Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6408 results about "Optical image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical image, the apparent reproduction of an object, formed by a lens or mirror system from reflected, refracted, or diffracted light waves. There are two kinds of images, real and virtual.
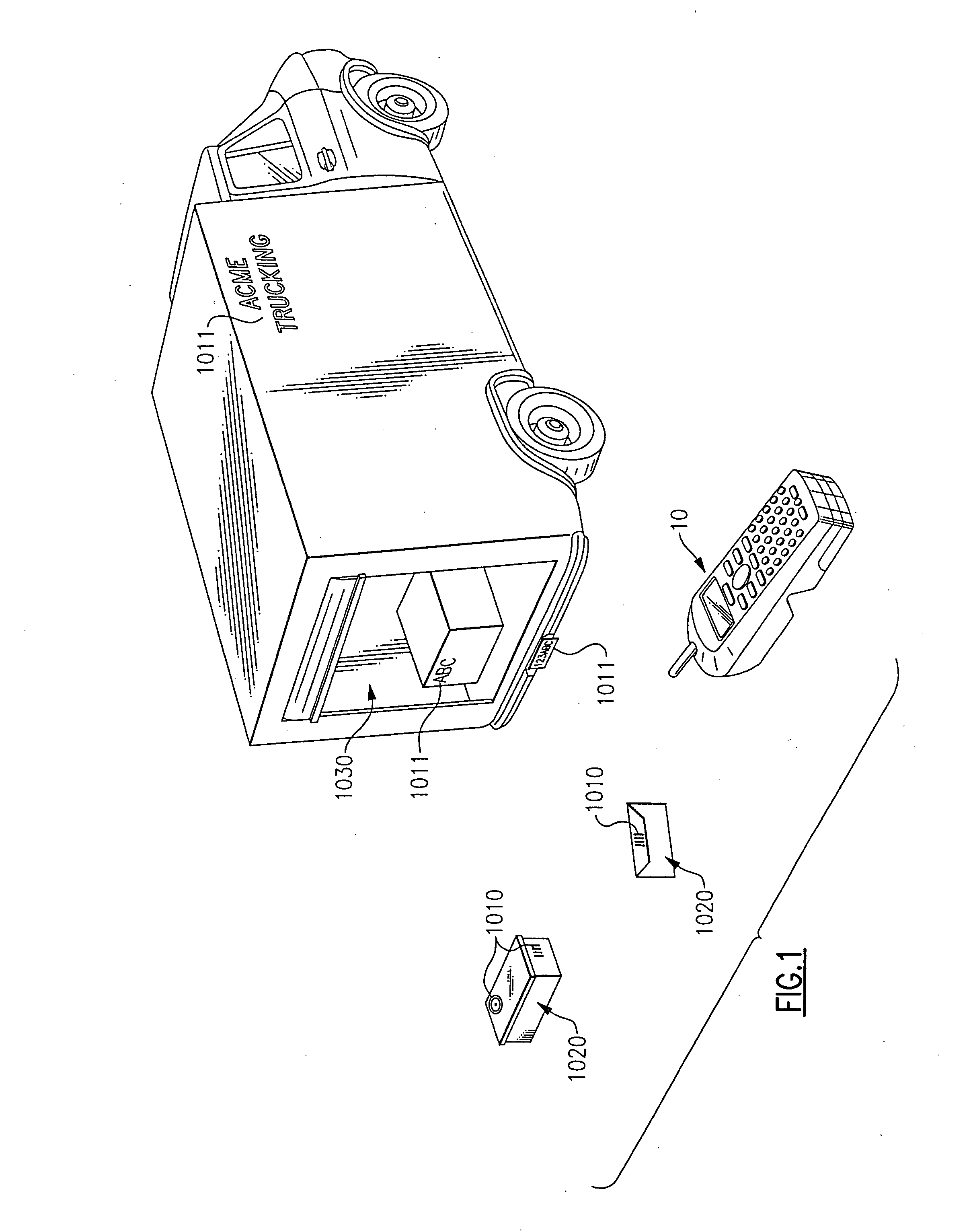
Method and system for acquiring three-dimensional teeth image
PCT No. PCT / IL96 / 00036 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 20, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 20, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 4, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 03622 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 6, 1997A method of obtaining a dental image, such as a three-dimensional image of teeth, providing a three-dimensional physical teeth model. The three-dimensional physical teeth model can be either: a negative teeth model that includes a matrix with a plurality of cavities or recesses, each corresponding to a tooth; or a positive teeth model, that includes a matrix with a plurality of projections or bulges, each corresponding to a tooth. The method also includes removing a portion of the model in a controlled, step-wise manner, and in each step acquiring an optical image of the model or of its removed portion, digitizing each of the optical images in order to obtain a plurality of digital images, and compiling the plurality of digital images to obtain a three-dimensional digital dental image.
