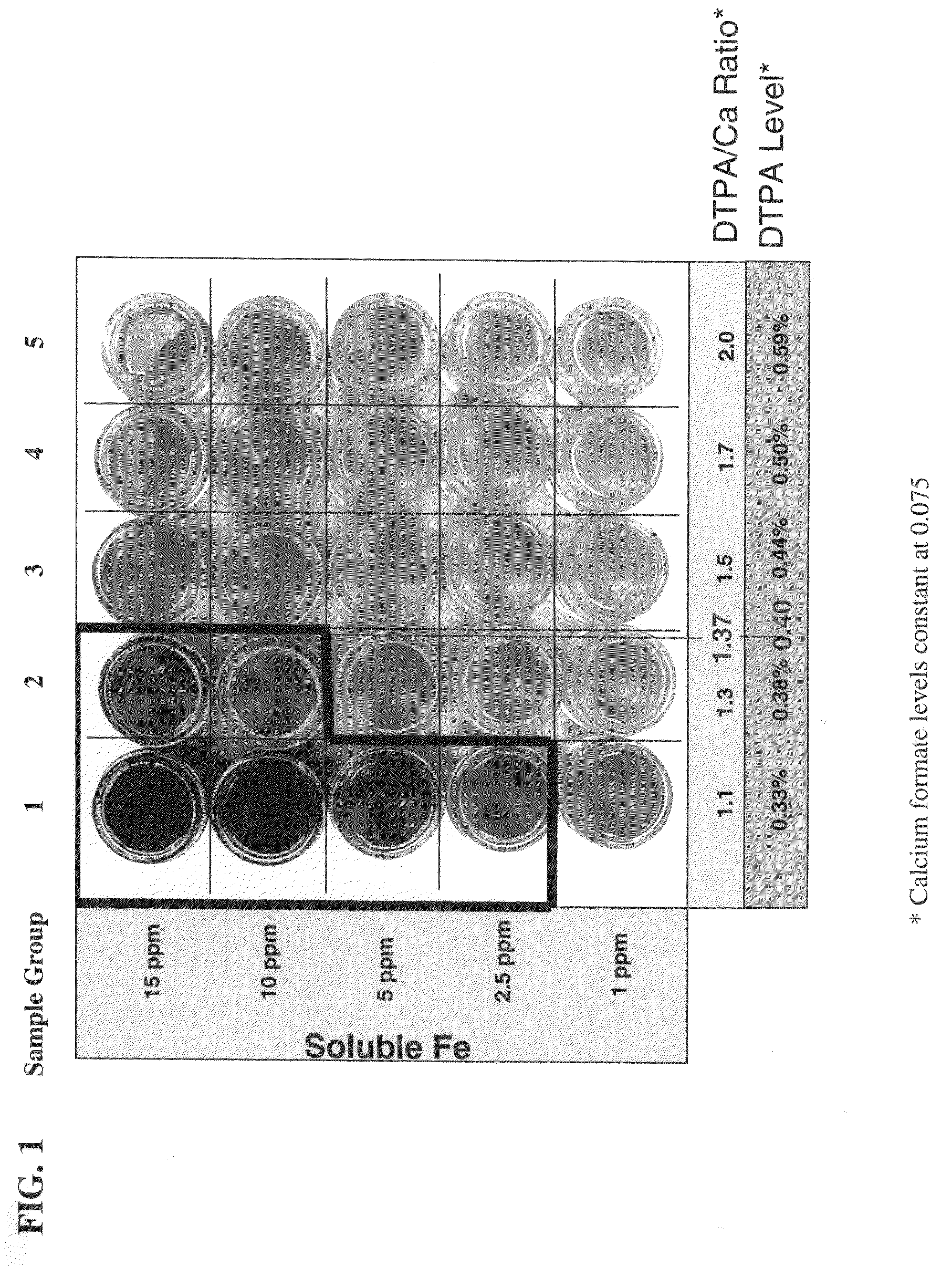
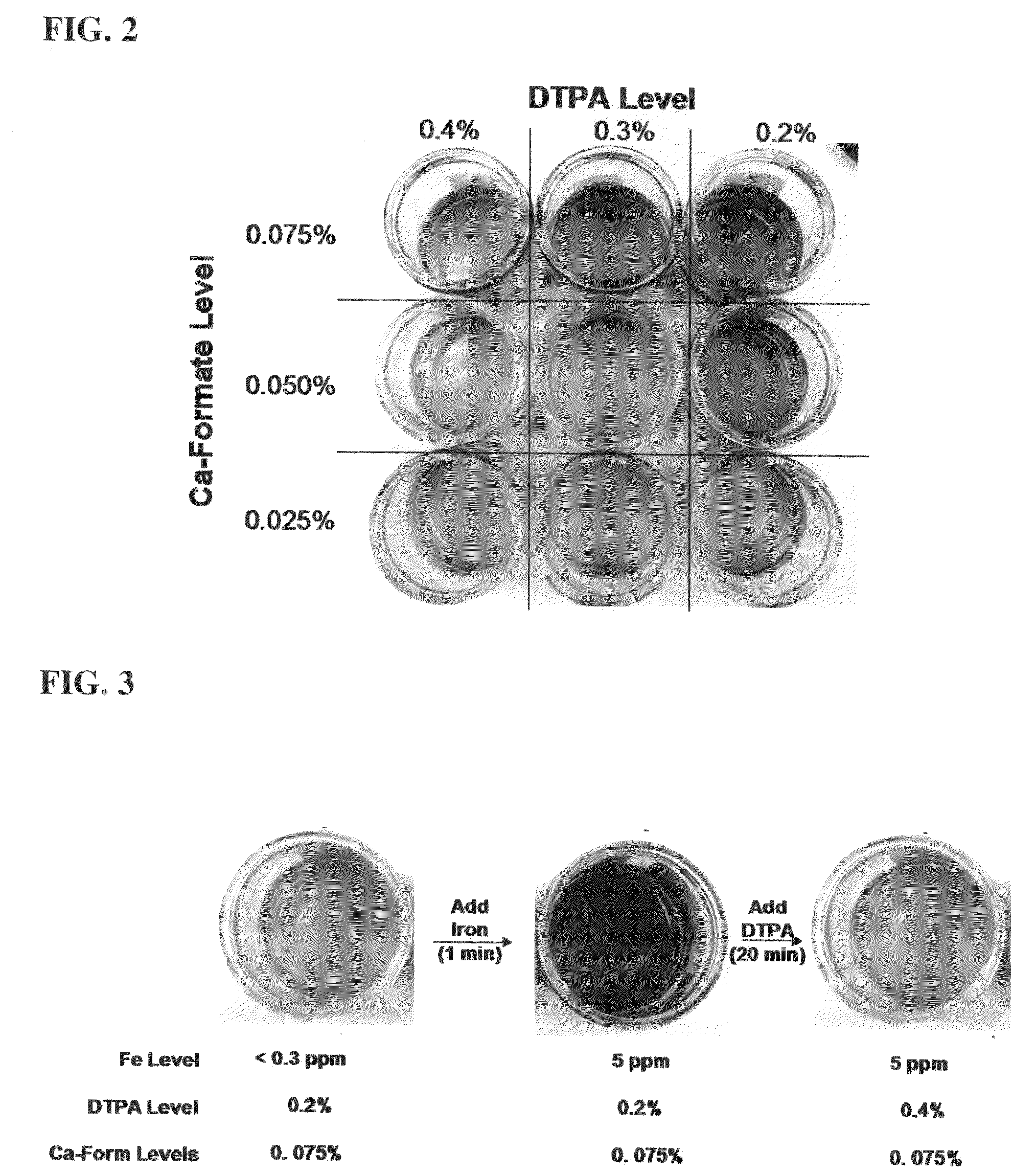
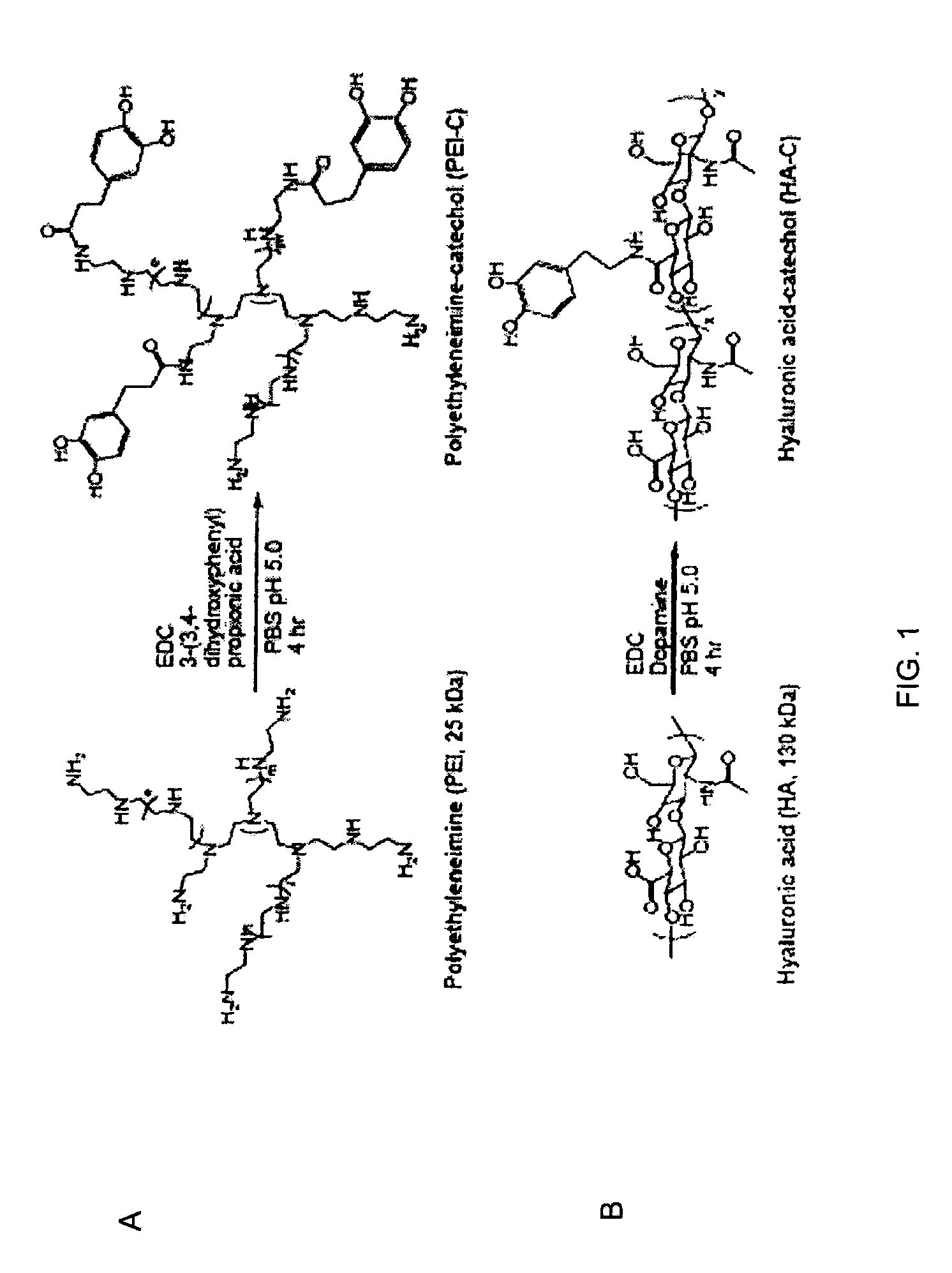
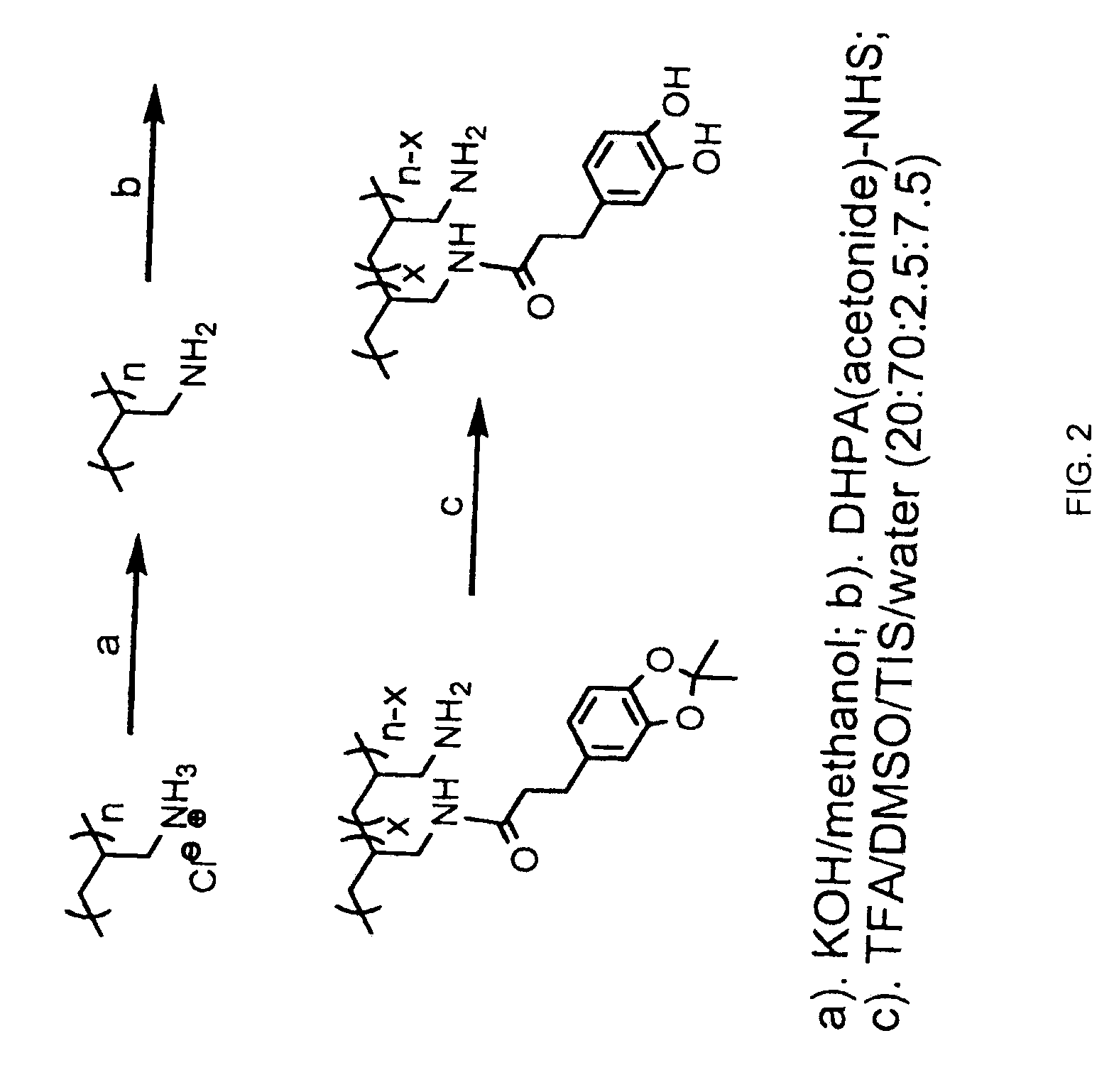
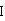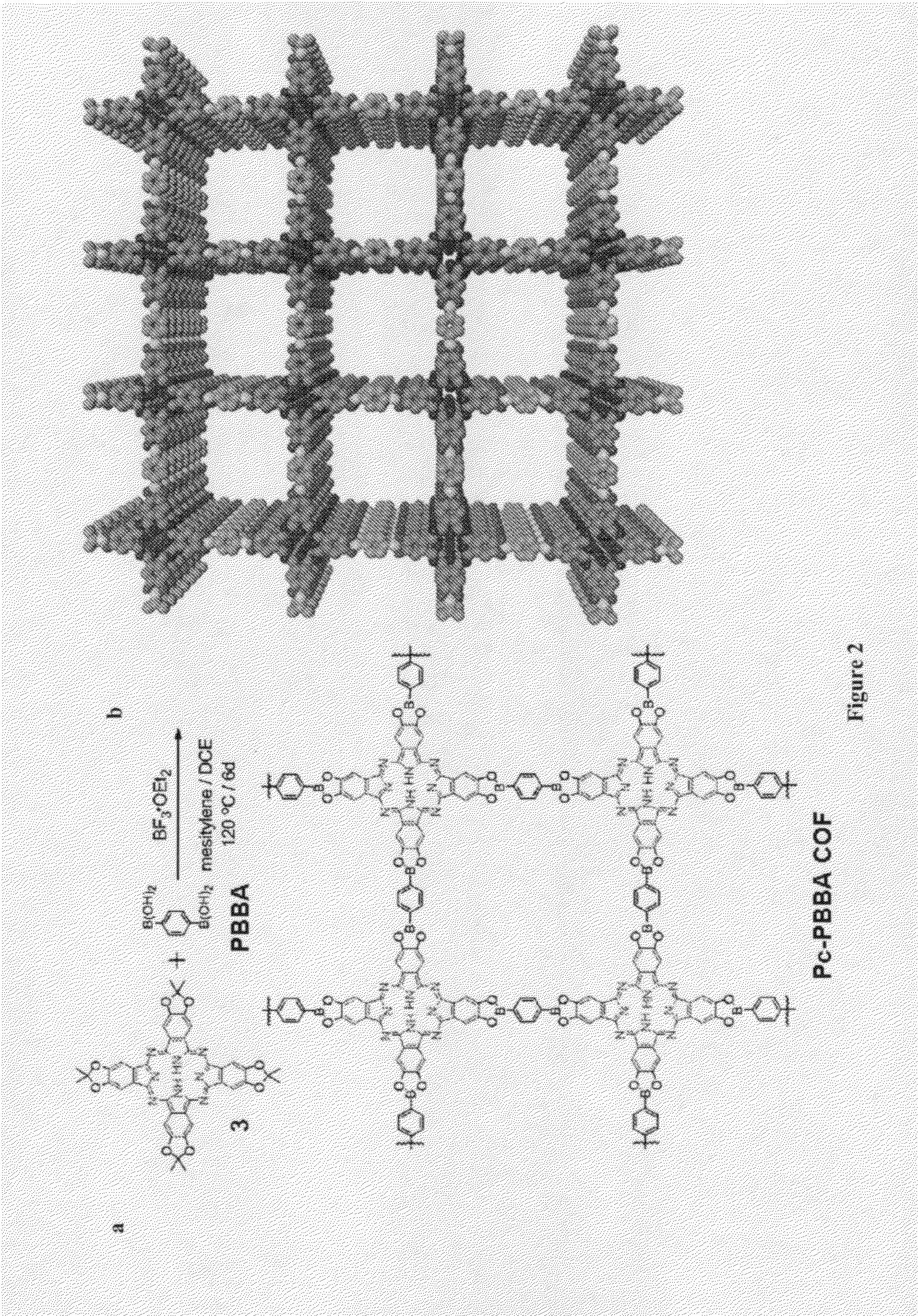Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1813 results about "Catechol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
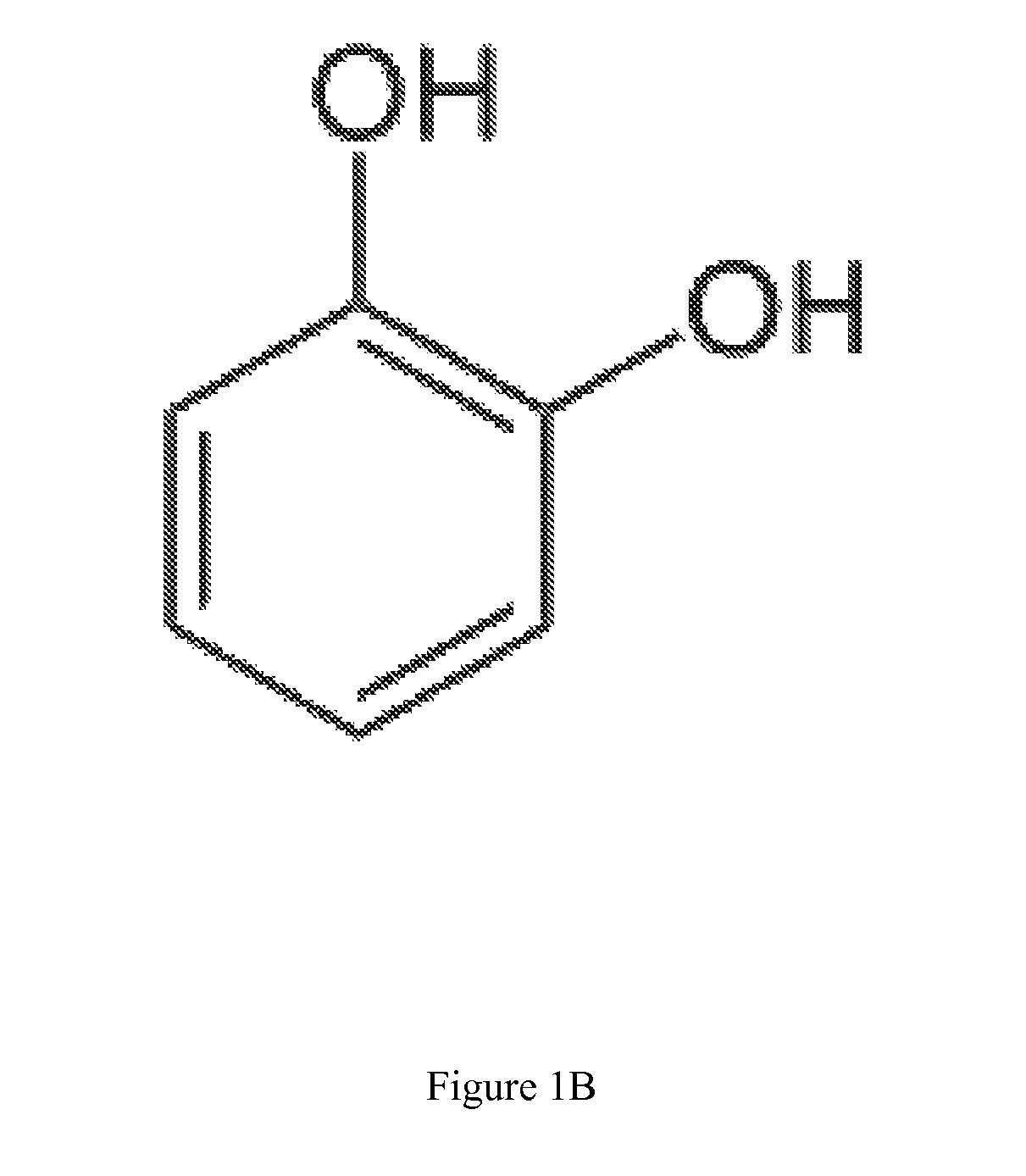
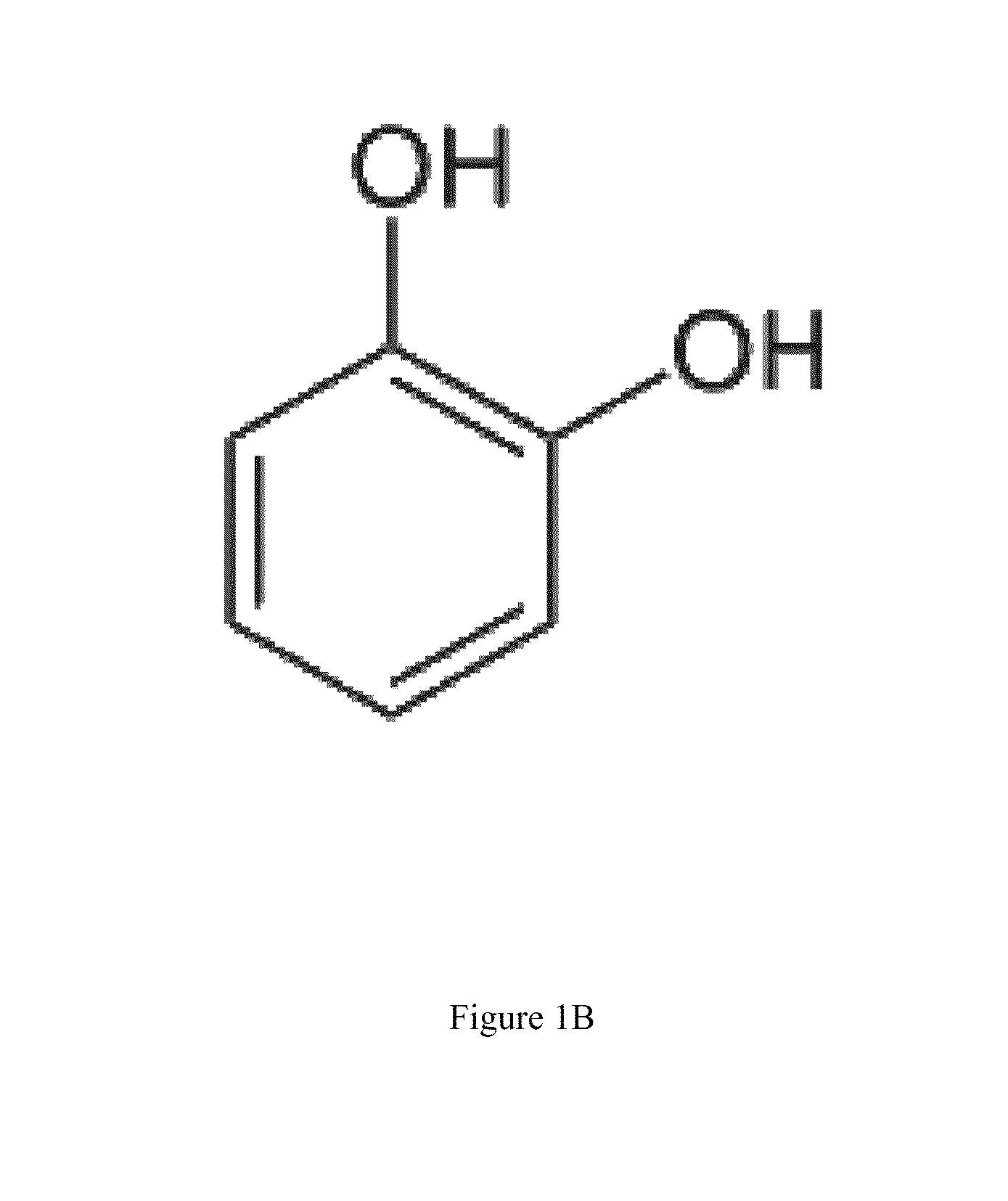
Catechol (/ˈkætɪtʃɒl/ or /ˈkætɪkɒl/), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C₆H₄(OH)₂. It is the ortho isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol is now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances.
Detergents having acceptable color
InactiveUS20090176684A1Reduce intensityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsBenzeneTitanium
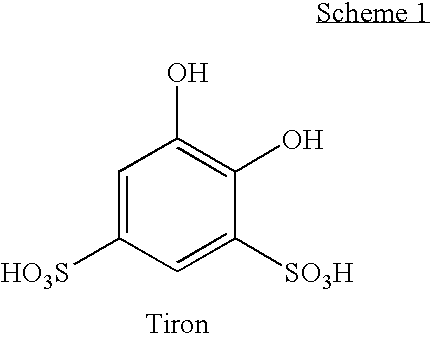
Detergent compositions containing catechols, such as tiron (1,2-dihydroxybenzene-3,5-disulfonic acid), which do not have or do not develop the reddish color associated with the catechol / ferric iron chelate are disclosed. Methods for reducing the intensity of red color in a tiron containing detergent composition are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Compositions containing anionically modified catechol and soil suspending polymers
InactiveUS7445644B2Organic detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsPolyphenolCatechol
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Bioadhesive polymers with catechol functionality
InactiveUS20050201974A1Good bioadhesionExtended stayNervous disorderPill deliveryArameHydrophobic polymer
Polymers with improved bioadhesive properties and methods for improving bioadhesion of polymers have been developed. A compound containing an aromatic group which contains one or more hydroxyl groups is grafted onto a polymer or coupled to individual monomers. In one embodiment, the polymer is a biodegradable polymer. In another embodiment, the monomers may be polymerized to form any type of polymer, including biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers. In some embodiments, the polymer is a hydrophobic polymer. In the preferred embodiment, the aromatic compound is catechol or a derivative thereof and the polymer contains reactive functional groups. In the most preferred embodiment, the polymer is a polyanhydride and the aromatic compound is the catechol derivative, DOPA. These materials display bioadhesive properties superior to conventional bioadhesives used in therapeutic and diagnostic applications. These bioadhesive materials can be used to fabricate new drug delivery or diagnostic systems with increased residence time at tissue surfaces, and consequently increase the bioavailability of a drug or a diagnostic agent. In a preferred embodiment, the bioadhesive material is a coating on a controlled release oral dosage formulation and / or forms a matrix in an oral dosage formulation.
