Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
381 results about "Fundus camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
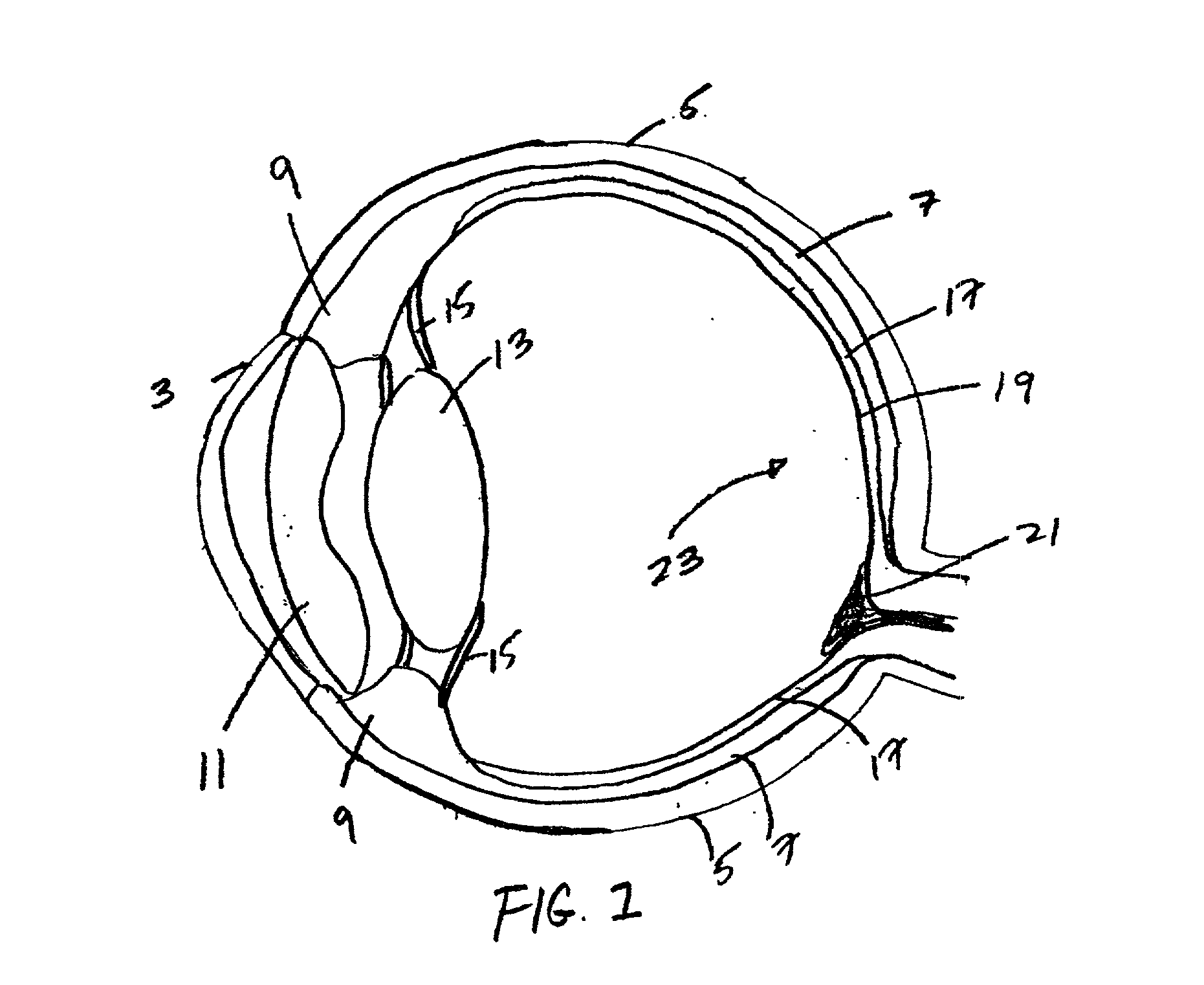
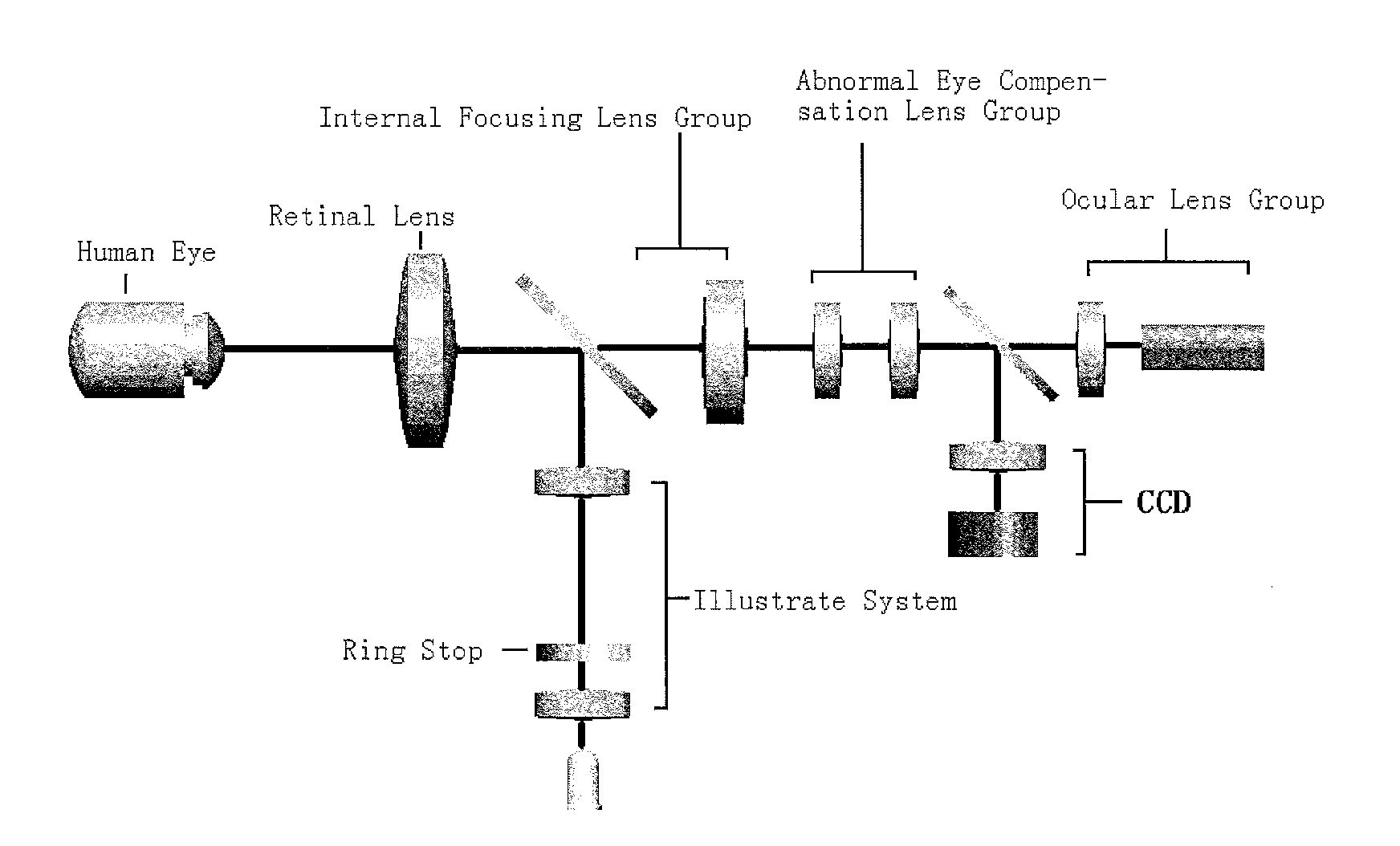
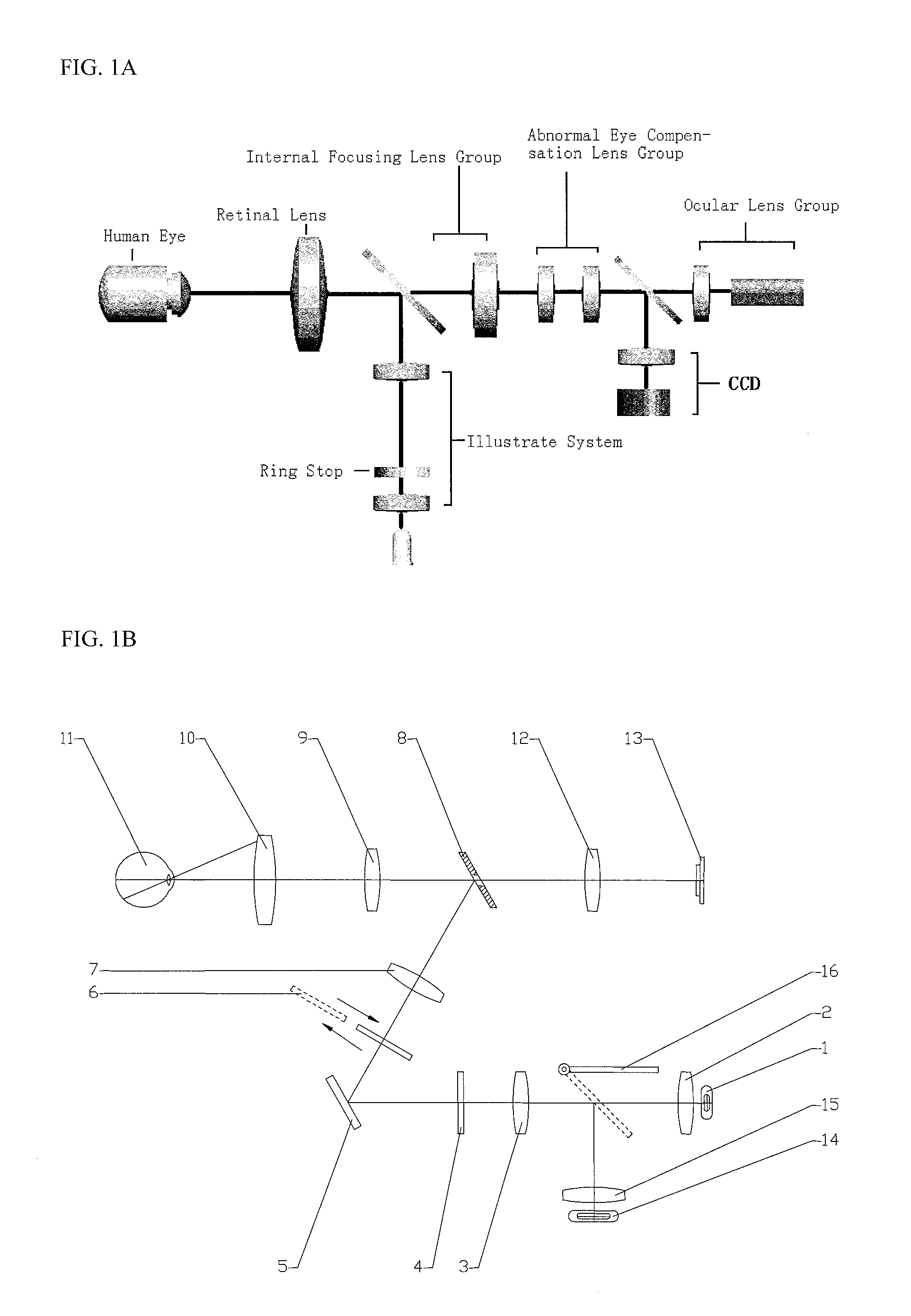
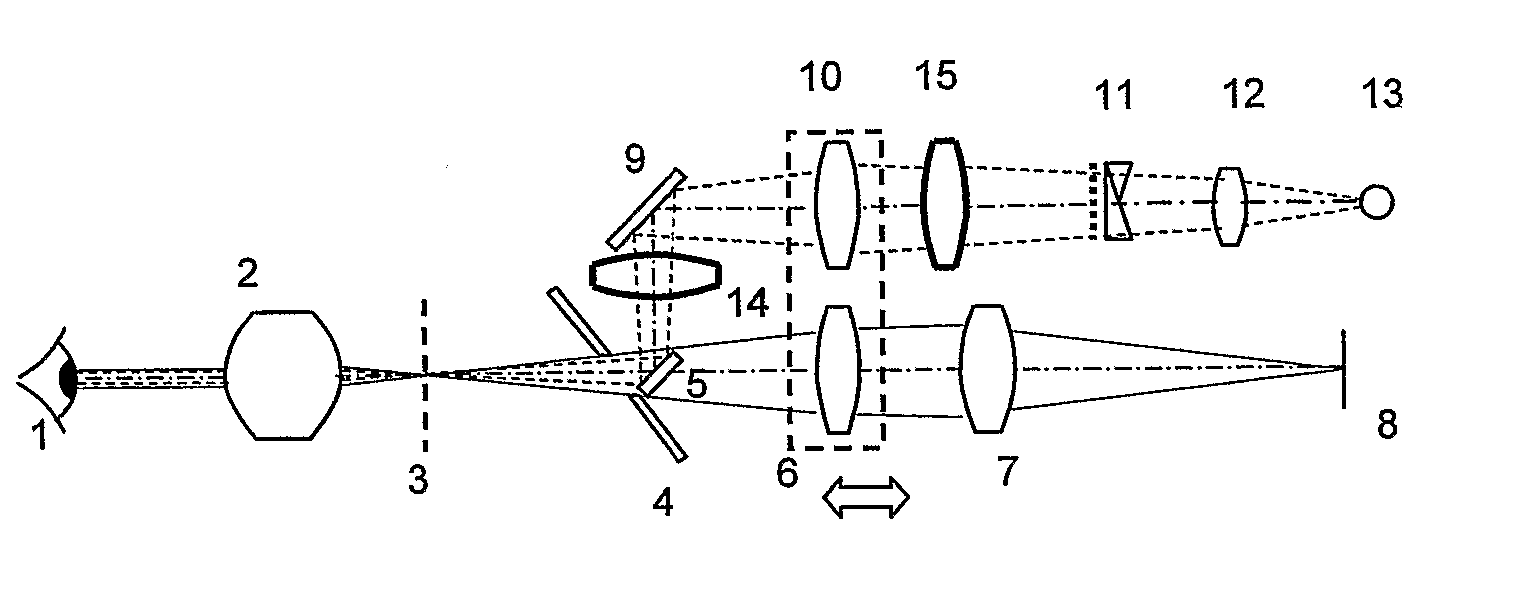
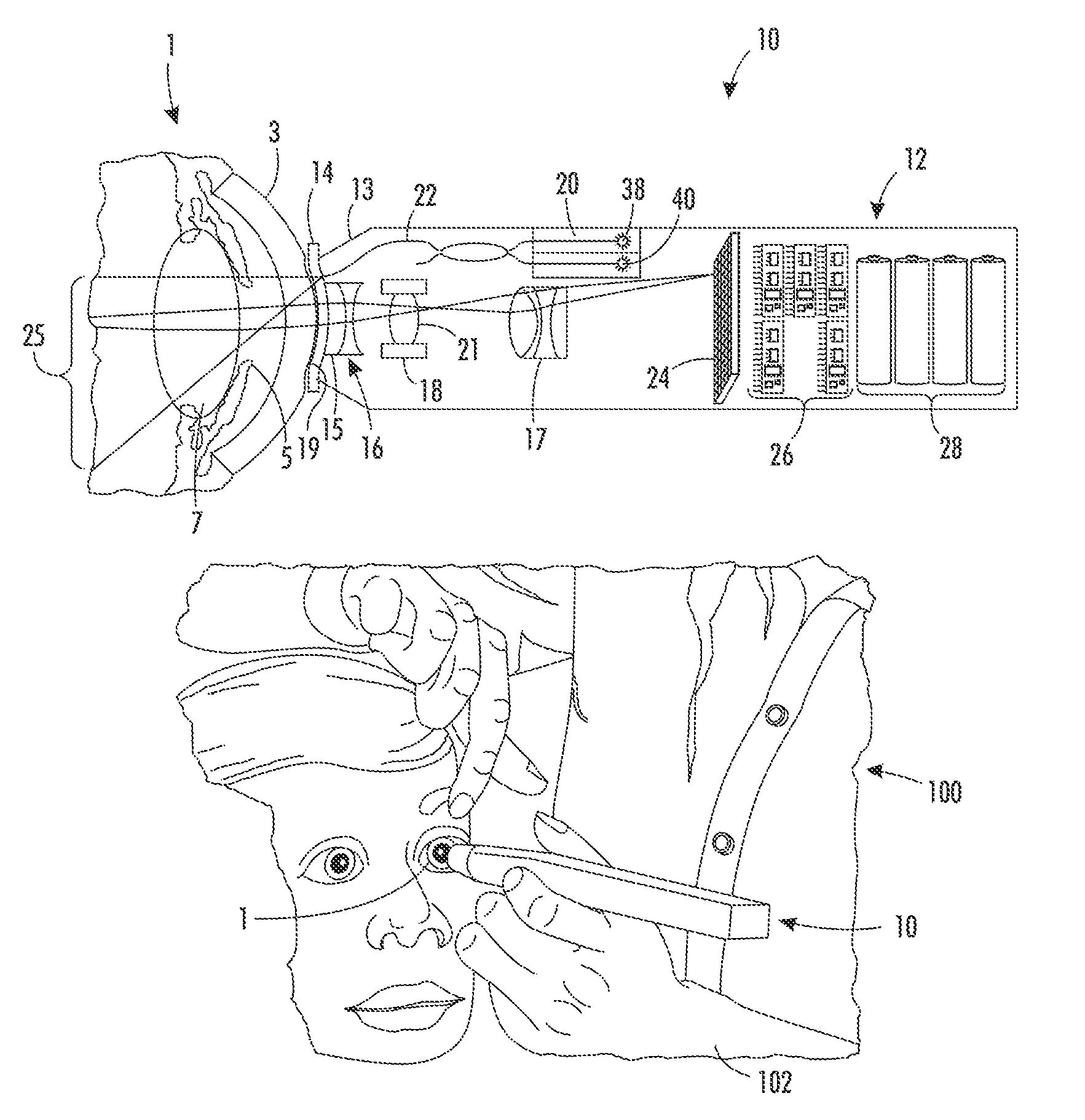
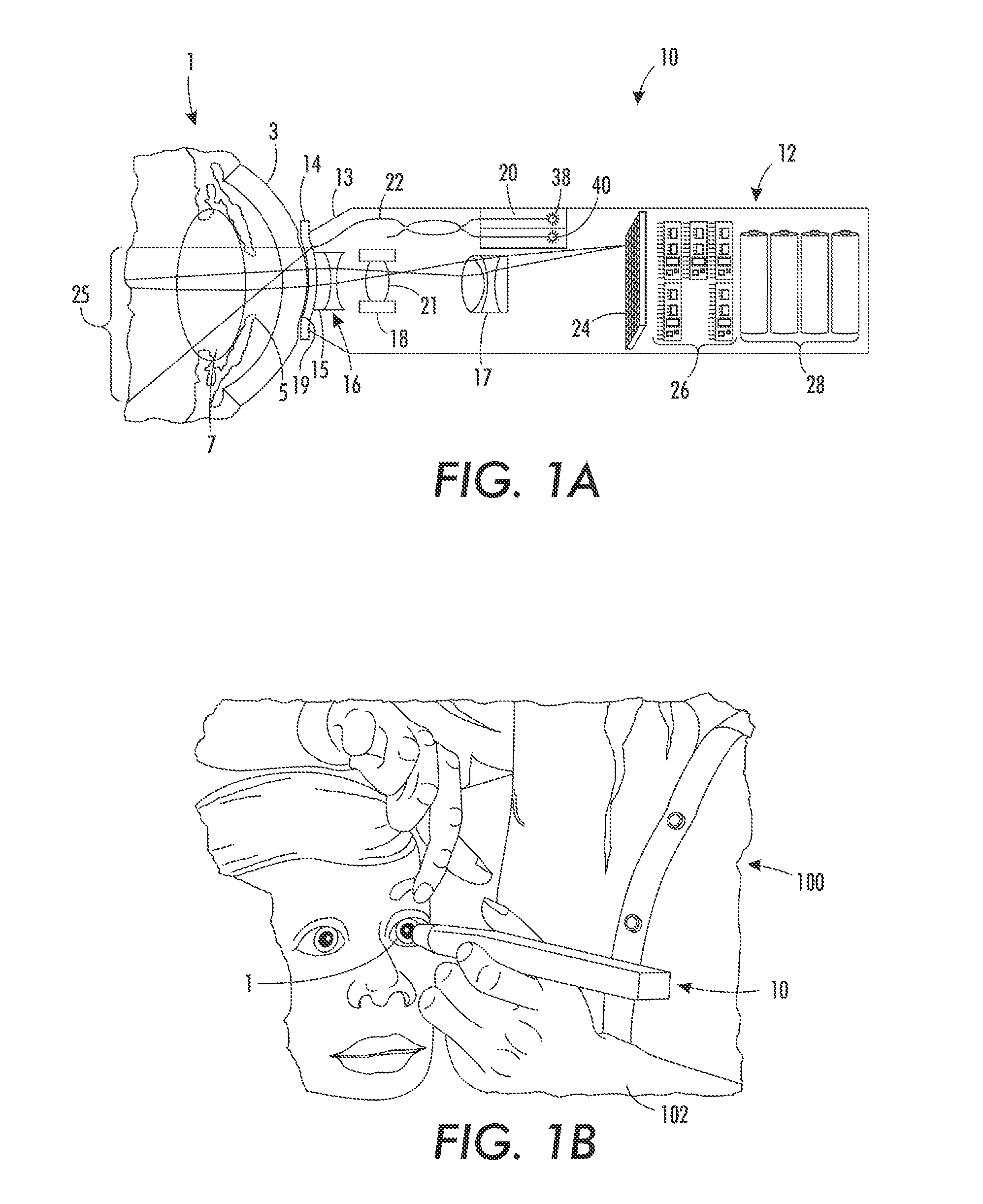
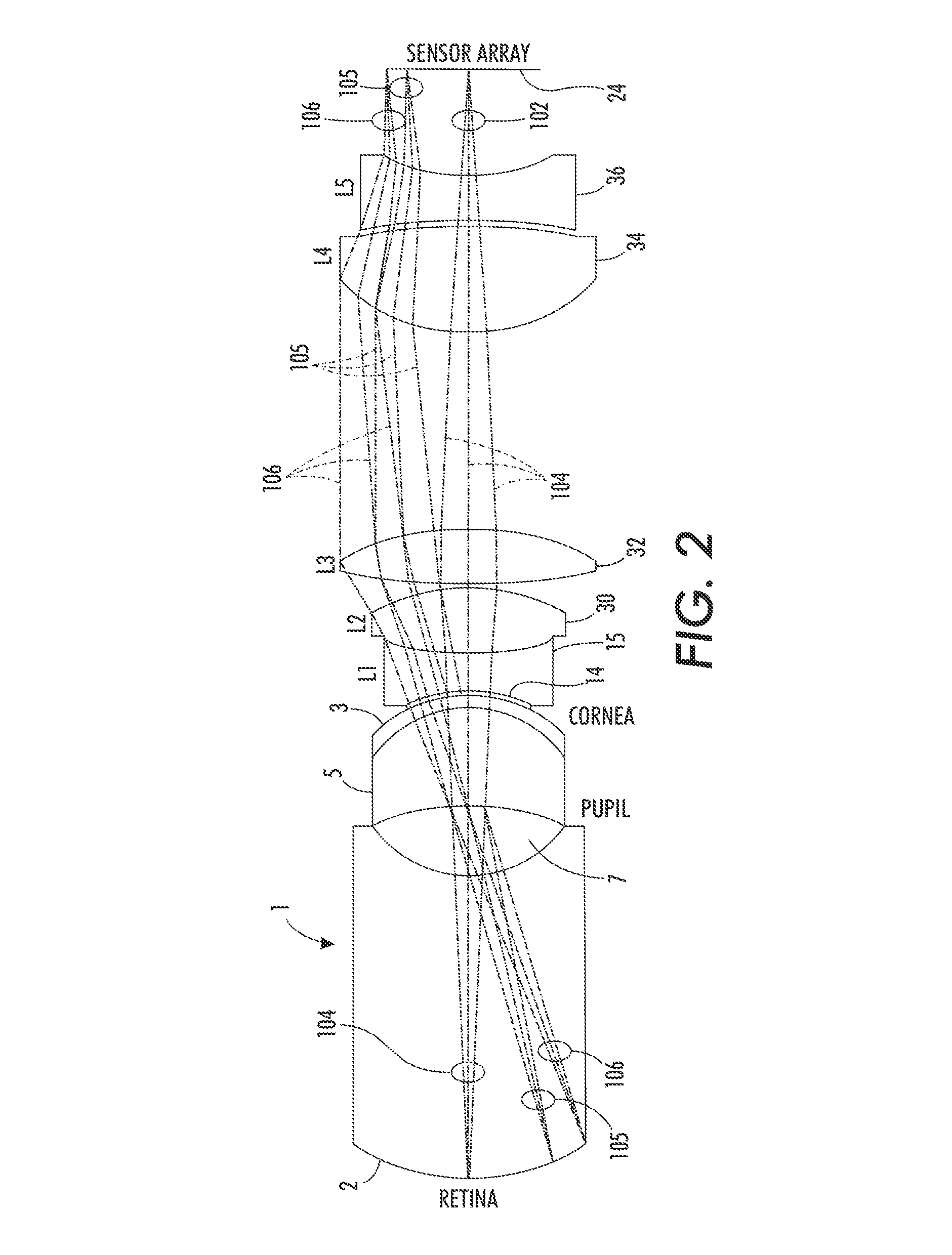
Specialized fundus cameras that consist of an intricate microscope attached to a flash enabled camera are used in fundus photography. The main structures that can be visualized on a fundus photo are the central and peripheral retina , optic disc and macula .