Owner:CADENT
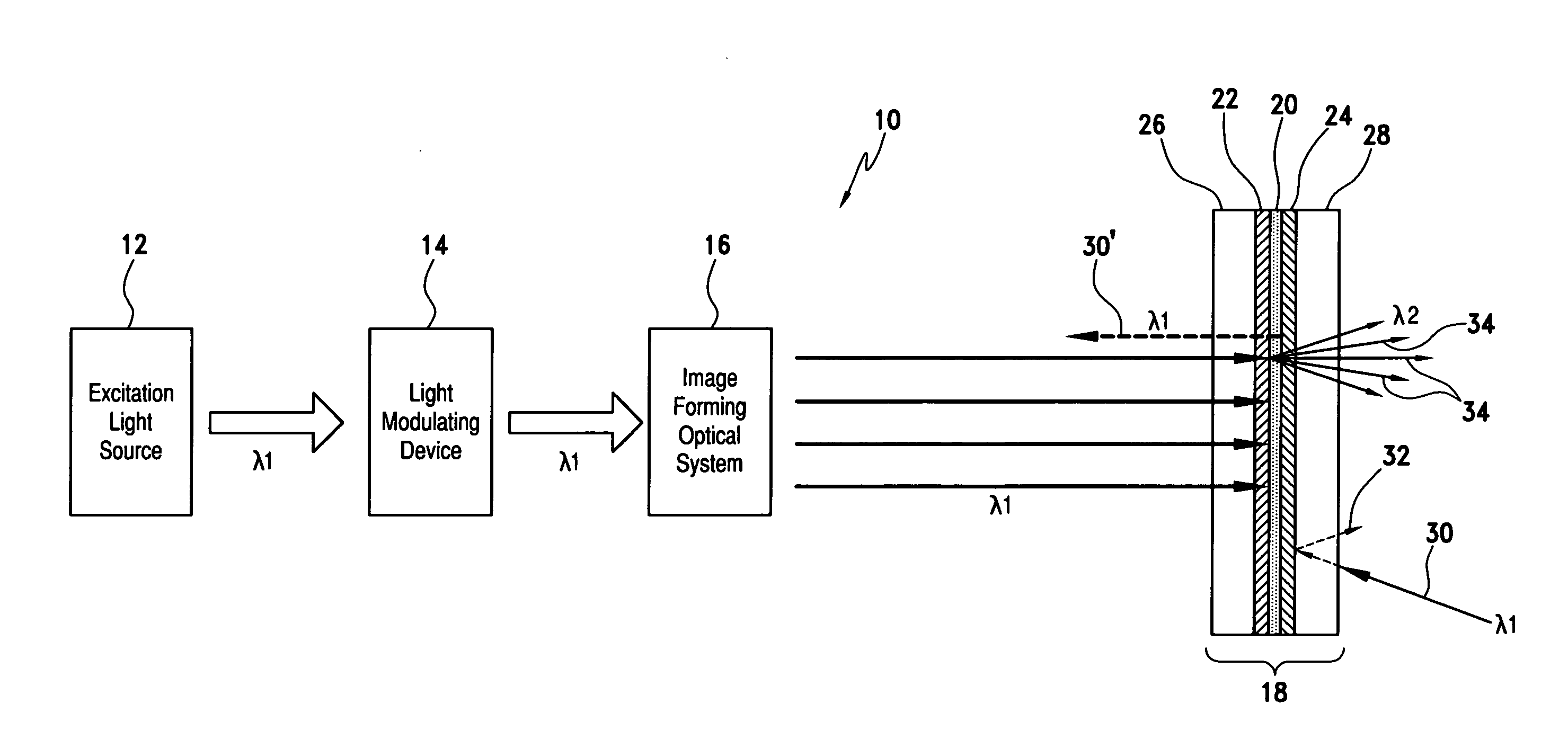
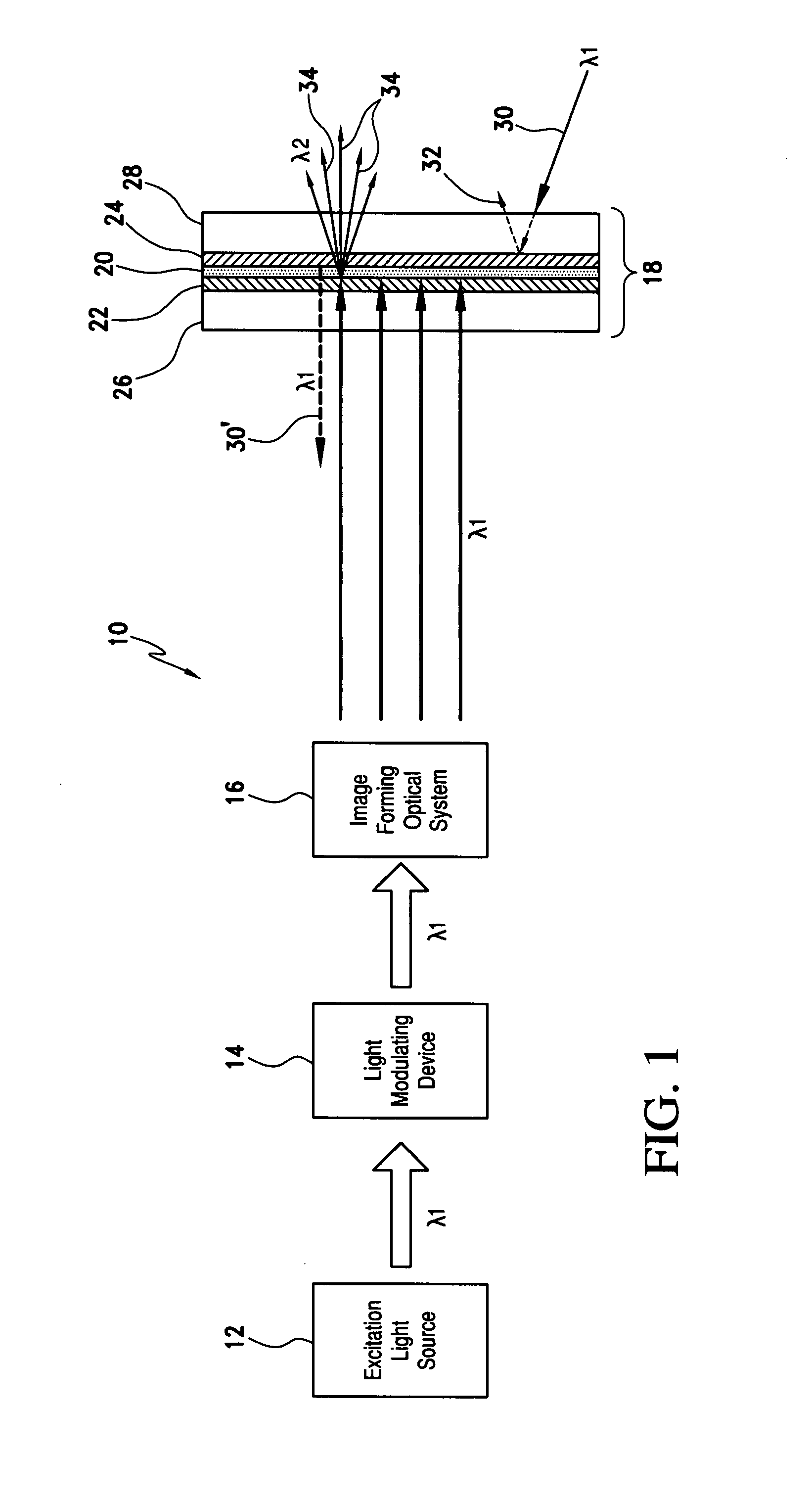
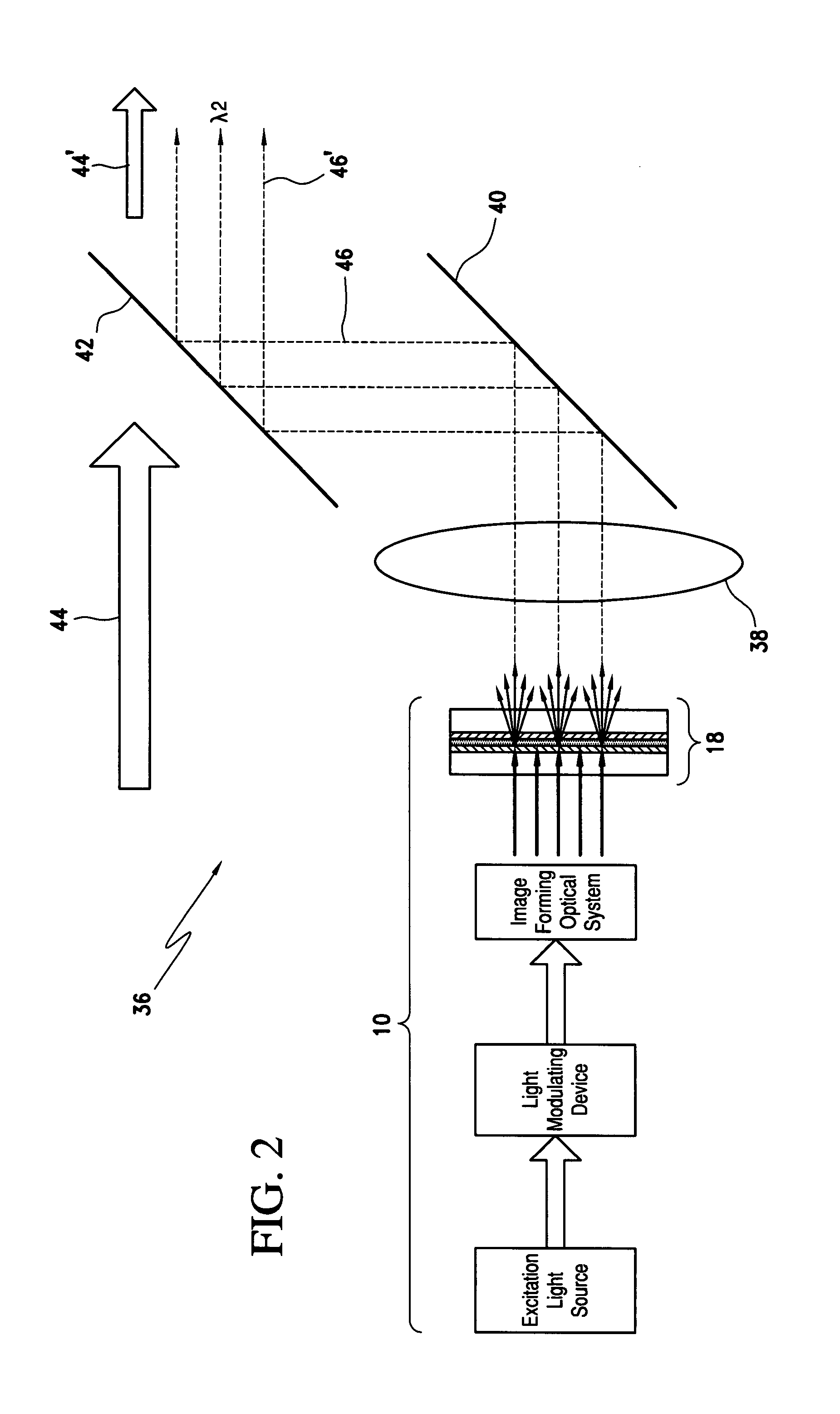
Phosphor screen and displays systems
InactiveUS7733571B1Good optical performanceImprove cooling effectOptical filtersNon-linear opticsPhosphorFluorescence
A phosphor screen for image forming including phosphor material being excitable by light in a wavelength λ1. The phosphor screen receives an optical image from an image forming optical system and produces the optical image at a second wavelength λ2. The phosphor screen includes a phosphor layer comprising the phosphor material. A short-pass reflective coating is positioned on a first side of the phosphor layer. The short-pass reflective coating transmits the wavelength λ1 and reflects the wavelength λ2. A long-pass reflective coating is positioned on a second side of the phosphor layer. The long-pass reflective coating transmits the wavelength λ2 and reflects the wavelength λ1. A first substrate is positioned over the short-pass reflective coating. The first substrate is formed of optically clear and thermal conductive material. A second substrate is positioned over the long-pass reflective coating. The second substrate is formed of long-pass absorptive optical filter material that transmits the wavelength λ2 and absorbs