Owner:SPHERICS
Electrical smoking system and method
InactiveCN1633247AReduce gaseous componentsIncandescent ignitionCigar manufactureIntegratorAcrylonitrile
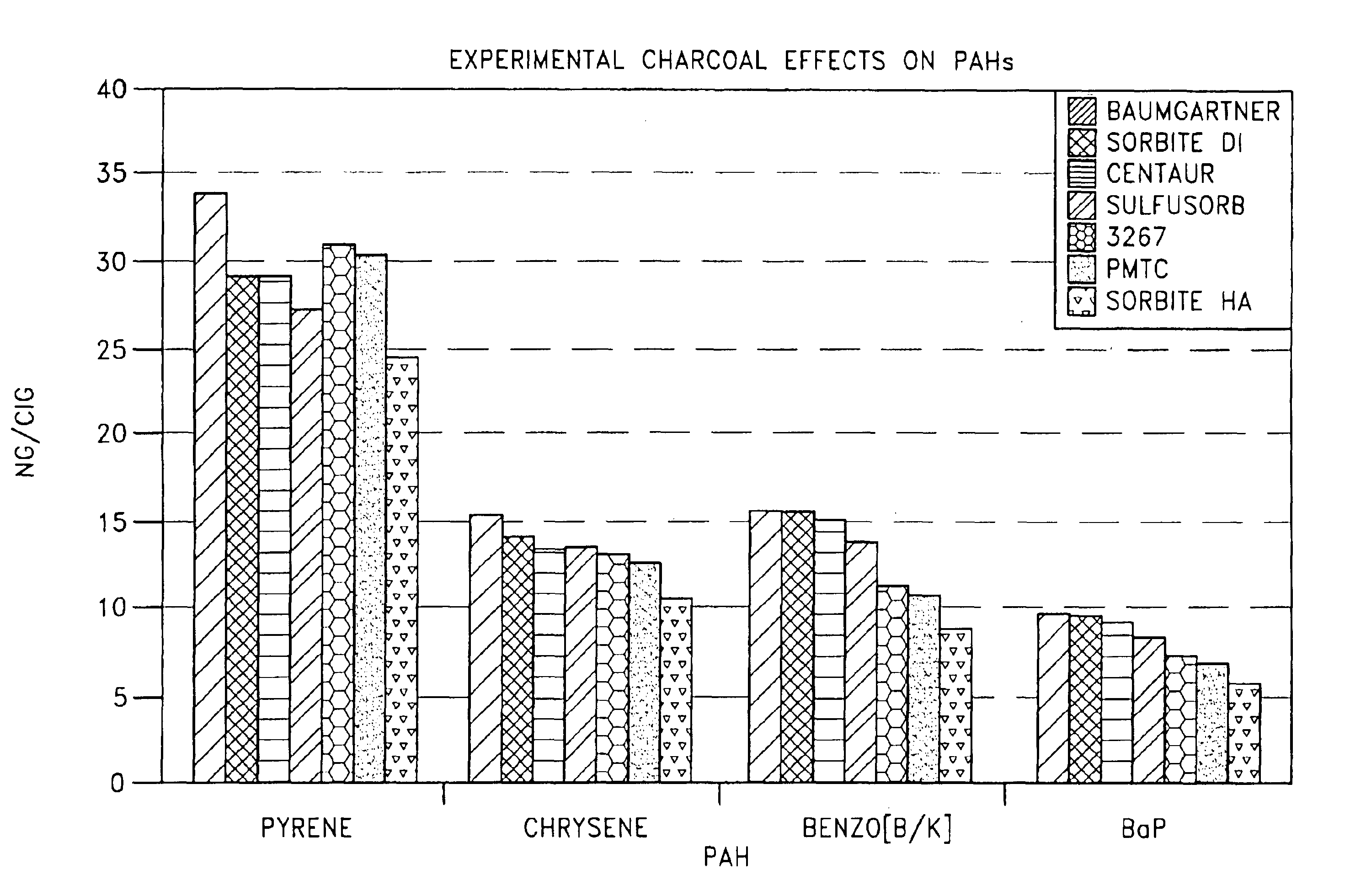
An electric smoking system includes a cigarette including a cylindrical tobacco web partially filled with tobacco material to define a filled tobacco rod portion and an unfilled tobacco rod portion, and an electric lighter. The wrapper includes a filler of ammonium-containing compounds effective to reduce the gaseous constituents of the smoke produced during smoking. The system includes a pilot burner including at least one heating vane and a controller adapted to control heating of the heating vane. The lighter is configured to at least partially contain the cigarette such that the heater blade heats the heating region of the cigarette. Manipulating the controller to limit the heating of the heater blades to a predetermined temperature range which allows the delivery of the smoke generated when the portion of the tobacco rod is heated while at least reducing the amount of smoke present in the smoke as compared to smoking a cigarette having only calcium carbonate as filler. A gaseous component. The gaseous components that can be reduced include carbon monoxide, 1,3 butadiene, isoprene, acrolein, acrylonitrile, hydrogen cyanide, 0-toluidine, 2-naphthylamine, nitrogen oxide, benzene, NNN, Phenol, catechol, benzanthracene and benzopyrene.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Method of making a smoking composition
The present invention relates to smoking articles such as cigarettes, and in particular to catalytic systems containing metallic or carbonaceous particles that reduce the content of certain harmful or carcinogenic substances, including polyaromatic hydrocarbons, tobacco-specific nitrosamines, carbazole, phenol, and catechol, in mainstream cigarette smoke and in side stream cigarette smoke.
Owner:VECTOR TOBACCO LLC
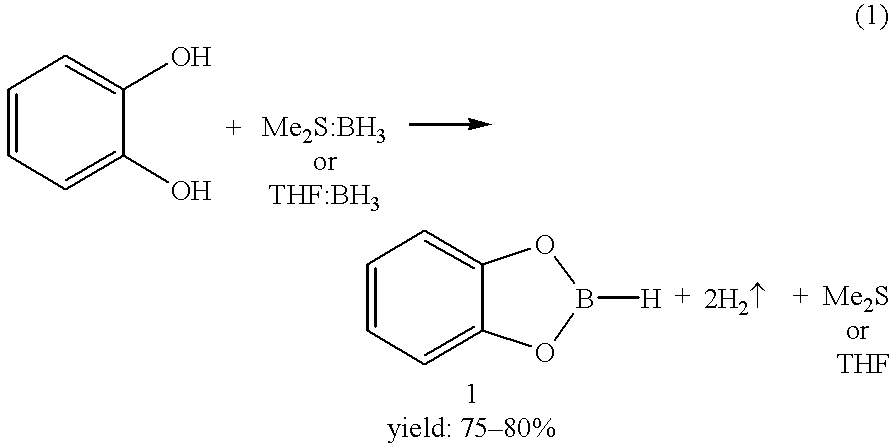
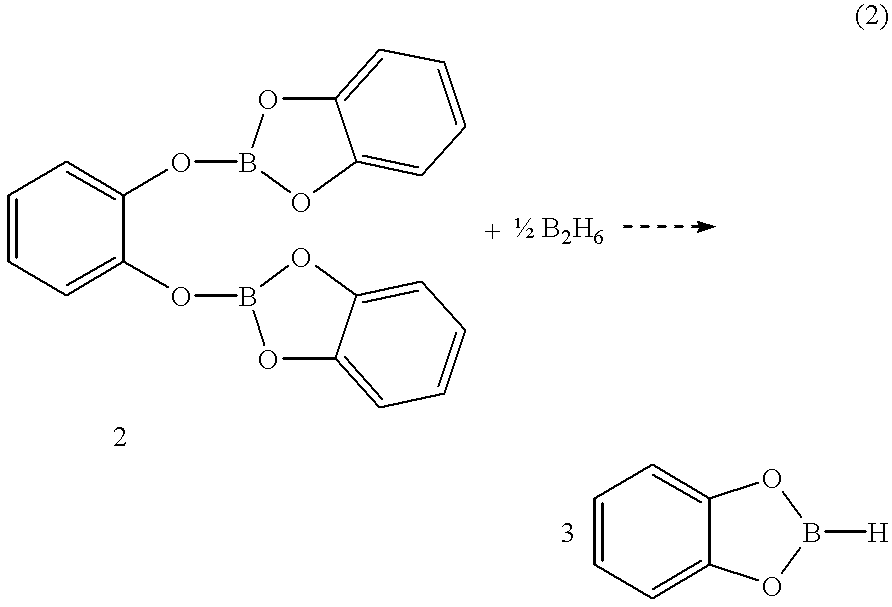
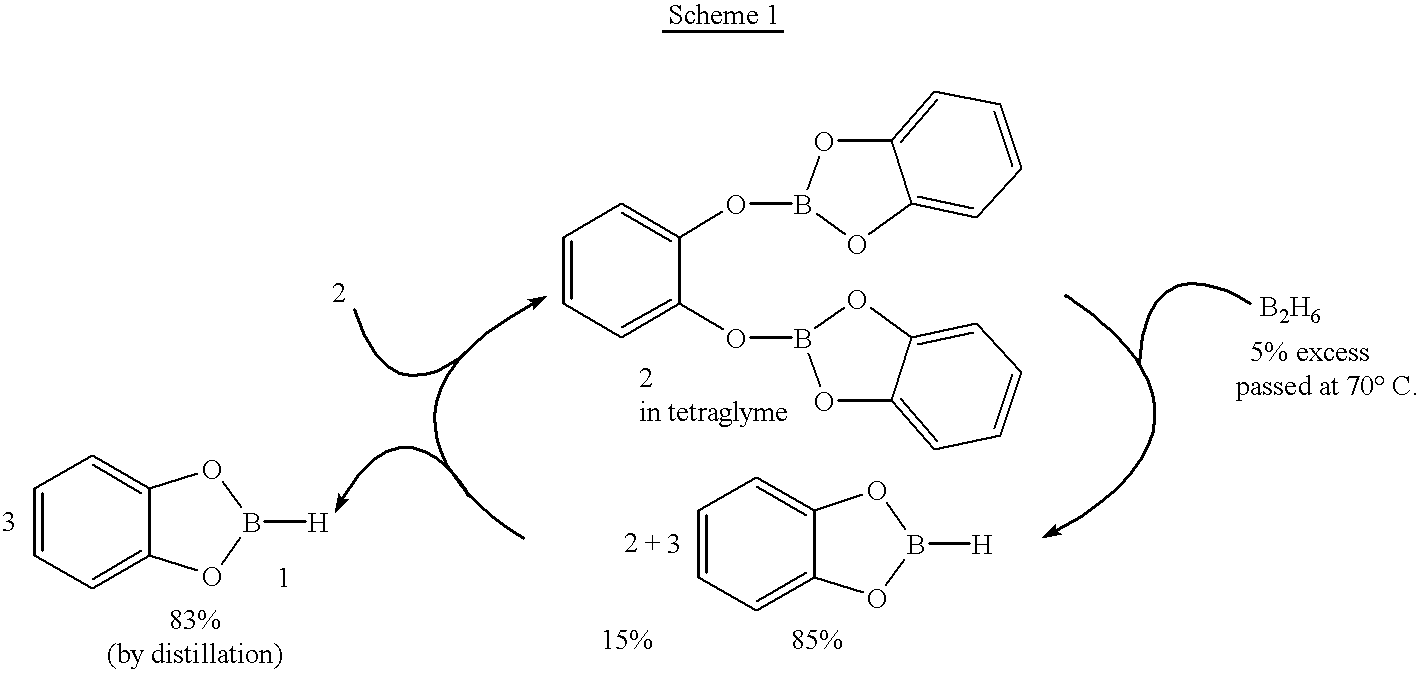
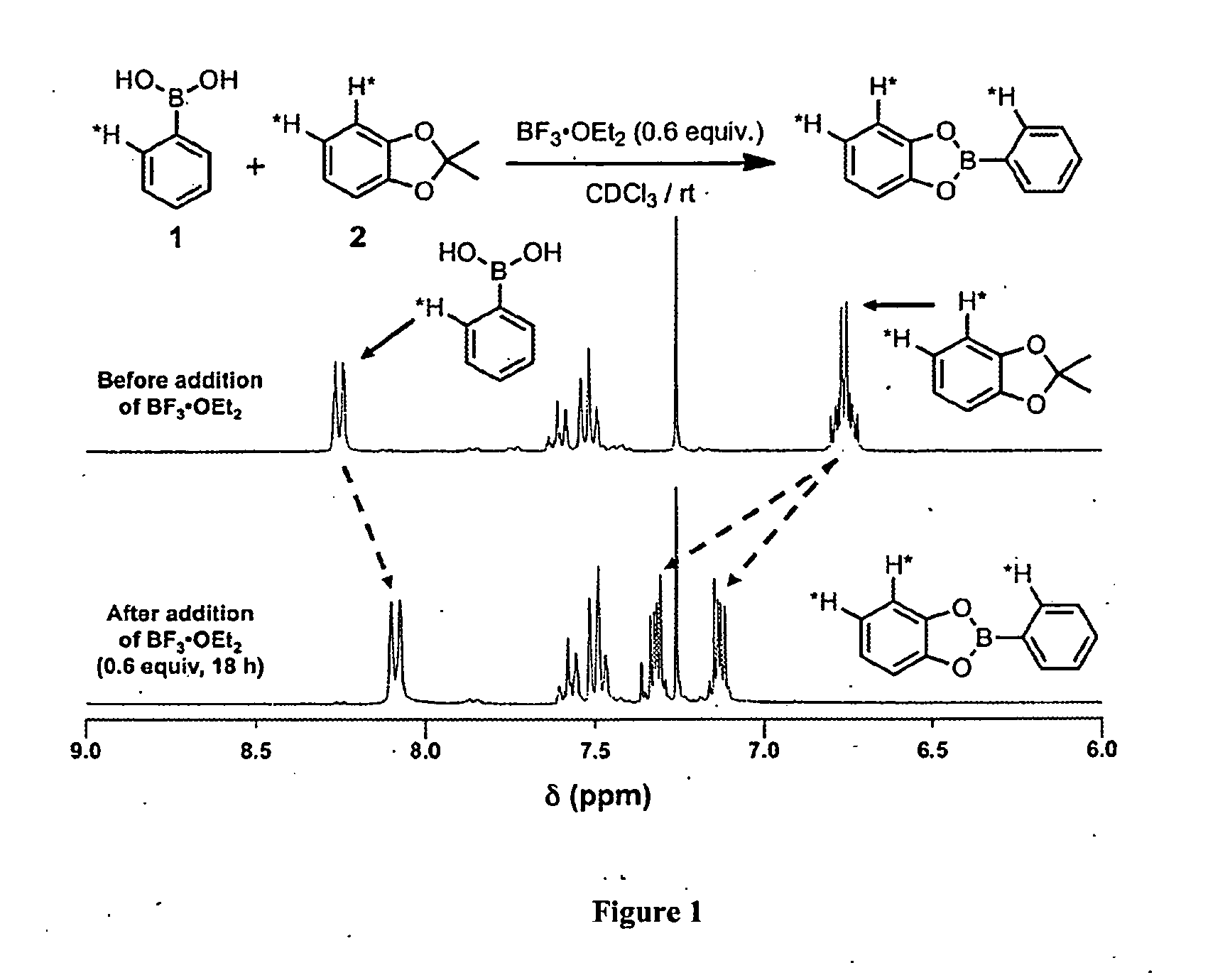
Economical and convenient procedures for the synthesis of catecholborane
New, economical and convenient procedures for the preparation of catecholborane in high chemically pure form using tri-O-phenylene bis borate readily prepared from the reaction of catechol with boric acid, and diborane or borane-Lewis base complexes.
