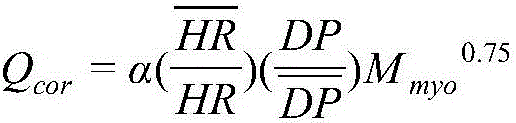Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
156 results about "Vessel diameter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The diameter of blood vessels ranges from 8 micrometer to 25000 micrometer. The type of blood vessels that has the smallest diameter is the capillary while the type with the largest diameter is the artery.
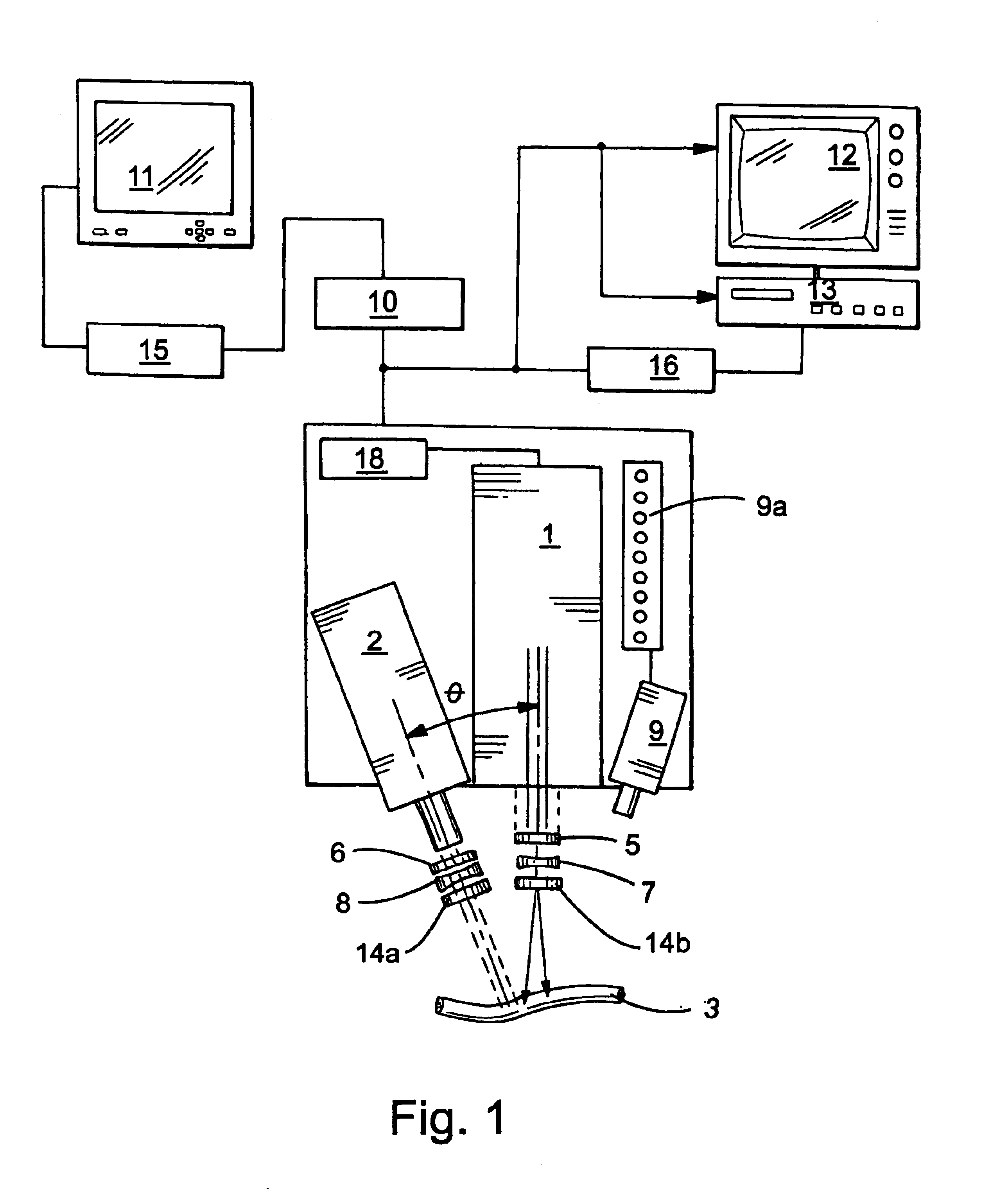
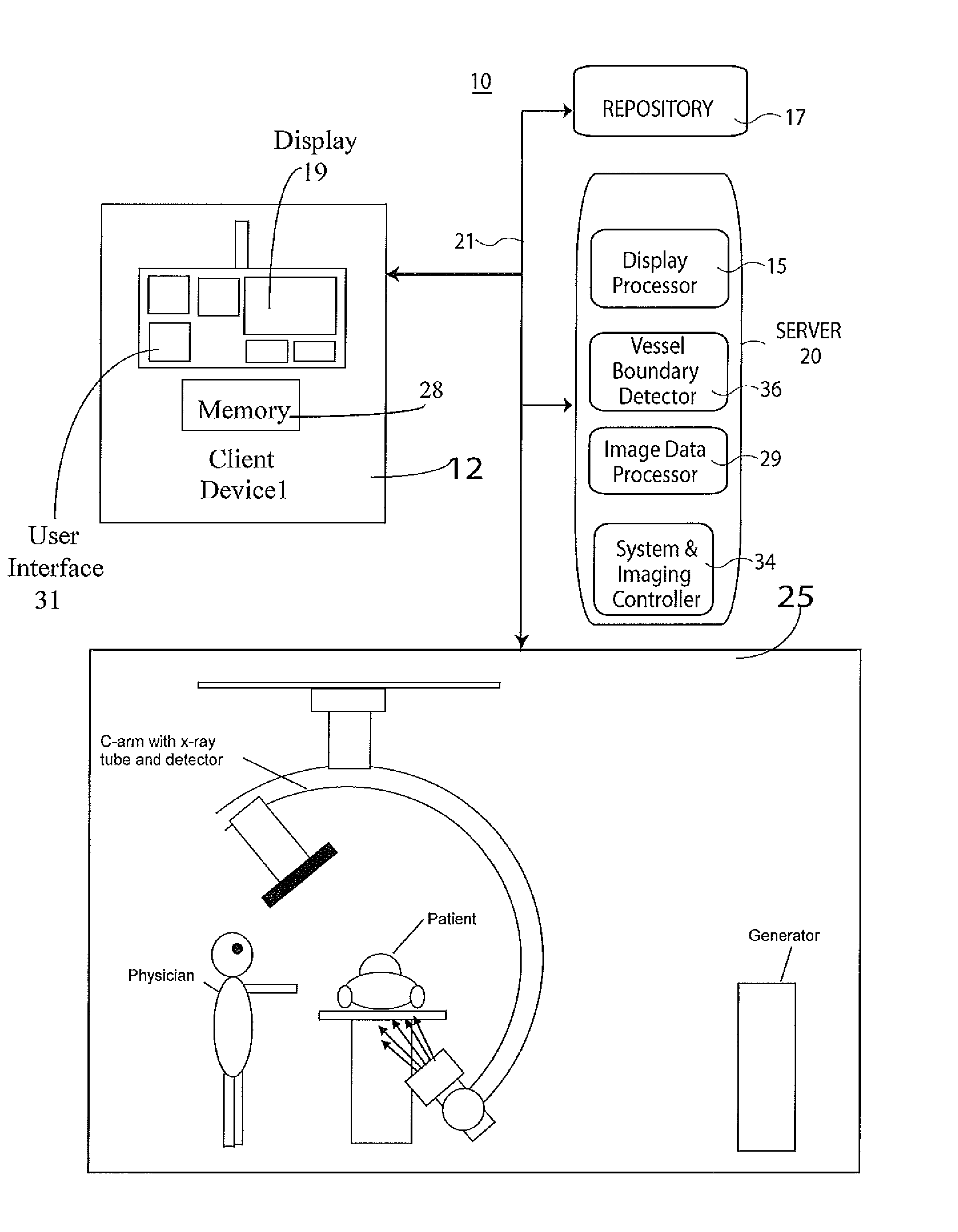
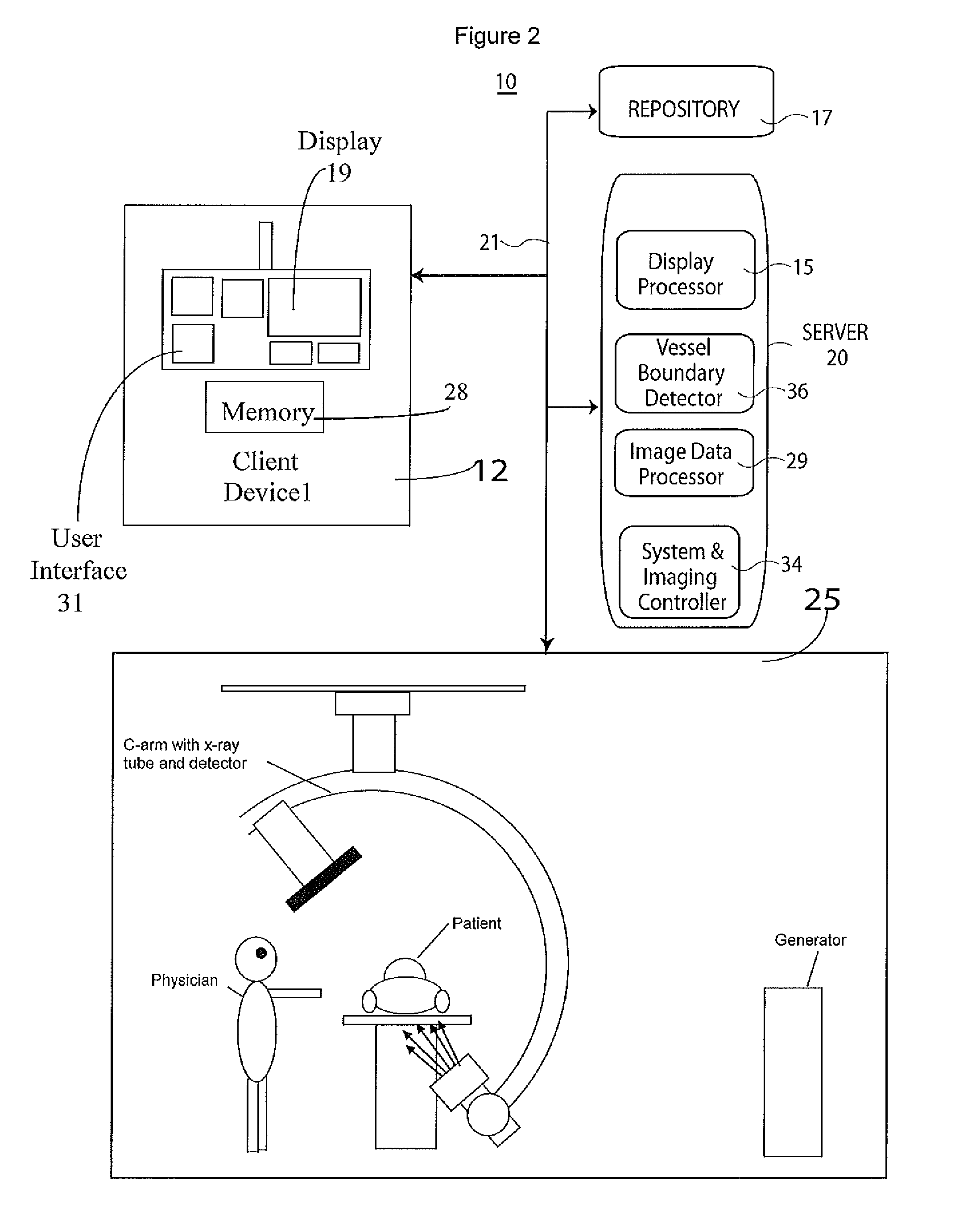
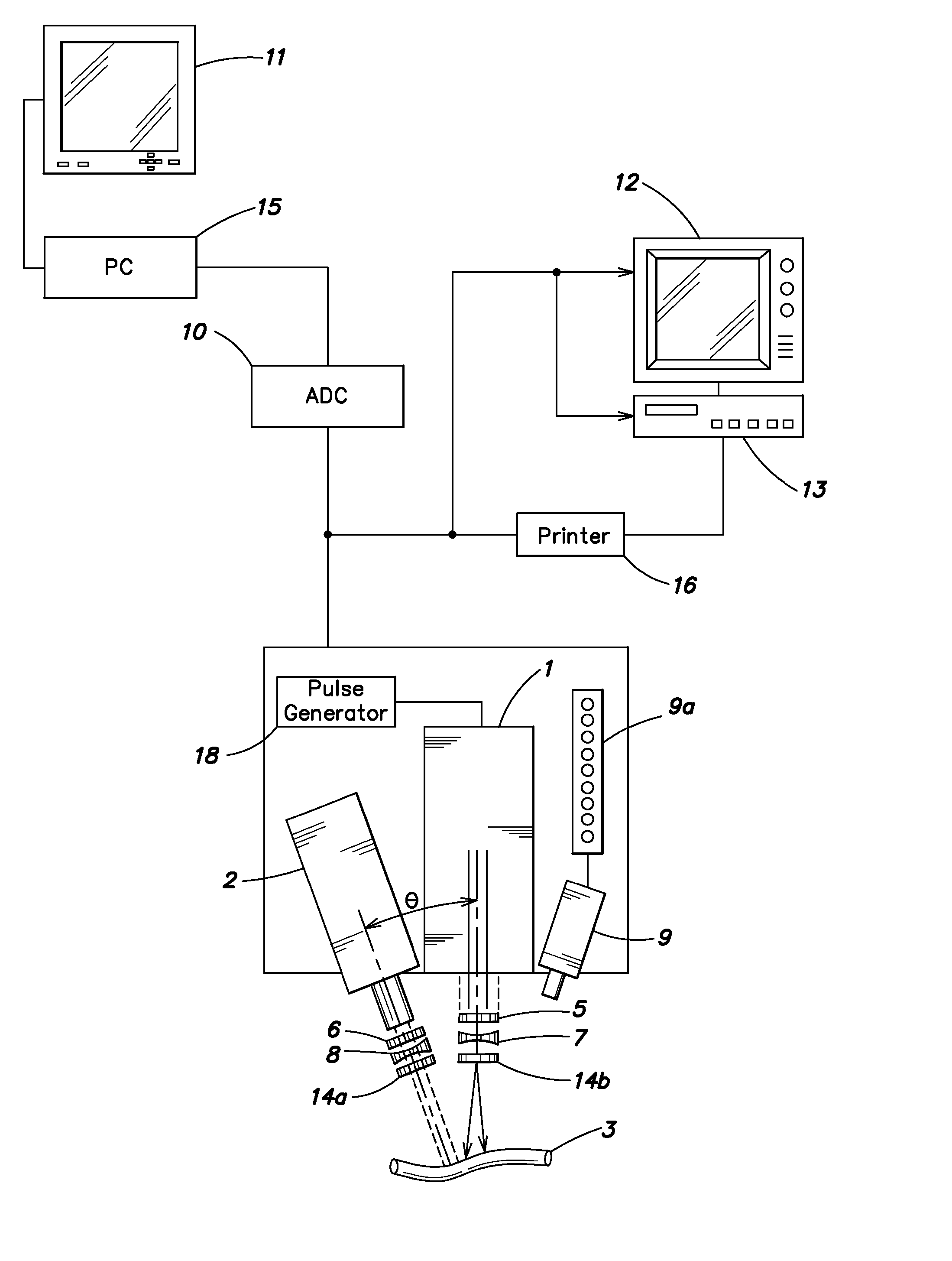
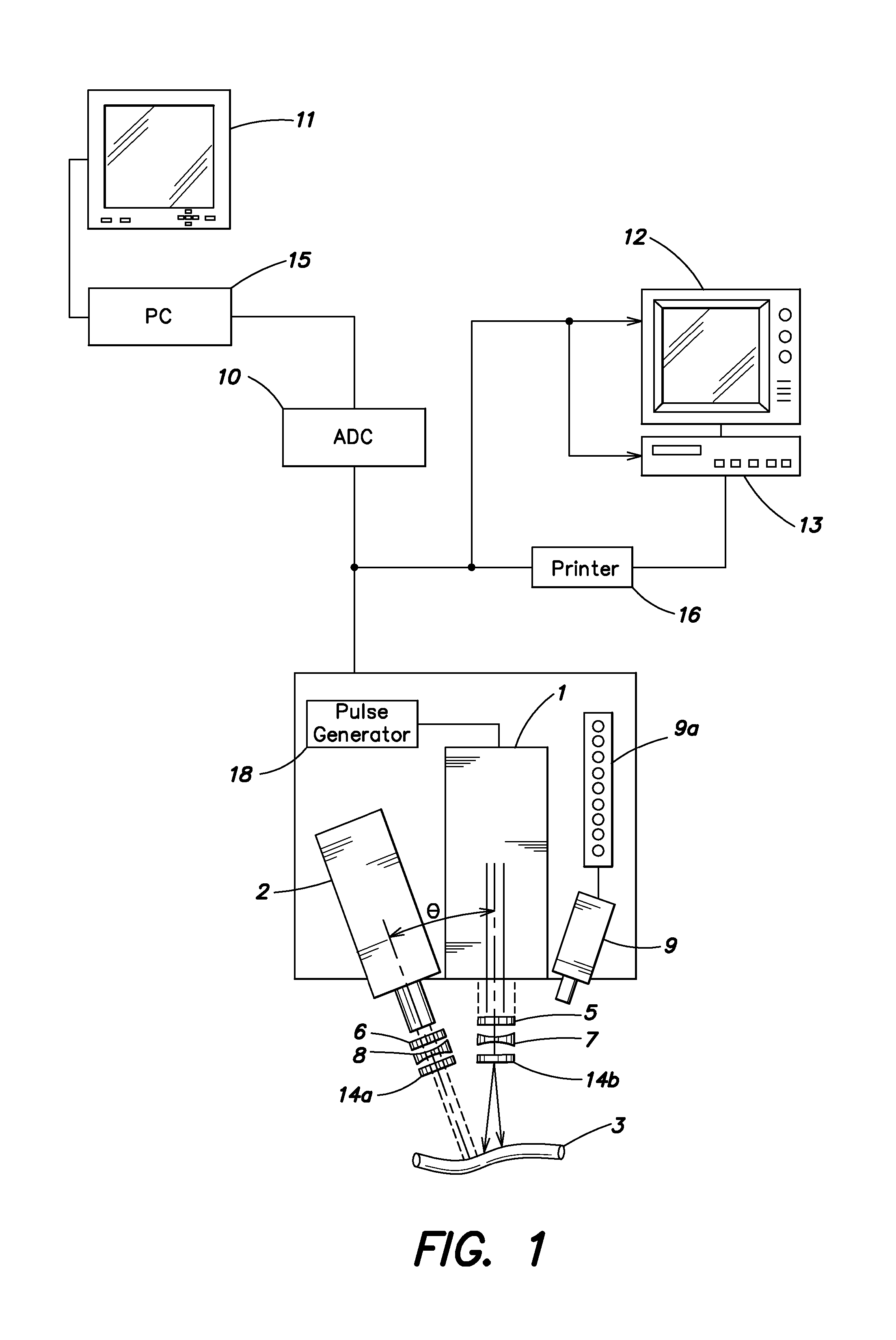
Lumen Morphology and Vascular Resistance Measurements Data Collection Systems, Apparatus and Methods
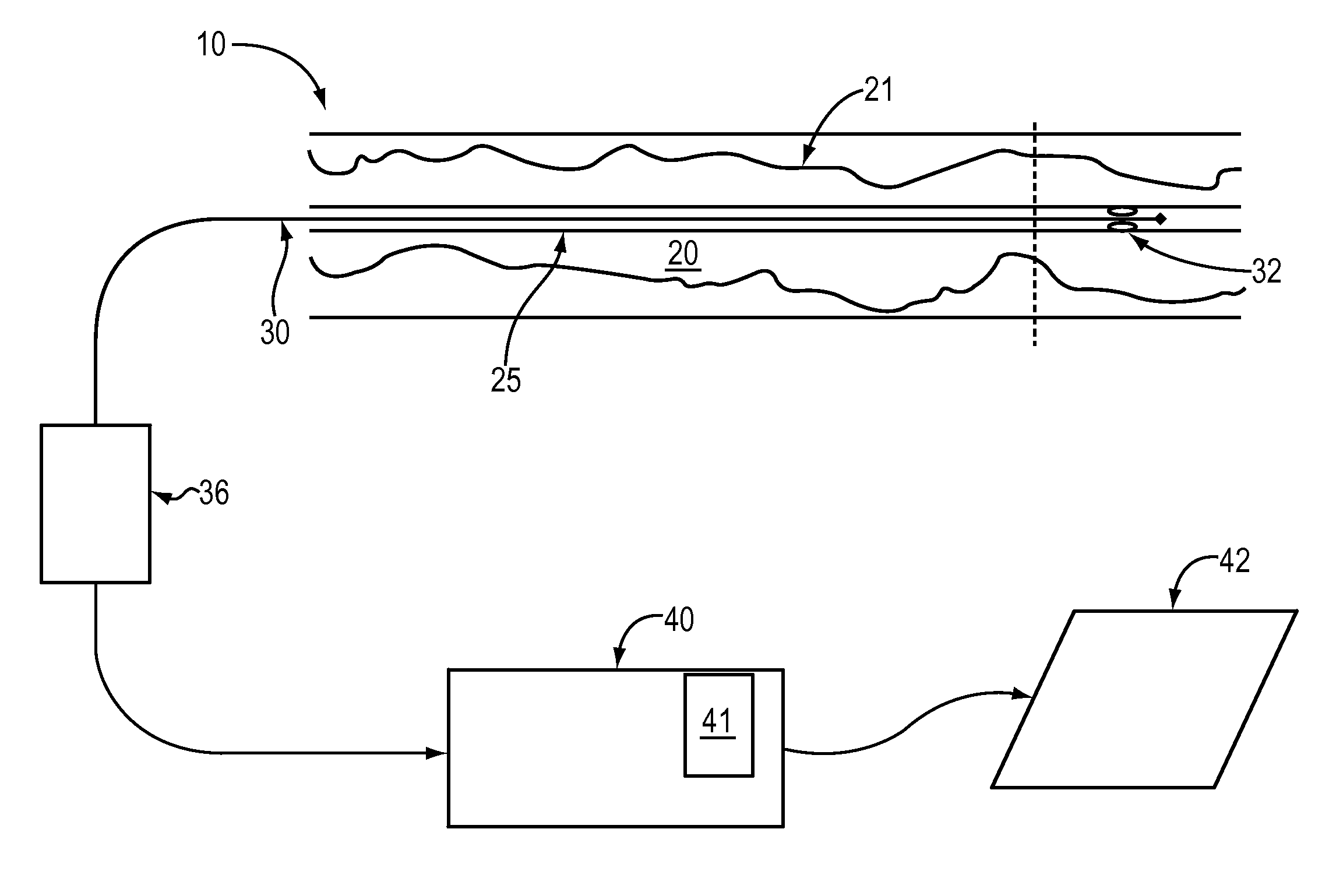
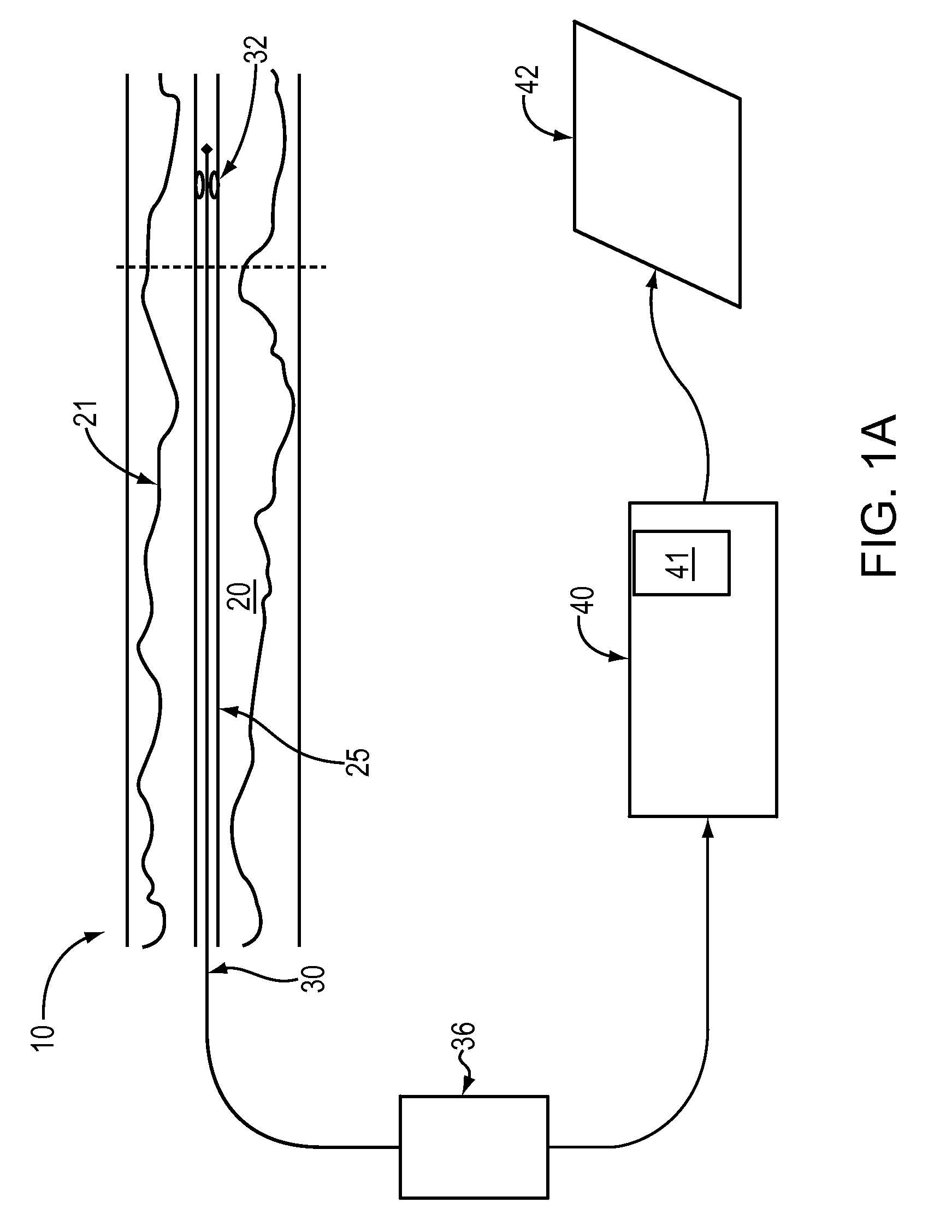
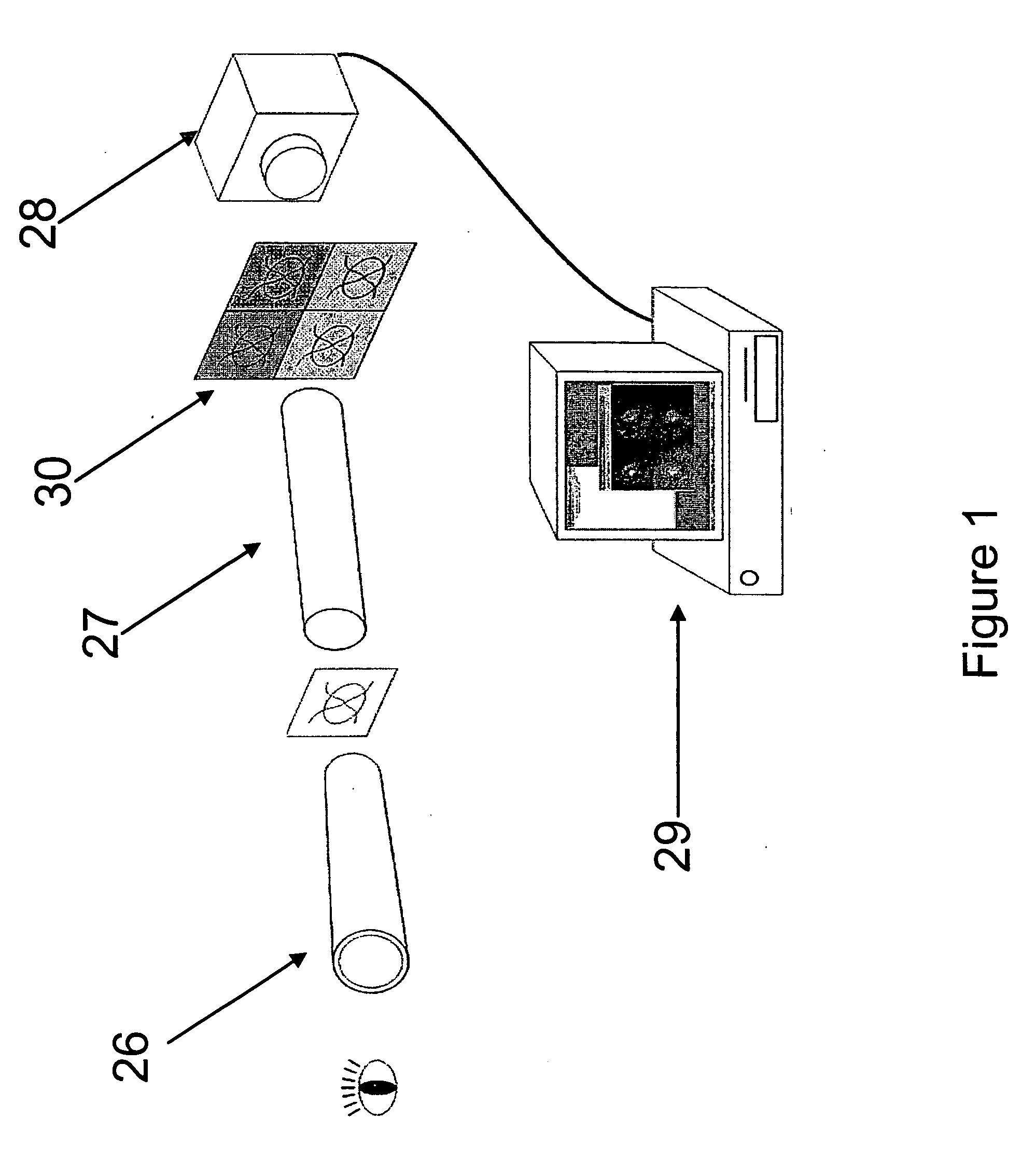
A method and apparatus of automatically locating in an image of a blood vessel the lumen boundary at a position in the vessel and from that measuring the diameter of the vessel. From the diameter of the vessel and estimated blood flow rate, a number of clinically significant physiological parameters are then determined and various user displays of interest generated. One use of these images and parameters is to aid the clinician in the placement of a stent. The system, in one embodiment, uses these measurements to allow the clinician to simulate the placement of a stent and to determine the effect of the placement. In addition, from these patient parameters various patient treatments are then performed.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
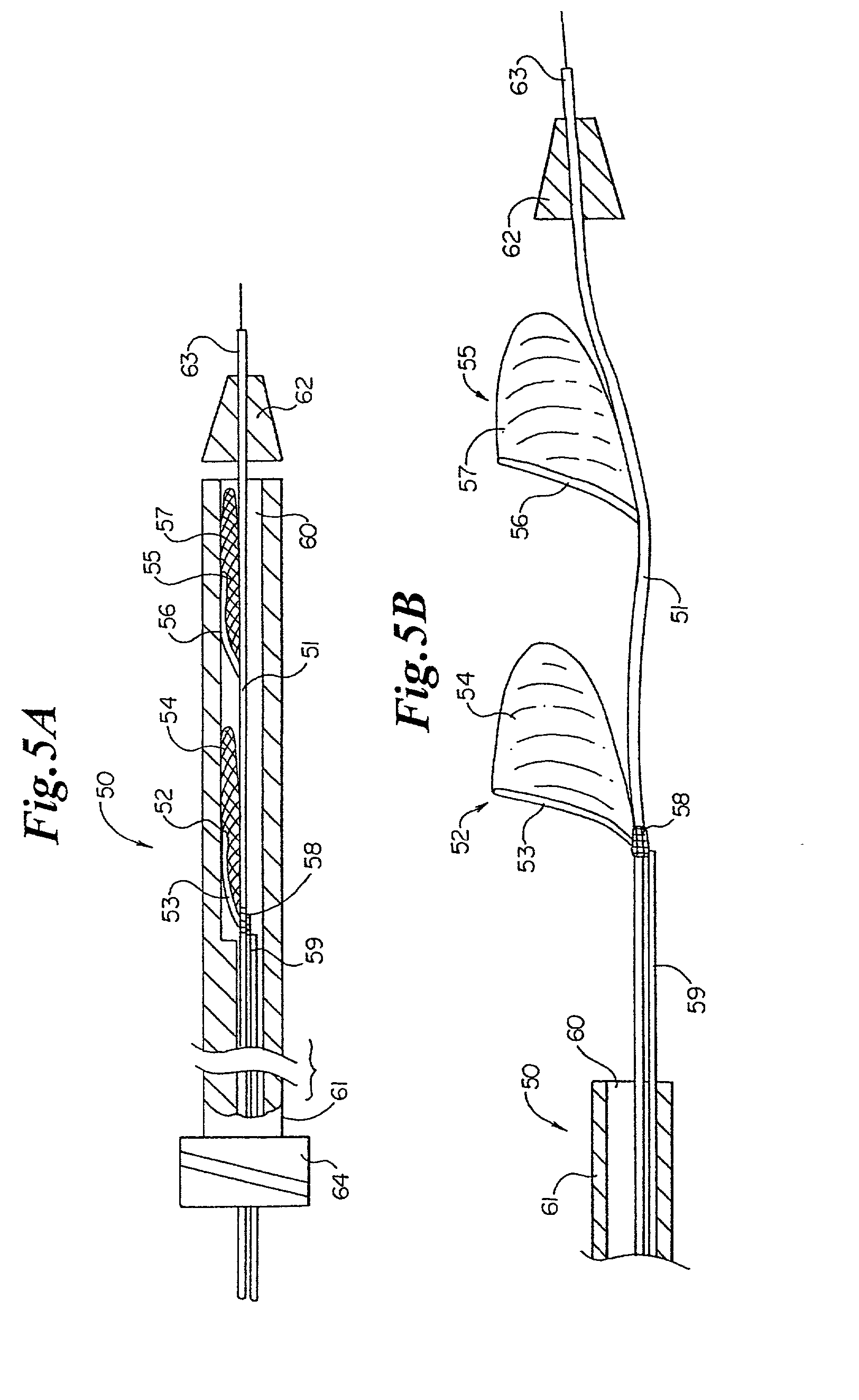
Vascular device for emboli and thrombi removal and methods of use
InactiveUS7306618B2Permit useFacilitate percutaneous introductionBalloon catheterInfusion syringesThrombusVascular device
Apparatus and methods are provided for use in filtering emboli from a vessel and / or performing thrombectomy and embolectomy, wherein a vascular device disposed on a guidewire comprises a support hoop disposed from a suspension strut. Alternately, a support hoop having an articulation region may be directly connected to a region proximate the distal end of the guidewire. A blood permeable sac is affixed to the support hoop to form a mouth of the blood permeable sac. The support hoop is disposed obliquely relative to the longitudinal axis of the guidewire and is capable of being properly used in a wide range of vessel diameters. The vascular device collapses during removal to prevent material from escaping from the sac. A delivery sheath and introducer sheath for use with the vascular device of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Method and apparatus for allowing blood flow through an occluded vessel
A device arranged to sustain and / or provide at least partial patency of a small blood vessel exhibiting an occlusion, the device constituted of a tubular body expandable from a first small diameter state for manipulation to, and through, the occlusion of the small blood vessel and a second large diameter state, the inner dimensions of the second large diameter state being no more than 50% of the diameter of the small blood vessel at the occlusion location, the device presenting a conduit for blood flow through the occlusion when in the large diameter state. In one embodiment the small blood vessel is an intracranial blood vessel.
Owner:PERFLOW MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for allowing blood flow through an occluded vessel
A device arranged to sustain and / or provide at least partial patency of a small blood vessel exhibiting an occlusion, the device constituted of a tubular body expandable from a first small diameter state for manipulation to, and through, the occlusion of the small blood vessel and a second large diameter state, the inner dimensions of the second large diameter state being no more than 50% of the diameter of the small blood vessel at the occlusion location, the device presenting a conduit for blood flow through the occlusion when in the large diameter state. In one embodiment the small blood vessel is an intracranial blood vessel.
Owner:PERFLOW MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for performing intra-operative angiography
InactiveUS6915154B1Accurately determine extentSensorsBlood flow measurementAfter treatmentAv fistulas
Method for assessing the patency of a patient's blood vessel, advantageously during or after treatment of that vessel by an invasive procedure, comprising administering a fluorescent dye to the patient; obtaining at least one angiographic image of the vessel portion; and evaluating the at least one angiographic image to assess the patency of the vessel portion. Other related methods are contemplated, including methods for assessing perfusion in selected body tissue, methods for evaluating the potential of vessels for use in creation of AV fistulas, methods for determining the diameter of a vessel, and methods for locating a vessel located below the surface of a tissue.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Bicuspid vascular valve and methods for making and implanting same
