Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
603results about How to "Reduce the amount of light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
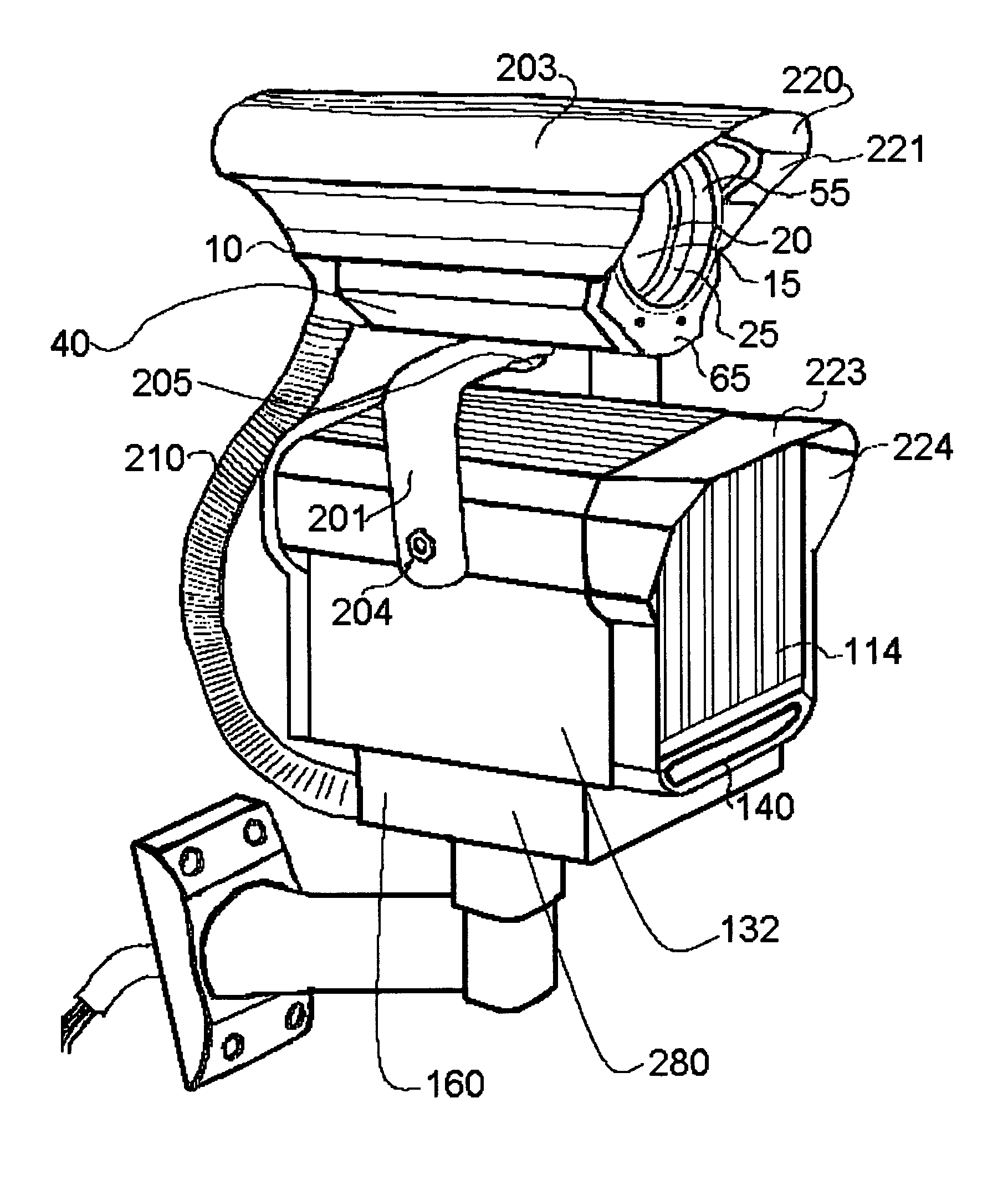
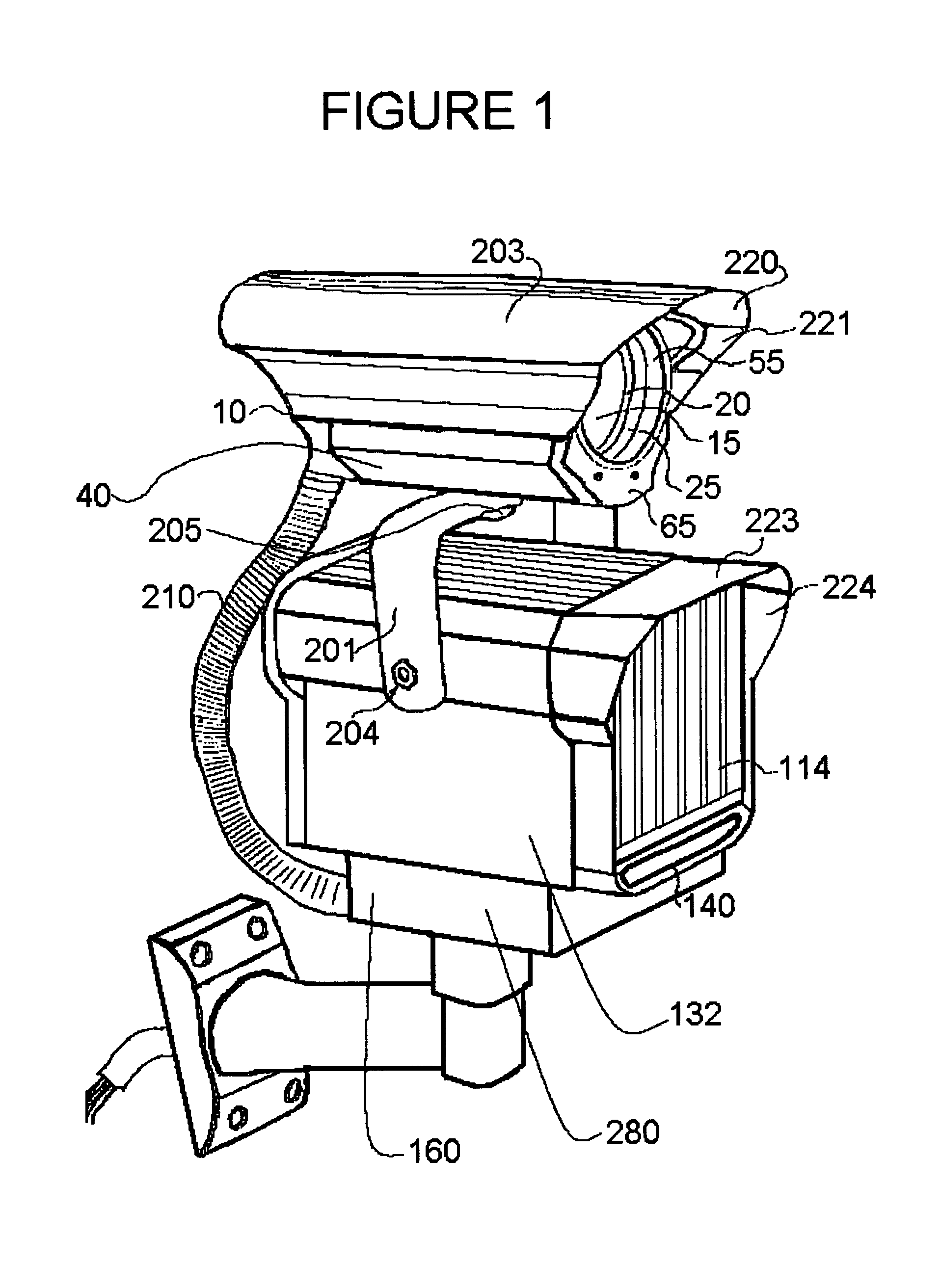
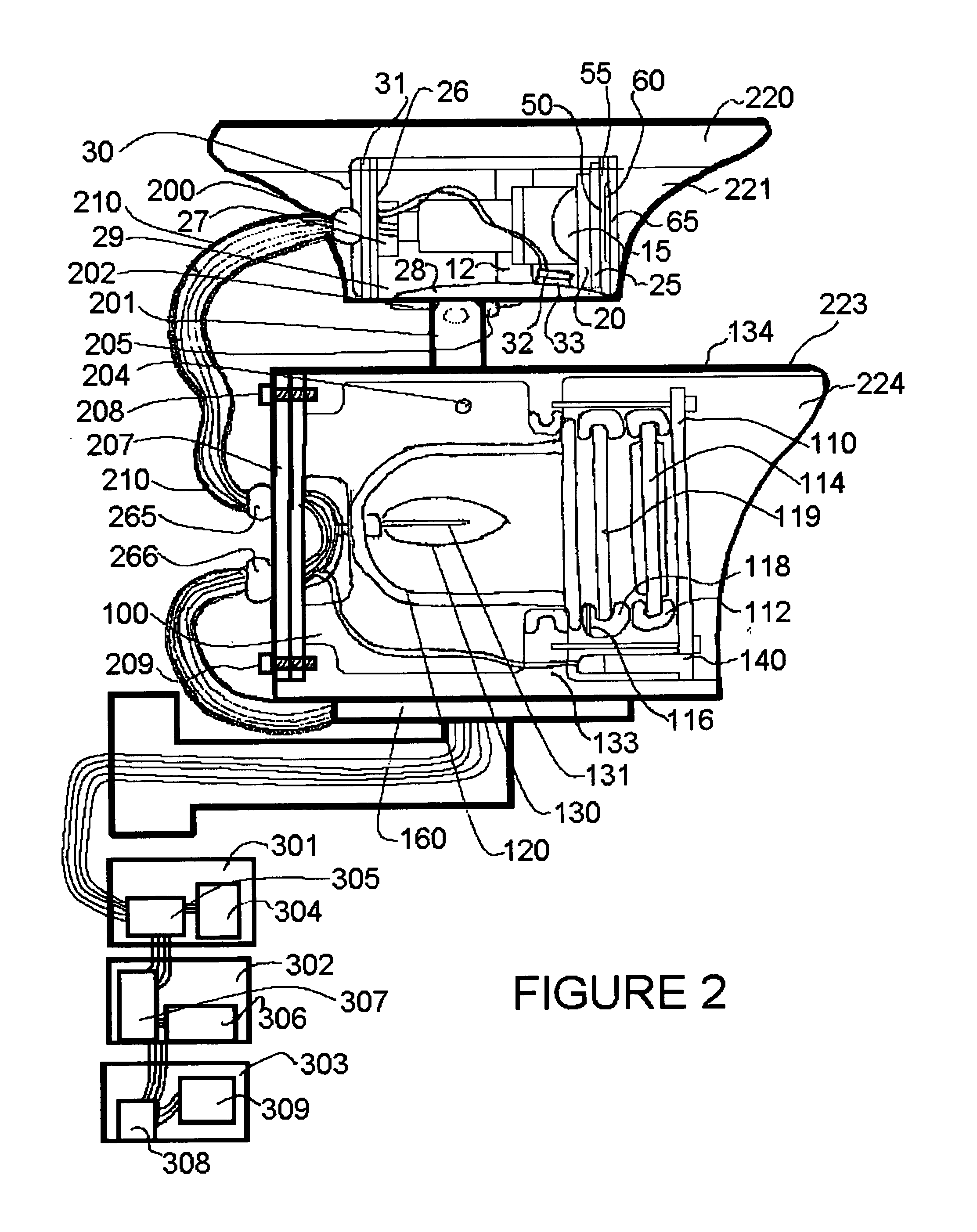
Vehicle license plate imaging and reading system for day and night
ActiveUS7016518B2Avoid sensor overload headlightAvoid reflected glareOptical rangefindersRoad vehicles traffic controlLicense numberInfrared
This invention provides an infrared illuminator and camera system for imaging of auto vehicle license plates. The system works in ambient light conditions, ranging from bright sunlight, to dim light, to dark, to zero ambient light. It yields high-contrast imaging of the letters and numbers on retro-reflective license plates. The images of the license letter and number combinations can be read manually by a remote operator. They can be converted to text format with optical character recognition computer hardware and software. The text data can then be compared to data files listing license numbers to provide further data about the owner of a licensed vehicle. A decision can be made quickly about whether to allow a vehicle to proceed through a gate, or whether to take other action. The system uses a mono camera that is enhanced for infrared sensitivity and combined with a high power infrared illuminator to maximize range at night, and with shutter speeds set up to capture clear license plate pictures even with fast moving vehicles and even with their headlights on and interfering with human observation of the license plates. Optical filtering to pass infrared in the range of the illuminator and to reduce light outside this range, combines with a lens set up, to avoid vertical smear and sensor overload caused by headlights at night and by highlight reflected glare from the sun in daytime.
