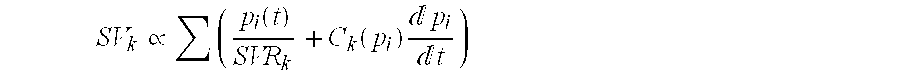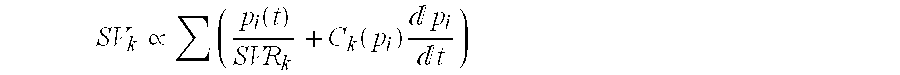Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Vascular resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
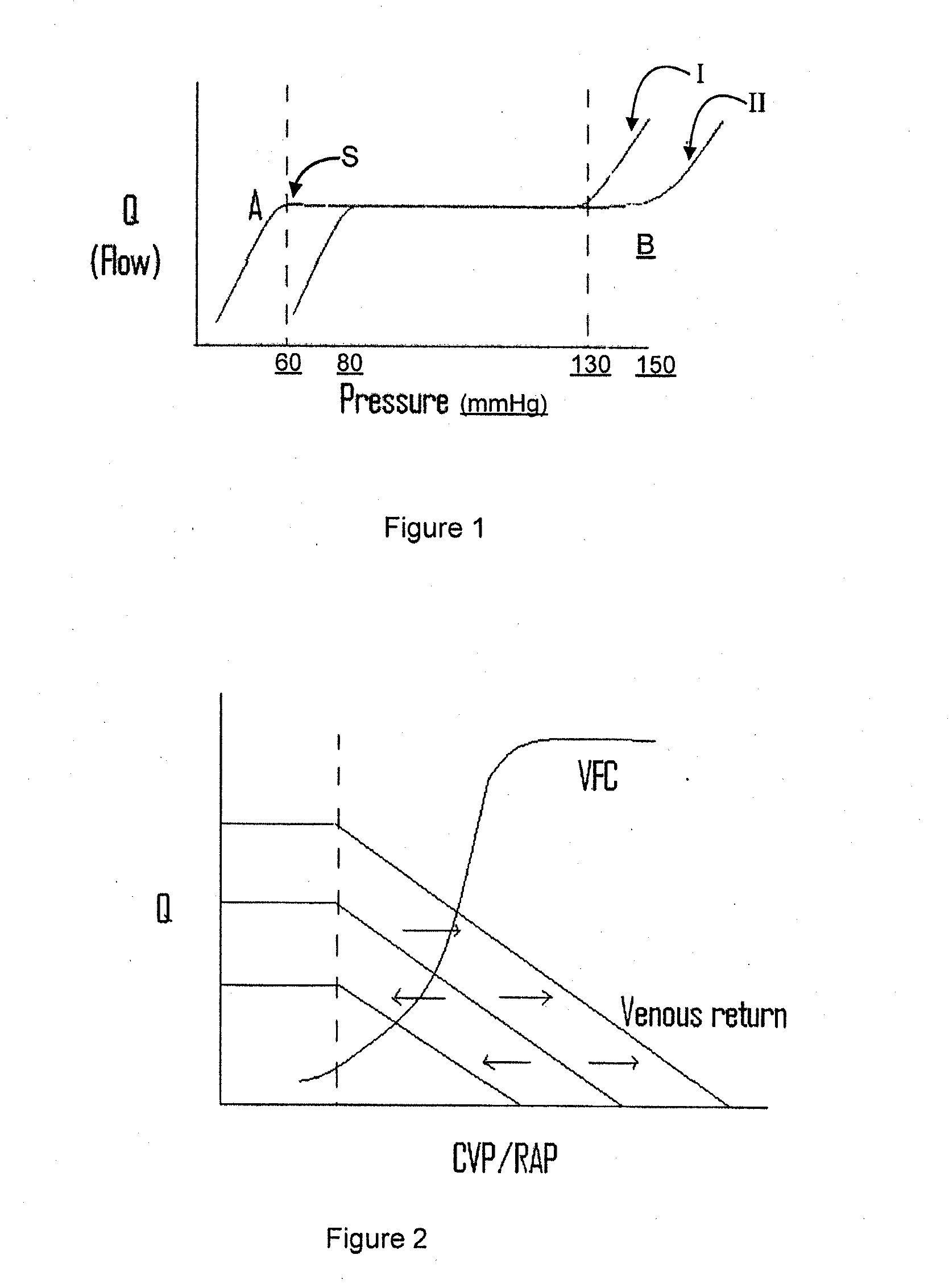
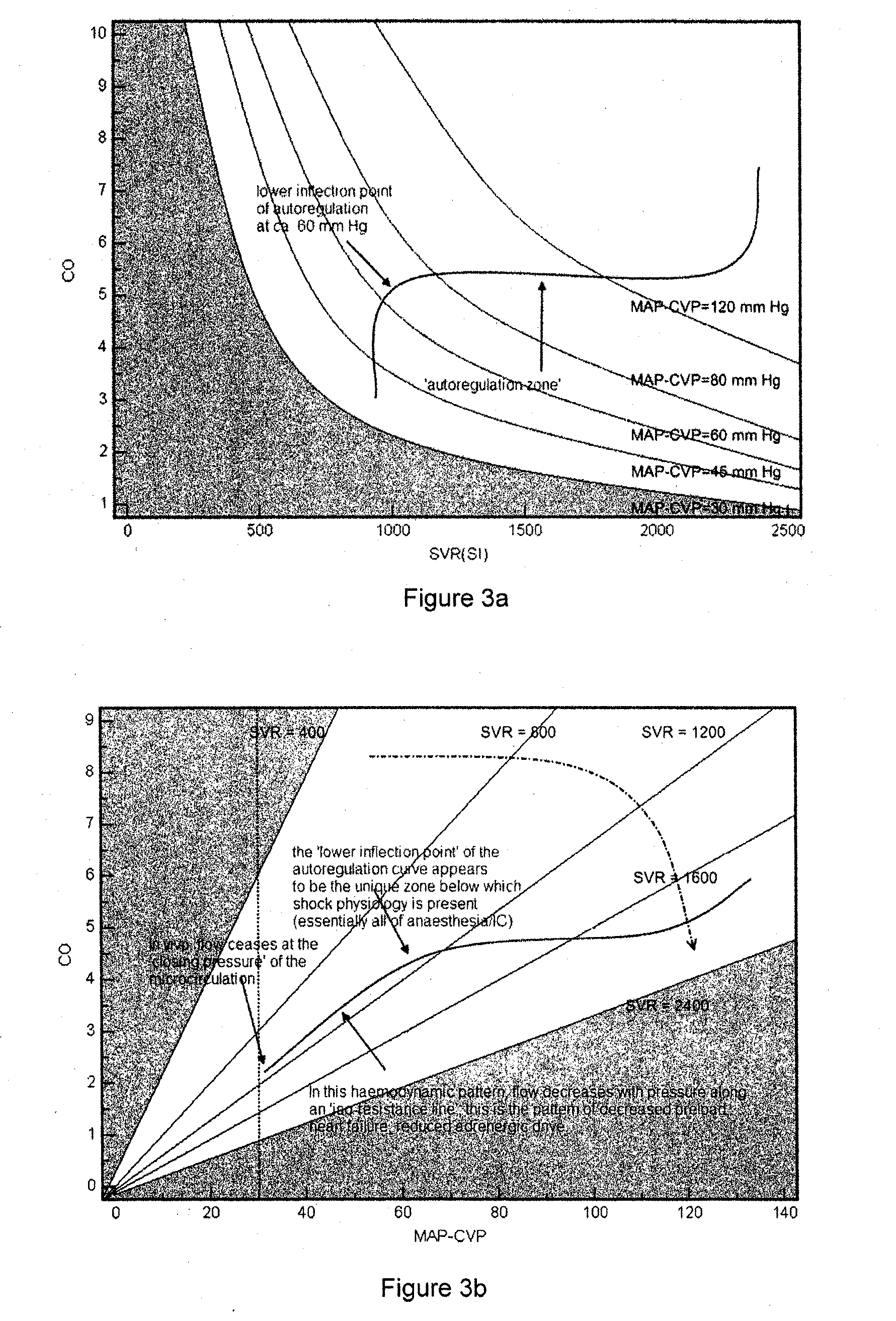
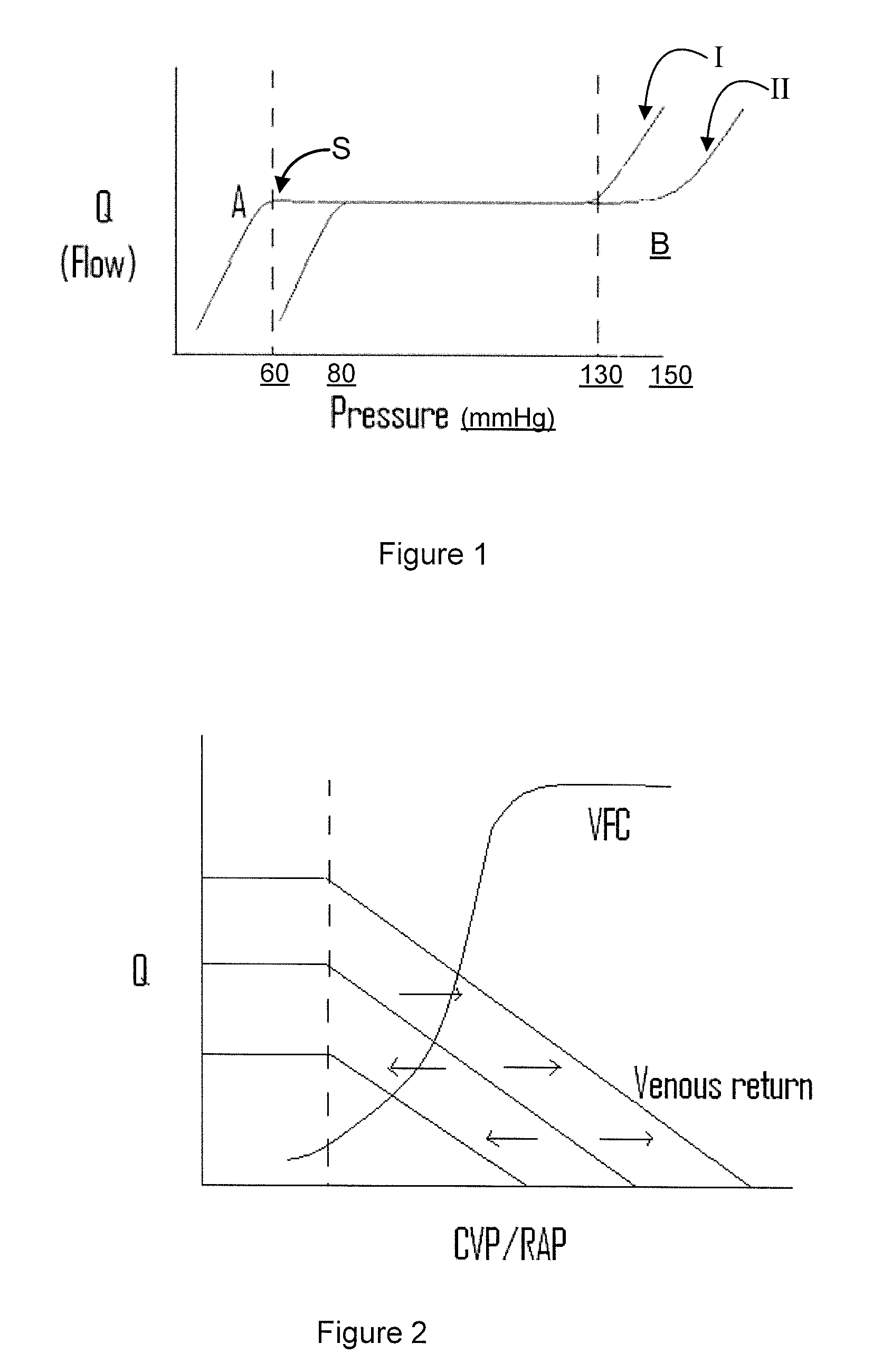
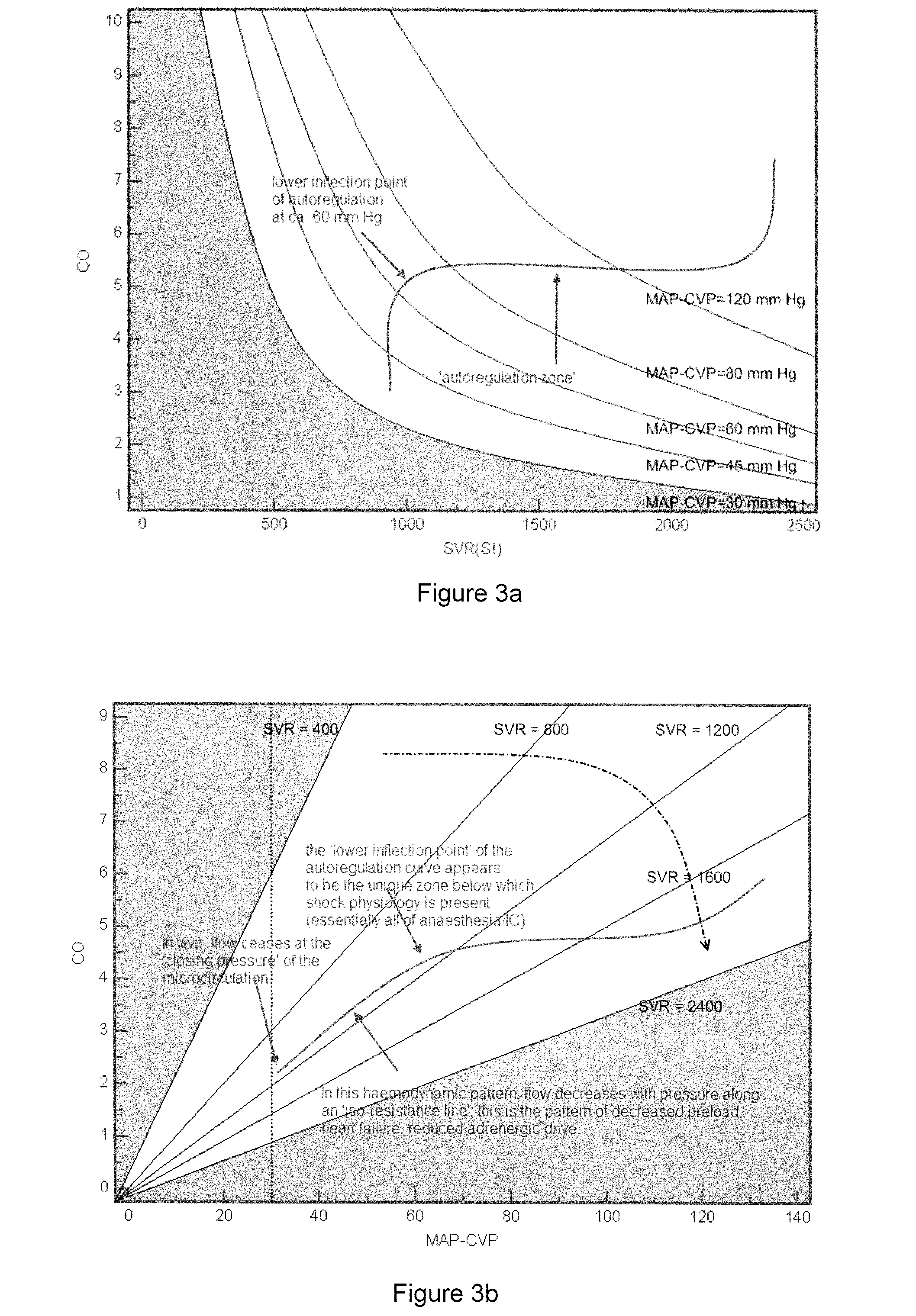
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome to push blood through the circulatory system and create flow. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) or may sometimes be called by the older term total peripheral resistance (TPR), while the resistance offered by the pulmonary circulation is known as the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR).
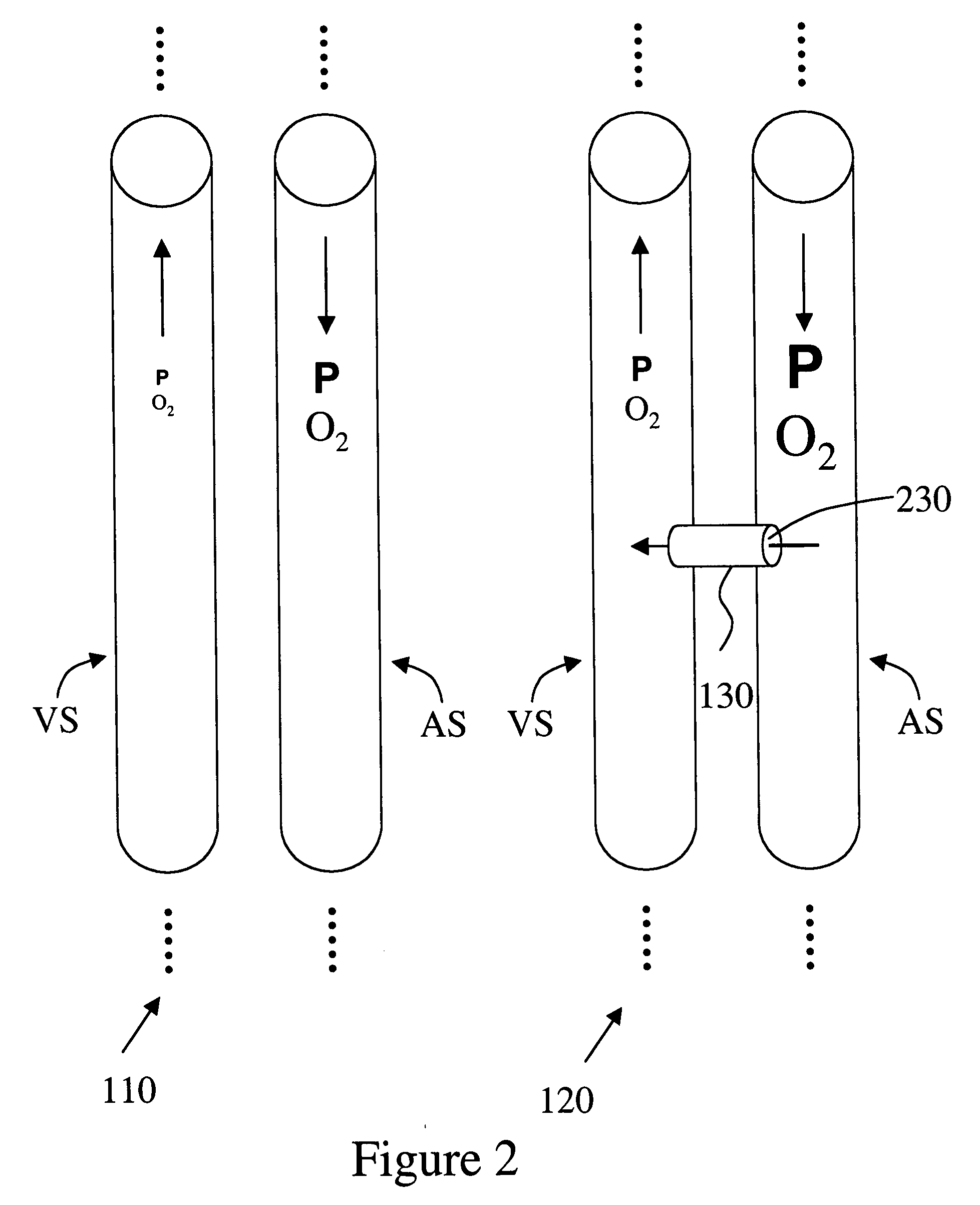
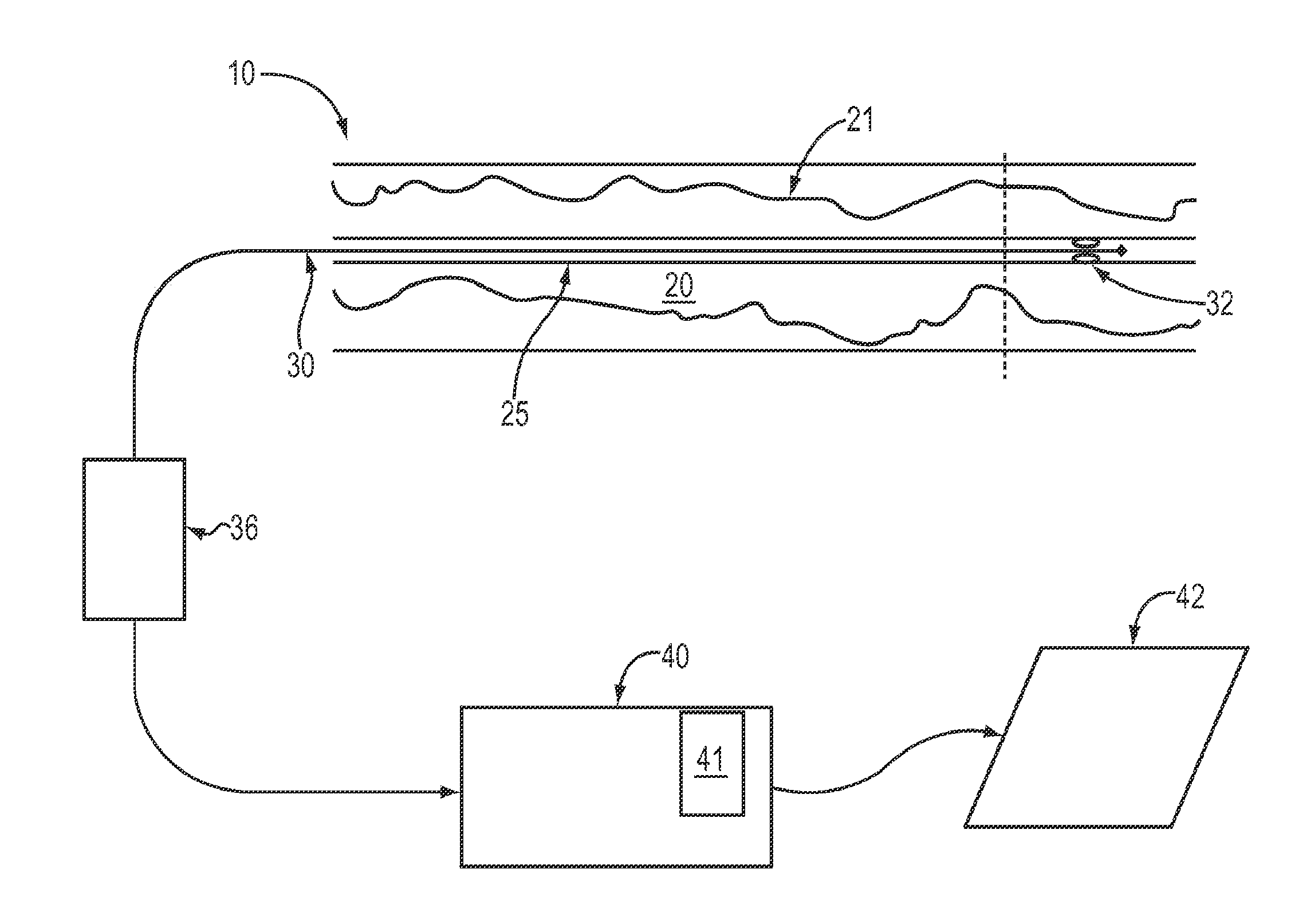
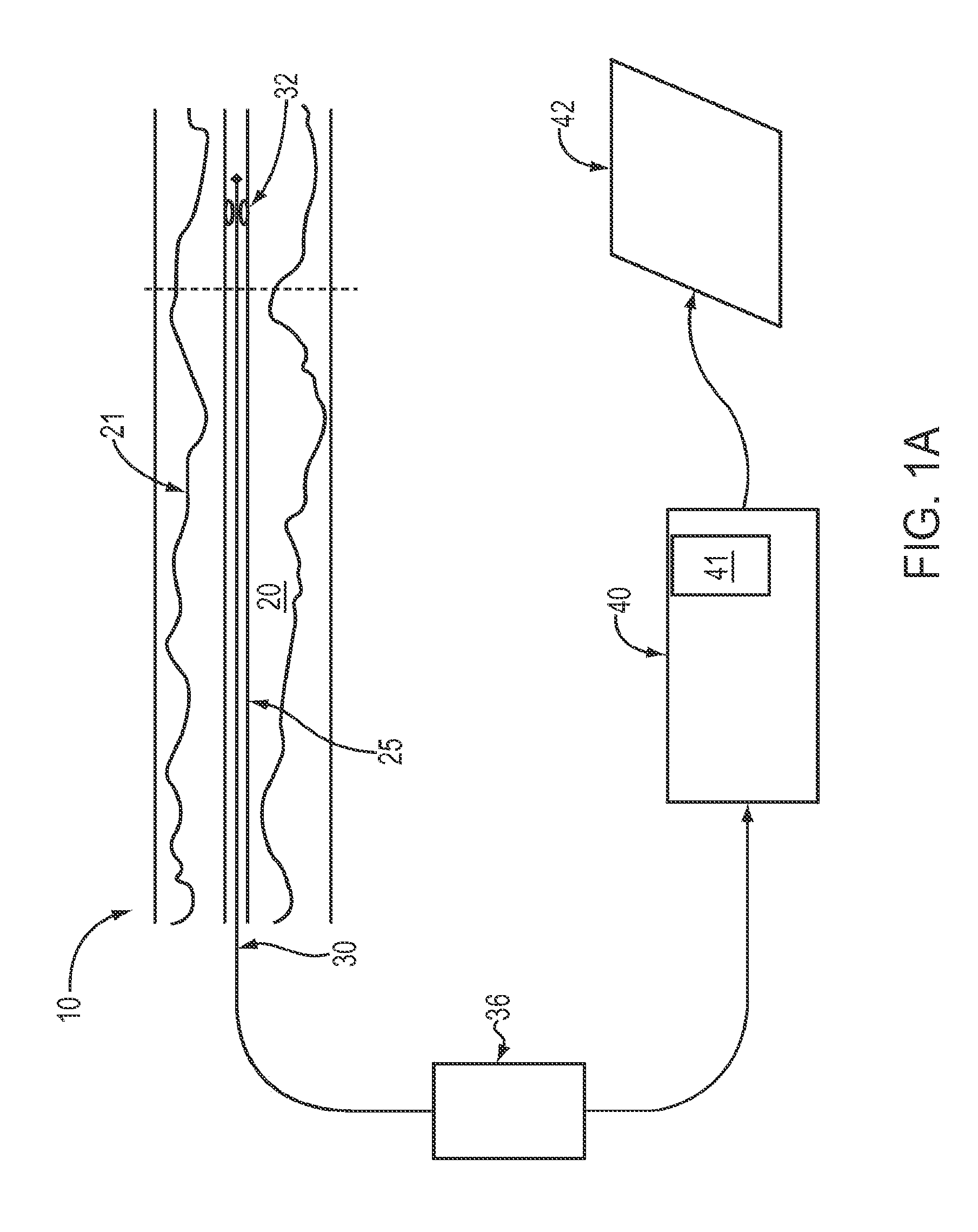
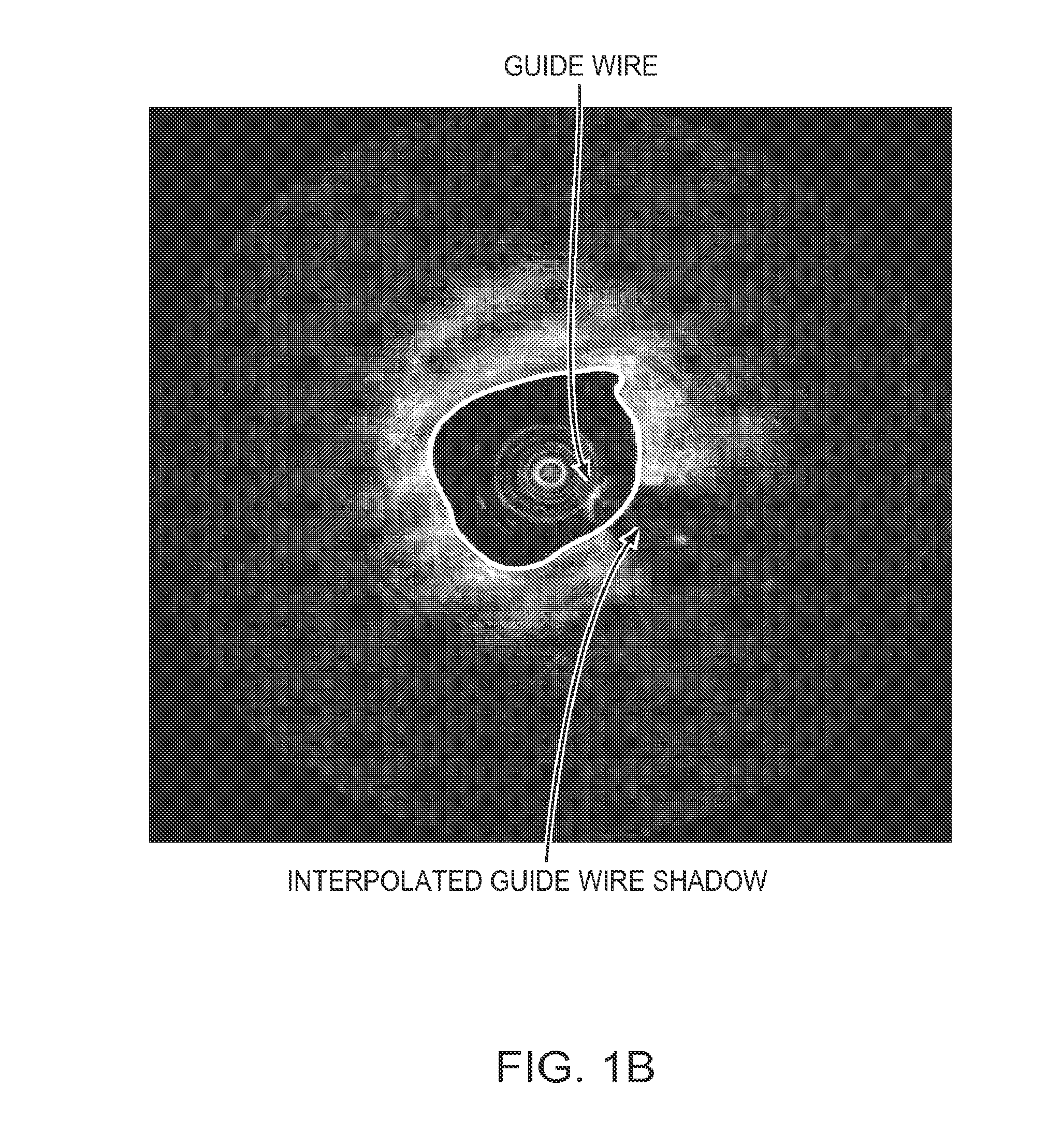
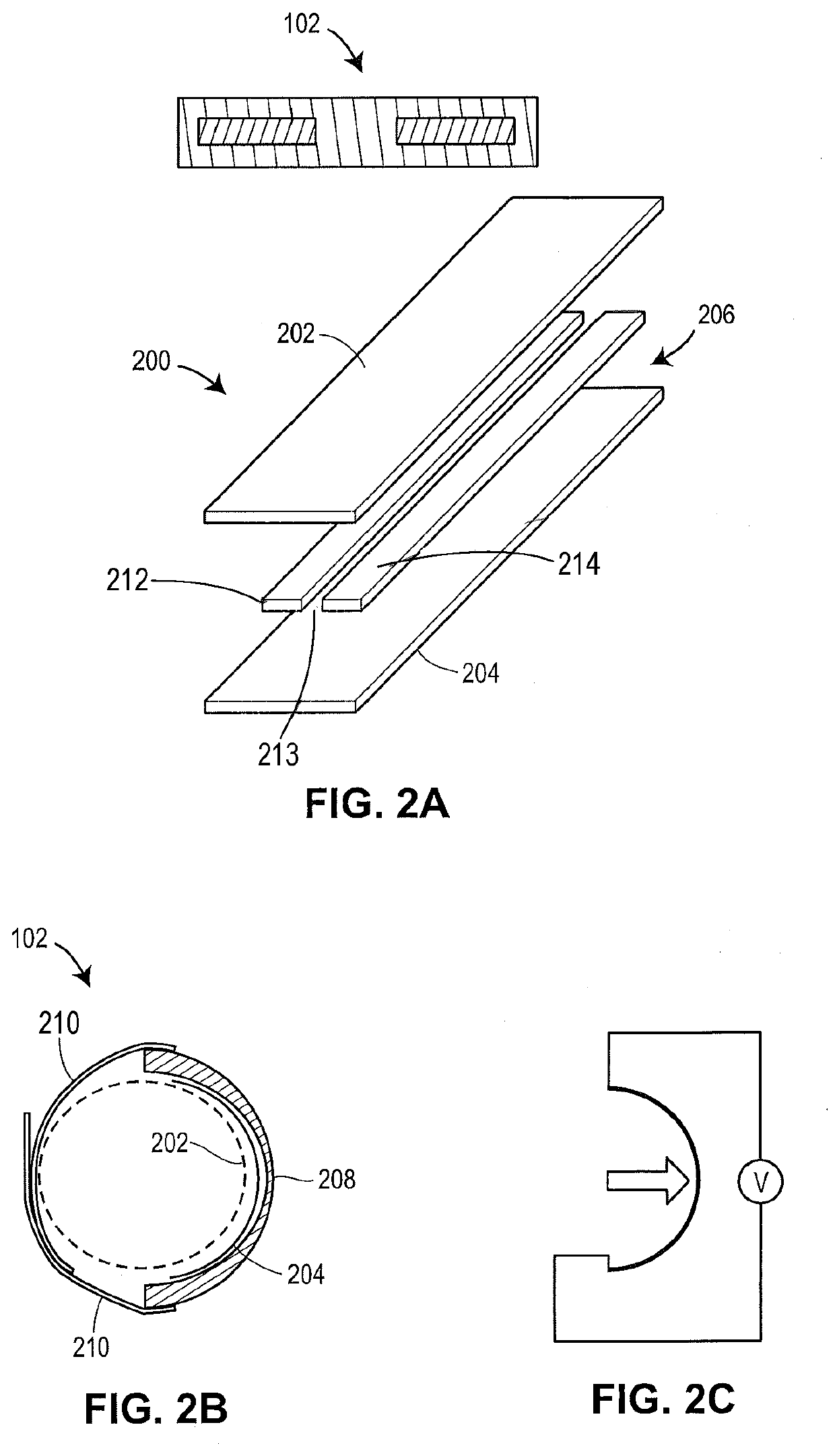
Lumen Morphology and Vascular Resistance Measurements Data Collection Systems, Apparatus and Methods
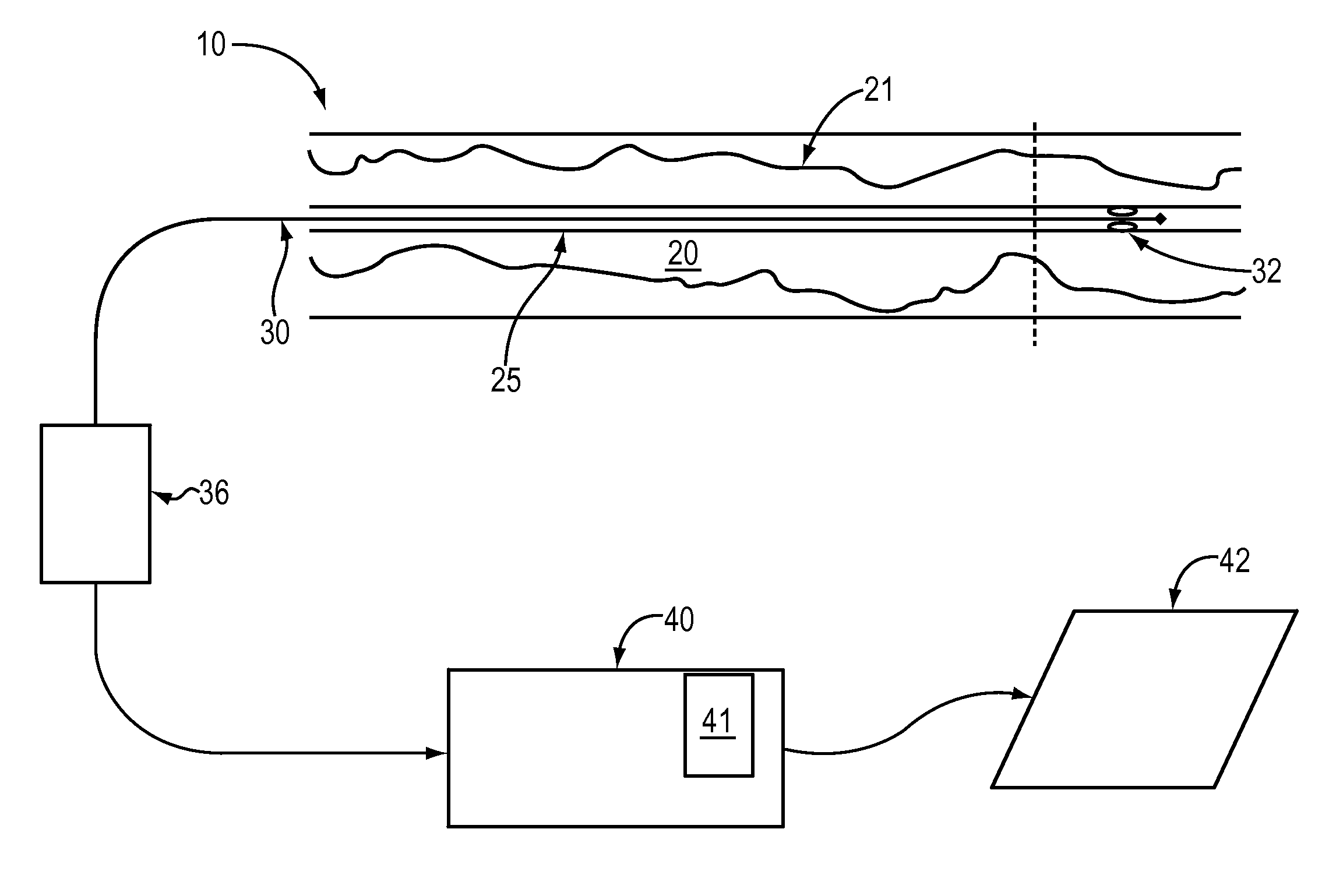
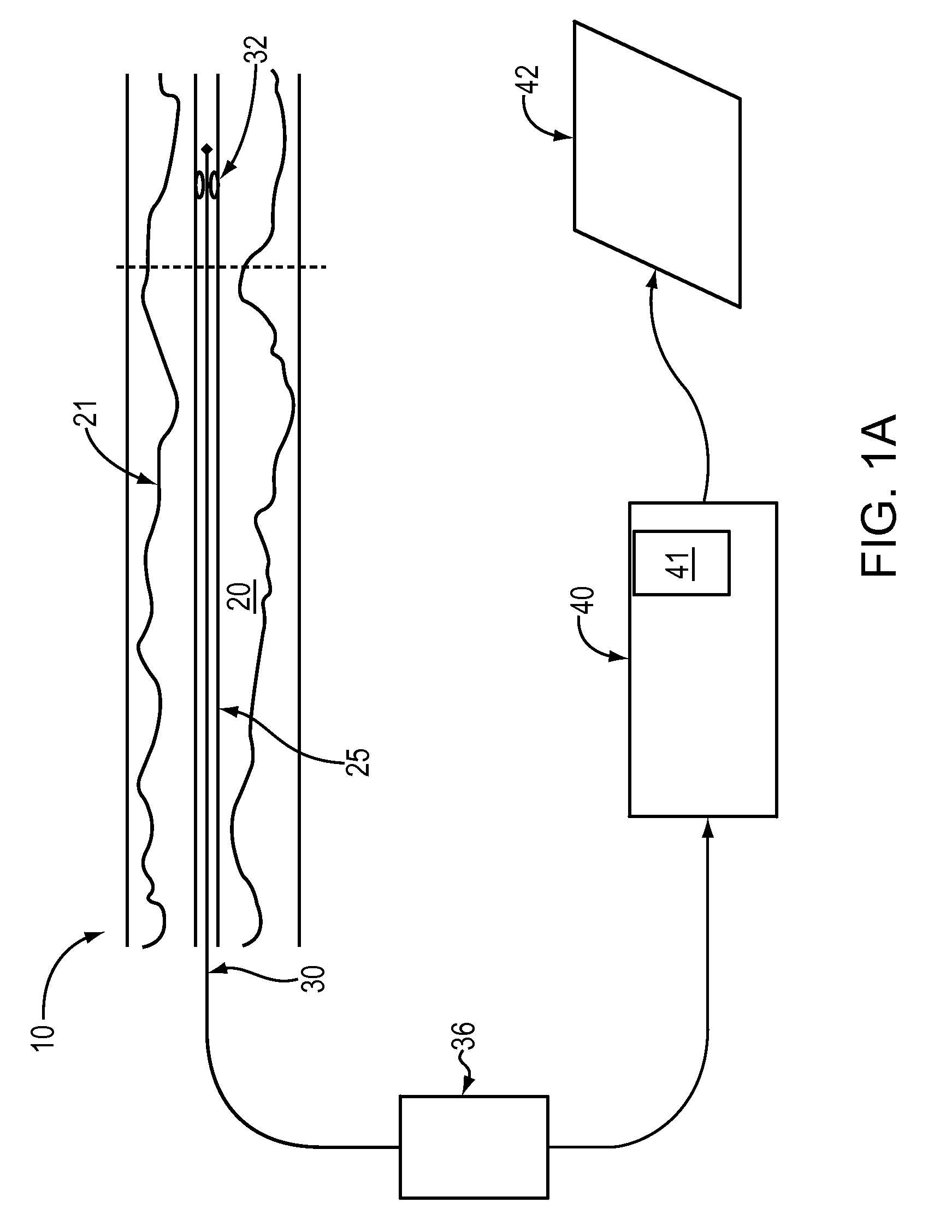
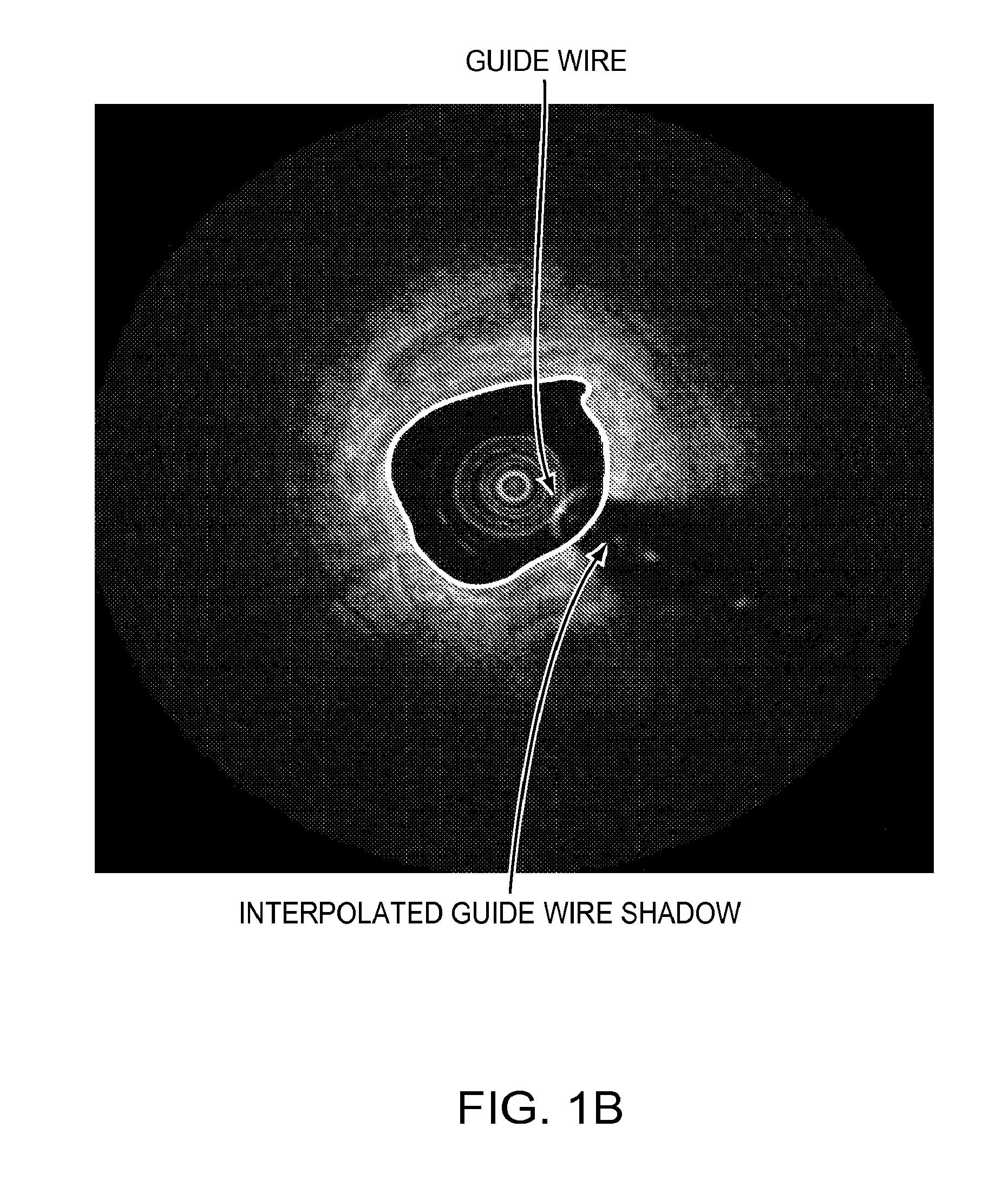
A method and apparatus of automatically locating in an image of a blood vessel the lumen boundary at a position in the vessel and from that measuring the diameter of the vessel. From the diameter of the vessel and estimated blood flow rate, a number of clinically significant physiological parameters are then determined and various user displays of interest generated. One use of these images and parameters is to aid the clinician in the placement of a stent. The system, in one embodiment, uses these measurements to allow the clinician to simulate the placement of a stent and to determine the effect of the placement. In addition, from these patient parameters various patient treatments are then performed.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Implantable arterio-venous shunt devices and methods for their use
InactiveUS20070299384A1Good blood pressureDecrease systemic vascular resistanceElectrocardiographySurgeryShunt DeviceBlood flow
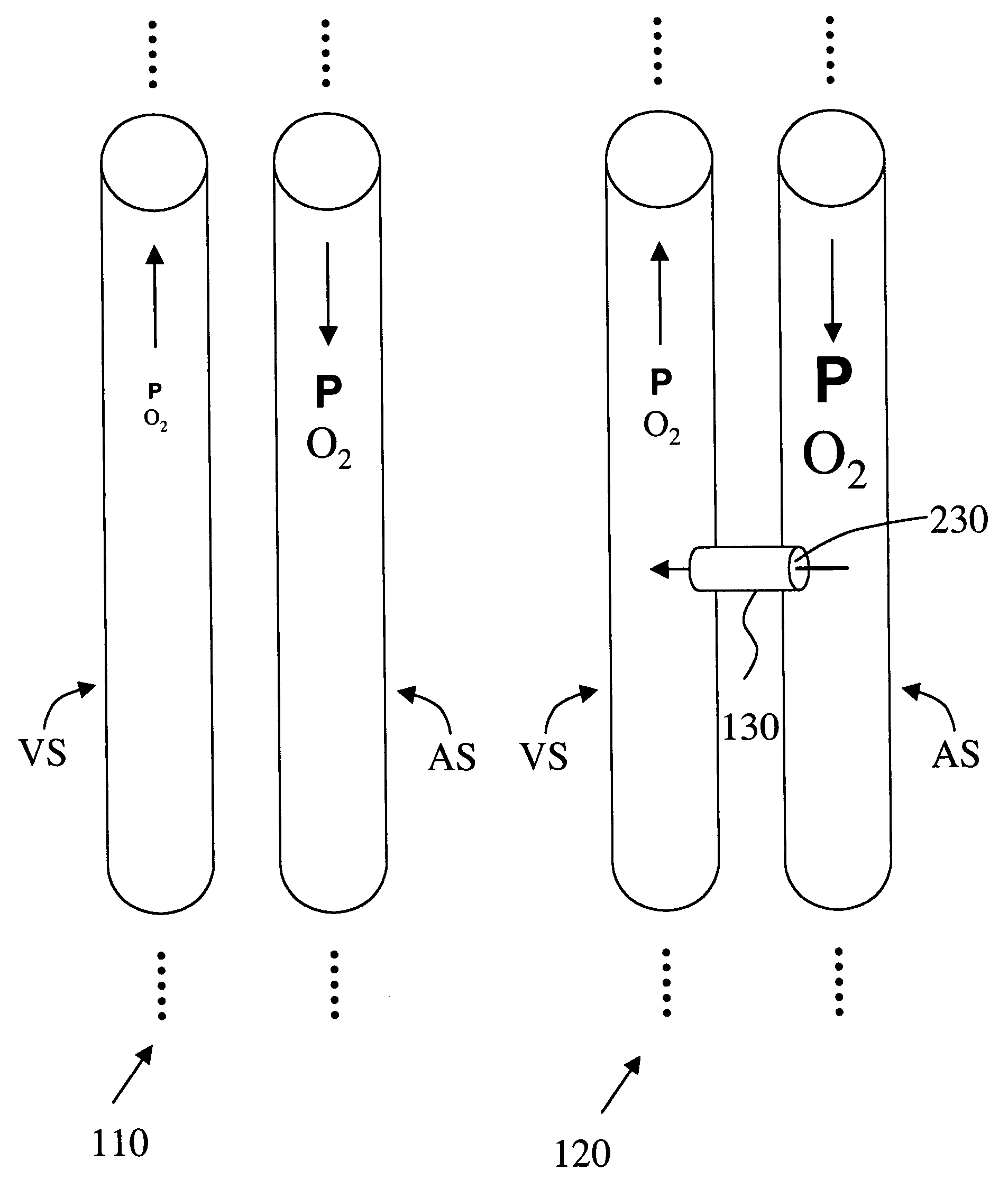
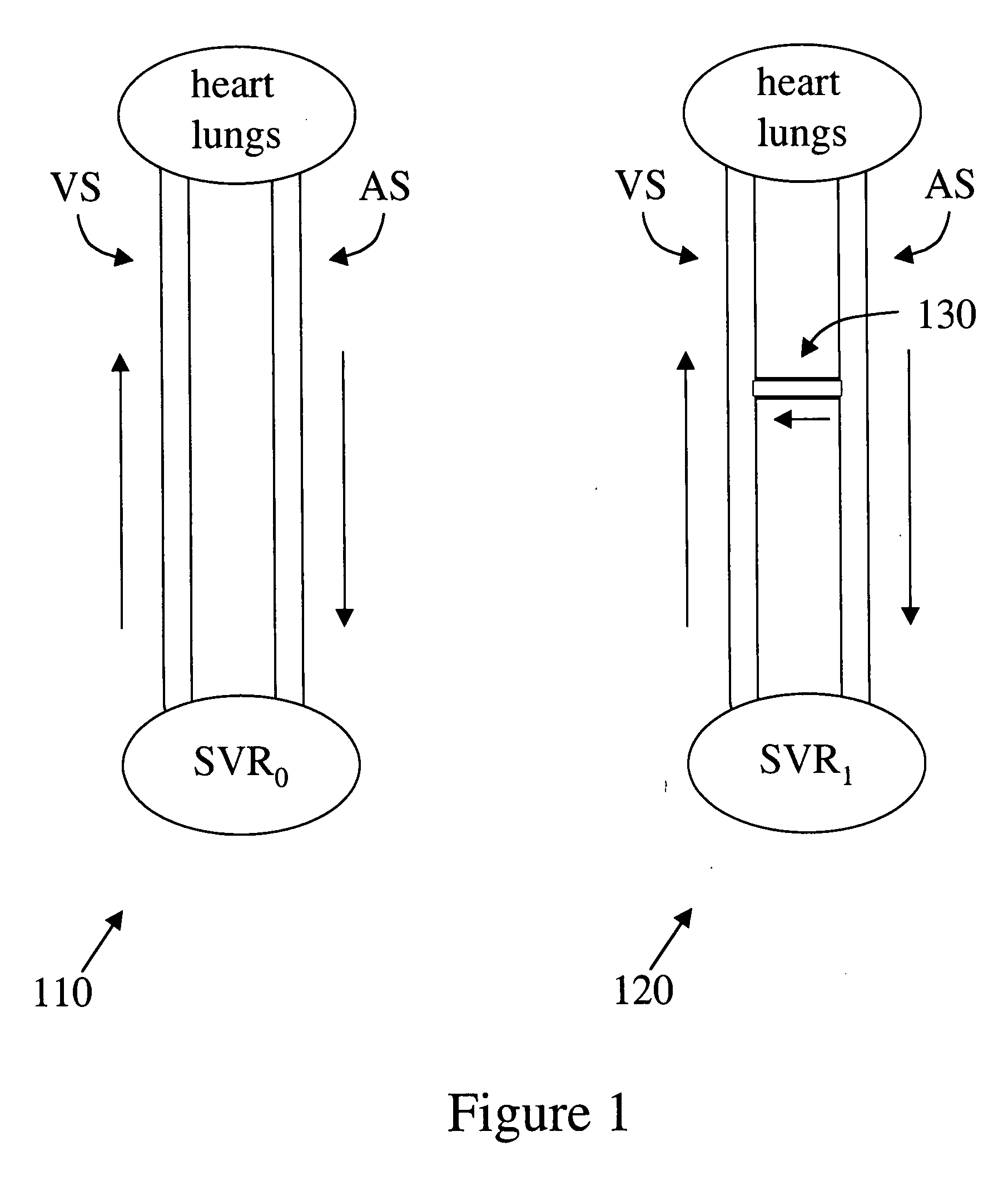
A long-term implantable arterio-venous shunt device or creation of a fistula is provided that can be used as a therapeutic method for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The shunt device is implanted between an artery and a vein, preferably between a peripheral artery and the inferior vena cava. The shunt device and method of creating a fistula increases cardiac output and