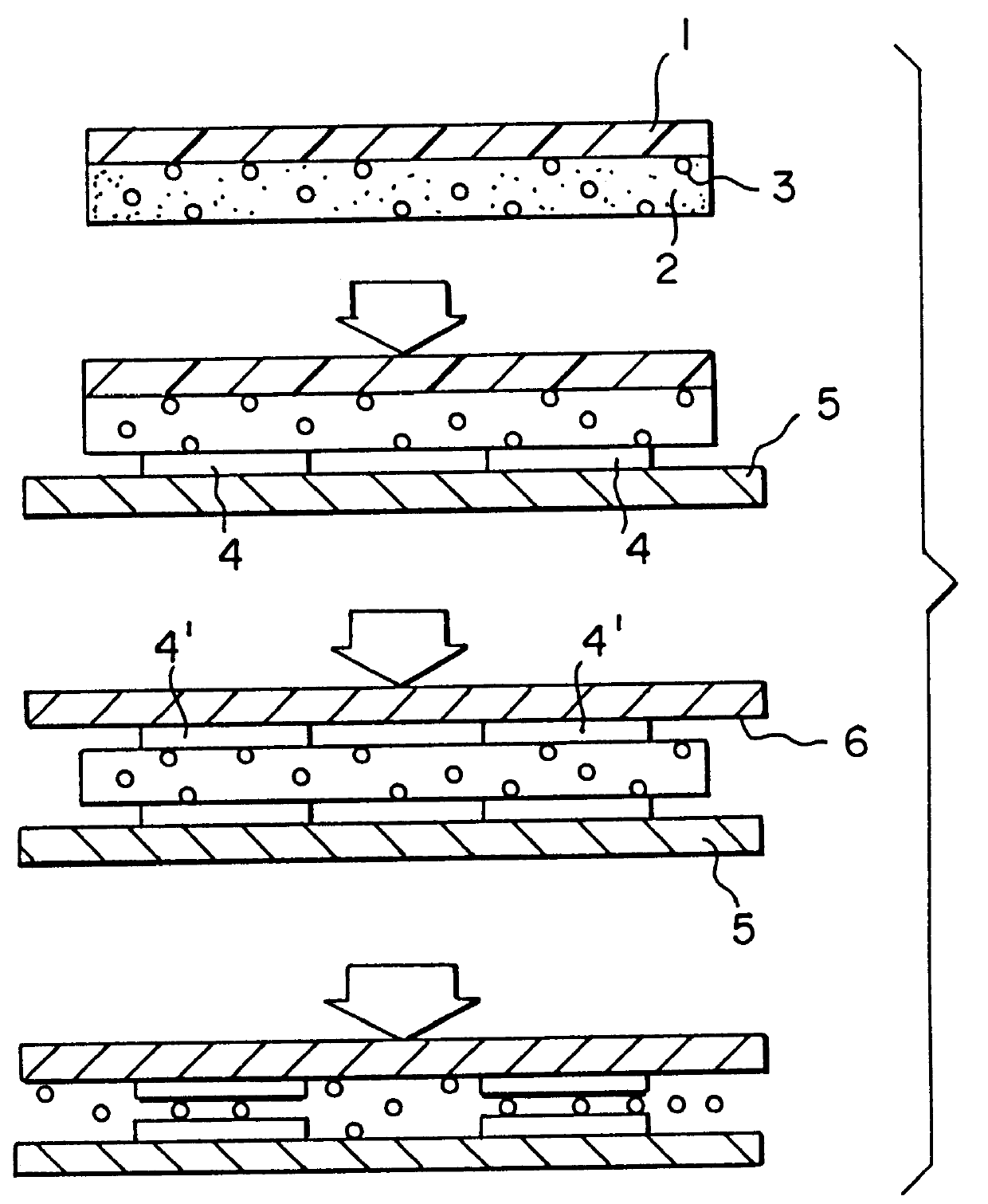
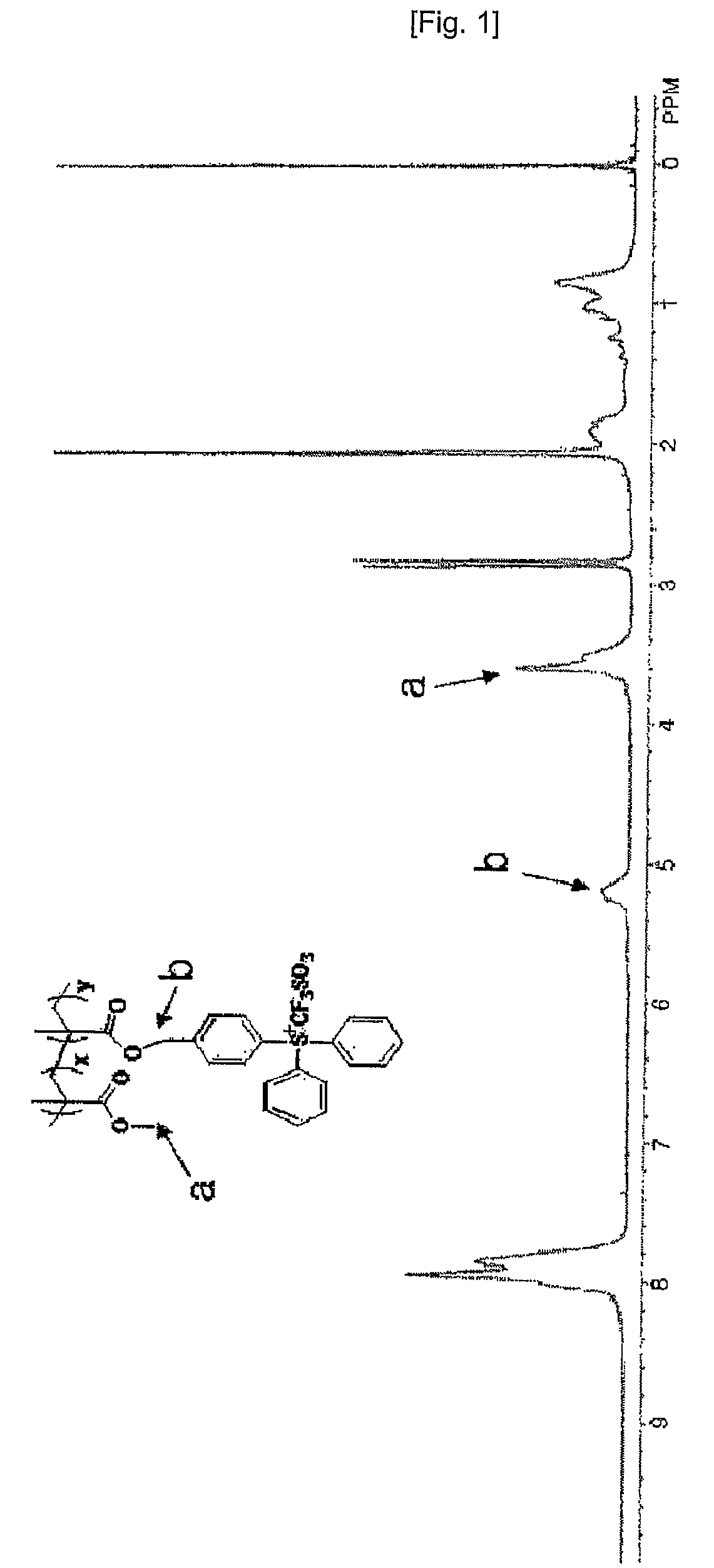
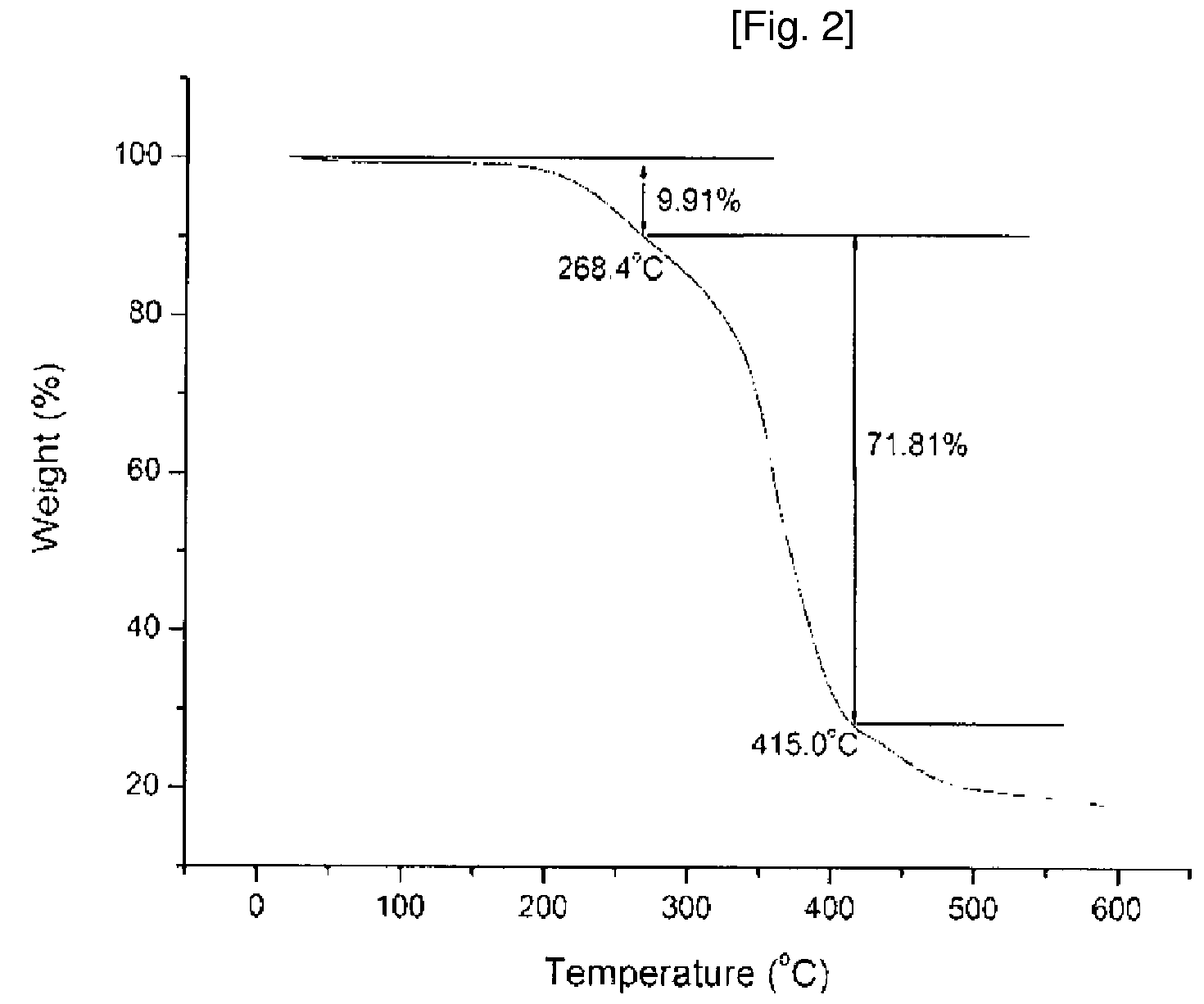
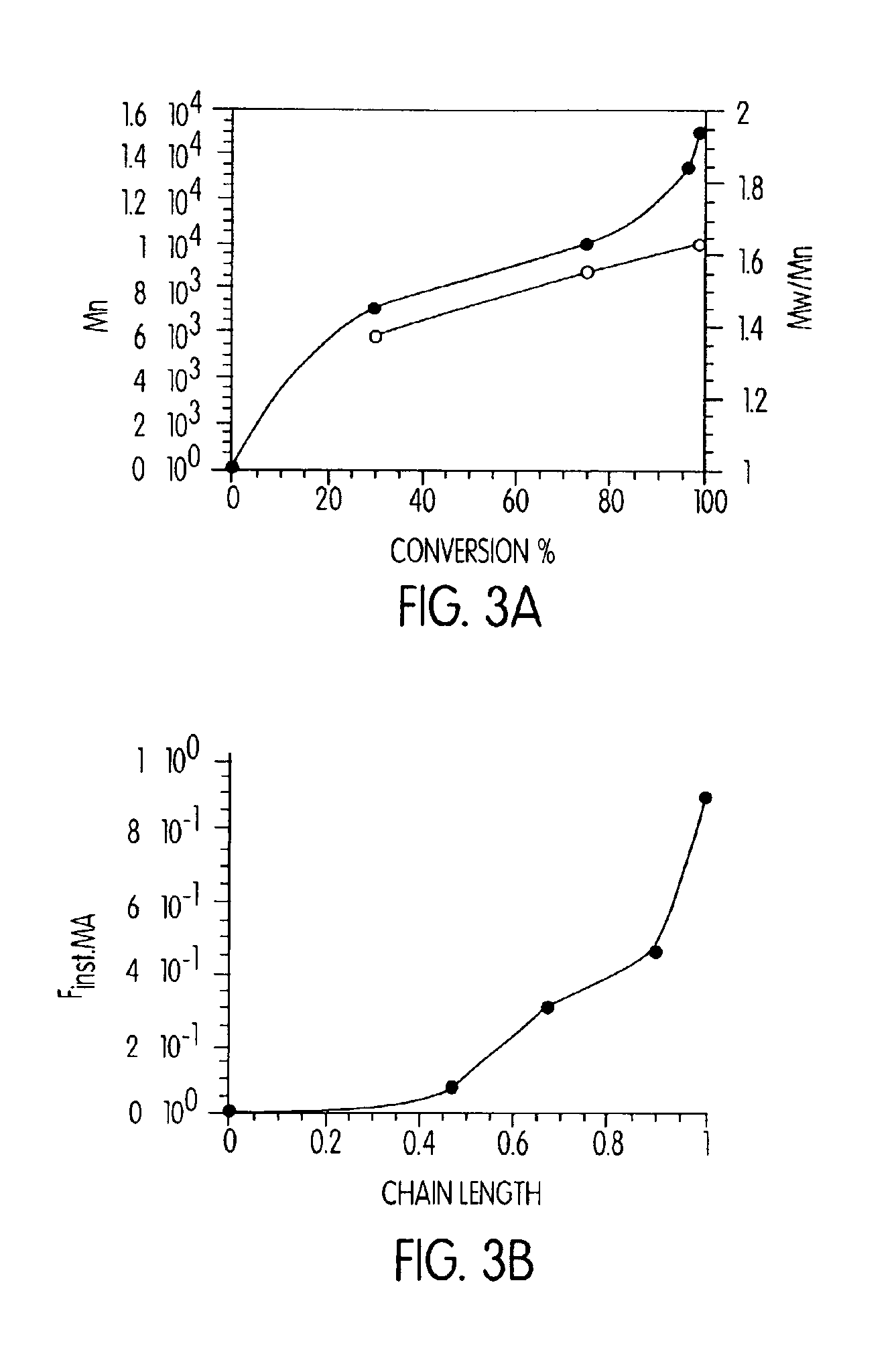
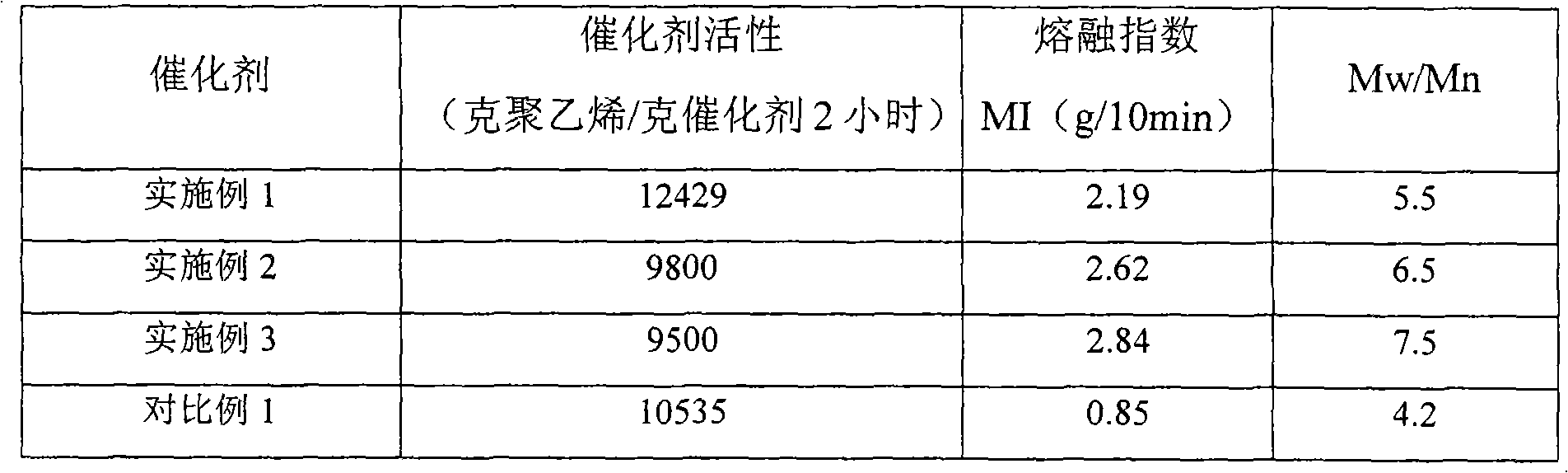
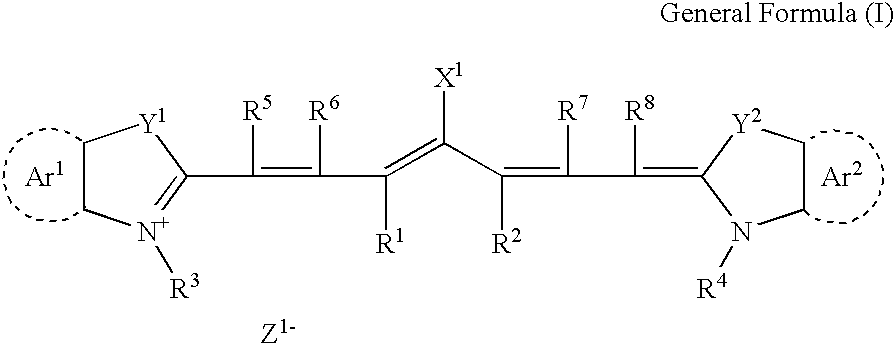
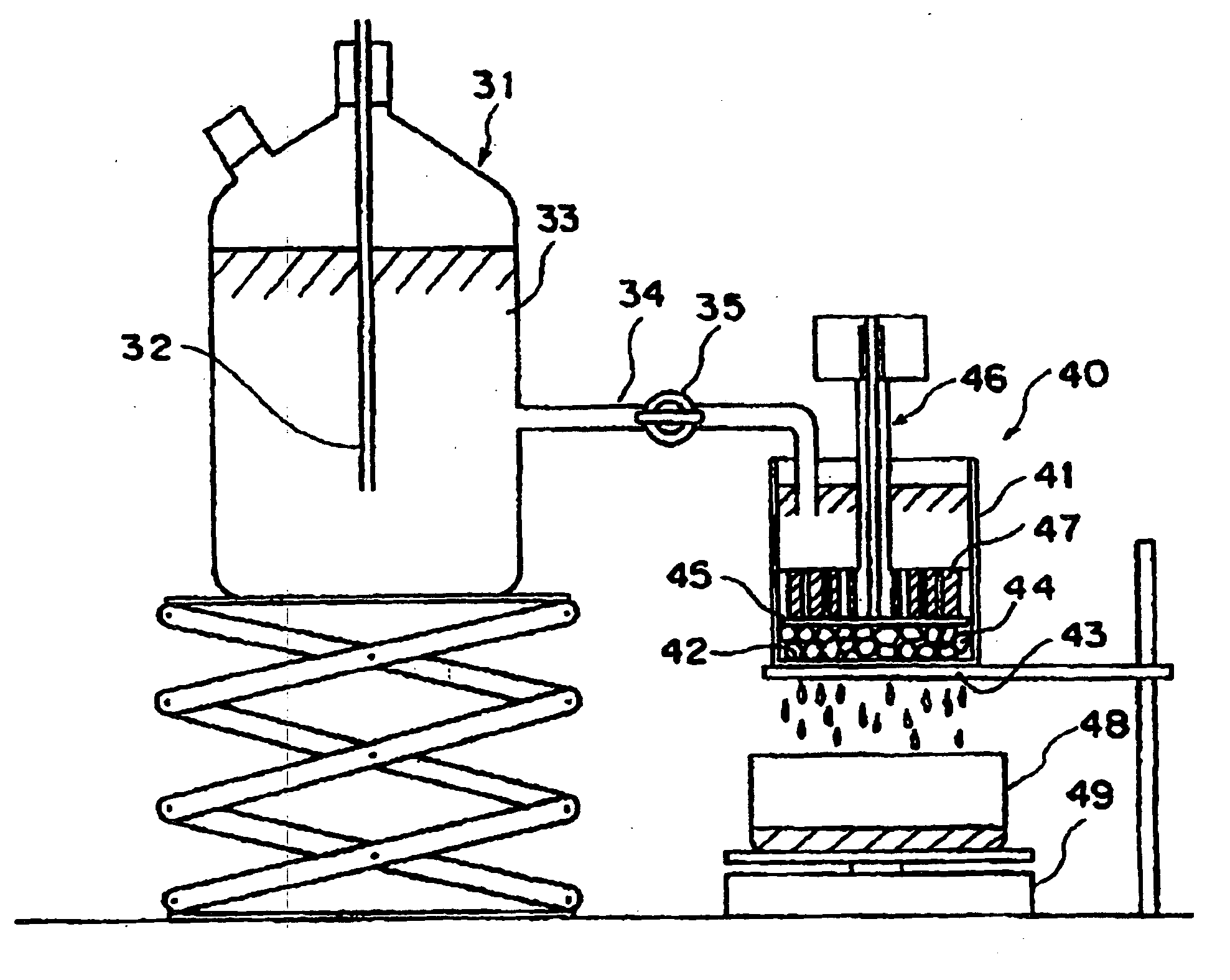
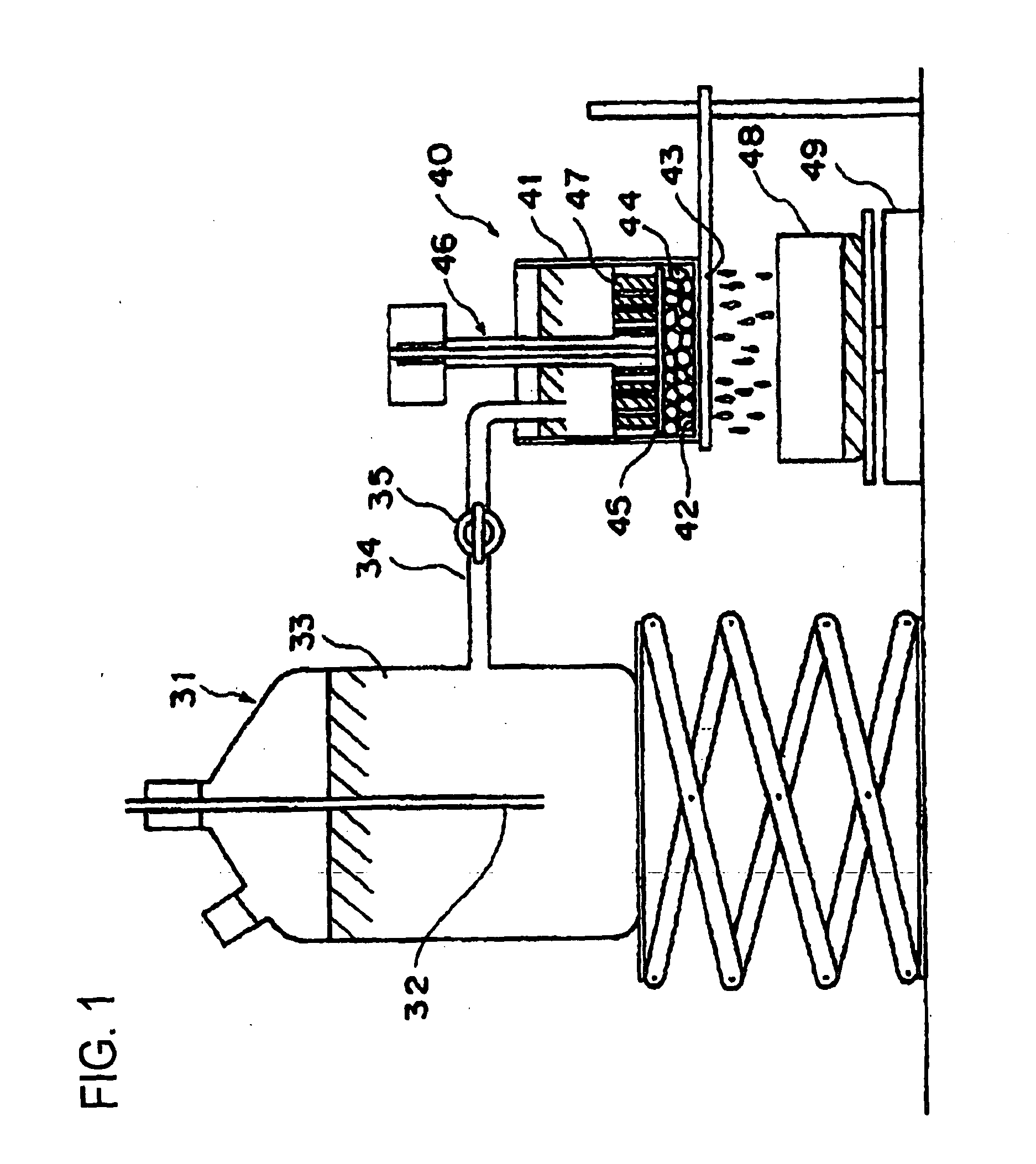
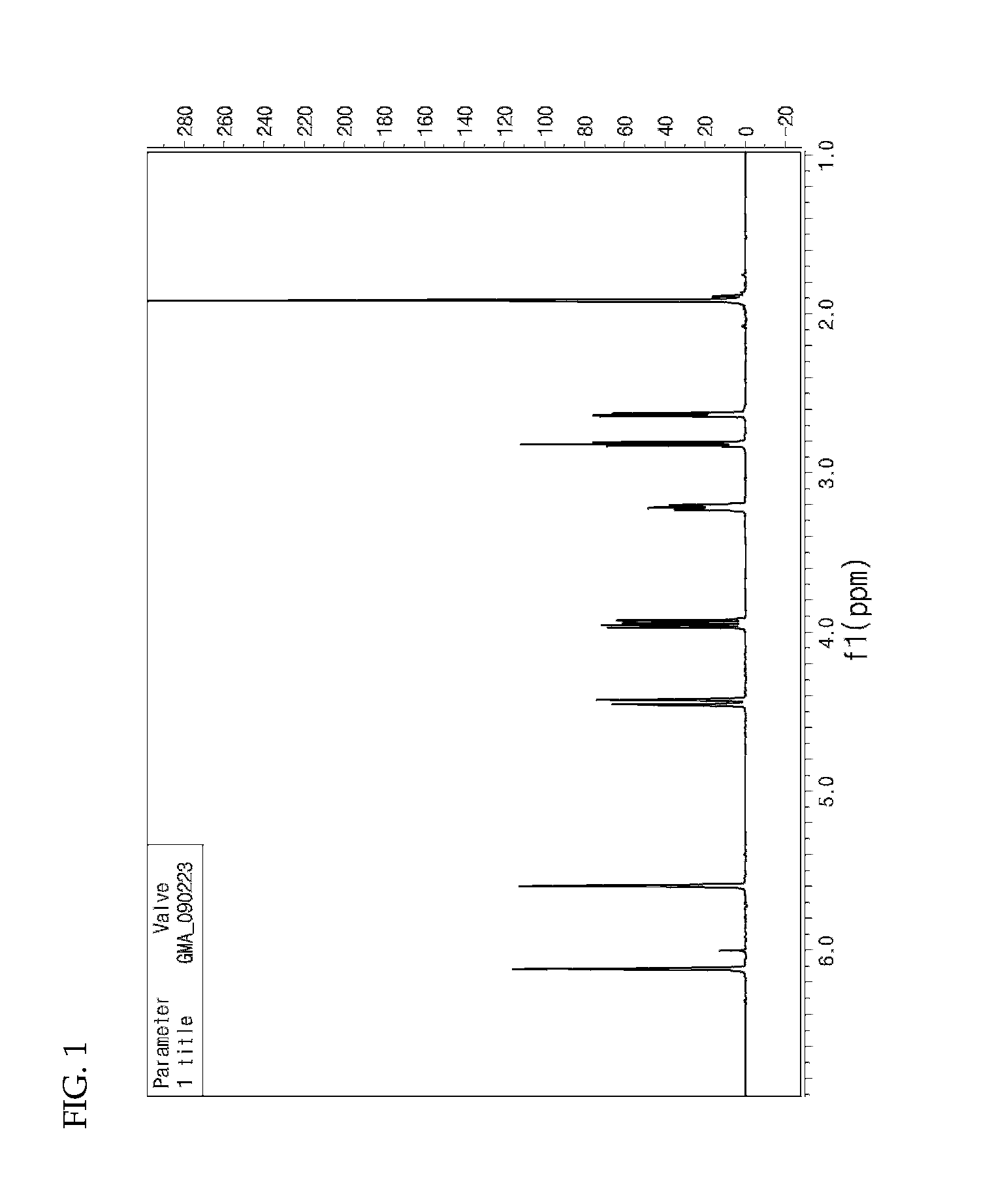
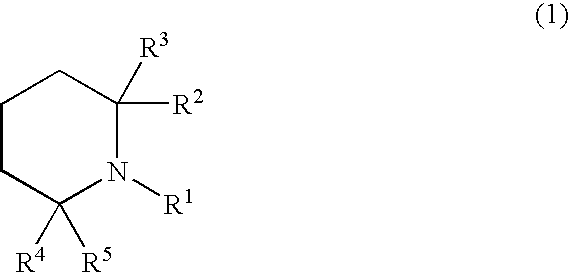
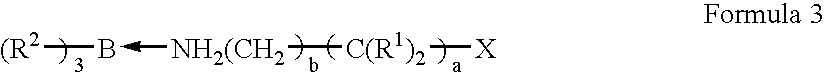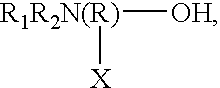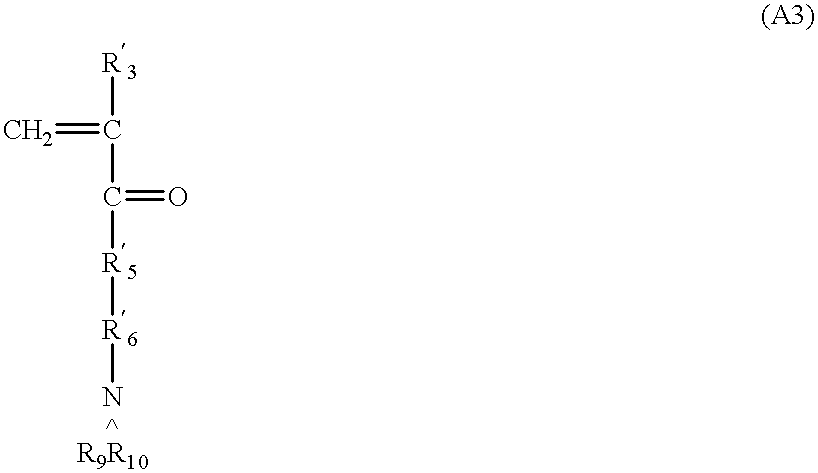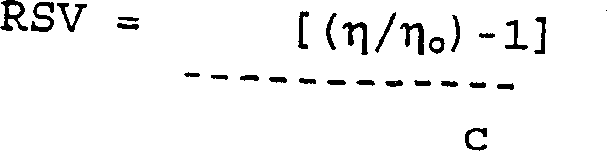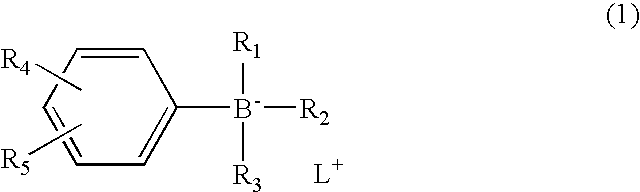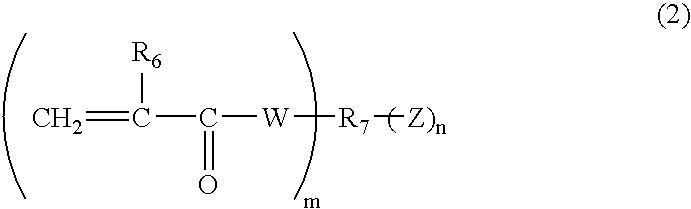Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5297 results about "Radical polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
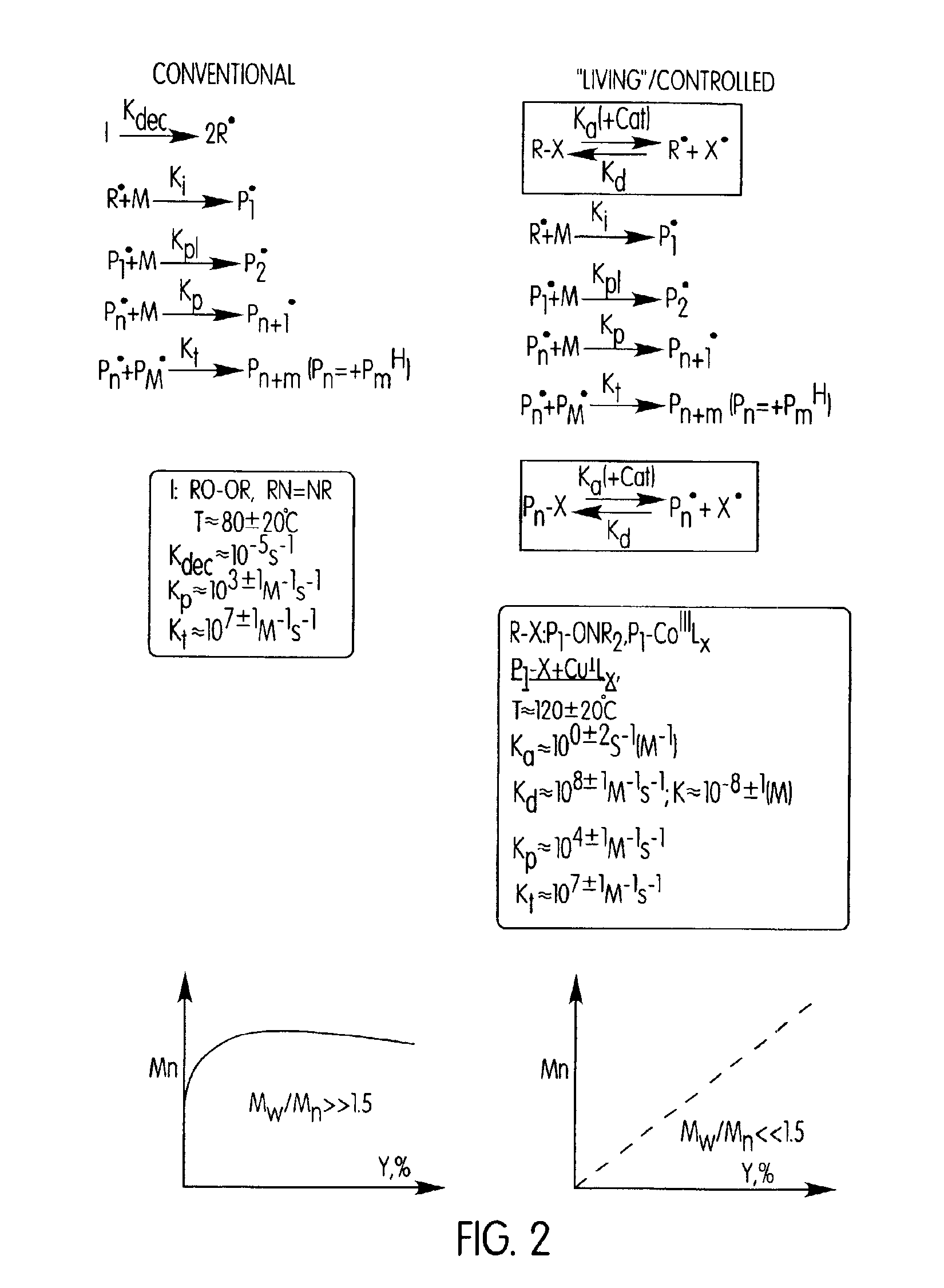
Free-radical polymerization (FRP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free-radical building blocks. Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms, usually involving separate initiator molecules. Following its generation, the initiating free radical adds (nonradical) monomer units, thereby growing the polymer chain.
Radiation-curable coating compounds
InactiveUS6605669B2Inhibition of polymerizationNo surface defectsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPrinting after-treatmentMeth-Functional monomer
Coating compounds curable by means of high-energy radiation, comprising as binderA) at least one (meth)acrylic copolymer containing olefinic double bonds capable of free-radical polymerization and hydroxyl groups with a C=C equivalent weight from 100 to 10,000 and an OH-value from 20 to 250 mg KOH / g, which is prepared from monomers comprising:A1) at least one olefinically unsaturated, epoxy-functional monomer capable of free-radical polymerization,A2) at least one olefinically unsaturated, carboxy-functional monomer capable of free-radical polymerization andA3) at least one further olefinically unsaturated monomer capable of free-radical polymerization which is different from A1) and A2), andB) at least one component with free isocyanate groups and process for multilayer coating using the coating compounds.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Preparation of novel homo- and copolymers using atom transfer radical polymerization
The present invention is directed to a process of atom (or group) transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of novel homopolymer or a block or graft copolymer, optionally containing at least one polar group, with well defined molecular architecture and narrow polydipersity index, in the presence of an initiating system comprising (i) an initiator having a radically transferrable atom or group, (ii) a transition metal compound, and (iii) a ligand, the present invention is also directed to the synthesis of a macromolecule having at least two halogen groups which can be used as a macroinitiator component (i) to subsequently form a block or graft copolymer by an atom or group transfer radical polymerization process; the present invention is also directed to a process of atom or group transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of a branched or hyperbranched polymer; in addition, the present invention is directed to a process of atom or group transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of a macroinitiator which can subsequently be used to produce a block or graft copolymer.