Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7956 results about "Pressure sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pressure sensing is the capacity for some system to sense the force exerted on a surface per unit area and express that force in the strength of an electric signal. For example, pressure sensing is what allows a robot to tell when it collides with something, or when something pushes against it.
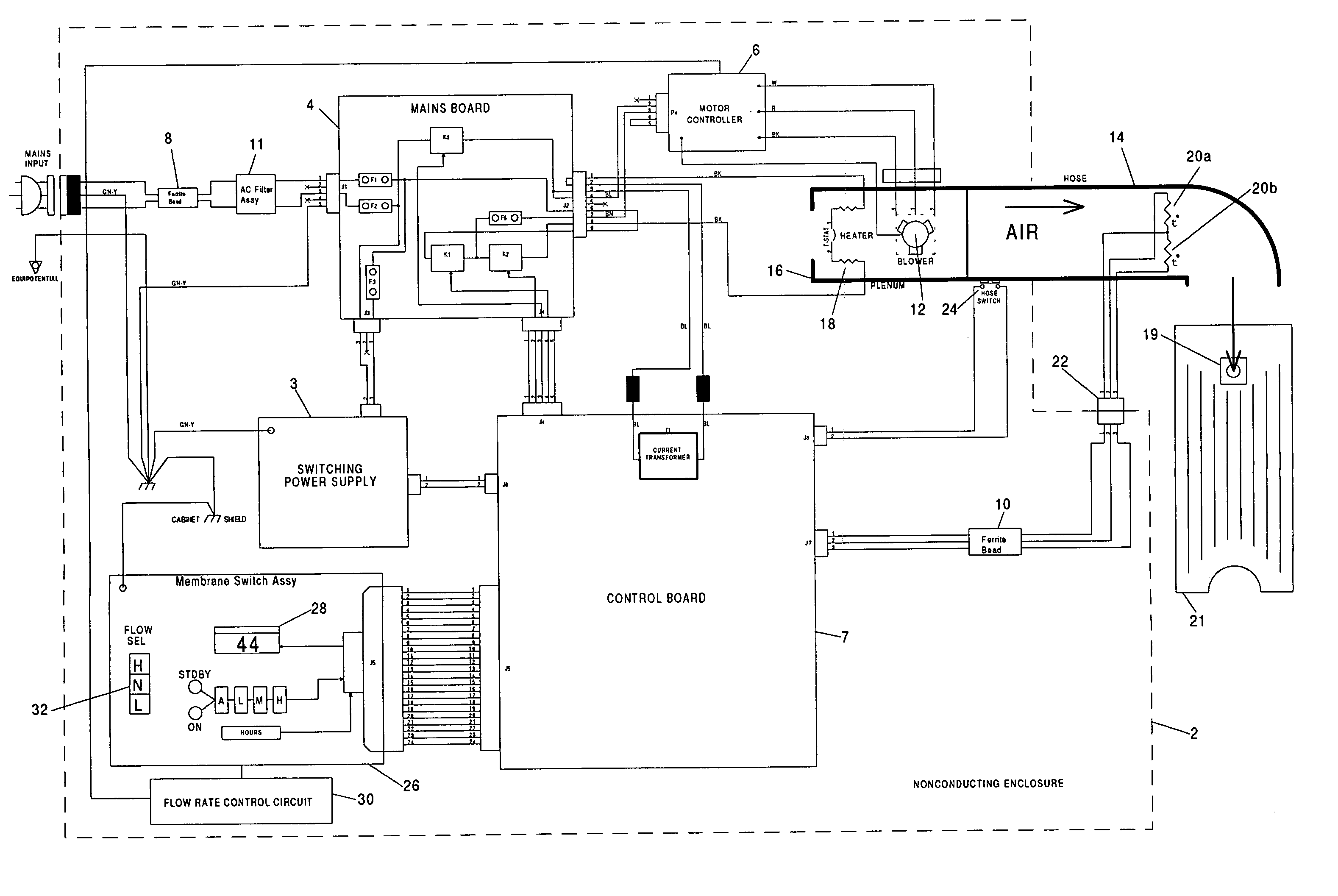
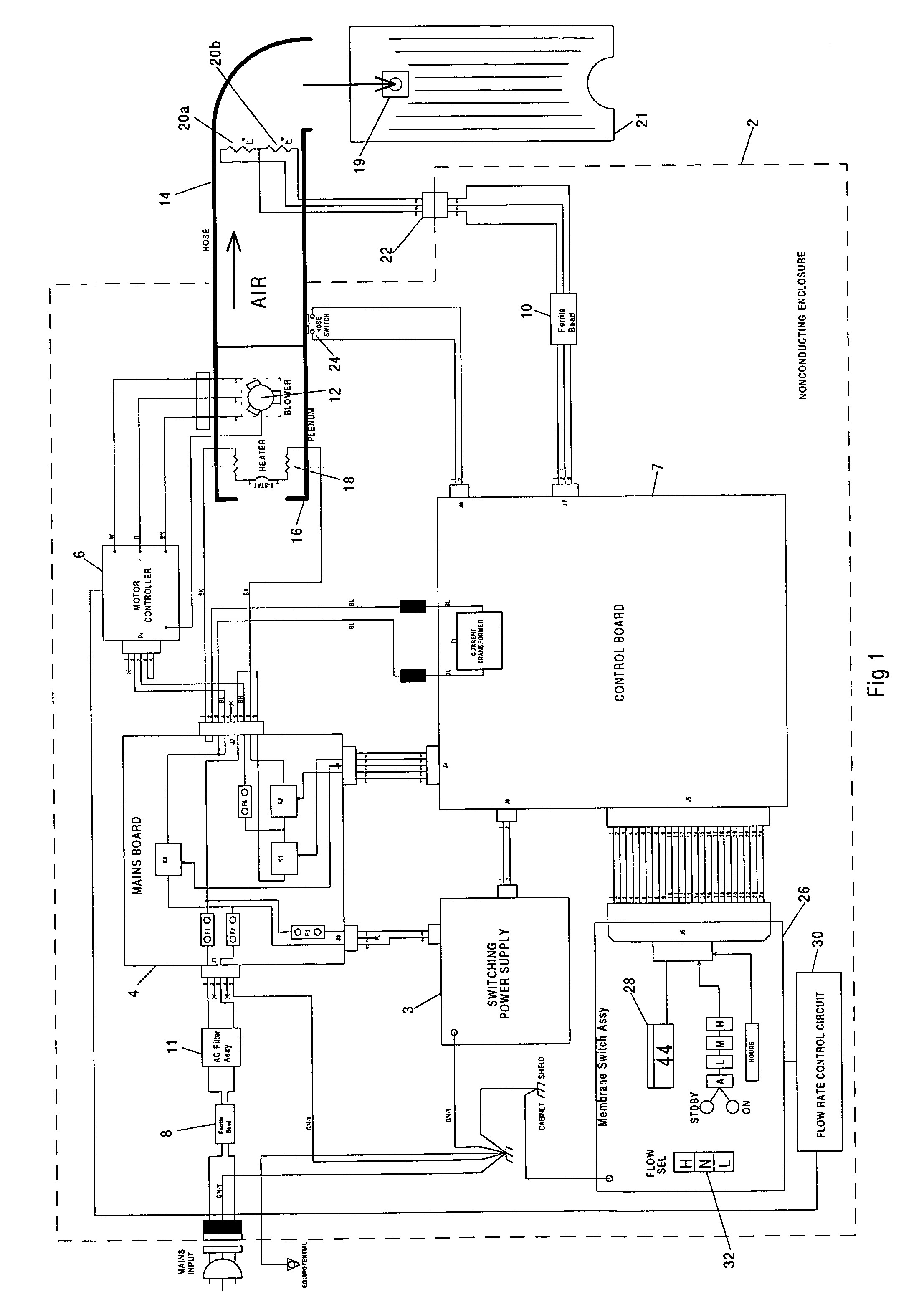
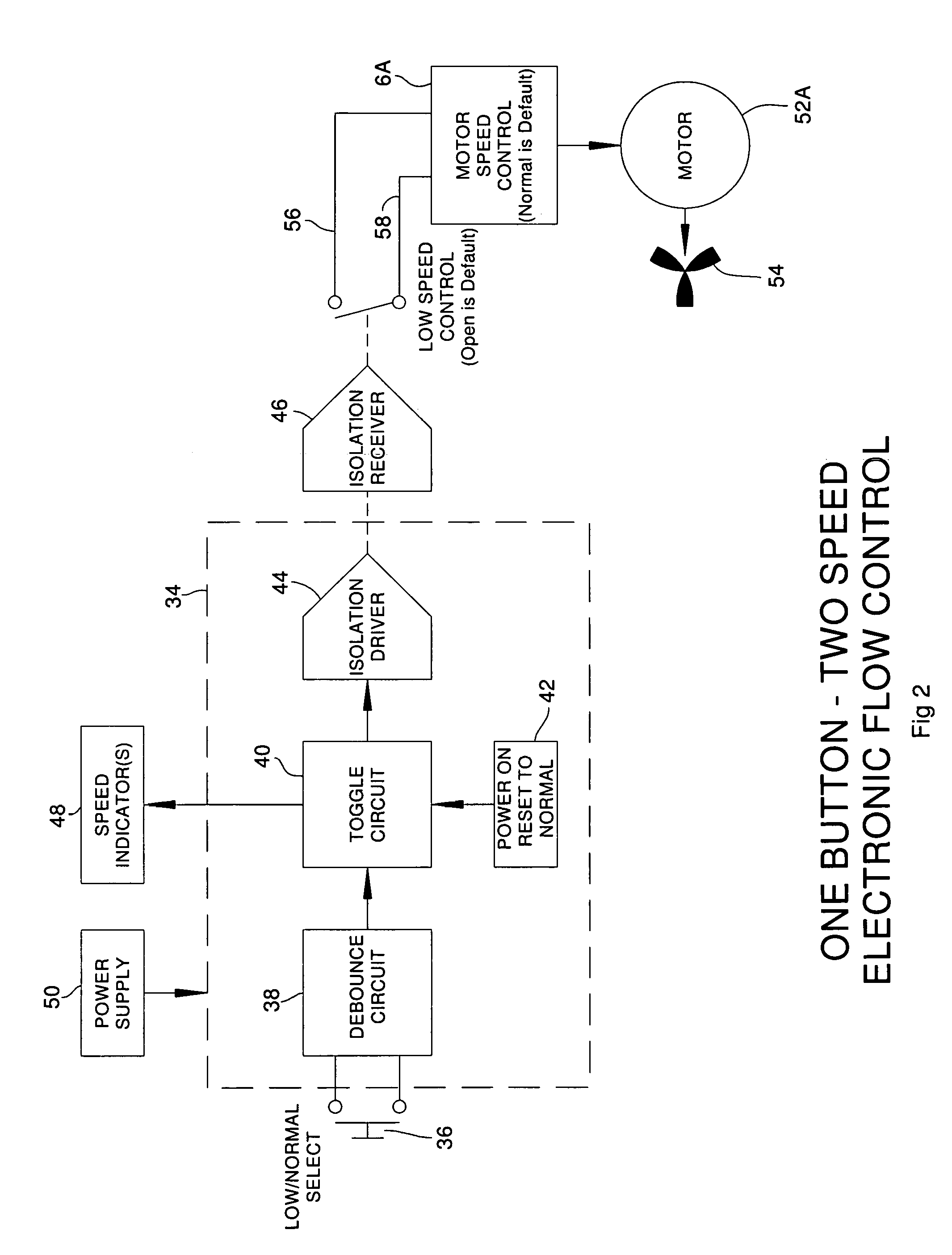
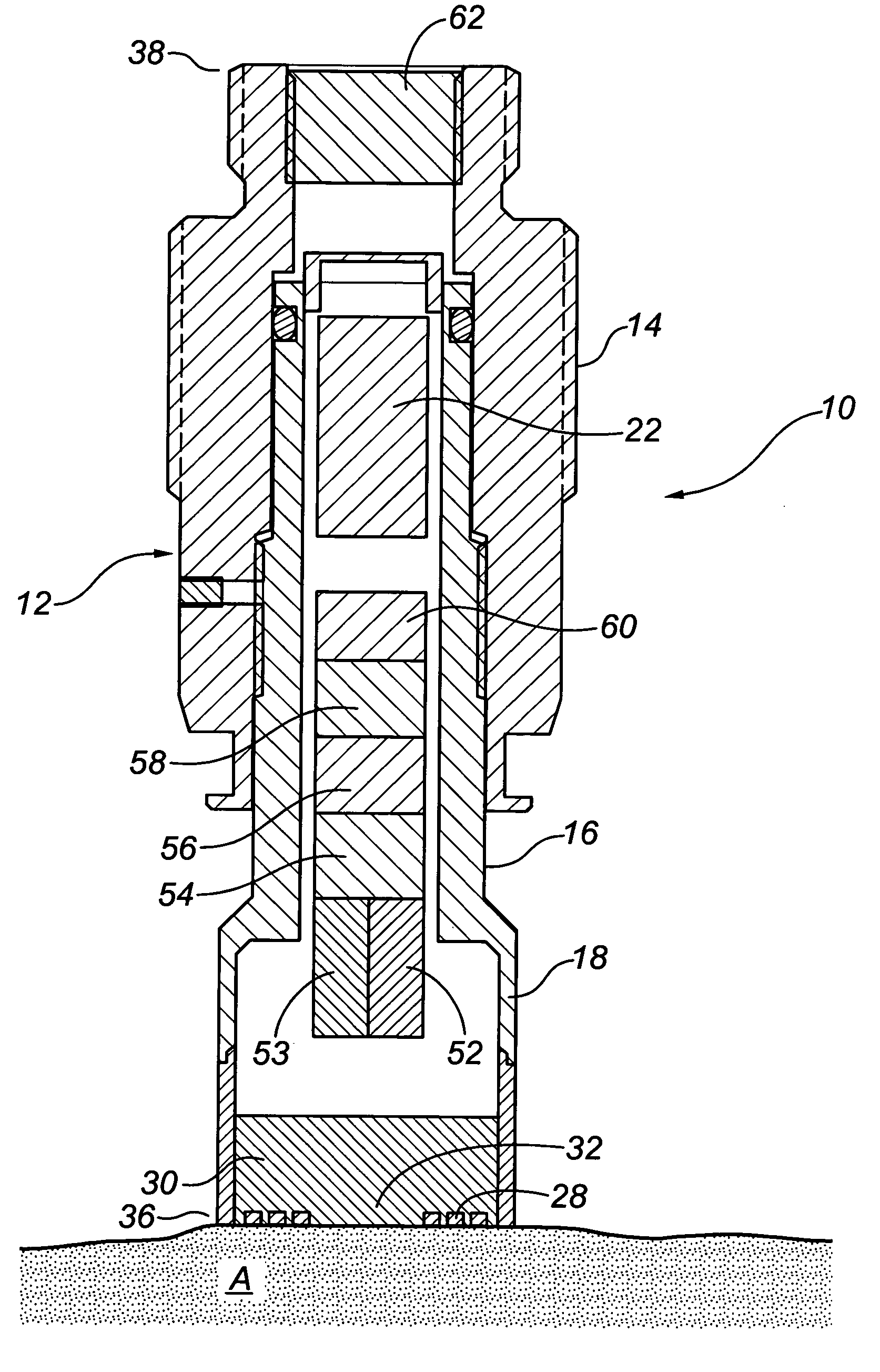
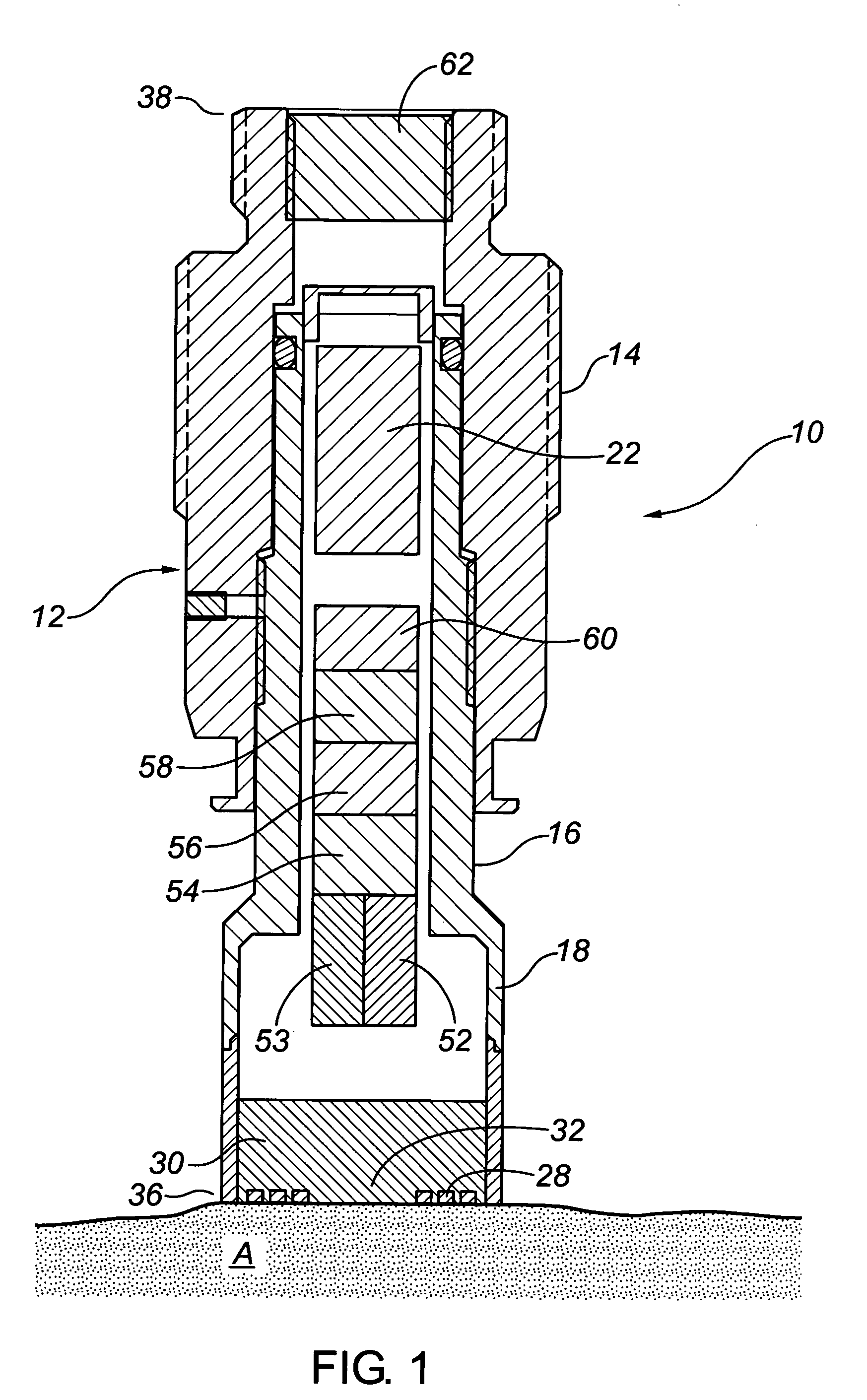
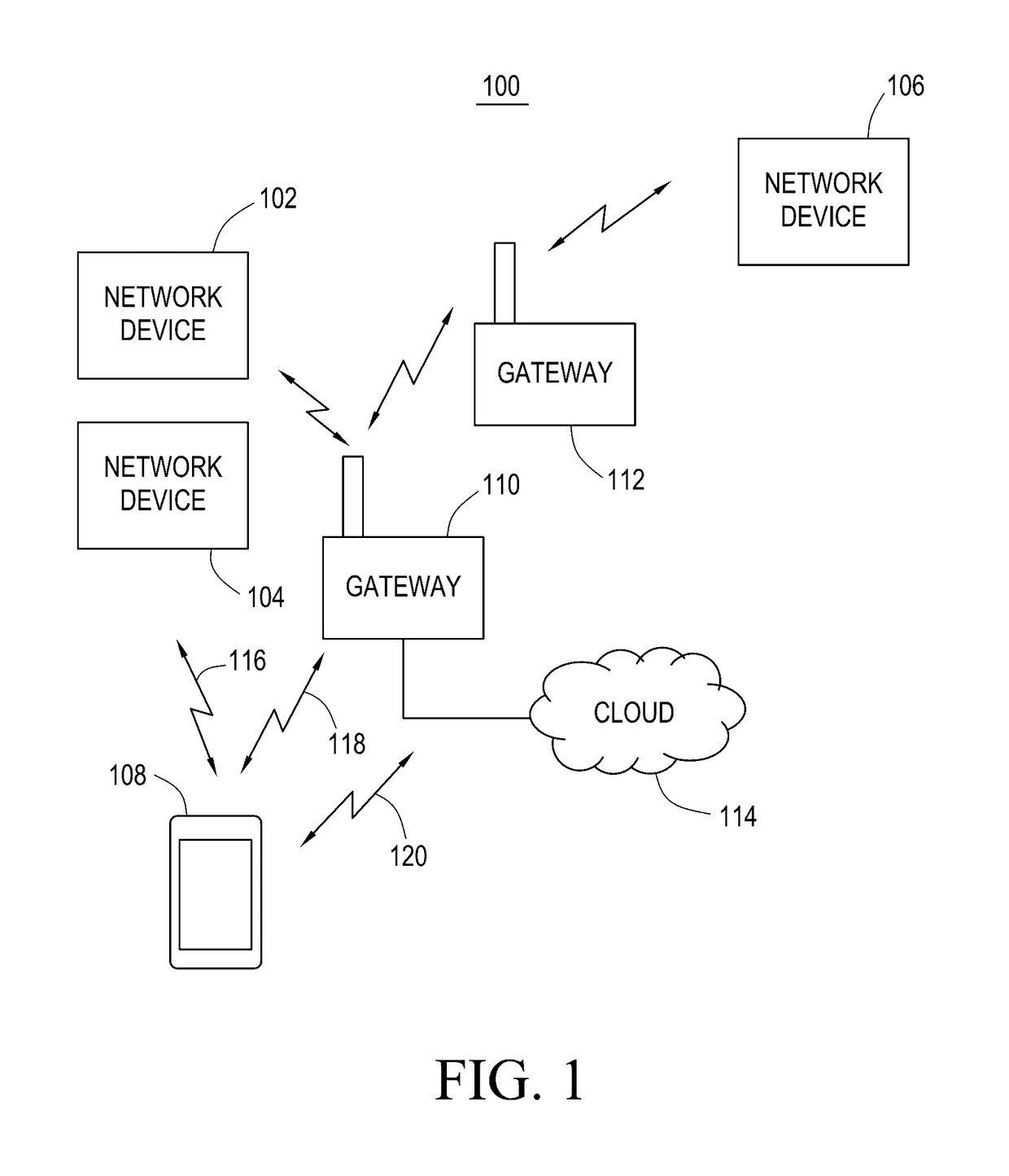
System for providing actuated optimal inflation to multiple temperature regulated blankets and method therefor
A convective warmer to which blankets of different dimensions may be connected is capable of providing air to the various blankets at flow rates that optimally inflate those blankets to achieve the optimal clinical result for the patients covered by those blankets. The blanket connected to the warmer may range from a full size adult warming blanket to a pediatric warming blanket. The convection warmer may have multiple fixed air flow rates each selectable by a user, via switch(es) either electronically or mechanically. For the electronic selection of a given flow rate, a motor adaptable to rotate a different speeds is used. To vary the flow rate mechanically, a valve is controlled to vary the amount of air that may pass to the blanket. Instead of different fixed flow rates, variable air flow rates, selectable by the user, may be used. Also, a feedback circuit that maintains the pressure sensed at the outlet of the warmer to a preset pressure may be used to eliminate the need for user intervention.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL ASD INC
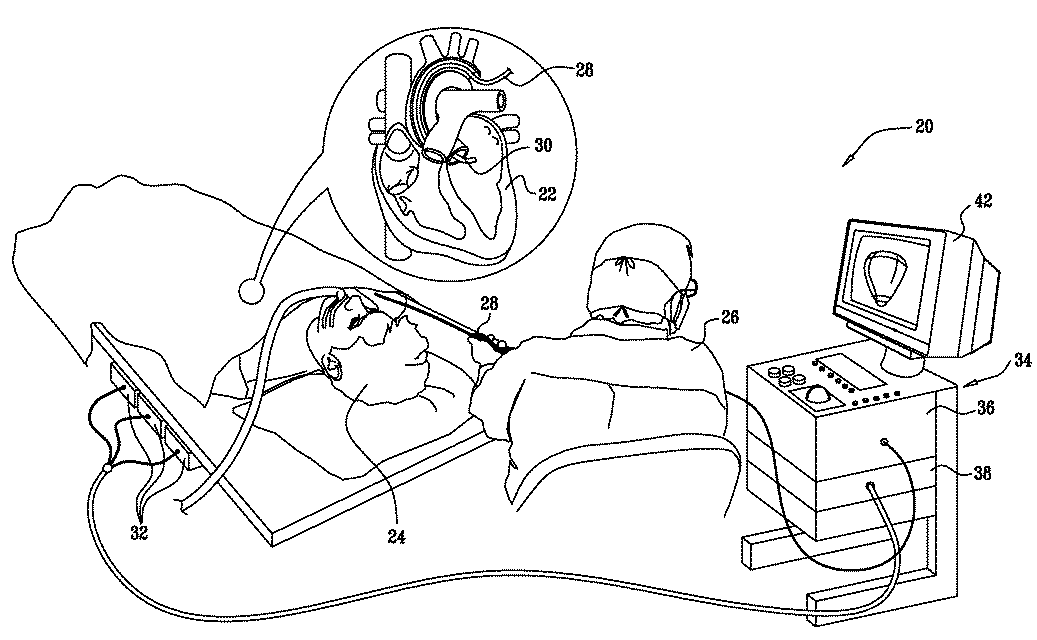
High-sensitivity pressure-sensing probe
ActiveUS20090138007A1Accurate inductionTransvascular endocardial electrodesEndoscopesMagnetic transducersSacroiliac joint
A medical probe includes an insertion tube, having a longitudinal axis and having a distal end. A distal tip is disposed at the distal end of the insertion tube and is configured to be brought into contact with a body tissue. A joint couples the distal tip to the distal end of the insertion tube. A joint sensor, contained within the probe, senses a position of the distal tip relative to the distal end of the insertion tube. The joint sensor includes first and second subassemblies, which are disposed within the probe on opposite, respective sides of the joint and each include one or more magnetic transducers.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Portable apparatus for peritoneal dialysis therapy
A portable peritoneal dialysis apparatus having (1) a hinged door for enclosing a disposable cassette that seals tightly shut using air pressure; (2) accurate pressure sensing of pressures applied to the patient through an enclosure in the disposable cassette; (3) two pumps that can operate separately or in tandem actuated by two separate stepper motors; and (4) a touch screen user interface where indicia of the operating mode is always visible along with indicia for the other possible operating modes and the mode can be changed by touching one of these indicia.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Tilting Touch Control Panel