decreases the systemic vascular resistance and allows a blood flow rate through the shunt device of at least 5 ml / min after the implantation. Based on the effects of the method and device to the respiratory, cardiac and circulatory system, the method and device are beneficial as a therapy to patients with problems or conditions related to these systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Lumen Morphology and Vascular Resistance Measurements Data Collection Systems, Apparatus and Methods
A method and apparatus of automatically locating in an image of a blood vessel the lumen boundary at a position in the vessel and from that measuring the diameter of the vessel. From the diameter of the vessel and estimate blood flow rate, a number of clinically significant physiological parameters are then determine and various user displays of interest generated. One use of these images and parameters is to aid the clinician in the placement of a stent. The system, in one embodiment, uses these measurements to allow the clinician to simulate the placement of a stent and to determine the effect of the placement. In addition, from these patient parameters various patient treatments are then performed.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Implantable arterio-venous shunt devices and methods for their use
InactiveUS7967769B2Increase volumeRelieves the shortness of breath and other symptoms sufferedElectrocardiographySurgeryShunt DeviceBlood flow
A long-term implantable arterio-venous shunt device or creation of a fistula is provided that can be used as a therapeutic method for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The shunt device is implanted between an artery and a vein, preferably between a peripheral artery and the inferior vena cava. The shunt device and method of creating a fistula increases cardiac output and decreases the systemic vascular resistance and allows a blood flow rate through the shunt device of at least 5 ml / min after the implantation. Based on the effects of the method and device to the respiratory, cardiac and circulatory system, the method and device are beneficial as a therapy to patients with problems or conditions related to these systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Lumen Morphology and Vascular Resistance Measurements Data Collection Systems, Apparatus and Methods
