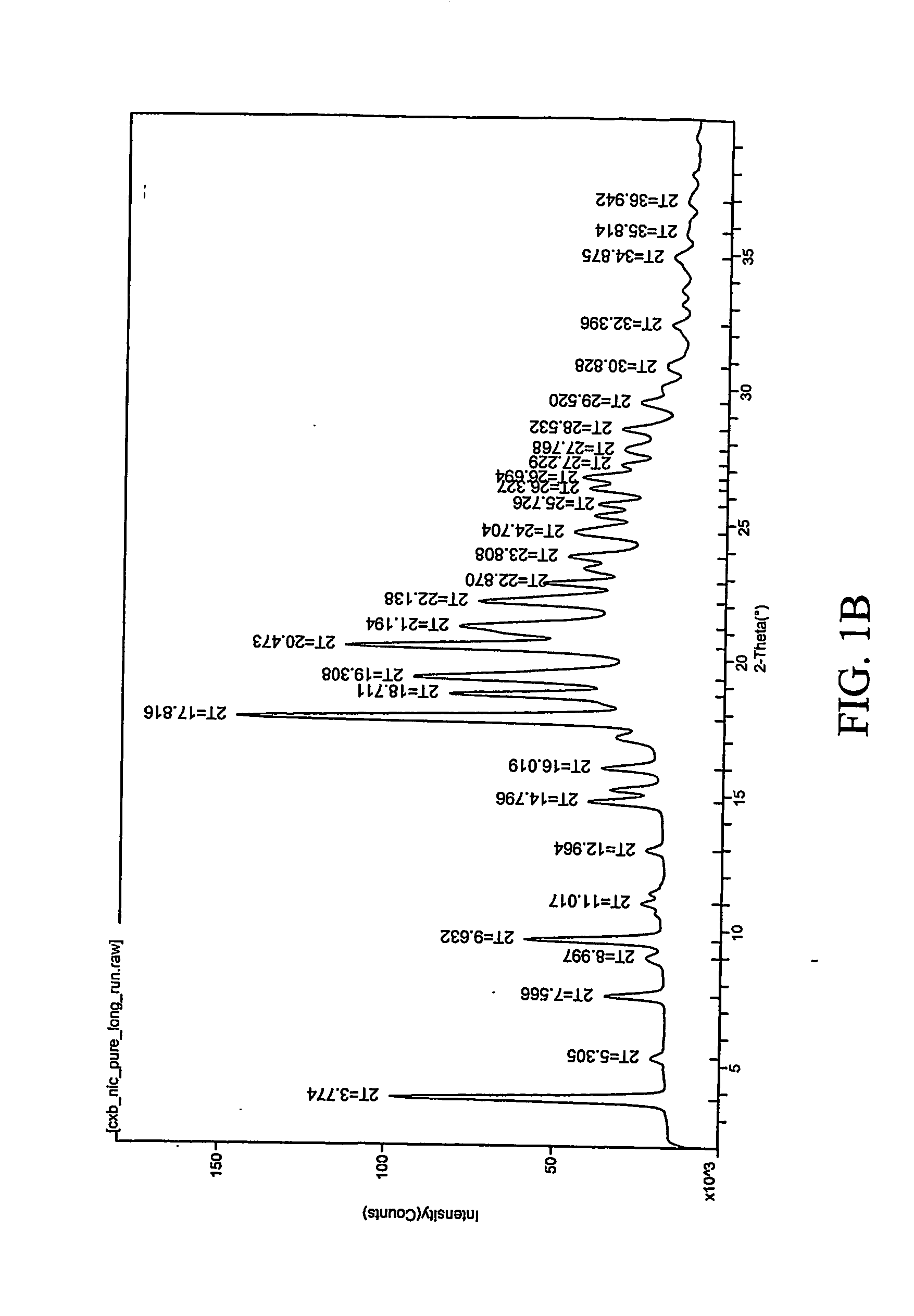
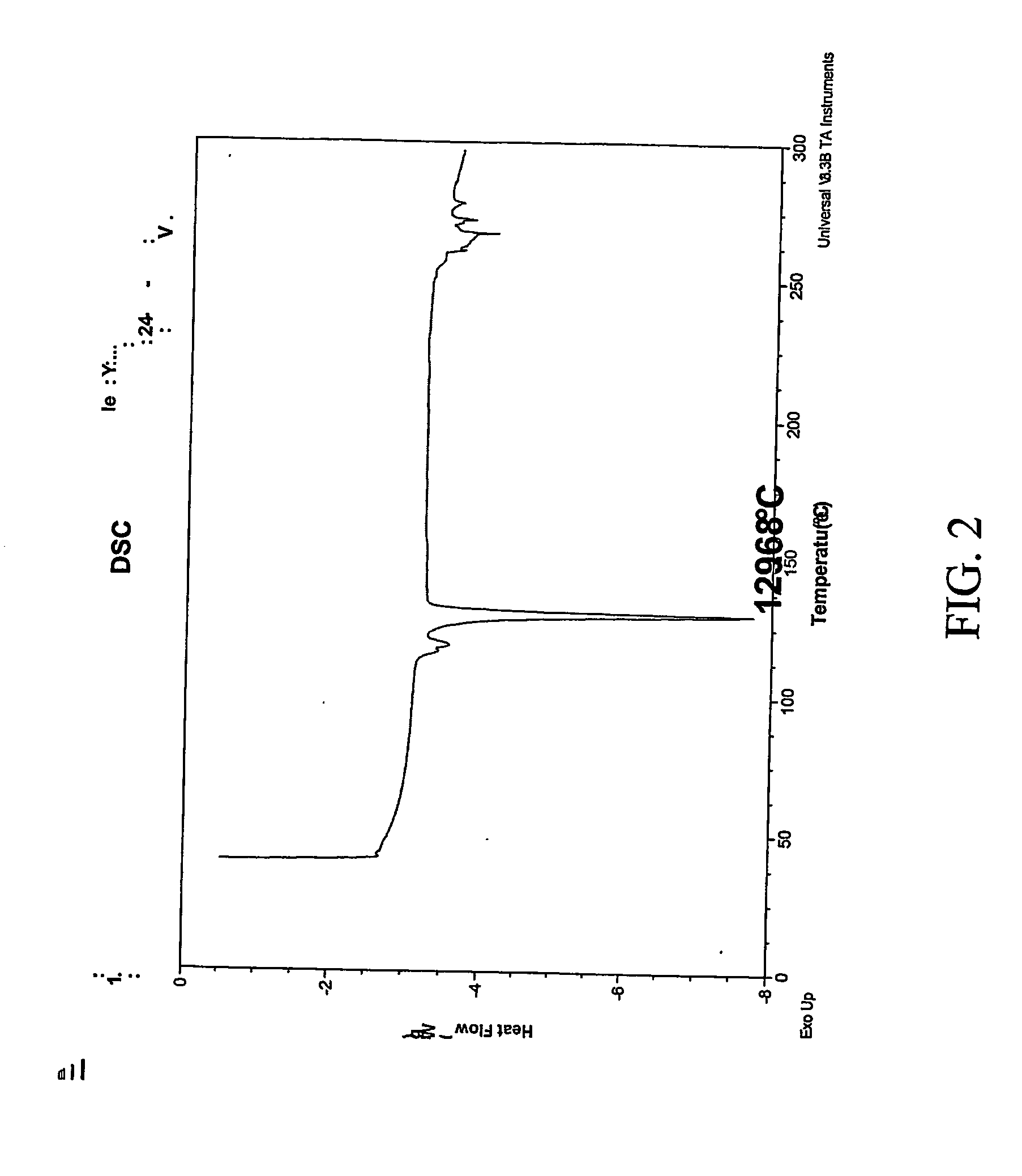
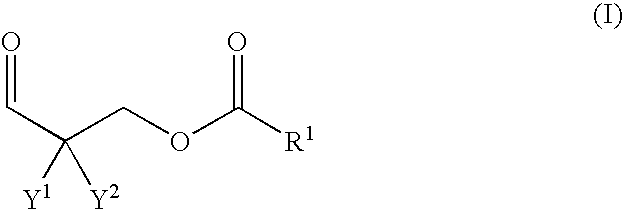
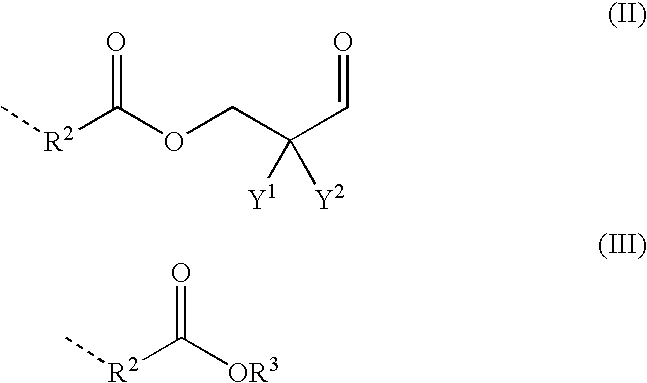
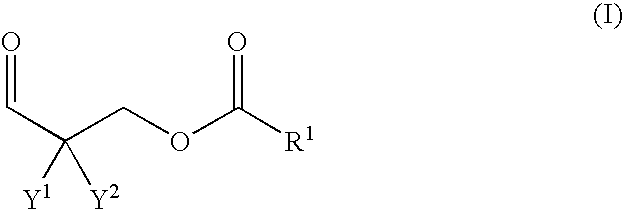
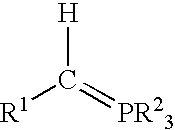
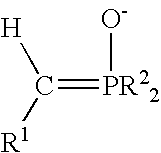
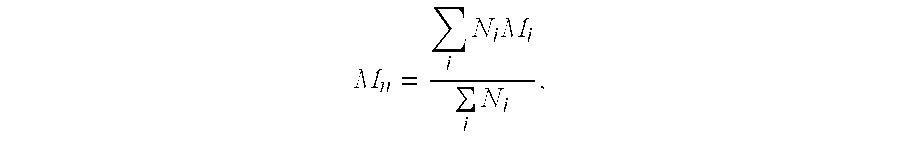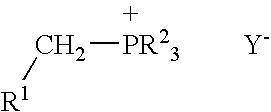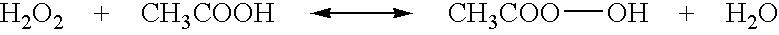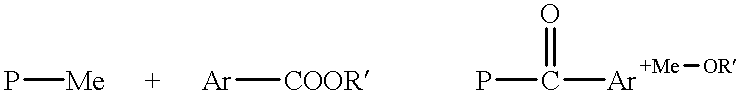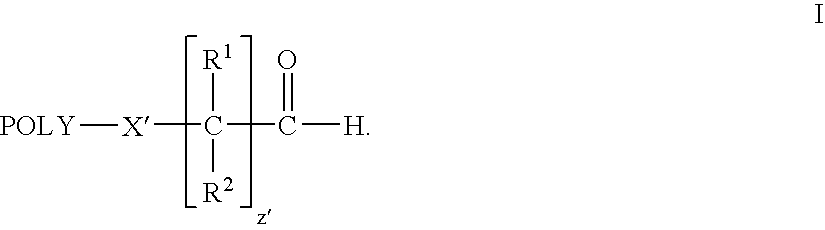Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1630 results about "Aldehyde formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An aldehyde /ˈældɪhaɪd/ or alkanal is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure −CHO, consisting of a carbonyl center (a carbon double-bonded to oxygen) with the carbon atom also bonded to hydrogen and to an R group, which is any generic alkyl or side chain.
