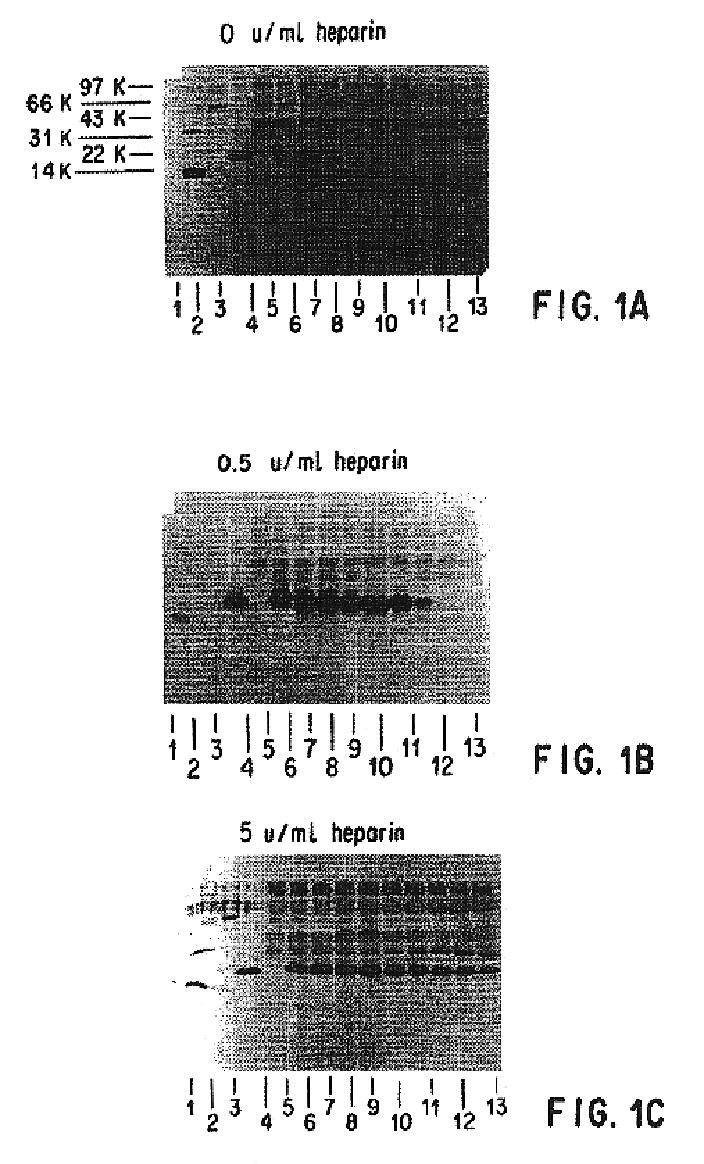
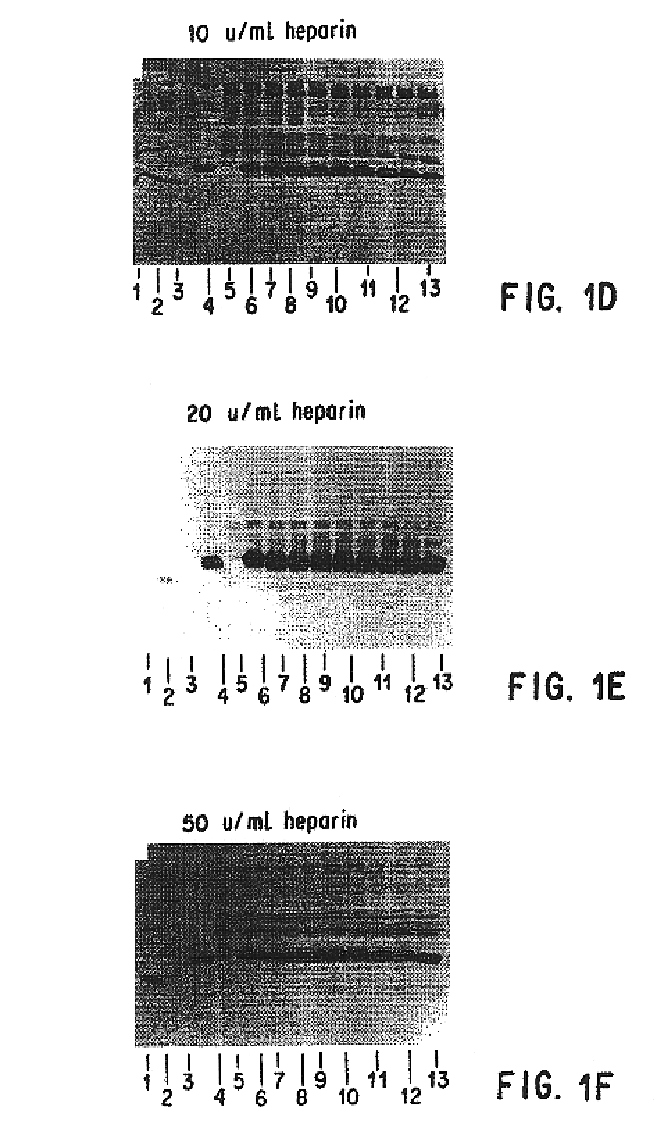
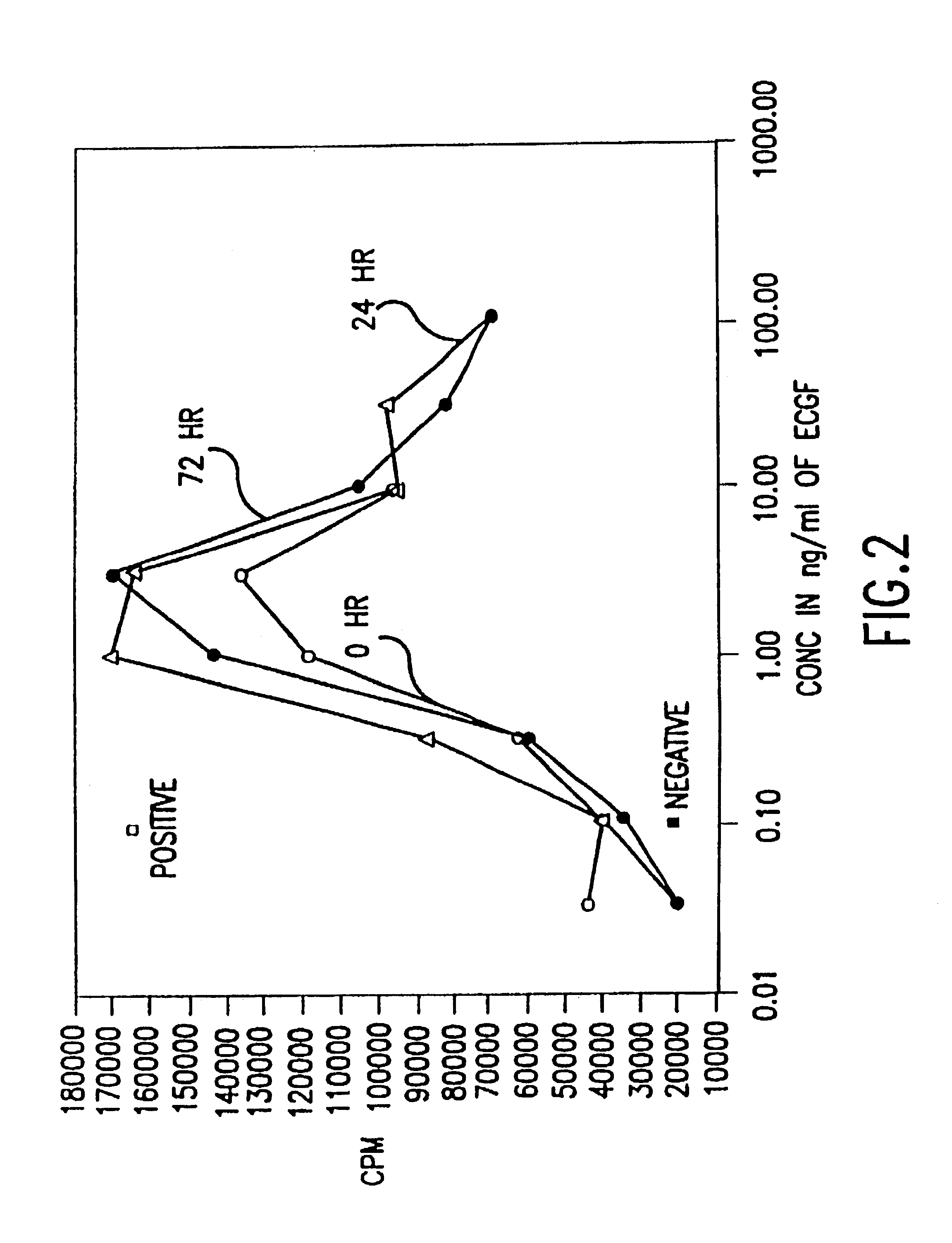
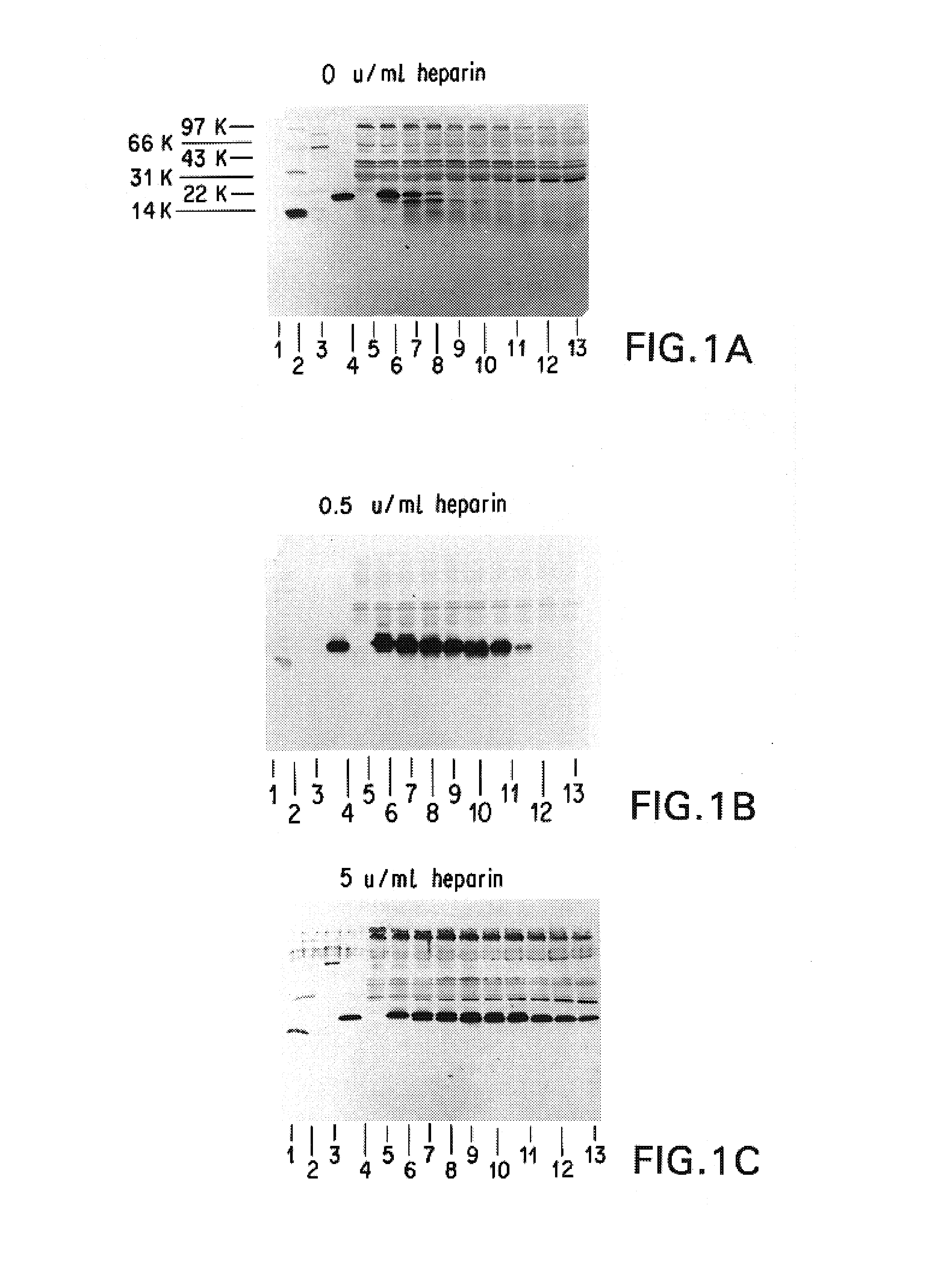
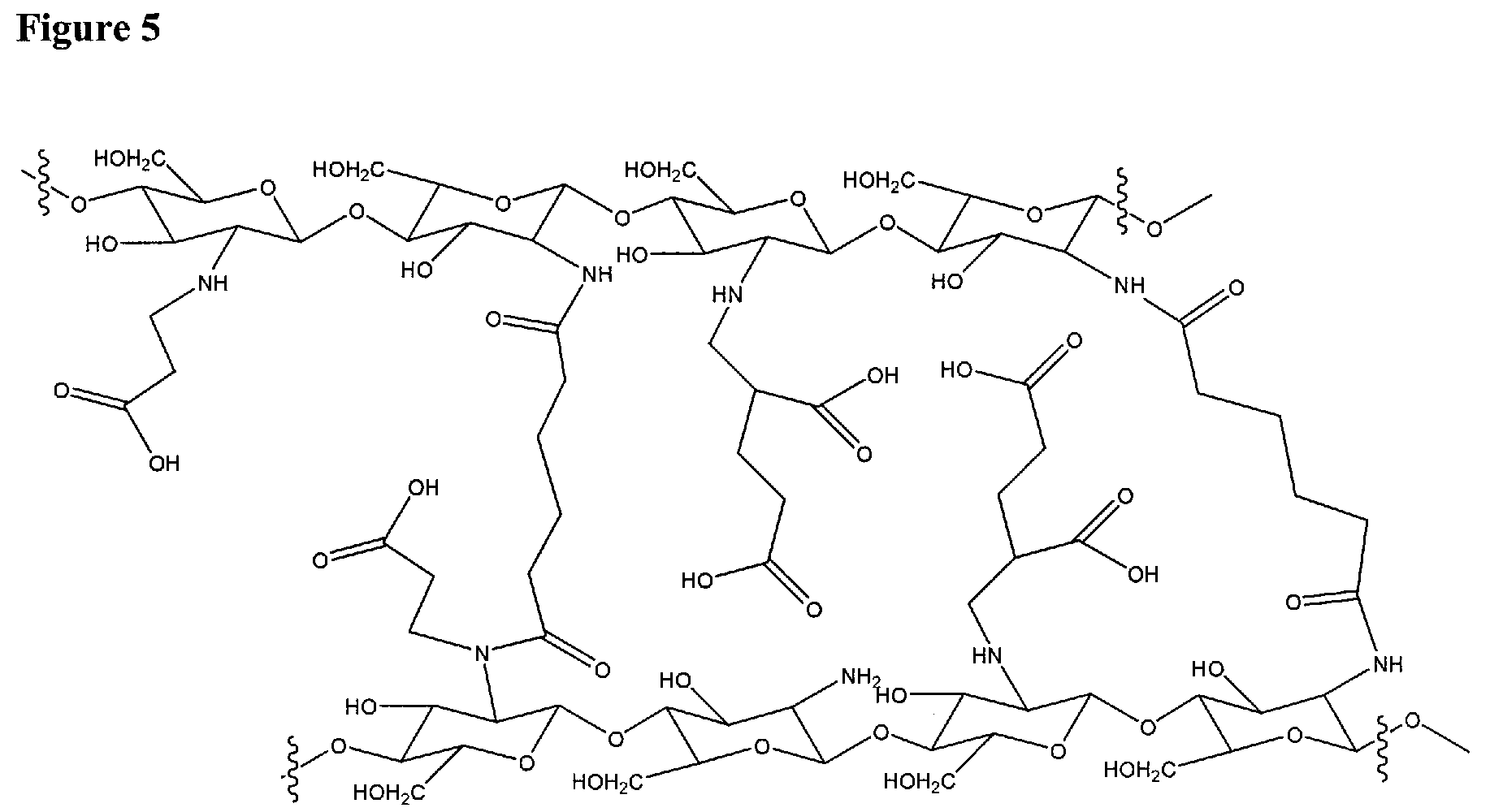
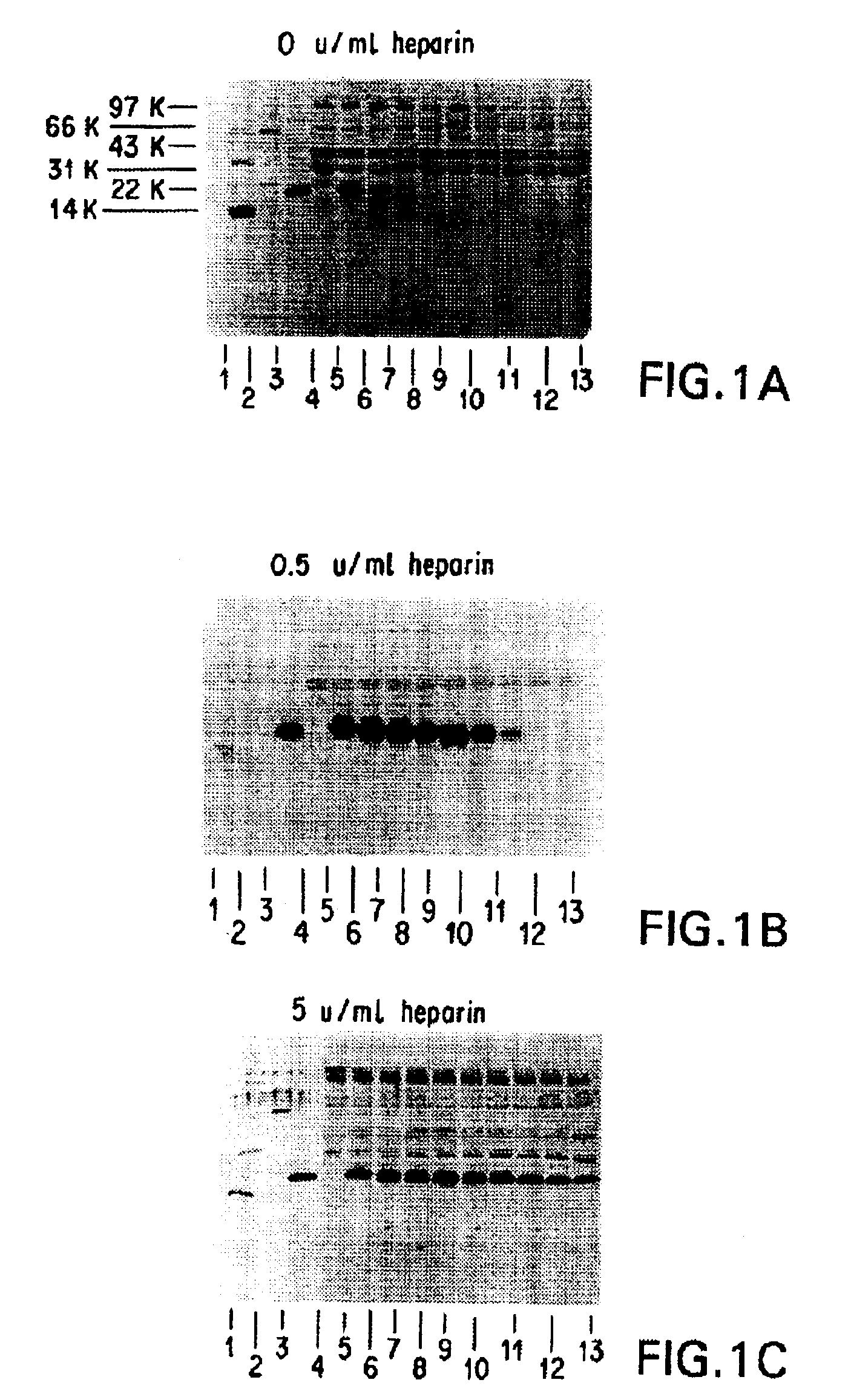
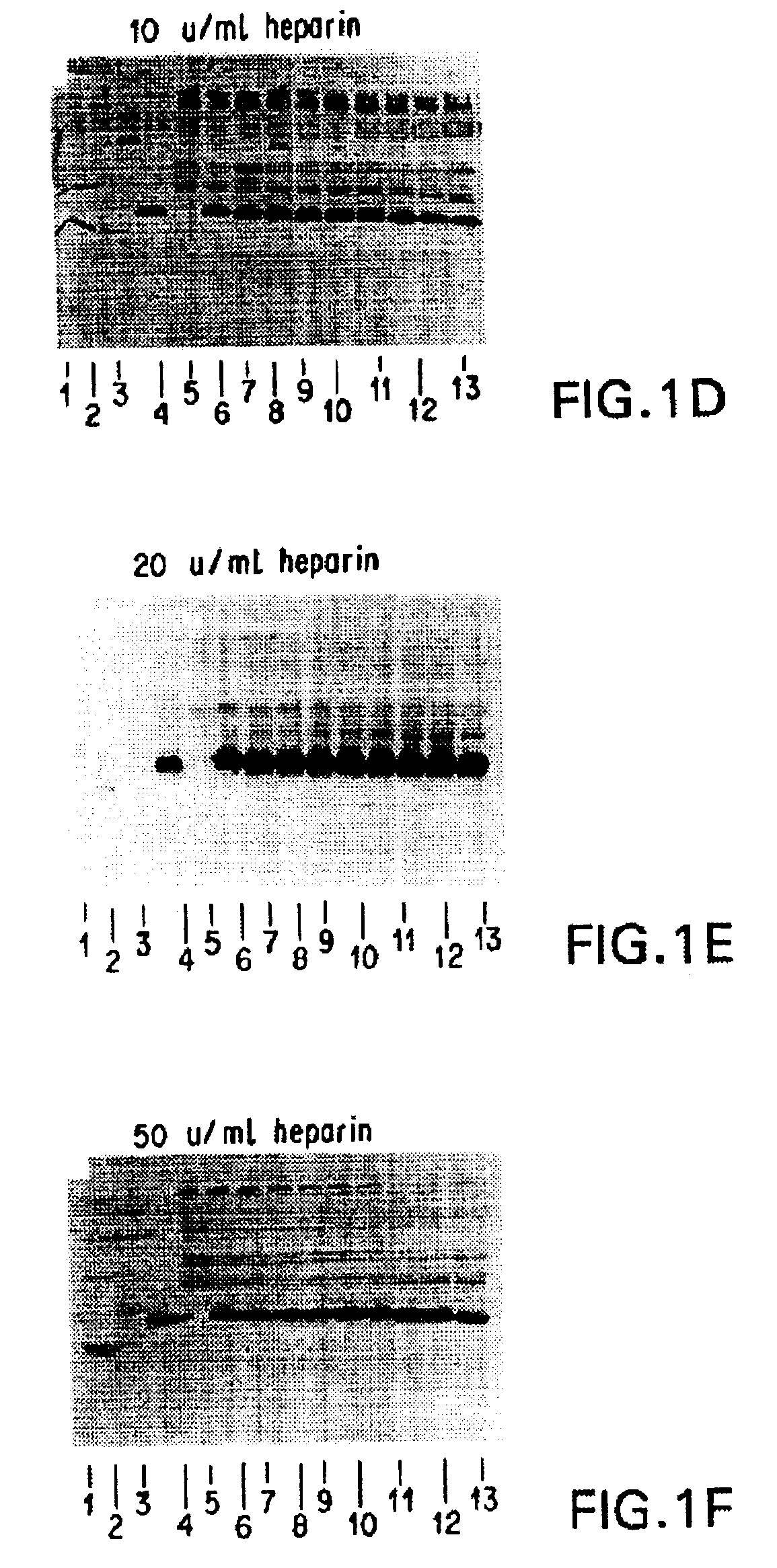
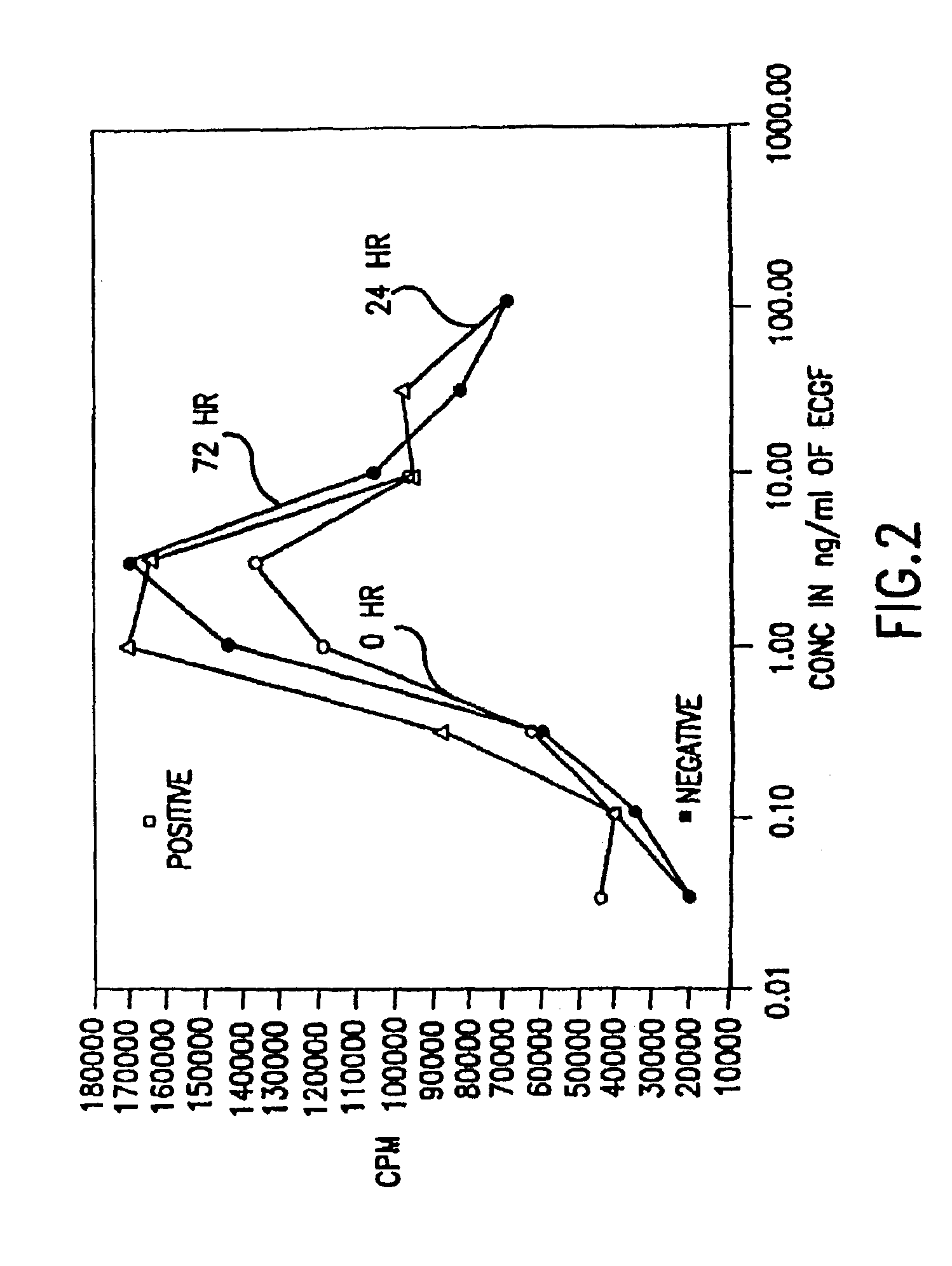
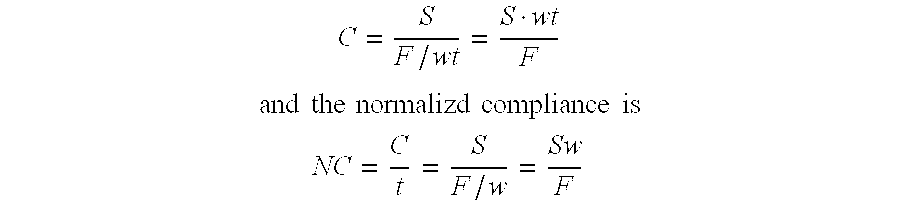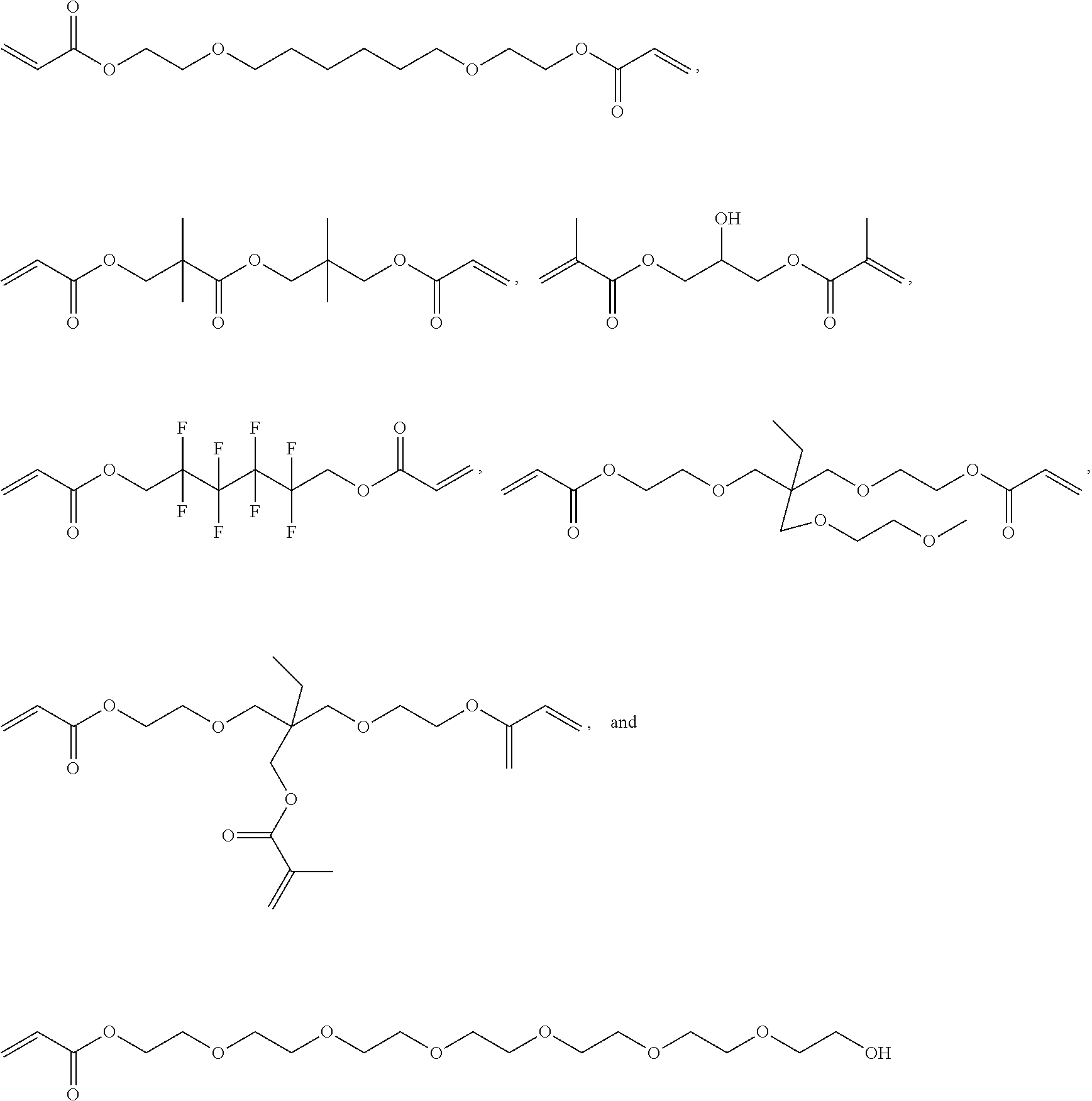Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Tissue sealant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tissue sealants are the products those binds and close the defect tissues. Hemostasis is a complex phenomenon between Platelets, Plasma Proteins, Coagulation and fibrinolysis pathways. Constriction of blood vessel to reduce blood flow, Platelets are activated at site of injury...