A method and apparatus of automatically locating in an image of a blood vessel the lumen boundary at a position in the vessel and from that measuring the diameter of the vessel. From the diameter of the vessel and estimated blood flow rate, a number of clinically significant physiological parameters are then determined and various user displays of interest generated. One use of these images and parameters is to aid the clinician in the placement of a stent. The system, in one embodiment, uses these measurements to allow the clinician to simulate the placement of a stent and to determine the effect of the placement. In addition, from these patient parameters various patient treatments are then performed.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
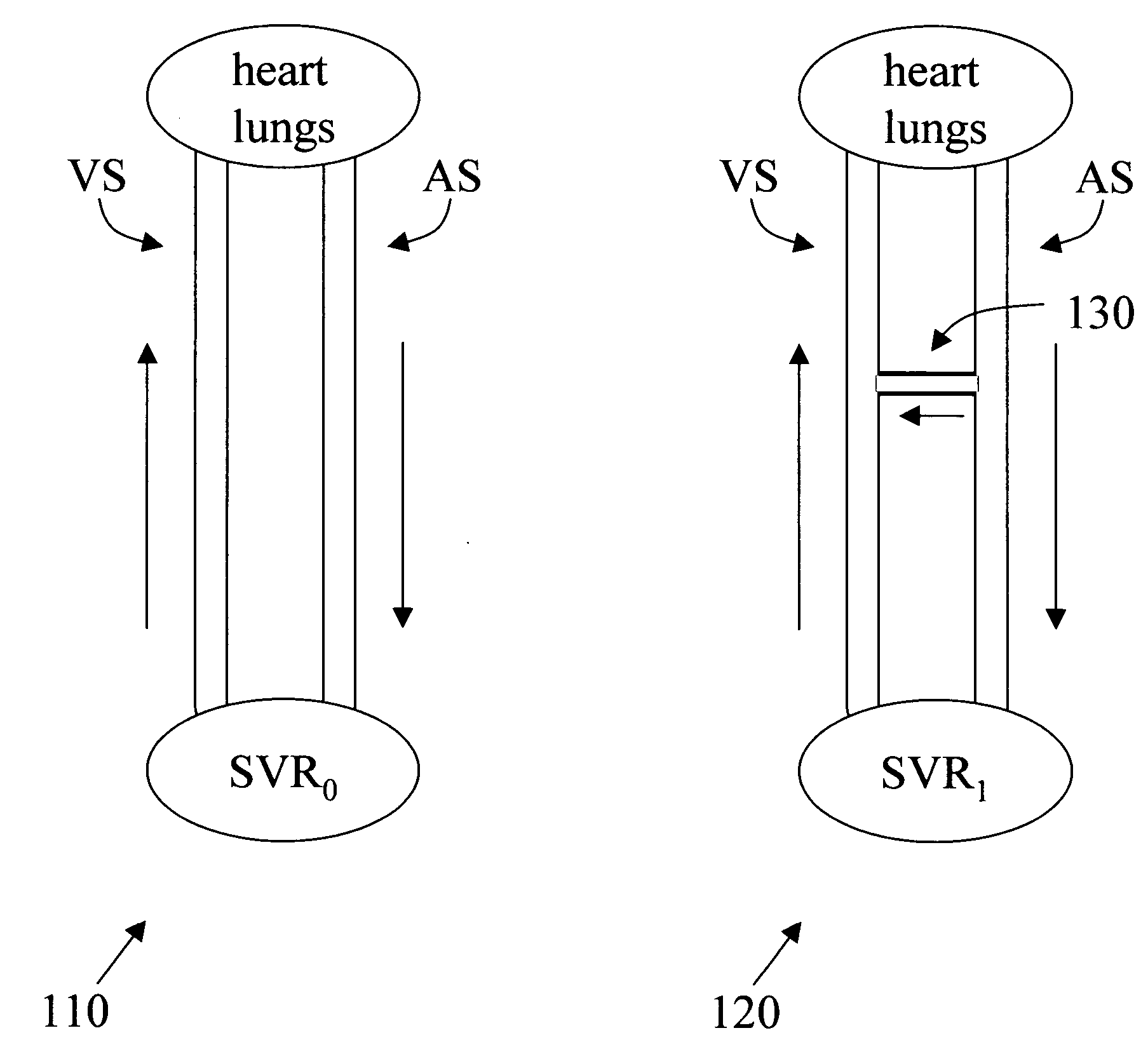
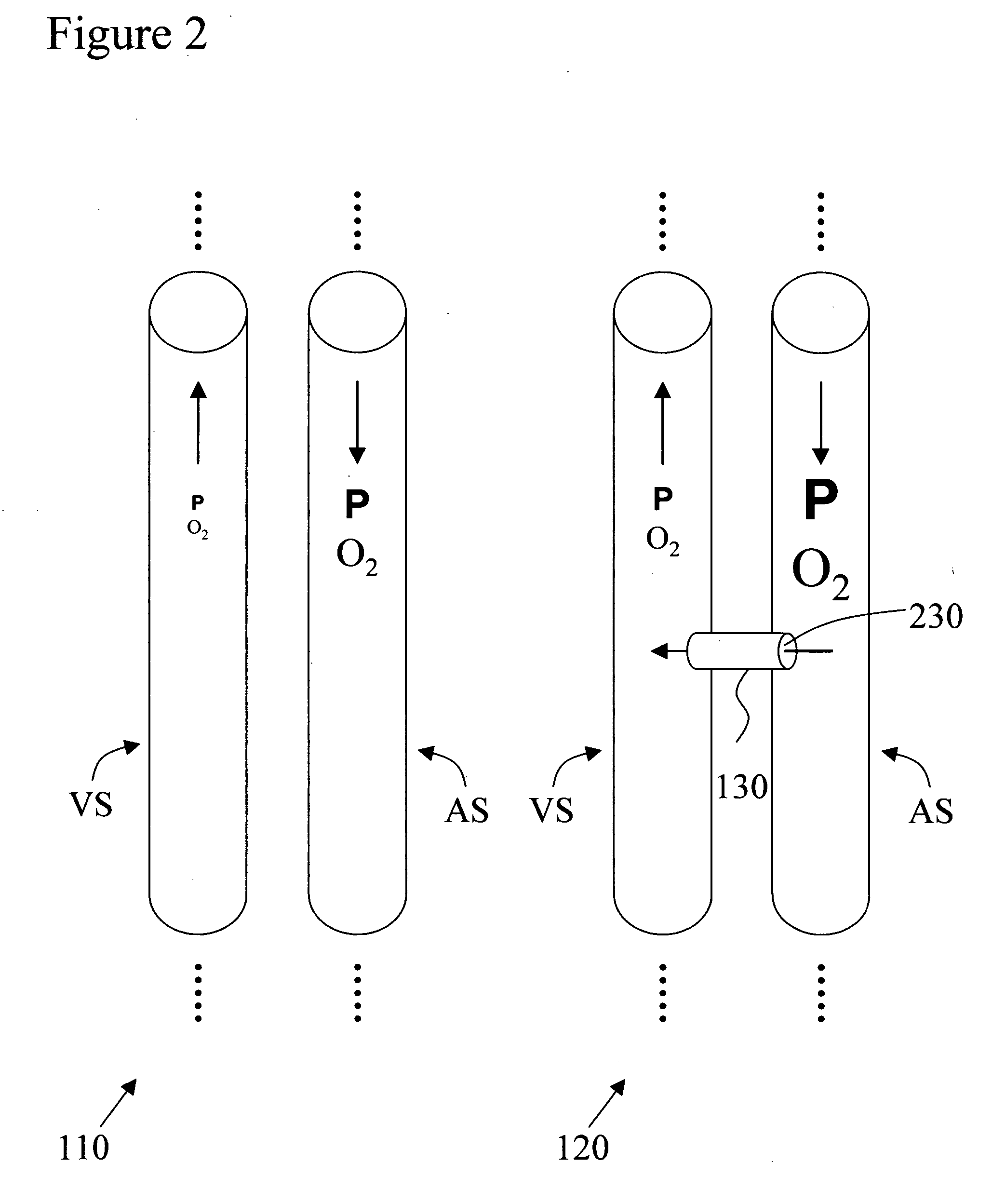
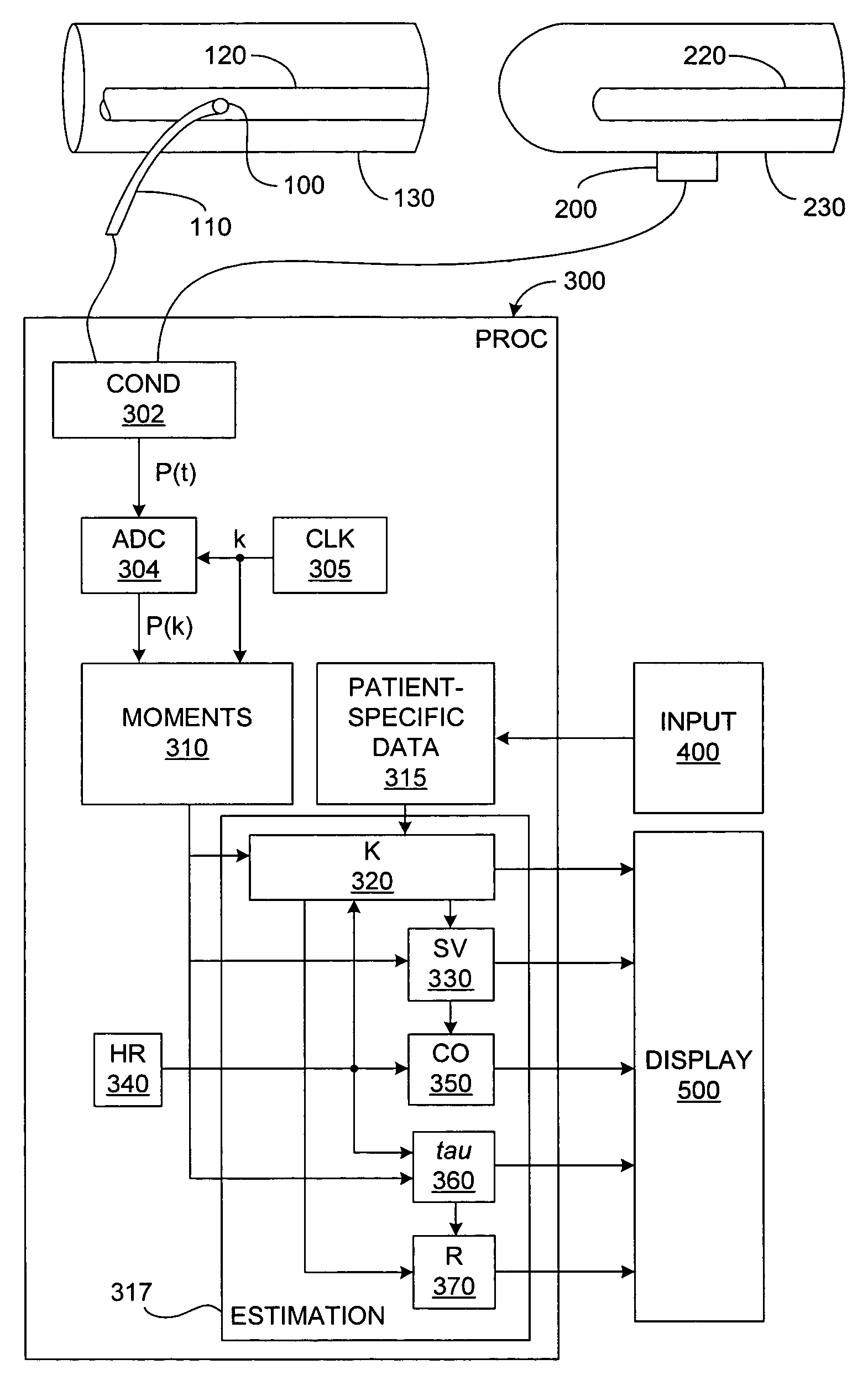
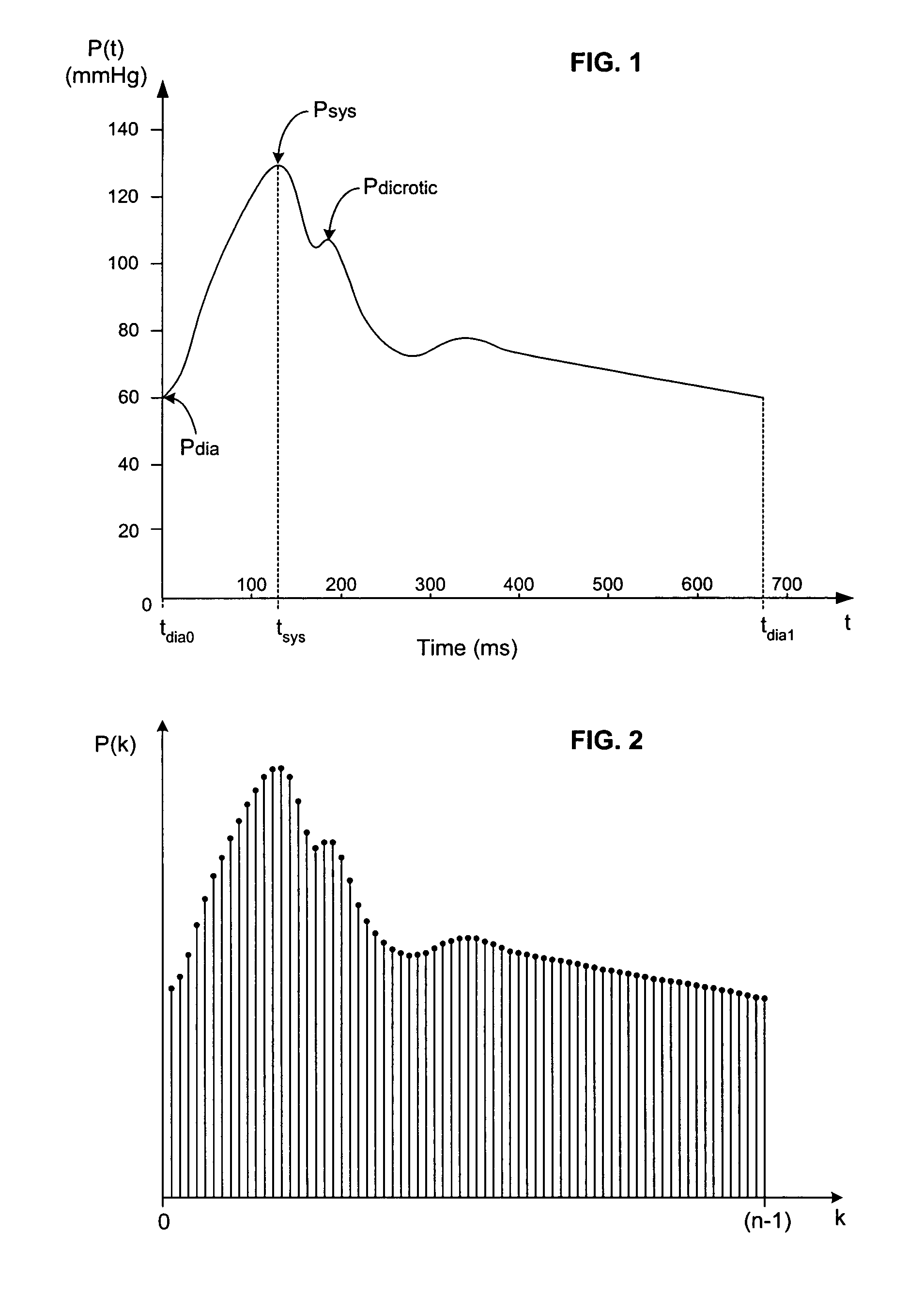
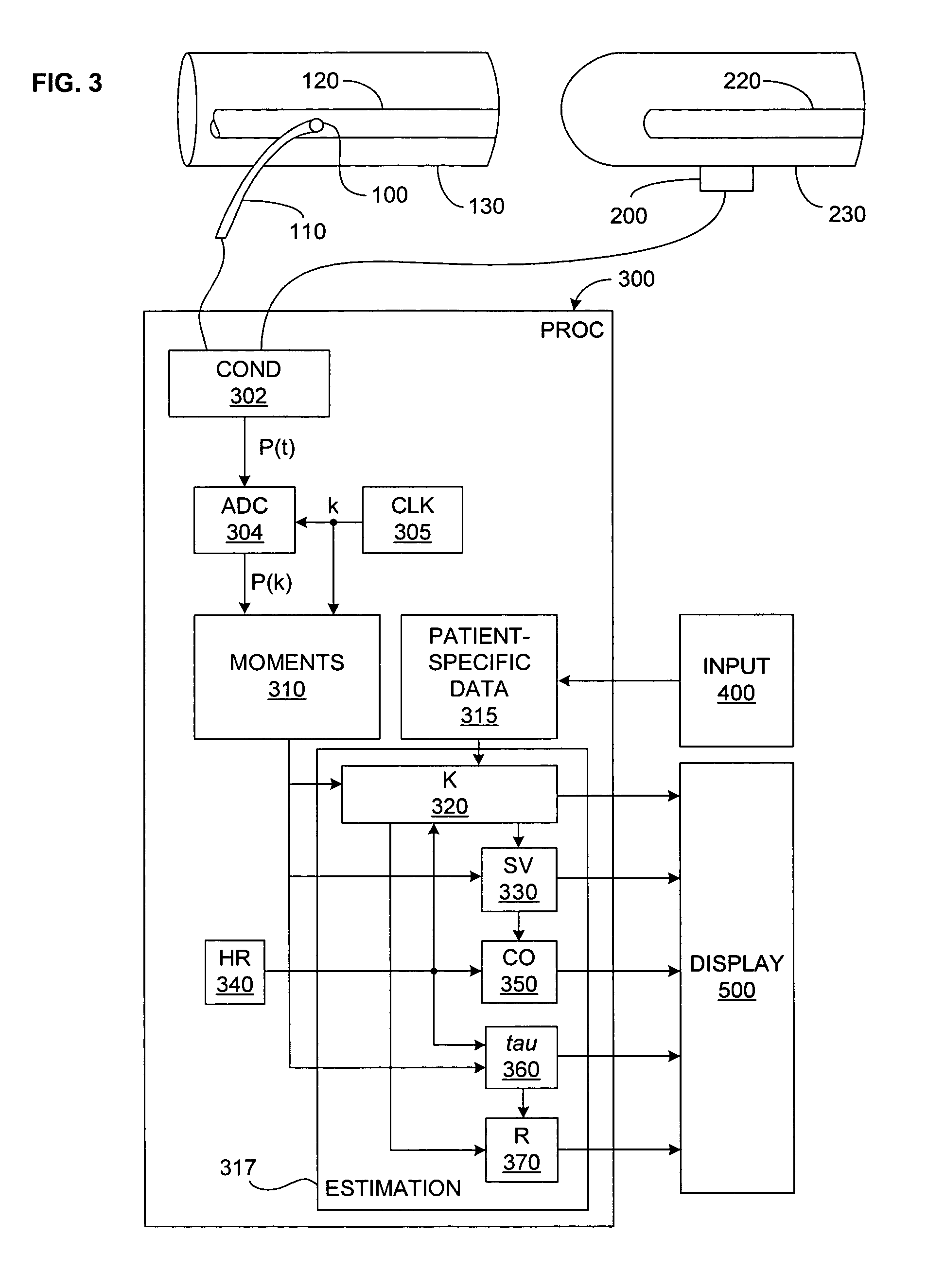
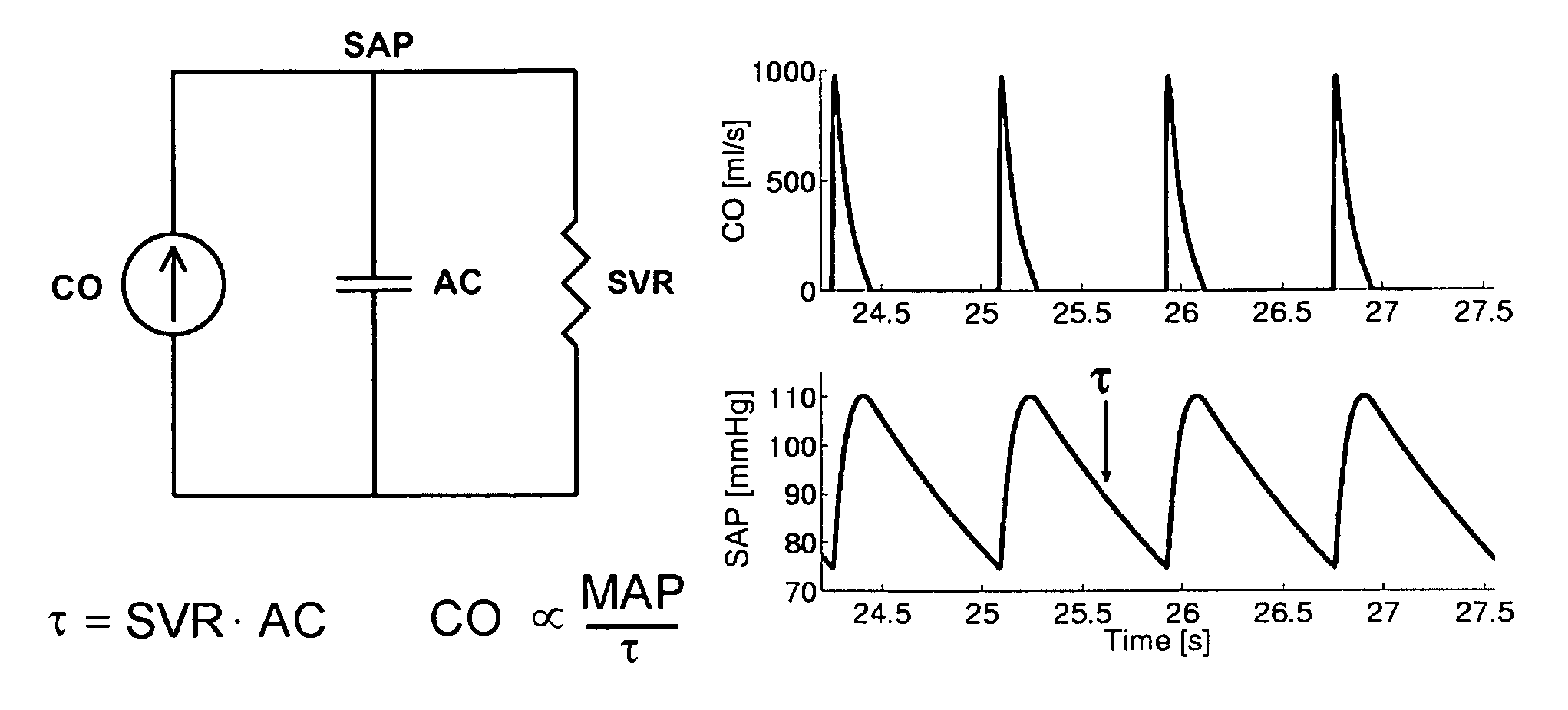
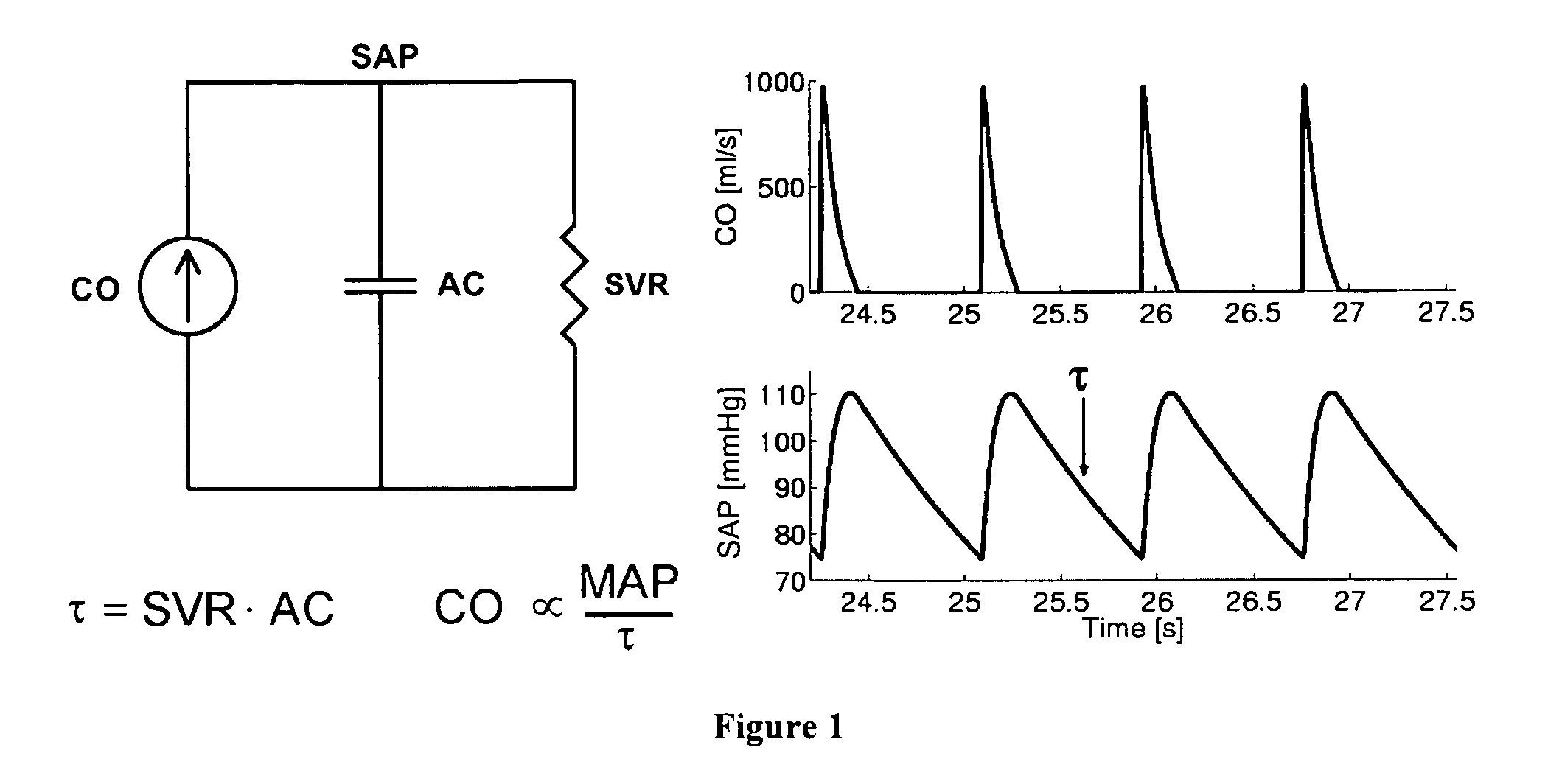
Arterial pressure-based, automatic determination of a cardiovascular parameter
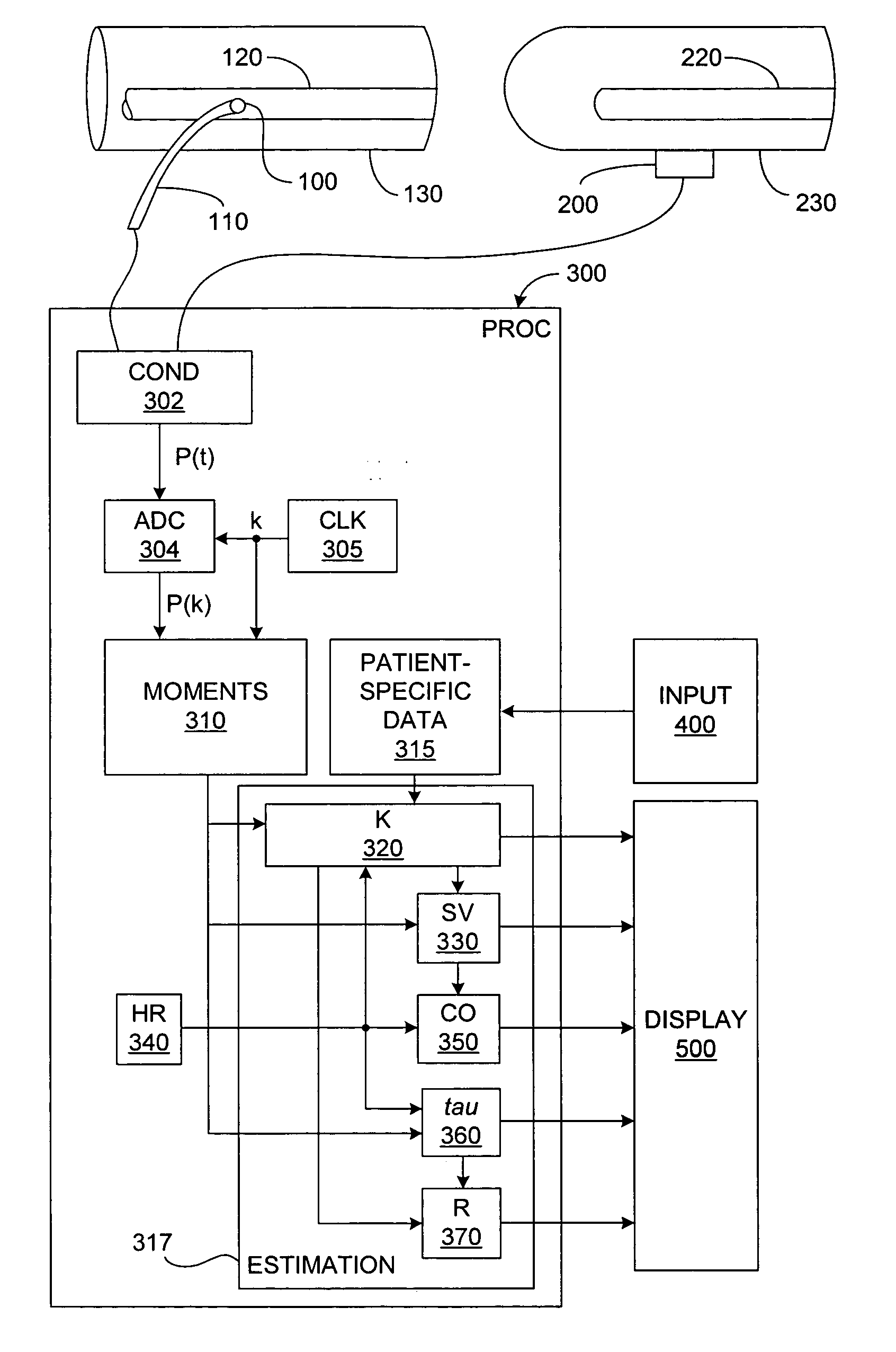
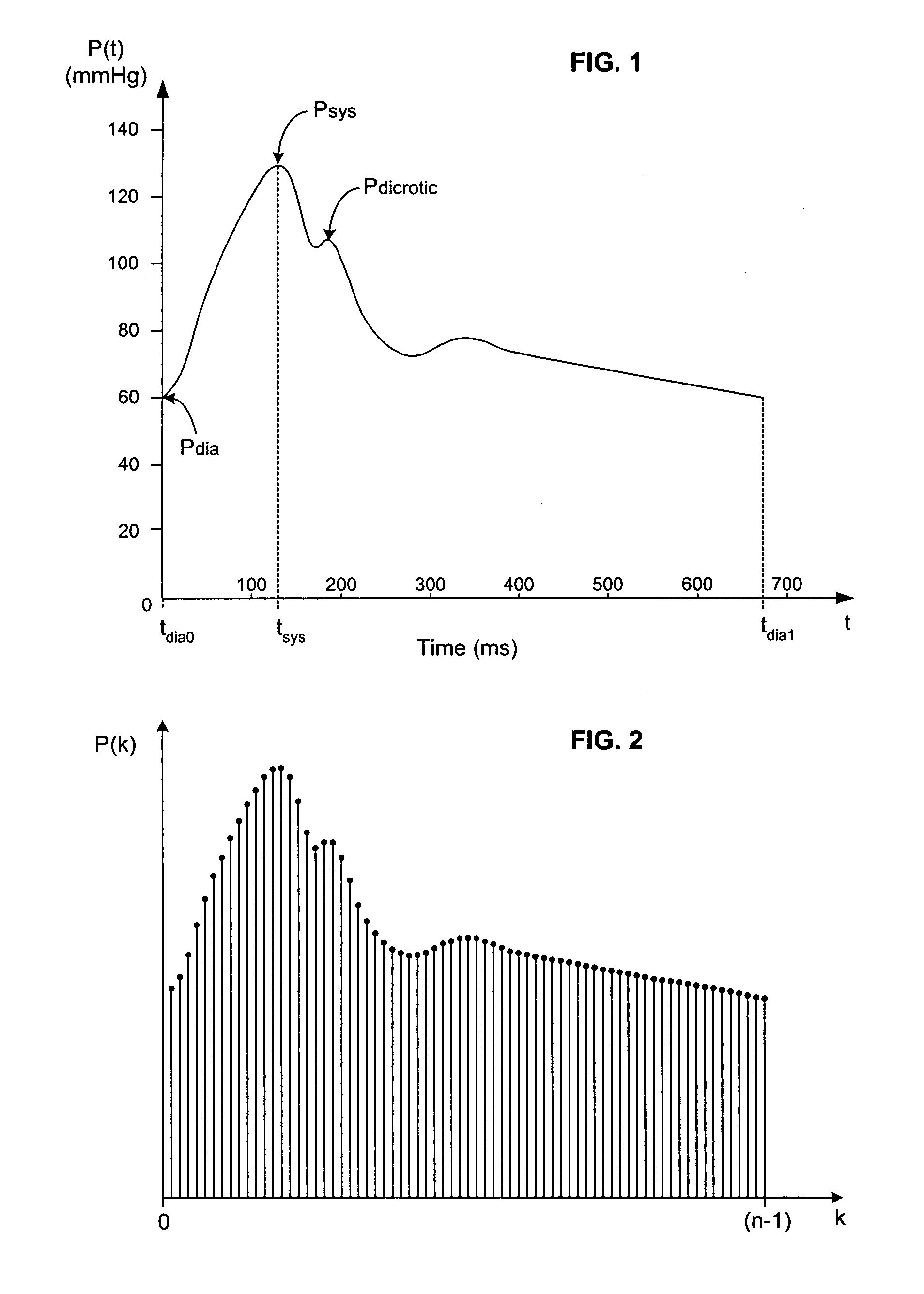
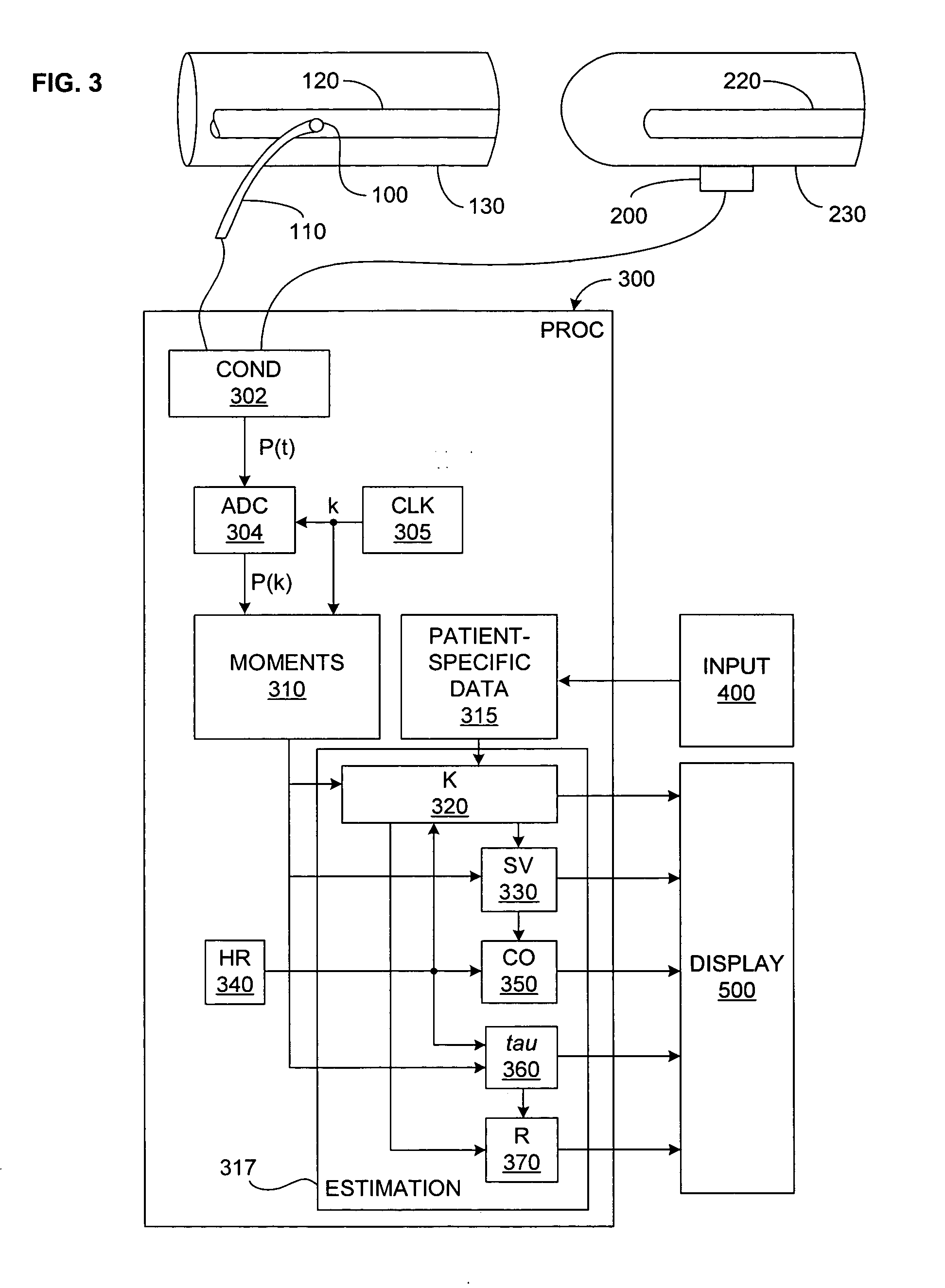
One or more cardiovascular parameters is estimated as a function of the arterial pressure waveform, in particular, using at least one statistical moment of pressure waveform having an order greater than one. Arterial compliance, the exponential pressure decay constant, vascular resistance, cardiac output, and stroke volume are examples of cardiovascular parameters that can be estimated using various aspects of the invention. In one embodiment of the invention, not only are the first four moments (mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis) of the pressure waveform used to estimate the cardiovascular parameter(s) of interest, but also heart rate, statistical moments of a set of pressure-weighted time values, and certain anthropometric patient measurements such as age, sex, body surface area, etc.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Implantable arterio-venous shunt devices and methods for their use
InactiveUS20050107733A1Good blood pressureReducing mean arterial pressureElectrocardiographyHeart valvesShunt DeviceWhole body
A long-term implantable arterio-venous shunt device is provided that can be used as a therapeutic method. The shunt device is implanted between an artery and a vein, preferably between the aorta and the inferior vena cava. The shunt device decreases the systemic vascular resistance and allows a blood flow rate through the shunt device of at least 5 ml / min after the implantation. The blood flow rate could be controlled either via an open loop or a closed loop control means. The shunt device could also be a self-adjustable shunt device to self-adjust its structure to control the blood flow rate through its lumen. Based on the effects of the shunt device to the respiratory, cardiac and circulatory system, the implantable shunt device could be beneficial as a therapy to patients with problems or conditions related to these systems.
