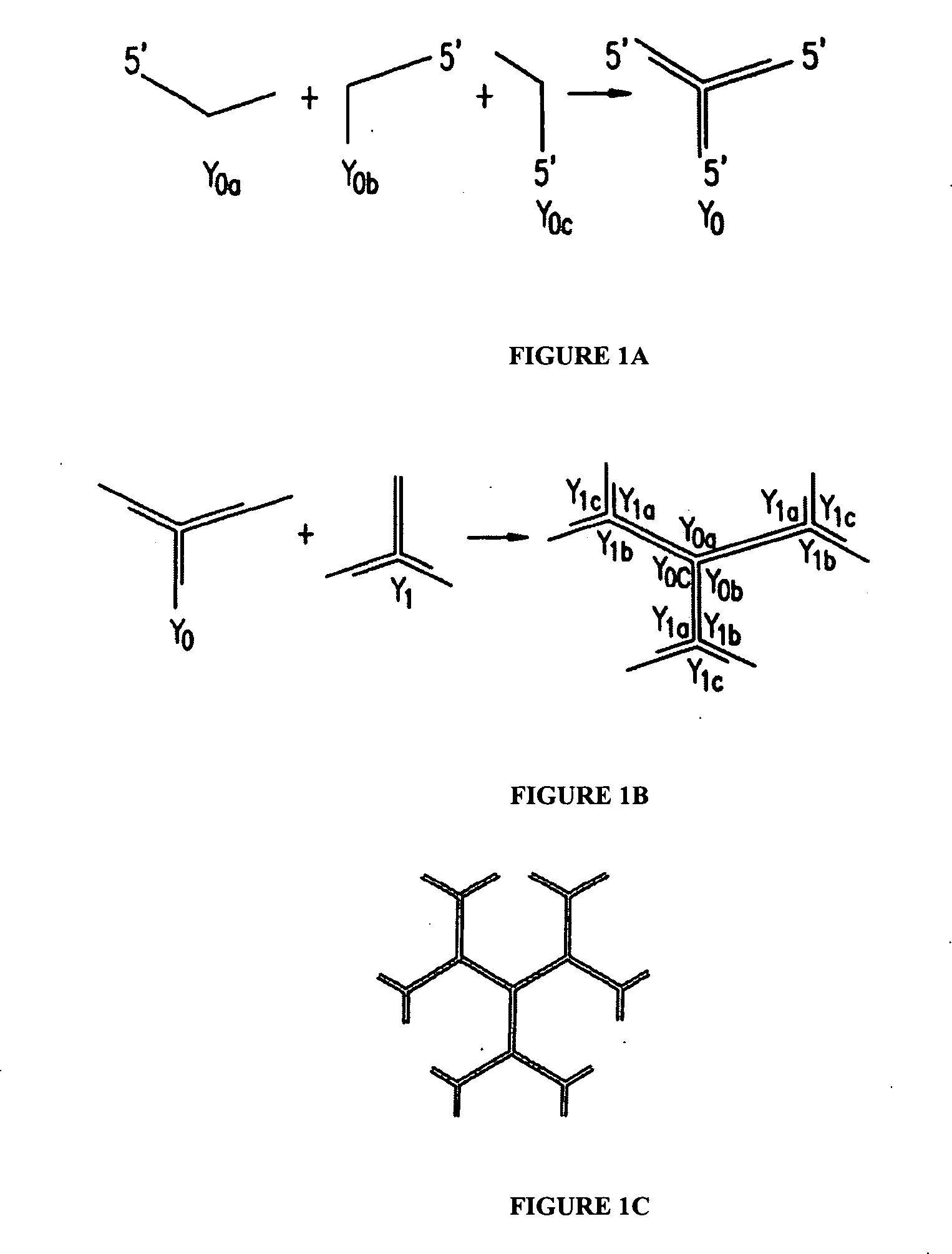
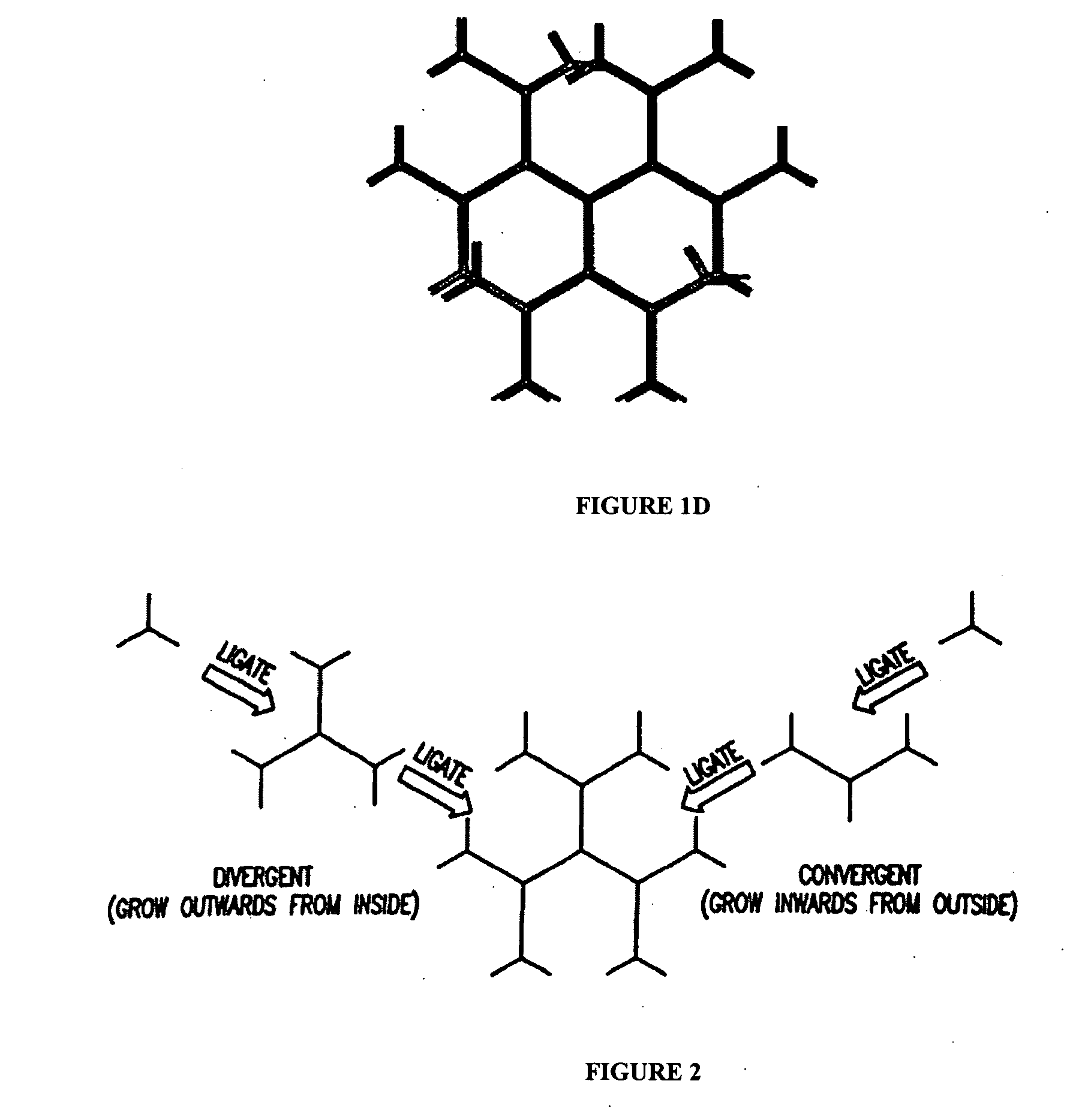
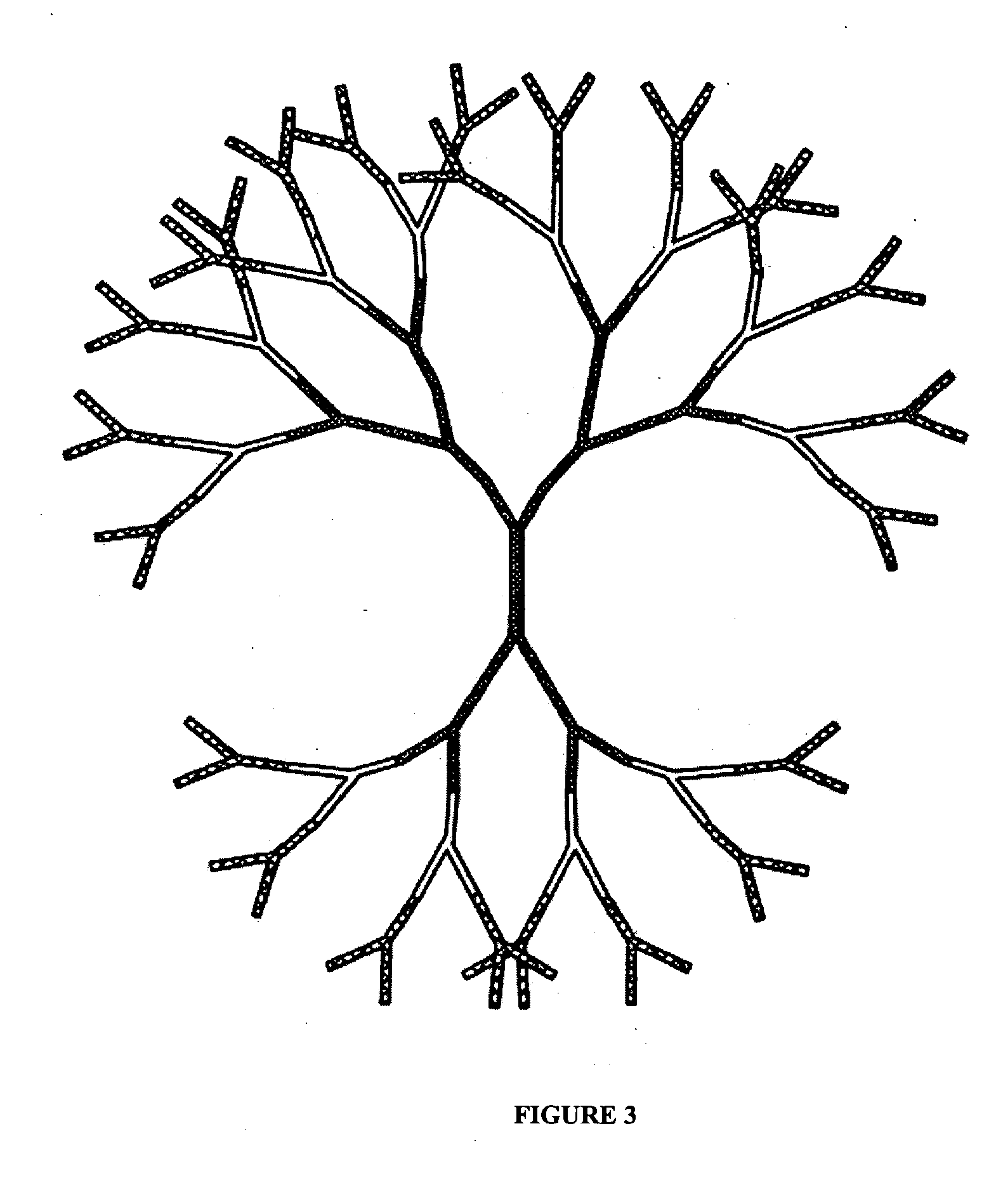
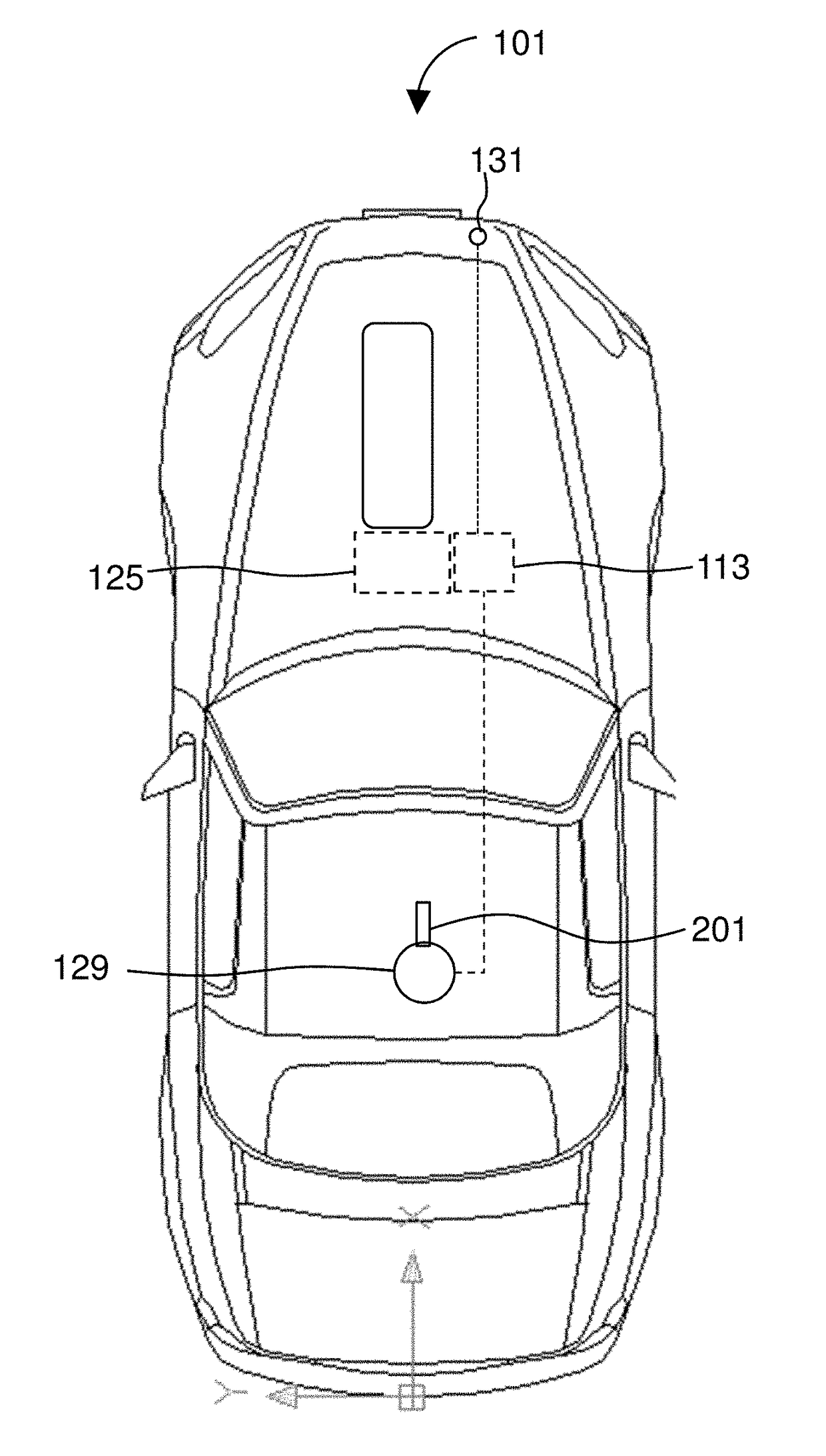
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
268results about How to "Detect presence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
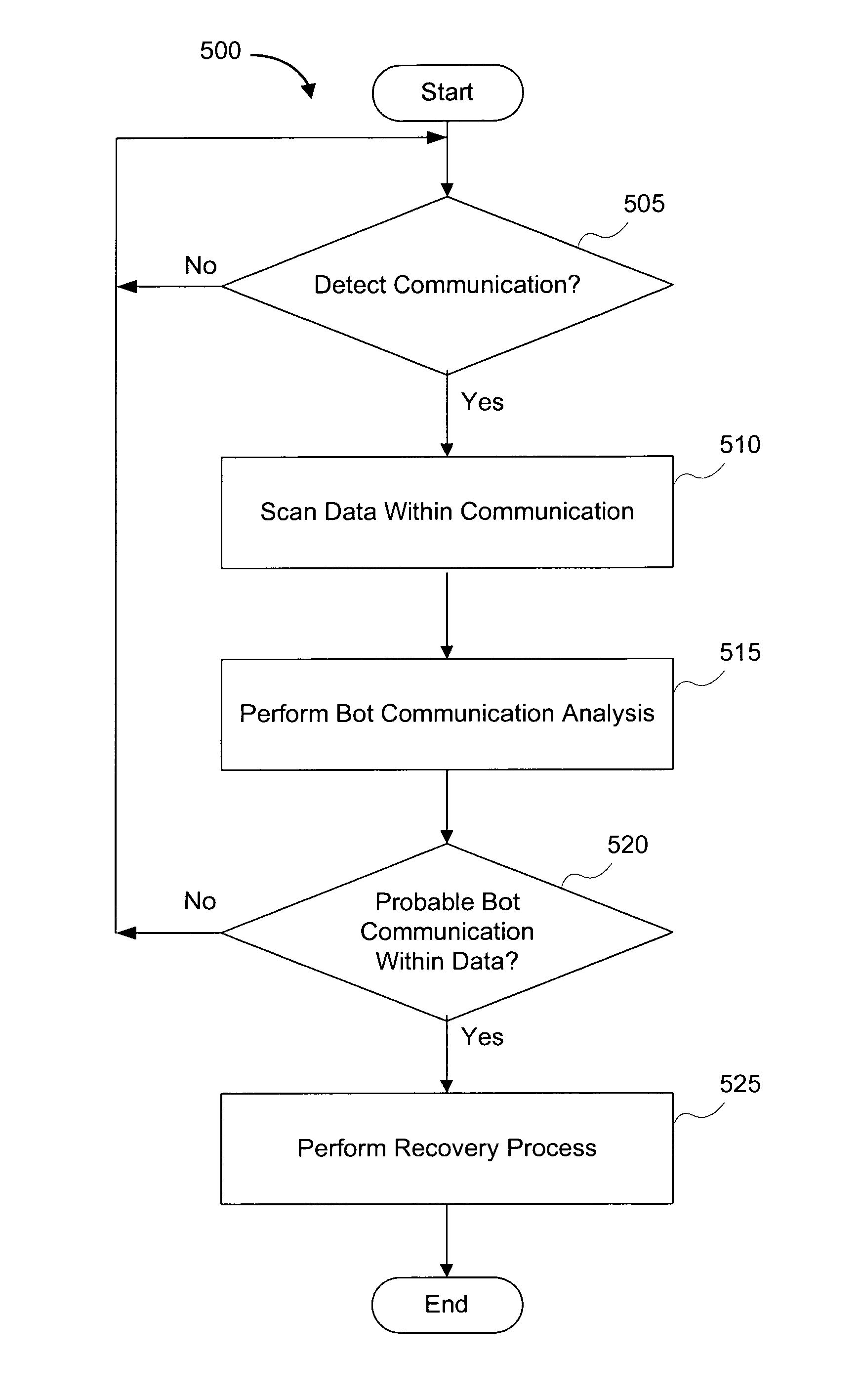
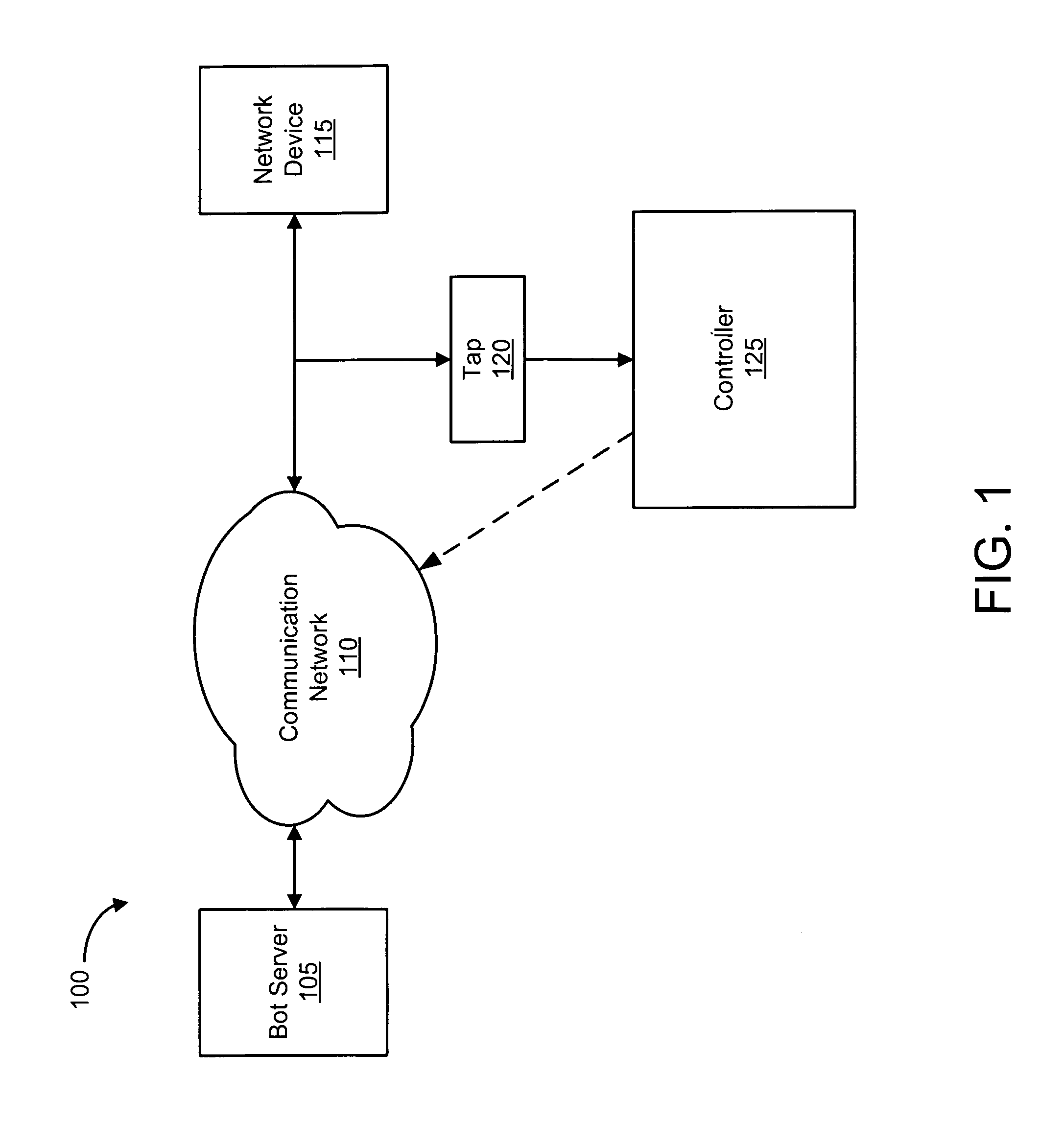
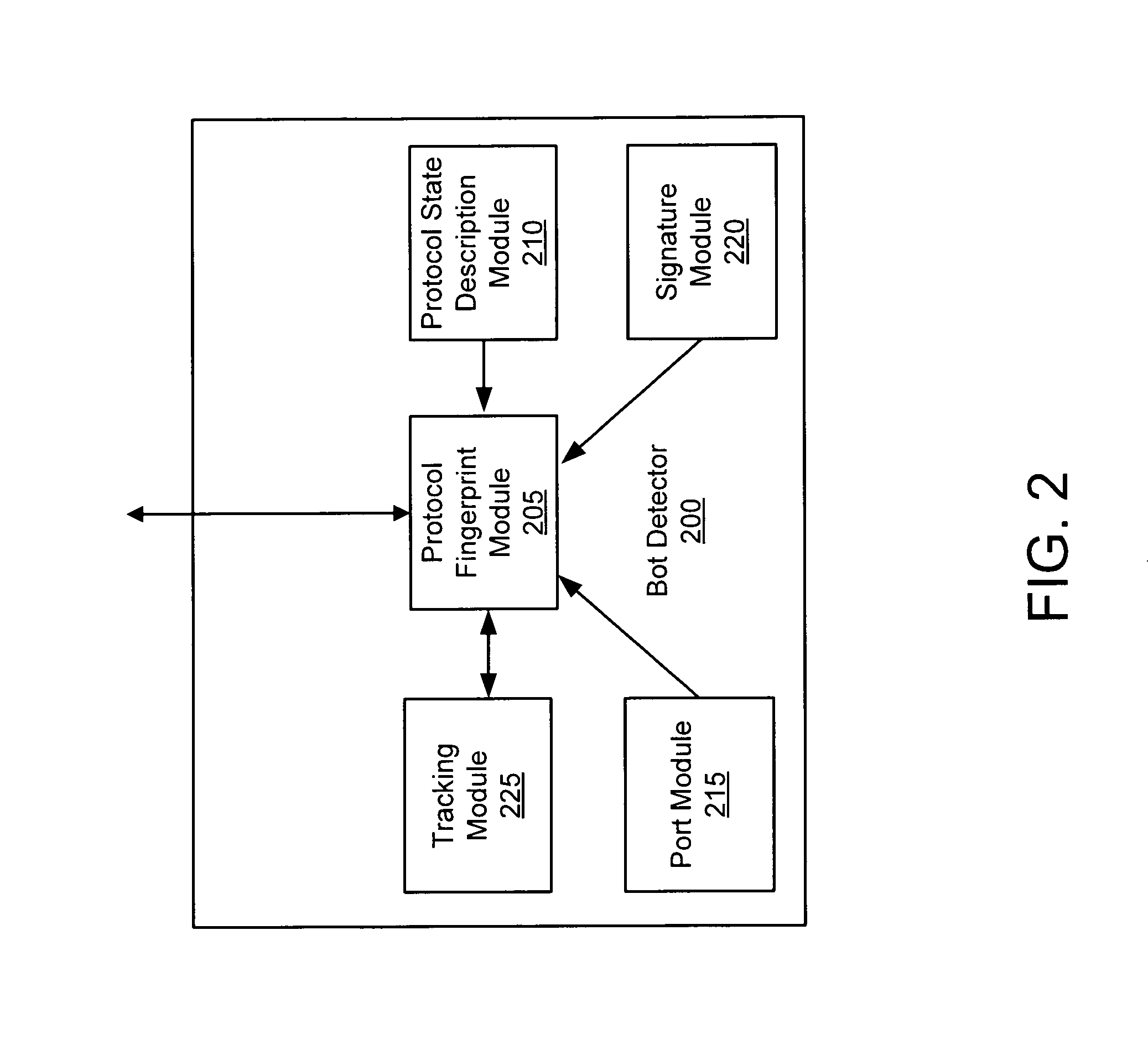
Systems and methods for detecting communication channels of bots
ActiveUS8561177B1Detect presenceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionBotnetComputer security
Exemplary systems and methods for detecting a communication channel of a bot. In exemplary embodiments, presence of a communication channel between a first network device and a second network device is detected. Data from the communication channel is scanned and used to determine if a suspected bot communication exists. If a bot communication is detected, then a recovery process may be initiated.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Wearable intravenous fluid heater
InactiveUS6175688B1Avoid contaminationReduce riskMedical devicesHeating element shapesTemperature controlEngineering
An intravenous fluid heater is provided that is dimensioned so as to be wearable adjacent a patient's intravenous fluid infusion situs. In one embodiment, the heater includes a heat exchanger for defining a flow path through the heater for fluid to be infused via the infusion situs. At least one controllable heating element is provided for heating the fluid in the flow path by heat conduction thereto through the heat exchanger. Sensors are included for sensing respective temperatures of entering and exiting fluids of the flow path. A controller controls, based upon the temperatures of the exiting fluids, heating of the fluid in the flow path by the heating element so as to cause the fluid in the flow path to be substantially uniformly heated to a desired infusion temperature prior to exiting the heater.