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Amine organoborane complex initiated polymerizable compositions containing siloxane polymerizable components
InactiveUS6777512B1Easy to useBroaden applicationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAminosilochromeOligomer
In one embodiment the invention is a polymerizable composition comprising a) an organoborane amine complex; b) one or more of monomers, oligomers or polymers having olefinic unsaturation which is capable of polymerization by free radical polymerization; c) one or more compounds, oligomers or prepolymers having a siloxane backbone and reactive moieties capable of polymerization; and d) a catalyst for the polymerization of the one or more compounds, oligomers or prepolymers having a siloxane backbone and reactive moieties capable of polymerization. This composition may further comprise a compound which causes the organoborane amine complex to disassociate. In a preferred embodiment, the two part composition further comprises a compound which is reactive with both the b) one or more of monomers, oligomers or polymers having olefinic unsaturation which is capable of polymerization by free radical polymerization; and the c) one or more compounds, oligomers or prepolymers having a siloxane backbone and reactive moieties capable of polymerization. This composition can be polymerized by contacting the two parts of the composition. In another embodiment the invention is an organoborane amine complex comprising an alkyl borane having ligands which are alkyl, cycloalkyl or both and an amino siloxane.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Bioprosthetic tissue preparation with synthetic hydrogels
ActiveUS20050119736A1Reduce calcificationReduce stiffnessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for treating xenogenic tissue for implantation into a human body including in-situ polymerization of a hydrogel polymer in tissue, and tissue treated according to those methods, where the polymerization takes place in tissue that has not been fixed with glutaraldehyde. The polymerization may only fill the tissue, bind the polymer to the tissue, or cross-link the tissue through the polymer, depending on the embodiment. One method includes free radical polymerization of a first vinylic compound, and can include cross-linking through use of a second compound having at least two vinyl groups. Another method utilizes nucleophilic addition polymerization of two compounds, one of which can include PEG and can further include hydrolytically degradable regions. In one embodiment, applicants believe the in-situ polymerization inhibits calcification, and