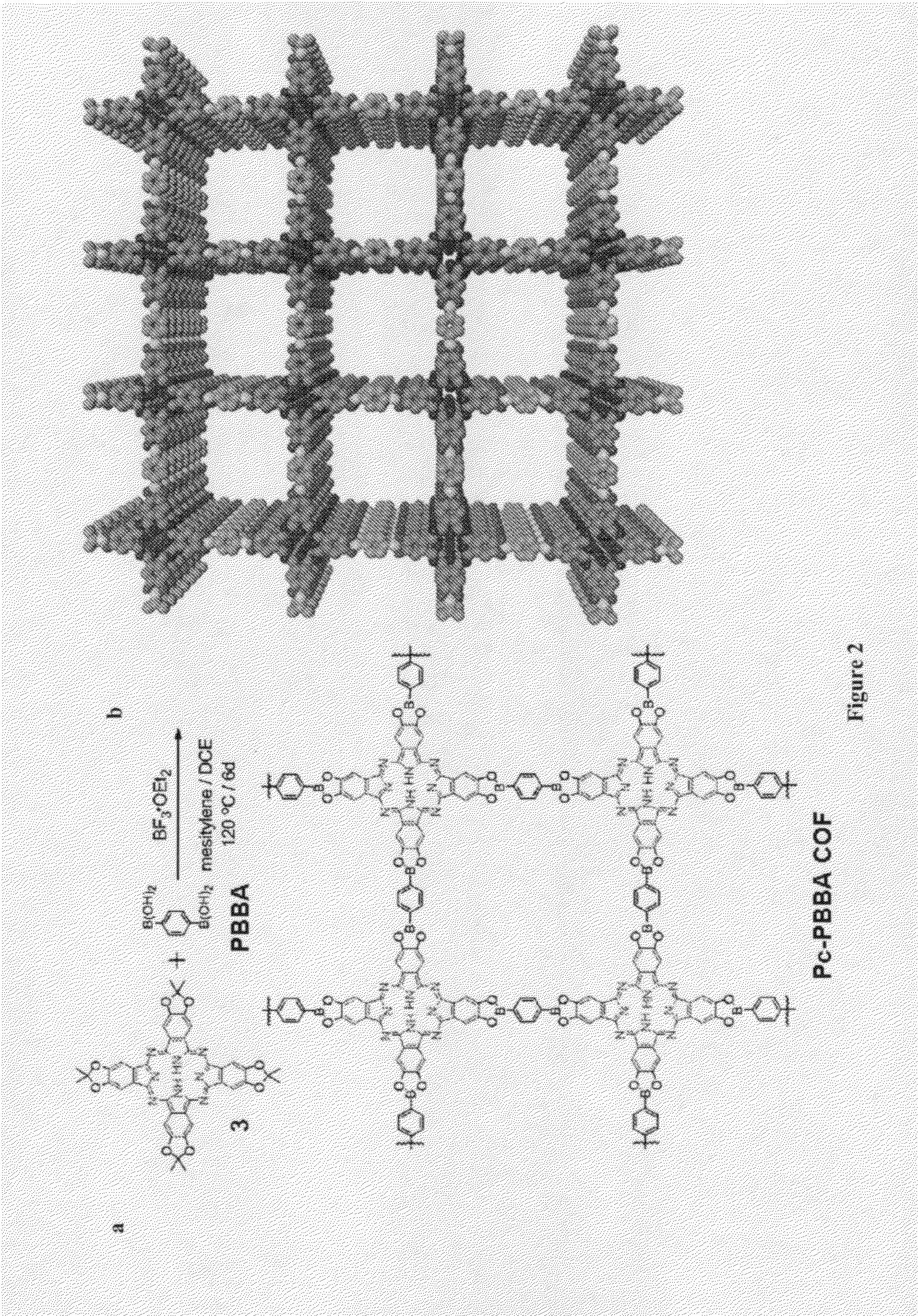Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1056 results about "Covalent organic framework" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
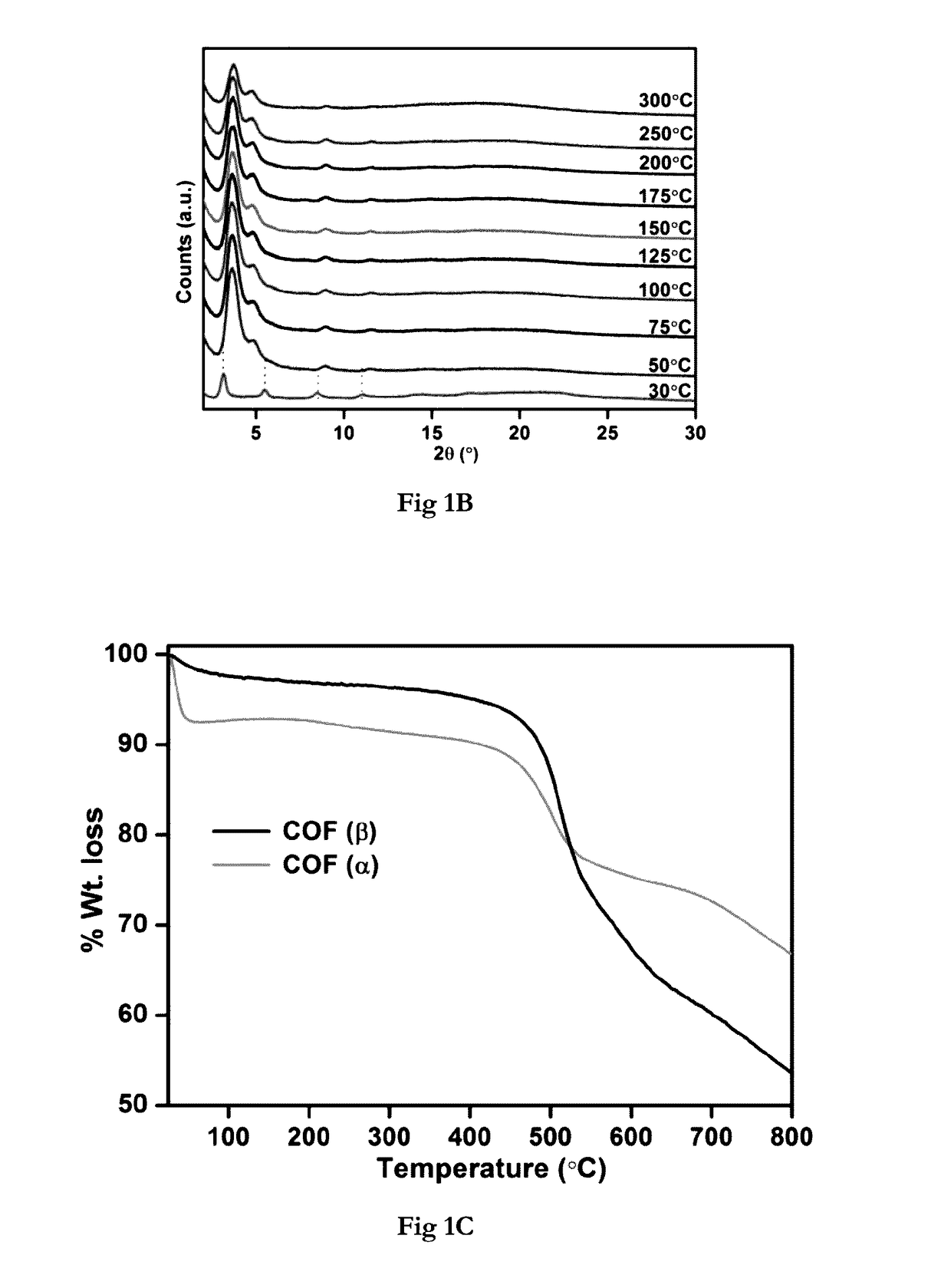
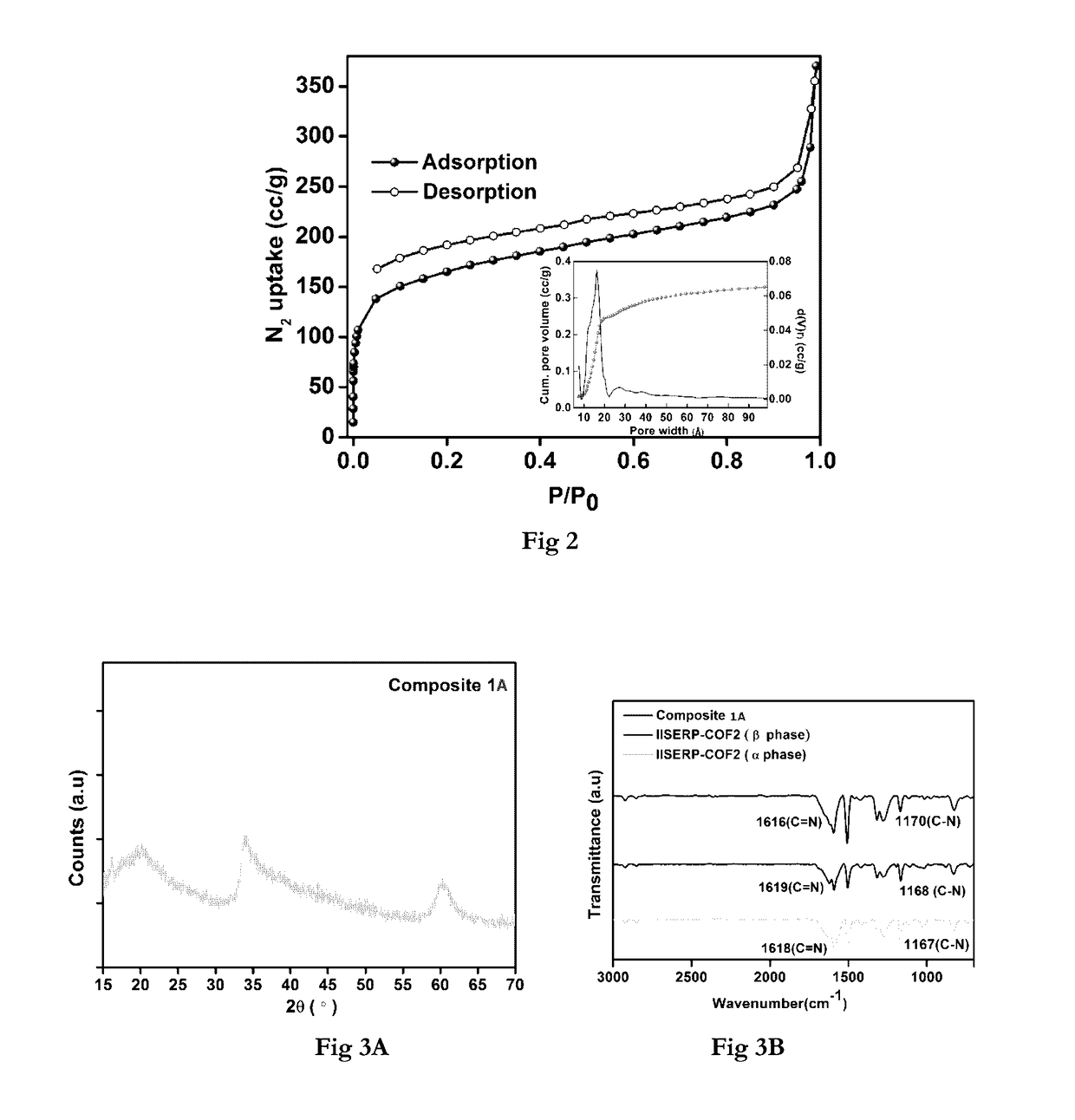
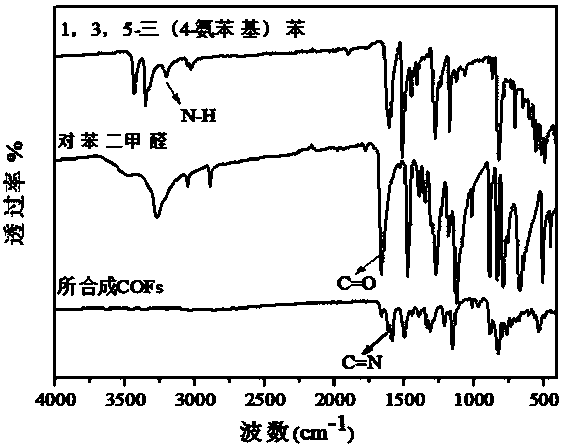
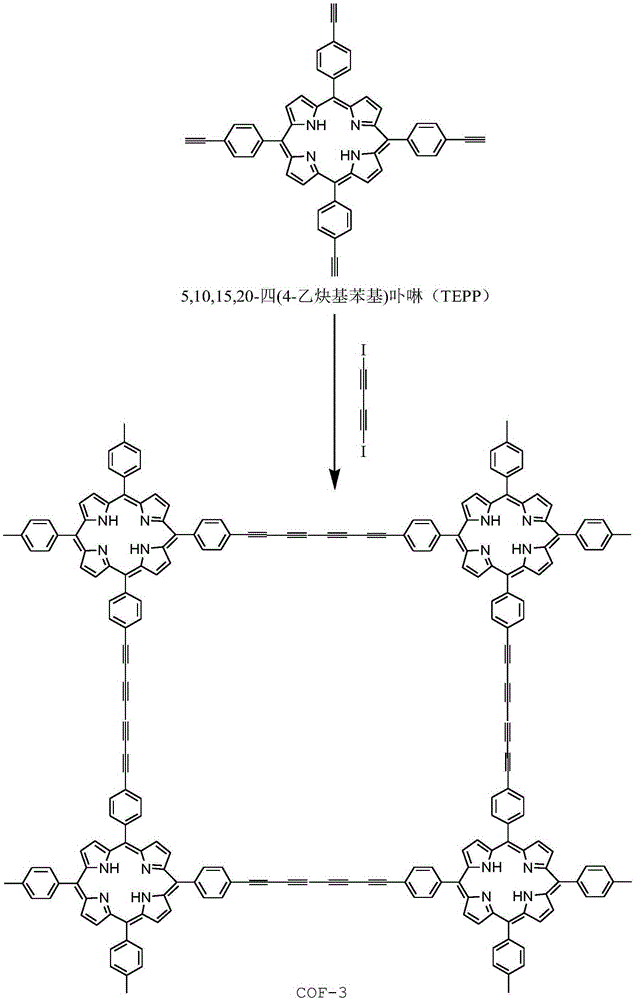
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are two-dimensional and three-dimensional organic solids with extended structures in which building blocks are linked by strong covalent bonds. COFs are porous and crystalline and are made entirely from light elements (H, B, C, N, and O) that are known to form strong covalent bonds in well-established and useful materials such as diamond, graphite, and boron nitride. Preparation of COF materials from molecular building blocks would provide covalent frameworks that could be functionalized into lightweight materials for diverse applications.
Imaging members for ink-based digital printing comprising structured organic films
ActiveUS8119315B1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternOrganic filmEngineering
An imaging member for ink-based digital printing having an outermost layer including a structured organic film (SOF) having a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be multi-segment thick.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Solid electrolyte for lithium ion battery and application thereof
ActiveCN102738510AImprove conductivityReduce crystallinitySecondary cellsCombustionMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a solid electrolyte for lithium ion battery and an application thereof. The electrolyte comprises a polyoxyethylene and / or polyoxyethylene derivative, an inorganic-organic hybrid framework and lithium salt. The inorganic-organic hybrid framework is one selected from a metal organic framework (MOF), a covalent-organic framework (COF) and a zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF). The prepared lithium ion cell electrolyte can be used to avoid safety problems such as cell combustion, even explosion and the like which are caused by leakage of traditional lithium ion batteries and has high lithium ion conductivity. By the use of the solid electrolyte, thinning of lithium ion batteries can be realized, so as to extend their application range.
Owner:王海斌
Imine coupled covalent organic framework material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106967216AGood chemical stabilityImprove thermal stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsOrganic reactionStructural formula
The invention provides an imine coupled covalent organic framework material and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of porous materials. The structural formula of the imine coupled covalent organic framework material is shown in the description, and the material can be prepared by triazinyl aromatic polyamine A and alkoxy substituted aromatic aldehyde B through simple Schiff base condensation reaction. Under visible light excitation condition, the prepared imine coupled covalent organic framework material can catalyze multiple types of organic reactions, specifically for example reaction for photocatalysis of N-aryl tetrahydroisoquinoline and nucleophilic reagent. The prepared covalent organic framework material has very good chemical stability and heat stability, high specific surface area and high crystallinity, has strong visible light absorption properties, can serve as an excellent heterogeneous photocatalyst and has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Synthetic method and application of covalent organic framework (COF) material