A vascular valve constructed from a biocompatible material that is designed to be surgically implanted in a patient's blood vessel, such as the right ventricular outflow tract. At the first end of the valve there is an orifice defined by at least two opposing free edges, and which can occupy either a first, closed position or a second, open position. At the second end of the valve there are at least two flexible members attachable to an anterior and a posterior wall of a patient's blood vessel. A length of the orifice between said at least two opposing free edges when the orifice is generally closed is equal to about 1.5 to 2 times the diameter of a patient's blood vessel. Optionally, the two flexible members to a stent or tubular graft. The valved stent or tubular graft can be inserted into a patient's blood vessel or heart.
Owner:QUINTESSENZA JAMES
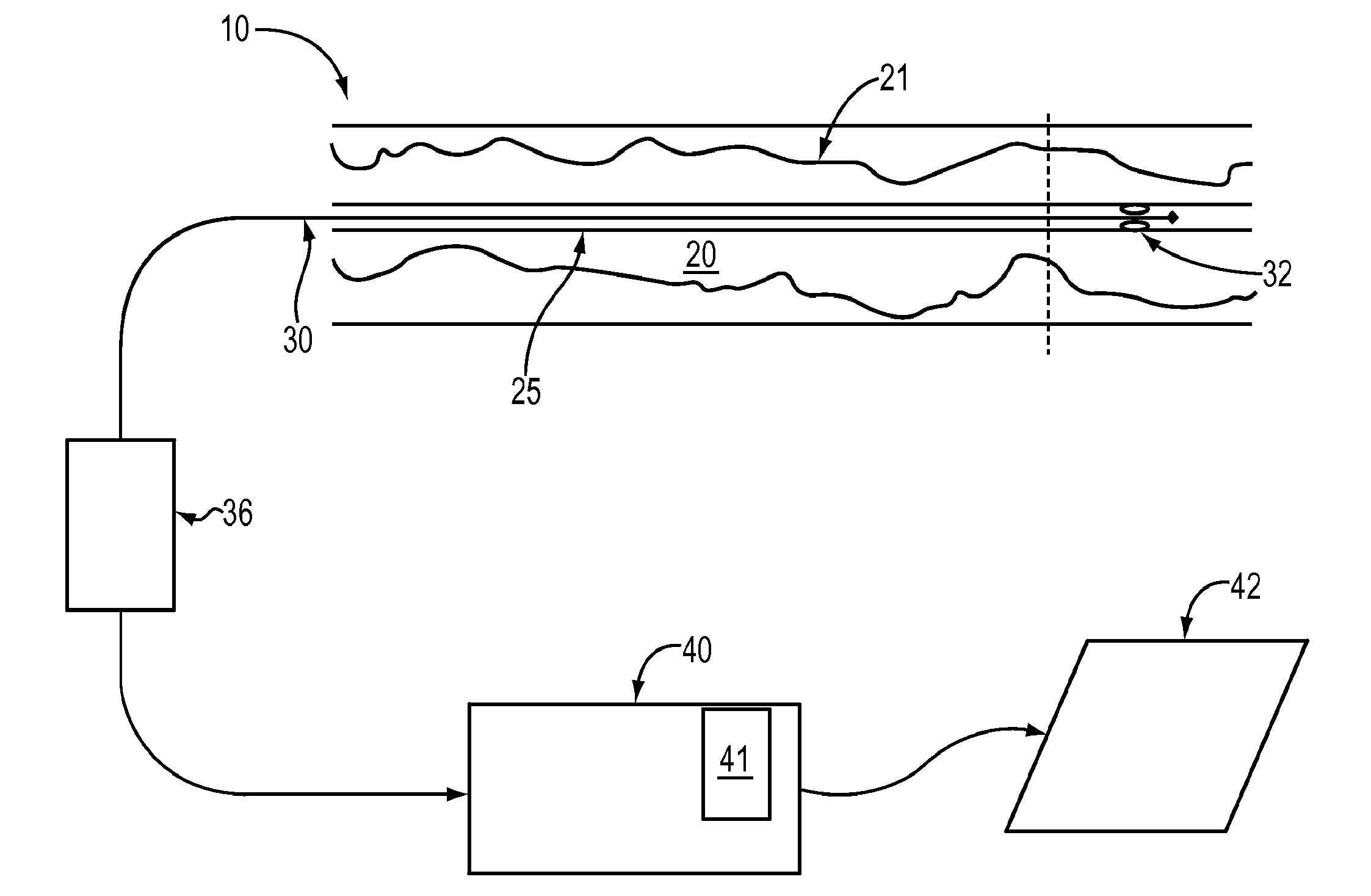
Automated System for Anatomical Vessel Characteristic Determination
ActiveUS20120051606A1Prevent false detectionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging dataUser interface
A system enables a user to mark a ROI of a vessel portion having detected boundaries and extend the detection of vessel boundaries into a region identified by the user. An anatomical blood vessel detection and display system includes a user interface enabling a user, via a display of an image presenting anatomical vessels, to, mark a region of interest in a vessel identified by detected boundaries in the image and extend the marked region of interest of the vessel. A detector automatically detects a boundary of the vessel in the extended marked region of interest by detecting an edge representing a change in luminance in data representing the image. An image data processor identifies a minimum vessel diameter in the extended marked region of interest between the detected boundaries and initiates identification of the location of the minimum vessel diameter in the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Lumen Morphology and Vascular Resistance Measurements Data Collection Systems, Apparatus and Methods
A method and apparatus of automatically locating in an image of a blood vessel the lumen boundary at a position in the vessel and from that measuring the diameter of the vessel. From the diameter of the vessel and estimated blood flow rate, a number of clinically significant physiological parameters are then determined and various user displays of interest generated. One use of these images and parameters is to aid the clinician in the placement of a stent. The system, in one embodiment, uses these measurements to allow the clinician to simulate the placement of a stent and to determine the effect of the placement. In addition, from these patient parameters various patient treatments are then performed.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
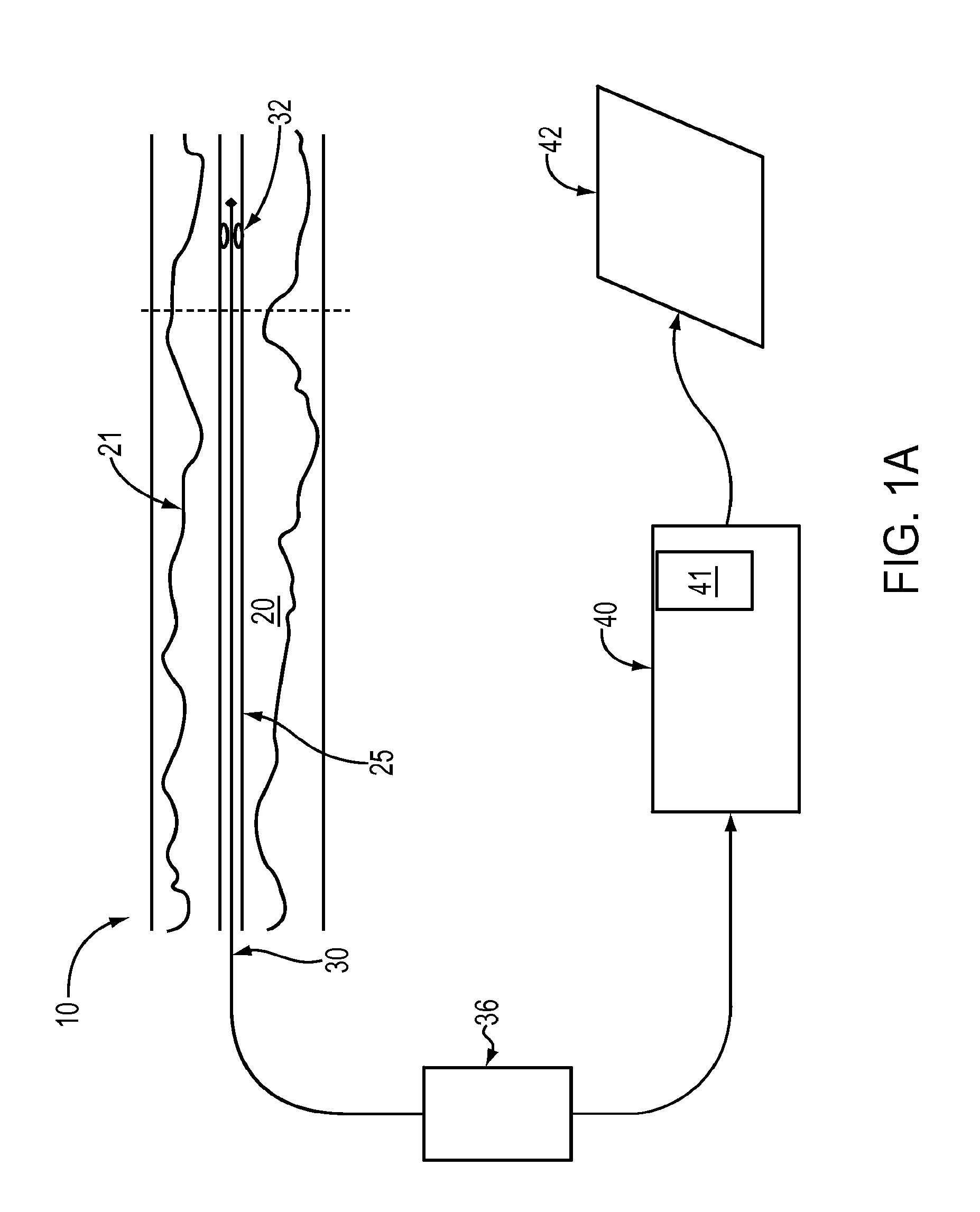
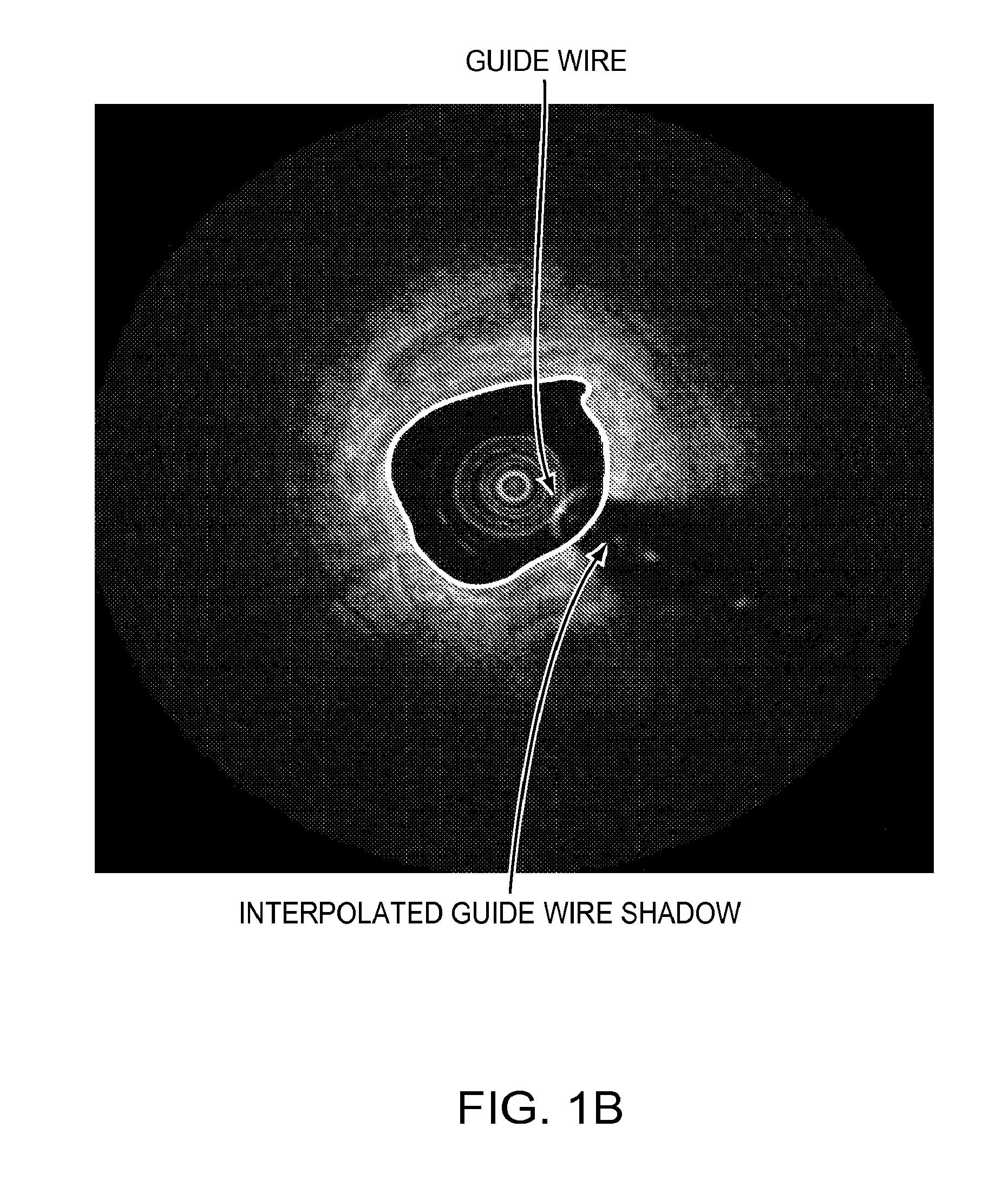
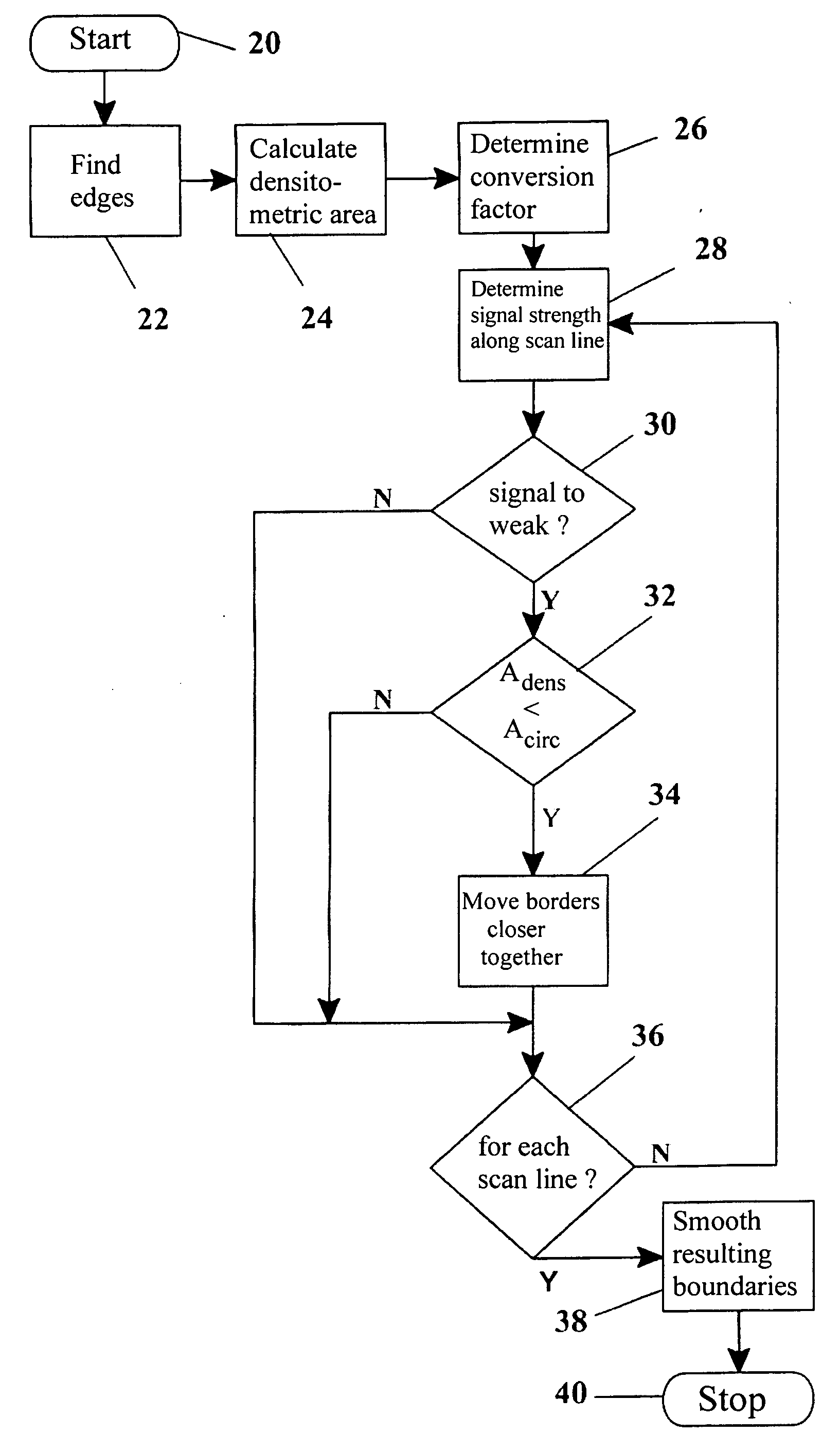
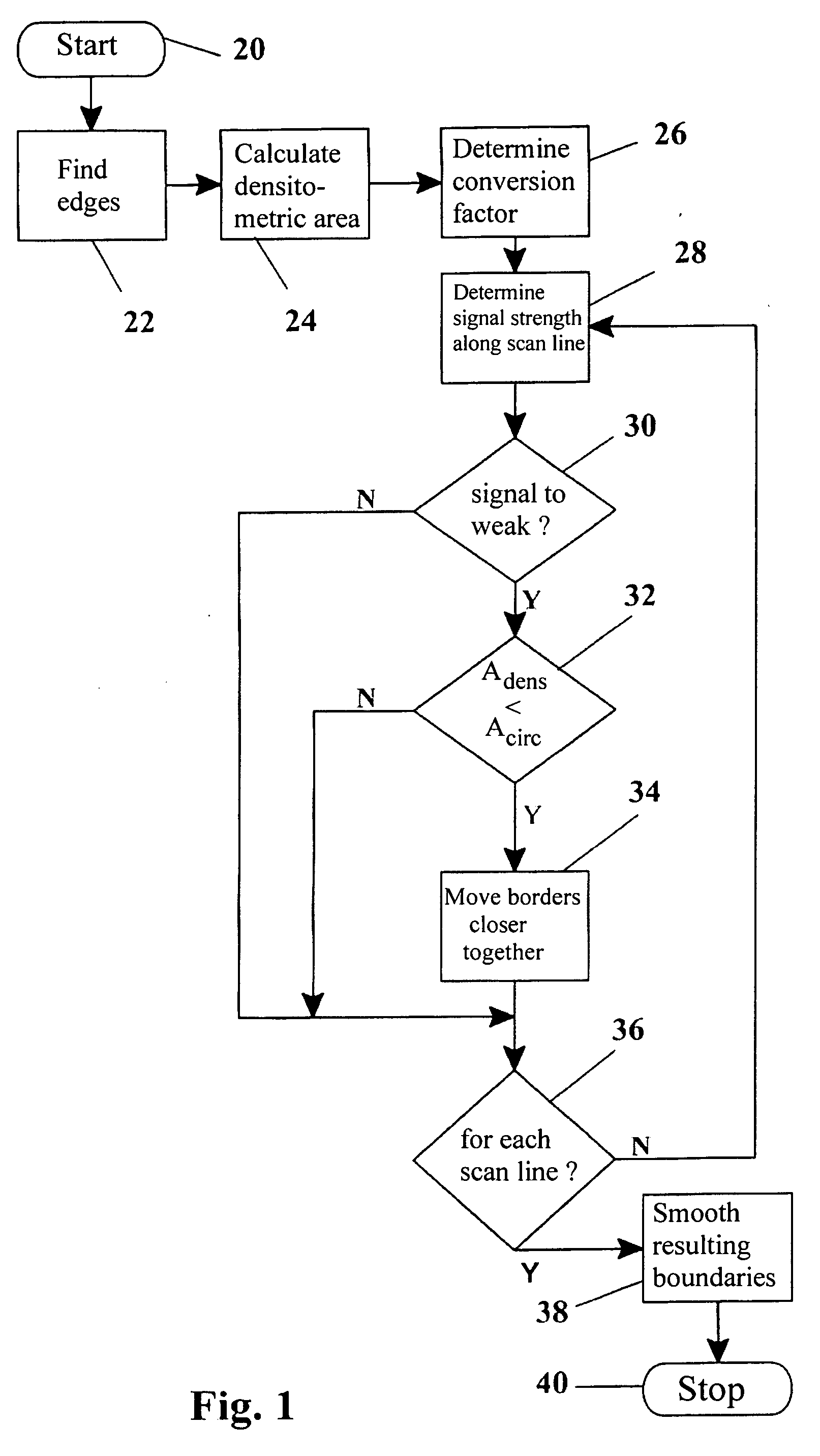
Method, apparatus and computer program for contour detection of vessels using x-ray densitometry
ActiveUS20070053558A1Simple processRobust resultImage enhancementImage analysisX ray densitometryConversion factor
A method has been described for deriving contour data in X-Ray images for vessels with differential absorption through applying a contour-finding algorithm on a shadow image and finding the vessel borders through segmentation based on image intensities. In particular, the method uses the following steps: finding a densitometric area of an above mentioned vessel, and displacing one or both of the borders inward until the densitometric measurement result between the borders after such displacing will start to change significantly. Furthermore, a specific procedure is introduced to automatically determine the conversion factor to equate the densitometrically based diameter to the contour based diameter of the vessel and to discriminate bifurcating or parallel vessels.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
Vascular device for emboli and thrombi removal and methods of use
InactiveUS20080058860A1Permit useLarge lateral deflectionBalloon catheterGuide wiresThrombusVascular device
