Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138 results about "Intraocular implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
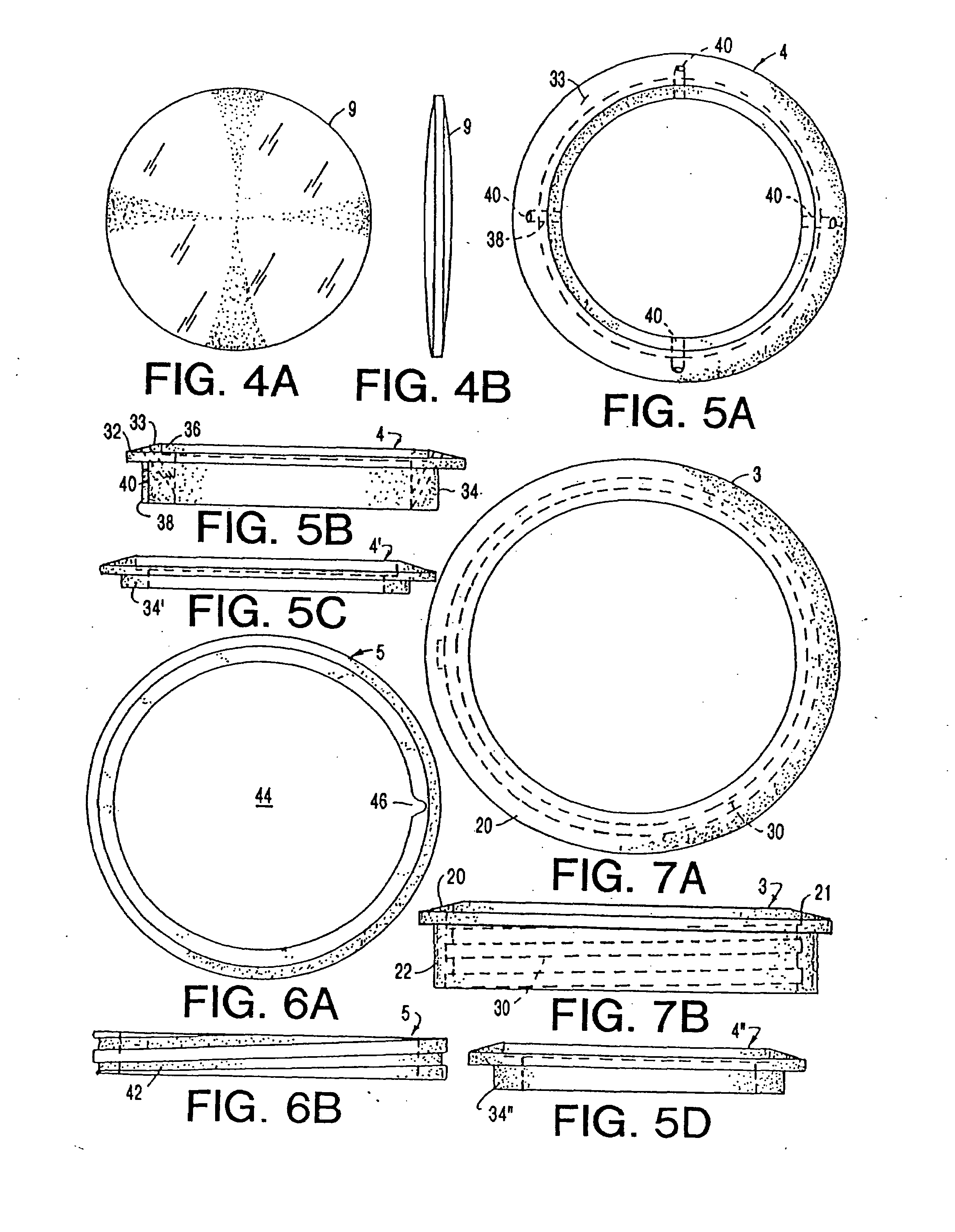
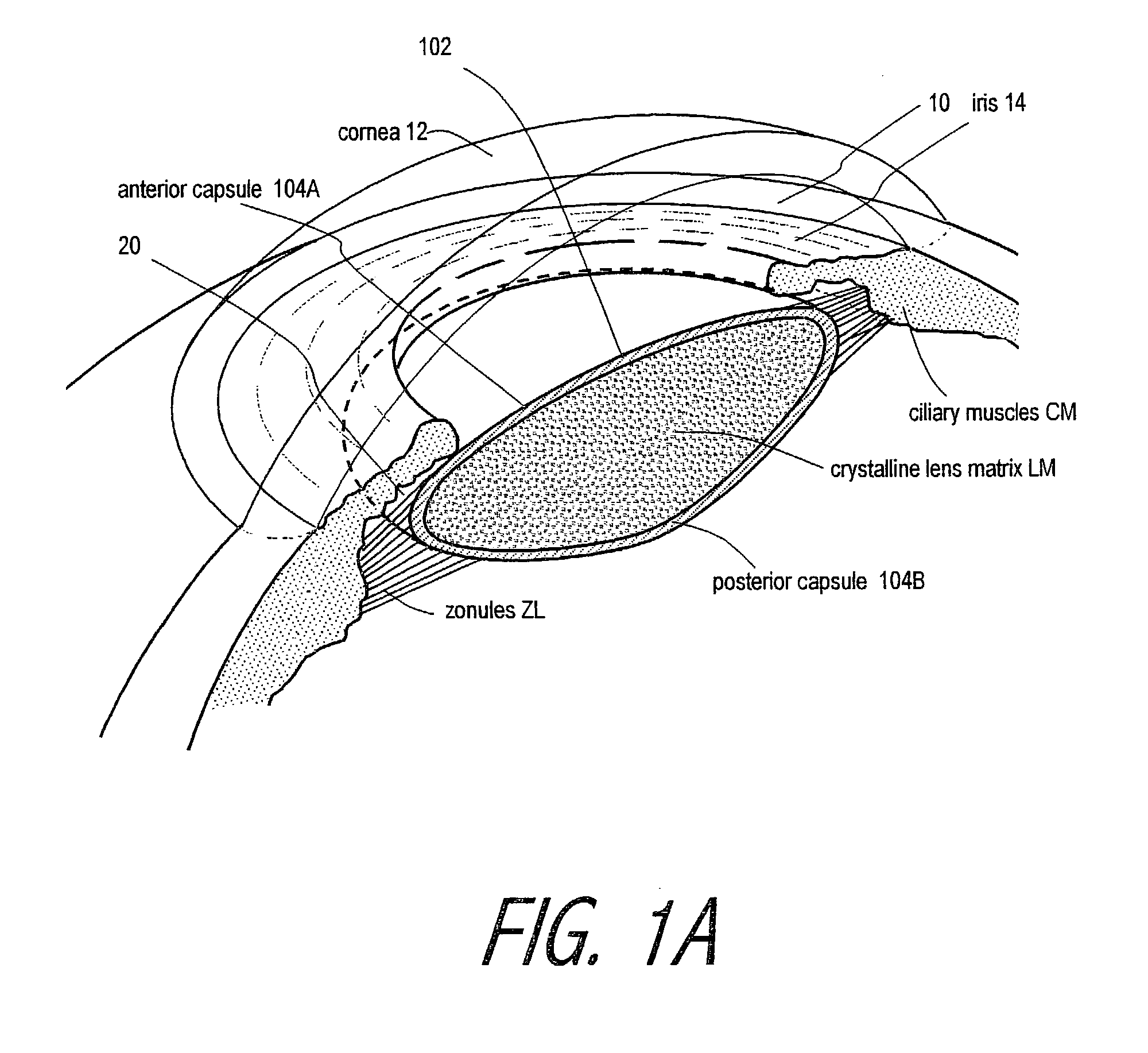
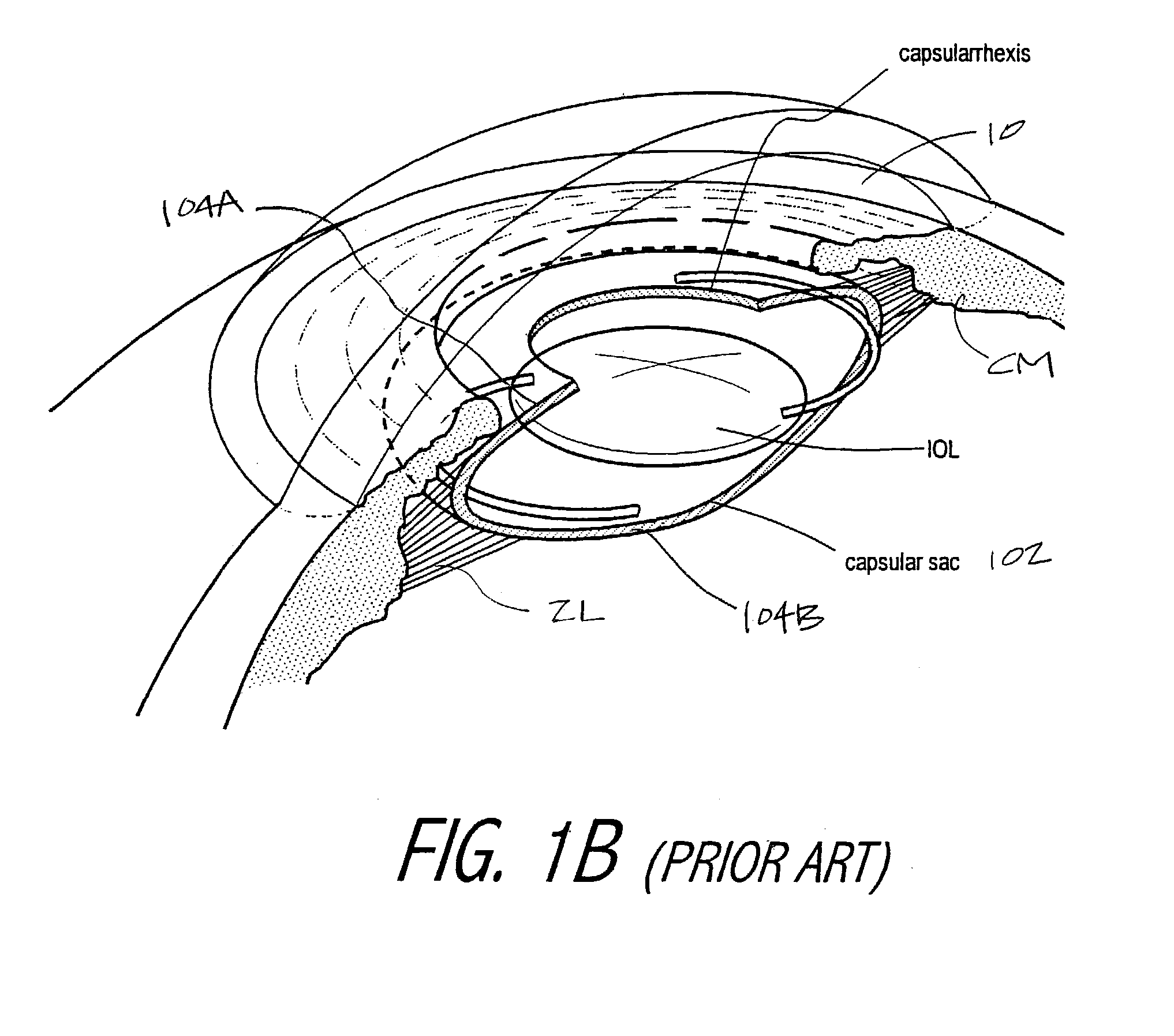
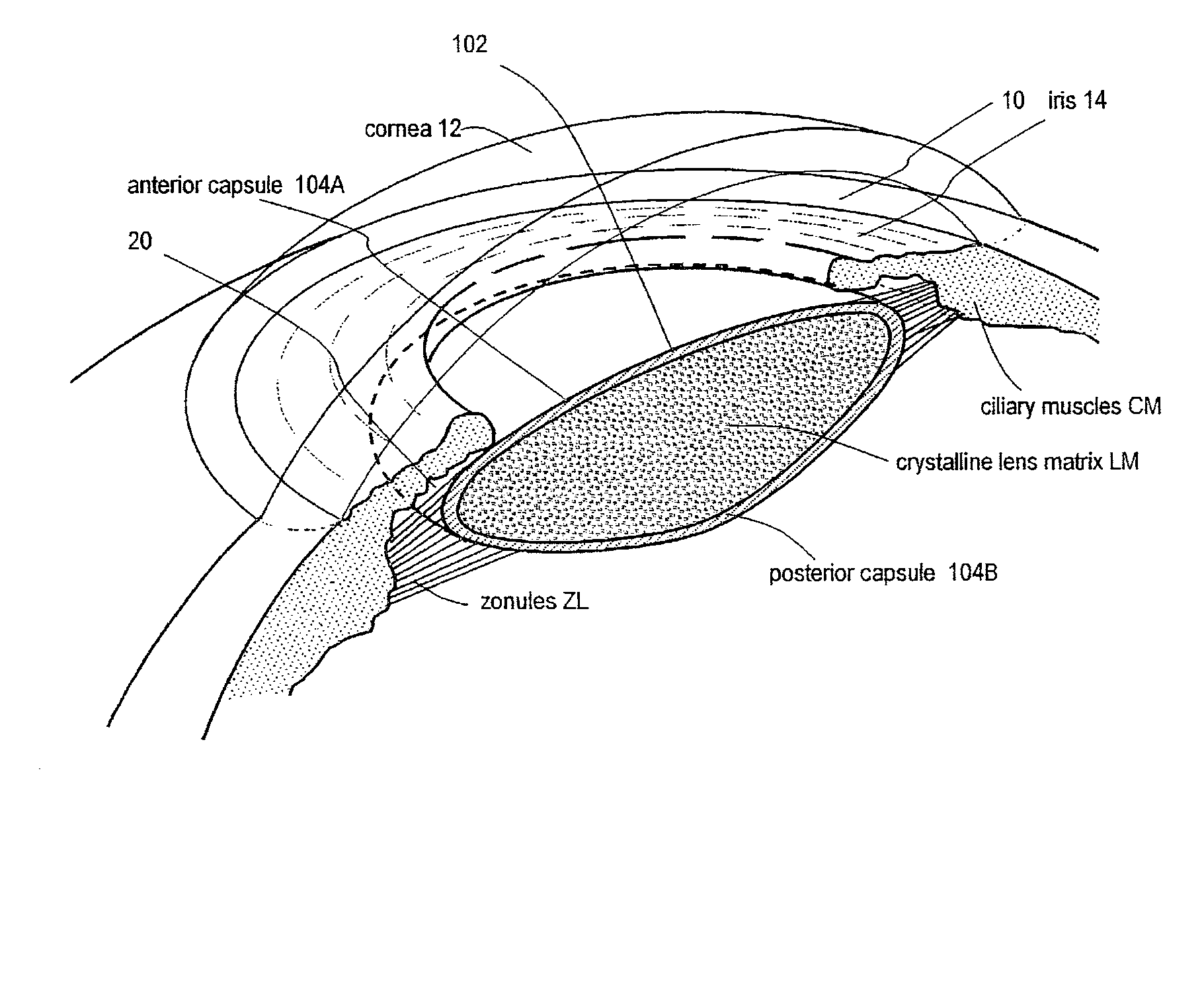
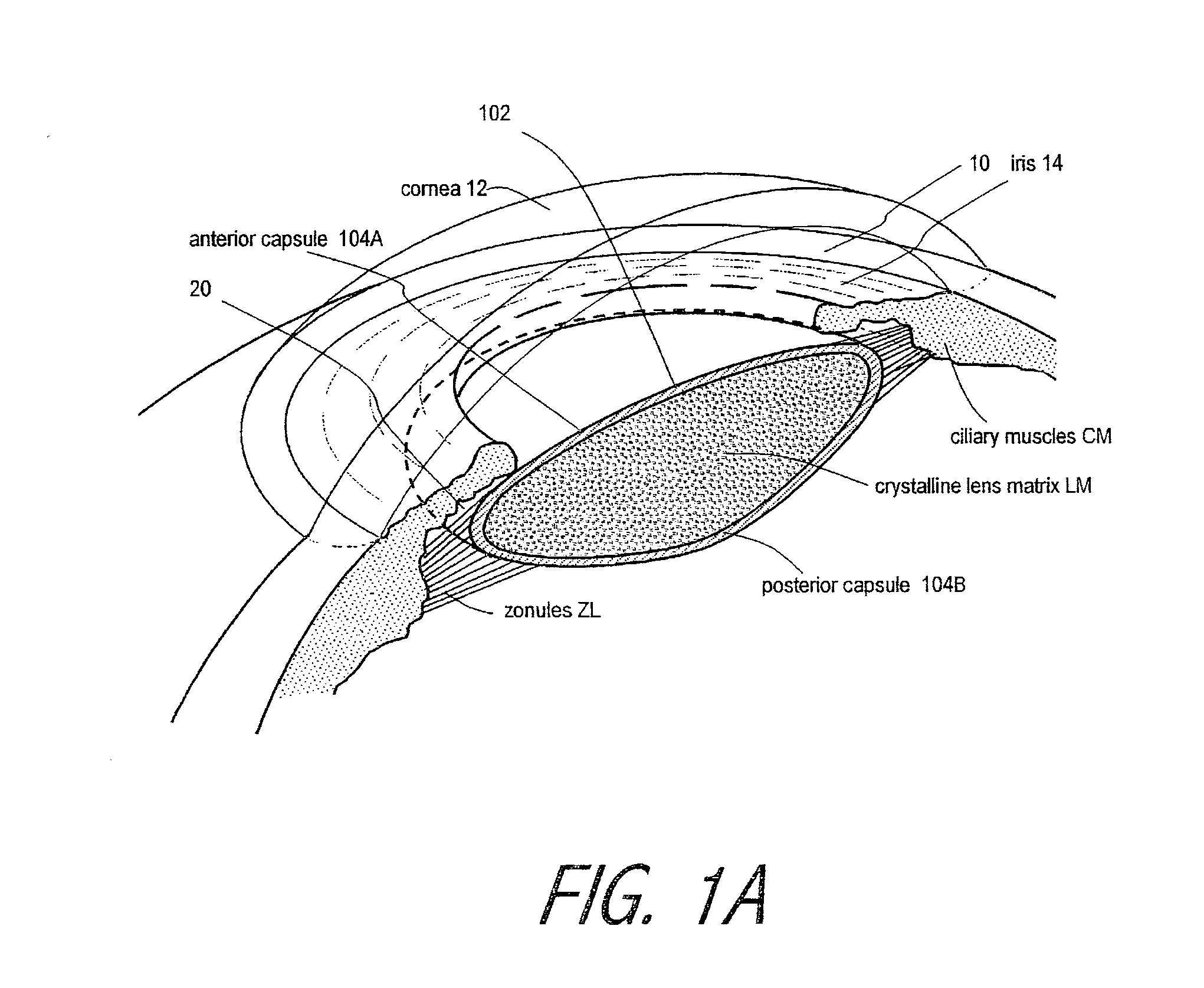
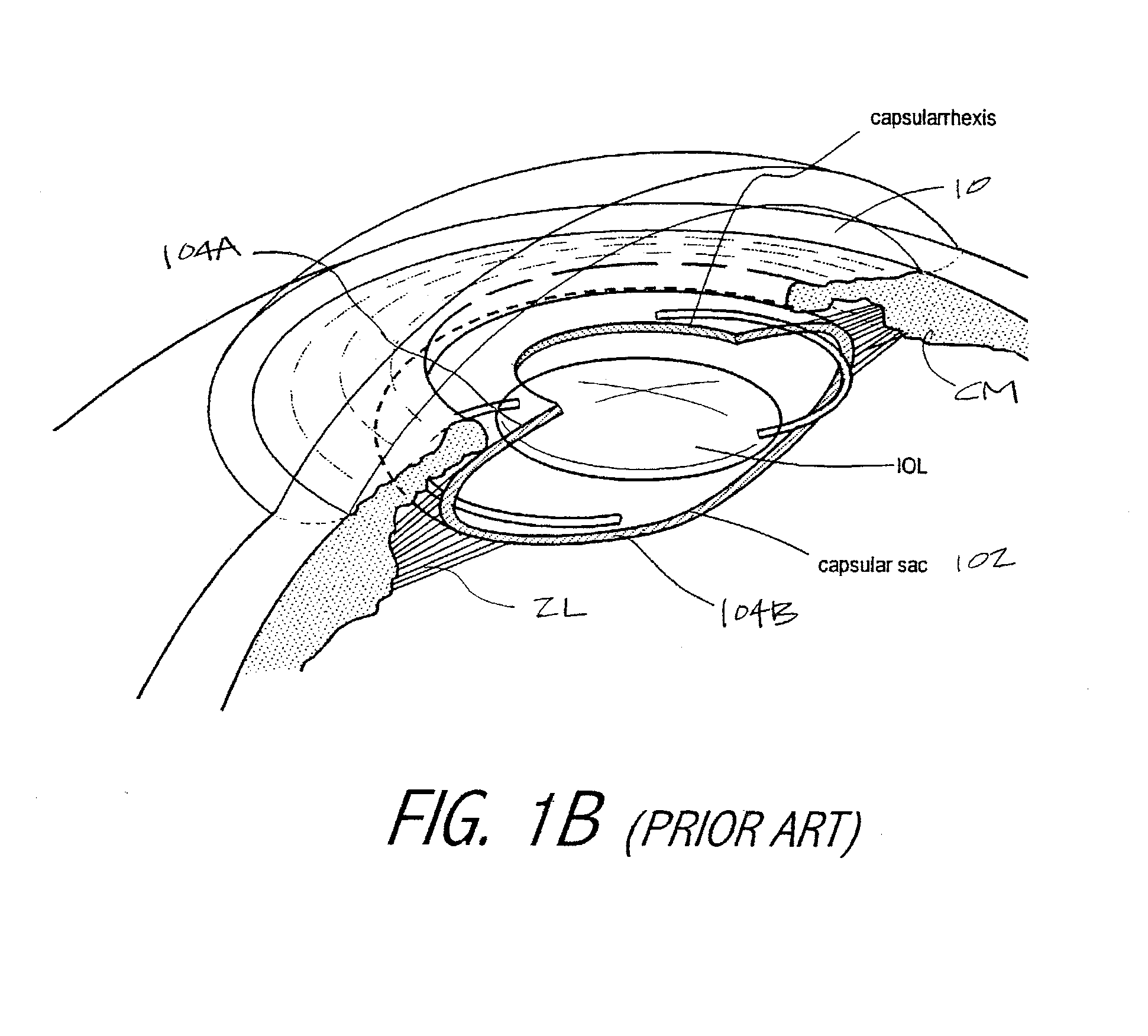
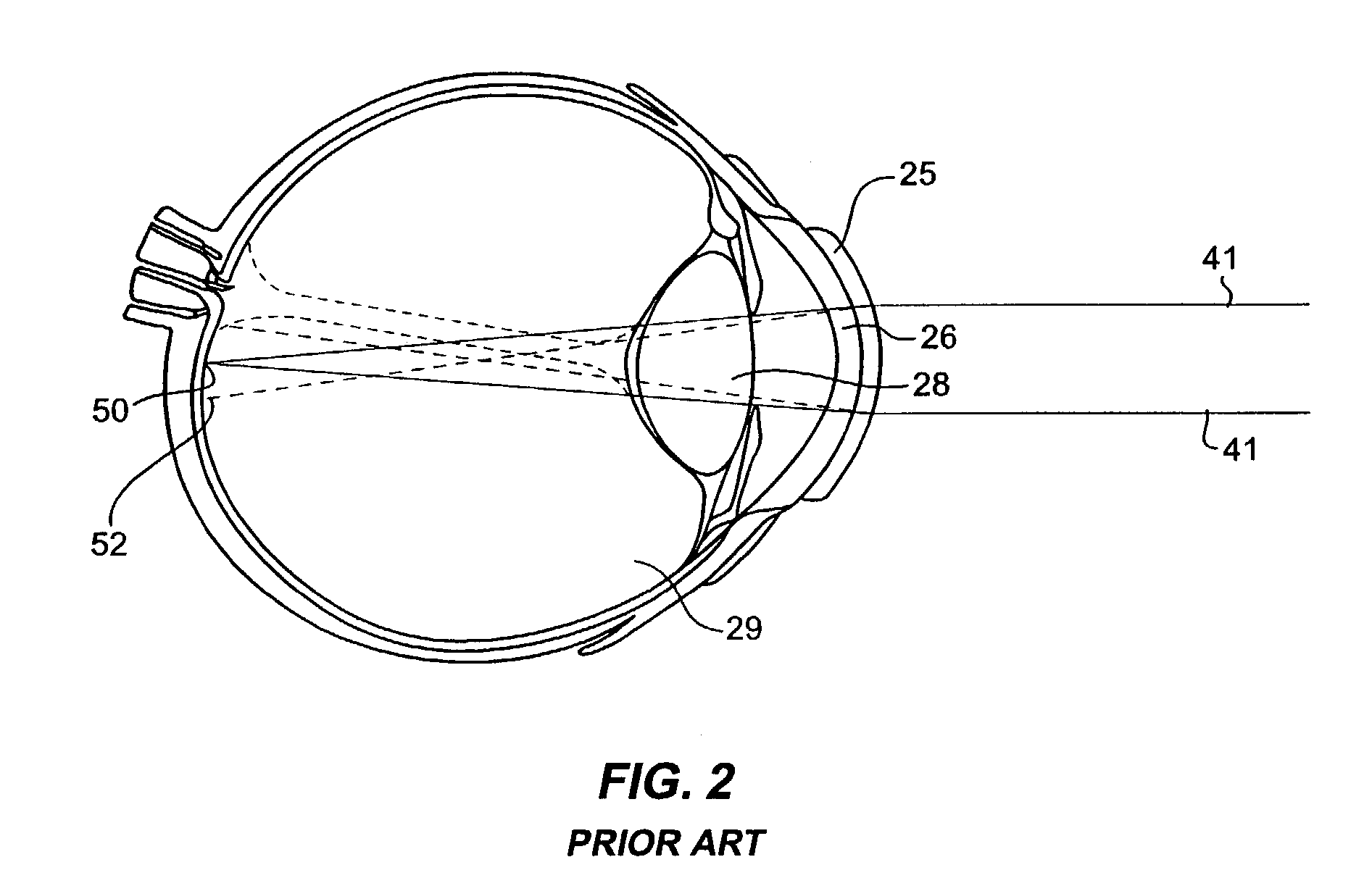
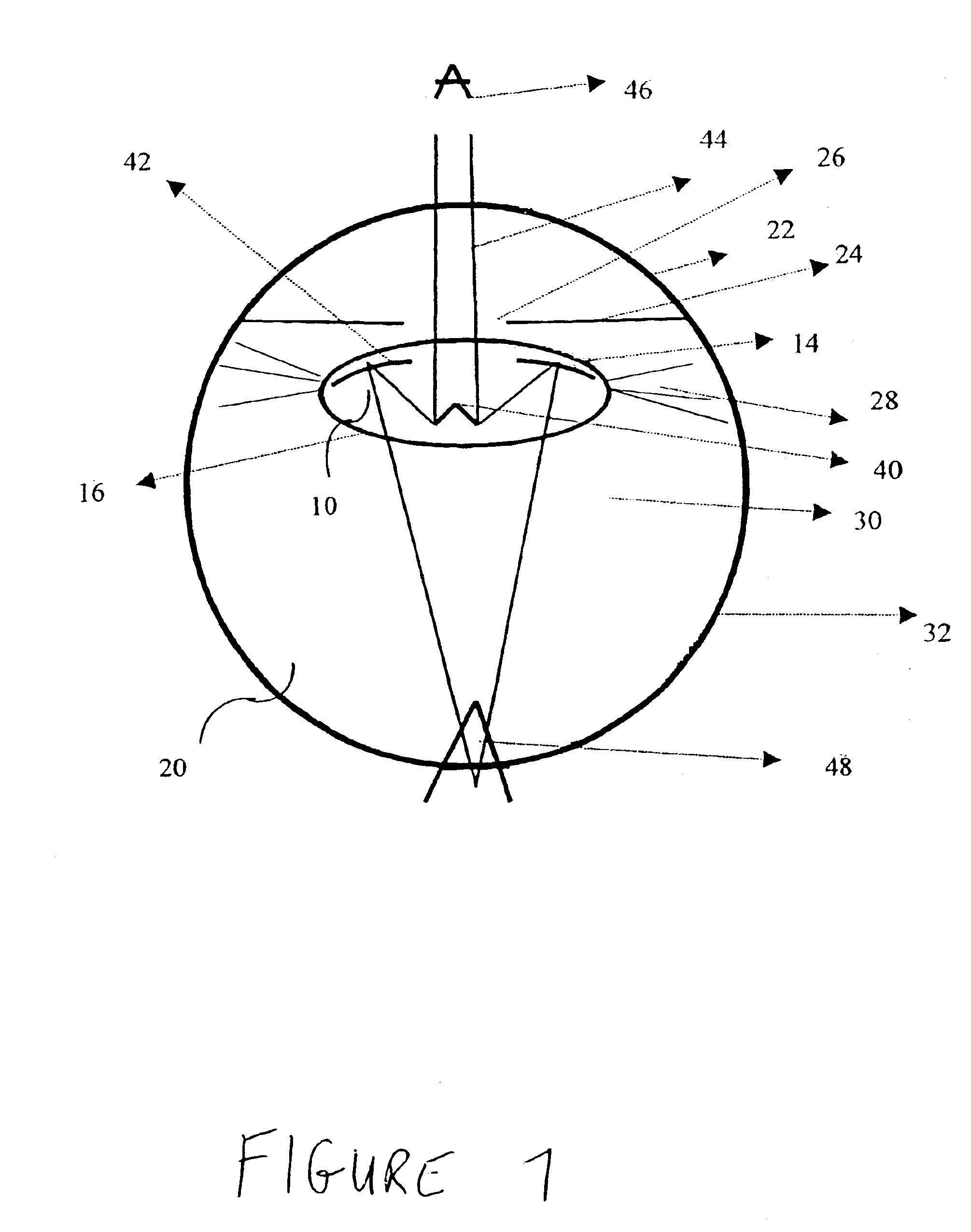
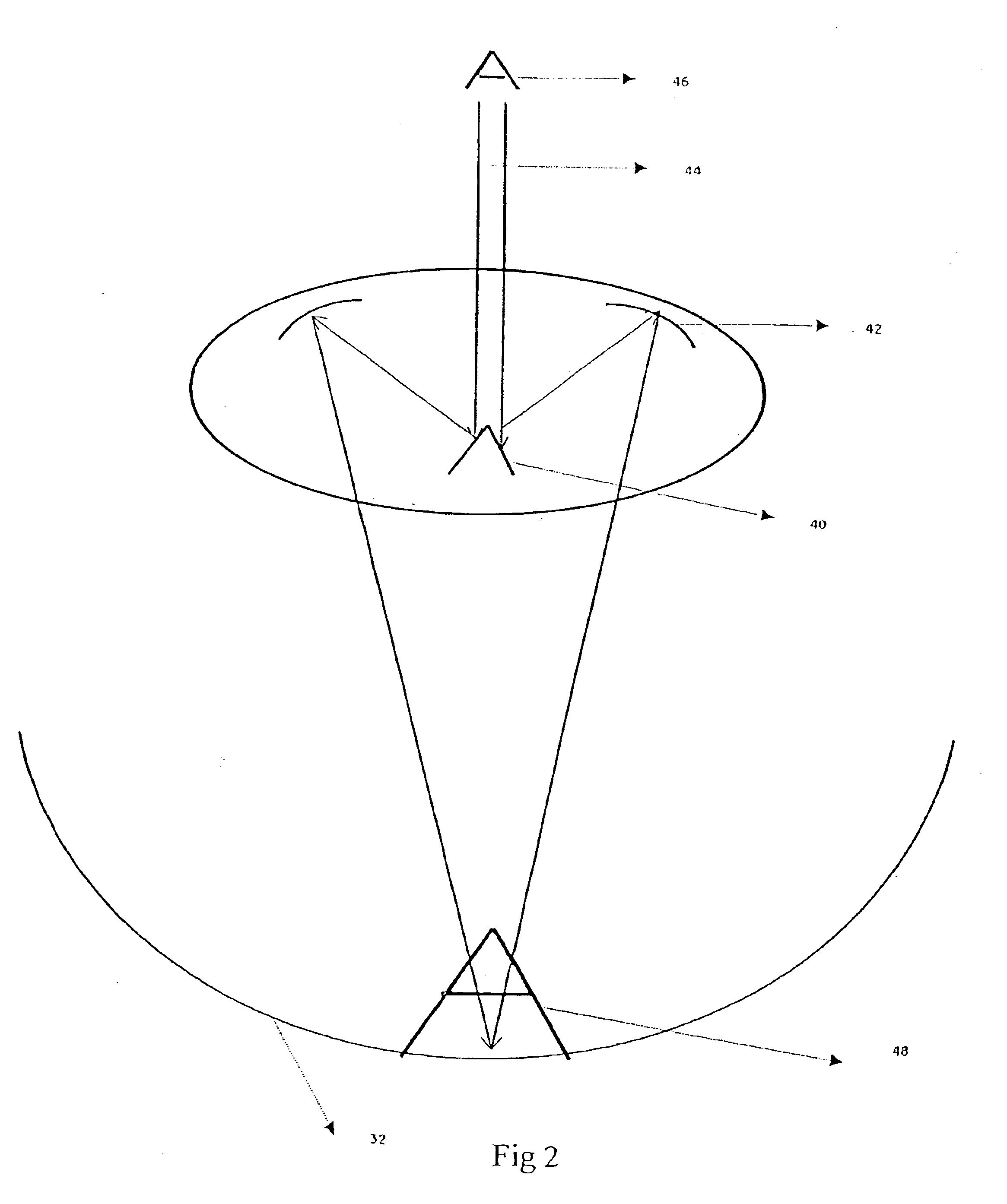
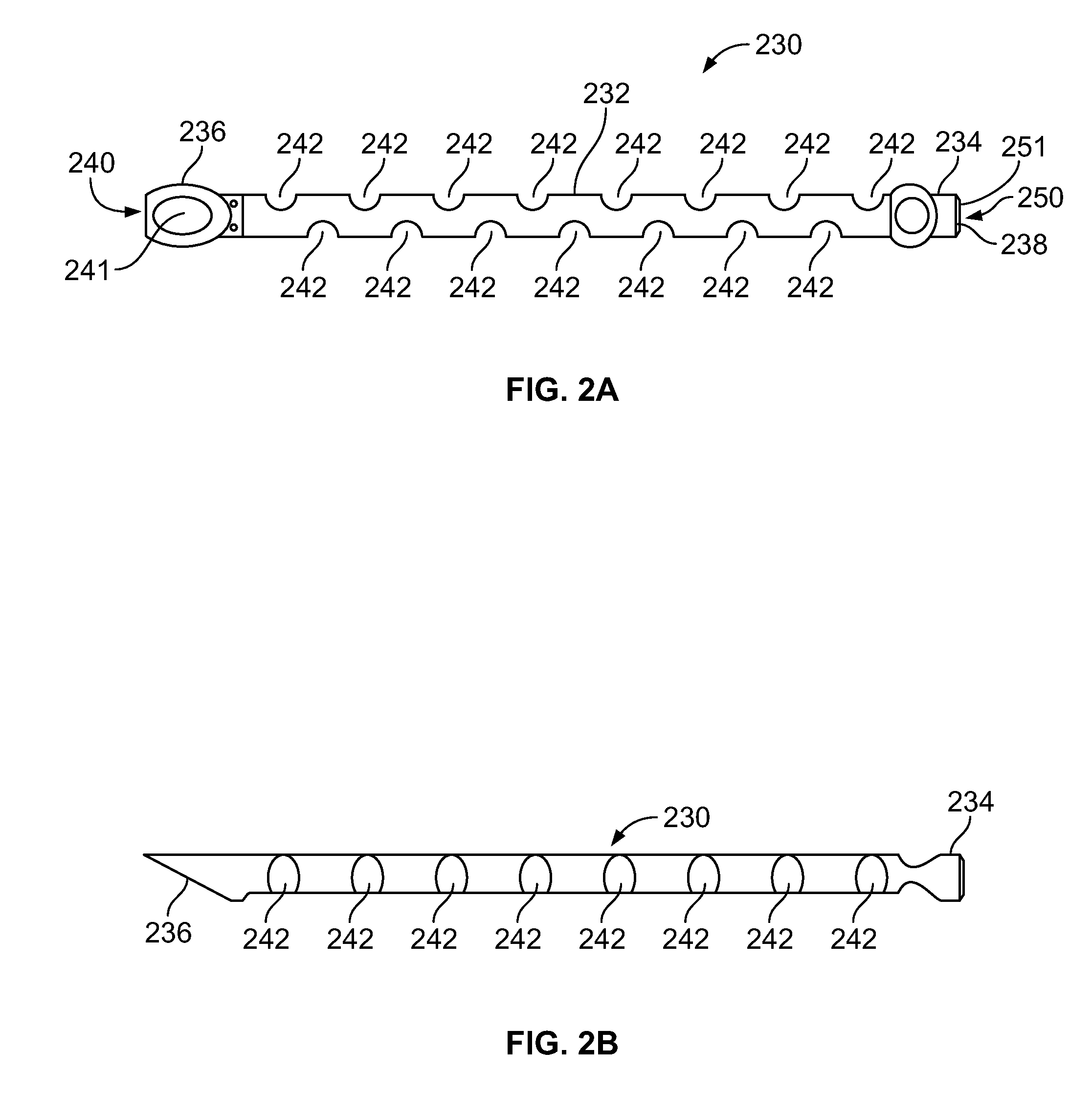
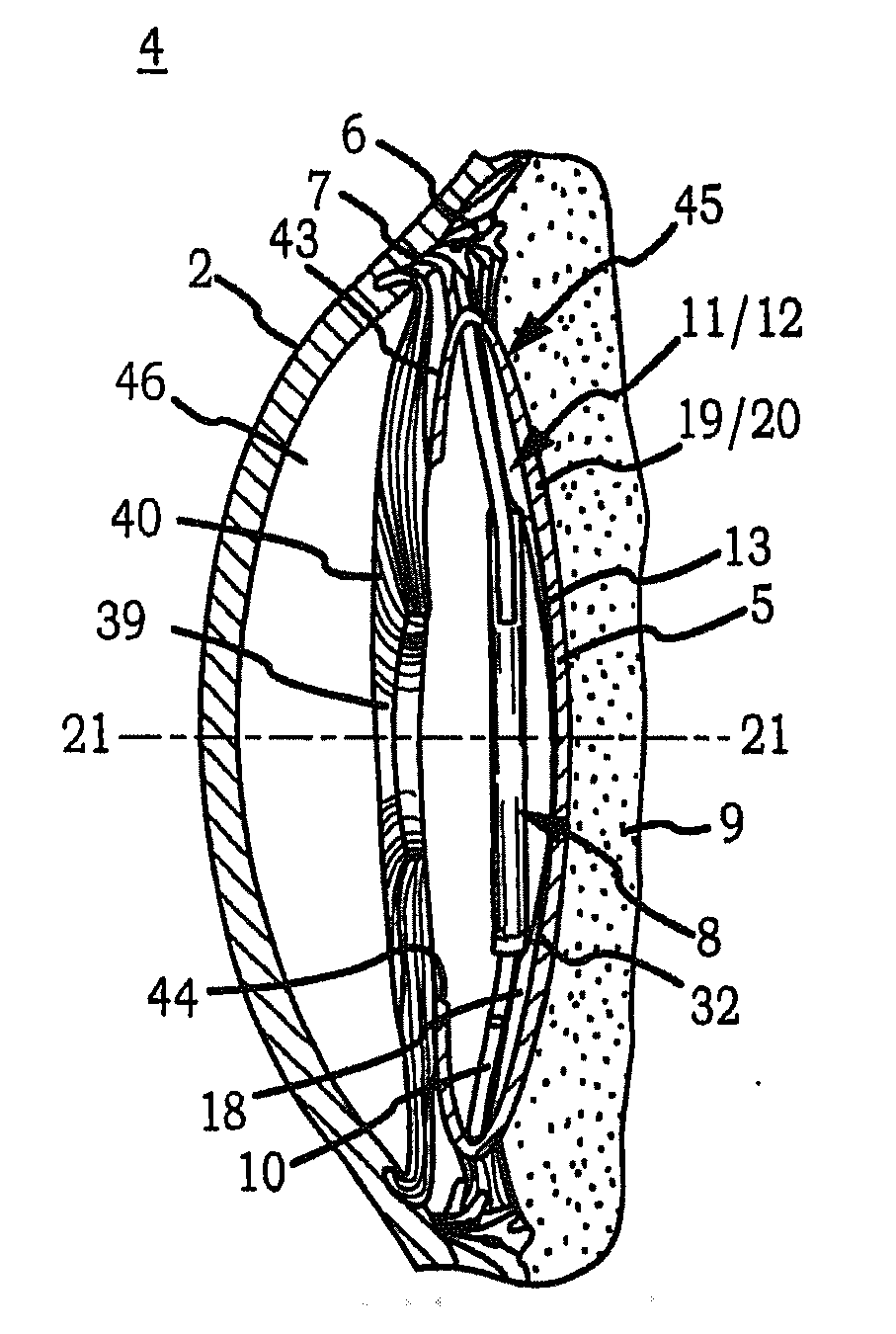
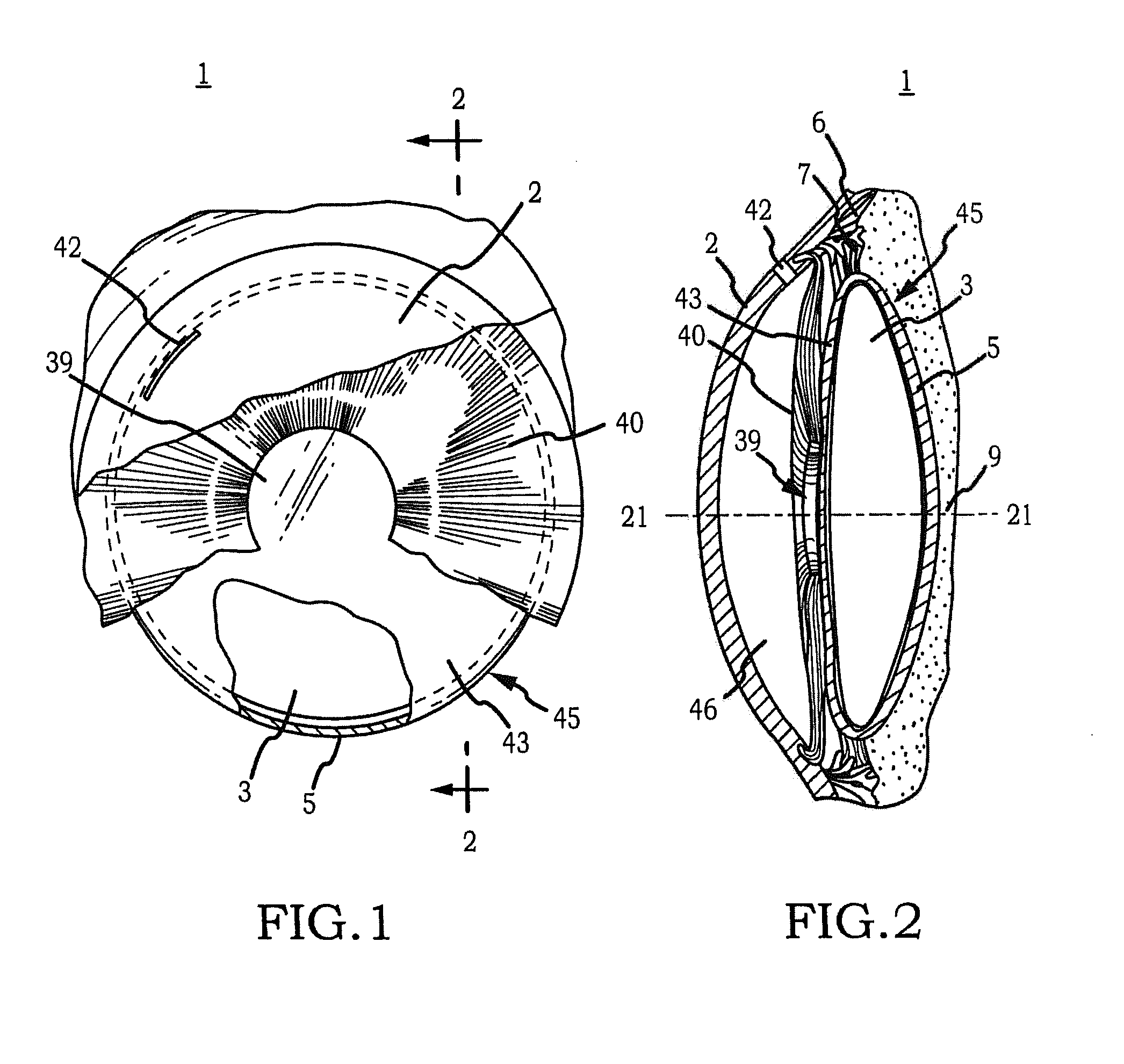
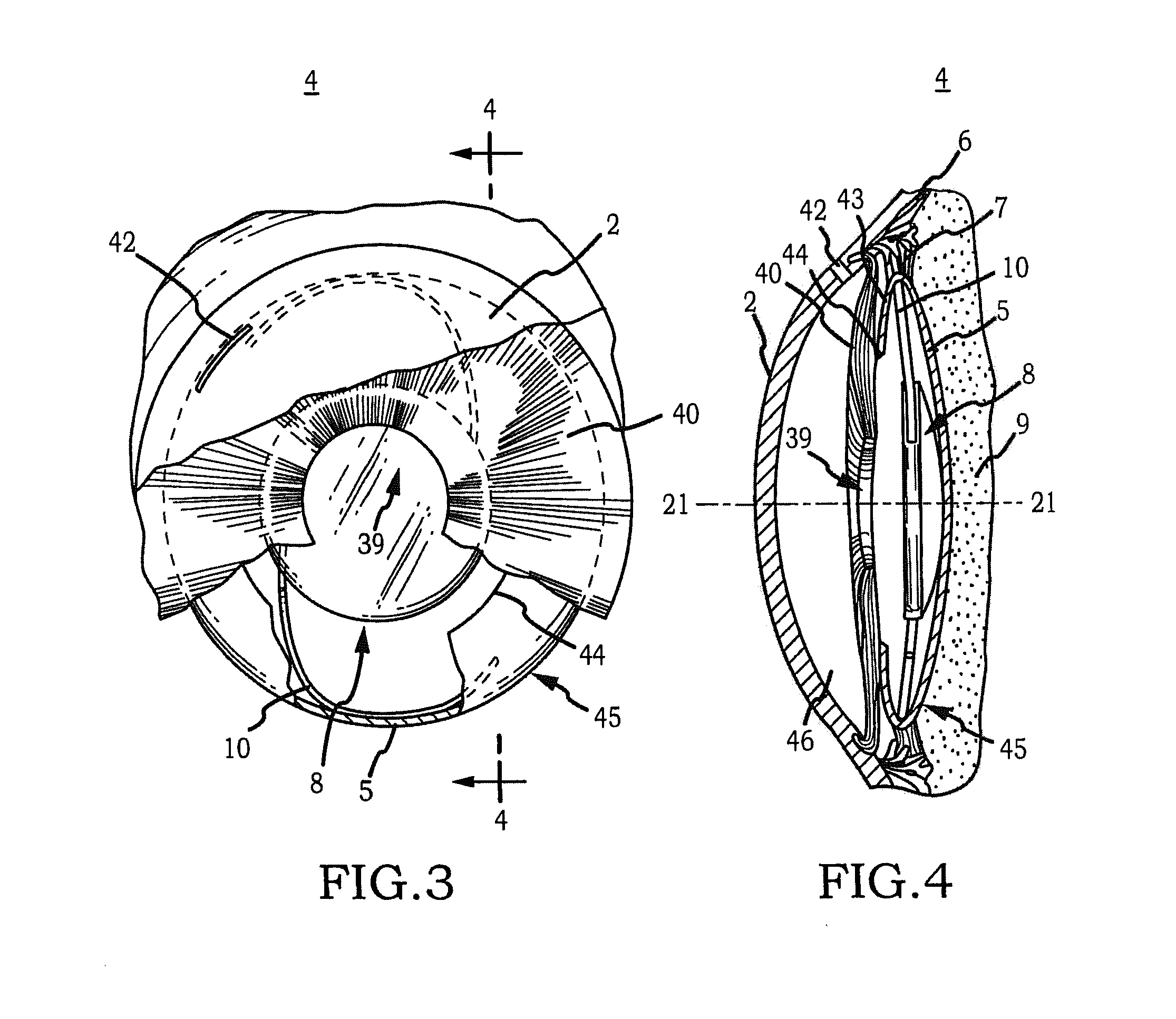
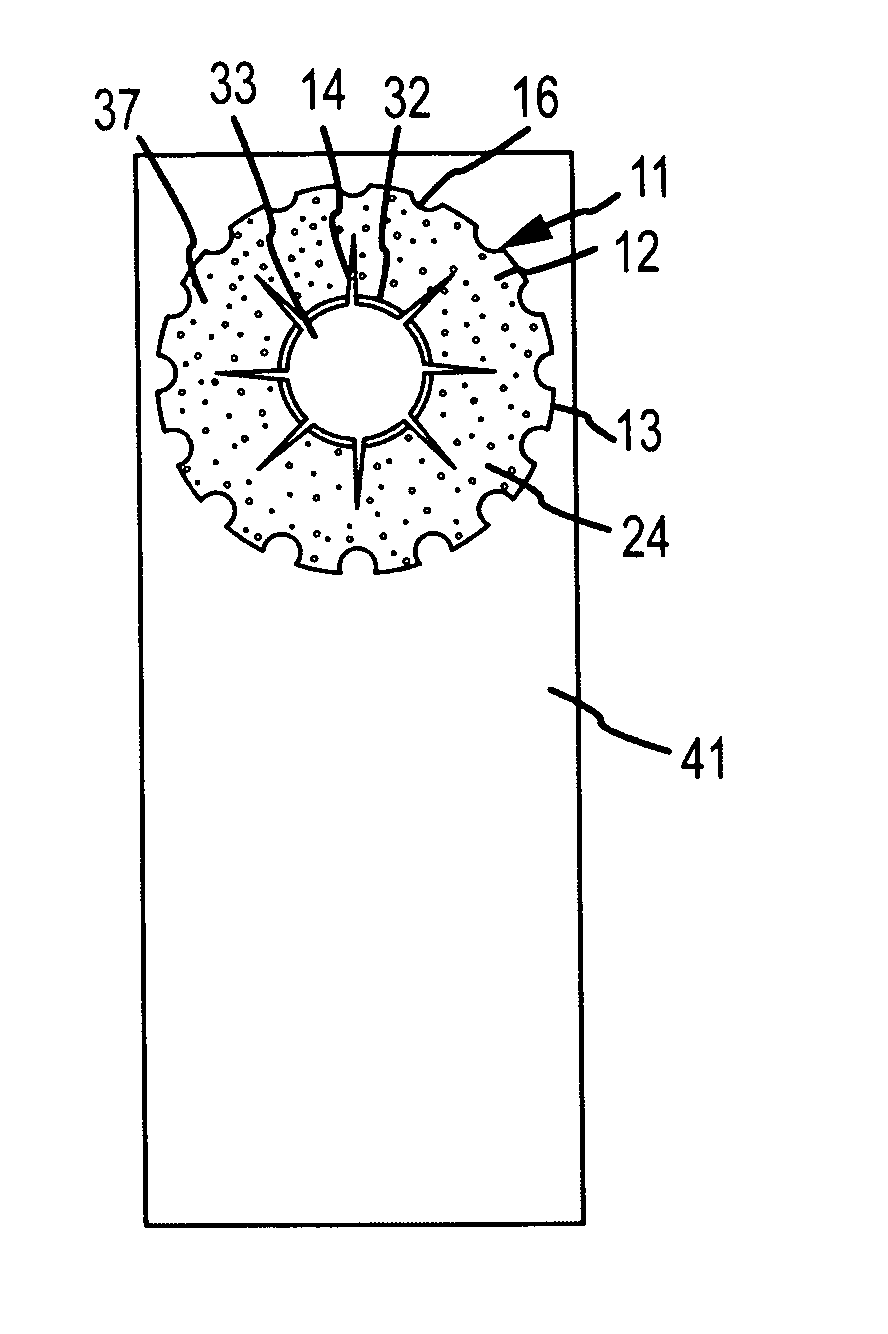
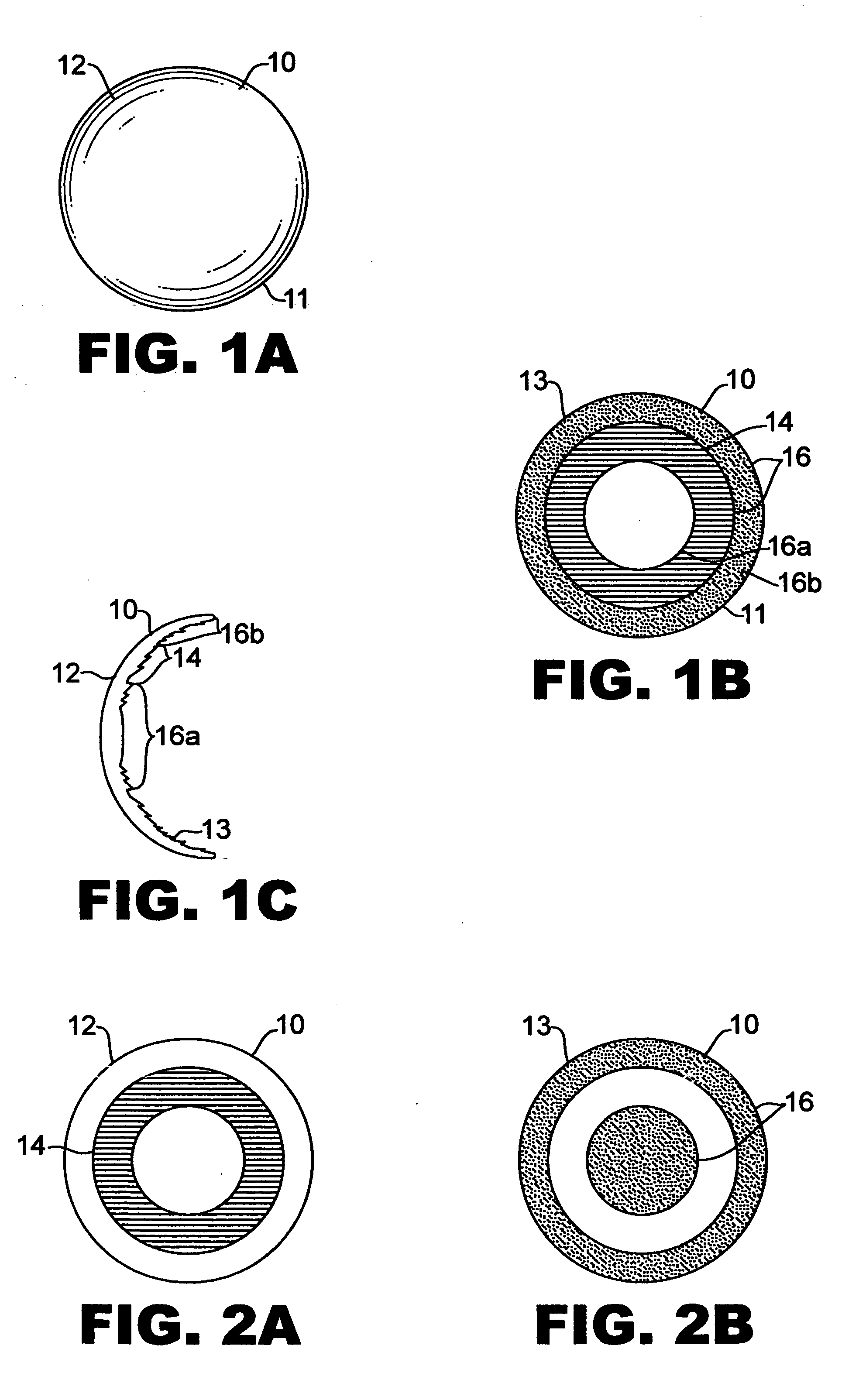