ActiveCN103755588AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrazide preparationMetal-organic frameworkNitromethane
The invention discloses a synthetic method of a covalent organic framework (COF) material. The method comprises the following steps: after mixing 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxaldehyde with 2,5-di(N,N-dimethyl)amino-1,4-benzdihydrazide uniformly in an organic solvent, reacting in the presence of a catalyst acetic acid to obtain the COF material, wherein the mole ratio of 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxaldehyde to 2,5-di(N,N-dimethyl)amino-1,4-benzdihydrazide is 1:(0.5-3). The COF material obtained by adopting the method has relatively large specific surface area and regular open framework structure with adjustable diameter, thus being beneficial for mass transfer of reactants and products in photoabsorption and catalytic processes; the material can serve as a photocatalyst and can increase the yield of the dehydrogenative coupling reaction between 2-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline and nitromethane from 39% in the absence of catalysts to 89%.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
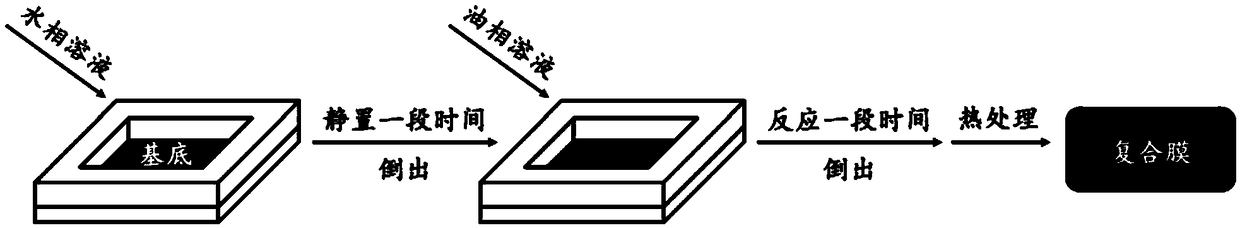
Method for preparing high-throughput covalent organic framework nano-filtration membrane on basis of interfacial polymerization
ActiveCN108889139AGood chemical stabilityHigh permeation fluxSemi-permeable membranesFiltration membraneBinding force
The invention provides a method for effectively preparing a high-throughput covalent organic framework (COFs) nano-filtration membrane on the basis of interfacial polymerization. The method comprisesthe following steps: sequentially applying an aqueous phase solution dissolved with polyamine monomers and an organic phase solution dissolved with polyaldehyde / polyketones monomers to the surface ofa porous carrier to carry out interfacial polymerization; diffusing the polyamine monomers in the aqueous phase solution saturated porous carrier to a water / oil interface to carry out schiff base reaction with polyaldehyde / polyketones in an organic phase, and gradually forming a covalent organic framework separating layer on the surface of the porous carrier by a conformal growth manner; and thencarrying out heat treatment on a composite membrane consisting of the separating layer and the porous carrier to enhance the binding force of the covalent organic framework separating layer and the porous carrier, and promoting crystallization and conversion of the covalent organic framework. The method not only is simple and convenient to operate and short in technological process, but also is well compatible with an existing process, thus, continuous product becomes possible, and the prepared composite membrane has high flux.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
METHOD FOR IN-SITU SYNTHESIS OF METAL ORGANIC FRAMEWORKS (MOFs), COVALENT ORGANIC FRAMEWORKS (COFs) AND ZEOLITE IMIDAZOLATE FRAMEWORKS (ZIFs), AND APPLICATIONS THEREOF
PendingUS20210016245A1Low desorption temperatureGreat energy requirementOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPhysical chemistryOrganic Metallic Compounds
The present invention relates to method for the synthesis in-situ of the class of compounds known generally as MOFs (metal organic frameworks or organometallic compounds), COFs (covalent organic frameworks), and ZIFs (Zeolitic imidazolate framework), within and onto different types of substrates, and to the applications of such substrates having in-situ synthesized MOFs, COFs and ZIFs.