wavelength λ1 from ambient light to prevent the phosphor layer from being excited by the ambient light. The phosphor screen may alternatively be used for a direct-view visual display apparatus. These principles can also be utilized for backlighting and general illumination applications.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Camera Adapter Based Optical Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20110043661A1Cancel noiseLow costTelevision system detailsInterferometersSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
The invention describes several embodiments of an adapter which can make use of the devices in any commercially available digital cameras to accomplish different functions, such as a fundus camera, as a microscope or as an en-face optical coherence tomography (OCT) to produce constant depth OCT images or as a Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography to produce a reflectivity profile in the depth of an object or cross section OCT images, or depth resolved volumes. The invention admits addition of confocal detection and provides simultaneous measurements or imaging in at least two channels, confocal and OCT, where the confocal channel provides an en-face image simultaneous with the acquisition of OCT cross sections, to guide the acquisition as well as to be used subsequently in the visualisation of OCT images. Different technical solutions are provided for the assembly of one or two digital cameras which together with such adapters lead to modular and portable high resolution imaging systems which can accomplish various functions with a minimum of extra components while adapting the elements in the digital camera. The cost of such adapters is comparable with that of commercial digital cameras, i.e. the total cost of such assemblies of commercially digital cameras and dedicated adapters to accomplish high resolution imaging are at a fraction of the cost of dedicated stand alone instruments. Embodiments and methods are presented to employ colour cameras and their associated optical sources to deliver simultaneous signals using their colour sensor parts to provide spectroscopic information, phase shifting inferometry in one step, depth range extension, polarisation, angular measurements and spectroscopic Fourier domain (channelled spectrum) optical coherence tomography in as many spectral bands simultaneously as the number of colour parts of the photodetector sensor in the digital camera. In conjunction with simultaneous acquistion of a confocal image, at least 4 channels can simultaneously be provided using the three color parts of conventional color cameras to deliver three OCT images in addition to the confocal image.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
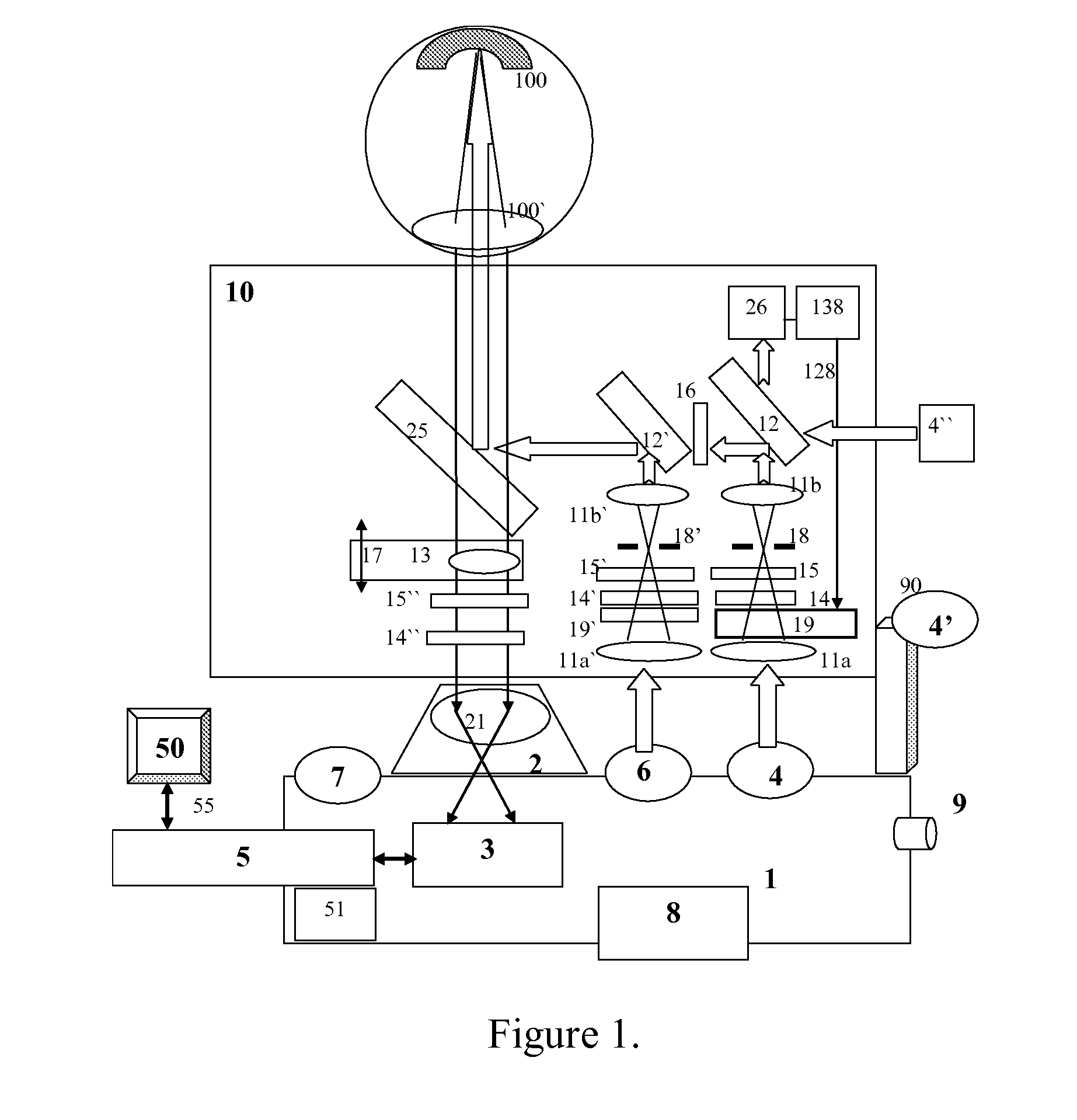
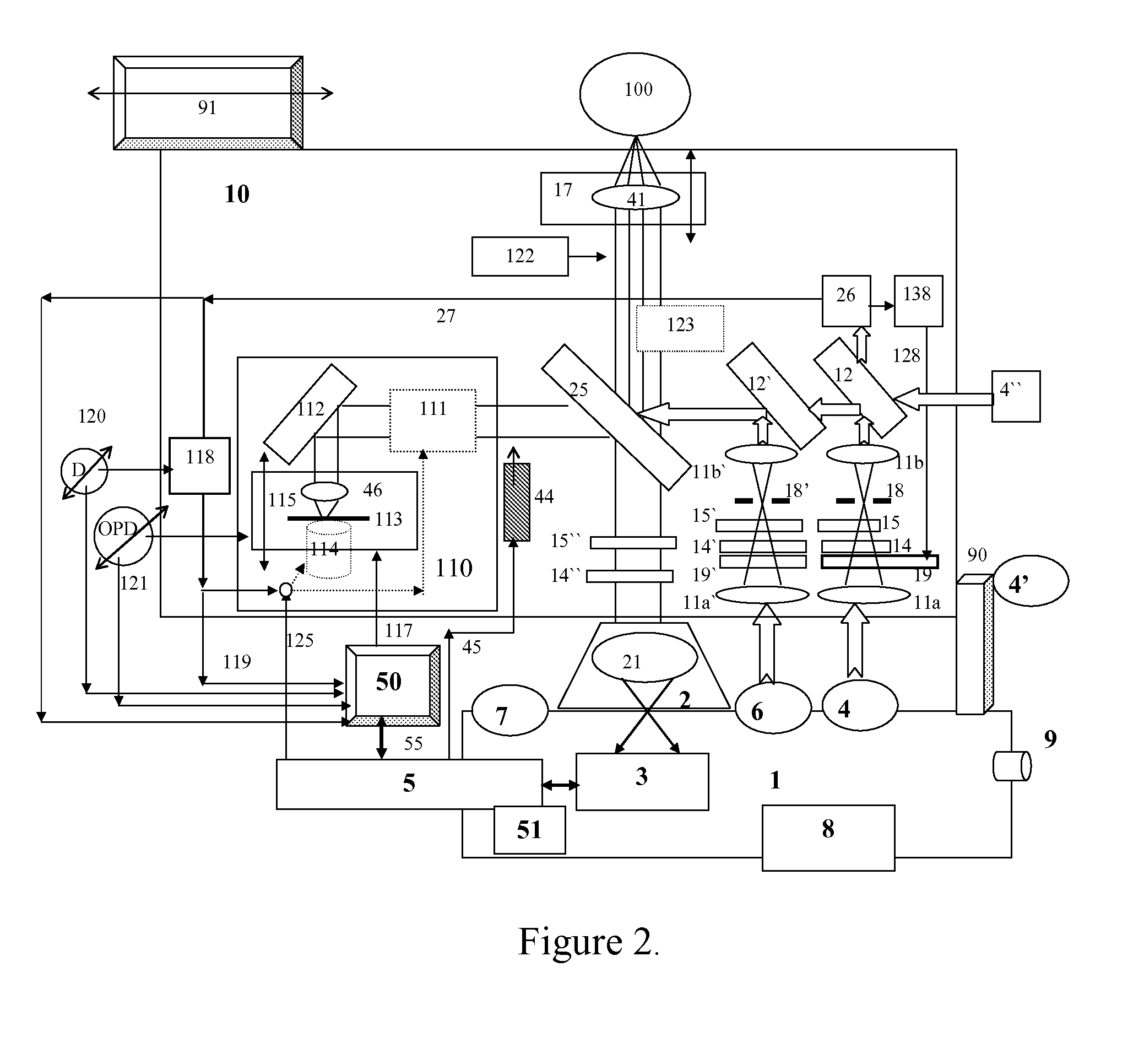
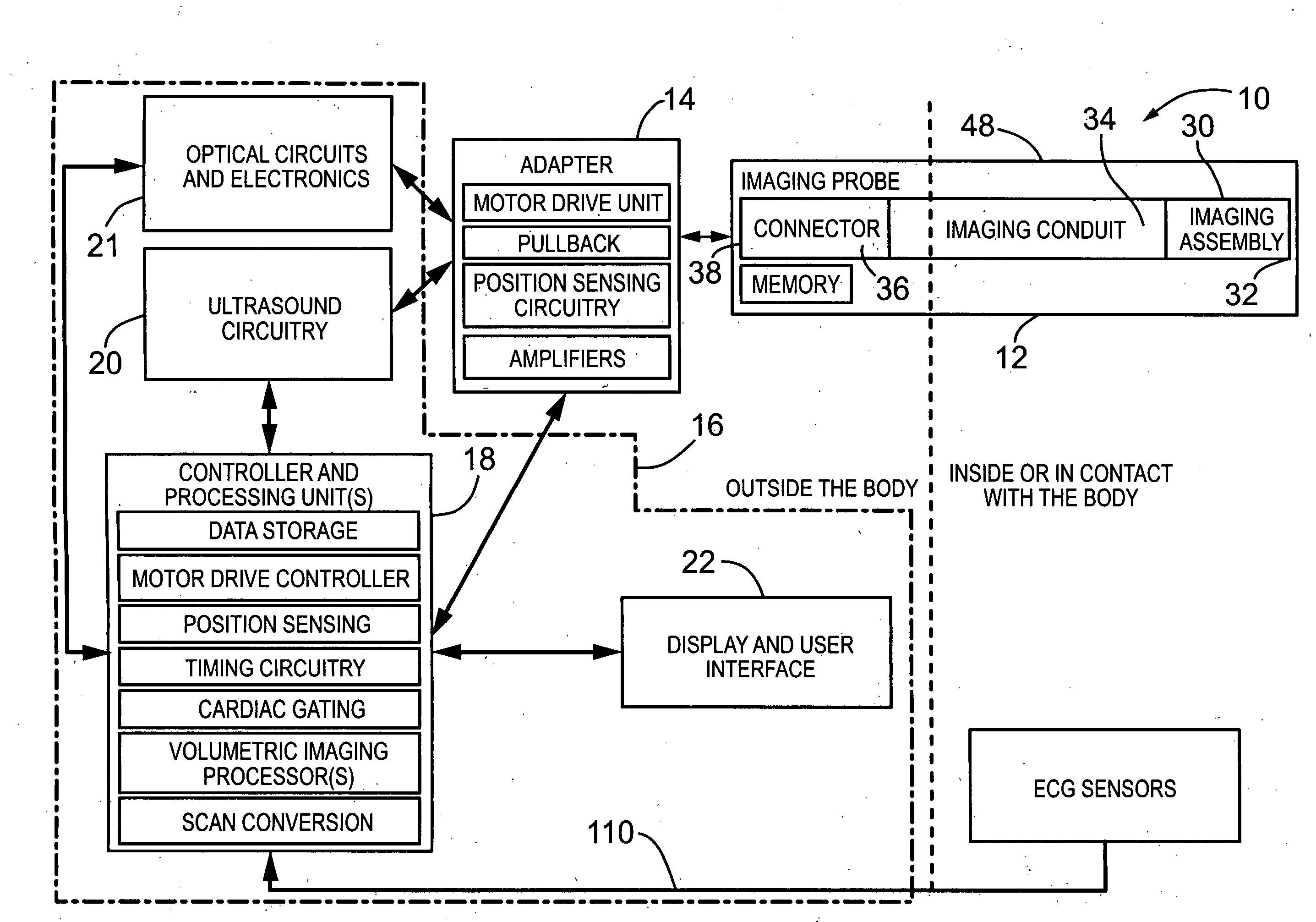
