Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
405 results about "Blood clotting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
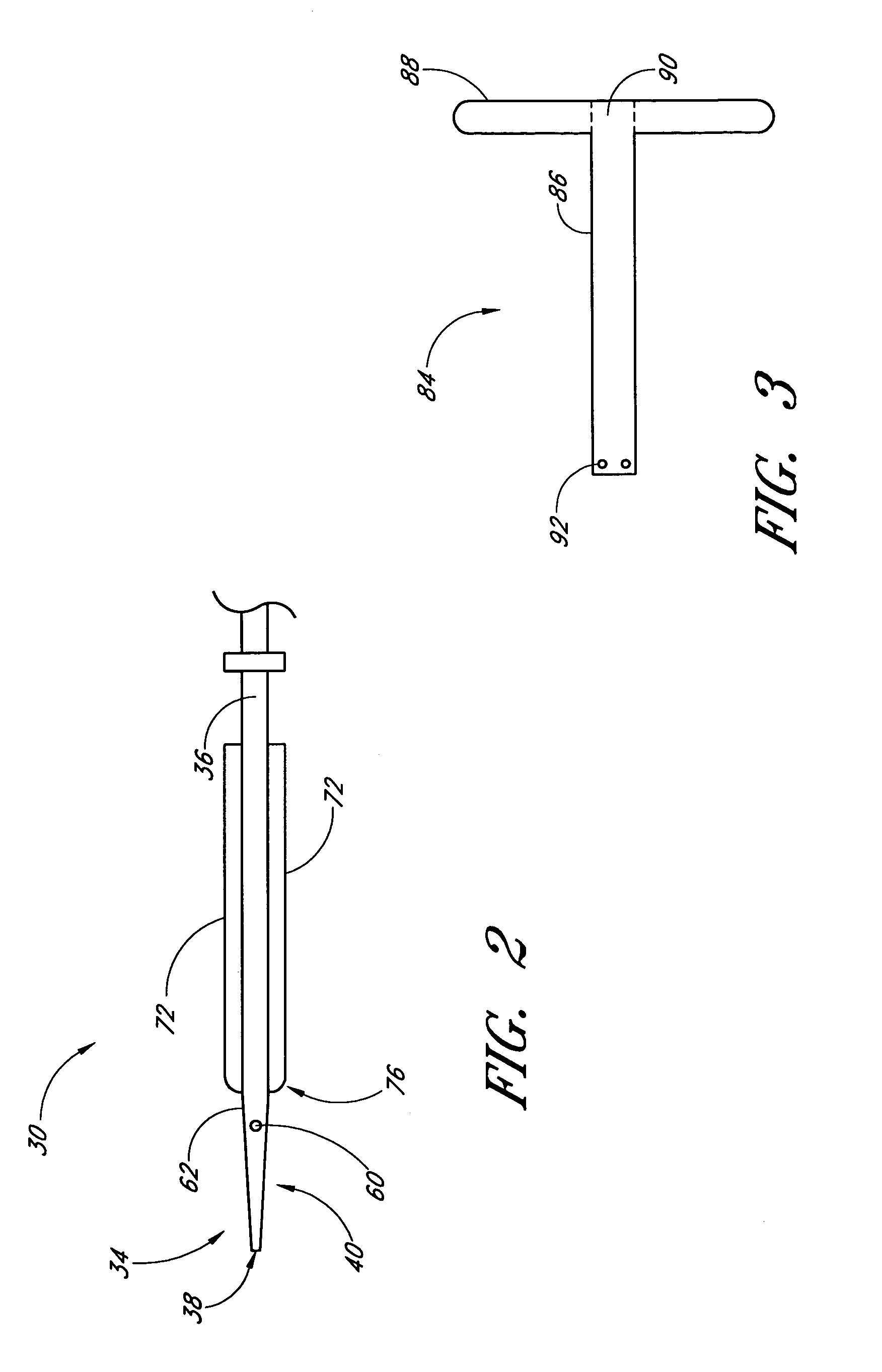
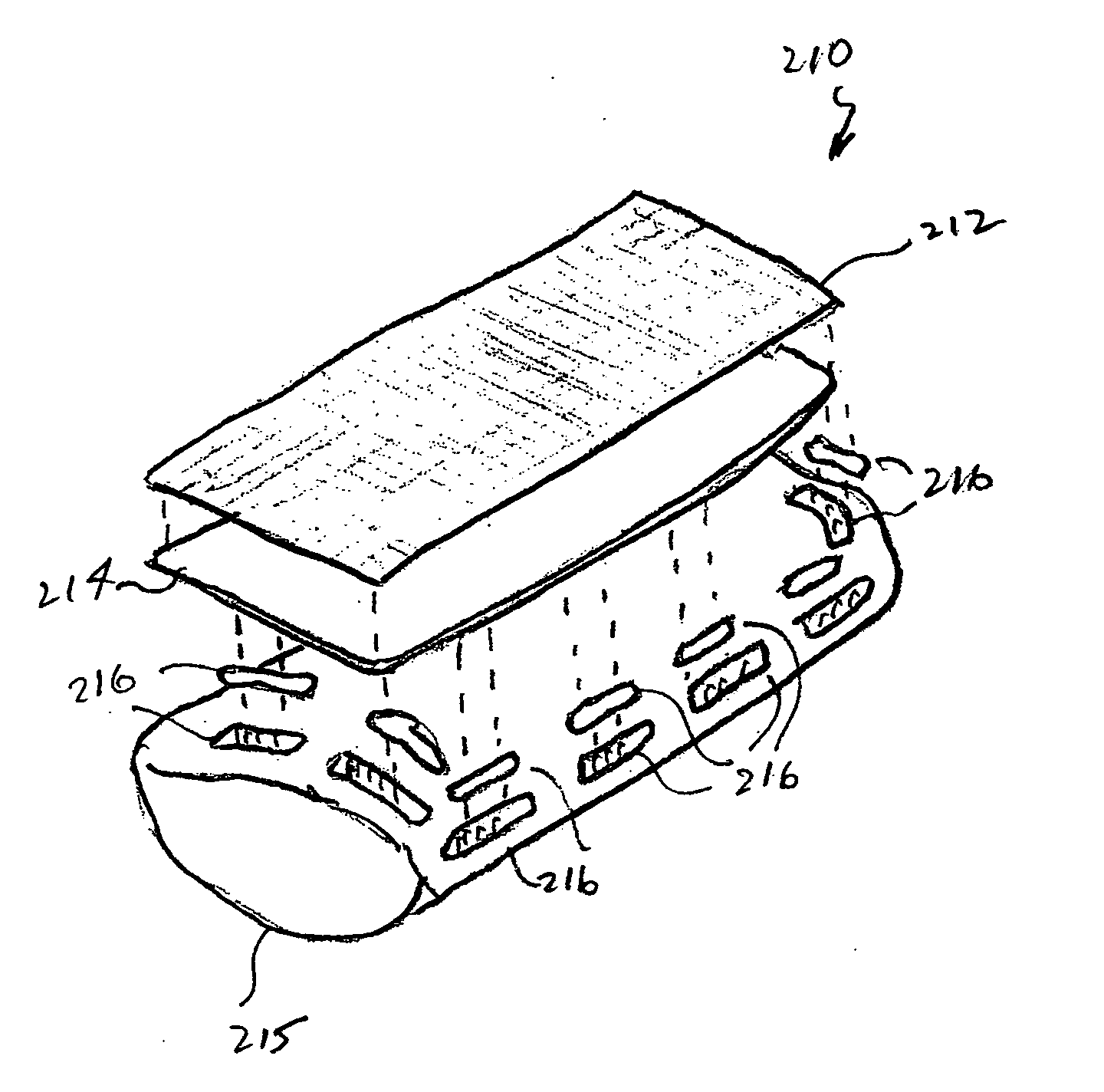
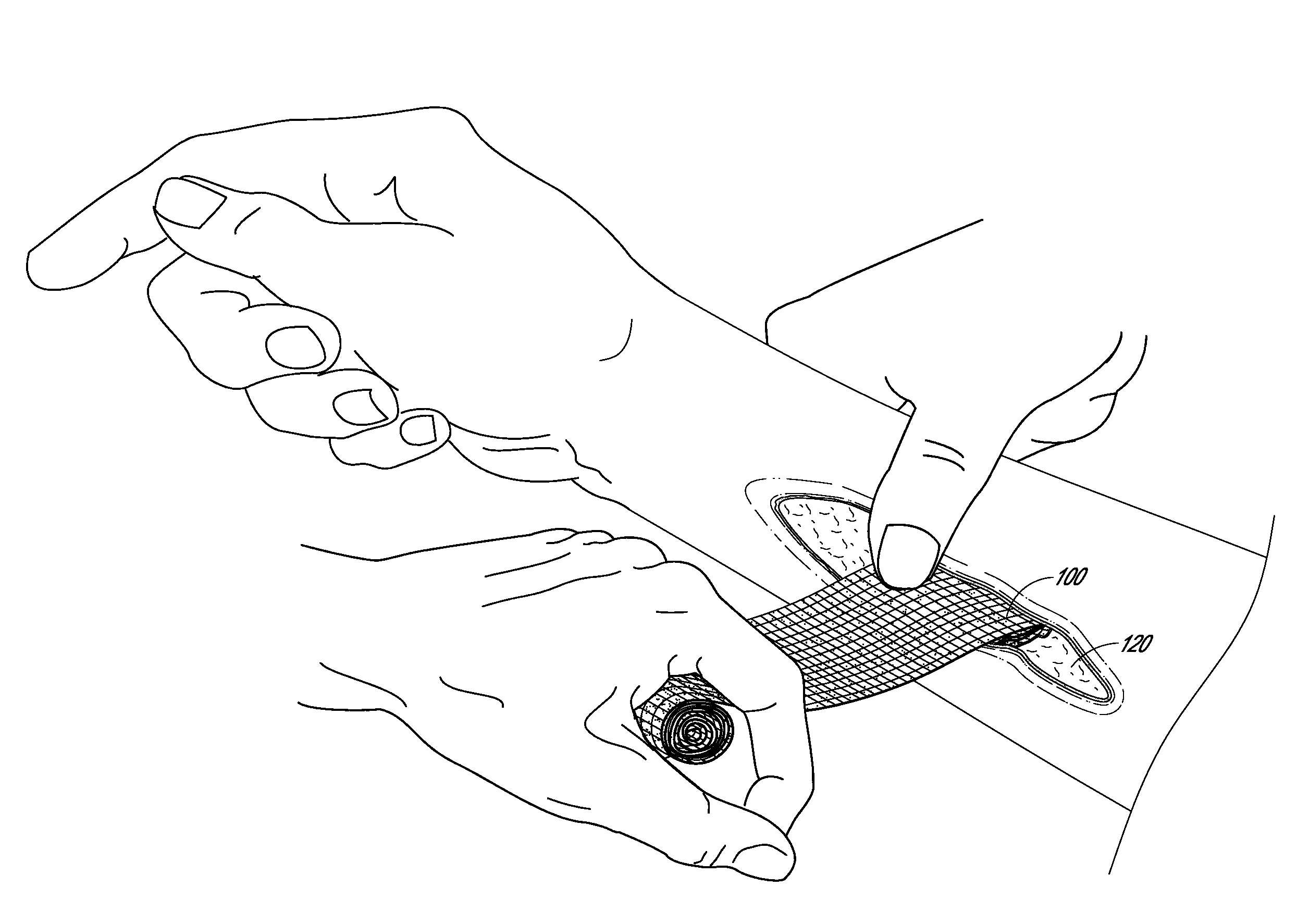
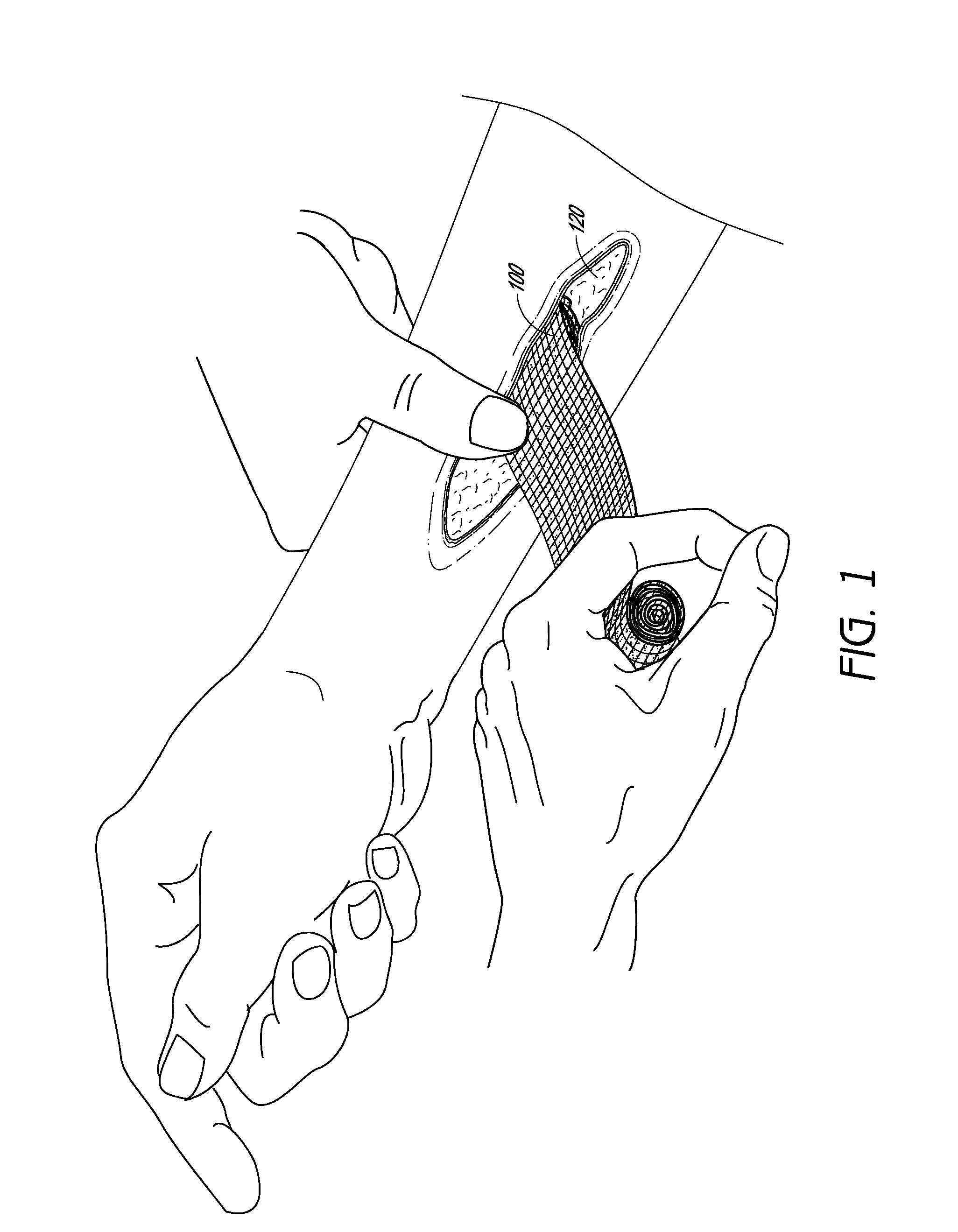
Agents and devices for providing blood clotting functions to wounds
InactiveUS20070190110A1Promote healingShorten the timePhysical treatmentAntithrombogenic treatmentNitrogen dioxideMedicine
Hemostatic agents and devices are made from oxidized cellulose fiber, the oxidized cellulose having a carboxylation content increased by the action of nitrogen dioxide on virgin cellulose fiber. A composition may be incorporated into the oxidized cellulose fiber to cause a pharmacological effect on a wound to which the hemostatic agents and devices are applied. When applied, the oxidized cellulose fiber causes blood emanating from the wound to clot. The oxidized cellulose fiber can either be resorbed into the wound or removed from the wound after healing. A hemostatic bandage includes a pad of unwoven oxidized cellulose fibers mounted on a substrate. Methods of arresting a flow of blood emanating from a wound using such devices are also disclosed. Methods of fabricating oxidized cellulose are also disclosed.
