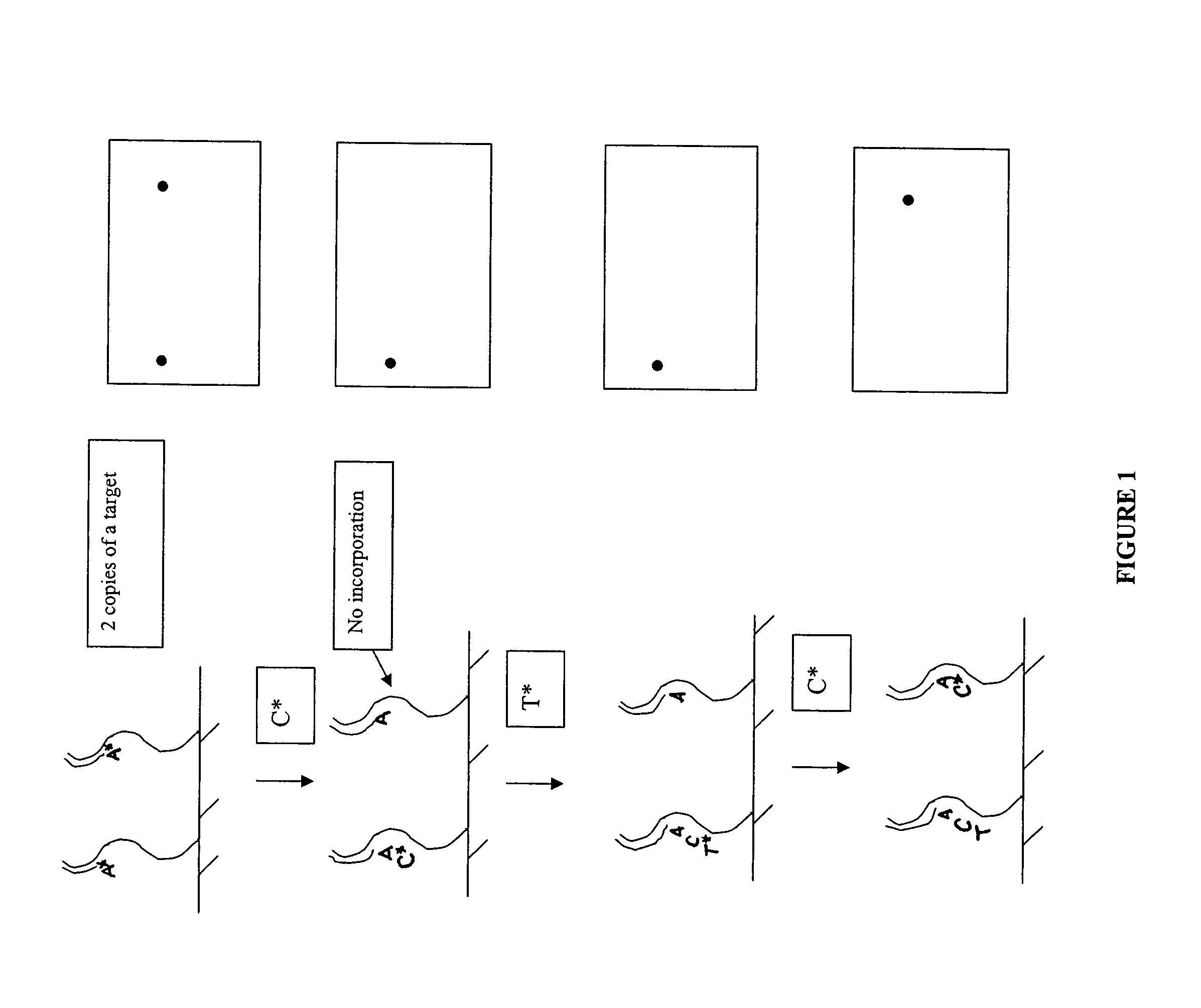
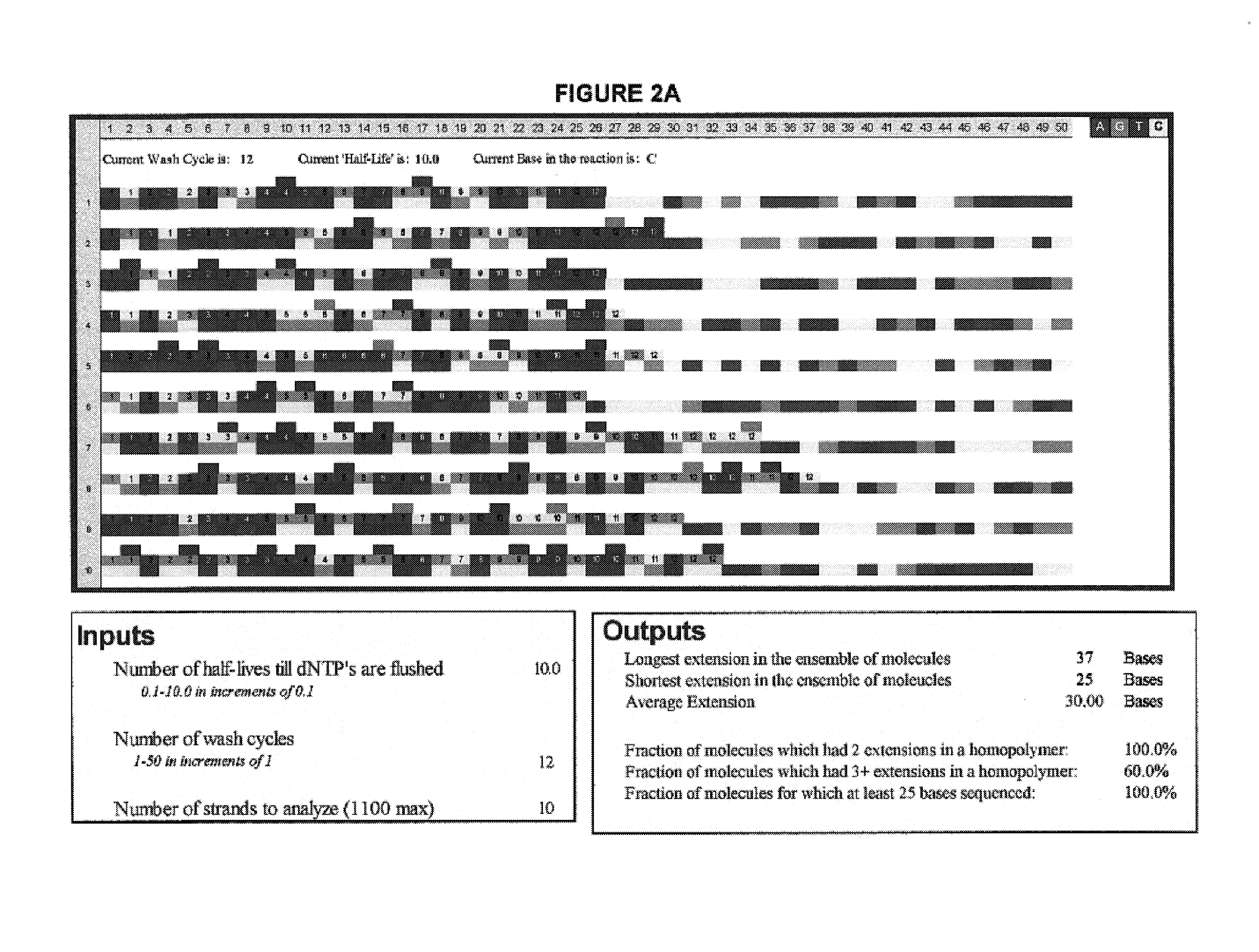
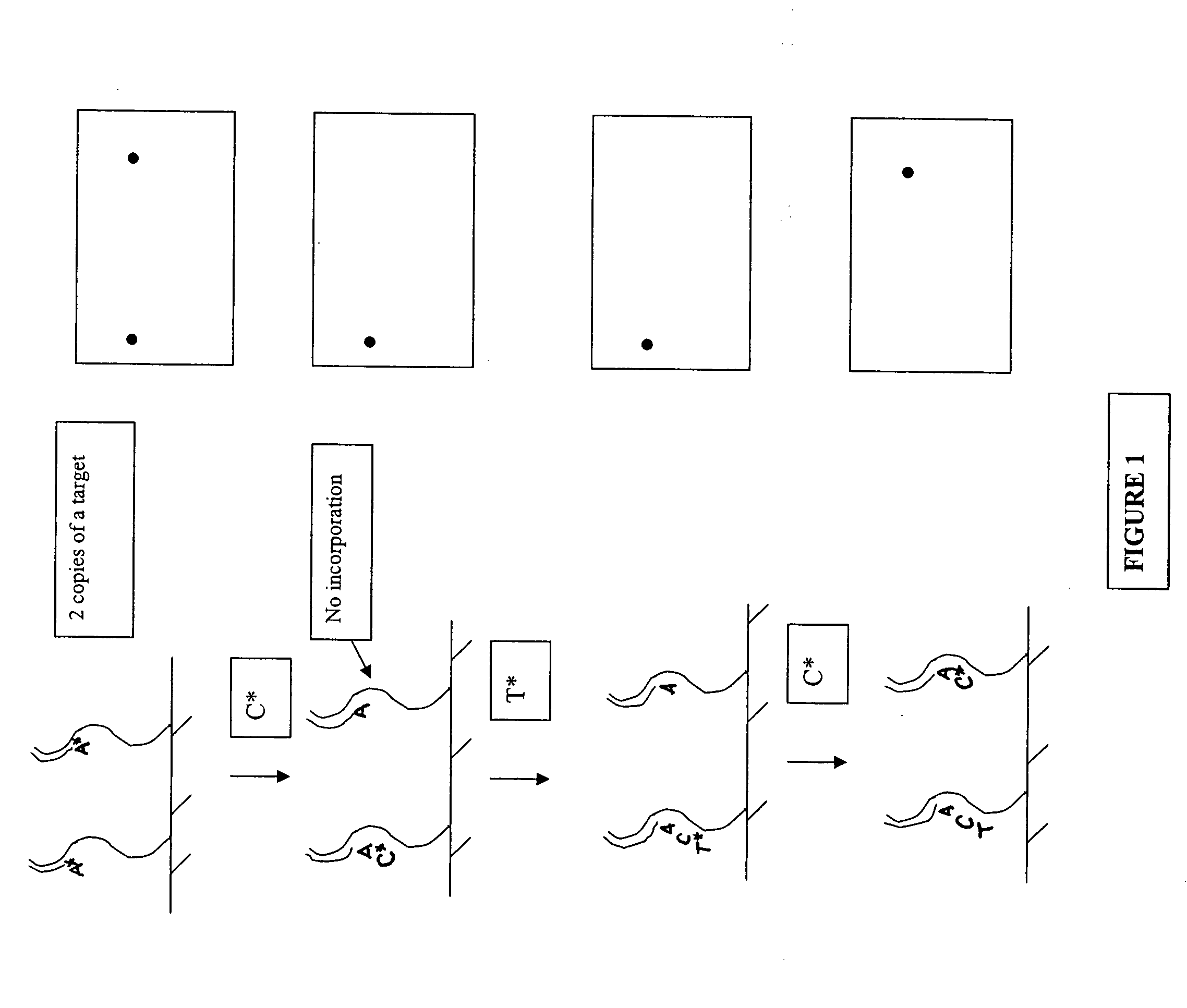
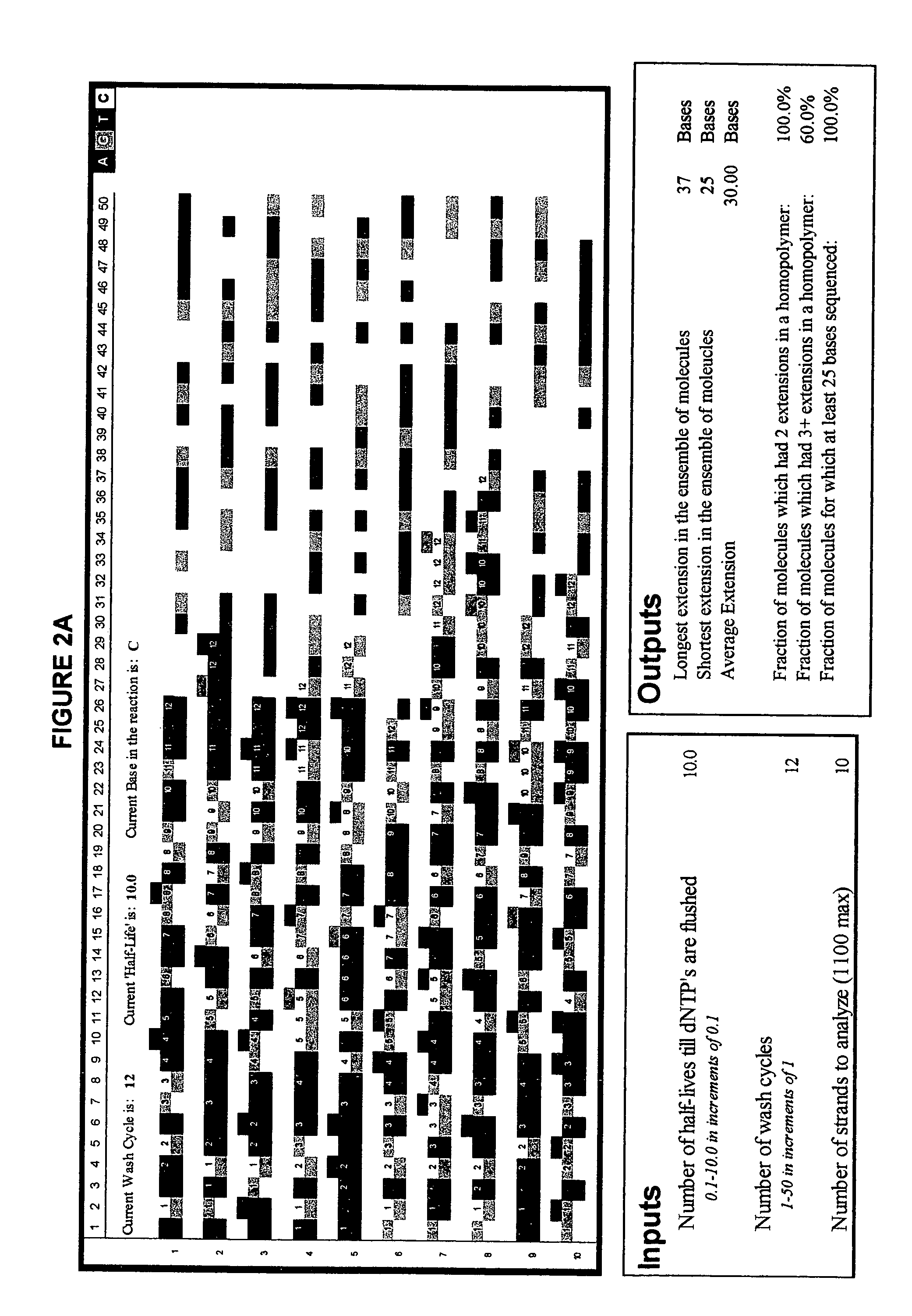
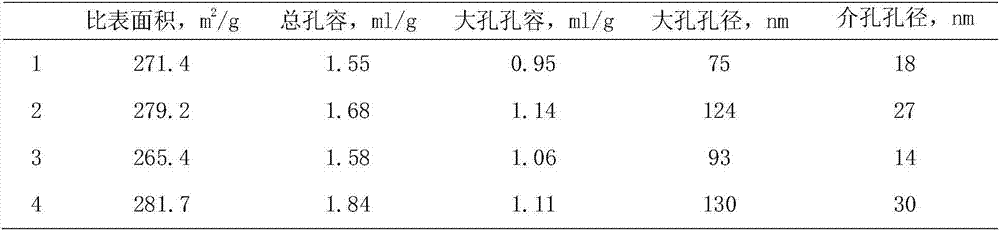
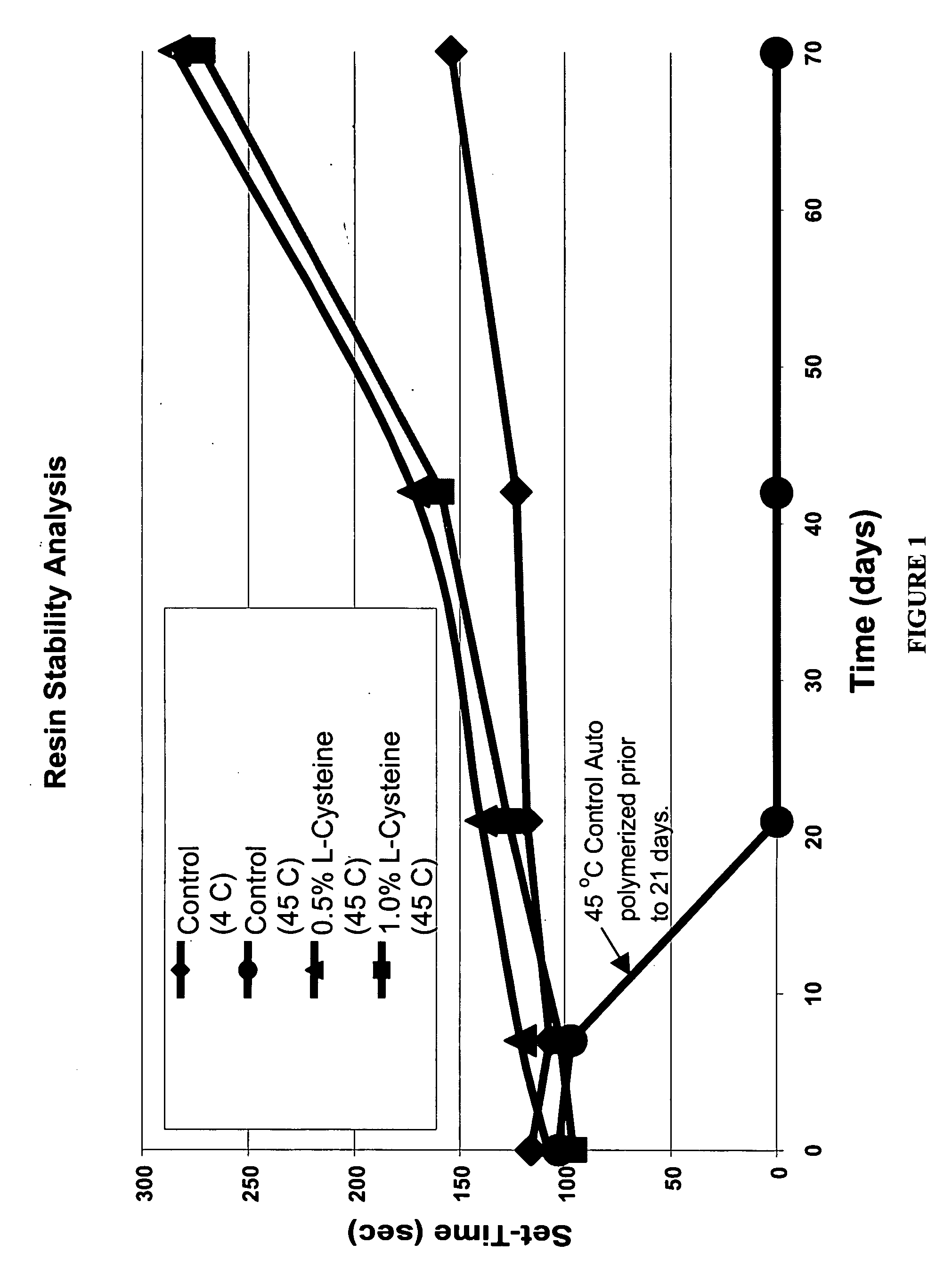
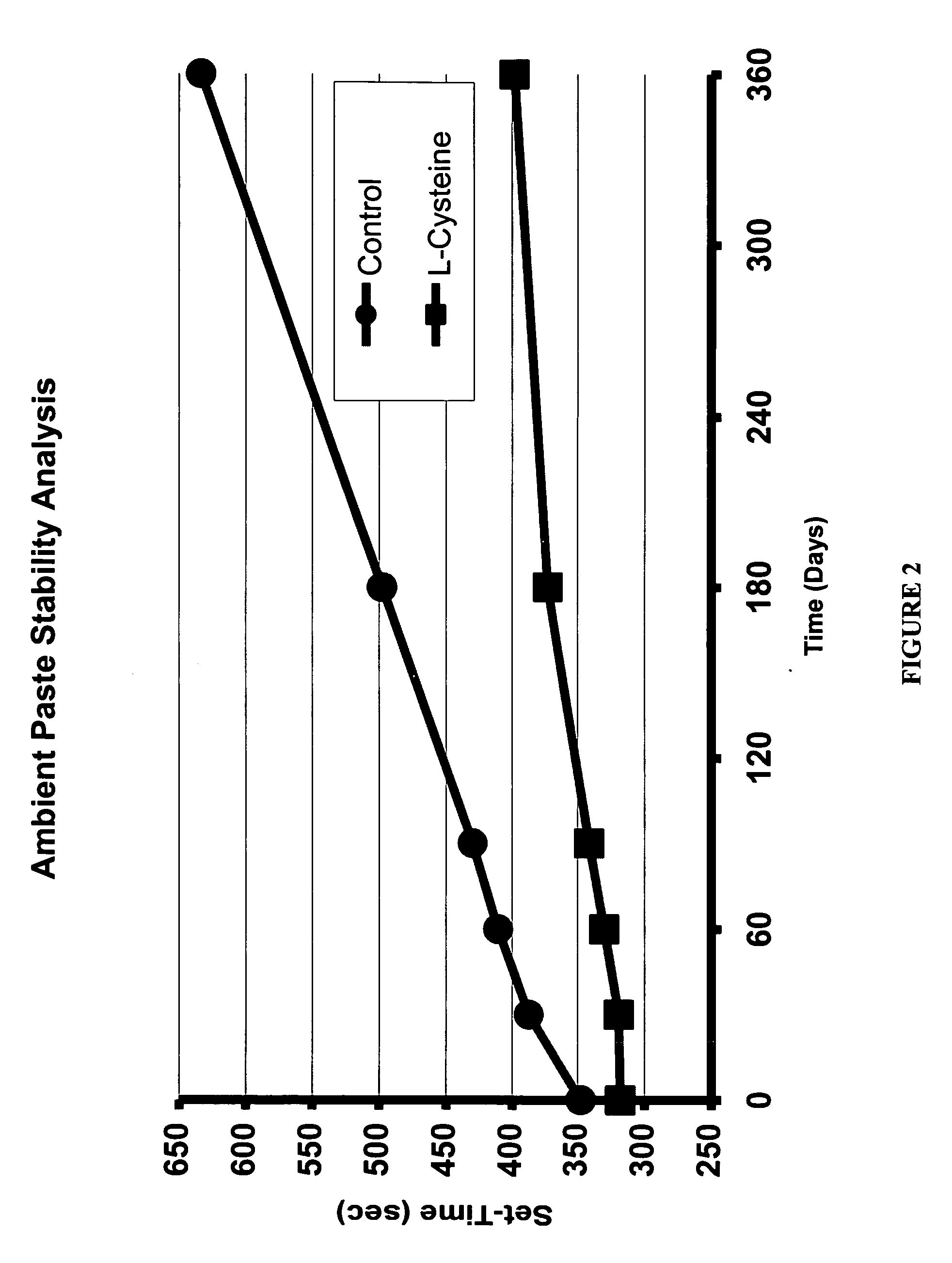
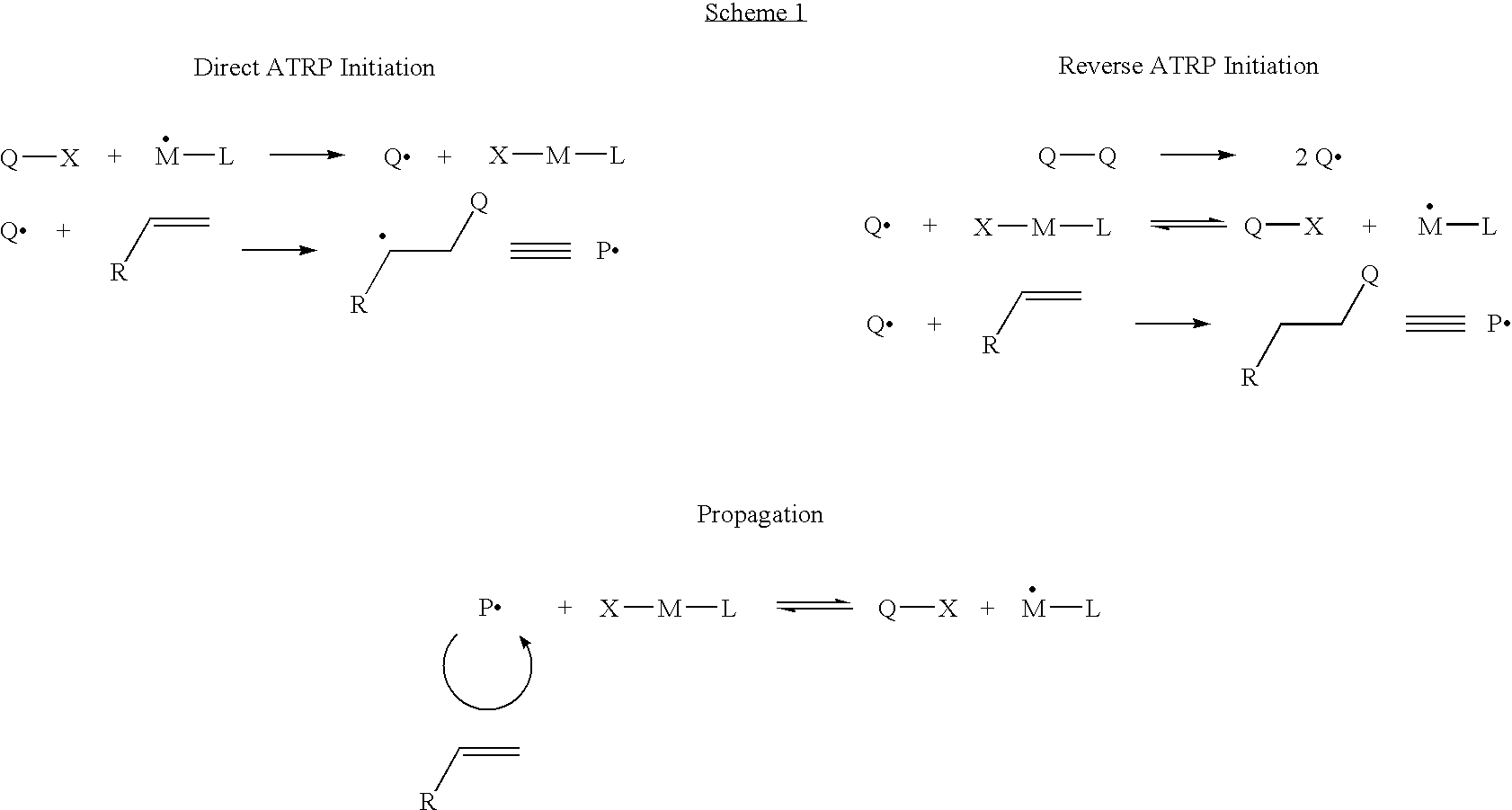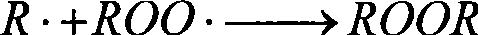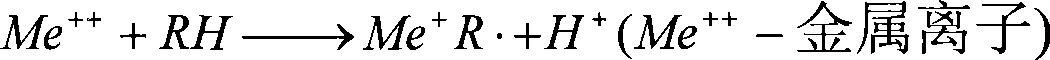Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
413results about How to "Inhibition of polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiation-curable coating compounds
InactiveUS6605669B2Inhibition of polymerizationNo surface defectsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPrinting after-treatmentMeth-Functional monomer
Coating compounds curable by means of high-energy radiation, comprising as binderA) at least one (meth)acrylic copolymer containing olefinic double bonds capable of free-radical polymerization and hydroxyl groups with a C=C equivalent weight from 100 to 10,000 and an OH-value from 20 to 250 mg KOH / g, which is prepared from monomers comprising:A1) at least one olefinically unsaturated, epoxy-functional monomer capable of free-radical polymerization,A2) at least one olefinically unsaturated, carboxy-functional monomer capable of free-radical polymerization andA3) at least one further olefinically unsaturated monomer capable of free-radical polymerization which is different from A1) and A2), andB) at least one component with free isocyanate groups and process for multilayer coating using the coating compounds.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
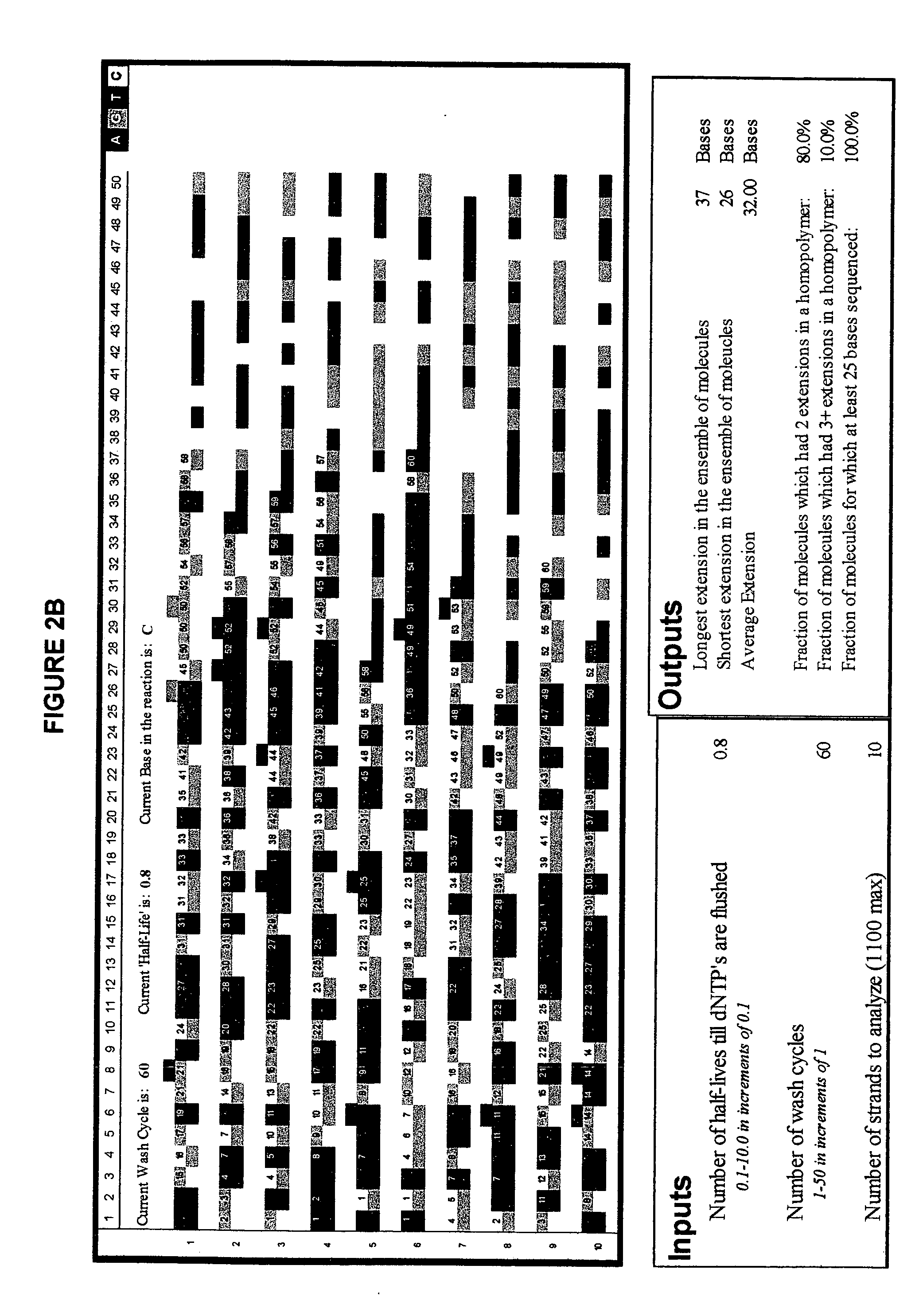
Short cycle methods for sequencing polynucleotides
InactiveUS7169560B2Increase resolution and reliabilityHigh throughput single molecule sequencingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideComputational biology
The invention provides methods for sequencing a polynucleotide comprising stopping an extension cycle in a sequence by synthesis reaction before the reaction has run to near or full completion.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Short cycle methods for sequencing polynucleotides
InactiveUS20050100932A1High throughput single molecule sequencingImprove resolutionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolynucleotideComputational biology
The invention provides methods for sequencing a polynucleotide comprising stopping an extension cycle in a sequence by synthesis reaction before the reaction has run to near or full completion.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
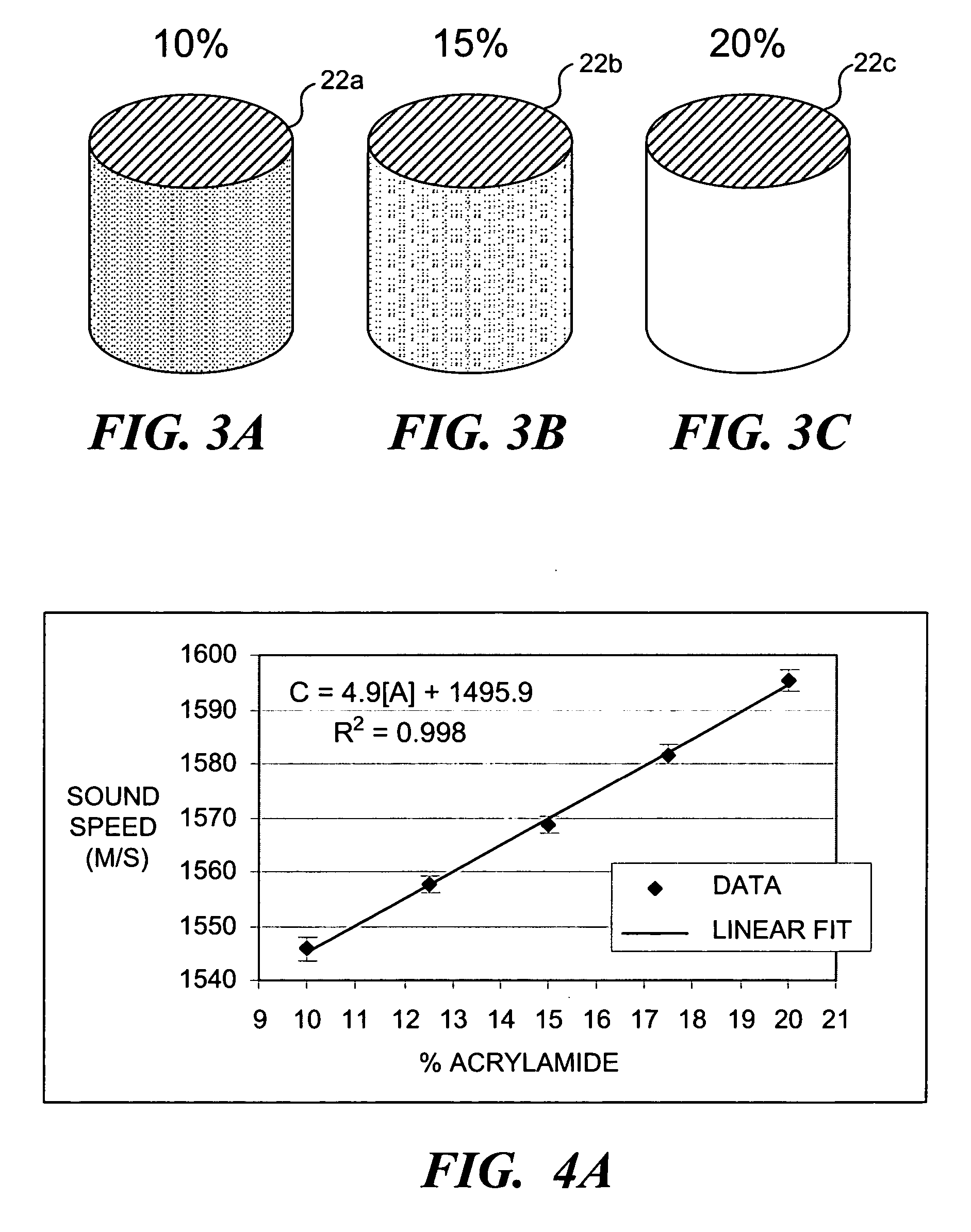
Solid hydrogel coupling for ultrasound imaging and therapy
InactiveUS20060184074A1Easy to useAvoid cloggingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsUltrasound imagingUltrasonic sensor
The present invention employs hydrogels as acoustic couplings for clinical applications of ultrasound imaging and therapy, but is particularly applicable to high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) based therapy. While other materials can be used, it has been determined that polyacrylamide is sufficiently robust and transmissive to withstand the high temperatures encountered in HIFU therapy. One embodiment of a hydrogel coupling is configured in shape and size (length) to ensure that a focal region of an ultrasound transducer is disposed proximate the target area when the distal tip of the transducer is in contact with tissue. These couplings can be shaped to correspond to the beam focus characteristics of specific transducers. Water can be applied to hydrate the tip of the hydrogel coupling during use, and medication absorbed into the hydrogel material can be applied to the tissue in contact with the distal surface of the hydrogel.