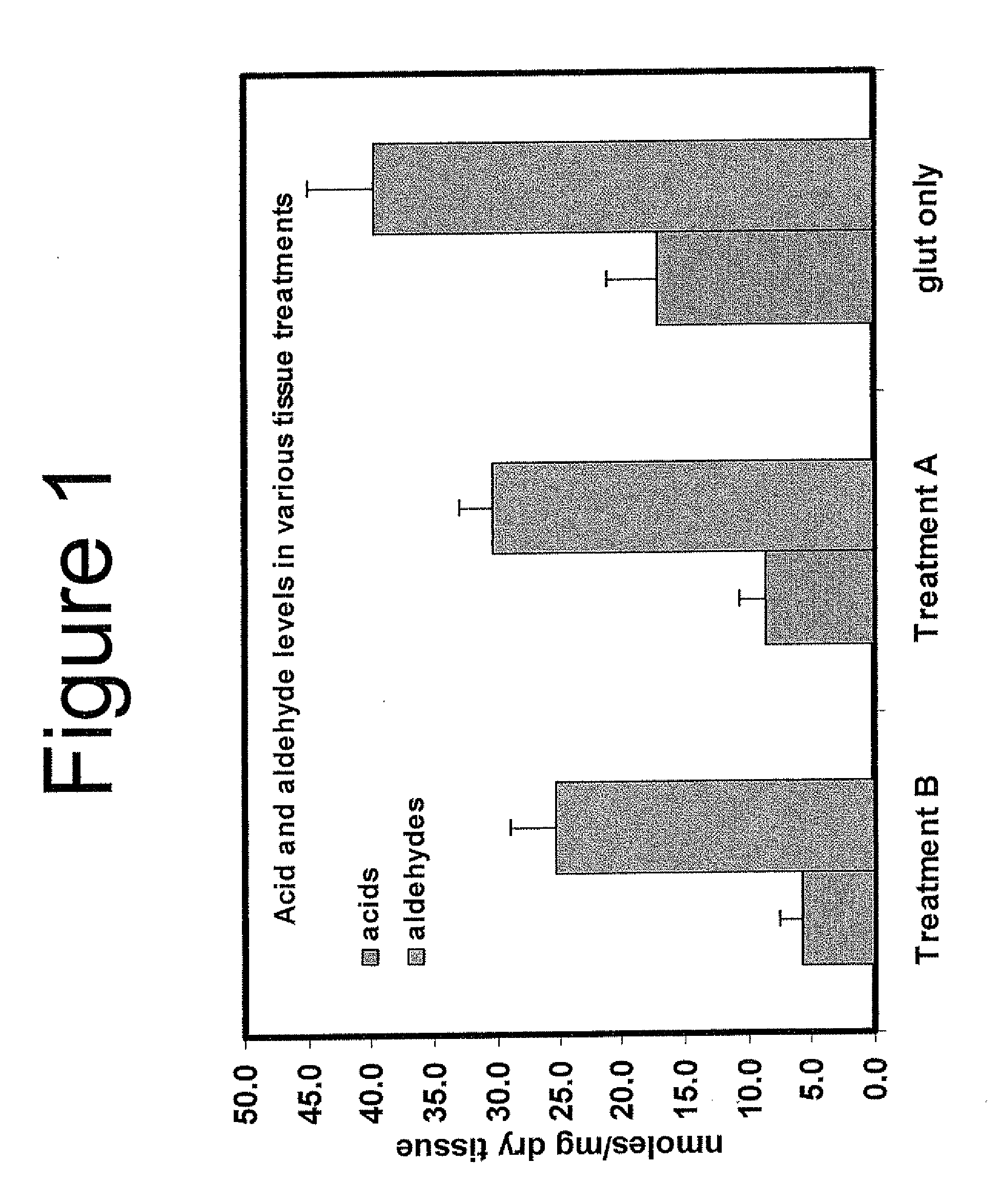
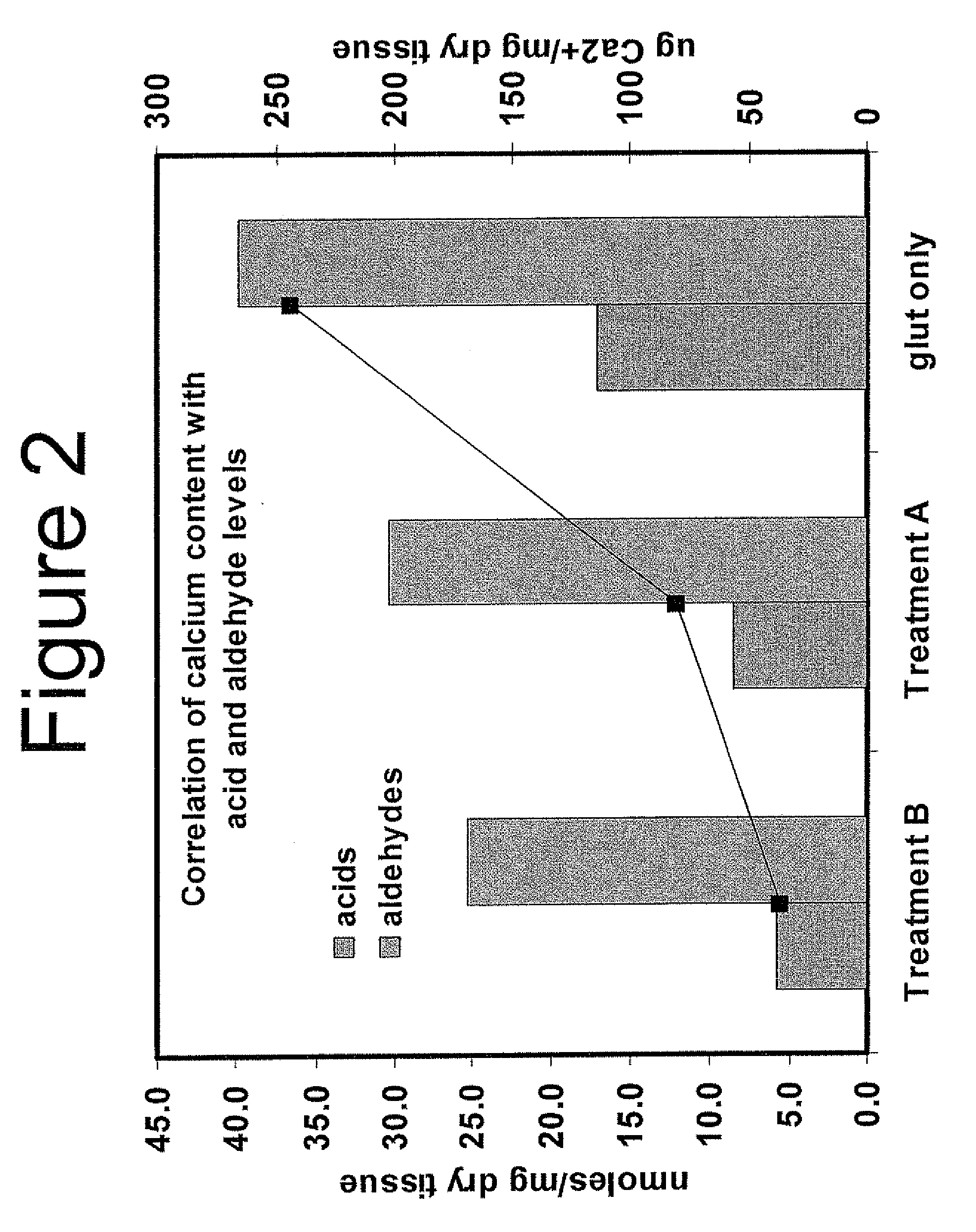
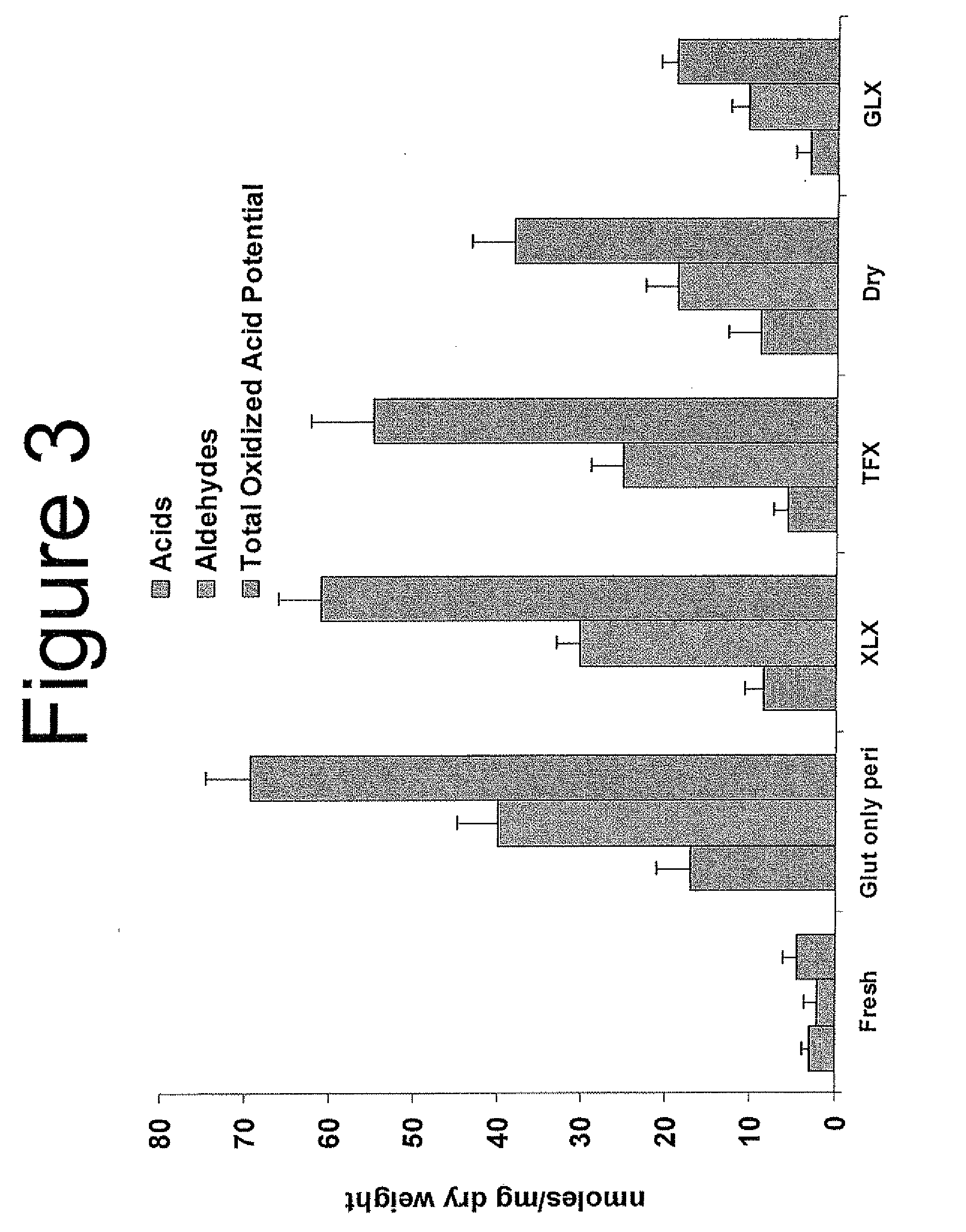
Capping Bioprosthetic Tissue to Reduce Calcification
A treatment for bioprosthetic tissue used in implants or for assembled bioprosthetic heart valves to reduce in vivo calcification. The method includes applying a calcification mitigant such as a capping agent or an antioxidant to the tissue to specifically inhibit oxidation in tissue. Also, the method can be used to inhibit oxidation in dehydrated tissue. The capping agent suppresses the formation of binding sites in the tissue that are exposed or generated by the oxidation and otherwise would, upon implant, attract calcium, phosphate, immunogenic factors, or other precursors to calcification. In one method, tissue leaflets in assembled bioprosthetic heart valves are pretreated with an aldehyde capping agent prior to dehydration and sterilization.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method of providing hemostasis to a wound
The present invention is directed to hemostatic wound dressings that contain a substrate for contacting a wound, wherein the substrate includes a wound-contacting surface and is fabricated at least in part from a biocompatible aldehyde-modified polysaccharide having covalently conjugated there with a hemostatic agent and to methods of providing hemostasis to a wound that include applying the wound dressing described herein to a wound.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Composite metal oxide for unsaturated aldehyde selective oxidation and preparing method thereof
A composite metallic oxide as catalyst for selective oxidization of unsaturated aldehyde, especially the acrylaldehyde or methyl acrylaldehyde to obtain acrylic acid or methyl acrylic acid, is composed of active components (Mo, V and Cu), stabilizer (at least Sb and Ti) and the composite oxide of Ni, Fe, Si, Al, alkali metal and alkali-earth metal. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:兰州金润宏成新材料科技有限公司
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
InactiveUS20070026078A1Improve solubilityLow hygroscopicityBiocidePowder deliveryThioketoneHydroxamic acid
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
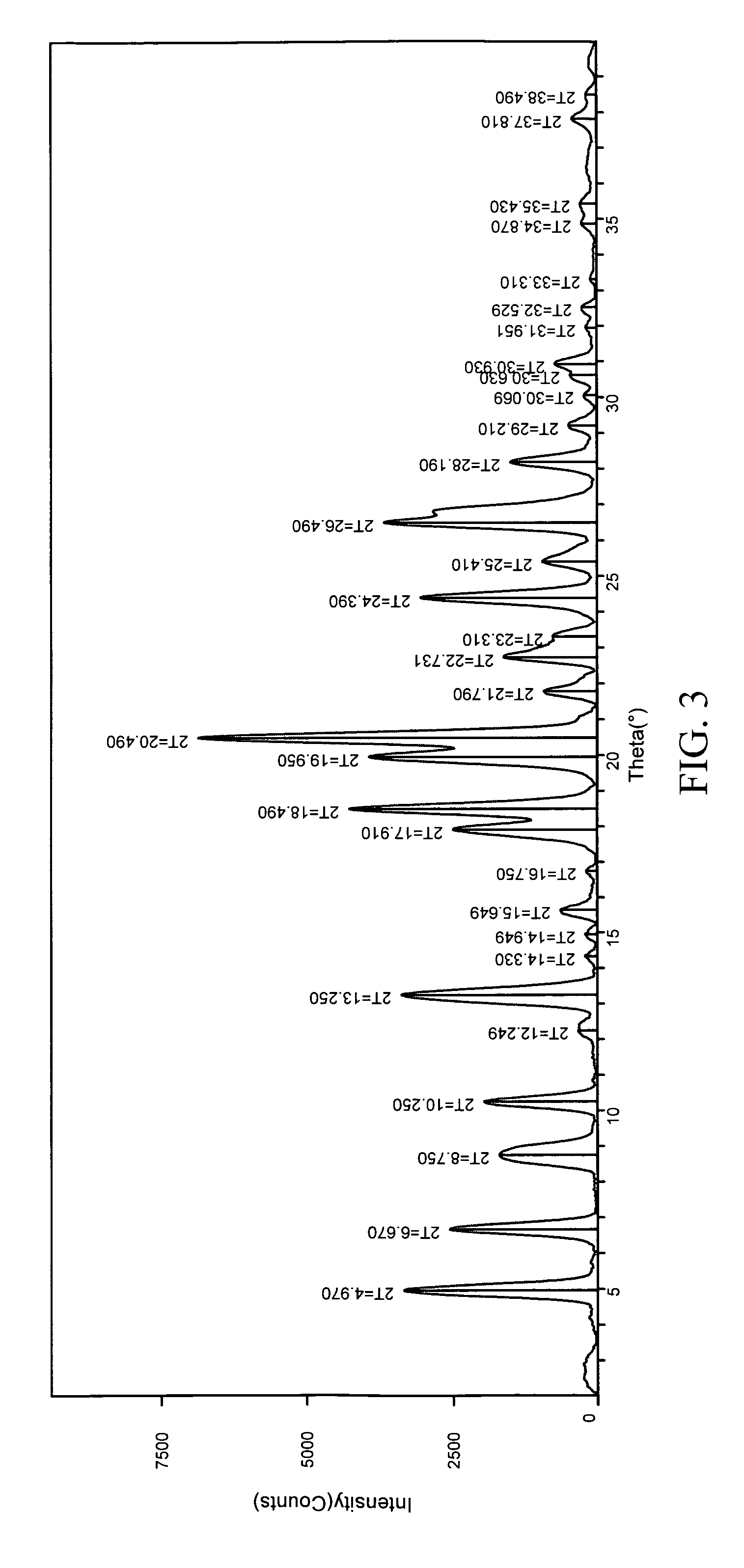
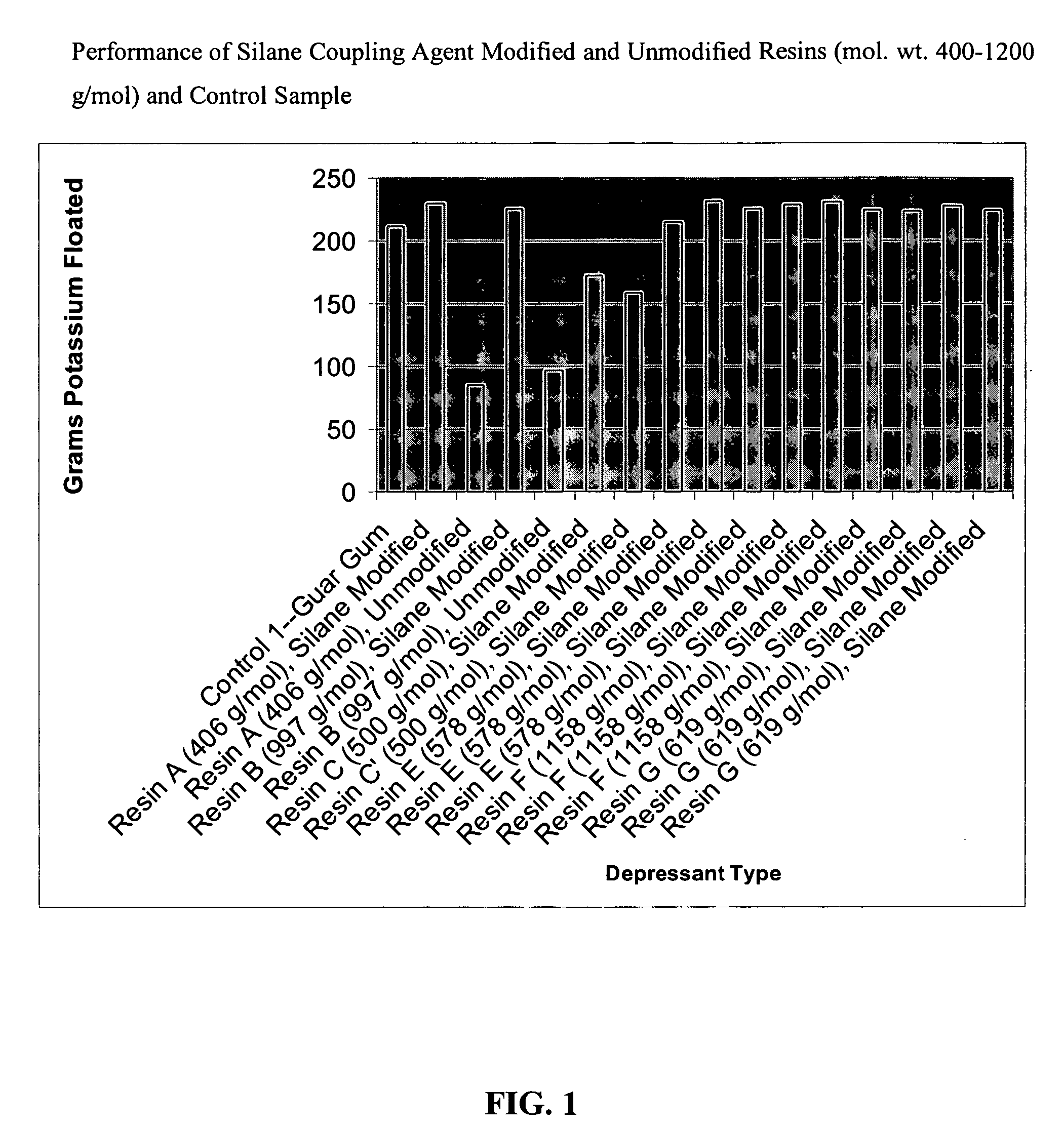
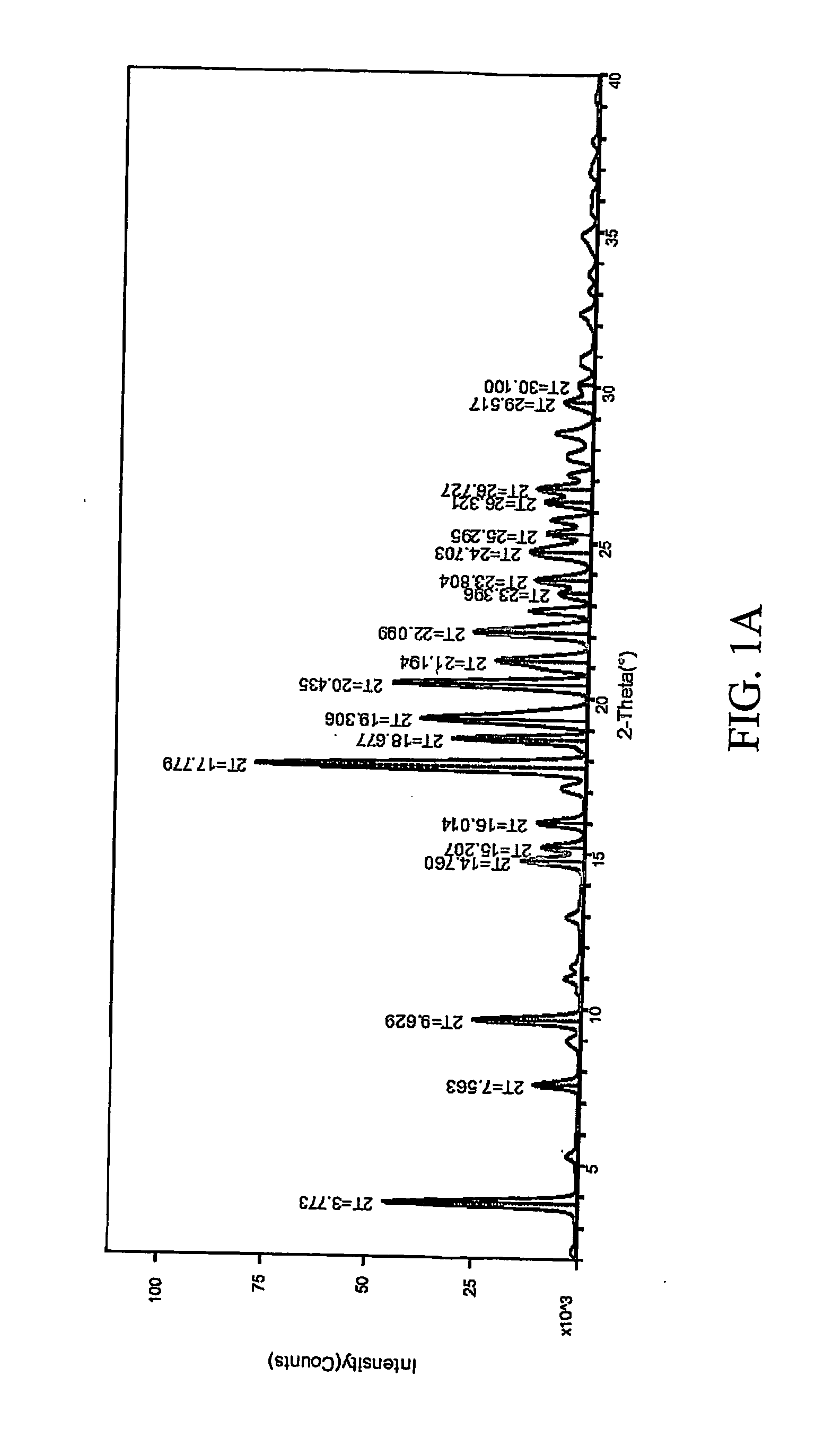
Modified amine-aldehyde resins and uses thereof in separation processes
InactiveUS20060151360A1Highly selective bindingWaste water treatment from quariesPigmenting treatmentIonAldehyde formation
Modified resins are disclosed for removing a wide variety of solids and / or ionic species from the liquids in which they are suspended and / or dissolved. These modified resins are especially useful as froth flotation depressants in the beneficiation of many types of materials (e.g., mineral and metal ores), including the beneficiation of impure coal comprising clay impurities, as well as in the separation of valuable bitumen from solid contaminants such as sand. The modified resins are also useful for treating aqueous liquid suspensions to remove solid particulates, as well as for removing metallic ions in the purification of water. The modified resins comprise a base resin that is modified with a coupling agent, which is highly selective for binding to solid contaminants and especially siliceous materials such as sand or clay.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Process for producing composite oxide catalyst
InactiveCN1697701AImprove conversion rateGood choiceOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAdditive ingredientSolvent