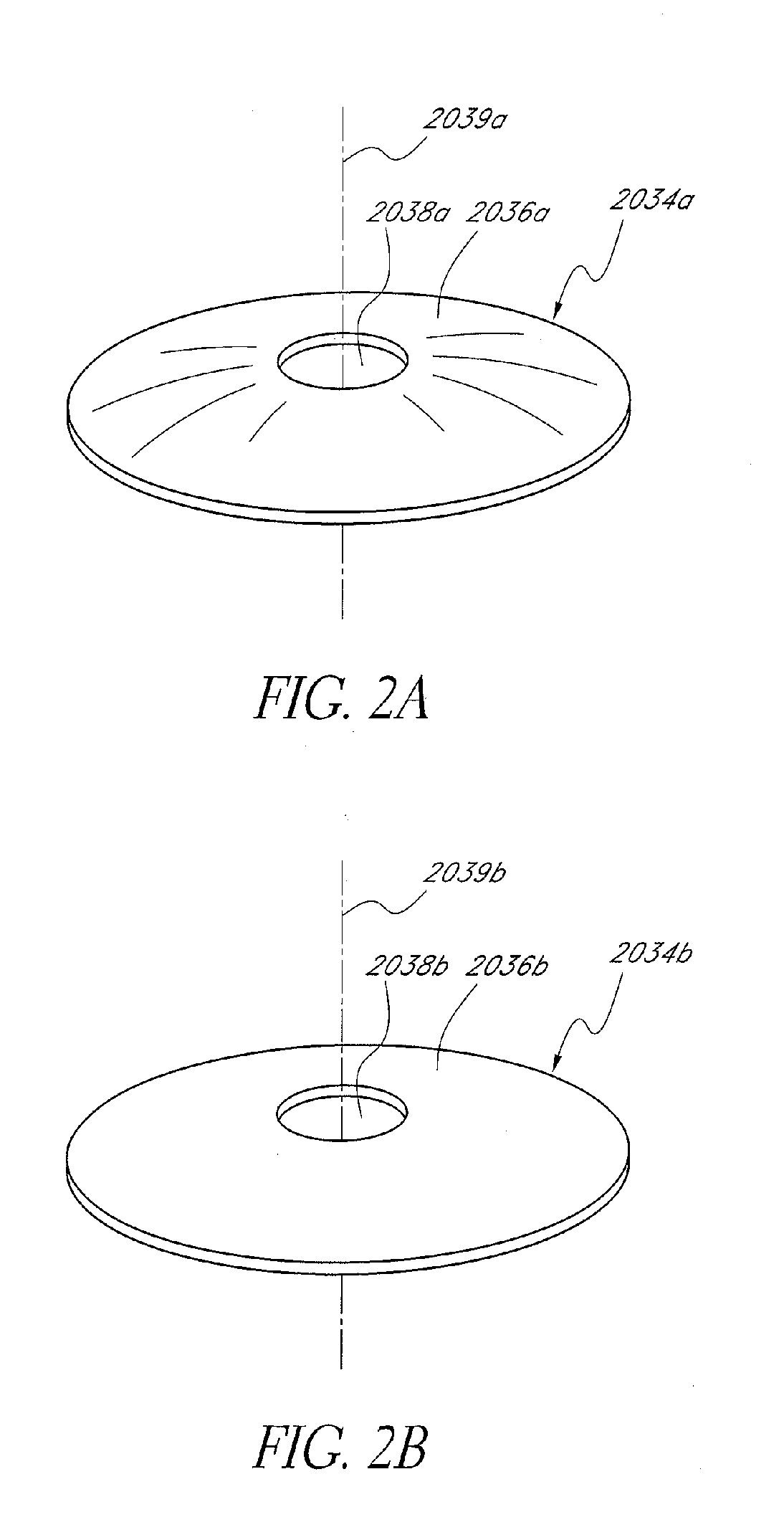
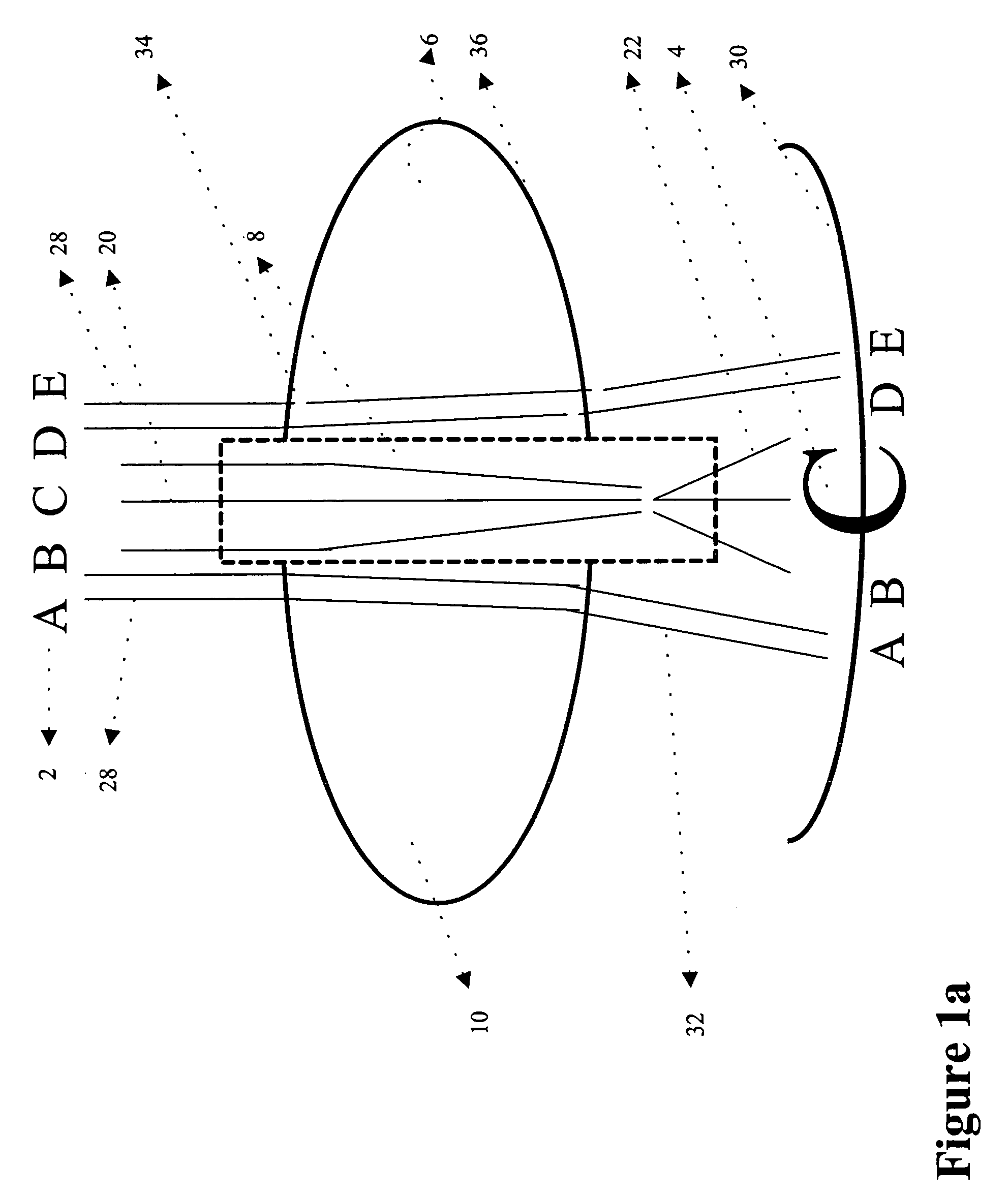
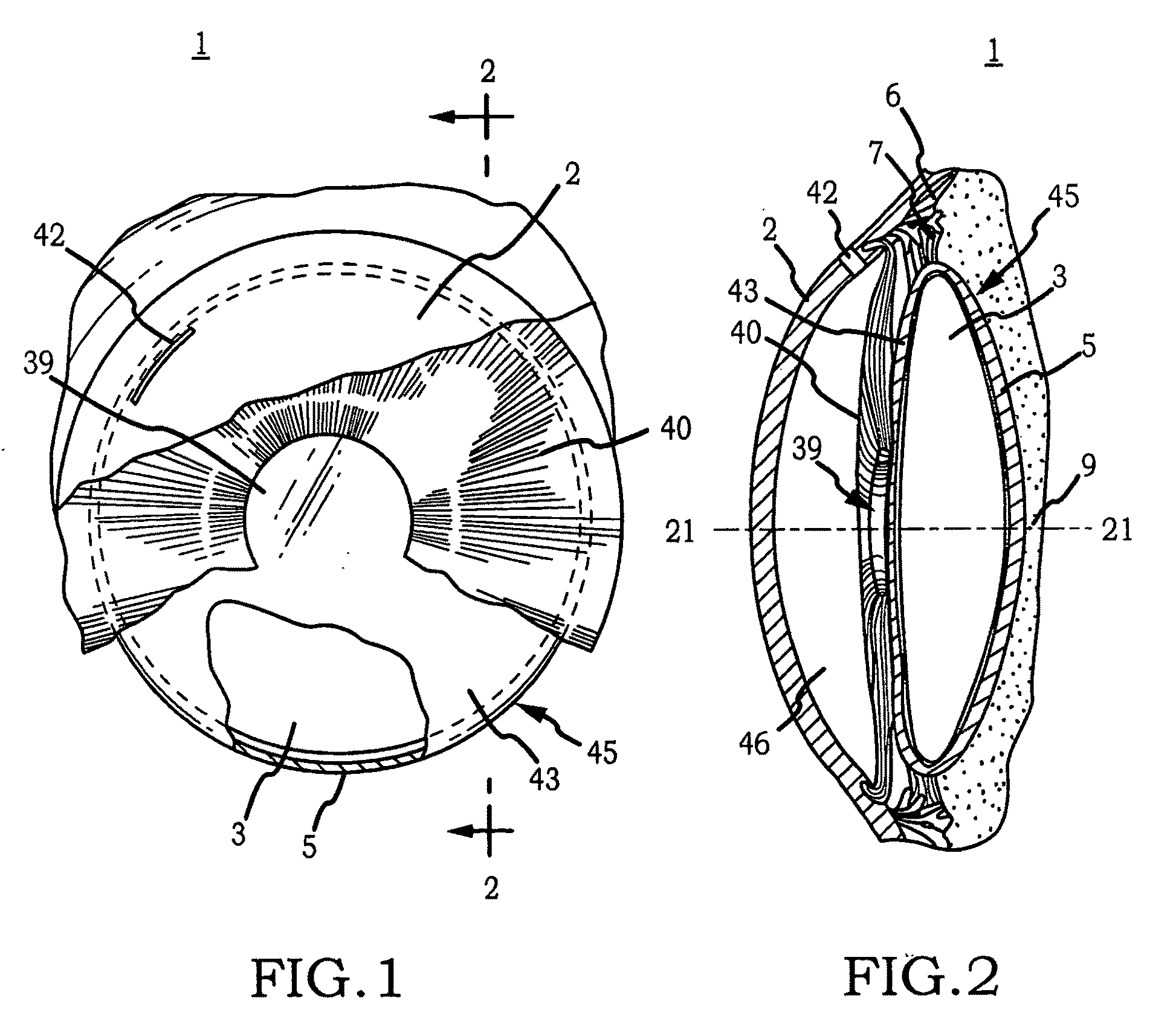
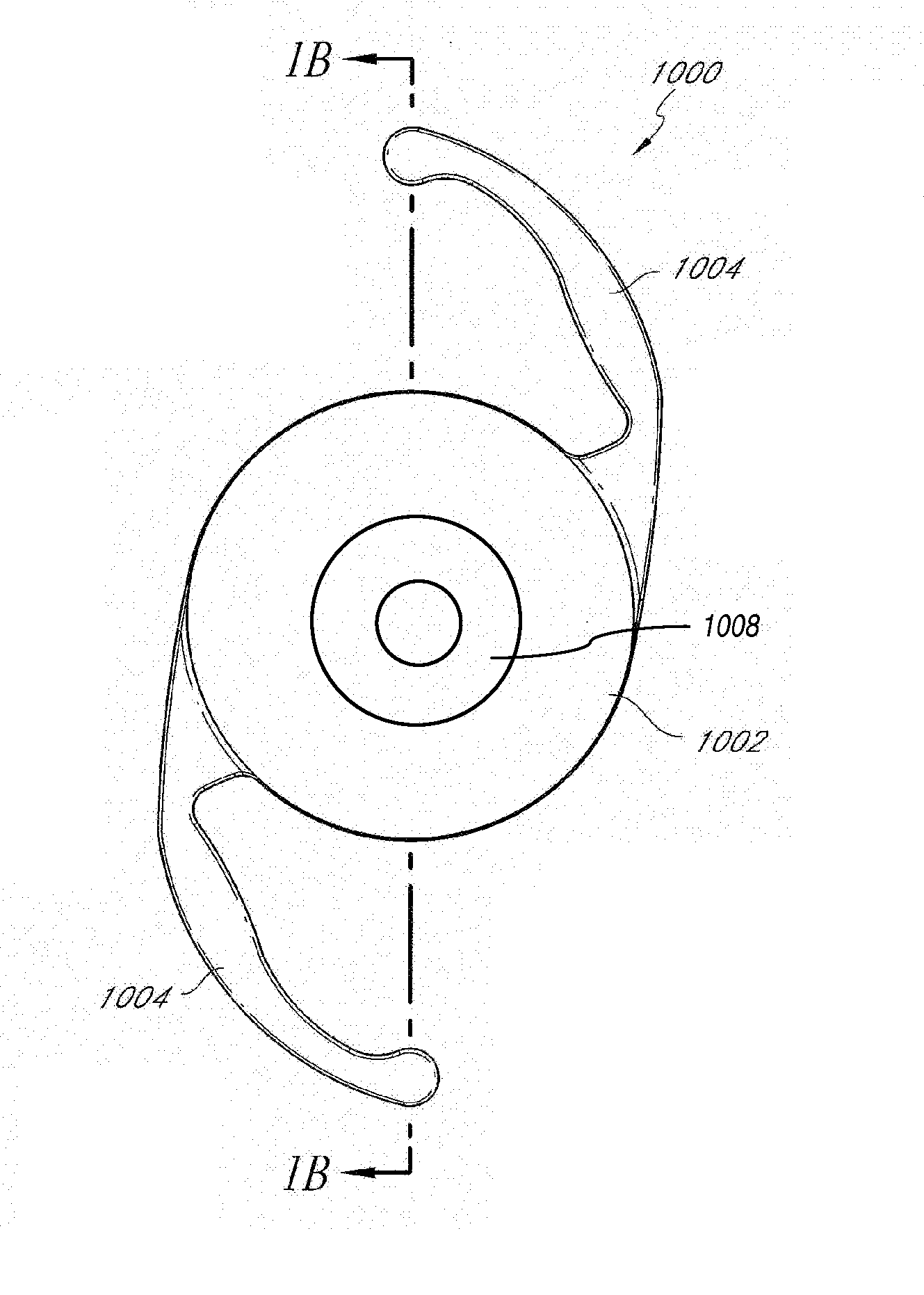
Intraocular implant and an artificial lens device
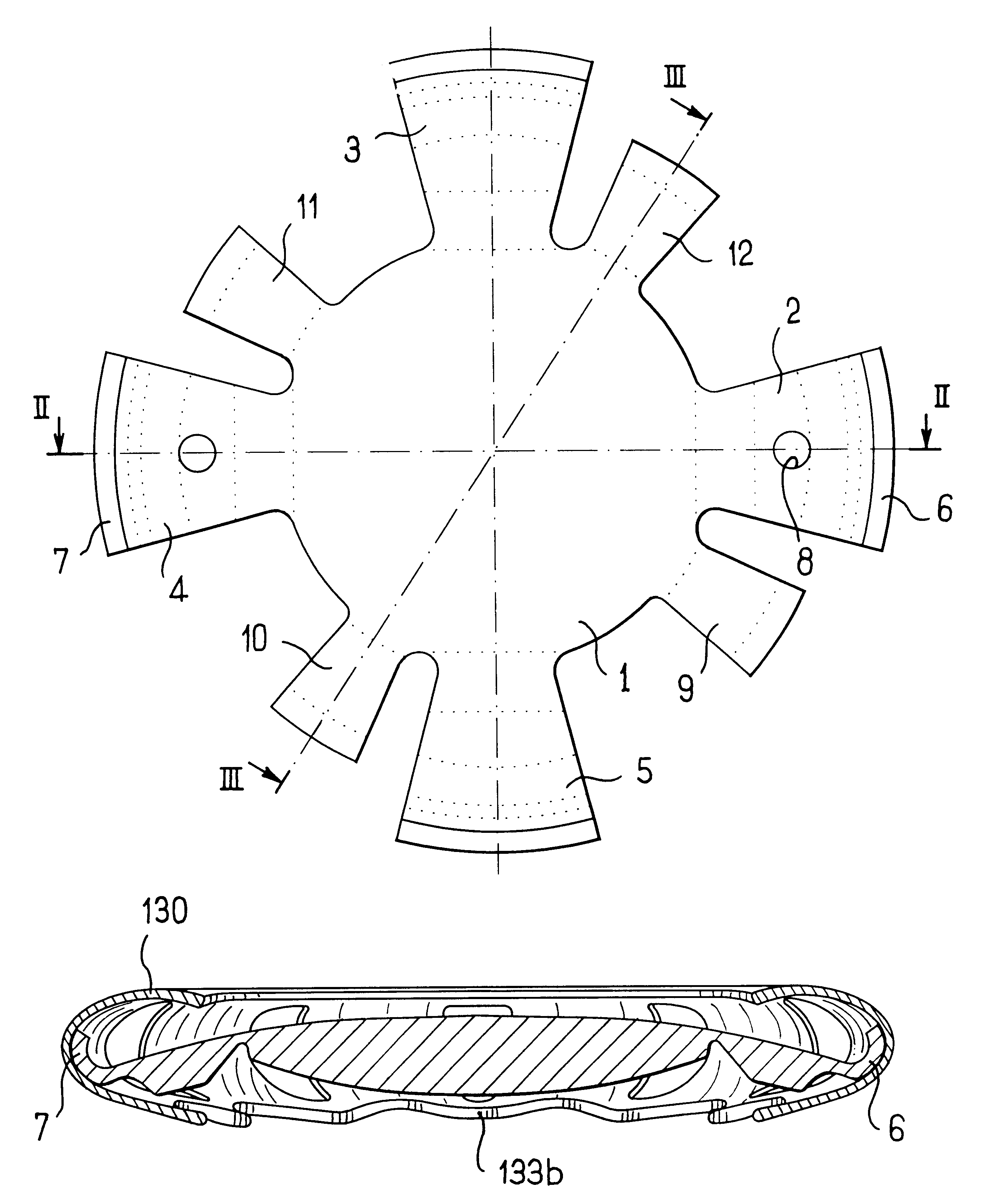
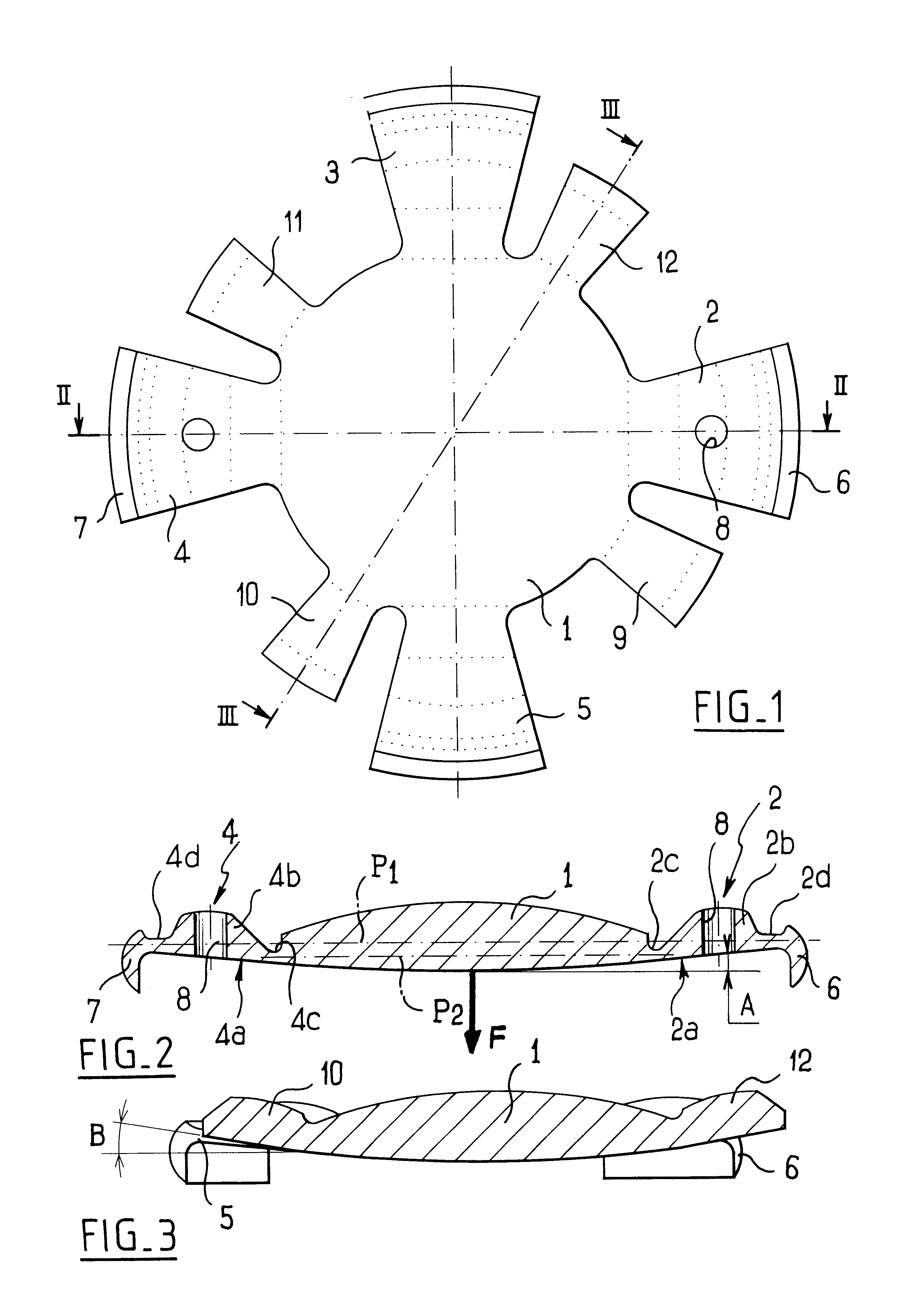
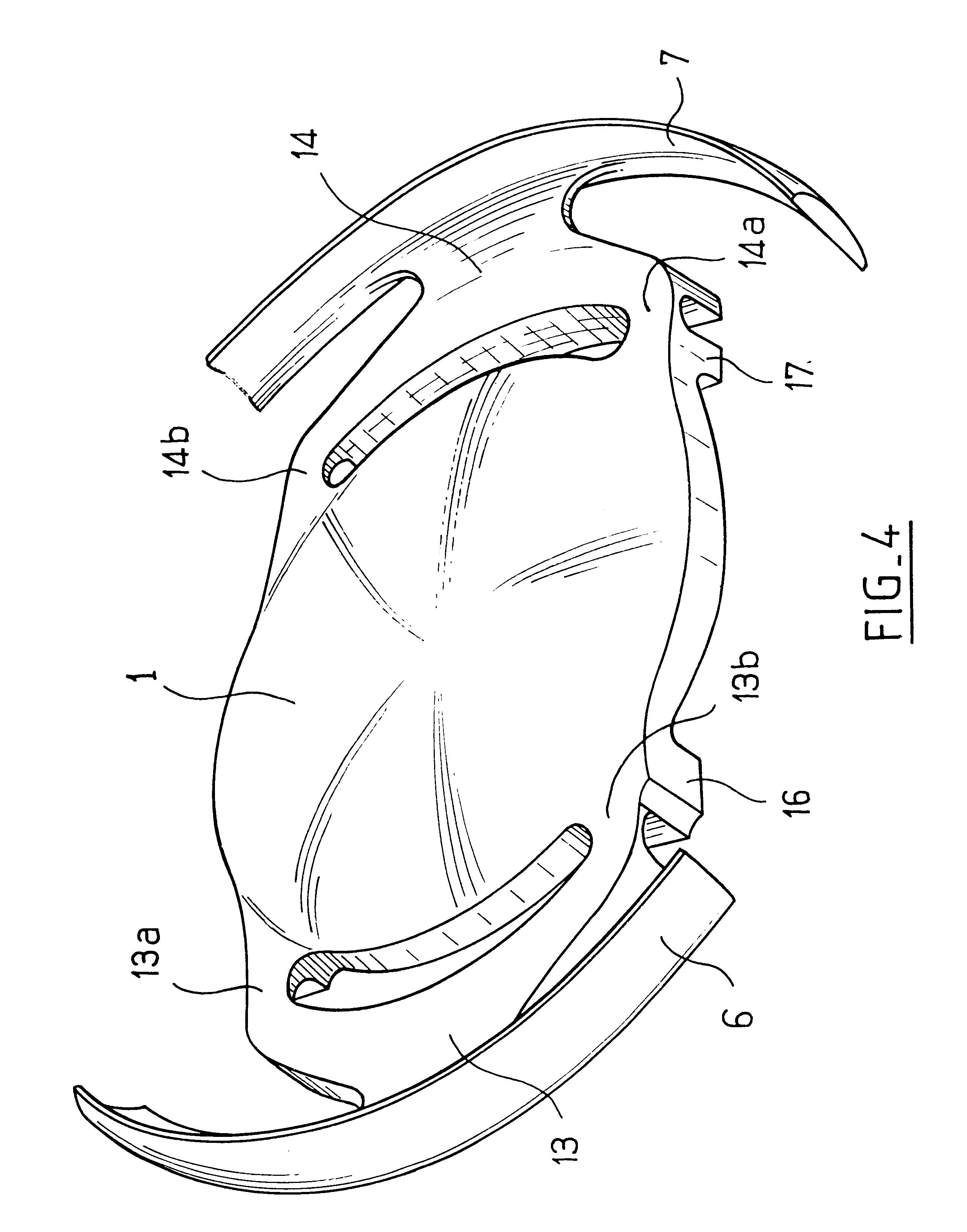
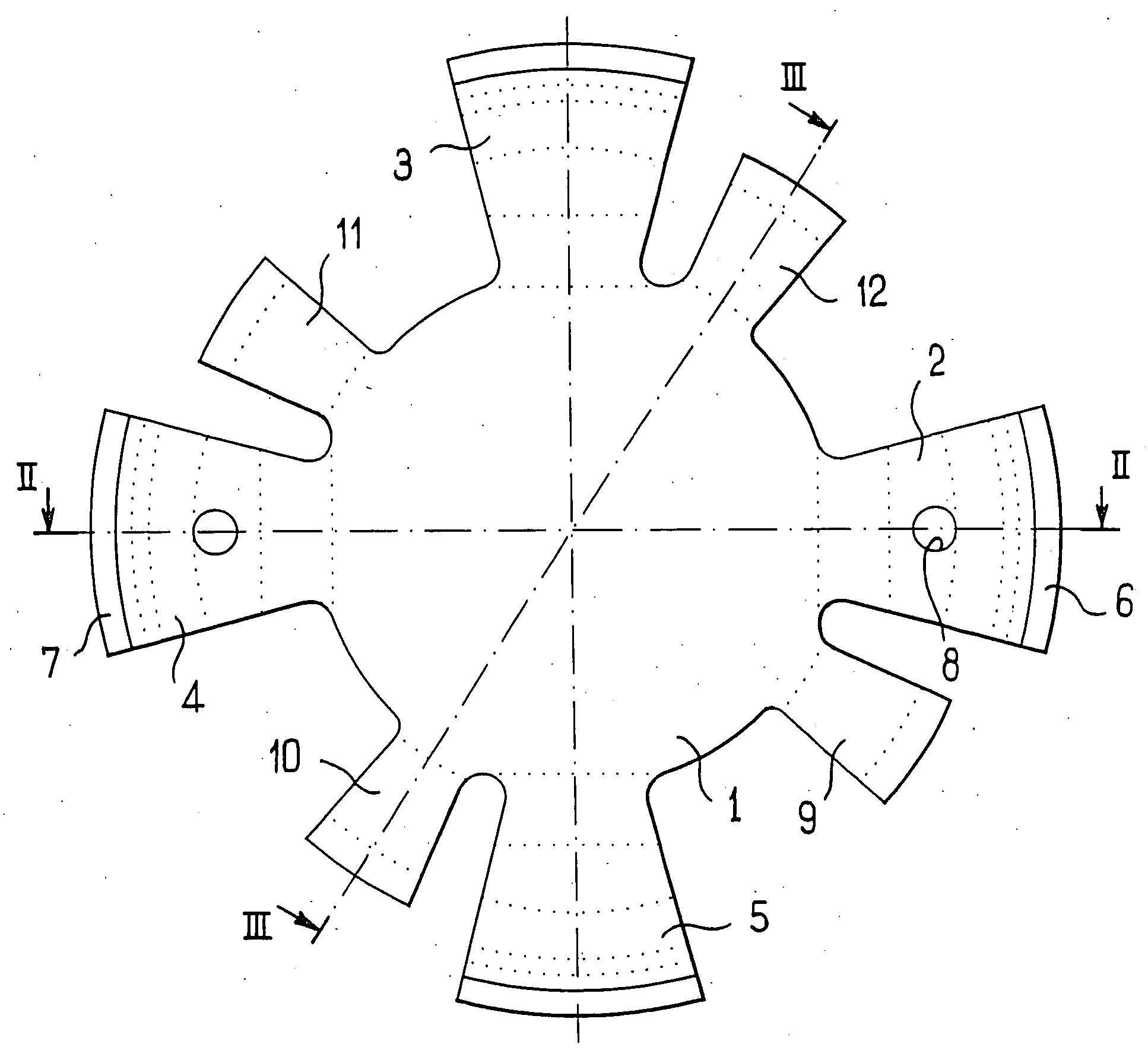
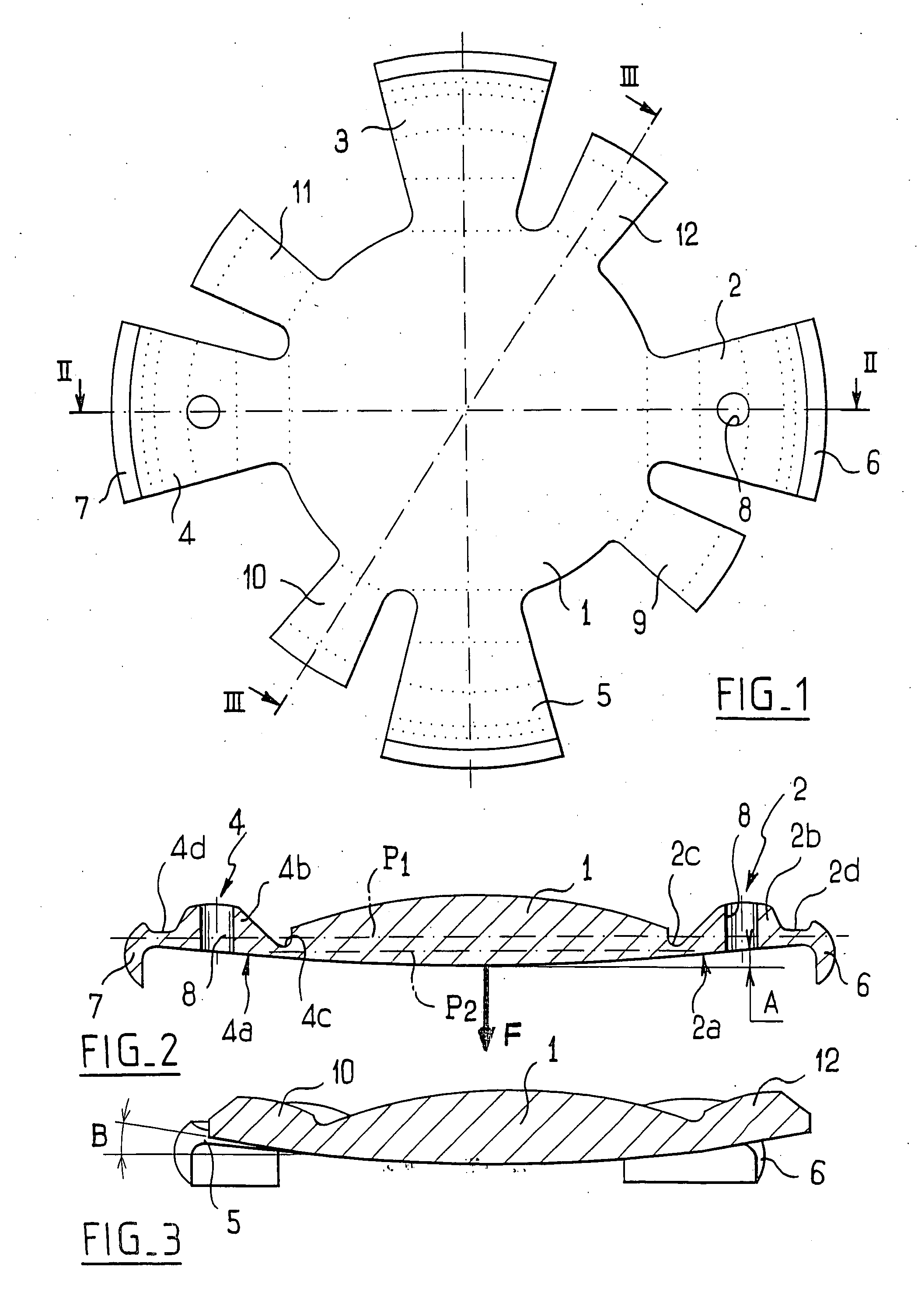
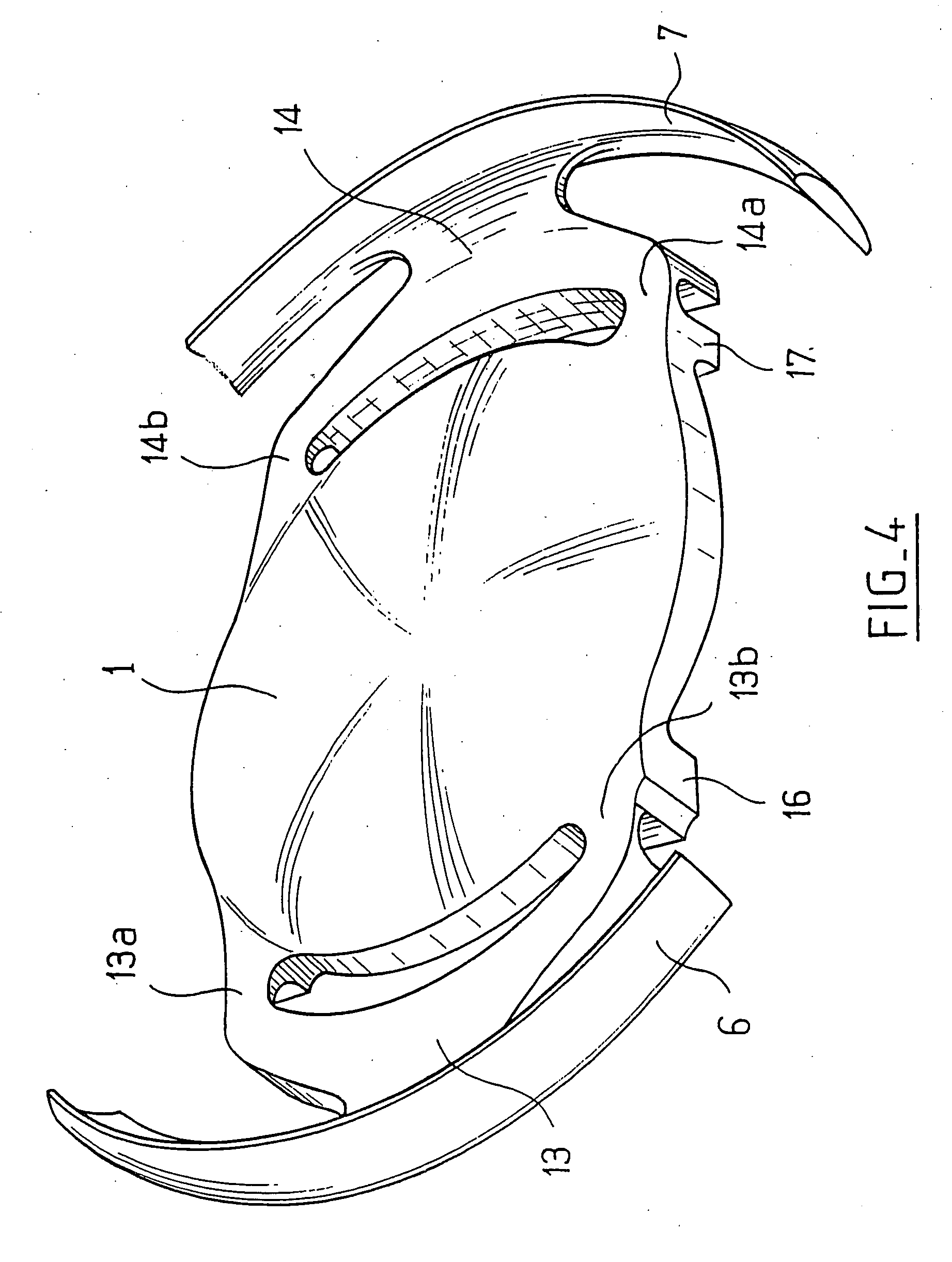
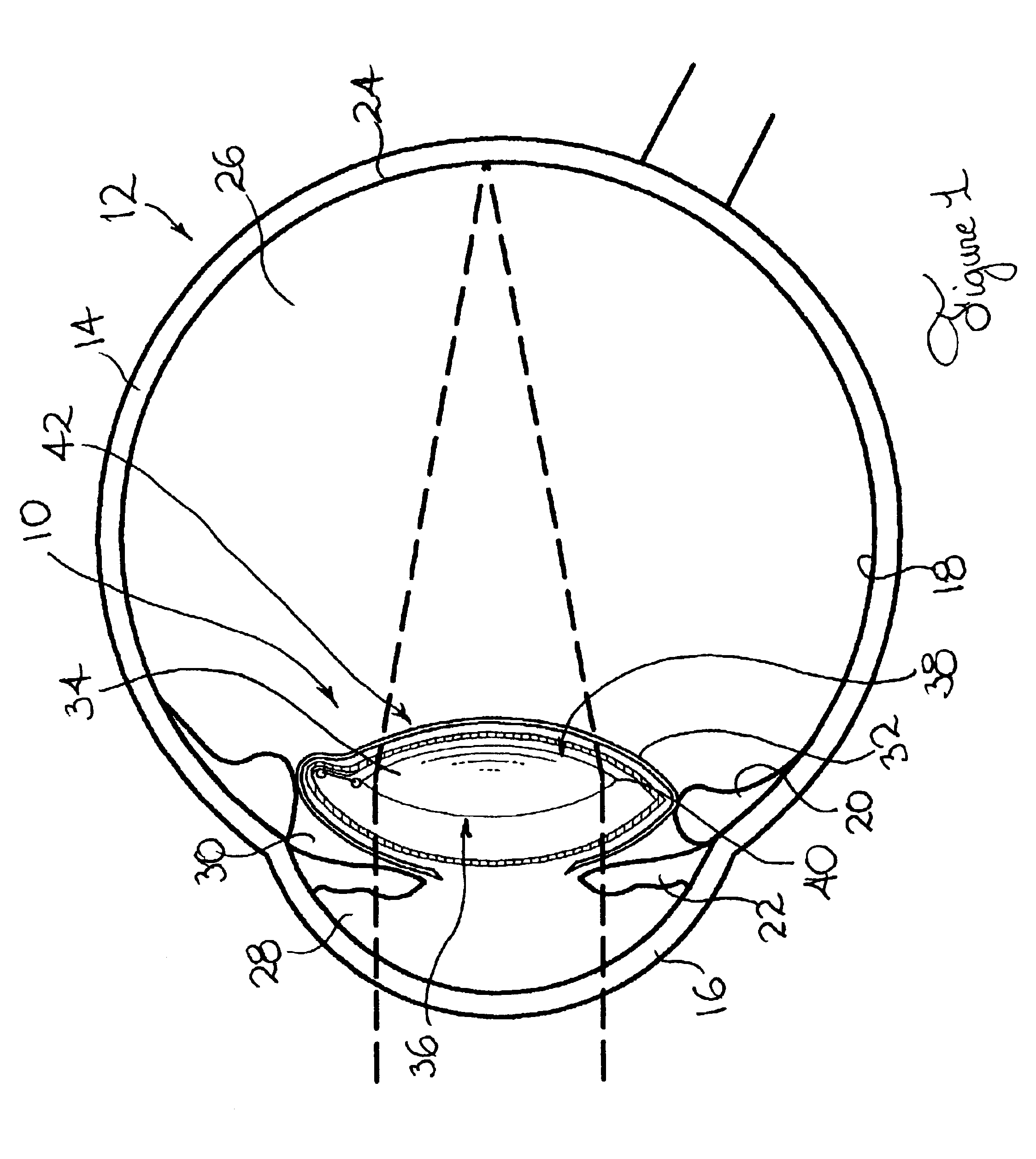
An accommodating intraocular implant for locating in the capsular bag, the implant comprising a single piece of elastically deformable material constituting a central lens (1) and at least two haptic portions (2, 4) in the form of radial arms for bearing via their free ends against the equatorial zone of the capsular bag, the free end of each radial arm (2, 4) being fitted with a shoe (6, 7) of substantially toroidal outside surface enabling the implant to bear against the equatorial zone of the bag, the connection between each shoe (6, 7) and the corresponding arm (2, 4) being of the hinge type situated in the vicinity of the posterior edge of the shoe (6, 7) and being formed by a first thin portion (2d, 4d) of the arm, while the connection between each arm and the lens is of the hinge type implemented at the anterior surface of the lens by a second likewise thin portion (2c, 4c) of the arm, the plane (P1) containing the first thin portions being situated behind the plane (P2) containing the second thin portions.
