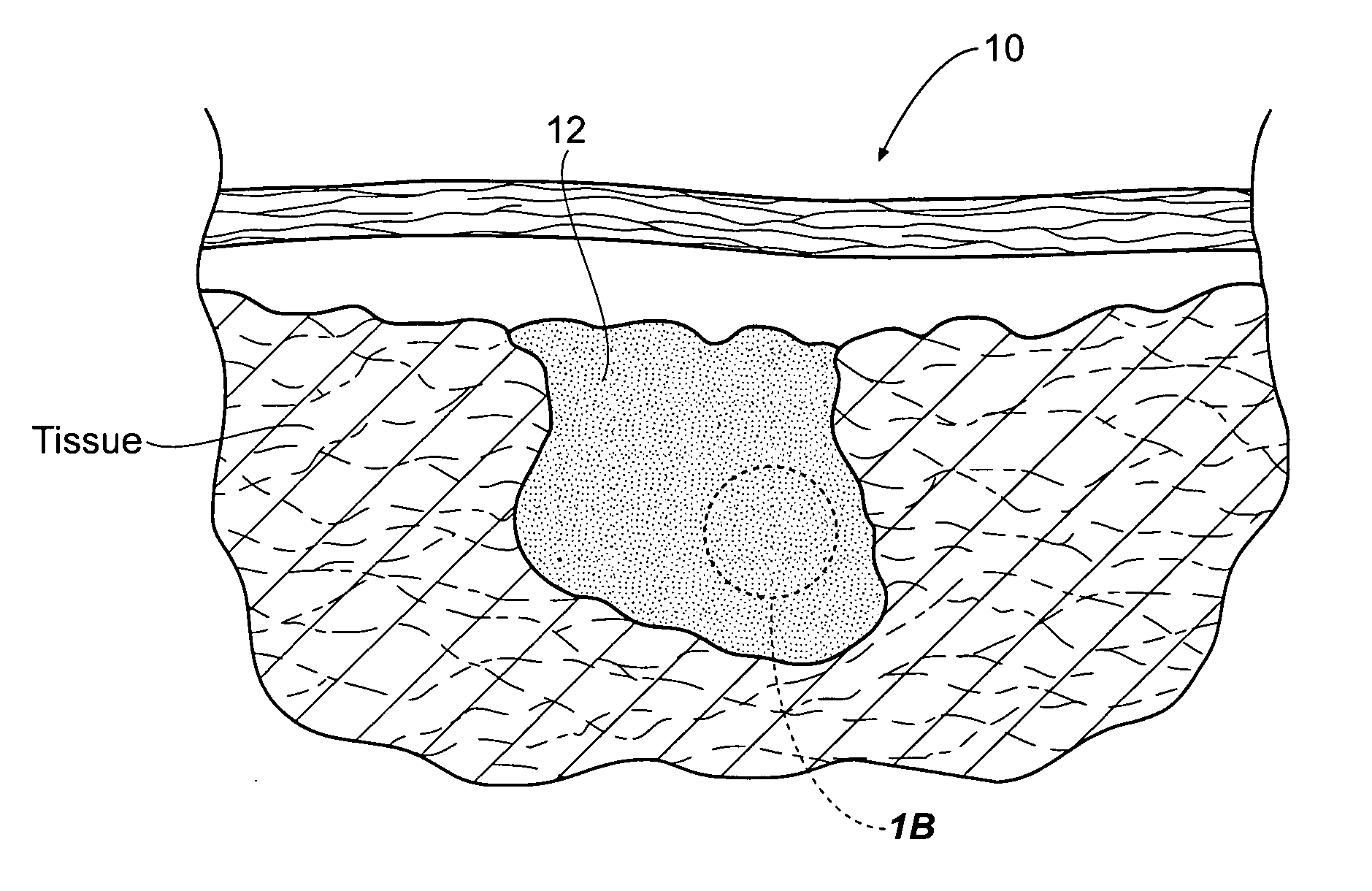
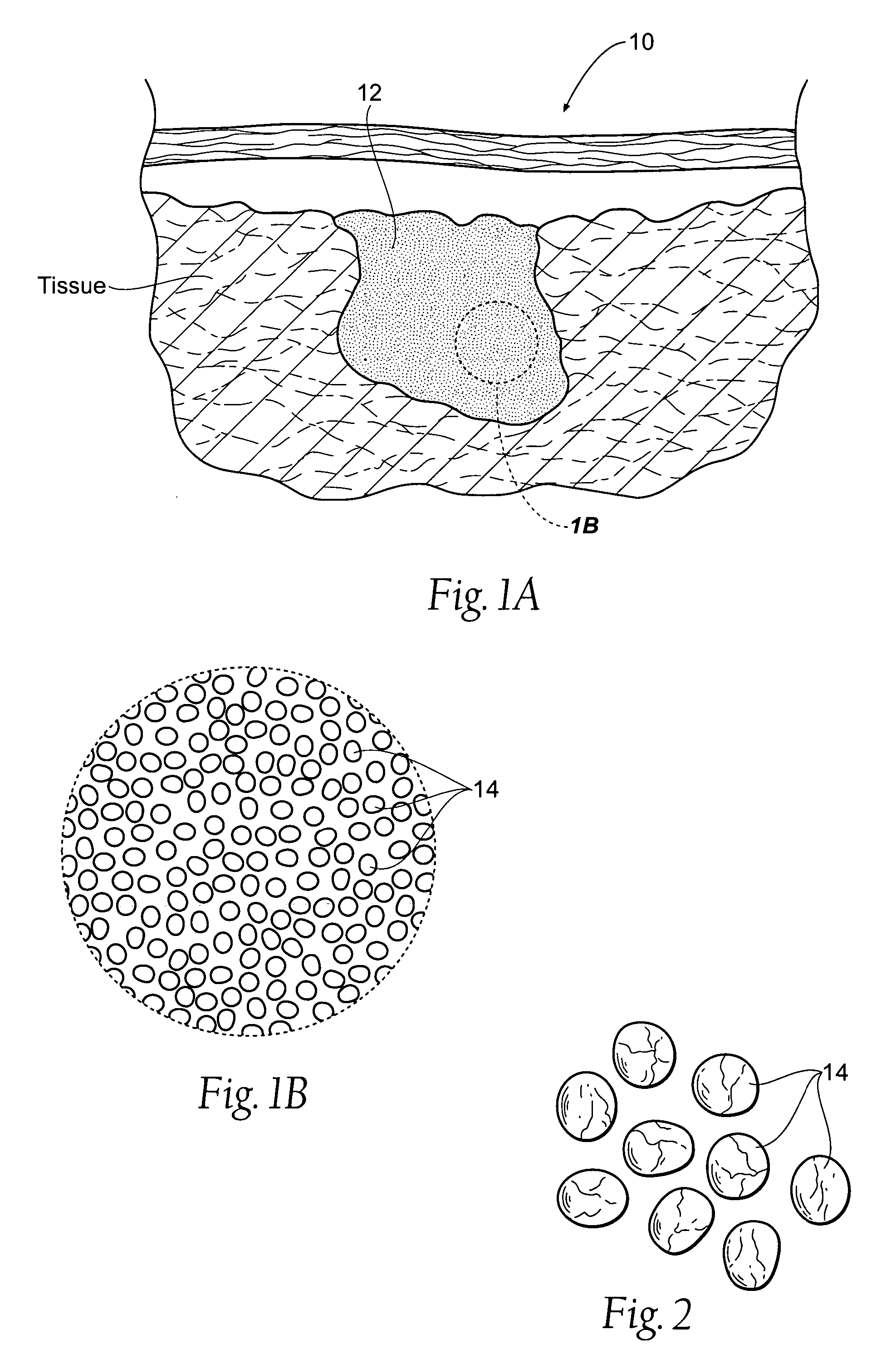
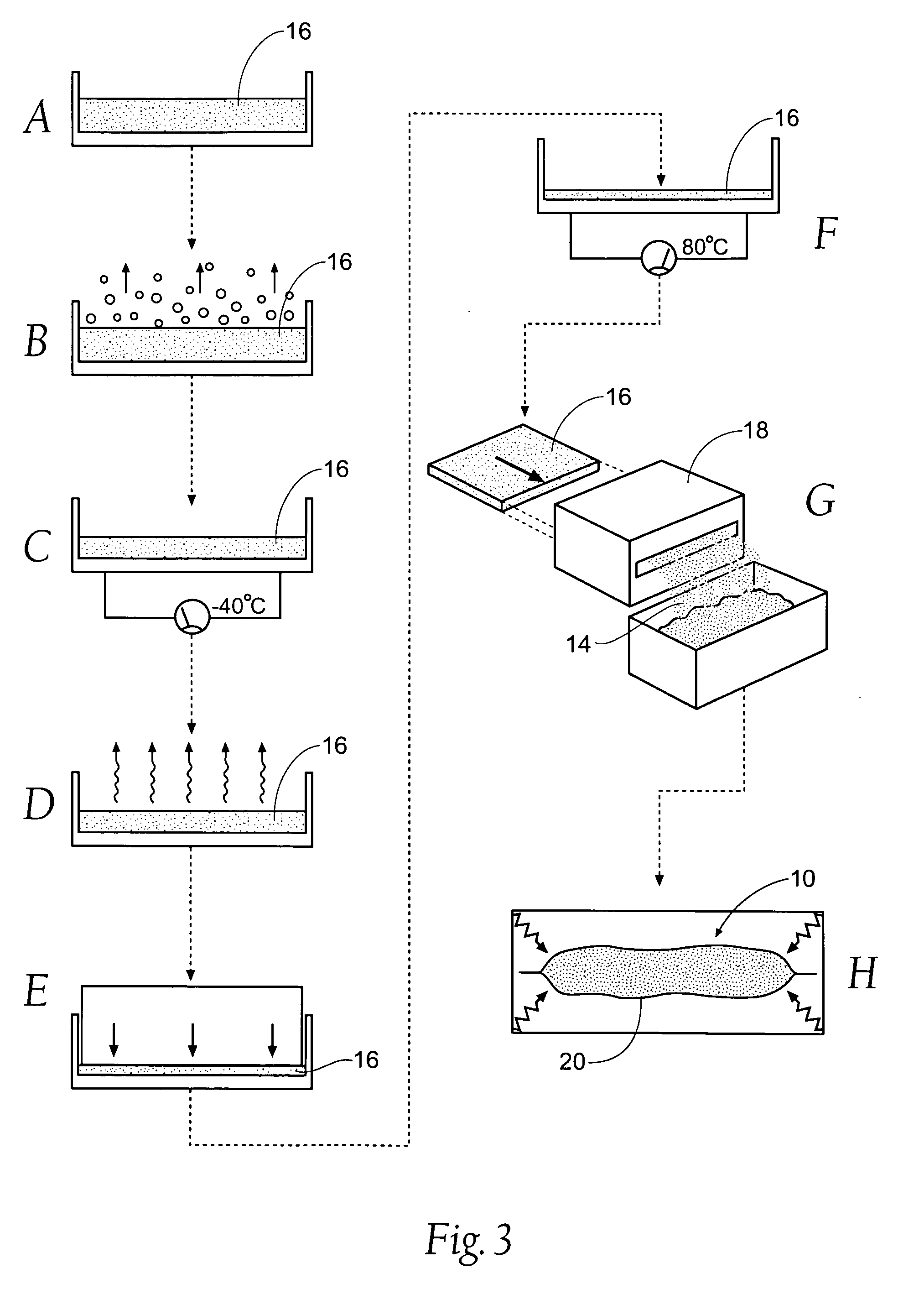
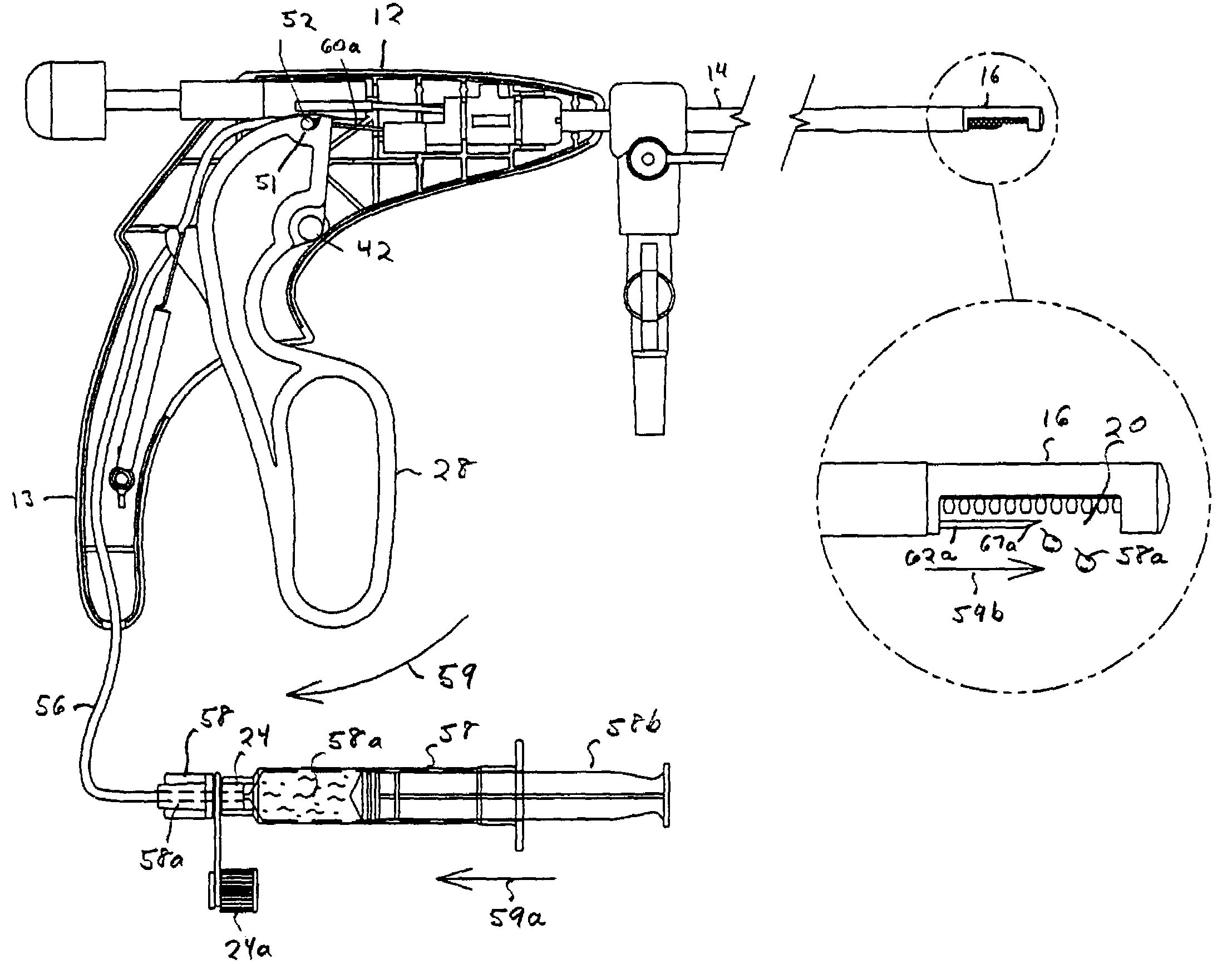
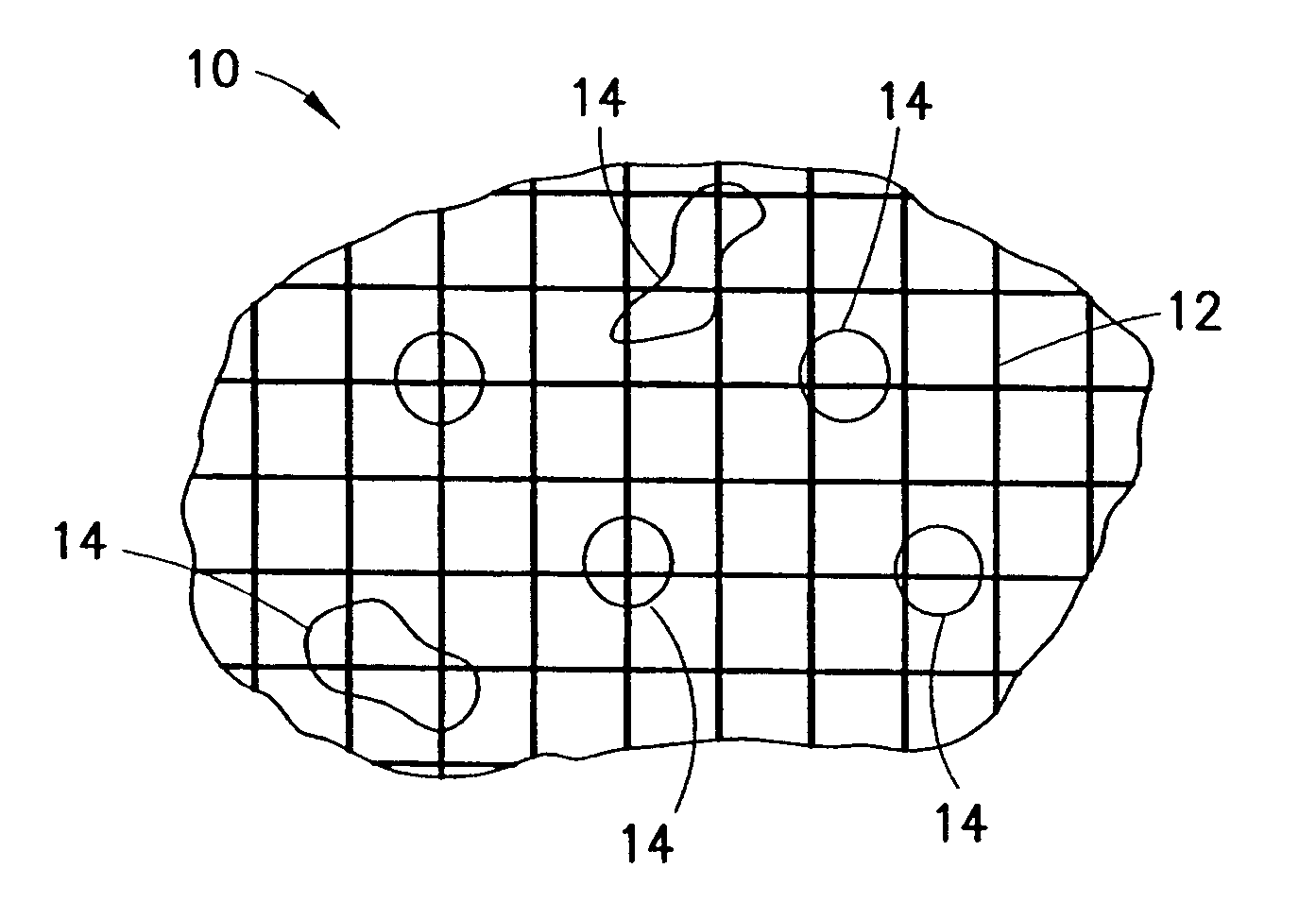
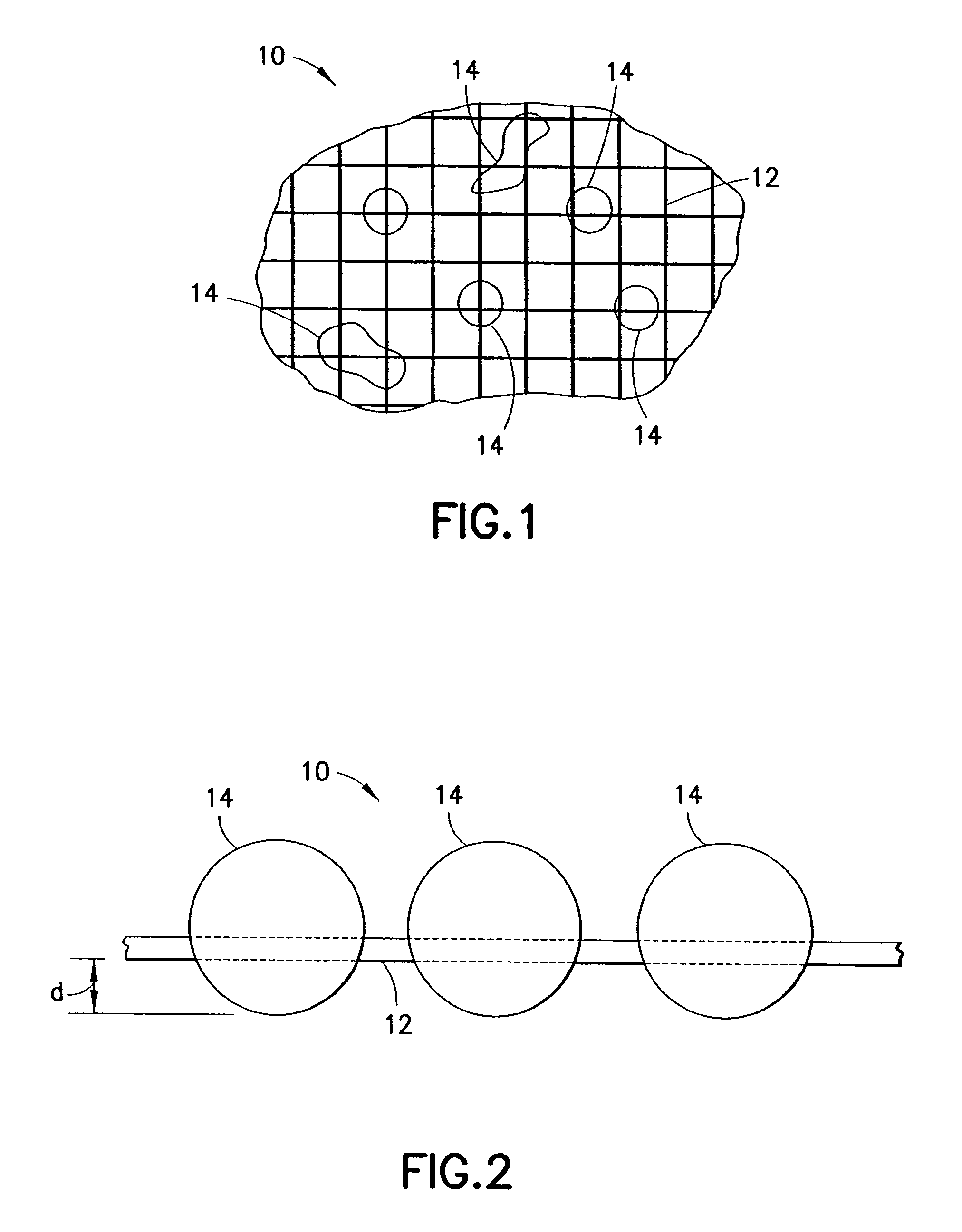
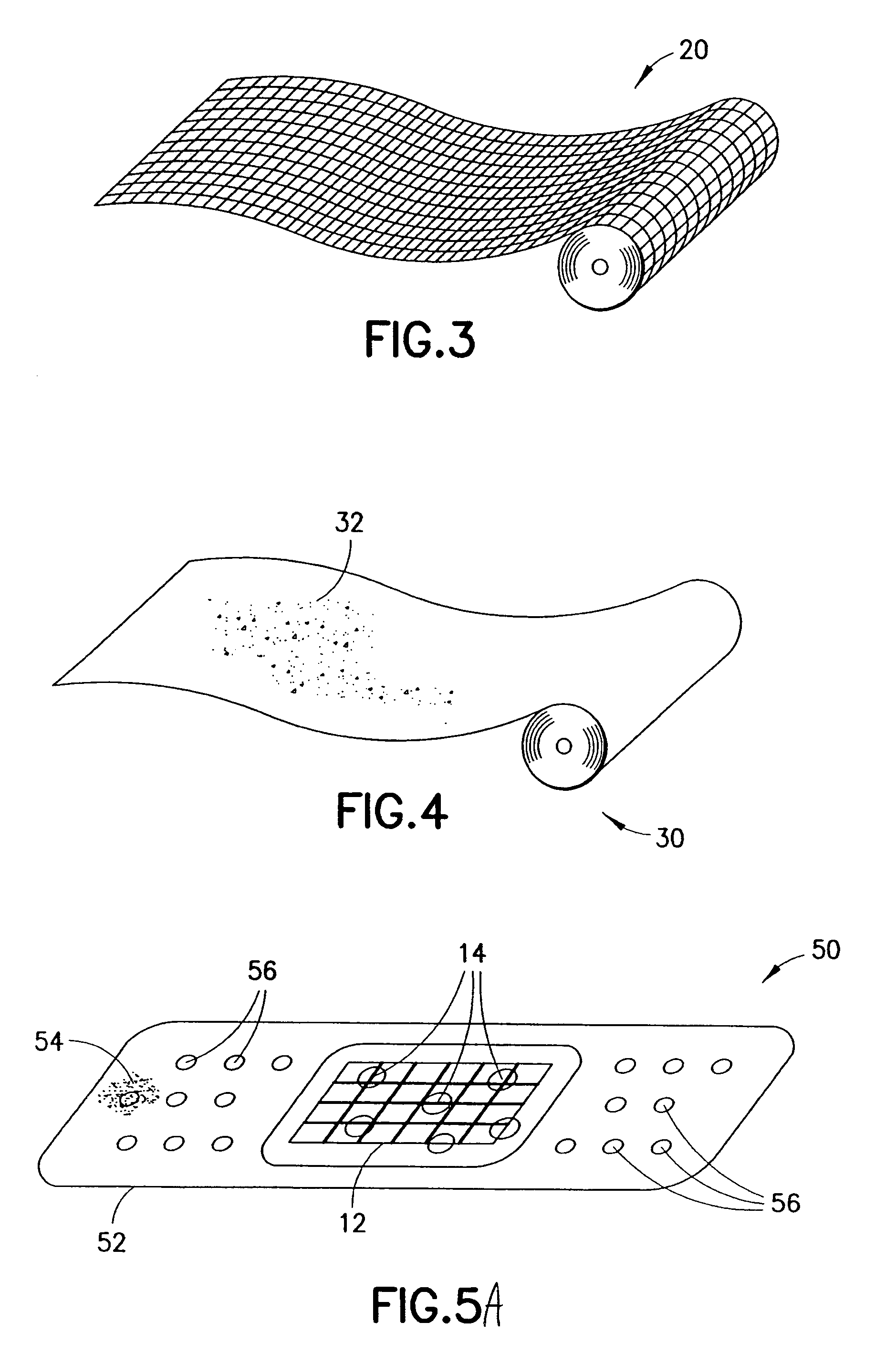
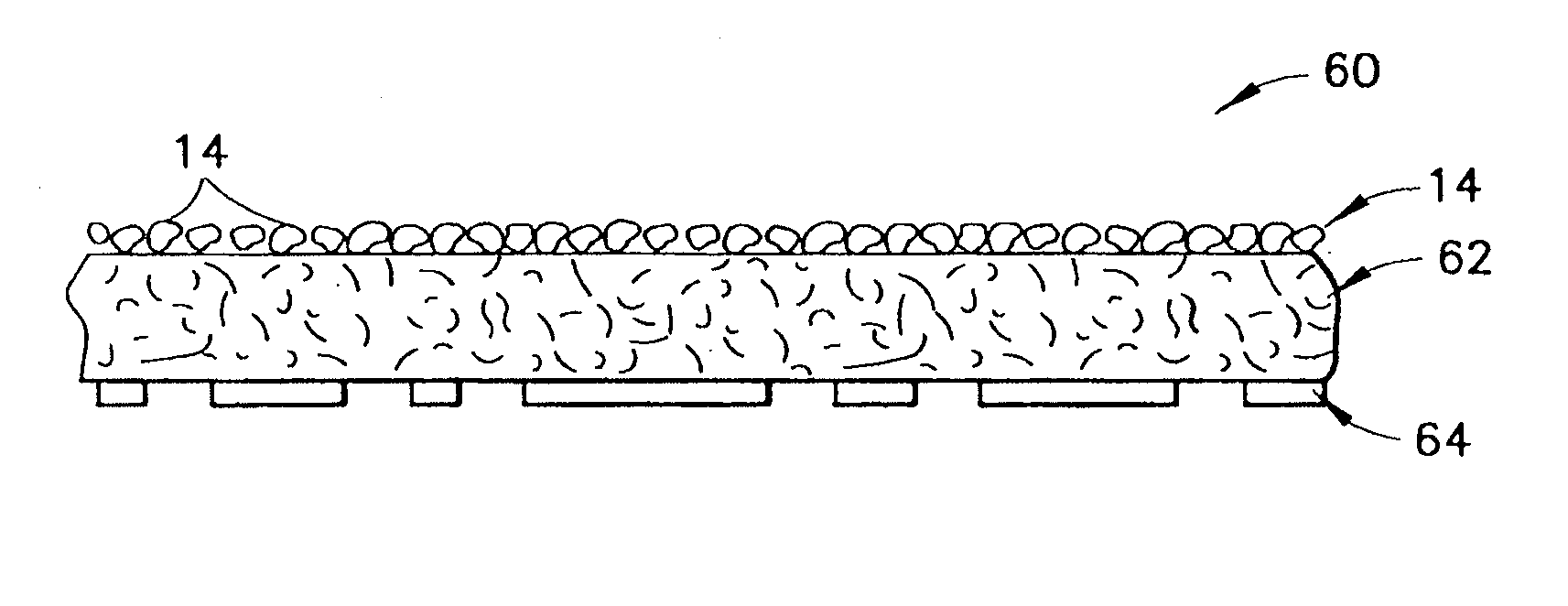
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
401 results about "Hemostatic Agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An agent that promotes hemostasis.
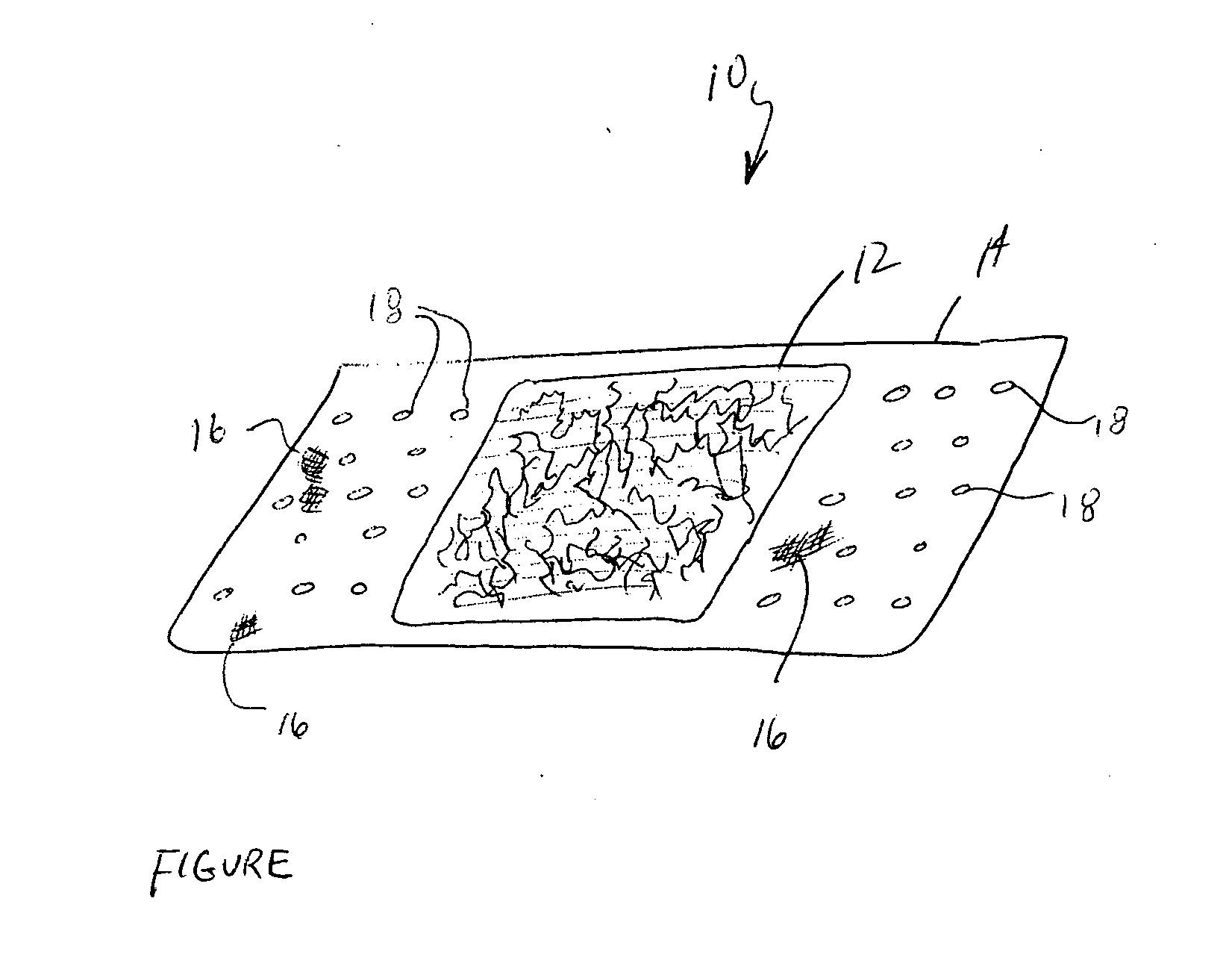
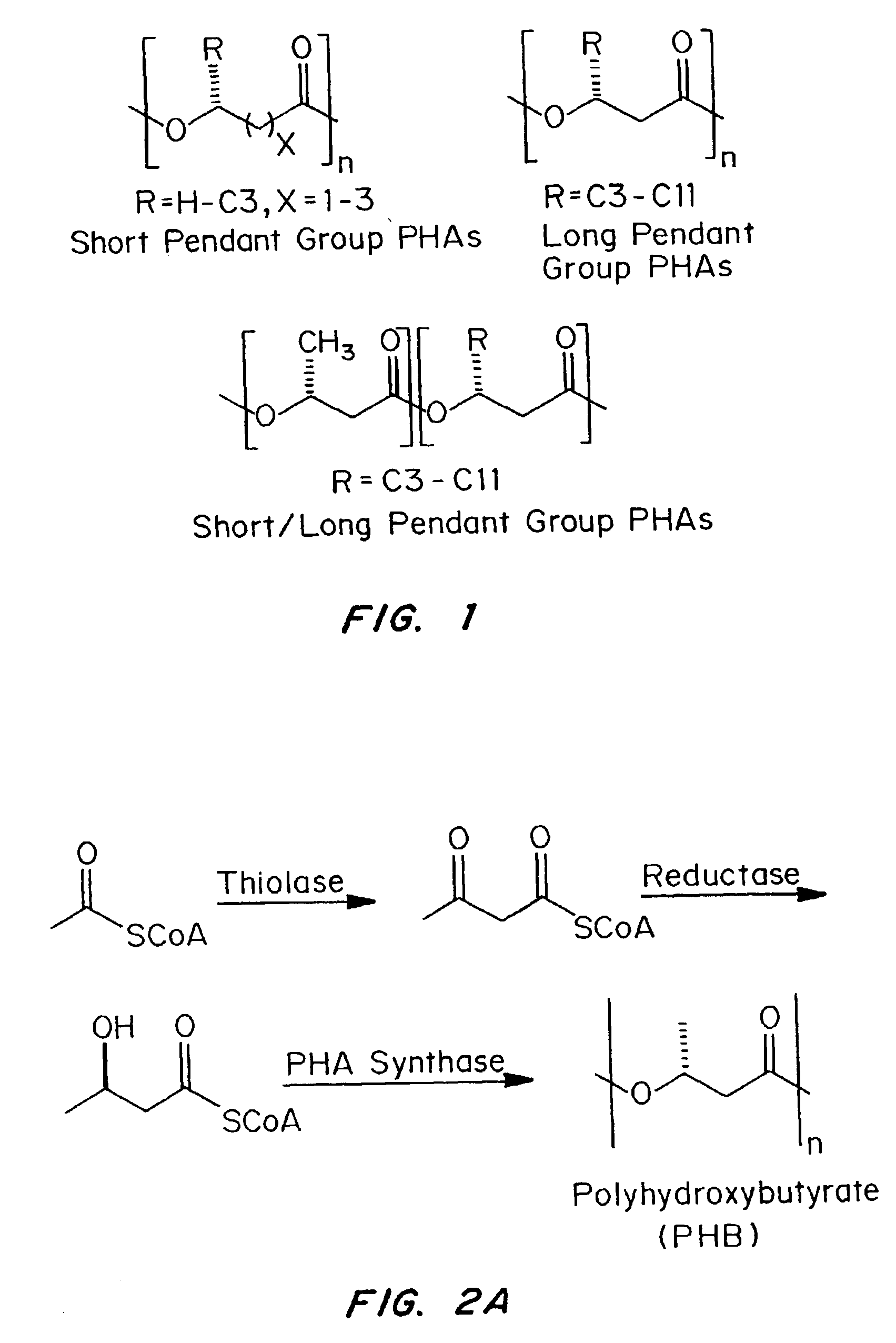
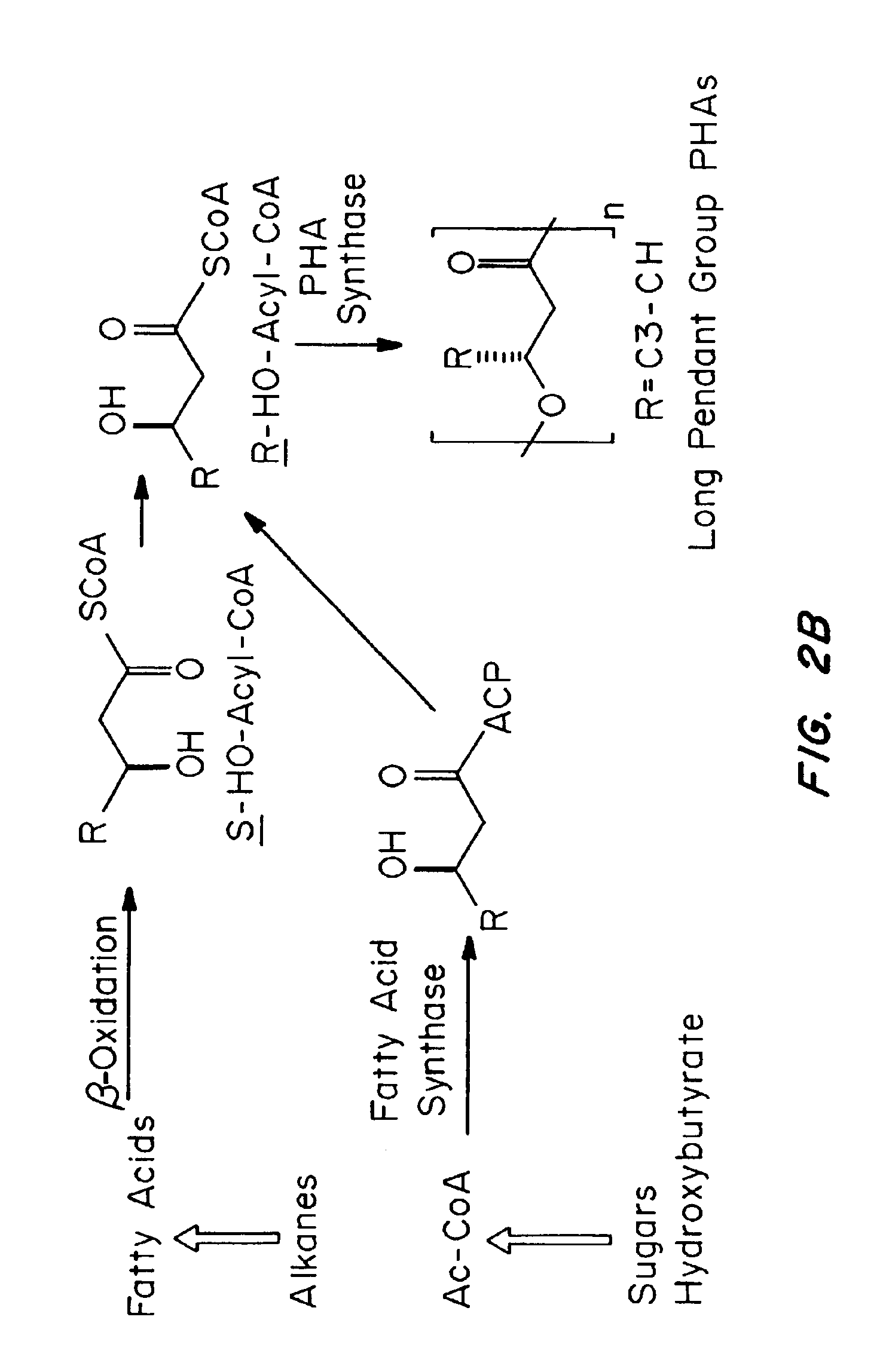
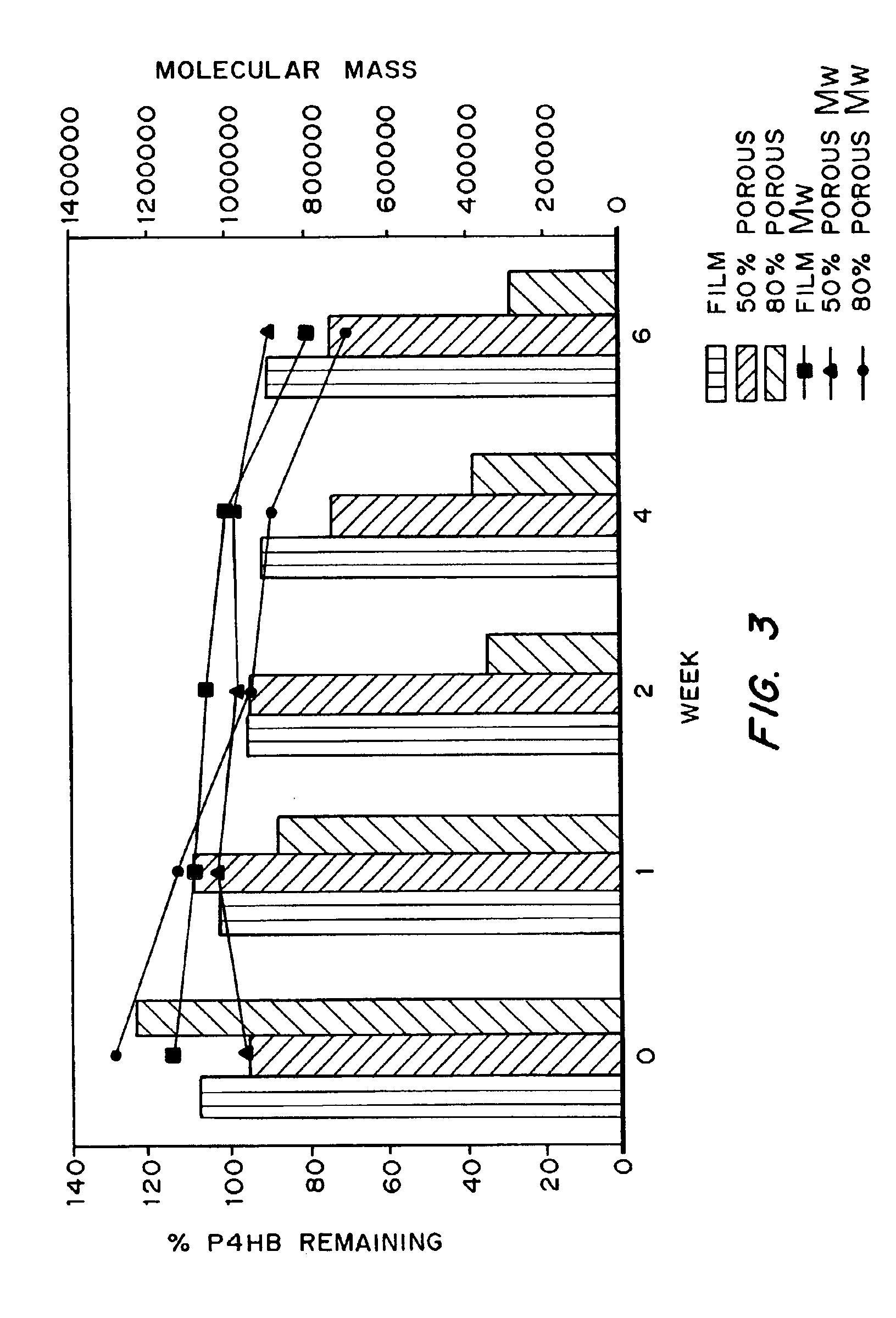