Owner:BELMONT INSTR LLC
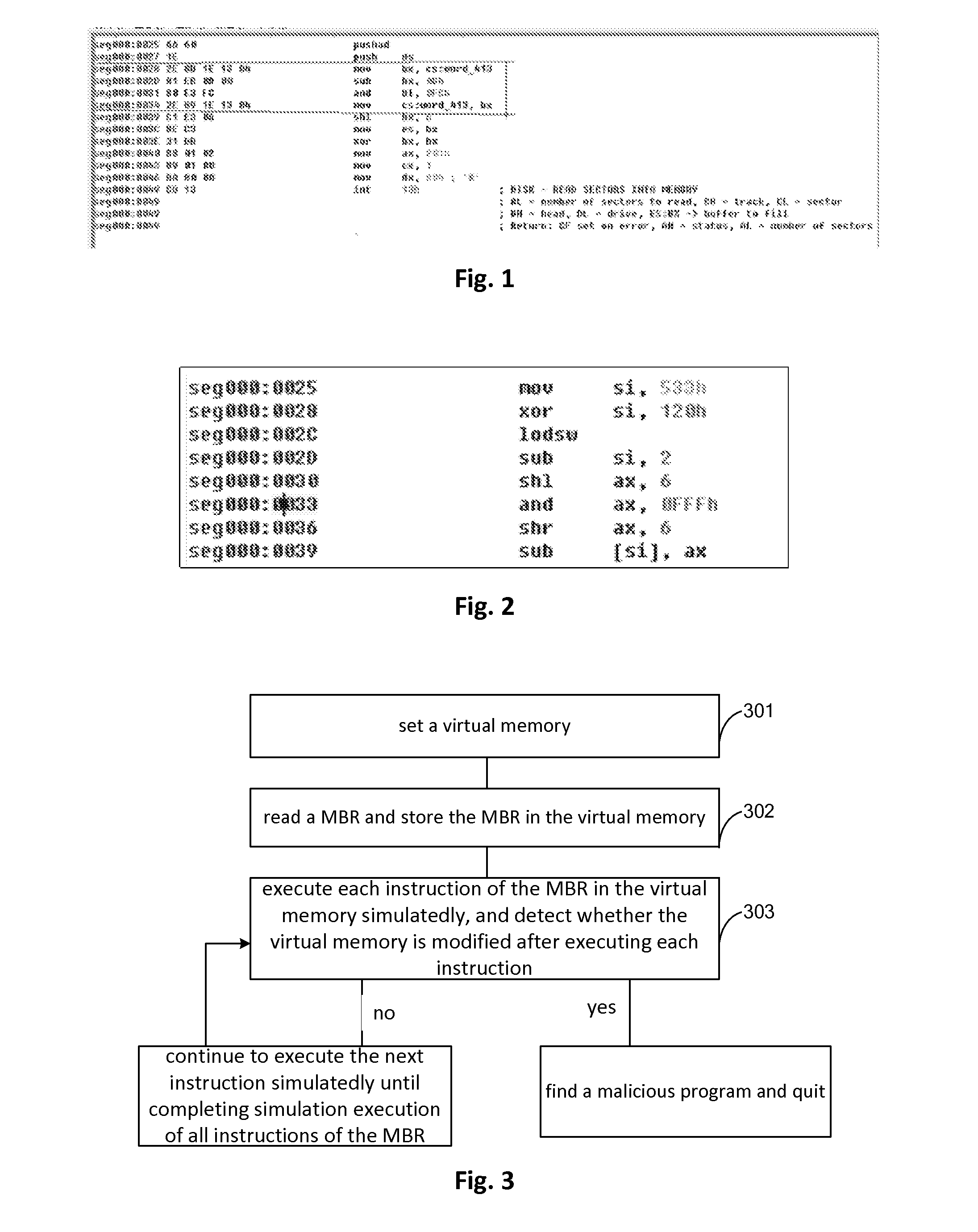
Method, apparatus and virtual machine for detecting malicious program
ActiveUS20140351935A1Detect presenceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionVirtual memoryVirtual storage
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD
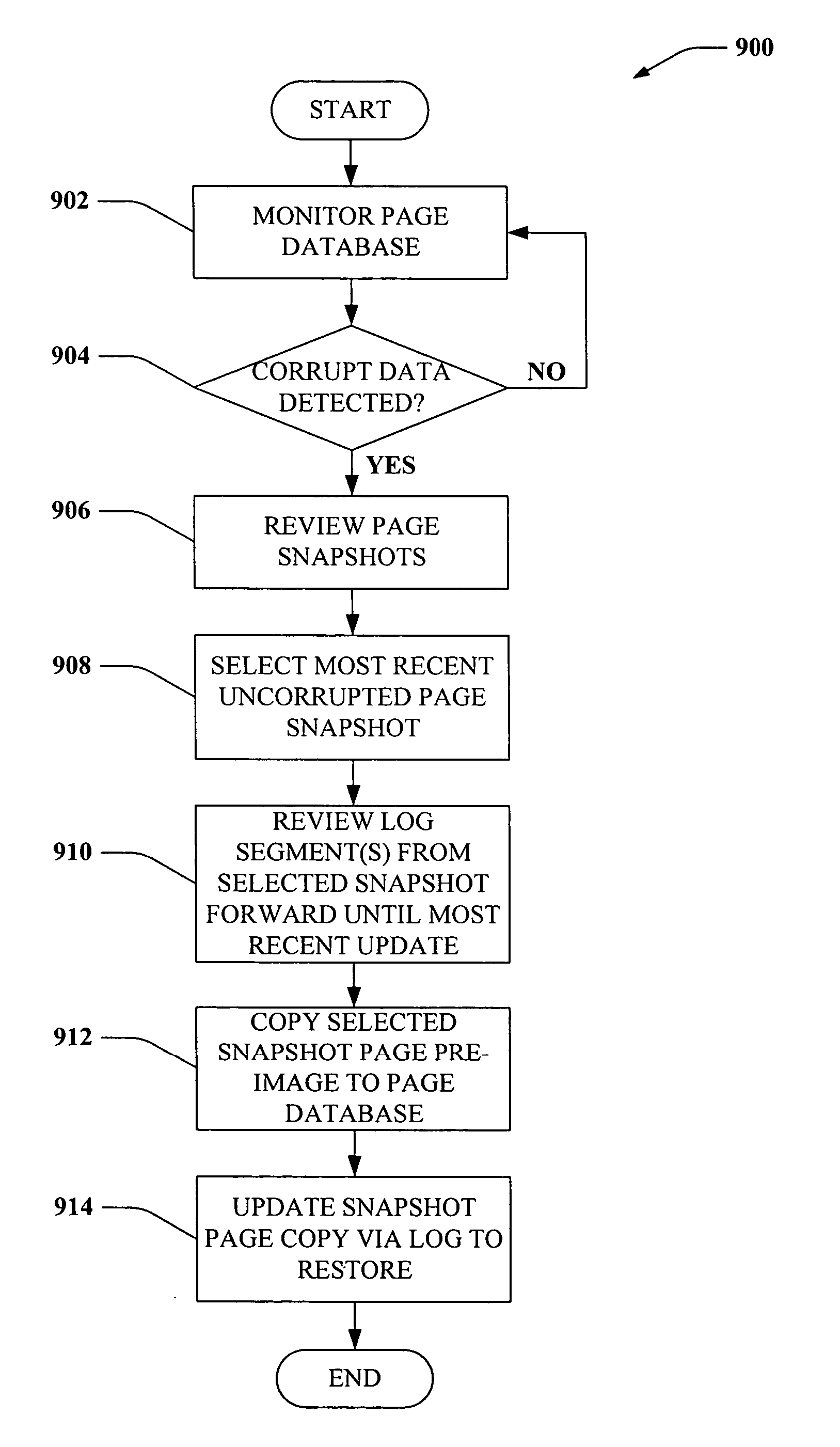
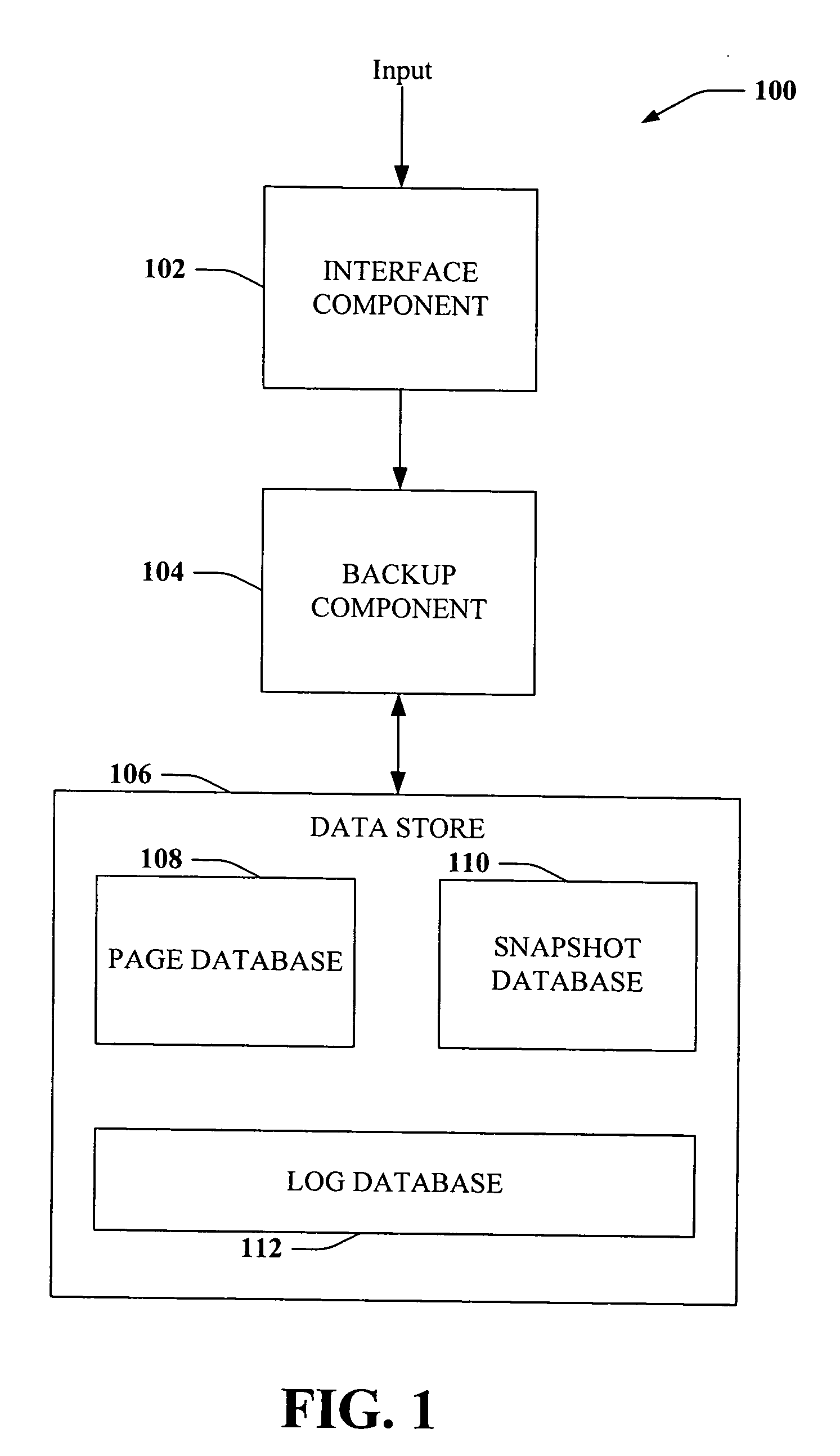
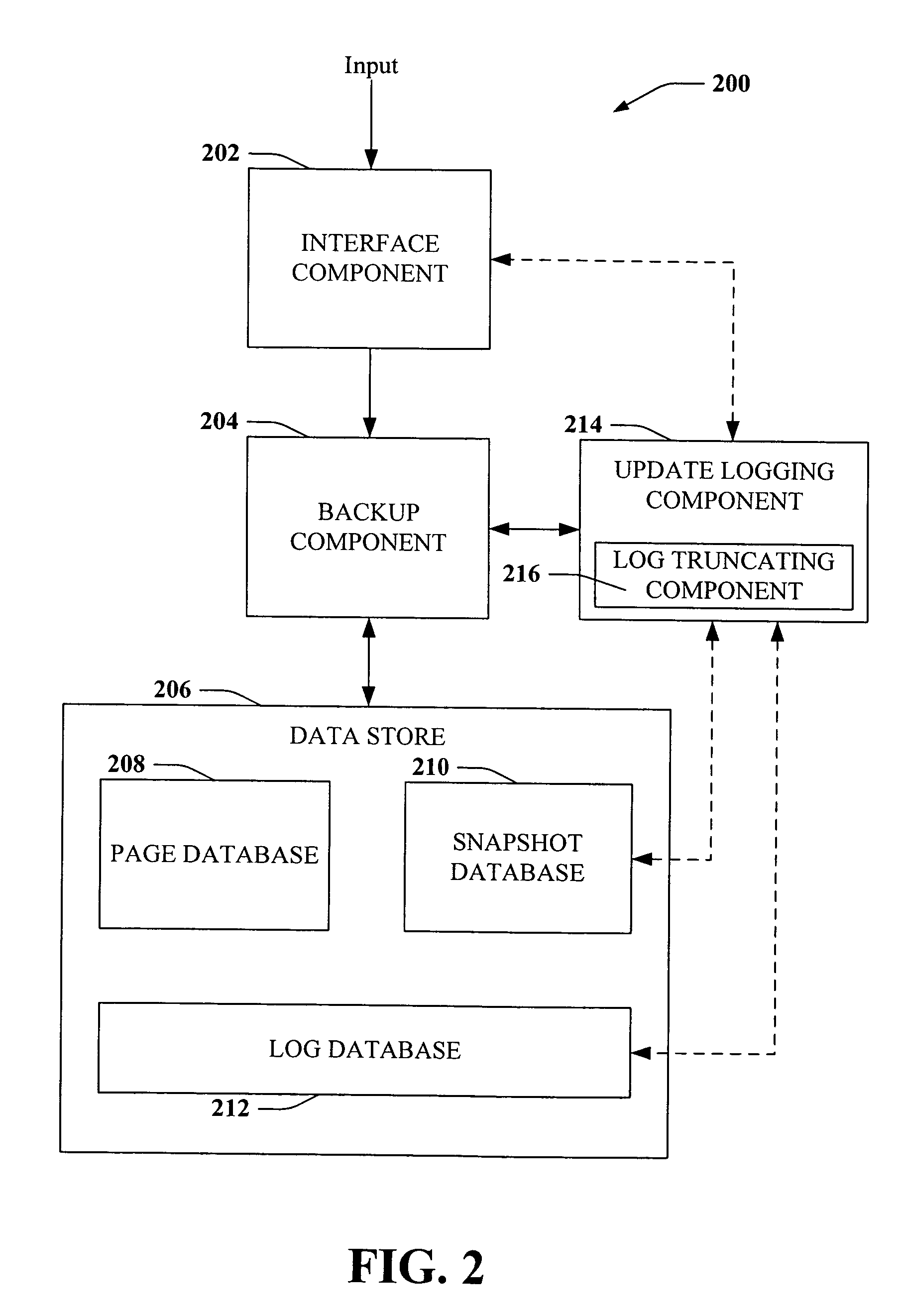
Page recovery using volume snapshots and logs
InactiveUS20060224636A1Promote recoveryImprove system efficiencyDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionDatabaseData page
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate providing page-level database restore functionality upon detection of a corruption event. Updates to a data page in a database can trigger generation of a snapshot of the data page, and an update log can be maintained that stores information related to page updates. Subsequent snapshots can be generated at predetermined intervals and can trigger truncation of a log segment and initiation of a new log segment. Upon detection of page corruption, a most-recent uncorrupt snapshot of the corrupt page can be identified, copied to the location of the corrupt page in the database, and modified according to the log segment associated with the uncorrupt snapshot to make the page current as of the corrupting event, all of which can be performed to restore the database without having to take the database offline.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
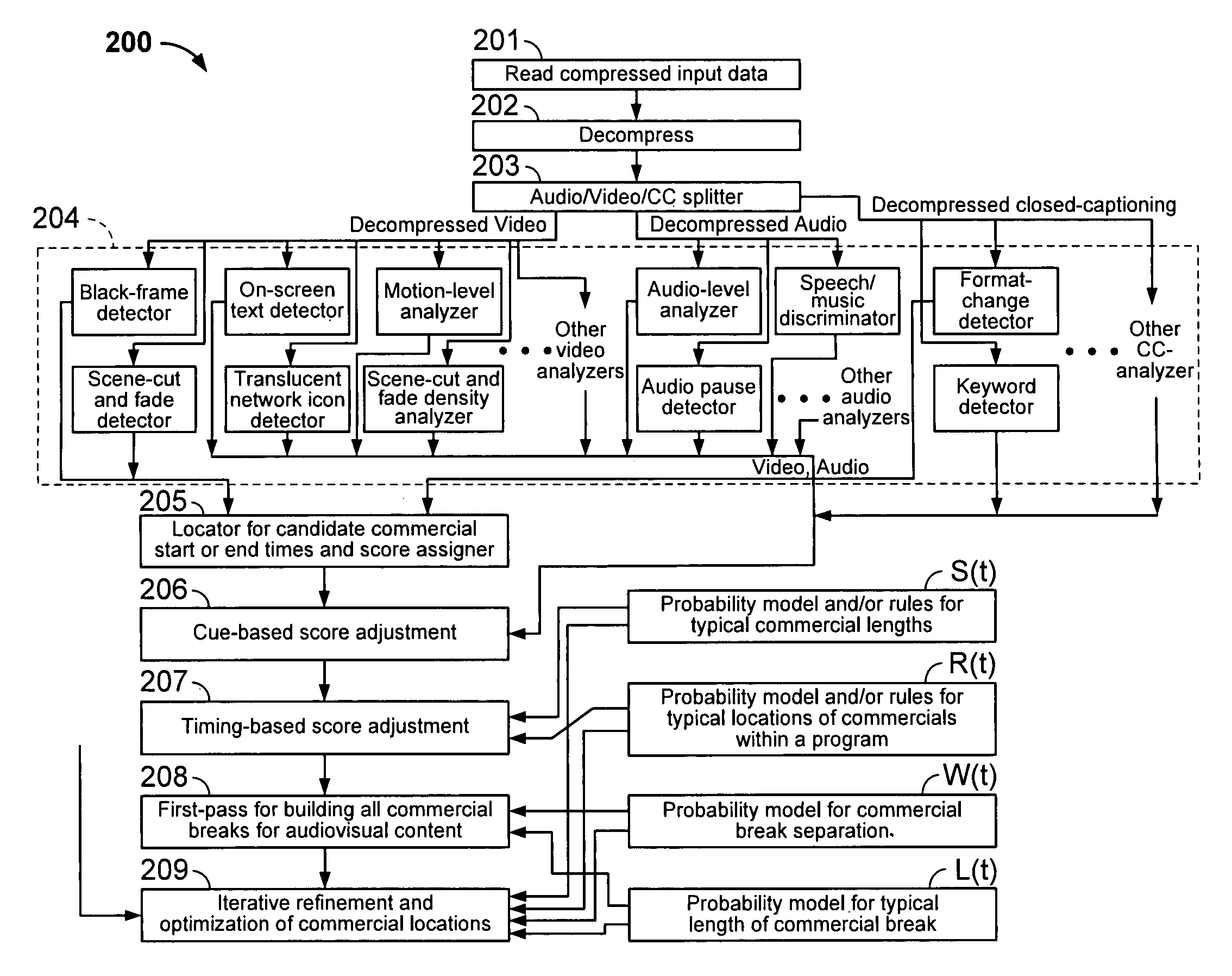
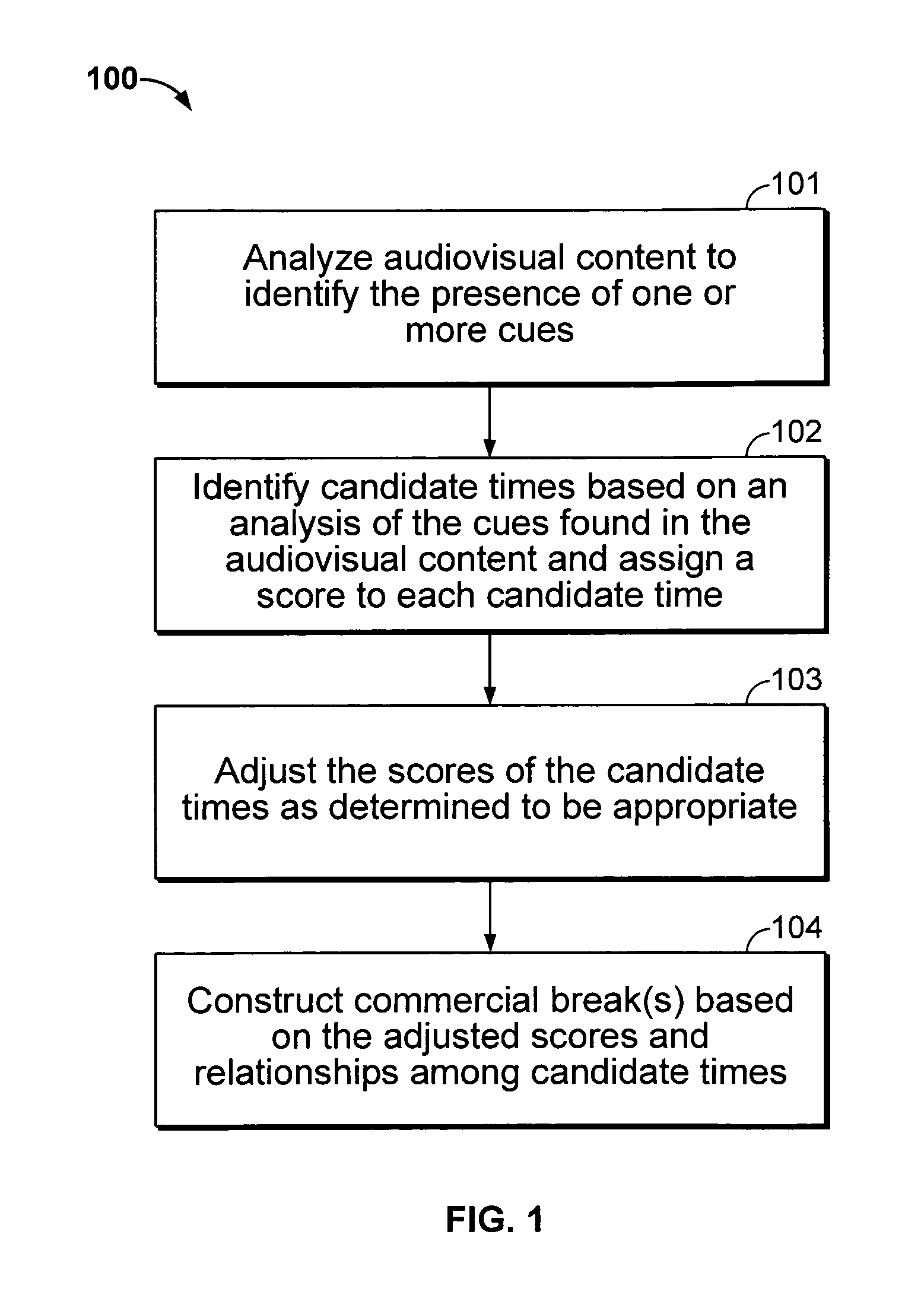
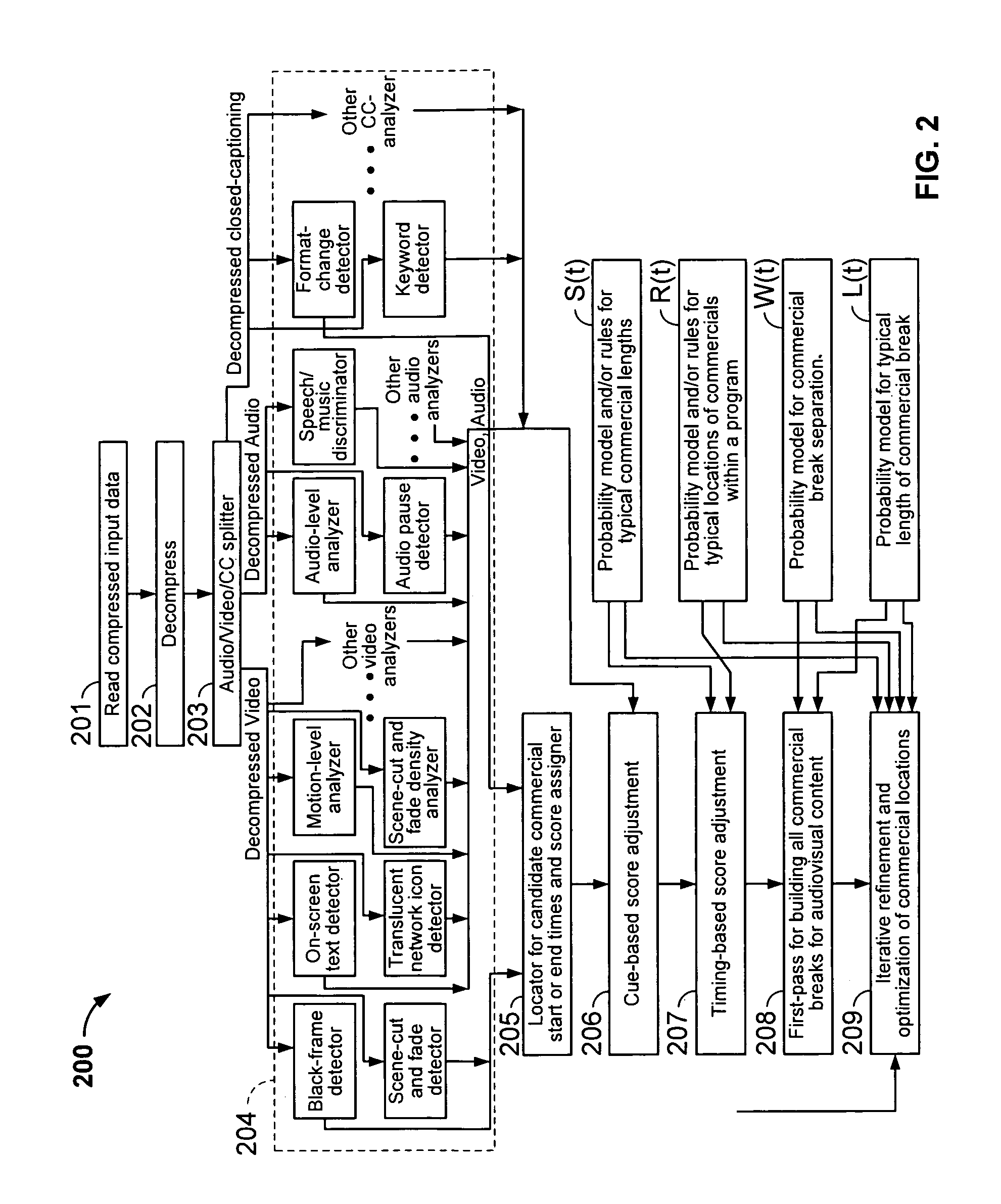
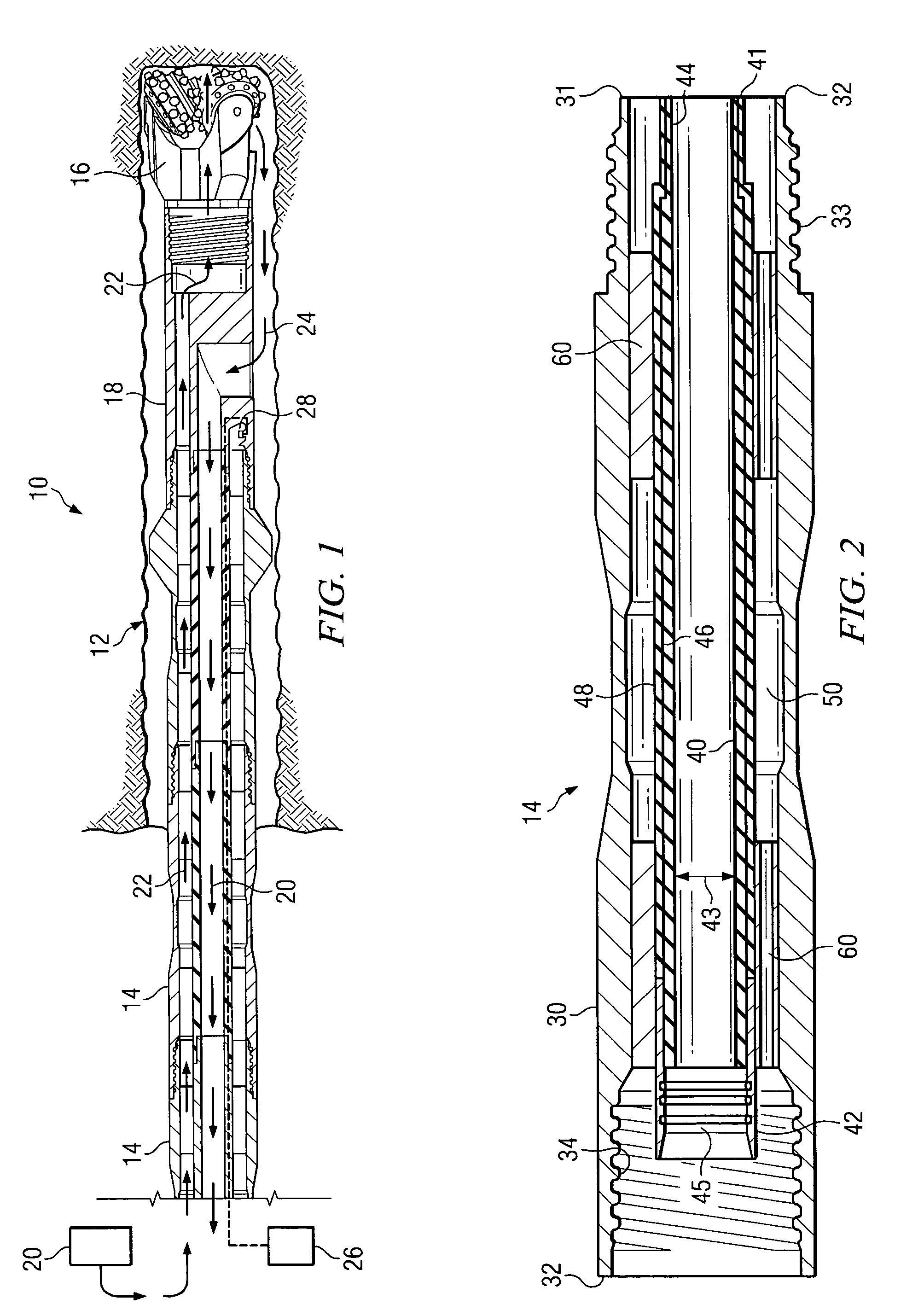
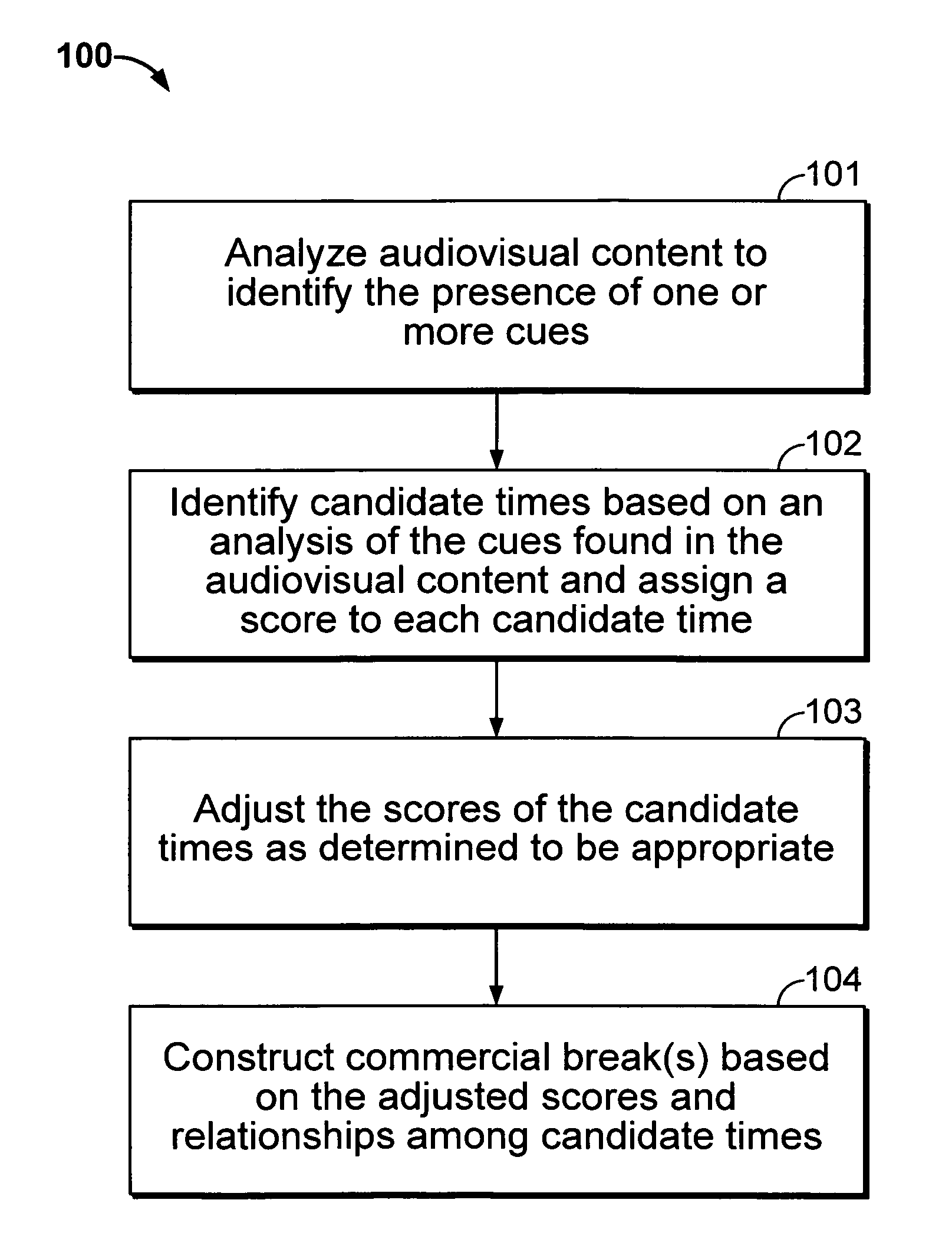
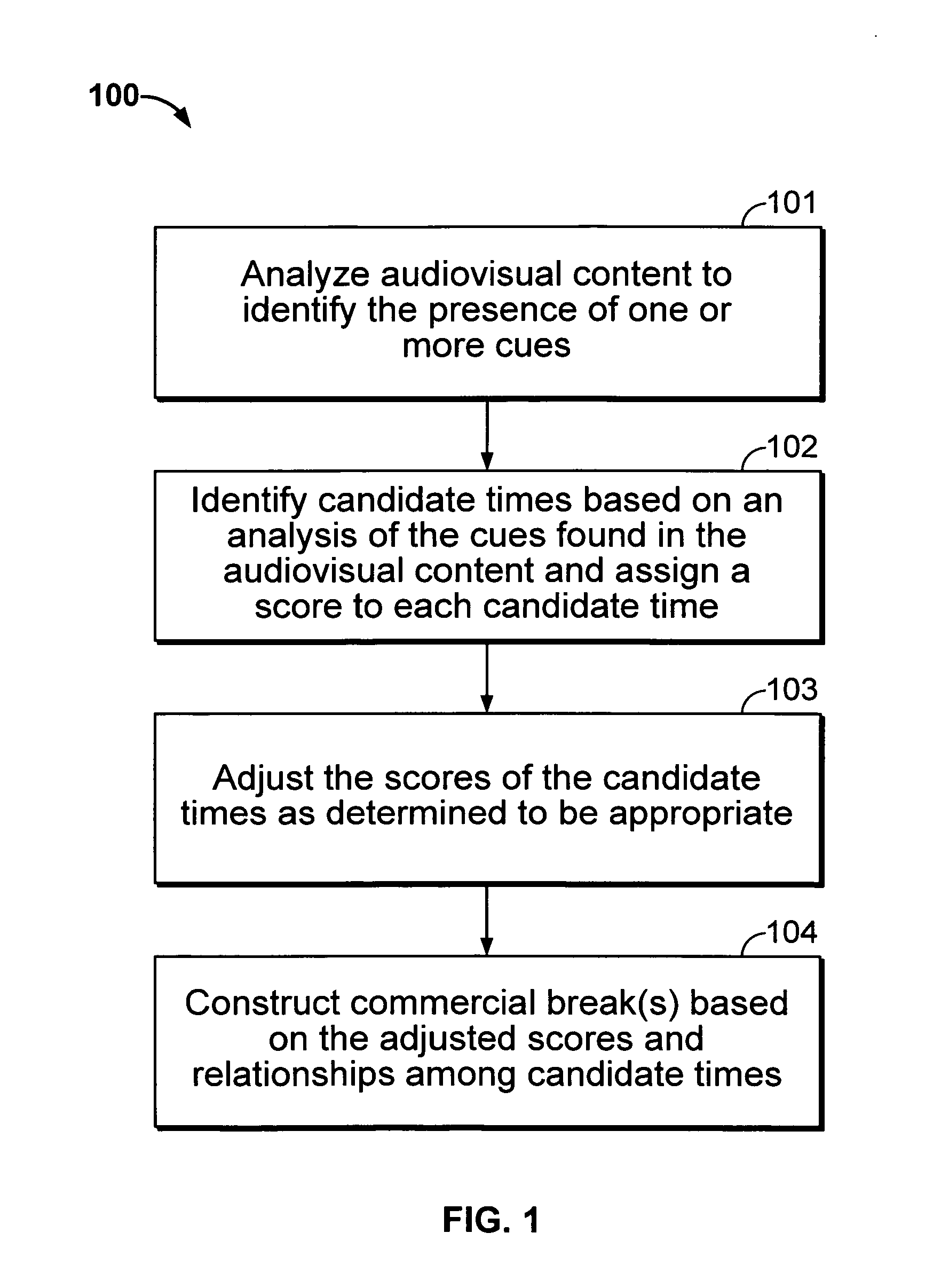
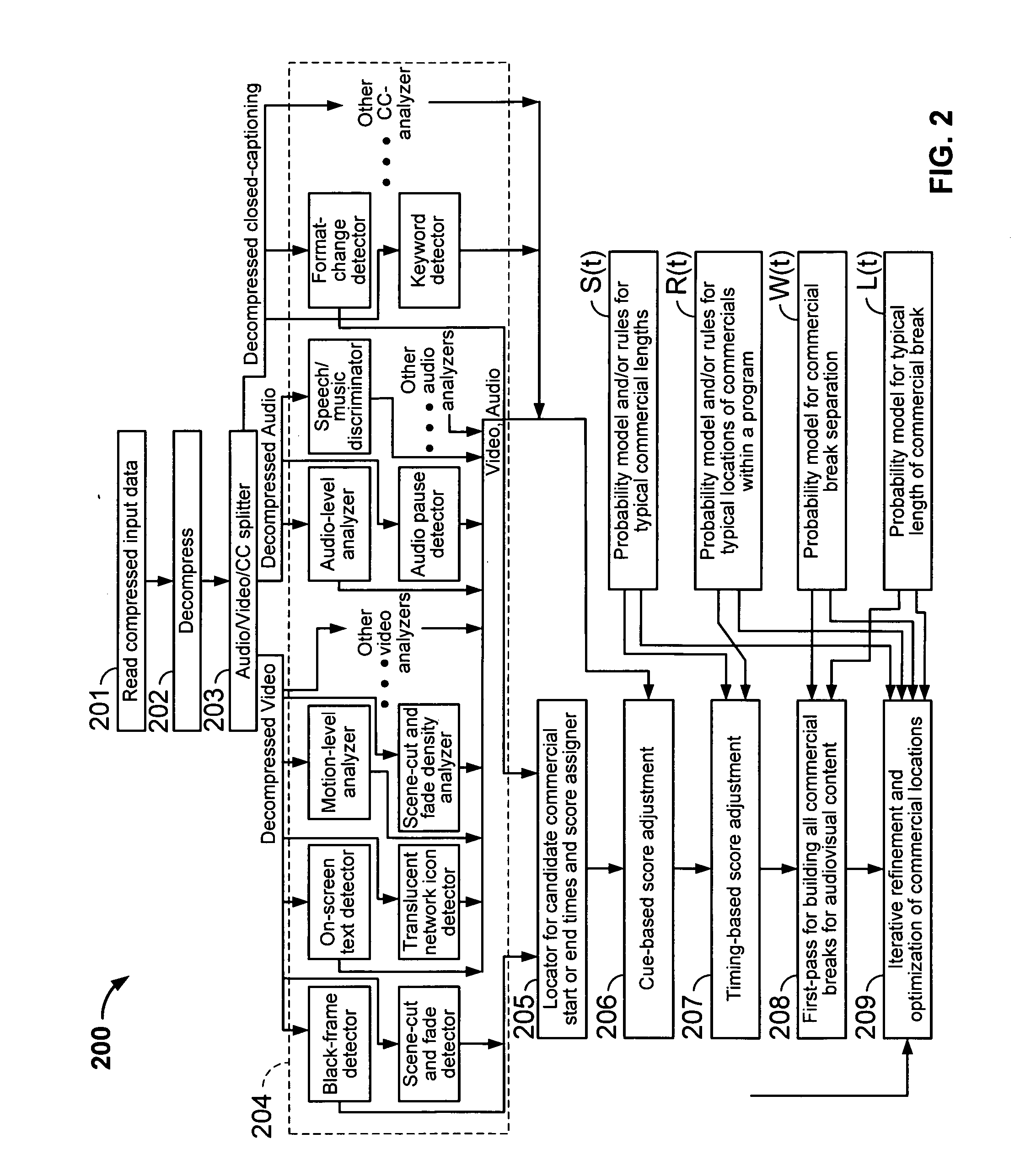
Iterative, maximally probable, batch-mode commercial detection for audiovisual content
InactiveUS6993245B1Improve accuracyPromote resultsTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsProbit modelLocation detection
Owner:INTERVAL RESEARCH CORPORATION
Cotton event MON15985 and compositions and methods for detection thereof
InactiveUS7223907B2Detect presenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceInsertion site
The present invention provides cotton plants, cotton tissues, and cotton seeds that include the MON15985 event, which confers resistance to Lepidopteran insect damage. Also provided are assays for detecting the presence of the MON15985 event based on the DNA sequence of the recombinant construct inserted into the cotton genome that resulted in the MON15985 event and / or the genomic sequences flanking the insertion site.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Wearable intravenous fluid heater