Owner:HANNA KHALIL PROF DR
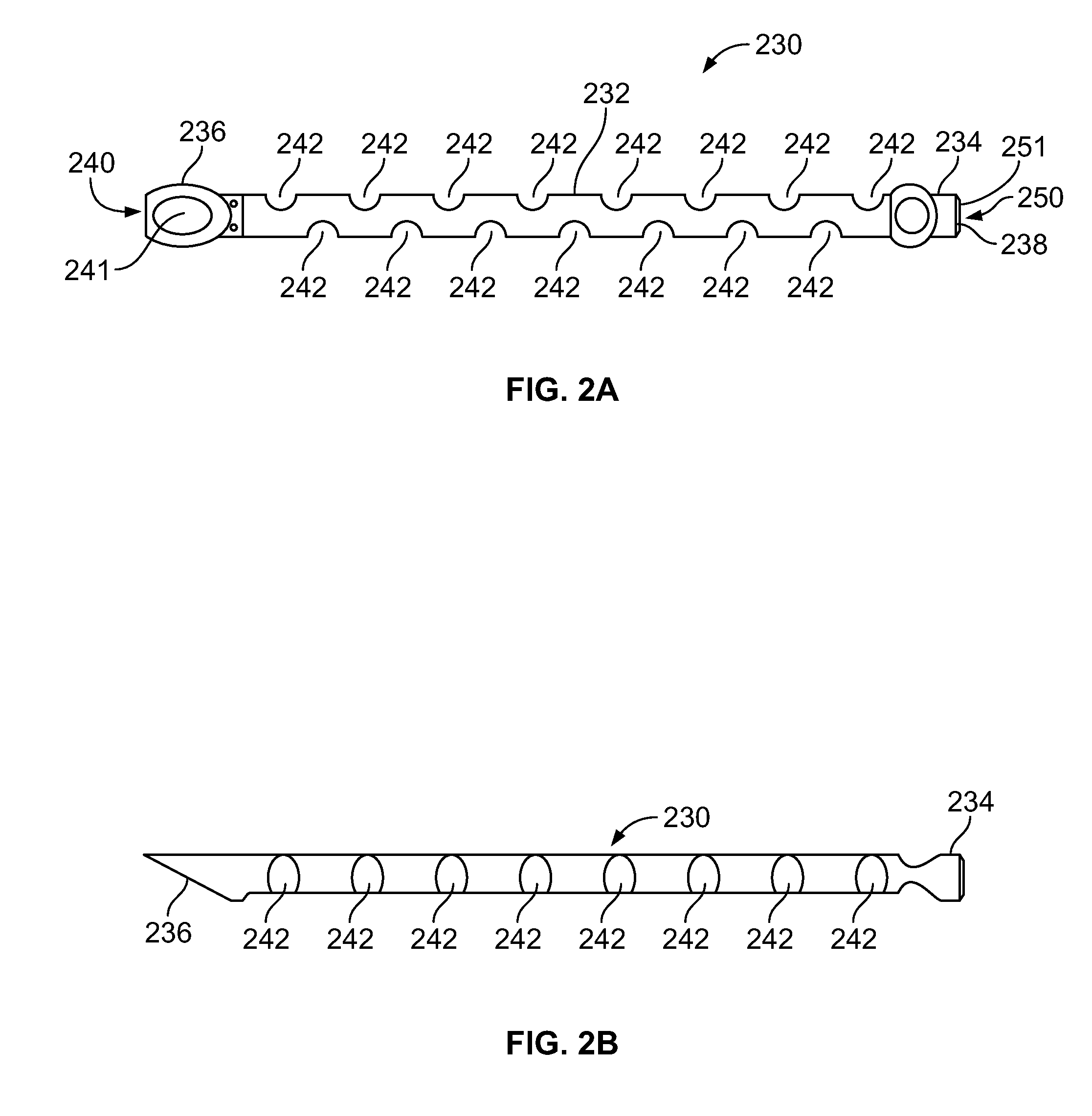
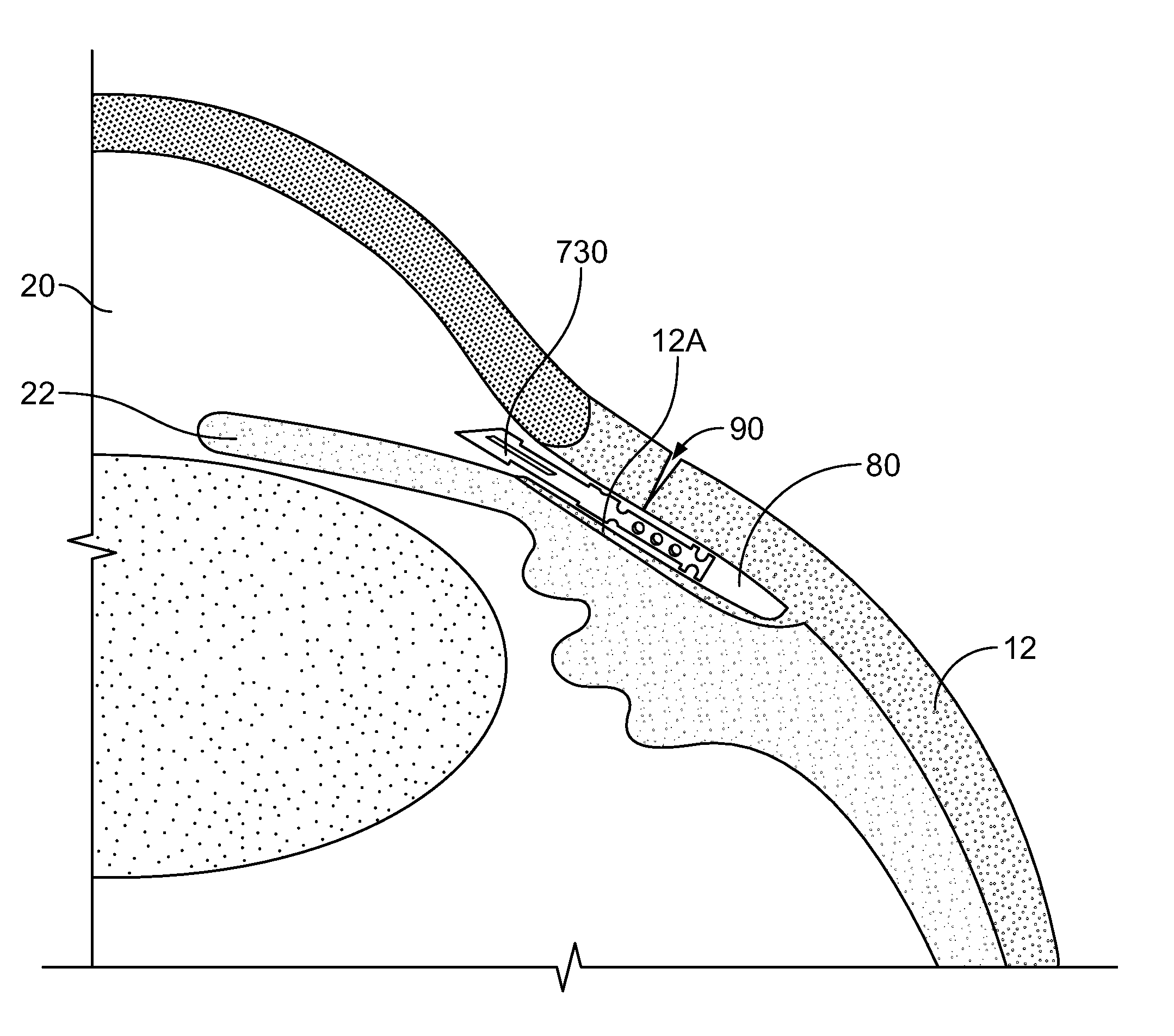
Fluid drainage device, delivery device, and associated methods of use and manufacture
The disclosure provides an intraocular implant for allowing fluid flow from the anterior chamber of an eye, the implant comprising a tube having an inlet end, an outlet end, and a tube passage, wherein the inlet end is adapted to extend into the anterior chamber of the eye, and wherein the outlet end is adapted to be implanted adjacent scleral tissue of the eye. The implant may be adapted to drain aqueous humor into a suprachoroidal space or a juxta-uveal space. The disclosure also provides associated delivery devices, methods of use, and methods of manufacture.
Owner:OPTONOL LTD
Modular intraocular implant
An adjustable ocular insert to be implanted during refractive cataract surgery and clear (human) crystalline lens refractive surgery and adjusted post-surgically. The implant comprises relatively soft but compressible and resilient base annulus designed to fit in the lens capsule and keep the lens capsule open. Alternatively the annulus may be placed in the anterior or posterior chamber. The annulus can include a pair of opposed haptics for secure positioning within the appropriate chamber. A rotatable annular lens member having external threads is threadedly engaged in the annulus. The lens member is rotated to move the lens forward or backward so to adjust and fine-tune the refractive power and focusing for hyperopia, myopia and astigmatism. The intraocular implant has a power range of approximately +3√0π−3 diopters.
Owner:EGGLESTON HARRY C
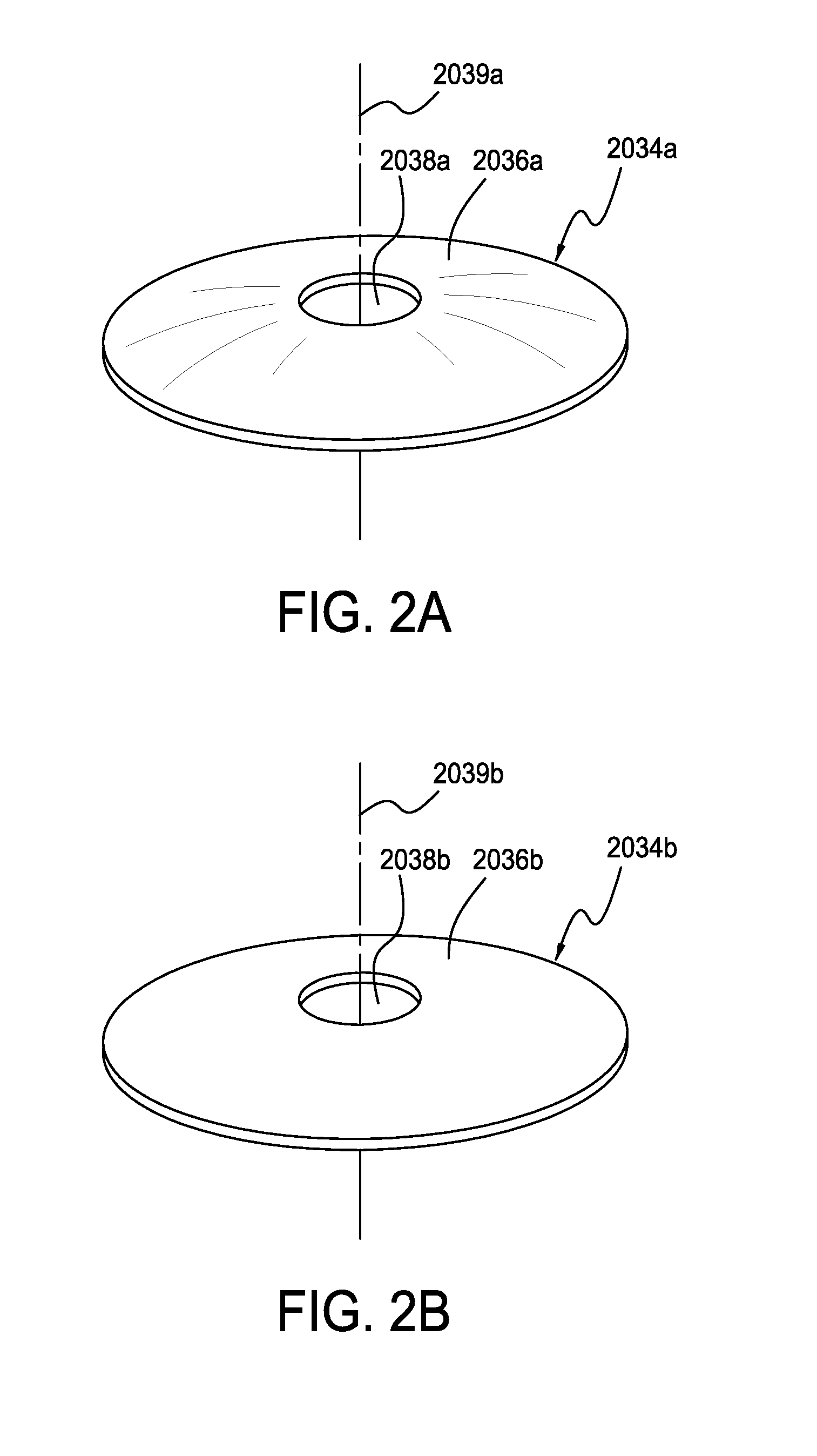
Masked intraocular implants and lenses
ActiveUS20110040376A1Improve eyesightIncrease depth of focusOptical articlesIntraocular lensMedicineOptical power
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implants can improve the vision of a patient, such as by increasing the depth of focus of an eye of a patient. In particular, the intraocular implants can include a mask having an annular portion with a relatively low visible light transmission surrounding a relatively high transmission central portion such as a clear lens or aperture. This construct is adapted to provide an annular mask with a small aperture for light to pass through to the retina to increase depth of focus. The intraocular implant may have an optical power for refractive correction. The intraocular implant may be implanted in any location along the optical pathway in the eye, e.g., as an implant in the anterior or posterior chamber.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Medical implants with a combination of compounds
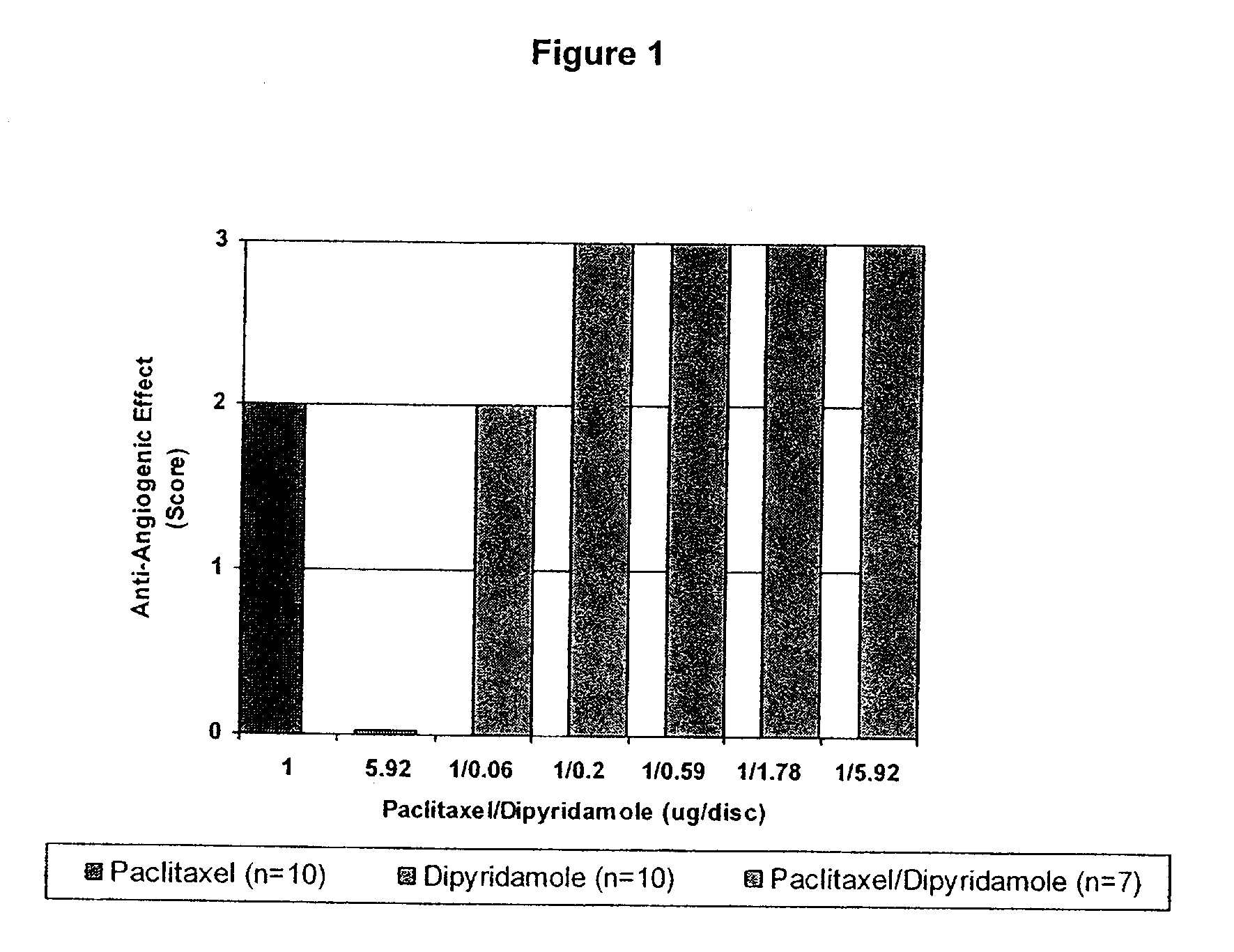
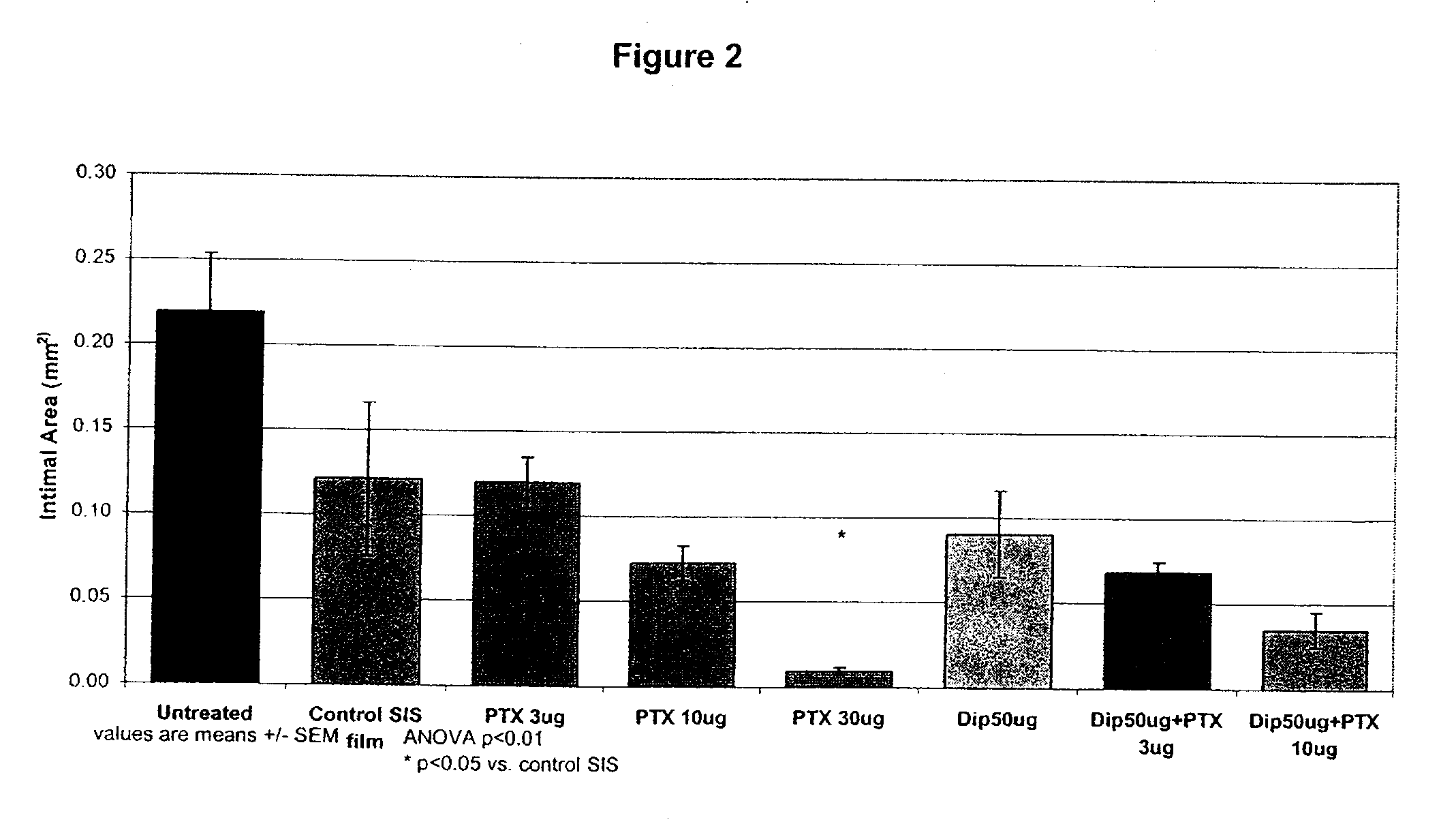
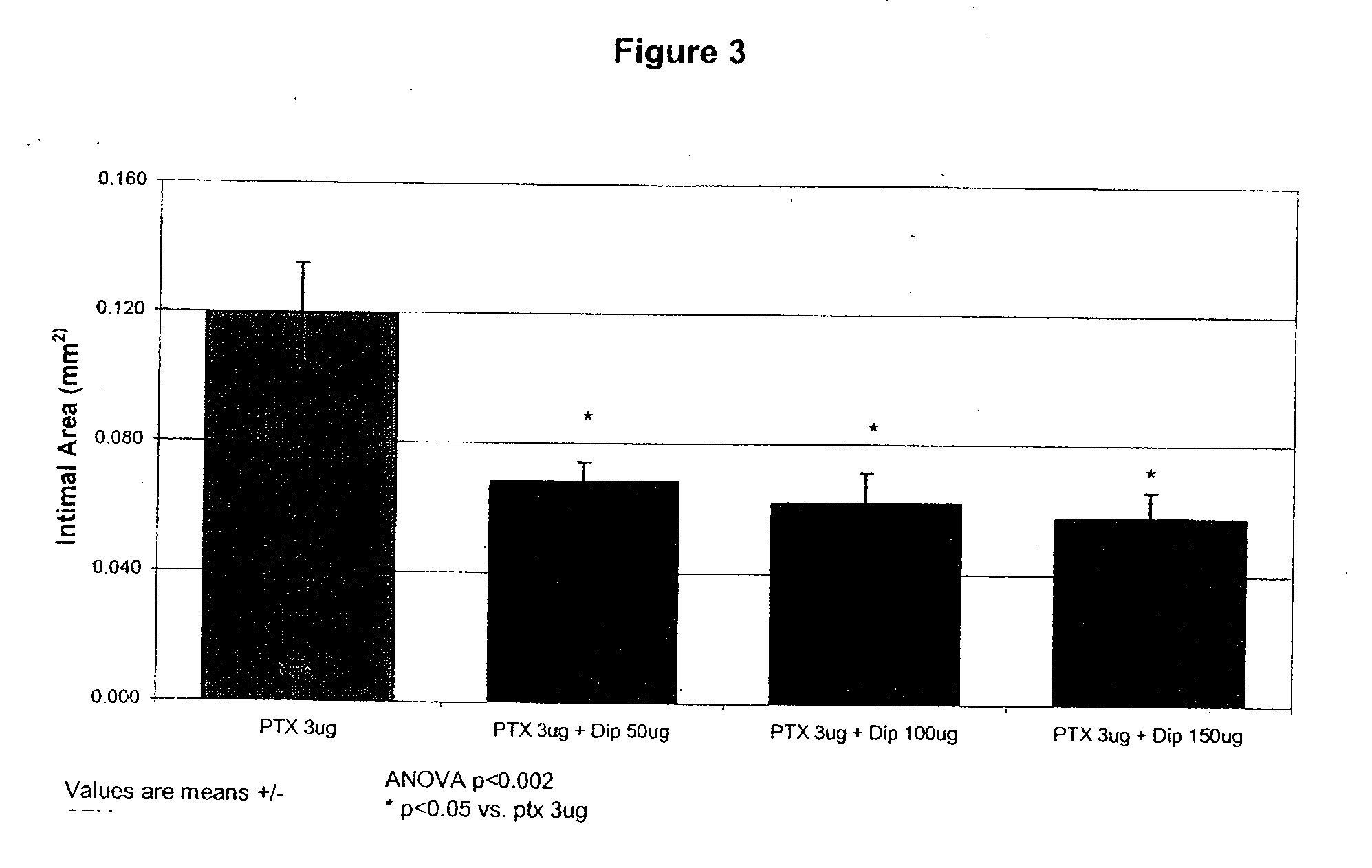
InactiveUS20100074934A1Minimize formationImprove biological effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDipyridamoleFibrosis
Implants are associated with a combination of paclitaxel or derivatives and dipyridamole or derivatives in order to inhibit fibrosis that may otherwise occur when the implant is placed within an animal. Exemplary implants include intravascular implants (e.g., coronary and peripheral vascular stents, catheters, balloons), non-vascular stents, pumps and sensors, vascular grafts, perivascular devices, implants for hemodialysis access, vena cava filters, implants for providing an anastomotic connection, electrical devices, intraocular implants, and soft tissue implants and fillers.