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Whitening and freckle-removing cream and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106580797AImprove antioxidant capacityEfficient hydrationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlycyrrhiza glabra RootGlycerol
The invention discloses whitening and freckle-removing cream and a preparation method thereof. The whitening and freckle-removing cream comprises water, butanediol, caprylic / capric triglyceride, isohexadecane, glycerol, cyclopentasiloxane, butyrspermum parkii butter, trehalose, cetearyl olivate, sorbitan olivate, cetearyl alcohol, cetearyl glucoside, magnolia sieboldii extract, citrus peel extract, hydrogenated lecithin, phytosterol, bisabolol, tocopheryl acetate, glycyrrhiza glabra root extract, thymus serpyllum extract, panthenol, sodium hyaluronate and the like. The whitening and freckle-removing cream disclosed by the invention can be used for inhibiting tautomerase activity of tyrosinase and dopachrome and hindering polymerization of DHI; the formation of melanin in a body is inhibited, the regeneration capability of pigment cells is improved, the pigment deposition is reduced and pigment cell detachment is promoted; the self-immunity of the cells is enhanced, and the skin elasticity and a metabolism function are improved; and the self-protection capability of skins is improved and the safe whitening and freckle-removing effects are realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KEYING COSMETICS CO LTD
Catalyst for high-selectivity preparation of light aromatic hydrocarbon by using synthesis gas and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106540740AImprove catalytic performanceHigh conversion rate of COHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMolecular sieve
The invention provides a catalyst for high-selectivity preparation of light aromatic hydrocarbon by using synthesis gas and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of catalysts. The catalyst is prepared from, by mass, 20%-60% of modified zeolite molecular sieve and 40%-80% of zirconium-containing composite oxide. The preparation method comprises the steps that the zirconium-containing composite oxide is added to a solvent, and ultrasonic dispersion is performed to obtain a solution A; the modified zeolite molecular sieve is added into the solution A; the mixture obtained after ultrasonic dispersion is subjected to suction filtration, and the obtained filter cake after washing is dried; the sample obtained after drying is grinded into powder; the powdery sample is calcinated, and the obtained sample is the catalyst for high-selectivity preparation of the light aromatic hydrocarbon by using synthesis gas. The light aromatic hydrocarbon can be prepared in a high-selectivity mode, and the stability is good. The preparation method of the catalyst for high-selectivity preparation of the light aromatic hydrocarbon by using the synthesis gas is simple and low in cost and has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing microcapsule by miniemulsion polymerization
InactiveUS20060281834A1Improve stabilityLow viscosityCoatingsMicroballoon preparationPolymer scienceSingle-core