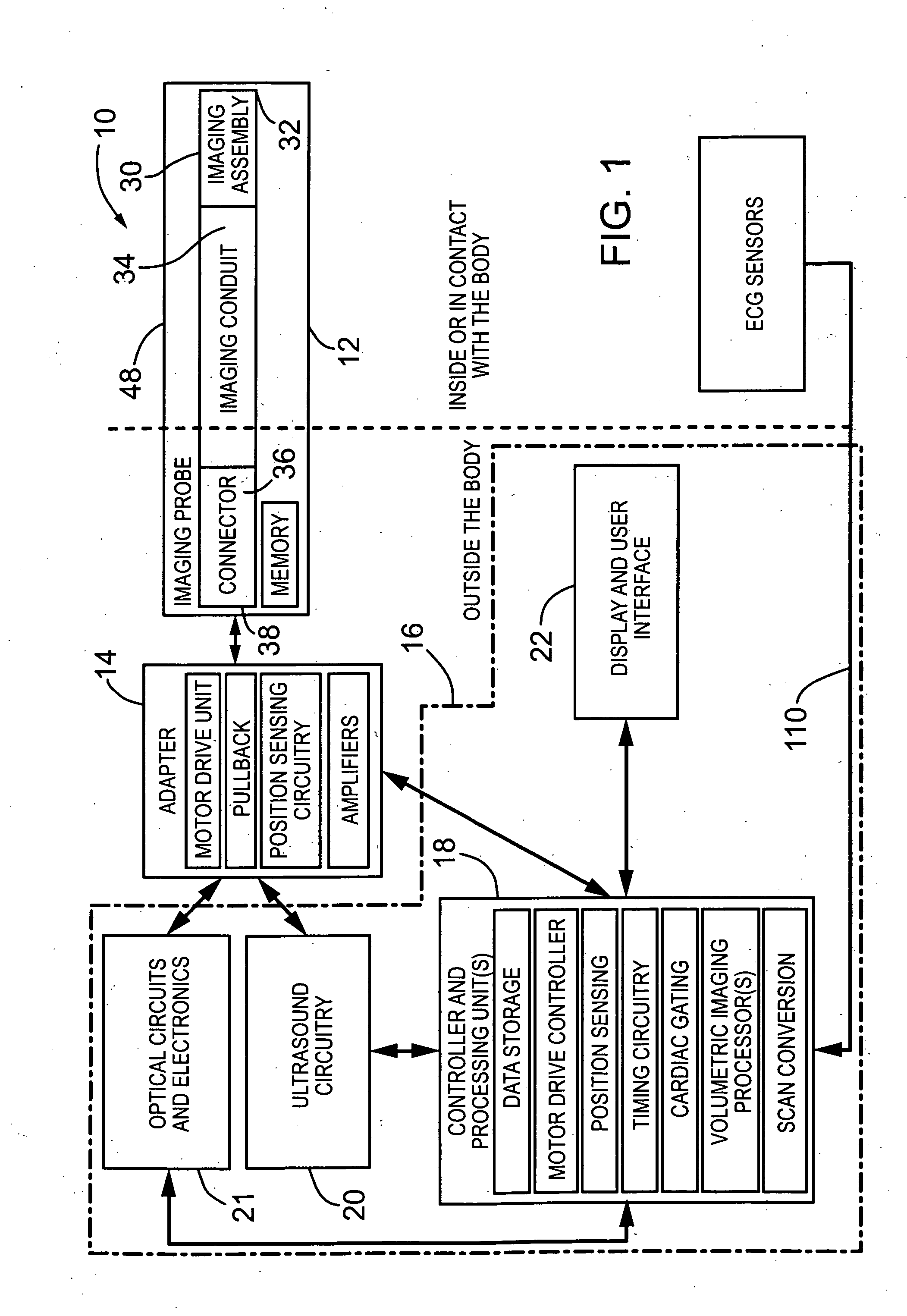
Imaging probe with combined ultrasounds and optical means of imaging
ActiveUS20080177183A1Provide goodFacilitates simultaneous imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryHigh resolution imagingMammalian tissue
The present invention provides an imaging probe for imaging mammalian tissues and structures using high resolution imaging, including high frequency ultrasound and optical coherence tomography. The imaging probes structures using high resolution imaging use combined high frequency ultrasound (IVUS) and optical imaging methods such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and to accurate co-registering of images obtained from ultrasound image signals and optical image, signals during scanning a region of interest.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
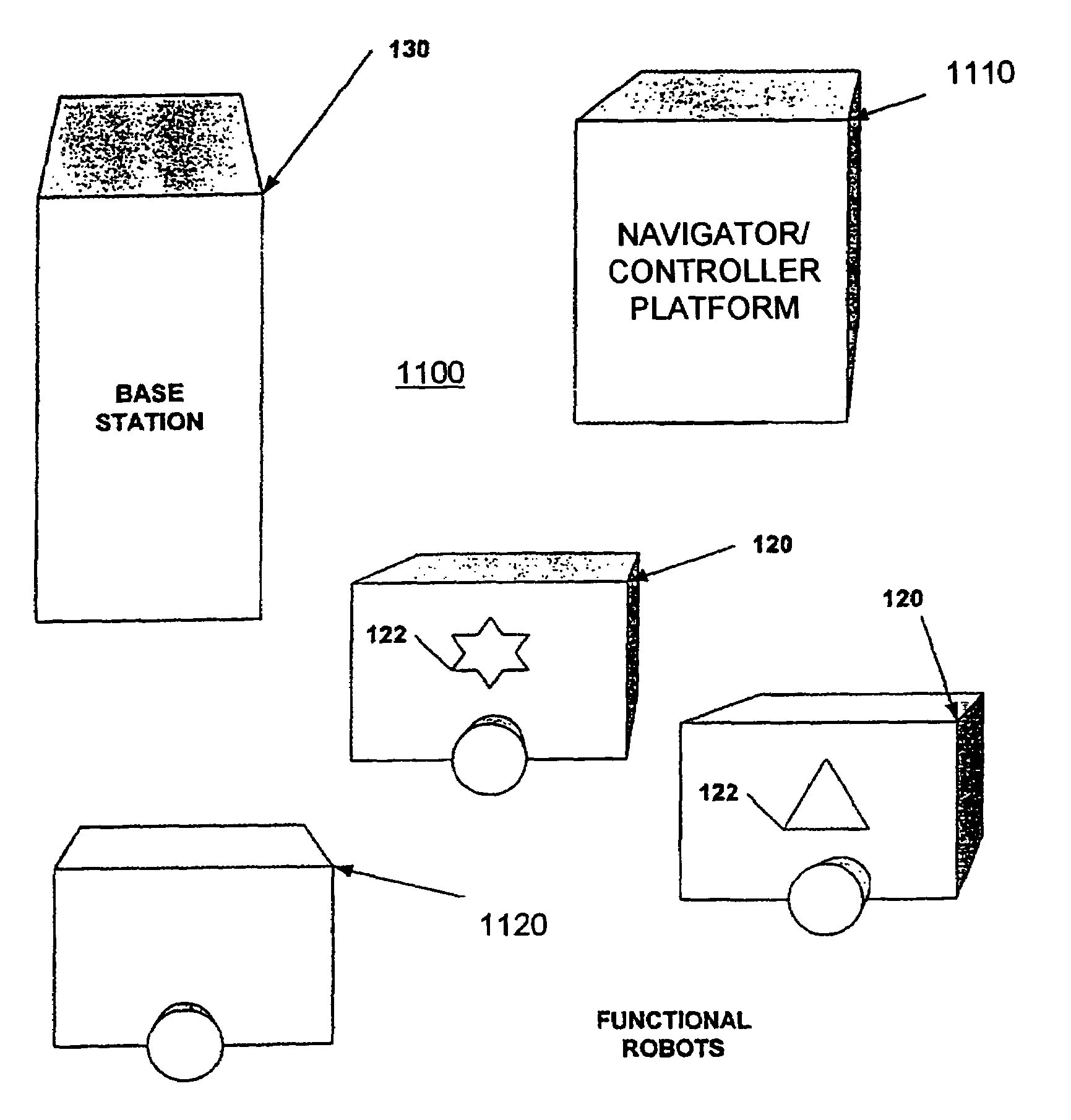
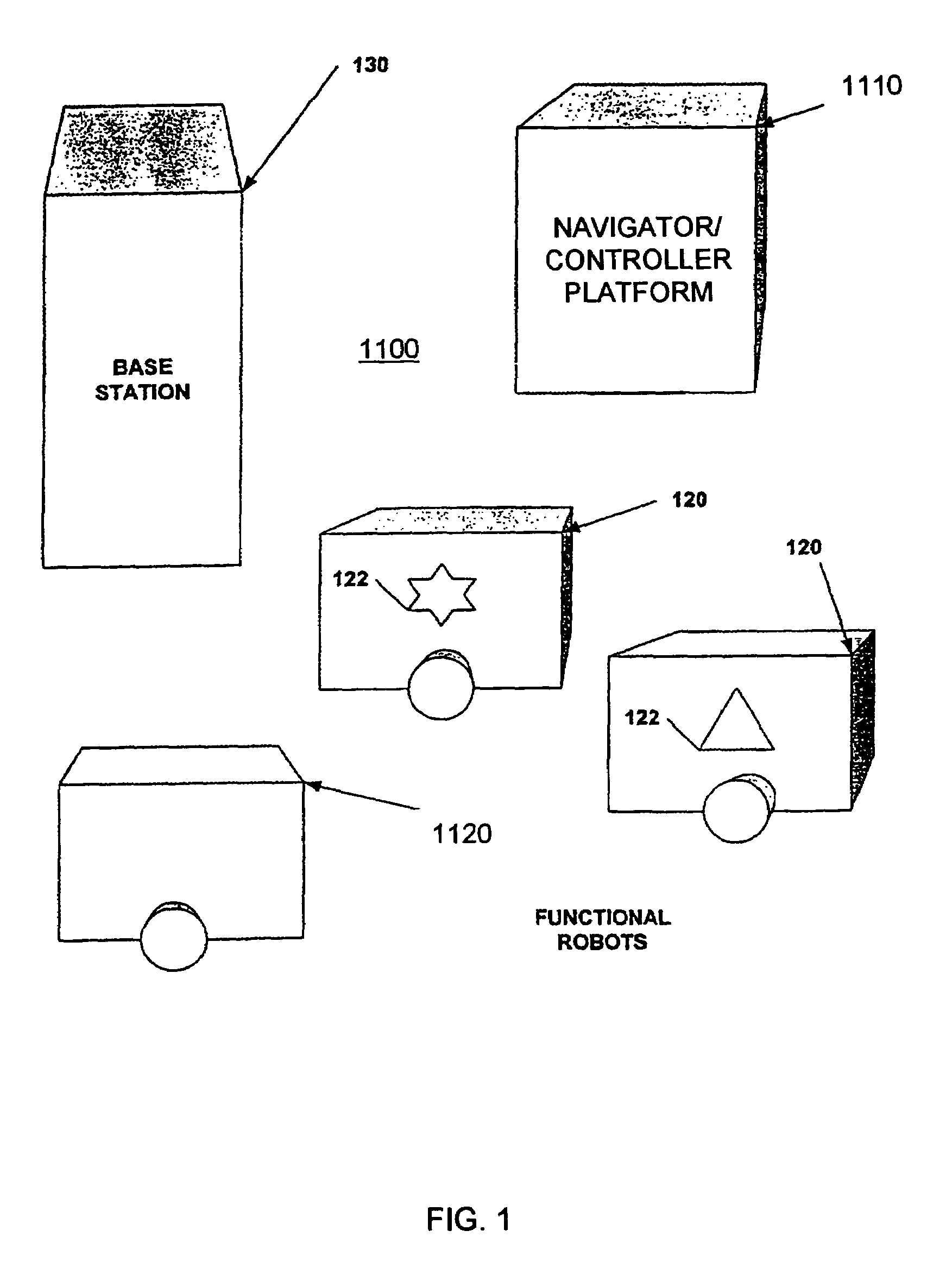
Sentry robot system
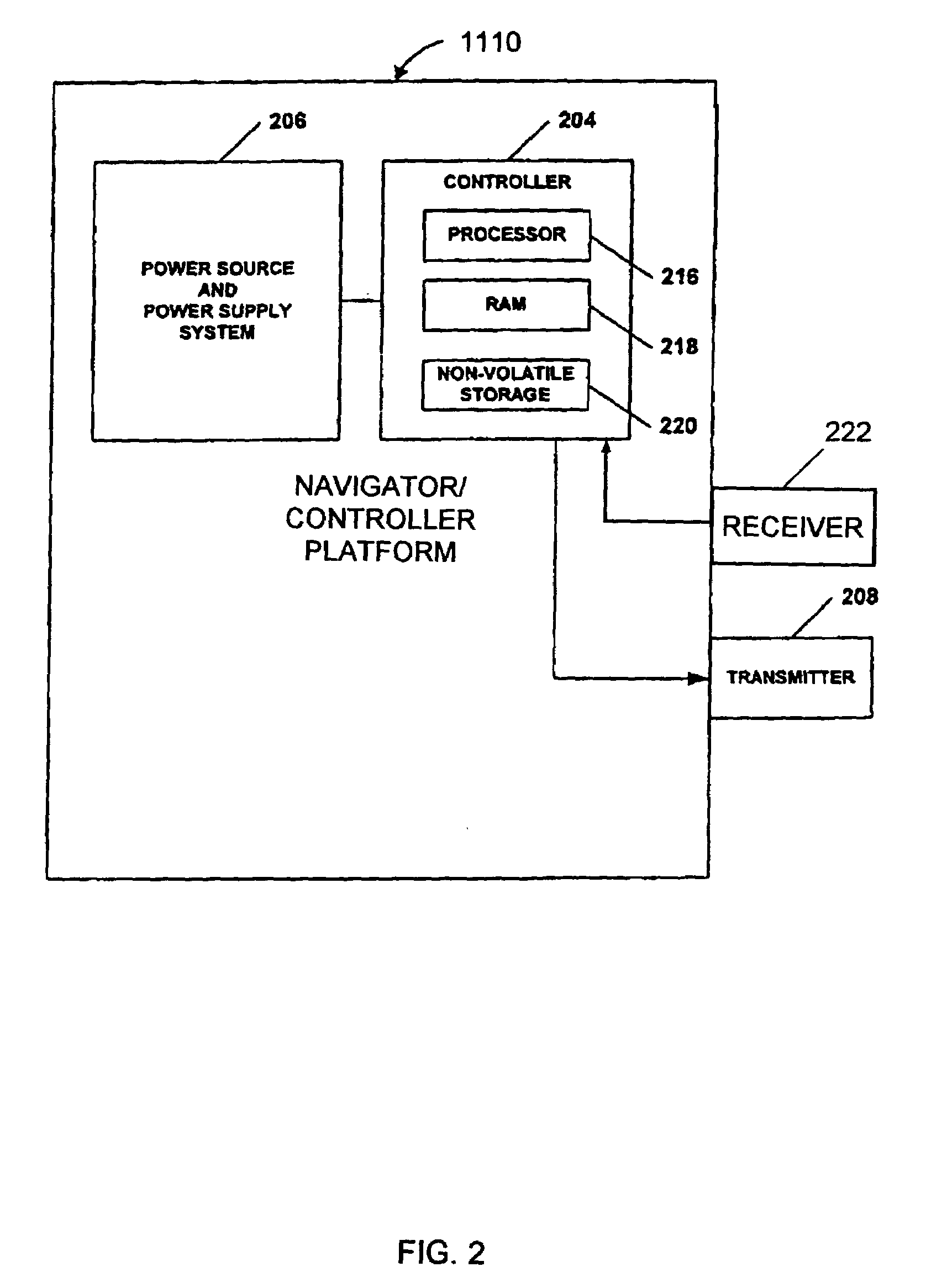
InactiveUS7054716B2Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsRobotic systemsSimulation
A sentry robot system and method for operating the system is provided. In one embodiment, the robot system includes at least one functional robot with one or more environmental sensors and at least one navigator / controller platform. In another embodiment, the robot system includes one or more functional robots, one or more environmental