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
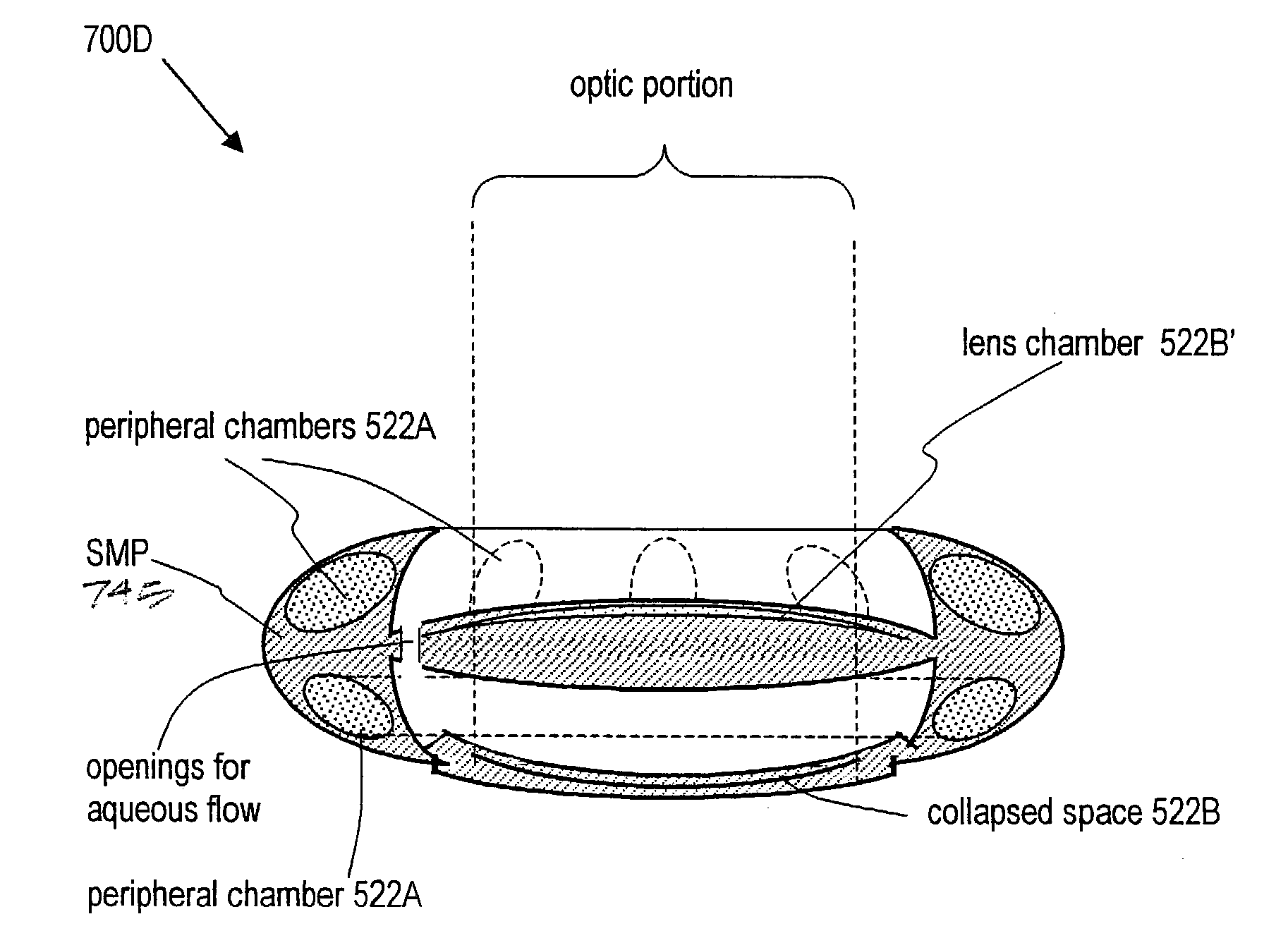
Intraocular implant devices
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
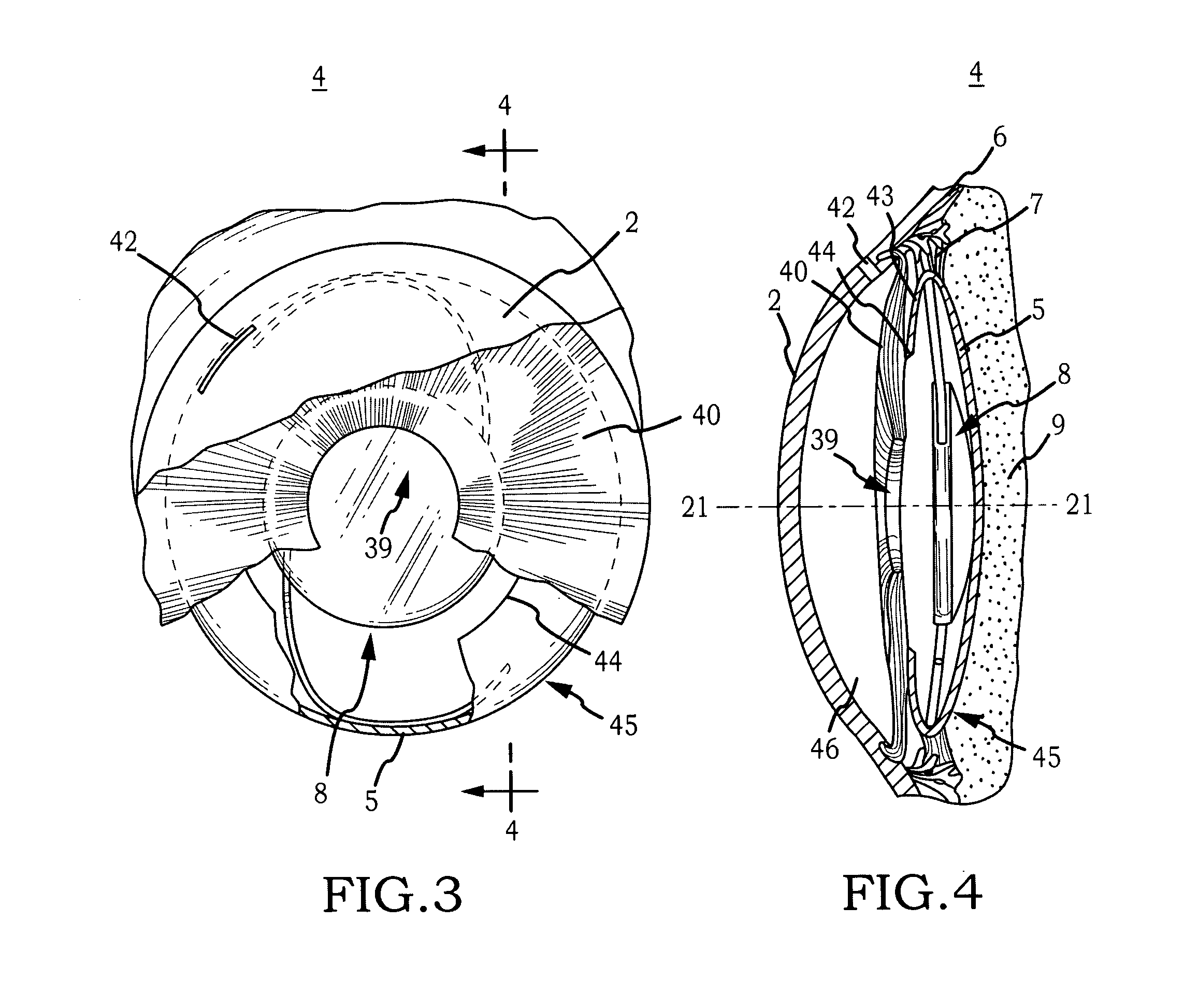
Accommodating Intraocular Lens
InactiveUS20100228344A1Minimal incisionSimplified lens exchangeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCataract surgery
A deformable intracapsular implant device for shaping an enucleated lens capsule sac for use in cataract procedures and refractive lensectomy procedures. In one embodiment, the intraocular implant devices rely on thin film shape memory alloys and combine with the post-phaco capsular sac to provide a biomimetic complex that can mimic the energy-absorbing and energy-releasing characteristics of a young accommodative lens capsule. In another embodiment, the capsular shaping body is combined with an adaptive optic. The peripheral capsular shaping body carries at least one fluid-filled interior chamber that communicates with a space in a adaptive optic portion that has a deformable lens surface. The flexing of the peripheral shaping body in response to zonular tensioning and de-tensioning provides an inventive adaptive optics mechanism wherein fluid media flows between the respective chambers “adapts” the optic to increase and decrease the power thereof. In one embodiment, the capsular shaping body carries a posterior negative power adaptive optic that can be altered in power during accommodation to cooperate with an independent drop-in exchangeable intraocular lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
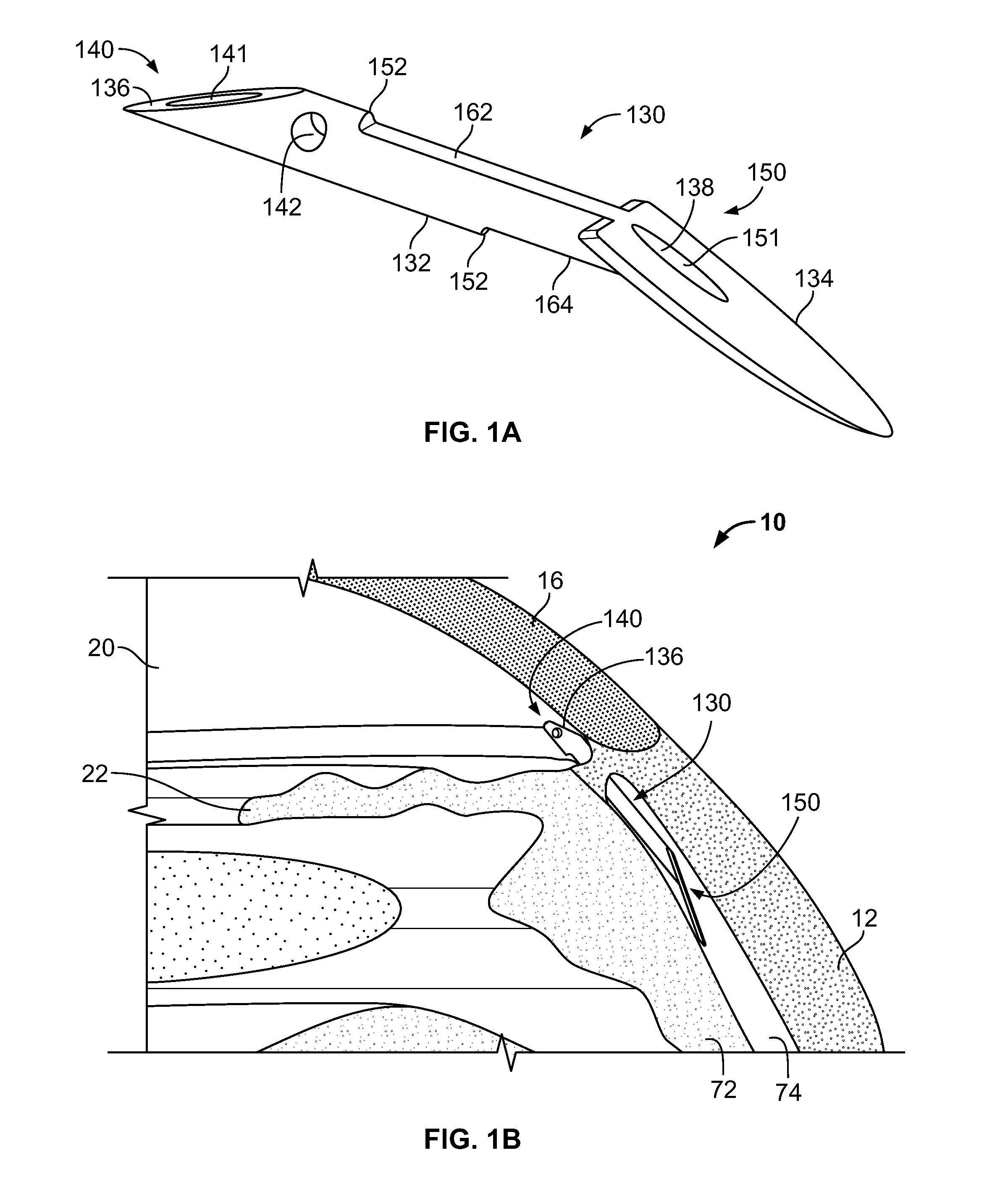
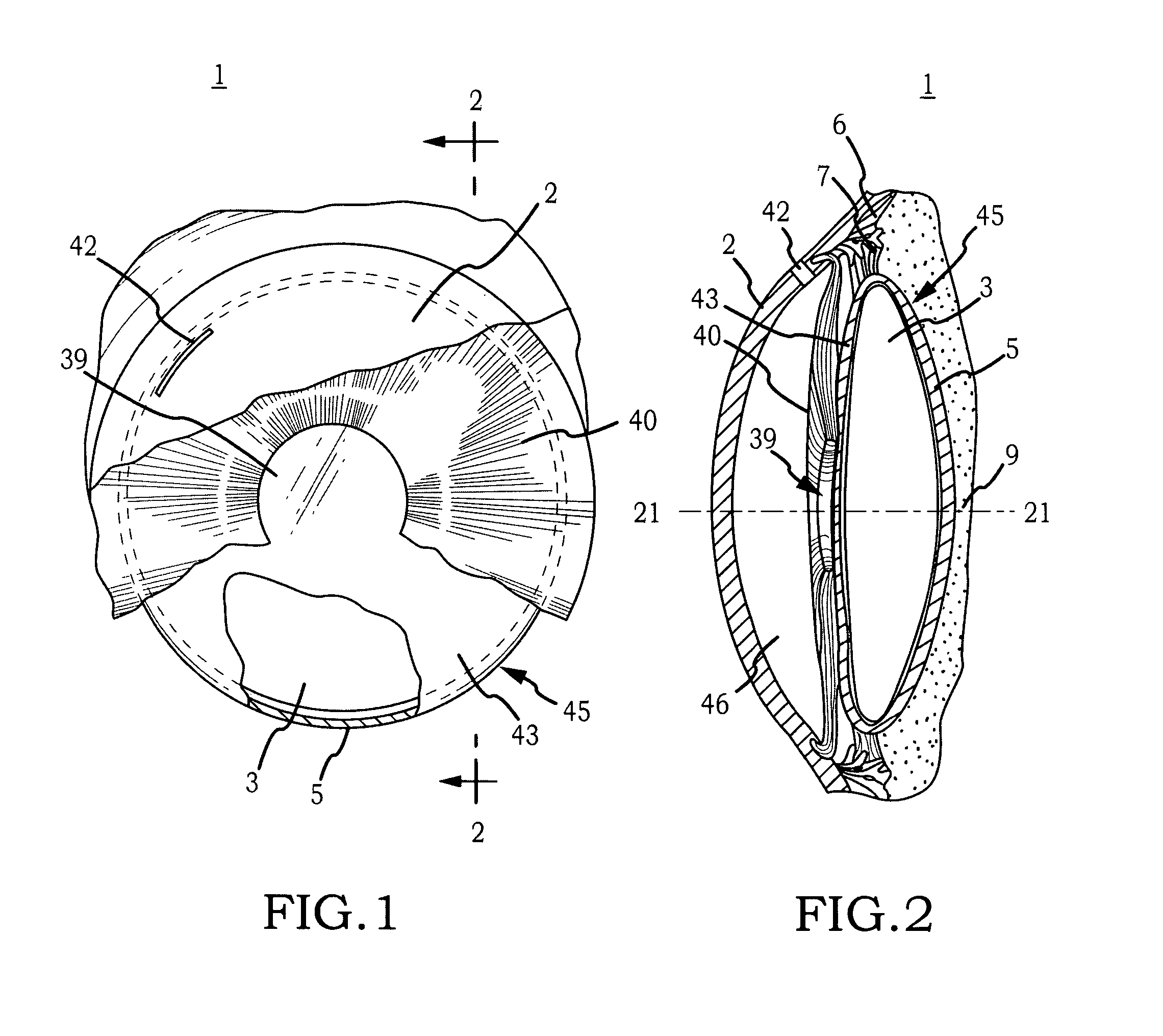
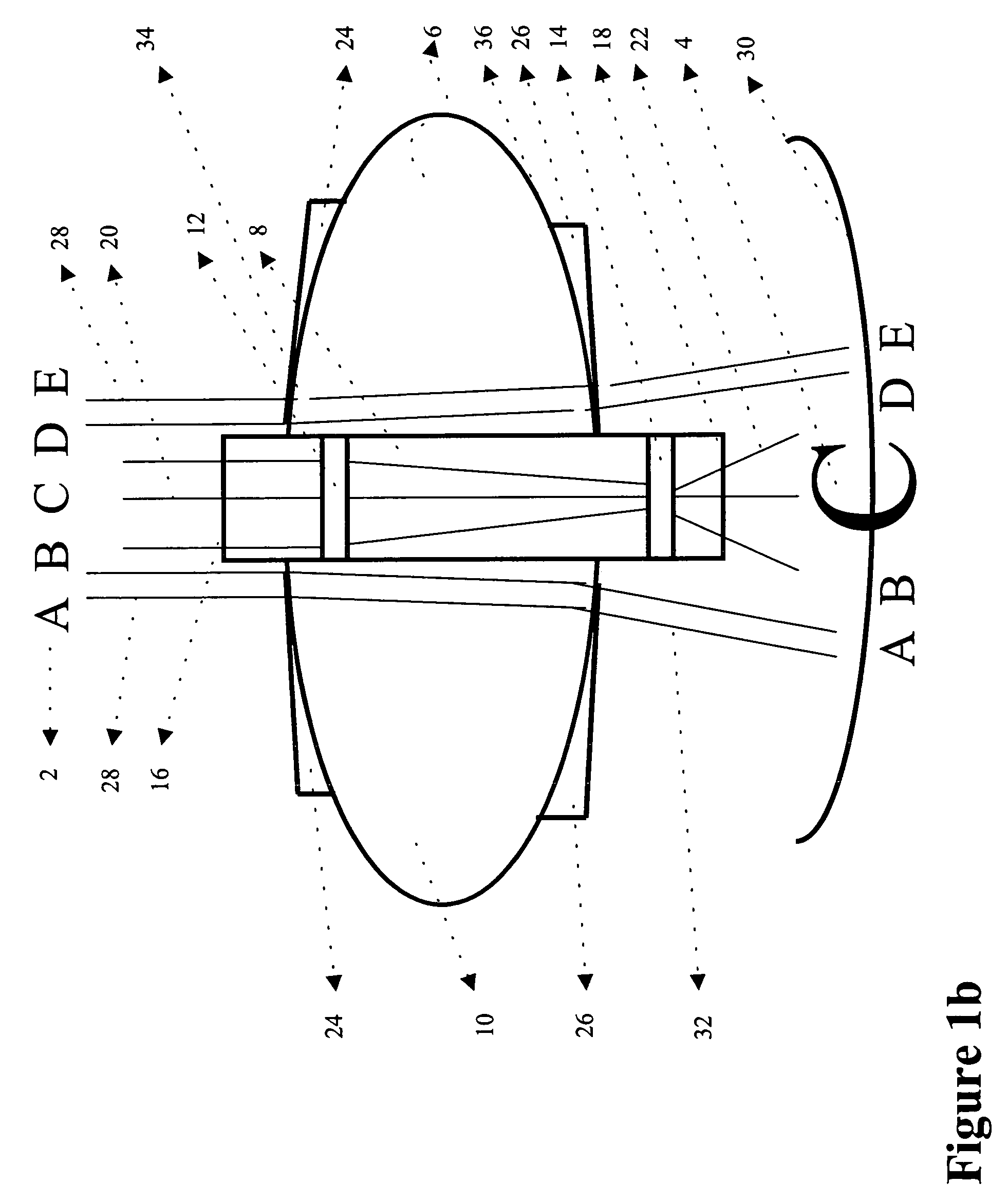
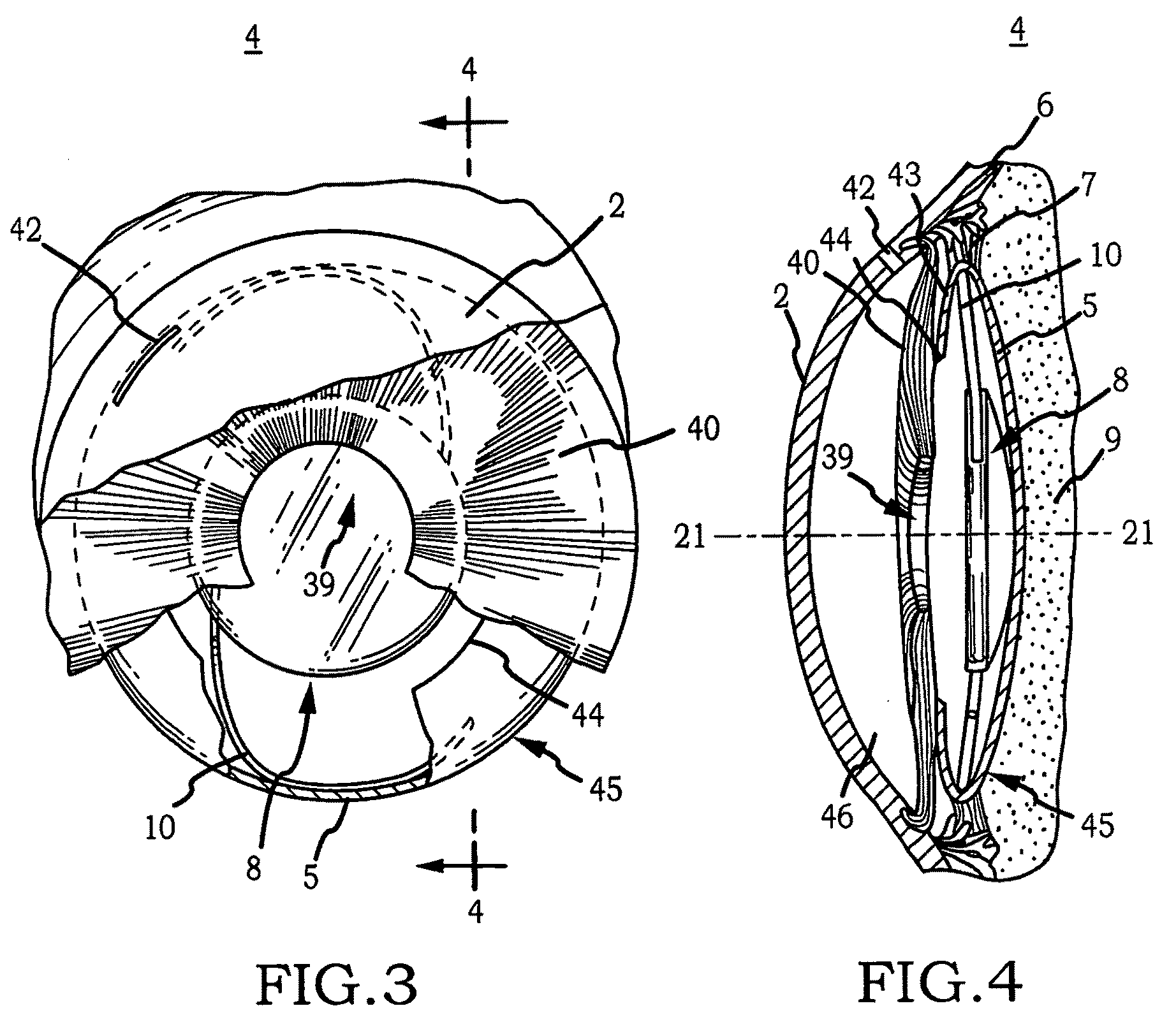
Intraocular implant and an artificial lens device
InactiveUS20050085907A1Improve abilitiesReduce productionIntraocular lensAnterior surfaceIntraocular implant
An accommodating intraocular implant for locating in the capsular bag, the implant comprising a single piece of elastically deformable material constituting a central lens (1) and at least two haptic portions (2, 4) in the form of radial arms for bearing via their free ends against the equatorial zone of the capsular bag, the free end of each radial arm (2, 4) being fitted with a shoe (6, 7) of substantially toroidal outside surface enabling the implant to bear against the equatorial zone of the bag, the connection between each shoe (6, 7) and the corresponding arm (2, 4) being of the hinge type situated in the vicinity of the posterior edge of the shoe (6, 7) and being formed by a first thin portion (2d, 4d) of the arm, while the connection between each arm and the lens is of the hinge type implemented at the anterior surface of the lens by a second likewise thin portion (2c, 4c) of the arm, the plane (P1) containing the first thin portions being situated behind the plane (P2) containing the second thin portions.
Owner:HUMANOPTICS AG
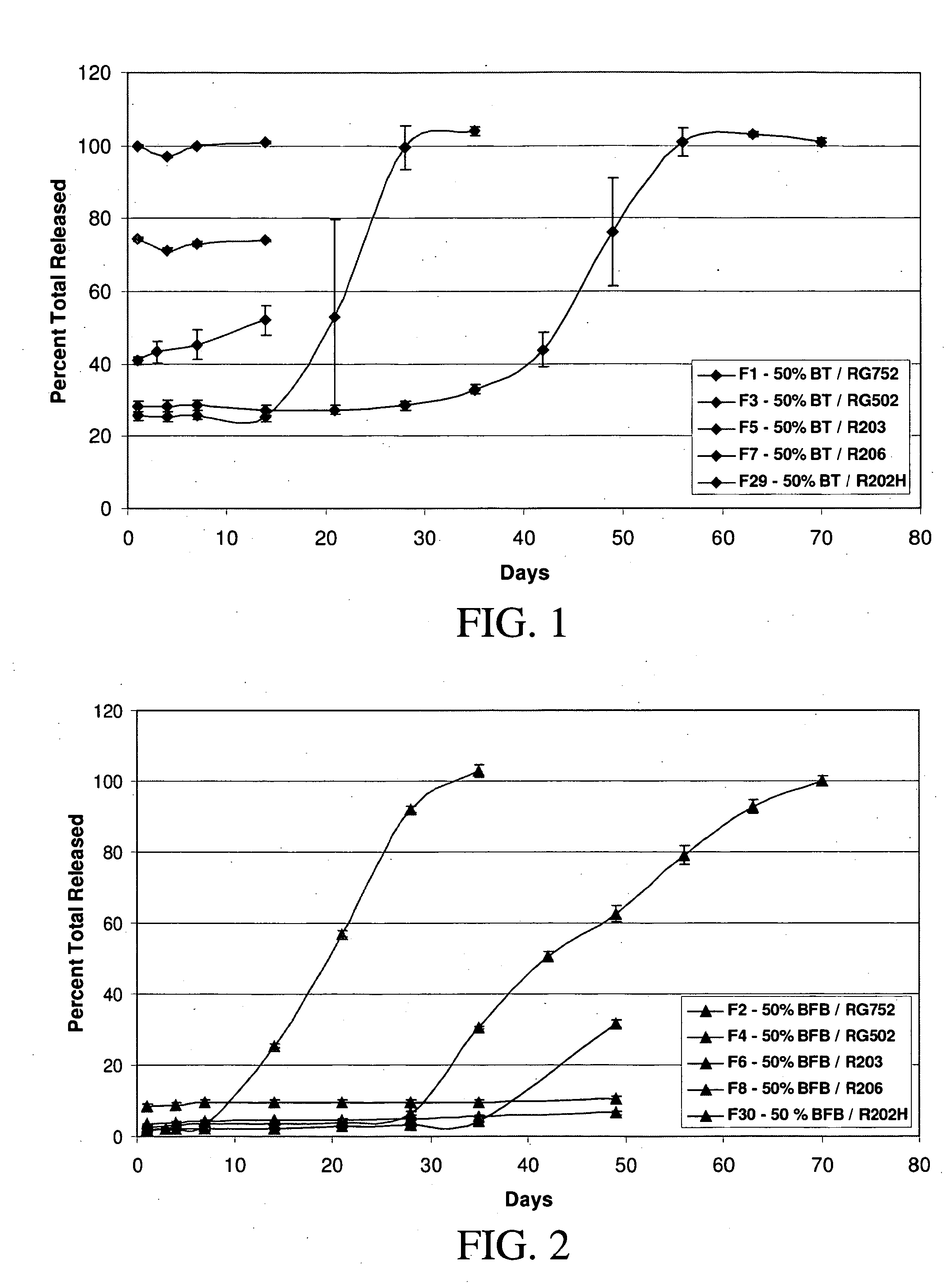
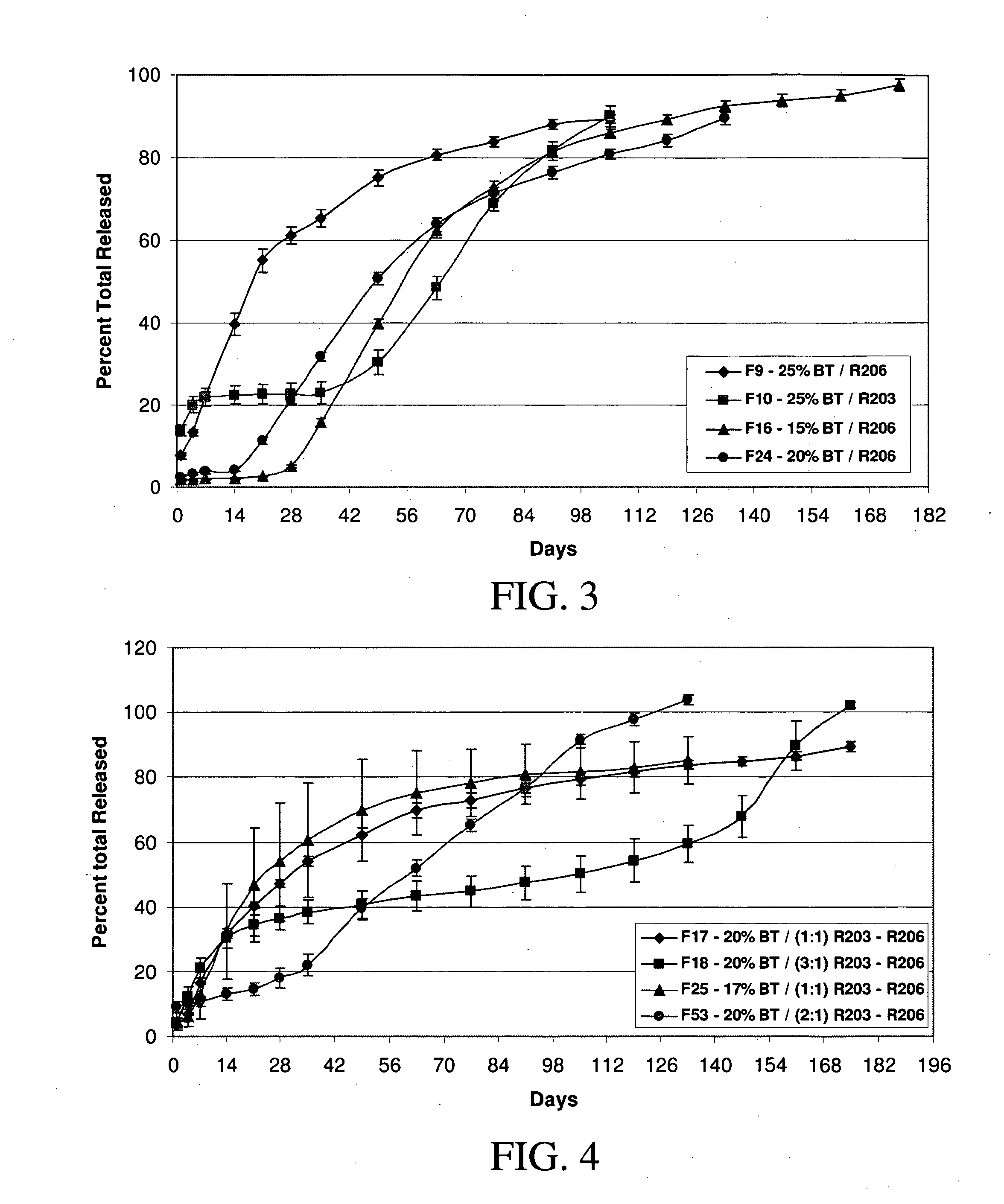
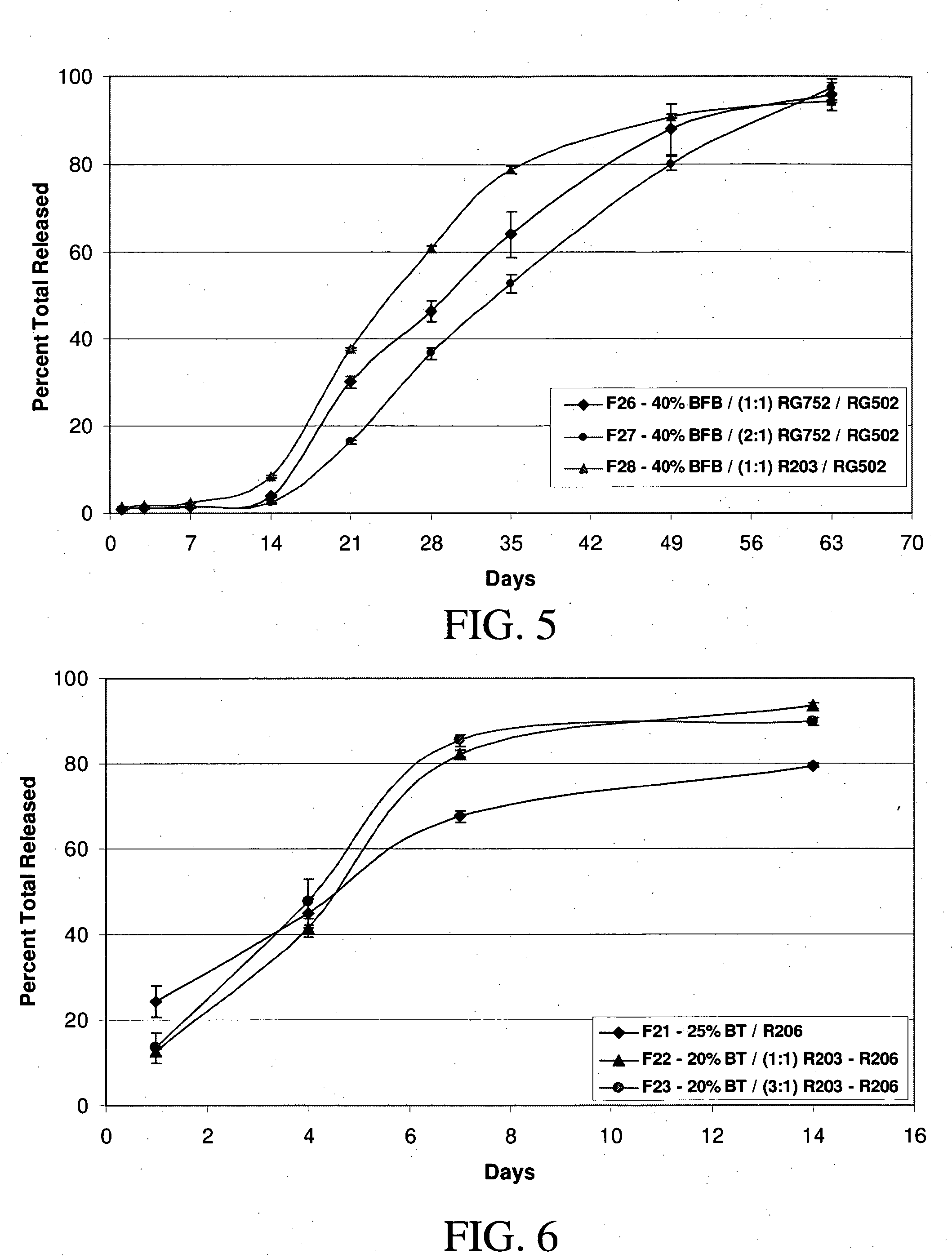
Sustained release intraocular implants and methods for preventing retinal dysfunction
InactiveUS20050244506A1Few and no negative side effectFacilitate obtaining successful treatment resultsPowder deliveryBiocideMicrosphereRetinal dysfunction