Owner:PAHWA DEEPAK +7
Porphyrin containing covalent organic frameworks and process for the preparation thereof
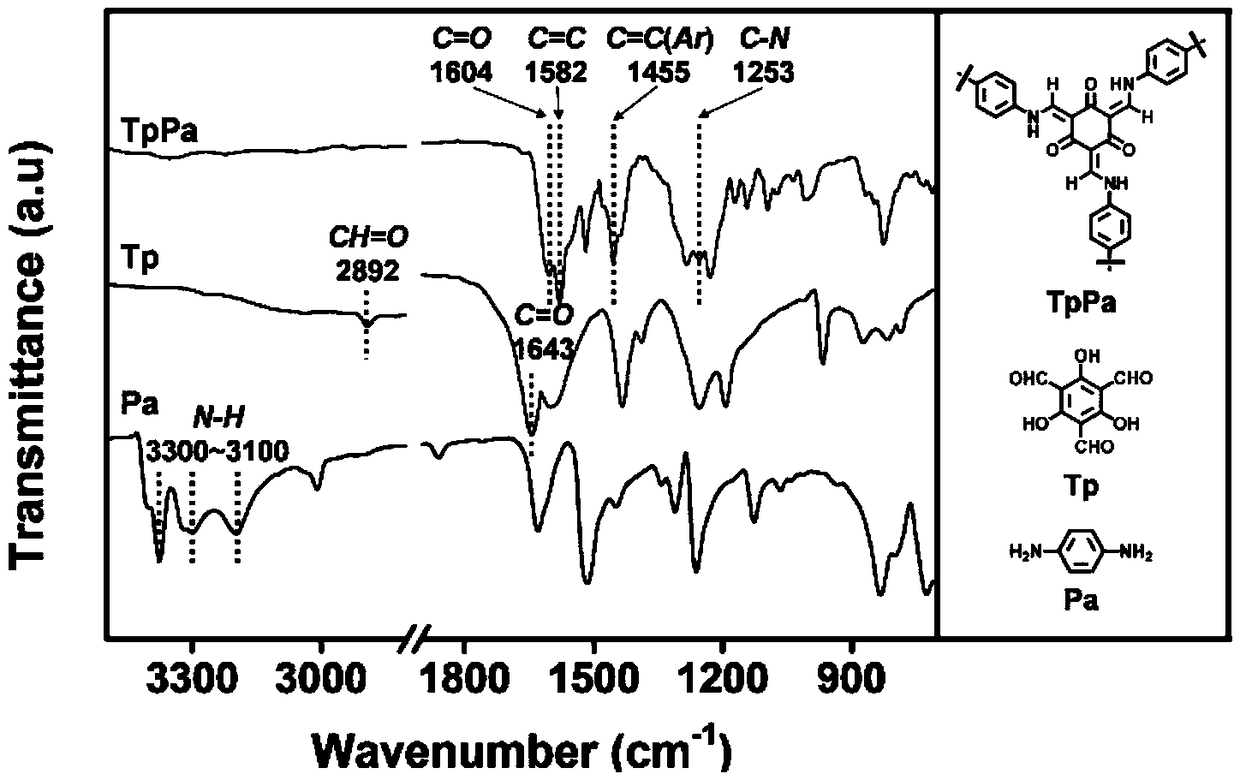
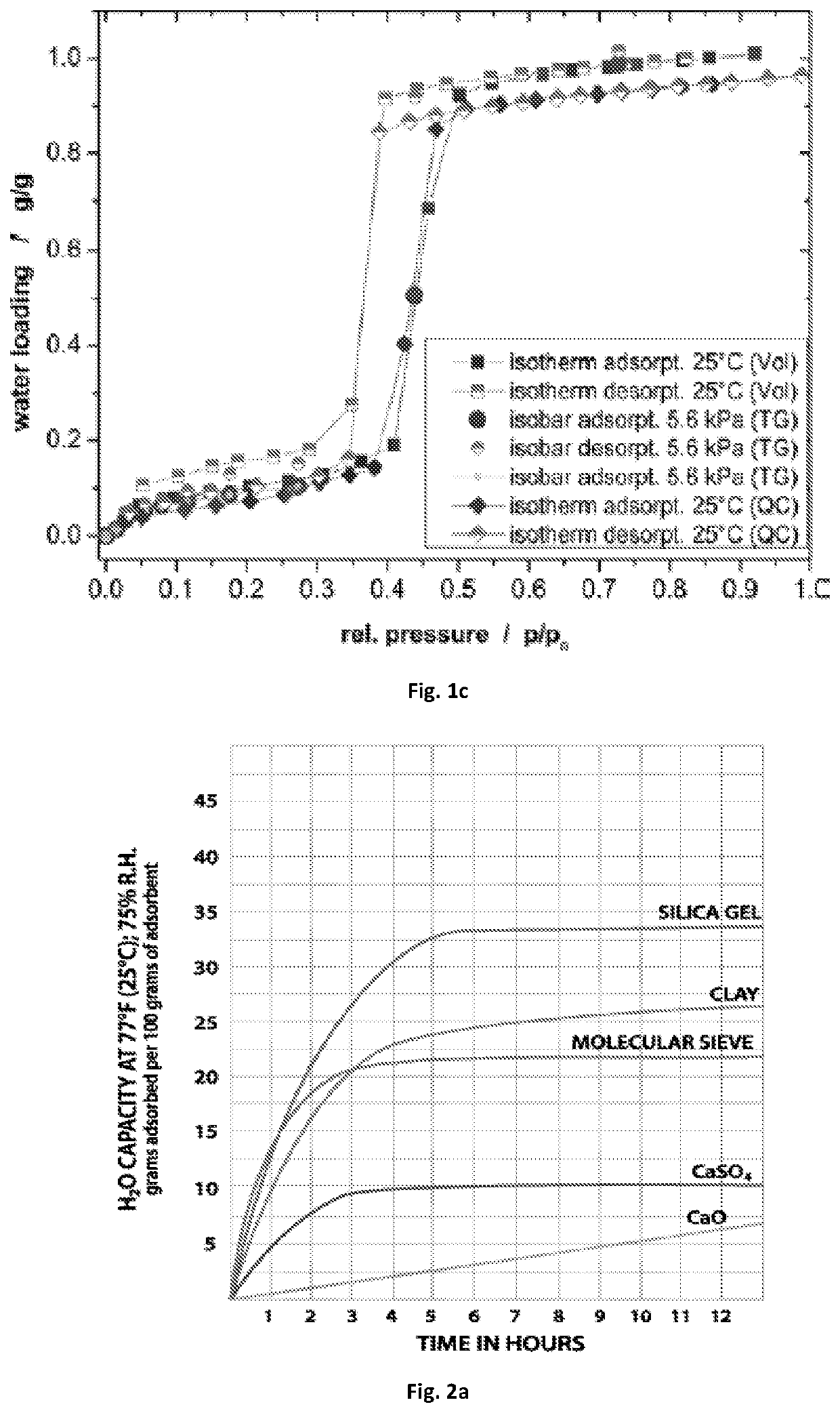
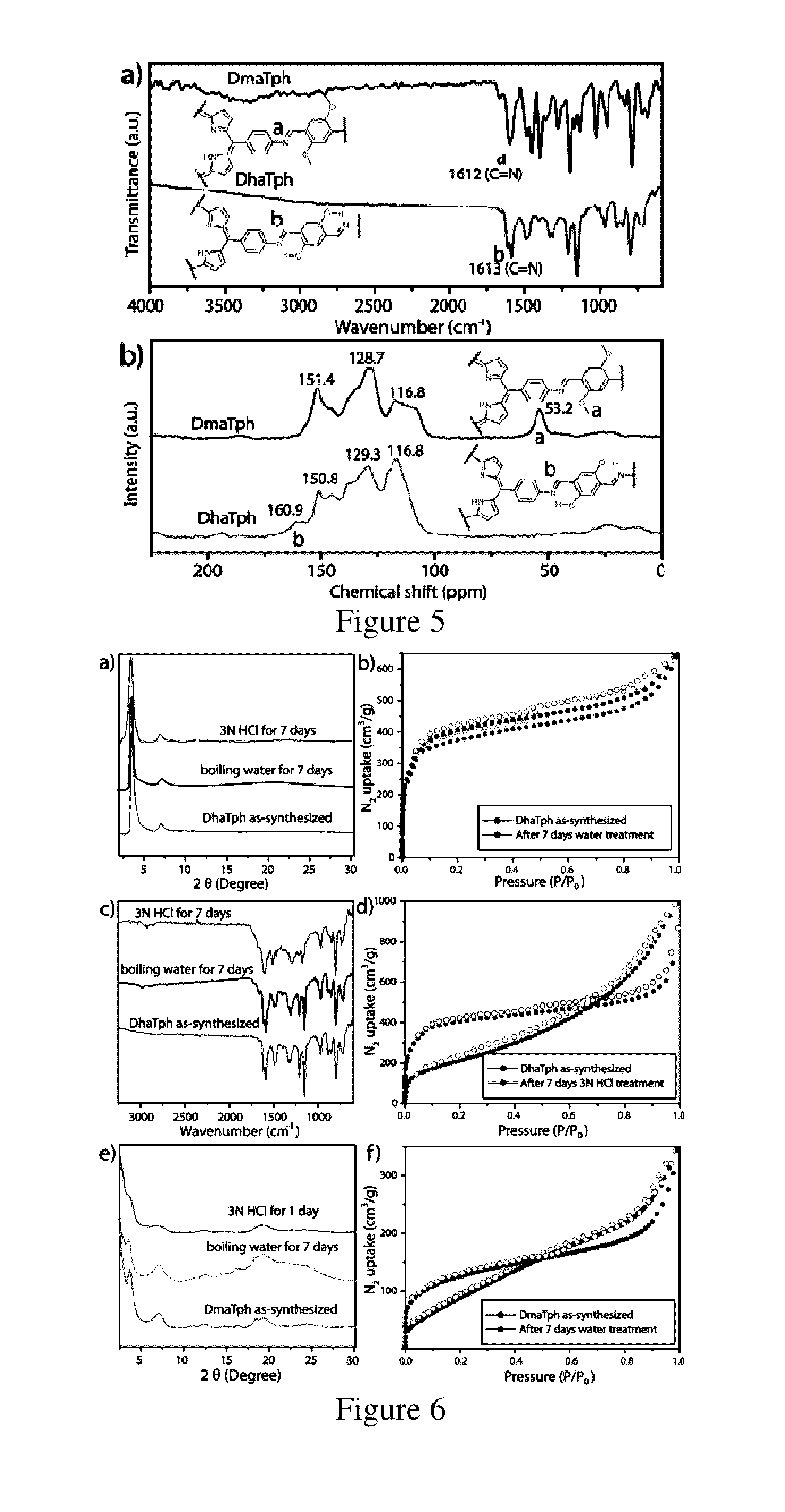
Disclosed herein is novel highly stable, crystalline porphyrin containing covalent organic frameworks and their synthesis using Schiff base reaction which are hydrophobic in nature having good selectivity towards alcohol uptake at low pressure over water. Particularly, present invention provides novel highly stable, porous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) comprising porphyrin linked hydroxyl aromatic compound by intramolecular O—H—N═C bonding; wherein porphyrin is tetra(p-amino-phenyl)porphyrin (Tph) and hydroxyl aromatic compound is selected from group consisting of Triformylphloroglucinol (Tp), 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde (Da).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Imaging devices comprising structured organic films
ActiveUS8119314B1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternOrganic filmSolvent
An imaging member for a xerographic liquid immersion development machine having an outermost layer including a solvent resistant structured organic film (SOF) having a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be multi-segment thick.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Covalent organic frameworks as porous supports for non-noble metal based water splitting electrocatalysts
ActiveUS20170130349A1Smooth connectionImprove performanceMultiple component coatingsElectrode with substrate and coatingMetal-organic frameworkManganese
The present invention discloses porous covalent organic frameworks (COF) supported noble metal-free nanoparticles which are useful as electrocatalysts for a water splitting system, and to the process for preparation of such electrocatalysts. The covalent organic frameworks (COF) supported noble metal-free nanoparticles have general formula (I):COF_AxBy(M)n (Formula I)wherein COF is selected from a Tris (4-formylphenyl)amine terephthaldehyde polymer or a benzimidazole-phloroglucinol polymer;‘A’ and ‘B’ each independently represent a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Zn, and mixtures thereof; or ‘A’ and ‘B’ together represent a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Ni, Co, Fe, Mn, Zn, and mixtures thereof;‘M’ represents hydroxide or a nitride ion;‘x’ and ‘y’ represent the weight % of the metal loadings; or a ratio of x:y is between 0:1 and 1:0; and‘n’ is an integer 1 or 2 or 3.
Owner:INDIAN INST OF SCI EUDCATION & RES
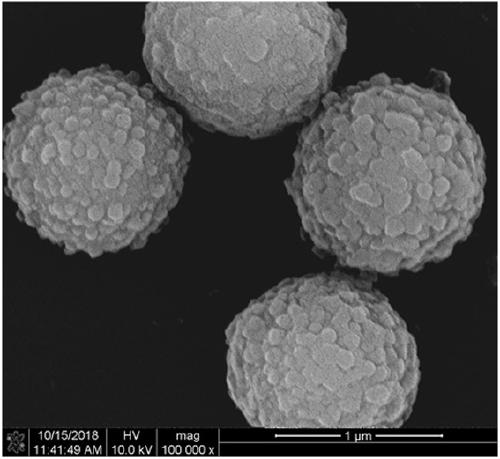
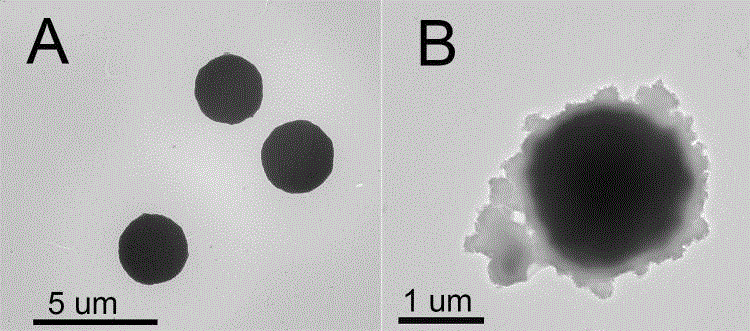
Spherical covalent organic framework material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109320734AGood size controlUniform pore sizeOther chemical processesStationary phaseOrganic solvent
The invention provides a spherical covalent organic framework material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving two covalent organic framework construction elements containing an amino group and an aldehyde group into an organic solvent respectively; after carrying out ultrasonic dispersion, rapidly adding a catalyst;carrying out Schiff base reaction at certain temperature to synthesize the spherical covalent organic framework material. The preparation method has a simple preparation process and the reaction is moderate; the prepared spherical covalent organic framework material has the advantages of controllable size, uniform pore diameter, large specific surface area, good crystal form structure, good chemical stability, good mechanical stability and the like; the spherical covalent organic framework material is used as a chromatography stationary phase and a sample loading amount can be greatly increased; the spherical covalent organic framework material contains a lot of benzene ring structures and has relatively strong hydrophobic performance, so that rapid separation of hydrophobic organic compounds is easy to realize; the spherical covalent organic framework material has a good application prospect.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Structured organic films
