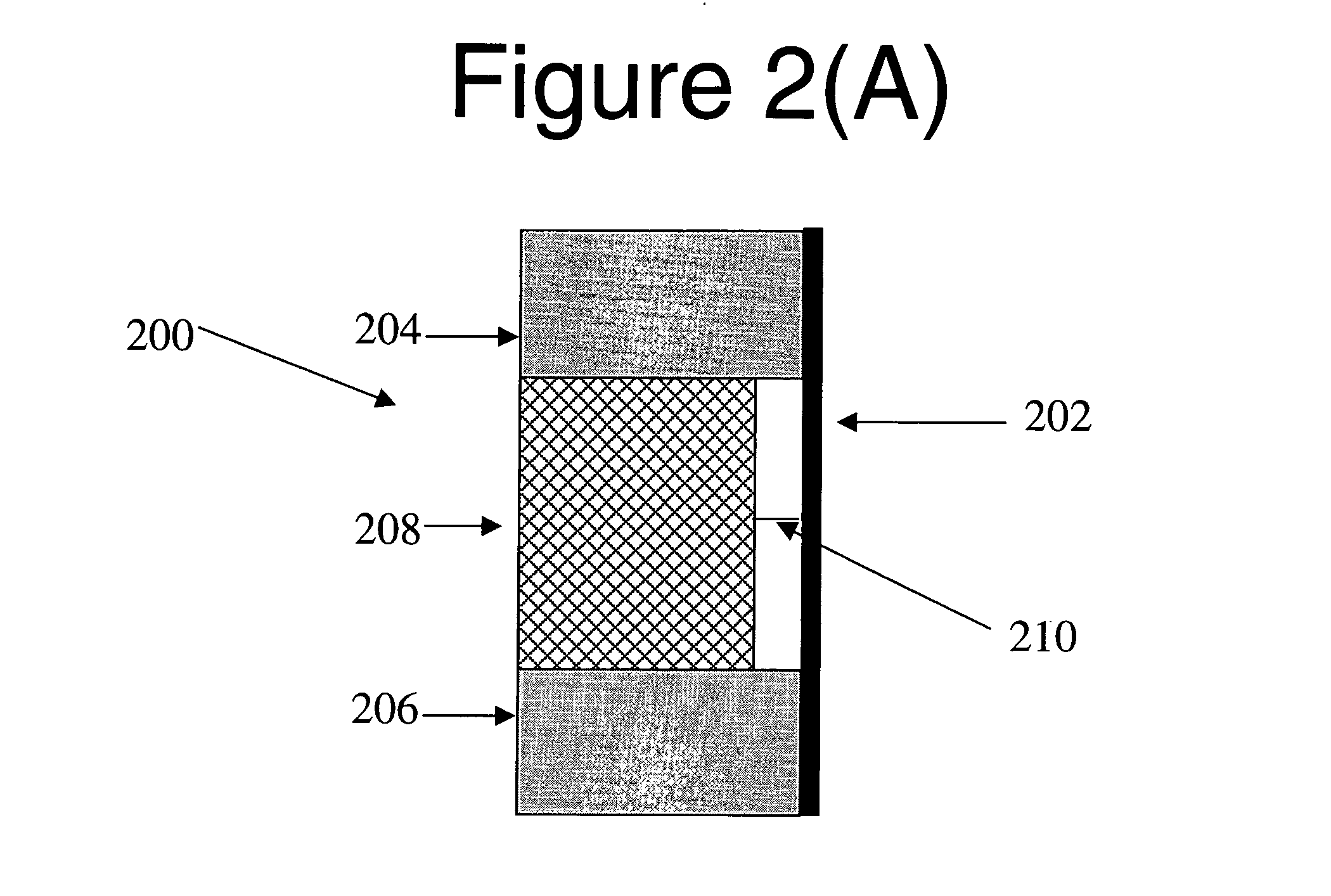
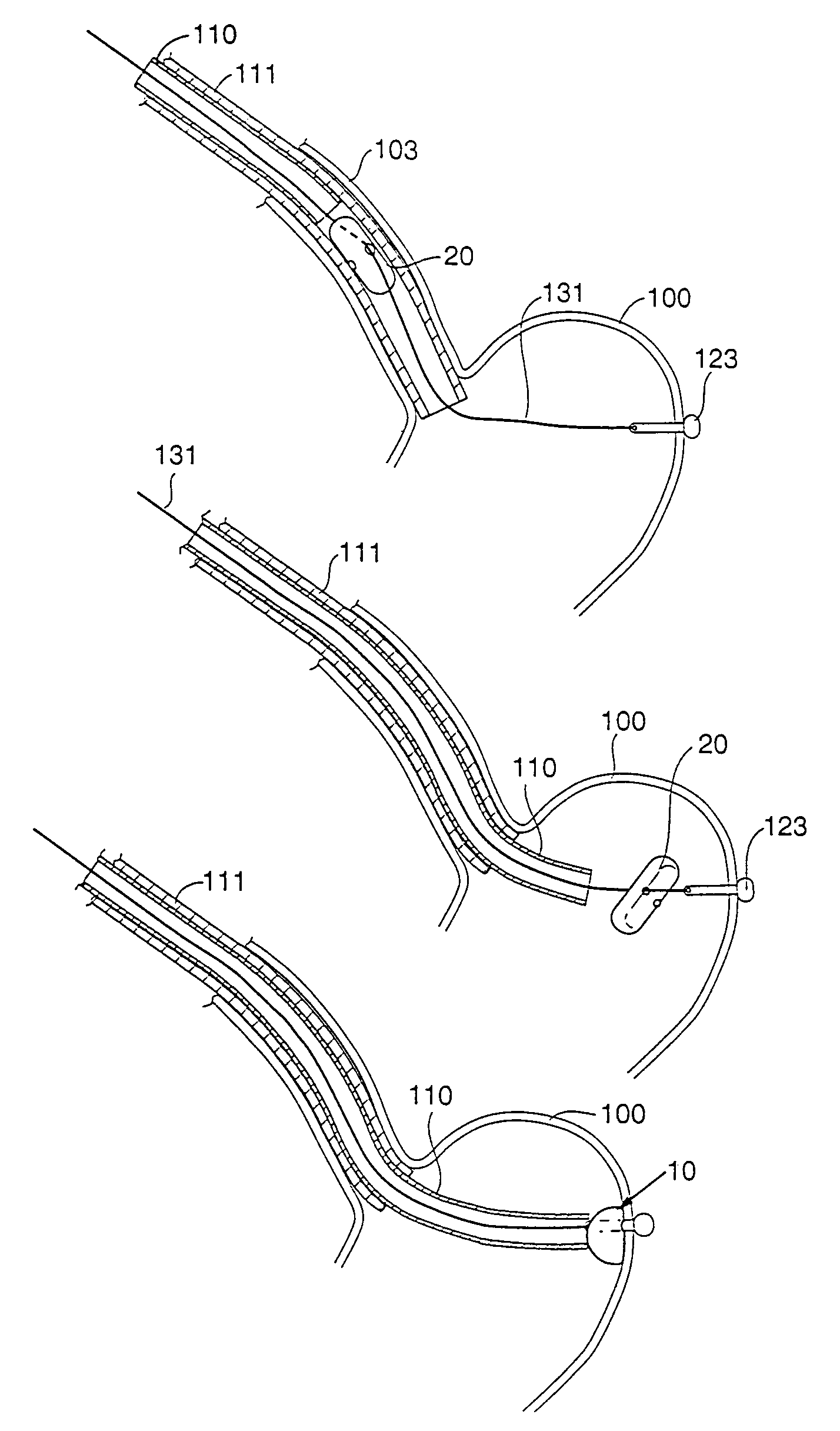
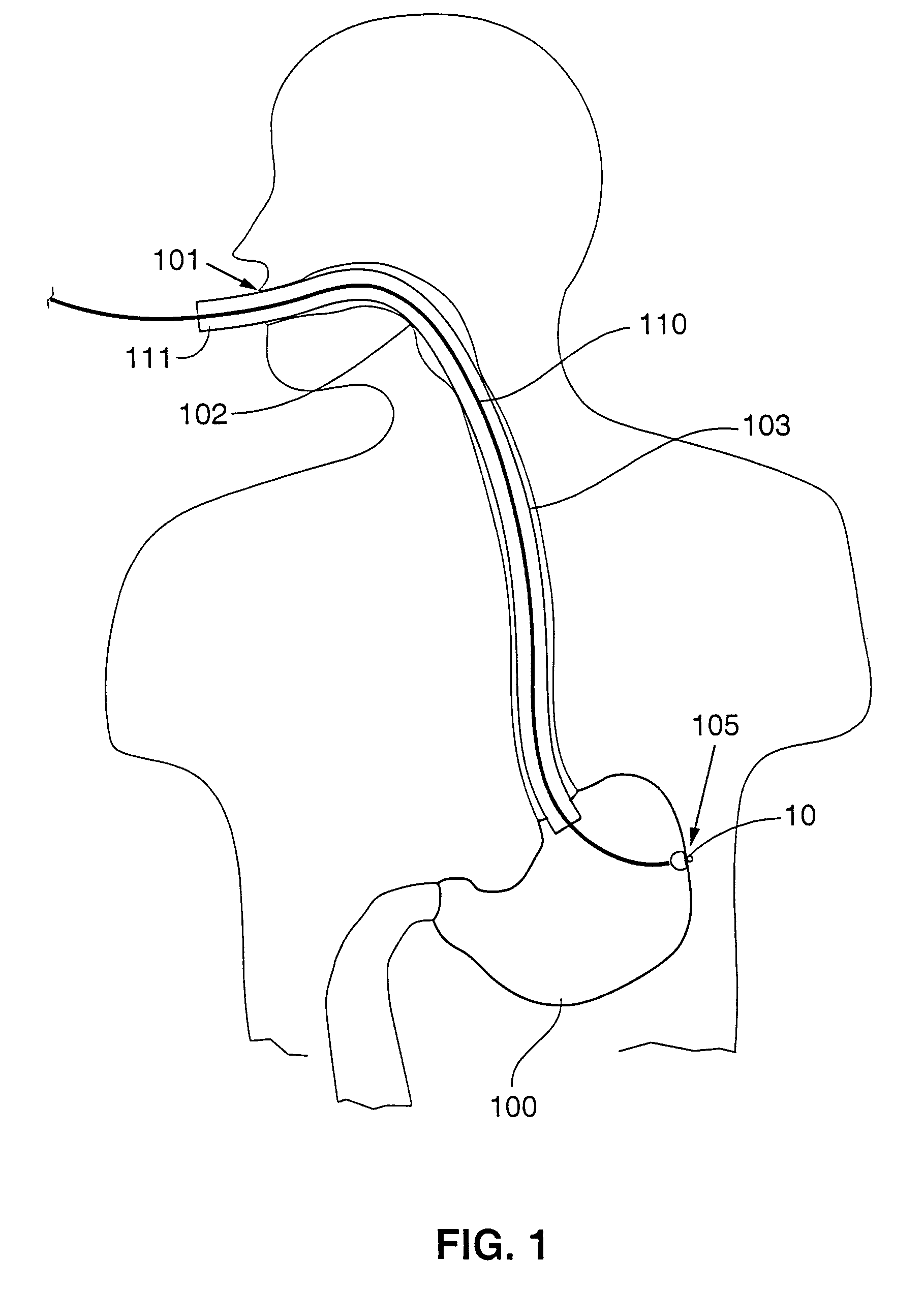
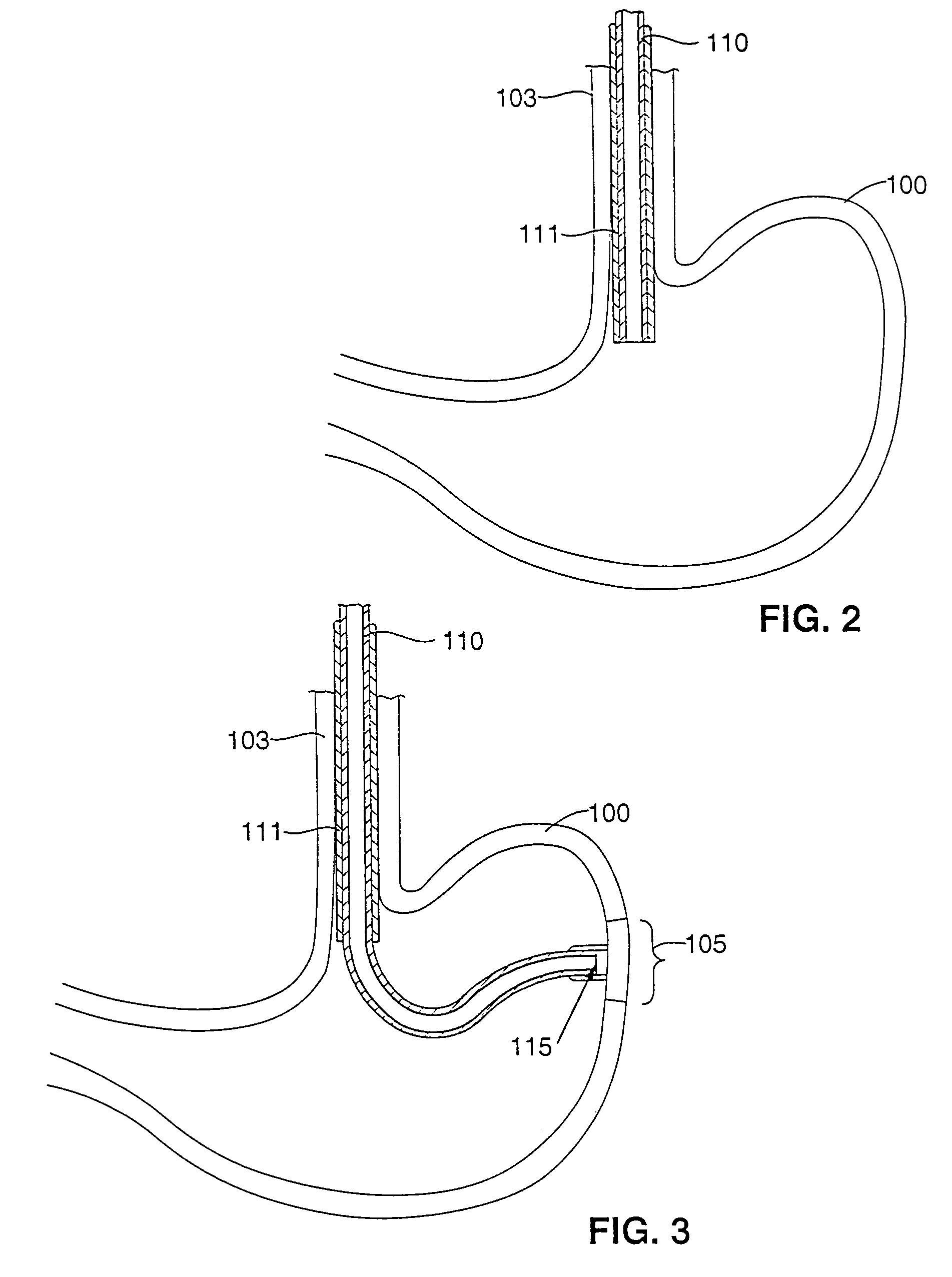
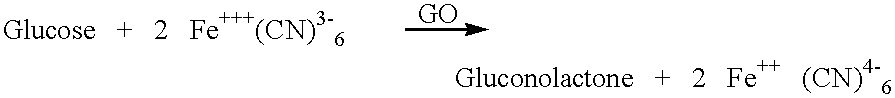Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11951results about "Material resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
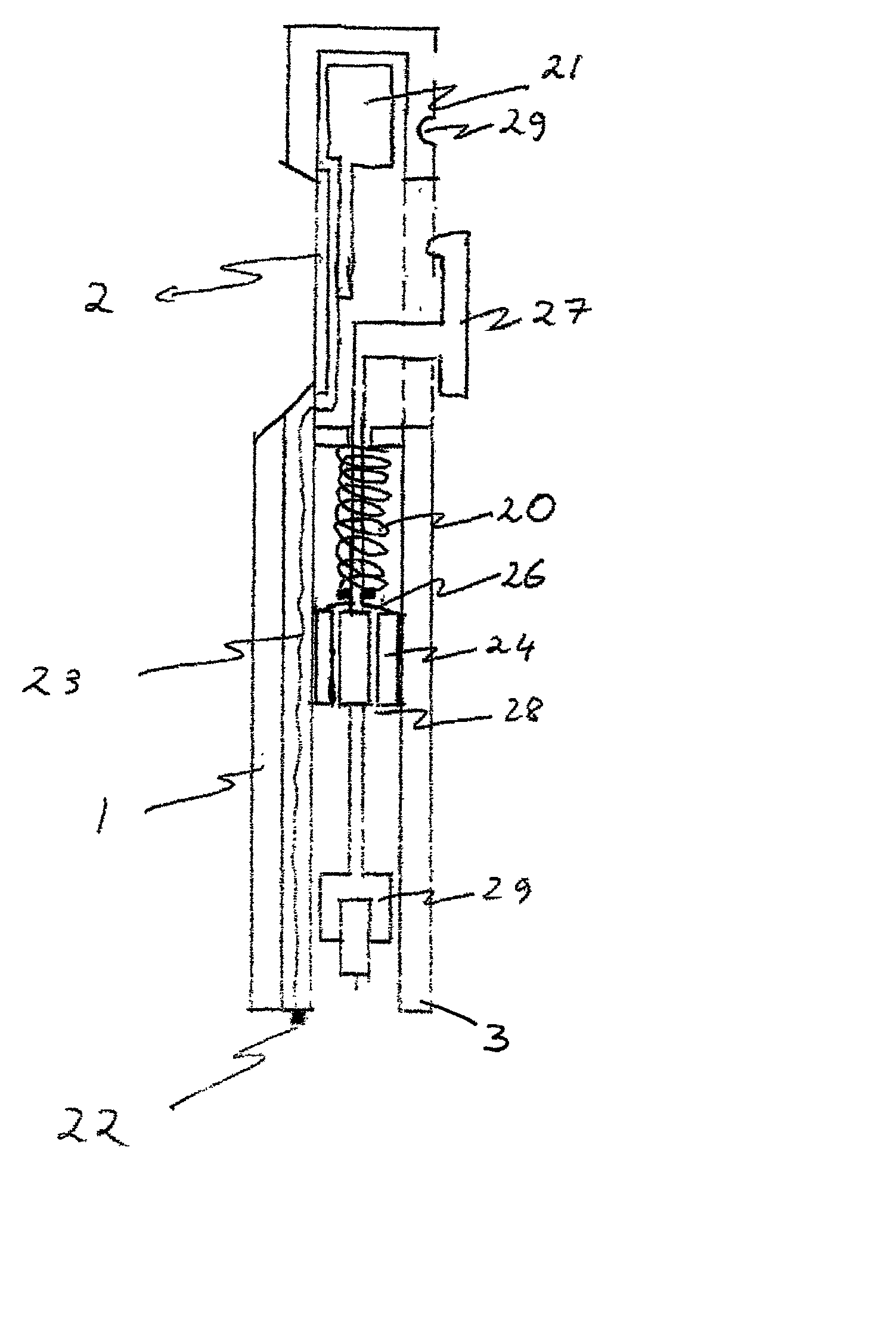
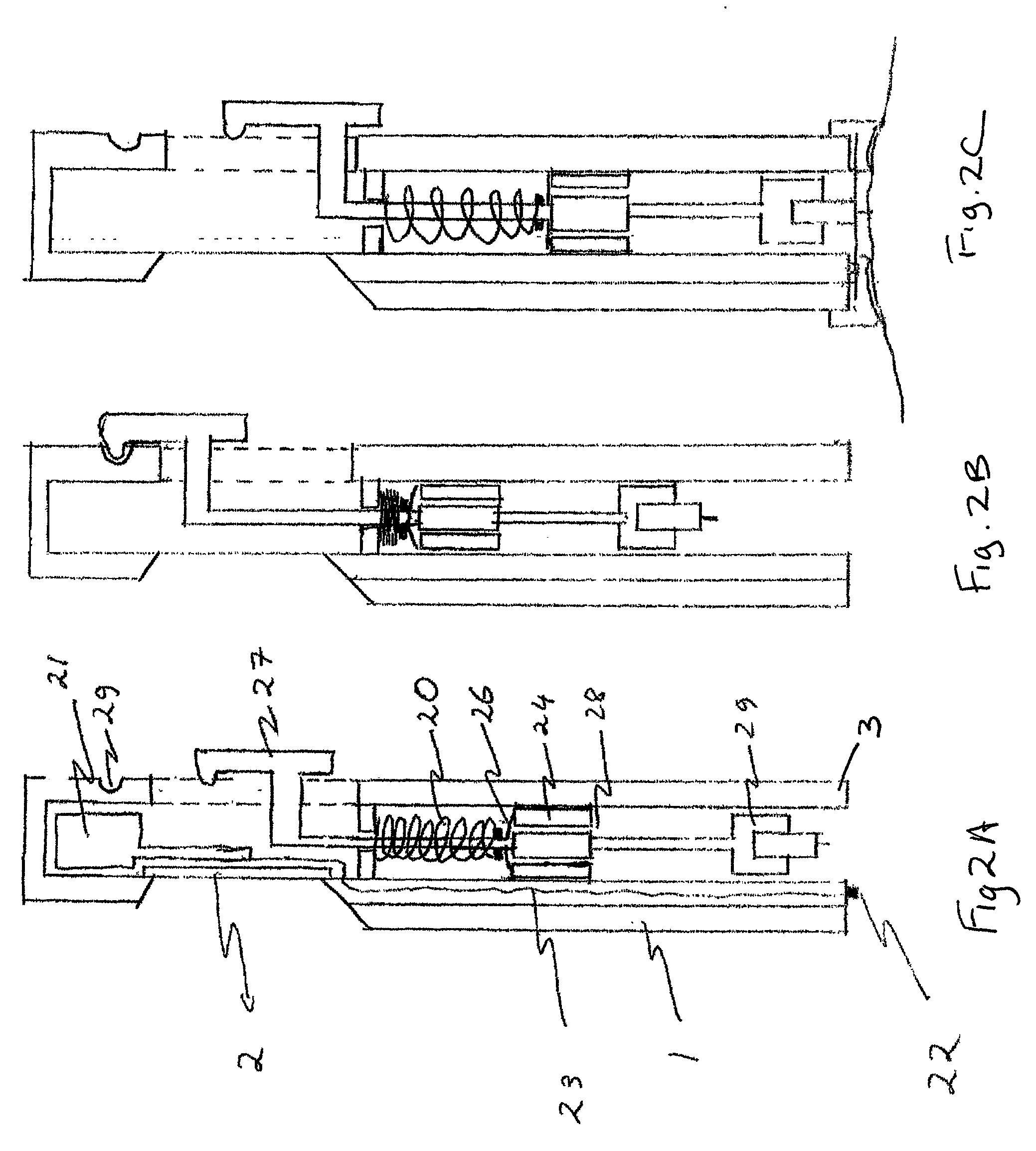
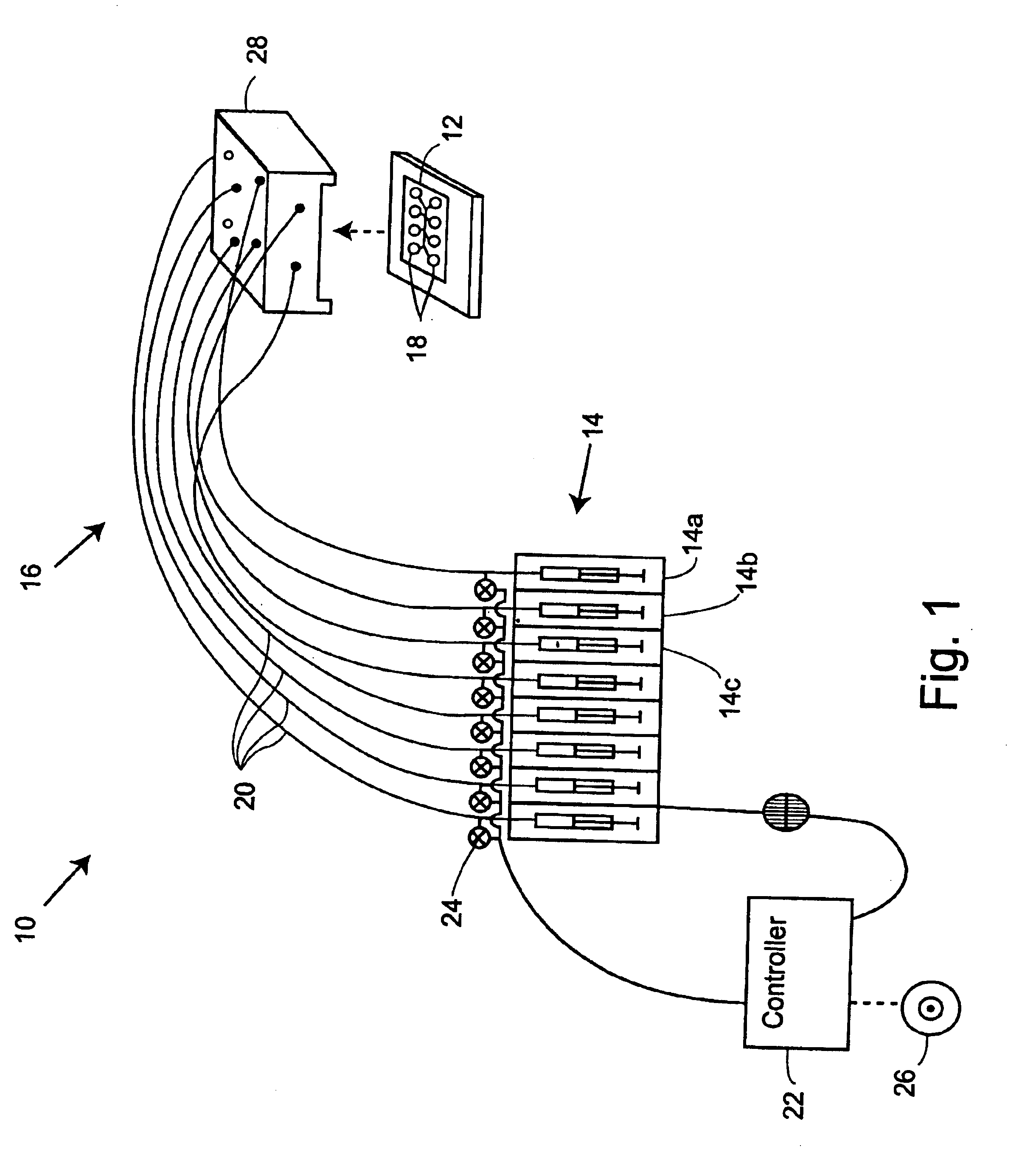
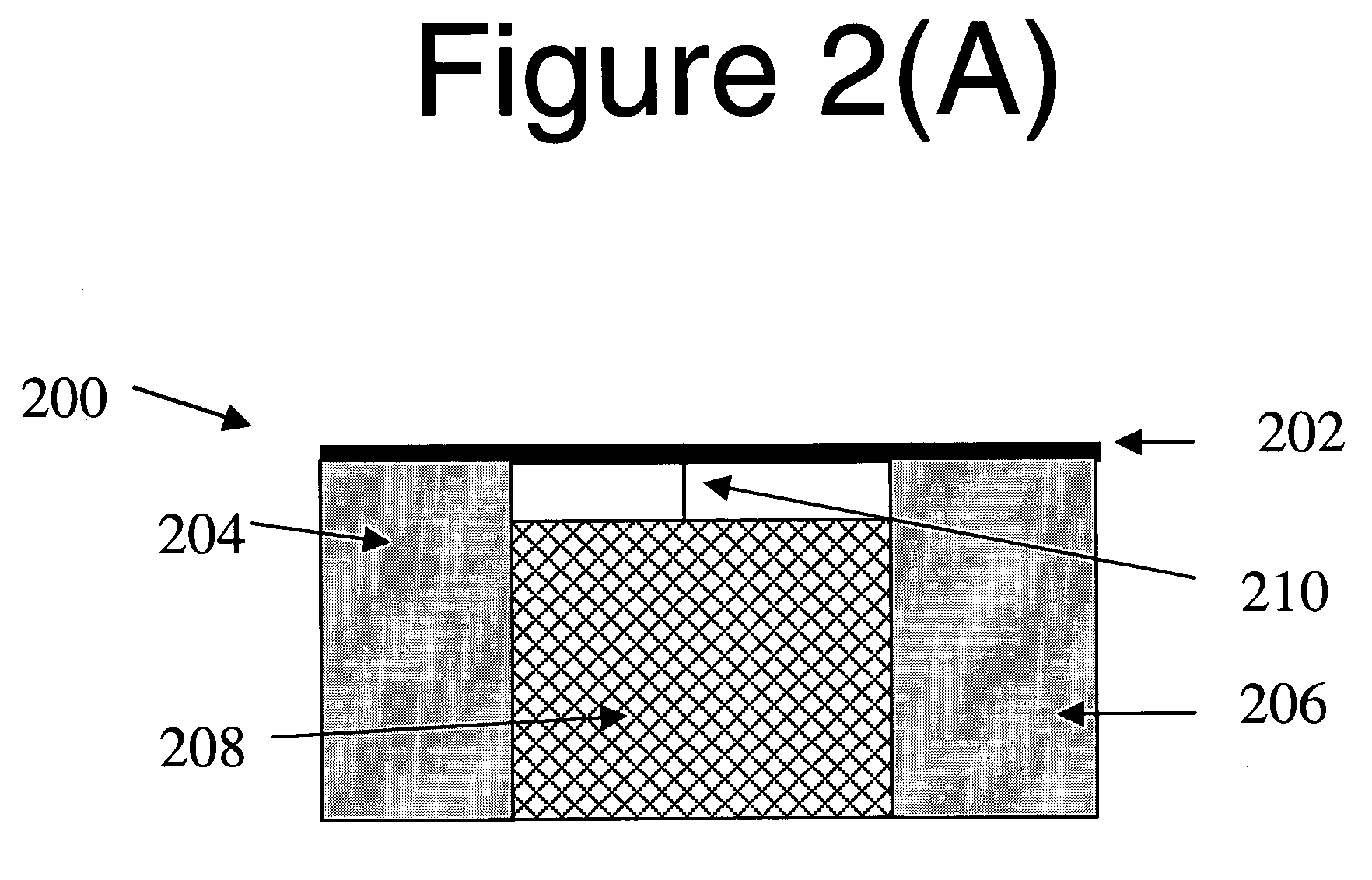
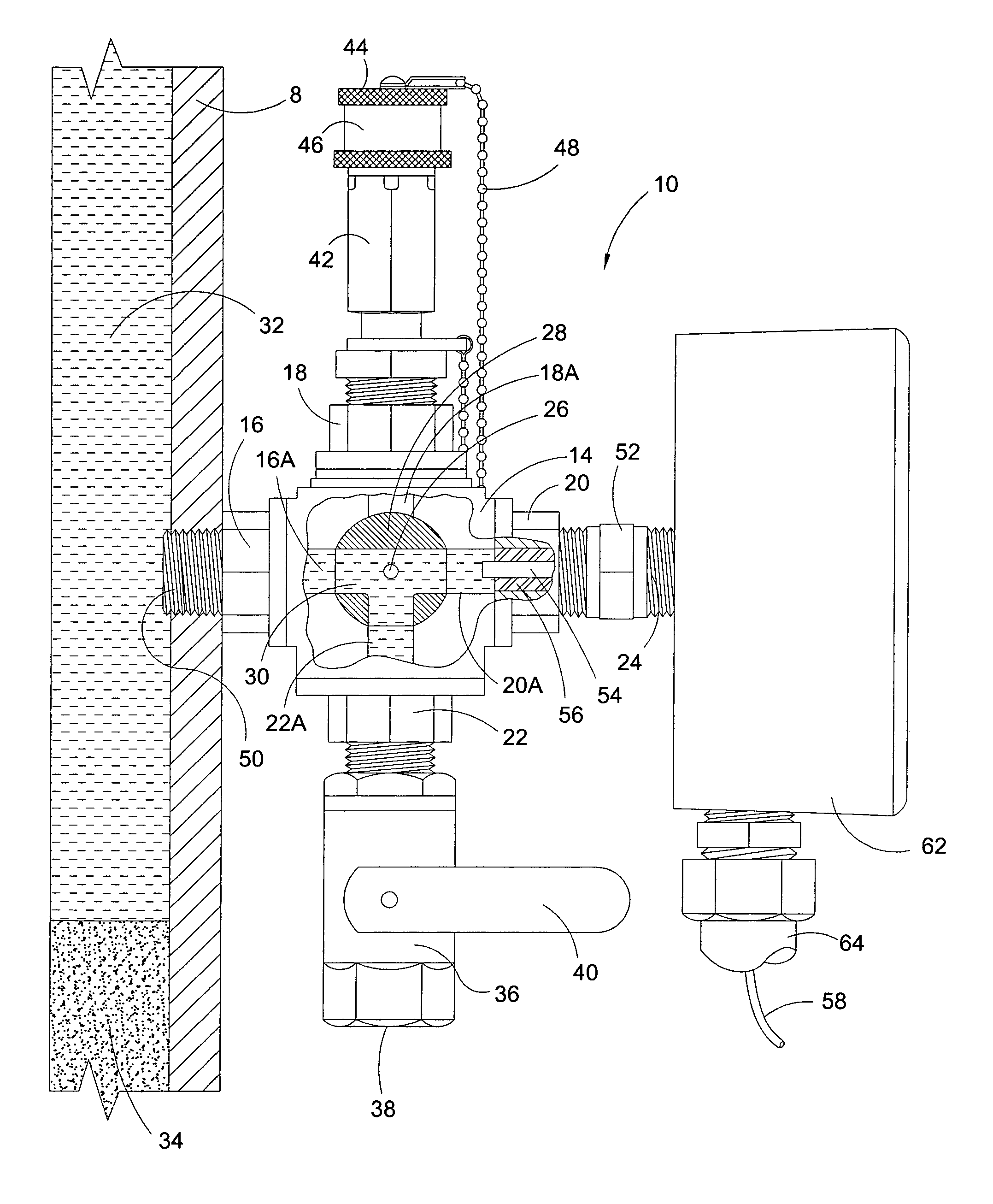
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
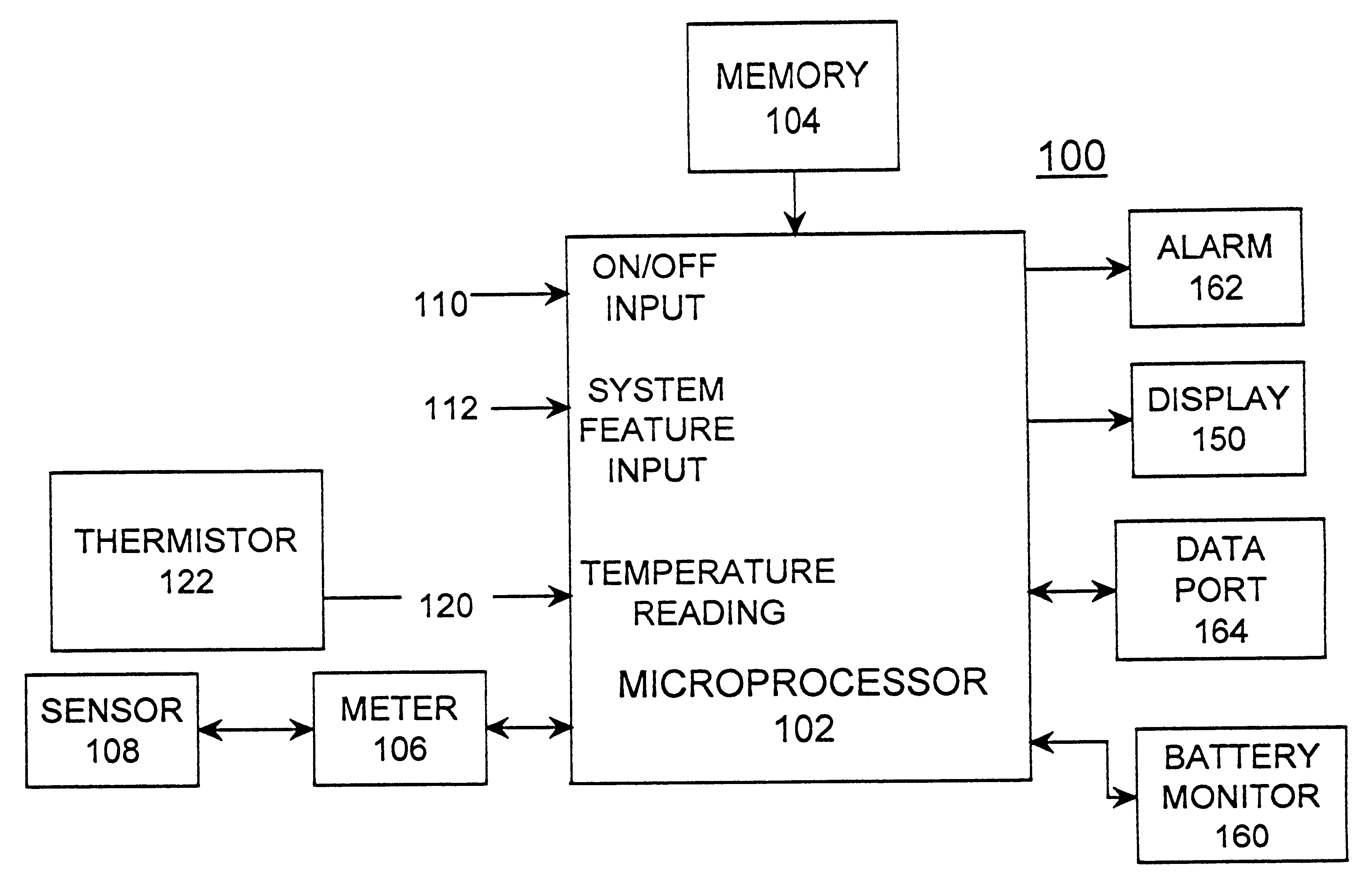
InactiveUS20020130042A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteDisplay device
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detect- able analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
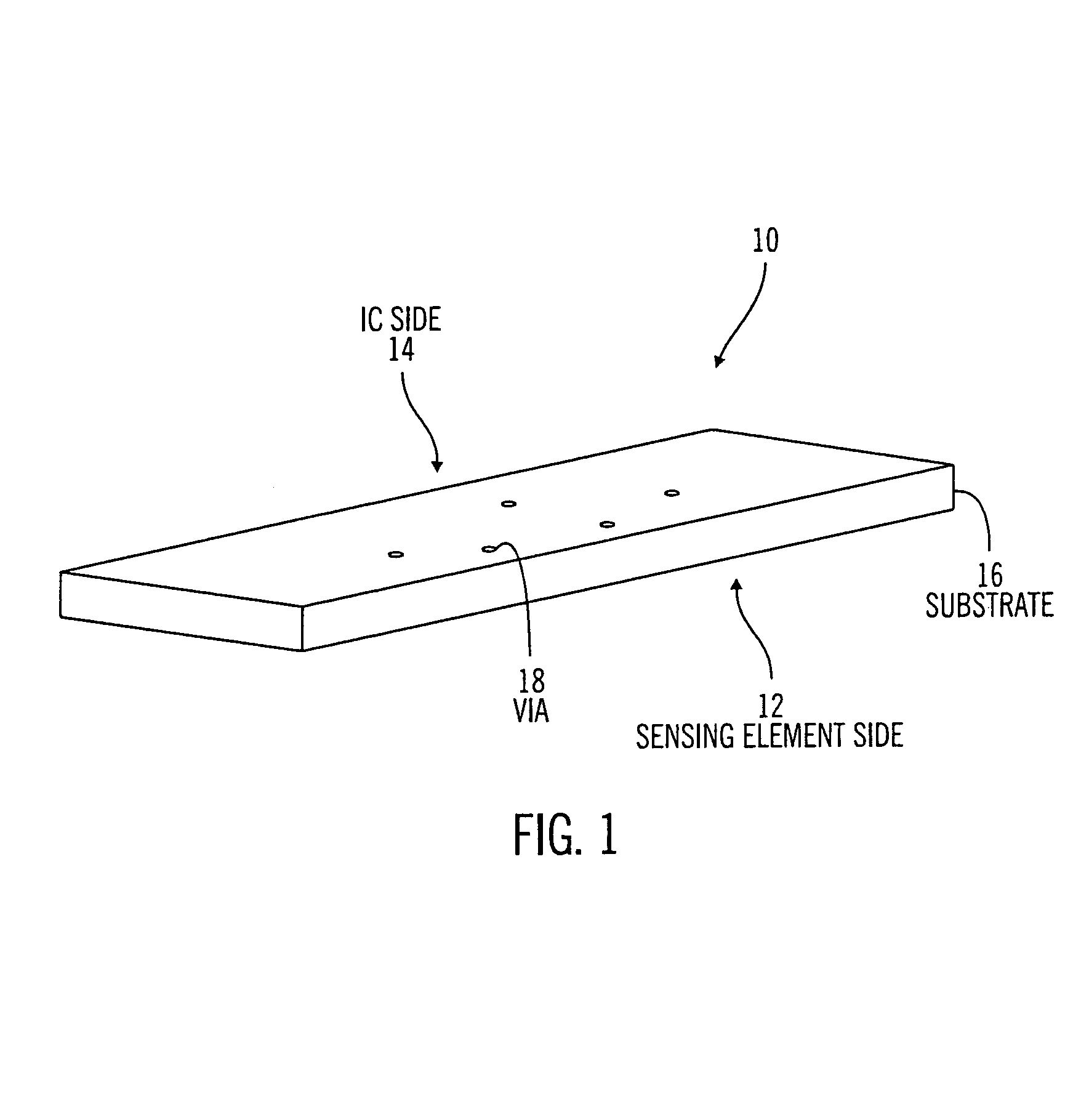
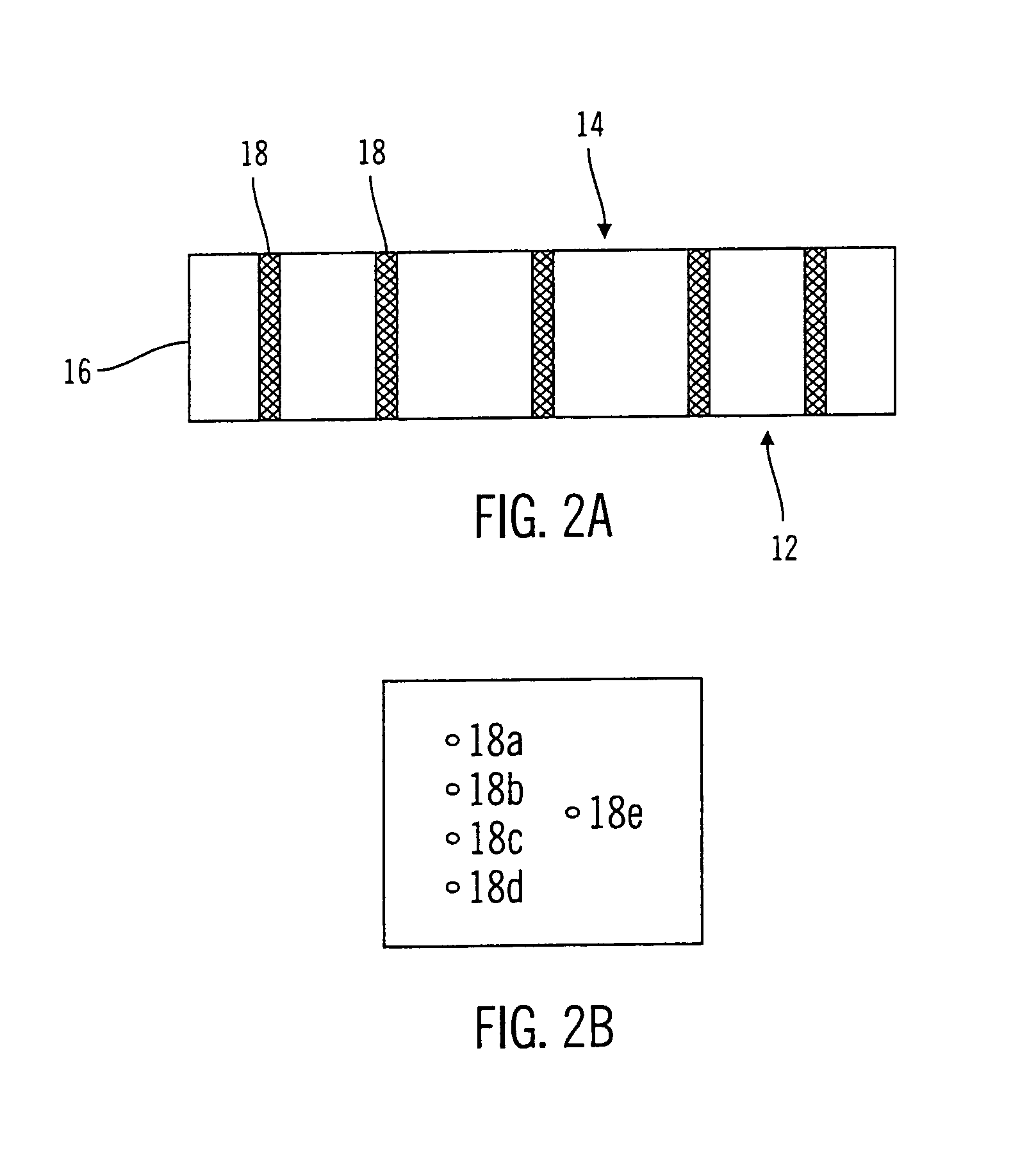
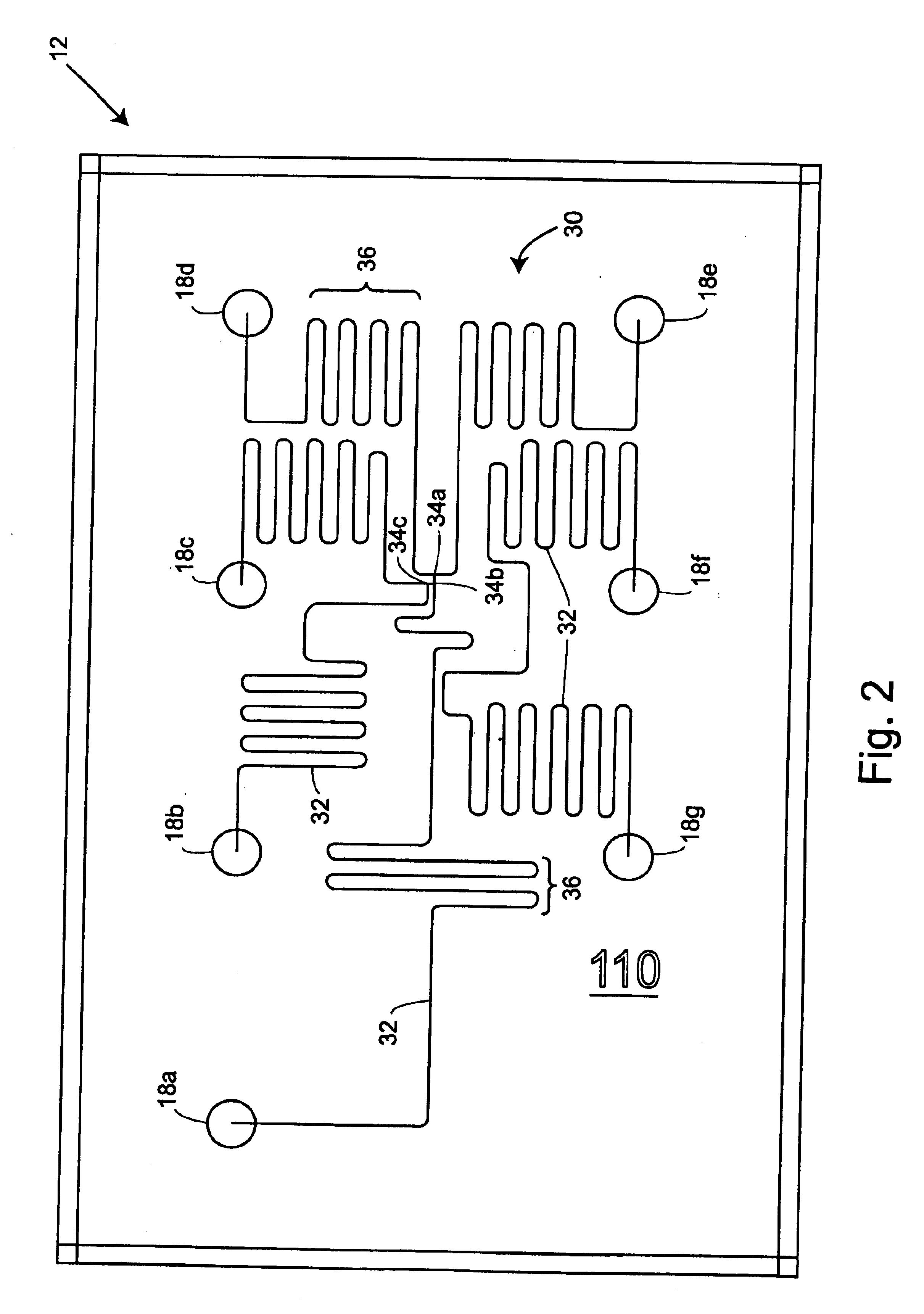
Sensor substrate and method of fabricating same
A substrate with hermetically sealed vias extending from one side of the substrate to another and a method for fabricating same. The vias may be filled with a conductive material such as, for example, a fritless ink. The conductive path formed by the conductive material aids in sealing one side of the substrate from another. One side of the substrate may include a sensing element and another side of the substrate may include sensing electronics.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
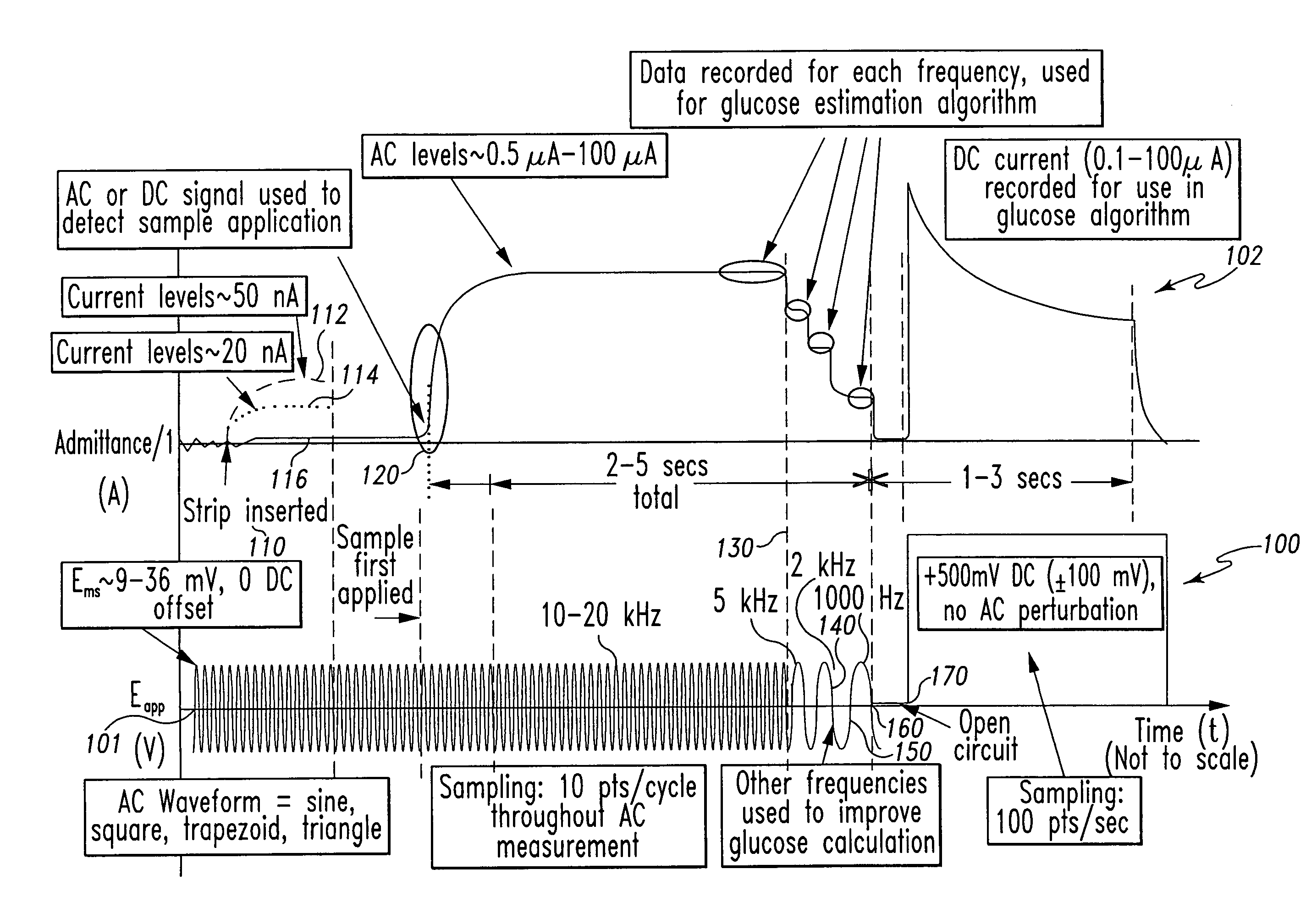
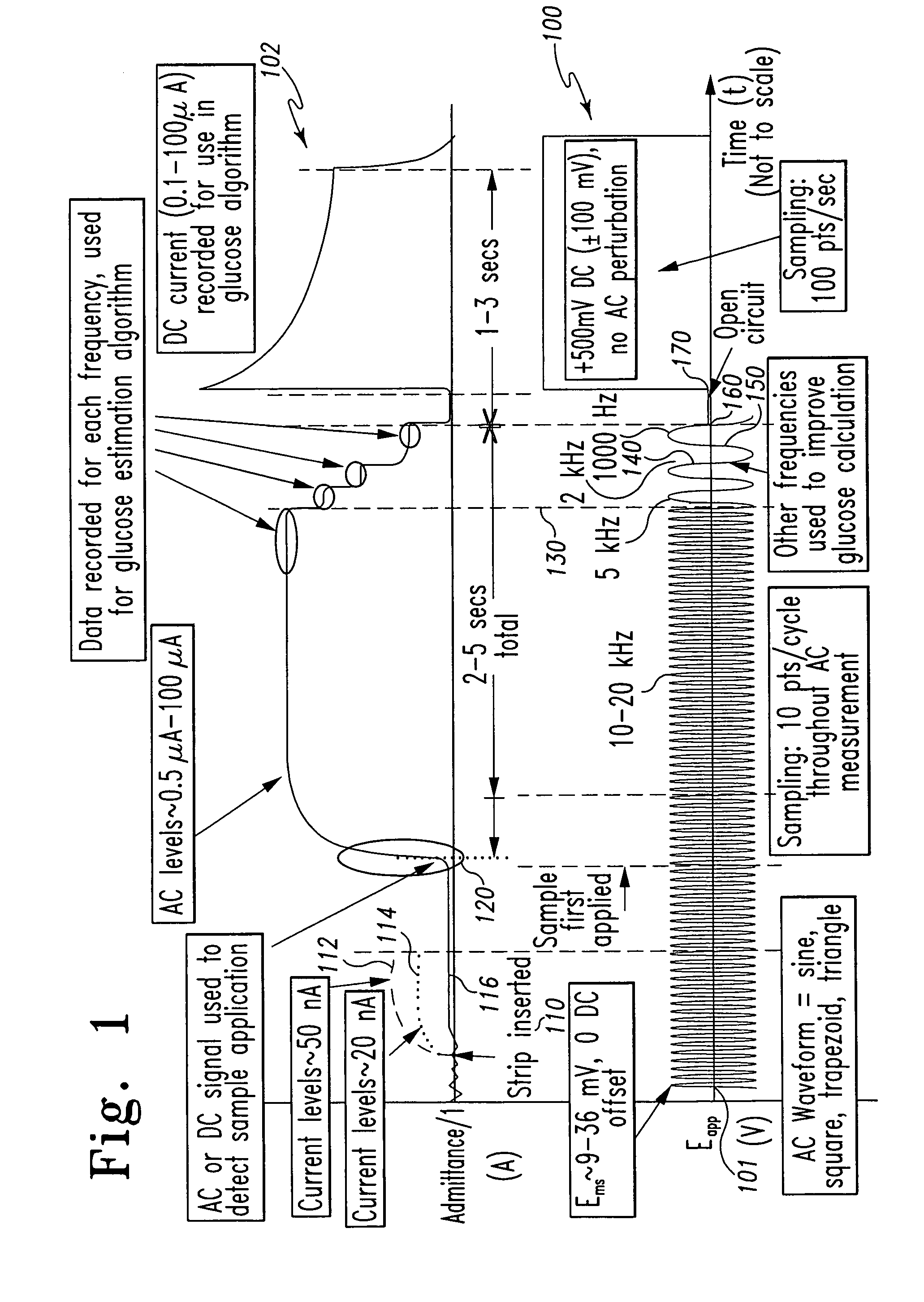
System and method for analyte measurement
InactiveUS7338639B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
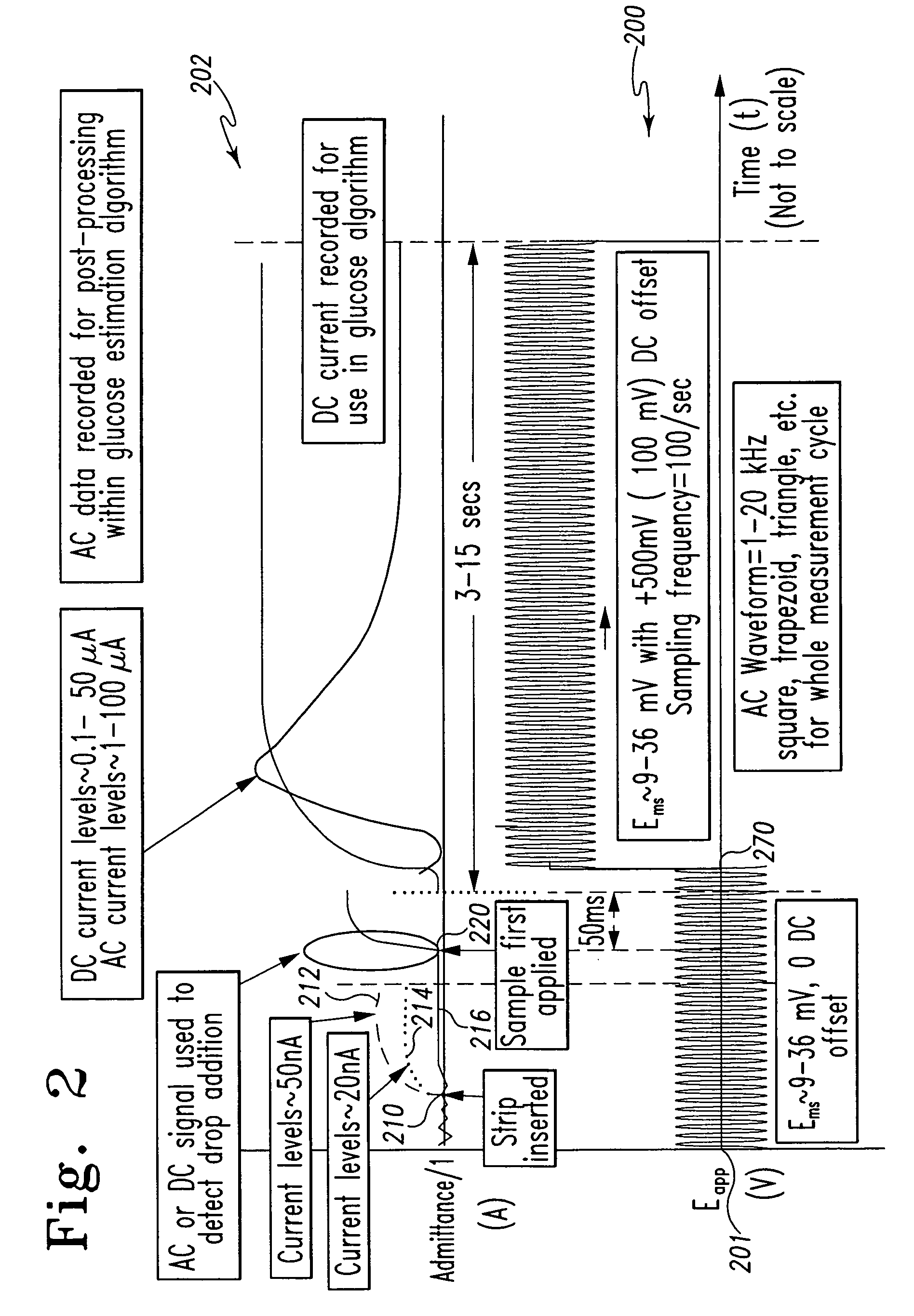
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Characterization of individual polymer molecules based on monomer-interface interactions
InactiveUS7189503B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologySingle strandDouble strand
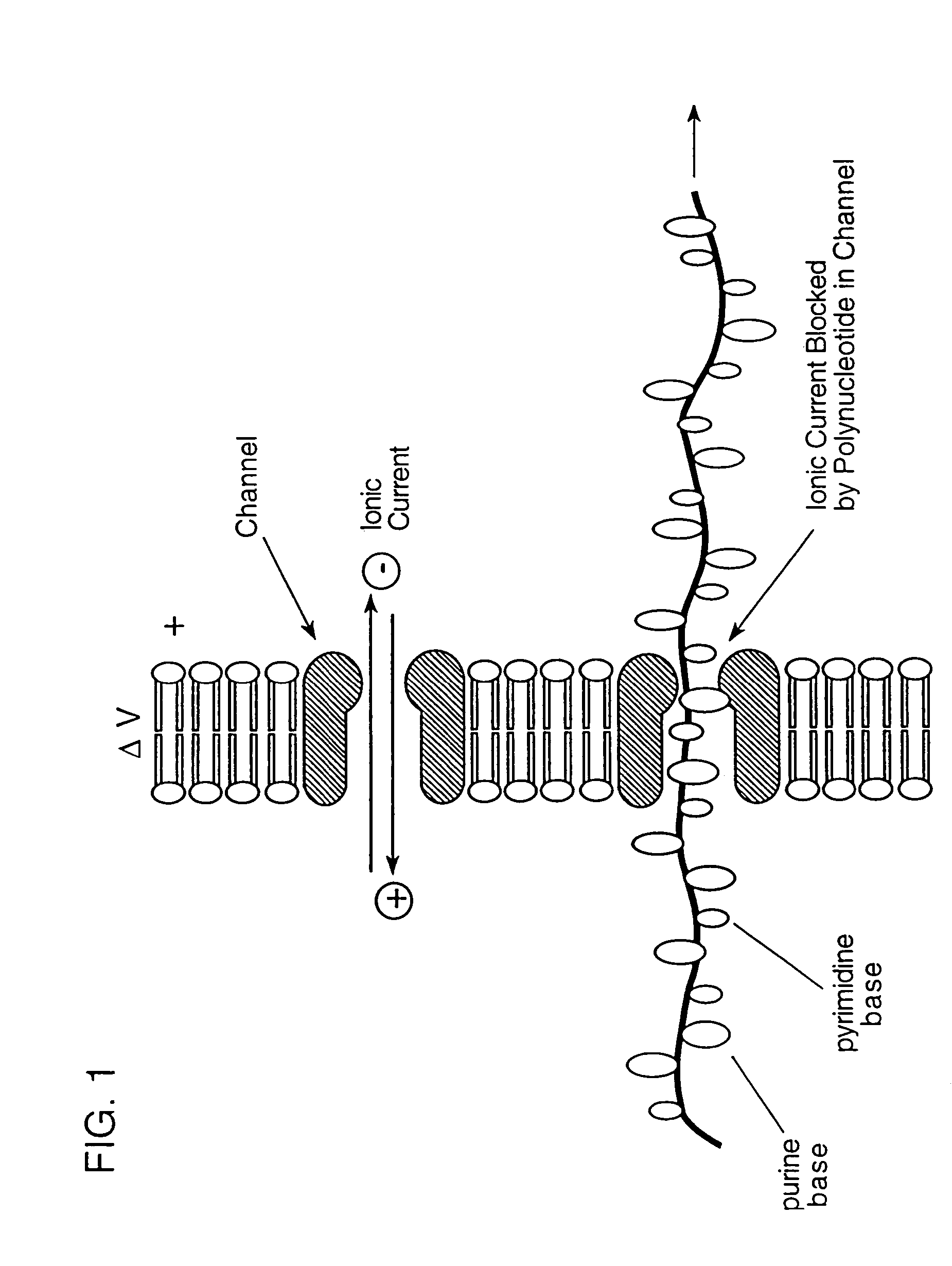
The invention relates to a method for detecting a double-stranded region in a nucleic acid by (1) providing two separate, adjacent pools of a medium and a interface between the two pools, the interface having a channel so dimensioned as to allow sequential monomer-by-monomer passage of a single-stranded nucleic acid, but not of a double-stranded nucleic acid, from one pool to the other pool; (2) placing a nucleic acid polymer in one of the two pools; and (3) taking measurements as each of the nucleotide monomers of the single-stranded nucleic acid polymer passes through the channel so as to differentiate between nucleotide monomers that are hybridized to another nucleotide monomer before entering the channel and nucleotide monomers that are not hybridized to another nucleotide monomer before entering the channel.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Interconnected networks of single-walled carbon nanotubes