Biocompatible intraocular microspheres and implants include an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist and a polymer associated with the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist to facilitate release of the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist into an eye for an extended period of time. The alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist may be associated with a biodegradable polymer matrix, such as a matrix of a two biodegradable polymers. The implants may be placed in an eye to treat or to prevent the occurrence of one or more ocular conditions, to reduce one or more symptoms of an ocular condition, such as an ocular neurosensory disorder and the like, to enhance normal retinal function and / or to lower intraocular pressure.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
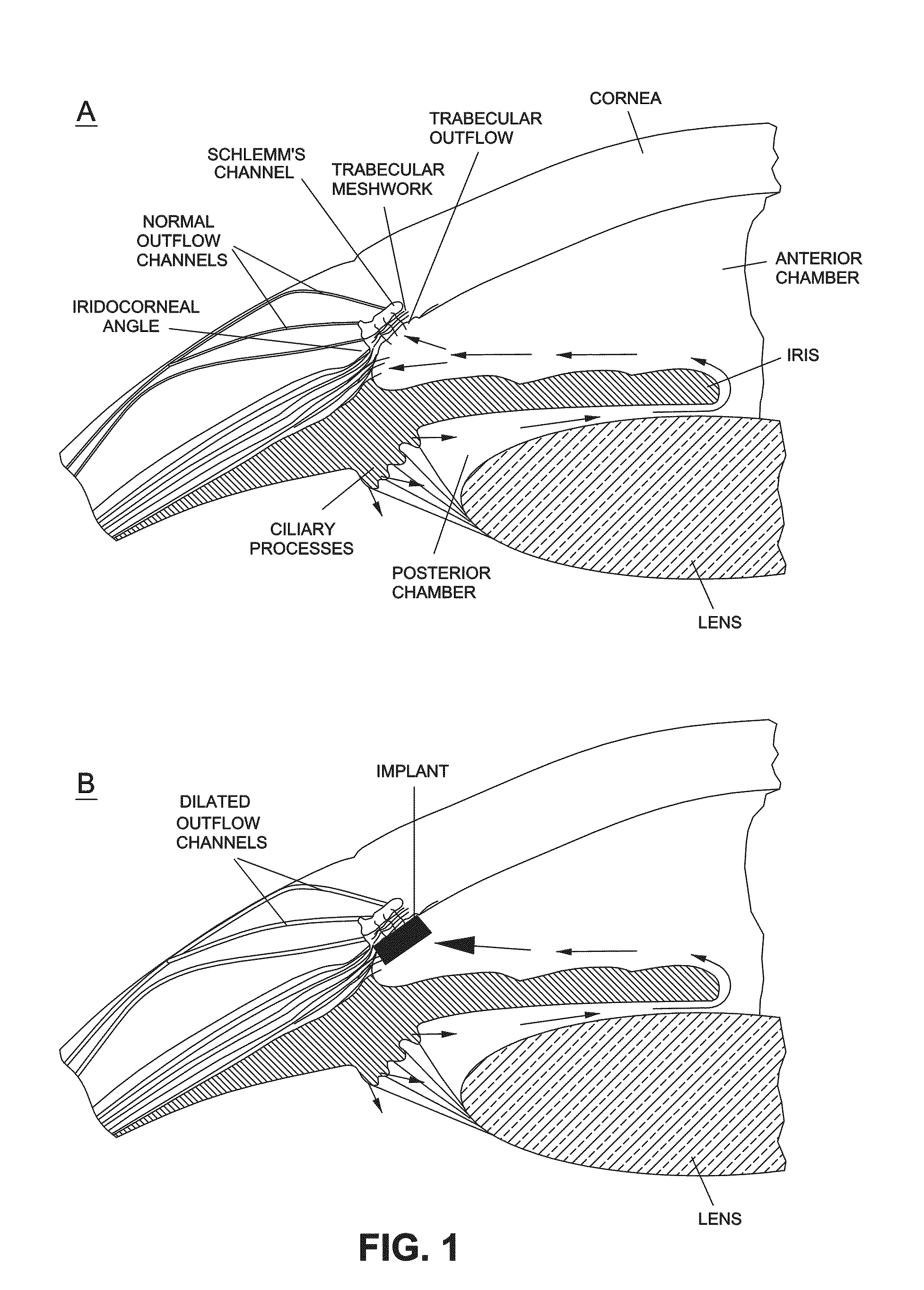
Intraocular pressure reduction with intracameral bimatoprost implants
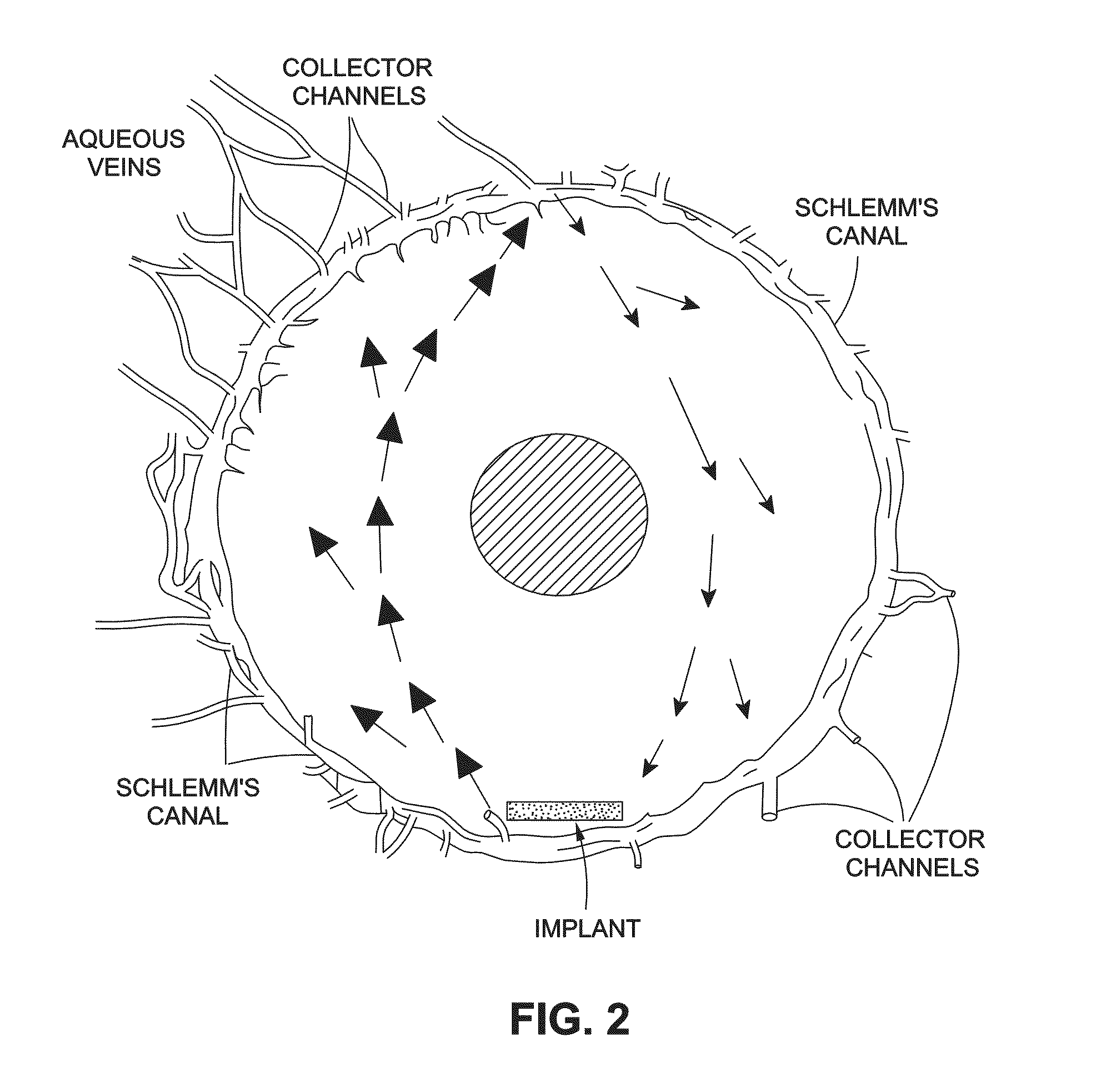
ActiveUS20100278898A1Inhibit progressLower eye pressureBiocideSenses disorderSchlemm's canalIntraocular pressure
The present invention provides a method of treating an ocular condition in an eye of a patient, comprising the step of placing a biodegradable intraocular implant in an eye of the patient, the implant comprising a prostamide and a biodegradable polymer matrix that releases drug at a rate effective to sustain release of an amount of the prostamide from the implant to provide an amount of the prostamide effective to prevent or reduce a symptom of an ocular condition of the eye, wherein said ocular condition is elevated IOP and said implant is placed in an intracameral location to dilate the outflow channels of the eye emanating from Schlemm's Canal.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
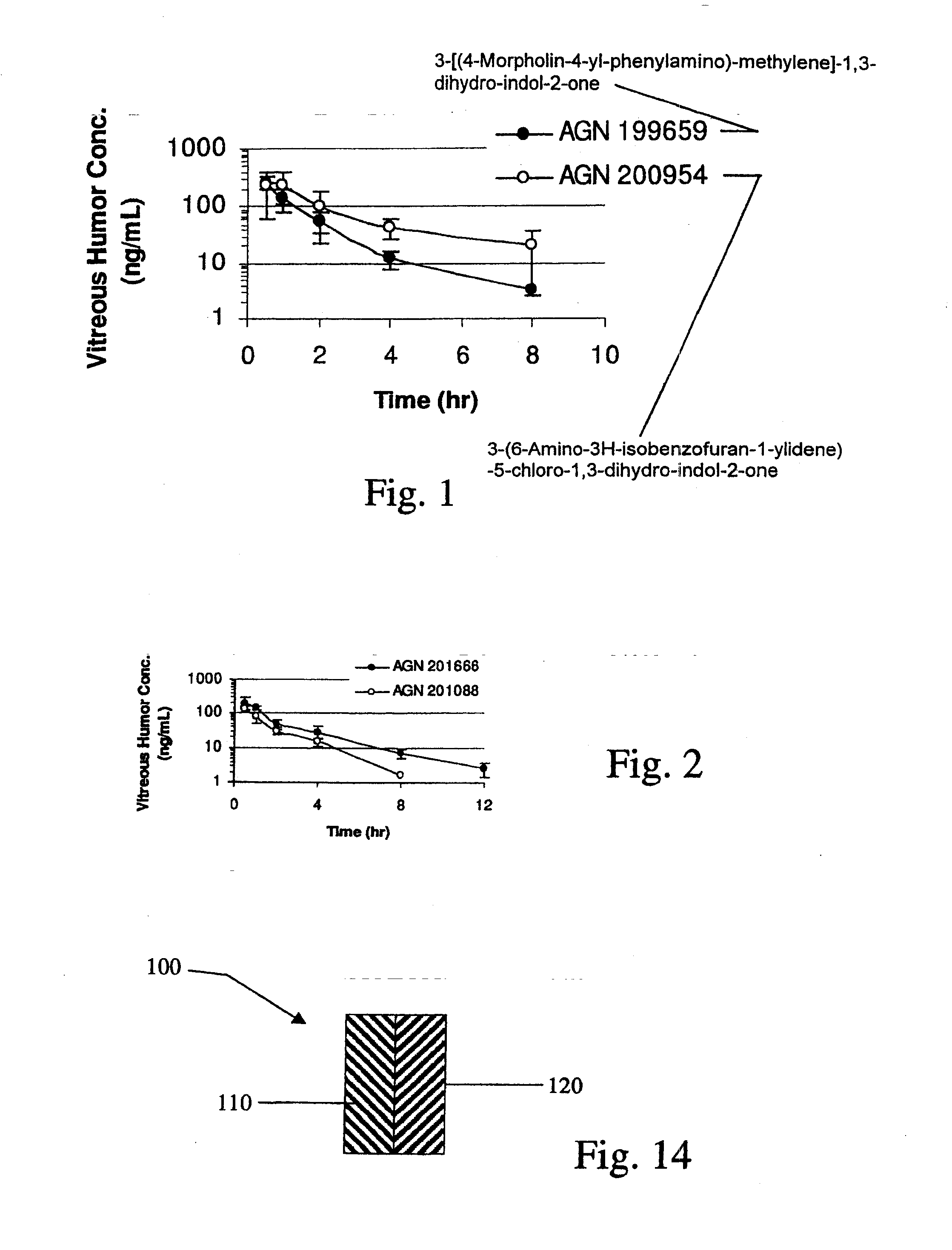
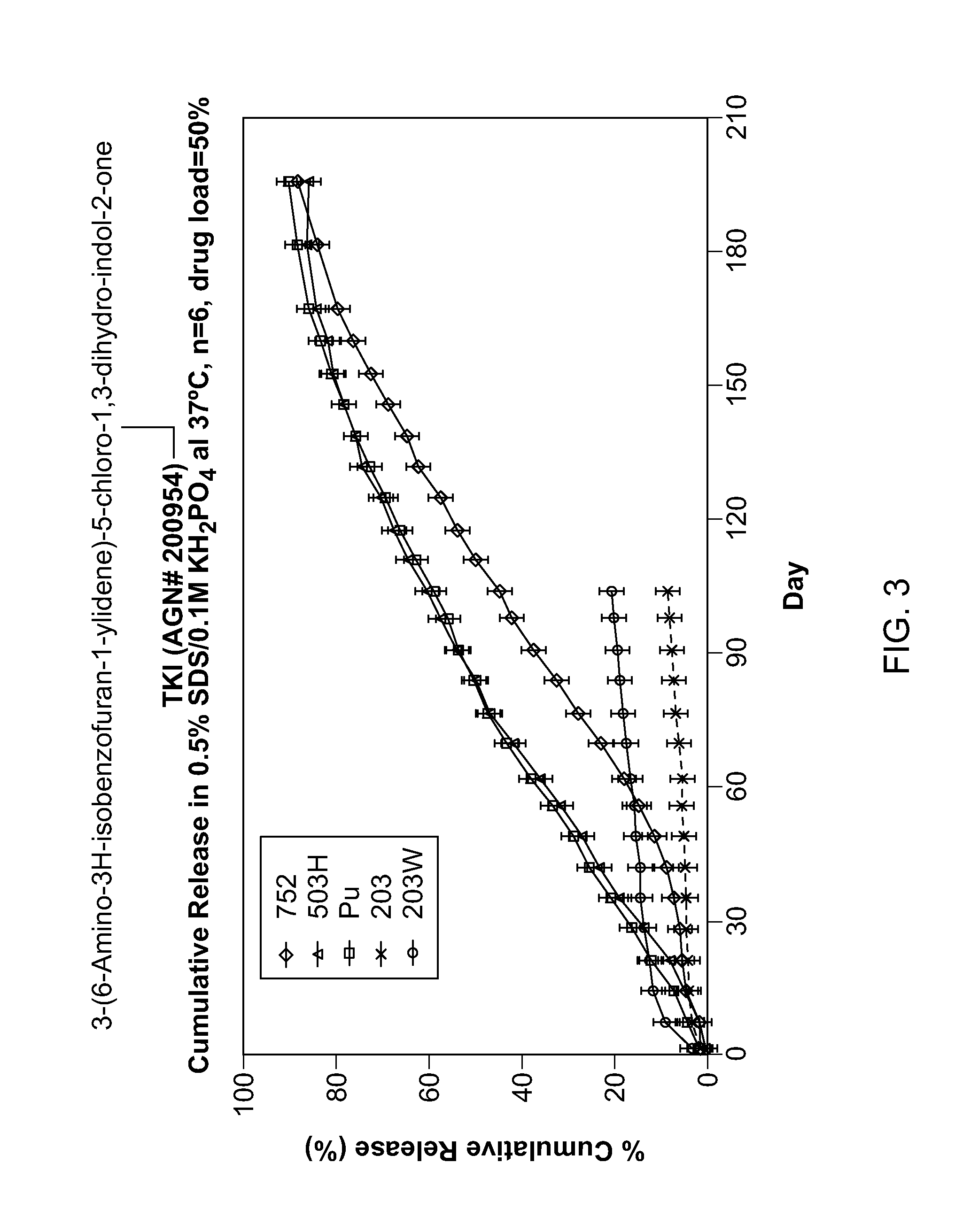
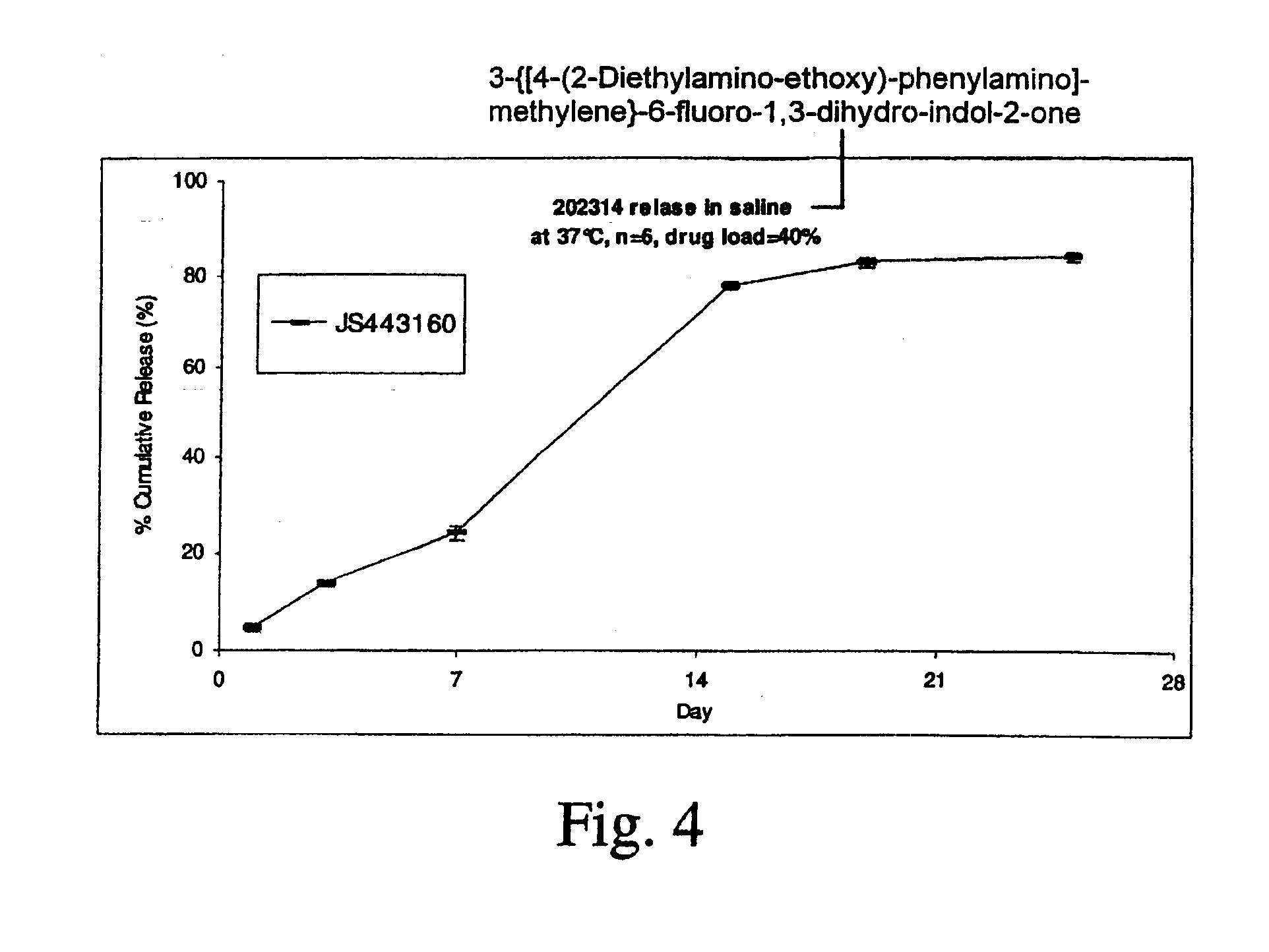
Biodegradable Intravitreal Tyrosine Kinase Implants
ActiveUS20140031408A1Reduce deliveryFacilitate obtaining successful treatment resultsBiocideSenses disorderOphthalmologyPolyvinyl alcohol
Biocompatible intraocular implants include a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and a biodegradable polymer that is effective to facilitate release of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor into the vitreous of an eye for an extended period of time. The therapeutic agents of the implants may be associated with a biodegradable polymer matrix, such as a matrix that is substantially free of a polyvinyl alcohol. The implants can be placed in an eye to treat or reduce the occurrence of one or more ocular conditions.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
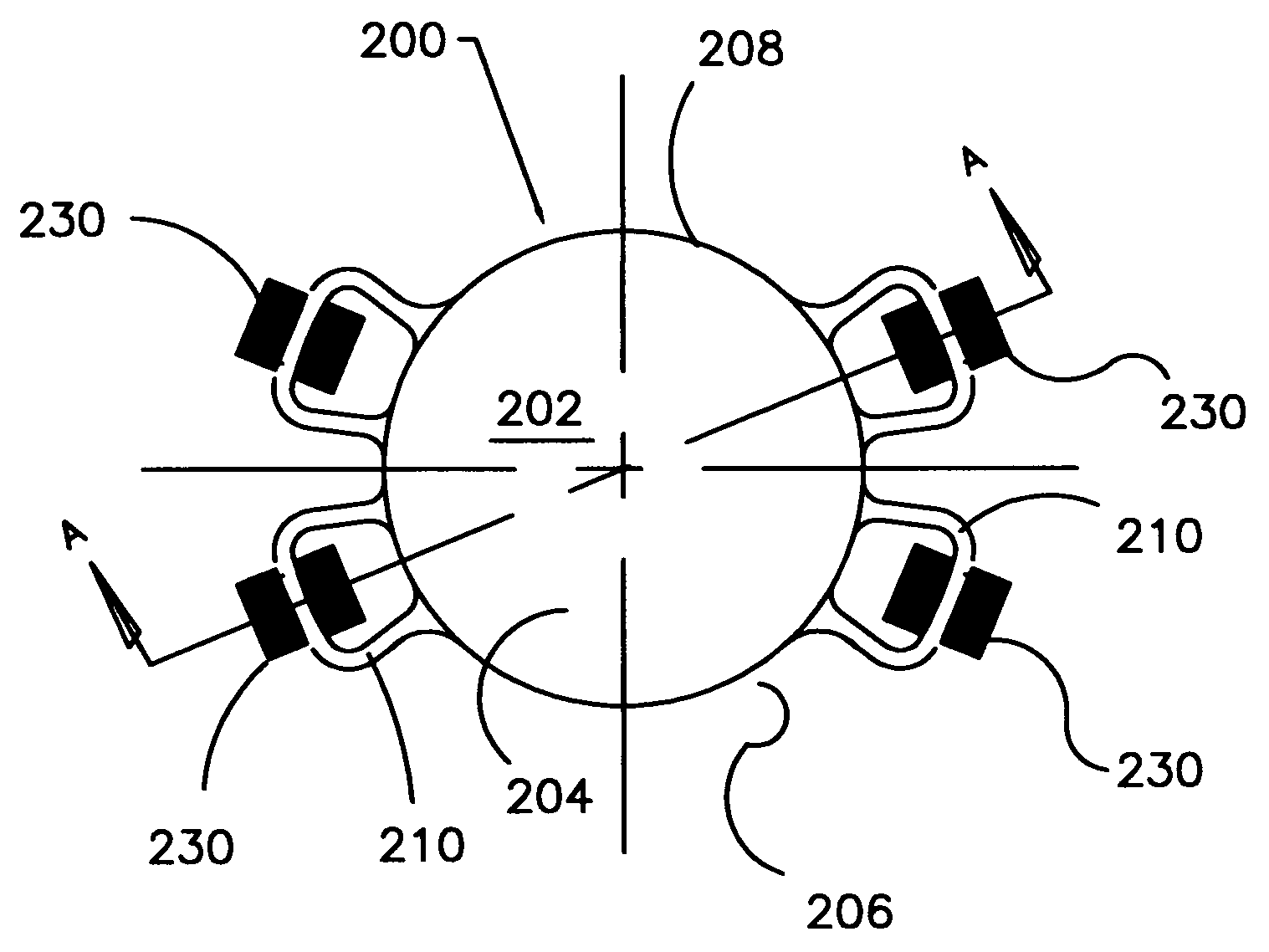
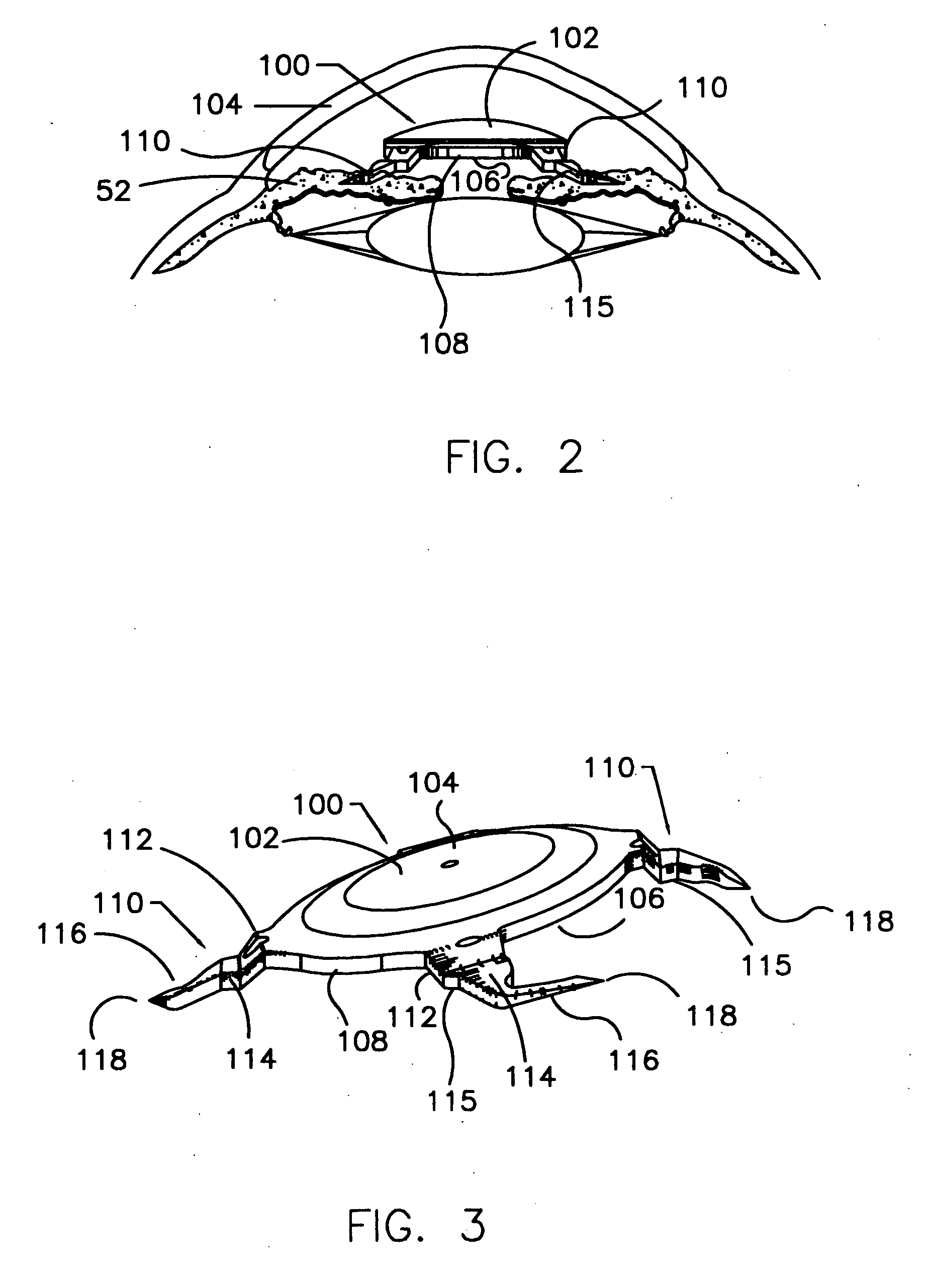
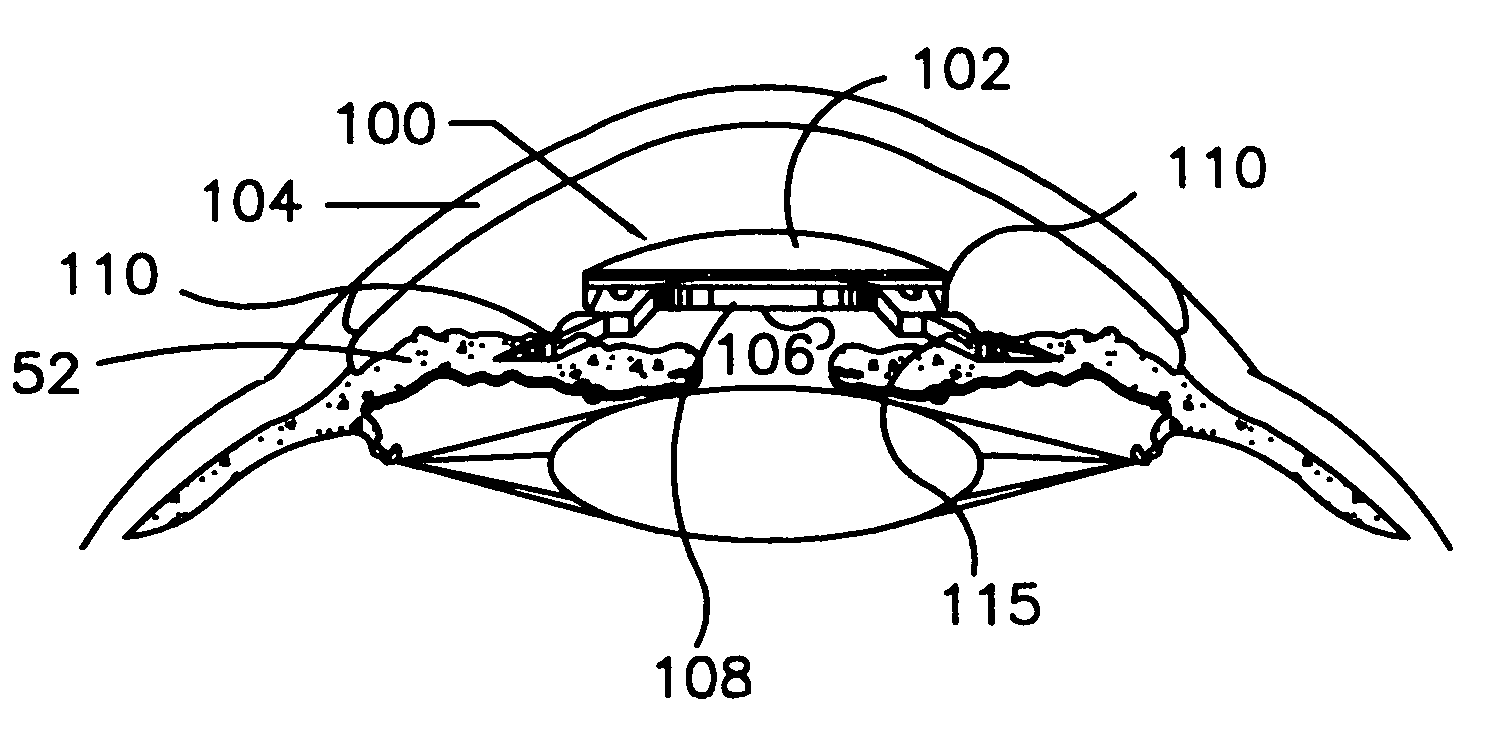
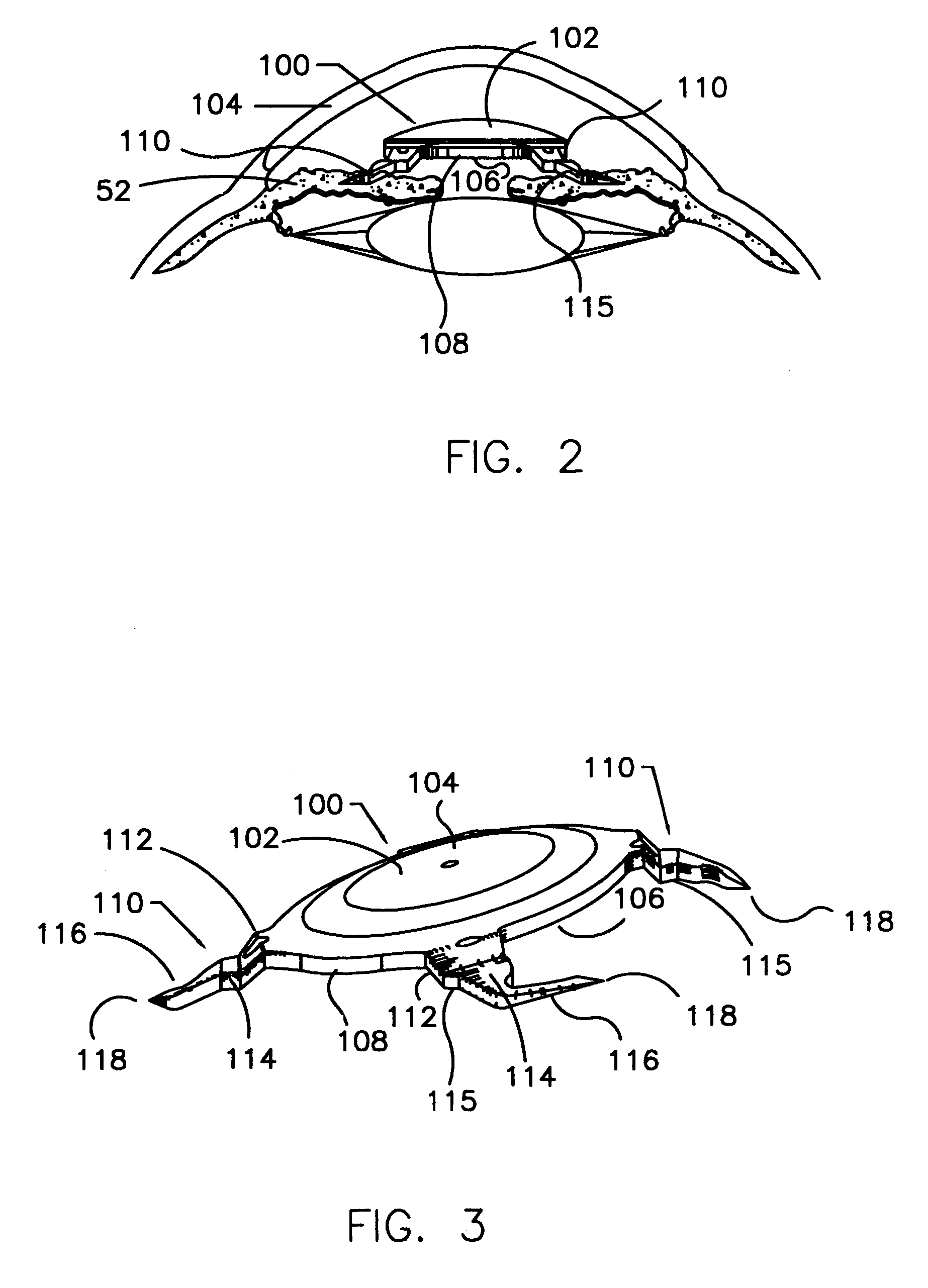
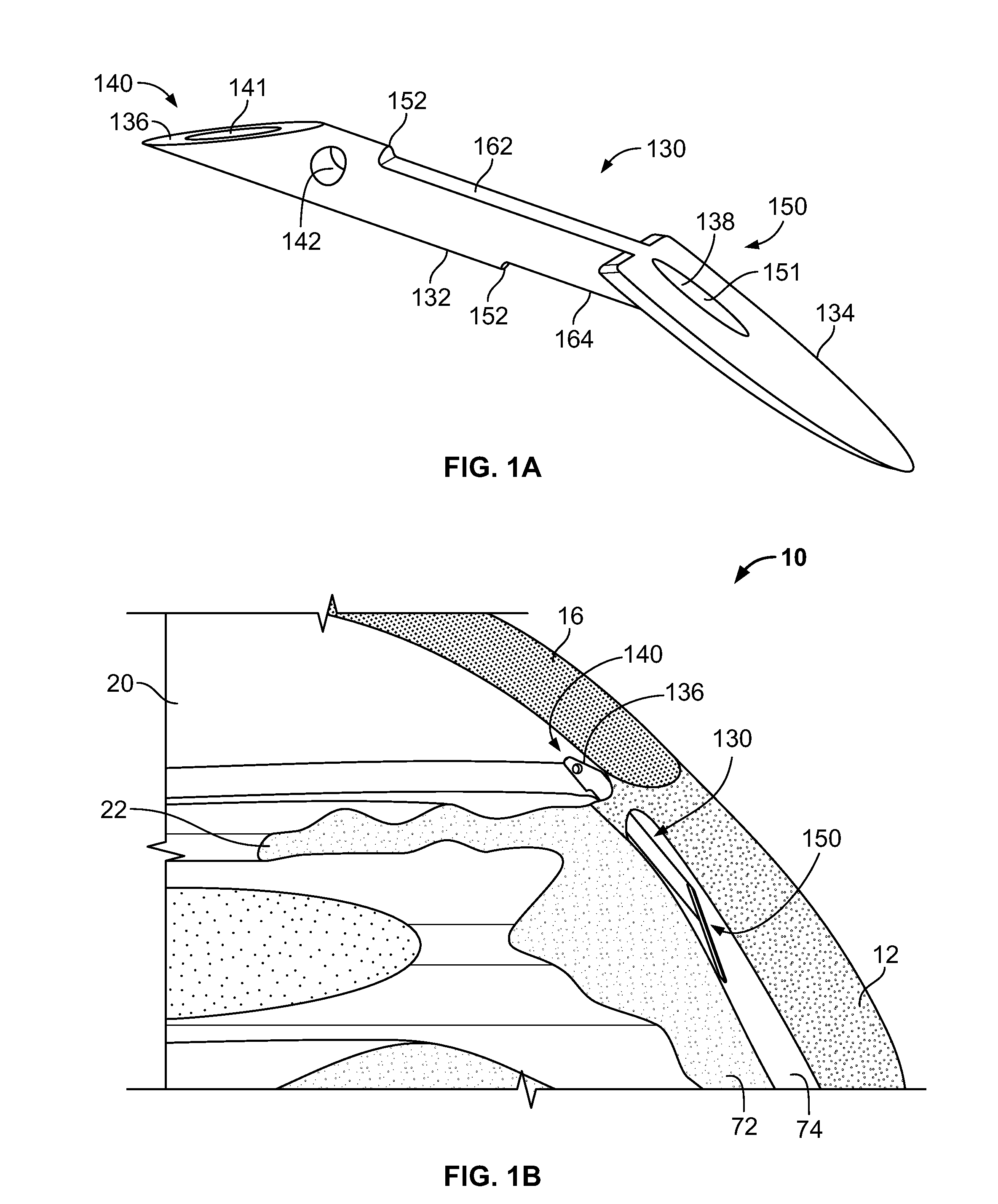
Refractive intraocular implant lens and method
InactiveUS20050015143A1Easy to insertEasy to removeEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular implantLens implant
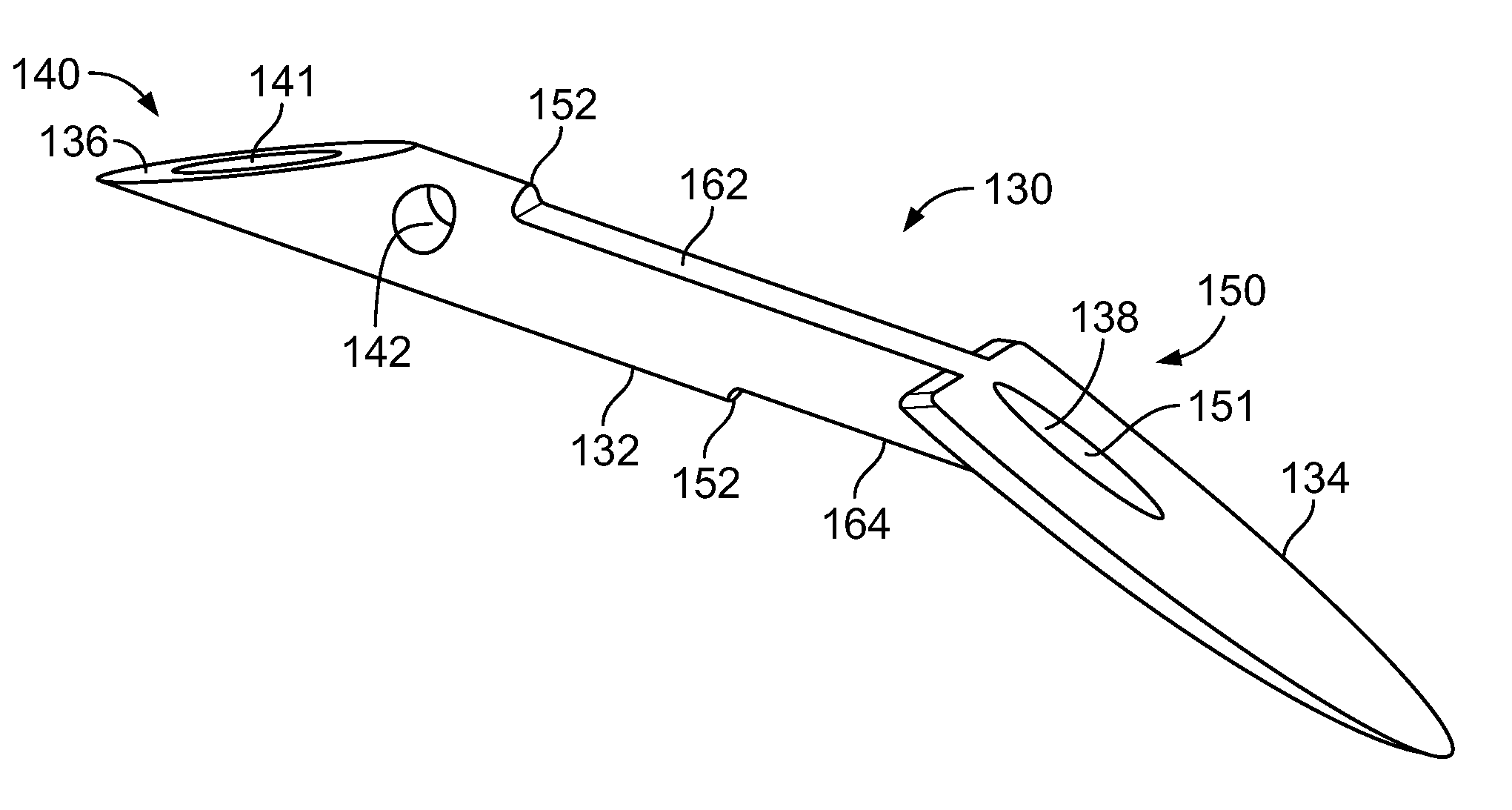
A refractive intraocular lens (104) and method of locating the lens within the eye and attaching the lens to the iris. The refractive intraocular lens (104) may be attached via a staple (230), a fastener (312), anchor (412) or by the tip of the haptic (118).