A structured organic film comprising a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be a multi-segment thick structured organic film.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Sulfide functionalized covalent organic frame material and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN103694469AHas a mesoporous structureHigh reaction yieldWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSynthesis methodsSolvent
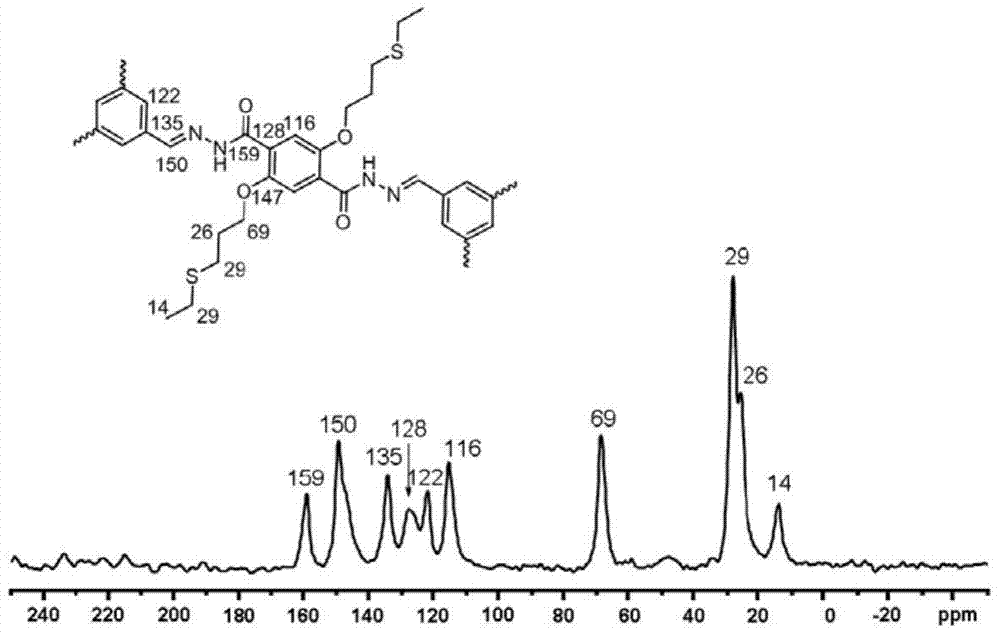
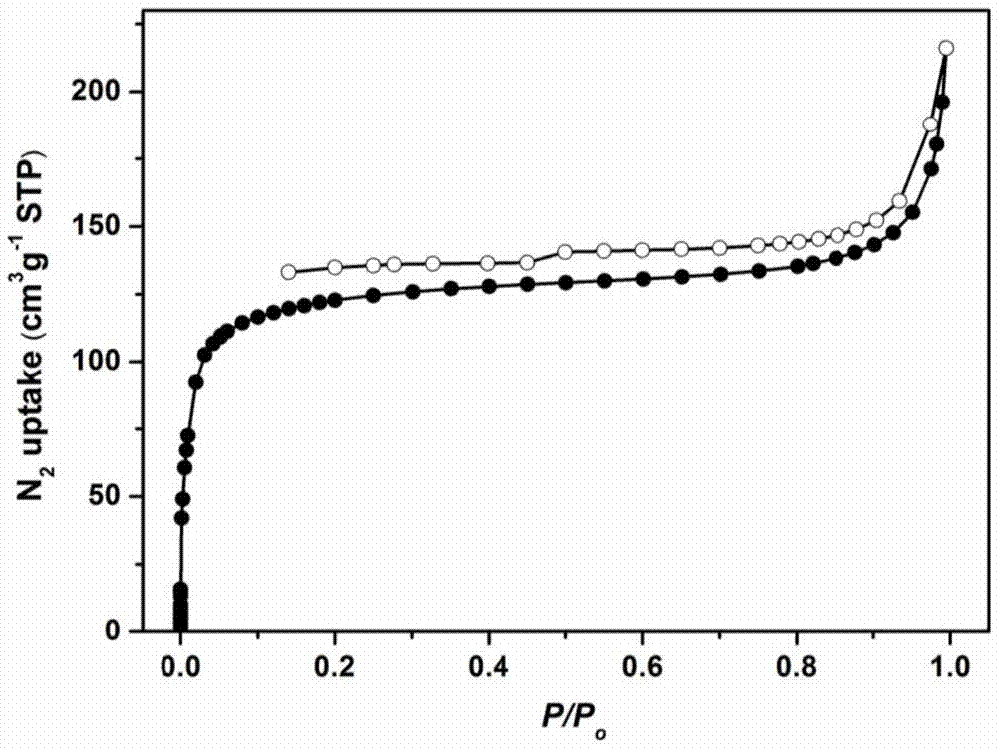
The invention discloses a sulfide functionalized covalent organic frame material, The material has a structural unit shown in the specification, and is obtained by the following steps: adding 2,5-Bis(3-(ethylthio)propoxy)-terephthalohydrazide and benzenetricarboxaldehyde into a mixed solvent of 1,4-dioxane and mesitylene, adding an aqueous acetic acid solution into the above mixture and reacting at 120 DEG C for 1-3 days. The material has a mesoporous structure, has BET specific surface area of 470-480 m<2>?g<-1>, has good selective identification for mercury ions, and can be used for removal of the mercury ions.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Porous crystalline frameworks, process for the preparation therof and their mechanical delamination to covalent organic nanosheets (CONS)
ActiveUS20150266885A1Simple and safe and environmentally-friendly mechanical grindingStable exposureProductsGas treatmentNeutral phCrystallization
The invention disclosed herein provides, Porous Crystalline Frameworks (PCFs) also known as Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) that exhibit stability towards acidic, basic and neutral pH conditions. Further the invention discloses economical, environmentally-friendly process for the synthesis thereof.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
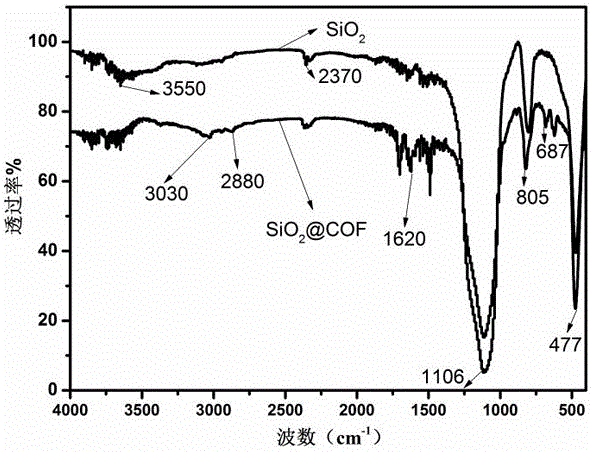
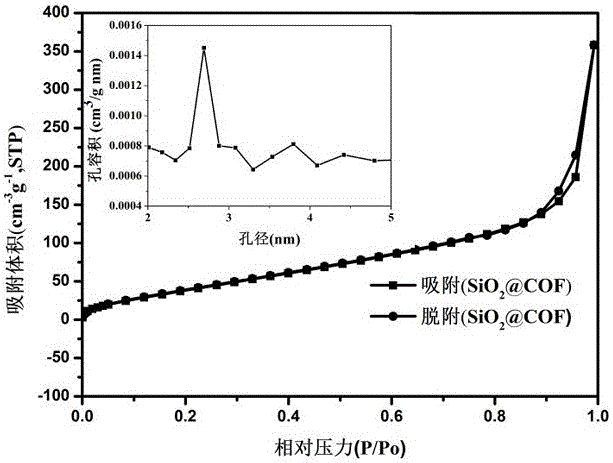
Preparation method of covalent organic framework composite microspheres with core-shell structures
InactiveCN107175053AMild preparation conditionsRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationMicrosphereSolid phase extraction
The invention relates to a preparation method of covalent organic framework composite microspheres with core-shell structures. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving silicon dioxide microspheres, a first construction element and a second construction element in an organic solvent; and after adding a catalyst, rapidly synthesizing into the composite microspheres with core-shell structures at a certain temperature. In a preparation process, reaction conditions are gentle, the method is simple, and the yield is high; the prepared covalent organic framework composite microspheres have the advantages of good core-shell morphology, high specific surface area, ordered pore structures, good mechanical stability, thermal stability, chemical stability and the like, if the microspheres are used as a chromatographic stationary phase, the chromatographic mass transfer resistance can be reduced effectively, the theoretical plate height is improved, and finally, column efficiency and degree of separation are improved; and if the microspheres are used as solid-phase extracting filler, the enrichment effect can be improved remarkably. The covalent organic framework composite microspheres with core-shell structures have good application prospects in the aspect of separation and enrichment of small organic molecules.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Structured organic films
A structured organic film comprising a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be a multi-segment thick structured organic film.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Imaging devices comprising structured organic films
ActiveUS20120040282A1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternOrganic filmSolvent
