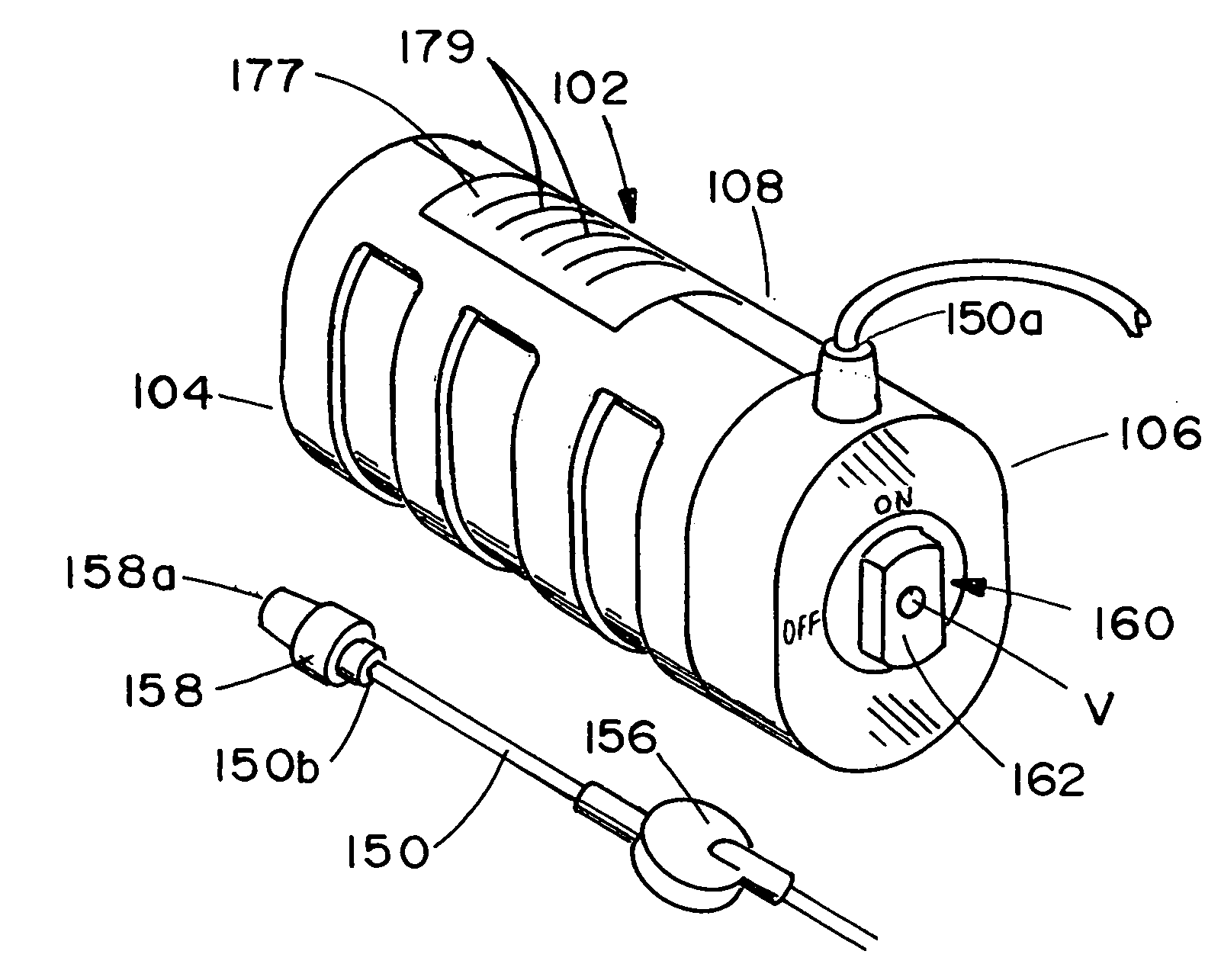
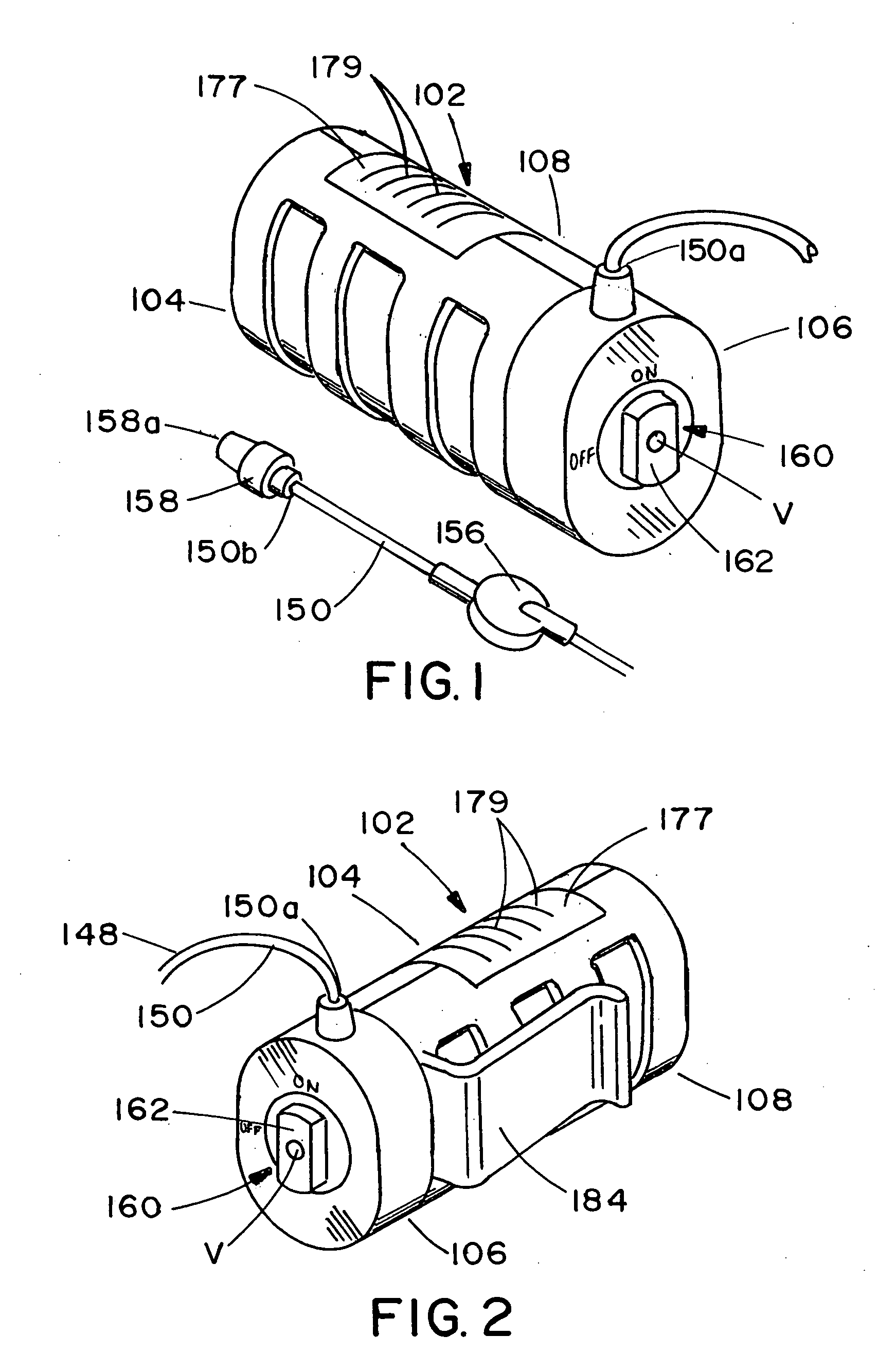
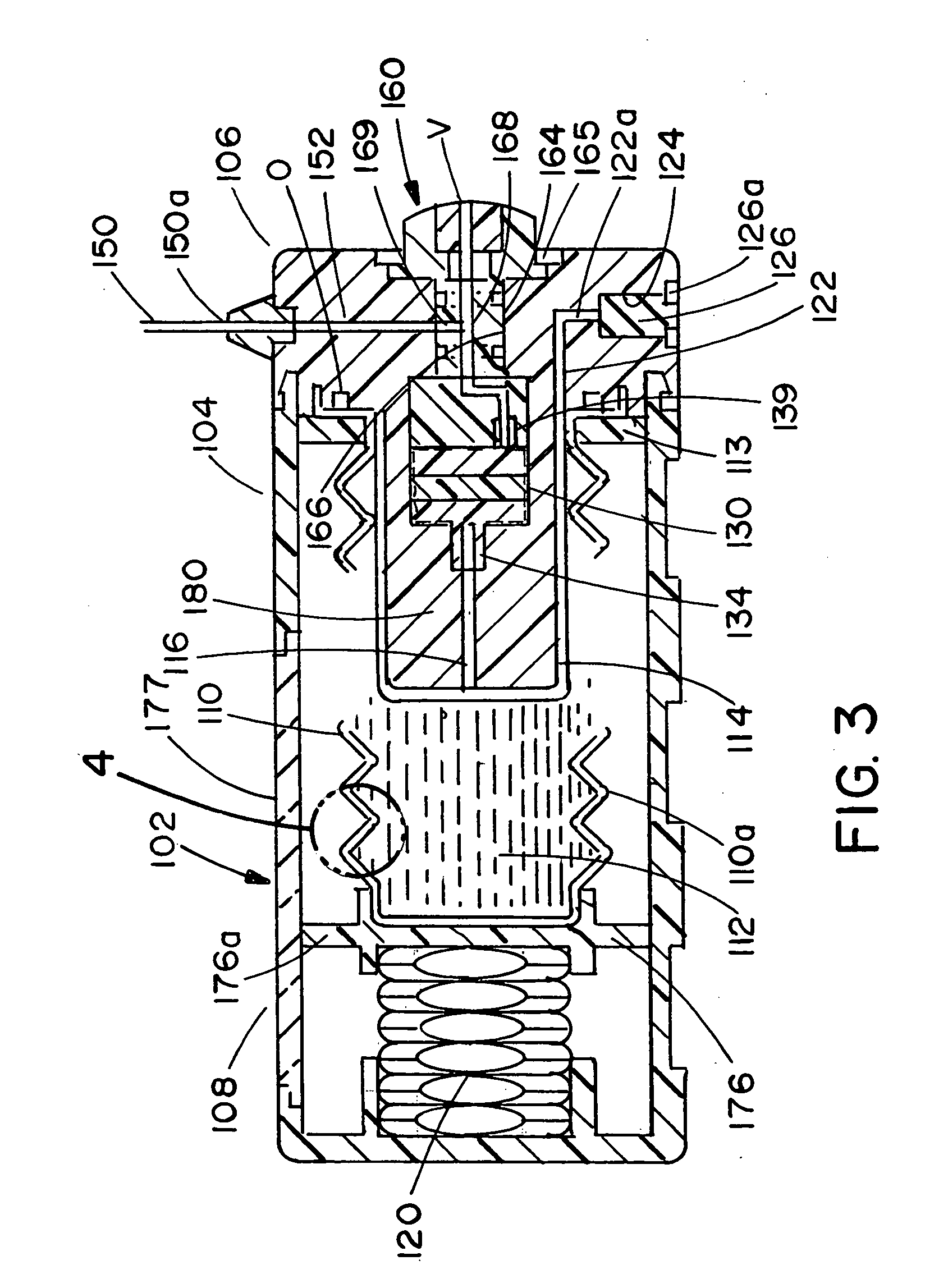
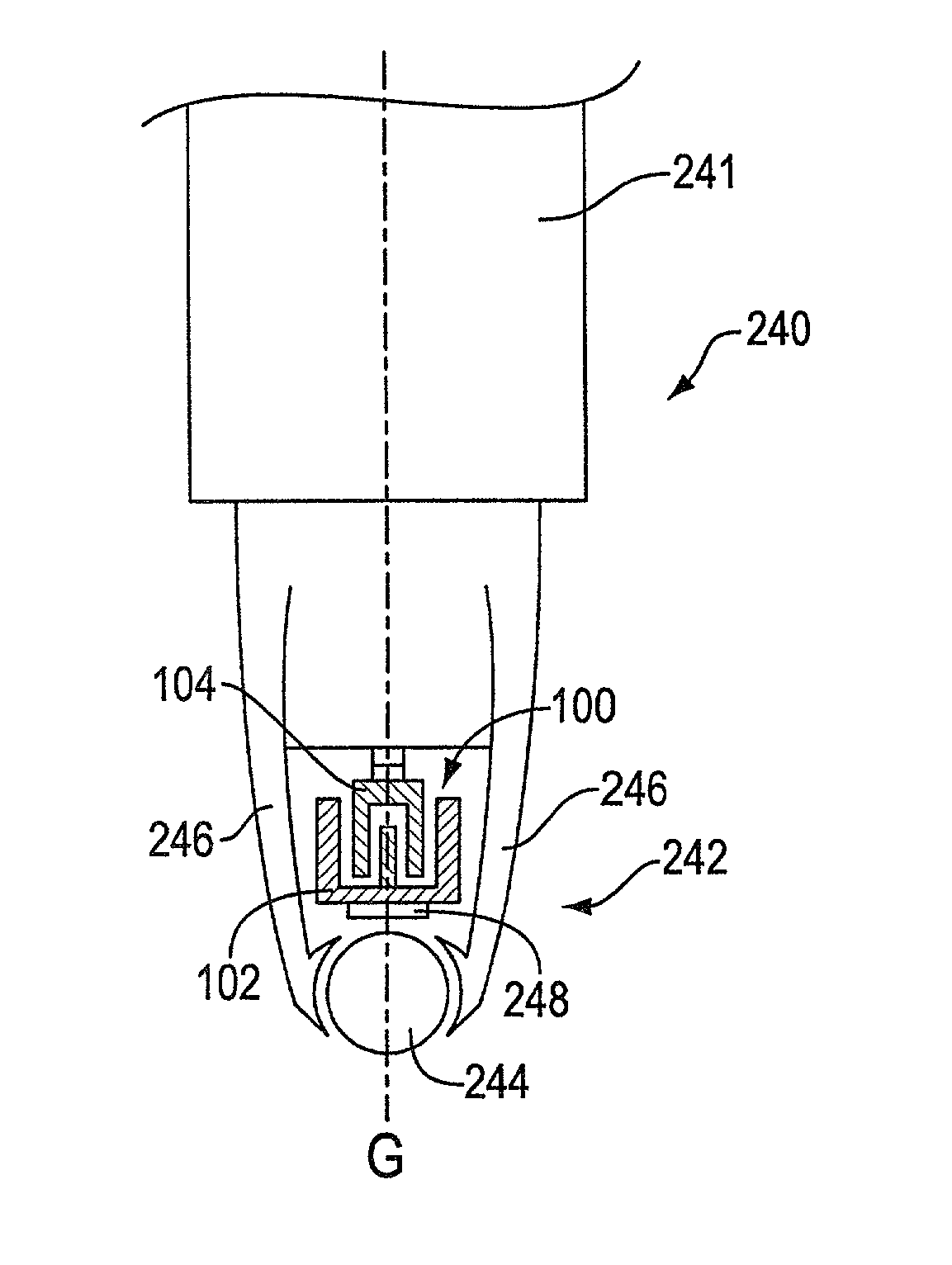
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1370 results about "Constant force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A constant force is one type of force effect that may be used in a force feedback stimulus. A constant force applies a constant force in a specified direction. You define a constant force with the keyword constant_force.
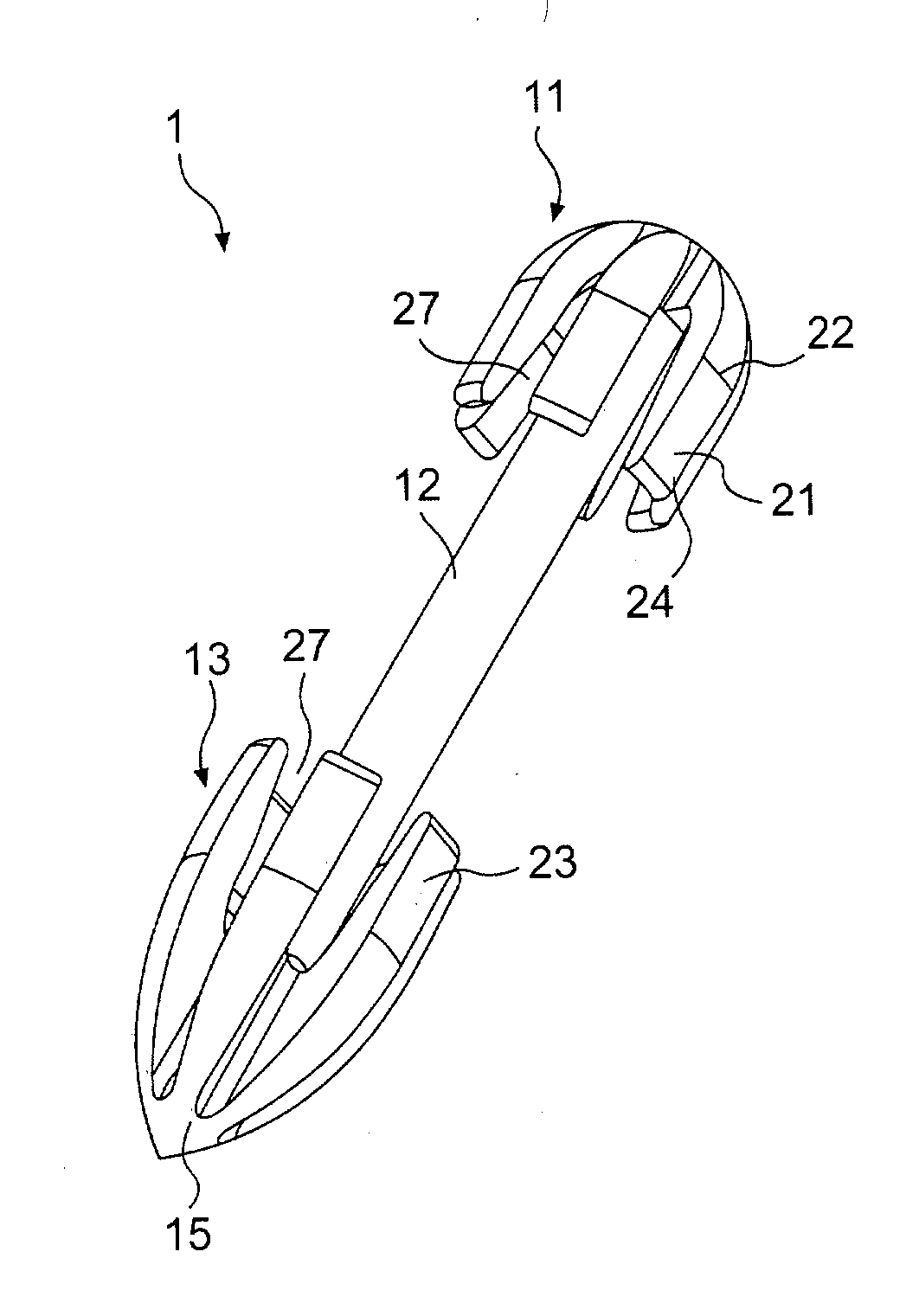
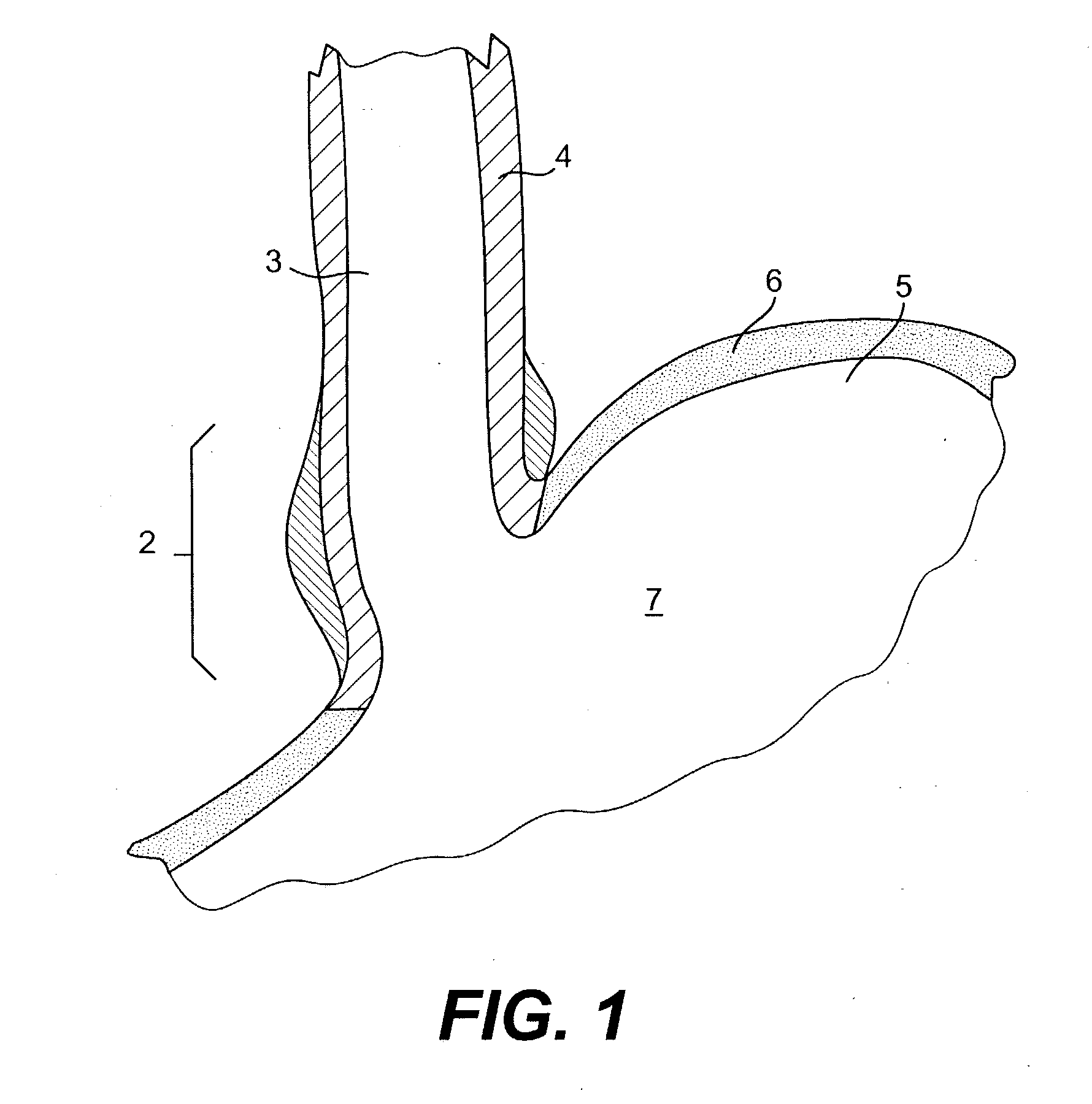
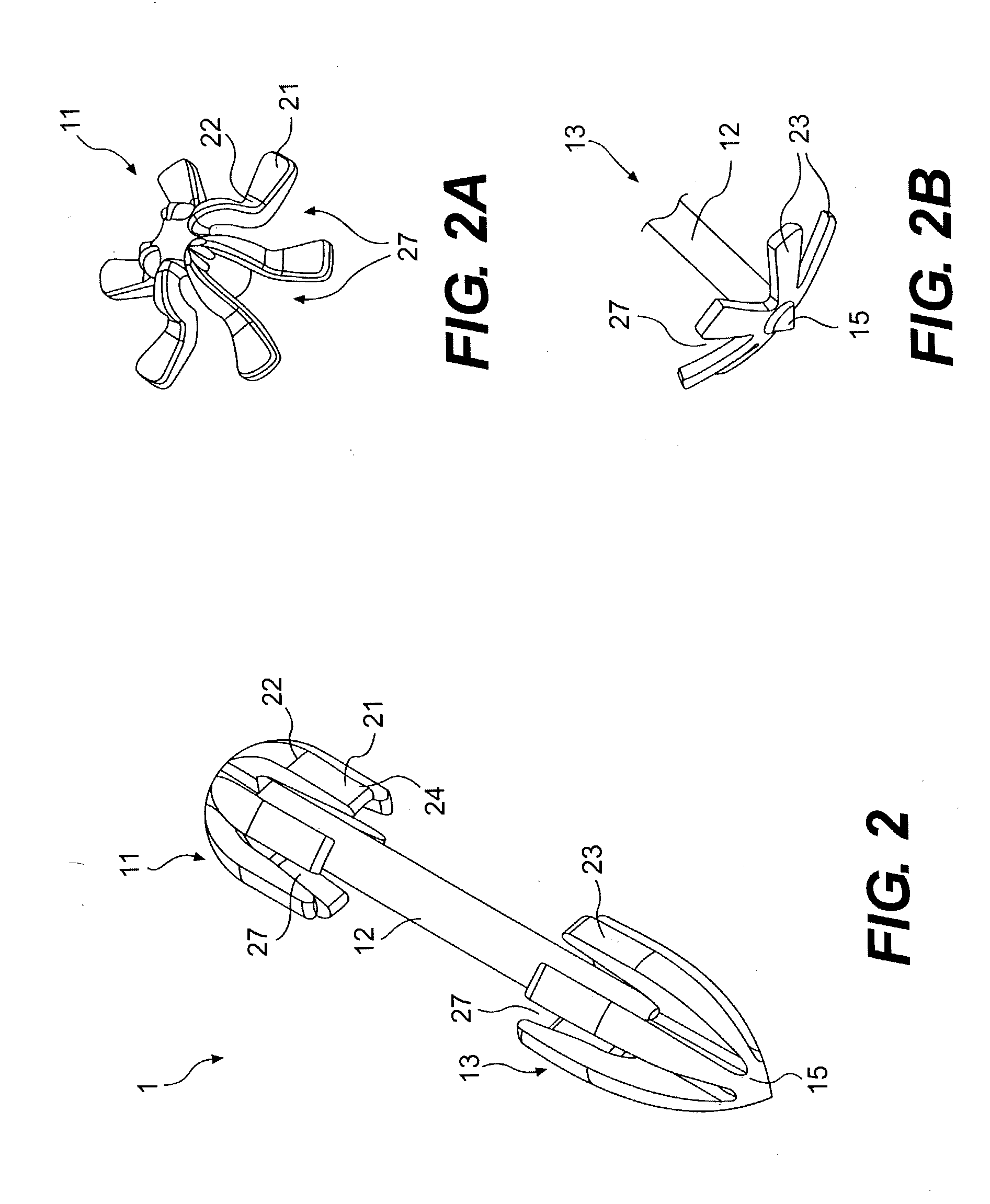
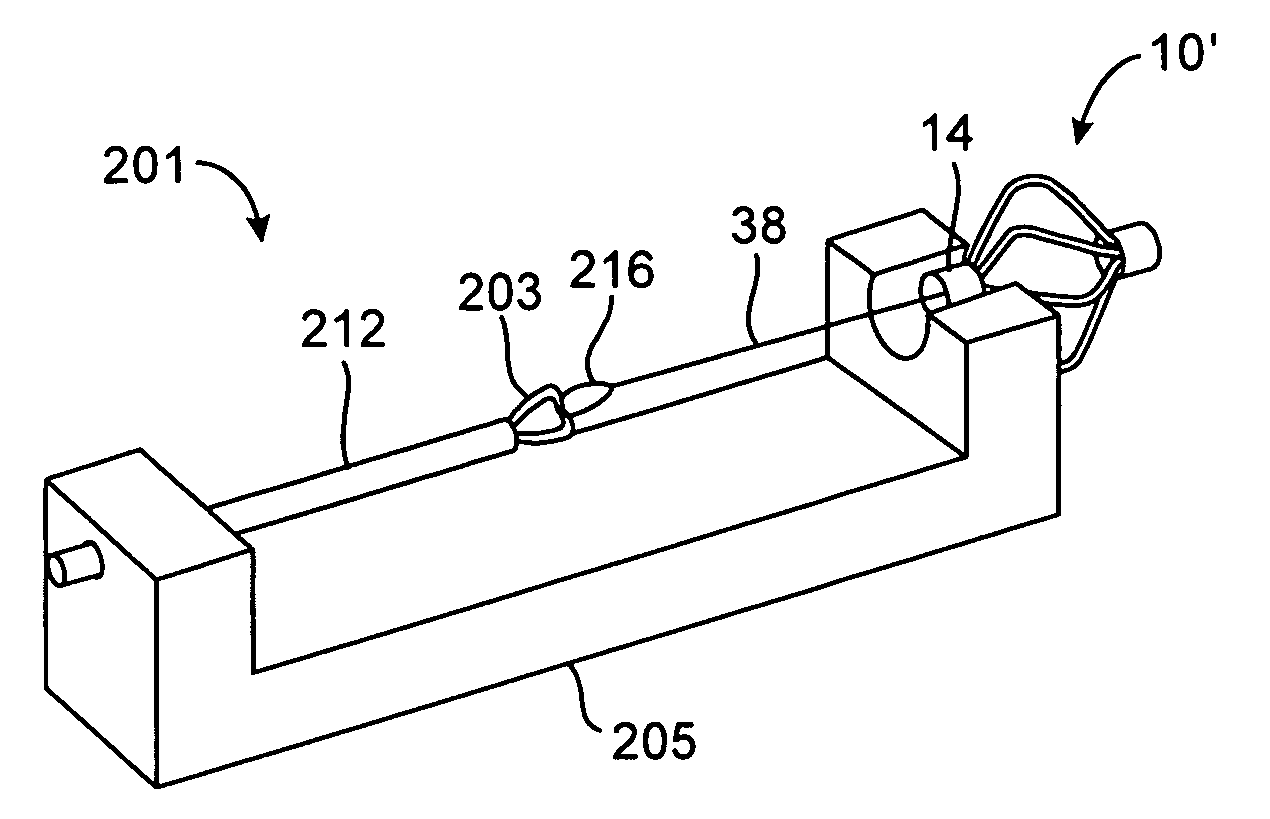
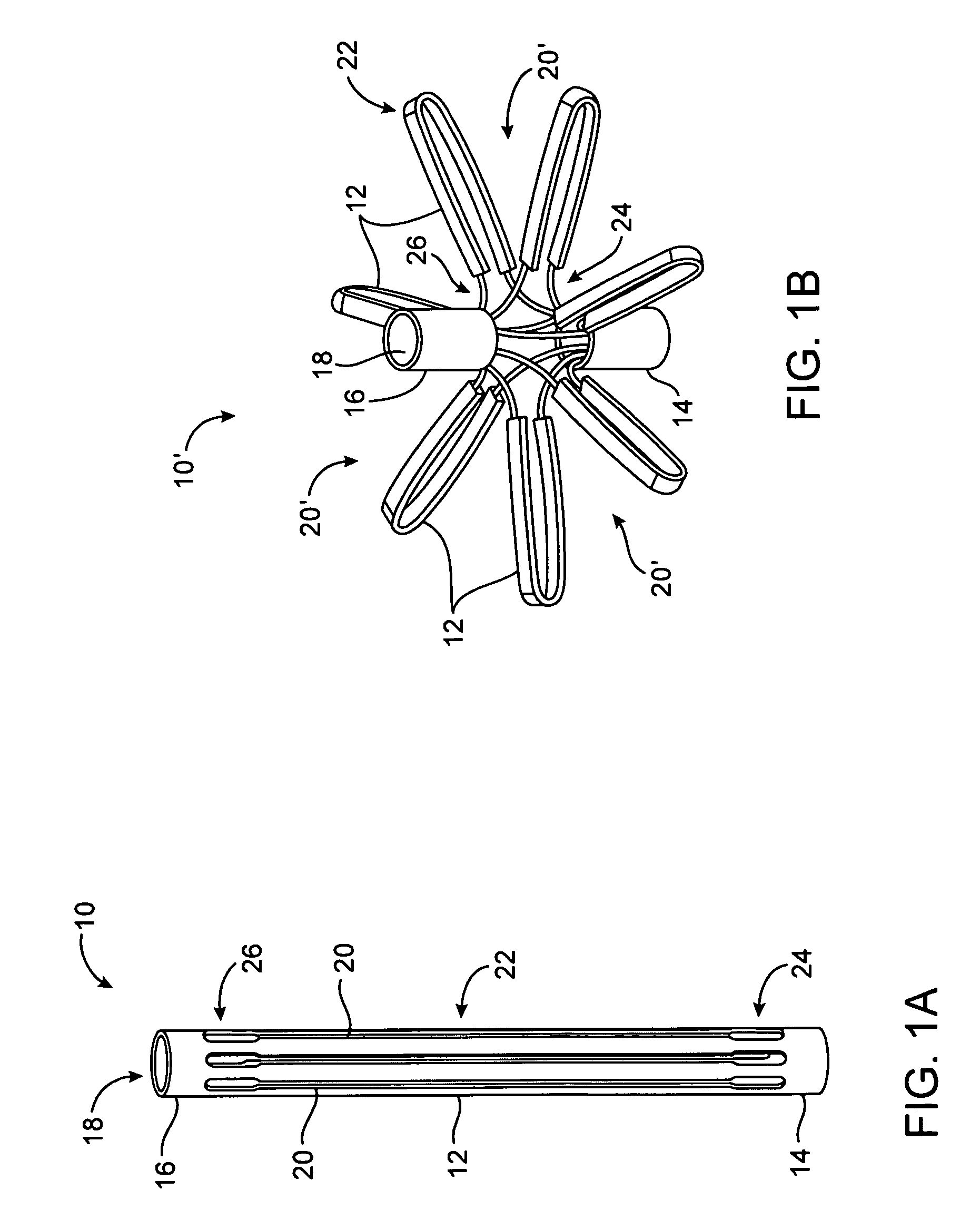
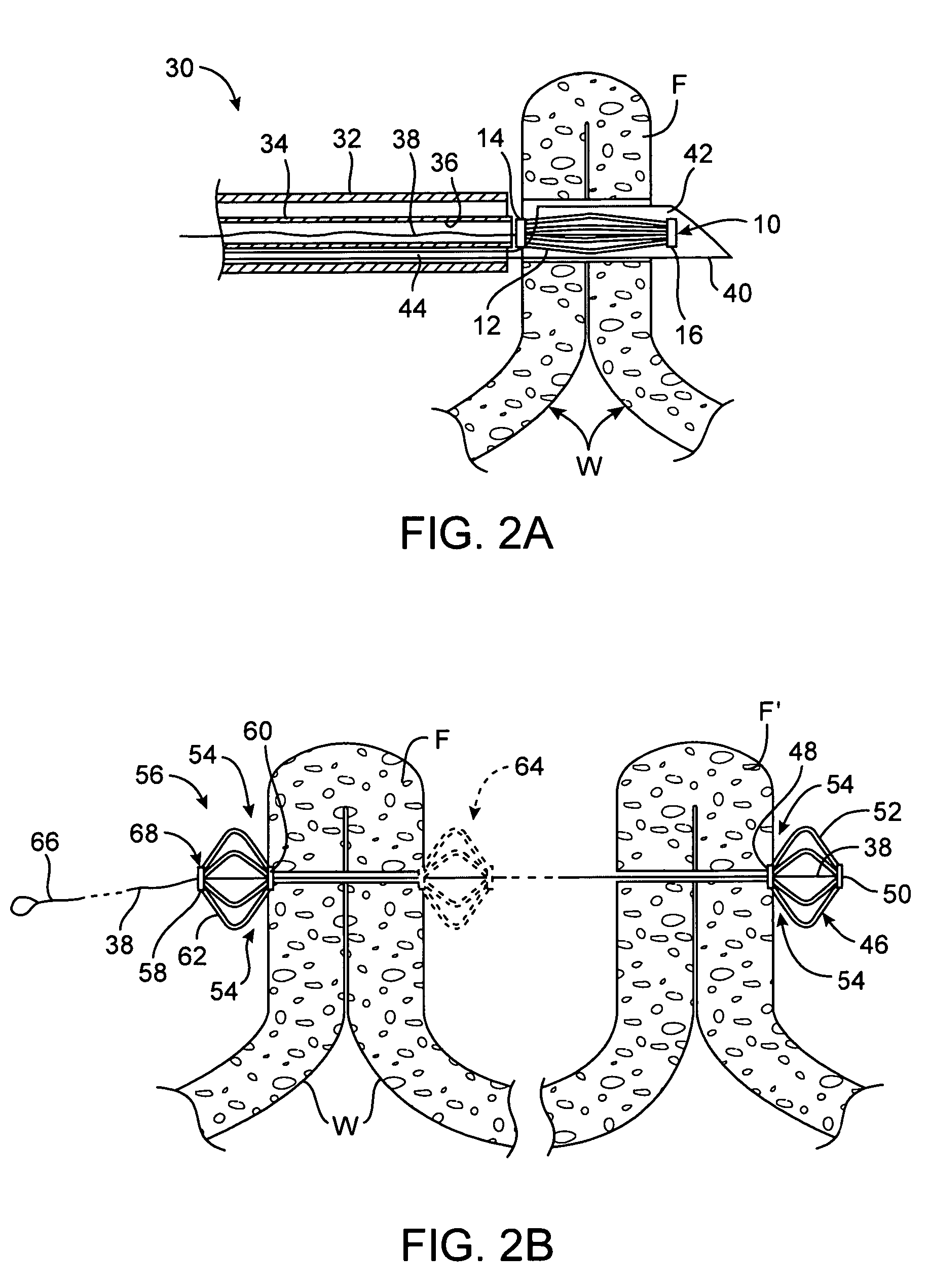
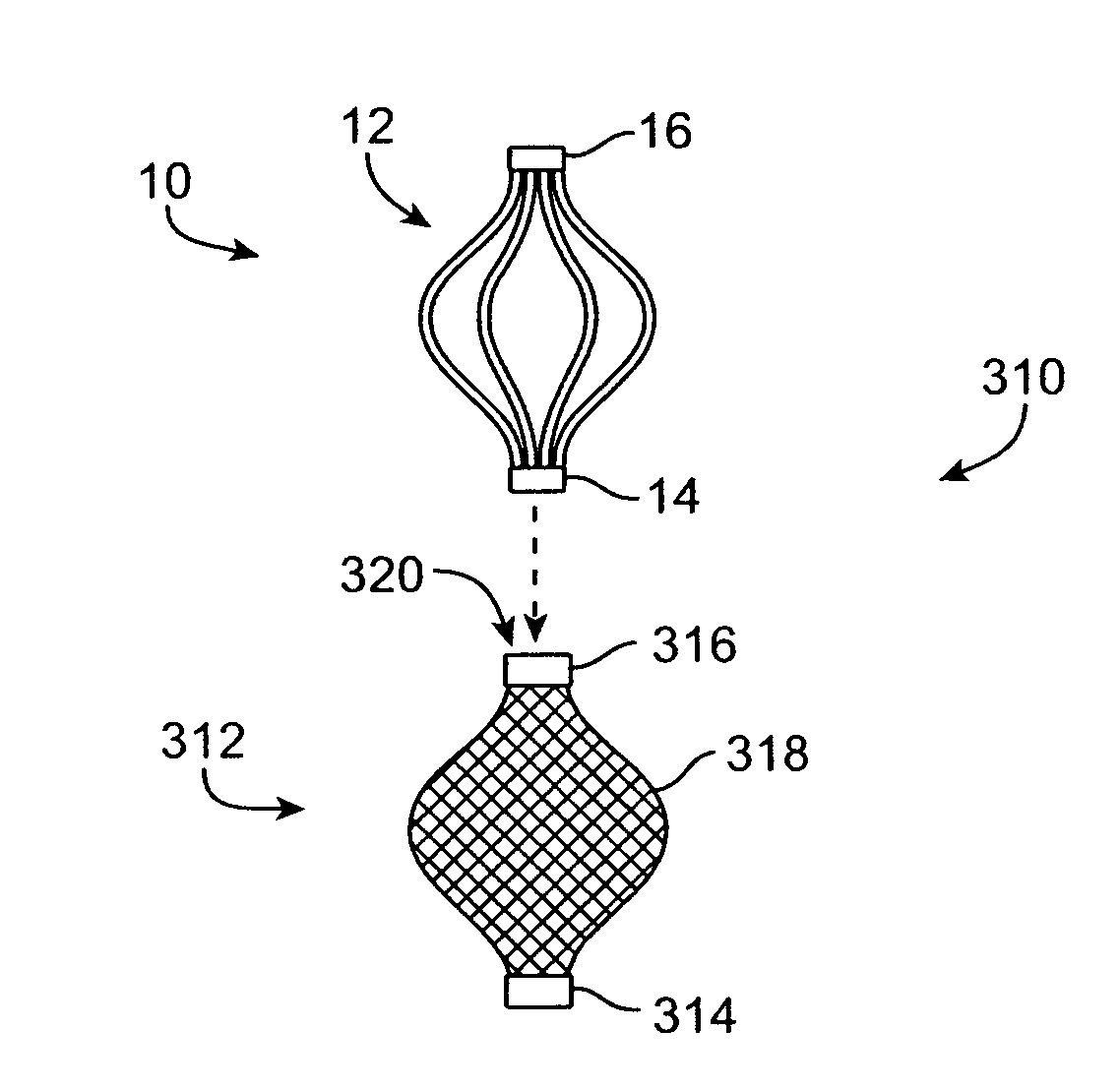
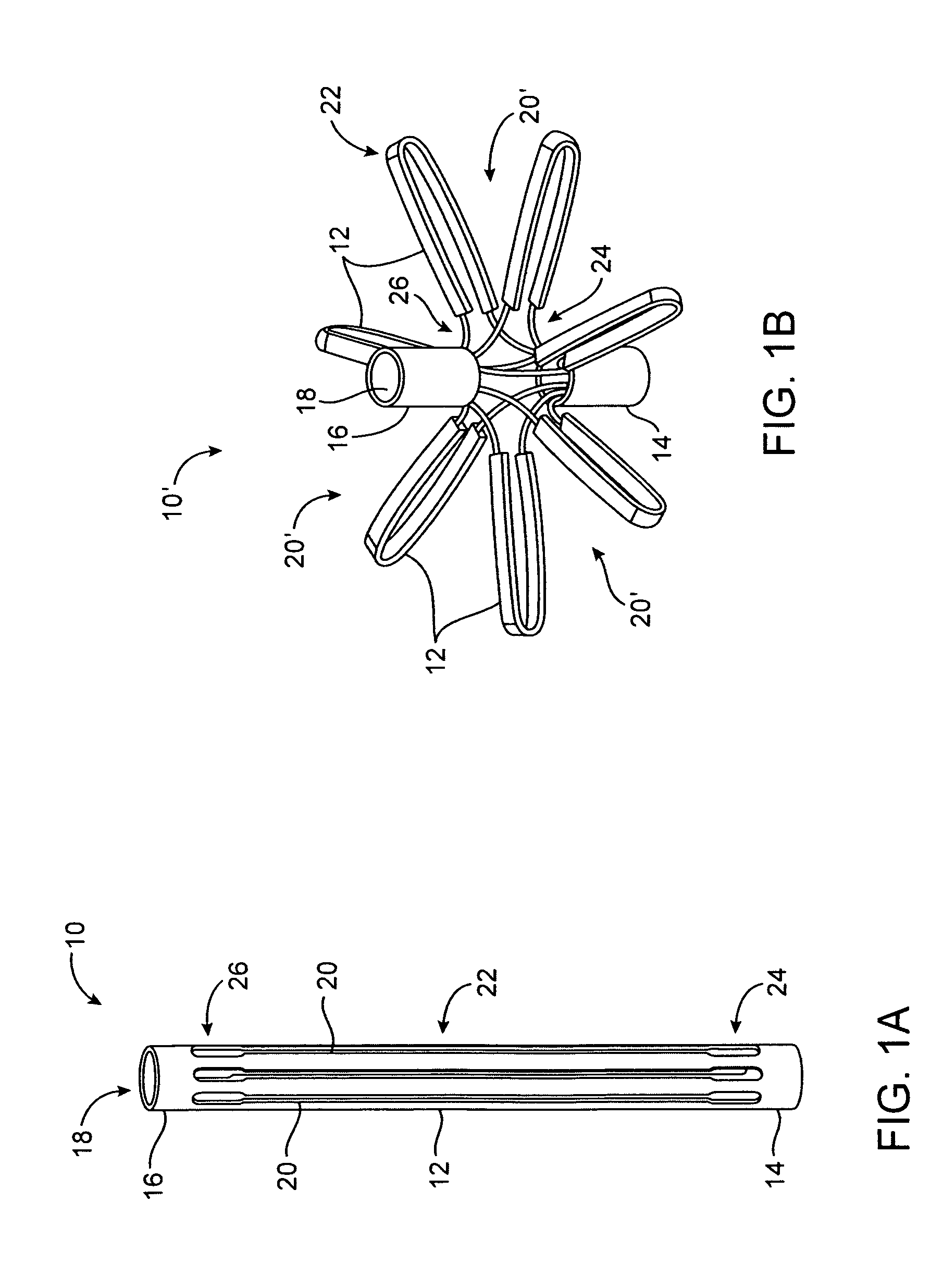
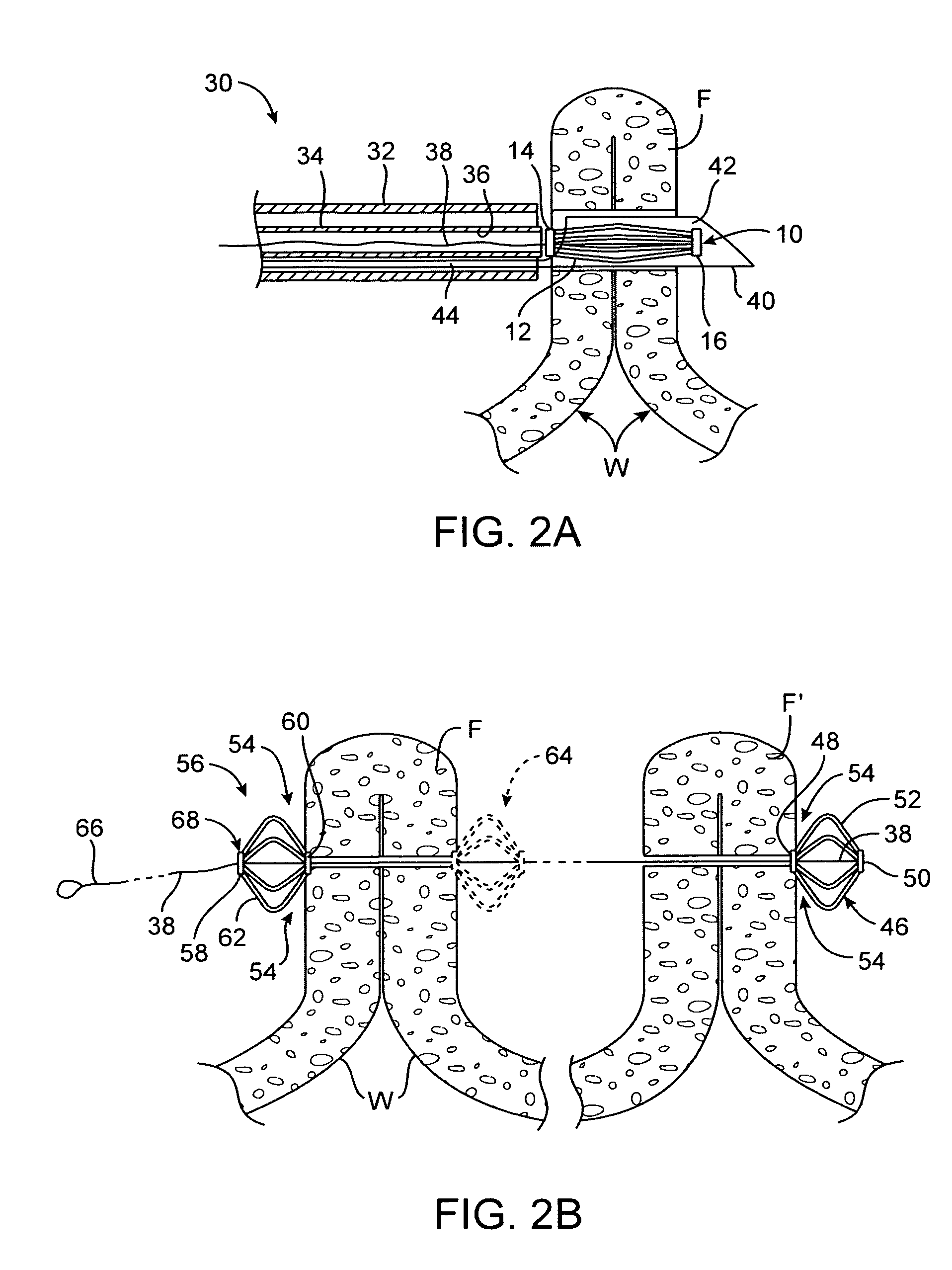
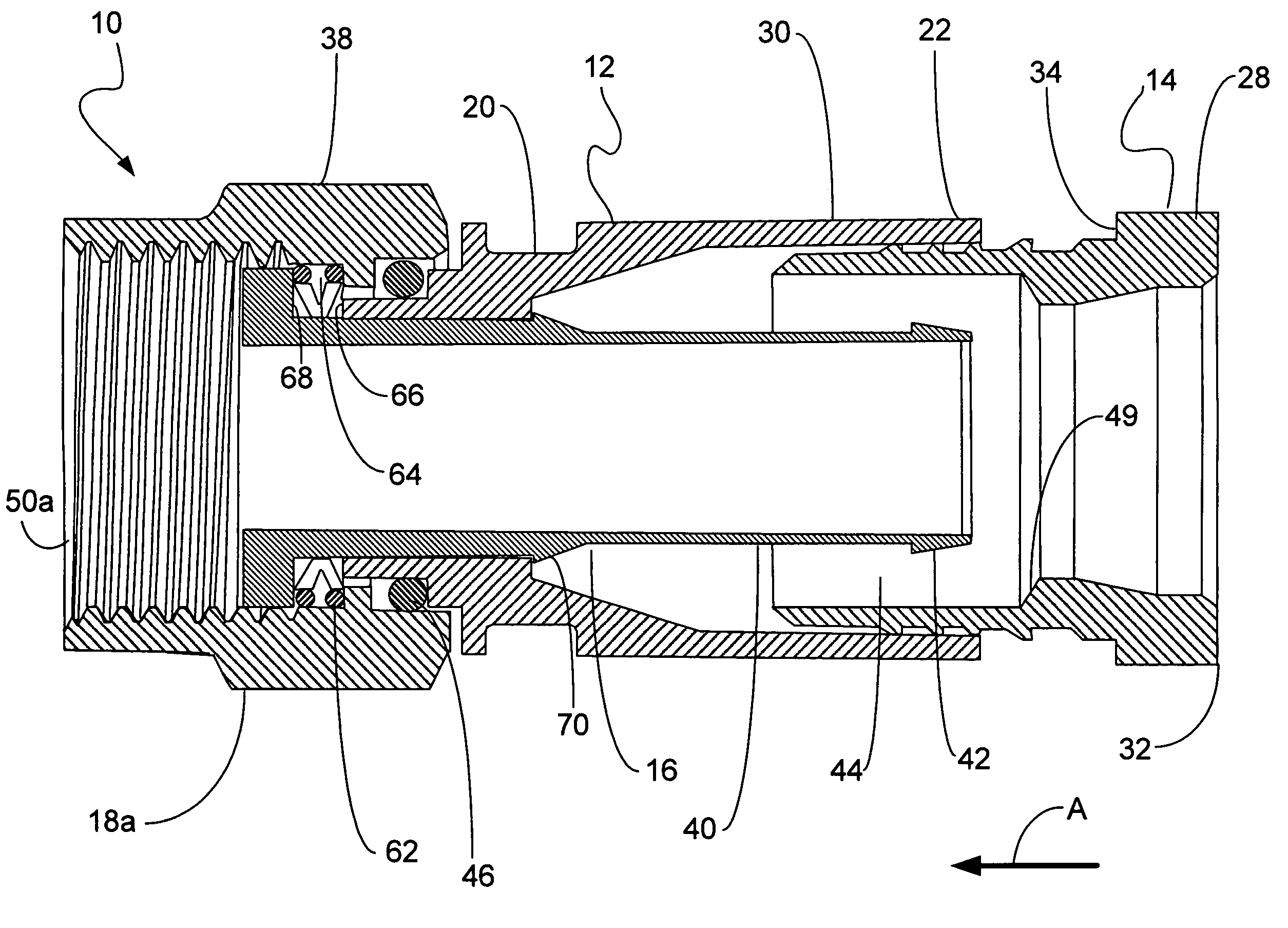
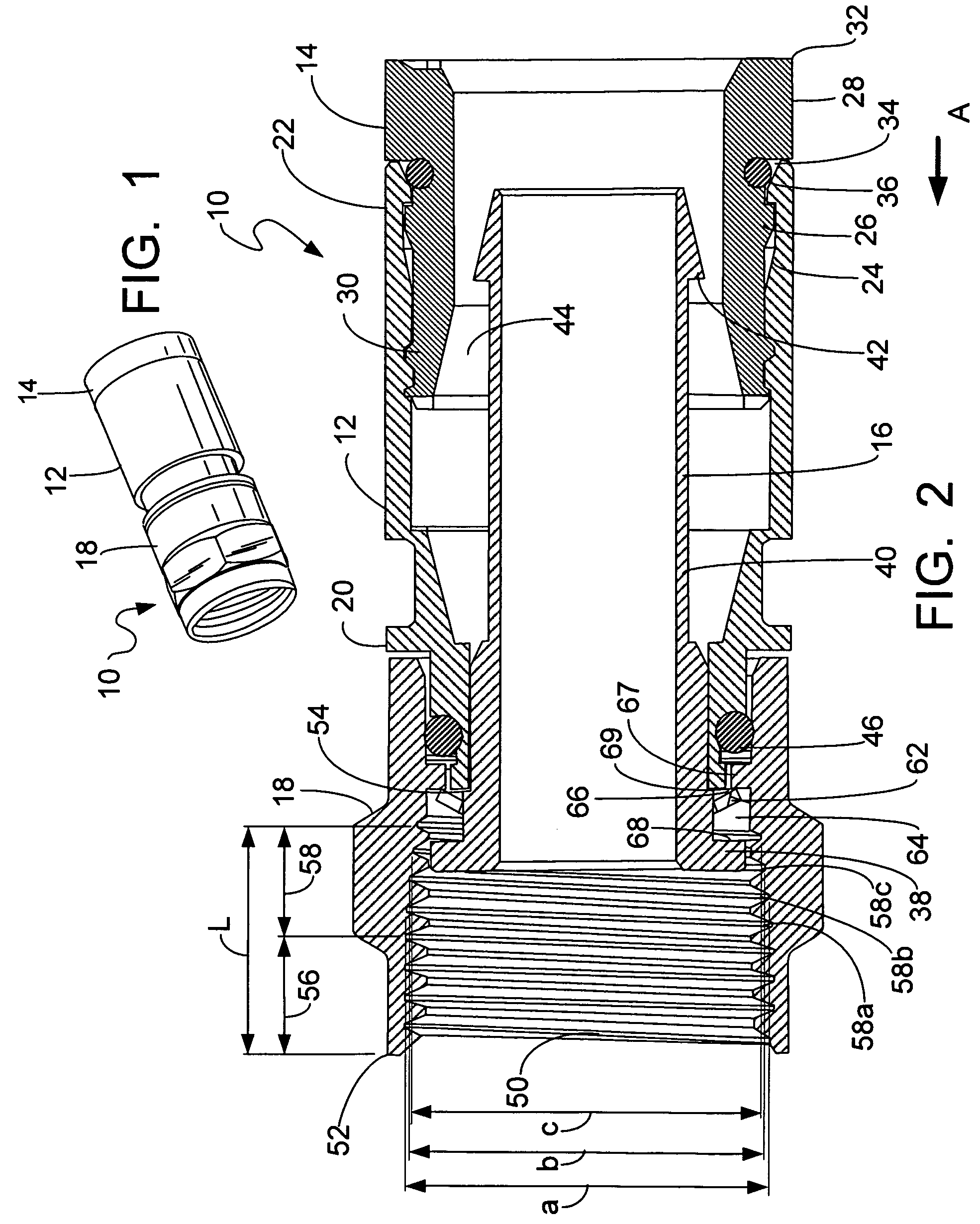