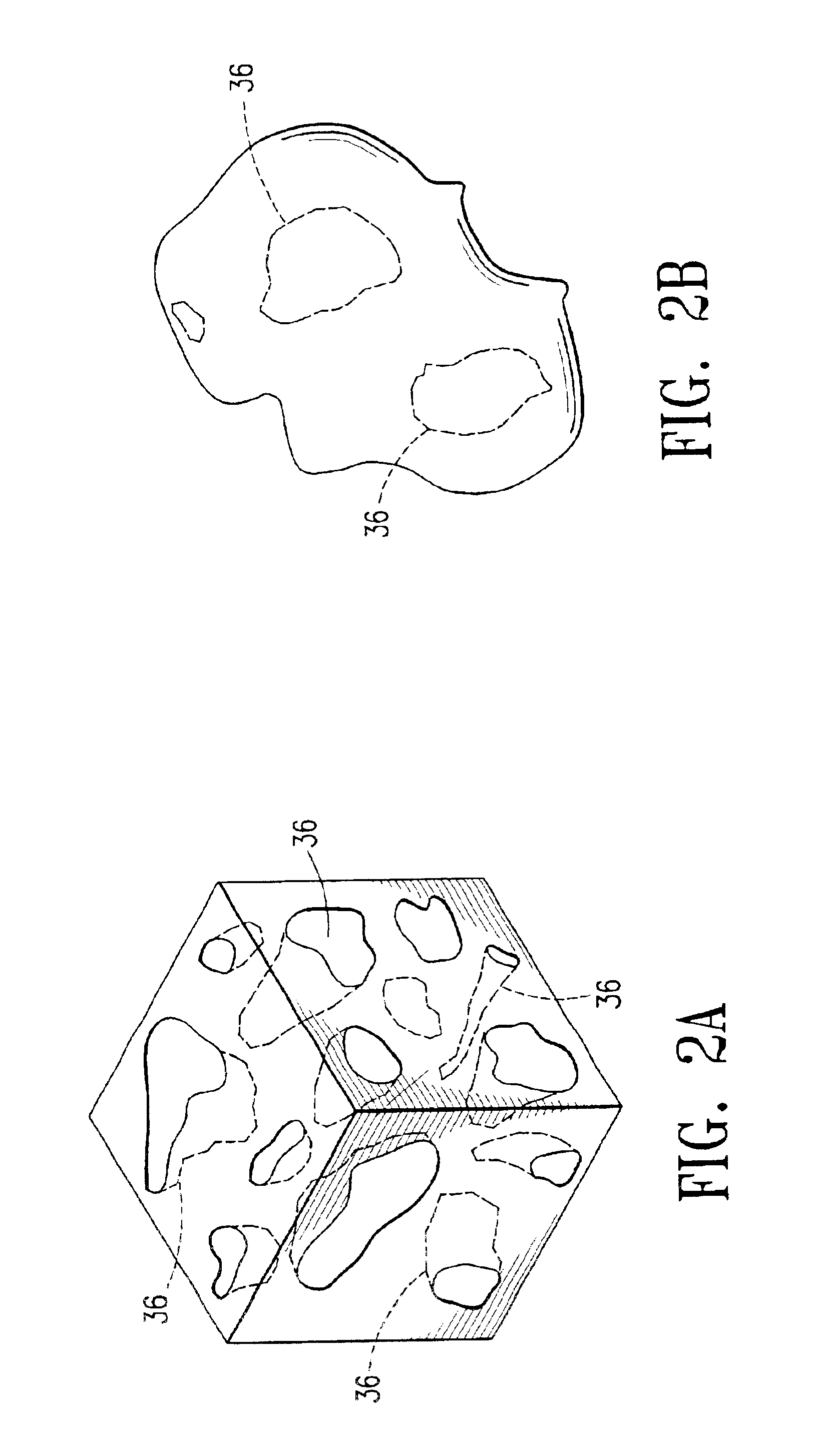
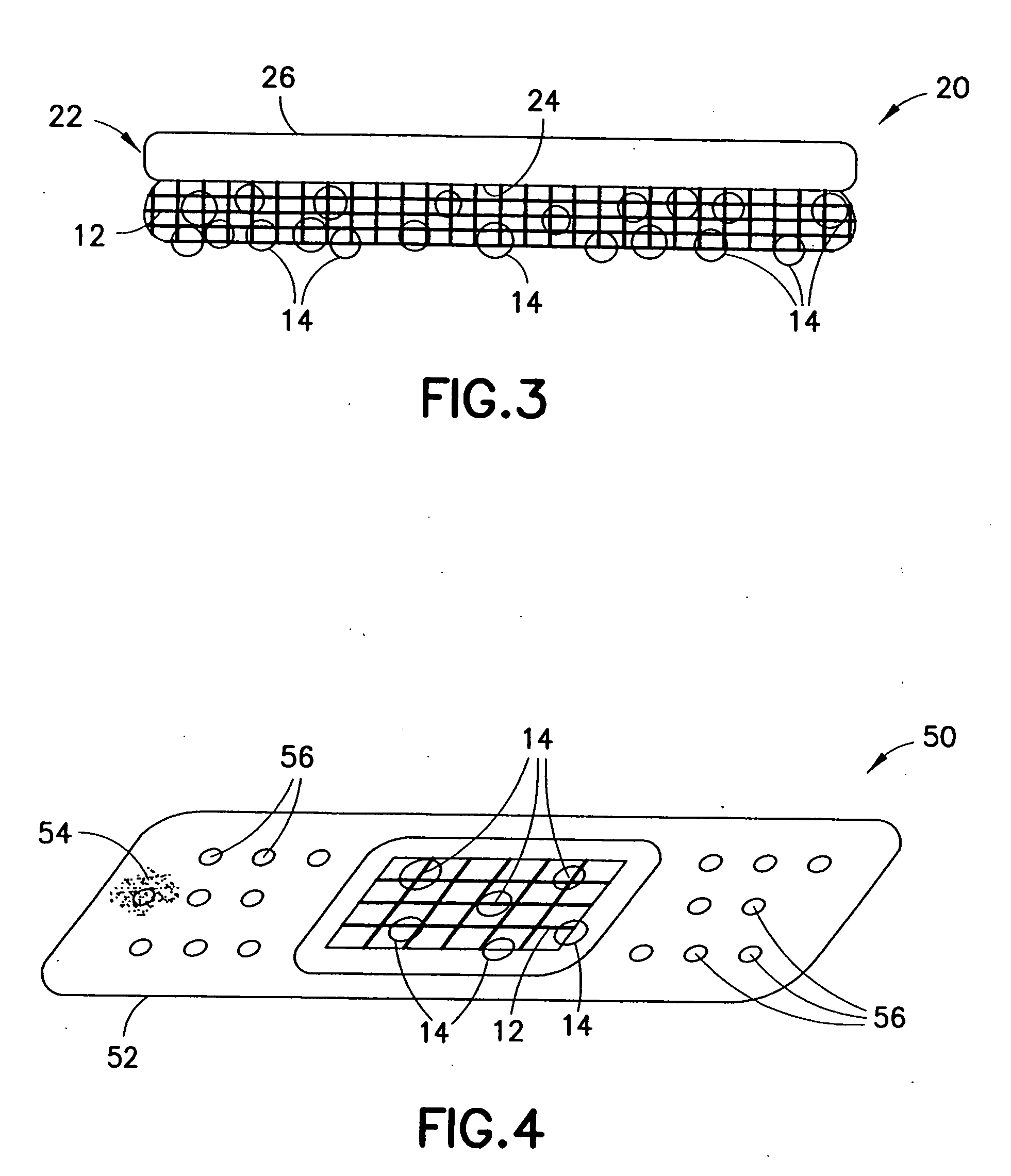
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
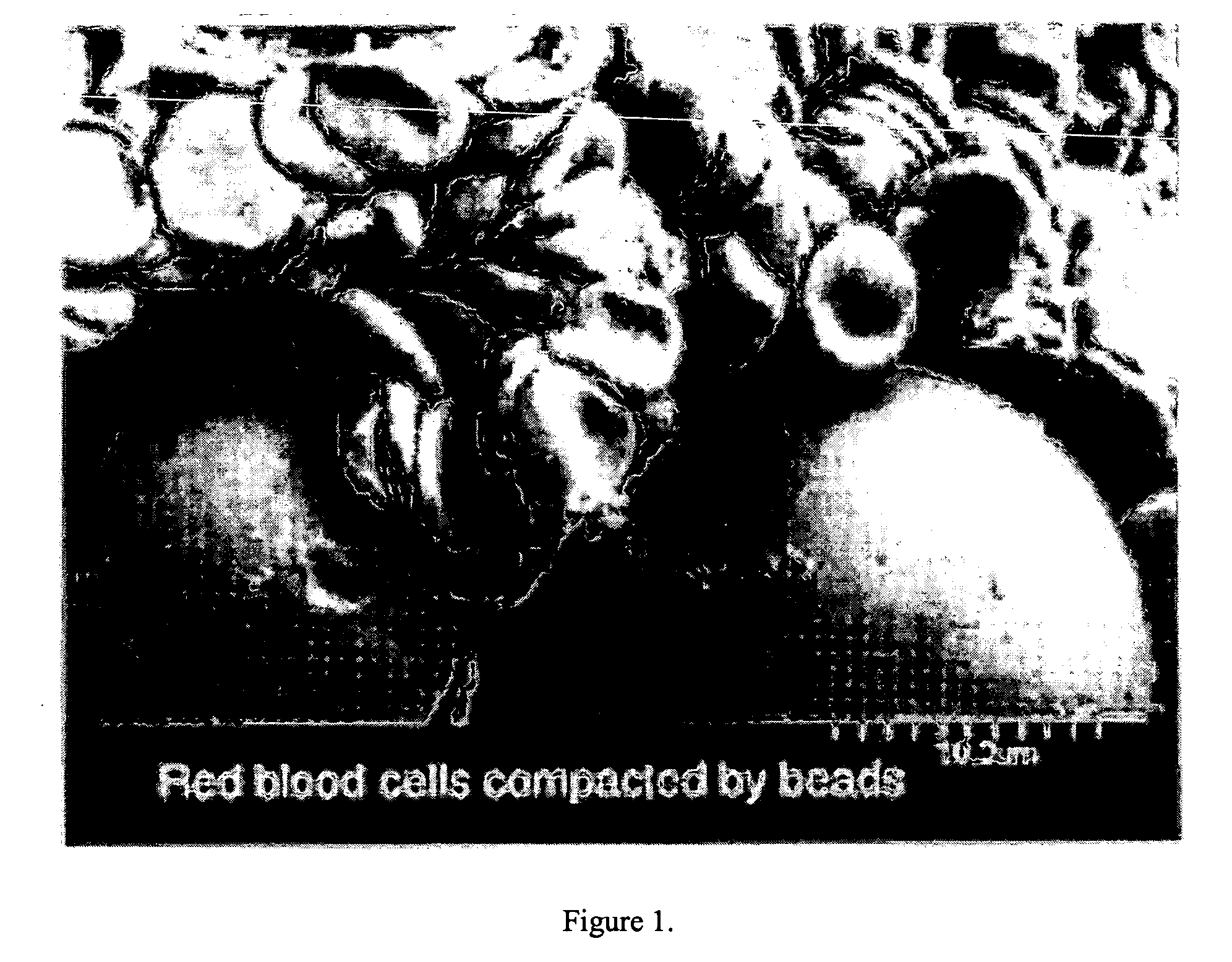
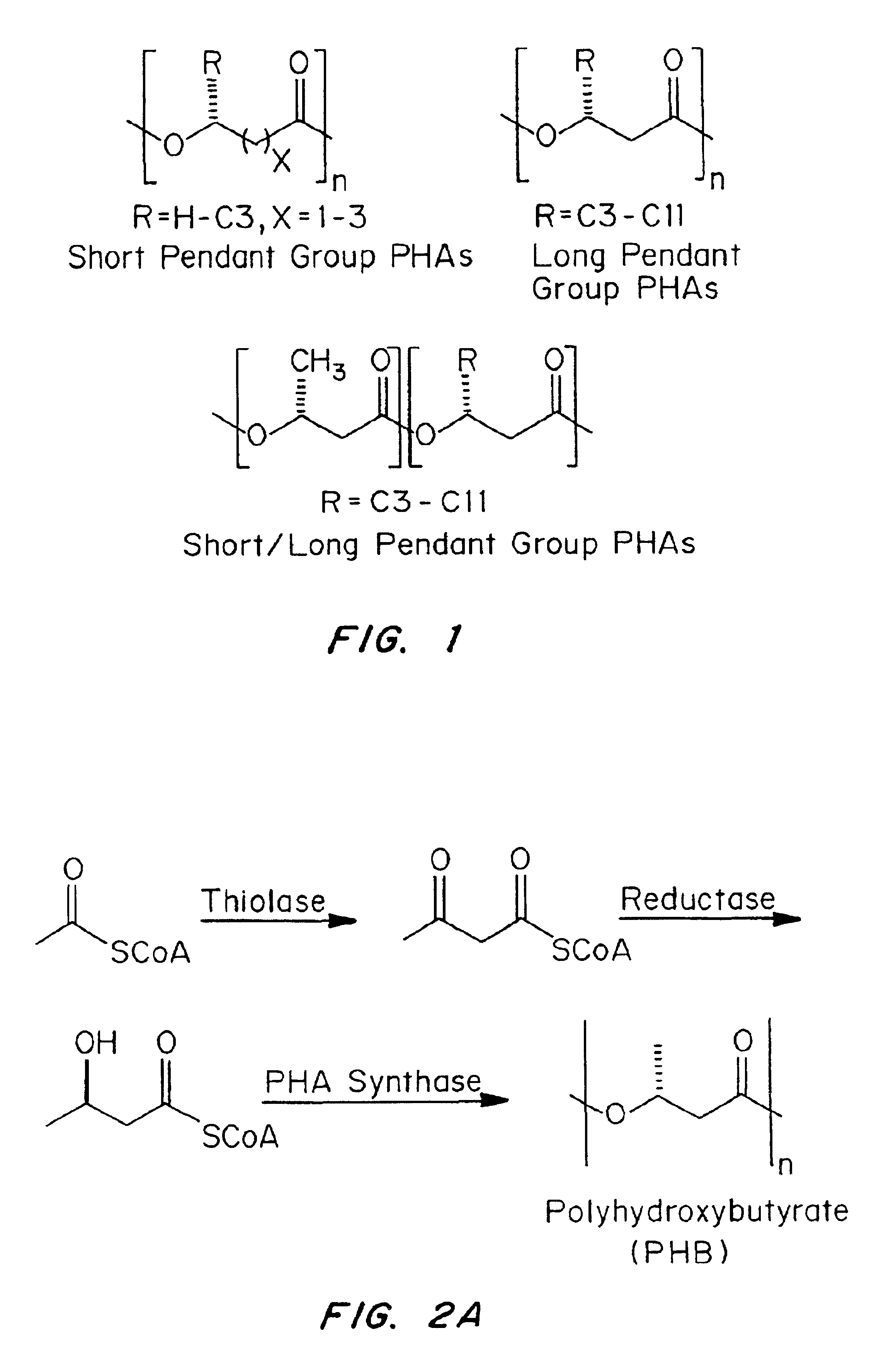
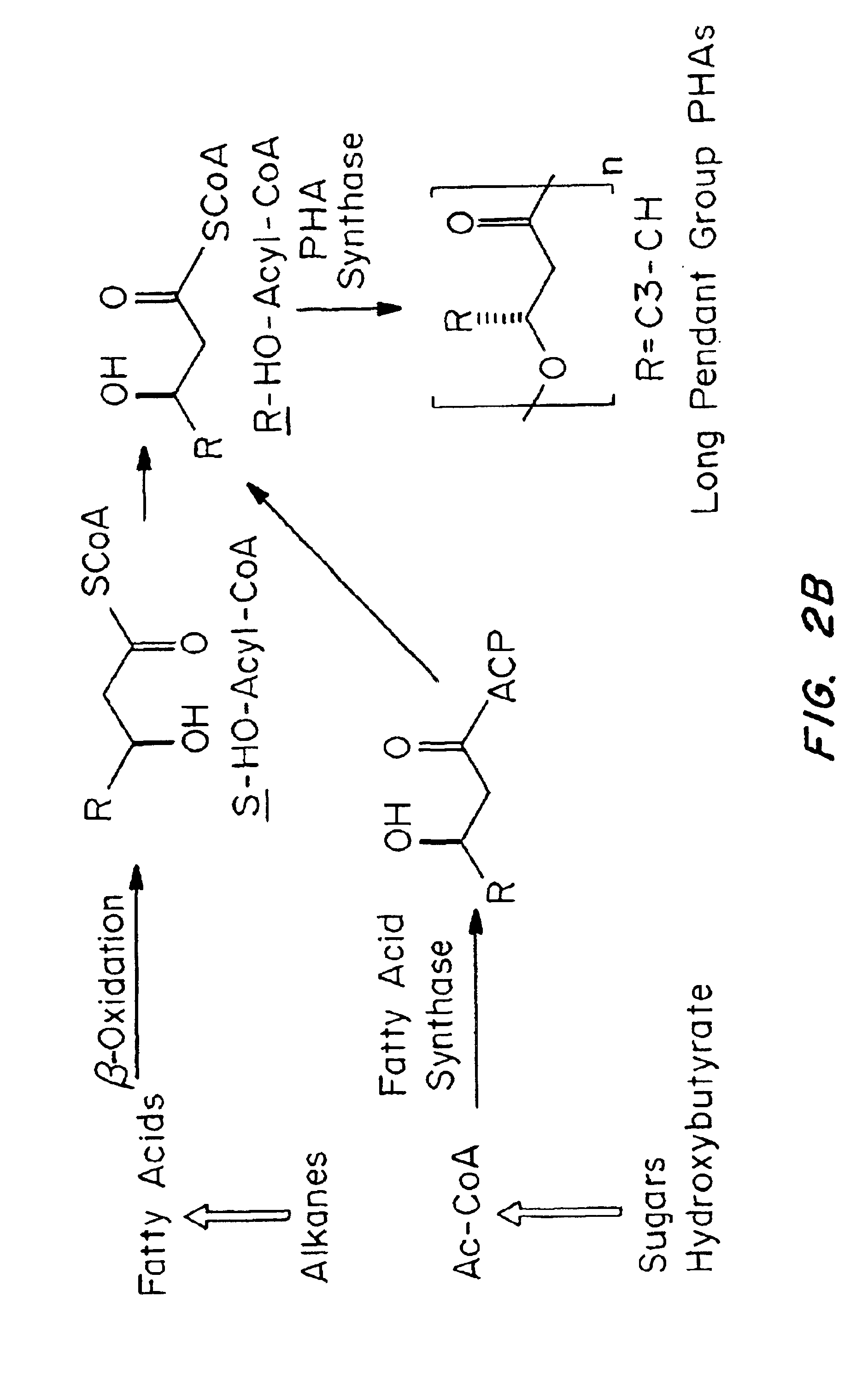
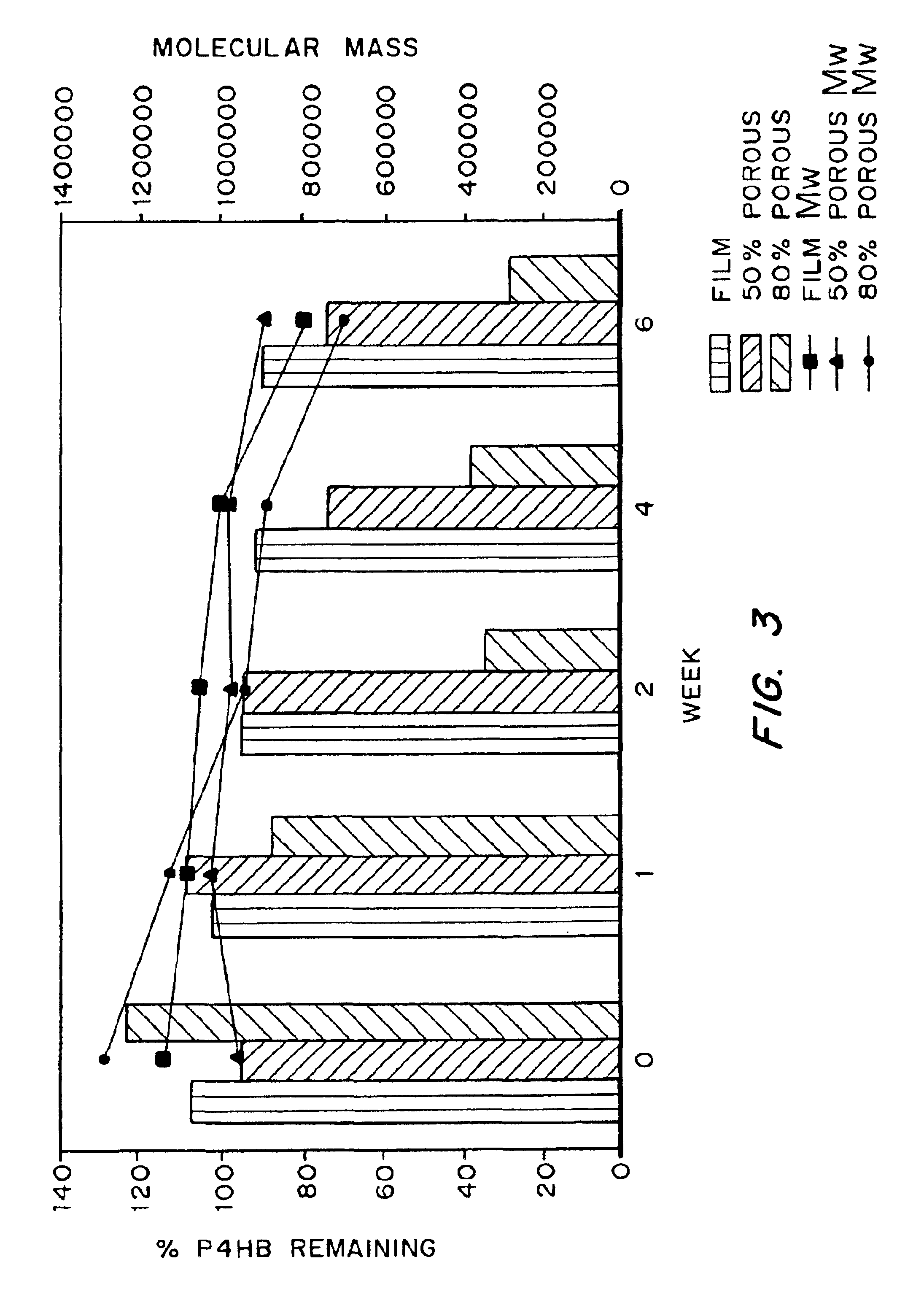
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Agents and devices for providing blood clotting functions to wounds
InactiveUS20070190110A1Promote healingShorten the timePhysical treatmentAntithrombogenic treatmentNitrogen dioxideMedicine
Hemostatic agents and devices are made from oxidized cellulose fiber, the oxidized cellulose having a carboxylation content increased by the action of nitrogen dioxide on virgin cellulose fiber. A composition may be incorporated into the oxidized cellulose fiber to cause a pharmacological effect on a wound to which the hemostatic agents and devices are applied. When applied, the oxidized cellulose fiber causes blood emanating from the wound to clot. The oxidized cellulose fiber can either be resorbed into the wound or removed from the wound after healing. A hemostatic bandage includes a pad of unwoven oxidized cellulose fibers mounted on a substrate. Methods of arresting a flow of blood emanating from a wound using such devices are also disclosed. Methods of fabricating oxidized cellulose are also disclosed.