An electronic device having an interconnected network of carbon nanotubes on the surface of a substrate, and two or more electrical leads. The network forms an electrical connection between the leads.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Multi-reservoir pressure control system
InactiveUS6915679B2Sufficient oscillationAccurate and stable and reliable assayAnalysis by electrical excitationLaboratory glasswaresFluid transportFlow resistivity
Improved microfluidic devices, systems, and methods allow selective transportation of fluids within microfluidic channels of a microfluidic network by applying, controlling, and varying pressures at a plurality of reservoirs. Modeling the microfluidic network as a series of nodes connected together by channel segments and determining the flow resistance characteristics of the channel segments may allow calculation of fluid flows through the channel segments resulting from a given pressure configuration at the reservoirs. To effect a desired flow within a particular channel or series of channels, reservoir pressures may be identified using the network model. Viscometers or other flow sensors may measure flow characteristics within the channels, and the measured flow characteristics can be used to calculate pressures to generate a desired flow. Multi-reservoir pressure modulator and pressure controller systems can optionally be used in conjunction with electrokinetic or other fluid transport mechanisms.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Sensor platform using a horizontally oriented nanotube element
Sensor platforms and methods of making them are described, and include platforms having horizontally oriented sensor elements comprising nanotubes or other nanostructures, such as nanowires. Under certain embodiments, a sensor element has an affinity for an analyte. Under certain embodiments, such a sensor element comprises one or more pristine nanotubes, and, under certain embodiments, it comprises derivatized or functionalized nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, a sensor is made by providing a support structure; providing a collection of nanotubes on the structure; defining a pattern within the nanotube collection; removing part of the collection so that a patterned collection remains to form a sensor element; and providing circuitry to electrically sense the sensor's electrical characterization. Under certain embodiments, the sensor element comprises pre-derivatized or pre-functionalized nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, sensor material is derivatized or functionalized after provision on the structure or after patterning. Under certain embodiments, a large-scale array includes multiple sensors.