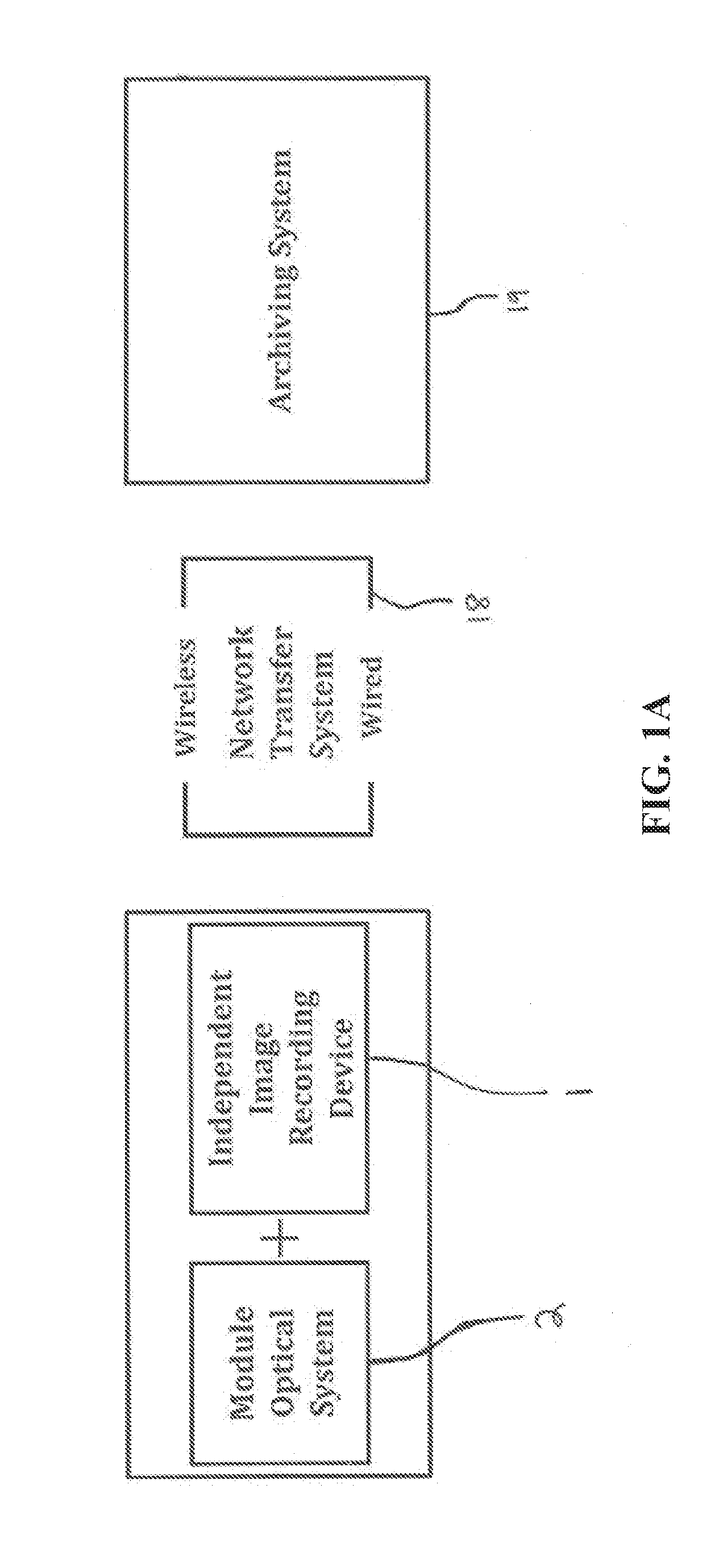
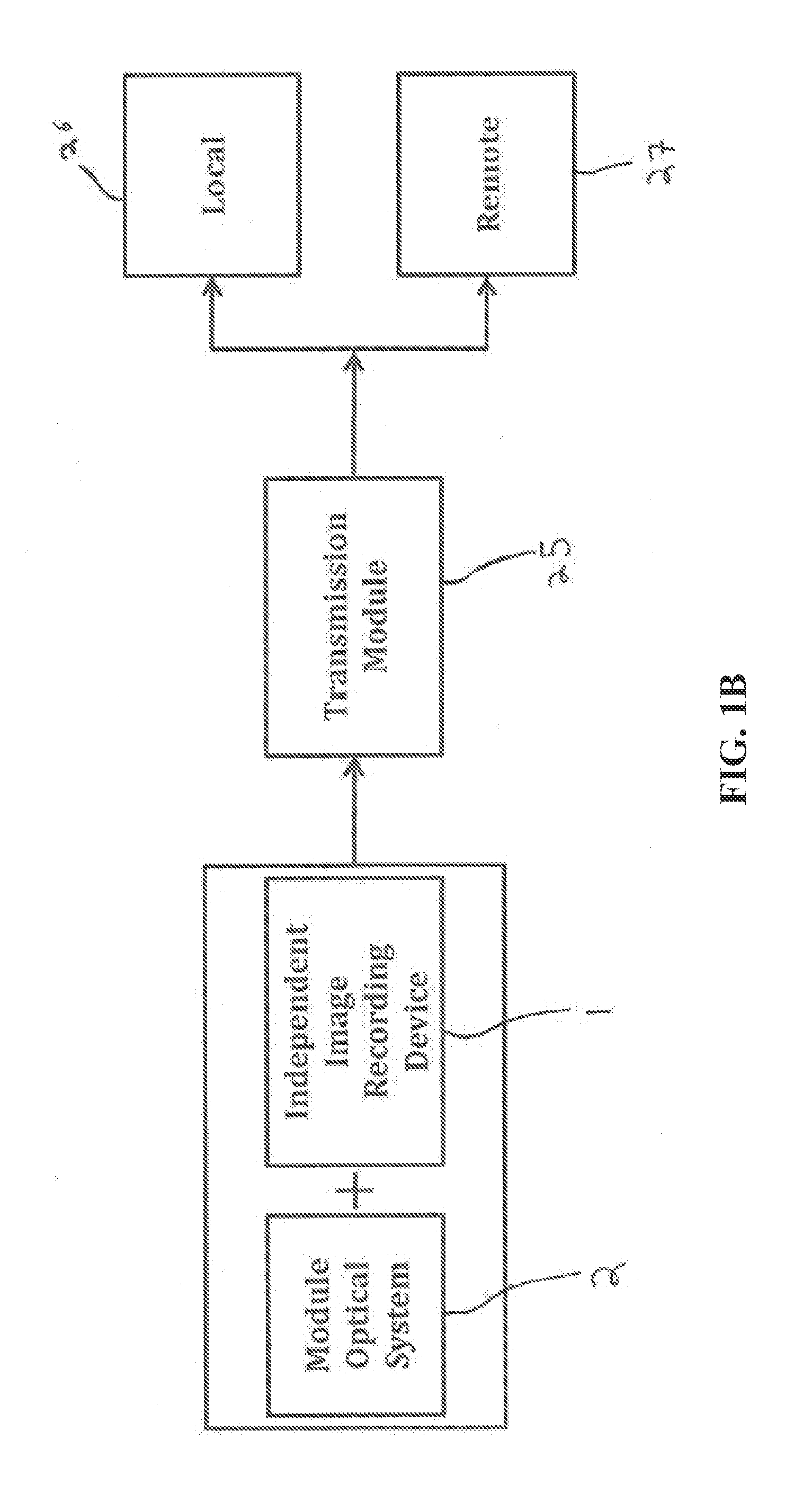
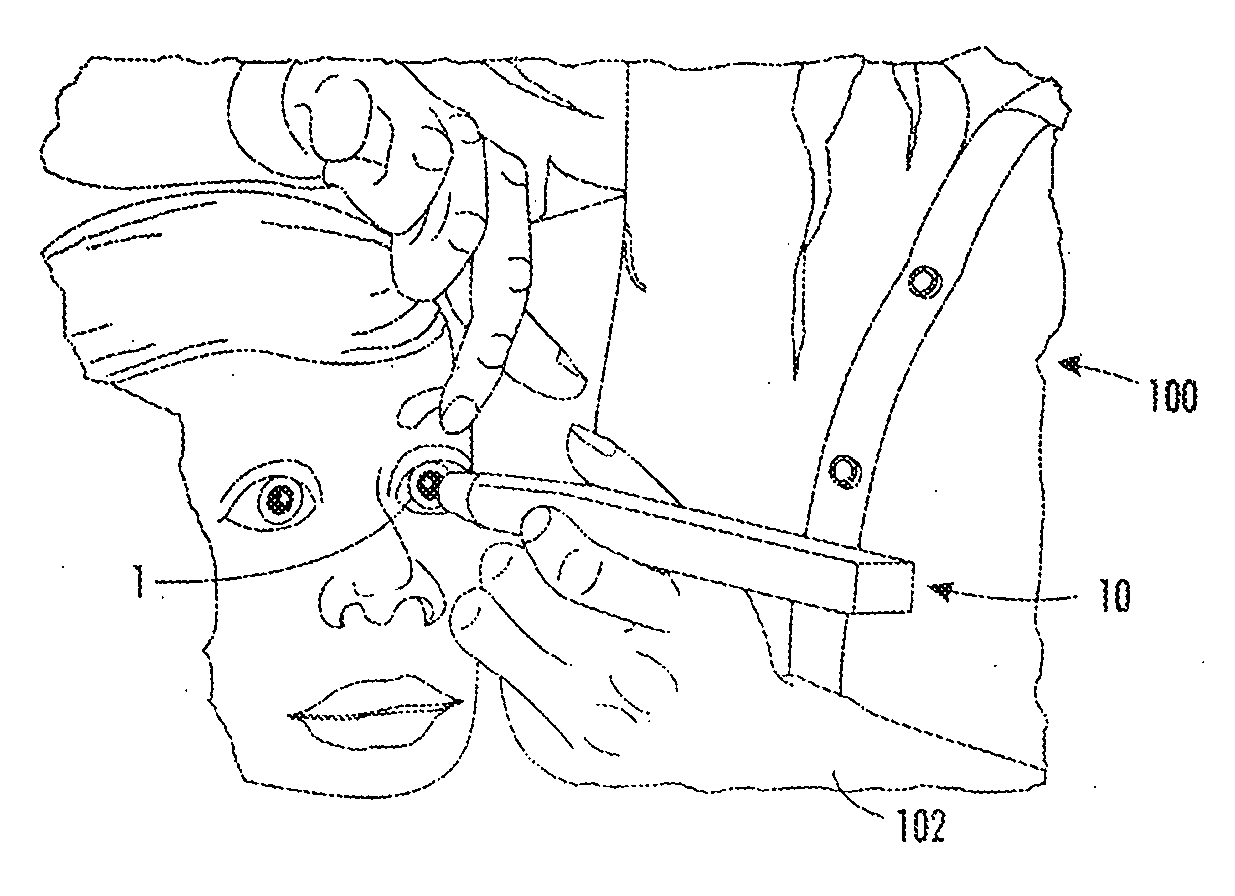
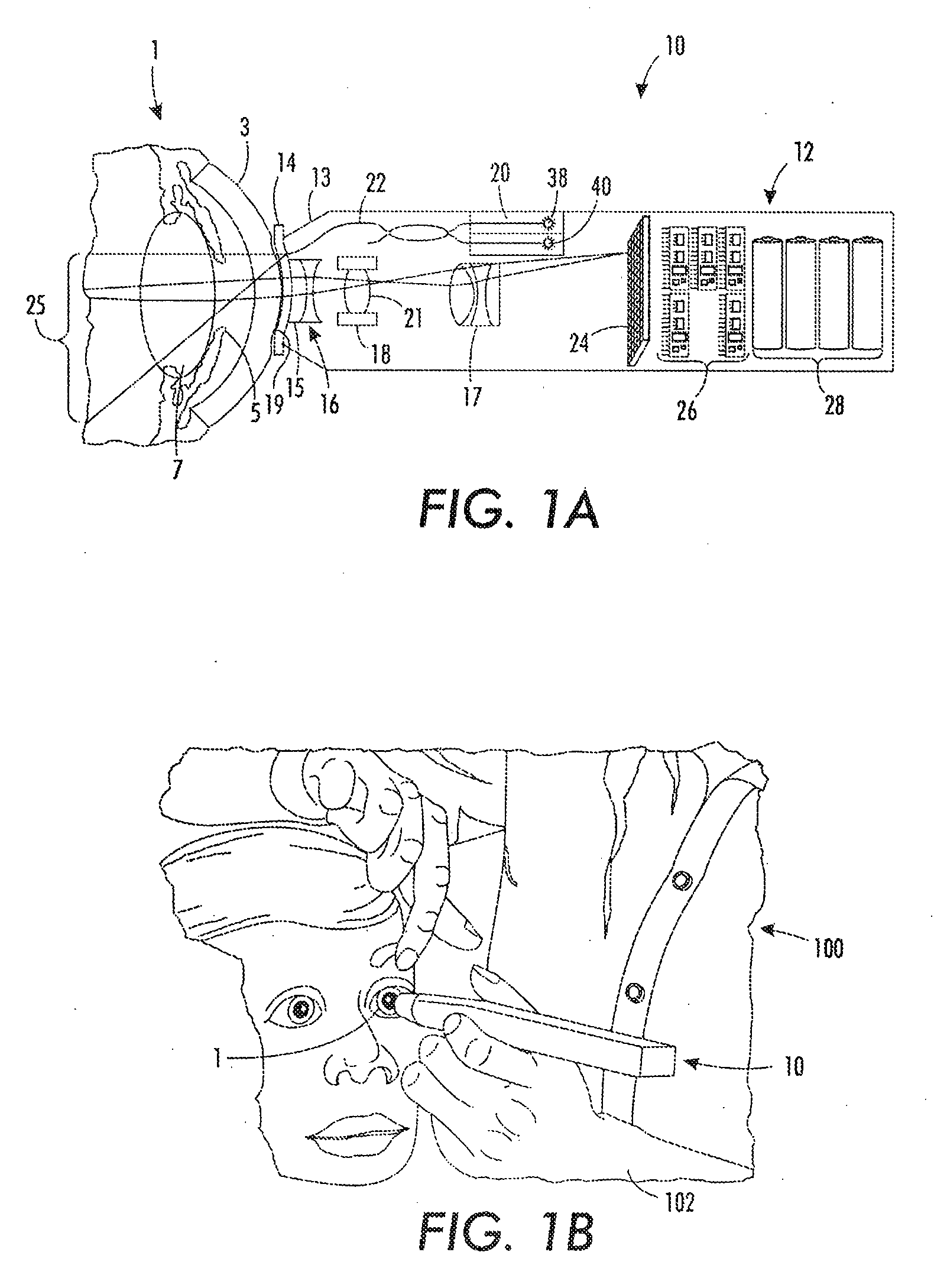
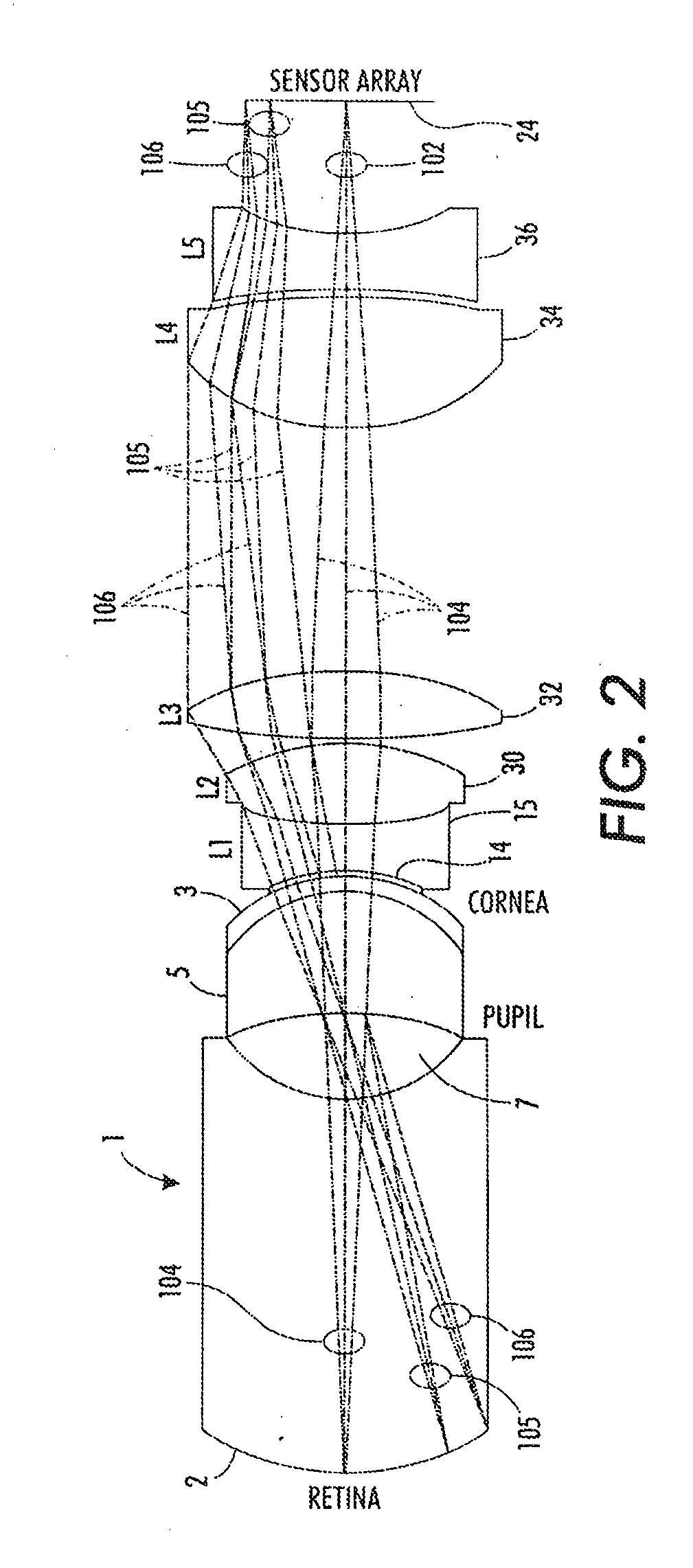
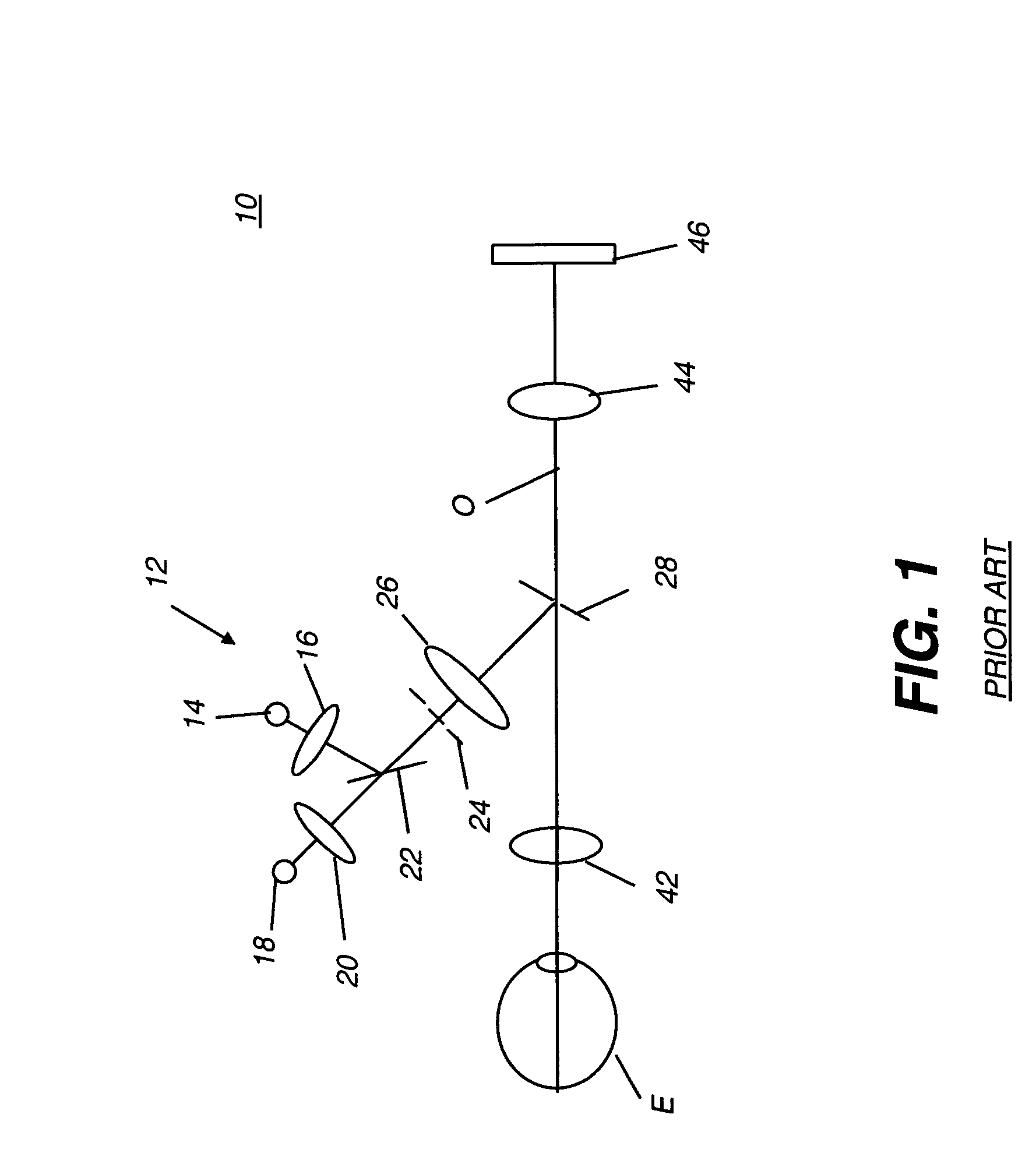
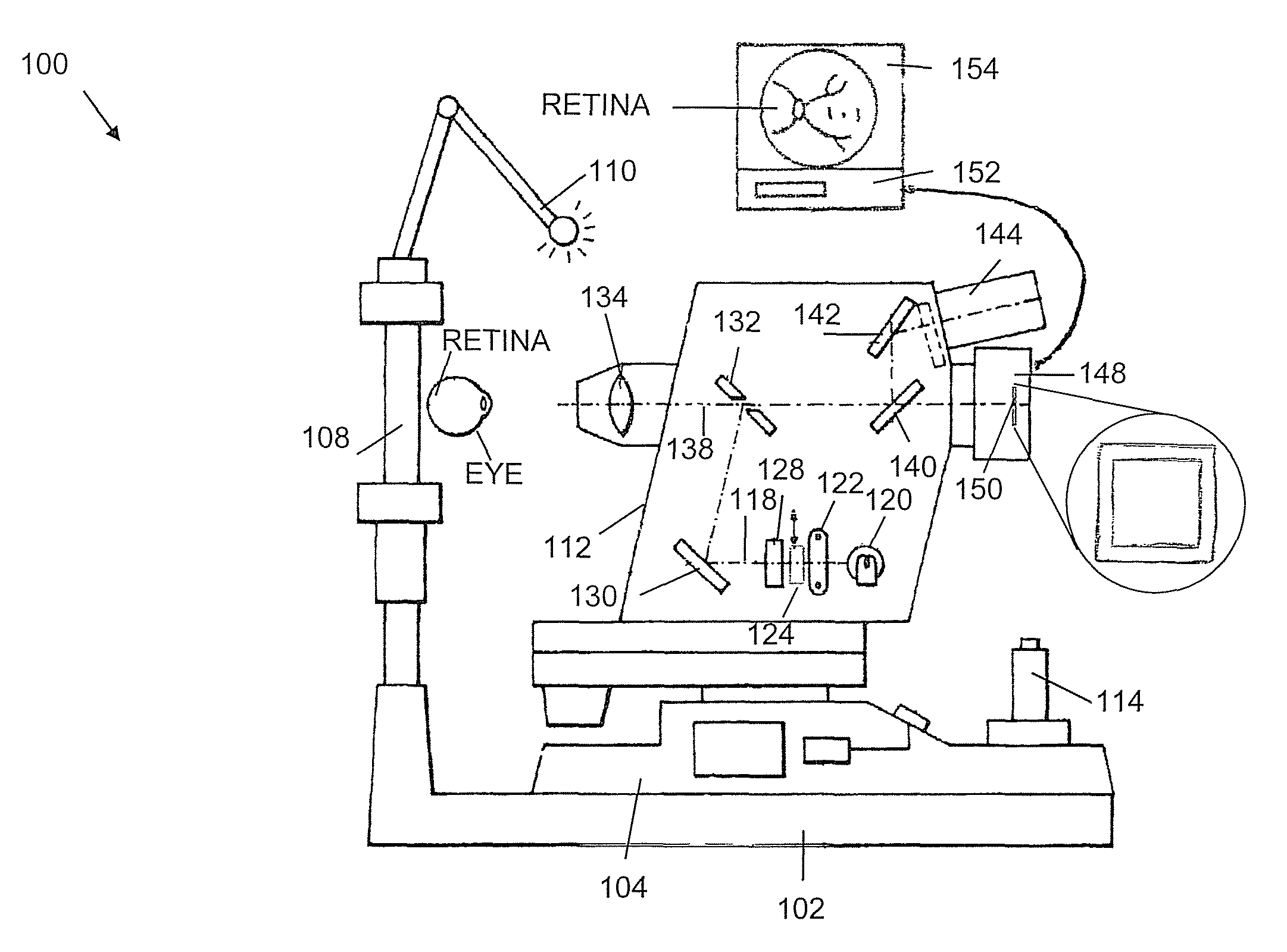
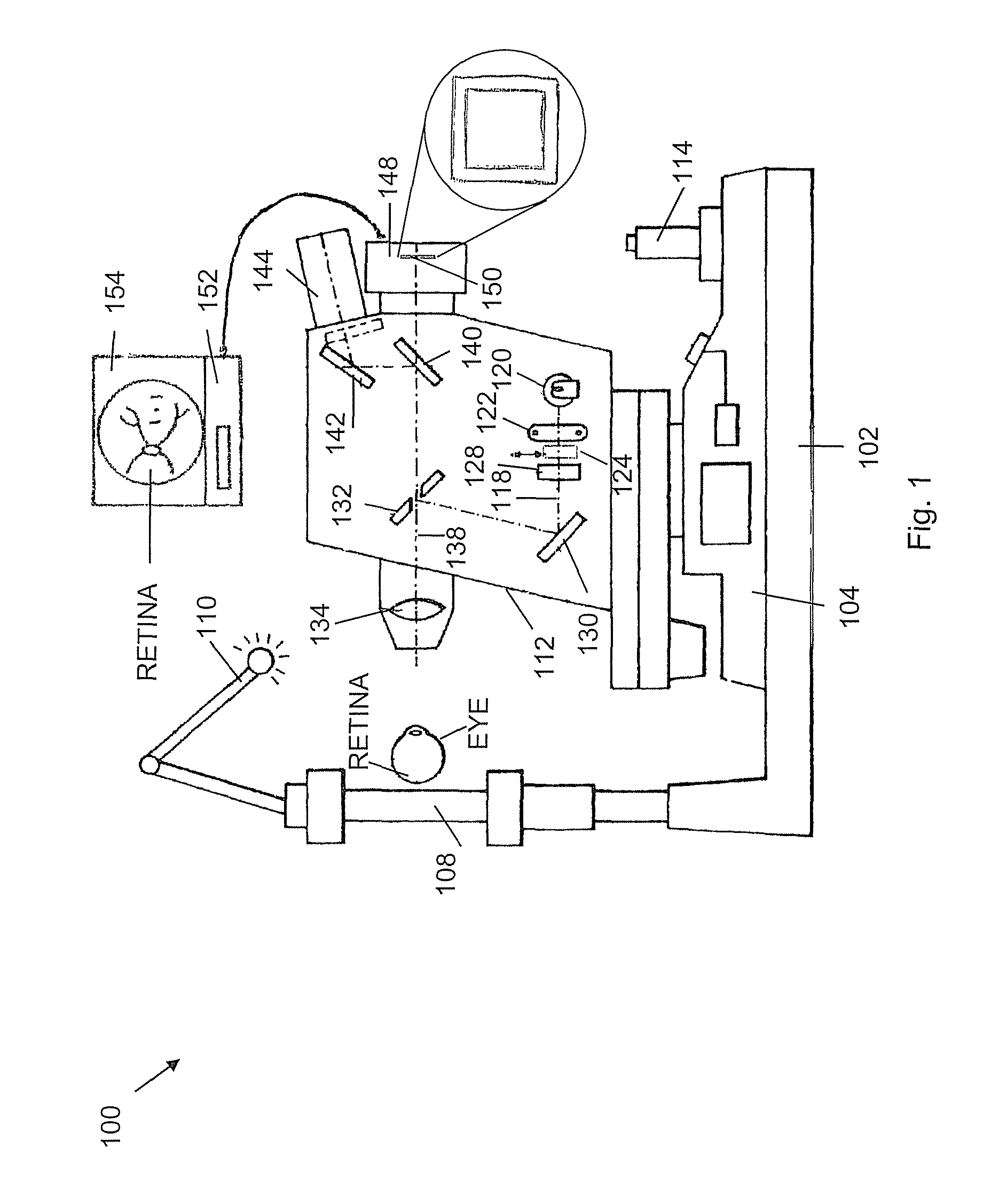
Camera Adapter Based Optical Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20110043661A1Cancel noiseLow costTelevision system detailsInterferometersSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
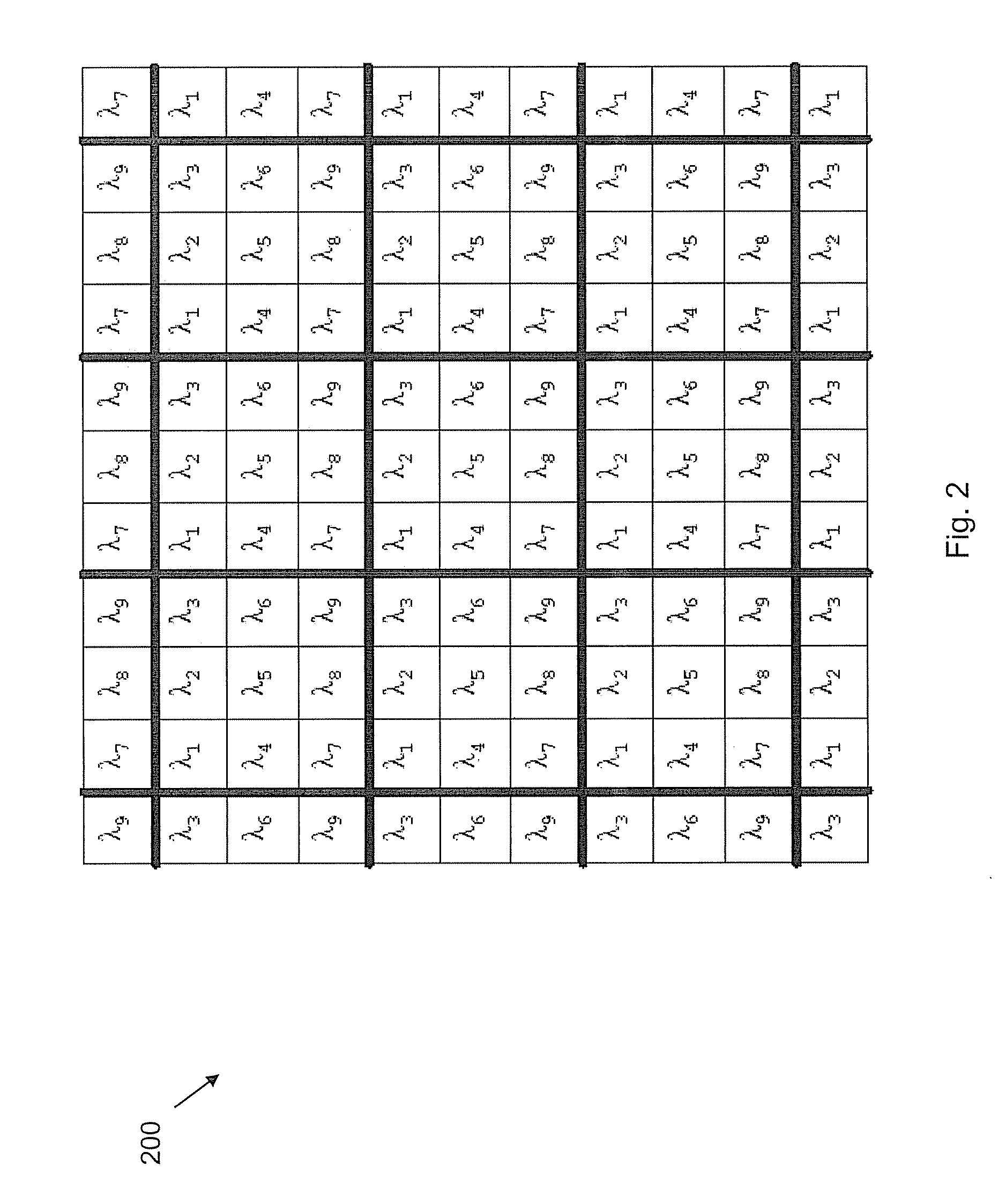
The invention describes several embodiments of an adapter which can make use of the devices in any commercially available digital cameras to accomplish different functions, such as a fundus camera, as a microscope or as an en-face optical coherence tomography (OCT) to produce constant depth OCT images or as a Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography to produce a reflectivity profile in the depth of an object or cross section OCT images, or depth resolved volumes. The invention admits addition of confocal detection and provides simultaneous measurements or imaging in at least two channels, confocal and OCT, where the confocal channel provides an en-face image simultaneous with the acquisition of OCT cross sections, to guide the acquisition as well as to be used subsequently in the visualisation of OCT images. Different technical solutions are provided for the assembly of one or two digital cameras which together with such adapters lead to modular and portable high resolution imaging systems which can accomplish various functions with a minimum of extra components while adapting the elements in the digital camera. The cost of such adapters is comparable with that of commercial digital cameras, i.e. the total cost of such assemblies of commercially digital cameras and dedicated adapters to accomplish high resolution imaging are at a fraction of the cost of dedicated stand alone instruments. Embodiments and methods are presented to employ colour cameras and their associated optical sources to deliver simultaneous signals using their colour sensor parts to provide spectroscopic information, phase shifting inferometry in one step, depth range extension, polarisation, angular measurements and spectroscopic Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography in as many spectral bands simultaneously as the number of colour parts of the photodetector sensor in the digital camera. In conjunction with simultaneous acquistion of a confocal image, at least 4 channels can simultaneously be provided using the three color parts of conventional color cameras to deliver three OCT images in addition to the confocal image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
Hand-held portable fundus camera for screening photography
ActiveUS20120229617A1Low costEasy to useTelevision system detailsAcquiring/recognising eyesFundus cameraHand held
System and Method pertaining to the modification and integration of an existing consumer digital camera, for example, with an optical imaging module to enable point and shoot fundus photography of the eye. The auto-focus macro capability of existing consumer cameras is adapted to photograph the retina over an extended diopter range, eliminating the need for manual diopter focus adjustment. The thru-the-lens (TTL) auto-exposure flash capability of existing consumer cameras is adapted to photograph the retina with automatic flash exposure eliminating the need for manual flash adjustment. The consumer camera imaging sensor and flash are modified to allow the camera sensor to perform both non-mydriatic focusing of the retina using infrared illumination and standard color flash photography of the retina without the need for additional imaging sensors or mechanical filters. These modifications and integration of existing consumer cameras for fundus photography of the eye significantly improve ease of manufacture and usability over existing fundus cameras.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Snapshot Spectral Imaging of the Eye
ActiveUS20090225277A1Minimizes problemStrong robustnessSpectrum investigationDiagnostic recording/measuringFundus cameraPupil
Obtaining spectral images of an eye includes taking an optical system that images eye tissue onto a digital sensor array and optically fitting a multi-spectral filter array and the digital sensor array, wherein the multi-spectral filter array is disposed between the digital sensor array and an optics portion of the optical system. The resulting system facilitates acquisition of a snap-shot image of the eye tissue with the digital sensor array. The snap shot images support estimation of blood oxygen saturation in a retinal tissue. The resulting system can be based on a non-mydriatic fundus camera designed to obtain the retinal images without administration of pupil dilation drops.
Owner:MERGE HEALTHCARE
Modular adaptive optical subsystem for integration with a fundus camera body and CCD camera unit and improved fundus camera employing same
InactiveUS20030007124A1Reduce complexityLow costLaser surgeryRefractometersWavefront sensorOptical Module
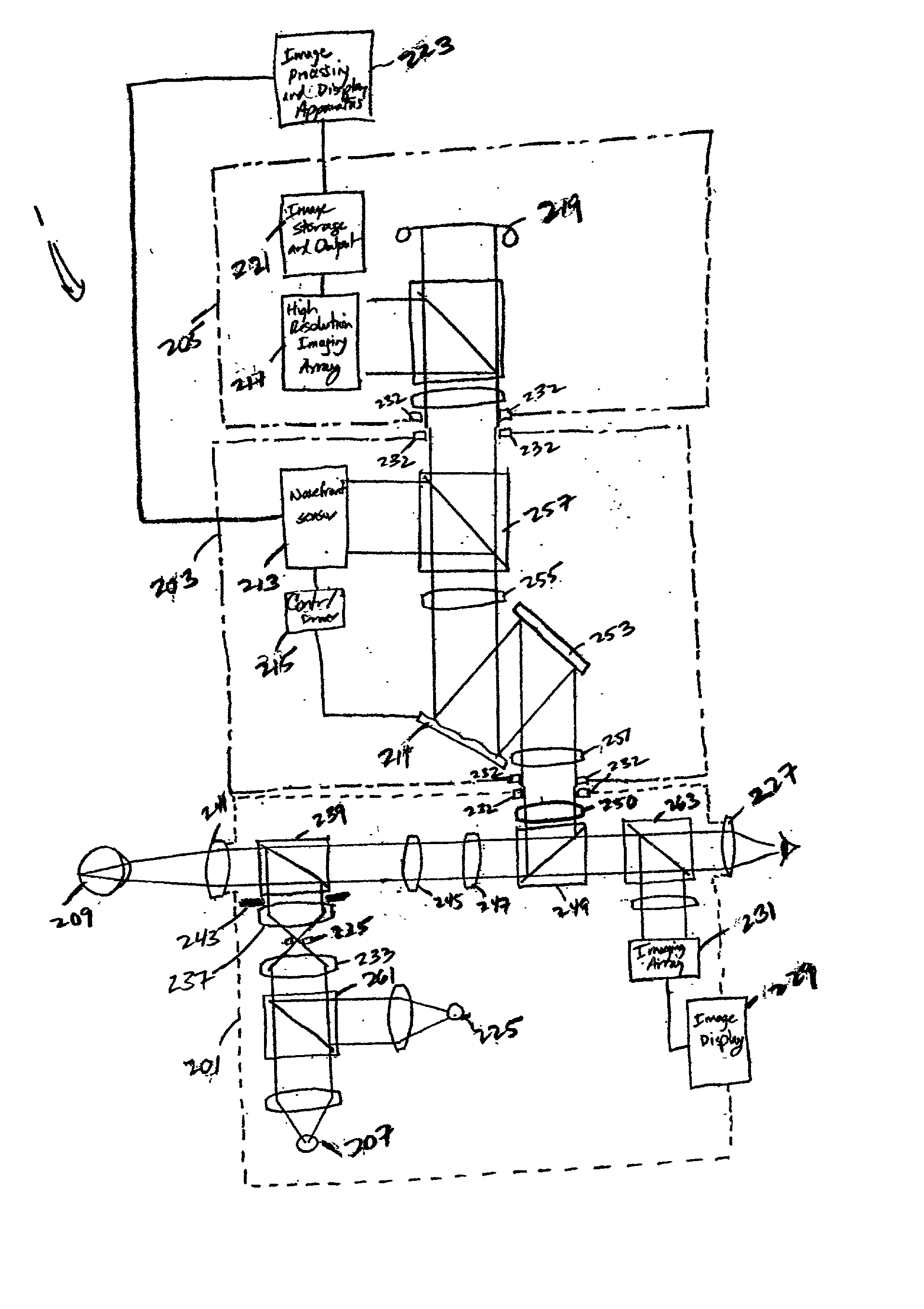
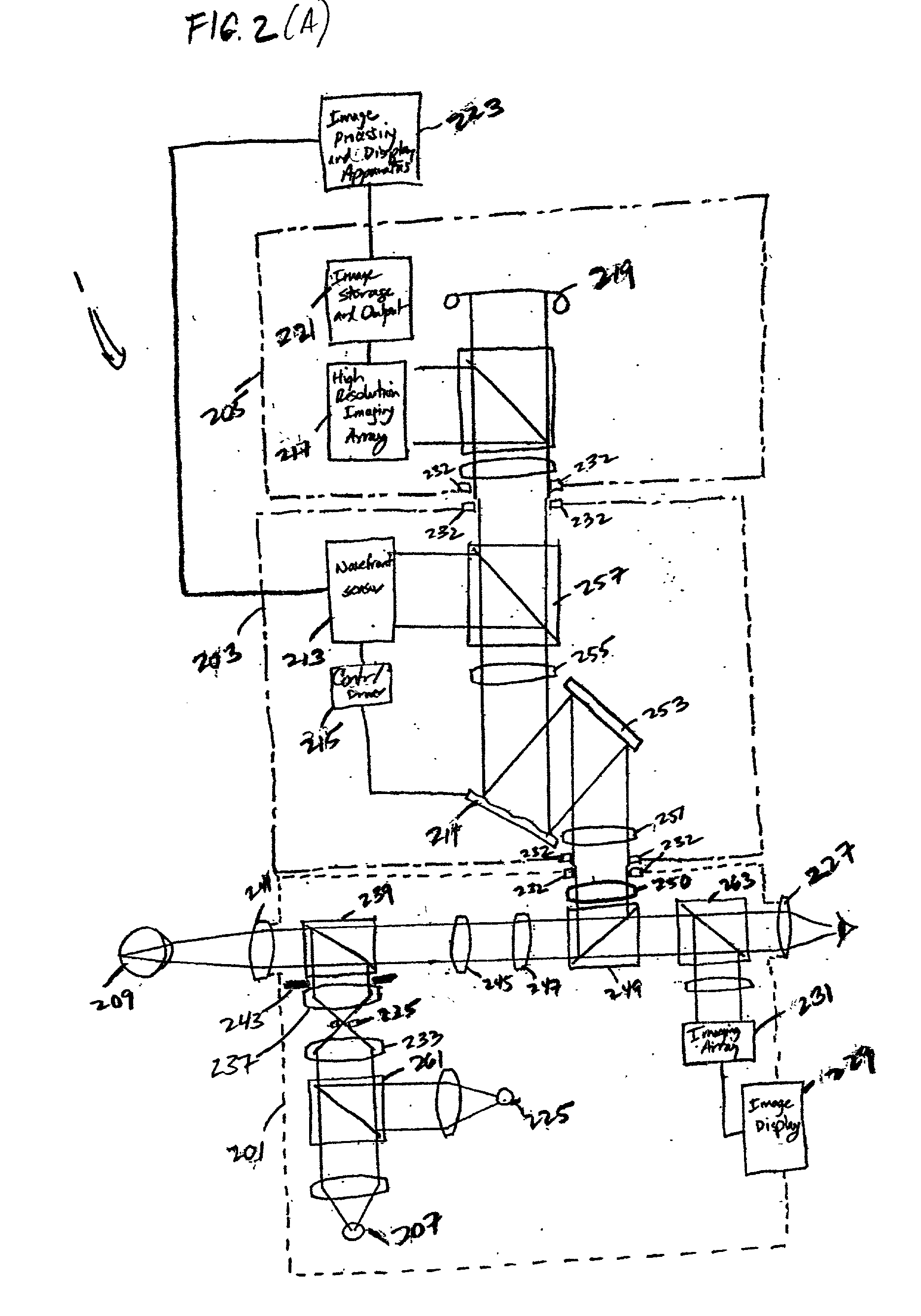
A modular fundus camera including an adaptive optical module that detachably interfaces to a fundus camera body and image capture subsystem. The fundus camera body directs light produced from a first light source into the human eye and that collects and collimates retinal reflections. The adaptive optical module includes a wavefront sensor, controller and phase-compensating optical element. The wavefront sensor measures phase aberrations in the retinal reflections and operates in a closed-loop fashion with the controller to control the phase-compensating optical element to compensate for such phase aberrations to produce phase-compensated retinal reflections for output to the image capture subsystem.