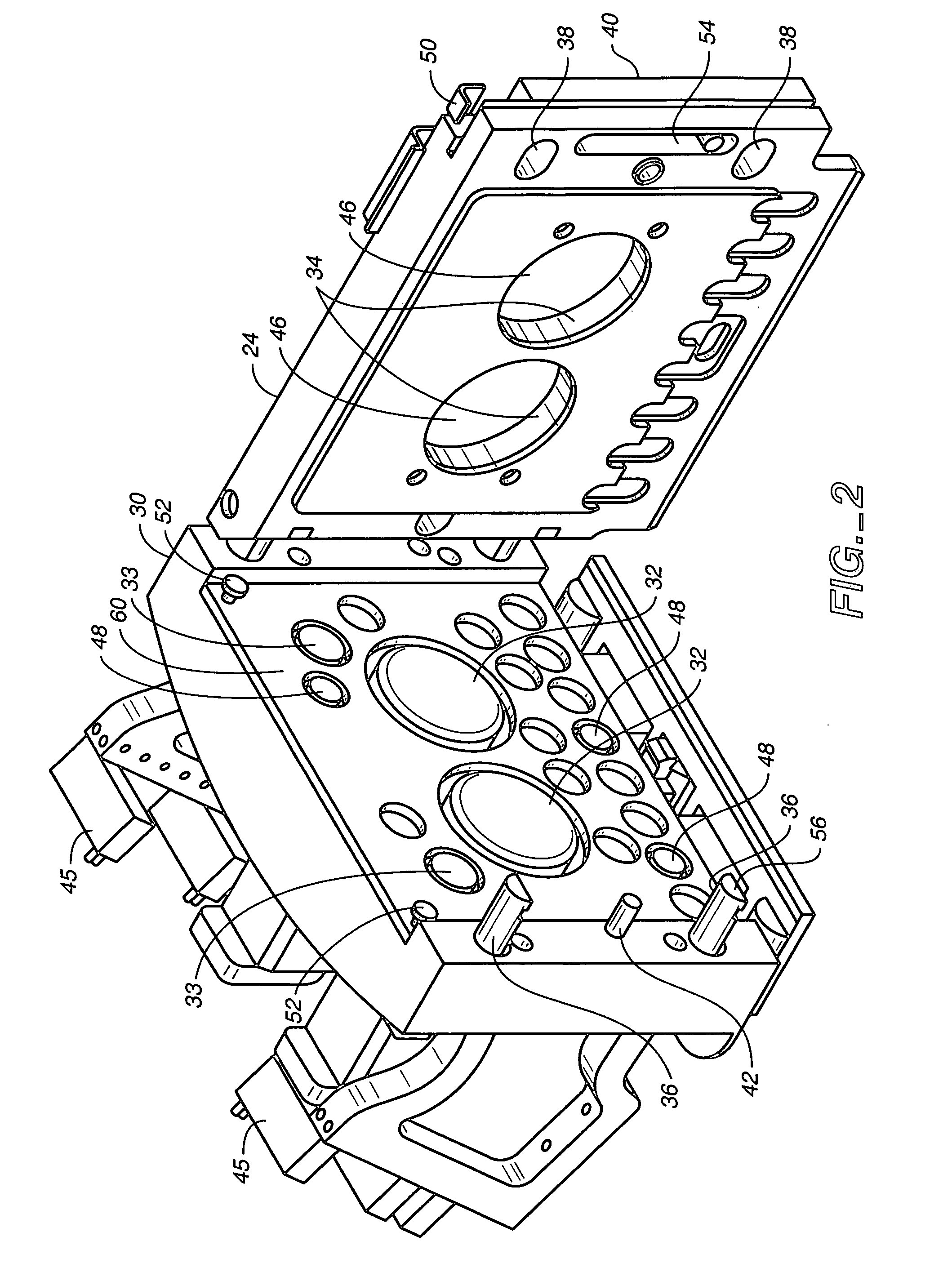
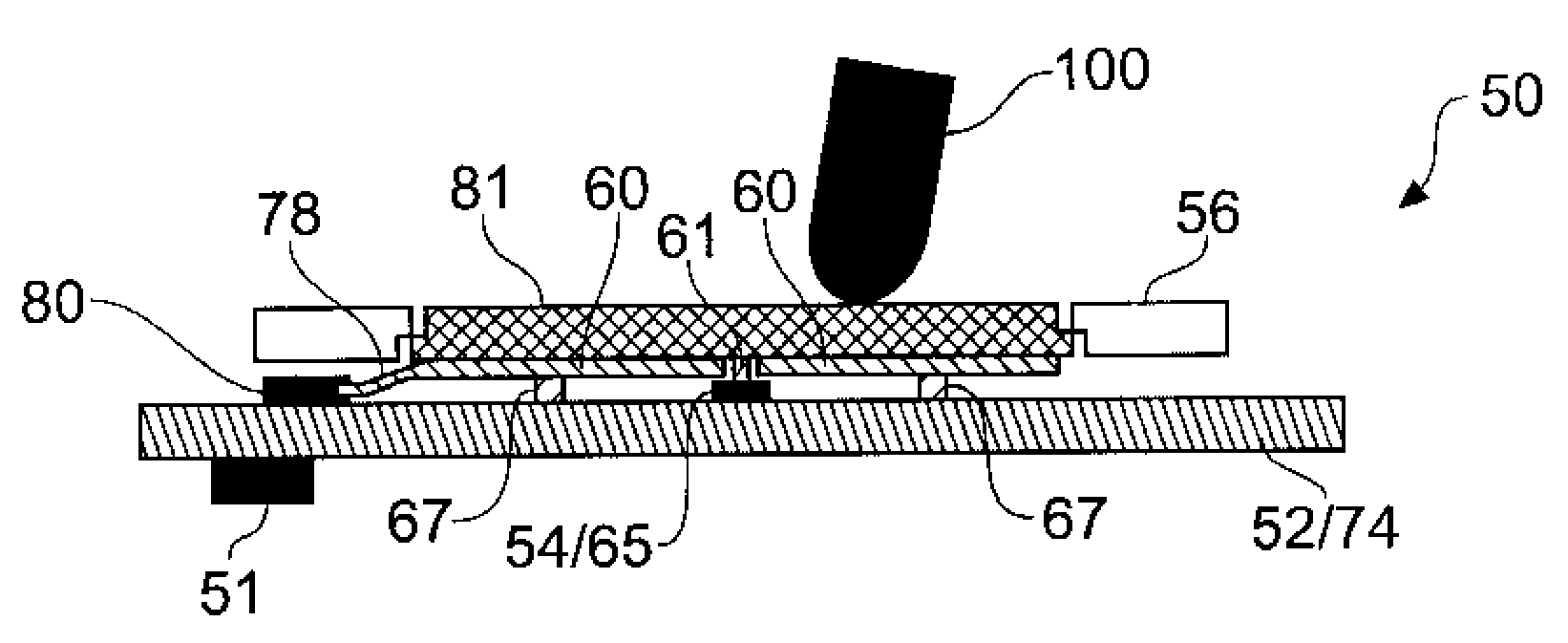
InactiveUS20080202824A1Displacement is detectedExtend your lifeInput/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsPressure senseEngineering
A control panel for controlling a device in response to user indications, the control panel comprising, a position sensing element (60) having a sensing surface, and a position interface circuit (76). The position interface circuit (76) is operable to determine a position of an object (100) on the sensing surface, when the object (100) is applied to the sensing surface of the position sensing element (60). At least one pressure sensing device (54, 66) and the sensing surface of the position sensing element (60) are arranged with the effect that a displacement of the sensing surface with respect to the pressure sensing device in response to the pressure applied by the object is detectable by the pressure sensing device. As such, in one example, the position interface circuit (76) is operable to identify one or more of a plurality of user indicated signals by correlating the position of the object on the sensing surface with a pressure detected by the pressure sensing device. The sensing surface may include pre-designated and pre-determined locations representing virtual buttons so that by determining whether the object is at one of a plurality of pre-determined locations on the sensing surface of the position sensing element, the position interface circuit (76) can identify the user indicated signal by correlating the position of the object at one of the predetermined locations with the detected pressure, each of the pre-determined location corresponding to one of the plurality of user indicated signals.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Telemetry method and apparatus using magnetically-driven MEMS resonant structure
InactiveUS20070236213A1High quality factorImprove reliabilityMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringIntraocular pressurePressure sense
A telemetry method and apparatus using pressure sensing elements remotely located from associated pick-up, and processing units for the sensing and monitoring of pressure within an environment. This includes remote pressure sensing apparatus incorporating a magnetically-driven resonator being hermetically-sealed within an encapsulating shell or diaphragm and associated new method of sensing pressure. The resonant structure of the magnetically-driven resonator is suitable for measuring quantities convertible to changes in mechanical stress or mass. The resonant structure can be integrated into pressure sensors, adsorbed mass sensors, strain sensors, and the like. The apparatus and method provide information by utilizing, or listening for, the residence frequency of the oscillating resonator. The resonant structure listening frequencies of greatest interest are those at the mechanical structure's fundamental or harmonic resonant frequency. The apparatus is operable within a wide range of environments for remote one-time, random, periodic, or continuous / on-going monitoring of a particular fluid environment. Applications include biomedical applications such as measuring intraocular pressure, blood pressure, and intracranial pressure sensing.