Owner:NANTERO
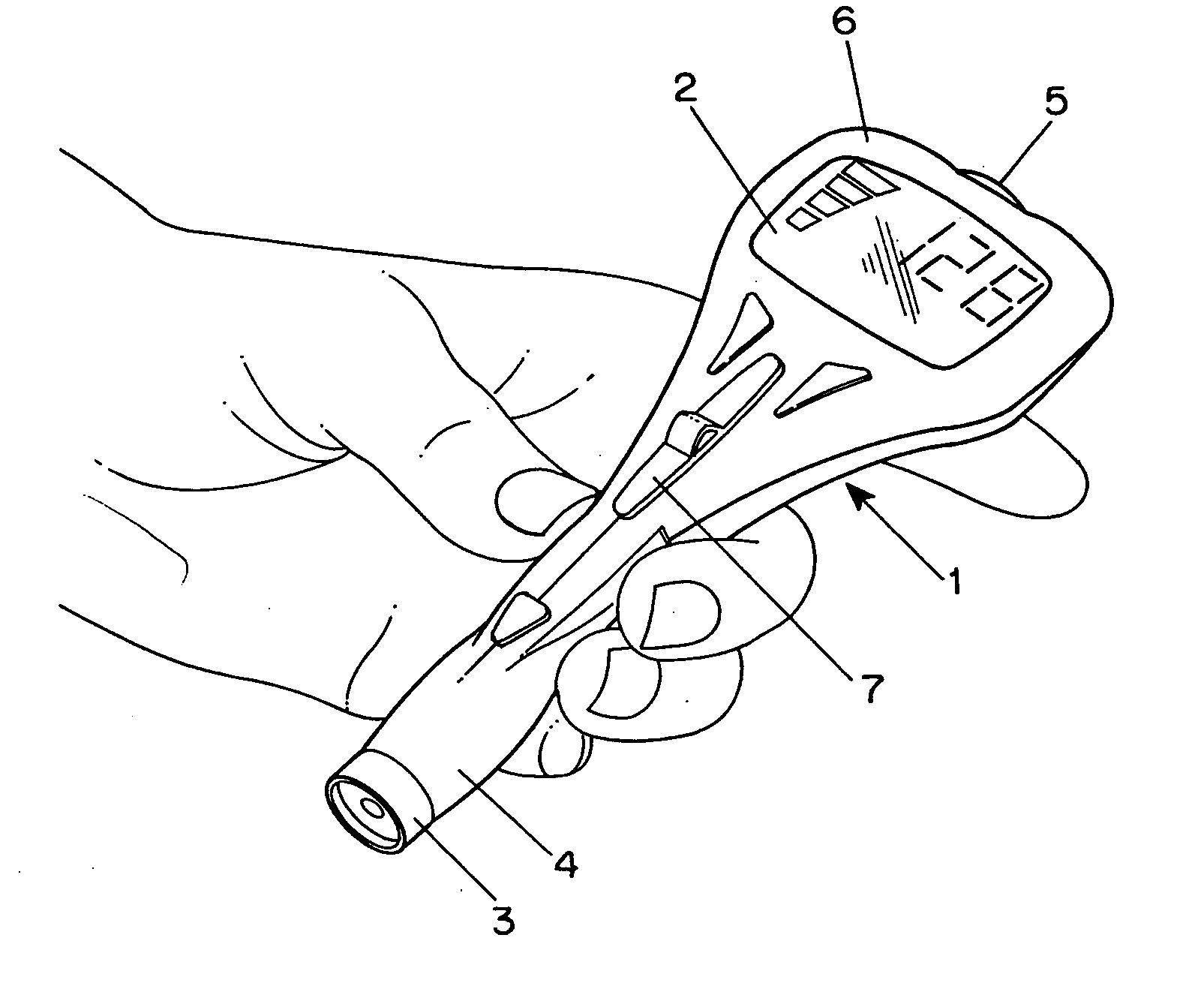
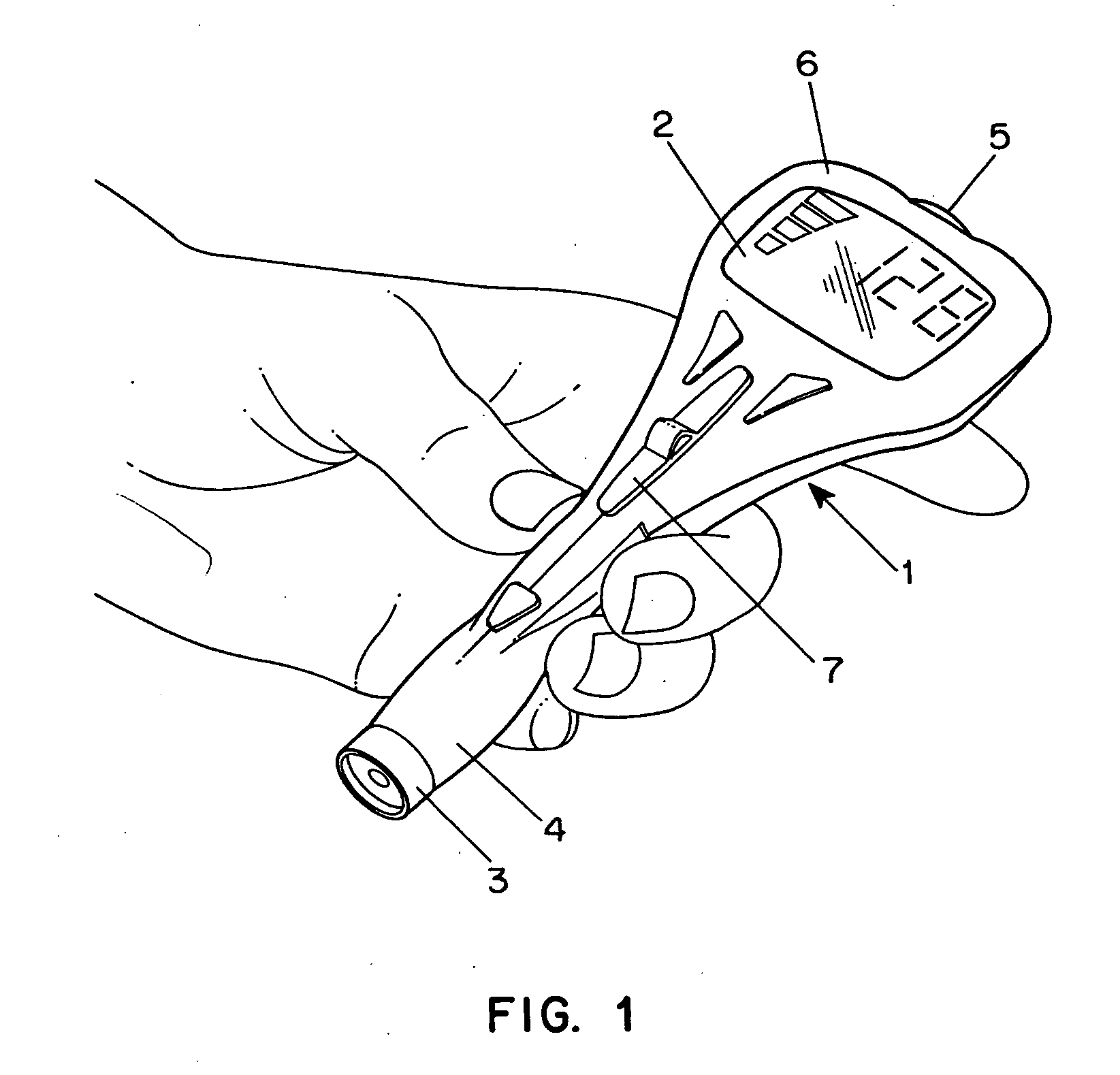
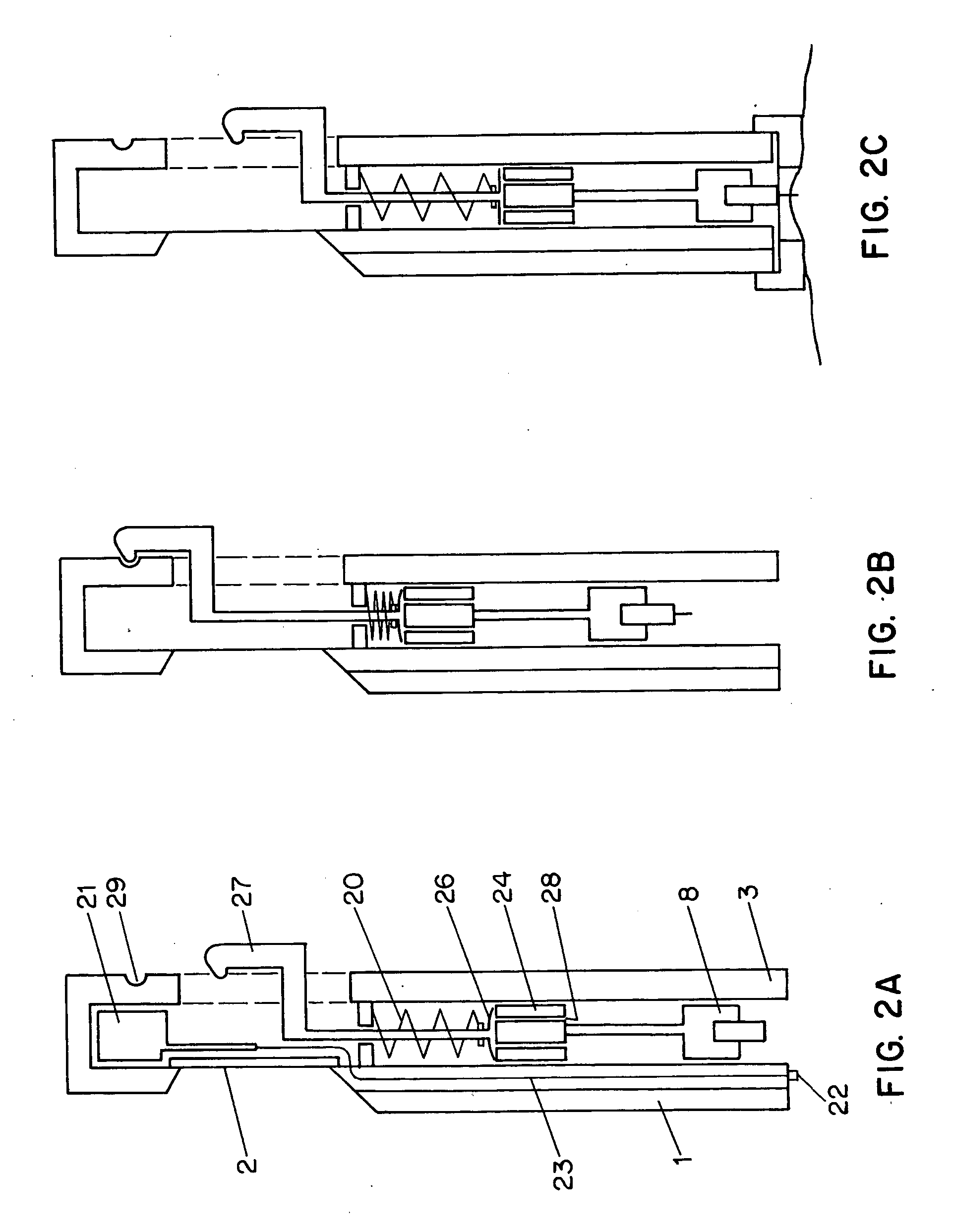
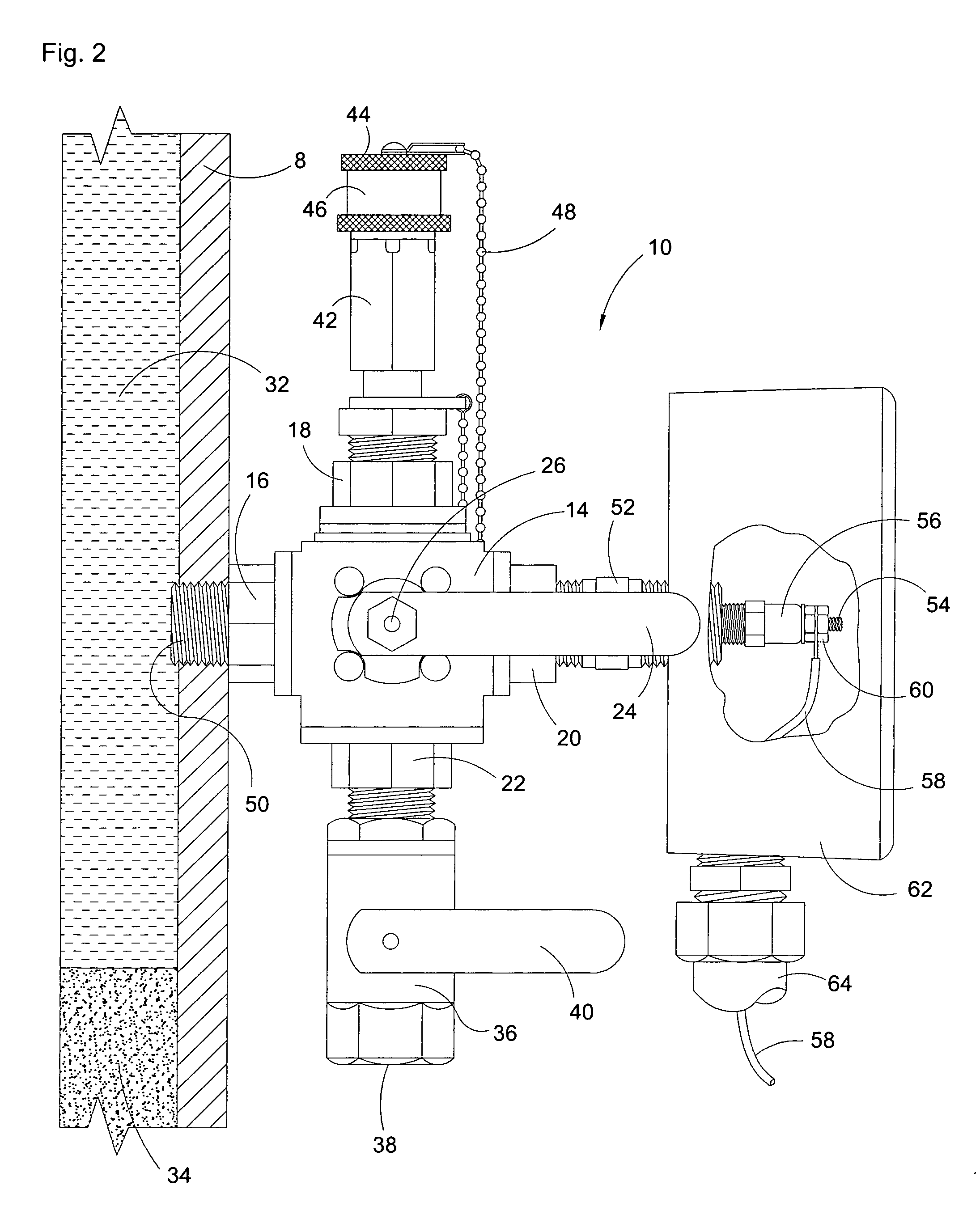
Combined lancet and electrochemical analyte-testing apparatus
InactiveUS20050011759A1Easy to takeReduces and eliminates disposal issueImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue fluidDisplay device
An apparatus for detection and quantitation of an electrochemically-detectable analyte, such as glucose, in blood or interstitial fluid includes a meter unit, a lancet and an electrochemical sensor. Of these components, the meter is preferably reusable, while the lancet and the electrochemical sensor are preferably incorporated in assemblies intended for single-use. The meter unit has a housing, within which a lancet is engaged with a mechanism for moving then lancet; a connector disposed within the housing for engaging an electrochemical sensor specific for the analyte and transmitting a signal indicative of the amount of analyte, and a display operatively-associated with a connector for displaying the amount of the analyte to user. The electrochemical sensor is adapted for detection of a particular analyte. In addition, the electrochemical sensor has an absorptive member for uptake of a sample of blood or interstitial fluid. In one version, the lancet moves from a initial position to a piercing position in which skin of the user is pierced and optionally back to a retracted position. The electrochemical sensor is disposed such that the absorptive member takes up a sample from the pierced skin of the user when it is pierced by the lancet without movement of the apparatus. In an alternative version, the lancet is a hollow cannula through which blood or interstitial fluid is transported from the puncture site to an absorbent portion of the electrochemical sensor. In either version, the apparatus provides single-step operation in which sample acquisition and analysis occur as a result of the single action of pressing, the apparatus against the users skin.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
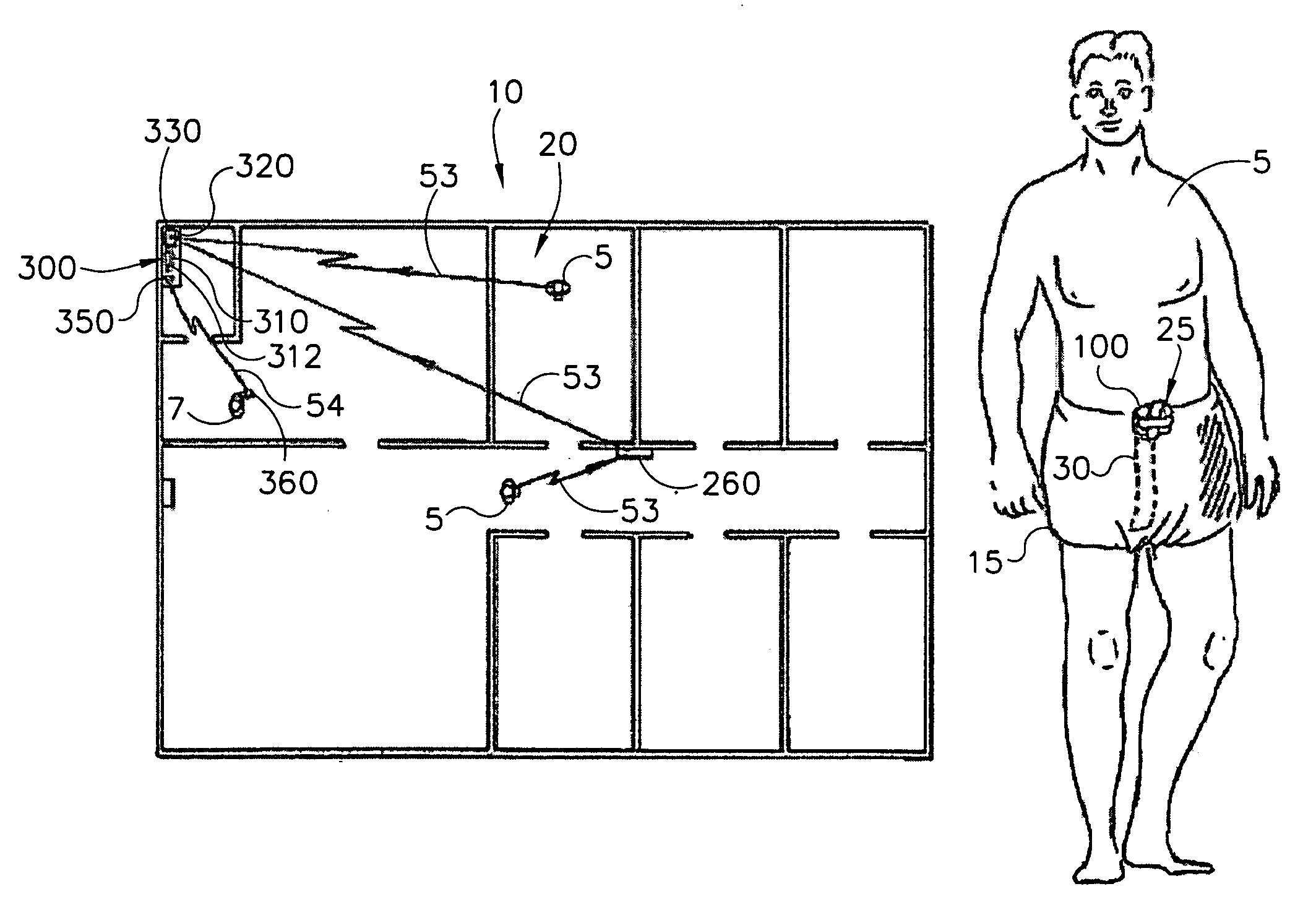
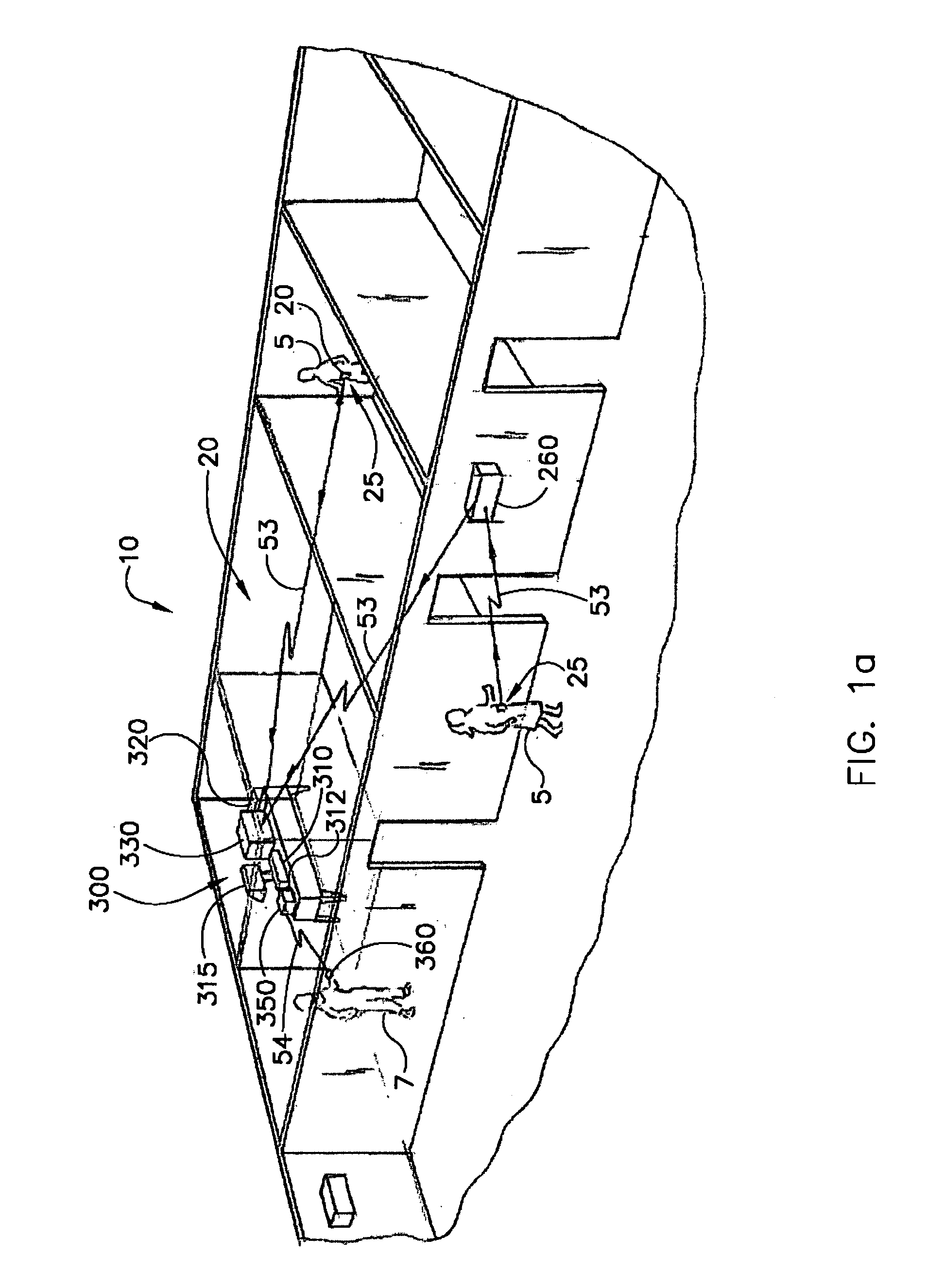
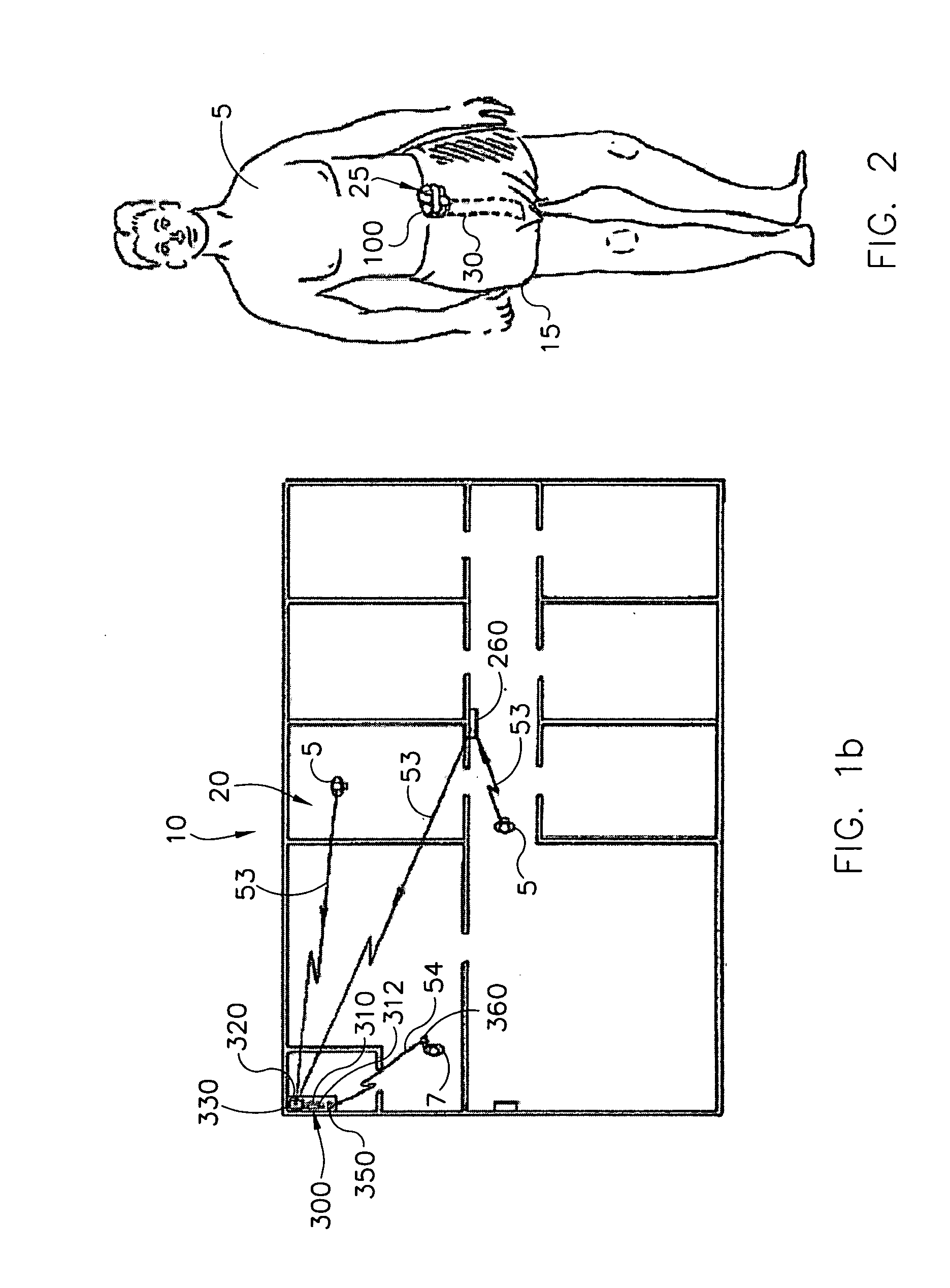
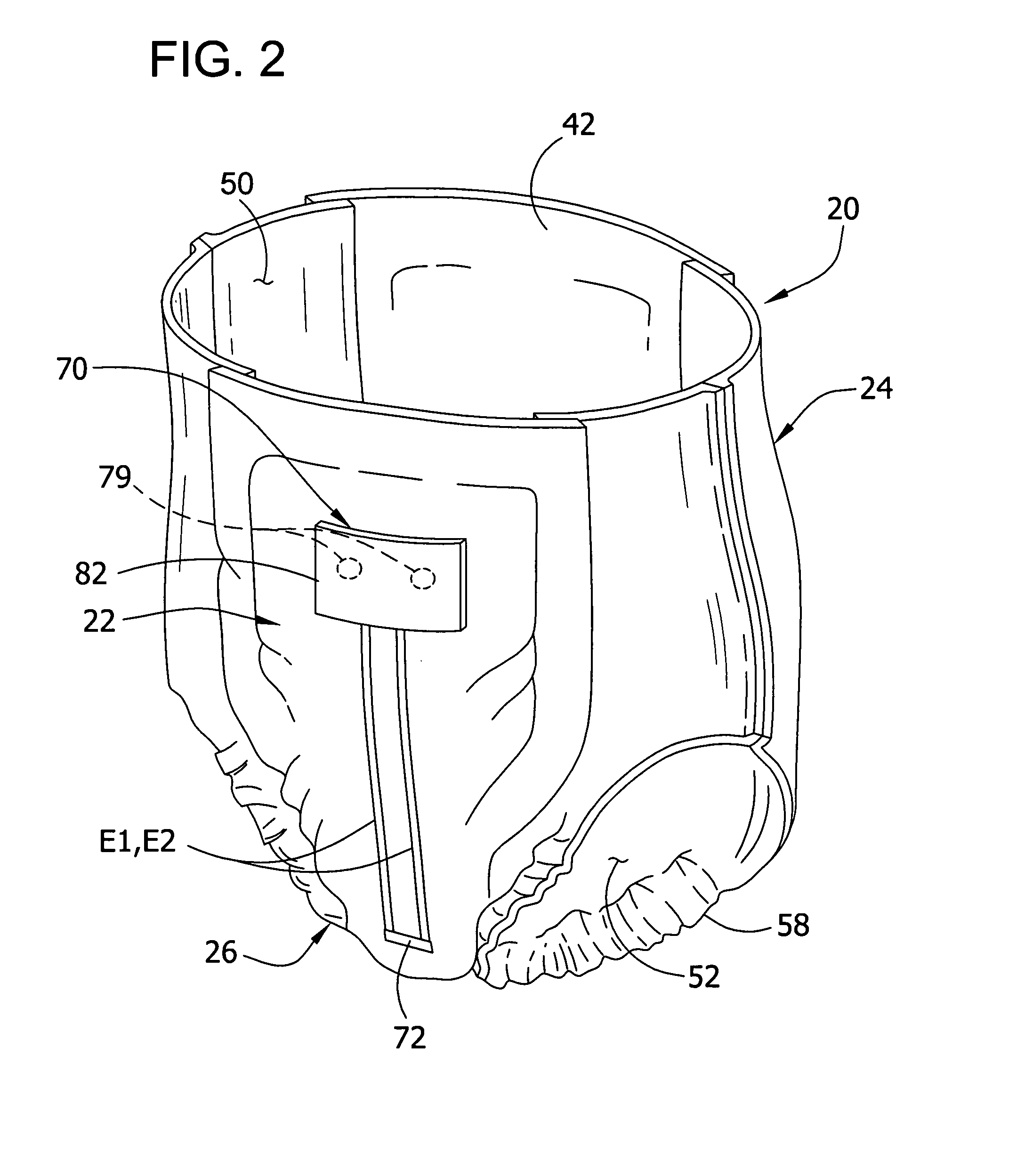
Wetness monitoring system
InactiveUS7250547B1Reduce operating costsLower annual operating costsBaby linensAlarmsData acquisitionMonitoring system
The present invention relates to a wetness monitoring system that includes a data collection device that sends wetness measurement data to a central computer that detects changes in wetness measurement data caused by the presence of urine or other dielectric fluids. The data collection device includes a semi-reusable sensor and reusable data collector that are worn on a garment of the person. The data collector includes an internal power source so that the person can live a normal ambulatory life. The data collector has an electrical circuit that uses the changing resistance characteristics in the sensor to gather wetness measurement data. The data collector periodically generates and transmits a signal containing the actual wetness measurement data. The signals are coded to identify the particular data collector or person sending the signal. The data collector is programmed to conserve power by sending signals less frequently during periods when the sensor is clearly dry. Signals are sent more frequently when the sensor is damp or a wetness event may have occurred. The central computer receives the signals containing the wetness measurement data and compares the measurement data to an adjustable wetness sensitivity level to determine if a wetness event has occurred. When the central computer determines that a wetness event has occurred, the computer displays the name of the particular person wearing the data collector and the approximate time that the wetness event occurred. The system then pages an appropriate healthcare worker to inform them that the particular individual needs attention and tracks the approximate response times to ensure that the patient is continuously receiving prompt care.