An imaging member for a xerographic liquid immersion development machine having an outermost layer including a solvent resistant structured organic film (SOF) having a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be multi-segment thick.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Covalent organic framework material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108219158AReduce energy consumptionEasy to operateGas treatmentOther chemical processesRoom temperatureBoric acid
The invention discloses a covalent organic framework material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of preparation of covalent organic framework materials. Multiple covalent organic framework materials are quickly synthesized under a room temperature and an open system by utilizing ionothermal reaction, and include a Schiff-base type covalent organic framework material and a boric-acid type covalent organic framework material, and also include covalent organic framework materials with two-dimensional and three-dimensional structures. The synthetic method has the advantages of short reaction time, low energy consumption, no pollution of volatile organic matters, no additive, simple operation and the like. Ironic liquid can be reused for at least three times after being simply filtered and separated. The covalent organic framework material synthesized by the method has potential application in the aspects of gas storage and separation and the like because ofloading the ironic liquid.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Capped structure organic film compositions
A capped structured organic film comprising a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be a multi-segment thick structured organic film.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Imaging members for ink-based digital printing comprising structured organic films
ActiveUS20120040283A1Electrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternOrganic filmEngineering
An imaging member for ink-based digital printing having an outermost layer including a structured organic film (SOF) having a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be multi-segment thick.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105348303AImprove performanceExcellent rate performanceOrganic chemistryHybrid capacitor electrodesPotassiumPorphyrin
The invention belongs to the fields of a metal ion battery and a super capacitor, and concretely relates to a porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer, and a preparation method and an application thereof. A structural formula of the porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer is shown in formula (I), wherein m=0 or 1, n=0 or 1. The porphyrin two-dimension covalent organic framework conjugated polymer can be directly used as a cathode material of the metal ion battery and the super capacitor, so that the cathode material shows excellent properties, which include good cycle performance, high specific capacity and excellent rate capability; the polymer powder also has the same effects and properties, and can be used as a cathode material of other metal ion (sodium, potassium, zinc, nickel, etc.) batteries and super capacitors.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
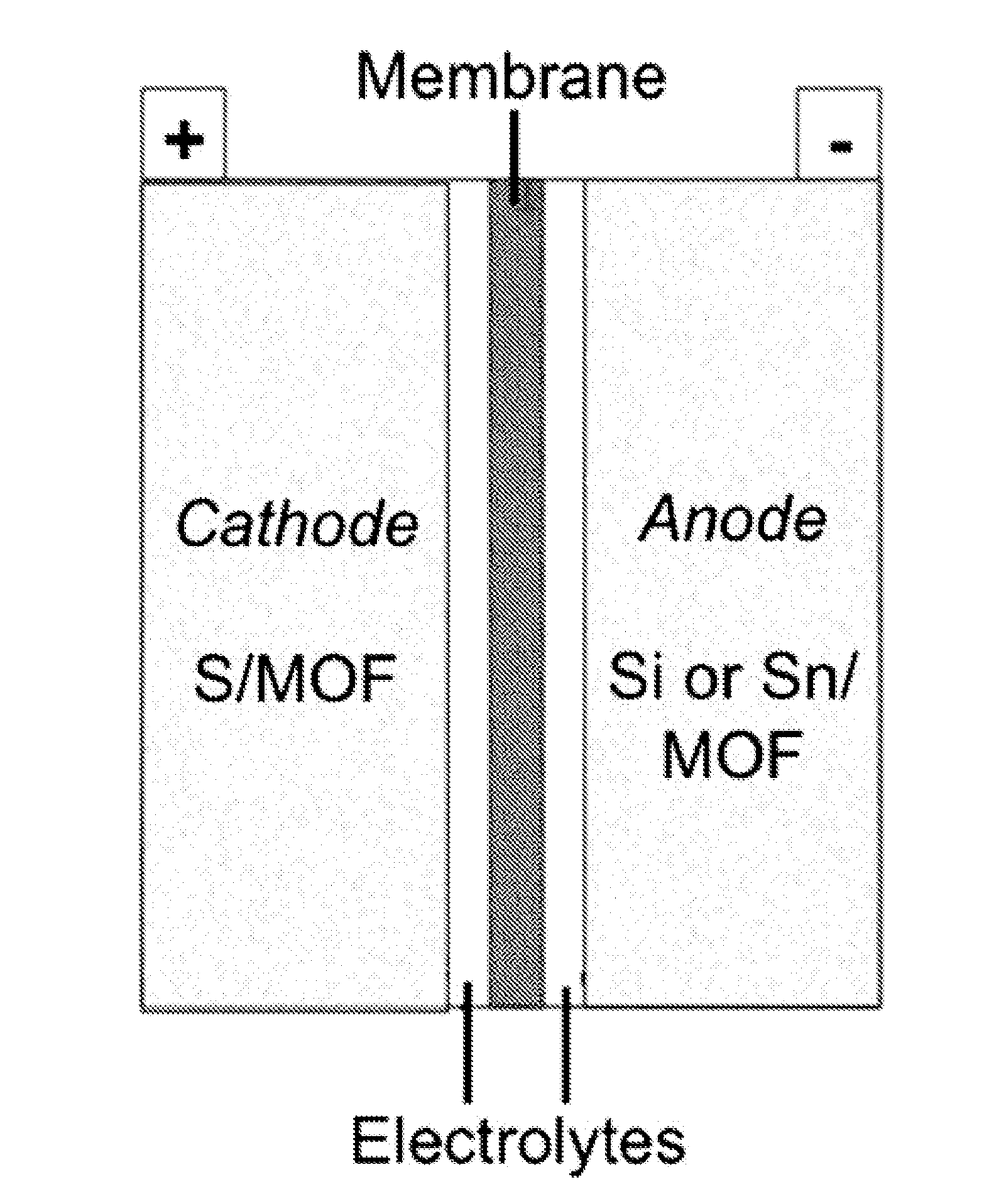
Open framework composites, methods for producing and using such composites
InactiveUS20170012277A1Equally distributedSuitable for useElectrode carriers/collectorsLi-accumulatorsTinIon
Provided herein are composites made up of open frameworks encapsulating sulfur, silicon and tin, and mechanochemical methods of producing such composites. Such open frameworks may include metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), including for example zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), and covalent organic frameworks (COFs). Such composites may be suitable for use as electrode materials, or more specifically for use in batteries. For example, sulfur composites may be used as cathode materials in Li-ion batteries; and silicon or tin composites may be used as anode materials in Li-ion batteries.