Provided is a method for preparing uniformly sized and shaped, mono-dispersed microcapsules using miniemulsion polymerization. In microcapsules prepared by the method, a liquid or solid core encapsulated by a polymer shell has 10 to 80% by volume of the microcapsules. Since miniemulsion particles produced at an early stage of the method are stable, an organic material which is well dissolved in monomer particles and has a higher interfacial tension with water, relative to the polymer shell, can be uniformly positioned in polymer particles. Furthermore, when a crosslinking agent is added during the polymerization, single-core microcapsules can be obtained. In addition, use of an oil-soluble initiator can prevent formation of secondary particles and addition of a secondary initiator during the polymerization can increase the yield of the uniformly sized and shaped microcapsules.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Ink container and method of storing ink
ActiveUS20070229612A1Excellent stabilityPrevent polymerizationMeasurement apparatus componentsInksEngineeringAir liquid interface
There is provided a method of storing a light-curable ink composition. Air and the light-curable ink composition are introduced into a container. The distance from an air-liquid interface to a bottom portion of the container is equal to or less than 5 cm. The amount of oxygen dissolved in the light-curable ink composition is maintained so as to be equal to or more than 3 ppm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
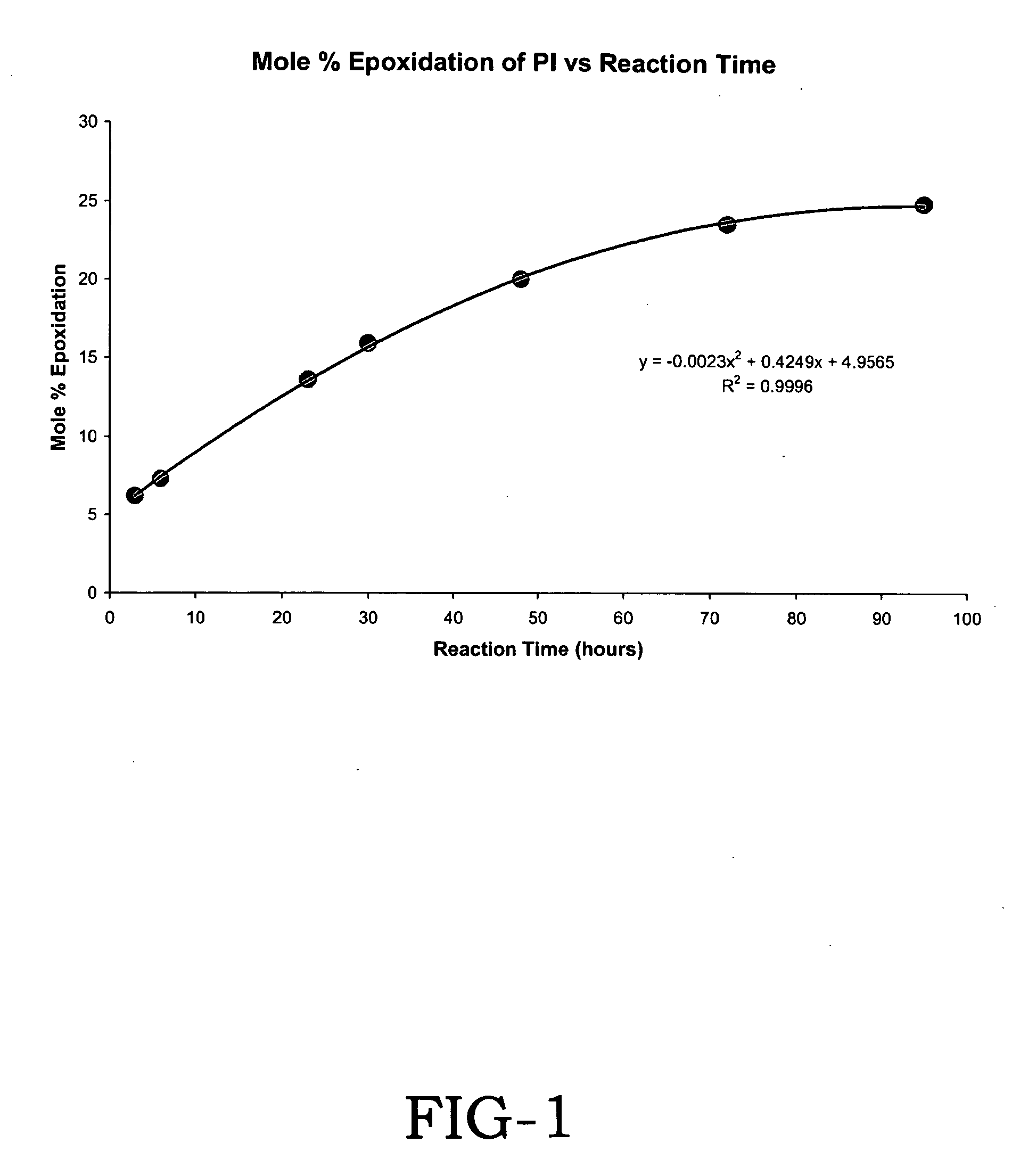
Hydrogenation and epoxidation of polymers made by controlled polymerization
InactiveUS20050256253A1Simple and versatile and highly effectiveInhibition of polymerizationGranular deliveryPolymer sciencePolymer adhesive
The present invention discloses a process for synthesizing a hydrogenated polymer that comprises: (1) preparing a aqueous polymerization medium which is comprised of (a) at least one monomer, (b) a polymerization control agent, and an emulsifier, wherein the emulsifier is prepared in-situ within the aqueous polymerization medium; (2) initiating polymerization of said monomer within the aqueous polymerization medium to produce a latex of an unsaturated polymer; (3) treating the latex of the unsaturated polymer with (a) an oxidant selected from the group consisting of oxygen, air and hydroperoxides; (b) a reducing agent selected from the group consisting of hydrazine and hydrates of hydrazine; and (c) a metal ion activator to produce the hydrogenated polymer. The present invention further discloses a process for synthesizing a hydrogenated polymer that comprises: (1) preparing a monomer solution which is comprised of (a) at least one monomer, (b) a conjugate acid of a surfactant with a pKa of less than about 14, and (c) a controlled free radical polymerization agent; (2) preparing an aqueous medium which is comprised of (a) water, and (b) a conjugate base of a weak acid wherein the pKb of the base is less than about 14; and (3) mixing the monomer solution with the aqueous medium under conditions that result in the in-situ formation of an emulsifier; (4) initiating free radical polymerization to produce a latex of an unsaturated polymer; and (5) treating the latex of the unsaturated polymer with (a) an oxidant selected from the group consisting of oxygen, air and hydroperoxides; (b) a reducing agent selected from the group consisting of hydrazine and hydrates of hydrazine; and (c) a metal ion activator to produce the hydrogenated polymer.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Process for inhibiting a polymerization in a vacuum section of an easily polymerizable compound purification system