Owner:LAUNCHPOINT TECH
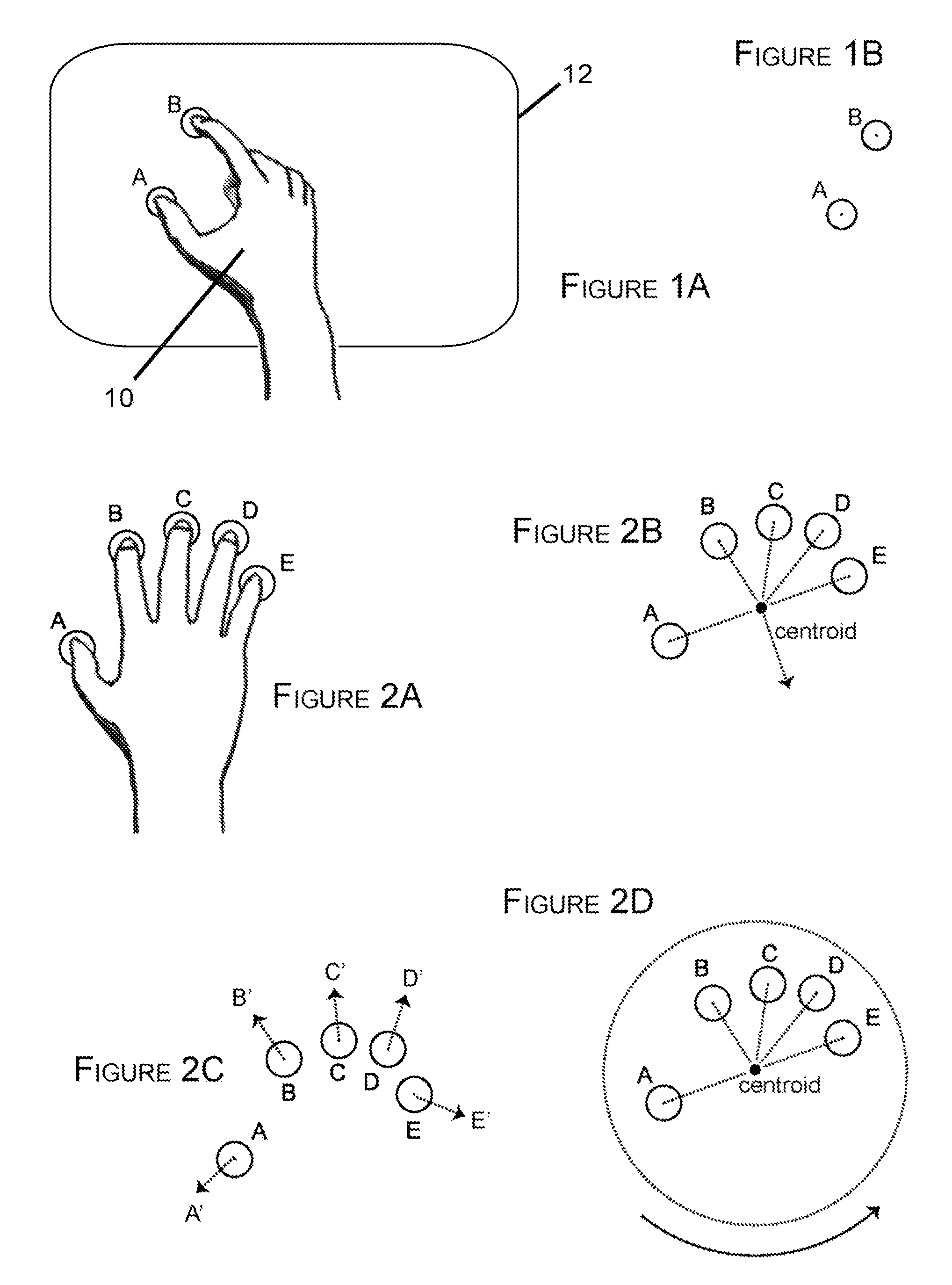
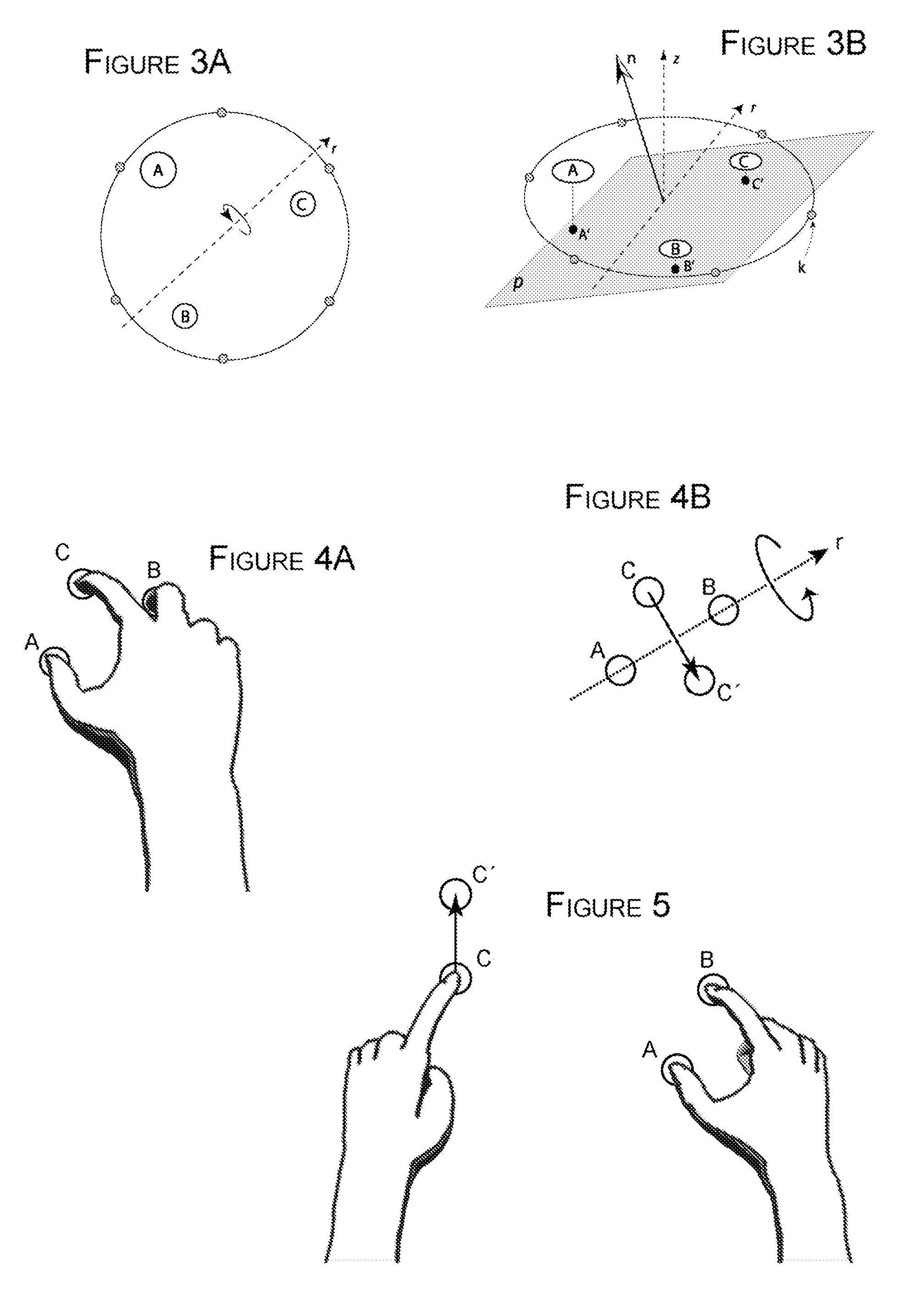
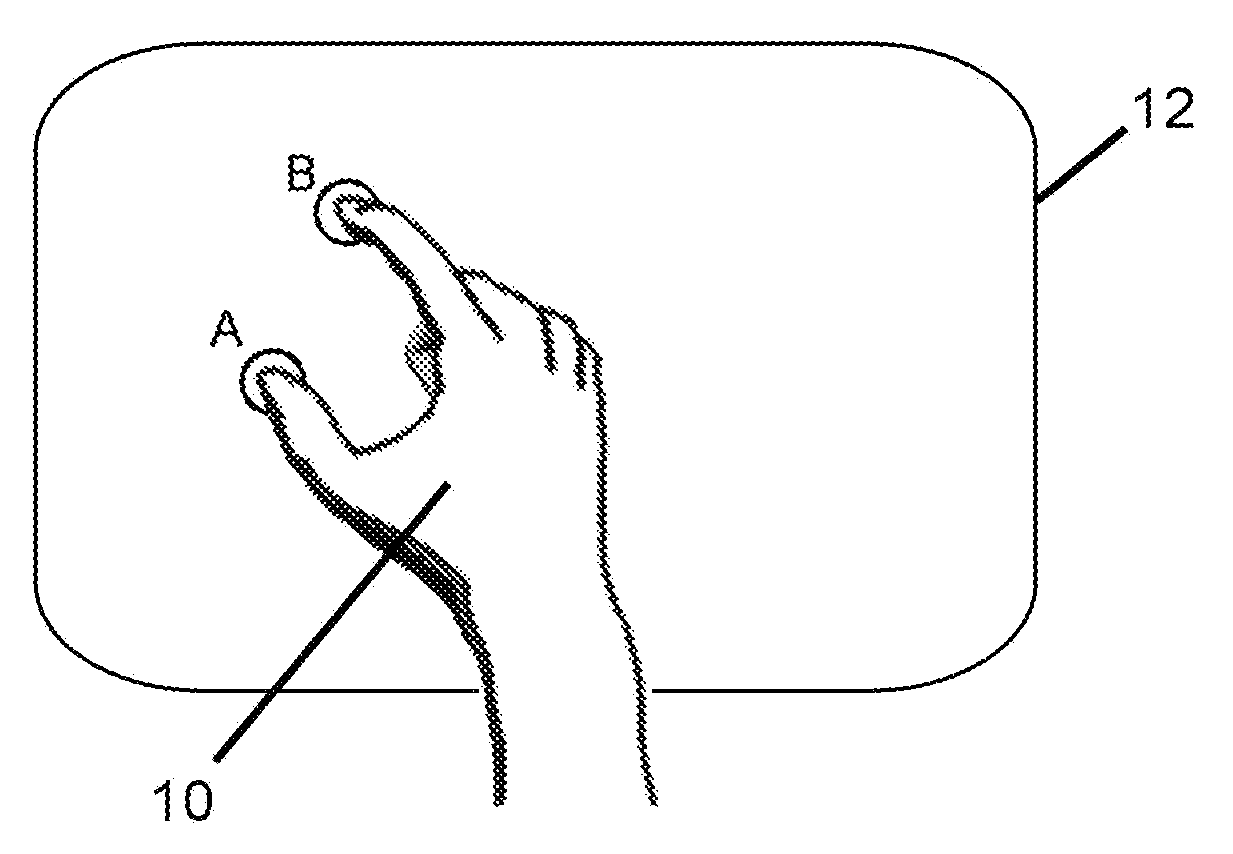
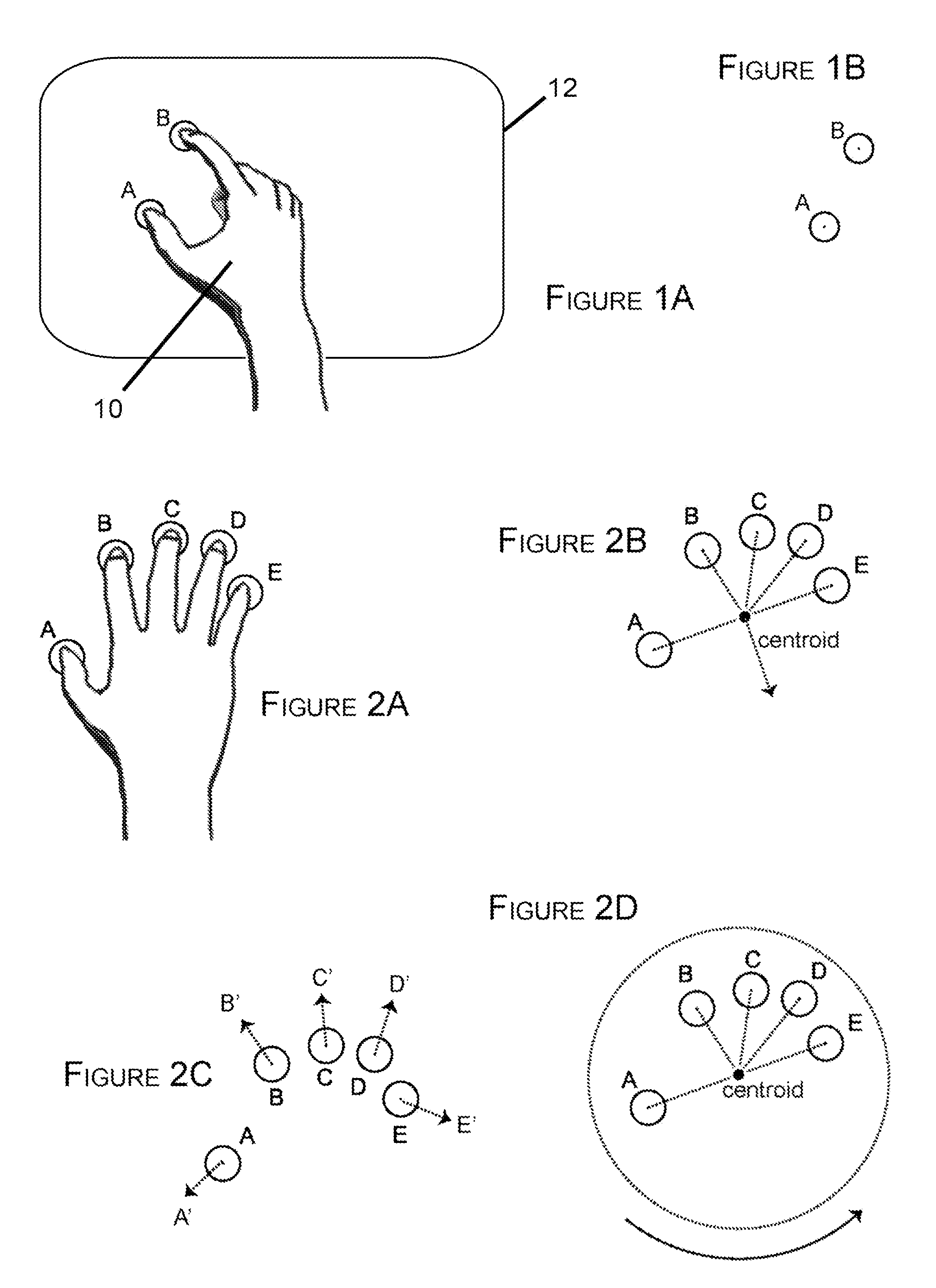
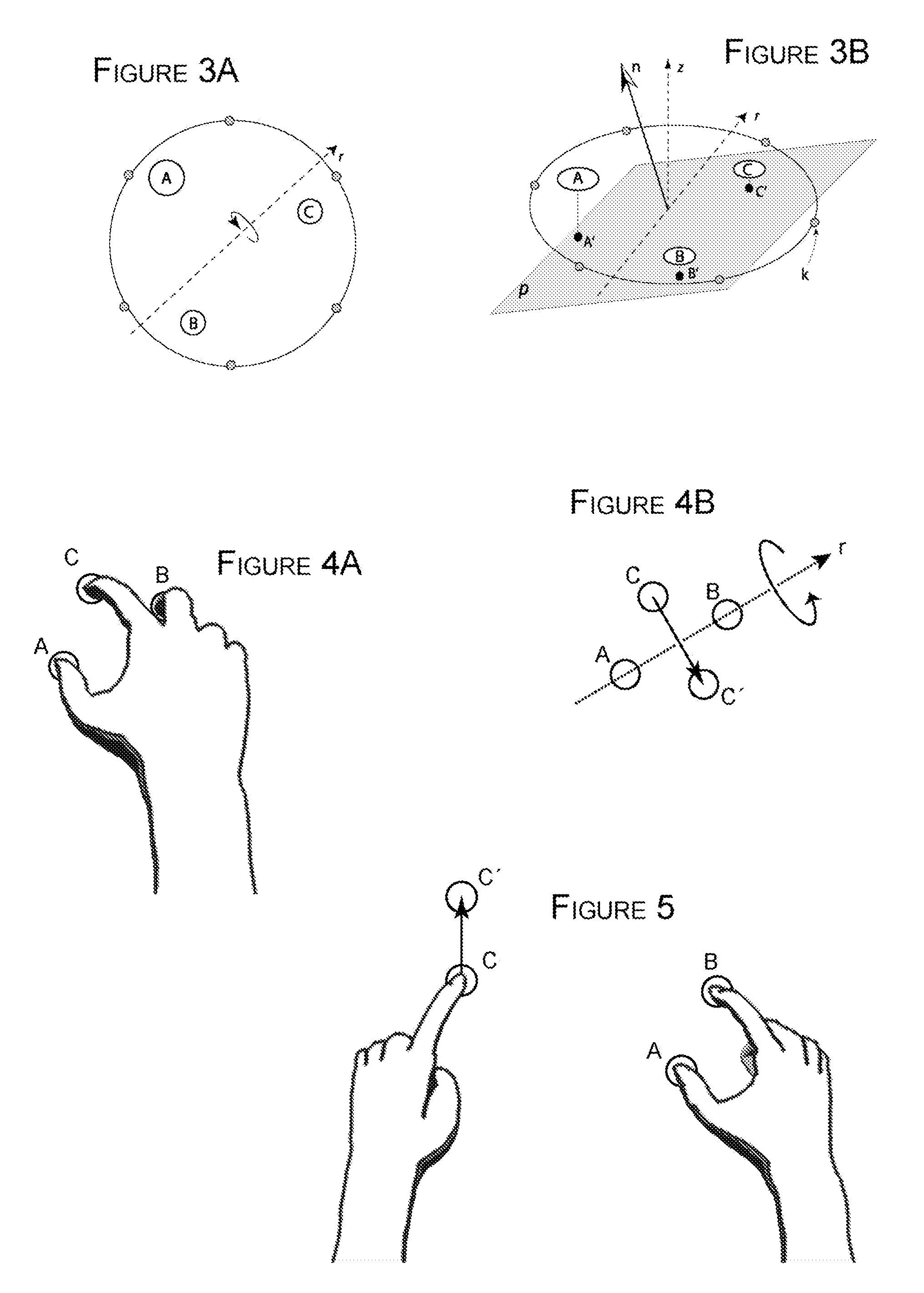
Methods of interfacing with multi-point input devices and multi-point input systems employing interfacing techniques
ActiveUS20080180406A1Improve human-computer interactionInput/output processes for data processing3d imageRotation control
Methods and systems for interfacing with multi-point input devices employ various techniques for controlling displayed images, including 2D and 3D image translation, scale / zoom, rotation control and globe axis tilt control. Various techniques employ three or more simultaneous inputs, changes in characteristics of those inputs, and pressure sensing, among other things.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
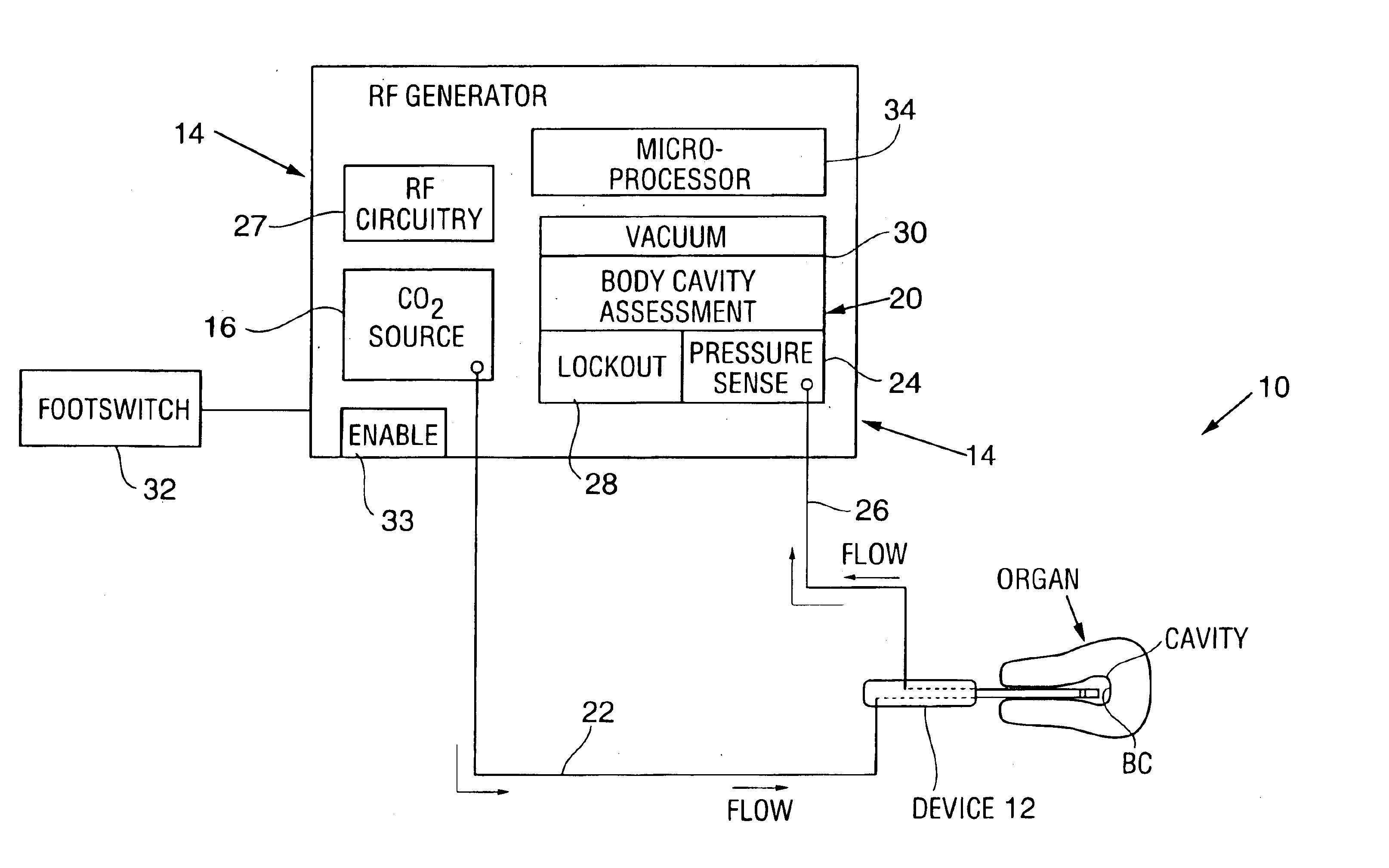
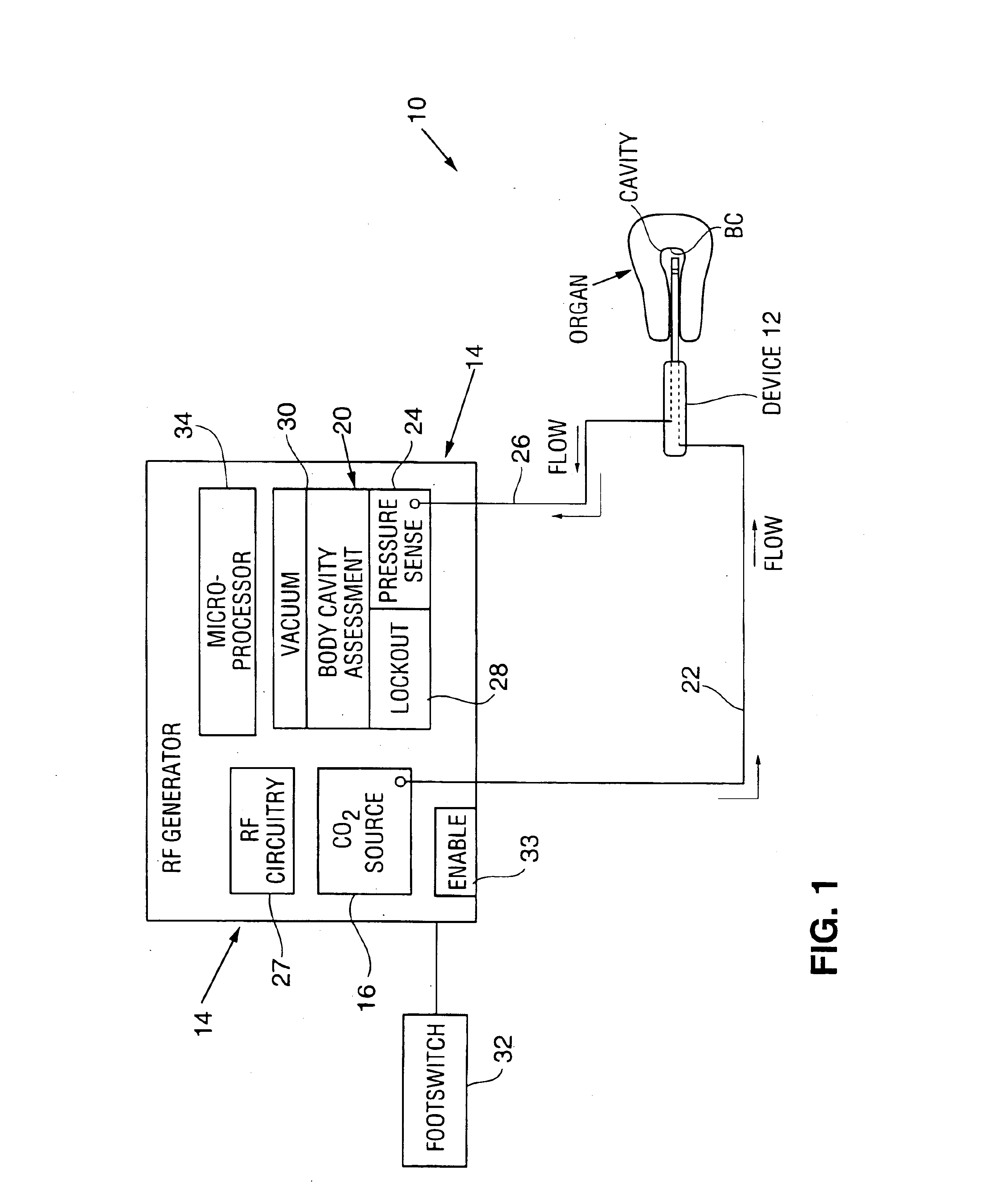
System and method for detecting perforations in a body cavity
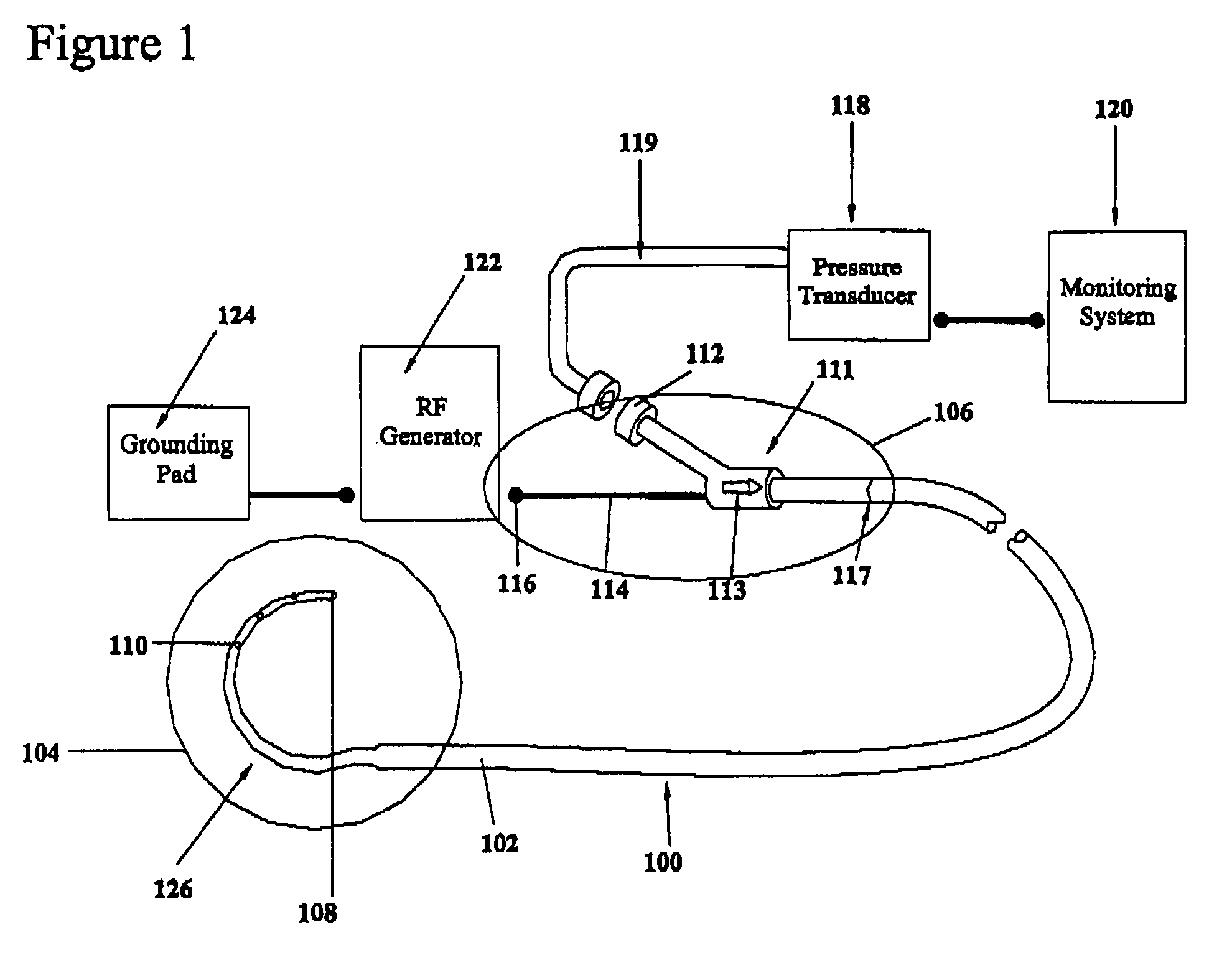
A system and method for detecting perforations in a body cavity. In accordance with the method of the invention, a fluid (liquid or gas) is delivered into a body cavity to slightly pressurize the cavity. A pressure sensing system monitors the pressure within the cavity for a predetermined test period. If cavity pressure is not substantially sustained during the test period, the physician is alerted to further assess the cavity for perforations before initiating treatment within the cavity. In a preferred form of the system, a medical treatment system such as an RF ablation system is provided with perforation detection functionality. The system preferably includes a pre-test and post-test lockout system. The lockout system prevents RF power delivery unless, during a predetermined test period, the pressure sensing system determines that no perforation exists, or unless a previously performed perforation detection procedure determined a perforation was present but the lockout system was subsequently overridden by the physician.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Display unit with touch panel
ActiveUS7312791B2Easy to identifyComplete banking machinesInput/output for user-computer interactionPressure senseTouchscreen
There is provided a display unit including a touch panel disposed on a display screen of a display panel to detect a touch position of a pointing device, operation being conducted by touching a touch operation member displayed on the screen. The display unit includes a sensor for sensing a pushing pressure caused when touching the touch operation member, and a control section for conducting first processing concerning the touch operation member pushed by the pointing device when the pressure sensed by the sensing unit satisfies a first predetermined pressure condition, and conducting second processing concerning the touch operation member, when the pushing pressure has changed from the first condition to a second one. Upon the change from the first condition to the second one, a function of moving the screen in a direction of pushing pressure caused by the pointer is executed by the second processing.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
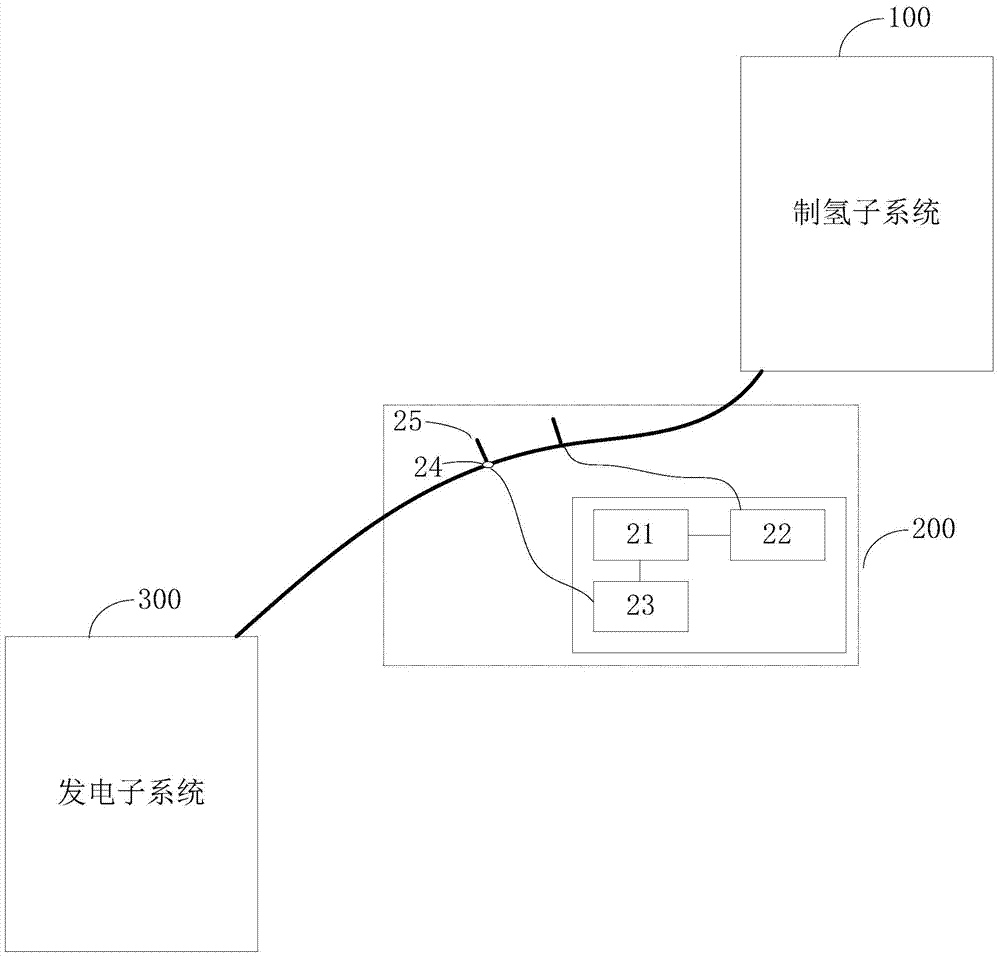
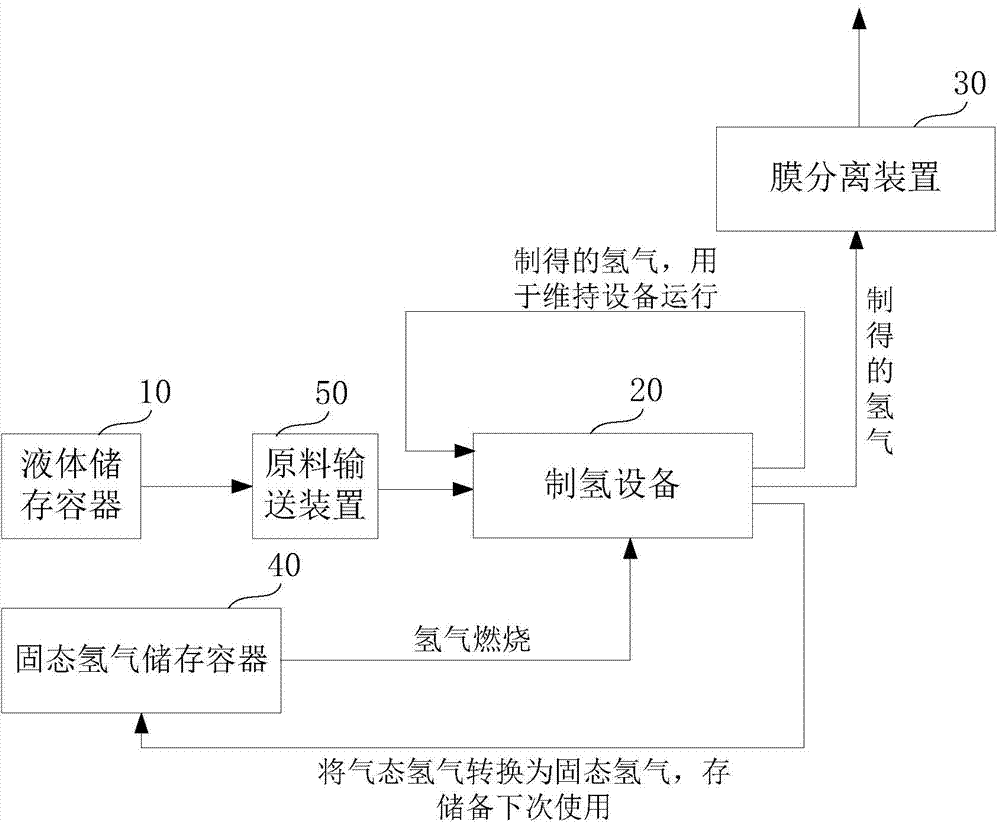
System and method for instant hydrogen production and power generation
The invention discloses a system and a method for instant hydrogen production and power generation. The system comprises a hydrogen production subsystem, an air pressure adjusting subsystem and a power generation subsystem, wherein the hydrogen production subsystem is used for preparing hydrogen from methanol water and transmitting the prepared hydrogen to the power generation subsystem in real time through a transmission pipeline; the transmission pipeline is provided with the air pressure adjusting subsystem for adjusting air pressure inside the transmission pipeline; the power generation subsystem is used for generating power by virtue of hydrogen prepared by the hydrogen production subsystem; the air pressure adjusting subsystem comprises a microprocessor, an air pressure sensor, a valve controller and an air outlet valve; the air pressure sensor is arranged in the transmission pipeline, and is used for sensing data of the air pressure inside the transmission pipeline and sending the data of the air pressure to the microprocessor; the microprocessor is used for controlling the on and off of the air outlet valve according to the data of the air pressure sensed by the air pressure sensor. Power can be generated by instantly prepared hydrogen, a hydrogen buffer tank is not required, and thus the portability and mobility of the hydrogen production and power generation system can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HYDROGEN MOBILE REFRMER INSTR
Methods of interfacing with multi-point input devices and multi-point input systems employing interfacing techniques
ActiveUS20080180404A1Improve human-computer interactionInput/output processes for data processing3d imageComputer science