Owner:PAMEIJER CORNELIS H +1
Vascular wound closure device and method
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes an apparatus that can be threaded over a guidewire into place at or adjacent the wound. The apparatus includes a chamber that encloses a hemostatic material therein. When the apparatus is positioned adjacent the wound as desired, the hemostatic material is deployed from the chamber. A blocking member distal of the hemostatic material functions as a barrier to prevent the hemostatic material from entering the wound. Blood contacts the hemostatic material, and blood clotting preferably is facilitated by a hemostatic agent within the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
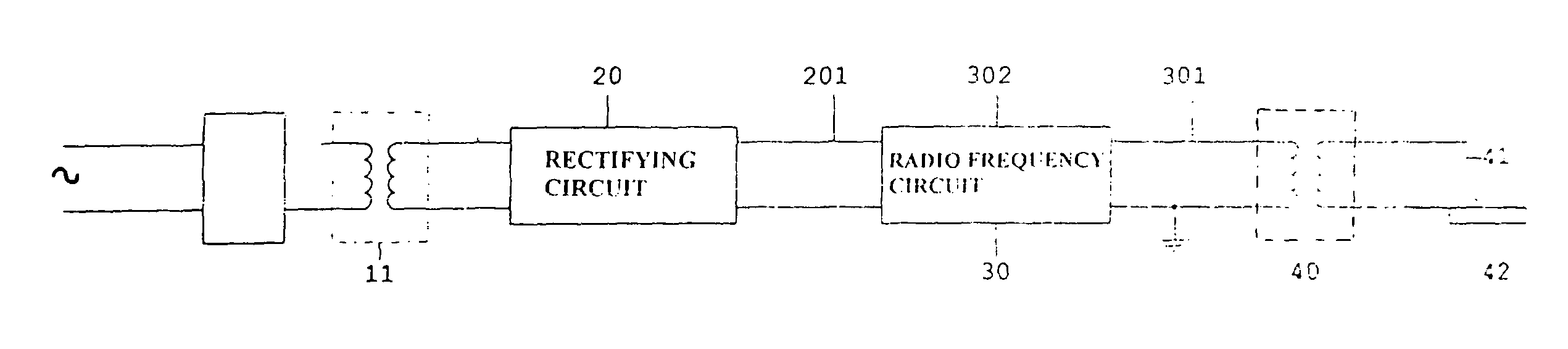
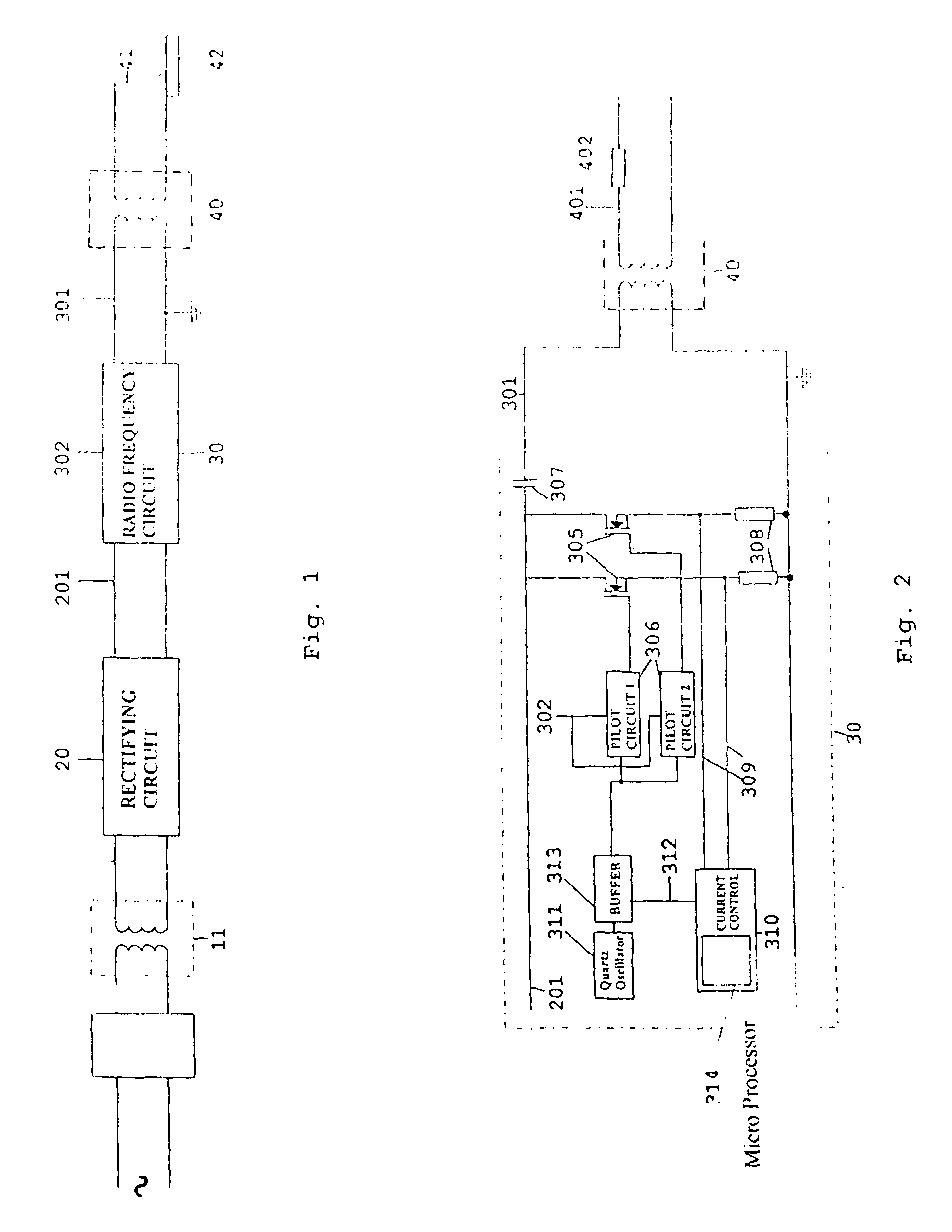
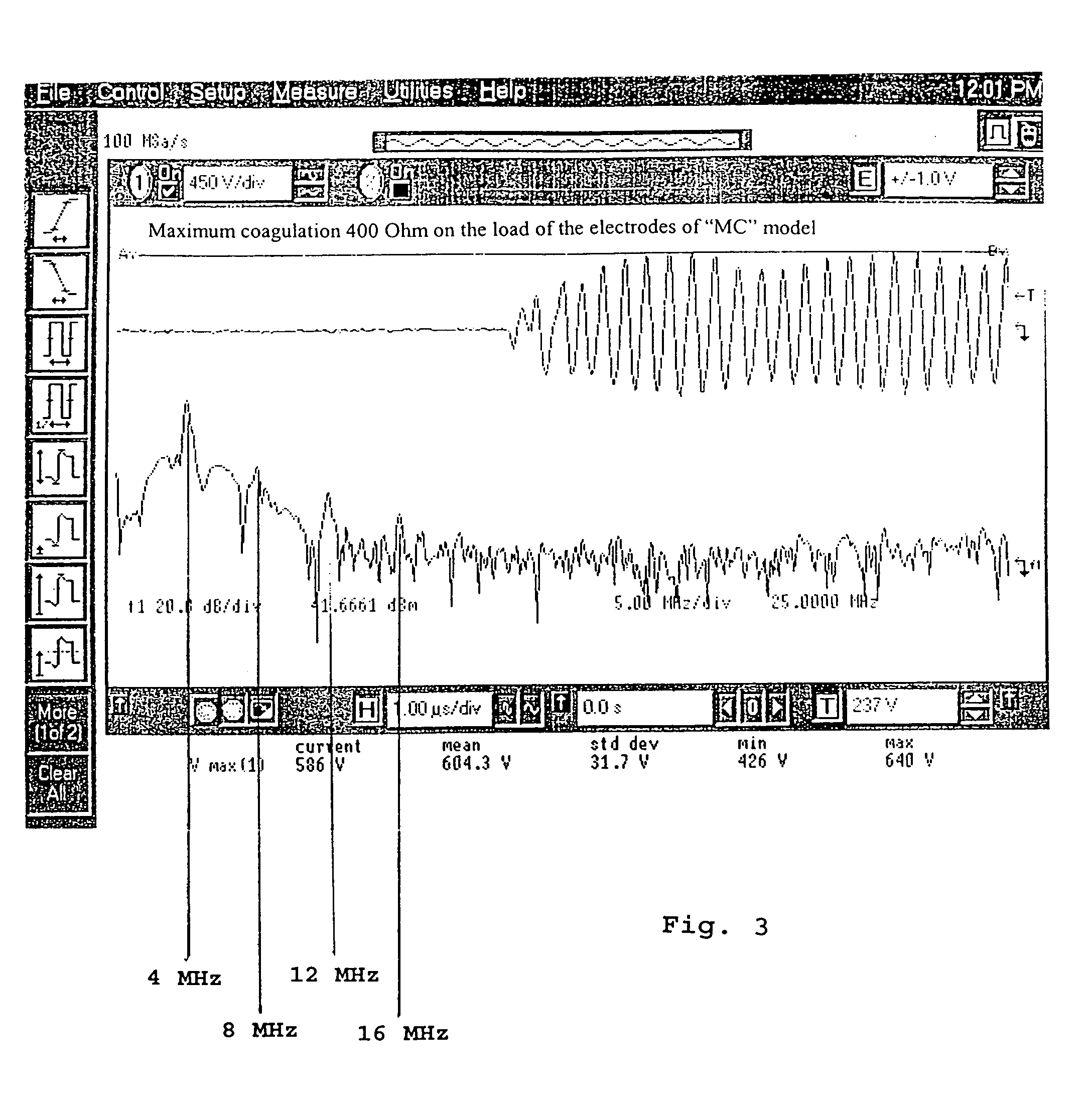
Electronic coagulation scalpel
ActiveUS7713267B2Suppress crashRule out the possibilitySurgical instruments for heatingElectricityTransformer
The invention relates to a method of regulating the power available at the manipulator of an electronic scalpel so as to make said manipulator adapted to be used to obtain blood clotting, said electronic scalpel being of the kind comprising: at least a mains voltage rectifying circuit supplying rectified and direct voltage to at least a radio frequency circuit adapted to emit as output a current carrier signal at a main frequency set by an oscillator, said current signal feeding said manipulator through a radio frequency transformer, wherein said method consists in applying to the manipulator a wave form resulting from the sum of the carrier