Owner:RF TECH
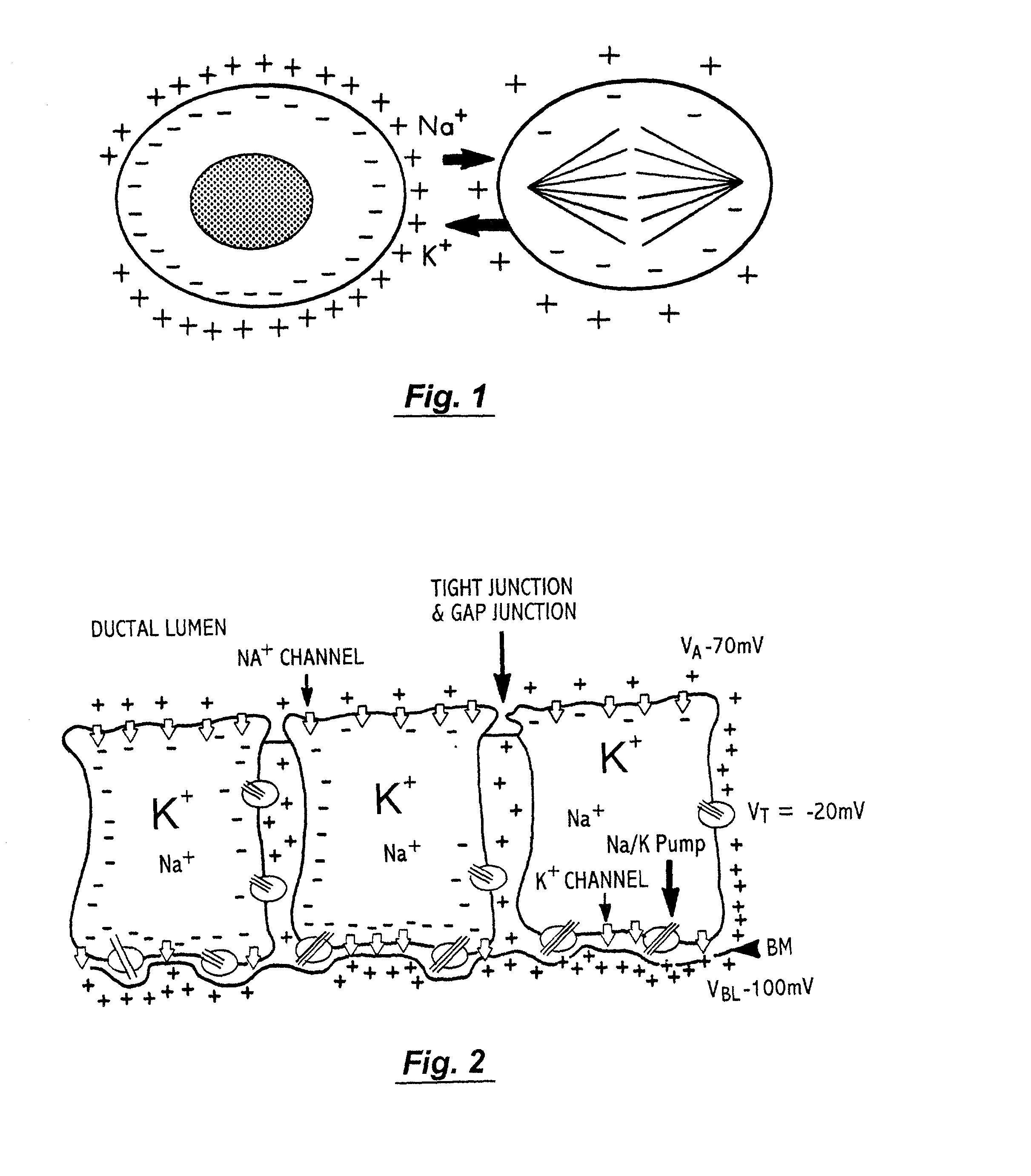
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
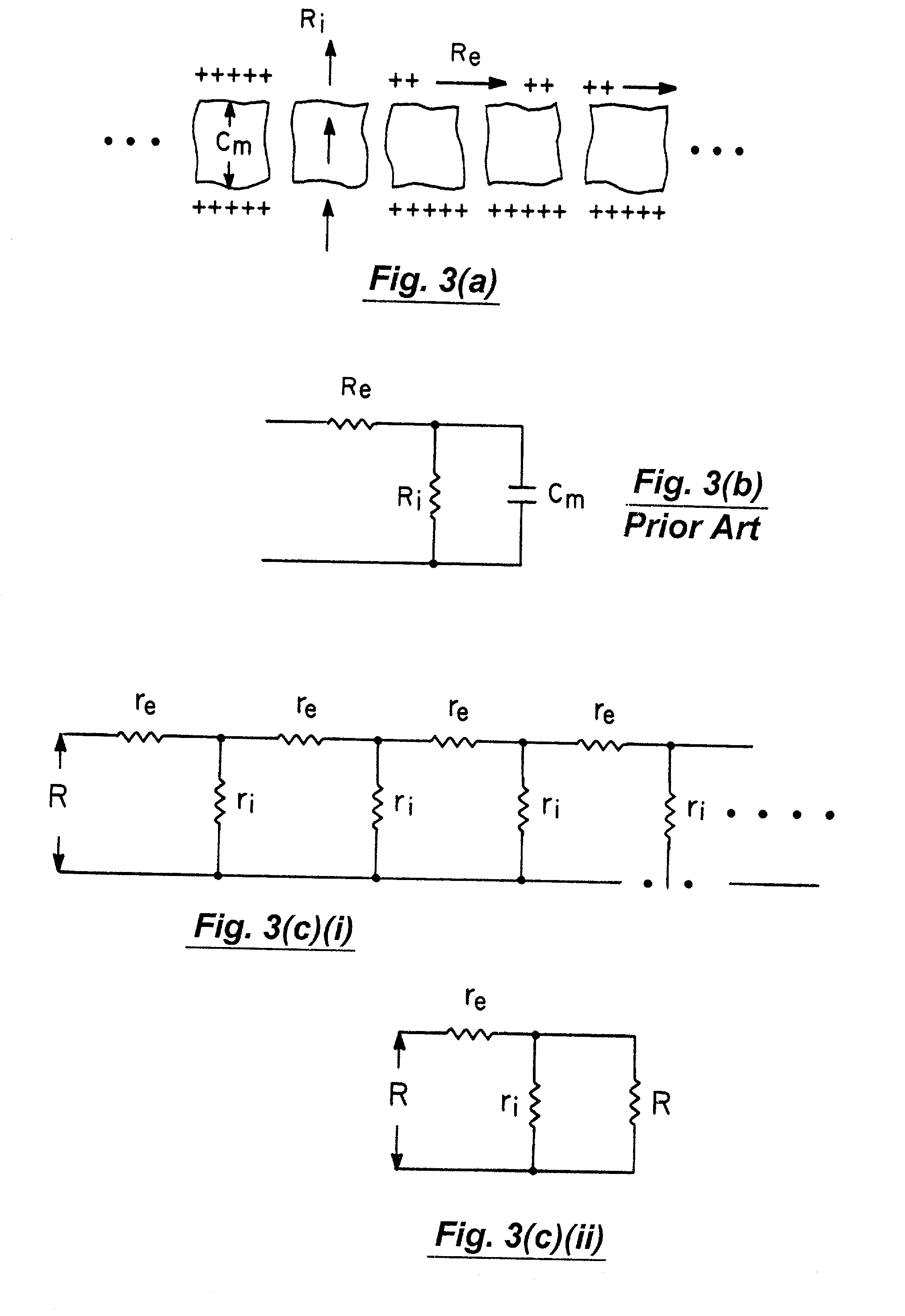
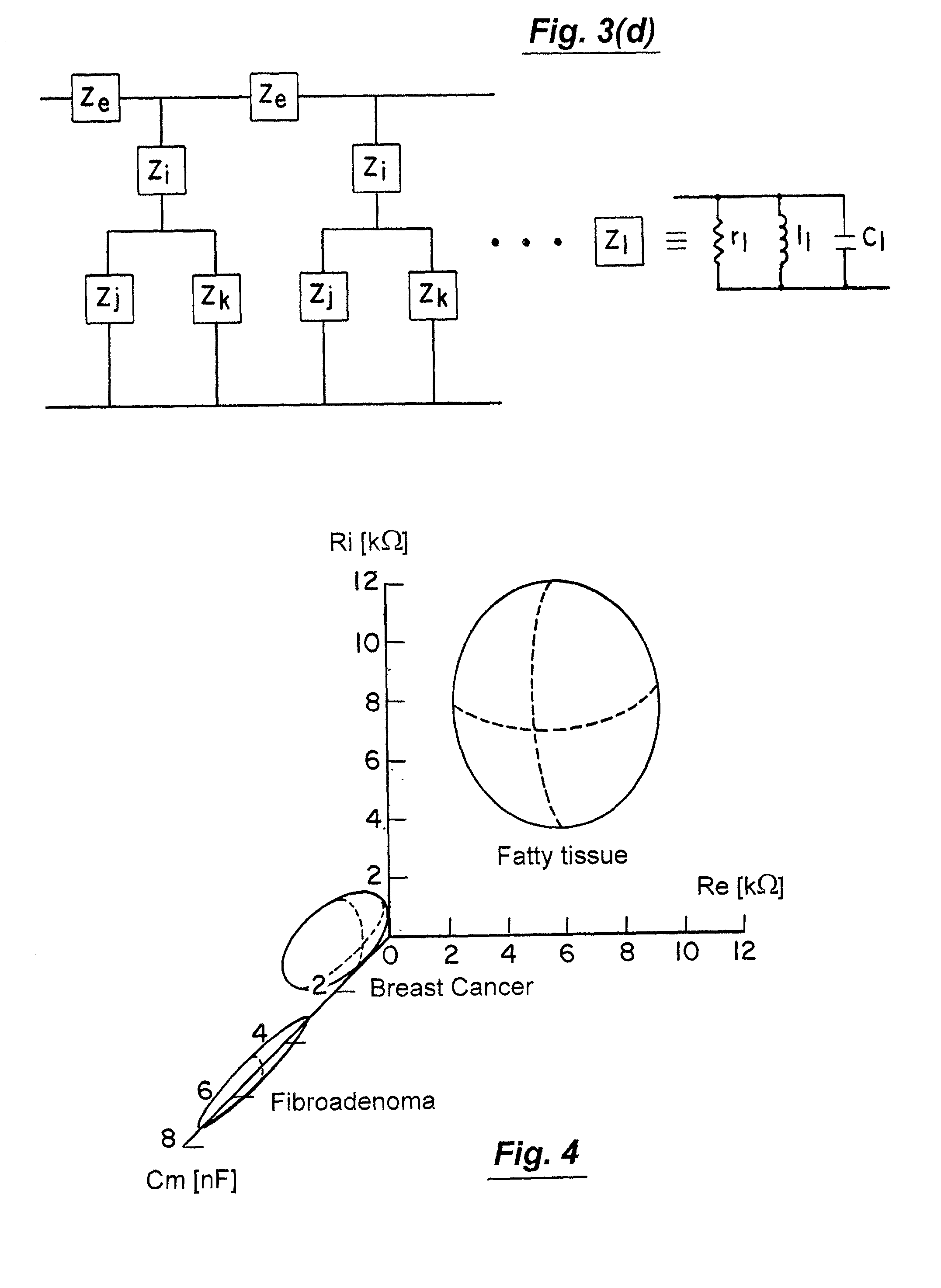
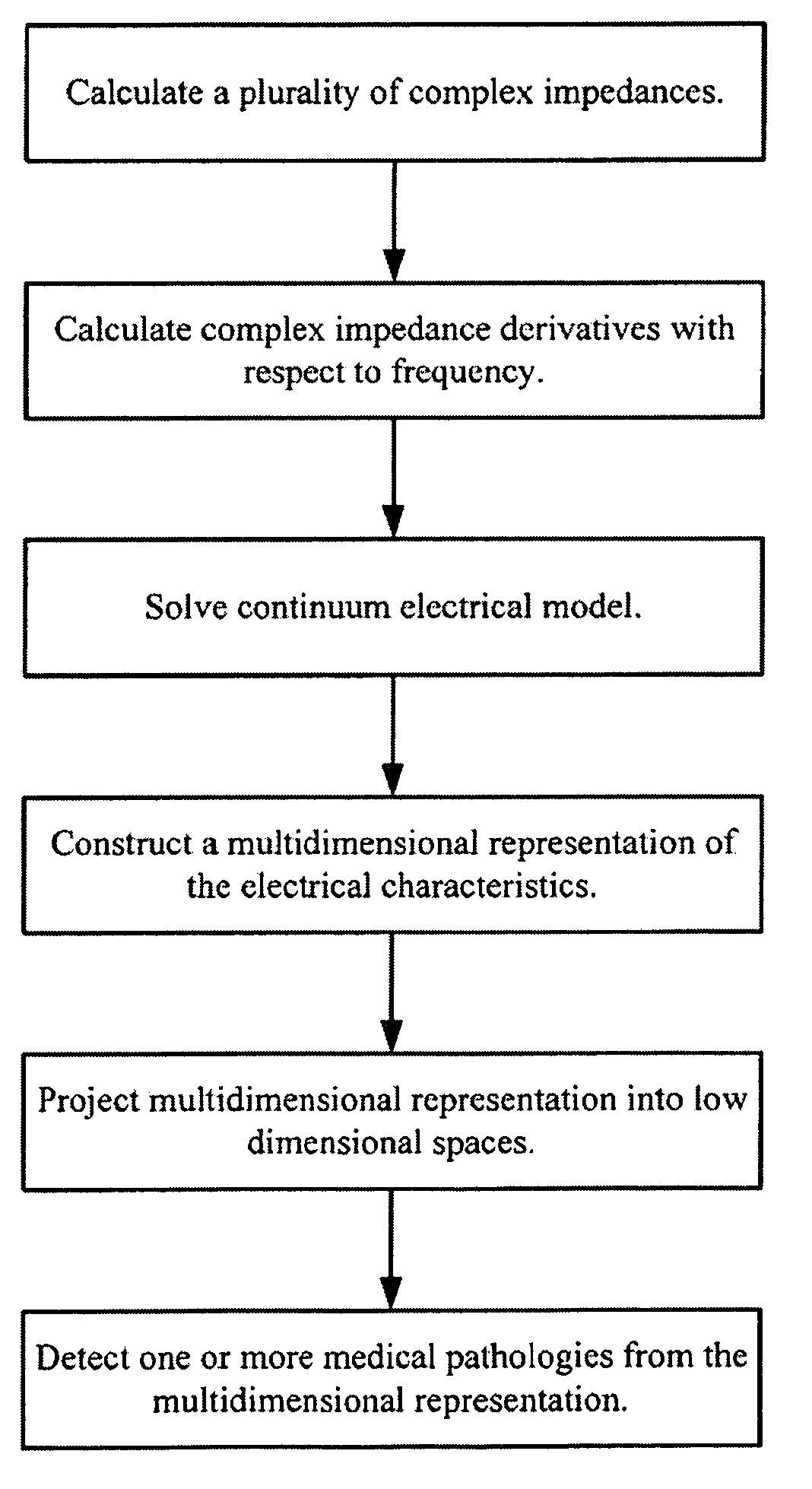
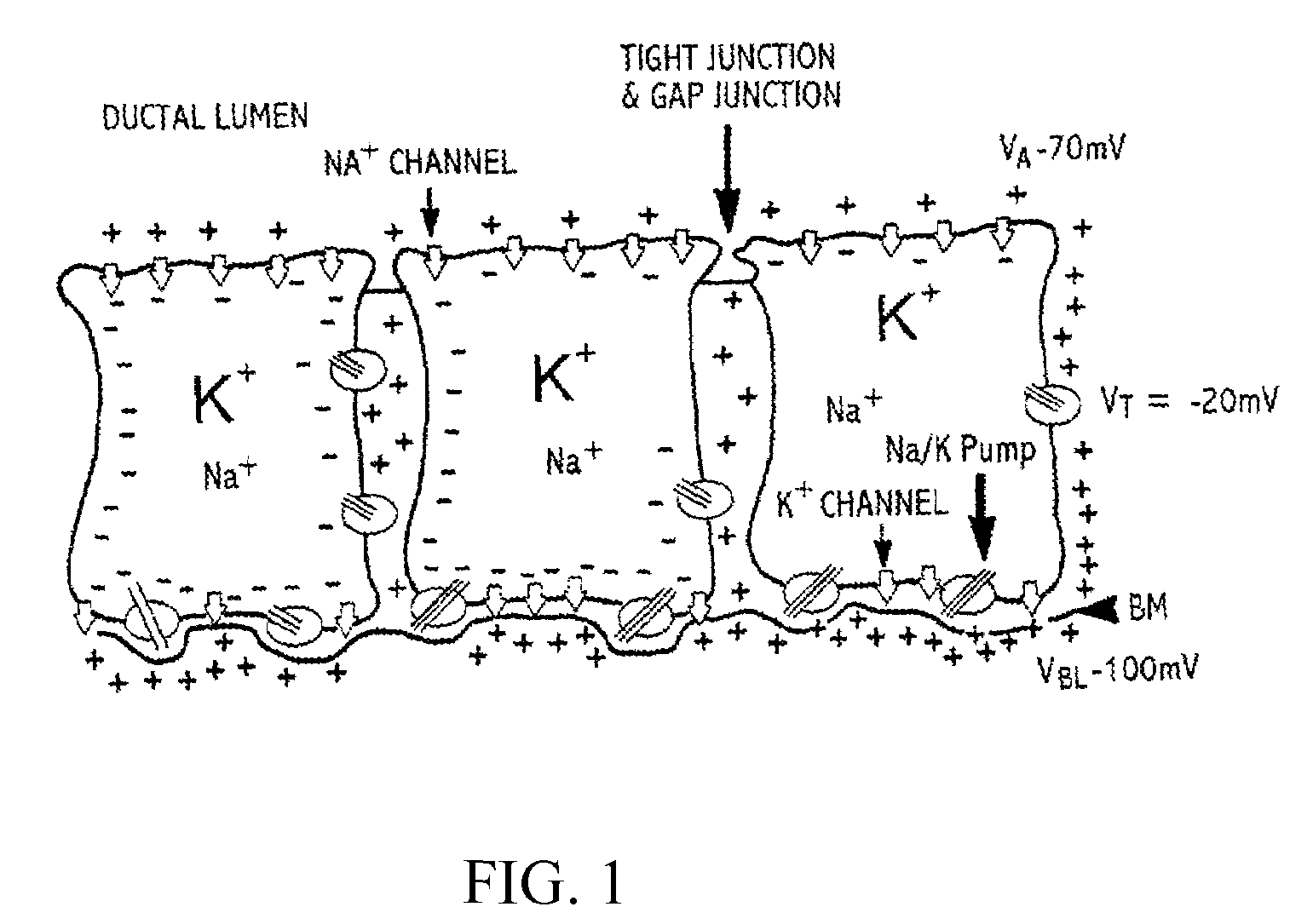
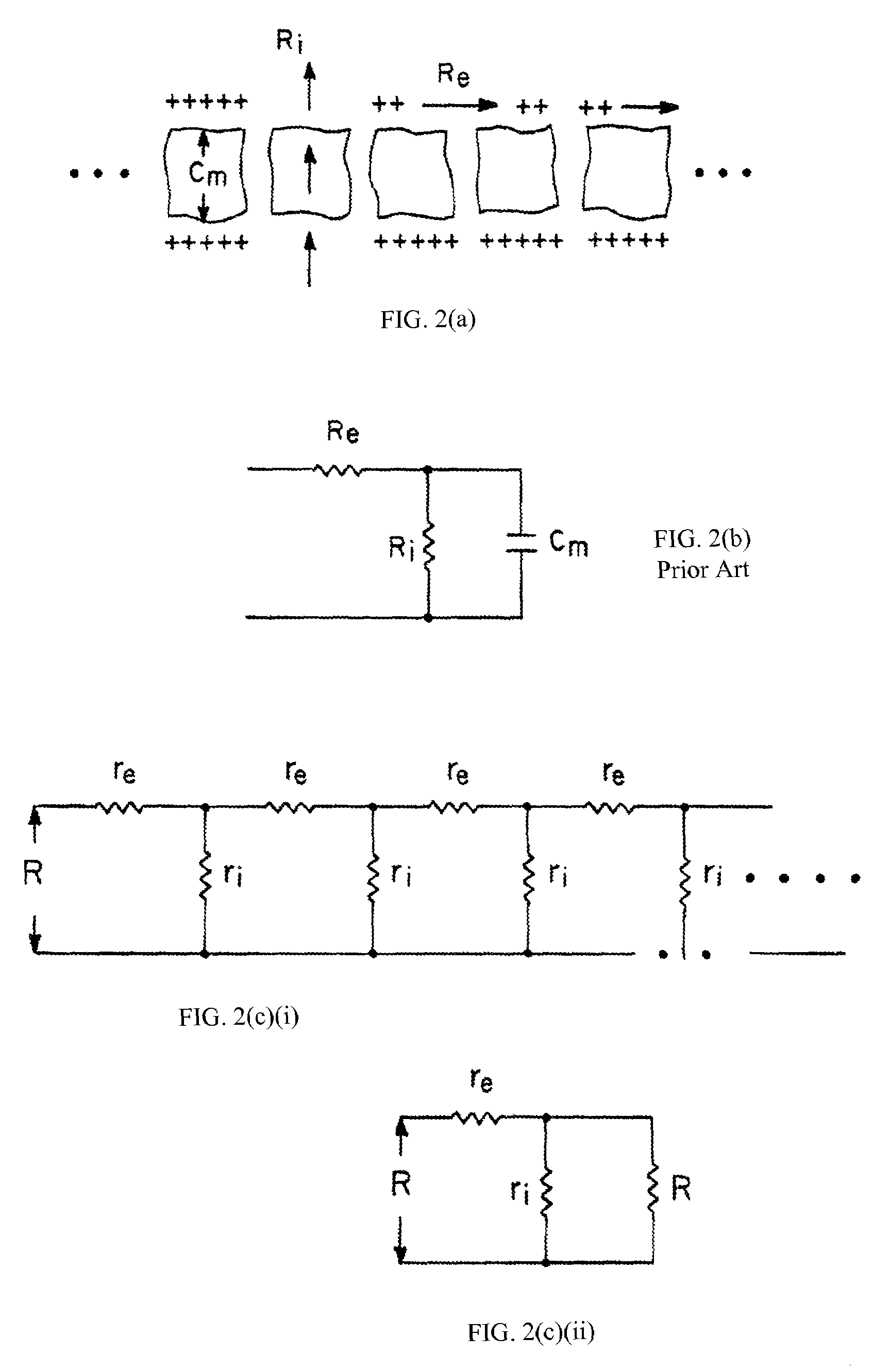
A method and apparatus that use complex impedance measurements of tissue in human or animal bodies for the detection and characterization of medical pathologies is disclosed. An analysis of the complex impedance measurements is performed by a trained evaluation system that uses a nonlinear continuum model to analyze the resistive, capacitive, and inductive measurements collected from a plurality of sensing electrodes. The analysis of the impedance measurements results in the construction of a multidimensional space that defines the tissue characteristics, which the trained evaluation system uses to detect and characterize pathologies. The method and apparatus are sufficiently general to be applied to various types of human and animal tissues for the analysis of various types of medical pathologies.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
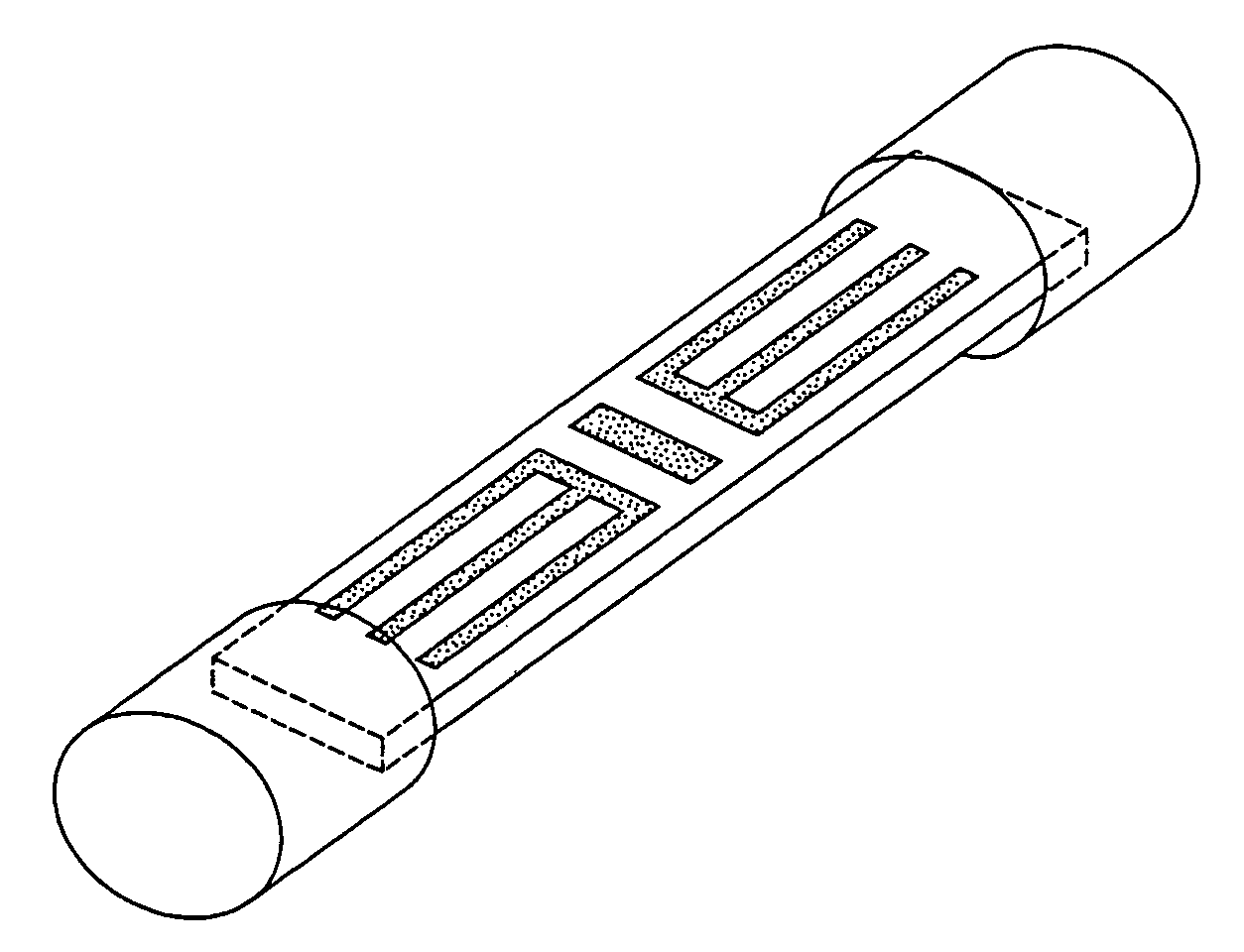
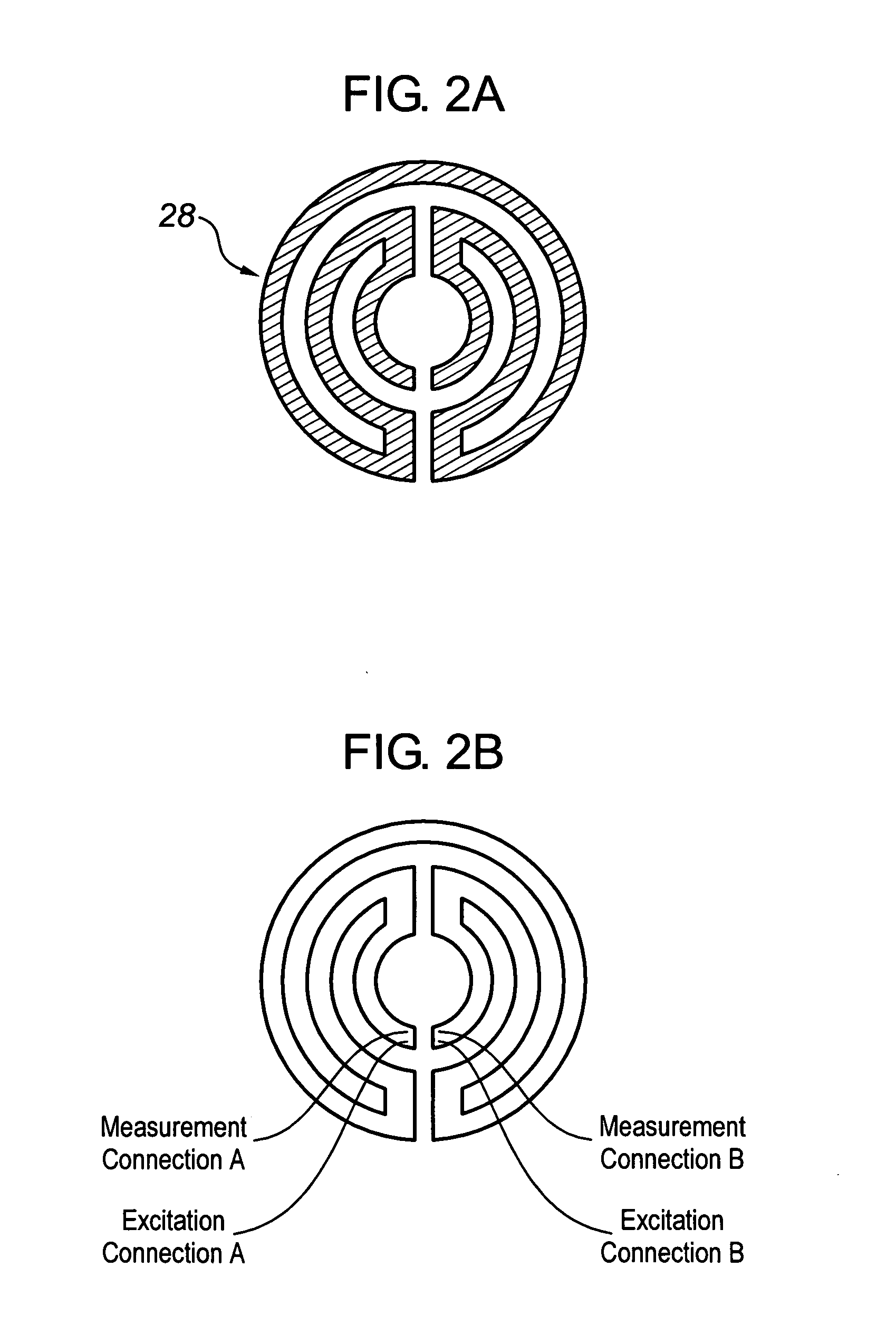
Analyte test sensor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060144704A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical resistance and conductanceAnalyte
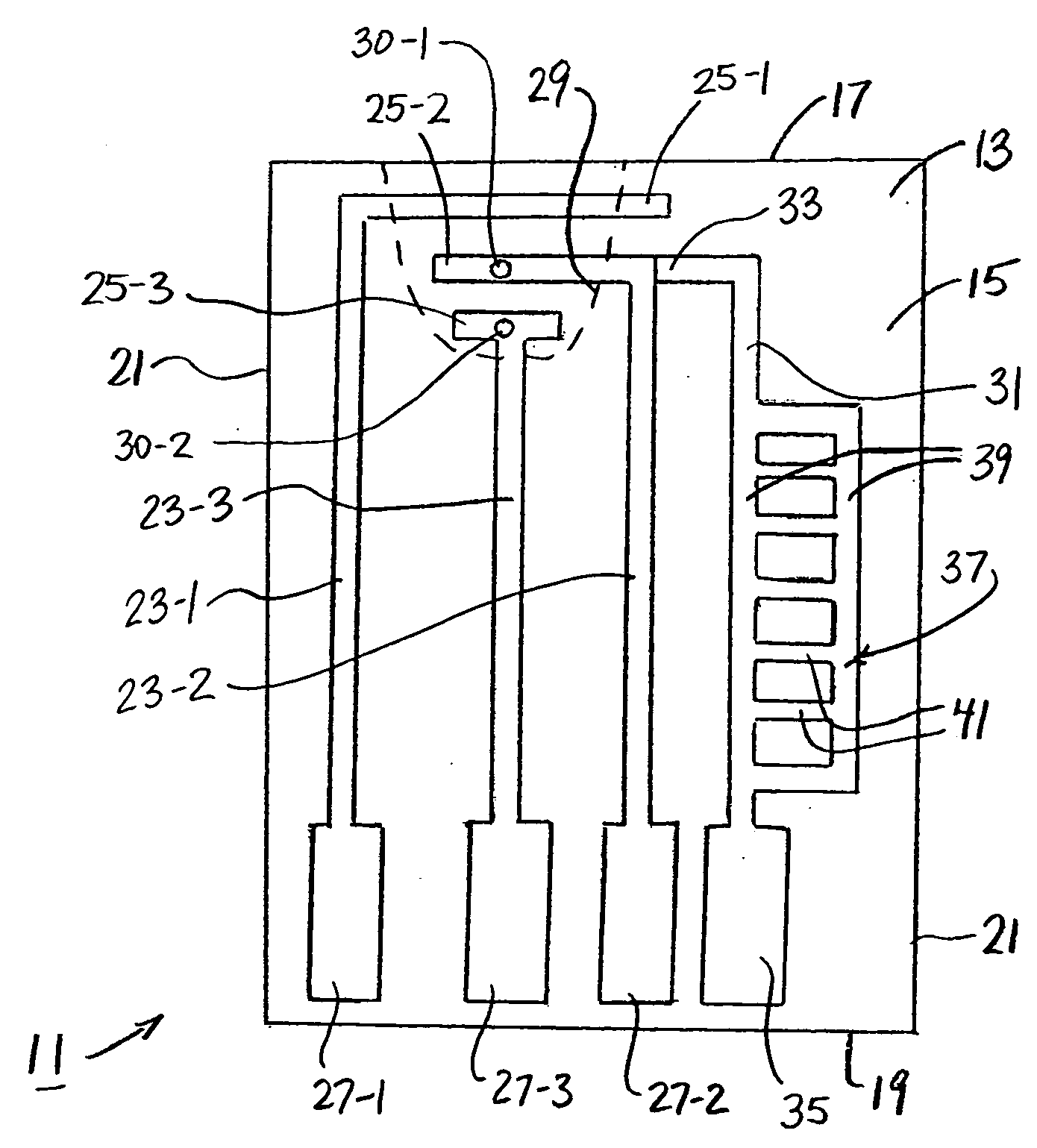
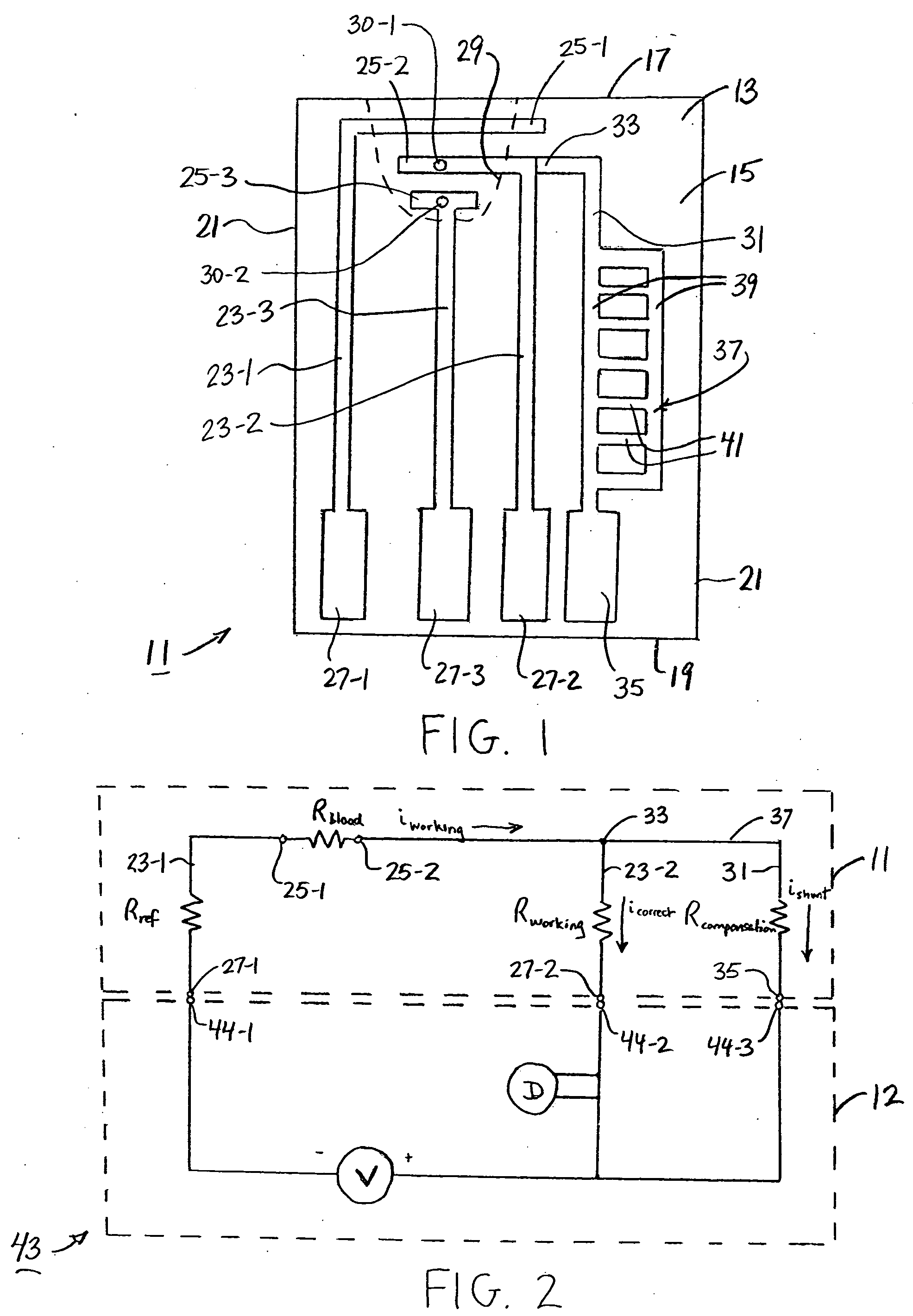
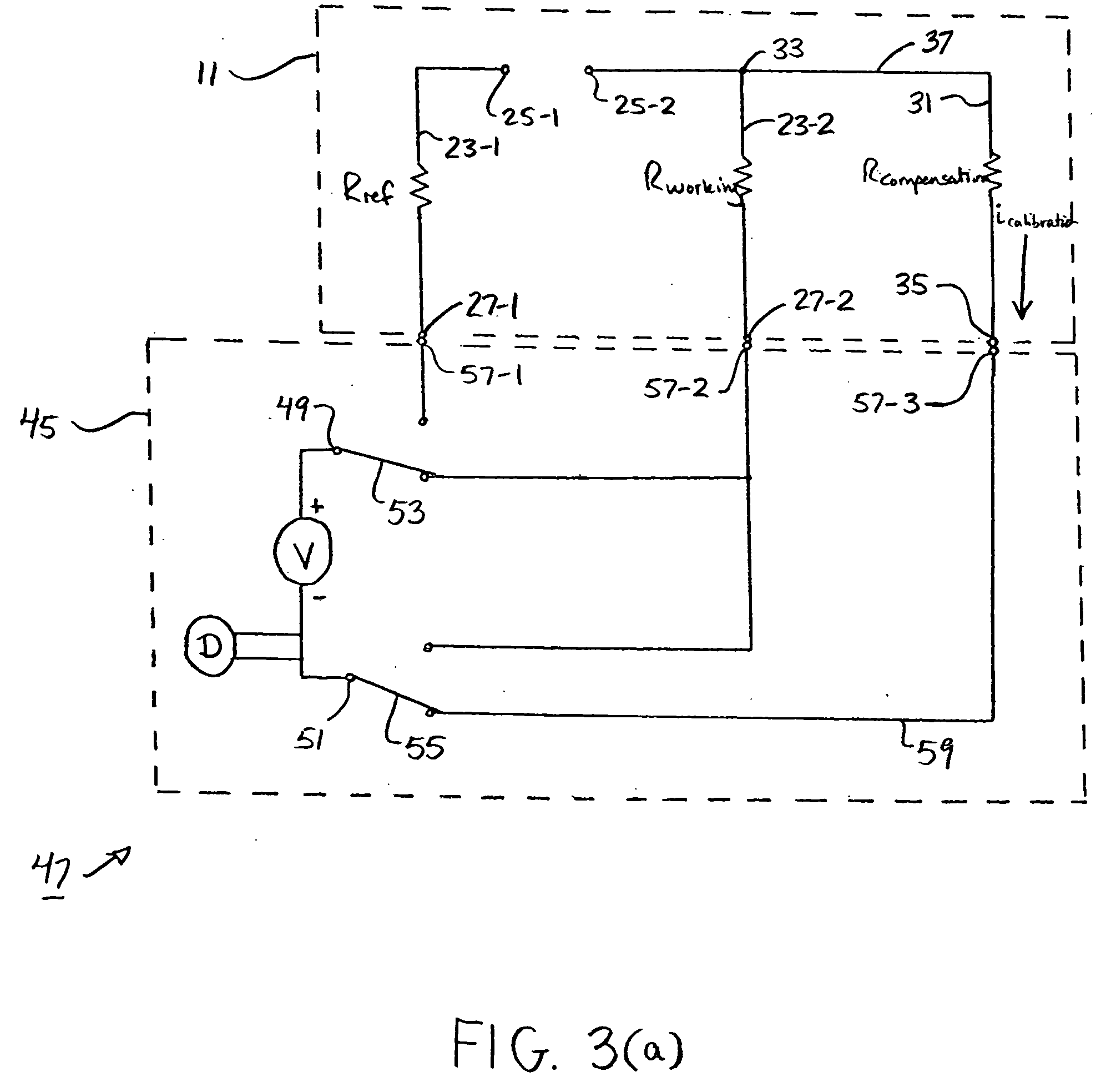
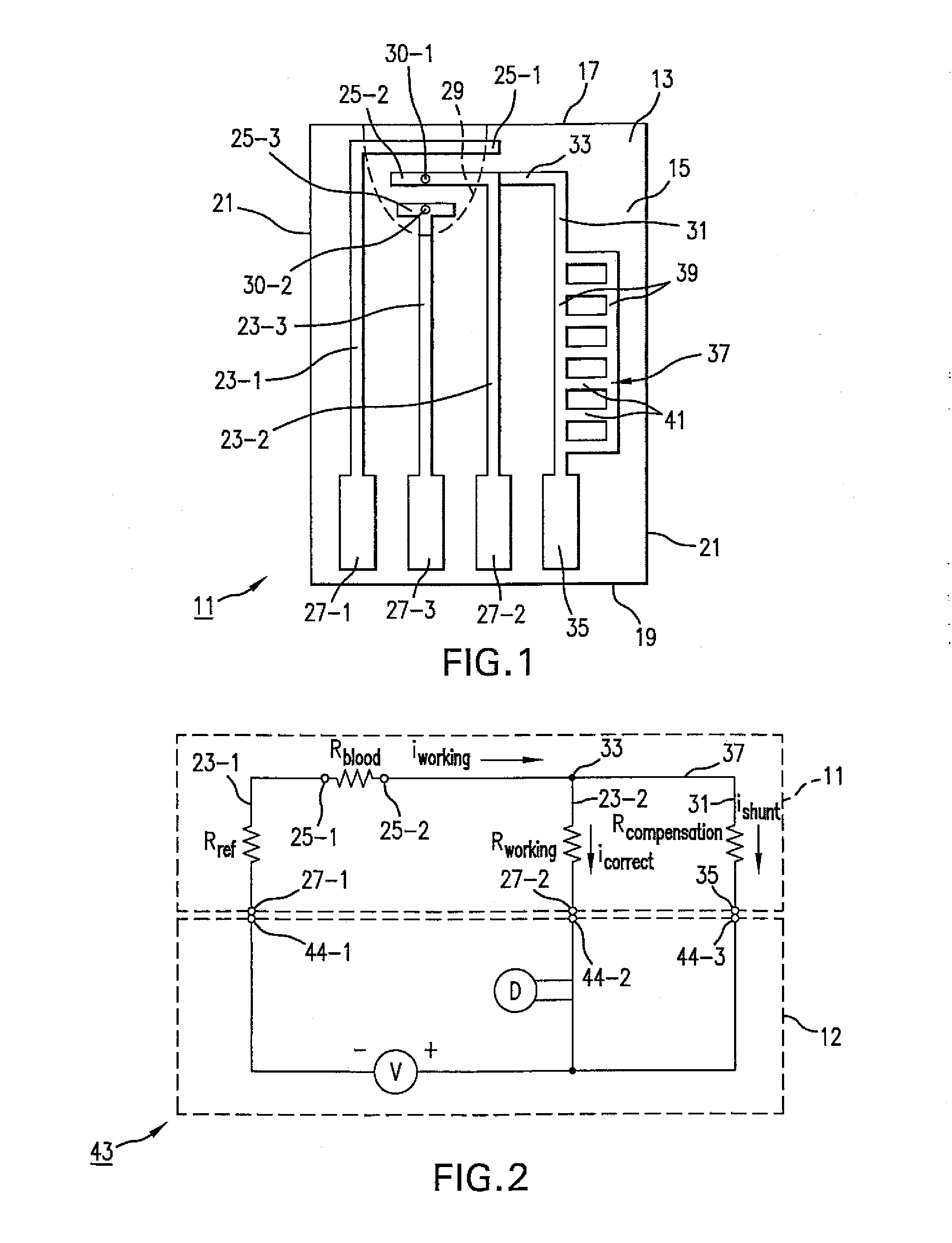
An analyte test sensor for use in measuring the concentration of a particular analyte in a test sample includes a non-conductive substrate, a reference electrode deposited on the substrate, a working electrode deposited on the substrate and a compensation electrode deposited on the substrate. The compensation electrode is provided with a resistive ladder and is designed to correct for test result inaccuracies which are the result of variances in the manufacturing of the test sensor. Specifically, in one embodiment, the compensation electrode corrects for test result inaccuracies in an analog manner by shunting a portion of the working current away from working electrode. In another embodiment, the compensation electrode corrects for test result inaccuracies in a digital manner by providing a calibration code which is proportional its resistance value. A batch of analyte test sensors are preferably manufactured in the following manner. An initial batch of the test sensors is constructed. Then, a limited sampling of the sensors is tested for accuracy using a control sample. Based on the test results, the resistance value of the compensation electrode for each remaining sensor in the batch is adjusted accordingly.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Method and apparatus for correcting ambient temperature effect in biosensors