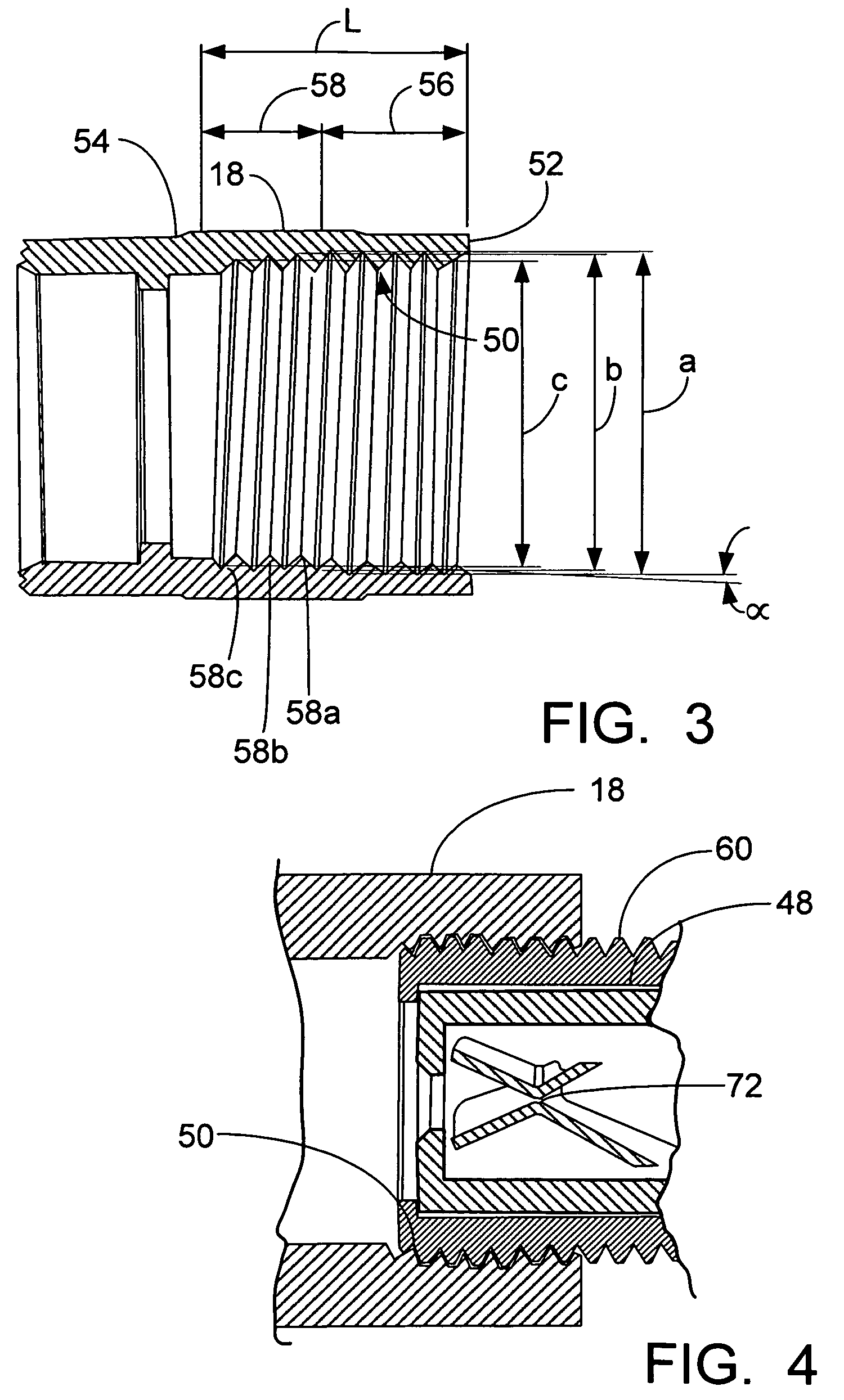
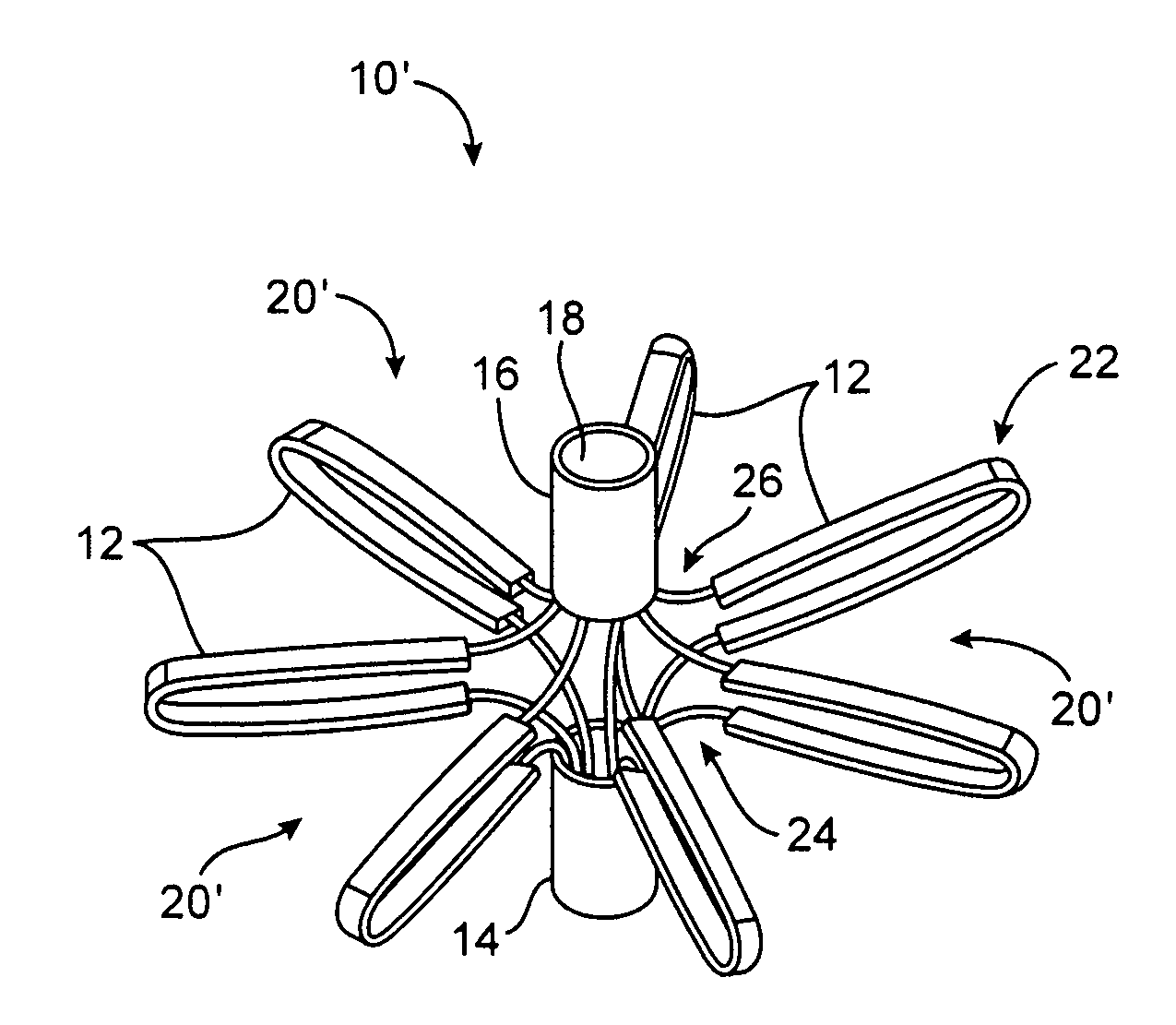
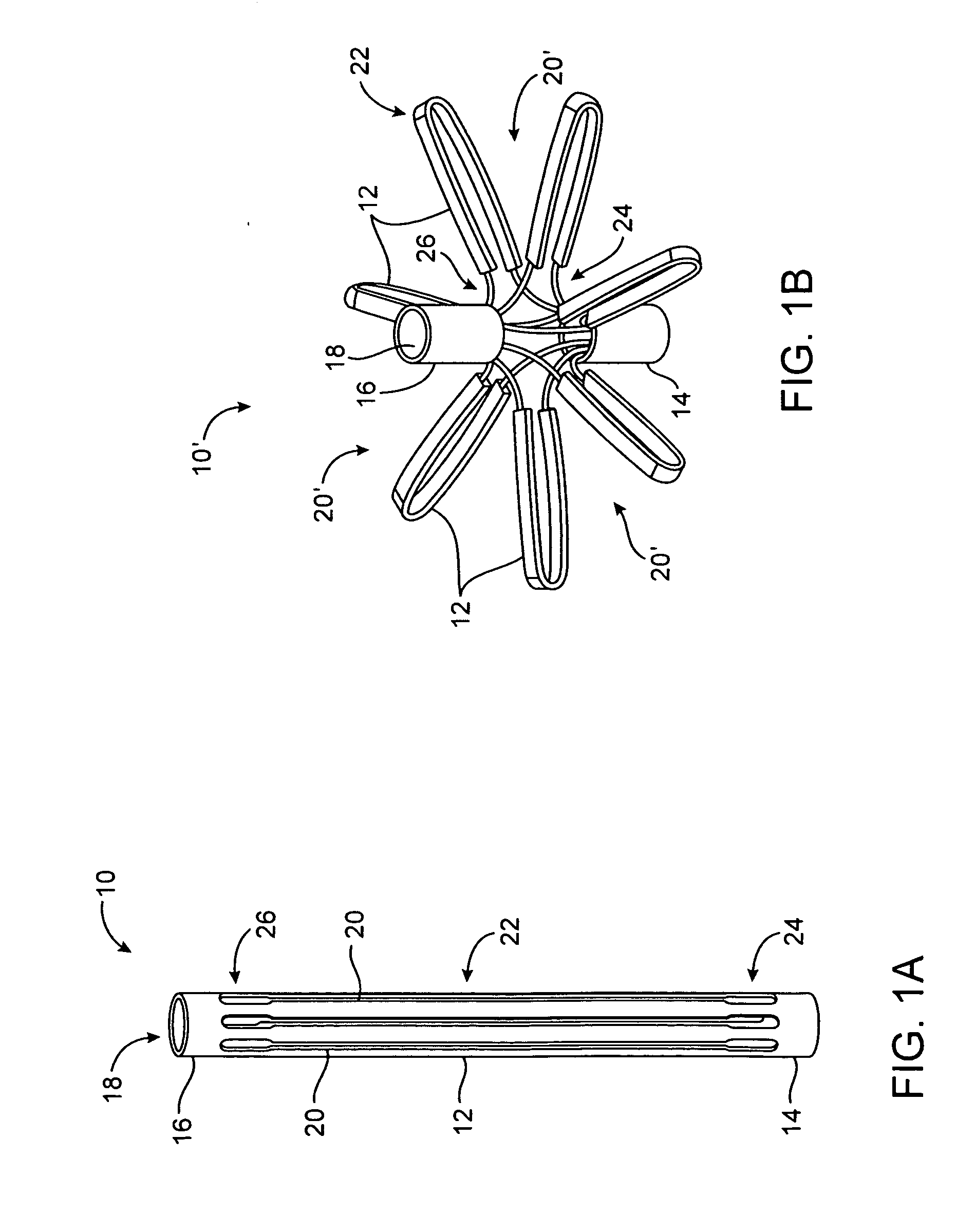
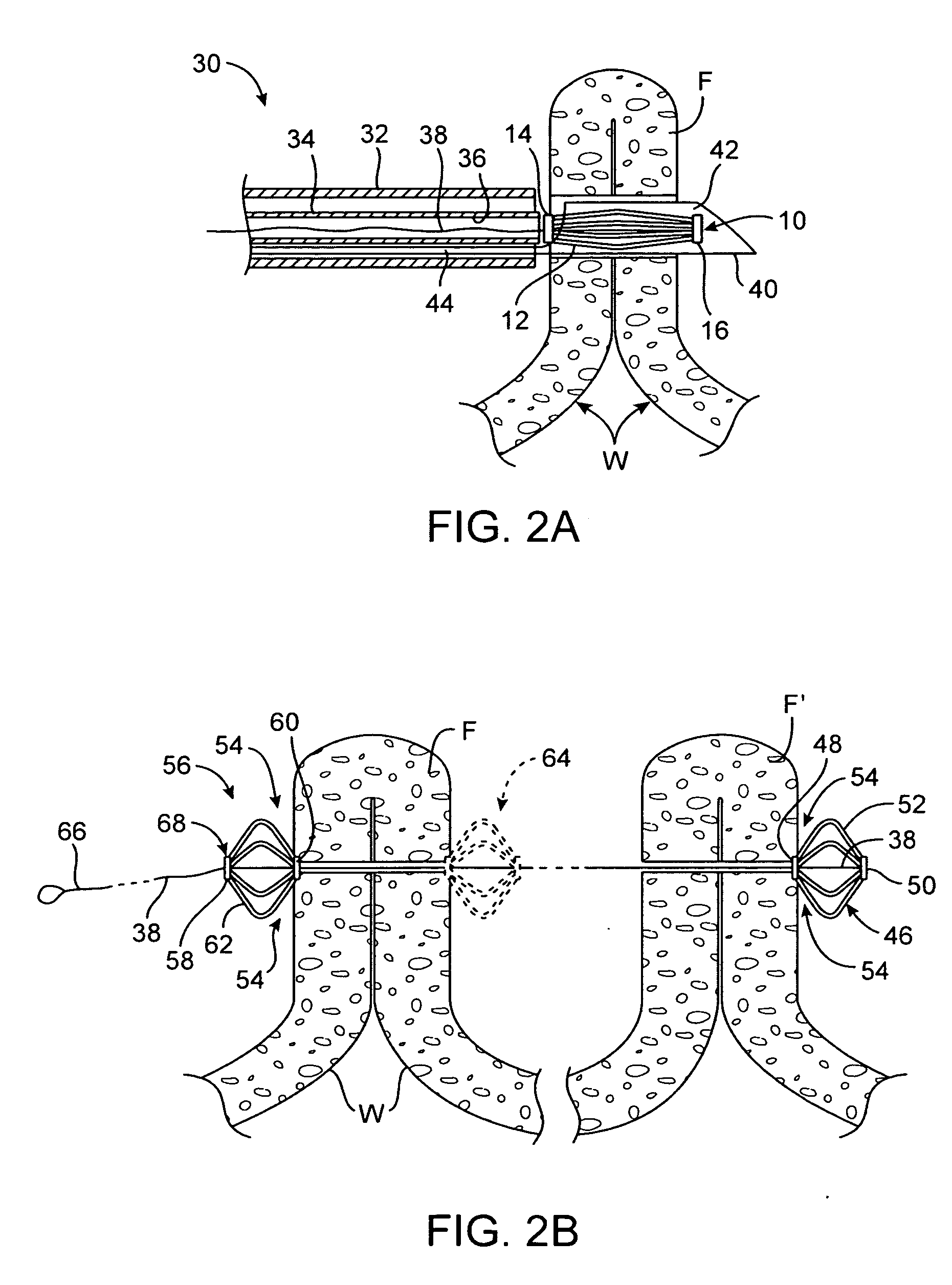
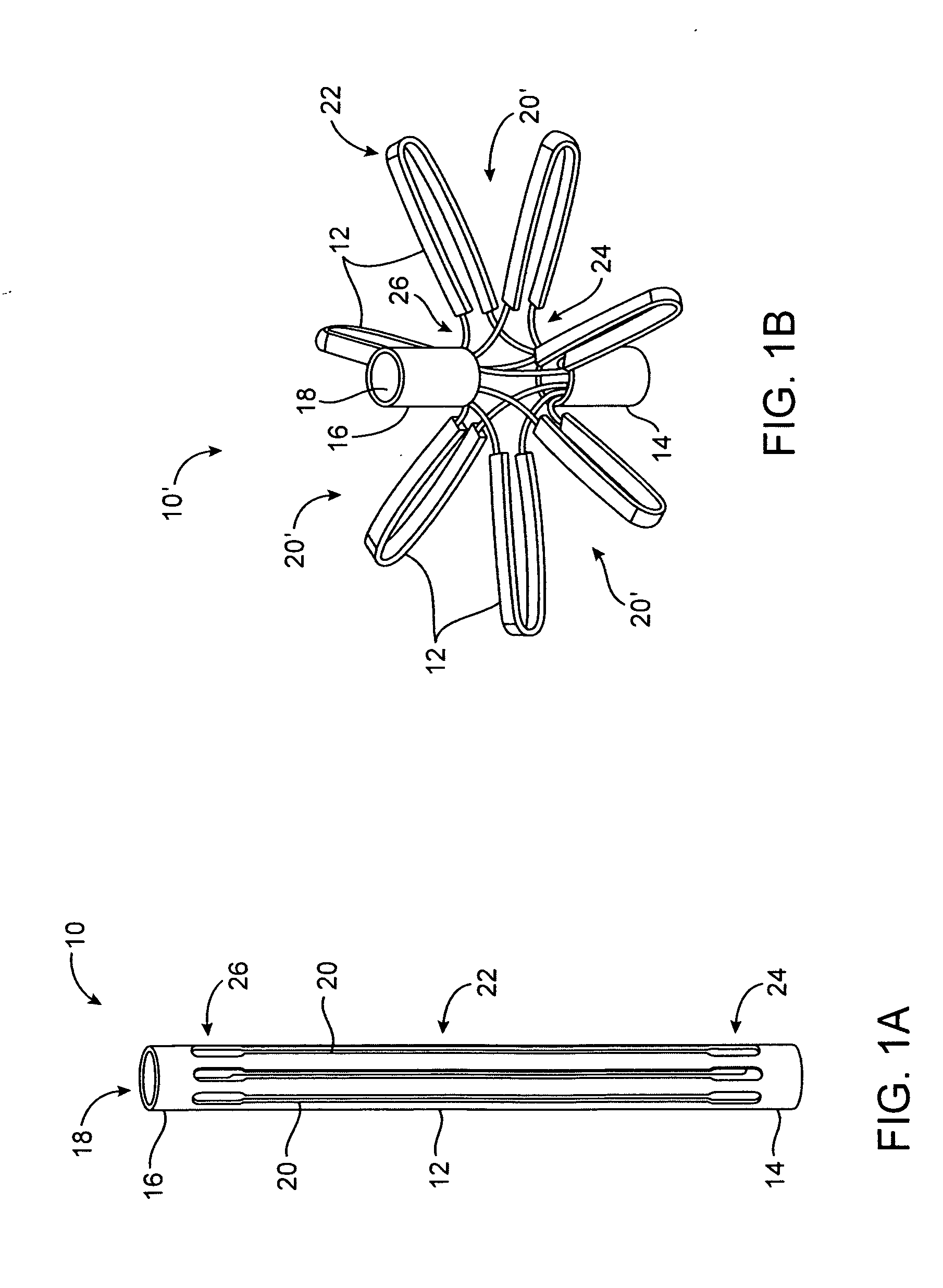
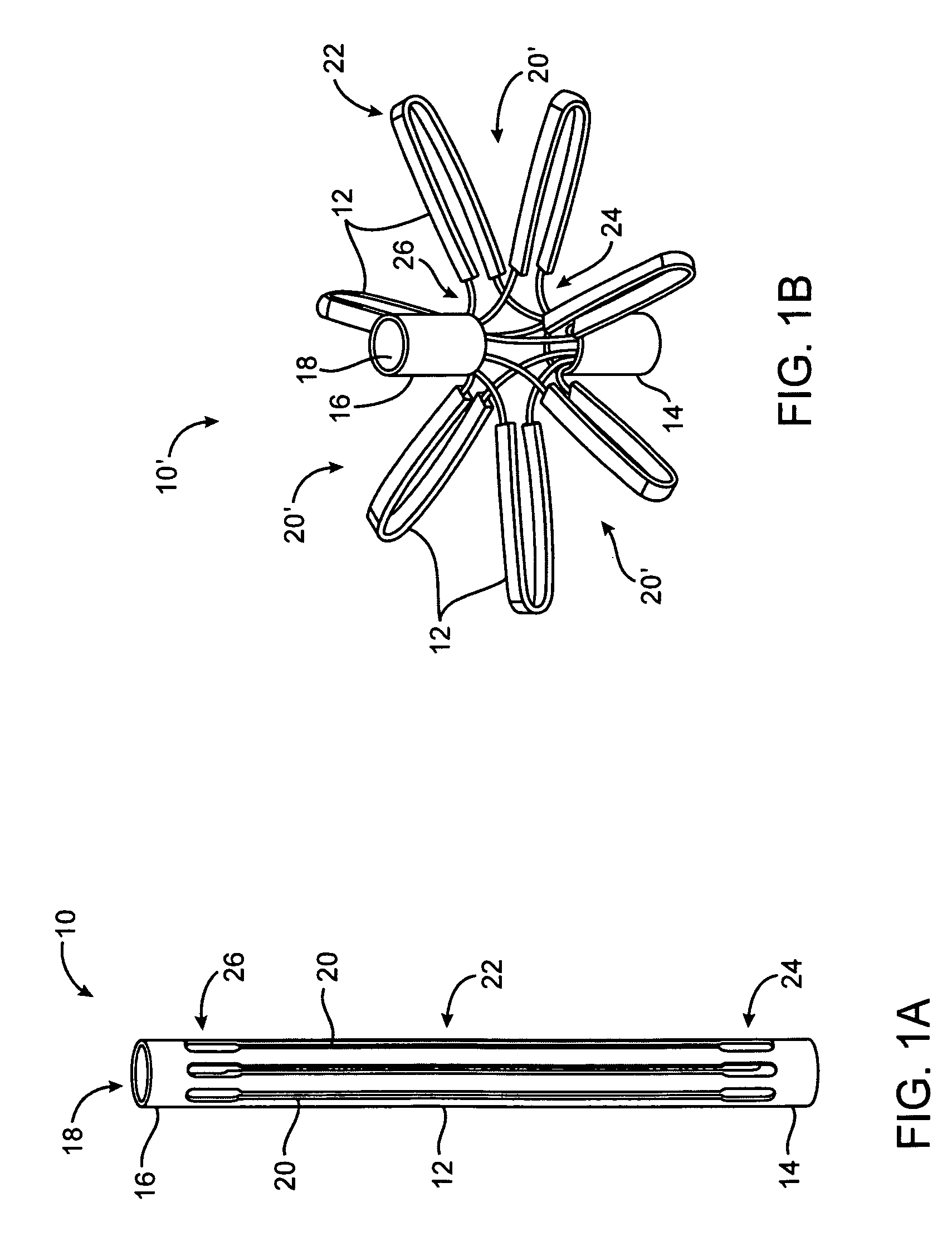
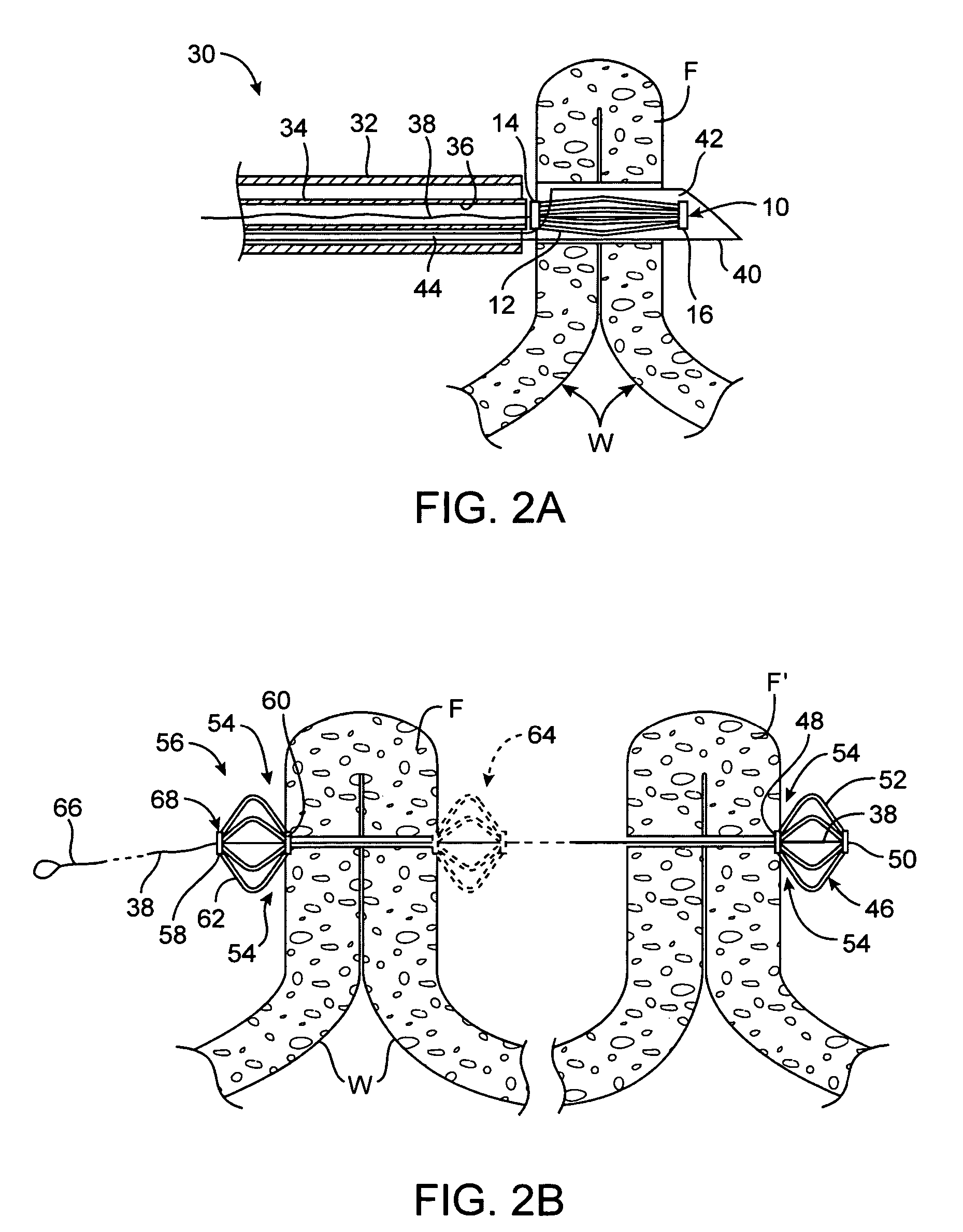
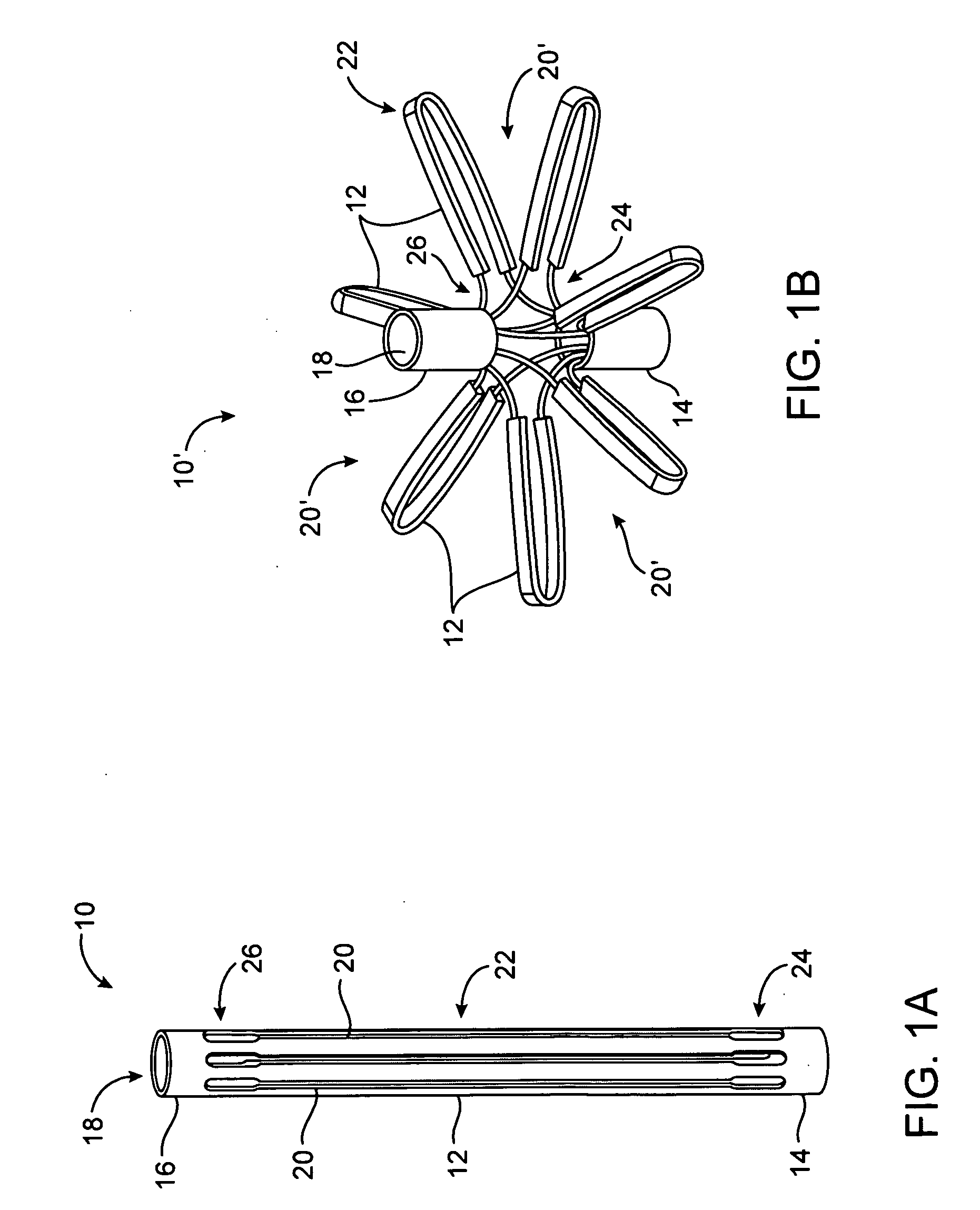
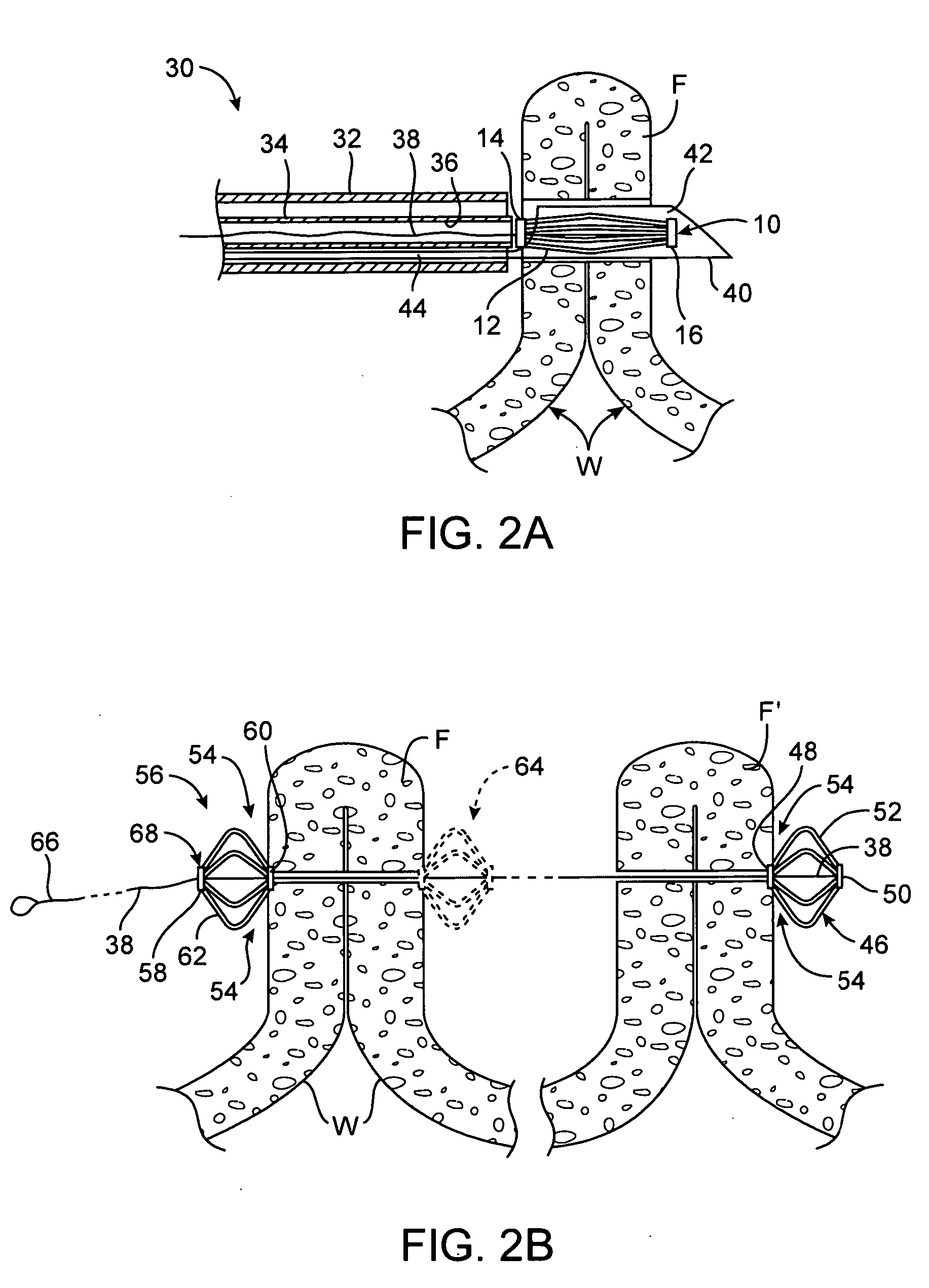
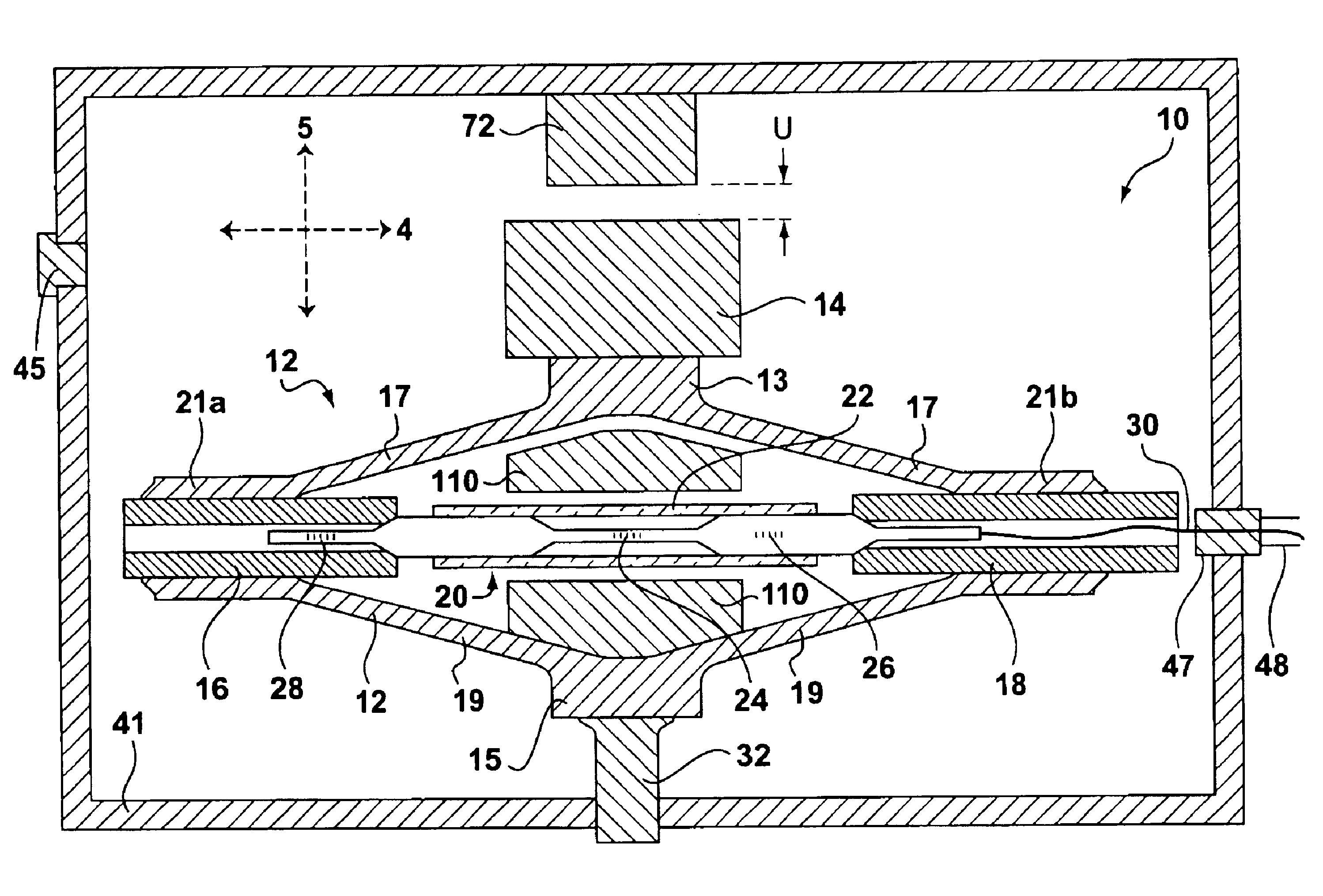
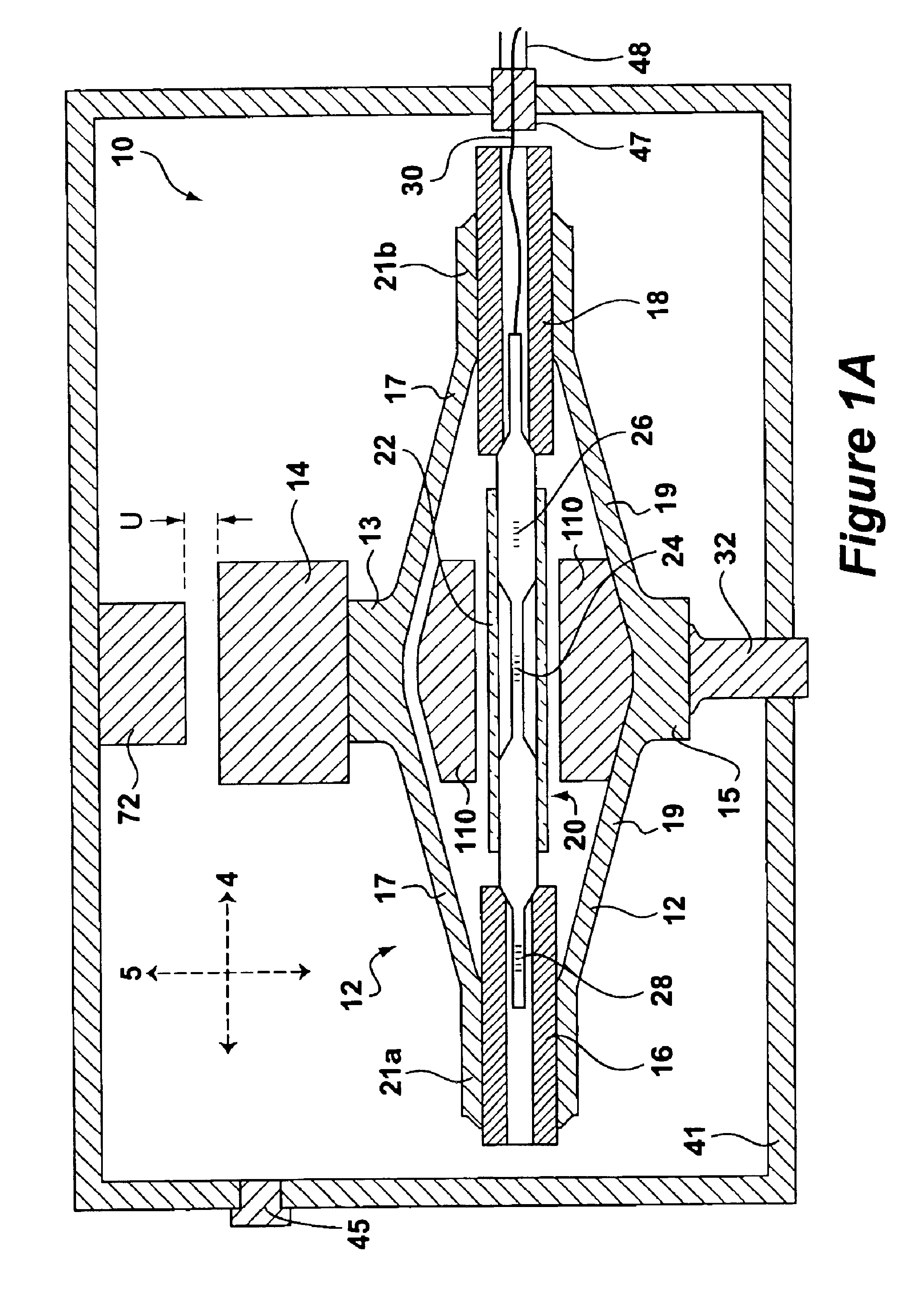
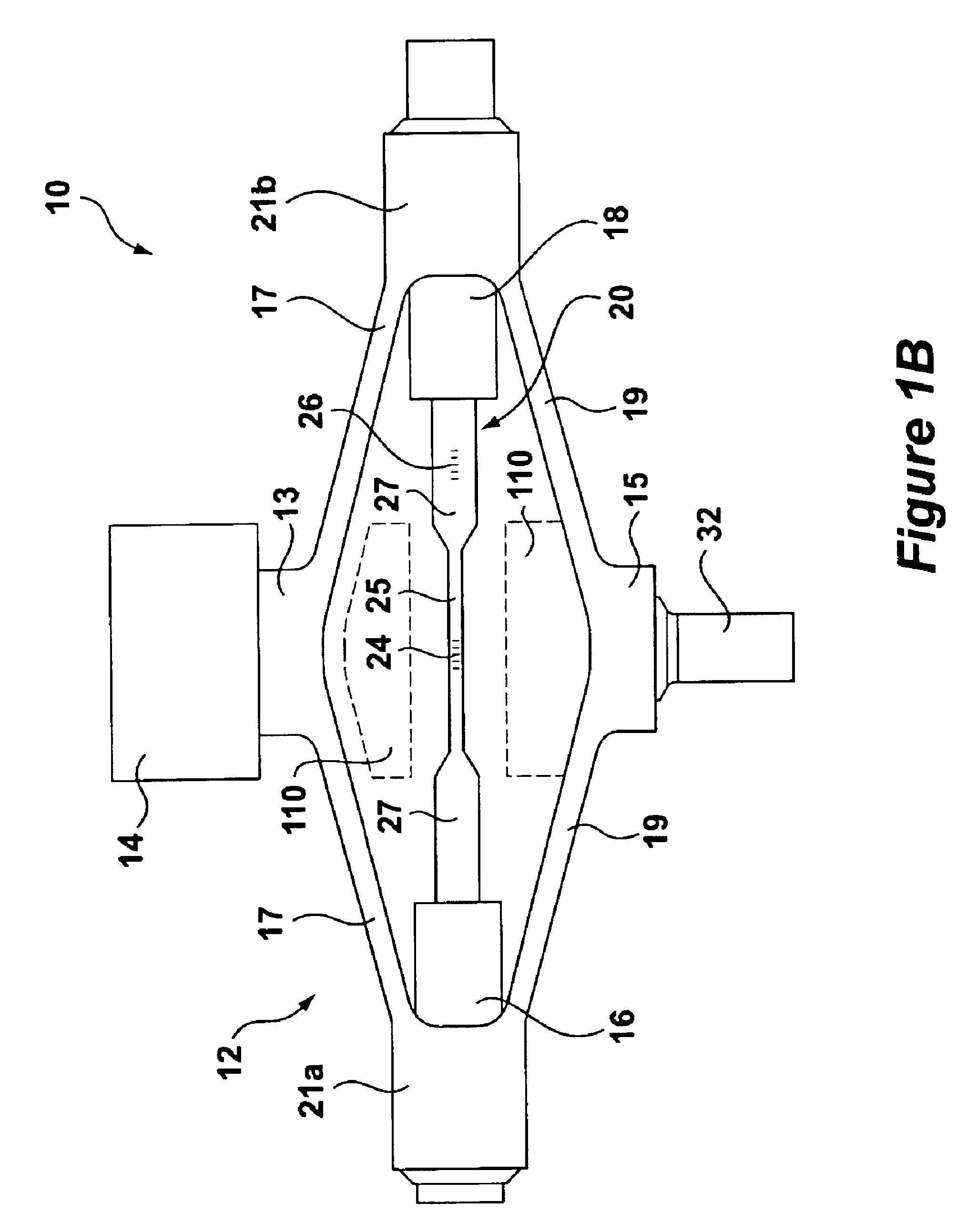
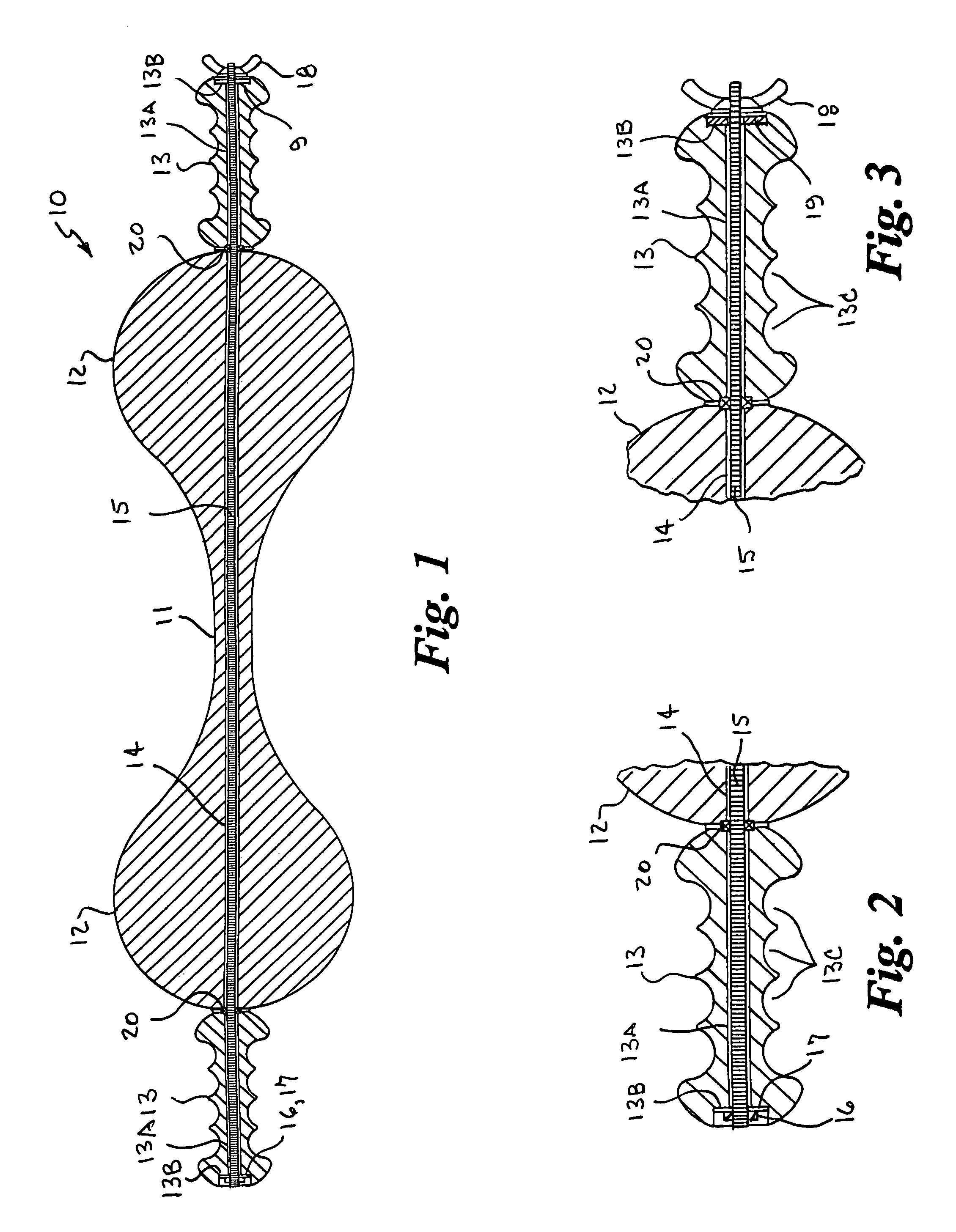
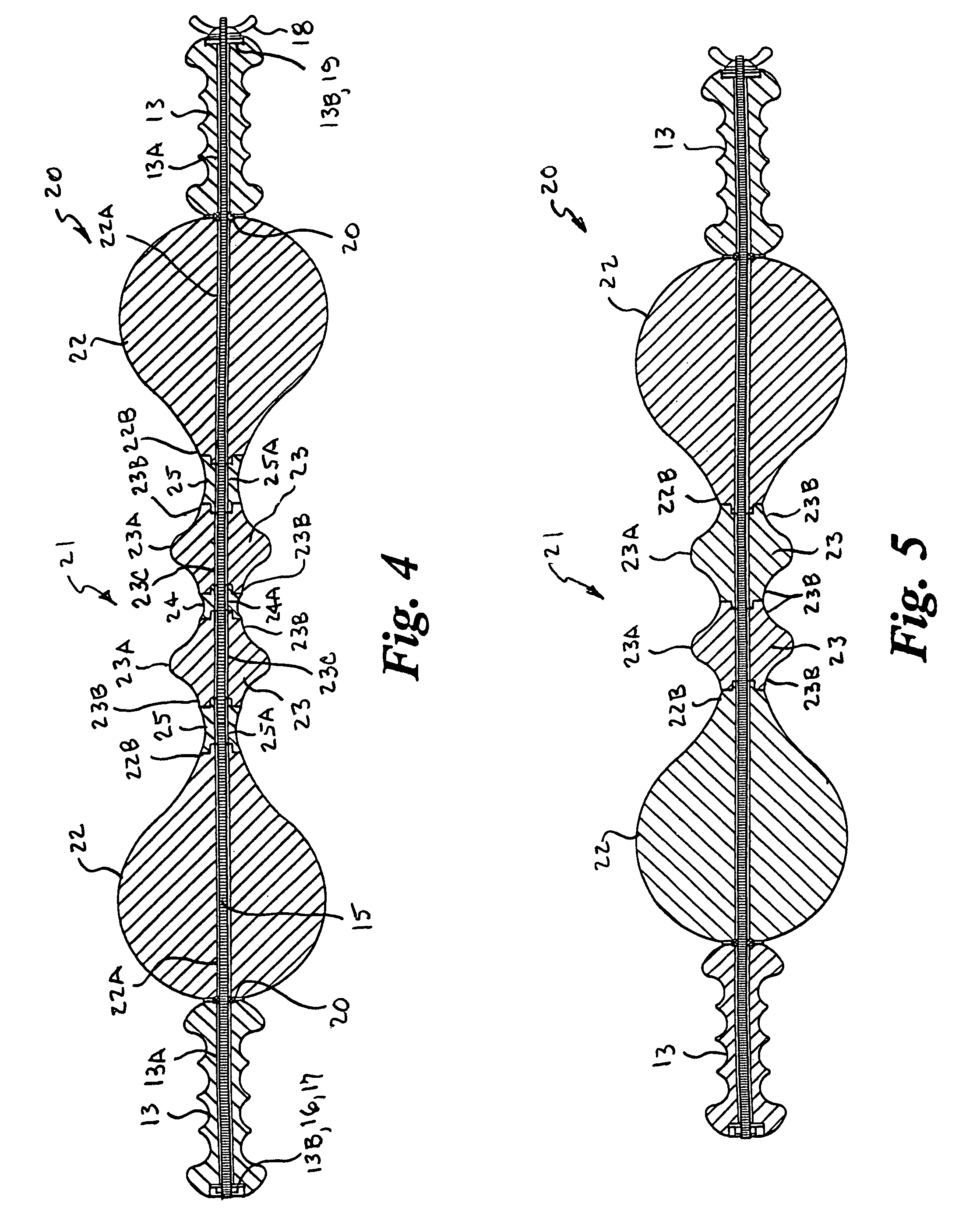
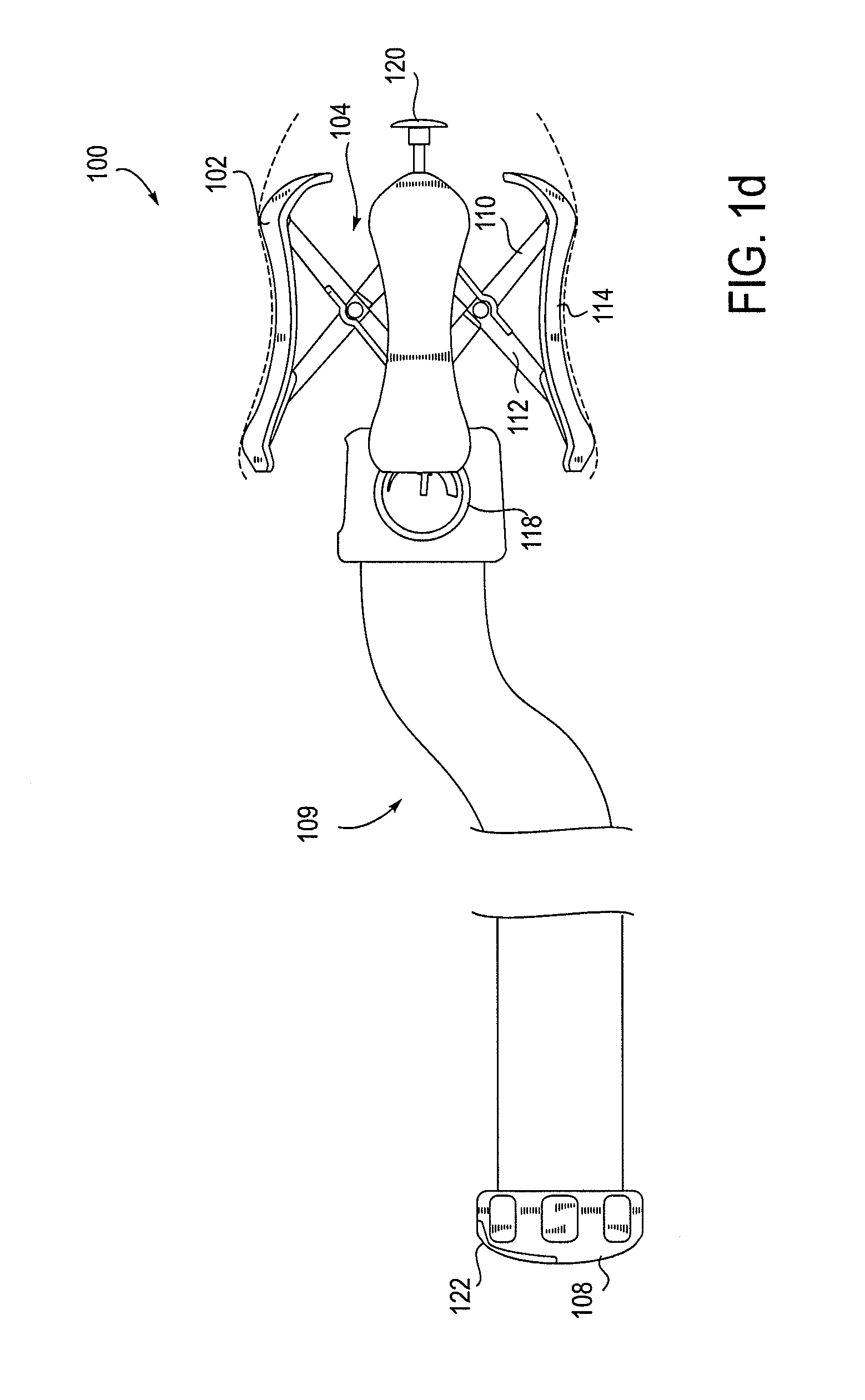
Tissue fasteners and related deployment systems and methods
Surgical tissue fasteners and related deployment systems and methods are disclosed. A tissue fastener used to join multiple tissue layers includes a first member, a second member, and a connecting member connecting the first and second members. In some embodiments, the first and second members are configured to expand from a delivered state