wave and a modulating wave of such frequency that the energy transmitted to the tissue to be coagulated is such to raise the temperature of the tissue to be coagulated until denaturation of the fibrinogen contained therein is caused and transforming it into fibrin. The invention relates also to the electronic scalpel carrying out such a method
Owner:TELEA MEDICAL GRP SRL
Infusion apparatus
ActiveUS20050277882A1Easy to useEasy constructionAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesDrugs solutionStored energy
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as, antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a substantially constant-force, compressible-expandable wave spring that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of medicament solution to the patient.
Owner:MARSHALL S KRIESEL REVOCABLE TRUST
Catheter infusion port
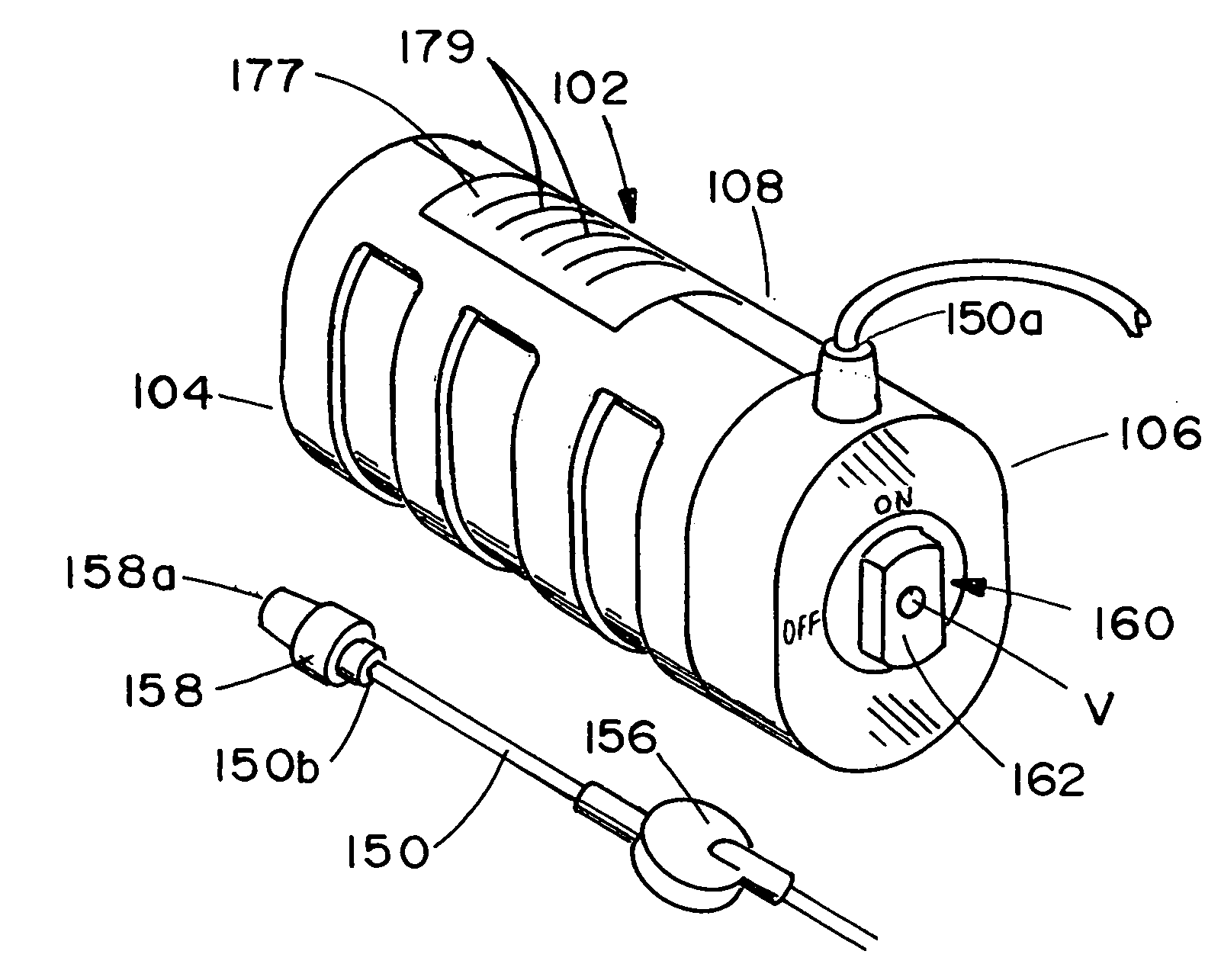
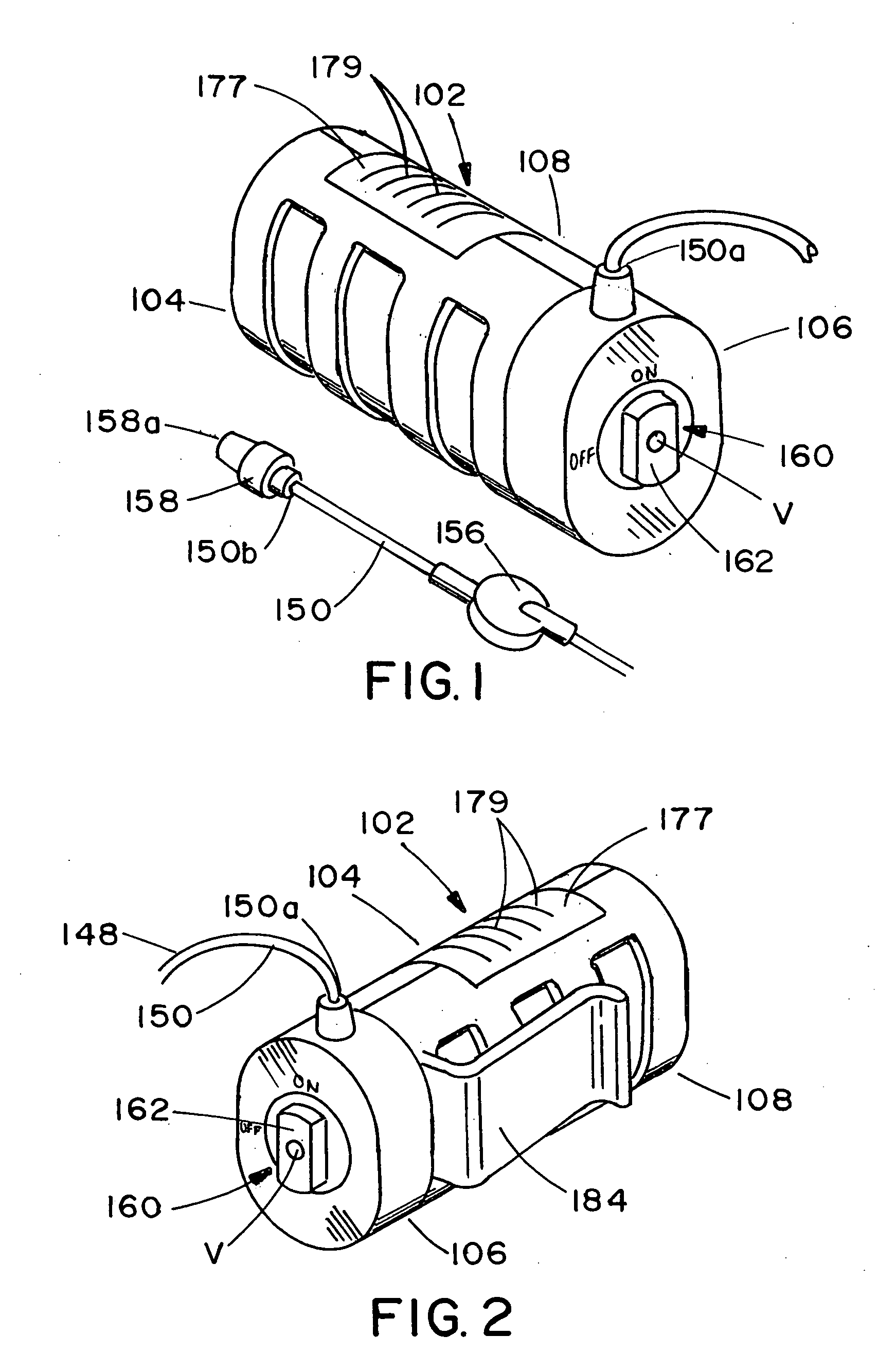
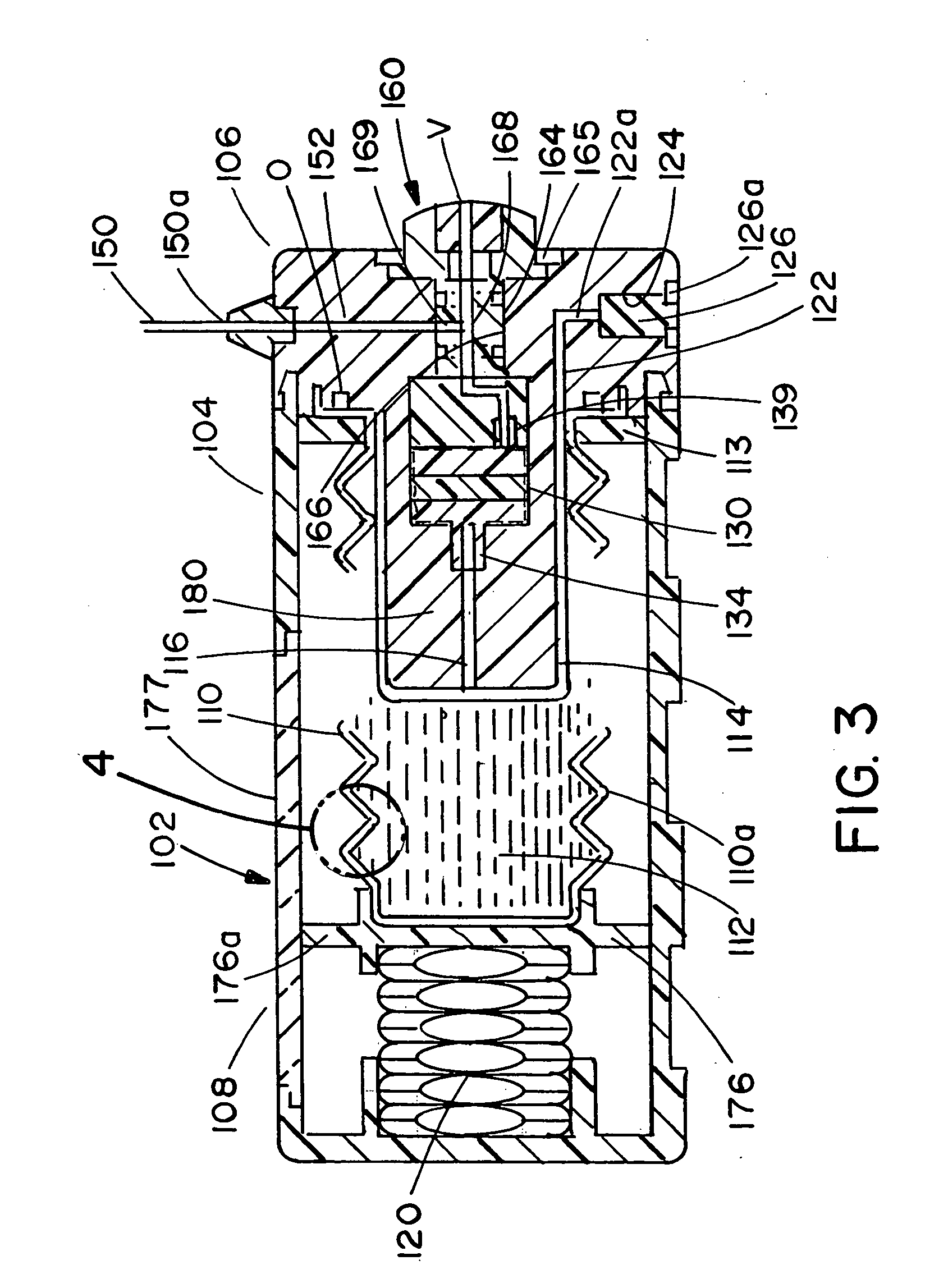
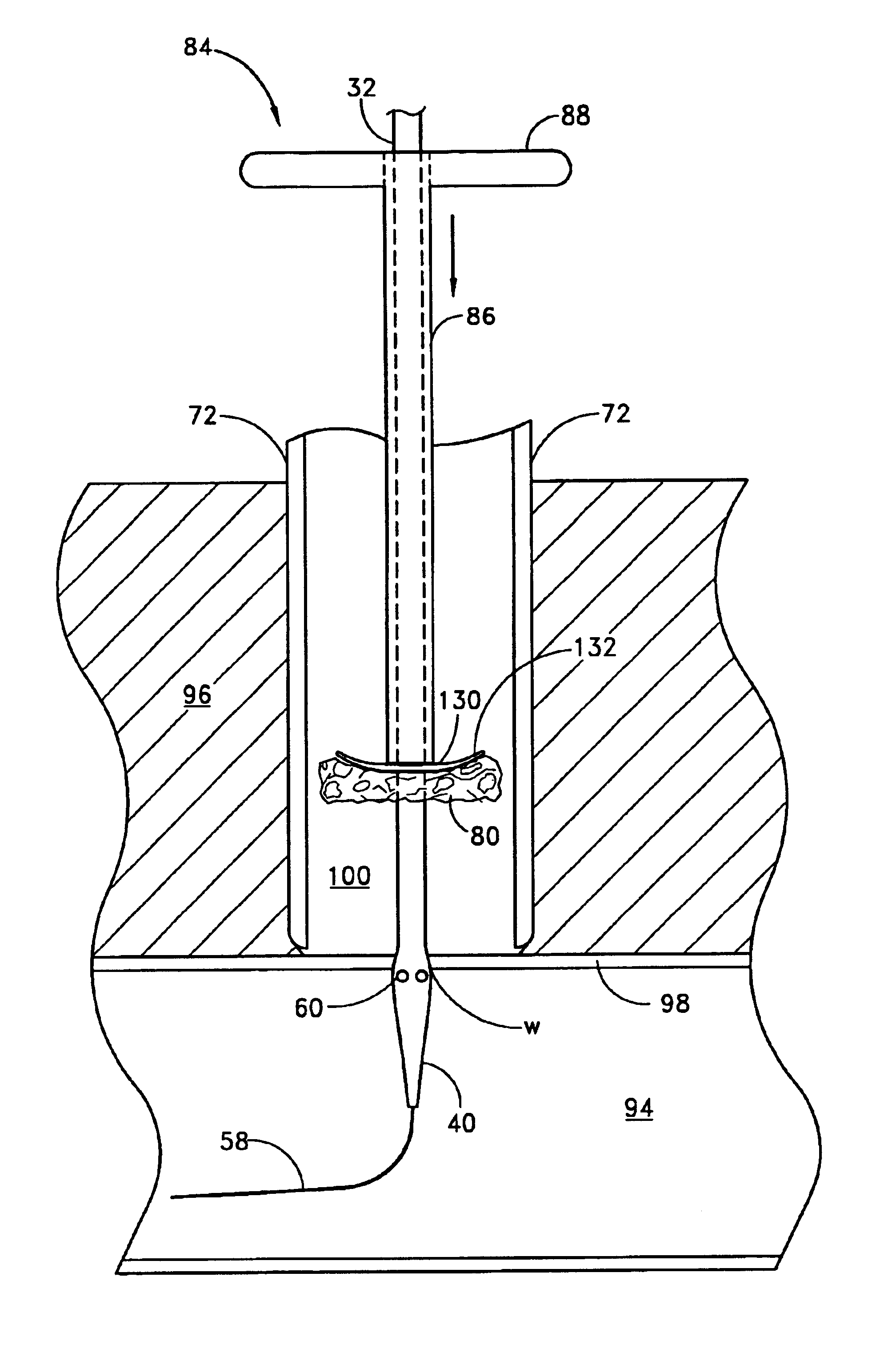
ActiveUS20060184142A1Unwanted growthEliminating an avenue of blood clotting and unwanted growthsMedical devicesSyringe needleGuide tube
A port (100) for a catheter assembly (200), including a body (102) and a cover (150) and having a distal discharge port (116) for connection to an implanted catheter assembly. Within the body is a longitudinal U-shaped channel (120) extending to a proximal body wall (104) from the distal body wall (106) along a longitudinal axis parallel to the axis of the discharge port (116). The channel has a rounded bottom (122) and is also rounded at the channel ends (126,124) at the distal and proximal body walls. The cover (150) provides for penetration by a syringe needle and seals upon needle withdrawal, with the cover having an inside surface (152) that is concave and rounded between the distal and proximal ends and also longitudinally, being generally smoothed into the channel sides and ends. The port has no inner sharp edges or corners and eliminates blood clotting and unwanted growth sites.
Owner:TWINCATH +1
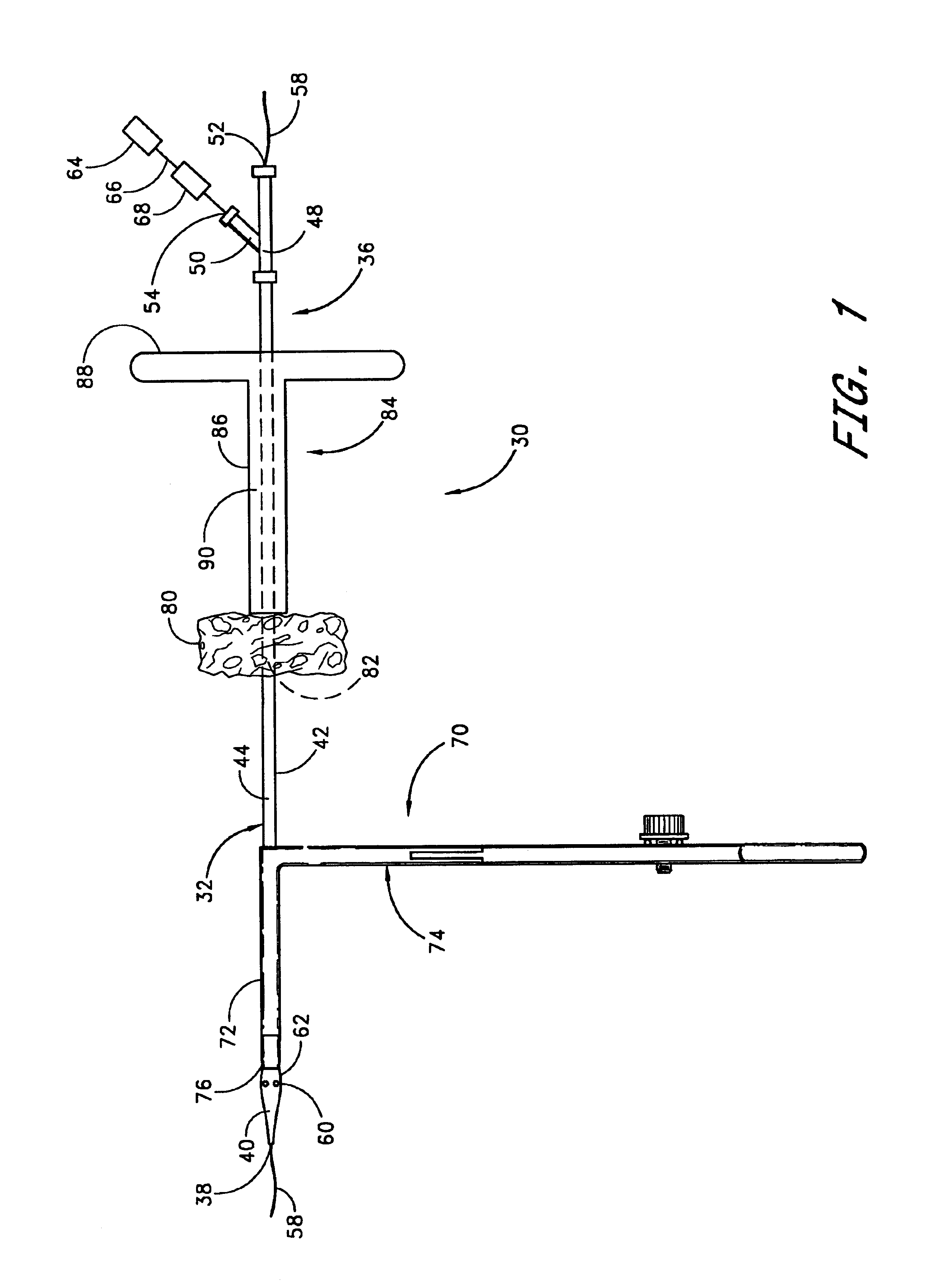
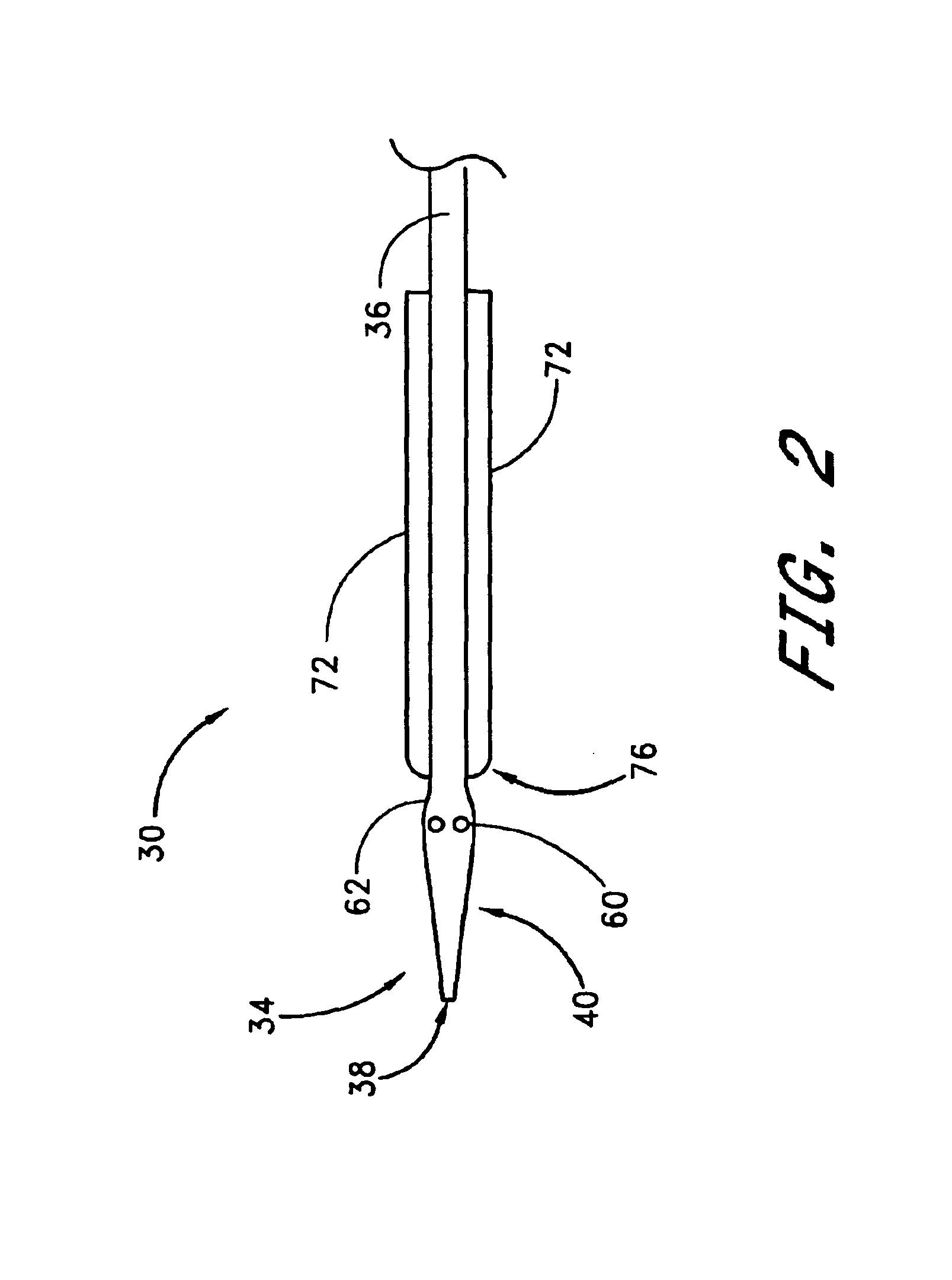
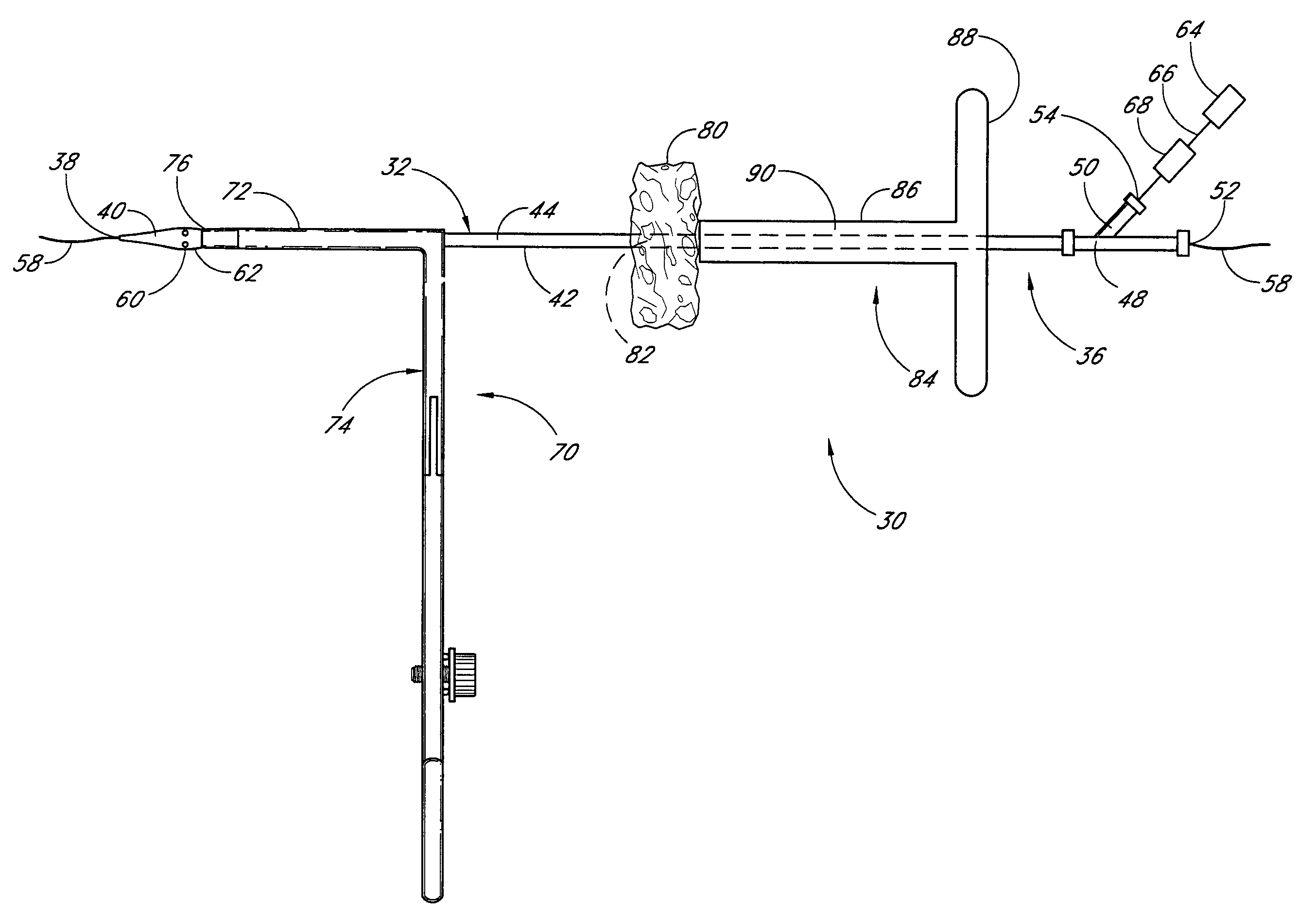
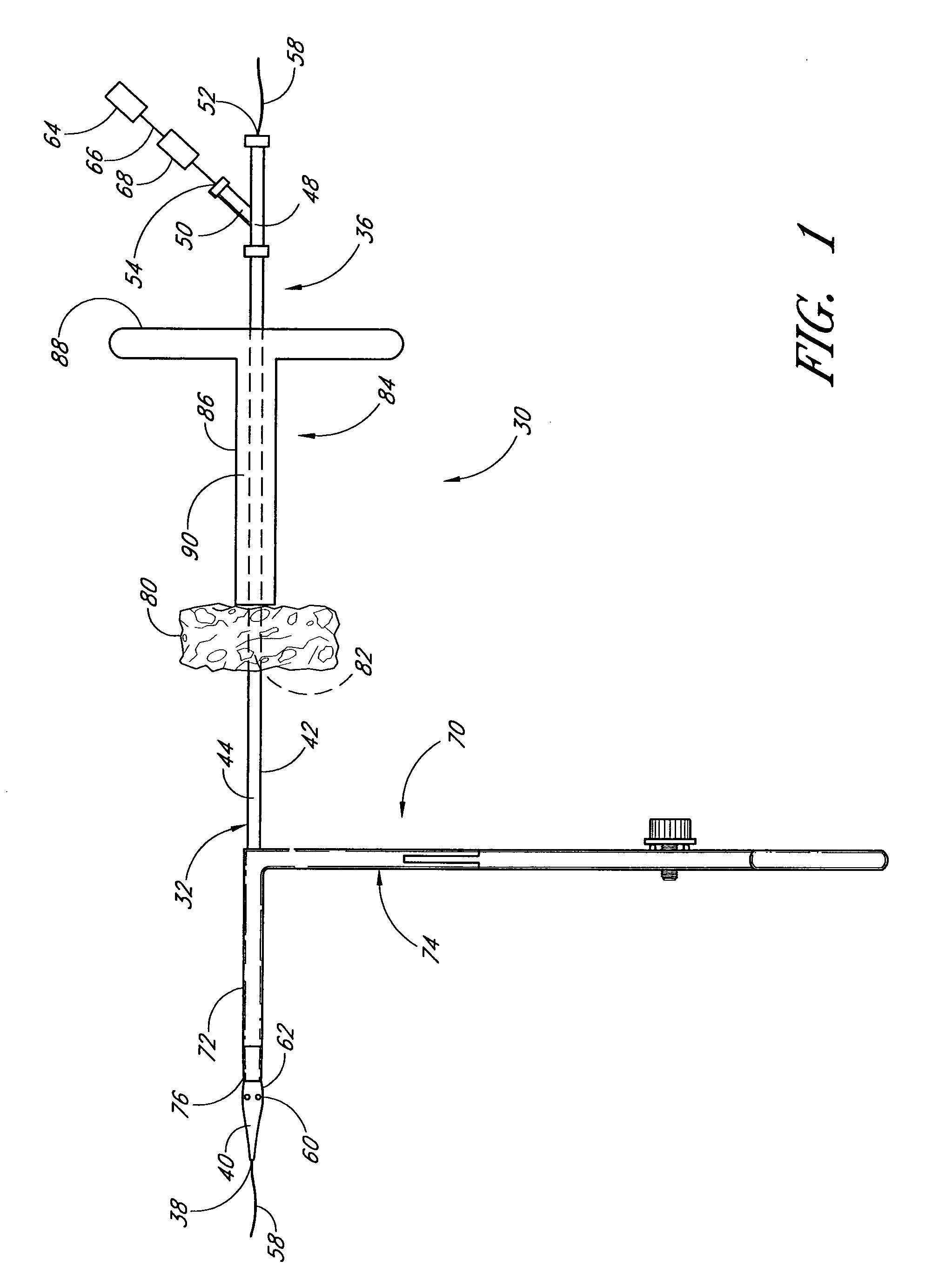
Method and apparatus for closing vascular puncture using hemostatic material
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes a guidewire and / or other surgical implement extending from the wound. A hemostatic material is advanced over the surgical implement and into contact with an area of the blood vessel surrounding the wound. The surgical implement is removed. Blood soaks the hemostatic material, and blood clotting is facilitated by the hemostatic agent within the material. A sealing layer of adhesive can be applied to the hemostatic material, confining the blood flow to the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by natural blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY
Vascular wound closure device and method
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes an apparatus that can be threaded over a guidewire into place at or adjacent the wound. The apparatus includes a chamber that encloses a hemostatic material therein. When the apparatus is positioned adjacent