InactiveUS6236809B1Avoid contaminationReduce riskMedical devicesLiquid transferring devicesTemperature controlEngineering
Owner:BELMONT INSTR LLC
Control system for a water heater
InactiveUSRE37745E1Detect presenceHarmful and dangerousMachines/enginesFuel injecting pumpsCombustorControl system
A multi-function controller for a water heater is advanced comprising a control panel and a plurality of sensors that monitor a variety of functions that impact the operation of a water heater. A flammable gas sensor, placed in proximity to the air intake, detects the presence of an unsafe concentration of gas and issues a signal to the control panel, which subsequently discontinues the operation of the burners. Detection of a blocked vent pipe is achieved by a carbon monoxide sensor placed near the draft hood. The control panel is equipped with circuitry which monitors usage of the heater for a specified time period to develop a pattern of use. Subsequent to the monitoring period, the controller will activate the burners a predetermined time prior to an anticipated period of high use. During periods of low use, the controller will decrease the temperature to which the water is to be heated, thereby resulting in a more efficient heater. Non-volatile memory records data from the sensors so that the operation status of the heater may be ascertained subsequent to a power outage. The control panel contains a plurality of visual alarms, each of which corresponds to a sensor. Consequently, repair and maintenance are simplified because the cause of a malfunction is quickly recognized.
Owner:AOS HLDG CO
Motion component dominance factors for motion locking of touch sensor data
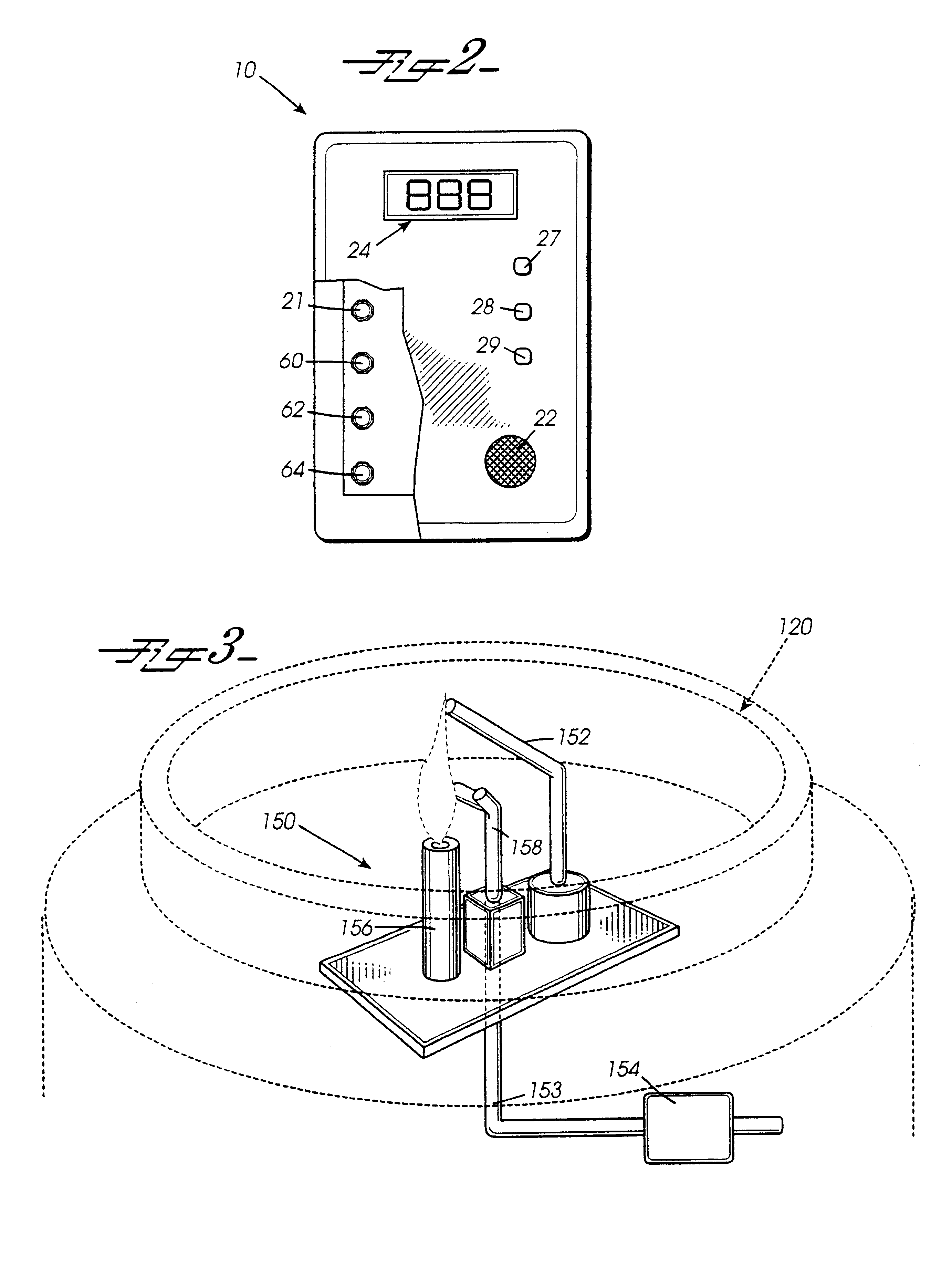
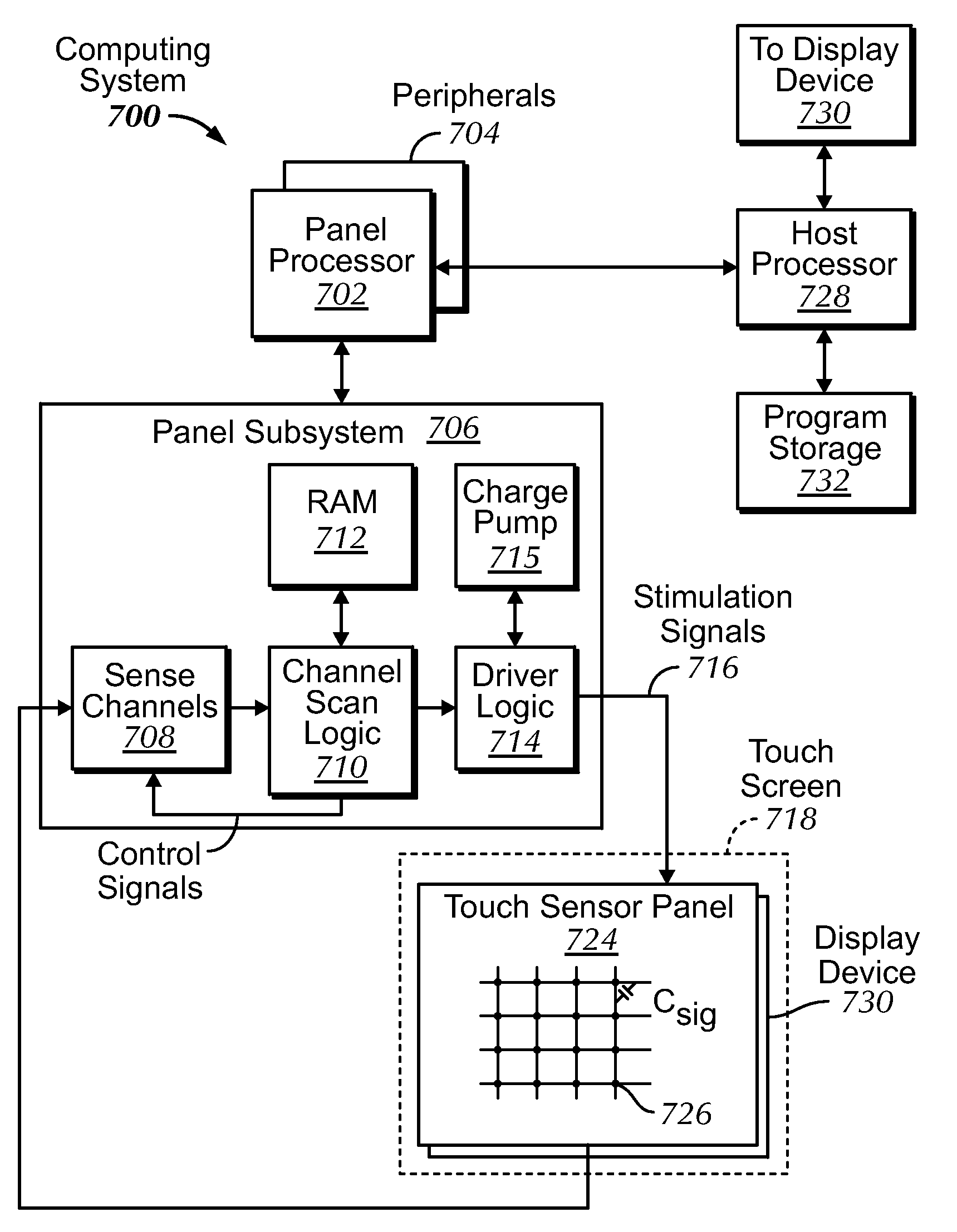
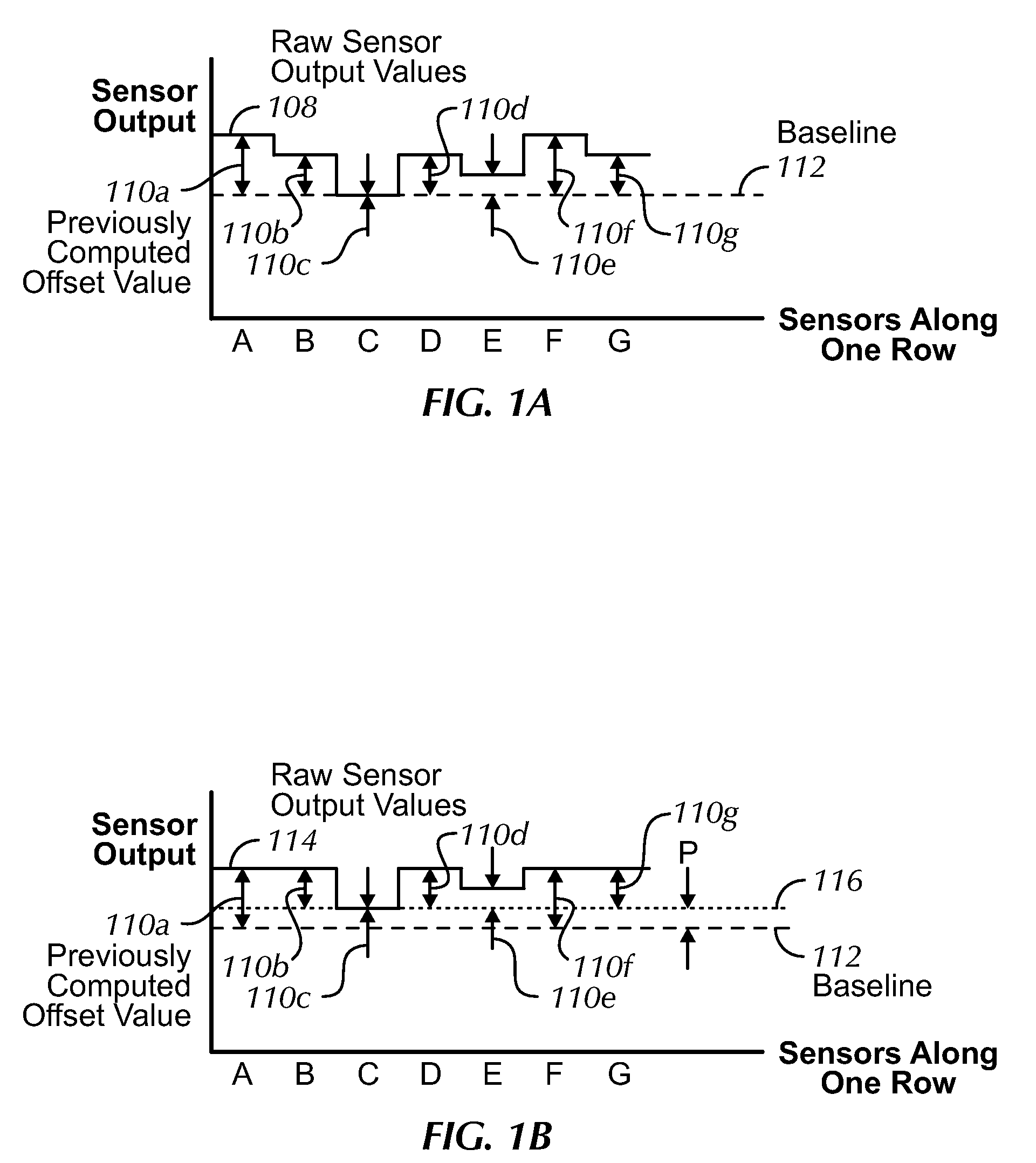
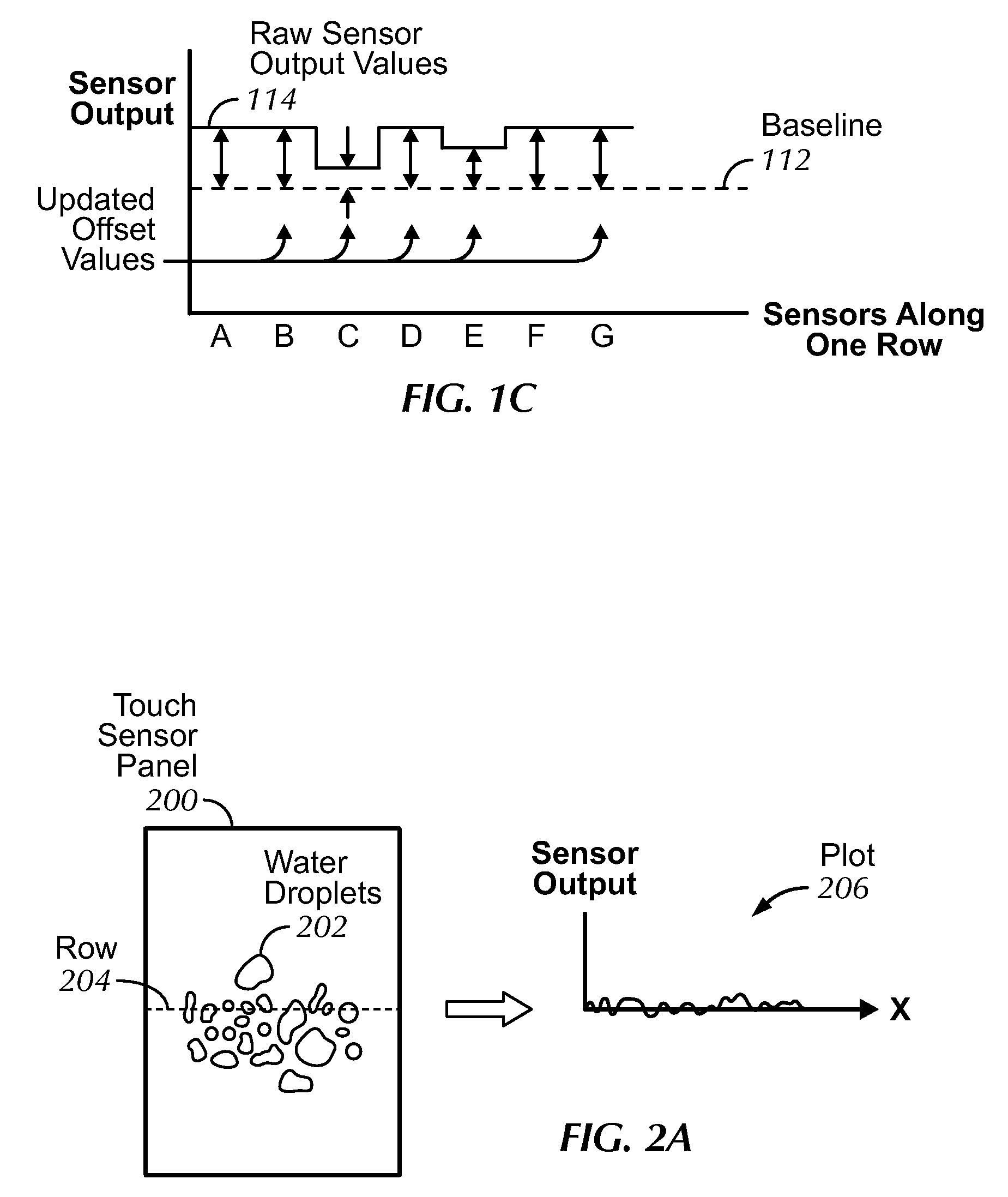
InactiveUS20090174676A1Improve accuracyDetect presenceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLine sensorStandardization
An image jaggedness filter is disclosed that can be used to detect the presence of ungrounded objects such as water droplets or coins, and delay periodic baseline adjustments until these objects are no longer present. To do otherwise could produce inaccurate normalized baseline sensor output values. The application of a global baseline offset is also disclosed to quickly modify the sensor offset values to account for conditions such as rapid temperature changes. Background pixels not part of any touch regions can be used to detect changes to no-touch sensor output values and globally modify the sensor offset values accordingly. The use of motion dominance ratios and axis domination confidence values is also disclosed to improve the accuracy of locking onto dominant motion components as part of gesture recognition.