A catalyst for producing from an olefin the corresponding unsaturated aldehyde and unsaturated carboxylic acid in high yield; and a process for producing the catalyst. The process is for producing a composite oxide catalyst which is for use in catalytically oxidizing an olefin in a vapor phase with a gas containing molecular oxygen to produce the corresponding unsaturated aldehyde and corresponding unsaturated carboxylic acid, and which comprises (A) molybdenum, (B) bismuth, (C) cobalt and / or nickel, and (D) iron. It is characterized in that catalyst precursor particles produced through a preceding step in which an aqueous dispersion containing a raw material for the ingredient (A), raw material for the ingredient (C), and raw material for the ingredient (D) which have been united with one another and having a nitric acid radical content satisfying the relationship 1.2<=NO3 / (3xFe+2x(Co+Ni)) is dried and then heated are united with a raw material for the ingredient (B) in a water-miscible solvent and the resultant united matter is dried and burned. In the relationship, NO3, Fe, Co, and Ni indicate the molar contents of nitric acid radicals, iron, cobalt, and nickel, respectively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Perfume for capsule composition
InactiveUS20070149424A1Improving capsule hardnessCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGreek letter betaFlavor
The invention relates to a core shell capsule containing in the core an oil or waxy solid, wherein the oil or waxy solid comprises: (1) 50-100% by weight of a perfume composition, which is a mixture of at least two perfume ingredients-selected from: a) aldehydes, including alpha beta unsaturated aldehydes, which constitute 0-20% by weight of the perfume composition; b) primary or secondary amines constituting 0-10% by weight of the perfume composition; c) perfume ingredients having ClogP>4.0, which constitute 0-25% by weight of the perfume composition; d) perfume ingredients having ClogP>5.0, which constitute 0-20% by weight of the perfume composition; and e) perfume ingredients having ClogP<2.0, which constitute 0-20% by weight of the perfume composition, and (2) 0-50% by weight of benefit agents other than perfume ingredients.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions of drugs such as carbamazepine, celecoxib, olanzapine, itraconazole, topiramate, modafinil, 5-fluorouracil, hydrochlorothiazide, acetaminophen, aspirin, flurbiprofen, phenytoin and ibuprofen
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphinic acid, phosphonic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, imine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, S-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, N-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, 0-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +3
L-threonine producing bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia and method for producing L-threonine
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Polyurethane composition containing polyaldimine
The invention relates to compositions containing at least one polyurethane prepolymer A which has isocyanate end groups and is produced from at least one polyisocyanate and at least on polyol, and at least one polyaldimine B which can be obtained from at least one polyamine C having aliphatic primary amino groups and at least one aldehyde D. The invention also relates to the production of said compositions, and to the production of the polyaldimine. Disclosed is also the use of said compositions as an adhesive, a sealant, a coating or a lining. The invention further relates to methods for gluing, sealing or coating, and to articles having a surface which has been at least partially brought into contact with one such composition. Said compositions have a significant advantage in that they are odourless before during and after the hardening thereof.