Owner:ADAPTIVE OPTICS ASSOC
Portable fundus camera
ActiveUS20120287255A1Speed flowEconomically beneficialUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcquiring/recognising eyesFundus cameraHand held
A portable hand-held camera for imaging the fundus of an eye, the camera comprising a housing comprising an internal cavity terminating at a forward housing end, a forward lens, and a light source configured to direct light from locations distributed around the perimeter of the forward lens forwardly out of the housing end. In other embodiment, a portable hand-held camera for imaging the fundus of an eye includes optics configured to focus light reflected back from the fundus onto an image receptor, with the optics being capable of varying the field of view among differing portions of the fundus. Methods to ensure unique image identification and storage are described.
Owner:LUMETRICS
Eye fundus image characteristics extraction method for diabetic retinopathy
InactiveCN103870838AEasy diagnosisImage symptoms are clearImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCotton wool patchesDiabetes retinopathy
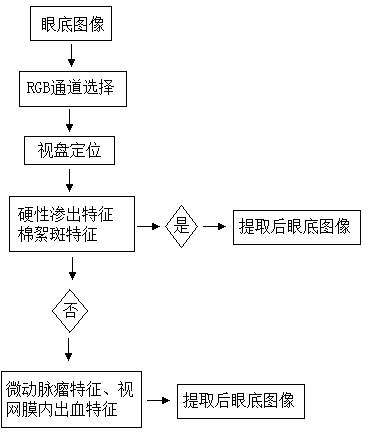
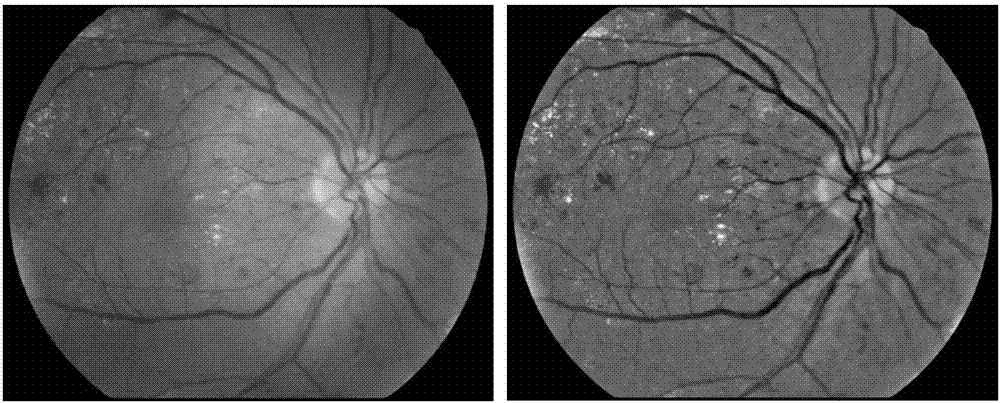
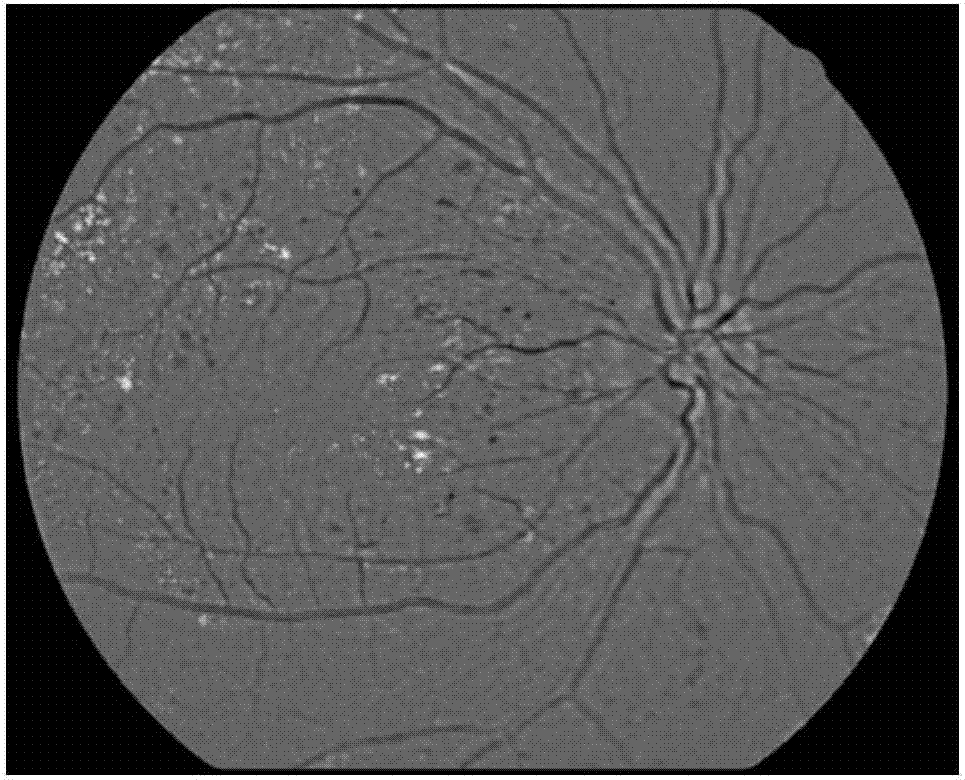
The invention discloses an eye fundus image characteristics extraction method for diabetic retinopathy by utilizing an eye fundus image shot by a digital mydriatic-free eye fundus camera. The method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting an RGB channel of the eye fundus image; (2) positioning the optic disk of the eye fundus image; (3) extracting the hard exudate characteristics and the cotton wool spot characteristics of the eye fundus image, generating an extracted eye fundus image if at least one characteristic is discovered, if no characteristic is discovered, extracting microaneurysm characteristics and retinal hemorrhage characteristics, and generating an extracted eye fundus image. The method belongs to a non-intrusive technology, and is simple, rapid, convenient and effective, and the processed image is clear and obvious in symptom, so the diagnosis of a doctor is facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
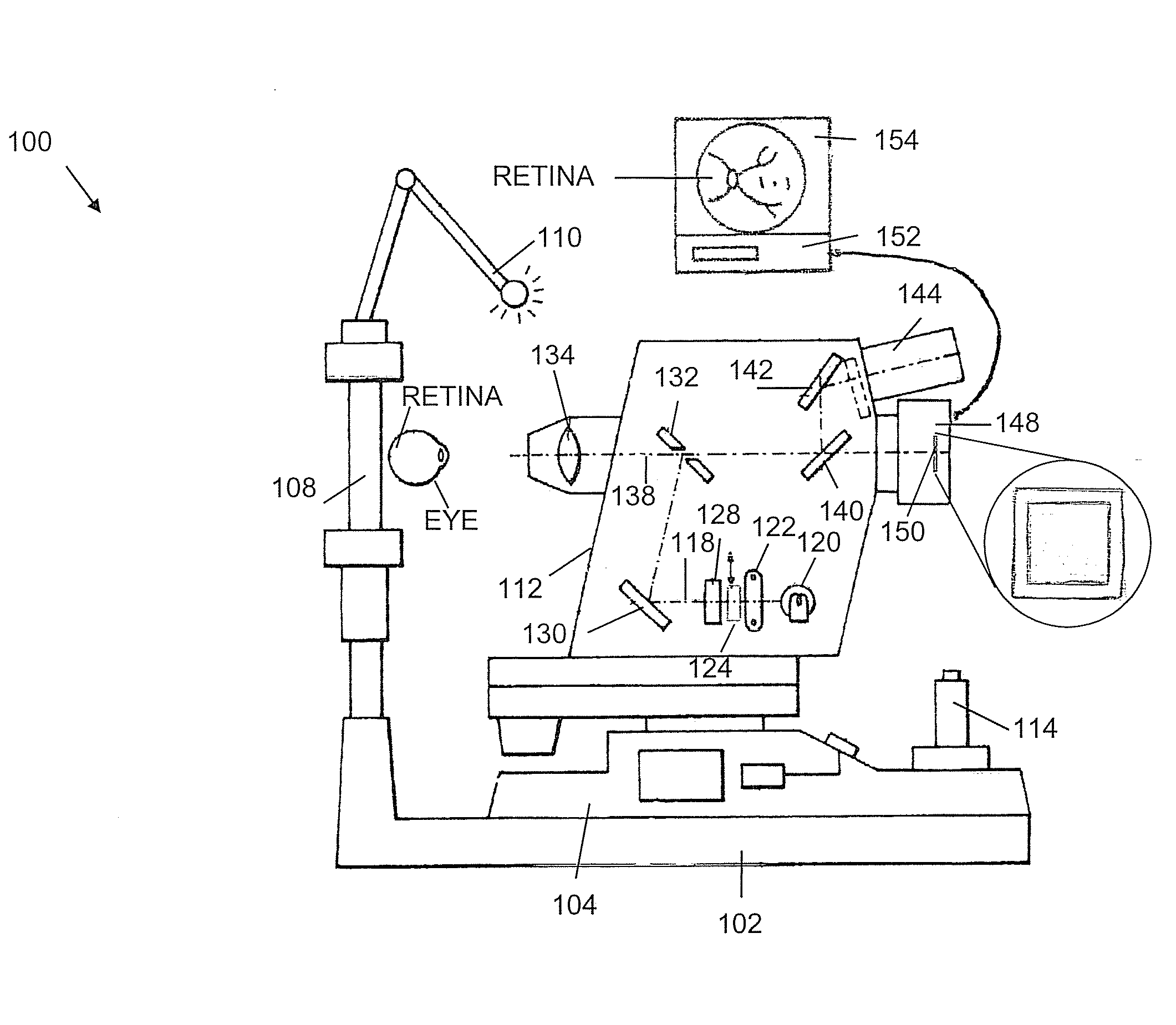
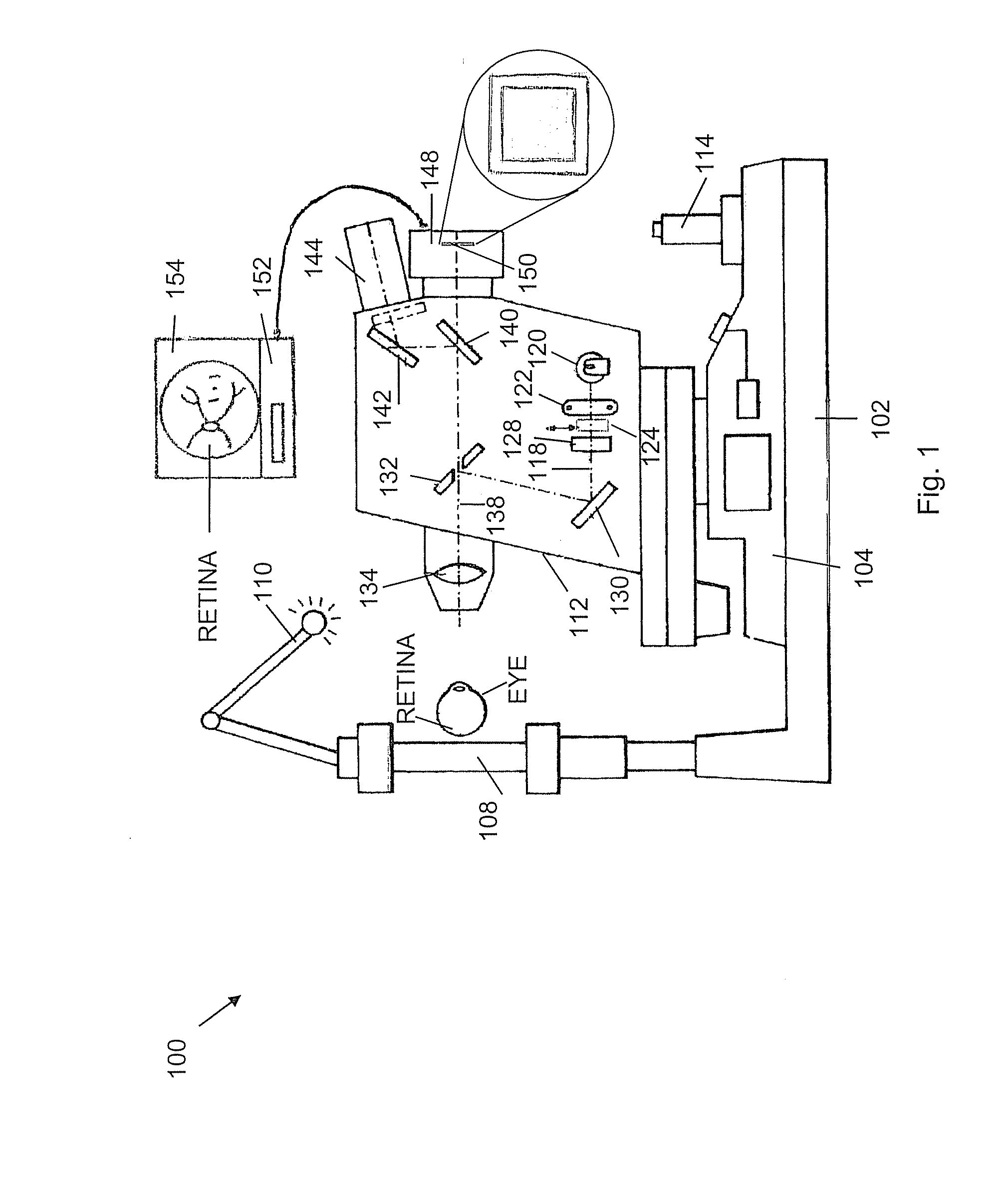
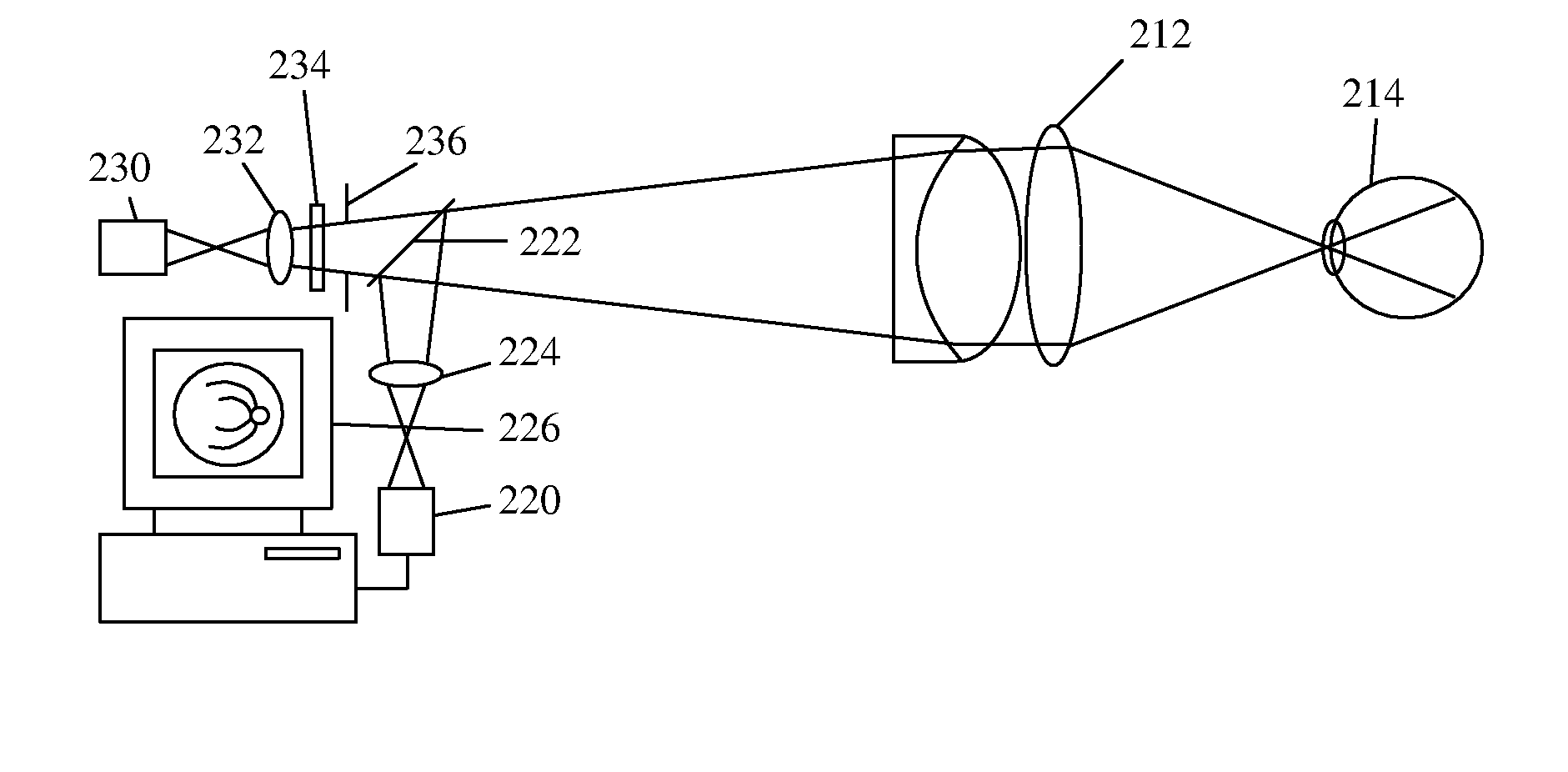
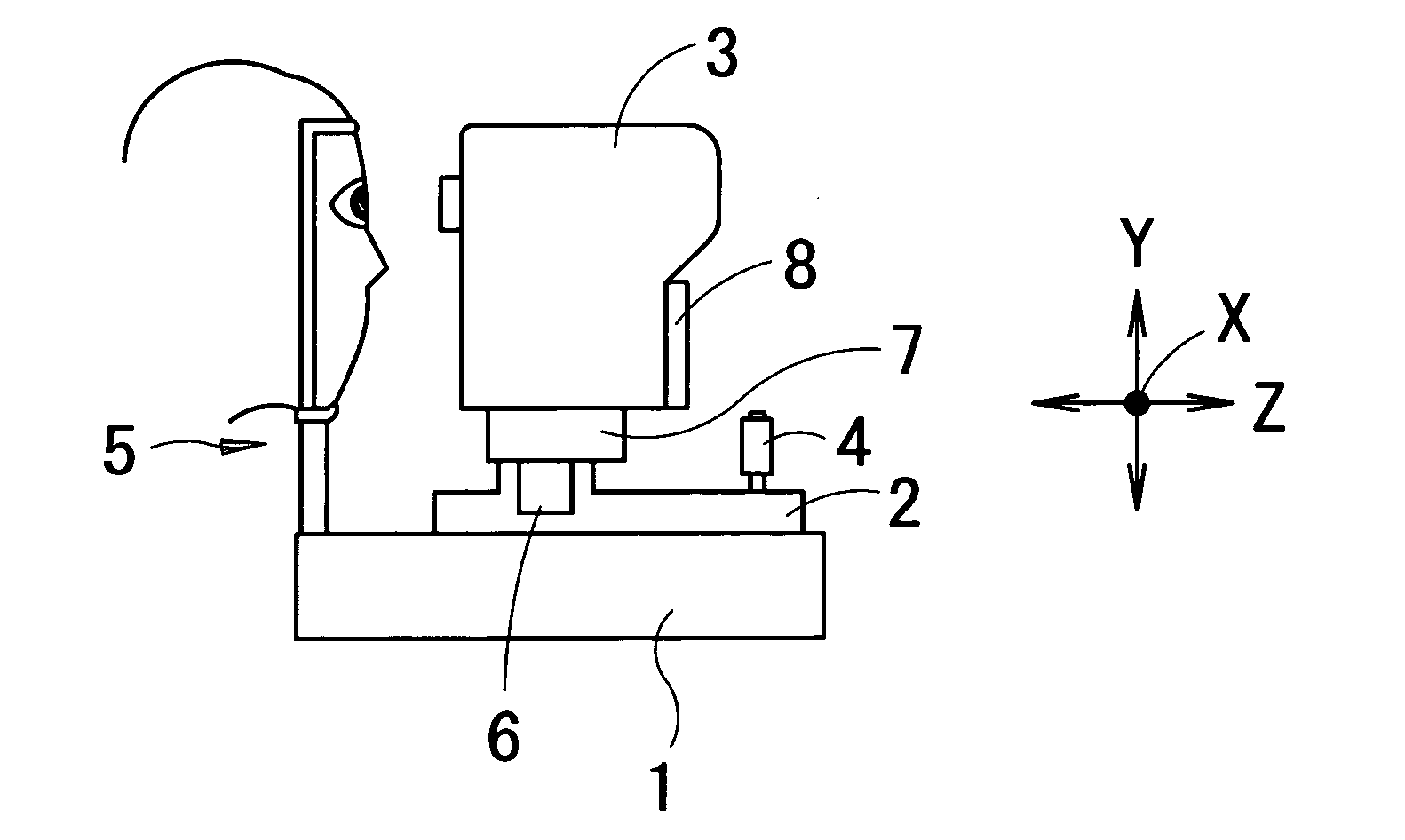
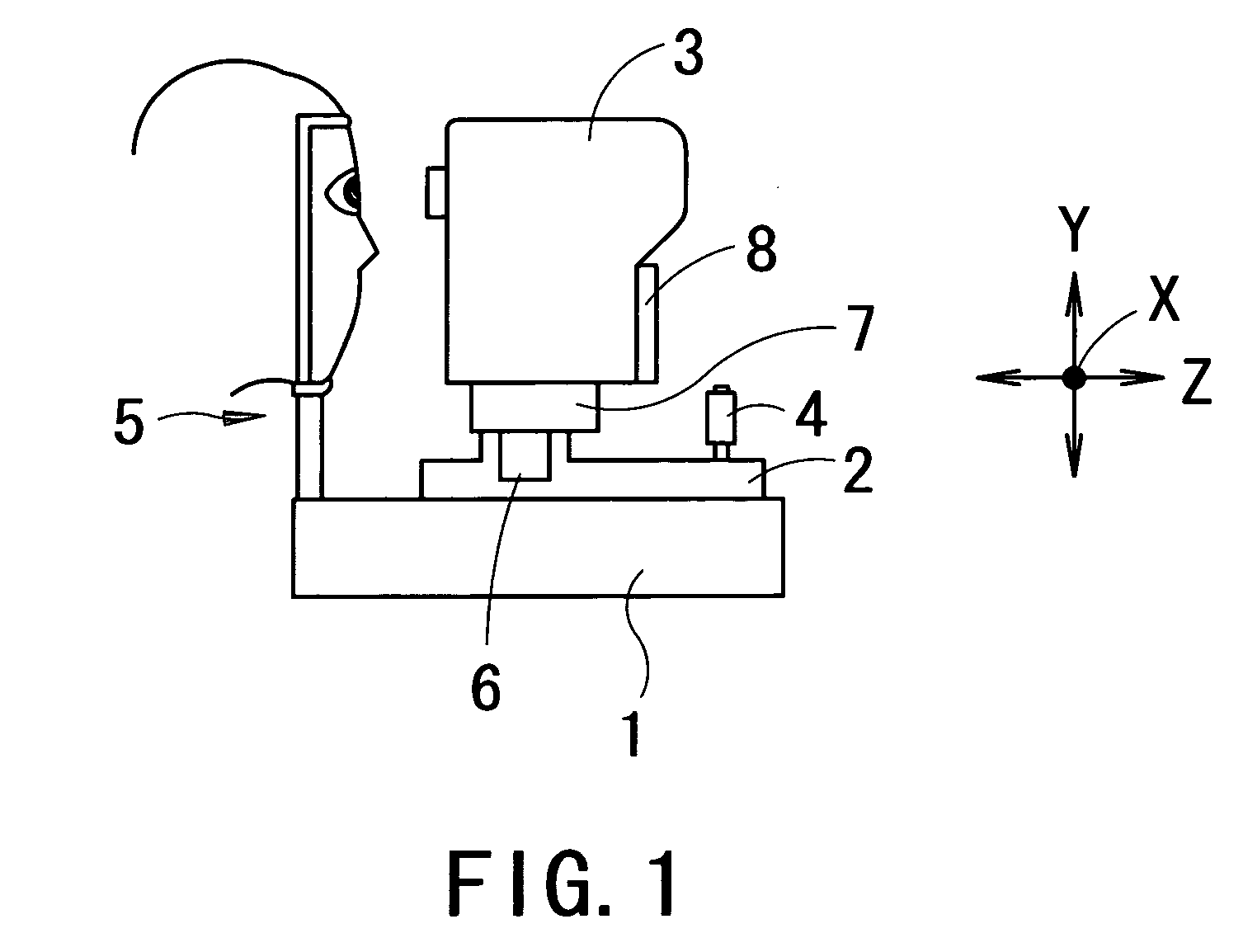
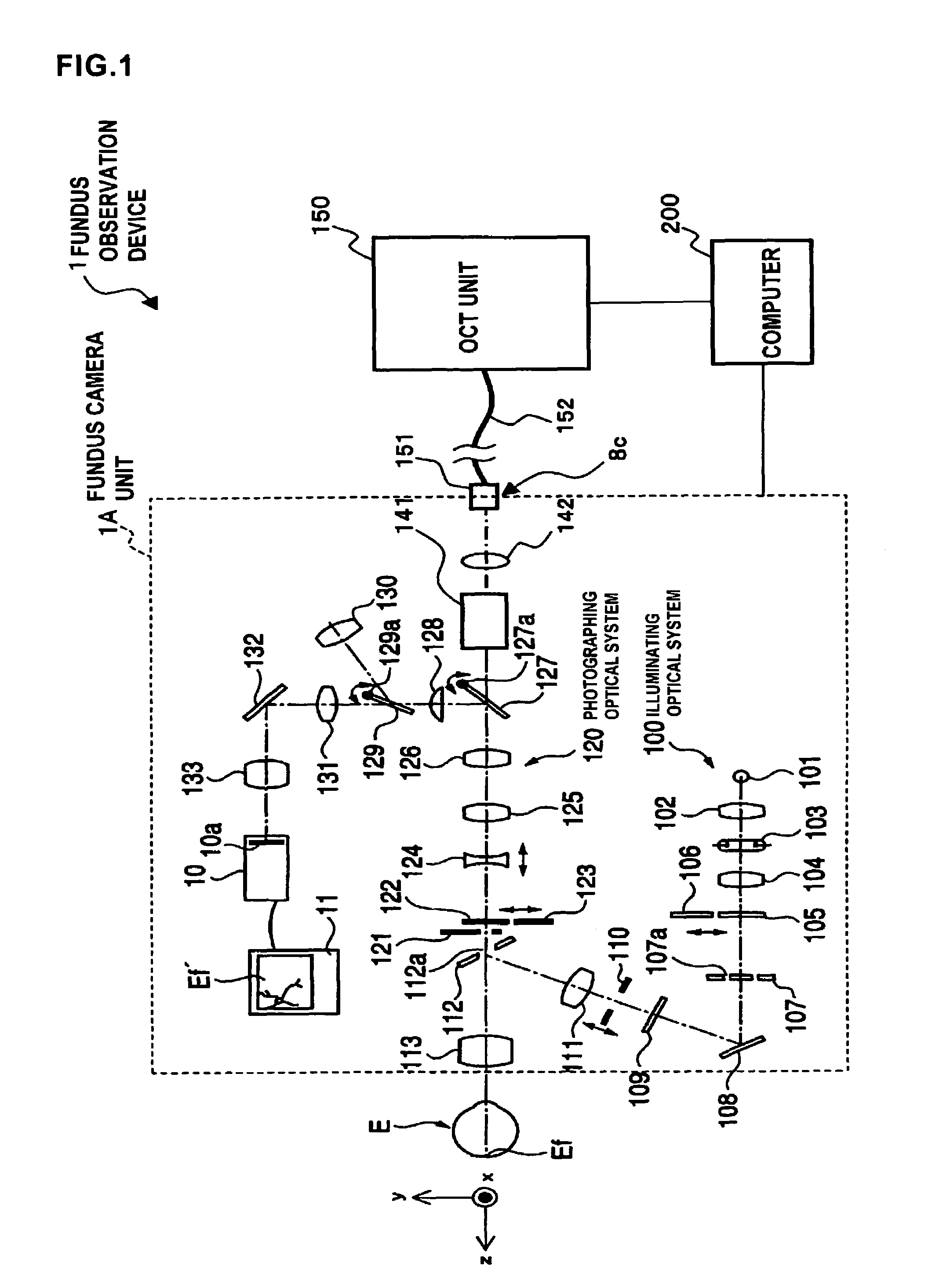
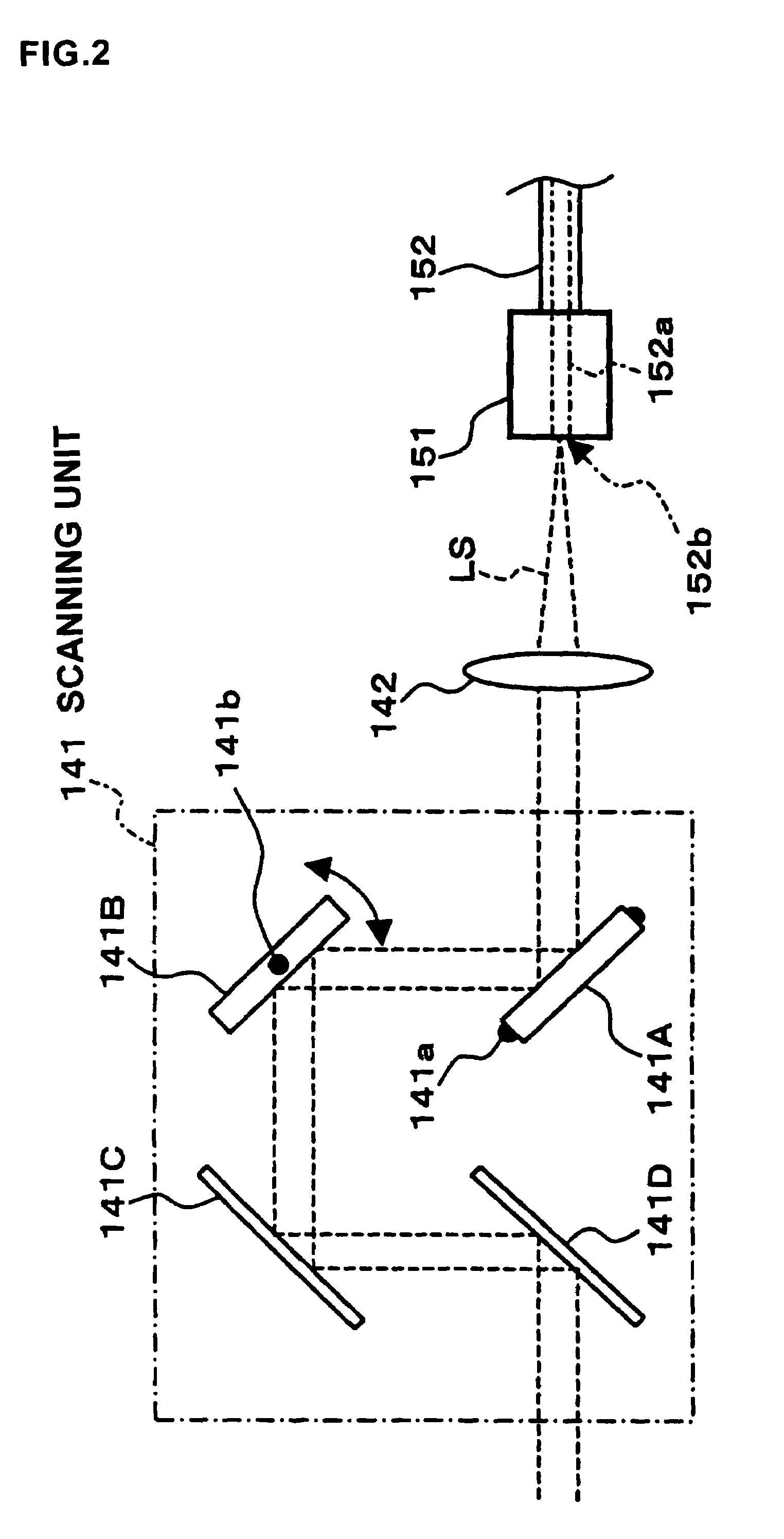
Fundus observation device, fundus image display device and fundus observation program
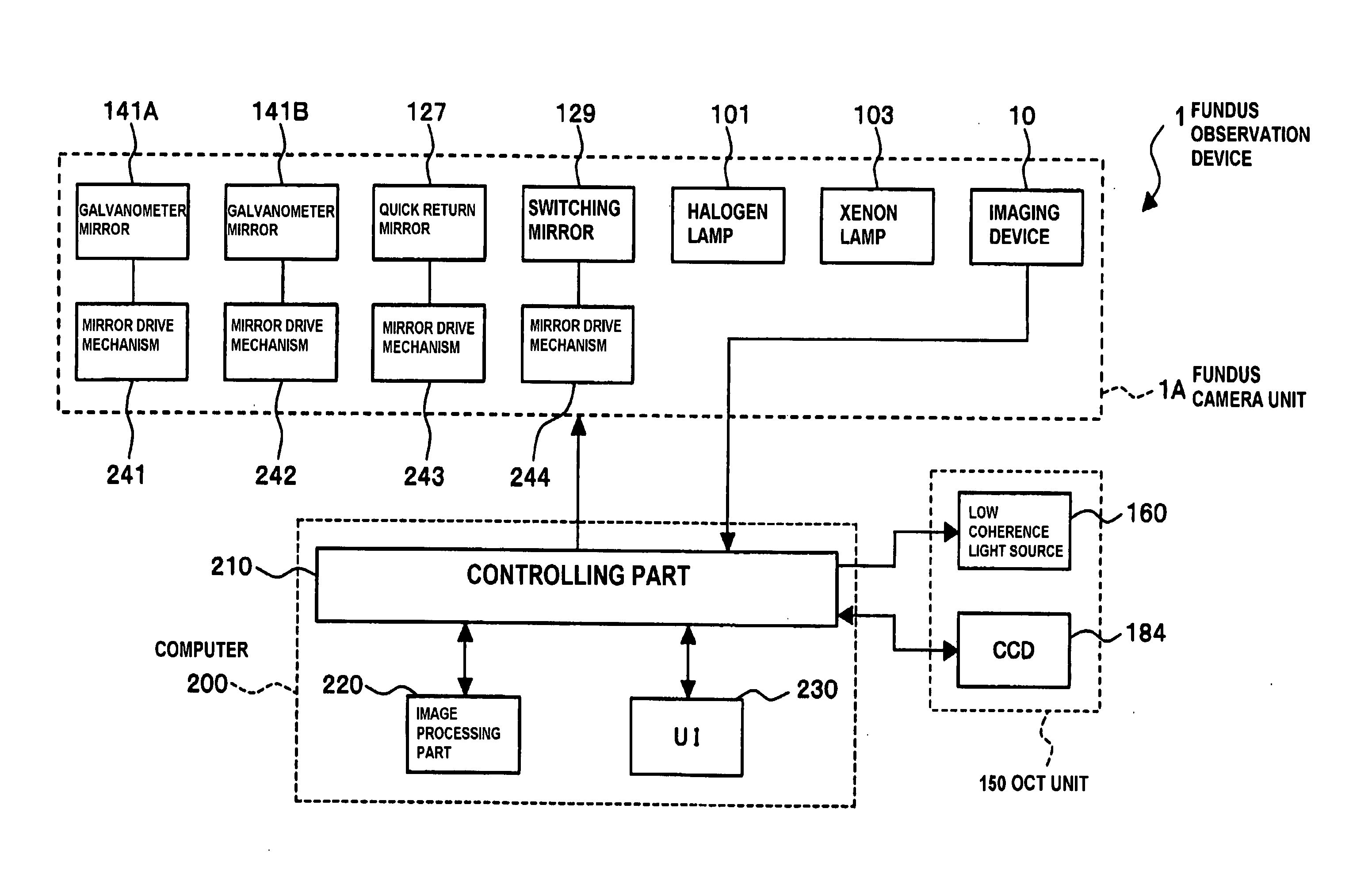
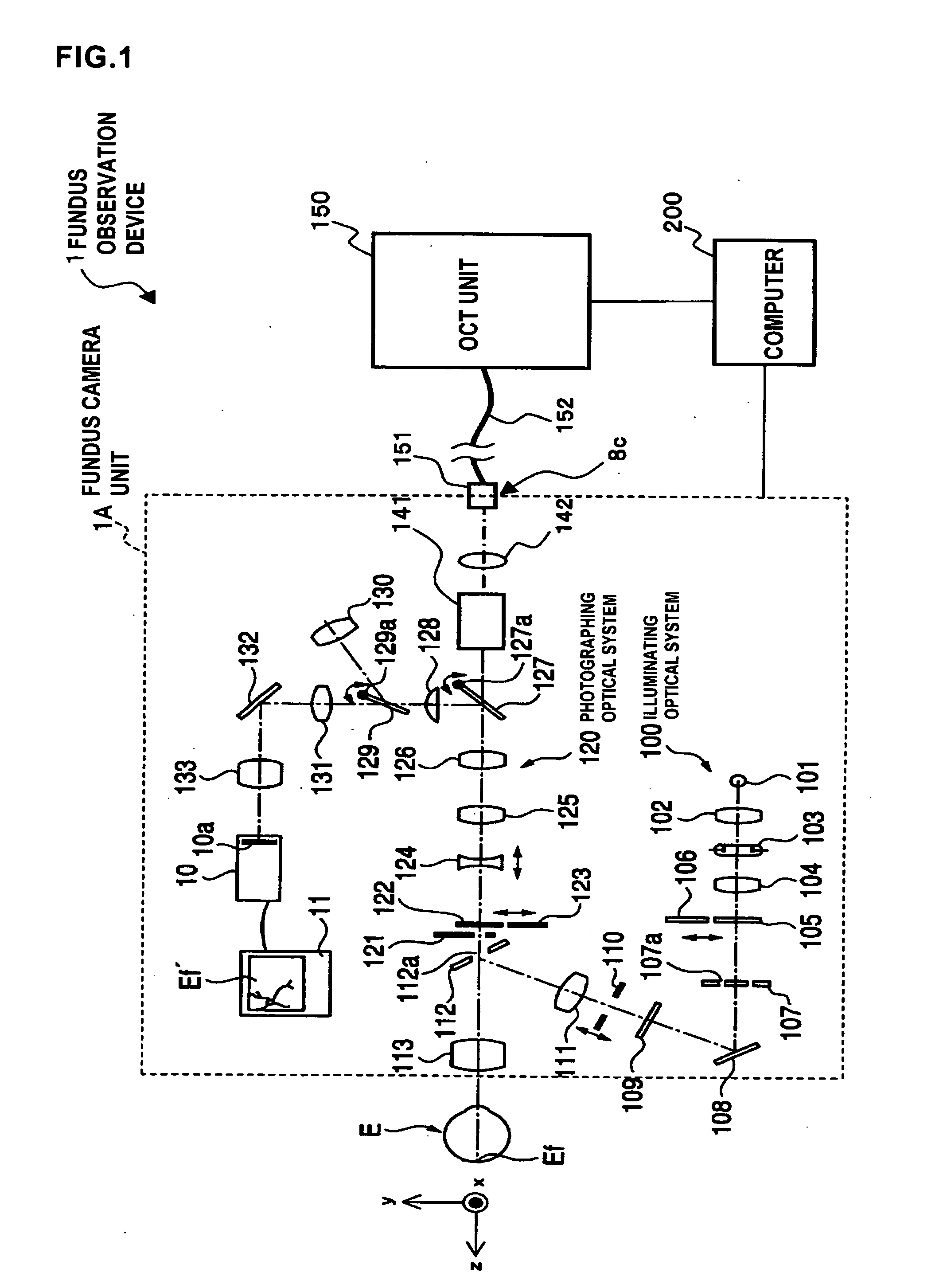
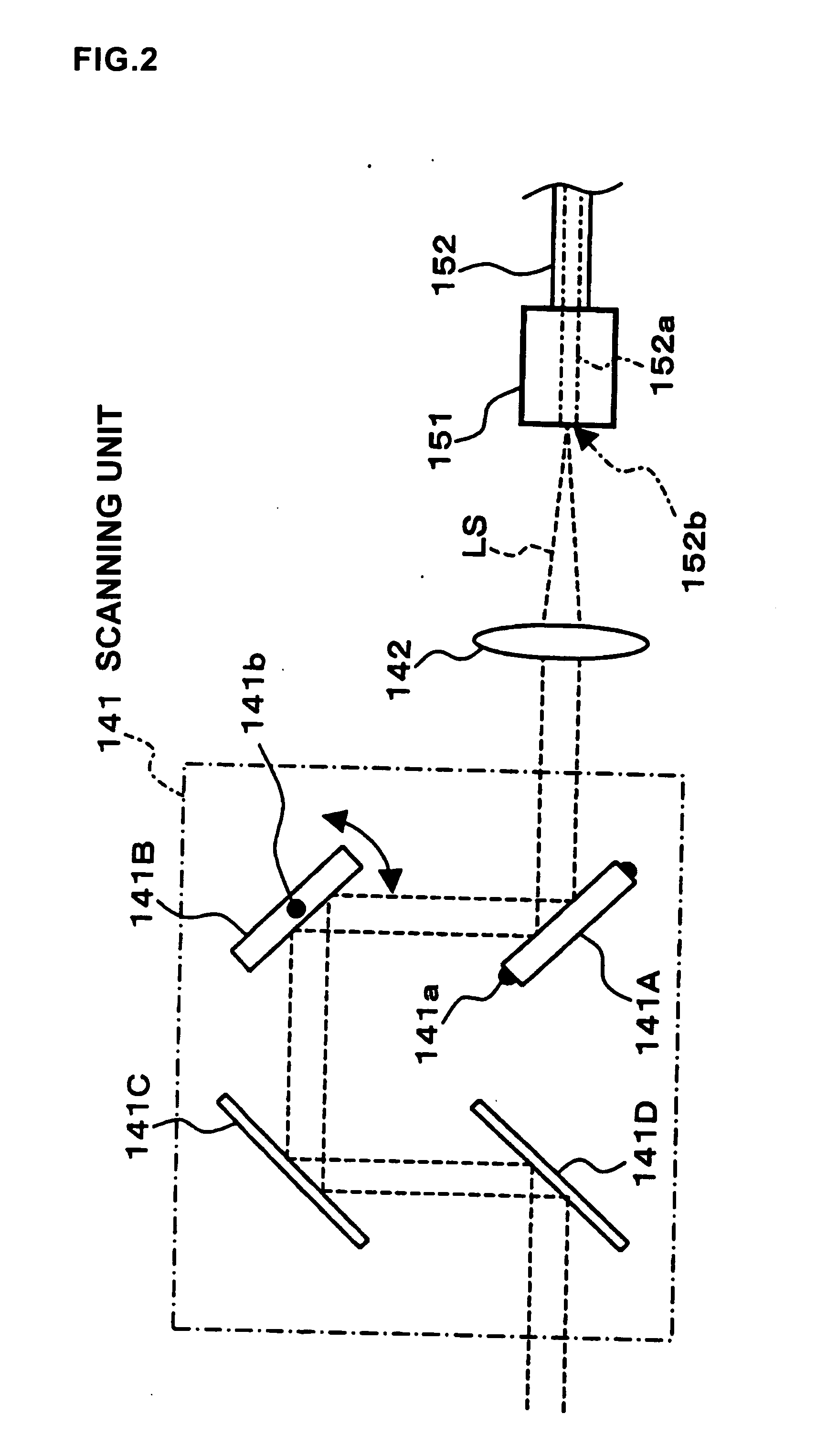
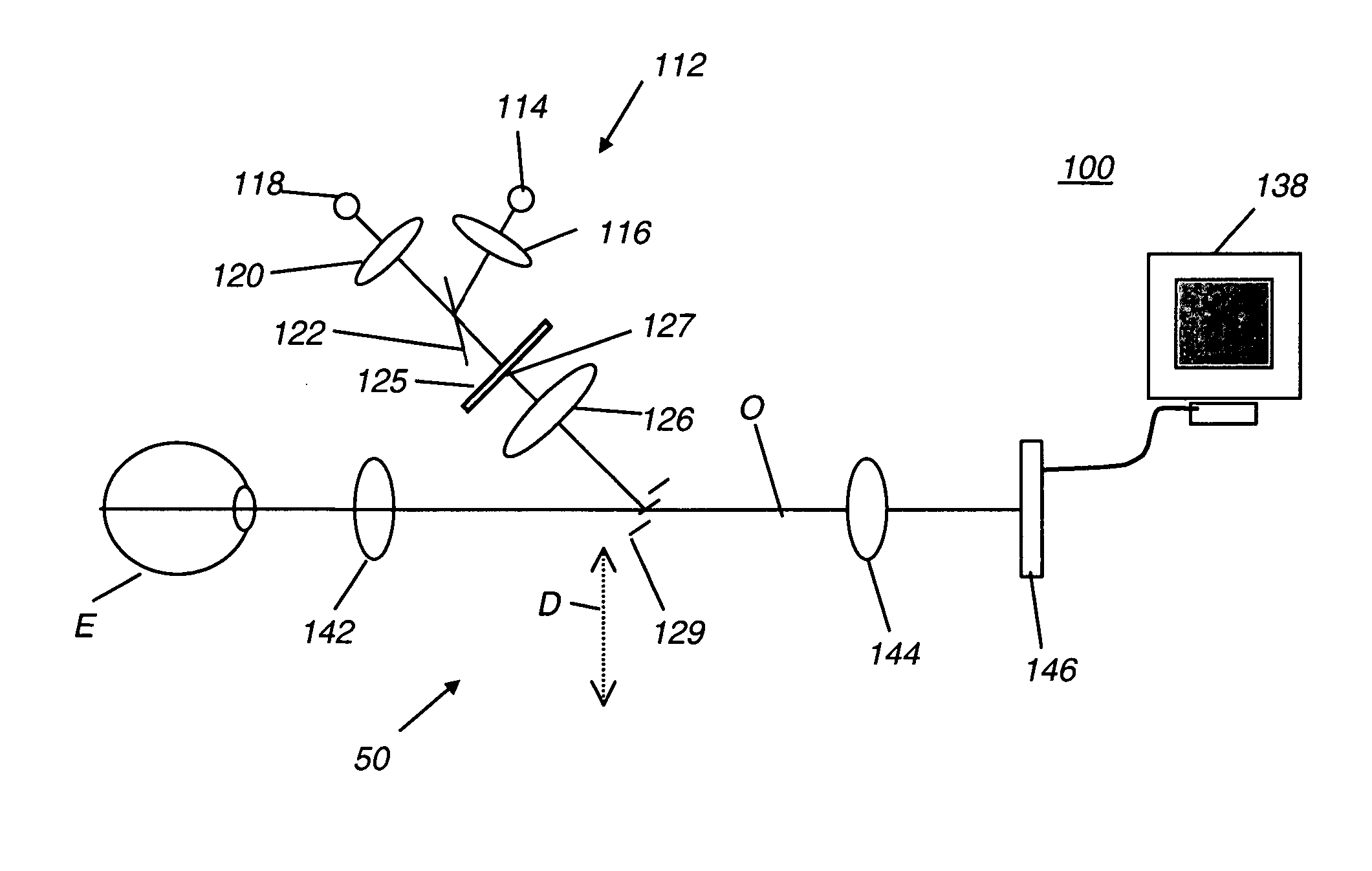
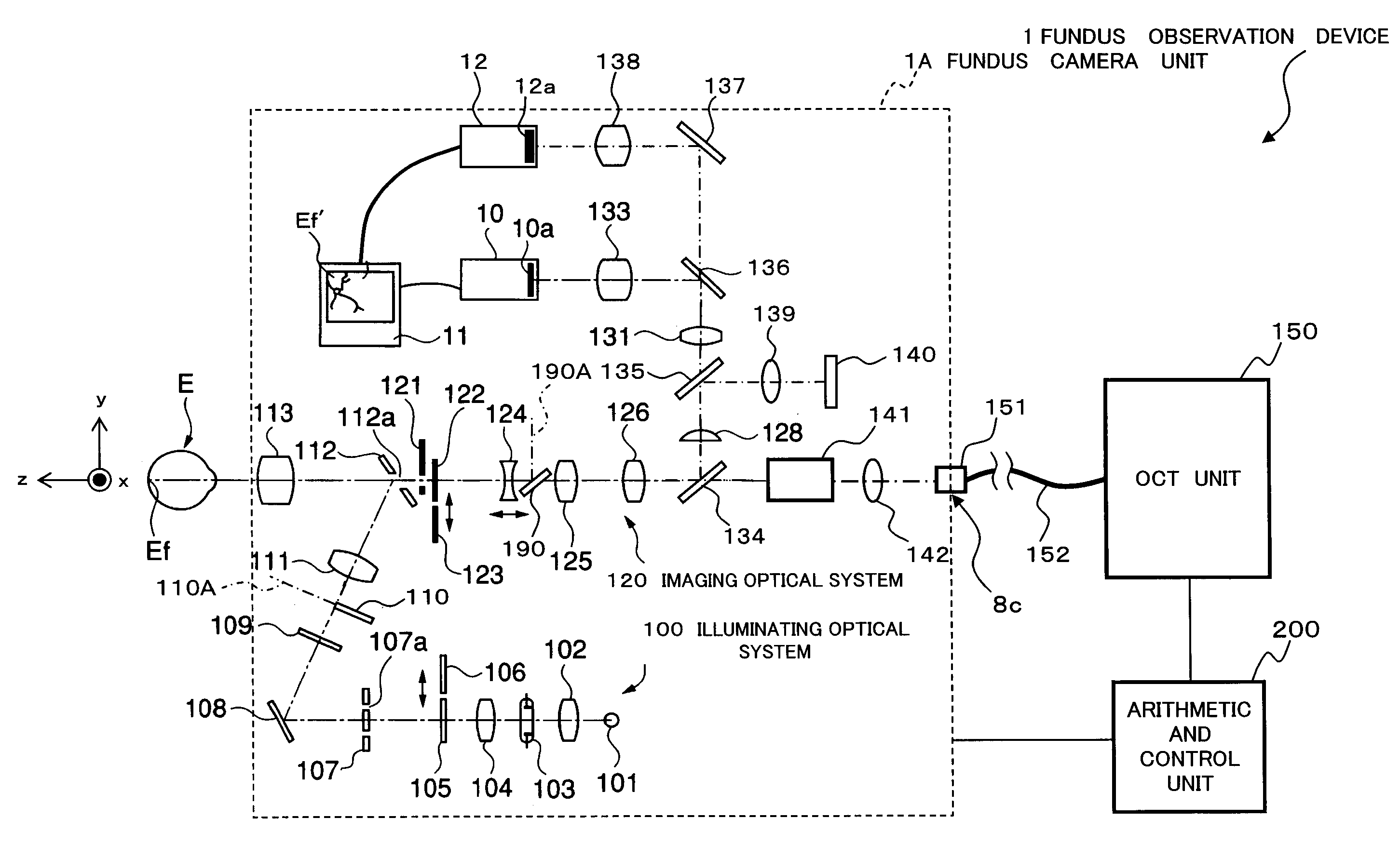
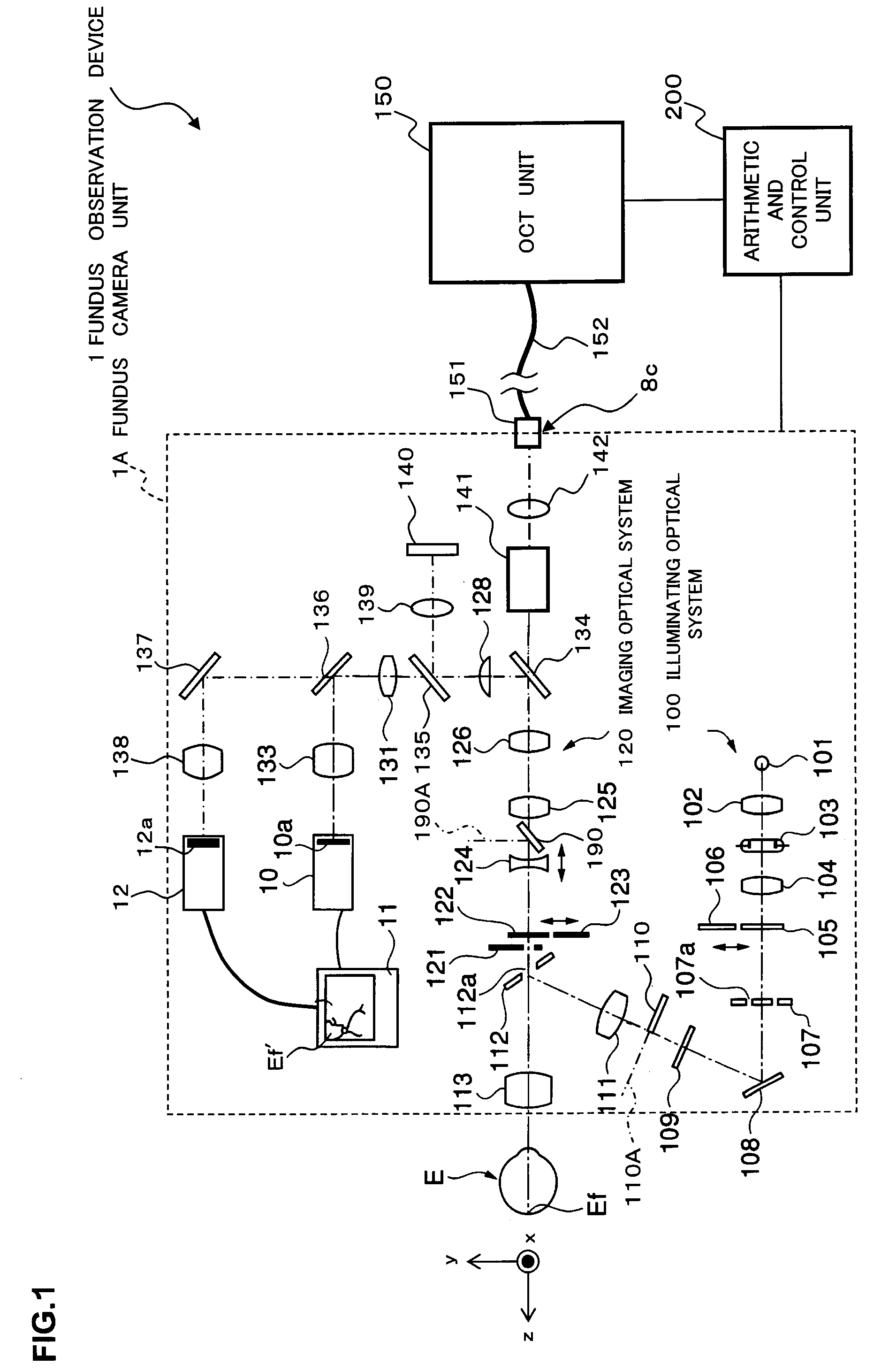
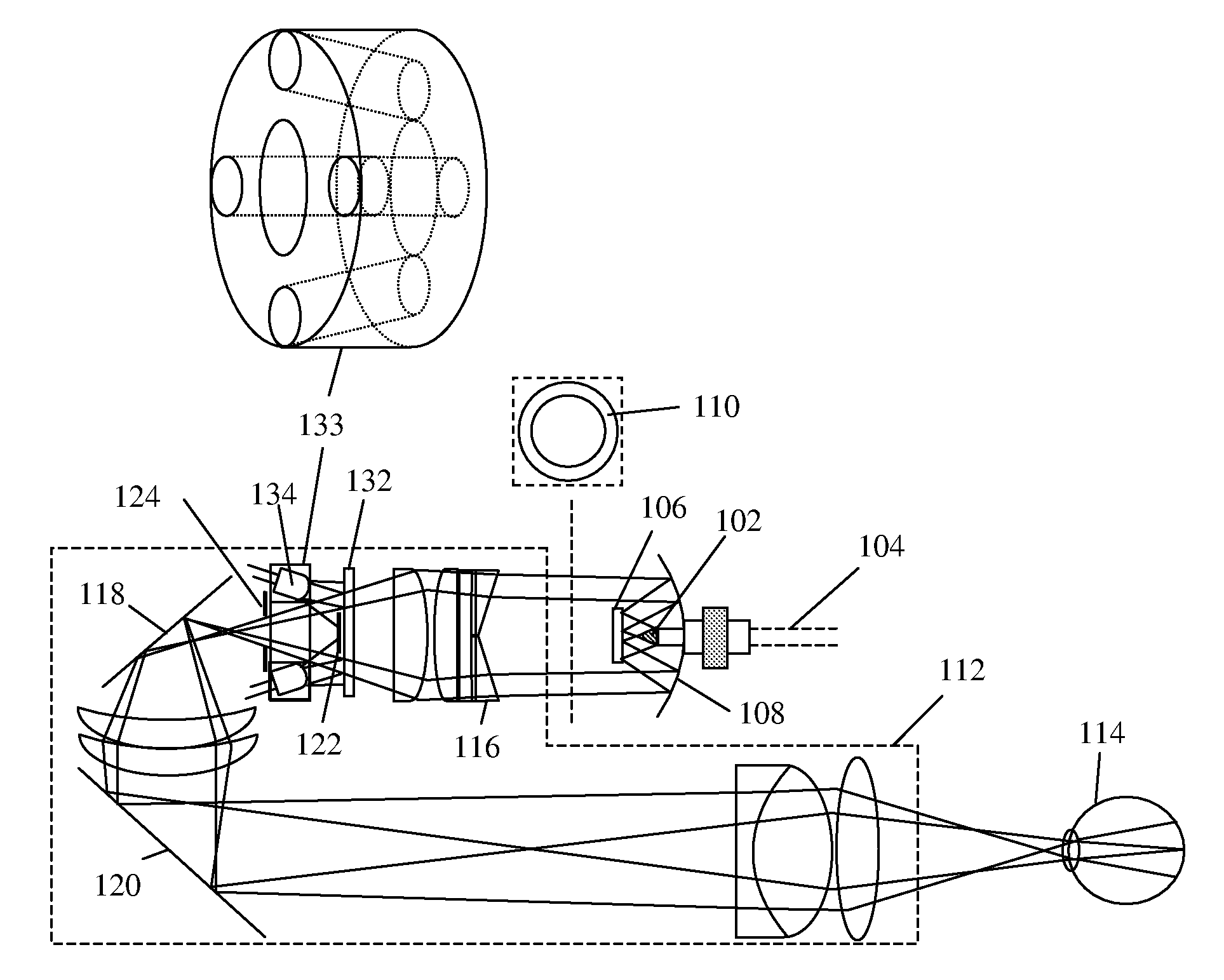
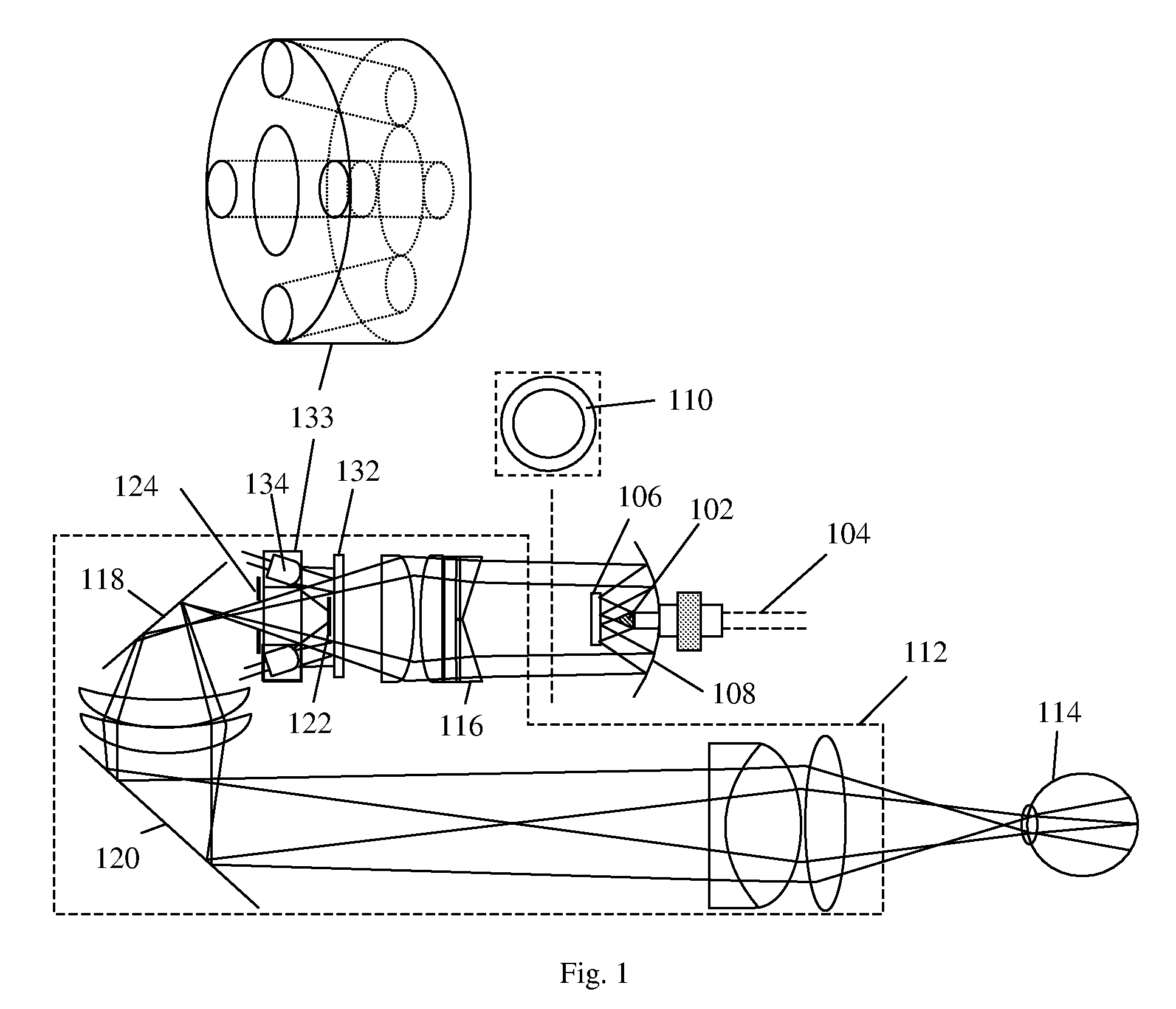
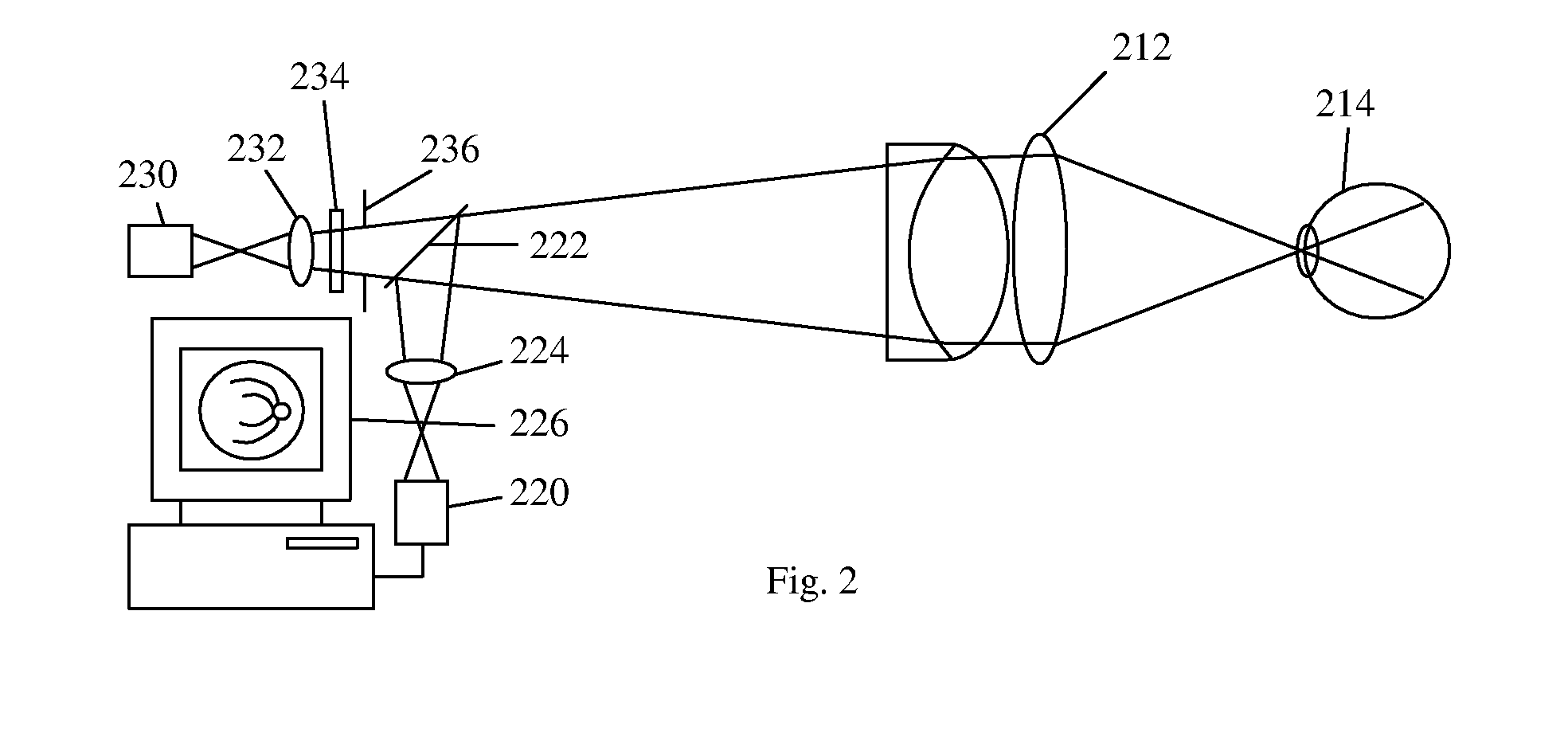
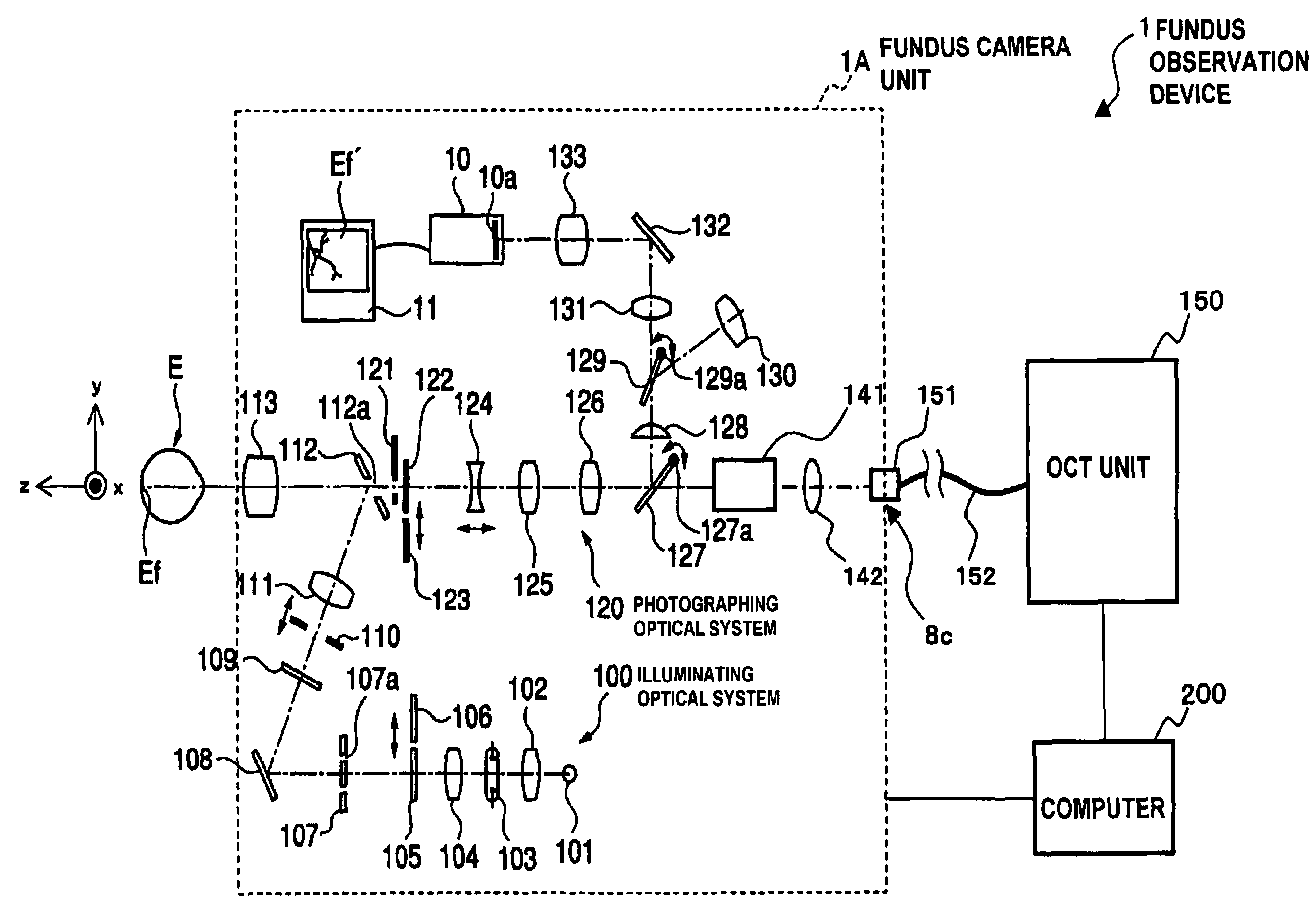
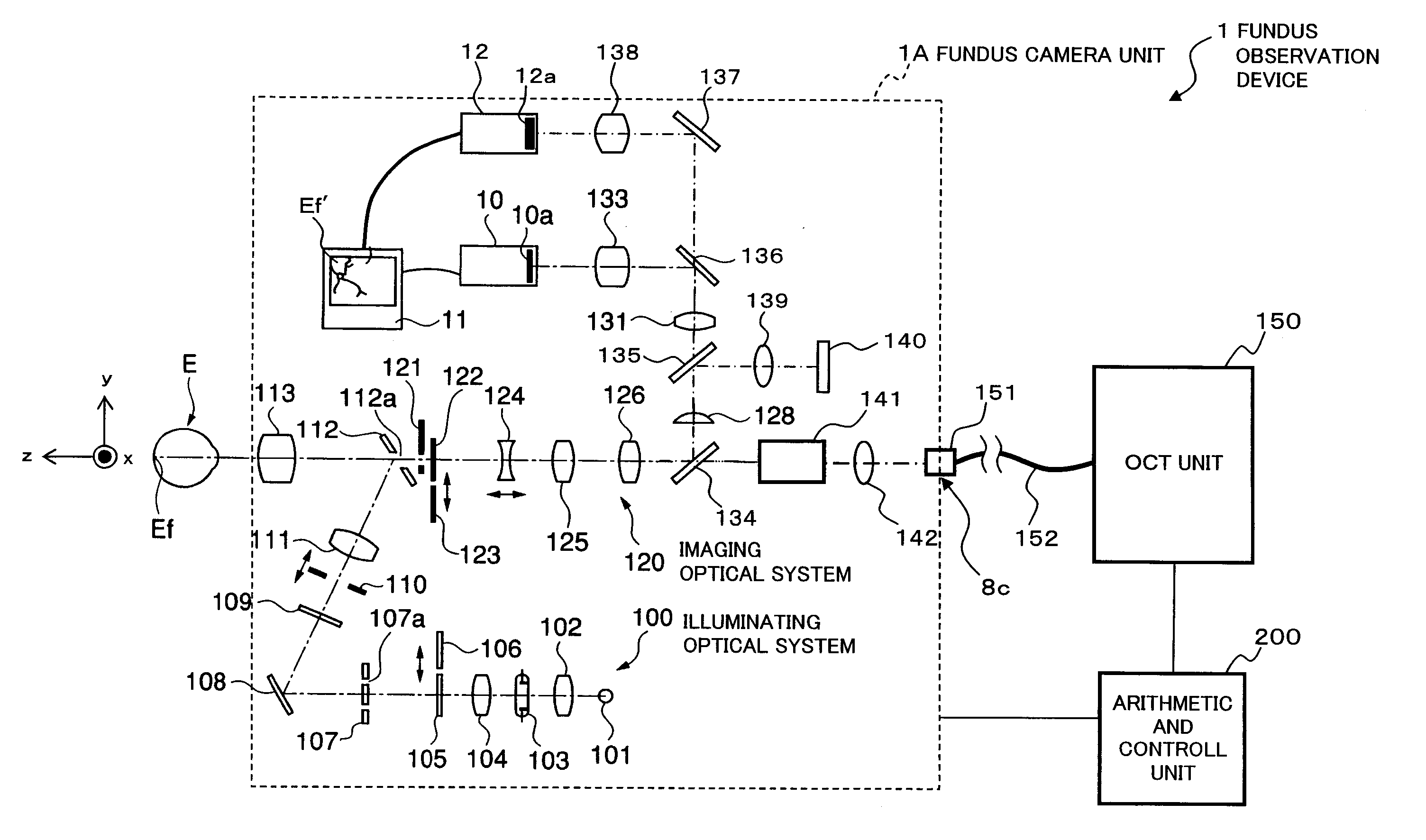
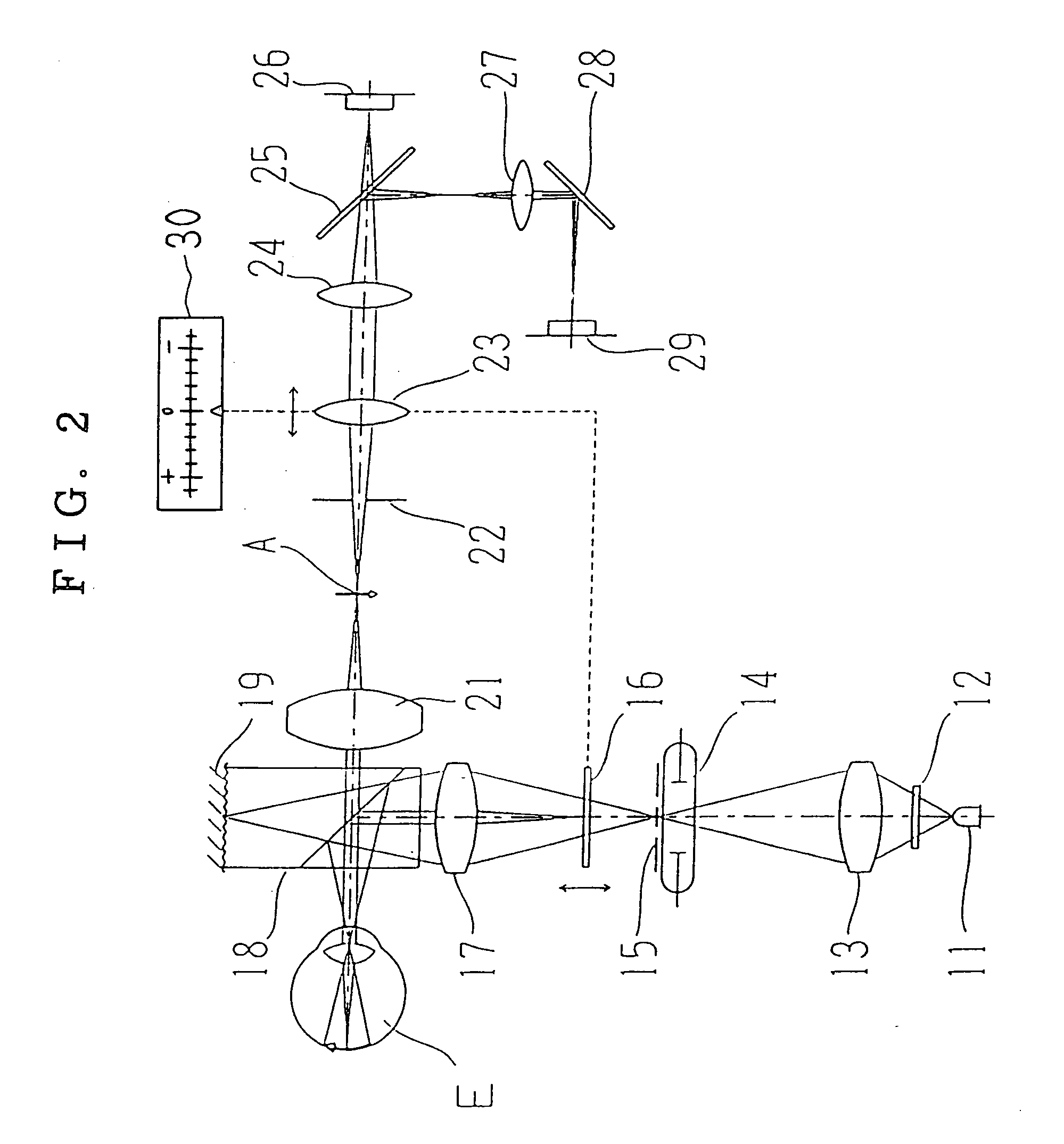
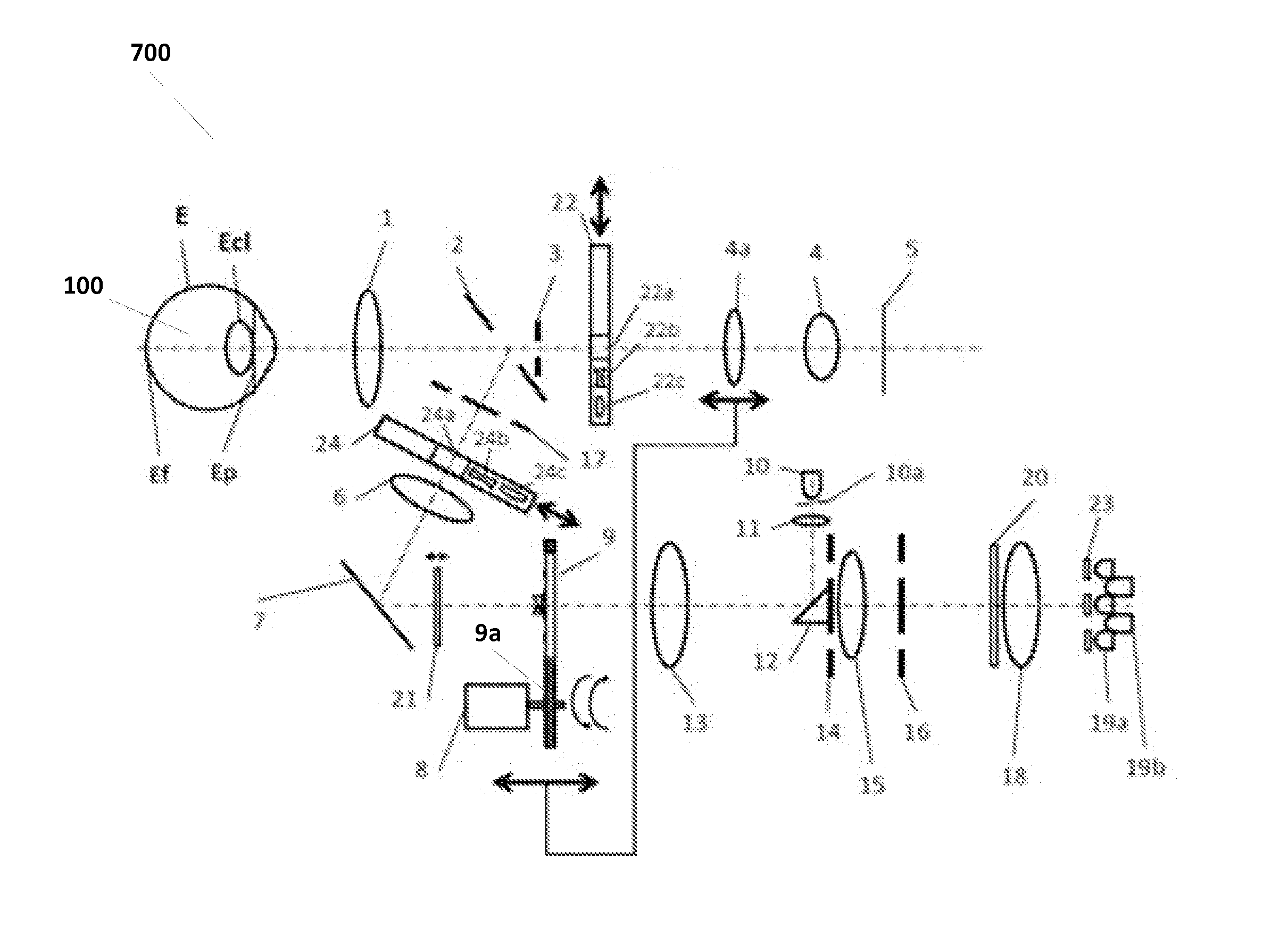
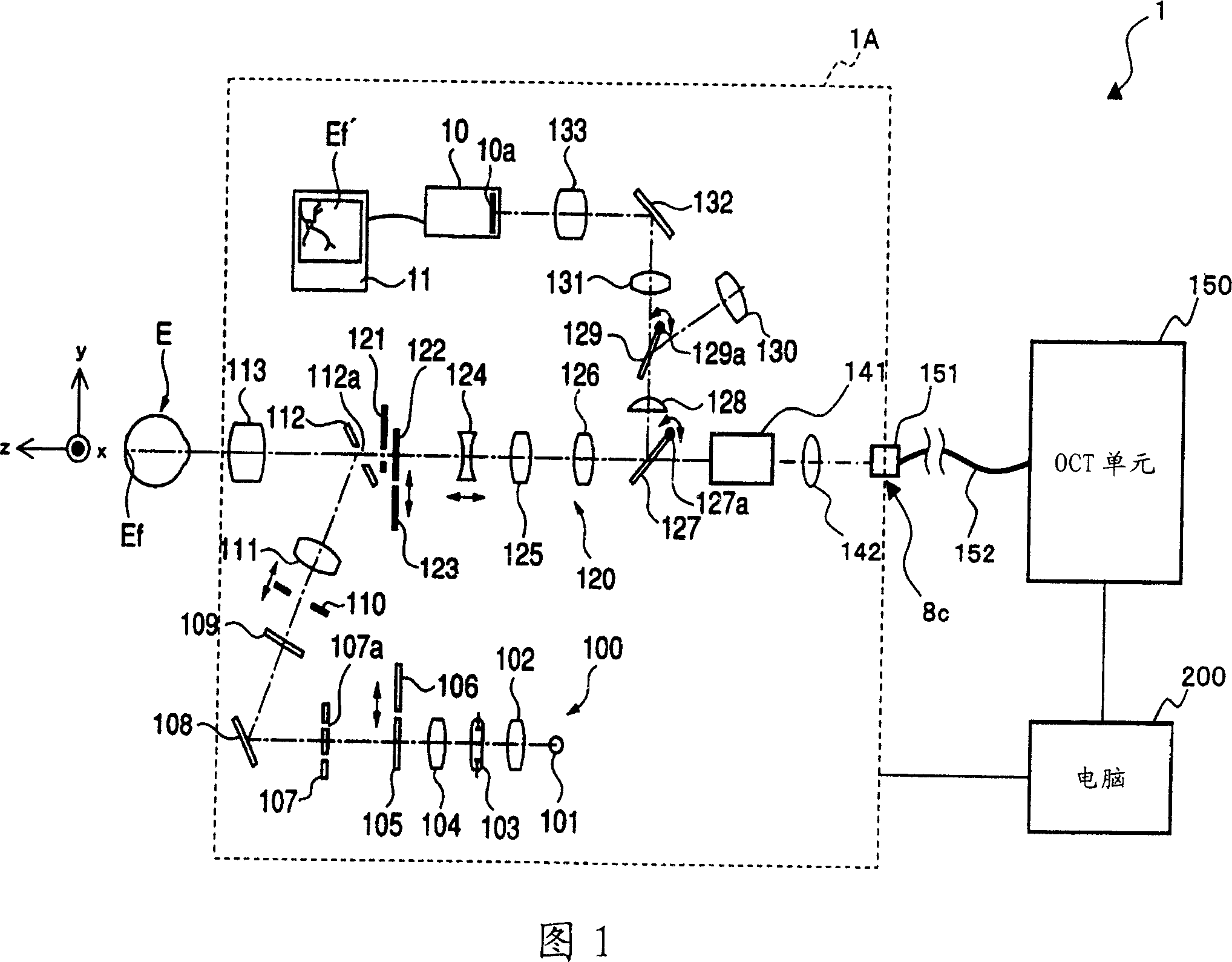
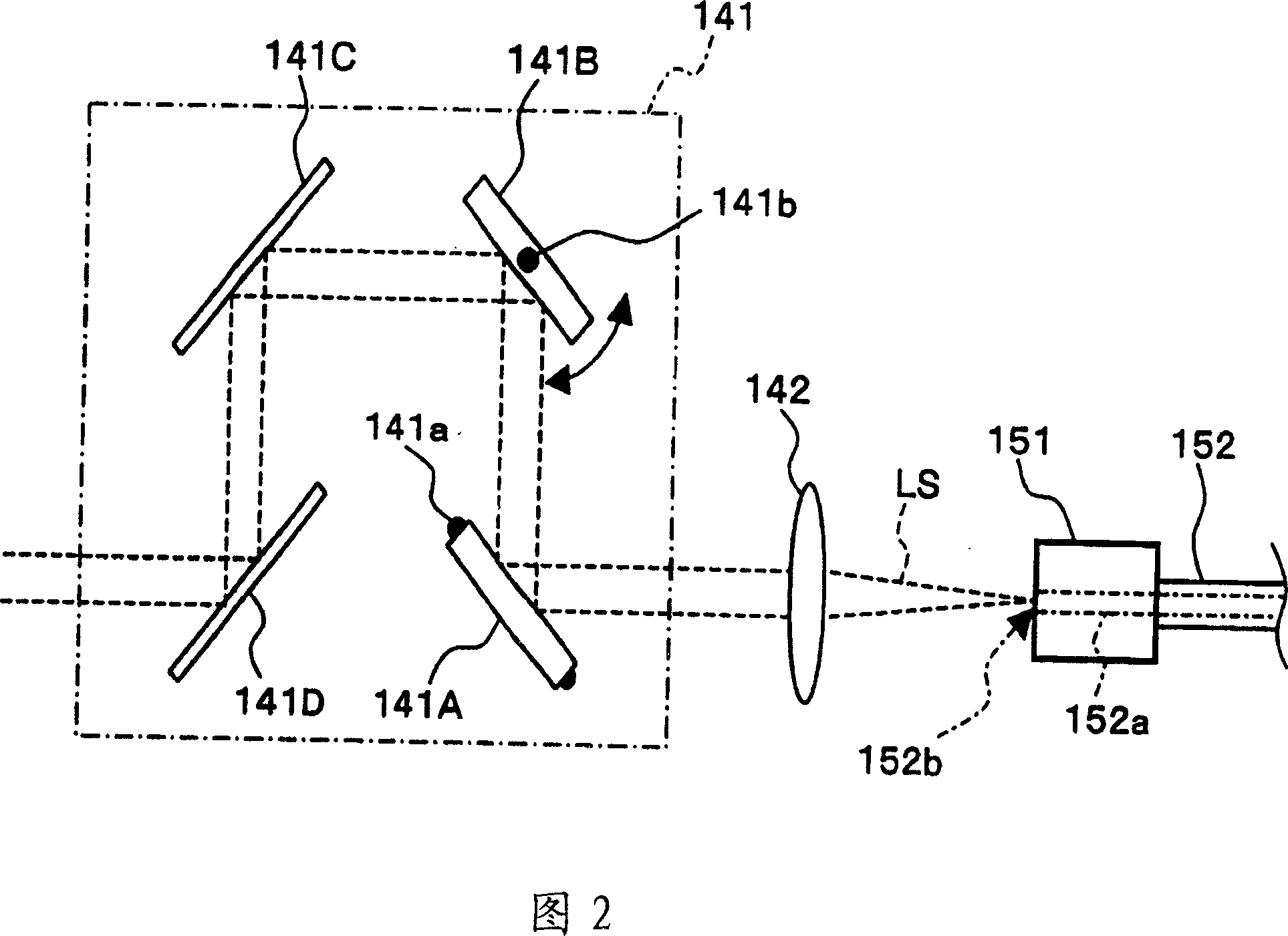
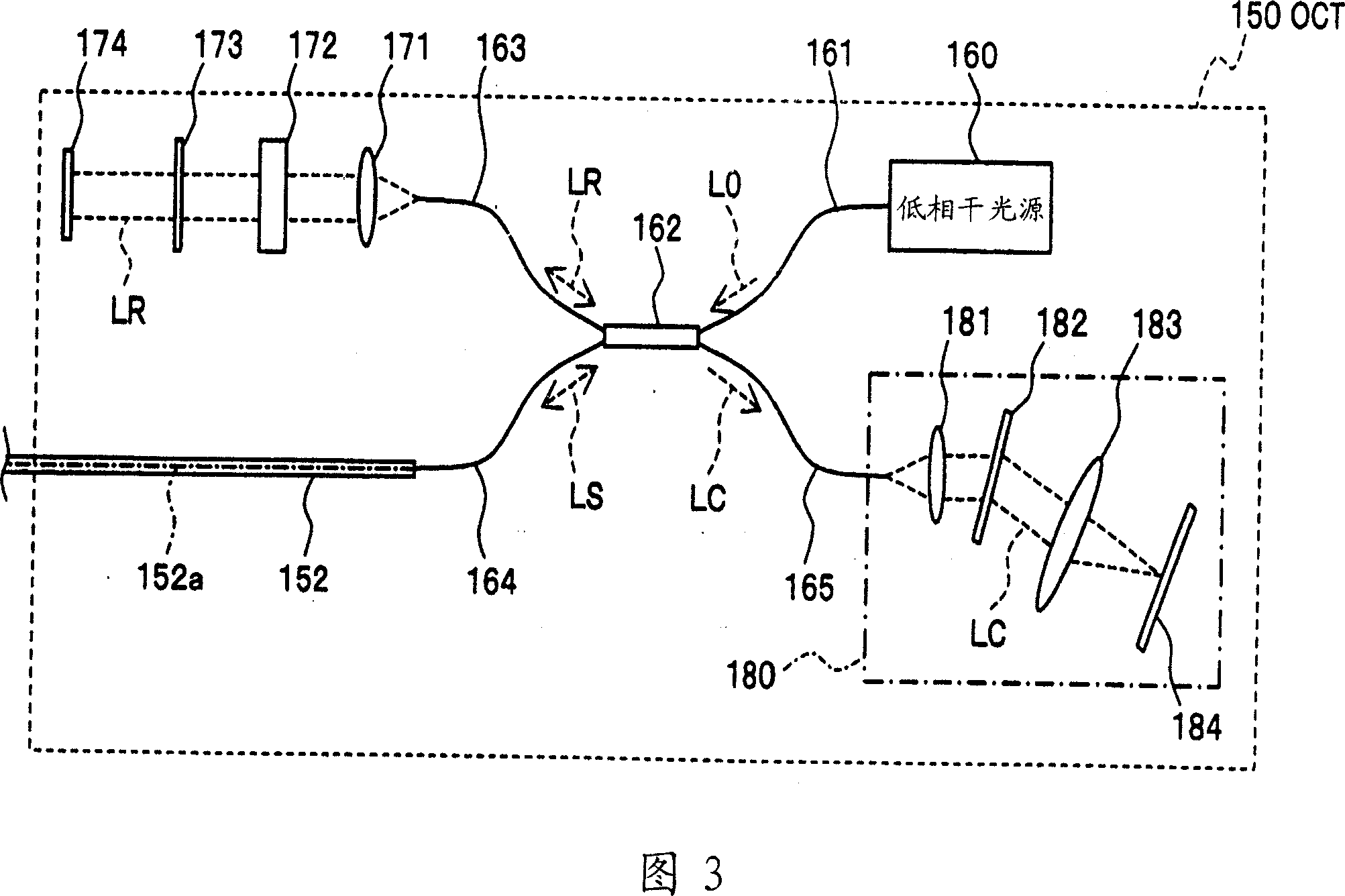