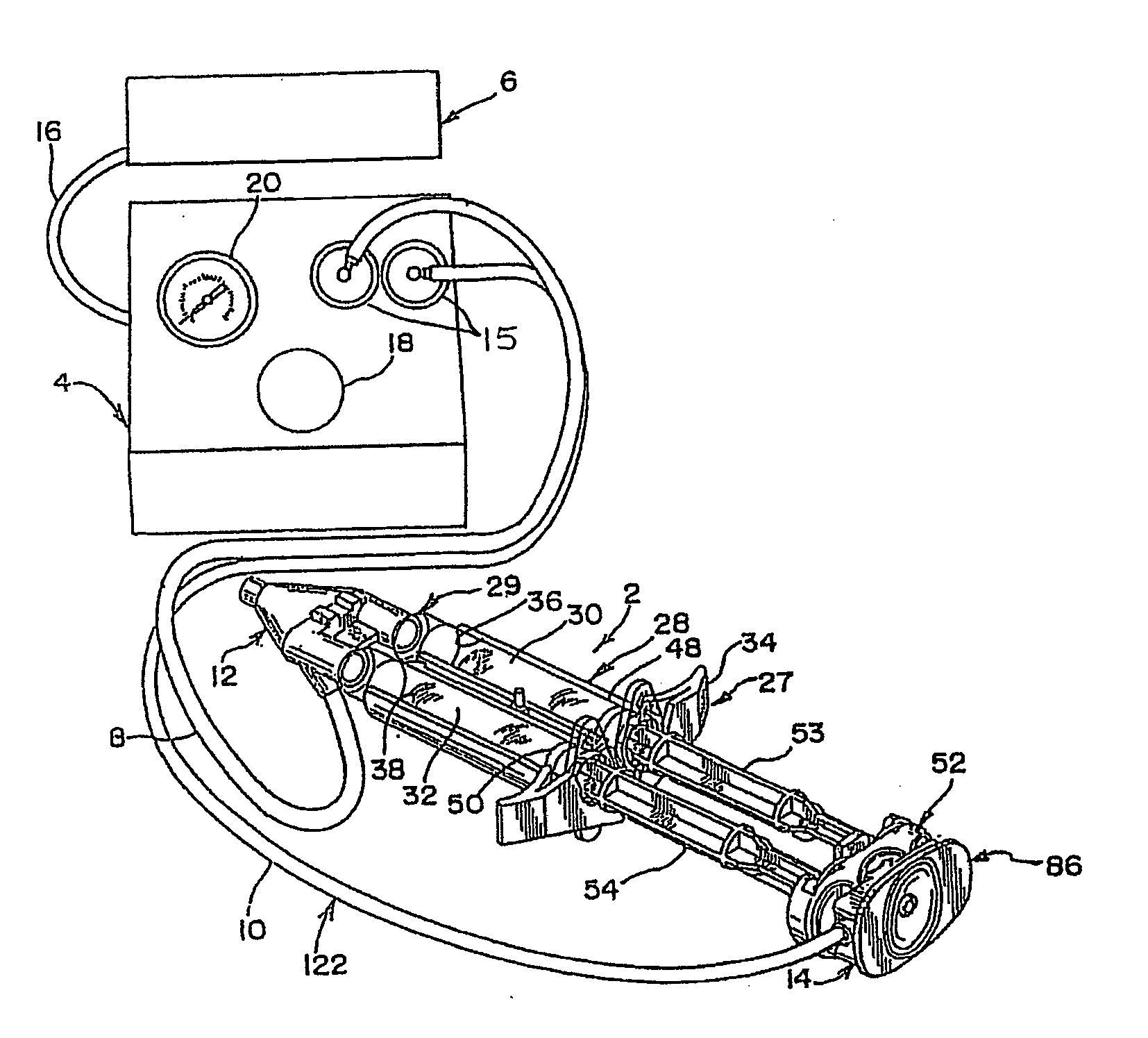
Apparatus for applying tissue sealant
InactiveUS6132396AEasy to fillEasy to assembleLiquid surface applicatorsSurgeryTissue sealantGear wheel
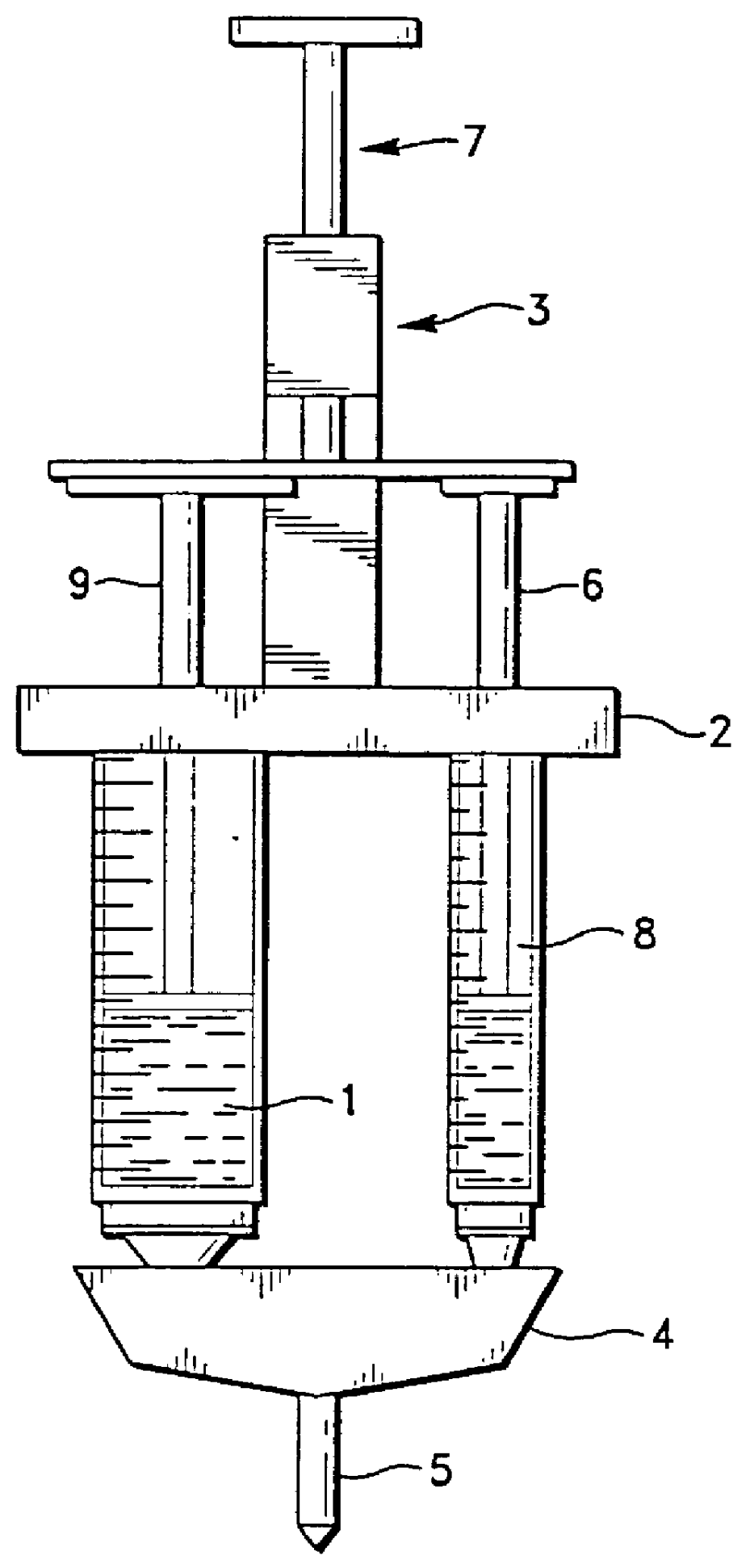
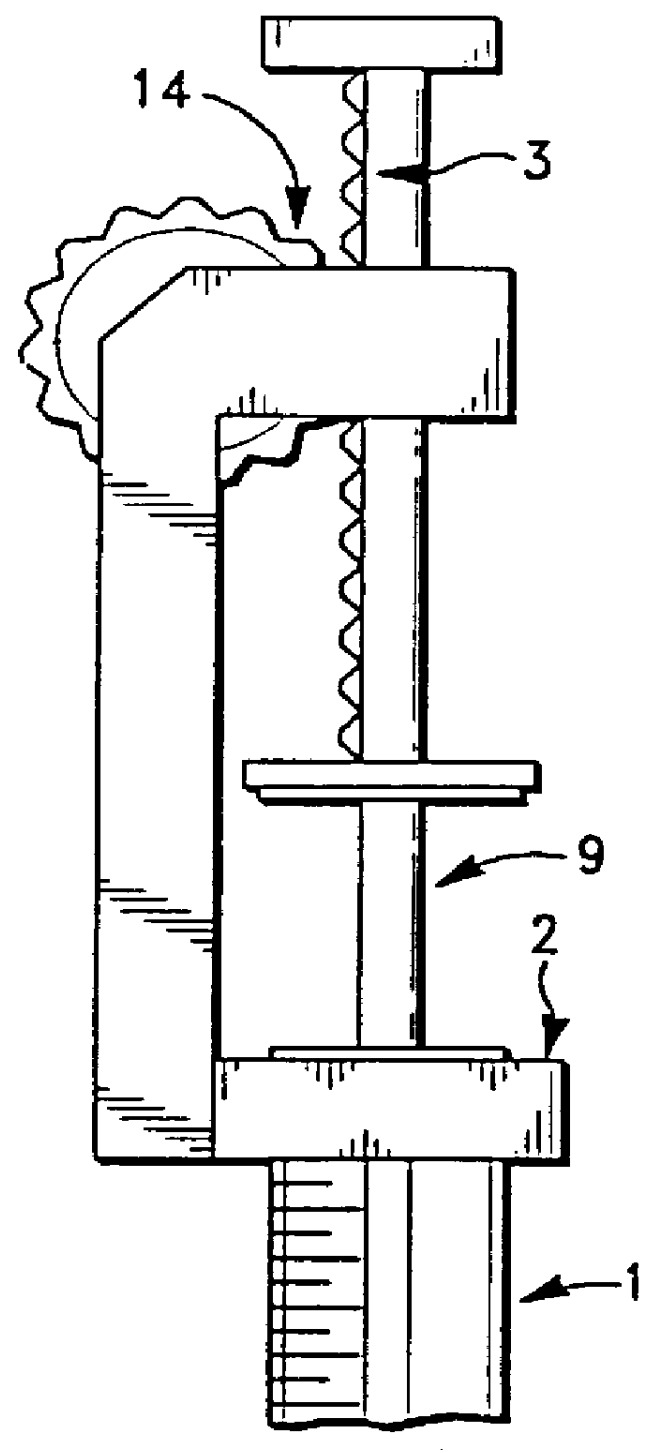
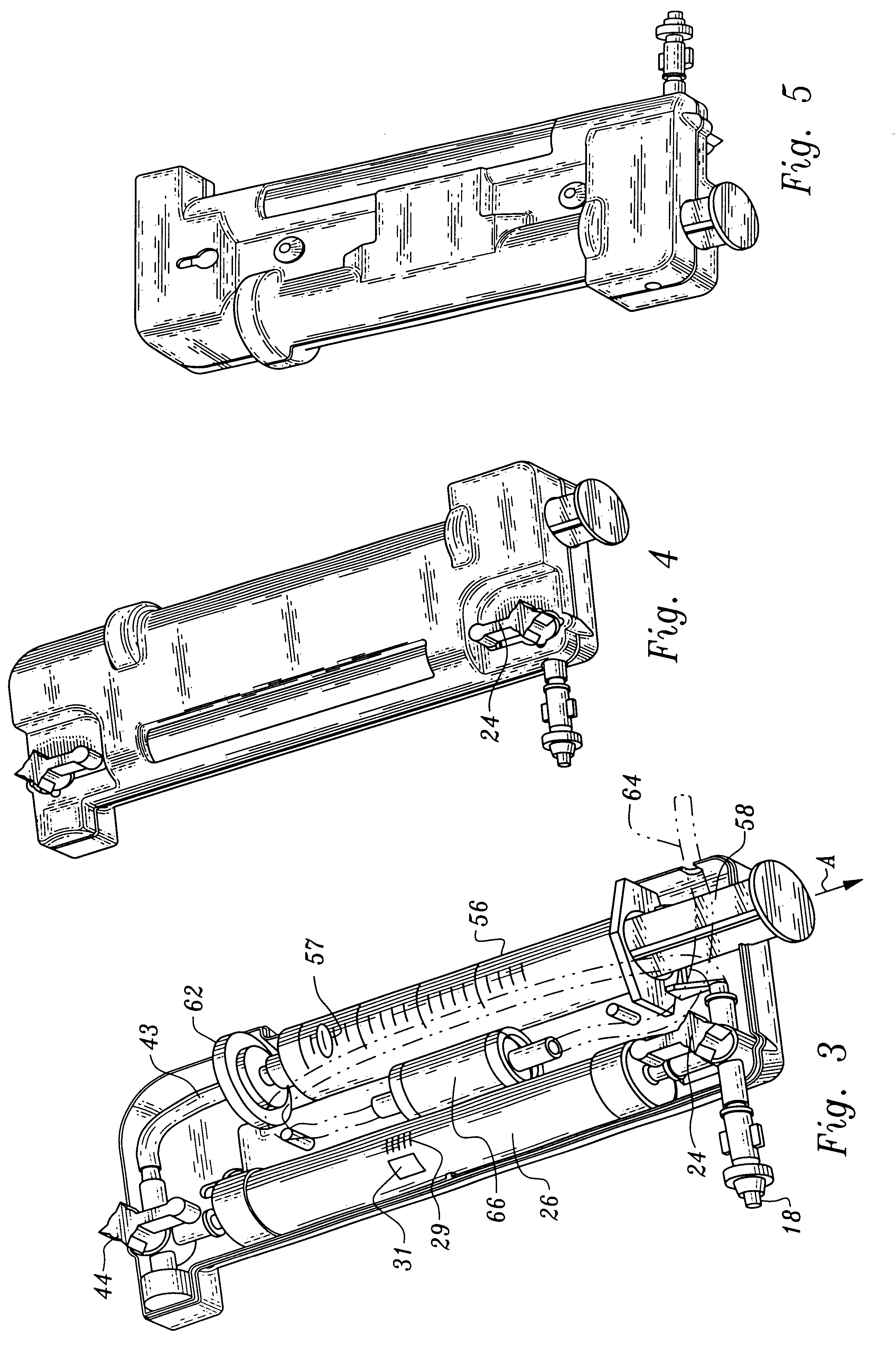
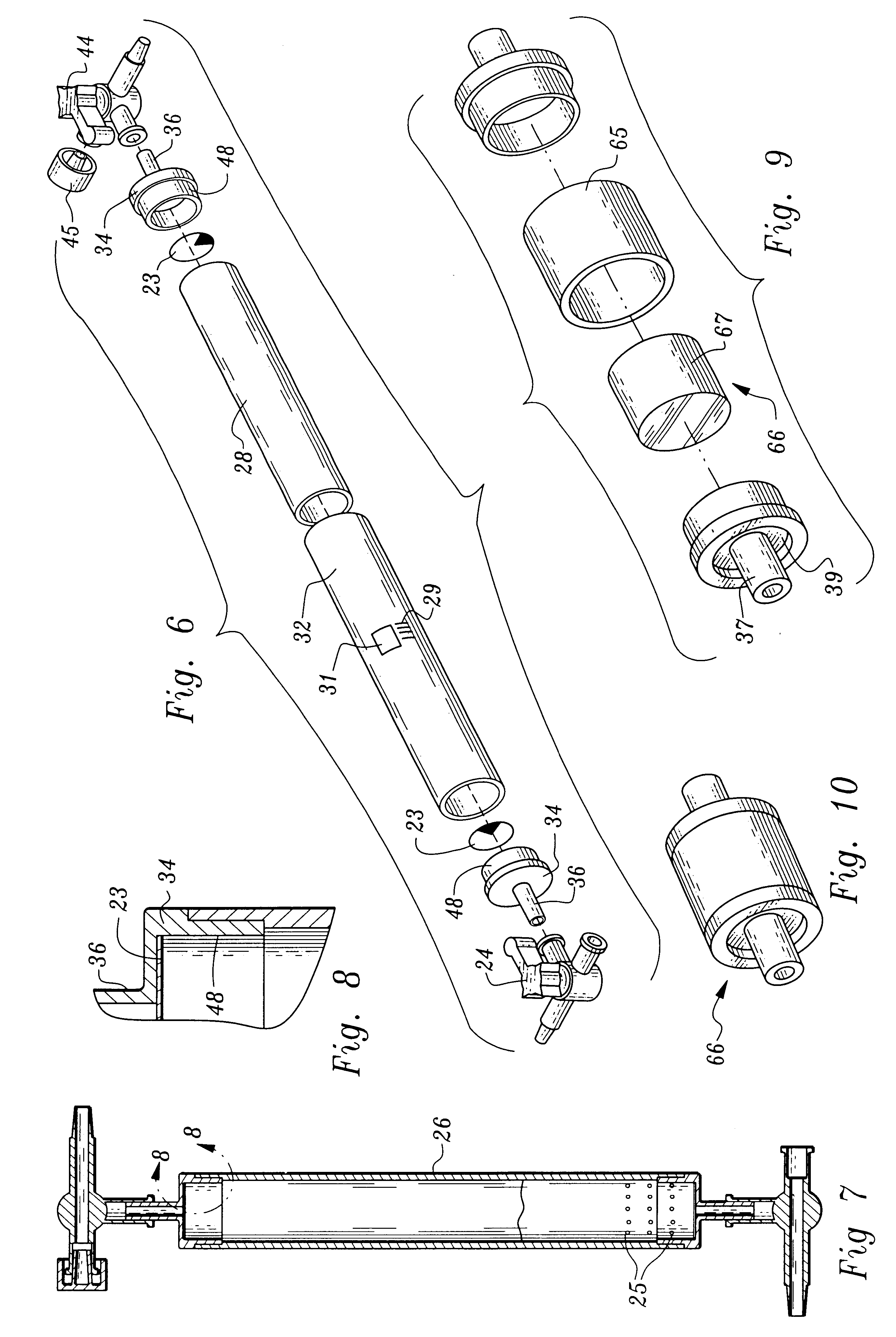
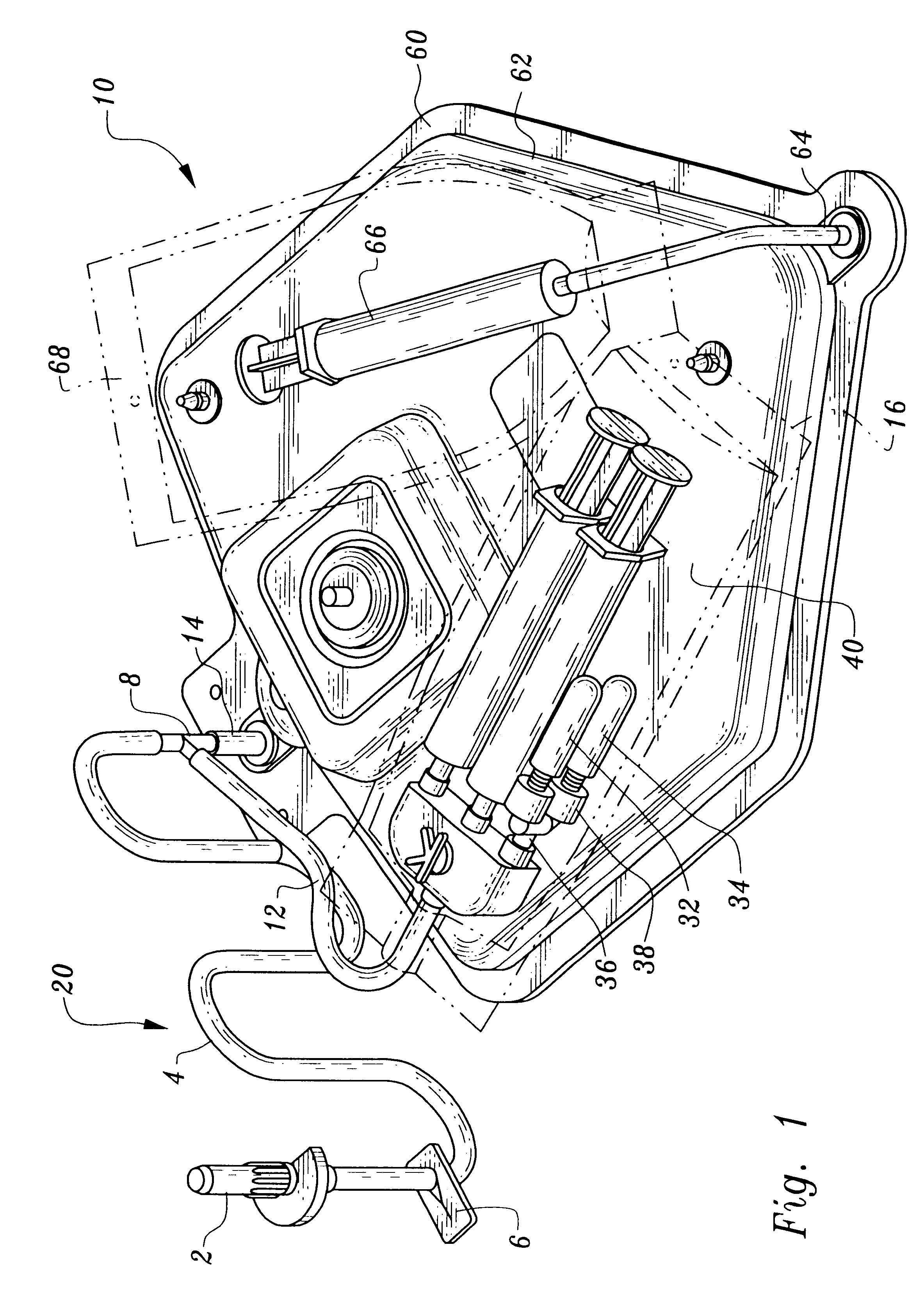
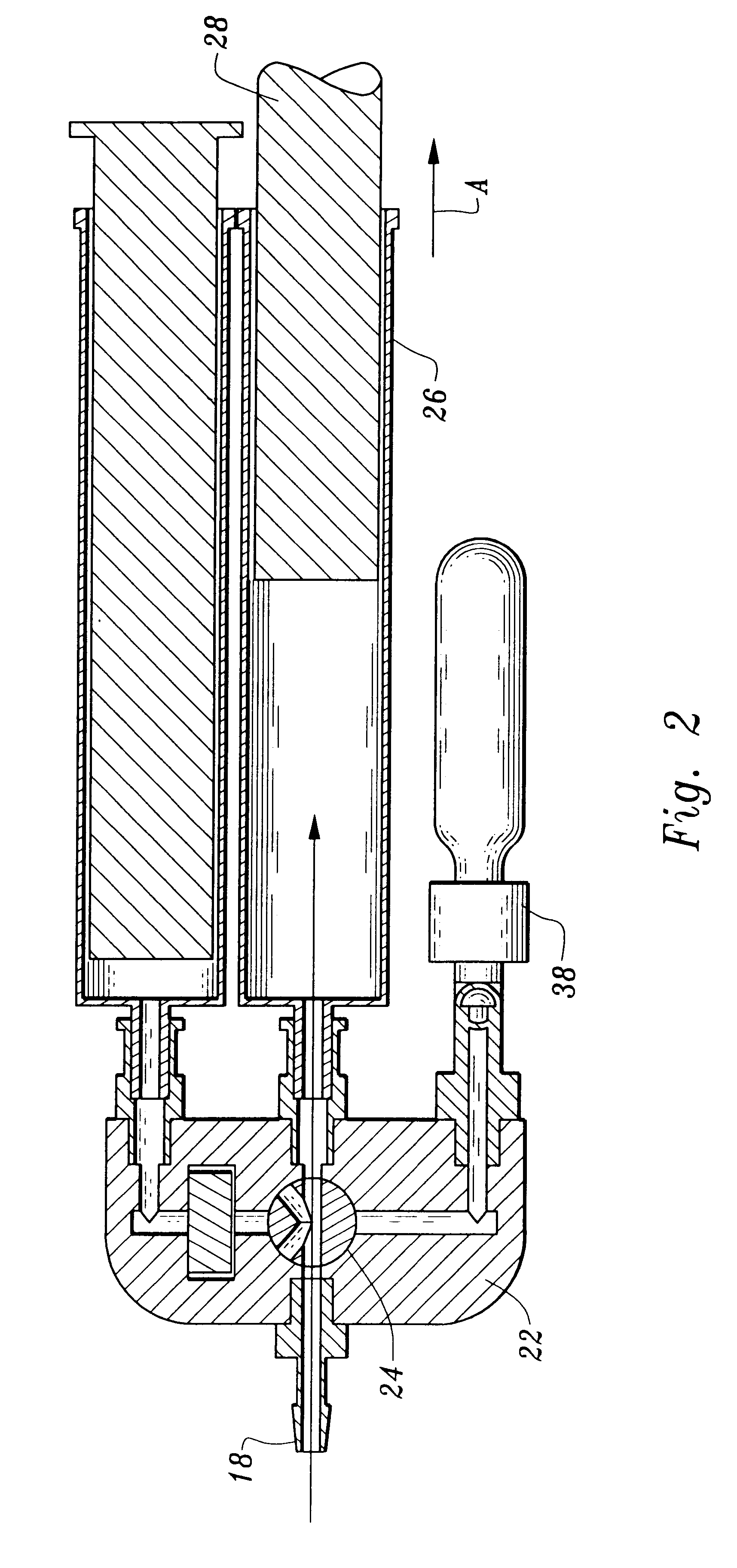
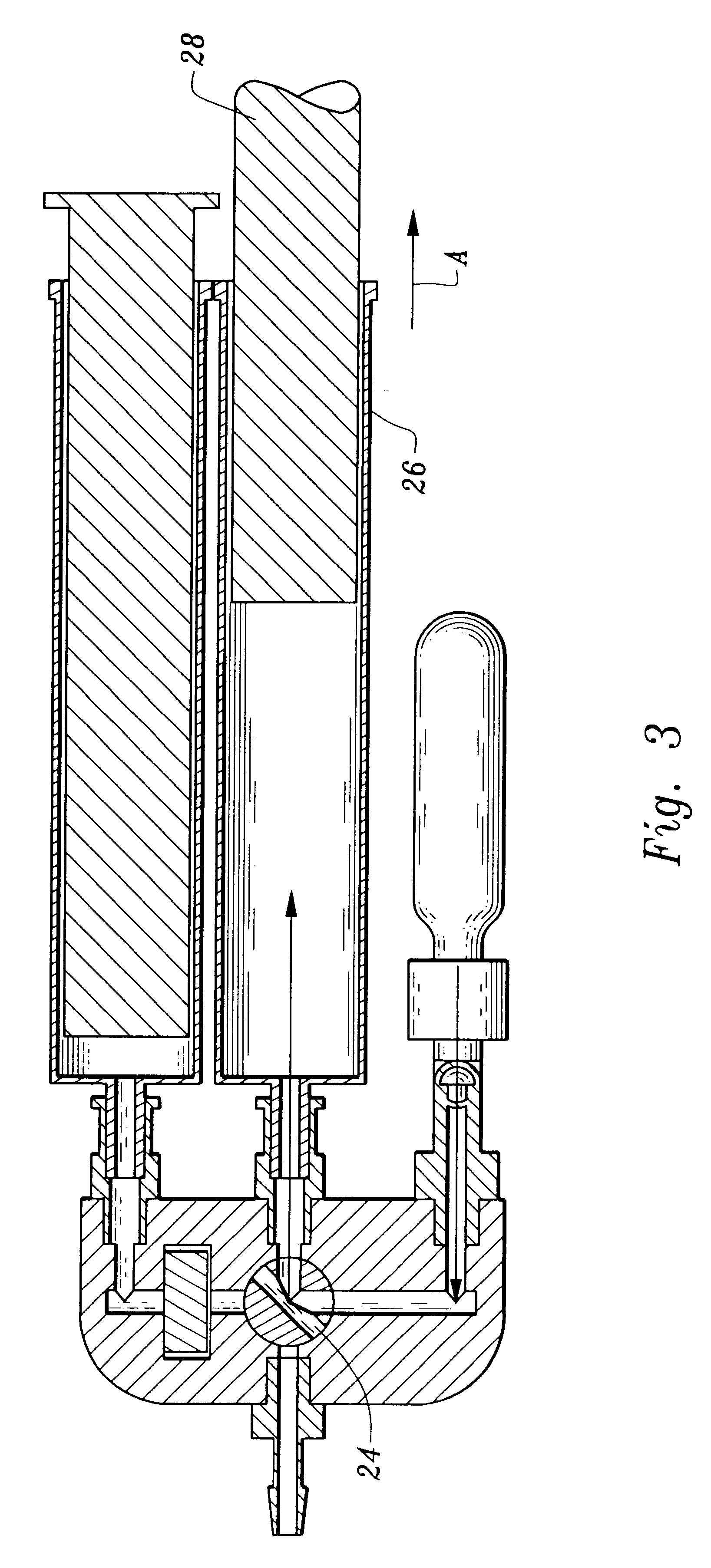
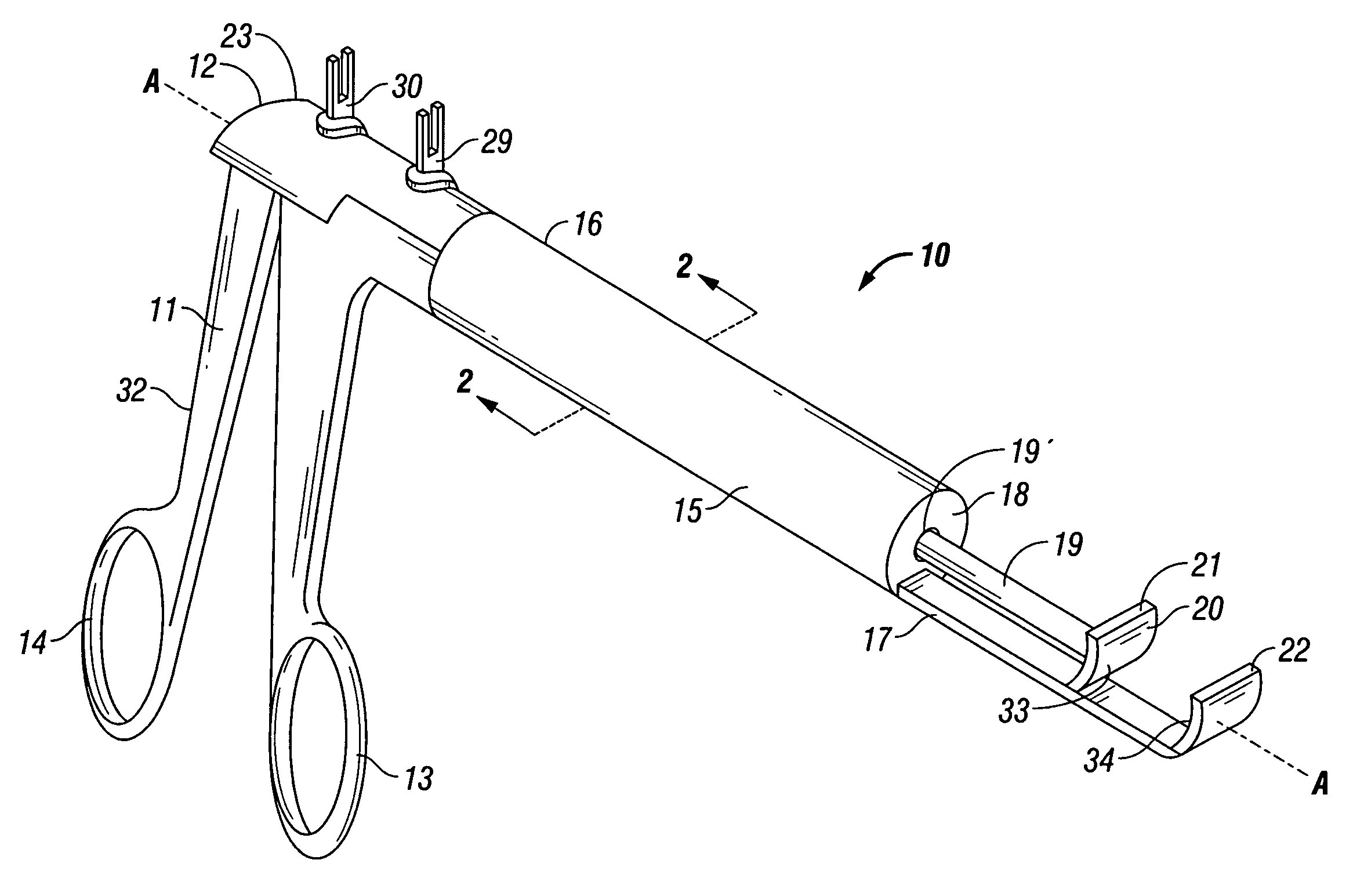
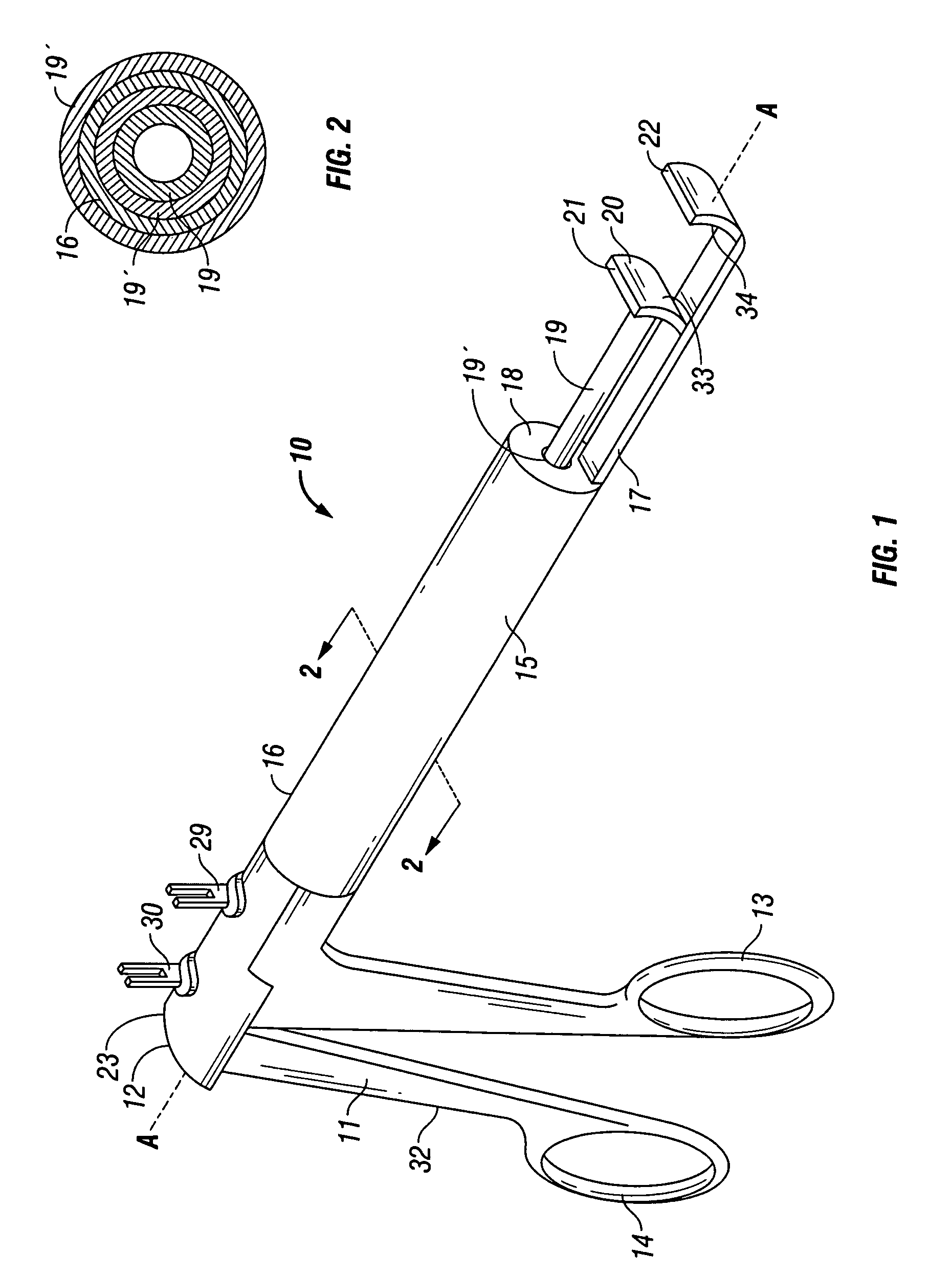
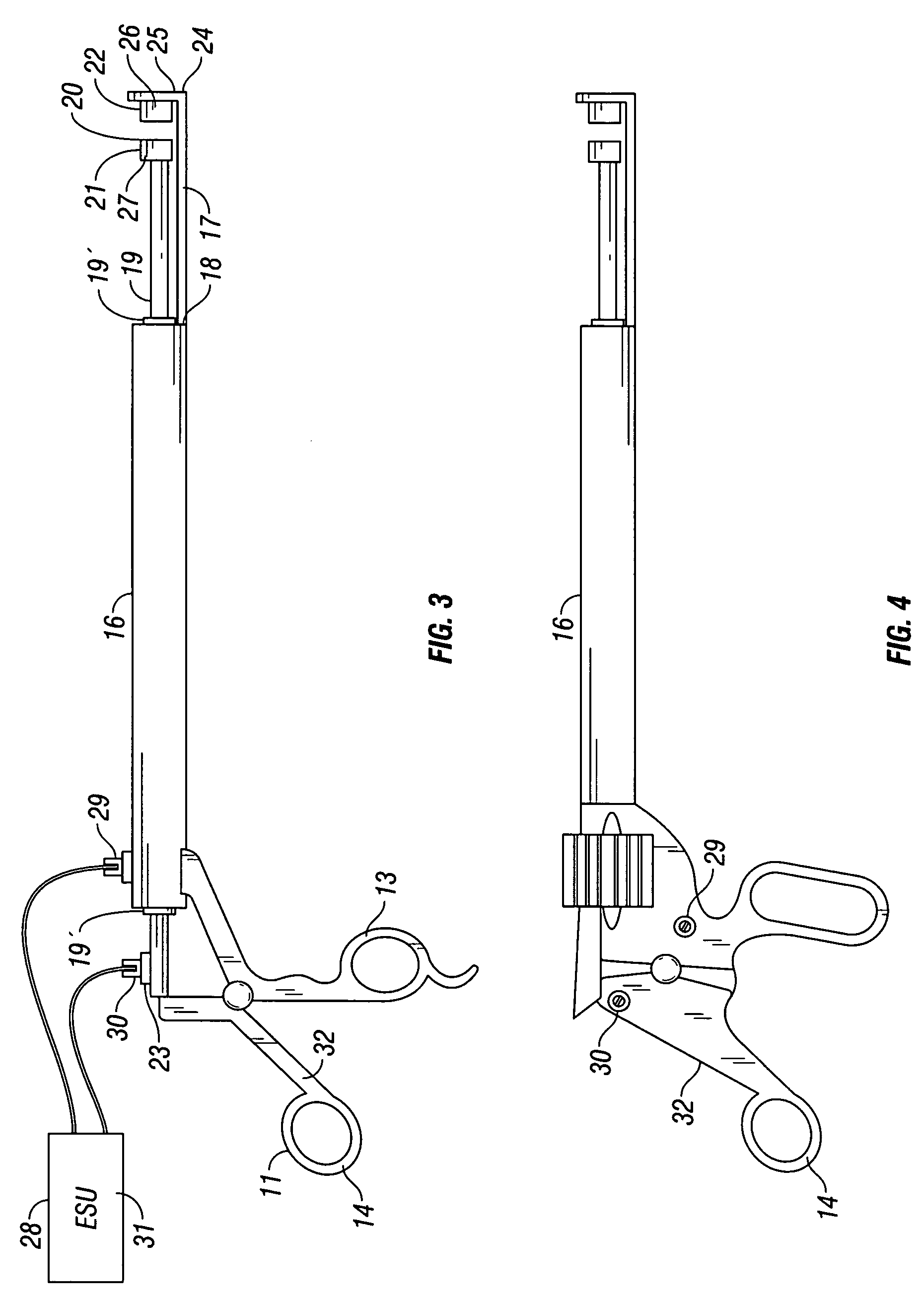
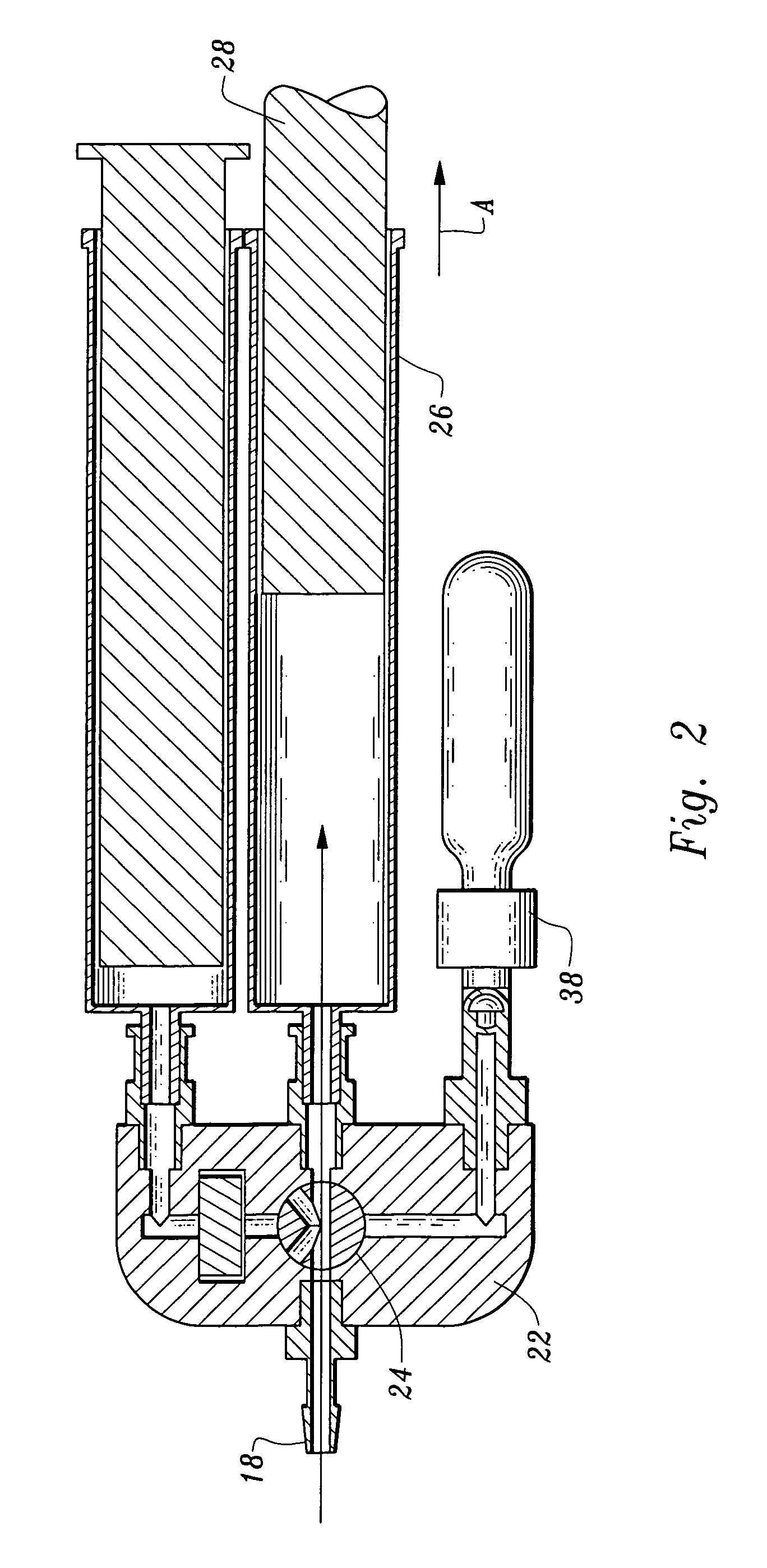
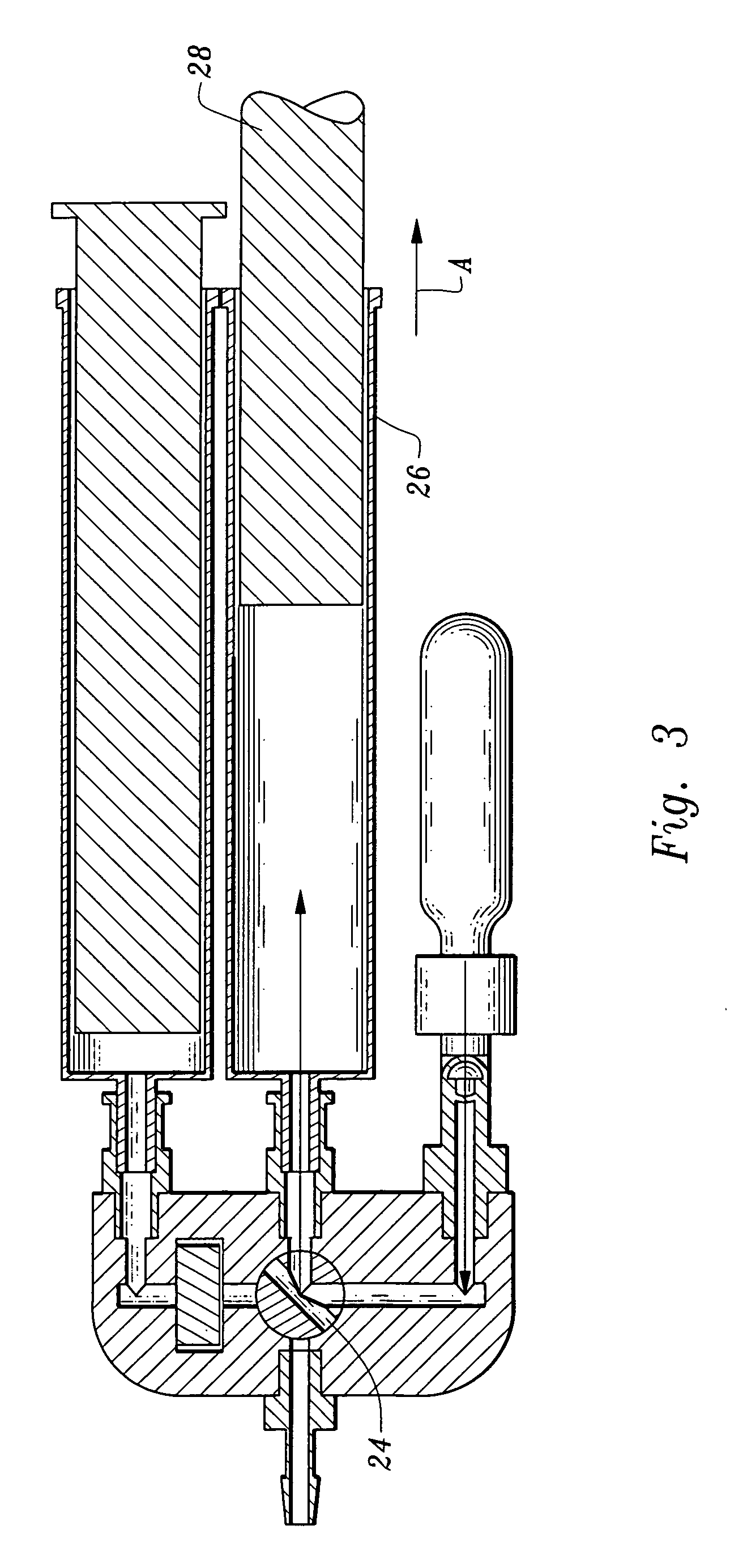
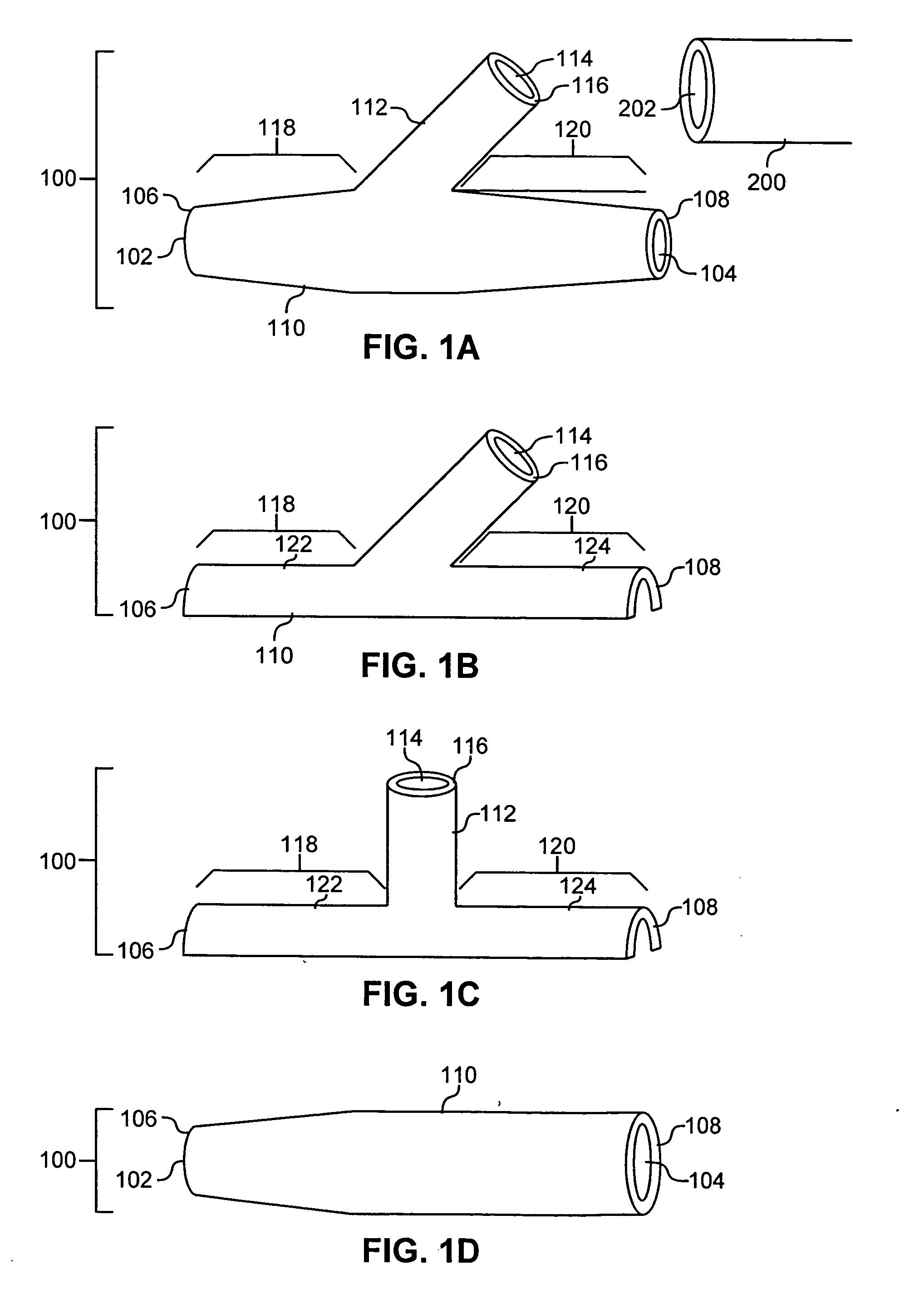
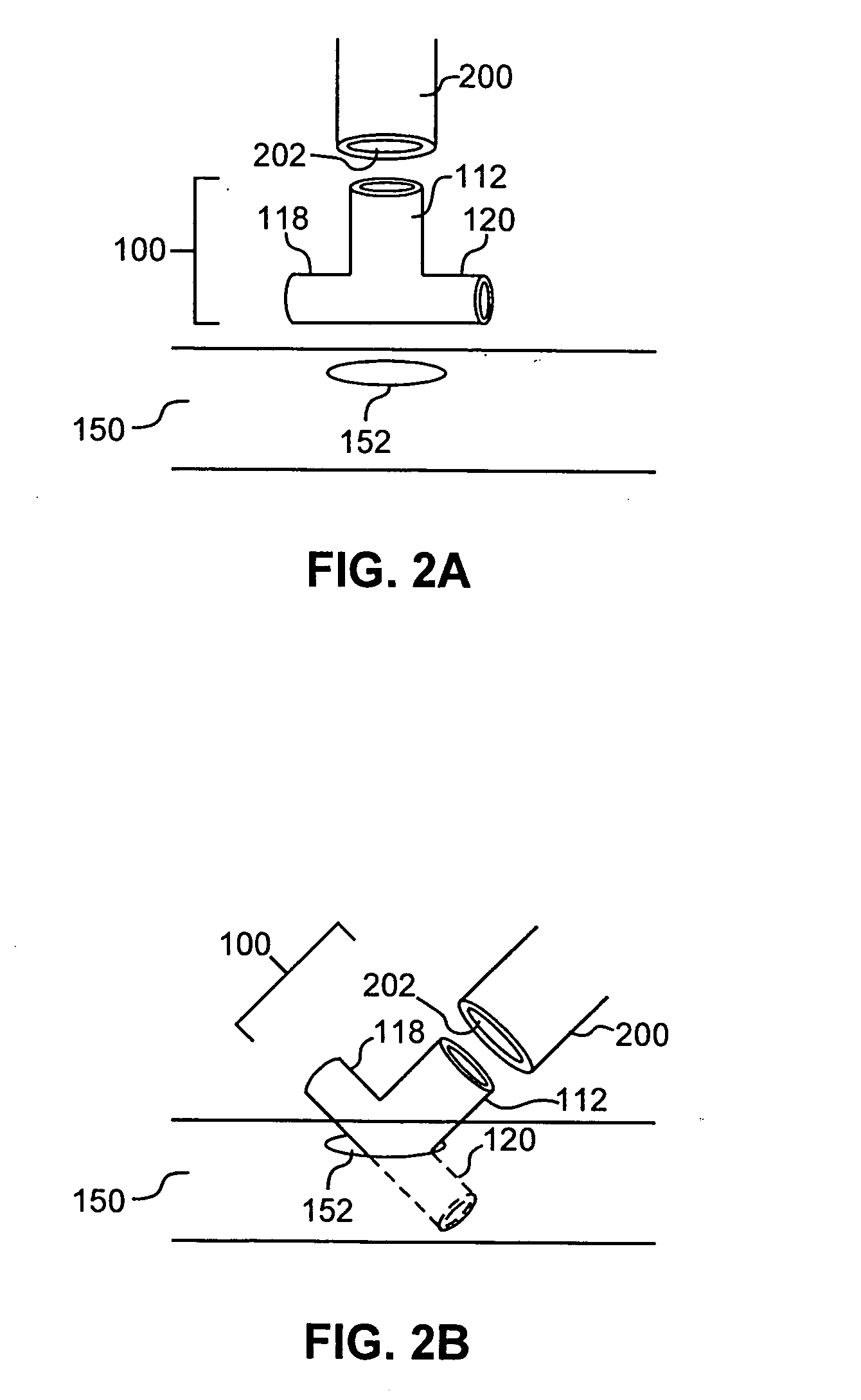
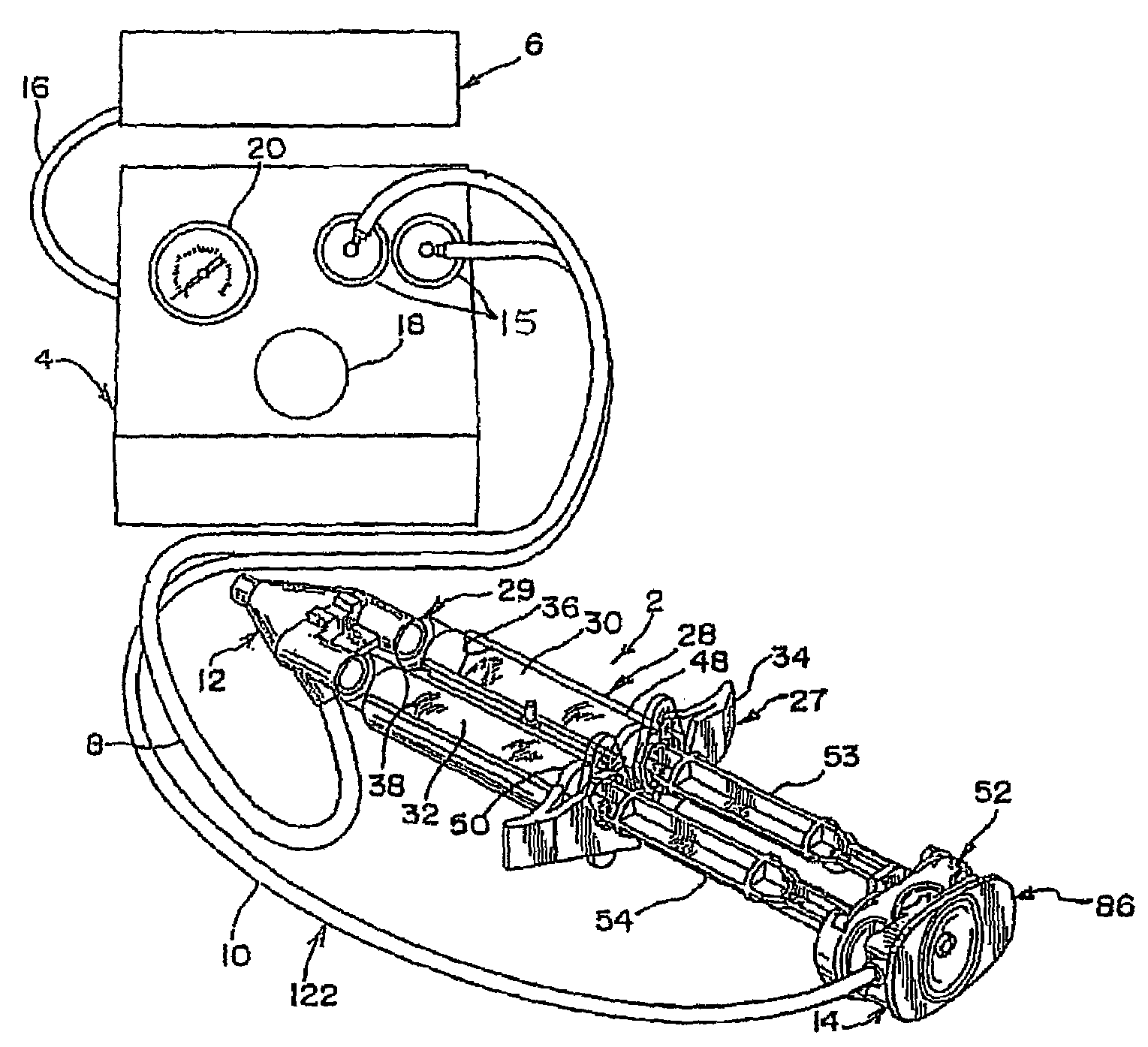
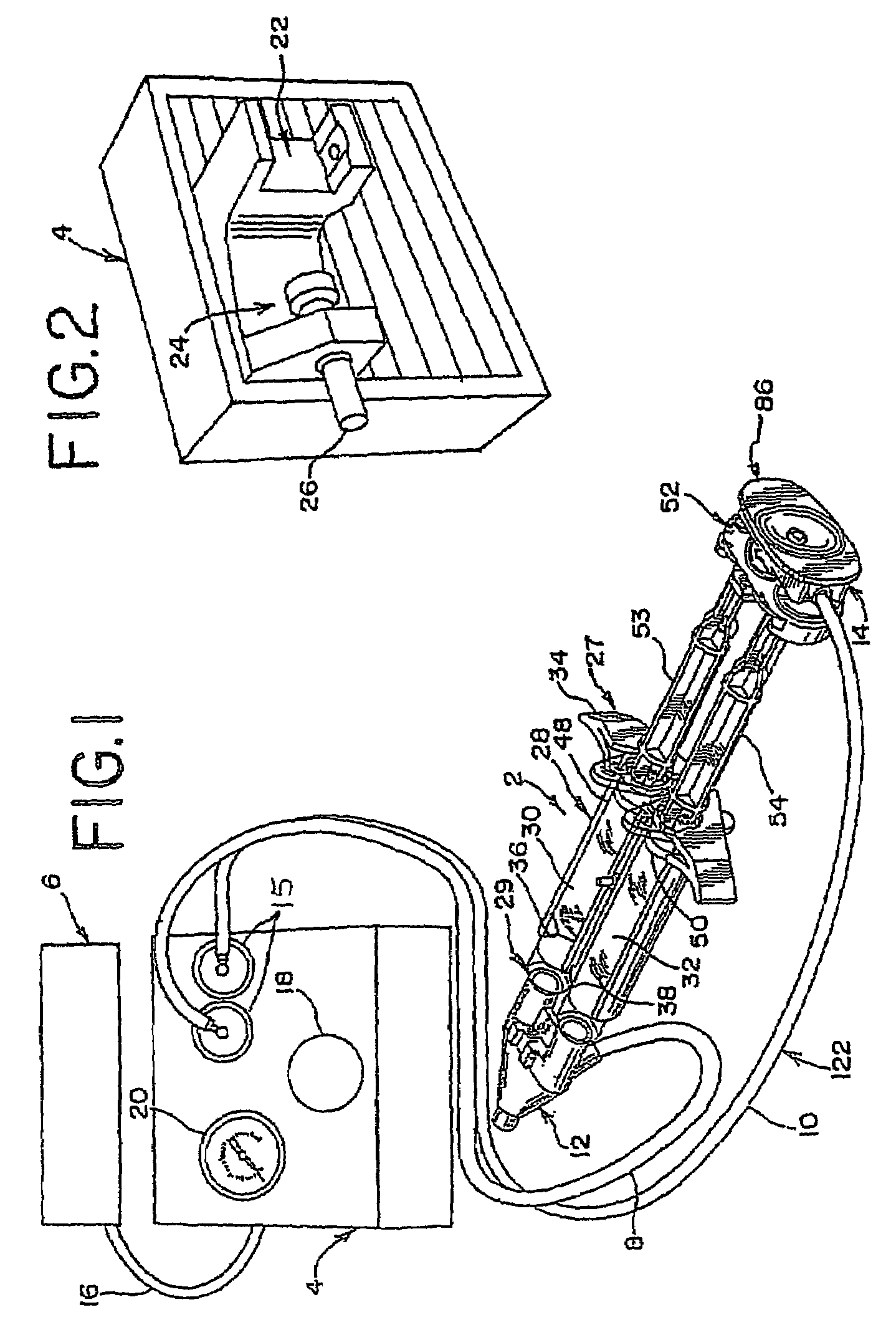
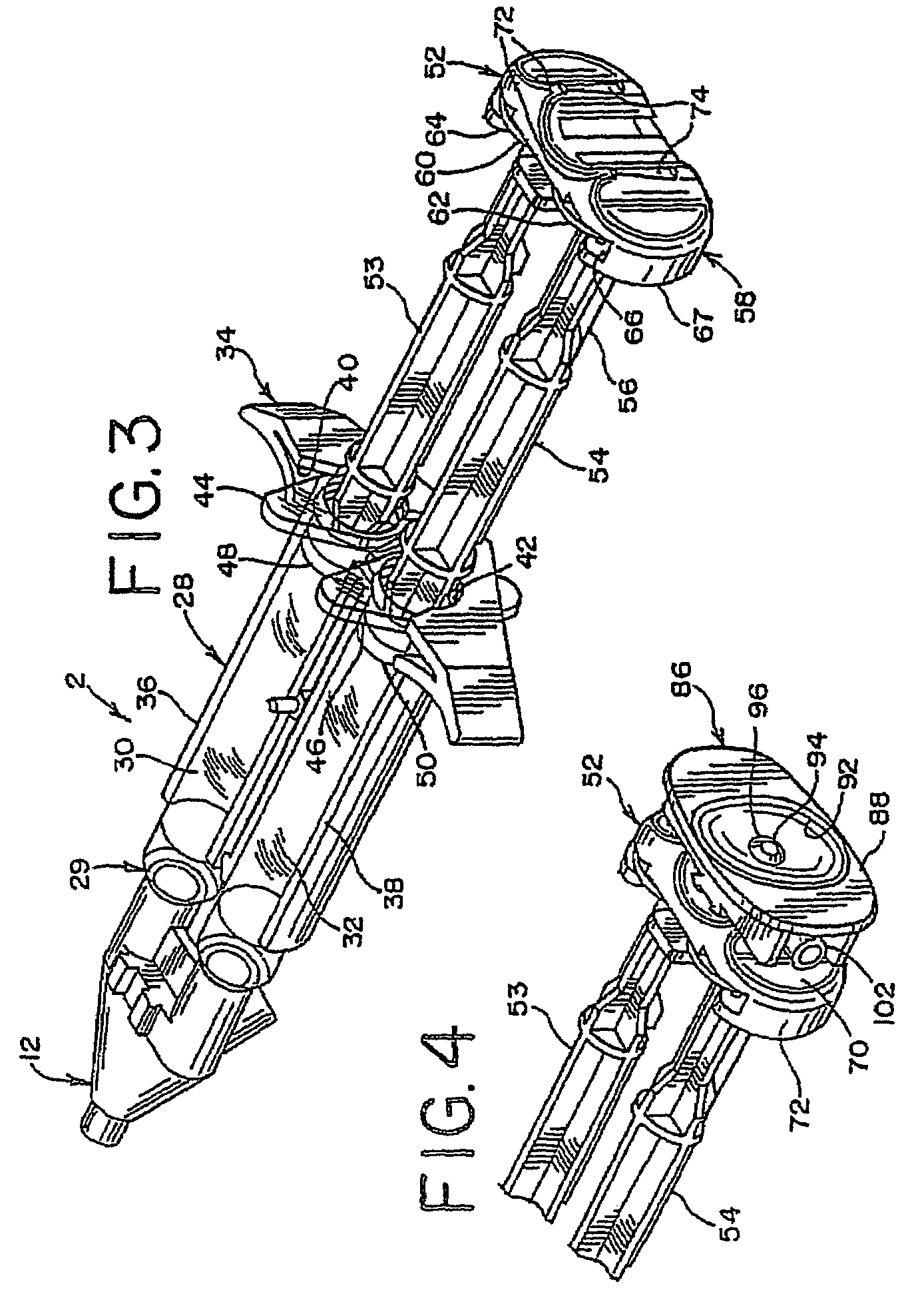
A device and method for applying a fibrinogen-based tissue sealant to seamlessly connect human or animal tissues or organ parts, to seal wounds, stop bleeding and the like by mixing fibrin or fibrinogen with blood clot-promoting coagulation factors are disclosed. The device includes two cylindrical compartments for separately containing the separate fluid components of the sealant preparation, which are simultaneously displaced from the respective compartments by plungers commonly depressable with the same effective strokes. The plungers may be depressed directly or by a common mechanism (e.g., rack and pinion) for accurately controlling the rate of dispensing fluid. The cylindrical compartments are of the same or different cross-sectional area and are arranged either concentrically or side-by-side. The device further includes structure for merging the two fluid components within an outer sleeve housing an inner needle. The sleeve and needle contain conduits for the flow of the two fluid sealant components as they are expressed from the respective compartments. Also disclosed are a convenient device for filling the two compartments, structure for mixing the fluid components, and for atomizing the effluent sealant fluid stream (i.e., spraying).
Owner:PLASMASEAL
Method for preparing thrombin for use in a biological glue
InactiveUS6472162B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component and the clotting and adhesive proteins component are harvested simultaneously from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Apparatus and method of preparation of stable, long term thrombin from plasma and thrombin formed thereby
InactiveUS6274090B1Derive fast acting, stable autologous thrombinSimple preparatory procedureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component is harvested simultaneously from the clotting and adhesive proteins component from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