Methods and systems for interfacing with multi-point input devices employ various techniques for controlling displayed images, including 2D and 3D image translation, scale / zoom, rotation control and globe axis tilt control. Various techniques employ three or more simultaneous inputs, changes in characteristics of those inputs, and pressure sensing, among other things.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
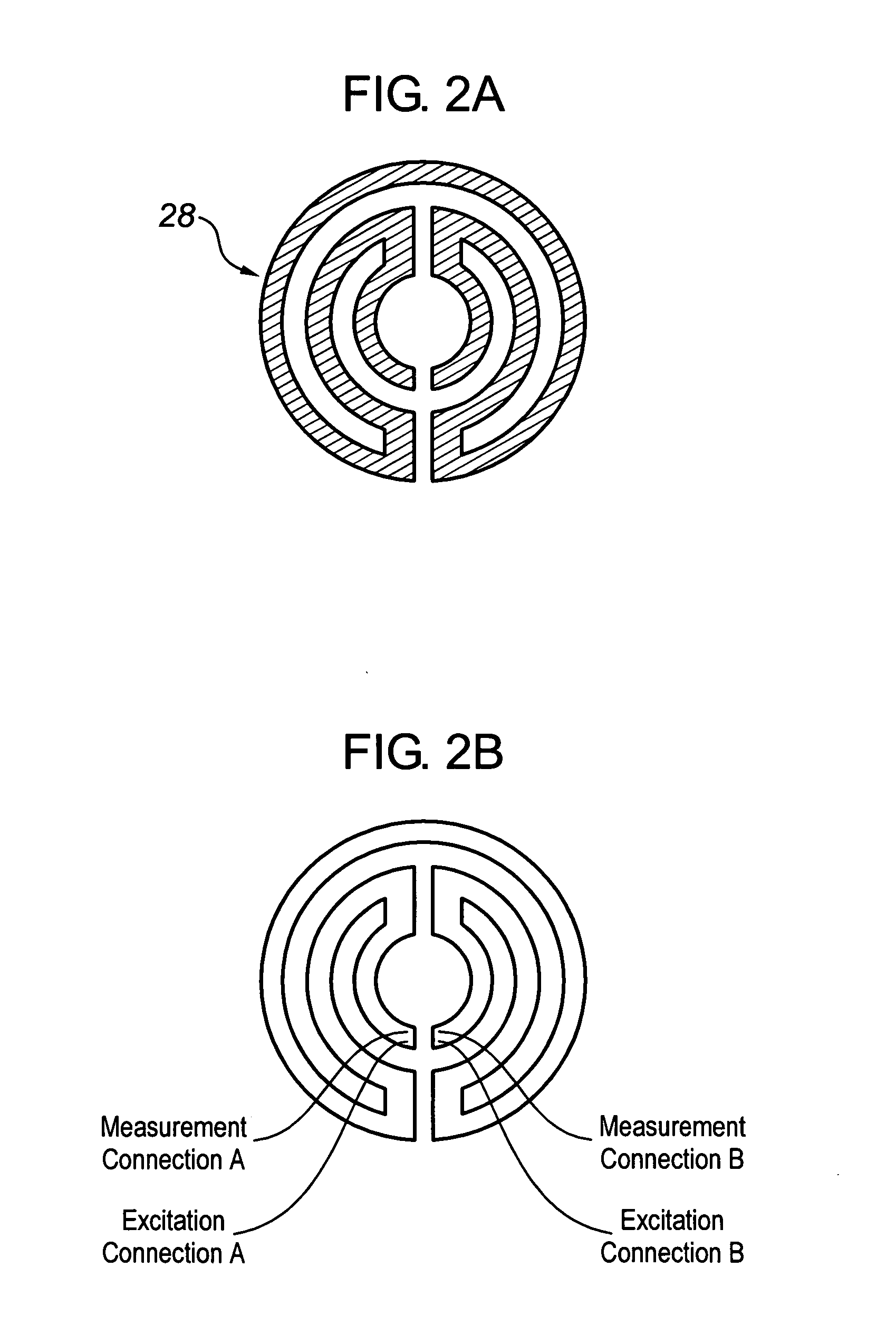
Pressure sensing or force generating device
ActiveUS20120055257A1Few contactsShorten the counting processPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceCapacitive effect
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a pressure sensing / force generating device comprising a non-planar substrate, a printed pressure sensitive element comprising (a) a piezoelectric material containing ink composition capable of producing a piezoelectric effect / piezoresistive effect and / or (b) a dielectric material containing ink composition capable of producing a capacitive effect. It also includes a first printed electrode comprising a conductive ink composition, and a second printed electrode comprising a conductive ink composition. The first and second electrodes are in electrical contact with the printed pressure sensitive element. The first and second printed electrodes and the printed pressure sensitive element collectively form a pressure sensitive junction, which is coupled to the non-planar substrate. The present invention further relates to medical devices comprising the pressure sensing / force generating device and methods of making such devices.
Owner:MICROPEN TECH CORP
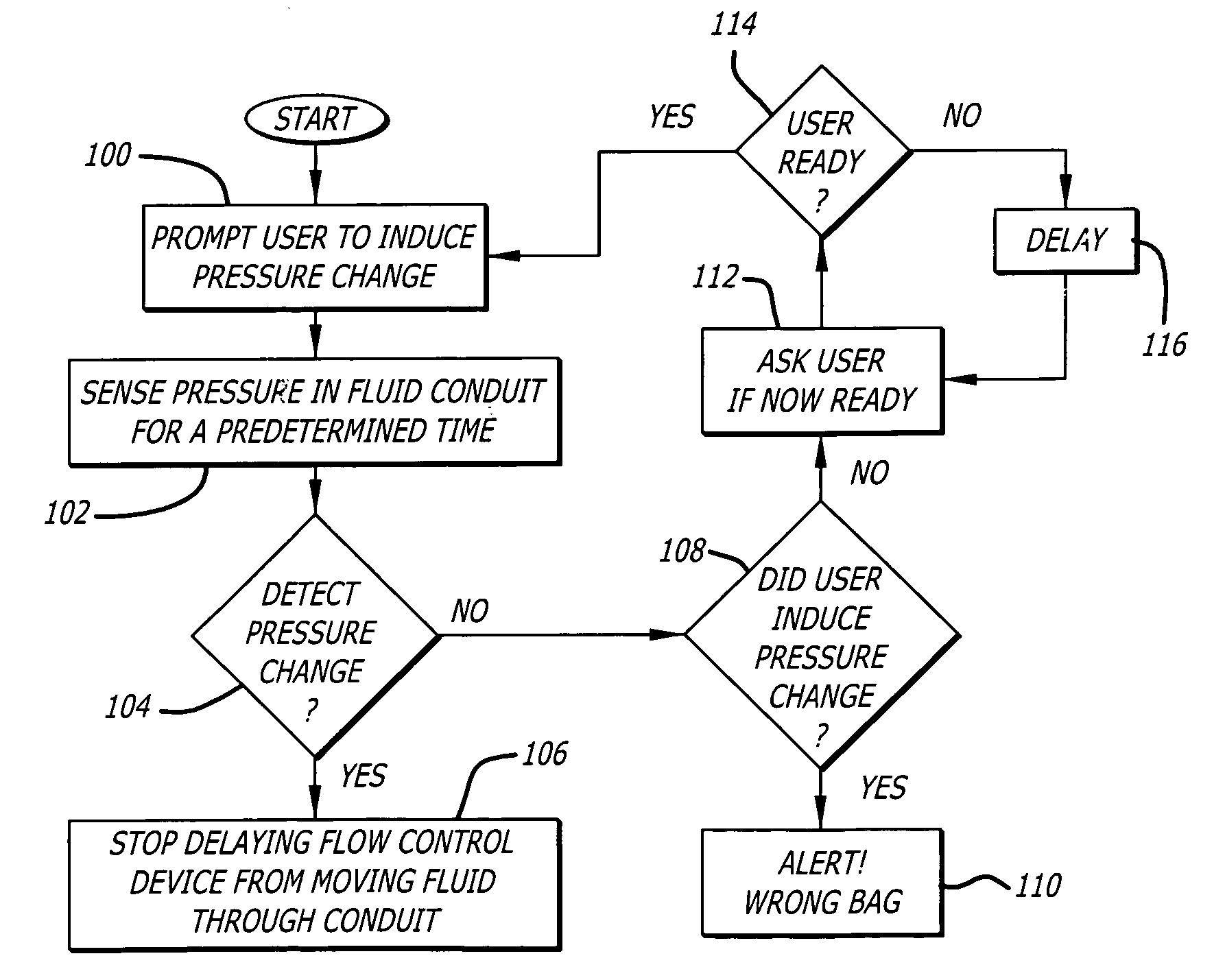
System and method for verifying connection of correct fluid supply to an infusion pump
A system and method for verifying that a particular fluid supply is connected to an infusion pump or pump channel. An upstream pressure sensor coupled to a fluid conduit associated with the fluid supply is used to provide pressure signals in response to pressure sensed in the conduit to a processor. In a connection verification mode, the processor is configured to receive the pressure signals and delay the flow control device of the infusion pump from moving fluid through the conduit until the processor detects a pressure change in the conduit indicated by the pressure signals to thereby verify that the particular fluid supply is connected to the infusion pump.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Extragastric Balloon
InactiveUS20070233170A1Increase heightLonger-term implantationSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyPatient managementNose
In one embodiment, a pressure sensing system is described which transmits data to a patient management system external to a patient. The pressure sensing system can rigidly couple to an implantable port or flexibly couple to an implantable port. In some embodiments, the pressure sensing system communicates with a hydraulic actuating system. In some embodiments, the pressure sensing system is implantable and comprises a circuit capable of wireless transmission through the skin of a patient to an external receiver which is part of a patient management system. A patient management system is described which receives up to date as well as historical data from the pressure sensing system and manages the these data in the context of a patient database. In some embodiments, an extragastric balloon is described in which the balloon is contoured to fit a portion of the stomach but not circumscribe the stomach. In some embodiments, electroactive polymers or nitinol structures are utilized to create restriction on the stomach in response to food boluses entering the stomach. In some embodiments, a nasogastric connector is described with two expandable structures translateable toward and away from one another so as to create pressure between two organ lumens when brought toward each other and fixed with respect to one another.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL
Device and method for biopsy guidance using a tactile breast imager
InactiveUS20040267121A1Provide real-timeIncreased sensitivity and repeatability and accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesBiopsy procedurePressure sense
A biopsy guidance device is enclosed based on a tactile imaging probe adapted to accept a biopsy gun. The tactile imaging probe includes a pressure sensing surface providing real-time 2-D images of the underlying tissue structures allowing to detect a lesion. A cannula is provided supported at a center point by a ball and socket joint. The joint is equipped with linear and angular sensors and supports the cannula with the ability to rotate thereof about the center point. The position, linear and angular displacement and direction of the needle tip of a biopsy needle placed inside the cannula is therefore known at all times and provided as a feedback signal to a physician. Also provided to a physician is a position of the target site at a lesion, as well as a linear and angular deviation of the needle tip away from the target site. Such audio, light, or visual feedback allows the physician to correct the insertion angle and depth to confidently reach the target site to perform a biopsy. Method is also disclosed to guide the biopsy procedure.