Owner:NIVO SYST
Process for preparing structured organic films (SOFS) via a pre-sof
A processes for preparing structured organic film (SOF) comprising a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be a multi-segment thick structured organic film by reaction of a pre-SOF.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Application of heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material in photocatalysis
ActiveCN108889334AStructure location is clearAdjustable performanceWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMonomerPhotochemistry
The invention belongs to the field of photocatalyst application of organic semiconductors and in particular relates to application of a heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material in photocatalysis. The heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material serves as a photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: introducing heteroatoms through heterocyclic aldehyde group monomers, carrying out a condensation polymerization reaction with binary or poly-element amidino compounds in the presence of a basic catalyst, thereby obtaining theproduct. The material serves as the photocatalyst, and is capable of degrading organic pollutants in water and producing hydrogen under light conditions by virtue of water splitting. According to themethods, the heteroatom-containing triazine covalent organic framework material is introduced to serve as the photocatalyst, and is high in catalytic efficiency, high in applicability and suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adsorption systems using metal-organic frameworks
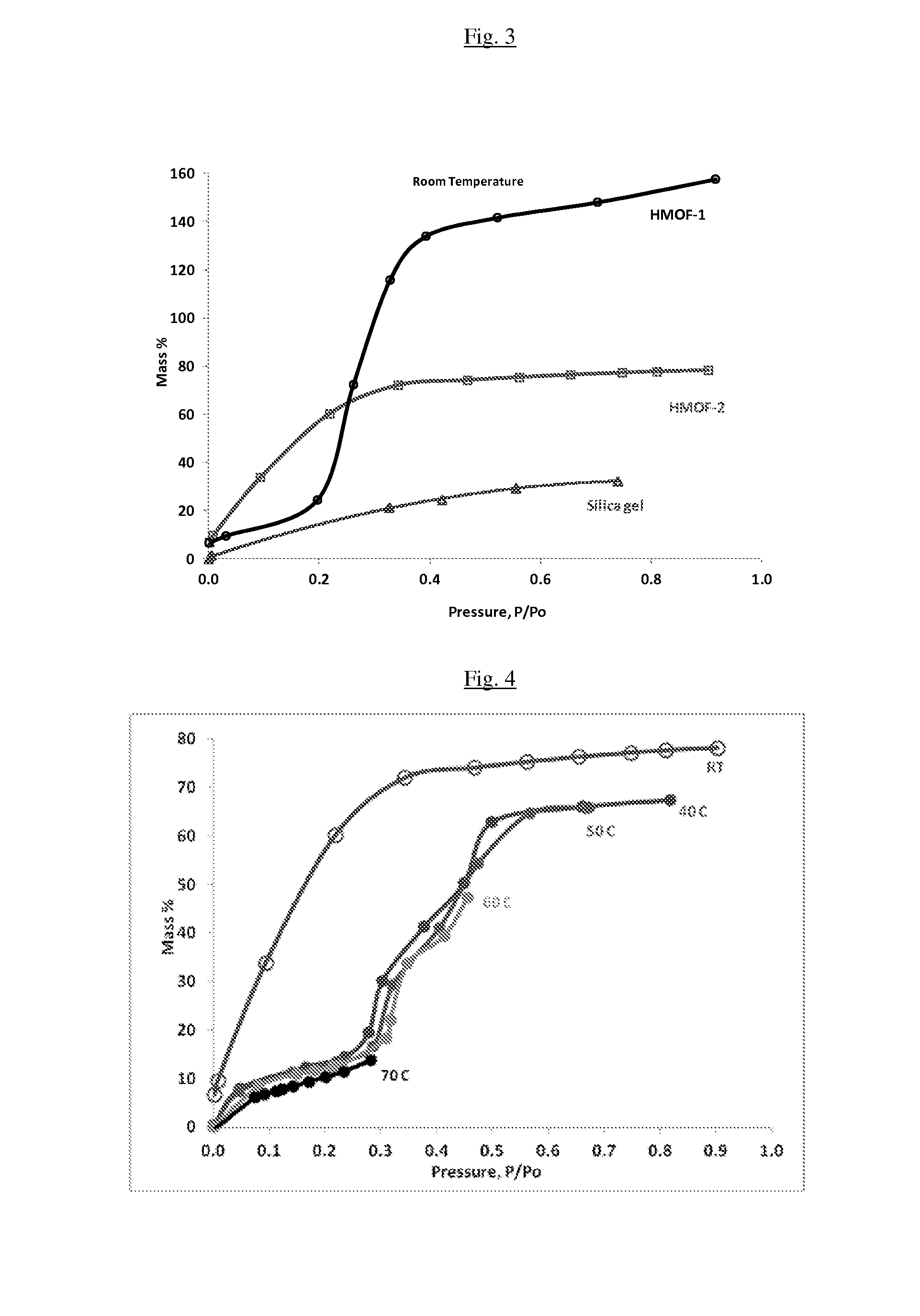
InactiveUS20150291870A1High mass loadingReduce heat of adsorptionGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesComplex cyanidesAdsorption chillerSorbent
The present invention relates to sorbants such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), covalent organic frameworks (COFs), porous aromatic frameworks (PAFs) or porous polymer networks (PPNs) for separations of gases or liquids, gas storage, cooling, and heating applications, including, but not limited to, adsorption chillers.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST +1
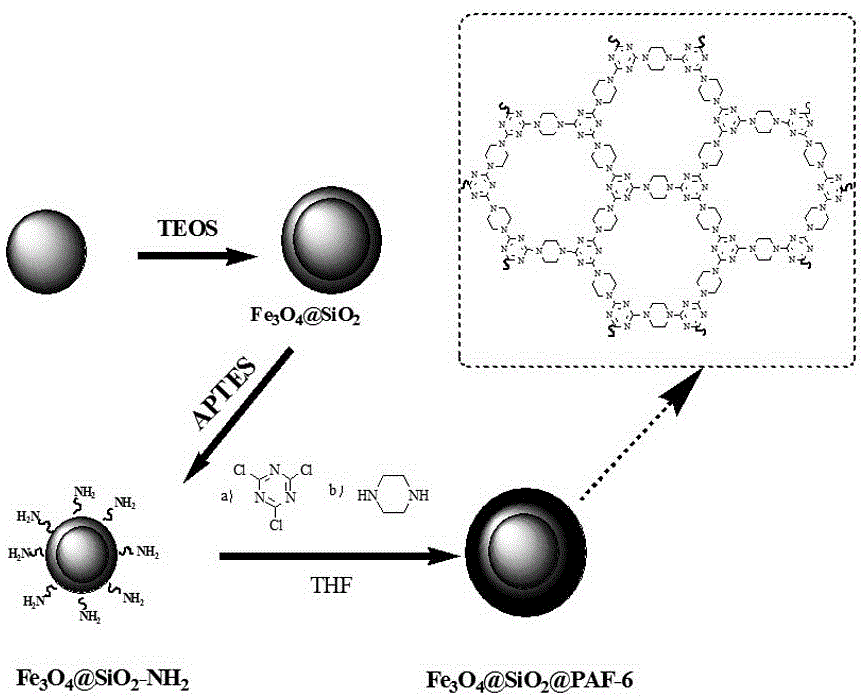
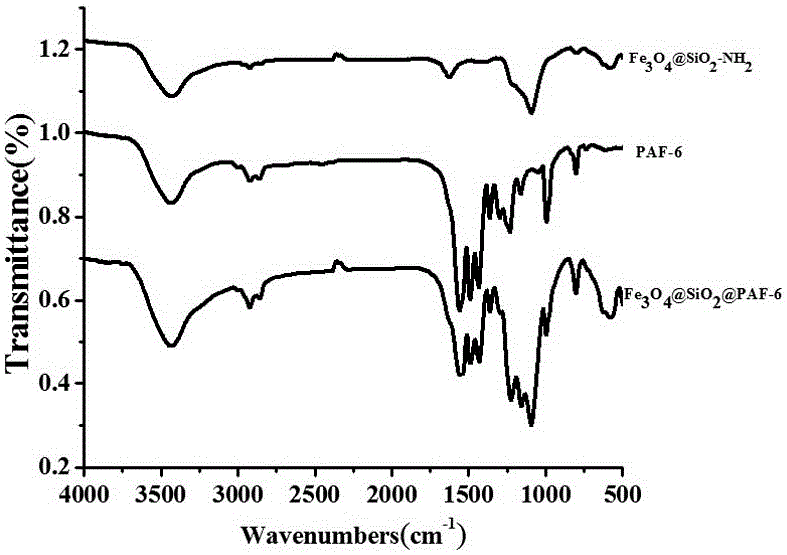
Magnetic PAFs solid-phase extracting agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105879842AEasy to separateAvoid inconvenienceOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSilanesCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a magnetic PAFs solid-phase extracting agent. A preparation method of the magnetic PAFs solid-phase extracting agent includes allowing 3-aminopropyl triethoxy silylation ferroferric oxide to have a temperature-programmed reaction with piperazine and cyanuric chloride in the presence of N, N-diisopropylethylamine to obtain the magnetic PAFs solid-phase extracting agent. The magnetic PAFs solid-phase extracting agent and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the prepared magnetic PAFs solid-phase extracting agent is good in dispersity and stable in core-shell structure; the preparation method is simple, low in cost, widely applicable, capable of achieving repeated material recycling, and the like; a covalent organic framework bonded to the ferroferric oxide can provide various action sites such as an inclusion interaction site, a hydrogen-bond interaction site, a pi-pi interaction site and an anion exchange site, so that the covalent organic framework has specific recognition and retention acting force on polar substances such as phenols and carboxylic acids.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