Owner:EXTREME CCTV
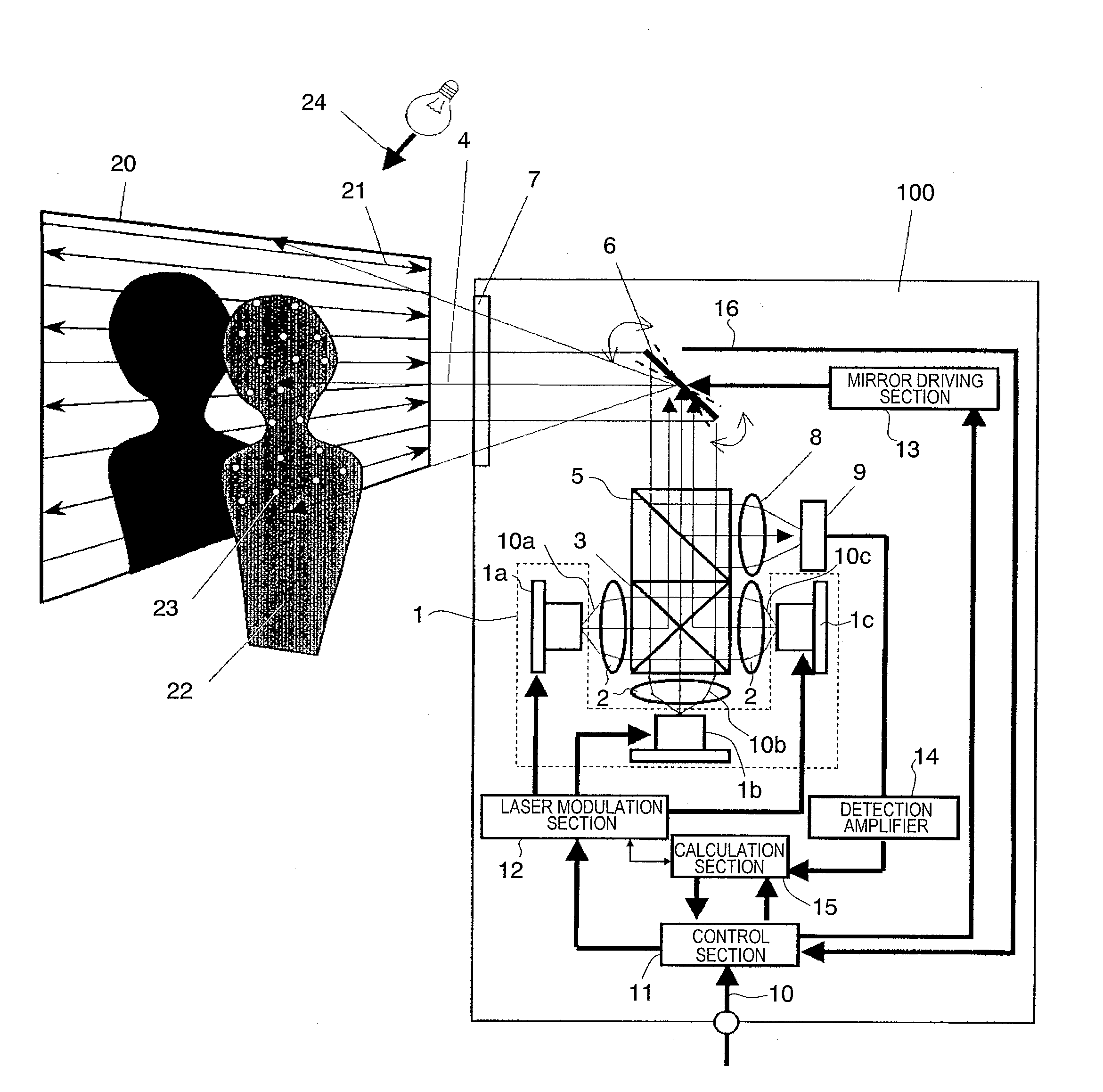
Image projection device
InactiveUS20090147224A1DownsizingReduce the number of partsProjectorsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsLaser light
An image projection apparatus according to the present invention includes a light source for outputting laser light and a mirror section for reflecting and projecting the laser light having been output from the light source, and displays an image with at least a portion of the projected laser light. The image projection apparatus includes a detection section for detecting at least a portion of the laser light returning from a projection direction of the laser light, and a calculation section for determining an image displayable region based on the detected light. The mirror section reflects at least a portion of the laser light returning from the projection direction of the laser light so as to be led into the detection section.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light mixer and backlight module having the same
ActiveUS7654687B2Easy to makeSimplify the manufacturing processNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOptoelectronicsReflective layer
Owner:HKC CORP LTD
Light emitting device
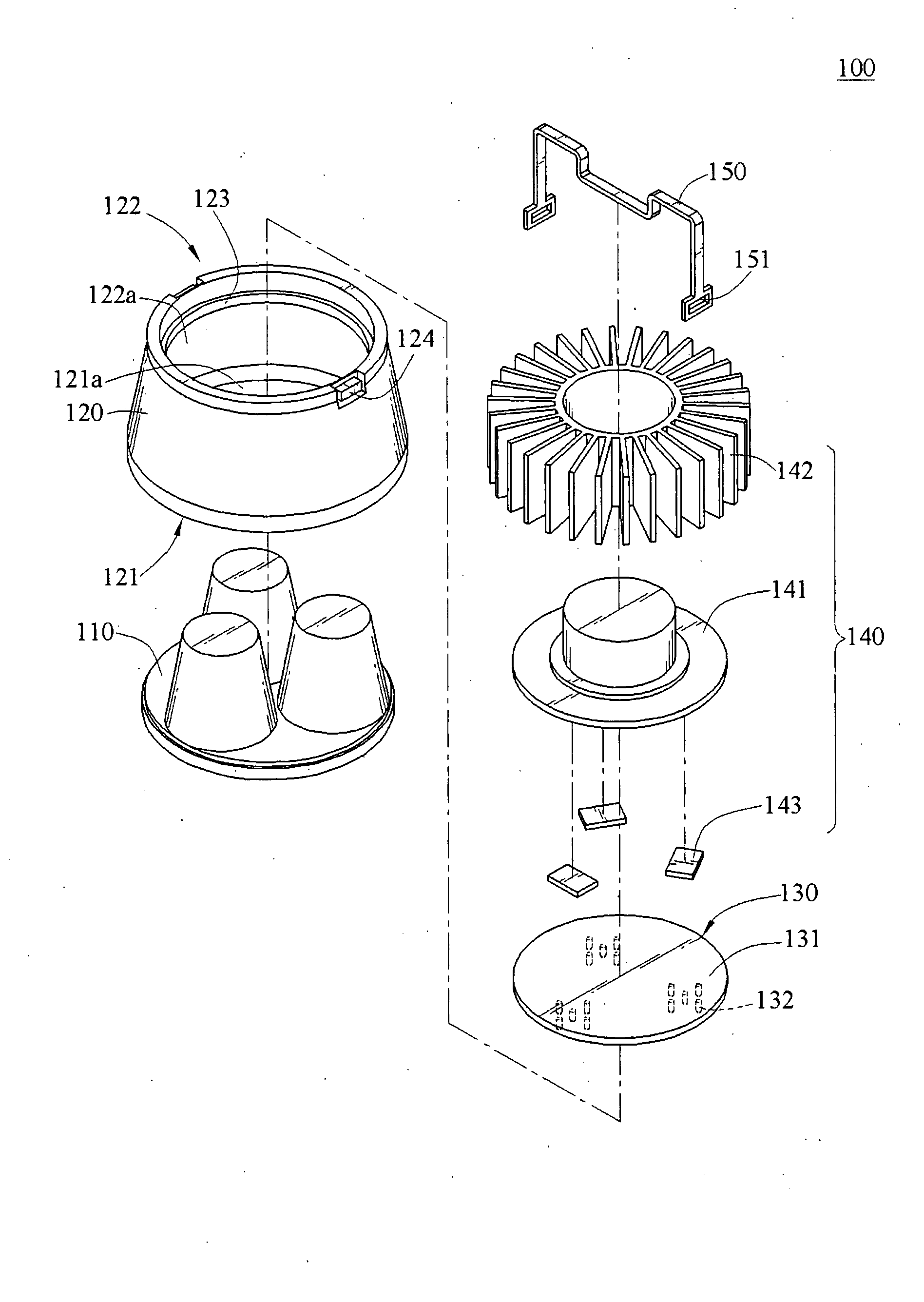
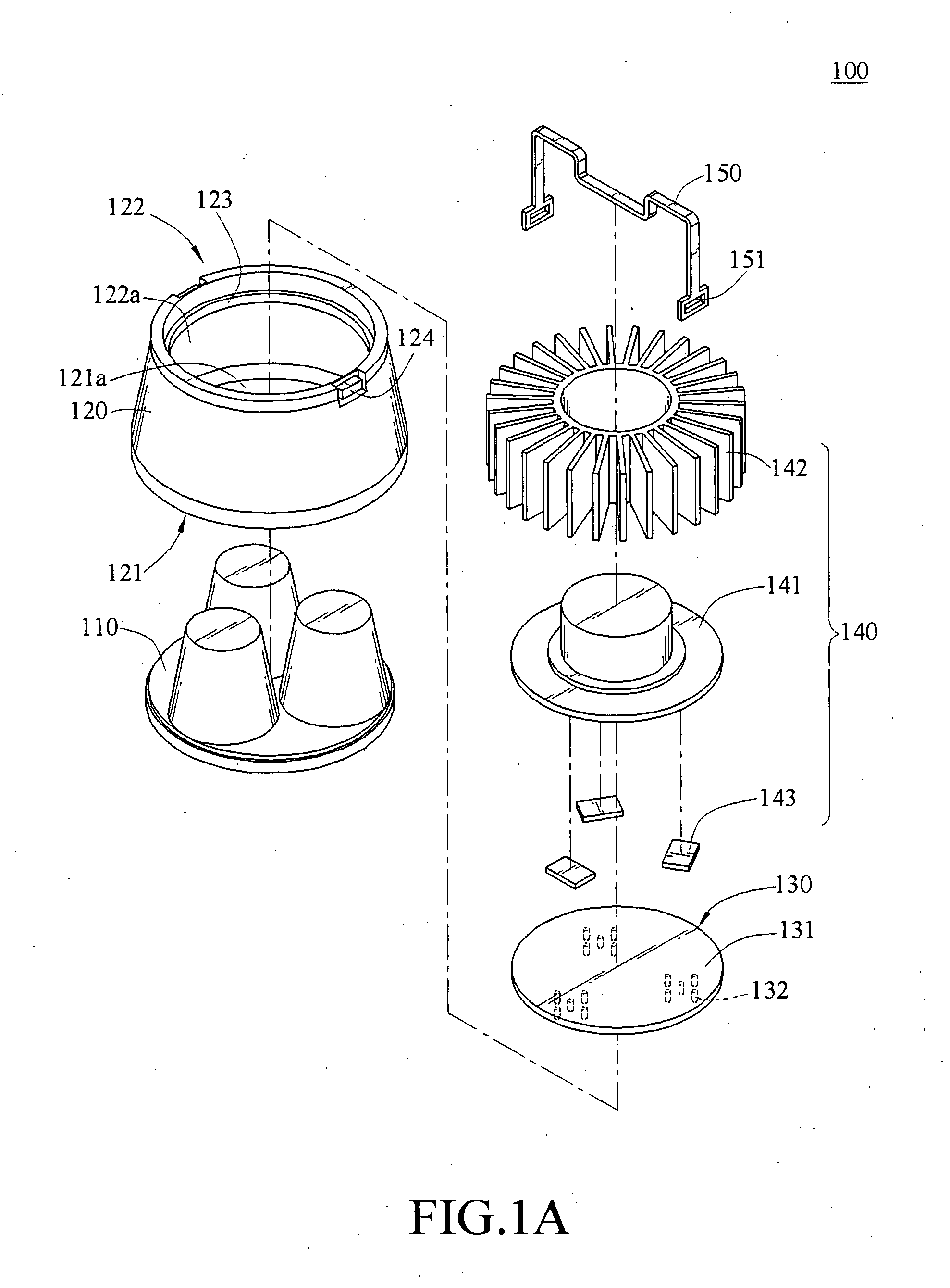
InactiveUS20080192436A1Improve cooling effectReduce the amount of lightPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringLight emitting device
A light emitting device including a housing, a light emitting unit, and a heatsink is provided. The housing has a projection end and a heat dissipation end, and a first opening and a second opening are respectively formed in the projection end and the heat dissipation end. The light emitting unit is disposed inside the housing, and is corresponding to the heat dissipation end, for projecting a light toward the projection end and through the first opening. The heatsink is fixed to the heat dissipation end of the housing, and in contact with one side of the light emitting unit that faces the second opening, for dissipating the heat generated by the light emitting unit to the outside air.
Owner:COOLER MASTER CO LTD
Photoelectric conversion device
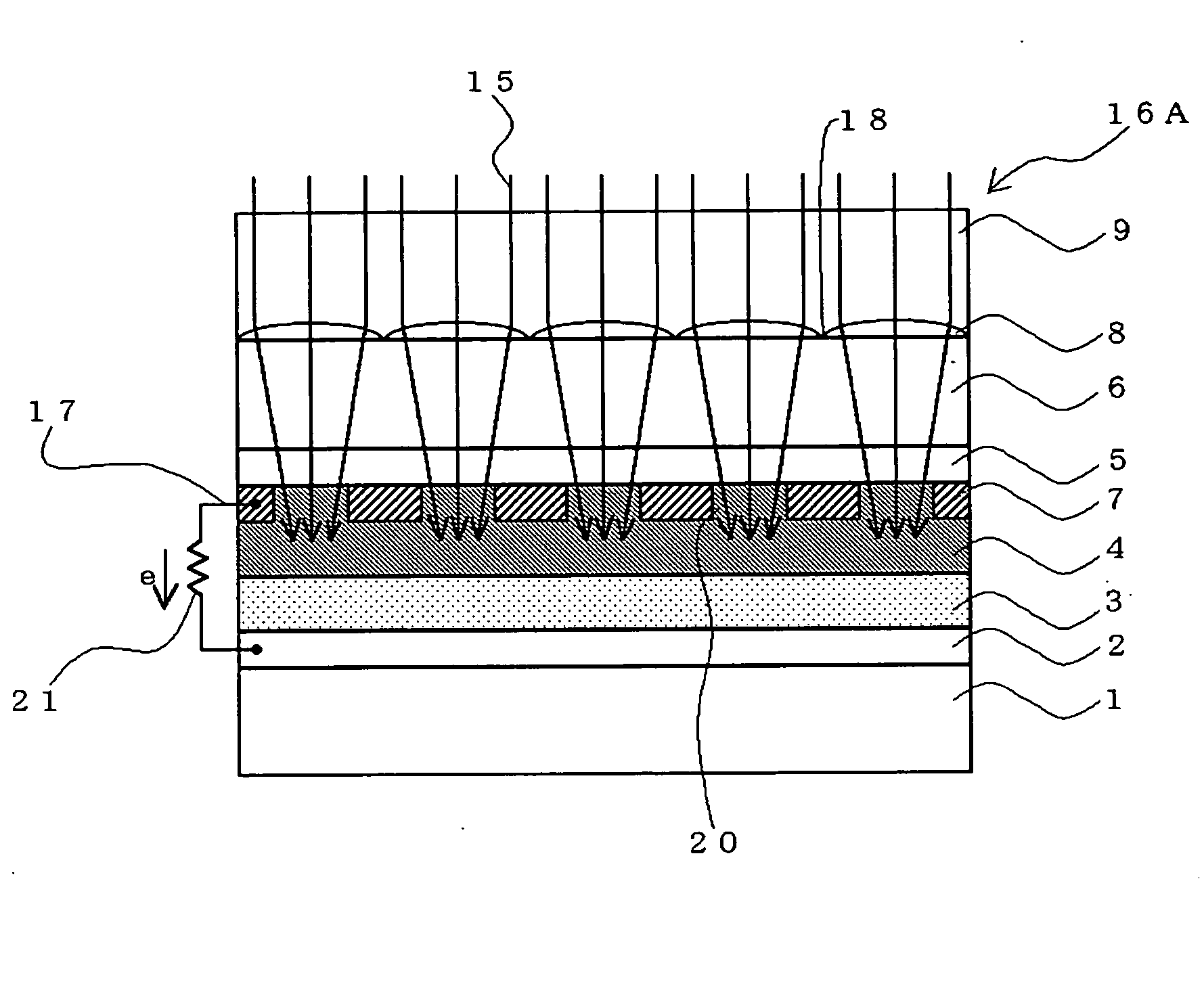
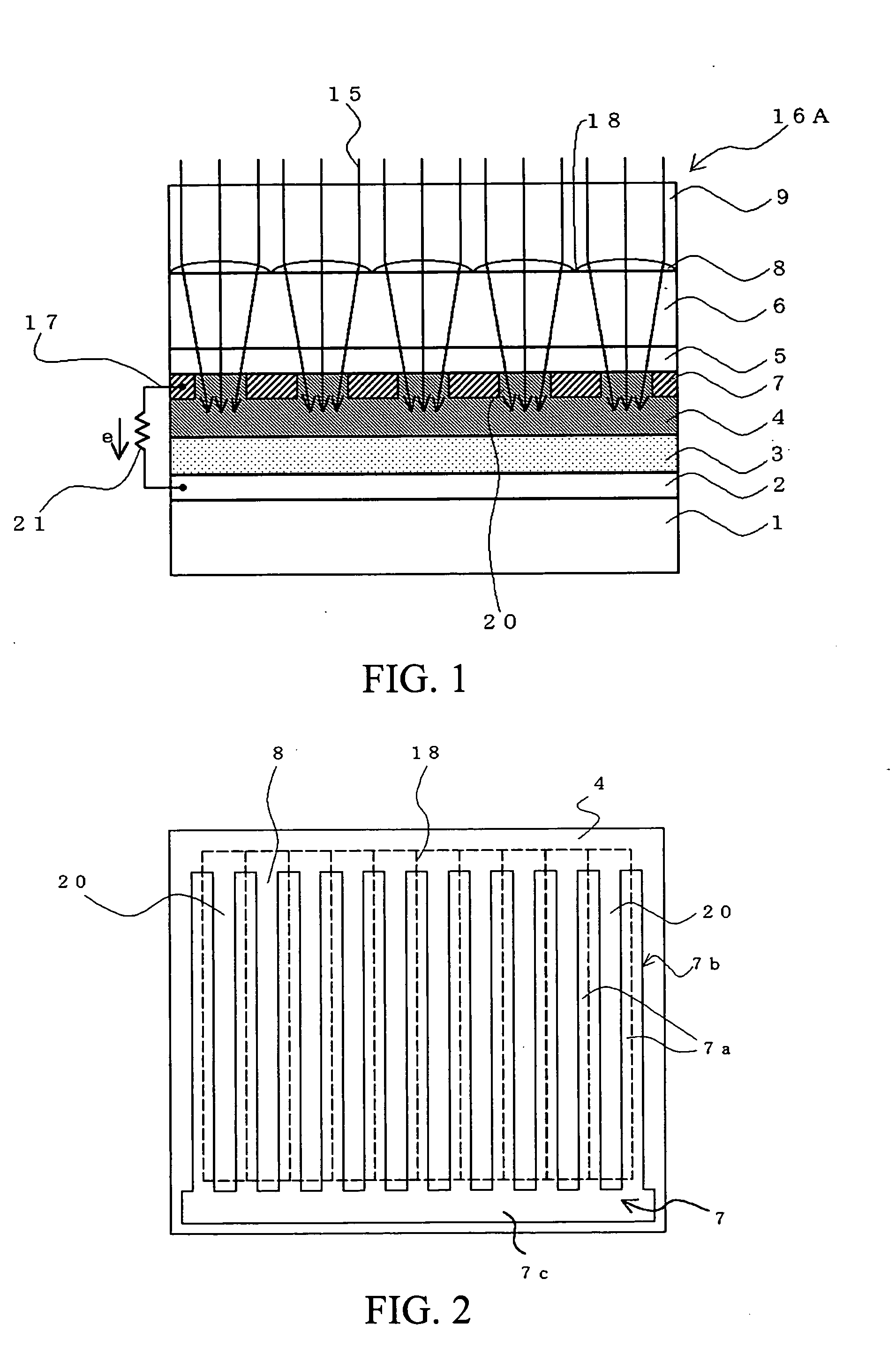
InactiveUS20050166957A1Conductor loss is reducedImprove mobilityLight-sensitive devicesPV power plantsLight energyTransducer
A photoelectric transducer having a relatively simple structure and capable of reducing the loss of light energy of incident light and conductor loss due to electrical resistance. A photoelectric transducer 16A includes a conductive layer 2; a electrolytic layer 3 that is in contact with the conductive layer 2; a charge separating layer 4; a transparent conductive layer 5 and a metal lines 7, which are in contact with the charge separating layer 4; and convex lenses 8 converging incident light 15 on openings 20 provided between the metal lines 7, the incident light 15 being converged on the charge separating layer 4 by the convex lenses 8. Electrons generated by photoelectric conversion move to the exterior through an external circuit 17 having a low resistivity.