Owner:ALDRICH CHEM
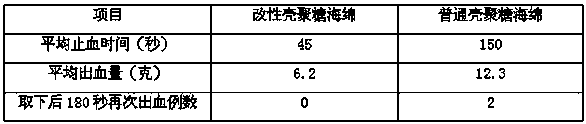
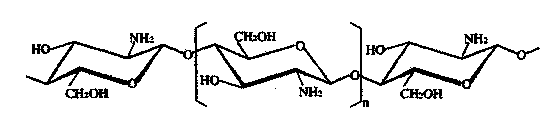
Modified chitosan having catechol group and biomedical material prepared from modified chitosan
The invention discloses a biomedical material and a product thereof. The biomedical material has main characteristic that a compound having a catechol group structure is grafted on chitosan to form a chitosan biomedical material having the catechol group structure; or the grafted chitosan is cross-linked to prepare a novel macromolecular biomedical material. The catechol has cell adhesion, so that tissue adhesiveness of the chitosan can be changed, and blood cells can be adsorbed on the material surface to achieve better bleeding-steeping effect. By virtue of the mediation, performance of the chitosan is improved, and tissue affinity is improved. The material is prepared into a novel bleeding-stopping sponge by freeze-drying, and prepared into novel dressing by spinning or prepared into powder dressing by reverse flocculating.
Owner:HAINAN JIANKE PHARMA
Preparation method of supported metal catalyst
InactiveCN105562116ALow costHigh operational controllabilityCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDispersityDyeing wastewater
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a supported metal catalyst. The supported metal catalyst comprises carrier framework materials and nano particles, loaded on the surfaces of the carrier framework materials, of metal or metal oxide, or metal ions chelated on the surfaces of the carrier framework materials, wherein the metal ions and nano particles of the metal or metal oxide are loaded on the surfaces of the carrier framework materials through the polymerization layers, adhered to the surfaces of the carrier framework materials, of catechol derivatives. The preparation method of the supported metal catalyst has the advantages that the method is simple, various carrier framework materials are used, one or more metal ions or nano particles can be loaded, and universality is achieved; the supported metal catalyst is good in active metal dispersity, large in carrier specific surface area, low in use amount, low in cost, and the like; the catalyst loaded with noble metal is catalyst material which is widely used and environmental friendly and is efficiently applicable to environmental chemical engineering fields such as dye wastewater decoloring, wastewater organic pollutant removing, car tail gas treatment, air purification, hydrogenation and reforming catalytic reaction, gas sensors and fuel cells.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Powder coating fluoropolymer compositions with aromatic materials
Provided is a composition comprising an aromatic material selected from a polythiol aromatic compound or resin, a hydroxythiophenol compound or resin, a catechol novolak resin, a catechol cresol novolak resin, a polyhydroxy aromatic resin or compound comprising at least one aromatic ring having at least one hydroxyl group attached directly to the aromatic ring wherein at least one hydroxyl group is a phenolate salt, or a combination thereof, and a salt former compound capable of forming a salt with the aromatic material, a fluoropolymer, and optionally a phase transfer catalyst. Also provided are articles comprising powder-coated fluoropolymers with aromatic compounds, and methods for making the compositions and articles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Rubber compositions comprising catechols and/or resorcinols and the use thereof in golf balls
The present invention is directed to a golf ball having at least one layer formed from a rubber composition comprising a base rubber, a free radical initiator, and a catechol. The present invention is also directed to a golf ball having at least one layer formed from a rubber composition comprising a base rubber, a free radical initiator, and a resorcinol. Rubber compositions of the present invention may be present in any one or more of a core layer, a cover layer, or an intermediate layer.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
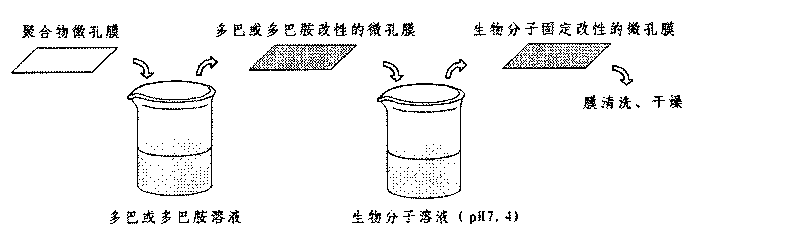
Method for fixing biological molecules on polymer microporous membrane surface