to a deployed state in which the fastener secures the tissue layers together. Other tissue fastener embodiments include means for applying a substantially constant force on the tissue layers and / or means for adjusting a length of the connecting member between the first and second members.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
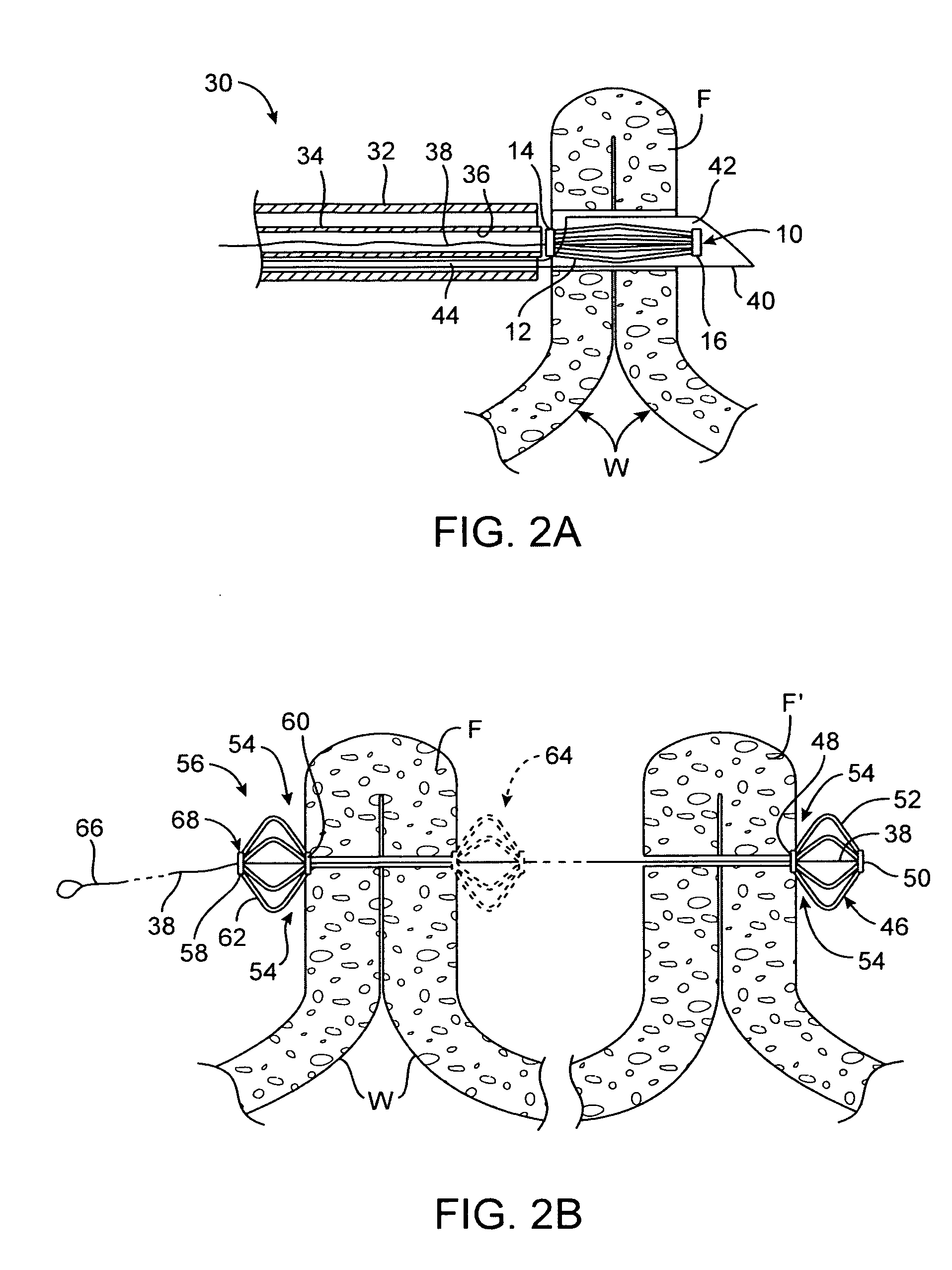
System for optimizing anchoring force
ActiveUS7695493B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Systems for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS7736379B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Apparatus & methods for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Constant force coaxial cable connector
ActiveUS7566236B2High retention rateTrend downEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsTwo pole connectionsInterference fitMating connection
Owner:PPC BROADBAND INC
Apparatus and methods for optimizing anchoring force
ActiveUS20050277981A1Avoid exposurePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Apparatus and methods for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS20050277966A1Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Apparatus & methods for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS7678135B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
System for optimizing anchoring force
ActiveUS20050277983A1Avoid exposureConstant force against the tissueSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Systems for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Infusion apparatus
ActiveUS20050277882A1Easy to useEasy constructionAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesDrugs solutionStored energy
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as, antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a substantially constant-force, compressible-expandable wave spring that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of medicament solution to the patient.
