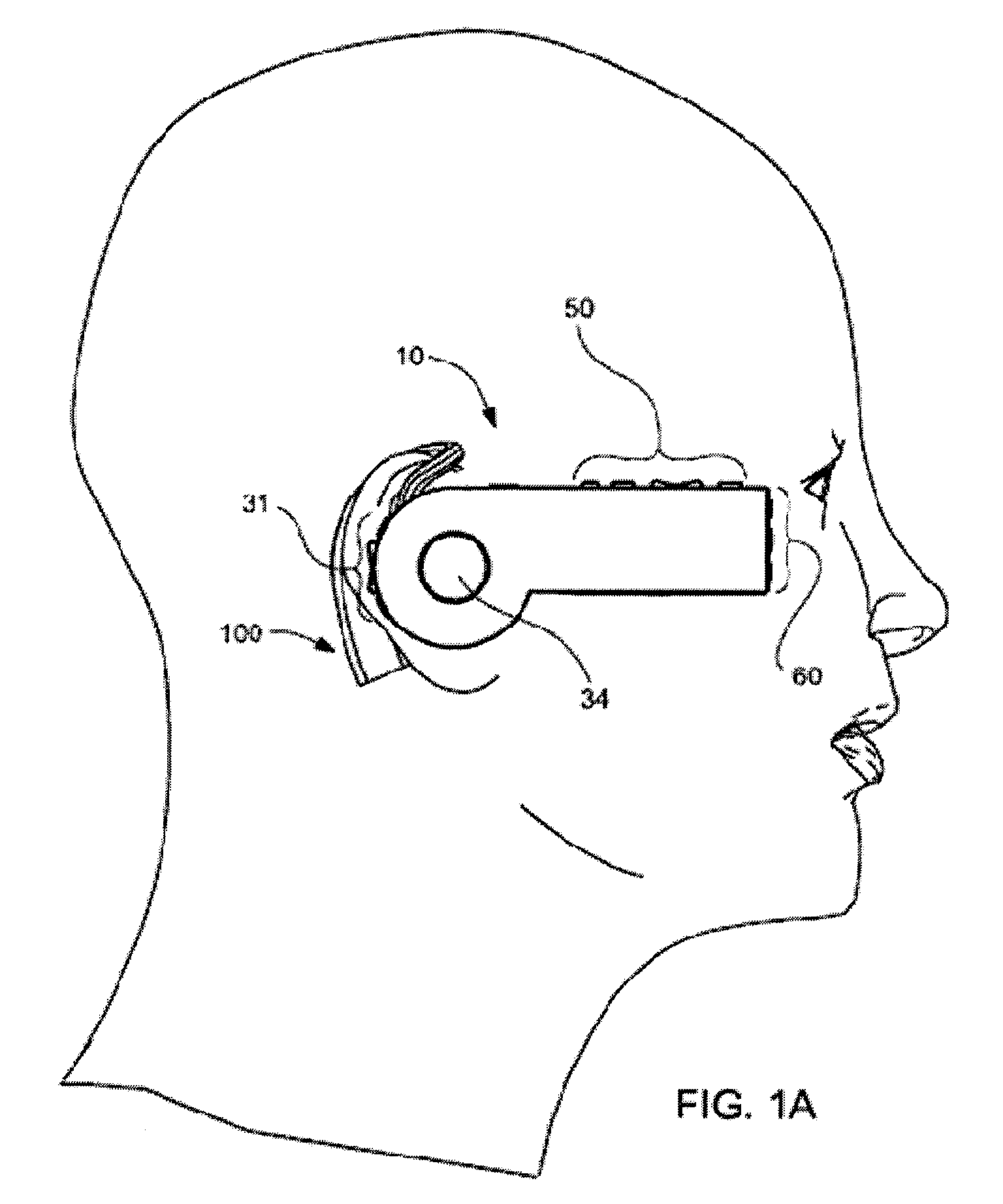
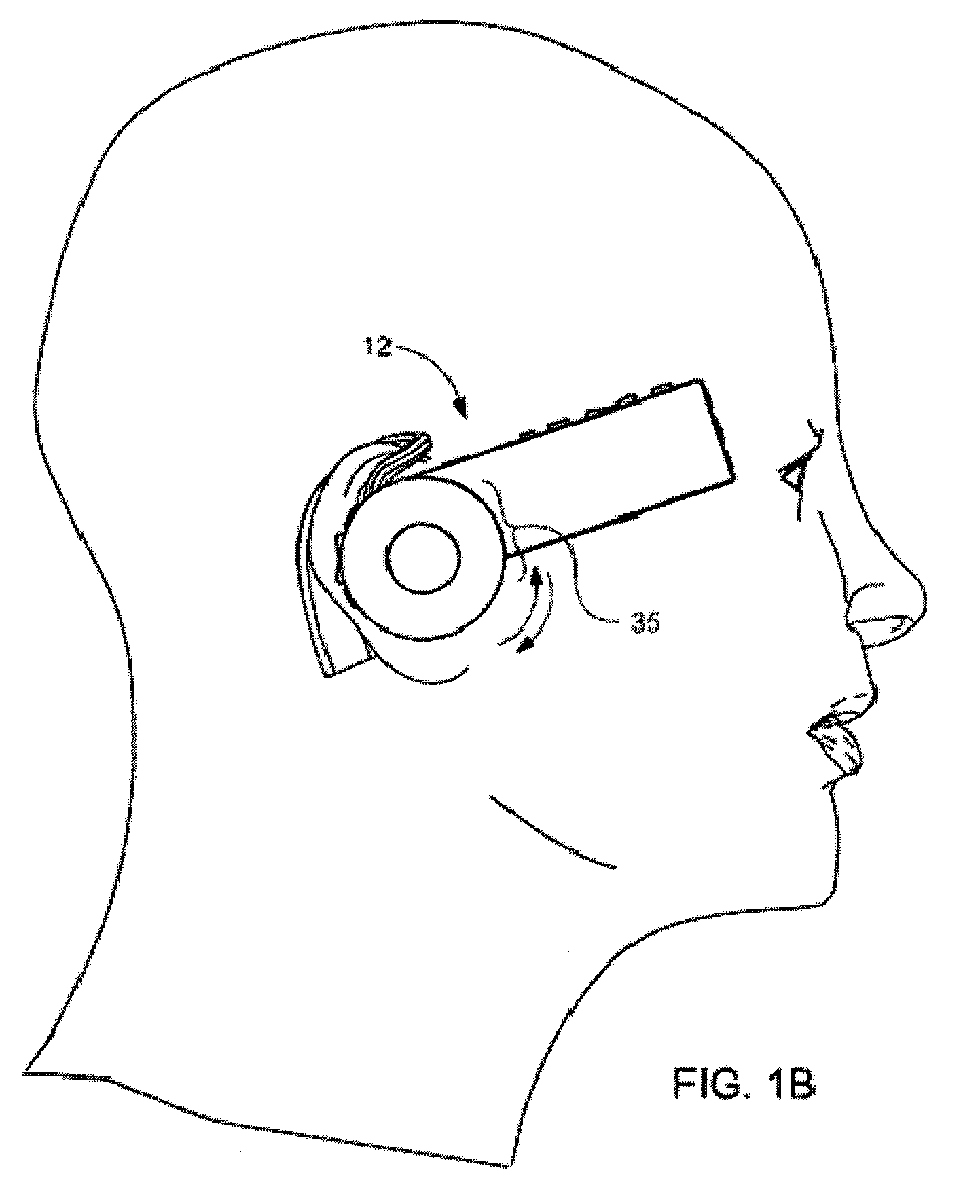
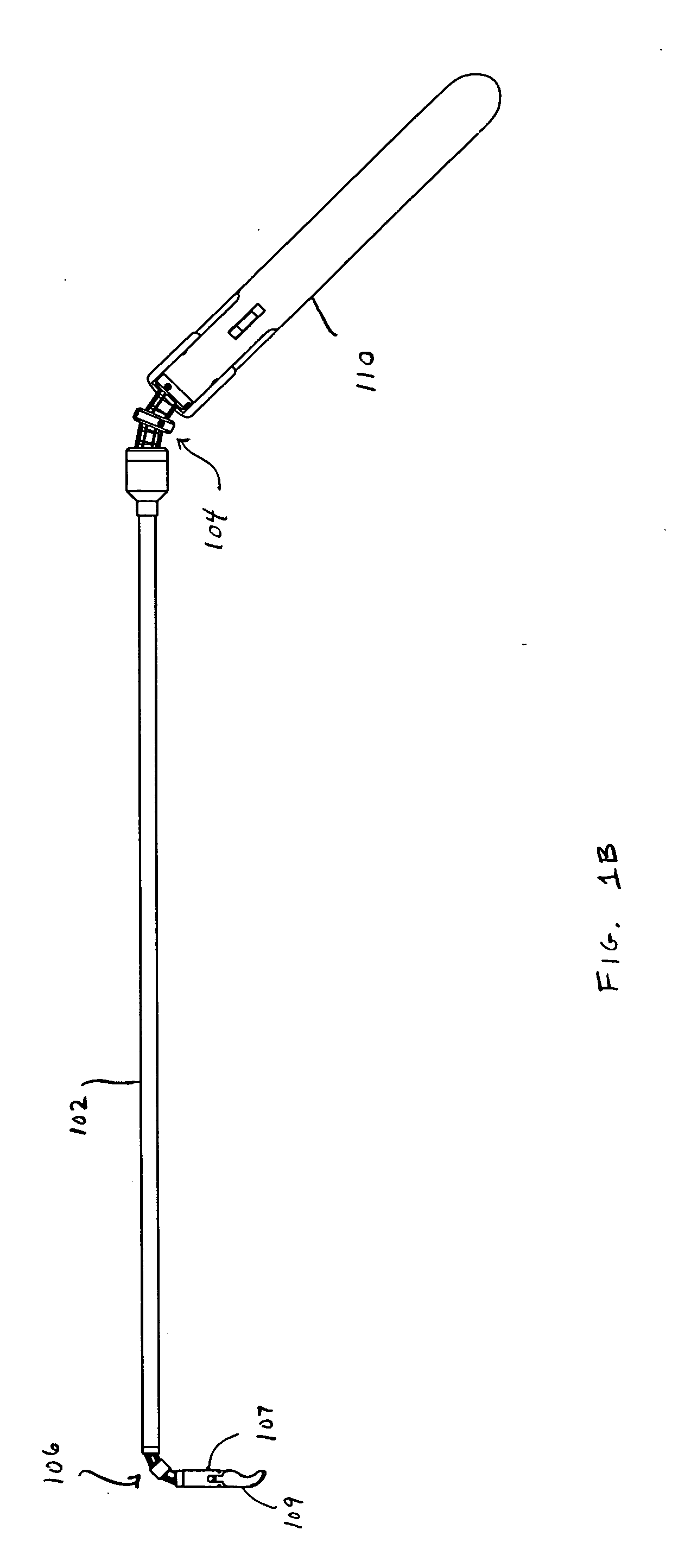
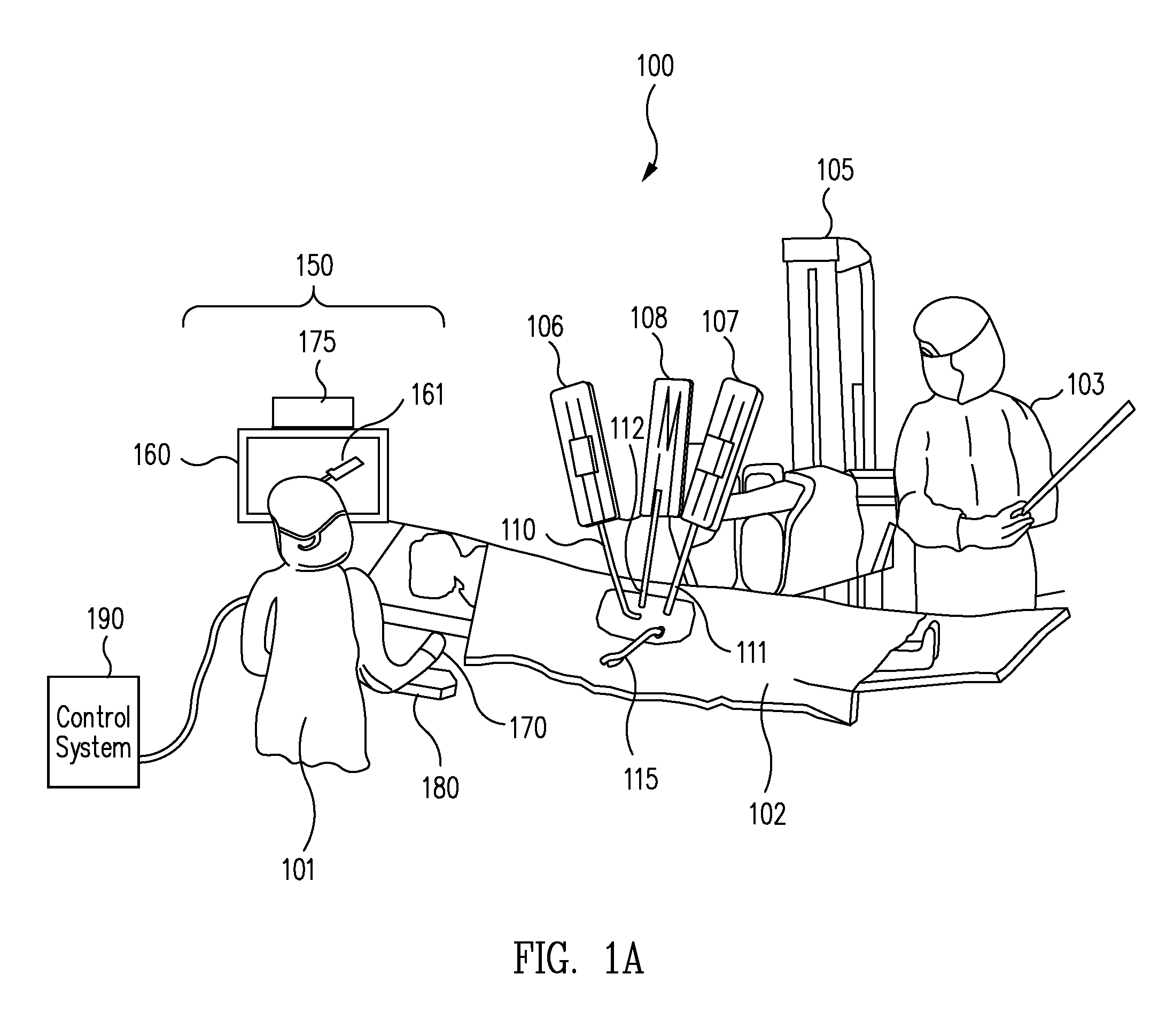
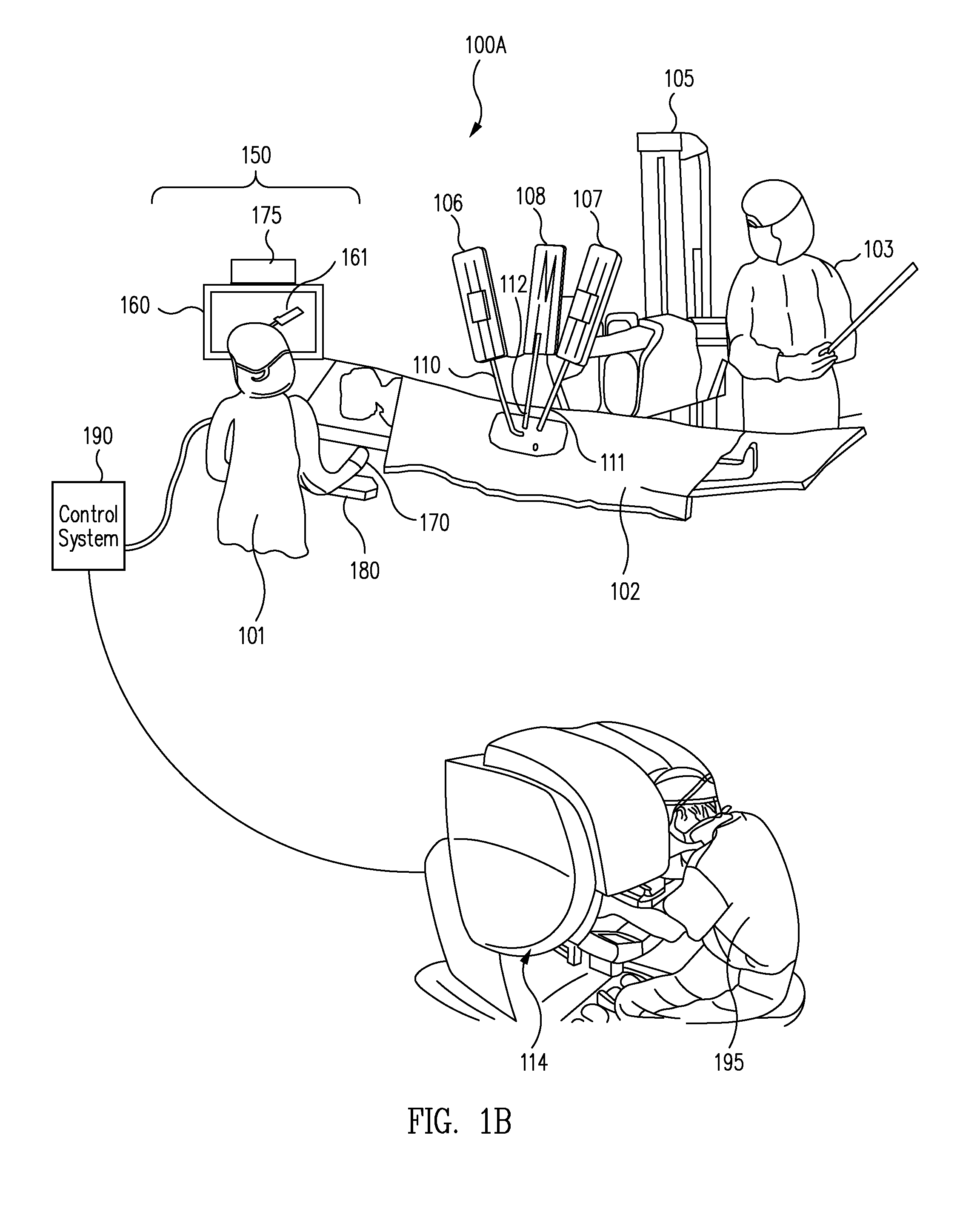
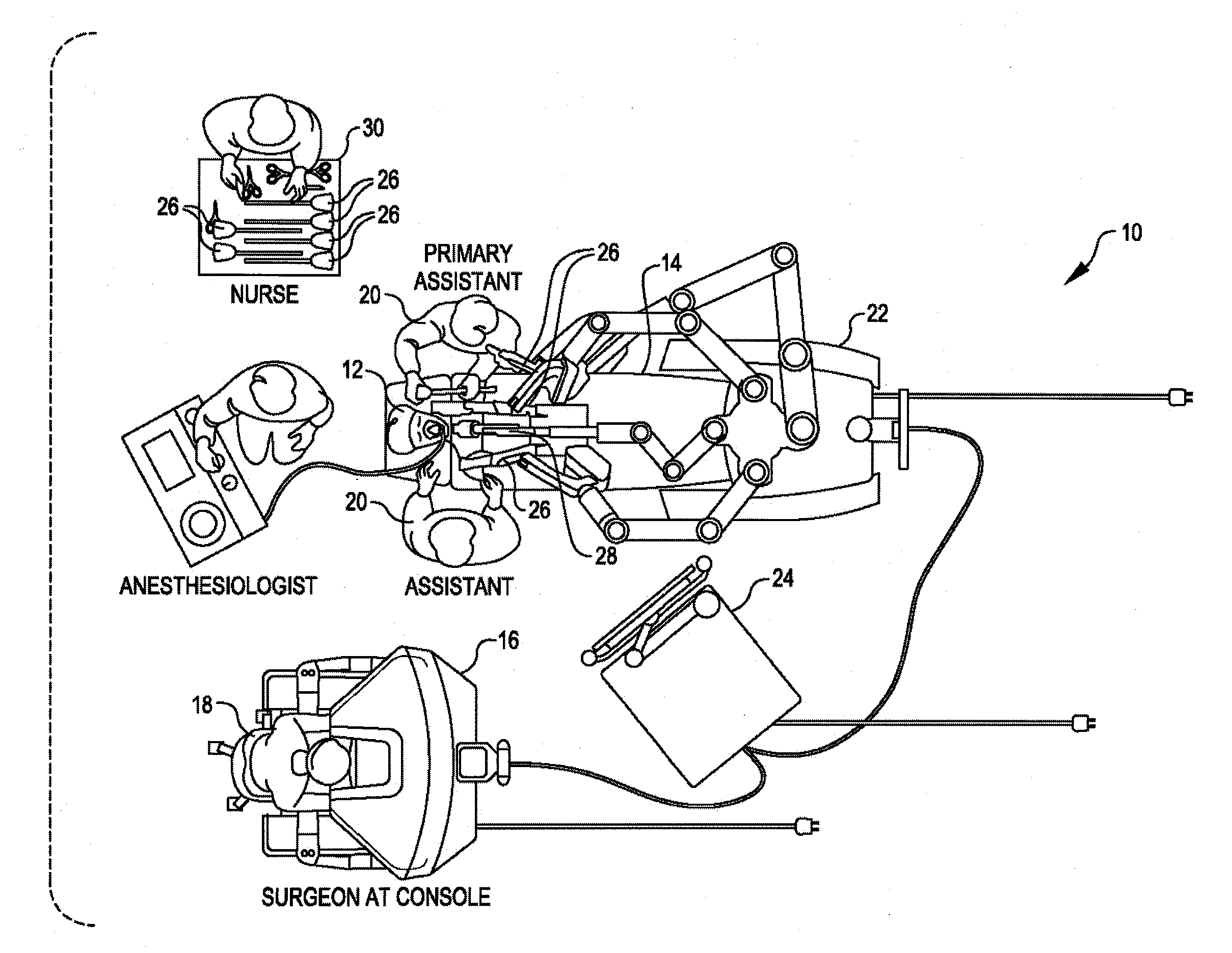
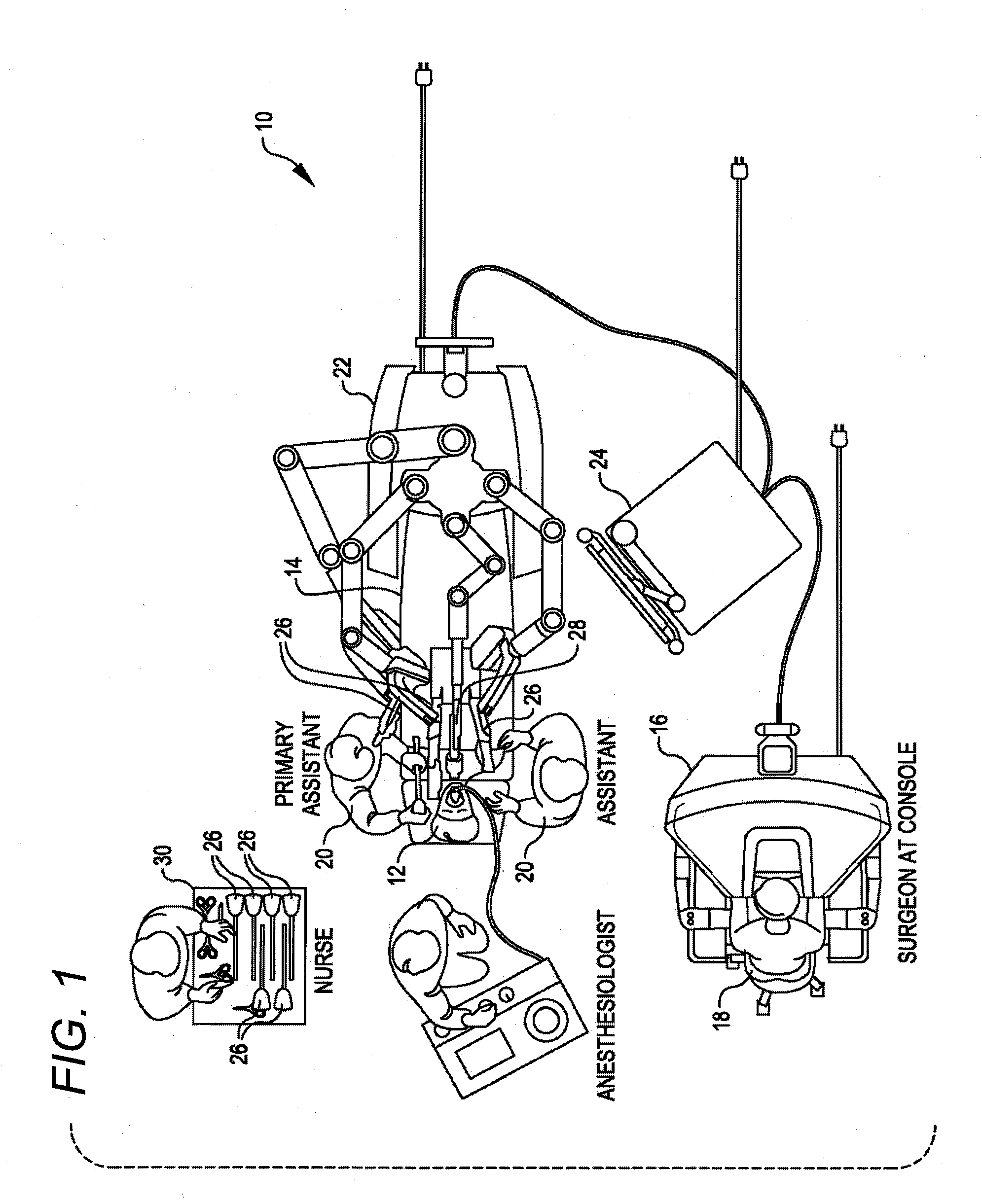
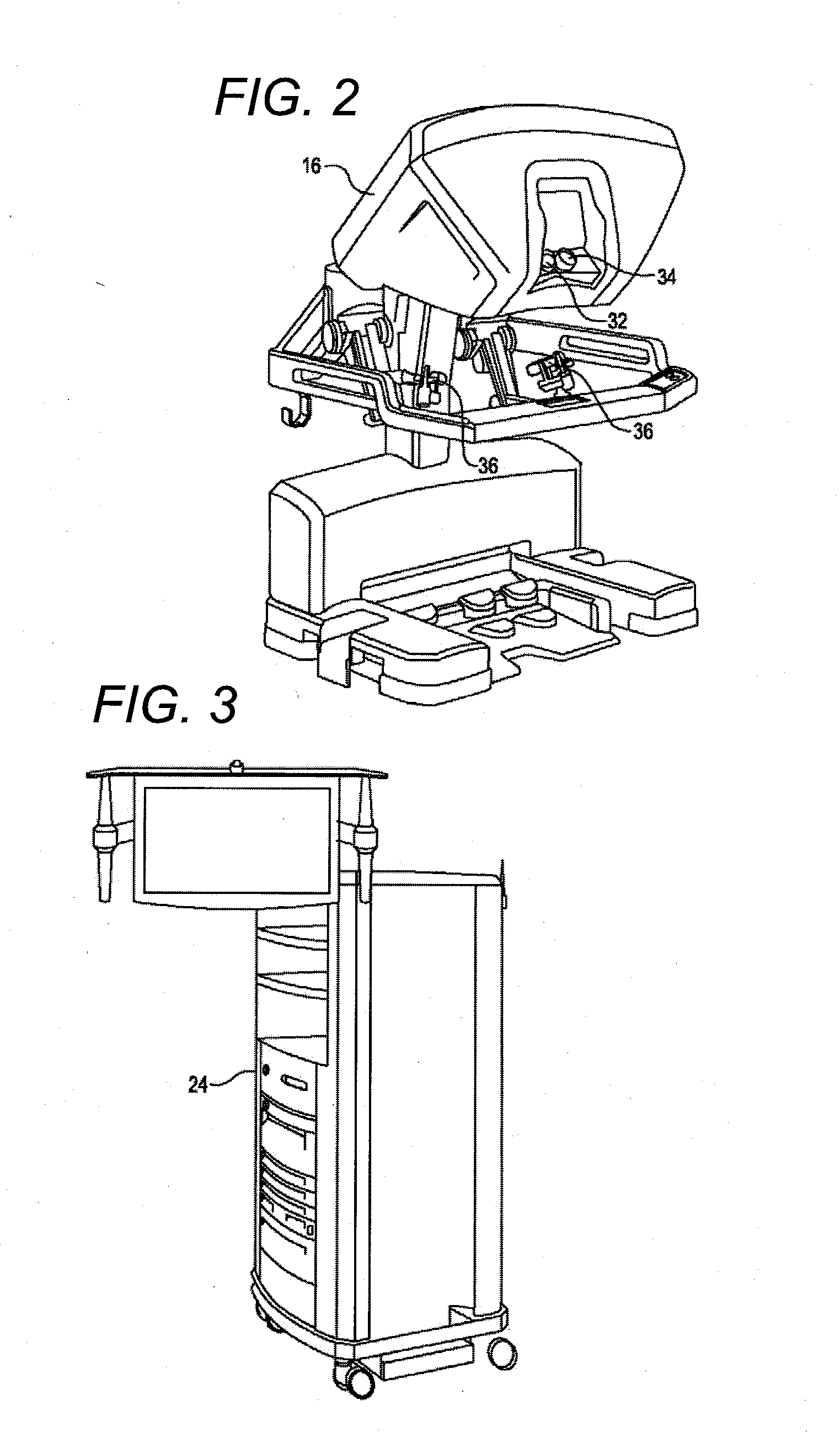
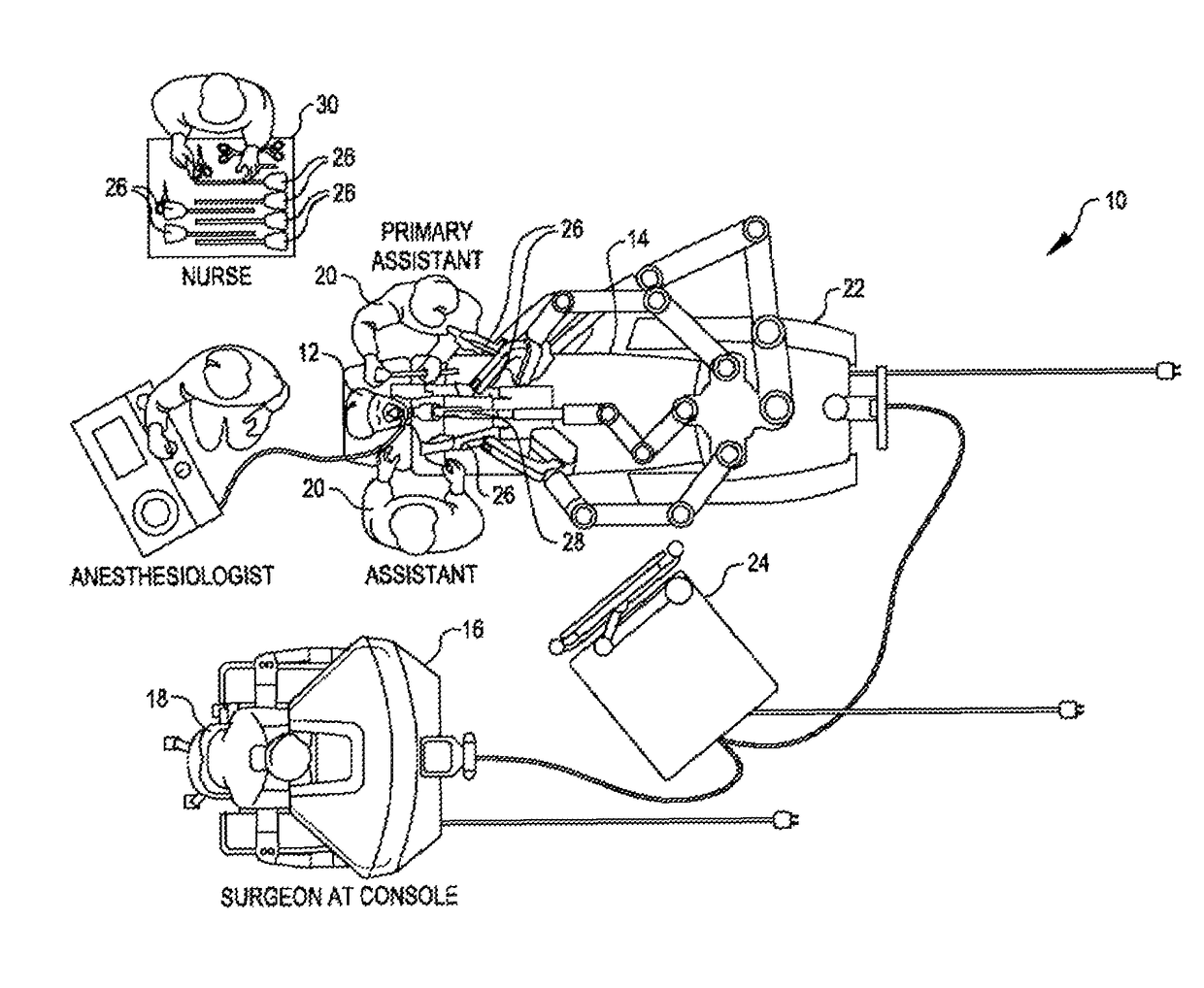
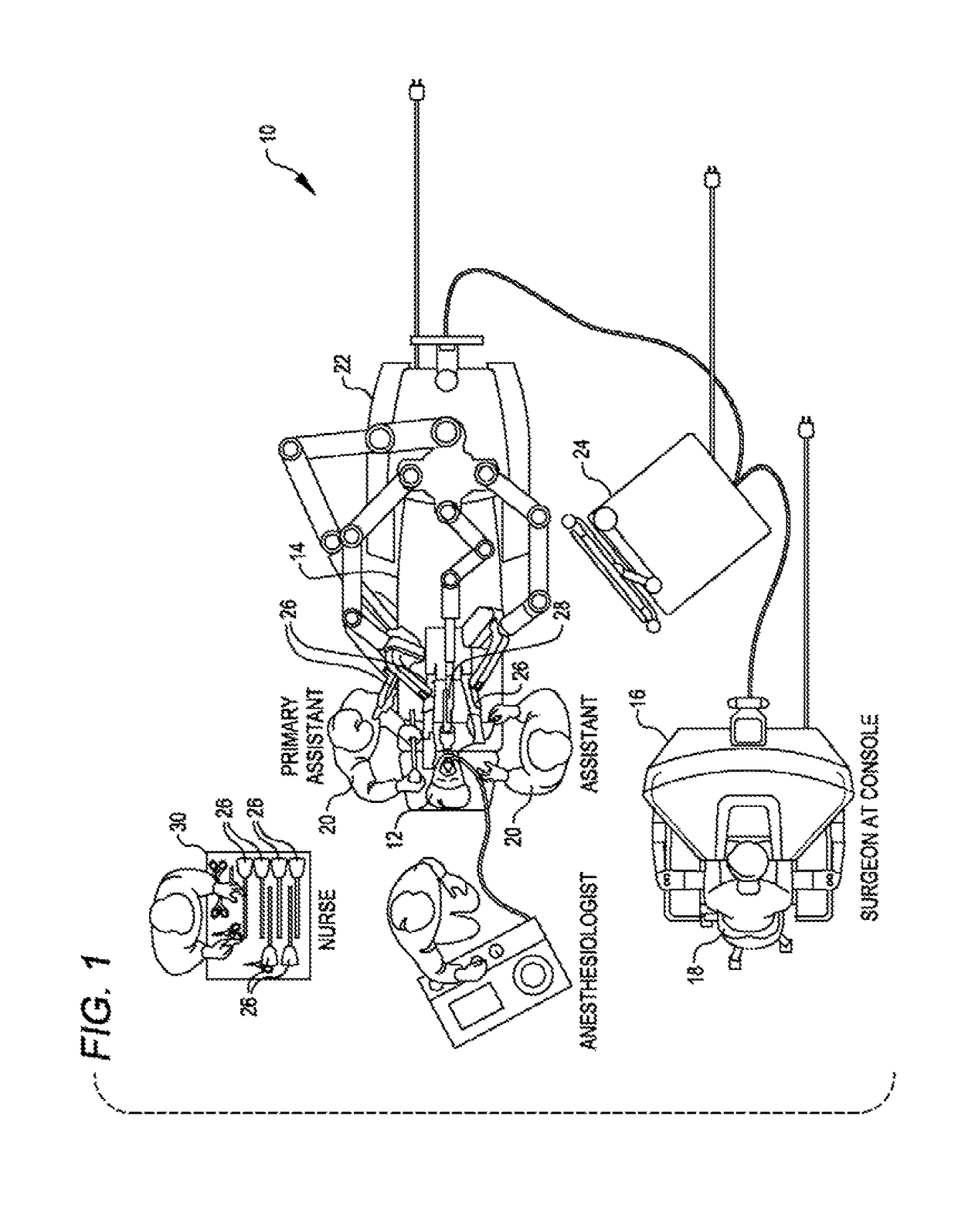
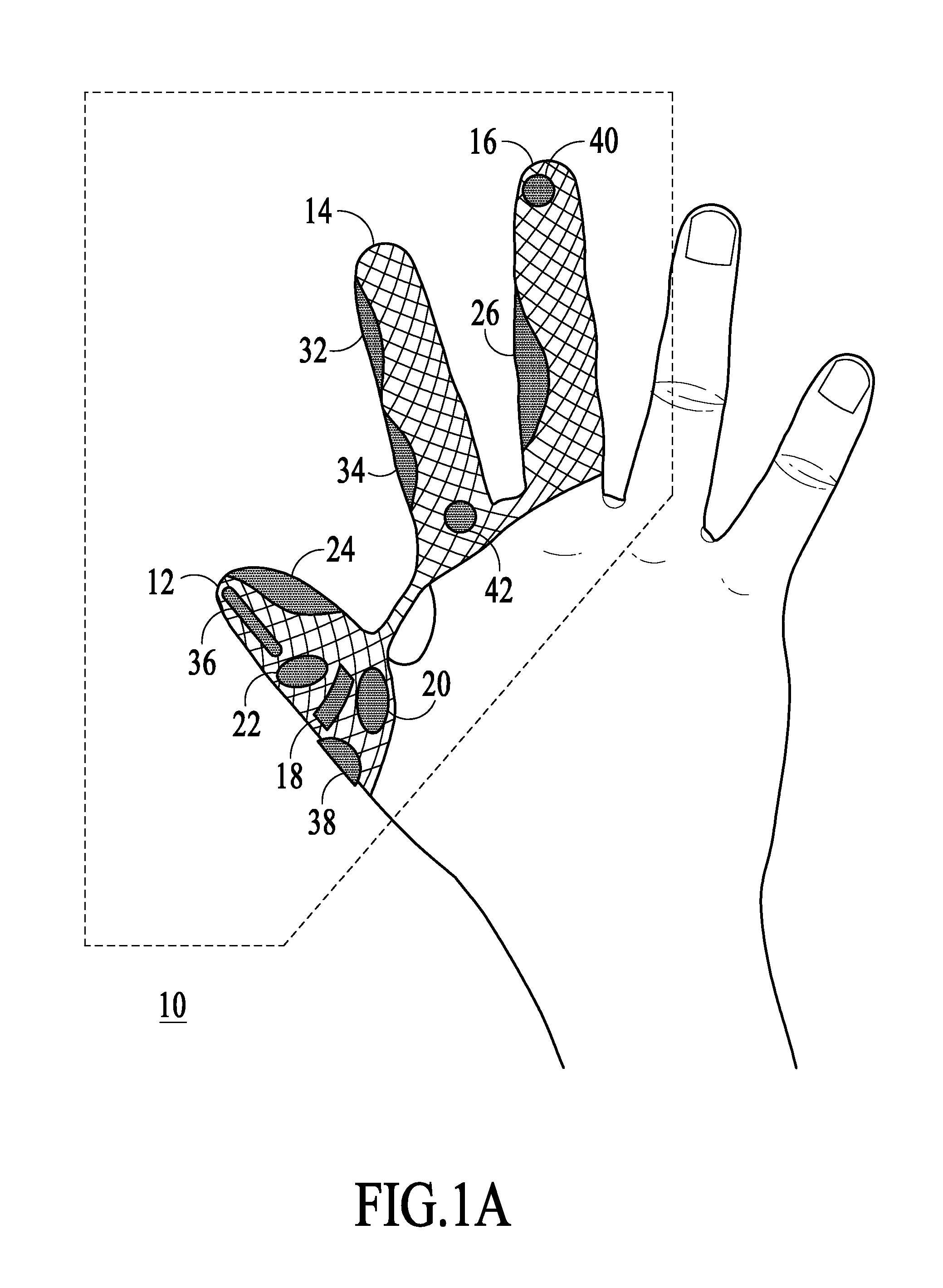
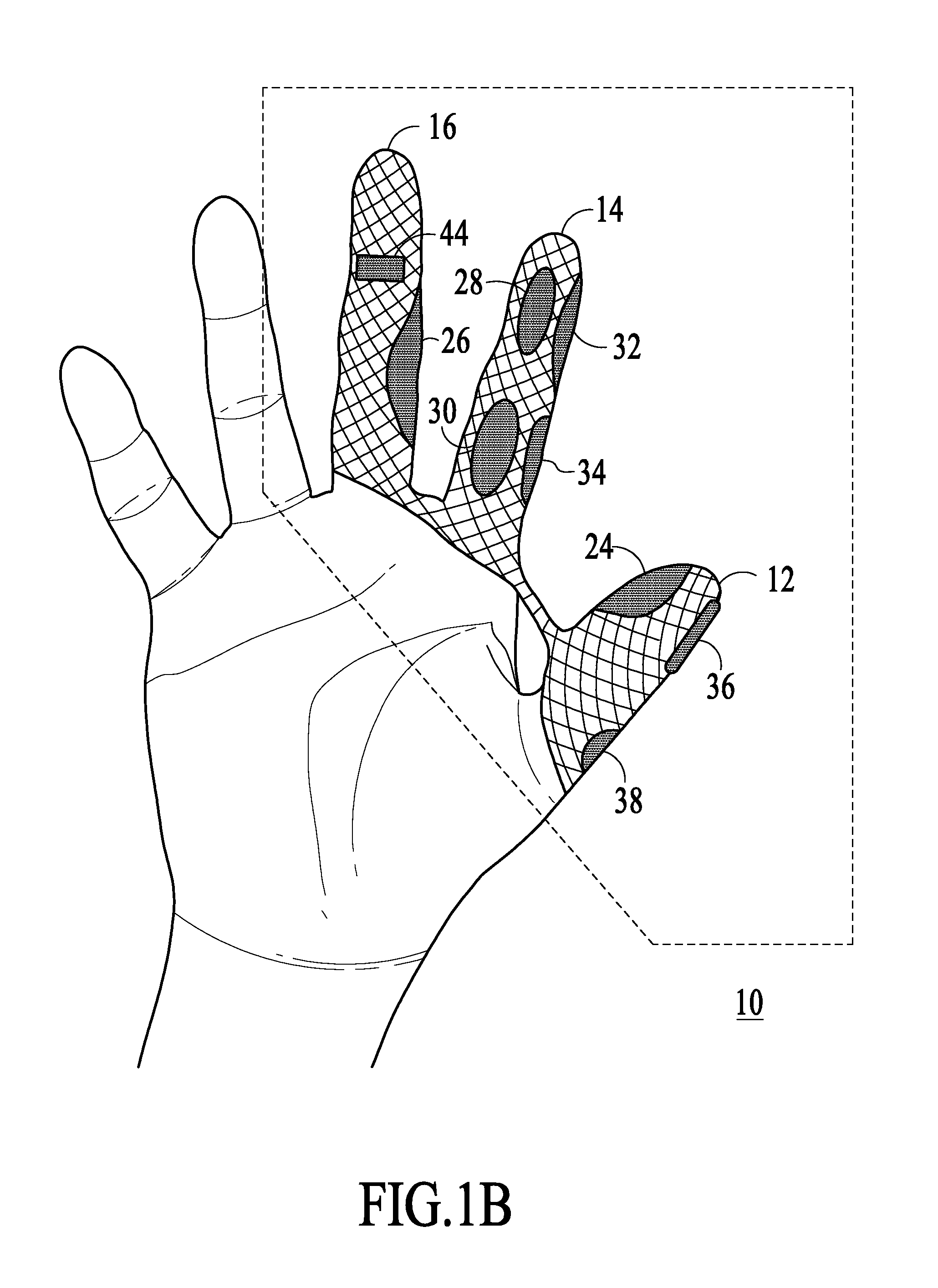
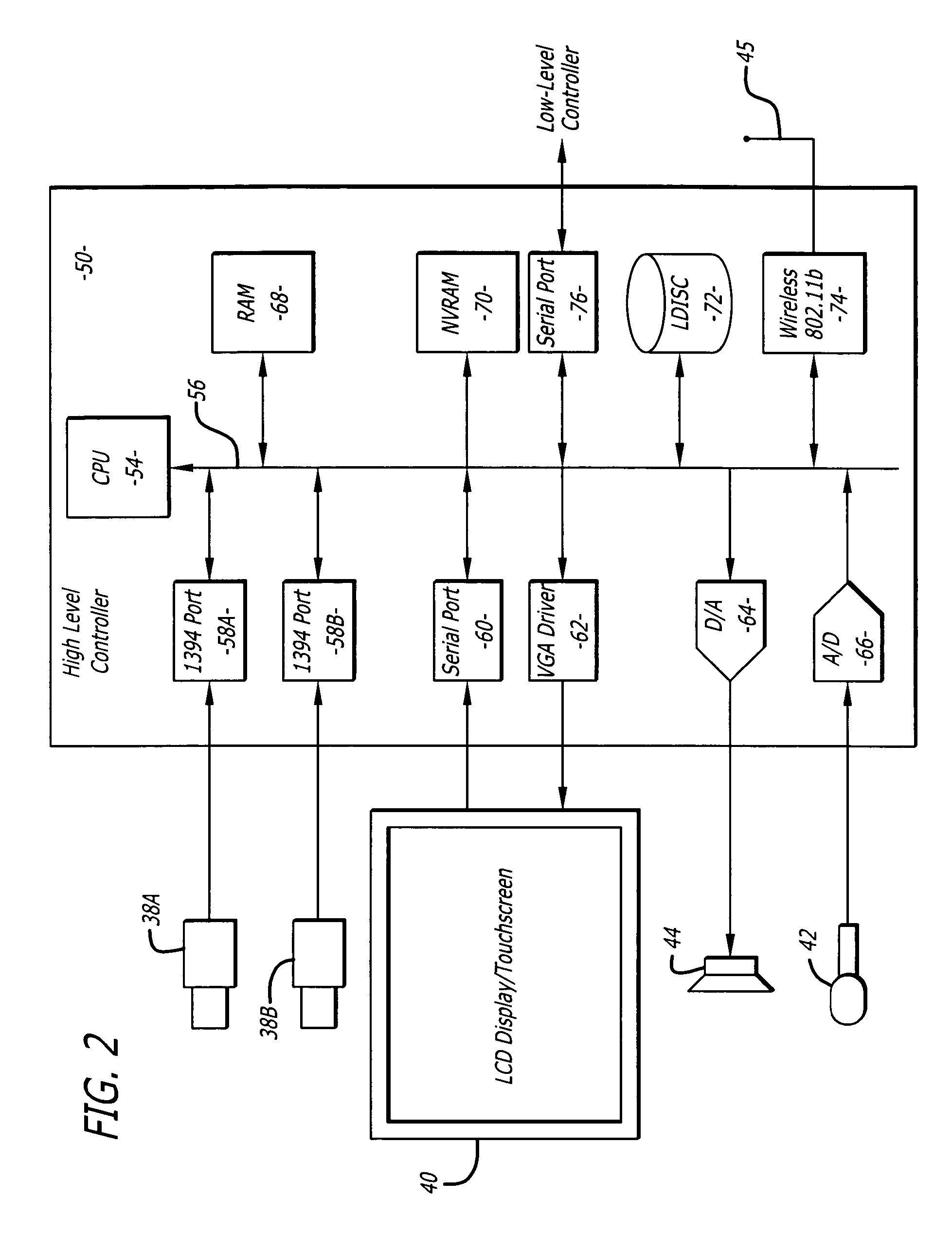
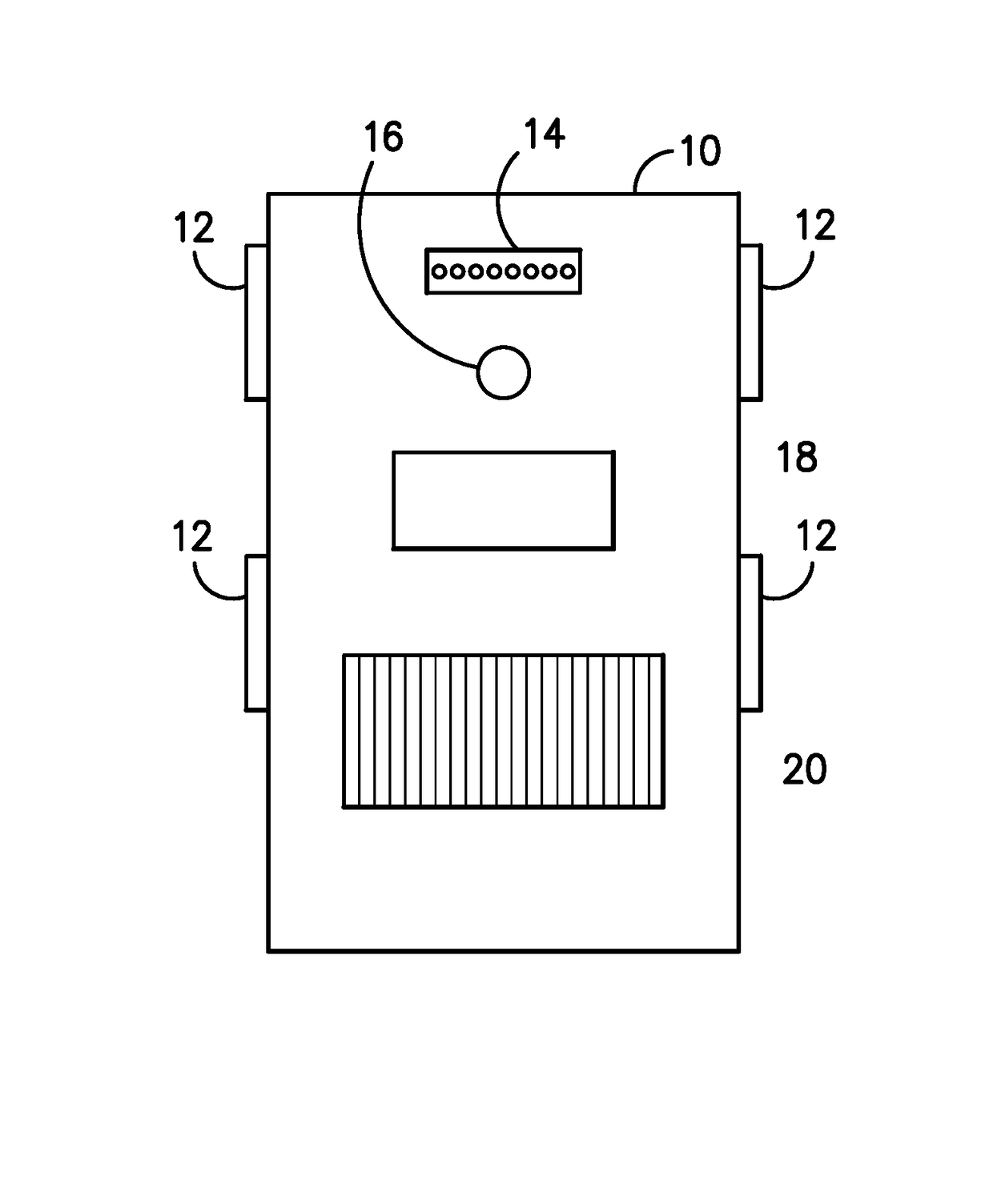
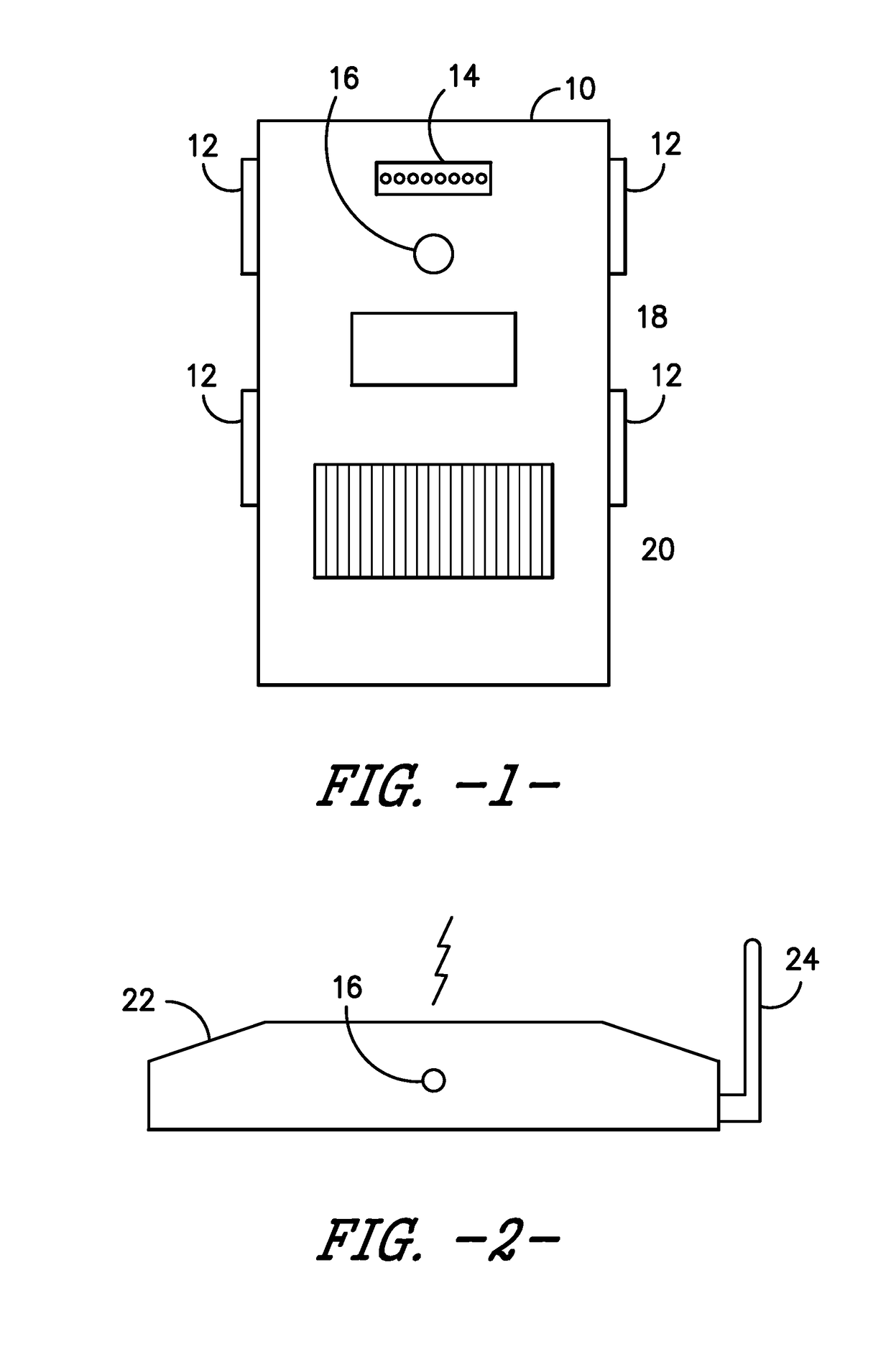
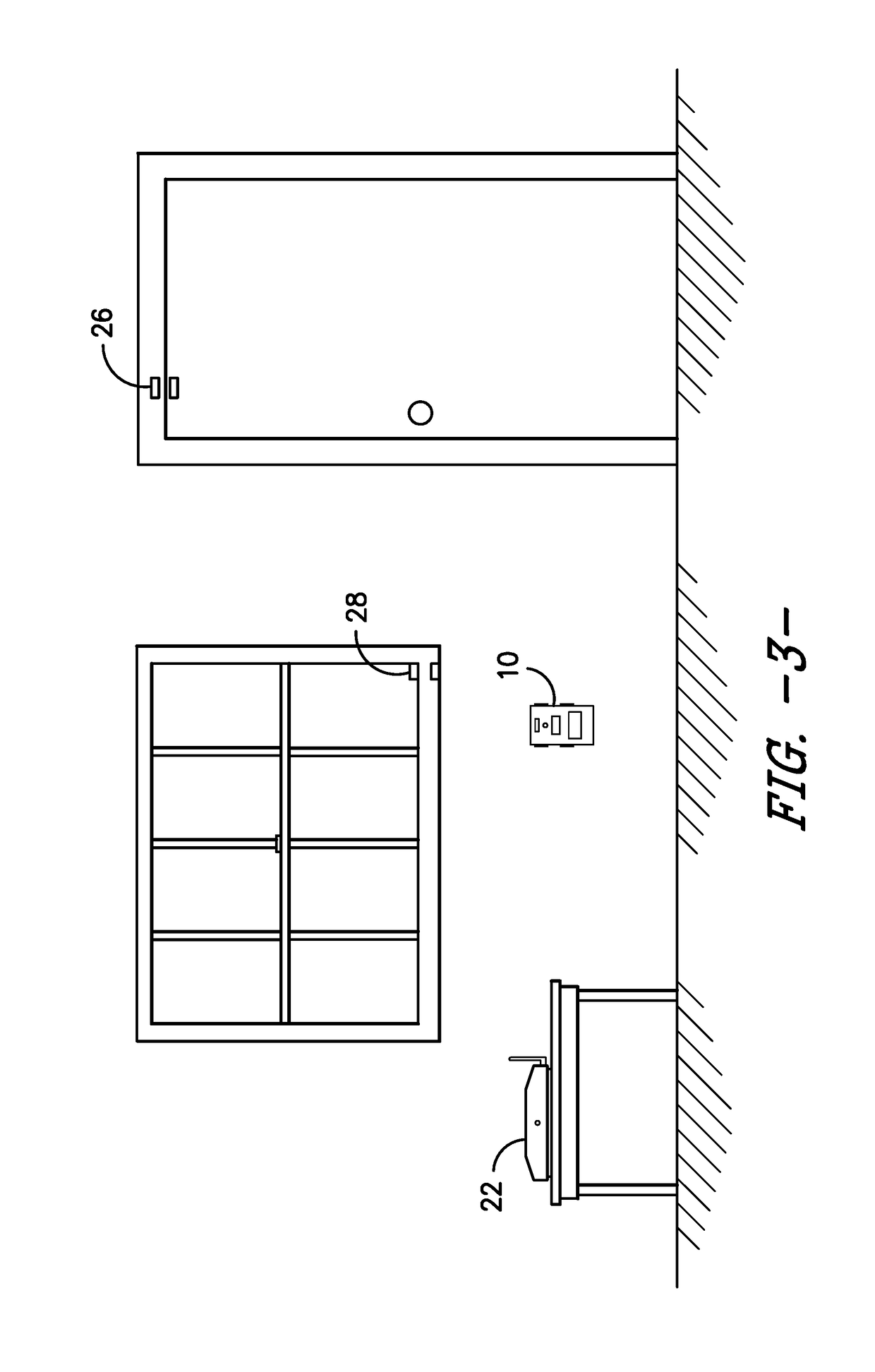
Patient-side surgeon interface for a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical instrument
A patient-side surgeon interface provides enhanced capabilities in using a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical system. The patient-side surgeon interface has components within the sterile surgical field of the surgery. The components allow a surgeon to control teleoperated slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field. The patient-side surgeon interface permits a surgeon to be in the sterile surgical field adjacent a patient undergoing surgery. Controlling minimally invasive slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field permits minimally invasive surgery combined with direct visualization by the surgeon. The proximity to the patient allows the surgeon to control a teleoperated slave surgical instrument in tandem with controlling manually controlled instruments such as a laparoscopic instrument. Also, the surgeon, from within the sterile surgical field, can use the patient-side surgeon interface to control at least one proxy visual in proctoring another surgeon.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Headset-Based Telecommunications Platform
ActiveUS20100245585A1Extend battery lifeTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersData streamPeer-to-peer
A hands-free wireless wearable GPS enabled video camera and audio-video communications headset, mobile phone and personal media player, capable of real-time two-way and multi-feed wireless voice, data and audio-video streaming, telecommunications, and teleconferencing, coordinated applications, and shared functionality between one or more wirelessly networked headsets or other paired or networked wired or wireless devices and optimized device and data management over multiple wired and wireless network connections. The headset can operate in concert with one or more wired or wireless devices as a paired accessory, as an autonomous hands-free wide area, metro or local area and personal area wireless audio-video communications and multimedia device and / or as a wearable docking station, hot spot and wireless router supporting direct connect multi-device ad-hoc virtual private networking (VPN). The headset has built-in intelligence to choose amongst available network protocols while supporting a variety of onboard, and remote operational controls including a retractable monocular viewfinder display for real time hands-free viewing of captured or received video feed and a duplex data-streaming platform supporting multi-channel communications and optimized data management within the device, within a managed or autonomous federation of devices or other peer-to-peer network configuration.