Owner:PAMEIJER CORNELIS H +1
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Method for preparing thrombin for use in a biological glue
InactiveUS6472162B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component and the clotting and adhesive proteins component are harvested simultaneously from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
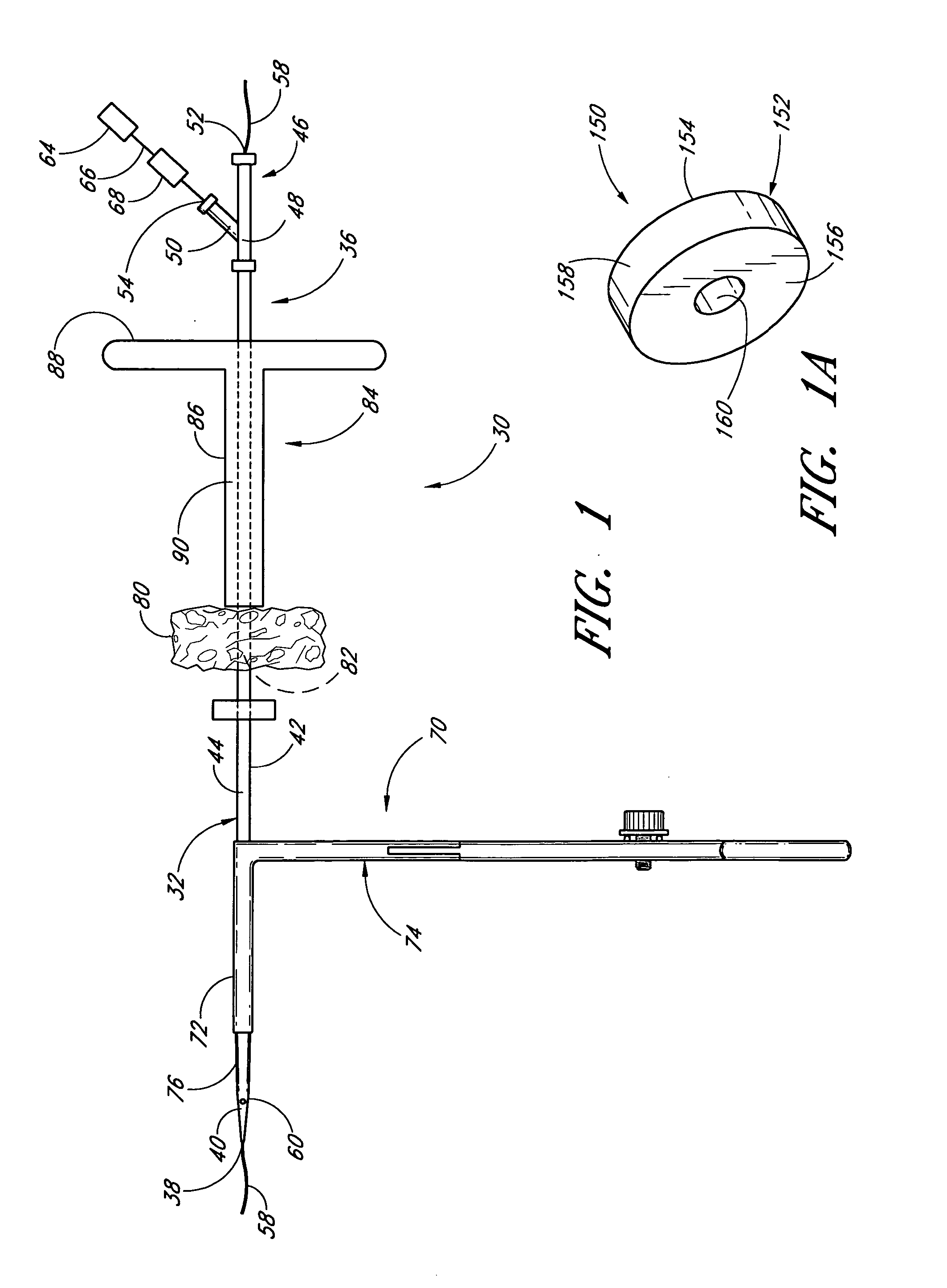
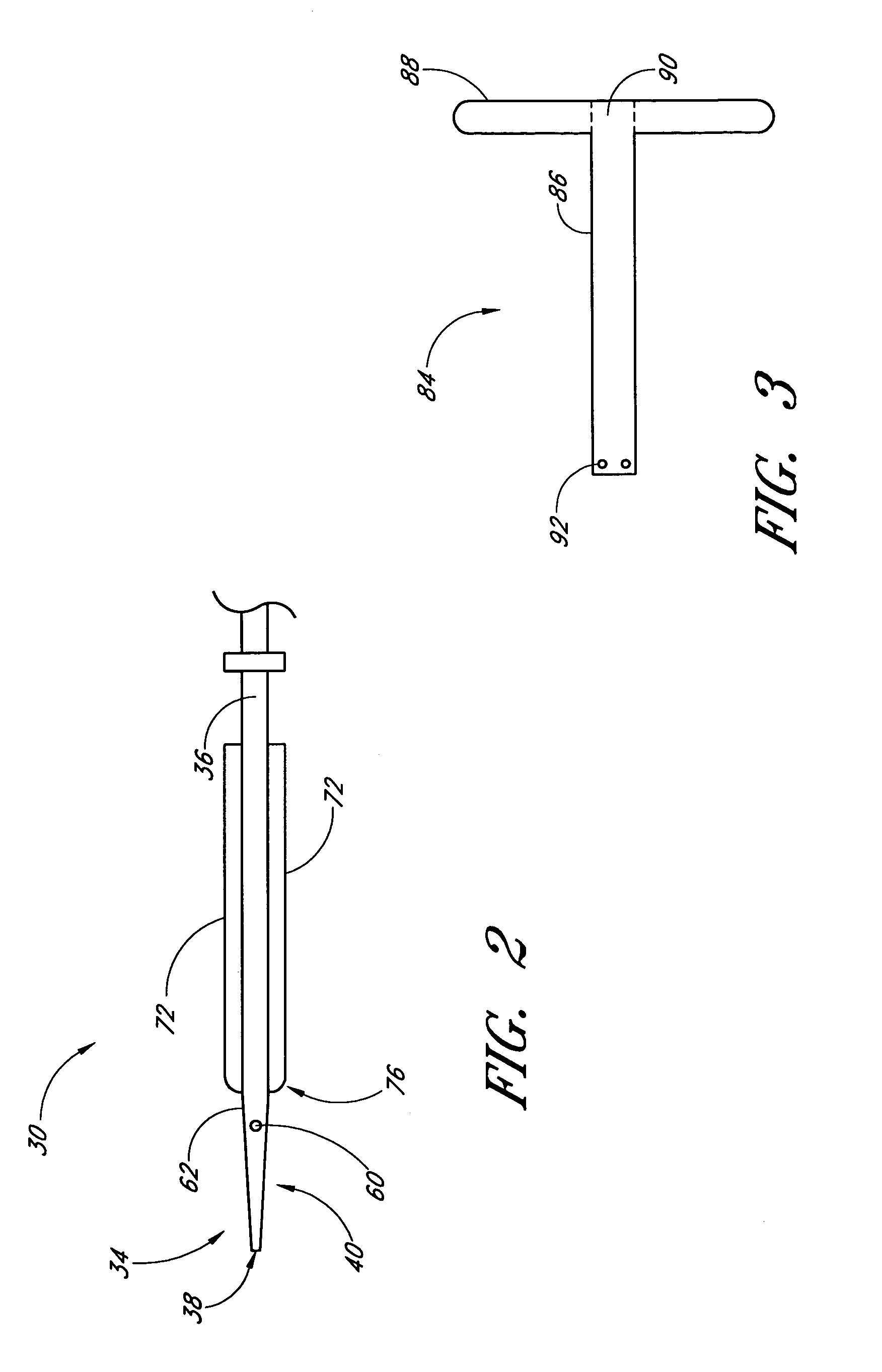
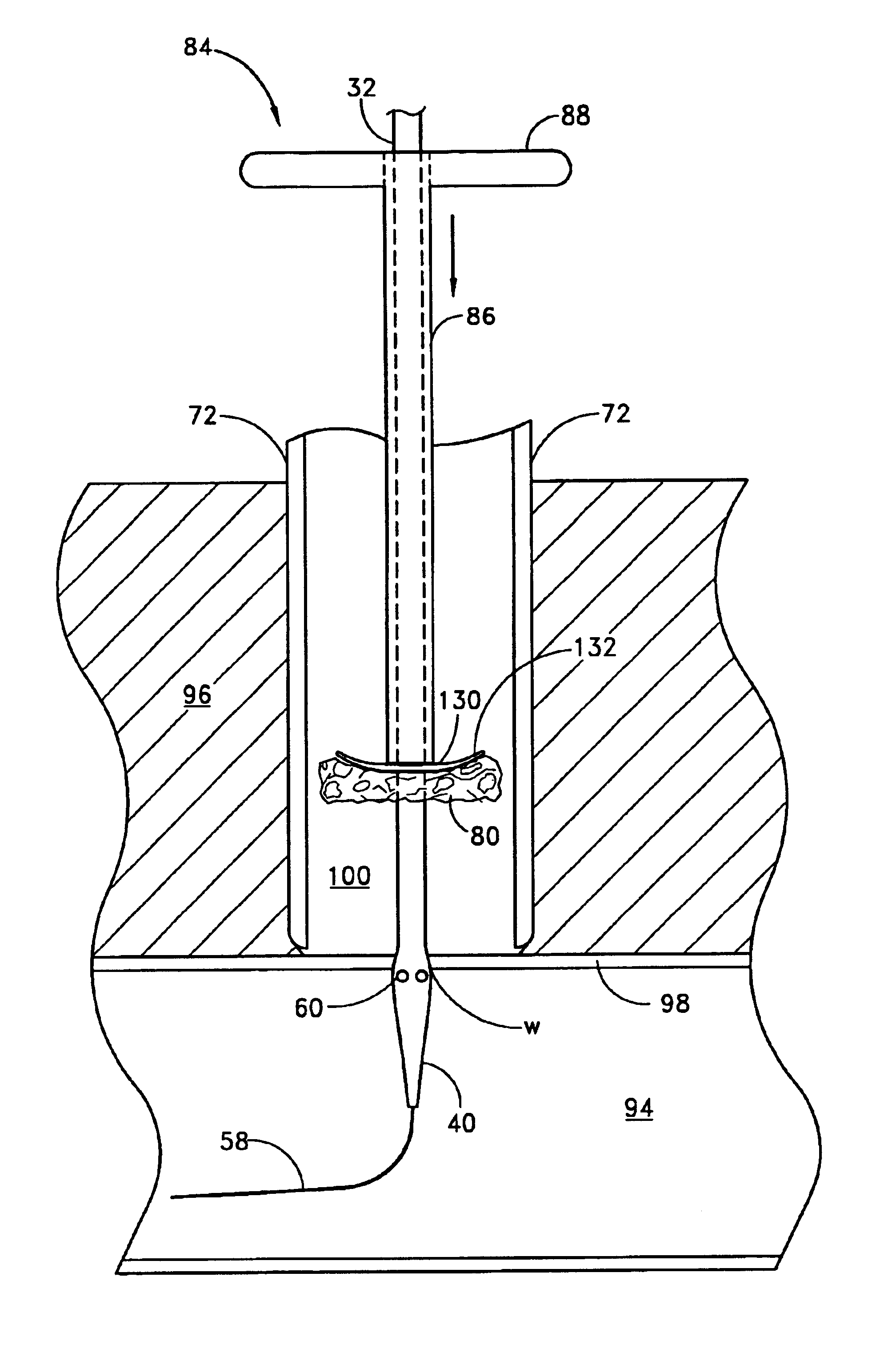
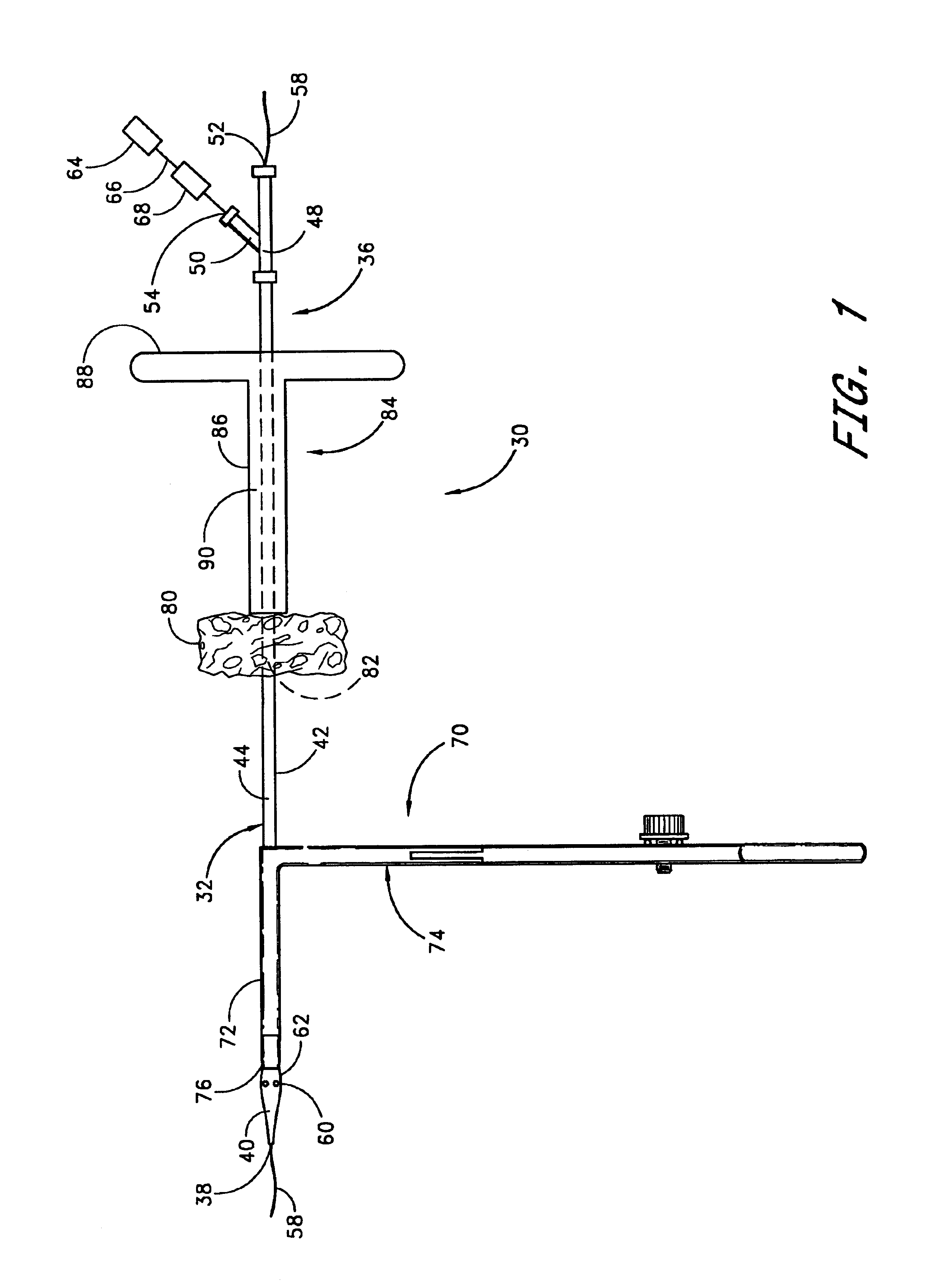
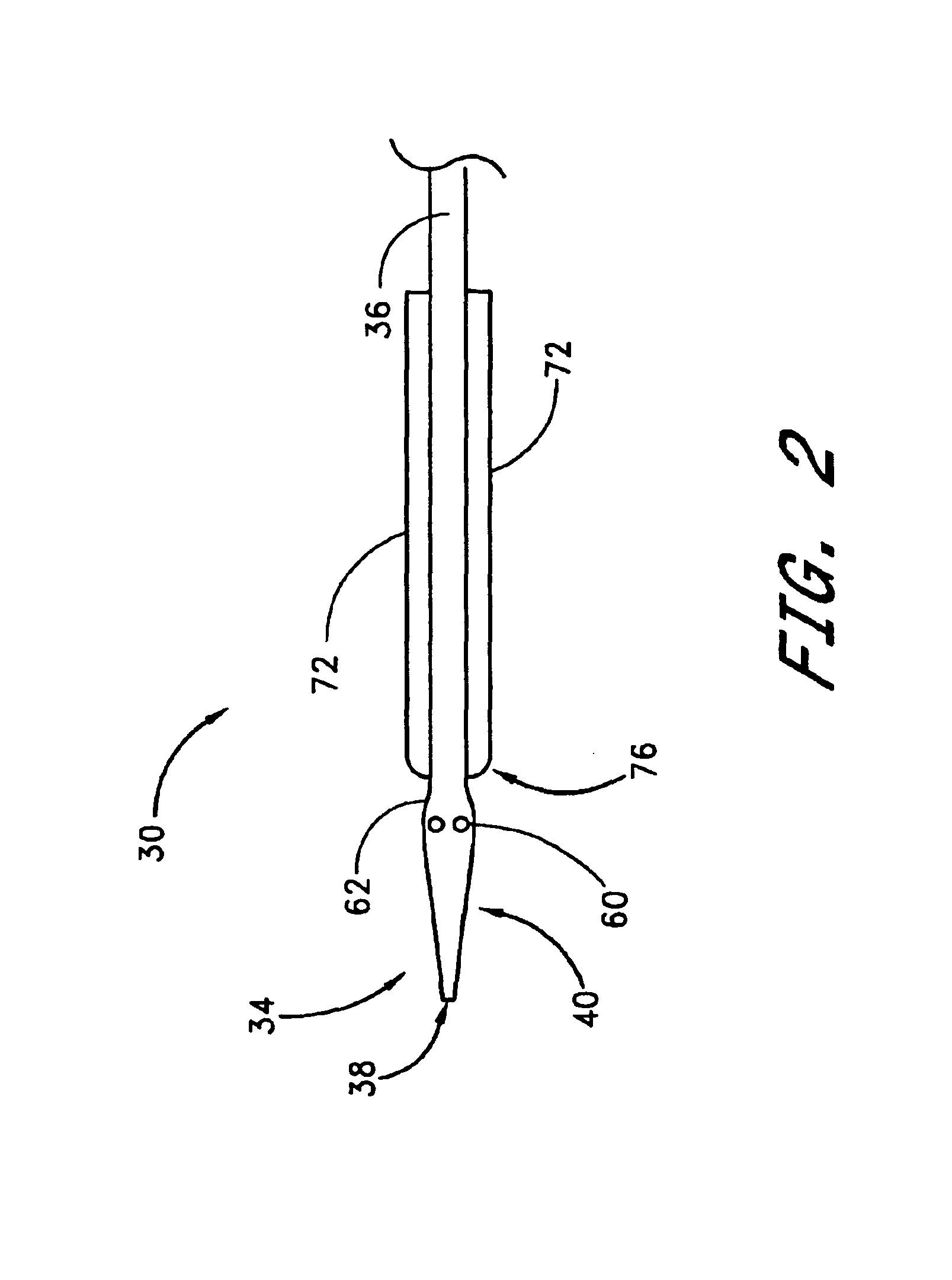
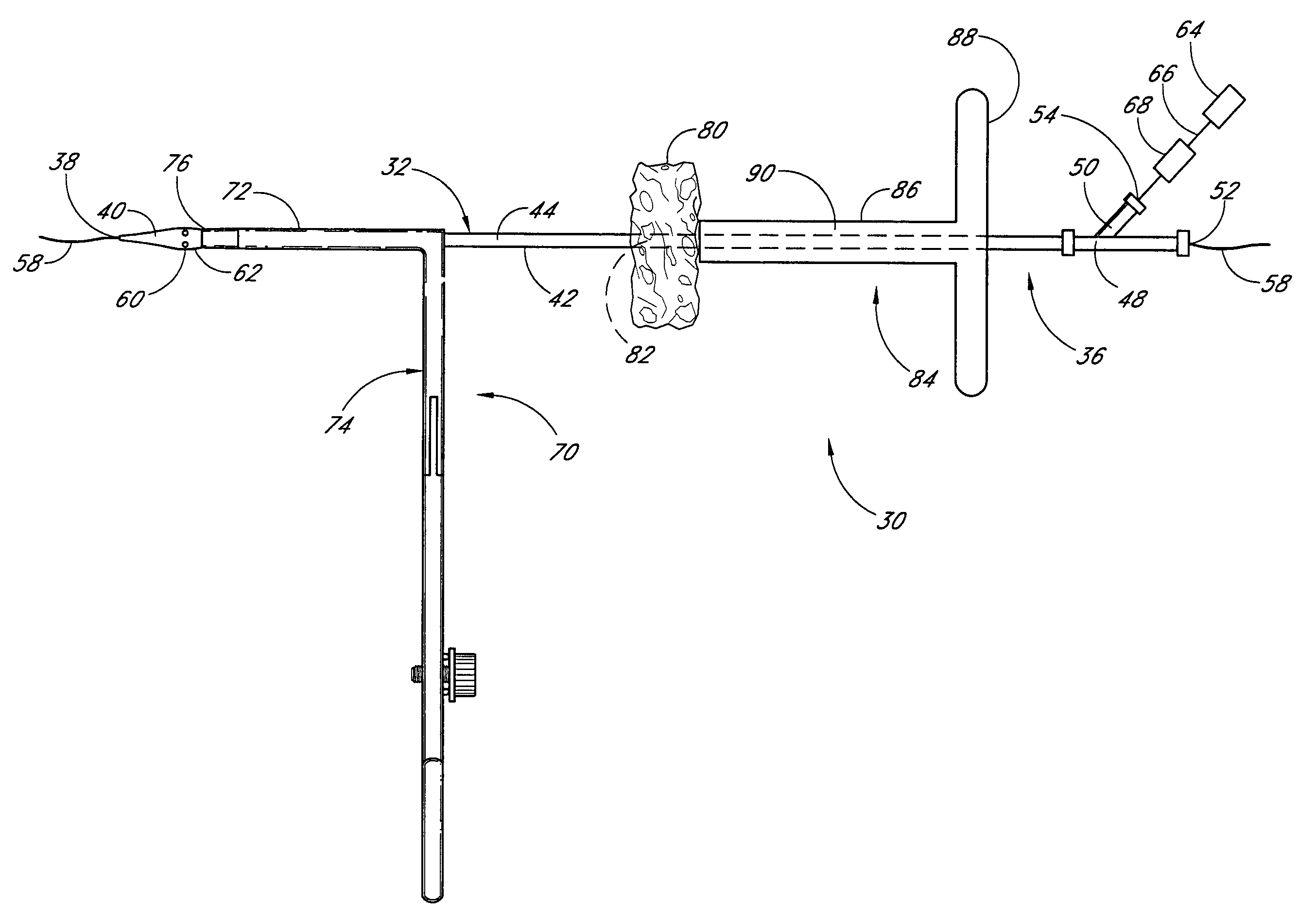
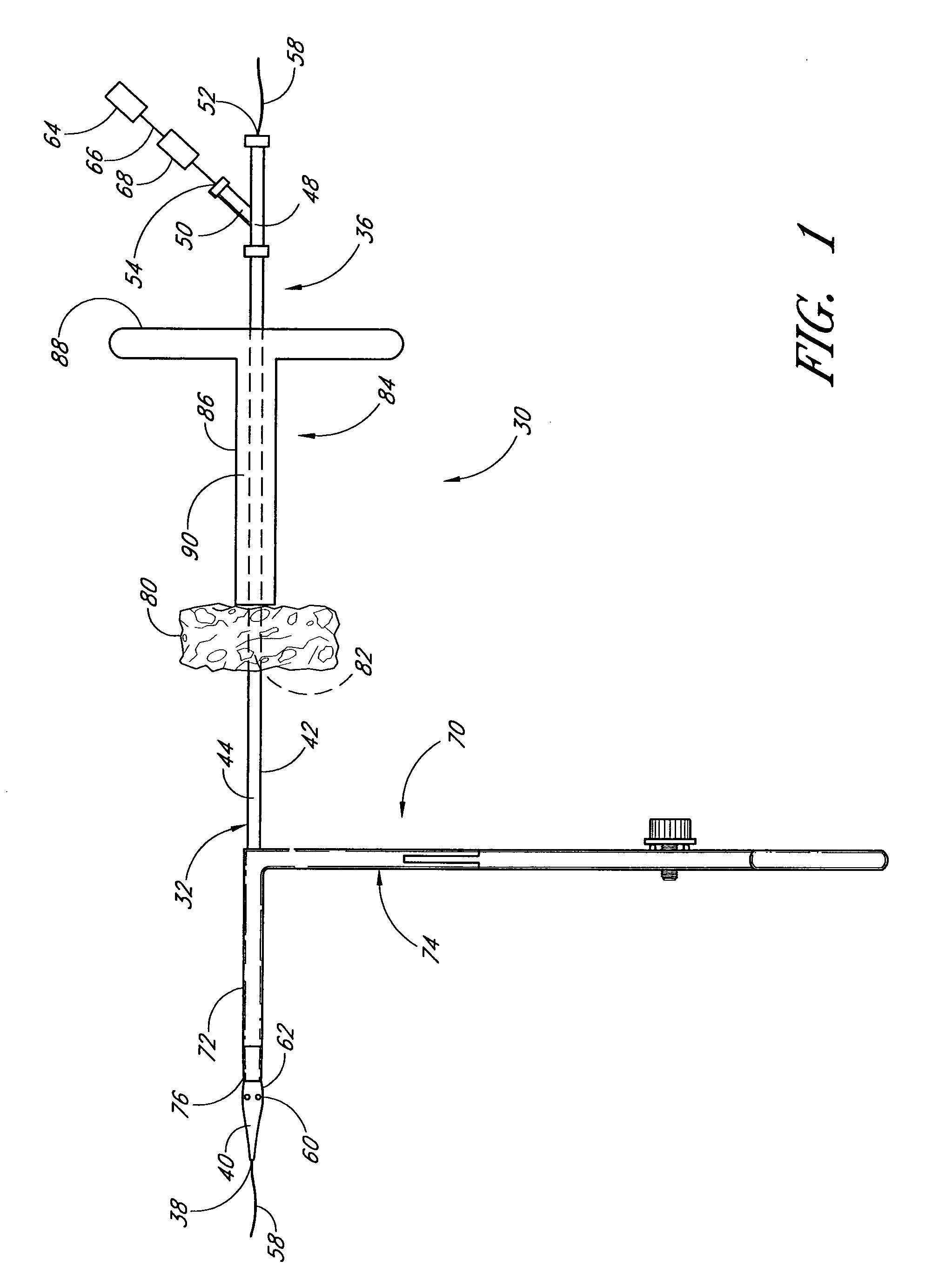
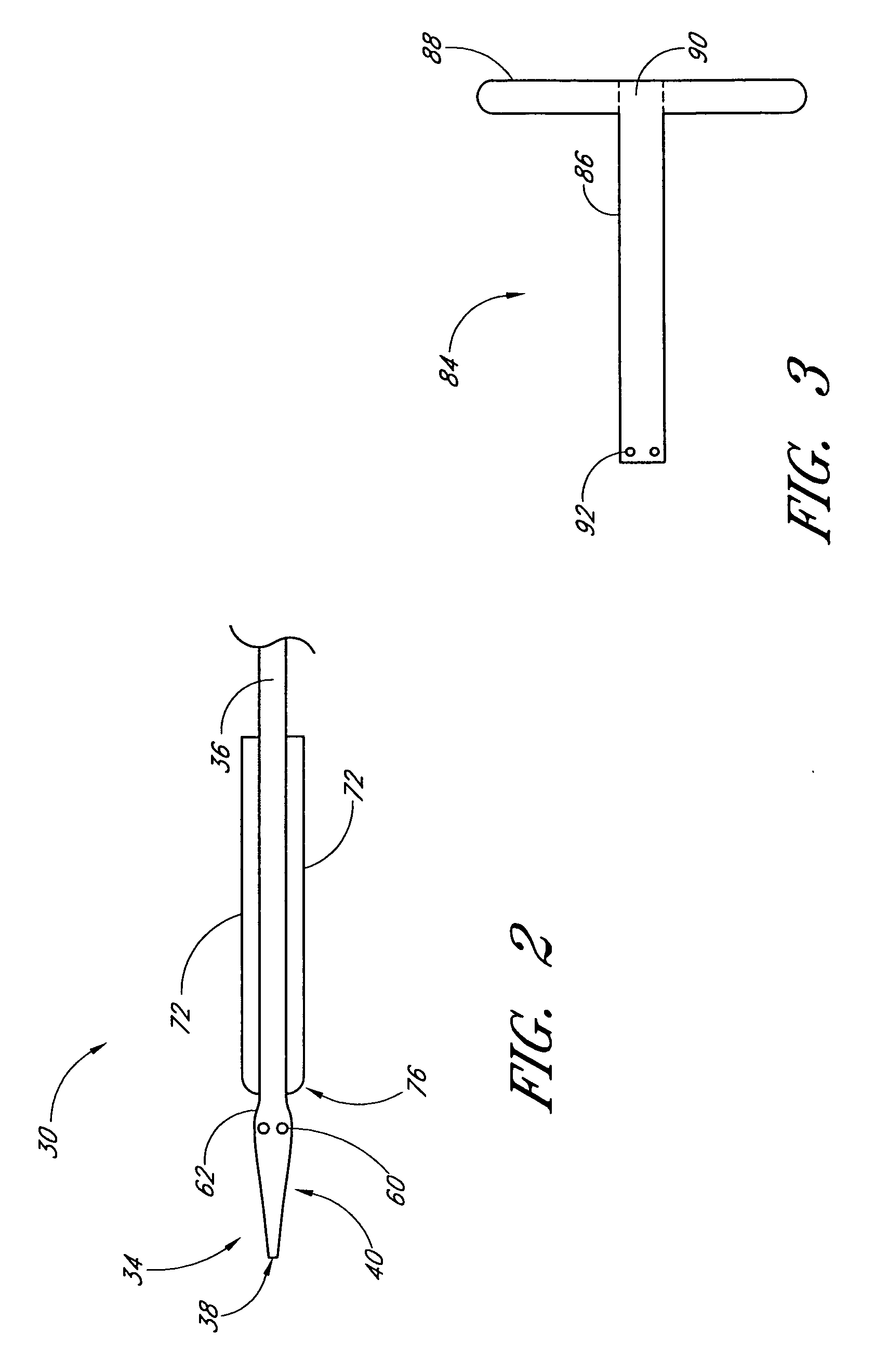
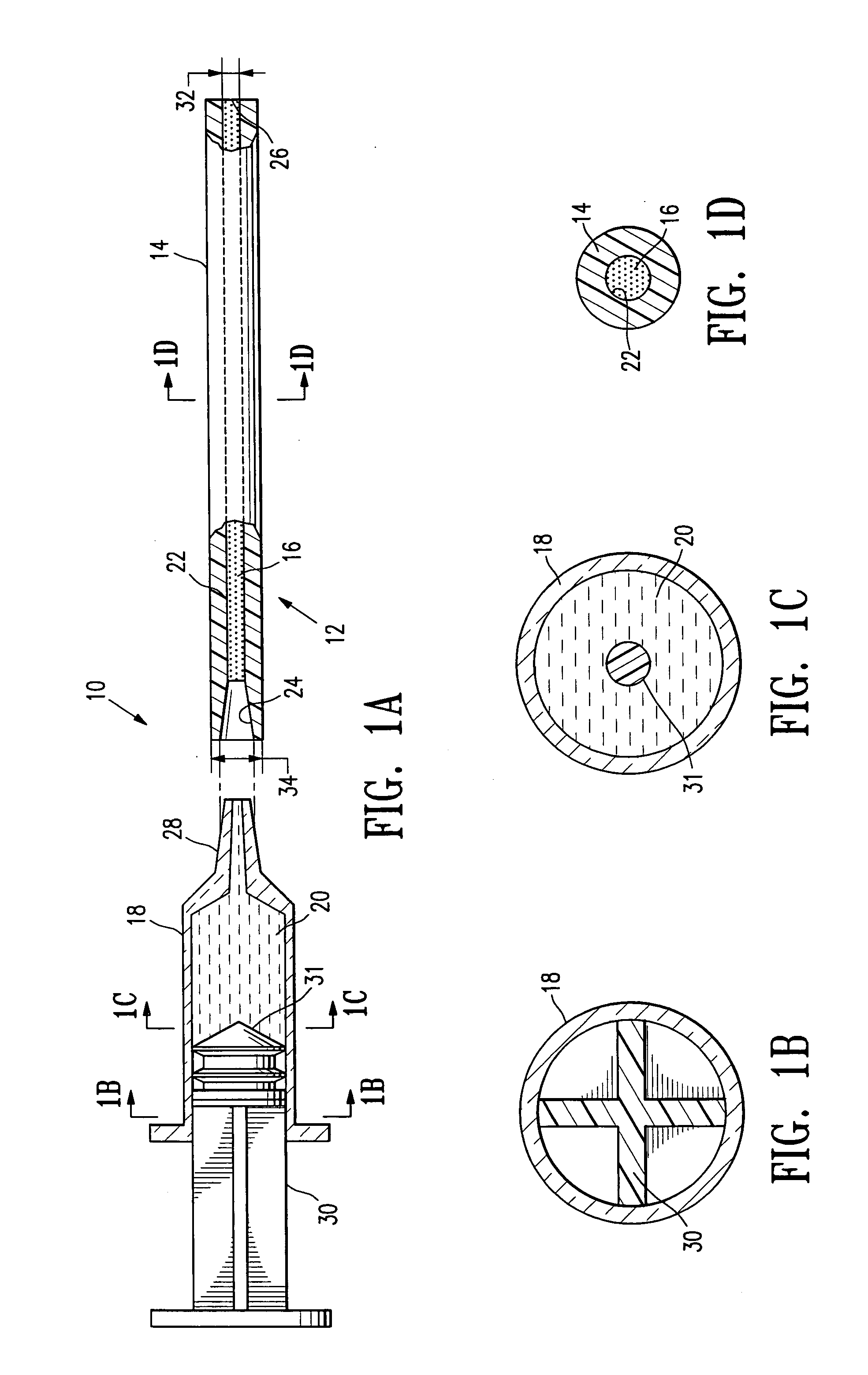
Vascular wound closure device and method
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes an apparatus that can be threaded over a guidewire into place at or adjacent the wound. The apparatus includes a chamber that encloses a hemostatic material therein. When the apparatus is positioned adjacent the wound as desired, the hemostatic material is deployed from the chamber. A blocking member distal of the hemostatic material functions as a barrier to prevent the hemostatic material from entering the wound. Blood contacts the hemostatic material, and blood clotting preferably is facilitated by a hemostatic agent within the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
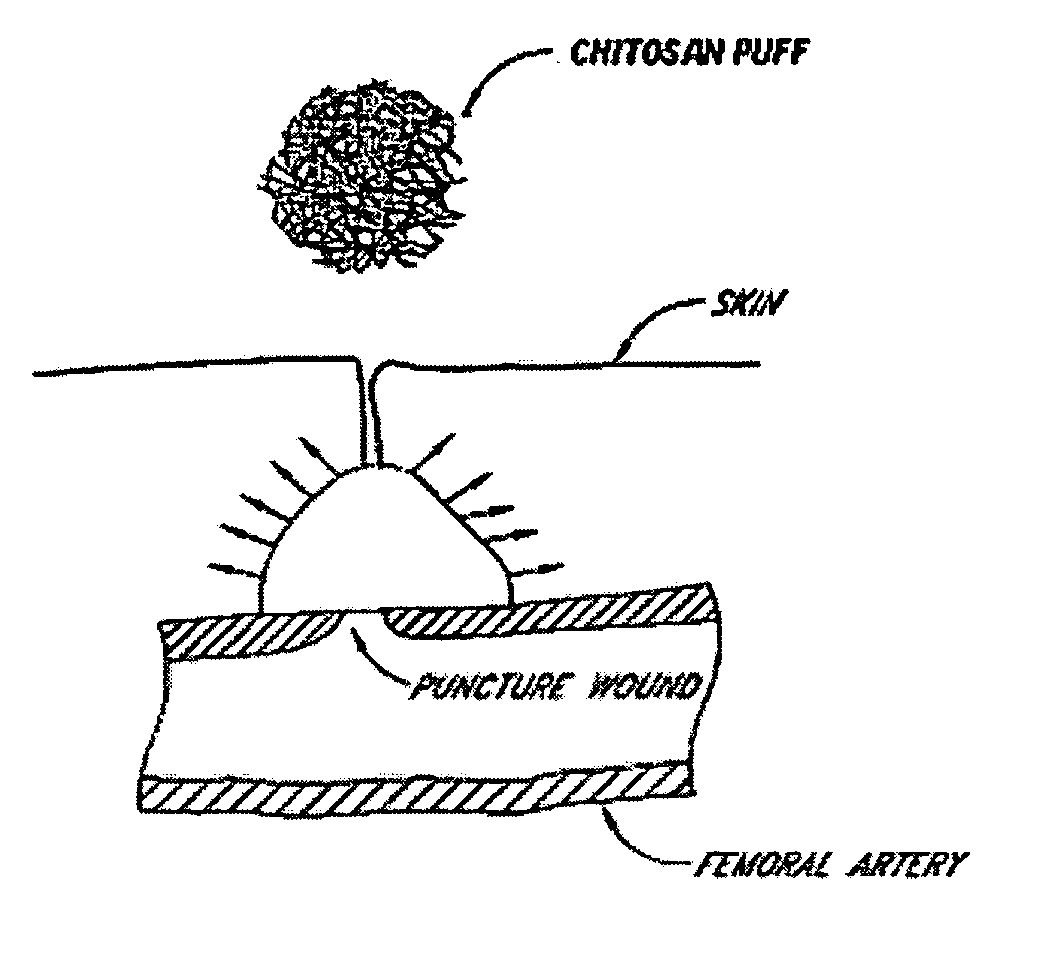
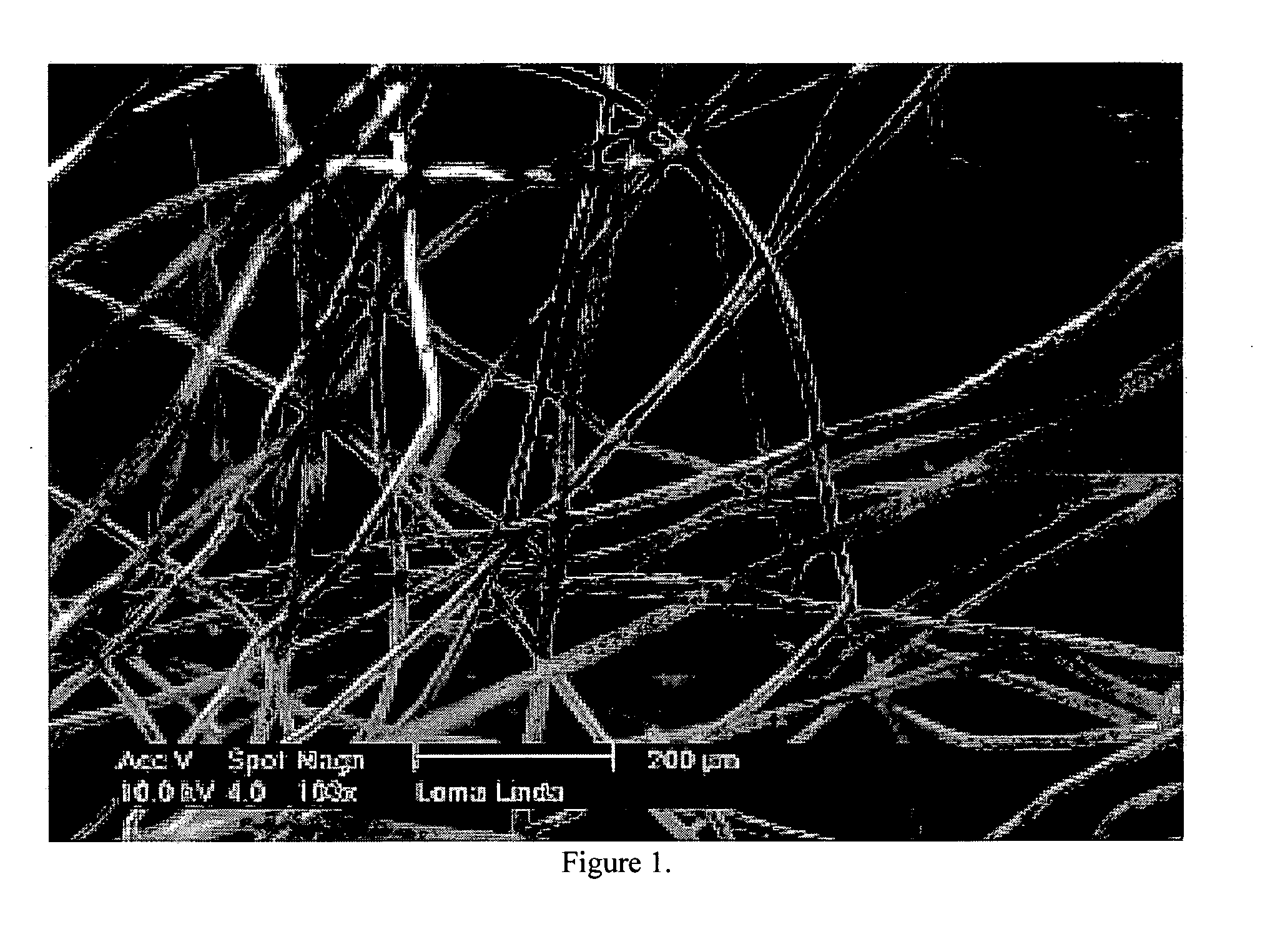
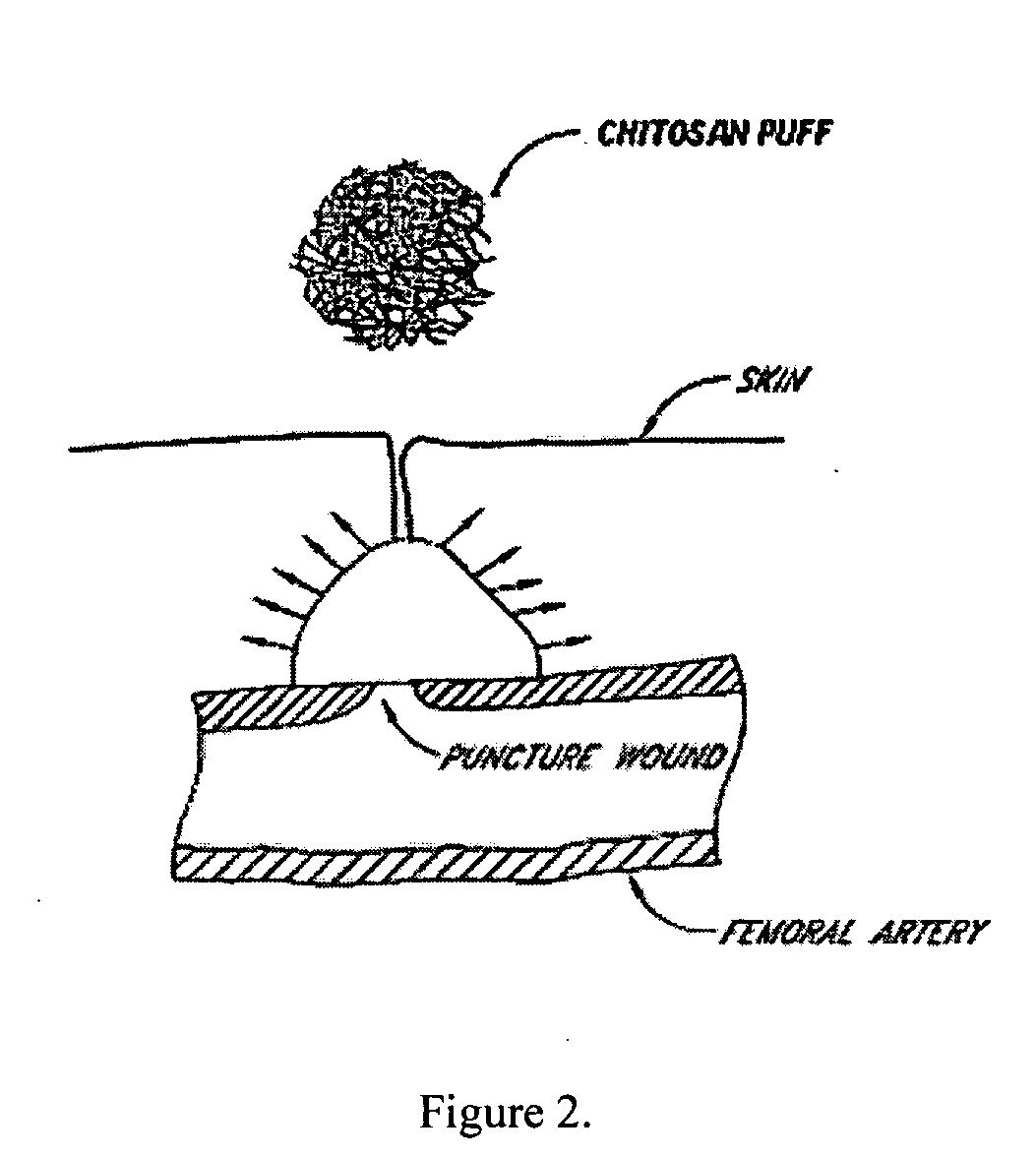
Deployable multifunctional hemostatic agent
InactiveUS20050123588A1Good hemostasisRapid and effective hemostasisSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsVeinMicrosphere
This invention relates to deployable hemostatic materials comprising chitosan fibers upon which hemostatic microporous polysaccharide microspheres and a medicament or biologically active substance are deposited. The hemostatic materials are suitable for use in controlling active bleeding from artery and vein lacerations, sealing femoral artery punctures, and controlling oozing from tissue.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Apparatus and method of preparation of stable, long term thrombin from plasma and thrombin formed thereby
InactiveUS6274090B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component is harvested simultaneously from the clotting and adhesive proteins component from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
