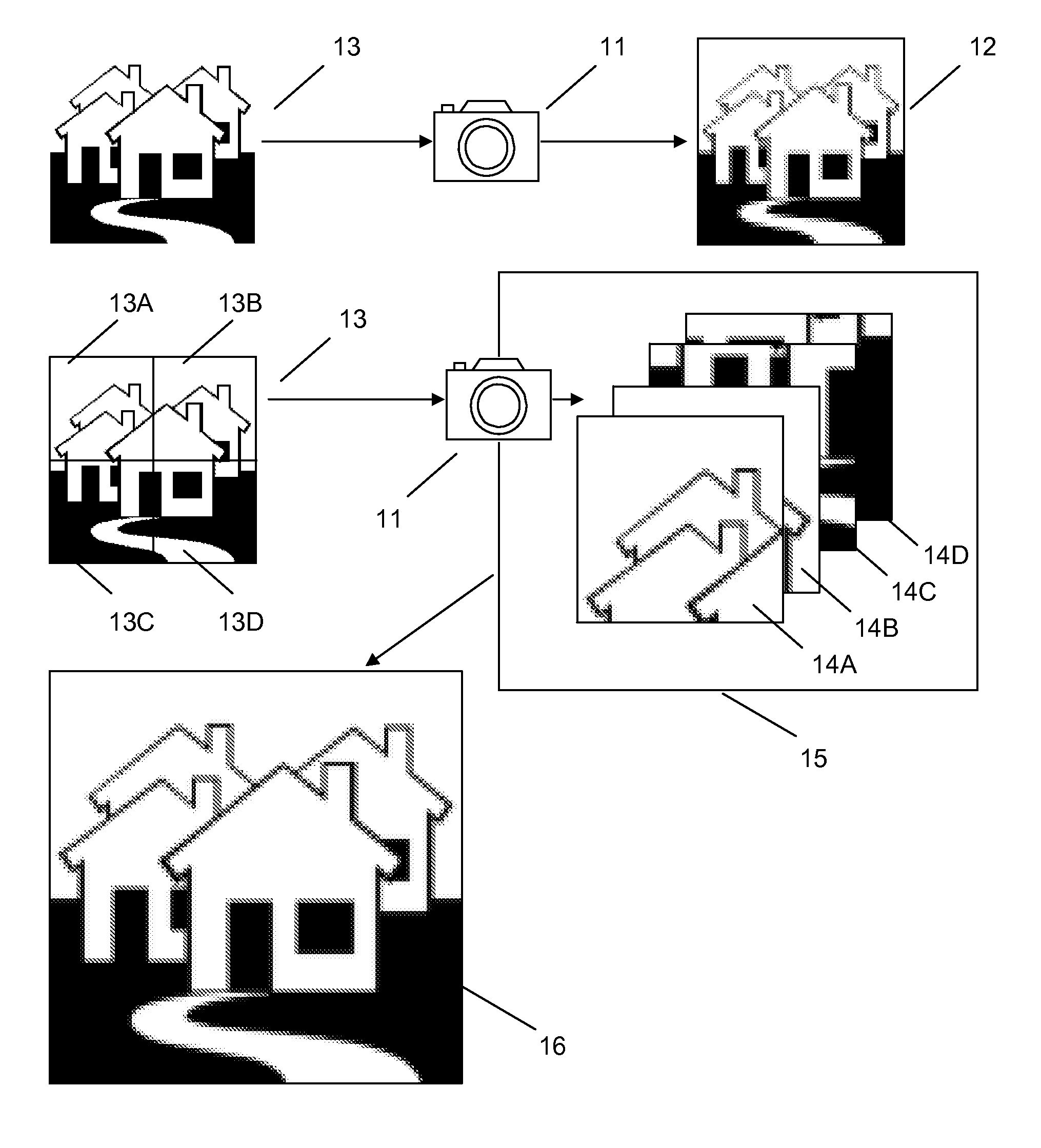
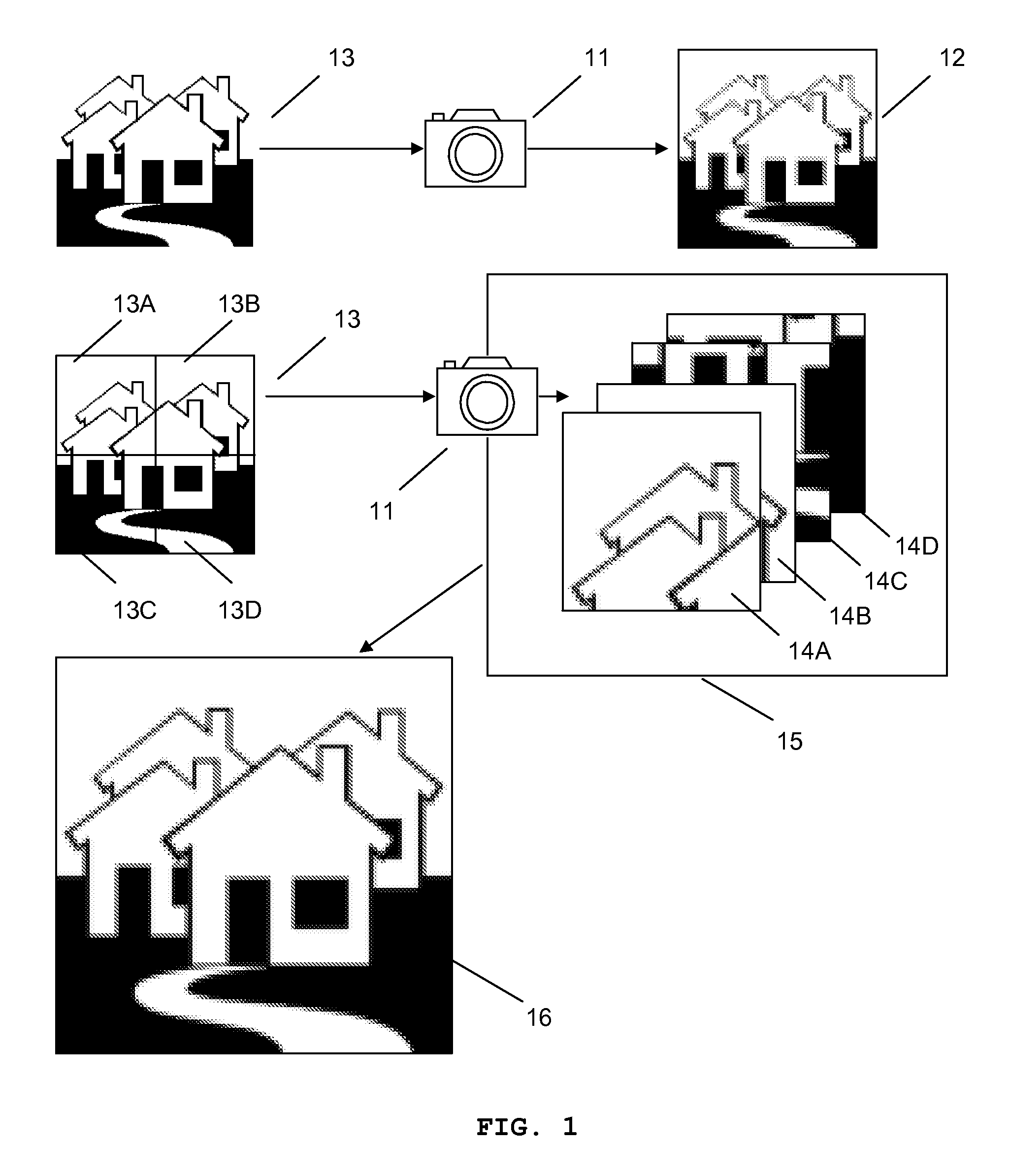
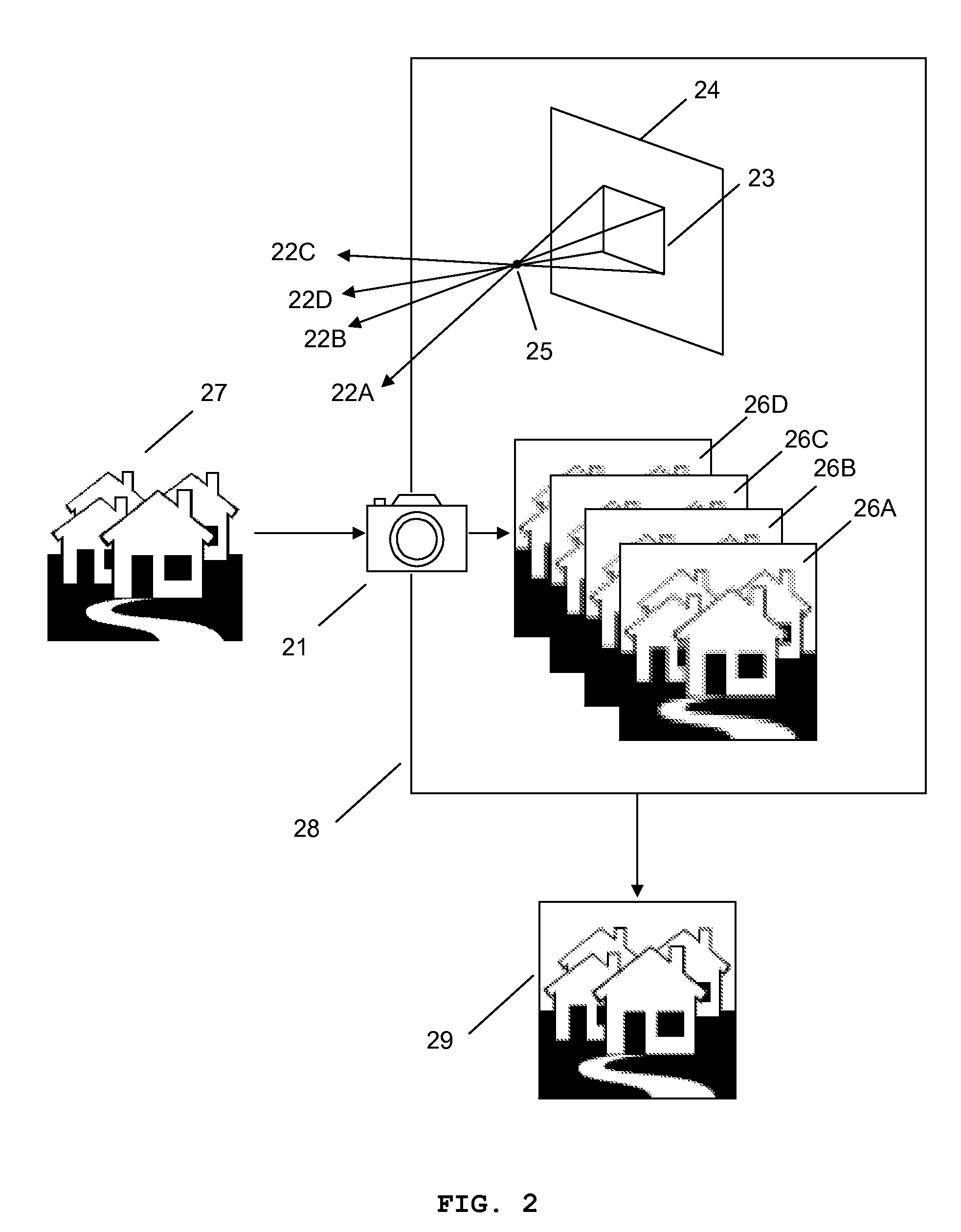
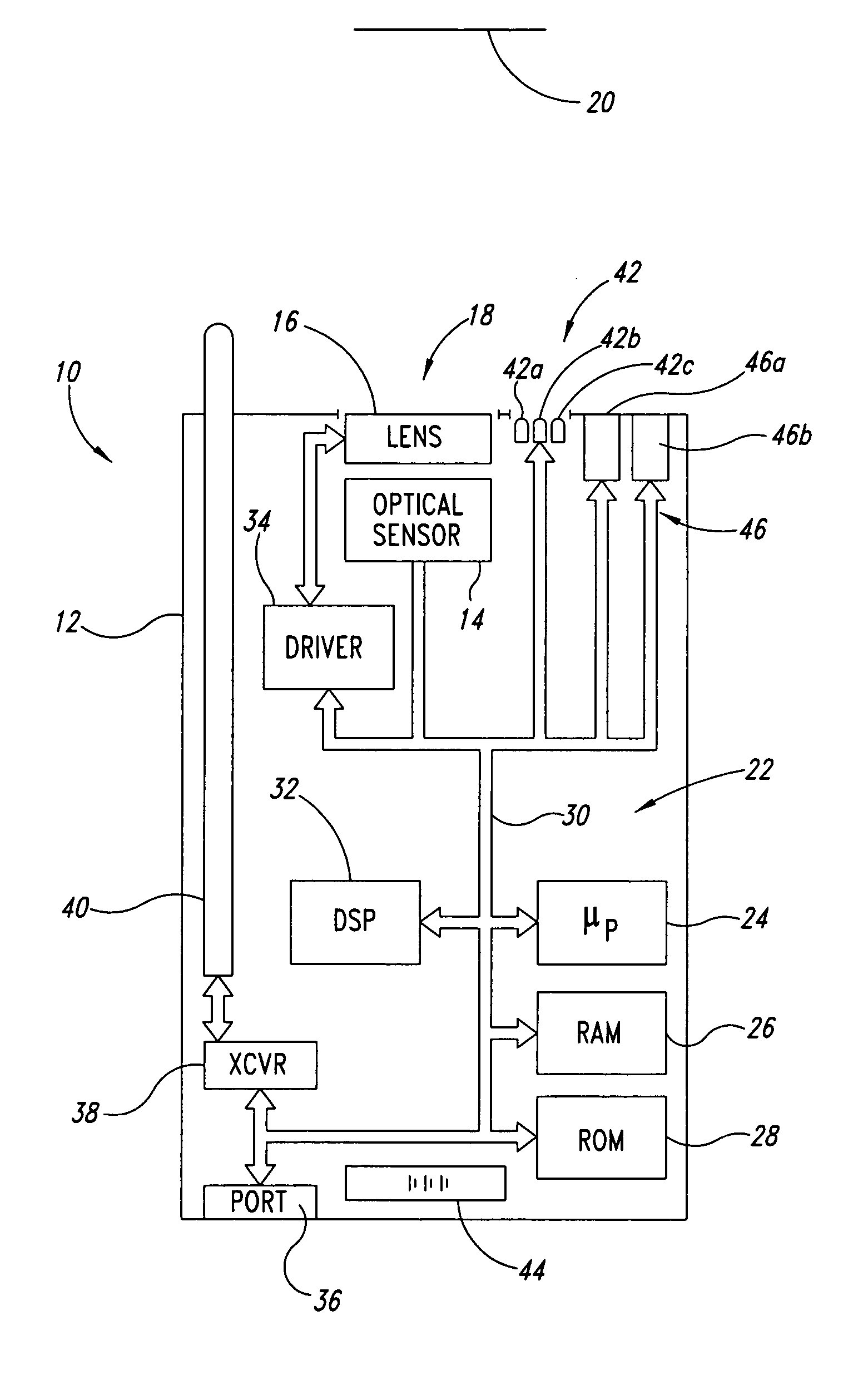
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2670 results about "Autofocus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
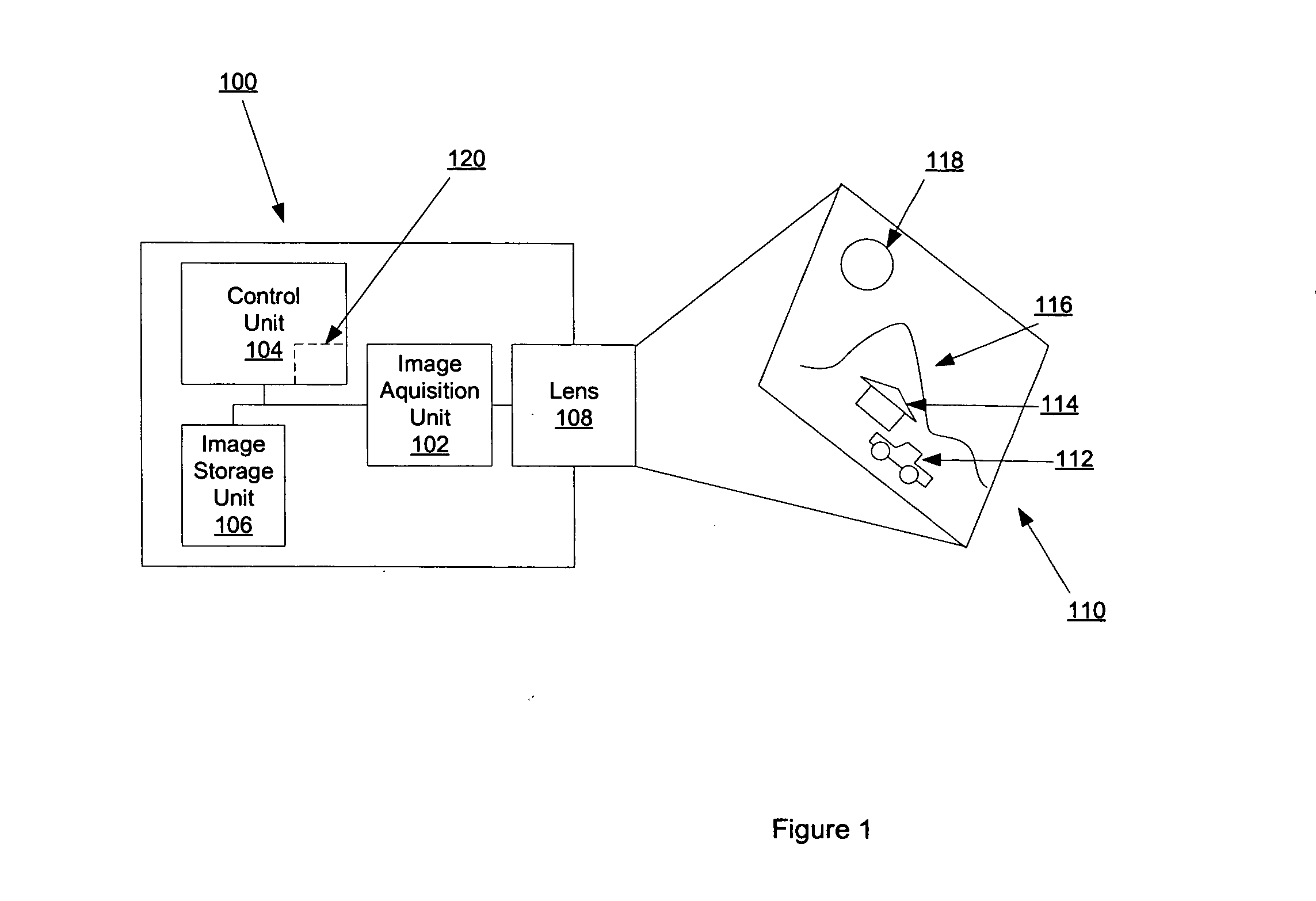
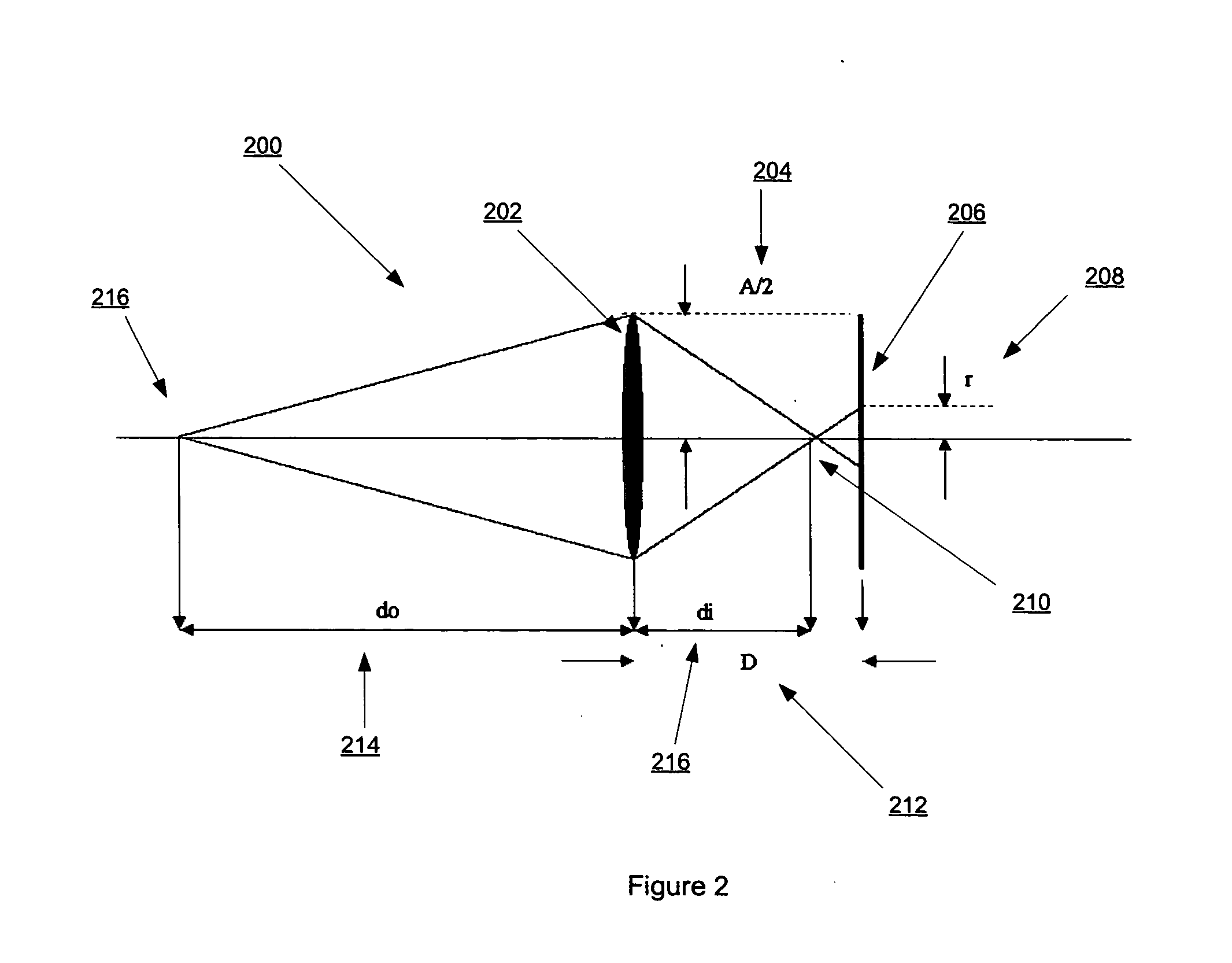
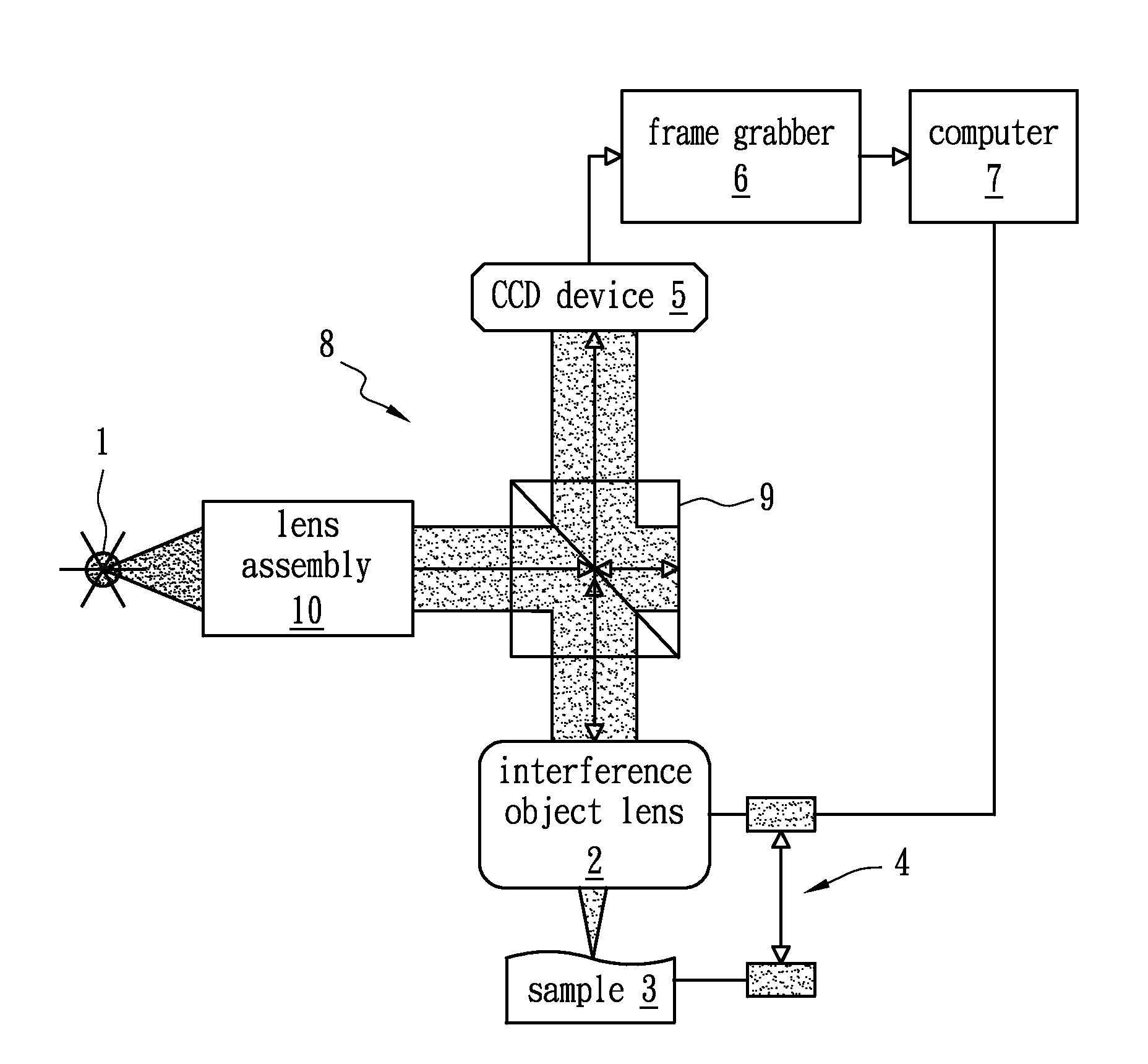
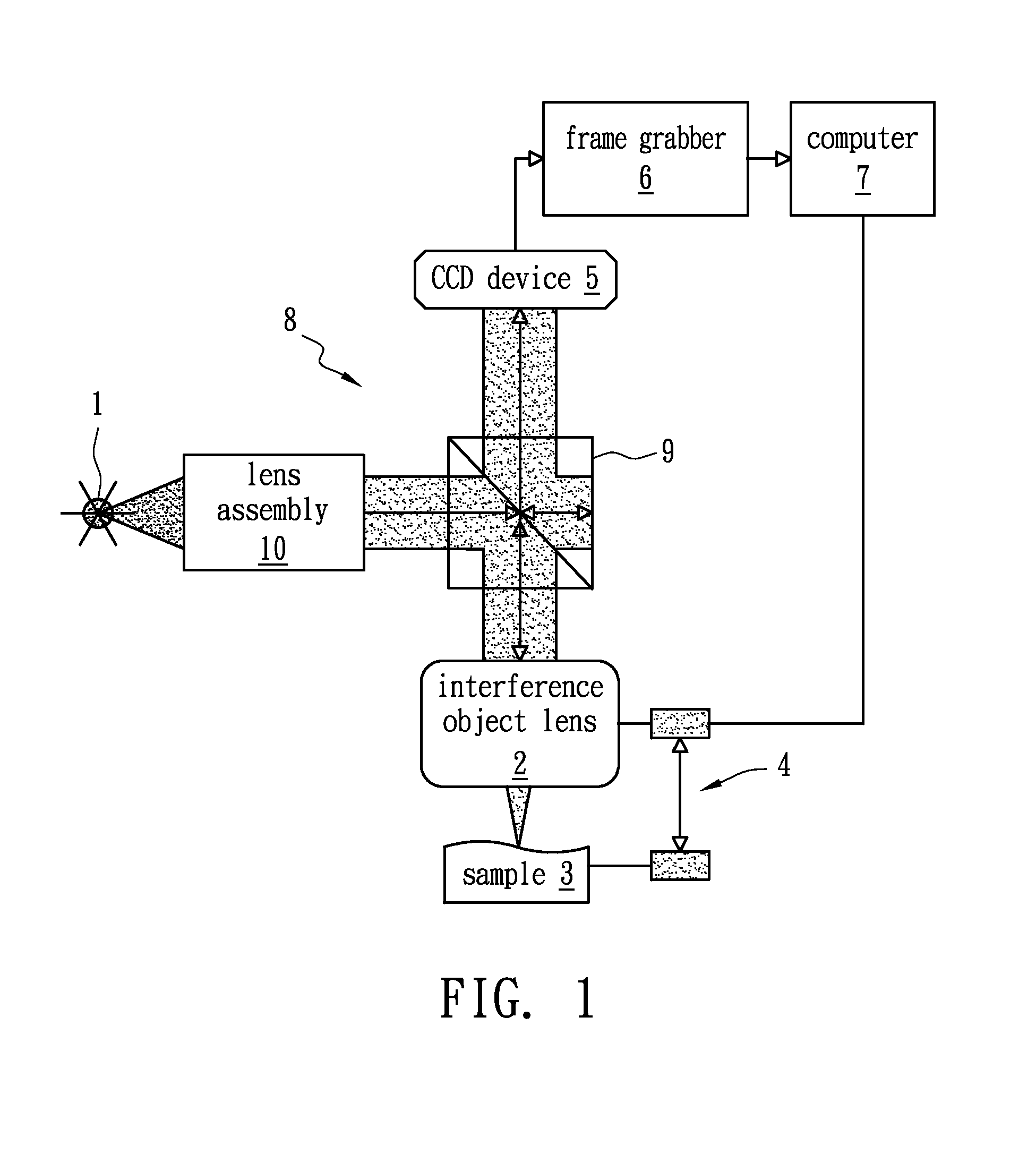
An autofocus (or AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication. Autofocus methods are distinguished by their type as being either active, passive or hybrid variants.