that the polymerization of tissue un-fixed by glutaraldehyde allows for improved penetration of the polymer. The methods find one use in the treatment of porcine heart valve tissue, intended to extend the useful life of the valves by inhibiting calcification. The incorporation of degradable hydrogel regions may initially fill the tissue and reduce any initial inflammatory response, but allow for later infiltration by cells to remodel the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Anisotropic conductive adhesive and method for preparation thereof and an electronic apparatus using said adhesive
InactiveUS6039896AReduce weightEasy to manufactureNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesDigital data processing detailsEpoxyPhosphoric Acid Esters
An anisotropic conductive adhesive contains conductive particles dispersed in a resin composition, wherein the resin composition includes a radical polymerization resin (A), an organic peroxide (B), a thermoplastic elastomer (C) and a phosphoric ester (D). The resin composition can further contain an epoxy silane coupling agent (E) represented by formula (2) or (3). The resin composition is mixed with other components after the radical polymerization resin (A), the thermoplastic elastomer (C), the phosphoric ester (D) and the epoxy silane coupling agent (E) are reacted. It is also possible to preliminarily react only the phosphoric ester (D) and the epoxy silane coupling agent (E) and to react the product of the preliminary reaction with the radical polymerization resin (A) and the thermoplastic elastomer (C), and then to add other components. The anisotropic conductive adhesive of the present invention can be used for electrical joining of electronic or electric parts of electrical apparatus.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Monomer substituted photoacid generator of fluoroalkylsulfon and a polymer thereof
InactiveUS7534844B2Reduce solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic chemistryPhotomechanical apparatusSolubilityMethacrylate
The present invention relates to a novel compound with a fluoroalkylsulfonium photoacid generating group and novel copolymers having superior solubility in organic solvents, which is prepared from radical polymerization of the novel compound with methacrylate monomers.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Low viscosity polymer polyols
The present invention relates to low viscosity polymer polyols and to a process for the preparation of these low viscosity polymer polyols. These polymer polyols comprise the free-radical polymerization product of (A) a base polyol, (B) a pre-formed stabilizer, and (C) at least one ethylenically unsaturated monomer, in the presence of (D) at least one free-radical polymerization initiator, and (E) at least one polymer control agent. The total amount of polymer control agent present in the polymer polyols of the present invention ranges from greater than about 5.0% up to about 20% by weight, based on 100% by weight of the polymer polyol.