InactiveUS6391645B1Improve accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnalyteTest sample
A method and apparatus are provided for correcting ambient temperature effect in biosensors. An ambient temperature value is measured. A sample is applied to the biosensors, then a current generated in the test sample is measured. An observed analyte concentration value is calculated from the current through a standard response curve. The observed analyte concentration is then modified utilizing the measured ambient temperature value to thereby increase the accuracy of the analyte determination. The analyte concentration value can be calculated by solving the following equation:where G1 is said observed analyte concentration value, T2 is said measured ambient temperature value and I1, I2, S1, and S2 are predetermined parameters.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG +1
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
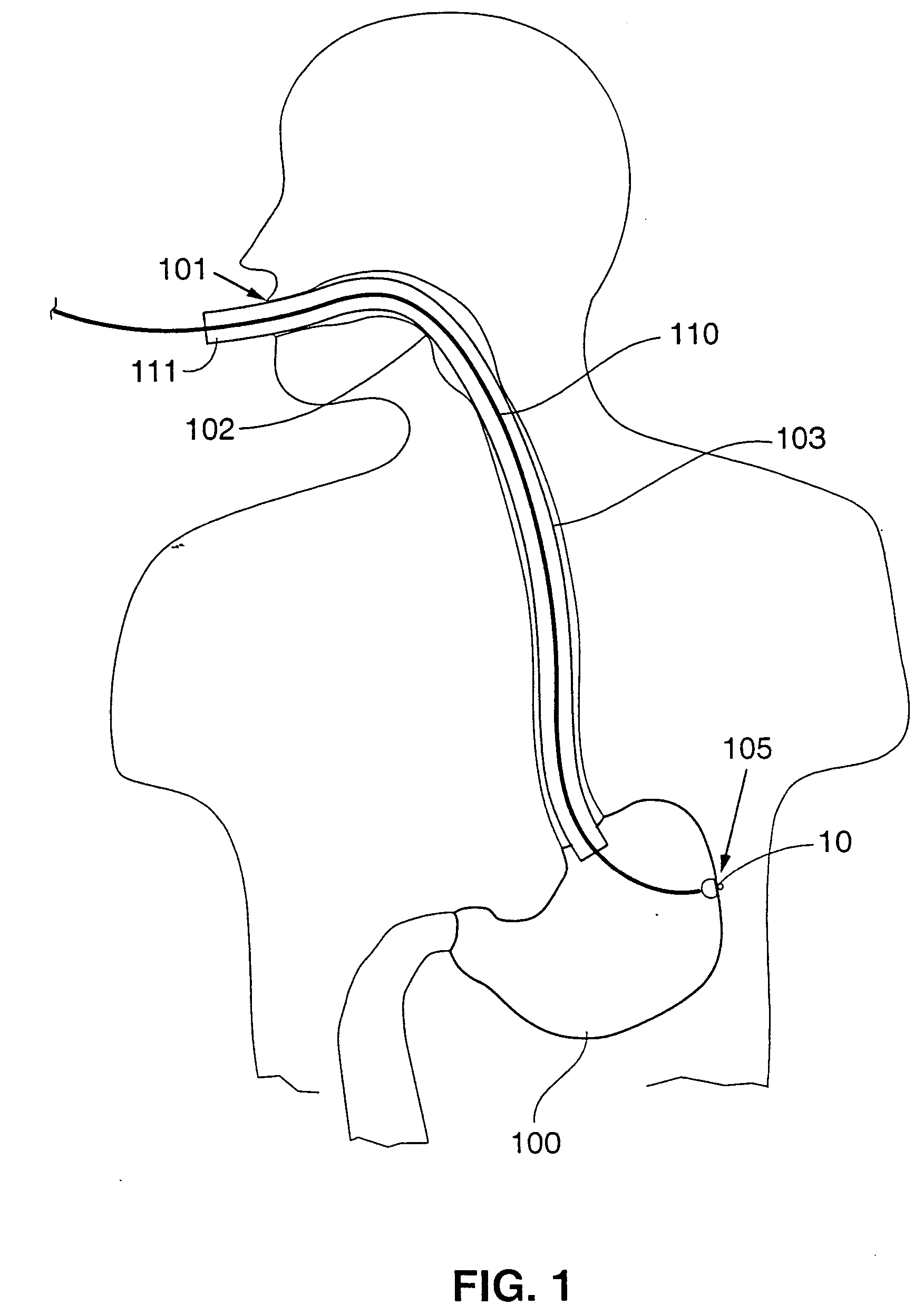
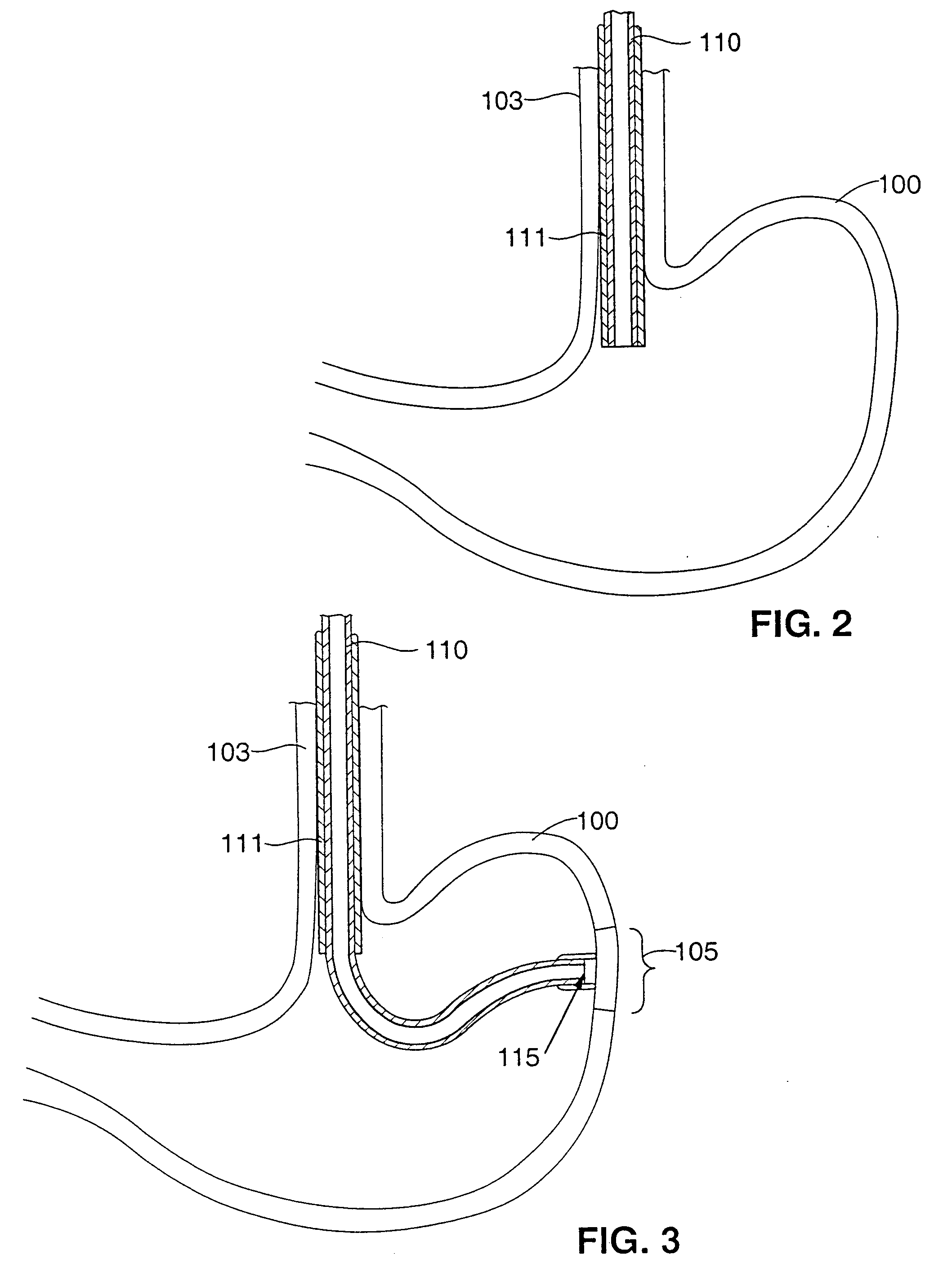
Gastric treatment and diagnosis device and method
InactiveUS20040088023A1Minimize stressReduce potential tissue damageCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGastric Disorders
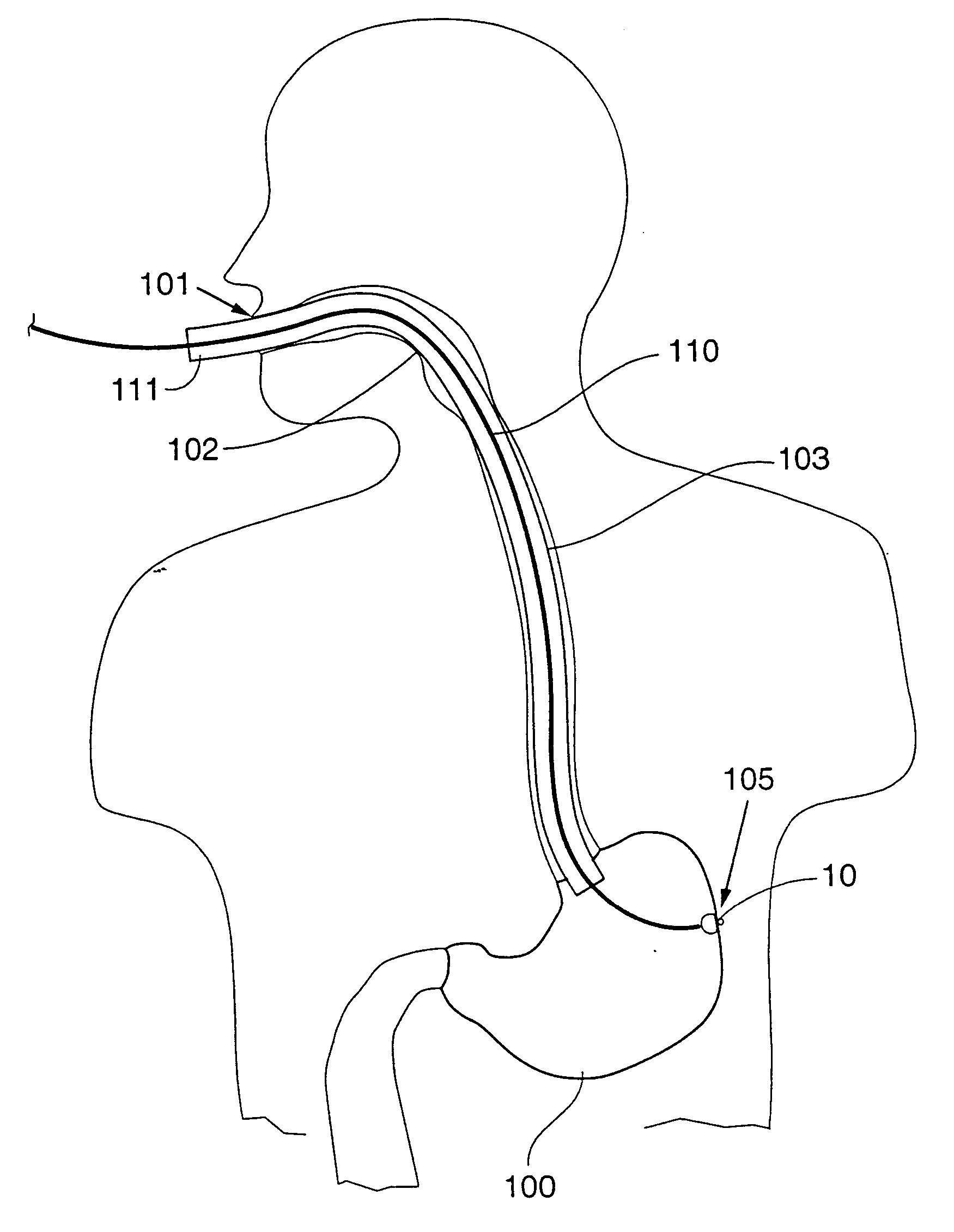
A device, system and method for diagnosing and treating gastric disorders is provided. A functional device resides within the patient's stomach and is secured to the stomach wall by an attachment device. The functional device may be a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The functional device in one embodiment provides a device, system and method for gastric electrical stimulation where stimulating electrodes are secured to the wall of the stomach by the attachment device or otherwise. A preferred device includes: at least one stimulating electrode in electrical contact with the stomach wall; an electronics unit containing the electronic circuitry of the device; and an attachment mechanism for attaching the device to the stomach wall. The functional devices may be programmed to respond to sensed information or signals. An endoscopic delivery system delivers the functional device through the esophagus and into the stomach where it is attached the stomach wall. The endoscopic instruments attach or remove the attachment devices and functional devices from the stomach and may be used to assist in determining the optimal attachment location.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Method of processing a substrate
InactiveUS7329608B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsDispersed particle separationReactive gasGas phase
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
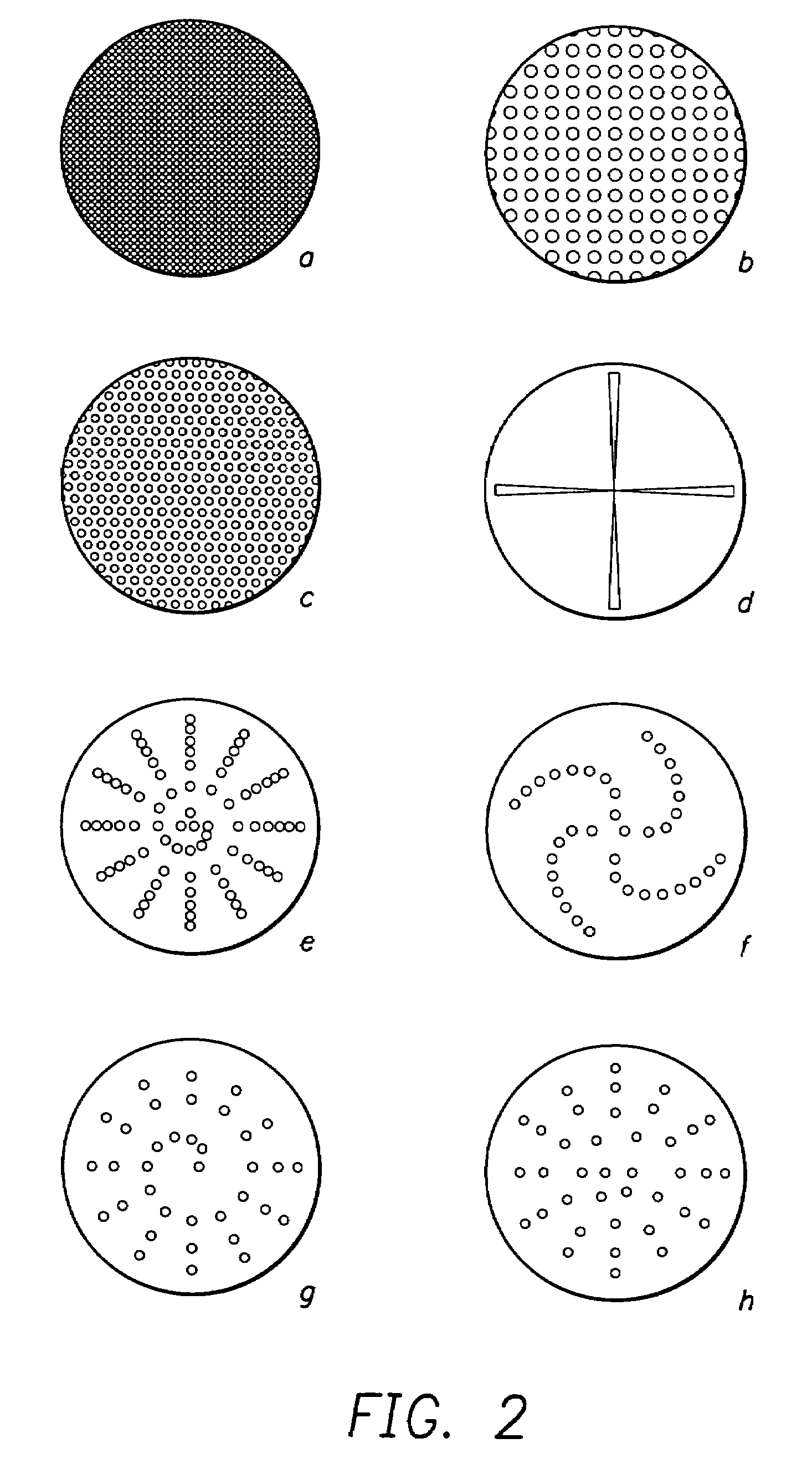