Owner:MARSHALL S KRIESEL REVOCABLE TRUST
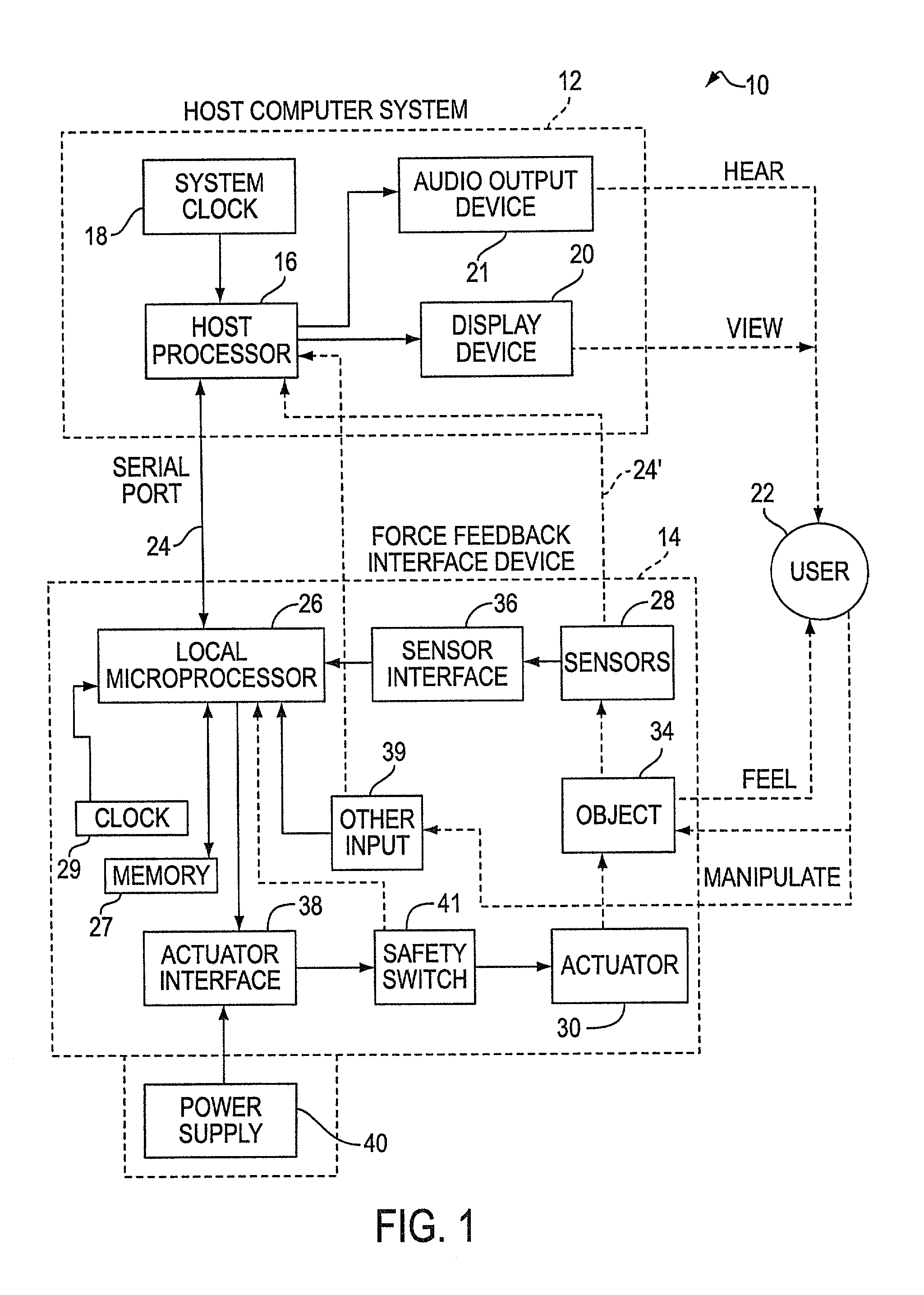
Haptic feedback stylus and other devices
InactiveUS7265750B2Low costSimpler and low force feedbackInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsTouch Perception
A force feedback interface and method including an actuator in a non-primary axis or degree of freedom. The force feedback interface device is connected to a host computer that implements a host application program or graphical environment. The interface device includes a user manipulatable object, a sensor for detecting movement of the user object, and an actuator to apply output forces to the user object. The actuator outputs a linear force on the user object in non-primary linear axis or degree of freedom that is not used to control a graphical object or entity implemented by the host computer, and movement in the non-primary degree of freedom is preferably not sensed by sensors. The axis extends through the user object, and there are preferably no other actuators in the device, thus allowing the force feedback device to be very cost effective. Force sensations such as a jolt, vibration, a constant force, and a texture force can be output on the user object with the actuator. The force sensations can be output in a direction perpendicular to a planar degree of freedom, radial to spherical degree of freedom, and / or along a lengthwise axis of the user object.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Infusion apparatus
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as, antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a substantially constant-force, compressible-expandable wave spring that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of medicament solution to the patient.
Owner:MARSHALL S KRIESEL REVOCABLE TRUST
Constant force actuator
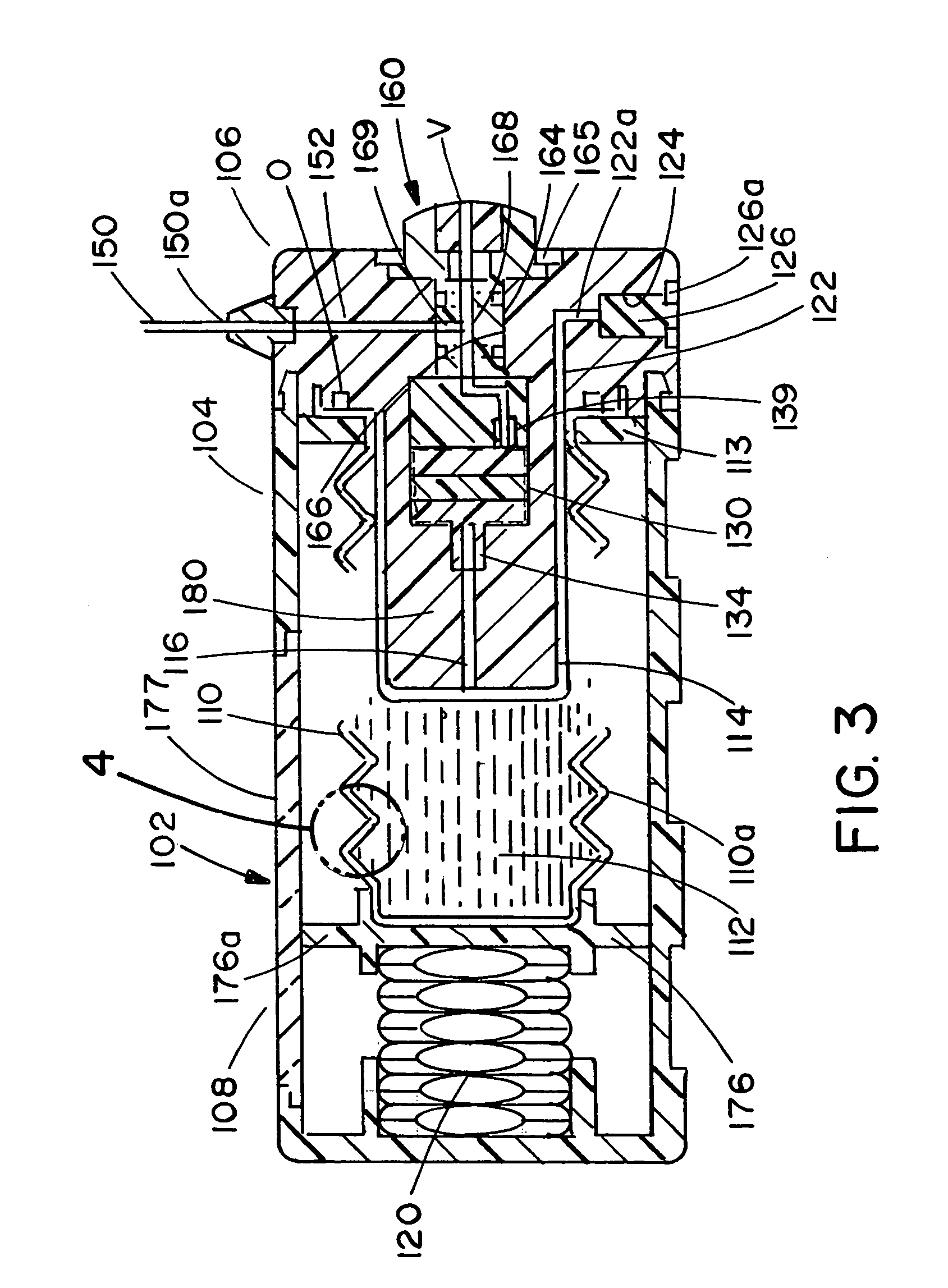
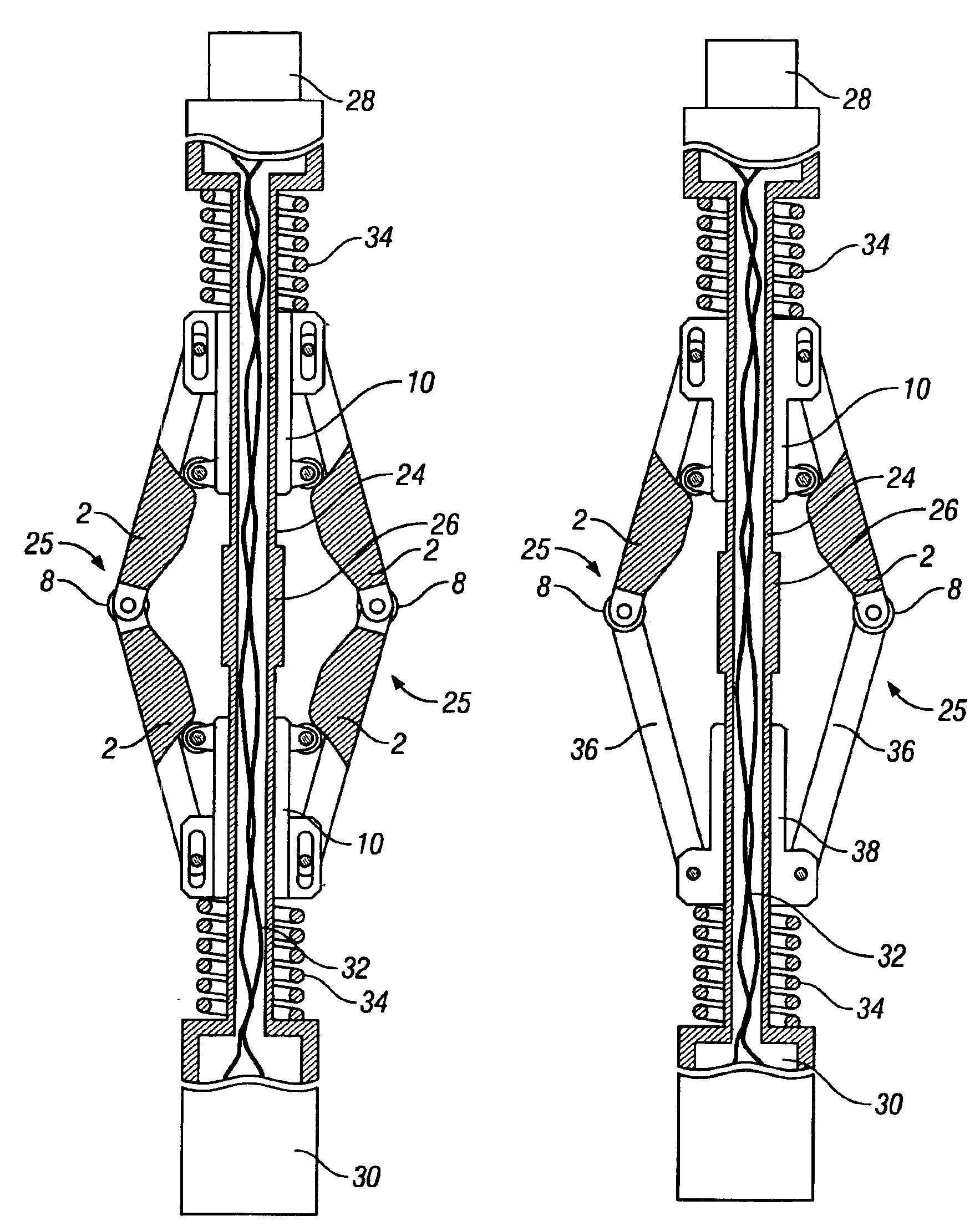
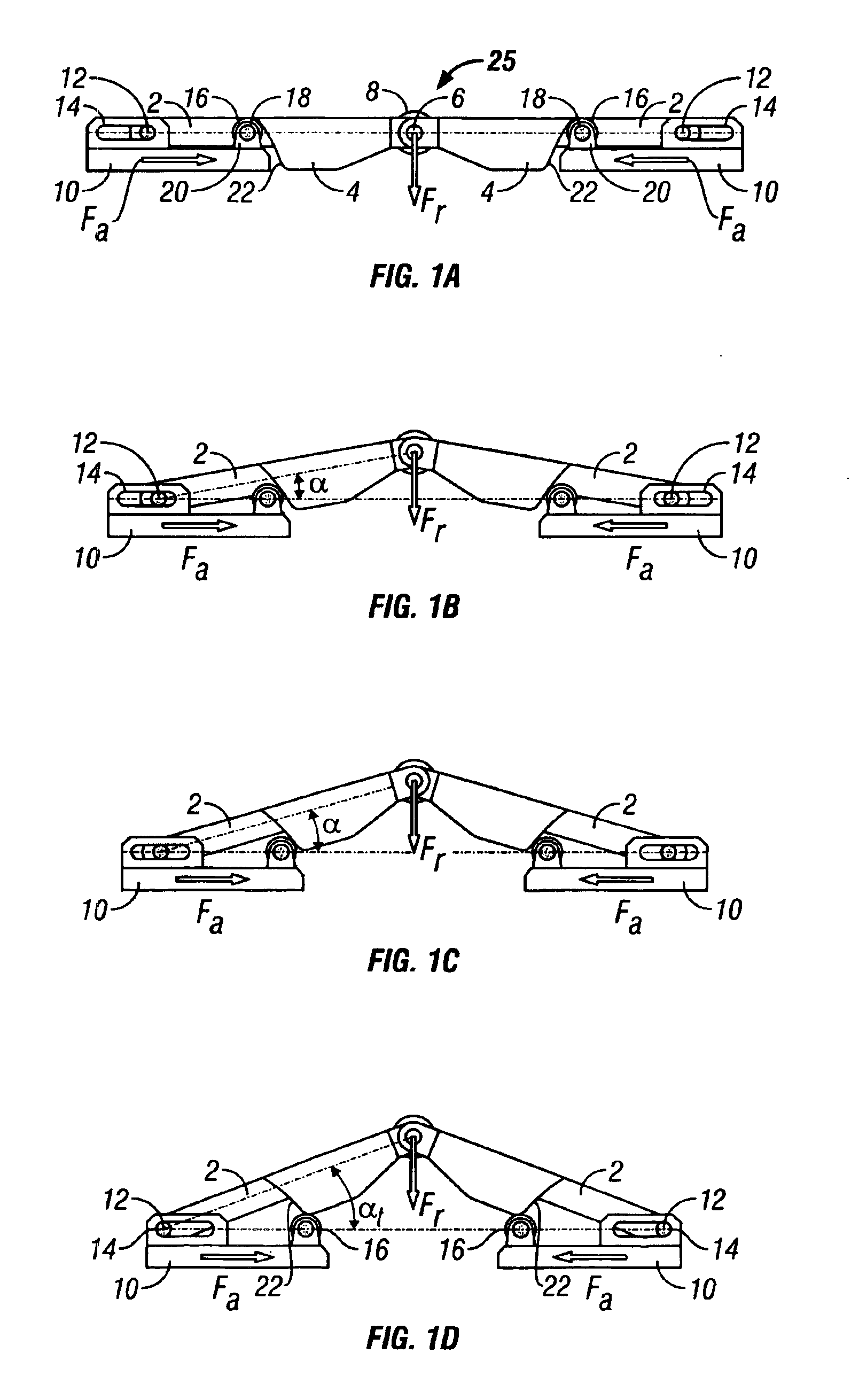
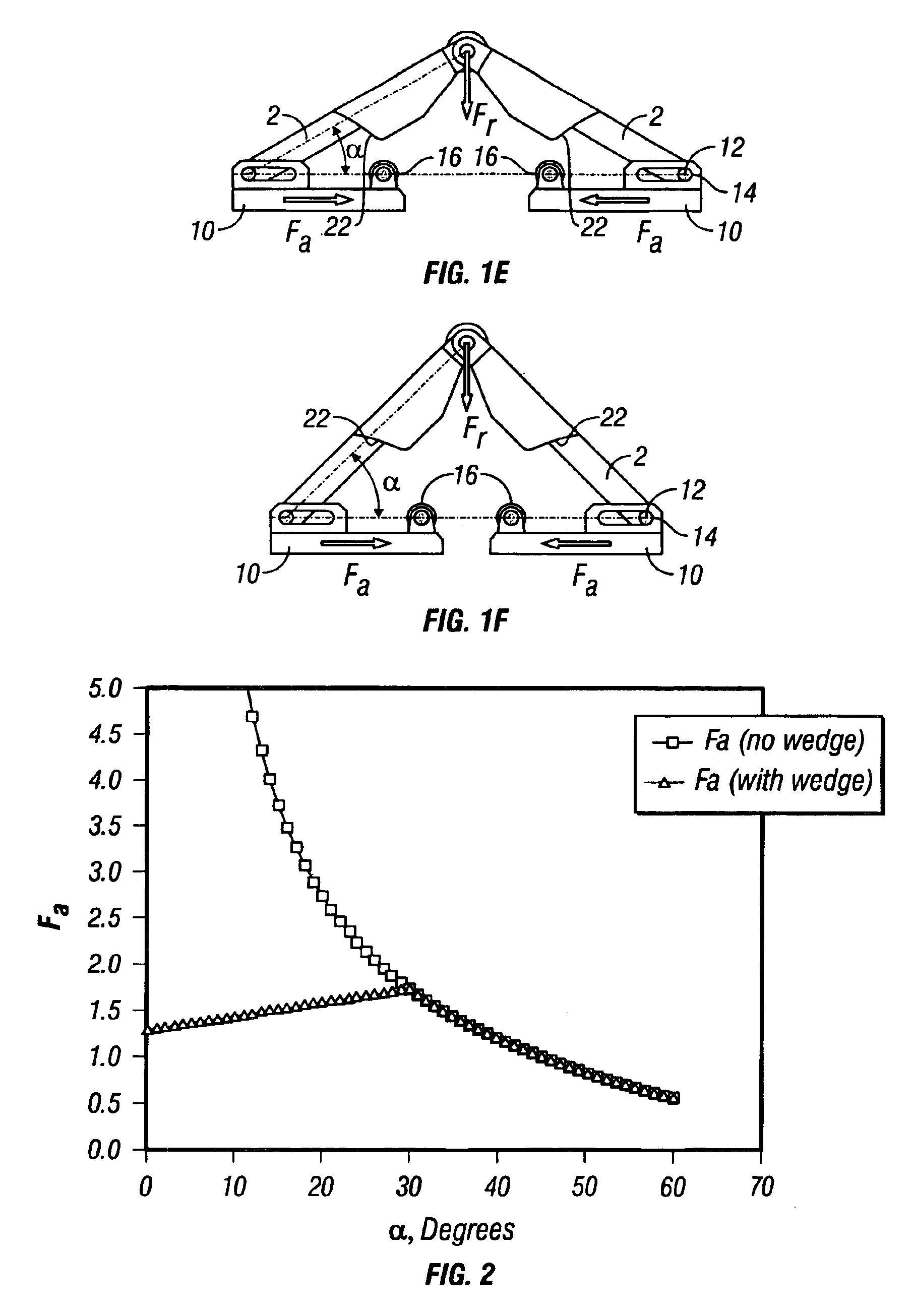
A substantially constant force actuator that is applicable to centralizers, anchors and tractors for use in wells and is applicable to lifting devices such as jacks and load supporting devices. One or more sets of linkage arms are angularly movable by the force of one or more force transmitting members from a minimum angle with the force transmitting members at maximum spacing to a maximum angle with the force transmitting members at minimum spacing to impart a substantially constant force to an object or surface, with the direction of the force being substantially perpendicular to the direction of relative linear movement of the force transmitting members. With the linkage arms at their minimum angles, movement control elements on at least one of the force transmitting members react with guide surfaces of the linkage arms to achieve angular linkage movement and to develop a substantially constant force during angular linkage movement.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Optical accelerometer or displacement device using a flexure system
InactiveUS6955085B2Radiation pyrometryAcceleration measurement using interia forcesFiberAccelerometer
Disclosed herein is an accelerometer and / or displacement device that uses a mass coupled to a rhomboidal flexure to provide compression to an optical sensing element preferably having a fiber Bragg grating (FBG). The transducer includes a precompressed optical sensor disposed along a first axis between sides of the flexure. The top portion of the flexure connects to the mass which intersects the flexure along a second axis perpendicular to the first axis. When the mass experiences a force due to acceleration or displacement, the flexure will expand or contract along the second axis, which respectively compresses or relieves the compression of the FBG in the optical sensing element along the first axis. Perturbing the force presented to the FBG changes its Bragg reflection wavelength, which is interrogated to quantify the dynamic or constant force. A temperature compensation scheme, including the use of additional fiber Bragg gratings and thermal compensators axially positioned to counteract thermal effects of the optical sensing element, is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Spinal and soft tissue mobilizer
A spinal and soft tissue mobilizer of modular construction for physical therapy has an elongate generally spool-shaped roller with a reduced diameter mid portion and larger diameter teardrop-shaped outer end portions rollers that apply pressure to the thoracic vertebrae, rib cage and muscles of the back without directly contacting the vertebrae. The mid portion may have lateral rollers with laterally spaced larger diameter portions that straddle the vertebrae of the spine and apply pressure to the muscles surrounding the straddled vertebrae without directly contacting the vertebrae. Interchangeable spacers of various lengths may be installed between the lateral rollers and / or between the lateral rollers and the teardrop-shaped outer end portions to provide proper lateral spacing for a particular individual. An individual may use the device without assistance, by placing the device on the floor underneath his / her back and moving back and forth over the device, or an operator may grip the handles and roll the device up and down along the back and spinal area of an individual laying face down on a flat surface. The device may also be mounted horizontally in doorway whereby the user can move his or her back up and down while at the same time applying a reasonably constant force against the device.
Owner:LAPHAM ROGER
Macrocellular cushion and folding elastomer truss
InactiveUS6284346B1Reducing effective buckling lengthPreventing unnecessary outward (lateral) bucklingLayered productsLight effect designsElastomerCardboard
An improved closed-cell foam sheet stock and method for producing constant force characteristics in elastomer cushions. A closed cell foam is formed as a corrugated cardboard with regular cavities and support elements between two surface sheets. The resulting stock material possesses similar flexibility to foam stock but with an elongated force curve. A method for modifying this or other corrugated elastomers for efficient constant force curves is further provided where alternating support members are conjoined or buttressed to fold in controlled sigmoid shape under load. The resulting collapsible truss or space frame structure produces a cushion with improved cushioning, load distribution, shock absorption and resistance from lateral collapse while folding uniformly and efficiently to a smooth, compact and comfortable support under full compression. The orthopedic constant force profile allows uses in shoes, furniture, mattresses, sports padding, aircraft seats or packaging applications and extends the dynamic range of more resilient elastic, plastic or foam materials including very lightweight closed cell foam. For packaging applications both the collapsing truss or the less sophisticated corrugated profiles provide lighter weight and improved impact absorption over solid closed-cell foams.
Owner:SHERIDAN TIMOTHY BRIAN
Exercise apparatus with rotational grips
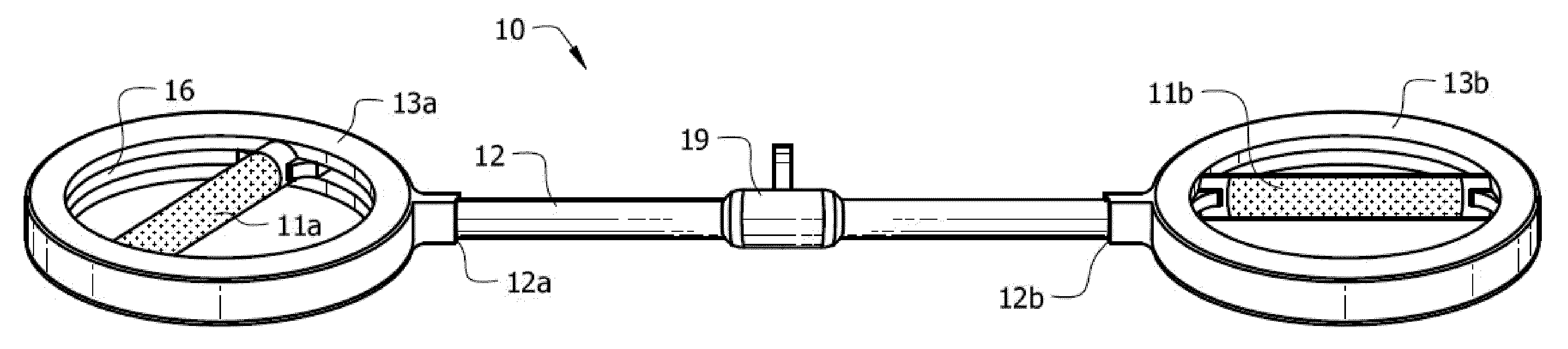
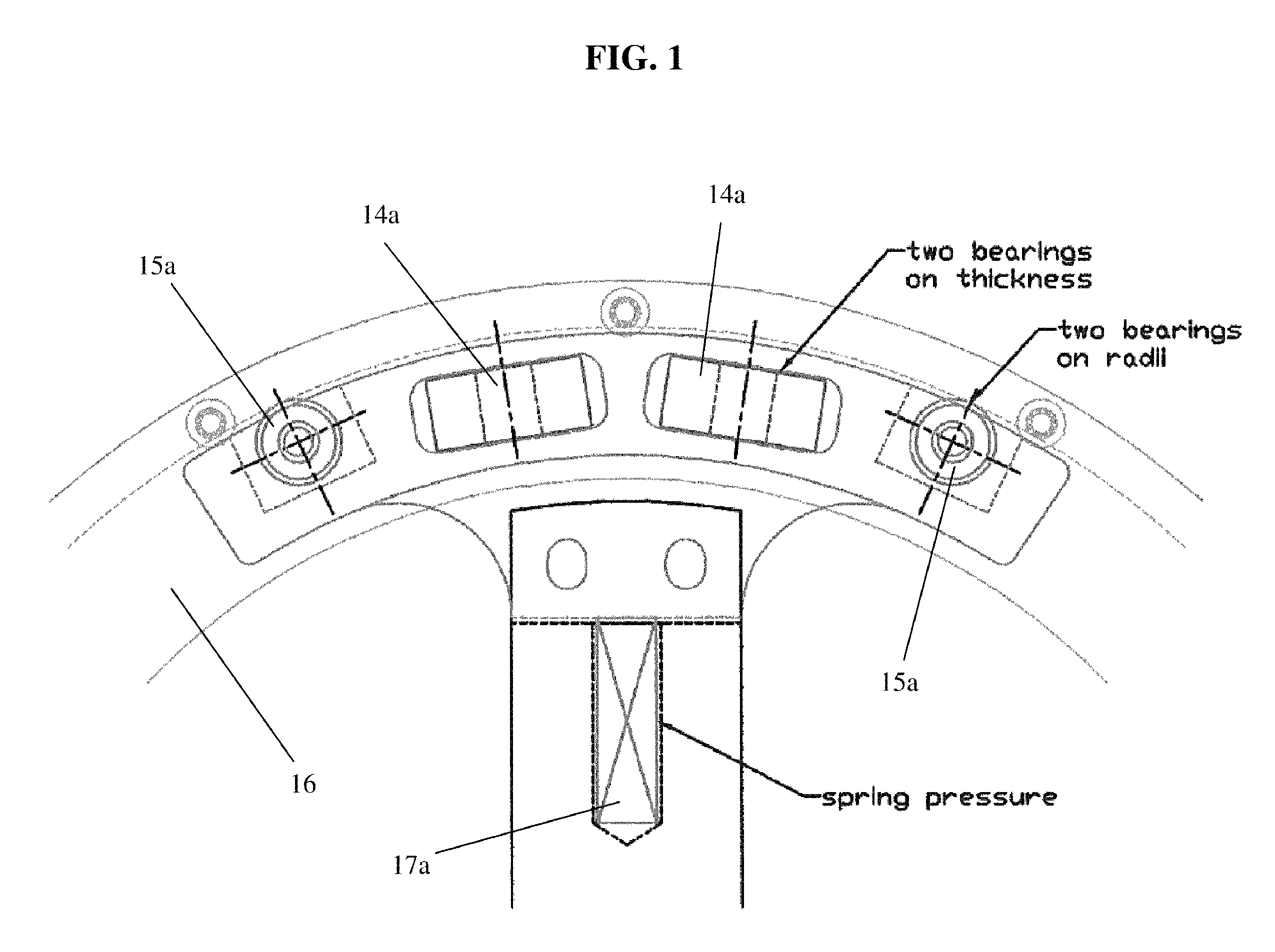
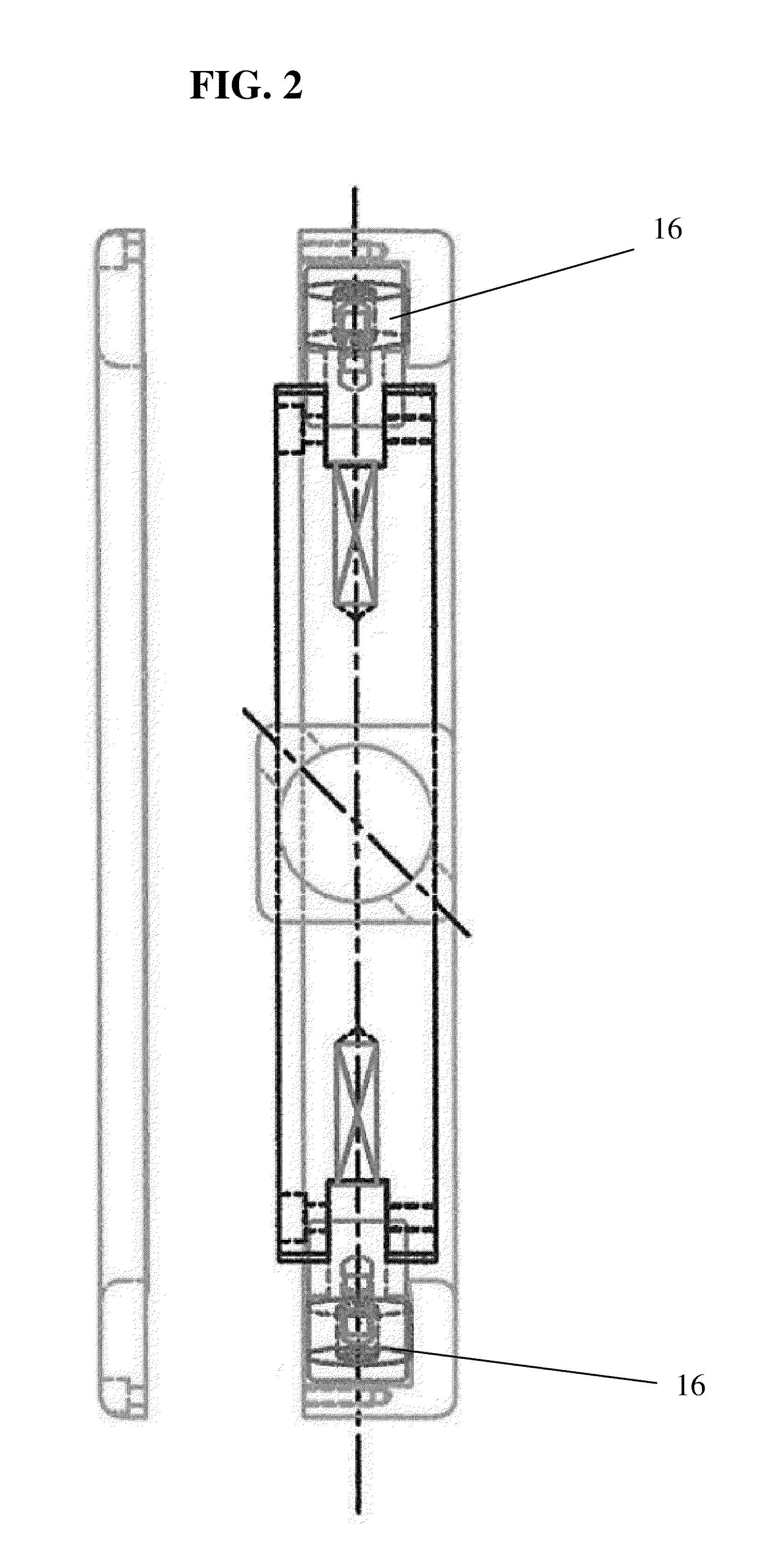
A barbell with rotational grips. The barbell includes a center bar with two grip housings of annular configuration mounted to opposite ends of the barbell. Handgrips are located within the grip housings. Two sets of bearings are diametrically opposed to one another at the ends of each handgrip. A first set of radial wall bearings are perpendicular to the rotational axis of the handgrip, and a second set of sidewall bearings are parallel to the rotational axis of the handgrip. Each grip housing has an interior circumferential groove, with radial and sidewall bearings operatively secured within the groove. Each hand grip is spring-loaded so that a constant force is applied perpendicular to the rotational axis of the handgrips.