Owner:APPLE INC
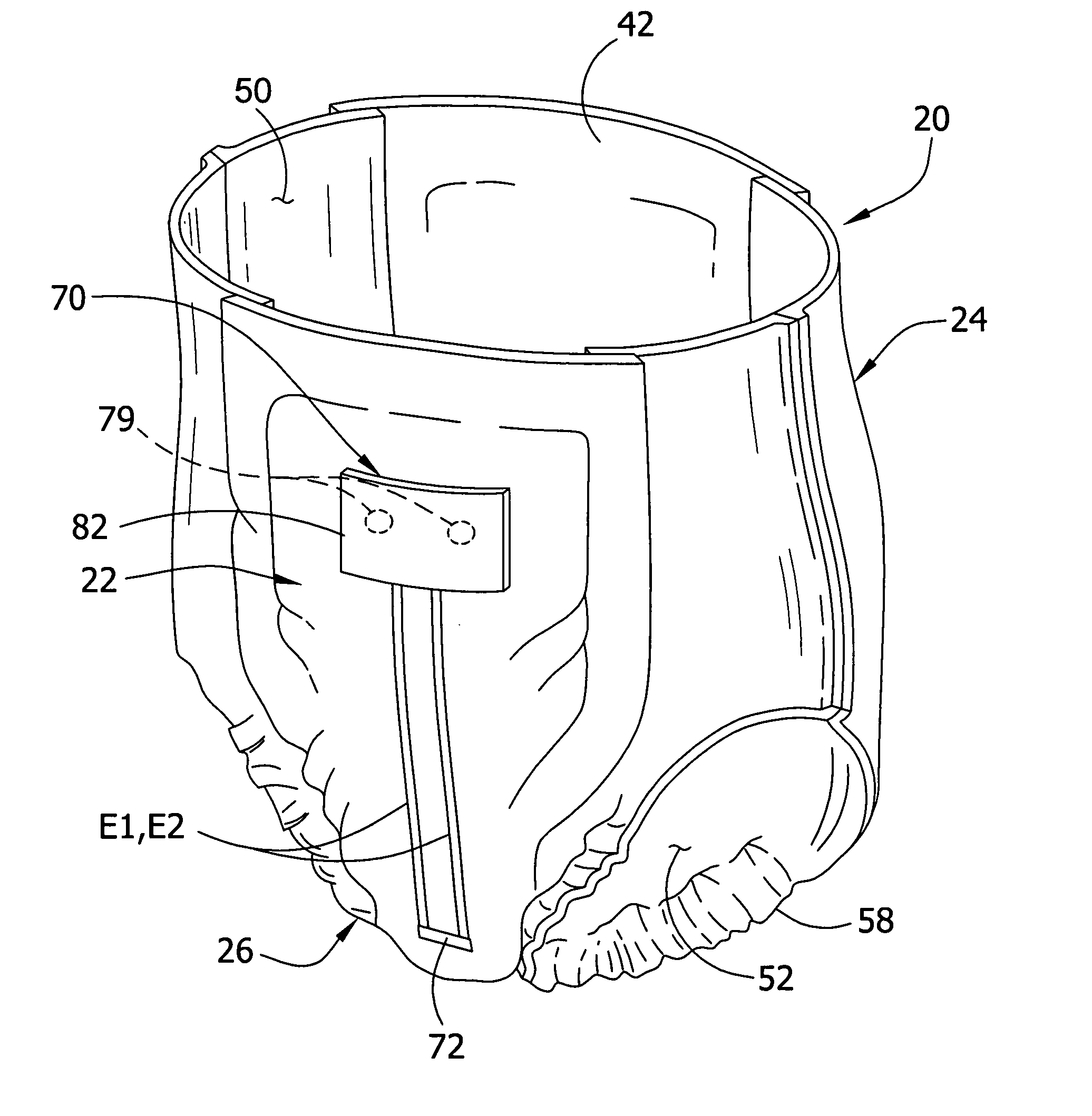
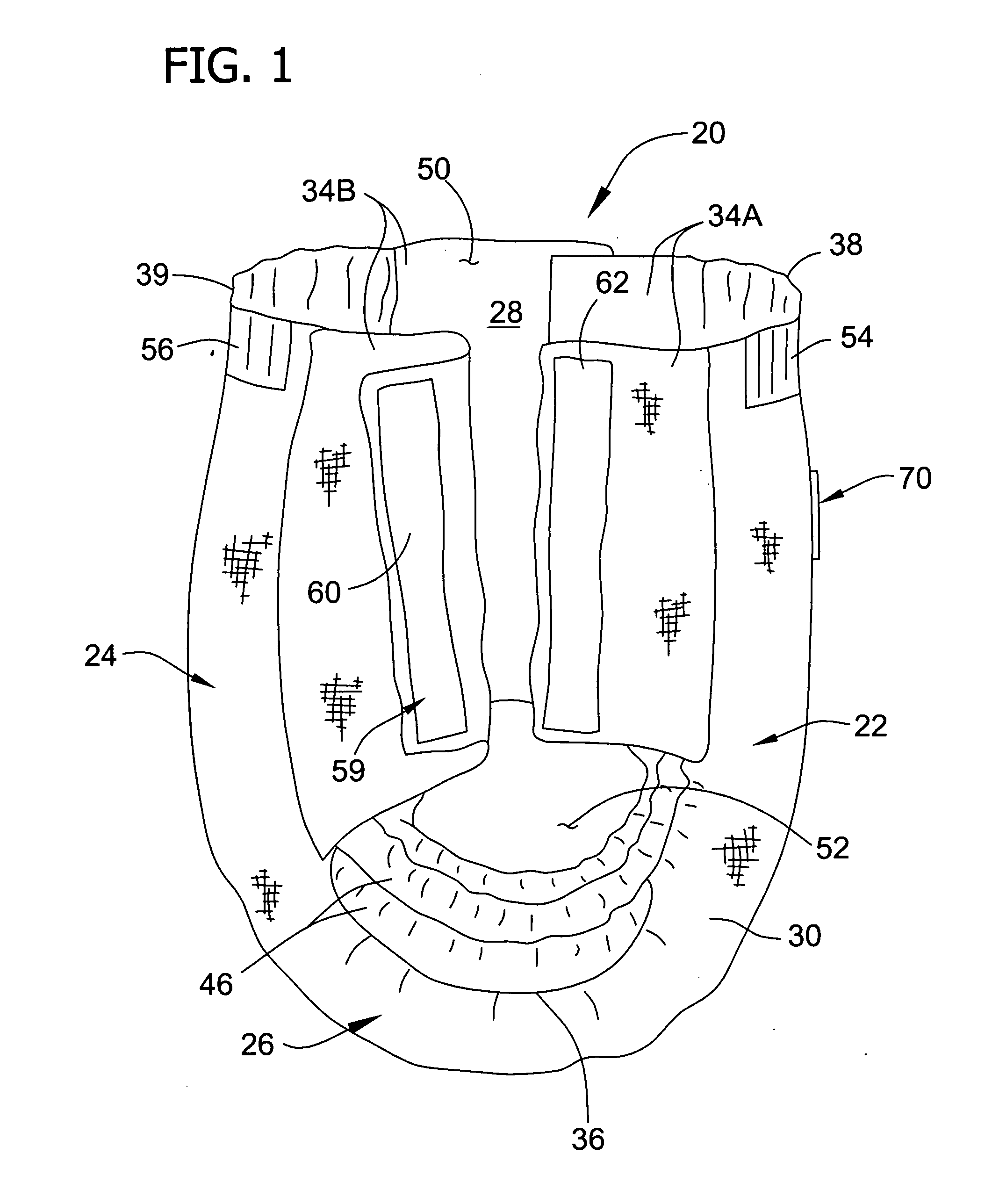
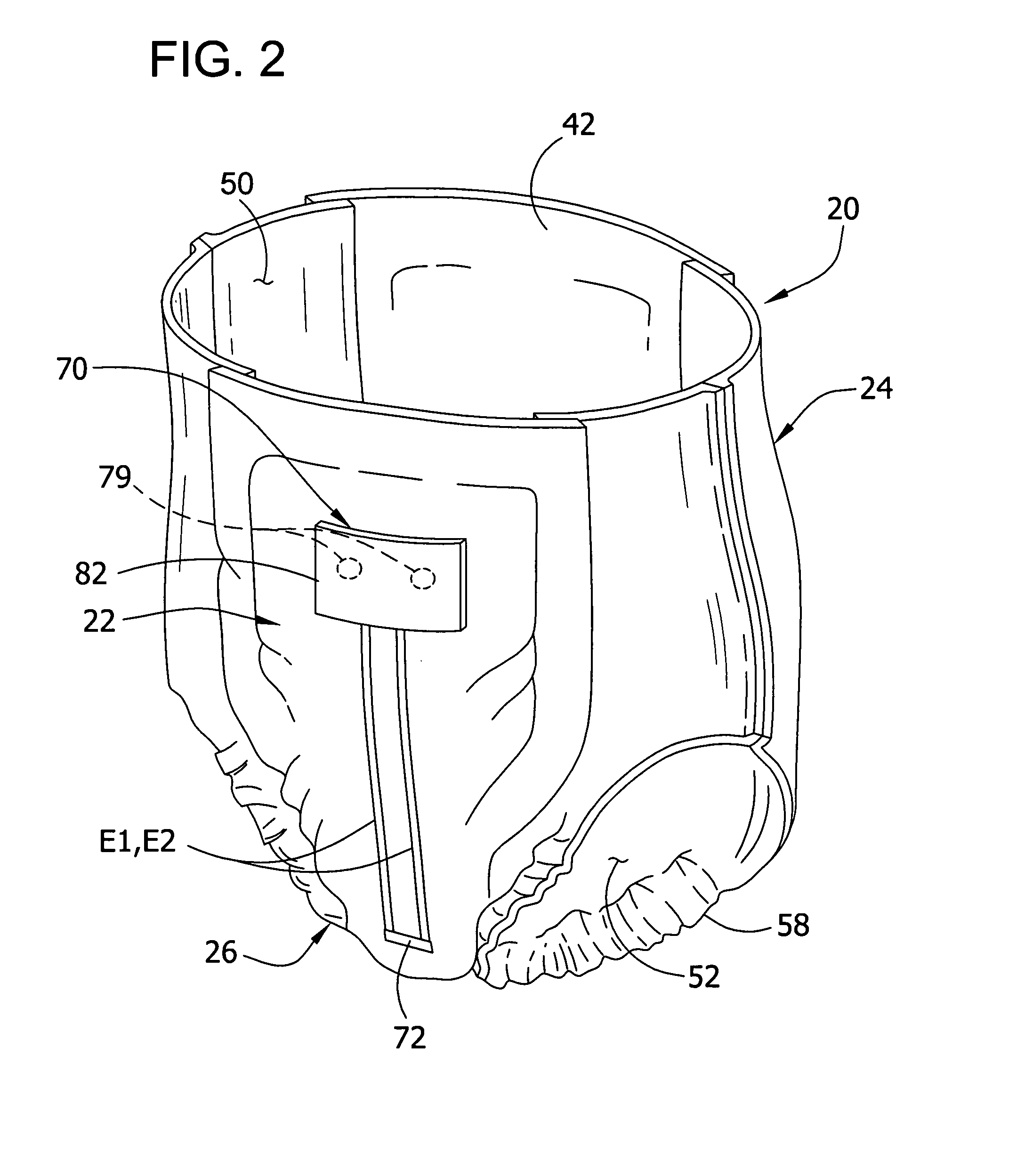
Personal care products with microchemical sensors for odor detection
ActiveUS20070142799A1Quickly and accurately determineDetect presenceBaby linensMaterial resistanceCaregiver personChemiresistor
Absorbent articles comprising one or more sensors capable of detecting the presence of a body waste in the absorbent article are described. In particular, the absorbent articles comprise at least one chemiresistor capable of detecting the presence of volatile organic compounds associated with a body waste. When a body waste is detected, an indicator means signals a caregiver and / or a user of the absorbent article that an insult has occurred
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
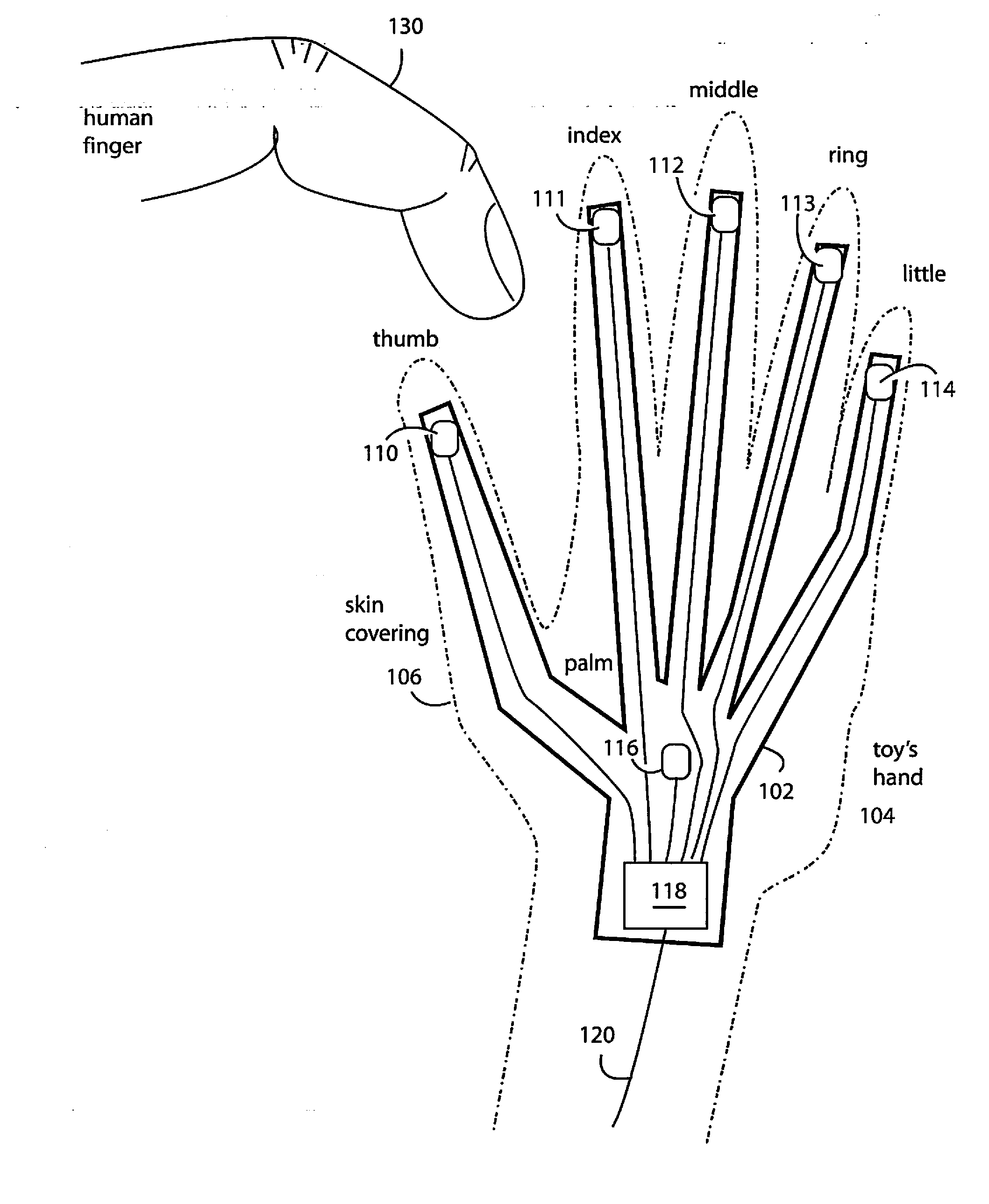
Pressure and touch sensors on flexible substrates for toys
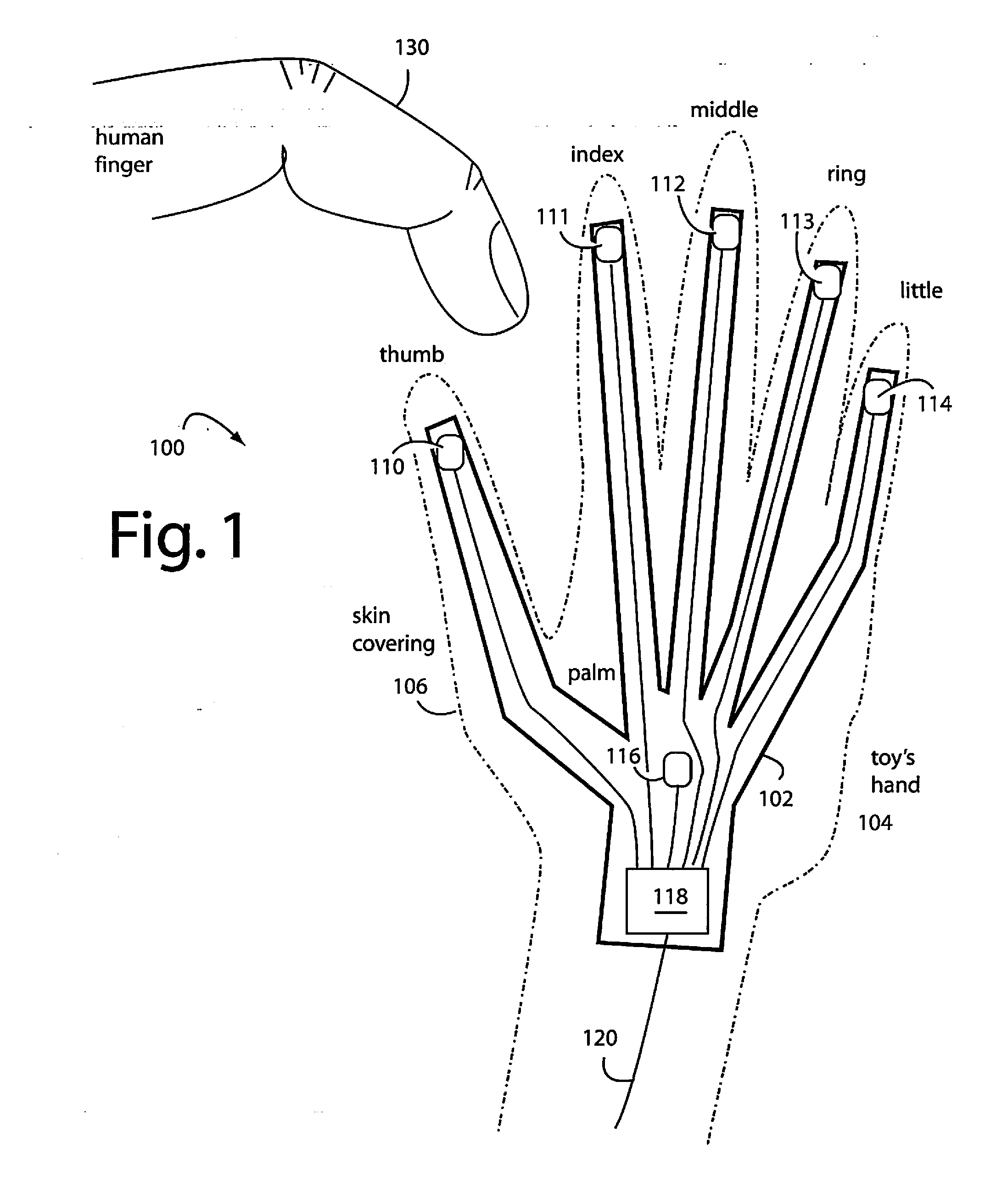
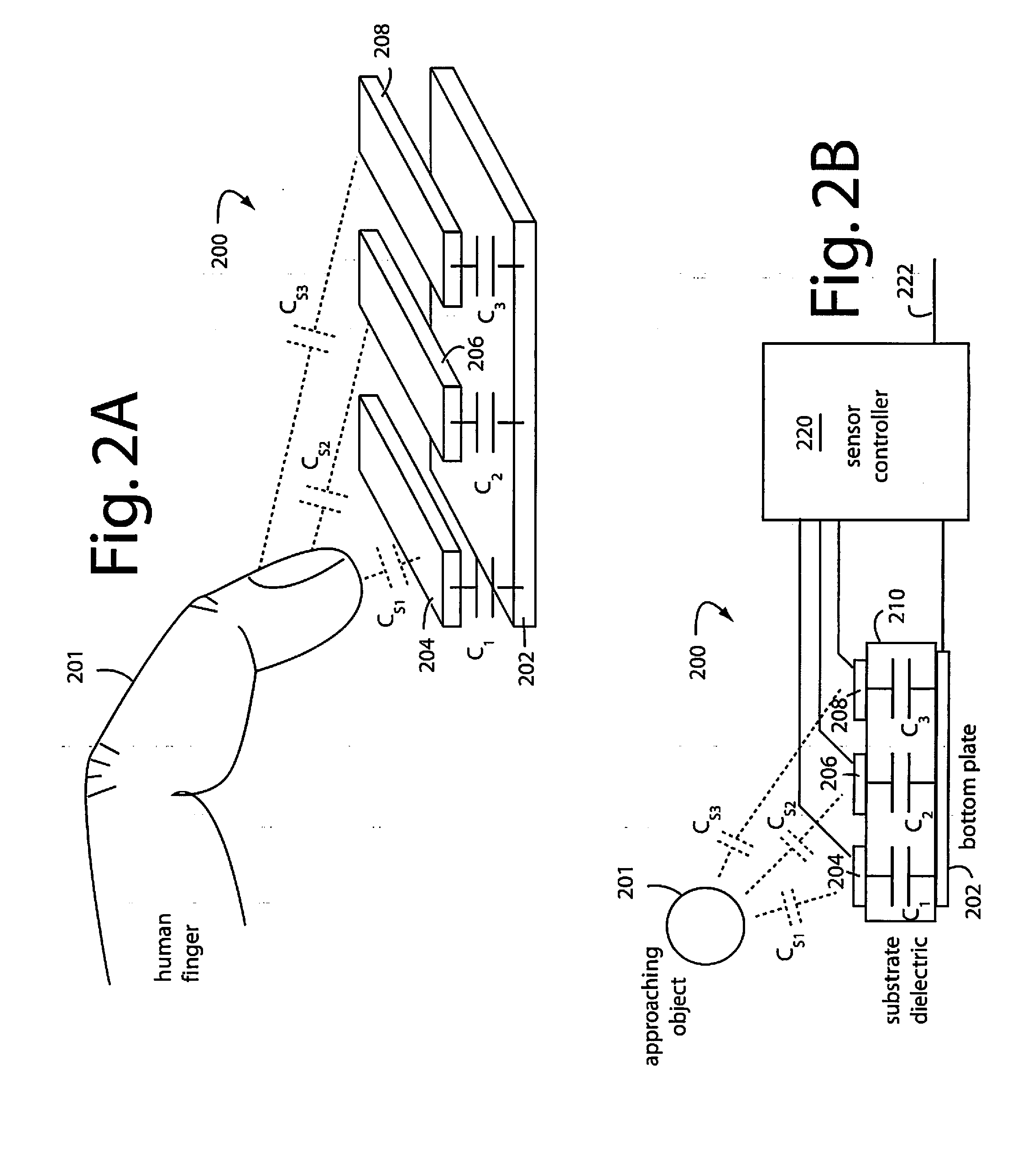
InactiveUS20110018556A1Detect presenceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingDielectricOpen cell
A capacitive sensor comprises patterned electrodes and printed wires of conductive material integrated with sensing circuits on flexible circuit substrates. The flexible circuit substrates are fingered or otherwise elongated to distribute sensing points to the limbs in a toy doll or animal, or squares on a board game. Such sensing points can detect the presence of a finger even though actual contact is not made by measuring the proportions and changes in stray capacitance attaching to the various electrodes. Touch sensors are therefore possible even when the capacitor sensor's sensing points are covered by a doll's plastic skin or a plush animal's fur. Including an interlayer of open cell foam under the flexible circuit substrate further implements a pressure sensor because applied pressures will deform the geometries of the capacitor electrodes and dielectrics enough to produce a measurable change in capacitance.