ActiveUS7189410B1Low antigenicityDecreasing thrombogenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides a fibrin sealant bandage, wherein said fibrin sealant may be supplemented with at least one composition selected from, for example, one or more regulatory compounds, antibody, antimicrobial compositions, analgesics, anticoagulants, antiproliferatives, anti-inflammatory compounds, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and / or using the unsupplemented or supplemented fibrin sealant bandage.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
InactiveUSRE39321E1Decreasing thrombogenicityLow antigenicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides a fibrin sealant dressing, wherein said fibrin sealant may be supplemented with at least one composition selected from, for example, one or more regulatory compounds, antibody, antimicrobial compositions, analgesics, anticoagulants, antiproliferatives, antiinflammatory compounds, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Also disclosed are methods of preparing and / or using the unsupplemented or supplemented fibrin sealant dressing.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Methods for treating wound tissue and forming a supplemented fibrin matrix
InactiveUS7196054B1Low antigenicityDecreasing thrombogenicityOrganic active ingredientsSurgical adhesivesTissue sealantVascular dilatation
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Biopolymer system for tissue sealing
InactiveUS20080075657A1Avoid bacterial infectionReduce pressurePowder deliverySurgical adhesivesActive agentTissue sealant
The invention provides a method of treating degenerative disc disease and discogenic pain by disposing a hydrogel tissue sealant within the intervertebral disc, where the hydrogel fills voids and tears in the annulus fibrosus and replaces leaked material from the nucleus pulposus. The hydrogel is formed in situ from a substantially liquid premix, which can be emplaced with a syringe needle or a catheter into the intervertebral disc, where it forms the hydrogel by gelation. The hydrogel can also include a therapeutic or a protective material, or a radiopaque or MRI-active agent to aid in visualization.
Owner:ENDOMEDIX
Apparatus and method for sealing and cutting tissue
InactiveUS20060020265A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingTissue sealantBipolar electrosurgery