Apparatus and methods are provided for use in filtering emboli from a vessel and / or performing thrombectomy and embolectomy, wherein a vascular device disposed on a guidewire comprises a support hoop disposed from a suspension strut. Alternately, a support hoop having an articulation region may be directly connected to a region proximate the distal end of the guidewire. A blood permeable sac is affixed to the support hoop to form a mouth of the blood permeable sac. The support hoop is disposed obliquely relative to the longitudinal axis of the guidewire and is capable of being properly used in a wide range of vessel diameters. The vascular device collapses during removal to prevent material from escaping from the sac. A delivery sheath and introducer sheath for use with the vascular device of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Blood vessel of brain circulation kinetic analysis method and apparatus
InactiveCN101172042ACalculation method is simpleEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsData processing applicationsNetwork modelAnalog-to-digital converter
The invention relates to a brain vascular blood circulation dynamic analysis method and the apparatus thereof. According to the cerebral circulation vascular bed anatomical model, an equivalent network model which comprises 12 pipeline units simulating the brain circulation blood dynamics is built, and the relevant parameter calculation formulas are confirmed, by utilizing the formulas, the flow rate waveform and the value inside the cartid artery, the pressure waveform, the blood pressure of the body, the diameter of the blood vessel, the flow rate waveform and the valve of the vertebral artery and the front, the middle and the rear parts on two sides inside the skull, and the characteristic and the parameter of the cartid artery and each blood vessel section inside the skull can be determined, the apparatus designed by the invention can be performed, the detecting system comprises the vessel diameter detecting of the cartid artery outside the skull, the blood pressure detecting, theblood flow rate detecting of the cartid artery outside the skull, the pressure waveform detecting of the cartid artery outside the skull, and the blood flow rate detecting on the artery inside the skull; the control system comprises a control module and a power supply module; the calculation and analysis system comprises a host computer, a peripheral equipment, and an analog-digital converter, the invention can fully analyze the brain circulation dynamic characteristic, thereby having notable effect on the early stage and the ultra early stage diagnosis and therapy of the brain vascular illness.
Owner:SHANGHAI KUANGFU MEDICAL EQUIP DEV
Automatic registration of images
ActiveUS20060276698A1Reliable measurementOptical density ratios are more reliably and easily obtainedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVisual perceptionImage contrast
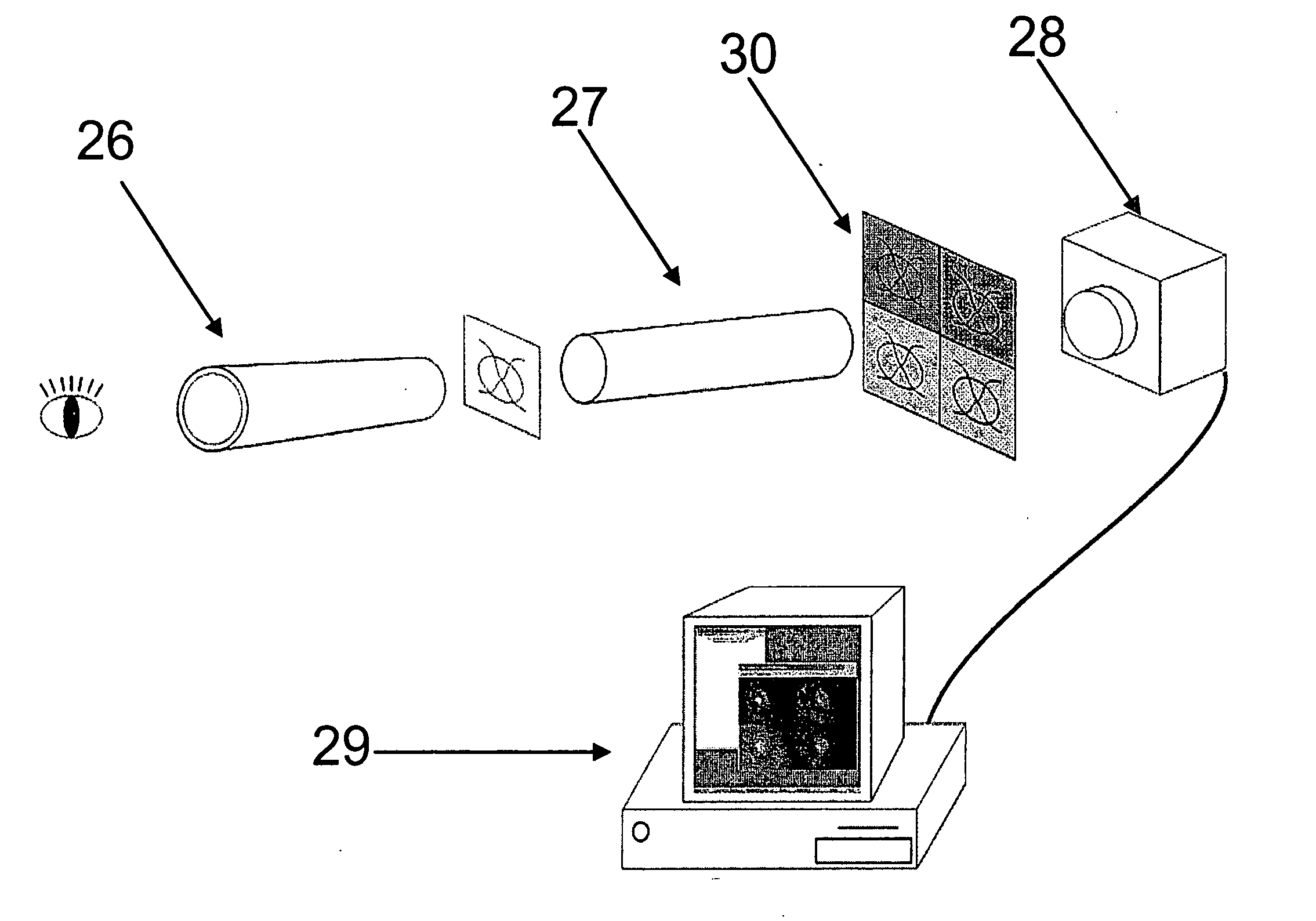
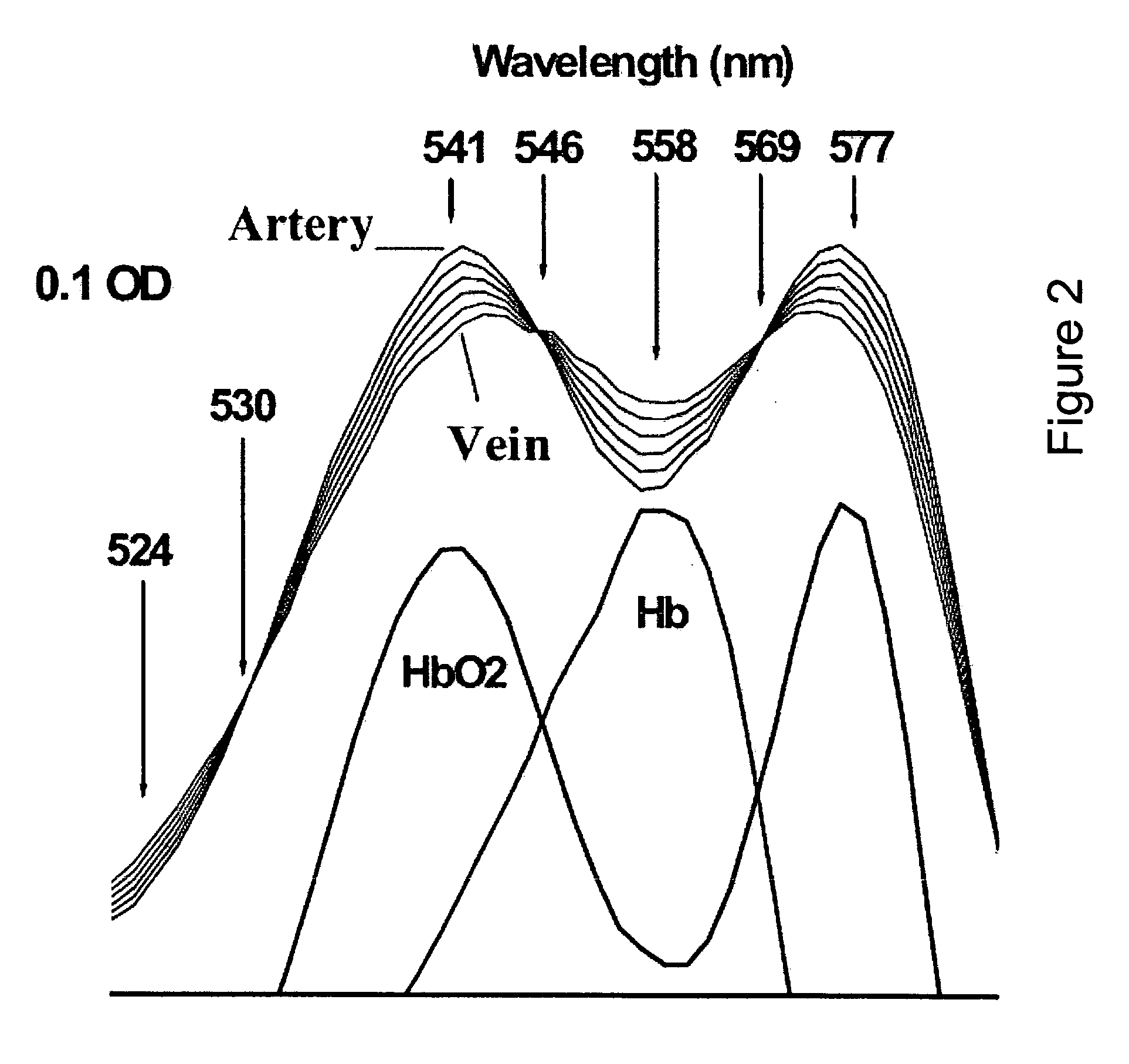
The present invention relates to a system for automatically evaluating oxygen saturation of the optic nerve and retina, said system comprising: image capturing system further comprising: a fundus camera (26), a four wavelengths beam splitter (27), a digital image capturing device (28), a computer system, image processing software performing in real-time the steps of: registering set of multi-spectral images (1) by, binarizing the multi-spectral image (7), find the all the border regions of each image by finding the region including the straight line that passes the most number of points in the region (8), use the orientation of the borders to evaluate the orientation of each spectral image (9), equalize the orientation of each spectral image by rotating the spectral image (10), edge detect each spectral image (11), estimate the translation between the spectral images based on the edges of adjacent images (12), transform the images to a stack of registered images (13), locating blood vessels (2) in each of the multi-spectral images by, retrieving registered spectral images (14), for each spectral image, remove defective pixels (15), enhance image contrast (16), perform top-hat transform using structuring element larger than the largest vessel diameter (17), binarize each image (18), apply filter for smoothing the image (19), combine all the spectral images using binary AND operator (20), skeletonize the resulting image (21), prune the skeleton image (22), re-grow the pruned image (23), locate junction points (24), evaluating the width of the blood vessels (3) by calculating the normal vector to the vessel direction to, estimate the direction and position of the vessel profile, evaluate positions of vessel walls based on the vessel profile obtained, evaluate vessel width based on the position of the vessel walls, selecting samples for calculating optical density, calculating the optical density ratio (4), evaluating oxygen saturation level (5), and presenting the results (6), wherein presenting the results may include presenting numerical and visual representation of the oxygen saturation.