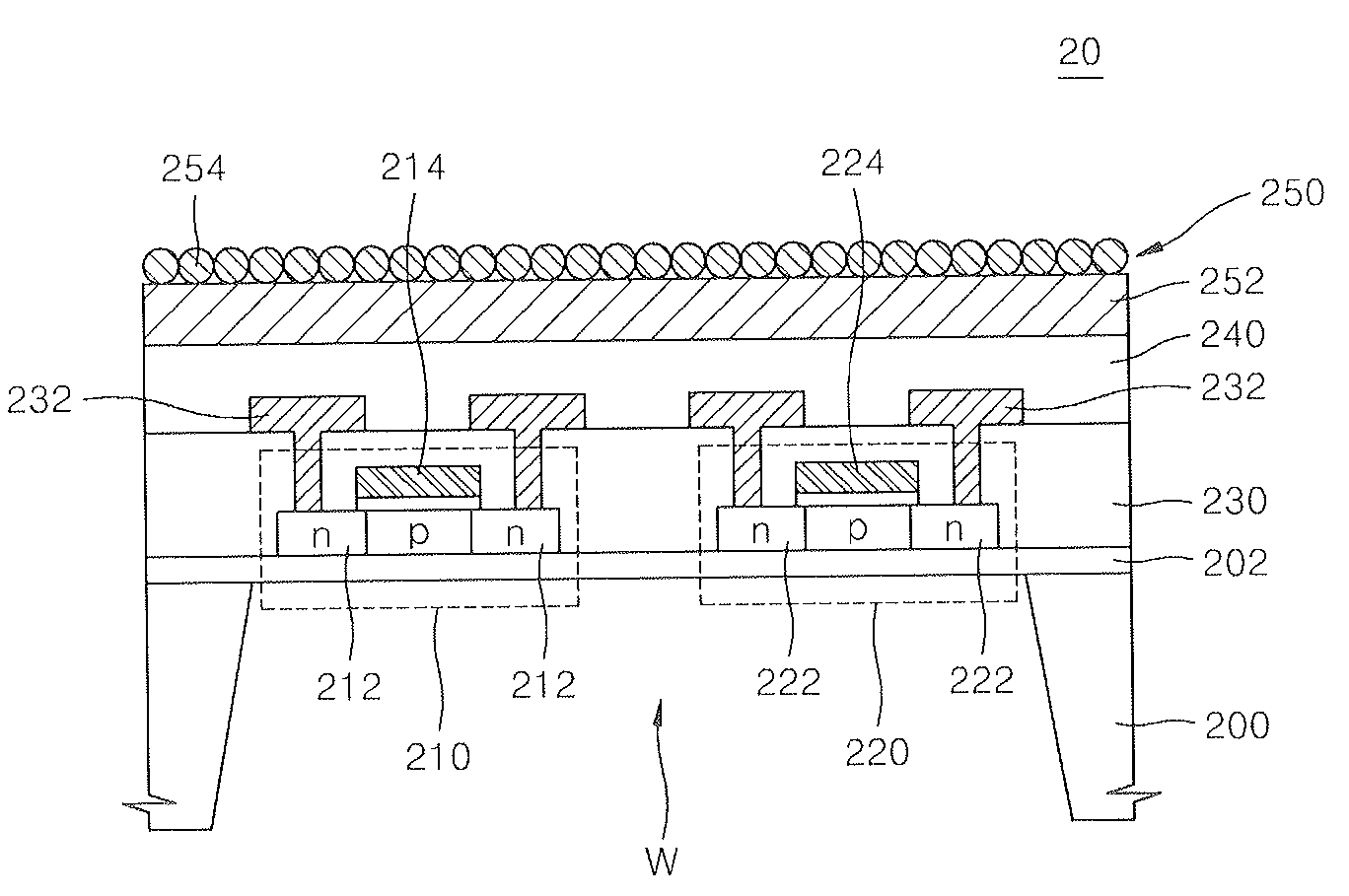
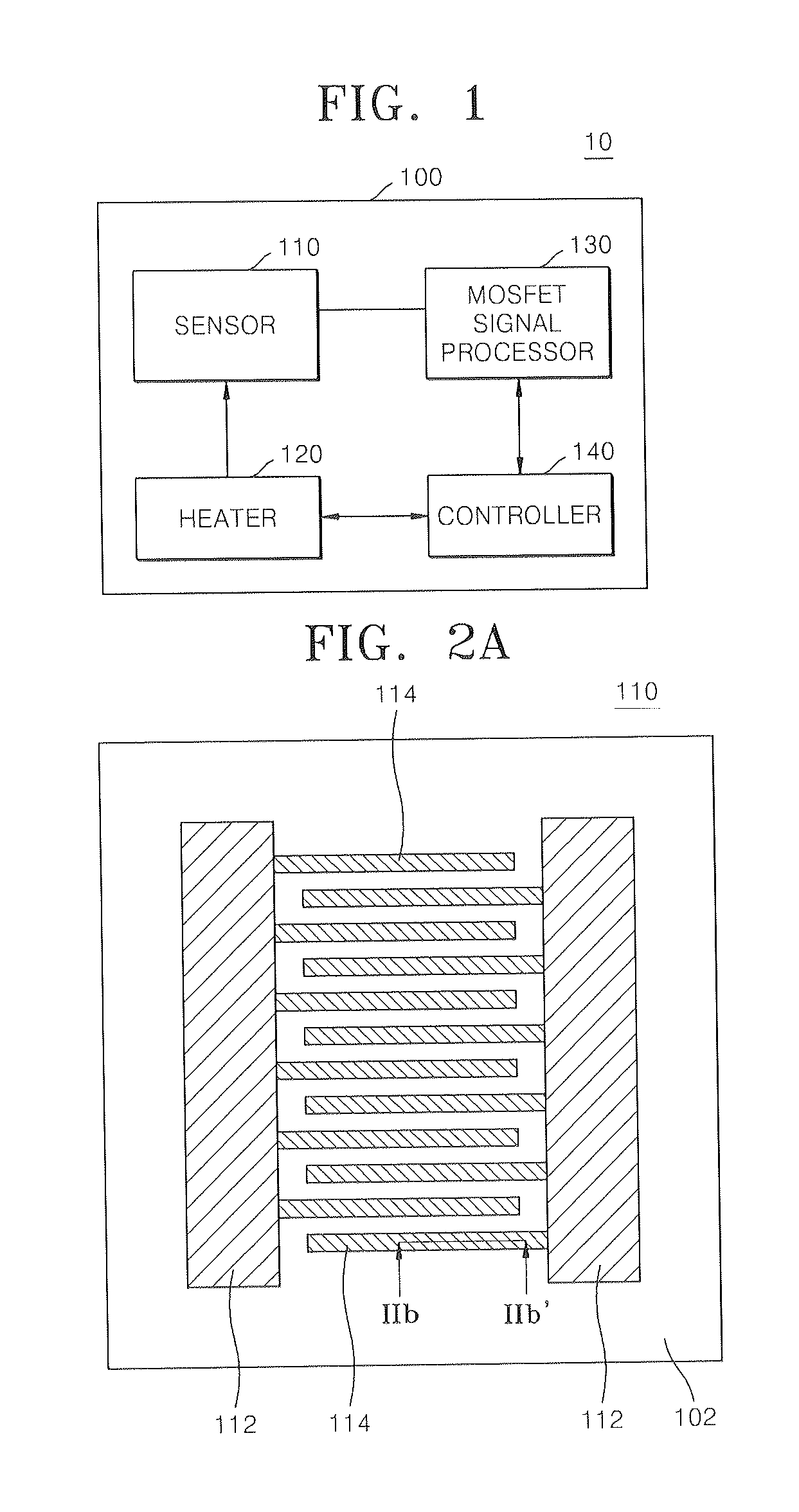
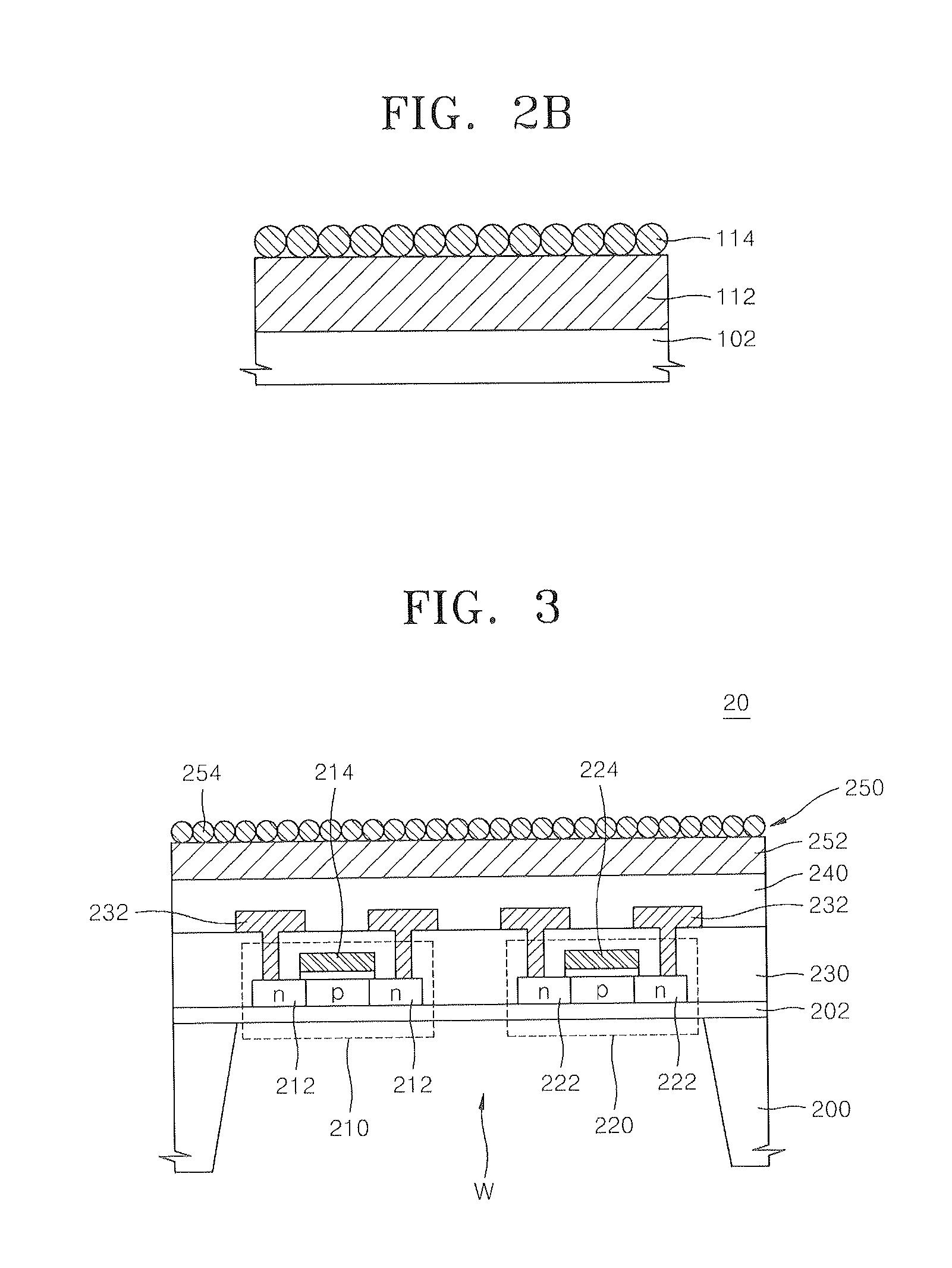
Method of forming sensor for detecting gases and biochemical materials, integrated circuit having the sensor, and method of manufacturing the integrated circuit
InactiveUS20080121946A1Characteristics degradation of an integrated circuit caused by heating the unit devices when forming the sensor can be preventedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanosensorsMOSFETNano structuring
A method of forming a sensor for detecting gases and biochemical materials that can be fabricated at a temperature in a range from room temperature to 400° C., a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET)-based integrated circuit including the sensor, and a method of manufacturing the integrated circuit are provided. The integrated circuit includes a semiconductor substrate. The sensor for detecting gases and biochemical materials includes a pair of electrodes formed on a first region of the semiconductor substrate, and a metal oxide nano structure layer formed on surfaces of the pair electrodes. A heater is formed to perform thermal treatment to re-use the material detected in the metal oxide nano structure layer. Also, a signal processor is formed by a MOSFET to process a predetermined signal obtained from a quantity change of a current flowing through the pair of electrodes of the sensor. To form the sensor, the metal oxide nano structure layer is formed on surfaces of the pair of electrodes at a temperature in a range from room temperature to 400° C.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
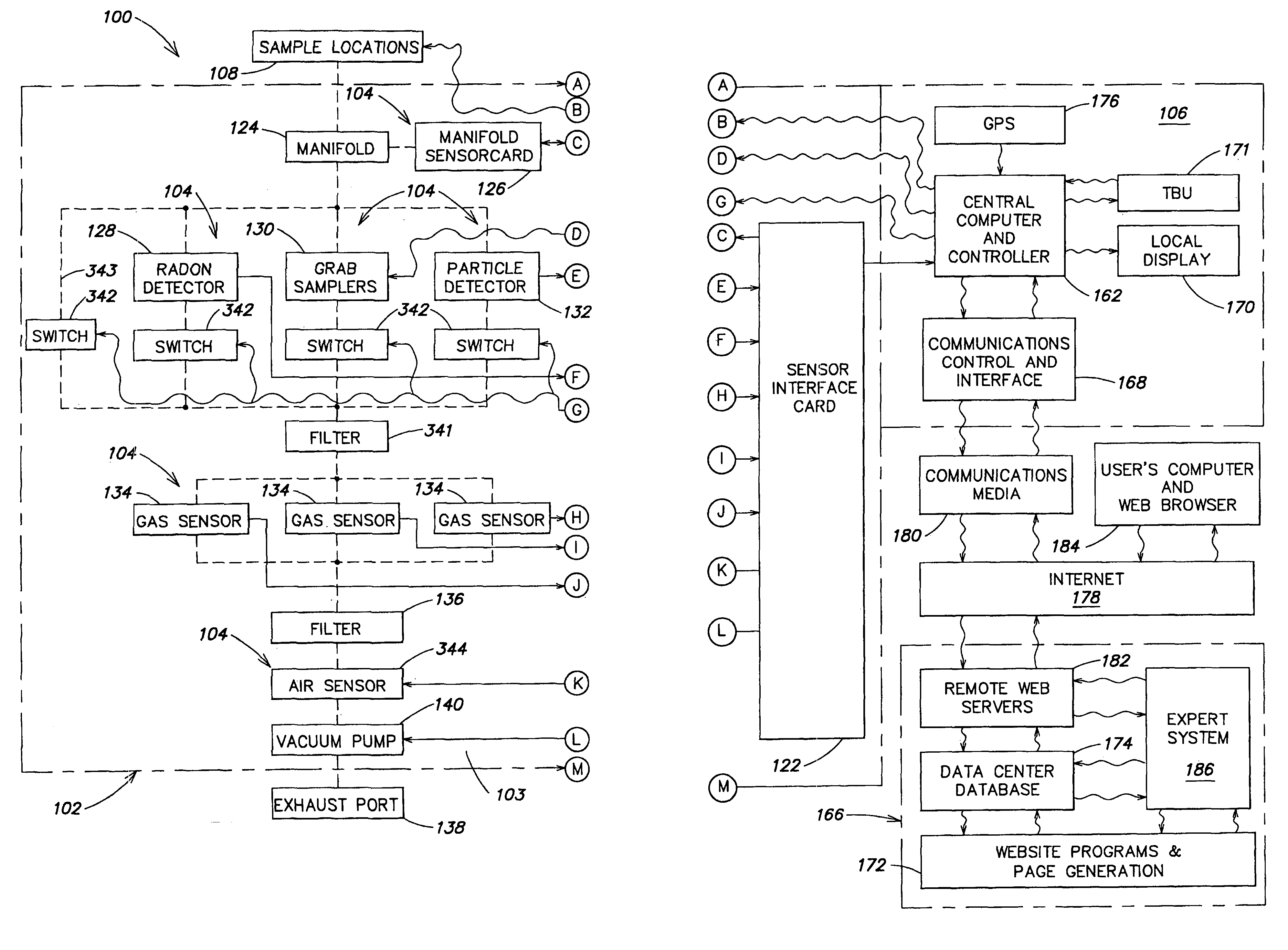
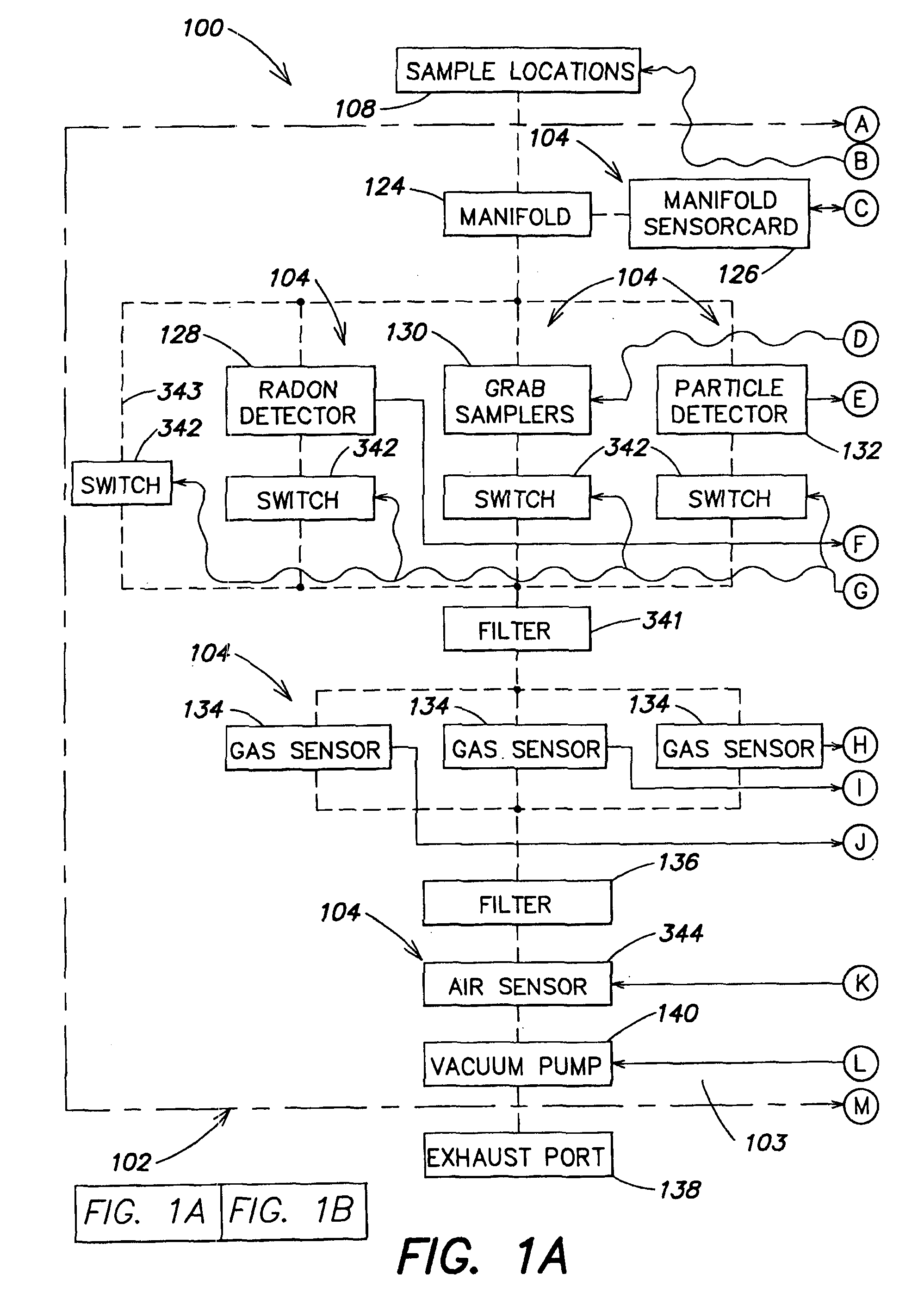
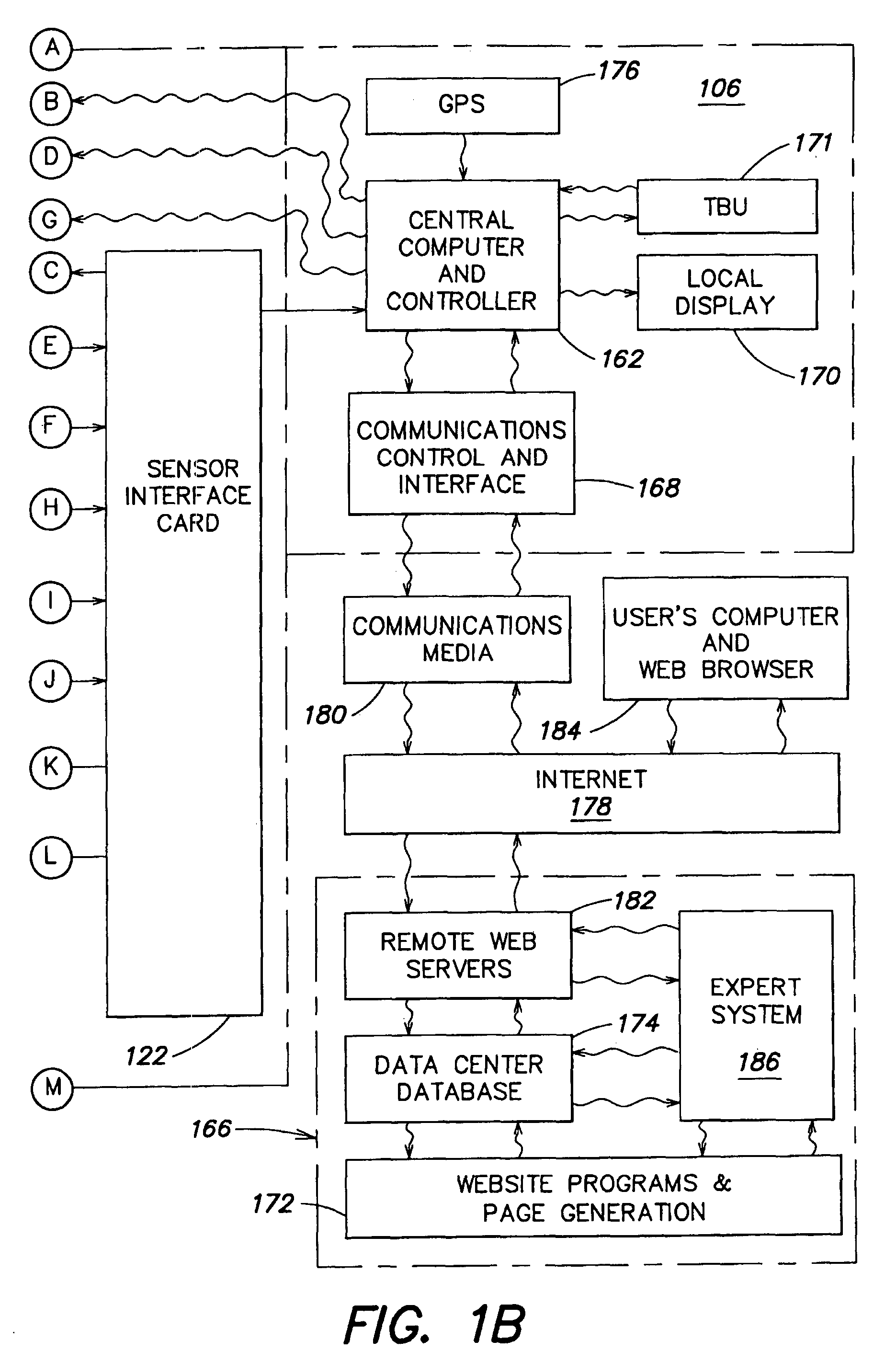
Air quality monitoring systems and methods
InactiveUS7302313B2Accurate locationRoom for correctingLighting and heating apparatusTemperatue controlAir monitoringData center
An air monitoring system is disclosed having an air monitoring unit with at least one sensor for measuring data of an air quality parameter and a computer for storing the air quality parameter data received from the sensor. The air monitoring unit may use an installed or a portable system, or a combination of both, for measuring the air quality parameters of interest. A remote data center may be provided, and the data may be uploaded to the data center from the unit by a communications media such as the Internet. Information or instructions may also be downloaded from the data center to the unit via the communications media for controlling or modifying the function of the unit. An expert system may be provided with the air monitoring system for controlling the unit. The information or instructions downloaded to the unit may be generated by the expert system.