Owner:SONY CORP
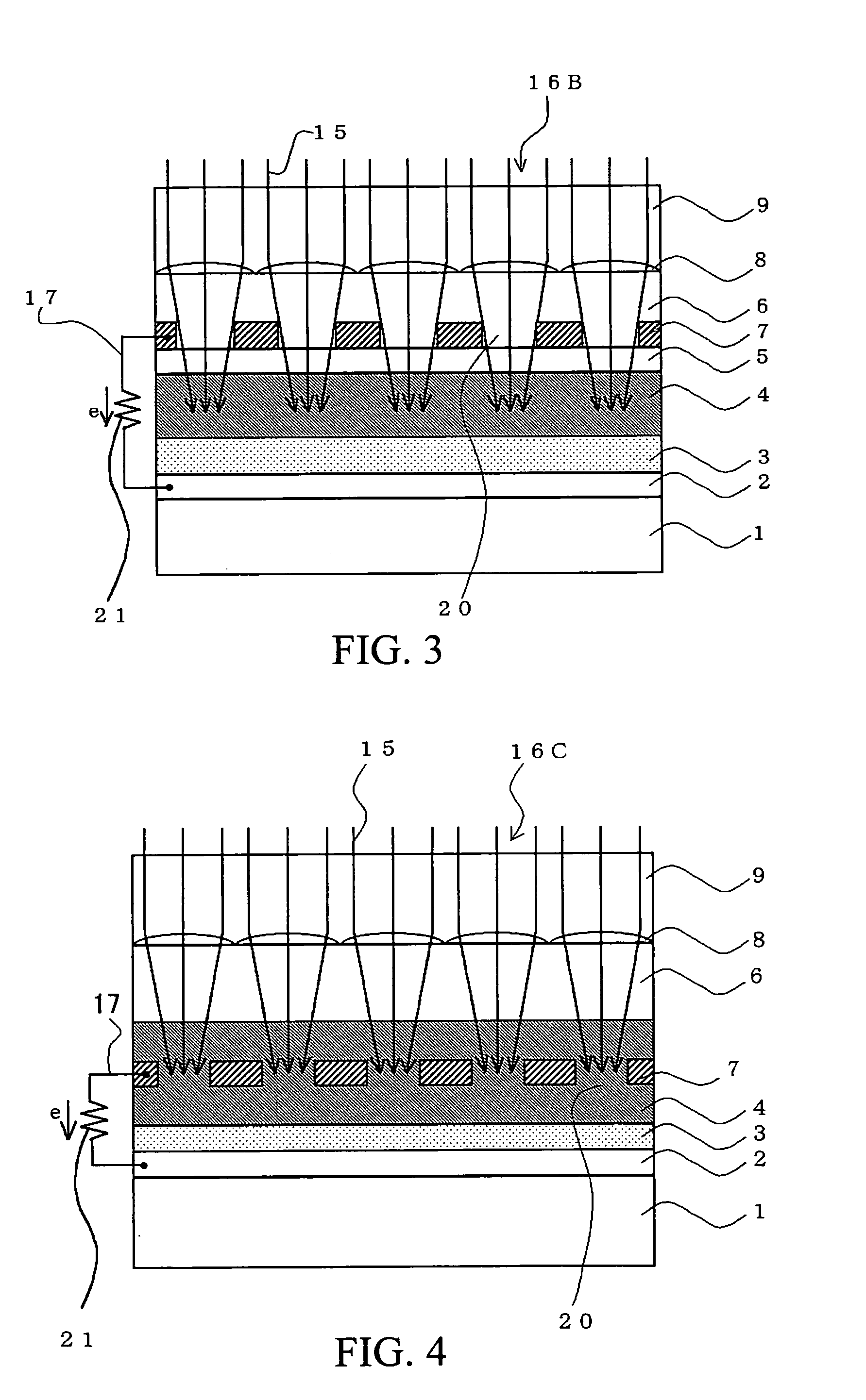
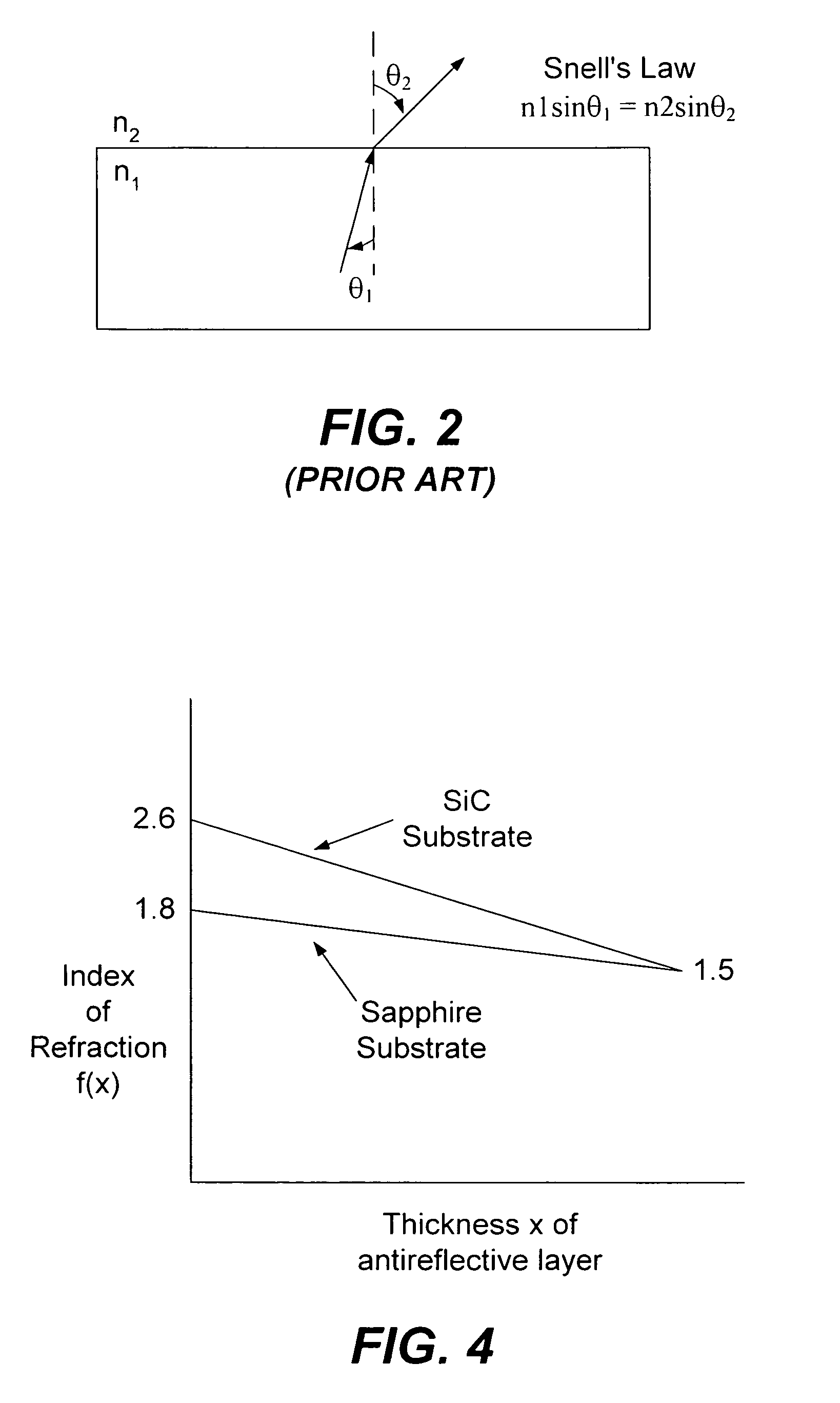
Methods of forming light-emitting devices having an antireflective layer that has a graded index of refraction
ActiveUS7087936B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce the amount of lightSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptical radiationRefractive index
A light-emitting device includes a substrate that is at least partially transparent to optical radiation and has a first index of refraction. A diode region is disposed on a first surface of the substrate and is configured to emit light responsive to a voltage applied thereto. An encapsulation layer is disposed on a second surface of the substrate and has a second index of refraction. An antireflective layer is disposed between a second surface of the substrate and the encapsulation layer. The antireflective layer has a graded index of refraction having values in a range between about the first index of refraction at a first surface of the antireflective layer and about the second index of refraction at a second surface of the antireflective layer. The encapsulation layer may also be omitted and the antireflective layer may separate the substrate, which has a first index of refraction, from air, which has a second index of refraction. Non “flip-chip” embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:CREELED INC
Exposure apparatus, microdevice, photomask, method of exposure, and method of production of device
InactiveUS6842225B1Reduce amount of lightImprove accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringPhotomask
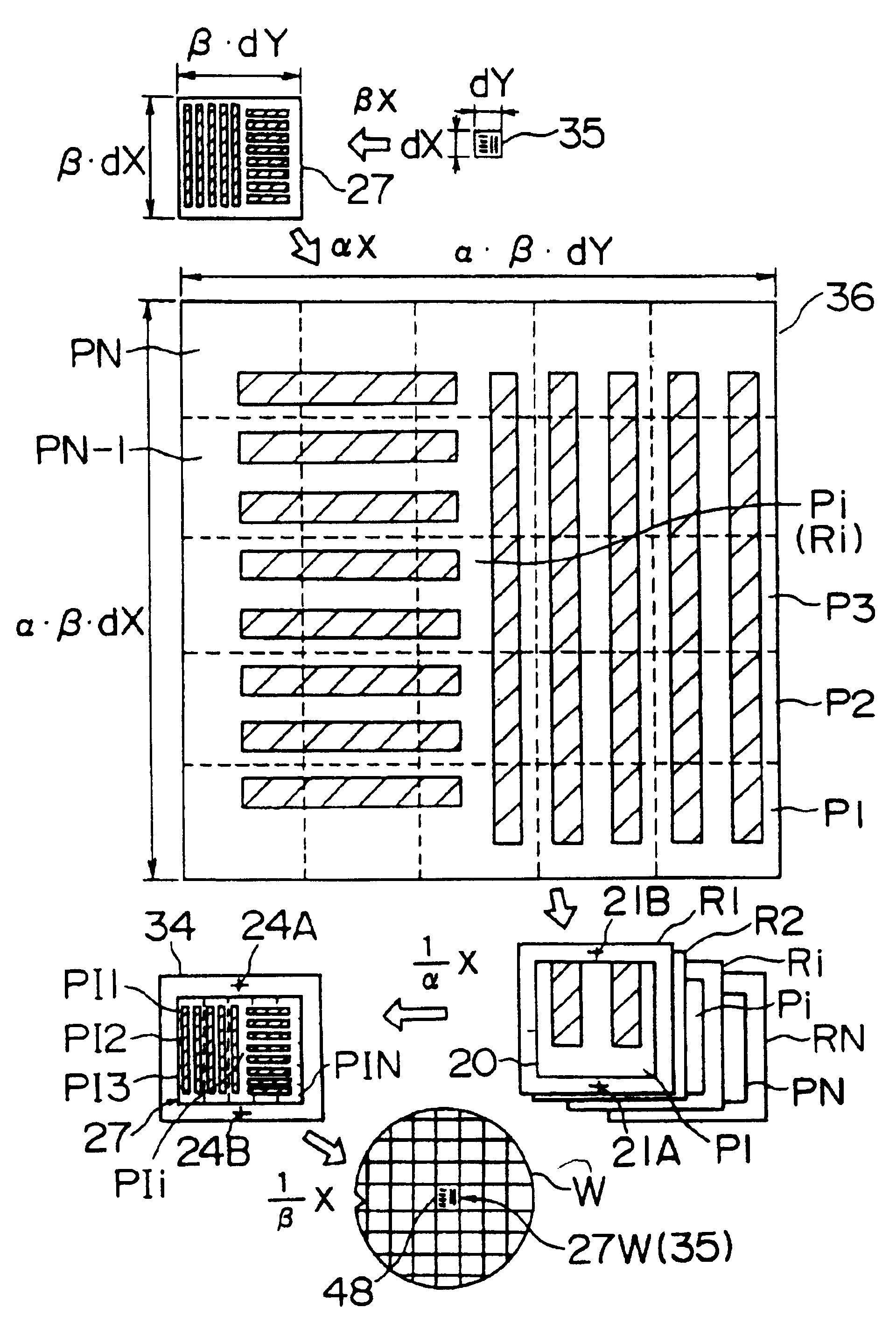
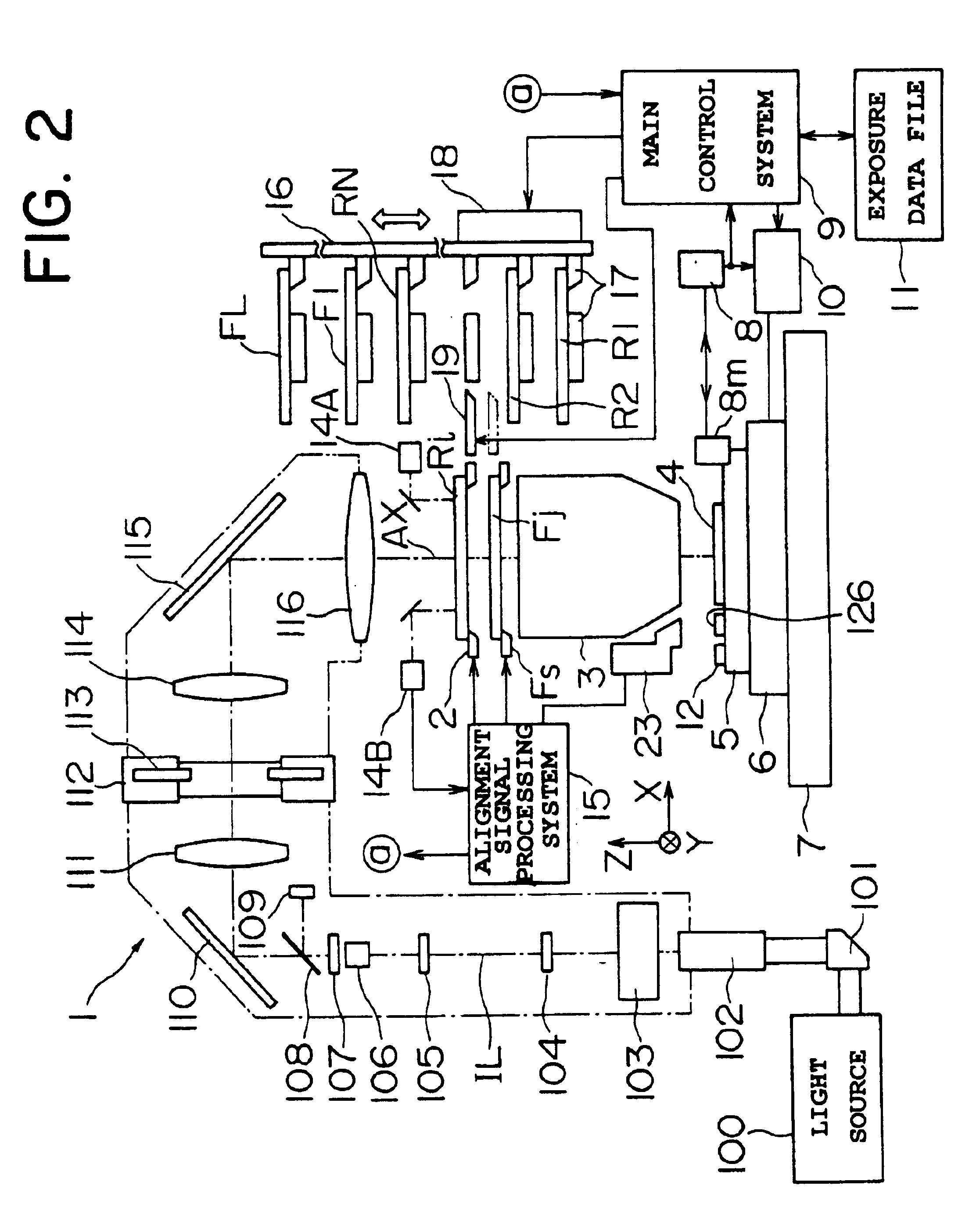
A stitching type exposure apparatus for successively exposing an image of a pattern of a reticle (Ri) on different areas of a surface of a substrate (4) while overlaying parts of the same, wherein a density filter (Fj) having a light attenuating part for reducing the amount of light of overlaid parts of the image of the pattern in a sloping manner is provided in the vicinity of the reticle (Ri), the density filter (Fj) is held at a filter stage (FS) for adjusting the posture, the posture of the density filter (Fj) is detected by an illumination uniformity sensor (126) on the substrate stage (6), and the posture of the density filter (Fj) is matched with the posture of the reticle (Ri) by the filter stage (FS).