ActiveCN101745327ALow costEase of mass industrial productionSemi-permeable membranesBiocompatibility TestingPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for fixing biological molecules on a polymer microporous membrane surface, comprising the following steps: (1) respectively dissolving DOPA compounds and the biological molecules in a trihydroxymethyl aminomethane - muriatic acid buffer solution and a phosphoric acid buffer solution to prepare solutions; (2) immersing a polymer microporous membrane in a DOPA compound solution and oscillating to cause the DOPA compounds to be auto-polymerized-compounded on the membrane surface and to be closely attached to the membrane surface and a membrane pore wall; (3) immersing the polymer microporous membrane modified by the DOPA compounds in a biological molecule solution, and fixing the biological molecules on the polymer microporous membrane surface by the addition reaction between catechol groups of the membrane surface and amidogen in the biological molecules. The method for fixing biological molecules on the polymer microporous membrane surface has simple process, the prepared polymer microporous membrane has good hydrophilic property and biocompatibility, and the method has important meaning for improving the permeability and the biocompatibility of the polymer microporous membrane.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
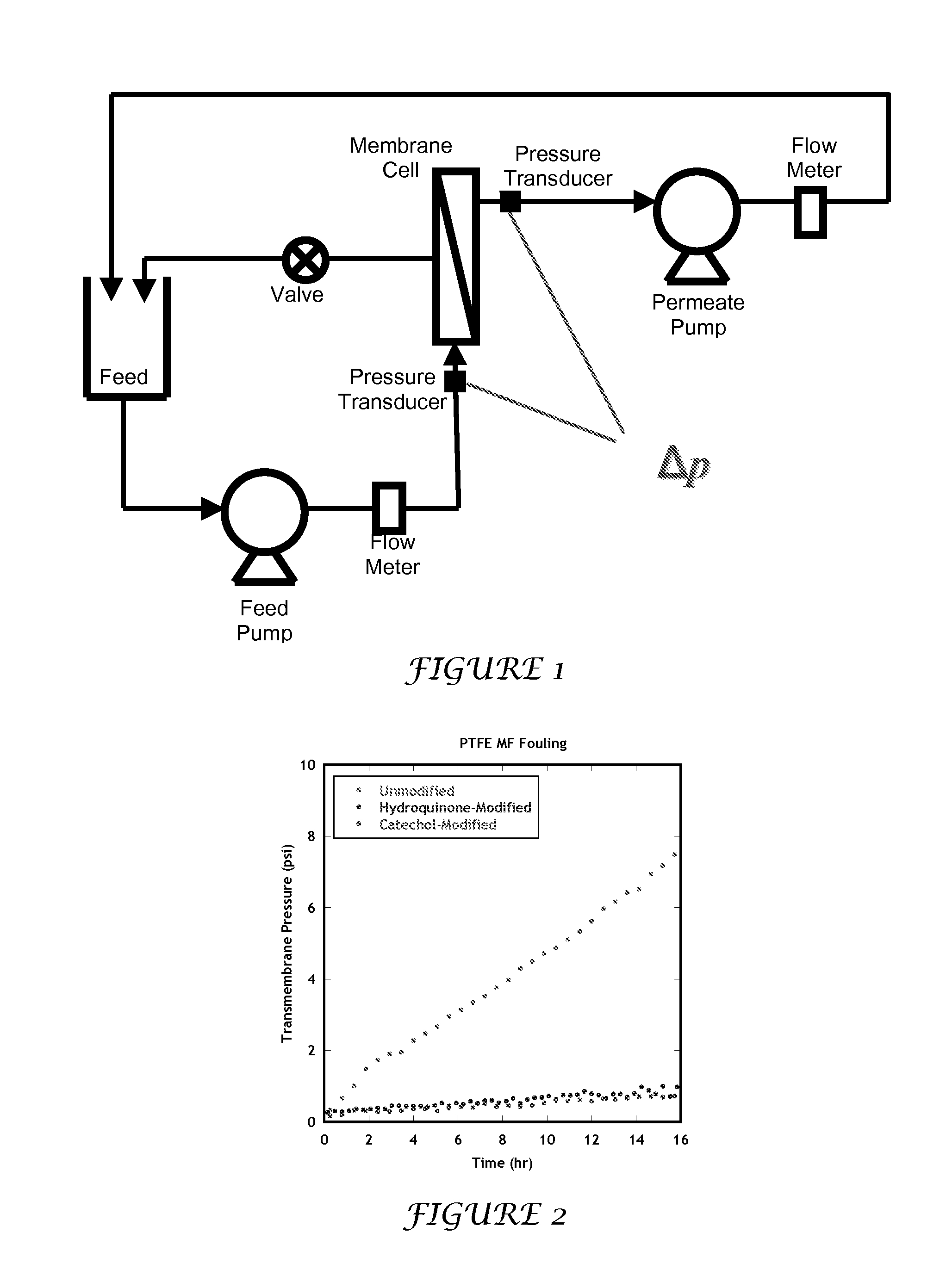
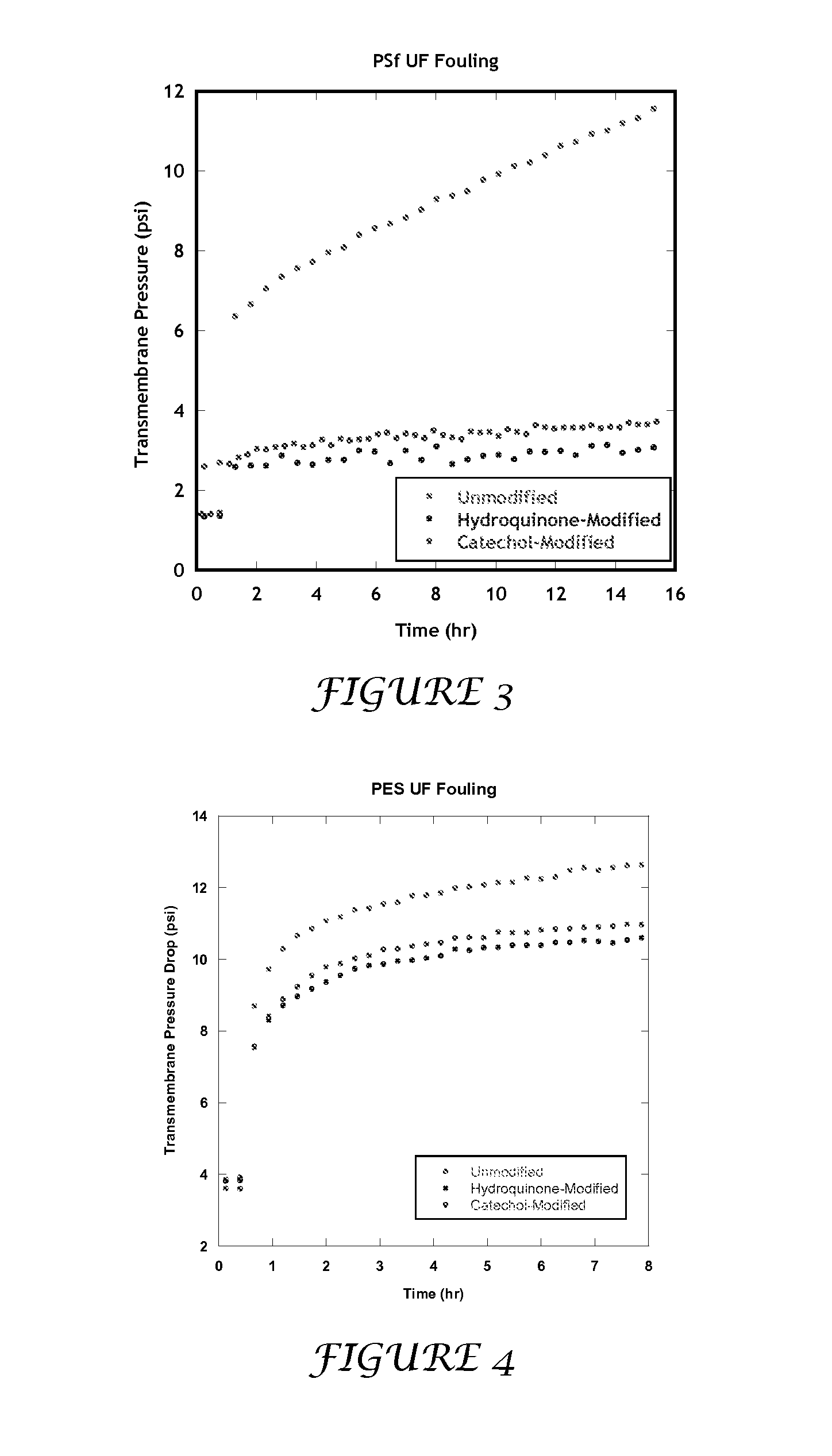
Surface Deposition of Small Molecules to Increase Water Purification Membrane Fouling Resistance
InactiveUS20120111791A1Efficient use ofEasy to retouchMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCoated membraneHydroquinone Compound
The present invention includes methods and compositions for liquid separation and water purification. The present invention includes a purification membrane having a polymer matrix purification membrane that has been treated with hydroquinone, catechol, and / or dopamine coated membrane with a high water flux.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
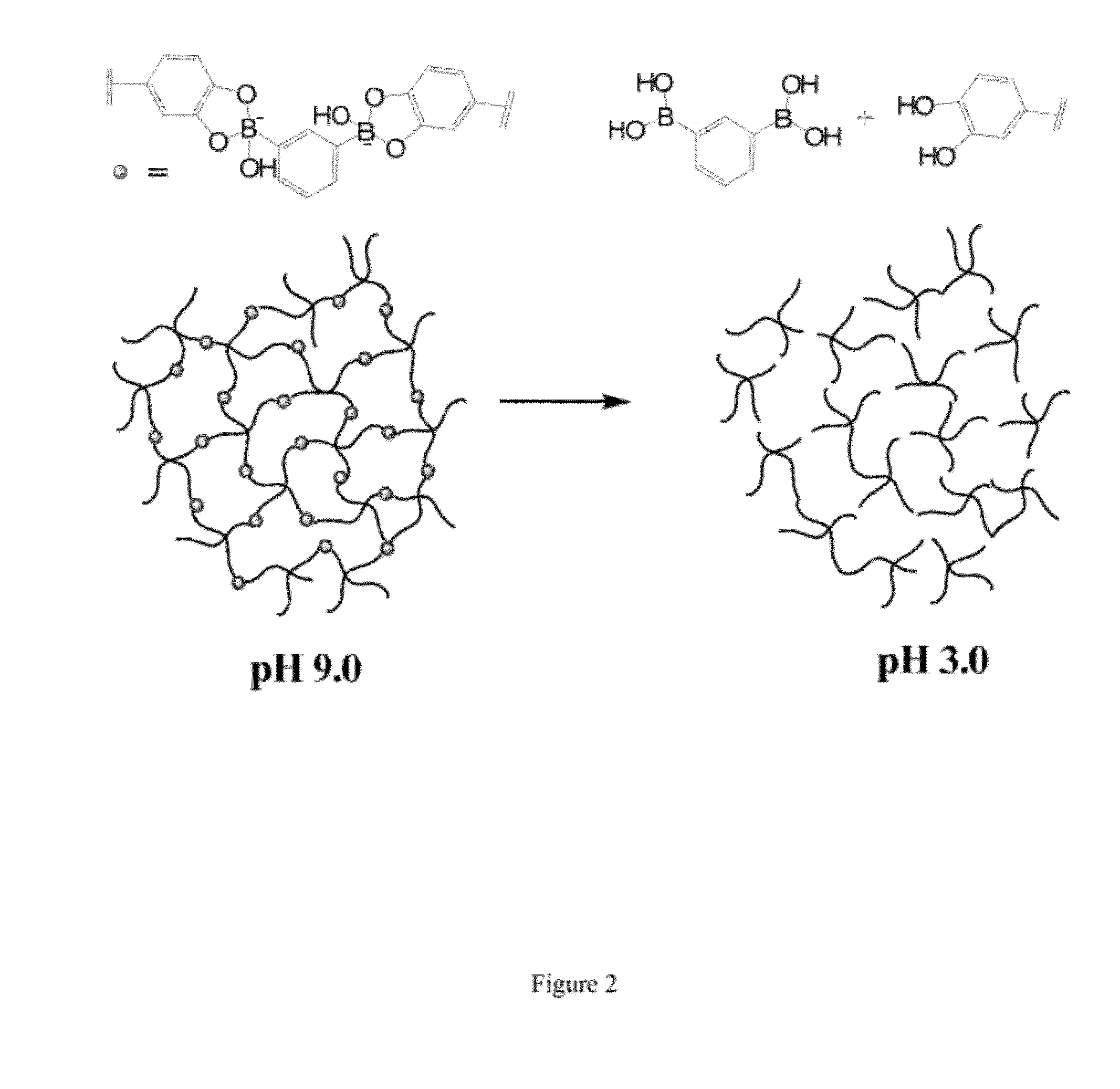
pH Responsive Self-Heating Hydrogels Formed By Boronate-Catechol Complexation
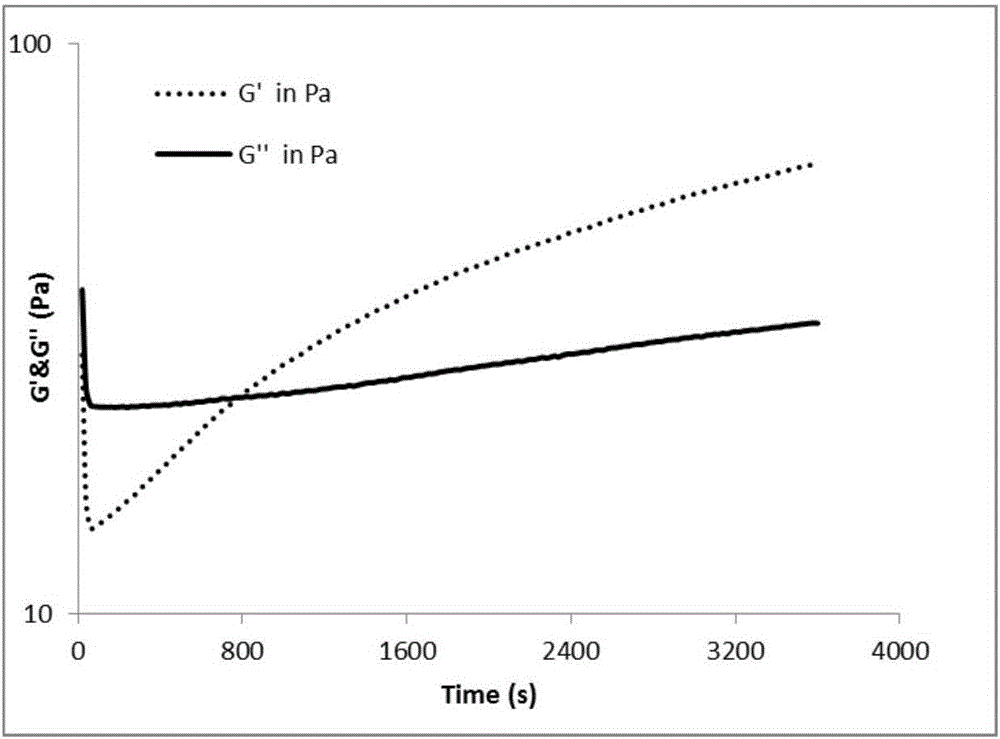
Biocompatible hydrogels made from cross-linked catechol-borate ester polymers are disclosed, along with methods of synthesizing and using such hydrogels. The hydrogels of the present invention are prepared by boronic acid-catechol complexation between catechol-containing macromonomers and boronic acid-containing cross-linkers. The resulting hydrogels are pH-responsive and self-healing, and can be used in a number of different biomedical applications, including in surgical implants, in surgical adhesives, and in drug delivery systems is data provides further evidence of the viability of using the disclosed hydrogels for in vivo in biomedical applications.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Smoke desulphurization agent and smoke desulphurization method
ActiveCN101721884AHigh desulfurization rateReduce absorptionDispersed particle separationAbsorption capacityDesorption
The invention provides a smoke desulphurization agent. The desulphurization agent is aqueous solution containing a main absorption component, an activating agent, an anti-oxidation component and acid, wherein the main absorption component is one or more of alkyl piperazine, hydroxyalkyl piperazine and hydroxyalkyl piperazine ketone; the activating agent comprises piperazine and diazabicyclo; and the anti-oxidation component is at least one of 4-tert-butyl catechol, 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-phenylcresol, acetone oxime and N,N-bi (2-ethoxy) glycine. The smoke desulphurization agent provided by the invention can remove and reclaim sulfur dioxide in the smoke, and has higher desulphurization rate; moreover, even if the smoke desulphurization agent is strongly oxidized and then is recycled, the absorption capacity for the sulfur dioxide is still stable; and in addition, the rich liquor formed by desulphurization after adopting the desulphurization agent has better desorption performance such as high desorption rate.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
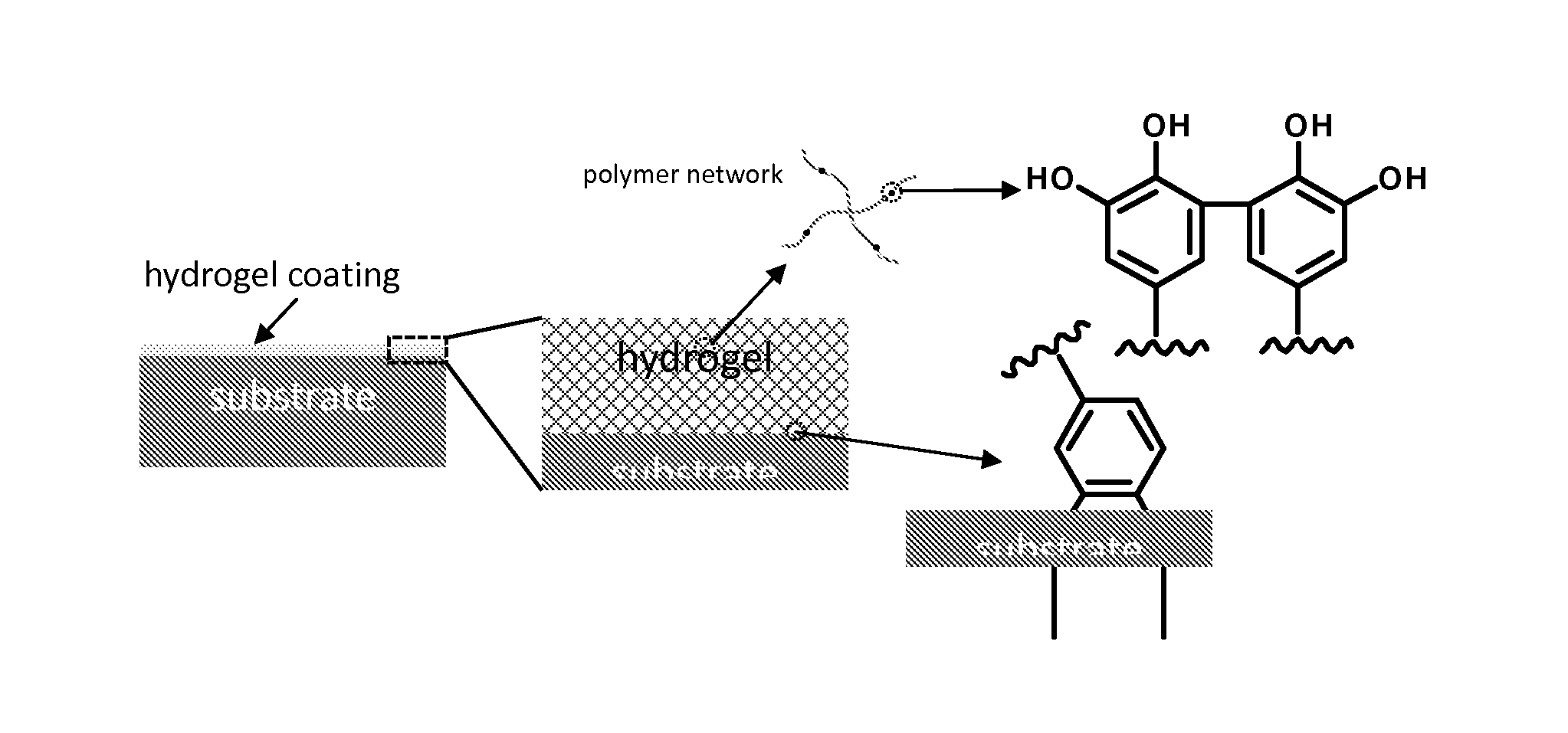
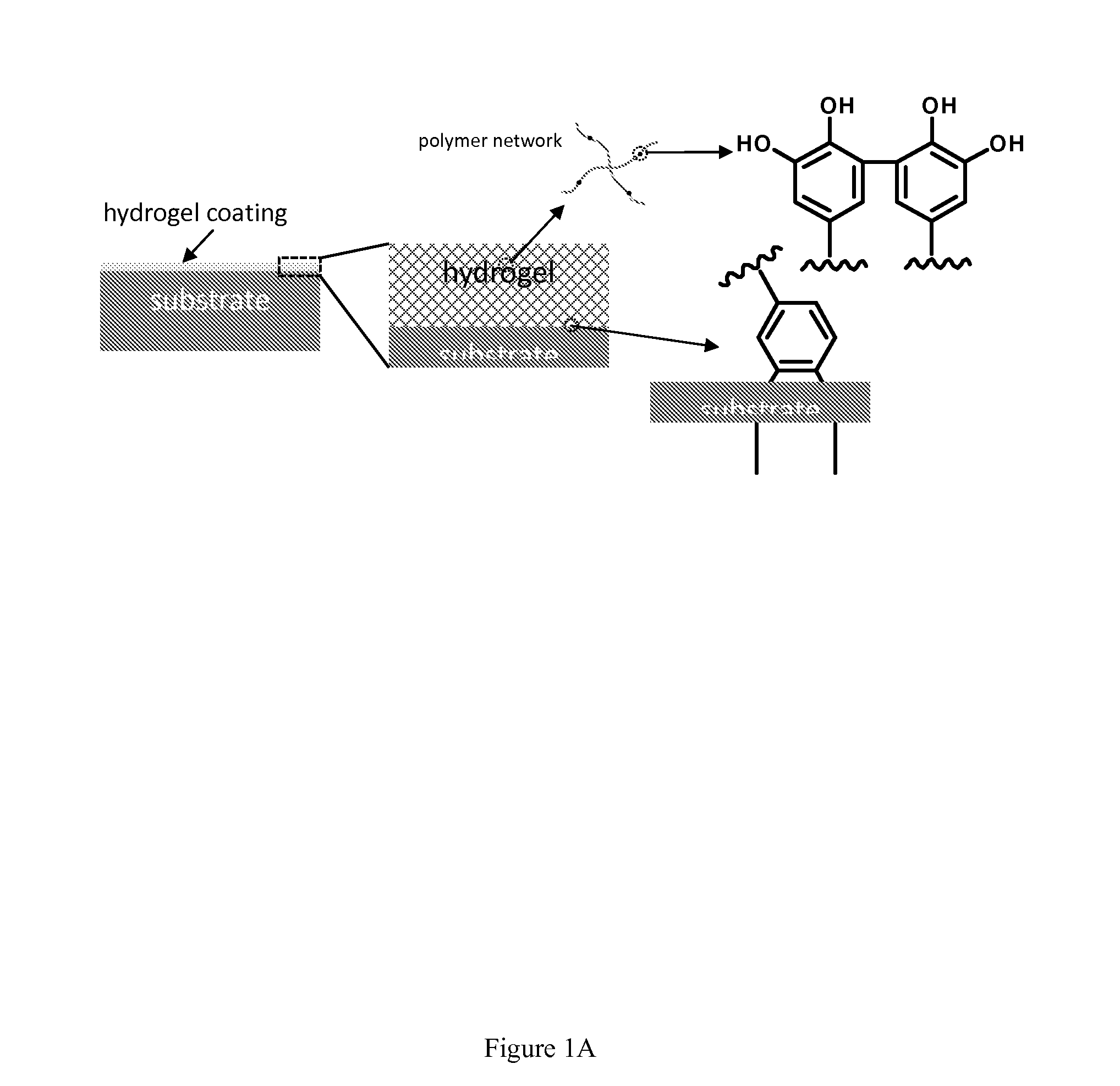
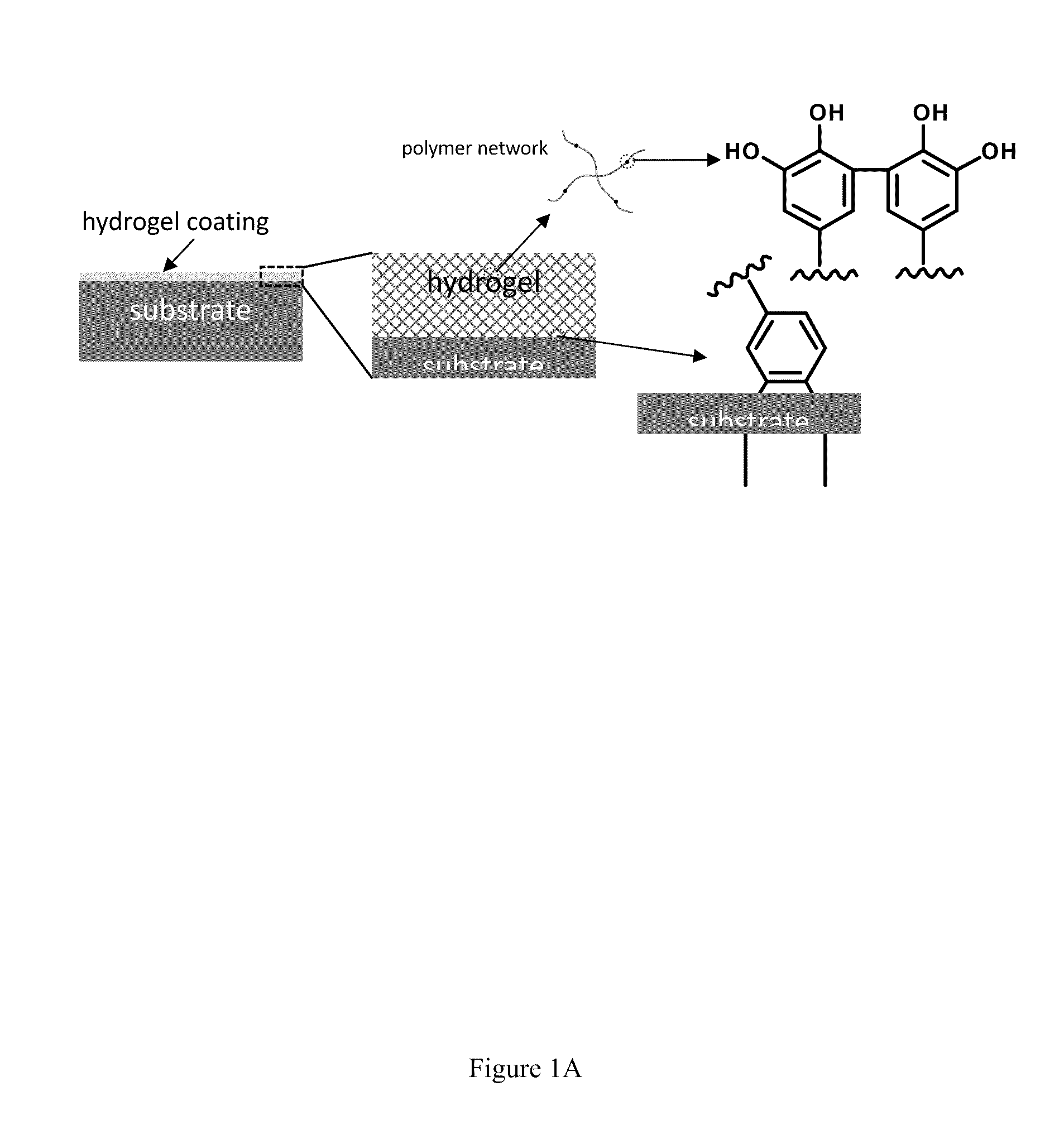
Substrate-Independent Layer-by-Layer Assembly Using Catechol-Functionalized Polymers