Owner:AIRCUITY
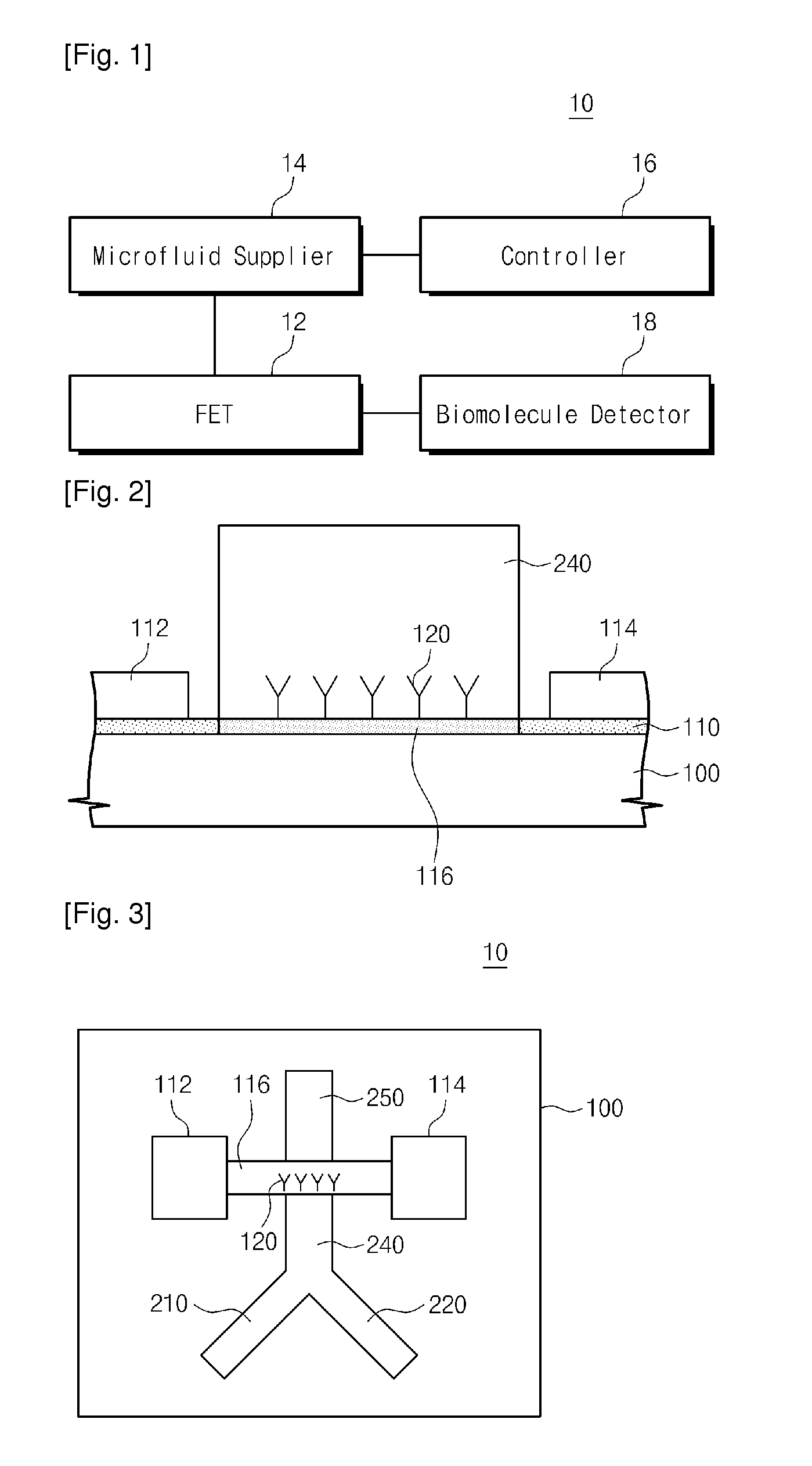
Apparatus and method for detecting biomolecules
ActiveUS20110165557A1Increase ionic strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBuffer solutionAnalytical chemistry
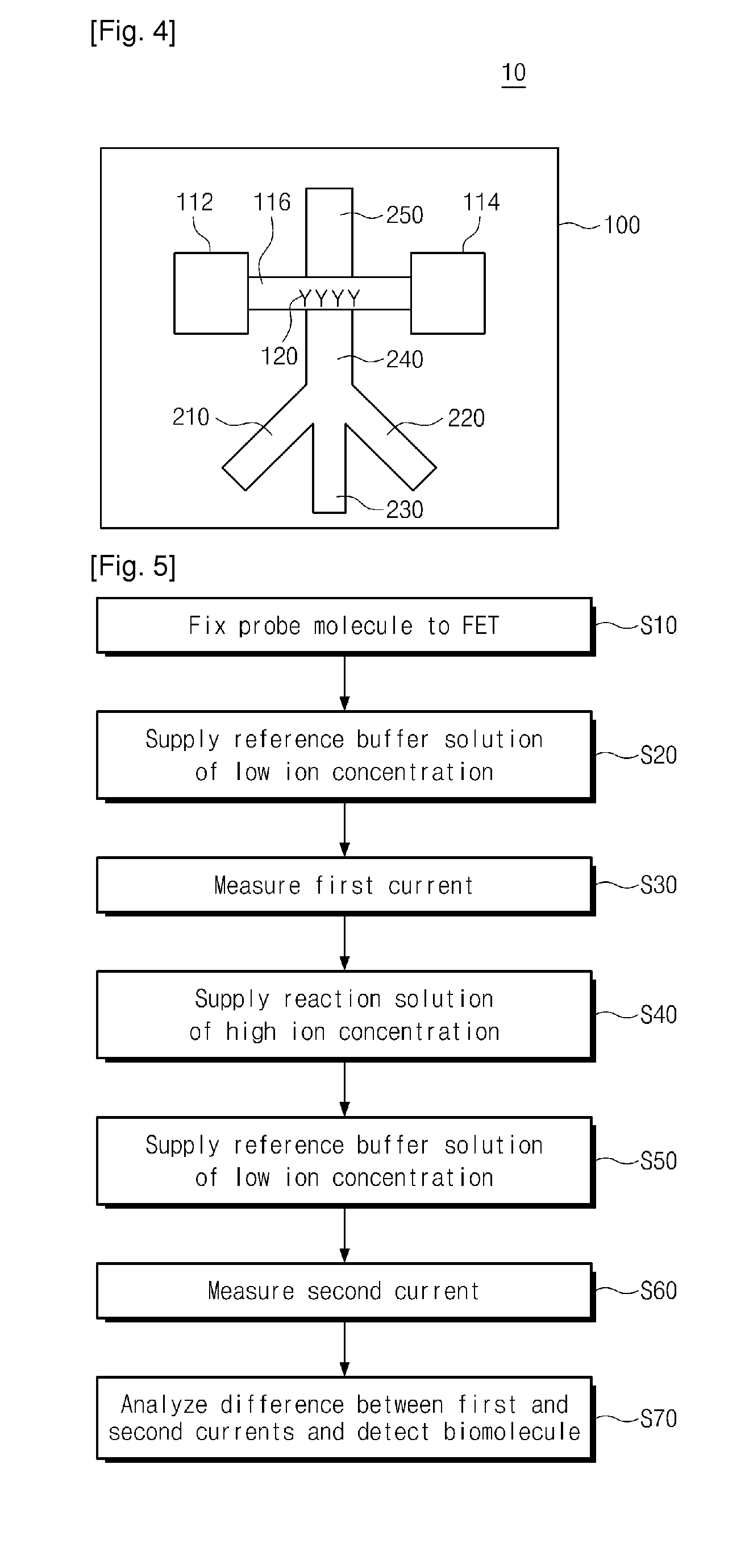
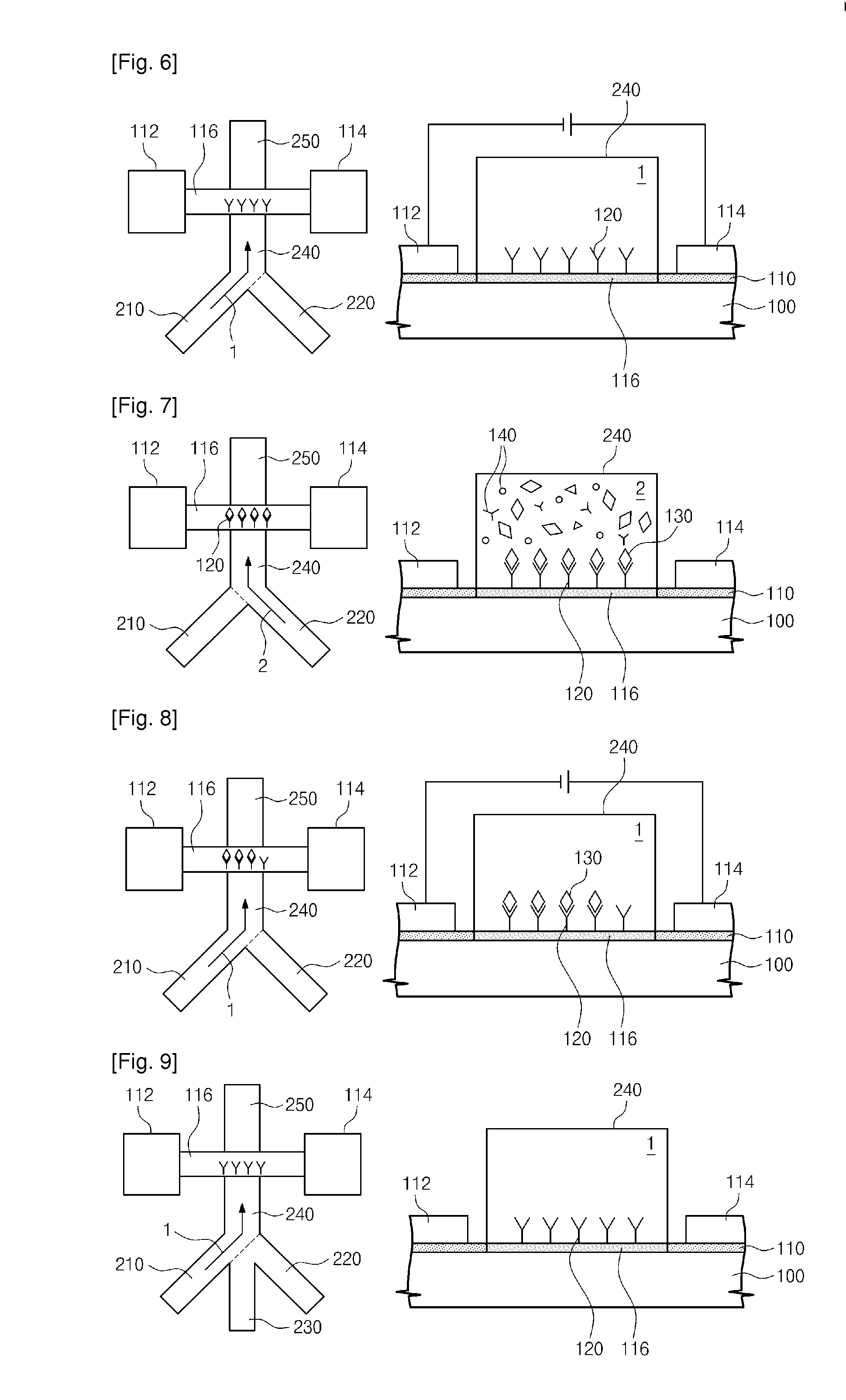
Provided are an apparatus and method for detecting biomolecules. The apparatus includes a FET having a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a channel region between the source and drain electrodes, and probe molecules fixed to the channel region, wherein the source and drain electrodes are separated on the substrate, a microfluid supplier selectively supplying one of a reference buffer solution of low ionic concentration and a reaction solution of high ionic concentration containing target molecules, to the channel region of the FET to which the probe molecules are fixed, and a biomolecule detector detecting the target molecules by measuring a first current value of the channel region of the FET, and a second current value of the channel region of the FET to which the target molecules and the probe molecules that bind to each other in the reaction solution of high ionic concentration are fixed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Sensor platform using a non-horizontally oriented nanotube element
Sensor platforms and methods of making them are described. A platform having a non-horizontally oriented sensor element comprising one or more nanostructures such as nanotubes is described. Under certain embodiments, a sensor element has or is made to have an affinity for an analyte. Under certain embodiments, such a sensor element comprises one or more pristine nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, the sensor element comprises derivatized or functionalized nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, a sensor is made by providing a support structure; providing one or more nanotubes on the structure to provide material for a sensor element; and providing circuitry to electrically sense the sensor element's electrical characterization. Under certain embodiments, the sensor element comprises pre-derivatized or pre-functionalized nanotubes. Under other embodiments, sensor material is derivatized or functionalized after provision on the structure or after patterning. Under certain embodiments, a large-scale array of sensor platforms includes a plurality of sensor elements.
Owner:NANTERO
Gastric anchor and method
Owner:INTRAPACE
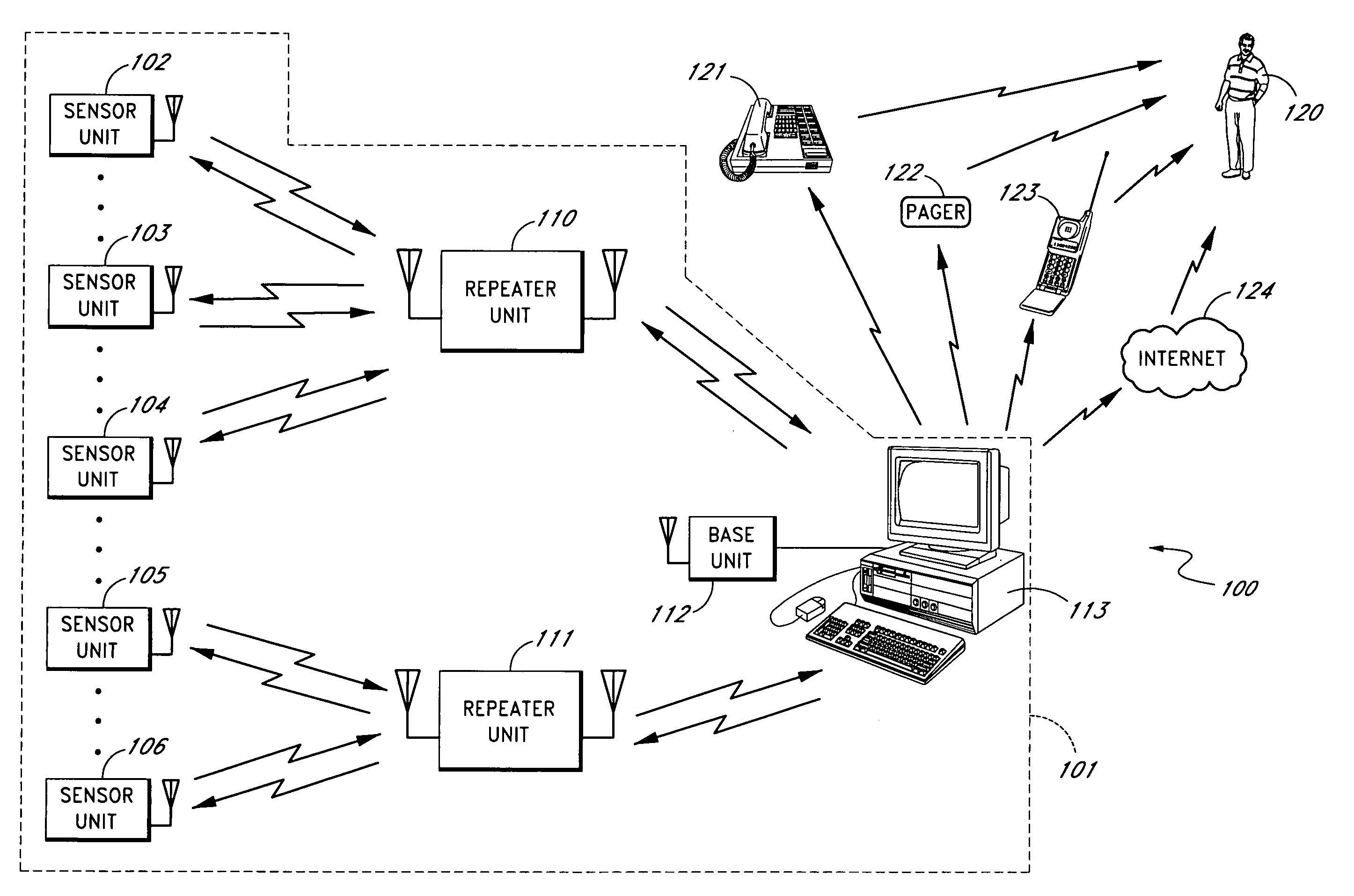
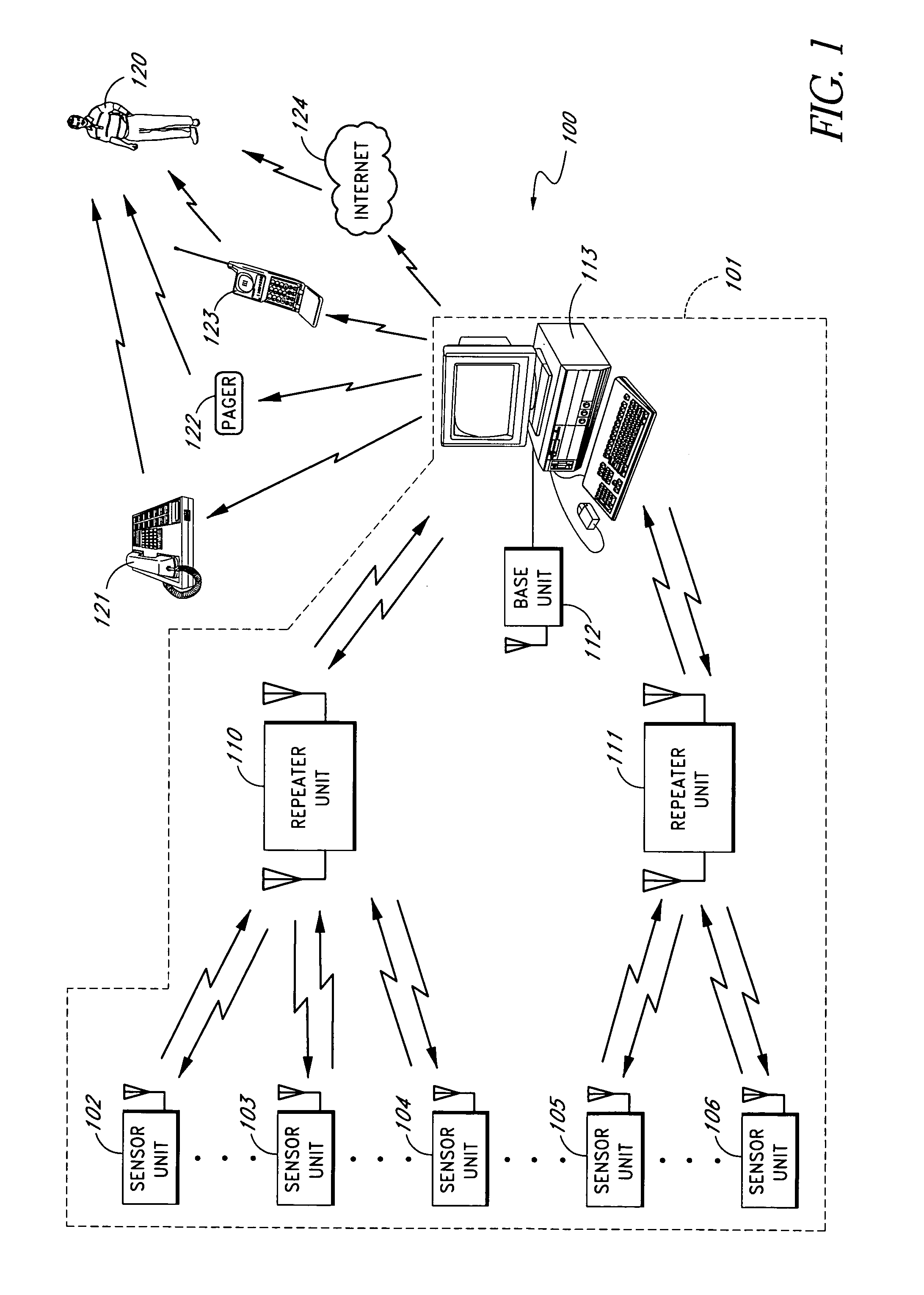
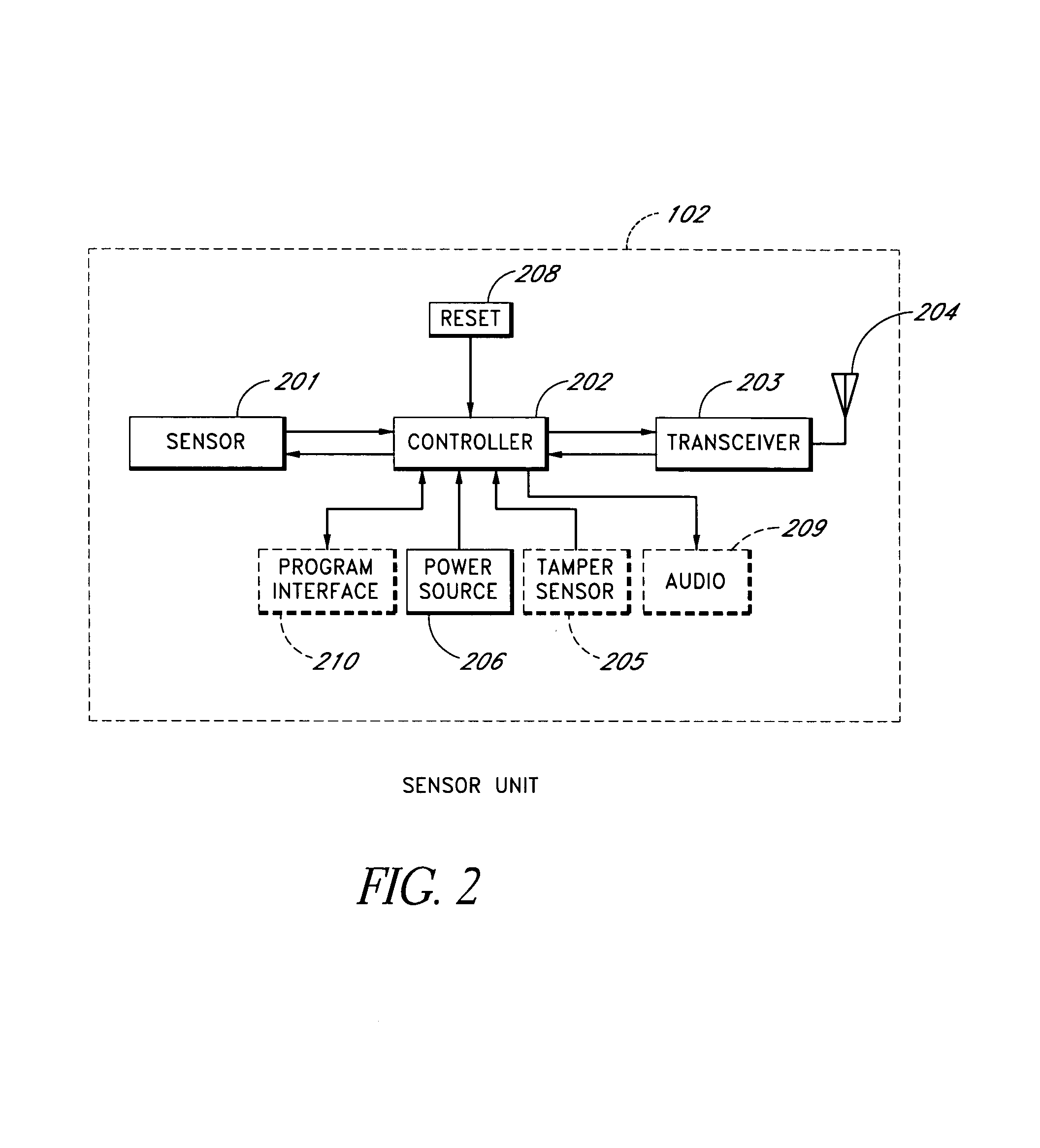
Method and apparatus for detecting moisture in building materials
ActiveUS7142123B1Low costIncrease rangeElectric signal transmission systemsBuilding constructionsPagerThe Internet
A moisture sensor system is described. In one embodiment, the system provides an adjustable threshold level for the sensed moisture level. The adjustable threshold allows the moisture sensor to adjust to ambient conditions, aging of components, and other operational variations while still providing a relatively sensitive detection capability. In one embodiment, the adjustable threshold moisture sensor is used in an intelligent sensor system that includes one or more intelligent sensor units and a base unit that can communicate with the moisture sensor units. When one or more of the moisture sensor units detects a excess moisture the moisture sensor unit communicates with the base unit and provides data regarding the moisture condition. The base unit can contact a supervisor or other responsible person by a plurality of techniques, such as, telephone, pager, cellular telephone, Internet (and / or local area network), etc. In one embodiment, one or more wireless repeaters are used between the moisture sensor units and the base unit to extend the range of the system and to allow the base unit to communicate with a larger number of sensors.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Nanoscale wires and related devices
InactiveUS7301199B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantTunnel diode
The present invention relates generally to sub-microelectronic circuitry, and more particularly to nanometer-scale articles, including nanoscale wires which can be selectively doped at various locations and at various levels. In some cases, the articles may be single crystals. The nanoscale wires can be doped, for example, differentially along their length, or radially, and either in terms of identity of dopant, concentration of dopant, or both. This may be used to provide both n-type and p-type conductivity in a single item, or in different items in close proximity to each other, such as in a crossbar array. The fabrication and growth of such articles is described, and the arrangement of such articles to fabricate electronic, optoelectronic, or spintronic devices and components. For example, semiconductor materials can be doped to form n-type and p-type semiconductor regions for making a variety of devices such as field effect transistors, bipolar transistors, complementary inverters, tunnel diodes, light emitting diodes, sensors, and the like.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
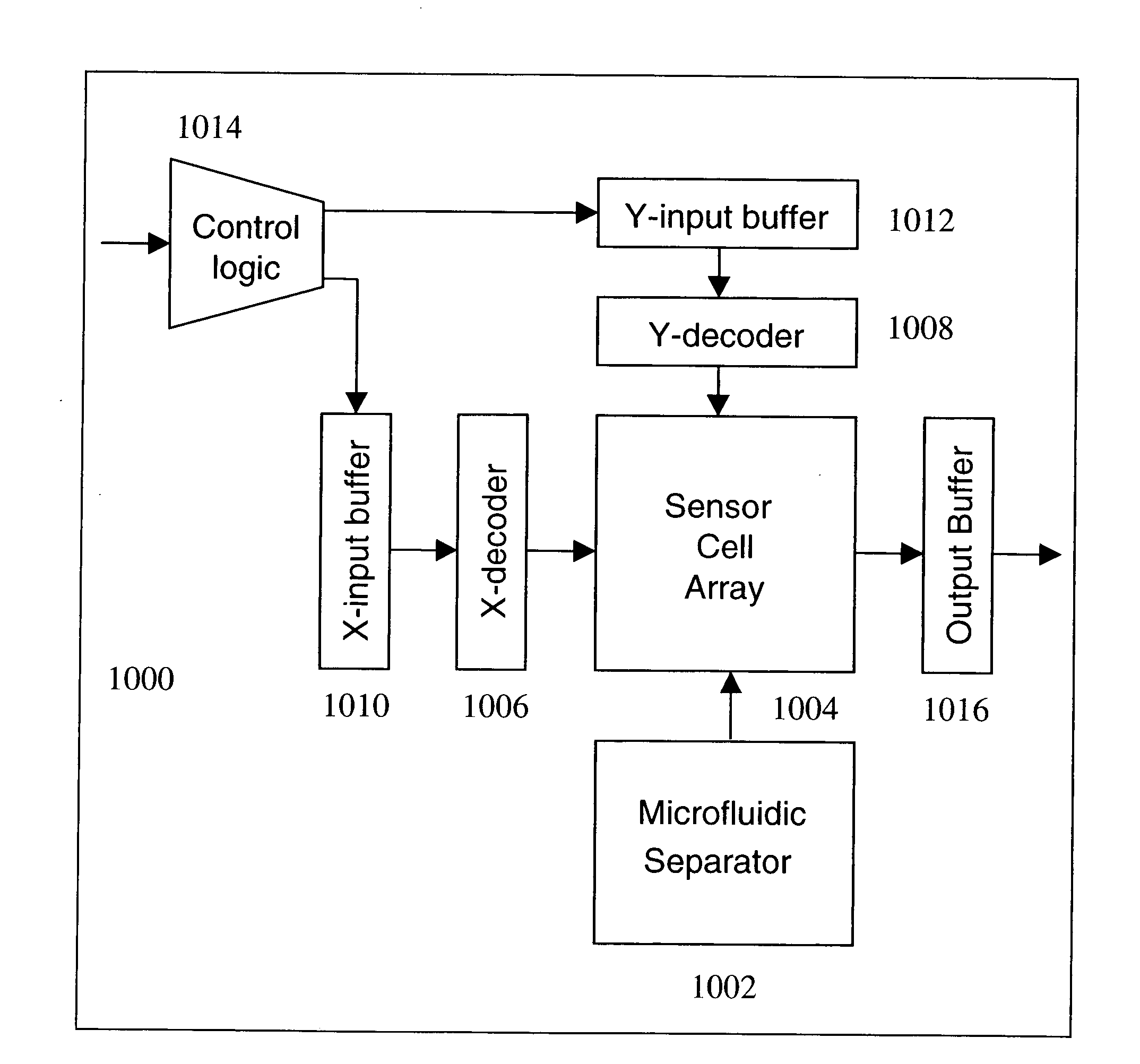
Microfluidic analytical system with position electrodes
ActiveUS6990849B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A microfluidic analytical system for monitoring an analyte (for example, glucose) in a liquid sample (e.g., ISF) includes an analysis module with at least one micro-channel for receiving and transporting a liquid sample, at least one analyte sensor for measuring an analyte in the liquid sample and at least one position electrode. The analyte sensor(s) and position electrode(s) are in operative communication with the micro-channel. The microfluidic system also includes a meter configured for measuring an electrical characteristic (such as impedance or resistance) of the position electrode(s). Moreover, the measured electrical characteristic is dependent on the position of the liquid sample in the micro-channel that is in operative communication with the position electrode for which an electrical characteristic is measured.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +2
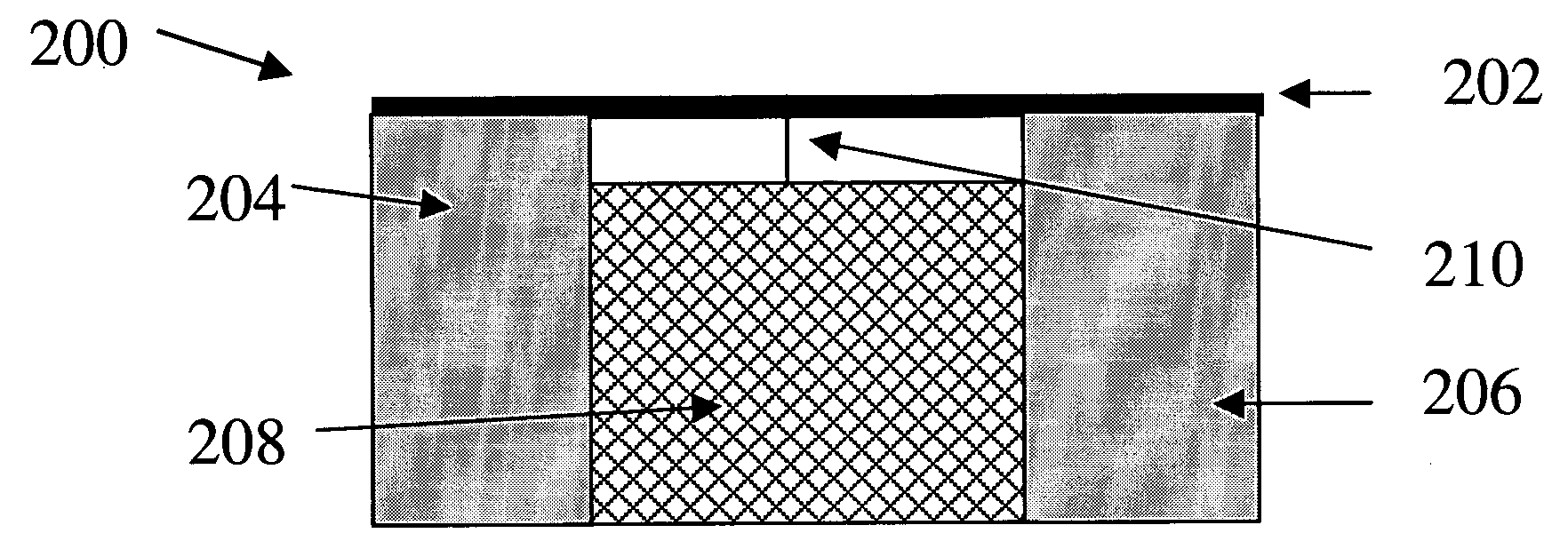
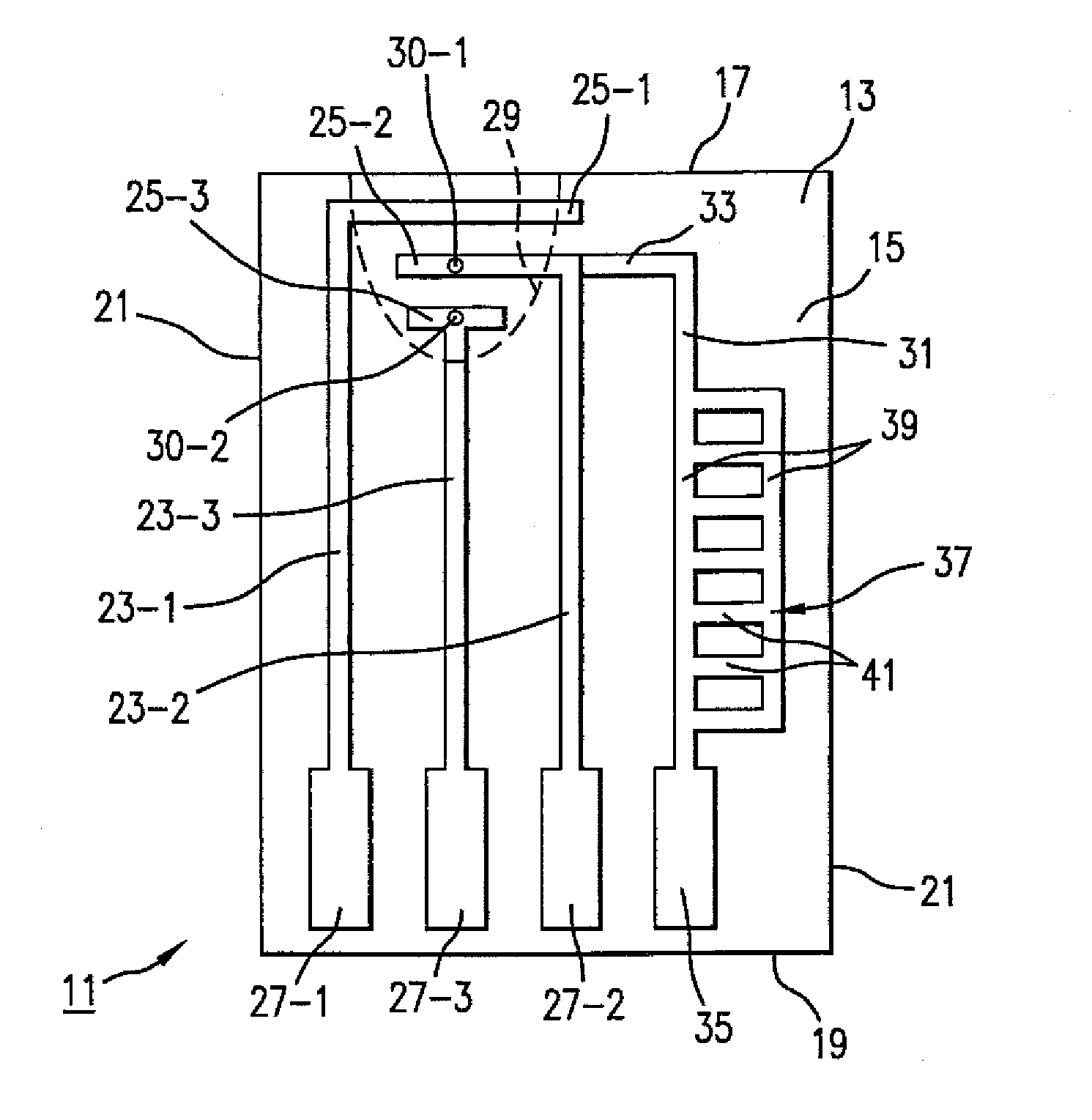
Sensing system for monitoring the structural health of composite structures
ActiveUS20050284232A1Easy to stickImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementGrid patternState of health
A sensing system for use in monitoring the structural health of a structure such as a polymeric matrix composite structure is provided. The system includes a sensor formed from a conductive ink containing carbon nanofibers and a polymeric resin, and a data acquisition system for acquiring and evaluating data from the sensor. The conductive ink may be applied directly to the structure to be monitored in the form of a grid pattern. Damage to the structure may be detected by measuring changes in resistance values detected from the sensor.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