Owner:COVESTRO LLC
Production of dyed polymer microparticles
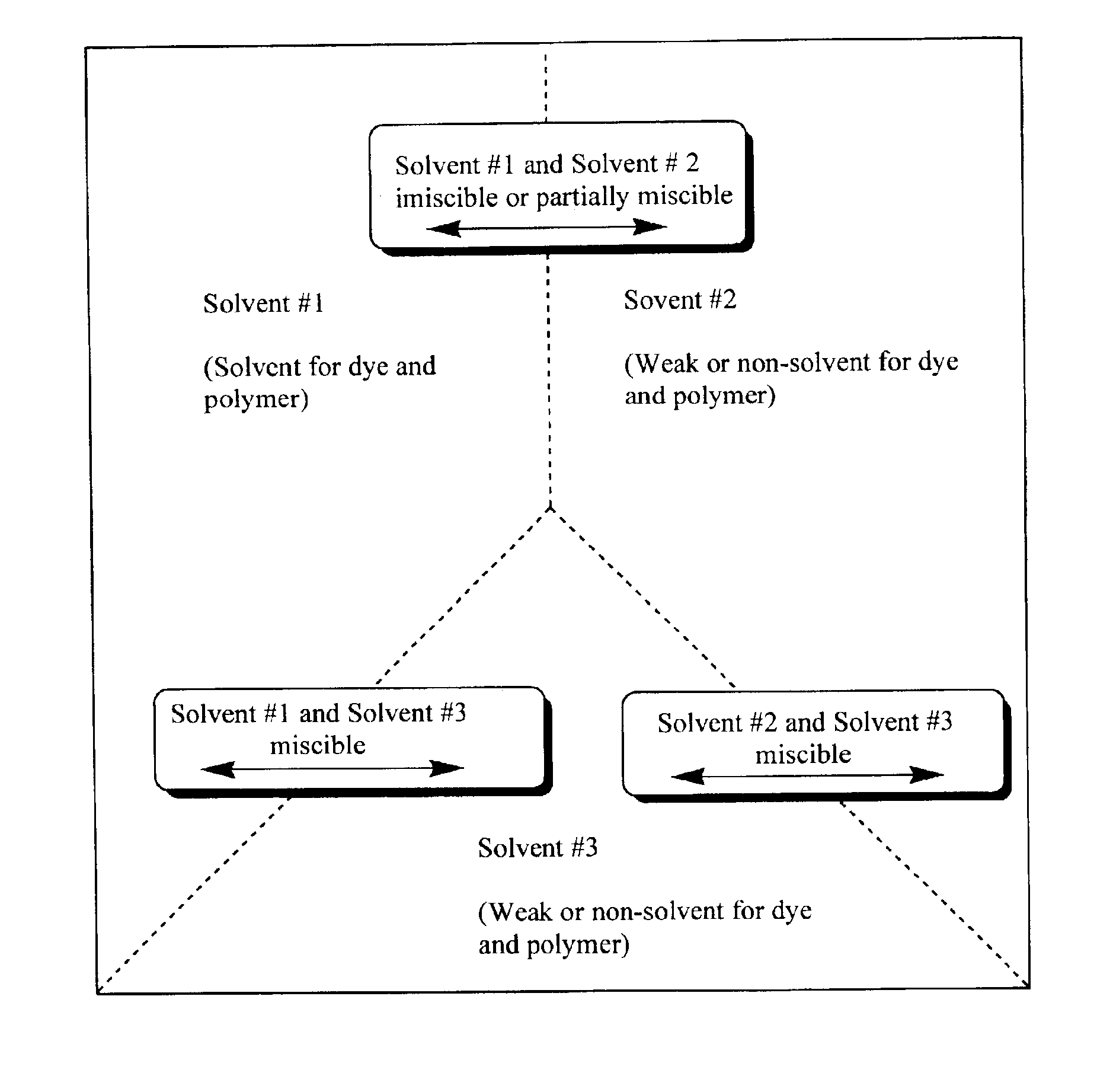
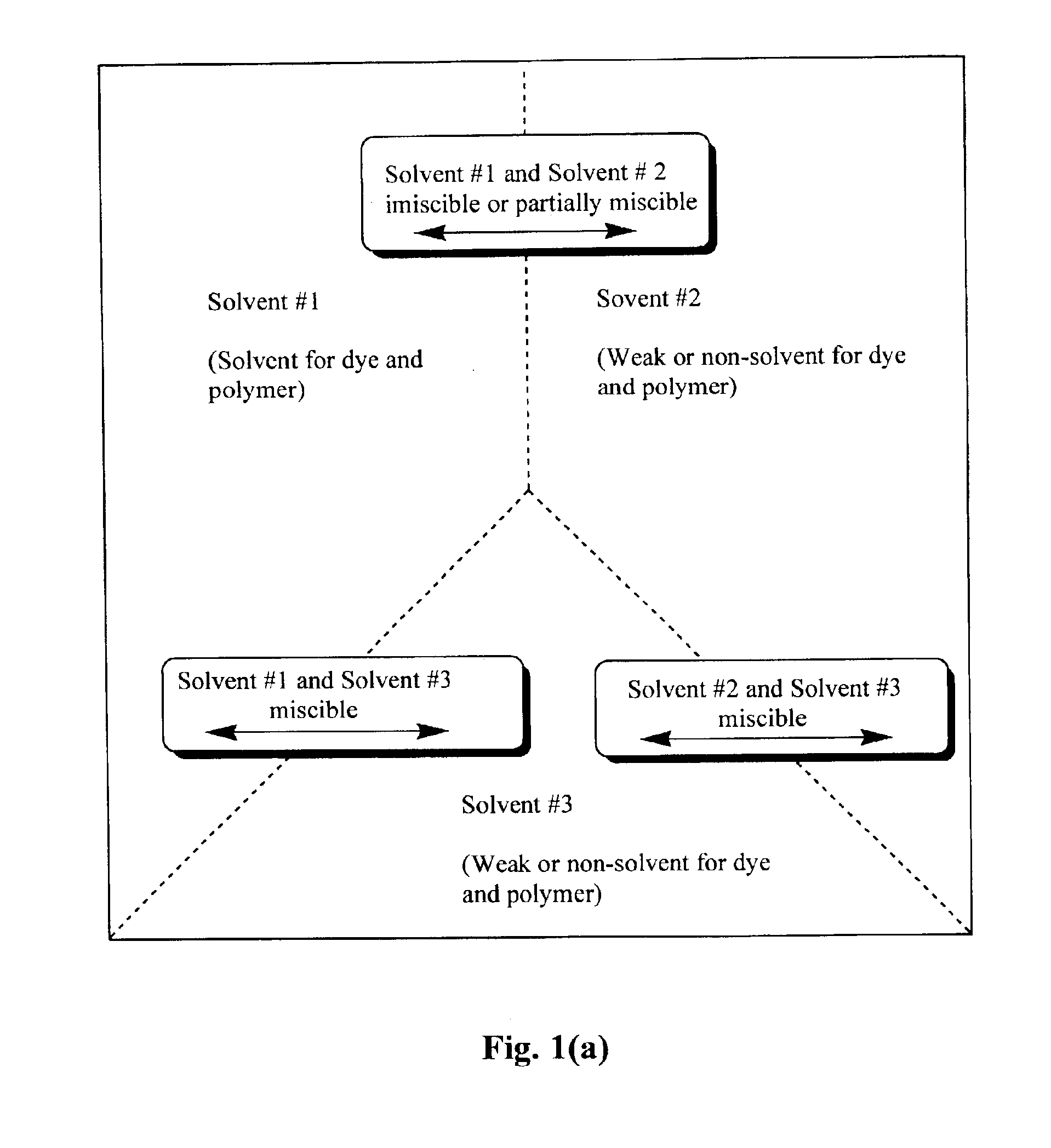
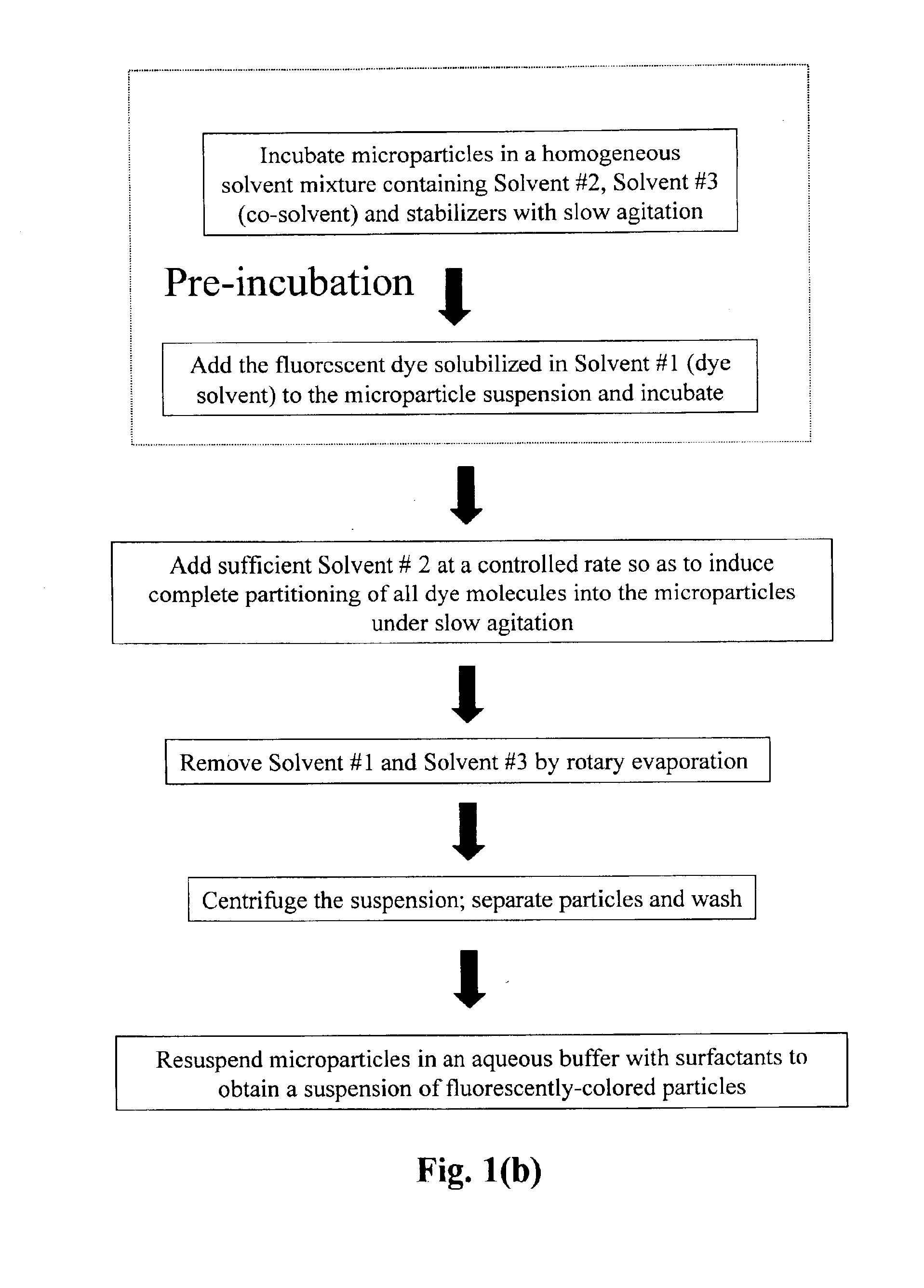
A dye, such as a fluorescent dye, is incorporated into polymer microparticles using a solvent system composed of a first solvent in which the dye and the microparticle polymer are soluble, a second solvent in which the dye and the microparticle polymer are not or only weakly soluble, and a third solvent in which the dye and the microparticle polymer are not or only weakly soluble. The first and second solvents are immiscible with each other, or at most partially miscible. The third solvent is miscible with the first and second solvents. The formulation provides substantially complete partitioning of the dye to the microparticles. The method may be used to obtain dyed polymer microparticle formed of cross-linked or non-cross-linked polymers. Libraries are provided comprising two or more sets of microparticles of different dye loadings. Fluorescent core-shell microparticles are produced from a mixture of microparticle cores incorporating one or more fluorescent dyes, a polymerization mixture comprising at least one polymerizable shell monomer, at least one free radical polymerization initiator comprising a water-insoluble oxidizing agent, and at least one water-soluble reducing agent.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Ink-jet printing ink compositions having superior smear-fastness
InactiveUS6417249B1Improve printing effectGood printing performanceInksCoatingsPolyesterPolymer science
Specific core-shell binders and additives for use in ink-jet printing ink compositions are provided. One class of specific core / shell binders has the general formula [AmBnC'p]x, where A and B are hydrophobic components in which A exhibits a glass transition temperature Tg between about -150° and +25° C. and B exhibits a glass transition temperature greater than 25° C., C' is a component that forms a hydrophilic or water-soluble component in the polymer chain, and has an ionic or non-ionic structure, m<30 wt %, n>40 wt %, and p<30 wt %, with the total of m+n+p=100 wt %, and x=1 to 100,000. The molecular weight (weight average) of the polymer is between about 1,000 and 2,000,000. The polymers useful in the practice of the invention are prepared by emulsifying the monomers and then conducting a free-radical polymerization in water. The foregoing binder polymer is used in conjunction with additives comprising either (a) amine alcohols having the general formulawhere R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, and phenoxy, R is alkyl, X is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl, -OH, -COOH, -CHO, and substituted groups or (b) organic acids (water-soluble or water-dispersive), including polymeric acids. Other additives include amines, polyalcohols, polyamines, and polyesters. In the ink compositions of the present invention, the ratio of binder (1) to colorant (pigment) is greater than 1 to 10. The concentration of the additive is within the range of 0.005 to 50 wt %. The general ink formulation comprises: 5 to 50 wt % water-miscible solvent; 0.5 to 10 wt % colorant; 0.005 to 50 wt % additive; and water.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Processes based on atom (or group) transfer radical polymerization and novel (co)polymers having useful structures and properties
InactiveUS6887962B2Increase in the rate of side reactionsReduce rateWater solubleRadical polymerization
Improved processes for atom (or group) transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and novel polymers have been developed and are described. In certain embodiments, novel copolymers comprising a least one polymeric branch or polymeric block with a predominantly alternating monomer sequence are described. Novel copolymers comprising a least one polymeric branch or polymeric block with a gradient monomer structure are described. Additionally, novel copolymers comprising a least one polymeric branch or polymeric block with a predominantly periodic monomer sequence are also described. Novel copolymers having a water soluble backbone and at least two hydrophobic polymeric branches grafted to the water soluble backbone are also described.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Ink-jet printing ink compositions having magnetic properties and specific core/shell binder
InactiveUS6248805B1Improve propertiesImprove magnetic propertiesIron oxides/hydroxidesDuplicating/marking methodsCharge-transfer complexPrinting ink