Owner:NIKON CORP
EL display panel and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20090262047A1Minimize impactAccurate operationStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsActive matrixThreshold voltage
Disclosed herein is an electroluminescence display panel including pixel circuits corresponding to an active-matrix drive system, the electroluminescence display panel including a structure configured to include first light-emitting areas corresponding to an emission color that is strongest in a characteristic of changing a threshold voltage of a thin film transistor and second light-emitting areas that correspond to another emission color and are each disposed between the first light-emitting areas, wherein a sampling transistor in each of the pixel circuits for driving the second light-emitting areas is disposed in an area corresponding to a range of one fourth to three fourths of a length from a peripheral edge of one of two first light-emitting areas that are adjacent to each other with intermediary of the second light-emitting area of the sampling transistor to a peripheral edge of the other of the two first light-emitting areas.
Owner:SONY CORP
Solar cell fabrication with faceting and ion implantation
ActiveUS20090308450A1Reduce amountReduce the amount of lightLiquid surface applicatorsFinal product manufactureElectron hole recombinationArea density
Solar cells in accordance with the present invention have reduced ohmic losses. These cells include photo-receptive regions that are doped less densely than adjacent selective emitter regions. The photo-receptive regions contain multiple four-sided pyramids that decrease the amount of light lost to the solar cell by reflection. The smaller doping density in the photo-receptive regions results in less blue light that is lost by electron-hole recombination. The higher doping density in the selective emitter region allows for better contacts with the metallic grid coupled to the multiple emitter regions. Preferably, the selective emitter and photo-receptive regions are both implanted using a narrow ion beam containing the dopants.
Owner:INTEVAC
Imaging device and electronic camera
InactiveUS20110076001A1Reduce the amount of lightLow costTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhase differenceOptical axis
An imaging device includes an arrayed imaging element group configured to receive light passing through a photographic lens, wherein the imaging element group includes a plurality of photographic elements used for photographic image data generation and a plurality of phase difference detection elements used for phase difference detection for focus detection of the photographic lens, each of the photographic elements and each of the phase difference detection elements include: an on-chip microlens configured to collect light passing through the photographic lens; a photoelectric conversion element configured to receive the light passing through the on-chip microlens; and an internal microlens disposed between the on-chip microlens and the photoelectric conversion element, the photographic element is configured such that an optical axis of the on-chip microlens matches an optical axis of the internal microlens, and the phase difference detection element is configured such that the optical axis of the on-chip microlens is shifted from the optical axis of the internal microlens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image sensor and image-capturing device
ActiveUS20100188532A1Reduce the amount of lightTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementLight beamLuminous flux
An image sensor includes: a plurality of image-capturing pixels that, upon each receiving a partial light flux within a predetermined wavelength range, which is part of a photographic light flux used to form an optical image, output image signals corresponding to the optical image; a plurality of focus detection pixels that receive a pair of focus detection light fluxes in a wider wavelength range than the predetermined wavelength range and output a pair of focus detection signals; and a reduction unit that adjusts a signal level of the focus detection signals output from the plurality of focus detection pixels to be equal to or less than a signal level of the image signals each output from one of the plurality of image-capturing pixels under a given light receiving condition.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Light emitting element, light emitting device, manufacturing method of light emitting device, and sheet-like sealing material
ActiveUS20080018231A1Reduce the amount of reflectionImprove lighting efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesRefractive indexLight emitting device
A method to improve light extraction efficiency of a light emitting element such as an electroluminescent element is disclosed. Over a substrate, a first electrode, a light emitting layer, and a second electrode are sequentially stacked. The first electrode is a reflective electrode. The second electrode is an electrode which transmits visible light, and light emitted from the light emitting layer is extracted from the second electrode. In contact with a surface of the second electrode, many fine particles are provided. The fine particles have a refractive index which is equal to or higher than that of the second electrode. Light which passes through the second electrode is scattered and refracted by the fine particles. Accordingly, the amount of light which is totally reflected at an interface between the second electrode and a gas is reduced, and light extraction efficiency is improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
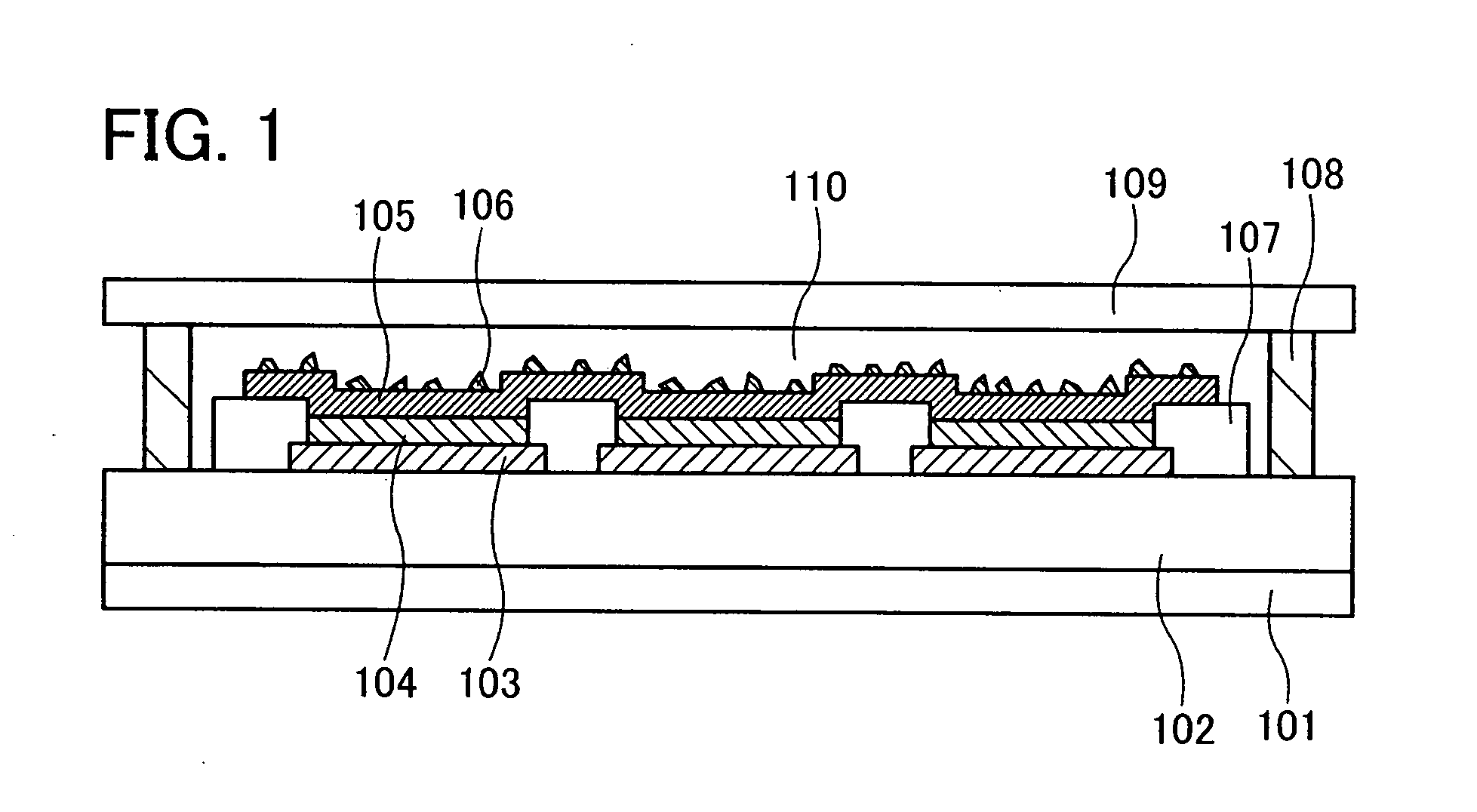
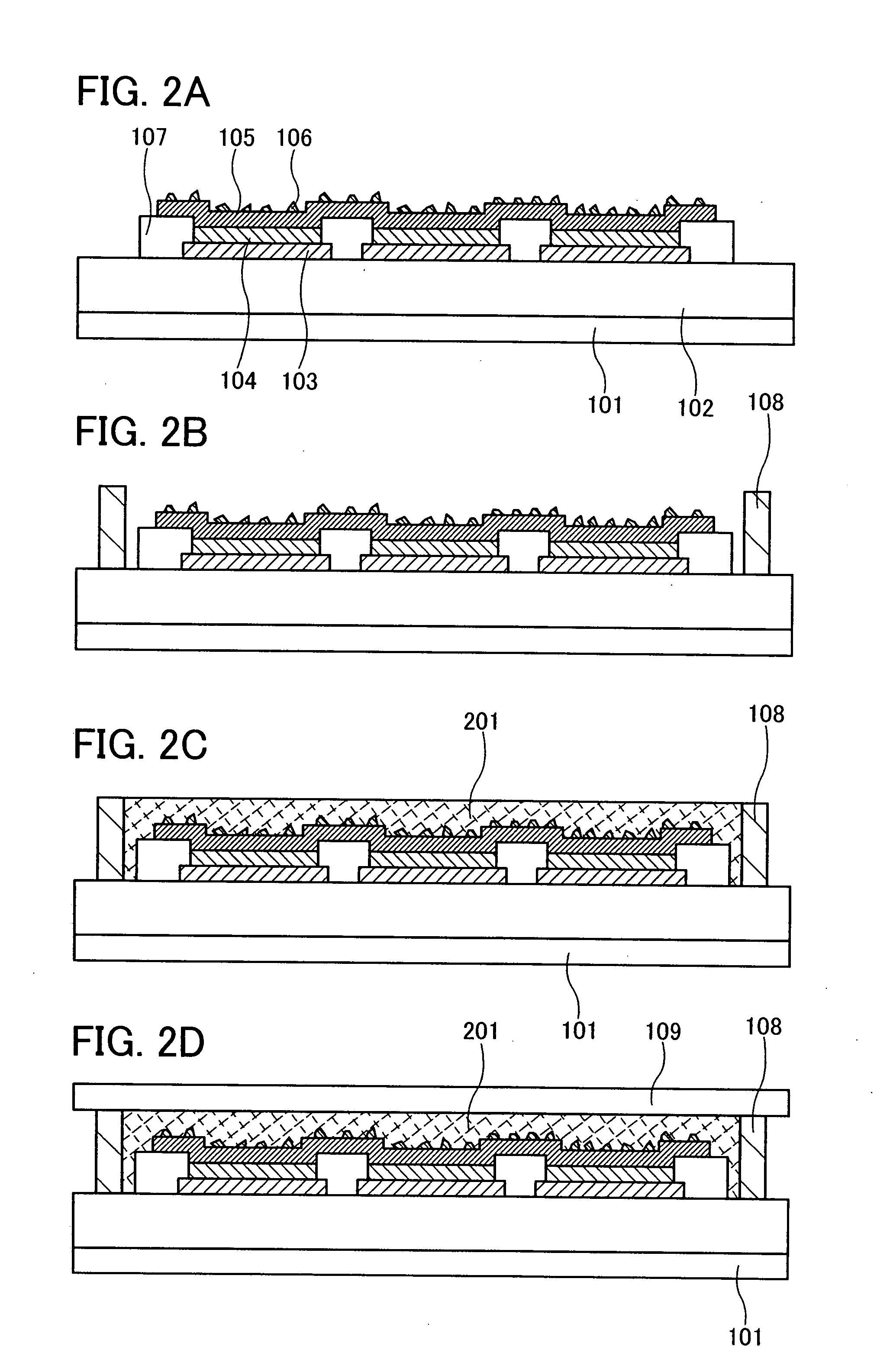
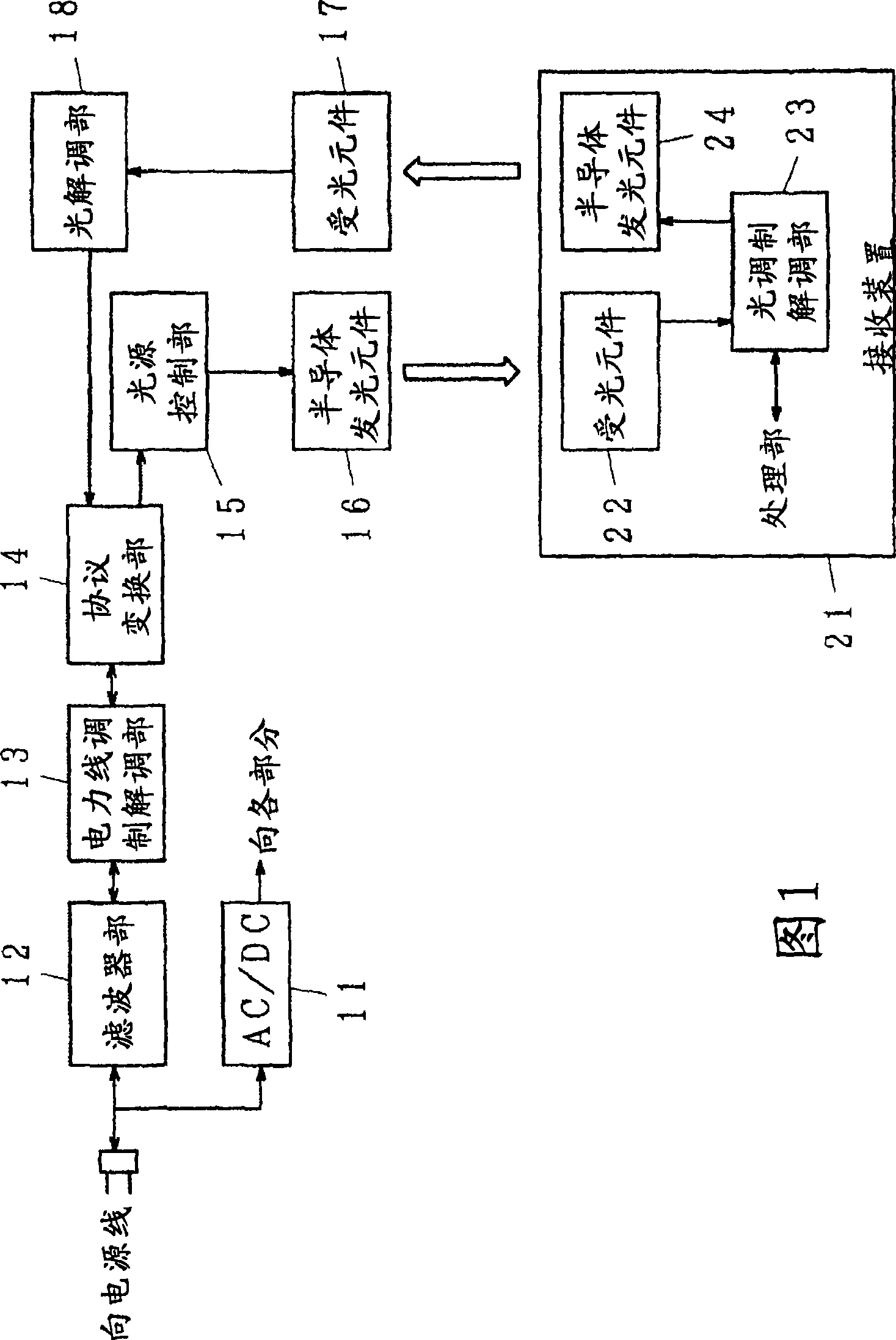
Illuminating light communication device
InactiveCN101432997AReduce the amount of lightSuppress changesPower distribution line transmissionLine-of-sight transmissionCommunications systemElectric power system
An illuminating light communication device is provided to construct a communication system in which, when data are transmitted by using an electric power line and illuminating light, light intensity fluctuations of the illuminating light are suppressed and communication by means of the electric power line and the illuminating light can be well carried out. When data to be transmitted are sent through an electric power line, signal components are extracted in a filter (12), they are demodulated in an electric power line modulating unit (13), so that data are obtained. The obtained data are tentatively stored in a protocol converting unit (14). The data are then converted to an optical communication protocol, a semiconductor light emitting element (16) is turned on or off, or its light quantity is controlled to modulate illuminating light in accordance with data to be transmitted by a light source controller (15). Thus, the data are transmitted by making use of the illuminating light. As a modulation system for the light communication, multiple-value PPM may be used, wherein an existing pulse is set to OFF while a non-existing pulse is set to ON.