Owner:EYECAM INC
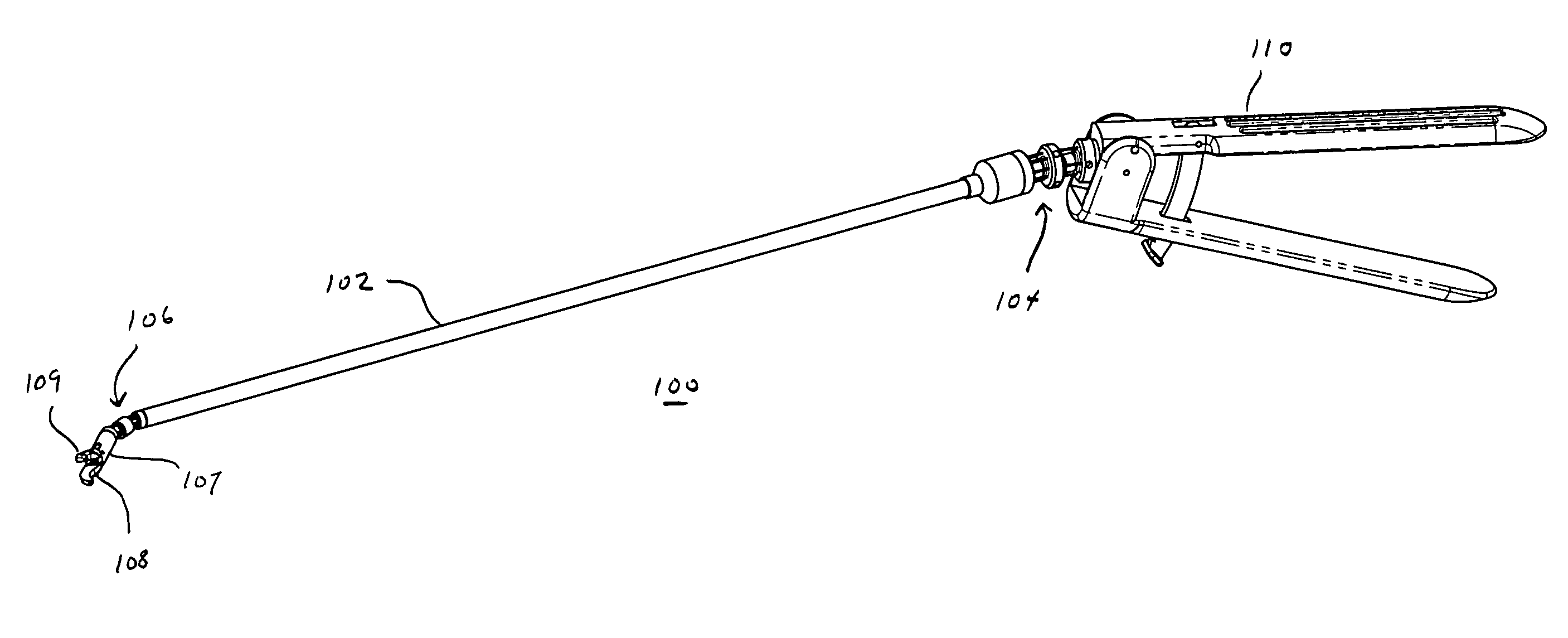
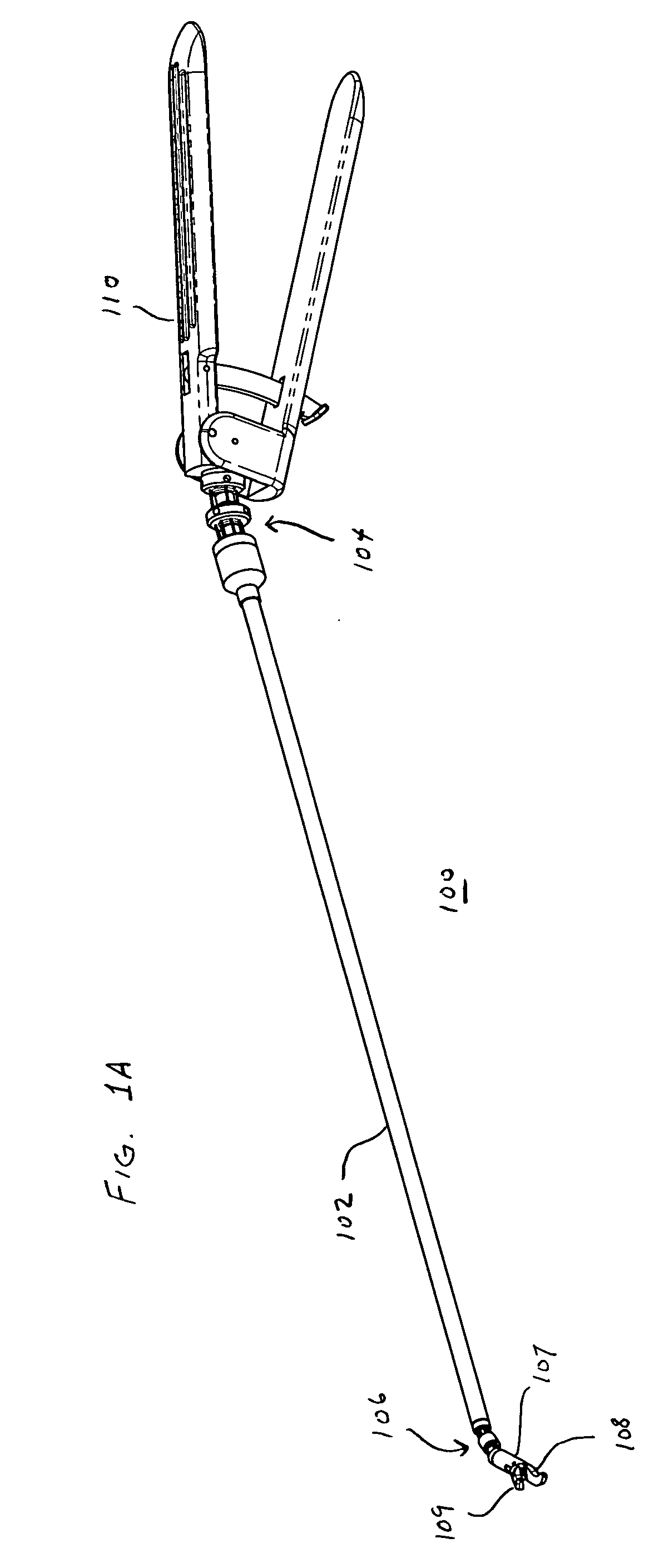
Link systems and articulation mechanisms for remote manipulation of surgical or diagnostic tools
ActiveUS20050273084A1Reduce and eliminate excess cable slackReduce and eliminate and tensionEar treatmentEndoscopesEngineeringDiagnostic instrument
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
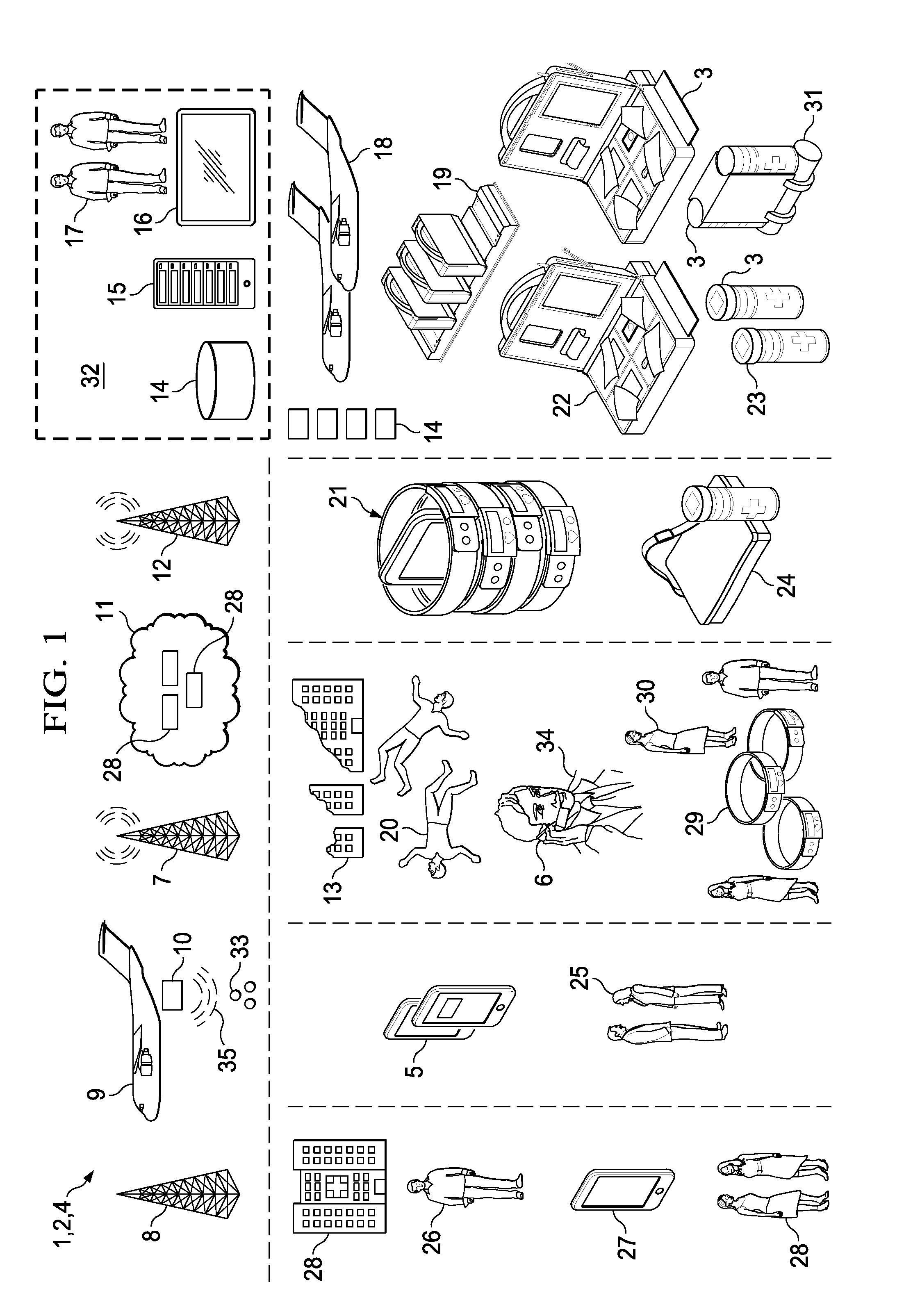
Systems, Methods and Devices for the Rapid Assessment and Deployment of Appropriate Modular Aid Solutions in Response to Disasters.
InactiveUS20110130636A1Rapid deploymentElectric testing/monitoringRemote controlled aircraftTriageModularity
The invention relates generally to systems, devices and methods for global disaster response, more particularly to the rapid detection, qualified assessment and monitoring of disasters and electronic triage of victims, communication, alert and evacuation systems, provision of suitable modular sensing or medical aid solutions, and their rapid deployment via delivery platforms such as disaster messaging formats and resources on client mobile phone applications or physically via remote operated vehicles (unmanned aerial sea or land systems) or targeted air delivery.
Owner:DANIEL SIMON R +4
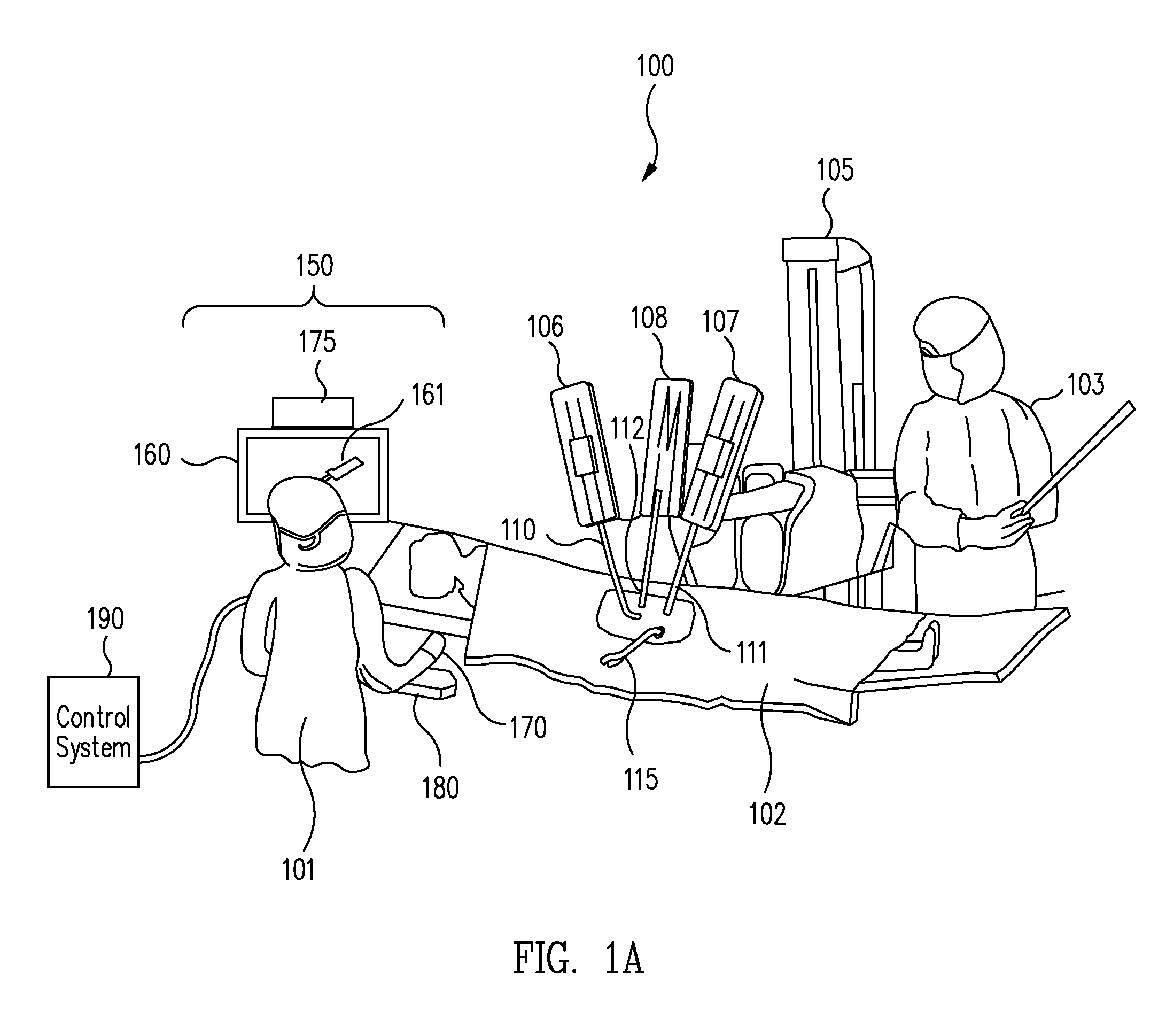
Patient-side surgeon interface for a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical instrument
A patient-side surgeon interface provides enhanced capabilities in using a minimally invasive, teleoperated surgical system. The patient-side surgeon interface has components within the sterile surgical field of the surgery. The components allow a surgeon to control teleoperated slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field. The patient-side surgeon interface permits a surgeon to be in the sterile surgical field adjacent a patient undergoing surgery. Controlling minimally invasive slave surgical instruments from within the sterile surgical field permits minimally invasive surgery combined with direct visualization by the surgeon. The proximity to the patient allows the surgeon to control a teleoperated slave surgical instrument in tandem with controlling manually controlled instruments such as a laparoscopic instrument. Also, the surgeon, from within the sterile surgical field, can use the patient-side surgeon interface to control at least one proxy visual in proctoring another surgeon.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
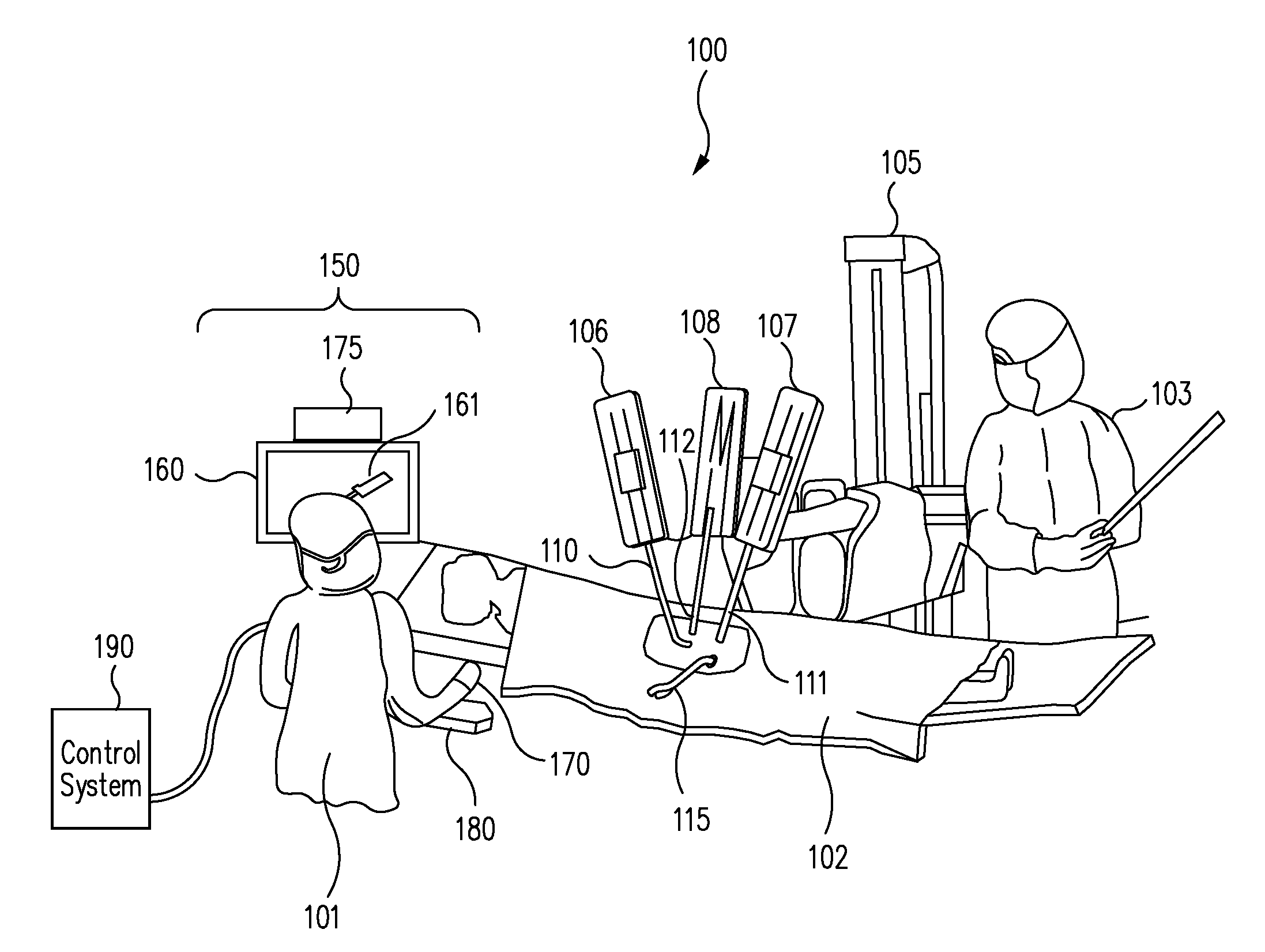
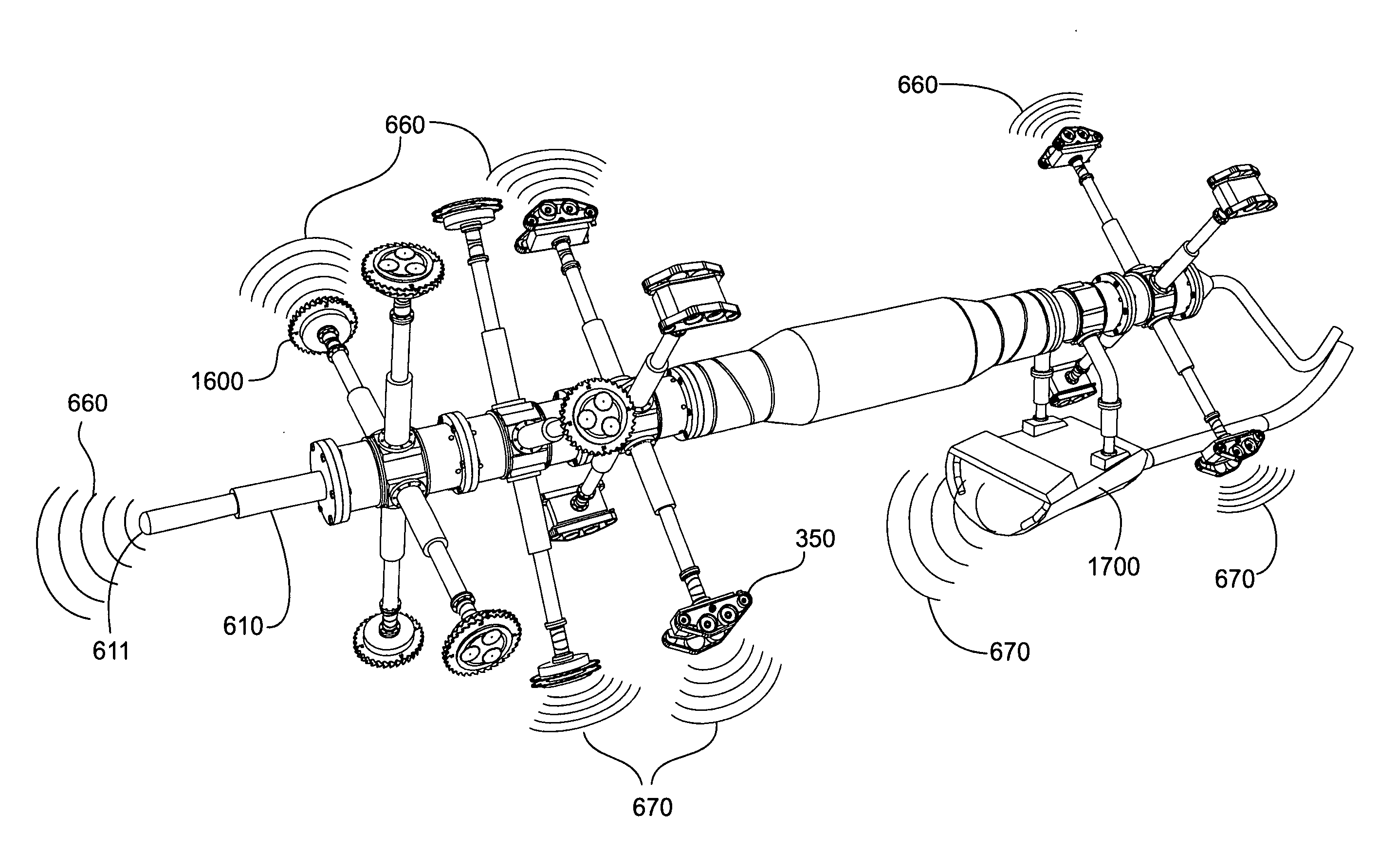
Multi-port surgical robotic system architecture
ActiveUS20130325033A1Improve mobilityEasy and fast setupPortable framesDiagnosticsRobotic systemsEngineering
A robotic surgery system includes an orienting platform, a support linkage movably supporting the orienting platform, a plurality of surgical instrument manipulators, and a plurality of set-up linkages. Each of the manipulators includes an instrument holder and is operable to rotate the instrument holder around a remote center of manipulation (RC). At least one of the manipulators includes a reorientation mechanism that when actuated moves the attached manipulator through a motion that maintains the associated RC in a fixed position.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
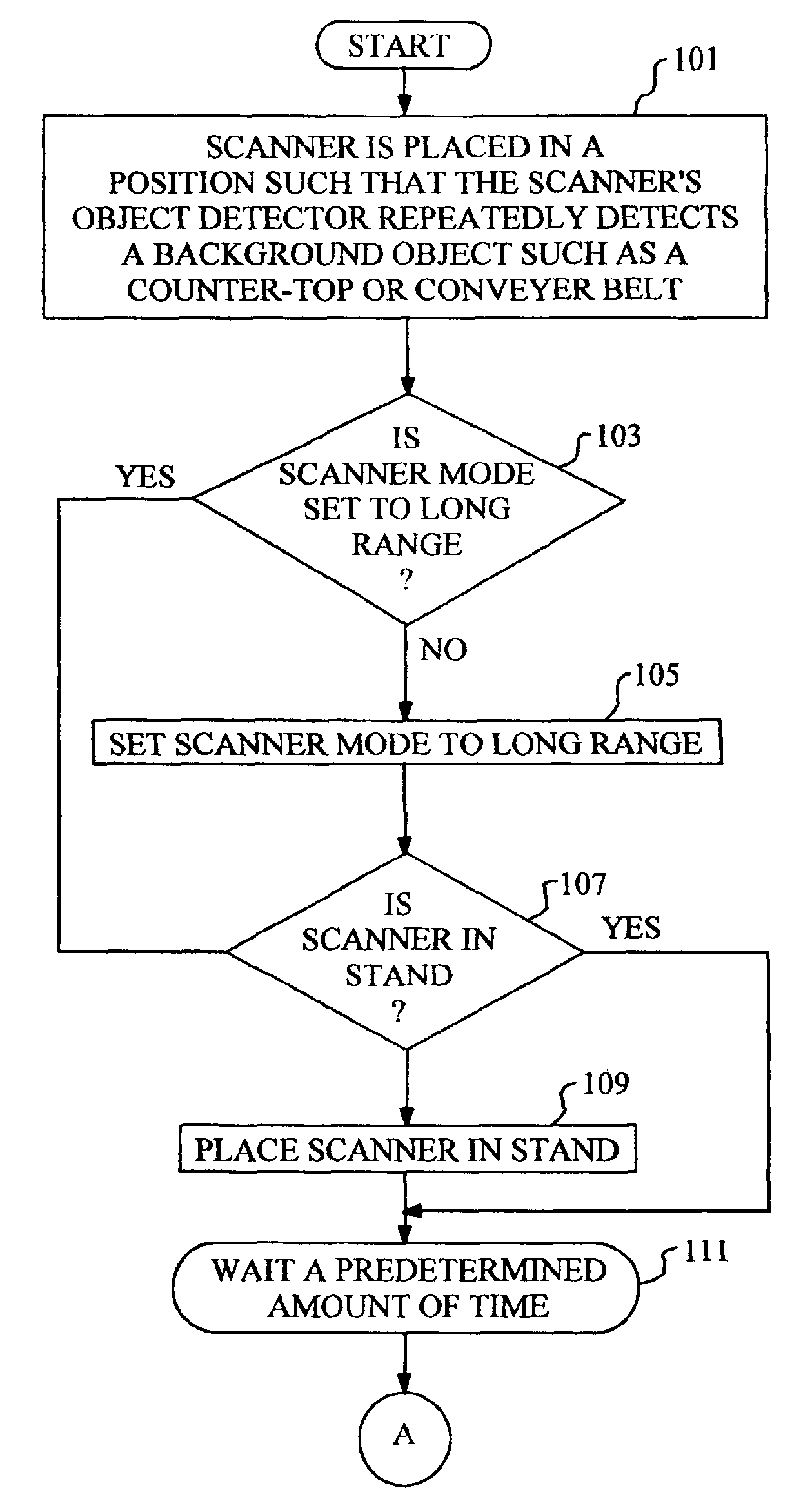
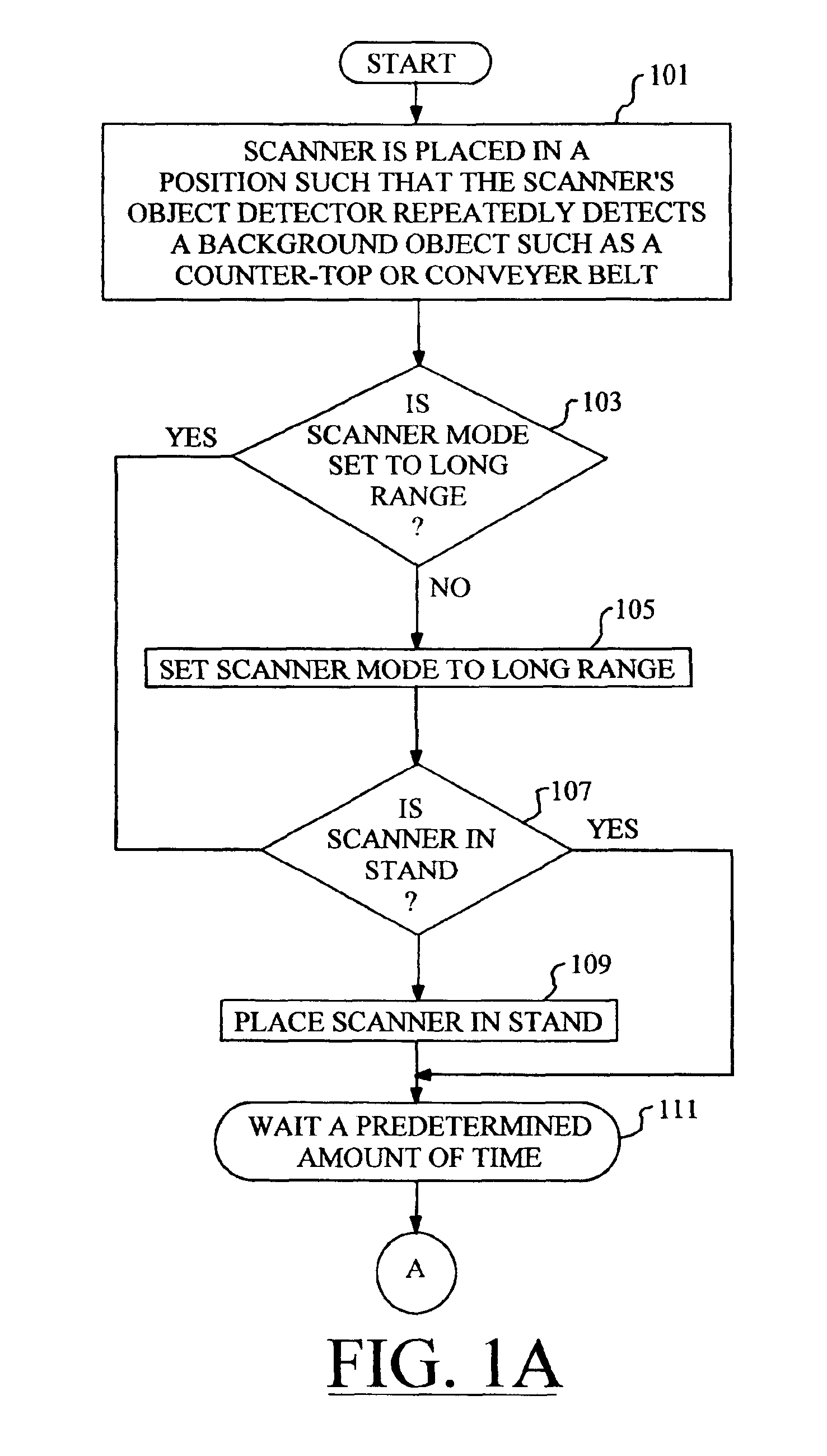
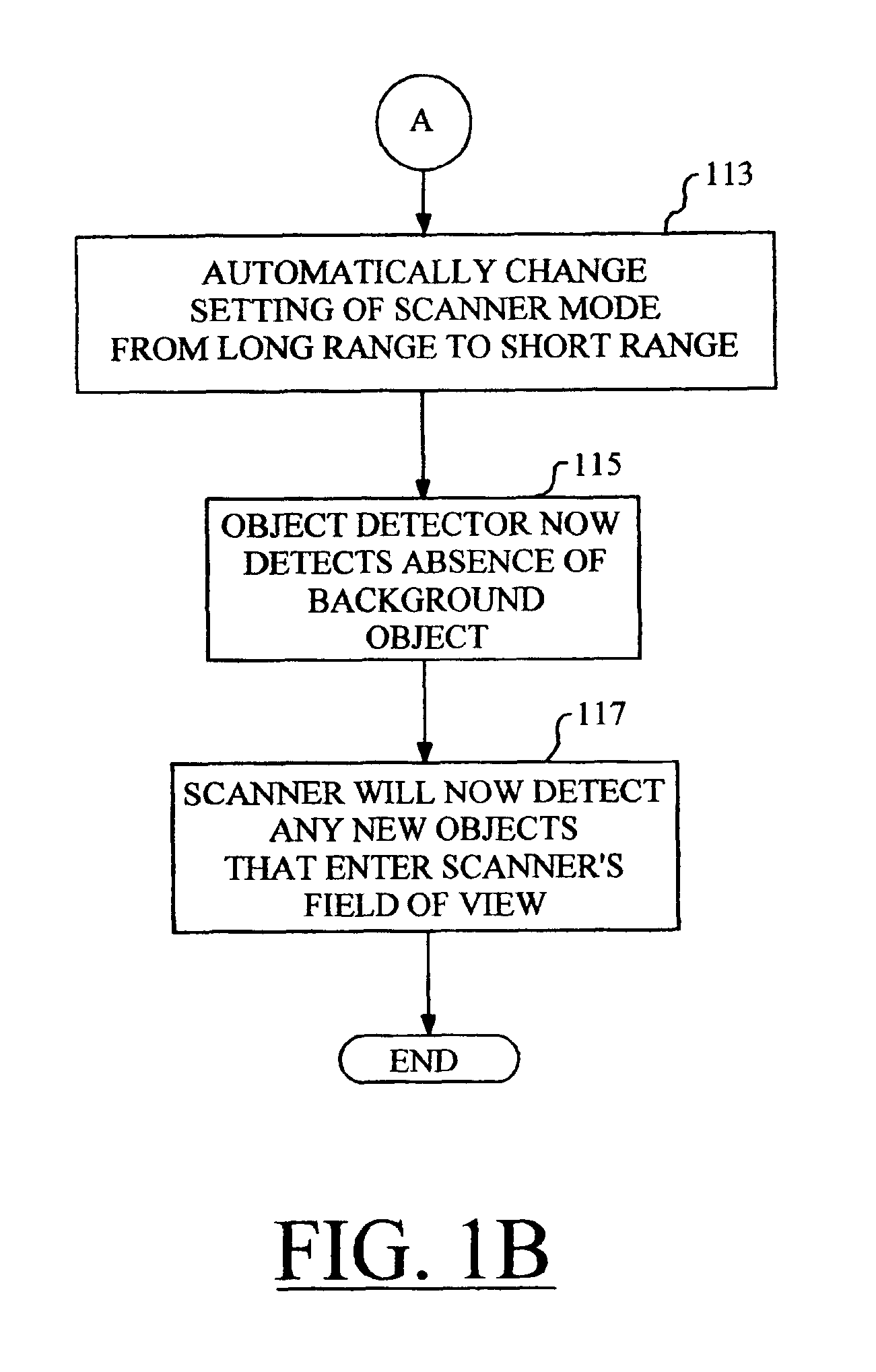
Automatic range adjustment techniques for stand-mountable bar code scanners
By automatically adjusting the object detection mechanism of a bar code scanner from a long range mode of operation to a short range mode of operation, the scanner will remain capable of detecting and decoding bar codes even if the object detection mechanism repeatedly detects the presence of a background object. The techniques of the present invention commence when the bar code scanner is placed in a position such that the scanner's object detection mechanism repeatedly detects a background object such as a counter top or conveyer belt. The object detection mechanism is set to the long range mode of operation if it is not already so set. In the case of a stand-mounted scanner, a test is performed to ascertain whether or not the scanner is in its stand, and the method will only proceed once the scanner is resting in the stand. Next, the scanner is programmed to wait for a predetermined amount of time, after which the operational mode of the object detection mechanism is changed from the long range mode to the short range mode. At this time, the object detection mechanism no longer detects the presence of the background object. The scanner will now detect any new objects that enter the field of view of the object detection mechanism, and attempt to read any bar codes which may be present
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
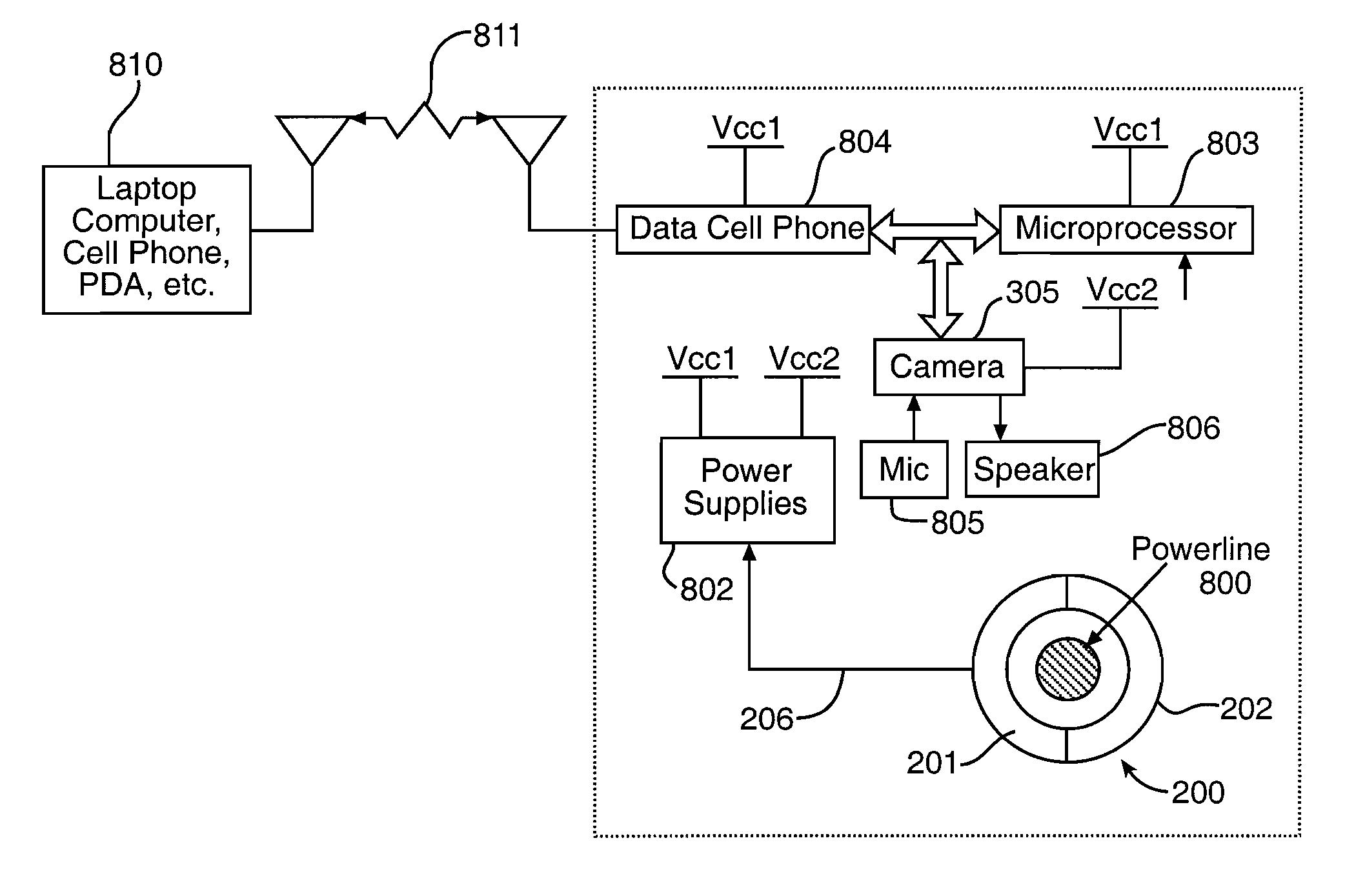
High voltage power line multi-sensor system
InactiveUS8767071B1Limited powerOvercome problemsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
A multi-sensor system can be attached to a high voltage power line, draw power from the power line inductively, and convert the power to lower voltages and direct currents for operating cameras, sensors, a processor, and communications equipment that provide persistent intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities. The multi-sensor system can detect and track targets in detection regions and transmit such detection data and other data from the camera and sensors to a remote operator who can initiate response actions and send control instructions to the multi-sensor system from the remote location.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Systems and methods for obstacle avoidance
ActiveUS20070193798A1Detect presenceAutonomous decision making processAutomatic initiationsControl systemObstacle avoidance