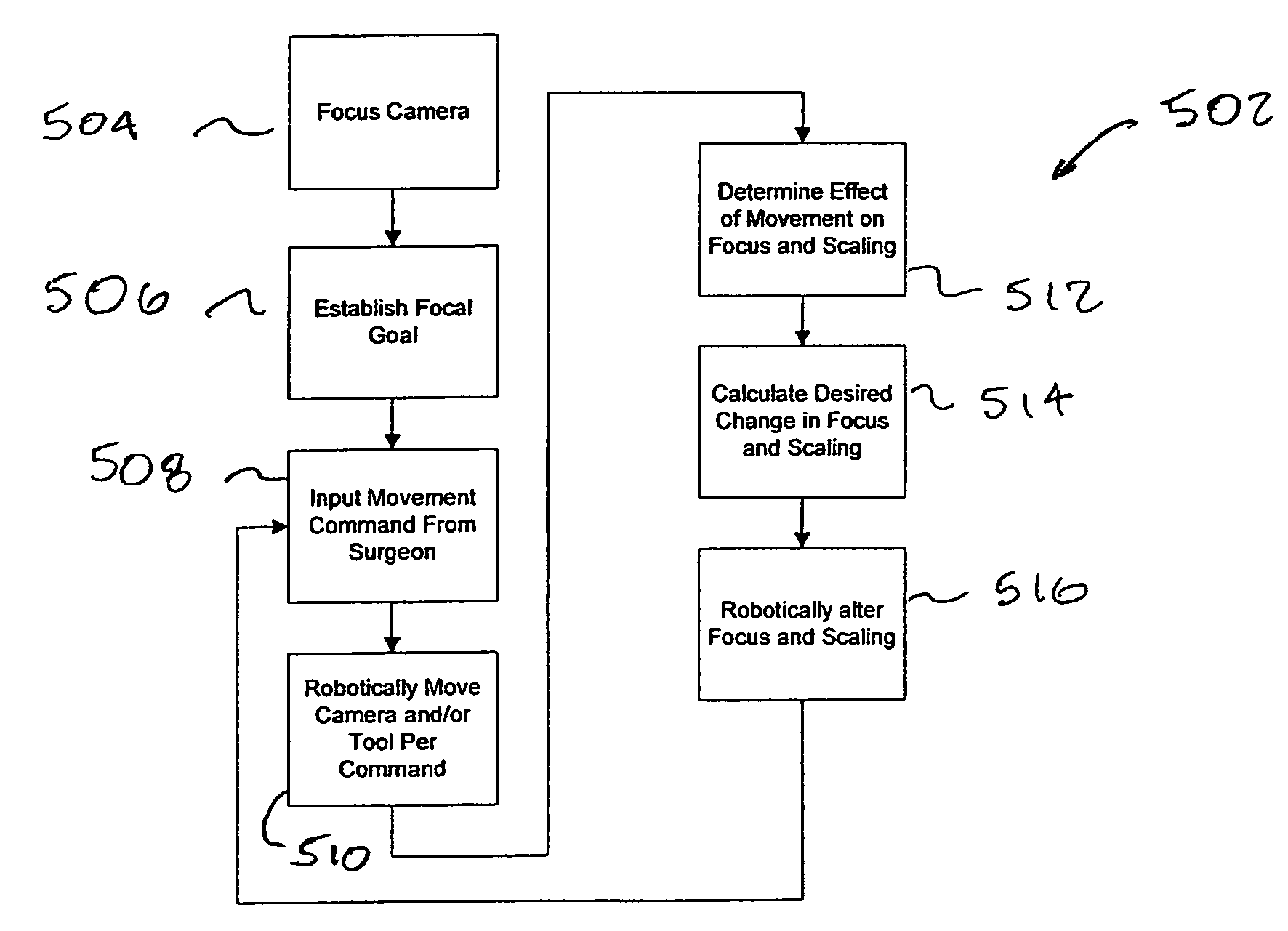
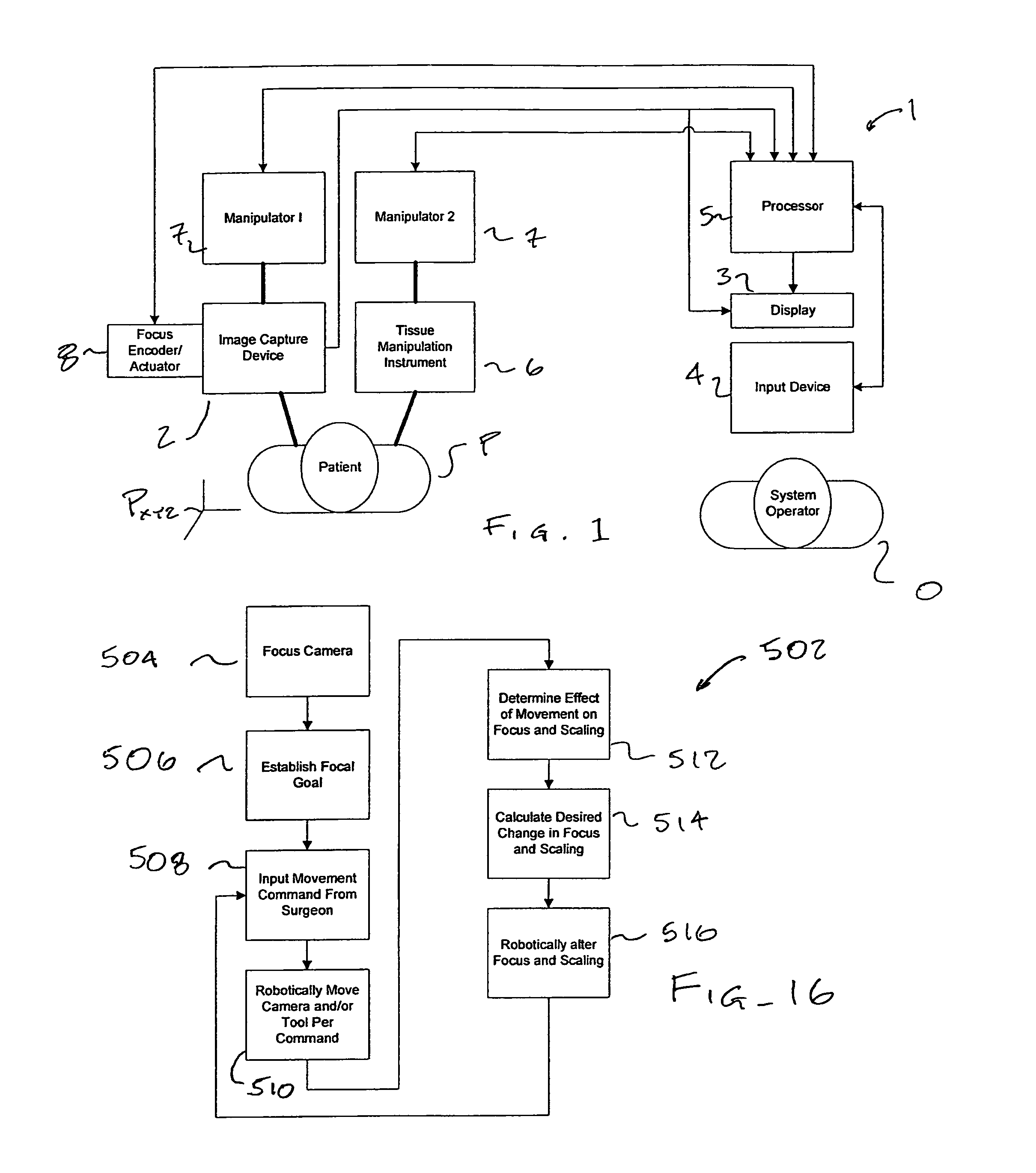
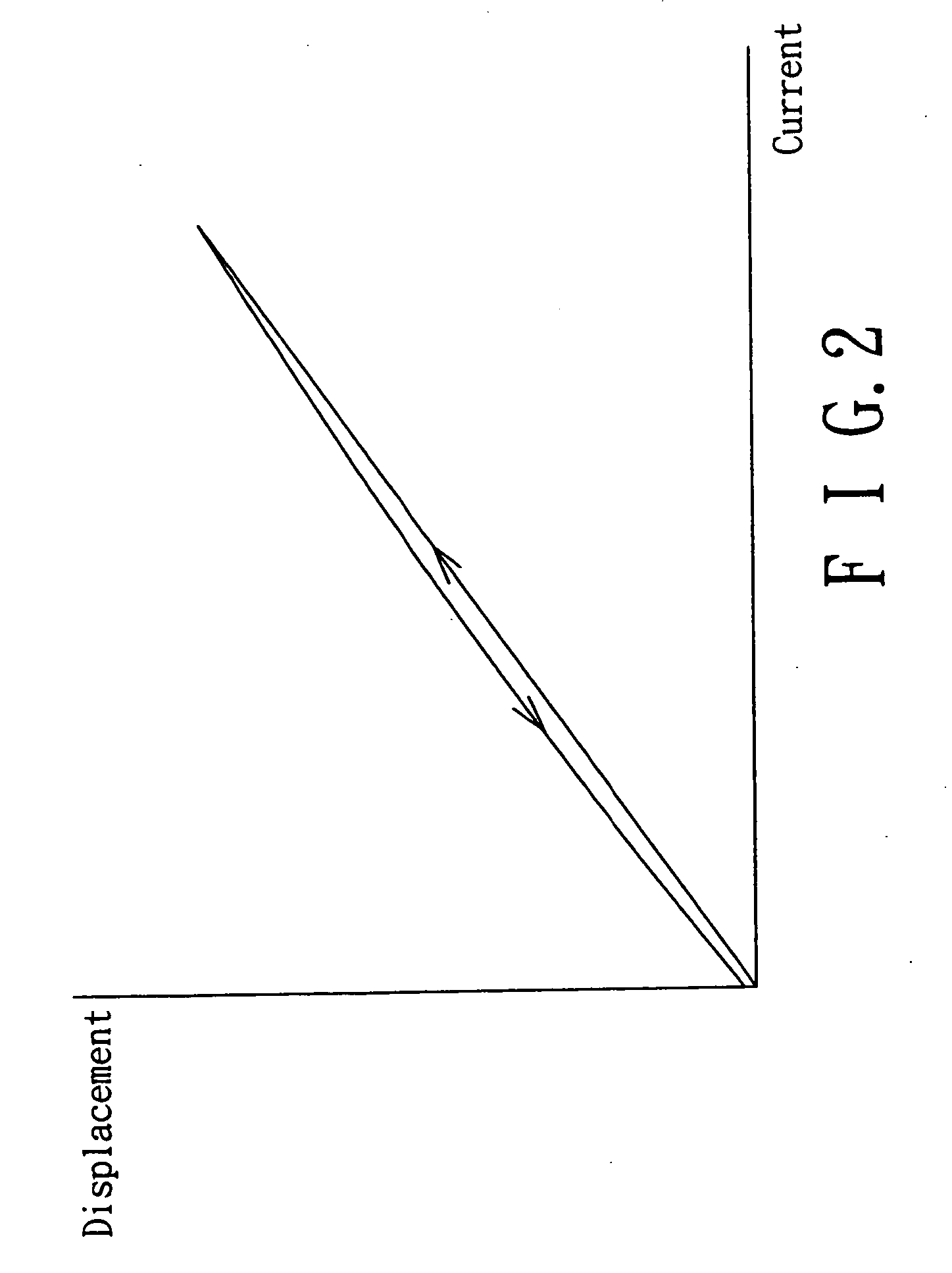
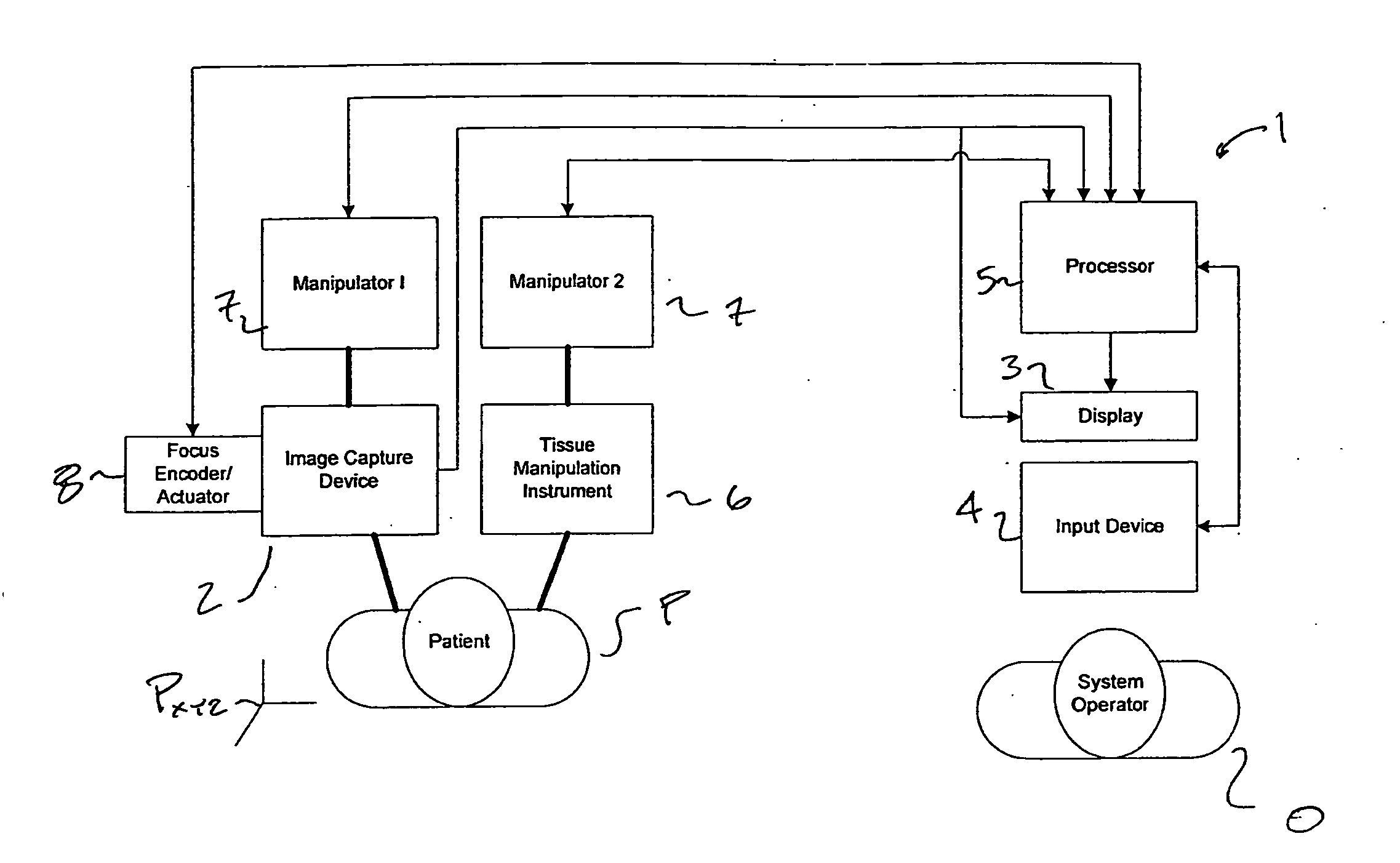
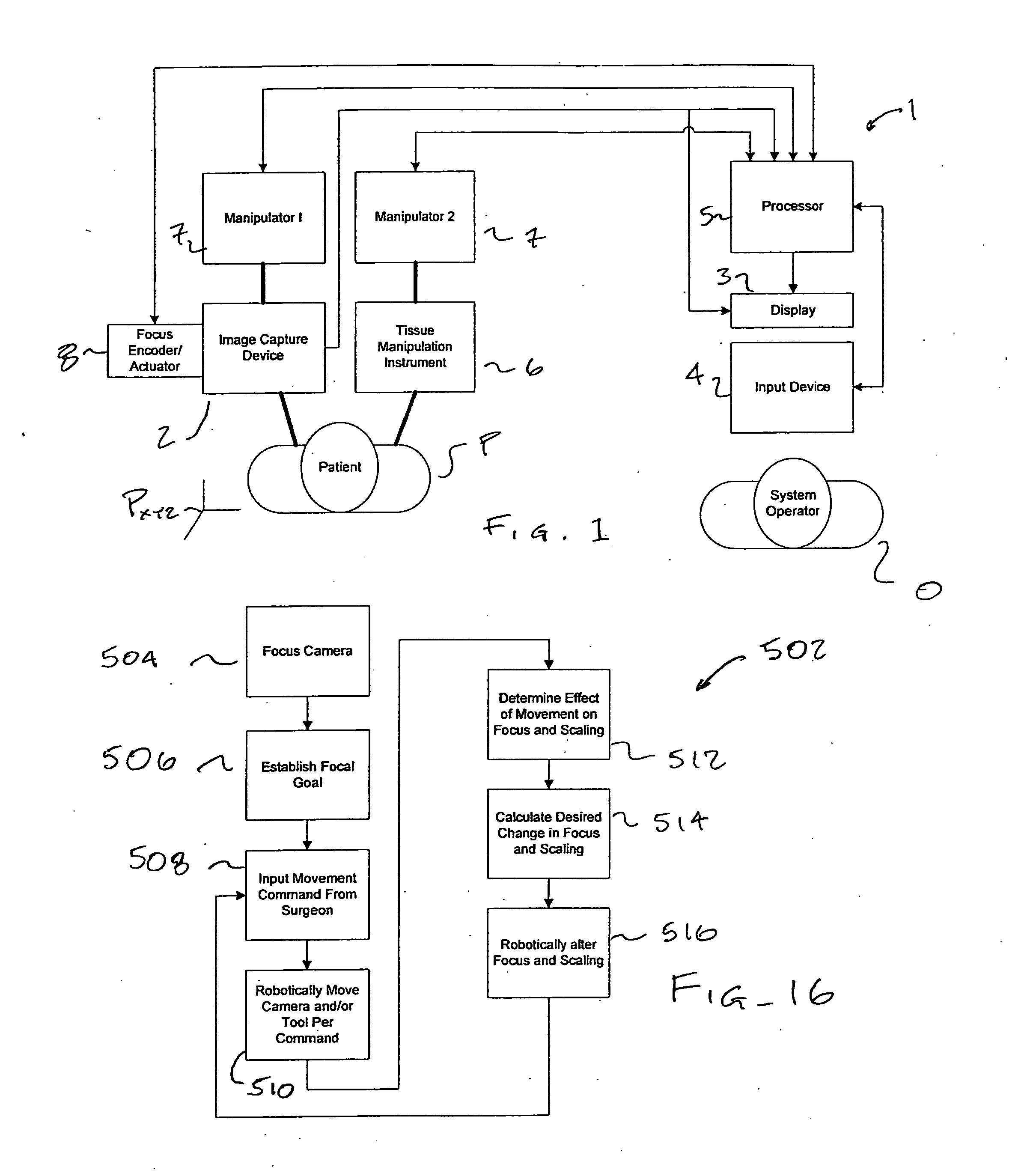
Autofocus and/or autoscaling in telesurgery
ActiveUS8079950B2Enhance perceived correlationComputer controlSimulator controlRemote surgeryComputer graphics (images)
Robotic, telerobotic, and / or telesurgical devices, systems, and methods take advantage of robotic structures and data to calculate changes in the focus of an image capture device in response to movement of the image capture device, a robotic end effector, or the like. As the size of an image of an object shown in the display device varies with changes in a separation distance between that object and the image capture device used to capture the image, a scale factor between a movement command input may be changed in response to moving an input device or a corresponding master / slave robotic movement command of the system. This may enhance the perceived correlation between the input commands and the robotic movements as they appear in the image presented to the system operator.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
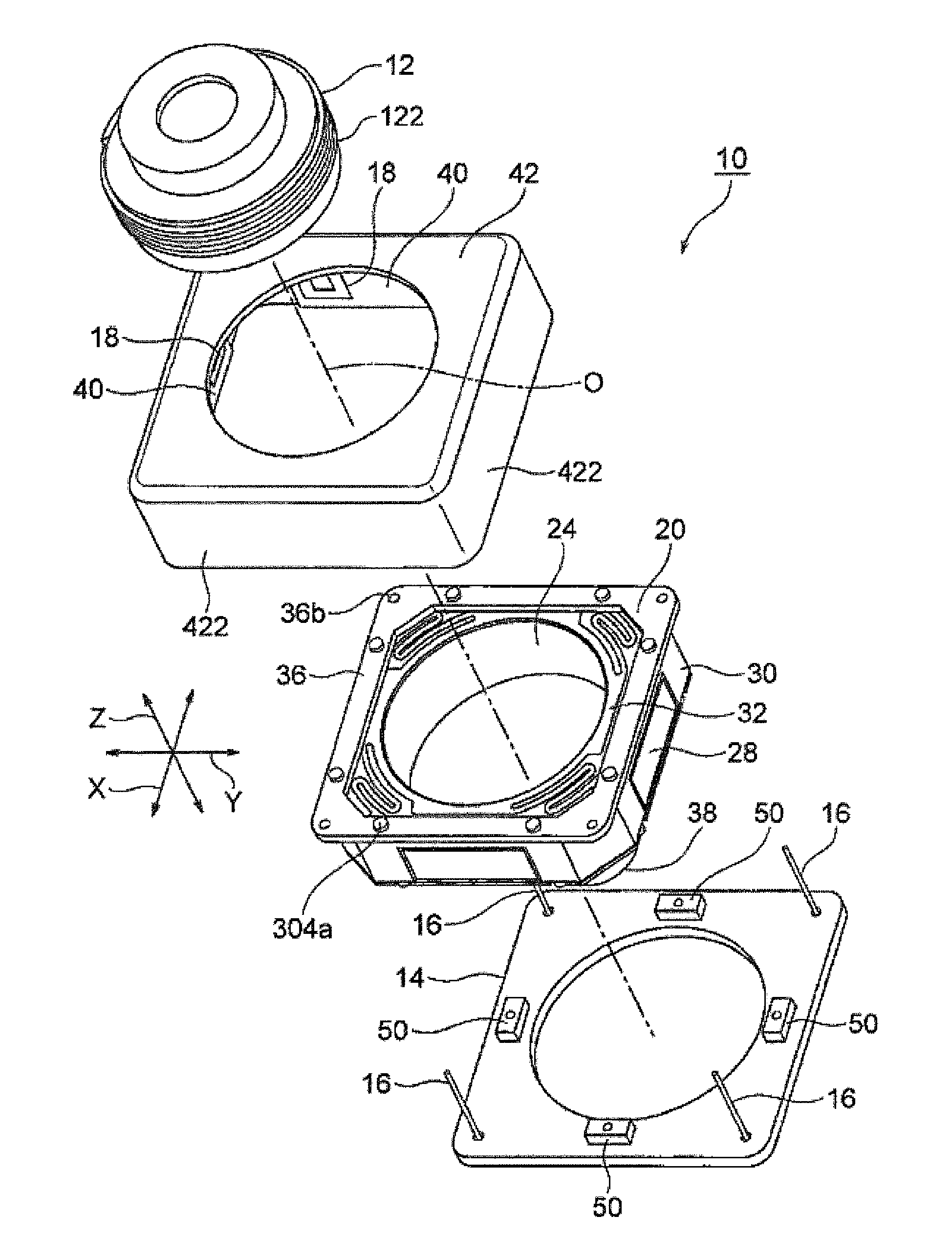
Camera-shake correction device
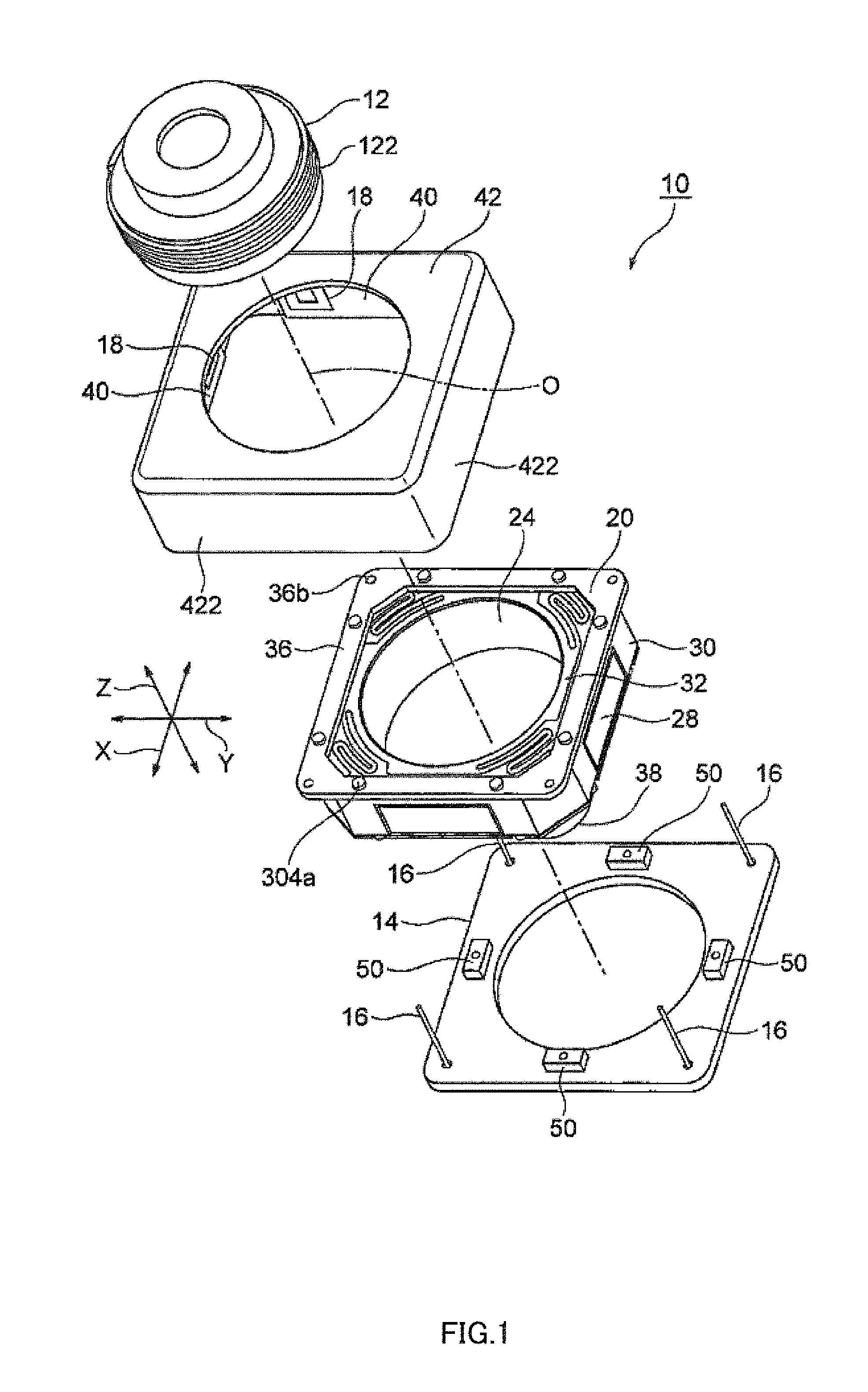
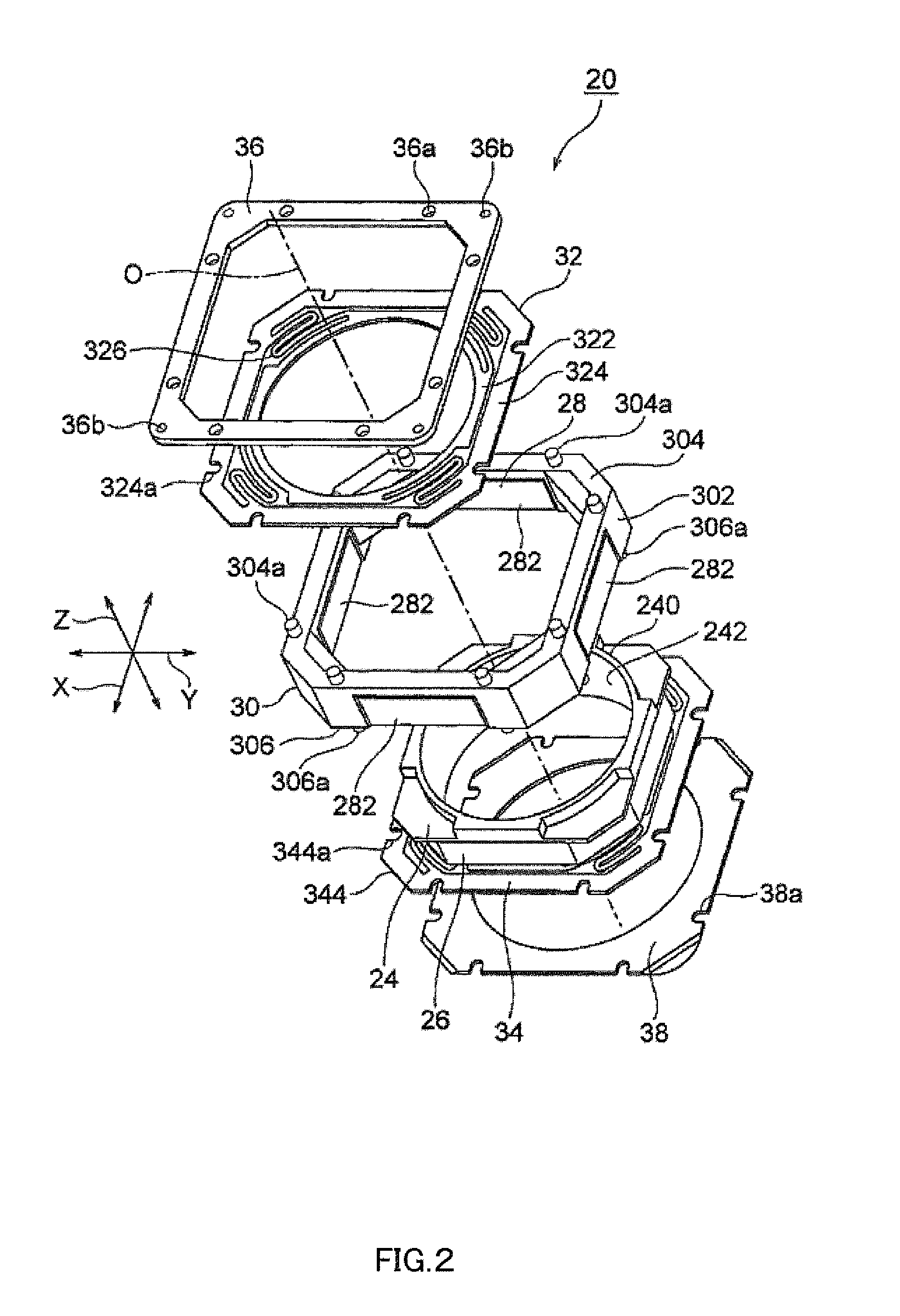
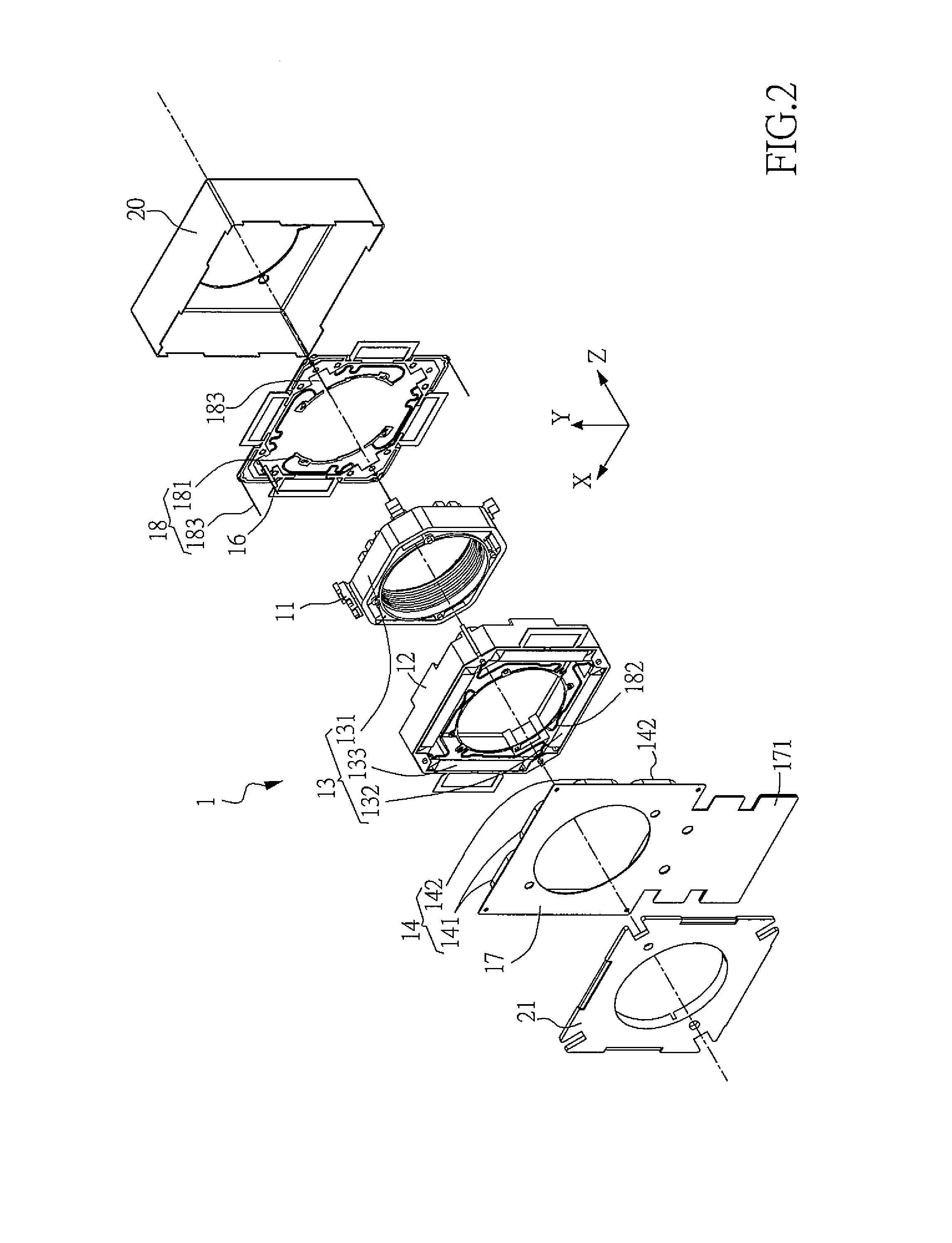
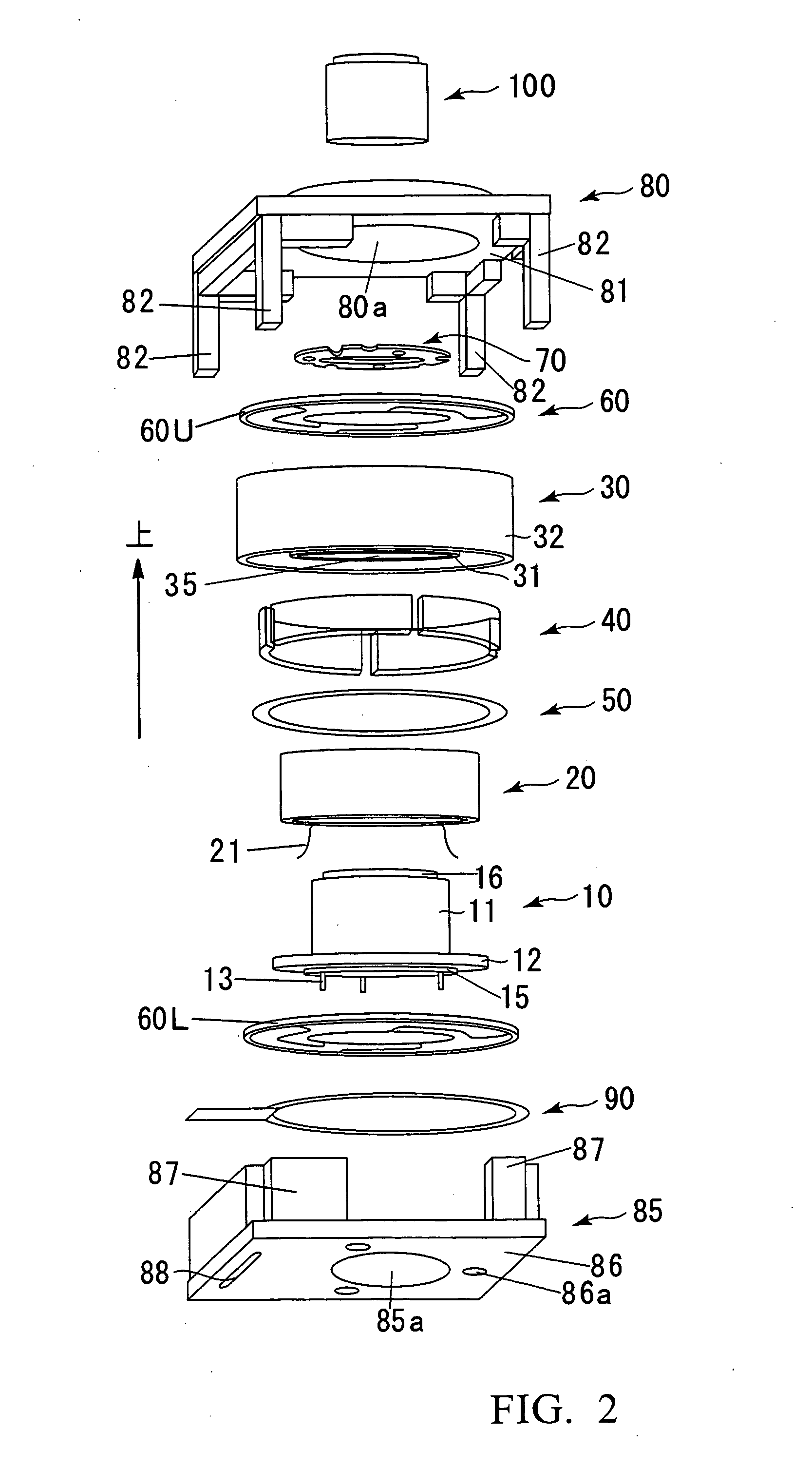
InactiveUS20120154614A1Small sizeLow profileTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisMagnet
A small size, low profile camera-shake correction device. A camera-shake correction device (10) corrects camera shake by moving the entire auto-focusing lens drive device (20) in a first direction (X) and a second direction (Y) which are perpendicular to the optical axis (O) and are perpendicular to each other, the auto-focusing lens drive device (20) being provided with a focusing coil (26) and a permanent magnet (28) which is disposed on the outside of the focusing coil. The camera-shake correction device (10) includes: a base (14) disposed so as to be spaced from the bottom surface of the auto-focusing lens drive device (20); suspension wires (16) which each have one end affixed to the outer peripheral section of the base, which extend along the optical axis (O), and which support the entire auto-focusing lens drive device (20) in such a manner that the auto-focusing lens drive device (20) is rockable in the first direction (X) and the second direction (Y); and a camera-shake correcting coil (18) disposed so as to face the permanent magnet (28).