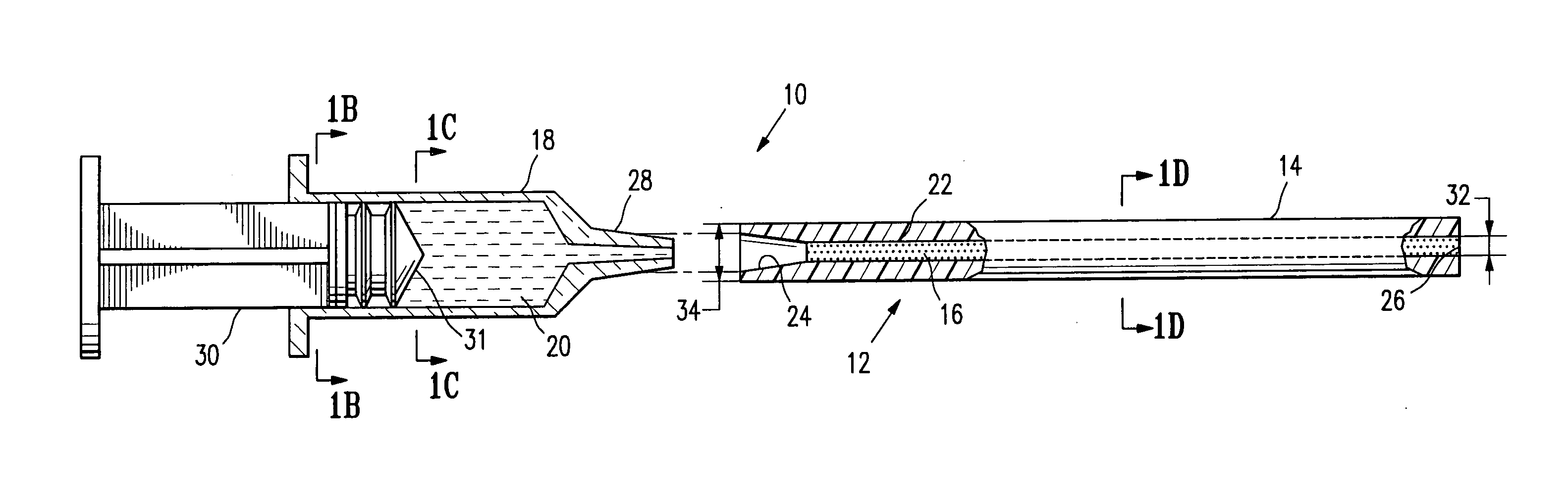
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS6862470B2Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
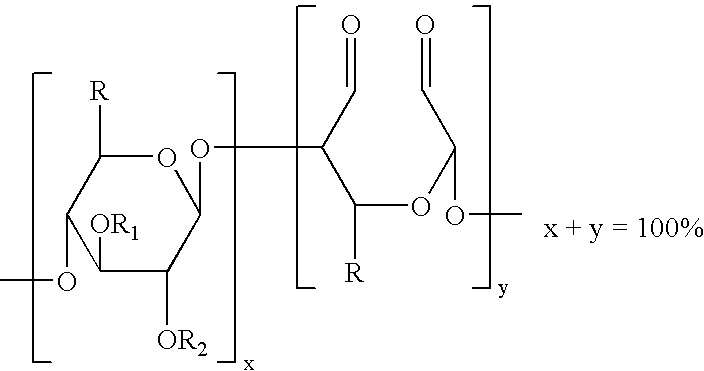
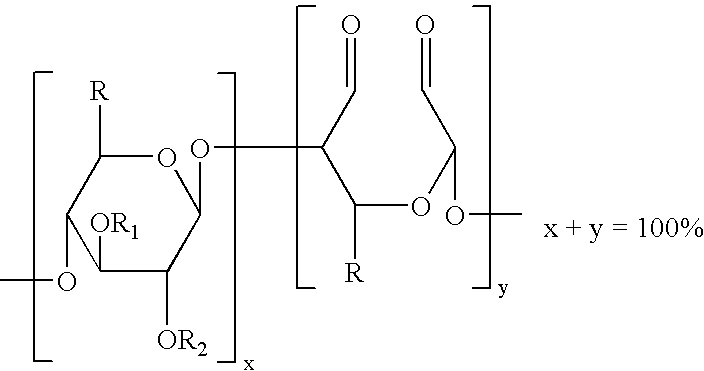
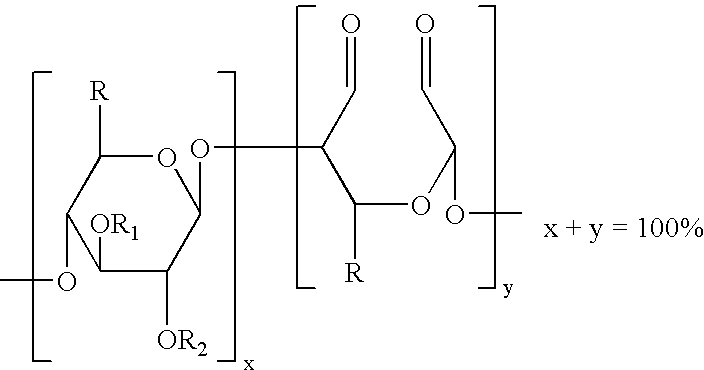
Method of providing hemostasis to a wound
The present invention is directed to hemostatic wound dressings that contain a substrate for contacting a wound, wherein the substrate includes a wound-contacting surface and is fabricated at least in part from a biocompatible aldehyde-modified polysaccharide having covalently conjugated there with a hemostatic agent and to methods of providing hemostasis to a wound that include applying the wound dressing described herein to a wound.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Hemostatic textile
ActiveUS20070160653A1Quick activationNon-adhesive dressingsPeptide/protein ingredientsLactideSisal fiber
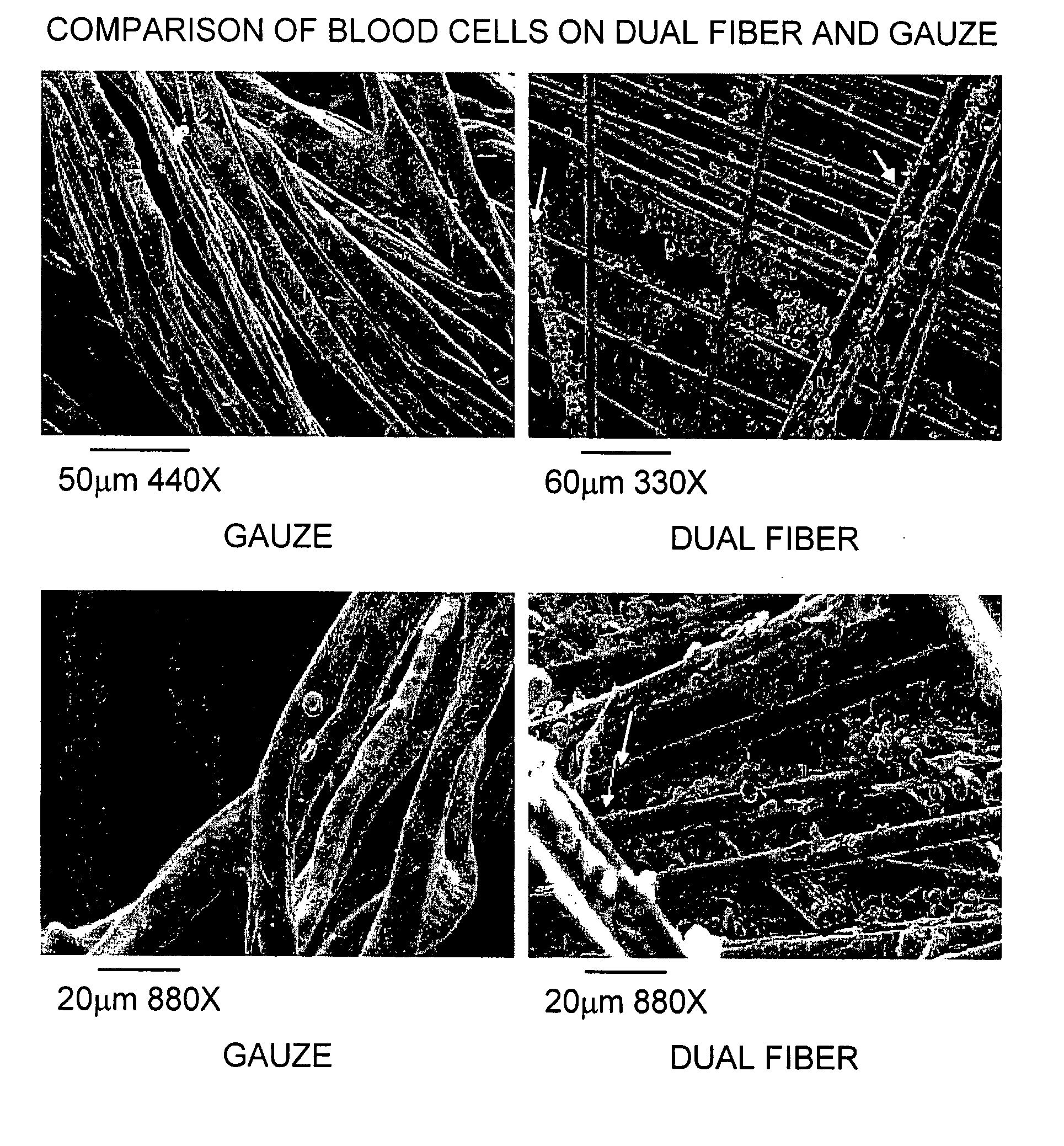
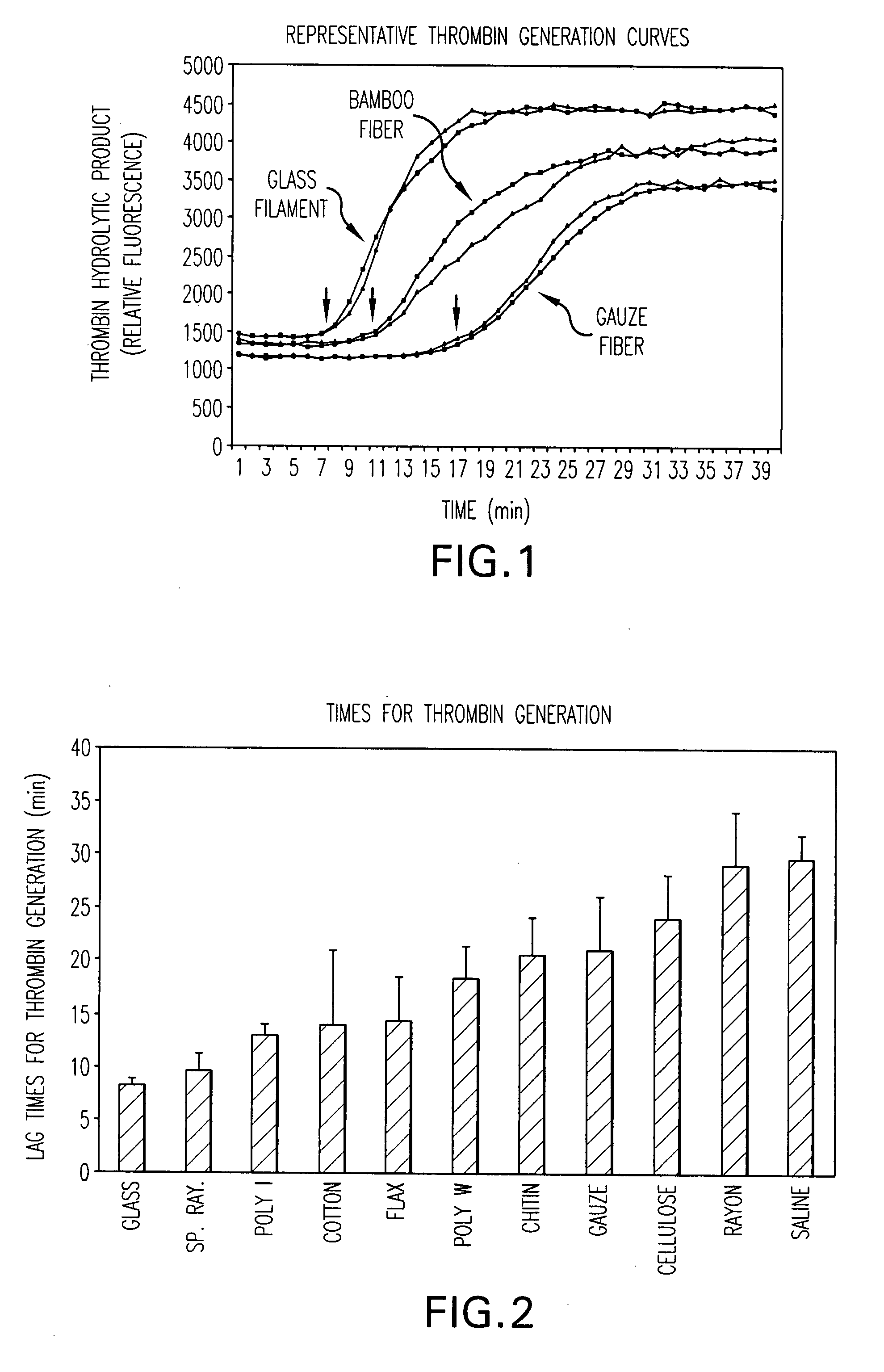
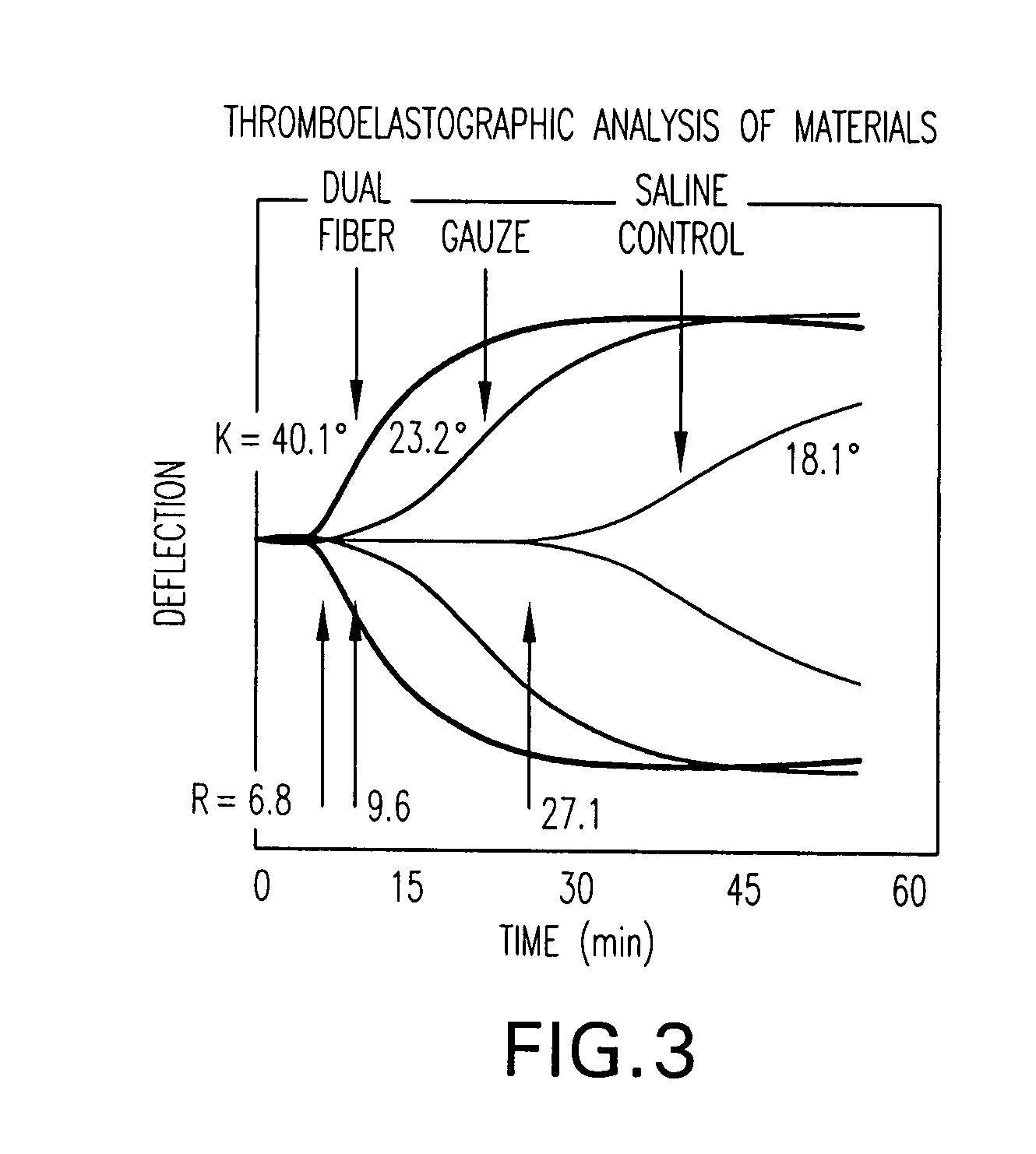
The present invention is directed to a hemostatic textile, comprising: a material comprising a combination of glass fibers and one or more secondary fibers selected from the group consisting of silk fibers; ceramic fibers; raw or regenerated bamboo fibers; cotton fibers; rayon fibers; linen fibers; ramie fibers; jute fibers; sisal fibers; flax fibers; soybean fibers; corn fibers; hemp fibers; lyocel fibers; wool; lactide and / or glycolide polymers; lactide / glycolide copolymers; silicate fibers; polyamide fibers; feldspar fibers; zeolite fibers, zeolite-containing fibers, acetate fibers; and combinations thereof; the hemostatic textile capable of activating hemostatic systems in the body when applied to a wound. Additional cofactors such as thrombin and hemostatic agents such as RL platelets, RL blood cells; fibrin, fibrinogen, and combinations thereof may also be incorporated into the textile. The invention is also directed to methods of producing the textile, and methods of using the textile to stop bleeding.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Method and apparatus for closing vascular puncture using hemostatic material