Owner:ARTANN LAB
Obesity treatment systems
InactiveUS20080147002A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSuture equipmentsPatient managementPatient database
In one embodiment, a pressure sensing system is described which transmits data to a patient management system external to a patient. The pressure sensing system can rigidly couple to an implantable port or flexibly couple to an implantable port. In some embodiments, the pressure sensing system communicates with a hydraulic actuating system. In some embodiments, the pressure sensing system is implantable and comprises a circuit capable of wireless transmission through the skin of a patient to an external receiver which is part of a patient management system. A patient management system is described which receives up to date as well as historical data from the pressure sensing system and manages the these data in the context of a patient database. In some embodiments, an extragastric balloon is described in which the balloon is contoured to fit a portion of the stomach but not circumscribe the stomach. In some embodiments, electroactive polymers or nitinol structures are utilized to create restriction on the stomach in response to food boluses entering the stomach. In some embodiments, a nasogastric connector is described with two expandable structures translateable toward and away from one another so as to create pressure between two organ lumens when brought toward each other and fixed with respect to one another.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL ERIC
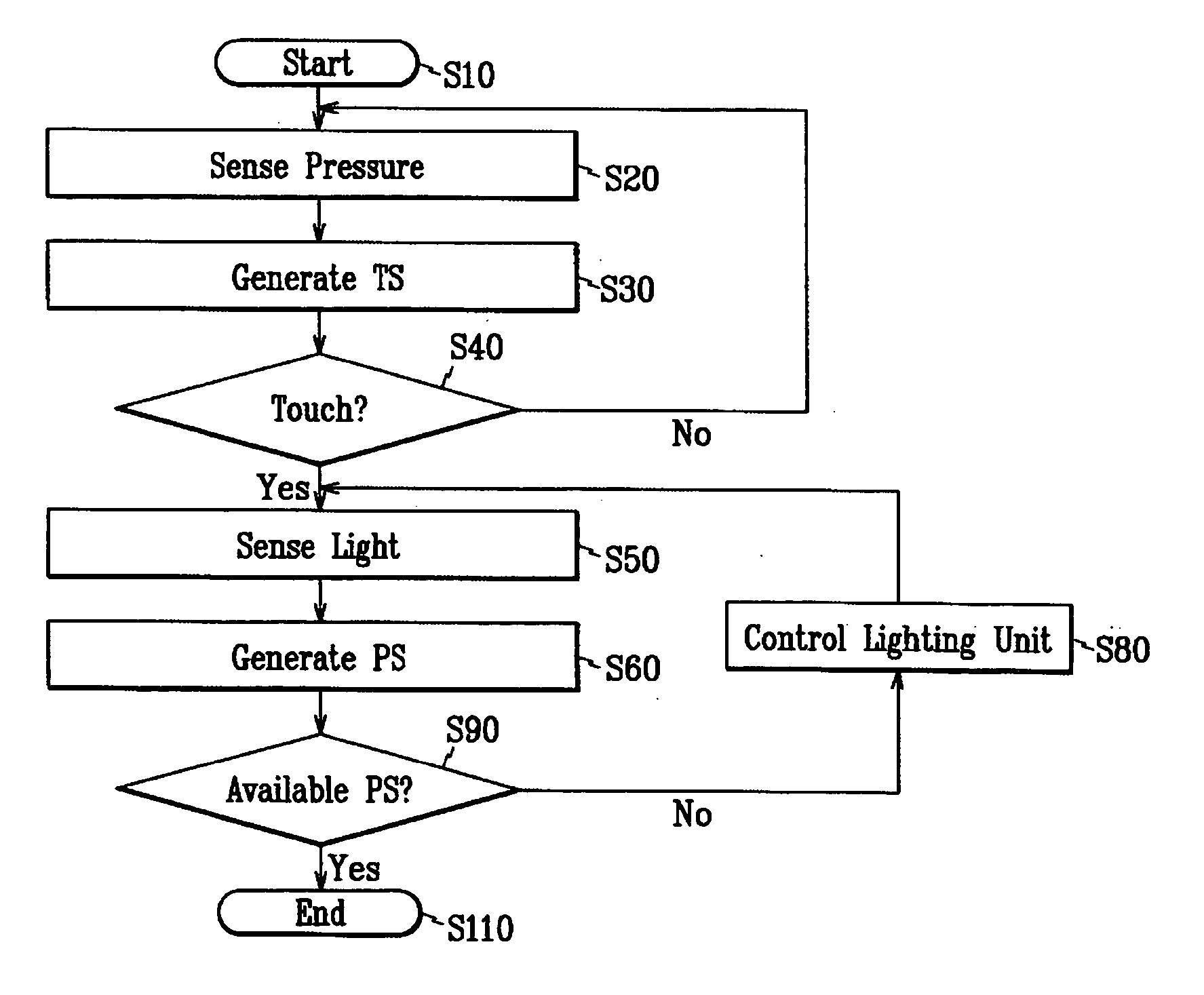
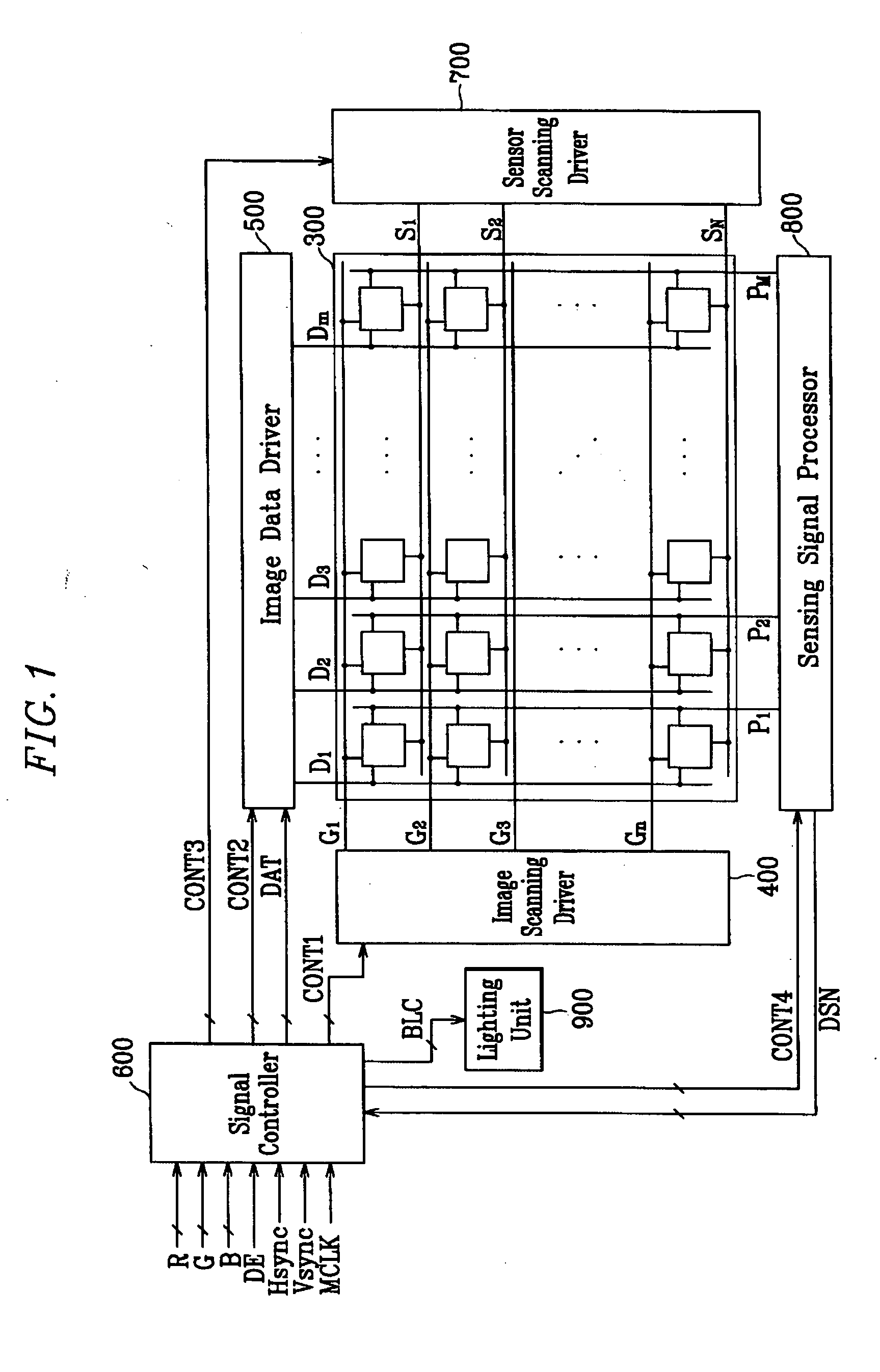
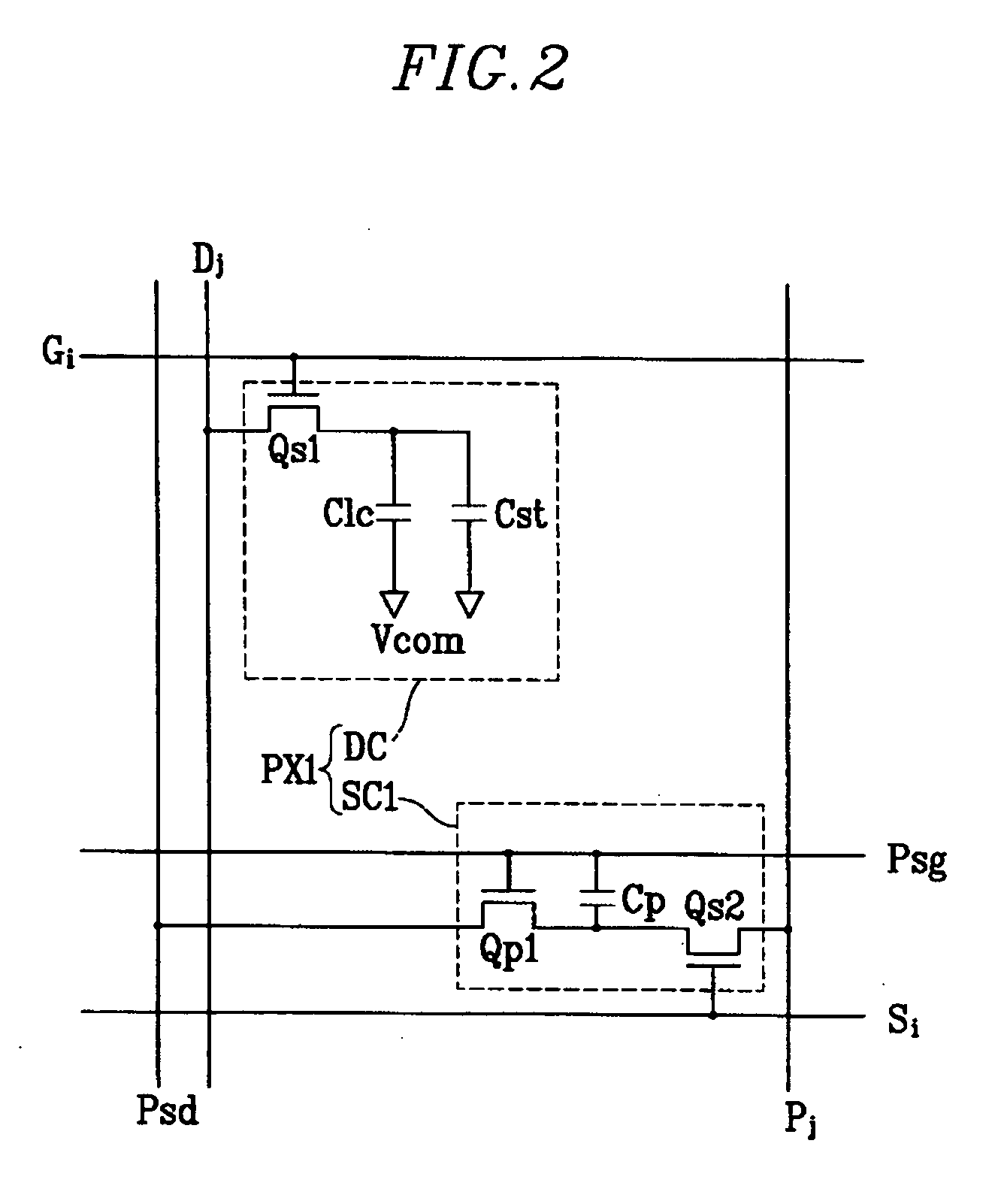
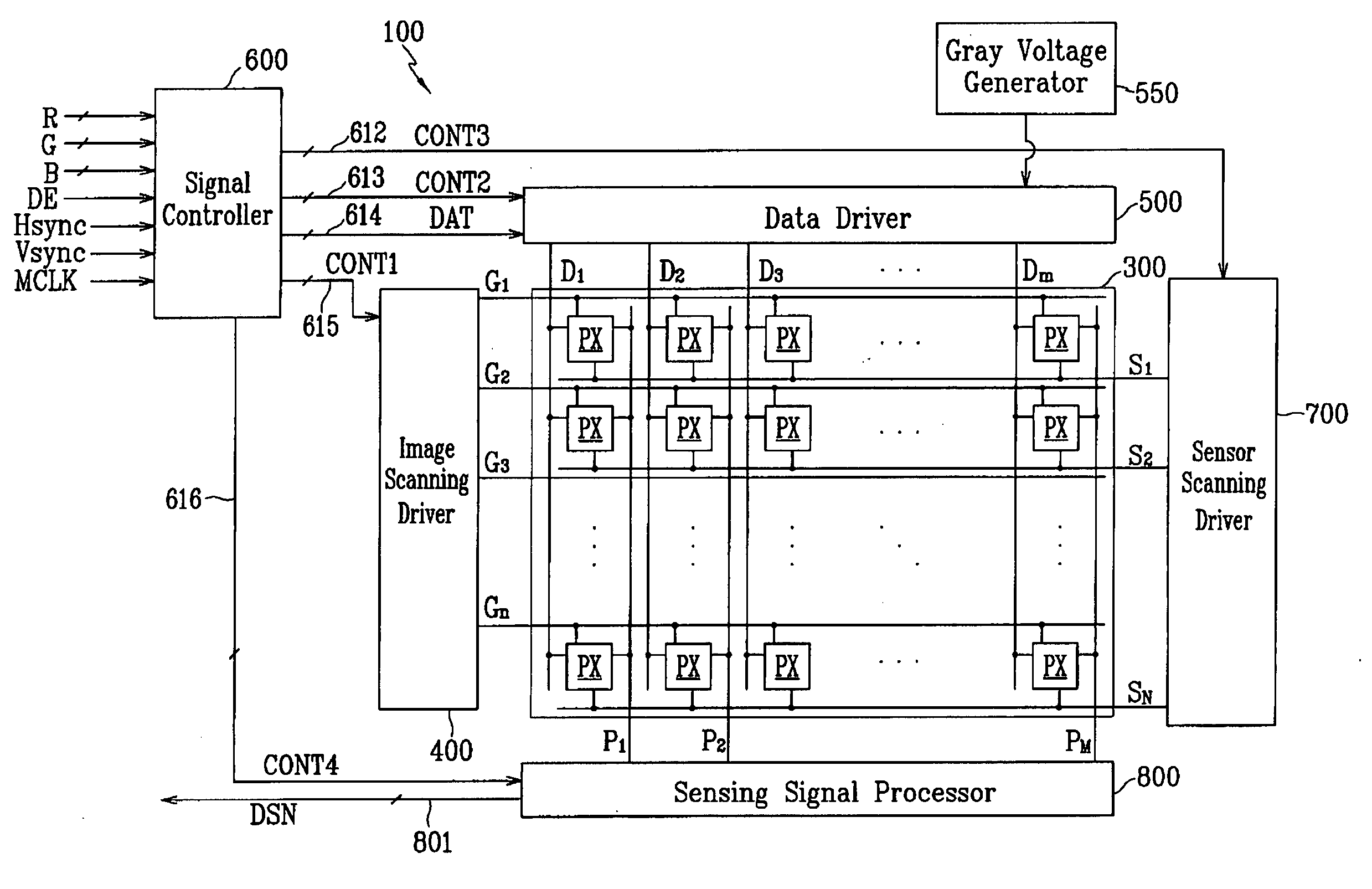
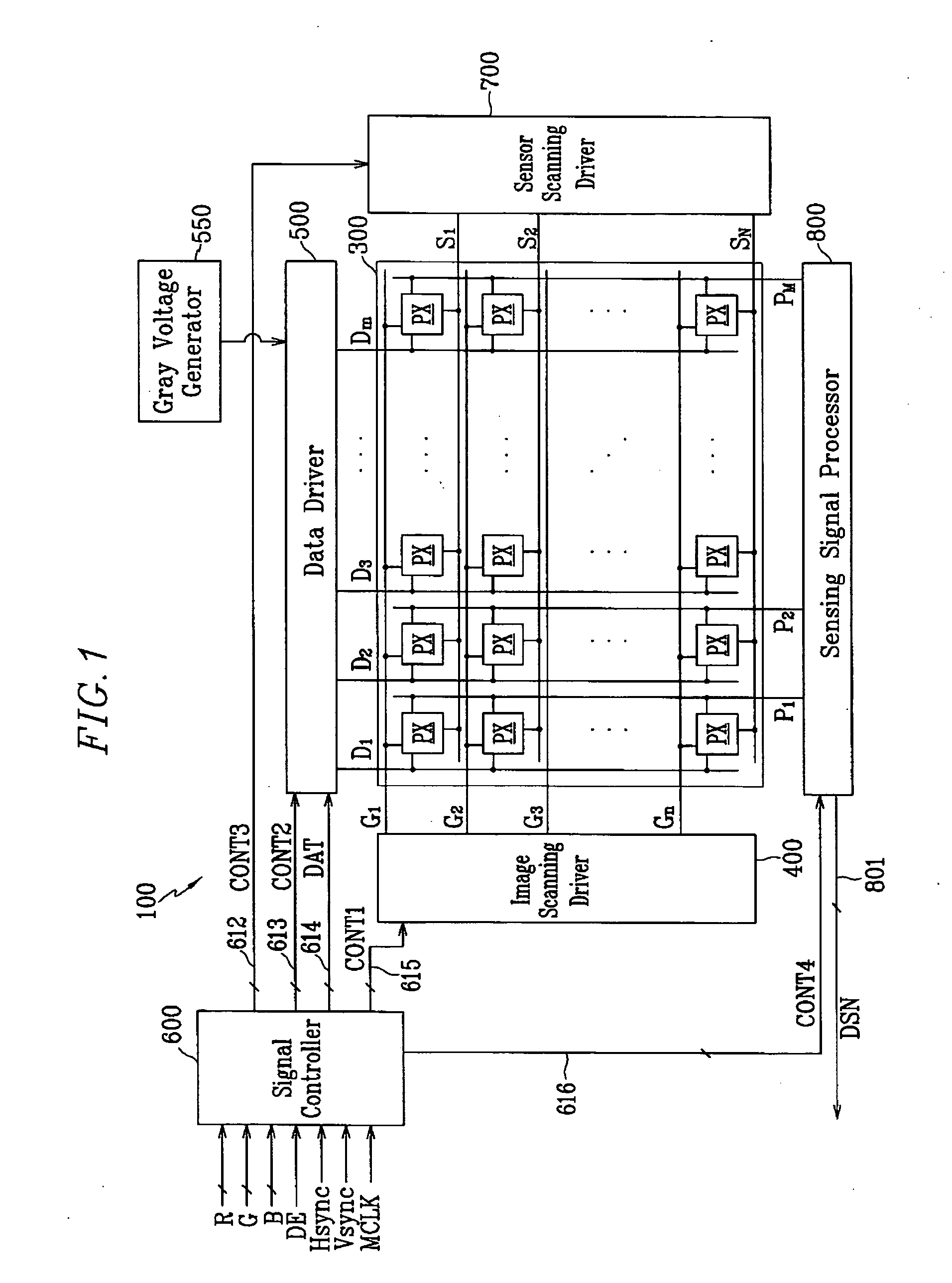
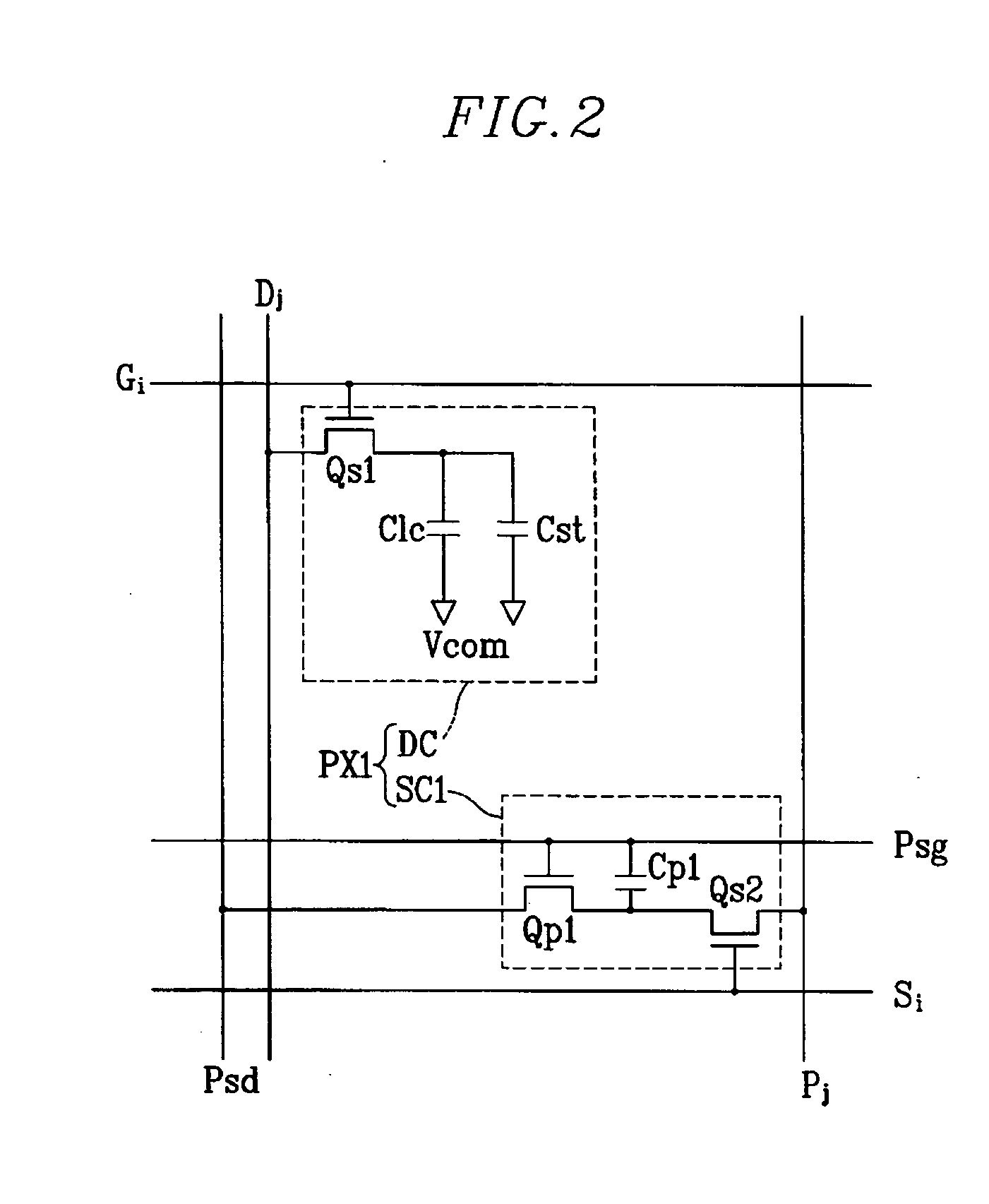
Touch detectable display device and driving method thereof
A display device is disclosed which includes: a display panel; a lighting unit to illuminate the display panel and having a state in response to a lighting control signal; a pressure sensing unit generating a first sensor output signal according to a touch on the display panel; a light sensing unit receiving light from the lighting unit and ambient light and generating a second sensor output signal according to the touch on the display panel; a sensor scanning driver outputting sensor scanning signals to the pressure sensing unit and the light sensing unit in response to a sensor scanning control signal; and a sensing controller generating the lighting control signal and the sensor scanning control signal based on the first and the second sensor output signals and outputting the lighting control signal to the lighting unit and the sensor scanning control signal and the sensor scanning driver.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
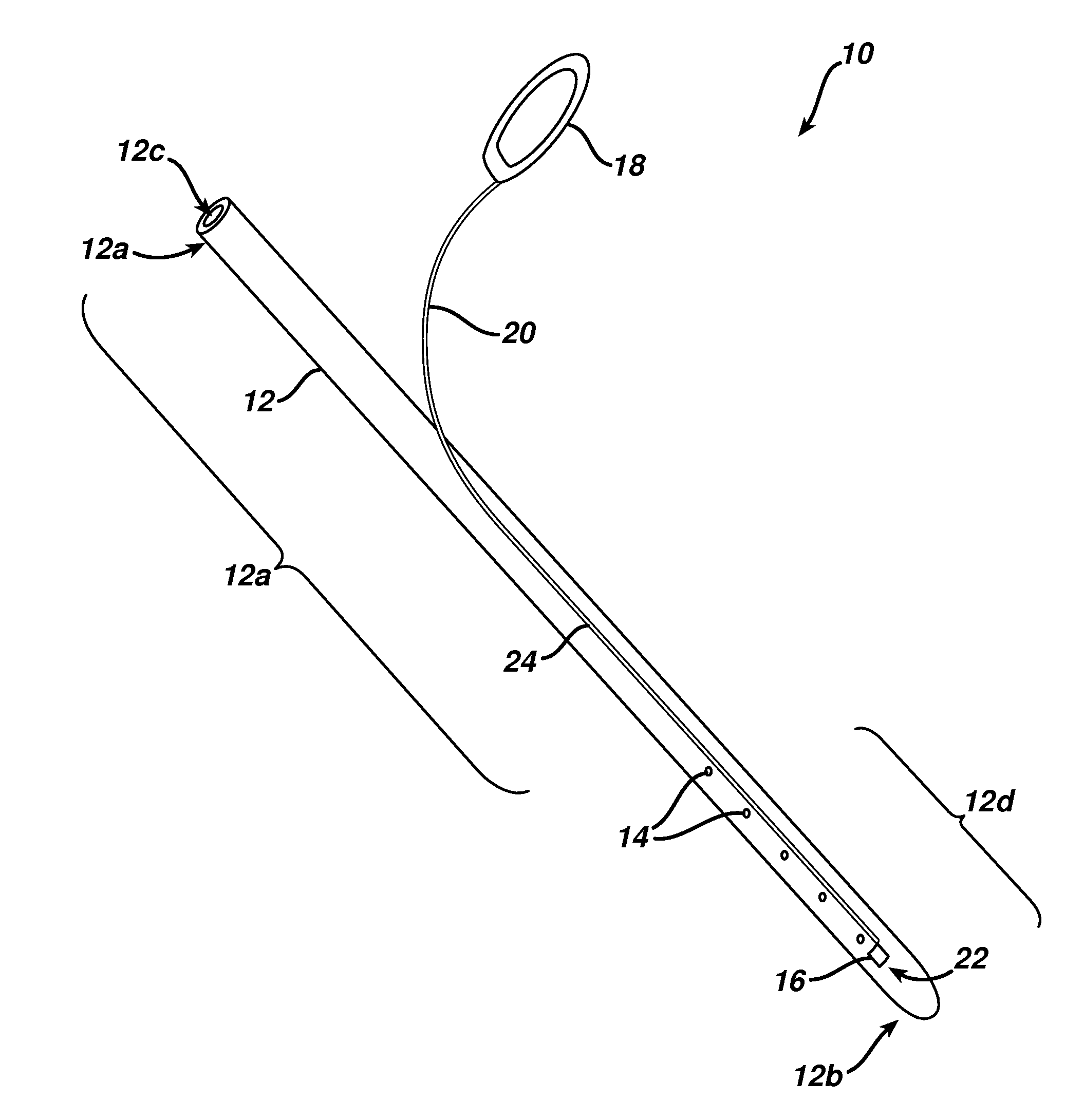
Surgical perforation device with curve
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
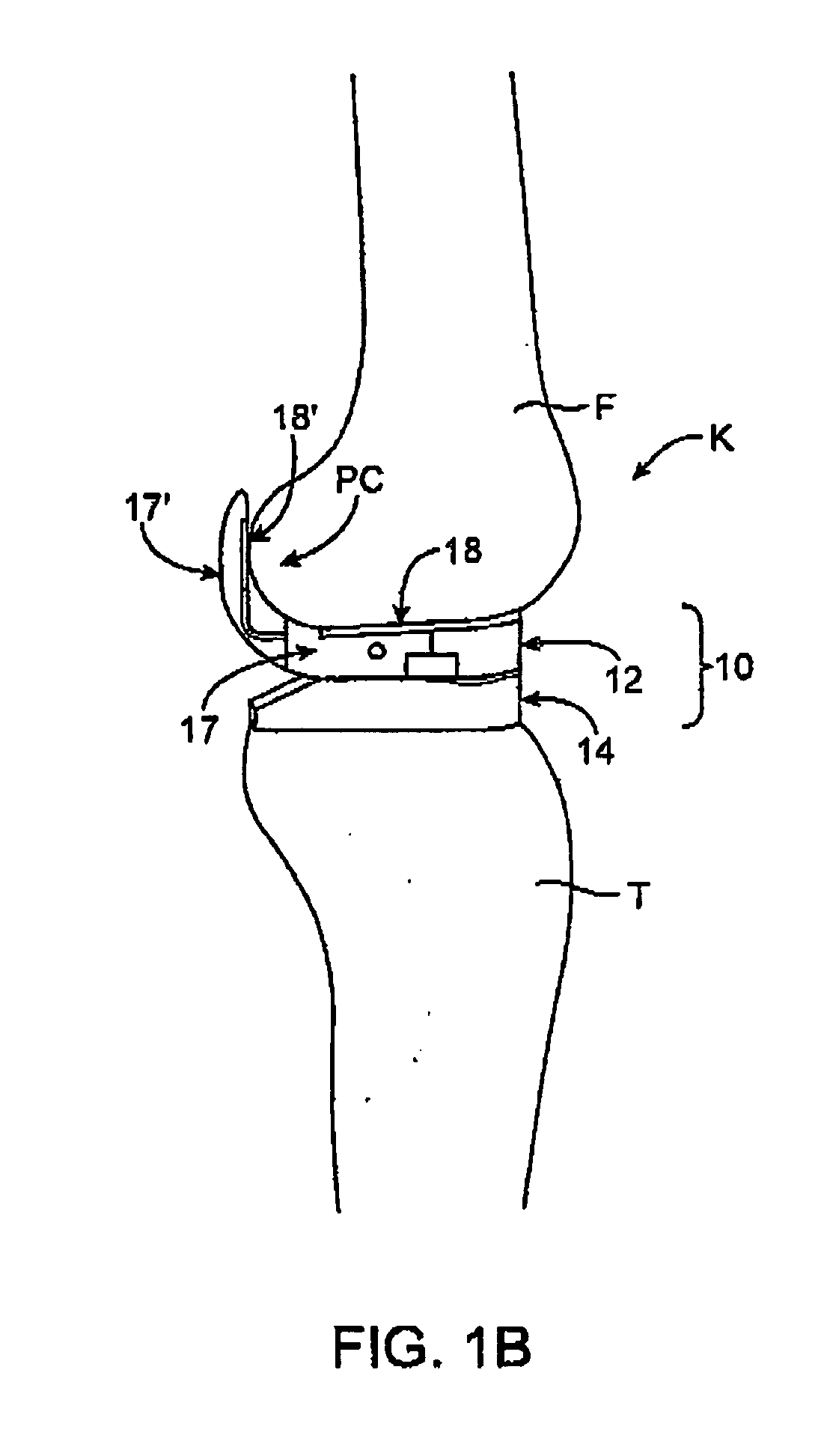
Dynamic knee balancer with pressure sensing
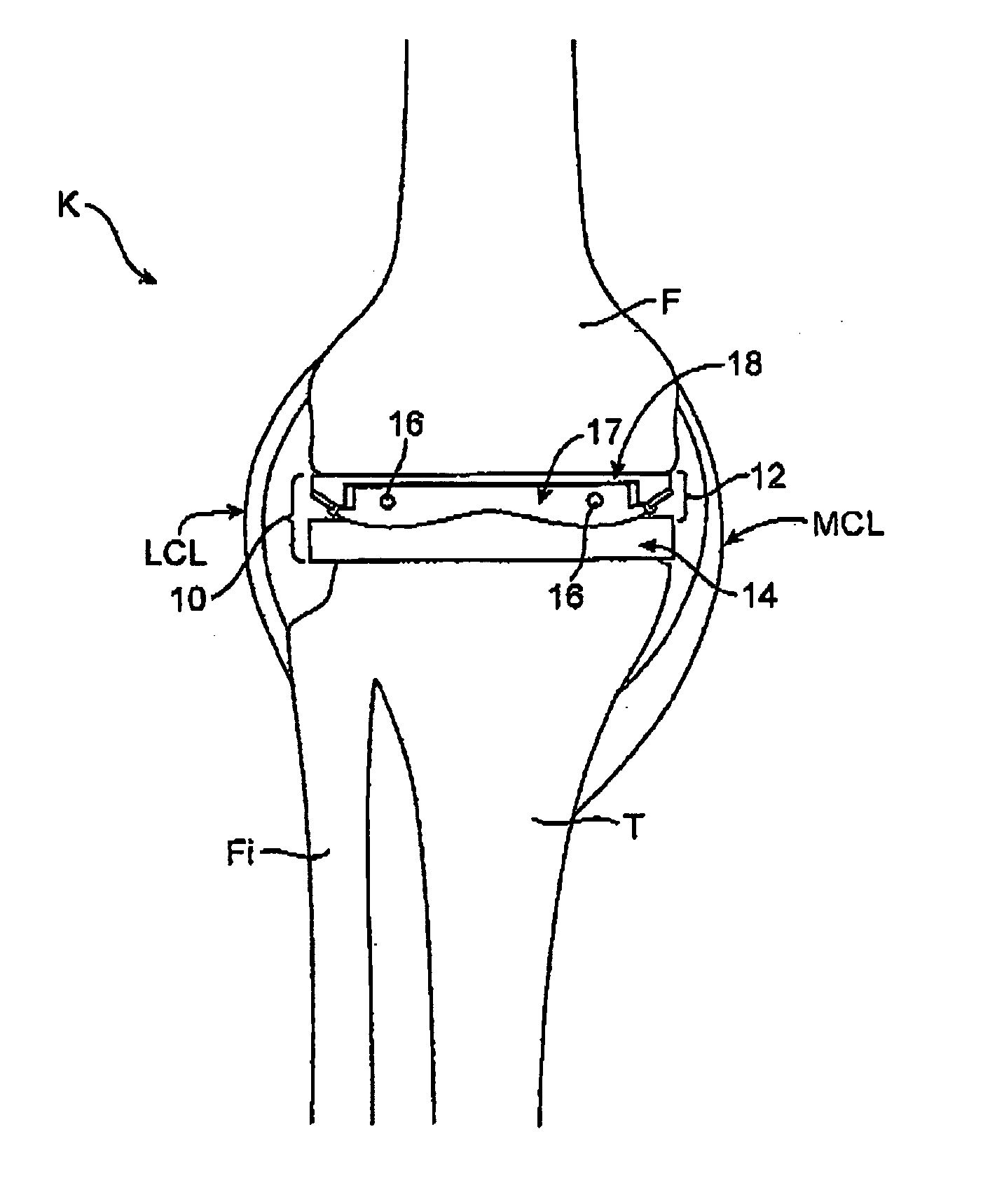
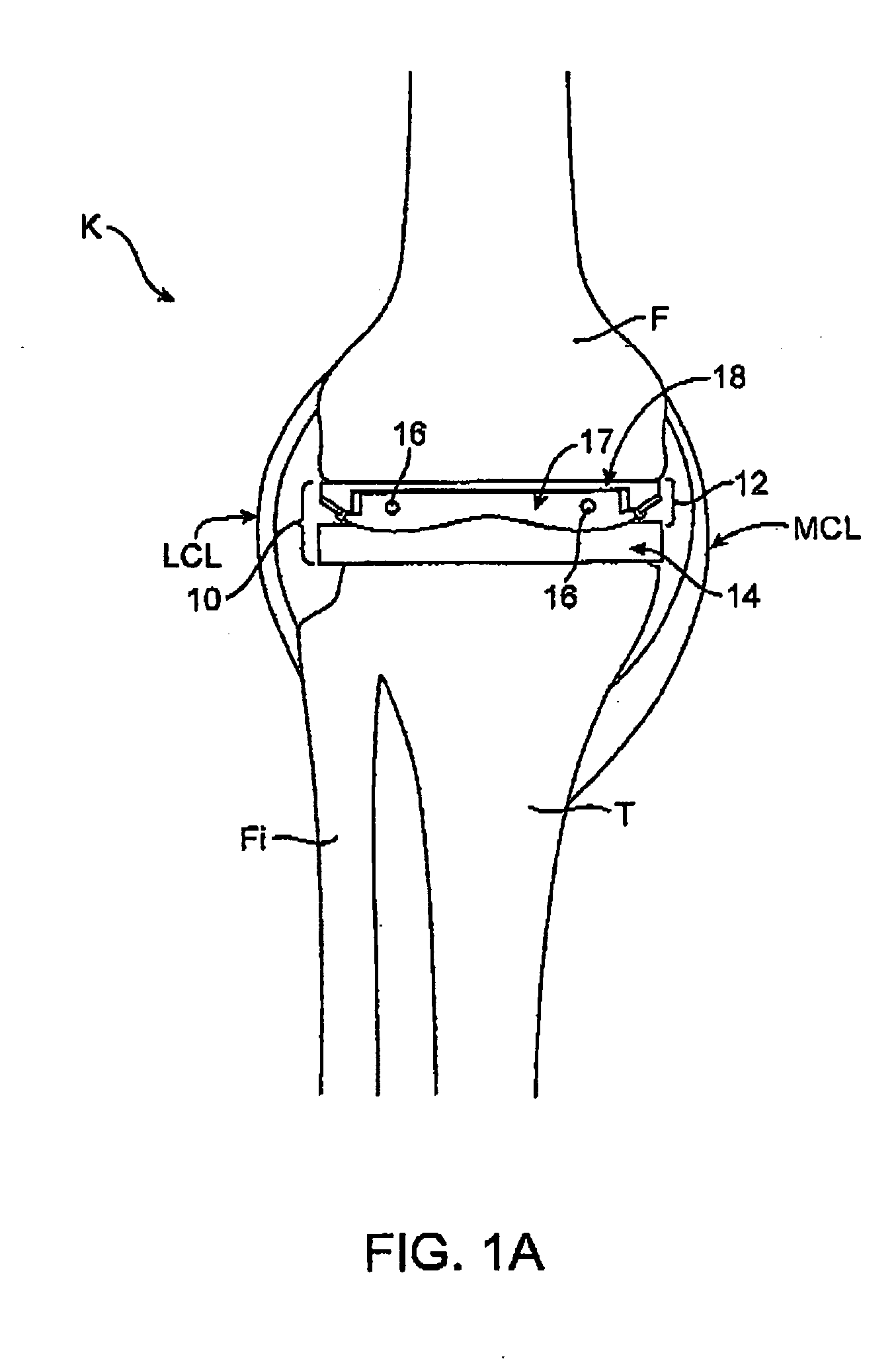
ActiveUS20050177170A1Enhancing knee surgery procedureAccelerated programPerson identificationJoint implantsTibiaRelative pressure
A device for performing a surgical procedure on a knee includes an adjustable femoral portion, a tibial portion and at least one sensor coupled with the femoral and / or tibial portions to sense pressure exerted by the femoral and tibial portions against one another. The femoral portion is adapted for removably coupling with a distal end of a femur to adjust tension in soft tissue adjacent the knee and has at least one positioning feature adapted to move relative to the distal end of the femur as the femoral portion is adjusted, thus helping position a femoral prosthetic on the distal end of the femur. The sensor(s) may be adapted to sense pressure at medial and lateral sides of the knee, and relative pressures may be displayed as data on a visual display. Adjustments to the femoral member may be made to balance pressure at flexion and extension of the knee.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Obesity Treatment Systems