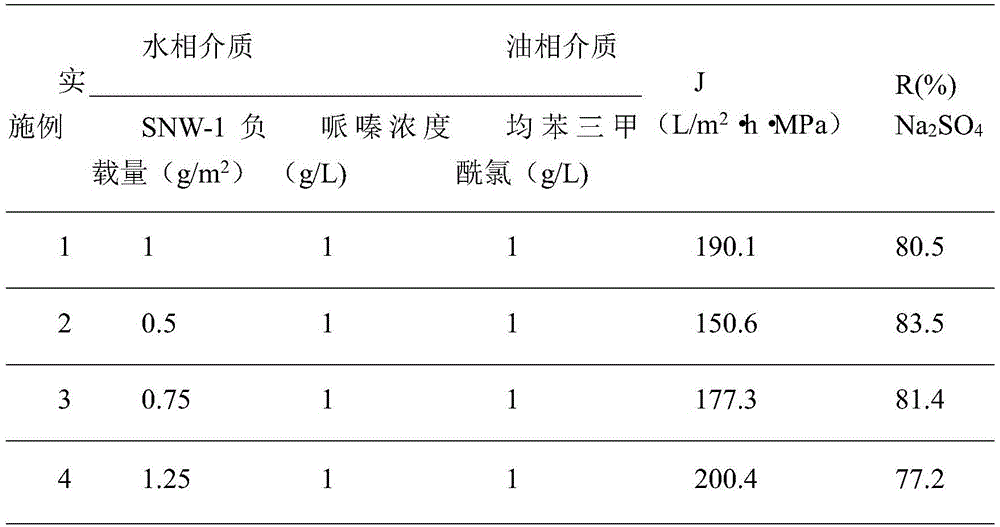
Polyamide/COFs hybridized nanofiltration composite membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105642133AImprove interface compatibilityHigh retention rateSemi-permeable membranesPolymer sciencePolyamide
The invention provides a polyamide / COFs hybridized nanofiltration composite membrane. The composite membrane comprises a composite layer and a loaded porous frame material. The composite layer is a layer of polyamide compound formed by conducting polymerization reaction on piperazine and trimesoyl chloride, and the thickness is 100-500 nm. The porous frame material is SNW-1 obtained when melamine and terephthalaldehyde react, and is a compound layer with the loading amount of 0.5-3 g / m<2>. A covalent organic framework is effectively hybridized in a separation layer of the composite membrane, and more water channels are provided for the nanofiltration membrane. By means of the method, various types of COFs can be introduced onto a polyether sulfone base membrane, the water flux can reach 200 L / m<2>.h.MPa and increased by 2 times, the sodium sulfate retention rate of the nanofiltration membrane is still kept at 80% or above, and the high water flux and the high retention rate are achieved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
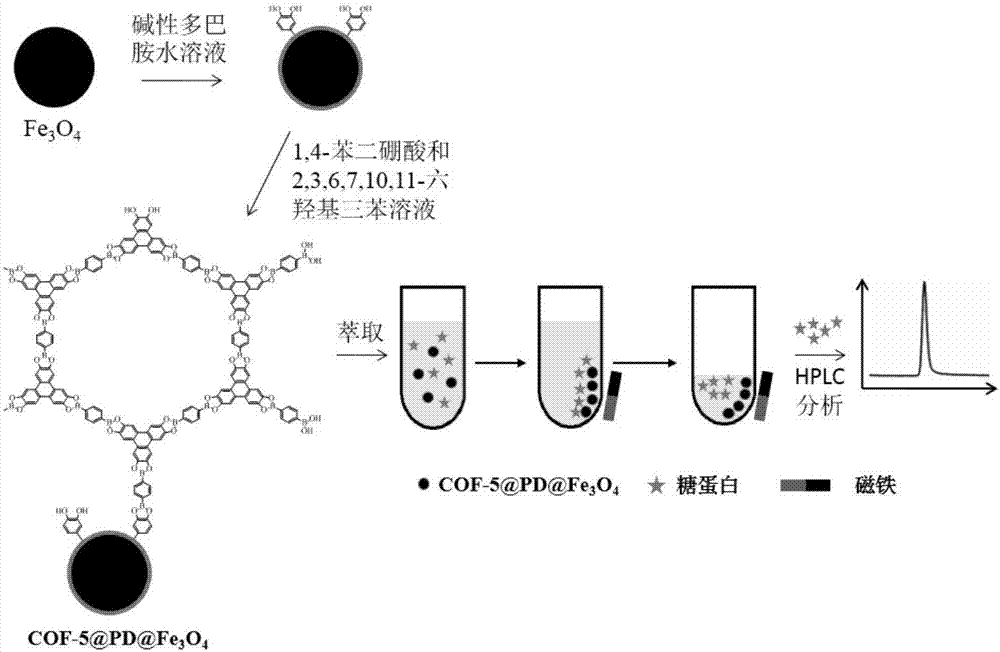
Method for fixing covalent organic framework material, and application thereof
ActiveCN105214340AEasy to separateSimple processSolid sorbent liquid separationBenzeneElectrochromatography
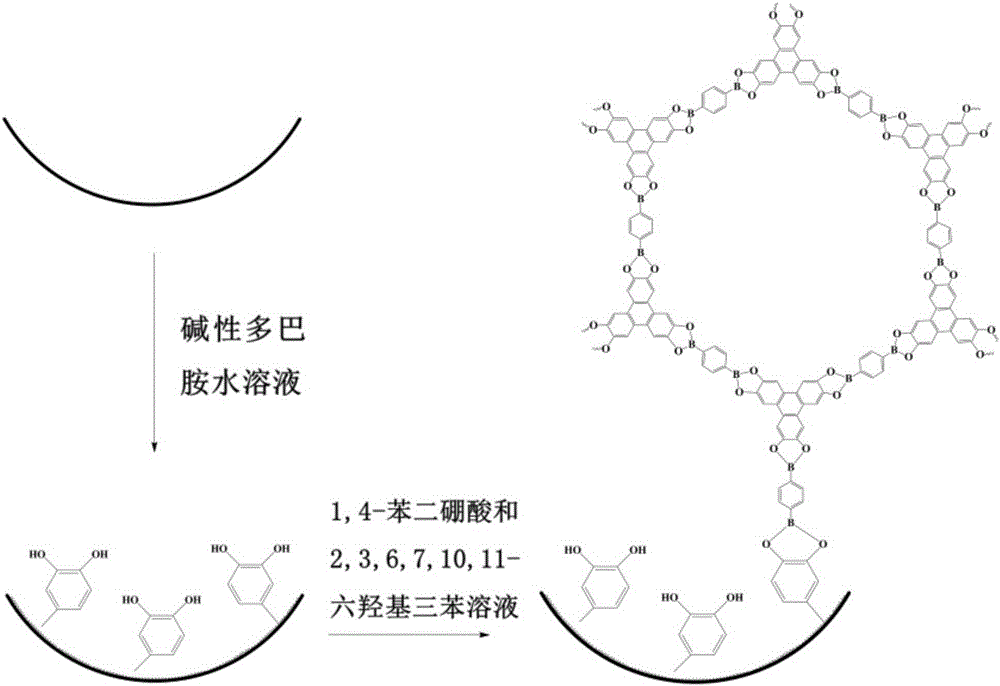
The invention provides a polydopamine-assisted method for fixing a covalent organic framework material, and an application thereof. First, a dopamine water solution is prepared; the pH value is regulated to weakly alkaline, and an oxidation treatment is carried out; a carrier with a clean surface is added under room temperature, and the surface of the carrier is modified with a polydopamine coating; the modified carrier is placed in a mixed solution of binary boric acid and 2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydroxyl triphenyl; one boric acid group is subjected to a reaction with o-phenyldihydroxyl site provided by the polydopamine coating, and another boric acid group participates in COFs framework formation, such that COFs crystal is formed on site and fixed on the surface of the carrier. The preparation process provided by the invention is simple. With the wide adaptability of polydopamine modification, synthesis and fixing of COFs on the surfaces of various substrates can be realized. The method is applied in preparing open tubular electrochromatography columns. Prepared open tubular column based on COF-5 has good separation effect upon electrically neutral benzene-series substances in an electrochromatography mode.