An axial elongate bipolar tissue sealer / cutter and method of use by a surgeon for electrosurgery on tissue has a handle. A chassis on the handle extends axially for axial movement. A tube may move axial relative to the chassis. An effector on a distal end of the chassis first contacts tissue with axial movement. The effector provides bipolar electrosurgery. A member extending from the distal end is opposite the patient end of the tube. A part on the member is transverse to the axis to conduct electrosurgery. First and second bipolar electrodes on the effector and part are electrically isolated. A generator for bipolar electrosurgery supplies the electrodes. An activator is movably supported on the handle connects to the tube and / or chassis to axially move the patient end and its effector relative to the part. Tissue and bodily fluid therebetween are sealed or cut through application of compression and bipolar electrosurgery between the first and second electrodes. The effector and the part have complimentary sealing or cutting surfaces for partial mating engagement upon axial movement toward one another. The effector and the part can be removably attached to the distal end or member, respectively The partial mating complimentary surfaces may be normal or skewed relative to the axis and may be curvelinear, flat, parallel, circular, elliptical, triangular or have at least one conjugating rib and slot. A method of use has the steps of holding and manipulating the sealer / cutter, moving the chassis relative to the tube, positioning the effector and the port to contact tissue, along the axis coupling bipolar electrodes to the effector and par; electrically isolating the electrodes, selectively coupling the generator to the electrodes for supplying bipolar electrosurgery. Supporting the activator for moving axially relative to one another, the patient part and the effector so tissue therebetween is sealed or cut by applying compression and bipolar electrosurgery across the first and second electrodes are steps.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
Tissue Sealant for Use in Non Compressible Hemorrhage
InactiveUS20110066182A1Excellent hemostatic agent candidateLeast riskSuture equipmentsPowder deliveryTissue sealantThoracic cavity
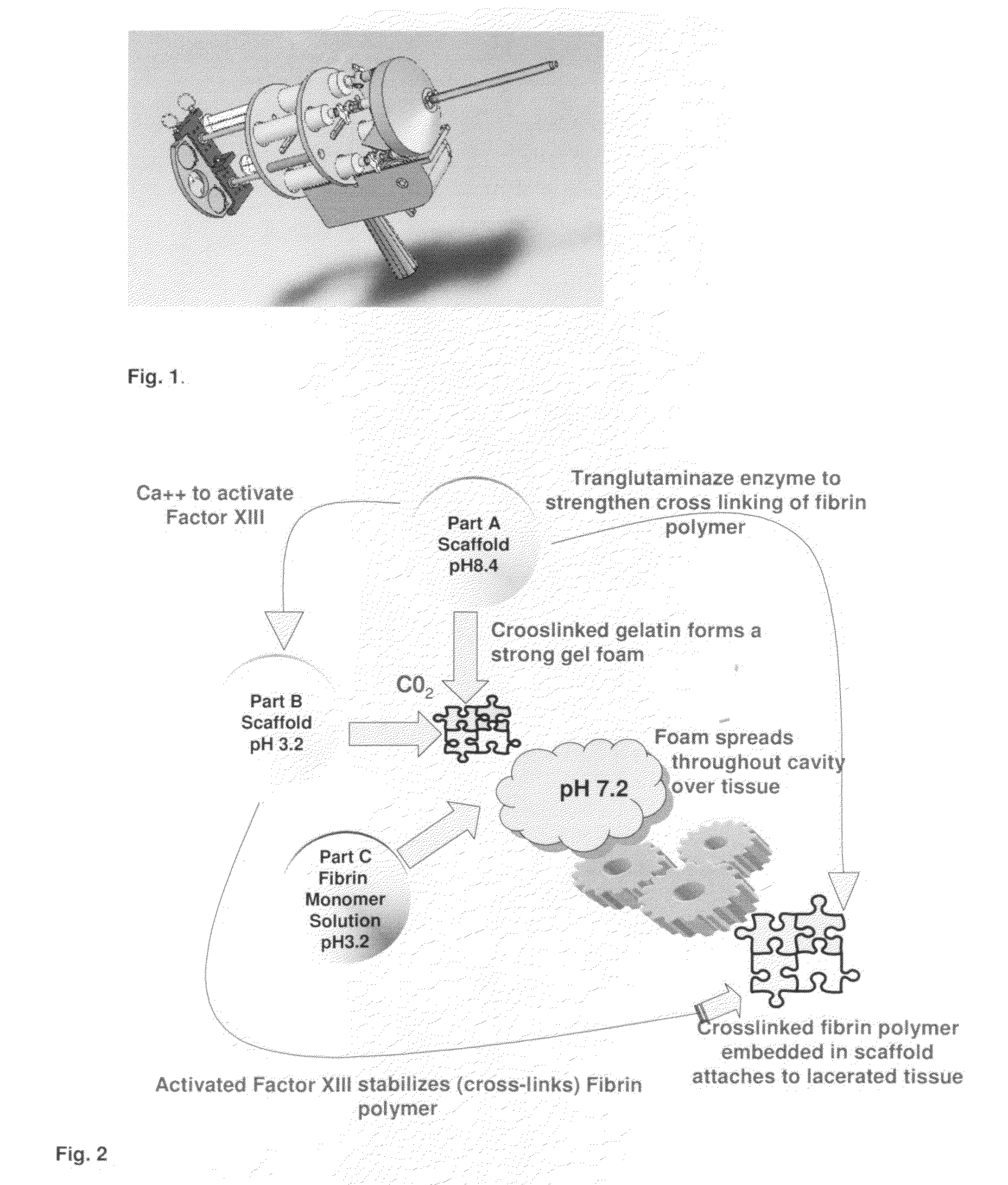
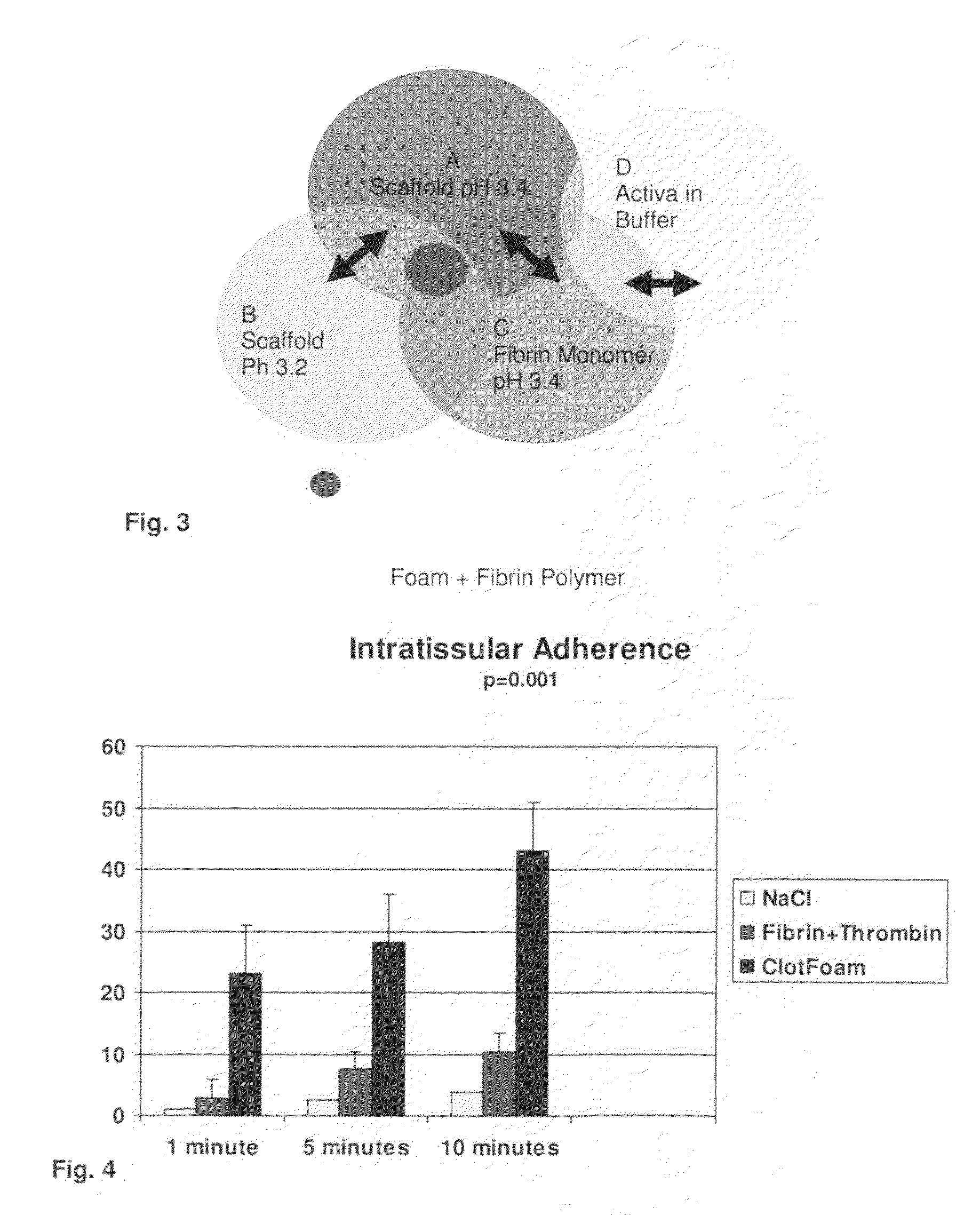
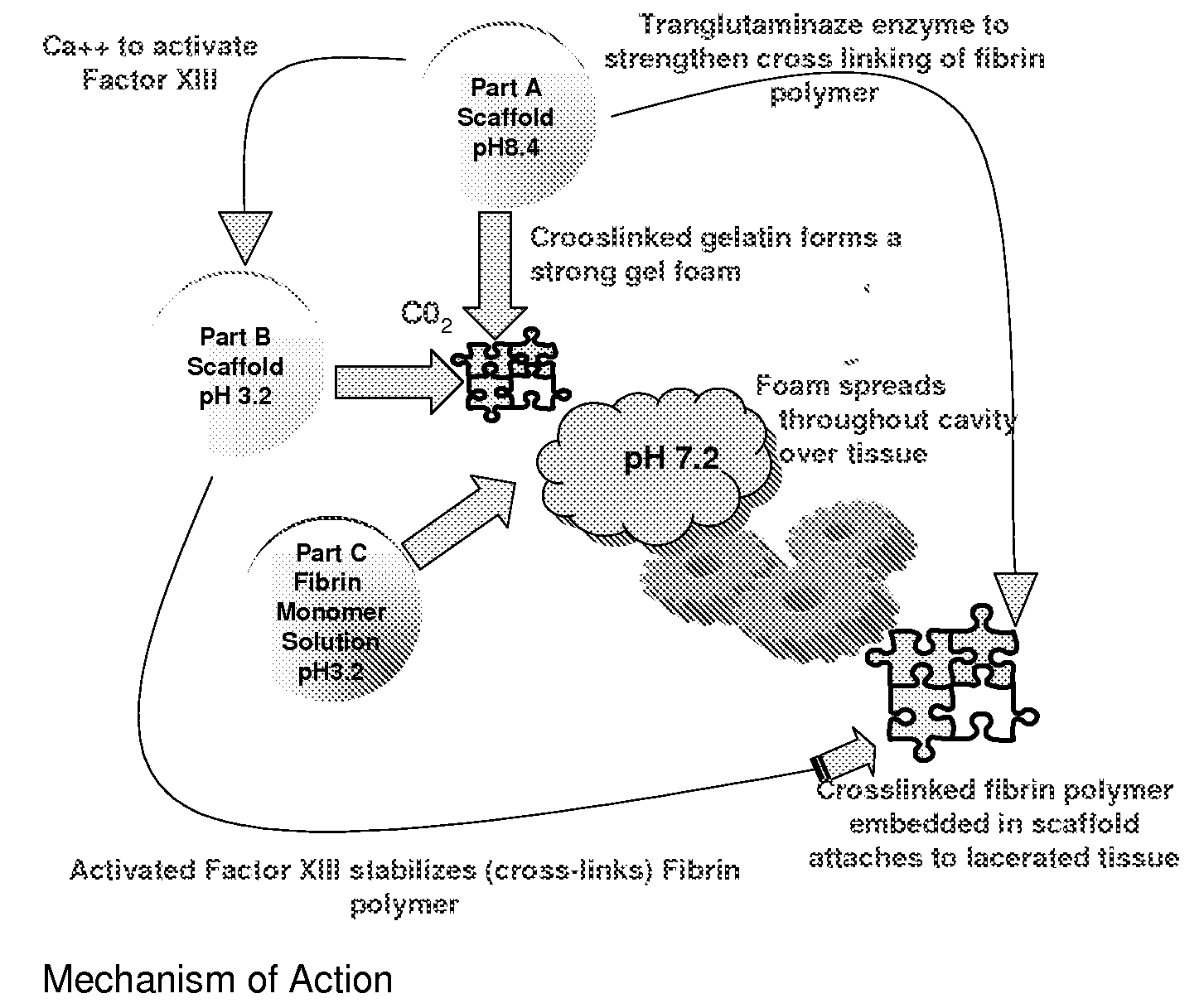
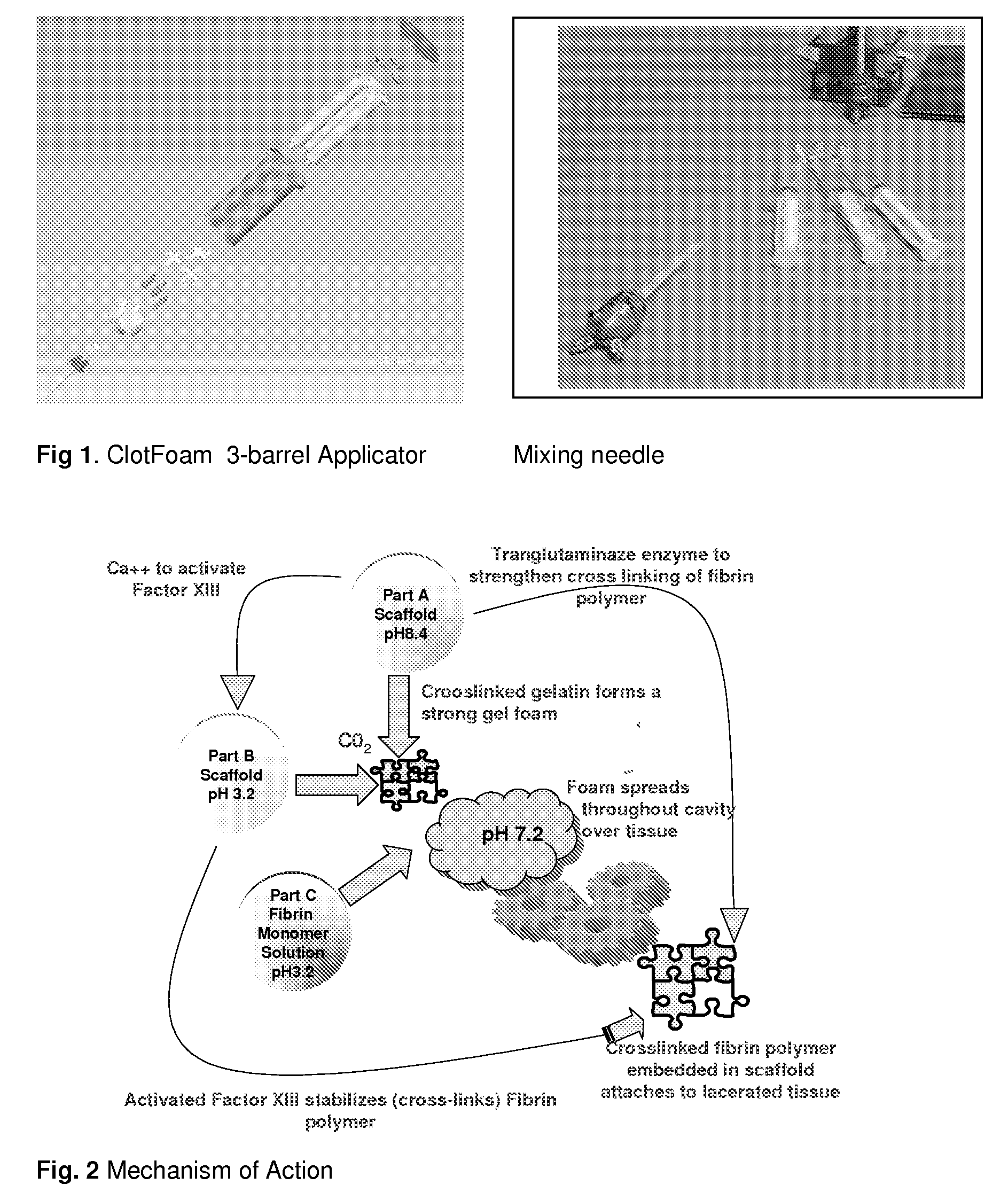
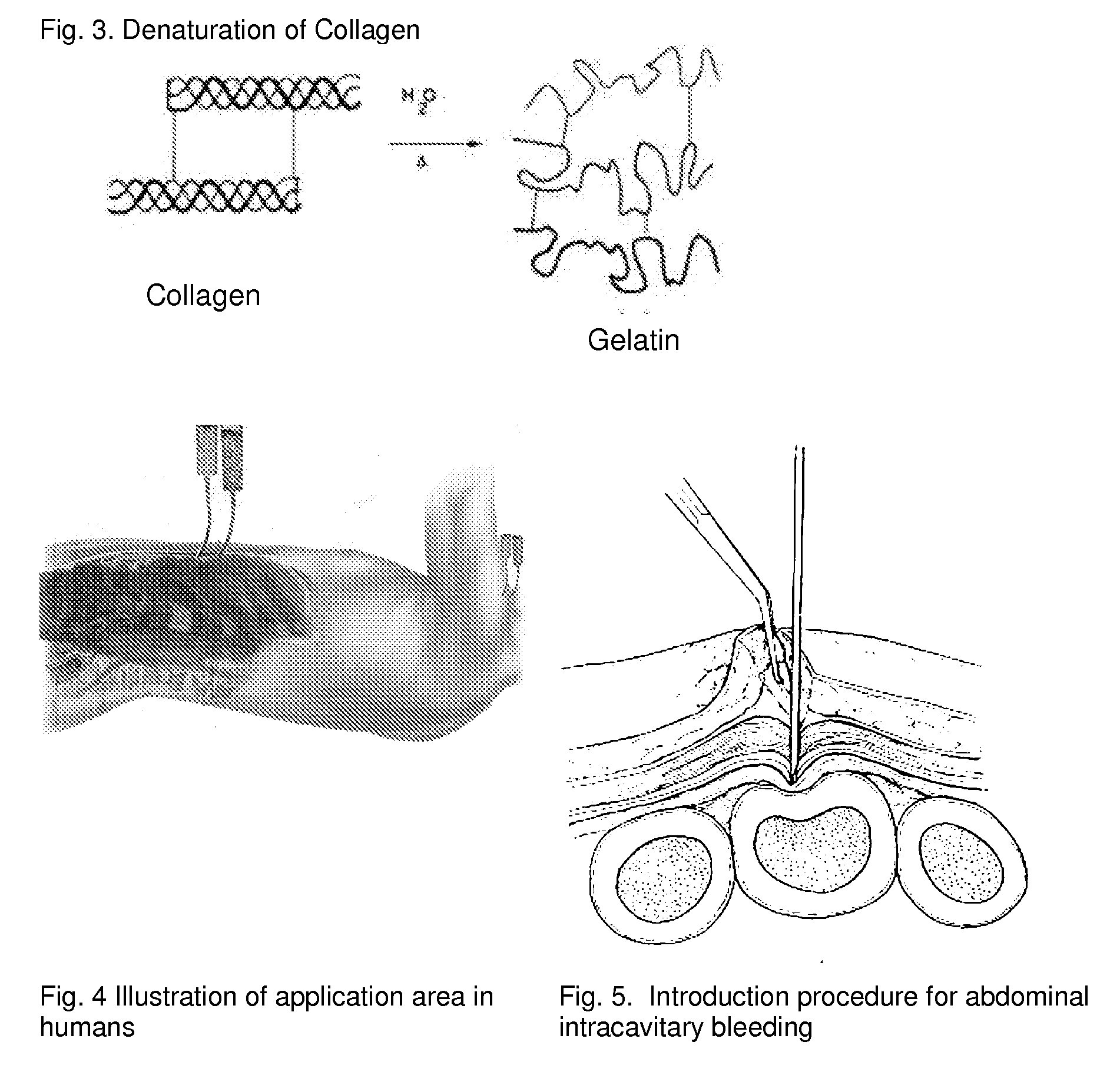
ClotFoam is a surgical sealant and hemostatic agent designed to be used in cases of non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied in the operating room through laparoscopic ports, or directly over lacerated tissue in laparotomy procedures or outside the operating room through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, Clotfoam produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade.The viscoelastic attachment properties of the foam as well as the rapid formation of a fibrin clot that ensure that the sealant remains at the site of application without being washed away by blood or displaced by movement of the target tissue .