Owner:WILLIS TIMOTHY R
Methods for reducing or preventing transplant rejection in the eye and intraocular implants for use therefor
InactiveUS7033605B2Reduce and prevent transplant rejectionReducing and preventing transplant rejectionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderTransplant rejectionOphthalmology
Methods for reducing or preventing transplant rejection in the eye of an individual are described, comprising: a) performing an ocular transplant procedure; and b) implanting in the eye a bioerodible drug delivery system comprising an immunosuppressive agent and a bioerodible polymer.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
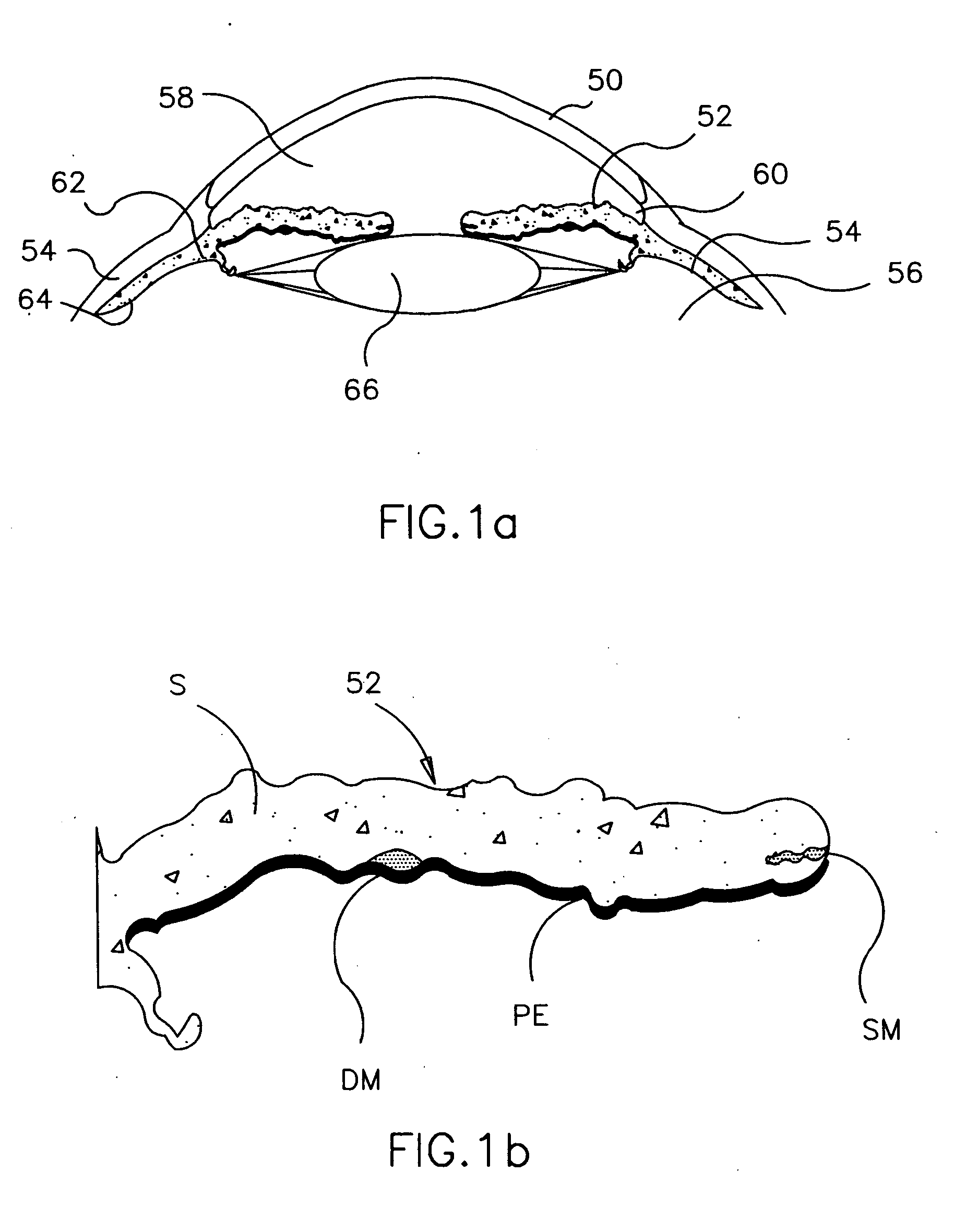
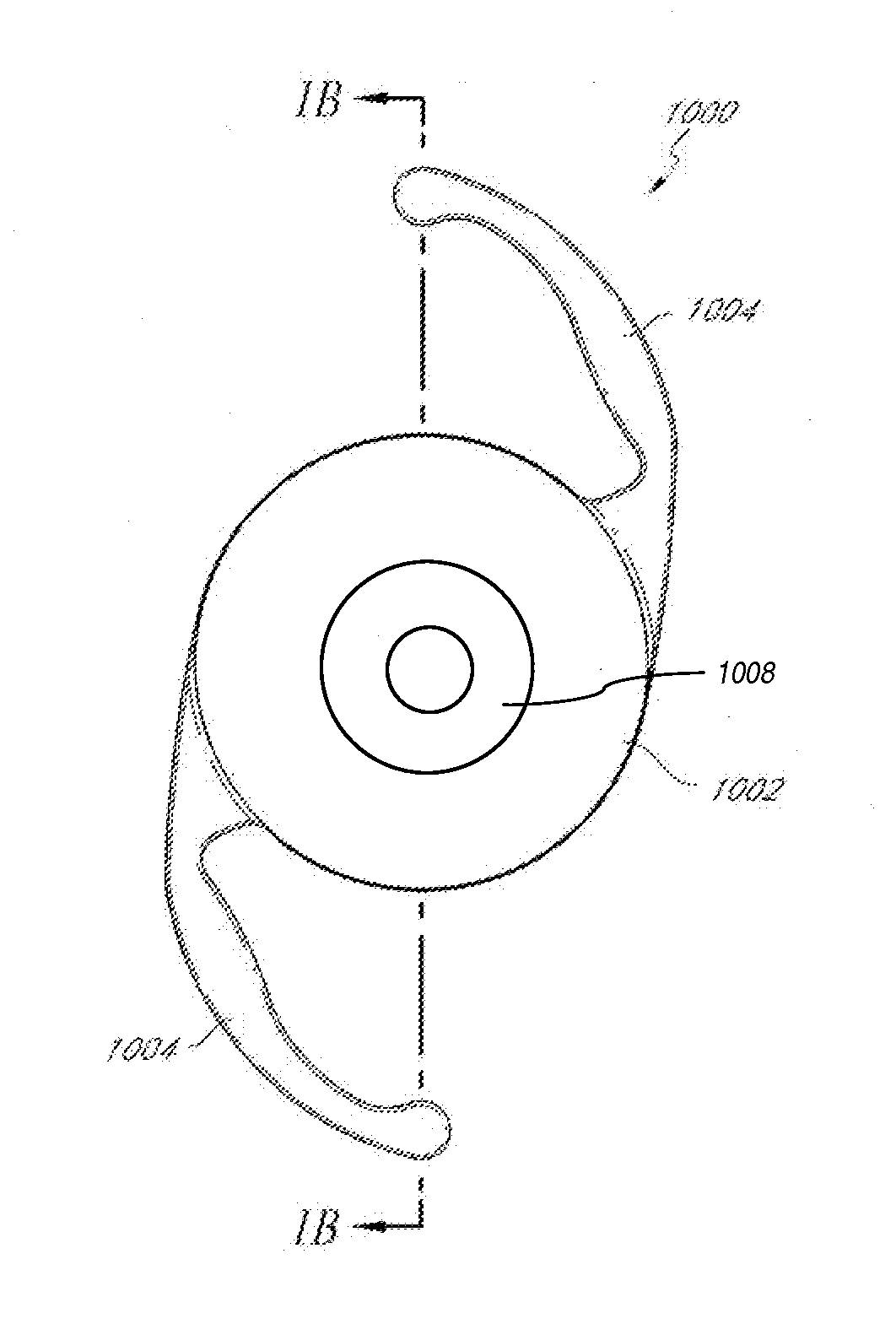
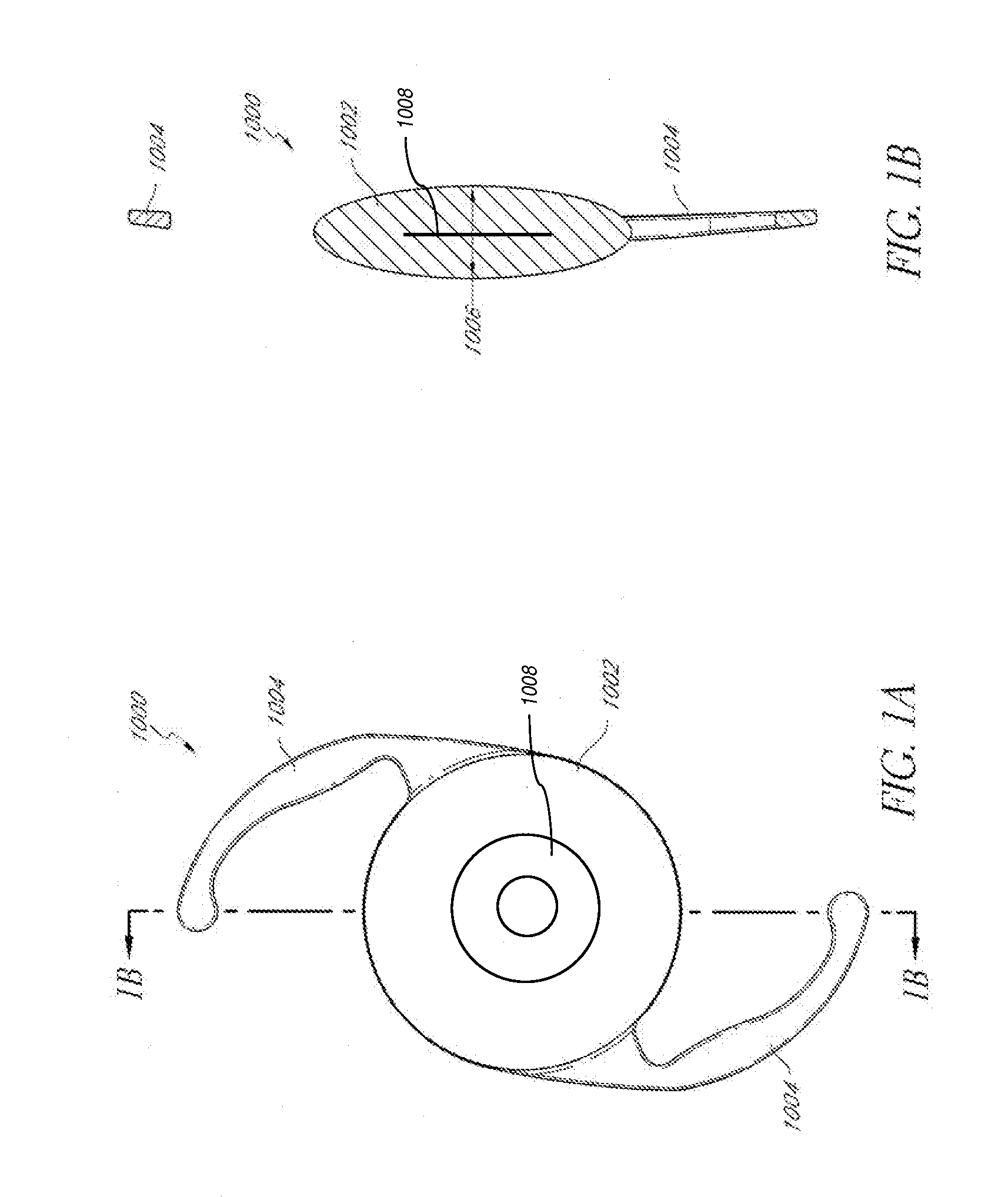
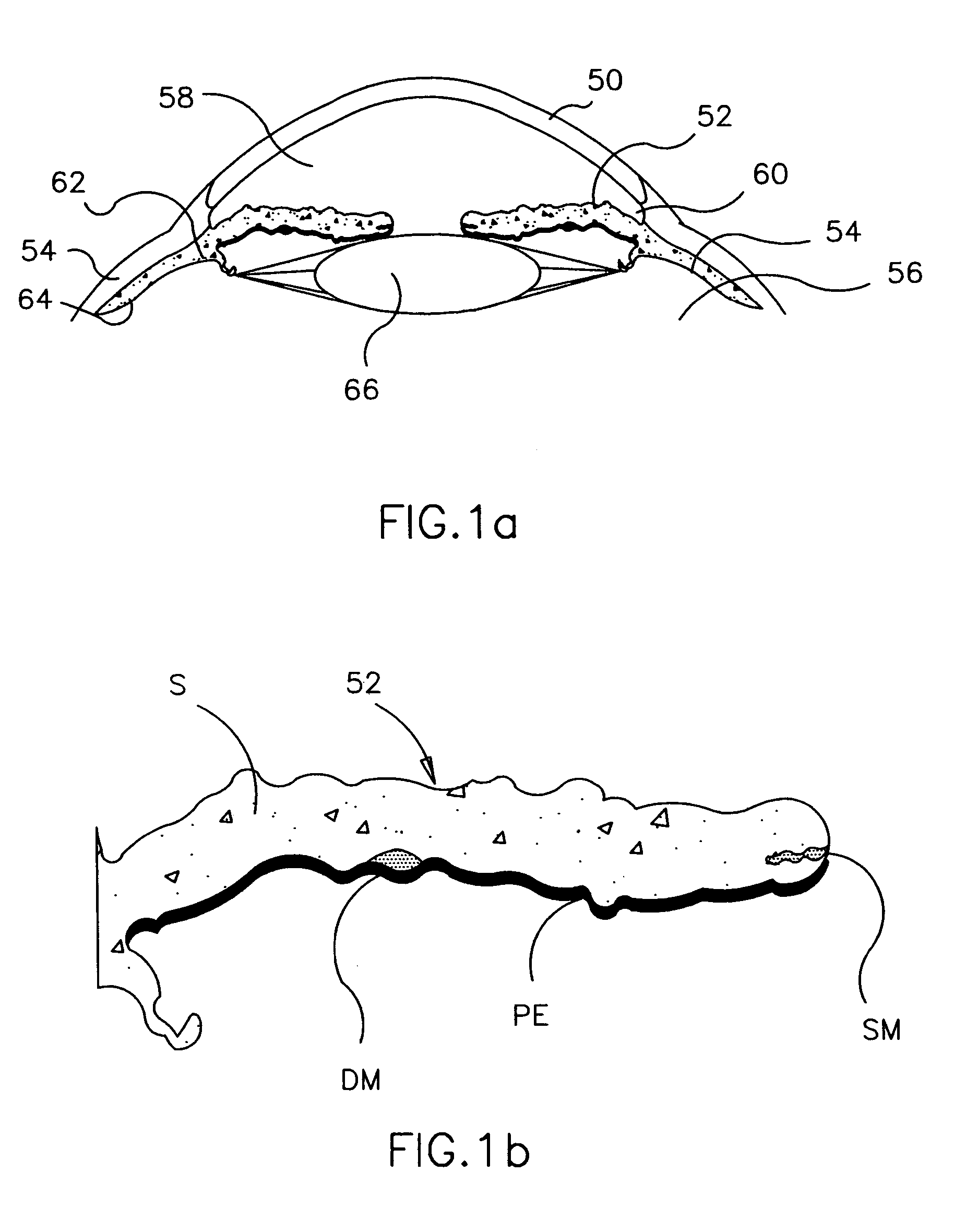
Intraocular lens implant having accommodative capabilities
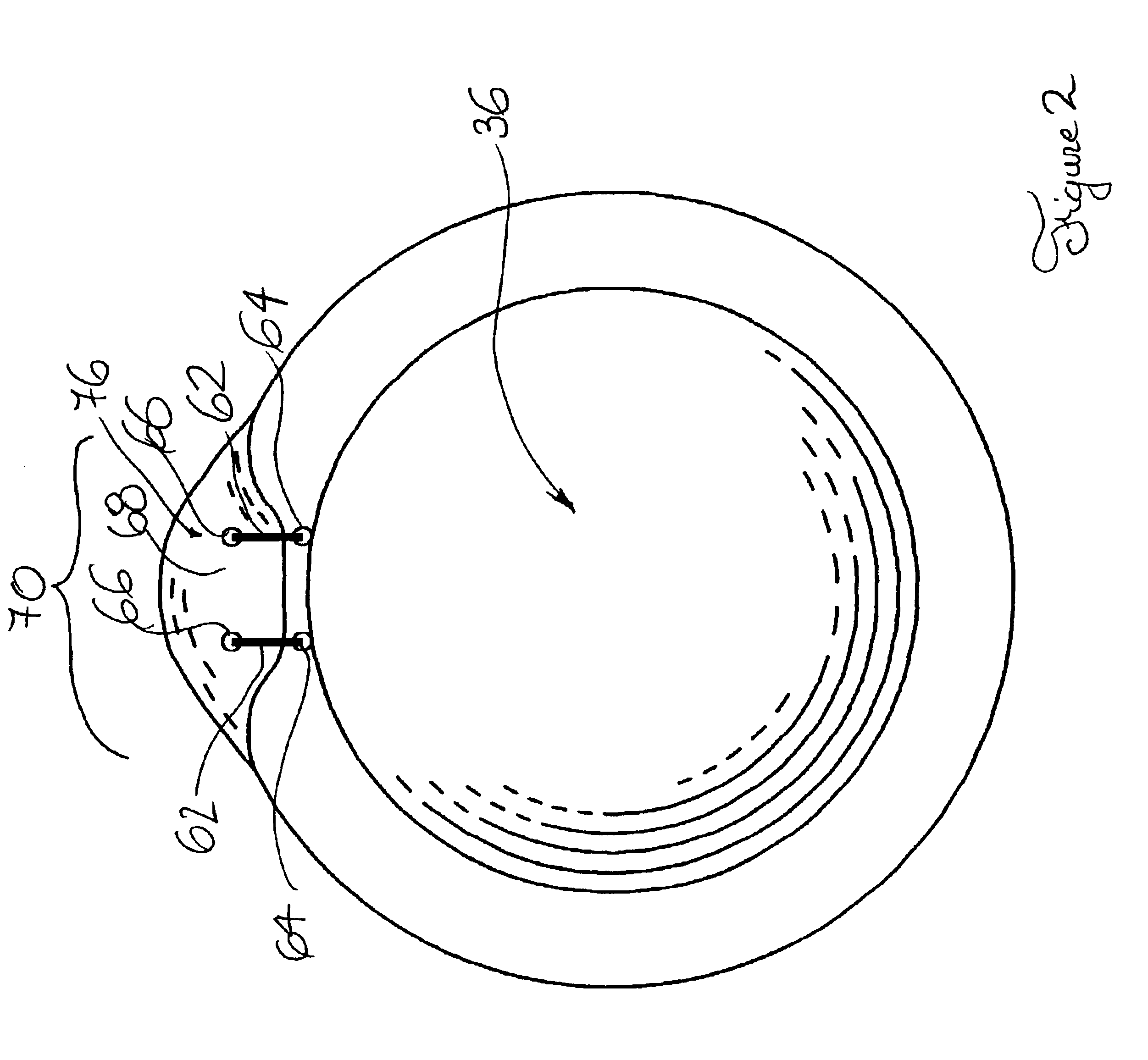
An intraocular implant including a lens and a shell component. The shell component includes a shell peripheral wall encompassing a shell inner volume for protectively enclosing the lens and allowing the latter to move therein between lens accommodating positions. The lens is pivotable within the shell inner volume between a lens first position wherein the lens is in a substantially proximal relationship relative to a shell wall first segment and a lens second position wherein the lens is in a substantially proximal relationship relative to a shell wall second segment. In one embodiment of the invention, the lens peripheral edge defines a lens edge pivot portion and the shell segment joining edge defines a corresponding shell edge pivot portion, the lens and shell edge pivot portion being complementarily configured and sized so that when the lens abuttingly rests against the peripheral wall inner surface, the lens and shell edge pivot portions interact with each other for allowing the lens to pivot between the lens first and second positions.In another embodiment of the invention, the lens is pivotally suspended within the shell component for pivotal movement between the lens first and second position. In both embodiments, the lens may also pivot to a lens intermediate position in a spaced relationship relative to both the the shell wall first and second segments.
Owner:KHOURY ELIE
Extended depth of field optics for human vision
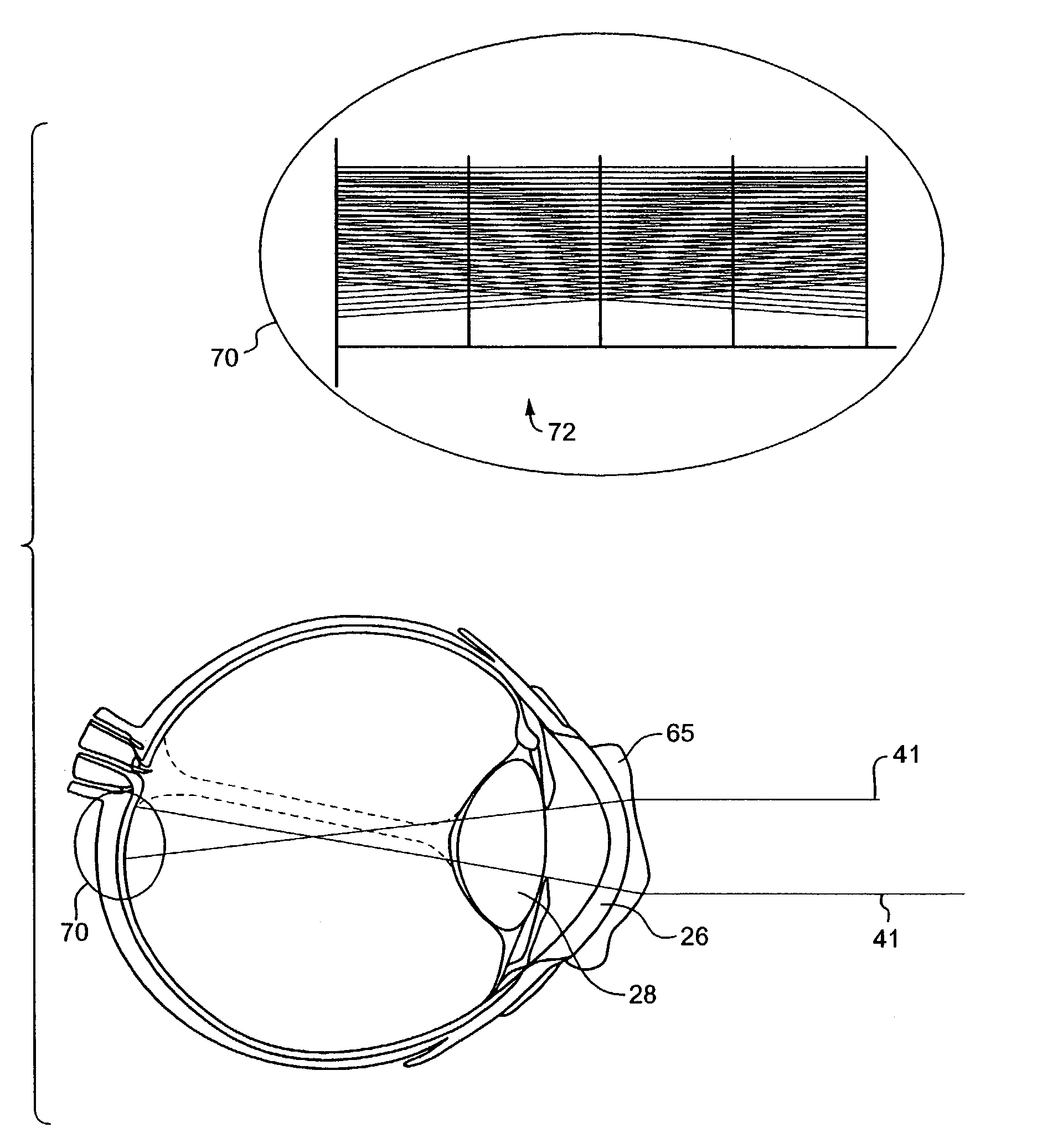
The present invention provides extended depth of field to human eyes by modifying contact lenses, intraocular implants, and / or the surface of the eye itself. This may be accomplished by applying selected phase variations to these optical elements (e.g., by varying surface thickness of the cornea of the eye). The phase variations EDF-code the wavefront and cause the optical transfer function to remain essentially constant within a range of distances from the in-focus position. This provides a coded image on the retina. The human brain decodes this coded image, resulting in an in-focus image over an increased depth of field.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Intraocular lens implant with mirror
InactiveUS6902577B2Reduce the amount of lightIncrease the amount of lightIntraocular lensOptical propertyAnterior surface
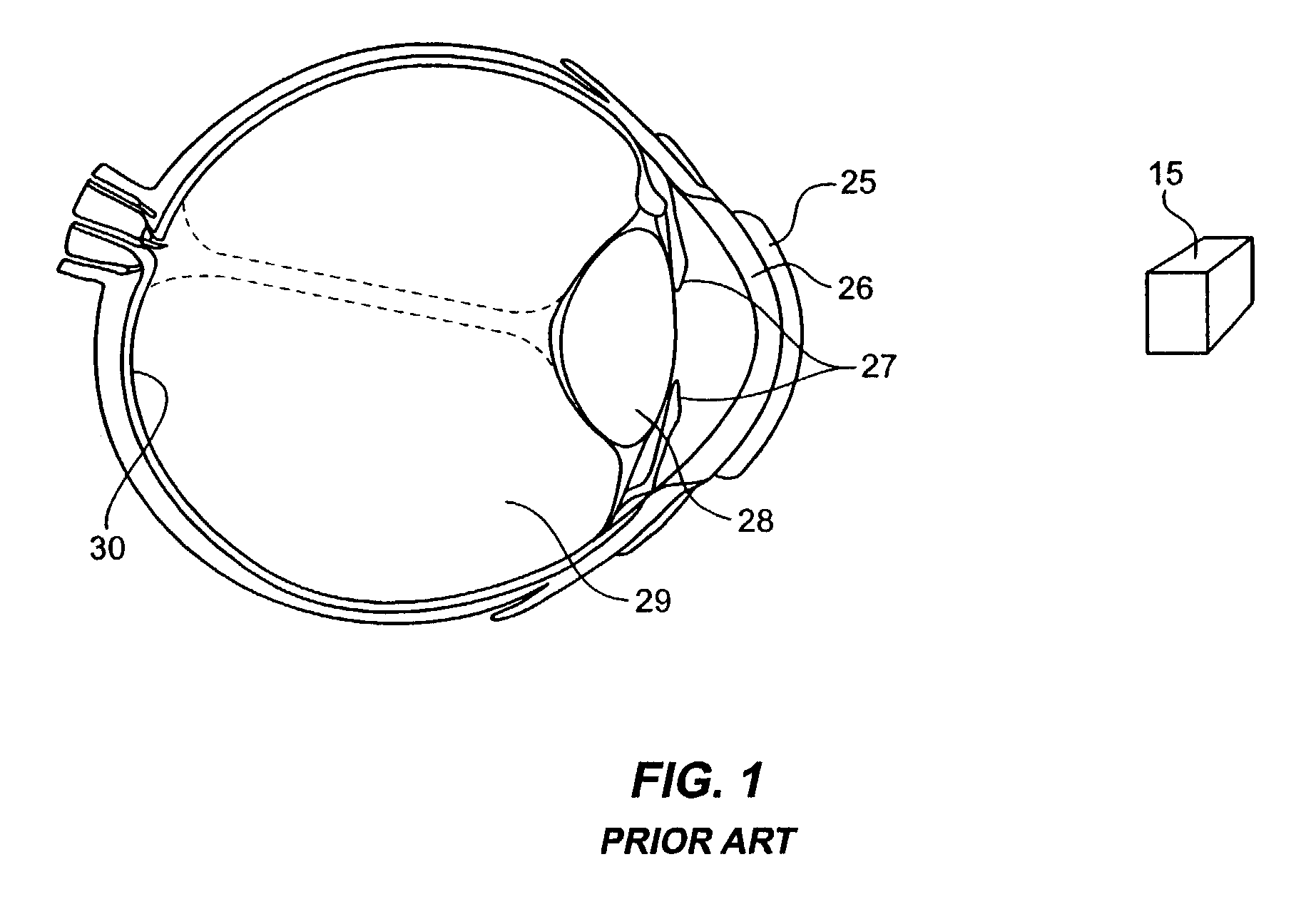
An intraocular implant for implantation into the interior of an eye is disclosed. The intraocular implant includes a body member, the body member has an anterior surface and a posterior surface, and has optical properties, and, at least one mirror, wherein the at least one mirror is contained within the body member.
Owner:ISAAC LIPSHITZ
Apparatus und Method for Rendering a Virtual Monitor on Smart Ophthalmic Devices in Augmented Reality Environments
InactiveUS20170336641A1Minimize discomfortReduce simulator sicknessStatic indicating devicesImage data processingVirtualizationGeolocation
An apparatus and a method are described herein related to the art of augmented reality type monitor virtualization. A monitor-virtualization system, such as a head-mountable device, an ophthalmic device or an intraocular implant, can render a virtual monitor in augmented reality. A liquid lens or an optical phased array can position the virtual monitor in space by optical means. A dimmable occlusion matrix can be additionally operated such as to make the image of the virtual monitor substantially opaque. A coordinator module can synchronize the activities of monitor positioning and occlusion masking. The virtual monitor can be anchored to real-world artifacts using bokode technology. Various dimming modes of the occlusion matrix reduce operator fatigue. The apparatus may operate in smart sunglass mode when the virtual monitor function is paused. The virtual monitor can be hidden or visualized differently when thresholds in terms of user geolocation or viewing angle are breached.
Owner:VON & ZU LIECHTENSTEIN MAXIMILIAN RALPH PETER
Biodegradable intraocular implants containing prostamides
InactiveCN1950091AFacilitated releaseGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGlaucomaIntraocular implant
Biocompatible intraocular implants include a prostamide component and a biodegradable polymer that is effective in facilitating release of the prostamide component into an eye for an extended period of time. The prostamide component may be associated with a biodegradable polymer matrix, such as a matrix of a two biodegradable polymers. The implants may be placed in an eye to treat or reduce a at least one symptom of an ocular condition, such as glaucoma.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Intraocular lens implant with mirror
InactiveUS6913620B2Guaranteed functionReduce the amount of lightIntraocular lensOptical propertyAnterior surface
Owner:LIPSHITZ ISAAC
Fluid drainage device, delivery device, and associated methods of use and manufacture
The disclosure provides an intraocular implant for allowing fluid flow from the anterior chamber of an eye, the implant comprising a tube having an inlet end, an outlet end, and a tube passage, wherein the inlet end is adapted to extend into the anterior chamber of the eye, and wherein the outlet end is adapted to be implanted adjacent scleral tissue of the eye. The implant may be adapted to drain aqueous humor into a suprachoroidal space or a juxta-uveal space. The disclosure also provides associated delivery devices, methods of use, and methods of manufacture.