InactiveUS6878239B1Inhibition of polymerizationImprove purification effectOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationMeth-Product gas
A process for inhibiting a polymerization of an easily polymerizable compound purification system is disclosed.According to the present invention, the polymerization of the easily polymerizable compound such as (meth)acrylic acid and (meth)acrylate flowed into a vacuum section can be inhibited by contacting a liquid containing a polymerization inhibitor with the compound directly in the vacuum section.When the vacuum section includes a gas and liquid contact chamber (usually a condenser), the liquid containing a polymerization inhibitor may be supplied to the chamber. When the vacuum section includes a liquid ejector and / or a nash pump as a vacuuming device, the liquid containing a polymerization inhibitor may be circulated by the liquid ejector and / or the nash pump for reducing a pressure of a purifying section. Examples of easily polymerizable compounds are (meth)acrylic acid and (meth)acrylates. The process of the invention is capable of inhibiting the polymerization of the easily polymerizable compound such as (meth)acrylic acid and (meth)acrylate in a vacuum section of a purifying system. The system of the invention is suitable for purifying the easily polymerizable compound.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Supported platinum group catalyst applied to propane dehydrogenation propylene preparation and preparation method of supported platinum group catalyst
InactiveCN105251486AImprove thermal stabilityImprove stabilityHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a supported platinum group catalyst applied to propane dehydrogenation propylene preparation and a preparation method of the supported platinum group catalyst and relates to propylene. The catalyst is prepared from PtSnN2 / N1-Al2O3, wherein N1 is selected from rare earth metals of La and Ce, and N2 is selected from alkali metals of Cs, K and Na. The catalyst is prepared from, by mass, 0.1%-0.5% of Pt, 0.2%-1.0% of Sn, 0.5%-6% of N1, 0.5%-5% of N and the balance Al2O3. The preparation method includes the steps that a cerous nitrate solution or a lanthanum nitrate solution containing the N1 component is added in the preparation process or forming process of an alumina precursor, and a modified carrier of the propane dehydrogenation propylene preparation catalyst is prepared after drying and calcination; Pt and Sn are co-steeped or steeped on the carrier step by step, the catalyst precursor PtSn / N1-Al2O3 is obtained after drying and calcination and then steeped in an N2 component solution, and the catalyst is prepared after drying and calcination.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Protection of fragrance in a wax candle using an antioxidant
InactiveUS20040031191A1Outstanding propertyProtects the candle from fragrance discolorationSolid fuelsCandle ingredientsParaffin waxFlavor
Disclosed is a fragranced wax candle and fragranced wax composition comprising paraffin wax, a fragrance containing an antioxidant, with or without vegetable wax and / or beeswax, saturated fatty acid, hindered amine, and an additive. Also disclosed is a method for incorporating an antioxidant into the fragranced candle wax composition.