InactiveUS20080161717A1Increase heightLonger-term implantationSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyPatient managementPatient database
In one embodiment, a pressure sensing system is described which transmits data to a patient management system external to a patient. The pressure sensing system can rigidly couple to an implantable port or flexibly couple to an implantable port. In some embodiments, the pressure sensing system communicates with a hydraulic actuating system. In some embodiments, the pressure sensing system is implantable and comprises a circuit capable of wireless transmission through the skin of a patient to an external receiver which is part of a patient management system. A patient management system is described which receives up to date as well as historical data from the pressure sensing system and manages the these data in the context of a patient database. In some embodiments, an extragastric balloon is described in which the balloon is contoured to −..it..i poi.jLυπo± the stomach nur not circumscribe the stomach. In some embodiments, electroactive polymers or nitinol structures are utilized to create restriction on the stomach in response to food boluses entering the stomach. In some embodiments, a nasogastric connector is described with two expandable structures translateable toward and away from one another so as to create pressure between two organ lumens when brought toward each other and fixed with respect to one another.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL ERIC
Optical capacitive thumb control with pressure sensor
A small sensor surface designed to control a smart phone or Mobile Internet Device (MID). The sensor surface may be mounted on the side of the proposed device in a position where a user's thumb or finger naturally falls when holding the device in his / her hand. The sensor surface is simultaneously convex and concave, providing both visual and physical cues for the use of the sensor surface. The sensor may include capacitive sensing, optical sensing and pressure sensing capabilities to interpret thumb gestures into device control.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Selectable switching of implantable sensors to provide fault toleance for implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20070265671A1Avoiding and positively resolvingAvoid formingElectrocardiographyEndoradiosondesSet screwHigh energy
The present disclosure provides one or more structures, techniques, components and / or methods for avoiding or positively resolving failure modes for an implanted medical device coupled to one or more sensors. A common fault scenario involves unintended stimulation during therapy delivery. A pacing stimulus can couple to exposed conductive portion(s) of a medical electrical lead (e.g., a tip portion) that includes a sensor to cause the stimulation. Stimulation also occurs due to insulation breaches of a lead. Stimulation can also result from a breach in insulation surrounding a conductive set screw that couples the lead to active circuitry. Stimulation also results when high energy therapy energy shunts to sensor circuitry (e.g., sensor bus) via insulation breach of the sensor lead and / or the circuitry. Such unintended stimulation is avoided by disconnecting the pressure sensing lead and sensor: during therapy delivery, when impedance measurement or current measurement to the sensor indicate unintended stimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for verifying connection of correct fluid supply to an infusion pump
A system and method for verifying that a particular fluid supply is connected to an infusion pump or pump channel. An upstream pressure sensor coupled to a fluid conduit associated with the fluid supply is used to provide pressure signals in response to pressure sensed in the conduit to a processor. In a connection verification mode, the processor is configured to receive the pressure signals and delay the flow control device of the infusion pump from moving fluid through the conduit until the processor detects a pressure change in the conduit indicated by the pressure signals to thereby verify that the particular fluid supply is connected to the infusion pump.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
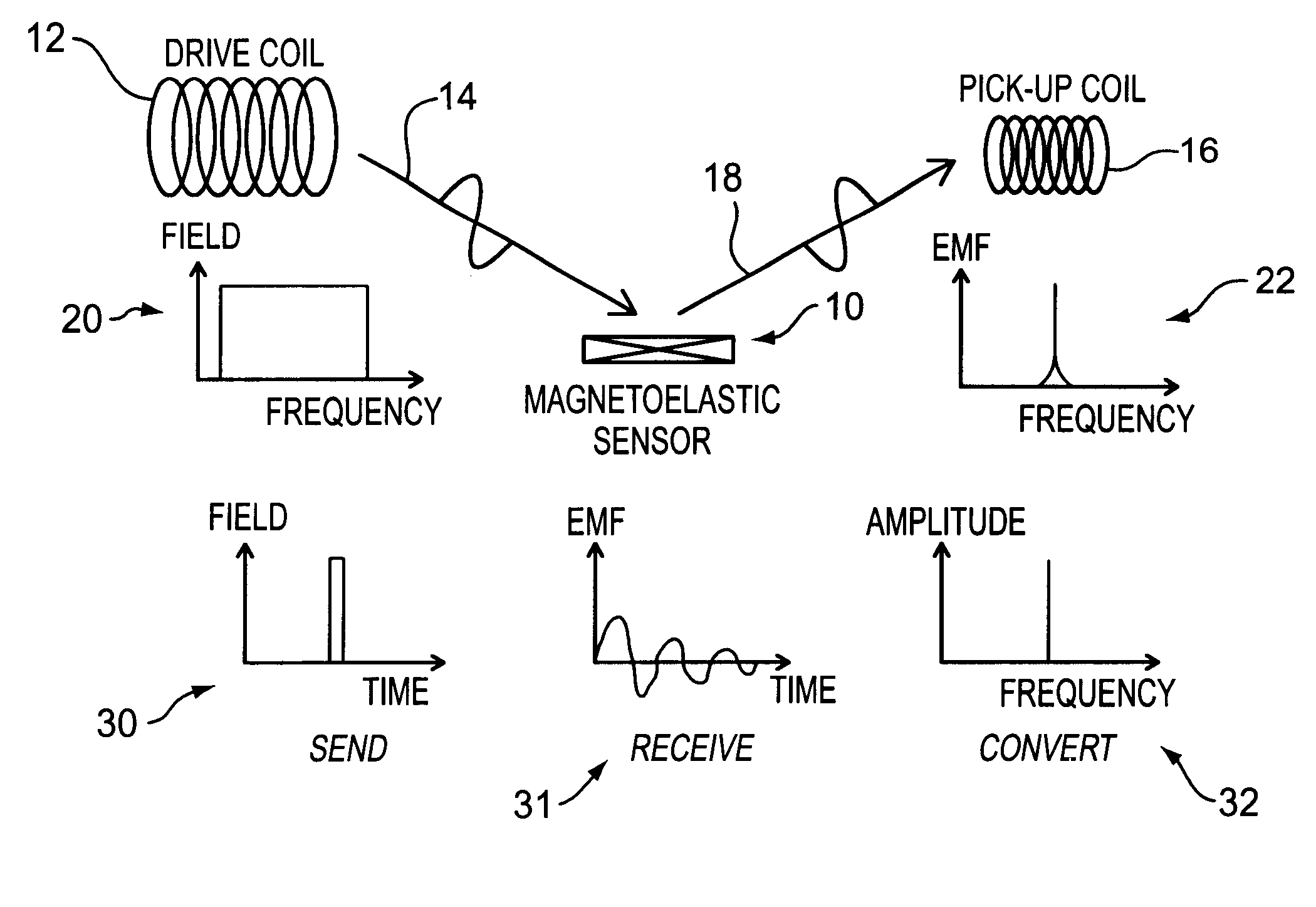