Owner:OXYMAP EHF
Assessment of microvascular circulation
InactiveUS20130070201A1Improve acquisitionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensorsConjunctivaIntervention design
Methods and compositions are disclosed to quantitatively measure in vivo blood vessel diameter, blood velocity, and other flow dynamics. Such methods and compositions can optimize therapeutic interventions designed to prevent or reduce the risk of cardiovascular and blood disorders. In one aspect, the methods and apparatus involve calculating blood vessel characteristics from a two dimensional image of a blood vessel in the conjunctiva of a subject's eye. In another aspect, a series of temporal images of a blood vessel are obtained to determine blood flow properties. The apparatus can include, for example, a biomicroscope, an illuminating light source and a high speed camera to acquire the series of temporal images with the data then analyzed by a programmed processor.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Prevention of tissue ischemia, related methods and compositions
ActiveUS8236313B2Increase blood flowIncrease oxygenationPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCoronary artery diseaseWhole body
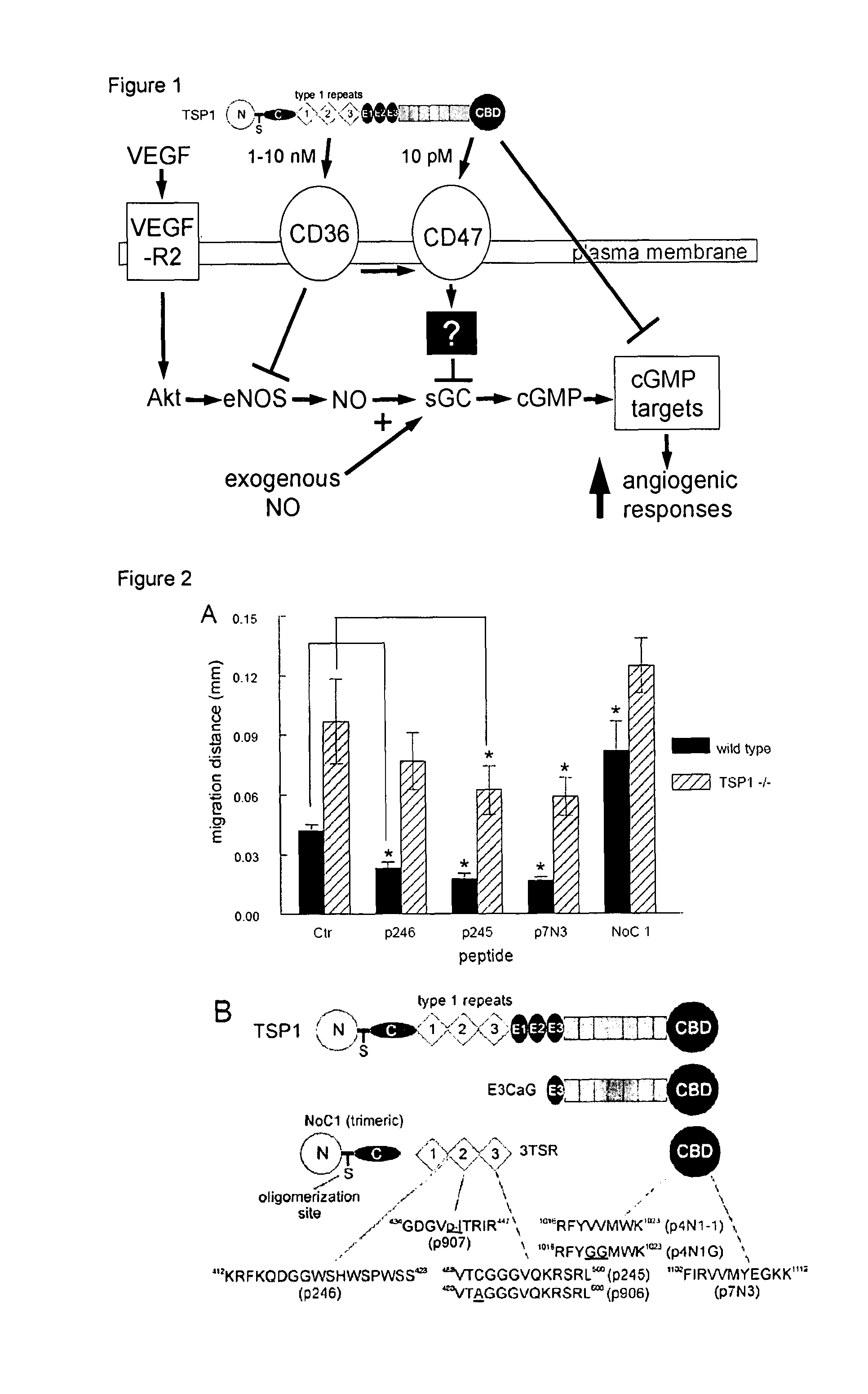
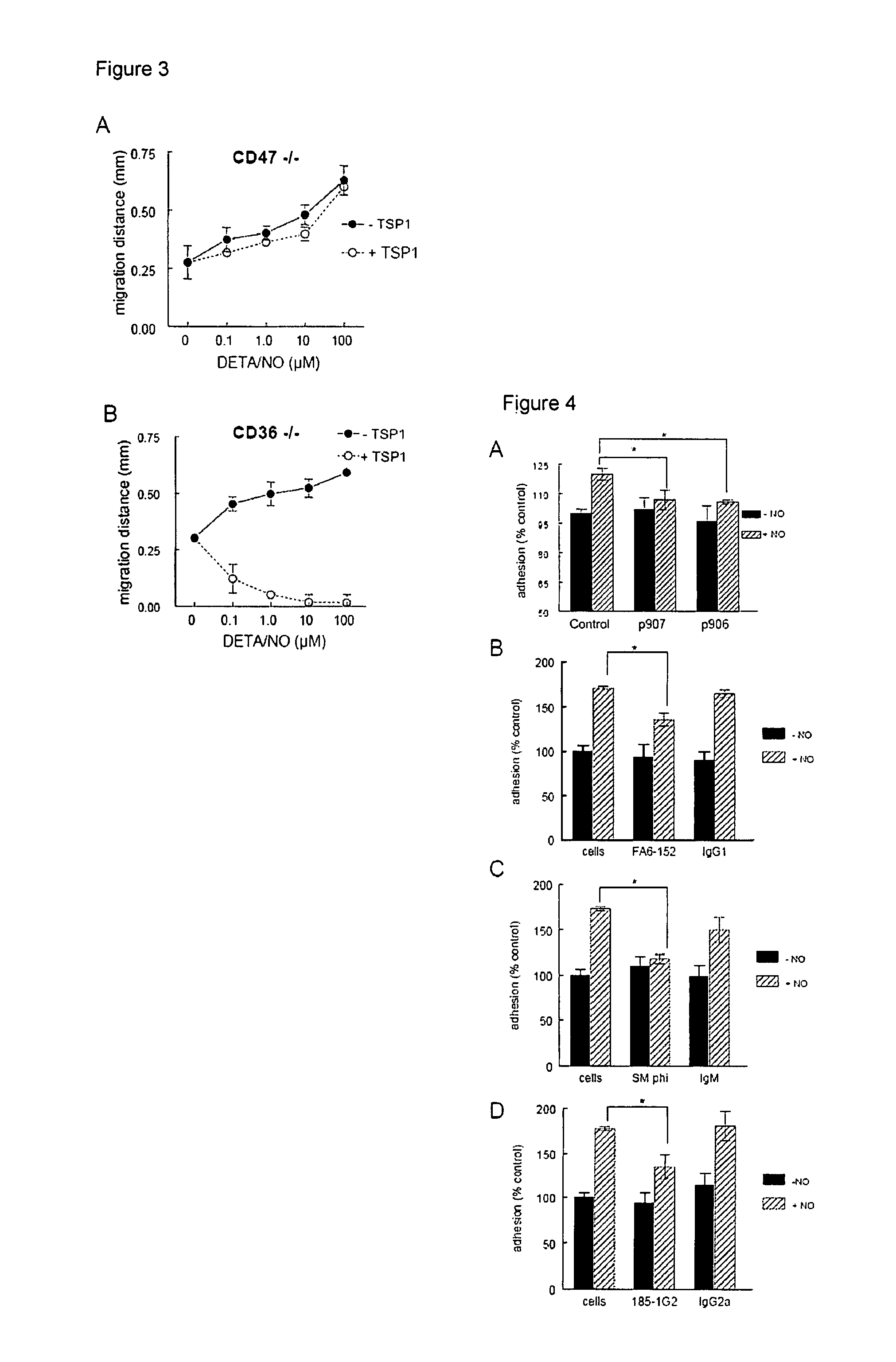
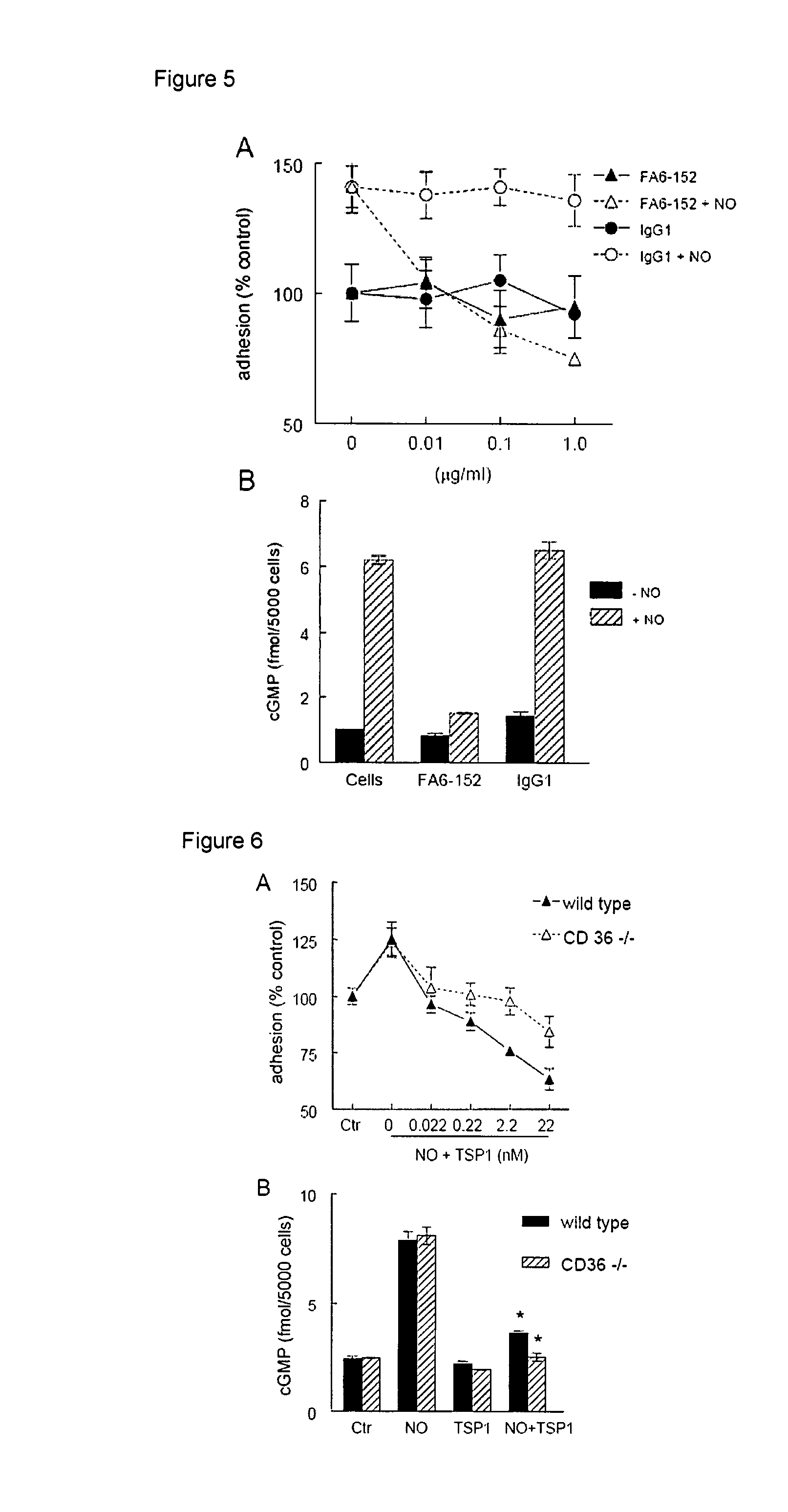
Provided herein are compositions and methods for preventing, ameliorating, and / or reducing tissue ischemia and / or tissue damage due to ischemia, increasing blood vessel diameter, blood flow and tissue perfusion in the presence of vascular disease including peripheral vascular disease, atherosclerotic vascular disease, coronary artery disease, stroke and influencing other conditions, by suppressing CD47 and / or blocking TSP1 and / or CD47 activity or interaction. Influencing the interaction of CD47-TSP1 in blood vessels allows for control of blood vessel diameter and blood flow, and permits modification of blood pressure and cardiac function. Under conditions of decreased blood flow, for instance through injury or atherosclerosis, blocking TSP1-CD47 interaction allows blood vessels to dilate and increases blood flow, tissue perfusion and tissue survival. This in turn reduces or prevents tissue necrosis and death. The therapeutics identified herein allow for precise regulation of blood flow to tissues and organs which need it, while substantially avoiding systemic complications. Methods and compositions described herein can be used to increase tissue survival under conditions of trauma and surgery, as well as conditions of chronic vascular disease. Also disclosed are methods for the treatment of elderly subjects using agents that affect TSP1 and CD47 and thereby affect tissue perfusion. Additionally, provided herein are compositions and methods for influencing blood coagulation, allowing for controlled increased or decreased blood clotting. Additionally, provided herein are compositions and methods for decreasing blood flow, as in the case of cancer through mimicking the effects of TSP1 and CD47 on blood vessel diameter and blood flow.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +1
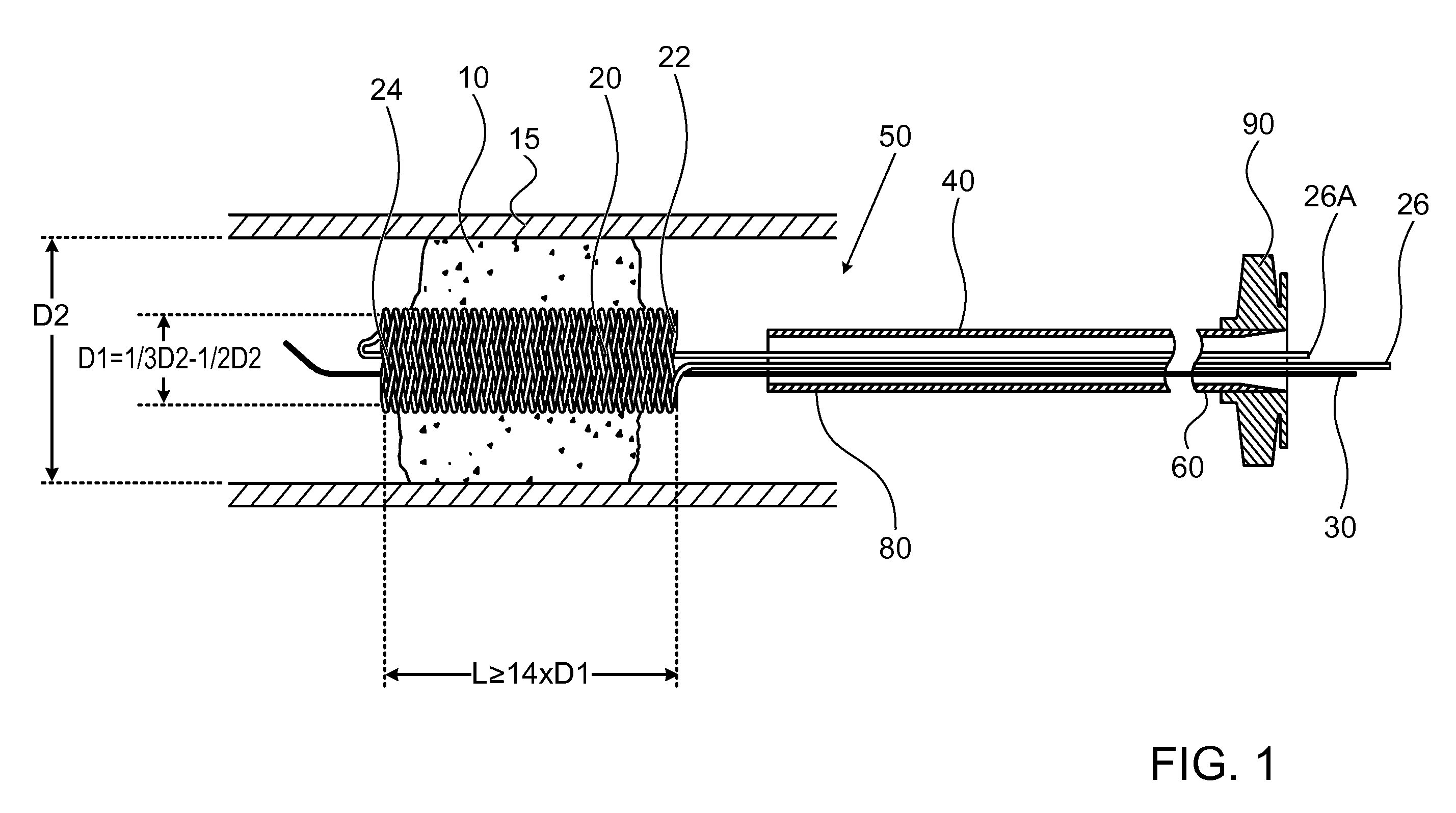
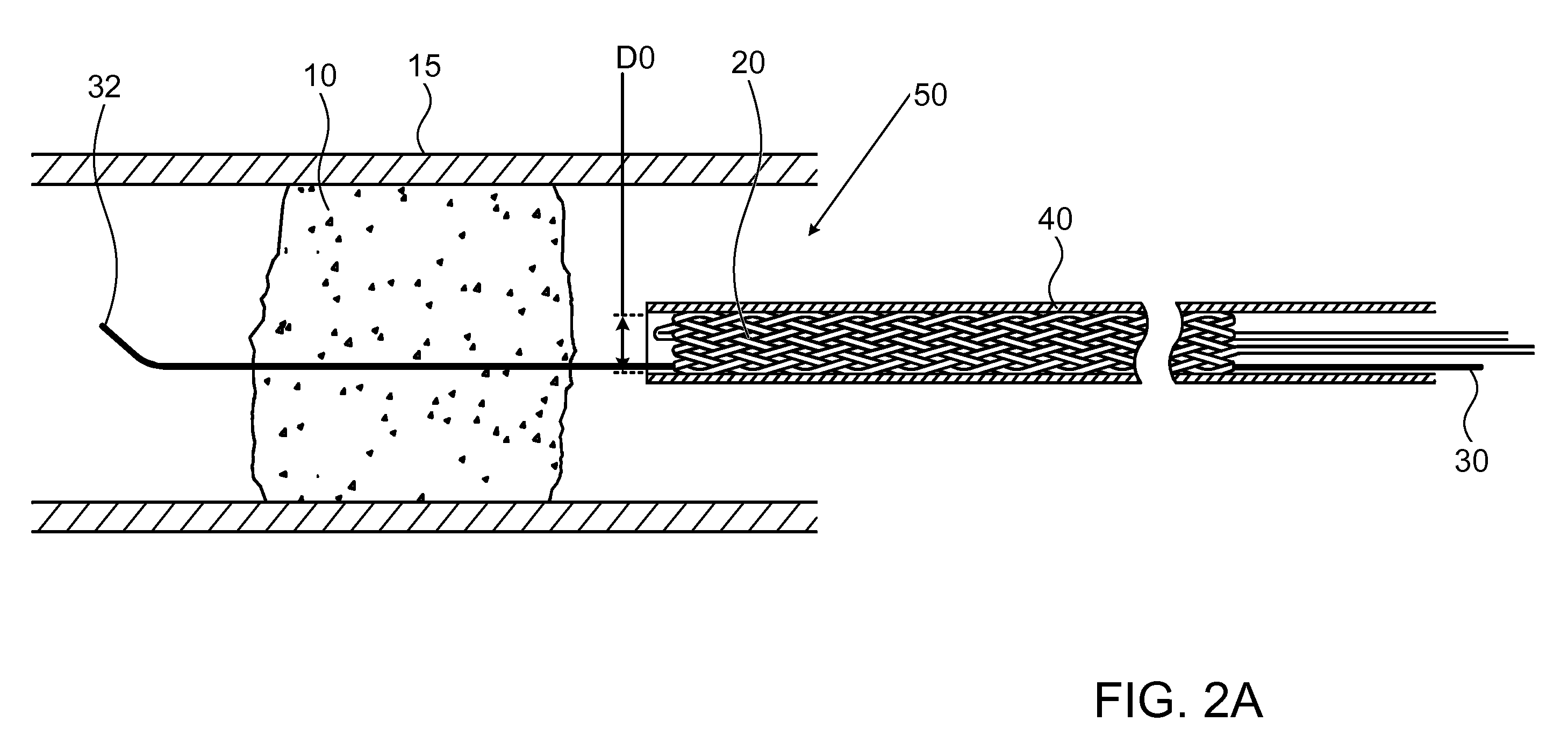
Intravascular material removal device