the wound as desired, the hemostatic material is deployed from the chamber. Blood contacts the hemostatic material, and blood clotting preferably is facilitated by a hemostatic agent within the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Infusion apparatus
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as, antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a substantially constant-force, compressible-expandable wave spring that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of medicament solution to the patient.
Owner:MARSHALL S KRIESEL REVOCABLE TRUST
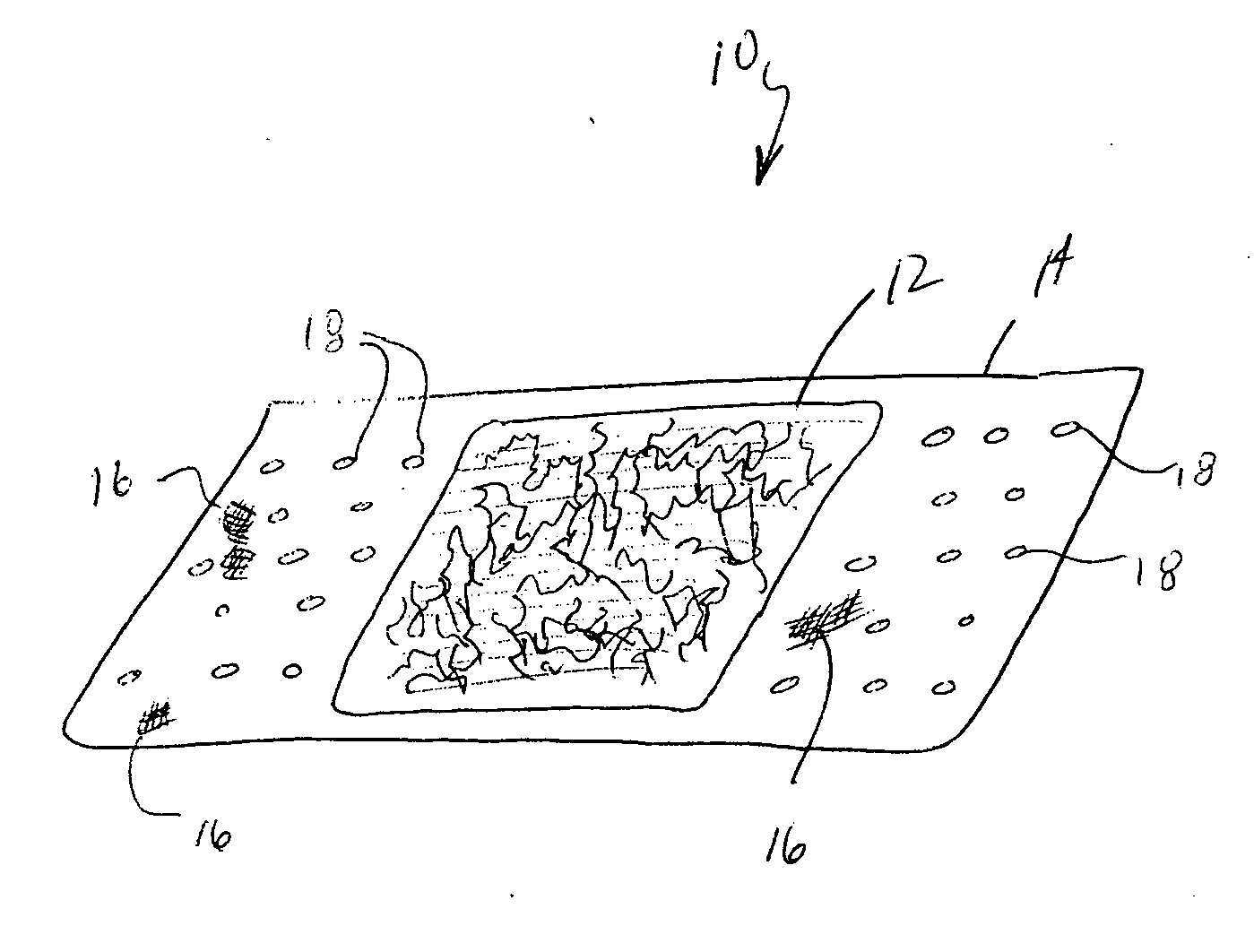
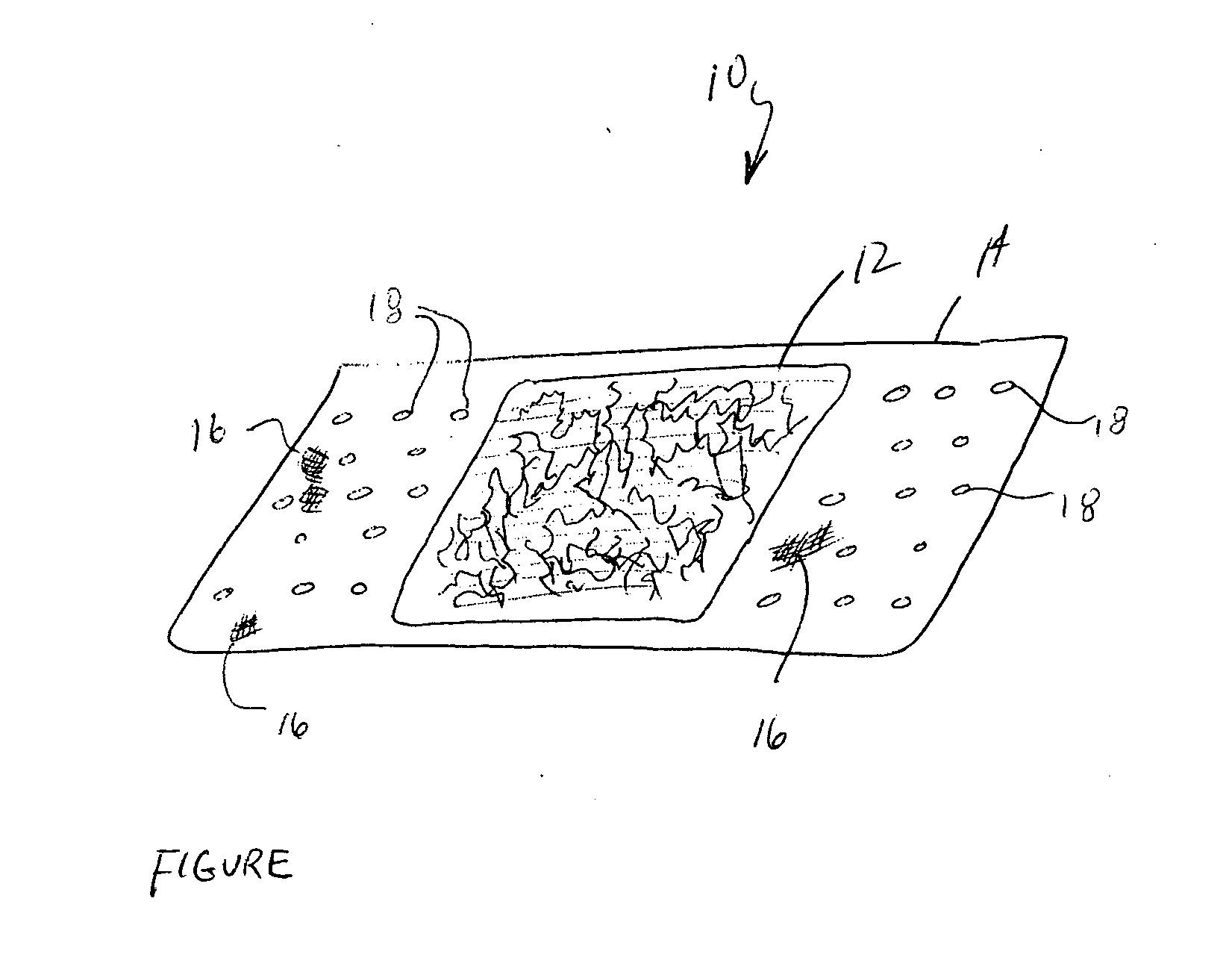
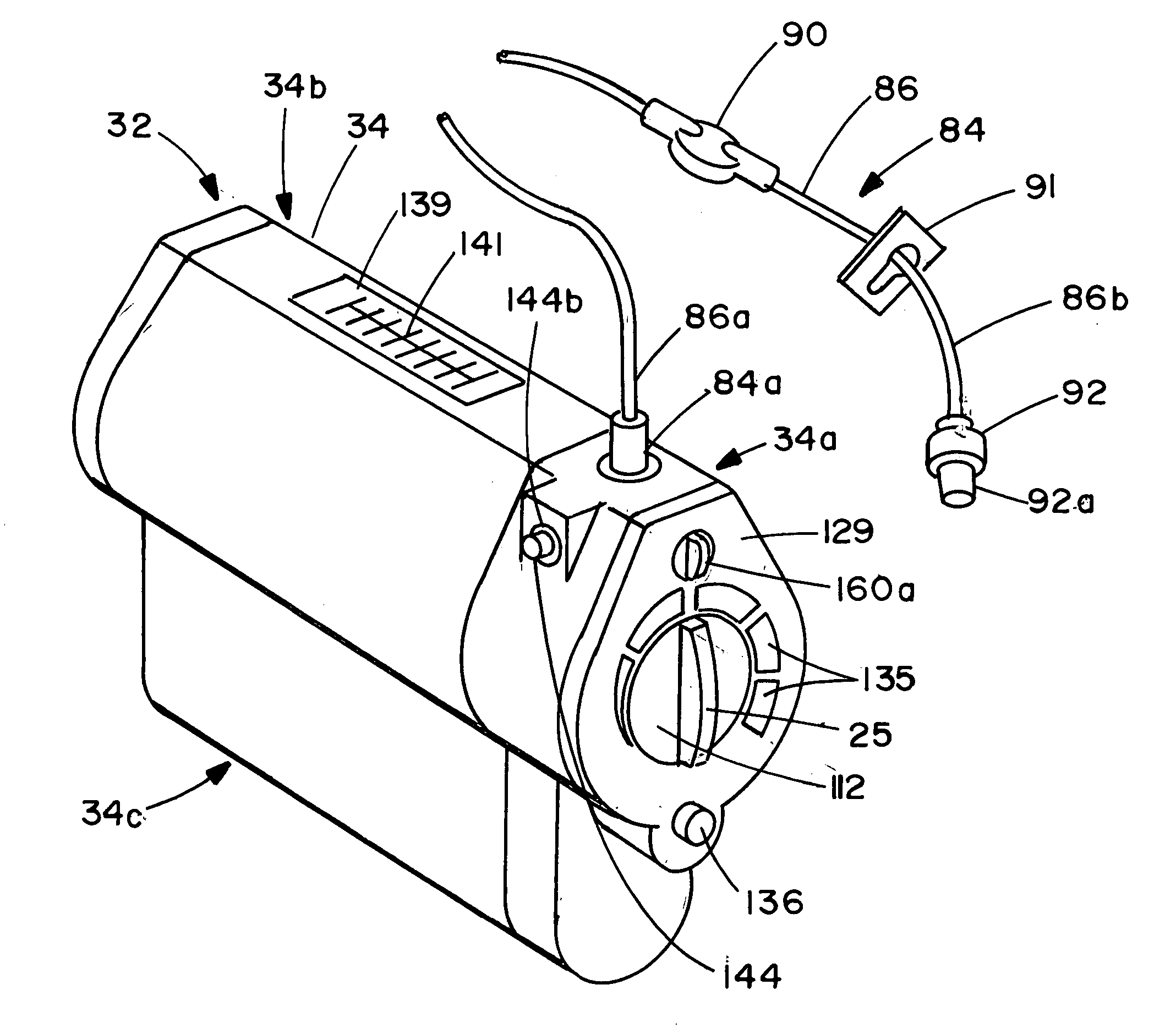
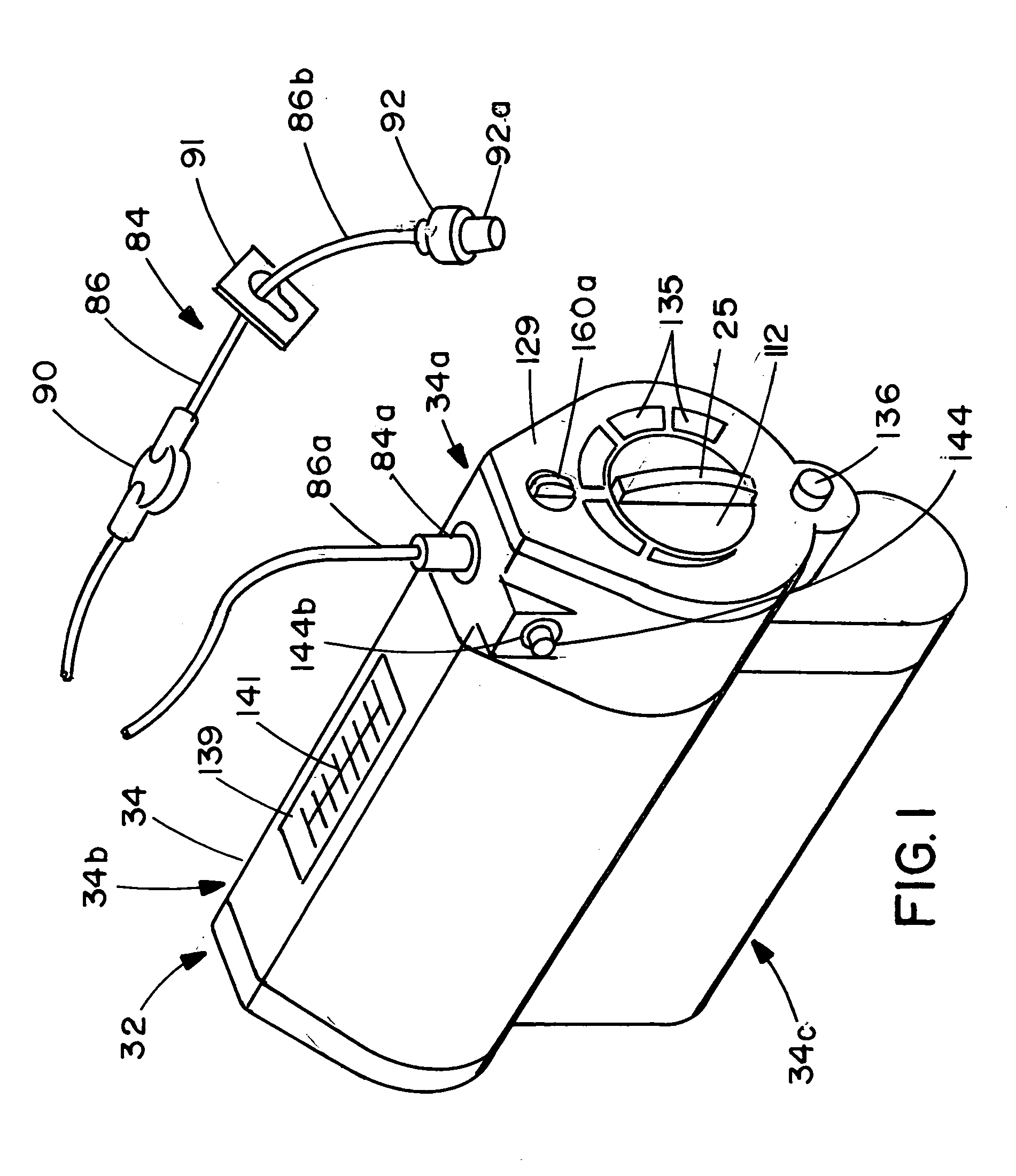
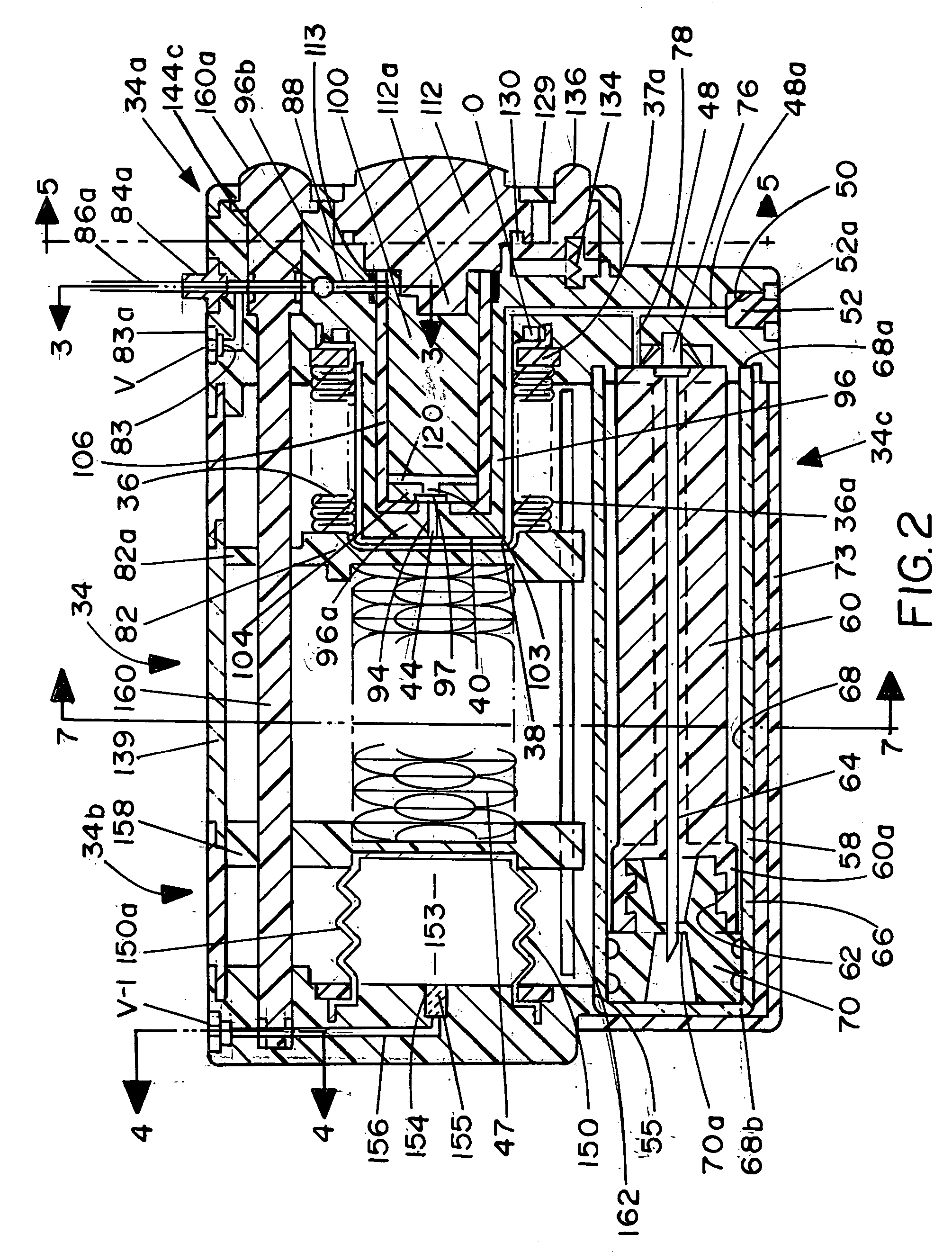
Device for the delivery of blood clotting materials to a wound site
InactiveUS20060211965A1Efficient use ofGood coagulationHead bandagesFinger bandagesChinMolecular sieve
A sleeve for covering a portion of a limb at a wound site incorporates a molecular sieve material which is at least partially exposed so that blood flowing from a wound site over which the sleeve is positioned contacts the molecular sieve material to facilitate clotting. One end of the sleeve may be closed to form a stocking or a mitten. The molecular sieve material may also be incorporated into a cap or similar device for wearing on the head of a victim. A chin strap may be attached to the cap to facilitate the retaining of the cap on the victim's head. The molecular sieve material may also be incorporated into a bandage that is directly wearable on a wound.