Owner:FALUS GEORGE D PHD
Apparatus and method of preparation of stable, long term thrombin from plasma and thrombin formed thereby
InactiveUS7056722B1Precise repeatable fast slow polymerizationVarious disease riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue sealantDonors plasma
A sterile method for preparing stable thrombin component from a single donor's plasma in which the thrombin component is harvested simultaneously from the clotting and adhesive proteins component from the same donor plasma in less than one hour. The combined components provide an improved biological hemostatic agent and tissue sealant by virtue of its freedom from the risk of contaminating viruses or bacteria from allogenic human or bovine blood sources. The thrombin provides polymerization of the clotting and adhesive proteins in less than five seconds, and is sufficiently stable to provide that fast clotting over a six hour period. Further, the clotting times can be predictably lengthened by diluting the thrombin with saline.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Compliant tissue sealants
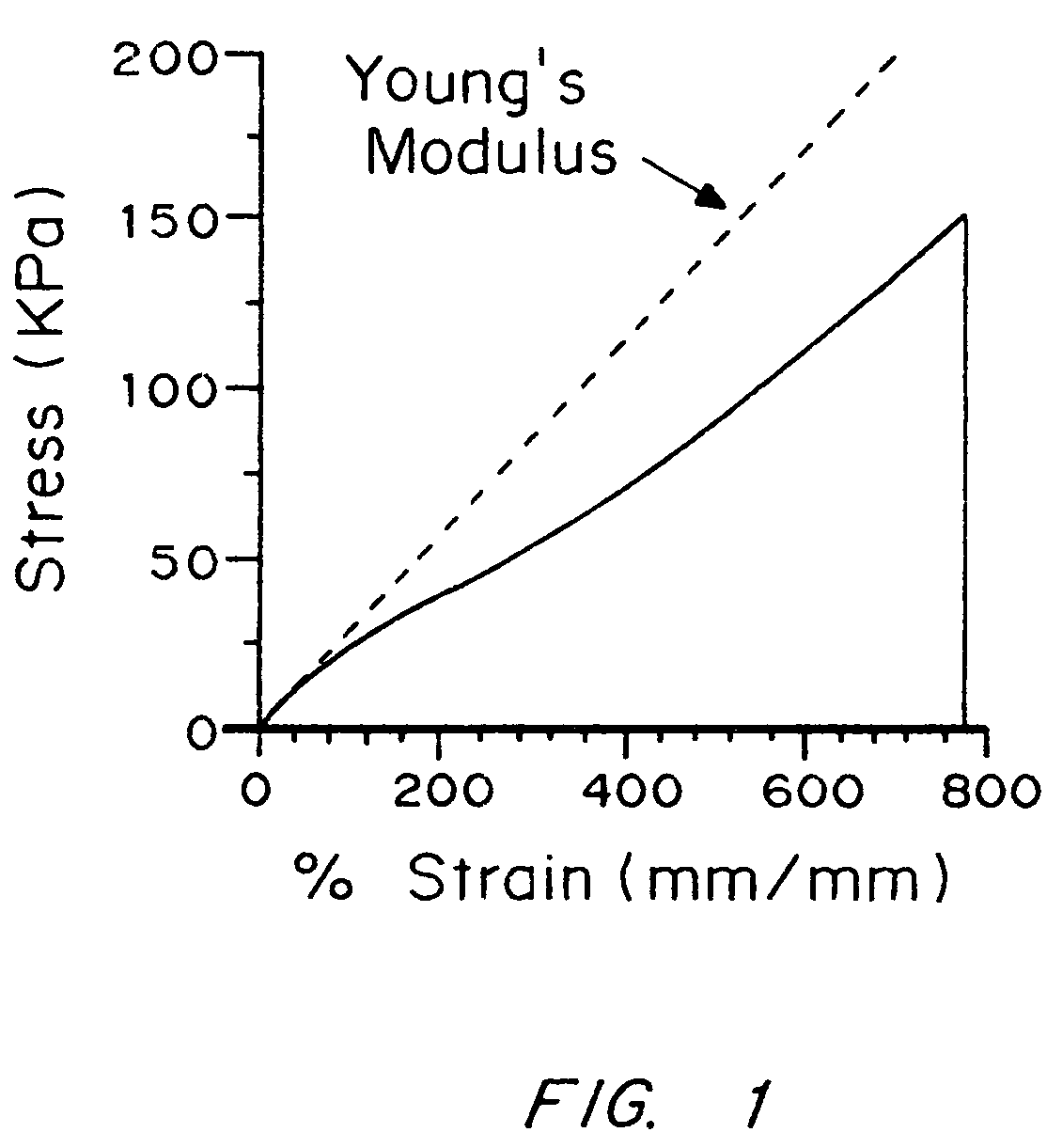
An improved barrier or drug delivery system which is highly adherent to the surface to which it is applied is disclosed, along with methods for making the barrier. In the preferred embodiment, the system is compliant, in that it is capable of conforming to the three dimensional structure of a tissue surface as the tissue bends and deforms during healing processes. The barrier or drug delivery systems is formed as a polymeric coating on tissue surfaces by applied a polymerizable monomer to the surface, and then polymerizing the monomer. The polymerized compliant coating preferably is biodegradable and biocompatible, and can be designed with selected properties of compliancy and elasticity for different surgical and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Advanced functional biocompatible polymeric matrix used as a hemostatic agent and system for damaged tissues and cells
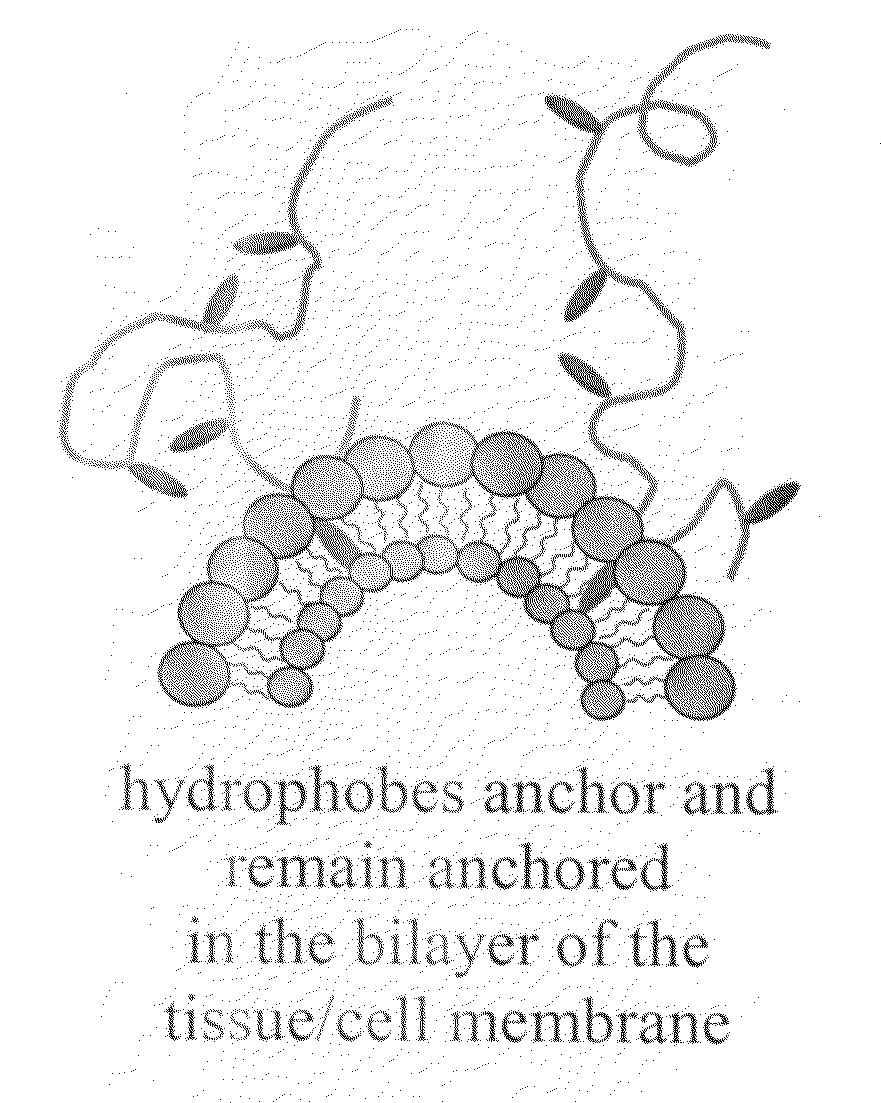
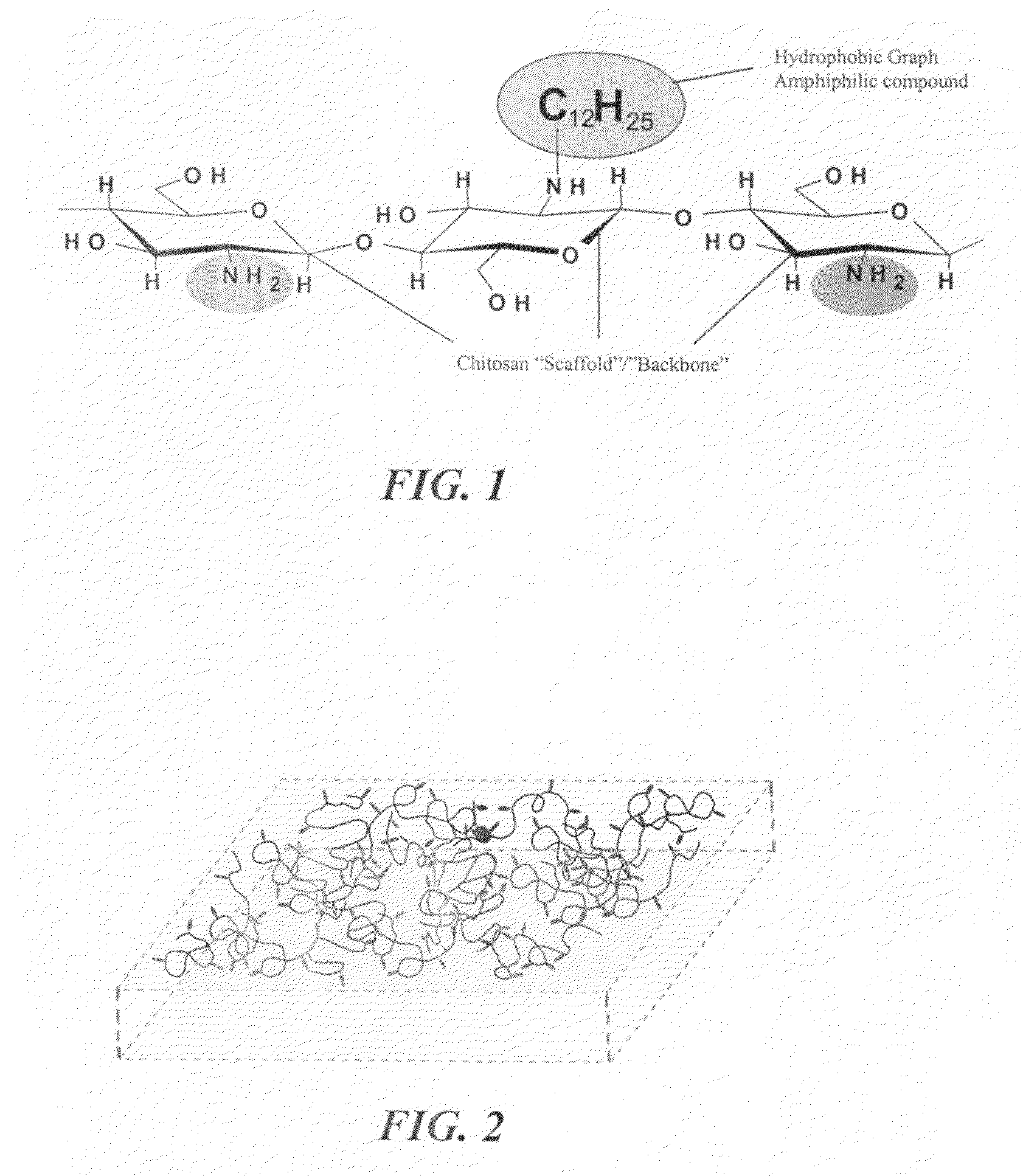
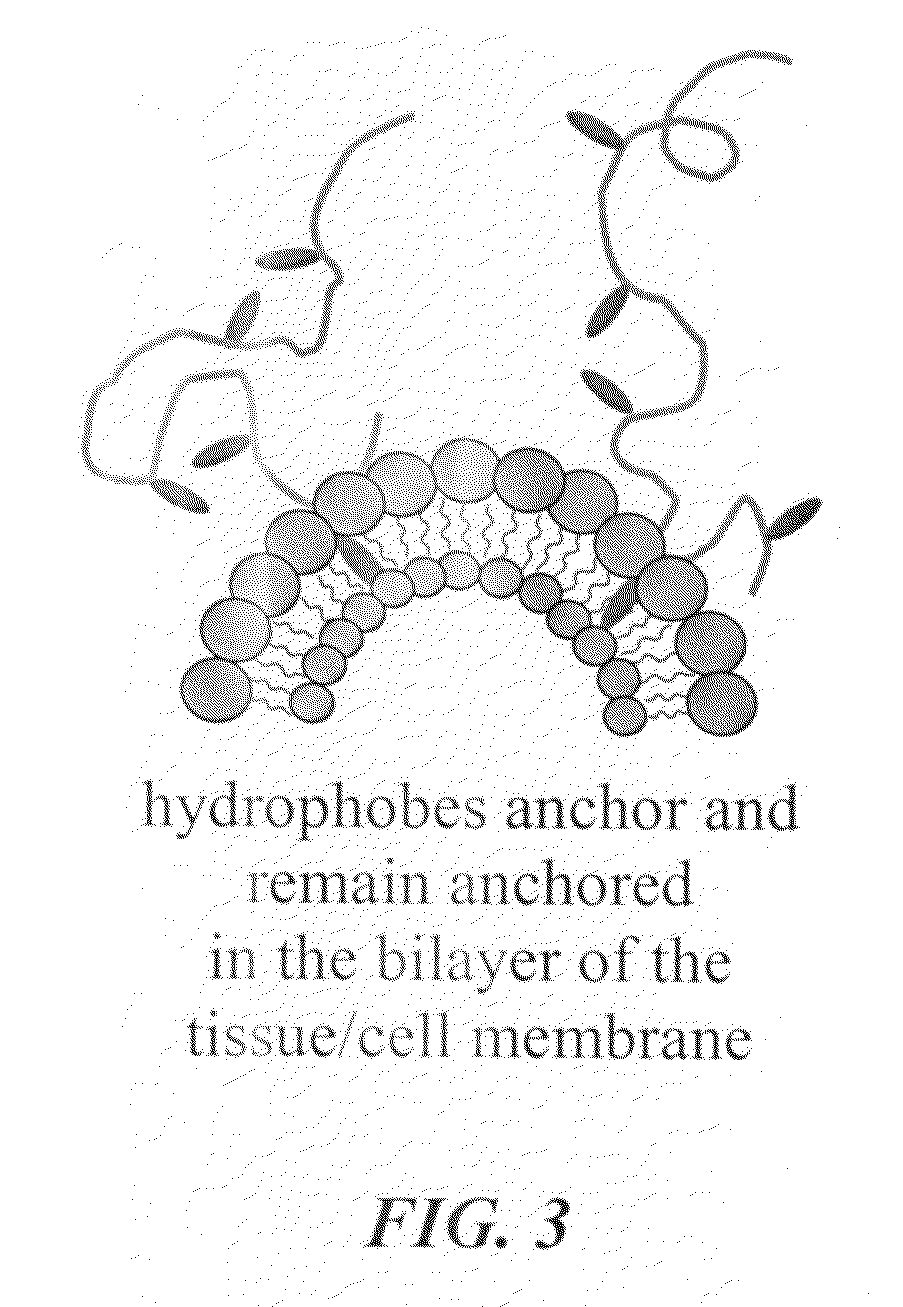
A hemostatic tissue sealant sponge and a spray for acute wounds are disclosed. The sponge comprises hydrophobically modified polymers that anchor themselves within the membrane of cells in the vicinity of the wound. The seal is strong enough to substantially prevent the loss of blood inside the boundaries of the sponge, yet weak enough to substantially prevent damage to newly formed tissue upon recovery and subsequent removal of the sponge. In examples, the polymers inherently prevent microbial infections and are suitable for oxygen transfer required during normal wound metabolism. The spray comprises hydrophobically modified polymers that form solid gel networks with blood cells to create a physical clotting mechanism to prevent loss of blood. In an example, the spray further comprises at least one reagent that increases the mechanical integrity of the clot. In another example, the reagent prevents microbial infection of the wound.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Compliant tissue sealants
An improved barrier or drug delivery system which is highly adherent to the surface to which it is applied is disclosed, along with methods for making the barrier. In the preferred embodiment, the system is compliant, in that it is capable of conforming to the three dimensional structure of a tissue surface as the tissue bends and deforms during healing processes. The barrier or drug delivery systems is formed as a polymeric coating on tissue surfaces by applied a polymerizable monomer to the surface, and then polymerizing the monomer. The polymerized compliant coating preferably is biodegradable and biocompatible, and can be designed with selected properties of compliancy and elasticity for different surgical and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Biopolymer system for tissue sealing
ActiveUS20070243131A1Outstanding advantageGood dimensional stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryTissue sealantBiopolymer
A tissue sealant for use in surgical and medical procedures for sealing the tissues of a living mammal is provided. The tissue sealant comprises a hydrogel which is formed by gelation of a premix disposed on the tissue to be sealed. The premix comprises alkylated chitosan or a gelatin, and a polybasic carboxylic acid or an oxidized polysaccharide, in an aqueous medium. The premix can also include a dehydrating reagent, a carboxyl activating reagent, or both. A specific use of the tissue sealant is in the repair of the dura mater after brain surgery to prevent leakage of cerebrospinal fluid. The tissue sealant may include a therapeutic or protective agent such as an antibiotic or an anti-inflammatory drug.
Owner:ENDOMEDIX
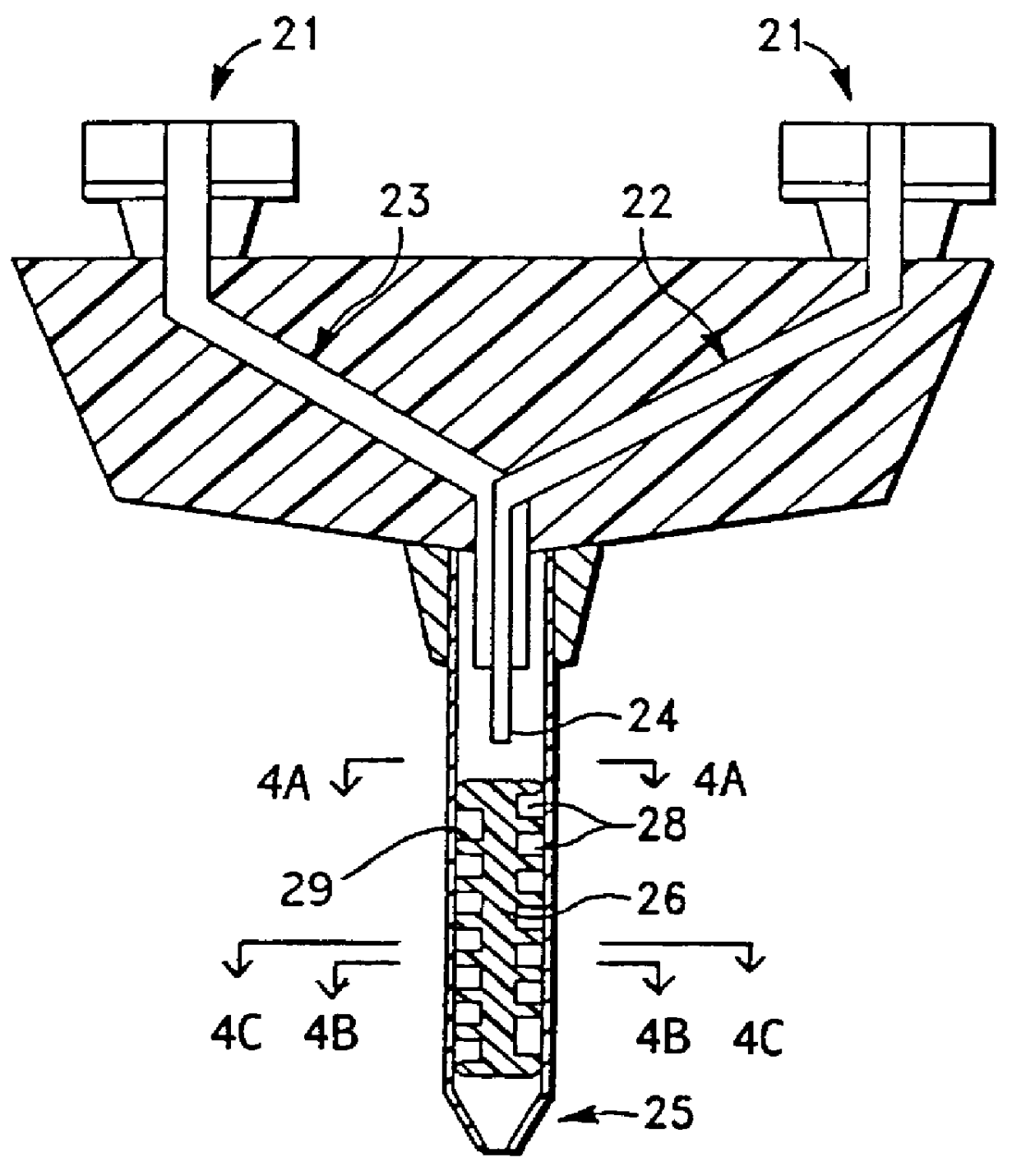
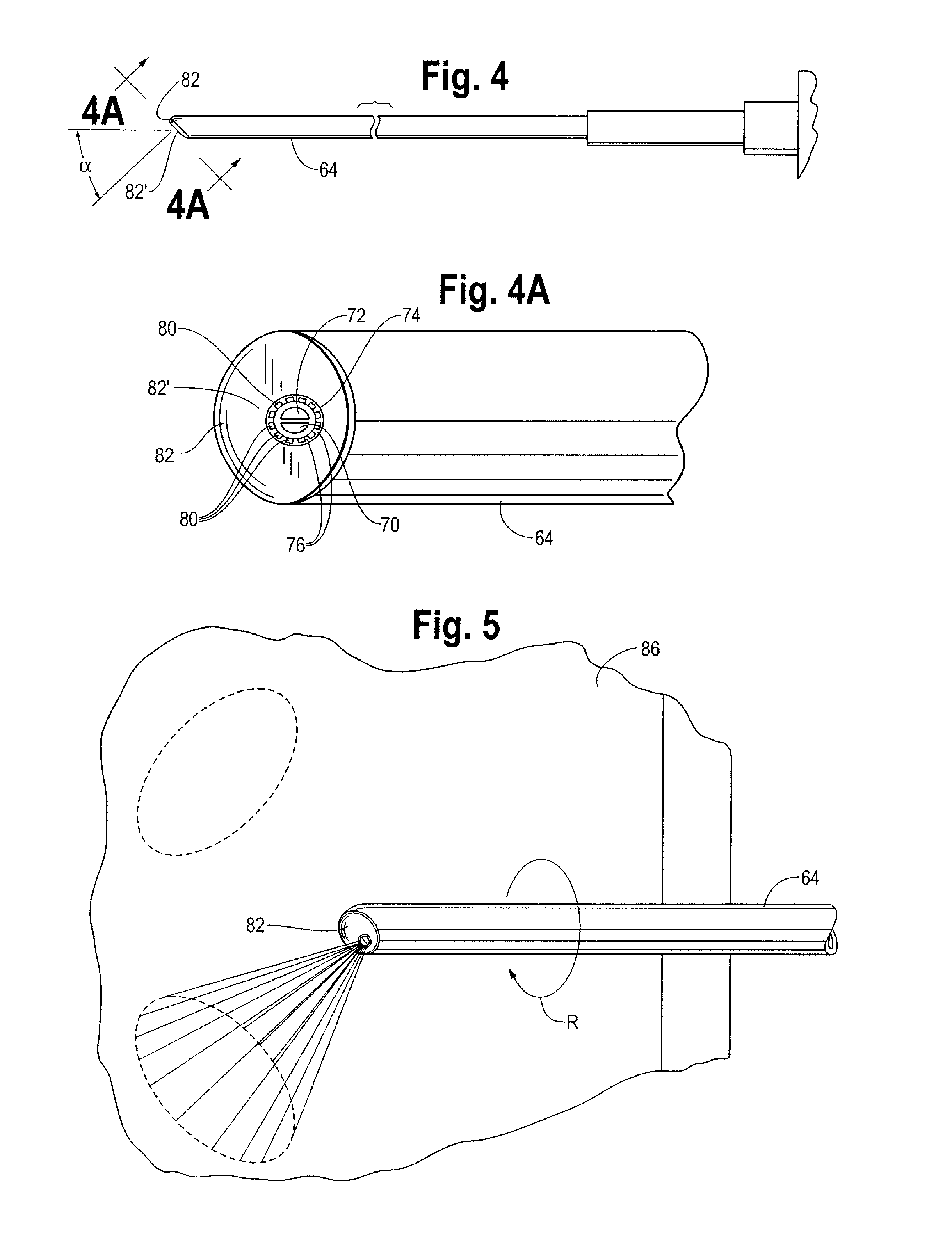
Hand triggered tissue sealant spray apparatus and system
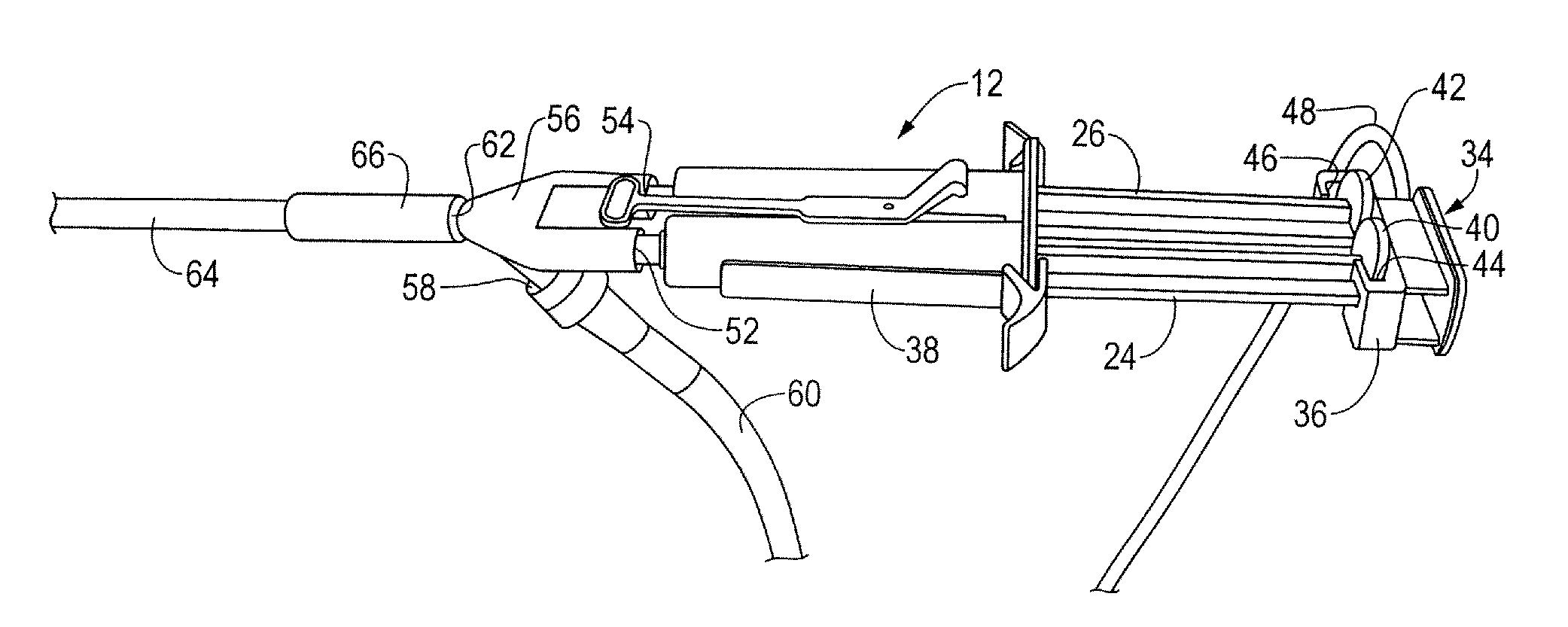
The present invention is generally directed to various structures for applying a sealant to a work surface. In one aspect of the invention, a sealant applicator assembly is provided for use with an apparatus of the type having an elongated body defining an interior bore and having a piston movably positioned in the bore and a pusher member operatively associated with the piston. The assembly comprises a spray adaptor adapted to communicate with the bore of the body and defining a distal outlet. A first gas passageway is cooperatively associated with the distal outlet and configured to direct gas to create a spray discharge of the sealant. An actuating member is adapted to be cooperative associated with a pusher member to eject sealant through the distal outlet and is operative to simultaneously actuate a supply of gas to the first gas passageway for creating a spray discharge of sealant.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Biopolymer system for tissue sealing
ActiveUS7854923B2Good dimensional stabilityReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryTissue sealantBiopolymer
A tissue sealant for use in surgical and medical procedures for sealing the tissues of a living mammal is provided. The tissue sealant comprises a hydrogel which is formed by gelation of a premix disposed on the tissue to be sealed. The premix comprises alkylated chitosan or a gelatin, and a polybasic carboxylic acid or an oxidized polysaccharide, in an aqueous medium. The premix can also include a dehydrating reagent, a carboxyl activating reagent, or both. A specific use of the tissue sealant is in the repair of the dura mater after brain surgery to prevent leakage of cerebrospinal fluid. The tissue sealant may include a therapeutic or protective agent such as an antibiotic or an anti-inflammatory drug.