InactiveUS7416555B2Low profileReduce deliveryCannulasExcision instrumentsMaterial removalBlood vessel
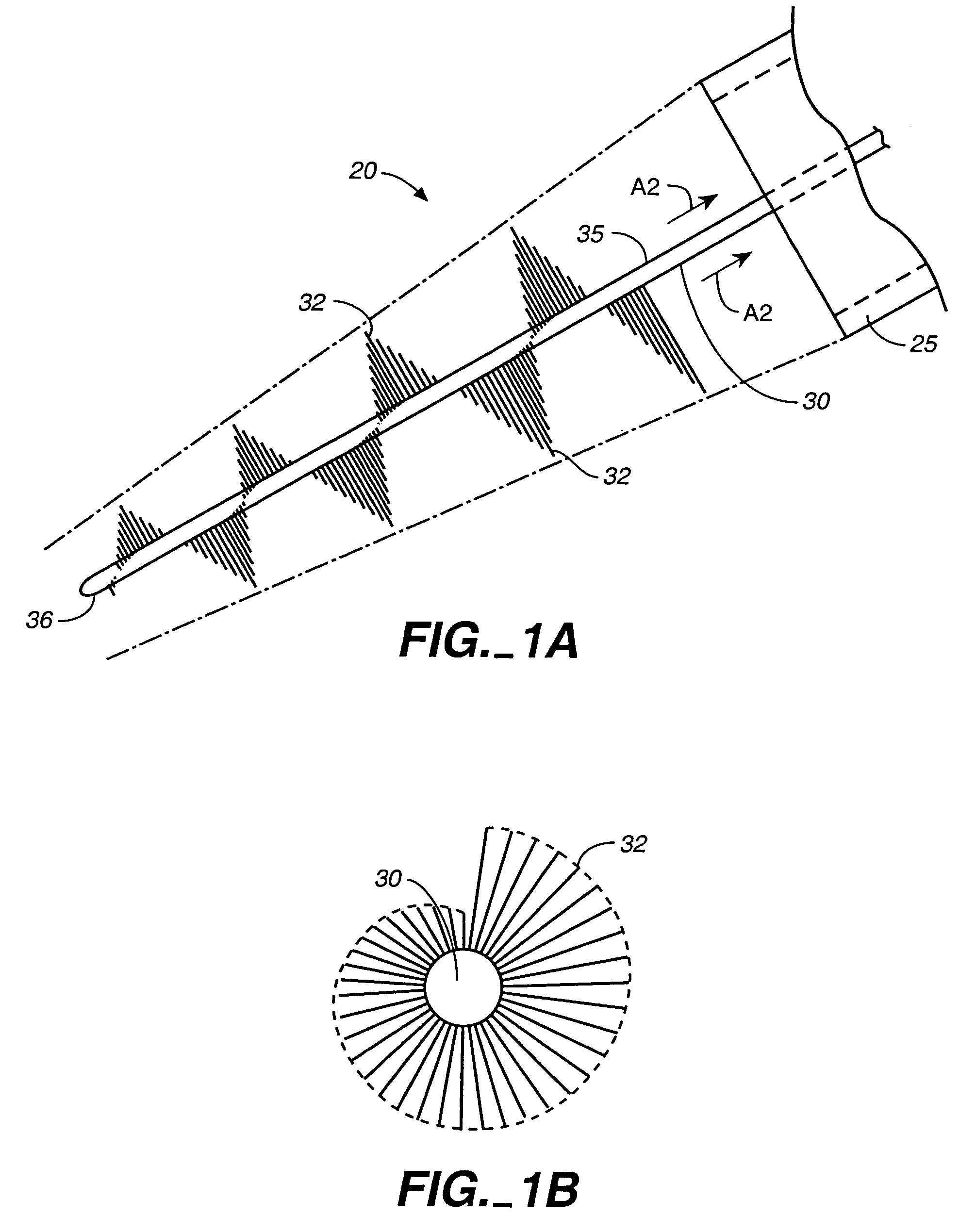
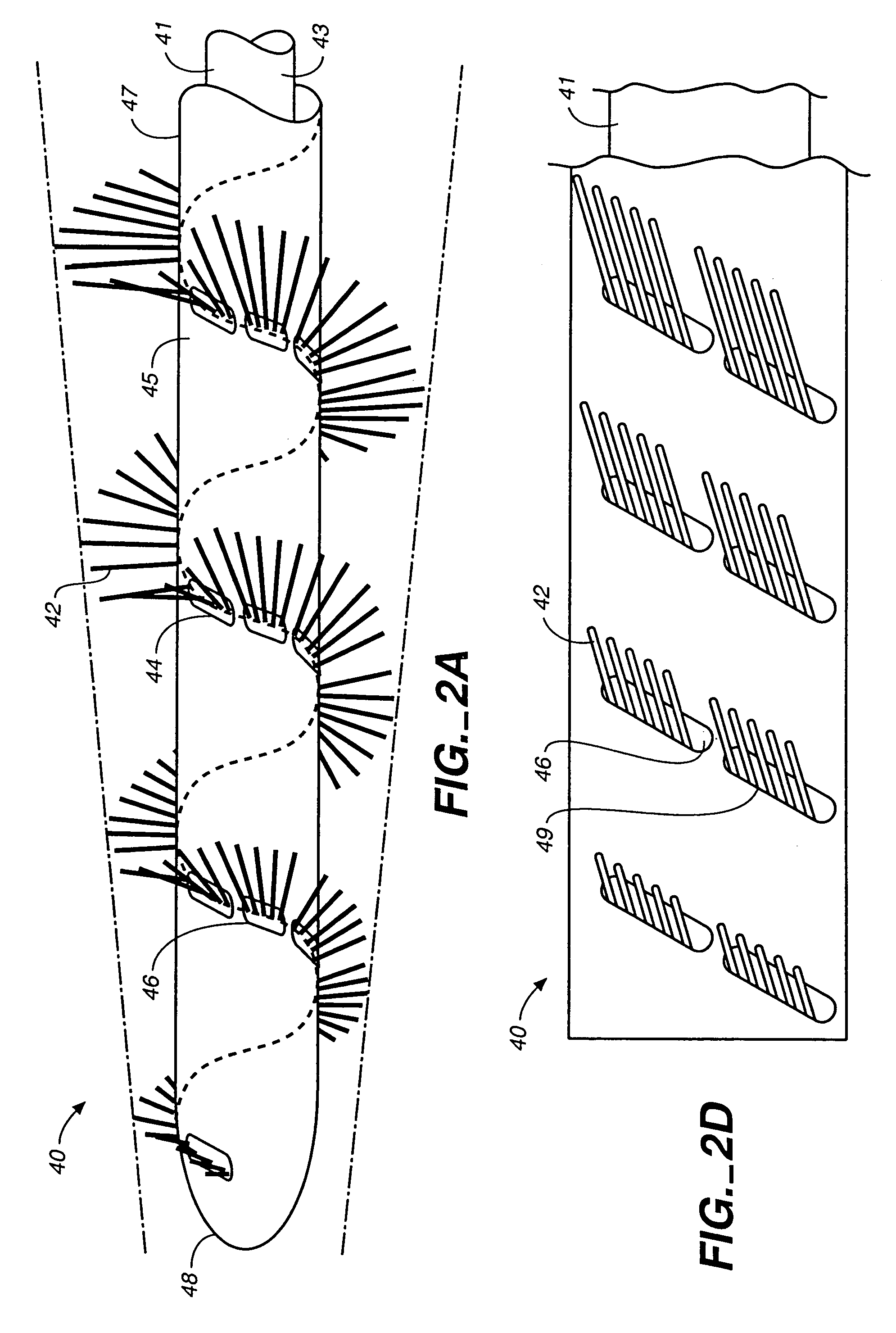
An intravascular material removal device that removes material from a vessel wall and creates flow dynamics that draw the material into a catheter device for removal from the vessel is provided. A collapsible device that provides a relatively low delivery profile while being expandable in use to adapt to varying and variable vessel diameters is also provided. A spiral configured material removing element is provided that can adapt to varying vessel diameters and to remove material forming blockages or occlusions from the inner wall of a vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Blood vessel diameter measuring method based on digital image processing technology
InactiveCN101984916AImprove computing efficiencyLow image quality requirementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityLine fitting
The invention provides a blood vessel diameter measuring method based on digital image processing technology. The method includes that: (1) Gauss matched filtering method is utilized to enhance a blood vessel image; (2) the image is normalized and binarized; (3) according to related theory of mathematical morphology, the image is refined, and skeleton is extracted; (4) straight line fitting method is used for solving slope of a section of blood vessel, pixel number of blood vessel is detected along the direction vertical to the blood vessel, and then the blood vessel diameter is solved according to dot pitch. The invention is used for measuring medical image blood vessel diameter, computing efficiency is high, requirement on image quality is low, and computation is accurate.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
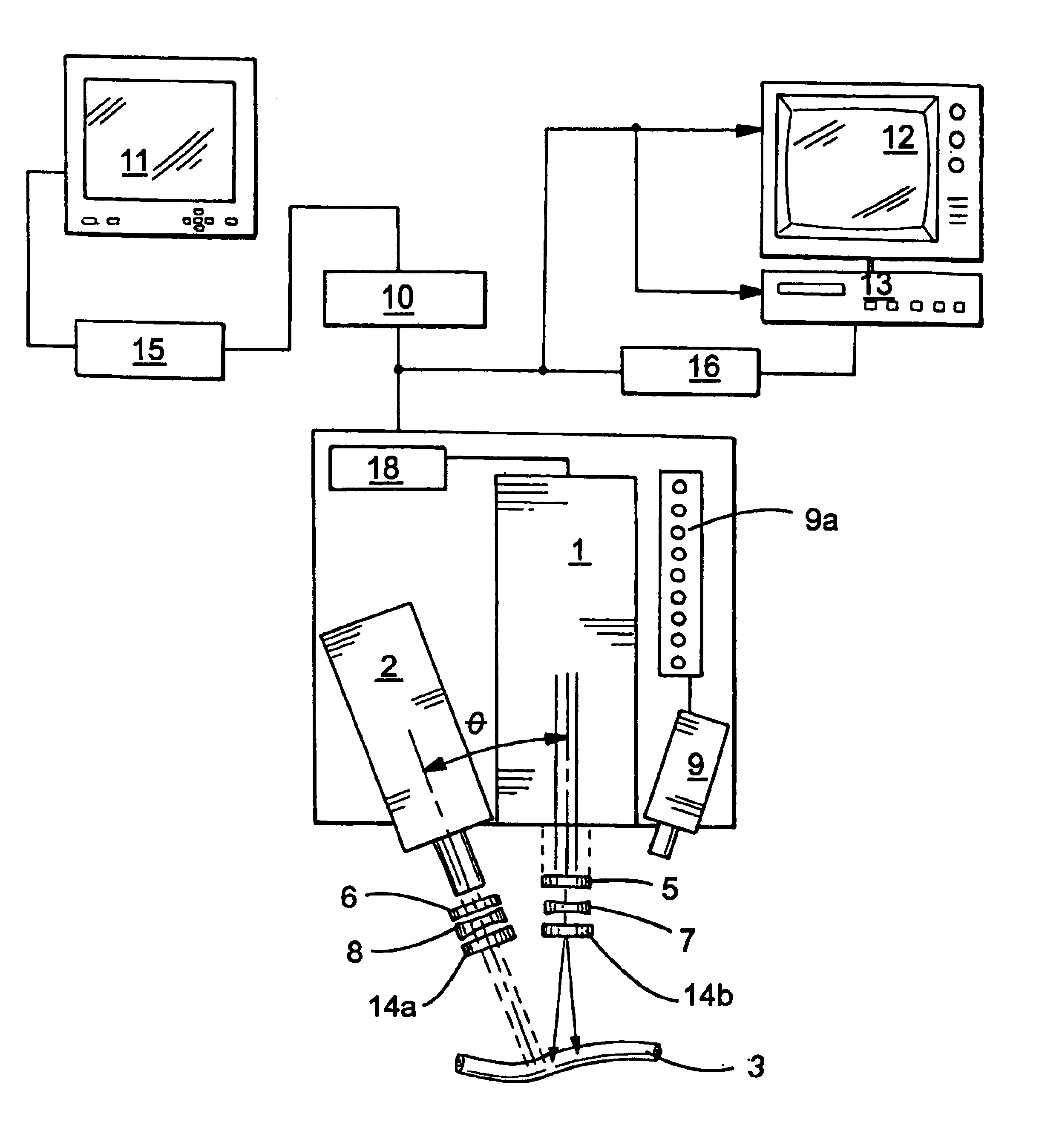
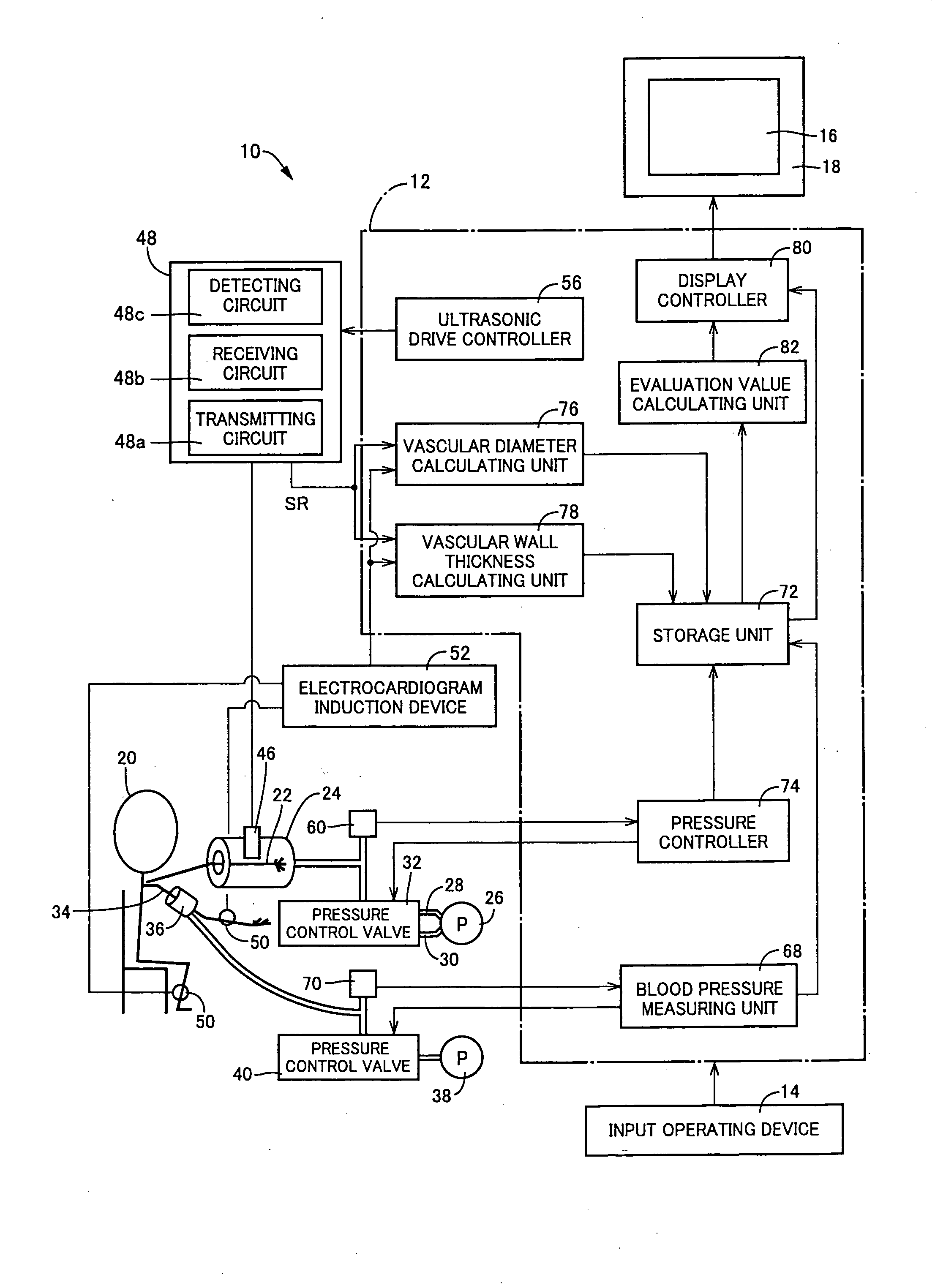
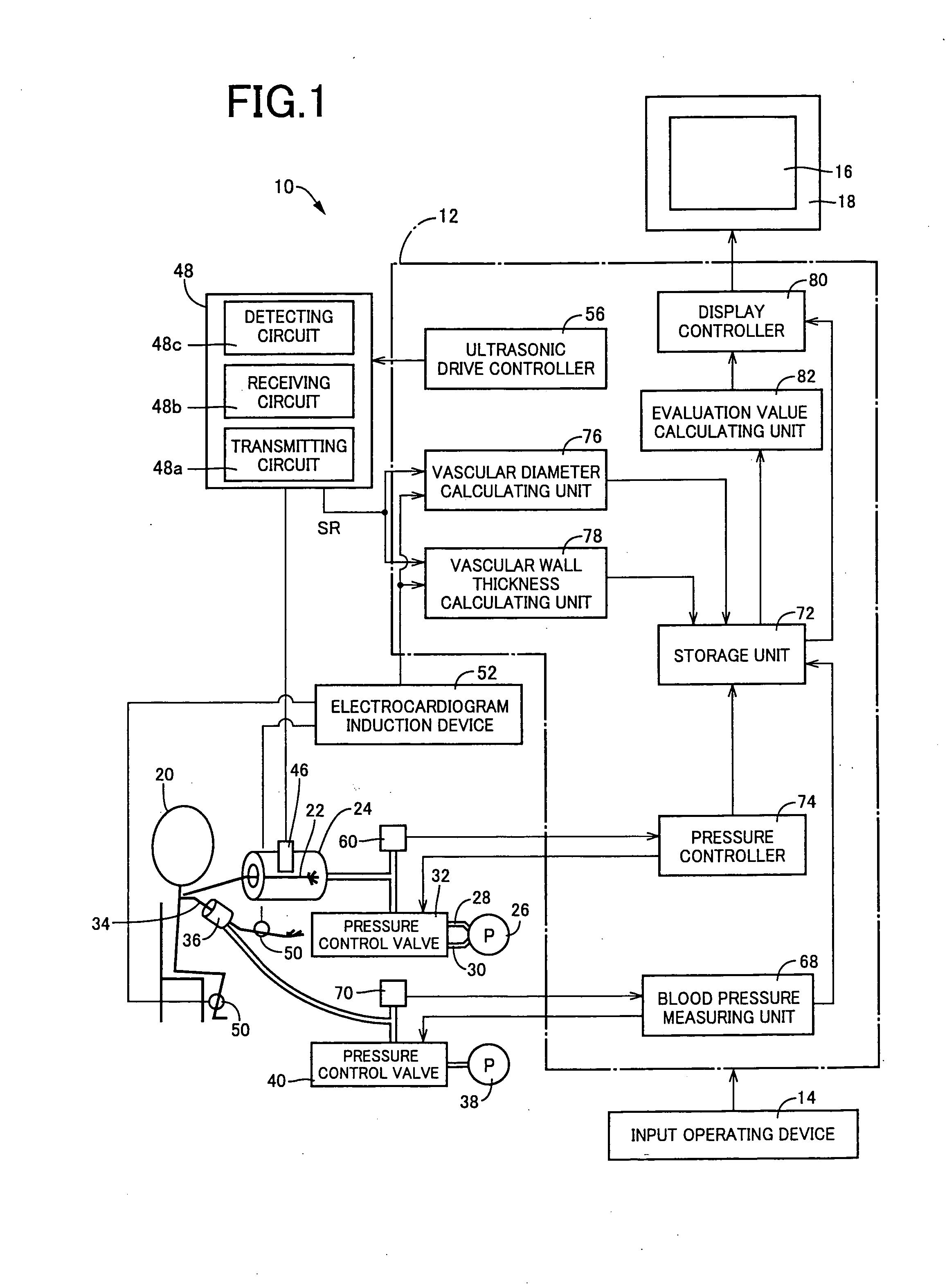
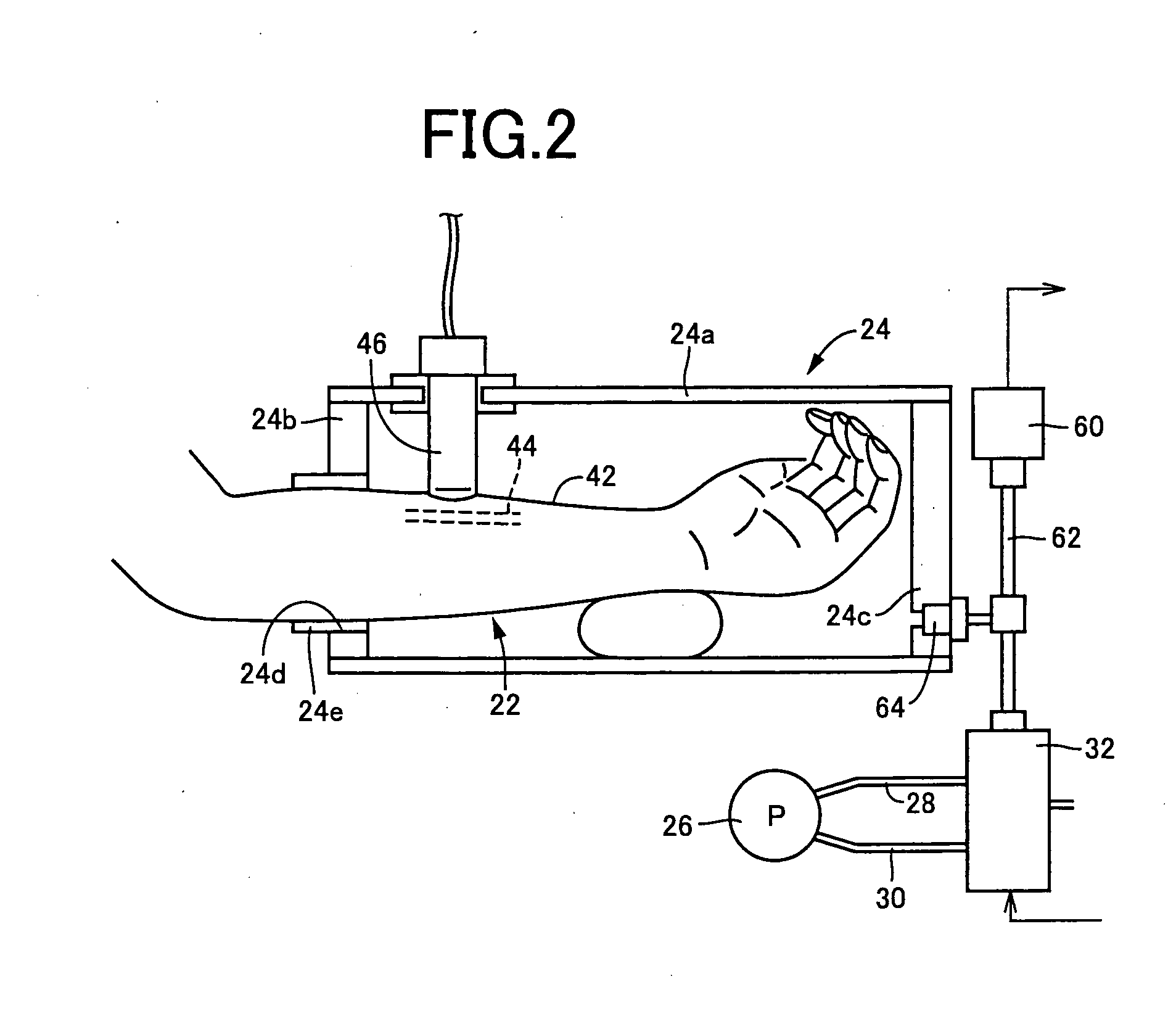
Biological luminal body evaluating apparatus
InactiveUS20080214961A1Accurate assessmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPerson identificationInternal pressureDisplay device
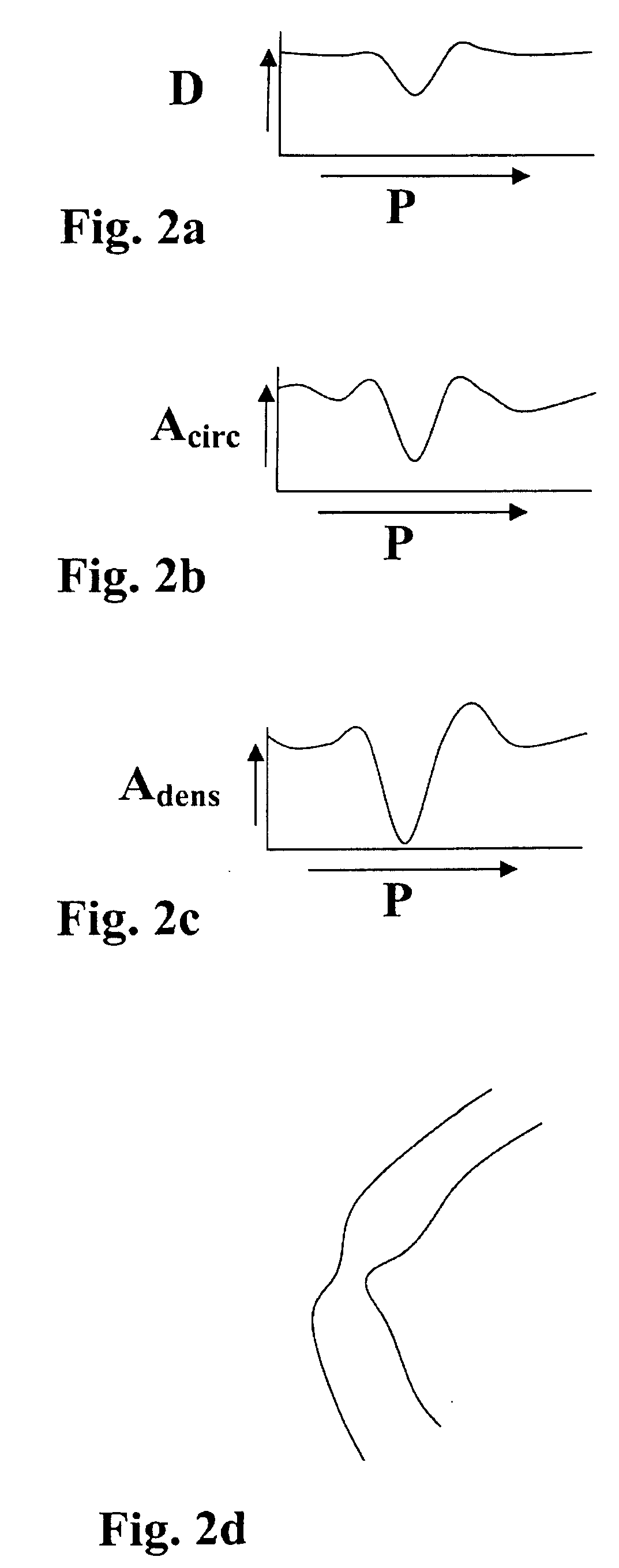
In a process of varying pressure of a pressure container (24) accommodating a forearm (22) of a subject (20) in a pressure range including negative pressure, a diameter (cross-sectional shape value) (D) of an artery 44 in the forearm (22) accommodated in the pressure container (24) is measured non-invasively by a vascular diameter calculating unit (76). In addition, a display controller (display controlling means) (80) operates to display on a displaying device (16) a variation of an internal pressure (Pc) in the pressure container (24) and a variation of the diameter (D) of the artery (44) varying depending thereon. Based on the diameter (D) of the artery (44) obtained in the high pressure region, the variation of the internal pressure Pc in the pressure container 24 and the variation of the diameter (D) of the artery 44 varying depending thereon i.e. mechanical properties of the artery (44) are displayed on the displaying device (16). The artery (44) can be evaluated accurately based on the mechanical properties.