Owner:SCENT2MARKET
Process for manufacturing an intraocular lens with an embedded mask
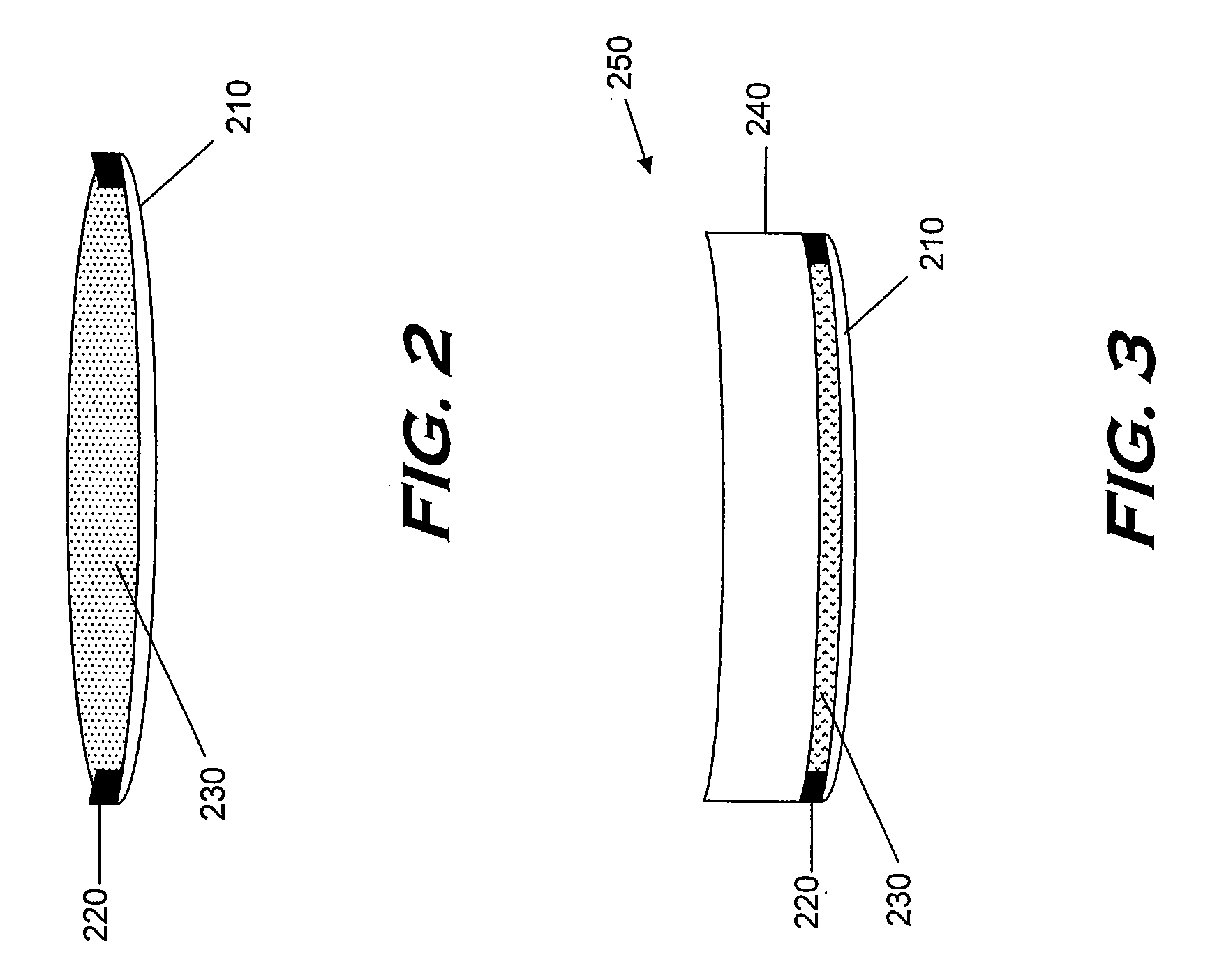
ActiveUS20140264981A1Inhibition of polymerizationOptical articlesAuxillary shaping apparatusIntraocular lensMedicine
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implant can include a mask adapted to increase depth of focus. The method of manufacturing the implant can include positioning the mask with an aperture on a protruding pin of a positioning mold portion. The protruding pin can be configured to center the mask in the intraocular lens.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
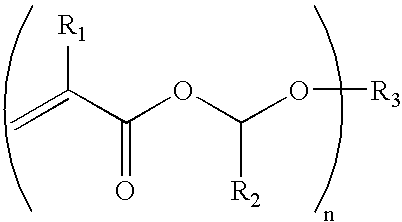
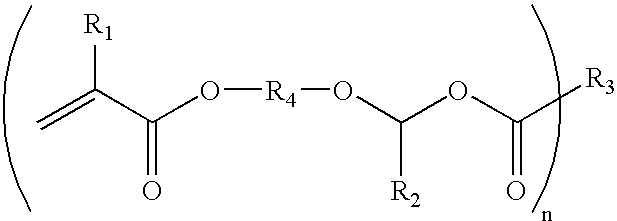
Multi-functional alpha-alkoxyalkyl acrylate and methacrylate ester compositions and reworkable polymers formed therefrom
InactiveUS20050101689A1Easy and less-expensive to prepareEasy to degradeOptical articlesCoatingsMethacrylatePolymer science
Adhesive compositions are disclosed which include acrylates, their polymers, and free radical initiators. The compositions include a multi-functional alpha-alkoxyalkyl(meth)acrylate compound and a free radical initiator. The multi-functional alpha-alkoxyalkyl(meth)acrylate compound is the reaction product of: (a) a (meth)acrylic acid or a (meth)acrylate ester having a free carboxylic acid group; and (b) a compound including two or more 1-alkenyl ether groups and free of acetal and ketal groups, or a compound free of acetal and ketal groups and including one or more 1-alkenyl ether groups and a (meth)acrylate group. The compositions are easier and less expensive to prepare than conventional acrylate compositions and degrade when contacted with an acid medium or when heated. The compositions are useful in a wide range of applications and are compatible with conventional adhesive additives.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
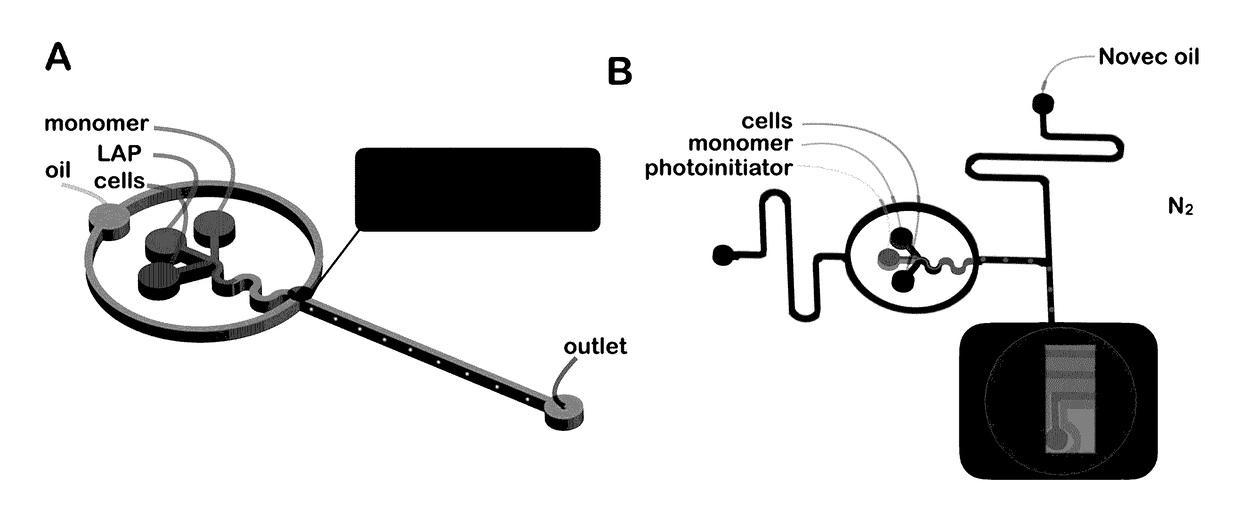
Methods of Generating Microparticles and Porous Hydrogels Using Microfluidics
PendingUS20170145169A1Ability to control the amount of oxygen presentInhibition of polymerizationFlow mixersTransportation and packagingMicrofluidicsAqueous droplet
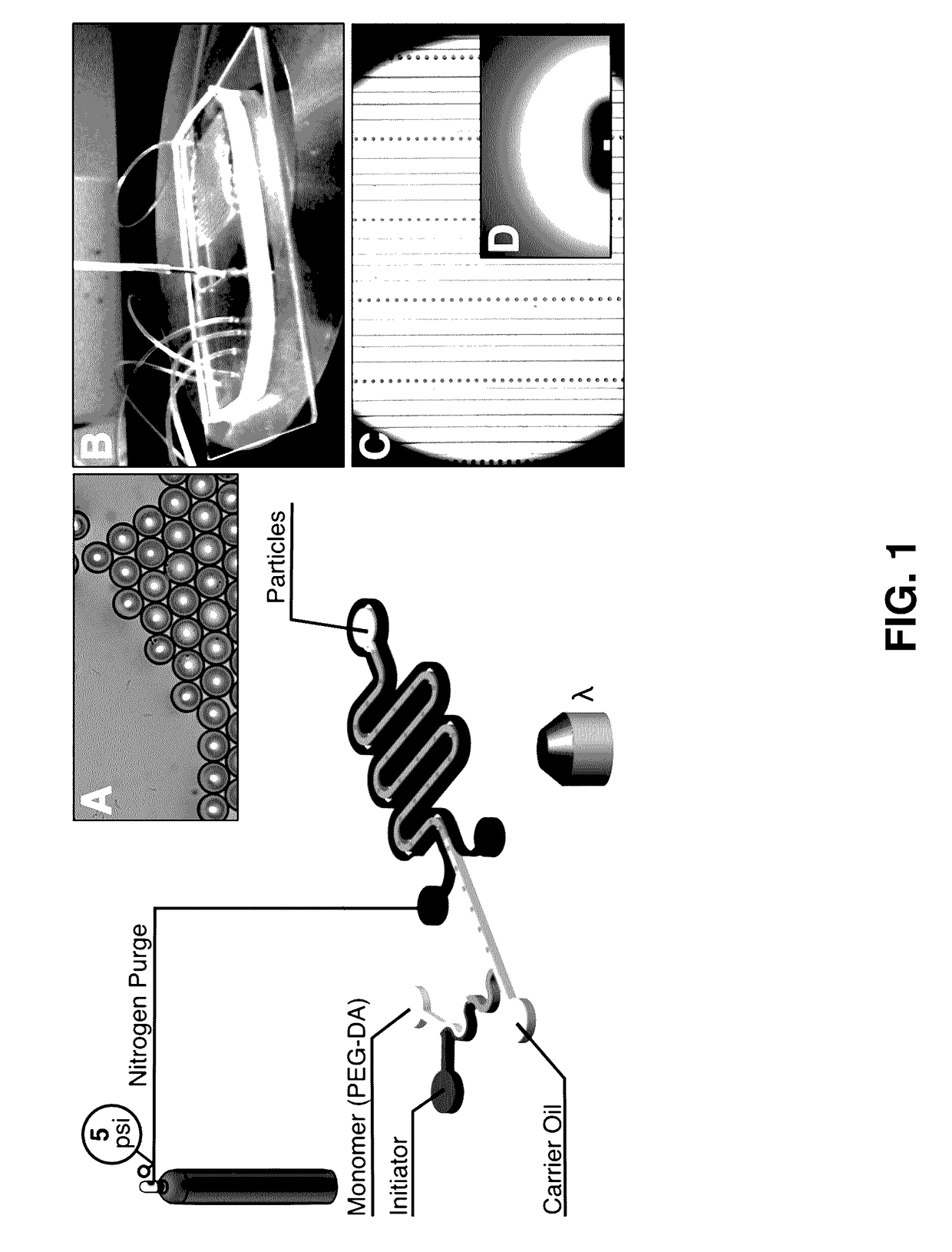
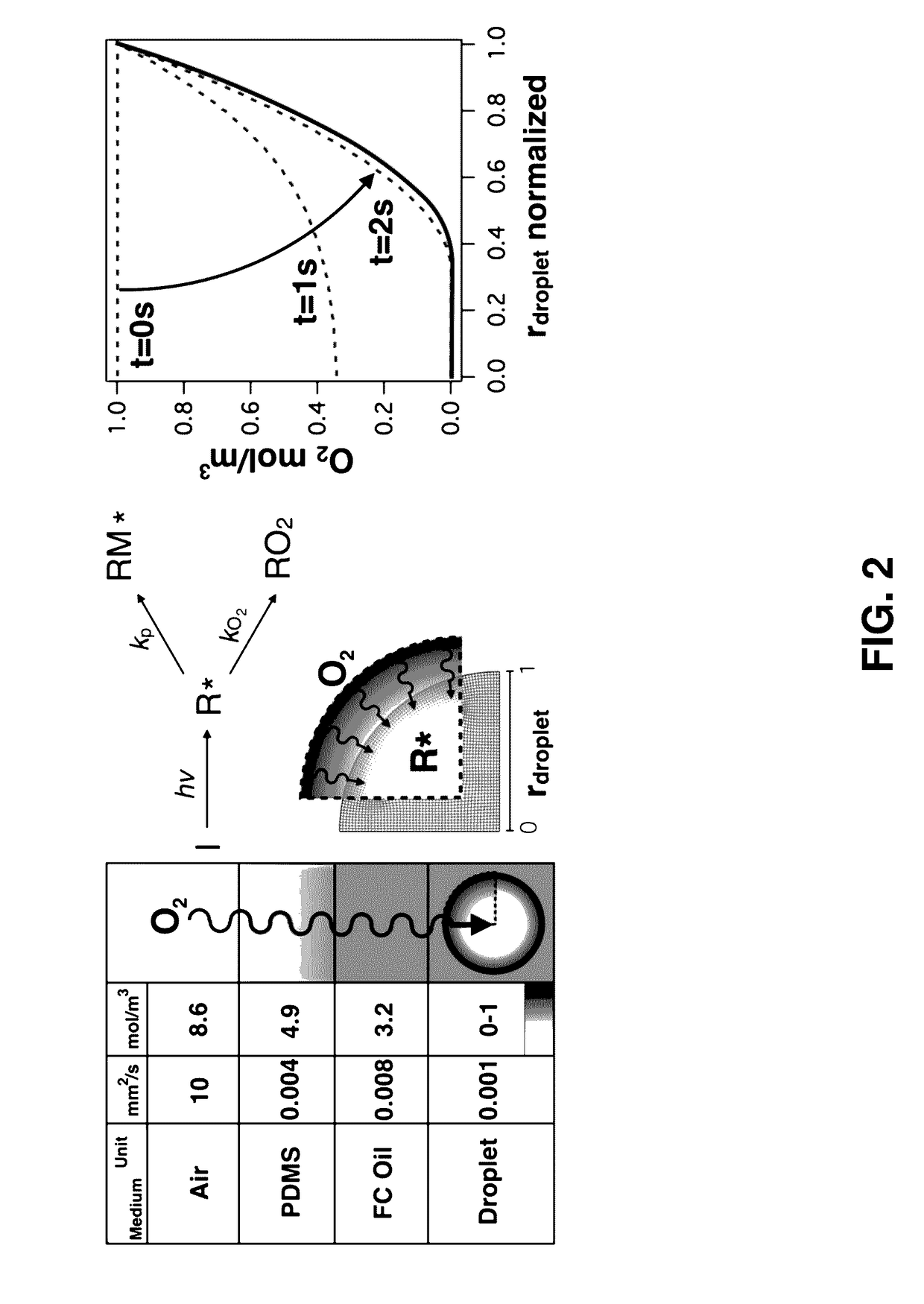
Provided herein are methods utilizing microfluidics for the oxygen-controlled generation of microparticles and hydrogels having controlled microparticle sizes and size distributions and products from provided methods. The included methods provide the generation of microparticles by polymerizing an aqueous solution dispersed in a non-aqueous continuous phase in an oxygen-controlled environment. The process allows for control of size of the size of the aqueous droplets and, thus, control of the size of the generated microparticles which may be used in biological applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Monomers and polymers for optical elements
ActiveUS20080068723A1Inhibition of polymerizationSpectales/gogglesSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxyPolyester
An optical element includes a first lens; a cover; and a cured matrix polymer sandwiched between the first lens and the cover; the matrix polymer, prior to curing, having a monomer mixture dispersed therein; the matrix polymer being selected from the group consisting of polyester, polystyrene, polyacrylate, thiol-cured epoxy polymer, thiol-cured isocyanate polymer, and mixtures thereof; and the monomer mixture comprising a thiol monomer and at least one second monomer selected from the group consisting of ene monomer and yne monomer.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Controlled polymerization
InactiveUS6992156B2Simple and versatile and highly effectiveInhibition of polymerizationSpecial tyresPolymer scienceActive agent
The present invention discloses an emulsion polymerization process that comprises: (1) preparing an aqueous polymerization medium which is comprised of (a) at least one monomer, (b) a polymerization control agent, and an emulsifier, wherein the emulsifier is prepared in-situ within the aqueous polymerization medium; and (2) initiating polymerization of said monomer within the aqueous polymerization medium. The subject invention more specifically reveals an emulsion polymerization process that comprises: (1) preparing a monomer solution which is comprised of (a) at least one monomer, (b) a conjugate acid of a surfactant with a pKa of less than 14, and (c) a controlled free radical polymerization agent; (2) preparing an aqueous medium which is comprised of (a) water, and (b) a conjugate base of a weak acid wherein the pKb of the base is less than 14; and (3) mixing the monomer solution with the aqueous medium under conditions that result in the in-situ formation of an emulsifier, and (4) initiating free radical polymerization.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Dental illumination device and method
InactiveUS20080002402A1Reduce light intensityGuaranteed to workPhotometrySurgeryLight equipmentMedicine
A dental illumination device is provided that comprises a plurality of light-emitting diodes capable of emitting light of selected wavelengths that do not activate initiator molecules contained within dental restorative material such as dental composite, or at an intensity which is insufficient to initiate substantial polymerization of the dental restorative material. Typically, the dental illumination device produces light having wavelengths not in a range selected from 400 nm to 500 nm, 350 nm to 470 nm and below 350 nm to 420 nm. The dental illumination device may further comprise a switch that allows the aforementioned wavelengths to be switched off or reduced in intensity as required. The dental illumination device may operate as a stand-alone unit or may be fitted to an existing dental light.