Owner:ENDOMEDIX
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
InactiveUSRE39192E1Increased longevityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides supplemented tissue sealants, methods for their production and use thereof. Disclosed are tissue sealants supplemented with at least one cytotoxin or cell proliferation inhibiting composition. The composition may be further supplemented with, for example, one or more antibodies, analgesics, anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory compounds, antimicrobial compositions, cytokines, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, deminearlized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Polyalkylene glycol viscosity-enhancing polymeric formulations
InactiveUS20020127196A1ChangeIncrease shear rateBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTissue sealantHyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid and polyalkylene glycol (PAG) based materials have been found to exhibit a synergistic interaction, in which the viscosity of the mixture is more than twice as high as the viscosity expected from the viscosity of the individual components. The mixture otherwise has similar properties to those of its constituents, and in particular will crosslink to form covalently crosslinked gels if the PEG carries crosslinkable groups. The viscous formulation adheres well to tissue, and has applications as a tissue sealant and in tissue coating, prevention of adhesions, cell immobilization, regeneration of cartilage, bone and other tissue, as well as in controlled delivery of hyaluronic acid to sites in the body. Related materials exhibit similar effects.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Polymeric tissue sealant
ActiveUS20080253987A1High mechanical strengthReduces and prevents leakageOrganic active ingredientsImpression capsTissue sealantActive agent
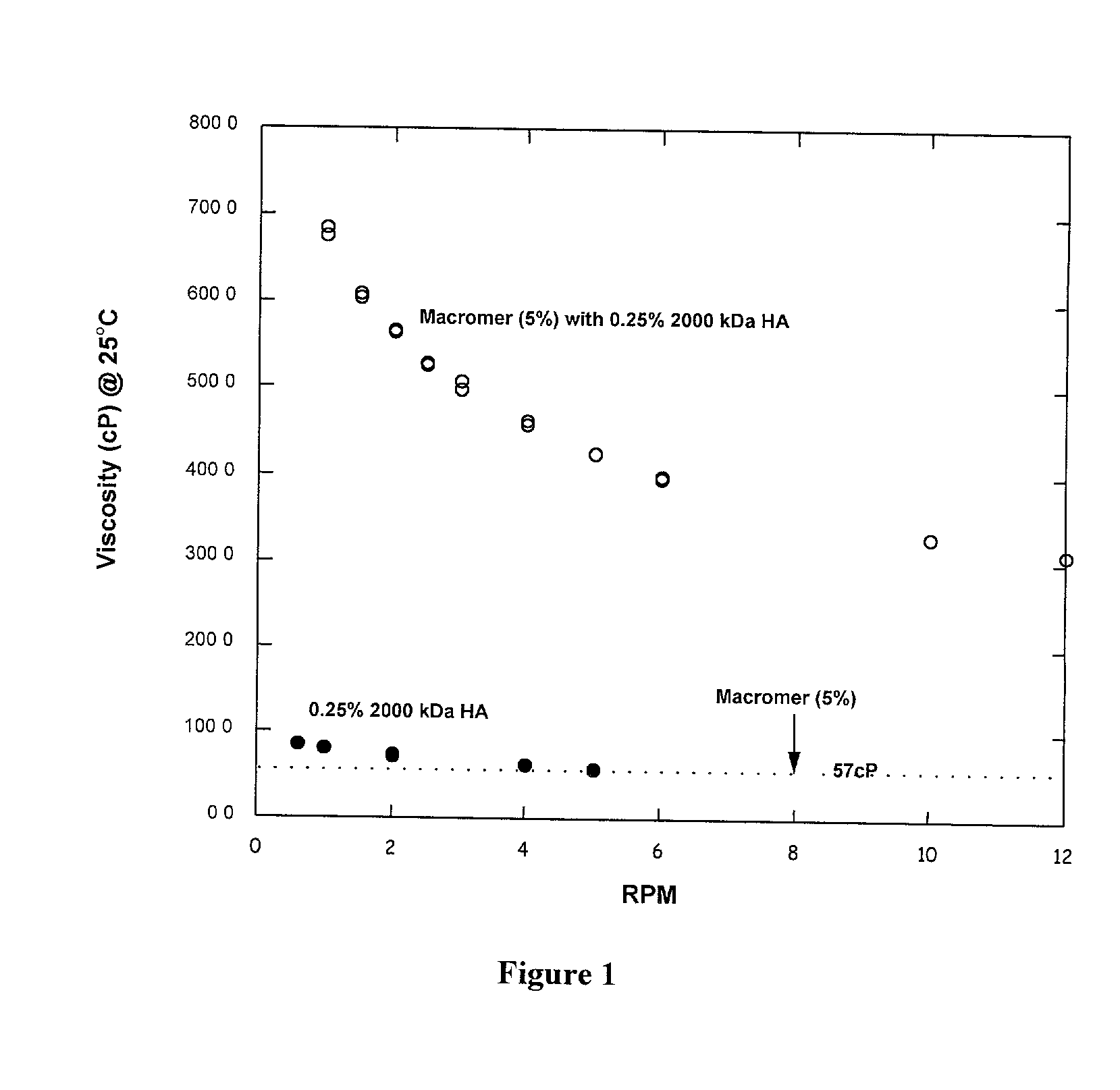
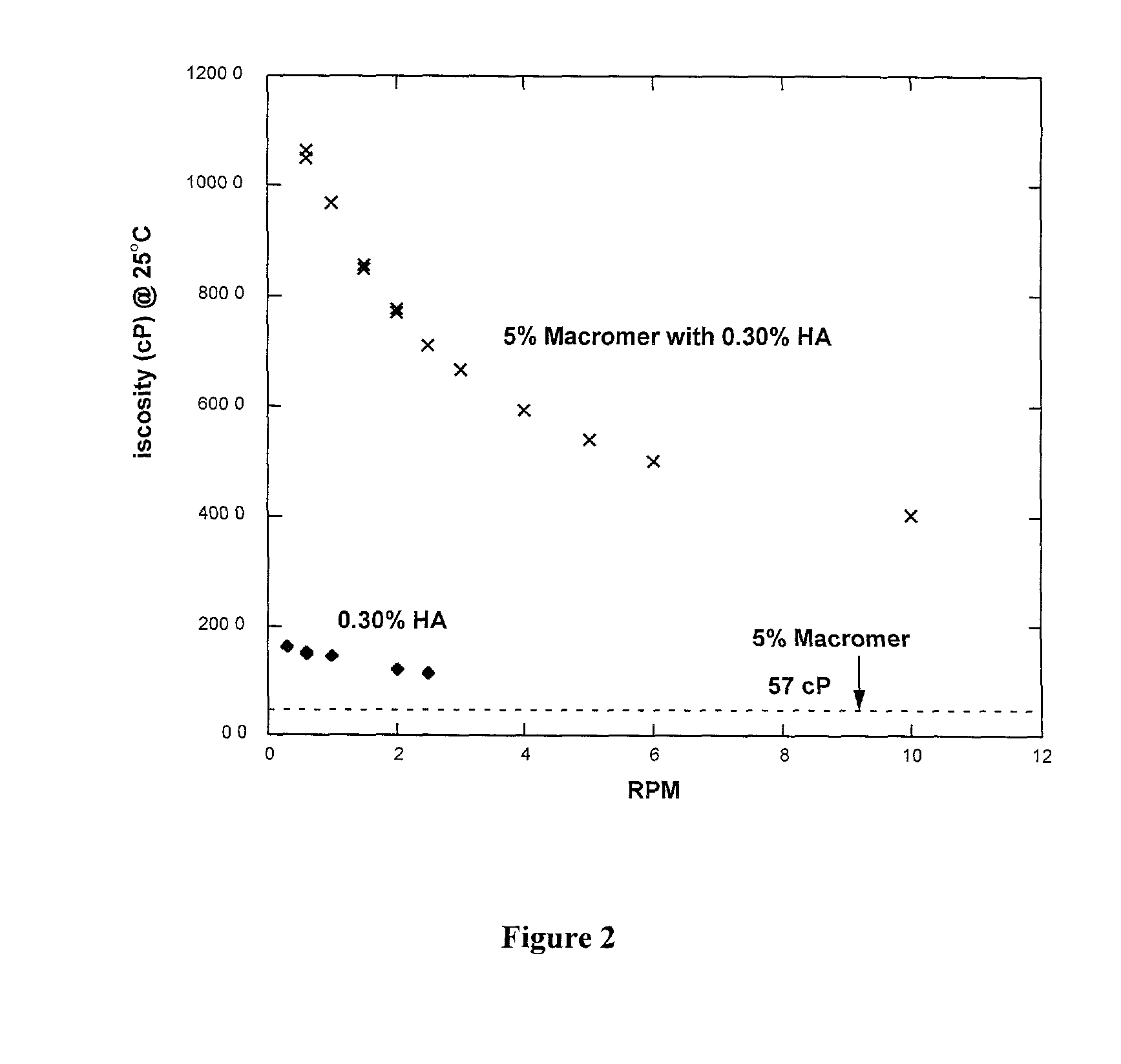
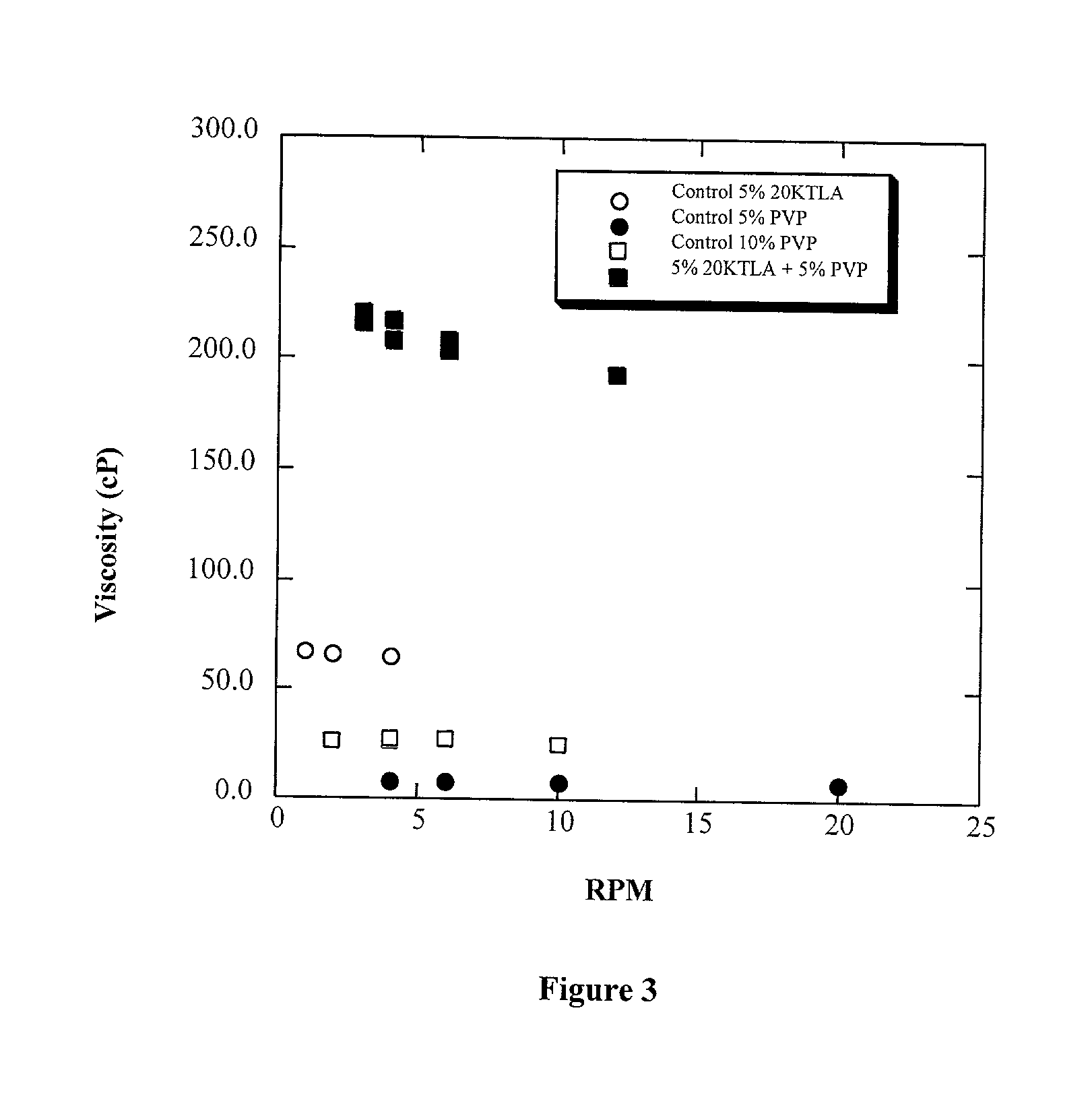
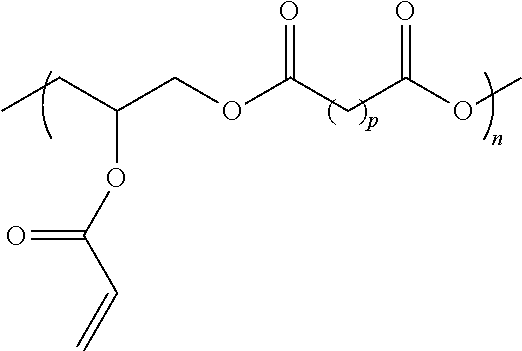
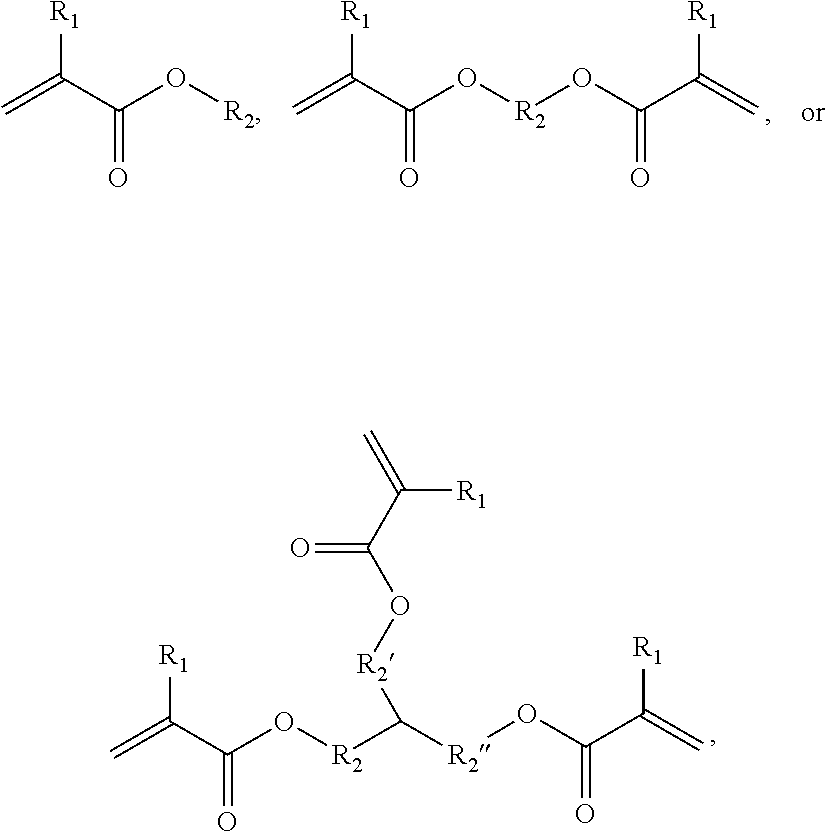
Methods for making biomaterials for use as a tissue sealant, kits containing precursors for forming the biomaterials, and the resulting biomaterials are described herein. The biomaterials are formed from a composition comprising at least a first and a second precursor molecule, wherein:i) the first precursor molecule is a poly(ethylene glycol) based polymer having x nucleophilic groups selected from the group consisting of thiol or amino groups, wherein x is greater than or equal to 2ii) the second precursor molecule is of the general formula:A-[(C3H6O)n—(C2H4O)m—B]i wherein m and n are integers from 1 to 200i is greater than 2A is a branch pointB is a conjugated unsaturated groupThe precursors are selected based on the desired properties of the biomaterial. Optionally, the biomaterials contain additives, such as thixotropic agents, radiopaque agents, or bioactive agents. In the preferred embodiment, the biomaterials are used to reduce, inhibit, or contain loss of a biological fluid or gas in a patient.
Owner:KUROS BIOSURGERY AG
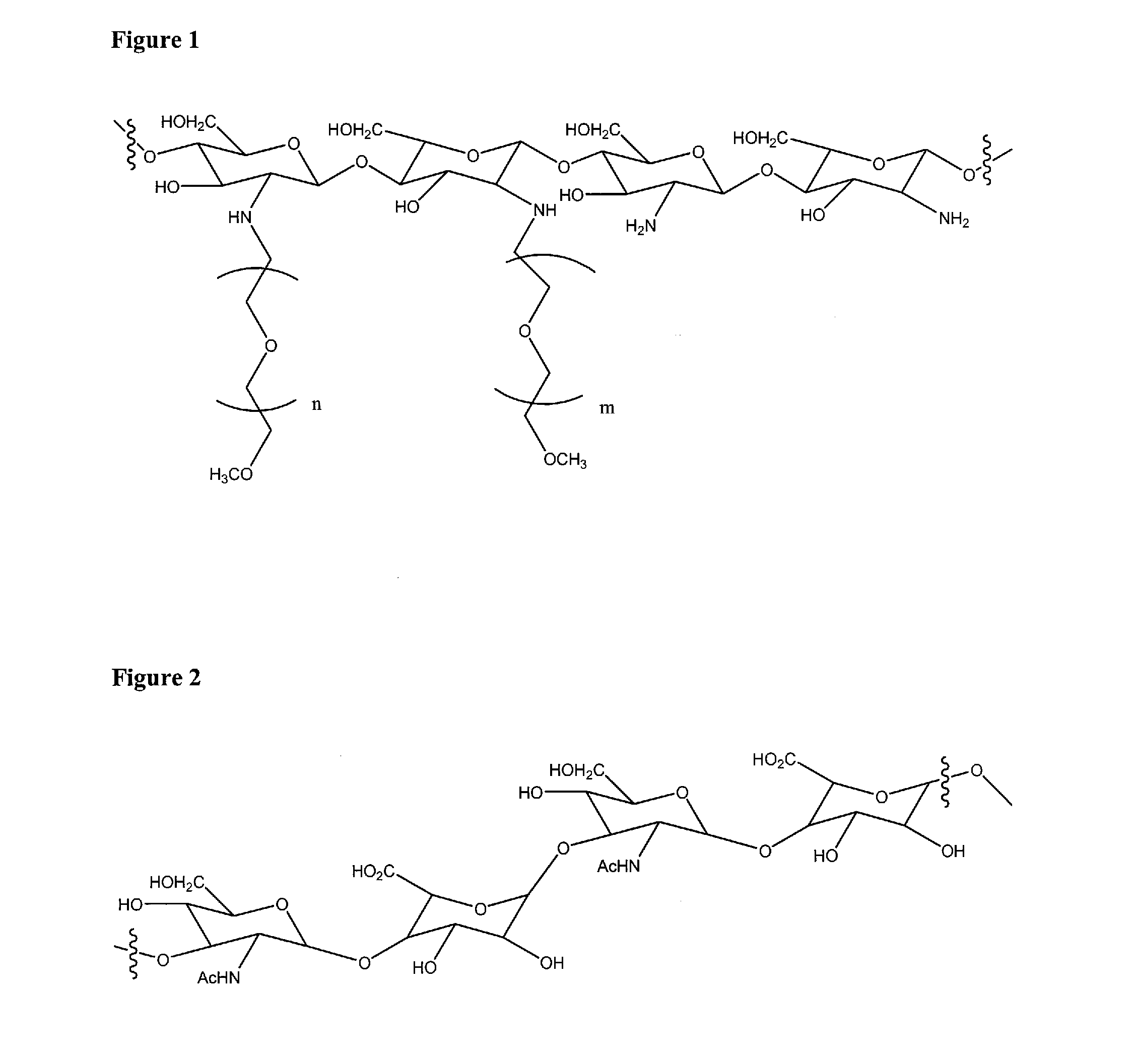
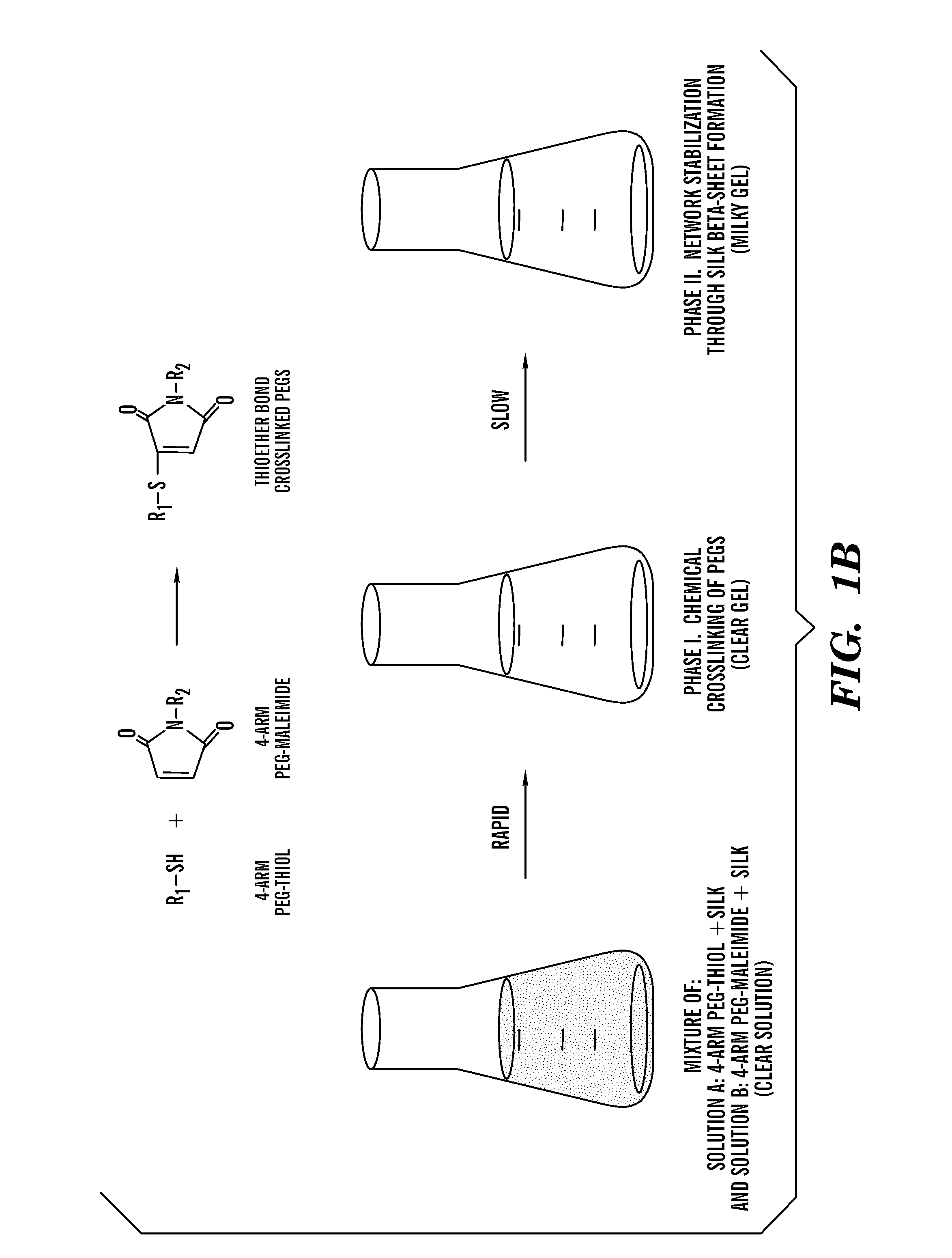
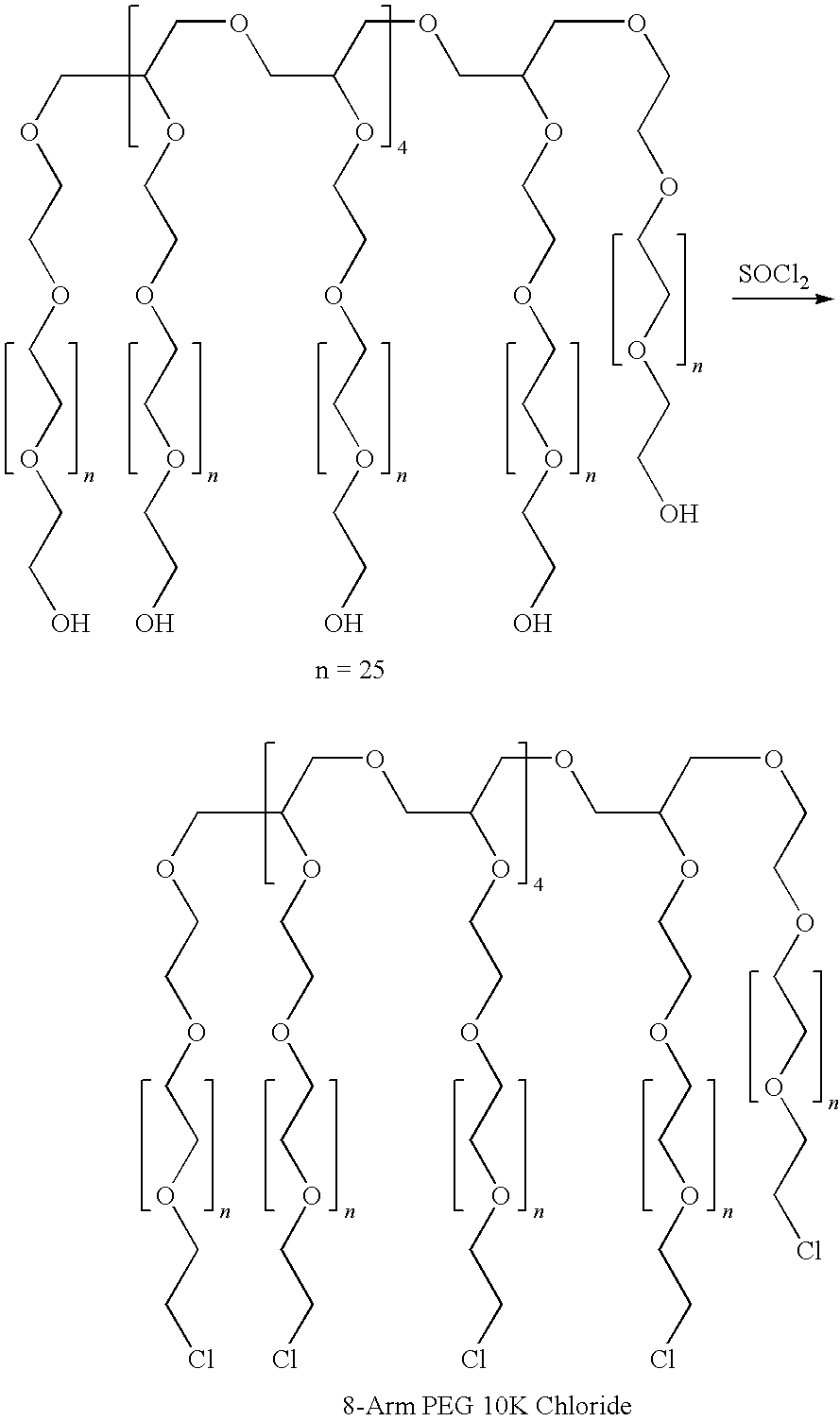
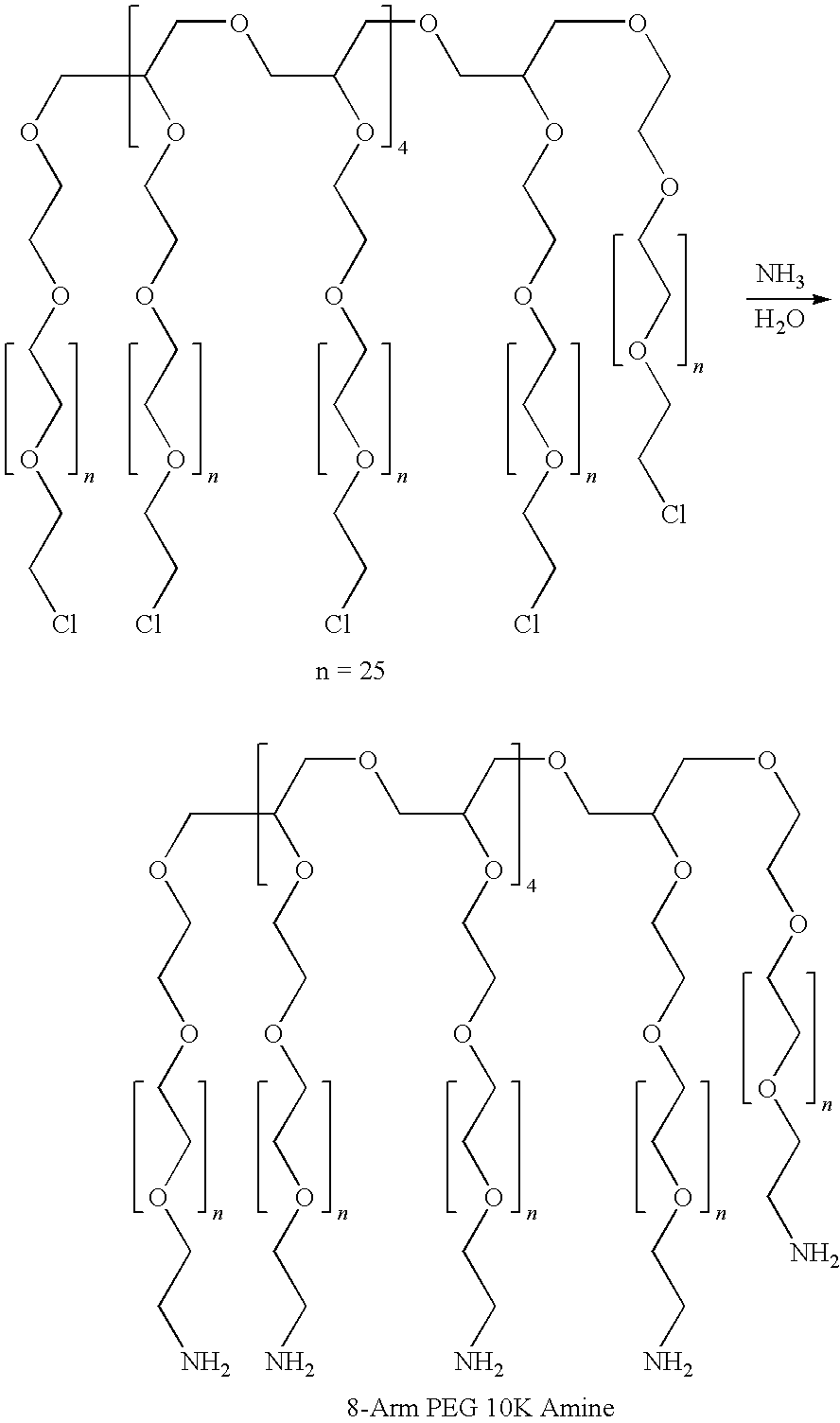
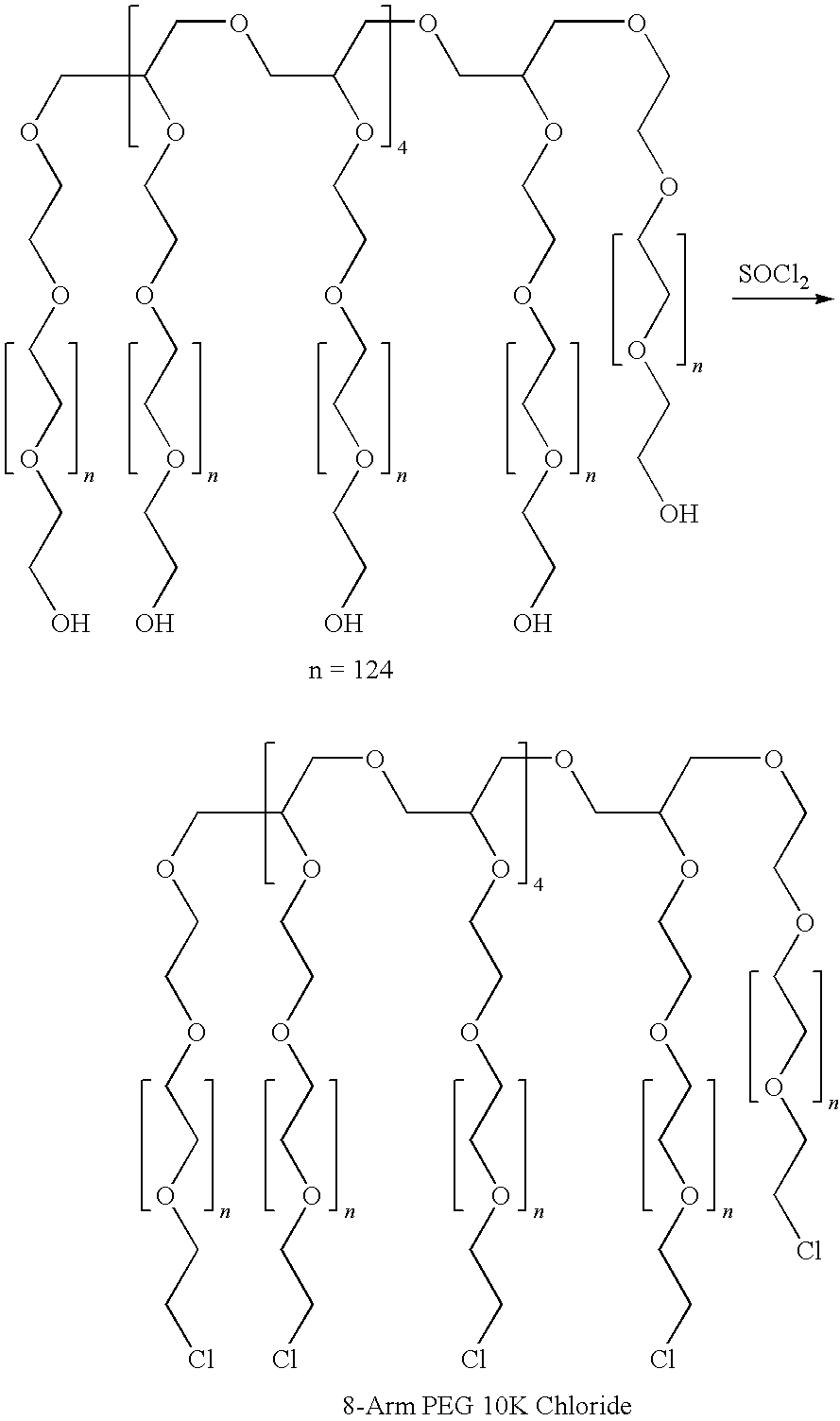
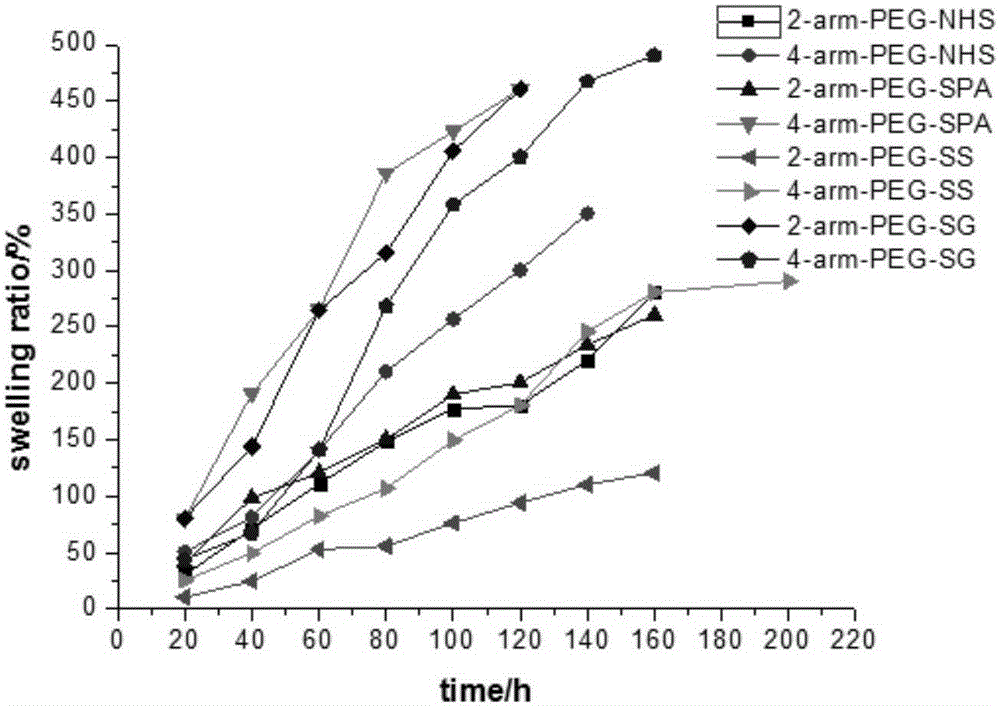