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for use in camera and systems employing same
ActiveUS20070002159A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesControl signalImage resolution
There are many inventions described herein. Some aspects are directed to methods and / or apparatus to provide relative movement between optics, or portion(s) thereof, and sensors, or portion(s) thereof, in a digital camera. The relative movement may be in any of various directions. In some aspects, relative movement between an optics portion, or portion(s) thereof, and a sensor portion, or portion(s) thereof, are used in providing any of various features and / or in the various applications disclosed herein, including, for example, but not limited to, increasing resolution, optical and electronic zoom, image stabilization, channel alignment, channel-channel alignment, image alignment, lens alignment, masking, image discrimination, range finding, 3D imaging, auto focus, mechanical shutter, mechanical iris, multi and hyperspectral imaging, and / or combinations thereof. In some aspects, movement is provided by actuators, for example, but not limited to MEMS actuators, and by applying appropriate control signal thereto.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
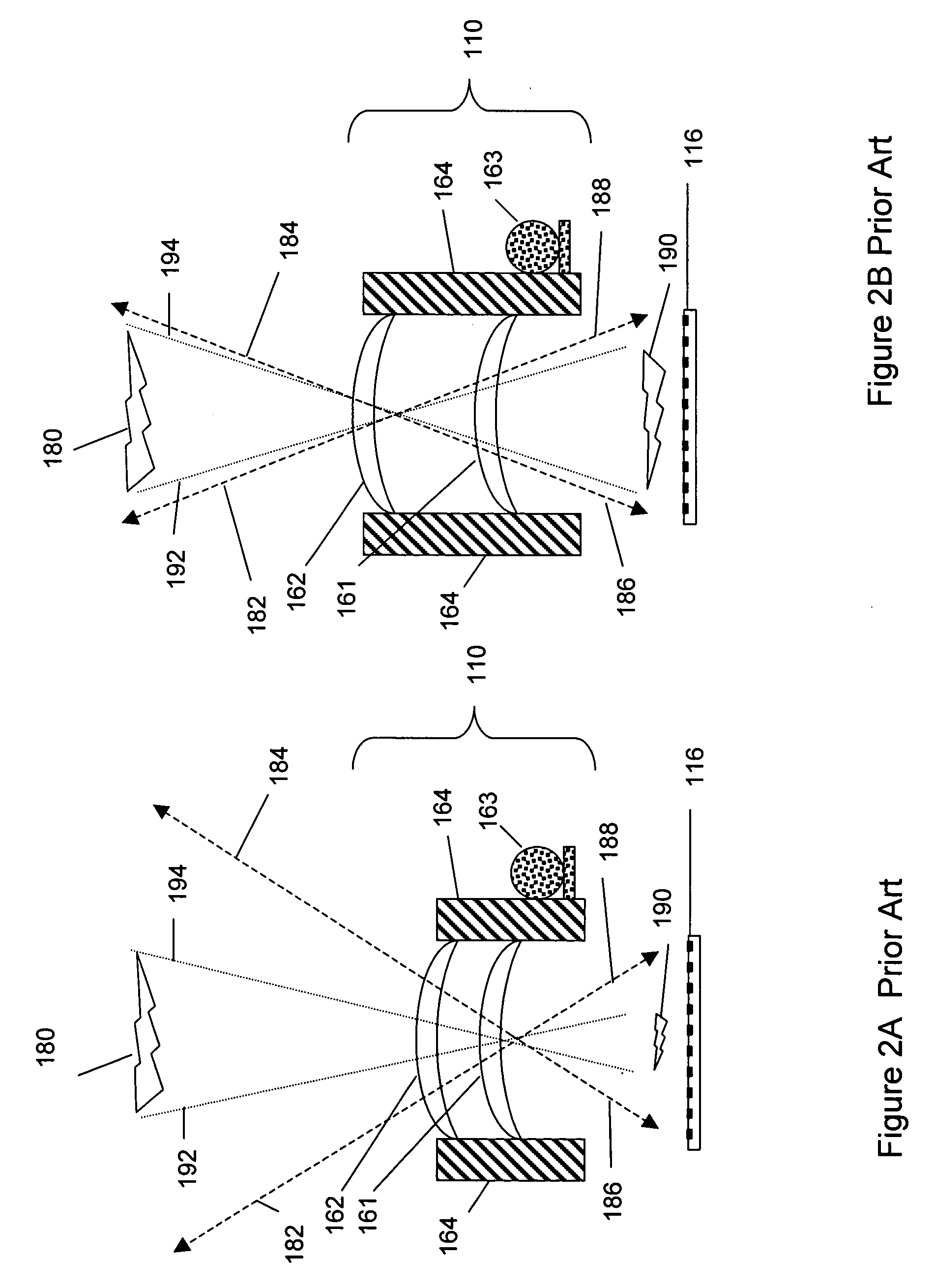
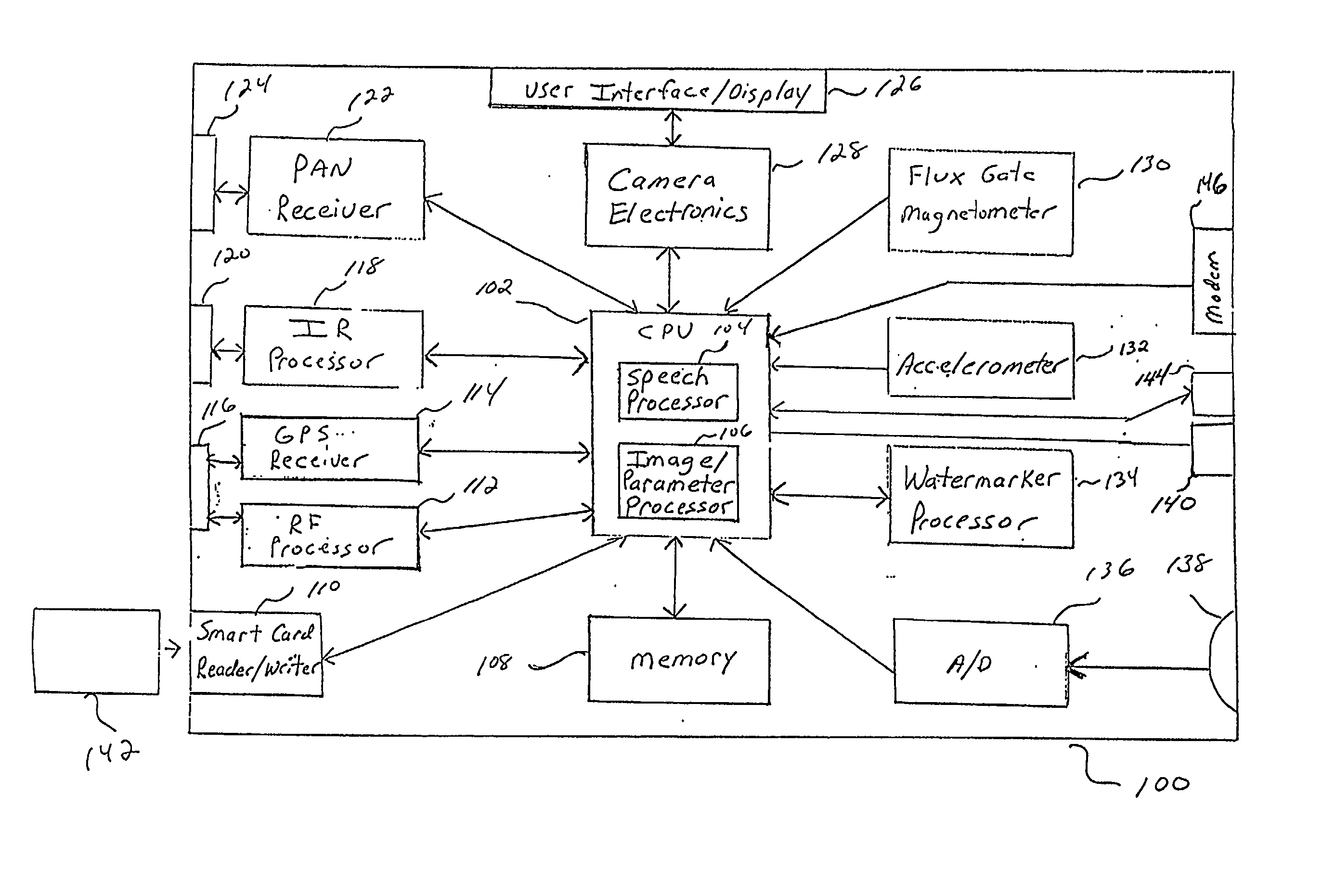
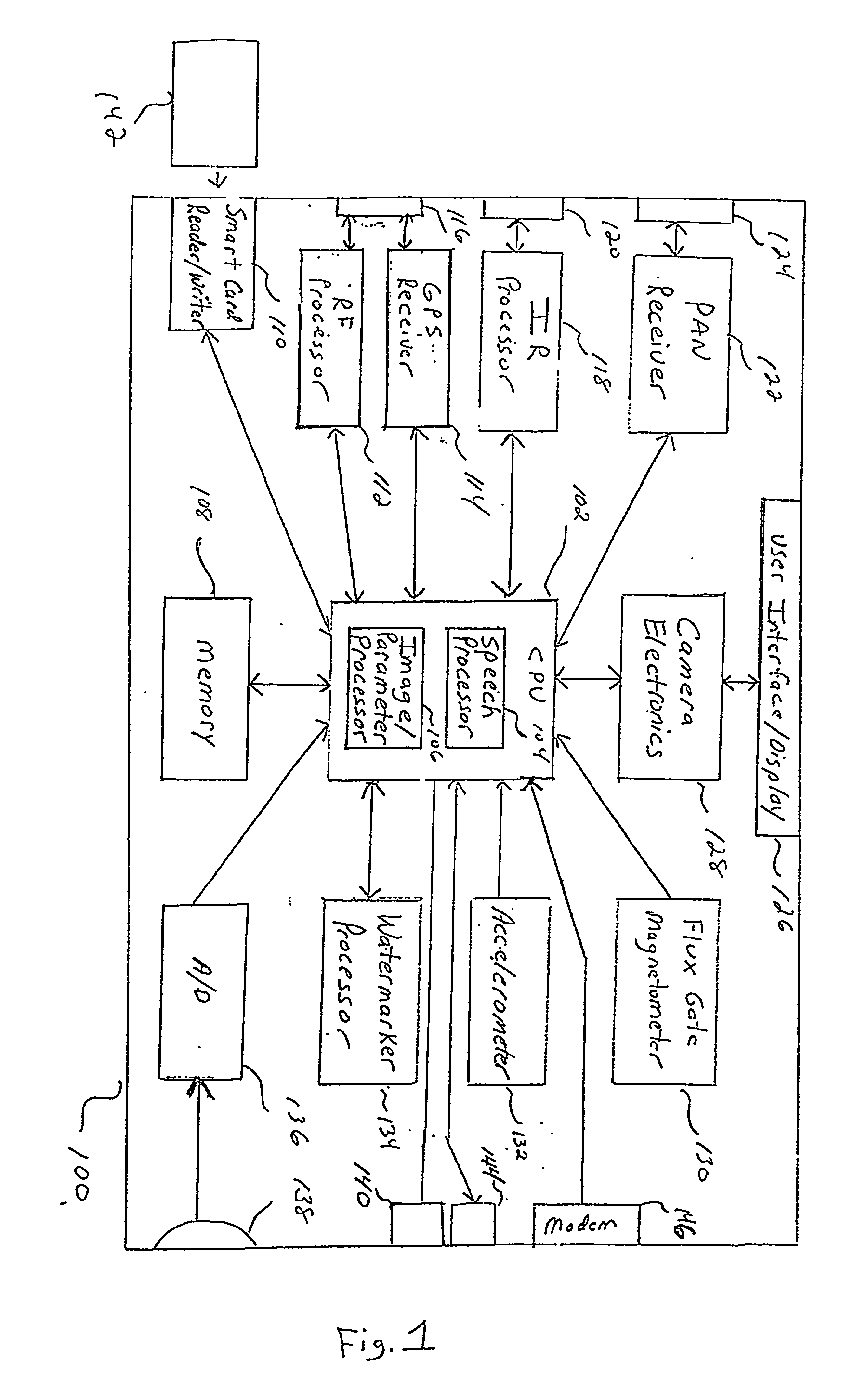
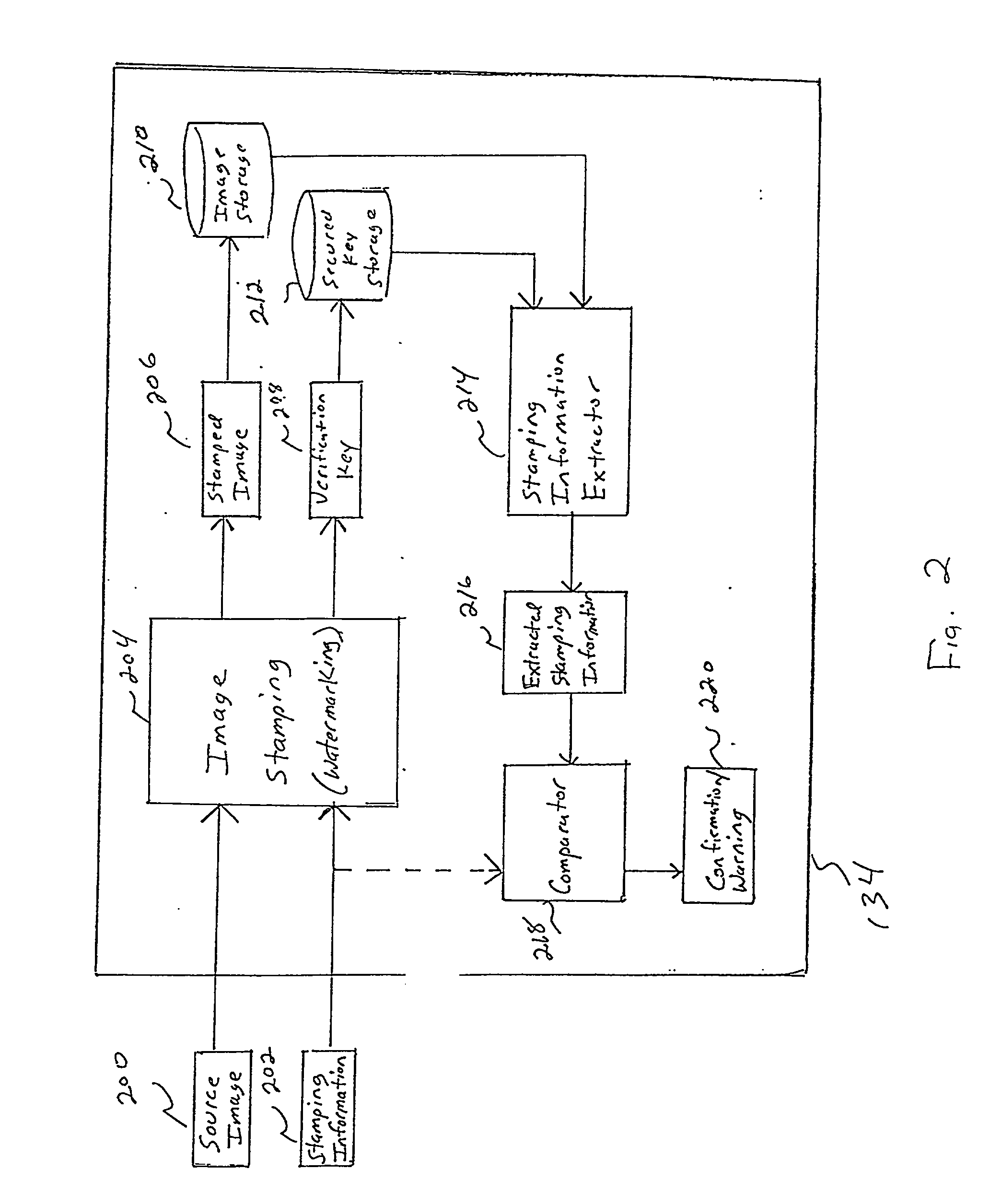
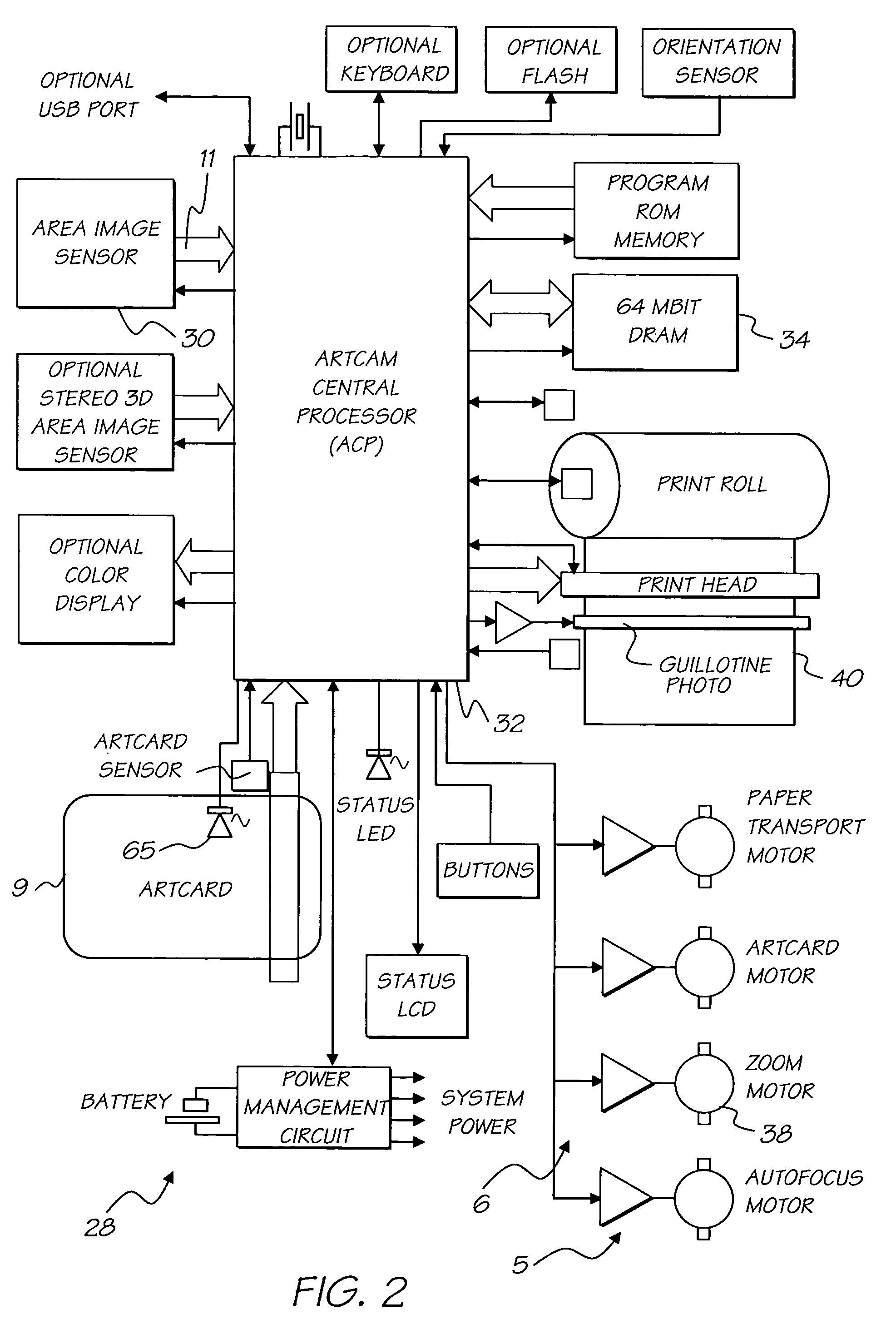
Image capturing system and method for automatically watermarking recorded parameters for providing digital image verification
An image capturing system and method for automatically watermarking a plurality of recorded camera and image parameters such as the location (latitude, longitude and altitude), orientation of the principal axis of the camera, whether the camera is in landscape mode or portrait mode, camera velocity, photographer information, time and date, zoom factor, shutter speed, flash on / off, autofocus distance, lightmeter reading, focal length and aperture into every captured image. This watermarked data can be subsequently extracted and compared with the originally recorded data so as to verify the authenticity of a corresponding image. Since the critical data is invisibly watermarked into the image, it is difficult to modify the image without affecting the watermarked data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Depth information for auto focus using two pictures and two-dimensional gaussian scale space theory
InactiveUS20070036427A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree-dimensional spaceAutofocus
An imaging acquisition system that generates a depth map from two pictures of a three dimensional spatial scene is described. According to one aspect of the invention, the system generates the depth map based on the relative blur between the two pictures and the absolute blur contributed by the system. According to another aspect of the invention, the system calculates the depth map directly from the relative blur between the two pictures.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
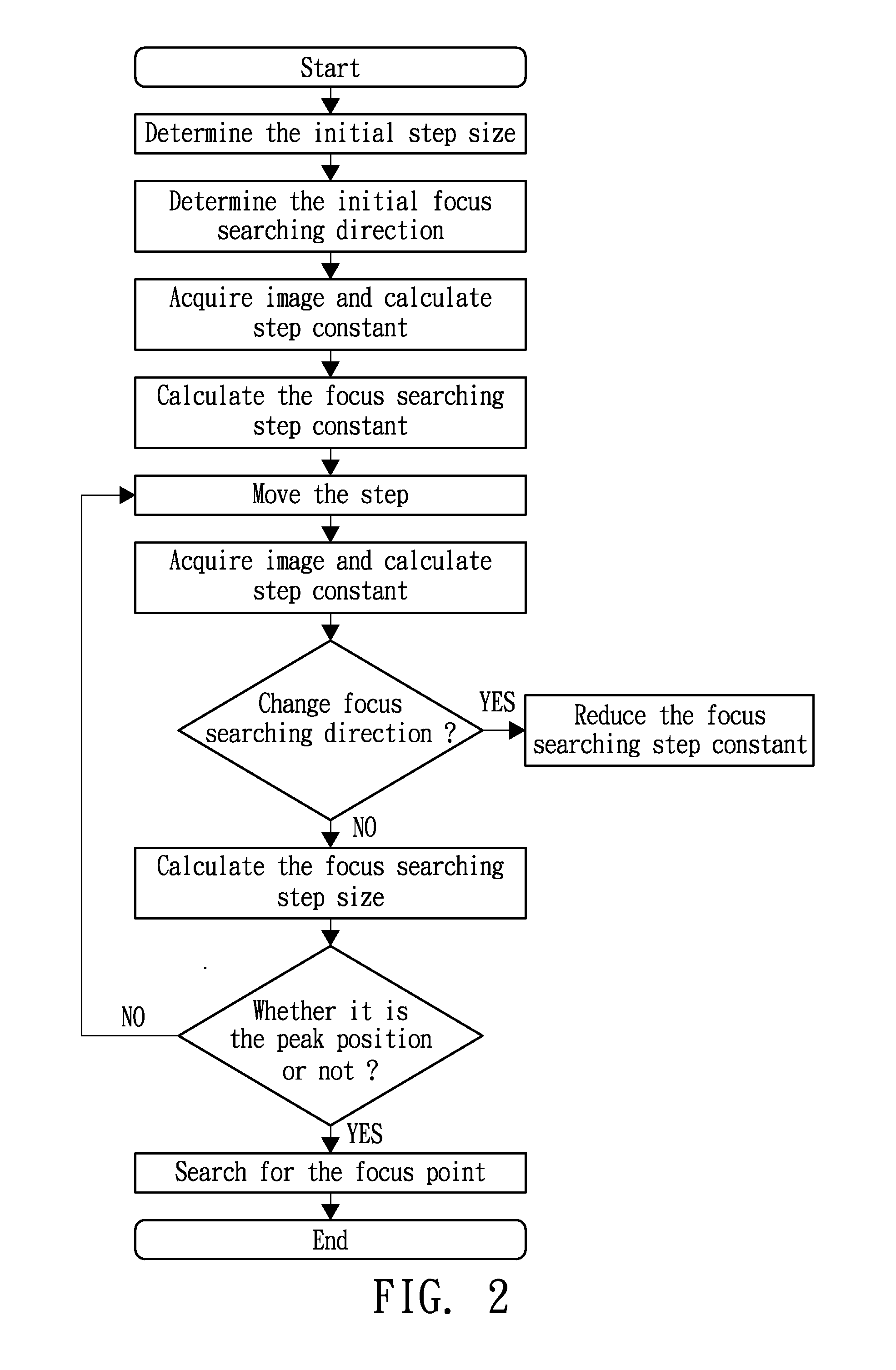
Autofocus searching method
An autofocus searching method includes the following procedures. First, focus values of images, which are acquired during the movement of the object lens, are calculated, in which the focus value includes at least the intensity value of the image derived from the intensities of the pixels of the image. Next, focus searching is based on a first focus-searching step constant and a first focus-searching direction, in which the first focus-searching step constant is a function, e.g., the multiplication, of the focus value and a focus-searching step. If the focus searching position moves across a peak of the focus values, it is then amended to be based on a second focus-searching direction and a second focus-searching step constant, in which the second focus-searching step constant is smaller than the first focus-searching step constant, and the second focus-searching direction is opposite to the first focus-searching direction.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
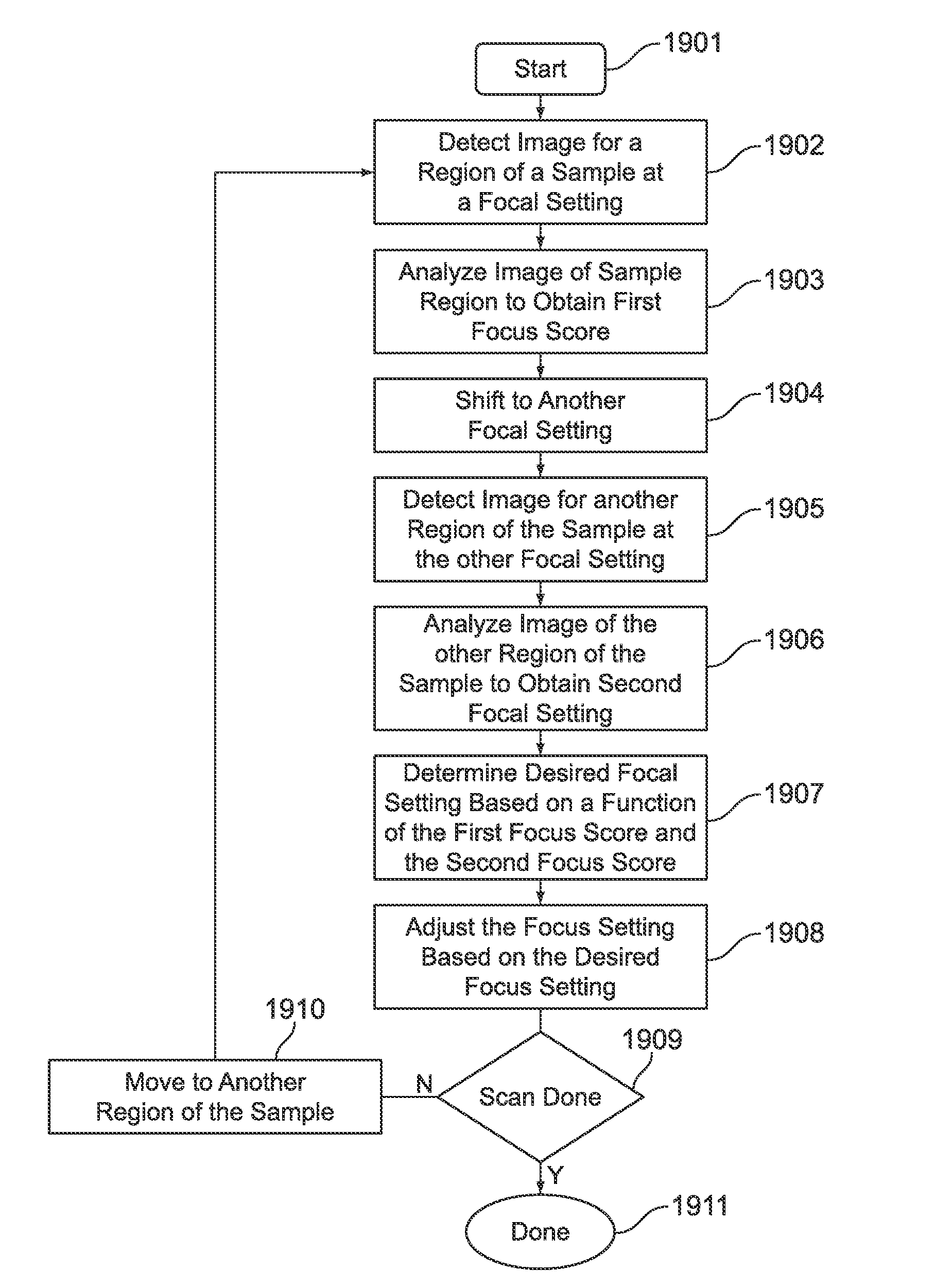
Dynamic autofocus method and system for assay imager
InactiveUS20100157086A1Television system detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayAssociate degree
A method and system are provided for controlling focus dynamically of a sample imager. The method comprises scanning a sample with an optical assembly that apportions the sample into regions based on a scan pattern. The optical assembly has a focal setting with respect to the sample. The method further comprises shifting the focal setting of the optical assembly during scanning of the sample, and detecting one or more images representative of one of the regions from the sample. The one or more images have associated degrees of focus corresponding to the focal setting of the optical assembly. The method analyzes the image(s) to obtain a focus score or scores corresponding thereto, where the focus scores represent a degree to which the optical assembly was in focus when detecting the images. The method adjusts the focus setting based on the focus score(s).