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for obstacle avoidance. In some embodiments, a robotically controlled vehicle capable of operating in one or more modes may be provided. Examples of such modes include teleoperation, waypoint navigation, follow, and manual mode. The vehicle may include an obstacle detection and avoidance system capable of being implemented with one or more of the vehicle modes. A control system may be provided to operate and control the vehicle in the one or more modes. The control system may include a robotic control unit and a vehicle control unit.
Owner:IROBOT CORP +1
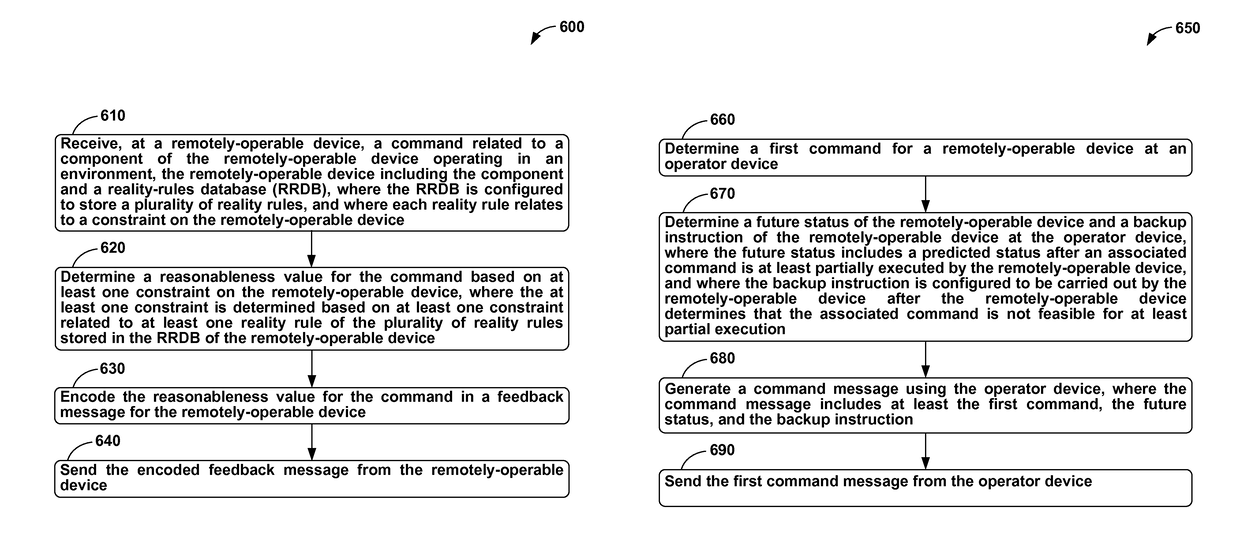
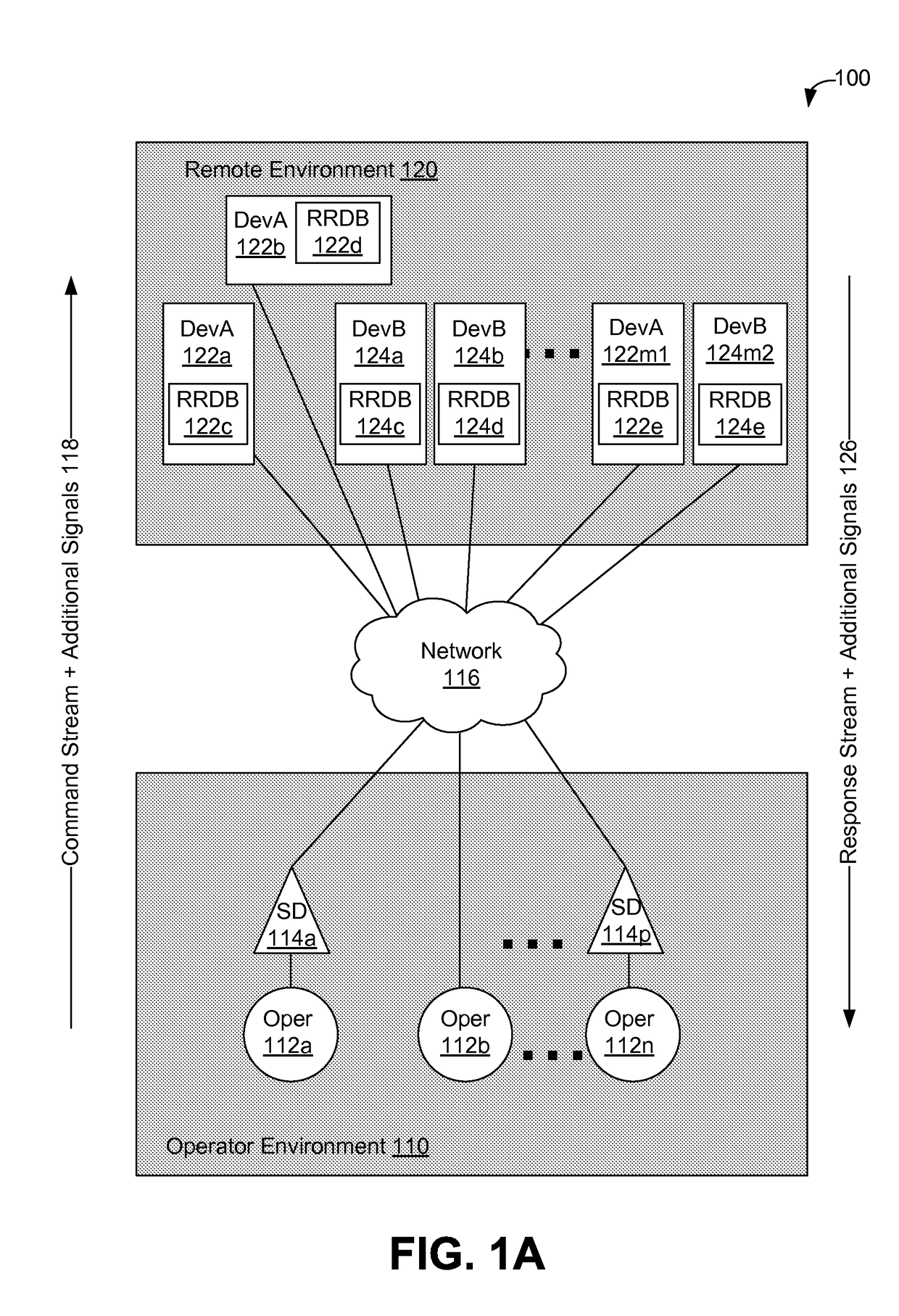
Using supplemental encrypted signals to mitigate man-in-the-middle attacks on teleoperated systems
ActiveUS9686306B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTelemedicineMan-in-the-middle attackOperational system
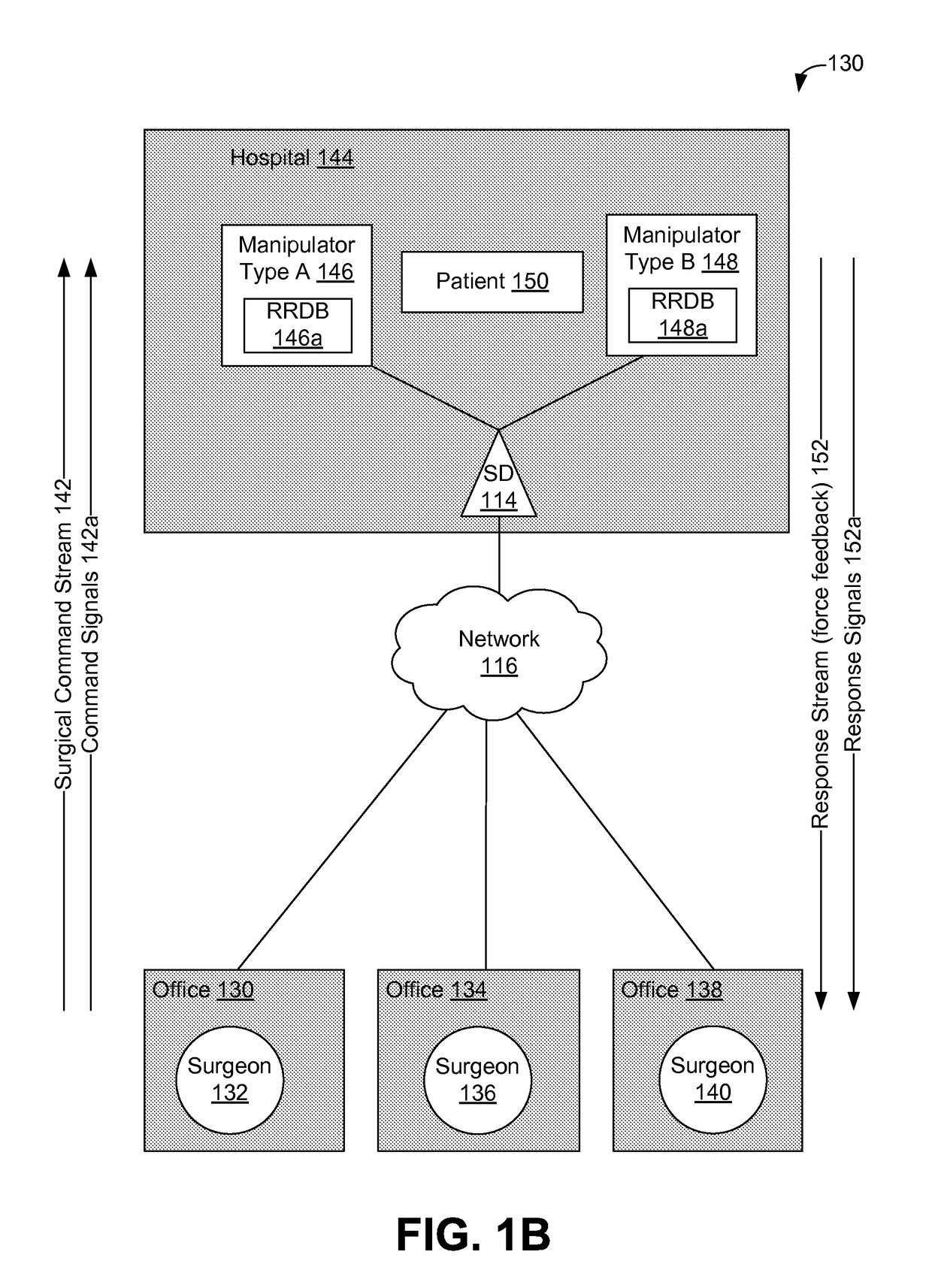
Methods and systems for securing remotely-operable devices are provided. A remotely-operable device can receive a command related to a component of the remotely-operable device operating in an environment. The remotely-operable device can include a reality-rules database (RRDB) that is configured to store a plurality of reality rules with each reality rule relating to a constraint on the remotely-operable device. The remotely-operable device can determine a reasonableness value for the command based on a constraint, where the constraint is determined based on a constraint related to at least one reality rule of the plurality of reality rules stored in the RRDB. The remotely-operable device can encode the reasonableness value for the command in a feedback message. The remotely-operable device can send the encoded feedback message from the remotely-operable device.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Control input accuracy for teleoperated surgical instrument
A surgical system having a patient side cart having at least one telesurgically operated instrument, the at least one telesurgically operated instrument comprising a surgical end effector having a plurality of effector components. A transmission is coupled to a motor. The drive train includes at least a first effector drive train and a second effector drivetrain. A controller comprises at least one processor for controlling the transmission. The controller is performs a method by locking an output gear of the second effector drivetrain rotating a camshaft to shift coupling of the motor from the first effector drivetrain to the second effector drivetrain; determining that the output gear is aligned by driving the locked output gear using a first torque; determining that the output gear is properly braked by driving the locked output gear using a second torque; disengaging the lock from the output gear; and driving the second effector drivetrain using the motor.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
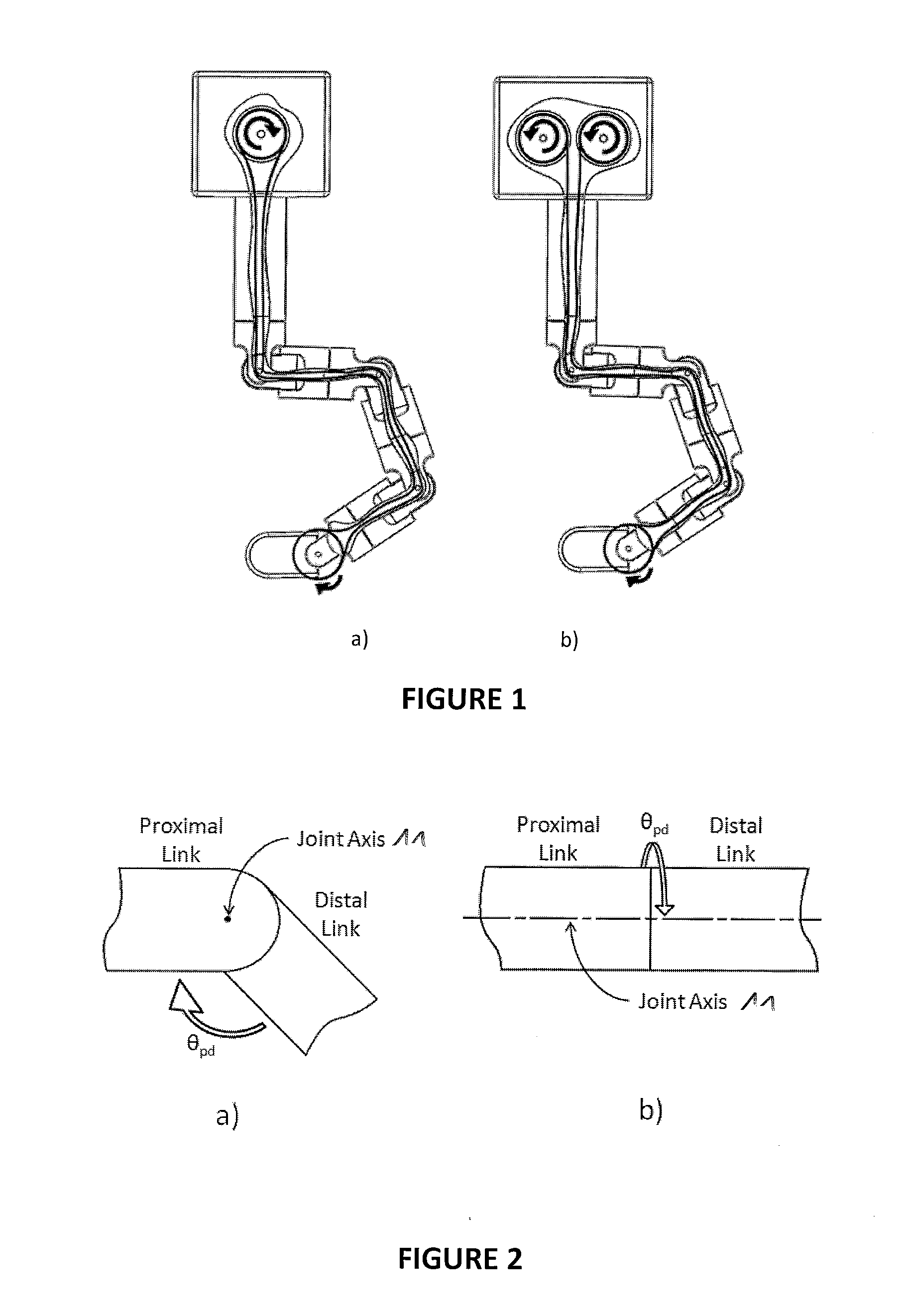
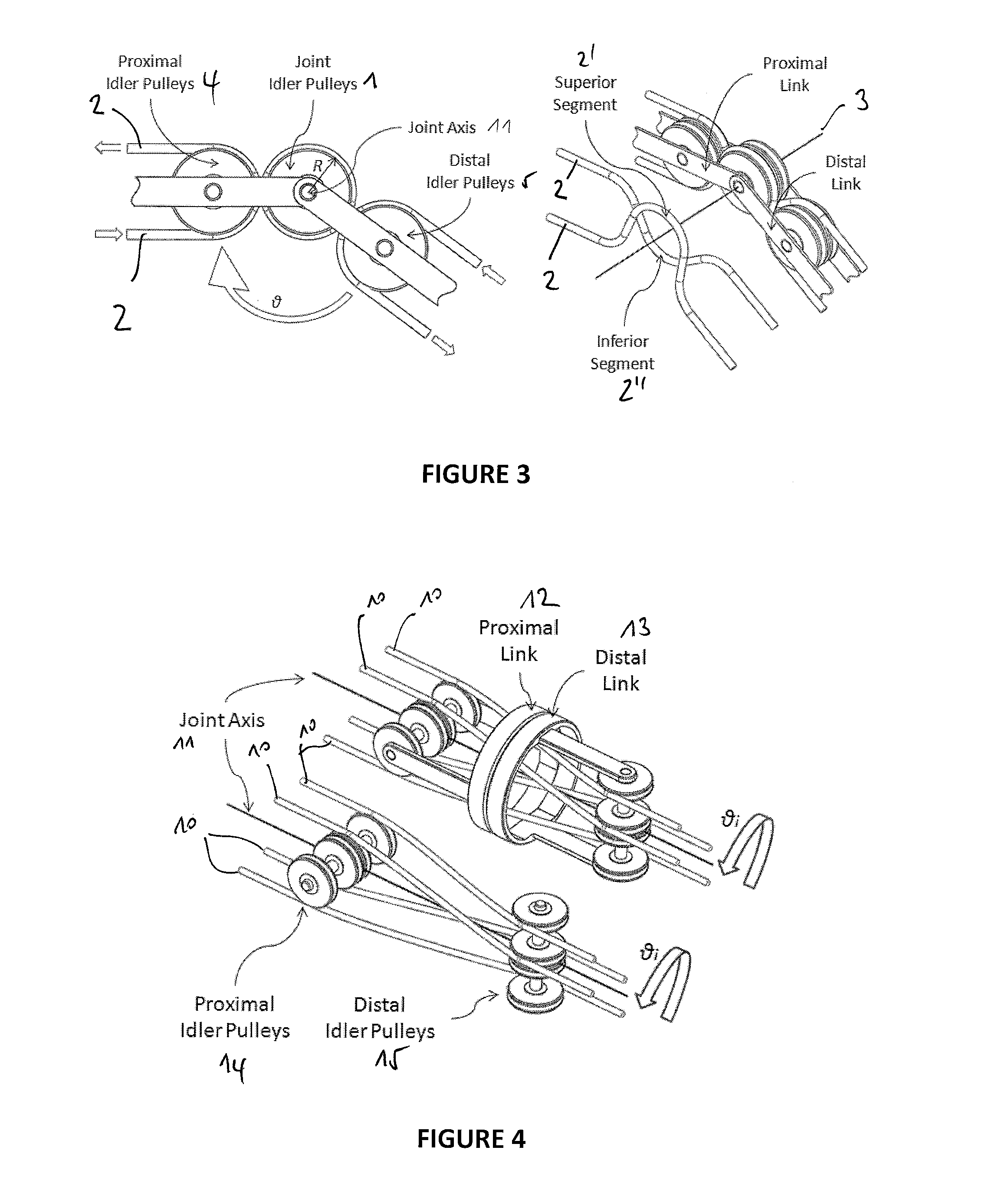
Mechanical manipulator for surgical instruments
ActiveUS20130304084A1Solve the lack of stiffnessSolve the lack of precisionDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsConventional laparoscopyEngineering
A novel mechanical system, based on a new cable driven mechanical transmission, able to provide sufficient dexterity, stiffness, speed, precision and payload capacity to actuate multi-DOF micro-manipulators. Besides the possibility of being used in several articulated surgical instruments and robotic systems for surgery or other applications involving remote manipulation, it enables the design of a novel fully mechanical surgical instrument, which offer the advantages of conventional laparoscopy (low cost, tactile feedback, high payload capacity) combined with the advantages of single port surgery (single incision, scarless surgery, navigation through several quadrants of the abdominal cavity) and robotic surgery (greater degrees of freedom, short learning curve, high stiffness, high precision, increased intuition). The unique design of the proposed system provides an intuitive user interface to achieve such enhanced manoeuvrability, allowing each joint of a teleoperated slave system to be driven by controlling the position of a mechanically connected master unit.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Submersible robotically operable vehicle system for infrastructure maintenance and inspection
InactiveUS20120215348A1Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsElectric powerInstrumentation
A configurable robotic apparatus and system is disclosed that is remotely operable in difficult, hazardous, subterranean, or submerged environs. The apparatus merges diverse disciplines to effect inspecting, cleaning, treating, repairing or otherwise maintaining a wide variety of materials and conditions. Deployment environments include power, municipal water and wastewater plants, surface and submerged infrastructures (pipes, lines, conduits), and like industrial applications. Extensible and articulating modules, configurable through standardized and interchangeable connectors, provide unique flexibility, scalability and versatility to accommodate a wide range of shapes, surfaces, and obstacles. In-module intelligence and instrumentation eliminates the need for constant manual control through autonomous operation capable of simultaneous optimization and synchronization of multiple work processes, but manual override and remote control is provided to overcome unanticipated limitations. Benefits include improved efficiency, cost, and safety over prior art. High-performance, one-pass operation reduces facility downtime while incorporating environmentally responsible debris recovery.