Owner:ROX MEDICAL +1
Arterial pressure-based, automatic determination of a cardiovascular parameter
One or more cardiovascular parameters is estimated as a function of the arterial pressure waveform, in particular, using at least one statistical moment of pressure waveform having an order greater than one. Arterial compliance, the exponential pressure decay constant, vascular resistance, cardiac output, and stroke volume are examples of cardiovascular parameters that can be estimated using various aspects of the invention. In one embodiment of the invention, not only are the first four moments (mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis) of the pressure waveform used to estimate the cardiovascular parameter(s) of interest, but also heart rate, statistical moments of a set of pressure-weighted time values, and certain anthropometric patient measurements such as age, sex, body surface area, etc.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
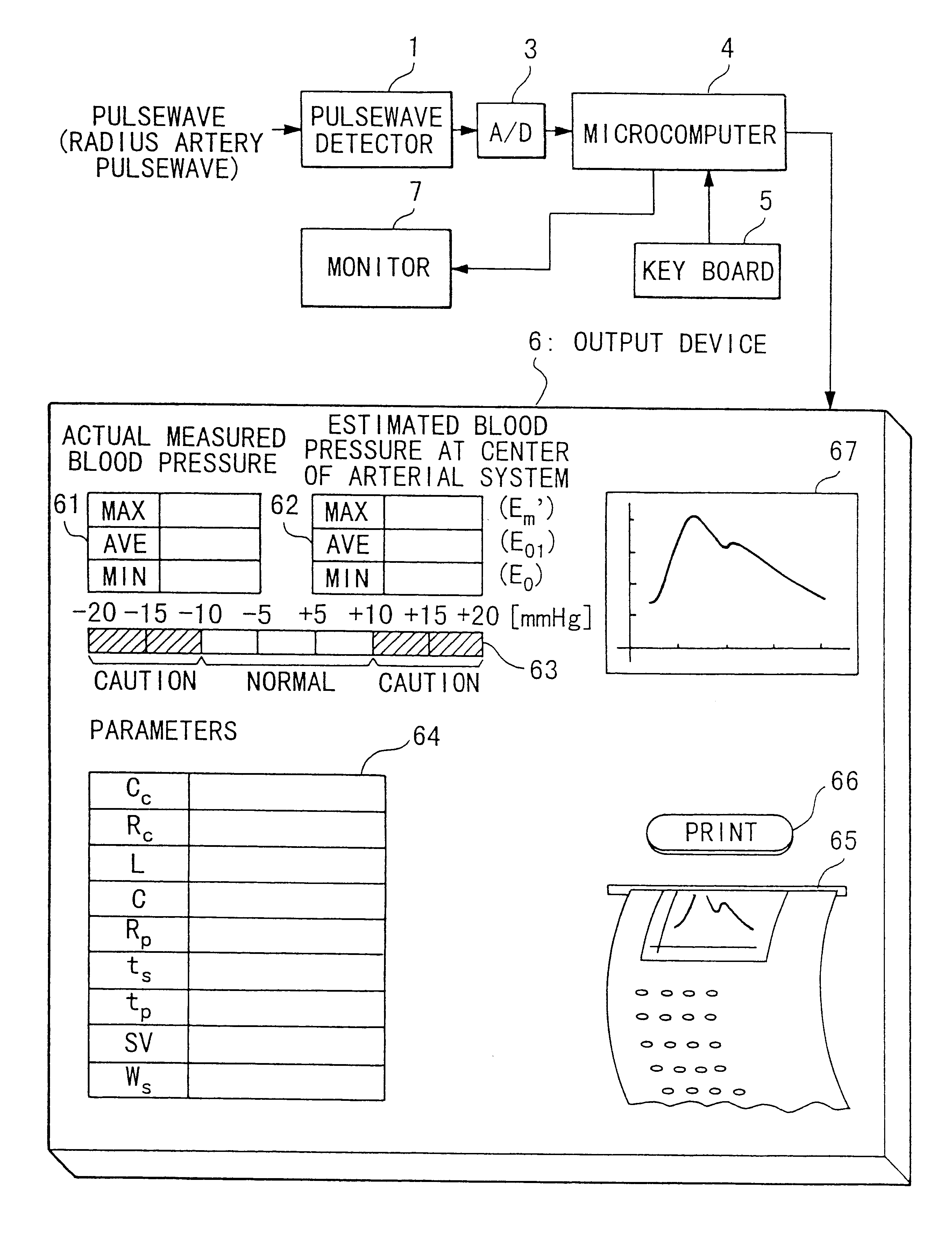
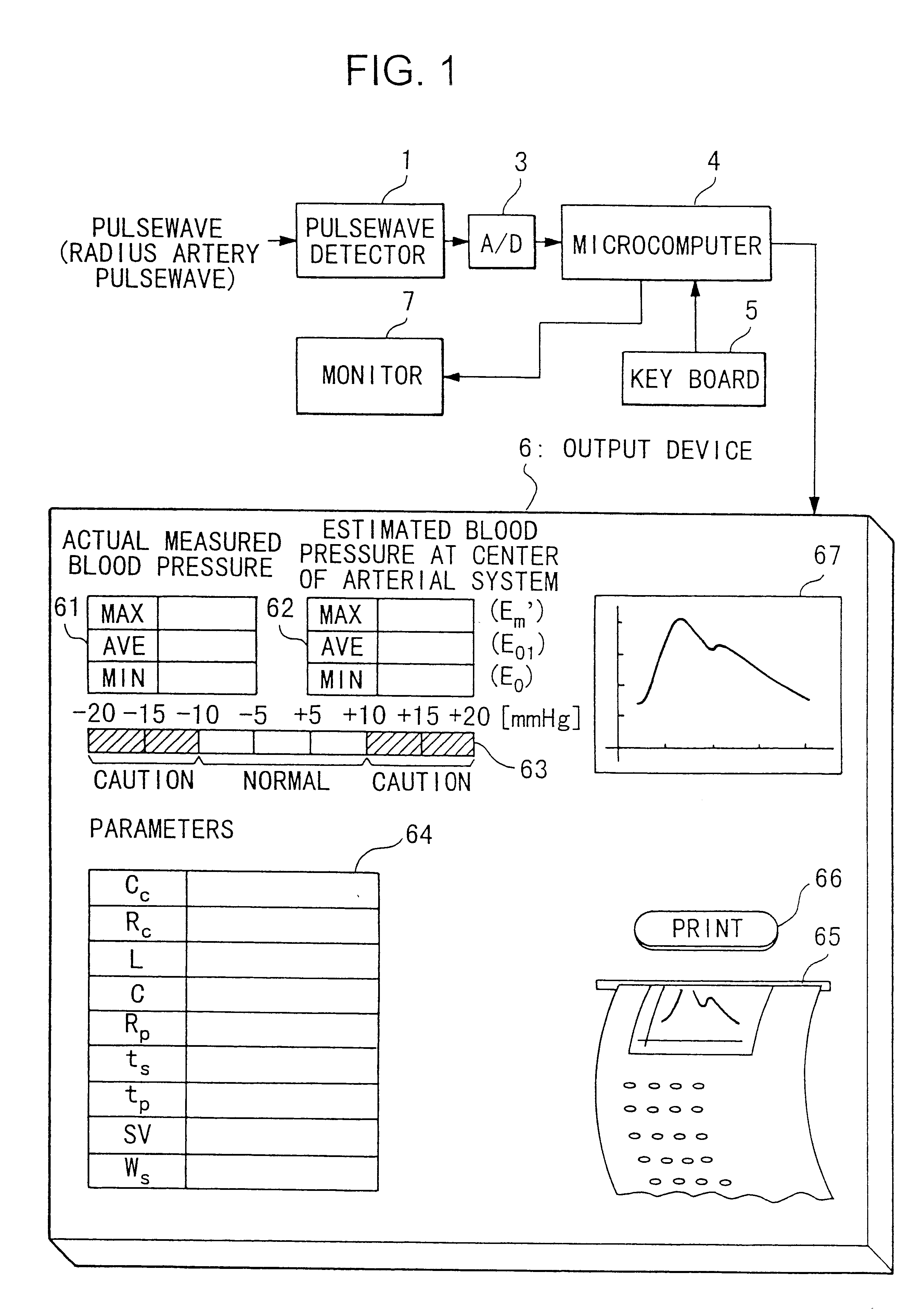
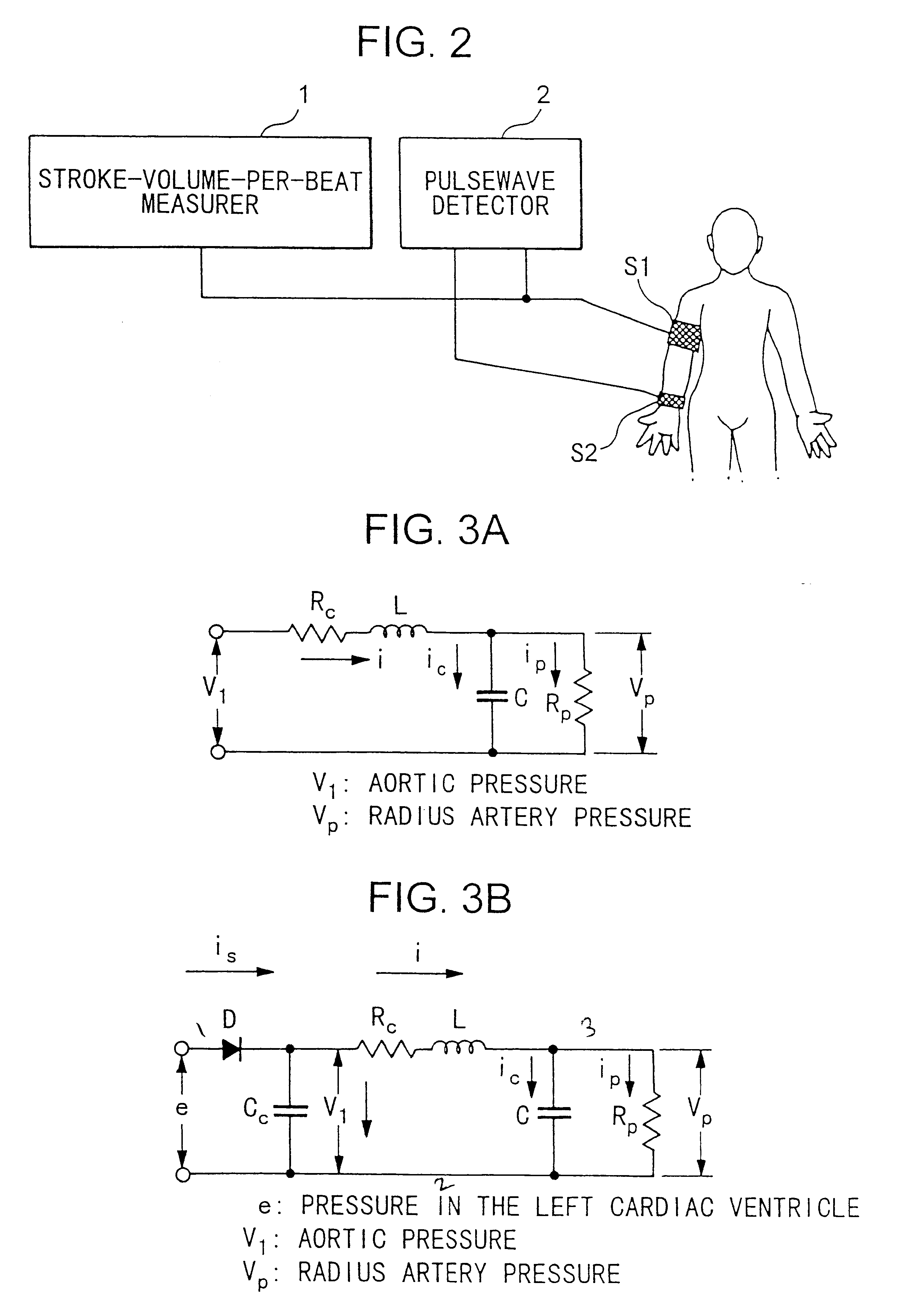
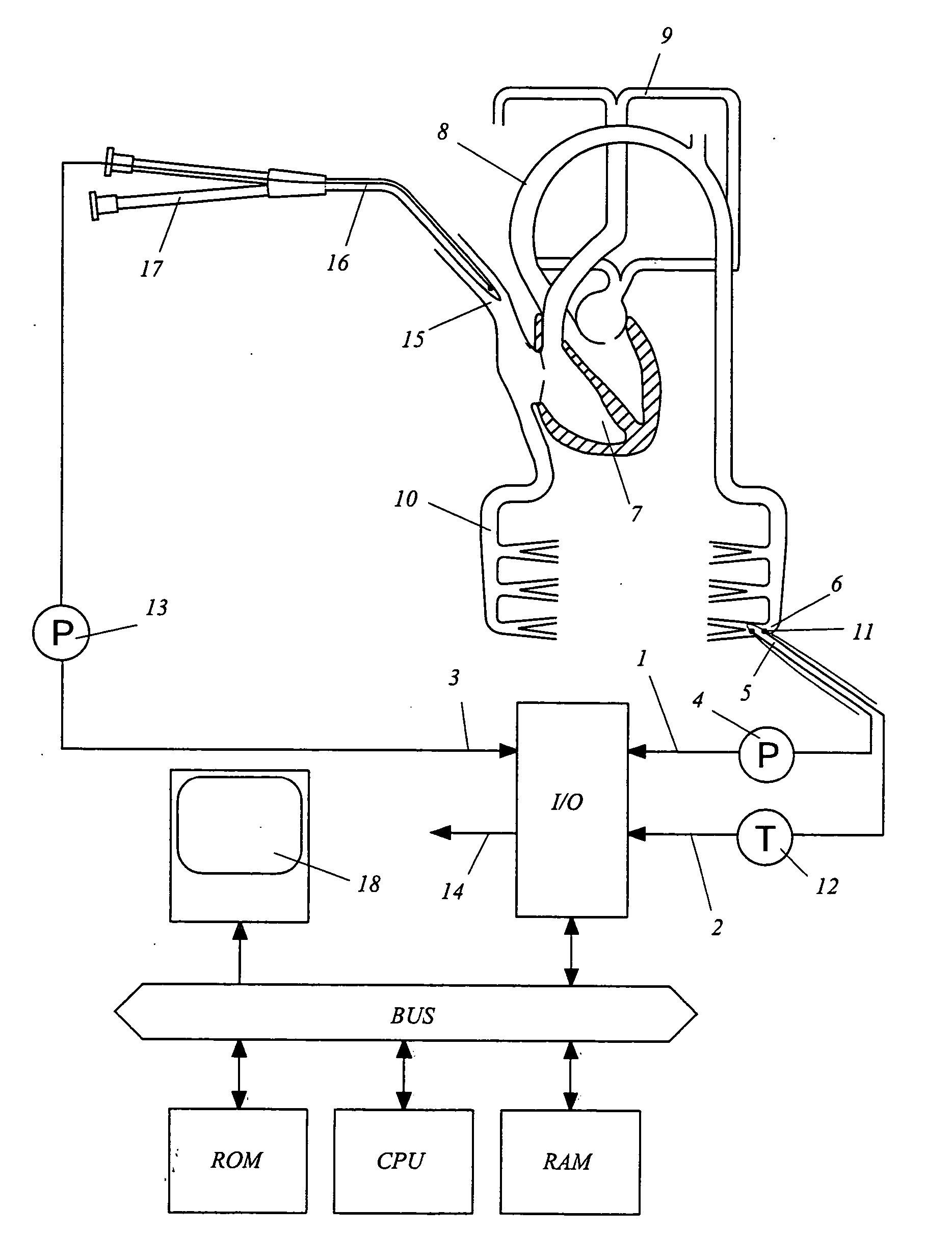
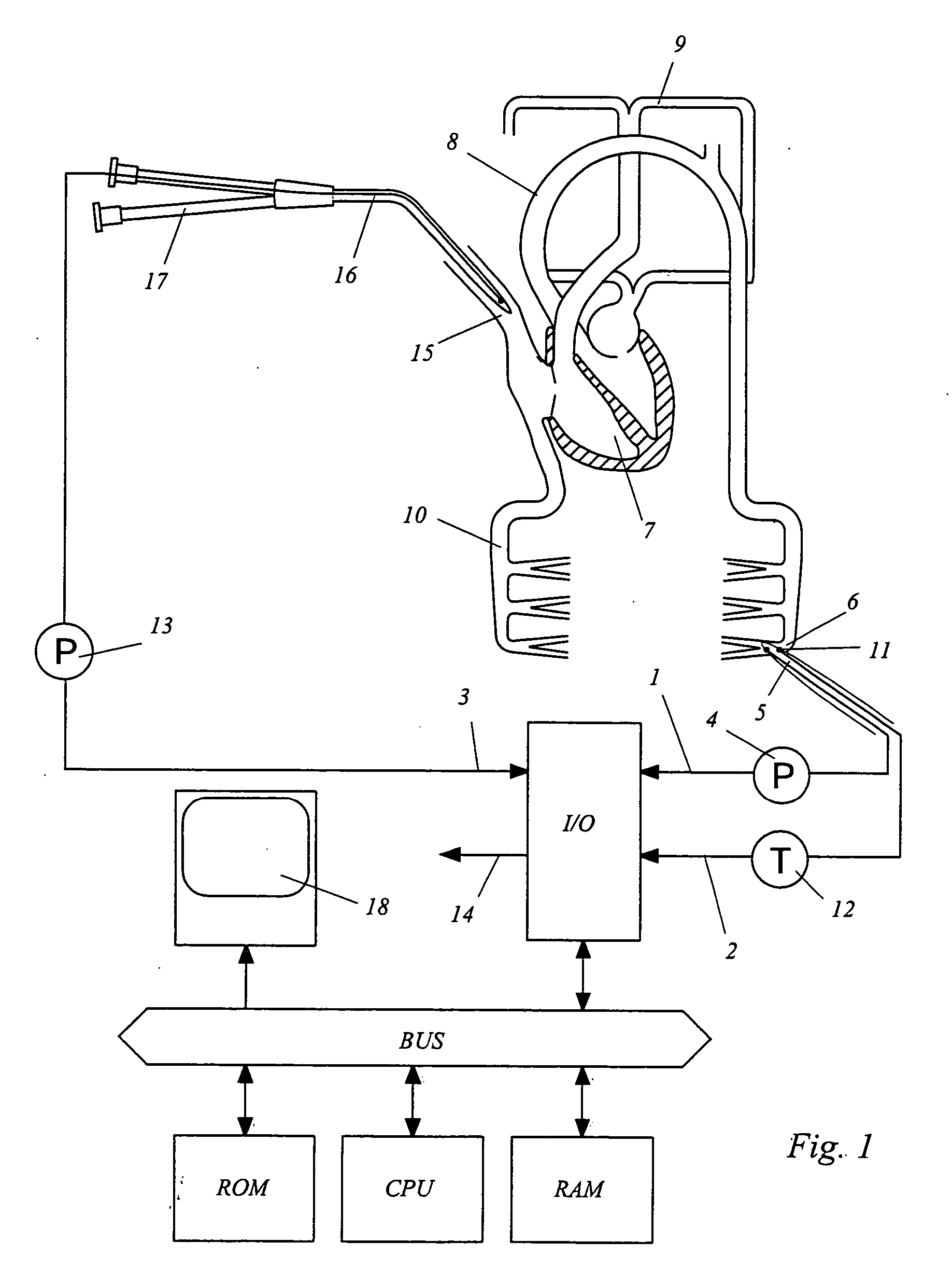
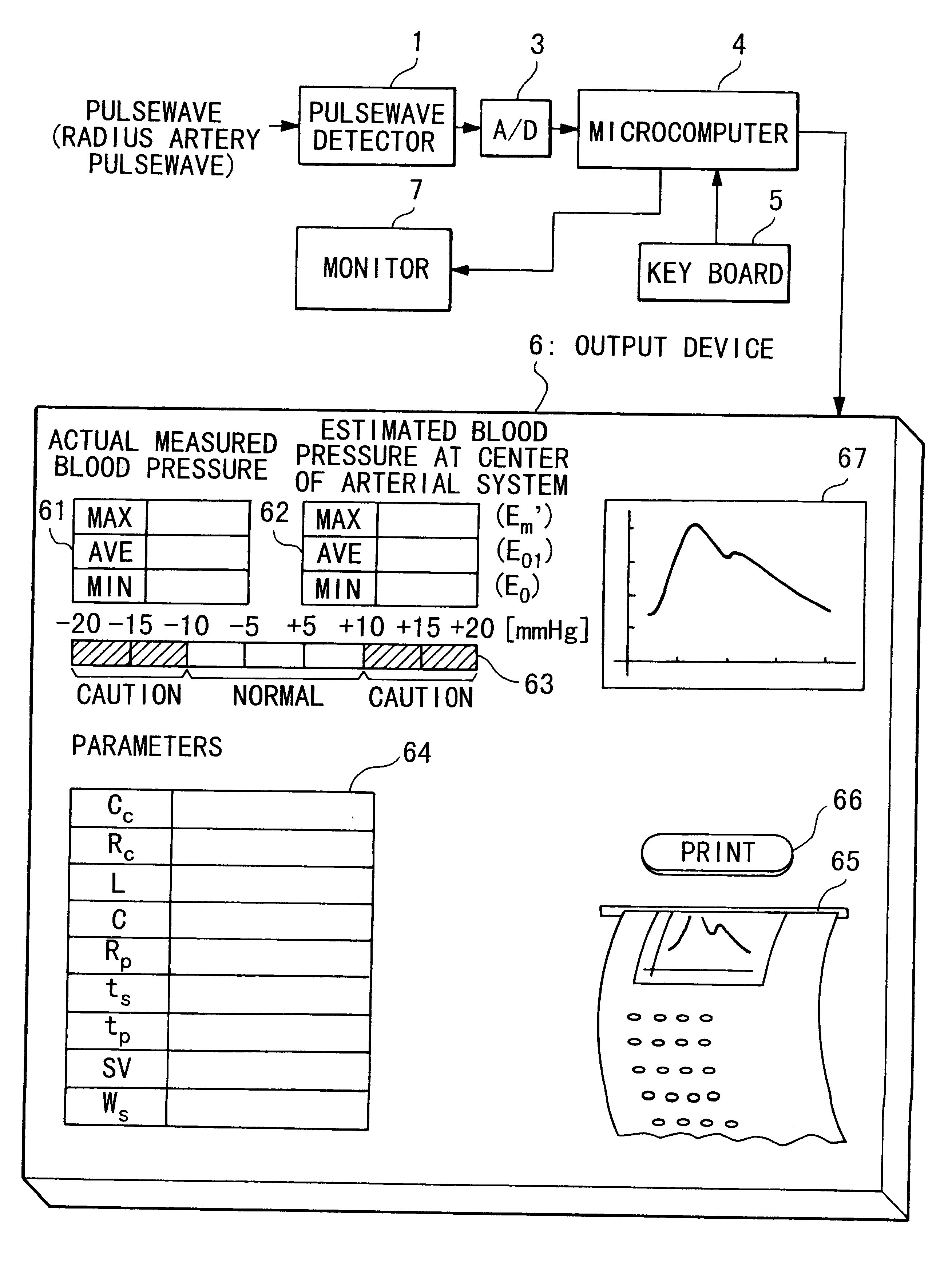
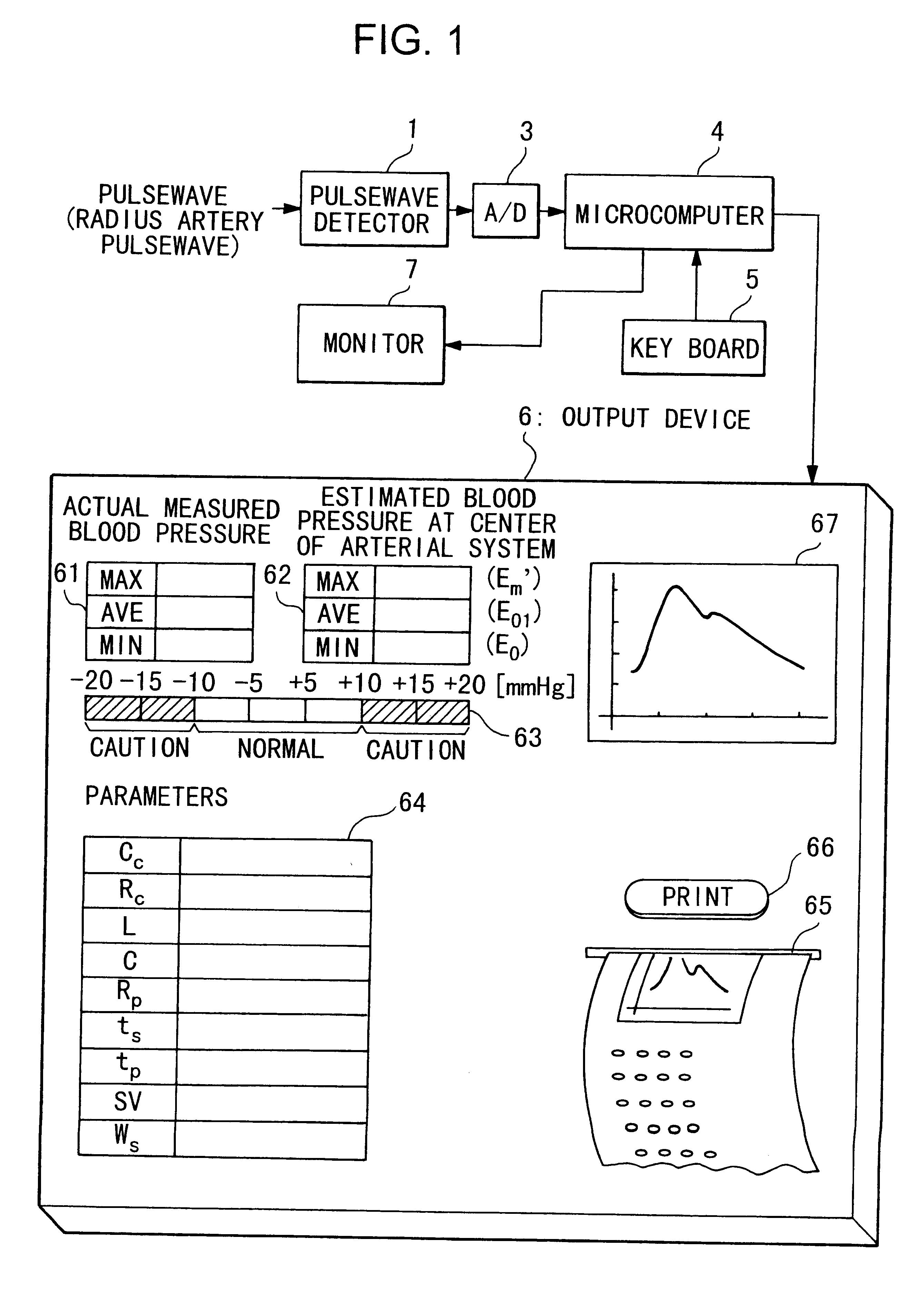
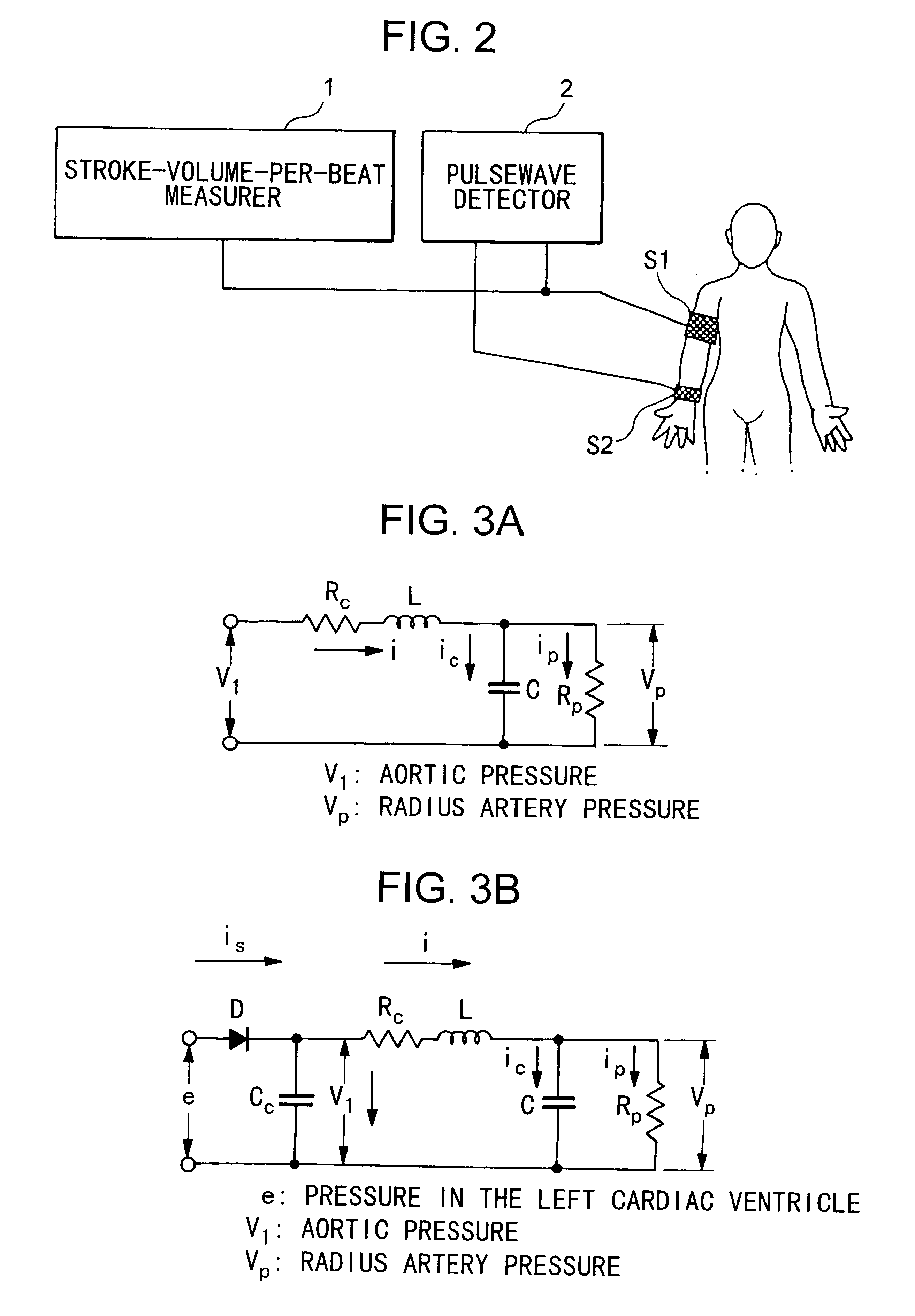
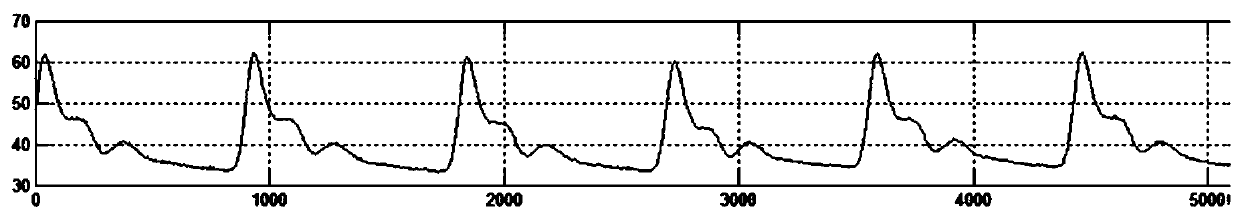
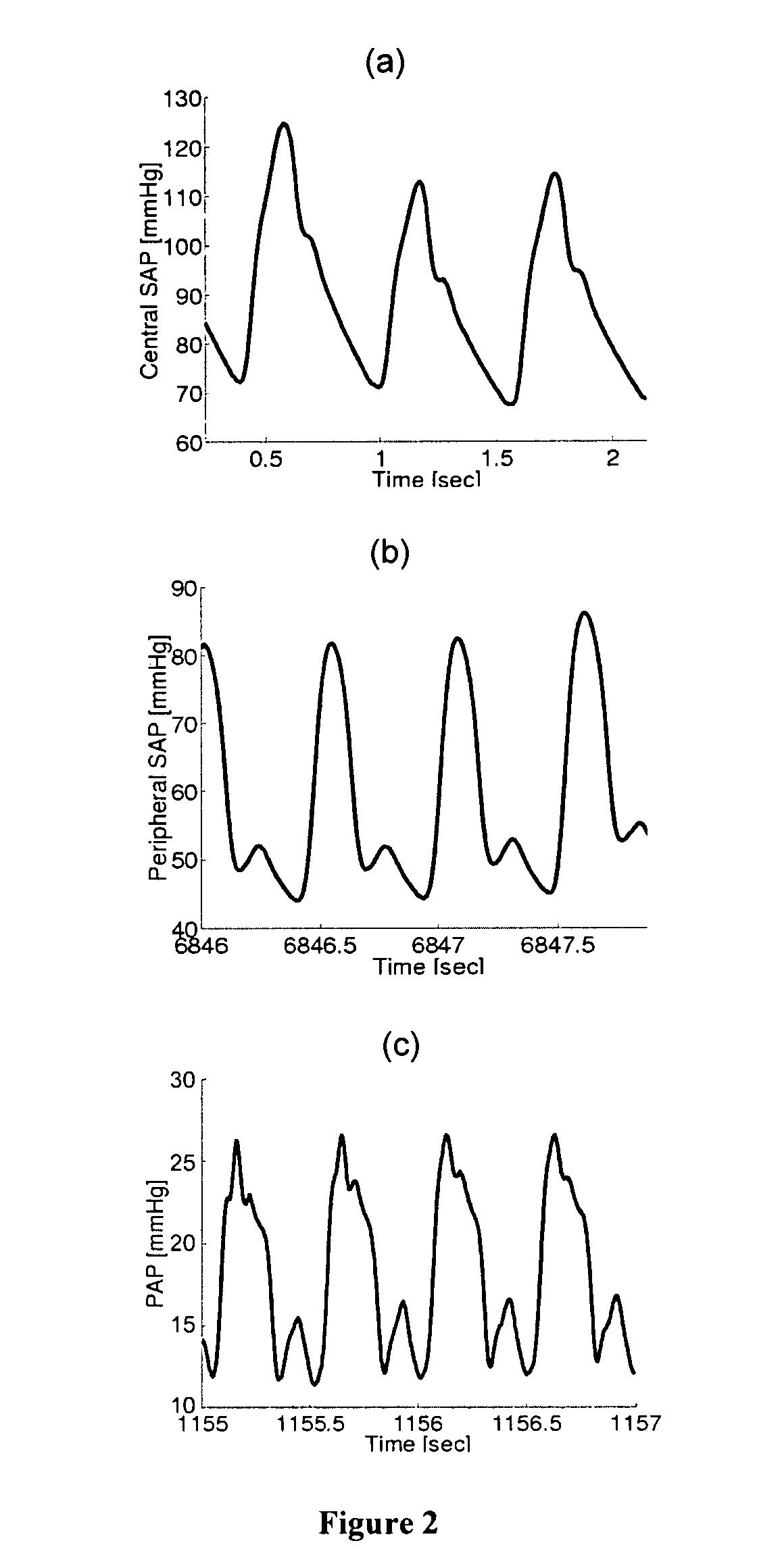
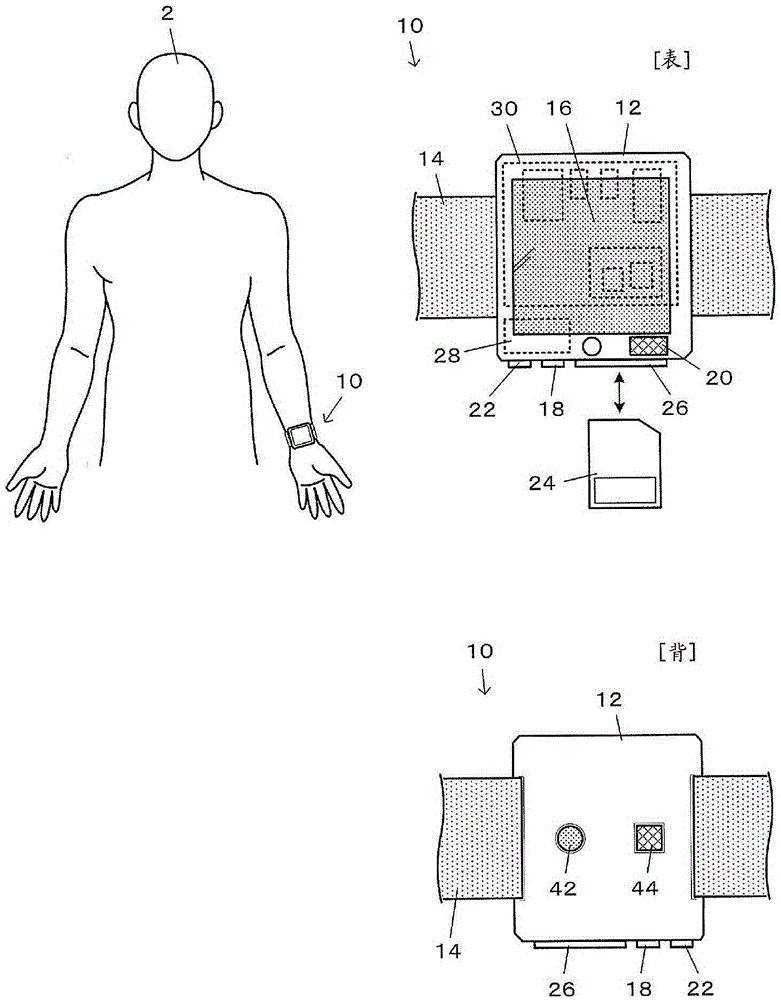
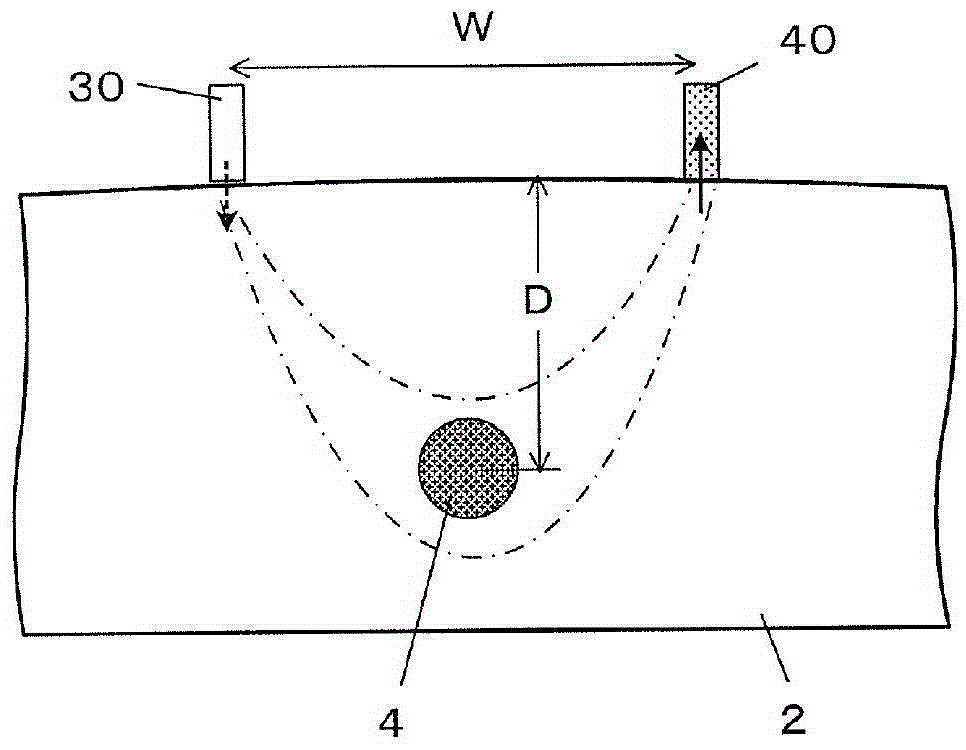
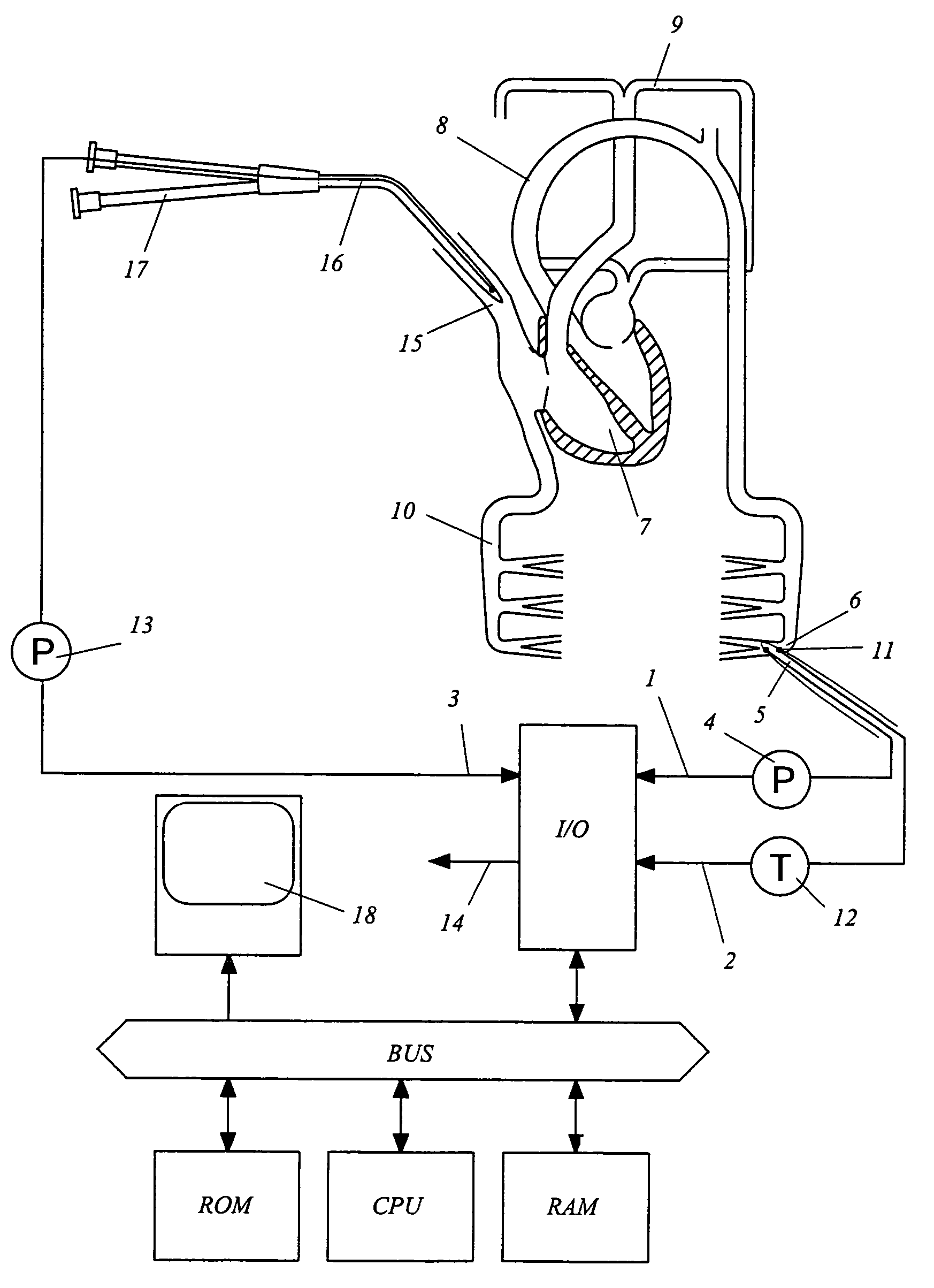
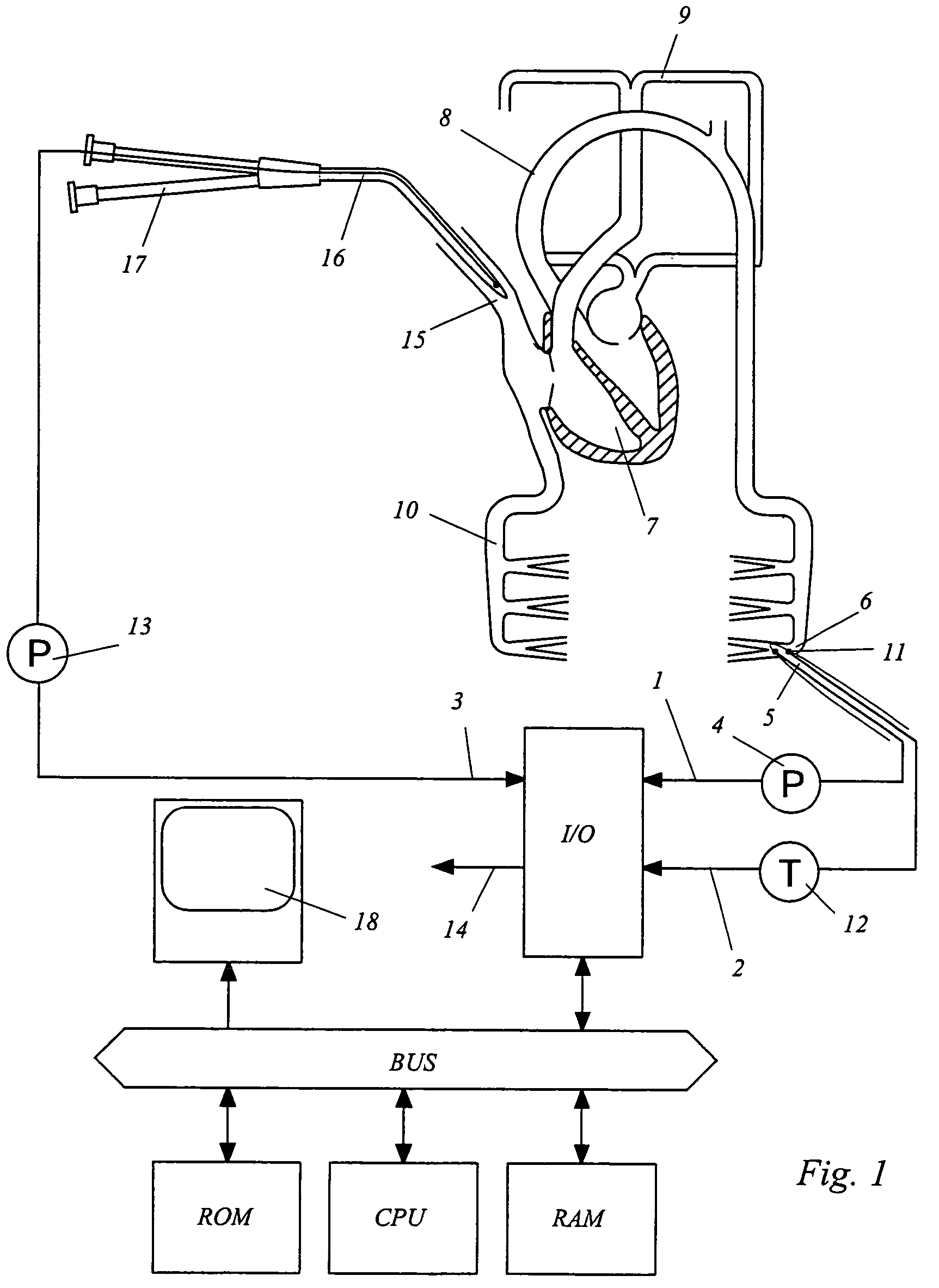
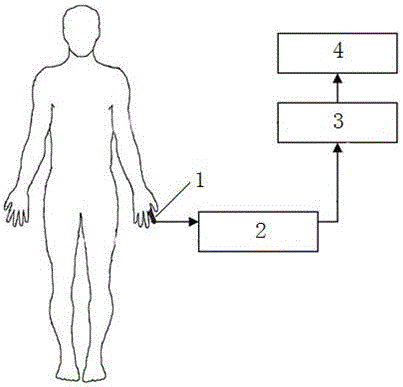
Device for measuring physiological state
A non-invasive device for evaluating circulatory state parameters, and specifically, a pulsewave analysis device capable of evaluation by separating blood vessel compliance and blood vessel resistance into central and peripheral components of the arterial system is provided. Microcomputer 4 detects the waveform at a test subject's radius artery via pulsewave detector 1, and uptakes the stroke volume in the test subject which is measured by a stroke-volume measurer. Next, based on the measured stroke volume, microcomputer 4 adjusts the values of each element in a lumped five parameter model made up of an electrical circuit which models the arterial system