Owner:SIKA TECH AG
Method for preparing load type rhodium catalyst for making high-carbon aldehyde using hydroformylation of higher olefins
InactiveCN101116816AImprove stabilityCatalyst activation/preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide reactionAlkaline earth metalFormylation reaction
A modified activated carbon supported rhodium type catalyst for high carbene hydrocarbon hydrogen formylation reaction is provided. The preparation of the catalyst comprises the techniques such as carrier pretreatment-activity rhodium solid-phase bound reagent combination, and used for gas-liquid-solid three phase catalyst system, which is characterized in that: a certain amount of alkali or alkaline earth metal hydroxide and salt modification activated carbon is used as a carrier, and the supported rhodium catalyst is prepared by using multiple impregnation method. The catalyst of the present invention is high in activity and selectivity. The catalyst is easy to be separated from products after reaction, capable of being used repeatedly, stable in performance, and suitable for the production process of high carbene hydrocarbon or mixed olefin hydrogen formylation made high carbon aldehyde, which has good industrial application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Aqueous disinfectants and sterilants and related delivery systems
InactiveUS20060198876A1Effectively clean surfaceBiocideNon-surface-active detergent compositionsDisinfectantAldehyde formation
The present invention is drawn to disinfectant or sterilant compositions and associated methods of use. In one embodiment, an aqueous disinfectant or sterilant composition can comprise an aqueous vehicle, including water, from 0.001 wt % to 50 wt % of a peracid, and from 0.001 wt % to 25 wt % of a peroxide. Additionally, from 0.001 ppm to 50,000 ppm by weight of a transition metal based on the aqueous vehicle content can also be present. The disinfectant composition can be used in the manufacture of disinfectant wipes, disinfectant gels, and disinfectant fogs. In one embodiment, the composition can be substantially free of aldehydes. Alternatively or additionally, the transition metal can be in the form of a colloidal transition metal.
Owner:AXENIC GLOBAL LLC
Process for preparing functional group-containing olefinic compounds
ActiveUS6838576B1High yieldStereoselectivity can be controlledPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationCompound aLeaving group
A process for preparing functional group-containing olefinic compounds comprises the steps of (a) reacting at least one alkylidene phosphorane with at least one carbonyl-containing compound that comprises at least one group that is a leaving group, or that is capable of subsequent conversion to a leaving group, to form an olefinic compound that comprises at least one leaving group, the carbonyl-containing compound being selected from the group consisting of ketones and aldehydes; and (b) reacting the olefinic compound with at least one functional group-containing nucleophile to form a functional group-containing olefinic compound.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous sanitizers, disinfectants, and/or sterilants with low peroxygen content
InactiveUS20070053850A1Effectively clean surfaceAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsAlcoholFood grade
The present invention is drawn to disinfectant compositions, which are human safe, e.g., food grade or food safe. In one embodiment, an aqueous disinfectant composition can comprise an aqueous vehicle, including water, from 0.001 wt % to 10.0 wt % of a peroxygen, and an alcohol. Additionally, from 0.001 ppm to 50,000 ppm by weight of a transition metal based on the aqueous vehicle content can also be present. The composition can be substantially free of aldehydes. Alternatively or additionally, the transition metal can be in the form of a colloidal transition metal, such as colloidal silver or alloy thereof.
Owner:AXENIC GLOBAL LLC
Functionalized particles
InactiveUS20050084456A1Safe and effectiveSafely and selectivelyPowder deliveryMicroencapsulation basedPhysiologic BarrierMethyl group
The present invention provides functionalized particles and methods for delivering said particles capable of crossing a physiologic barrier and exerting an effect. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method of delivering a particle to a mammal comprising the steps of contacting a functionalized particle with a tag and introducing the functionalized and tagged particle to a mammal, wherein the functionalized portion of the particle is selected from the group consisting of acrylic acid, 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate, 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid, allylamine, carboxyl group, hydroxyl group, sulfonic group, aldehyde and amine group. The particle is a biodegradable or nodegradable polymer and less than 1.0 mm in diameter.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
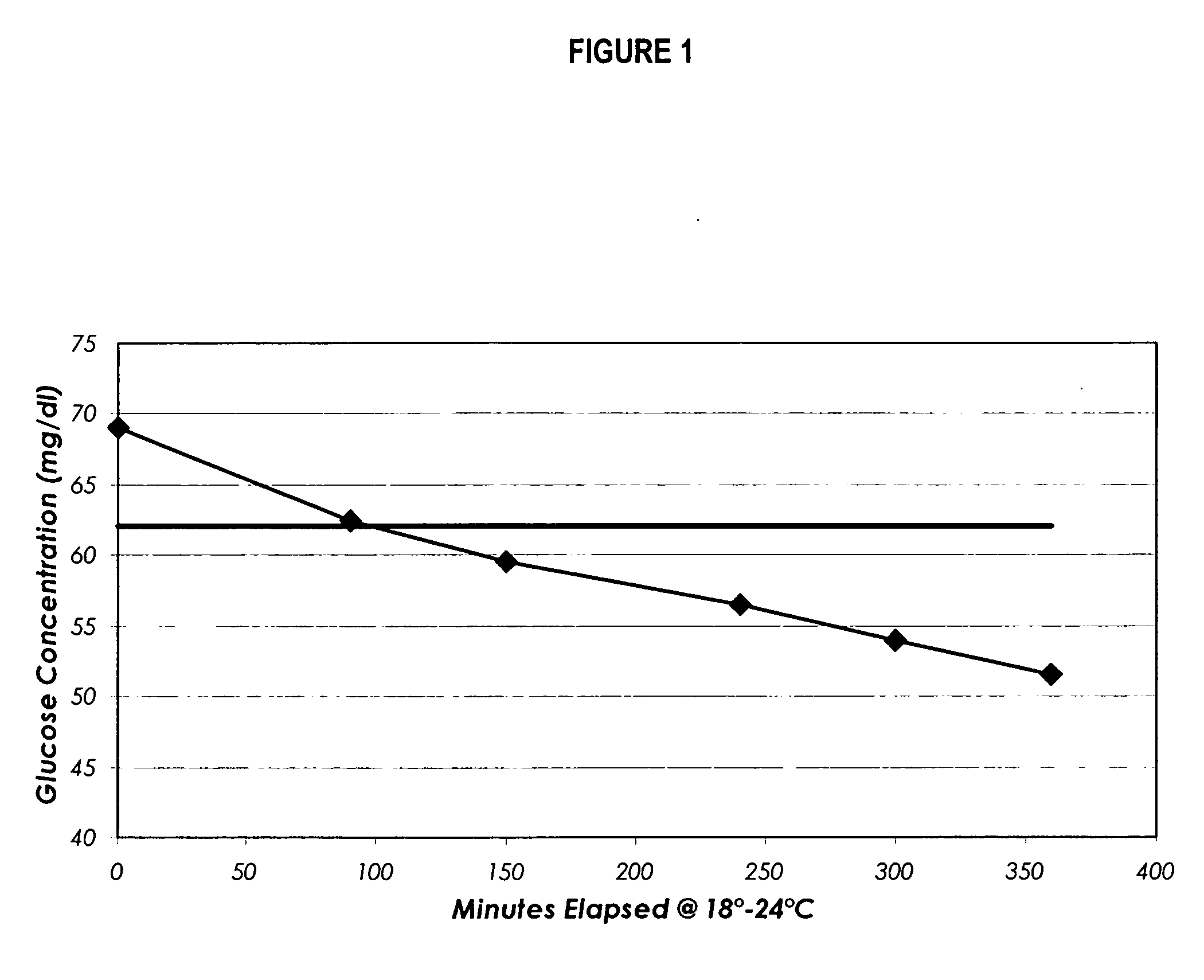
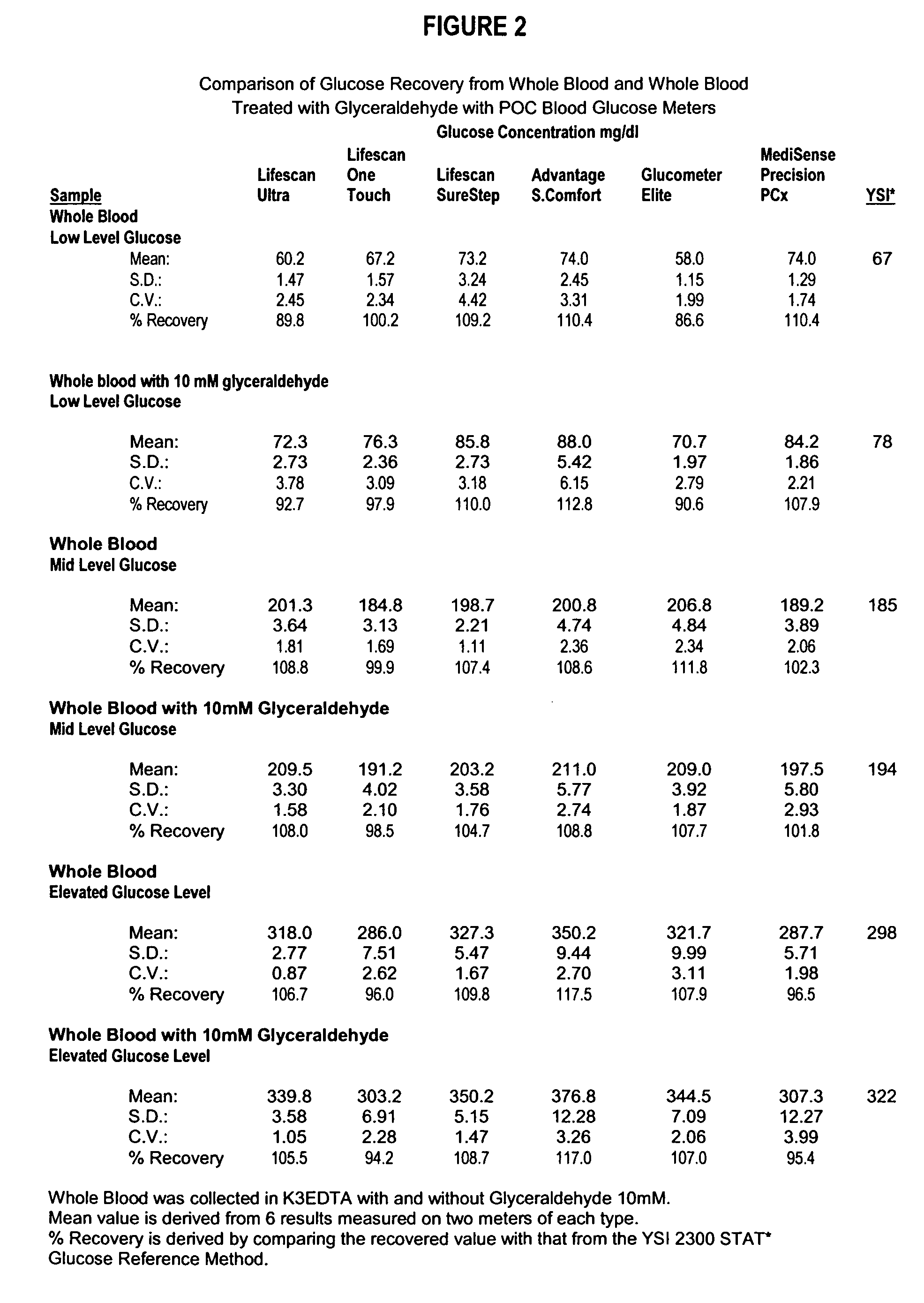
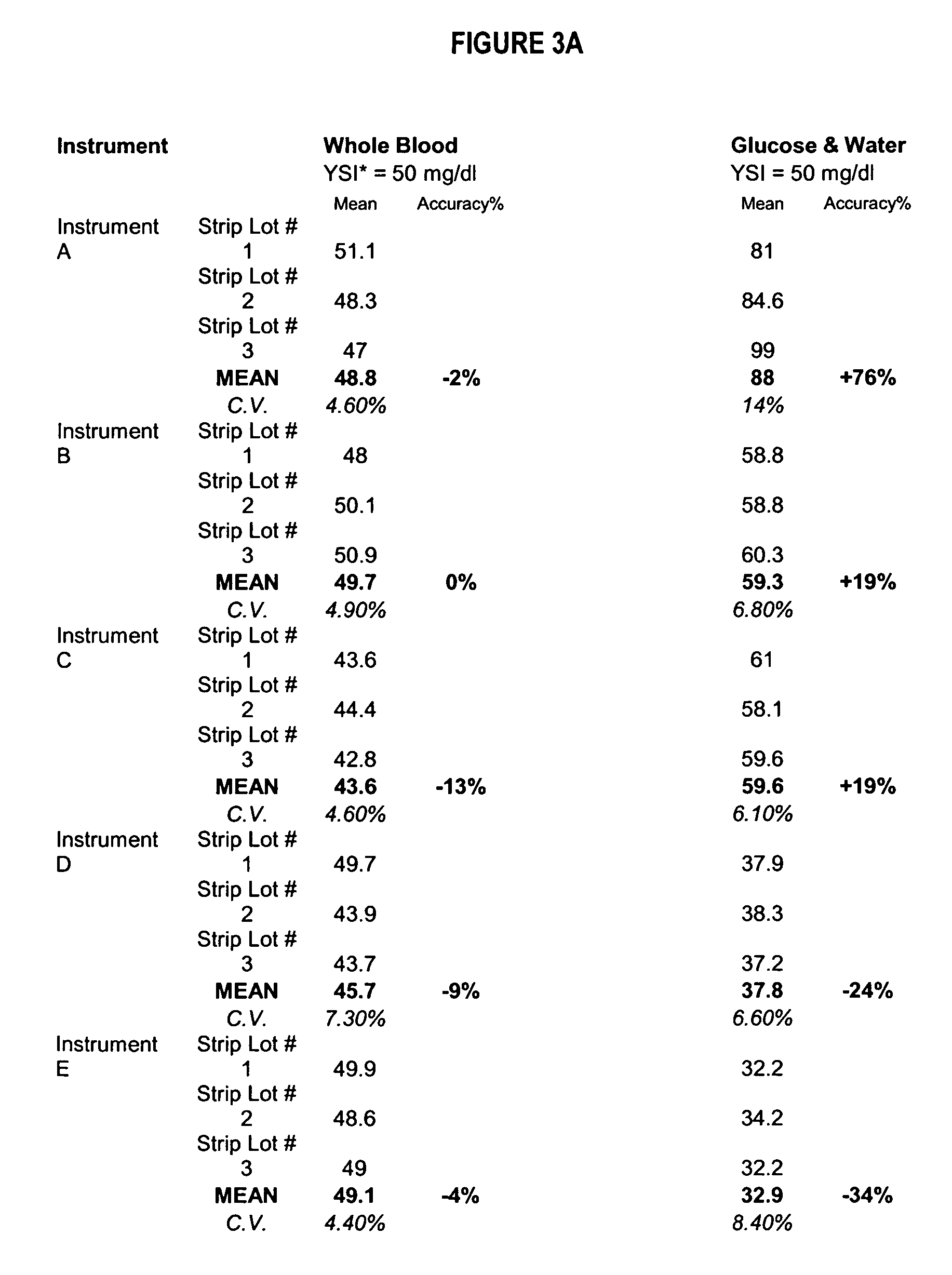
Process, composition and kit for providing a stable whole blood calibrator/control
InactiveUS20060188995A1Quality improvementSimple and elegantMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingMedicineMeasuring instrument
The present invention is directed toward a stable calibrator and / or control, kit and process for using in a glucose monitoring instrumentation. Principally, the instant invention teaches a glycolyzed red blood cell component, which has been treated with a glycolysis stabilizing effective amount of at least one non-crosslinking aldehyde compound. The glycolyzed red blood cell component may be added to fresh plasma along with an amount of glucose to form a simulated whole blood glucose control product, effective for maintaining a particular and essentially stable glucose concentration over a period of time sufficient for accurate measurement and calibration of a glucose measuring instrument.