Owner:NAKAGAWA LAB INC
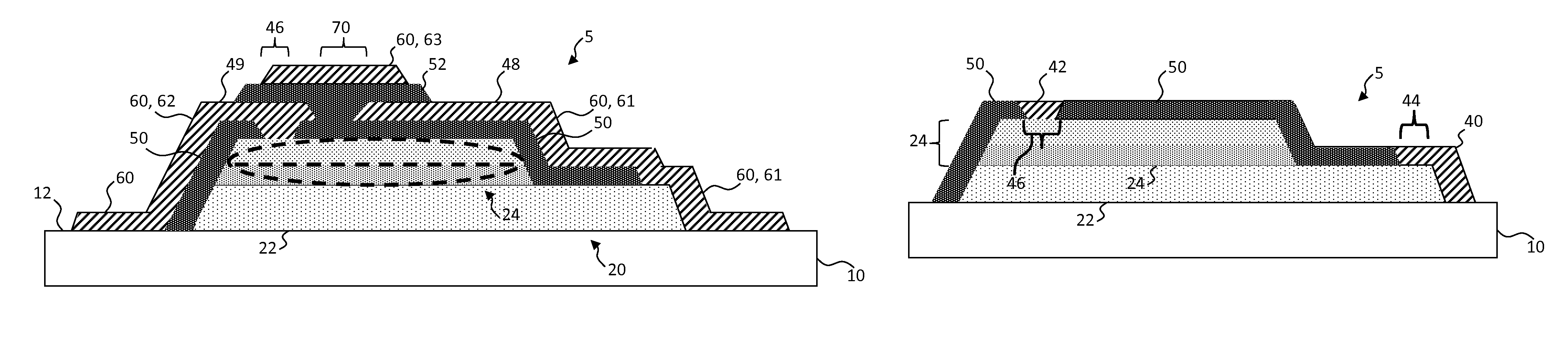
Inorganic light-emitting diode with encapsulating reflector
ActiveUS9537069B1Improve efficiencyImprove light outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesReflective layerLight-emitting diode
An inorganic light-emitting diode structure includes a transparent substrate and an inorganic semiconductor having a conduction layer and a light-emitting layer over and in contact with only a portion of the conduction layer. A first metal contact is in electrical contact with the conduction layer and a second metal contact is in electrical contact with a second contact portion of the light-emitting layer so that a current supplied between the first metal contact and the second metal contact through the inorganic semiconductor causes the light-emitting layer to emit light. A dielectric layer is located over at least a portion of the light-emitting layer and a reflective layer is located over at least a portion of the dielectric layer. The reflective layer encapsulates the light-emitting layer exclusive of the portion of the conduction layer in contact with the light-emitting layer.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
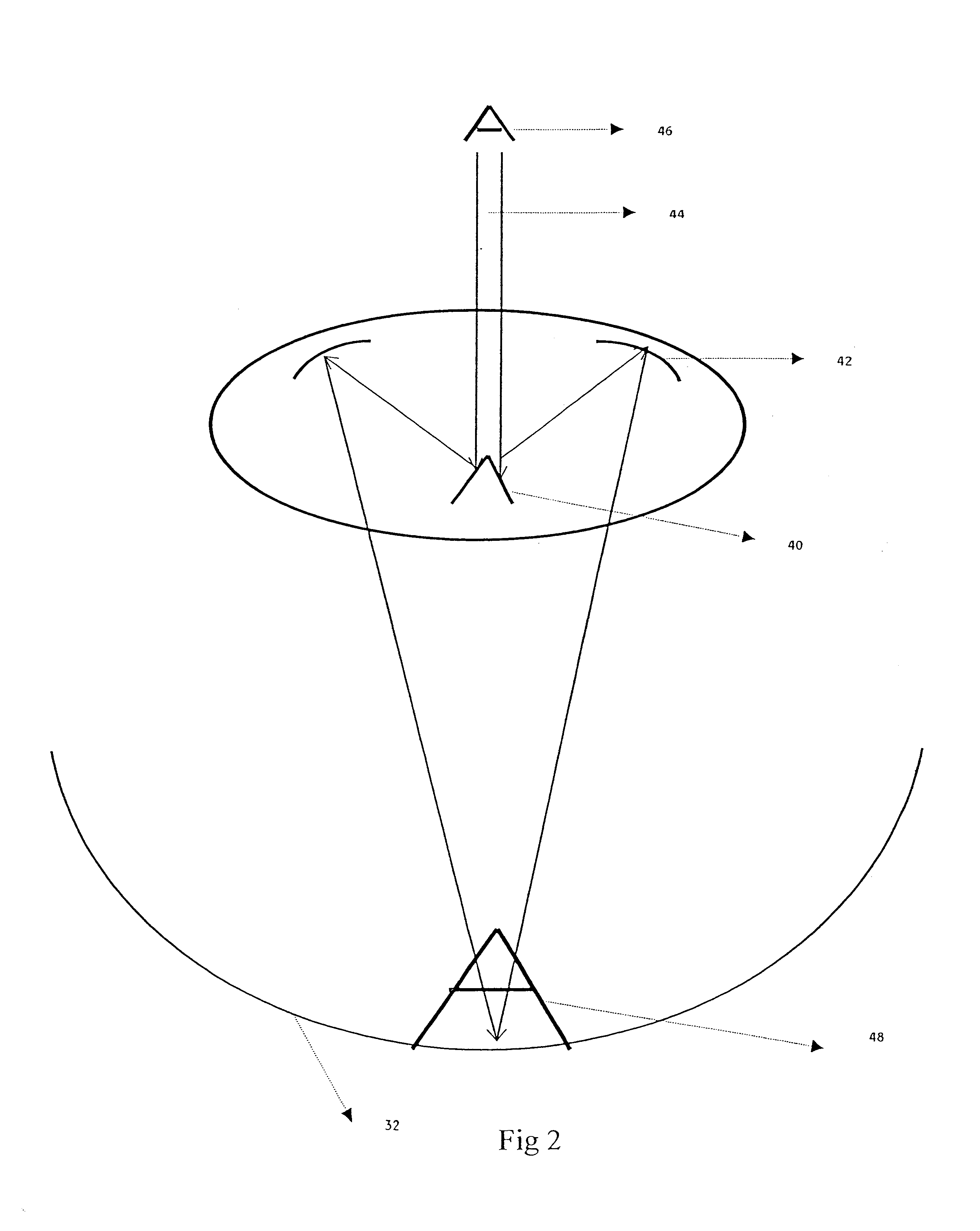
Intraocular lens implant with mirror
InactiveUS6902577B2Reduce the amount of lightIncrease the amount of lightIntraocular lensOptical propertyAnterior surface
An intraocular implant for implantation into the interior of an eye is disclosed. The intraocular implant includes a body member, the body member has an anterior surface and a posterior surface, and has optical properties, and, at least one mirror, wherein the at least one mirror is contained within the body member.
Owner:ISAAC LIPSHITZ
Display apparatus
InactiveUS20110069254A1Improve image qualityReduce the amount of lightNon-linear opticsLensFocal positionOptoelectronics
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
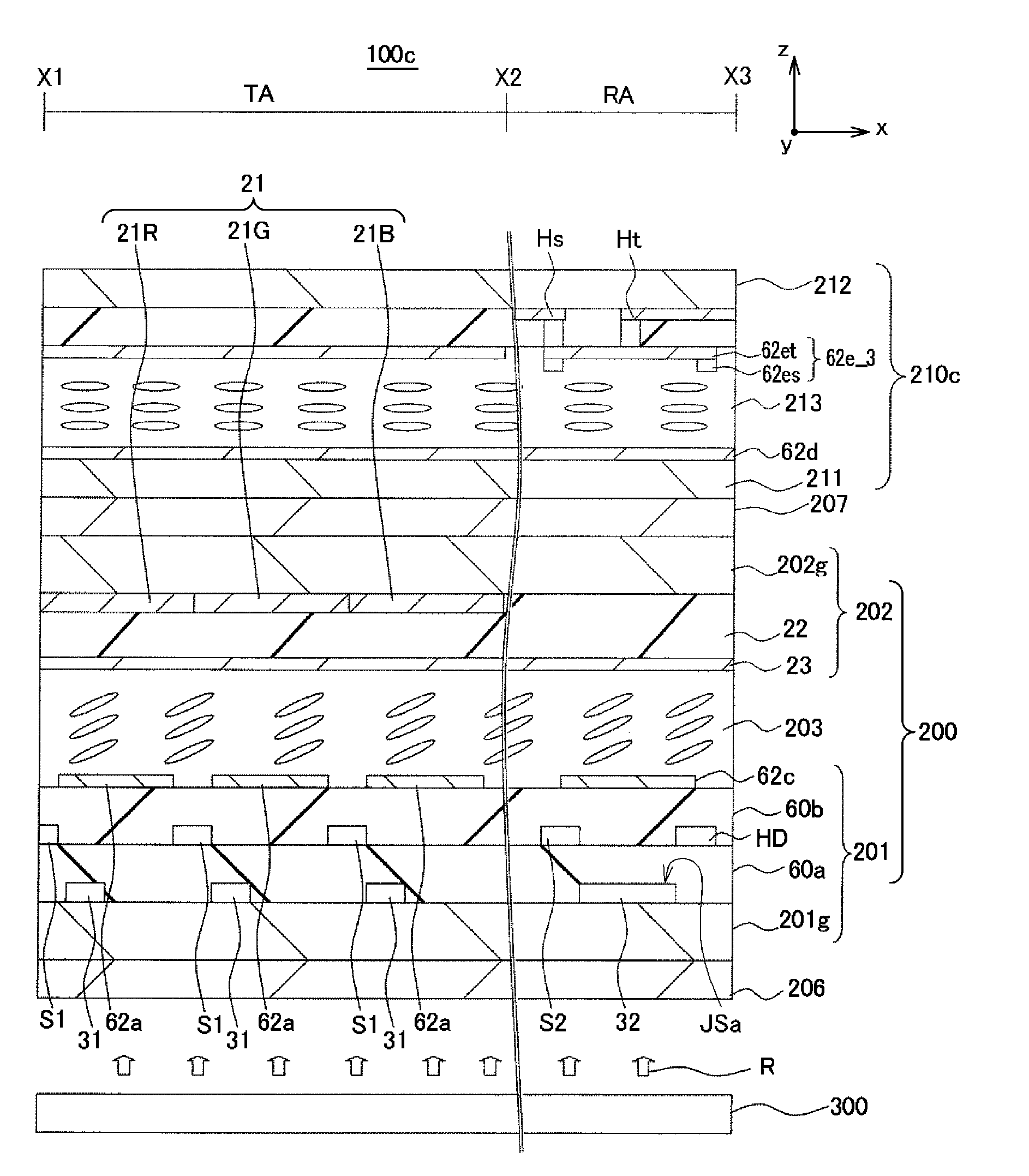
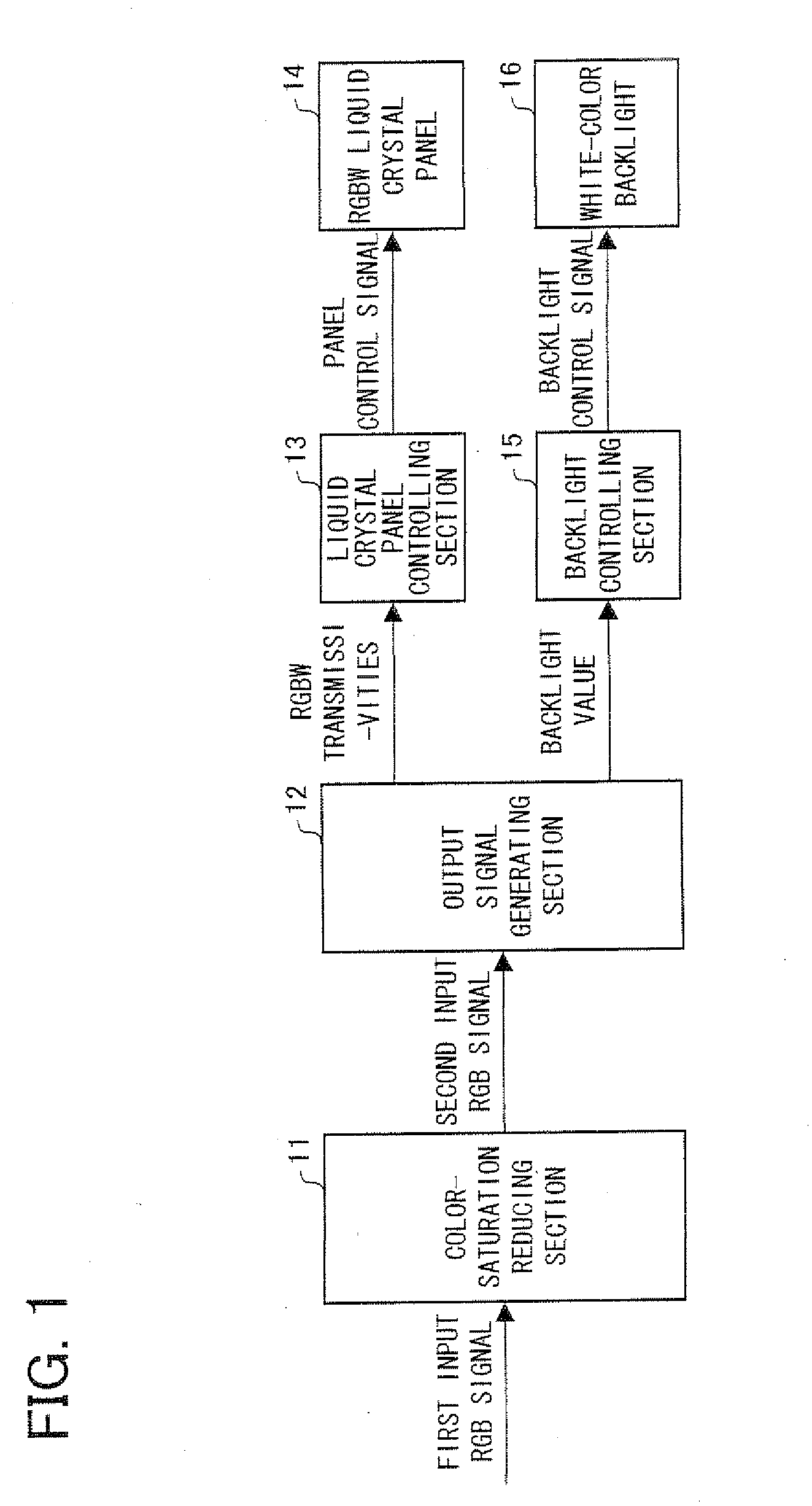
Transmissive-type liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20080150863A1Reduce power consumptionNo loss (or little loss)Color signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayTransmittance