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes a guidewire and / or other surgical implement extending from the wound. A hemostatic material is advanced over the surgical implement and into contact with an area of the blood vessel surrounding the wound. The surgical implement is removed. Blood soaks the hemostatic material, and blood clotting is facilitated by the hemostatic agent within the material. A sealing layer of adhesive can be applied to the hemostatic material, confining the blood flow to the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by natural blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY
Vascular wound closure device and method
A method and apparatus for closing a vascular wound includes an apparatus that can be threaded over a guidewire into place at or adjacent the wound. The apparatus includes a chamber that encloses a hemostatic material therein. When the apparatus is positioned adjacent the wound as desired, the hemostatic material is deployed from the chamber. Blood contacts the hemostatic material, and blood clotting preferably is facilitated by a hemostatic agent within the material. Thus, the vascular puncture wound is sealed by blood clot formation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Compositions and methods for treating diverticular disease
InactiveUS20050277577A1Induce adhesionEasy to fillOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineDiverticulitis
Agents, compositions, and implants are provided herein for treating diverticular disease (e.g., diverticulosis and diverticulitis). In particular, fibrosis-inducing agents, hemostatic agents, and / or anti-infective agents, or compositions containing one or more of these agents are provided for use in methods for treating diverticular disease.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Hemostatic agent for topical and internal use
ActiveUS20050240137A1Good hemostasisRapid and effective hemostasisSuture equipmentsSurgical adhesivesVeinDermatology
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
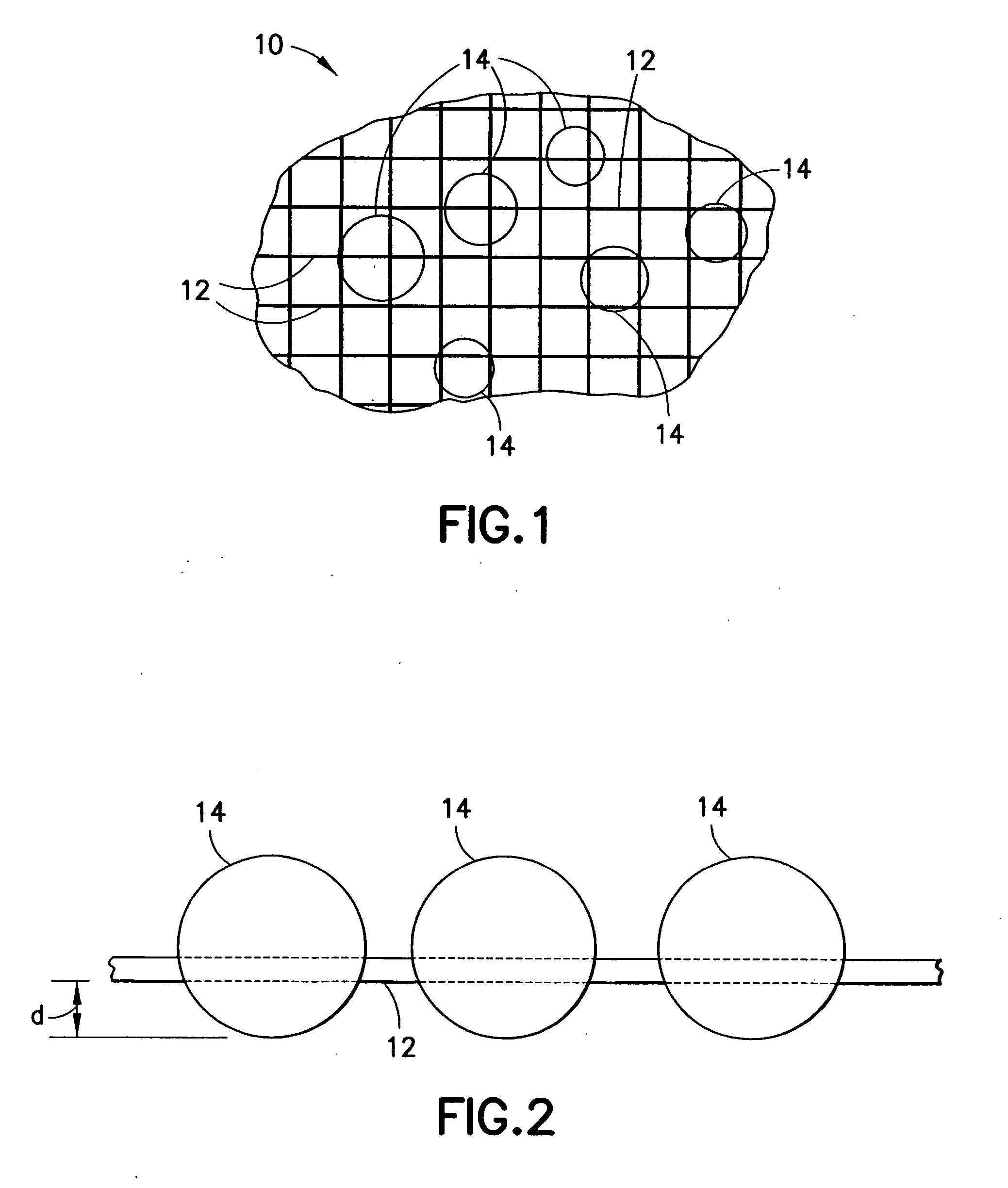
Hemostatic compositions, assemblies, systems, and methods employing particulate hemostatic agents formed from hydrophilic polymer foam such as chitosan
ActiveUS20070021703A1Safe and effective deliveryIncrease ratingsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsParticulatesPolymer
Improved hemostatic agents take the form of granules or particles that can be used to stanch, seal, or stabilize a site of hemorrhage, including a noncompressible hemorrhage.