Owner:STRECK INC
Heterogeneous catalysts for alkene hydroformylation reaction and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103521268AHigh activityImprove stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide reactionFormylation reactionMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a supported metal catalyst under double modification of an anchoring ligand and an auxiliary and a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst comprises an active component, an auxiliary, a carrier and a ligand, wherein the active component is one or more of metals Rh, Ru and Co; the auxiliary is one or more of Al, K, Zn, Cu and Ag; the carrier is a molecular sieve SiO2, Al2O3, MCM-41 or SBA-15; the ligand is an N or P-containing organic ligand capable of acting with silicon hydroxyl. In the catalyst, the metal component and the auxiliary are directly fixed on the carrier, and then the anchoring ligand and the metal generate a coordination action to in-situ generate an active species; due to the double modification of the ligand and the auxiliary, the activity and stability of the catalyst are remarkably improved. The catalyst can be applied to alkene hydroformylation to prepare various organic aldehydes, has relatively high catalytic activity and excellent stability, and is easy to separate.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modification of polymers with basic N-groups and ion exchange groups in the lateral chain
InactiveUS20020045729A1Improve stabilityThe degree of freedom becomes largerIon-exchange process apparatusNon-metal conductorsAlkaneIon exchange
A method for lateral chain modification of aryl main chain polymers with aromatic ketones or aldehydes containing tertiary basic N-groups is described. The modification can be accomplished via addition of an aromatic carboxylic acid or an acid derivative containing a tertiary amine moiety to a metallized polymer. The tertiary amines on the modified polymer can be converted to quaternary amines with halogen alkanes. Modification of the aryl main chain polymers with aromatic groups containing sulphonic acid radicals is also described. The polymers formed can be crosslinked and prepared for use in a wide variety of membrane technologies including ion exchange, dialysis, reverse osmosis, nanofiltration.
Owner:UNIV STUTTGART
Process and catalyst for the preparation of aldonic acids
InactiveUS20070027341A1Organic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationPlatinumGluconic acid
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of aldonic acids (in particular gluconic acid) by oxidation of aldoses with oxygen or with a gas containing oxygen, in the presence of supported bimetallic catalysts based on gold and platinum.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
Impregnated filter element, and methods
InactiveUS20060130451A1High molecular weightCombination devicesGas treatmentKetoneAldehyde formation
A contaminant-removal filter for removing carbonyl-containing compounds from a gas stream, such as air. Examples of common airborne carbonyl-containing compounds include ketones, including acetone, and aldehydes, including formaldehyde. The filter has a porous or fibrous body that includes a plurality of passages extending from a first, inlet face to a second, outlet face, the passages providing flow paths. The body has a reactant material impregnated throughout the substrate. The reactant material is a sulfite, bisulfite, oxidant, or derivative of ammonia, specifically high molecular weight and stable amines. Strong alkali (basic) materials are particularly suitable for aldehyde removal. The filter is free of any humectants.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Method for synthesizing modified sodium alginate flocculating agent and application of flocculating agent
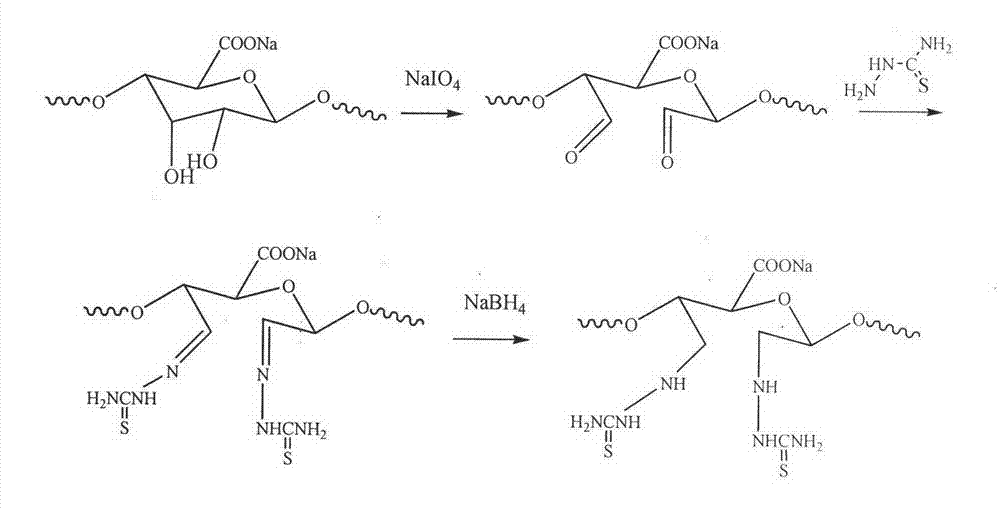
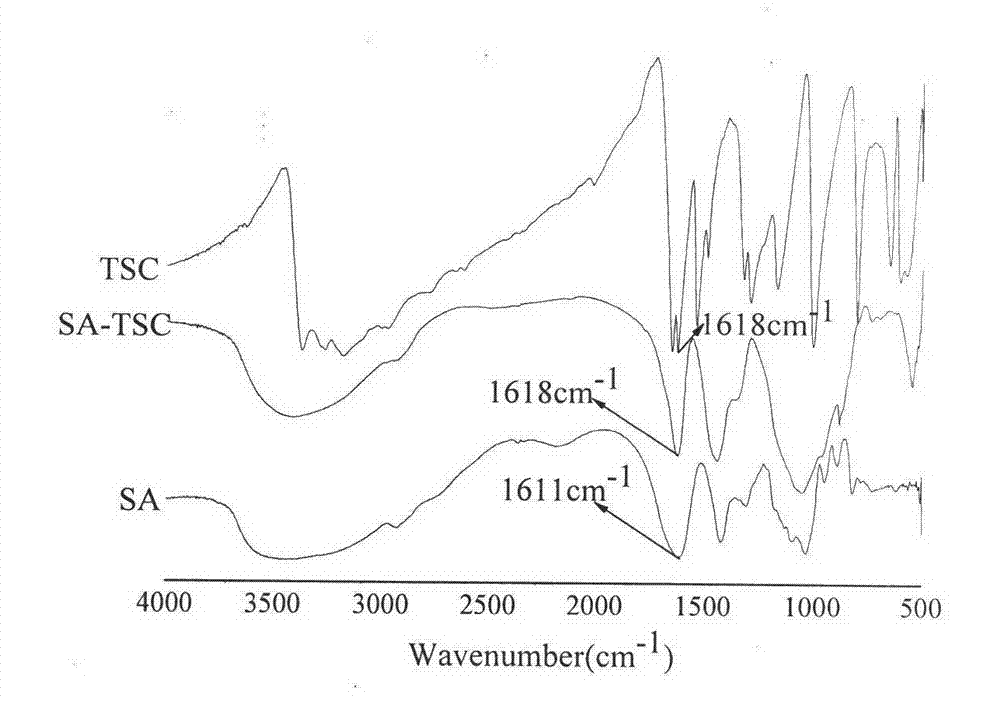
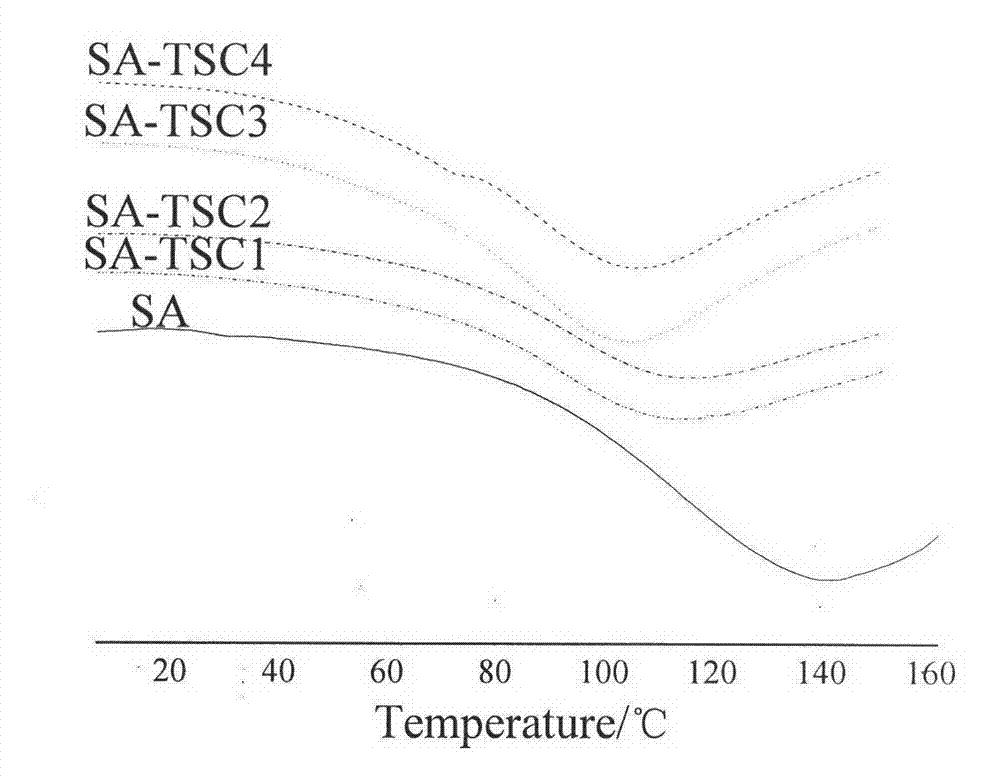
ActiveCN103359816ASimple production processLow costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationIonSchiff base
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a modified sodium alginate flocculating agent and an application of the flocculating agent. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting partially oxidized sodium alginate and a chelating agent thiosemicarbazide with a functional group in an aqueous solution to obtain a biodegradable natural high polymer flocculating agent. The method mainly comprises two reaction processes: (1) oxidizing the sodium alginate by using sodium periodate, and preparing the partially oxidized sodium alginate with a dialdehyde structure, wherein the oxidation degree is 68.2 percent; and (2) dissolving the oxidized sodium alginate in a phosphate buffer solution with the pH of 7.0 to prepare a uniform solution, adding the thiosemicarbazide to the uniform solution, reacting for 4 hours to generate a Schiff base, and adding NaBH4 to generate stable amine. The method is simple and easily controllable in process, low in cost and easy to popularize and apply, and raw materials are easily obtained. Nitrogen and sulfur elements are introduced into sodium alginate subjected to chemical modification, and the adsorption capacity and removal rate of the sodium alginate flocculating agent on heavy metal ions in sewage are greatly improved. The flocculating agent is biodegradable, and secondary pollutants are avoided.