Owner:BOREI CORP
Probe for analysis of target nucleic acids
The invention is a probe for detecting nucleic acids having a particular sequence. It is composed of two joint units. One unit is chemically different from natural nucleic acids, but has the ability to recognize a particular sequence of bases or base pairs in single or double-stranded DNA of RNA. The other unit is a compound whose detectable properties are altered upon binding to nucleic acids.
Owner:LIGHTUP TECH
Touch sensor and display device
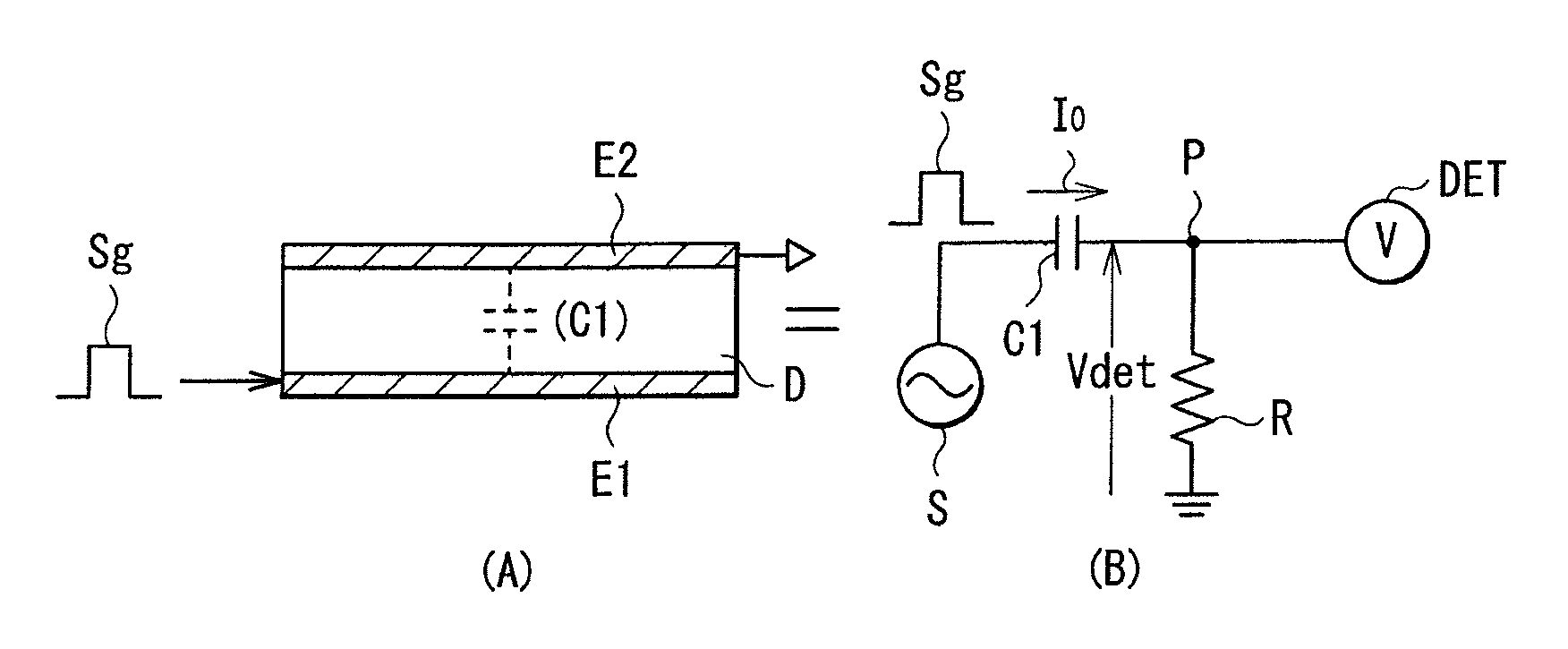
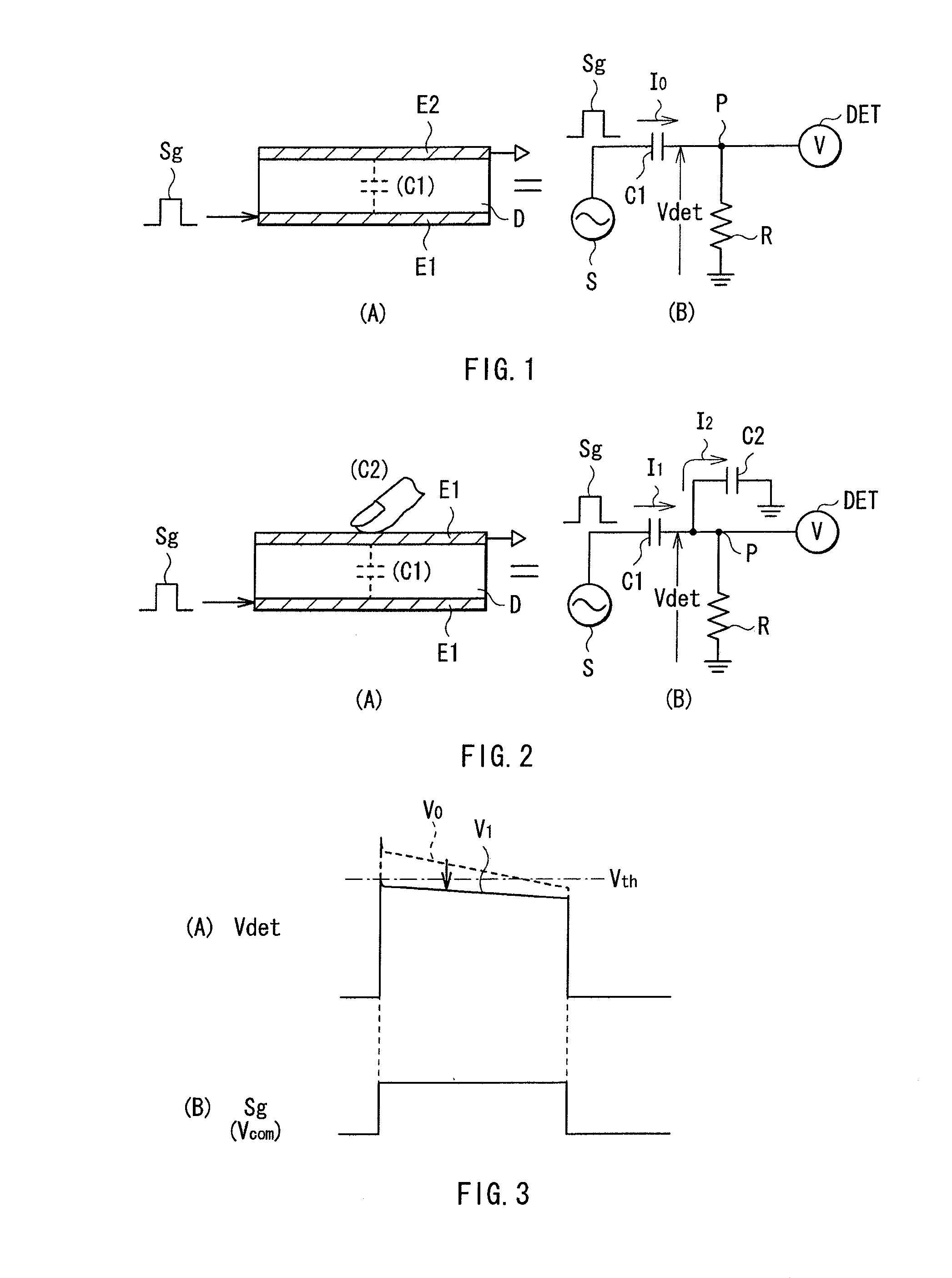
ActiveUS20100328259A1High detection sensitivityDetect presenceStatic indicating devicesElectronic switchingElectricityCapacitance
A touch sensor that may detect an object away from the sensor is provided. The touch sensor includes one or more drive electrodes; one or more detection electrodes forming capacitance in cooperation with the respective drive electrodes; a detection circuit applying drive signals to the respective drive electrodes to detect the object based on detection signals obtained from the respective detection electrodes in response to the respective drive signals; and a controller controlling to change a range of electric flux lines generated between the drive electrodes and the detection electrodes.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Dual wall drill string assembly
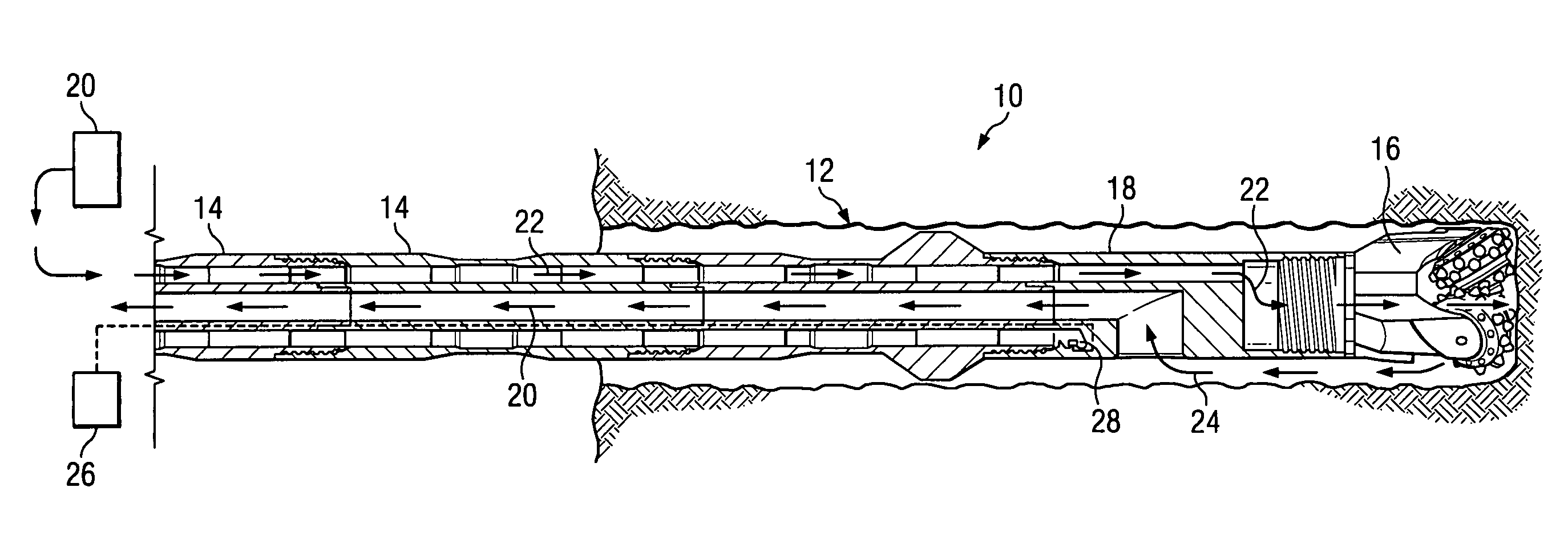
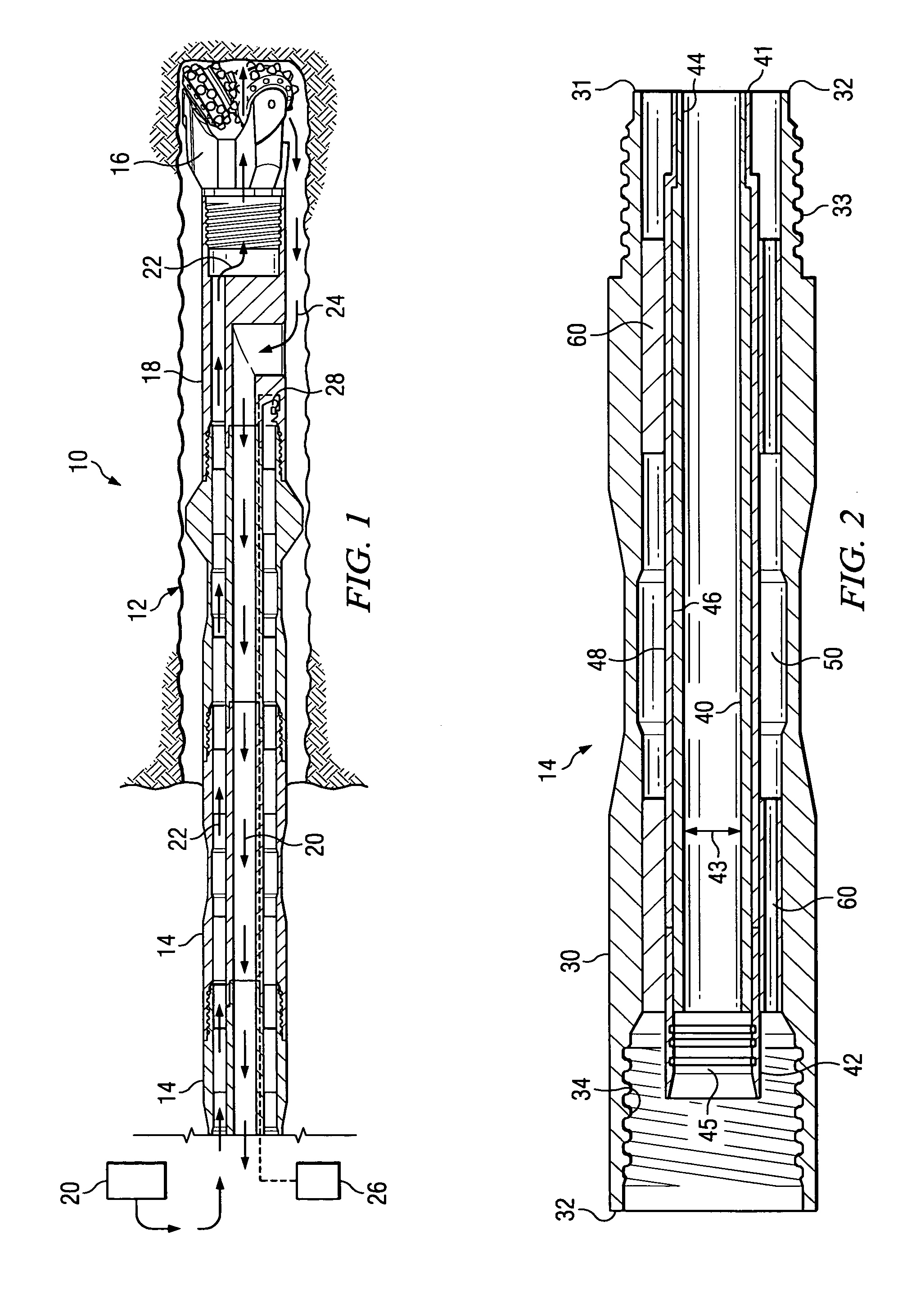
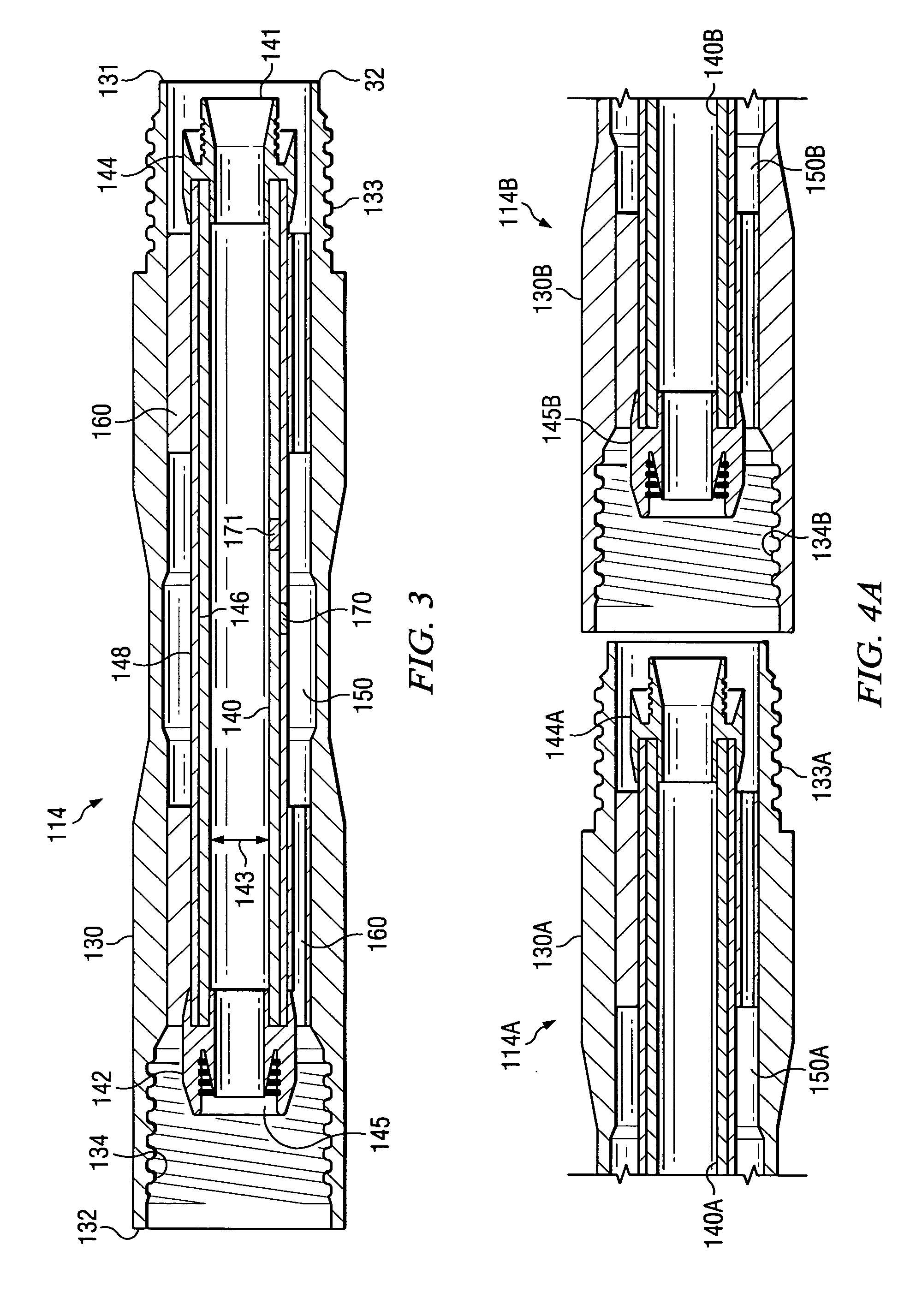
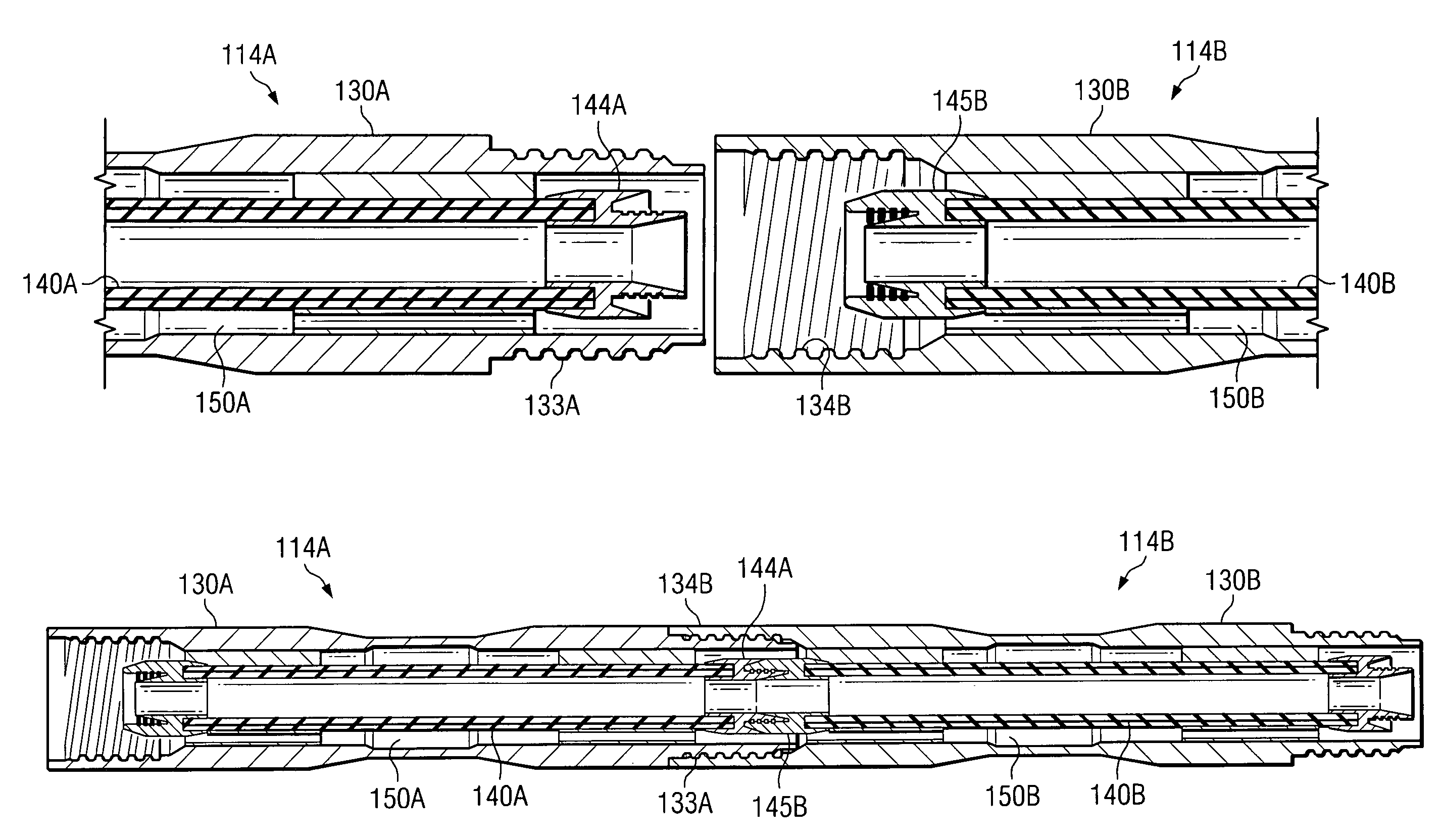
ActiveUS20050103527A1Little and no resistanceIncrease volumeDrilling rodsFlushingCoiled tubingEngineering
A coil tubing or jointed dual wall drill string assembly for subsurface drilling. The drill string assembly includes a metallic outer tube having an outer tube first end and an outer tube second end opposite the outer tube first end. The assembly also includes a flexible, substantially non-metallic inner tube that is substantially enclosed within and generally coaxially aligned with the outer tube. The flexible, substantially non-metallic inner tube has an inner tube first end, an inner tube second end opposite the inner tube first end, and an inner tube inner diameter. The inner tube and the outer tube define an annular channel therebetween. The drill string assembly also includes a means for conveying fluid through the annular channel toward the inner tube first end. The annular channel is adapted to convey drilling fluid under pressure toward the inner tube first end and the inner tube is adapted to convey cuttings toward the inner tube second end.