Owner:Z MEDICA LLC
Calcium zeolite hemostatic agent
ActiveUS20050074505A1Promote formationReduce heatBiocideInanimate material medical ingredientsBlood flowCalcium content
A composition for promoting the formation of clots in blood comprises a binder and a zeolite disposed in the binder, the zeolite having an adjusted calcium content. A method of forming a blood-clotting composition comprises the steps of providing a zeolite, combining the zeolite with a binder, and adjusting a calcium content of the zeolite to have an amount of calcium such that upon application of the composition to a wound, a heat of hydration is reduced and thereby heat transferred to the wound is reduced. A method of clotting blood flowing from a wound comprises the steps of applying a zeolite to the wound and maintaining the zeolite in contact with the wound for a predetermined amount of time. The zeolite preferably has an adjusted calcium content and is capable of producing a controllable blood clotting effect on the wound.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
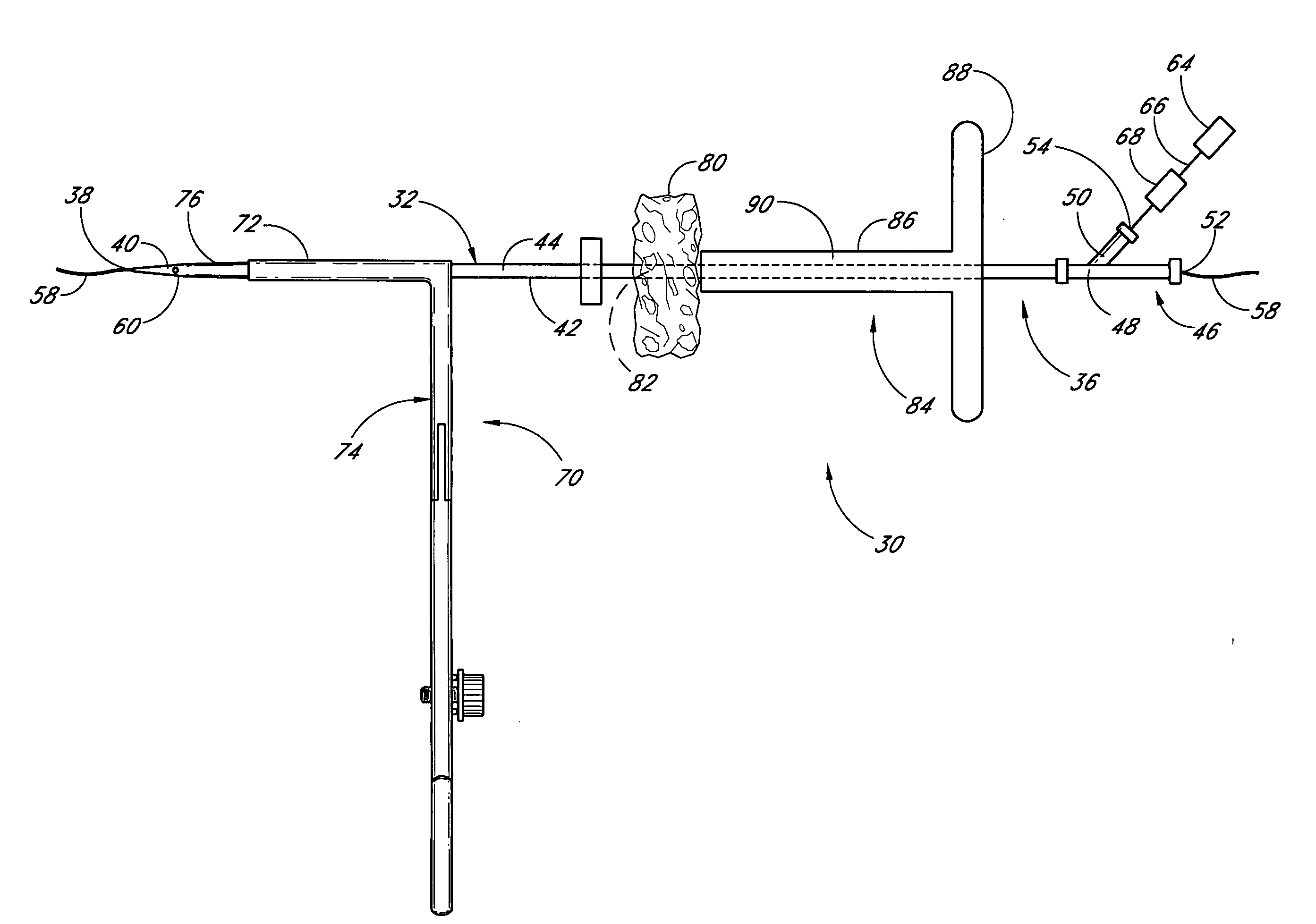
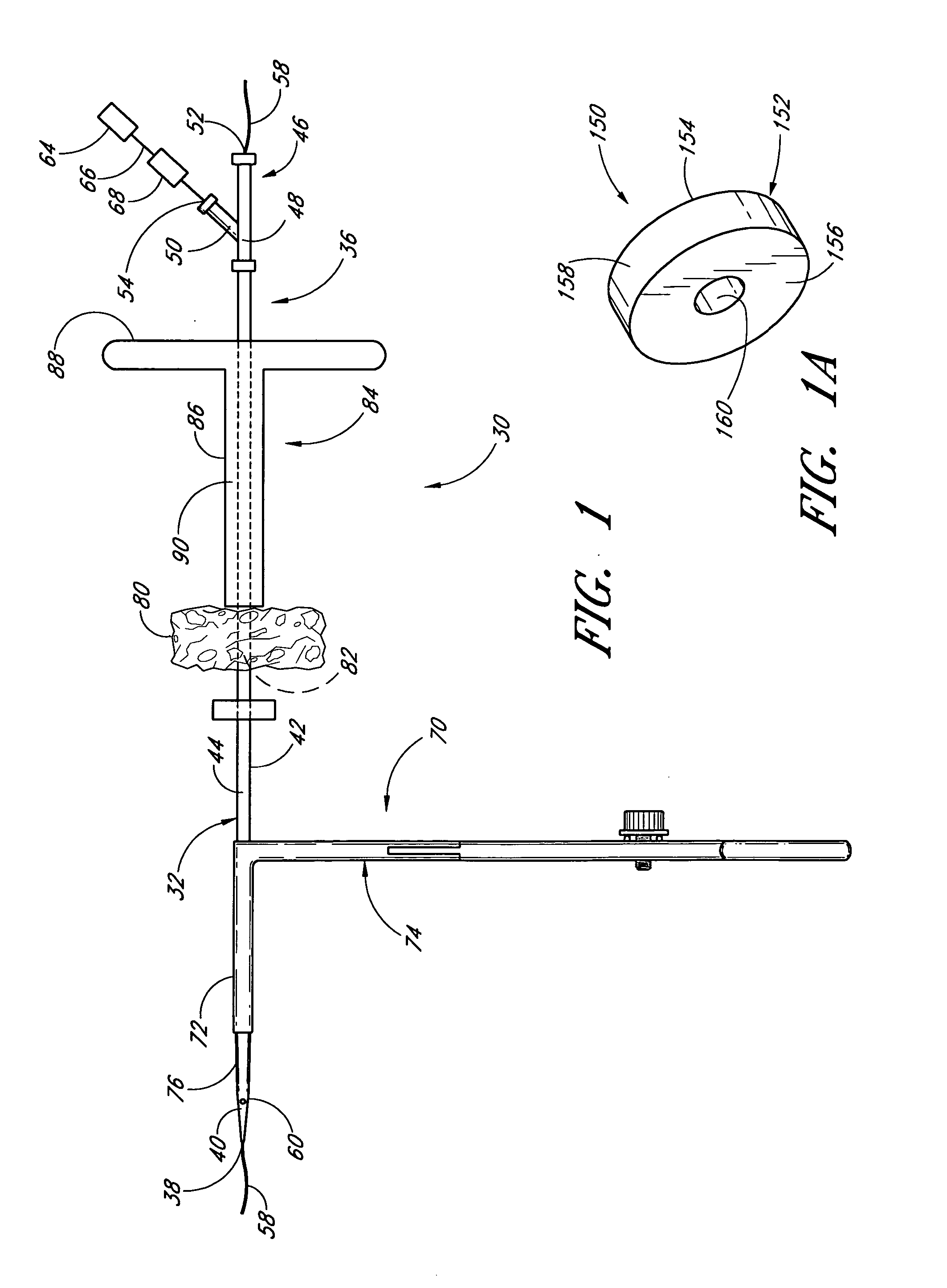
Devices and methods for promoting the formation of blood clots in esophageal varices
InactiveUS20070167971A1Inhibit injectionPromote formationBalloon catheterSurgeryThrombusSilicon dioxide
A device for promoting the clotting of blood in body cavities includes a flexible body portion; an expandable member located on the flexible body portion; and a blood clotting material attached to the expandable member. When used, insertion of at least a portion of the blood clotting material into the body cavity causes at least a portion of the blood clotting material to contact blood emanating from a bleed site. Methods of providing therapies to tube-shaped organs include the steps of providing suitable devices having expansion capabilities, positioning the devices at the appropriate bleed sites, and expanding the devices to cause blood clotting materials to contact the bleed sites. Materials that may be used as the blood clotting material include zeolites, molecular sieve materials, diatomaceous earth, clay, silica-based materials, oxidized cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, bioactive glass, biological hemostats, chitosan, and combinations of the foregoing.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Multichannel fluid delivery device
ActiveUS20050038387A1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureUniform rateMedical devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismStored energyAntibiotic Y
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from a plurality of prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a plurality of stored energy source that are provided in the form of compressible-expandable members of novel construction that provide the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from a plurality of device reservoirs. The apparatus further includes a plurality of fluid flow control assemblies that precisely control the flow of the medicament solutions from the plurality of device reservoirs to the patient.
Owner:BIOQ PHARMA
Temporary absorbable venous occlusive stent and superficial vein treatment method
InactiveUS20050107867A1Promotes localized blood clottingPromotes fibrosisSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSuperficial veinInsertion stent
A temporary absorbable venous occlusive stent for use in a varicose vein treatment method includes a stent body, a bio-absorbable material associated with the body, and a closure for blocking blood flow past the stent when implanted in a vein. The stent produces localized blood clotting, fibrosis and vein collapse as it is absorbed. A permanent blockage is produced that prevents the undesirable back flow of blood from above the blockage site, thereby reducing distension of a varicose vein below the blockage site.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Infusion apparatus with modulated flow control
InactiveUS20050033232A1Easy to useEasy constructionFlexible member pumpsMedical devicesStored energyConstant force
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a substantially constant-force, compressible-expandable wave spring that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of medicament solution to the patient. Additionally, the device includes a novel modulating assembly for controllably modulating the force exerted by the wave spring tending to expel the fluid from the device reservoir.
Owner:BIOQUIDDITY
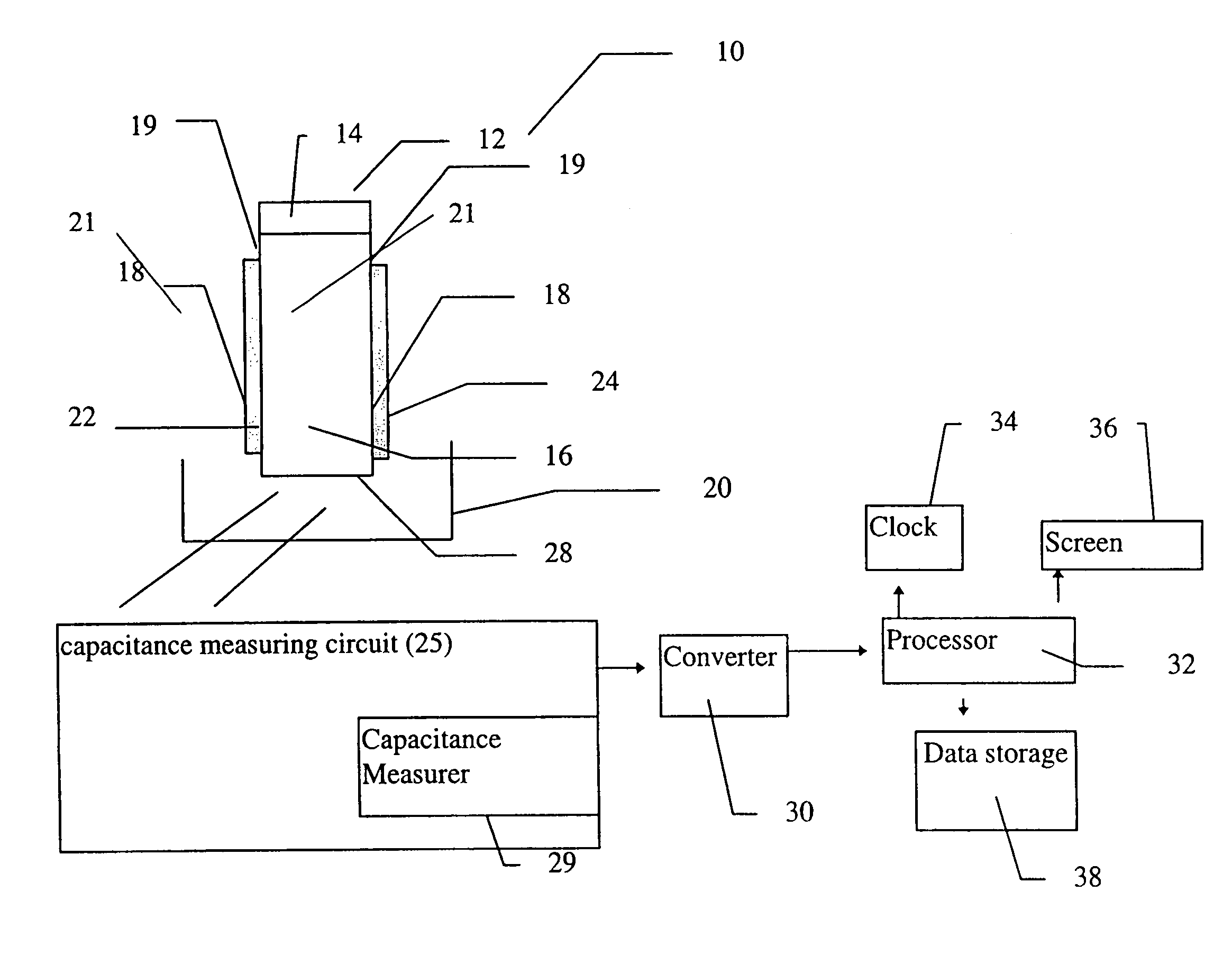
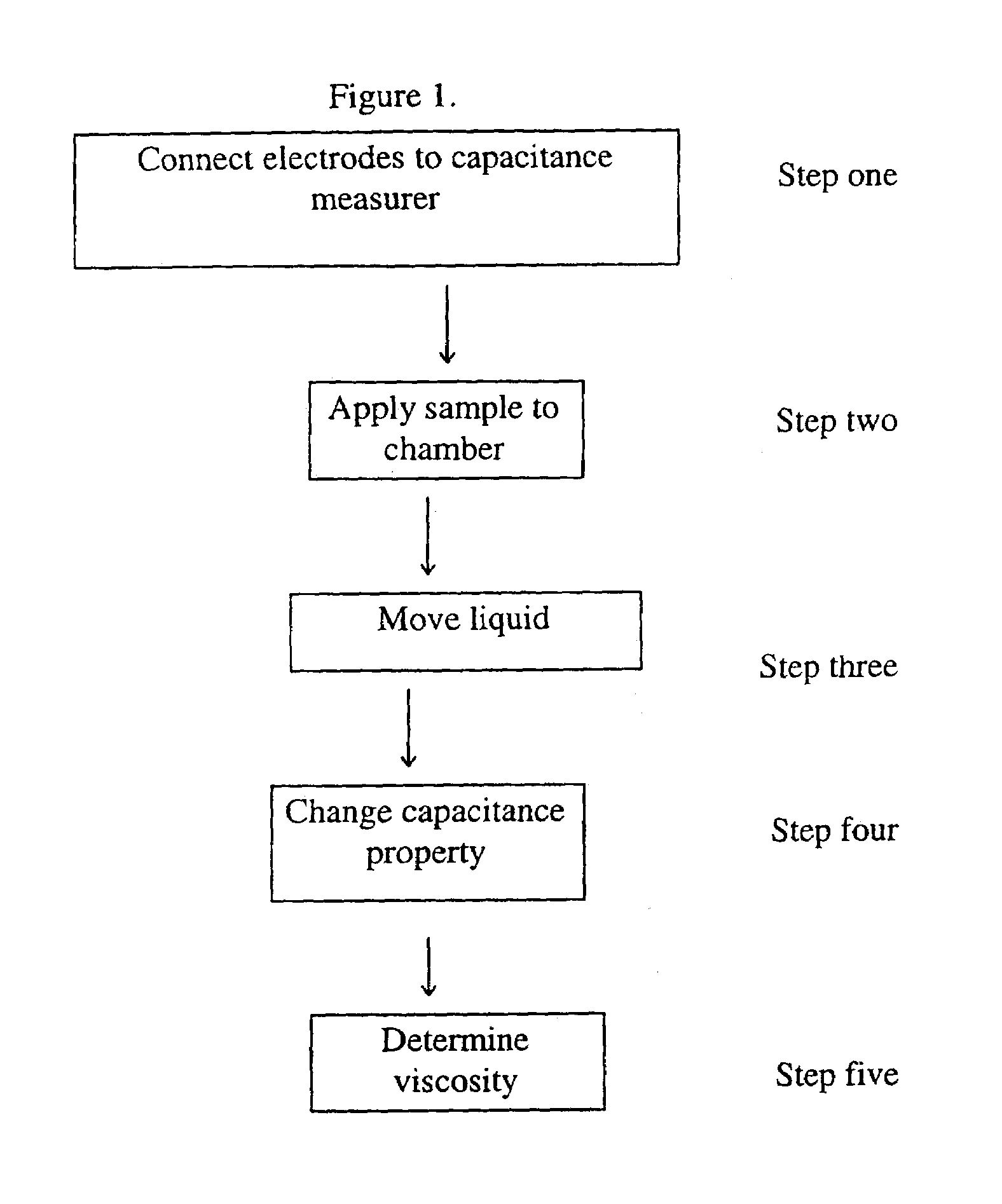
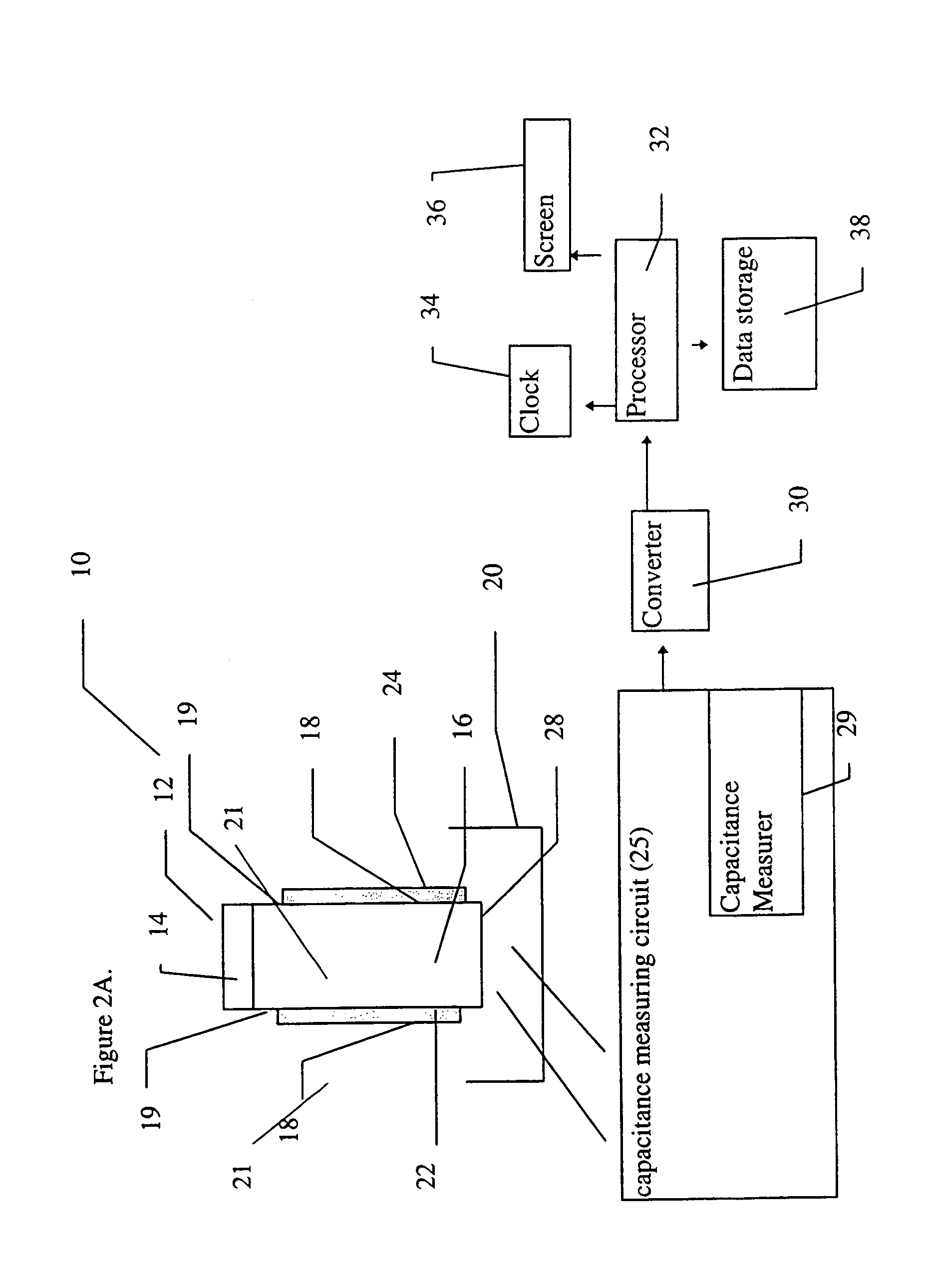
Device for the determination of blood clotting by capacitance or resistance
InactiveUS7021122B1Machines/enginesLubrication indication devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceViscosity
A sensor device (10) and a method for measuring a viscosity of a sample of a liquid. The sensor features a chamber (12) for receiving the sample of the liquid, two electrodes (18) disposed either on the surfaces of the chamber, but possibly isolated from contacting the sample, or electrodes located externally to the chamber, and a capacitance measuring circuit (25). The sensor is used by connecting to a measurer for determining a capacitance on the electrodes, such that the capacitance directly reflects a volume occupied by the sample of the liquid. Preferably, the liquid is blood and the capacitance is used to determine the clotting time of the blood. Also preferably, a cover for the chamber is provided with at least one aperture, which more preferably is a mesh. Alternatively, an electrical property such as the amplitude of current passed through the sample is used to determine clotting time. Also preferably, the time period required for the maximum capacitance to be reached could be measured. Alternatively, the capacitance could be measured after a fixed time period (34) had elapsed. Also alternatively, the time period required for the maximum current to be reached could be measured, or the amount of current could be measured after a fixed time period had elapsed. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, a kit for measuring the clotting time of blood is provided. In other preferred embodiments of the present invention, methods are provided for using the kit and device of the present invention.