InactiveUS20090123652A1Simple, non-destructive and versatileIncrease the number ofPretreated surfacesCoatingsNon destructivePolymer science
The present invention provides a simple, non-destructive and versatile method that enables layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly to be performed on virtually any substrate. A novel catechol-functionalized polymer which adsorbs to virtually all surfaces and can serve as a platform for LbL assembly in a surface-independent fashion is also provided.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
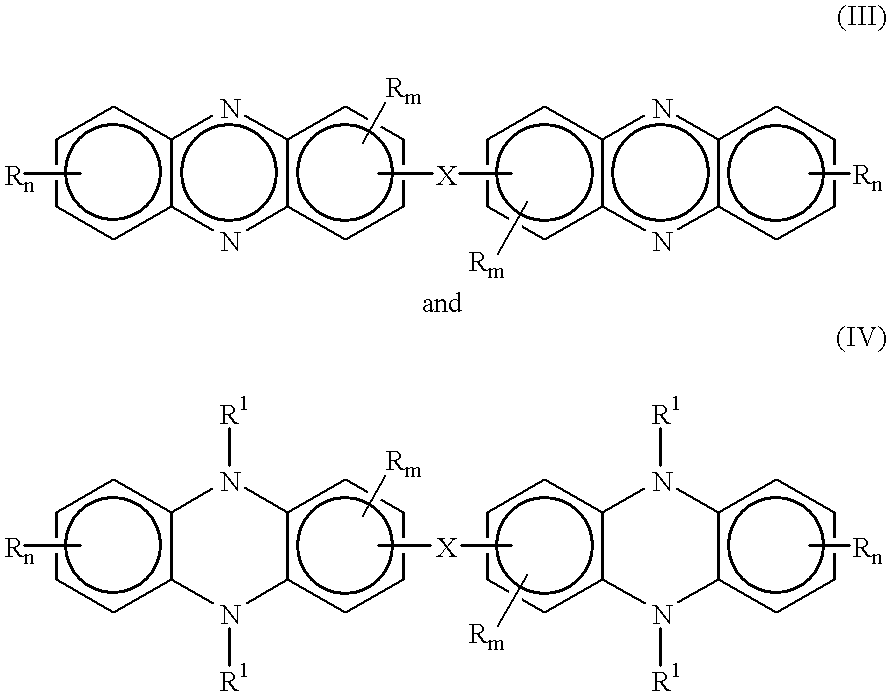
One pot synthesis of 5,10-dihydrophenazine compounds and 5,10-substituted dihydrophenazines
Dihydrophenazines and bis(dihydrophenazines) are prepared in high yield under commercially viable reaction conditions by reacting a catechol with a 1,2-diaminoaryl compound, wherein either the catechol or the 1,2-diaminoaryl compound is provided in at least 50% molar stoichiometric excess. The product may be oxidized to the corresponding phenazine, but is preferably derivatized at one or both of the 5,10-positions to form a monosubstituted or disubstituted dihydrophenazine or bis(dihydrophenazine). Most preferably, 5,10-dialkyl-5,10-dihydrophenazines are prepared starting from catechol and 1,2-diaminoaryl compound in a one pot synthesis. The products are useful as dyes, and in particular as chromophores in electrochromic systems.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure copolymer and preparation method and application thereof
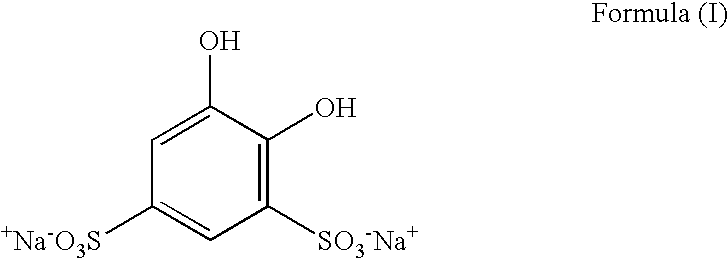
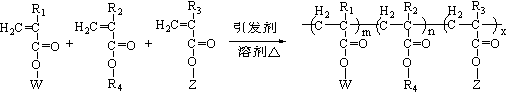
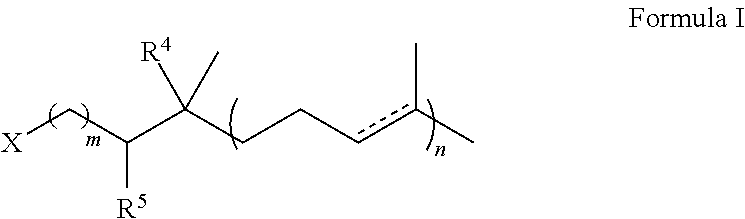
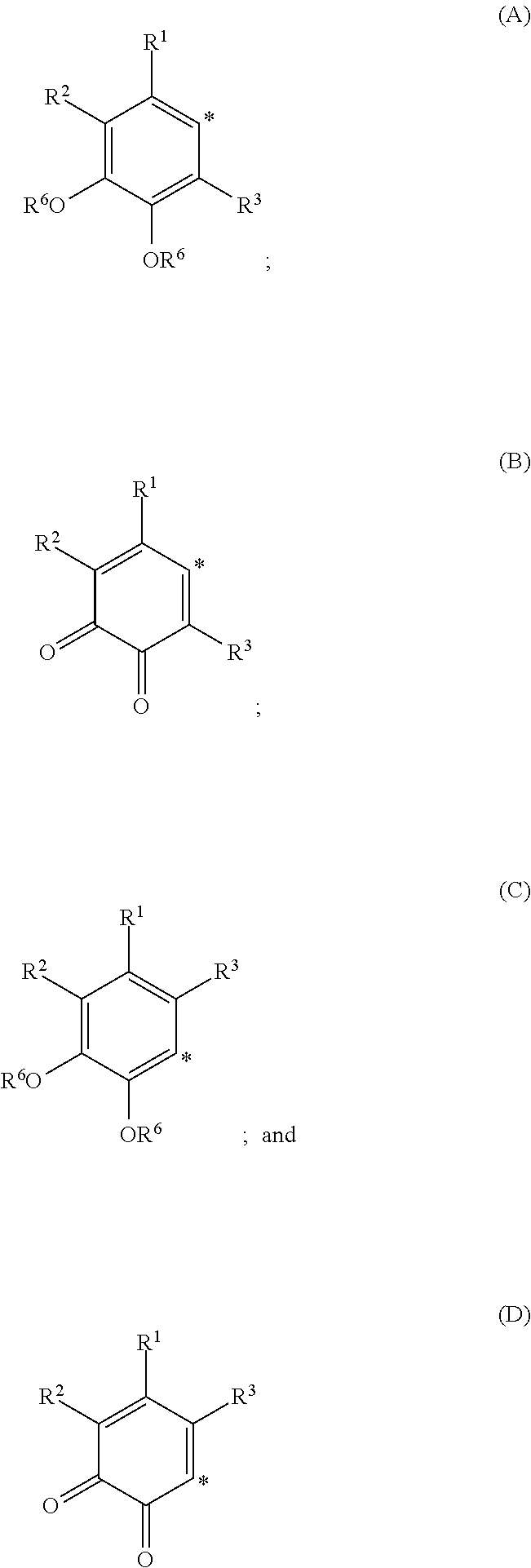
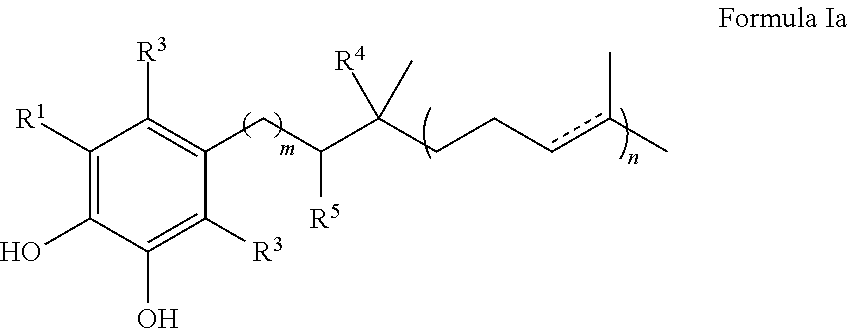
The invention discloses an imitation mussel attachment protein and cell membrane structure double-bionic copolymer shown by the structural formula (I), wherein m is an integer from 10 to 1,000, n is an integer from 0 to 500, and x is an integer from 5 to 500; in the m, n and x, the molar percentage of m is 30-90%, the molar percentage of n is 0-50%, and the molar percentage of x is 10-70%; R1, R2 and R3 are H or CH3; R4 is an alkyl with 4-18 carbon atoms; V is a catechol group with 2-300 carbon atoms in chain connection; W is a hydrophilic group with 2-8 carbon atoms in chain connection; and the hydrophilic group is a quaternary ammonium group, phosphorylcholine group, pyridinium, sulfonic acid group, phosphate group, carboxylic acid group or sulfuric acid group. According to the invention, the coating is in firm combination, the copolymer is almost suitable for an establishment method of a surface imitation cellulosa membrane structure of any material, and the surface hydrophilic performance and biocompatibility of artificial organ and related materials, medicine controlled-release systems, separation materials and other materials can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Method for surface modification on carbon fibers
The invention belongs to the technical field of surface modification and relates to a method for surface modification on carbon fibers. The method is characterized in that a material containing a catechol structure is used as a surface modifier and the surface modifier is coated on surfaces of carbon fibers so that carbon fiber surface characteristics are improved. After surface modification on carbon fibers by the material containing the catechol structure, the carbon fibers can be further subjected to surface modification by other chemical materials according to demands. The method can be operated simply and conveniently, has obvious effects and realizes effective modification on a specific matrix by simple operation. Through simple operation, the carbon fibers can be subjected to hydrophilic modification and the surfaces of the carbon fibers have lipophilicity. Through use of a group or a substance having special a function, the carbon fibers have special functions of bacterium resistance and luminescence. The method has wide application prospects in the field of carbon-fiber composite materials and other functional materials.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparation methods of graphene and graphene-oxide compound