To provide a technology that makes it easy to capture a positional relation of a 2-dimensional image of the surface of a fundus oculi and a tomographic image of the fundus oculi. The fundus observation device 1 is provided with a fundus camera unit 1A for forming a 2-dimensional image of the surface of a fundus oculi Ef of an eye to be examined, an OCT unit 150 for forming a tomographic image of the fundus oculi Ef, a scanning unit 141 as well as an image processing part 220, a display 207, and a controlling part 210 of a computer 200 for displaying the 2-dimensional image formed by the fundus camera unit 1A and a tomographic image formed by the OCT unit, etc. in parallel on the display 207, and also for displaying the cross-sectional position information (attention line L, attention region P) indicating the cross-sectional position of the tomographic image on the surface of the fundus oculi Ef, so as to be overlapped with the 2-dimensional image.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Handheld portable fundus imaging system and method
InactiveUS20130057828A1Reduce restrictionsLow costOthalmoscopesPhotographyCamera lensOff-axis illumination
A system and method for fundus imaging wherein selective illumination of a sector of the field of view of the fundus, using off-axis illumination, provides images of acceptable clarity, resolution, and size, with significantly reduced reflections, in a compact system. By rotating illumination around the optical axis, sectors of the fundus may be selectively and sequentially illuminated. An image of the entire field of view of the fundus is obtained by combining images, e.g. two or more half images, obtained within a single shutter exposure or capture period. An illumination system using LED light sources and a rotatable occluder provides for a lightweight, handheld and portable fundus imaging system. It may take the form of a fundus camera, a fundus imaging lens module for regular camera, or an adapter which couples to the standard lens of a camera to create a low cost fundus camera.
Owner:MASIDAH CORP
Fundus camera having scanned illumination and pupil tracking
InactiveUS20060077347A1Minimizes and eliminates requirementLarge field of viewUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPrintersSpatial light modulatorFundus camera
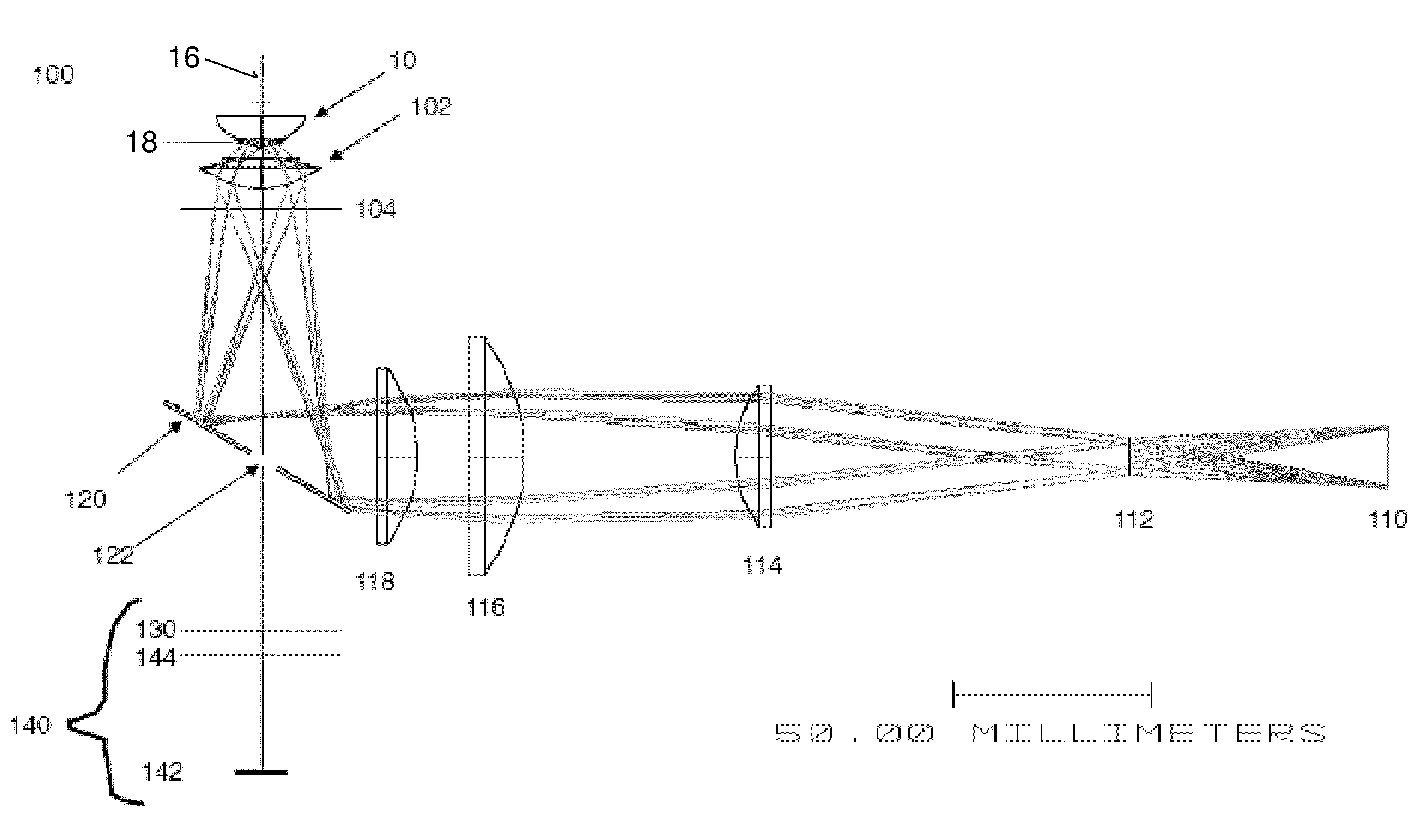
An apparatus (100) for obtaining an image of the eye, has an alignment section (160) for aligning the pupil of the eye along an optical axis and a pupil sensor (170) for identifying pupil location and dimensions. An illumination section (112) has a light source (114) for providing an illumination beam and a spatial light modulator (125) for positioning and shaping the illumination beam according to the sensed location and dimensions of the pupil. An illumination beam partitioning mechanism (50) segments the illumination beam directed toward the pupil of the eye into at least one light-bearing segment (150) and at least one blocked segment. An actuator (132) coupled to the illumination beam partitioning mechanism (50) scans the at least one light-bearing segment (150) of the illumination beam across the pupil of the eye. An image sensor (146), aligned along the optical axis, obtains reflected light from the eye.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
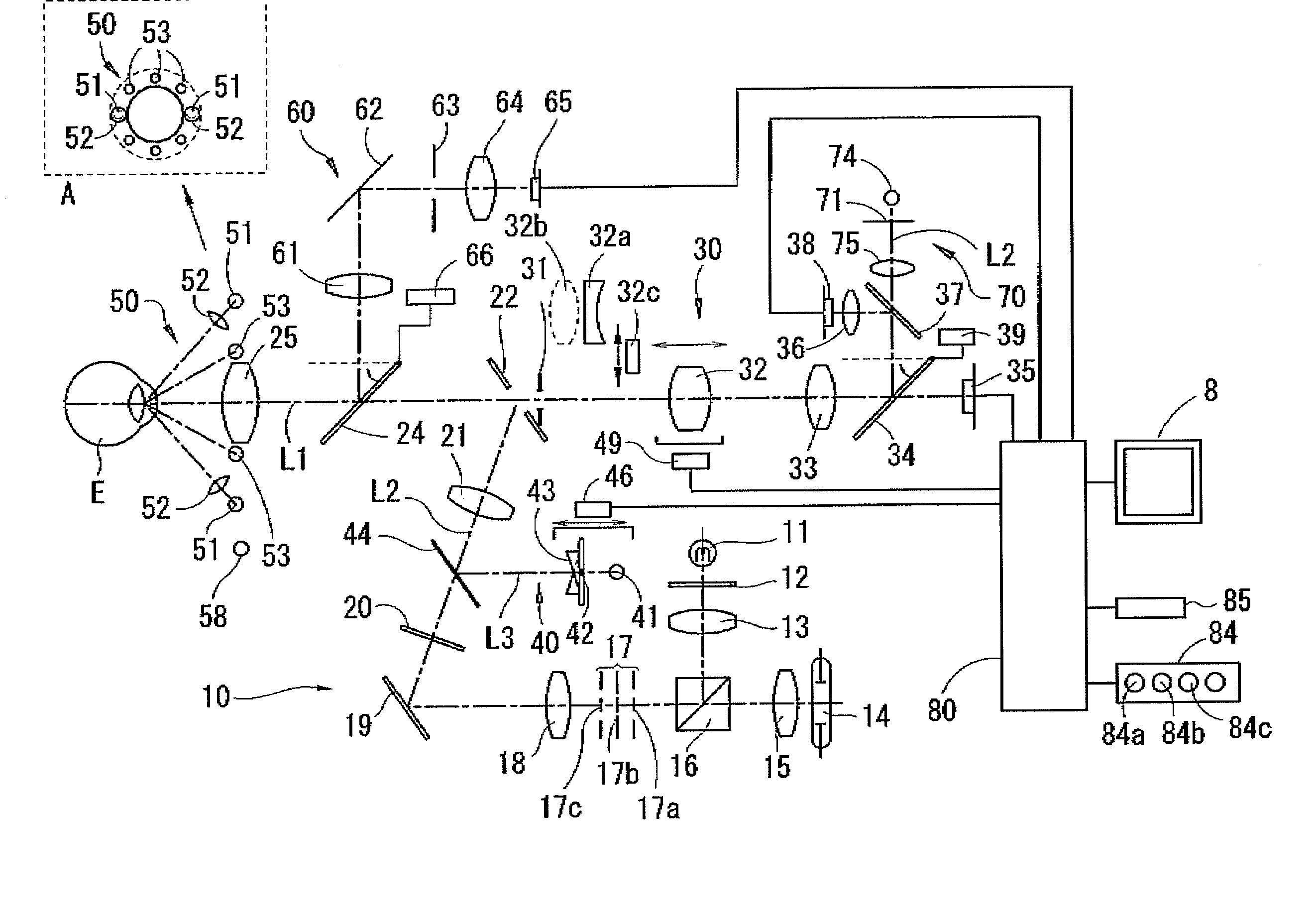
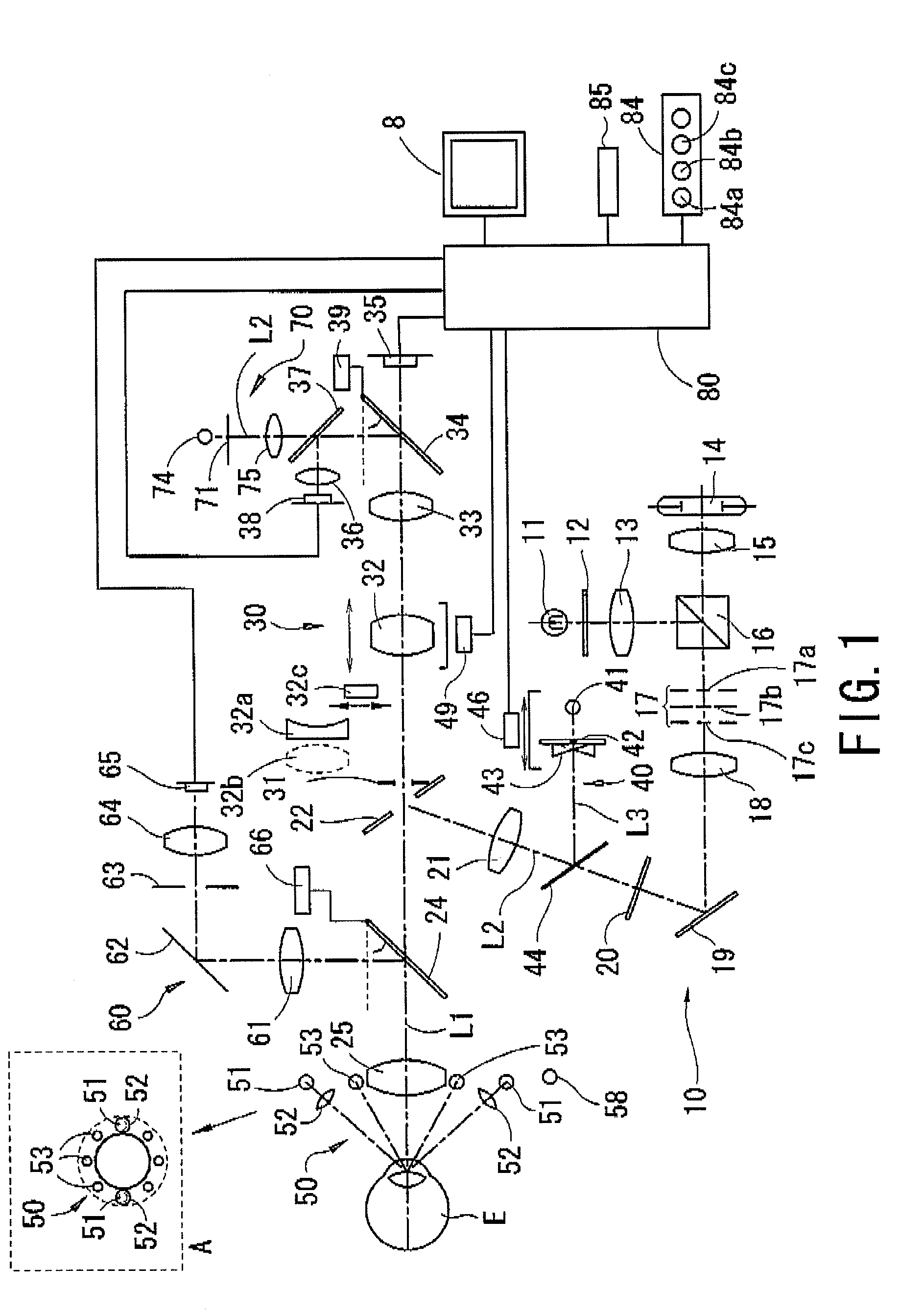