from the center to the periphery of the body, so that the response waveform obtained when an electric signal corresponding to the pressure waveform at the proximal portion of the aorta in a test subject is provided to the electric circuit coincides with the waveform at the radius artery. Microcomputer 4 then outputs the thus-obtained values of each element as circulatory state parameters. In addition, microcomputer 4 calculates the diastolic pressure value, systolic pressure value and pulse waveform at the proximal portion of the aorta from the values of each element, and outputs the calculated result to output device 6.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Device for determining a hemodynamic parameter
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYSTEMS SE
Determining hemodynamic performance
ActiveUS20130024176A2Improve clinical outcomesData visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesDisplay deviceAnimal subject
Owner:HUMAN CHIMP PTY LTD
Implantable arterio-venous shunt devices and methods for their use
InactiveUS20110270149A1Increase volumeRelieves the shortness of breath and other symptoms sufferedElectrocardiographySurgeryShunt DeviceWhole body
A long-term implantable arterio-venous shunt device or creation of a fistula is provided that can be used as a therapeutic method for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The shunt device is implanted between an artery and a vein, preferably between a peripheral artery and the inferior vena cava. The shunt device and method of creating a fistula increases cardiac output and decreases the systemic vascular resistance and allows a blood flow rate through the shunt device of at least 5 ml / min after the implantation. Based on the effects of the method and device to the respiratory, cardiac and circulatory system, the method and device are beneficial as a therapy to patients with problems or conditions related to these systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
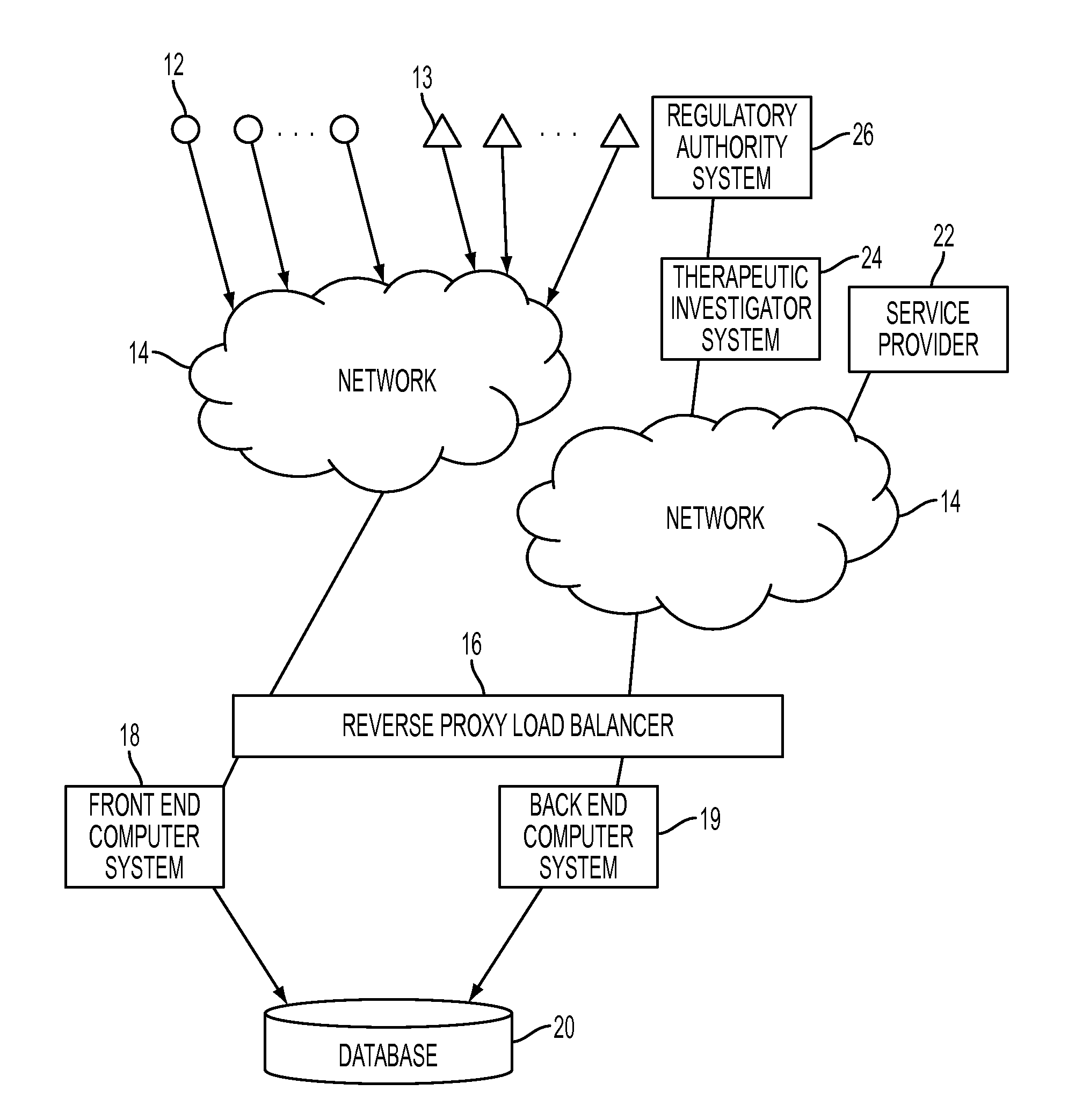
Systems and methods for using physiological information
Systems and methods using a database of physiological information for the design, development, testing and use of therapeutics. In one aspect, the physiological information can include at least one of: hemodynamic monitoring information, pulmonary arterial pressure, cardiac output, heart rate, respiratory rate, peripheral vascular resistance, total peripheral resistance or dicrotic notch information. Optionally, the cardiovascular physiology information can include ambulatory physiological information.