Owner:UNAX CORP
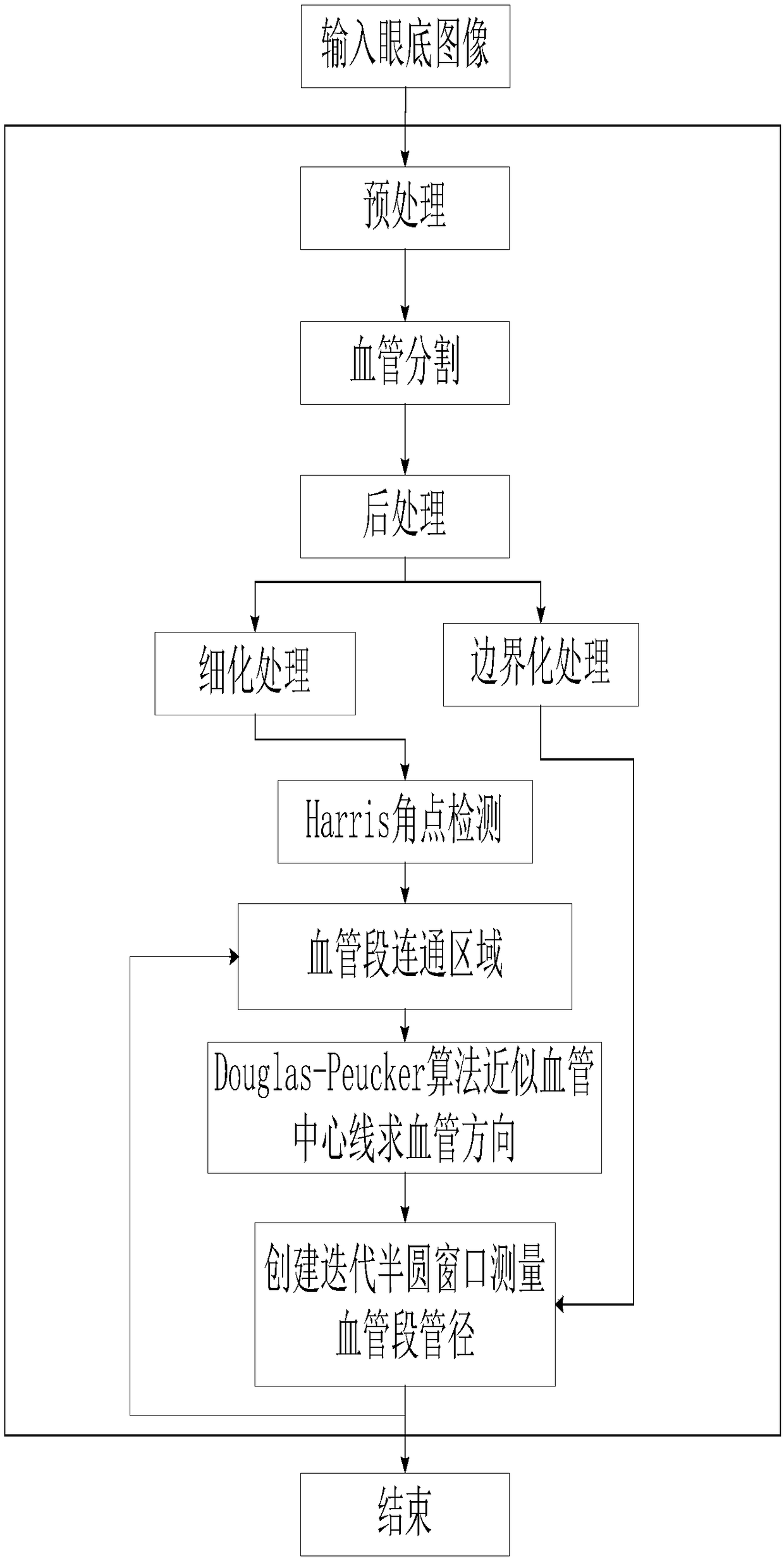
A retinal blood vessel morphology quantization method based on a connected region
ActiveCN109166124AEasy to judgeSolving Quantitative ProblemsImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyRetina
The invention provides a retinal blood vessel morphology quantization method based on a connected region. The method obtains a retinal blood vessel segmentation image after the fundus image is preprocessed, and then performs post-processing on the blood vessel segmentation image. On this basis, the vascular network is thinned and boundary treated, and the vascular centerline network and vascular boundary map are obtained. Corner detection is then performed and removed from the vascular centerline network so that the vascular segments of the vascular network form separate communication areas. Traversing is performed on the blood vessel segment, approximate the centerline of the blood vessel segments, and the blood vessel segment is changed into a broken line to calculate the direction of the blood vessel. At last, that initial diameter value is calculated, the center of the circle is selected by sliding on the centerline of the blood vessel segment, a semicircle window is created according to the direction of the circle cardiovascular and the diameter value measured in the early stage, and the distance between the window and the two intersection points of the blood vessel boundary is taken as a new diameter value. From this iteration, a set of vessel diameter values are measured, and the median value is the vessel diameter of the vessel segment. The invention is applicable to the quantification of large-scale retinal blood vessel morphology, and has high reliability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for tracking and extracting blood vessels from angiography image full-automatically
ActiveCN102819823AAccurate extractionEliminate human distractionImage enhancementImage analysisBlood vesselOperating speed
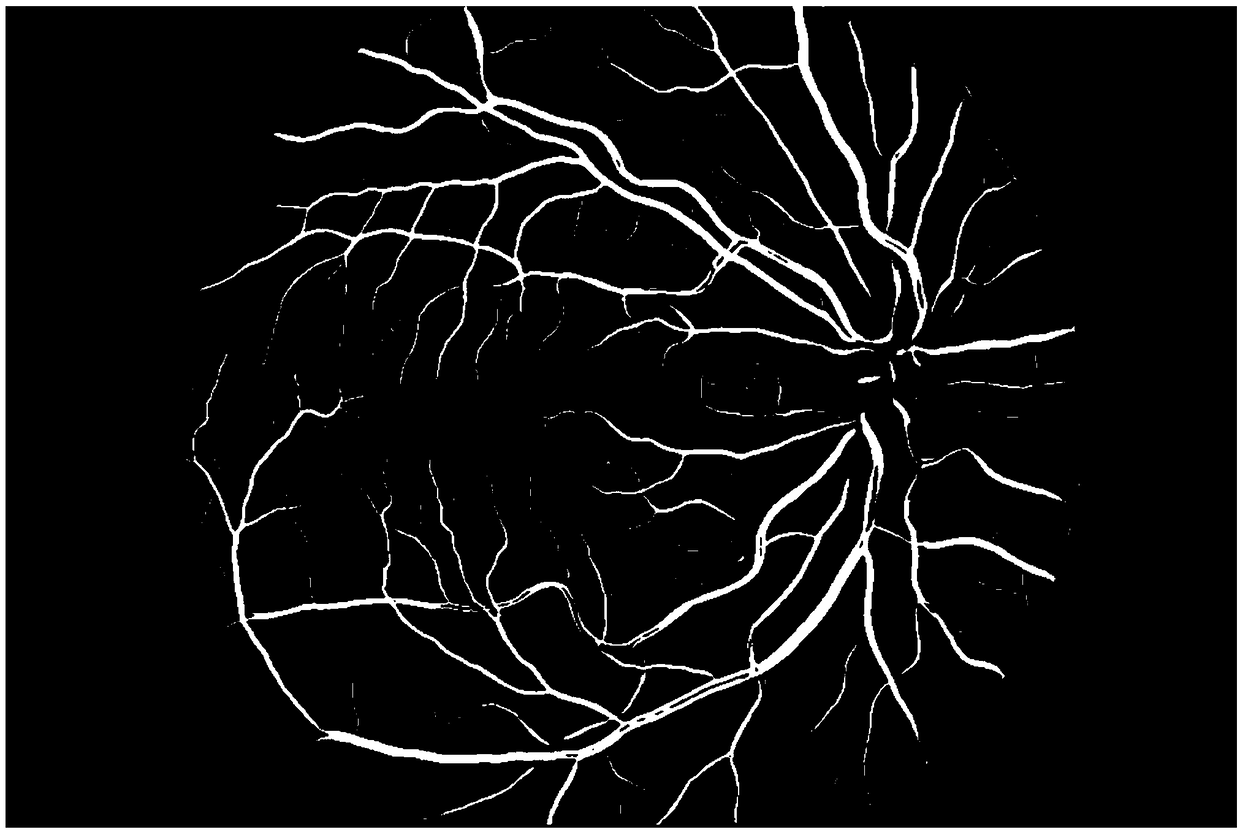
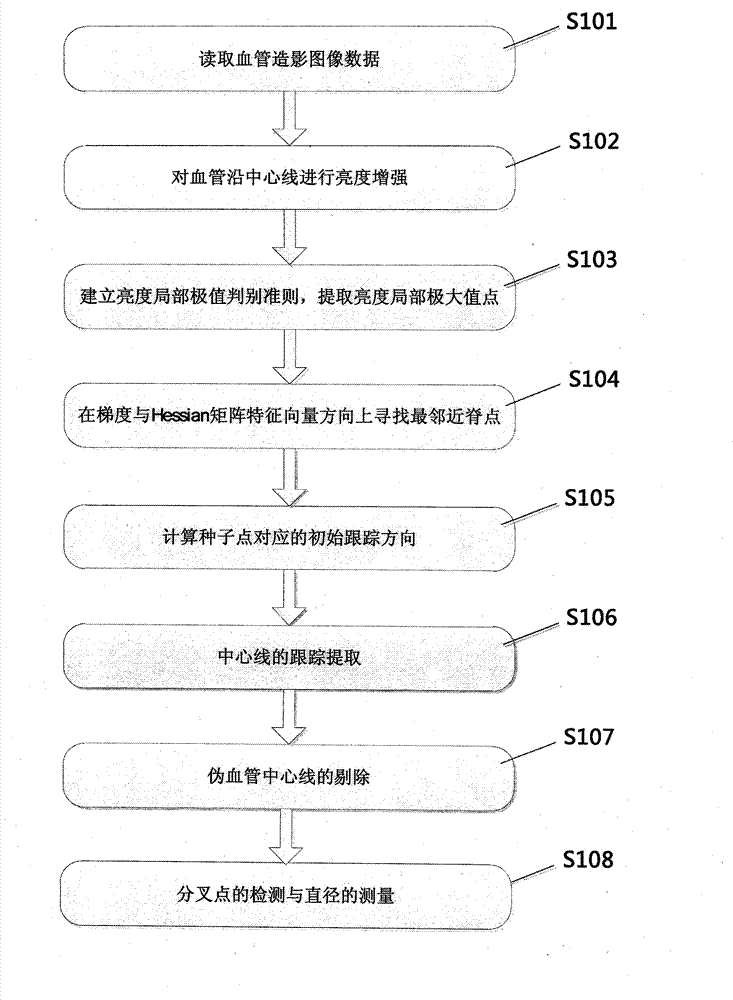
The structures of blood vessels can be segmented from a medical image, and the segmentation is significant for research and diagnosis and treatment of vascular diseases. In a conventional blood vessel extracting method, a large amount of labor force are engaged in the operation and calculated amount of related algorithms is large. The invention provides a method for tracking and extracting blood vessels from an angiography image full-automatically. The method comprises the steps of detecting a large amount of seed points which are located on central lines of blood vessels automatically based on the fact that blood vessels in the image is subjected to multi-scale ridge strengthening and calculating original tracking directions of the blood vessels; acquiring a candidate central line assembly through a method in which ridge points are tracked and extracted on the central lines of the blood vessels and rejecting false blood vessel central lines; and finally, analyzing discrete points on the central lines, and determining which point is a branching point of a blood vessel and calculating blood vessel diameter length corresponding to a ridge point on a central line of the blood vessel. The algorithm is high in operating speed, a topological structure of blood vessels can be extracted accurately without manual intervention, and the method can be used in a clinical diagnosis and treatment process of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Medical image sequence plaque stability index-based quick calculation method and system
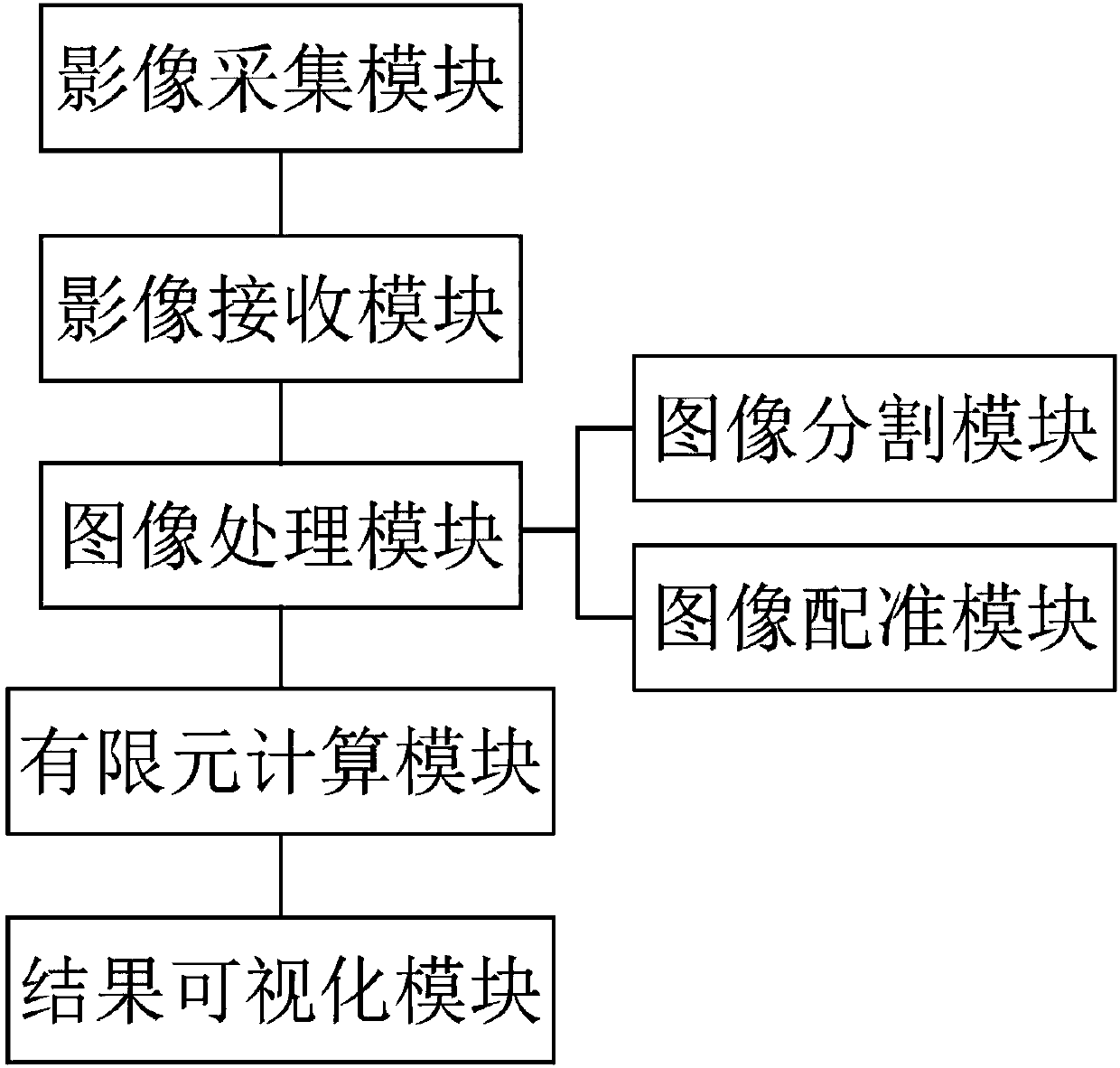
ActiveCN108038848AObserve comprehensivelyObserve completeImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionStability indexIn vivo
The invention provides a medical image sequence plaque stability index-based quick calculation method and system. The system comprises an image collection and receiving module, an image processing module, a plaque stability calculation module and a result visualization module. The image collection and receiving module is used for collecting, receiving and transmitting a dynamic two-dimensional vascular image sequence; the image processing module is used for performing local feature or global image registration based on dynamic information of artery real-time deformation in a two-dimensional image to obtain a displacement field function of space transformation; and the plaque stability calculation module performs calculation by utilizing the displacement field function to obtain a time-varying vascular diameter sequence, a lumen central line, a contour deformation parameter and a mechanics index. Based on an existing medical image function, information such as the time-varying vasculardiameter sequence, a lumen contour, area strain and stress, and the like is added to the two-dimensional image directly, so that the in-vivo assessment of plaque stability is simplified and effectively realized.
Owner:PULSE MEDICAL IMAGING TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
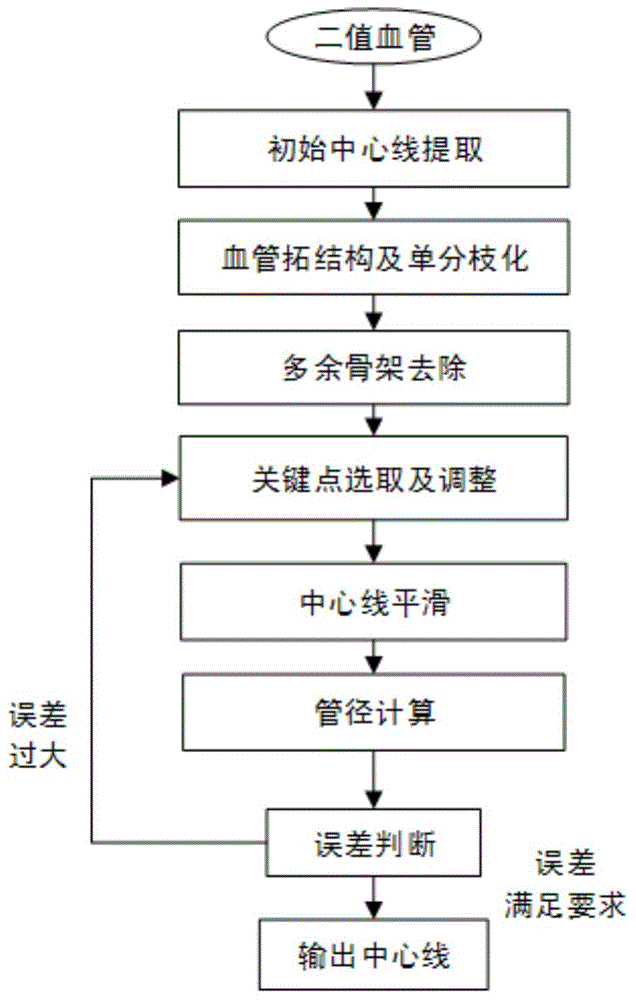
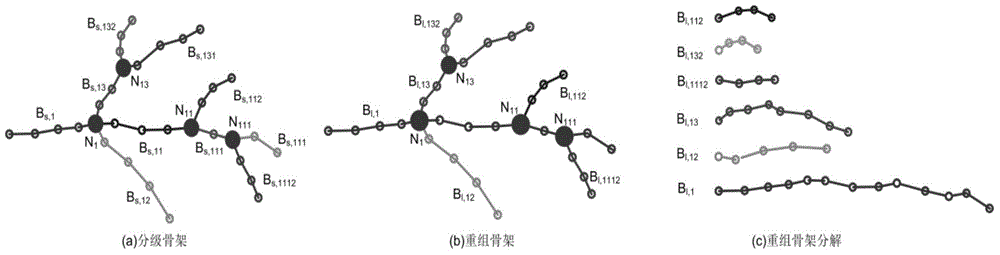
Vascular skeleton line reconstruction and precise vessel diameter calculation method
The invention provides a vascular skeleton line reconstruction and precise vessel diameter calculation method which includes the following steps: refining two-value vascular images in a CT (Computerized Tomography) image to form an initial skeleton line; dividing the vascular skeleton line into separate branches, and separating the skeleton line to form independent vascular sections; detecting the obtained branched vascular skeleton lines to remove surplus skeleton lines; smoothing all the obtained branched vascular skeleton lines to obtain precise center lines; outputting the smoothed vascular skeleton lines. The vascular skeleton line reconstruction and precise vessel diameter calculation method divides the initial skeleton line into separate branches to remove surplus skeleton lines and then smoothes the surplus skeleton lines, the obtained skeleton lines are located at the vascular center, and therefore a vascular model is made more accurate.