Working distance and alignment sensor for a fundus camera
In embodiments of optical arrangements of a working distance sensor in a fundus camera that can improve the determination of a correct working distance as well as the transverse positioning of the camera a number of near infrared light sources are arranged to project a number of near infrared illumination beams into the visible light illumination path of the fundus camera and a live view of the retina under near infrared illumination is captured and displayed on a monitor. These embodiments of optical arrangements and associated methods will enable an operator to directly determine if there is any undesirable flare or other artifact appearing within a designated region on the infrared retina view as a result of a wrong alignment of the fundus camera with respect to the eye in terms of not only the working distance but also the horizontal and vertical positions. Pattern recognition algorithms can be used to further enhance the positioning sensitivity of the working distance sensor. An additional iris alignment sensor can be added to achieve a coarse alignment and also function as a measure to determine if the dilation of the iris size is sufficient for different mode of fundus imaging.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Fundus camera
InactiveUS20070013867A1Not impairing convenienceEasy to operateOthalmoscopesFundus cameraComputer science
A fundus camera, in which operability is improved while not impairing the convenience of the function of automatic alignment, has a photographing part including a fundus photographing optical system, a moving unit which moves the photographing part, an observation optical system having a first image-pickup element which picks up a fundus image, an observation optical system having a second image-pickup element which picks up an anterior-segment image, a display unit capable of displaying the images, a control part which obtains information on alignment of the photographing part with the eye and controls driving of the moving unit based on the alignment information so that an alignment state satisfies a first reference condition, and a first input switch for inputting a signal for display switching from the fundus image to the anterior-segment image, wherein the control part prohibits the driving of the moving unit when the signal is inputted.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Snapshot spectral imaging of the eye
ActiveUS8109634B2Strong robustnessWithout reducing effective resolutionSpectrum investigationDiagnostic recording/measuringFundus cameraPupil
Obtaining spectral images of an eye includes taking an optical system that images eye tissue onto a digital sensor array and optically fitting a multi-spectral filter array and the digital sensor array, wherein the multi-spectral filter array is disposed between the digital sensor array and an optics portion of the optical system. The resulting system facilitates acquisition of a snap-shot image of the eye tissue with the digital sensor array. The snap shot images support estimation of blood oxygen saturation in a retinal tissue. The resulting system can be based on a non-mydriatic fundus camera designed to obtain the retinal images without administration of pupil dilation drops.