Owner:ORGENICS BOISENSORS
Multichannel fluid delivery device
ActiveUS7169128B2Uniform ratePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesStored energyAntibiotic Y
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from a plurality of prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a plurality of stored energy source that are provided in the form of compressible-expandable members of novel construction that provide the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from a plurality of device reservoirs. The apparatus further includes a plurality of fluid flow control assemblies that precisely control the flow of the medicament solutions from the plurality of device reservoirs to the patient.
Owner:BIOQ PHARMA
Devices for the delivery of molecular sieve materials for the formation of blood clots
InactiveUS20070104768A1Easily and cleanly pulled awayEasy to disassembleAbsorbent padsSheet deliveryCelluloseMolecular sieve
An apparatus for promoting the clotting of blood comprises a substrate and a zeolite in powder form deposited on the substrate. At least a portion of the substrate is selected from a group consisting of paper, polymer matrix, polyethylene sheet, hydrophilic macromolecules, and cloth. An agent for promoting the clotting of blood comprises a porous web structure and a compound capable of providing hemostasis incorporated into the porous web structure. The compound capable of providing hemostasis comprises at least one cationic species interspersed throughout and coulombically bound to the web structure such that the cationic species provides a positive charge to the web structure. A method of fabricating a blood clotting apparatus comprises the steps of providing a cellulose-based substrate; providing a zeolite; incorporating at least one cationic species into a structure of the zeolite to impart a positive charge thereto; and impregnating the cellulose-based substrate with the zeolite.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Temporary absorbable venous occlusive stent and superficial vein treatment method
InactiveUS20060190076A1Reduce bloatPromotes localized blood clotting, fibrosis and vein collapseSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSuperficial veinBlood flow
A temporary absorbable venous occlusive stent for use in a varicose vein treatment method includes a stent body, a bio-absorbable material associated with the body, and a closure for blocking blood flow past the stent when implanted in a vein. The stent produces localized blood clotting, fibrosis and vein collapse as it is absorbed. A permanent blockage is produced that prevents the undesirable back flow of blood from above the blockage site, thereby reducing distension of a varicose vein below the blockage site.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Pillow for the delivery of blood clotting materials to a wound site
A pillow for supporting a wounded victim at a wound site incorporates a molecular sieve material which is at least partially exposed so that blood flowing from a wounded area supported by the pillow contacts the molecular sieve material to facilitate the clotting of blood flowing from the wound. A removable flexible casing for a pillow incorporates a molecular sieve material capable of providing a clotting function to the blood. An overlay comprising a molecular sieve material can be placed on top of a conventional pillow, on a gurney, or on any other surface. A method of treating a bleeding wound includes providing a pillow having molecular sieve material in particle form retained therein and using the pillow to support a bleeding wound such that blood flowing from the wound comes into contact with the molecular sieve material, thereby causing the blood to coagulate.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
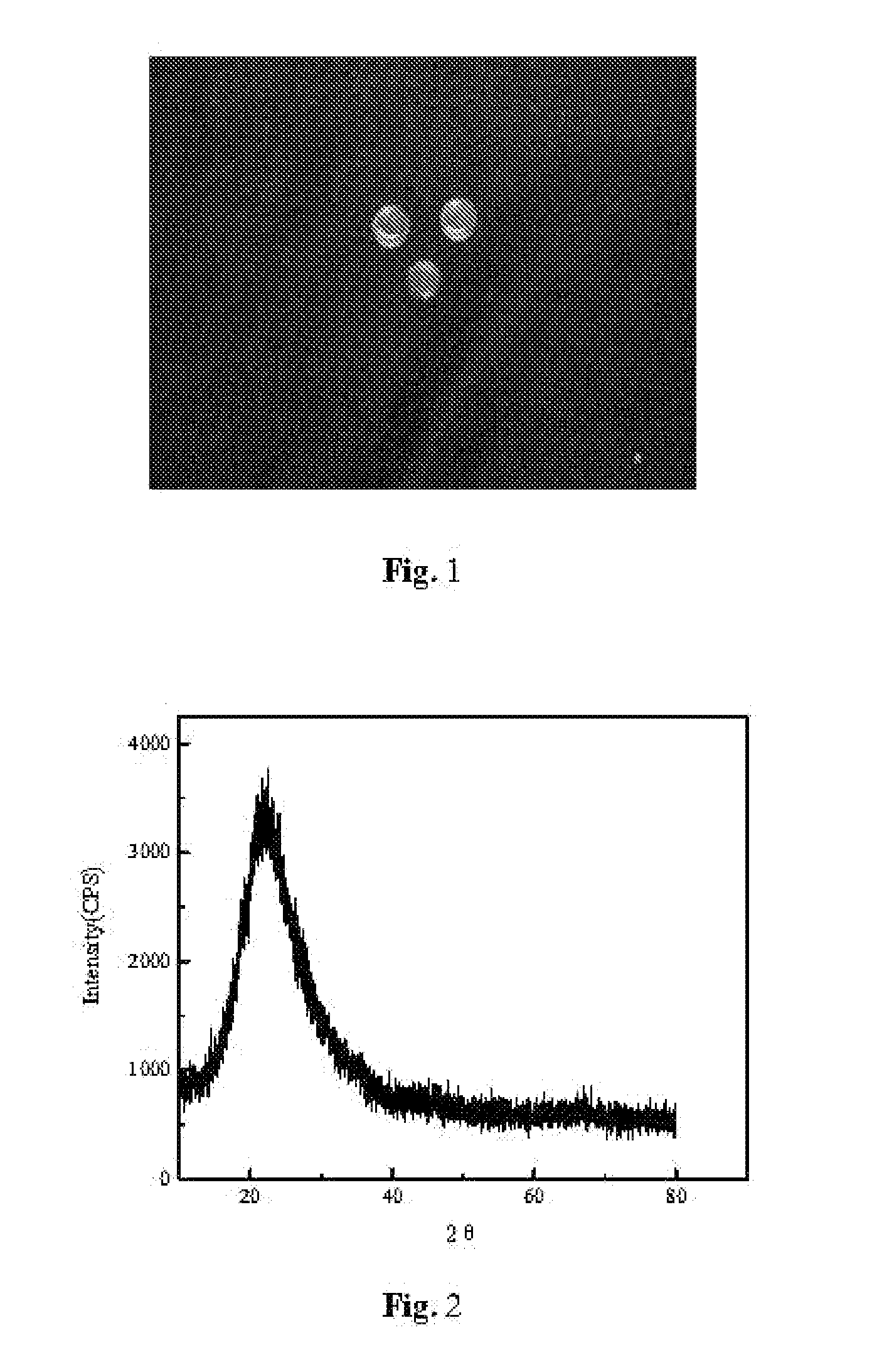
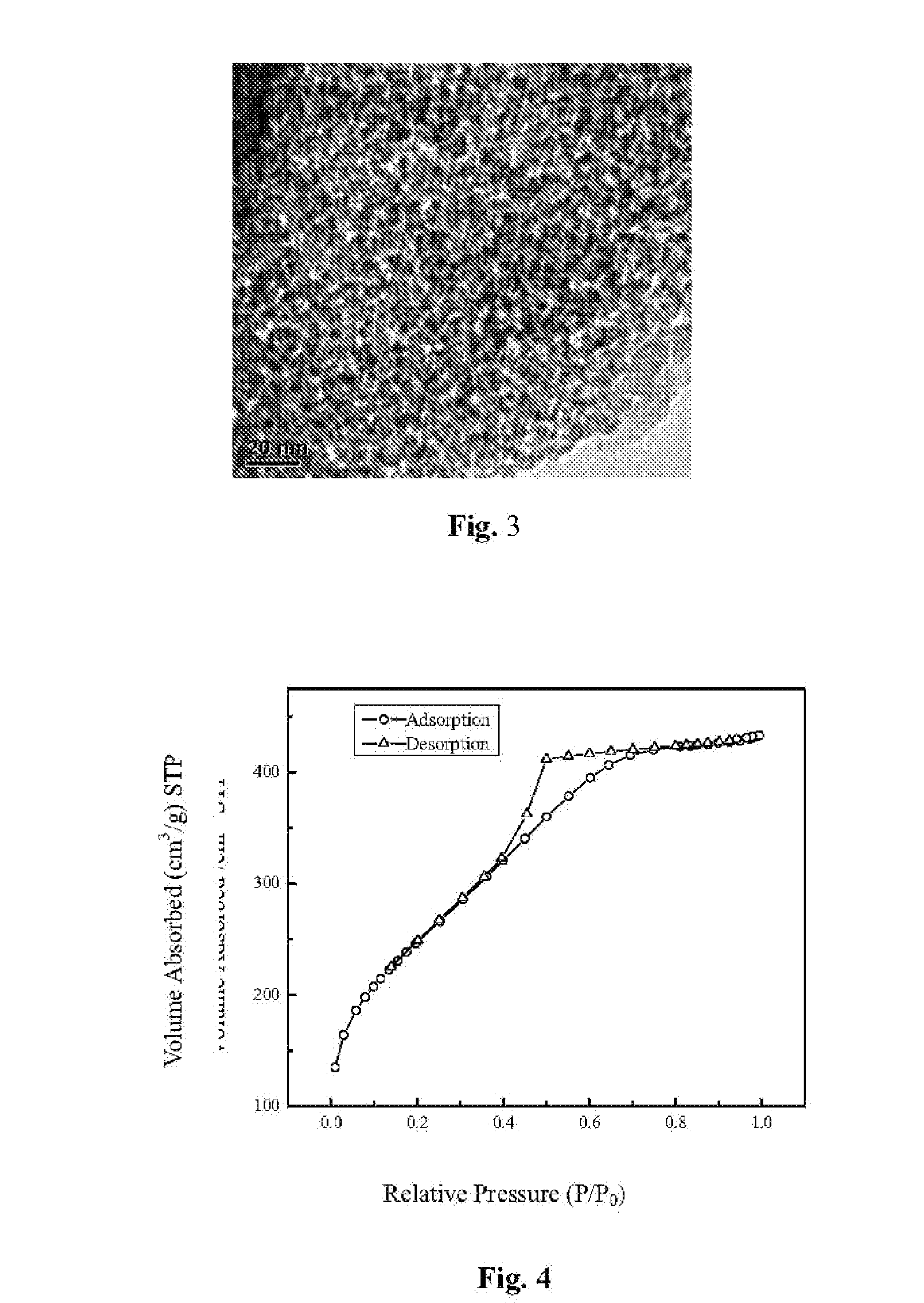
Nanometer mesoporous silica-based xerogel styptic material and its preparing process and application
ActiveUS20090232902A1Improve adsorption capacityHigh porosityBiocideSilicaAdditive ingredientTherapeutic effect
The invention disclosed a novel mesoporous silica-based xerogel and its use in hemorrhage control. The mesoporous silica-based xerogel material has tunable mesopores (1-50 nm), high specific surface area (100-1400 m2 / g), macroscopical morphology (powder, film, disc, column, etc.) and adjustable compositions (SiO2, CaO and P2O5, etc.) as well as good biodegradation. The mesoporous silica-based xerogels herein effectively promote the blood clotting under various conditions including slow and severe hemorrhage, even at the blood oozing site of bone defect. Meanwhile, the networks of silica-based xerogel with good elastic and mechanic properties, formed by adsorbing a large amount of water, can modulate the cell behavior and tissue growth, and thus promote the wound healing. Additionally, due to the mesoporous structure, the materials have the potential to load drug, thrombin and bioactive factors, which is favorable for the therapeutical efficacy.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIJI BIOTECH CO LTD
Calcium zeolite hemostatic agent
ActiveUS7595429B2Promote formationReduce heatBiocideInanimate material medical ingredientsCalcium contentCalcium EDTA
A composition for promoting the formation of clots in blood comprises a binder and a zeolite disposed in the binder, the zeolite having an adjusted calcium content. A method of forming a blood-clotting composition comprises the steps of providing a zeolite, combining the zeolite with a binder, and adjusting a calcium content of the zeolite to have an amount of calcium such that upon application of the composition to a wound, a heat of hydration is reduced and thereby heat transferred to the wound is reduced. A method of clotting blood flowing from a wound comprises the steps of applying a zeolite to the wound and maintaining the zeolite in contact with the wound for a predetermined amount of time. The zeolite preferably has an adjusted calcium content and is capable of producing a controllable blood clotting effect on the wound.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Hemostatic devices
ActiveUS20130344131A1Reduce the amount requiredConvenient and cost-effective for manufacturingBiocidePowder deliveryFiberSolubility
Hemostatic devices for promoting blood clotting can include a substrate (e.g., gauze, textile, sponge, sponge matrix, one or more fibers, etc.), a hemostatic material disposed thereon such as kaolin clay, and a binder material such as crosslinked calcium alginate with a high guluronate monomer molar percentage disposed on the substrate to substantially retain the hemostatic material material. When the device is used to treat a bleeding wound, at least a portion of the clay material comes into contact with blood to accelerate clotting. Moreover, when exposed to blood, the binder has low solubility and retains a majority of the clay material on the gauze. A bandage that can be applied to a bleeding wound to promote blood clotting includes a flexible substrate and a gauze substrate mounted thereon.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Devices and methods for the delivery of blood clotting materials to bleeding wounds
ActiveUS20070065491A1Easy to disassemblePromote formationAbsorbent padsSheet deliveryParticulatesReticular formation
An apparatus for promoting the clotting of blood and controlling bleeding comprises a receptacle for retaining blood clotting material in particulate form therein. A pad for controlling bleeding comprises a mesh structure and a support attached to the mesh structure to facilitate the application of pressure to the pad and the wound. A bandage applicable to a bleeding wound comprises a mesh structure and a flexible substrate attached to the mesh structure, the substrate being a cloth or plastic member that may be adhesively attachable to cover a wound. In any embodiment, at least a portion of the receptacle or mesh structure is defined by a mesh having openings therein, and at least a portion of the particulate blood clotting material is in direct contact with blood. The mesh may include a zeolite powder impregnated or otherwise incorporated therein.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
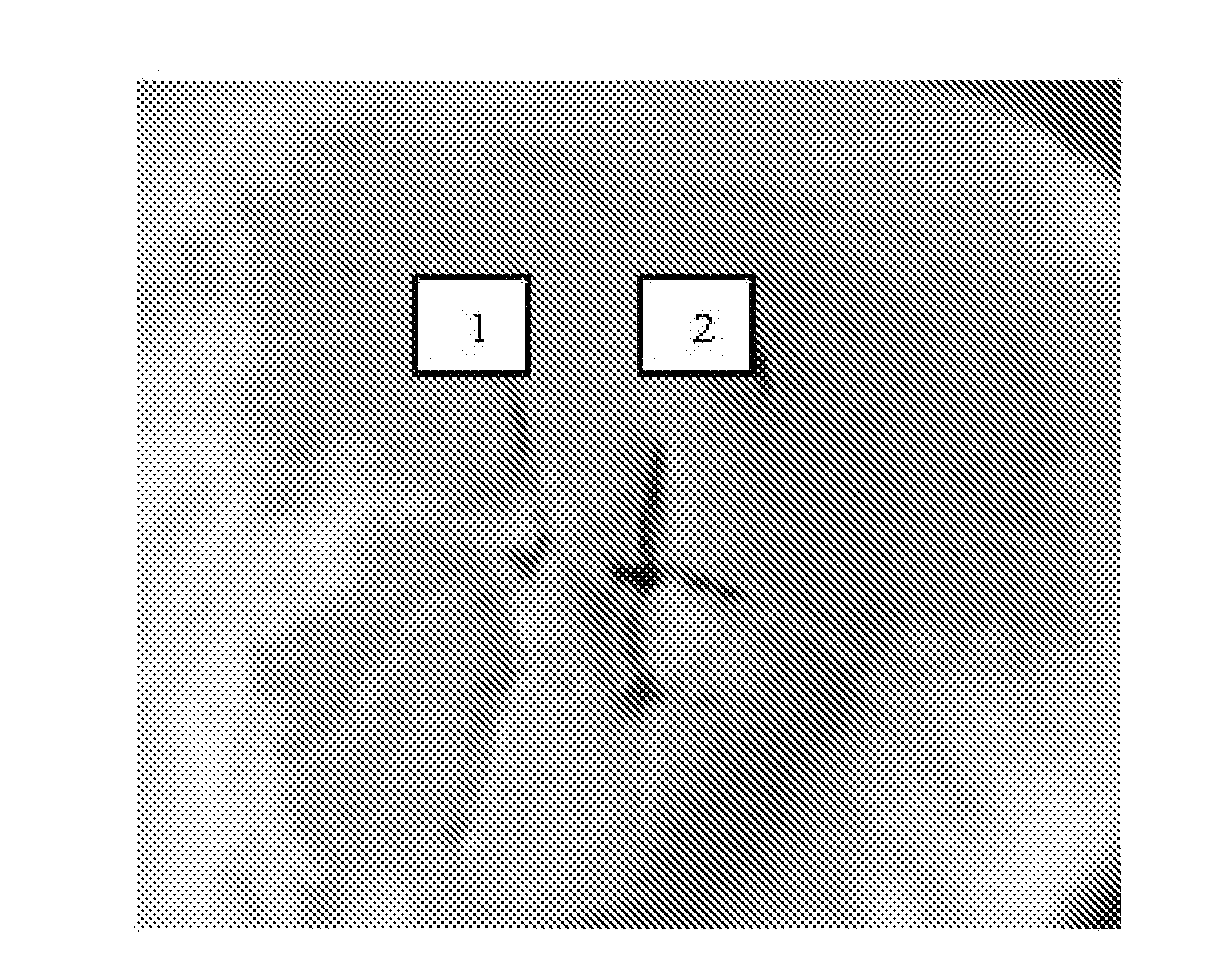
Method of measuring bleeding volume
A method of measuring blood clotting ability of a patient. A known volume of blood is dispensed on a reference disc of blotter paper, such that at least one reference blotch is formed on the reference disc. The surface area of the reference blotch formed on the reference disc, such that a relationship between the volume of blood and the surface area of the reference blotch can be obtained. An incision is made at the patient. A piece of blotter paper to the incision is applied to the incision to collect blood flowing therefrom, such that at least one blotch is formed on the piece of blotter paper. The surface area of the blotch formed on the piece of blotter paper is measured. The volume of the blood absorbed blood by the blotter paper is calculated according to the relationship between the blood volume and the surface area of the blotch.