In a transmissive-type liquid crystal display device including a liquid crystal panel and a backlight, the liquid crystal panel has pixels each divided into four subpixels red (R), green (G), blue (B), and white (W). The backlight is a white backlight by which luminance of emitted light is controllable. A color-saturation reducing section carries out a process of reducing color saturation on a first RGB input signal, which is an original input signal, so that the first RGB input signal becomes a second RGB input signal. Thereafter, an output signal generating section obtains a transmissivity and a backlight value on the basis of the second RGB input signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS6383898B1Increase light absorption coefficientReduce the amount of lightFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion device including a plurality of pin junction layers, wherein at least a p-layer adjacent to an n-layer is formed of a stack of an amorphous silicon layer as a first p-layer and an amorphous silicon layer as a second p-layer, the first p-layer having a thickness of 5 nm or less and containing a p-type impurity and an n-type impurity, and the second p-layer having a p-type impurity concentration gradually decreasing as it is closer to an i-layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
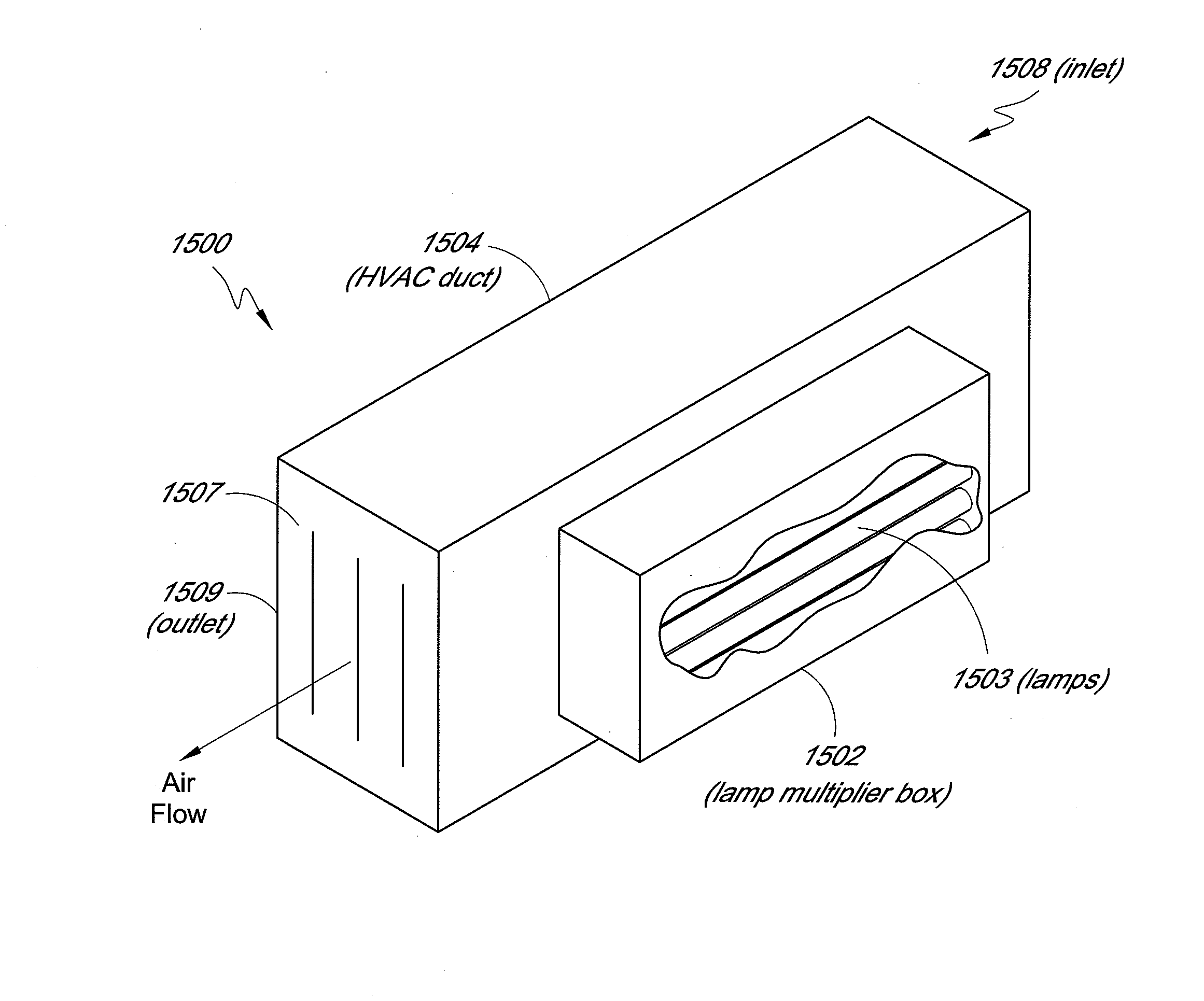
UV flux multiplication system for sterilizing air, medical devices and other materials
ActiveUS20080152548A1Reduced Power RequirementsReduce in quantityMechanical apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltraviolet lightsOptoelectronics
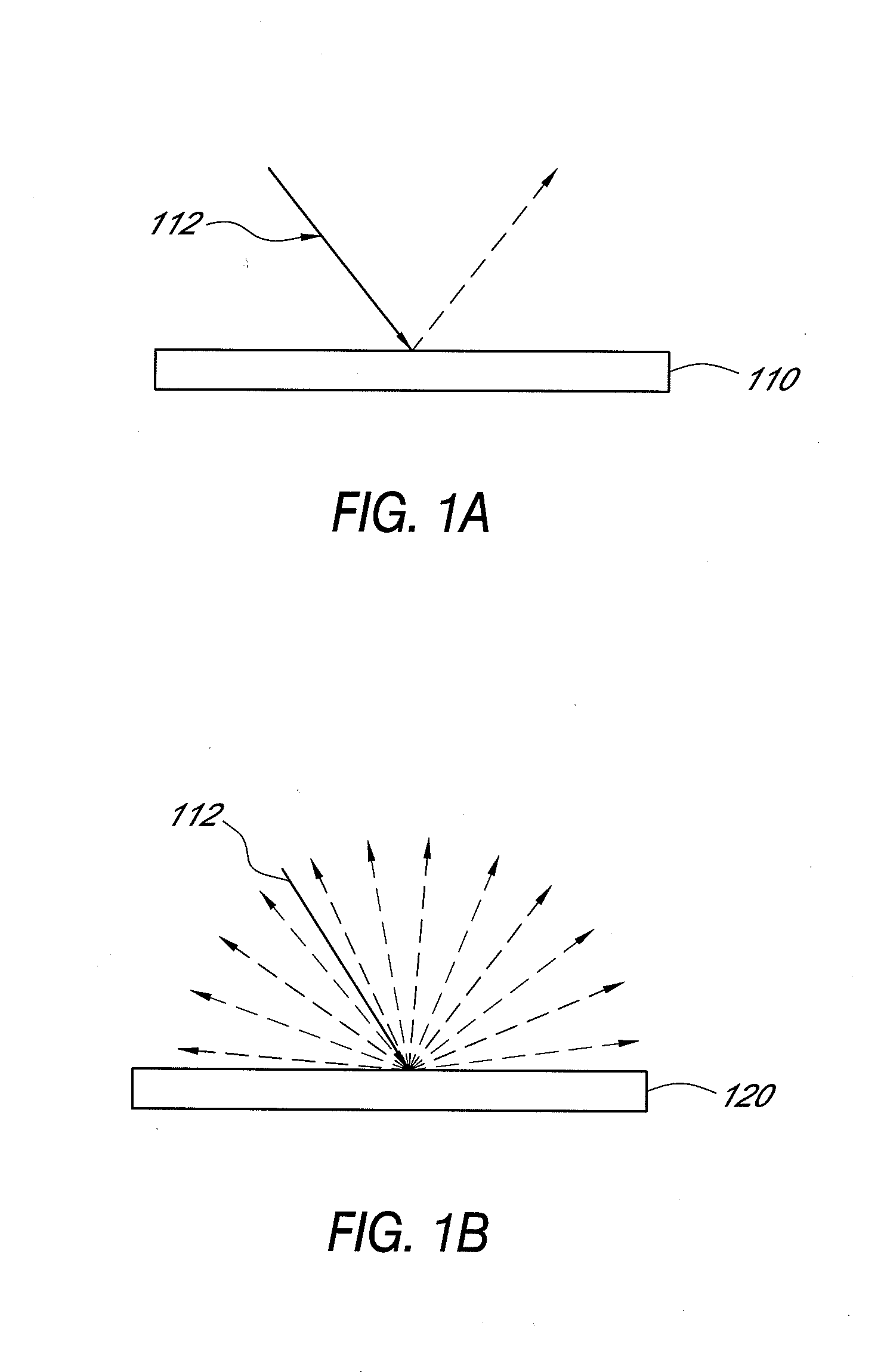
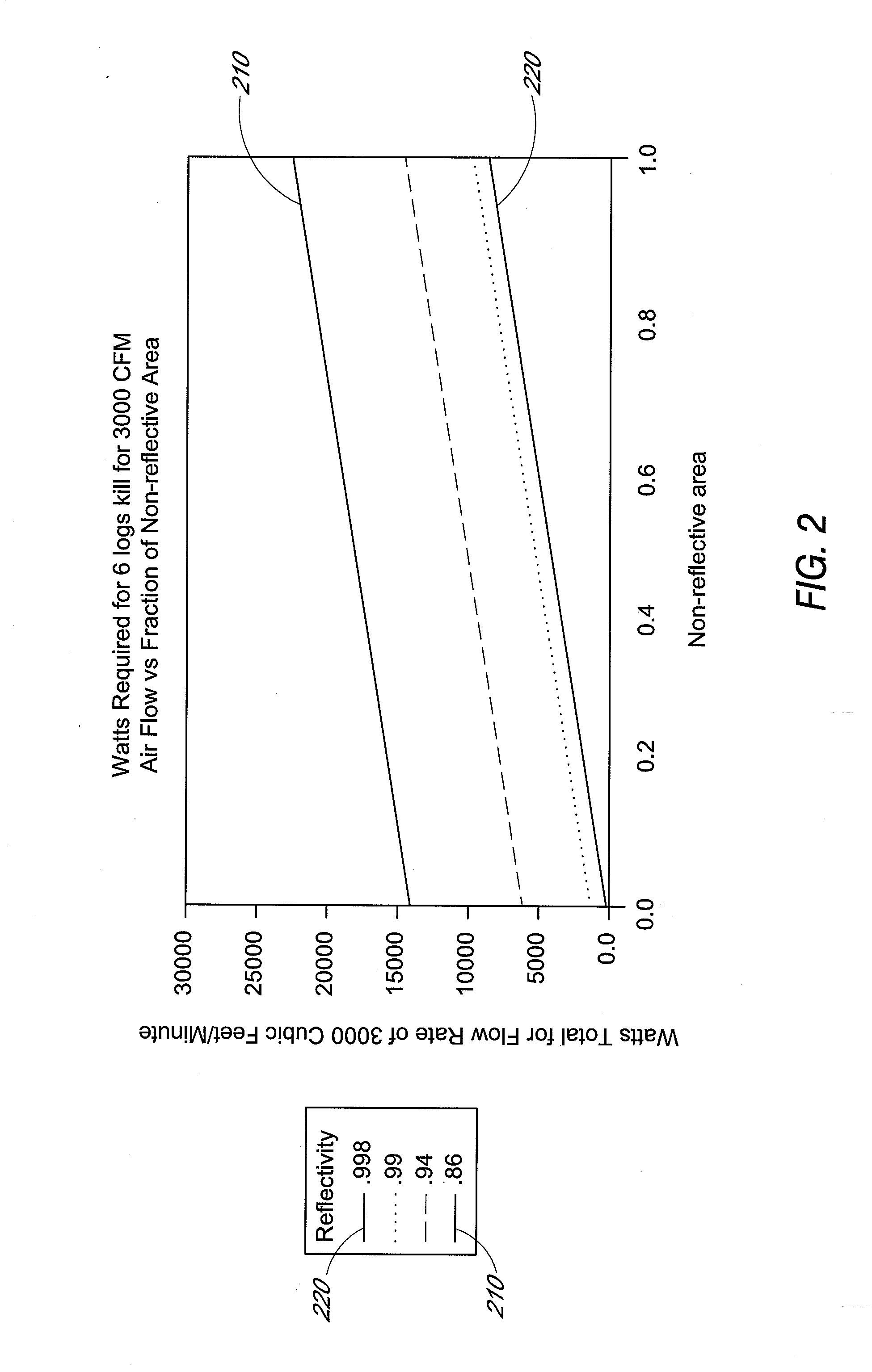
An ultraviolet flux multiplying air sterilization chamber comprises inner surfaces having a diffuse reflective behavior. The sterilization chamber includes an inlet aperture and an outlet aperture for air to flow through said chamber and a light source emitting an ultraviolet light. Due to the reflectivity of the inner surfaces of the chamber, a flux of the ultraviolet light is multiplied by reflecting multiple times from the inner surfaces of the chamber. The inlet and outlet apertures are advantageously configured to reduce the amount of light that escapes from the chamber and increase the amount of photons available in the chamber. In an exemplary embodiment, perforated end panels having diffuse, reflective interior surfaces may be provided over at least a portion of the inlet and outlet apertures.