Specific core-shell binders and magnetic additives for use in ink-jet printing ink compositions are provided. One class of specific core / shell binders has the general formula [AmBnC'p]x, where A and B are hydrophobic components in which A exhibits a glass transition temperature Tg between about -150° and +25° C. and B exhibits a glass transition temperature greater than 25° C., C' is a component that forms hydrophilic or water-soluble component in the polymer chain, and has an ionic or non-ionic structure, m<30 wt %, n>40 wt %, and p<30 wt %, with the total of m+n+p=100 wt %, and x=1 to 100,000. The molecular weight (weight average) of the polymer is between about 1,000 and 2,000,000. The polymers useful in the practice of the invention are prepared by emulsifying the monomers and then conducting a free-radical polymerization in water. The foregoing binder polymer is used in conjunction with magnetic additives comprising either (a) inorganic magnetic compound containing at least one of iron, cobalt, and nickel or (b) organic magnetic complexes containing at least one of iron, cobalt, and nickel or (c) organic charge transfer complexes that exhibit magnetic properties. The ratio of binder (I) to colorant (pigment) is greater that 1 to 10. The concentration of the magnetice additive is within the range of 1 to 30 wt %. The general ink formulation comprises: 5 to 50 wt % water-miscible solvent; 0.5 to 10 wt % colorant; 1 to 30 wt % magnetice additive; and water.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method for injection moulding moulded bodies consisting of (meth) acrylate copolymers
InactiveUS20040104501A1Reduce contentLittle reabsorptionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEndocrine system disorderPolymer scienceMeth-
The invention relates to a process for producing mouldings by injection moulding the steps in the process being a) melting and mixing of a (meth)acrylate copolymer composed of from 85 to 98% by weight of C1-C4-alkyl (meth)acrylates capable of free-radical polymerization and from 15 to 2% by weight of (meth)acrylate monomers having a quaternary ammonium group in the alkyl radical, with from 10 to 25% by weight of a plasticizer, and also from 10 to 50% by weight of a dryers [sic] and / or from 0.1 to 3% by weight of a release agent, and, where appropriate, with other conventional pharmaceutical additives or auxiliaries and / or with an active pharmaceutical ingredient, b) devolatilizing the mixture at temperatures of at least 120° C., thus reducing the content of the low-boiling constituents with a vapour pressure of at least 1.9 bar at 120° C. to not more than 0.5% by weight, and c) injecting the devolatilized mixture at a temperature of from 80 to 160° C. into the mould of an injection moulding system and removing the resultant moulding from the mould.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG +1
Catalyst for vinyl polymerization and method for preparing same
The invention provides a catalyst for vinyl polymerization. The catalyst contains titanium-containing active components and active agent components (organic aluminum compound), wherein an inorganic oxide carrier is loaded with at least one kind of magnesium dihalide, one kind of aluminum halide, at least one kind of titanium halide and at least one kind of electron donor, and the electron donor compound is ether, ester or ketone; and the general formula of the organic aluminum compound is AlRnX3-n, R is alkyl of which the number of hydrogen or carbon atoms is 1 to 20, X is halogen, and n is a numeral which is more than 1 and less than or equal to 3. When the catalyst is used for the vinyl polymerization, the catalyst has higher polymerization activity and hydrogen-adjusting sensitivity, and simultaneously the molecular weight distribution of the obtained polymers is wider.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Planographic printing plate precursor and planographic printing method
ActiveUS7005234B2Excellent plate-wear resistanceAvoid small quantitiesPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPlanographic printingPhotochemistry
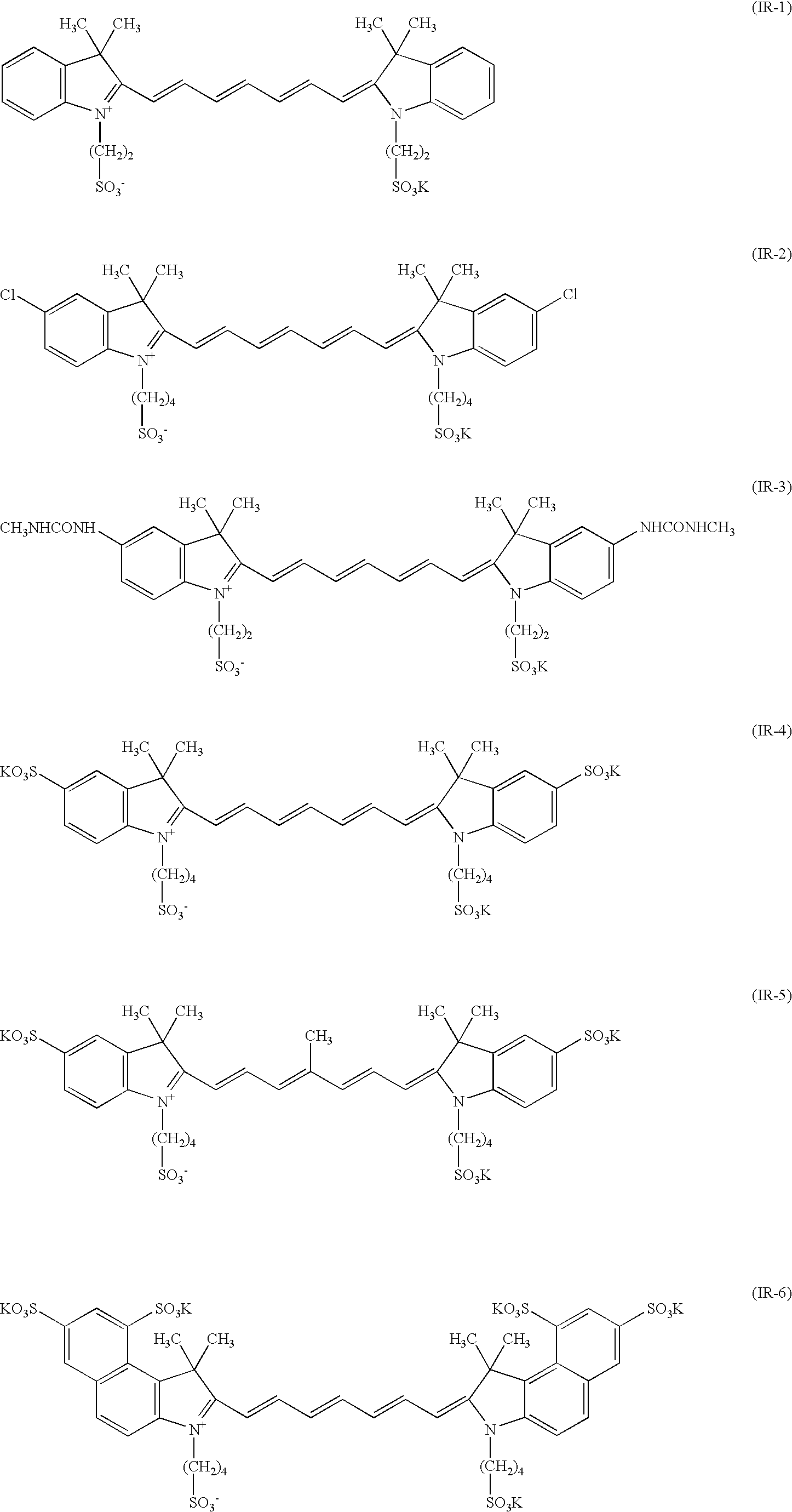
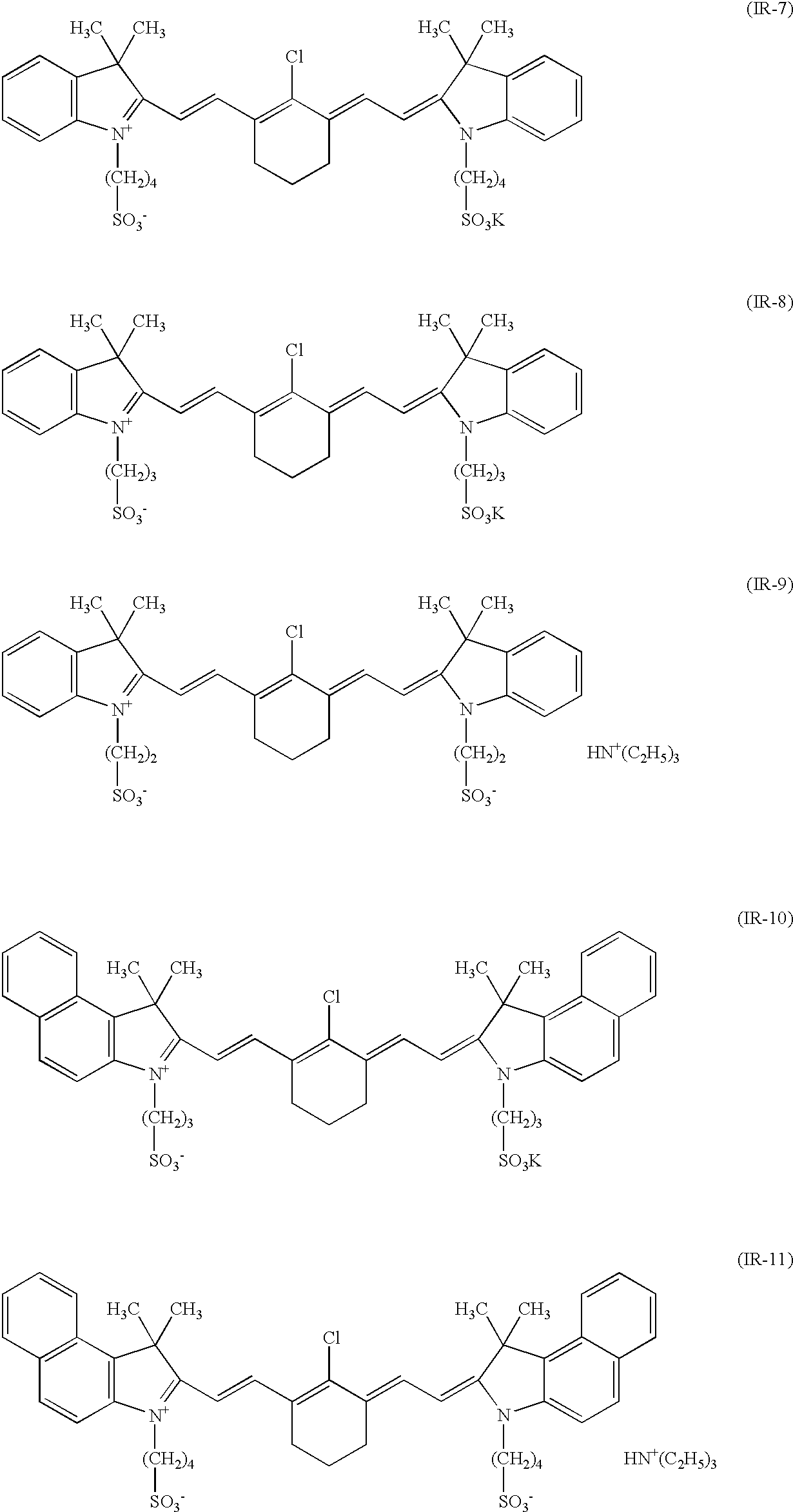
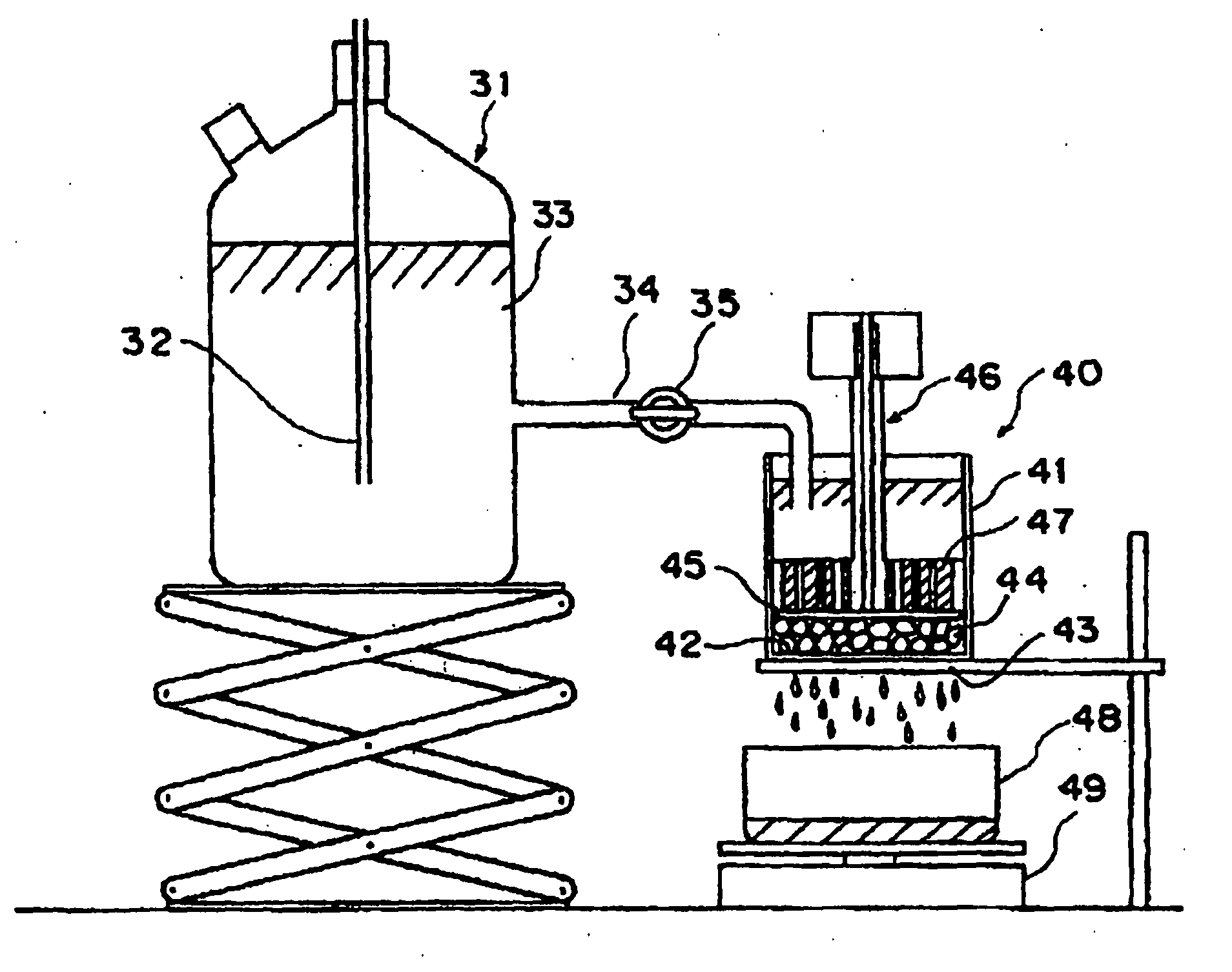
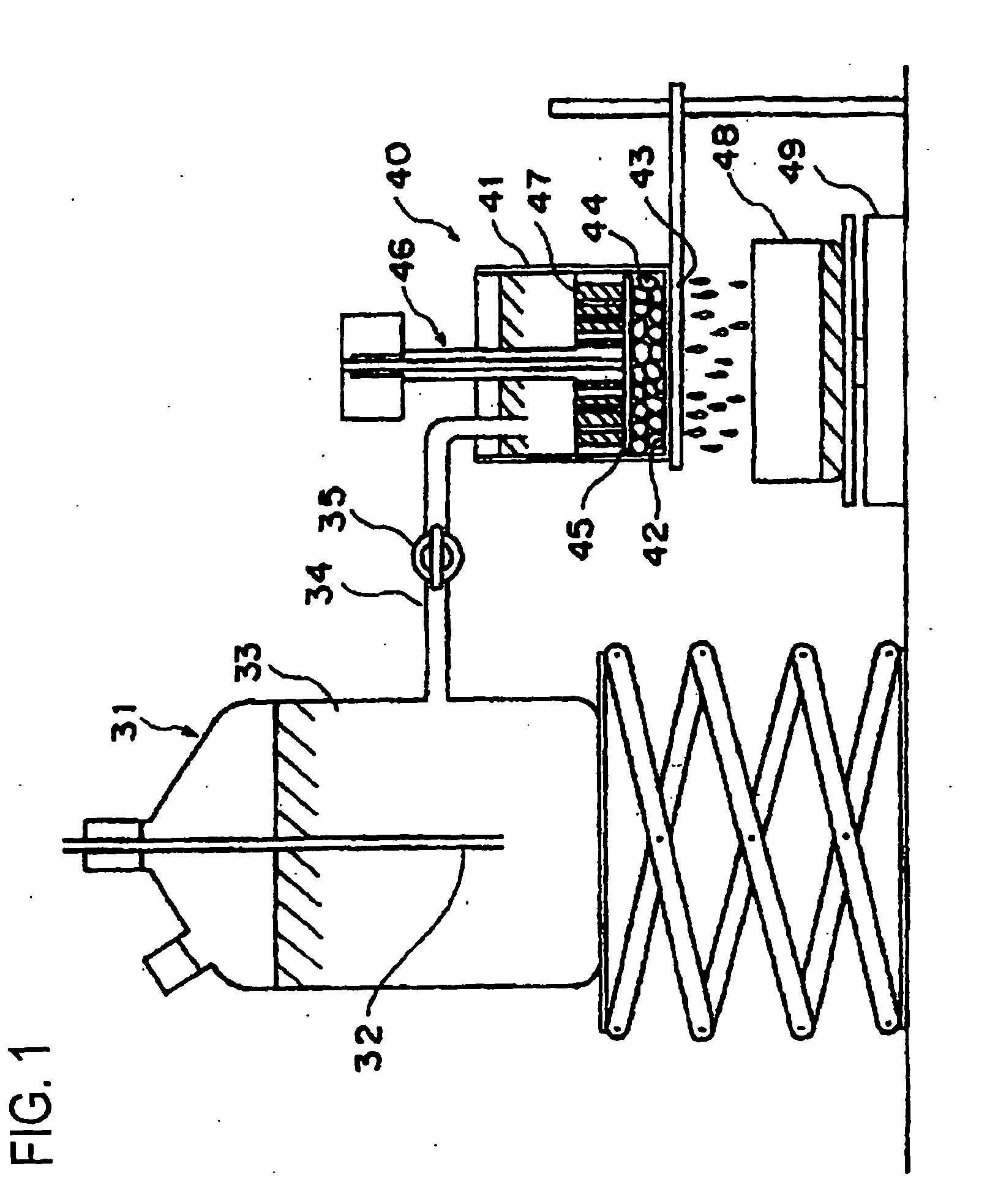