Owner:MERGE HEALTHCARE
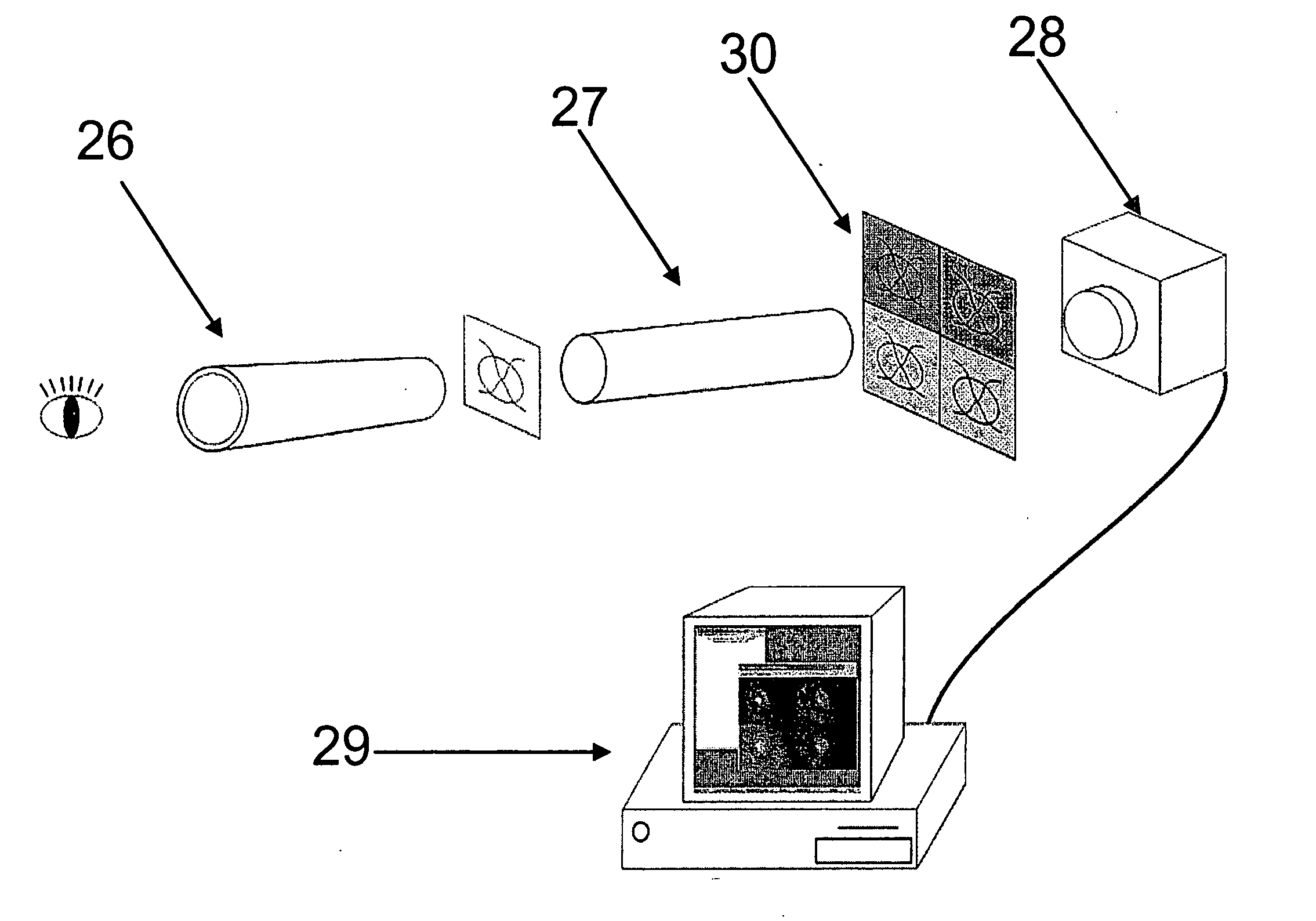
Automatic registration of images
ActiveUS20060276698A1Reliable measurementOptical density ratios are more reliably and easily obtainedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVisual perceptionImage contrast
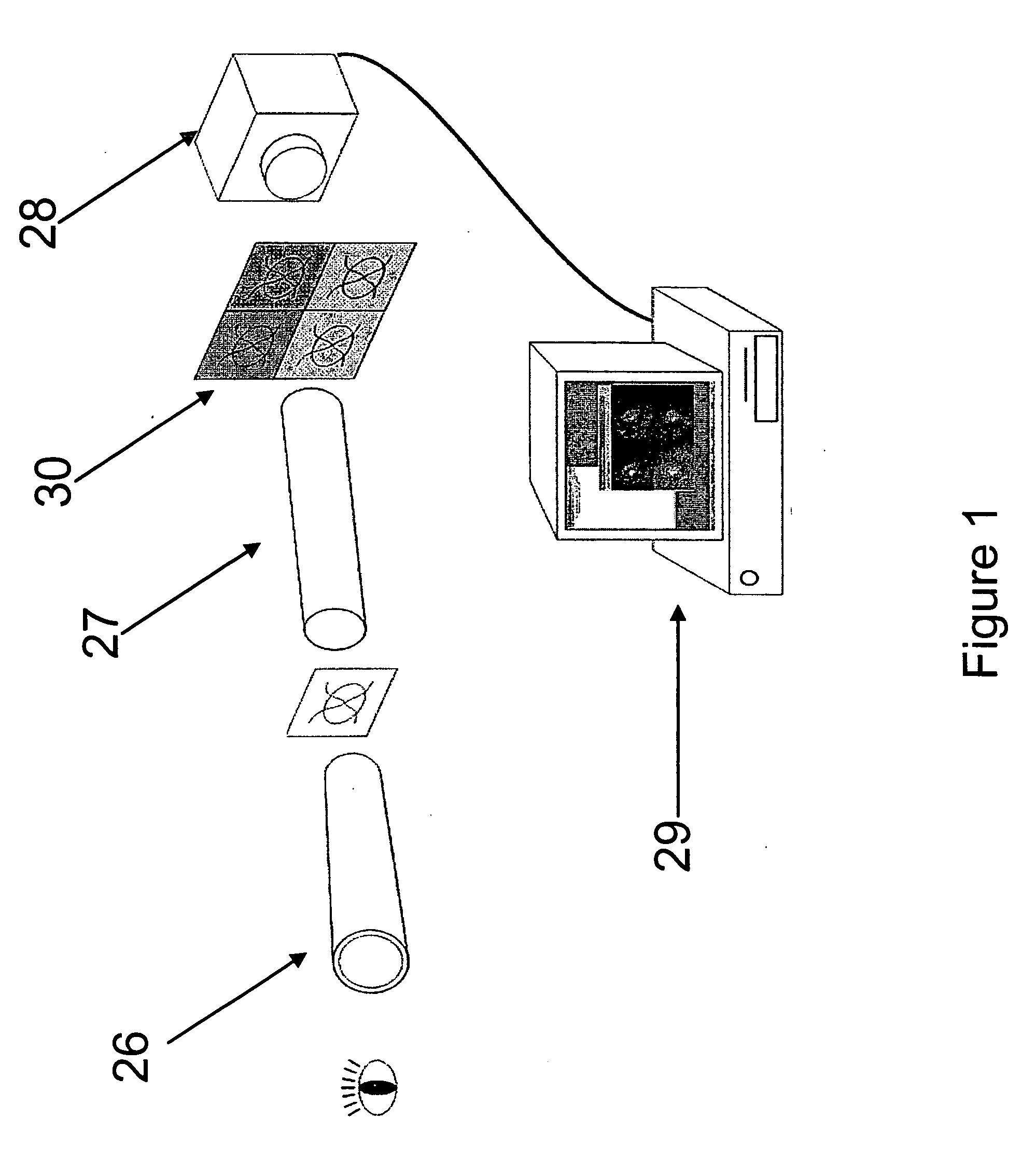
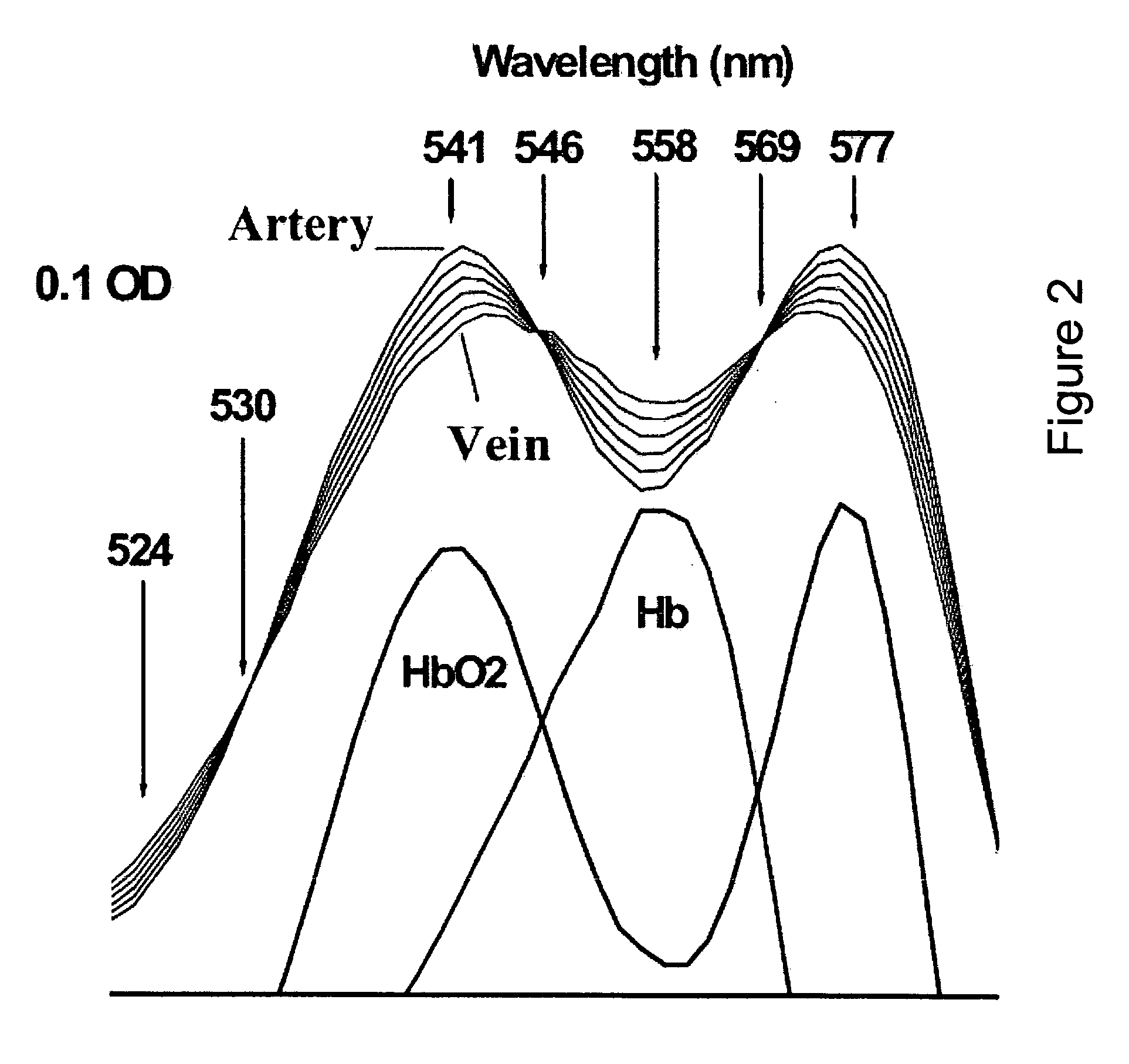
The present invention relates to a system for automatically evaluating oxygen saturation of the optic nerve and retina, said system comprising: image capturing system further comprising: a fundus camera (26), a four wavelengths beam splitter (27), a digital image capturing device (28), a computer system, image processing software performing in real-time the steps of: registering set of multi-spectral images (1) by, binarizing the multi-spectral image (7), find the all the border regions of each image by finding the region including the straight line that passes the most number of points in the region (8), use the orientation of the borders to evaluate the orientation of each spectral image (9), equalize the orientation of each spectral image by rotating the spectral image (10), edge detect each spectral image (11), estimate the translation between the spectral images based on the edges of adjacent images (12), transform the images to a stack of registered images (13), locating blood vessels (2) in each of the multi-spectral images by, retrieving registered spectral images (14), for each spectral image, remove defective pixels (15), enhance image contrast (16), perform top-hat transform using structuring element larger than the largest vessel diameter (17), binarize each image (18), apply filter for smoothing the image (19), combine all the spectral images using binary AND operator (20), skeletonize the resulting image (21), prune the skeleton image (22), re-grow the pruned image (23), locate junction points (24), evaluating the width of the blood vessels (3) by calculating the normal vector to the vessel direction to, estimate the direction and position of the vessel profile, evaluate positions of vessel walls based on the vessel profile obtained, evaluate vessel width based on the position of the vessel walls, selecting samples for calculating optical density, calculating the optical density ratio (4), evaluating oxygen saturation level (5), and presenting the results (6), wherein presenting the results may include presenting numerical and visual representation of the oxygen saturation.
Owner:OXYMAP EHF
Portable fundus camera
InactiveUS20140267668A1Speed flowEconomically beneficialTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensFundus camera
A portable hand-held ocular fundus camera system for imaging the fundus of the eye is disclosed. The camera system is comprised of a camera housing, one or more groups of lens in an internal cavity of the housing, a front group of lenses at the front end of the internal cavity, a contact member to contact at least a portion of the cornea, a light source configured to direct light from locations inside the camera through an annulus near the periphery of the front lens group, so that the light enters the eye through an annulus at the periphery of the pupil of the eye during contact with the cornea. Light from the light source that is reflected off of the fundus that passes through the center portion of the pupil of the eye is imaged onto an imager configured to acquire a sequence of images while an actuator coupled to the imager continuously varies the location of the imager along the optical axis of the camera.
Owner:LUMETRICS
Fundus Observation Device
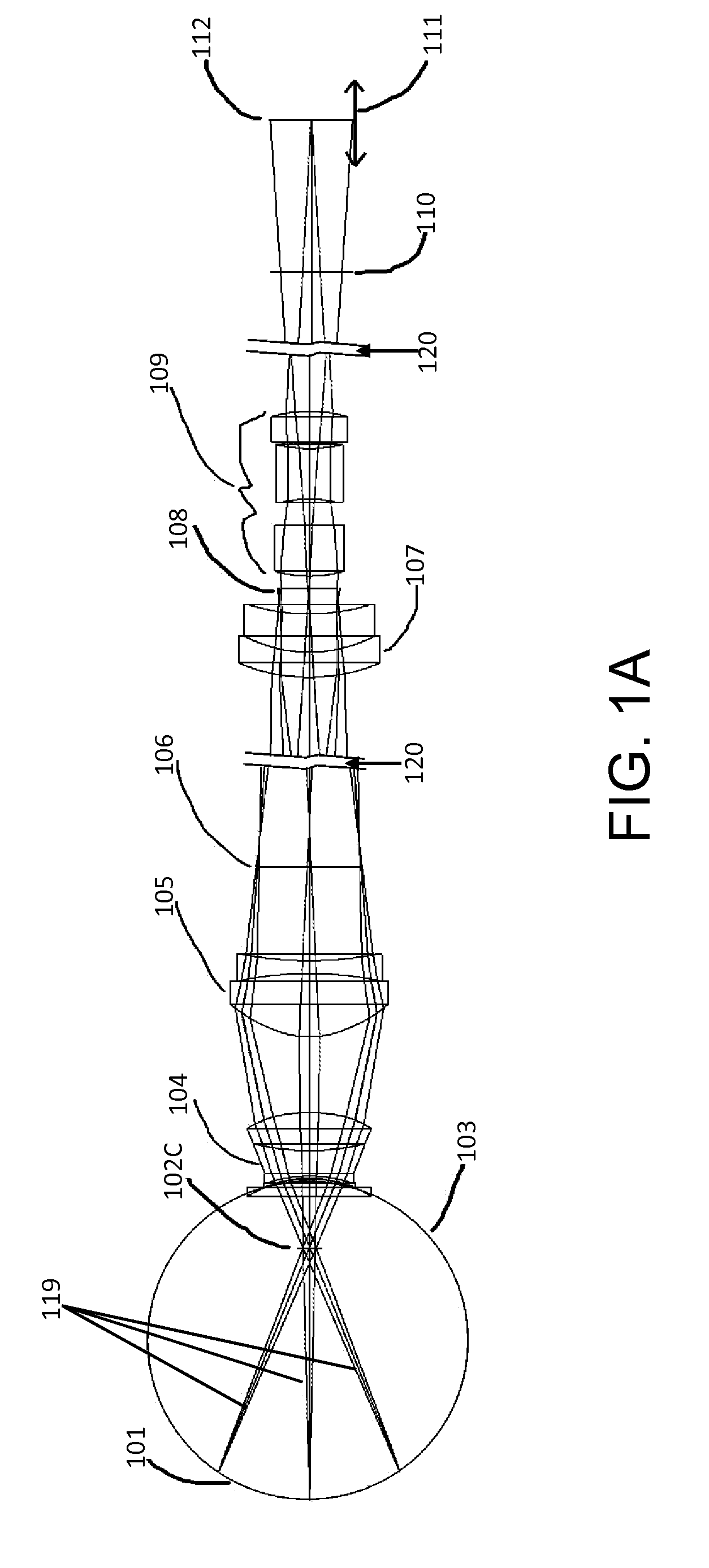
A fundus observation device is provided capable of capturing both images of the surface of the fundus oculi and tomographic images of the fundus oculi, and capable of preventing alignment indicators from being reflected in the image of the fundus oculi. Image forming part 220 operates to form surface images based on results of detecting the reflection light by the fundus oculi Ef of the illumination light obtained from a fundus camera unit 1A, and operates to form tomographic images based on results of detecting interference light LC by the OCT unit 150. The fundus camera unit comprises alignment optical systems 110A and 190A, which project an alignment indicator. Detection timing controlling part 210B controls a fundus camera unit 1A and makes it detect the illumination light substantially simultaneously with detection of the interference light. Before the interference light LC and illumination light are substantially simultaneously detected, the alignment controlling part 210 controls the alignment optical system 110A and 190A and terminates the projection of the alignment light indicator. Correction processing part 225 corrects the image position of tomographic images using the surface images obtained substantially simultaneously.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Working distance and alignment sensor for a fundus camera
In embodiments of optical arrangements of a working distance sensor in a fundus camera that can improve the determination of a correct working distance as well as the transverse positioning of the camera a number of near infrared light sources are arranged to project a number of near infrared illumination beams into the visible light illumination path of the fundus camera and a live view of the retina under near infrared illumination is captured and displayed on a monitor. These embodiments of optical arrangements and associated methods will enable an operator to directly determine if there is any undesirable flare or other artifact appearing within a designated region on the infrared retina view as a result of a wrong alignment of the fundus camera with respect to the eye in terms of not only the working distance but also the horizontal and vertical positions. Pattern recognition algorithms can be used to further enhance the positioning sensitivity of the working distance sensor. An additional iris alignment sensor can be added to achieve a coarse alignment and also function as a measure to determine if the dilation of the iris size is sufficient for different mode of fundus imaging.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Fundus observation device, fundus image display device and fundus observation program
To provide a technology that makes it easy to capture a positional relation of a 2-dimensional image of the surface of a fundus oculi and a tomographic image of the fundus oculi. The fundus observation device 1 is provided with a fundus camera unit 1A for forming a 2-dimensional image of the surface of a fundus oculi Ef of an eye to be examined, an OCT unit 150 for forming a tomographic image of the fundus oculi Ef, a scanning unit 141 as well as an image processing part 220, a display 207, and a controlling part 210 of a computer 200 for displaying the 2-dimensional image formed by the fundus camera unit 1A and a tomographic image formed by the OCT unit, etc. in parallel on the display 207, and also for displaying the cross-sectional position information (attention line L, attention region P) indicating the cross-sectional position of the tomographic image on the surface of the fundus oculi Ef, so as to be overlapped with the 2-dimensional image.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Fundus camera
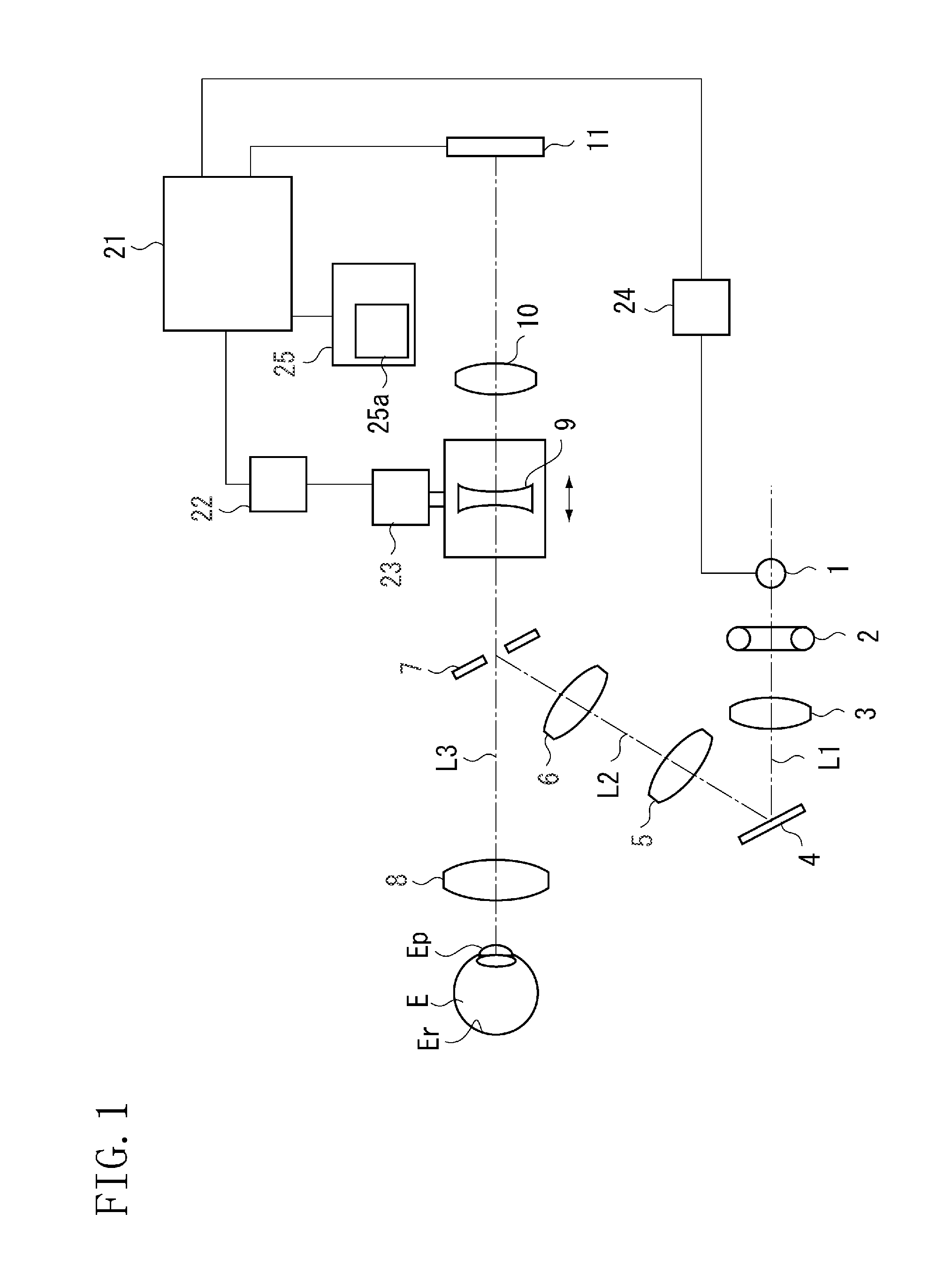
InactiveUS20090244483A1Improve performanceEasy to knowEye diagnosticsRefractive errorPhotovoltaic detectors
A fundus camera favorably performing focusing on a fundus of an examinee's eye without a black dot plate in a target projection optical system comprises an illumination optical system comprising a light source and an objective lens, a photographing optical system comprising a focusing lens movable in the optical axis direction and a diopter correction lens to correct a diopter of severe ametropia, a first moving mechanism comprising a first driving unit moving the focusing lens, a focus detection optical system comprising a projection optical system comprising a light source and a photo-receiving optical system comprising a photodetector, a second moving mechanism comprising a second driving unit moving a part of the detection optical system including at least one of the projection light source and the photodetector in the optical axis direction, a monitor, and a control unit controlling the second unit in conjunction with movement of the focusing lens.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Fundus camera
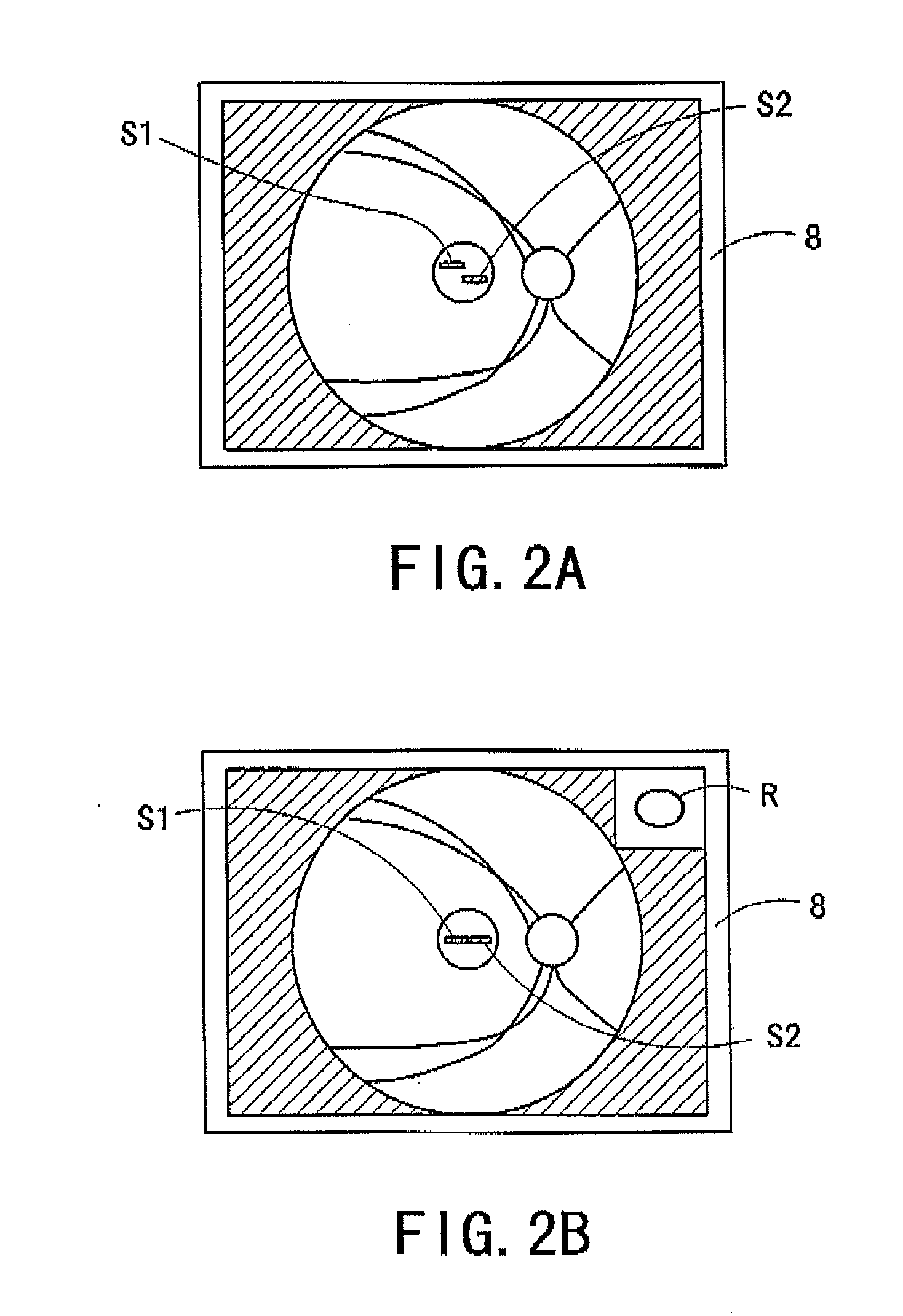
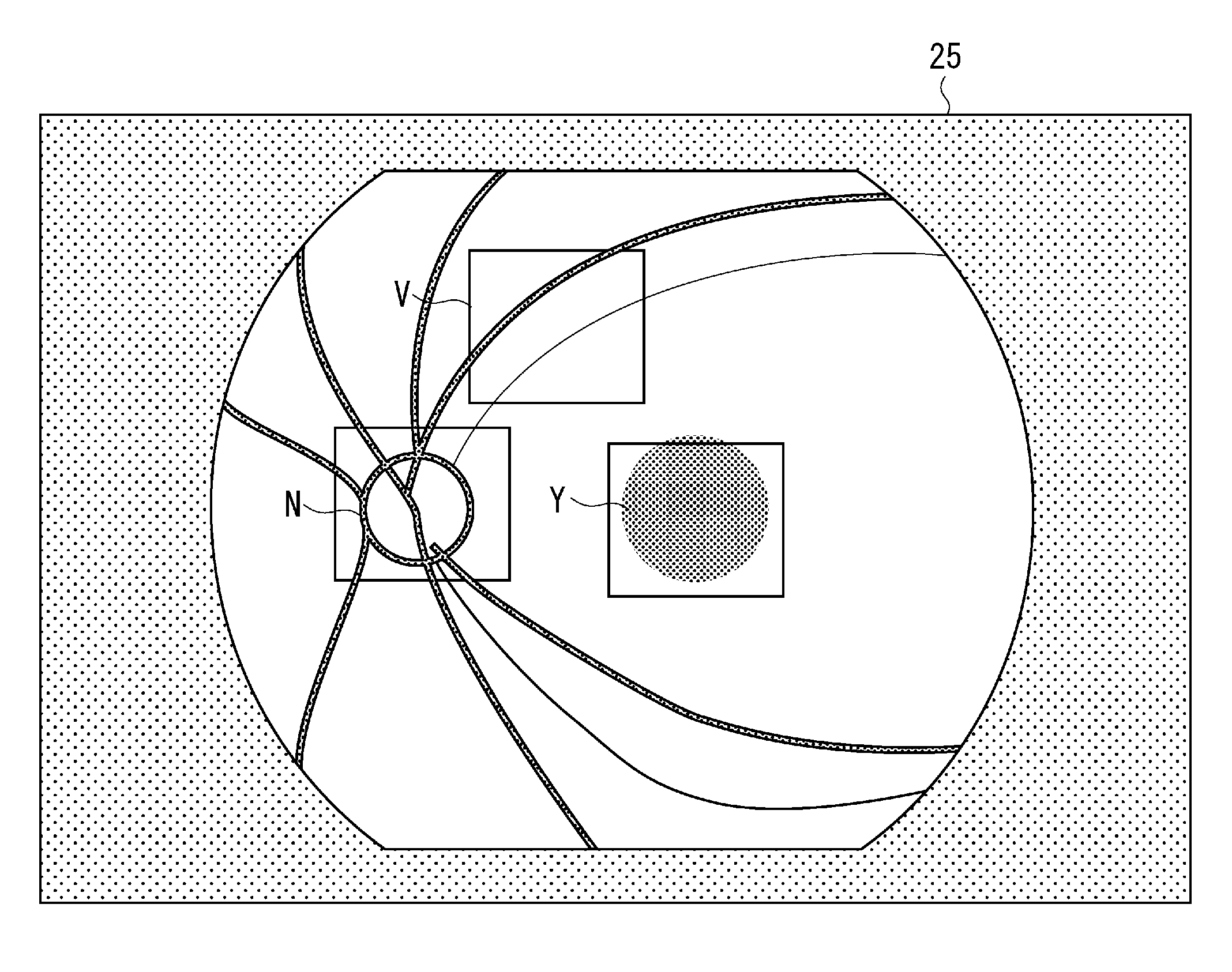
InactiveUS20110051087A1Easy alignmentImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFundus camera
When pattern recognition of a fundus image is started in step S1, output from a fundus image sensing unit is compared with a regional pattern of stored fundus image specific regions in step S2, and it is decided whether to proceed to pattern recognition. If pattern recognition is possible, based on an AF evaluation value, the lens is driven, with which automatic focusing is completed.