sensors associated with at least one of the functional robots, and one or more navigator / controller platforms. The navigator / controller platform in this embodiment includes a receiver, a controller, a memory, and a transmitter. In one embodiment, the method includes creating an image map of the environment from environment data, periodically moving the functional robot to predetermined locations, collecting new environment data using the optical image sensor at each predetermined location, and comparing the new environment data to corresponding locations in the image map, and periodically determining if intervention is required due to changed conditions within the environment.
Owner:ROYAL APPLIANCE MFG
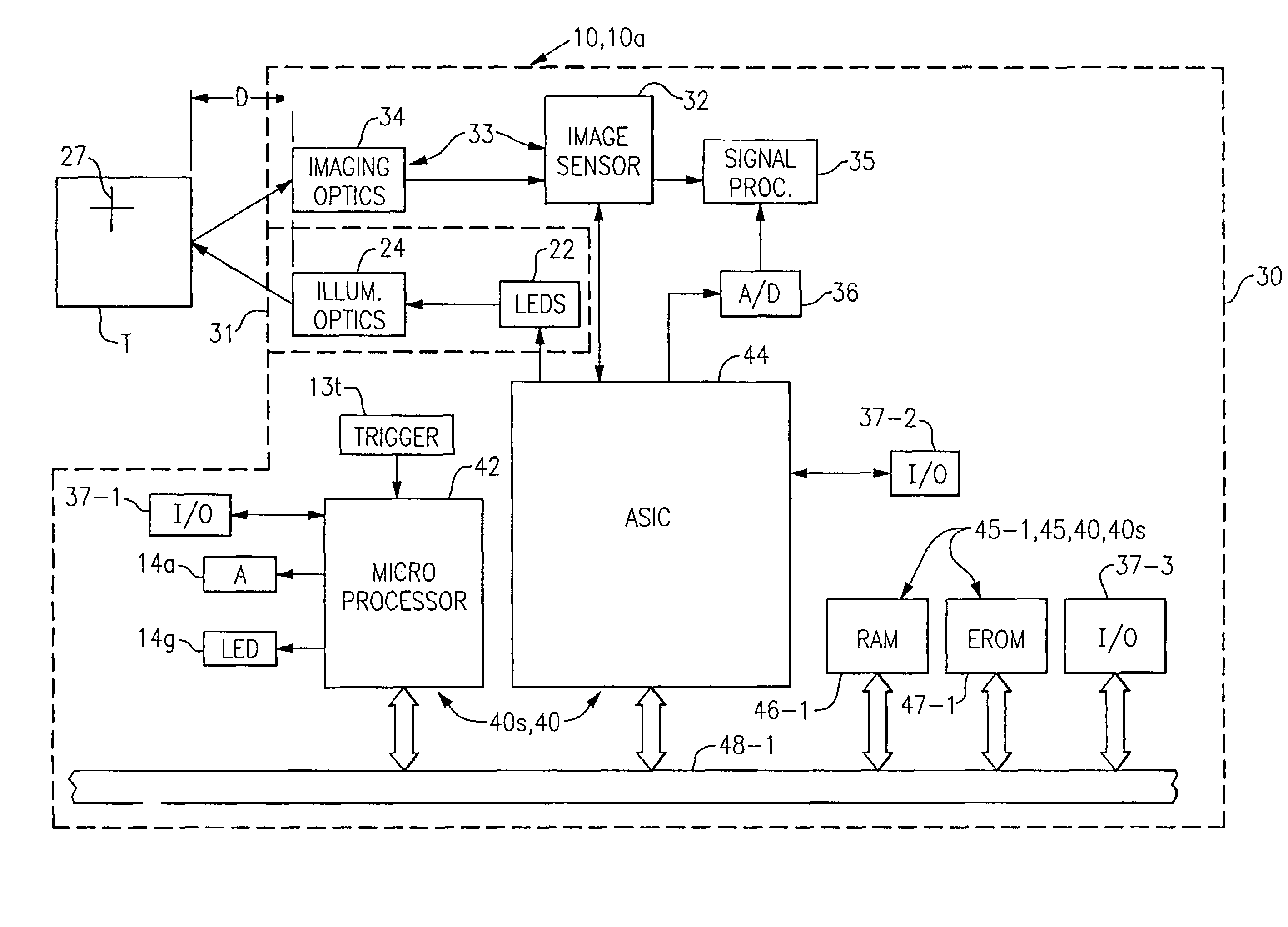
Adaptive optical image reader
InactiveUS7331523B2Character and pattern recognitionExposure controlDigital converterComputer science
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
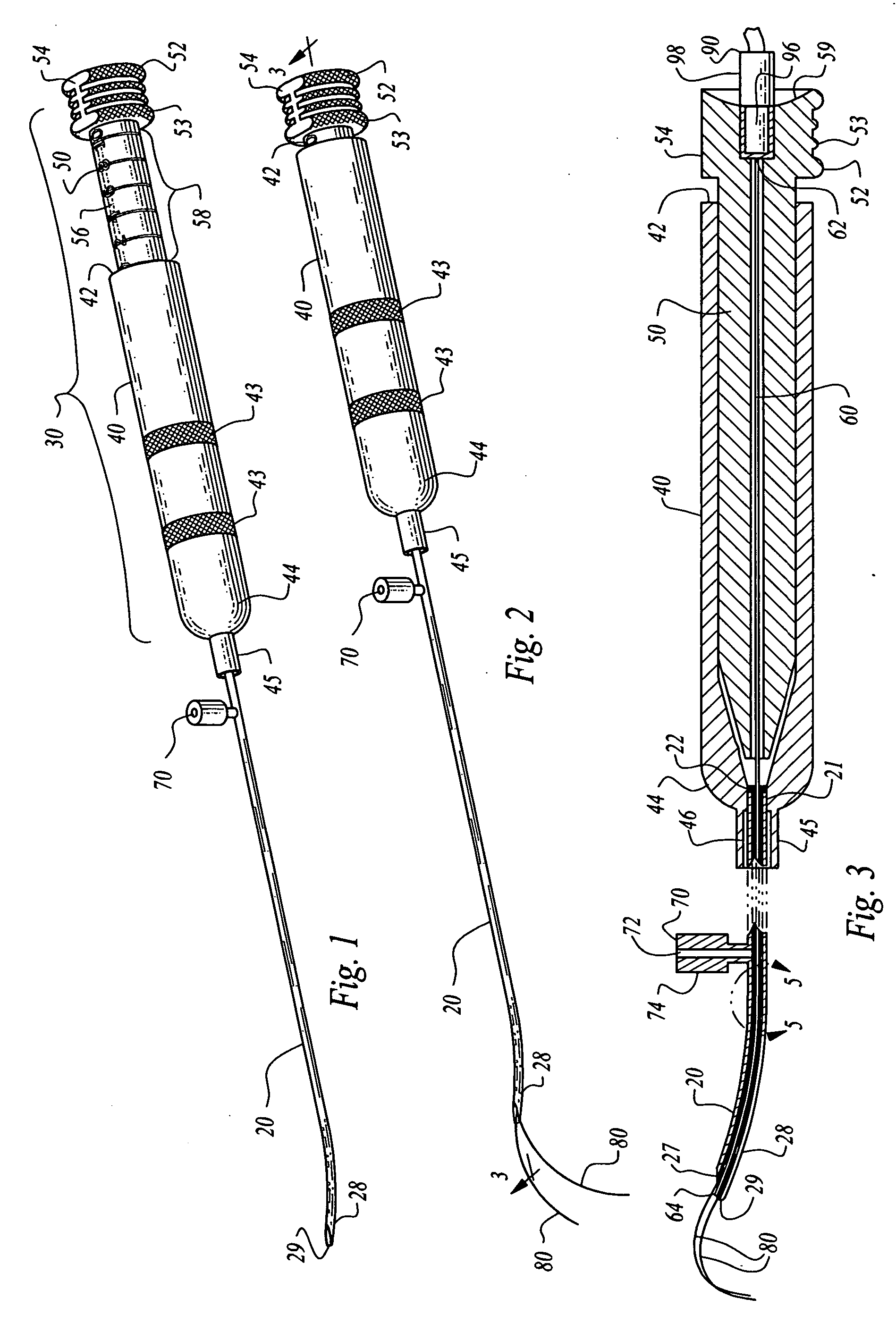
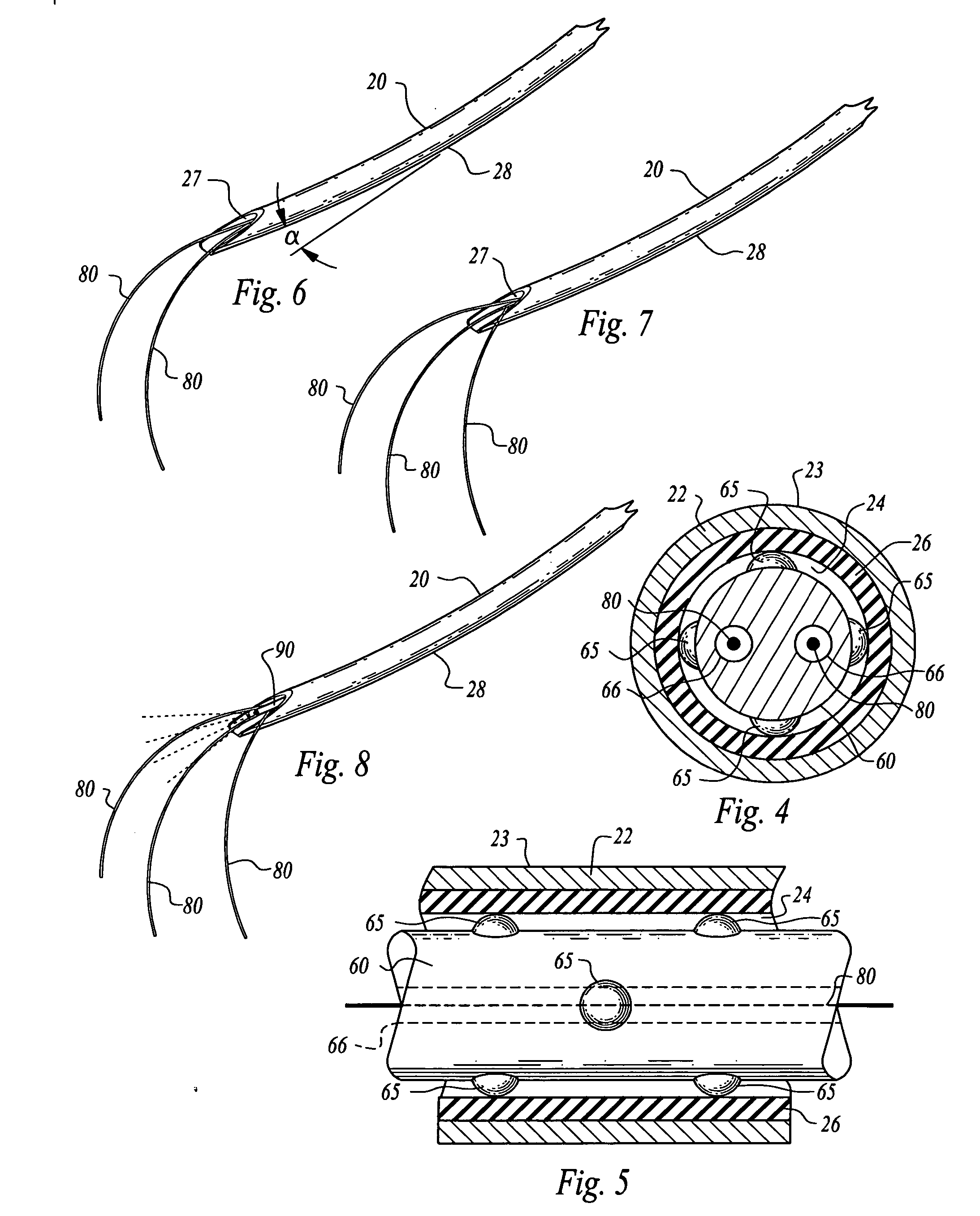
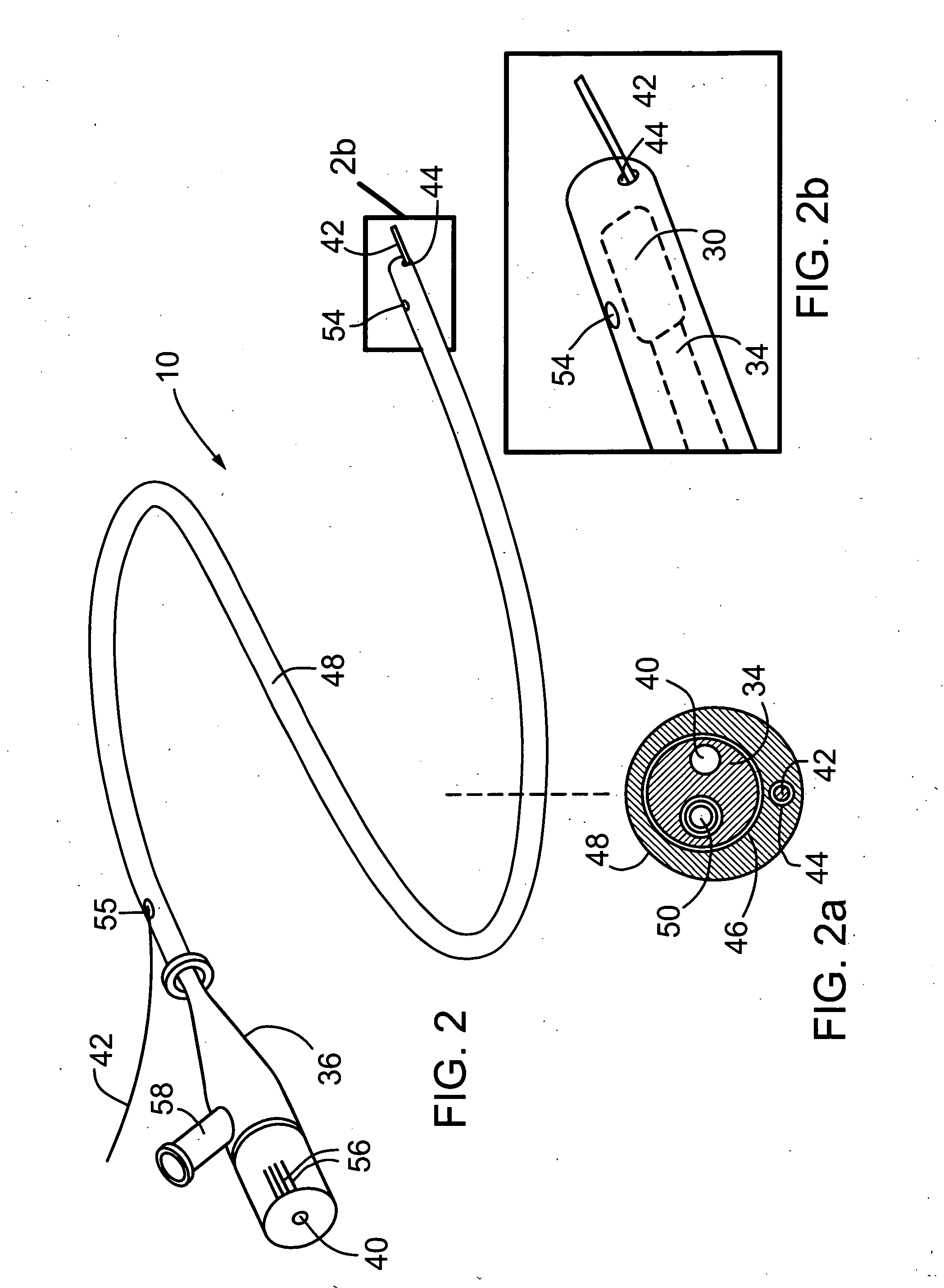
Combination imaging and treatment assemblies
Combination imaging and treatment assemblies are described herein which may utilize a deployment catheter in combination with an endoscopic system. The combined system comprises an open architecture to modularly incorporate any number of imaging devices (such as optical fiber, CMOS or CCD endoscopes) to provide high