Owner:AMERICAN AUGERS +1
Dual wall drill string assembly
InactiveUS7152700B2Little and no resistanceIncrease volumeDrilling rodsFlushingCoiled tubingDrilling fluid
Owner:AMERICAN AUGERS +1
Iterative, maximally probable, batch-mode commercial detection for audiovisual content
InactiveUS20060029368A1Improve accuracyPromote resultsTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsLocation detectionProbit model
Owner:INTERVAL RESEARCH CORPORATION
Data exploration system
InactiveUS20050179684A1Facilitate visual comparison and comprehensionEnhance abilityDrawing from basic elementsInput/output processes for data processingComplex data typeData science
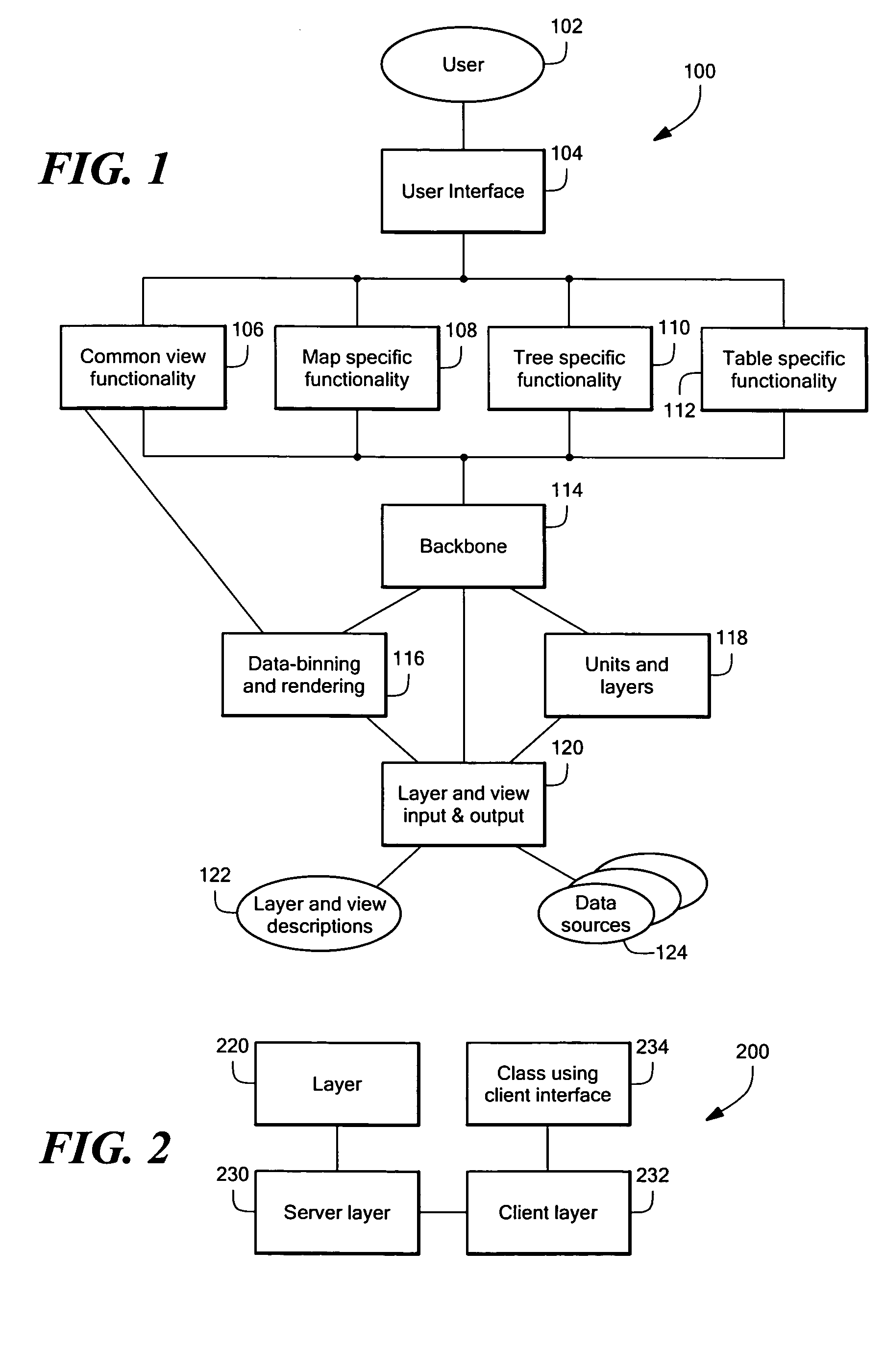
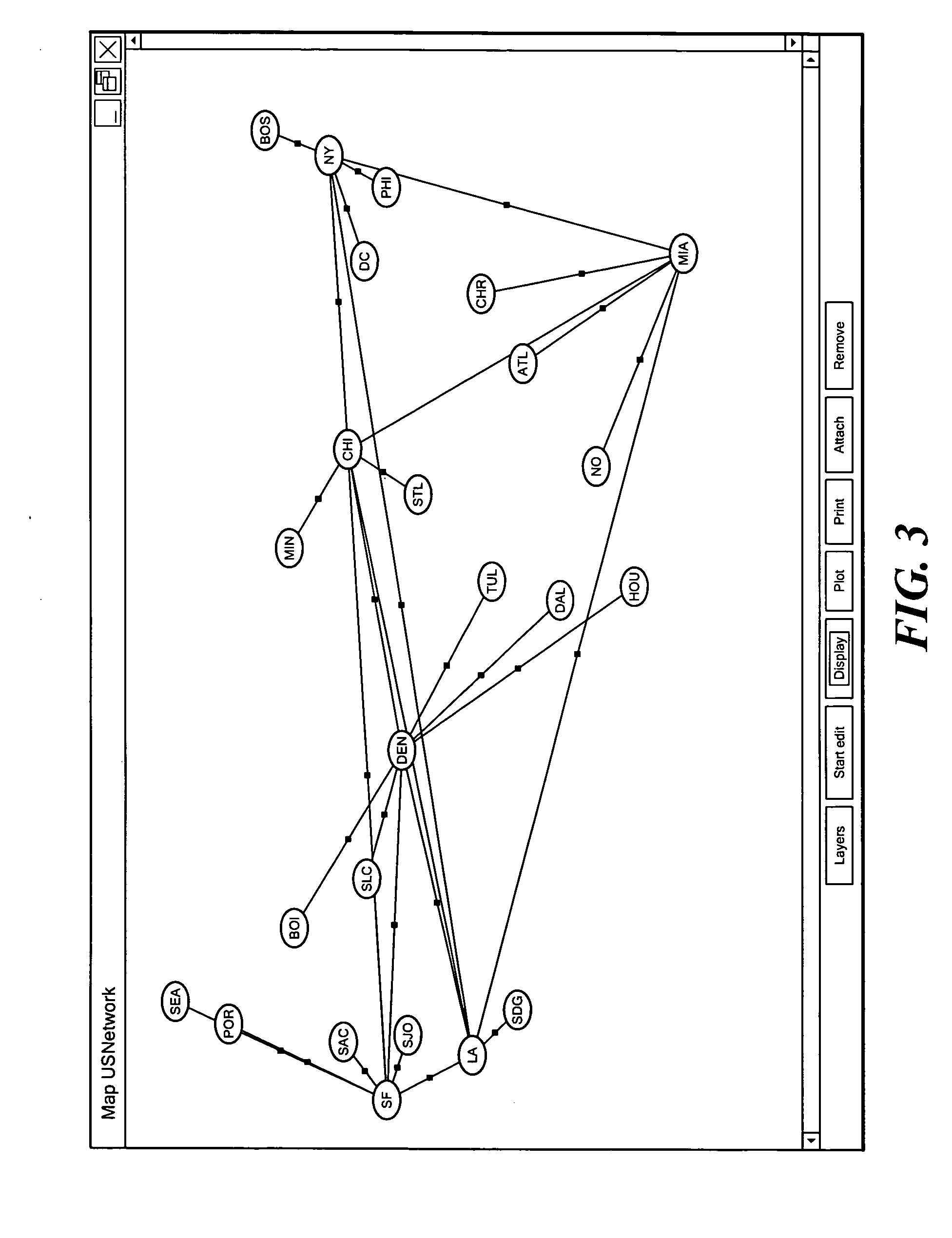
An improved data exploration system and method that can be used to analyze and to explore complex data sets involving multiple data dimensions and multi-variable data presentations. The data exploration system generates visual representations of complex data sets in map, table, and tree view formats. In each of these view formats, both the appearance and the arrangement of the symbols representing the data sets are based on the data itself to facilitate the comprehension of patterns and information relationships within the data sets. Further, the data can be viewed at different levels of density to perform detailed analysis of the data, and to detect the presence of overall trends within the data. Moreover, the data exploration system performs a suite of calculation operations to cast the data in different forms, and to facilitate the acquisition, integration, and analysis of the data.
Owner:WALLACE JAMES H
Method and apparatus for prevention of catheter air intake
InactiveUS20090163864A1Quantity minimizationEasy to removeMedical devicesIntravenous devicesEngineeringHemostasis valve
A system is disclosed for preventing air from entering a first catheter or cannula of a multi-catheter system. Air is prevented from entering the proximal end of the first catheter by an axially elongate chamber having an impeller, the chamber being affixed to the proximal end of the first catheter. The first catheter is affixed at an offset location, near the periphery of the chamber. The impeller is driven by a motor drive and imparts rotational energy to the fluid within the chamber forcing any air within the chamber to migrate to the center of the chamber by buoyancy effects. The air is removed through a port near the centerline of the chamber. Liquid removed with the air is returned to the chamber to minimize liquid loss during the procedure. Hemostasis valves or seals can be provided at the entrance and the exit of the chamber. A second catheter inserted through the chamber and into the first catheter is unable to entrain gas into the first catheter because any gas that enters the chamber is routed to the centerline of the chamber where it is removed. The first catheter can be a cannula or an introduction sheath, devices suited for endovascular access into the mammalian cardiovascular system where pressures may fall below ambient room pressure, a condition, which could encourage the possibility of air embolism to a patient. Inflow of fluid from an external pump scrubs the second catheter shaft of air bubbles attached by surface tension.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Explosives detection using differential ion mobility spectrometry
InactiveUS20050133716A1Easy to separateHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersFuel testingOptical spectrometerPhysical chemistry
System for control of ion species behavior in a time-varying filter field of an ion mobility-based spectrometer to improve species identification for explosives detection.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Multi-functional leak detection instrument along with sensor mounting assembly and methodology utilizing the same
A leak detection instrument may comprise a housing, a gas sensor supported relative to the housing, an AE sensor for generating a sound detection input signal upon exposure to gas leakage, processing circuitry for producing output signals, and an output device. The AE sensor may include an elongated mounting member, an AE sensor housing supported by the mounting member, and an AE sensor disposed therein. Improvements to leak detection instruments, an AE sensor mounting assembly and a method of monitoring a device to ascertain leakage of a target gas therefrom are also provided.
Owner:RADIAULICS
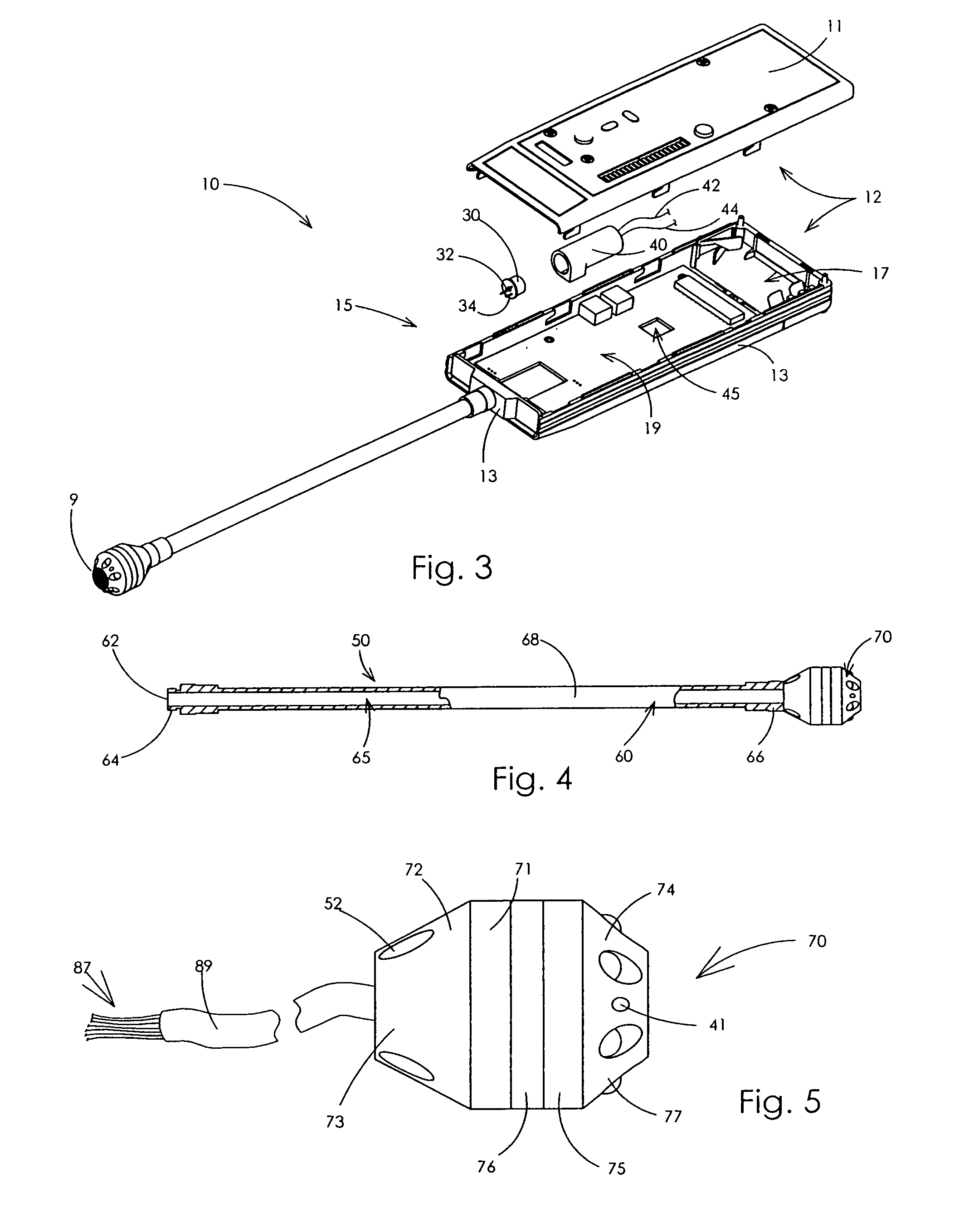
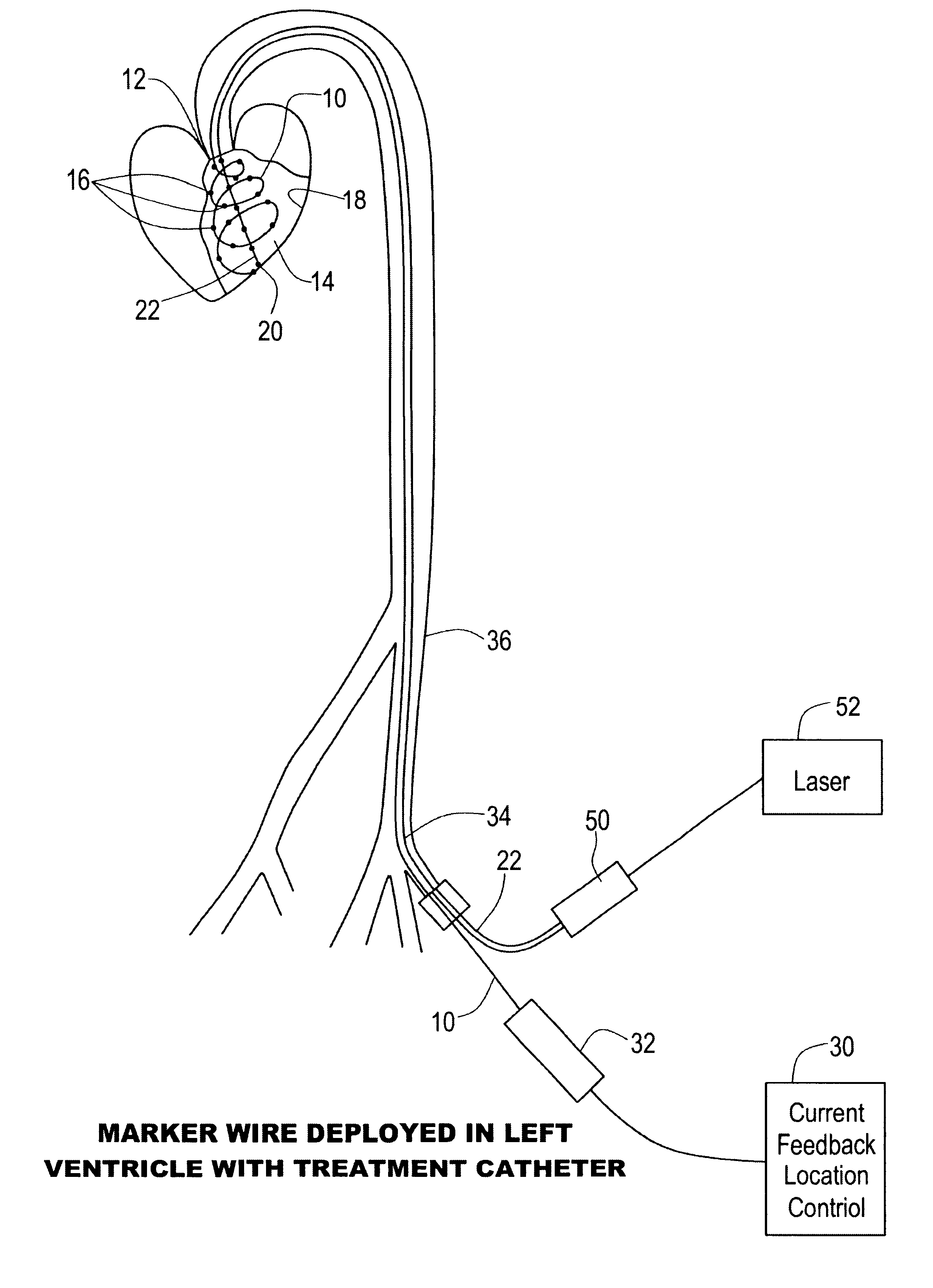
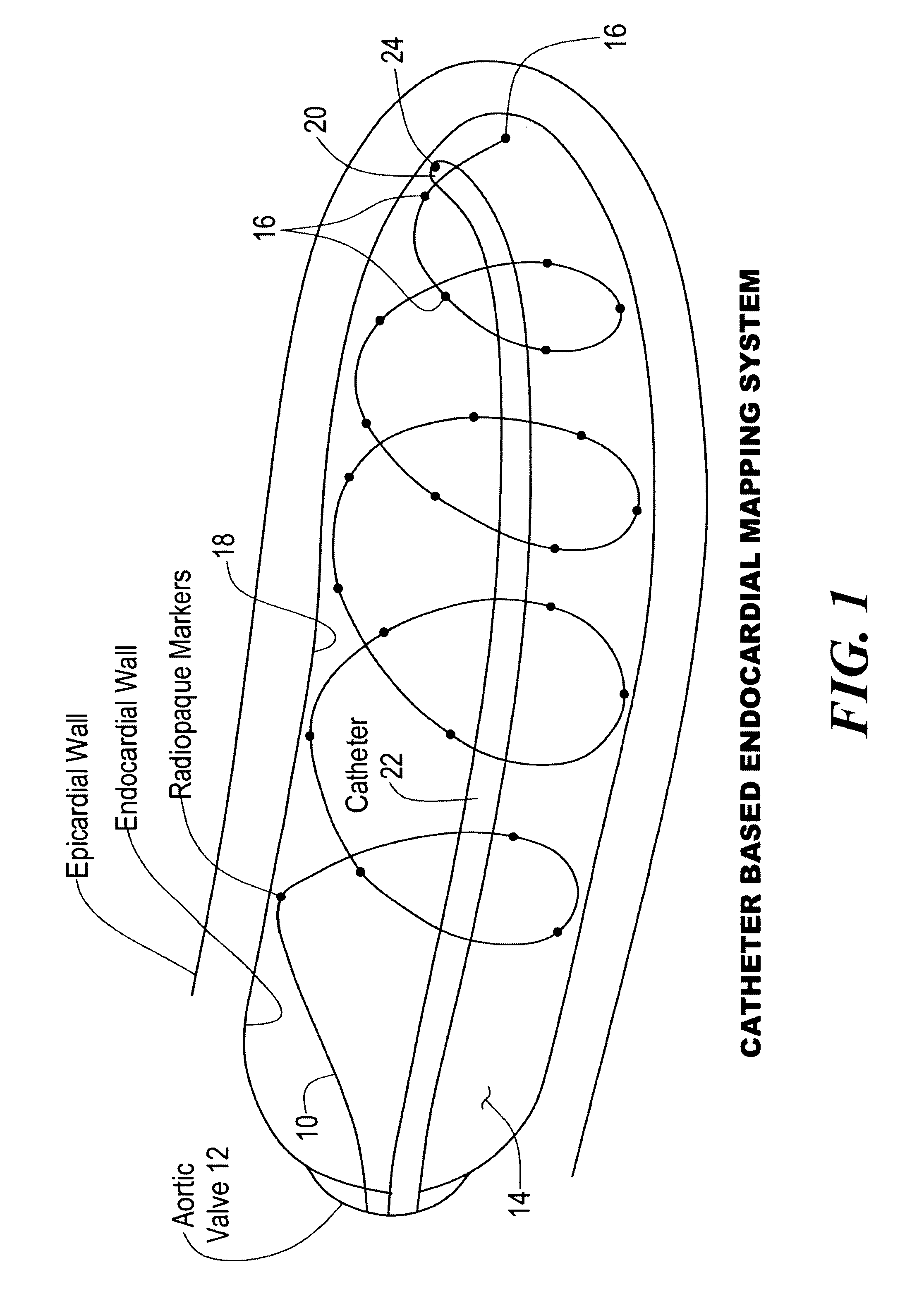
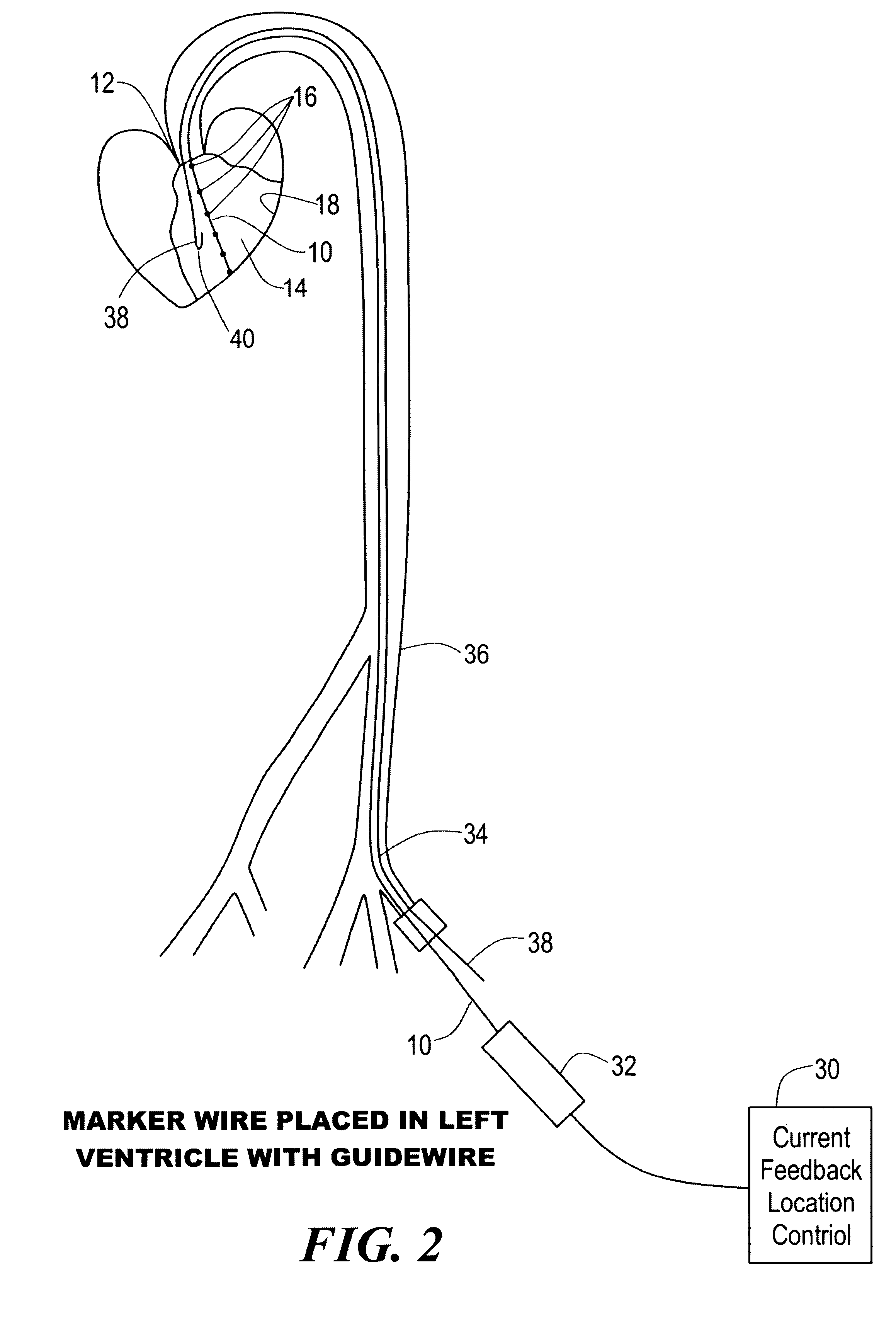
Percutaneous mapping system
InactiveUS6241665B1Simple and inexpensiveThe process is simple and effectiveElectrocardiographyCatheterRadiologyMapping system
A percutaneous mapping system includes a mapping wire, for percutaneous insertion into an internal body cavity, having a plurality of spaced imaging markers; and an insertion device for deploying the mapping wire in a spiral configuration inside the cavity with the markers distributed about the inner wall of the cavity.