Owner:SKRINDE RICHARD ARTHUR
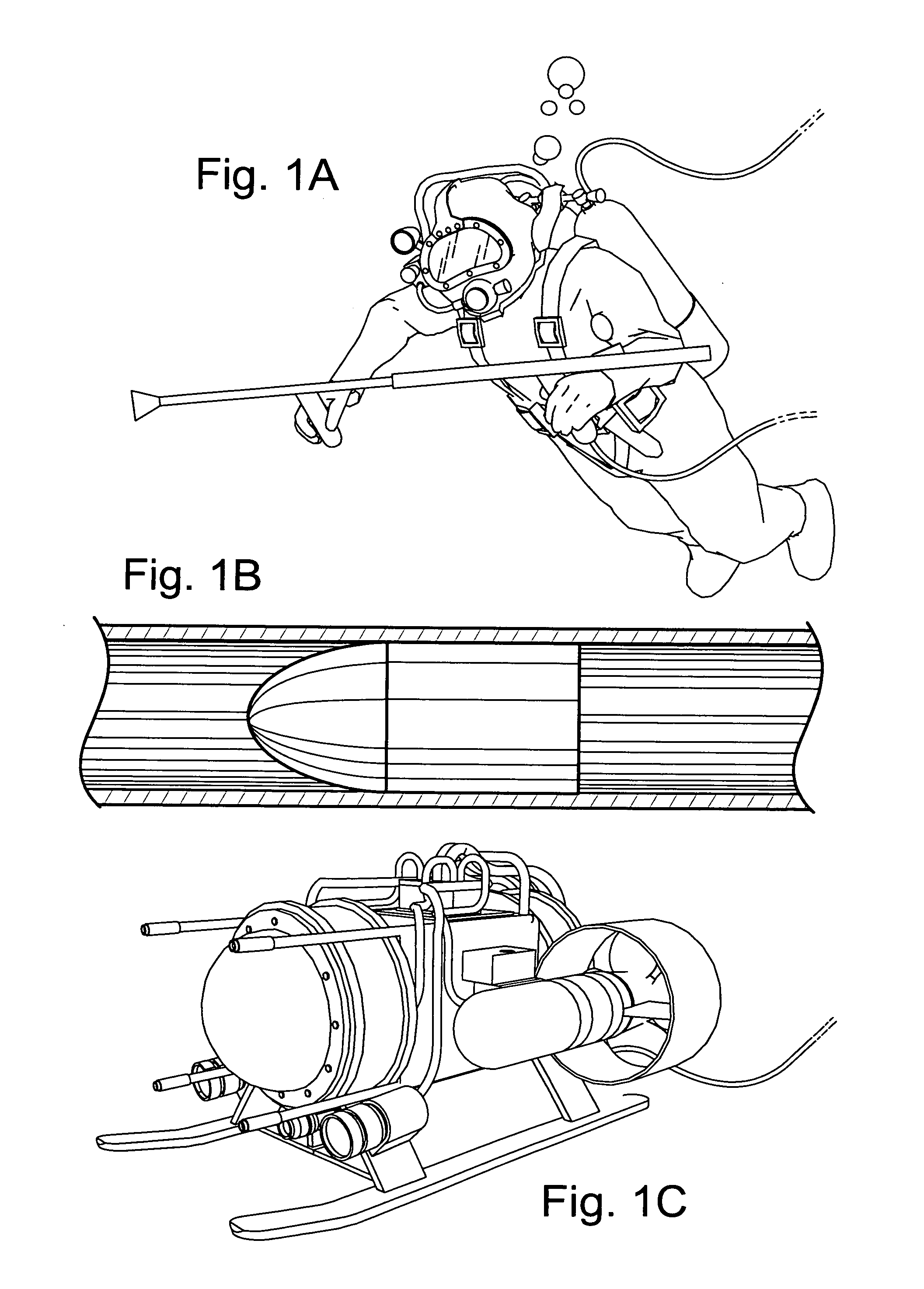
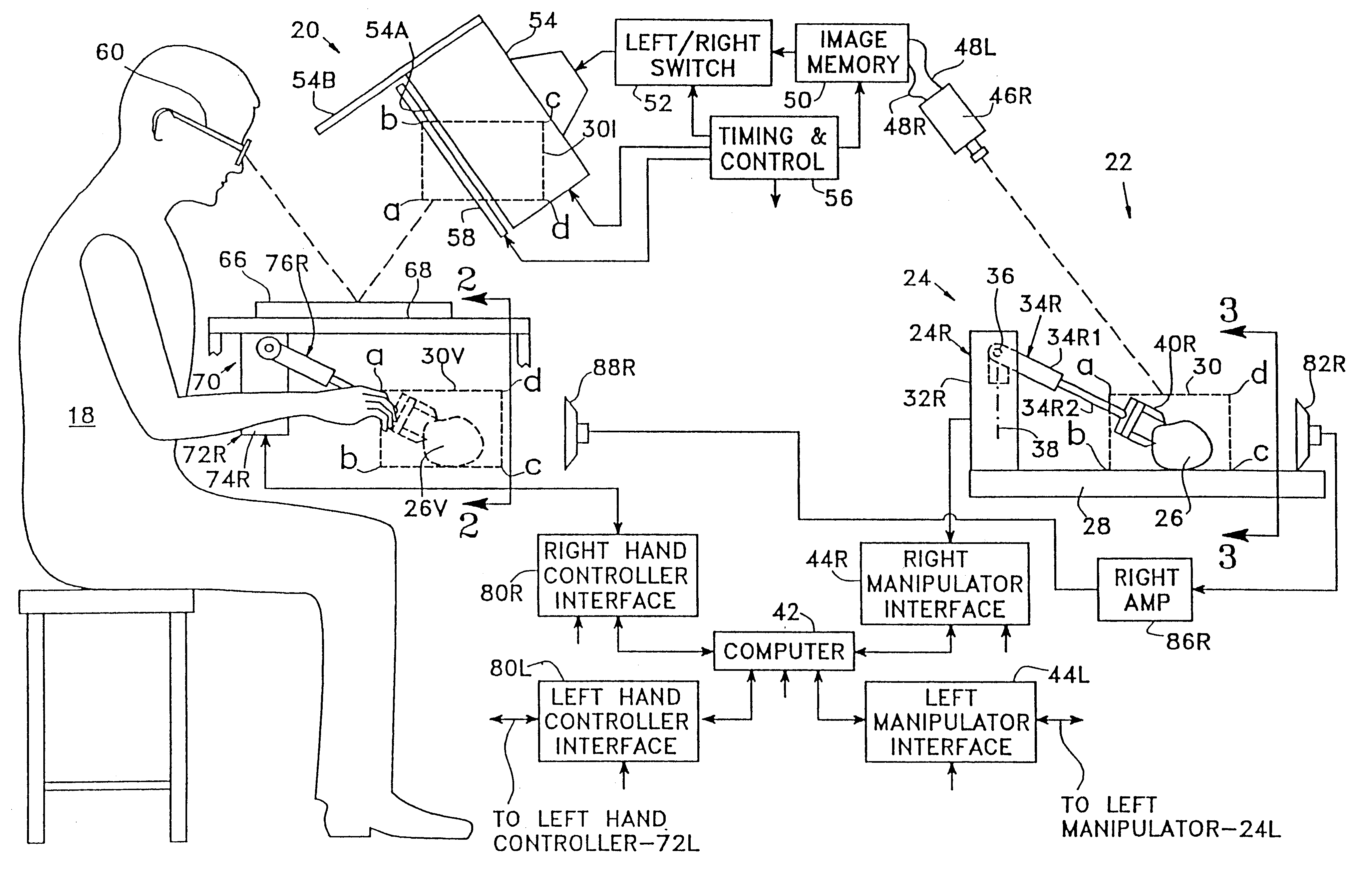
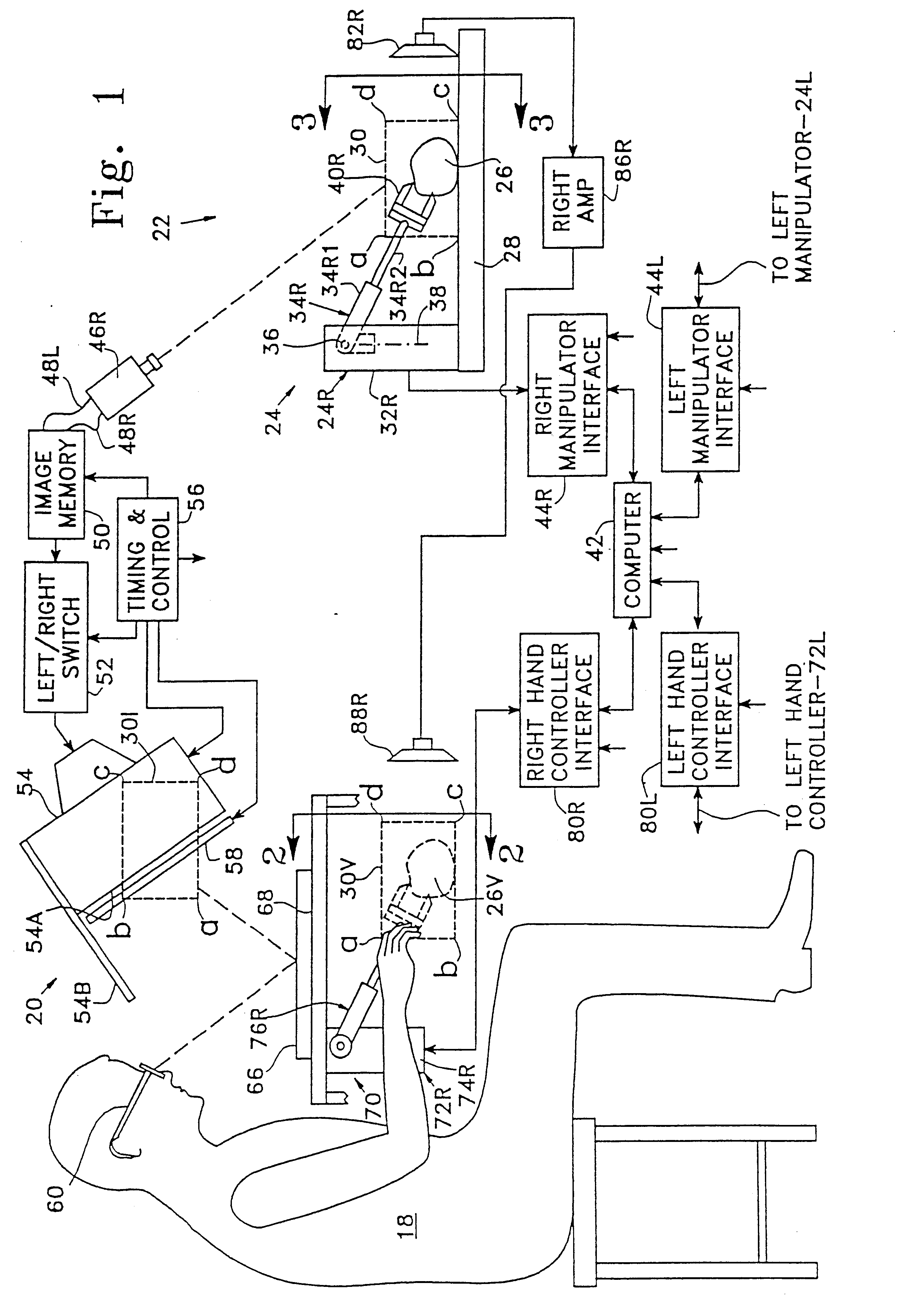
System and method for remote endoscopic surgery
InactiveUS6731988B1Improve satisfactionStrong sense of satisfactionComputer controlSimulator controlControl armDisplay device
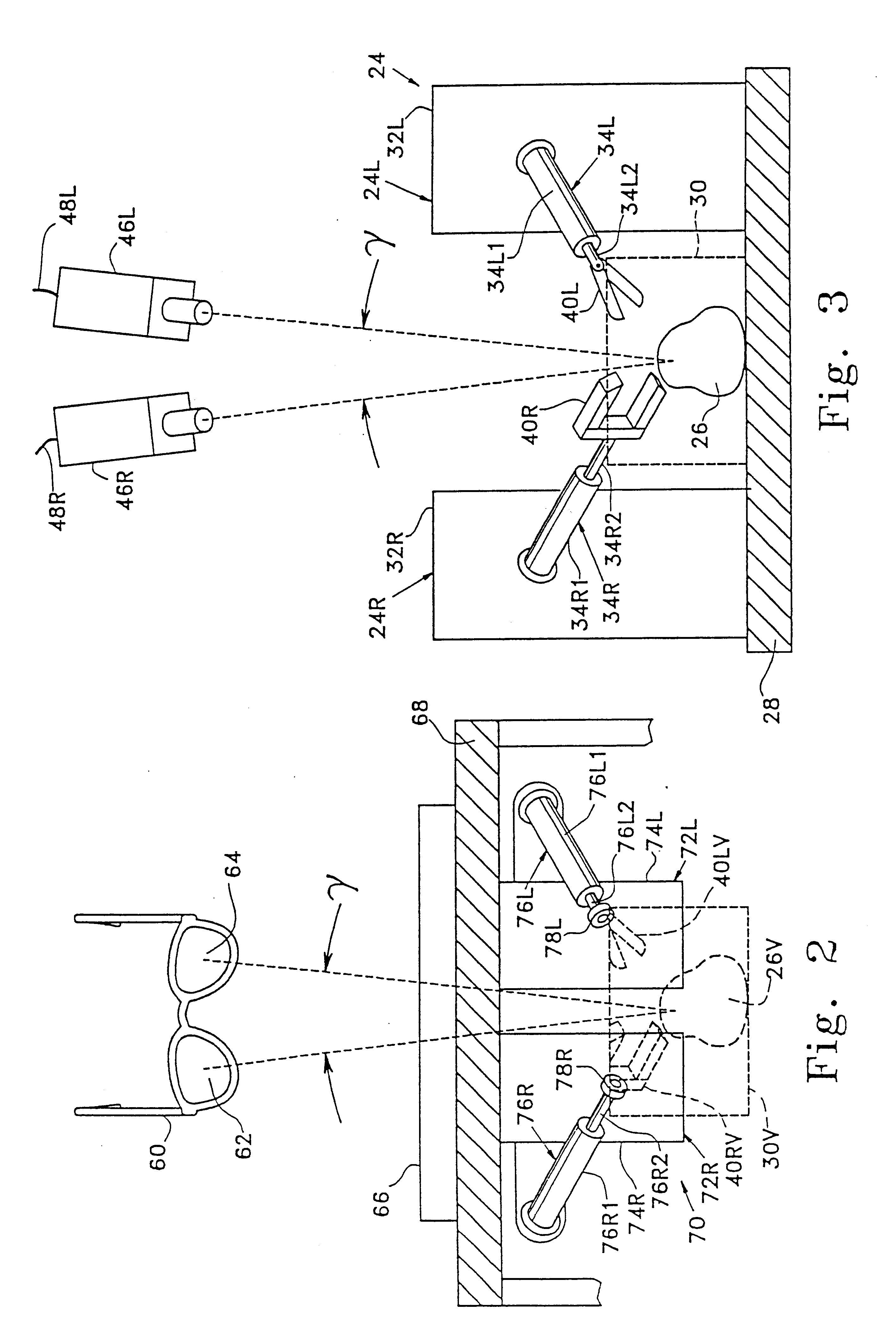
A teleoperator system with telepresence is shown which includes right and left hand controllers (72R and 72L) for control of right and left manipulators (24R and 24L) through use of a servomechanism that includes computer (42). Cameras (46R and 46L) view workspace (30) from different angles for production of stereoscopic signal outputs at lines (48R and 48L). In response to the camera outputs a 3-dimensional top-to-bottom inverted image (30I) is produced which, is reflected by mirror (66) toward the eyes of operator (18). A virtual image (30V) is produced adjacent control arms (76R and 76L) which is viewed by operator (18) looking in the direction of the control arms. By locating the workspace image (30V) adjacent the control arms (76R and 76L) the operator is provided with a sense that end effectors (40R and 40L) carried by manipulator arms (34R and 34L) and control arms (76R and 76L) are substantially integral. This sense of connection between the control arms (76R and 76L) and end effectors (40R and 40L) provide the operator with the sensation of directly controlling the end effectors by hand. By locating visual display (246) adjacent control arms (244R and 244L) image (240I) of the workspace is directly viewable by the operator (FIGS. 12 and 13). Use of the teleoperator system for surgical procedures is also disclosed (FIGS. 7-9 and 13).
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method and apparatus for controlling and optimizing seismic data acquisition
InactiveUS6590831B1Towing/pushing equipmentSeismic signal processingMarine engineeringData acquisition
A system and method for coordinating the operation of multiple manned, remotely operated or autonomous marine vessels engaged in marine seismic data acquisition to direct cooperating vessels from one point to the next while minimizing deviations in the desired spatial configuration of assets, risk to vessels and seismic assets, and personnel and to obtain optimal midpoint coverage by evaluating inputs from subsystems providing positioning information for cooperating vessels, prospect coverage, vessel capabilities, environmental information, and navigation hazards.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC +1
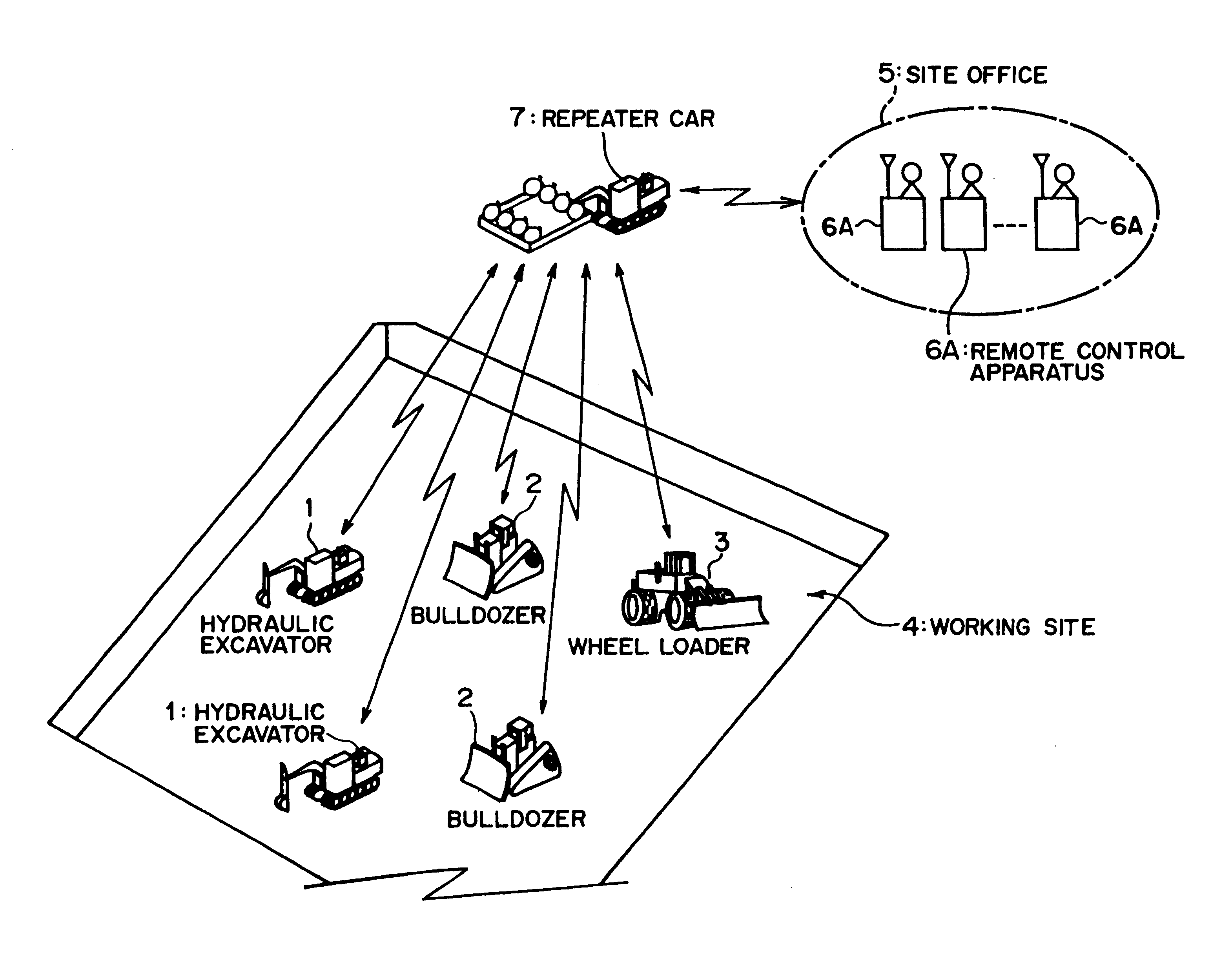
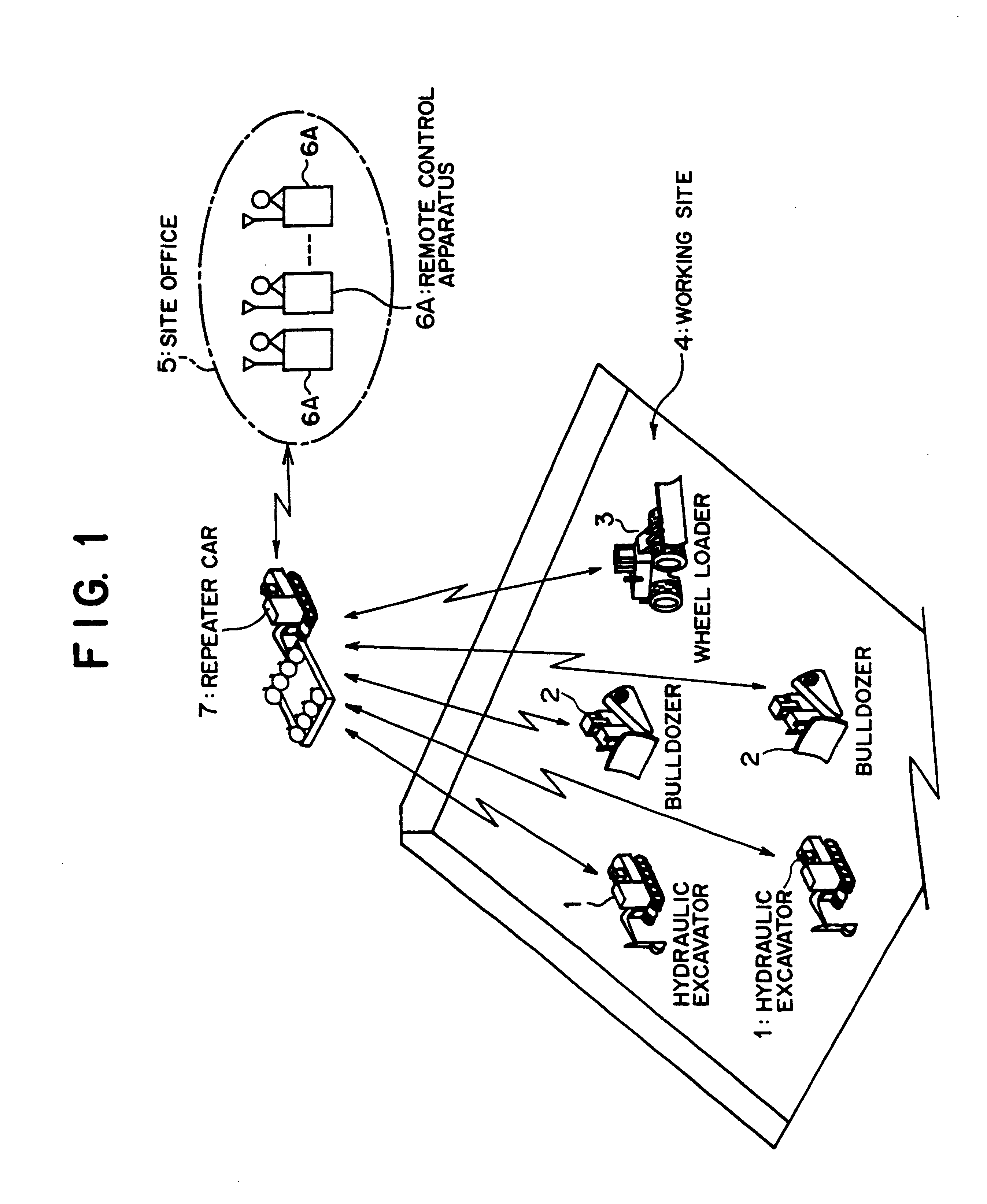
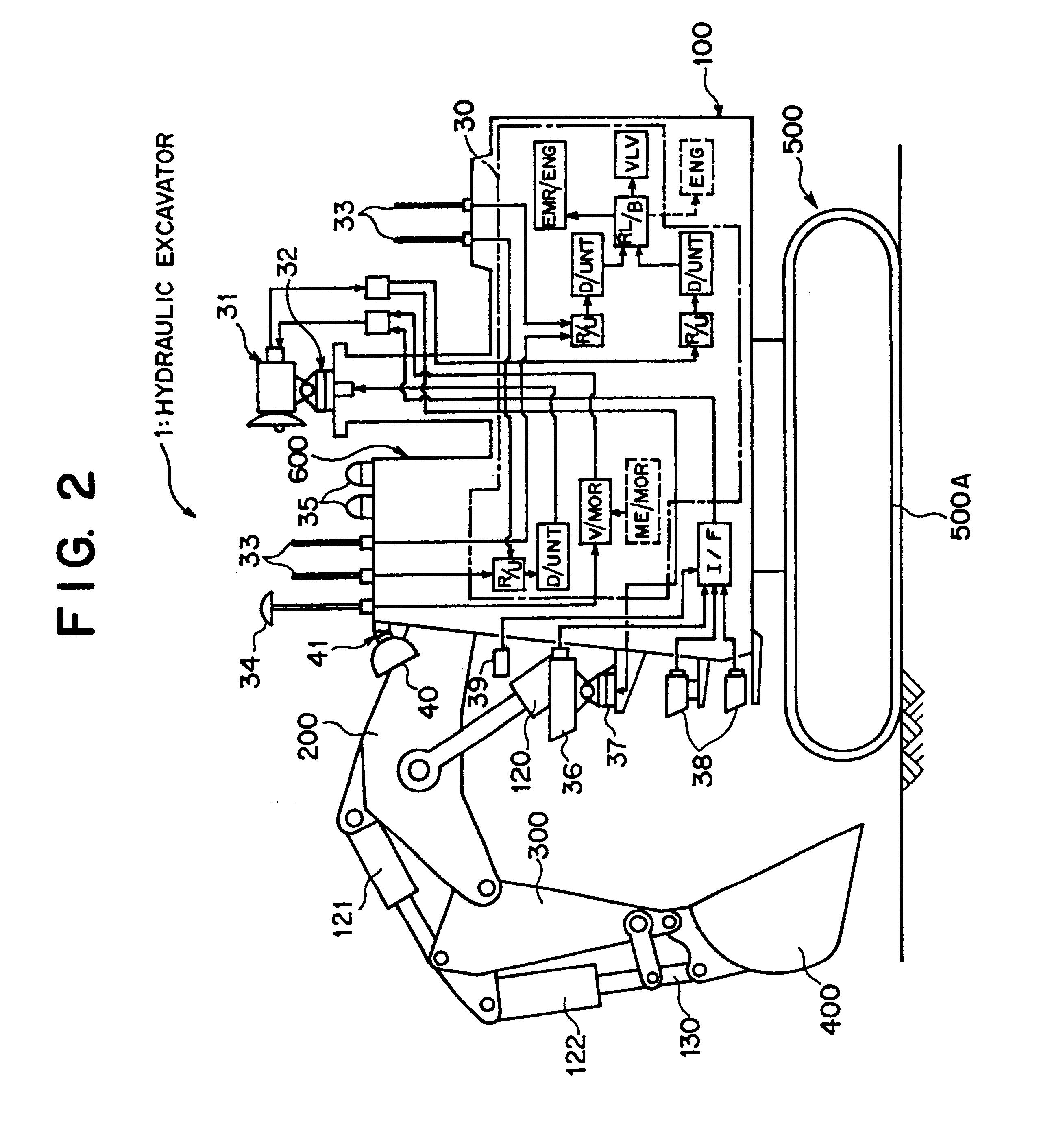
Remote radio operating system, and remote operating apparatus, mobile relay station and radio mobile working machine
InactiveUS6778097B1Improve reliabilityShort working hoursElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsMobile relayRemote control
The present invention relates to remote radio control technology, and a remote radio control system includes a radio movable working machine (1), a remote control apparatus (6A), and a movable repeater station (7). First bidirectional communication means (31, 71) having a high radio wave directionality and first automatic tracking means (32, 71A) are provided between the working machine (1) and the repeater station (7), and second bidirectional communication means (63, 76) having a high radio wave directionality, second automatic tracking means (63A, 76A), and emergency spread spectrum bidirectional communication means (64, 87) for enabling bidirectional communication between the remote control apparatus (6A) and the repeater station (7) when communication by the second bidirectional communication means (63, 76) is impossible are provided between the remote control apparatus (6A) and the repeater station (7). Consequently, even if communication between the working machine (1) and the movable repeater station (7) is disabled, each of the working machine (1) and the repeater station (7) is permitted to perform a minimum necessary operation, and any other person than those skilled in actual controlling operation of the working machine (1) can perform remote control easily.