Owner:CARDIOMEMS
Device for measuring physiological state
A non-invasive device for evaluating circulatory state parameters, and specifically, a pulsewave analysis device capable of evaluation by separating blood vessel compliance and blood vessel resistance into central and peripheral components of the arterial system is provided. Microcomputer 4 detects the waveform at a test subject's radius artery via pulsewave detector 1, and uptakes the stroke volume in the test subject which is measured by a stroke-volume measurer. Next, based on the measured stroke volume, microcomputer 4 adjusts the values of each element in a lumped five parameter model made up of an electrical circuit which models the arterial system from the center to the periphery of the body, so that the response waveform obtained when an electric signal corresponding to the pressure waveform at the proximal portion of the aorta in a test subject is provided to the electric circuit coincides with the waveform at the radius artery. Microcomputer 4 then outputs the thus-obtained values of each element as circulatory state parameters. In addition, microcomputer 4 calculates the diastolic pressure value, systolic pressure value and pulse waveform at the proximal portion of the aorta from the values of each element, and outputs the calculated result to output device 6.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
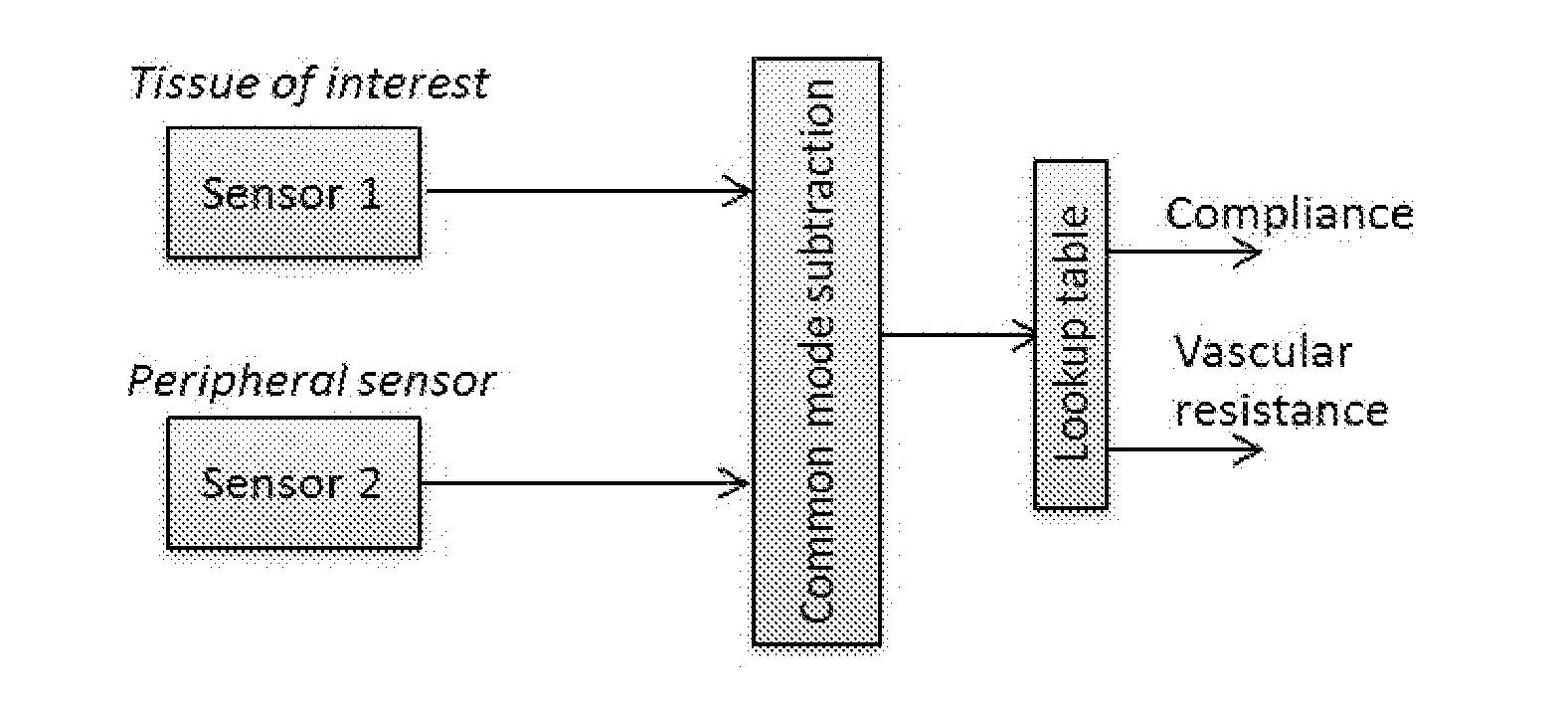
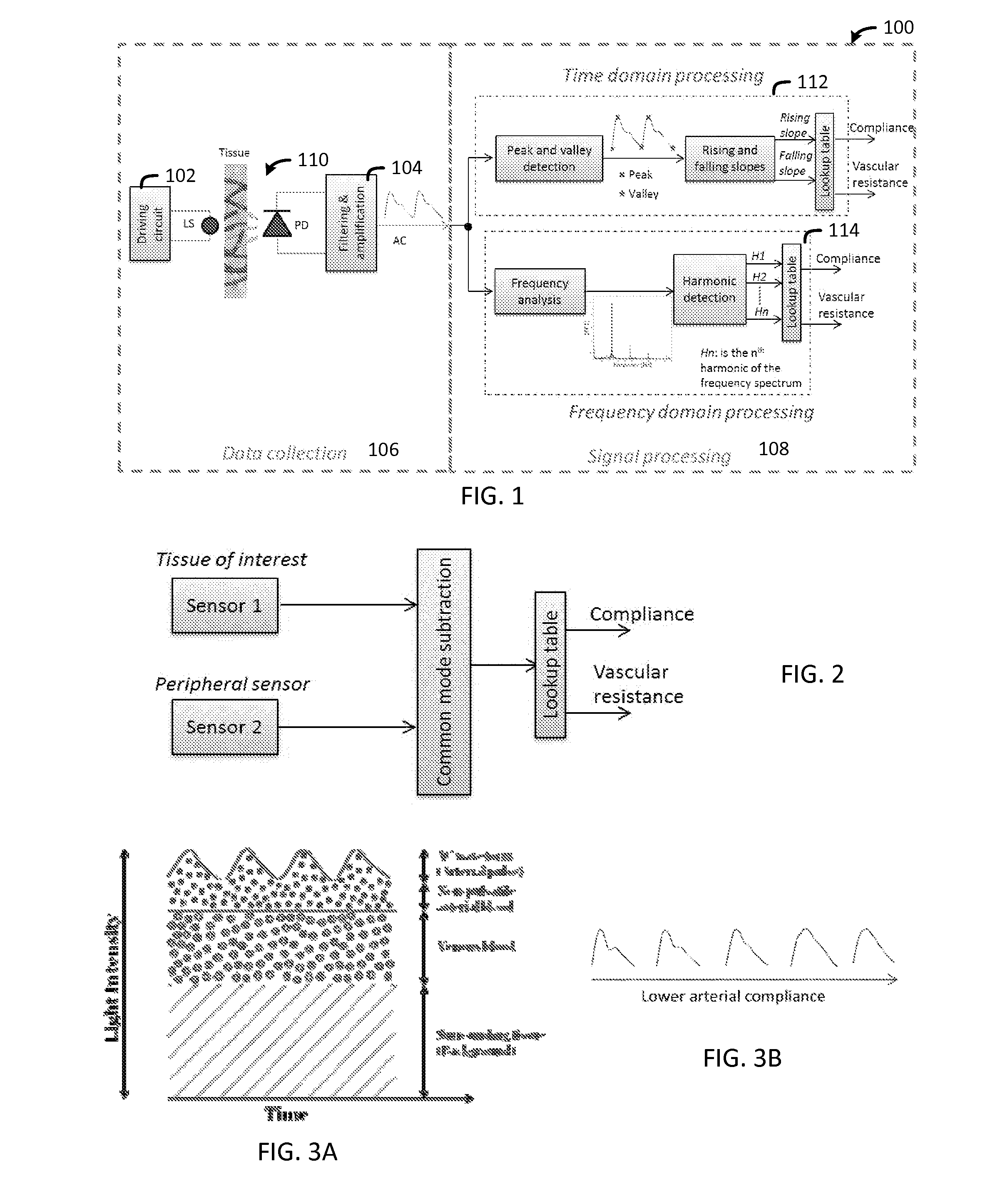
Non-Invasive Monitoring of Tissue Mechanical Properties
Methods and apparatuses for a tissue mechanical property monitoring system are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a tissue mechanical property monitoring system is disclosed. The tissue mechanical property monitoring system may comprise a probe, wherein the probe comprises a light source and a photodetector; and a main unit, wherein the main unit comprises a microcontroller and wireless transmitter. The probe may be hermetically sealed and may be capable of being implanted onto tissue. The photodetector may be capable of collecting reflectance data from the light emitted by the light source. The reflectance data may be capable of being sorted and processed into tissue mechanical property data such as tissue compliance, vascular resistance, and the like for the tissue illuminated with the probe.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +3
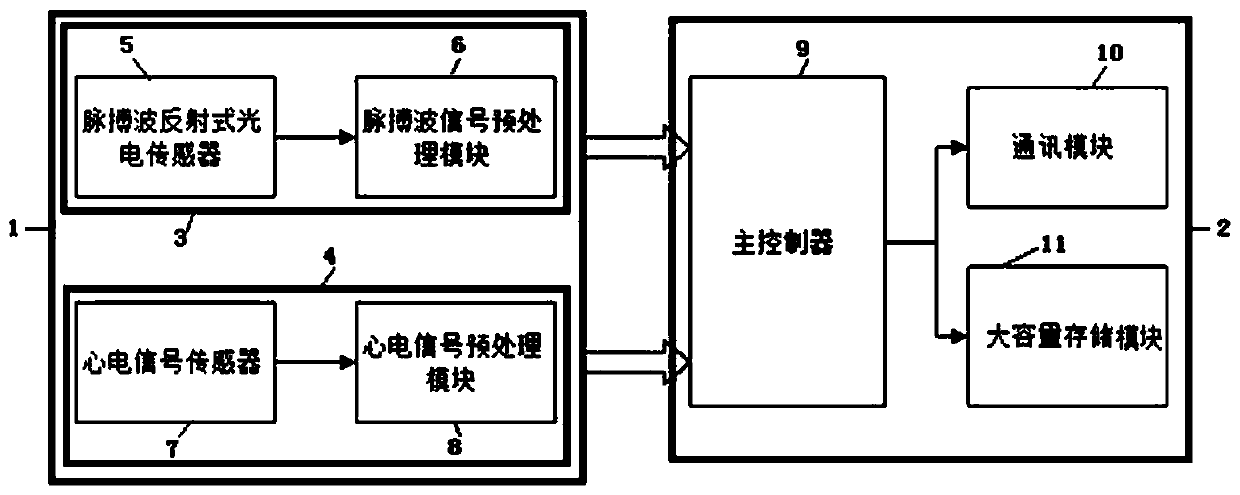
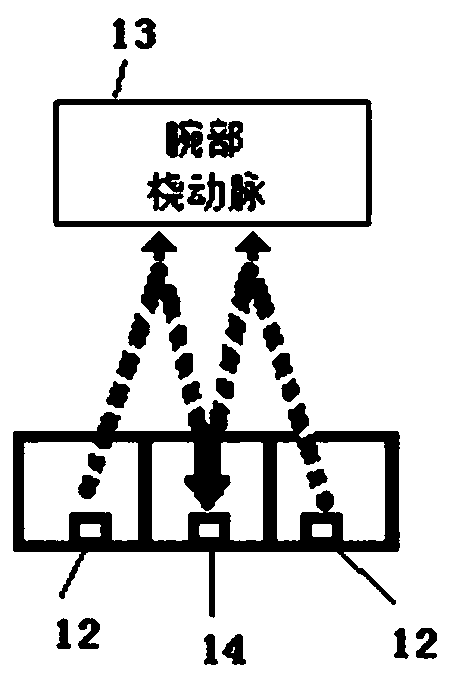
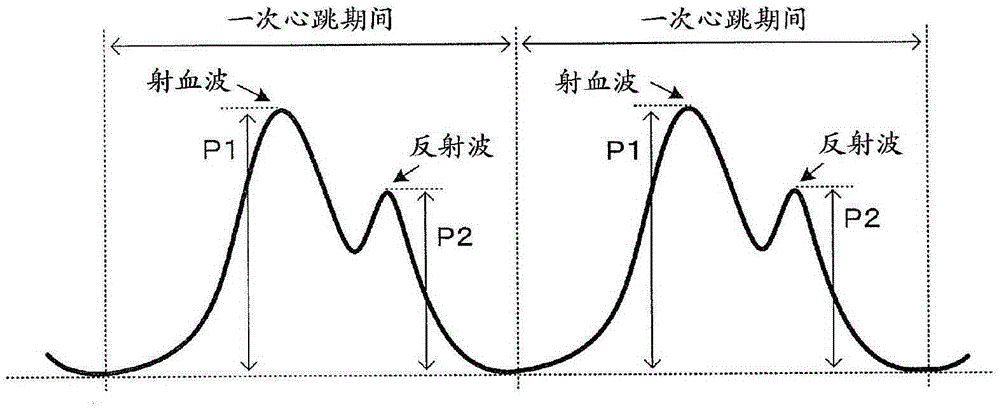
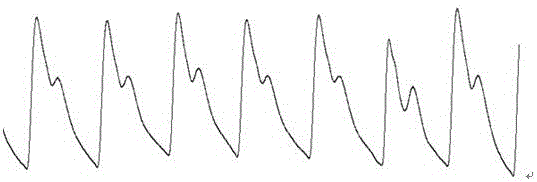
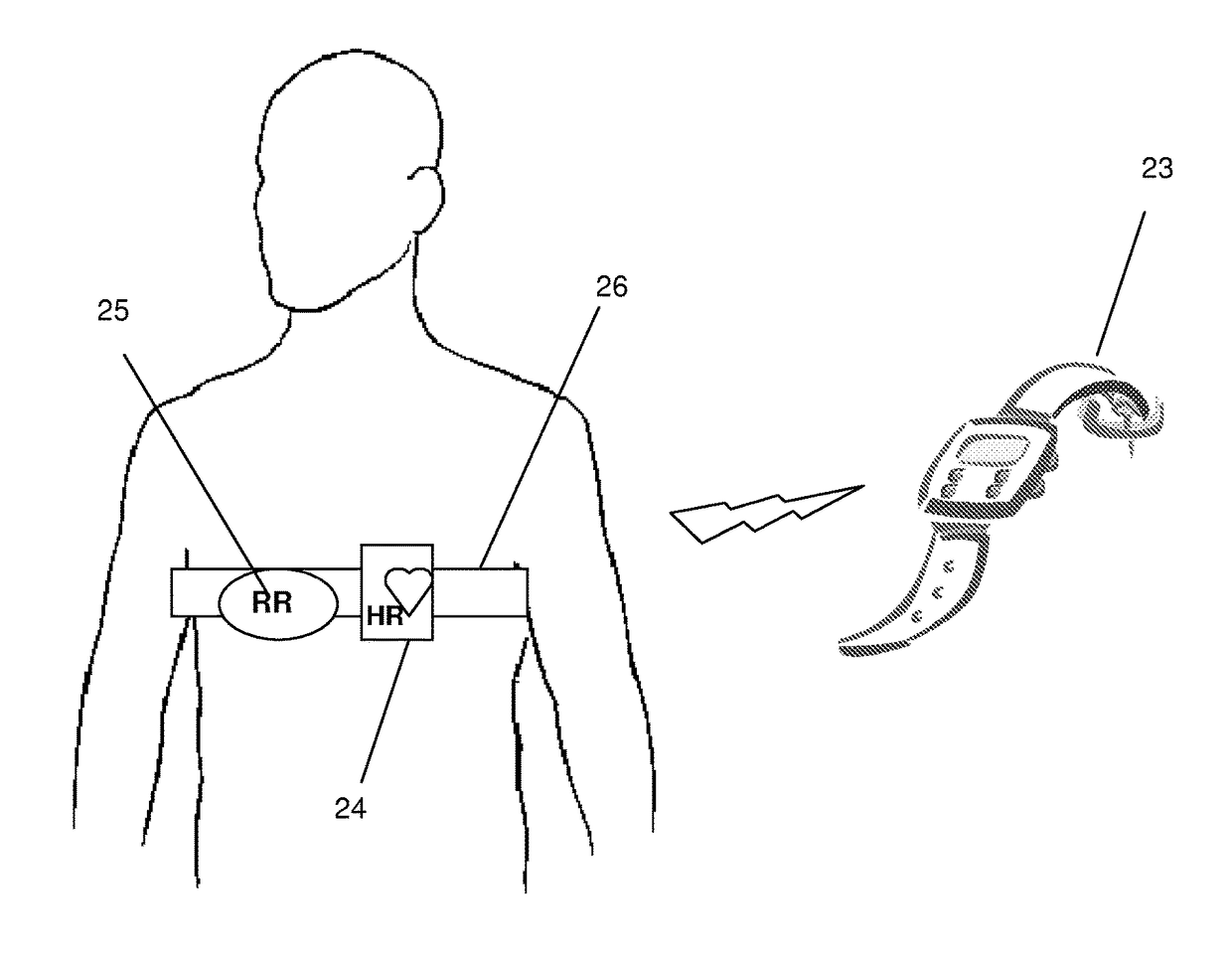
Peripheral vascular resistance detecting device and method based on ECG and pulse wave morphological parameters
InactiveCN108175387ALow costSimple and fast operationDiagnostics using lightCatheterElectricityEcg signal
The invention discloses a peripheral vascular resistance detecting device based on ECG and pulse wave morphological parameters. The device comprises a signal collecting module unit and a communicationstorage module unit which are connected with each other. The signal collecting module unit comprises a pulse wave signal collecting module and an ECG signal collecting module. The pulse wave signal collecting module is composed of a pulse wave reflecting type photoelectric sensor and a pulse wave signal preprocessing module which are electrically connected. The ECG signal collecting module is composed of an ECG signal sensor and an ECG signal preprocessing module which are electrically connected. The communication storage module unit comprises a main controller, and a communication module anda large-capacity memorizer which are connected with the controller. The output end of the pulse wave signal preprocessing module and the output end of the ECG signal preprocessing module are connected into two input ends of the main controller respectively. The peripheral vascular resistance detecting device is low in cost, easy to operate, convenient to measure and carry and suitable for families and individuals for detection. The invention meanwhile discloses a peripheral vascular resistance detecting method based on the ECG and pulse wave morphological parameters.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Methods and apparatus for determining cardiac output and left atrial pressure
Method and apparatus are introduced for determining proportional cardiac output (CO), absolute left atrial pressure (LAP), and / or other important hemodynamic variables from a contour of a circulatory pressure waveform or related signal. Certain embodiments of the invention provided herein include the mathematical analysis of a pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) waveform or a right ventricular pressure (RVP) waveform in order to determine beat-to-beat or time-averaged proportional CO, proportional pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and / or LAP. The invention permits continuous and automatic monitoring of critical hemodynamic variables with a level of invasiveness suitable for routine clinical application. The invention may be utilized, for example, to continuously monitor critically ill patients with pulmonary artery catheters installed and chronically monitor heart failure patients instrumented with implanted devices for measuring RVP.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Method of reducing pulmonary hypertension and atrial fibrillation after surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass
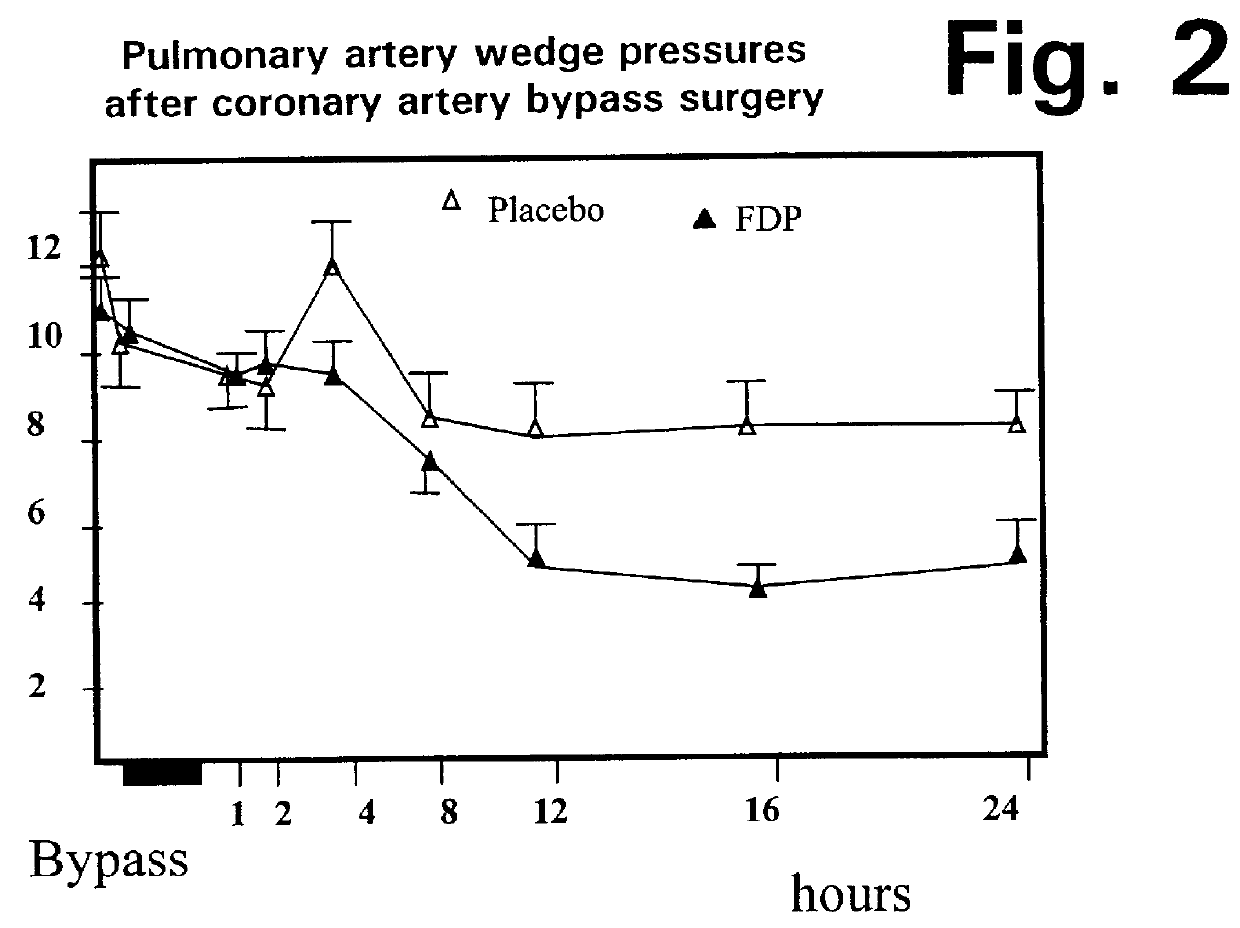
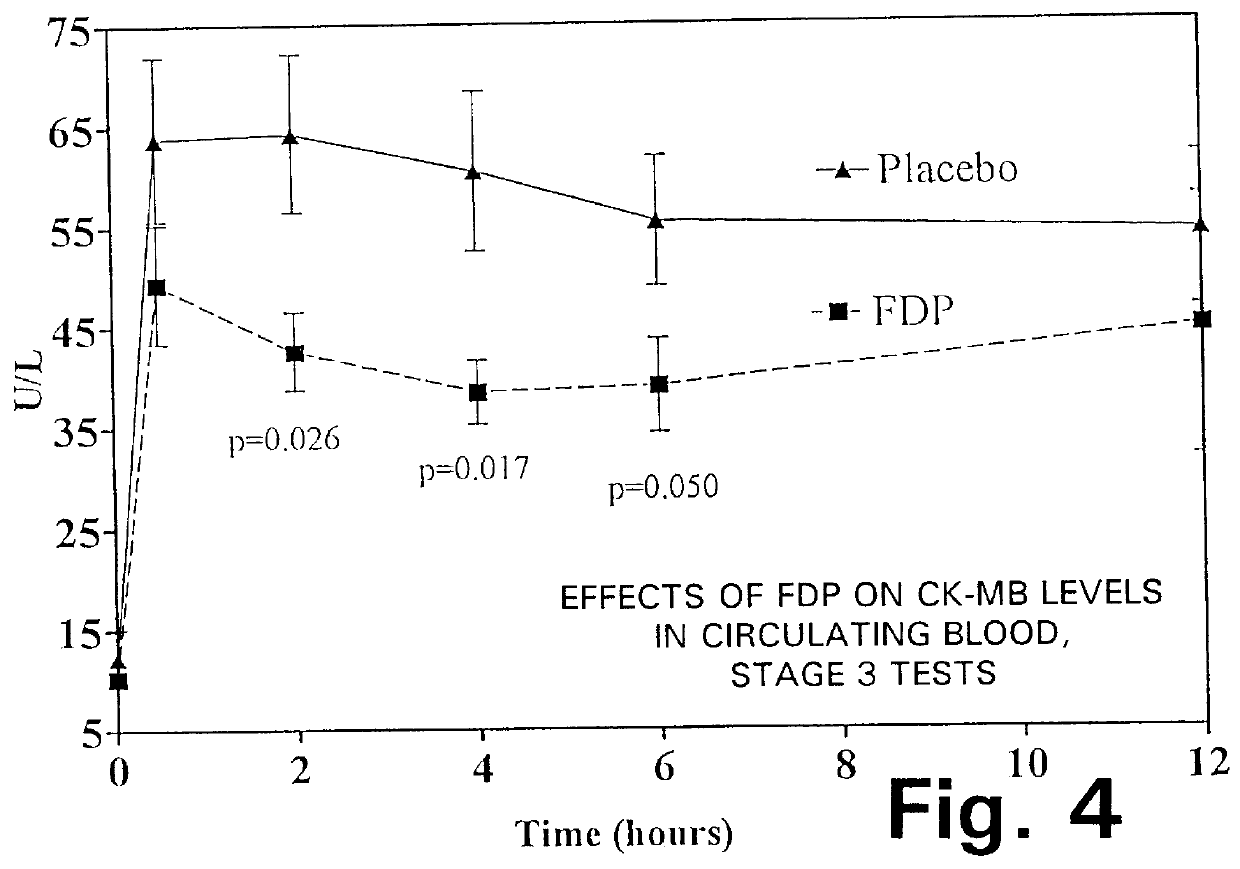
A method is disclosed for using fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) to reduce and prevent two very serious problems caused by surgery that requires cardiopulmonary bypass. Before bypass begins, a liquid that contains FDP is intravenously injected into the patient, preferably over a period such as about 10 to 30 minutes, to allow the FDP to permeate in significant quantity into the heart and lungs while the heart is still beating. FDP can be added to the cardioplegia solution that is pumped through the heart to stop the heartbeat, and / or during bypass. This treatment was found to reduce two very important and serious problems that have unavoidably plagued CPB surgery in the past, which are: (1) elevated levels of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), which includes pulmonary hypertension; and (2) high occurrence rates for atrial fibrillation. Prior to this discovery, there has never been any satisfactory treatment which could reduce the severity and occurrence rates for these two major problems. FDP also can be co-administered in this manner, along with (1) a buffering or alkalizing agent that counteracts acidosis, such as sodium bicarbonate or THAM, and / or (2) a drug that reduces the formation of lactic acid, such as dichloroacetate.