Owner:安徽紫薇帝星数字科技有限公司
Method of producing personalized biomimetic drug-eluting coronary stents by 3d-printing
ActiveUS20160256610A1Avoid influenceReduce complicationsStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusThrombusPercent Diameter Stenosis
A method for using 3D printing technology produces personalized biomimetic drug-eluting coronary stent and the product thereof. The process of manufacturing stent, based on coronary angiography imaging data, measures the diameter of diseased coronary and conducts 3D reconstruction. A personalized stent for each patient according to diameter, length, and morphological characteristics of target vessel that suited to the lesion is produced. The coronary stent is formed from biodegradable poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) or other materials. The stent is modeled by 3D printing and then coated with polymers carrying antiproliferative drug to reduce restenosis (the polymers is a mixture of antiproliferative drug and PDLLA at a ratio of 1:1). The biomimetic drug-eluting coronary stent produced by 3D printing technology is personalized stent for each patient according to different characteristics of diseased coronary, reduces the incidence of vascular injury, thrombosis, dissection and other complications caused by stent and vessel diameter mismatch.
Owner:ZHOU YUJIE +3
Bicuspid vascular valve and methods for making and implanting same
Owner:QUINTESSENZA JAMES
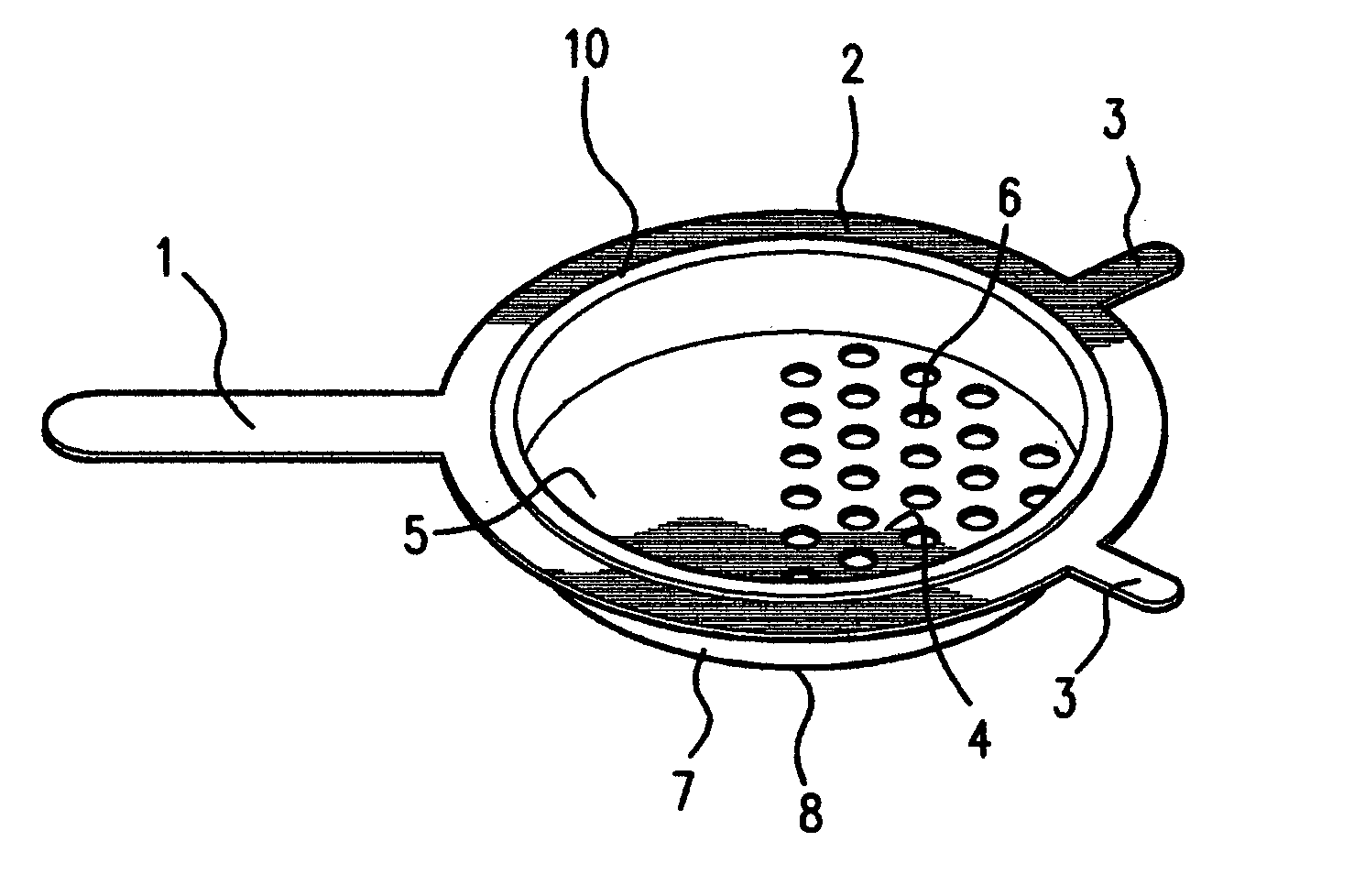
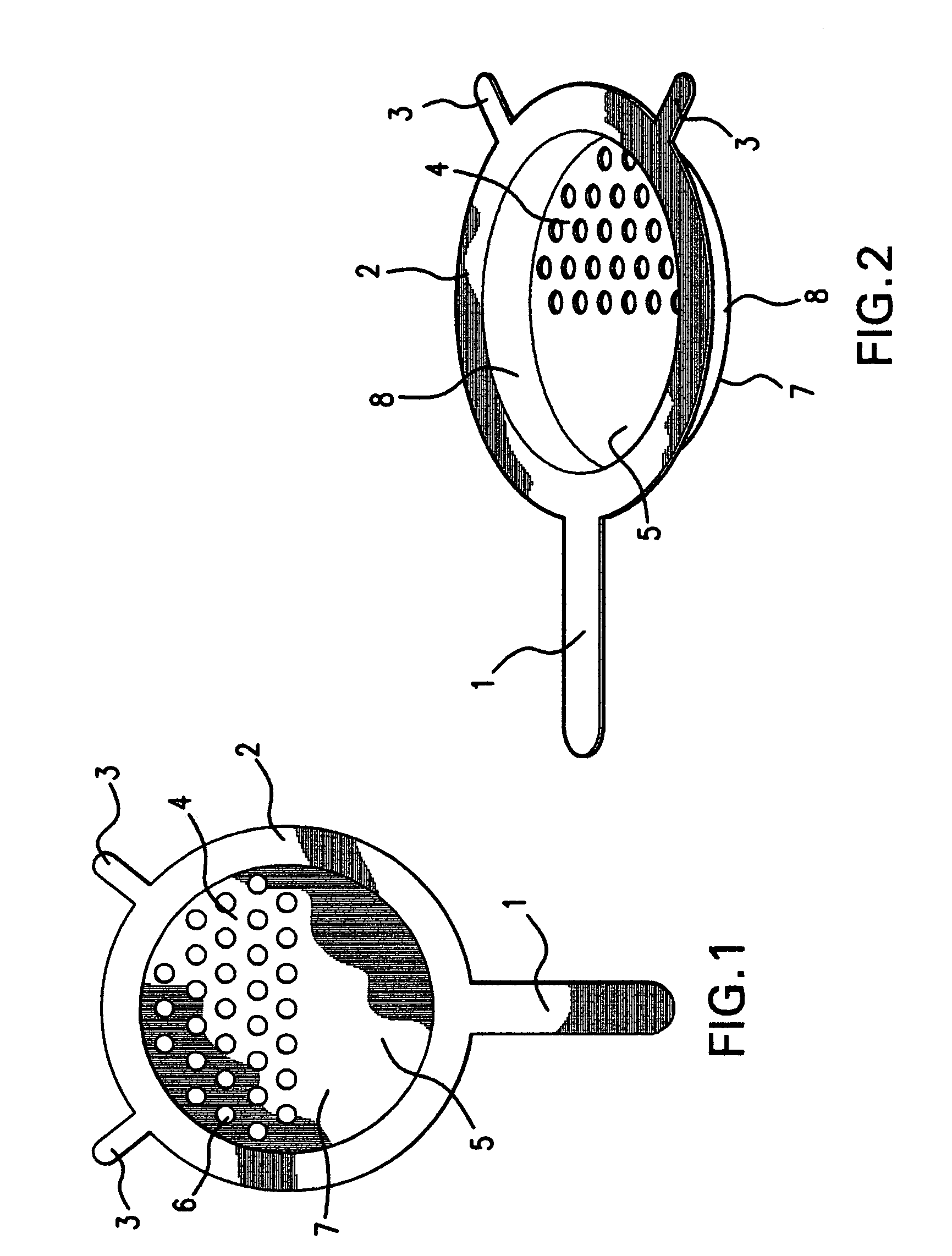
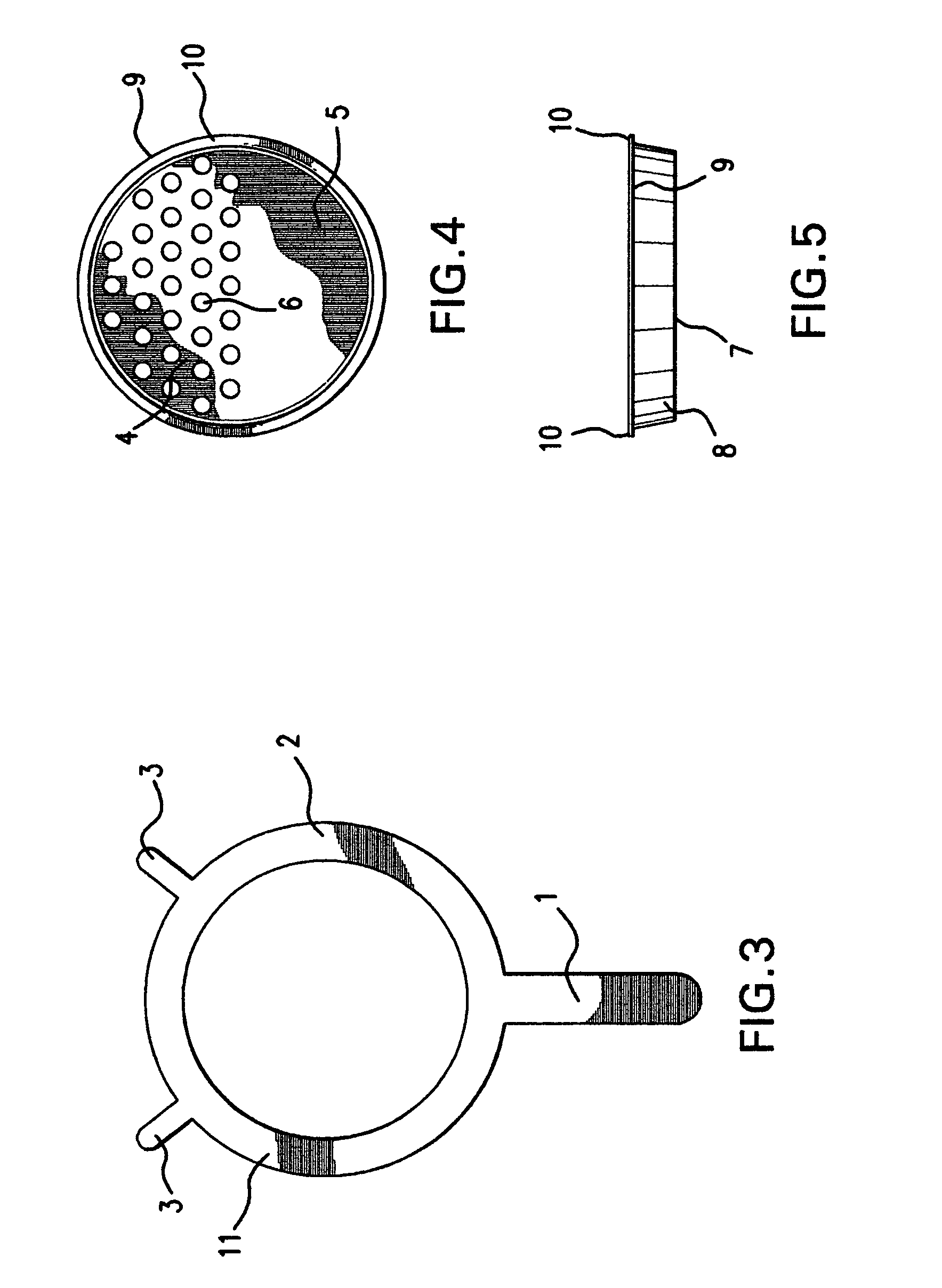
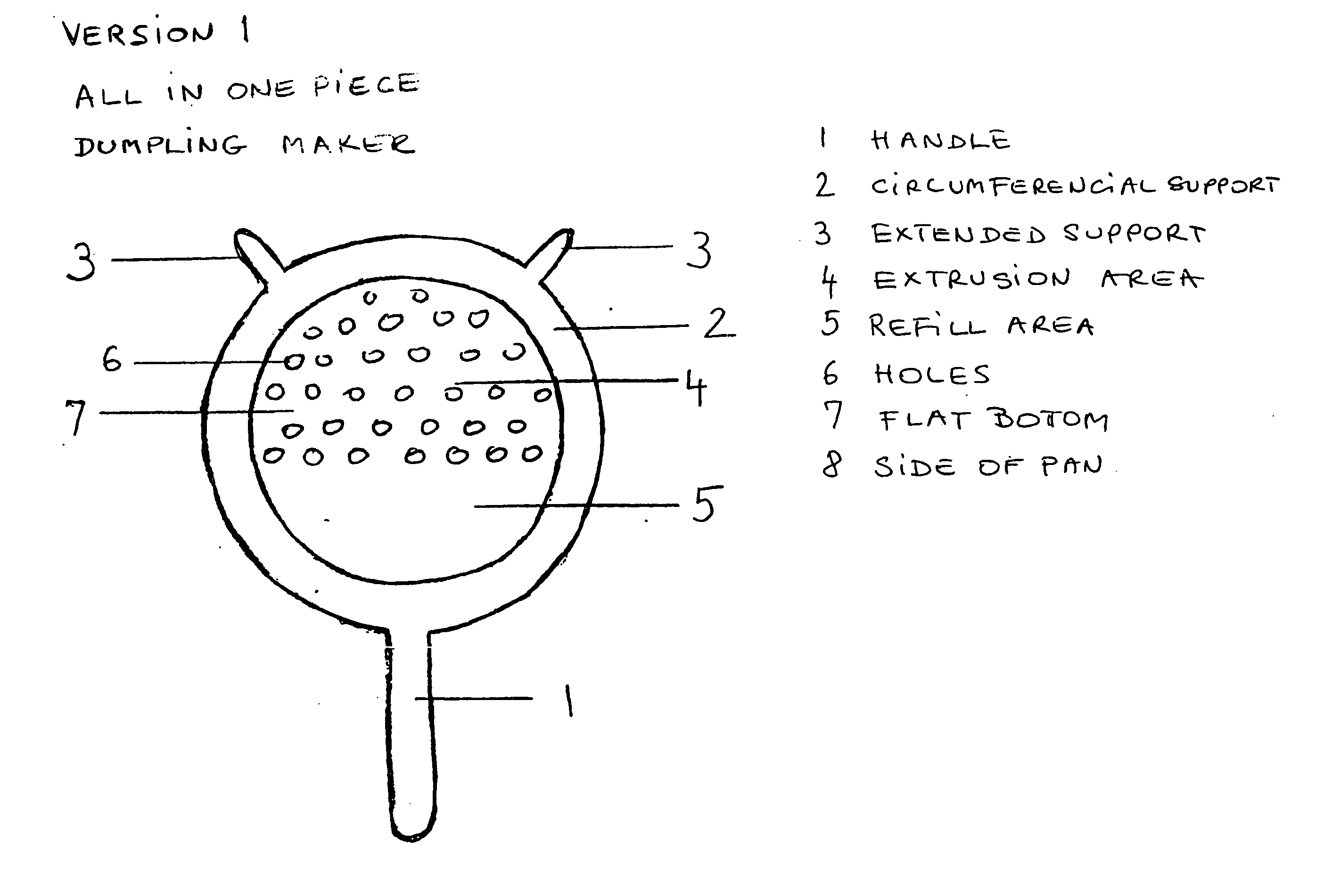
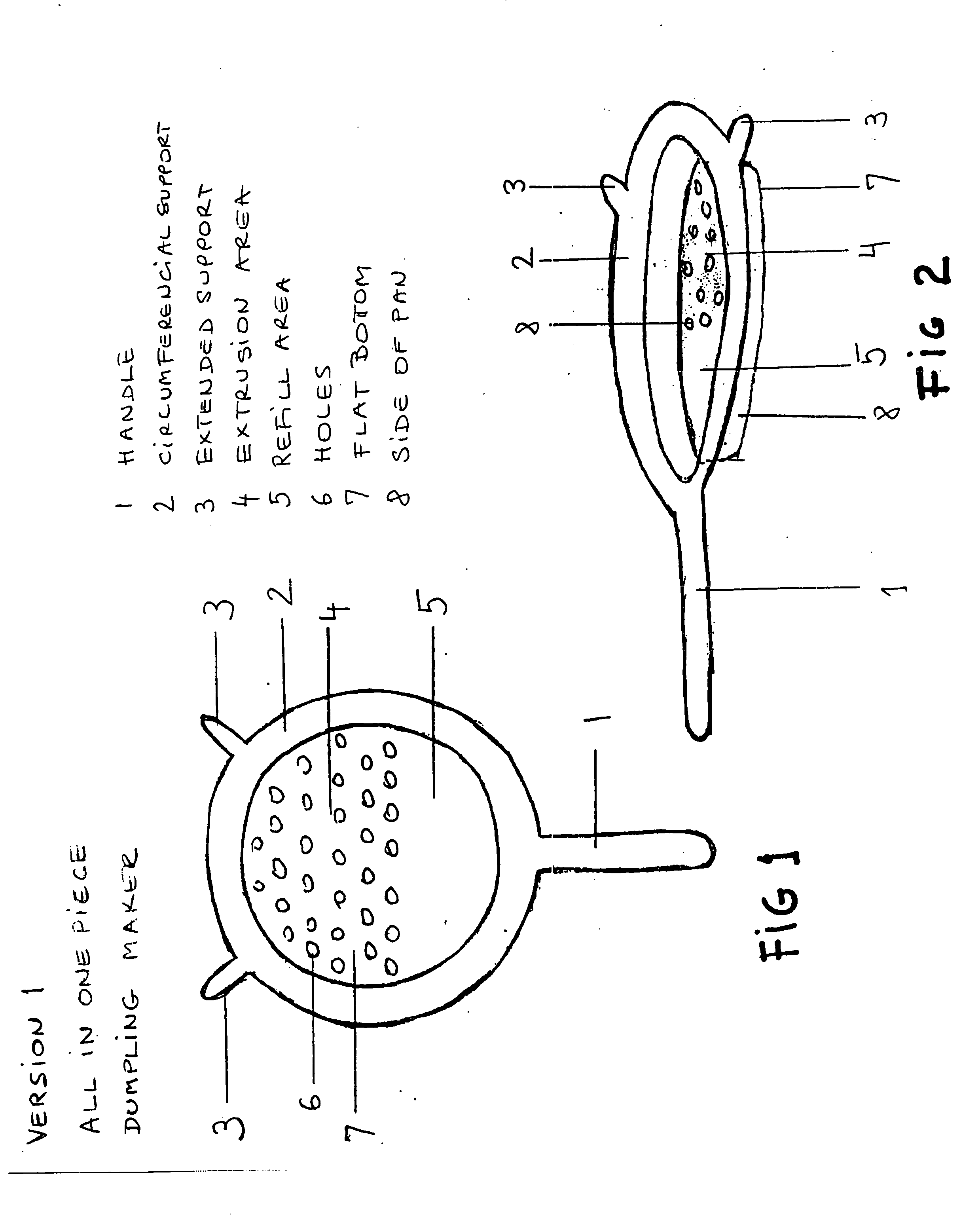
Dumpling maker
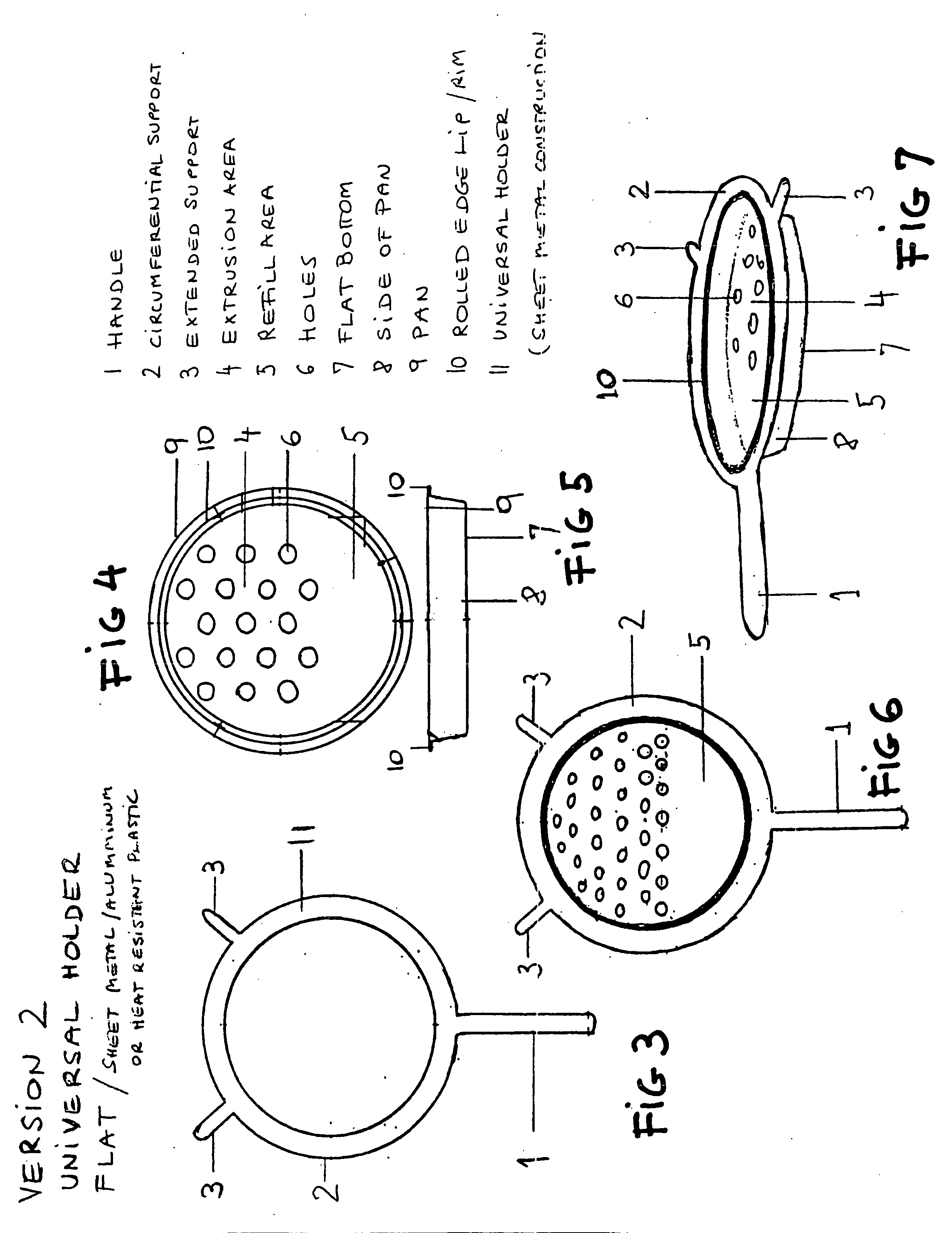
ActiveUS7008214B2Speed and safetyEasy to manufactureDough treatmentConfectioneryEngineeringVessel diameter
A cooking utensil includes an all-in-one device that incorporates a partially perforated pan, circular in shape, with a permanent and continuous circumferential holder with one or more supports that provide stability and safety during the extrusion process of the soft batter. At the same time, this cooking utensil fits easily on top of commonly used cooking vessels regardless of lip configuration or vessel diameter. This cooking utensil also includes versions for removable type holders in kit form that can be used interchangeably with several pans with different hole sizes while providing multiple support and stability over commonly used cooking vessels.