Owner:TOPSTORE
Anti-tartar detersive for quenching oil column of ethylene unit
ActiveCN101445749AImprove bindingInhibition of polymerizationHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsPhenolic antioxidantRoom temperature
The invention relates to an anti-tartar detersive for a quenching oil column of an ethylene unit. In order to solve the problems of the anti-tartar and cleaning of the quenching oil column, the invention provides the anti-tartar detersive for the quenching oil column. The anti-tartar detersive can inhibit the generation of dirt from the source; meanwhile, the detersive can also eliminate the generated dirt in the quenching oil column on line, thus providing necessary conditions for the long period operation of the ethylene unit. The anti-tartar detersive for the quenching oil column of the ethylene unit of the invention is characterized in that according to weight percentage, phenolic antioxidant is 1-18%, phosphorus metal ion deactivator is 8-20%, amine inhibitive substance is 5-35%, thiazolinyl succinimide dispersant is 2-18%, solvent is 30-70%; the substances are put into a container for heating, stirred and mixed evenly and cooled to room temperature, and then filtered to obtain the product.
Owner:浙江杭化科技股份有限公司
Self-healing dental composites and related methods
ActiveUS20080300340A1Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsIncrease polymerization rateImpression capsDentistry preparationsSelf-healingMicrosphere
Dental restorative composites having self-healing capabilities to repair discontinuities in the composite are provided. Dental restorative composites according to the present invention include a microsphere that encapsulates a monomer. When a fracture occurs, the microsphere is ruptured and the monomer fills the fracture. Depending on the monomer present in the microsphere, it is polymerized by a polymerization initiator or by an olefin metathesis catalyst present in the dental restorative composite. Self-healing dental restorative composites provide increased resistance to fracturing, and thus remain substantially intact for a longer period of time, preserving the remedial integrity of the dental repair or reconstruction.
Owner:PREMIER DENTAL PRODS
Method for selective hydrogenation through cracking of C5-C9 distillate
InactiveCN107159283AAperture size adjustableGood adhesive performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsRefining by selective hydrogenationPtru catalystHydrogenation reaction
The present invention relates to a method for selective hydrogenation through cracking of a C5-C9 distillate. According to the method, the catalyst comprises an alumina carrier having a macroporous structure and metal active components comprising nickel and tungsten and supported on the carrier, the nickel oxide content is 12-22 wt% based on the total weight of the catalyst, the tungsten oxide is 1.5-8 wt% based on the total weight of the catalyst, and the hydrogenation reaction process conditions are that the reaction inlet temperature is 40-55 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 2.0-3.5 MPa, the hydrogen oil volume ratio is 60-150, and the liquid volume space velocity is 3.0-5.5 h<-1>. According to the present invention, the catalyst has characteristics of good glue capacity, strong arsenic resistance, strong sulfur resistance, strong coking inhibition and low temperature activity; and the method provides strong adaptability for the cracking gasoline raw materials having different arsenic contents and different sulfur contents.
Owner:QINZHOU UNIV
Silicon-based negative electrode material with multi-buffer structure, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107623104AInhibition of polymerizationInhibit flakingCell electrodesElectrolytic agentMaterials processing
The invention relates to a silicon-based negative electrode material with a multi-buffer structure, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of material processing. According to the silicon-based negative electrode material provided by the invention, a nanometer titanium dioxide layer is coated on the surface of nanometer silicon powder, the stable structure of the nanometer titanium dioxide is used as a buffer layer of volume change of silicon particles in a lithium embedding and removing process to successfully inhibit the polymerization and peeling of the siliconparticles, and the electrochemical performance of the electrode material is also improved, then an amorphous carbon layer is coated to prepare a silicon-based electrode material with a double-layer coating structure, the volume expansion of the core of the activated silica is effectively buffered by the double-layer coating structure in a charge and discharge process, the stability of an electrode / electrolyte interface and a surface SEI film is maintained, and thus the composite material exhibits good cycle performance.
Owner:常州市宇科不绣钢有限公司
Stabilizers for polymerizable biocompatible materials
InactiveUS20050203217A1Easy to processIncrease flexibilityImpression capsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsOrganic chemistryAmino acid
The present invention provides polymerizable biocompatible materials stabilized by amino acids or reducing salts to improve shelf life. Methods of stabilizing a polymerizable biocompatible material are also provided that inhibit auto polmerization of the material over time.