Owner:SPINGRIP FITNESS
System and method for implementing a suspended personal radiation protection system
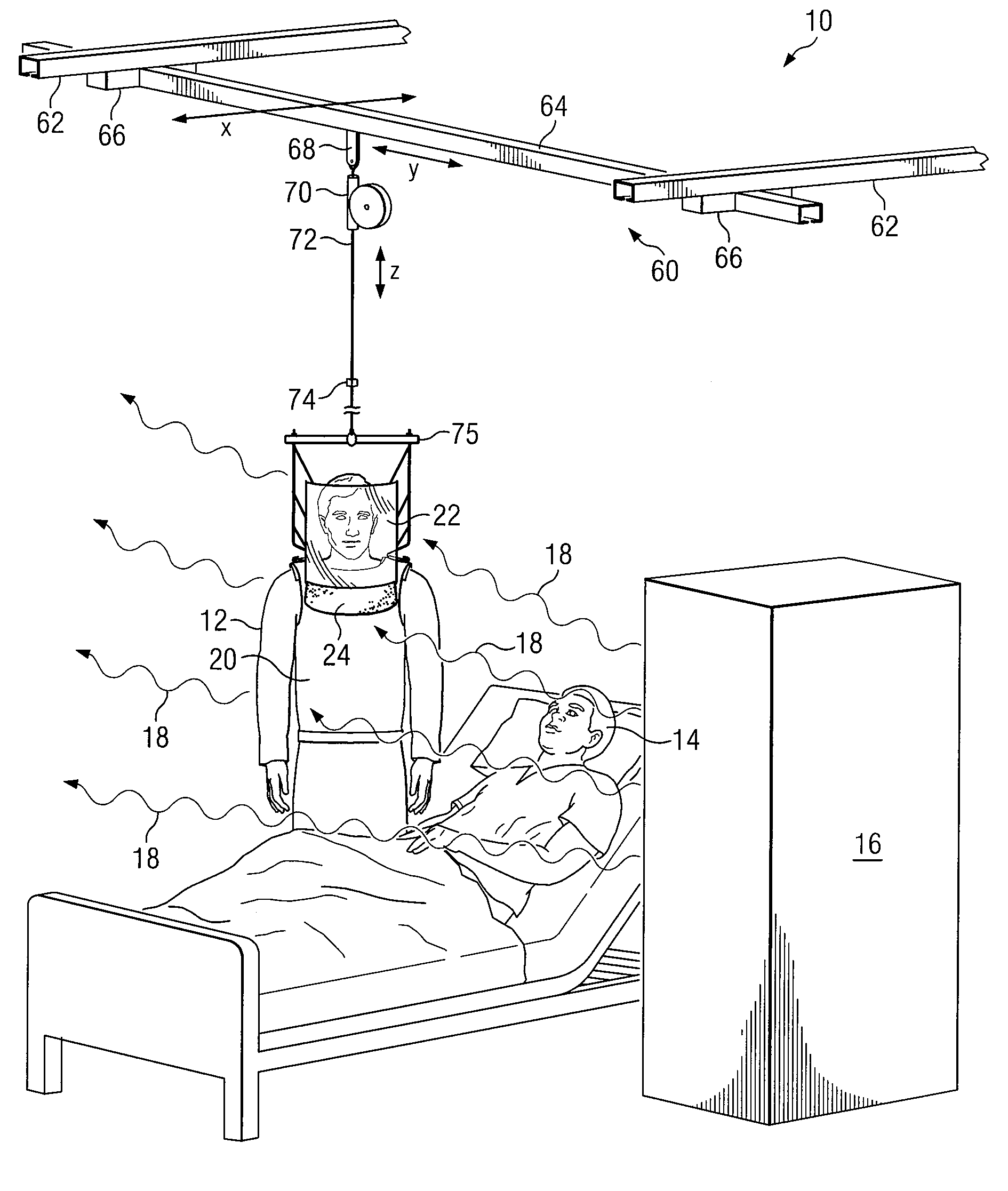
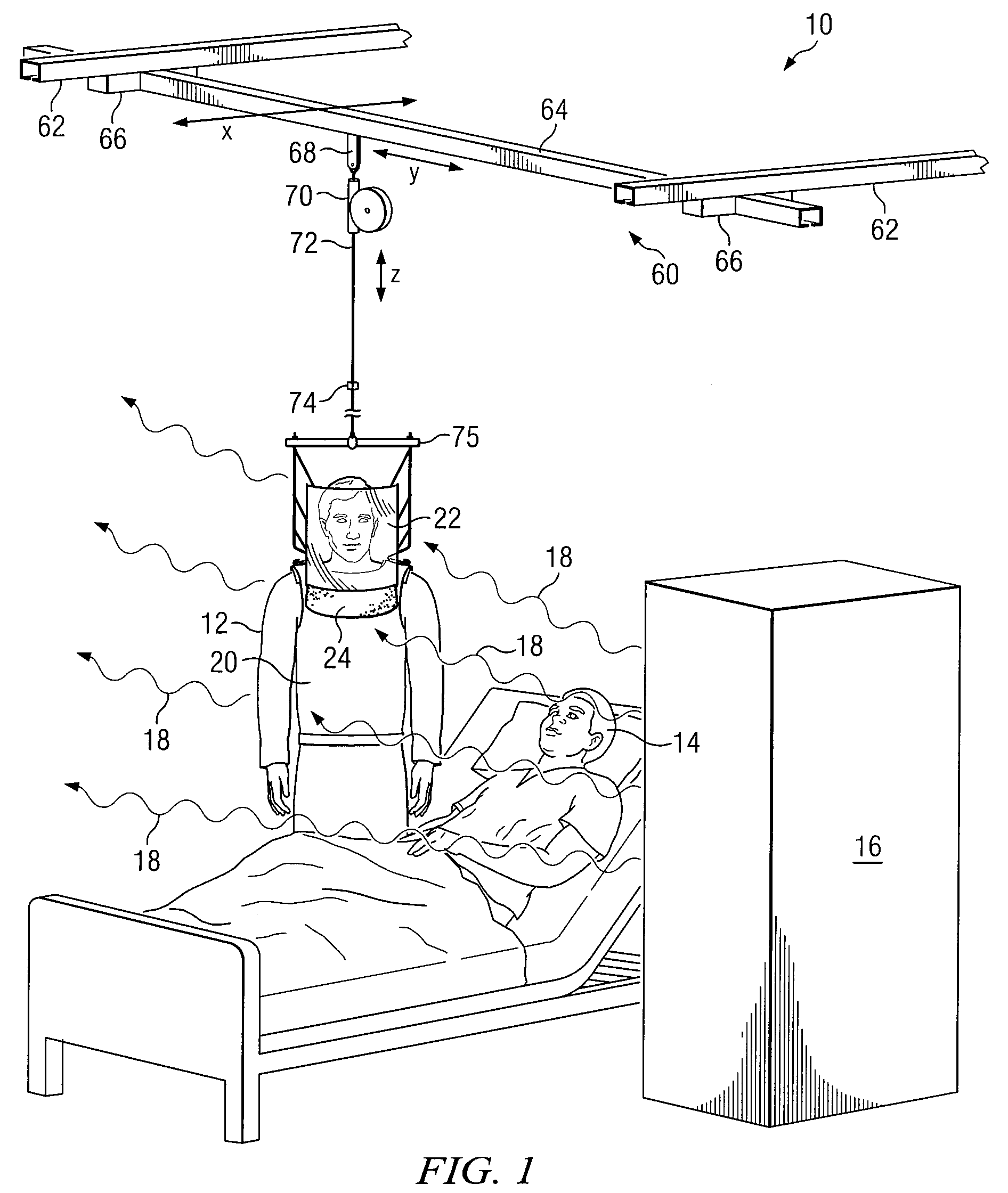
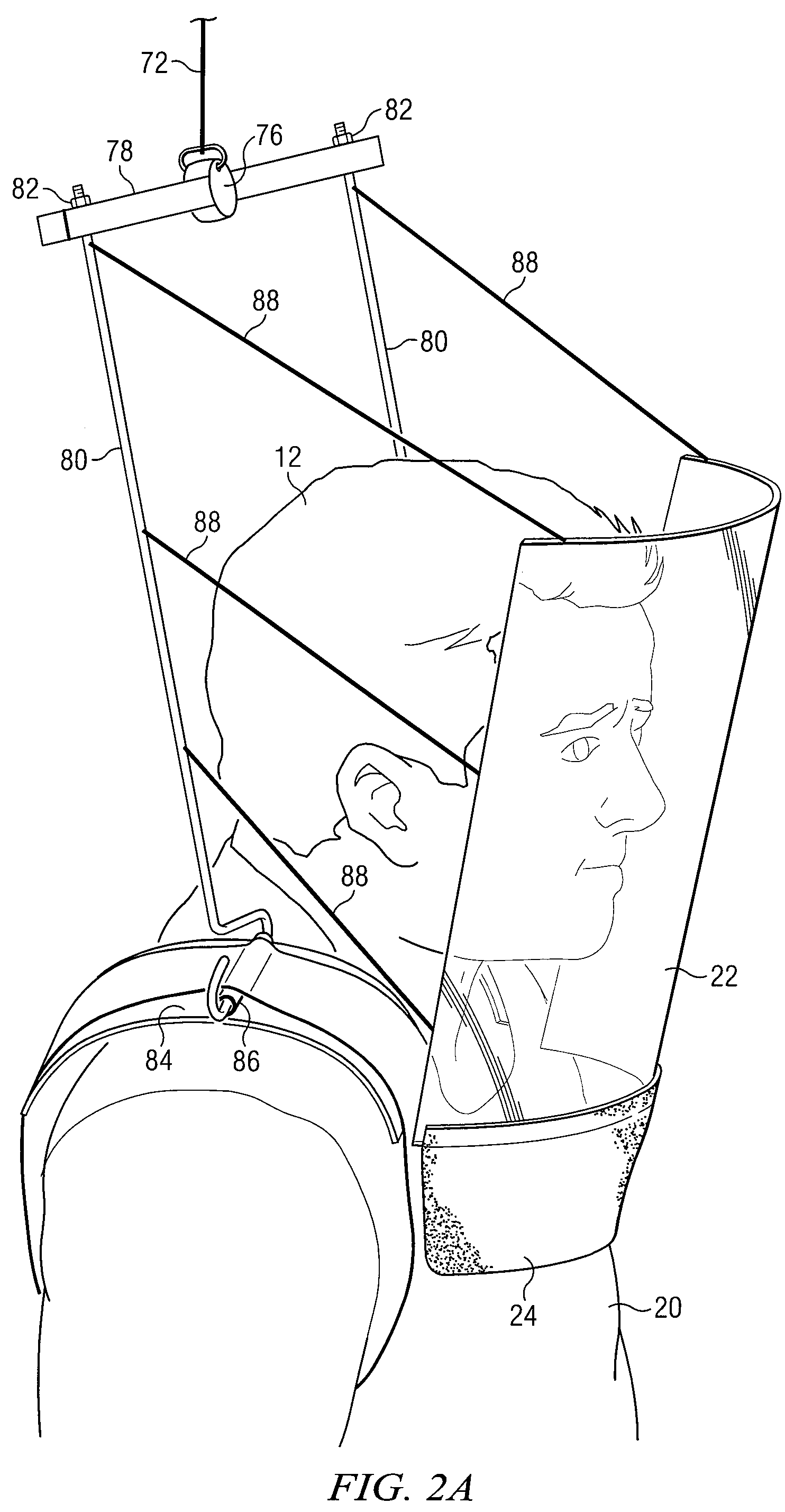
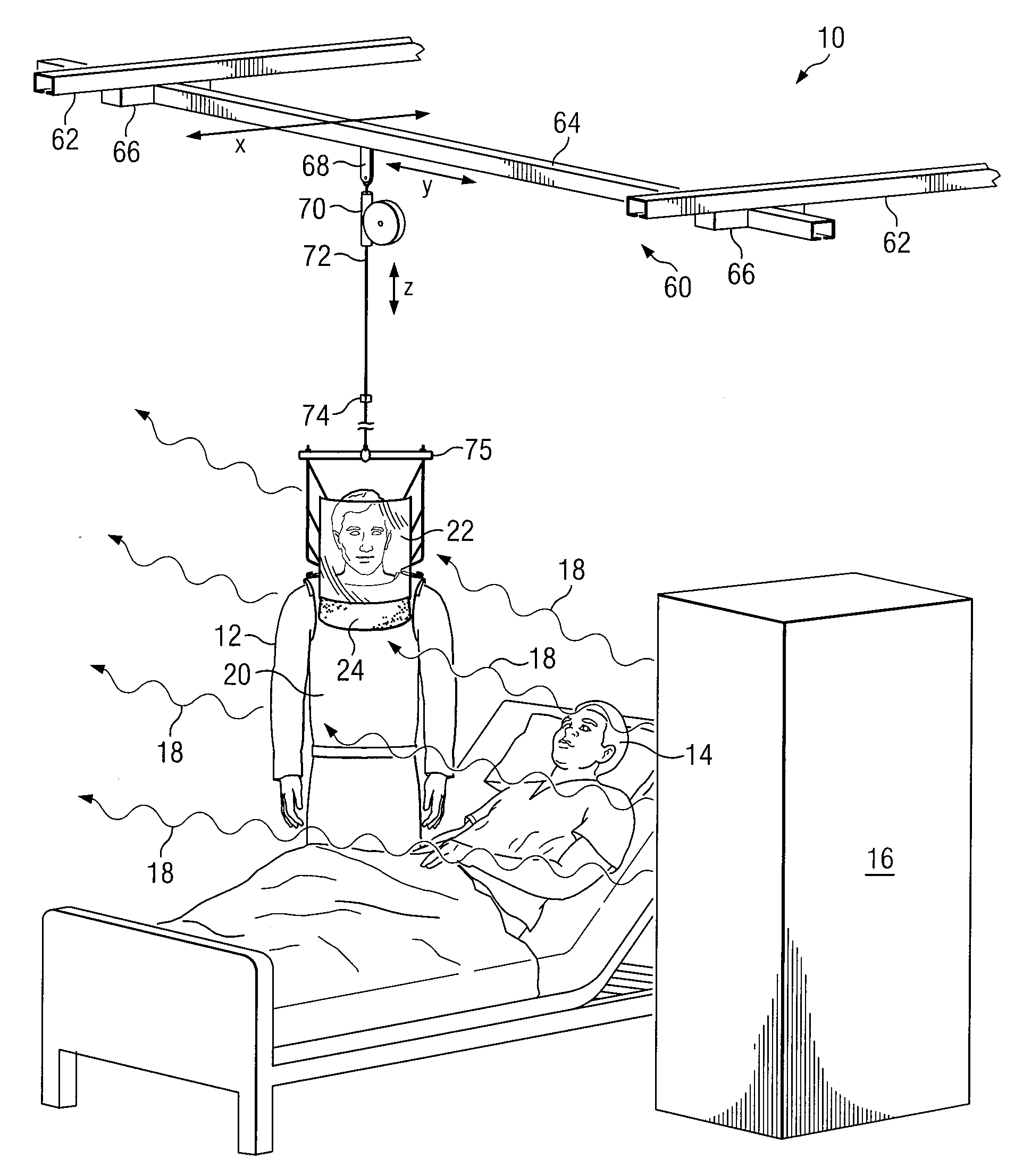
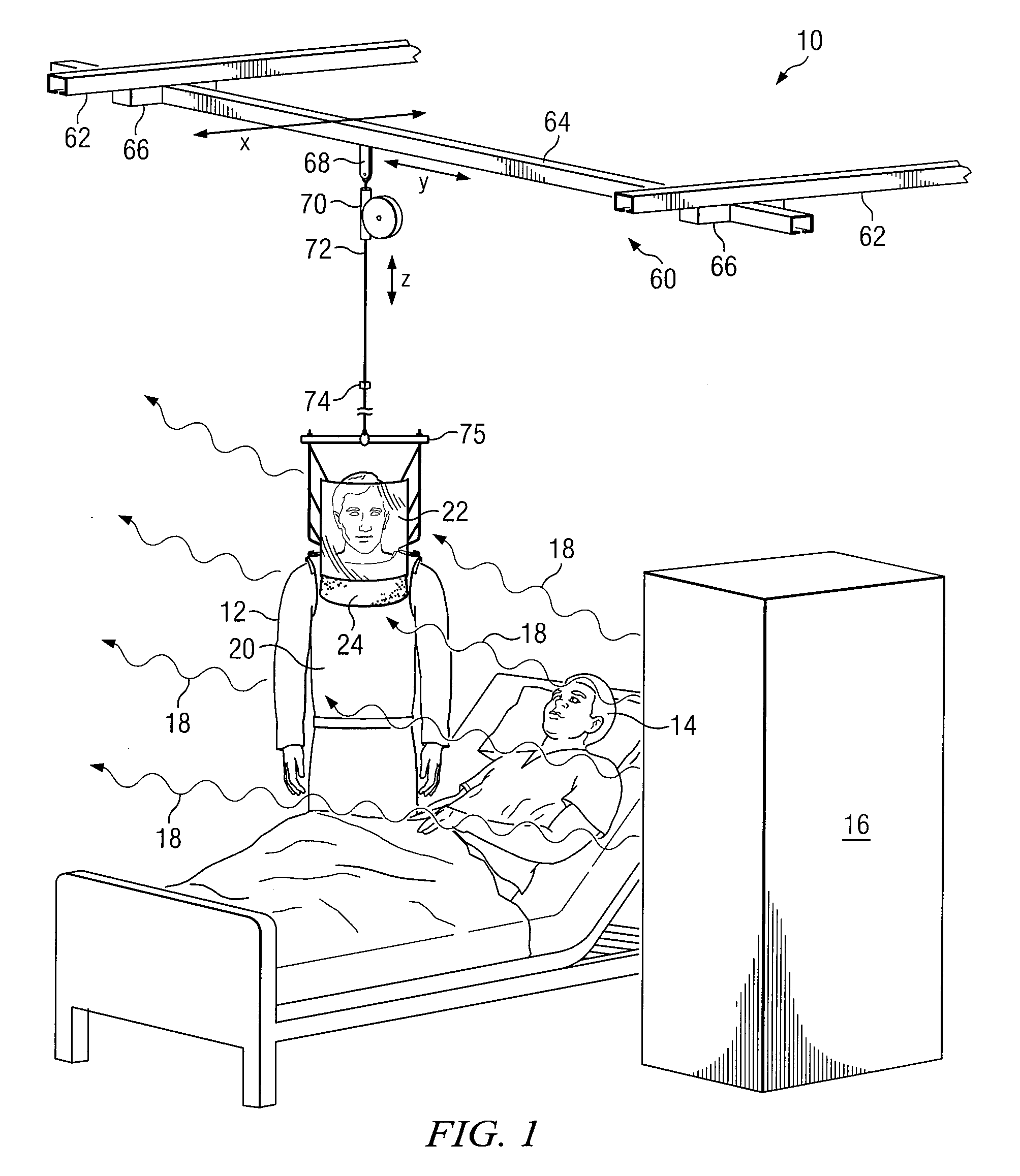
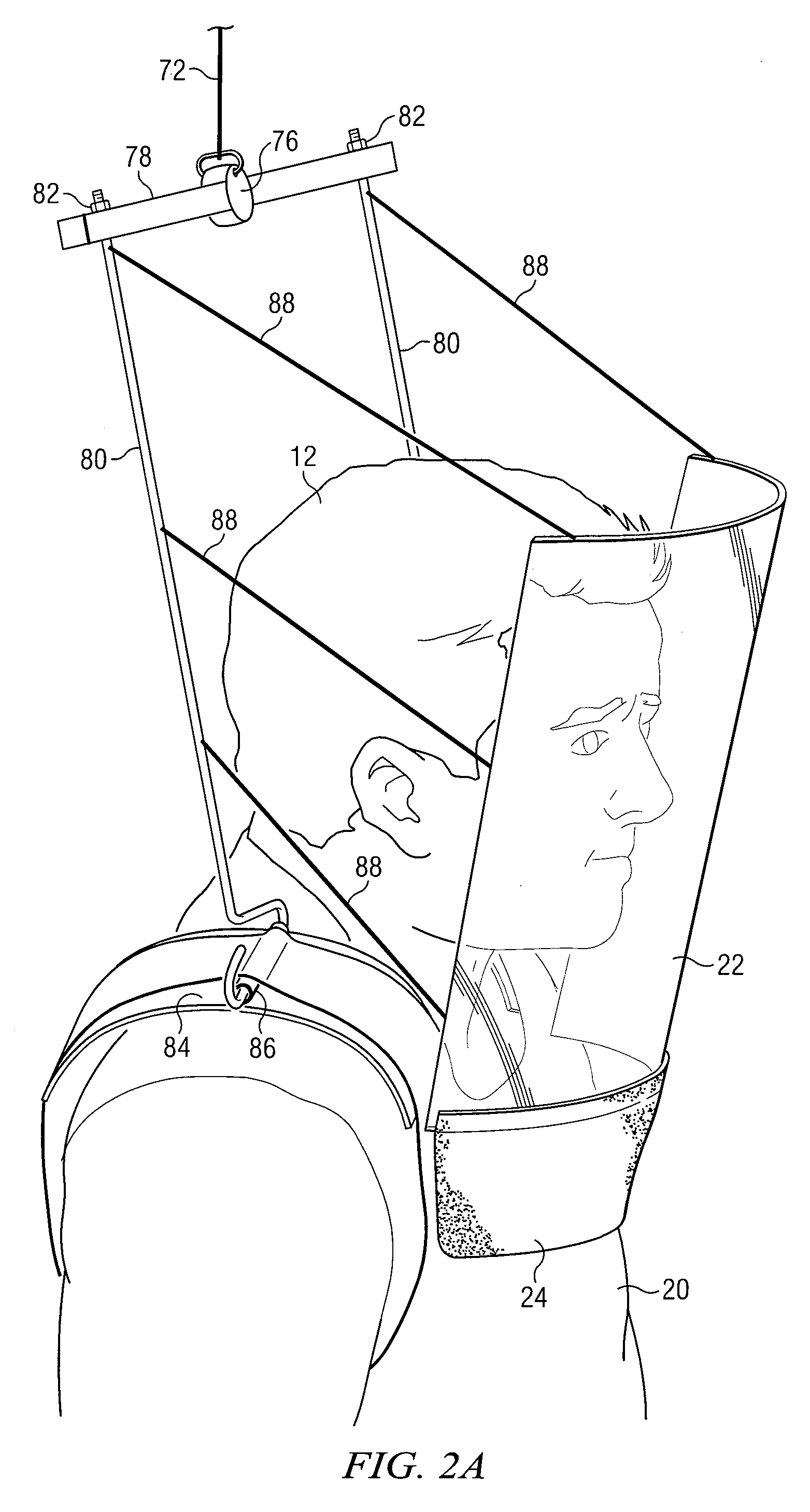
ActiveUS7608847B2Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemChemical protectionHeat protectionConstant forceBody contouring
A personal radiation protection garment that substantially contours to an operator's body is suspended from a suspension means. The garment is operable to protect the operator from radiation. The suspension means is operable to apply constant force. The suspension means allows operator wearing protective radiation garment to move freely in the X, Y, and Z spatial planes simultaneously, such that the protective radiation garment is substantially weightless to operator. A radiation protection face shield and flap can also be suspended from suspension means, such that face shield and flap are substantially weightless to operator. The suspension means can be mounted to a ceiling.
Owner:INTERVENTCO
Infusion apparatus with modulated flow control
InactiveUS20050033232A1Easy to useEasy constructionFlexible member pumpsMedical devicesStored energyConstant force
A compact fluid dispenser for use in controllably dispensing fluid medicaments, such as antibiotics, oncolytics, hormones, steroids, blood clotting agents, analgesics, and like medicinal agents from prefilled containers at a uniform rate. The dispenser uniquely includes a stored energy source that is provided in the form of a substantially constant-force, compressible-expandable wave spring that provides the force necessary to continuously and uniformly expel fluid from the device reservoir. The device further includes a fluid flow control assembly that precisely controls the flow of medicament solution to the patient. Additionally, the device includes a novel modulating assembly for controllably modulating the force exerted by the wave spring tending to expel the fluid from the device reservoir.