Owner:FADDI IBOLYA
Blood rheology measurement device and blood rheology measurement method
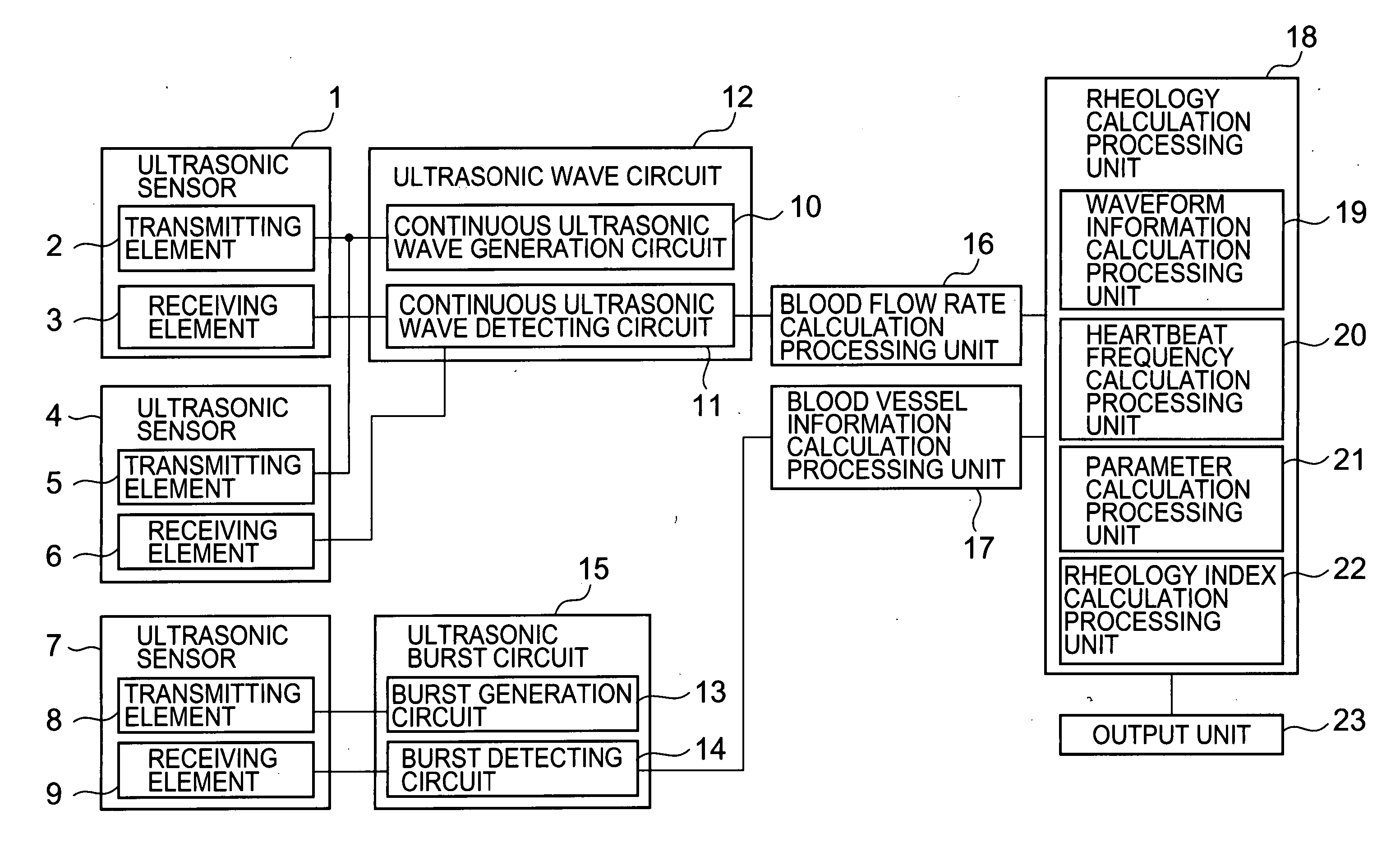
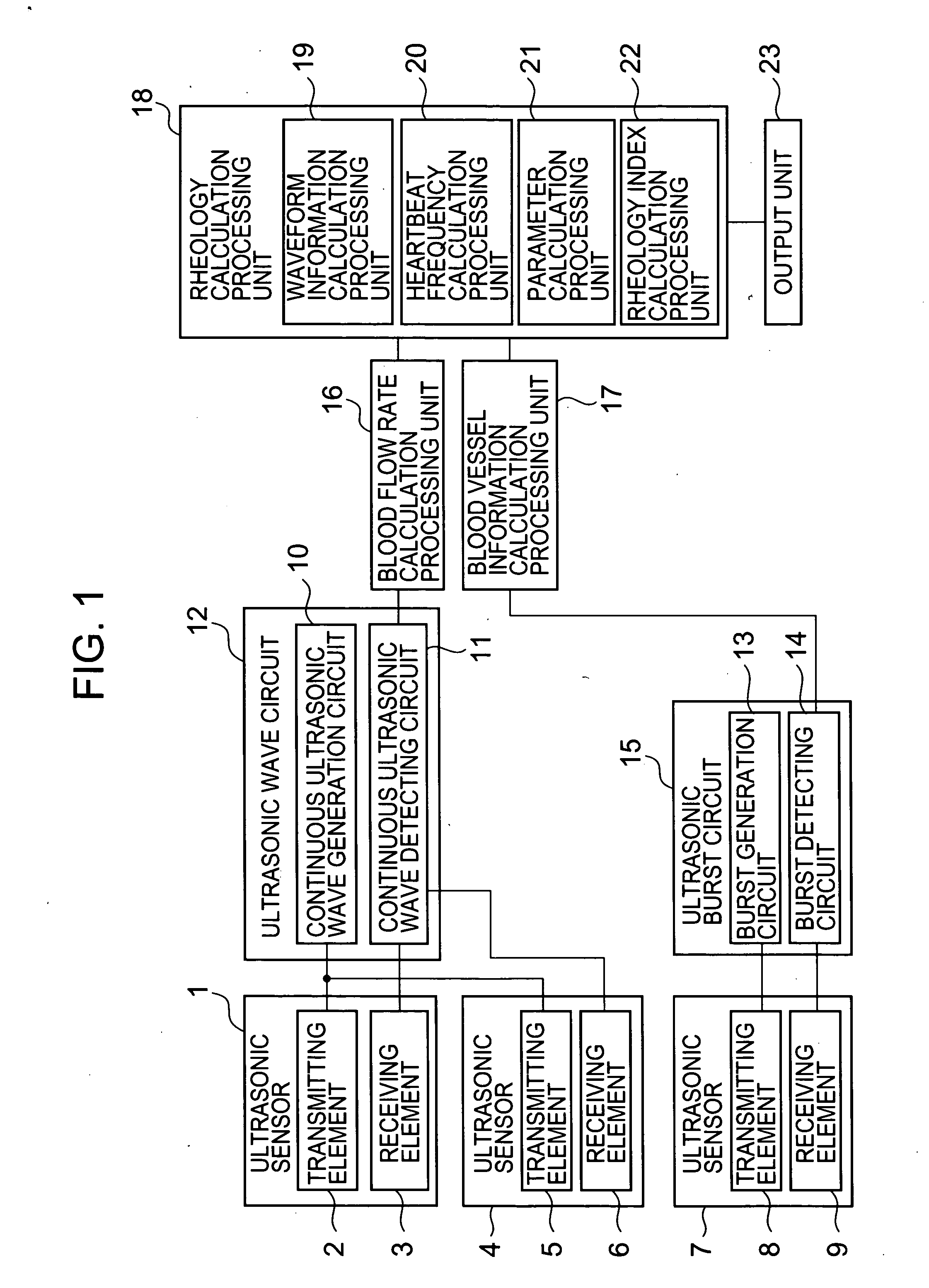
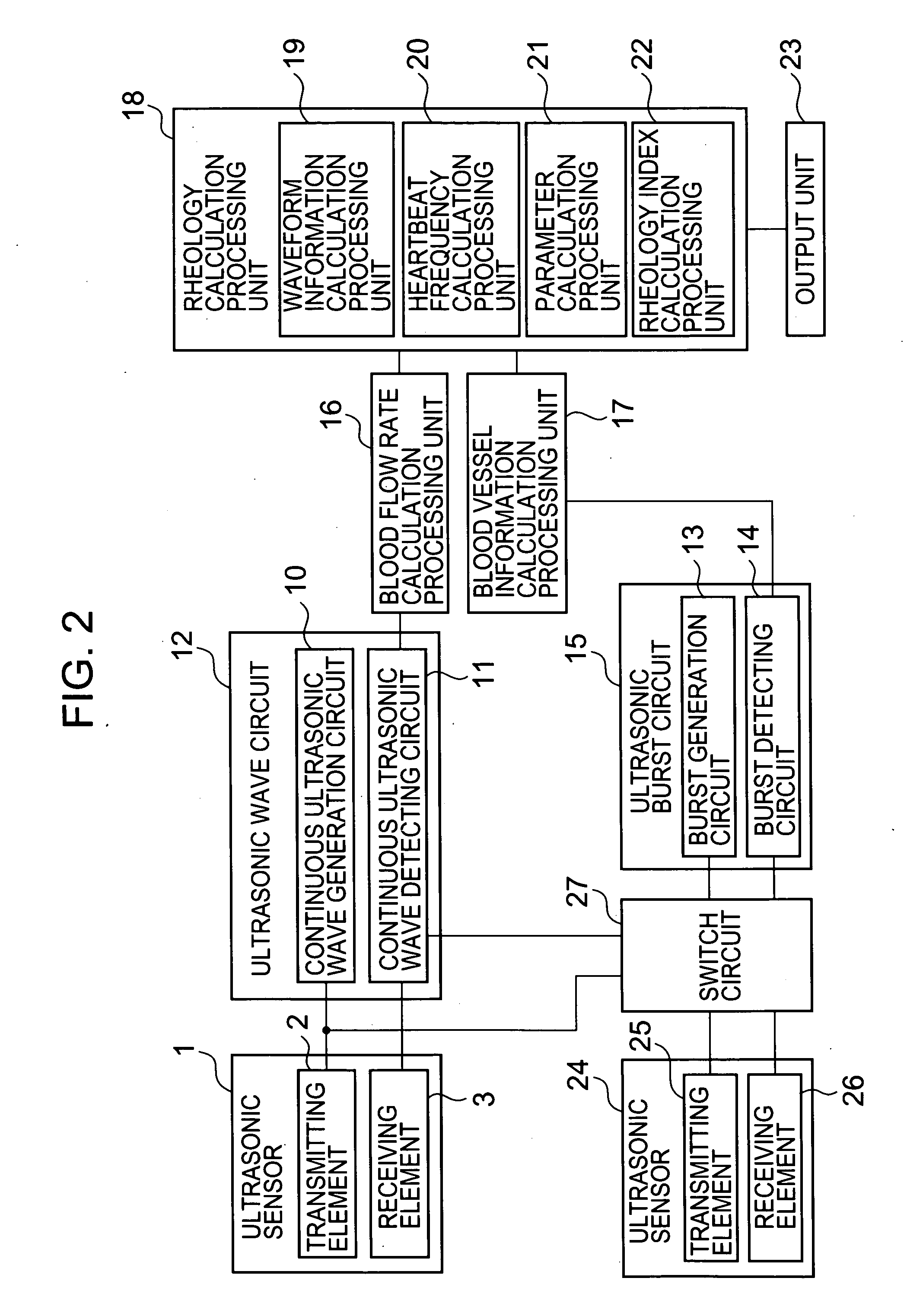
InactiveUS20060241460A1Good precisionSimple and high-precisionBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement devicePhase difference
There is disclosed a miniature blood rheology measurement device and a blood rheology measurement method which are capable of performing measurement of a portion such as a wrist or a fingertip with a high precision and which are simple without requiring measurement of a blood pressure. The method: detects an artery blood flow rate, a pulsatile displacement, an artery diameter, an artery wall thickness, a heartbeat frequency, and a phase difference or an amplitude ratio of the blood flow rate and the pulsatile displacement, which change with elapse of time, by use of a sensor including ultrasonic wave transmitting and receiving elements for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves between the surface of a living body and an artery blood flow in the living body; and calculates a blood kinematic viscosity by use of one of the phase difference and the amplitude ratio, the blood vessel diameter, and the heartbeat frequency to obtain an index value of a blood rheology.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
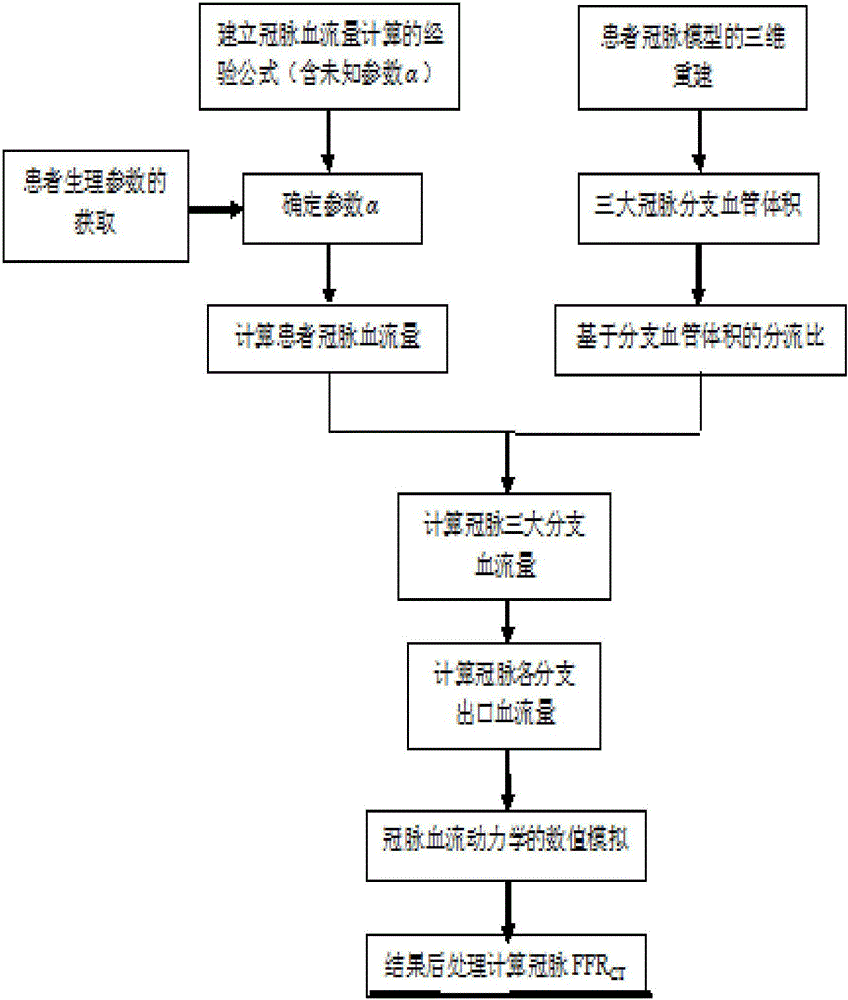
Method for computing FFR<CT> (fractional flow reserve <computed tomography>) on basis of personalized coronary artery branch blood flow volumes
InactiveCN106473731AEnabling Non-Invasive ComputingImprove calculation accuracyMedical simulationHealth-index calculationBiomechanicsEmpirical formula
The invention discloses a method for computing FFR<CT> (fractional flow reserve <computed tomography>) on the basis of personalized coronary artery branch blood flow volumes, and belongs to the field of biomechanics and haemodynamics. The method includes clinically acquiring physiological parameters of cardiac muscle masses, heart rates, blood pressures and the like of patients and establishing coronary blood flow volume computing empirical formulas on the basis of allometric growth laws; rebuilding three-dimensional geometric models of coronary arteries on the basis of CT images of the coronary arteries of the patients, acquiring the volumes of blood vessels of branches of the coronary arteries and the vessel diameters of the various branches and acquiring split ratios of the various branches on the basis of the volumes of the blood vessels of the branches and the Poiseuille law; combining the coronary blood flow volumes of the patients and the split ratios of the various branches with one another, acquiring the blood flow volumes of the various branches of the coronary arteries by means of computing and solving the FFR<CT> of the coronary arteries of the patients by the aid of the blood flow volumes of the various branches of the coronary arteries. The blood flow volumes of the various branches of the coronary arteries are used as coronary haemodynamics computing boundary conditions. The method has the advantages that FFR of the coronary arteries of human bodies can be noninvasively computed, simulation results can be similar to real blood flow states under the condition of the maximum congestion states of the coronary arteries of the patients owing to personalized coronary flow boundaries, and accordingly the coronary artery FFR<CT> computing accuracy can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing personalized bionic drug eluting coronary stent by using 3D printing technology
InactiveCN105877881AAvoid influenceImprove the quality of lifeStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusThrombusCoronary angiogram
The invention discloses a method for preparing a personalized bionic drug eluting coronary stent by using a 3D printing technology and a product. The method for preparing the personalized bionic drug eluting coronary stent comprises the step that according to image data of coronary angiogram, adopting a QCA technique for measuring the diameter of a diseased coronary artery and reconstructing in a three-dimensional manner. According to indexes such as lesion vascular diameter, lesion length and lesion vascular pattern, a personalized coronary stent can be made for each patient in a customized manner and a stent most suitable for the lesion state of a patient can be prepared. The personalized bionic drug eluting coronary stent can be made of degradable poly L-lactic acid (PLLA) or other materials, after 3D printing molding, the surface of the stent can be coated with a polymer with anti-proliferation medicines by using a conventional process, and in-stent restenosis can be reduced (the polymer is prepared by mixing a medicine with PDLLA in a ratio of the medicine to PDLLA being 1:1). The most suitable personalized bionic drug eluting coronary stent can be customized for the patient according to diseased coronary arteries of different states, requirements of different lesions can be met, customization of coronary stents can be achieved, and complications such as vascular injury, thrombus and coronary arterial dissection caused by mismatching of the diameter of the stent and that of the blood vessel can be reduced.
Owner:周玉杰 +3
Method for extracting two-dimensional dynamic blood vessel information based on ultrasonic echo in real time
InactiveCN102113899AHigh resolutionEasy to measureBlood flow measurement devicesFrequency spectrumSonification
The invention relates to a method for extracting two-dimensional dynamic blood vessel information based on ultrasonic echo in real time, which comprises the following steps: forming and displaying a blood vessel indication cursor on an ultrasonic two-dimensional image; conducting extraction on the information about the blood vessel diameter for the original blood vessel digital radio frequency echo data to obtain the blood vessel diameter data and the blood vessel diameter variation data, wherein the representation unit of the diameter information is the number of sampling points; determining the actual diameter and fluctuations of the blood vessel according to the blood vessel indication cursor and the information about the blood vessel diameter; and further calculating blood flow volume, the fluctuation range and characteristic points of the blood vessel as well as blood flow diameter arc graphs according to the blood vessel diameter information of the blood vessel diameter variation information by combining other existing information, namely electrocardiogram information and blood flow frequency spectrogram, thus obtaining real-time two-dimensional dynamic blood vessel information. According to the invention, an analysis tool is provided for dynamic assessment of blood flow / blood vessel and compliance / elastic analysis of the blood vessel, pressure signals in the axial and radial directions of the blood vessel are provided for pulse condition analysis and research, and the extraction method has the characteristics of practical applicability and clinical practice.
Owner:PHILIPS & NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST
Method and apparatus for performing intra-operative angiography
InactiveUS20080071176A1Accurately determine extentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAfter treatmentAv fistulas
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Dumpling maker
ActiveUS20050069602A1Speed and safetyEasy to manufactureDough treatmentFrozen sweetsEngineeringCooker
A cooking utensil includes an all-in-one device that incorporates a partially perforated pan, circular in shape, with a permanent and continuous circumferential holder with one or more supports that provide stability and safety during the extrusion process of the soft batter. At the same time, this cooking utensil fits easily on top of commonly used cooking vessels regardless of lip configuration or vessel diameter. This cooking utensil also includes versions for removable type holders in kit form that can be used interchangeably with several pans with different hole sizes while providing multiple support and stability over commonly used cooking vessels.
Owner:FADDI IBOLYA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com