Owner:NOVATRON
Spectrometer
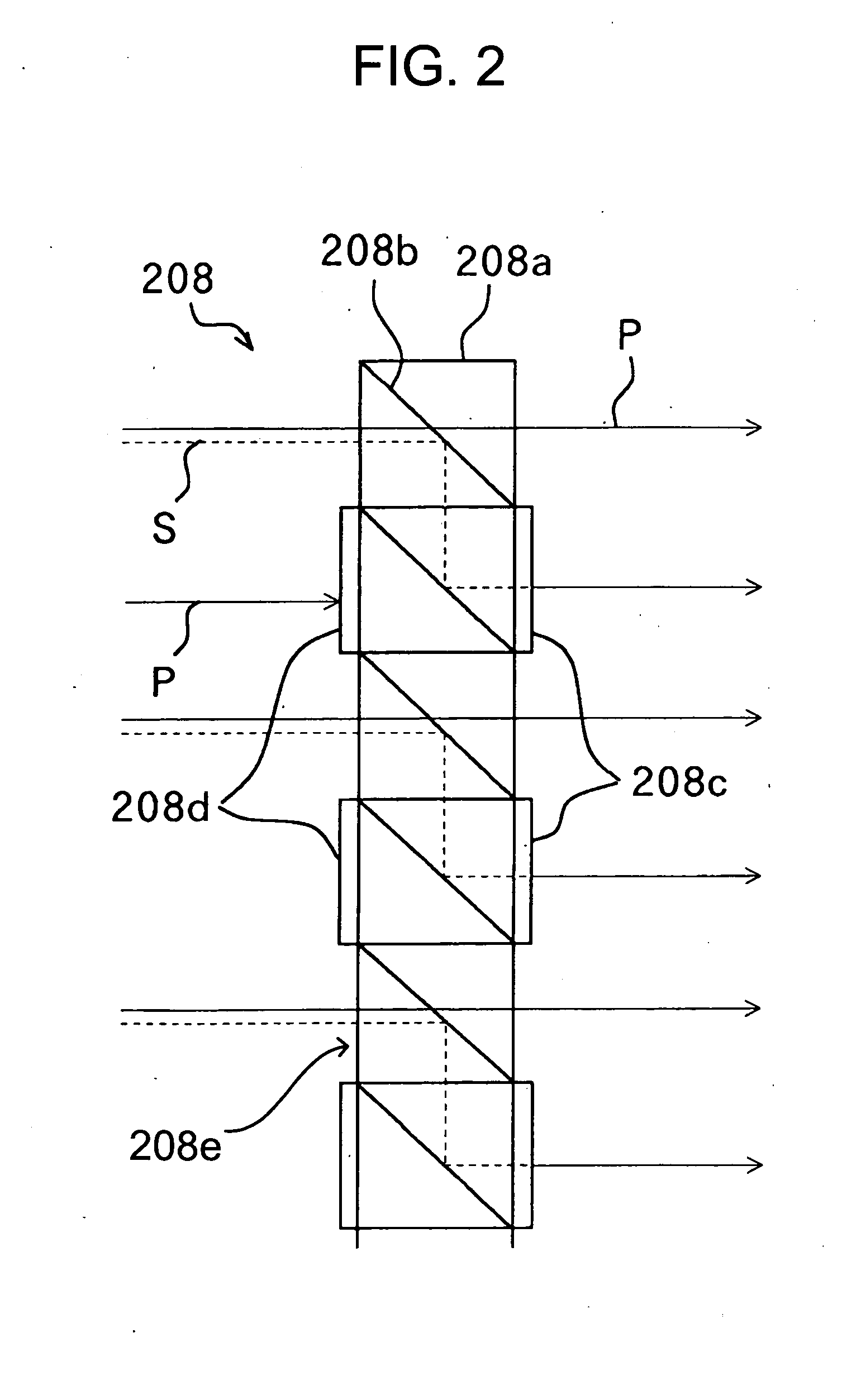
ActiveUS20140168636A1Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLength waveSpectrometer
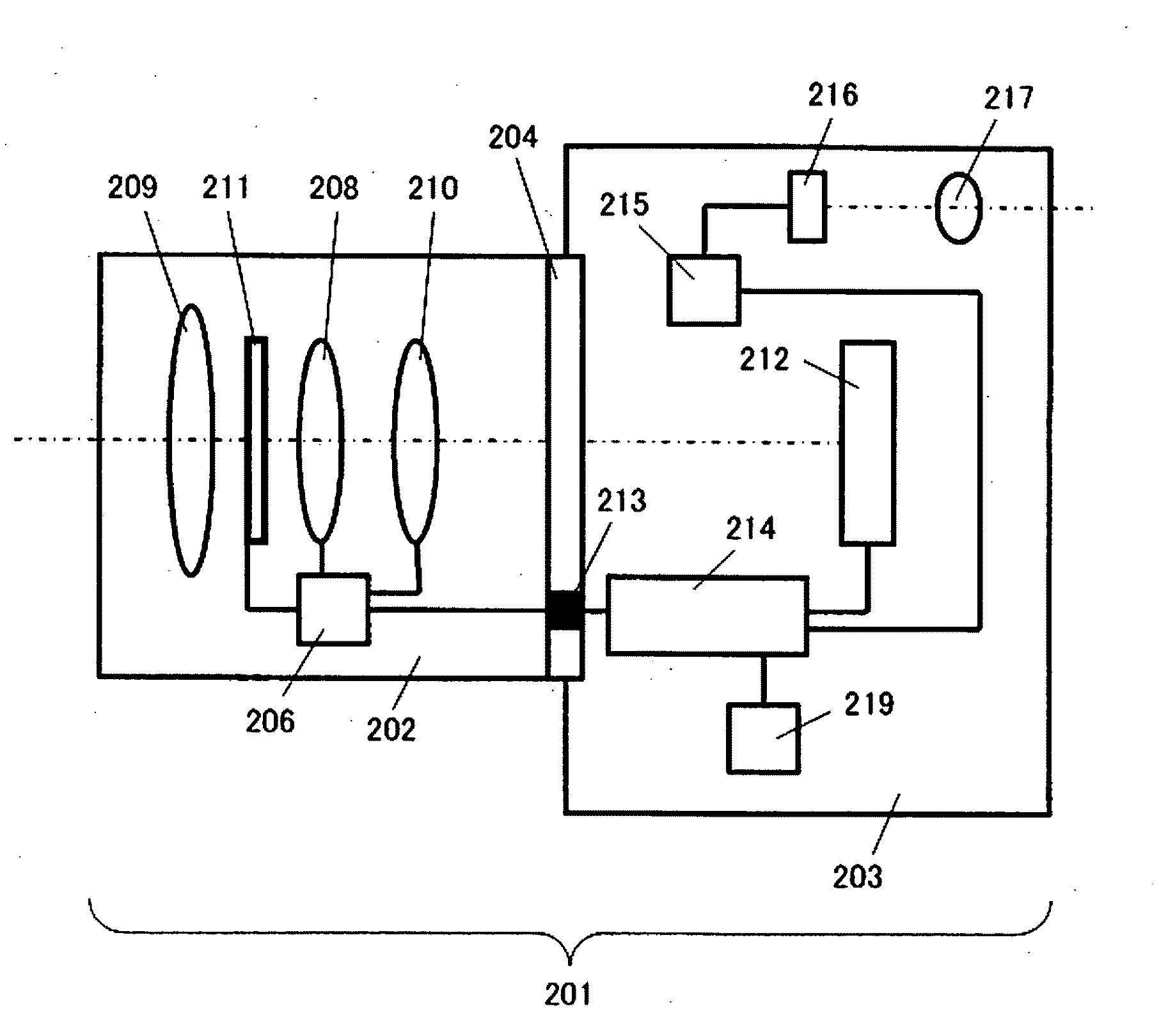
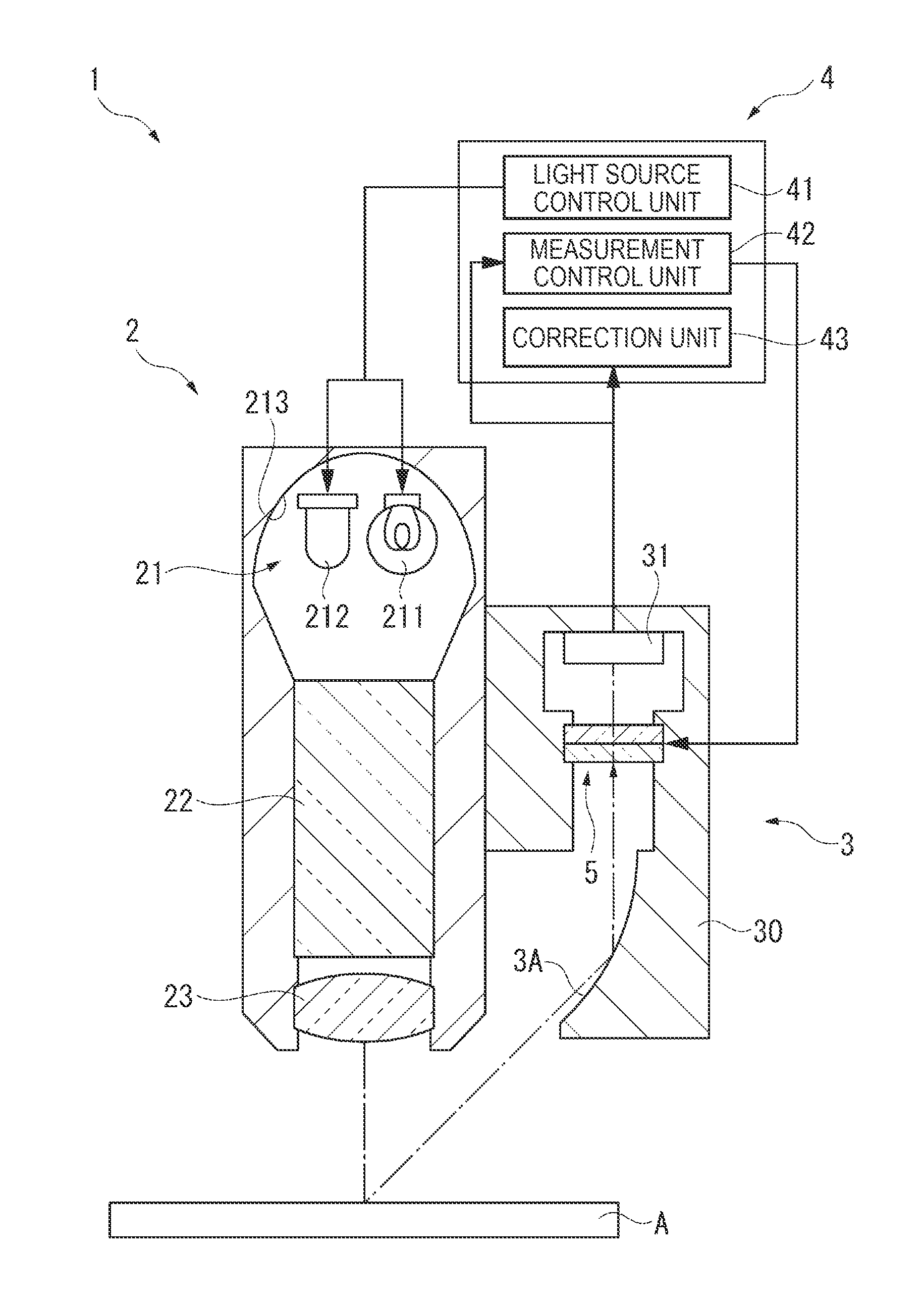
A spectrometer includes: a tungsten lamp which emits light with no peak wavelength within a wavelength range of visible light and having a light amount increasing as the wavelength becomes longer; a violet LED which emits light having a peak wavelength within the wavelength range of visible light; a light mixer which mixes light emitted from the tungsten lamp and the violet LED; an etalon which receives light mixed by the light mixer and transmits light contained in the received mixed light and having a particular wavelength; a light receiving unit which receives light transmitted by the etalon; and a measurement control unit which changes the wavelength of light that can pass through the etalon and measures spectral characteristics of the light having passed through the etalon based on the light received by the light receiving unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Photodetector
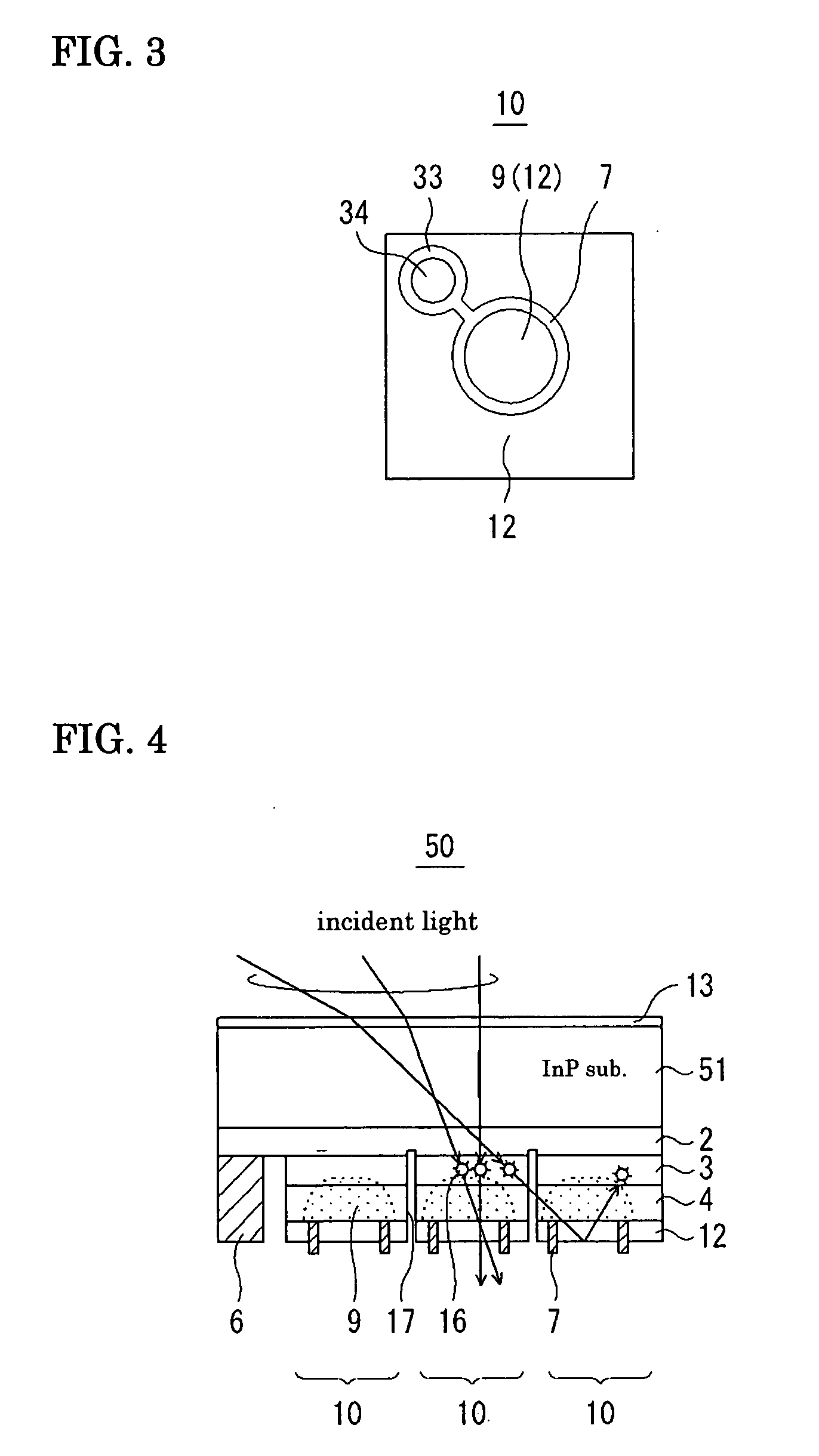
ActiveUS20070194401A1Reduce crosstalkImprove crosstalk characteristicTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
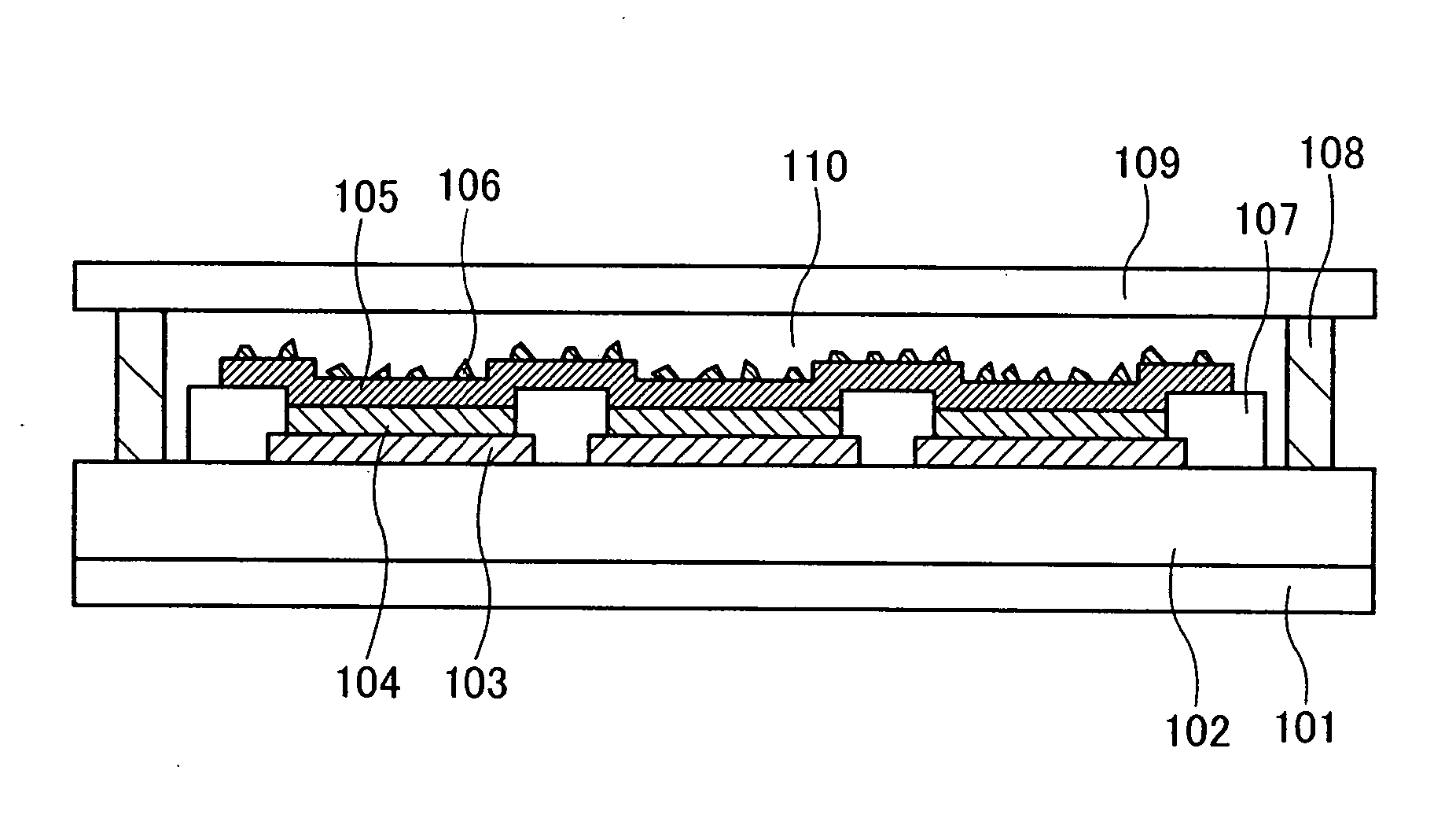
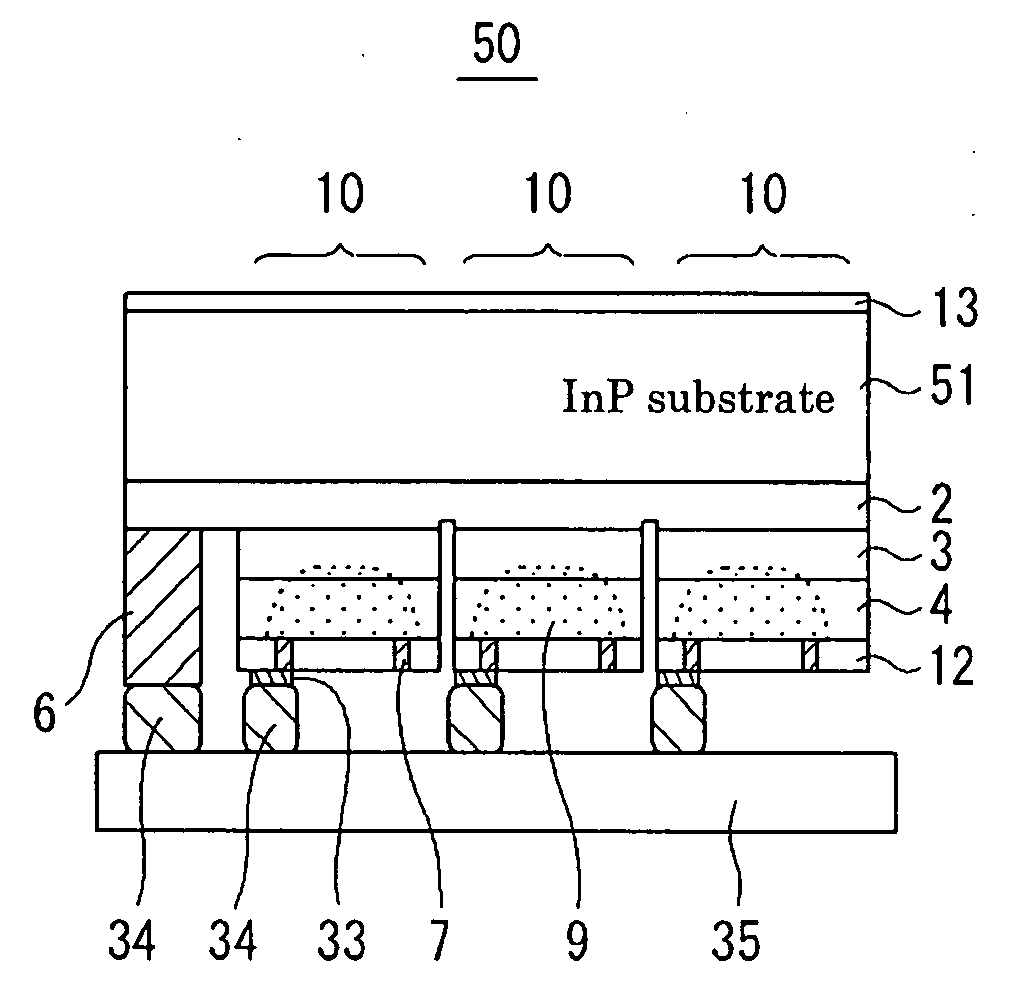
A photodetector having a mechanism of suppressing light crosstalk includes a plurality of photodiodes disposed on a common semiconductor substrate, each photodiode including an absorption layer epitaxially grown on the common semiconductor substrate and being provided with an epitaxial-side electrode. Each photodiode is provided with at least one of a ring-shaped or crescent-shaped epitaxial-side electrode, an incident-side-limited condensing part which condenses incident light that is directed to the corresponding photodiode only, and emission means which is disposed on a side opposite to a light-incident side of the absorption layer and which allows light entering from the light-incident side to be easily emitted out of the photodiode.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Illumination optical system and projection display optical system
InactiveUS20060203200A1Inhibition decreasedReduce the amount of lightTelevision system detailsPrismsIntegratorPolarization beam splitter
An illumination optical system is disclosed, which provides a luminous flux with a small incident angle on an illumination surface in one axis direction on a section of the luminous flux. The illumination optical system can suppress a reduction in light amount by a mask provided for a polarization conversion element. The illumination optical system has a light source and an optical integrator. The optical integrator uses a lens array to perform splitting of a luminous flux from the light source. The illumination optical system has the polarization conversion element including a polarization beam splitter array, a plurality of ½ wave plates, and a mask. The light source is a discharge gas exciting arc tube of a DC drive type.