Owner:TRICOL BIOMEDICAL INC
Instrument for surgically cutting tissue and method of use
InactiveUS7481817B2Easy diagnosisFacilitates accurate appositionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsVia incisionVascular structure
An instrument for precisely cutting tissue to controlled dimensions (length, width, depth, and shape) is provided for the removal of tissue specimens from remote sites in the body of a patient, such as from the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or vascular structures, or any tissue surface or soft tissue of the body. The instrument has a housing and a substantially flexible shaft extending from the housing to a distal end. The distal end of the instrument has an open cavity into which tissue is receivable. Suction can be communicated along the shaft to the distal end for distribution across the cavity utilizing a manifold having a grated tissue engaging surface with opening(s) for applying the suction, thereby pulling tissue adjacent to the distal end into the cavity against the tissue engaging surface of the manifold. One or more hollow needles are extendable from the housing through the shaft into the cavity to enable infusion of fluid, such as saline or a hemostatic agent, into the tissue. A blade in the distal end is extendable through the cavity over the manifold and across the opening to cut the tissue held by suction and stabilized by the needles in the cavity. The shape and depth of the tissue removed by the cuts is in accordance with the contour of the tissue engaging surface and the size and shape of the cavity at the distal end. The tissue so removed by the instrument may be for therapeutic intervention and / or represent a tissue specimen for biopsy suitable of diagnostic evaluation. The tissue edges in the patient's body left after cutting with this instrument readily avail themselves to apposition for enhanced healing.
Owner:LSI SOLUTIONS
Hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
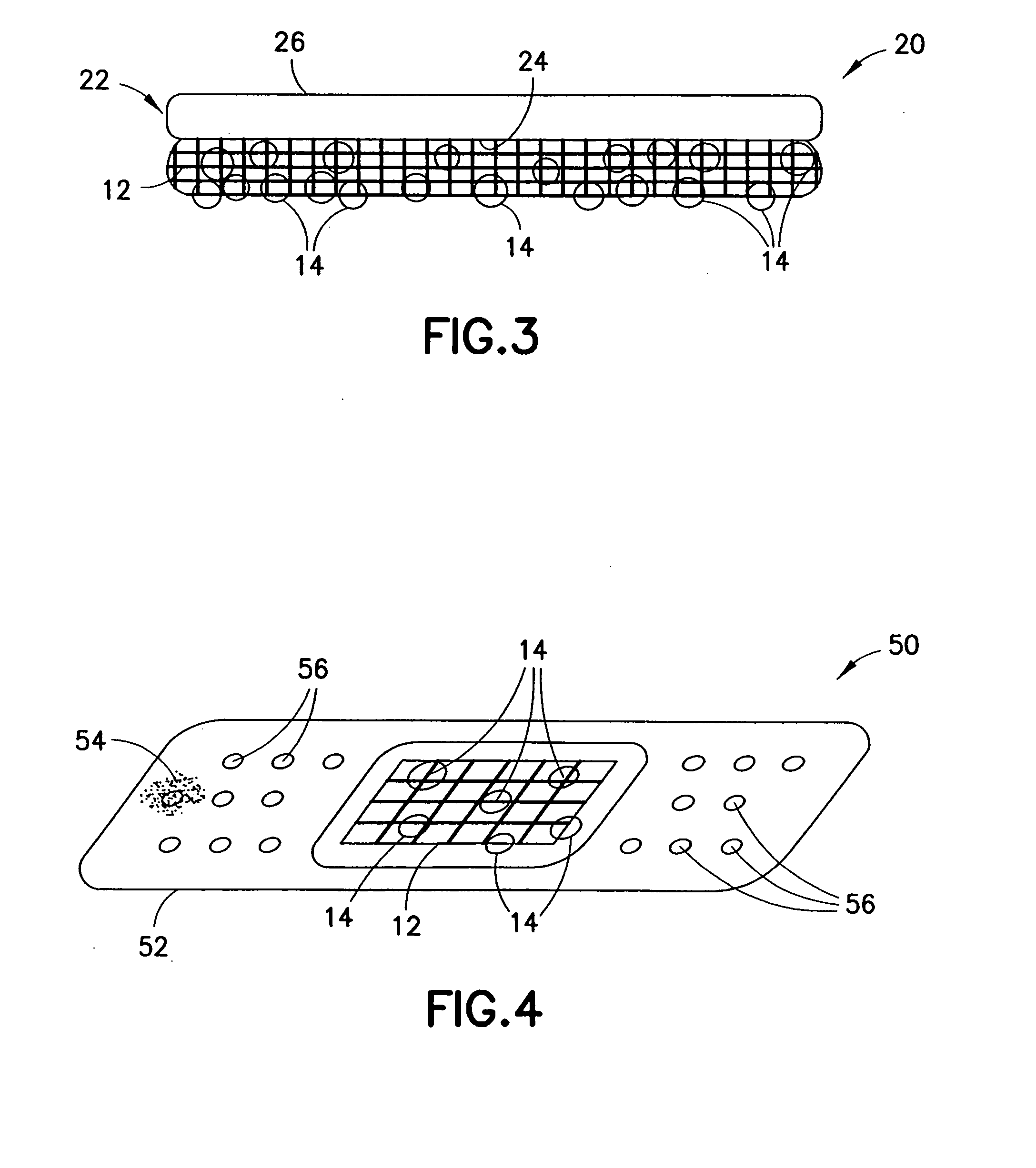
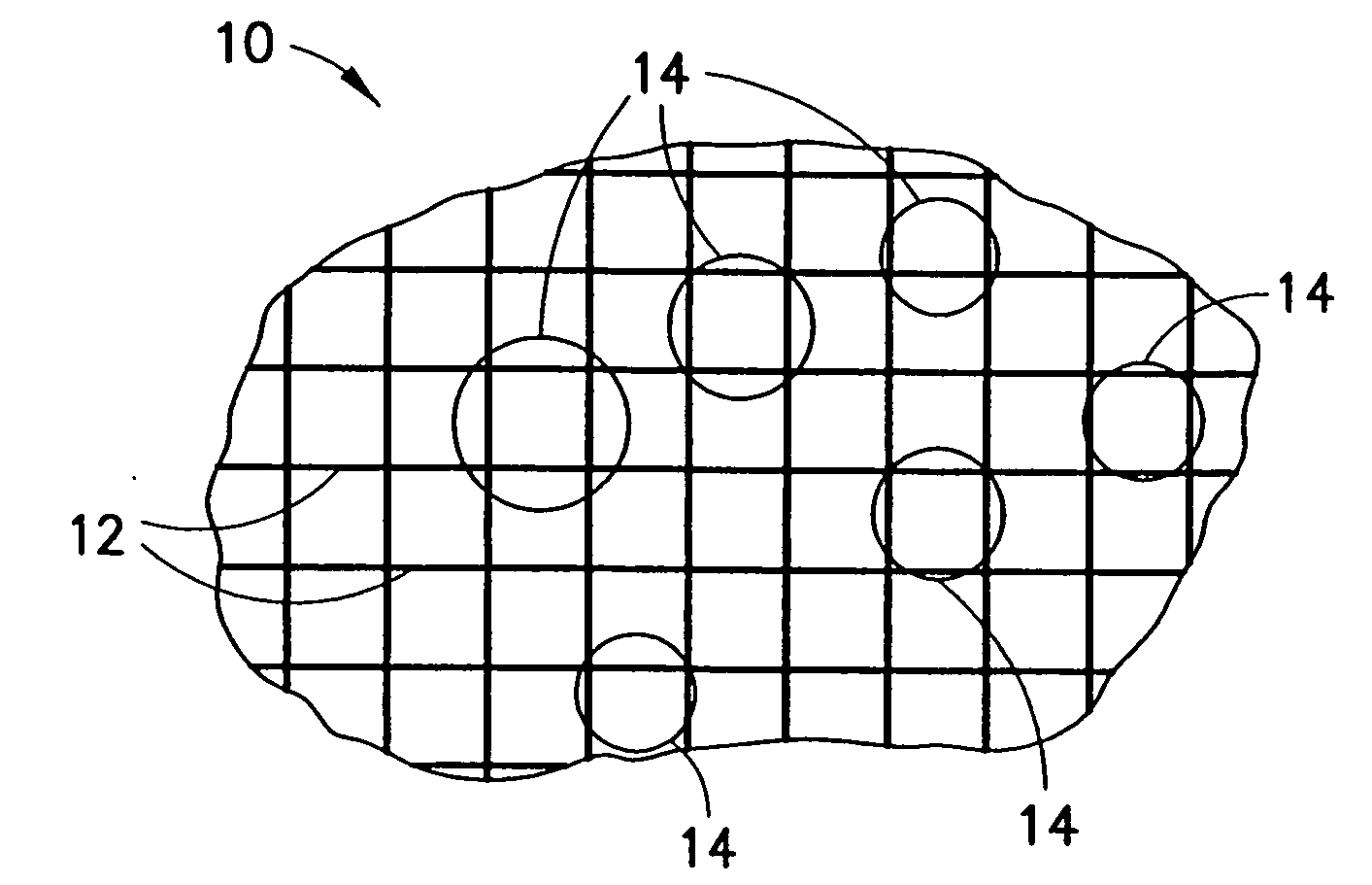
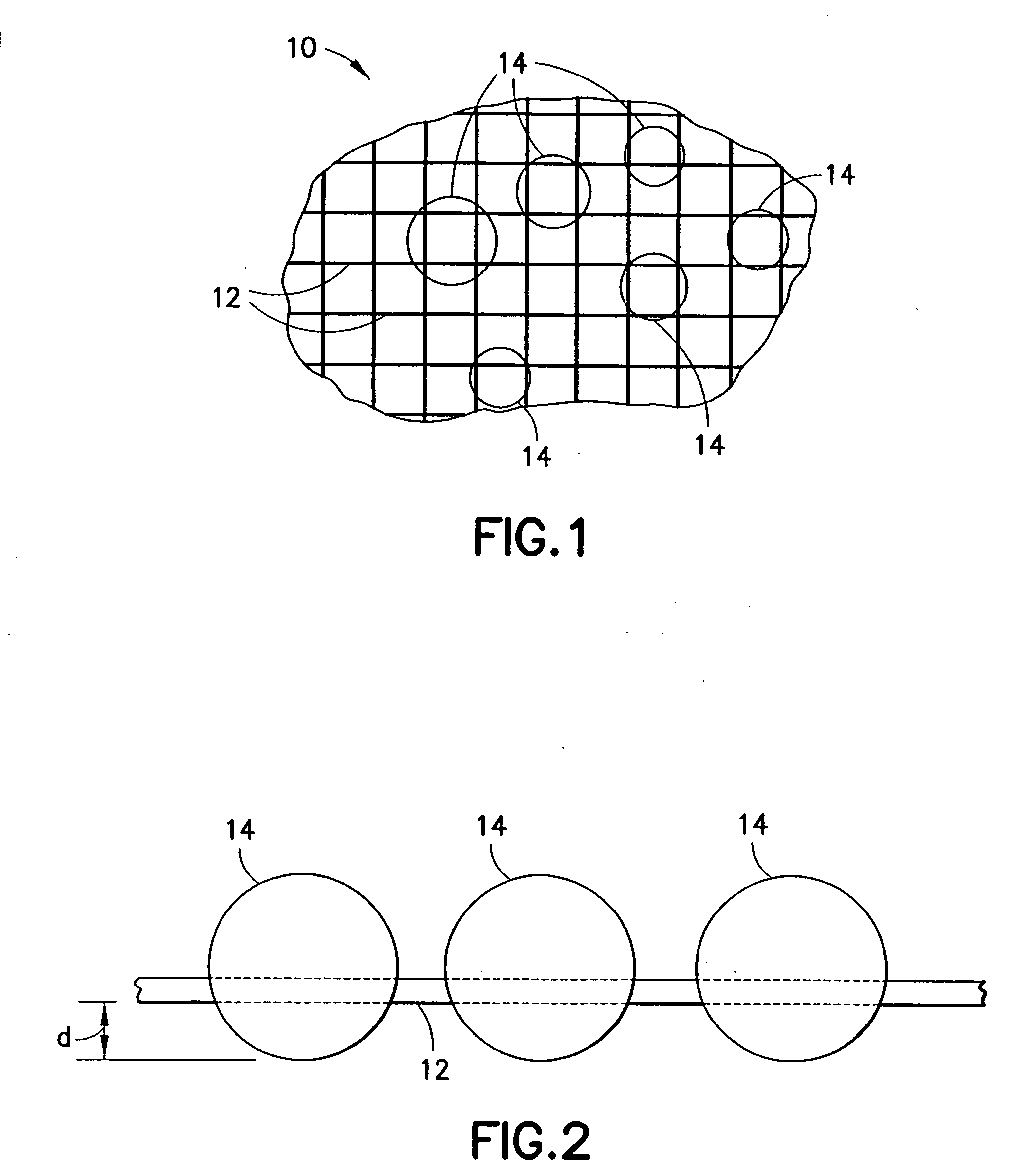
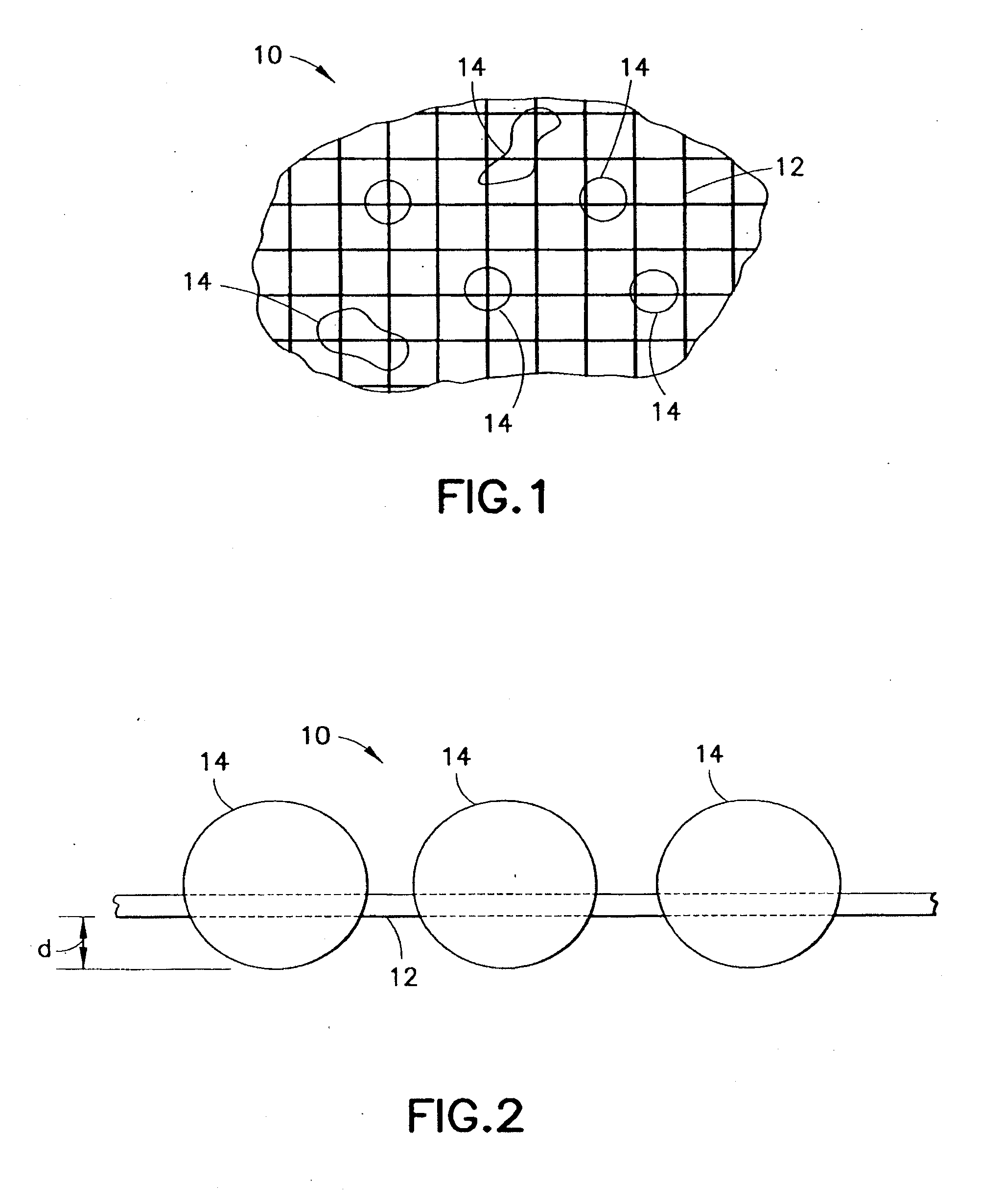
InactiveUS20070276308A1Minimize injuryEliminate feverNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersMedicineHemostatic Agent
A hemostatic agent comprises diatomaceous earth in particle form. Devices for promoting hemostasis comprise diatomaceous earth in particle form and a receptacle for retaining the particles therein. The receptacle is defined by a mesh having openings therein. A hemostatic sponge comprises a substrate, diatomaceous earth disposed on the substrate, and a release agent disposed on the substrate. A hemostatic sponge may also comprise a film into which diatomaceous earth is incorporated, or it may comprise a substrate, diatomaceous earth disposed on the substrate, and a film disposed over the diatomaceous earth. A hemostatic sponge may also comprise a first substrate, diatomaceous earth disposed on the first substrate, and a second substrate disposed on the diatomaceous earth. When treating a bleeding wound using any of the foregoing devices, application of the device causes the diatomaceous earth to come into contact with blood to cause a clotting effect.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Partially hydrated hemostatic agent
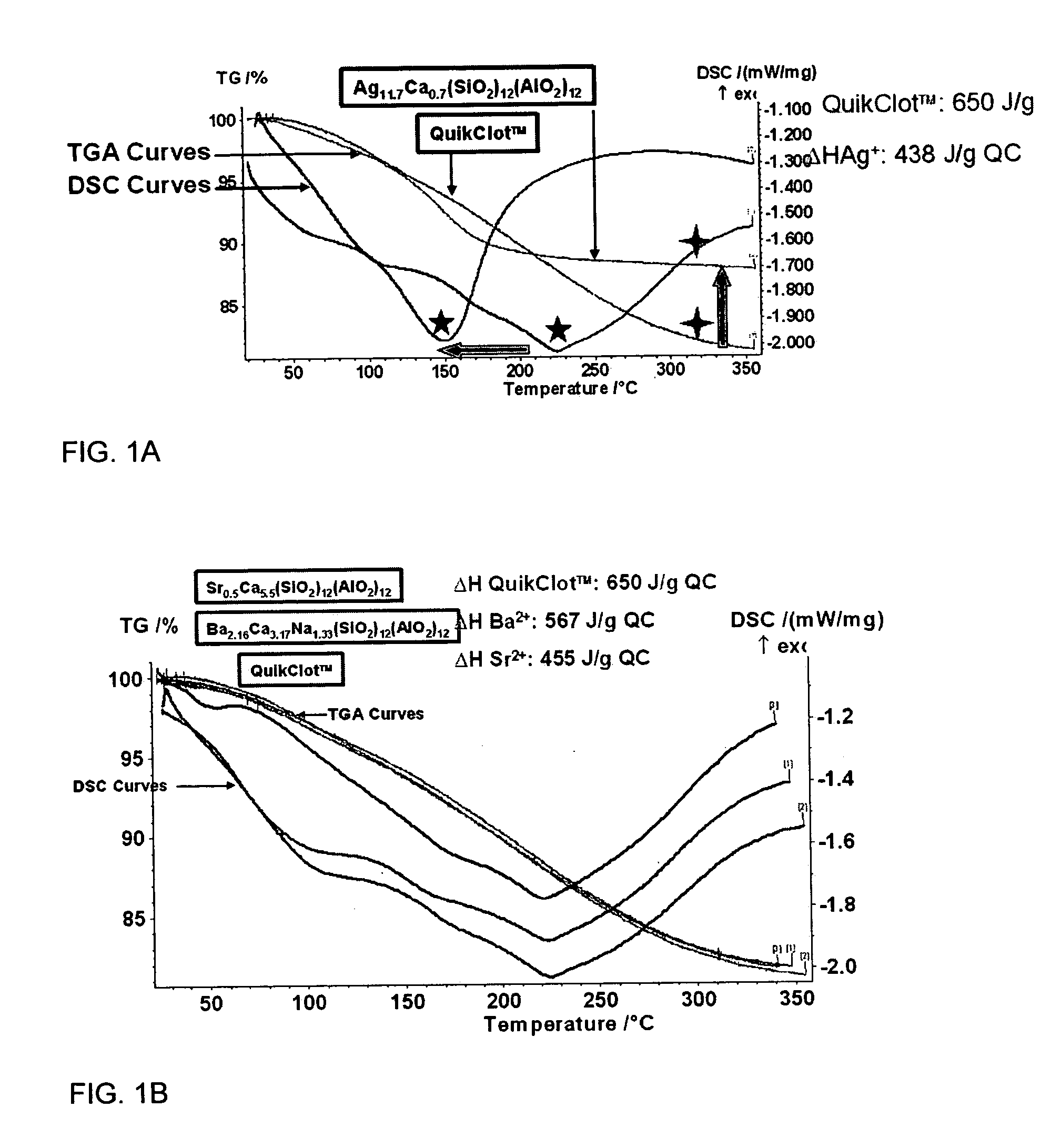
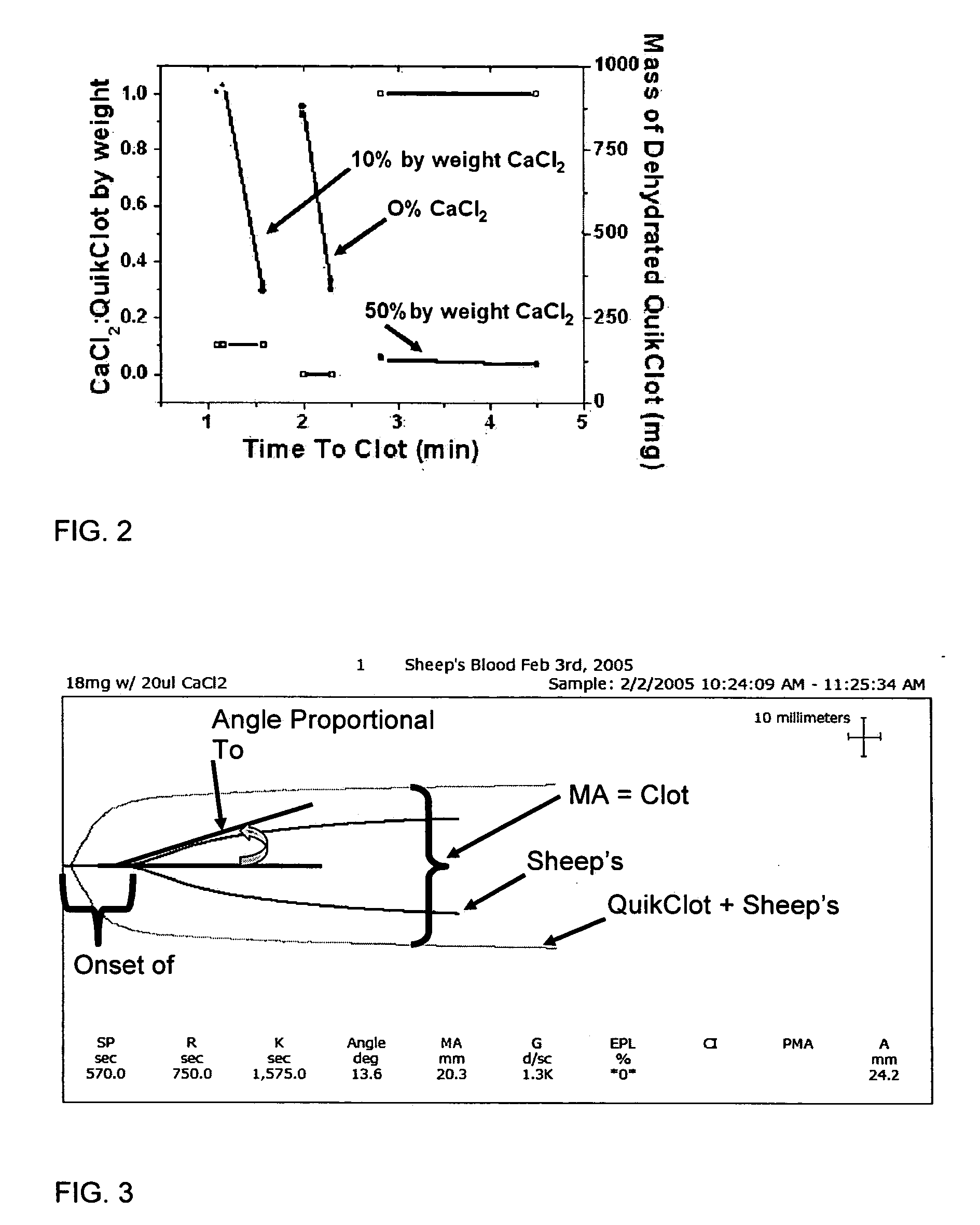
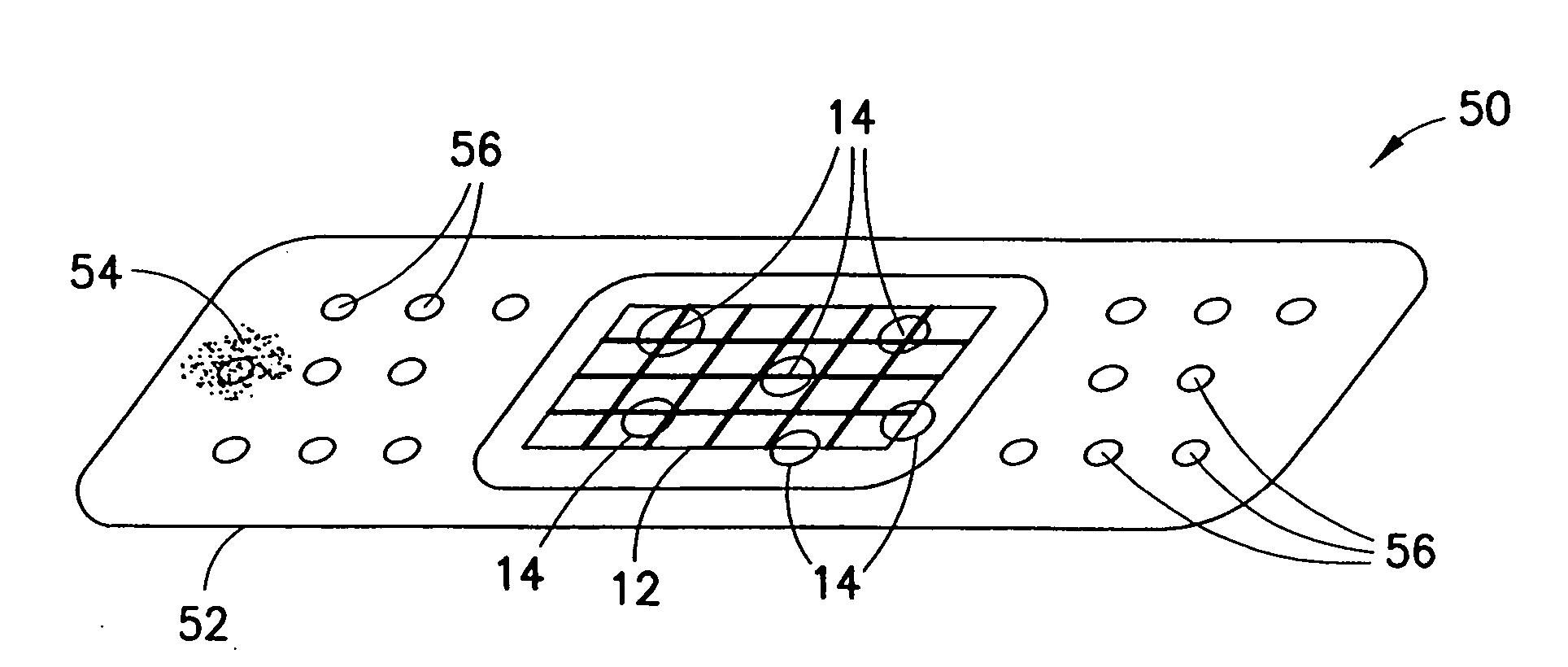
A composition for promoting the formation of clots in blood comprises a zeolite and a binder. The zeolite is adjusted to have a specific moisture content. Processes by which the moisture content is adjusted include drying, re-hydrating, and combinations of drying and re-hydrating. A method of forming the composition comprises the steps of providing a zeolite and adjusting the moisture content such that upon application of the composition to a wound, a heat of hydration is reduced and heat transferred to the wound is reduced. A method of clotting blood flowing from a wound comprises the steps of applying the zeolite to the wound and maintaining the zeolite in contact with the wound for a predetermined amount of time, the zeolite having an adjusted moisture content and being capable of producing a controllable exothermic effect on the wound.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Calcium zeolite hemostatic agent
ActiveUS20050074505A1Promote formationReduce heatBiocideInanimate material medical ingredientsBlood flowCalcium content
A composition for promoting the formation of clots in blood comprises a binder and a zeolite disposed in the binder, the zeolite having an adjusted calcium content. A method of forming a blood-clotting composition comprises the steps of providing a zeolite, combining the zeolite with a binder, and adjusting a calcium content of the zeolite to have an amount of calcium such that upon application of the composition to a wound, a heat of hydration is reduced and thereby heat transferred to the wound is reduced. A method of clotting blood flowing from a wound comprises the steps of applying a zeolite to the wound and maintaining the zeolite in contact with the wound for a predetermined amount of time. The zeolite preferably has an adjusted calcium content and is capable of producing a controllable blood clotting effect on the wound.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Disposable sheath for specula
A speculum sheath which covers a speculum and methods for using the sheath are described herein. A variety of different types of specula may be covered with the sheath, including anal, vaginal, ear, and nasal specula. The sheath is made of a compliant or partially compliant material, including latex, vinyl, natural and synthetic rubbers, silicone, nylon, polyethylene, polypropylene, and non-degradable or degradable elastomers. The material may be transparent or opaque. In the preferred embodiment, the material is transparent. The sheath may contain one or two openings. Optionally, the sheath contains an affixing means on the inside of or at least one of the openings on the sheath to prevent slippage when in contact with the speculum. Optionally, the sheath contains an active agent, such as hemostatic agents, anti-infectives, antibiotics, antimitotics anti-inflammatory, or other chemotherapeutic agents. In the preferred embodiment, the sheath is placed on a vaginal speculum and supports loose vaginal tissue when inserted into a patient. In the most preferred embodiment, the material is transparent so that medical provider may view the lumen.
Owner:ENDOLUMINAL THERAPEUTICS
Clay-based hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
ActiveUS20070275073A1Minimize injuryEliminate feverAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryBandageMaterials science
A device for promoting the clotting of blood comprises a clay material in particle form and a receptacle for containing the clay material. At least a portion of the receptacle is defined by a mesh. Another device comprises a gauze substrate and a clay material disposed on the gauze substrate. Another device is a bandage comprising a substrate, a mesh mounted on the substrate, and particles of a clay material retained in the mesh. A hemostatic sponge comprises a substrate, a hemostatic material disposed on a first surface of the substrate, and a release agent disposed on a second surface of the substrate. The release agent is disposed on the wound-contacting surface of the substrate. When treating a bleeding wound, application of the hemostatic sponge causes at least a portion of the hemostatic material to come into contact with blood through the release agent and through the substrate.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Chitosan wound dressing