Owner:BIOQUIDDITY
Vertical speed and flight path command algorithm for displacement collective utilizing tactile cueing and tactile feedback
ActiveUS20080234881A1Improve processing qualityEnhanced Situational AwarenessAircraft controlDigital data processing detailsLevel flightDetent
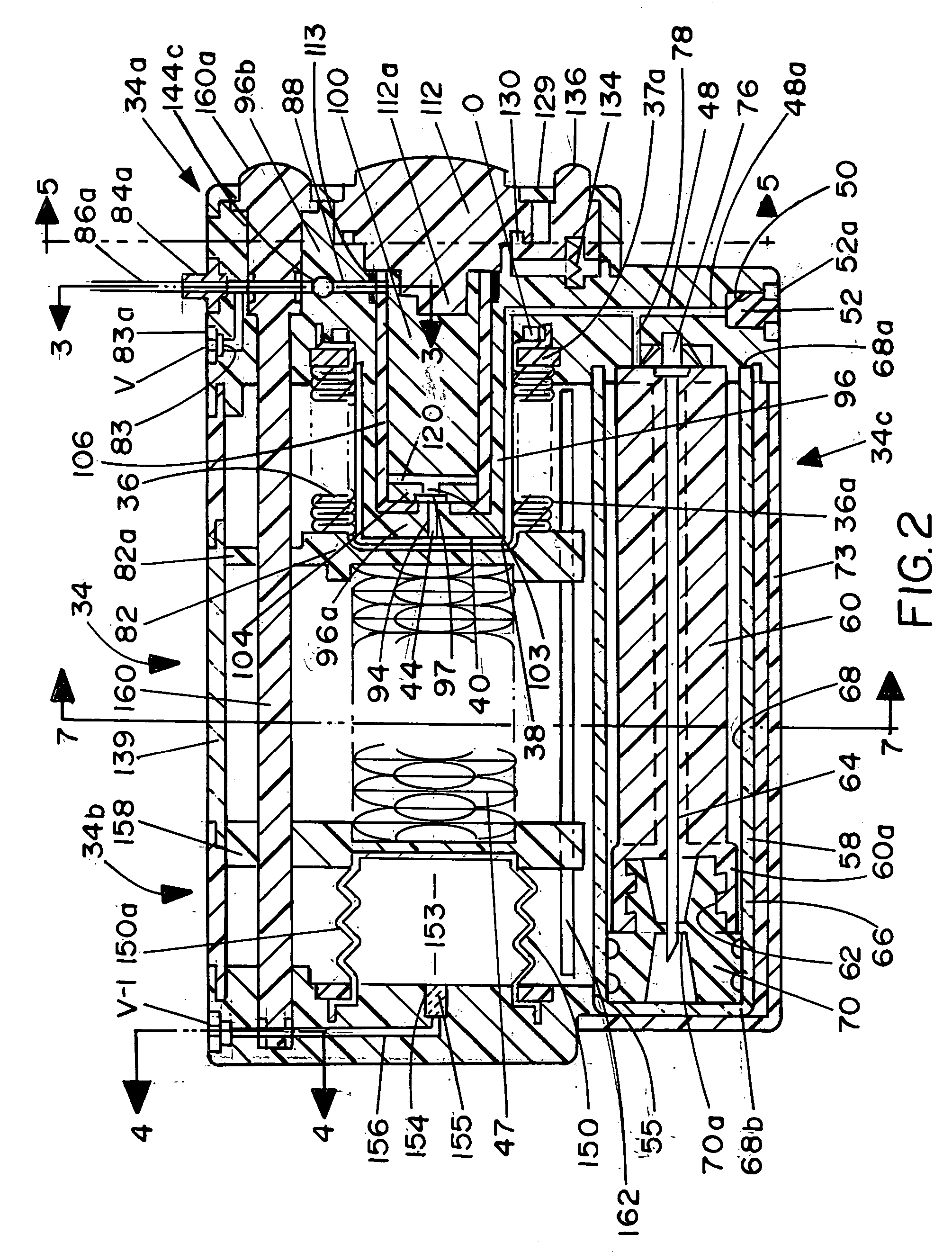
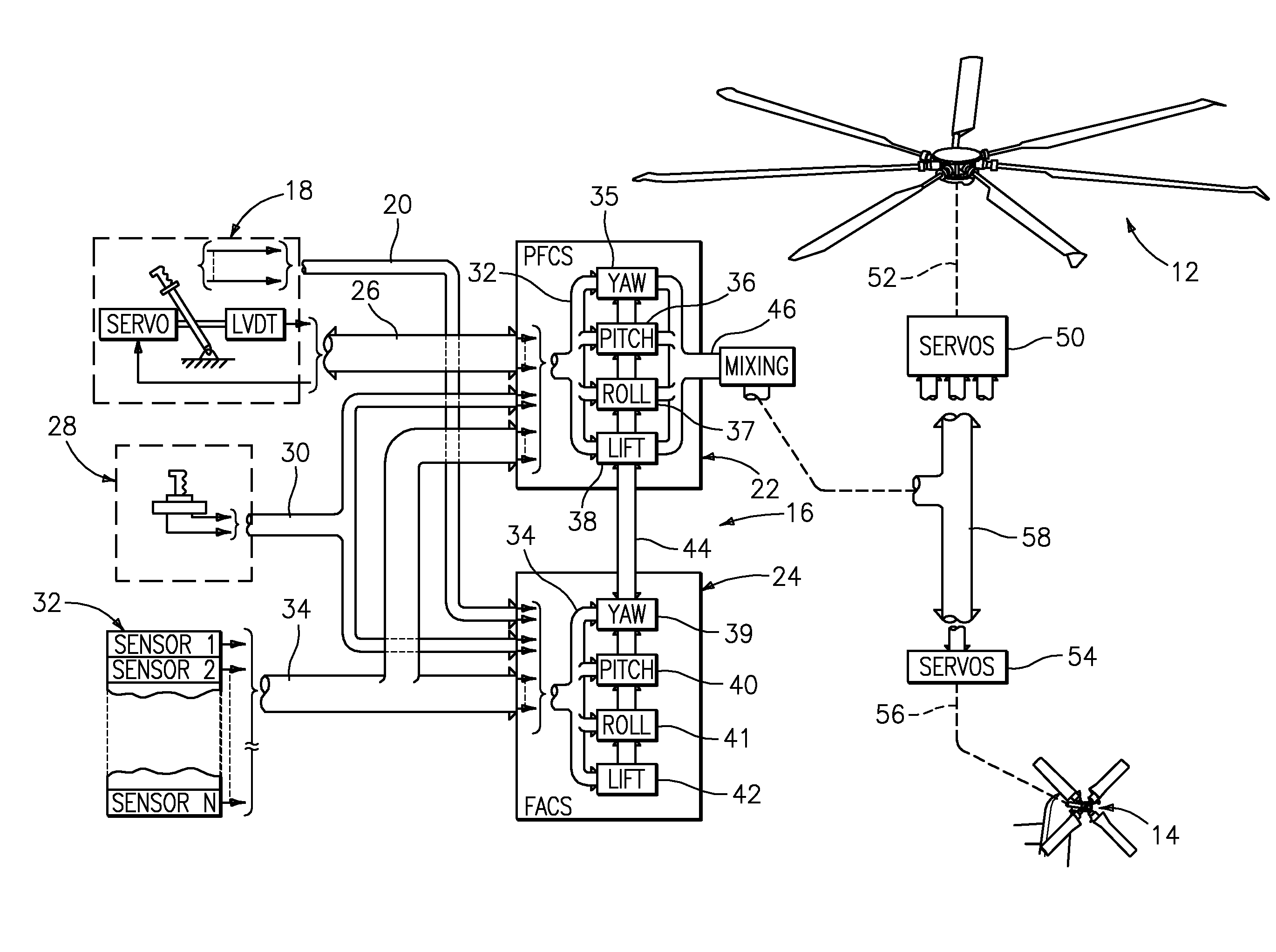
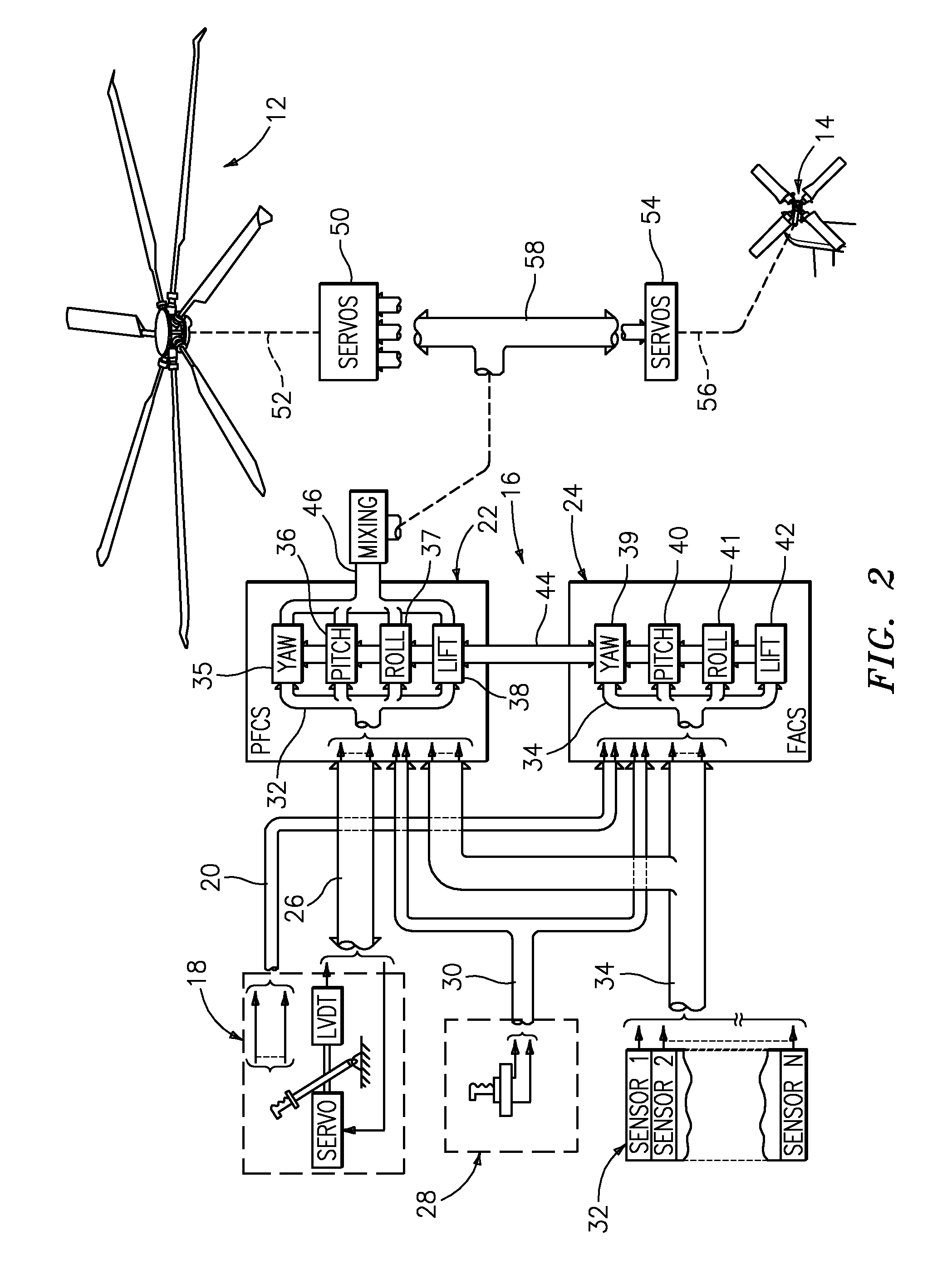
A flight control system includes a collective position command algorithm for a lift axis (collective pitch) which, in combination with an active collective system, provides a force feedback such that a pilot may seamlessly command vertical speed, flight path angle or directly change collective blade pitch. The collective position command algorithm utilizes displacement of the collective controller to command direct collective blade pitch change, while a constant force application to the collective controller within a “level flight” detent commands vertical velocity or flight path angle. The “level flight” detent provides a tactile cue for collective position to reference the aircraft level flight attitude without the pilot having to refer to the instruments and without excessive collective controller movement.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Vehicle suspension system
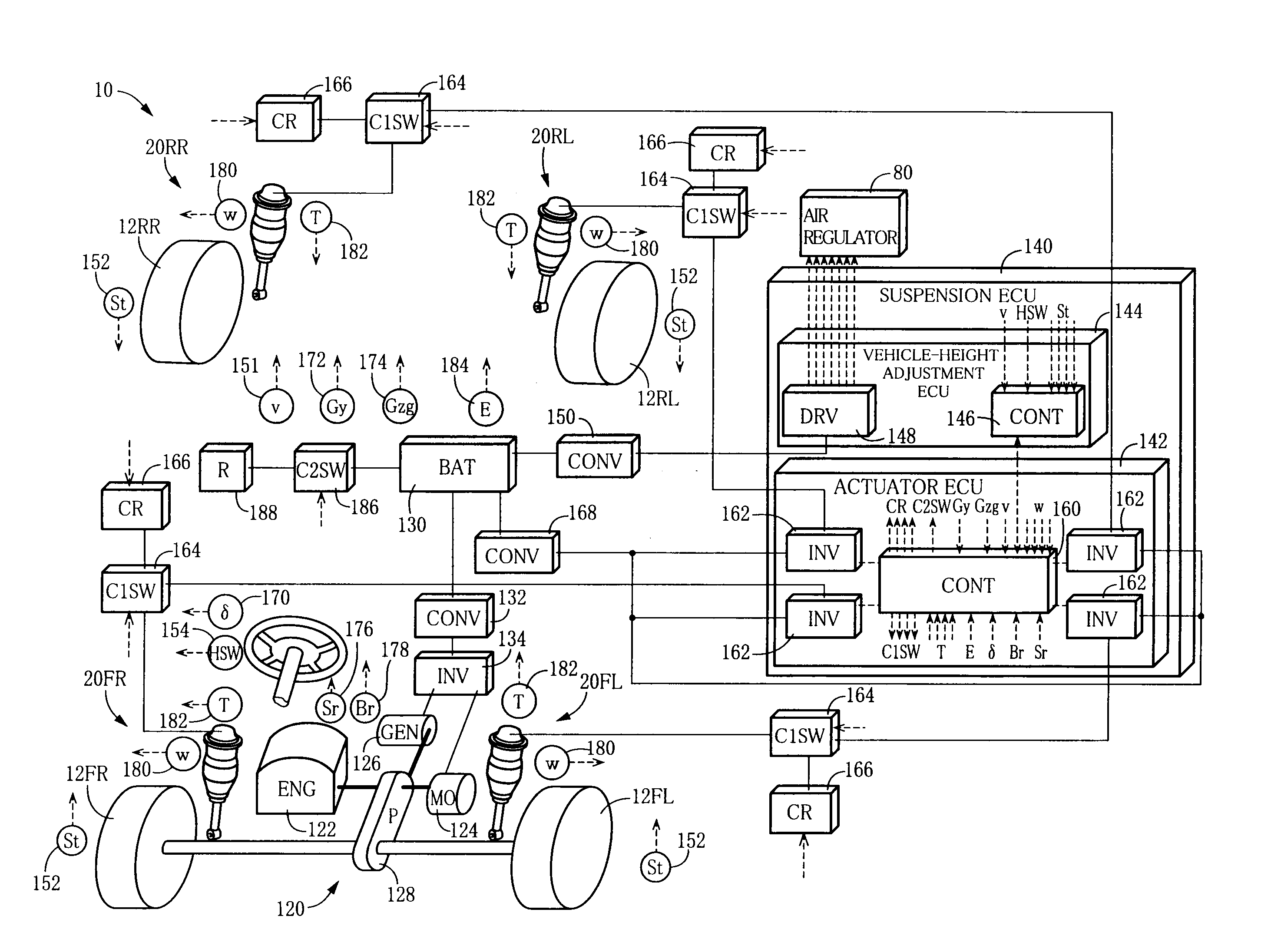
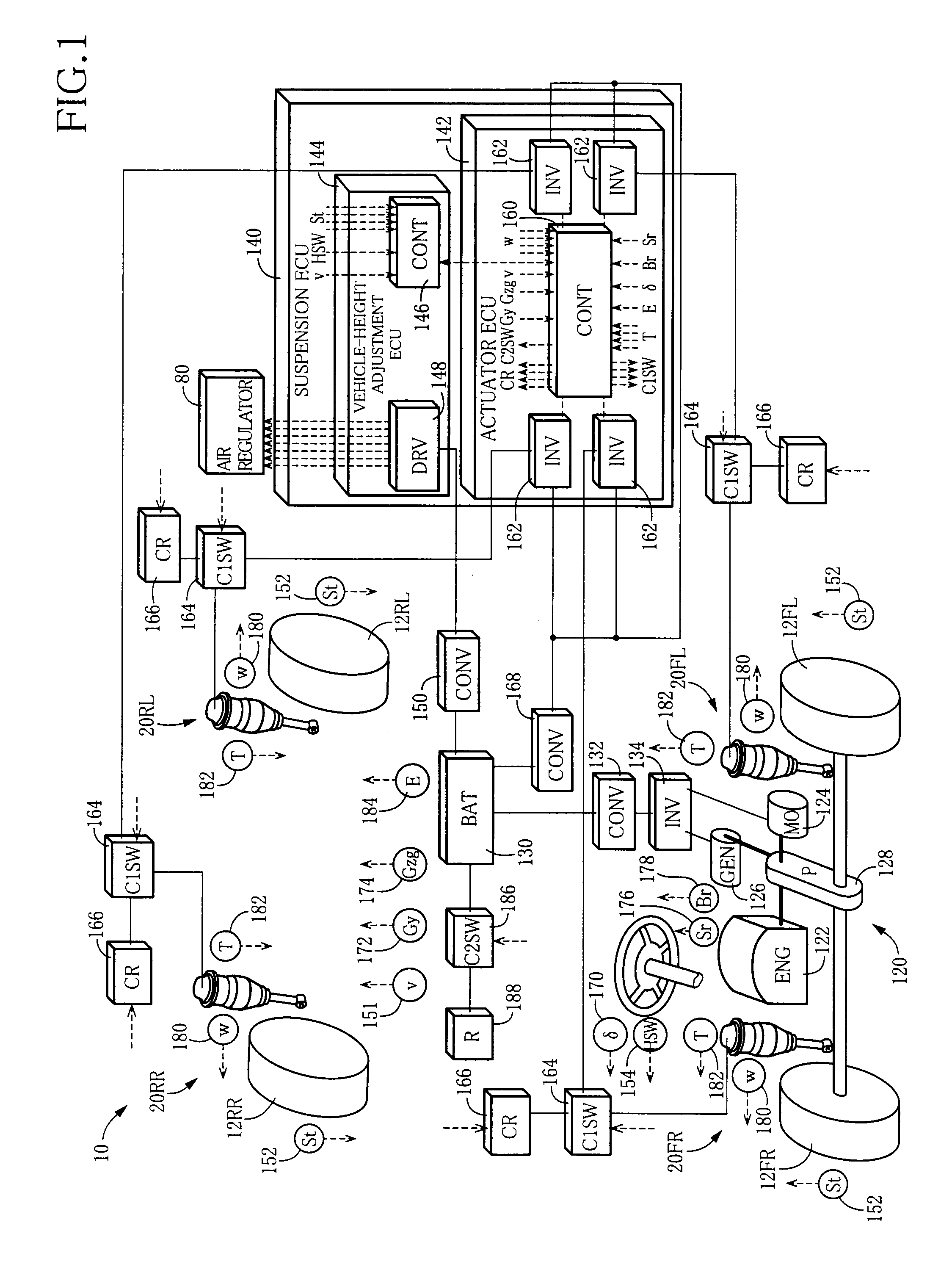
ActiveUS20100230876A1Effective controlImprove applicabilityMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionElectrical batteryConstant force
A vehicle suspension system including: (a) a suspension spring interconnecting a vehicle body and a wheel; (b) an actuator having an electric motor, such that the actuator is capable of generating, based on a force of the electric motor, an actuator force forcing the body and the wheel toward and away from each other, and causing the generated actuator force to act as a damping force against displacement of the body and the wheel; and (c) a control device for controlling the actuator force generated by the actuator, by controlling operation of the electric motor. The control device is capable of establishing a constant-force generating state in which the actuator force is constantly generated as a constant actuator force by the actuator with supply of an electric power thereto from a battery as an electric power source of the electric motor such that the generated constant actuator force acts in a rebound direction or a bound direction. The control device controls the constant-force generating state, based on a charge state of the battery.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
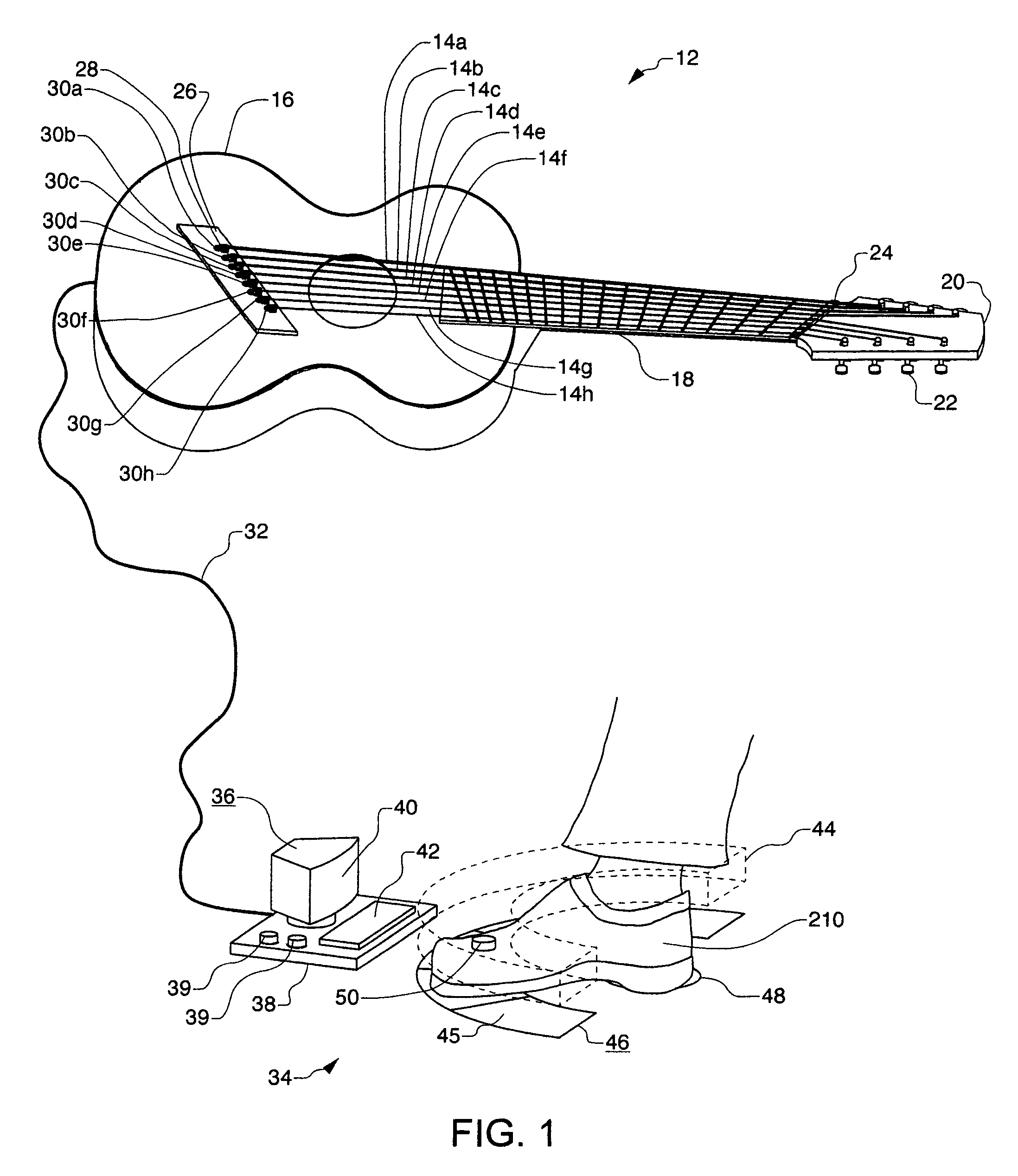
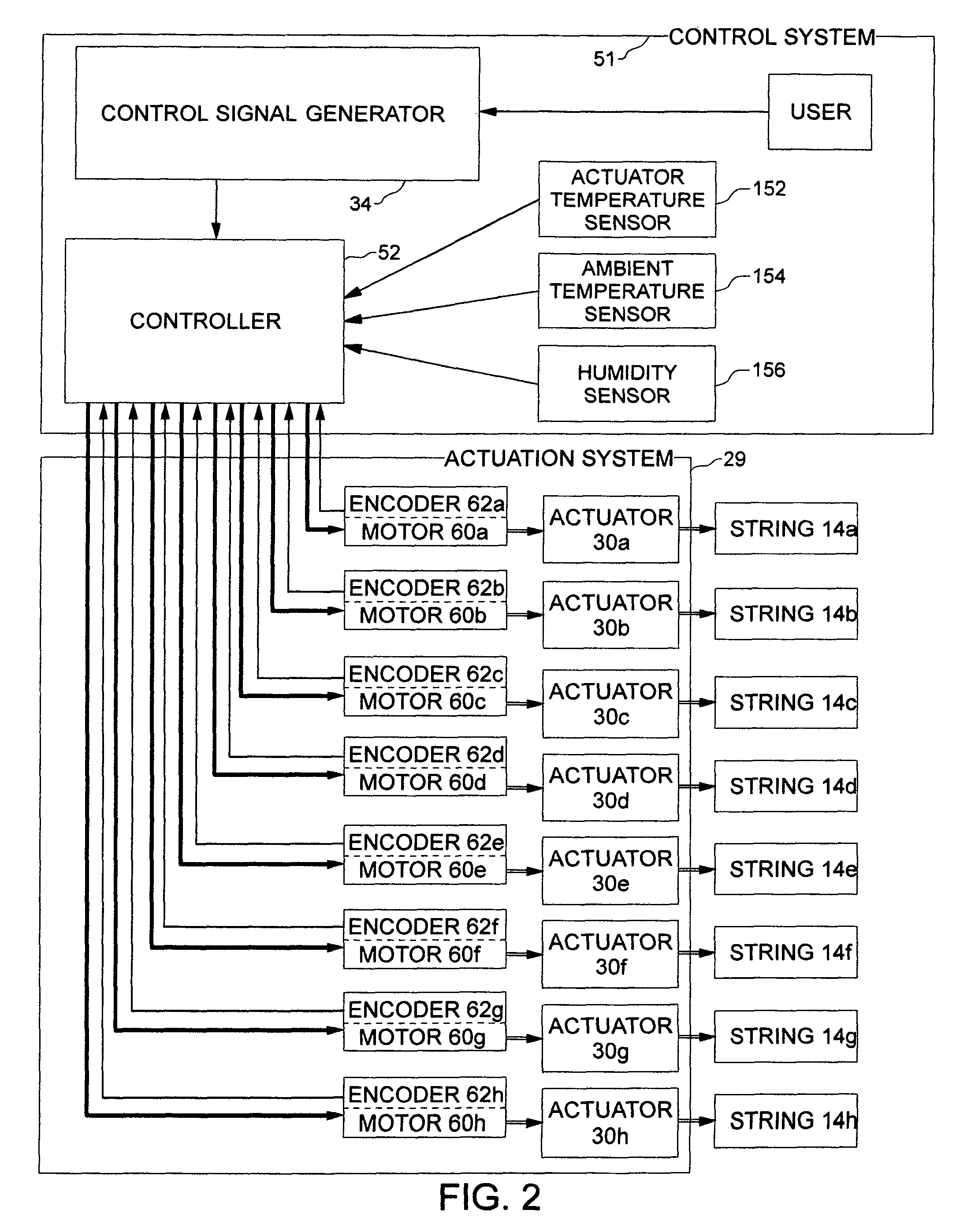
Method and apparatus for string load reduction and real-time pitch alteration on stringed instruments
ActiveUS7935876B1Reduce loadReduces string loadStringed musical instrumentsMusic aidsLoad optimizationControl signal
A method and apparatus for string load reduction and real-time pitch alteration on stringed instruments. A string load is substantially reduced with a camming surface actuator so that the pitch can be rapidly manipulated by an input force which is generated by human power or an electronically controlled motor. Various types of camming surfaces are provided as well as a load optimization calculation which determines the shape of a variable ratio camming surface. Multiple embodiments are described including a constant force pitch alteration device, a motorized control system with pitch compensation and real-time tracking of string pitch to multiple relative input signals, a control signal generator based on real-time position measurement of a control object relative to an electromagnetic radiation sensor, and methods for generating mechanical looping, vibrato, and polyphonic chorus effects which can be automated or dynamically controlled by a user. Other embodiments are described and shown.