Owner:CATEPILLAR SARL
Apparatus for remotely controlling computers and other electronic appliances/devices using a combination of voice commands and finger movements
An apparatus for remotely operating a computer using a combination of voice commands and finger movements. The apparatus includes a microphone and a plurality of control elements in the form of touch-sensitive touchpads and / or motion-sensitive elements that are used to operate the computer and to move an on-screen cursor. At least one touchpad is used to selectively switch between a command-mode of operation in which the computer interprets spoken words as commands for operating the computer and any software applications being used, and a text-mode of operation in which the computer interprets spoken words literally as text to be inserted into a software application. The apparatus is ergonomically designed to enable it to be easily worn and to enable a user to operate a computer from a standing, sitting or reclining position. The apparatus can be used to operate a computer for traditional computing purposes such as word processing or browsing the Internet, or for other purposes such as operating electronic devices such as a television and / or other household appliances. The apparatus eliminates the need for a keyboard and a mouse to operate a computer. In addition, the apparatus can be used as a telephone.
Owner:MILLER STEPHEN S
Remotely-operated robotic control system for use with a medical instrument and associated use thereof
A manipulator, for use with a robotic control system, to maneuver an existing instrument (e.g., medical instrument) to a desired location within a target zone includes at least one controller, a rotation mechanism in communication with the at least one controller and being rotated about a first axis, a horizontal movement mechanism in communication with the at least one controller and being displaced along a first path, and a deflection mechanism capable of receiving a portion of the existing instrument. Such a deflection mechanism is in communication with the at least one controller and displaced along a second path in such a manner that causes deflection of a distal end (e.g., portion of an insertion tube) of the existing medical instrument.
Owner:ELMED ELEKTRONIK VE MEDIKAL SANAYI VE TICARET ANONIM SIRKETI
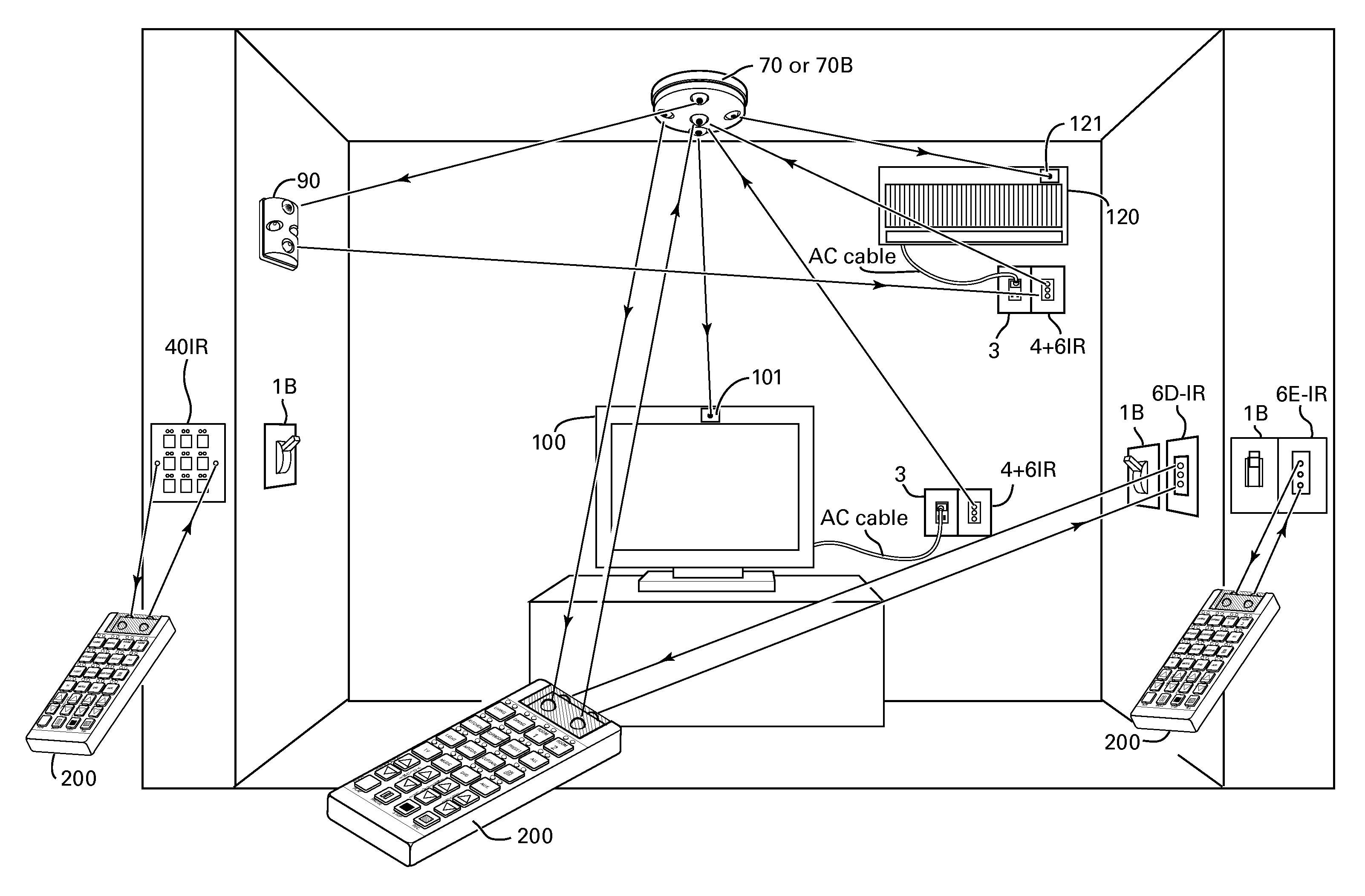
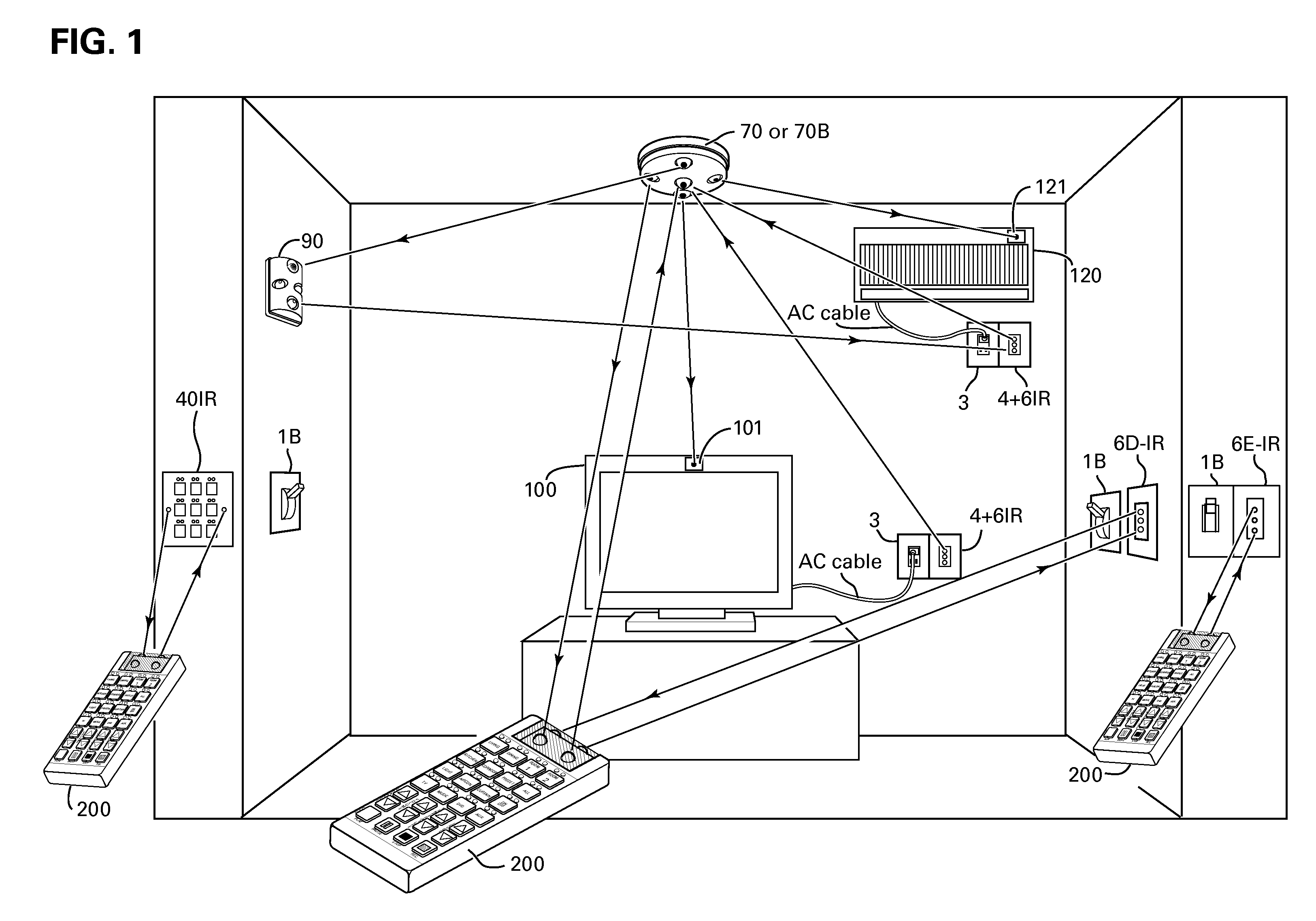
Method and apparatus for operating AC powered appliances via video interphones, two way IR drivers and remote control devices
InactiveUS7639907B2Effectively close missing linkLow costNon-electrical signal transmission systemsCoupling light guidesHand heldEngineering
A method for coupling at least one of a wall mount and a ceiling mount adjustable IR driver with a two way IR network of a home automation system controlled by a main controller selected from a group comprising a dedicated controller, a video interphone and a shopping terminal, the IR driver includes a plurality of adjustable IR transmitters and at least one IR receiver for propagating IR commands to at least one of hand held IR remote control units, electrical appliances and devices selected from a group comprising a remotely operated relays, an AC current sensors and a keypads, and for receiving from at least one of the devices a status data, said IR commands include at least a power on-off command for switching an appliance on and off and the status data pertaining to the on and off statuses of a commanded appliance.
Owner:ELBEX VIDEO LTD
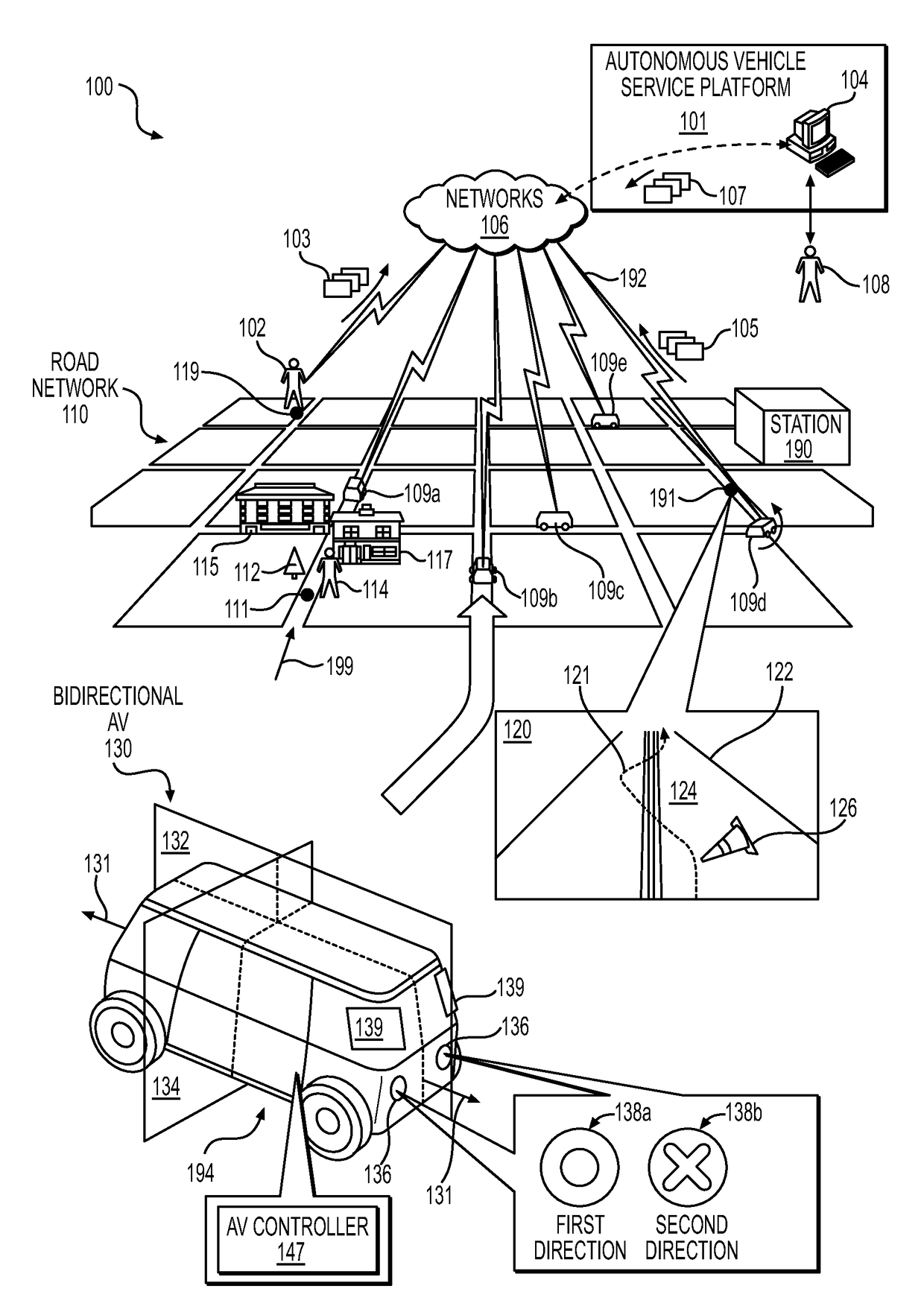
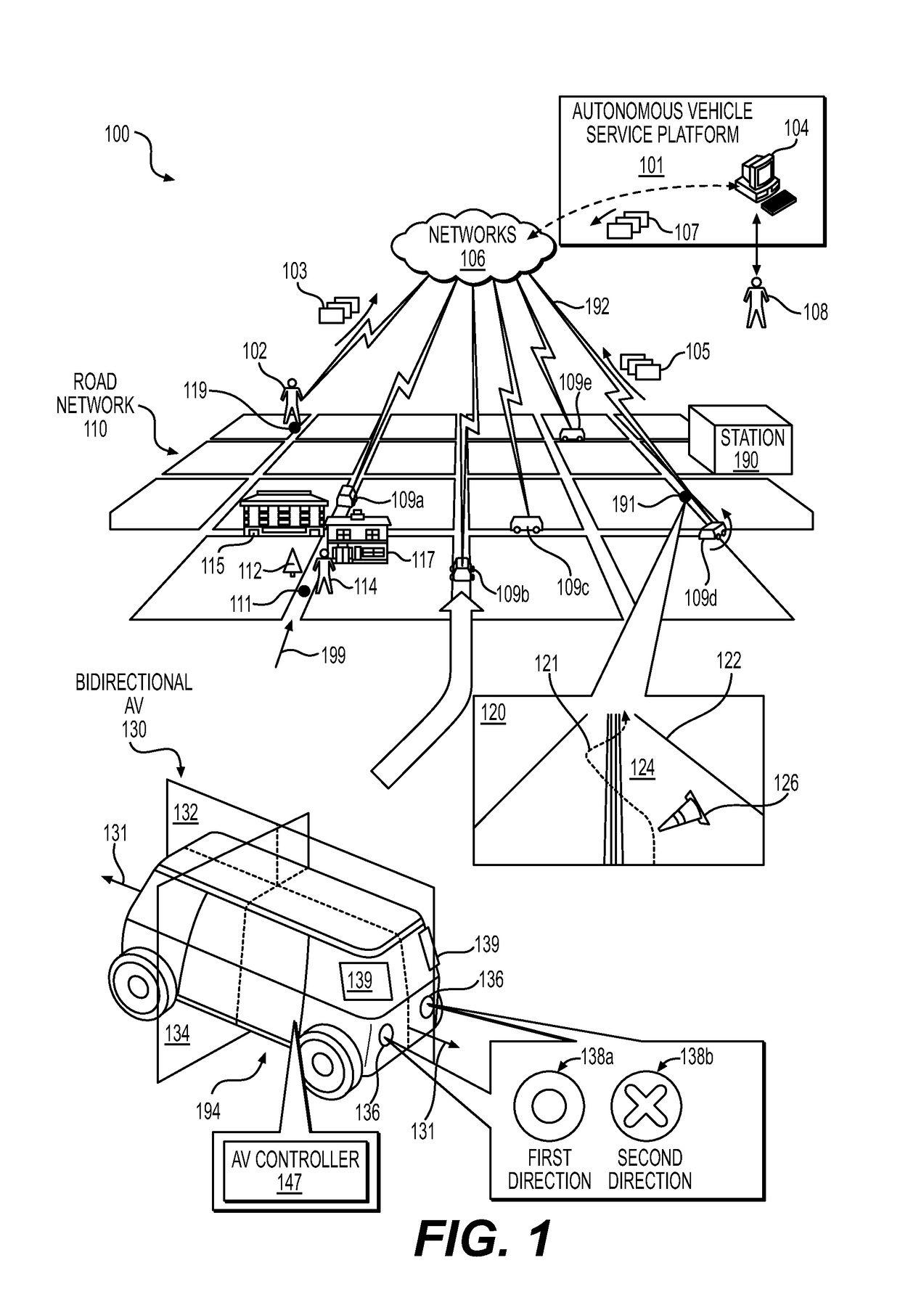
Teleoperation system and method for trajectory modification of autonomous vehicles
ActiveUS20180136651A1Autonomous decision making processDrawing from basic elementsOperational systemTelecommunications link
Various embodiments relate generally to autonomous vehicles and associated mechanical, electrical and electronic hardware, computer software and systems, and wired and wireless network communications to provide an autonomous vehicle fleet as a service. More specifically, systems, devices, and methods are configured to initiate modification of trajectories to influence navigation of autonomous vehicles. In particular, a method may include receiving a teleoperation message via a communication link from an autonomous vehicle, detecting data from the teleoperation message specifying an event associated with the autonomous vehicle, identifying one or more courses of action to perform responsive to detecting the data specifying the event, and generating visualization data to present information associated with the event to a display of a teleoperator computing device.
Owner:ZOOX INC
Aerially Deployed Illumination System
InactiveUS20120044710A1Create illusionReduce power consumptionAmmunition projectilesNon-electric lightingOptoelectronicsLighting system
An aerially deployed illumination system is provided which may be remotely operated or preprogrammed to illuminate a designated target, such as a geographic area, vehicle, or personnel. In particular, a remotely controlled UAV having an illumination system disposed thereon is provided, the illumination system comprised of a concentrated light source and light movement apparatus operable to rapidly scan the target with the light source, thereby providing an illusion of a large area of illumination. Preferably, a line is created from the light source, the line being rapidly moved over the target in specific patterns and at specific frequencies. The system may further include a plurality of UAV's capable of ad hoc networking, so as to illuminate both large areas, as well as stationary and moving targets. In addition, the UAV's having an illumination system disposed thereon may be disposed within a projectile, the projectile tube or gun launched, and the UAV ejected from the projectile over a designated target, thereby enabling quick delivery of the UAV to an area of interest.
Owner:JONES KENNETH R
Rotating biopsy device and biopsy robot
InactiveUS20090112119A1Easy to useAccurate samplingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy procedureNeedle localization
Embodiments of a needle biopsy device having a rotating needle mechanism to automatically cut sample tissue that can be operated remotely. A portable small biopsy robot can improve biopsy accuracy, reduce the pain and complications, and shorten the duration of the total biopsy time by using an automatic needle rotating mechanism and a needle localization system that allows a medical practitioner to perform the biopsy procedure from a remote distance. The needle biopsy device can include a cannula and a rotational biopsy needle with a blade the rotational biopsy needle axially and rotatably moveable within the cannula lumen, the blade configured to remove, cut, and / or separate a tissue sample from the target tissue site through rotation of the blade, and to hold the tissue sample in the rotational biopsy needle during proximal retraction from the patient.