Owner:QUESTCOR PHARMA
System for measuring pulsatile vascular resistance
ActiveUS7794403B2Diagnostic value can be improvedIncrease valueBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsWhole bodyArterial blood flow
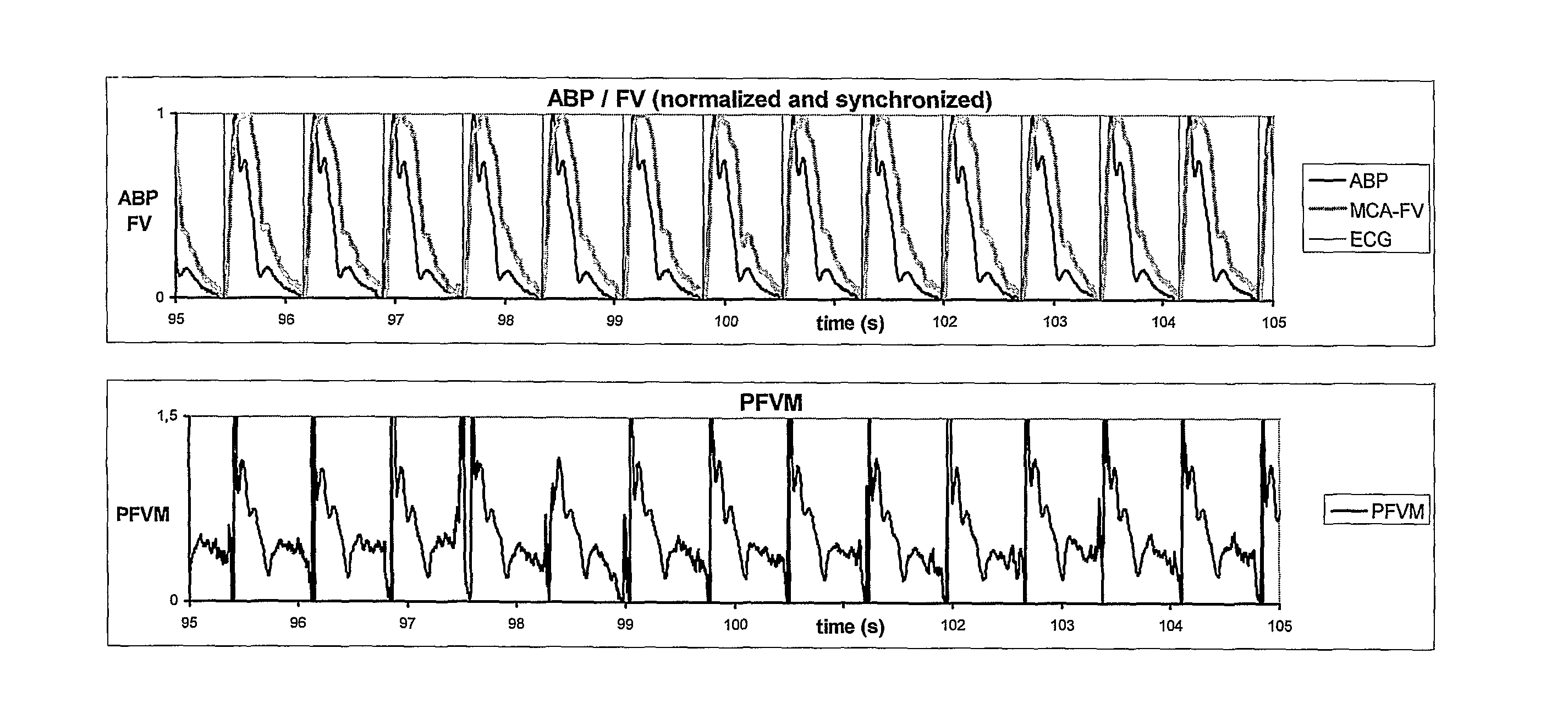
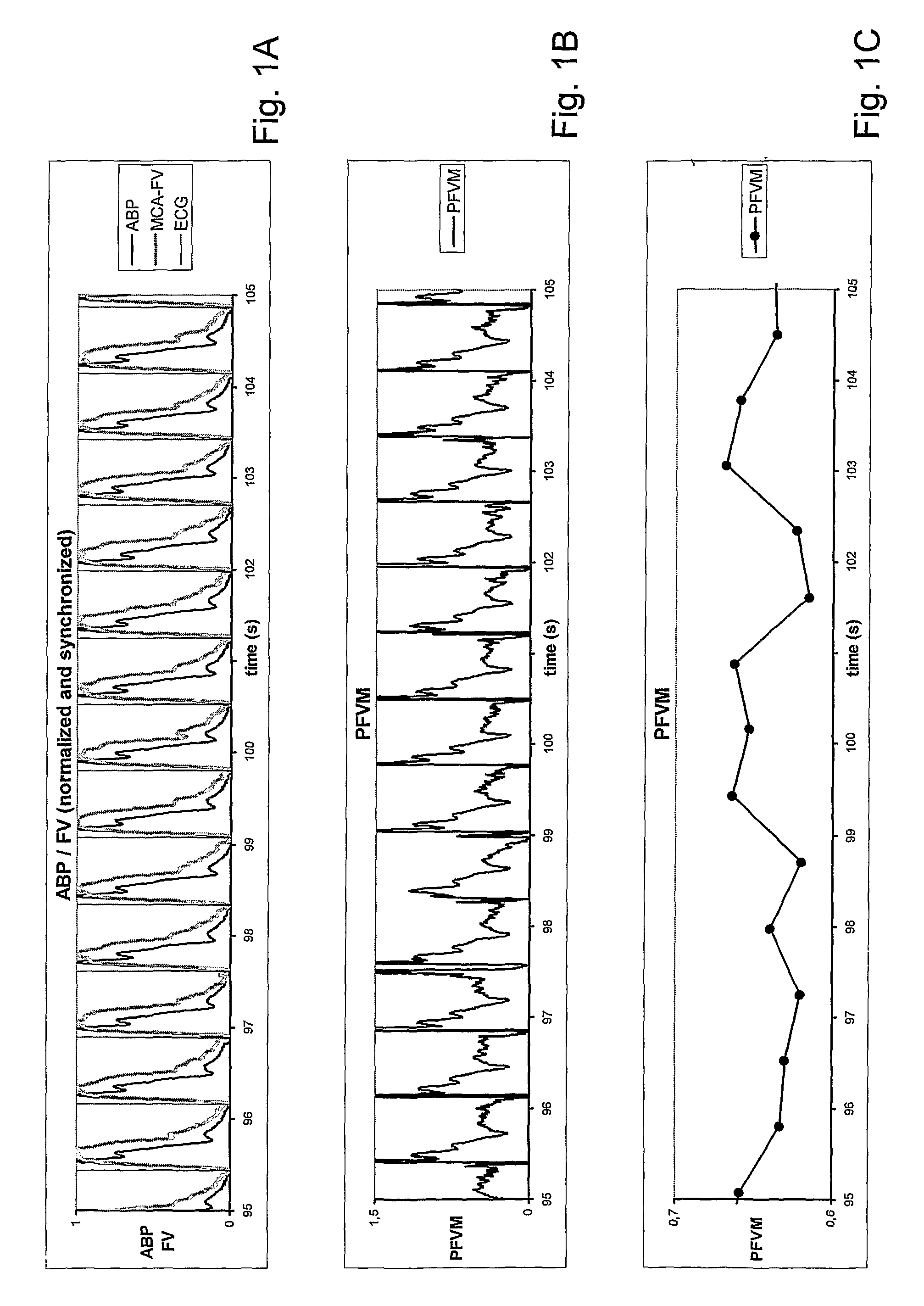
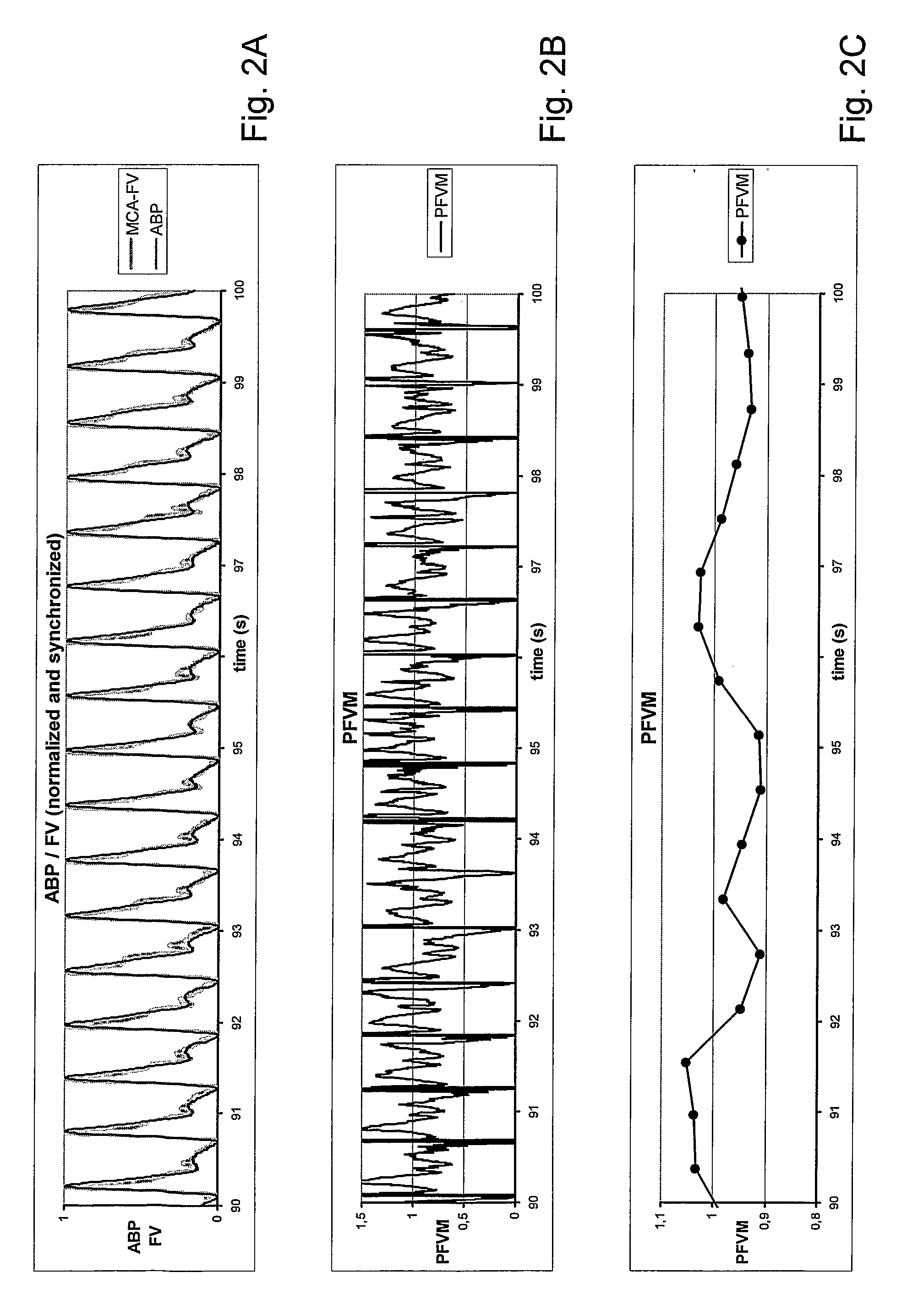
The invention relates to acquiring information concerning the hemodynamic status of the brain (or any other organ) by measuring and analysing the pulsatile properties of blood flow (velocities) in the organ's feeding vessels in relation to the pulsatile properties of the systemic arterial blood pressure. Provided is a system for the analysis of arterial blood flow velocity measurements, comprising means for receiving input signals delivered by an arterial blood flow velocity (FV) sensor and by an arterial blood pressure (BP) sensor, wherein said FV and BP signals are recorded simulataneously and continuously, further comprising means for processing and outputting signals, wherein said processing comprises calculating the pulsatile apparent resistance (PaR) or the Pulse Flow Velocity Mismatch (PFVM). Plotting PAR or PVFM against mean arterial blood pressure and / or end tidal CO2 levels can serve as an indicator for the effectiveness of imposed therapy.
Owner:MEAR HLDG
Injection of fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) prior to coronary artery bypass grafting surgery
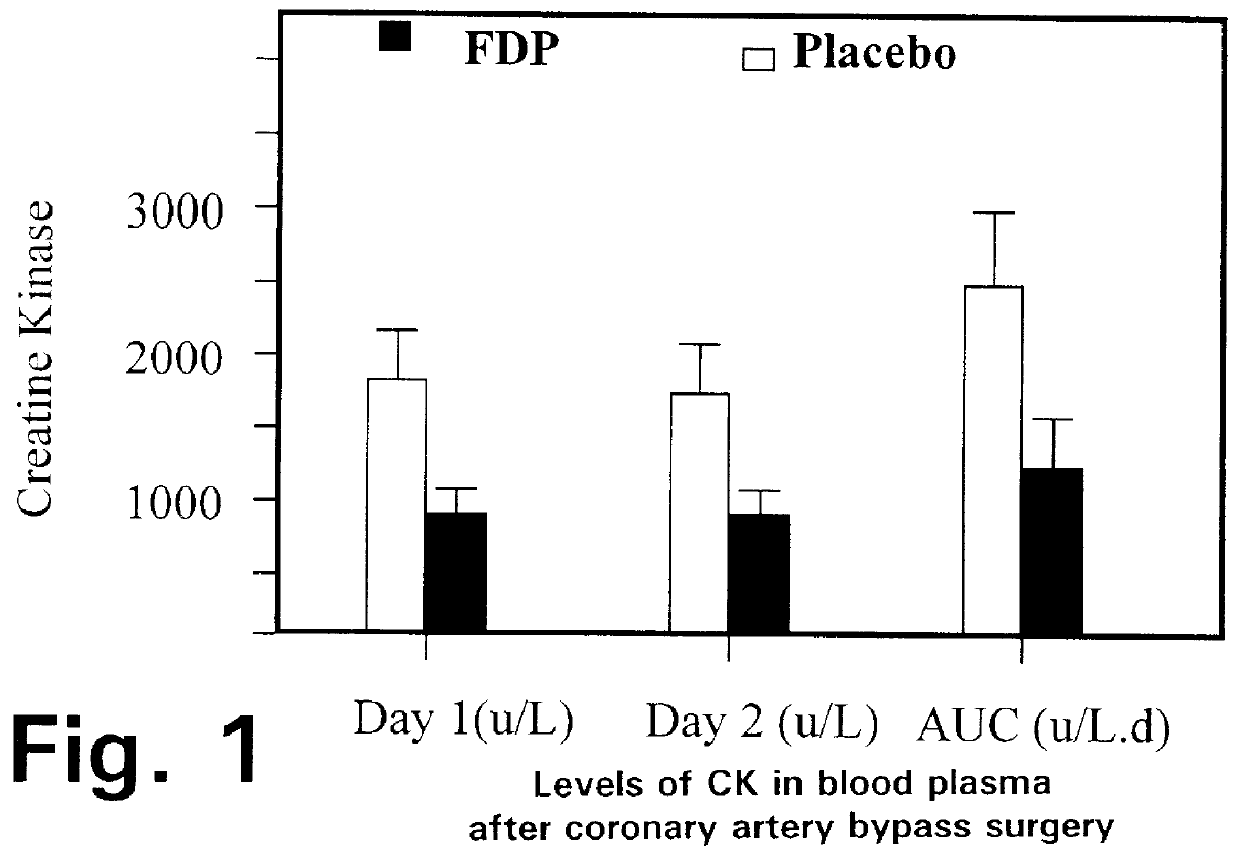
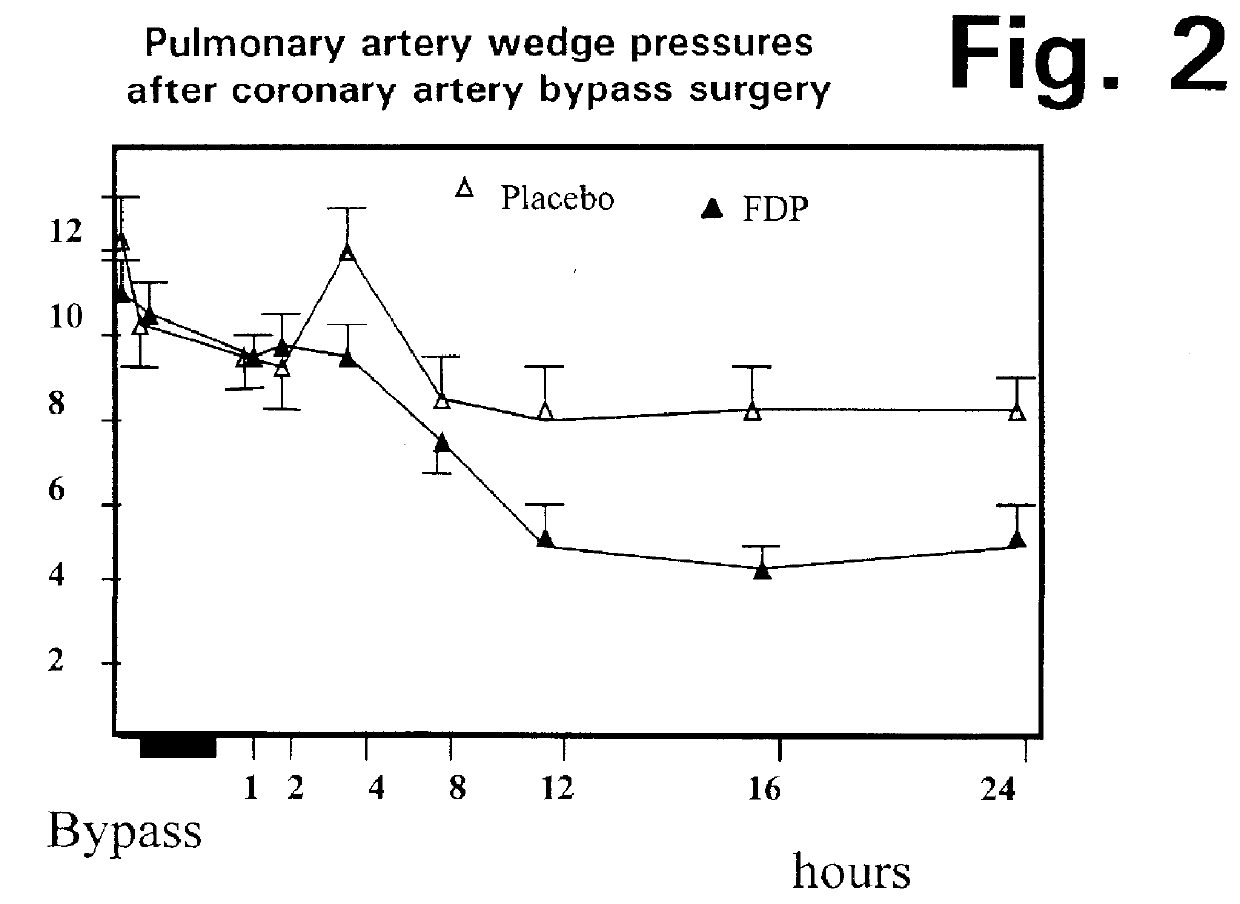
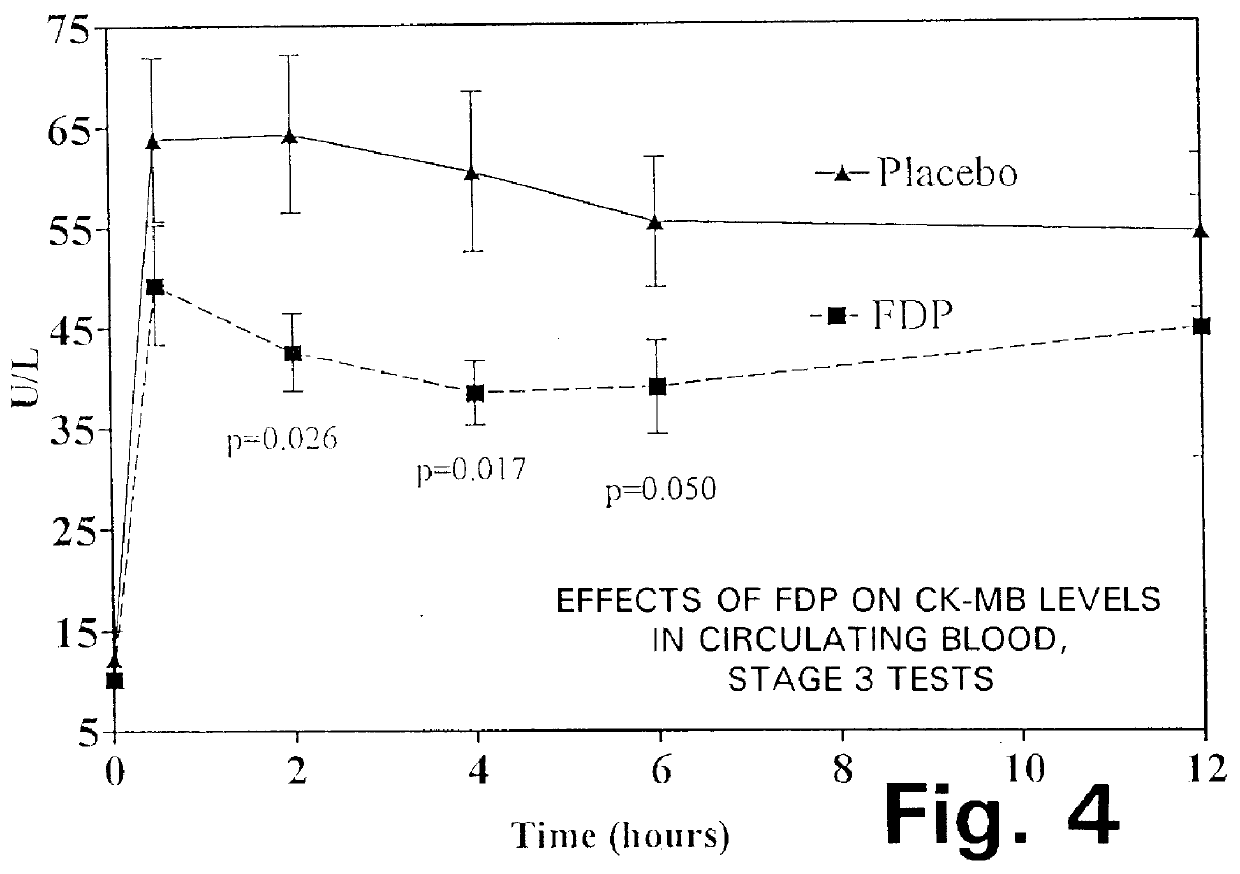
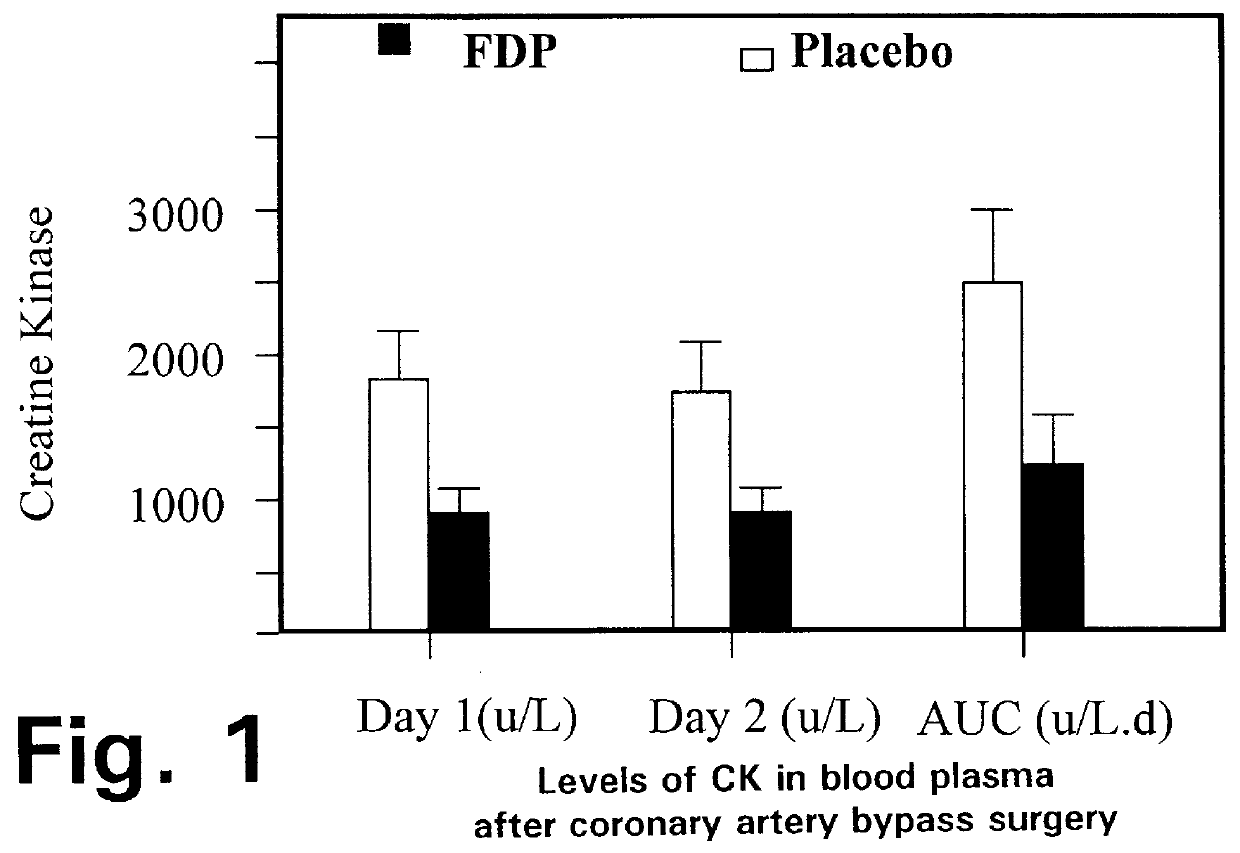
Fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) is used to treat patients who are undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Before cardiopulmonary bypass begins, a liquid that contains FDP is intravenously infused in the patient, preferably for about 10 to 30 minutes, to allow the FDP to enter the heart and lung tissue while the heart is still beating. FDP can also be added to cardioplegia solution; in addition, FDP can be injected after bypass is terminated, but if post-bypass injection is used, steps should be taken to avoid excess lactic acid accumulation, which appears to increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. To prevent or control lactic acidosis, a buffering or alkalizing agent, such as sodium bicarbonate, or an agent which reduces lactic acid formation, such as dichloroacetate, can be used. In double-blinded trials, this use of FDP substantially reduced heart damage and improved overall outcomes, as shown by lower levels of creatine kinase in blood, improvements in pumping performance, reduced requirements for vasodilator and inotropic drugs, and shorter stays in intensive care units. Certain dosages also reduced the likelihood of atrial fibrillation; however, FDP at high dosages increased the likelihood of A-fib. FDP also helped reduce pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR); this is an important finding, since pulmonary hypertension following cardiopulmonary bypass is a very difficult and often intractable problem, and is a contributing factor in nearly all deaths following CPB surgery.