InactiveUS20070237811A1Stop the bleedingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGel preparationWound dressing
A composition is described in which chitosan is prepared in a foamed gel that may be layered onto a suitable backing for use as a wound dressing, or the gel may be directly applied to wounds to effect hemostatic activity as a result of the action of the chitosan. The composition of the foamed chitosan gel has added to it medicaments, which include antimicrobial agents, in order to reduce the risk of microbial infections in wounds where hemostatic agents including the chitosan foamed gel preparation can be applied to effect hemostasis.
Owner:SCHERR GEORGE H
Inorganic materials for hemostatic modulation and therapeutic wound healing
InactiveUS20070031515A1Reduced heat of hydrationEliminate side effectsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsWound healingSide effect
The invention provides compositions, methods and devices relating to a silaceous oxide that generates a reduced heat of hydration upon contact with blood. By reducing the heat of hydration, the compositions provide a hemostatic agent that attenuates a tissue burning side effect of conventional hemostatic agents without adversely affecting the wound healing properties of the composition.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Devices and methods for the delivery of hemostatic agents to bleeding wounds
InactiveUS20080097271A1Less aggressive drawingLess aggressive drawing of moistureNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersParticulatesBandage
A hemostatic agent applicable to a bleeding wound to promote the clotting of blood comprises a first component and a second component, both components being in particle form and commingled with each other, and both components having hemostatic properties. A device incorporating such an agent comprises a receptacle for retaining the agent in particulate form therein. At least a portion of the receptacle is defined by a mesh having openings therein through which the blood may flow to come into contact with the particles of the hemostatic agent. A pad for controlling the flow of blood from a bleeding wound comprises a mesh structure and the hemostatic agent retained therein. A bandage applicable to a bleeding wound is defined by a substrate, a mesh mounted on the substrate, and the hemostatic agent retained in the mesh.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Hemorrhage control simulator
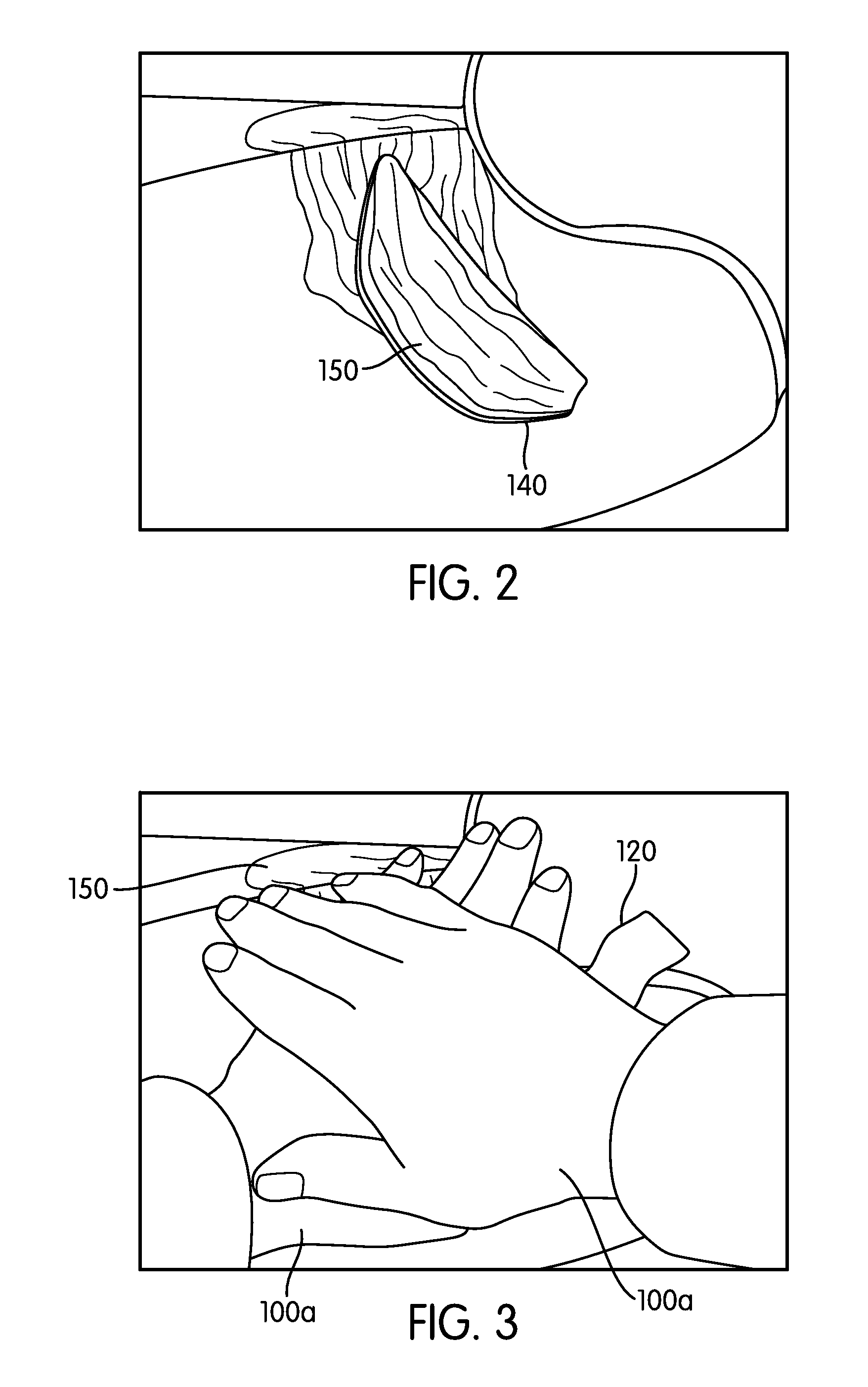
ActiveUS20120045742A1Improve effectivenessRetention of trainingEducational modelsTouch PerceptionTourniquet time
A simulator trains for hemorrhage control using hemostatic agents, tourniquets, and / or other hemorrhage control techniques in a simulator that works with a wide variety of existing human surrogates. The simulator merges a live video feed of the surrogate and trainee's hands (or objects interacting with the surrogate) with a computer-generated visual representation of the wound and hemorrhaging blood to provide an immersive display experience to the trainee without requiring different surrogates for different simulated wounds. The trainee may wear pulse-generating glove(s) that simulate the patient's pulse where the trainee's finger tip contacts the surrogate. A sensorized substrate (e.g., load sensors, haptic output generators) may automatically be moved between the trainee and the surrogate to sense interaction with the surrogate and provide haptic feedback. The substrate may replace the surrogate altogether. The simulator may alternatively simulate events and objects other than wounds and humans.
Owner:SIMQUEST
Heat mitigating hemostatic agent
InactiveUS20080125686A1Less aggressive drawingLess aggressive drawing of moistureSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismReticular formationBandage
A hemostatic agent in the form of particles comprises a first component and a second component bound thereto, each component having hemostatic properties. Additional components may also be included. The first component may be a zeolite and the second component may be clay. A device for promoting the clotting of blood comprises a receptacle for retaining particles of a hemostatic agent therein, at least a portion of the receptacle being defined by a mesh. A pad for controlling bleeding comprises a mesh structure defined by openings sized to accommodate the flow of blood therethrough and also by a hemostatic agent retained in the mesh structure. A bandage applicable to a bleeding wound comprises a substrate, a mesh mounted on the substrate, and a hemostatic agent retained in the mesh. The mesh is defined by a plurality of members arranged to define openings through which blood may flow.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Cavity-filling biopsy site markers
InactiveUS20050143656A1Easy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesAnesthetic AgentMaximum dimension
The invention provides materials, devices and methods for marking biopsy sites for a limited time. The biopsy-marking materials are ultrasound-detectable bio-resorbable powders, with powder particles typically between about 20 microns and about 800 microns in maximum dimension, more preferably between about 300 microns and about 500 microns. The powders may be formed of polymeric materials containing cavities sized between about 10 microns and about 500 microns, and may also contain binding agents, anesthetic agents, hemostatic agents, and radiopaque markers. Devices for delivering the powders include tubes configured to contain the powders and to fit within a biopsy cannula, the powders being ejected by action of a syringe. Systems may include a tube containing powder, and a syringe containing sterile saline. The tube may be configured to fit within a biopsy cannula such as a Mammotome® or SenoCor 360™ cannula.
Owner:SENORX
Clay-based hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
ActiveUS7604819B2Minimizing discomfort and further injuryEliminate feverPowder deliveryPhysical/chemical process catalystsPolyolGlycerol
A hemostatic device for promoting the clotting of blood includes a gauze substrate, a clay material disposed on the gauze substrate, and also a polyol such as glycerol or the like disposed on the gauze substrate to bind the clay material. When the device is used to treat a bleeding wound, at least a portion of the clay material comes into contact with blood emanating from the wound to cause the clotting. A bandage that can be applied to a bleeding wound to promote the clotting of blood includes a flexible substrate and a gauze substrate mounted thereon. The gauze substrate includes a clay material and a polyol. A hemostatic sponge also includes a gauze substrate and a dispersion of hemostatic material and a polyol on a first surface of the substrate.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Clay-based hemostatic agents and devices for the delivery thereof
ActiveUS20100228174A1Minimize injuryEliminate feverPowder deliveryPhysical/chemical process catalystsBiomedical engineeringHemostatic Agent
Disclosed are device for promoting the clotting of blood comprising a clay material and a release agent. In some embodiments, the clay material is disposed within a substrate and the release agent is disposed within a mesh. The release agent can be configured to make direct contact with a bleeding wound when the device is in particle form and the clay material can promote hemostasis.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com