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Simple method for calculating camera defocus from an image scene
ActiveUS20070216765A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementThree-dimensional spaceAutofocus
An imaging acquisition system that generates a picture depth from an auto focus curve generated from picture of a three dimensional spatial scene is described. The auto focus curve comprises a step edge. The system generates the depth based on the step edge and a reference auto focus normalization curve.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
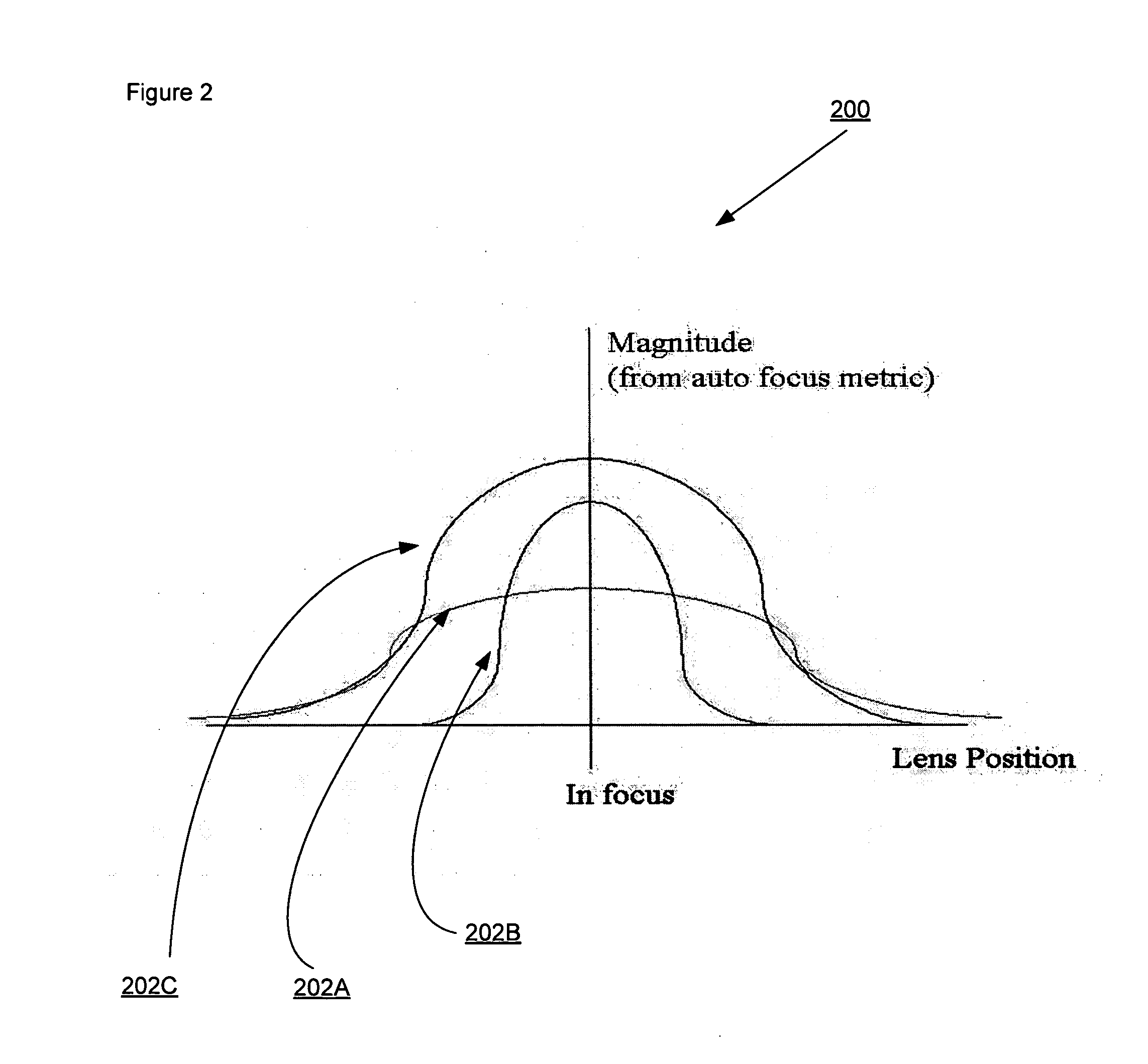
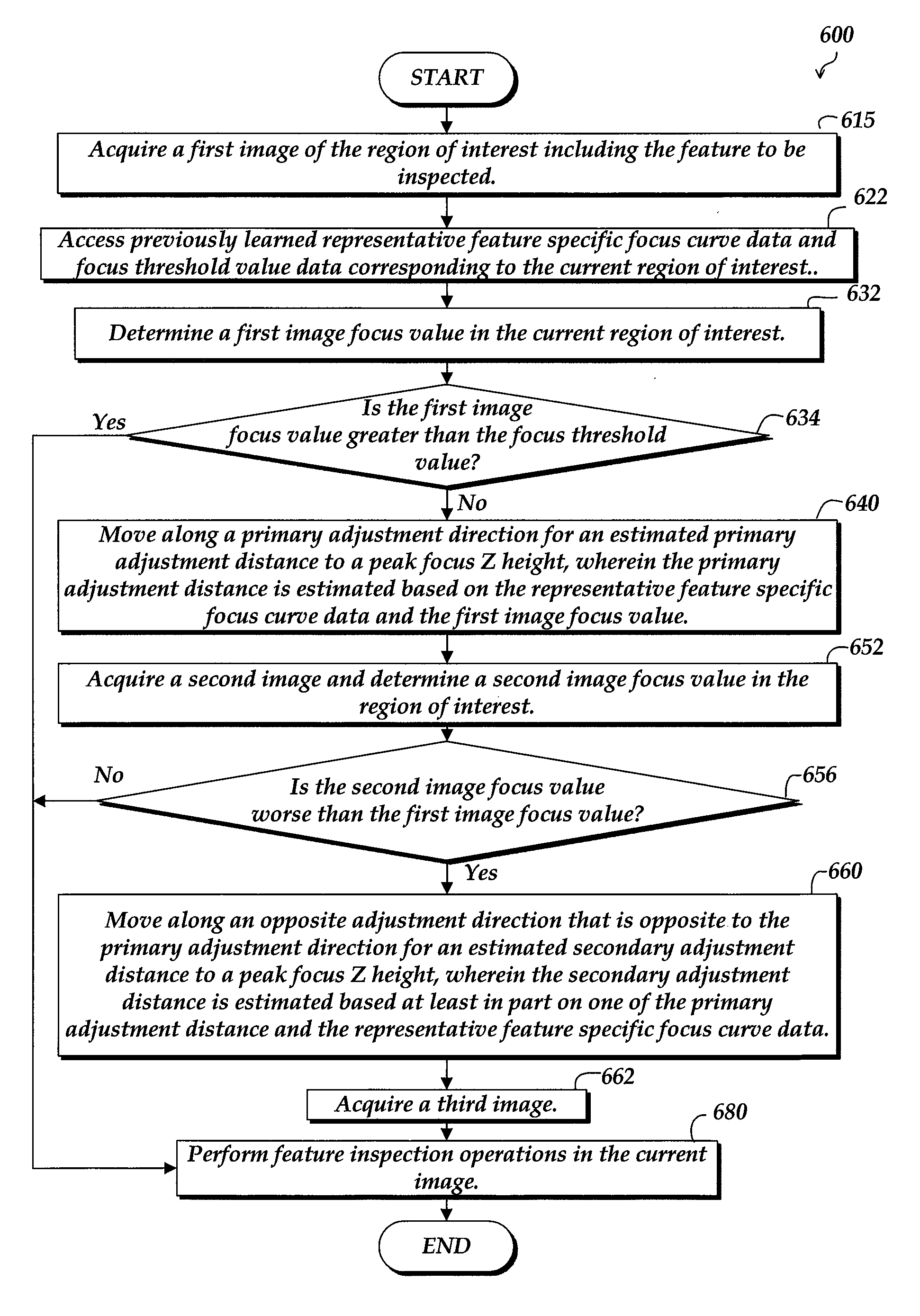
System and method for fast approximate focus
ActiveUS8111938B2Improve throughputQuick focusTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Engineering
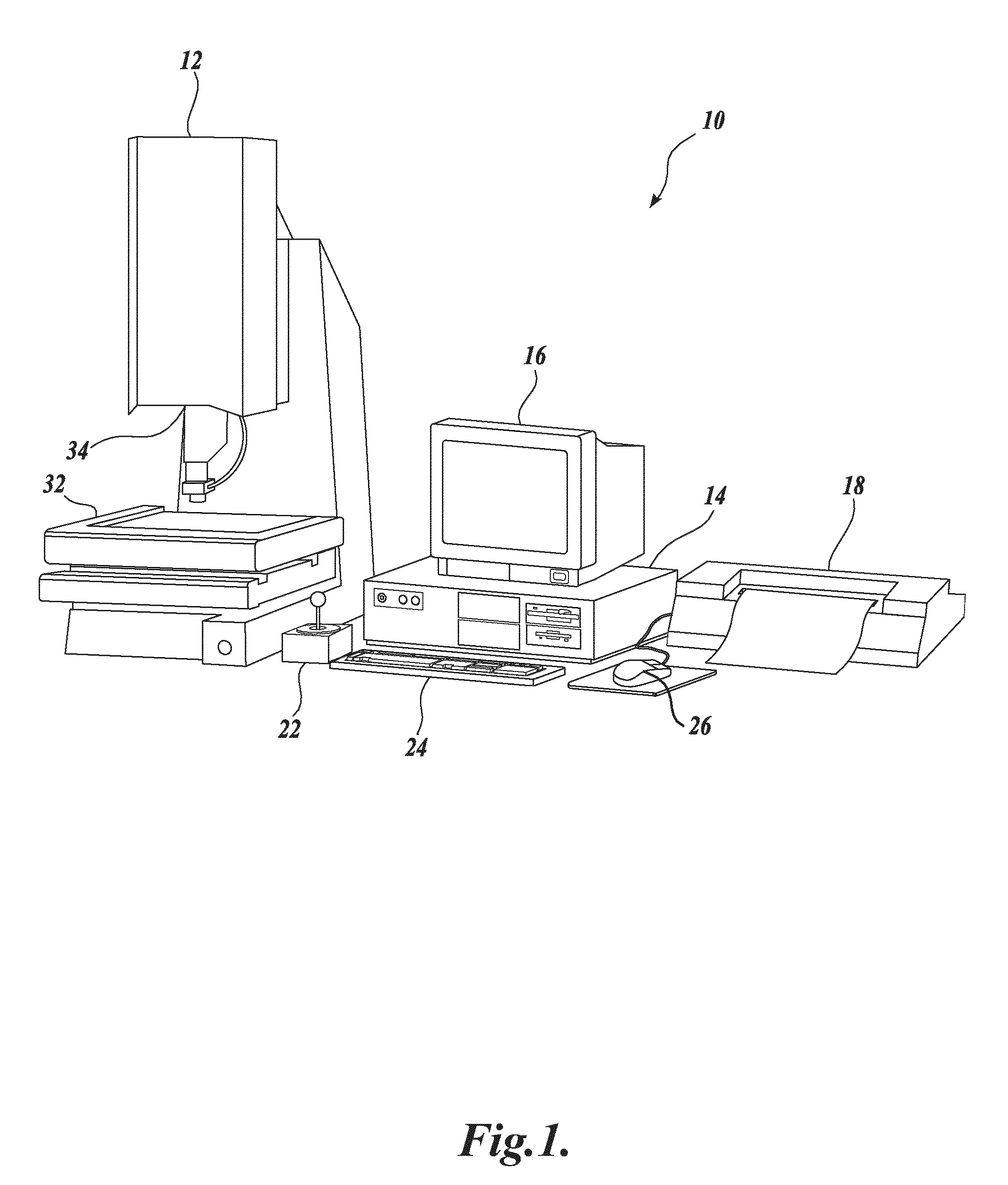
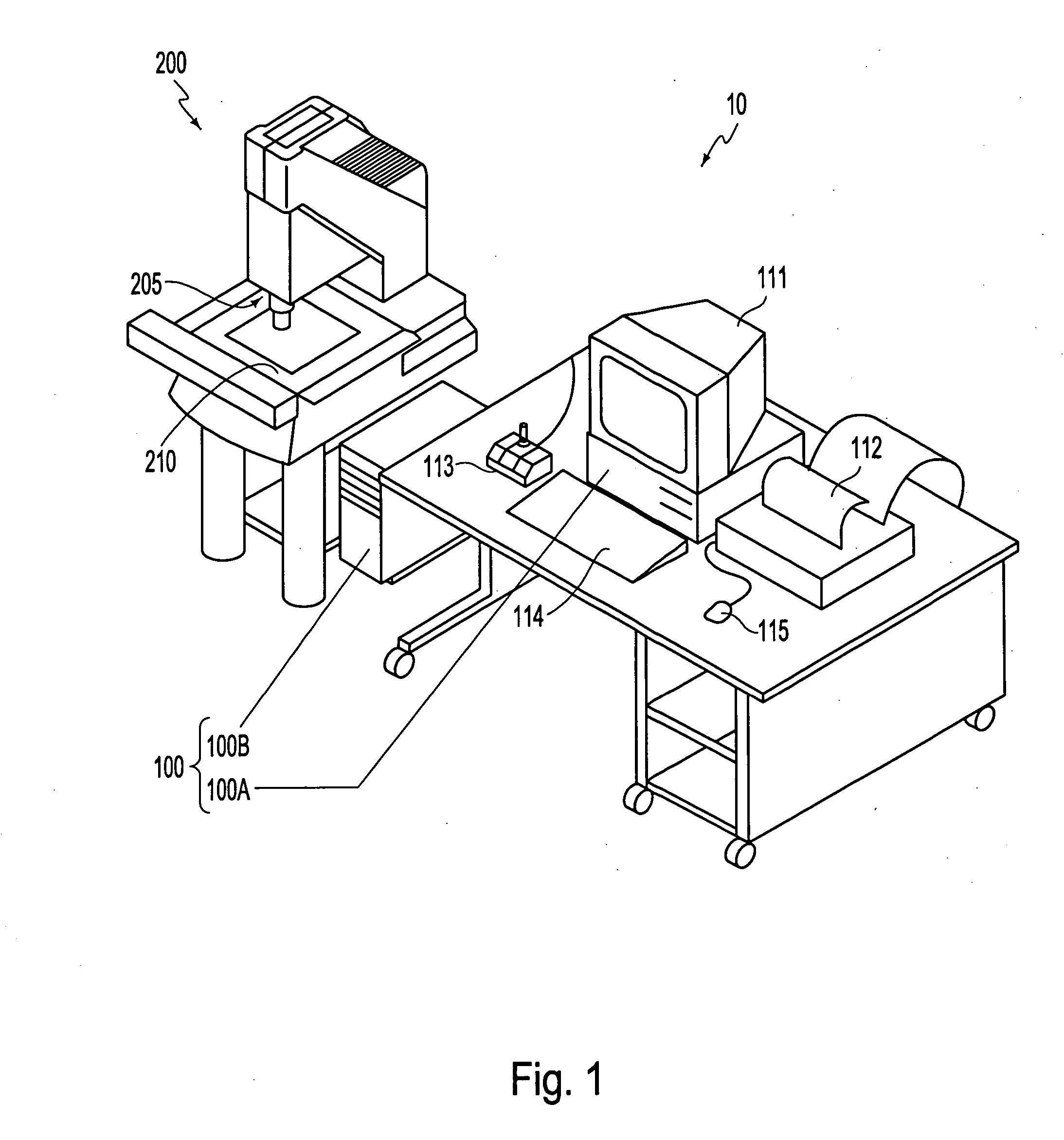
Fast approximate focus operations providing an approximately focused image that is sufficiently focused to support certain subsequent inspection operations. The operations are particularly advantageous when used to provide images for successive inspection operations that predominate when inspecting planar workpieces. Improved inspection throughput is provided because, in contrast to conventional autofocus operations, the fast approximate focus operations do not acquire an image stack during a run mode as a basis for determining a best focused image. Rather, during learn mode, a representative feature-specific focus curve and a focus threshold value are determined and used during run mode to provide an approximately focused image that reliably supports certain inspection operations. In one embodiment, an acceptable approximately focused inspection image is provided within a limit of two focus adjustment moves that provide two corresponding images. The adjustment moves are based on the representative feature-specific focus curve provided in learn mode.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Autofocusing eyewear, especially for presbyopia correction
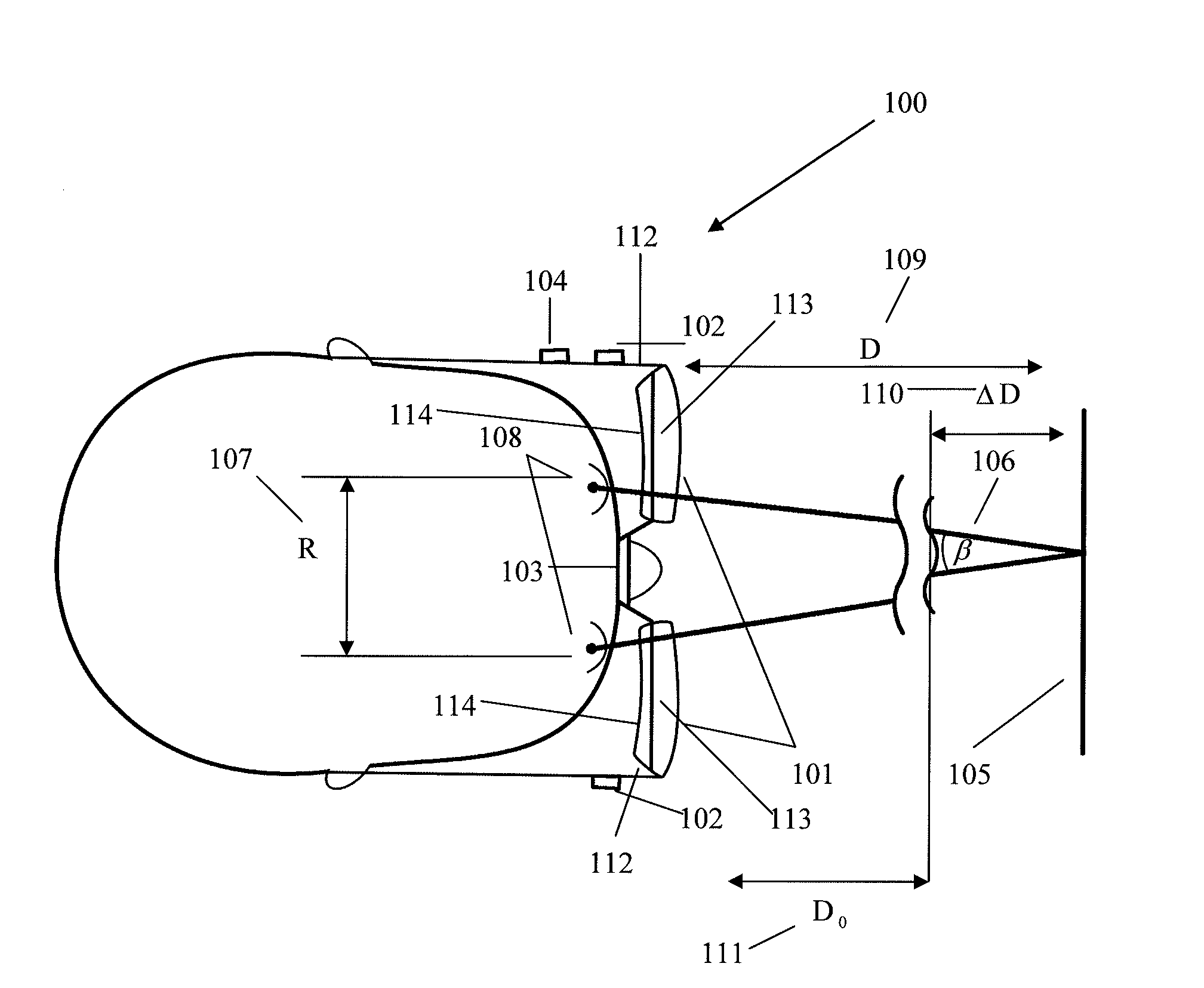
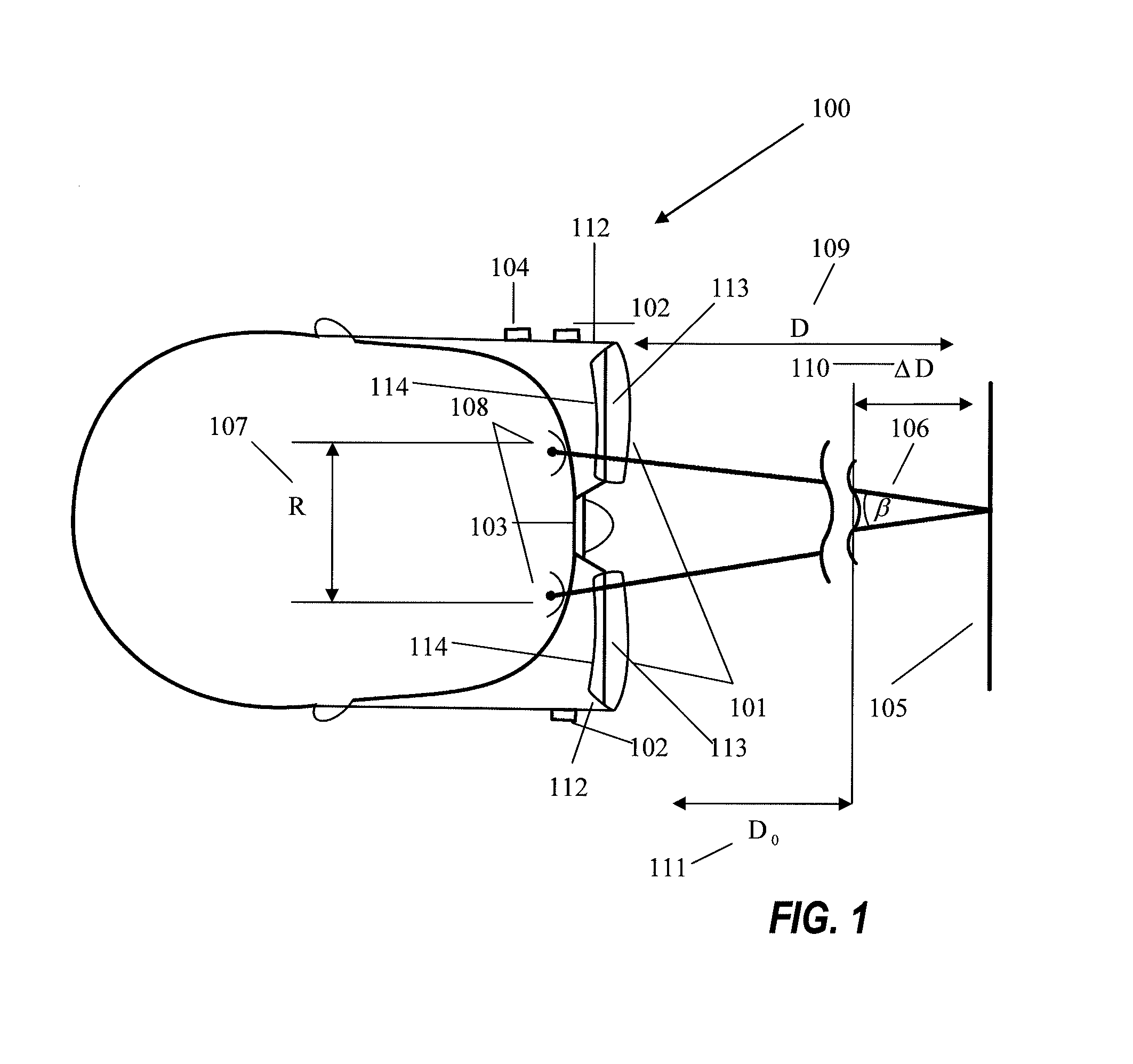
A pair of eyewear has transparent waveguides in each eyewear lens. An illumination subsystem directs a beam of light through the waveguides onto a wearer's eyes. A First Purkinje point imaging subsystem for each lens uses light reflected from the eyes through the waveguides. A controller calculates from the positions of the First Purkinje points the wearer's gaze parallax angle and / or the distance to an object of interest on which the gaze of the wearer's eyes converges. The output of the controller may drive variable-focus eyeglass lenses to enable a presbyopic wearer to focus on the object. Modified Alvarez variable-focus lenses are described.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
Autofocus video tool and method for precise dimensional inspection
ActiveUS8111905B2Reliable and robust determinationProvide accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Radiology
A refined autofocus method provides optimized lighting between iterative autofocus operations, to reliably provide the best possible autofocus Z-height precision. The method includes a quantitative initial focus Z-height determination based on initial focus curve data from initial autofocus images acquired using initial light control parameters. Then, the camera is set at that initial focus Z-height such that well focused images are provided. Refined (optimized) light control parameters are then determined based on at least one respective image acquired using respective light control parameters at that Z-height, such that an image acquired using the refined light control parameters provides a near-optimum value for a contrast-related metric (e.g., a focus metric) at that Z-height. Then, refined autofocus images are acquired using the refined light control parameters and a refined precise Z-height is quantitatively determined base on the resulting focus curve.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
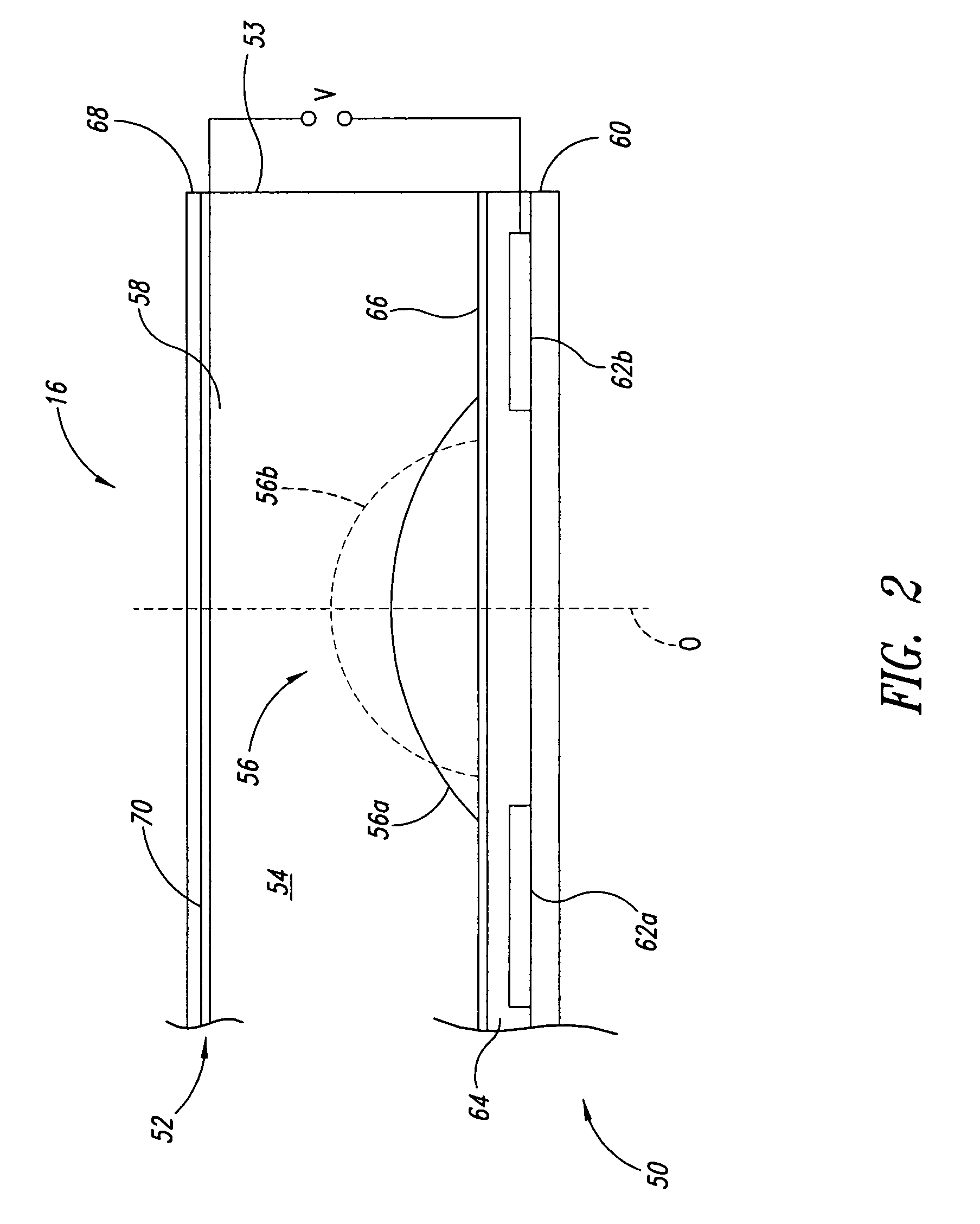
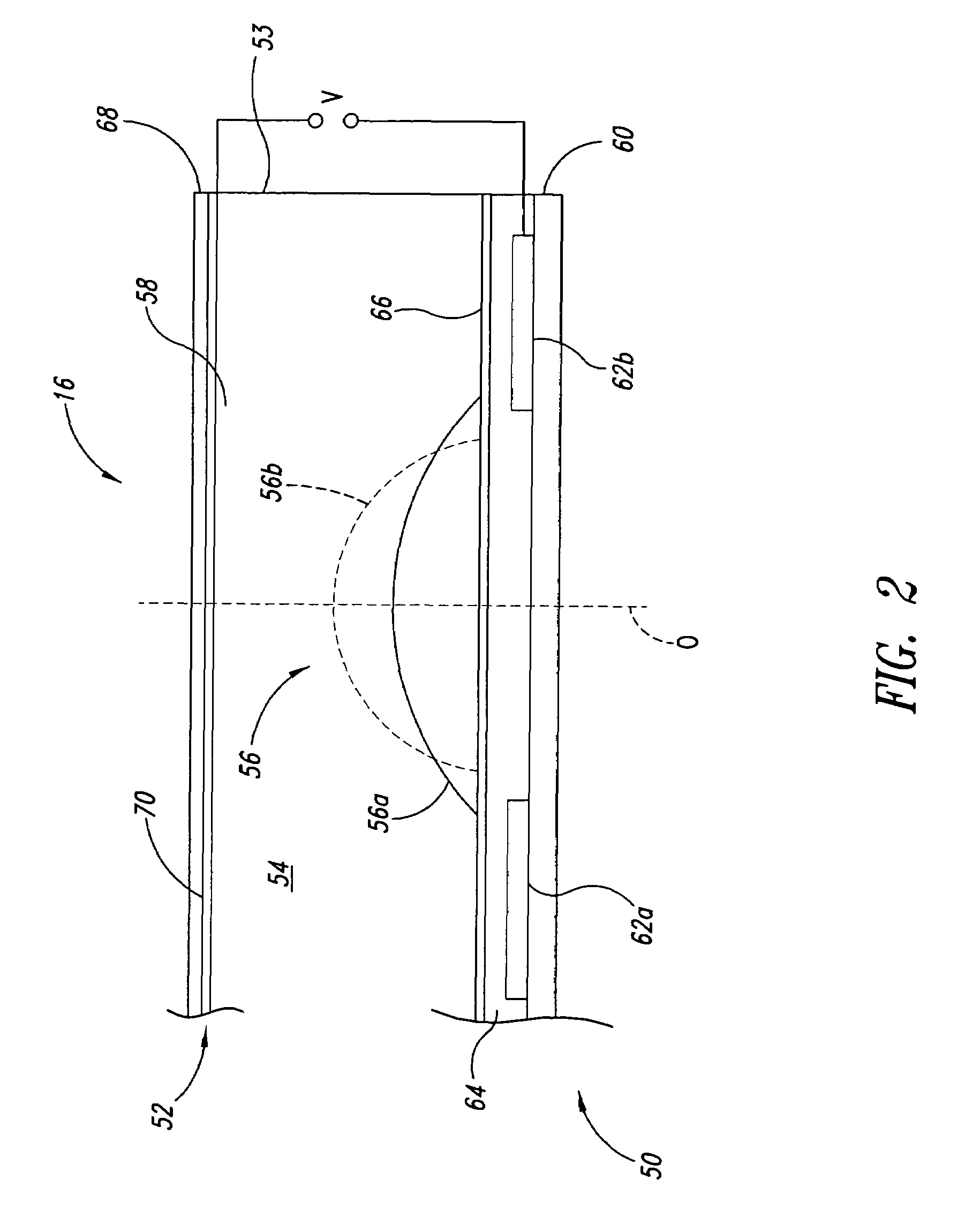
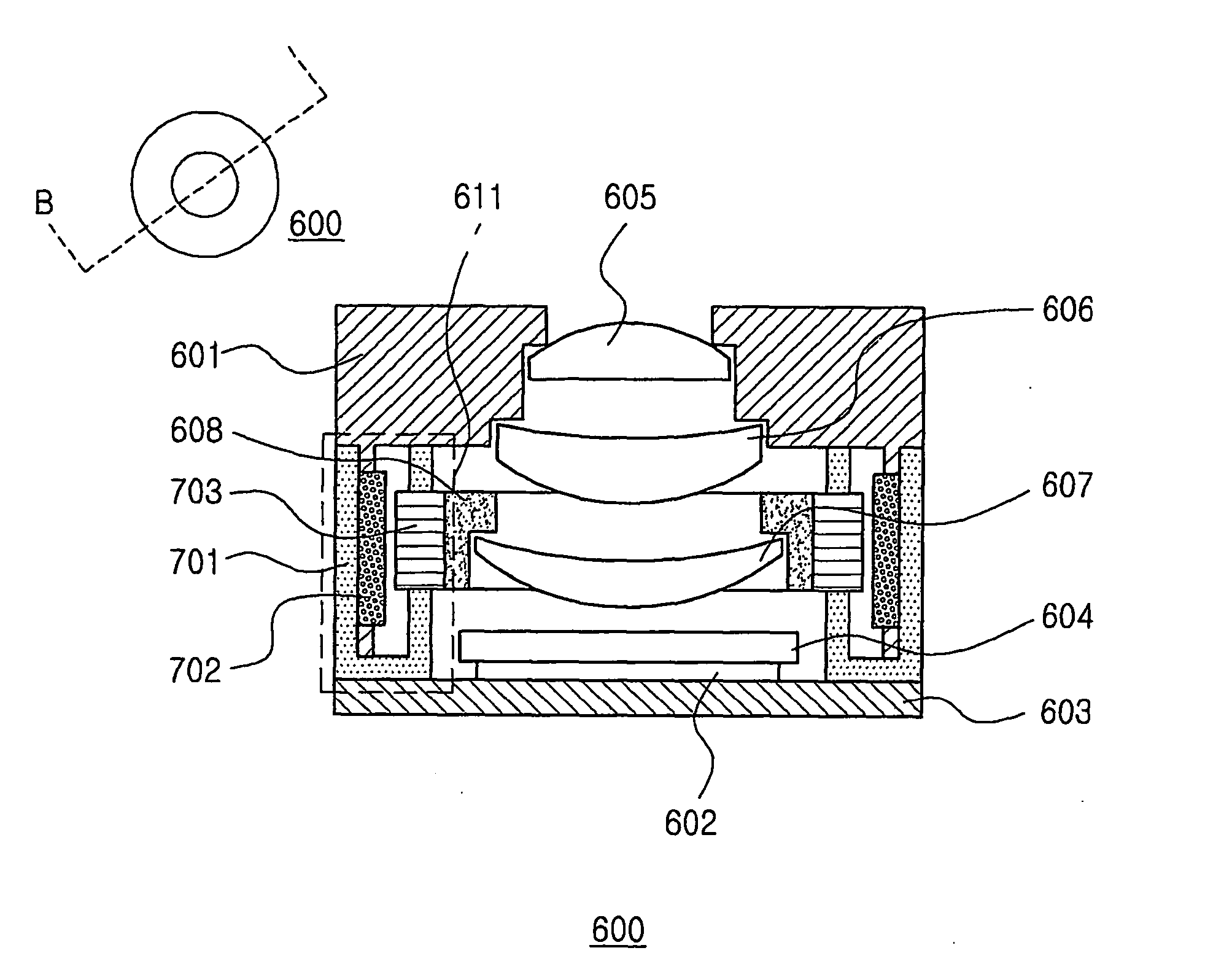
Tri-Axis Close Loop Feedback Controlling Module for Electromagnetic Lens Driving Device