Owner:MEDICAL SYST
Parking management system and method using lighting system
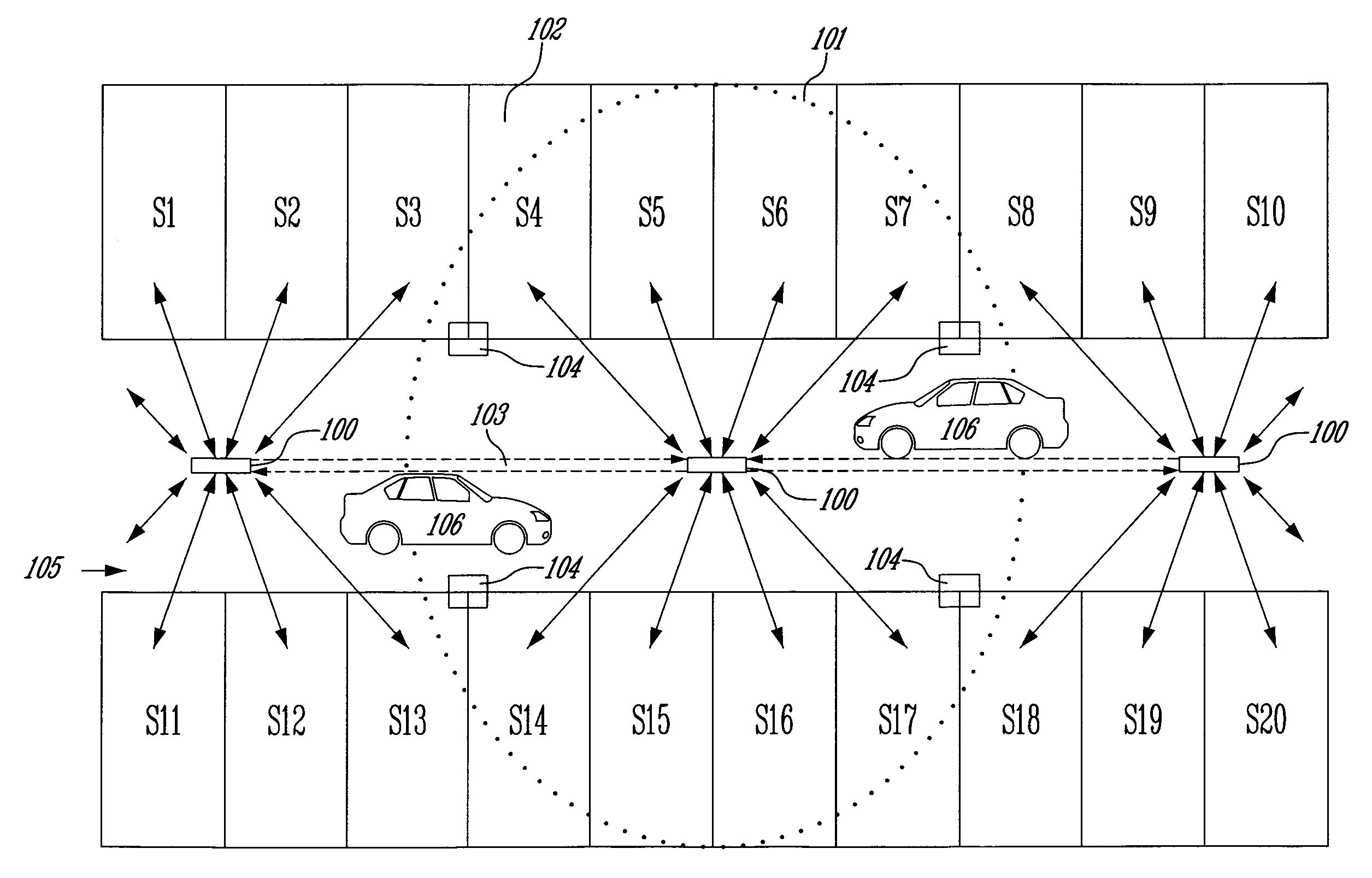
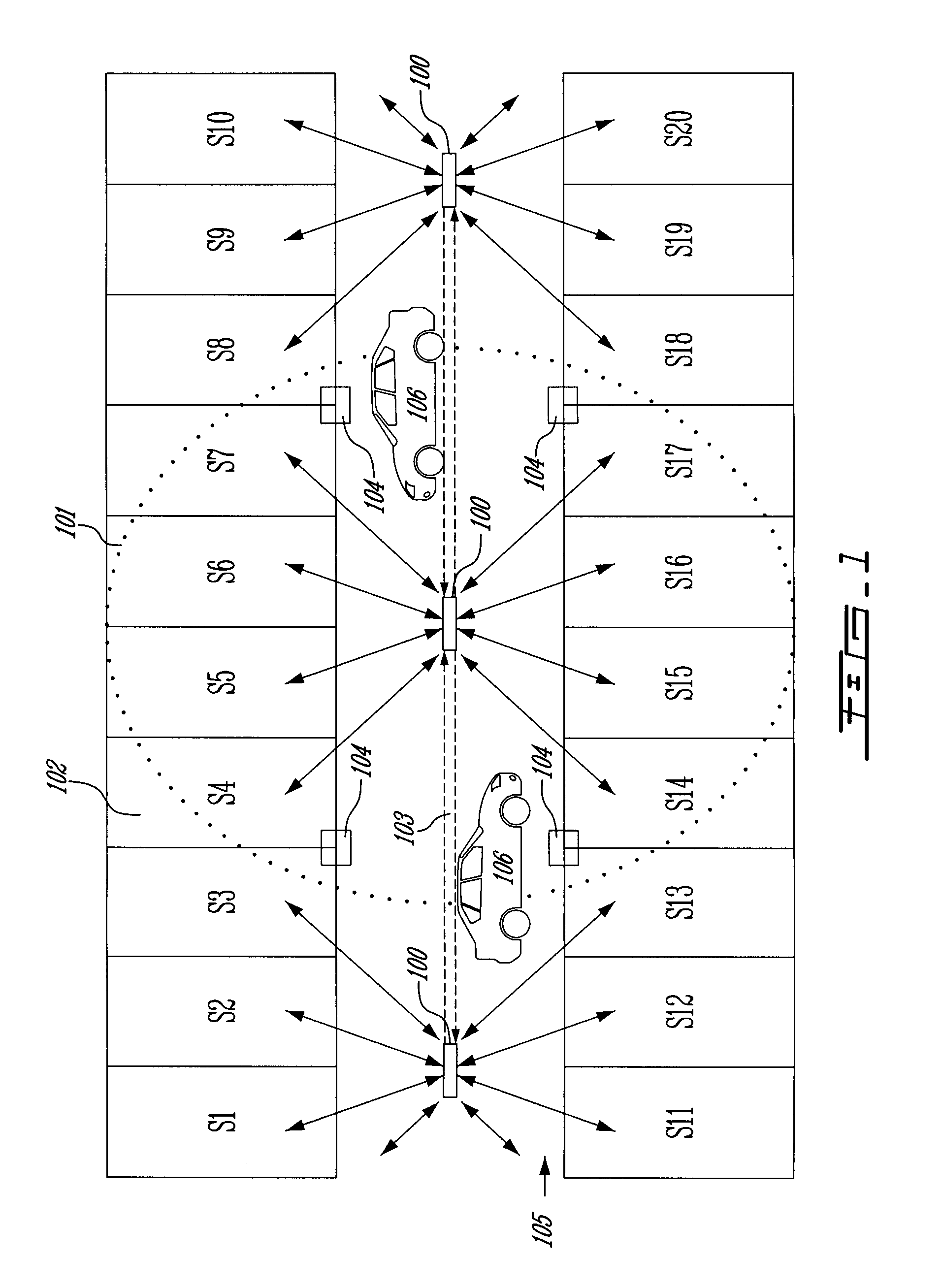
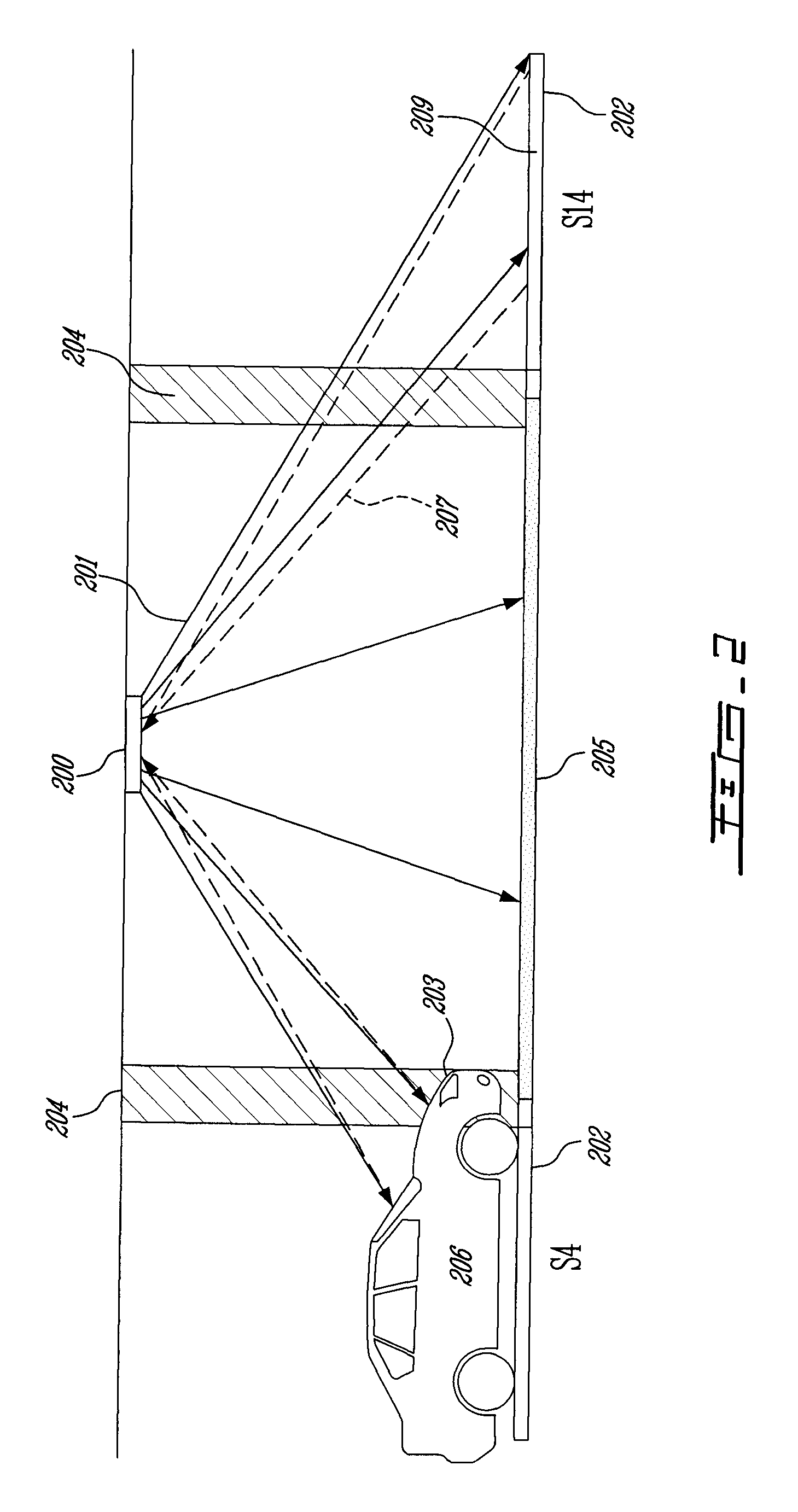
ActiveUS20100309024A1Detect presenceLow cost installationDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesParking spaceEngineering
A system and a method for detecting availability of a parking space in a parking facility are provided. A first method has the steps of providing a lighting system having at least one visible-light source for illumination of at least part of the parking space. Providing an available space time-of-flight trace. Providing an availability threshold value. Illuminating the at least part of the parking space using the at least one visible-light source. Emitting a status visible-light signal from the visible-light source in the predetermined direction toward the predetermined target in the parking space. Capturing a status reflection trace at the visible-light source. Determining a time-of-flight difference value by comparing the status reflection trace to the available space time-of-flight trace. Comparing the time-of-flight difference value with the availability threshold value and determining a status of the parking space to be one of available and not available. Another method has the steps of providing a lighting system having at least one visible-light source for illumination of at least part of the parking space. Providing a camera. Providing an available space region value. Providing an availability threshold value. Illuminating the at least part of the parking space using the at least one visible-light source. Emitting visible light from the visible-light source in the predetermined direction to the predetermined target in the parking space. Capturing a reflection of the emitted visible light at the camera and determining a status region value. Determining a region difference value by comparing the status region value to the available space region value. Comparing the region difference value with the availability threshold value and determining a status of the parking space to be one of available and not available.
Owner:LEDDARTECH INC
Method and Apparatus for Prevention of Catheter Air Intake
InactiveUS20110270182A1Quantity minimizationEasy to removeCatheterIntravenous devicesImpellerCatheter
A system for preventing air from entering a first catheter of a multi-catheter system. Air is prevented from entering the proximal end of the first catheter by an axially elongate chamber having an impeller, the chamber being affixed to the proximal end of the first catheter. The air is removed through a port near the centerline of the chamber. Liquid removed with the air is returned to the chamber to minimize liquid loss during the procedure. A second catheter inserted through the chamber and into the first catheter is unable to entrain gas into the first catheter because any gas that enters the chamber is routed to the centerline of the chamber where it is removed. Inflow of fluid from an external pump scrubs the second catheter shaft of air bubbles attached by surface tension.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
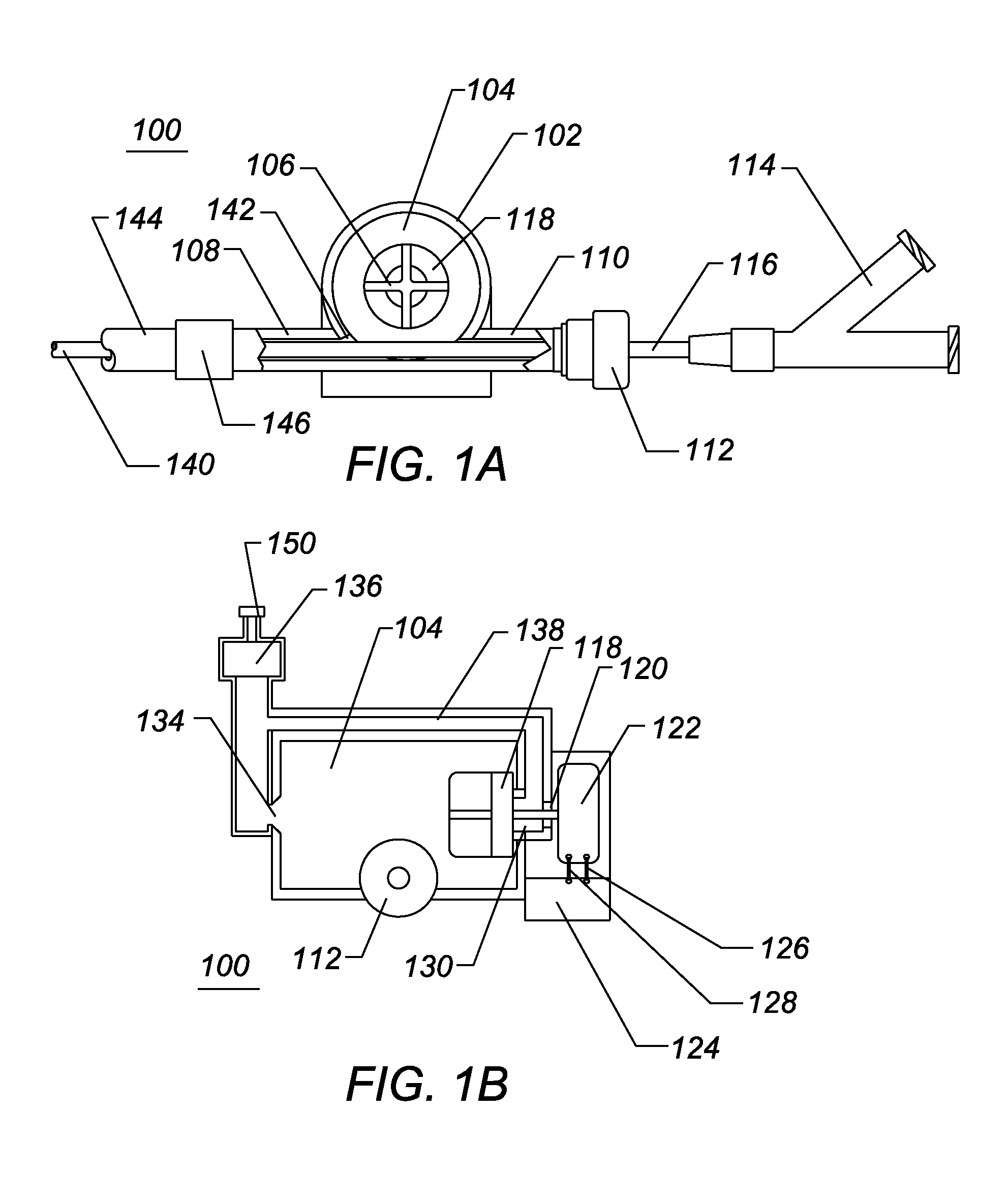
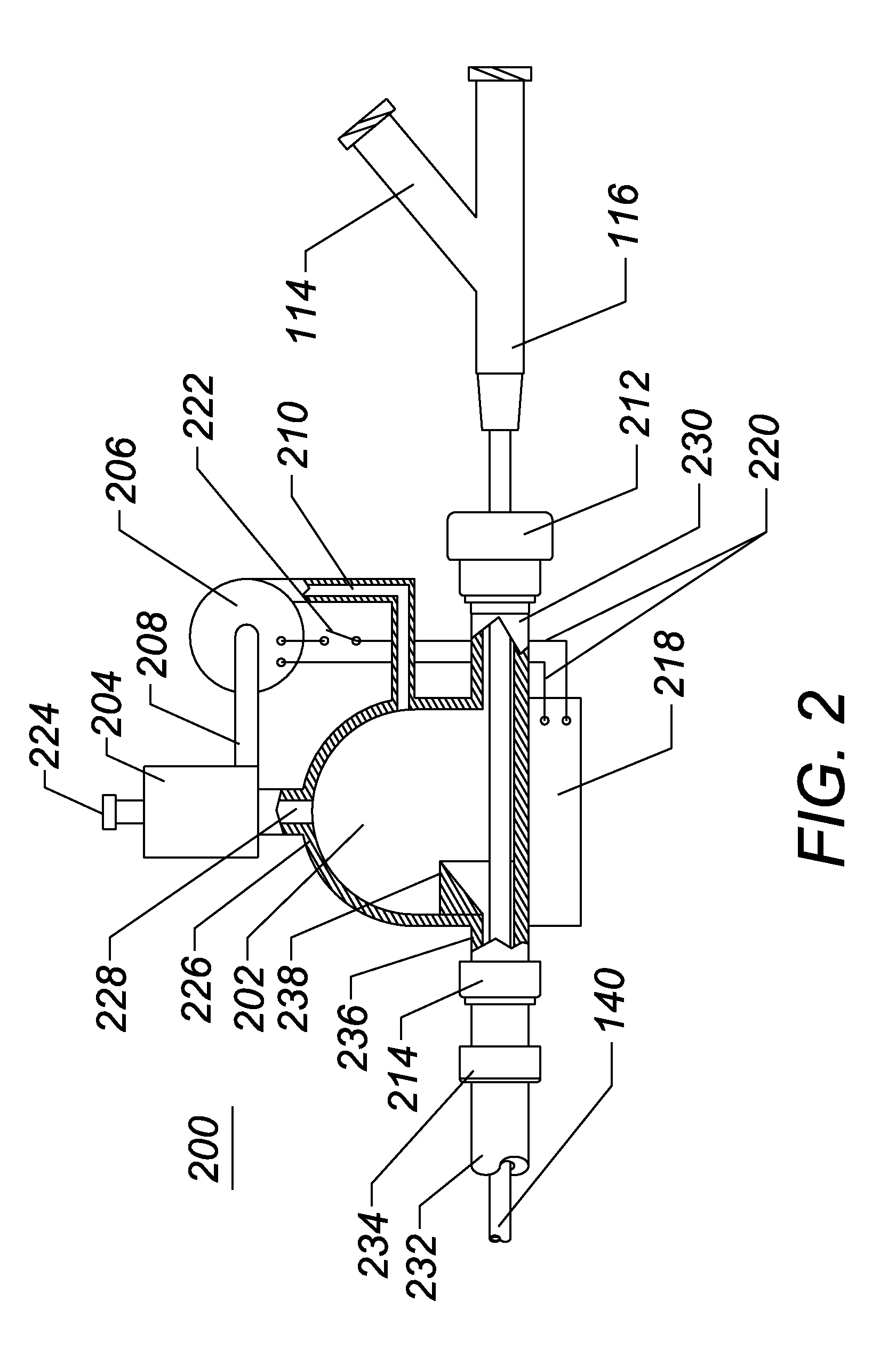
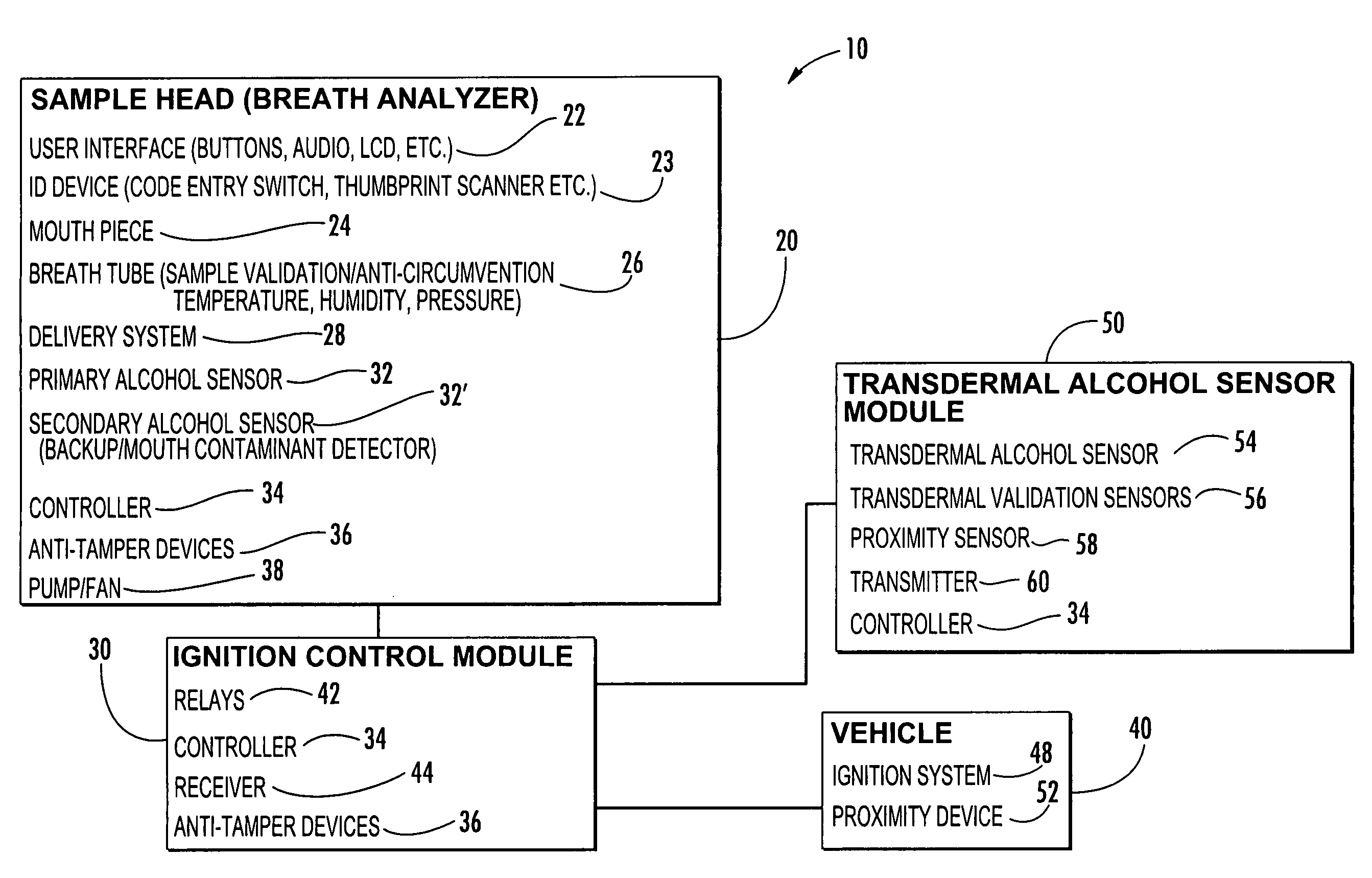
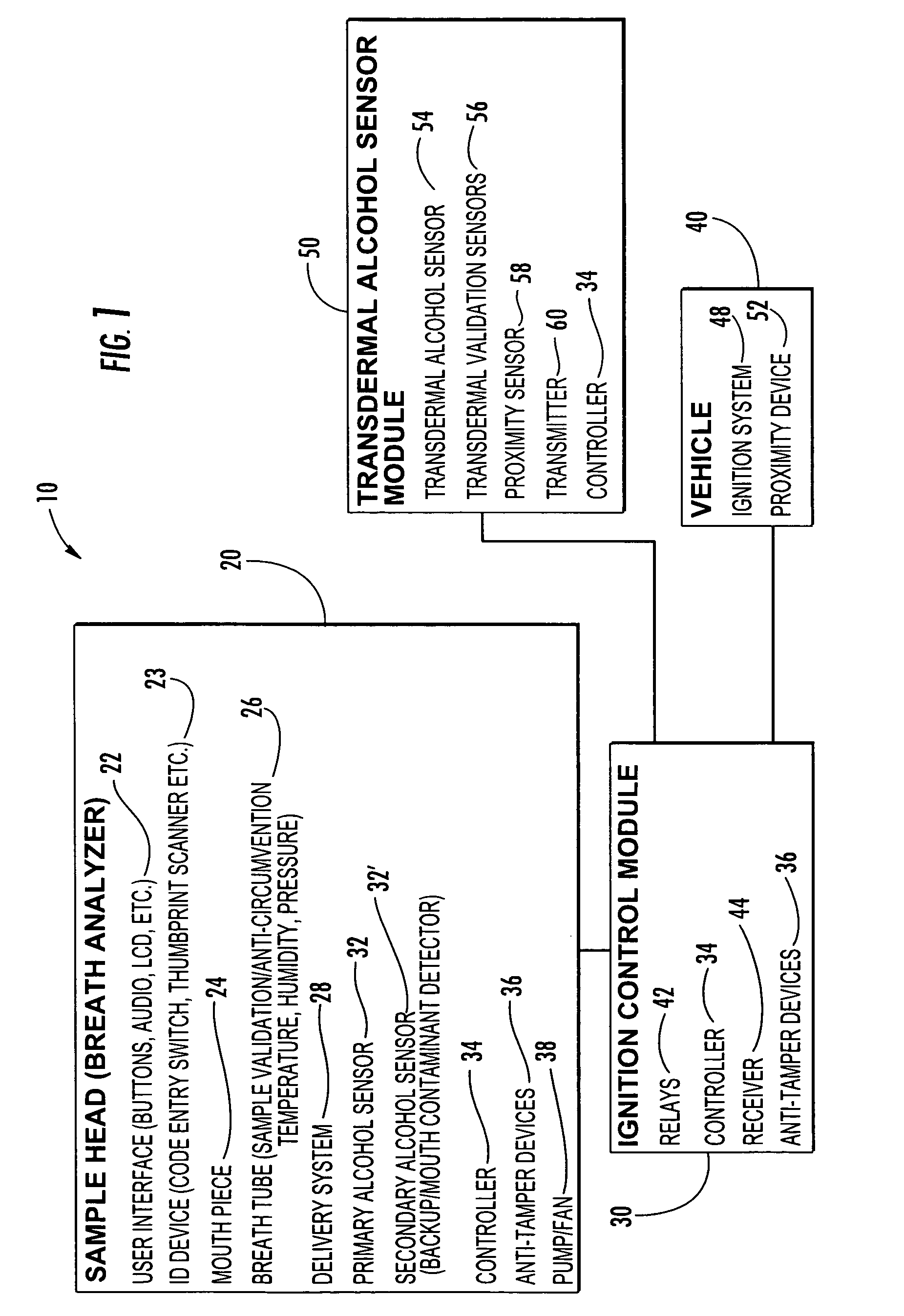
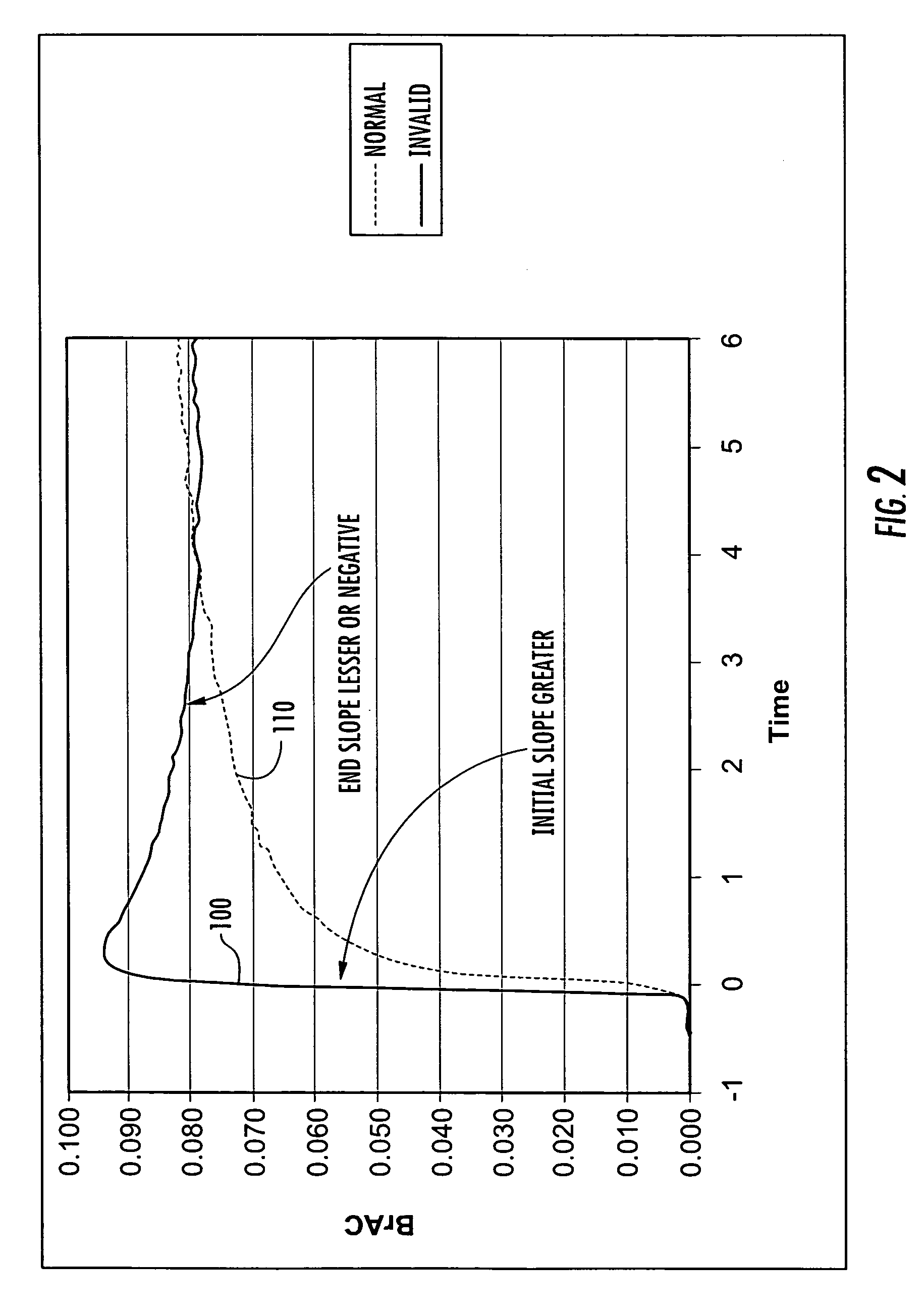
Vehicle ignition interlock systems with retesting frequency control
InactiveUS20060237253A1Reduce frequencyHigh frequencyElectric devicesElectrical apparatusControl theoryBreath analyzer
A vehicle ignition interlock system includes a breath analyzer and a controller operably connected to the breath analyzer and to an ignition system of the vehicle. The controller compares detected breath alcohol levels of the vehicle operator with a threshold value, and is configured to prevent vehicle ignition if a breath alcohol level detected by the breath analyzer is greater than or equal to a threshold value. The controller also requires the vehicle operator to periodically take breath analyzer retests after vehicle ignition in order to allow vehicle operation to continue. The controller can reduce the frequency of periodic retests in response to one or more retests when the breath alcohol level of the vehicle operator is below a threshold value. The system may include a transdermal alcohol sensor, a mouth contamination sensor, a mouth contamination sensor, and redundant alcohol sensors.