Owner:KIM STANLEY I
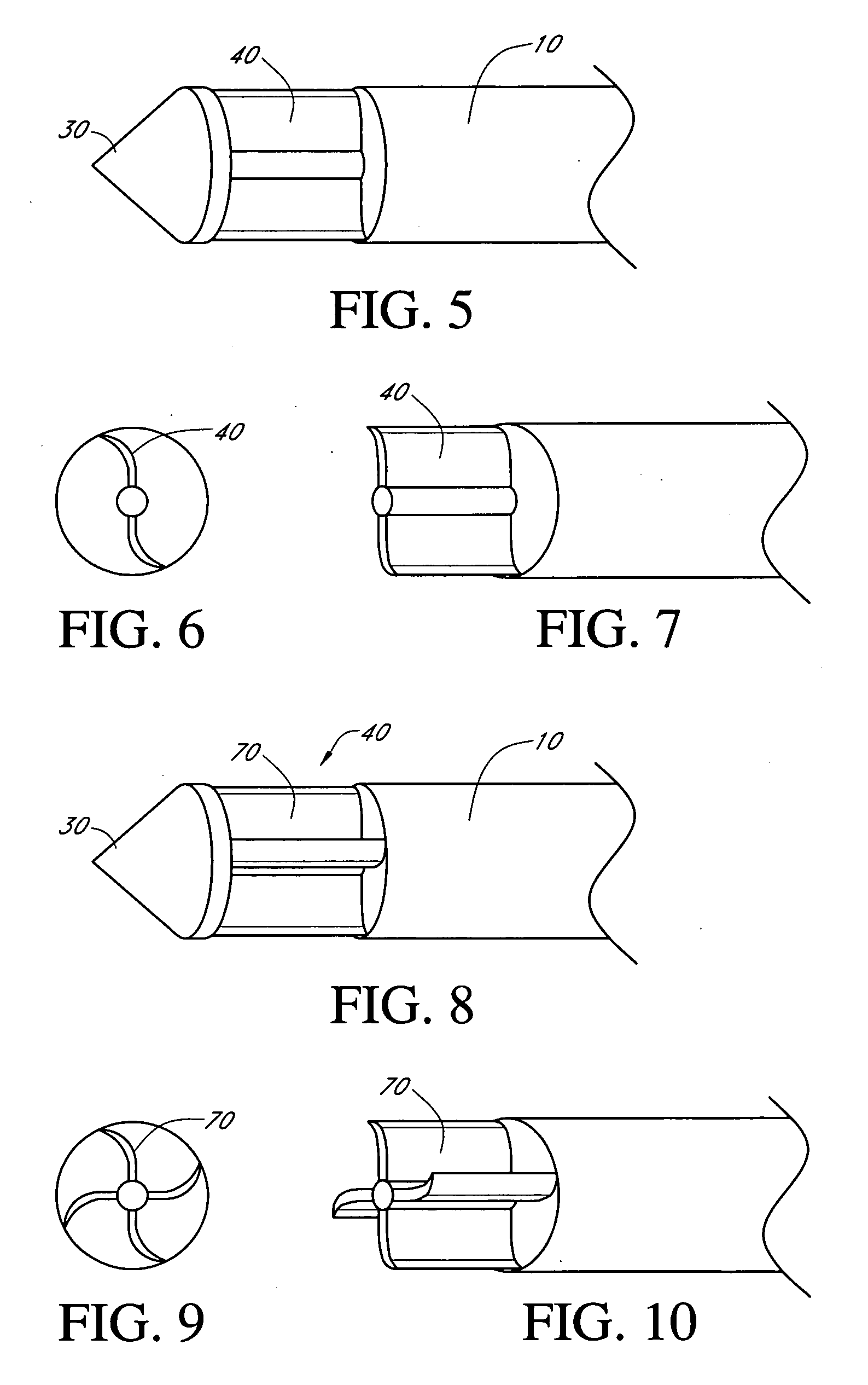
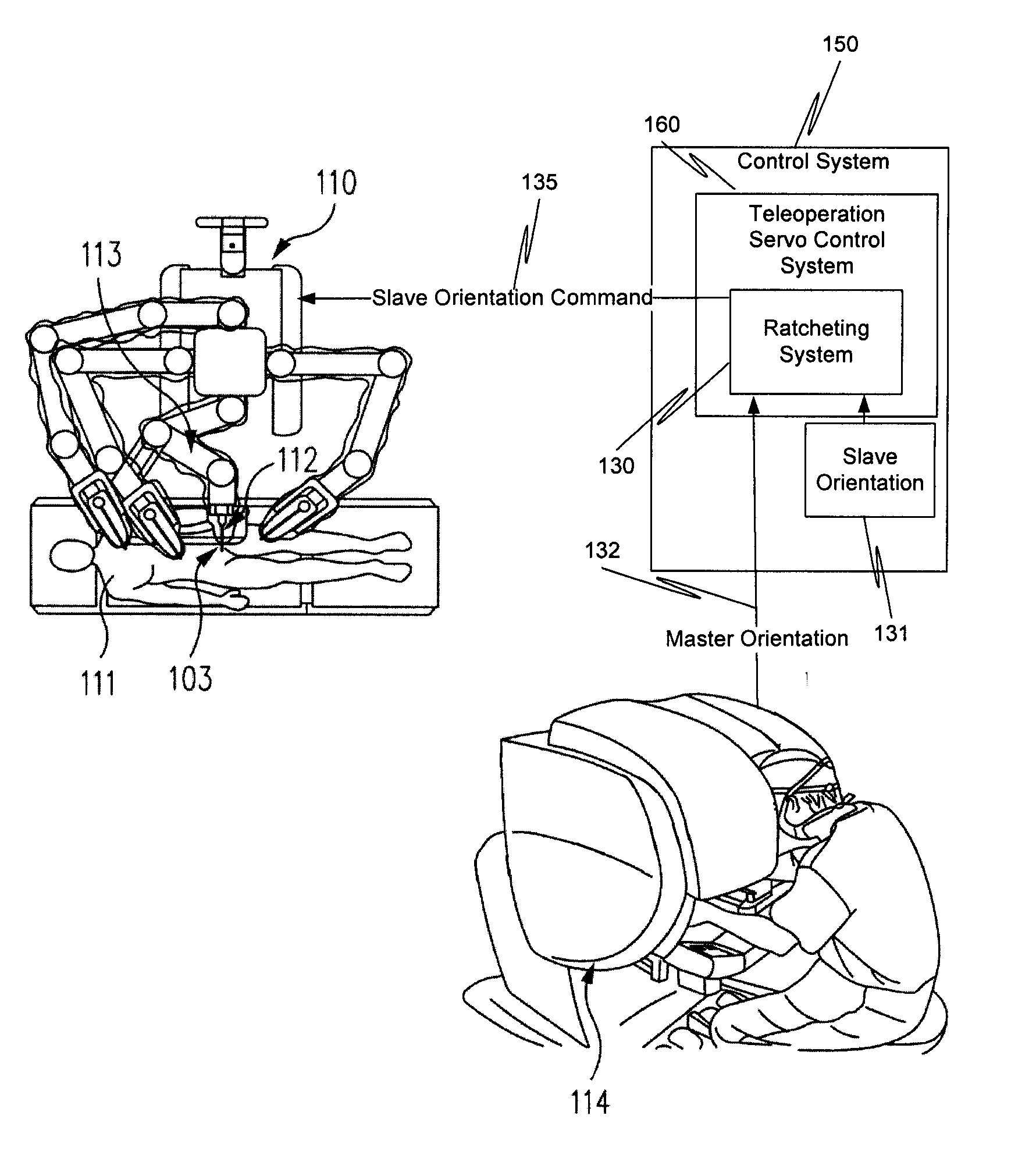
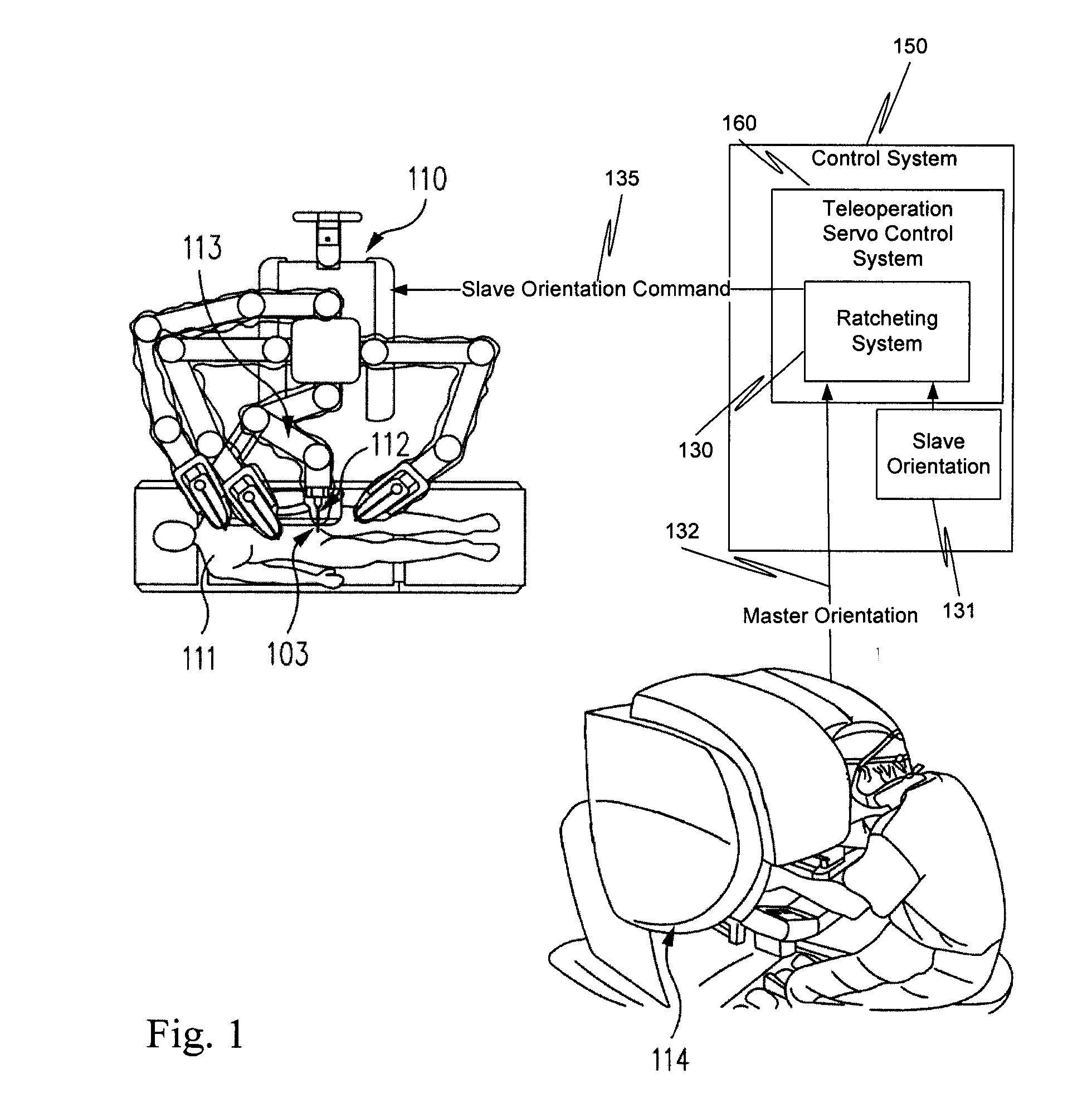
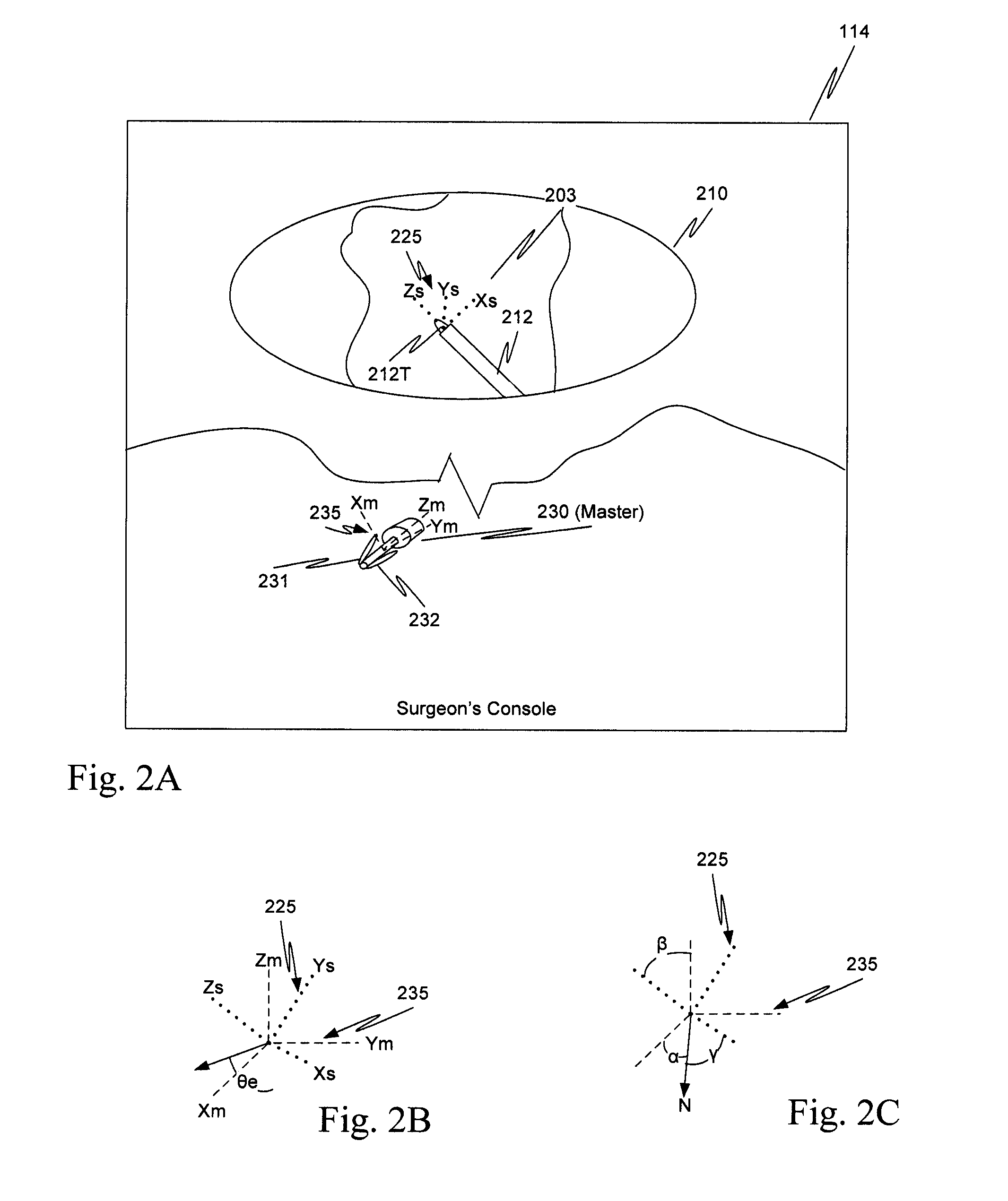
Ratcheting for master alignment of a teleoperated minimally-invasive surgical instrument
ActiveUS20100332031A1Easy alignmentLow costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorLess invasive surgeryEngineering
A minimally-invasive surgical system includes a slave surgical instrument having a slave surgical instrument tip and a master grip. The slave surgical instrument tip has an alignment in a common frame of reference and the master grip, which is coupled to the slave surgical instrument, has an alignment in the common frame of reference. An alignment error, in the common frame of reference, is a difference in alignment between the alignment of the slave surgical instrument tip and the alignment of the master grip. A ratcheting system (i) coupled to the master grip to receive the alignment of the master grip and (ii) coupled to the slave surgical instrument, to control motion of the slave by continuously reducing the alignment error, as the master grip moves, without autonomous motion of the slave surgical instrument tip and without autonomous motion of the master grip.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Tele-robotic videoconferencing in a corporate environment
A business to business mobile teleconferencing system. The system includes a mobile robot that can be remotely operated from a remote station. Both the robot and the remote station may have a camera, a screen, a microphone and a speaker to conduct a teleconference between a user at the remote station and personnel located in viewing proximity of the robot.
Owner:JONATA SUB TWO INC +1
Remote control method for television and system for remotely controlling television by same
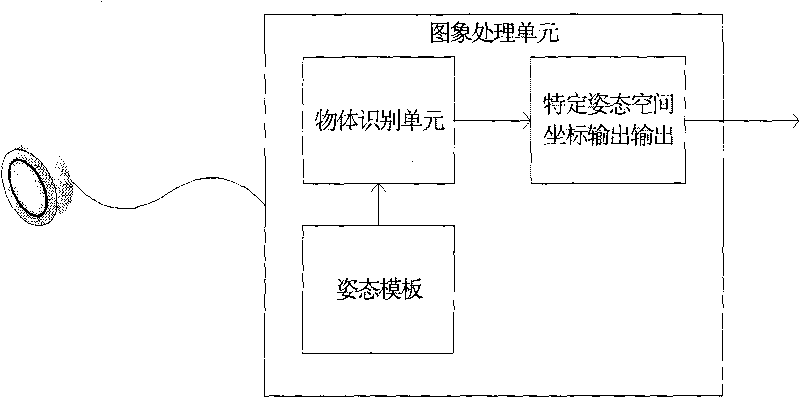
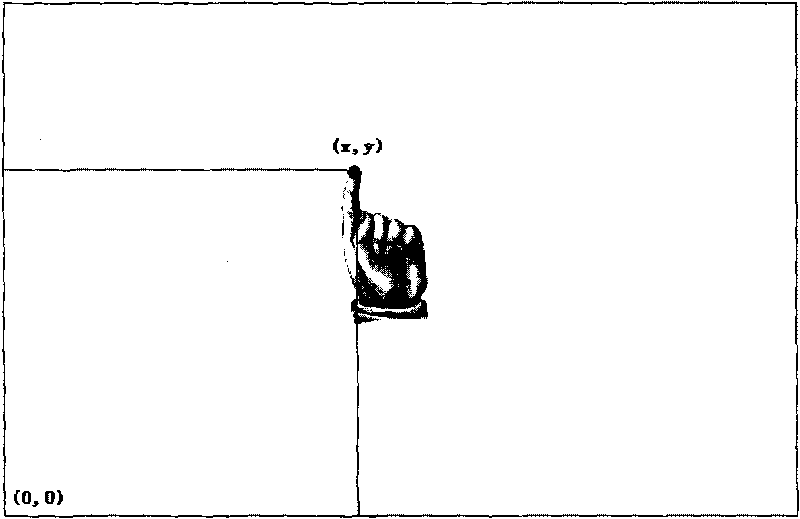
ActiveCN101729808ASimple and user-friendly remote control operationAdd entertainment functionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOperational systemRemote control
The invention discloses a remote control method for a television and a system for remotely controlling the television by same. The remote control method for the television is characterized by comprising the following steps: giving a specific gesture to a camera by an operator; transmitting the acquired specific gesture by the camera to a three-dimensional motion recognition module in the television for the three-dimensional motion and gesture recognition; acquiring three-dimensional motion coordinates of the specific gesture by the module, and outputting a control signal; executing corresponding programs according to the control signal by an executing device in the television. By utilizing the remote control method for the television, the remote control operation on the television can be performed by the gesture; and the remote control operation on the television becomes simpler and more humanized by means of a corresponding remote control operation system. In particular, the recreation functions which can be realized on a computer originally can be finished on the television without a mouse, a keyboard and other peripheral equipment of the computer based on the platform.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
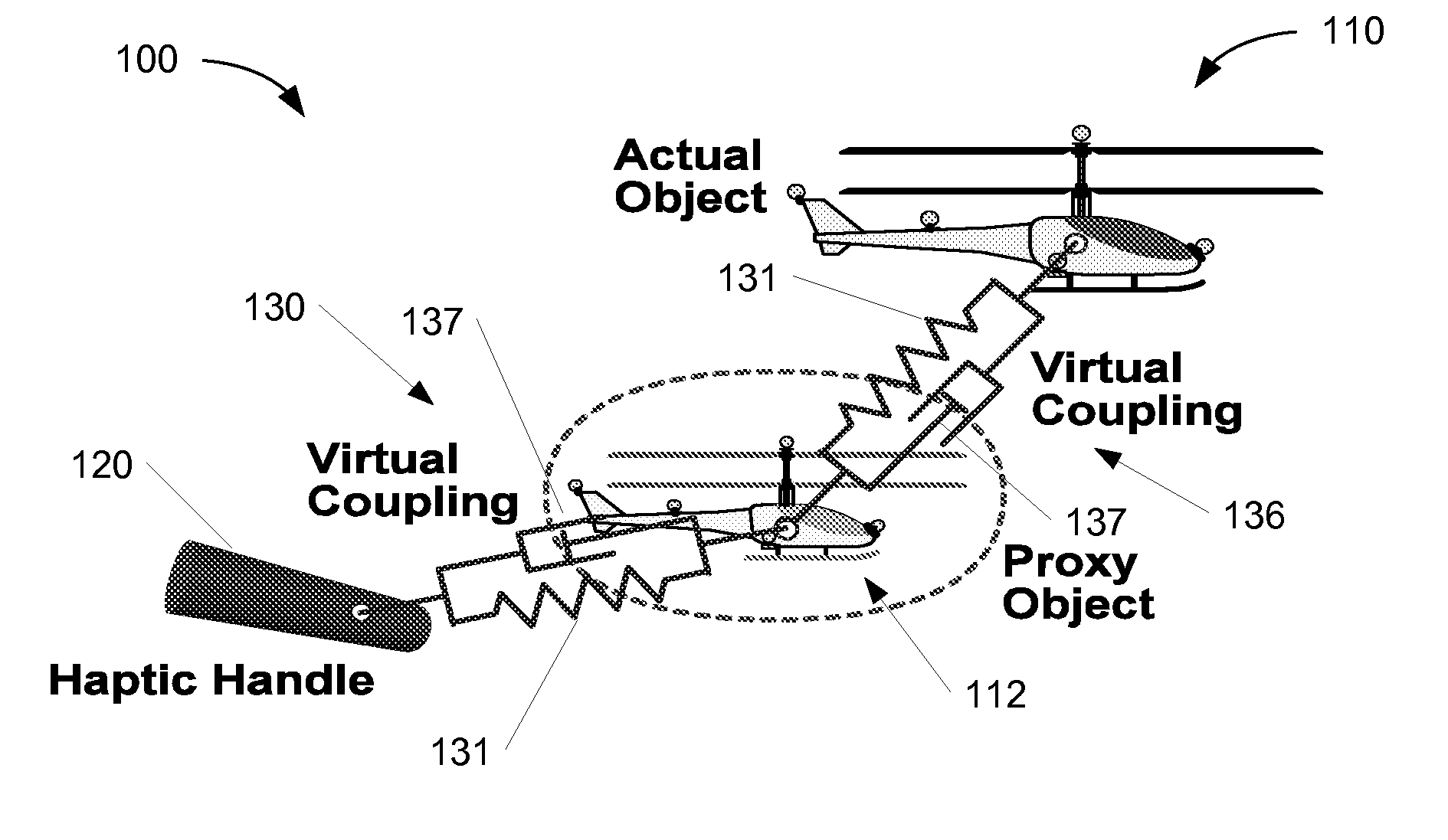
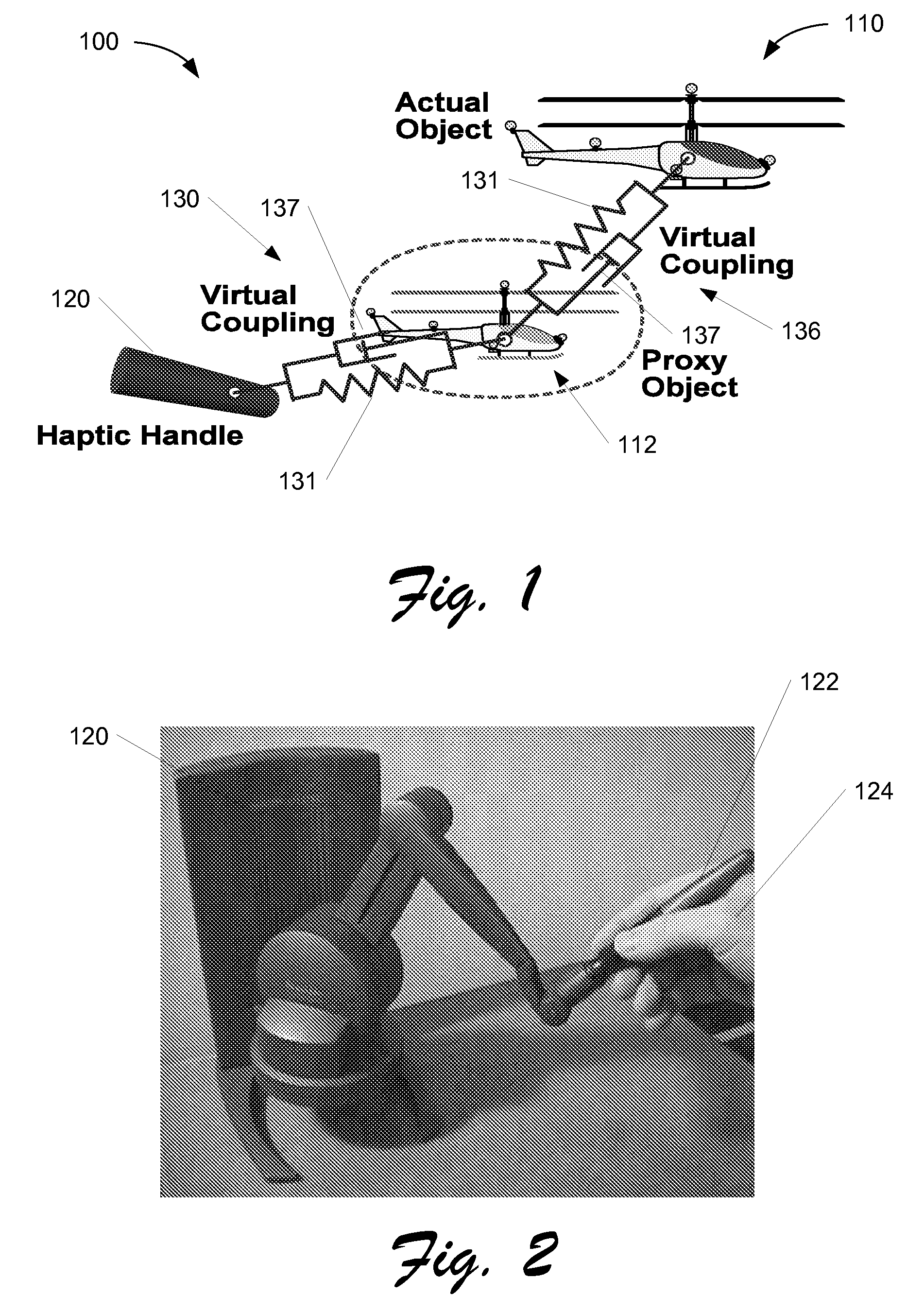
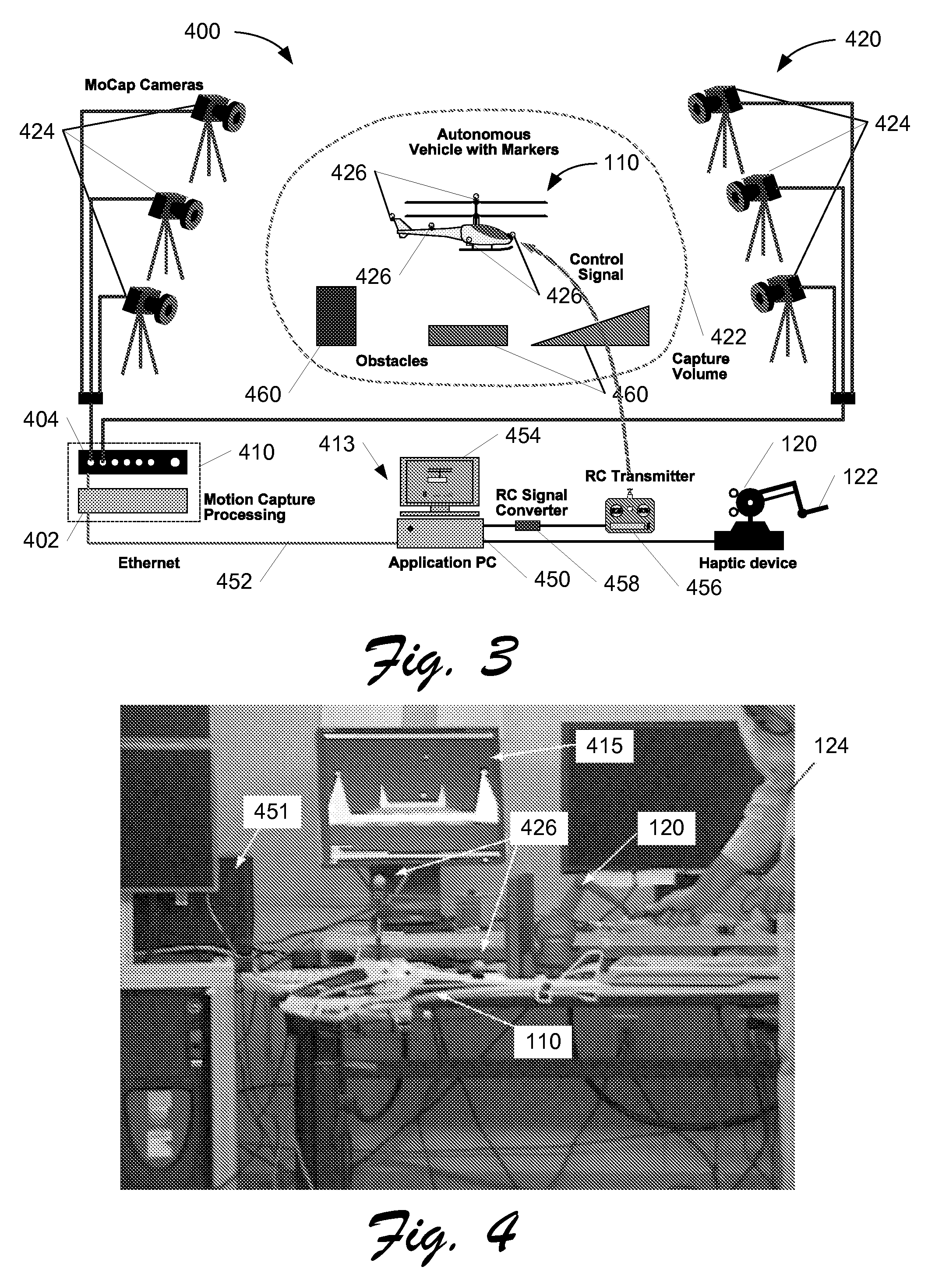
Systems and Methods for Haptics-Enabled Teleoperation of Vehicles and Other Devices
ActiveUS20080103639A1Easy to controlReduce capacityInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsLand basedClosed loop feedback
Systems and methods are disclosed for haptics-enabled teleoperation of vehicles and other devices, including remotely-controlled air, water, and land-based vehicles, manufacturing robots, and other suitable teleoperable devices. In one embodiment, a system for teleoperation of a vehicle comprises a control component configured to provide position and orientation control with haptic force feedback of the vehicle based on a position measurement of the vehicle and configured to function in a closed-loop feedback manner. In a particular embodiment, the position measurement may include six degree-of-freedom position data provided by a motion capture system to the control and / or haptic I / O components of the application. The system may also use differences in position and / or velocity between the vehicle and a haptic I / O device for feedback control.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Portable wireless remote monitoring and control systems
ActiveUS9769420B1Easy to installEasy to set upComputer controlHybrid transportSensor arrayThe Internet
A user-programmable portable wireless remote monitoring system includes a base unit, a series of sensor units and a remote control device. The base unit is connected to the internet, and receives wireless alerts from sensor arrays deployed in the sensor units. When the sensor units detect a problem, then they send an alert to the base unit, which then relays the alert to the remote control device that is preferably a smart phone, tablet, or the like, including software for operating the system. The system may also incorporate smart outlets that are remotely operable by the remote control device, various monitors, a touchscreen, and wearable tracking devices to monitor a person within the home. The system is designed to provide security, home system monitoring, personal medical monitoring, and remote control of various electrical appliances. The system may also be controlled by using oral commands.