Owner:武汉长林医药科技有限公司
Structured organic films having an added functionality
A structured organic film with an added functionality comprising a plurality of segments and a plurality of linkers arranged as a covalent organic framework, wherein the structured organic film may be a multi-segment thick structured organic film.
Owner:XEROX CORP
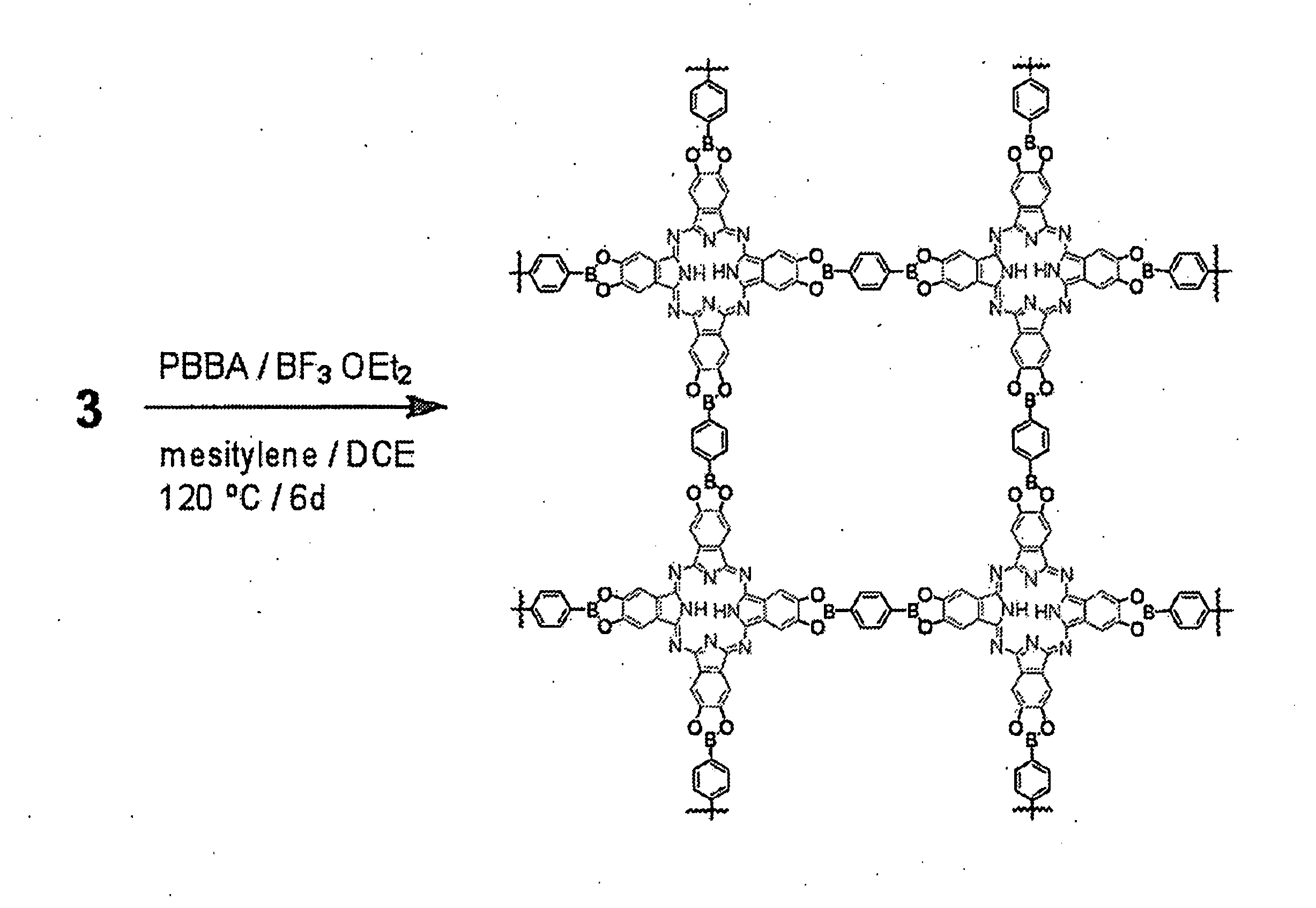
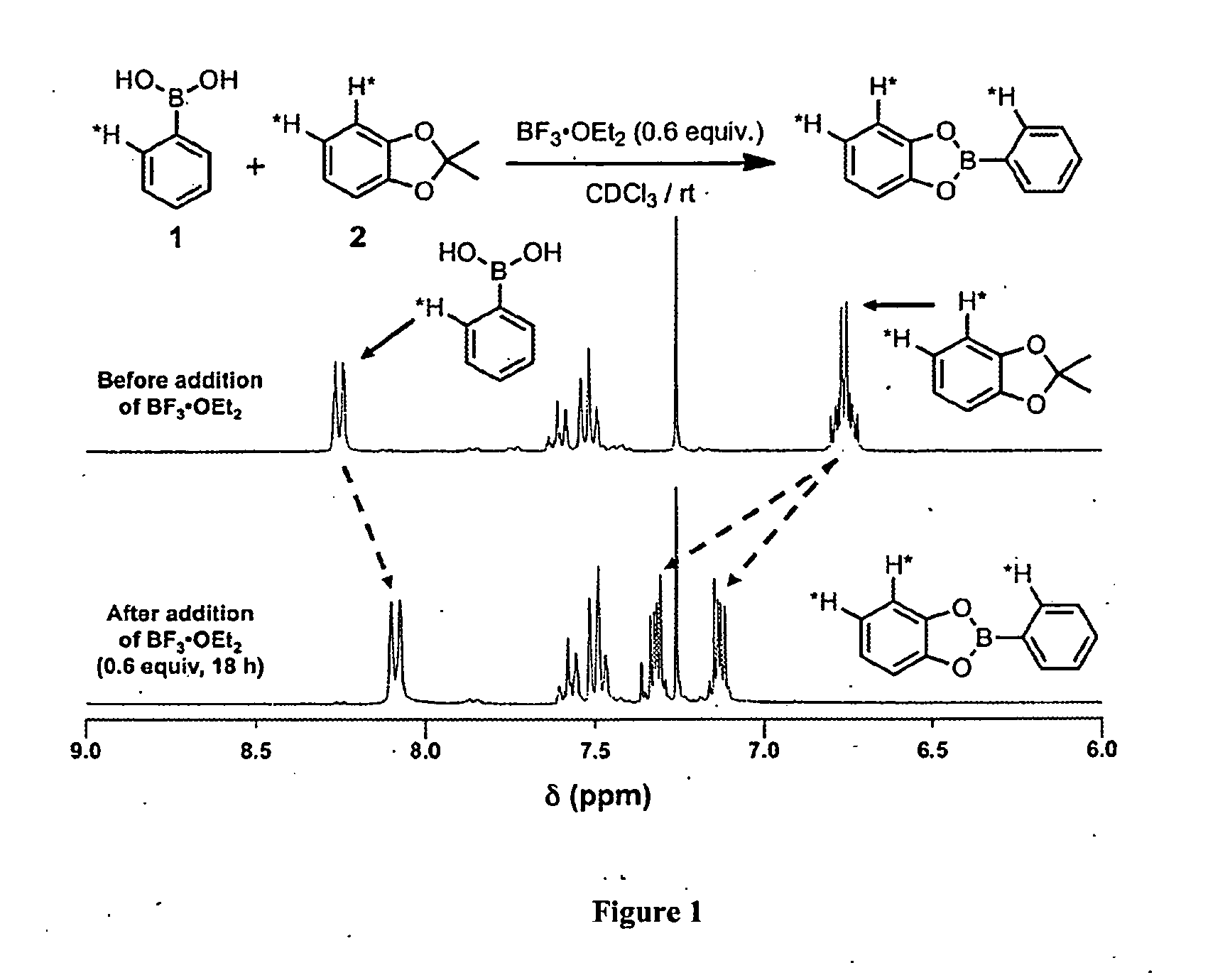
Covalent Organic Frameworks and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20140148596A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoron containingAcid catalyzed
Crystalline COFs comprising a phthalocyanine moiety and a boron-containing multifunctional linking group joined by boronate ester bonds. A method for making crystalline COFs comprising Lewis acid catalyzed formation of boronate ester bonds between protected catechol subunits and multifunctional linkers comprising boronic acid groups. The COFs can be used in applications such as, for example, electronic devices.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Magnetic solid-phase extraction agent based on covalent organic framework material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107413313ALarge specific surface areaModerate pore sizeIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesOrganic solventMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to a magnetic solid-phase extraction agent based on a covalent organic framework material and a preparation method and application thereof. The magnetic solid-phase extraction agent comprises a ferriferous oxide magnetic nanoparticle core, a polydopamine layer and a covalent organic framework material COF-5 layer, and the polydopamine layer and the covalent organic framework material COF-5 layer are sequentially coated outside the core. A method includes: adding functionalized magnetic nanoparticles into a to-be-treated glycoprotein sample, sufficiently stirring for extraction, using a magnet to separate the magnetic nanoparticles from a solution, adding elution liquid to elute off the glycoprotein from the magnetic nanoparticles, and measuring. The covalent organic framework material can selectively enrich glycoprotein and effectively separate the glycoprotein from impurities, so that the method has good extraction effect on the glycoprotein. The solid-phase extraction method is simple in operation step, short in time, high in recycling rate, low in organic solvent consumption and suitable for enrichment and measurement of the glycoprotein in complex biological samples like plasma and urine.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com