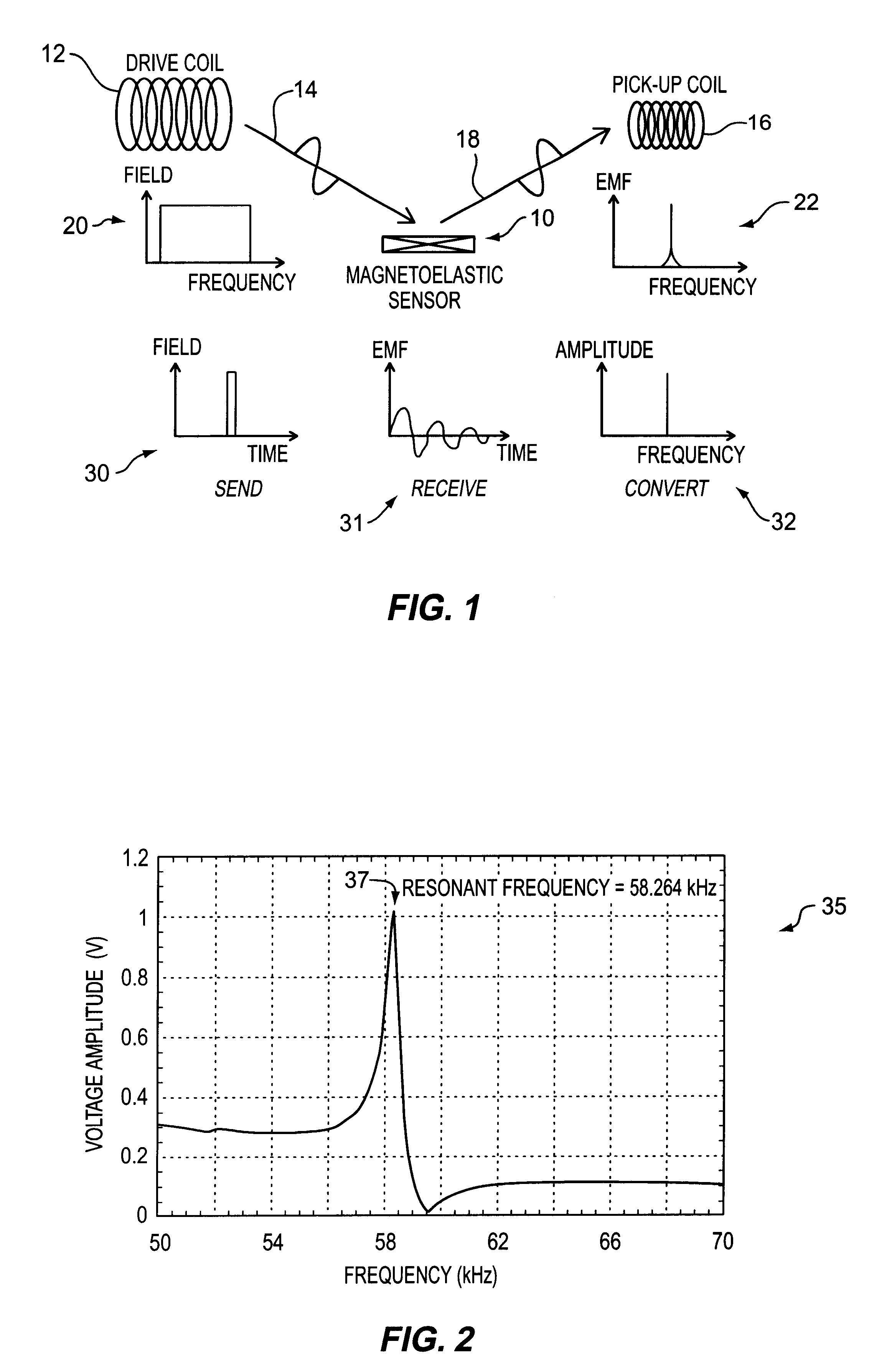
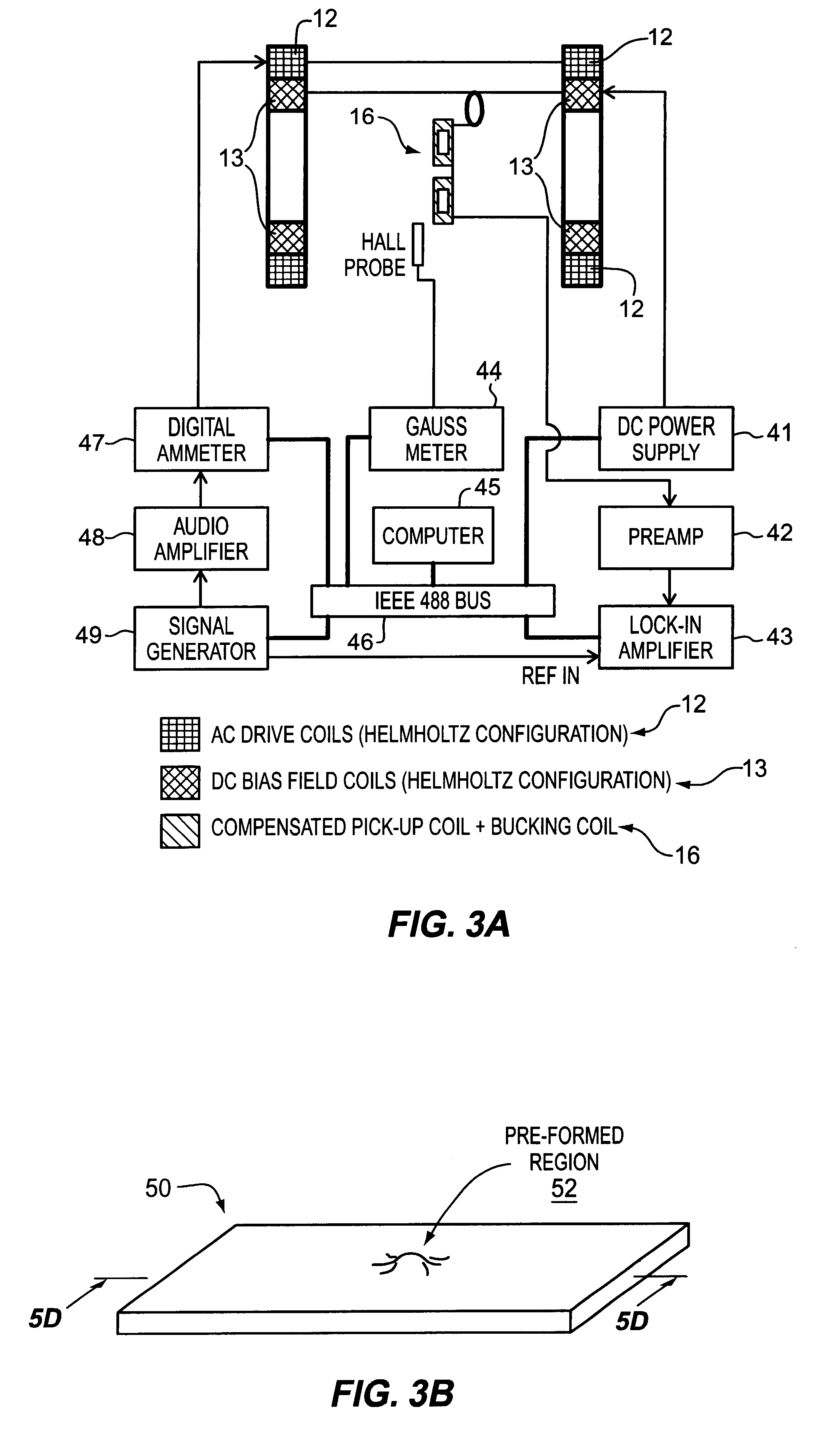
Magnetoelastic sensing apparatus and method for remote pressure query of an environment
InactiveUS6393921B1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementMagneto elasticPressure sense
A pressure sensing apparatus for operative arrangement within an environment, having: a sensor comprising a hermetically-sealed receptacle, at least one side of which has an flexible membrane to which a magnetically hard element is attached. Enclosed within the receptacle is a magnetostrictive element that vibrates in response to a time-varying magnetic field. Also included is a receiver to measure a plurality of successive values for magneto-elastic emission intensity of the sensor taken over an operating range of successive interrogation frequencies to identify a resonant frequency value for the sensor. Additional features include: (a) the magnetically hard element may be adhered to an inner or outer side of, or embedded within, the membrane; (b) the magnetostrictive element can include one or more of a variety of different pre-formed, hardened regions; (c) the magneto-elastic emission may be a primarily acoustic or electromagnetic emission; and (d) in the event the time-varying magnetic field is emitted as a single pulse or series of pulses, the receiver unit can detect a transitory time-response of the emission intensity of each pulse (detected after a threshold amplitude value for the transitory time-response is observed). A Fourier transform of the time-response can yield results in the frequency domain. Also, an associated method of sensing pressure of an environment is included that uses a sensor having a magnetostrictive element to identify a magneto-elastic resonant frequency value therefore. Using the magneto-elastic resonant frequency value identified, a value for the pressure of the environment can be identified.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Direct resistance measurement corrosion probe
InactiveUS7034553B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
A direct resistance measurement probe for measuring corrosion levels and material loss. The probe includes a hollow body having a resistive element at one end that is exposed to the environment. The probe can have an internal or external power source that is electrically connected to the resistive element. A meter measures the electrical resistance of the resistive element providing data from which corrosion rates may be ascertained. A temperature sensing device measures the temperature of the resistive element. A pressure sensing device measures the pressure of the environment that the resistive element is subjected to. The probe does not use a comparative or ratiometric reference element.
Owner:GILBOE DEREK
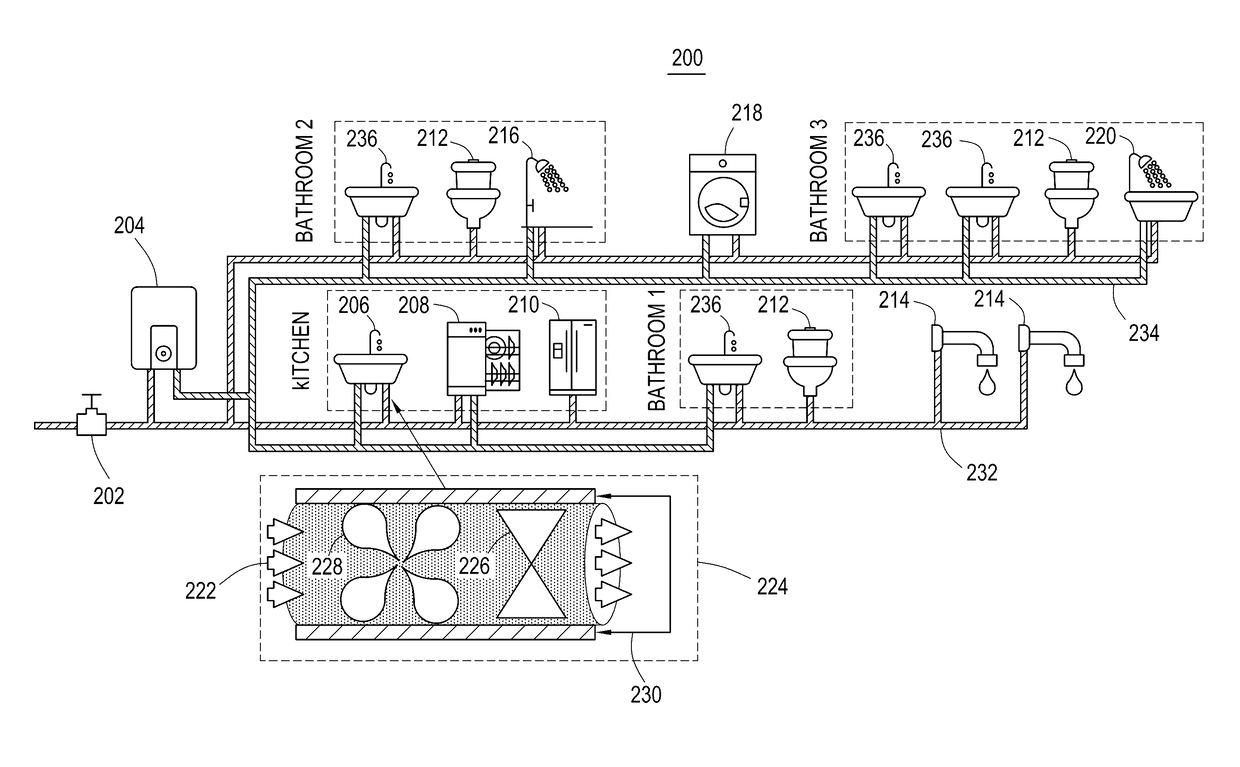
Water leak detection using pressure sensing
ActiveUS20170131174A1Inexpensive to fixWater consumptionMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateGeneral water supply conservationEngineeringWater leak
A system including a sensing device including a pressure sensor configured to measure pressure of water in a water system of a structure. The sensing device can be configured to generate pressure measurement data representing the pressure of the water as measured by the pressure sensor. The system also can include one or more processing units including one or more processors and one or more non-transitory storage media storing machine executable instructions configured when run on the one or more processors to perform detecting a non-cyclical pressure event corresponding to a water leak in the water system of the structure during a first time period based on an analysis of information including the pressure measurement data. The information analyzed in the analysis does not include any flow measurement data that represents a total amount of flow of the water in the water system of the structure during the first time period. The pressure sensor can be coupled to the water system of the structure at a single location of the water system of the structure when measuring the pressure of the water in the water system of the structure. Other embodiments are provided.