The tri-axis close-loop feedback controlling module for electromagnetic lens driving device comprises a 6-pin Hall element. Two pins of the Hall element are coupled to an auto-focus module for providing a current to drive the auto-focus module to conduct auto-focusing operations along the Z-axis; while other four pins of the Hall element are coupled to a control unit. The control unit detects the X-Y axial positions of the auto-focus module relative to an OIS module and generates a control signal which is then sent to the Hall element. Therefore, the Hall element not only can provide its own feedback controlling function according to the Z-axial position of lens, but also can drive the auto-focus module based on the control signal corresponding to the X-Y axial positions of the auto-focus module, so as to achieve the goal of tri-axis close-loop feedback controlling for the electromagnetic lens driving device.
Owner:TDK TAIWAN
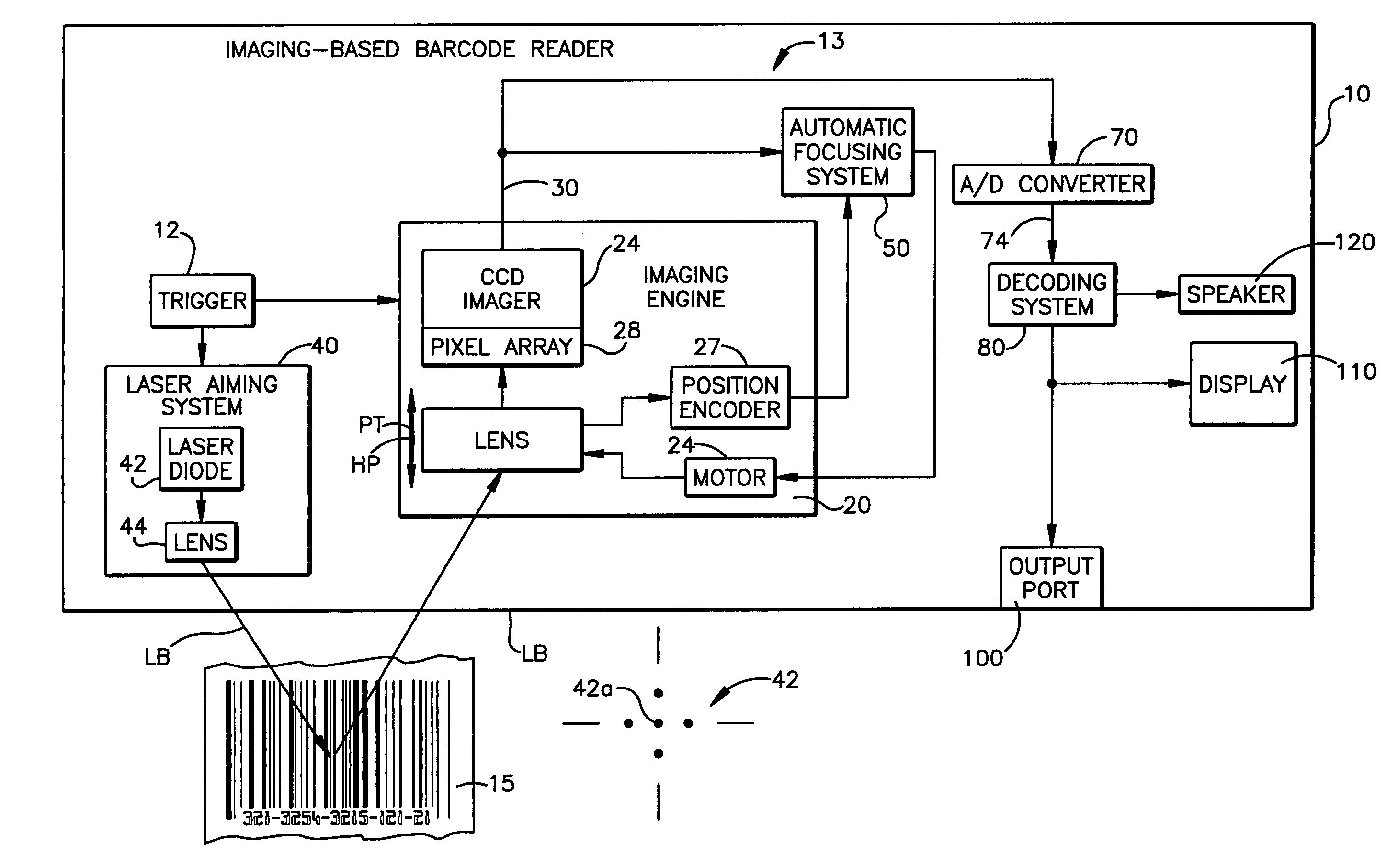
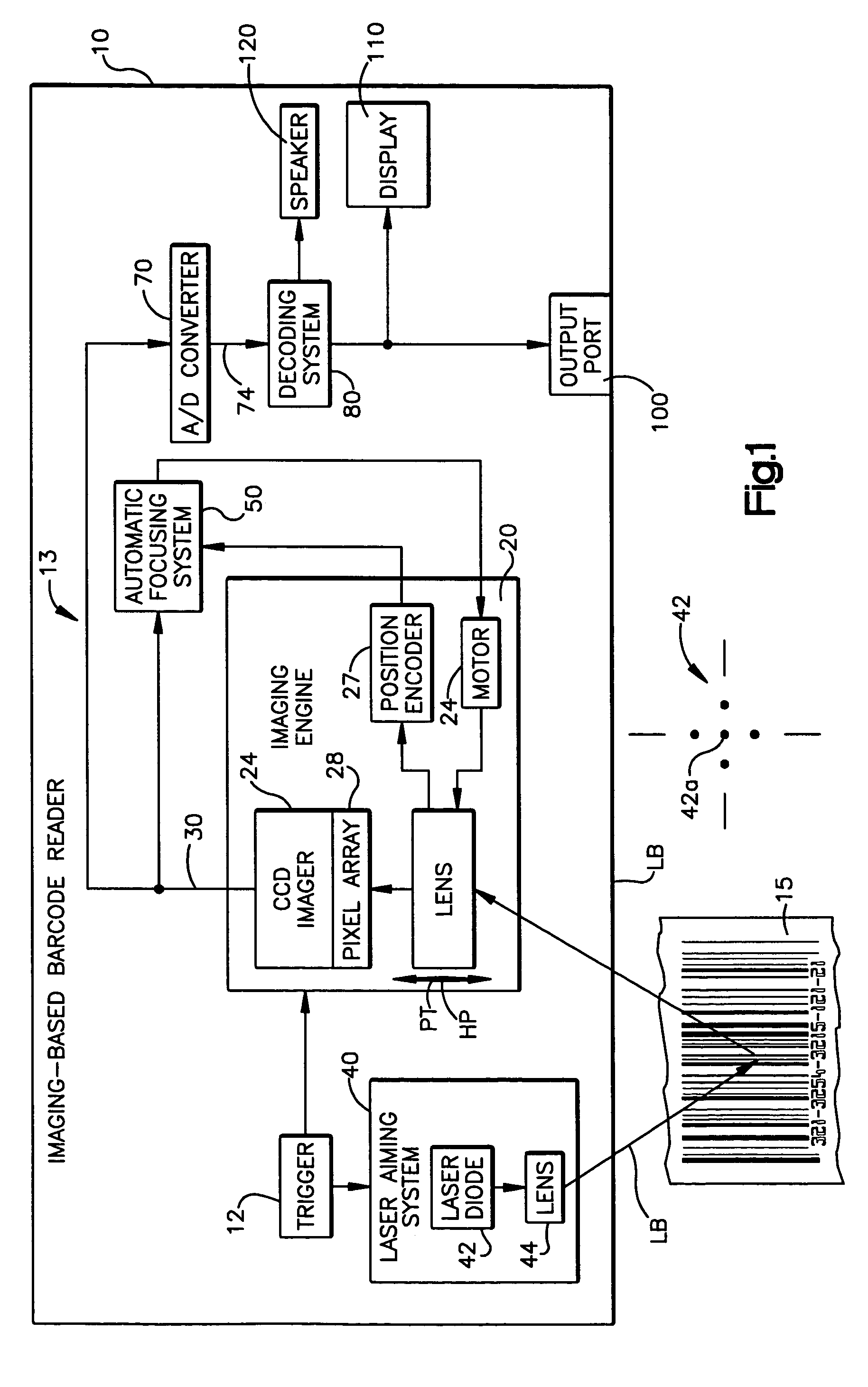
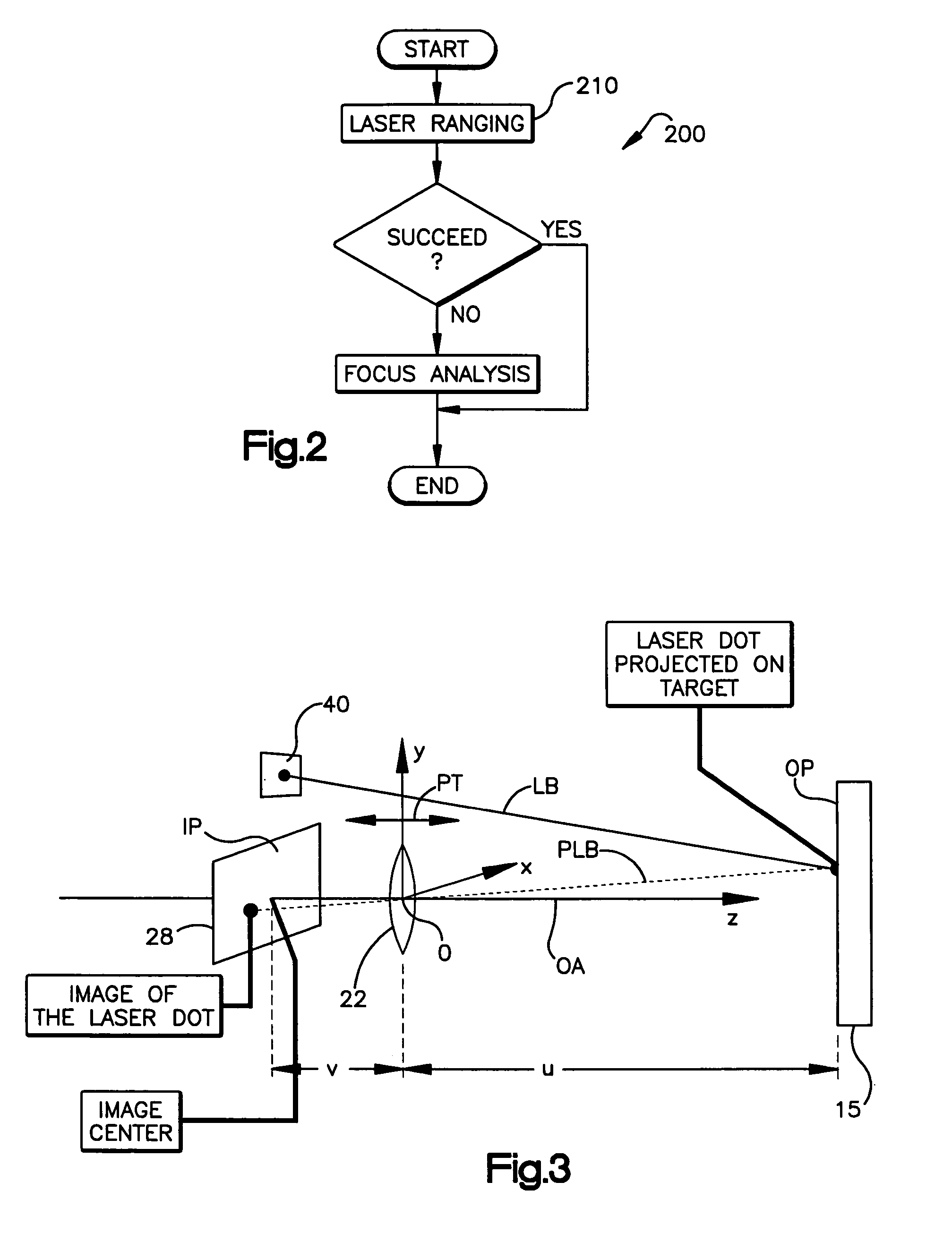
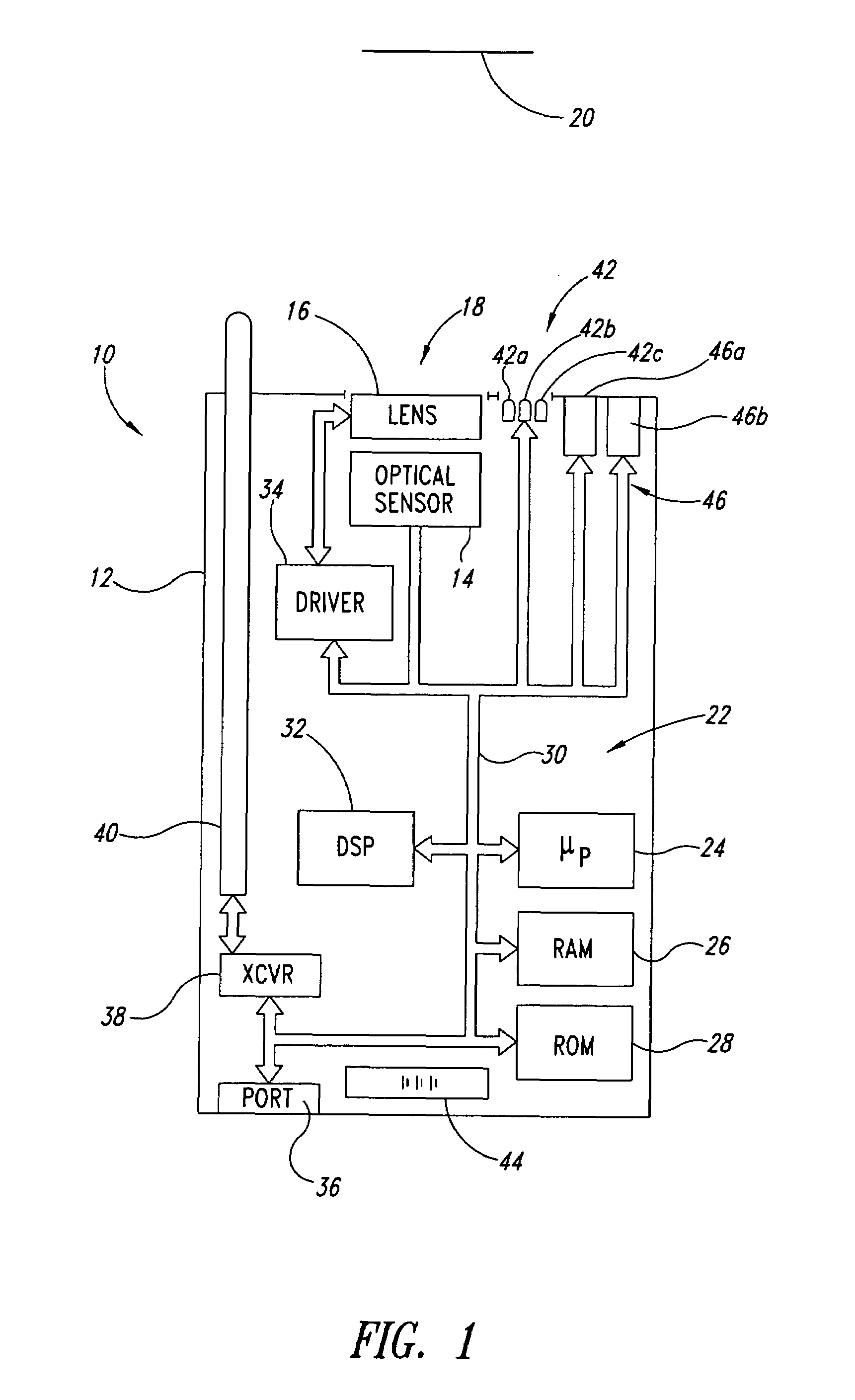
Automatic focusing system for imaging-based bar code reader
An automatic focusing system for an imaging-based bar code reader. The automatic focusing system employs a two step process for moving a lens of an imaging system along its path of travel such that a sharp image of a target bar code is projected or focused onto an imaging system pixel array. The first step is laser ranging which utilizes a laser beam for range finding. Laser ranging determines a distance between the imaging system pixel array and the target bar code. Given the determined distance, the automatic focusing system moves the lens to a suitable position for imaging the target bar code. If ambient conditions prevent laser ranging from properly working, the second step is focus analysis. Focus analysis involves moving the lens in accordance with a search routine and analyzing image frames of the target object to find a suitable focus position.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
High resolution imaging system
InactiveUS20070263113A1Compact and lightweightLow resolution imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh resolution imagingImage resolution
The present invention provides an imaging system generating a high resolution image using low resolution images taken by a low resolution image sensor. Also, the imaging system generates a wide angle of view image. Enhancement of resolution and enlargement of angle of view are accomplished by optical axis change, utilizing one or more micromirror array lenses without macroscopic mechanical movements of lenses. The imaging system also provides zoom and auto focusing functions using micromirror array lenses.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Autofocus barcode scanner and the like employing micro-fluidic lens
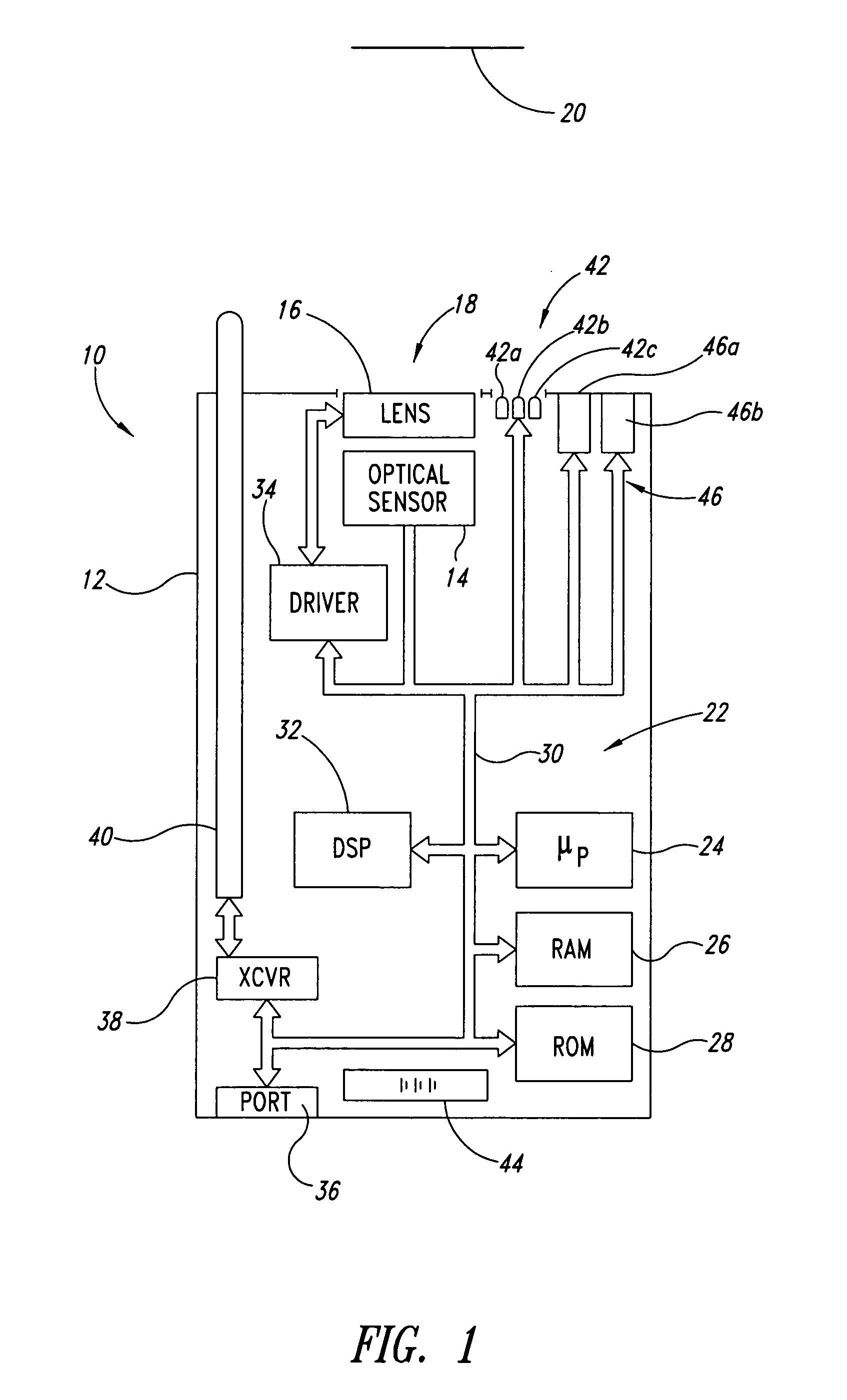
ActiveUS20050218231A1Wide spatial resolution rangeReduce and eliminate needProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementBarcodeAutofocus
A machine-readable symbol reader includes a microfluidic lens assembly providing responsive, reliable auto-focus functionality. A range finder may provide distance to a planar target (e.g., barcode symbol) information for use in auto-focusing, with or without localization. Illumination system, if included, is selectively controlled based on the distance to target and auto-focusing functionality to substantially reduce power consumption. The localization may color optical sensors.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Auto-focusing device with voice coil motor for position feedback and method for using same
InactiveUS20070047942A1Simple configurationSmall sizeTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementMagnetic tension forceAutofocus
An auto-focusing device with voice coil motor for position feedback comprises a lens holder, a sensor holder, a permanent magnet set, a yoke and a base. The lens holder holds a lens barrel and is wound around with at least two coils wound in opposite directions. The sensor holder holds an image sensor. The permanent magnet set includes at least two permanent magnets stacked together with opposing poles to form a multi-pole permanent magnet set. The permanent magnet set is furnished on the periphery of lens holder and corresponds to the two coils on lens holder. The permanent magnet set is disposed on the yoke to form a close-loop magnetism so as to increase the density of magnetic lines and the efficiency of magnetic force, save power consumption, and extend the service life of device.