Owner:ORTHOVITA INC
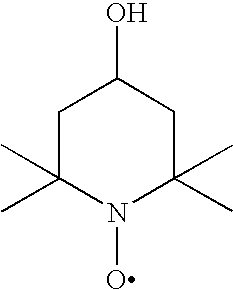
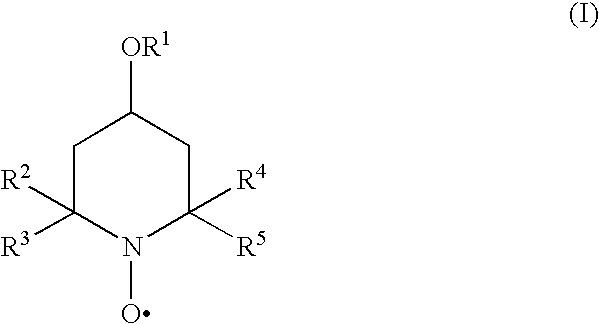
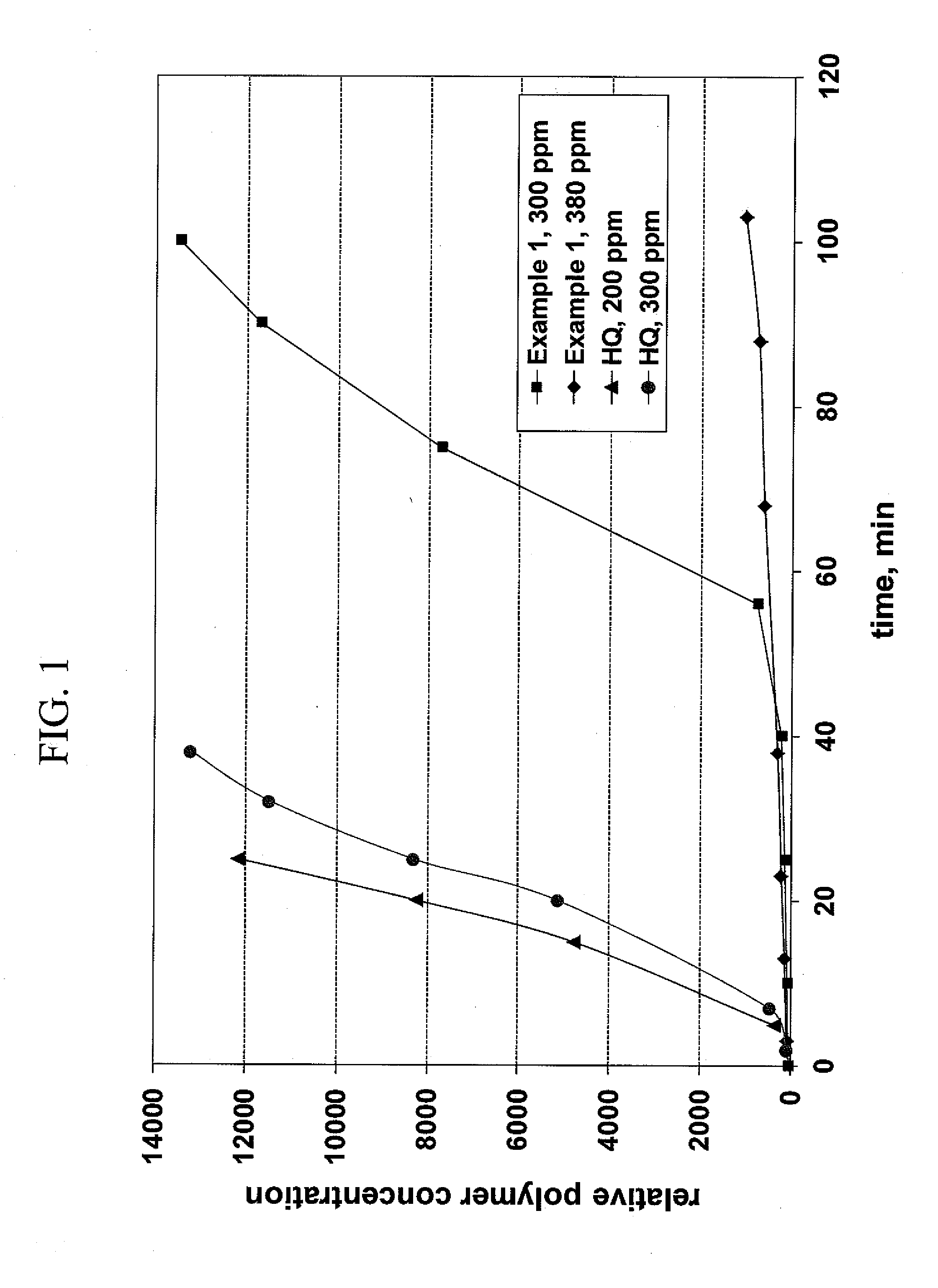
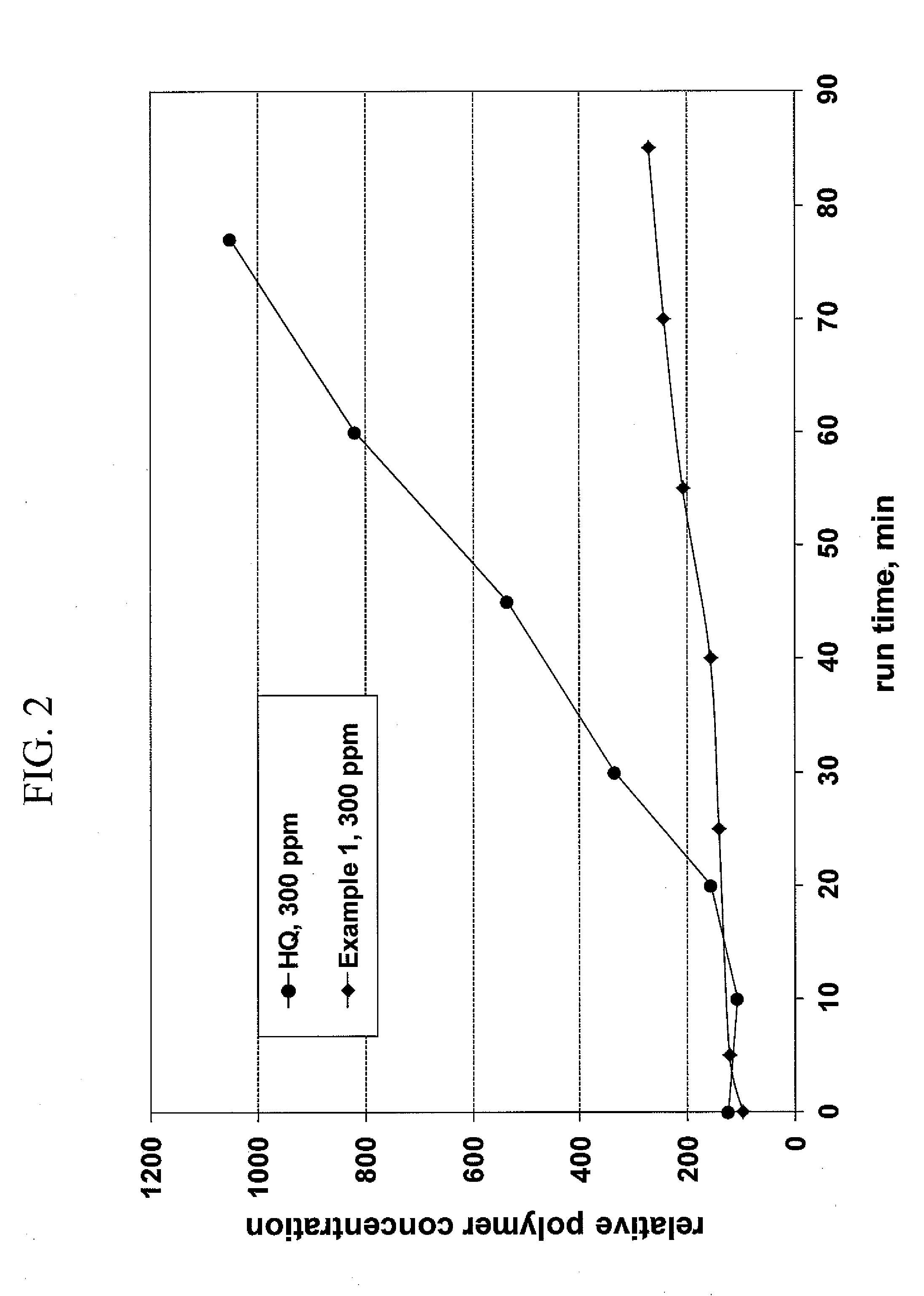
Inhibition of polymerisation
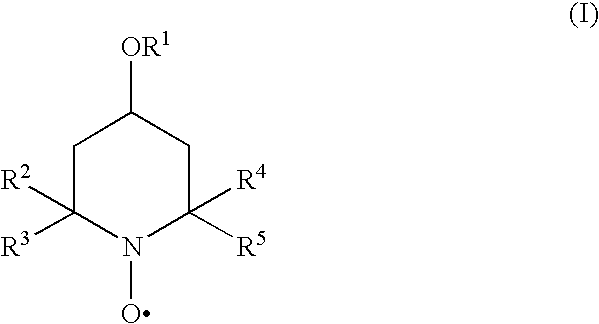
InactiveUS20100168434A1Inhibition of polymerizationGood miscibilityOrganic compound preparationOther chemical processesUnsaturated monomerChemistry
The present invention provides methods and compositions for inhibiting polymerisation of ethylenically unsaturated monomers, which involve the use of nitroxide compound of formula (I):whereinR1 is C4-20 hydrocarbyl; andR2, R3, R4 and R5 are independently each C1-6 alkyl.