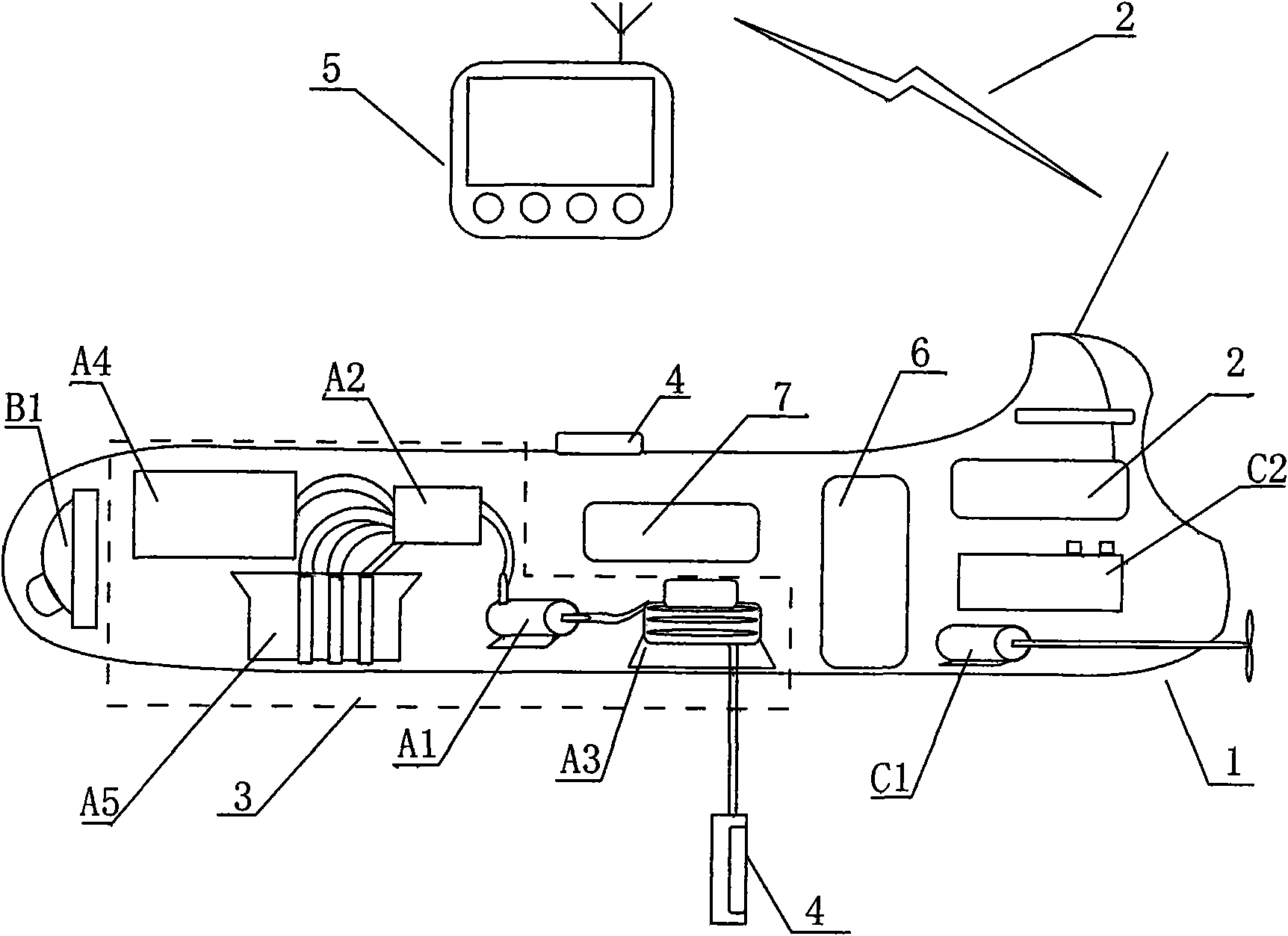
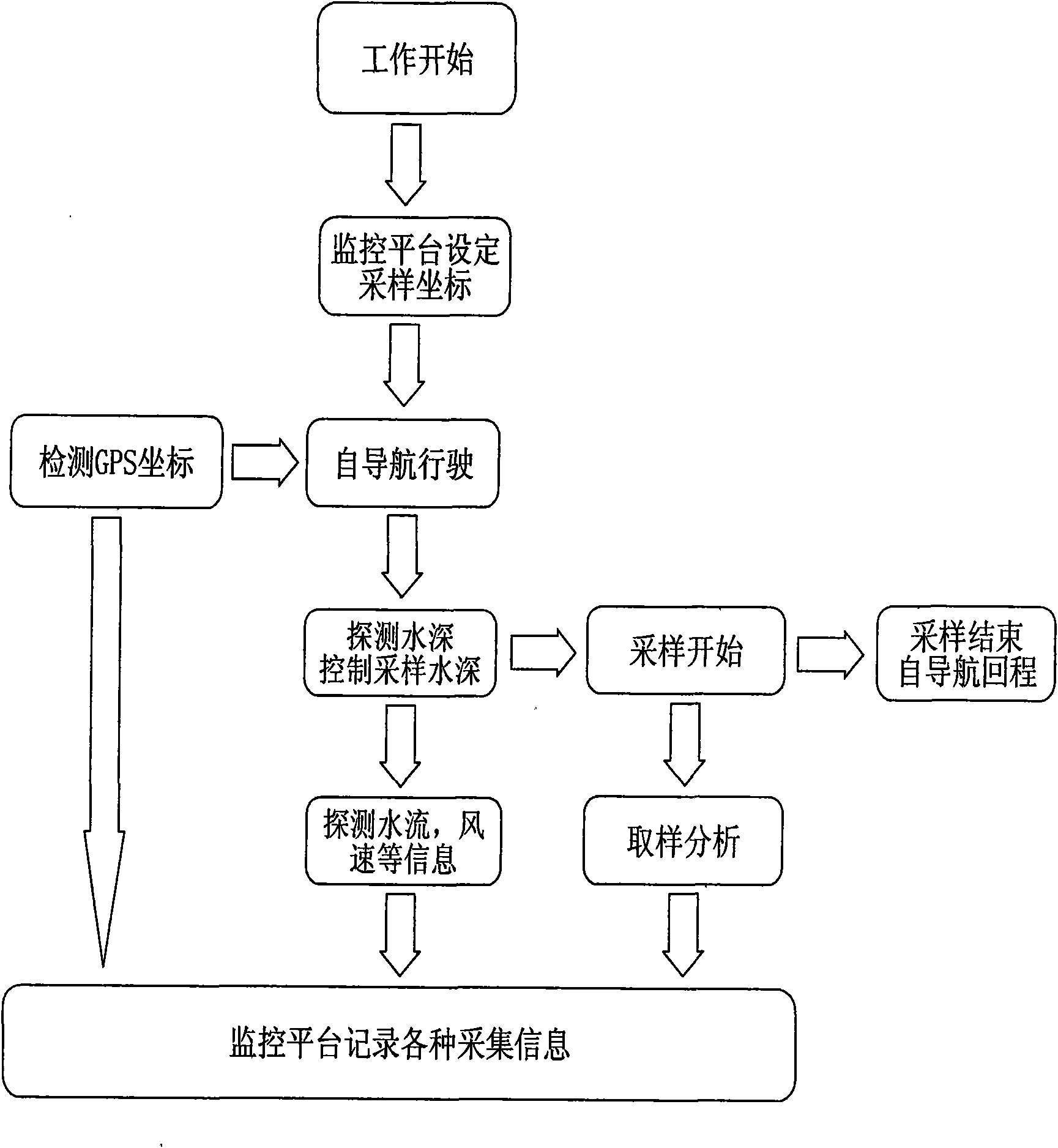
Remote-control self-navigation water quality sampling and analyzing device
InactiveCN101592649AAccurate water quality testing dataLow costRadiation pyrometryWithdrawing sample devicesSystem integrationSample water
A remote-control self-navigation water quality sampling and analyzing device belongs to the field of water quality monitoring, sampling and analyzing system integration in environmental protection, and in particular relates to self-navigation running and water quality sampling and analyzing detection technology. The device comprises a carrier [1], a wireless communication module [2], a sampling and analyzing module [3], an environmental sensor module [4], a remote monitoring platform [5], a self-navigation system [6], a control module [7], and the like. The device has the characteristics of remote monitoring, automatic acquisition, sample dividing storage, automatic record of related information and the like in the overall process of sampling water quality, and simultaneously has the advantage of quick and accurate acquisition of time and spacial information; and the water quality analyzing module of the device can acquire partial water quality analyzing results in the first time, so the device can greatly improve the accuracy, authenticity, timeliness, intellectuality and monitoring efficiency of water quality field sampling, can reduce sampling risk and cost, and has significance on water area water quality monitoring.
Owner:CENT TESTING INT GRP CO LTD +2
Personal care products with microchemical sensors for odor detection
ActiveUS20070142799A1Quickly and accurately determineDetect presenceBaby linensMaterial resistanceCaregiver personChemiresistor
Absorbent articles comprising one or more sensors capable of detecting the presence of a body waste in the absorbent article are described. In particular, the absorbent articles comprise at least one chemiresistor capable of detecting the presence of volatile organic compounds associated with a body waste. When a body waste is detected, an indicator means signals a caregiver and / or a user of the absorbent article that an insult has occurred
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
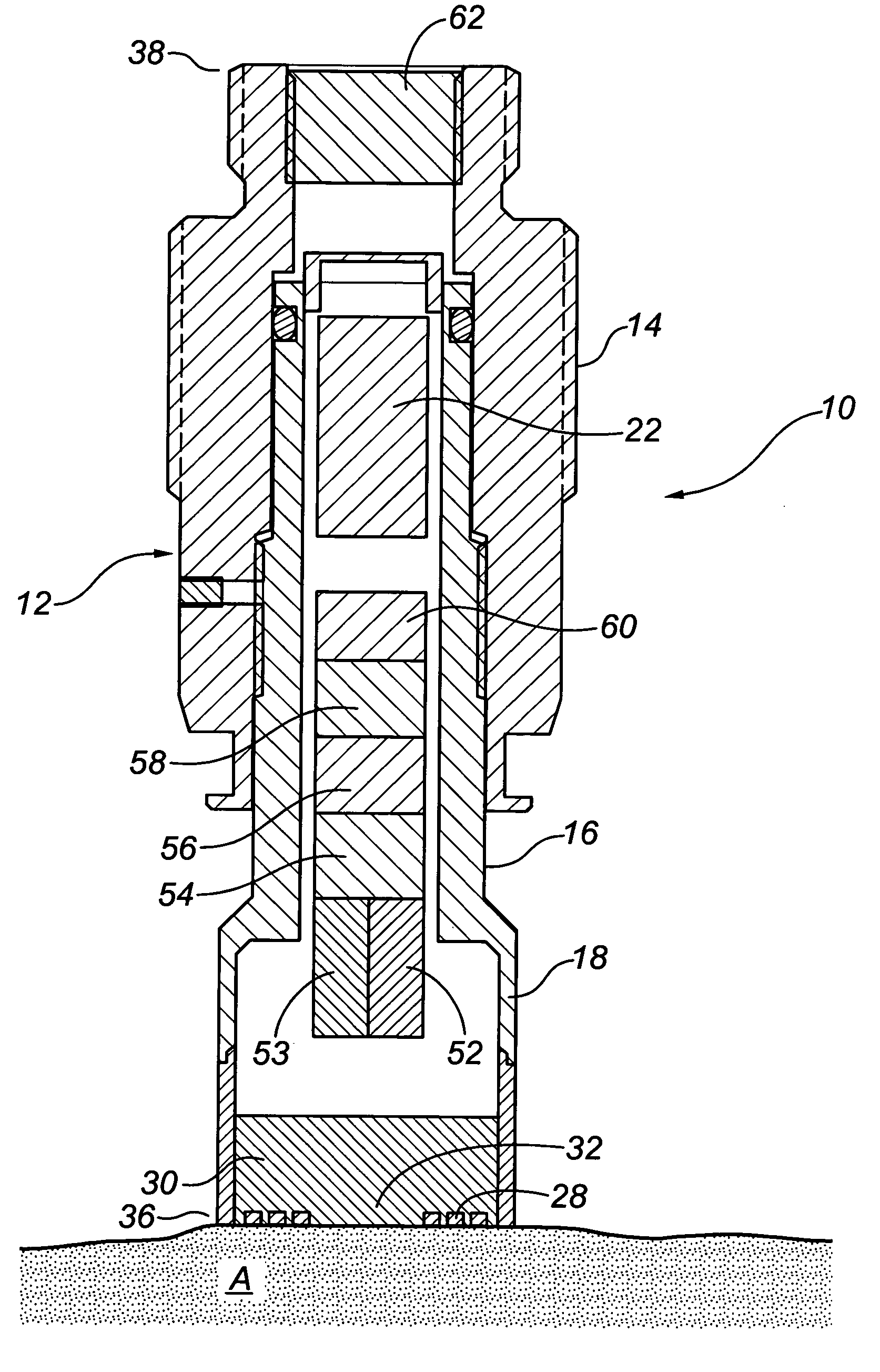
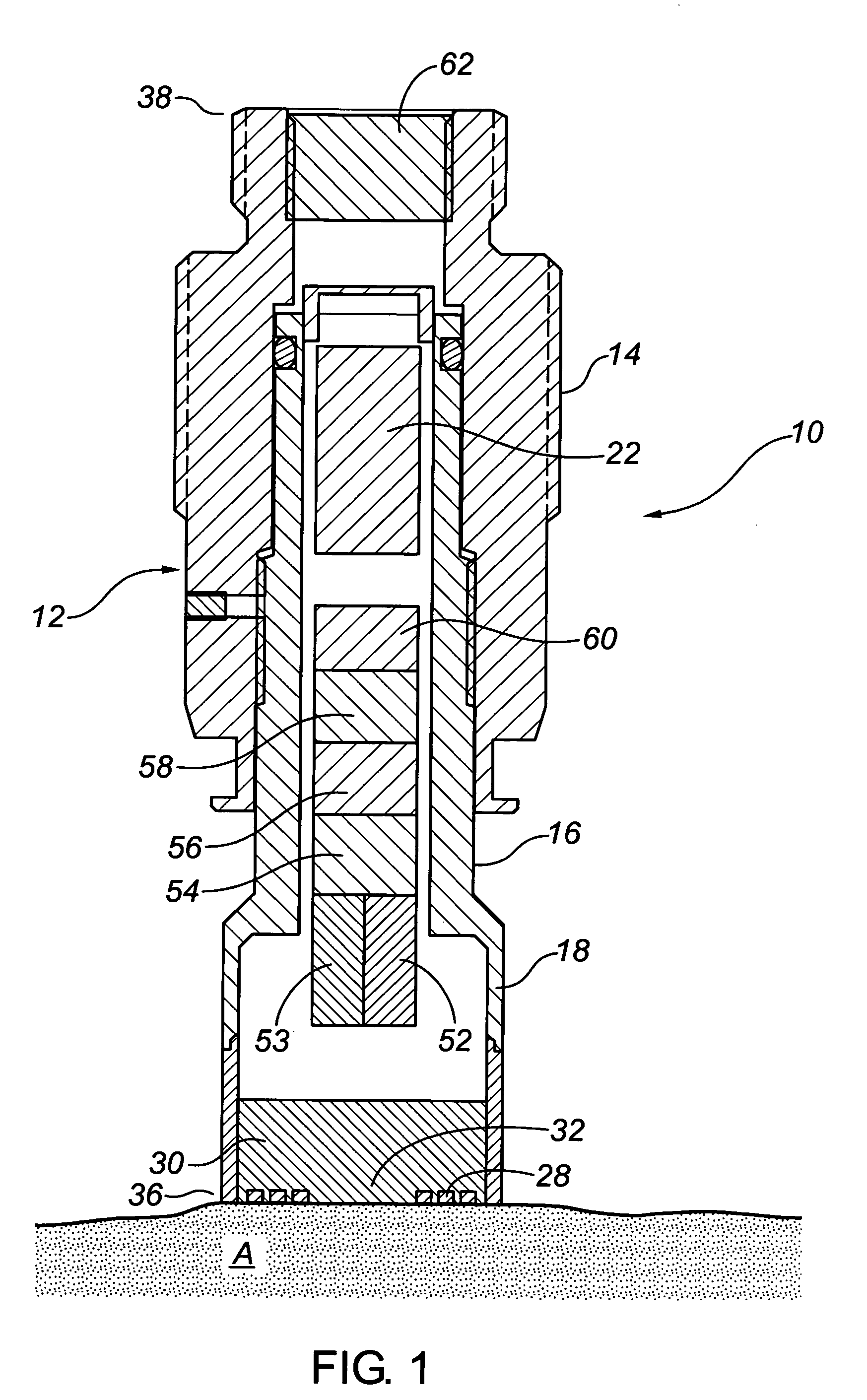
Direct resistance measurement corrosion probe
InactiveUS7034553B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A direct resistance measurement probe for measuring corrosion levels and material loss. The probe includes a hollow body having a resistive element at one end that is exposed to the environment. The probe can have an internal or external power source that is electrically connected to the resistive element. A meter measures the electrical resistance of the resistive element providing data from which corrosion rates may be ascertained. A temperature sensing device measures the temperature of the resistive element. A pressure sensing device measures the pressure of the environment that the resistive element is subjected to. The probe does not use a comparative or ratiometric reference element.
Owner:GILBOE DEREK
Electric conductivity water probe
ActiveUS7019541B2Precise functionComponent separationResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityEngineering
An electric conductivity water probe consisting of a test chamber having a wall, a fluids input / output port, and a water input port, the wall having a first and at least a second wall section, the first and at least second wall sections being electrically isolated from each other by an electrical insulator; and a valve connected operatively to the fluids input / output port, the valve being adapted for alternately and permitting and resisting flows of fluids through the fluids port.
Owner:CROWN PRODS
Analyte test sensor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7418285B2Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical resistance and conductanceAnalyte
An analyte test sensor for use in measuring the concentration of a particular analyte in a test sample includes a non-conductive substrate, a reference electrode deposited on the substrate, a working electrode deposited on the substrate and a compensation electrode deposited on the substrate. The compensation electrode is provided with a resistive ladder and is designed to correct for test result inaccuracies which are the result of variances in the manufacturing of the test sensor. Specifically, in one embodiment, the compensation electrode corrects for test result inaccuracies in an analog manner by shunting a portion of the working current away from working electrode. In another embodiment, the compensation electrode corrects for test result inaccuracies in a digital manner by providing a calibration code which is proportional its resistance value. A batch of analyte test sensors are preferably manufactured in the following manner. An initial batch of the test sensors is constructed. Then, a limited sampling of the sensors is tested for accuracy using a control sample. Based on the test results, the resistance value of the compensation electrode for each remaining sensor in the batch is adjusted accordingly.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Methods and devices for characterizing duplex nucleic acid molecules
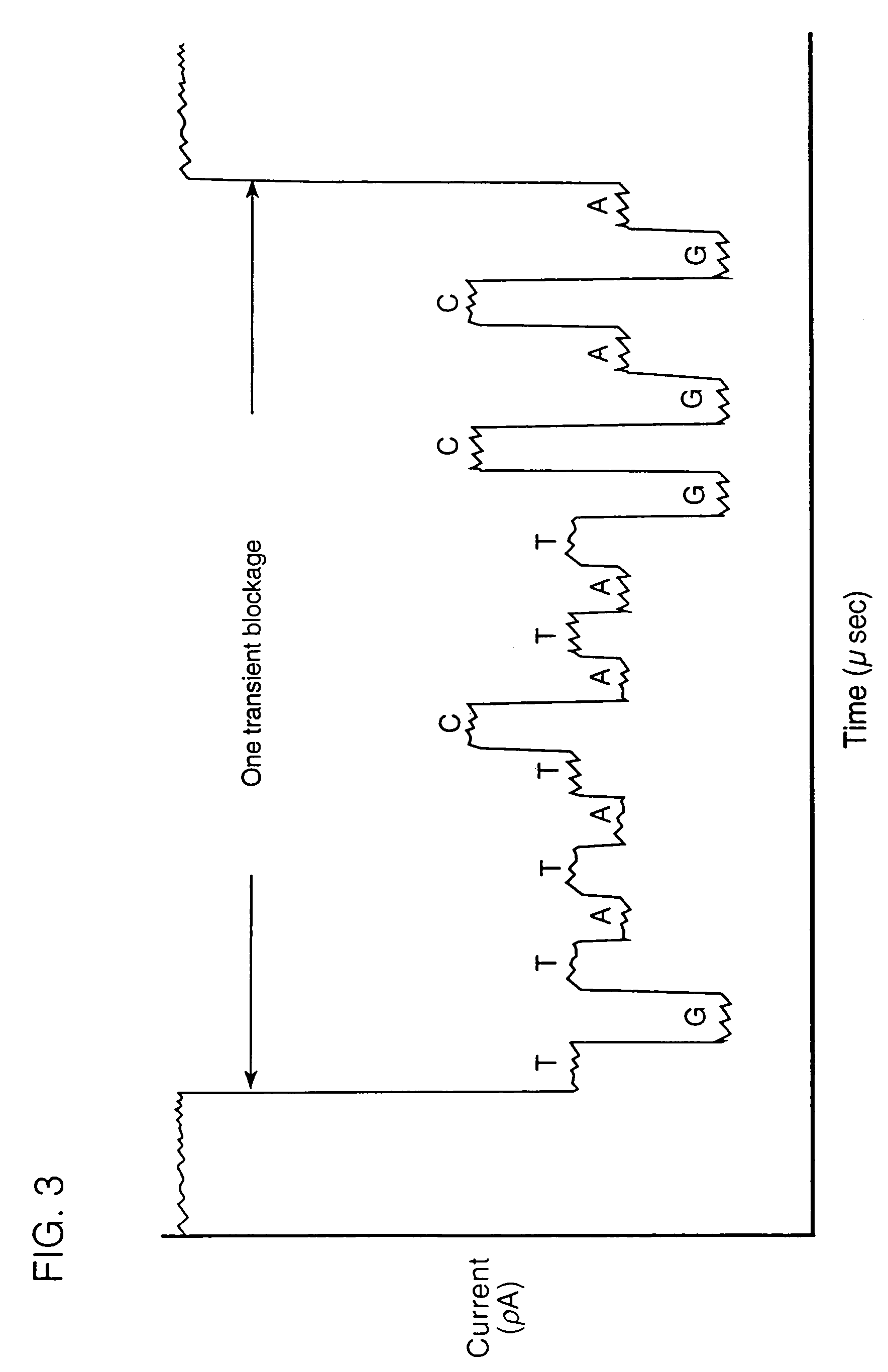
Methods and devices are provided for characterizing a duplex nucleic acid, e.g., a duplex DNA molecule. In the subject methods, a fluid conducting medium that includes a duplex nucleic acid molecule is contacted with a nanopore under the influence of an applied electric field and the resulting changes in current through the nanopore caused by the duplex nucleic acid molecule are monitored. The observed changes in current through the nanopore are then employed as a set of data values to characterize the duplex nucleic acid, where the set of data values may be employed in raw form or manipulated, e.g., into a current blockade profile. Also provided are nanopore devices for practicing the subject methods, where the subject nanopore devices are characterized by the presence of an algorithm which directs a processing means to employ monitored changes in current through a nanopore to characterize a duplex nucleic acid molecule responsible for the current changes. The subject methods and devices find use in a variety of applications, including, among other applications, the identification of an analyte duplex DNA molecule in a sample, the specific base sequence at a single nulceotide polymorphism (SNP), and the sequencing of duplex DNA molecules.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com