resolution optical images of tissue within an opaque environment. Additional variations may include an imaging hood or balloon member incorporated upon an endoscope or advanced through an endoscope working channel to visualize and treat tissue through blood.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
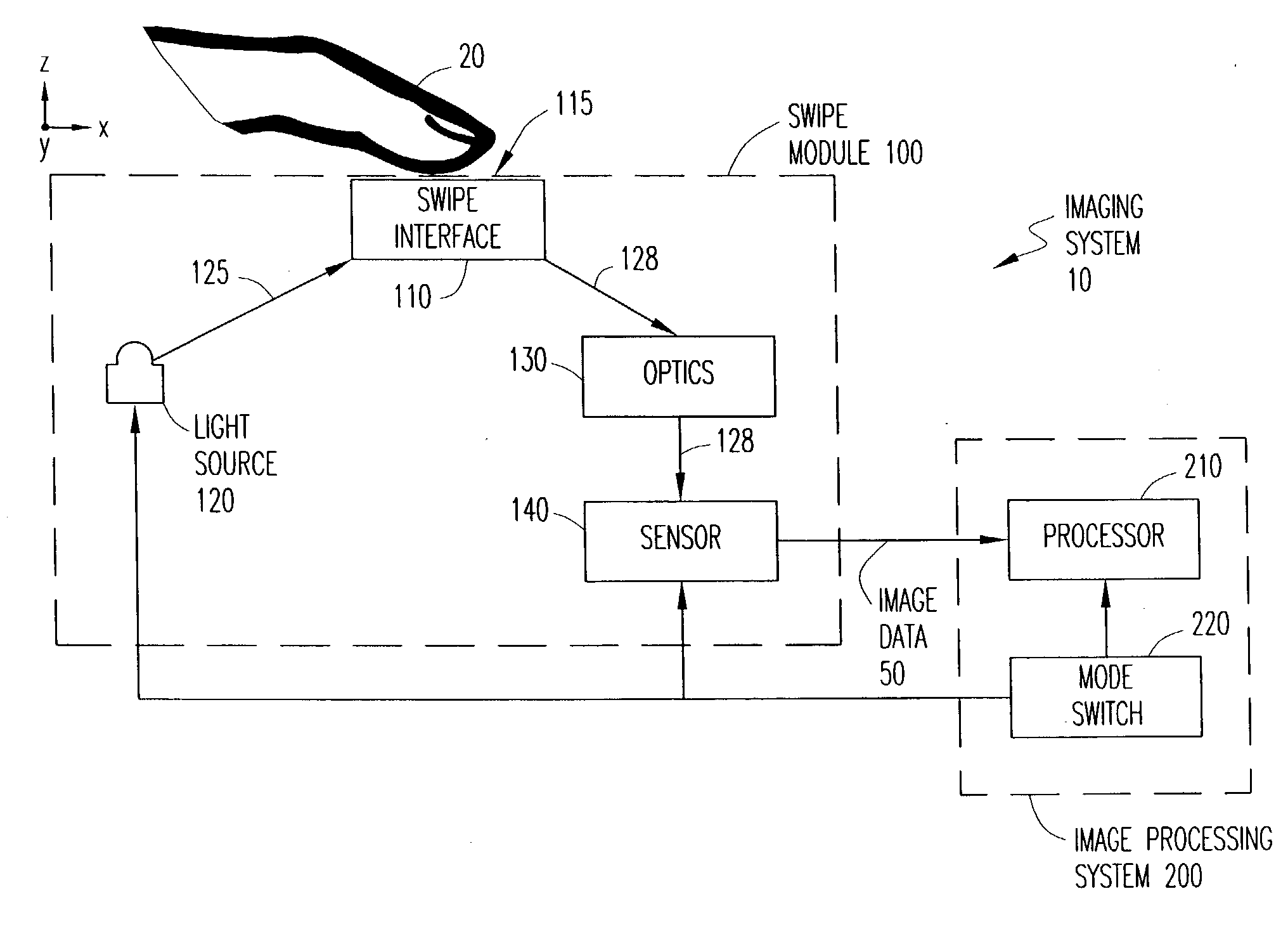
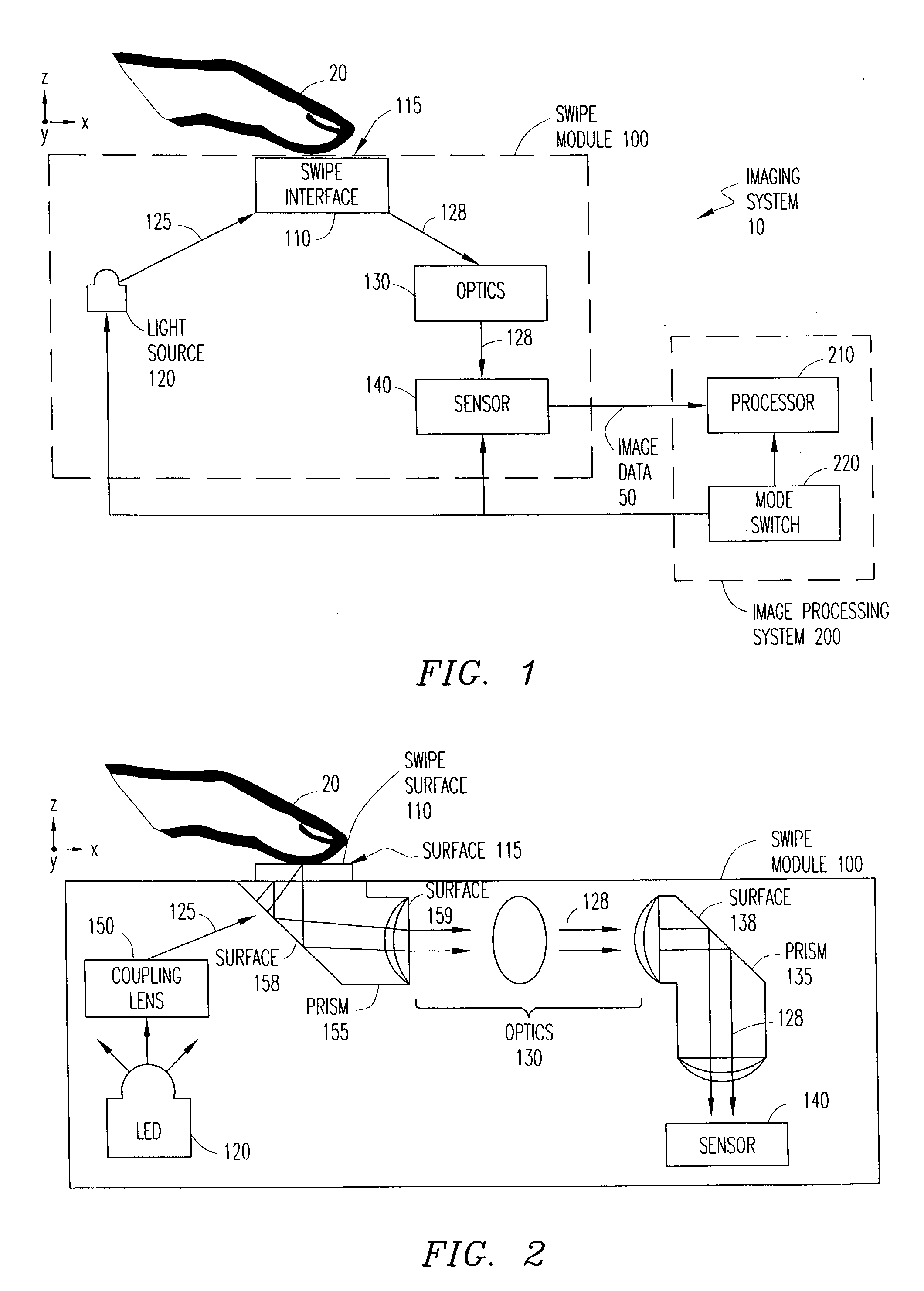
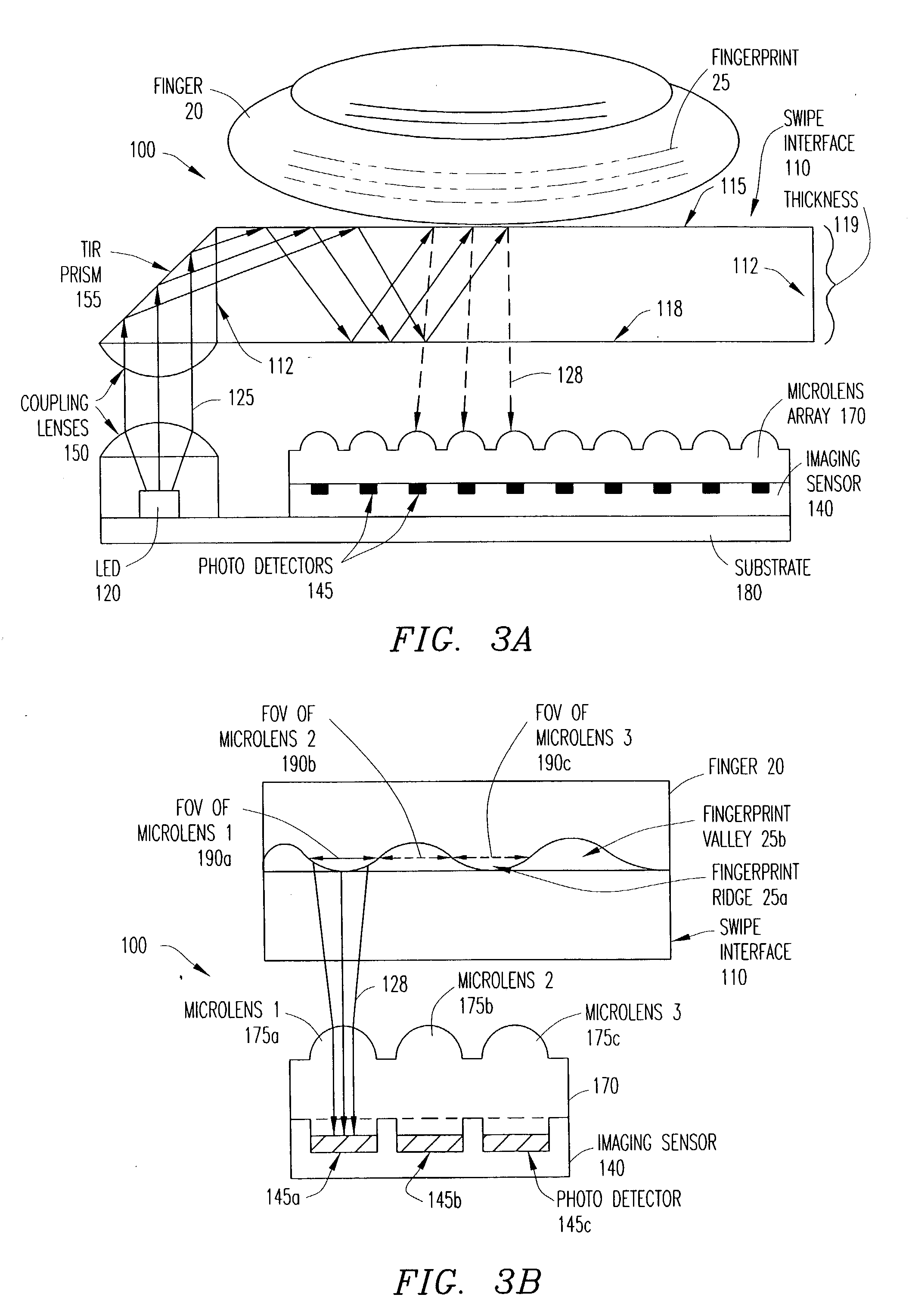
Imaging system and apparatus for combining finger recognition and finger navigation
ActiveUS20040208348A1Character and pattern recognitionSensing record carriersFinger vein recognitionMarine navigation
An imaging system for imaging a fingerprint operates in at least two different modes to provide both finger recognition and finger navigation applications. A light source illuminates a swipe interface having an elongated sensing area upon which a user swipes a finger. Light reflected from the finger is captured by an optical image sensor as image data representing a sequence of images resulting from motion of the digit over the sensing area of the swipe interface. The captured image data is output by the optical image sensor for processing of the data in one of the at least two different modes.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Diagnostic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050003323A1Reduce adverse effectsAccurate diagnostic image informationSurgeryEndoscopesFluorescenceHand held