Owner:MONITECH
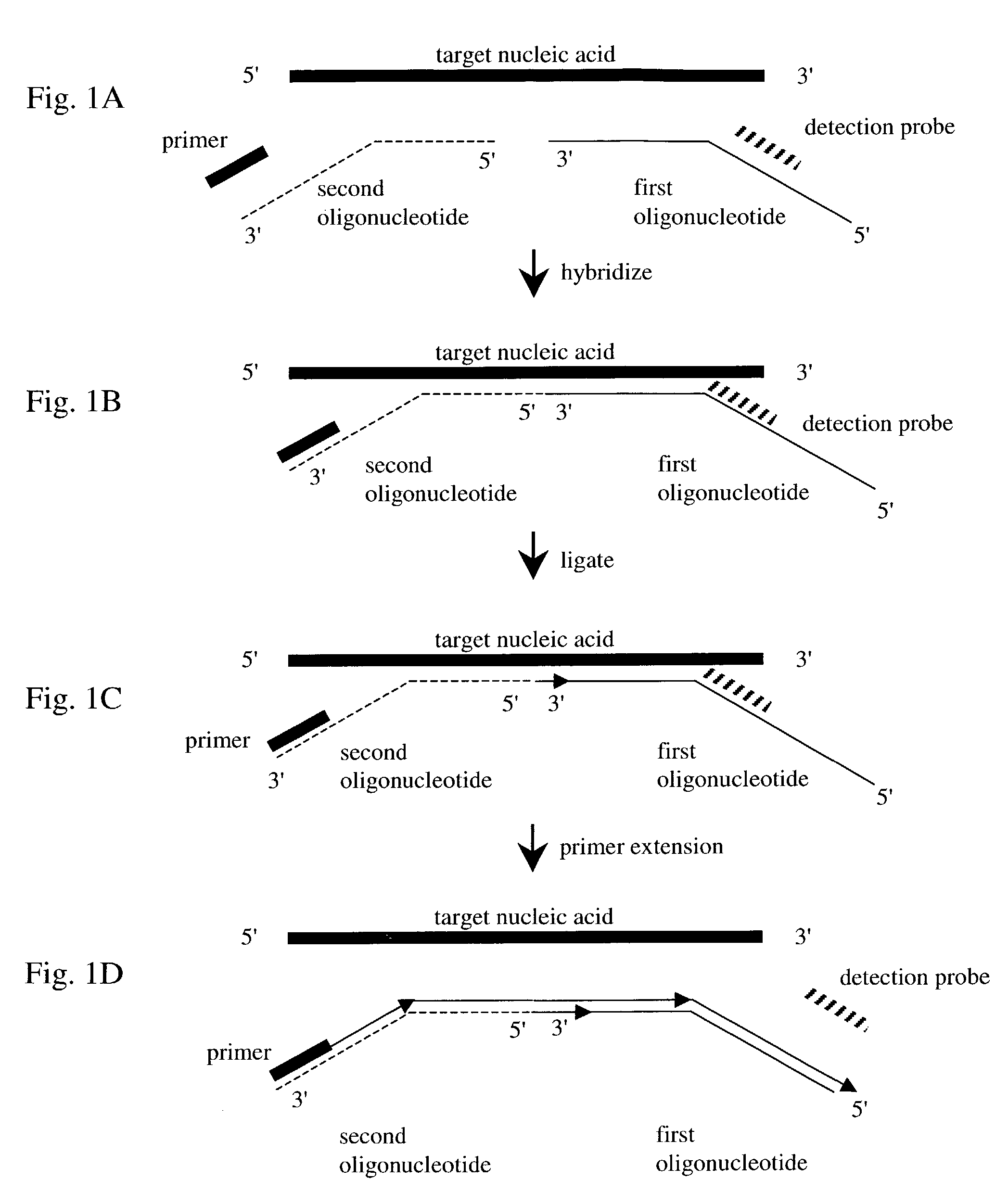
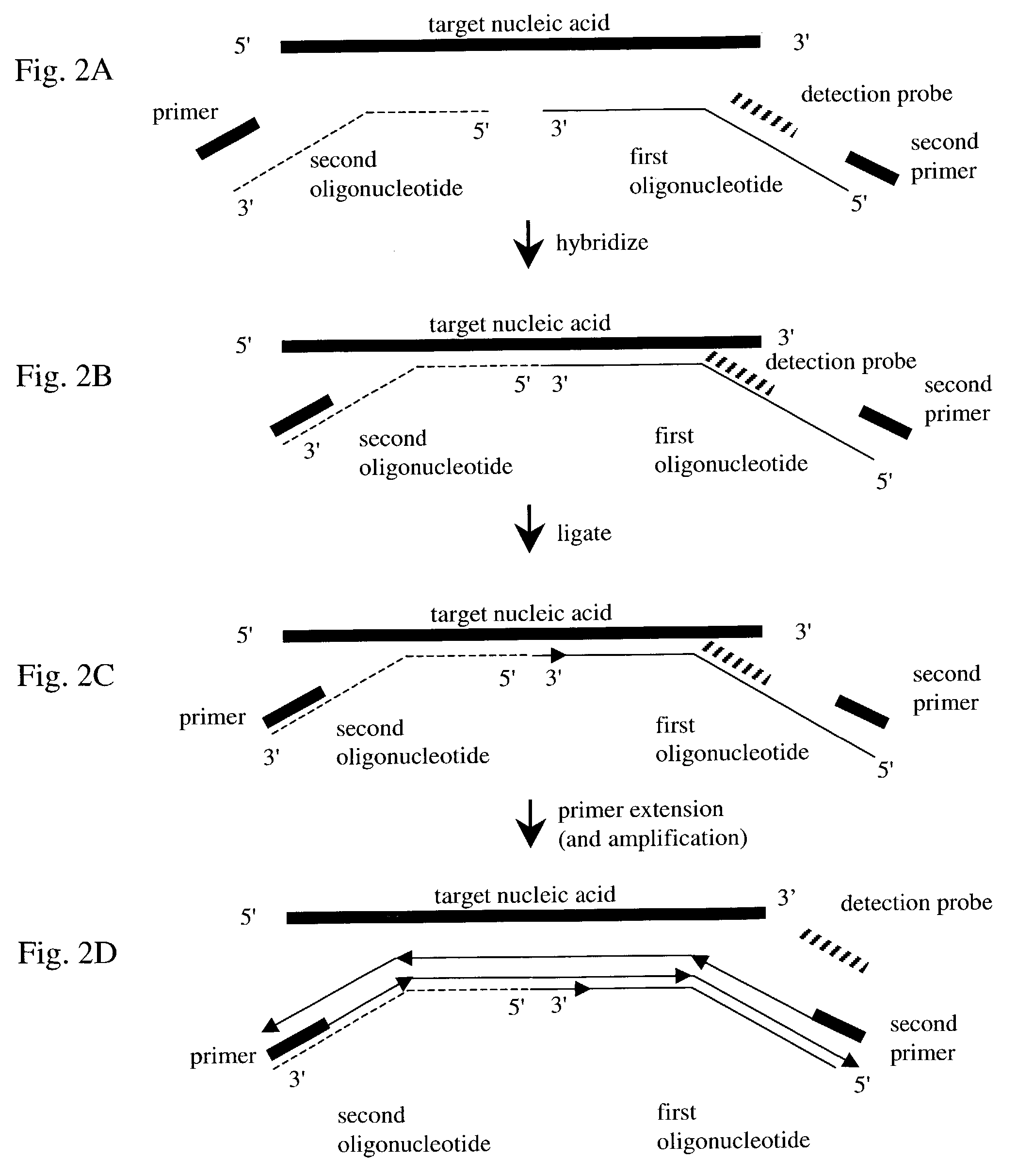
Nucleic acid detection method
InactiveUS7282355B2Rapid and reliable and cost-effectiveDetect presenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed are methods for detecting a target nucleic acid molecule having a known sequence among a plurality of nucleic acid molecules. The method includes hybridizing two oligonucleotides to adjacent nucleotide sequences on the target nucleic acid molecule, ligating the two oligonucleotides together, and extending a primer that hybrizes to the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide that hybrized to the 5′ nucleotide sequence on the target nucleic acid molecule. If the target nucleic acid molecule is present (and thereby allowing ligation of the two oligonucleotides), extension of the primer dislodges a detection probe hybridized to the 5′ end of the oligonucleotide that hybridized to the 3′ nucleotide sequence on the target nucleic acid molecule.Also disclosed are kits for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Live bioload detection using microparticles
ActiveUS20120009588A1Quick checkDetect presenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroparticleBiology
The present invention provides methods to concentrate cells onto microparticles, to concentrate the microparticles, and to detect the cells. The present invention also includes unitary sample preparation and detection devices to be used in accordance with the methods.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
System for monitoring quality of water system
InactiveUS20070257806A1Detect presenceProvide real-timeWater/sewage treatmentTesting waterComputer scienceControl logic
A monitoring, detection and alarm for water systems includes a plurality of sensing components for detecting the presence of target contaminants in water and for measuring the overall quality of the water. The apparatus contains water sensing components, a database for storing sensor data and processors for data analysis using artificial intelligence. The apparatus provides control logic to take responsive action based on the results of the detection of the target contaminants. Responsive action includes, but is not limited to, generation of reports and alarm signals that are delivered in near real-time to users of the system.
Owner:SOURCE SENTINEL
Detection of target molecules with labeled nucleic acid detection molecules
InactiveUS20070048759A1Easy to detectImprove utilizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionChemistry
The invention is directed to a detection molecule for detection of a target molecule. The detection molecule includes a probe specific to the target molecule. One or more multimer nucleic acid molecules are connected to the probe, whereby the multimer is also coupled to at least one detectable label. The detection molecules are utilized in a method to detect the presence of one or more target molecules in a sample.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Real-time hdr video for vehicle control
ActiveUS20180048801A1Improve utilizationImprove securityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsVehicle controlLight level
The invention provides an autonomous vehicle with a video camera that merges images taken a different light levels by replacing saturated parts of an image with corresponding parts of a lower-light image to stream a video with a dynamic range that extends to include very low-light and very intensely lit parts of a scene. The high dynamic range (HDR) camera streams the HDR video to a HDR system in real time—as the vehicle operates. As pixel values are provided by the camera's image sensors, those values are streamed directly through a pipeline processing operation and on to the HDR system without any requirement to wait and collect entire images, or frames, before using the video information.
Owner:CONTRAST INC
Living being presence detection system
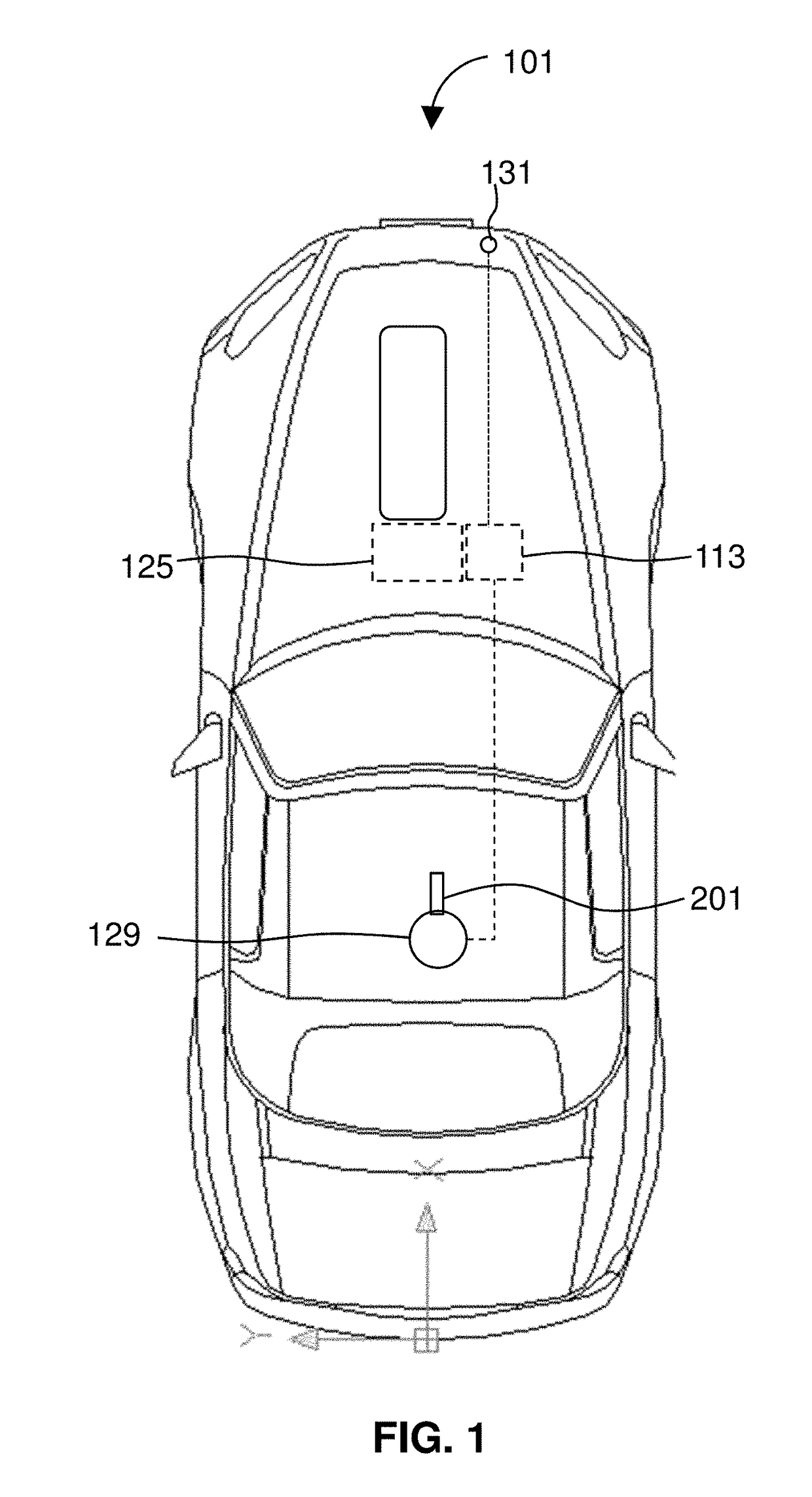
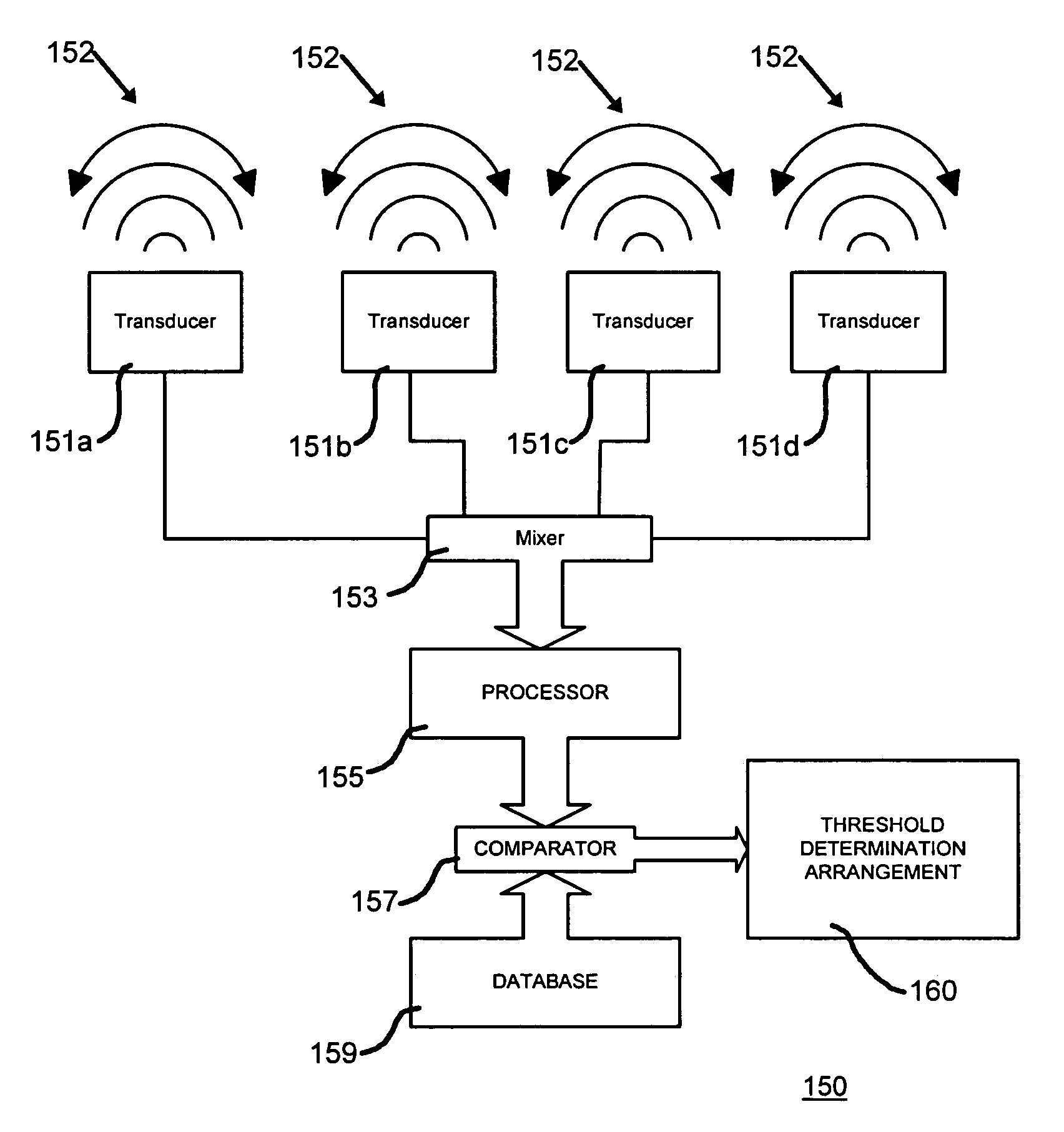
InactiveUS7417536B2Facilitates the rescue of living beingsDetect presenceFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital data processing detailsTransducerMems sensors
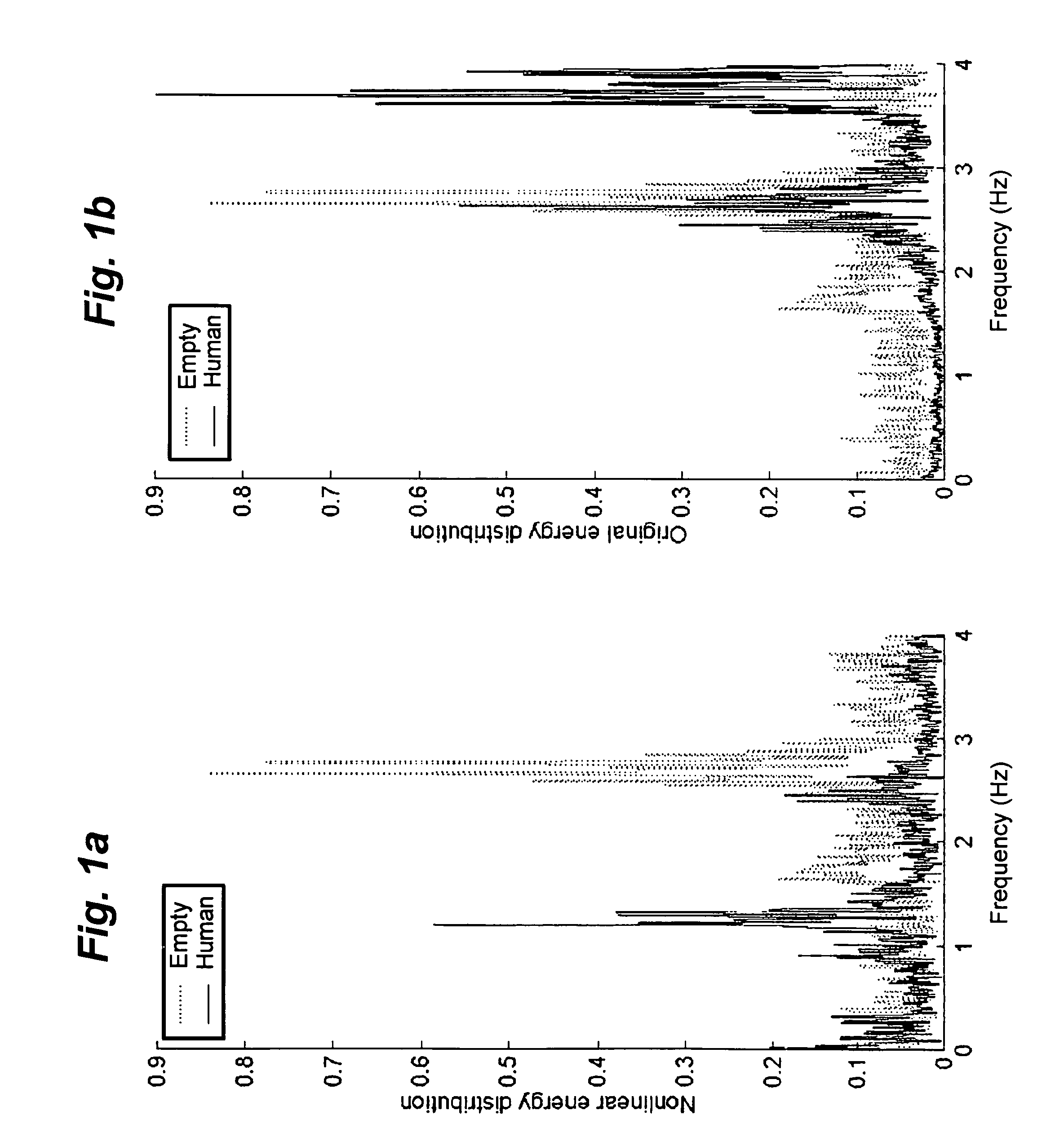
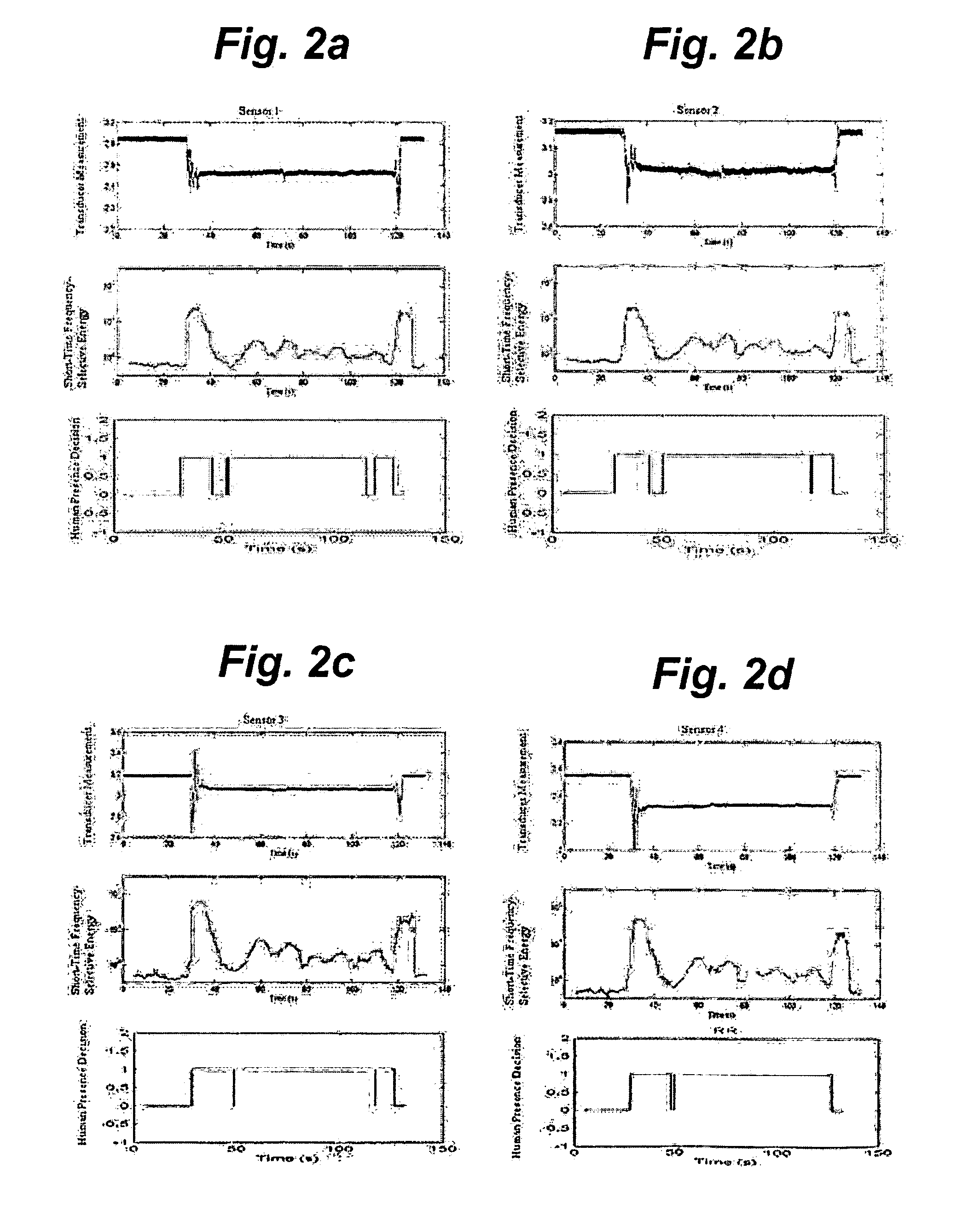
A system for distinguishing between a first condition corresponding to a living subject being directly in contact with an object of interest, and a second condition corresponding to the absence of contact between the living subject and the object of interest. A transducer, which may be a MEMs sensor, is disposed in predetermined relationship to the object of interest and produces a transducer signal responsive to a pressure wave resulting from the living subject being directly in contact the object of interest. A database stores data corresponding to the first condition and may contain additional data corresponding to the second condition. A processor calculates an algorithm of a non-linear short-term frequency-selective energy distribution of the transducer signal over time to produce transducer signal data. An arrangement, which may be a human listener or a processor system, determines a threshold between the first and second conditions in response to the transducer signal data and the first and second data. The direct contact may be a tap or stroking contact by a living subject. The transducer can be disposed within, or on the exterior of, the object of interest.
Owner:LAKSHMANAN SRIDHAR +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com