Owner:KLEIN JEFFREY A
Fluid delivery device
InactiveUS20050277883A1Easy to useEasy constructionAmpoule syringesMedical devicesDrugs solutionStored energy
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a compressible-expandable elastomeric member of novel construction that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of the medicament solution to the patient.
Owner:BIOQUIDDITY
Hemostatic Agent Composition and Method of Delivery
ActiveUS20080299226A1Good coagulationTerminate hemorrhagingBiocideNon-adhesive dressingsMedicineHemostatic Agent
A hemostatic agent composition that includes a clay hemostatic agent which is inert and non-reactive relative to blood clotting proteins and platelets, yet is capable of accelerating the formation of a stable clot when applied to an actively bleeding wound.
Owner:MENTKOW JACK +1
Vascular wound closure device and method
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes a guidewire and / or other surgical implement extending from the wound. A hemostatic material is advanced over the surgical implement and into contact with an area of the blood vessel surrounding the wound. The surgical implement is removed. Blood soaks the hemostatic material, and blood clotting is facilitated by the hemostatic agent within the material. A sealing layer of adhesive can be applied to the hemostatic material, confining the blood flow to the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by natural blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Blood clotting compositions and wound dressings
InactiveUS20090299253A1Efficient use ofEasy to disassembleInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMolecular sieveWound dressing
In general, the basic material forming the wound dressing, covering, and / or application system of the present invention for use in blood coagulation comprises a combination of one or more components selected from the group consisting of clay materials, a molecular sieve material, principally zeolite, and inorganic oxide materials. Although the actual process which enables the wound dressing, covering, and / or application system of the present invention to effectively coagulate flowing blood is unknown, it is believed that the molecular sieve material selectively absorbs small molecules, such as water, from the blood. Due to the absorption of the water molecules, it is believed that the rate of blood clotting is increased.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
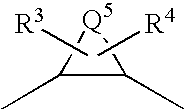
Diamine derivatives
A compound represented by the general formula (1):Q1-Q2-T0-N(R1)-Q3-N(R2)-T1-Q4 (1)wherein R1 and R2 are hydrogen atoms or the like; Q1 is a saturated or unsaturated, 5- or 6-membered cyclic hydrocarbon group which may be substituted, or the like; Q2 is a single bond or the like; Q3 is a groupin which Q5 is an alkylene group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms, or the like; and T0 and T1 are carbonyl groups or the like; a salt thereof, a solvate thereof, or an N-oxide thereof.The compound is useful as an agent for preventing and / or treating cerebral infarction, cerebral embolism, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, pulmonary infarction, pulmonary embolism, Buerger's disease, deep venous thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, thrombus formation after valve or joint replacement, thrombus formation and reocclusion after angioplasty, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), thrombus formation during extracorporeal circulation, or blood clotting upon blood drawing.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
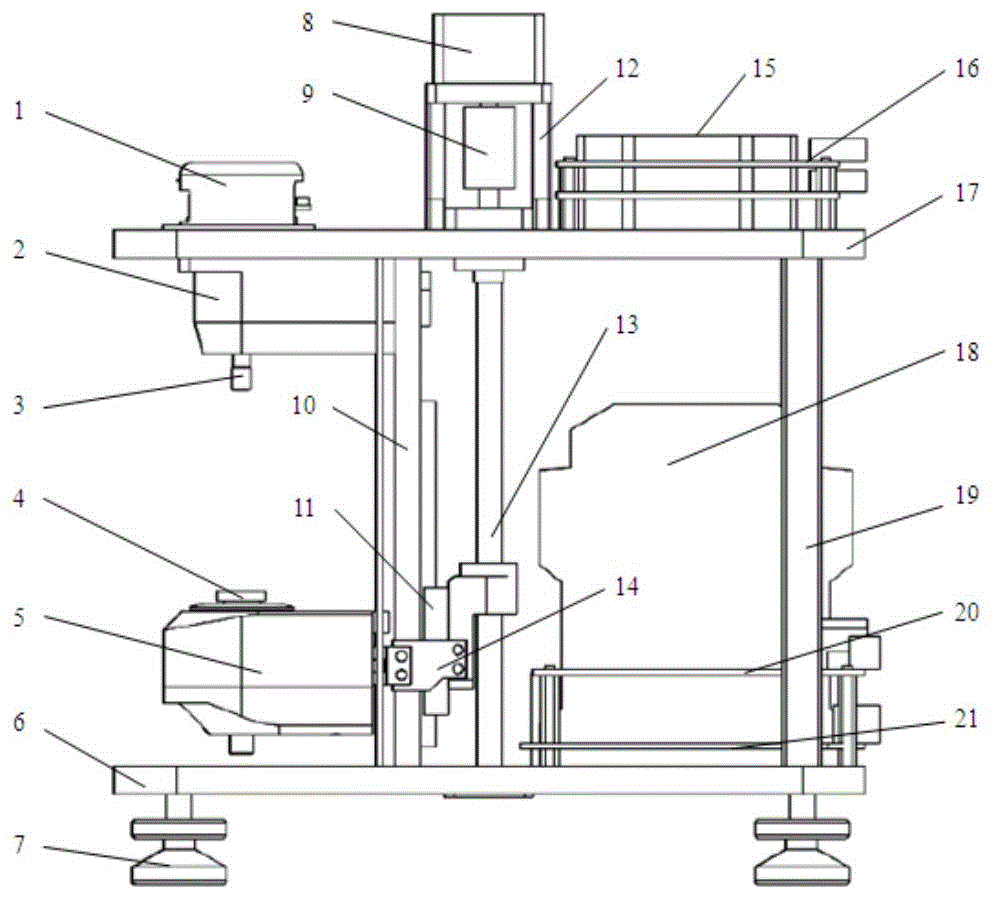
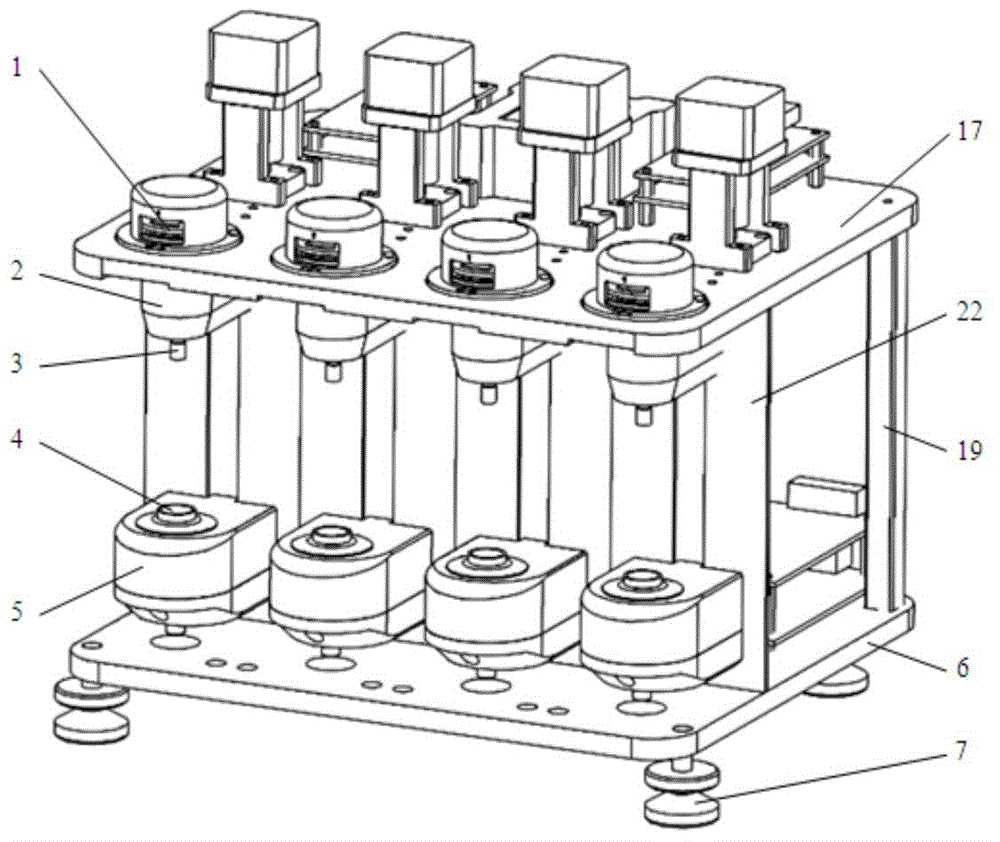
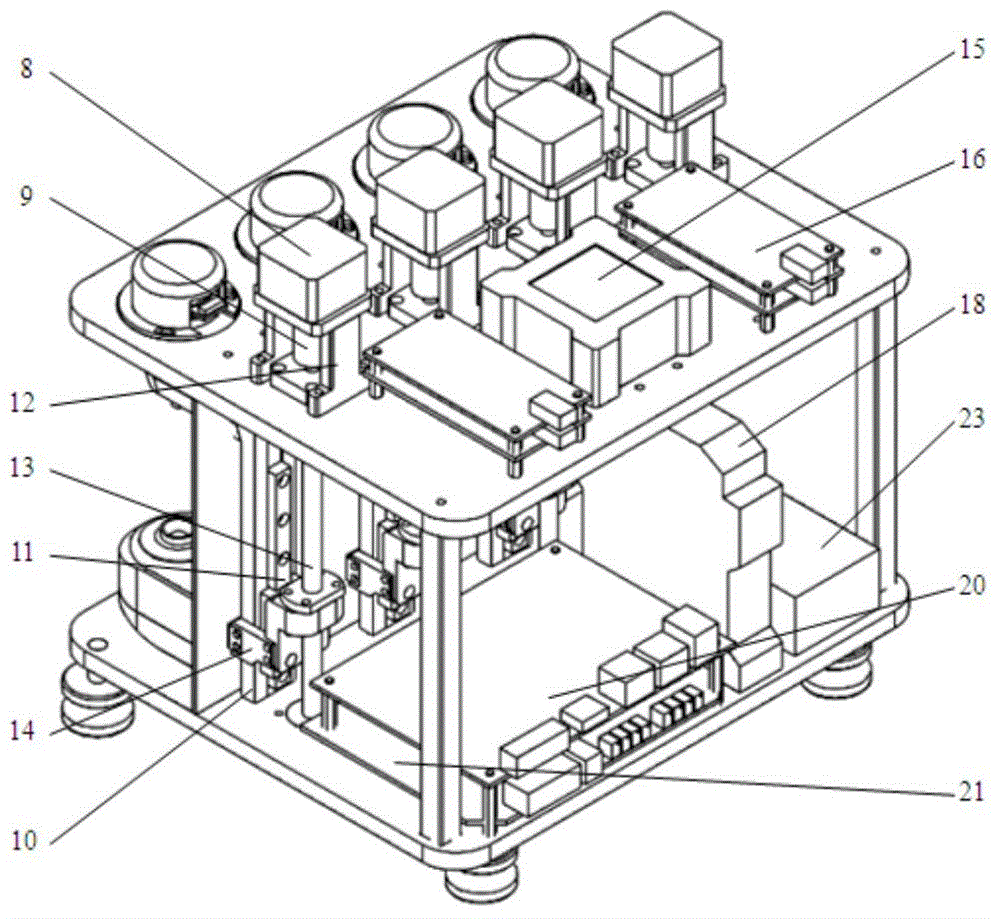
Thrombelastogram instrument
The invention discloses a thrombelastogram instrument, which comprises a structural module comprising a structural framework and an auxiliary motion execution mechanism, wherein the auxiliary motion execution mechanism is used for realizing cup loading, elevating and cup unloading motion of a test cup; a measure module comprising a measure assembly, a cup holder assembly, a level meter and a temperature controller; a signal control module comprising an amplification plate and a main control board; a storage processing module comprising host computer hardware; and an auxiliary module comprising a power supply, a switch, a button connecting line and an interface. The thrombelastogram instrument has the advantages of strong integrated level of a system, high automation degree and good anti-interference performance, clotting panorama of patients can be comprehensively detected, curative effect of certain medicines relative to blood clotting can be monitored, medicine or blood transfusion scheme can be adjusted, treatment scheme can be rapidly determined, patient cost is simultaneously reduced, detection period is shortened, treatment time is saved, and life span can be prolonged.
Owner:北京乐普诊断科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com