Owner:POWERGATE OPTICAL INC
Autofocus and/or autoscaling in telesurgery
ActiveUS20070083098A1Enhance perceived correlationProgramme controlComputer controlRemote surgeryDisplay device
Robotic, telerobotic, and / or telesurgical devices, systems, and methods take advantage of robotic structures and data to calculate changes in the focus of an image capture device in response to movement of the image capture device, a robotic end effector, or the like. As the size of an image of an object shown in the display device varies with changes in a separation distance between that object and the image capture device used to capture the image, a scale factor between a movement command input may be changed in response to moving an input device or a corresponding master / slave robotic movement command of the system. This may enhance the perceived correlation between the input commands and the robotic movements as they appear in the image presented to the system operator.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
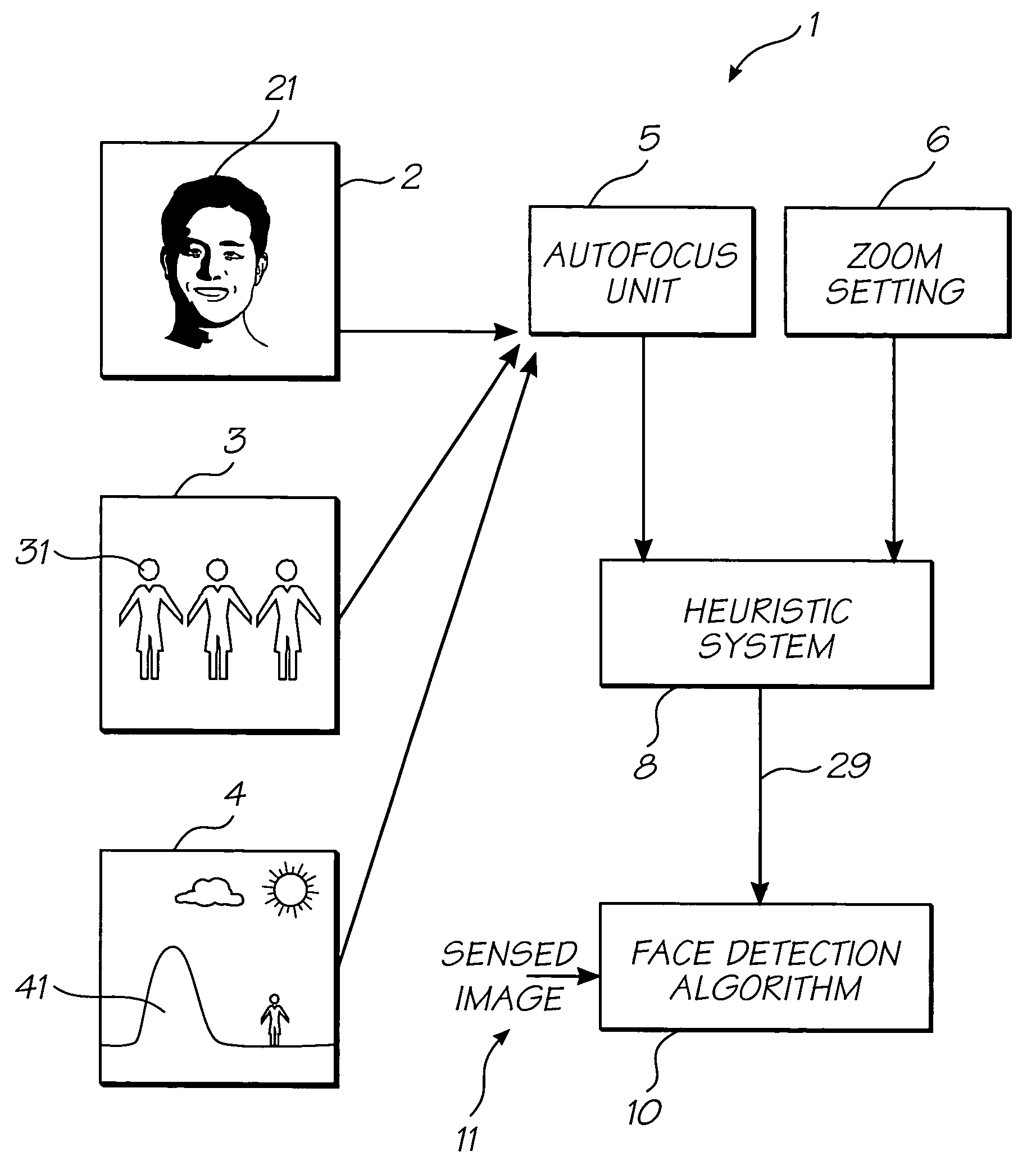
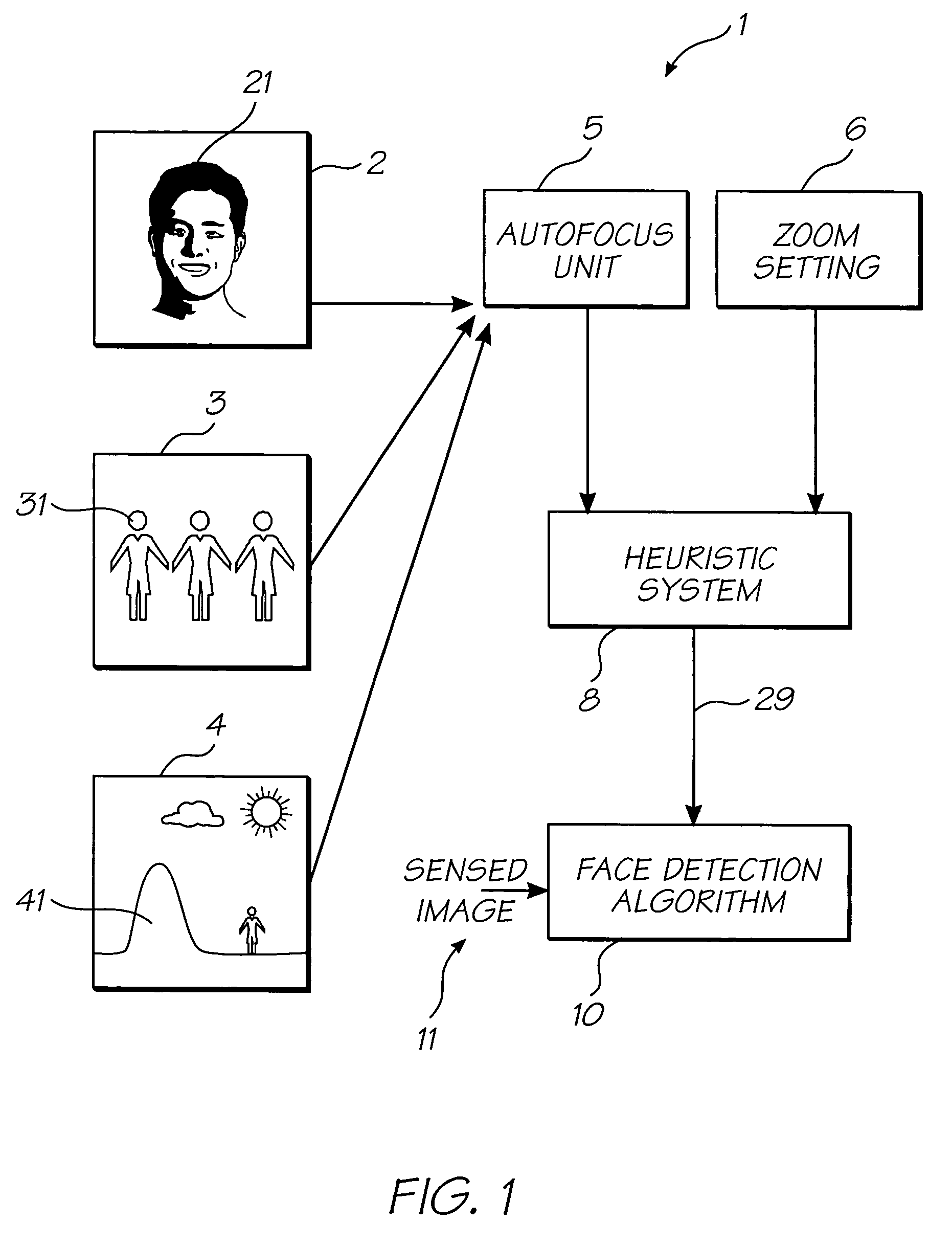
Digital camera utilizing autofocus settings for image manipulation
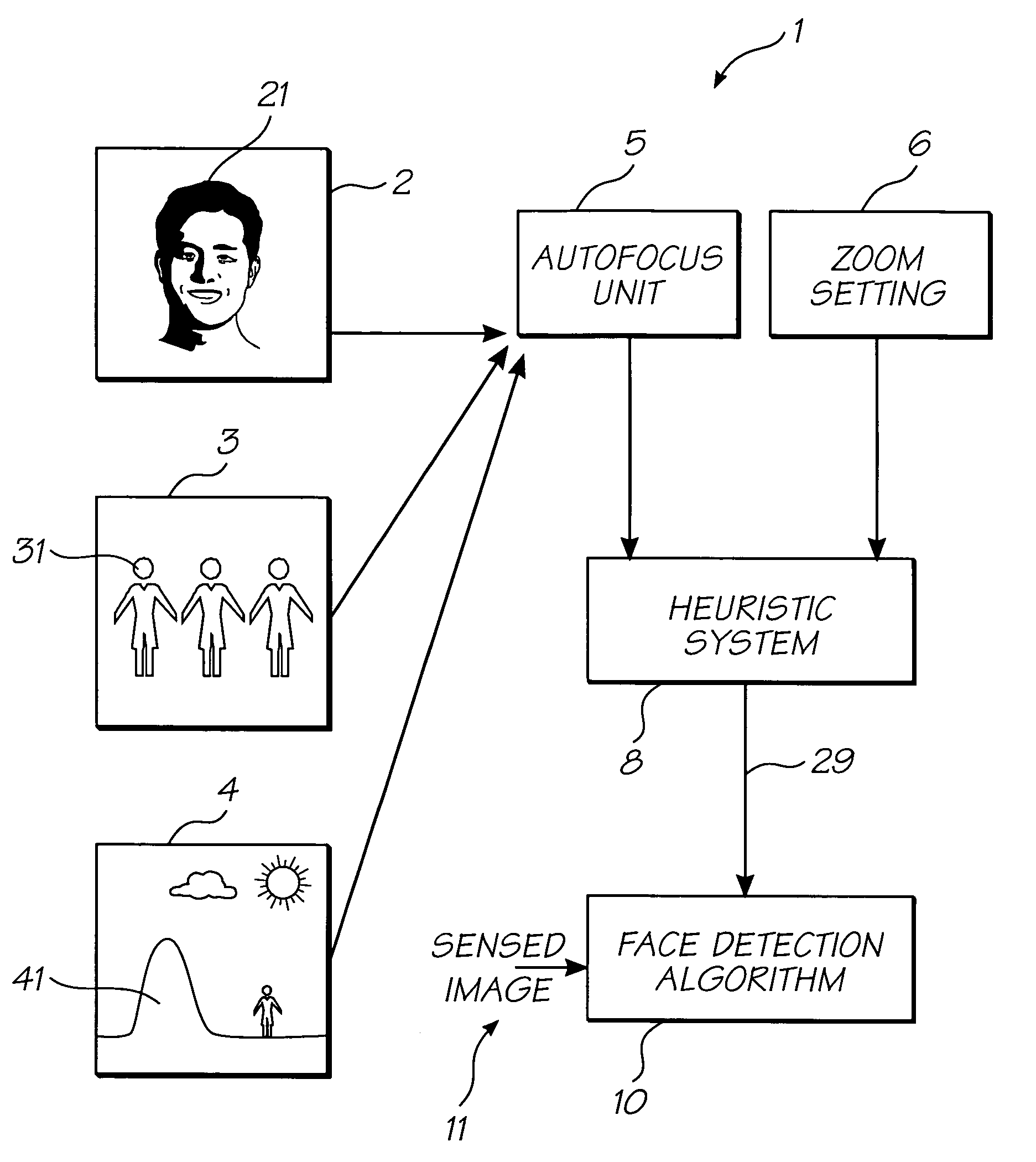
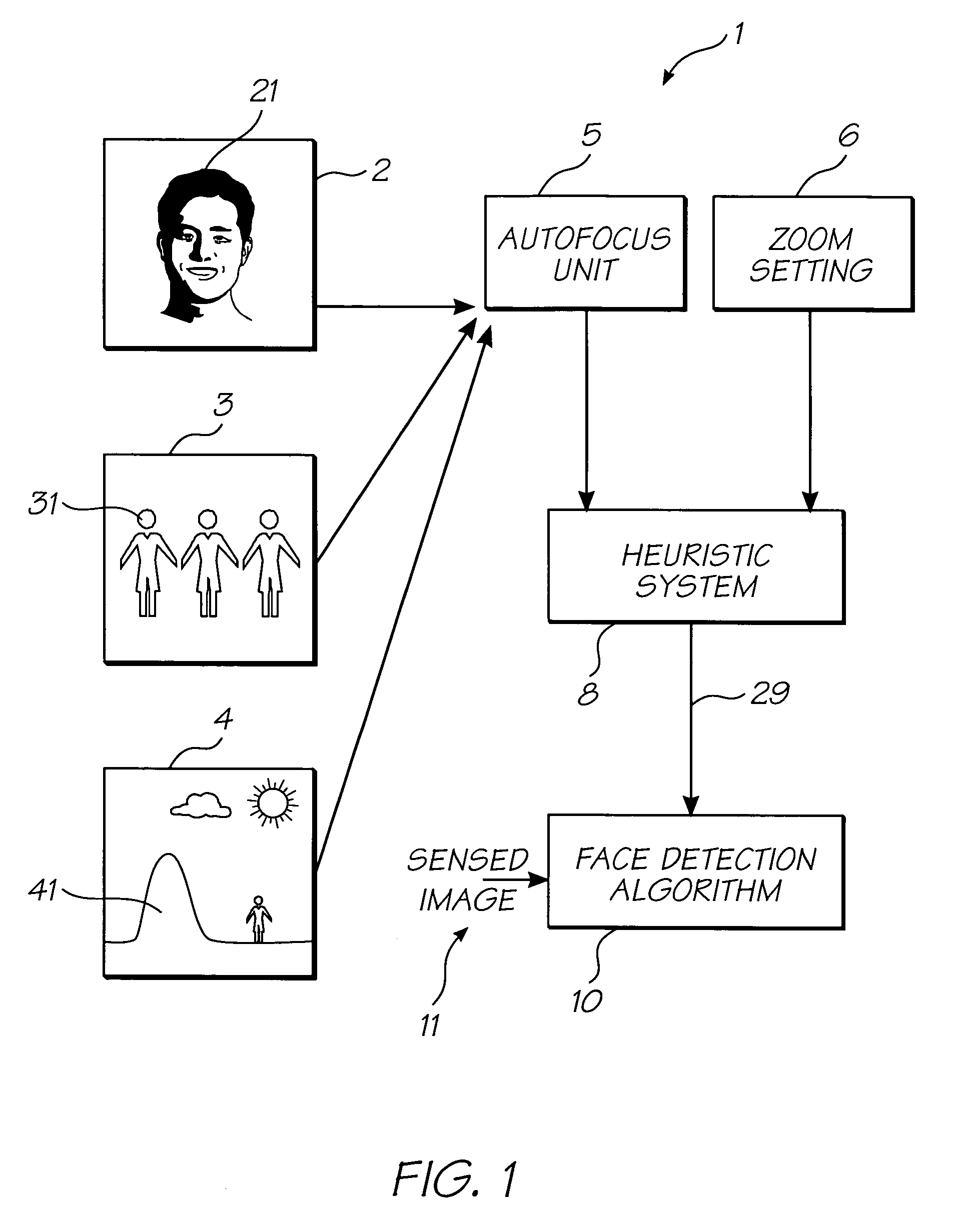
InactiveUS7385639B2Speed up the processImprove image processing capabilitiesTelevision system detailsMaterial nanotechnologyFace detectionAutofocus
A digital camera is provided for generating a manipulated output image. The camera focuses an image using an automatic focusing technique thereby generating focus settings. The focus settings are stored in a memory of the digital camera and used in manipulating the captured image to produce an enhanced image. The digital image manipulation process is selected from the group consisting of applying a face detection algorithm to the captured focussed image and producing a painting effect within the captured focussed image.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
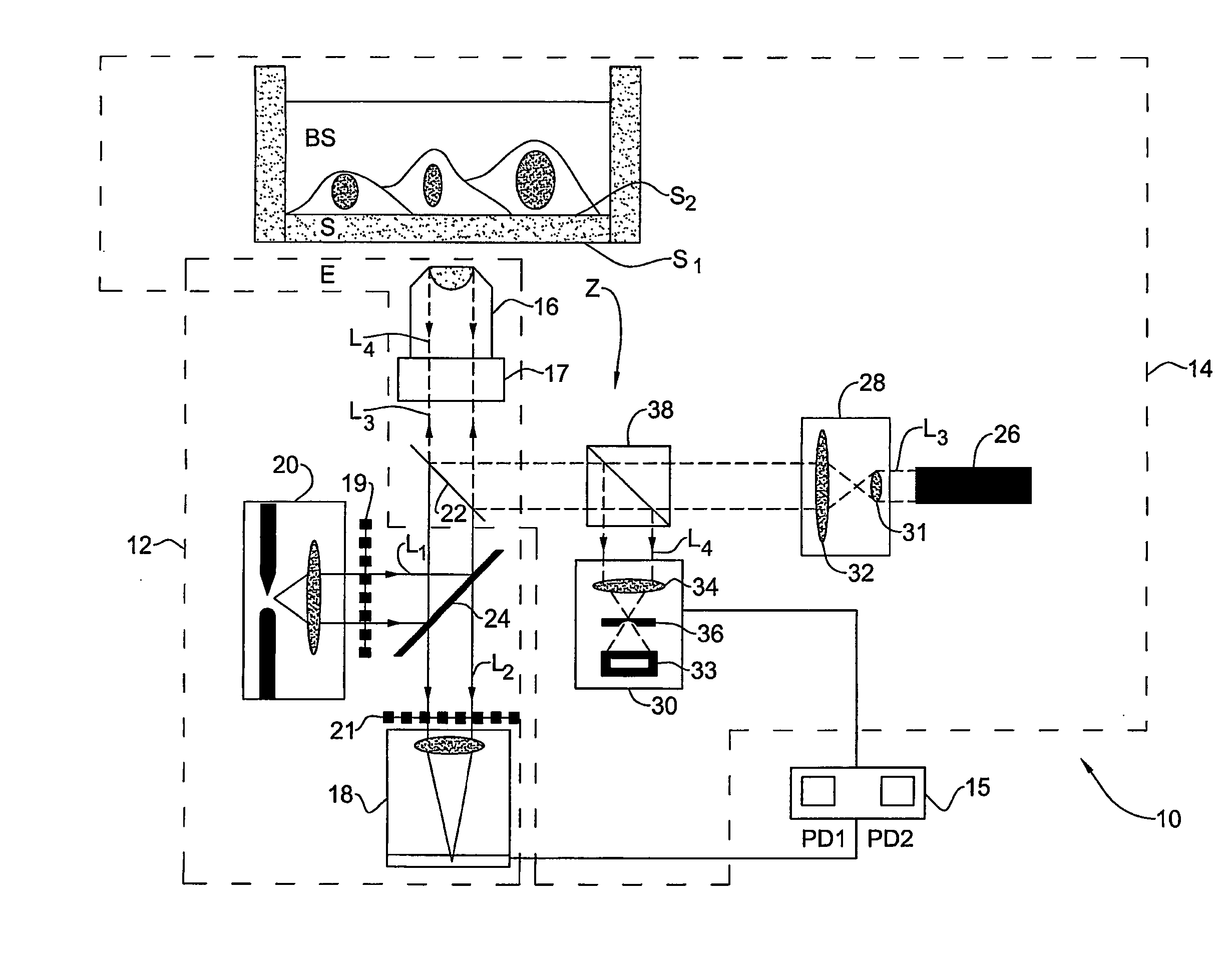
Auto-focusing method and device
InactiveUS20050121596A1Rapid positioningIncrease speedElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOptical axisElectromagnetic radiation
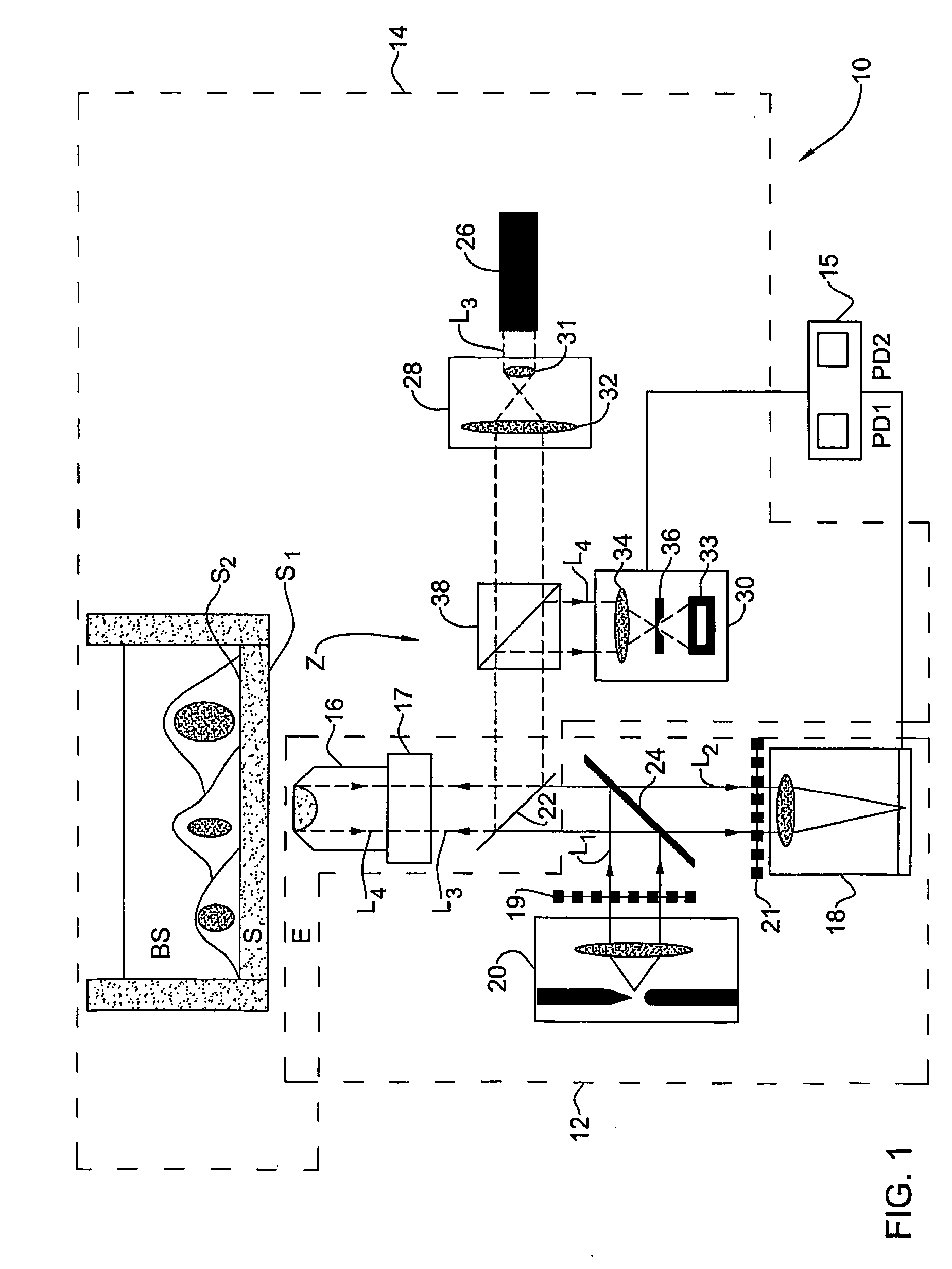
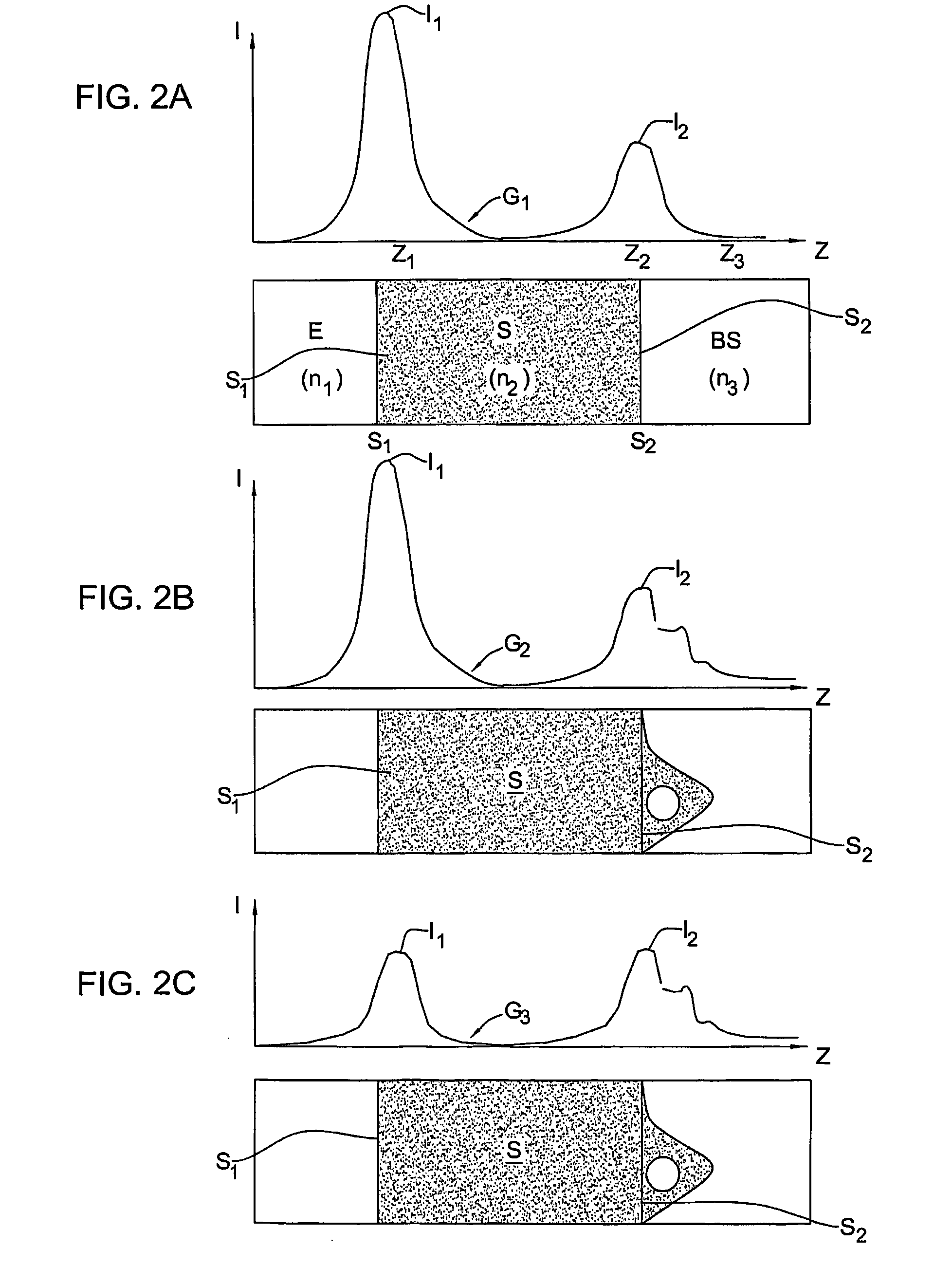
An auto-focusing method and device are presented for determining an in-focus position of a sample supported on a substrate plate made of a material transparent with respect to incident electromagnetic radiation. The method utilizes an optical system capable of directing incident electromagnetic radiation towards the sample and collecting reflections of the incident electromagnetic radiation that are to be detected. A focal plane of an objective lens arrangement is located at a predetermined distance from a surface of the substrate, which is opposite to the sample-supporting surface of the substrate. A continuous displacement of the focal plane relative to the substrate along the optical axis of the objective lens arrangement is provided, while concurrently directing the incident radiation towards the sample through the objective lens arrangement to thereby focus the incident radiation to a location at the focal plane of the objective lens arrangement. Reflected components of the electromagnetic radiation to a location objective lens arrangement are continuously detected. The detected reflected components are characterized by a first intensity peak corresponding to an in-focus position of said opposite surface of the substrate, and a second intensity peak spaced in time from the first intensity peak and corresponding to an in-focus position of said sample-supporting surface of the substrate. This technique enables imaging of the sample when in the in-focus position of the sample-supporting surface of the substrate.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Processing of digital images using autofocus settings for image enhancement
InactiveUS7557853B2Improve image processing capabilitiesTelevision system detailsMaterial nanotechnologyAutofocusDigital image
A method of processing a digital image comprising: using a digital camera, capturing the image utilising an adjustable focusing technique; storing the focusing settings within a memory of the digital camera; utilising the focusing settings as an indicator of the position of structures within the image; processing the image within a processor of the camera utilising the said focus settings to produce a manipulated image having effects specific to said focus settings; and printing out the image using a printer inbuilt to the camera body.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
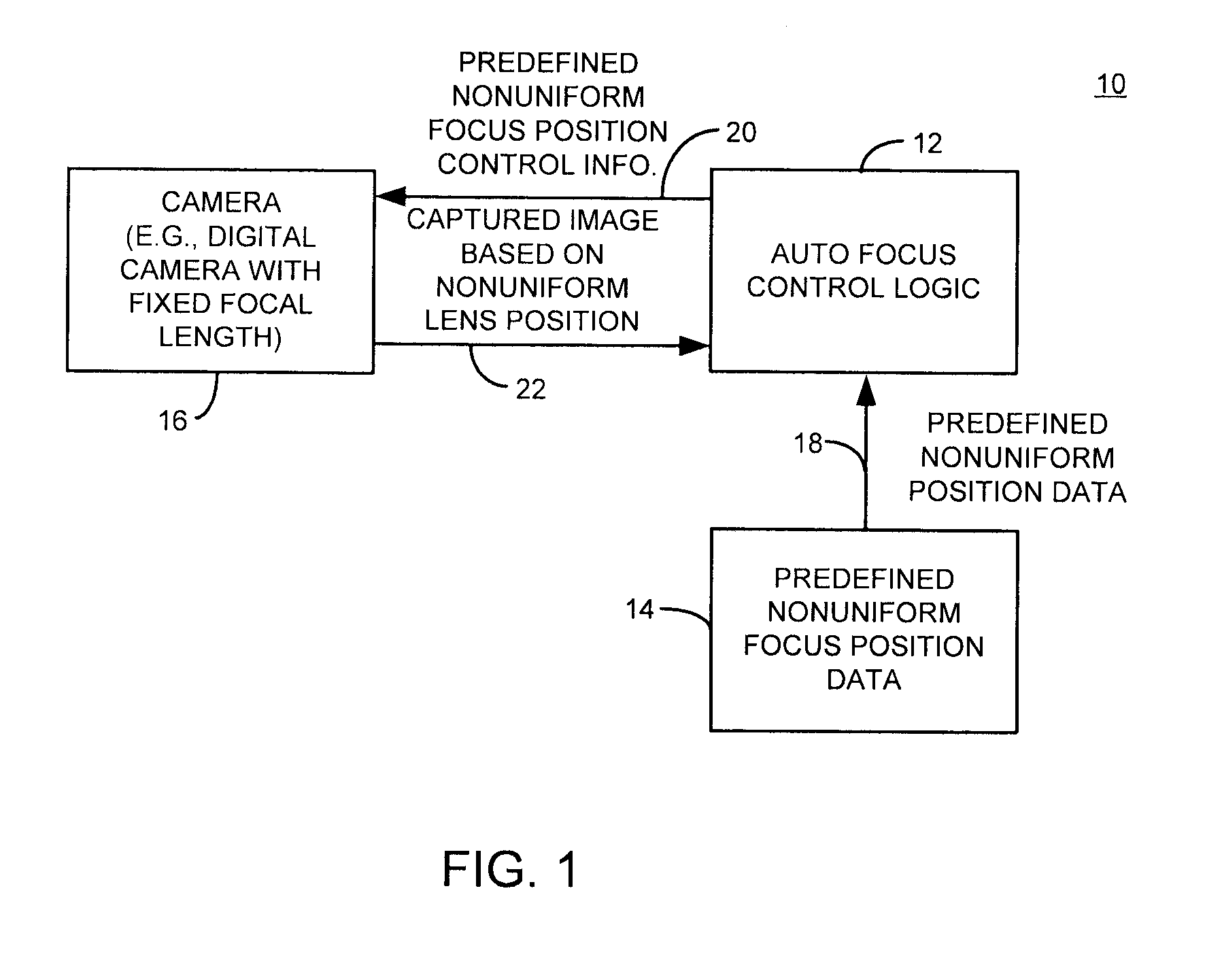
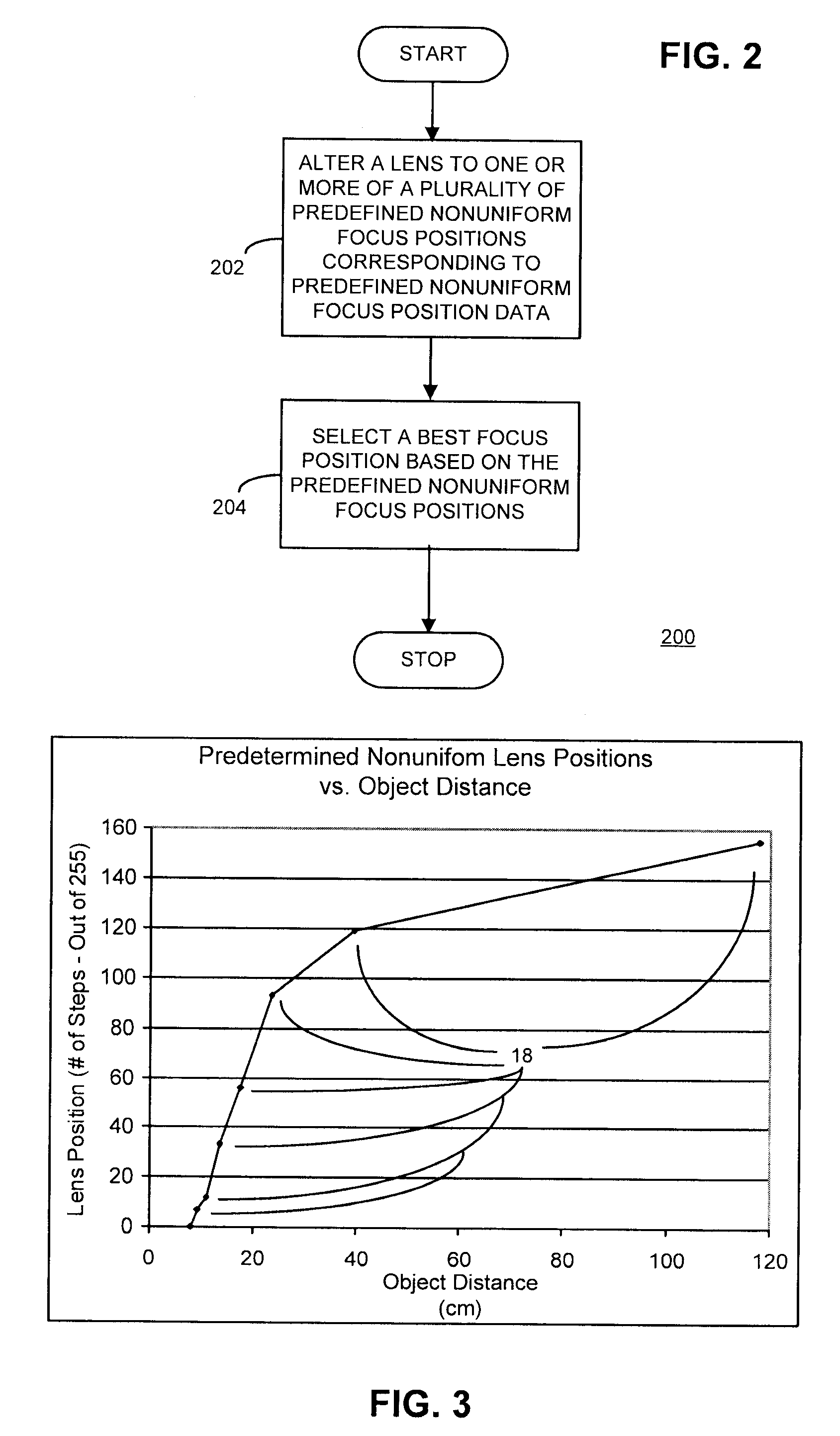
Method and apparatus with fast camera auto focus