ActiveCN103332678AFull reduction reactionHigh transparencySilicaGrapheneOxide compositeLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to the technical field of carbon material preparation and provides a preparation method of graphene. The preparation method comprises the following step that graphene oxide is dispersed in a solution of catechol or its derivatives and the mixed solution undergoes a hydrothermal reaction to produce the graphene having particle length and width of 10-200 microns. The invention also discloses a preparation method of a graphene-oxide compound comprising uniform-size and uniformly-dispersed oxide particles. The preparation method comprises that the graphene and an oxide precursor solution are dispersed in an aqueous solution and the mixed solution undergoes a hydrothermal reaction to produce the graphene-oxide compound. The preparation methods adopt a hydrothermal method and a water system, do not produce toxins and are environmentally friendly. The graphene has good transparency and small thickness. The graphene-oxide compound comprises the uniform-size oxide particles uniformly dispersed in the graphene, solves the problems of easy aggregation of the graphene and the oxide particles, uneven dispersion of the graphene and the oxide particles, complex preparation processes and high equipment requirements, and can be widely used in fields of supercapacitors, lithium ion batteries and electrochemical sensing.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
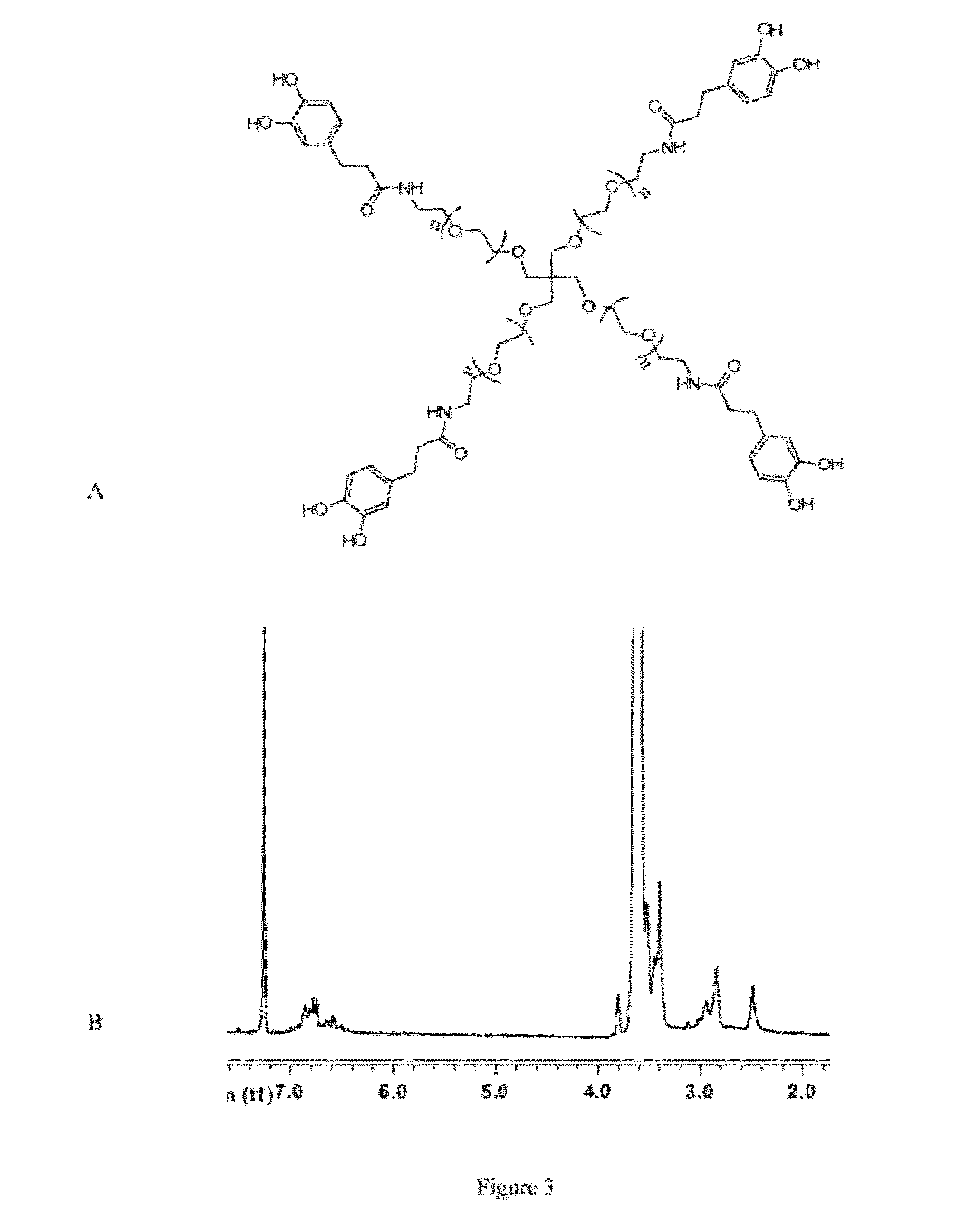
Cross-Linkable Polymeric Compositions
A class of bioinspired, cross linking polymers, created by working catechol functionalities into the backbone of a bulk polymer, is disclosed. Varied cross linking groups may be incorporated into different polymer backbones, and subsequently reacted with an array of reagents. An adhesive composition comprising a copolymer, the copolymer comprising pendant dihydroxyphenyl groups; and a crosslinking agent selected from the group consisting of, for example, oxidants, enzymes, metals, and light. A method of preparing an adhesive composition comprising copolymerizing a first monomer comprising pendant dihydroxy-protected dihydroxyphenyl groups; deprotecting the dihydroxy-protected dihydroxyphenyl groups; crosslinking the dihydroxyphenyl groups with a crosslinking agent.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
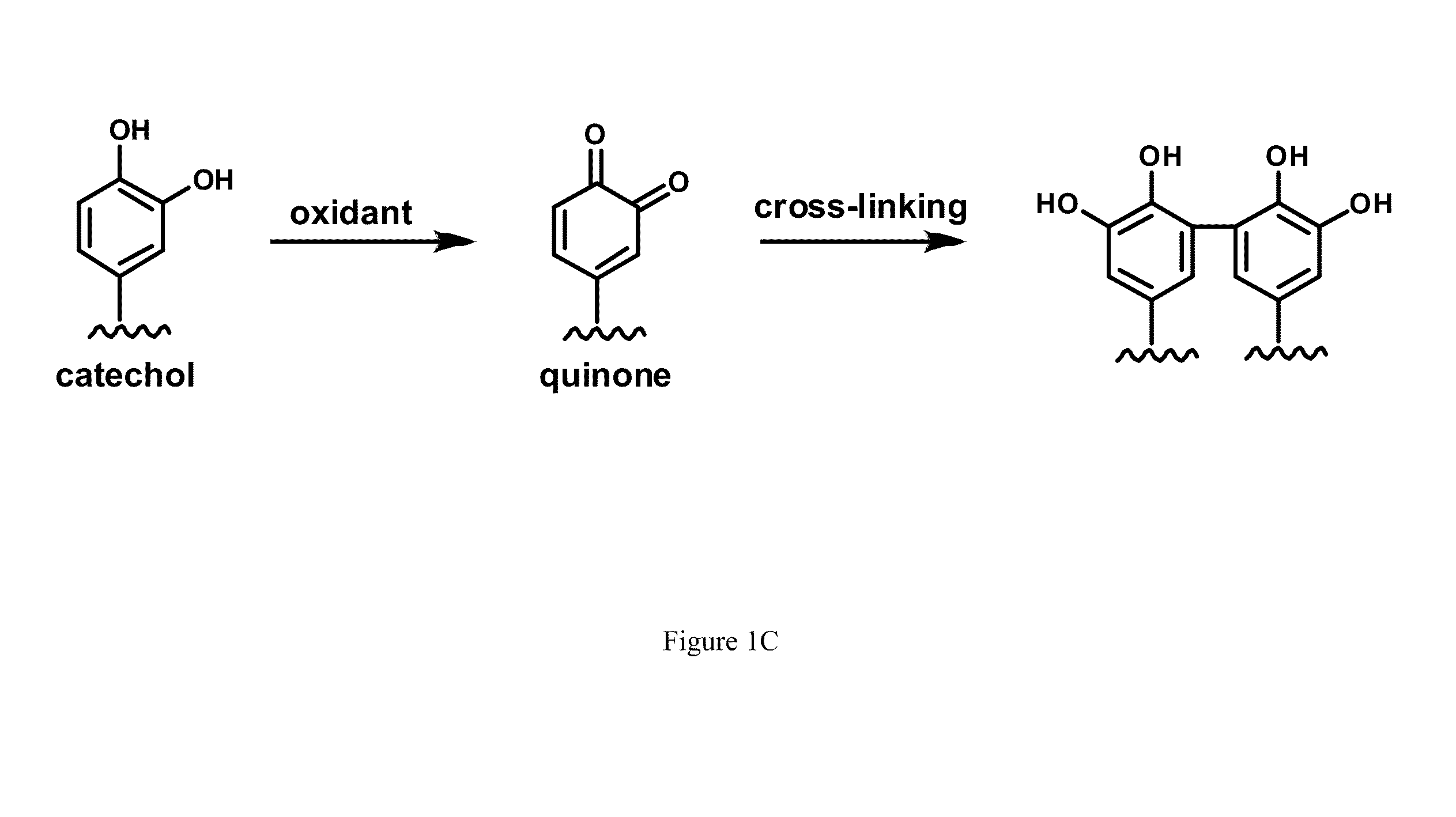
Catechol derivatives for treatment of oxidative stress diseases
Methods of treating or suppressing oxidative stress disorders affecting normal electron flow in the cells, including mitochondrial diseases, impaired energy processing disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, diseases of aging and diseases caused by reactive oxygen species are disclosed, as well as compounds useful in the methods of the invention, such as such as catechol or ortho-quinone derivatives of Formula (I).
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Preparation method of biological mimetic tissue adhesive
InactiveCN106390185AImprove activation efficiencyMild reaction conditionsSurgical adhesivesBiocompatibility TestingBioadhesive
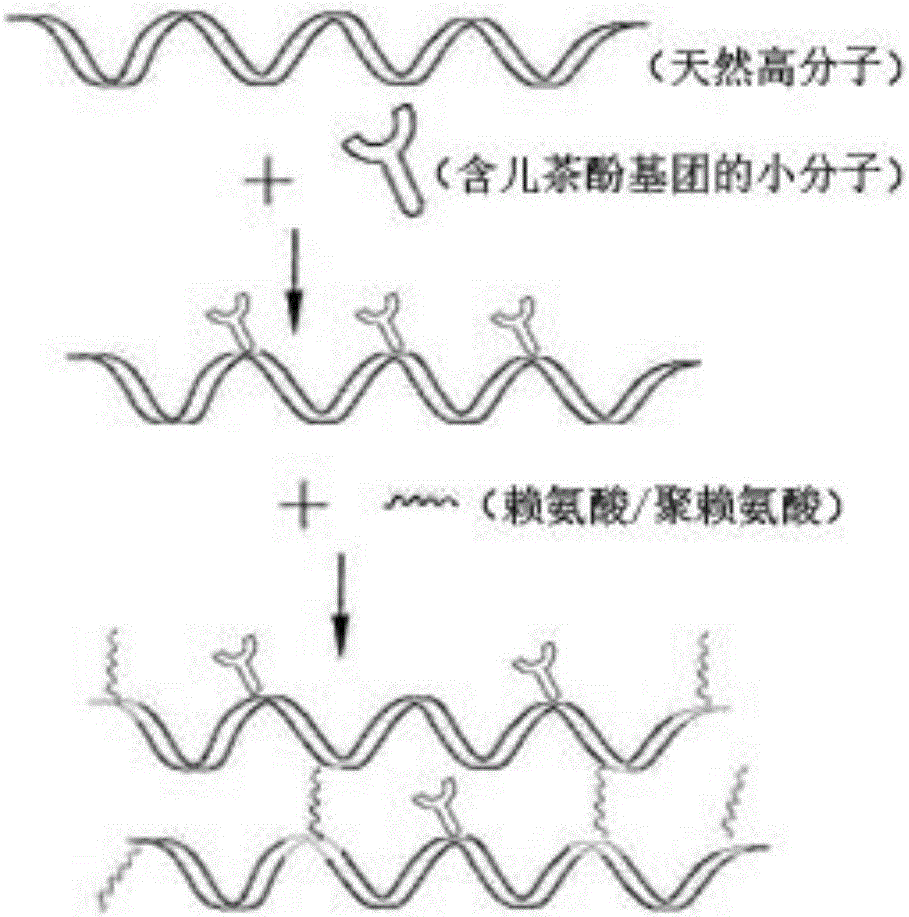
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biological mimetic and structural bionic tissue adhesive in order to overcome disadvantages of present technological technologies for preparing mussel mucoprotein bionic biological tissue adhesives and improve the viscosity, the biocompatibility and the structural bionic property of a material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: grafting a natural polymer material with dopamine or other catechol group-containing derivatives through an amidation reaction by adopting DMTMM as a carboxyl group activator; and further modifying the grafted natural polymer material with lysine or polylysine by adopting the same technology to obtain the novel biological mimetic and structural bionic tissue adhesive containing dopamine analog and polylysine analog. The tissue adhesive plays a full role in tissue adhesion in wet and physiologic environment, has good tissue adherence and high biological safety, and can be slowly degraded in the tissue healing process until complete degradation. The preparation method of the biological adhesive has the advantages of simplicity, mild reaction conditions, increase of the reaction efficiency, improvement of the operability of the enterprise production process, and facilitation of amplified production of enterprises.