Owner:MOSES THOMAS LAWRENCE
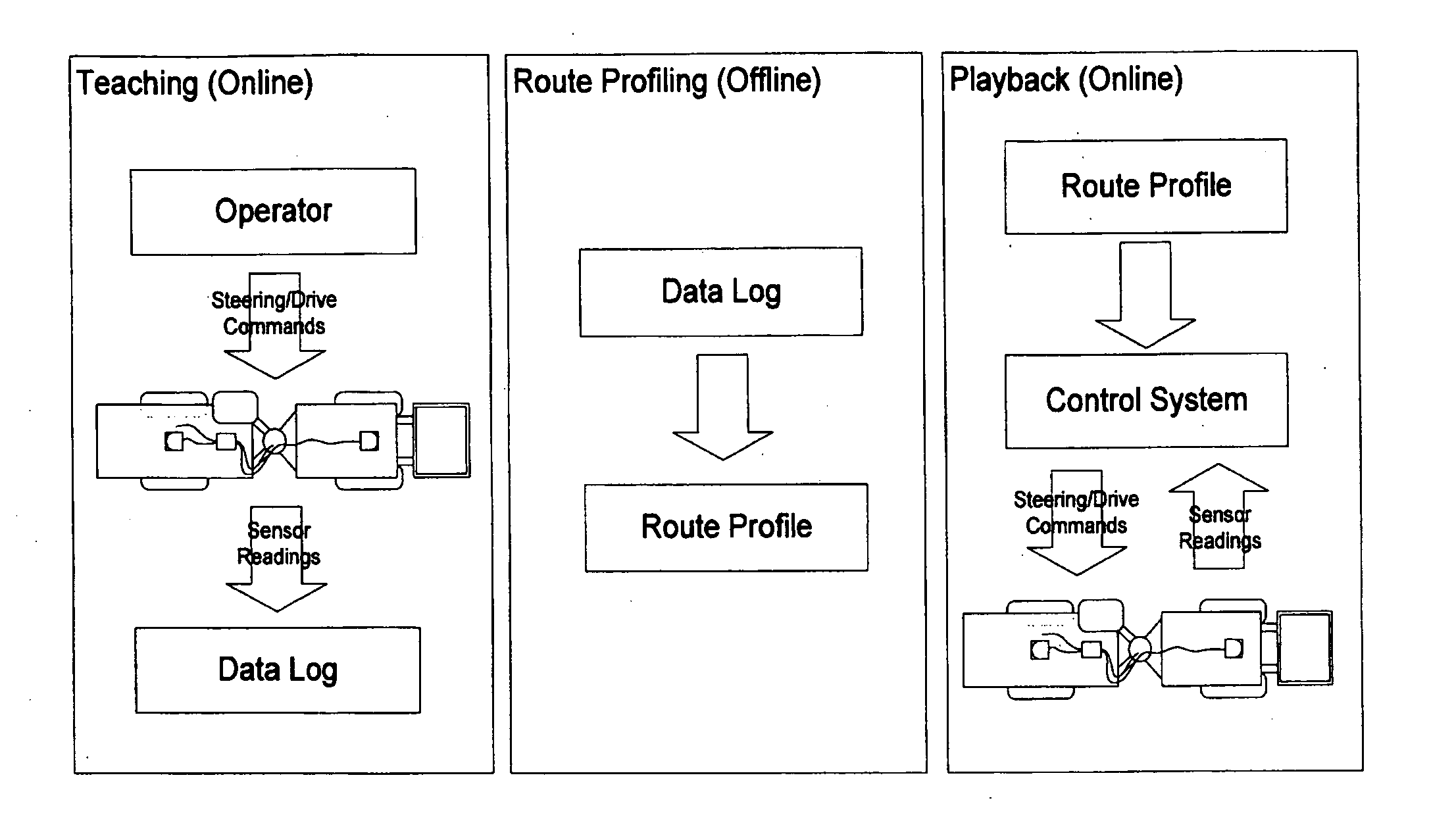
Guidance, Navigation, and Control System for a Vehicle
The present invention provides a guidance, navigation, and control method and system for an underground mining vehicle that allow said vehicle to be taught a route by a human operator and then have it automatically drive the route with no human intervention. The method works in three steps: teaching, route profiling, and playback. In the teaching step the vehicle is manually driven by a operator (or using tele-operation whereby the operator views a screen displaying live views from vehicle-mounted cameras and using remote controls) along a route which can consist of an arbitrary sequence of maneuvers including tramming forwards, switching directions, tramming backwards, turning, or pausing movement. During this phase raw data from vehicle-mounted sensors including odometric sensors and rangefinders are logged to a file throughout teaching for later processing. During the (offline) route profiling step, the raw data in the log file are processed into a route profile including a vehicle path, a sequence of local metric submaps located along the path, and a profile of desired speed as a function of distance along the path. During the playback step, the vehicle automatically repeats the route that was taught during the teaching phase, as represented by the route profile. This is accomplished by first determining where the vehicle is on the route using a localization method which uses the odometric and laser rangefinder sensors and the local metric maps to determine the vehicle location. A steering control method adjusts the vehicle's steering to ensure it tracks the intended path. A drive control method adjusts the vehicle's speed accordingly and safety method ensures the vehicle stops in the event that an obstruction is on the vehicle's intended path.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Method & apparatus for remotely operating a robotic device linked to a communications network
InactiveUS20090248200A1Programme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorTelecommunications linkRemote control
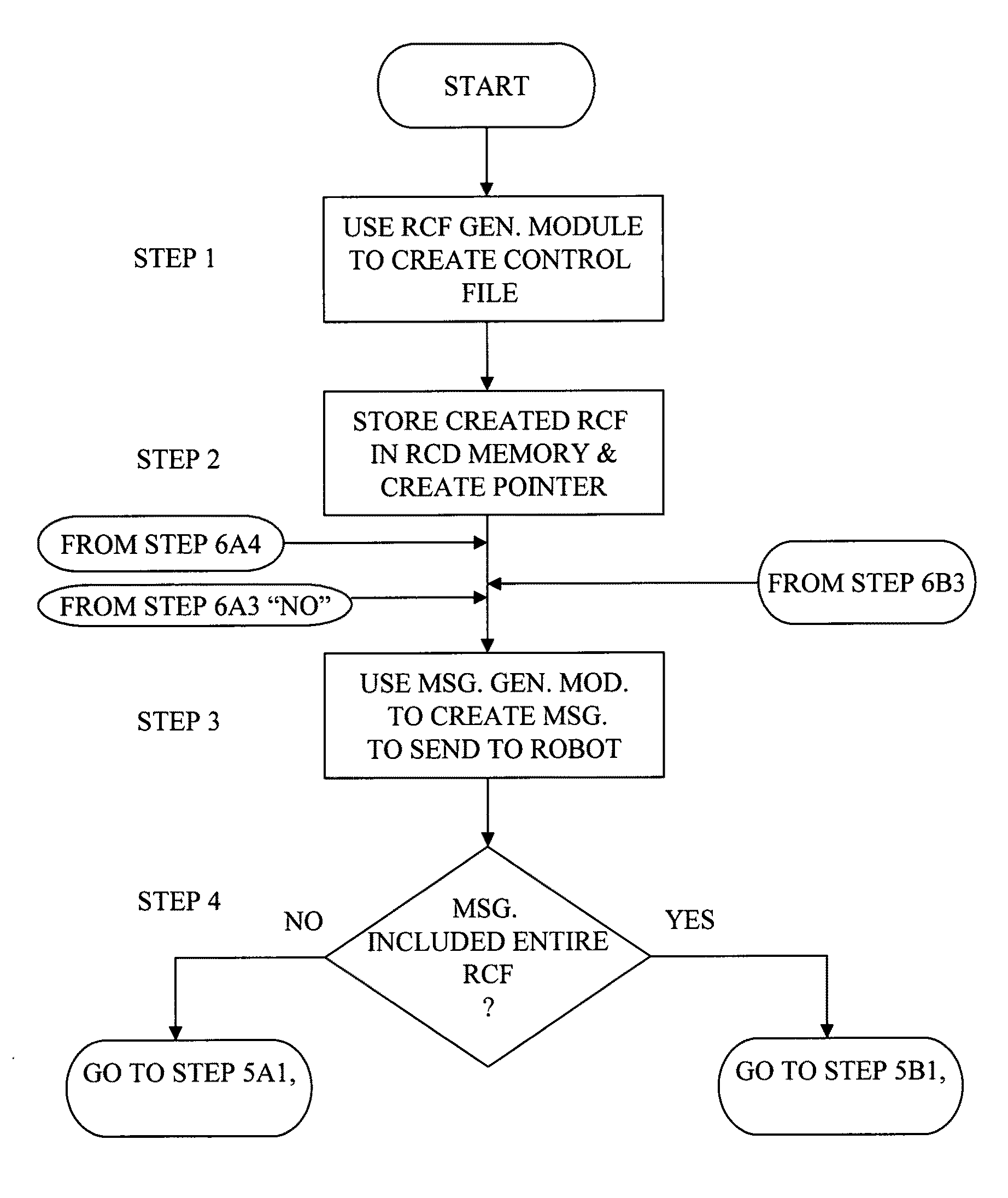
A remote control device able to connect to a communications network generates robot control messages are used for the remote control of a robot also able to be connected to the communications network. The remote control device creates a robot control file and an indirect reference to the robot control file which a user can select for inclusion in a robot control message. Once selected, the indirect reference to a robot control file causes the indirectly referenced robot control file to be included in a message generated by the remote control device. The remote control device establishes a communications link with the communications network, and sends the message, with the robot control file, to the robot also connected to the communications network. The robot receives the robot control message and performs at least one action according to the instruction included in the robot control message.
Owner:NORTH END TECH
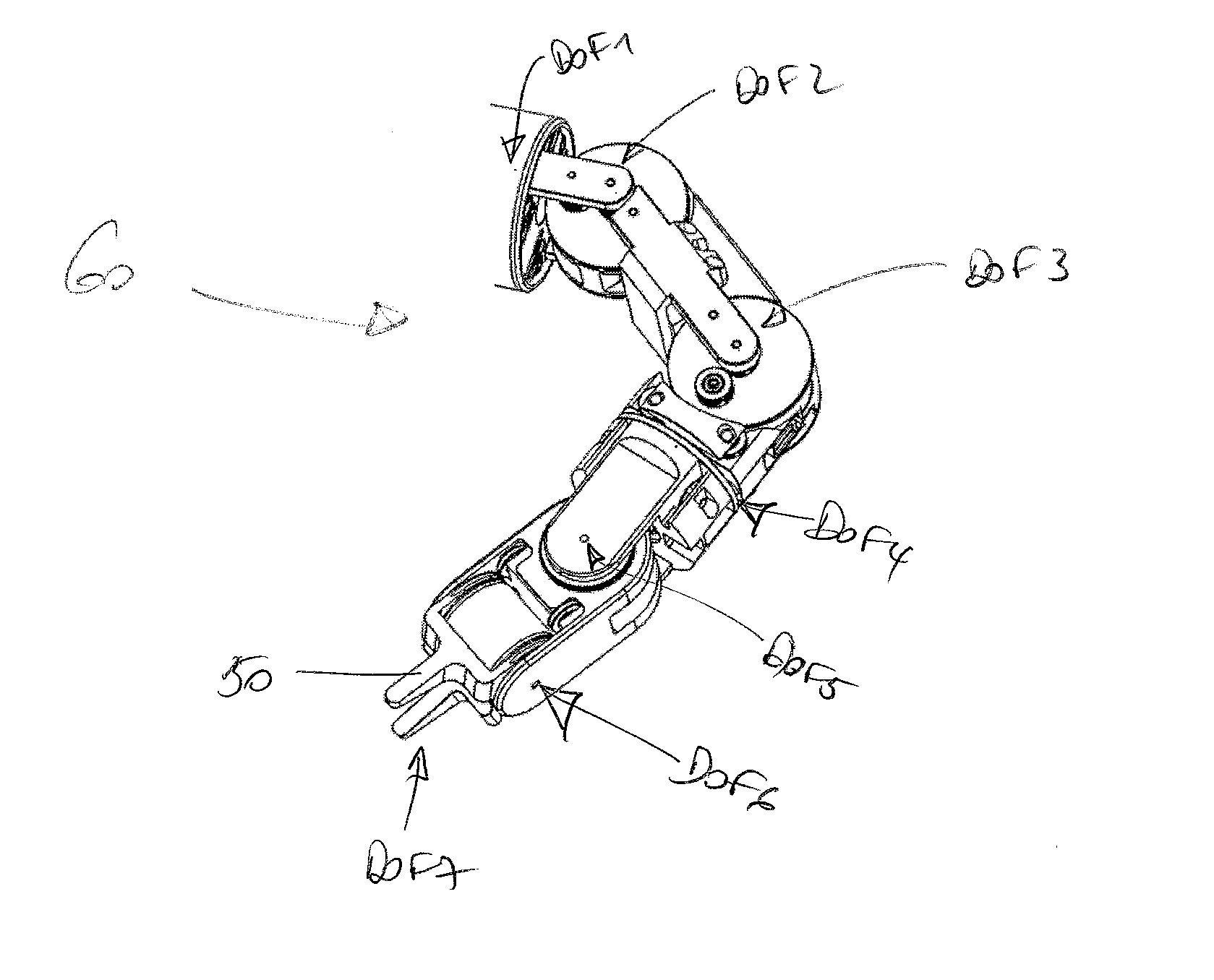
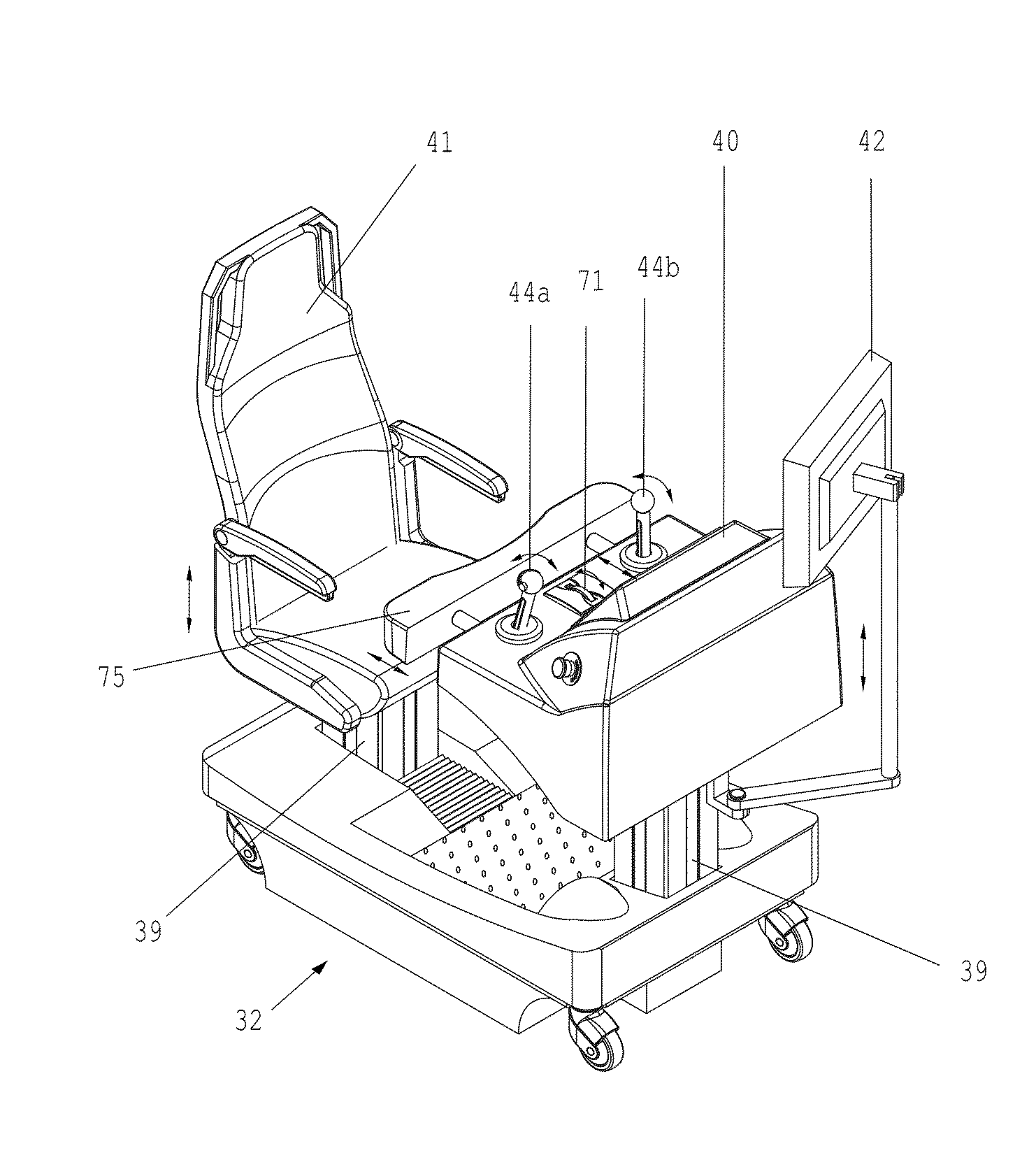
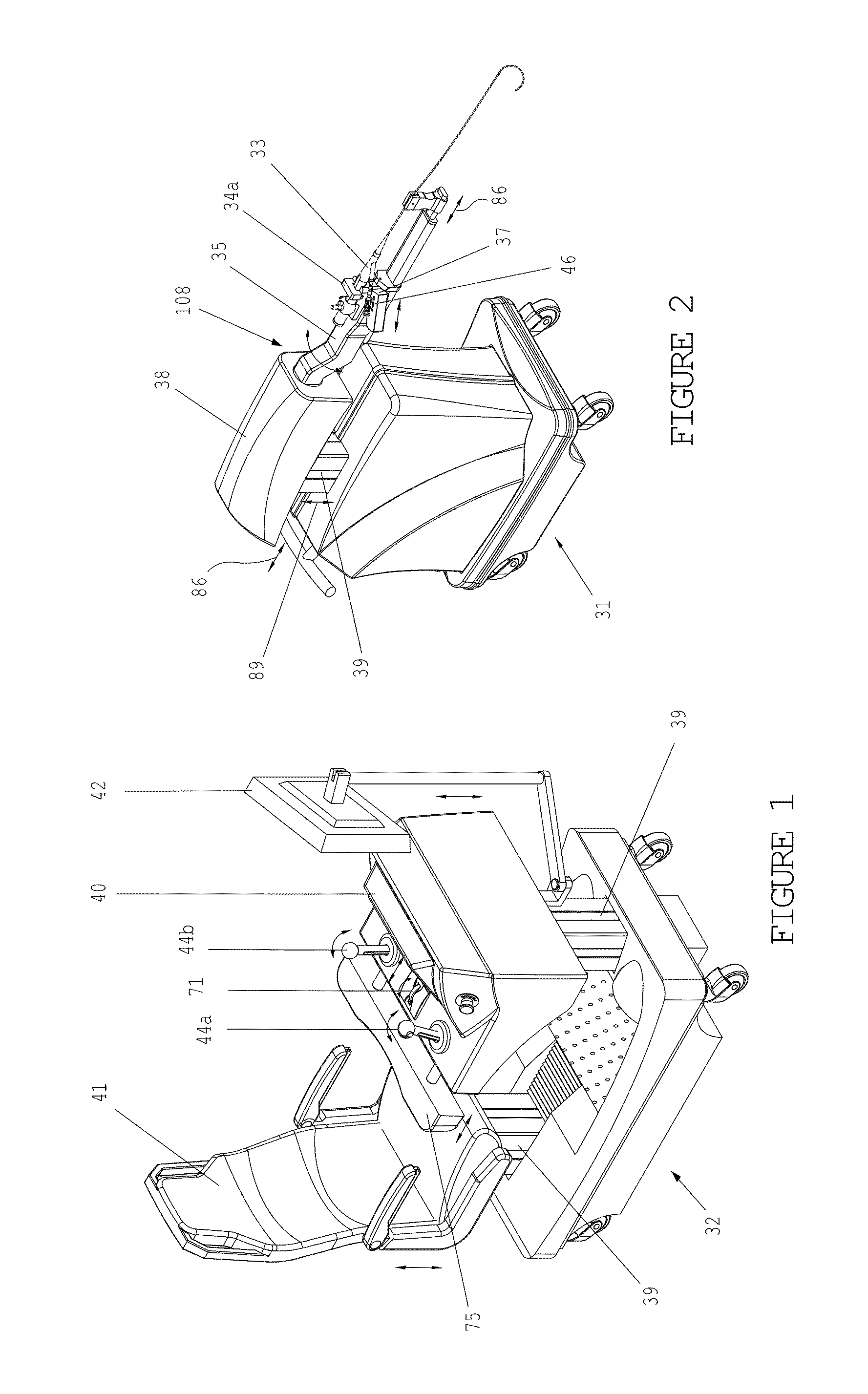
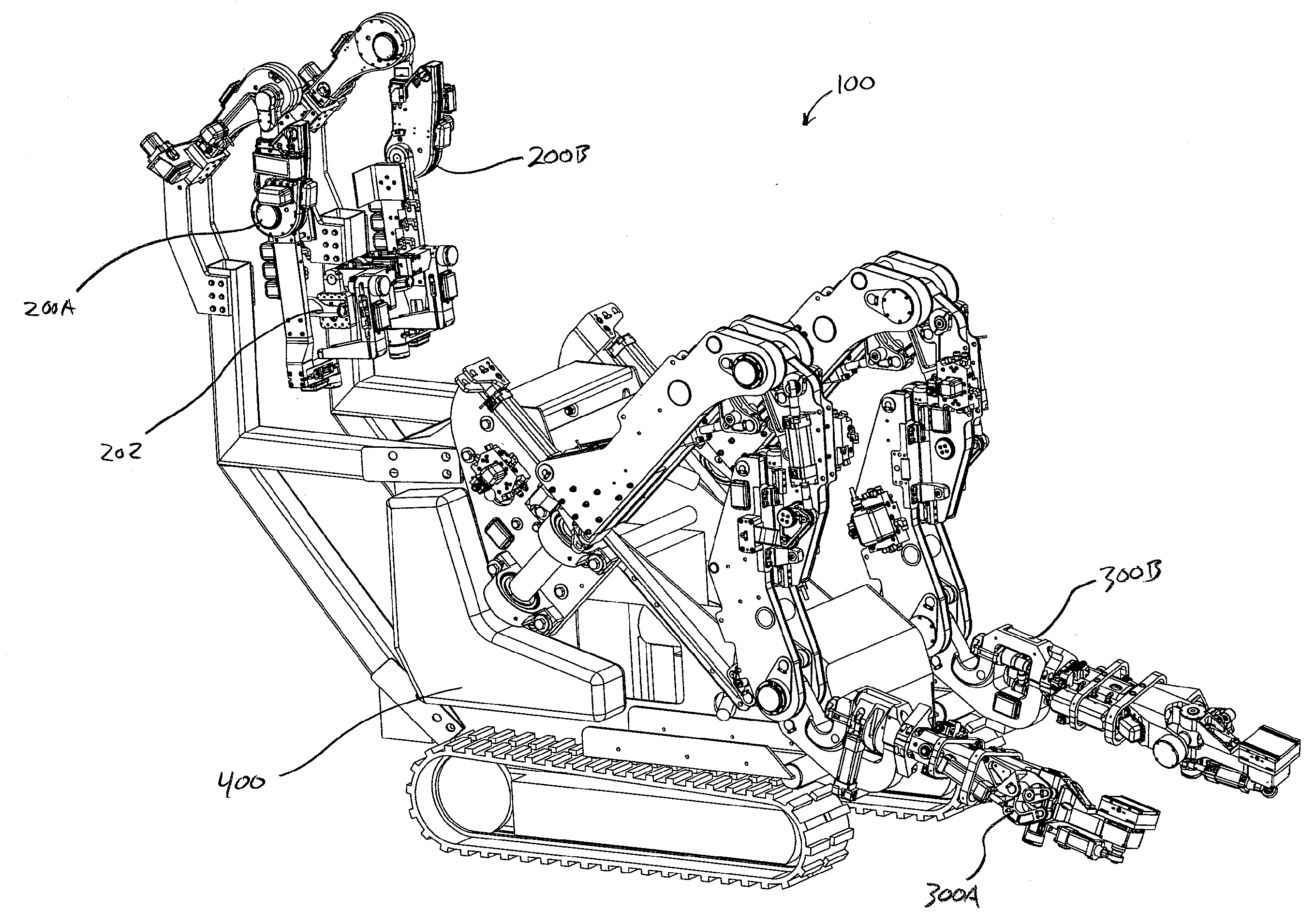
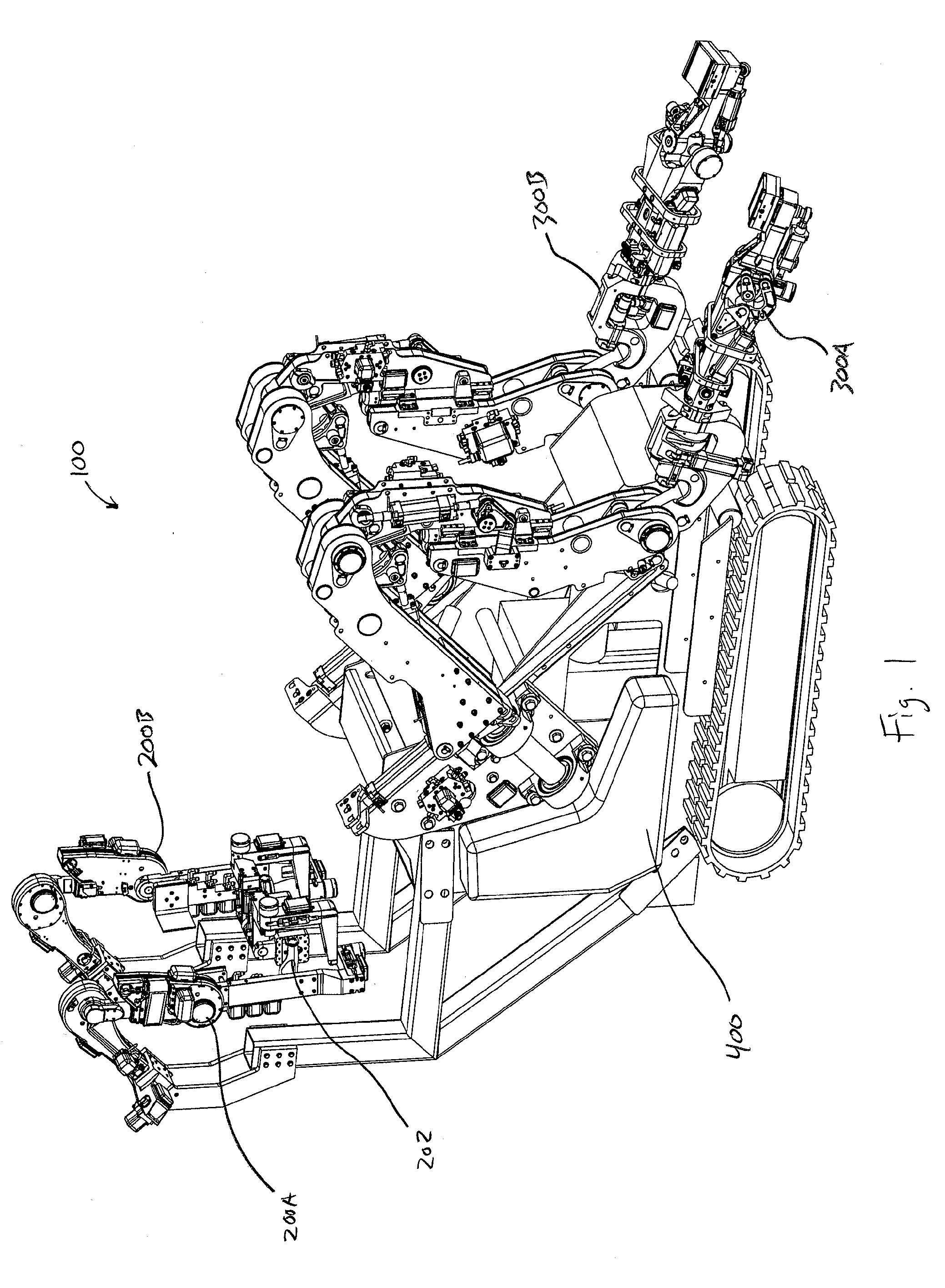
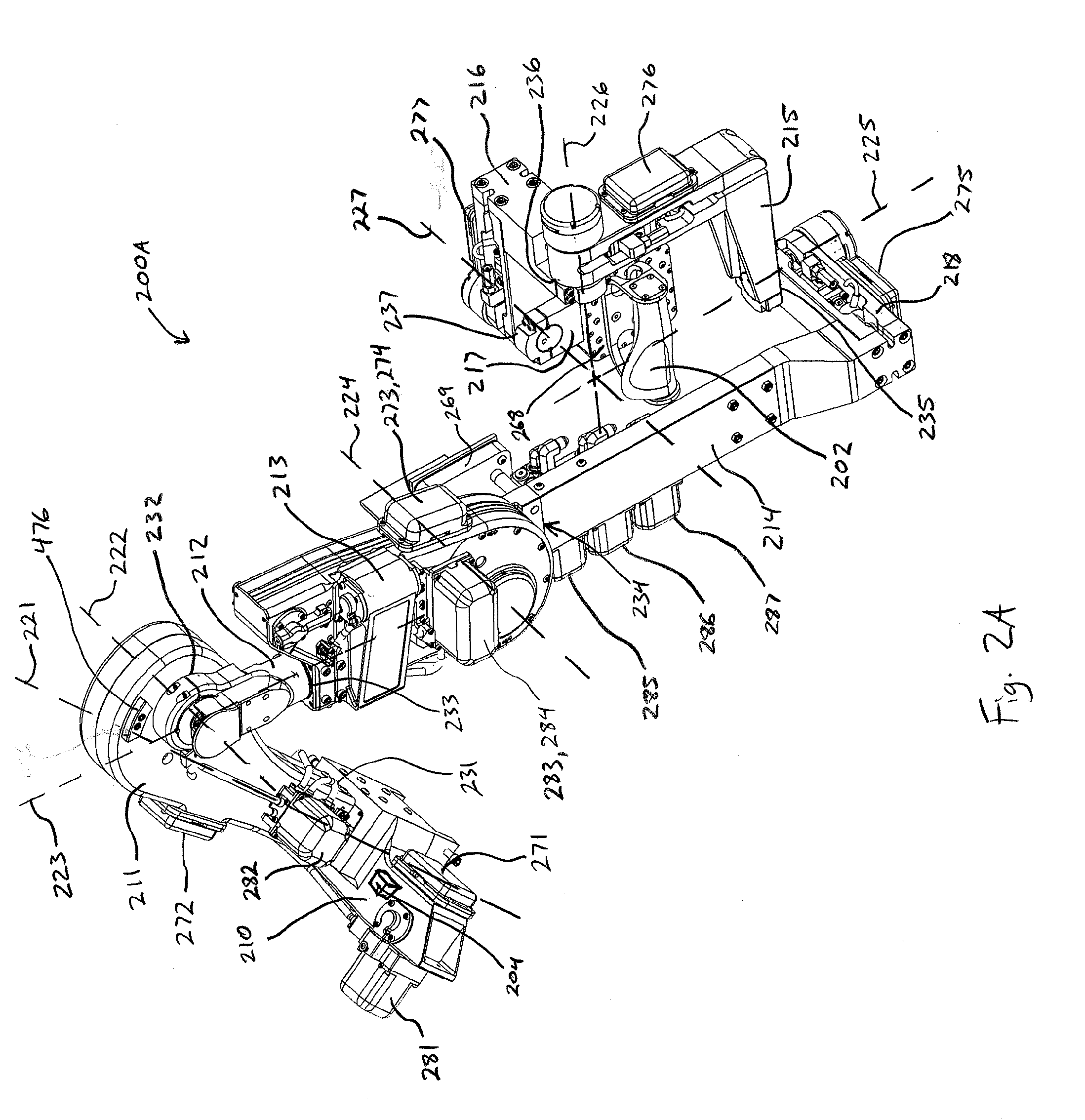
Teleoperated Robotic System
ActiveUS20120328395A1Programme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsTeleoperated robot
A teleoperated robotic system that includes master control arms, slave arms, and a mobile platform. In use, a user manipulates the master control arms to control movement of the slave arms. The teleoperated robotic system can include two master control arms and two slave arms. The master control arms and the slave arms can be mounted on the platform. The platform can provide support for the master control arms and for a teleoperator, or user, of the robotic system. Thus, a mobile platform can allow the robotic system to be moved from place to place to locate the slave arms in a position for use. Additionally, the user can be positioned on the platform, such that the user can see and hear, directly, the slave arms and the workspace in which the slave arms operate.
Owner:SARCOS LC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com