Owner:PHYN LLC
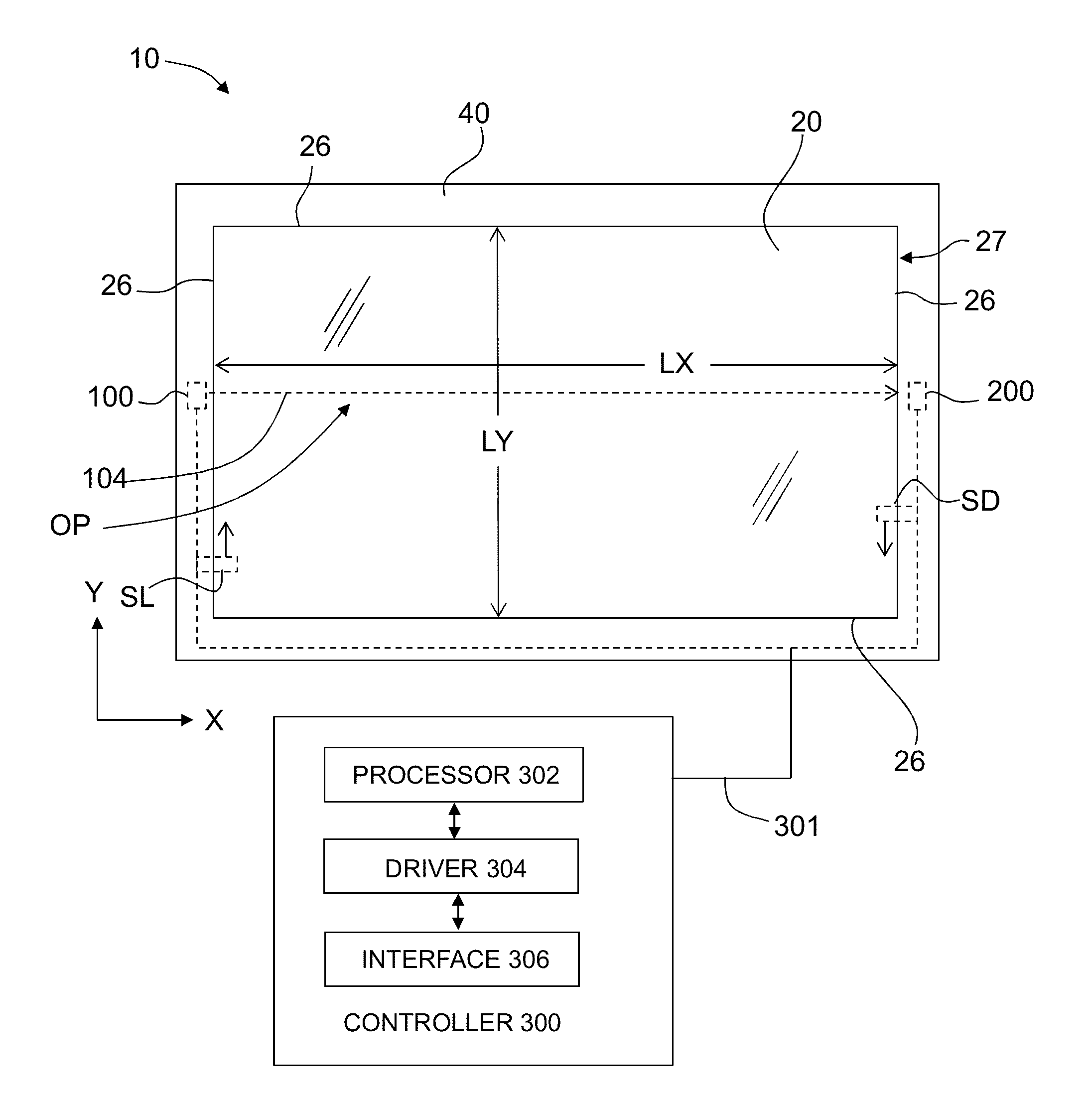
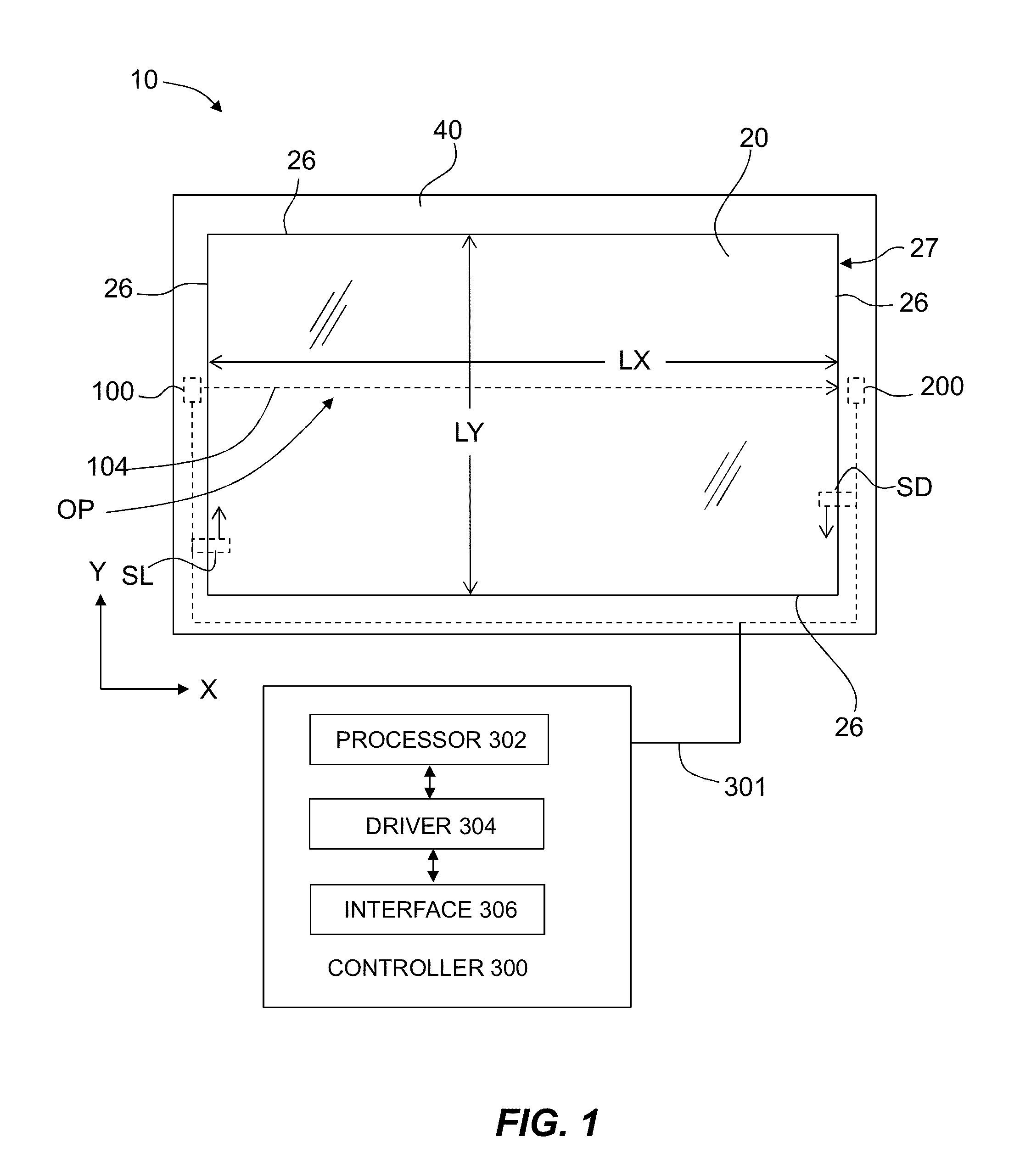
Pressure-sensing touch system utilizing optical and capacitive systems
A hybrid touch system that utilizes a combination of a capacitive touch system for position sensing and an optical touch system for pressure sensing is disclosed. The optical touch system includes a transparent sheet having a surface, at least one light source and at least one detector which are operably arranged relative to the transparent sheet to transmit light through the sheet and to detect the transmitted light. Performing position sensing using the capacitive touch system simplifies the pressure-sensing optical touch system.
Owner:CORNING INC
Non-invasive measurement of fluid pressure in an adjustable gastric band
A food intake restriction device for forming a restriction in a patient's gastro-intestinal tract and non-invasively communicating pressure data regarding the restriction to an external monitor. The device includes a food intake restriction device implanted substantially about a patient's gastro-intestinal tract to form a restricted opening in the tract. A port is connected to the restriction device. The port contains a working fluid for affecting the size of the restricted opening. A pressure sensing system communicates with the working fluid to measure the pressure of the working fluid. A transmitter communicates the measured fluid pressure to the external monitor.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Display device and driving apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20060138983A1Reliable and accurate touch sensingReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTStatic indicating devicesLight sensingA d converter
A display apparatus may include touch detection circuitry including a light sensing circuit and a physical parameter sensing circuit (e.g., a pressure sensing circuit). The display apparatus may further include processing circuitry implementing a power-saving mode and a normal mode, and configured to generate touch information. An display driver may include a photo sensing circuit and a pressure sensing circuit. An embodiment of the display driver may include: an amplifying unit amplifying a photo sensing signal and a pressure sensing signal; a parallel-to-serial converting unit converting the amplified photo sensing signal and the amplified pressure sensing signal into serial sensing signals; and an analog-to-digital converter converting the serial sensing signals into digital sensing signals, wherein the amplifying unit, the parallel-to-serial converting unit, and the analog-to-digital converter operate in one of a normal mode and a power saving mode according to the pressure sensing signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
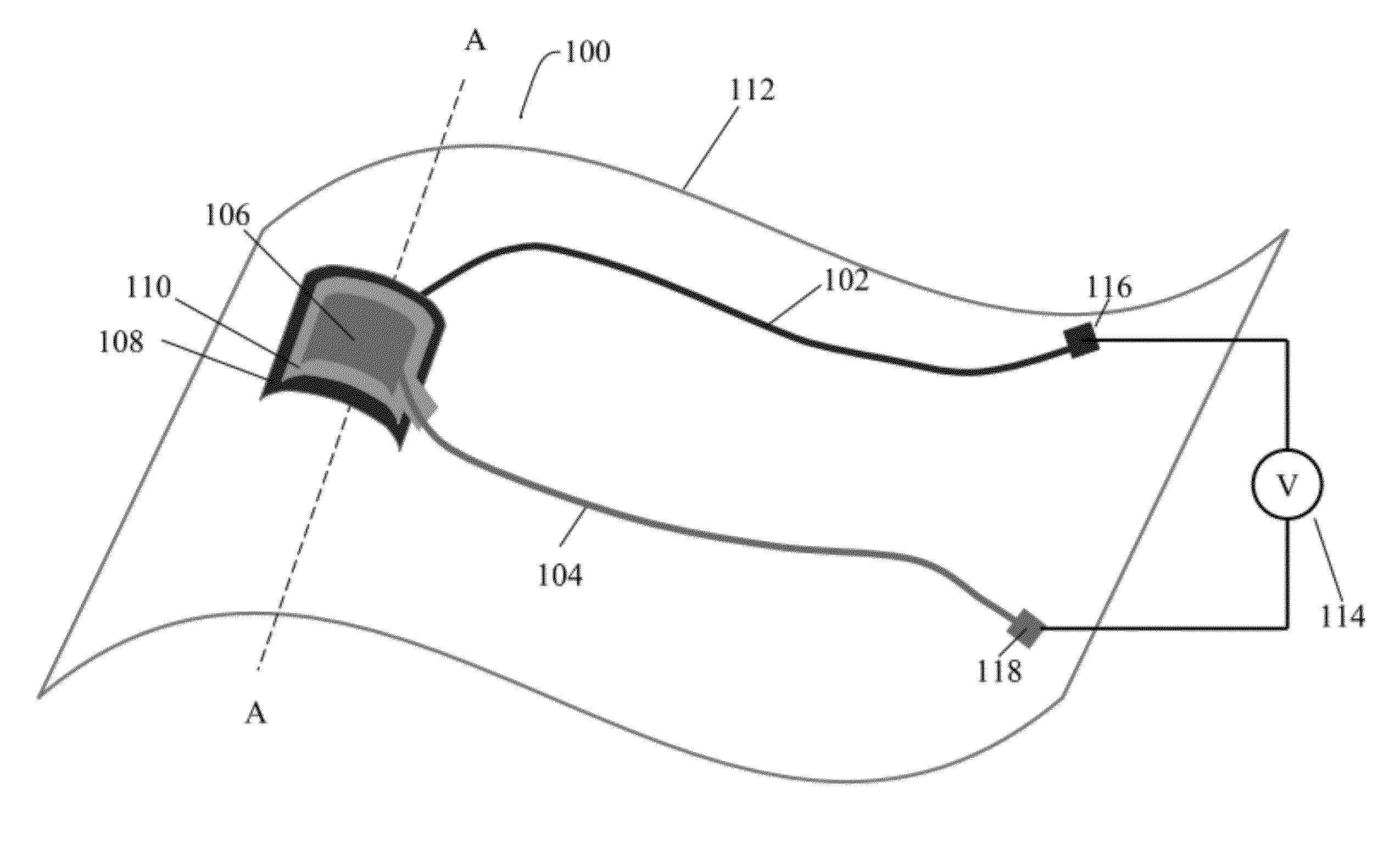
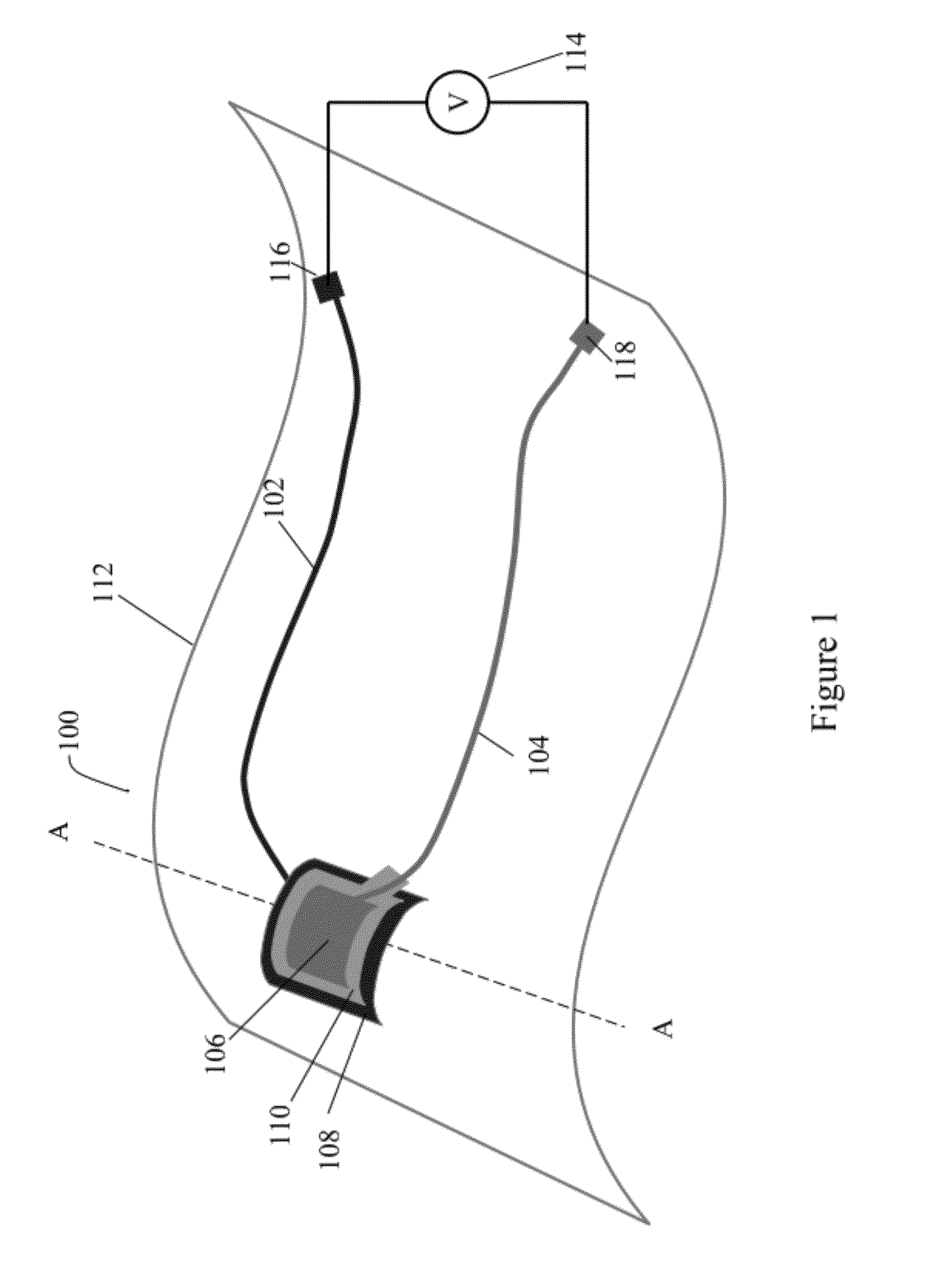
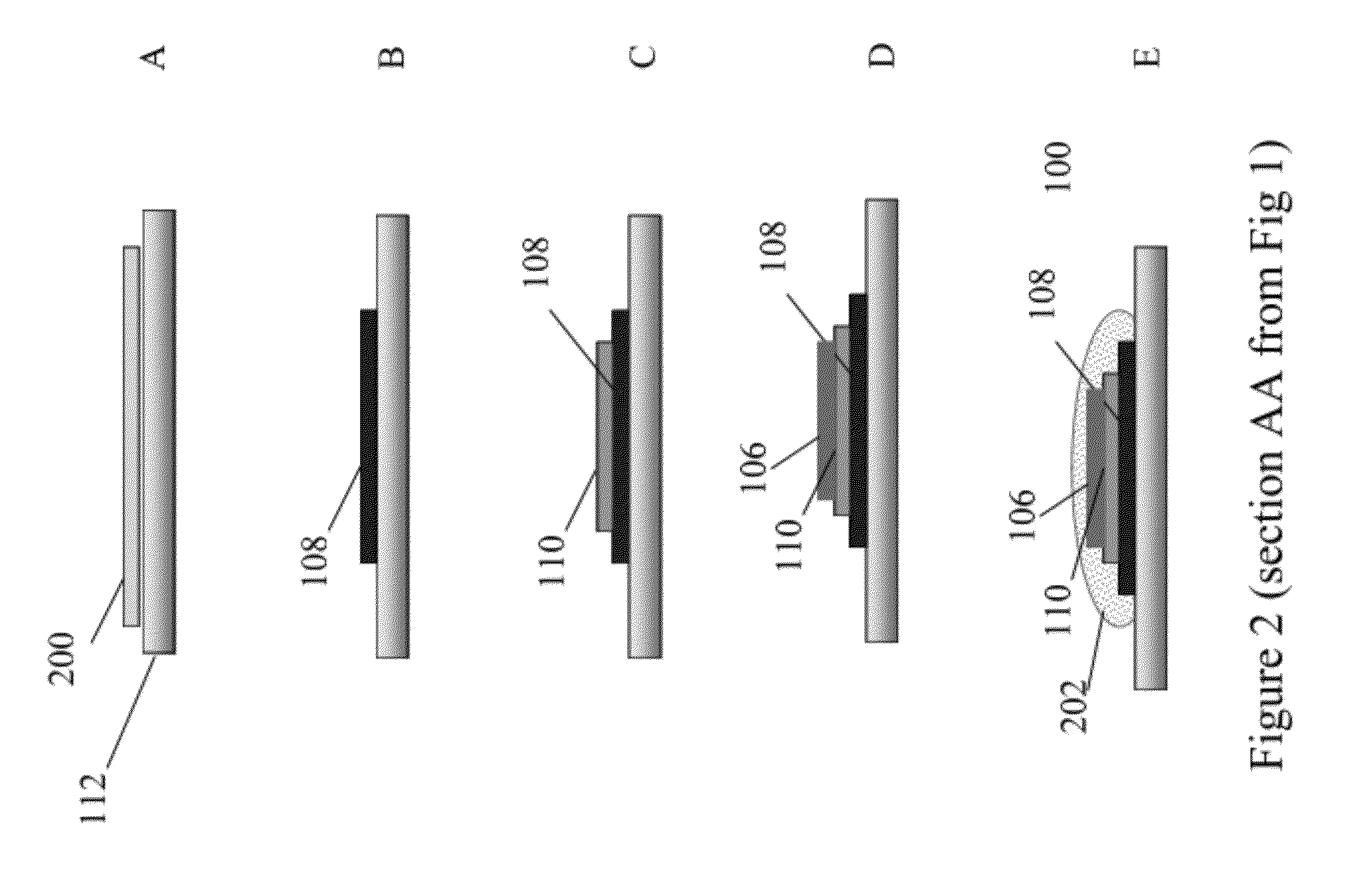
Pressure sensing devices
ActiveUS20060211944A1Inaccurate readingMeasure directlyCatheterIntracranial pressure measurementPressure senseEngineering
A pressure sensing catheter having a pressure sensor and an antenna that is coupled to the pressure sensor, e.g., by a connector, are provided. The pressure sensor can be adapted to measure a pressure surrounding the catheter, and the antenna can be adapted to telemetrically communicate the measured pressure to an external device. In an exemplary embodiment, the antenna, pressure sensor, and / or connector are hermetically sealed, e.g., by the catheter and / or a coating, to prevent the antenna, pressure sensor, and connector from coming into contact with fluid, thereby allowing the catheter to be permanently implanted or otherwise used for long term use. Exemplary methods for manufacturing and using pressure sensing catheters are also provided.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
One button remote control with haptic feedback
InactiveUS20090213066A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsRemote controlPressure sense
An input system for a TV remote control or other system has a single touch surface with a deformable haptic assembly below the touch surface such that a user placing a finger on the touch surface can feel deformation of the haptic assembly. A pressure sensing assembly is below the haptic assembly and sensing motion of a finger on the touch surface, with a processor receiving input from the pressure sensing assembly and providing output to the haptic assembly in response. Also, a display receives input sent by the processor in response to input from the pressure sensing assembly to cause the display to present a changing image of a keypad as a user moves a finger on the touch surface.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com