Owner:SHANGHAI QISHENG BIOLOGICAL PREPARATION CO LTD
Textile ink composition
A textile ink composition and a method of manufacturing a textile ink composition are disclosed. The textile ink composition is formed from a cationically charged metal oxide and a dye, and is capable of durably dyeing different types of fabric. The cationically charged metal oxide is typically an oligomer, such as an alumina oligomer. A suitable alumina oligomer is aluminum chlorohydrate. Typical dyes have anthraquinone, catechol, hydroxyazo or salicylic acid groups or are mordant dyes, such as Carminic Acid, Alizarin Red, Acid Blue 45, Acid Green 41, Hematoxylin, Chromoxane Cyanine R, Calconcarboxylic Acid, Plasmocorinth B, Pyrocatechol, Acid Alizarin Violet N, Alizarin Yellow GG, Mordant Yellow 12 and Mordant Blue 9.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Semiconductor process residue removal composition and process
InactiveUS7528098B2Efficient removalReduce rateOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationHydroxylamineGallic acid ester
A residue remover for removing polymeric material and etch residue includes 2-(2-aminoethylamino)-ethanol and optionally another two-carbon atom linkage alkanolamine compound, gallic acid or catechol, water, a polar organic solvent, and hydroxylamine. A process for removing photoresist or other residue from a substrate, such as an integrated circuit semiconductor wafer including titanium metallurgy, includes the steps of contacting the substrate with the above composition for a time and at a temperature sufficient to remove the photoresist or other residue from the substrate. Use of 2-(2-aminoethylamino)-ethanol in the composition and process provides superior residue removal without attacking titanium or other metallurgy on the substrate. The composition preferably has a flash point greater than about 130° C.
Owner:EKC TECH
Additive for lowering harmful constituents in cigarette flue gas and cigarette thereof
InactiveCN101692934AImprove adsorption capacityLarge aspect ratioTobacco treatmentHazardous substanceCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a cigarette additive and cigarette prepared by the additive. The additive can lower the tar contents in cigarette flue gas and can selectively absorb harmful substances such as polycyclic aromatics, phenols and the like in cigarette flue gas. The additive is carbon nanometer pipe preparation dispersed in water solution of surface active agent. The preparation is taken as cigarette cut tobacco additive and is sprayed on tobacco leaves in the cigarette production material feeding technique process according to 1 to 25% of the weight of the cut tobacco, and carbon nanometer pipes are evenly and dispersedly absorbed on the surface of the cut tobacco after silk drying processing. The additive can remove 6.2-38.8% of polycyclic aromatics such as Benzo(a)pyrene and the like and 3.0 to 28.3% of carbolic acid and catechol in cigarette main flow flue gas, and also can lower the tar contents in flue gas for 3.4 to 20.4%, and the original color and flavor of cut tobacco are not changed basically.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP
Antifouling hydrogels, coatings, and methods of synthesis and use thereof
InactiveUS20110052788A1Reducing and eliminating proteinReducing and eliminating and microorganism adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPharmaceutical containersPolymer modifiedEnd-group
The invention provides an antifouling hydrogel comprising an effective amount of antifouling polymer modified with a compound containing catechol functional groups to yield a modified antifouling polymer comprising at least one catechol functional end group; and an effective amount of at least one oxidizing reagent, wherein the at least one oxidizing reagent reacts with the modified antifouling polymer to provide a modified antifouling polymer comprising at least one oxidized catechol end group, wherein an antifouling hydrogel is provided. Methods of synthesis, methods of use and kits of the antifouling hydrogel are also provided.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Antifouling hydrogels, coatings, and methods of synthesis and use thereof
InactiveUS8796394B2Reducing and eliminating protein and microorganism adhesionReduces and eliminates protein and cell adhesionPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesPolymer modifiedSynthesis methods
The invention provides an antifouling hydrogel comprising an effective amount of antifouling polymer modified with a compound containing catechol functional groups to yield a modified antifouling polymer comprising at least one catechol functional end group; and an effective amount of at least one oxidizing reagent, wherein the at least one oxidizing reagent reacts with the modified antifouling polymer to provide a modified antifouling polymer comprising at least one oxidized catechol end group, wherein an antifouling hydrogel is provided. Methods of synthesis, methods of use and kits of the antifouling hydrogel are also provided.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
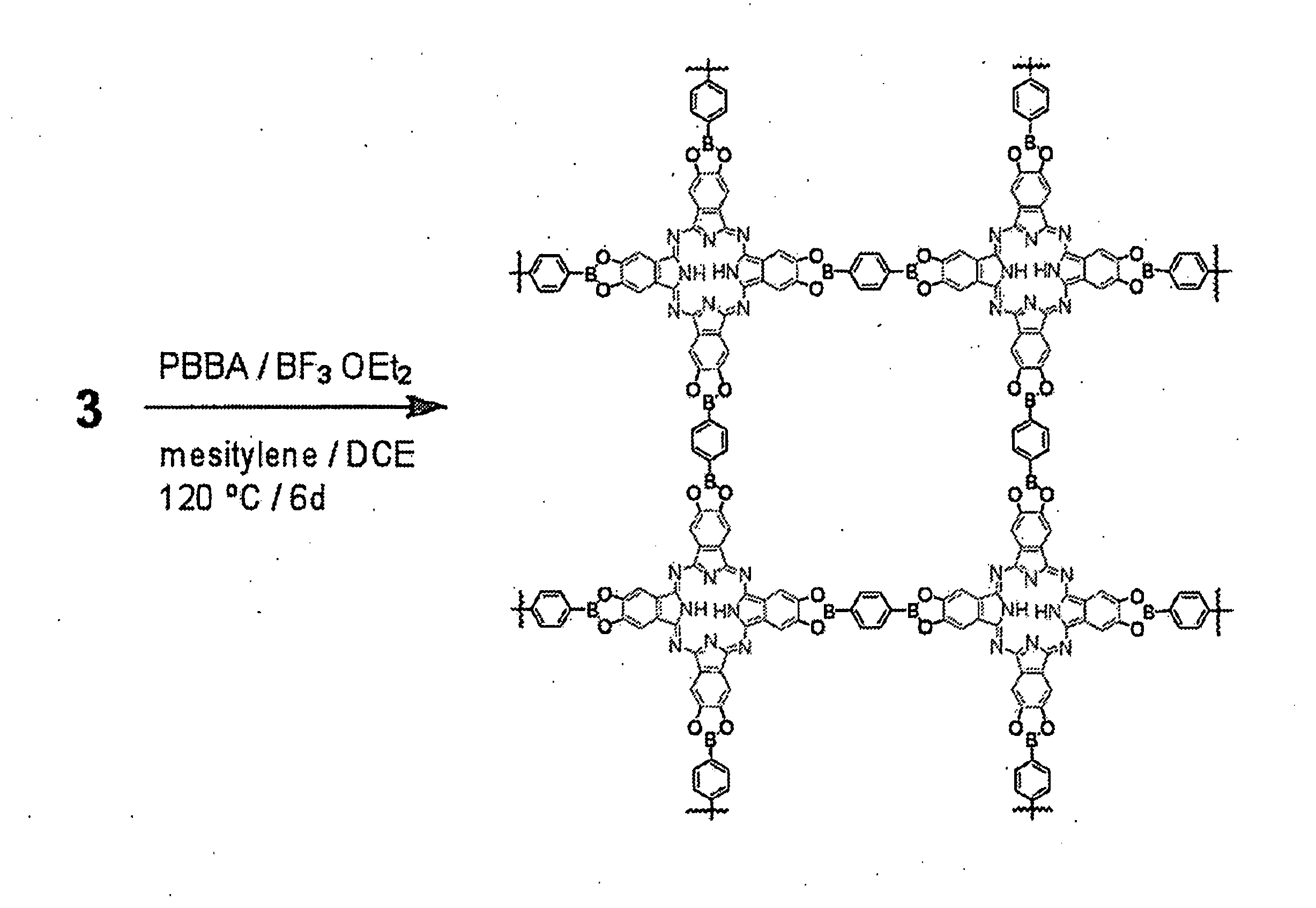
Covalent Organic Frameworks and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20140148596A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoron containingAcid catalyzed
Crystalline COFs comprising a phthalocyanine moiety and a boron-containing multifunctional linking group joined by boronate ester bonds. A method for making crystalline COFs comprising Lewis acid catalyzed formation of boronate ester bonds between protected catechol subunits and multifunctional linkers comprising boronic acid groups. The COFs can be used in applications such as, for example, electronic devices.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Synergistic flame retardant compositions and fiber blends including the same
A synergistic flame retardant composition comprising a phenolic compound comprising condensed tannin, hydrolysable tannin, lignin, cardanol, quercetin, catechin, epicatechin, anthocyanidin, catechol, dopamine, hydroxytyrosol, adrenaline, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, gallic acid, digallic acid, methyl gallate, ellagic acid, phloroglucinol, hexahydroxydiphenic acid, luteic acid, casuarictin, or a combination thereof; and a phosphorus-containing compound comprising a C5-7 carbocyclic polyol substituted with at least one phosphate group.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
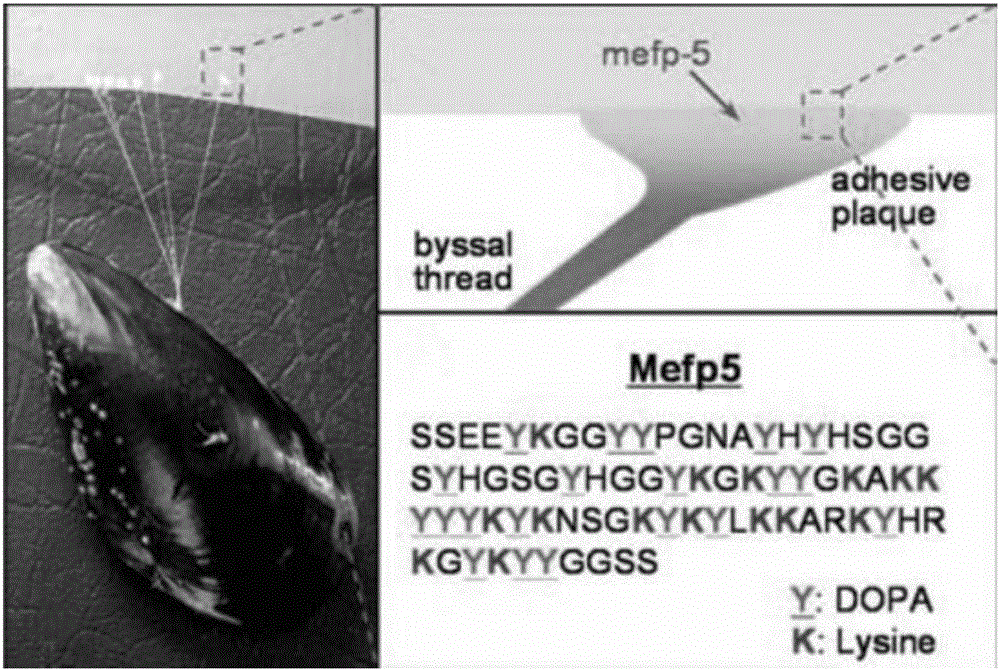
Preparation method for biomimetic mussel adhesive used for adhesion on wet surface and underwater curing
InactiveCN103965810AEfficient synthesisImprove bindingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer scienceAttachment protein
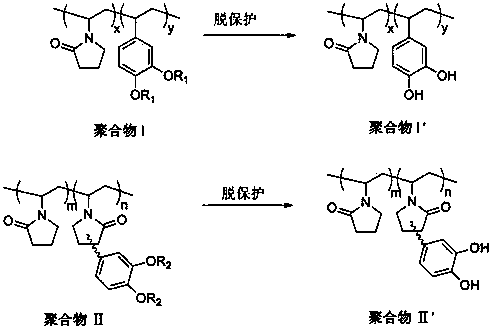
The invention relates to a preparation method for a biomimetic mussel adhesive used for adhesion on a wet surface and underwater curing. The method is characterized in that the biomimetic mussel adhesive is composed of two components including A and B, wherein the component A is a methanol solution of a polymer containing catechol groups; the polymer containing catechol groups is obtained in the manner that N-vinyl pyrrolidone and a polymerizable catechol derivative monomer are subjected to free radical polymerization and further subjected to deprotection; the component B is a crosslinking curing agent. The method has the advantages as follows: 1, the synthetic method is simple and efficient, raw material and reagents used in the reaction process are low in price and easy to get, and amplification in the operation process and industrial production are facilitated; 2, the biomimetic mussel adhesive has certain biocompatibility and initial adhesion performance, can be used for adhesion on the wet surface and underwater curing, and has the bonding strength being over 1 MPa, so as to be applied to adhesion of human tissue and adhesion in the wet environment of commonly-used base material as well as adhesion under the water. According to the invention, perfect combination between synthetic macromolecule and natural mussel attachment proteins is successfully realized, the technical bottleneck about the current biomimetic mussel adhesive is expected to break through, and meanwhile, a new approach for shellfish-based development of biomimetic high polymer material is provided.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com