Silk fibroin and polyethylene glycol-based biomaterials
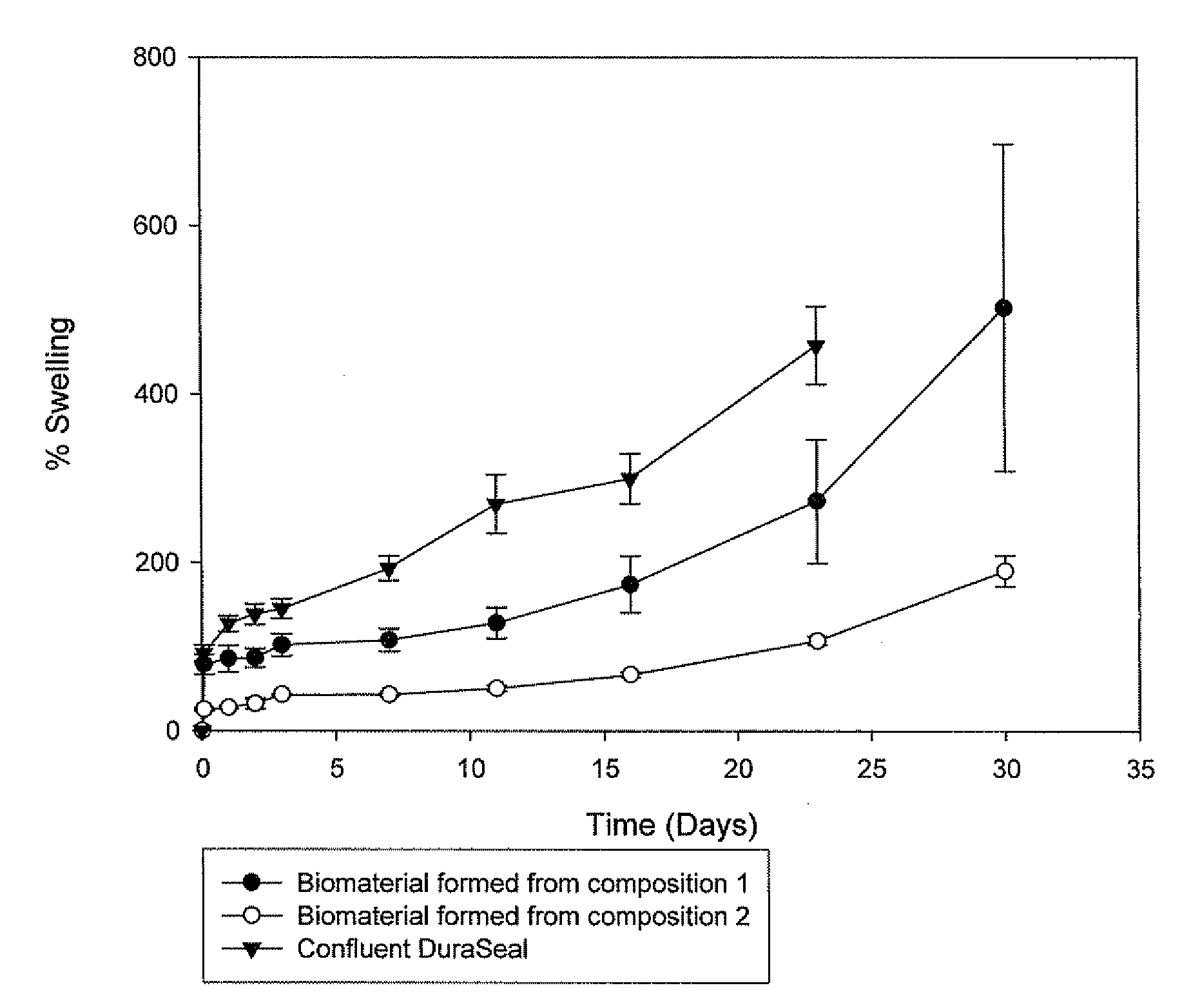
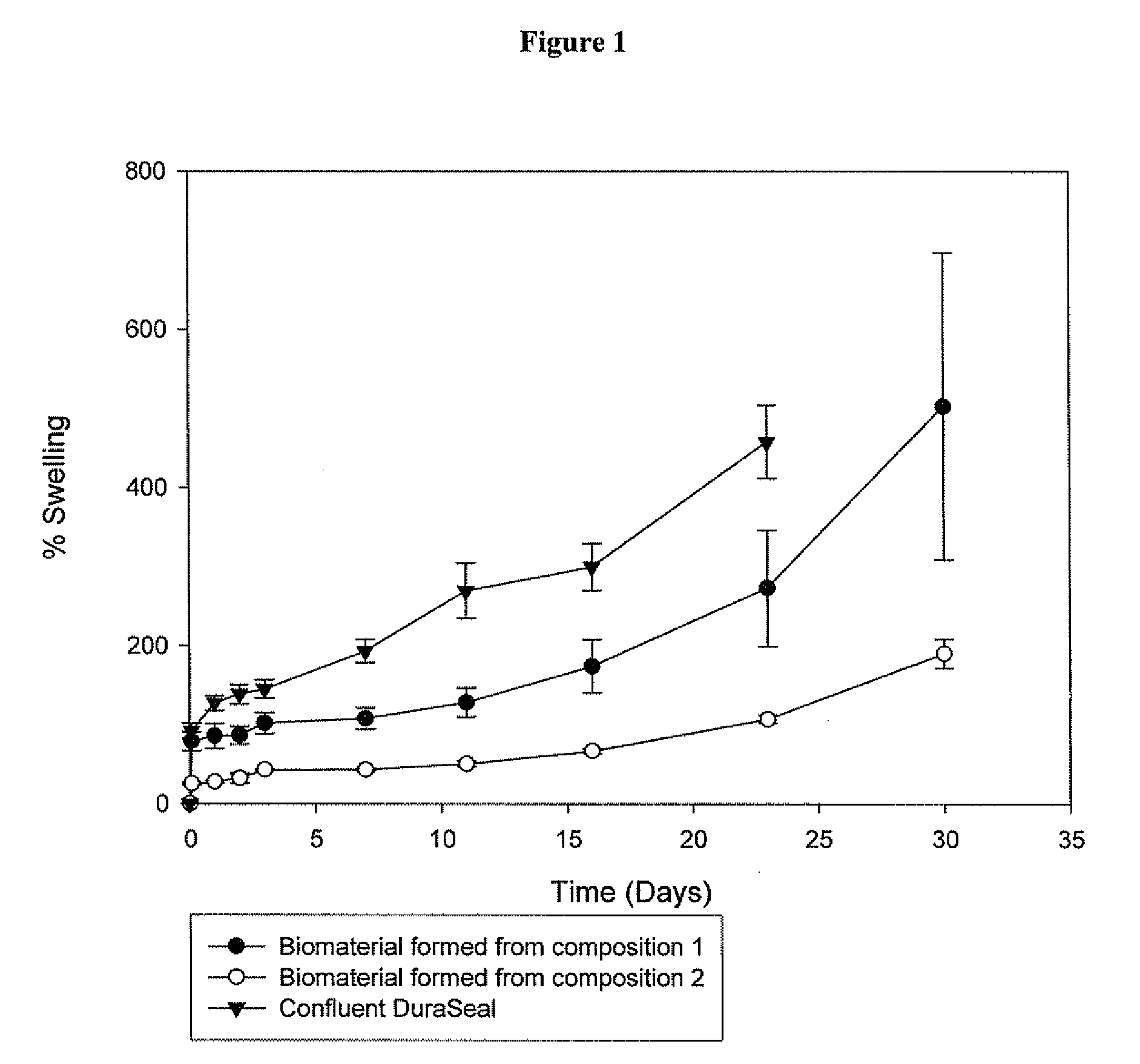
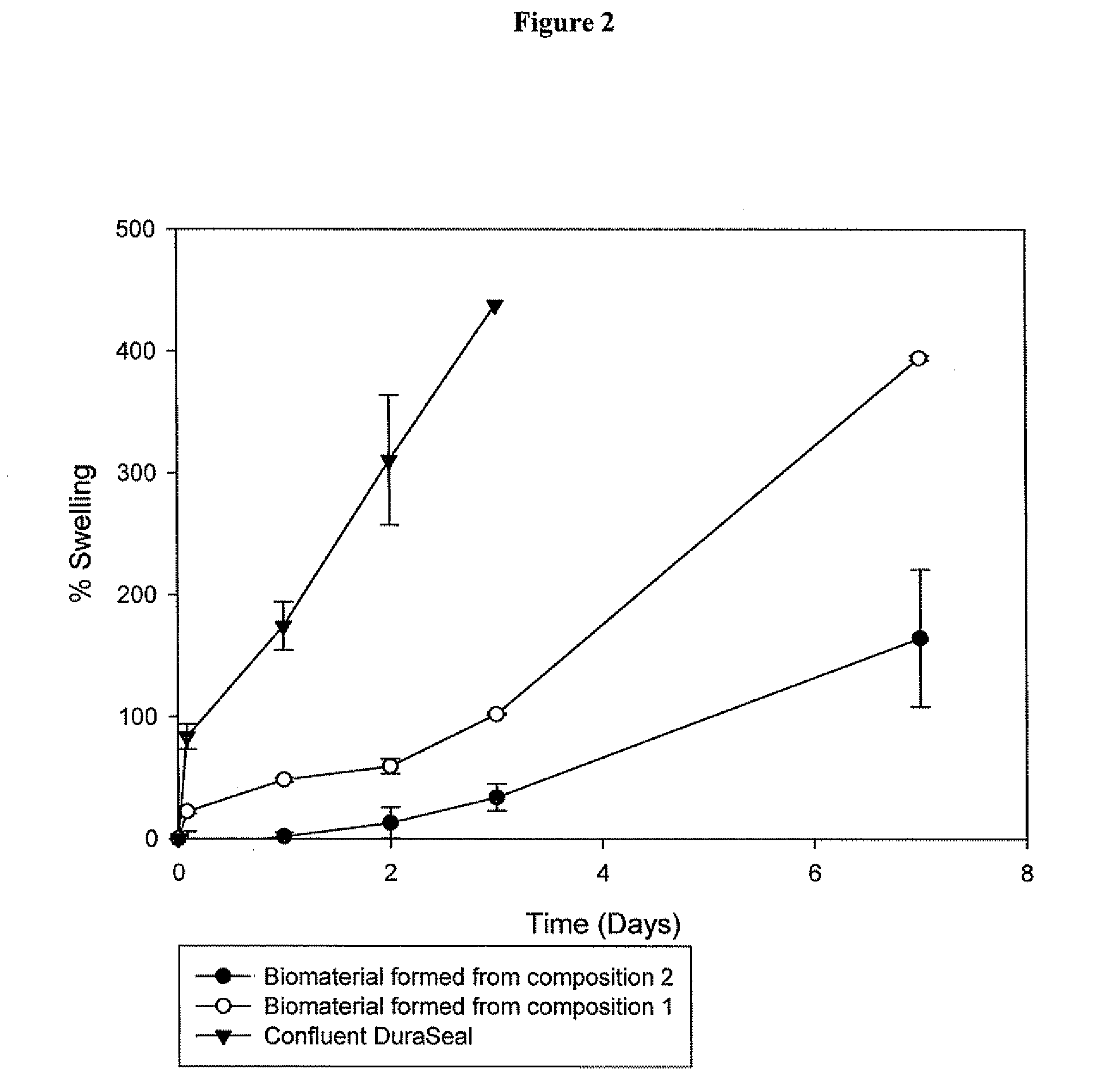
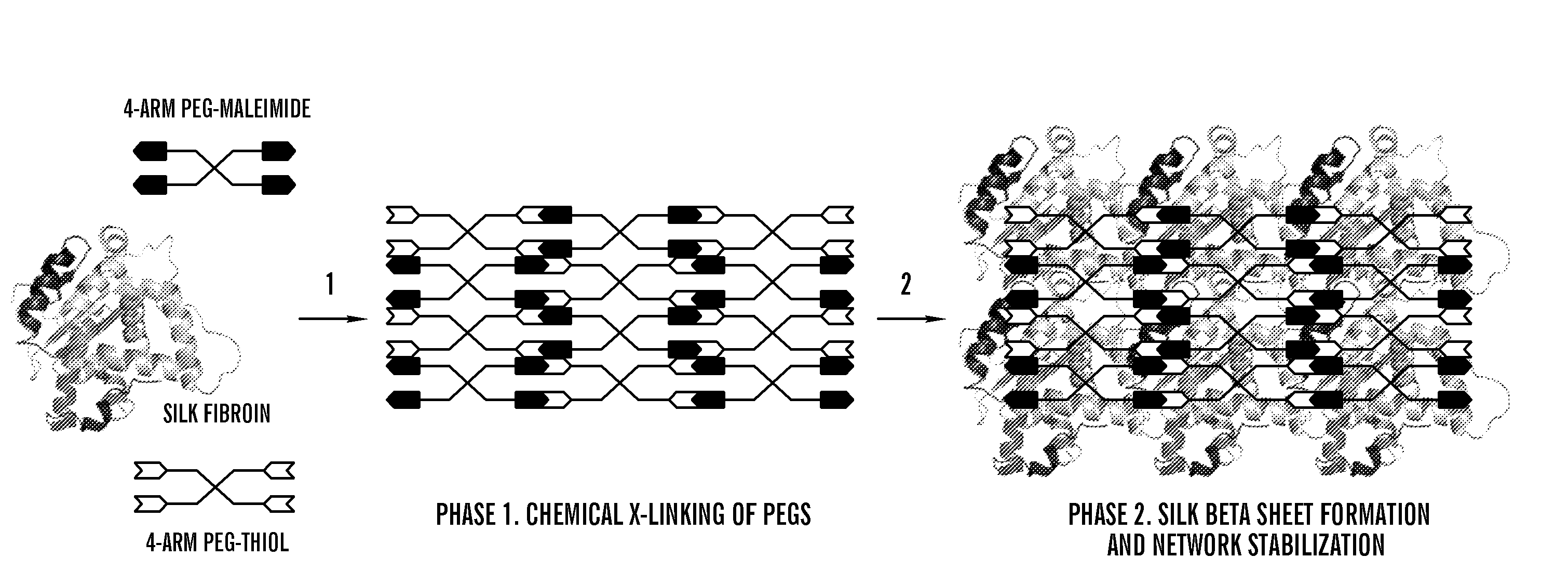
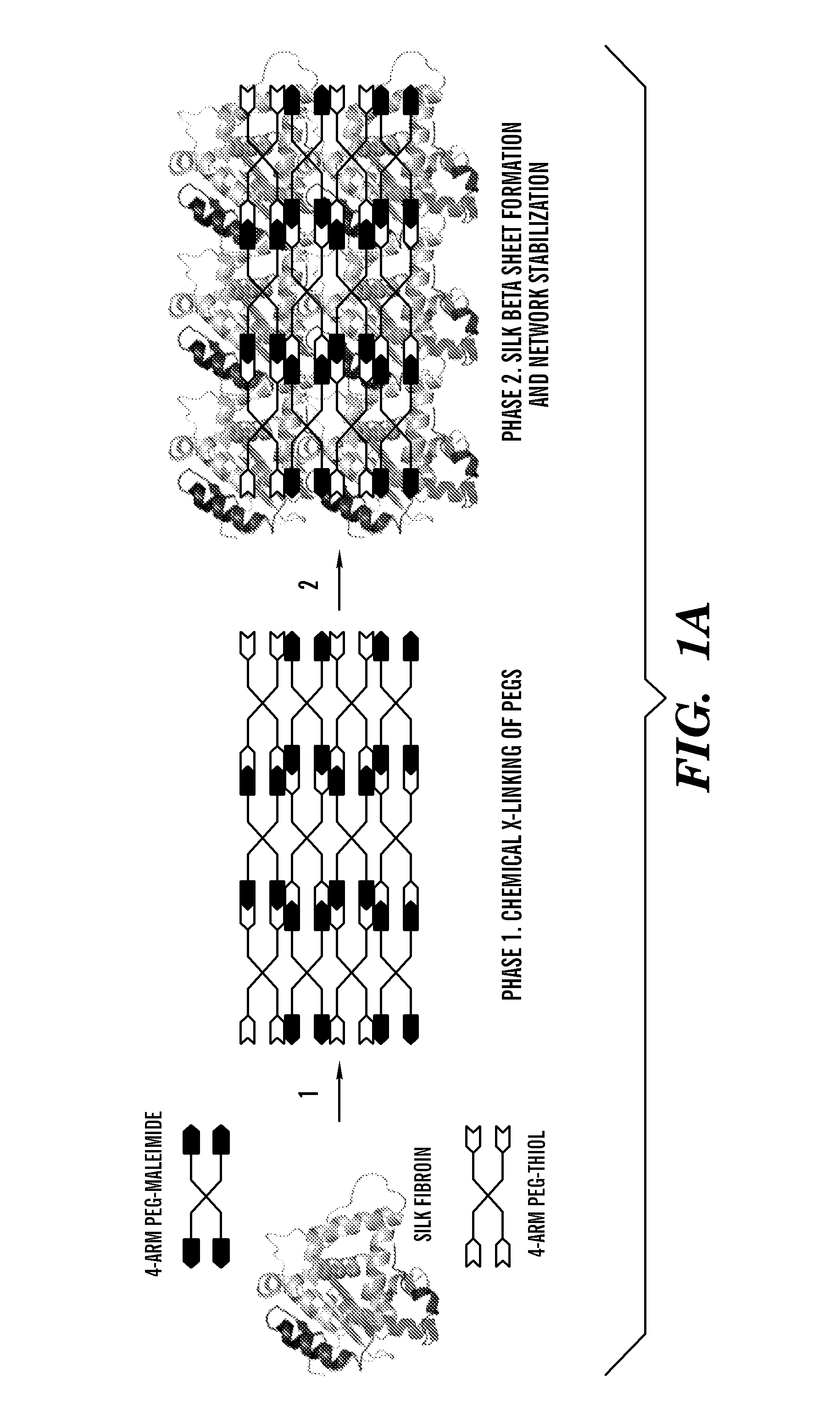
This invention relates to methods and compositions for preparation of silk-PEGs based biomaterials through crosslinking by chemically reacting active polyethylene glycols (PEGs) possessing different chemical groups (e.g., thiols and maleimides functionalized PEGs) that are additionally stabilized by the beta-sheet formation of silk fibroin. The crosslinked silk-PEGs biomaterials present strong adhesive properties, which are comparable to or better than the current leading PEG-based sealant, depending on the silk concentration in the silk-PEGs biomaterials. In addition, the silk-PEGs based biomaterials are cytocompatible, show decreased swelling behavior and longer degradation times, which make them suitable for hemostatic applications where the current available tissue sealant products can be contraindicated.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE
High swell, long-lived hydrogel sealant
A high swell, long-lived hydrogel sealant formed by reacting a highly oxidized polysaccharide containing aldehyde groups with a multi-arm amine is described. The hydrogel sealant may be particularly suitable for applications requiring high swell and slow degradation, for example, tissue augmentation, both cosmetic and reconstructive; void filling; tissue bulking, for example treatment of urinary incontinence and acid reflux; and embolization. The high swell, long-lived hydrogel sealant may also be useful as a tissue sealant and adhesive, and as an anti-adhesion barrier.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Supplemented and unsupplemented tissue sealants, methods of their production and use
InactiveUSRE39298E1Decreasing thrombogenicityLow antigenicityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryTissue sealantVascular dilatation
This invention provides methods for the localized delivery of supplemented tissue sealants, wherein the supplemented tissue sealants comprise at least one composition which is selected from one or more antibodies, analgesics, anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory compounds, antimicrobial compositions, antiproliferatives, cytokines, cytotoxins, drugs, growth factors, interferons, hormones, lipids, demineralized bone or bone morphogenetic proteins, cartilage inducing factors, oligonucleotides polymers, polysaccharides, polypeptides, protease inhibitors, vasoconstrictors or vasodilators, vitamins, minerals, stabilizers and the like. Further provided are methods of using the site-specific supplemented tissue sealants, including preparation of a biomaterial.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Resorbable anastomosis stents and plugs and their use in patients
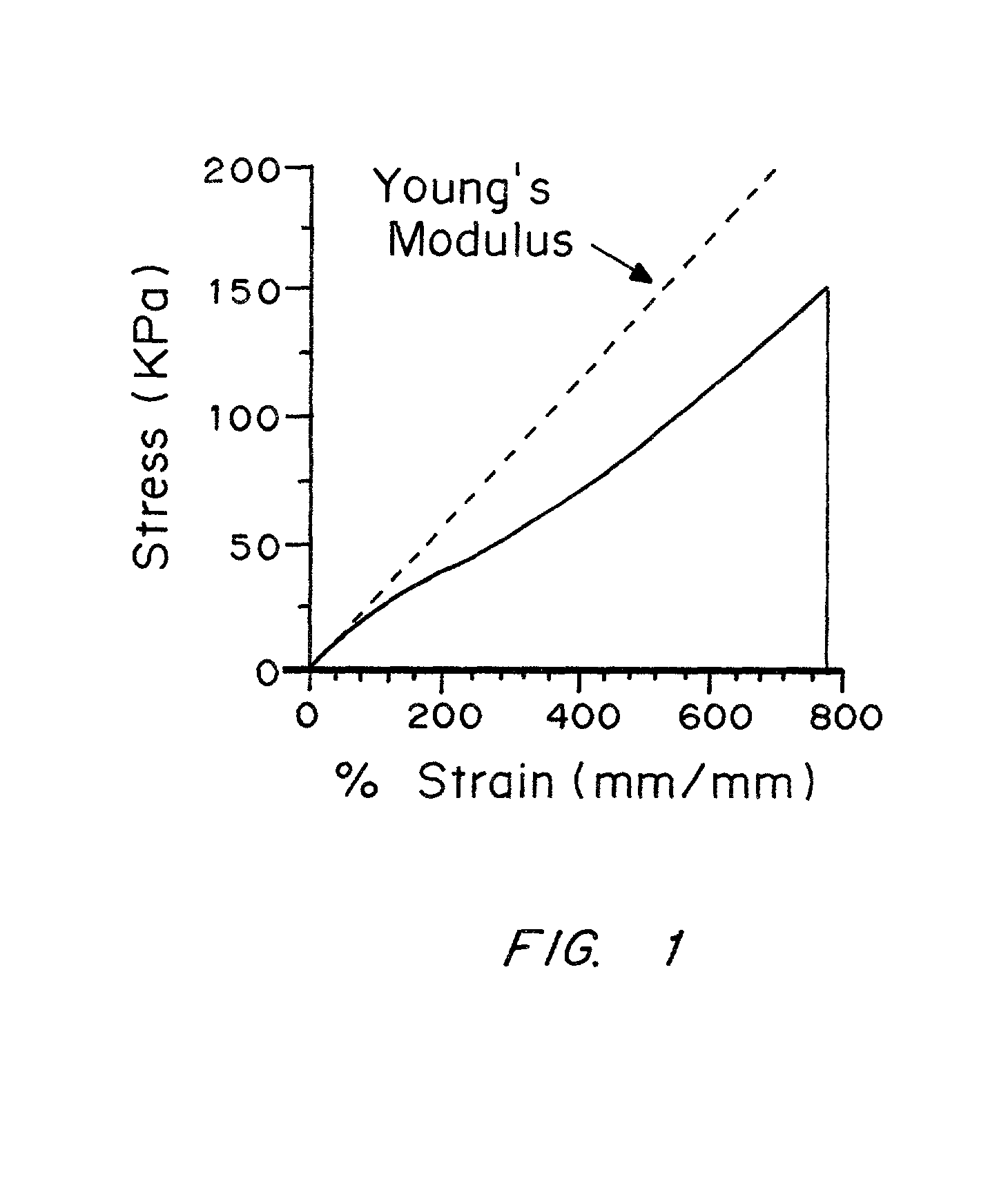
The invention relates to anastomosis stents and plugs comprised of a non-polyglycolic acid material that is resorbable by the patient in about a few minutes up to about 90 days. Such stents and plugs may be employed in surgical techniques wherein tissue is joined at an interface without need for sutures, optionally through use of a tissue sealant. As a result, interfacial tensile strengths of at least about 1.3N / cm2 may be achieved.