A method and apparatus improves an auto focus system by altering, such as by positioning, at least one lens of a digital camera to a plurality of predetermined nonuniform lens positions corresponding to predetermined nonuniform lens position data. The method and apparatus selects a final lens position for the lens based on the predetermined nonuniform lens position data. In one example, a fixed number of predetermined nonuniform lens positions define a set of lens positions used to capture images during an auto focus operation. A final image is captured using a final lens position. The final lens position is determined by comparing focus metric information from each of the frames obtained at the various predetermined nonuniform focus lens positions and selecting the frame with, for example, the best focus metric as the lens position to be used for the final picture or image capture.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Integrated lens barrel
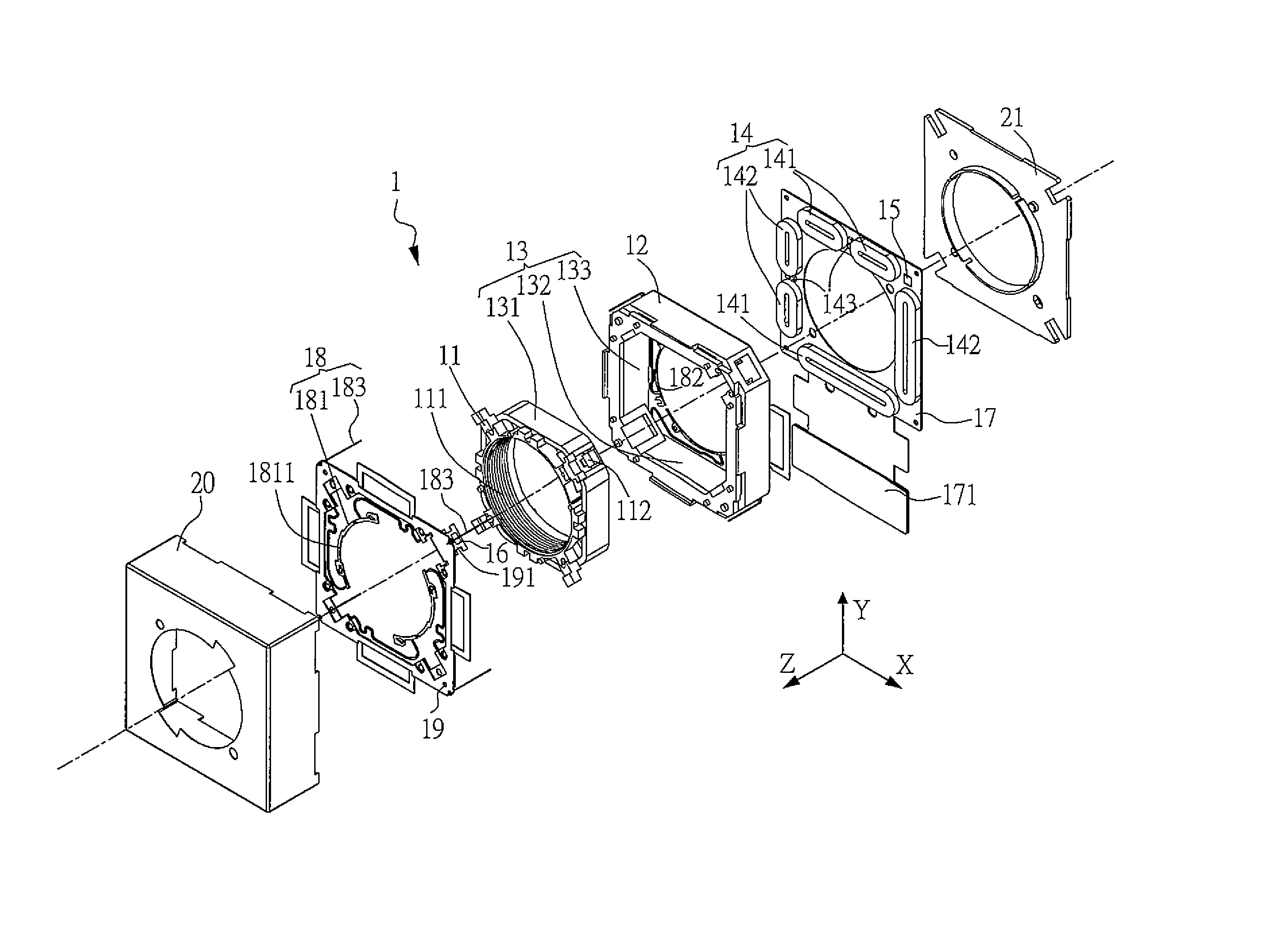
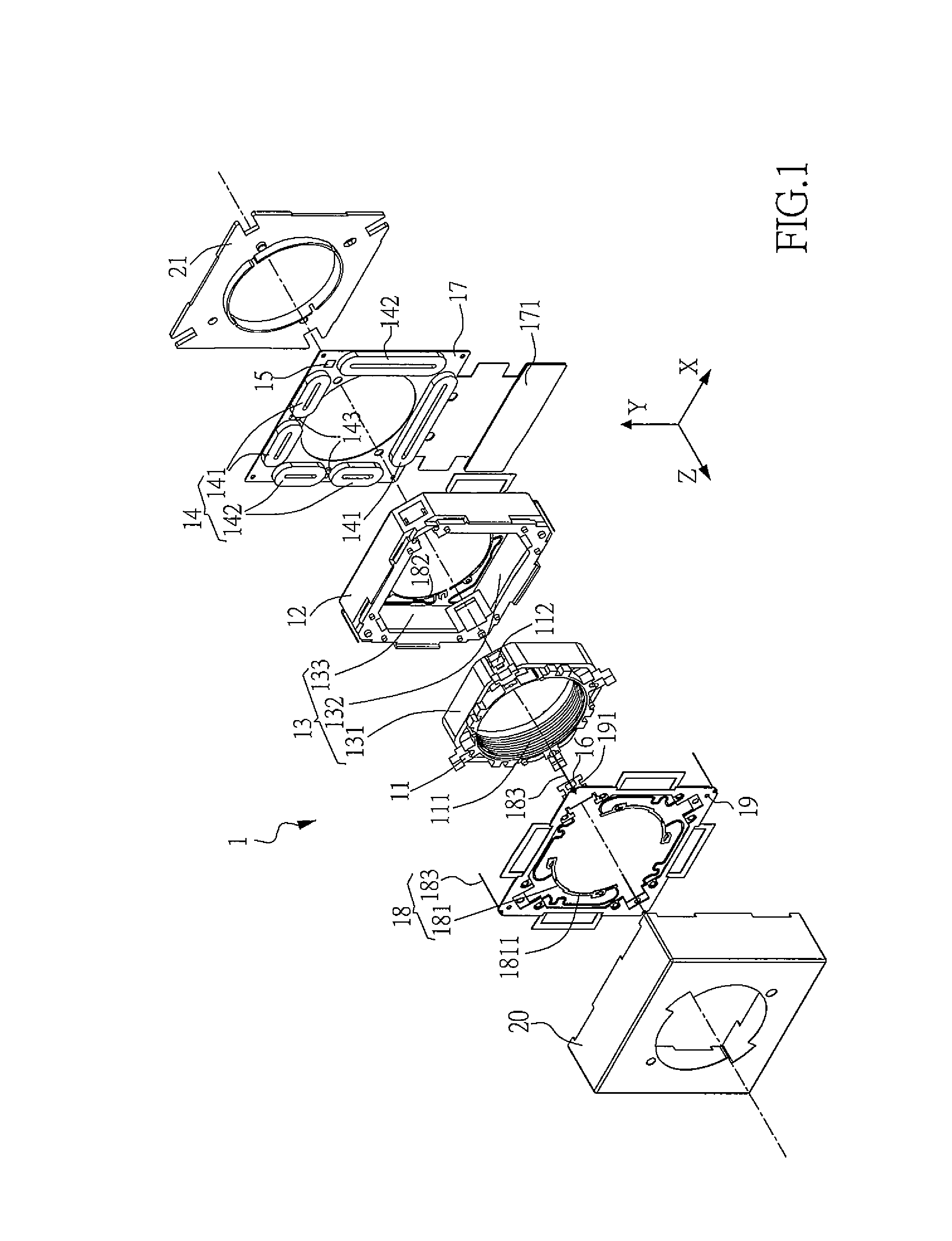
ActiveUS20100284081A1Increase the lengthConvenient lengthProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementEngineeringImage stabilization
An integrated lens barrel for a miniature camera is disclosed. The lens barrel can include components such as a shutter, an autofocus mechanism, a zoom mechanism, and / or an image stabilization mechanism. These and / or components can define a portion of the lens barrel that increases the length of the lens barrel. An electrostatic MEMS actuator can be used to effect movement of the autofocus mechanism, zoom mechanism, and / or image stabilization mechanism. Integrating the shutter, autofocus mechanism, zoom mechanism, and / or image stabilization mechanism into the lens barrel facilitates the construction of a substantially smaller camera that is suitable for use in personal electronic devices, such as cellular telephones.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS MEMS
Autofocus barcode scanner and the like employing micro-fluidic lens
ActiveUS7296749B2Wide spatial resolution rangeReduce and eliminate needProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementBarcodeDistance to target
A machine-readable symbol reader includes a microfluidic lens assembly providing responsive, reliable auto-focus functionality. A range finder may provide distance to a planar target (e.g., barcode symbol) information for use in auto-focusing, with or without localization. Illumination system, if included, is selectively controlled based on the distance to target and auto-focusing functionality to substantially reduce power consumption. The localization may color optical sensors.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
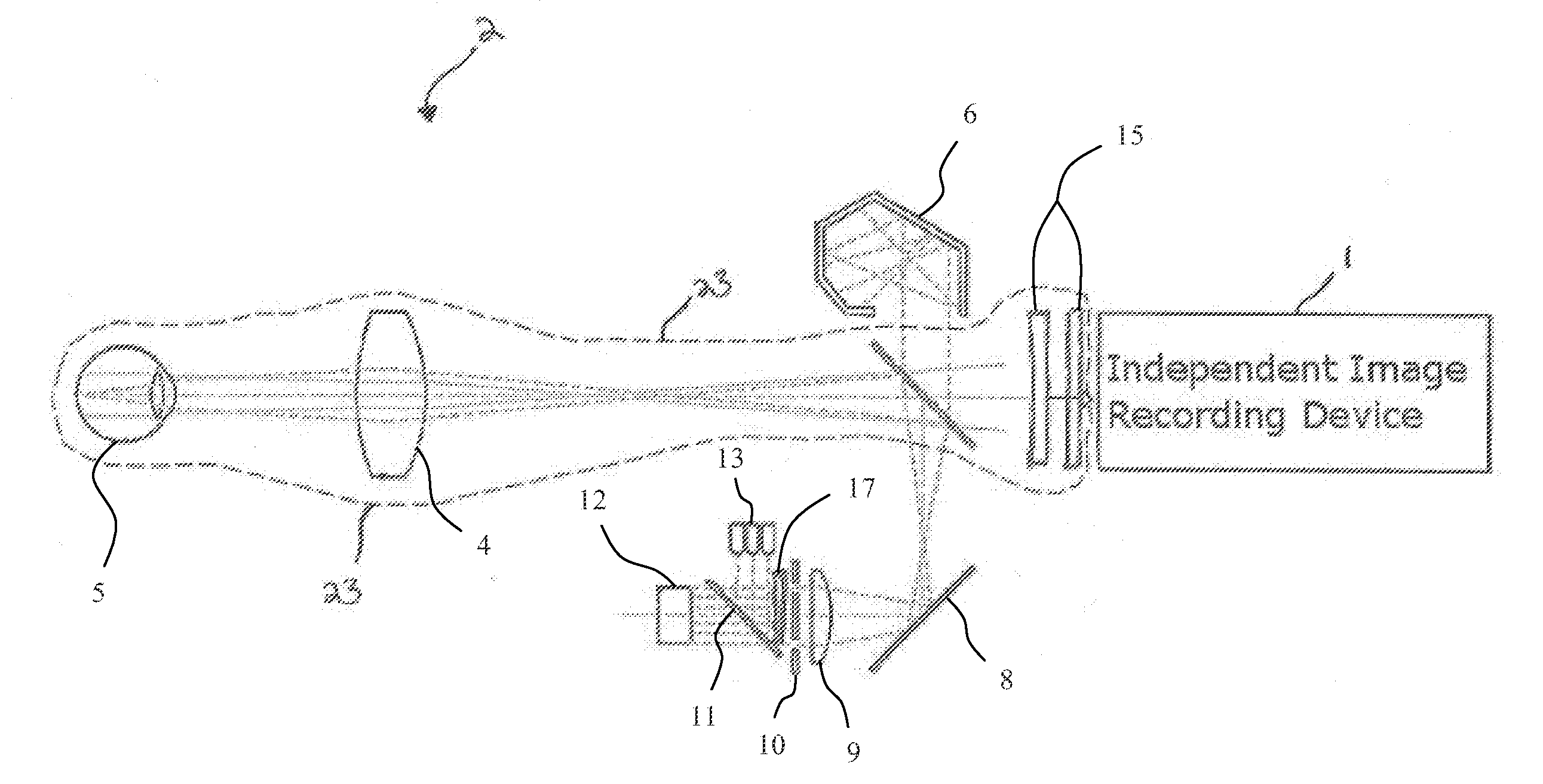
Hand-held portable fundus camera for screening photography
ActiveUS20120229617A1Low costEasy to useTelevision system detailsAcquiring/recognising eyesFundus cameraHand held
System and Method pertaining to the modification and integration of an existing consumer digital camera, for example, with an optical imaging module to enable point and shoot fundus photography of the eye. The auto-focus macro capability of existing consumer cameras is adapted to photograph the retina over an extended diopter range, eliminating the need for manual diopter focus adjustment. The thru-the-lens (TTL) auto-exposure flash capability of existing consumer cameras is adapted to photograph the retina with automatic flash exposure eliminating the need for manual flash adjustment. The consumer camera imaging sensor and flash are modified to allow the camera sensor to perform both non-mydriatic focusing of the retina using infrared illumination and standard color flash photography of the retina without the need for additional imaging sensors or mechanical filters. These modifications and integration of existing consumer cameras for fundus photography of the eye significantly improve ease of manufacture and usability over existing fundus cameras.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Image capture systems, devices, and methods that autofocus based on eye-tracking
Image capture systems, devices, and methods that automatically focus on objects in the user's field of view based on where the user is looking / gazing are described. The image capture system includes an eye tracker subsystem in communication with an autofocus camera to facilitate effortless and precise focusing of the autofocus camera on objects of interest to the user. The autofocus camera automatically focuses on what the user is looking at based on gaze direction determined by the eye tracker subsystem and one or more focus property(ies) of the object, such as its physical distance or light characteristics such as contrast and / or phase. The image capture system is particularly well-suited for use in a wearable heads-up display to capture focused images of objects in the user's field of view with minimal intervention from the user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Image photographing apparatus
InactiveUS20070154198A1Quality improvementImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementAutofocusImaging quality
An image photographing apparatus for automatically focusing a photographed image to improve the image quality. The image photographing apparatus automatically focuses the image through a zoom actuator for changing a zoom ratio and a focus actuator for controlling the focus to thereby enhance the image quality. Also, the image photographing apparatus adds a zooming function to diversify the application fields of image photographing.