The present invention provides a planographic printing plate precursor comprising a photosensitive layer on a support, the photosensitive layer including an infrared absorbent, a radical polymerization initiator and a radical polymerizing compound, the photosensitive layer being recordable with irradiation with an infrared ray, and being at least one of soluble and dispersible in water.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for production of modified water absorbent resin
InactiveUS20090298963A1Improve production efficiencyOutstanding propertyAbsorbent padsBandagesWater solublePolymer chemistry
This invention is to provide a method for producing a modified water absorbent resin excelling in water absorbing properties. This invention relates to a method for producing a modified water absorbent resin, which comprises a) mixing a water absorbent resin and a water-soluble radical polymerization initiator or a heat-degradable radical polymerization initiator without addition of an ethylenically unsaturated monomer and b) irradiating the resultant mixture with active energy rays. The method is particularly capable of exalting the absorbency against pressure and the saline flow conductivity.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Structurally-modified polymer flocculants
InactiveCN1426429ASludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSedimentation separationCross-linkStructural Modifier
This invention is directed to structurally-modified water-soluble polymers prepared by initiating polymerization of an aqueous solution of monomers under free radical polymerization conditions to form a polymer solution and adding at least one structural modifier to the polymer solution after at least 30 % polymerization of the monomers has occurred, and to use of the water-soluble cross-linked polymers as flocculating agents.
Owner:ONDEO NALCO
Plastic body provided with a microstructured surface
InactiveUS20060121248A1Lamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticPoly methacrylate
The invention relates to a process for the production of a plastics article with a microstructured surface via production of a composite composed of a backing layer composed of a thermoplastic or thermoelastic with one or more structure layers, characterized in that the structure layer(s) is / are composed of from 1 to 100% by weight of a polymethacrylate moulding composition which comprises from 80 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized methyl methacrylate units and from 0 to 20% by weight of other comonomers capable of free-radical polymerization, and which has an average (weight-average) molar mass Mw of from 30 000 g / mol to 70 000 g / mol and, where appropriate, is present in a. mixture with up to 99% by weight of a polymethacrylate moulding composition which is composed of from 80 to 100% by weight of free-radical-polymerized methyl methacrylate units and from 0 to 20% by weight of other comonomers capable of free-radical polymerization, and which has an average (weight-average) molar mass Mw of from 90 000 g / mol to 200 000 g / mol and the structure layer(s) obtain microstructuring via known structuring processes, after production of the composite. The invention further relates to the plastics articles themselves which are capable of production according to the invention, and also to their uses.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG
Water-based primer-topcoat braking paint and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a water-based primer-topcoat braking paint and a preparation method thereof. The braking paint comprises the following materials by weight percentage: 30-40 of water-based acrylic resin, 2-10 of amino resin, 1-3 of neutralizing agent, 2-5 of compound rustproofing pigment, 1-3 of tinting pigment, 10-20 of filling agent, 0.1-0.5 of defoaming agent, 0.1-0.5 of flatting agent and 25-40 of deionized water, wherein the water-based acrylic resin is a free radical polymerization resultant which comprises the following materials by weight percentage: 10-30 of monomer containing hydroxy acrylic acid, 5-20 of monomer containing carboxyl acrylic acid, 2-8 of internal crosslinking monomer, 20-40 of other acrylic acid monomer, 15-30 of phenyl ethylene monomer, 1-5 of evocating agent and 40-50 of alcohol ether latent solvent. When the paint is prepared, the dispersion and the abrading condition of the pigments and the filling agents are reasonably controlled to ensure that each component of the paint fully plays the respective function. The paint ensures the corrosion prevention effect and the decoration of a coating and realizes the combination of a primer and a topcoat.