Owner:ANHUI RONGJING FENGDAN BIOTECH
Hexahydrotriazines, synthesis and use
InactiveUS20130118996A1Organic chemistryRefining with acid-containing liquidsTriazineAldehyde formation
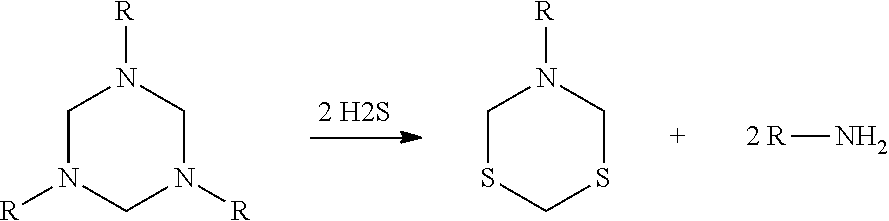
Methods for making asymmetrical triazines are provided. The methods comprise first forming a mixture of at least two primary amines then reacting the mixture with an aldehyde. Methods for removing sulfides from hydrocarbon streams are also provided. The triazines may be added to the hydrocarbon stream in a molar ratio of triazine:H2S of about 10:1 to about 1:2.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
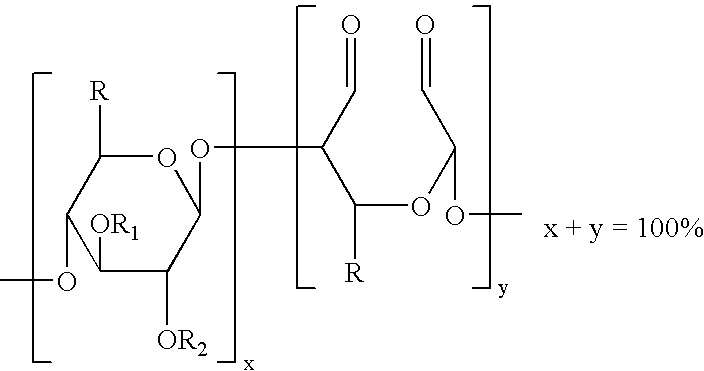
Water-soluble polymer alkanals
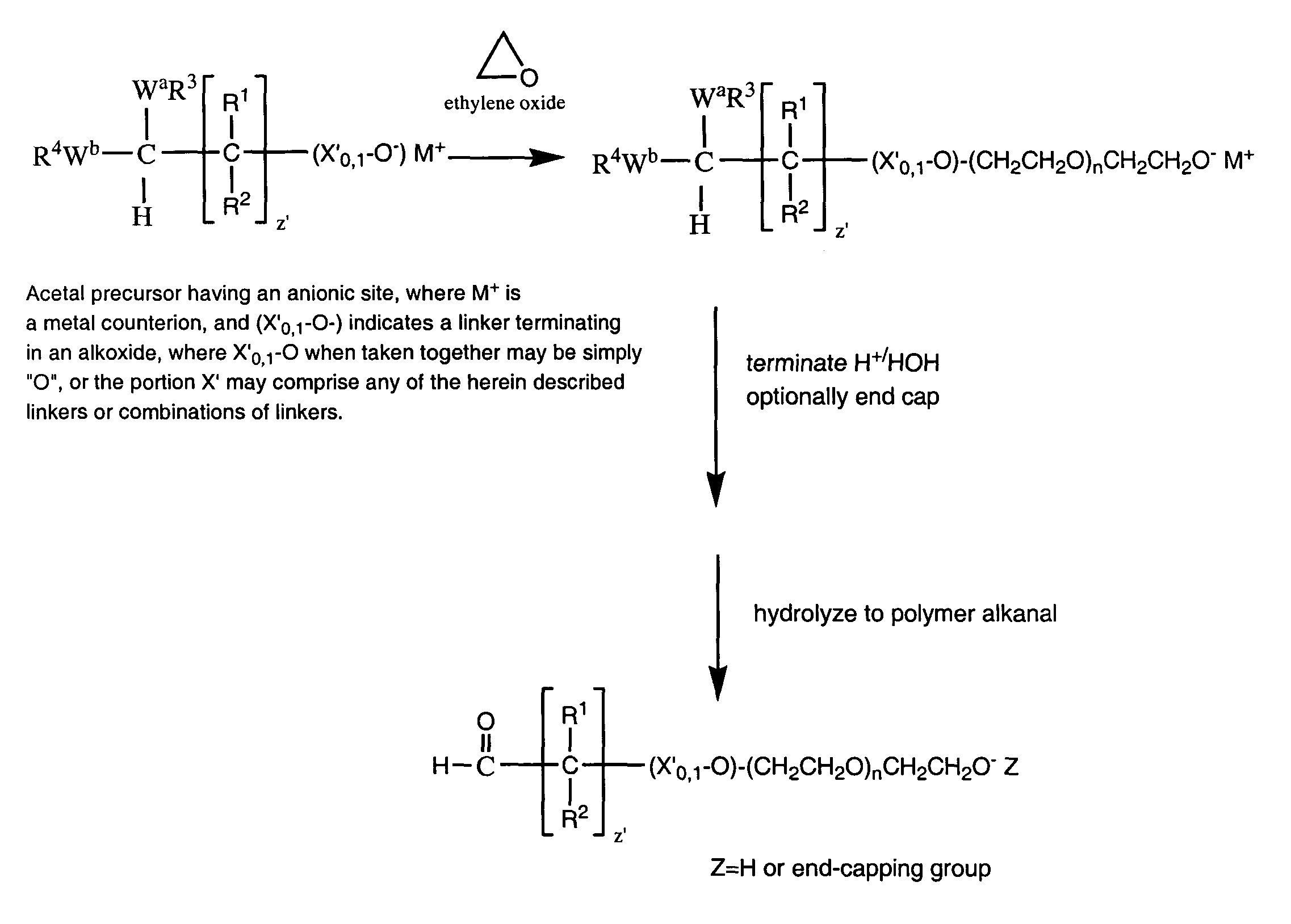
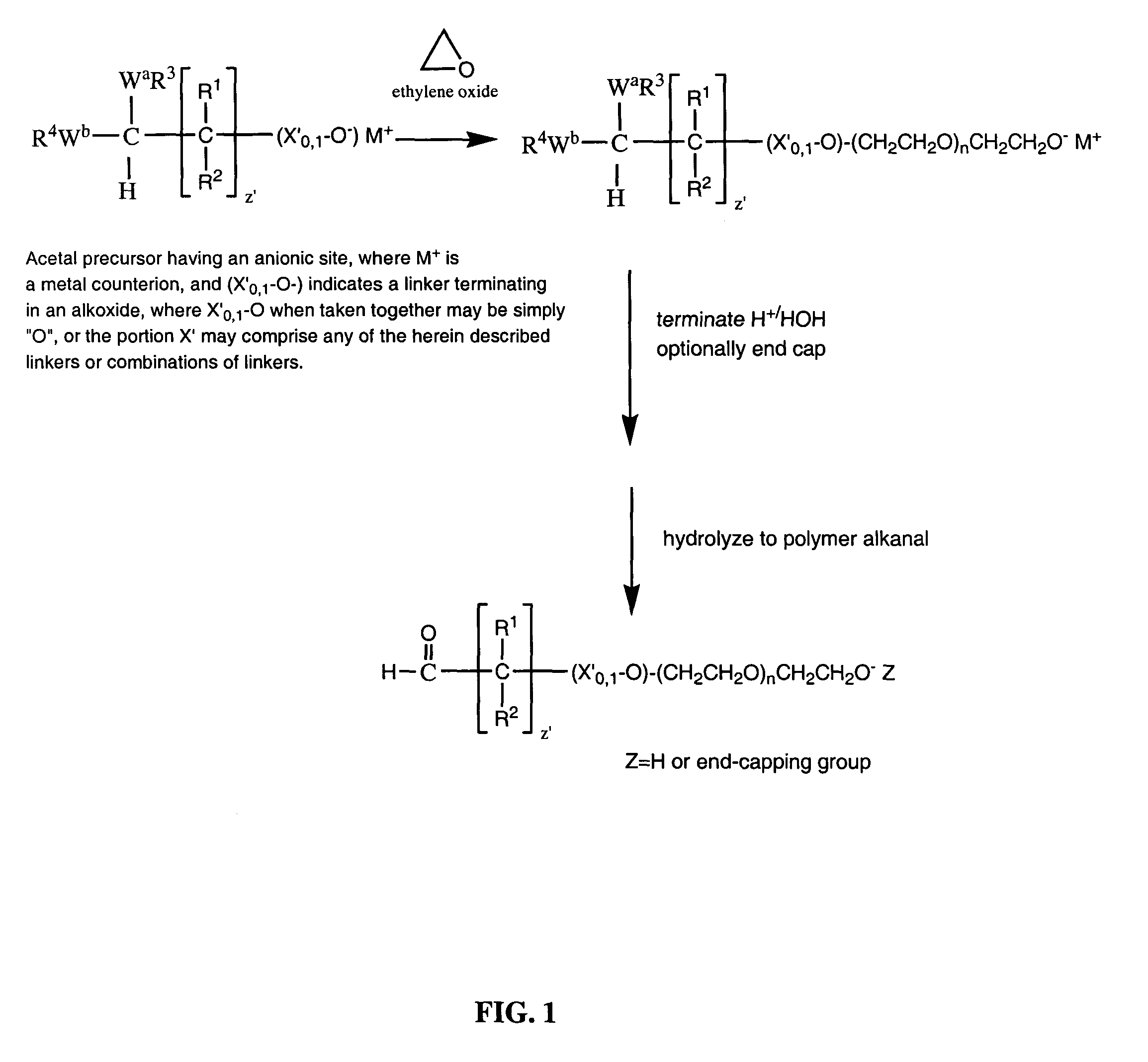
ActiveUS7157546B2Less reactiveHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceWater soluble
The present invention is directed to alkanal derivatives of water-soluble polymers such as poly(ethylene glycol), their corresponding hydrates and acetals, and to methods for preparing and using such polymer alkanals. The polymer alkanals of the invention are prepared in high purity and exhibit storage stability.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for producing surfaces that resist non-specific protein binding and cell attachment
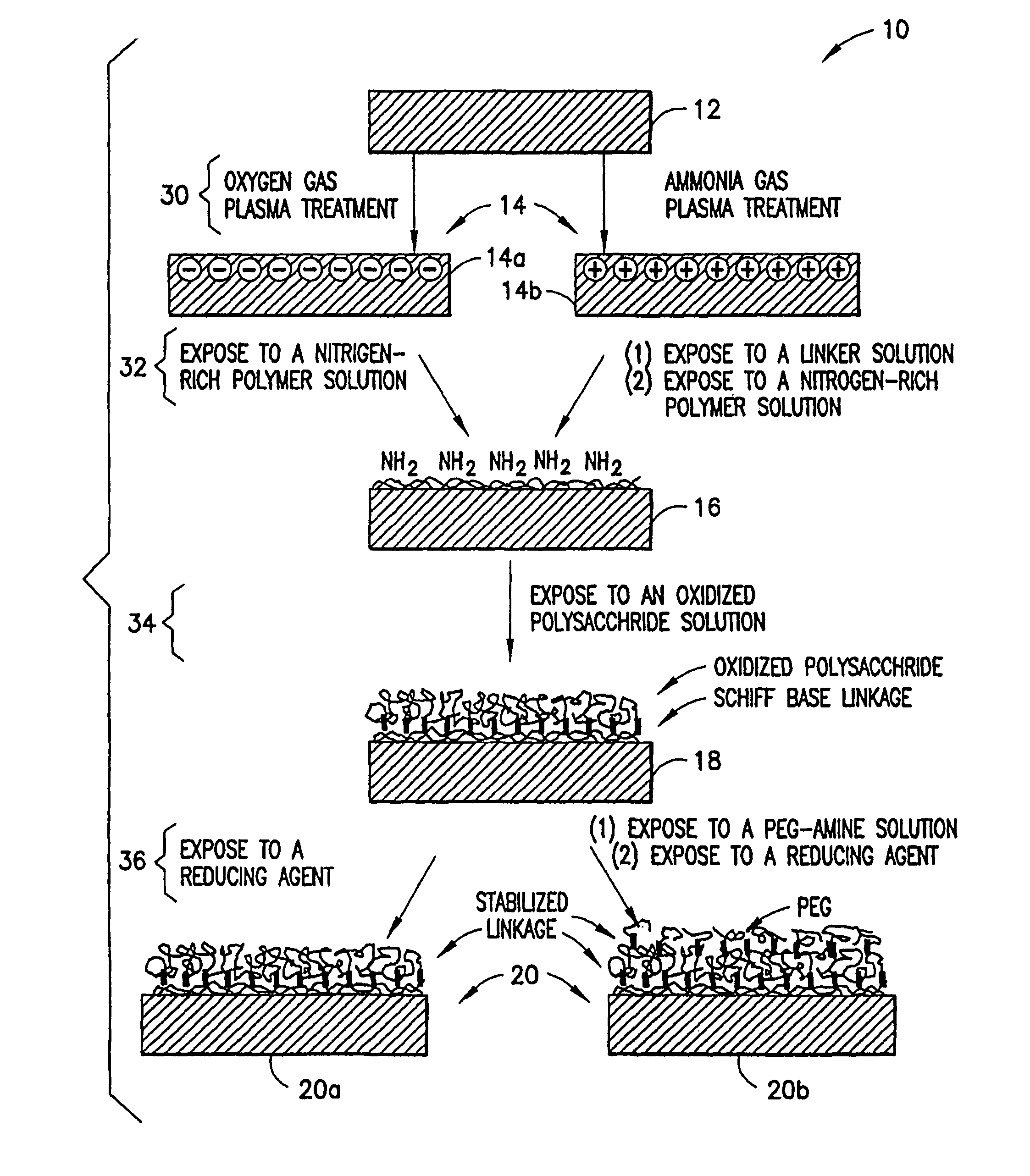
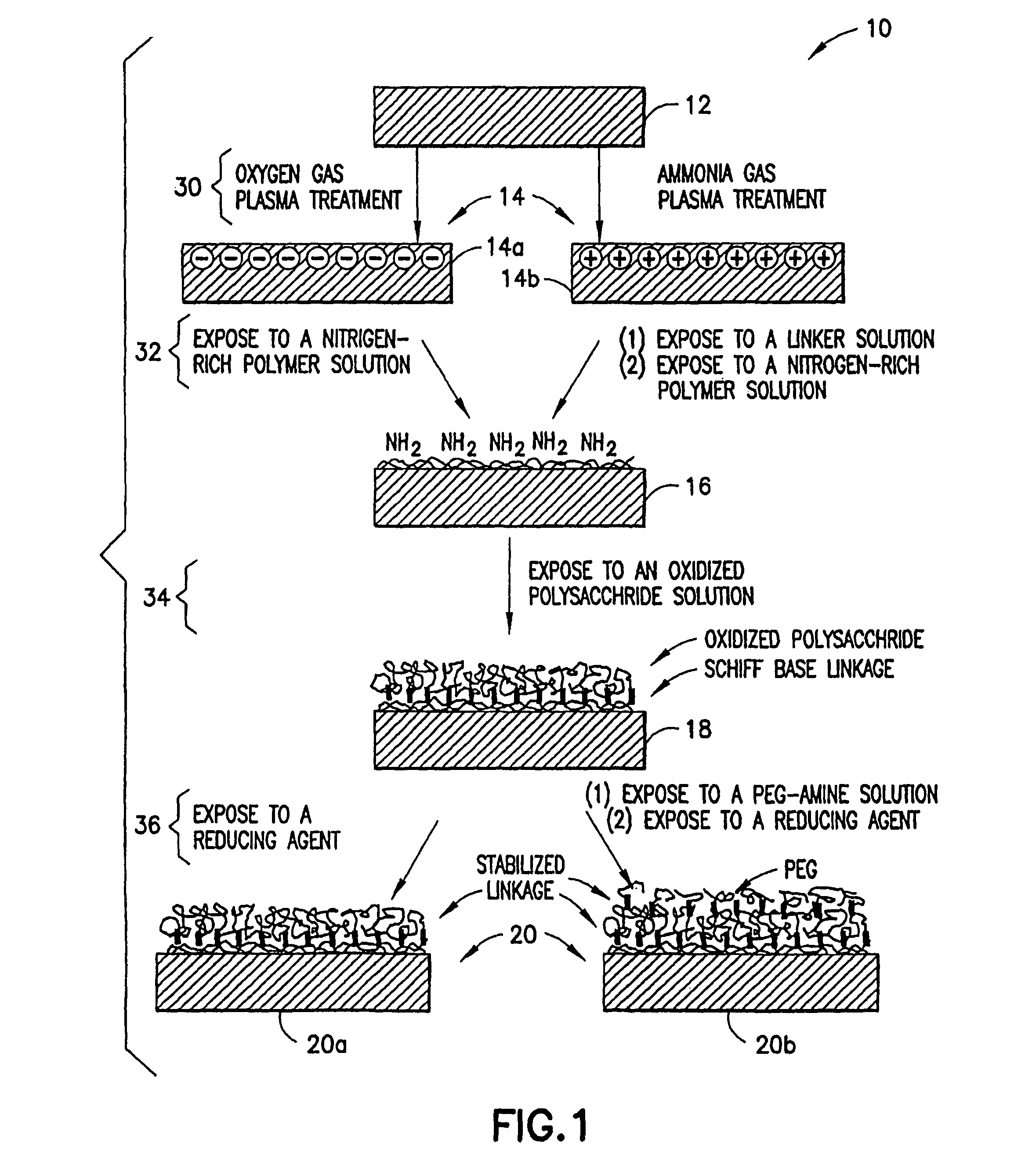
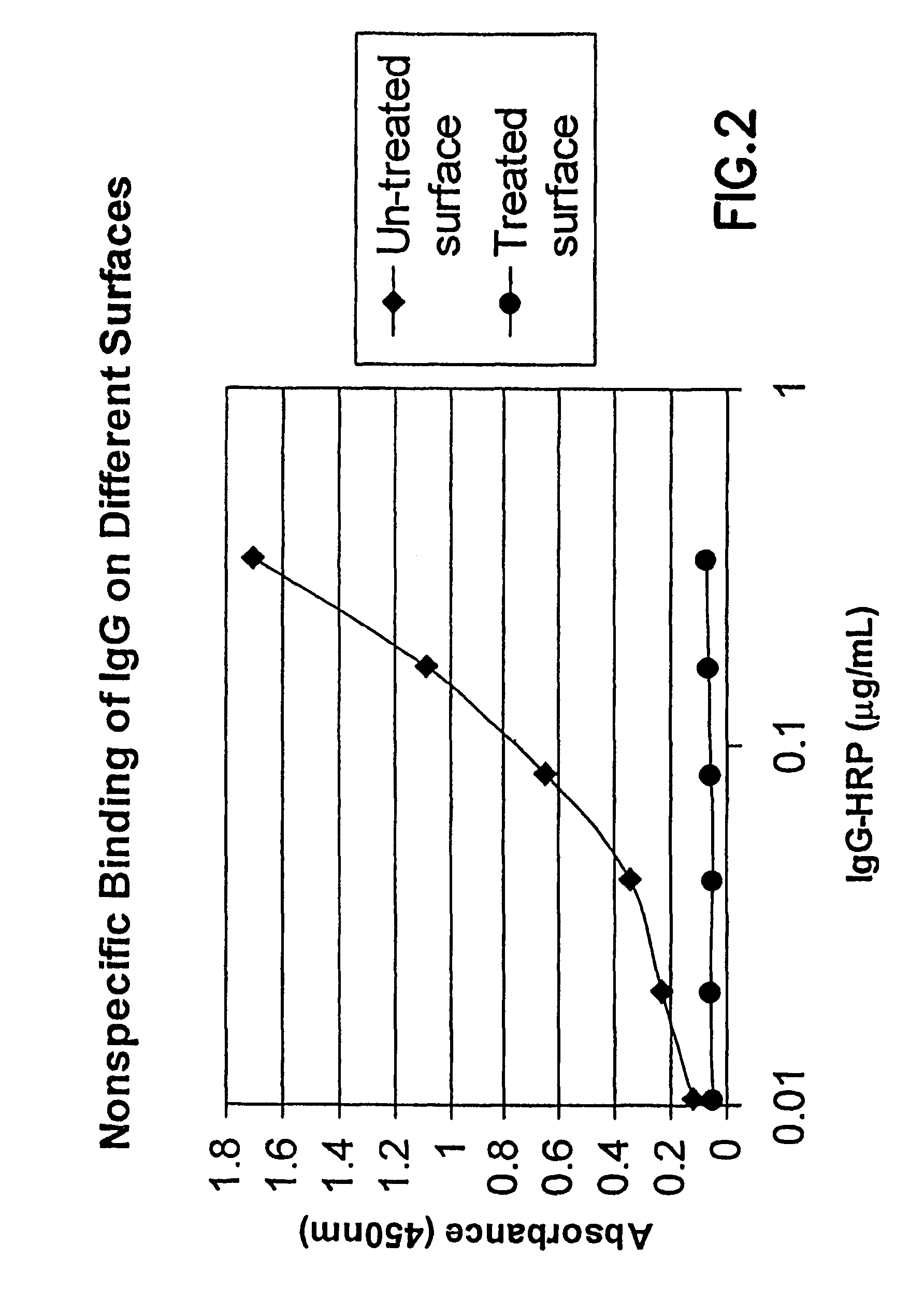
ActiveUS8475886B2Preparing sample for investigationSynthetic resin layered productsPolymeric surfaceChemical reaction
A method is disclosed herein for treating a polymeric surface to resist non-specific binding of biomolecules and attachment of cells. The method includes the steps of: imparting a charge to the polymeric surface to produce a charged surface; exposing the charged surface to a nitrogen-rich polymer to form a polymerized surface; exposing the polymerized surface to an oxidized polysaccharide to form an aldehyde surface; and exposing the aldehyde surface to a reducing agent. Advantageously, a method is provided which produces surfaces that resist non-specific protein binding and cell attachment and that avoids the use of photochemical reactions or prior art specially designed compounds.
Owner:CORNING INC
Process for making amine compounds
There is provided a process for producing amine reaction product, in particular suitable for industrial process, whereby high yields of the amine reaction product is obtained. This is achieved by having a selected temperature range upon the contacting of the amine containing compound with the active aldehyde and / or ketone.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Polyamide/COFs hybridized nanofiltration composite membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105642133AImprove interface compatibilityHigh retention rateSemi-permeable membranesPolymer sciencePolyamide
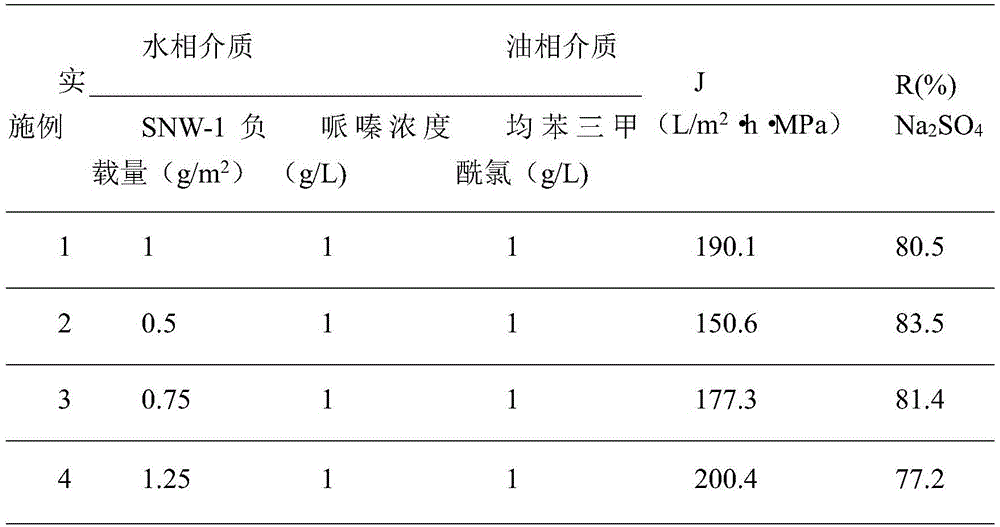