Owner:HYSONIC
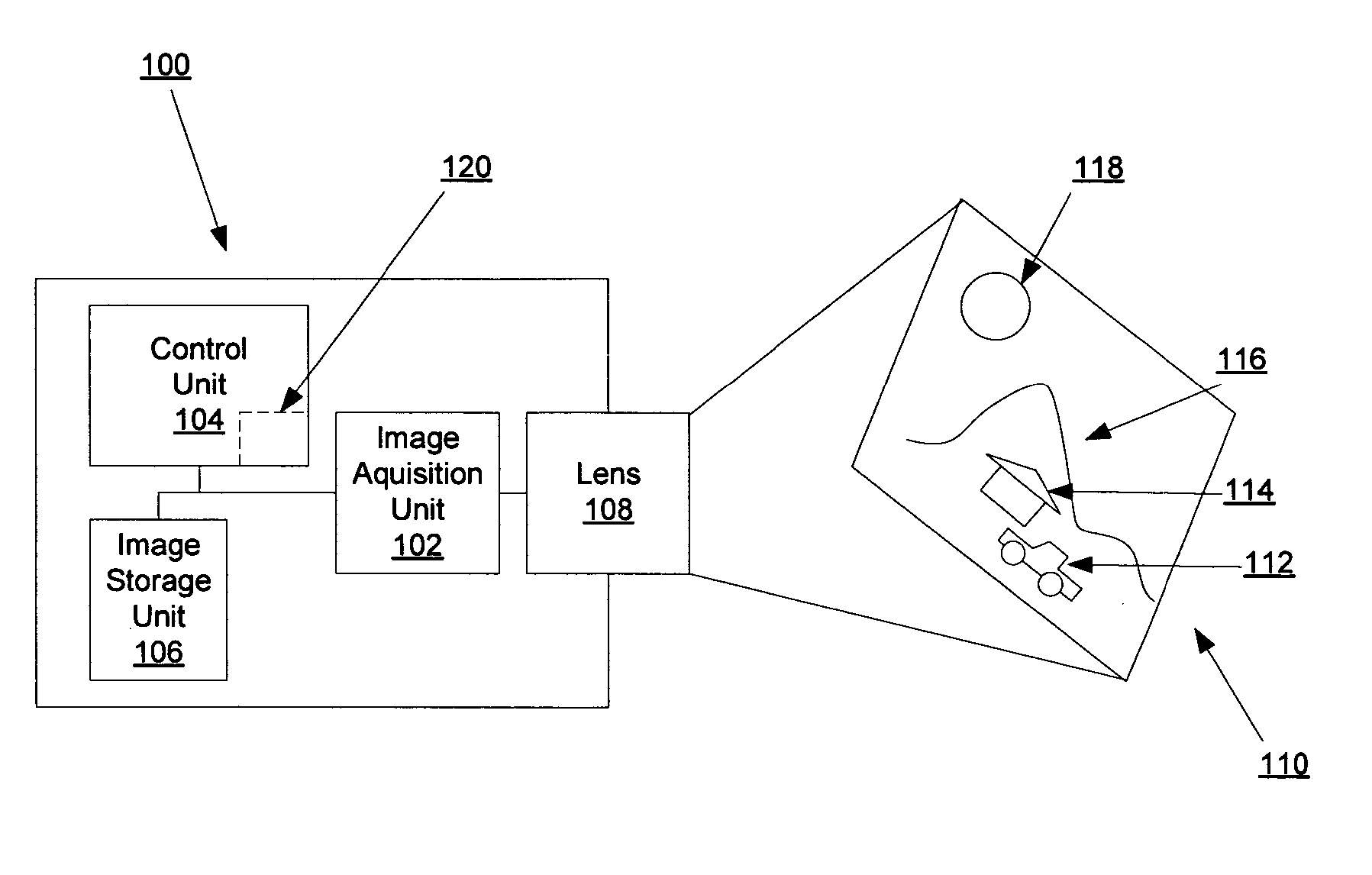
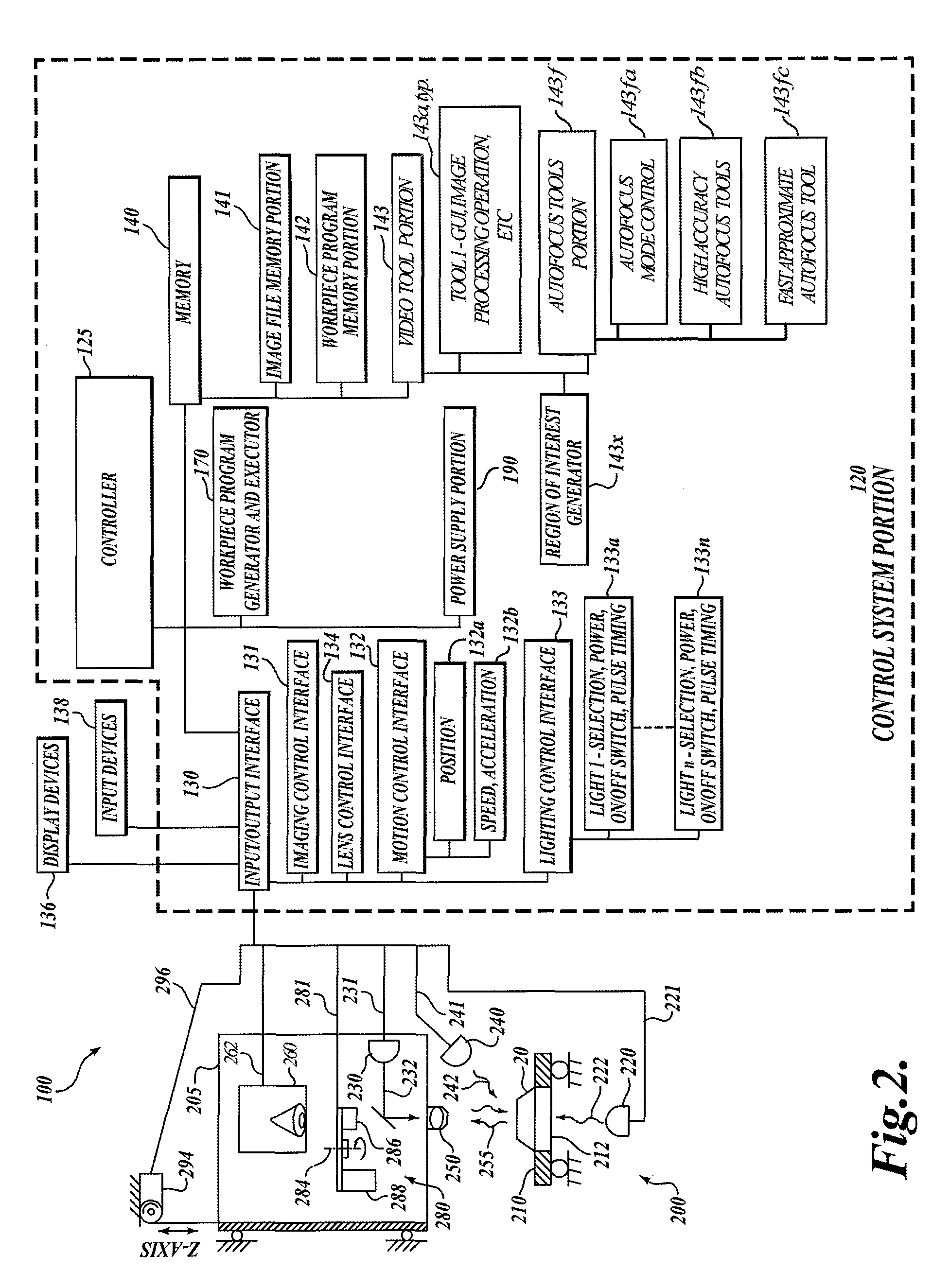
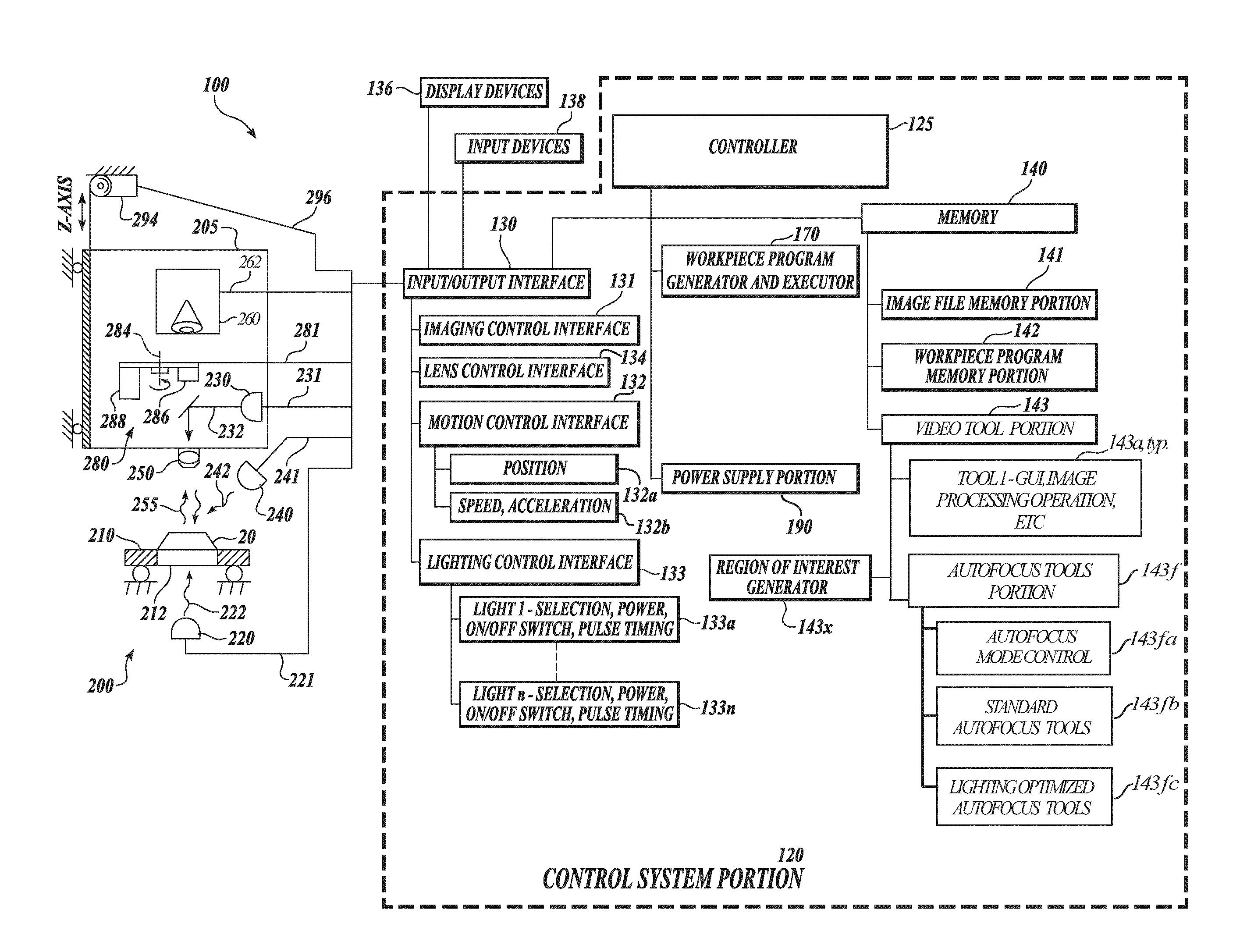
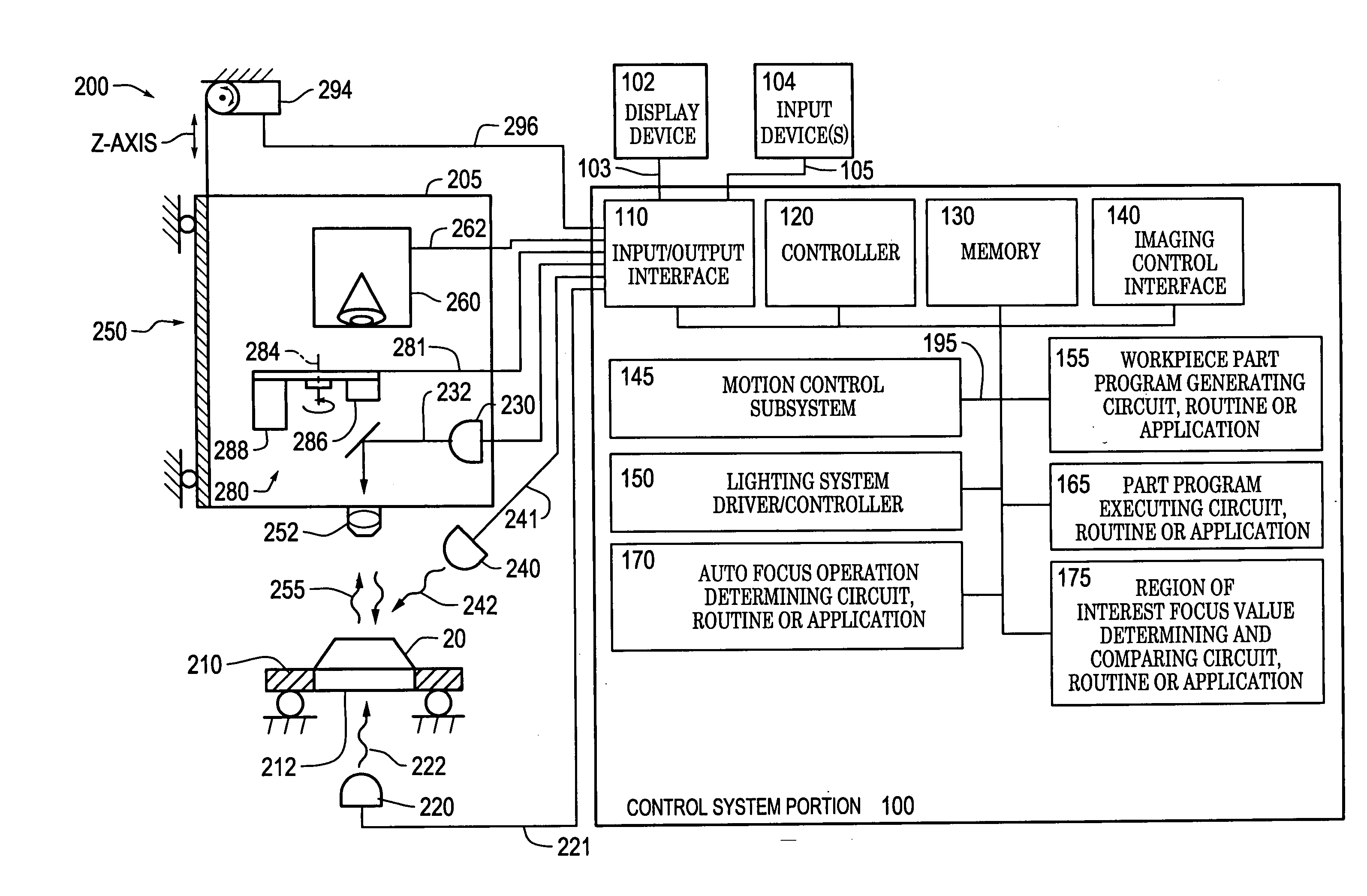
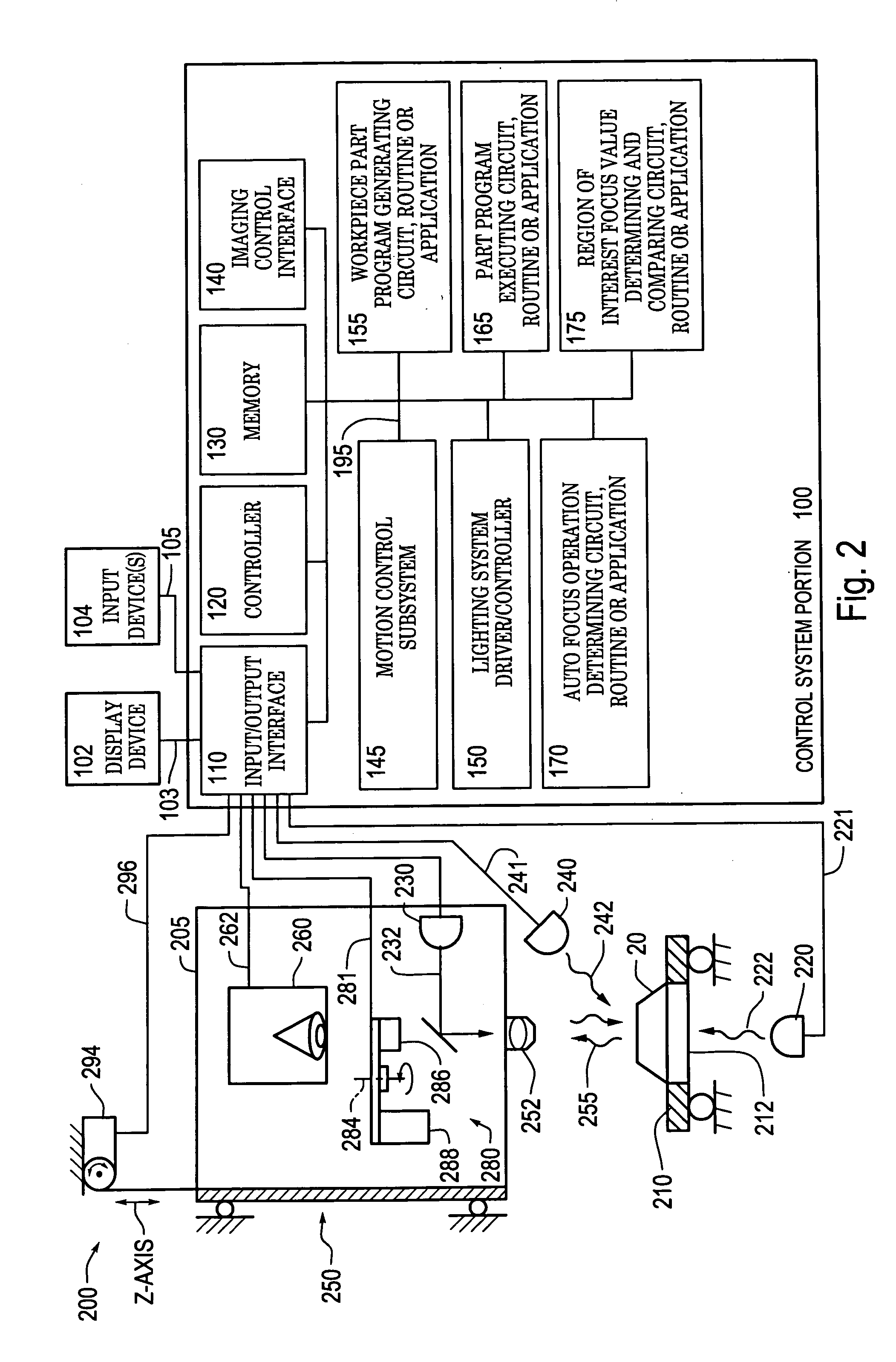
Systems and methods for rapidly automatically focusing a machine vision inspection system
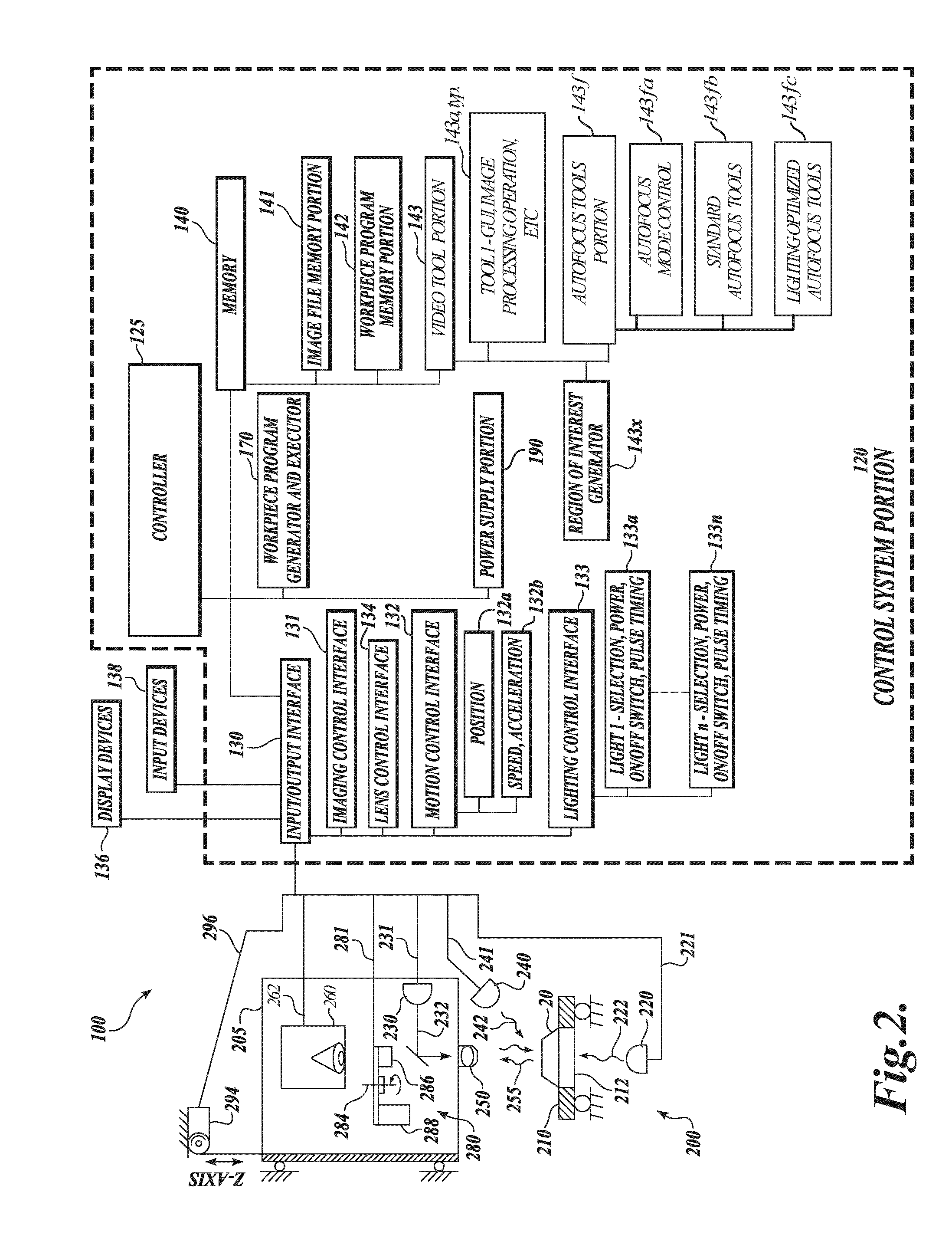
ActiveUS20050109959A1Increase speedAccurate autofocusTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesMachine visionMetrology
Auto focus systems and methods for a machine vision metrology and inspection system provide high speed and high precision auto focusing, while using relatively low-cost and flexible hardware. One aspect of various embodiments of the invention is that the portion of an image frame that is output by a camera is minimized for auto focus images, based on a reduced readout pixel set determined in conjunction with a desired region of interest. The reduced readout pixel set allows a maximized image acquisition rate, which in turn allows faster motion between auto focus image acquisition positions to achieve a desired auto focus precision at a corresponding auto focus execution speed that is approximately optimized in relation to a particular region of interest. In various embodiments, strobe illumination is used to further improve auto focus speed and accuracy. A method is provided for adapting and programming the various associated auto focus control parameters.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Autofocus actuator
ActiveUS20060034599A1Easy to produceImprove bindingProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementEngineeringAutofocus
An autofocus actuator is provided with a yoke 320 that comprises an inner cylindrical portion 321 defining an insertion bore 35 through which a hollow body portion of a holder is adapted to be received and an outer cylindrical portion 322 provided outside of the inner cylindrical portion with a predetermined spacing left between the inner cylindrical portion and the outer cylindrical portion by a connecting portion 324. Four tab-shaped portions 325 are integrally formed with an end surface of the outer cylindrical portion 322 of the yoke in such a manner that the tab-shaped portions remain flush with the end surface of the outer cylindrical portion and extend outwardly from the outer cylindrical portion. The tab-shaped portions 325 are so formed as to leave a concave portion 327 between the adjacent tab-shaped portions. This assures that the tab-shaped portion 325 can make contact with a leaf spring in a broader area, thus enabling the leaf spring to be reliably bonded to the yoke 320. Moreover, the yoke 320 can be aligned with ease by disposing a part of a support frame within the concave portions 327 formed between the adjacent tab-shaped portions 325.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Lens holder driving device including fracture preventing member for suspension wires
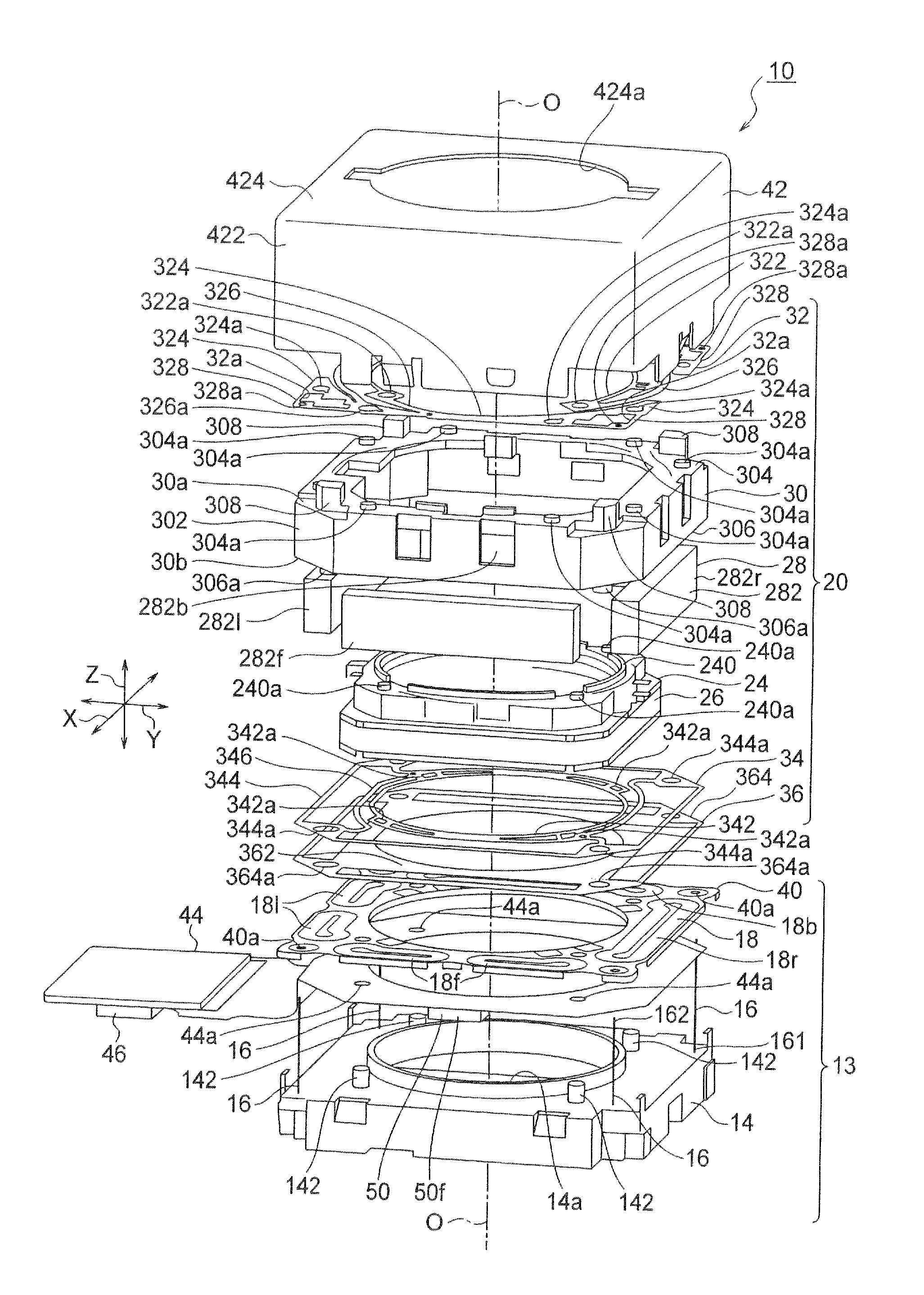
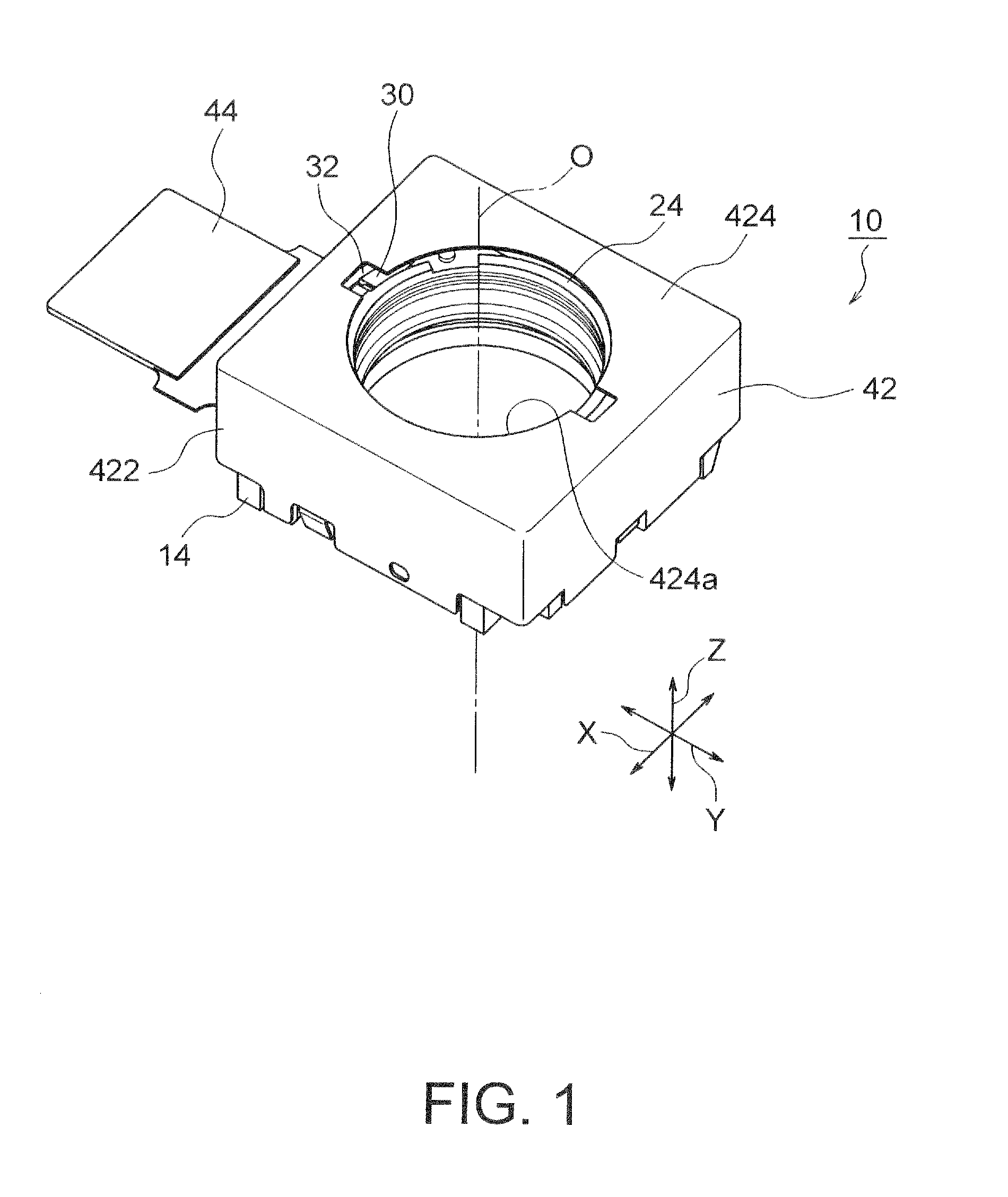
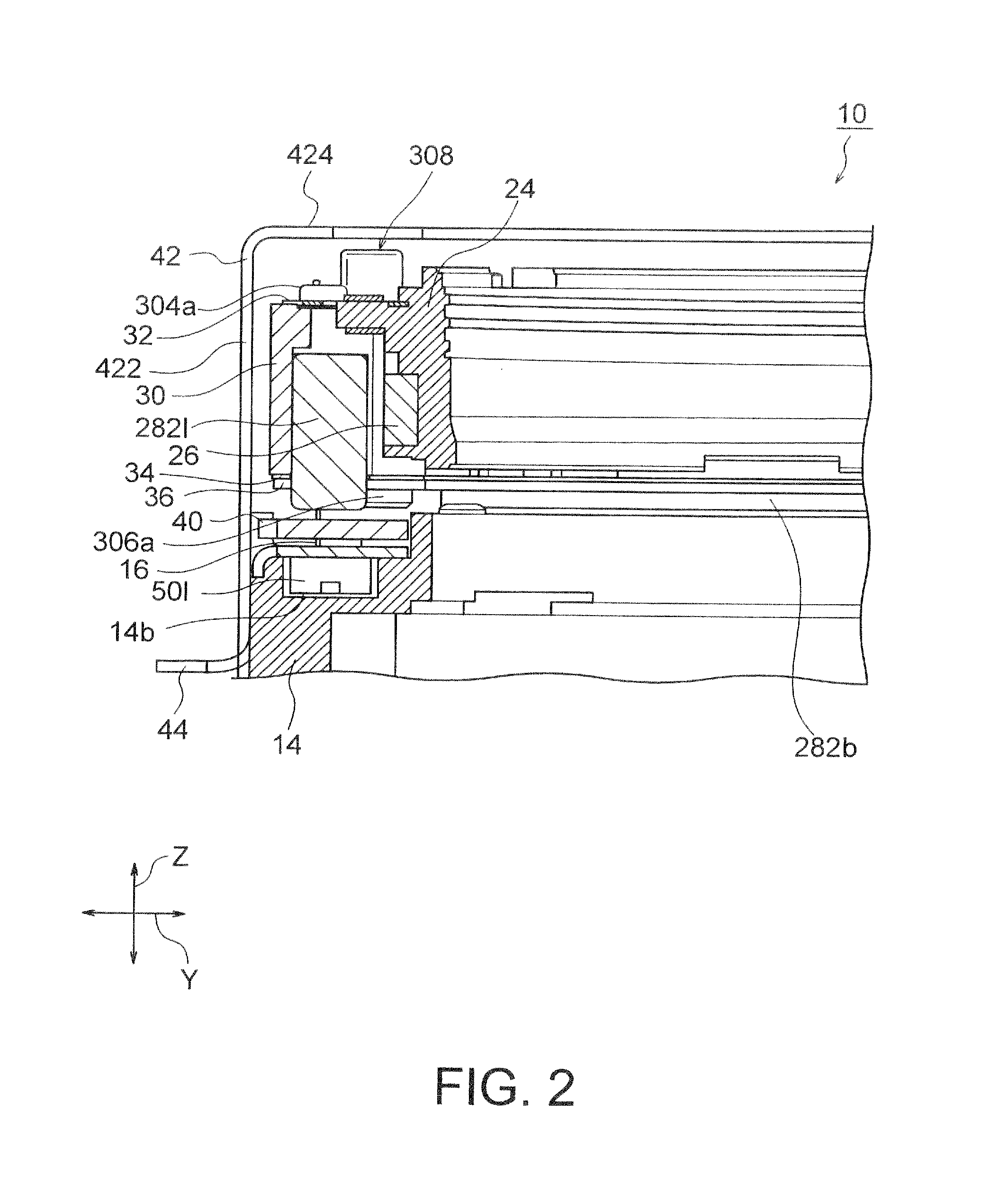
ActiveUS20130016428A1Improve impact resistanceTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisEngineering
A lens holder driving device includes an auto-focusing lens holder driving portion moving a lens holder holding a lens barrel along an optical axis, and an image stabilizer portion stabilizing image blurred by moving the auto-focusing lens holder driving portion in first and second directions which are orthogonal to the optical axis and which are perpendicular to each other. The image stabilizer portion includes: a fixed portion disposed apart from the auto-focusing lens holder driving portion in the direction of the optical axis; a plurality of suspension wires having first end portions fixed to the fixed portion at outer regions thereof, extending along the optical axis, having second end portions fixed to the auto-focusing lens holder driving portion, and swingably supporting the auto-focusing lens holder driving portion in the first direction and the second direction; and a fracture preventing member preventing the suspension wires from fracturing.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Active autofocus window
ActiveUS20080007626A1Easy to controlLarge apertureImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage recordingDisplay device
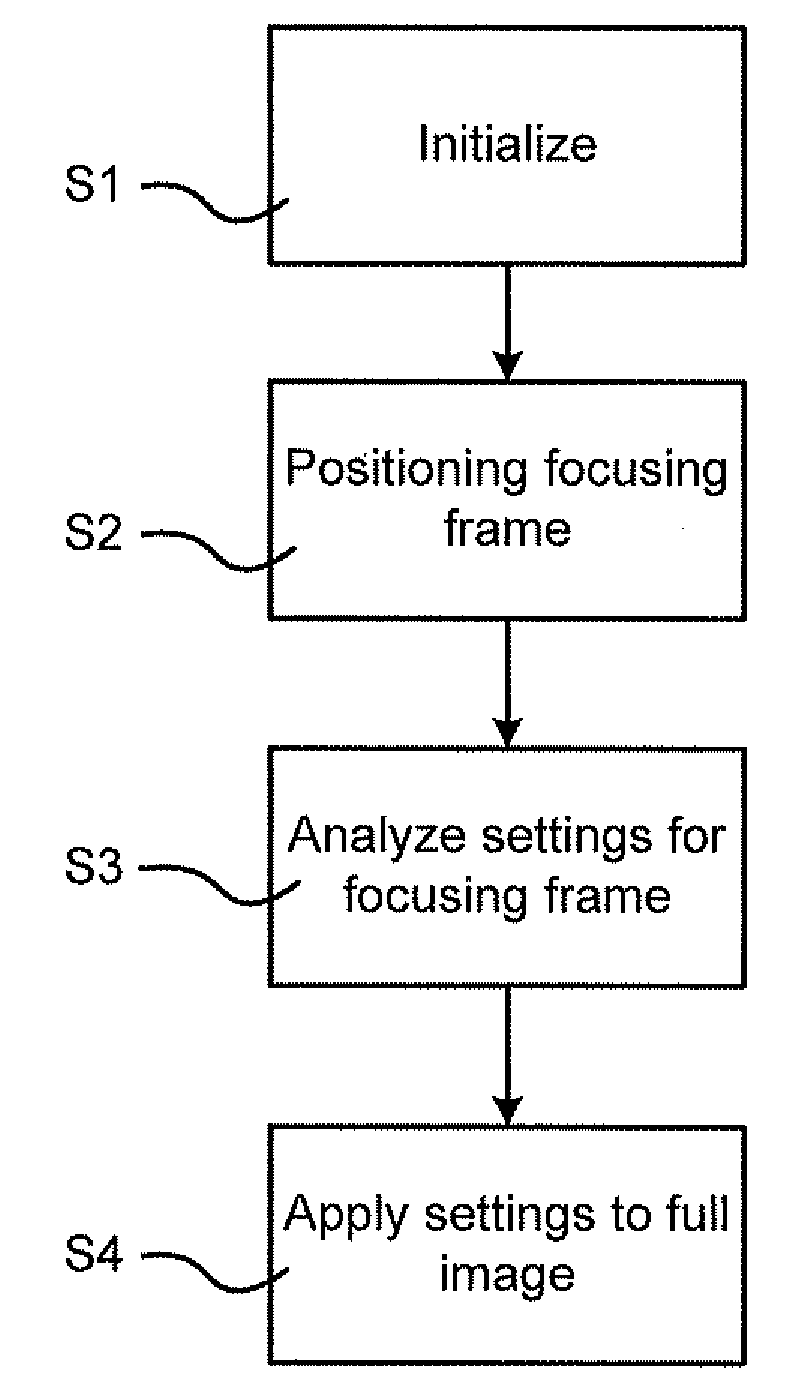
A method for changing the depth at which an image is focused is provided in a portable imaging device that includes an image recording arrangement that has a lens system, an image sensor for recording images, and a display arrangement for presentation of the recorded images. The method includes moving a movable focusing frame covering a part of a recorded image presented on the display to identify an area of interest in the presented image. The method also includes analyzing the image within the frame to obtain a setting required to focus the image within the frame and applying the obtained setting to the full presented image to focus the presented image at the depth defined by the current position of the movable focusing frame.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com