Owner:NUFARM LTD
Extraction distillation solvent
ActiveCN1962013AImprove relative volatilityEasy to separateDistillation purification/separationExtractive distillationSolventBoiling point
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Dental adhesive compositions and methods
InactiveUS20070299157A1Good adhesionIncreased durabilityImpression capsDentistry preparationsEtchingDental Adhesives
Owner:SANG JUNJIE +2
Multi-component polymerization inhibitors for ethylenically unsaturated monomers
ActiveUS20120203020A1Inhibition of polymerizationOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationArylHydroxylamine
The invention provides a composition and a method of using the composition for inhibiting the unwanted polymerization of ethylenically unsaturated monomers. The composition is prepared by reducing a nitroxide stable free radical to its corresponding hydroxylamine through reaction with a dialkyl / aryl hydroxylamine and subsequent addition of a polymerization prevention component selected from phenolic antioxidants, phenylenediamine and phenylenediamine derivatives, or phenothiazine and phenothiazine derivatives targeted towards ethylenically unsaturated monomers. The conversion of the nitroxide by the dialkyl / aryl hydroxylamine is to prevent it or the polymerization prevention component from being “spent” by reaction with each other, impurities or any other incompatible components. This allows previously incompatible combinations to now work effectively. In fact, the combination is more efficacious as the combination exerts a synergy due to the presence of various polymerization prevention reagents. The composition is a synergistic combination of various polymerization inhibition compounds for the inhibition of the unwanted polymerization of ethylenically unsaturated monomers.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Peptides for binding fibrinogen and fibrin
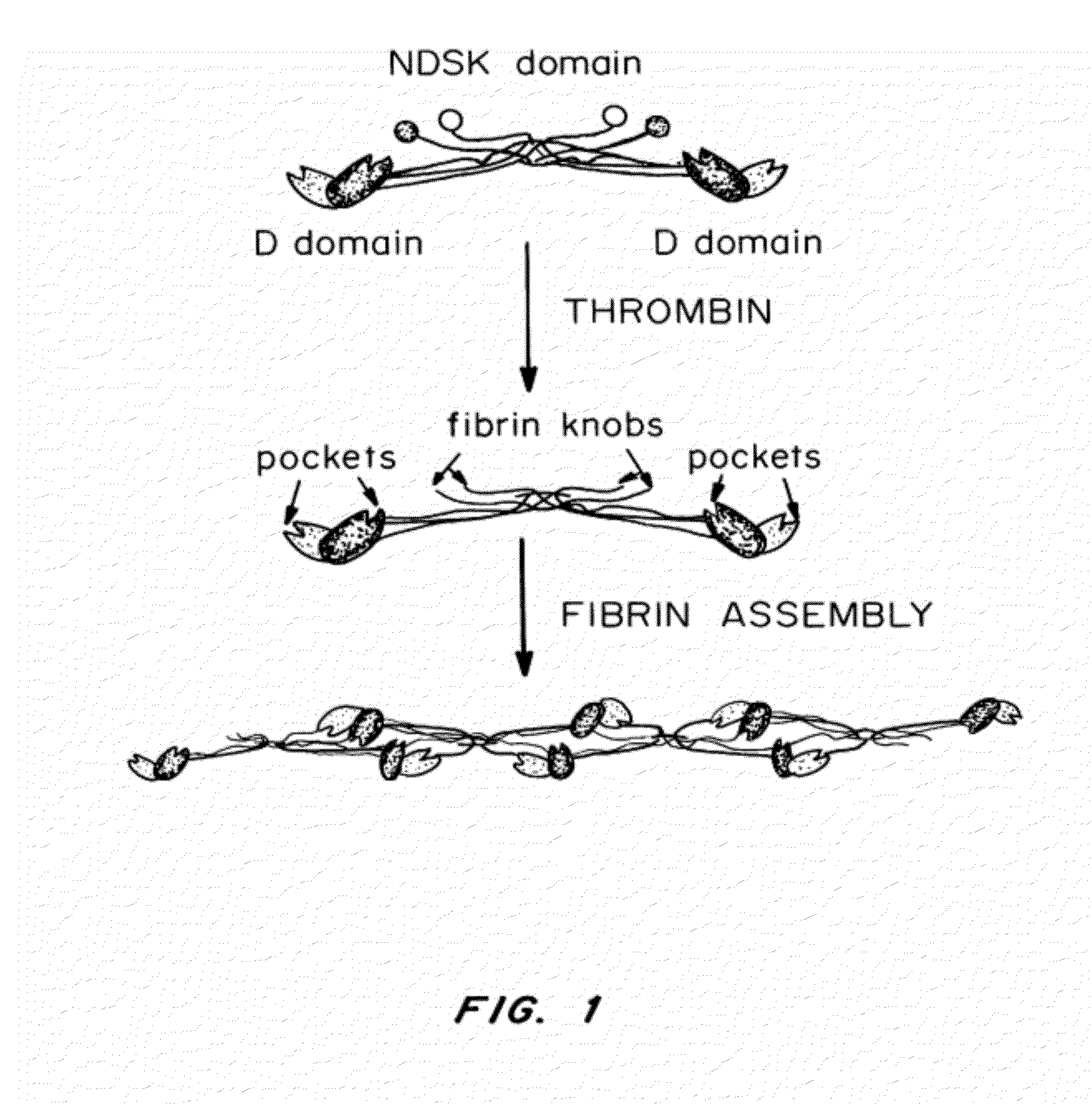
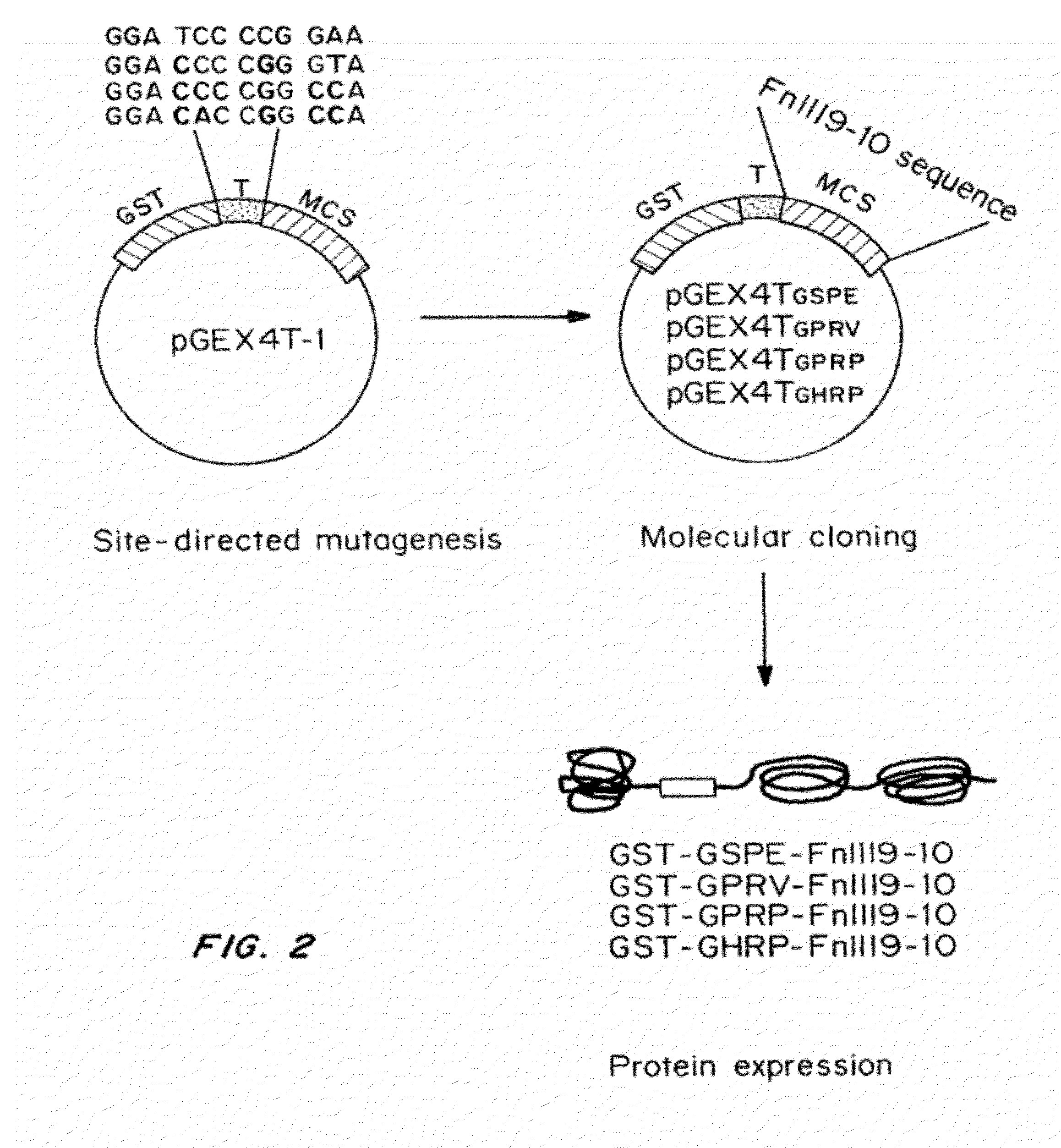
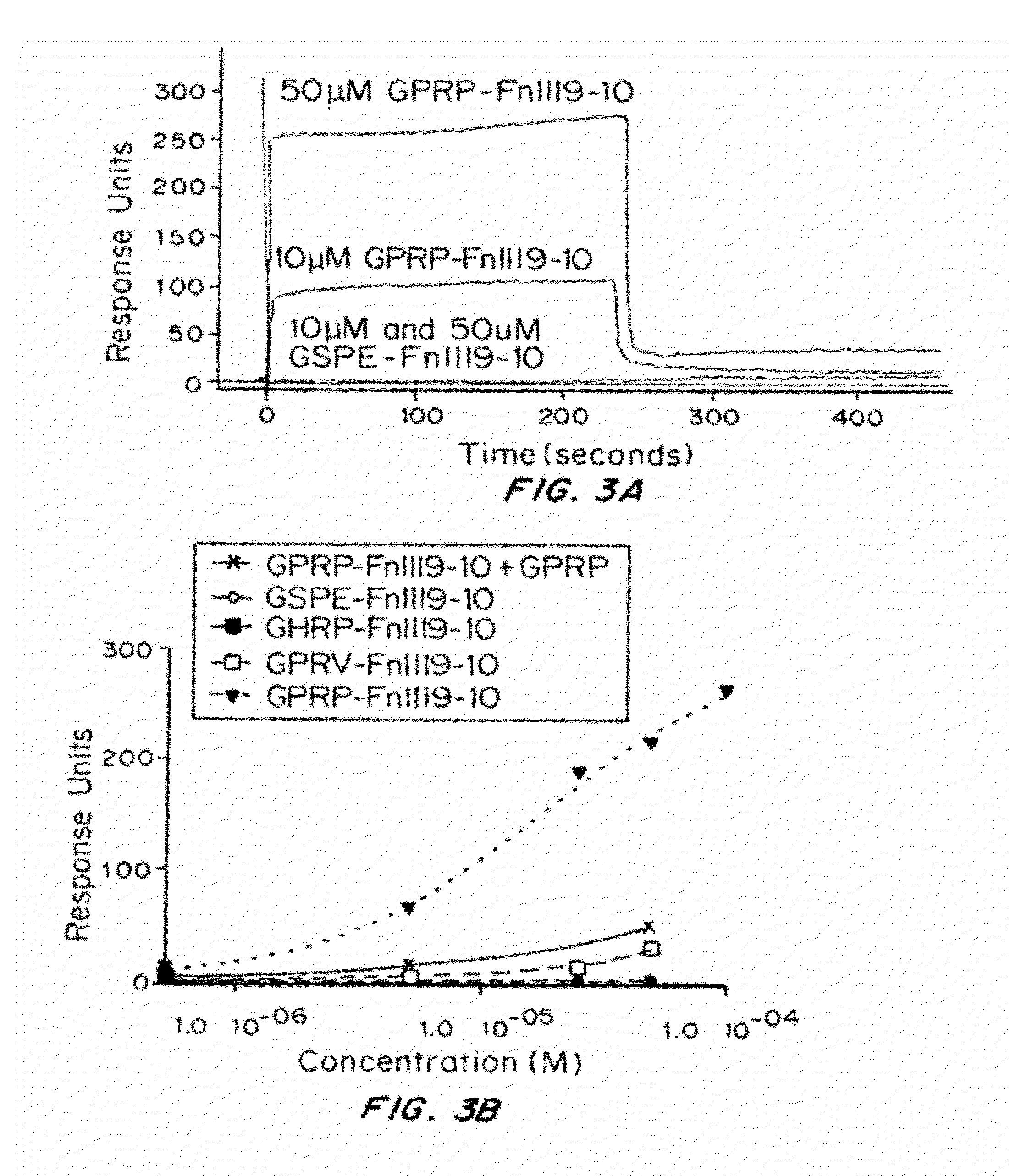
ActiveUS20120114682A1Promote healingPromote fibrinolysisFibrinogenSerum albuminCrystallographyFibrin Monomer
Compositions and methods for targeting substances to fibrinogen, fibrin monomers, or fibrin polymers are provided. These compositions and methods generally involve the use of fibrin knob peptides that bind fibrin(ogen), which can be used to detect fibrin(ogen) and modulate fibrin polymerization and fibrinolysis.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Mannich condensation products useful as sequestering agents
ActiveUS7964543B2Prevent oxidationInhibition of polymerizationOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsMannich condensationAmino acid
The present invention is directed to Mannich condensation product sequestering agents or mixtures of Mannich condensation product sequestering agents for use in fuels and lubricating oils. The present invention is also directed to a process for preparing the Mannich condensation product sequestering agents. The present invention is also directed to a product formed by combining, under reaction conditions, a polyisobutyl-substituted hydroxyaromatic compound, an aldehyde, an amino acid or ester thereof, and an alkali metal base to form the Mannich condensation product sequestering agent. The present invention is also directed to a lubricating oil composition, a lubricating oil concentrate, a fuel composition, and a fuel concentrate having the Mannich condensation product sequestering agents of the present invention.
Owner:CHEVRON ORONITE CO LLC
Process for preparing iminodiacetonitrile
ActiveCN1830953AAvoid the defect that the mixing temperature is the reaction temperatureLess side effectsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceAcetonitrile
A process for preparing iminodiacetonitrile from hydroxy acetonitrile and ammonia water includes such steps as respective pre-heating, mixing and reacting.
Owner:CHONGQING UNISPLENDOUR CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com