Owner:CNOOC CHANGZHOU PAINT & COATINGS IND RES INST +1
Emulsion deep profile/displacement control agent and preparation method of emulsion deep profile/displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of core shell structure
The invention relates to a preparation method of an emulsion deep profile / displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of a core shell structure. According to the method, materials are fed many times to carryout inverse emulsion low-temperature oxidation and reduction to initiate free radical polymerization so that water-solubility monomers (including acrylamide, ionic monomer I, the ionic monomer II and the third monomer) react with a cross-linking agent to generate the emulsion deep profile / displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of a core shell structure. The invention also relates to the emulsion deep profile / displacement control agent containing gel microspheres of a core shell structure, which is prepared by using the method. The profile / displacement control agent is a water-solubility microgel oil displacement material containing gel microspheres from nano scale to micron scale; with small initial grain size, the profile / displacement control agent can enter into the deep part of stratum; in addition, the profile / displacement control agent has high emulsion active component content and good flowability, can have volume expansion and mutual cementation under the actions of formation water and temperature according to the condition whether charges carried by the ionic monomers at a core layer and a shell layer are same or not; therefore the profile / displacement control requirements of different geological oil deposits of oil fields can be met.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for surface-treatment of water absorbent resin
InactiveUS20090239966A1Improve production efficiencyEffecting introduction of a surface crosslink simplyPhotomechanical apparatusOptical articlesSaline waterAbsorption ratio
This invention is to provide a method for surface-treatment of a water absorbent resin excelling in water absorption properties. This invention relates to a method for the surface-treatment of a water absorbent resin, which comprises: a) mixing 100 parts by weight of a water absorbent resin, 0.01-20 parts by weight of at least one radical polymerization initiator selected from the group-consisting of persulfates, hydrogen peroxide, and azo compounds, and a radically polymerizing compound and b) irradiating the resultant mixture with active energy rays. The treatment particularly exalts the absorption ratio against pressure and the saline flow conductivity.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
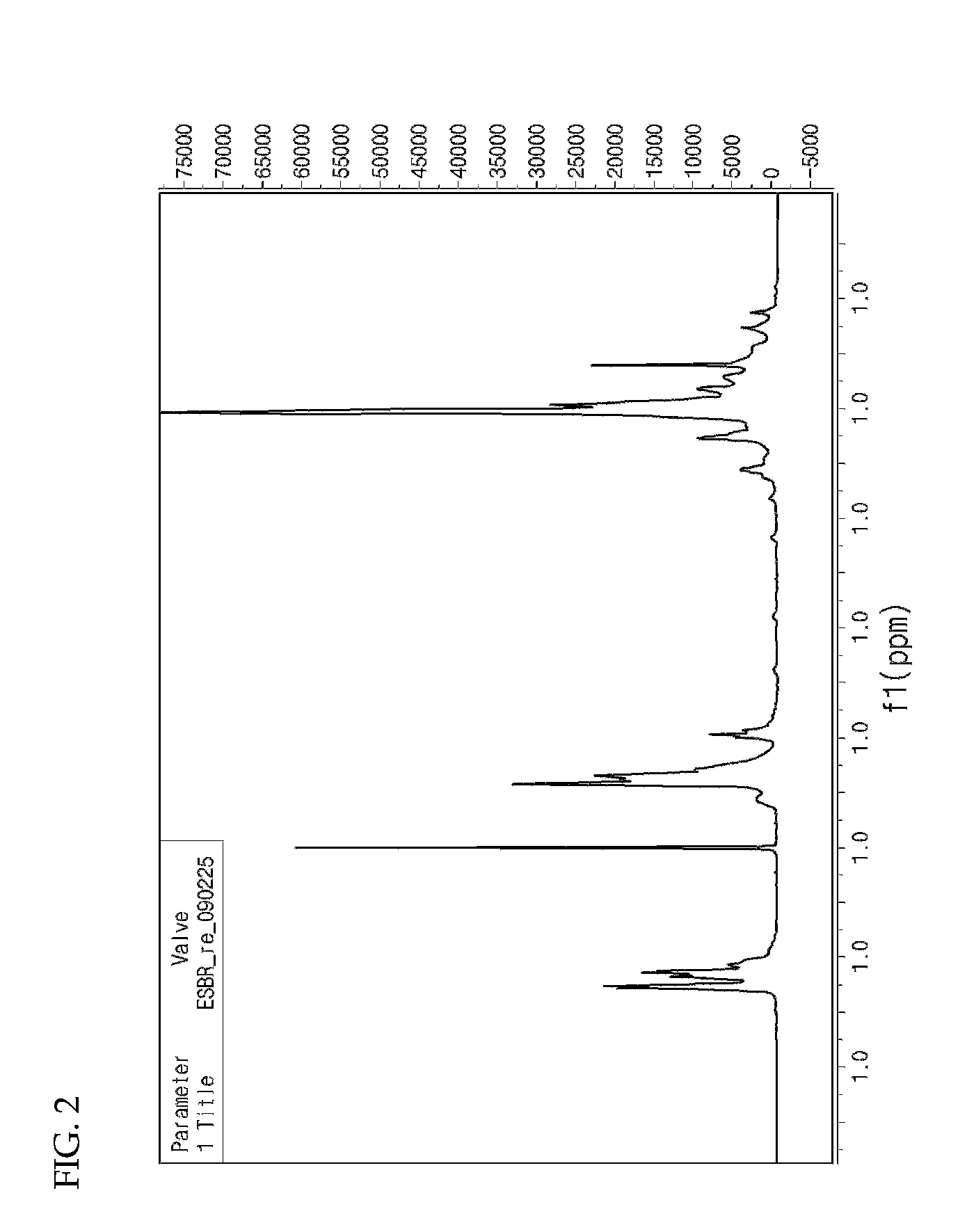
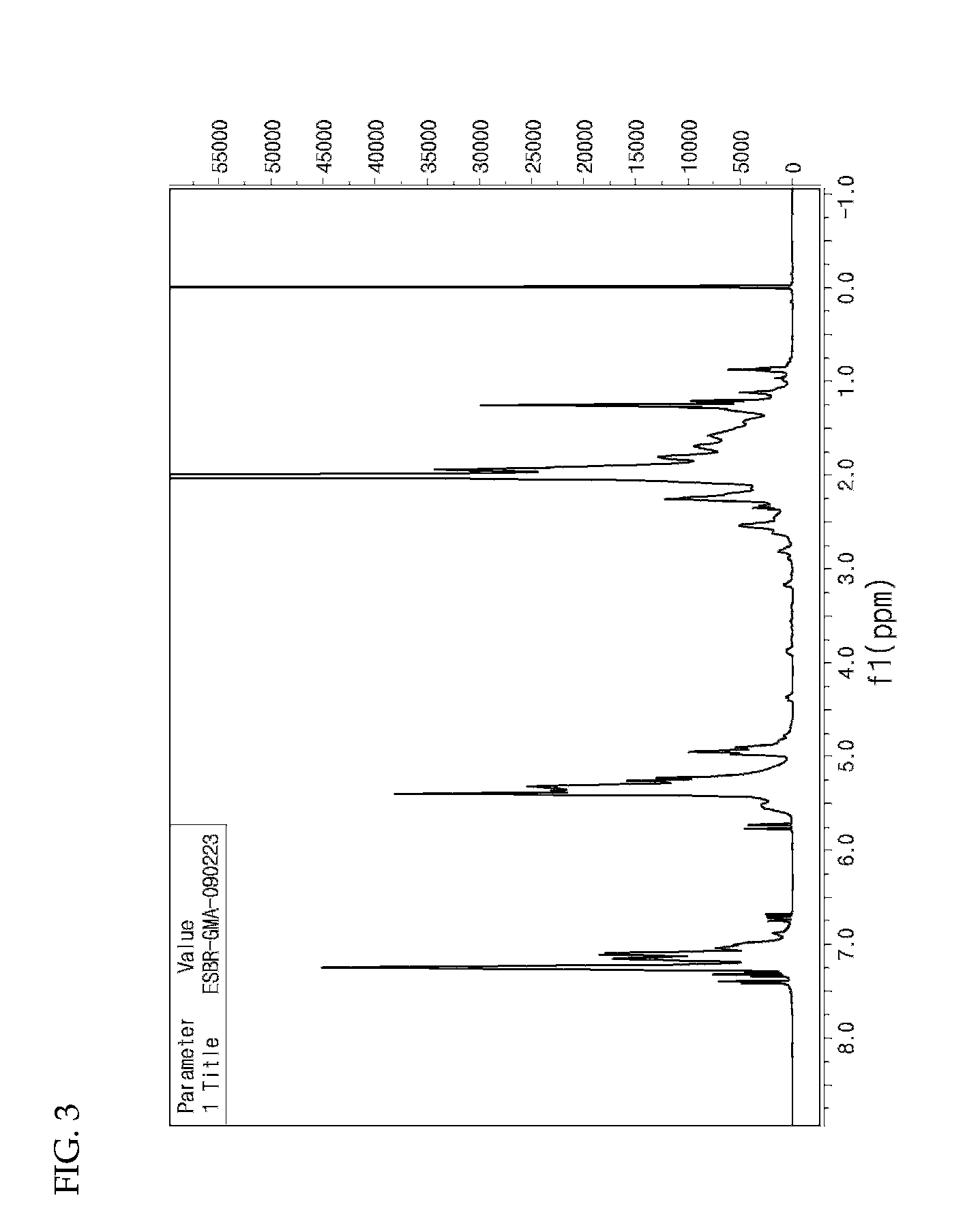
Functional styrene-butadiene copolymer
A functional styrene-butadiene copolymer is disclosed. More specifically, the copolymer is prepared by radical polymerization of a styrene monomer, a butadiene monomer and an epoxy acrylate monomer in an emulsion state and ring-opening of the resultant styrene-butadiene-epoxy acrylate copolymer. When blended with silica, the disclosed copolymer provides excellent wet stopping performance and superior wear resistance. Therefore, it can be usefully applied for industrial materials including fuel-efficient tires, snow tires, belts, hoses, etc.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Graphene/polysiloxane composite coating material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106752926AImprove scratch resistanceImprove wear resistanceFireproof paintsAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxyResin-Based Composite
The invention provides a graphene / polysiloxane composite coating material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: modifying the graphene surface with active groups by a chemical modification technique to obtain modified graphene, mixing the modified graphene with a silane compound, a dispersion medium, a non-essential comonomer and a non-essential accelerator, and carrying out hydrolytic condensation or hydrolytic condensation-free radical polymerization to generate a graphene / polysiloxane composite resin in situ; and mixing the resin with a non-essential blend resin, a non-essential curing agent, a non-essential solvent, a non-essential pigment and filler and a non-essential aid, and carrying out physical blending, amino epoxy addition reaction, Michael addition reaction and the like to form a film, thereby obtaining the graphene / polysiloxane composite coating material. The uniformly dispersed graphene lamellae and polysiloxane have strong interface effects, also have the gas / liquid barrier and heat shielding effects, and endow the coating with excellent corrosion resistance, flame retardancy and the like, thereby greatly enhancing the mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, scratch resistance, wear resistance and the like of the coating.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Molding material containing a matting agent
The invention relates to a moulding composition, comprising a) 50 to 99.9% by weight of a matrix composed of a thermoplastic polymer and b) from 0.1 to 50% by weight of a matting agent in the form of a (meth)acrylate copolymer dispersed in the matrix, characterized in that the matting agent is a (meth)acrylate copolymer which has been prepared from the following monomers, b1) from 50 to 95% by weight of methyl methacrylate b2) from 5 to 50% by weight of C1-C6-alkyl acrylates b3) from 0.01 to less than 0.5% by weight of a crosslinking monomer and / or graft-linking agent having two or more ethylenically unsaturated radicals capable of free-radical polymerization, b4) from 0 to 20% by weight of one or more other, non-crosslinking ethylenically unsaturated monomers capable of free-radical polymerization, where the entirety of the constituents b1) and b2) and, where appropriate, b3) and / or b4) gives 100% by weight, and the glass transition temperature Tmg of the matting agent is at least 20° C.
Owner:ROEHM GMBH & CO KG
Radical polymerization catalyst and adhesive kit for dental use
InactiveUS20050009946A1High polymerization activityEasy to handleImpression capsPhysical/chemical process catalystsArylVanadium Compounds
According to the present invention, there are disclosed a radical polymerization catalyst comprising an aryl borate compound, an acidic compound and a +tetravalent and / or +pentavalent vanadium compound; and a curable composition, a dental composition, a dental adhesive, a dental pretreatment agent, a dental adhesive kit, etc. all containing the radical polymerization catalyst.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP +1
Ink composition for inkjet-recording and method for inkjet-recording
InactiveUS20080131618A1Improving desired propertyStable ink-ejecting propertyInksCoatingsPliabilityIrradiation
An ink composition for inkjet-recording, which shows a high sensitivity to irradiation with actinic radiation and is able to form an image with superior curability, permitting the image formed after curing to have sufficient adhesiveness to a recording medium, as well as to have excellent flexibility in the formed image portion, and an inkjet-recording method using the same is provided:wherein the ink composition for inkjet-recording comprises (A) a compound having a polymerizable unsaturated bond and a cyclic amine structure in the molecule, (B) a compound having a polymerizable unsaturated bond and an alicyclic structure in the molecule, and (C) a radical polymerization initiator.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
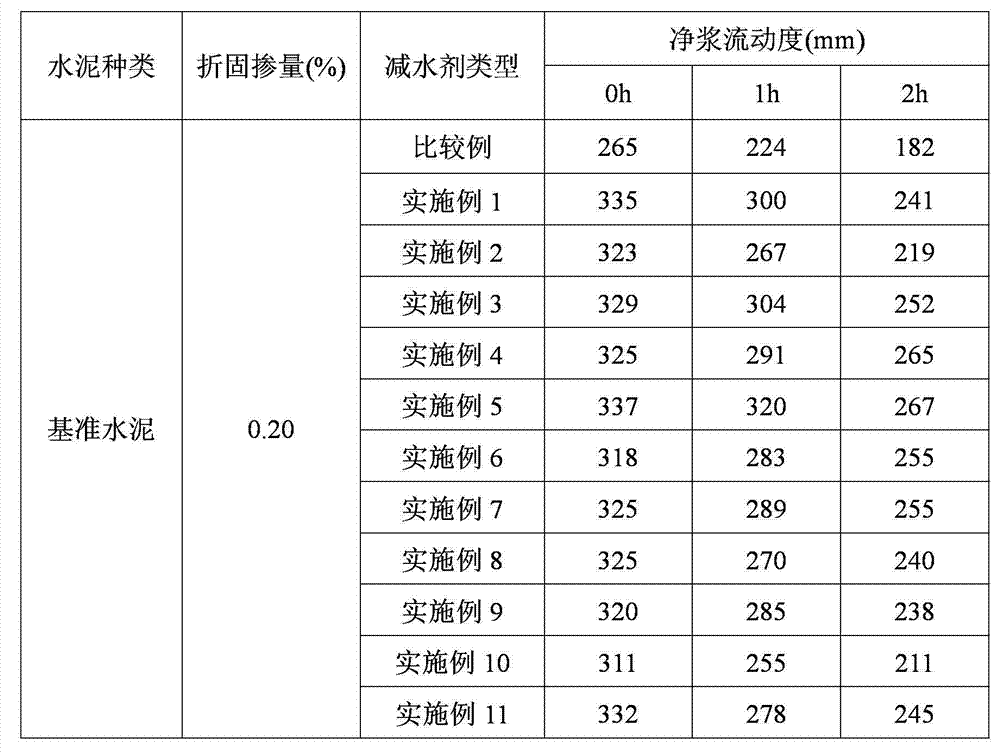
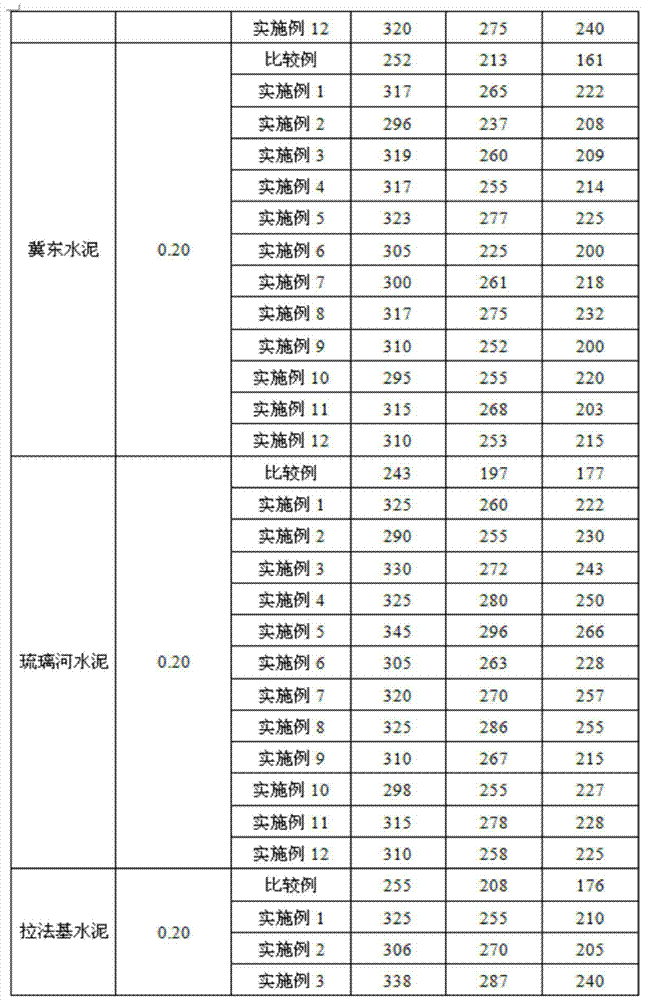
Preparation method of star polycarboxylic acid high-performance water reducing agent
ActiveCN102887979AExtended Dionon Design-Structure-PropertyExpanding the theoretical connotation of the design-structure-performance of moleculesWater reducerPollution
The invention relates to a preparation method of a star polycarboxylic acid high-performance water reducing agent. Polybasic alcohol and (methyl) acrylic acid used as main raw materials for esterification are esterified and polymerized to prepare the star polycarboxylic acid high-performance water reducing agent material: the (methyl) acrylic acid and polybasic alcohol used as reactants are esterified under the action of a catalyst to firstly prepare a star polymerizable active terminal, and free-radical polymerization reaction is carried out with unsaturated polyethenoxy ether, molecular weight regulator and unsaturated carboxylic acid monomer under the action of an initiator to prepare the star polycarboxylic acid high-performance water reducing agent. The invention is easy to control, and has the advantages of high polymerization degree, low cost and no pollution; the esterification reaction is carried out form an active core, and the free-radical polymerization is carried out to generate the chain arm, thereby implementing the polycarboxylic acid high-performance water reducing agent in a star molecular structure; and under the condition of common doping amount and low doping amount, the star polycarboxylic acid high-performance water reducing agent has better cement paste flowability and holding capacity than the traditional linear and comb polycarboxylic acid water reducing agents, and has favorable cement adaptability and concrete application performance.