Owner:OPTONOL LTD
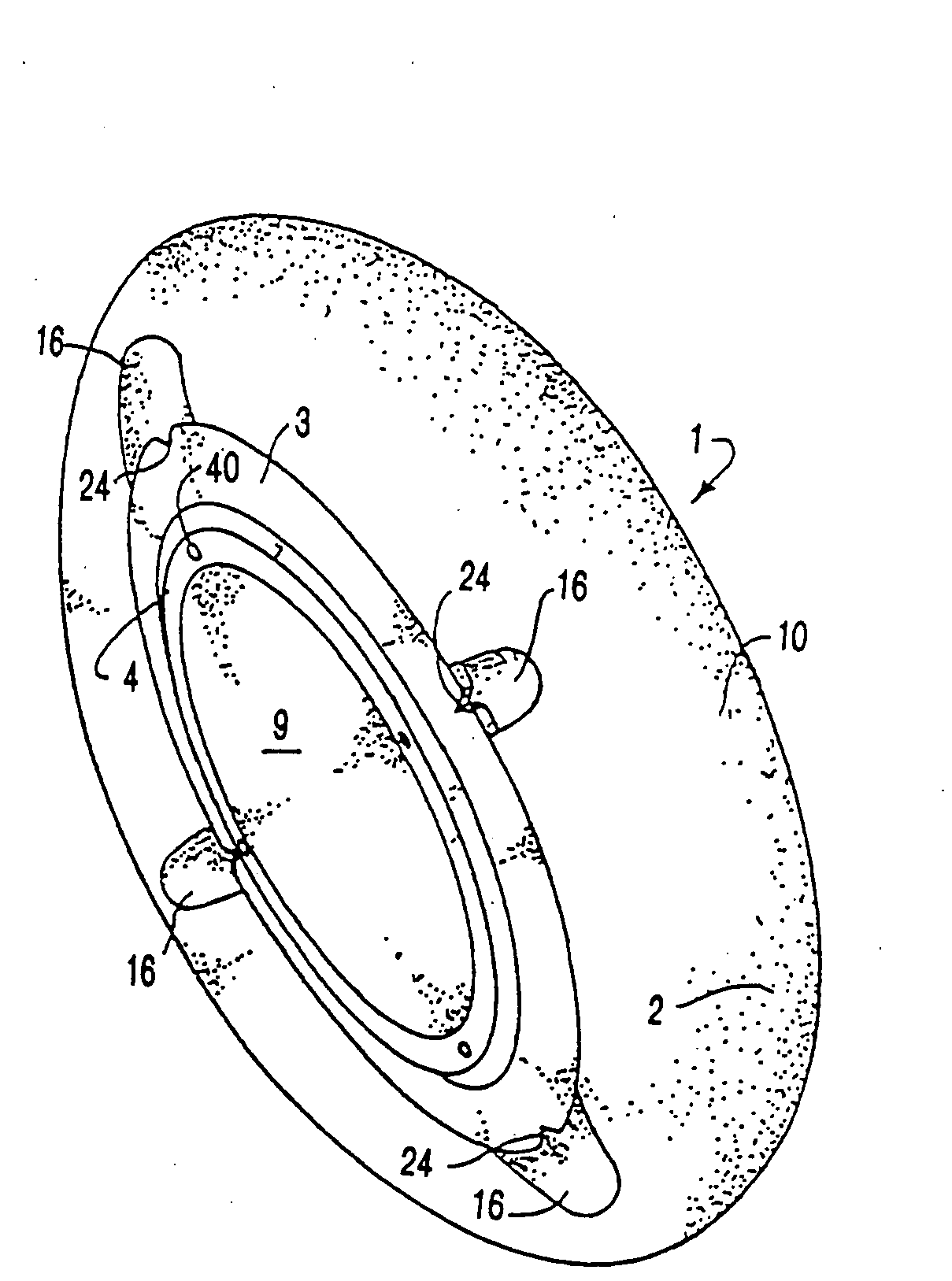
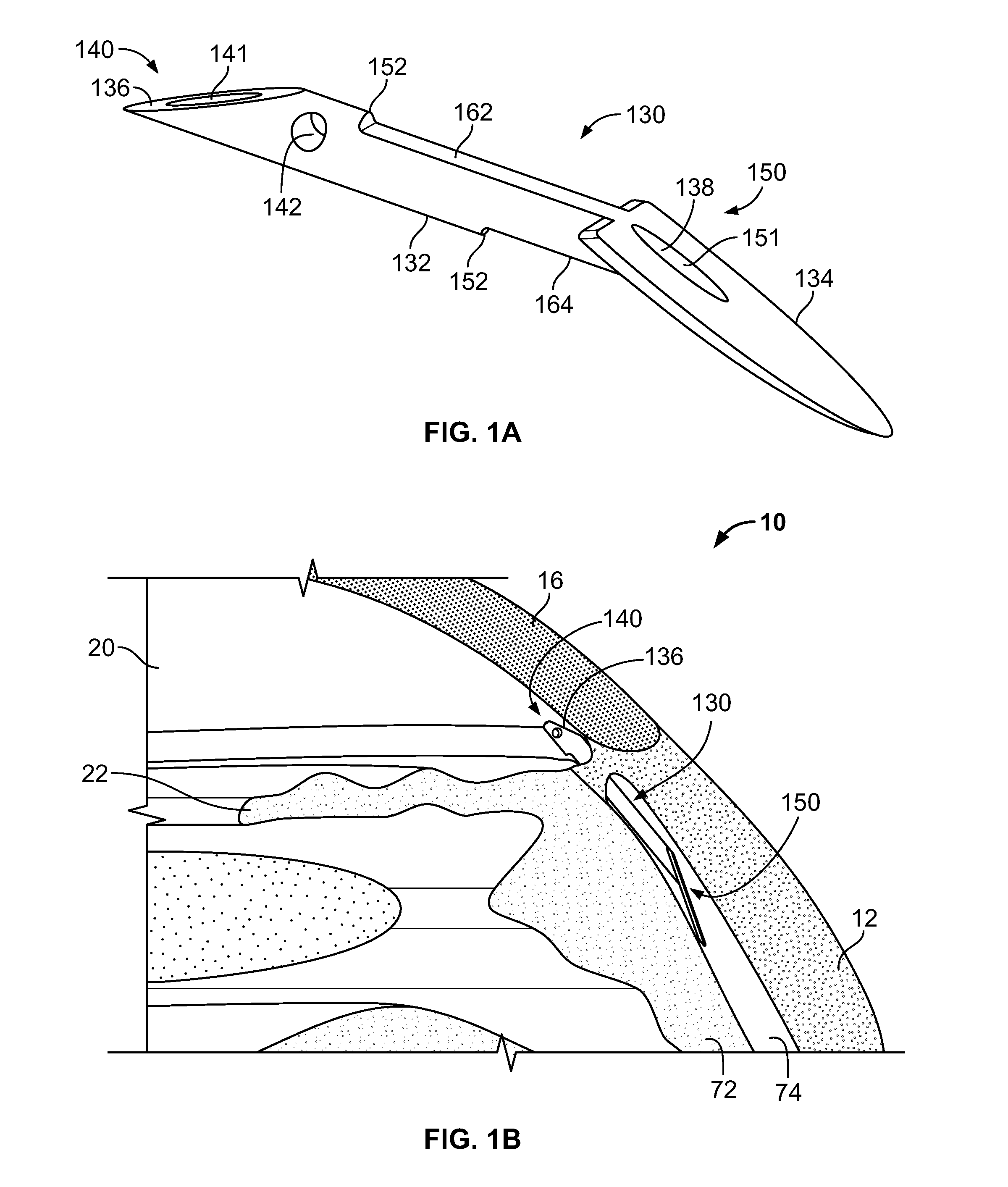
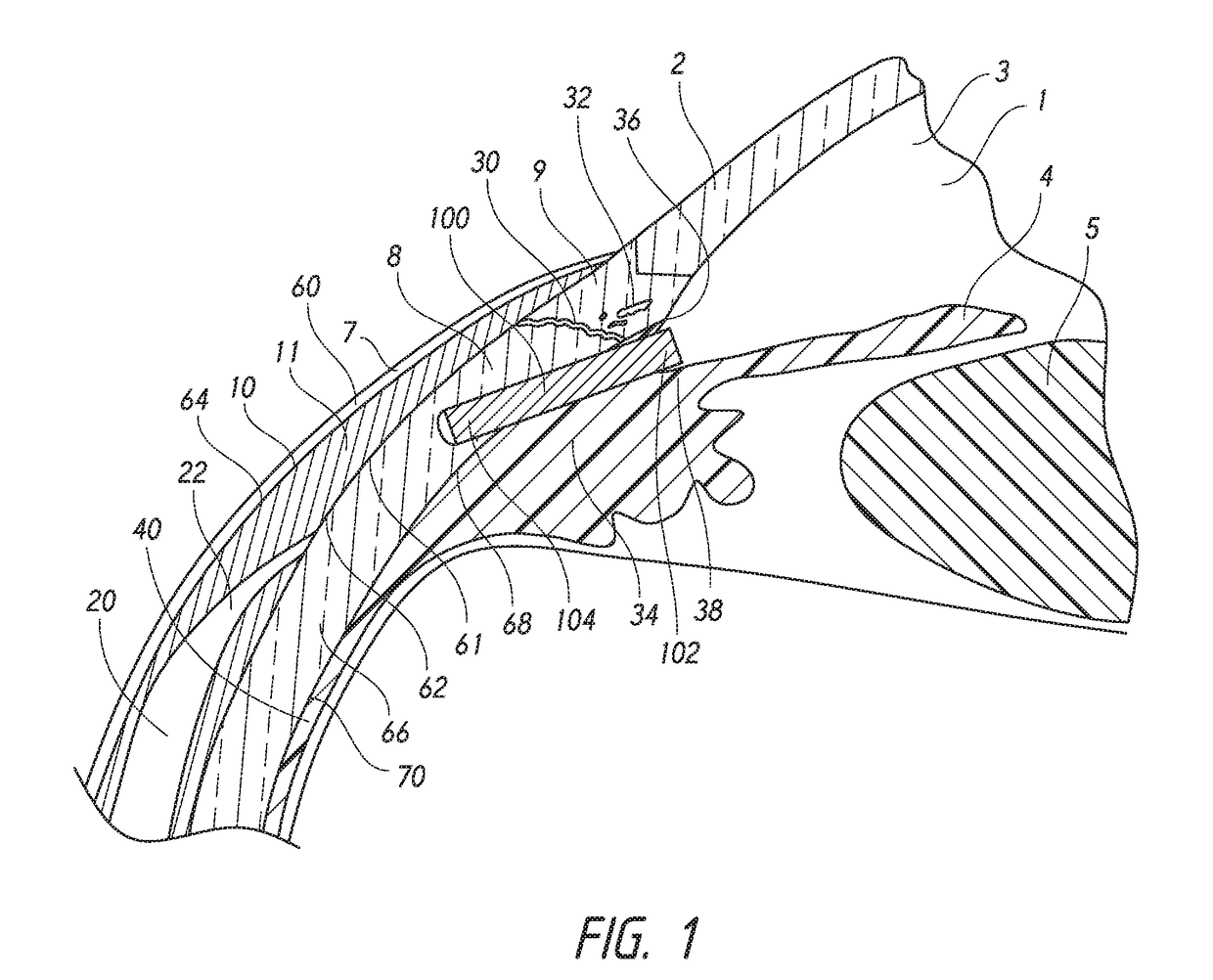
Intraocular Lens Cell Migration Inhibition System
InactiveUS20120232649A1Inhibit migrationReduce posterior capsule opacificationEye treatmentTissue regenerationPosterior capsular opacificationLens epithelial cell
Generally, an intraocular implant and methods for treating an ocular condition. In particular, an intraocular implant which implanted between an intraocular lens and the surface of the posterior capsule of the eye inhibits migration of residual lens epithelial cells after cataract surgery by providing structural barriers to reduce posterior capsule opacification of the eye.
Owner:INSIGHT INNOVATIONS
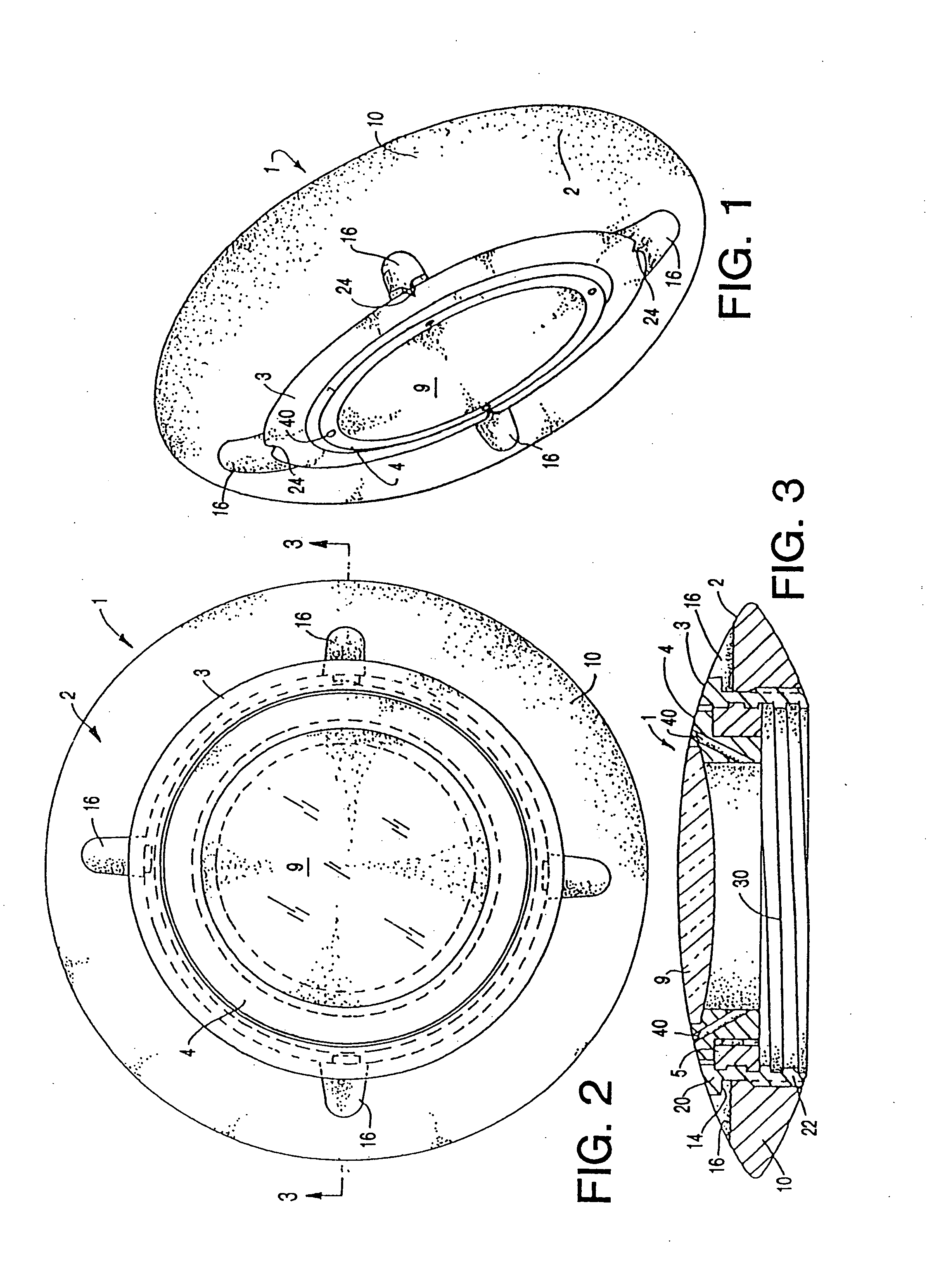
Biocompatible biodegradable intraocular implant system
InactiveUS20110230963A1Prevent proliferationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEye treatmentIntraocular lensActive agent
Generally, an intraocular implant and methods for treating an ocular condition. As to certain embodiments, an intraocular biocompatible biodegradable implant (11) which can provide a biocompatible biodegradable material in the form of a flexible membrane (12) containing an active agent (24) which implanted between an intraocular lens (8) and the surface of the posterior capsule (5) of the eye (1)(4) inhibits migration of residual lens epithelial cells after cataract surgery by providing structural or pharmaceutical barriers to reduce posterior capsule (5) opacification of the eye (1)(4).
Owner:INSIGHT INNOVATIONS
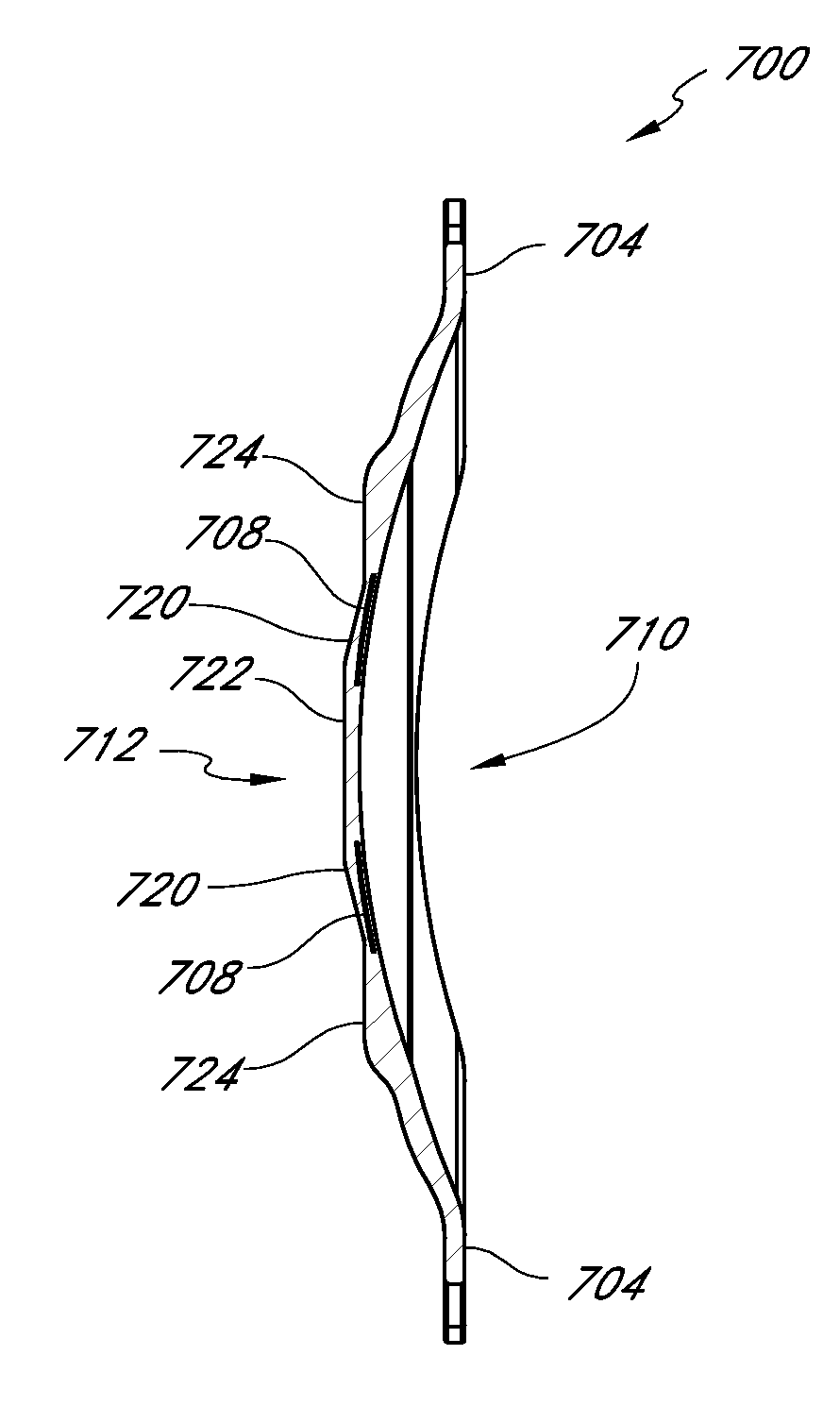
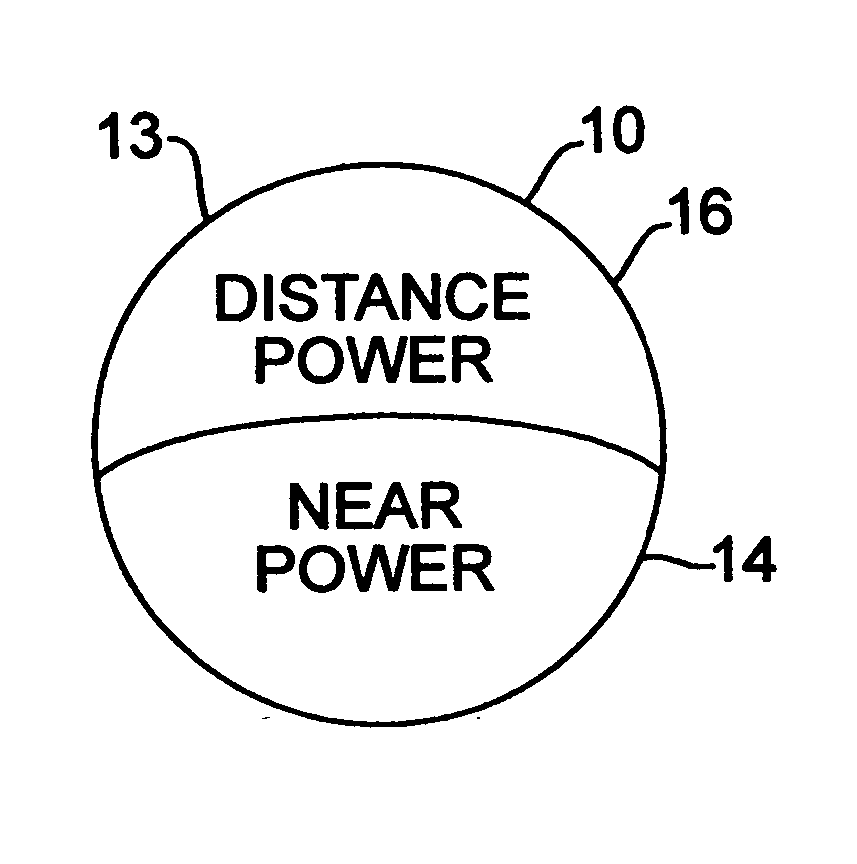
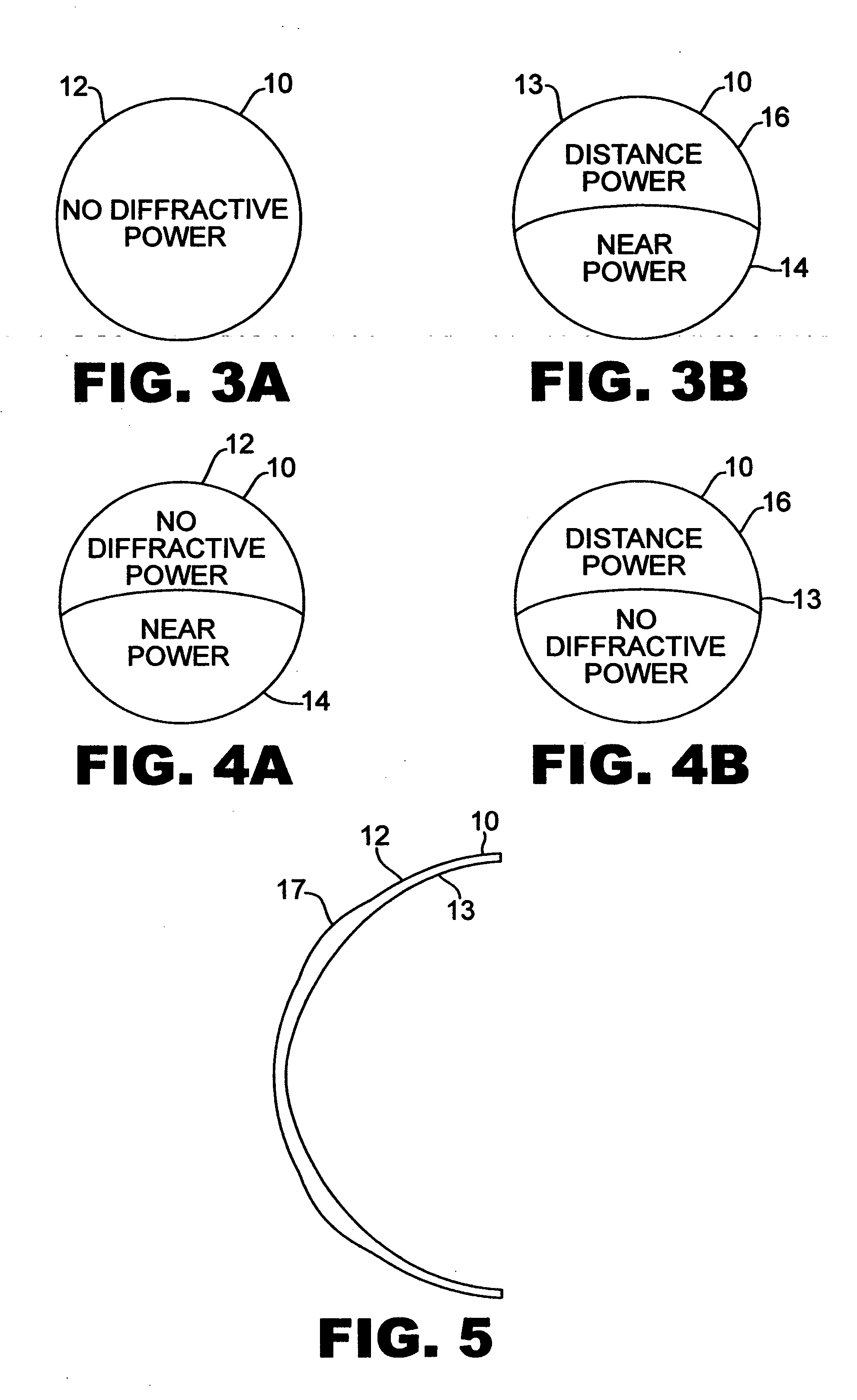
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. Such one or more first regions may represent one or more annular rings, or other portion of the lens, and the second region may occupy the portion of the lens aperture outside the first region. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. When multiple optical elements are used, the multiorder diffractive structures may be located along an interior surface of the lens. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. The lens may represent a contact lens, a spectacle lens, or the optic portion of an intraocular implant (IOL). Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for performance for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Intraocular lens with elastic mask
ActiveUS20150073549A1Increase depth of focusOptical articlesDomestic articlesIntraocular lensMedicine
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implant can include a lens body having a lens material and a mask having a mask material. The lens body can be secured to the mask. The mask material can include a modulus of elasticity that is greater than or equal to a modulus of elasticity of the lens material.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Refractive intraocular implant lens and method
InactiveUS7008449B2Easy to insertEasy to removeEye surgeryIntraocular lensIntraocular implantLens implant
A refractive intraocular lens (104) and method of locating the lens within the eye and attaching the lens to the iris. The refractive intraocular lens (104) may be attached via a staple (230), a fastener (312), anchor (412) or by the tip of the haptic (118).
Owner:WILLIS TIMOTHY R
Fluid drainage device, delivery device, and associated methods of use and manufacture
The disclosure provides an intraocular implant for allowing fluid flow from the anterior chamber of an eye, the implant comprising a tube having an inlet end, an outlet end, and a tube passage, wherein the inlet end is adapted to extend into the anterior chamber of the eye, and wherein the outlet end is adapted to be implanted adjacent scleral tissue of the eye. The implant may be adapted to drain aqueous humor into a suprachoroidal space or a juxta-uveal space. The disclosure also provides associated delivery devices, methods of use, and methods of manufacture.
Owner:ALCON INC
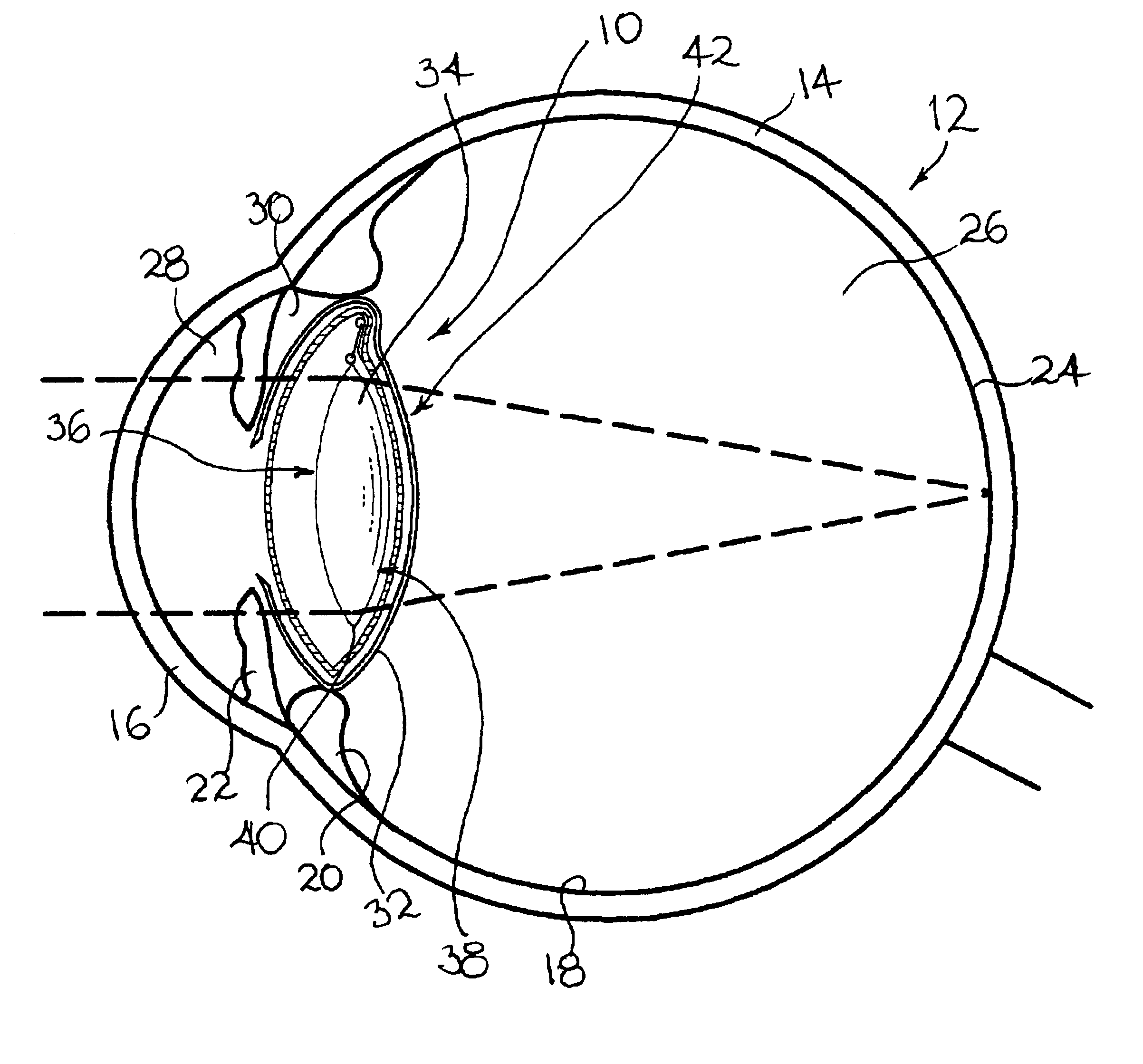
Intraocular implant for retinal diseases
An intraocular implant for implantation into the interior of a human eye, the eye having a retina, the implant comprising a body member and an optical arrangement. The body member has an anterior surface, a posterior surface and optical properties. The optical arrangement is configured for forming a first image on the retina. The first image is an image of at least part of the central visual field. The body member and / or the optical arrangement are configured for forming a second image on the retina. The second image is an image of at least part of the peripheral visual field.
Owner:LIPSHITZ ISAAC
Intraocular implant cell migration inhibition system
InactiveUS20110295367A1Inhibit migrationReduce posterior capsule opacificationEye surgeryTissue regenerationPosterior capsular opacificationLens epithelial cell
Generally, an intraocular implant and methods for treating an ocular condition. In particular, an intraocular implant which implanted between an intraocular lens and the surface of the posterior capsule of the eye inhibits migration of residual lens epithelial cells after cataract surgery by providing structural barriers to reduce posterior capsule opacification of the eye.
Owner:INSIGHT INNOVATIONS
Process for manufacturing an intraocular lens
Intraocular implants and methods of making intraocular implants are provided. The intraocular implant can include a mask adapted to increase depth of focus. The method of making the intraocular implant can include suspending the mask along an optical axis of the intraocular implant using a centration tool.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
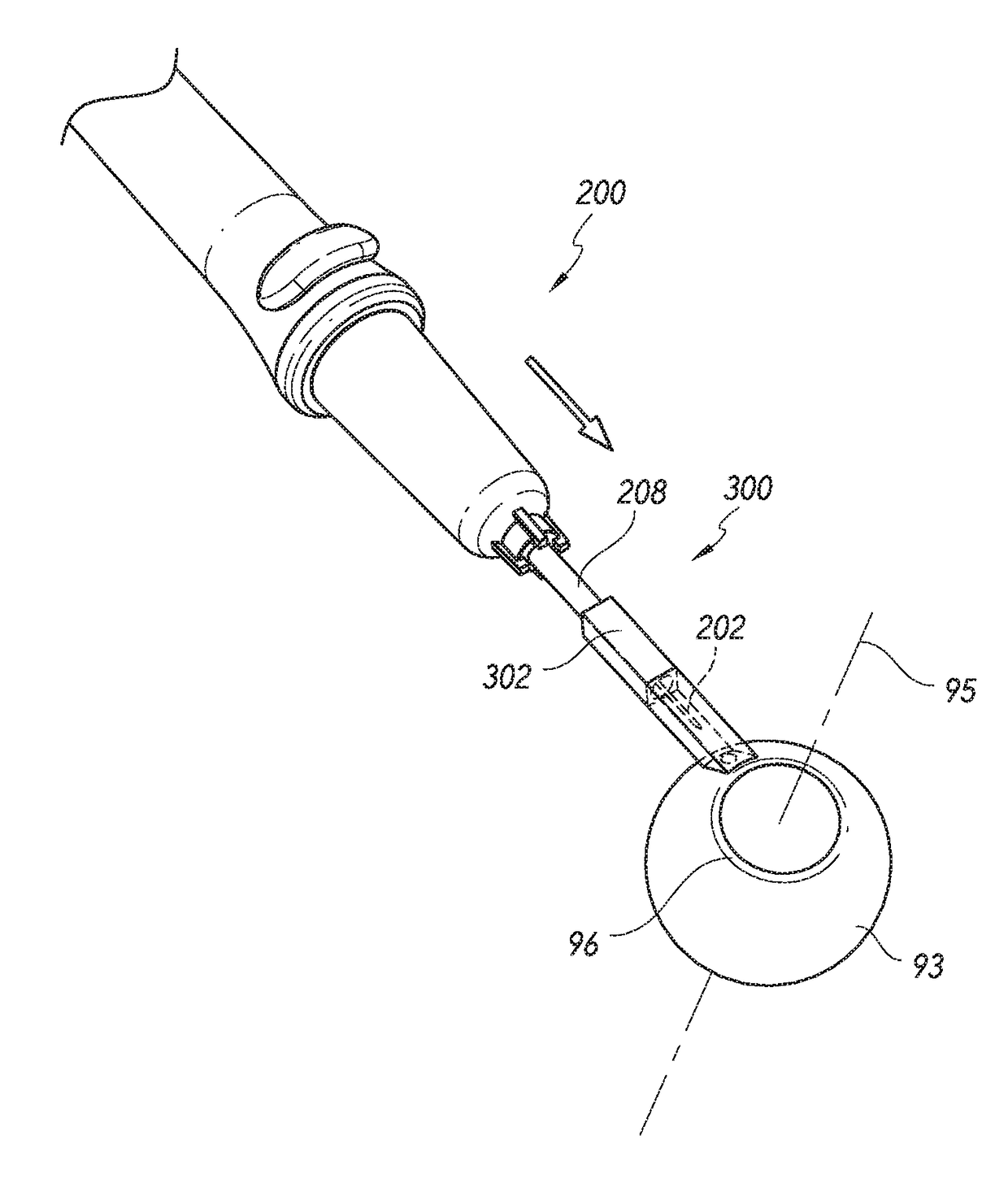
Intraocular drug delivery
An ab externo method of placing an intraocular implant into an eye can include advancing a needle, in which the implant is disposed, into the eye through conjunctiva and sclera of the eye. The implant can include a drug deliverable to the eye. The implant can thereafter be released to be anchored in the eye and elute the drug to the eye.
Owner:AQUESYS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com