Owner:GLISSPHONIC
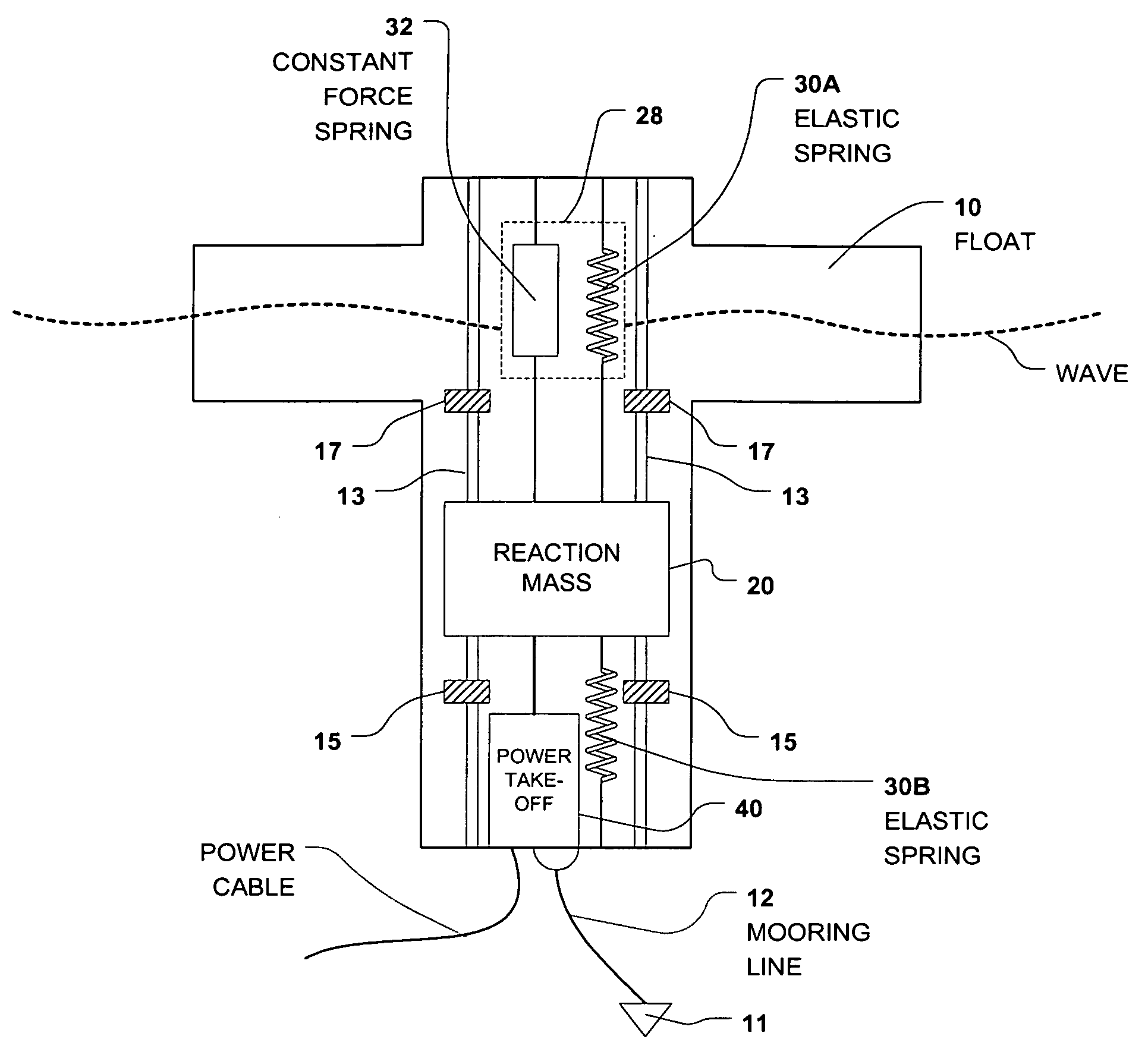
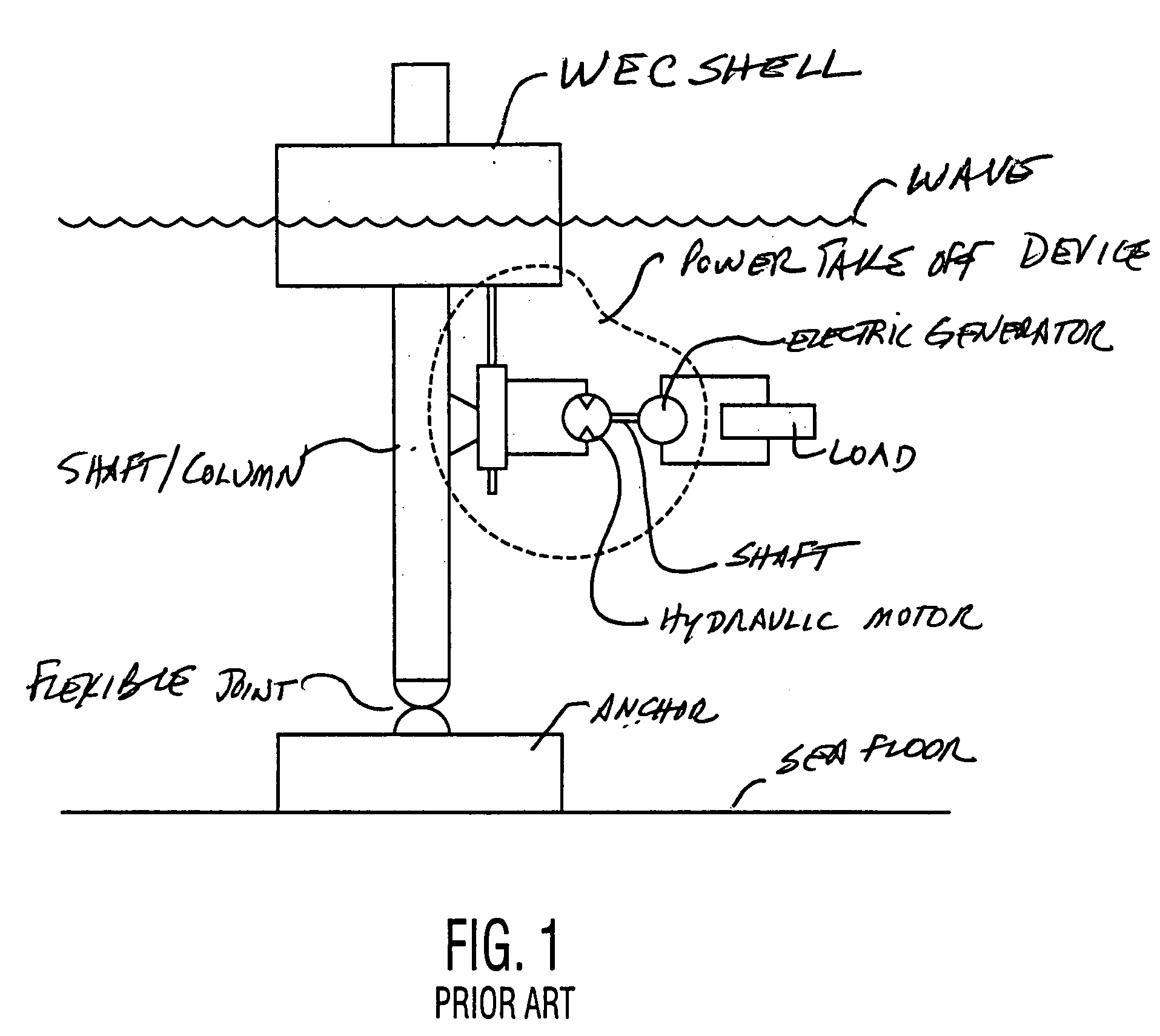
Wave energy converter with internal mass on spring oscillator
ActiveUS20090085357A1Reduce capacityIncrease the lengthMachines/enginesEngine componentsConstant forceRelative motion
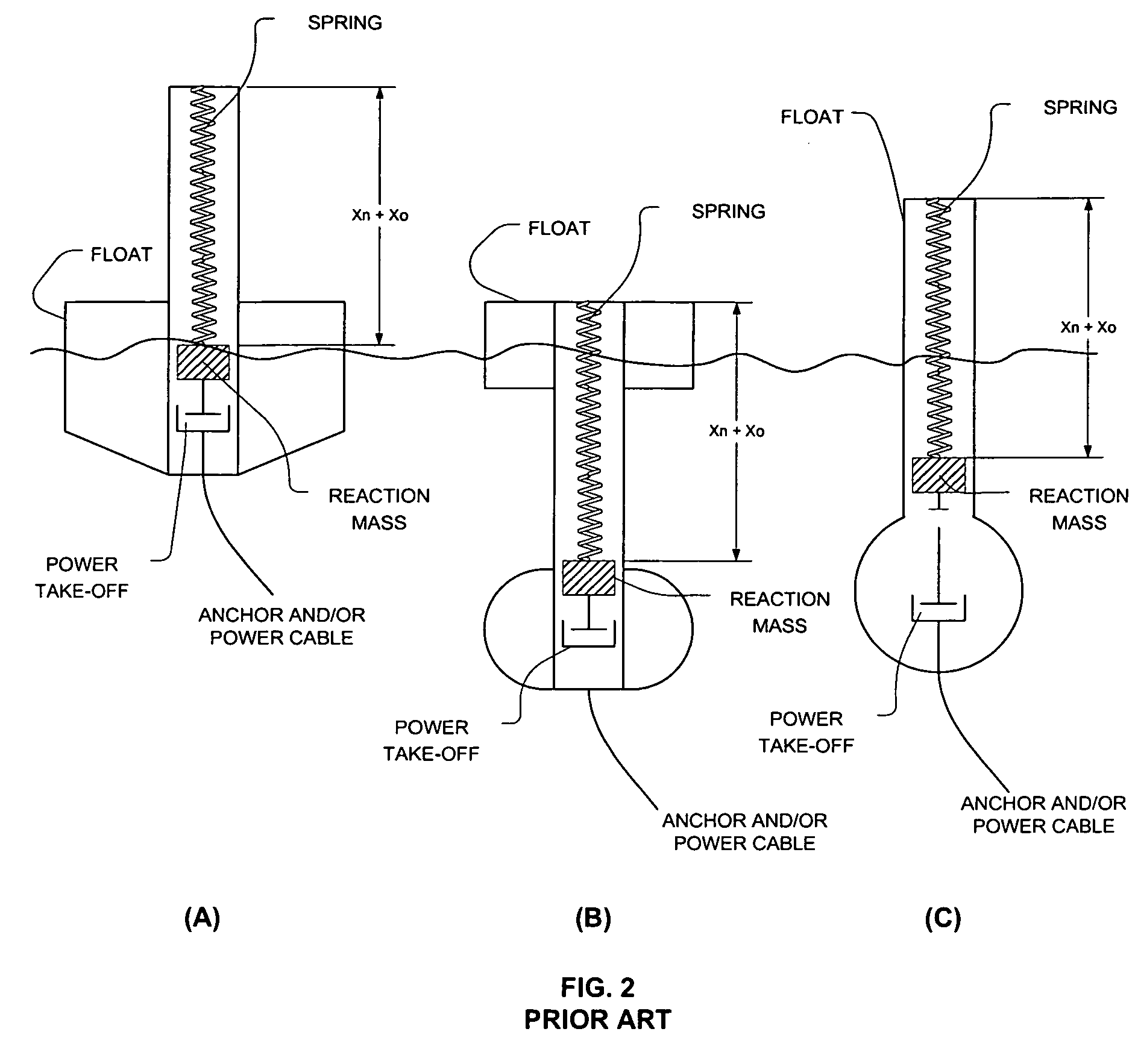
A wave energy converter (WEC) system includes a shell containing an internal oscillator comprised of a reaction mass suspended from the shell by an elastic spring in parallel with a constant force spring. The constant force spring provides a relatively constant force (Fc) to counterbalance the static weight of the reaction mass and reduce the extension “static” length of the elastic spring while the elastic spring exerts a force (Fes) on the reaction mass that is proportional to the displacement, x, of the elastic spring. A power take-off (PTO) device, located within the shell, coupled between the shell and the internal oscillator converts their relative motion into electrical energy.
Owner:OCEAN POWER TECHNOLOGIES
Metal-to-metal seal with soft metal insert
An annular metal-to-metal sealing system, for use in wellhead systems and having many other uses, has a metal member defining an annular internal or external sealing surface for which sealing is intended. An annular seal body composed of high strength metal material is positioned in concentric relation with the annular sealing surface and is sufficient flexible to become spring loaded, typically during assembly, for continuous application of a spring force. The annular seal body defines one or more annular seal retainer grooves each having an annular soft metal sealing insert therein, with a portion thereof exposed for sealing engagement with the annular sealing surface. The spring loaded characteristic of the annular seal body applies constant force to maintain the soft metal seal insert in constantly energized sealing relation with the annular sealing surface and maintains effective sealing even when dimensional changes to the sealing surface occur due to temperature or pressure changes.
Owner:FMC CORP
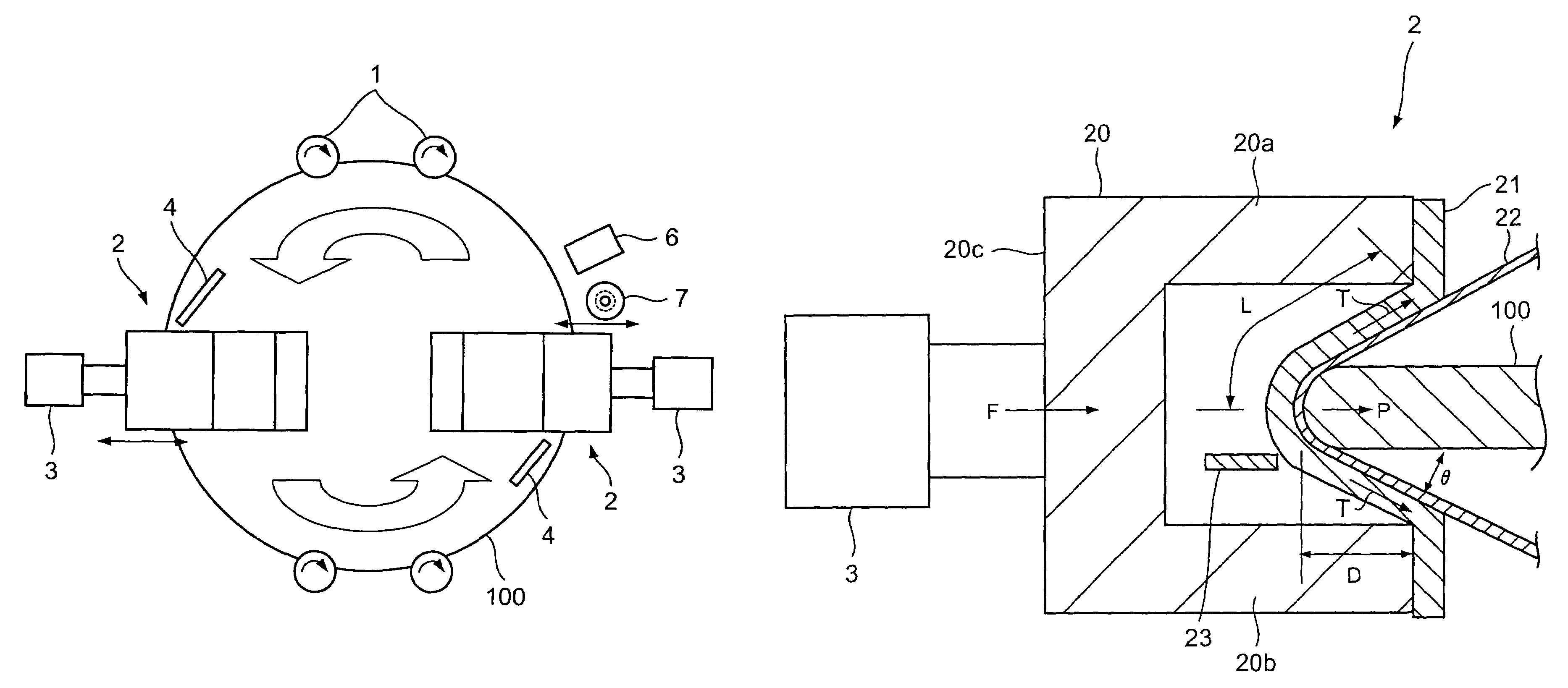
Substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS7367873B2Eliminate surface roughnessShort timeEdge grinding machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesConstant forceEngineering
A substrate processing apparatus has a polishing tape and a polishing head for pressing the polishing tape against a peripheral portion of a semiconductor wafer. The substrate processing apparatus polishes the wafer due to sliding contact of the polishing tape and the wafer. The polishing head has an elastic body for supporting the polishing tape. The substrate processing apparatus has an air cylinder for pressing the polishing head so that the elastic body of the polishing head presses the polishing tape against the predetermined portion of the wafer under a constant force.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
System and Method for Implementing a Suspended Personal Radiation Protection System
ActiveUS20070138415A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemChemical protectionHeat protectionConstant forceBody contouring
A personal radiation protection garment that substantially contours to an operator's body is suspended from a suspension means. The garment is operable to protect the operator from radiation. The suspension means is operable to apply constant force. The suspension means allows operator wearing protective radiation garment to move freely in the X, Y, and Z spatial planes simultaneously, such that the protective radiation garment is substantially weightless to operator. A radiation protection face shield and flap can also be suspended from suspension means, such that face shield and flap are substantially weightless to operator. The suspension means can be mounted to a ceiling.
Owner:INTERVENTCO
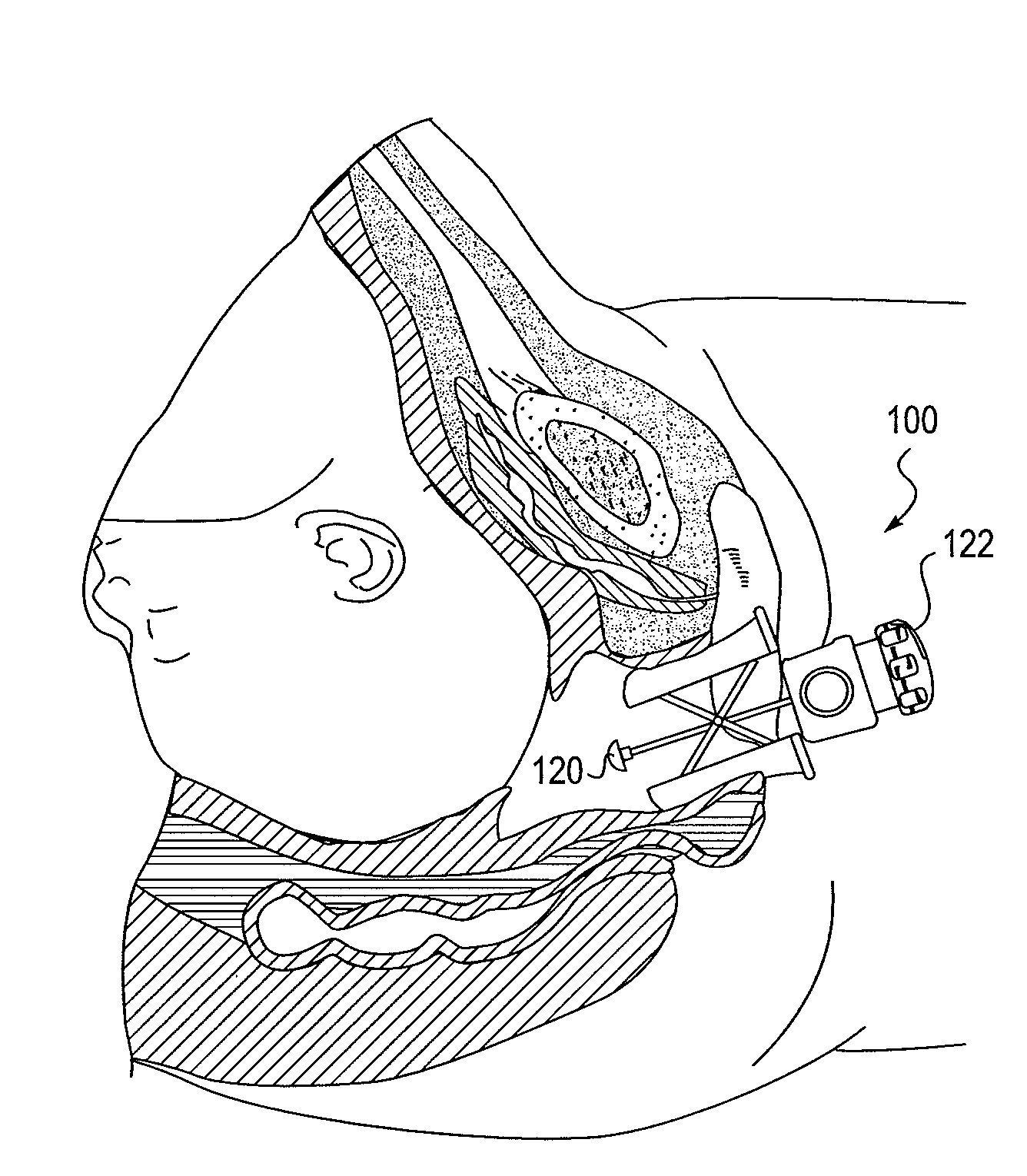
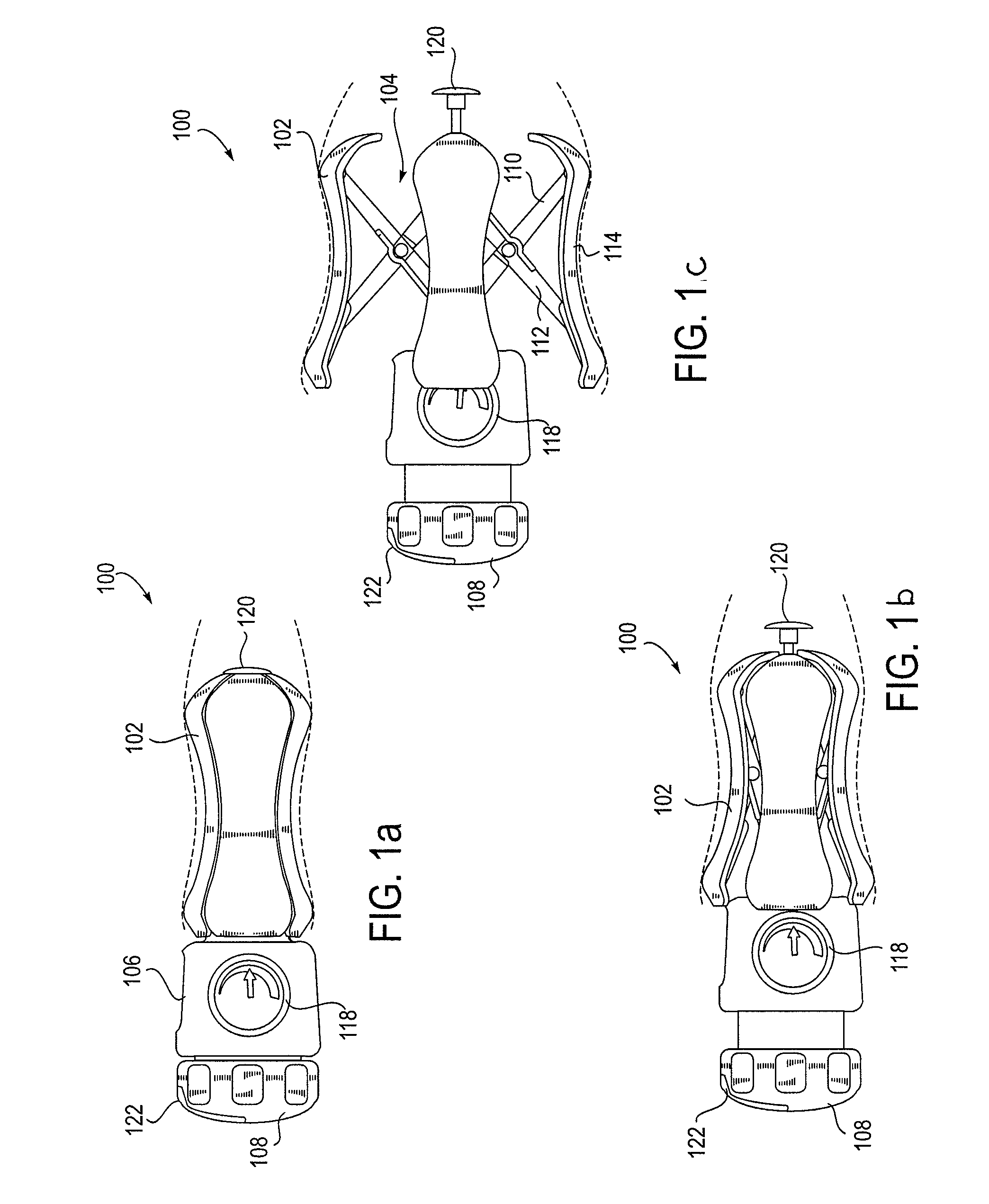
Methods and apparatus for preventing vaginal lacerations during childbirth
ActiveUS20130053863A1Avoid overexpansionPrevent pressureCannulasDilatorsVaginal dilationAutomatic control
A vaginal dilation device is provided that may include any of a number of features. One feature of the vaginal dilation device is that it is configured to dilate vaginal tissue during labor to prevent tissue damage. Another feature of the vaginal dilation device is that it can be manually controlled to dilate vaginal tissue, or can be automatically controlled to dilate vaginal tissue. In some embodiments, the vaginal dilation device is configured to measure a force applied by the device to tissue. In other embodiments, the vaginal dilation device is configured to apply a constant force to tissue. In other embodiments, the vaginal dilation device is configured to expand at a constant rate. Methods associated with use of the vaginal dilation device are also provided.
Owner:MATERNA MEDICAL
Computer monitor lift and storage mechanism
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
High resilience flanged earplug
ActiveUS20070221232A1Increase elasticityIncrease deflectionEar supported setsStethoscopeMaximum diameterConstant force
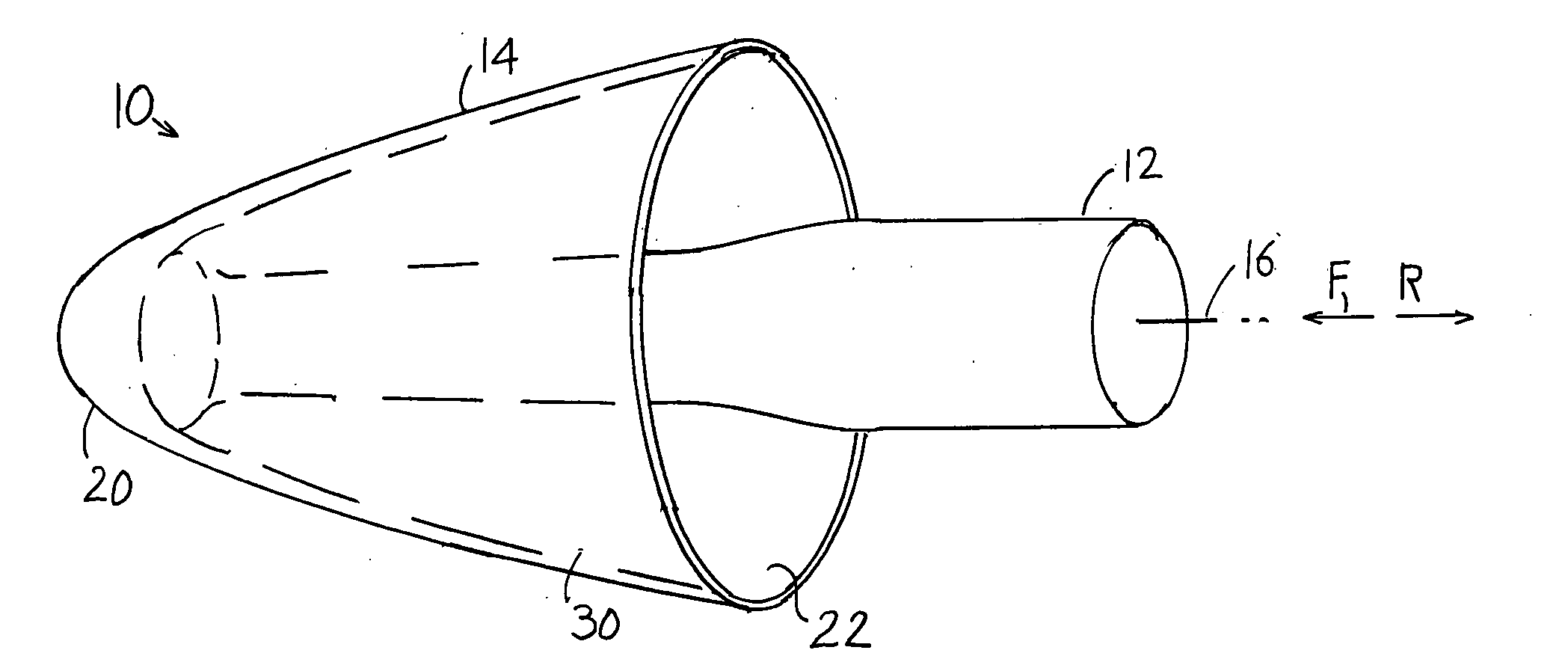
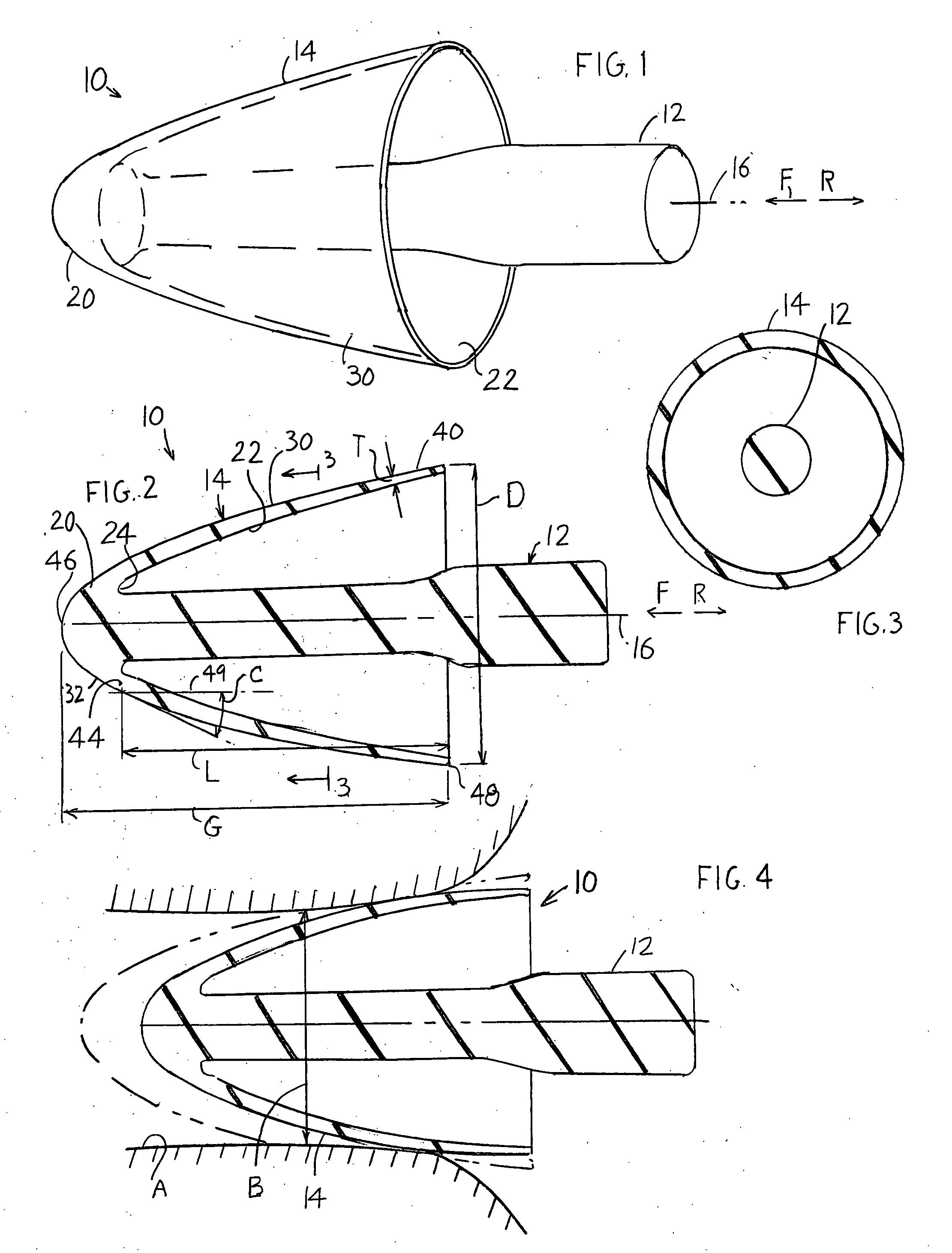
An earplug (10) of the type that is molded of elastomeric material and that has a flange (14) that seals to the walls of a person's ear canal as a stem (12) is pushed forward into the ear canal. Instead of using three or four flanges, applicant's earplug has a single very long main flange (14) with a maximum diameter (D) that is at least 80% of the length (L) of the main flange, and at least 55% of the entire length (B) of the earplug except for the stem. This allows the outside of the long flange to extend at a very small angle (C) to the axial direction, and apply a constant force against the walls of the ear canal, for good and comfortable sealing to the ear canal.
Owner:HONEYWELL SAFETY PROD USA
Integrated resistance spring force machine
An integrated resistance spring force assembly machine which is incorporated into an exercise machine and having a plurality of internal transverse sections with each section having respective constant force springs to output a respective magnitude of a spring resistance force, which serves as the respective force loads when in use, and a force selection mechanism which can be used to selectively activate the respective springs so that the respective force loads can be output to a combined level of resistance for an exercise routine.
Owner:EHRLICH MICHAEL J +2
Downhole position locating device with fluid metering feature
A tool for multiple purposes features one ore more dogs that can engage a collar groove or restriction sub in the wellbore. The dogs are extendable through a sleeve biased in opposed directions and are supported from a mandrel. The dogs can retract into mandrel grooves to clear restrictions on the trip into the well. On the way up to a collar that has just been passed, the dogs engage and an upward pull on the mandrel displaces fluid through a restriction to allow enough time to get a meaningful surface signal of the overpull force. Thereafter, the applied force can be reduced as the dogs release at a lower applied force to reduce the slingshot effect. The tool can be inverted and used to keep a constant force on a bottom hole assembly during offshore drilling where a heave compensator is employed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com