Owner:GUIZHOU DR SHI TECH
Organic-inorganic hybrid super-hydrophilic coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102241939AEasy to prepareMild reaction conditionsPretreated surfacesCoatingsHydrophilic monomerPtru catalyst
The invention discloses an organic-inorganic hybrid super-hydrophilic coating as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises: firstly carrying out hydrolysis condensation polymerization by a sol-gel method with ethyl orthosilicate used as a precursor, hydrochloric acid used as a catalyst, ethanol used as a solvent, a silane coupling agent used as a modifier and a proper amount of water to obtain a modified silica sol, then carrying out free radical polymerization on the modified silica sol and reactive hydrophilic monomers to obtain an organic-inorganic hybrid material, and carrying out solvent replacement to obtain an aqueous organic-inorganic hybrid super-hydrophilic coating. The coating is coated on plastics, glass or metal substrates through dipping or brushing to form a coating layer, the coating layer has a contact angle with water less than 5 degrees, the adhesion force with the substrates of level-0 and the hardness greater than 6H, and water drops can spread out quickly on the coating layer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
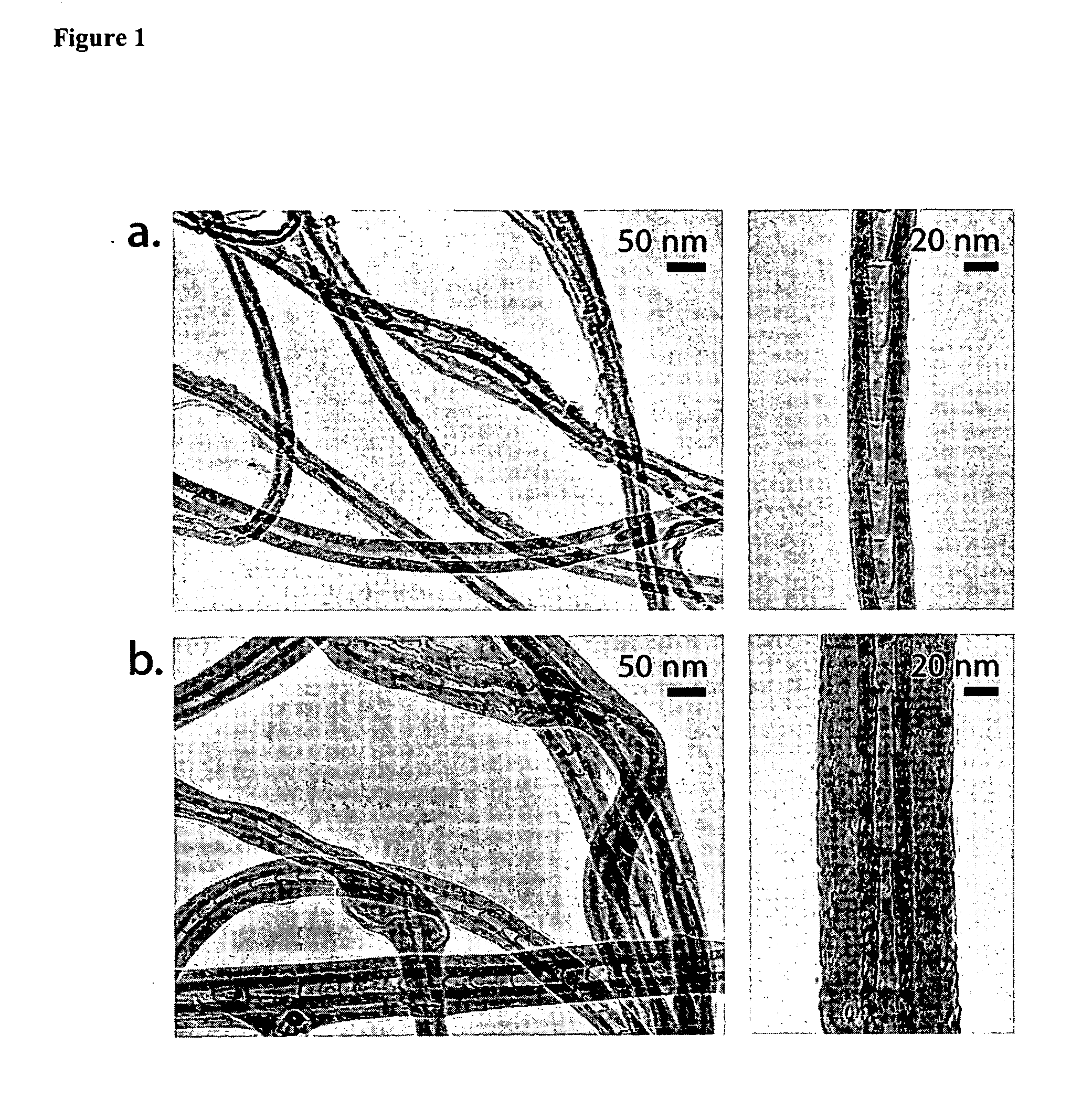
Initiated chemical vapor deposition of vinyl polymers for the encapsulation of particles
ActiveUS20070104860A1Quality improvementClear processPretreated surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseConformal coating
One aspect of the present invention relates to an all-dry encapsulation method that enables well-defined polymers to be applied around particles of sizes down to the nanoscale. In certain embodiments, the methods are modified forms of initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) using a thermally-initiated radical polymerization to create conformal coatings around individual particles while avoiding agglomeration. The present invention also enables the coating of particle surfaces with a range of functional groups via direct incorporation of the functionality into the monomers used or indirectly through a subsequent modification of the surface of a coated particle. In certain embodiments, the method produces high quality functional polymer coatings.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
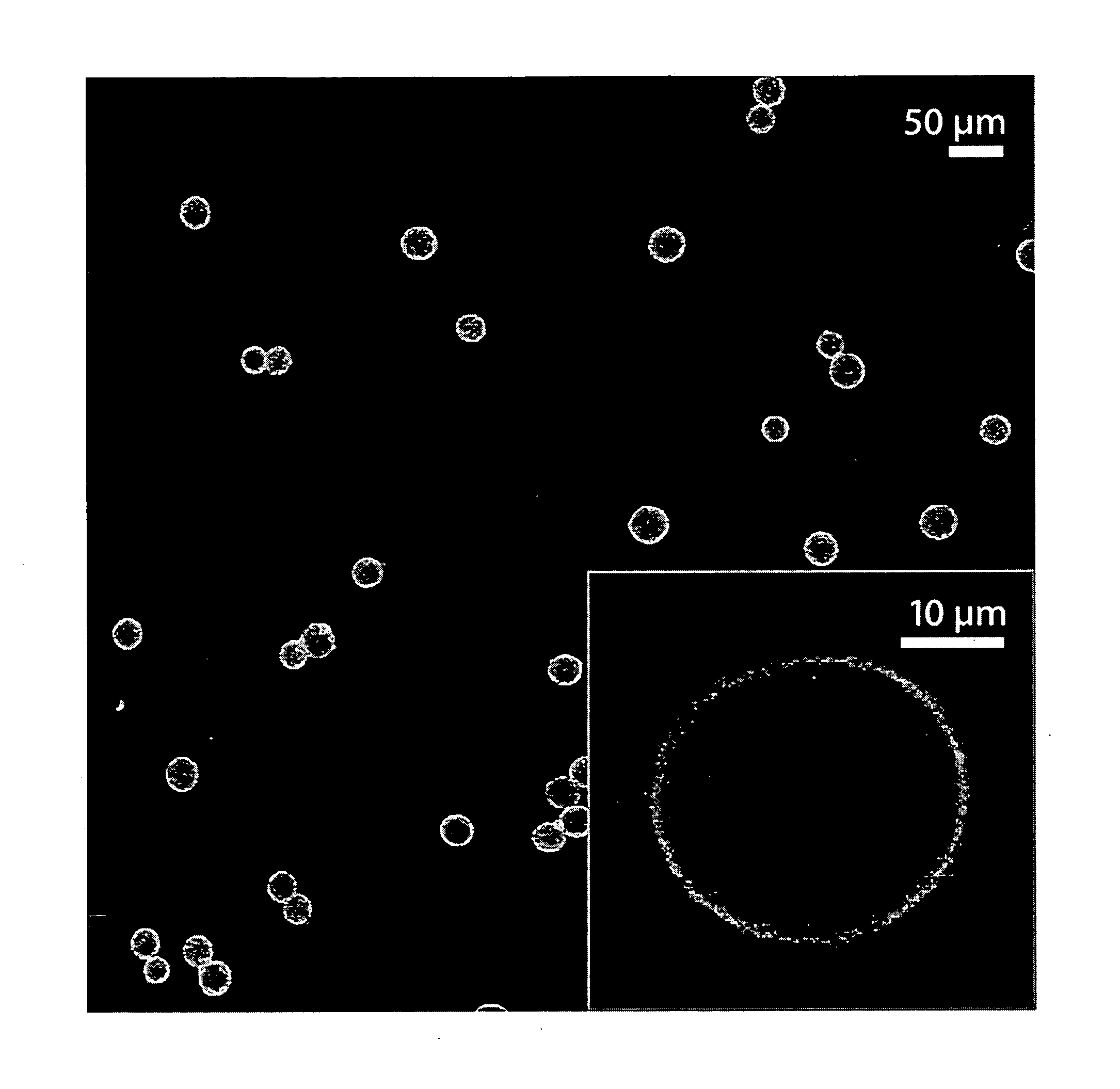
Electrophoretic particle, process for its production, and its use
ActiveUS20050270628A1Improve the display effectGood dispersionStatic indicating devicesMicroballoon preparationPolymer scienceElectrophoresis
An electrophoretic particle including: a pigment particle having an average particle diameter of 1 μm or smaller; and a polymer layer having an average thickness of 1 to 500 nm formed on a surface of the pigment particle, wherein 50% or higher of an entire surface of the pigment particle is coated with the polymer layer. The electrophoretic particle can be produced by radical polymerization using a polymerization initiator in a state where a pigment particle and monomer components are present in a solvent. The electrophoretic particle can be used in a microcapsule and a sheet for electrophoretic display, as well as an electrophoretic display device and an electronic equipment.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Self-repairing polyurethane hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a self-repairing polyurethane hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The polyurethane hydrogel comprises the following components in parts by mass: 10-30 parts of polyisocyanate, 30-50 parts of hydrophilic polyester polyol or hydrophilic polyether polyol, 10-50 parts of acrylamide monomer, 0.5-3 parts of chain extender, 3-10 parts of methacrylic acid functional monomer containing an UPy unit, 0.5-2 parts of catalyst and 0.5-3 parts of photoinitiator. The preparation method comprises the following steps of firstly preparing a hydrophilic polyurethane macromonomer terminated with an acrylic acid monomer and carrying out radical polymerization with the methacrylic acid functional monomer containing the UPy unit under the action of photo-initiation. According to the self-repairing polyurethane hydrogel, the self-repairing of the damage of the polyurethane hydrogel can be completed without need of any repairing agent or specific environmental requirements, the polyurethane hydrogel has the advantages of high repairing efficiency, high mechanical strength and low cost and the repeatedly repairing function can be achieved on the same site.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com