Owner:CANON KK
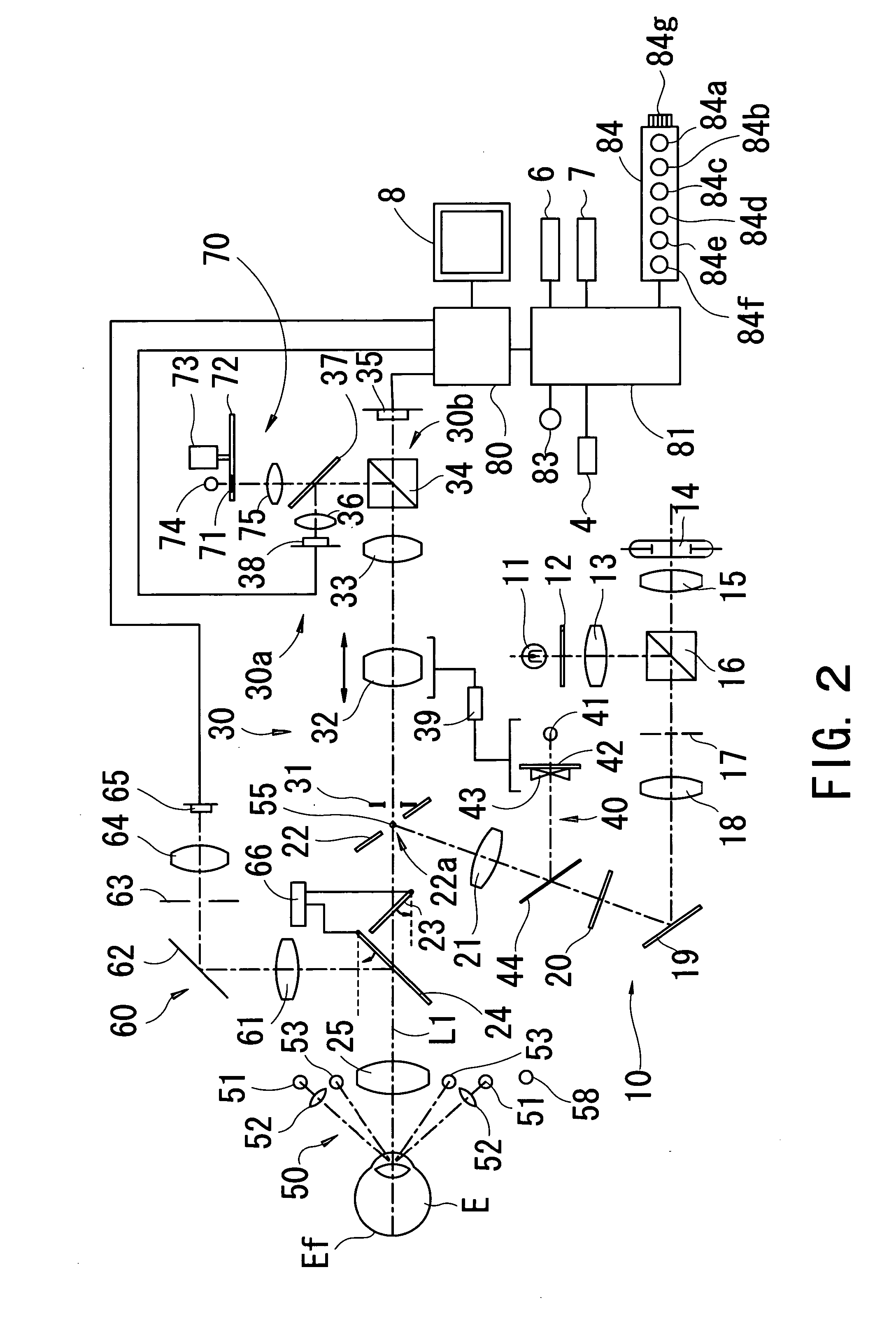
Fundus Observation Device
ActiveUS20070159595A1Interference can be controlledHigh interference efficiencyOthalmoscopesFundus cameraOphthalmology
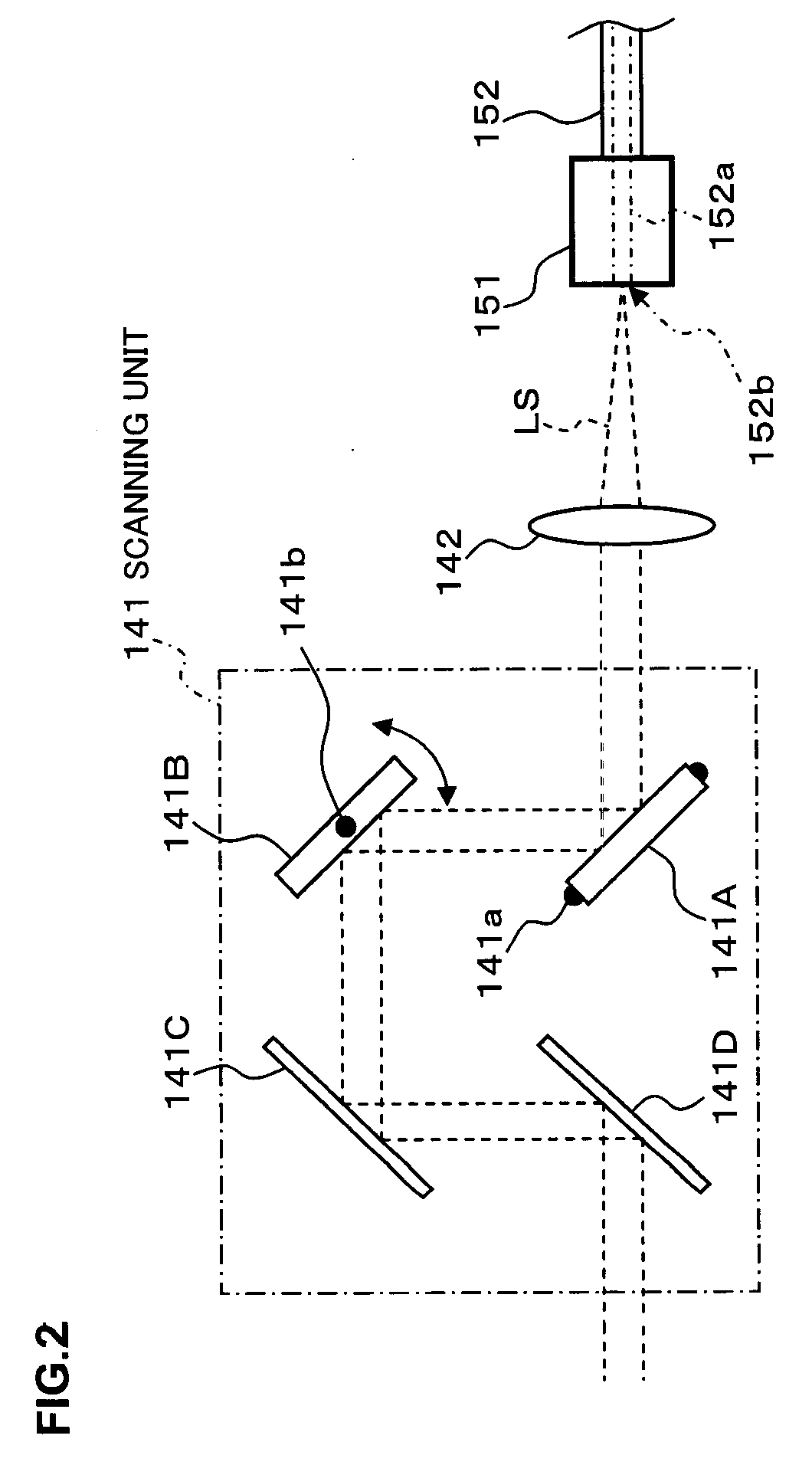
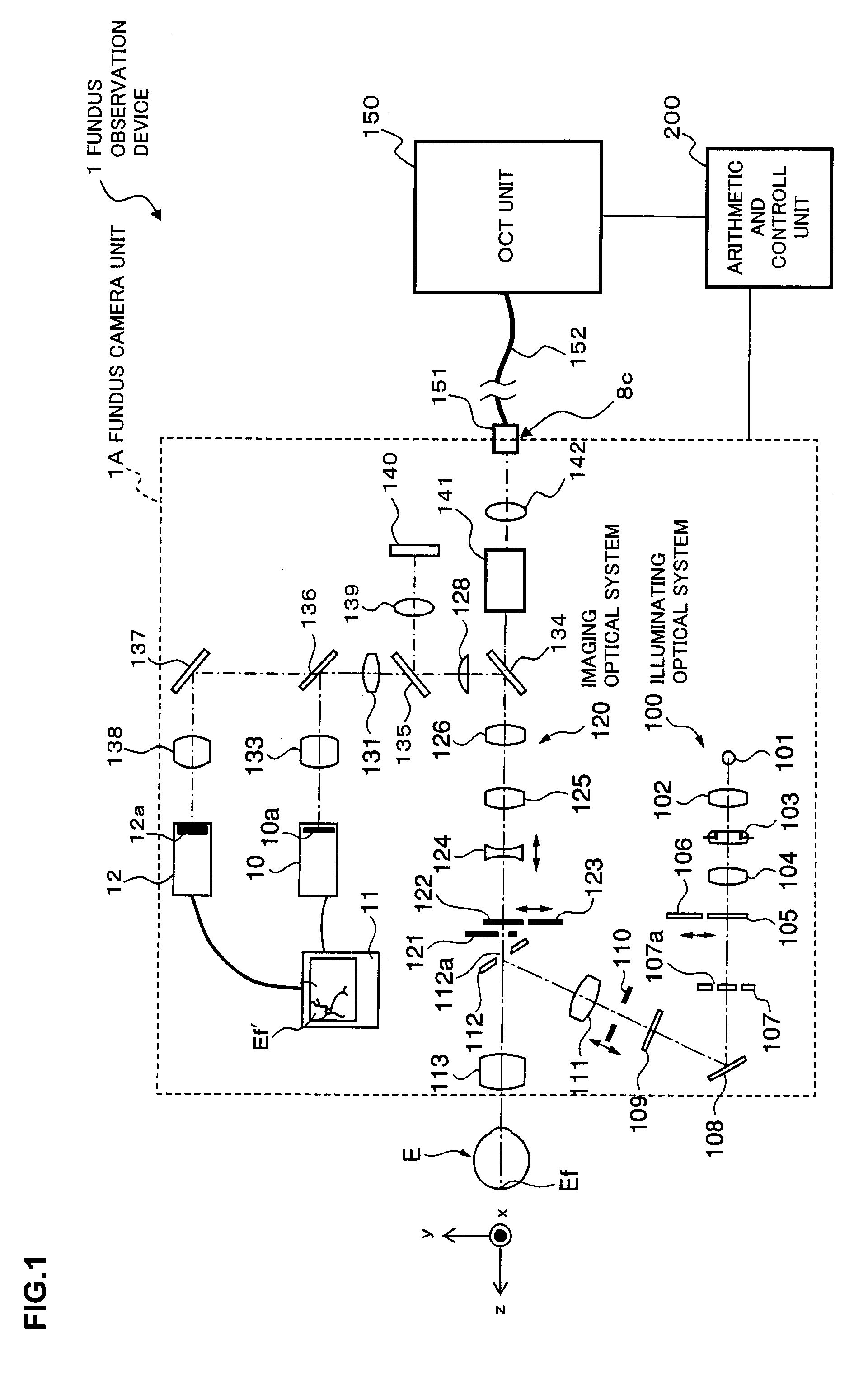
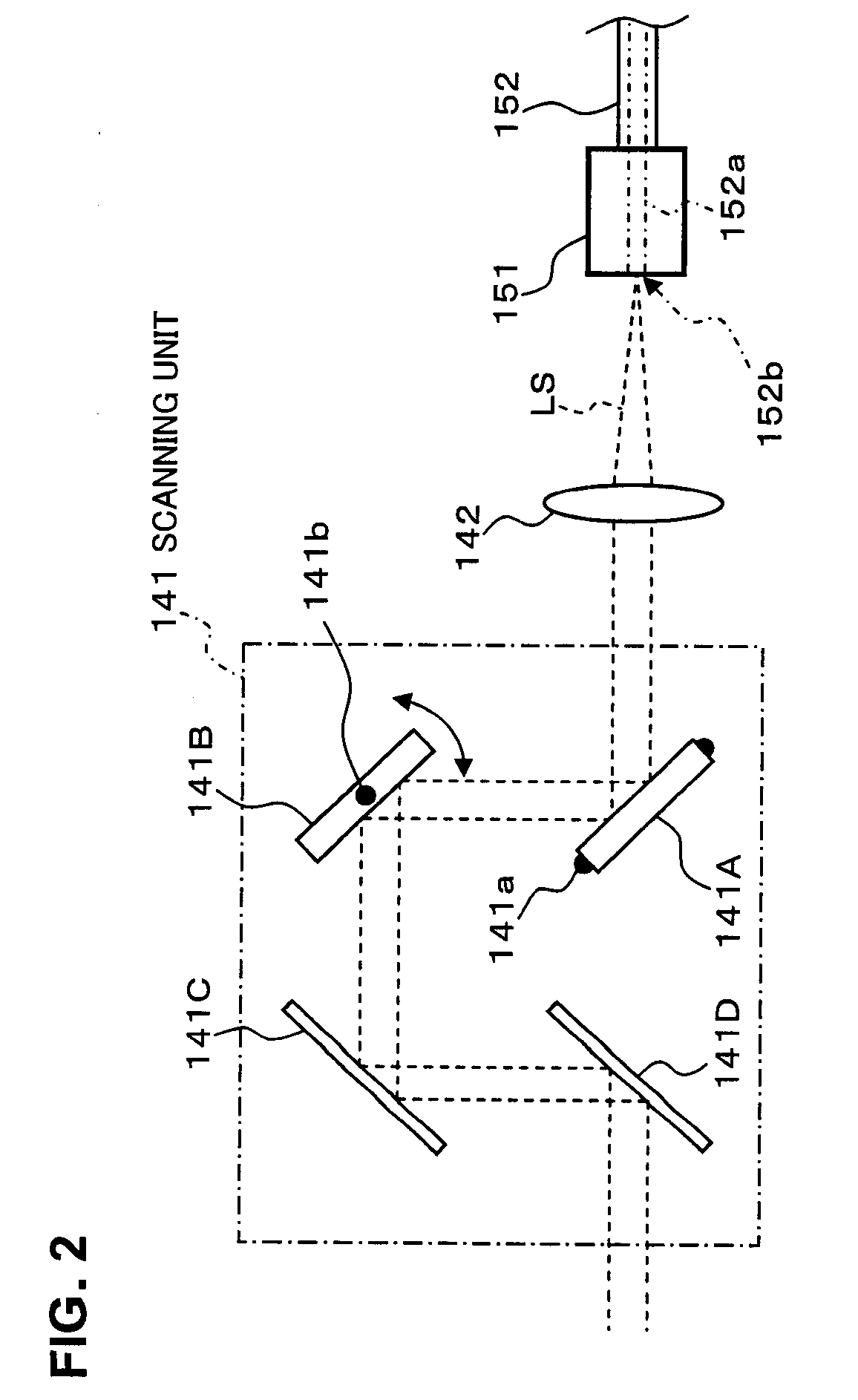
A fundus observation device which can simultaneously capture both surface images and tomographic images of the fundus oculi is provided. The fundus observation device 1 has a fundus camera unit 1A, an OCT unit 150, and an arithmetic and control unit 200. The fundus camera unit 1A has an illuminating optical system 100 and an imaging optical system 120. The arithmetic and control unit 200 forms the surface image of fundus oculi Ef based on signals from fundus camera unit 1A. The OCT unit 150 divides low coherence light LO into the signal light LS and the reference light LR, and detects the interference light LC that can be obtained from the signal light LS passing through fundus oculi Ef and the reference light LR passing through reference mirror 174. The arithmetic and control unit 200 forms tomographic images of fundus oculi Ef based on these detecting results. A Dichroic mirror 134 combines the optical path of the signal light LS toward fundus oculi Ef into the optical path for imaging of the imaging optical system 120, and separates the optical path of the signal light LS towards fundus oculi Ef from the optical path for imaging.
Owner:KK TOPCON
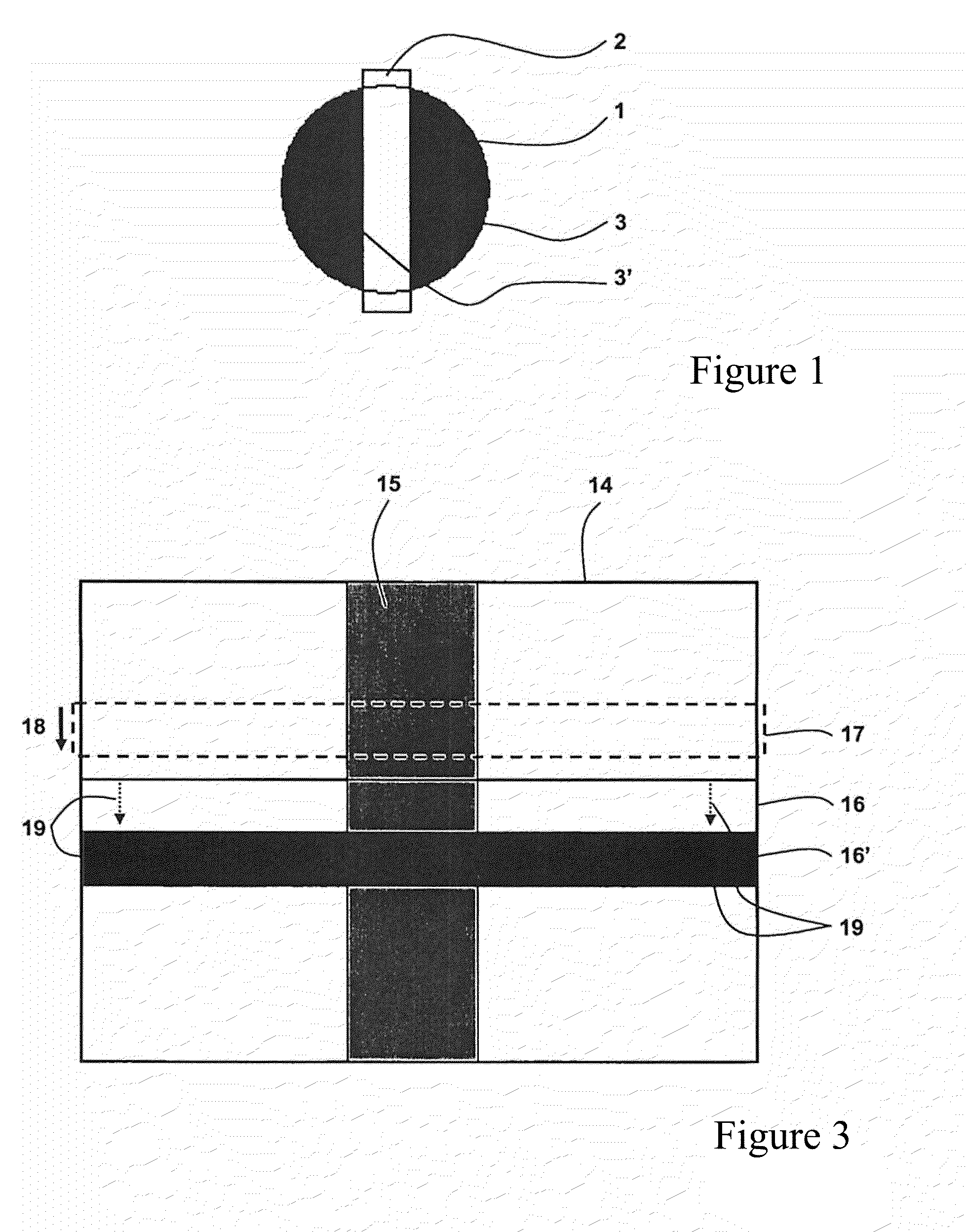
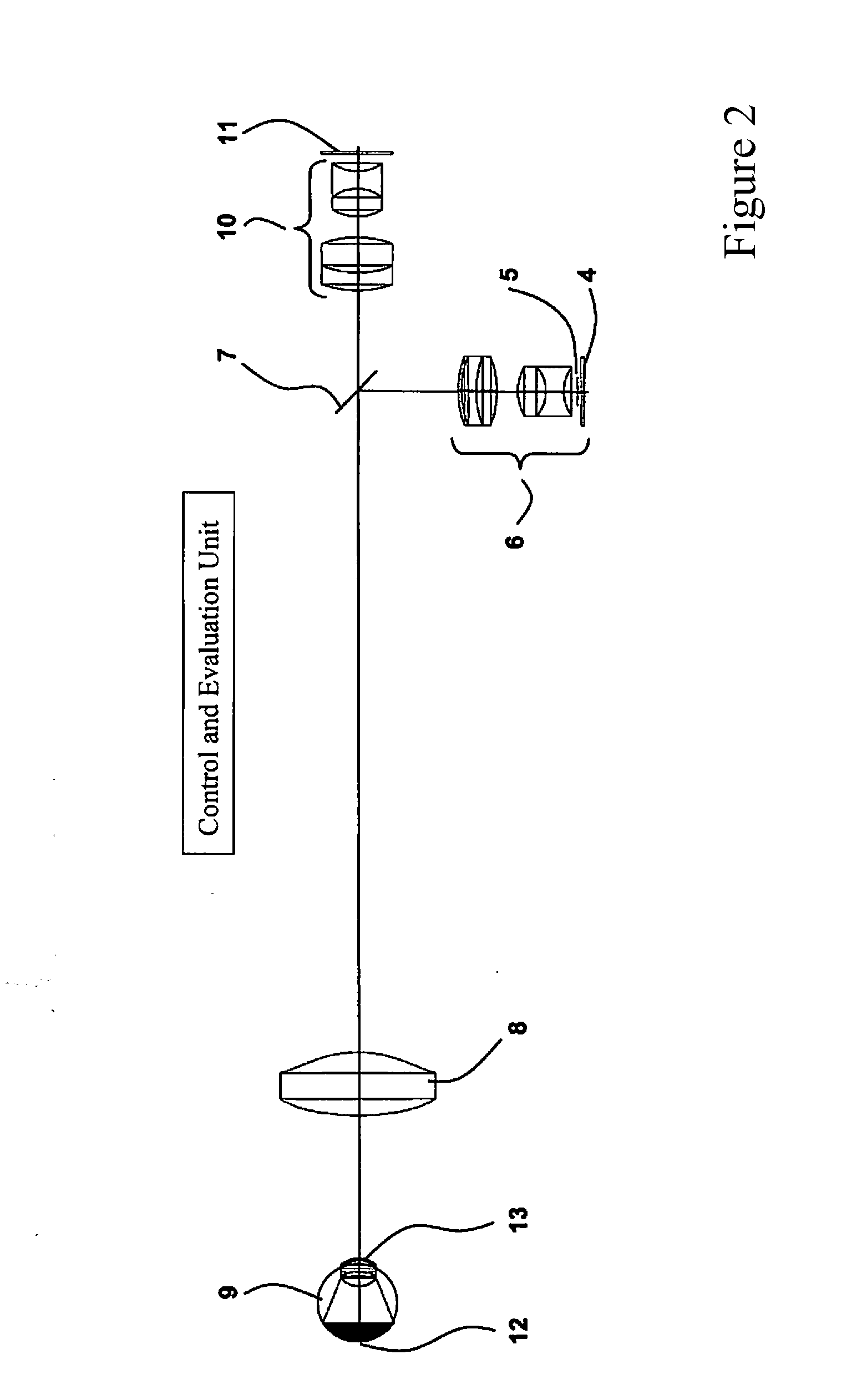
Fundus camera with strip-shaped pupil division, and method for recording artifact-free, high-resolution fundus images
ActiveUS20130222763A1Eliminate contactReduce manufacturing costOthalmoscopesSpatially resolvedRecord artifact
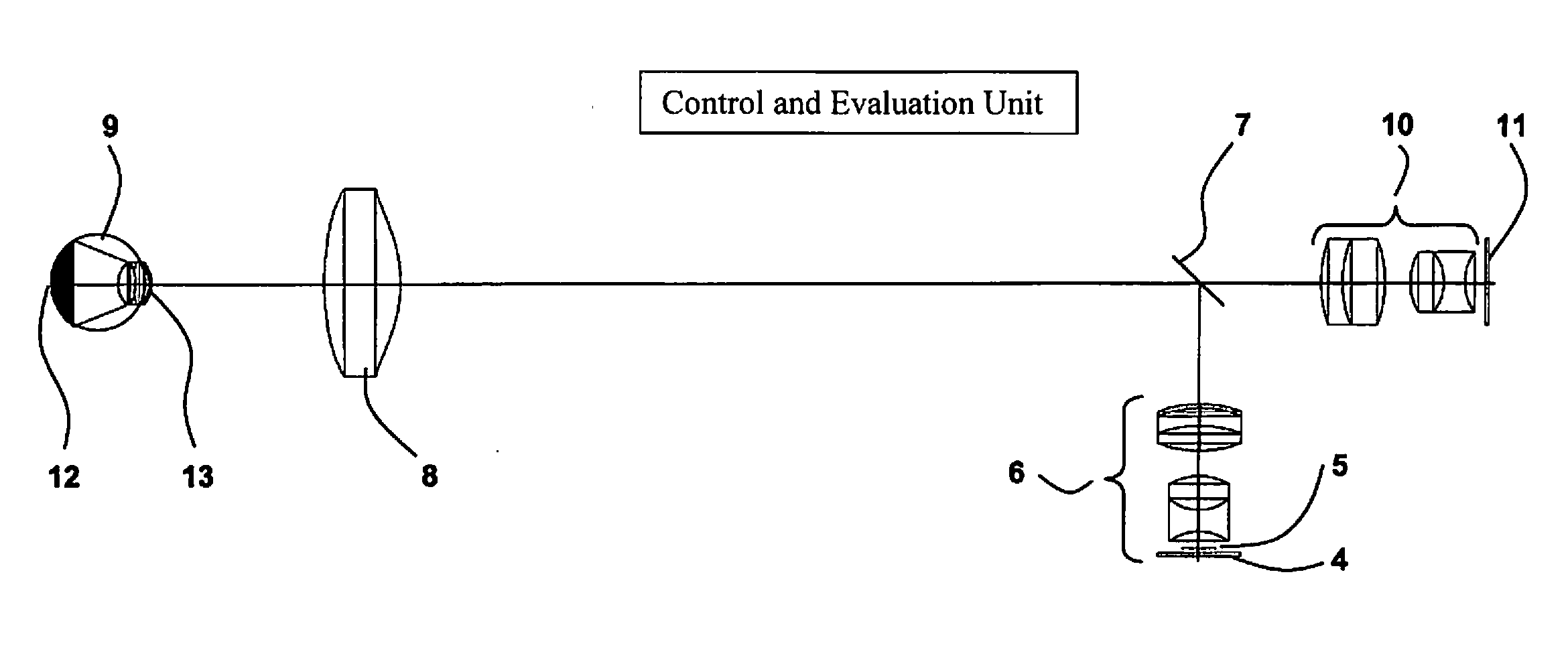
A fundus camera for the recording of high-resolution colour images of the fundus of non-dark-adapted eyes, and without the use of a mydriatic. The fundus camera has a strip-shaped pupil division, and includes a coherent or incoherent illumination source with illumination optics, a deflection mirror and an ophthalmoscope lens for illuminating the eye, detection optics and a detector for detecting the light reflected by the eye, and a control and evaluation unit. The deflection mirror has a strip shape, and the spatially resolving detector can be activated and read out in sectors. The control and evaluation unit connects the data read out in sectors in the form of a bright image from the detector and produce a resulting fundus image. The fundus camera records images of the fundus when the eyes are not dark-adapted for this purpose and no mydriatic has been used.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Fundus camera
InactiveUS20070146535A1Compactness and lighteningReduce irresolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFundus cameraDisplay device
A fundus camera having a photographing optical system for photographing a fundus of an eye to be examined, the camera providing, a first illumination optical system for illuminating the fundus of the eye with using infrared light, a second illumination optical system for illuminating the fundus of the eye with using visible light for photography by sharing a part of optical path with the first illumination optical system, a target projecting optical system for projecting a target for focusing on the fundus of the eye, an observation optical system provided with a focusing lens and photographic element having sensitivity in an infrared area, for observing the fundus of the eye which is illuminated by the infrared light of the first illumination optical system and a target image of a target plate projected on the fundus of the eye, displaying device for displaying an image obtained by the observation optical system, moving device for moving by interlocking the focusing lens of the observation optical system and the target plate, travel-distance displaying device for displaying travel distances by the moving device.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Fundus camera
An apparatus and method of providing an ophthalmic image is presented. In accordance with embodiments of the present invention, an illumination path with a focus index optical assembly and a first diopter compensator is provided and an imaging path with a sensor and a second diopter compensator is provided. The first diopter compensator and the second diopter compensator can be adjusted to provide focus according to a focus index from the focus index optical assembly.