The invention provides a polyamide / COFs hybridized nanofiltration composite membrane. The composite membrane comprises a composite layer and a loaded porous frame material. The composite layer is a layer of polyamide compound formed by conducting polymerization reaction on piperazine and trimesoyl chloride, and the thickness is 100-500 nm. The porous frame material is SNW-1 obtained when melamine and terephthalaldehyde react, and is a compound layer with the loading amount of 0.5-3 g / m<2>. A covalent organic framework is effectively hybridized in a separation layer of the composite membrane, and more water channels are provided for the nanofiltration membrane. By means of the method, various types of COFs can be introduced onto a polyether sulfone base membrane, the water flux can reach 200 L / m<2>.h.MPa and increased by 2 times, the sodium sulfate retention rate of the nanofiltration membrane is still kept at 80% or above, and the high water flux and the high retention rate are achieved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Composite bracket made of multialdehyde sodium alginate crosslinked calcium polyphosphate/chitosan and preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101301491AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisDefect repairBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a composite frame of multi-aldehyde sodium alginate cross-linked polyethylene / chitosan for bone or cartilage repair and treatment, as well as preparation and application of the material of the framework. The framework is made from Calcium polyphosphate, chitosan and multi-aldehyde sodium alginate. As organic matrix multi-aldehyde sodium alginate cross-linked chitosan derived from nature which is the main component of the composite frameworks of the invention, therefore the composite framework is safe and non-toxic, has good biocompatibility and biodegradability, and cell identificaton signal existed on the surface provides physical support and the best chemical environment for bone or cartilage regeneration and reconstruction, the network structure makes the mechanical properties improved greatly. In addition, the components of the inorganic strengthened calcium polyphosphate are consistent with those of human bone tissue, has the property of activity which promotes bone or cartilage growth and the controllable degradation. The composite of the invention can be used as defect repair of bone or cartilage and tissue engineering, drug delivery carrier.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Processes for synthesizing borohydride compounds
InactiveUS20030092877A1HydrogenMonoborane/diborane hydridesAlkaline earth metalCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to processes for producing borohydride compounds. In particular, the present invention provides efficient processes and compositions for the large-scale production of borohydride compounds of the formula YBH.sub.4 by the reaction of a boron-containing compound represented by the formula BX.sub.3 with hydrogen or an aldehyde to obtain diborane and HX, and reacting the diborane with a Y-containing base selected from those represented by the formula Y.sub.2O, YOH and Y.sub.2CO.sub.3 to obtain YBH.sub.4 and YBO.sub.2. Y is selected from the group consisting of the alkali metals, pseudo-alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, an ammonium ion, and quaternary amines of the formula NR.sub.4.sup.+, wherein each R is independently selected from hydrogen and a straight- or branched-chain C.sub.1-4 alkyl group, and X is selected from the group consisting of halide ions, --OH, --R' and --OR' groups, chalcogens, and chalcogenides, wherein R' is a straight- or branched-chain C.sub.1-4 alkyl group.