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA US
Method to produce fibrin monomer in acid media for use as tissue sealant
InactiveUS8367802B2Prevent re-bleedingReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFiberTissue sealant
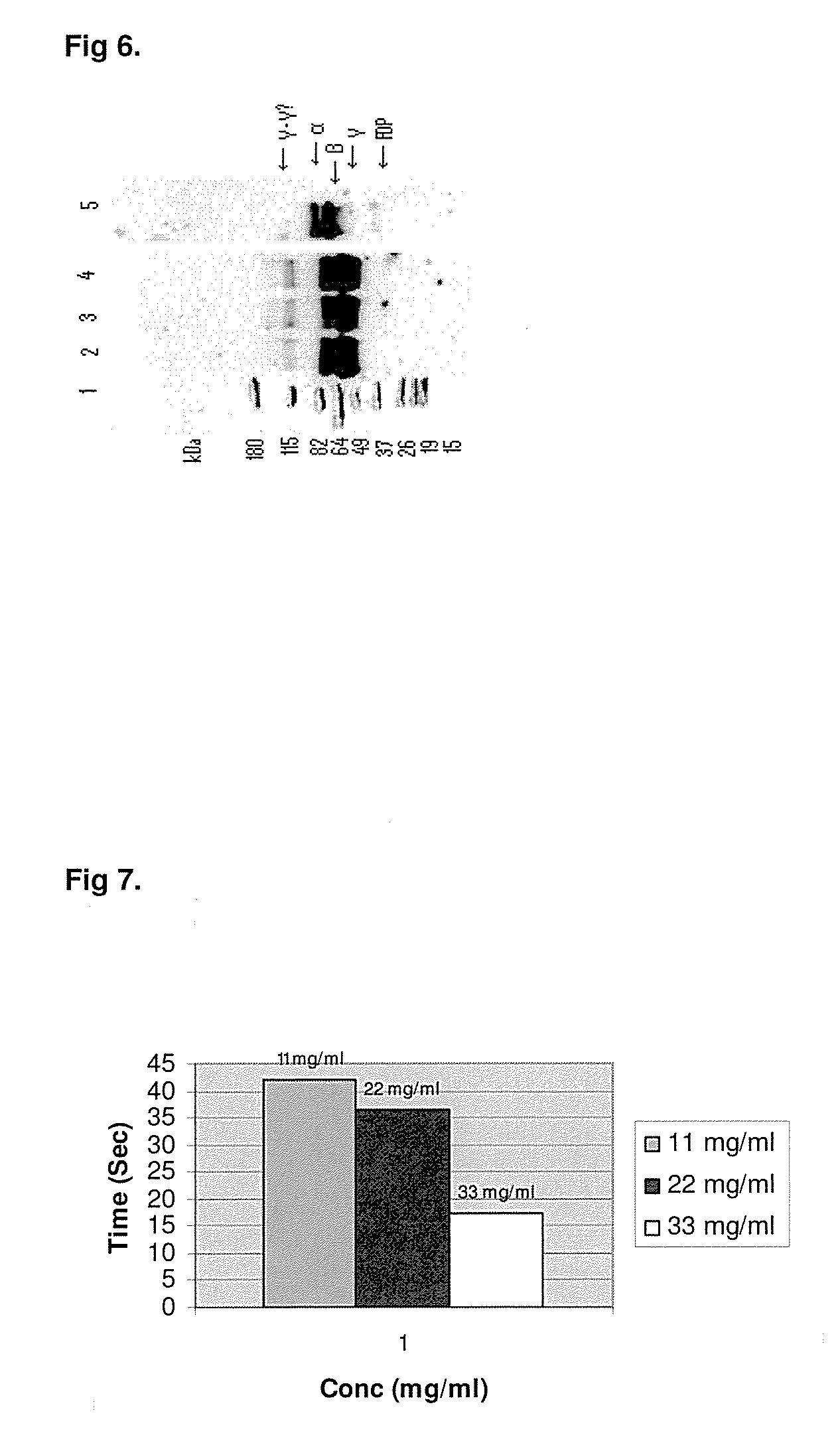
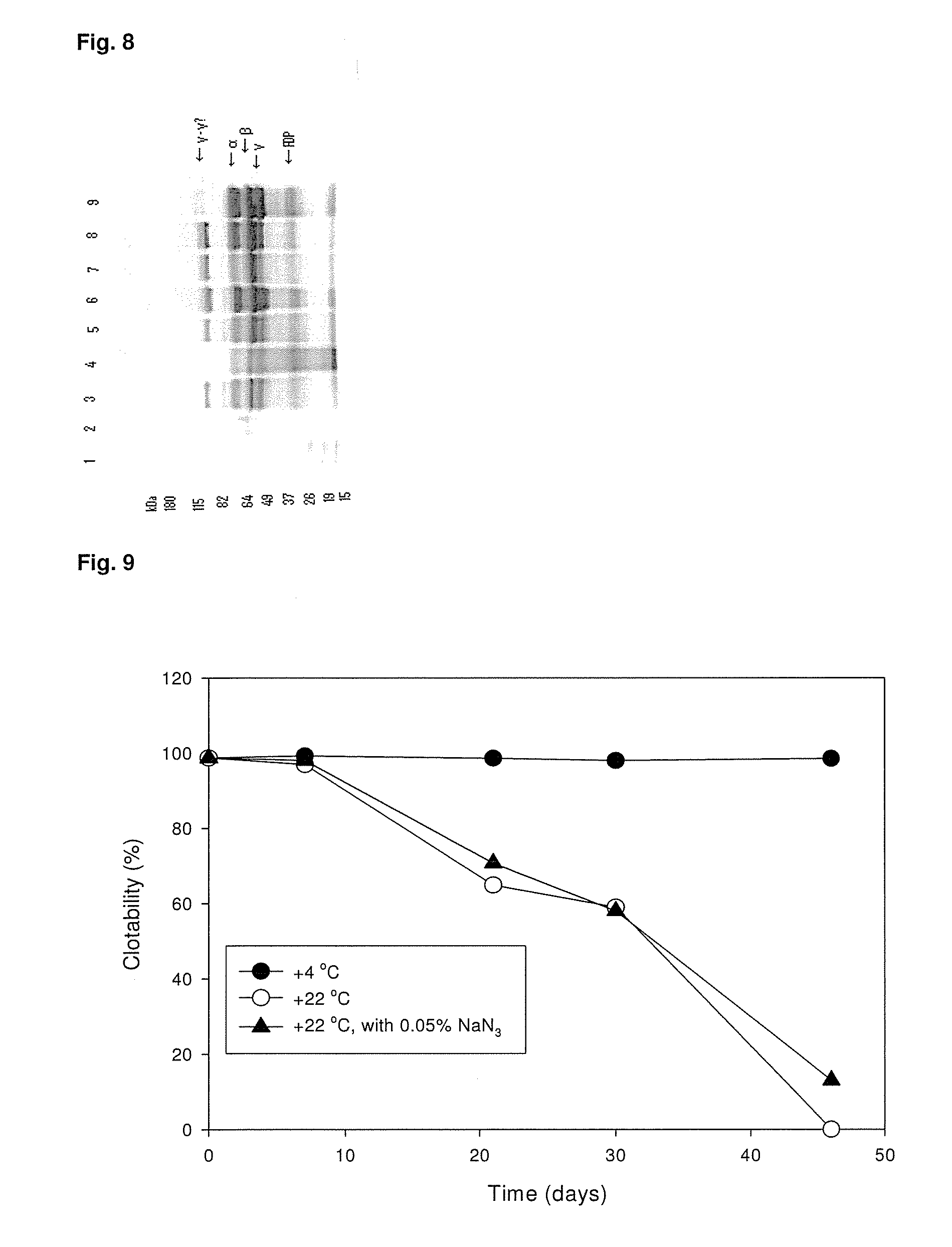
A hemostatic agent designed for use in cases of non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis, or it can be used for laparoscopic procedures or other surgical procedures in which compression is not possible or recommended. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, it produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade. The fibrin components are produced by a novel dialysis method which does not present thrombin to the immune system and can be maintained in solution for six weeks without significant proteolytic degradation.
Owner:MEDVED LEONID PHD +1
Tissue sealant for use in noncompressible hemorrhage
InactiveUS20100256671A1Excellent hemostatic agent candidateLeast riskBiocidePowder deliveryLaparoscopyTissue sealant
ClotFoam is an hemostatic agent designed for non-compressible hemorrhage. It can be applied outside the operating room through a mixing needle and / or a spray injection method following abdominal, chest, extremities or other intracavitary severe trauma to promote hemostasis, or it can be used in the operating room for laparoscopic procedures or other surgical procedures in which compression is not possible or recommended. Its crosslinking technology generates an adhesive three-dimensional polymeric network or scaffold that carries a fibrin sealant required for hemostasis. When mixed, Clotfoam produces a foam that spreads throughout a body cavity reaching the lacerated tissue to seal tissue and promote the coagulation cascade. The viscoelastic attachment properties of the foam as well as the rapid formation of a fibrin clot that ensure that the sealant remains at the site of application without being washed away by blood or displaced by movement of the target tissue .
Owner:BIOMEDICA MANAGEMENT
Hand triggered tissue sealant spray apparatus and system
The present invention is generally directed to various structures for applying a sealant to a work surface. In one aspect of the invention, a sealant applicator assembly is provided for use with an apparatus of the type having an elongated body defining an interior bore and having a piston movably positioned in the bore and a pusher member operatively associated with the piston. The assembly comprises a spray adaptor adapted to communicate with the bore of the body and defining a distal outlet. A first gas passageway is cooperatively associated with the distal outlet and configured to direct gas to create a spray discharge of the sealant. An actuating member is adapted to be cooperative associated with a pusher member to eject sealant through the distal outlet and is operative to simultaneously actuate a supply of gas to the first gas passageway for creating a spray discharge of sealant.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Tissue sealing system and apparatus
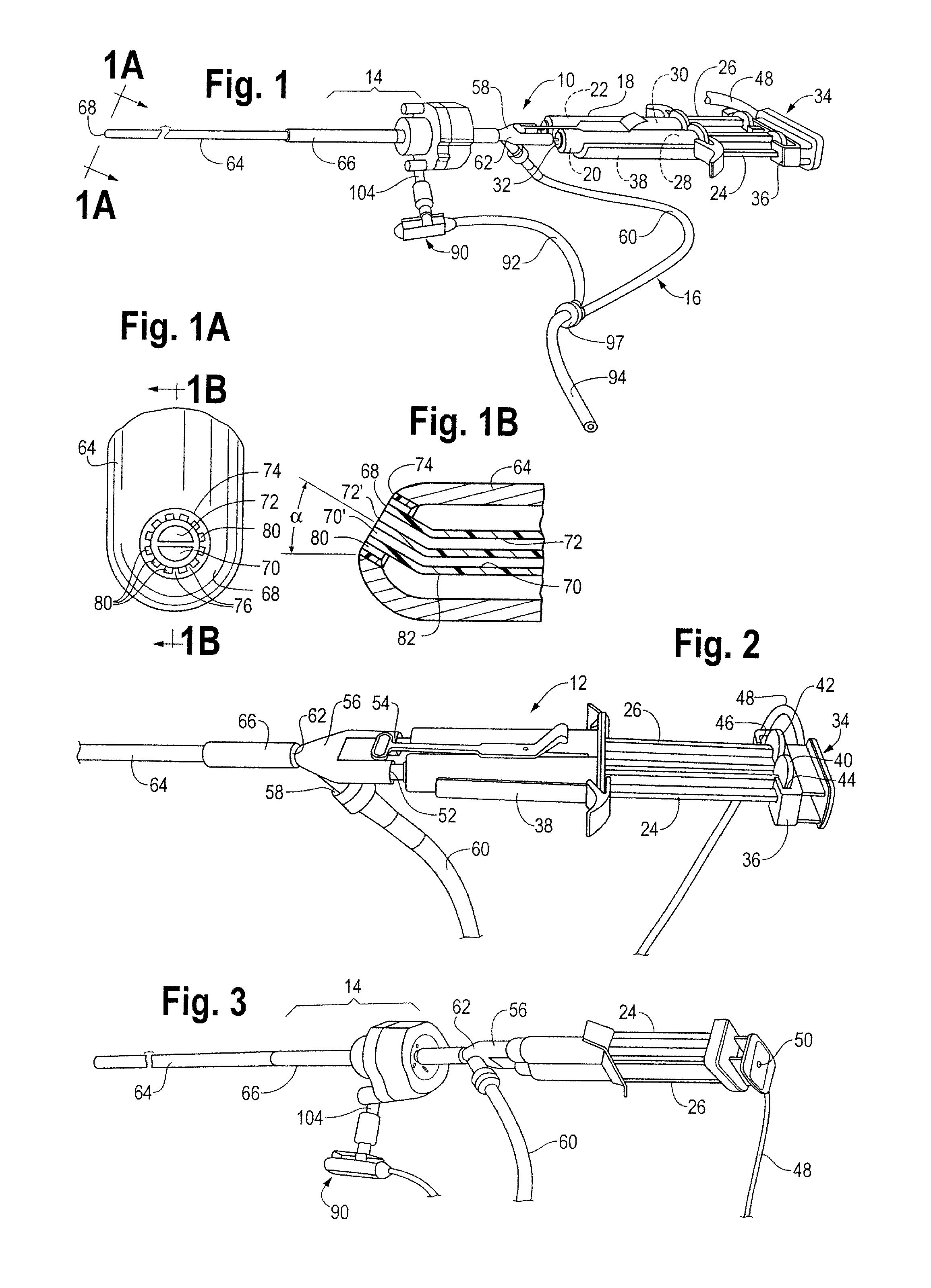
A laparoscopic tissue sealant spray apparatus and system having a laparoscopic tissue sealant spray assembly combined with a trocar assembly, the tissue sealant spray assembly having an elongate delivery tube. A spray outlet at a distal end of the elongate delivery tube may be rounded or angled. A ring member provided at the distal end of the elongate delivery tube directs a spray cone toward a portion of a target tissue site, and the spray cone may be repositioned to a different portion of the target tissue site by rotation of the elongate delivery tube. The trocar assembly includes a vent opening that connects to a venting valve member that provides a vent path which passively opens upon operation of the tissue sealant spray assembly, avoiding excessive pressure build-up within a body cavity.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
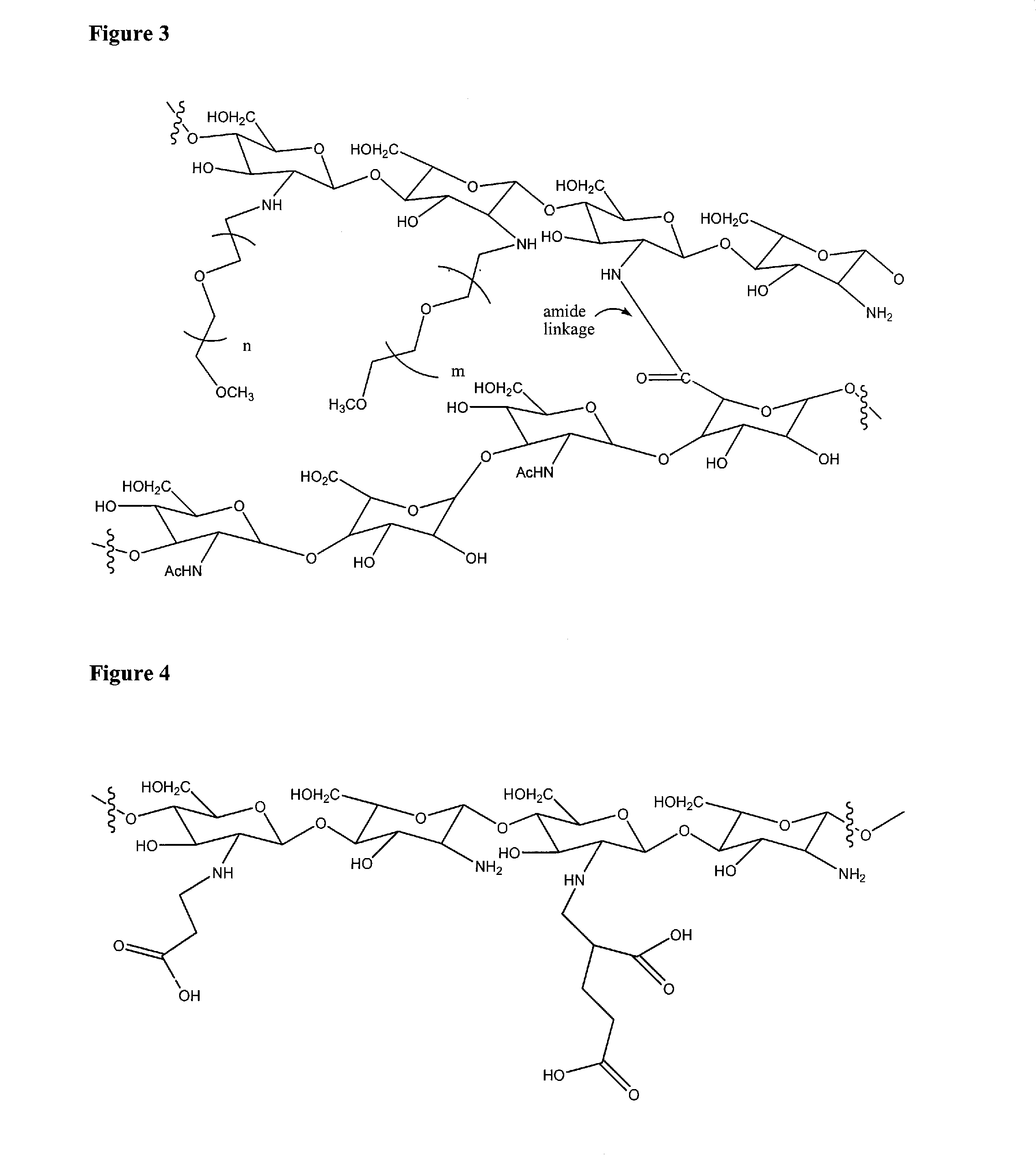
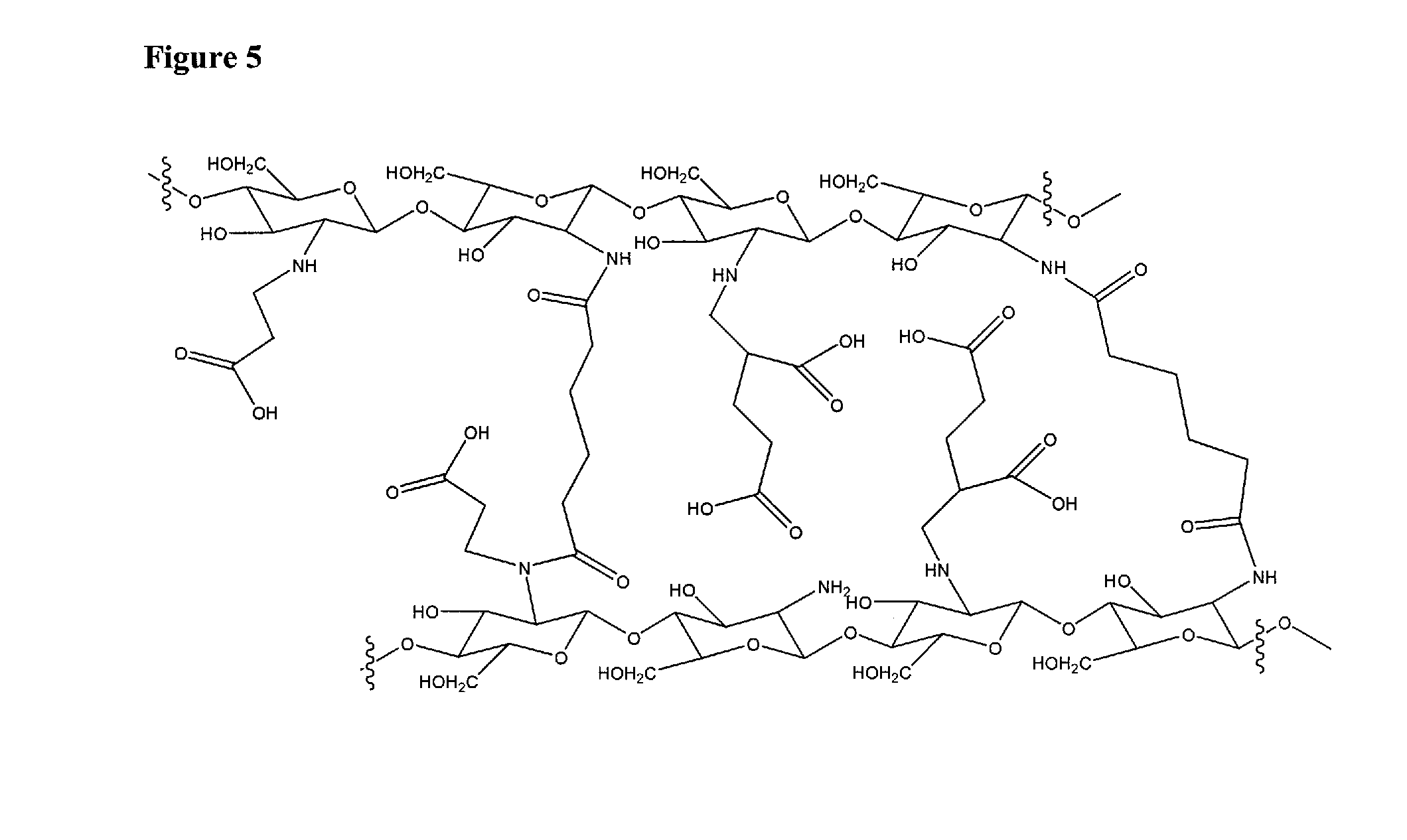
Tissue sealant and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105169469AAvoid stickingAvoid risk of transmissionSurgical adhesivesTissue sealantPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a tissue sealant and a preparation method and application thereof. The sealant mainly comprises hydrophilic raw material, nucleophilic raw material, a marker and physiological thinner, wherein the hydrophilic raw material mainly refers to the derivatives of polyethylene glycol and the nucleophilic raw material mainly refers to polyamino acid. The preparation method includes: physically mixing the hydrophilic raw material, the nucleophilic raw material, the marker and the physiological thinner through a mixing tool, and performing covalent cross-linking to form hydrogel. The tissue sealant has the advantages that the sealant mainly used for sealing small wounds after eye surgery is good in tissue cohesive force and film-forming property, good in biocompatibility, capable of promoting epithelization healing and preventing seepage leakage, simple in preparation method, capable of being quantified to form a stable production line, and good in clinical application value.
Owner:NKD PHARMA CO LTD
Hydrophobic Tissue Adhesives
ActiveUS20140348896A1Reduce deliveryHigh bonding strengthSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue sealantCatheter
Pre-polymers for use as tissue sealants and adhesives, and methods of making and using thereof are provided. The pre-polymers have flow characteristics such that they can be applied through a syringe or catheter but are sufficiently viscous to remain in place at the site of application and not run off the tissue. The pre-polymers are also sufficiently hydrophobic to resist washout by bodily fluids. The pre-polymers are stable in bodily fluids; that is the pre-polymer does not spontaneously crosslink in bodily fluids absent the presence of an intentionally applied stimulus to initiate crosslinking. Upon crosslinking, the adhesive exhibits significant adhesive strength in the presence of blood and other bodily fluids. The adhesive is sufficiently elastic that it is able to resist movement of the underlying tissue. The adhesive can provide a hemostatic seal. The adhesive is biodegradable and biocompatible, causing minimal inflammatory response.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com