Owner:CANON KK
Transmissive liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090160747A1Reduce power consumptionReduce the amount of lightTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
In a transmissive liquid crystal display device including a liquid crystal panel and a backlight, the liquid crystal panel has pixels each divided into four subpixels, namely red (R), green (G), blue (B), and white (W) subpixels. Further, the backlight is a white backlight whose light emission luminance is controllable. Furthermore, a color-saturation conversion section performs a color-saturation reduction process on a first input RGB input signal serving as an original input signal, and then a gamma-correction section performs a gamma-correction process on the first RGB input signal. An output signal generation section calculates transmittances and a backlight value in accordance with gamma-corrected RGB input signal obtained after the gamma-correction process has been performed by the gamma-correction section.
Owner:SHARP KK
Transmissive liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090085847A1Optimal backlight valueReduce backlight power consumptionStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayMaterials science
In a transmissive liquid crystal display device including a liquid crystal panel and a backlight, the liquid crystal panel contains pixels each divided into four subpixels, a red (R), a green (G), a blue (B), and a white (W) subpixel. The backlight is a white backlight emitting light with controllable emission luminance. A luminance lowering section performs luminance lowering processing on input RGB signals (original input signals) for transformation into luminance-lowered RGB signals. An output signal generating section obtains transmittances and a backlight value from the luminance-lowered RGB signals.
Owner:SHARP KK
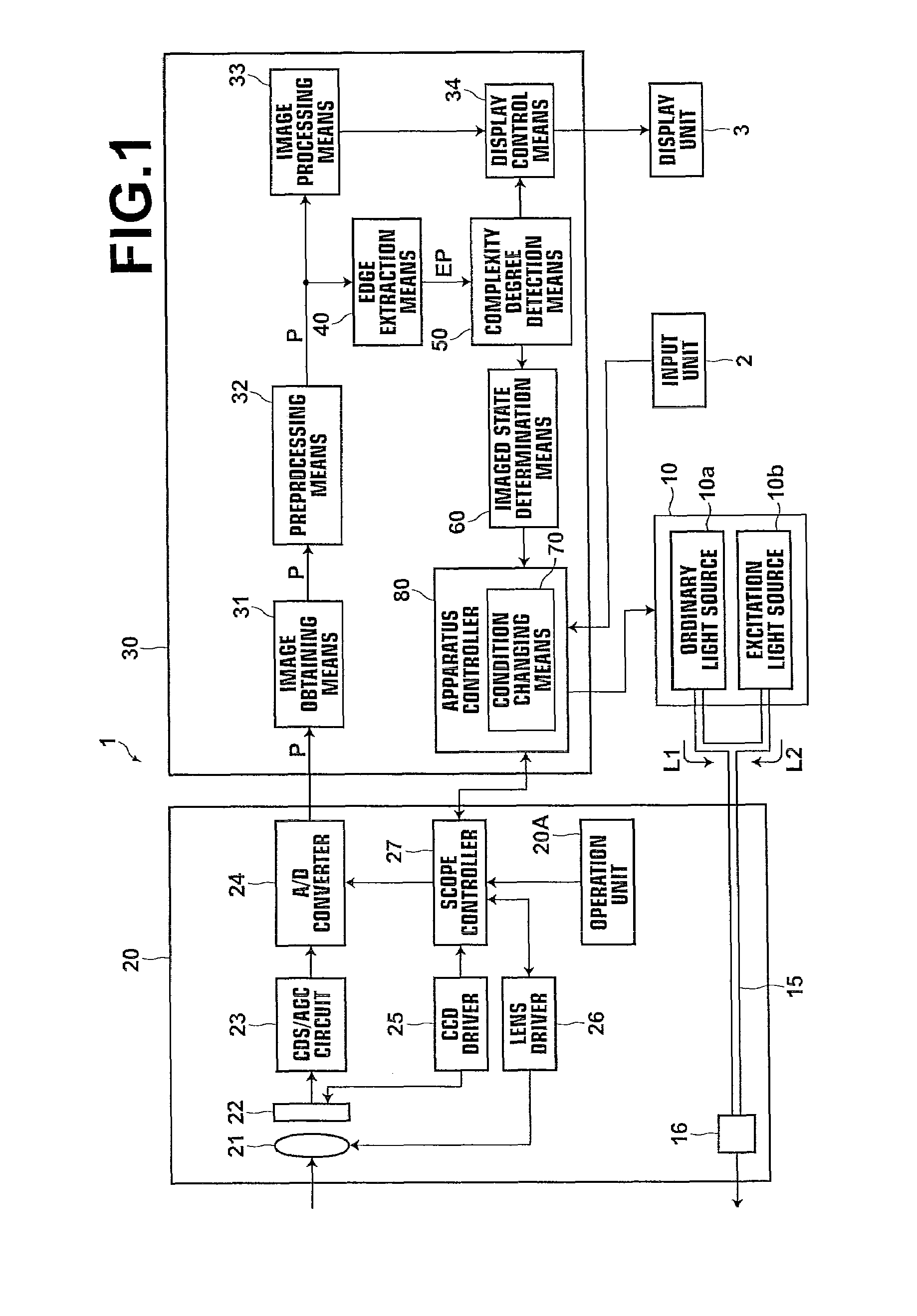
Endoscope apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS20100097454A1Optimize timingReduce the amount of lightImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging conditionNear sight
An endoscope image is obtained by imaging a subject with a scope. Then, an edge portion of the endoscope image is extracted and a complexity degree of the edge portion is detected. Thereafter, a determination is made as to whether the endoscope image is an image obtained through near view imaging or distant view imaging according to the complexity degree and an imaging condition is changed according to the determined near view imaging or distant view imaging.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical recording medium and optical recording medium recording device
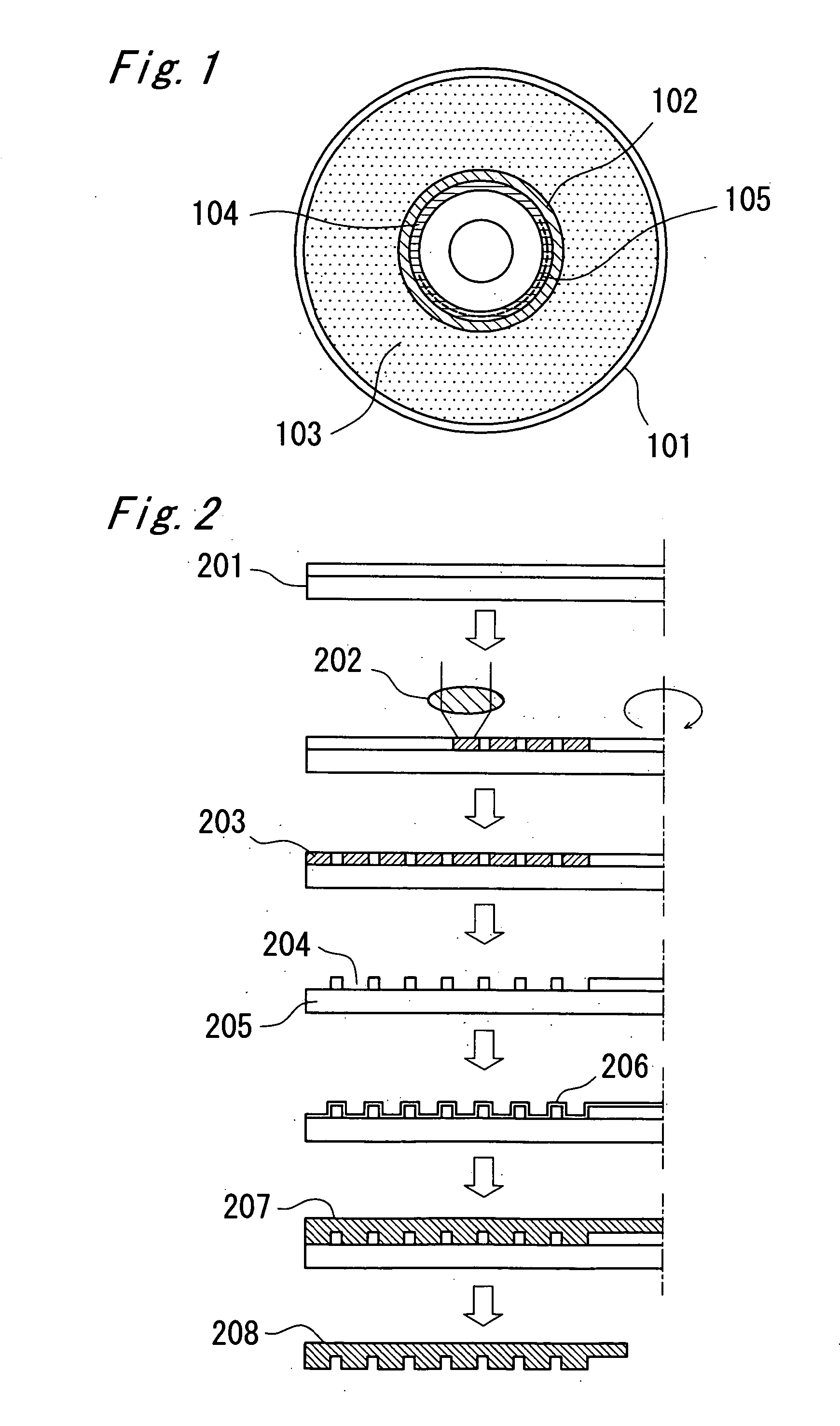
InactiveUS20060098559A1Difficult to forgeEffective protectionOptical overwritingRecord information storageOptical recordingData recording
An optical recording medium such as DVD has a data recording area (103) in which data can be rewritten and a write-once area (104) in which data can be written only once and not be erased. A medium specific ID (105) which is specific to an optical recording medium is recorded in the write-once area (104). In the data recording area (103), a reflectance ratio of a part where the data is recorded is different from a reflectance ratio in a part where the data is not recorded. A reflectance ratio of a recording pit formed in the write-once area (104) is higher than the higher one of the reflectance ratios in the part where the data is recorded and in the part where the data is not recorded in the data recording area (103). Data recoding in the write-once area (104) is performed by irradiating to the write-once area (104) a laser beam with heat amount of three to 25 times heat amount necessary for recording rewritable data in the data recording area (103).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Endoscope system with scanning function
ActiveUS20100123775A1Brightness adjustableIncrease the amount of lightTelevision system detailsSurgeryEndoscopeLightness
An endoscope system has a light source system configured to emit illumination light on a target area, a scanner configured to periodically scan the illumination light over a target area at predetermined time intervals, and an imager configured to receive the illumination light reflected from the target area and to acquire in succession a sequence of image-pixel signals. Further, the endoscope system has a luminance detector that detects in succession a sequence of luminance data of the object image from the sequence of image-pixel signals; and a brightness adjuster that adjusts the brightness of an observed image on the basis of the sequence of luminance data. Then, the brightness adjuster adjusts an amount of illumination light in accordance with a scanning position of the illumination light.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method and system for the three-dimensional representation
InactiveUS7046271B2Reduce the amount of lightReduce in quantityMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsGratingComputer vision
A method for three-dimensional display in which a plurality of individual image elements αij are made visible simultaneously in a raster of columns i and lines j, wherein the image elements αij reproduce partial information from a plurality of views Ak (k1 . . . n) of a scene / object, and adjacent image elements αij radiate light of different wavelengths or wavelength regions is provided. In a method of the type described above, wavelength-dependent propagation directions are predetermined for the light radiated from the image elements αij. The propagation directions within an observation space in which an observer is situated intersect in a plurality of intersection points which correspond to observation positions. From each observation position, one eye of an observer perceives predominantly partial information of a first selection and the other eye perceives predominantly partial information of a second selection from views Ak (k=1 . . . n).
Owner:PHOENIX 3D INC
Blade driving device for use in cameras
InactiveUS7156564B2Simple processSimple structureShuttersCamera diaphragmsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:COPAL CO LTD
Color emitting device
InactiveUS20060158403A1Reduce the amount of lightReduce light intensityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesLength waveLight emitting device
A color emitting device (1) comprising an emitting device (10) and a color conversion member (21) which absorbs light emitted from the emitting device (10) and emits light; the emitting device (10) including at least a first reflecting section (12) and a second reflecting section (15) provided in that order in a light-outcoupling direction, and an organic emitting layer (14) positioned between the first and second reflecting sections; the color conversion member (21) being positioned on a light-outcoupling side of the second reflecting section (15); and the emitting device (10) having a reflectance of 50% or more for a peak wavelength of the light emitted from the color conversion member (21).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com