Owner:MILLENNIUM CELL
Compositions and methods useful for treatment of respiratory illness
Disclosed are compositions including phenylephrine, its free and addition salt forms, and mixtures thereof, alone, or in combination with other pharmaceutical actives. The compositions have a pH of about 2 to about 5 and are substantially free of aldehydes. Also disclosed are methods of treating respiratory illness through administration of a composition comprising phenylephrine, its free and addition salt forms, and mixtures thereof alone, or in combination with other pharmaceutical actives, wherein the composition has a pH of from about 2 to about 5 and is substantially free of aldehydes.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
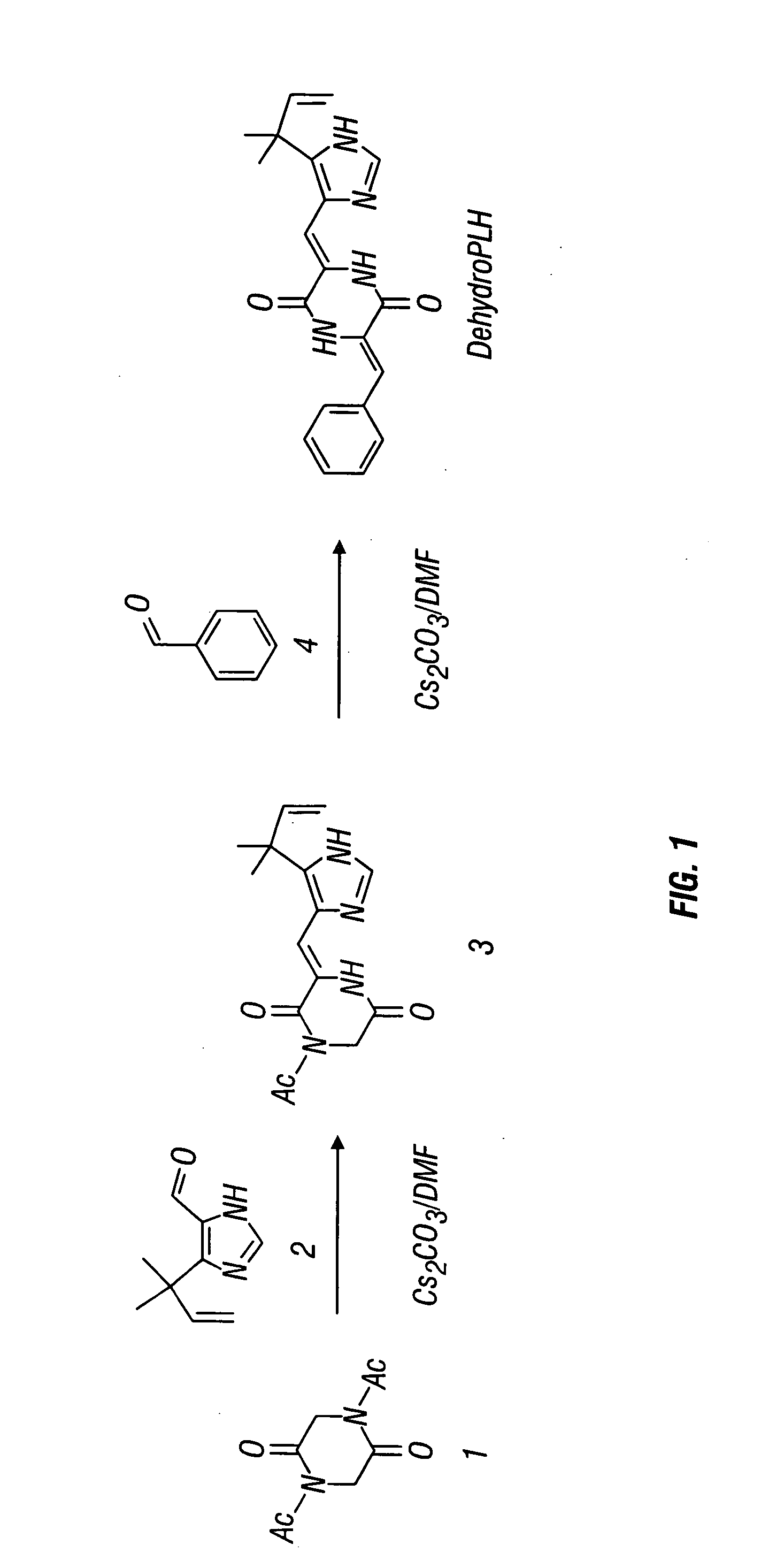
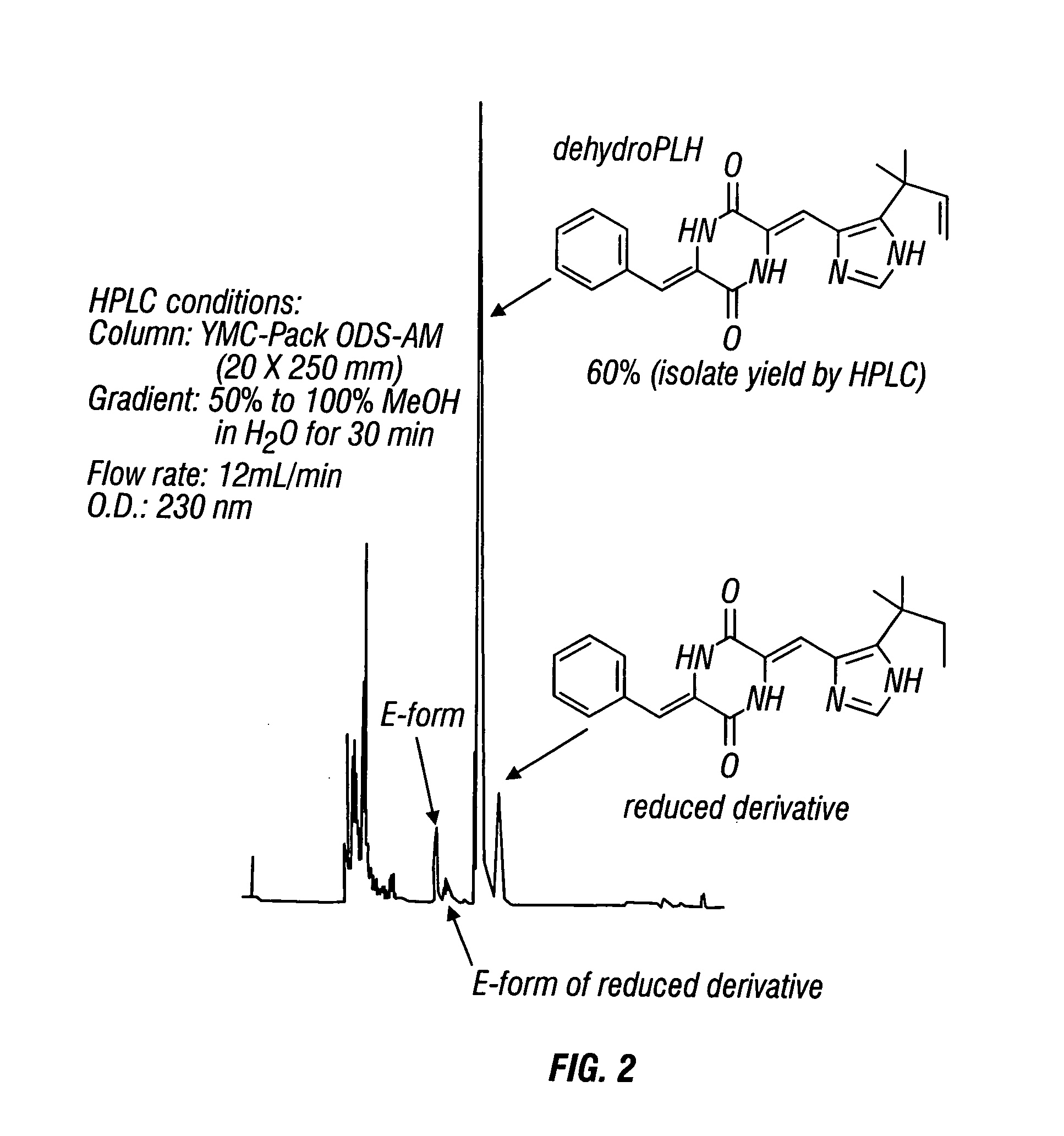
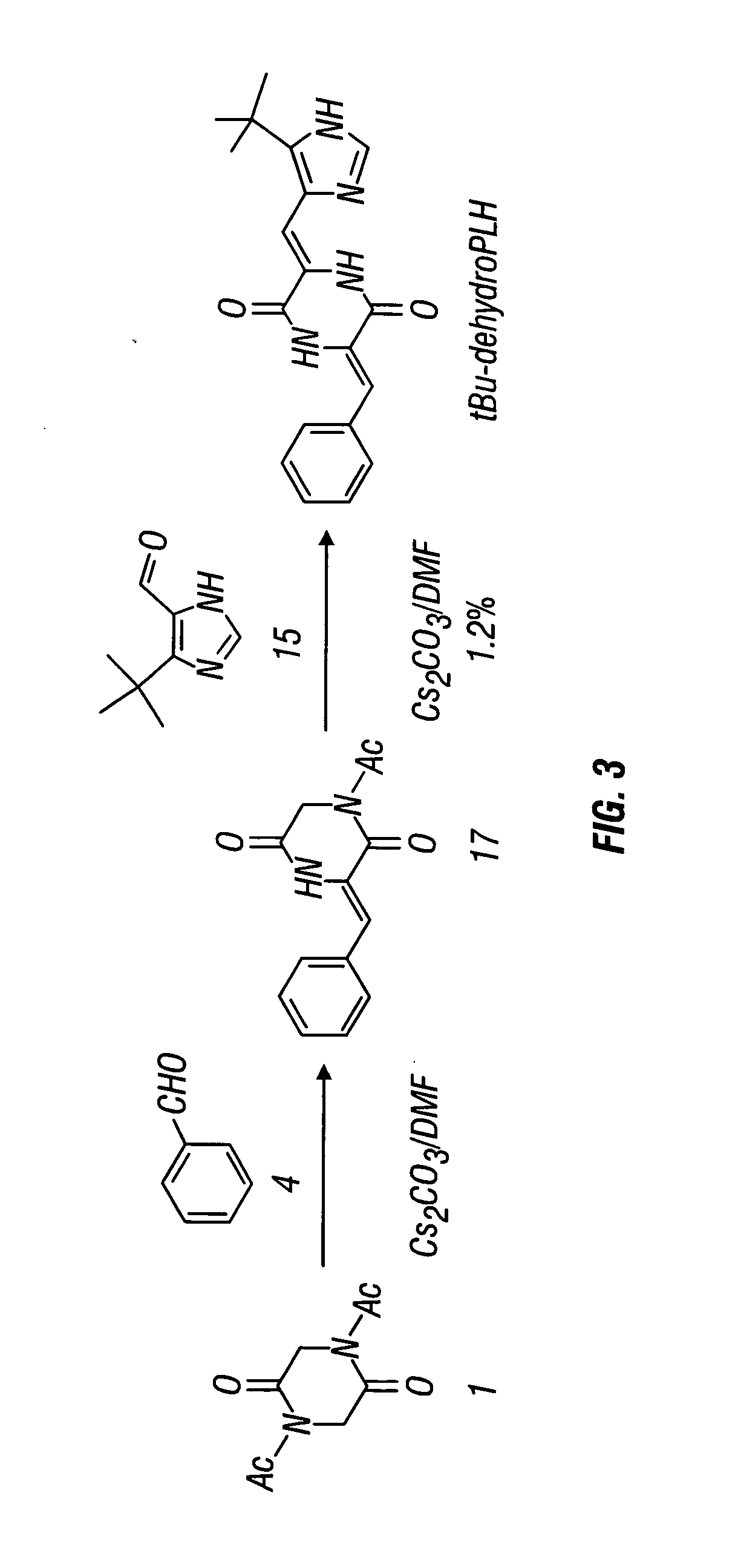
Dehydrophenylahistins and analogs thereof and the synthesis of dehydrophenylahistins and analogs thereof
ActiveUS20050197344A1Reduce spreadReduce vascular densityOrganic active ingredientsVascular proliferationBenzaldehyde
Compounds represented by the following structure (I) are disclosed: as are methods for making such compounds, wherein said methods comprise reacting a diacyldiketopiperazine with a first aldehyde to produce an intermediate compound; and reacting the intermediate compound with a second aldehyde to produce the class of compounds with the generic structure, where the first aldehyde and the second aldehydes are selected from the group consisting of an oxazolecarboxaldeyhyde, imidazolecarboxaldehyde, a benzaldehyde, imidazolecarboxaldehyde derivatives, and benzaldehyde derivatives, thereby forming the above compound wherein R1, R1′, R1″, R2, R3, R4, R5, and R6, X1 and X2, Y, Z, Z1, Z2, Z3, and Z4 may each be separately defined in a manner consistent with the accompanying description. Compositions and methods for treating vascular proliferation are also disclosed.
Owner:BEYONDSPRING PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com