Owner:QUESTCOR PHARMA
Lumen Morphology and Vascular Resistance Measurements Data Collection Systems, Apparatus and Methods
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Blood pressure measurement device, electronic device, and blood pressure measurement method
The invention relates to a blood pressure measurement device an electronic device and a blood pressure measurement method. The blood pressure measurement device includes: a light emitting unit configured to irradiate a living body with measurement light; a light receiving unit configured to receive reflected or transmitted light of the measurement light; and a computational unit configured to calculate a blood flow and a volume pulse wave based on a light-receiving result from the light receiving unit, and to calculate blood pressure based on the blood flow and blood vessel resistance that is obtained from the volume pulse wave.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Device for determining a hemodynamic parameter
Owner:PULSION MEDICAL SYSTEMS SE
Orally taken traditional Chinese medicine for treating migraine
InactiveCN103751570ALong courseNervous disorderLeech/worm material medical ingredientsAngelica Sinensis RootBlood flow
The invention discloses an orally taken traditional Chinese medicine for treating migraine, and belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicines. The traditional Chinese medicine is prepared from the following raw materials: astragalus root, lumbricus, ligusticum wallichii, atractylodes macrocephala, Chinese parsnip root, tuckahoe, red paeony root, semen cassiae, radix paeoniae alba, prepared rehmannia root, large-leaved gentian, selfheal, red flower, schizonepeta, chrysanthemum, peach seeds, asarum, radix bupleuri, codonopsis pilosula, angelica sinensis, gastrodia elata, angelica root and fructus viticis. The traditional Chinese medicine is mainly used for realizing the effects of promoting circulation of qi, relieving depression, activating blood, dredging collaterals, reducing phlegm, removing stagnation, expelling wind and alleviating pain, and also achieving the purposes of improving circulation of blood, reducing drag of blood vessels, and increasing the microcirculation blood flow rate. The traditional Chinese medicine has the advantages that the effect is instant, the treatment course is short, the cost is low, and the like.
Owner:王怀方
Determining hemodynamic performance
ActiveUS20120130697A1Restoring non-optimal haemodynamic performanceData visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesBlood flowDisplay device
Owner:WOODFORD STEPHEN
Method for evaluating cardiac function by using pulse waves
A method for evaluating a cardiac function by using pulse waves includes the following steps: (1) acquiring a finger tip photoelectric capacity pulse wave signal through a photoelectric capacity sensor; (2) amplifying and filtering the finger tip photoelectric capacity pulse wave signal; (3) separating alternating quantity; (4) performing analog-to-digital conversion on the alternating quantity, and performing re-sampling on the converted digital signal to acquire a pulse waveform; (5) determining the pulse rate PR by using feature points of the pulse waveform; (6) segmenting the signal by using ascending ramus start point of the pulse waveform, acquiring waveform feature parameters for reflecting the human body cardiovascular resistance and a microvessel microcirculation state, and acquiring parameters including the cardiac output, the cardiac index, the stroke volume, and the stroke index which can reflect the cardiac function. The method can acquire the pulse wave signal of a human body through photoelectric capacity pulse waves, can evaluate the cardiac function through the pulse waves without drawing blood, can avoid injure, is high in adaptability, is simple in detection, is high in efficiency, and can accurately reflect the health condition of the cardiac function.
Owner:SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER CENT HOSPITAL
Traditional Chinese medicine preparation for purifying blood
InactiveCN101804110AGood hypolipidemic effectImprove solubilityAnthropod material medical ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseasePropolis
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for purifying blood, which comprises the following components: hawthorn, Astragalus root, leech, cortex moutan, safflower, hemlock parsley, suberect spatholobus stem, vinegar-radix paeoniae alba, angelica, trogopterus dung, salviae miltiorrhizae, propolis, calendula officinalis root, ginkgo leaf and gynostemma pentaphylla. The traditional Chinese medicine composite has the obvious effect of reducing blood lipid, can promote the decomposition of blood lipid, reduces blood viscosity, and resists atherosclerosis; the traditional Chinese medicine composite has the obvious effects of anticoagulation and anti-thrombosis, can inhibit the aggregation of thrombocyte, improves the activity of plasmin, and promotes fibrinolysis; the traditional Chinese medicine composite has favorable effects of heart strengthening, decompression and arrhythmia resistance, can slow heart rate, dilates coronary artery and blood vessel of brain, increases blood flow, lightens myocardial ischemic injury degree, lowers myocardial oxygen consumption, has obvious prevention effect on ischemic cerebrovascular diseases, can dilate peripheral vessel, reduces vascular resistance and promotes blood circulation; and the traditional Chinese medicine composite can promote the generation of haemoglobin and erythrocyte.
Owner:杨勤峰
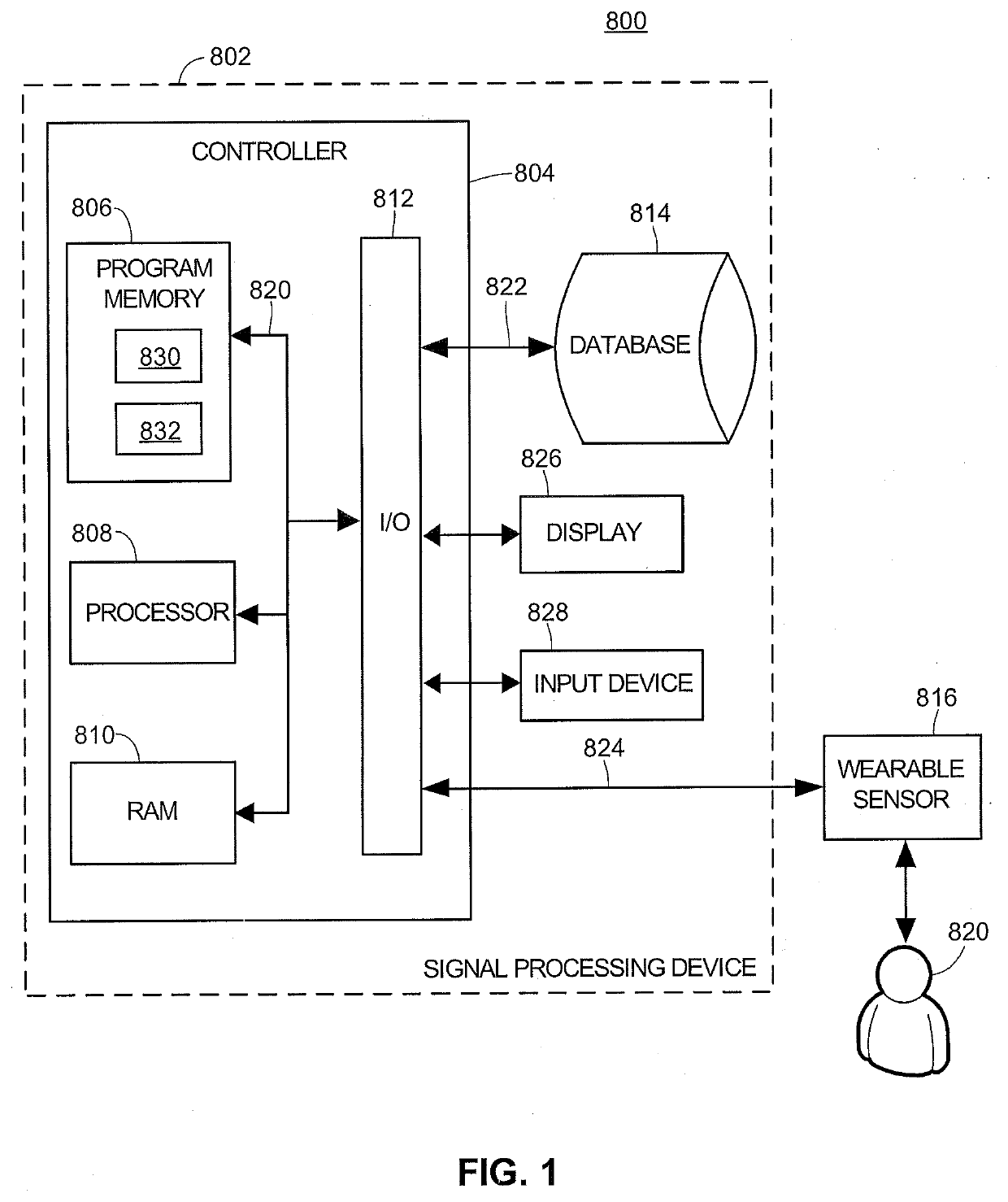
Estimation of peripheral vascular resistance using a miniature piezoelectric sensor
ActiveUS20200054221A1Accurate trackingStrain gaugeEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood flowPiezoelectric sensor
A wearable assembly has a pulse plethysmography (PPG) sensor and a piezoelectric pressure sensor and is attachable to a patient's finger or other area corresponding to a peripheralvascular region, and further includes a signal processor configured to monitor blood flow dependent measurements and pressure measurements over time, comparing these measurements to determine properties of the vascular region, such as vascular resistance of a blood vessel, vascular radius of the blood vessel, vascular stiffness of the vascular region, blood pressure, and / or cardiac vascular power. The signal processor may apply a hysteresis comparison of the sensor outputs, e.g., using an elliptical model, and in some examples may apply an extended Kalman filter for optimizing output of the vascular region properties.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Systems and methods for using physiological information
InactiveUS20120064006A1Improve indication effectReduce the impactPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHaemodynamic monitoringCardiovascular physiology
Systems and methods using a database of physiological information for the design, development, testing and use of therapeutics. In one aspect, the physiological information can include at least one of: hemodynamic monitoring information, pulmonary arterial pressure, cardiac output, heart rate, respiratory rate, peripheral vascular resistance, total peripheral resistance or dicrotic notch information. Optionally, the cardiovascular physiology information can include ambulatory physiological information.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
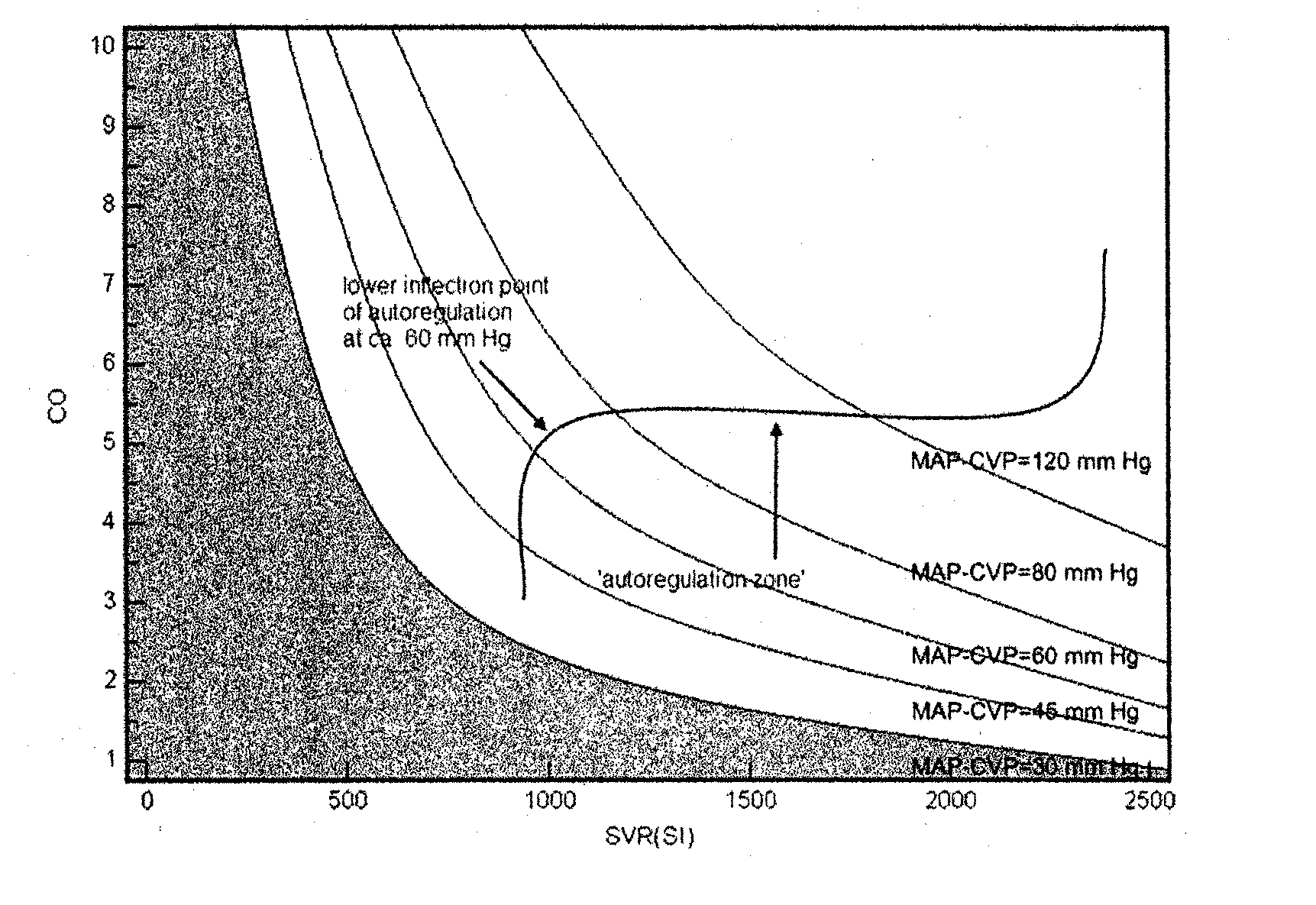
Method and system for estimating momentary cardiovascular performance reserve
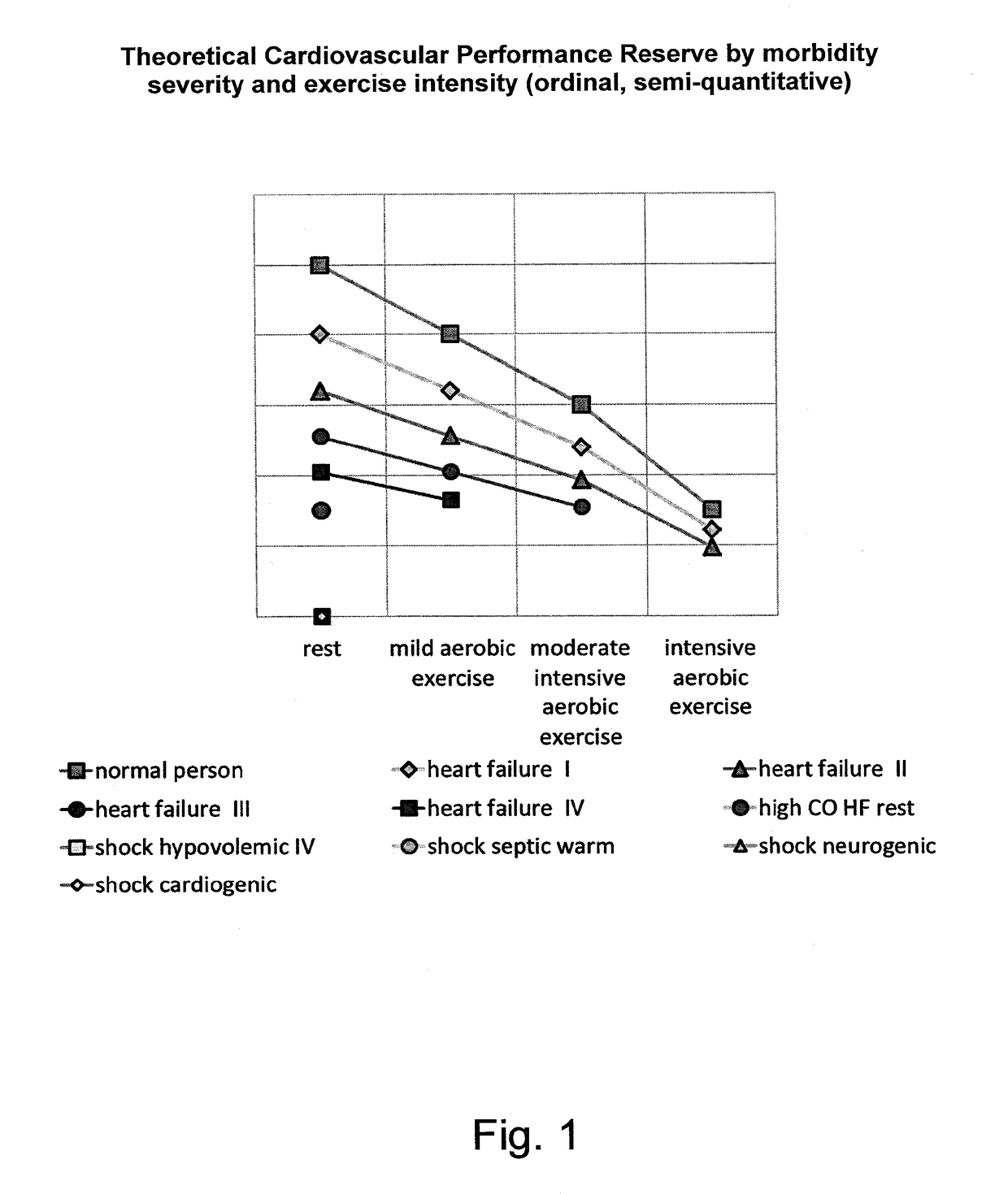
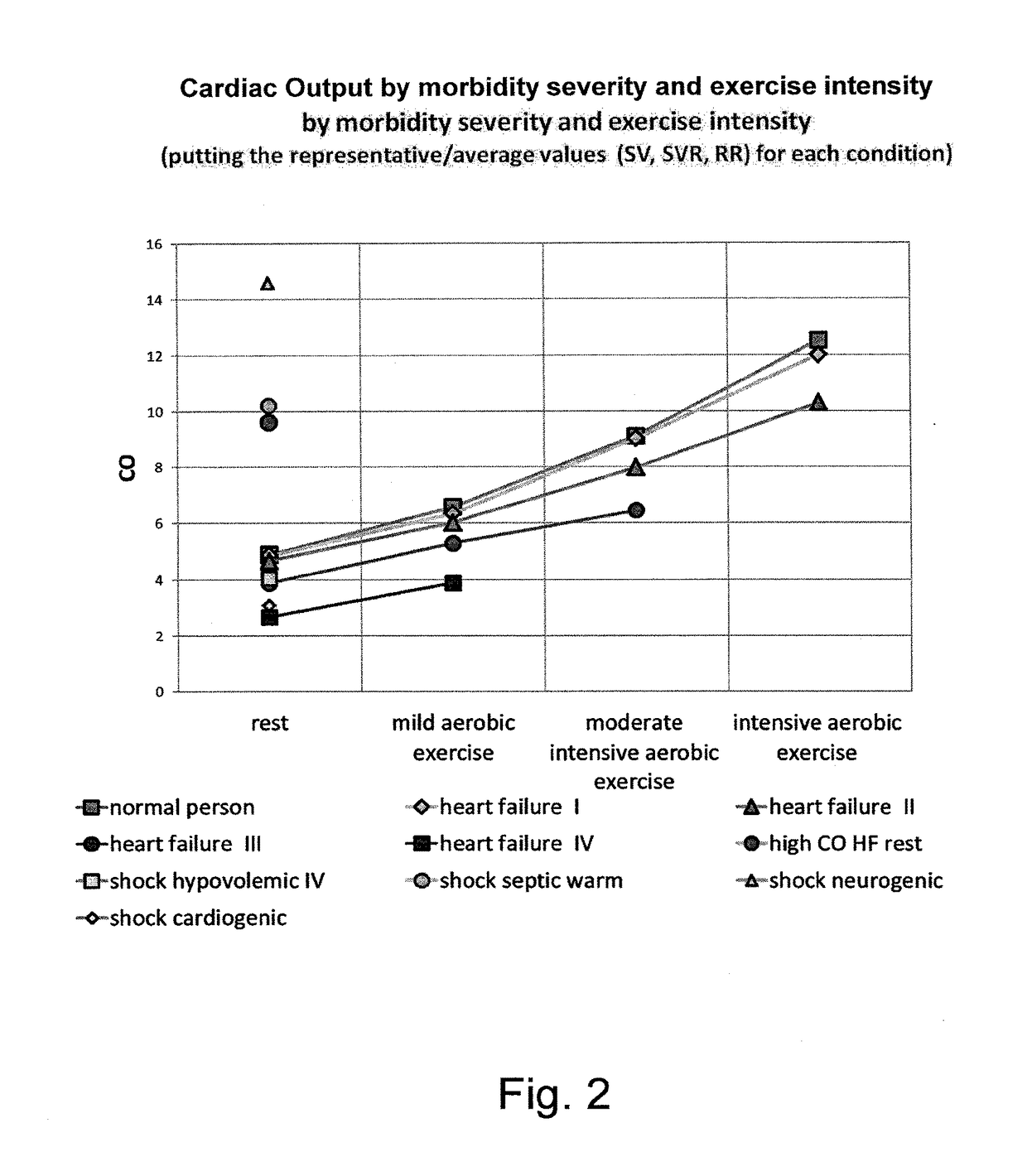
The invention relates to a method for determining a cardiovascular performance reserve for each individual patient, comprising the steps of: a) receiving input physiological data from the patient for obtaining a parameter Z which is or approximates the product of the Stroke Volume (SV) by the Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR); b) providing a value representing the Respiratory Rate (RR) of said patient, wherein the Respiratory Rate (RR) value is provided by measurements using dedicated device(s), calculations from the input physiological data or manually by using best estimate; c) providing anthropometric data of said patient for calculating the Body Surface Area (BSA) of said individual, wherein the anthropometric data includes at least body dimensions (such as height and weight) of said patient; d) calculating the Cardiovascular Reserve (CVR) by using said Z parameter and said RR according to following formula: CVR=(Z / RR); e) calculating a Cardiovascular Reserve Index (CVRI) by standardizing said CVR (by said BSA) and normalizing it to a scale of 1 according to the following formula: CVRI=CVR / (BSA*4); and outputting said Cardiovascular Reserve Index.
Owner:CARDIO SCALE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com