Owner:OPTOVUE
Apparatus and method for non-invasive diabetic retinopathy detection and monitoring
ActiveUS20120249959A1Robust identificationEnhance vesselImage analysisAcquiring/recognising eyesDiabetes retinopathyOphthalmology
A fundus camera using infrared light sources, which included an imaging optical path and an optical path for focusing and positioning and two optical paths share a common set of retina objective lens, and a computer-assisted method for retinal vessel segmentation in general and diabetic retinopathy (DR) image segmentation in particular. The method is primarily based on Multiscale Production of the Matched Filter (MPMF) scheme, which together the fundus camera, is useful for non-invasive diabetic retinopathy detection and monitoring.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
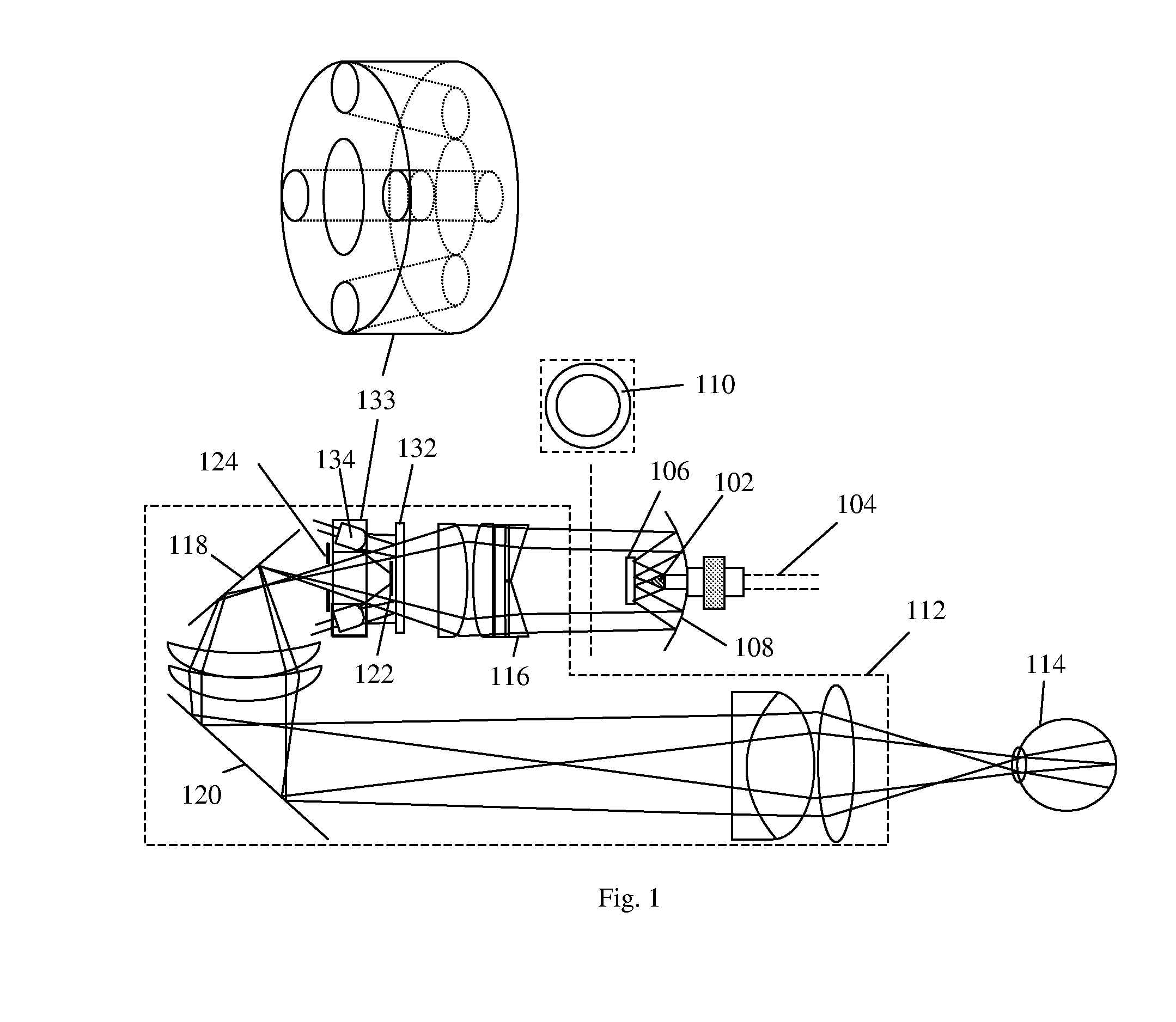
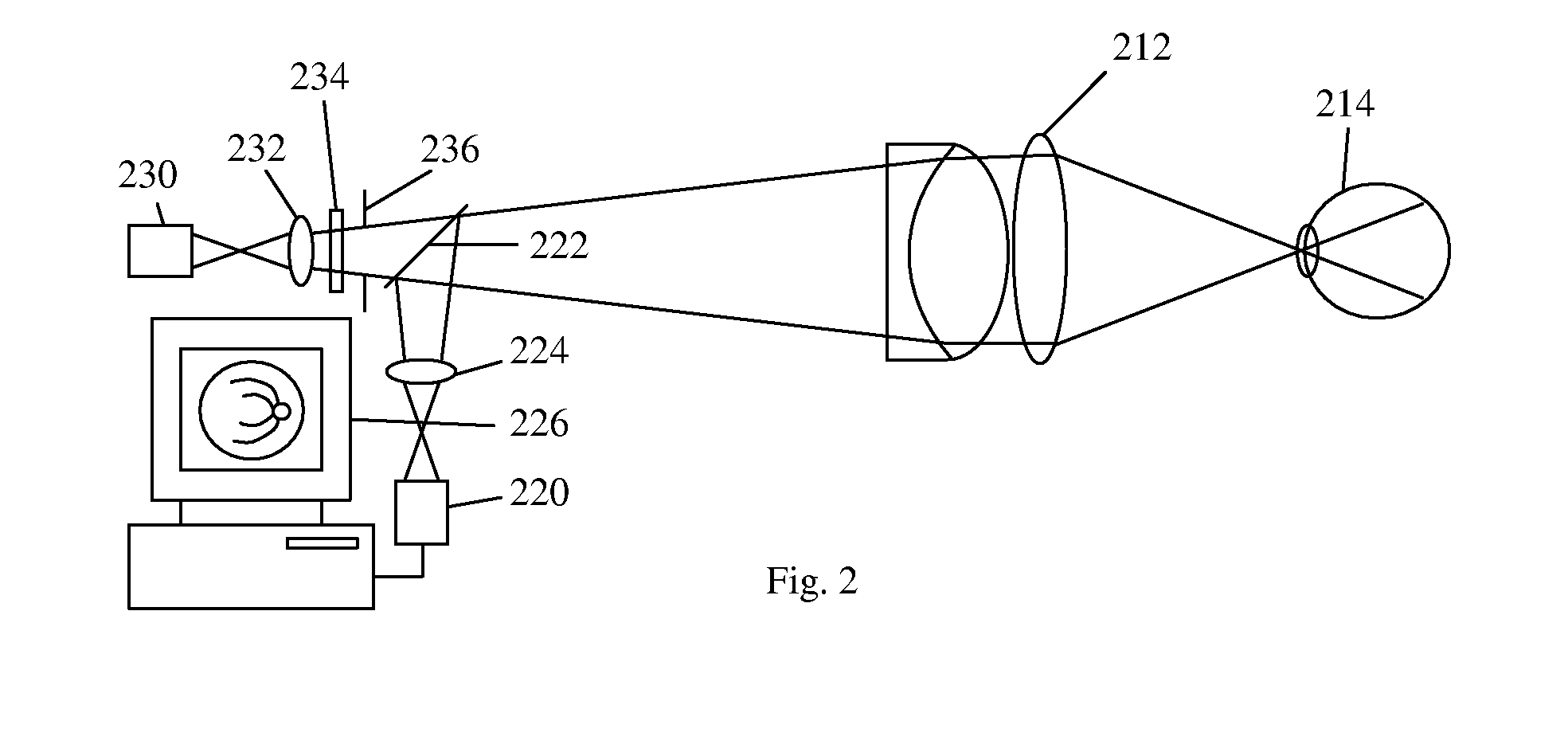
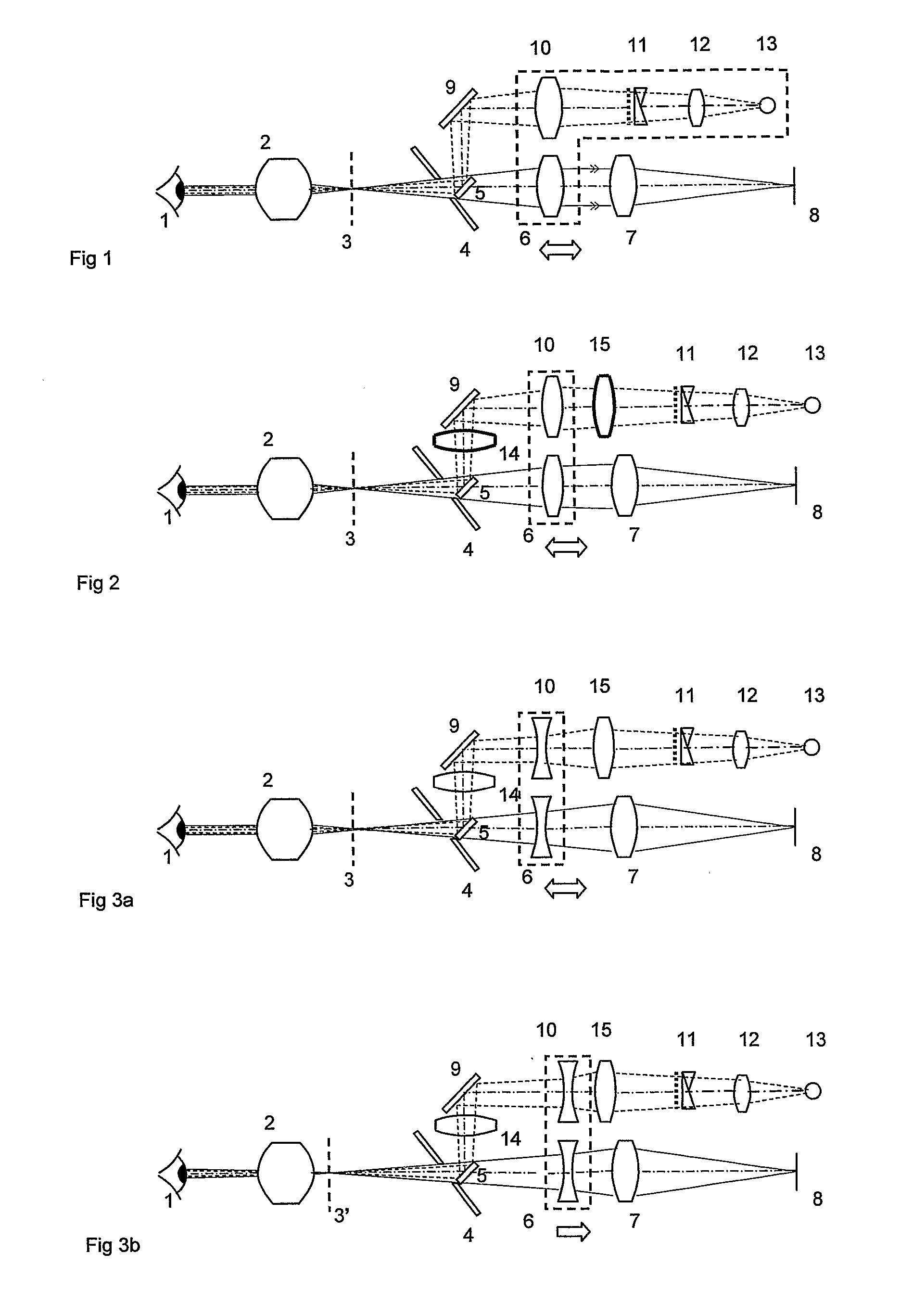
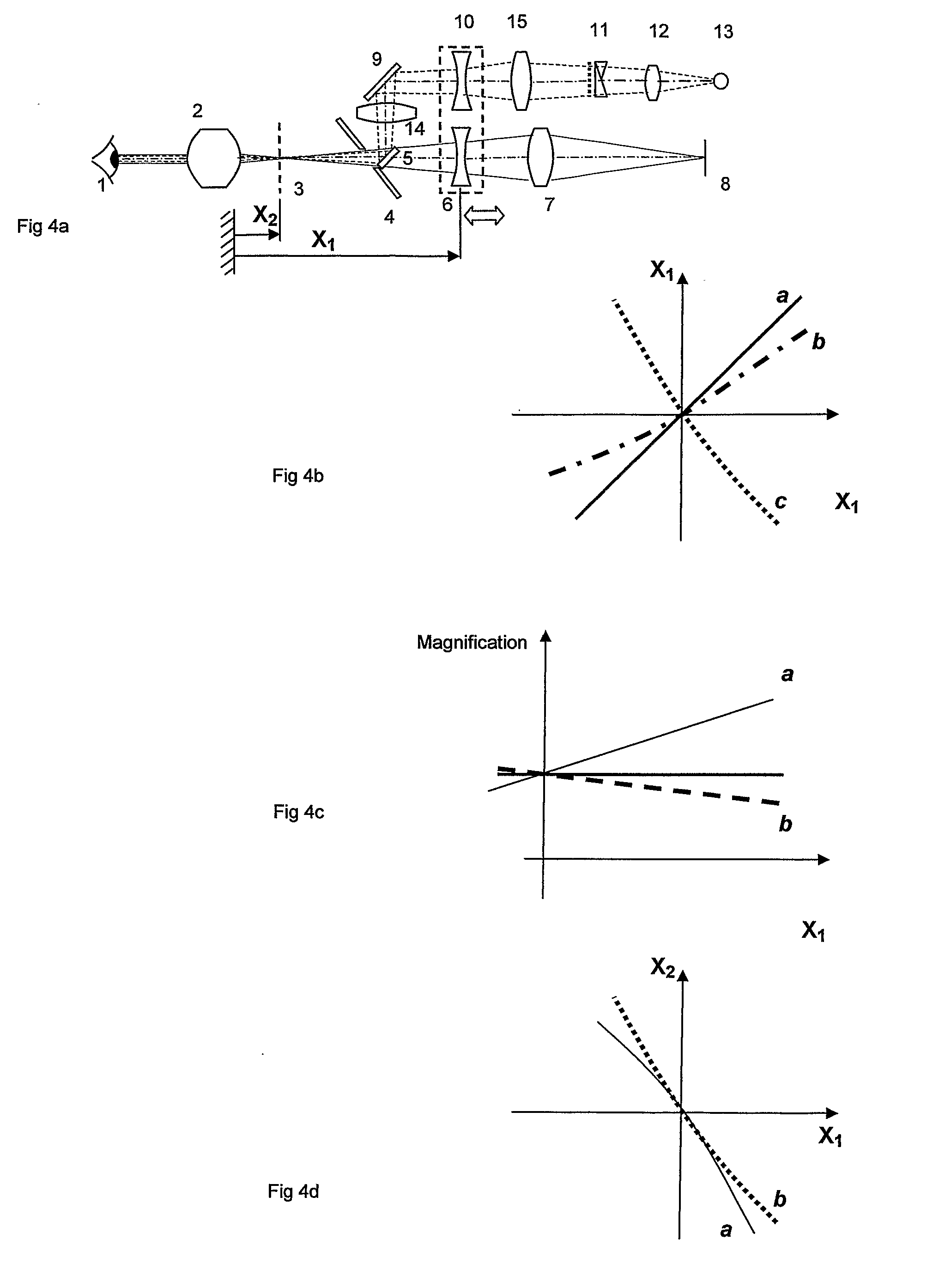
Devices to Facilitate Alignment and Focussing of a Fundus Camera
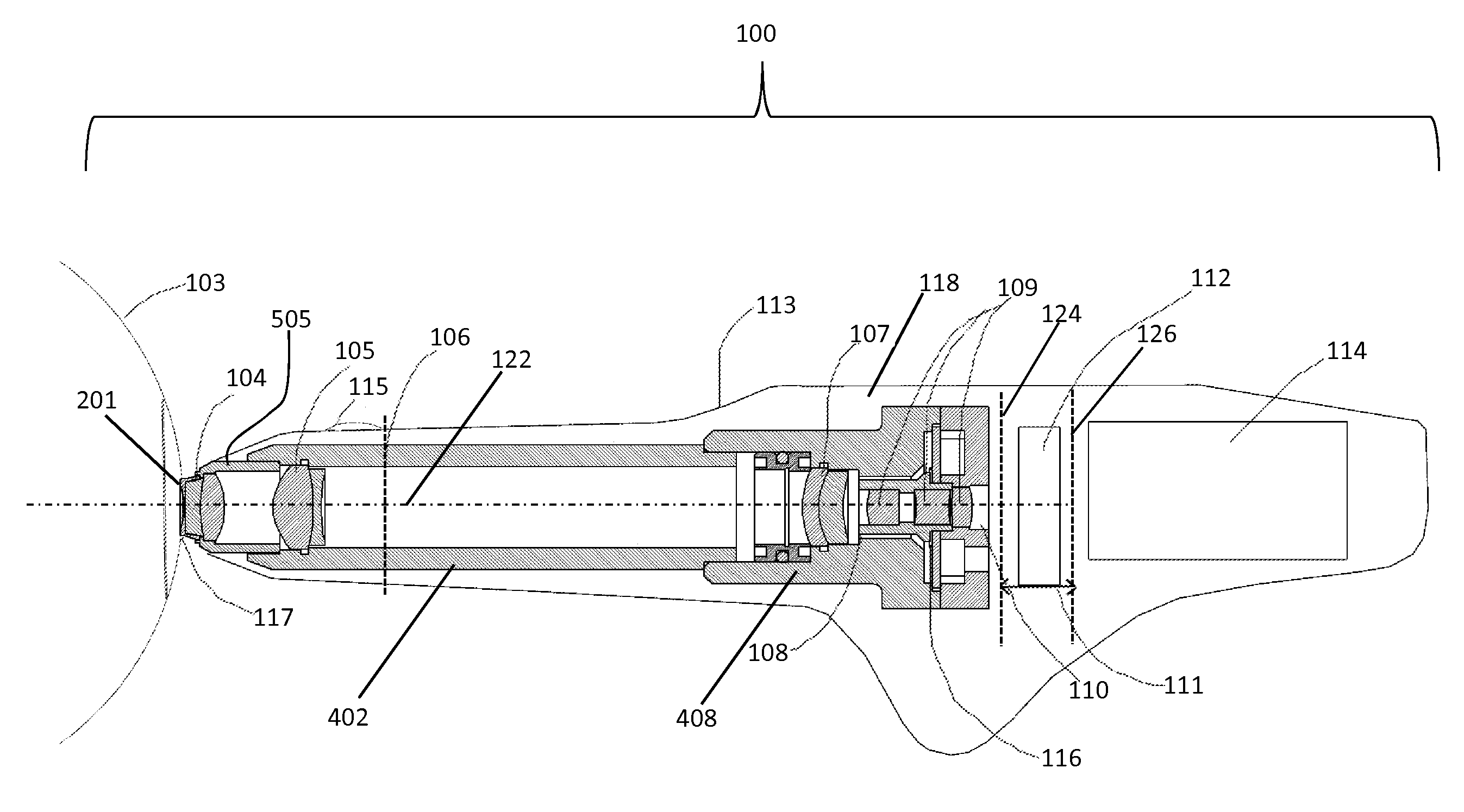
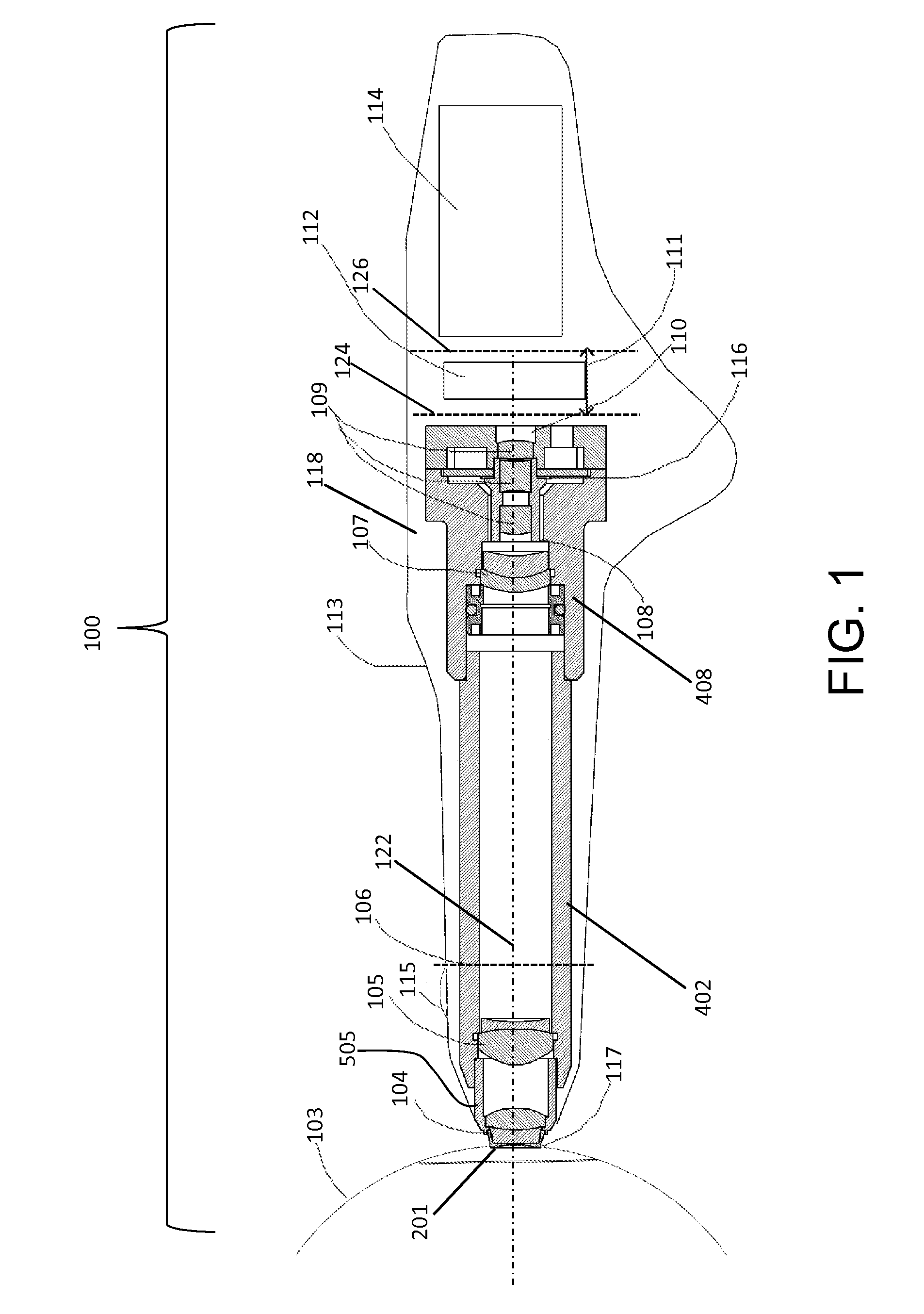
InactiveUS20070253688A1Increase powerEasy constructionPrintersProjectorsFundus cameraProjection system
A fundus camera is provided with a focus aid mark projection system (5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13) that includes a focus aid mark focussing lens (10) and other optical components such that the focus aid mark focussing lens (10) is attached to the focussing lens (6) of the imaging system and moves with that lens, thereby maintaining the focal planes of the focus aid mark projection system and the imaging system co-planar. An associated alignment mark projection system (35, 34, 33, 32) includes optics that utilise part of the existing fundus camera illumination system (35) to project a plurality of alignment marks onto the iris of the subject eye.
Owner:VISION BIOSYST
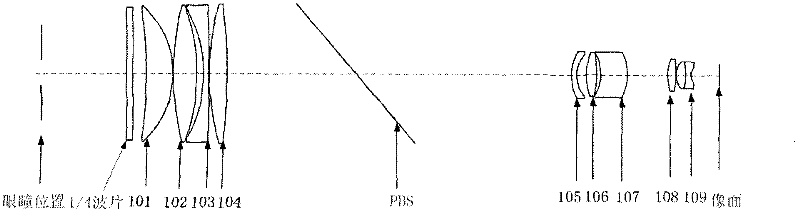
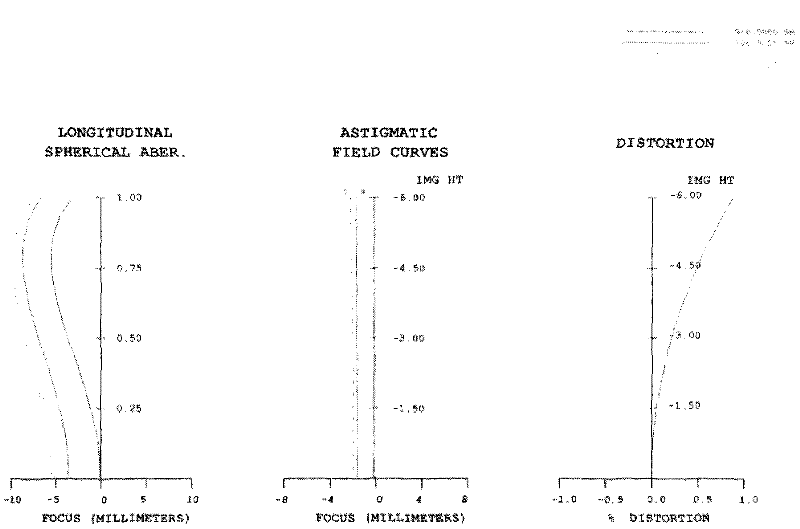
Novel mydriasis-free portable fundus camera
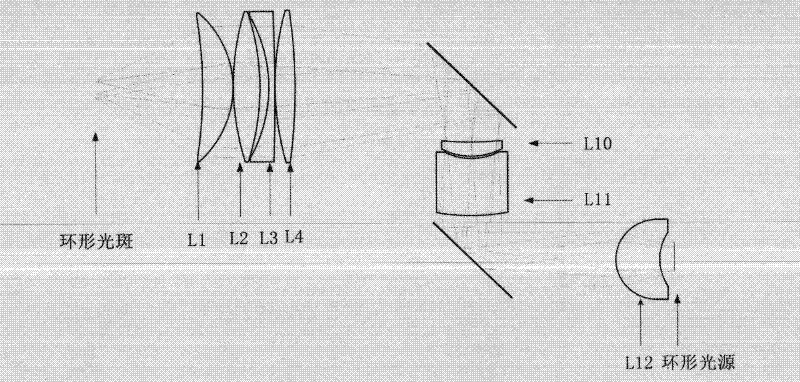
The invention provides a fundus camera optical system for detecting lesion of human eyes, and particularly provides a novel mydriasis-free portable fundus camera. The novel mydriasis-free portable fundus camera comprises a lighting system and an imaging system. The imaging system comprises an eye objective lens and an imaging objective lens, wherein the eye objective lens consists of first, second, third and fourth lenses from left to right, the imaging objective lens consists of fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth and ninth lenses, fundus is imaged on a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) by the imaging system and displayed in real time by an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). The lighting system consists of an annular light source, a dodging lens and an eye objective lens, wherein the dodging lens consists of tenth, eleventh and twelfth lenses, and the eye objective lens and the imaging system are commonly used. PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) and a quarter wavelength plate are added in the system so as to eliminate the ghost image generated by the eye objective lens. According to the invention, the 2-megapixel CCD is adopted as the camera, the MTF (Mechanical Time Fuse) value is larger than 0.2 at a position of 120lp / mm, the full field angle is 60 degrees, the distortion value is smaller than 5%, and the fundus camera can be universally applicable to human eyes of minus 8D to positive 10D through adjusting the positions of the CCD.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
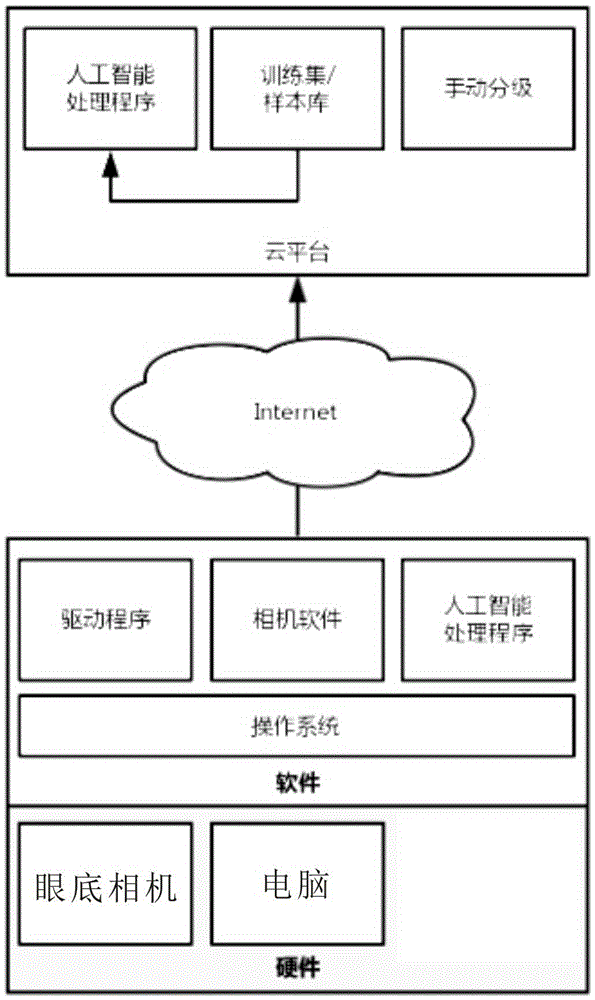
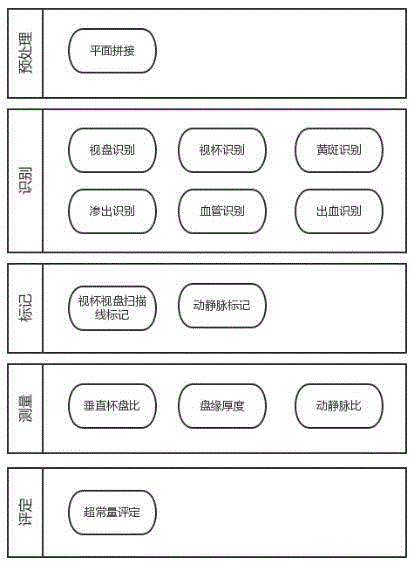
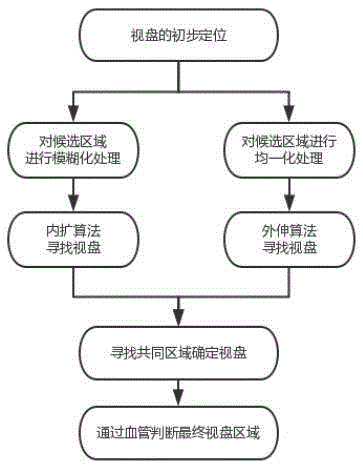
Eye ground picture and image intelligent obtaining and recognizing system
ActiveCN105411525AFast diagnosisGuaranteed accuracyOthalmoscopesEffective solutionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an eye ground picture and image intelligent obtaining and recognizing system which comprises an eye ground camera, a computer and artificial intelligent processing program installed in the computer. The artificial intelligent processing program comprises an eye ground picture and image feather recognition unit, an eye ground picture and image feature marking unit, an eye ground image feature measuring unit and an eye ground picture and image evaluation unit. According to the obtaining and recognizing system, after eye ground pictures are taken, a normal grading report is directly given for eye ground pictures more than constant quantity automatically through an eye ground picture artificial intelligent processing program built in the obtaining and recognizing system, cases of suspected lesion are sent to an artificial intelligent processing cloud platform of the obtaining and the recognizing system, and cloud automatic evaluation is provided through a larger sample library and higher computing power. Meanwhile, ophthalmologists are allowed to carry out manual classification through a cloud computing platform, and the system is an effective solution of remarkably increasing eye ground disease diagnosis speed on the premise that accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HEALGOO INTERACTIVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Portable fundus camera
ActiveUS8836778B2Speed flowEconomically beneficialUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcquiring/recognising eyesFundus cameraHand held
A portable hand-held camera for imaging the fundus of an eye, the camera comprising a housing comprising an internal cavity terminating at a forward housing end, a forward lens, and a light source configured to direct light from locations distributed around the perimeter of the forward lens forwardly out of the housing end. In other embodiment, a portable hand-held camera for imaging the fundus of an eye includes optics configured to focus light reflected back from the fundus onto an image receptor, with the optics being capable of varying the field of view among differing portions of the fundus. Methods to ensure unique image identification and storage are described.
Owner:LUMETRICS
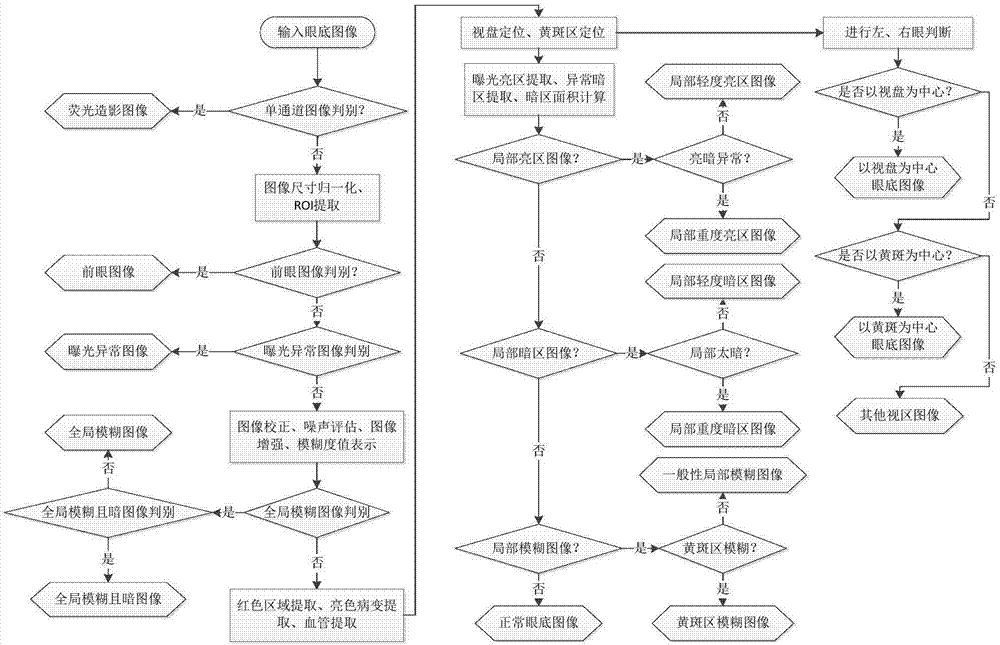
Eye fundus image quality control method
ActiveCN107451998AControl resource usageReduce technical requirements for shootingImage enhancementImage analysisFundus cameraQuality control
The invention discloses an eye fundus image quality control method which includes the following steps: processing a target eye fundus image; extracting local bright regions and local dark regions of the target eye fundus image from a region of interest ROI of the target eye fundus image; determining whether the brightness of the target eye fundus image is abnormal; and carrying out image screening based on the judgment on brightness. Through the method, the quality of color eye fundus images can be discriminated, and images with local bright regions and / or local dark regions can be distinguished from normal eye fundus images. The quality of color eye fundus images taken by cameras of various models can be controlled, evaluated and classified. The visual area of an eye fundus image can be identified, and the quality of the eye fundus image can be evaluated. Unqualified images are prevented from entering the detection link to occupy resources. The method is used together with eye fundus camera hardware. Problems can be found at the source, and the feedback time can be reduced. The shooting technology requirement for medical workers is lowered.
Owner:北京大恒普信医疗技术有限公司
Fundus observation device, fundus image display device and memory media for fundus observation program
InactiveCN1939208AEasy mutual positional relationshipEasy to masterOthalmoscopesImaging processingFundus camera
To provide a technology that makes it easy to capture a positional relation of a 2-dimensional image of the surface of a fundus oculi and a tomographic image of the fundus oculi. The fundus observation device 1 is provided with a fundus camera unit 1A for forming a 2-dimensional image of the surface of a fundus oculi Ef of an eye to be examined, an OCT unit 150 for forming a tomographic image of the fundus oculi Ef, a scanning unit 141 as well as an image processing part 220, a display 207, and a controlling part 210 of a computer 200 for displaying the 2-dimensional image formed by the fundus camera unit 1A and a tomographic image formed by the OCT unit, etc. in parallel on the display 207, and also for displaying the cross-sectional position information (attention line L, attention region P) indicating the cross-sectional position of the tomographic image on the surface of the fundus oculi Ef, so as to be overlapped with the 2-dimensional image.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com