A diagnostic imaging apparatus of hand piece type suitable for medical or dental use, comprising a main body held by operator's fingers, a luminous means for irradiating at least one of lights selected from excitation light, infrared light and ultraviolet light, and an imaging means provided in a forward portion of the main body. The imaging means comprises a solid-state image sensing device and an optical means for forming an optical image of a diagnosis object to be examined on the solid-state image sensing device and is so constructed as to output a predetermined diagnostic image information by receiving the light reflected from the diagnosis object and / or the fluorescence generated from the diagnosis object when irradiation of light from the luminous means to the diagnosis object is performed.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
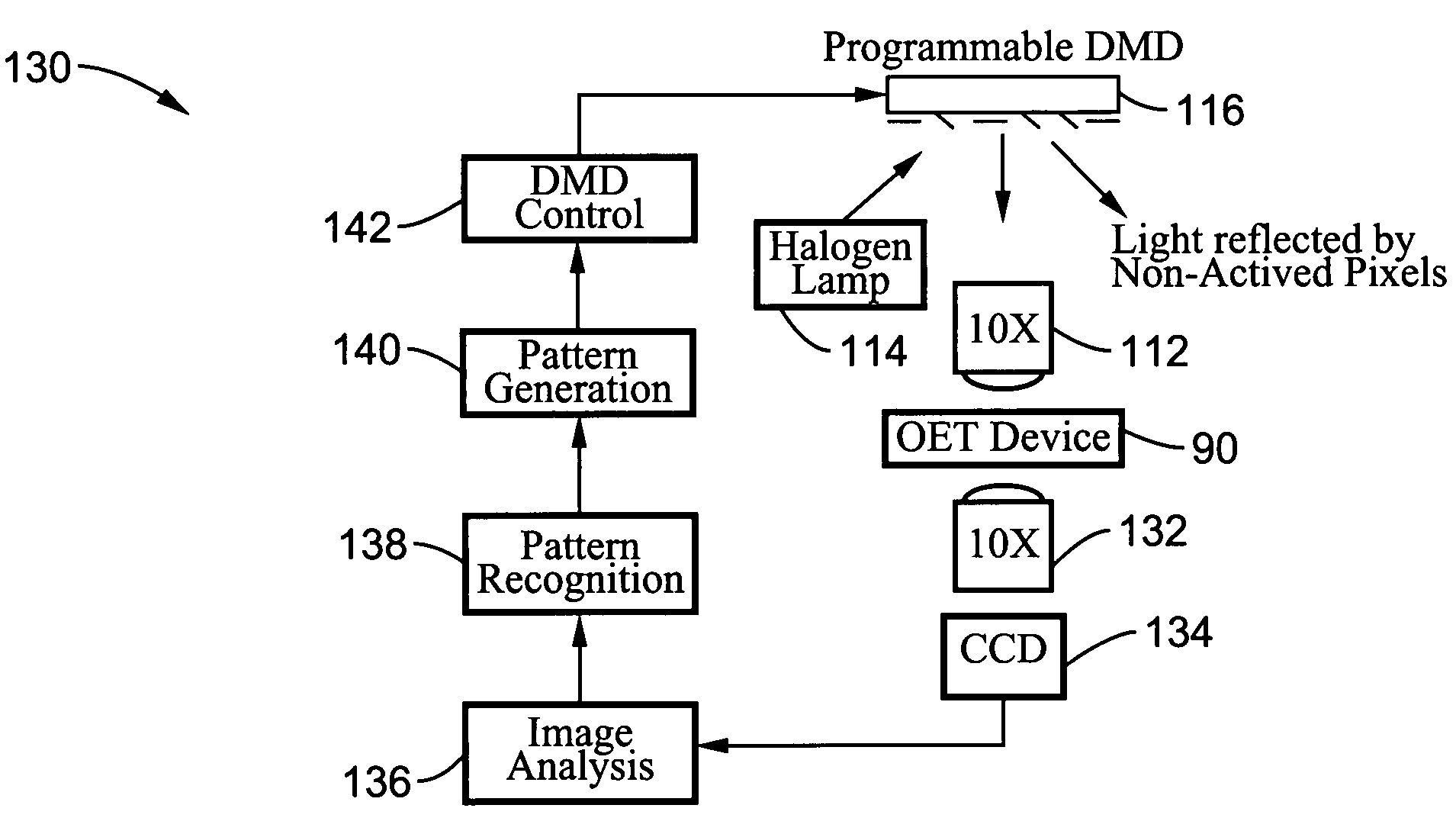
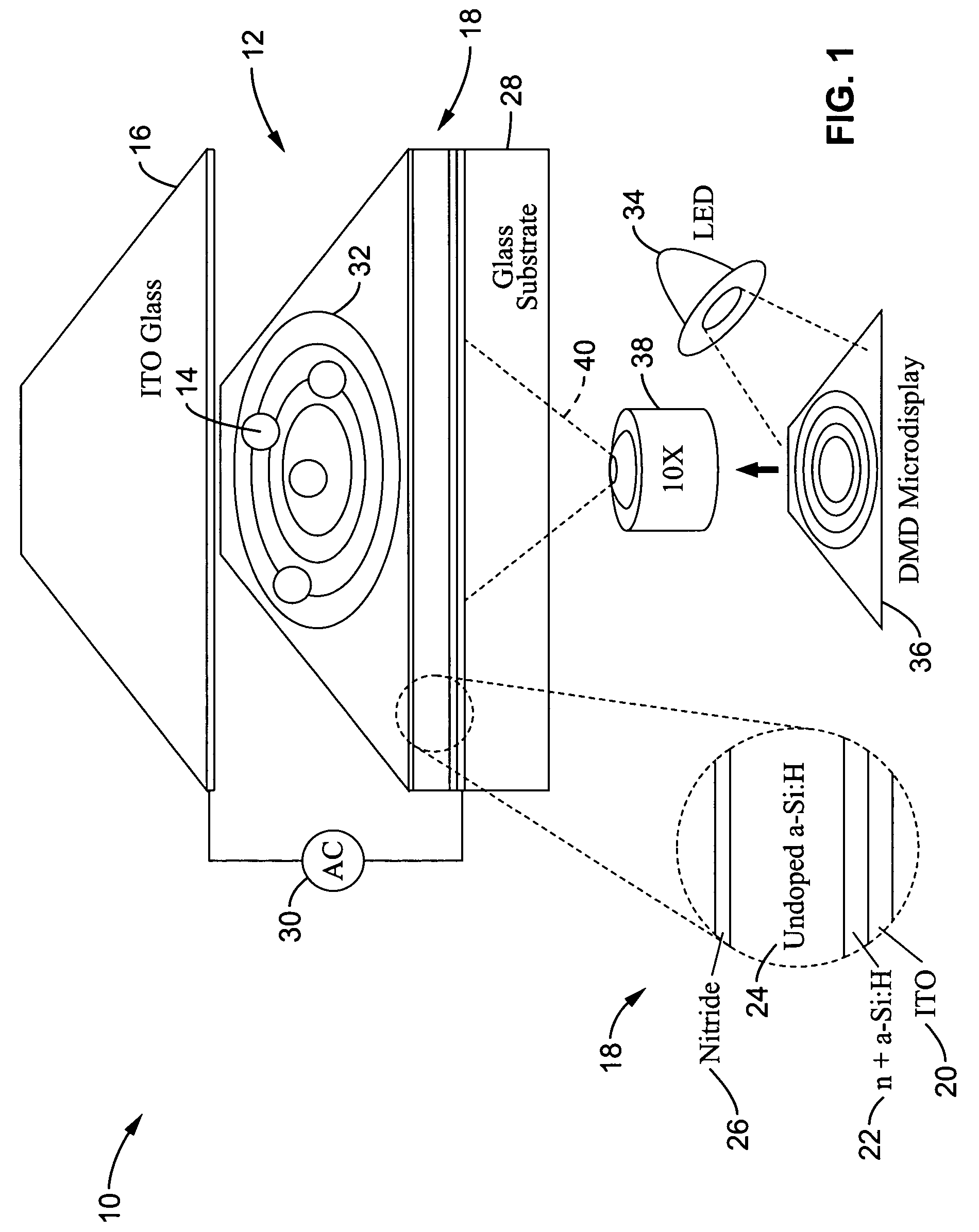
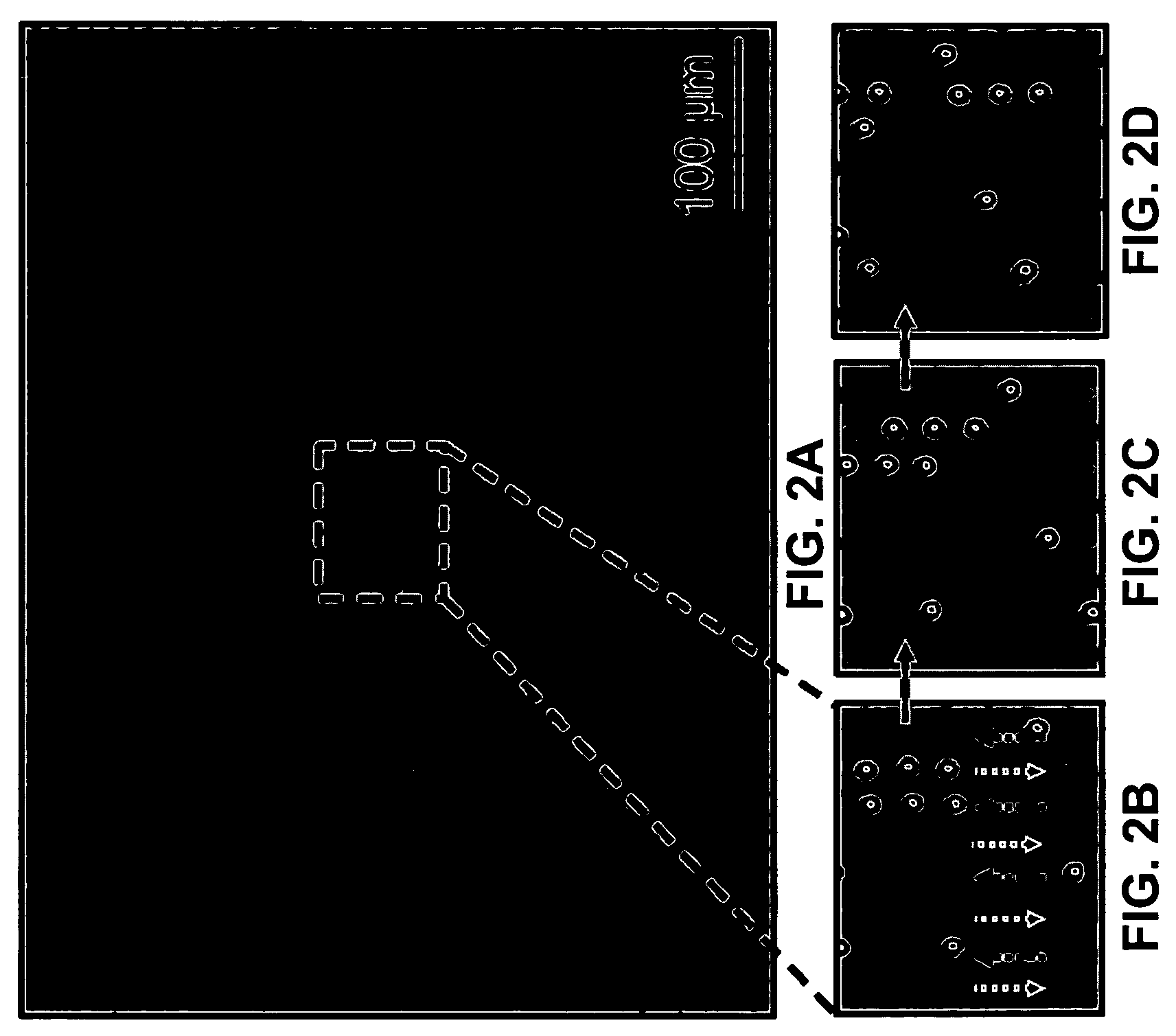
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS7612355B2Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleOpto electronic
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
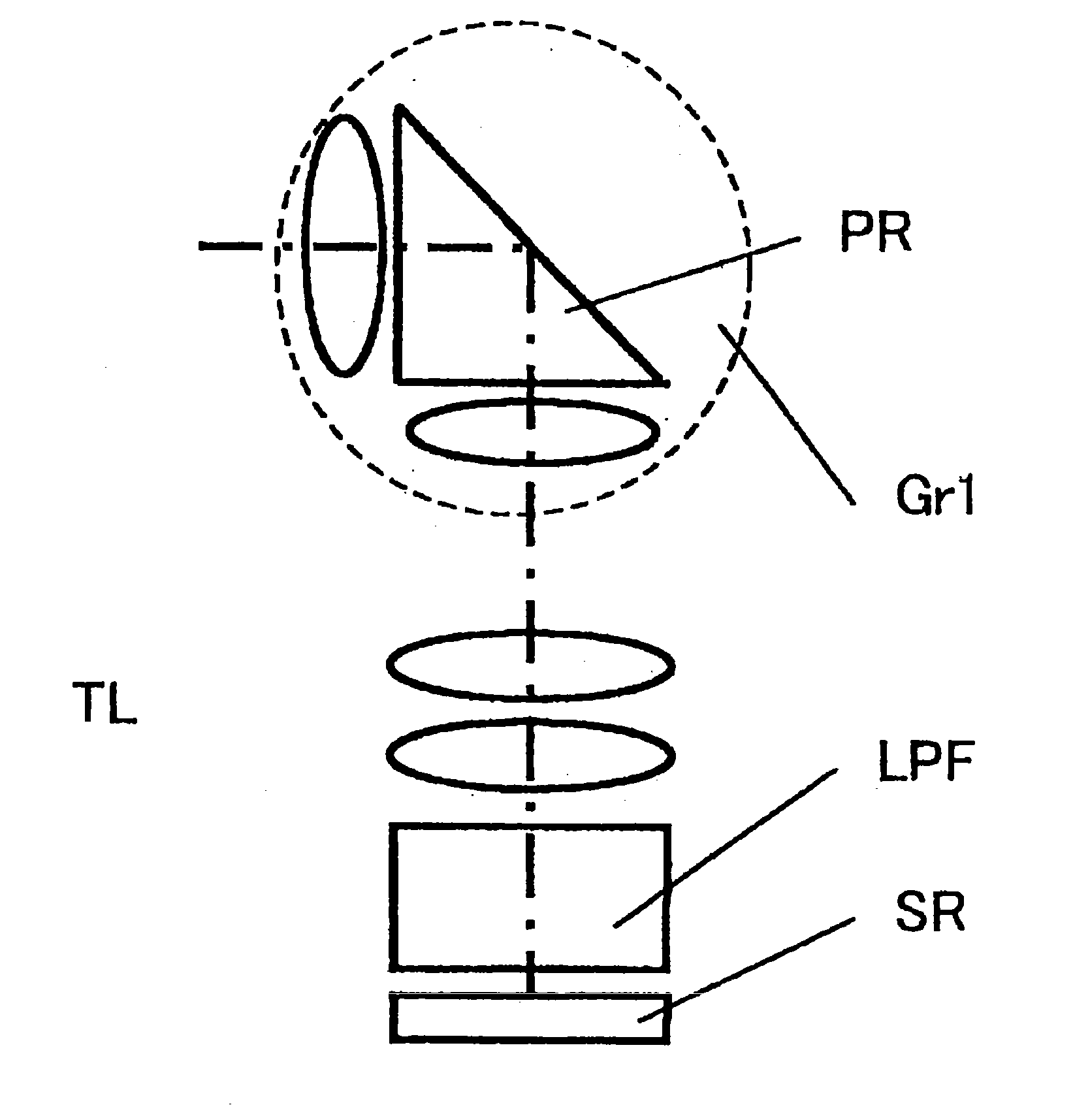
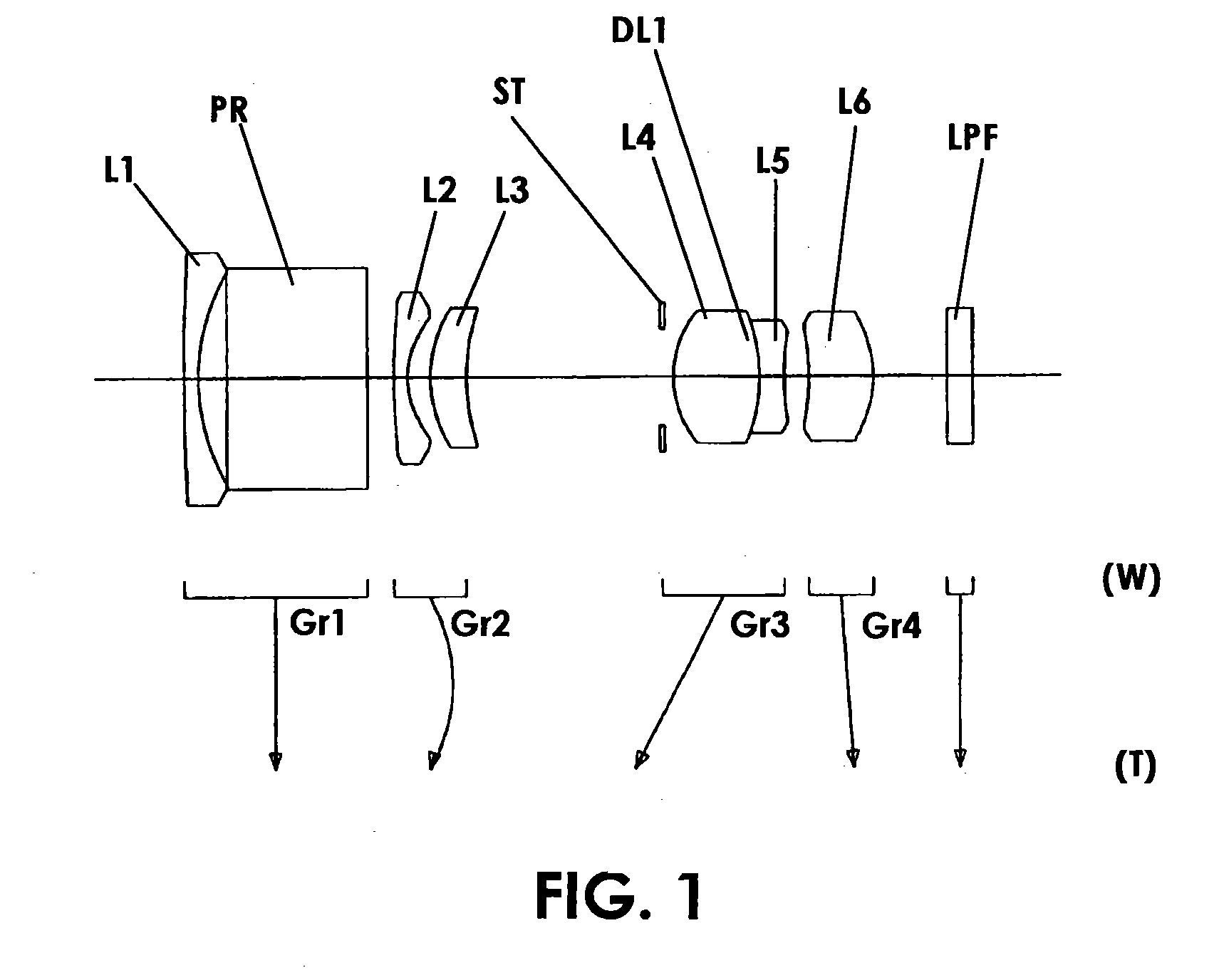
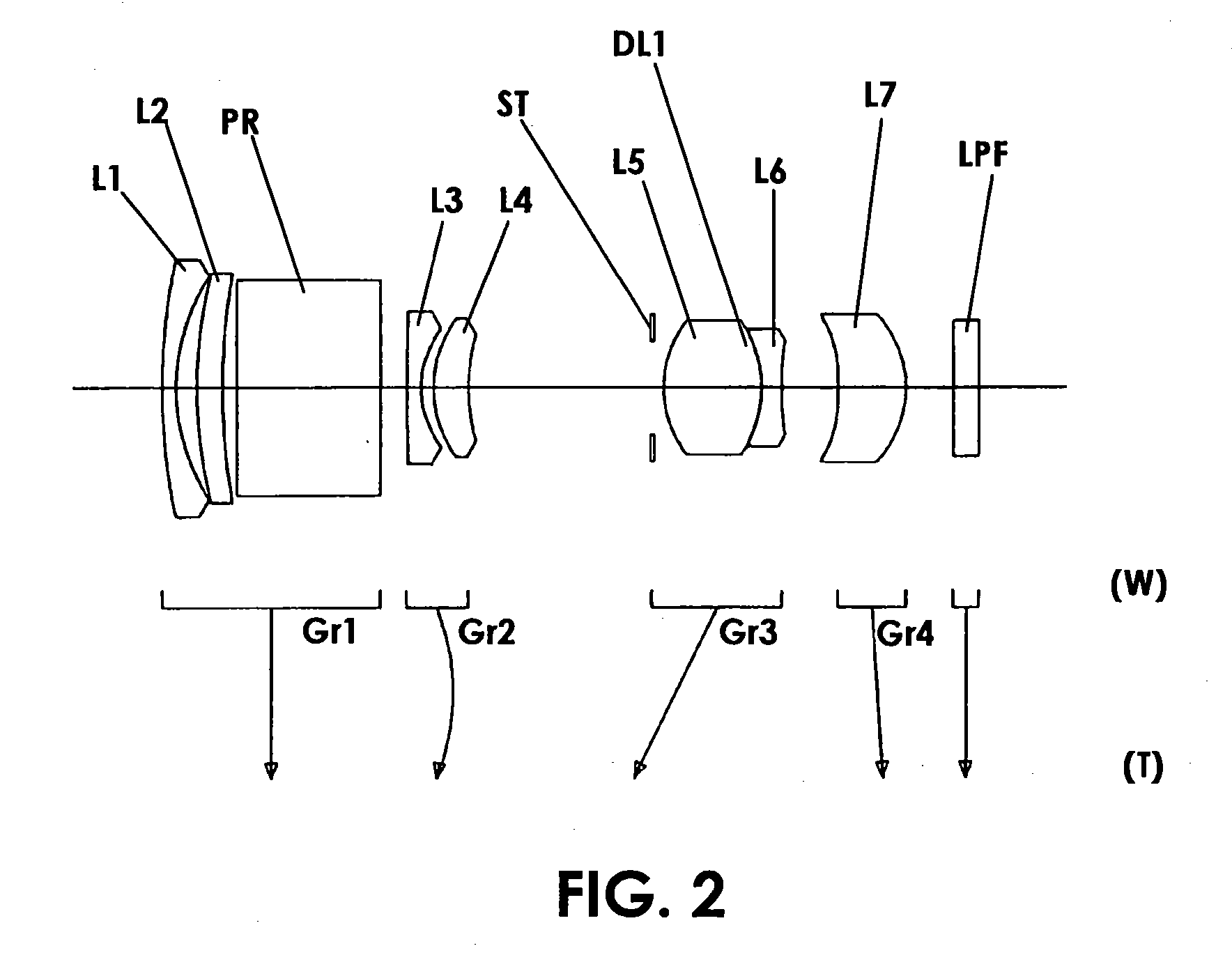
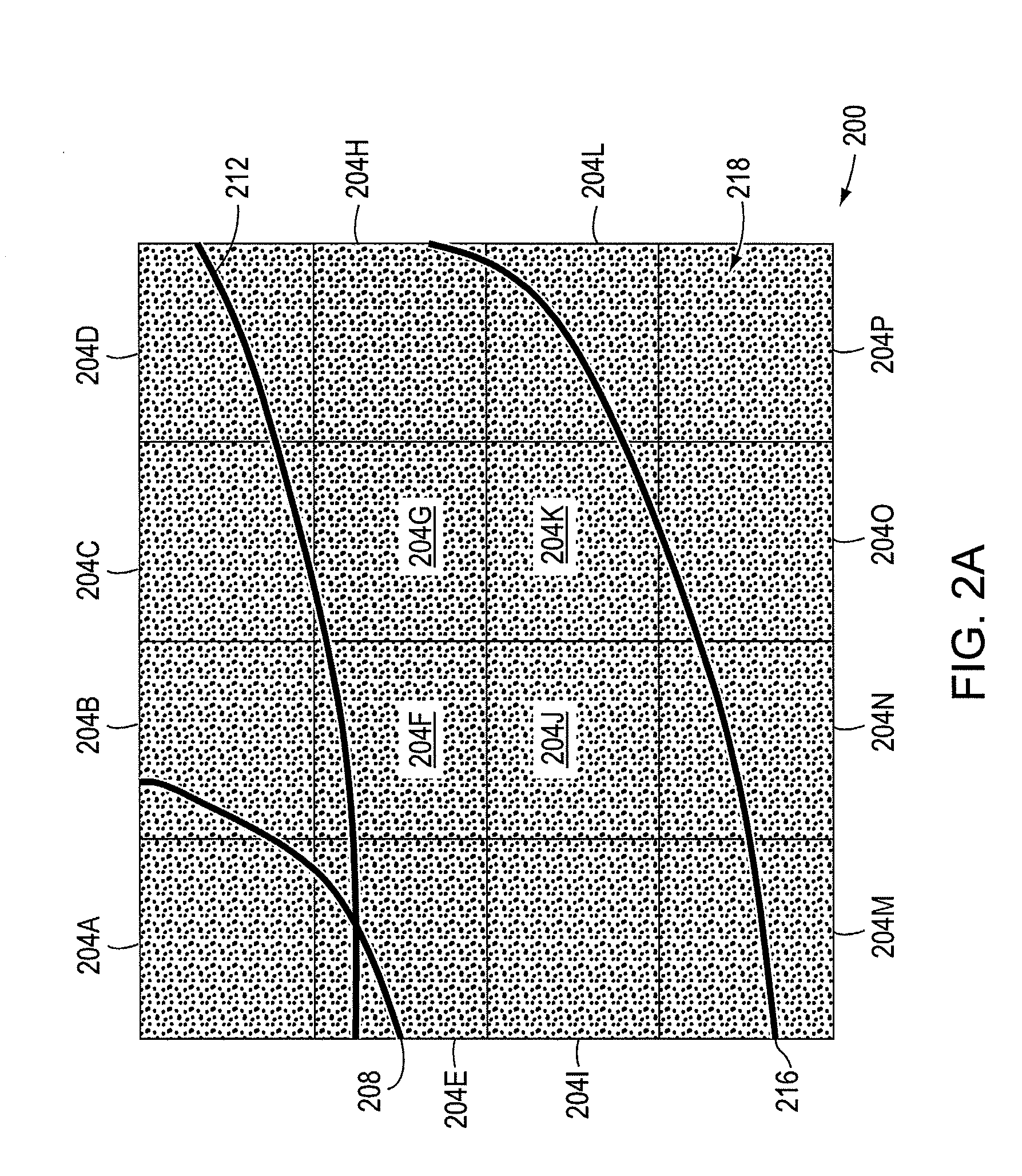
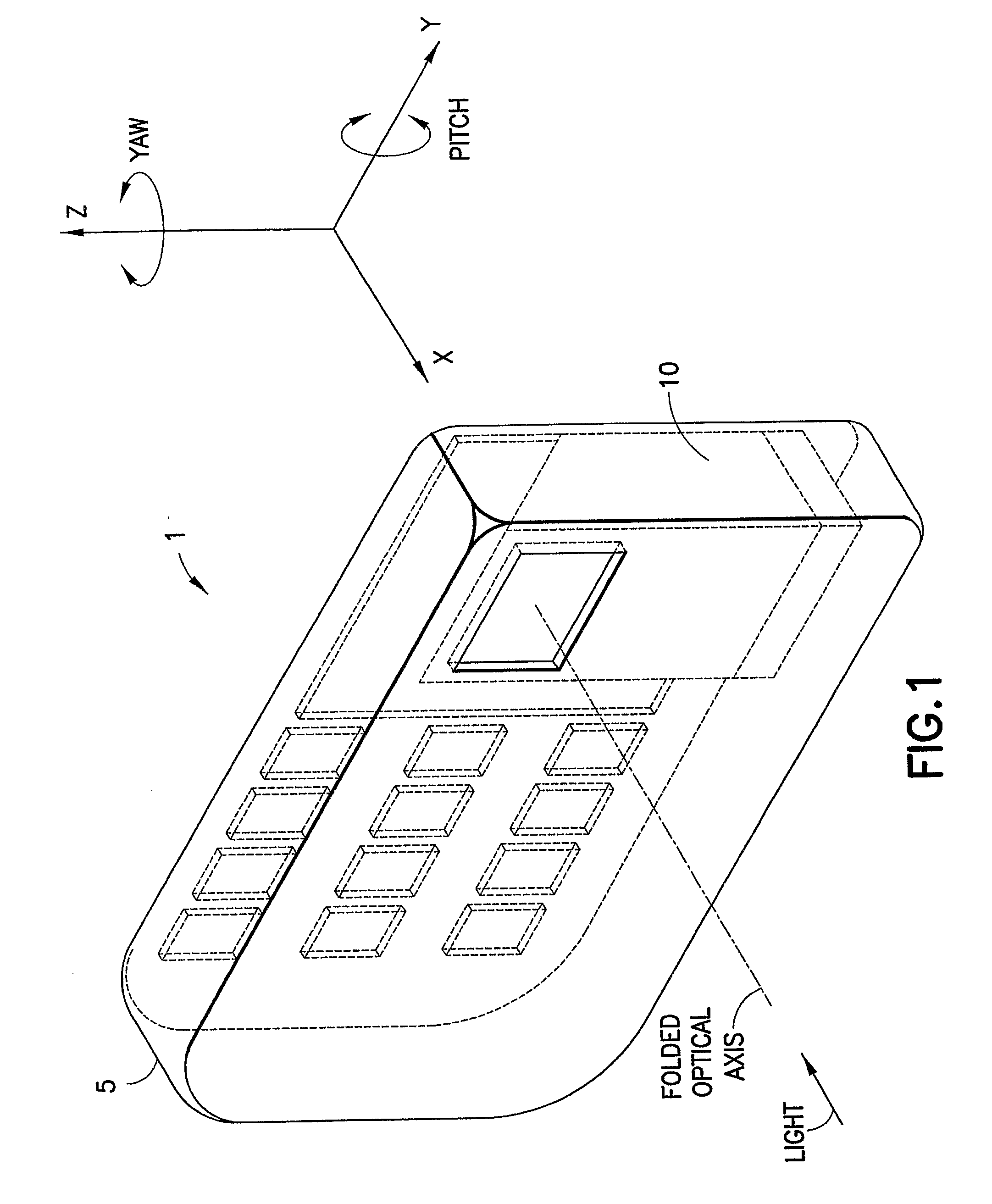
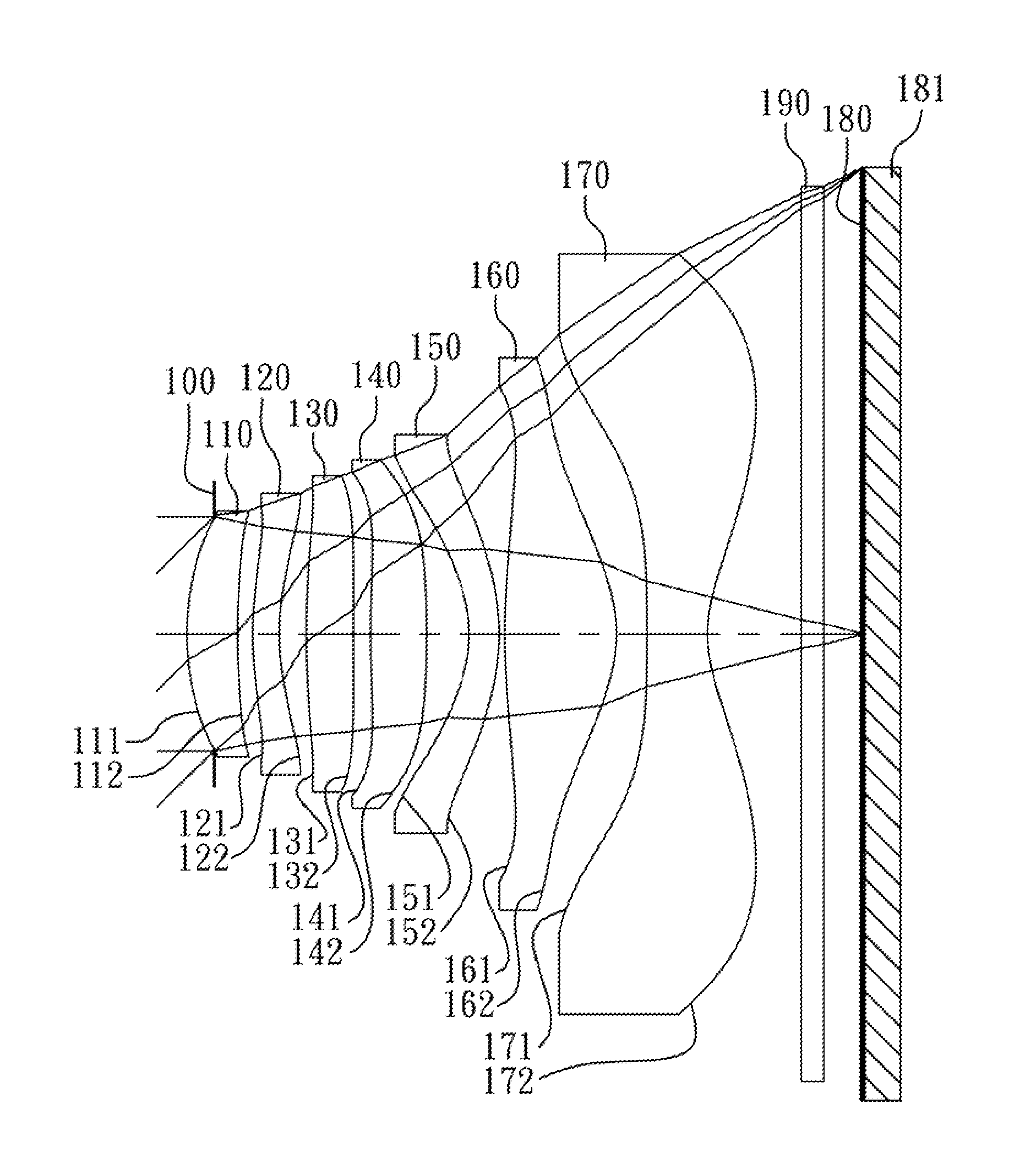
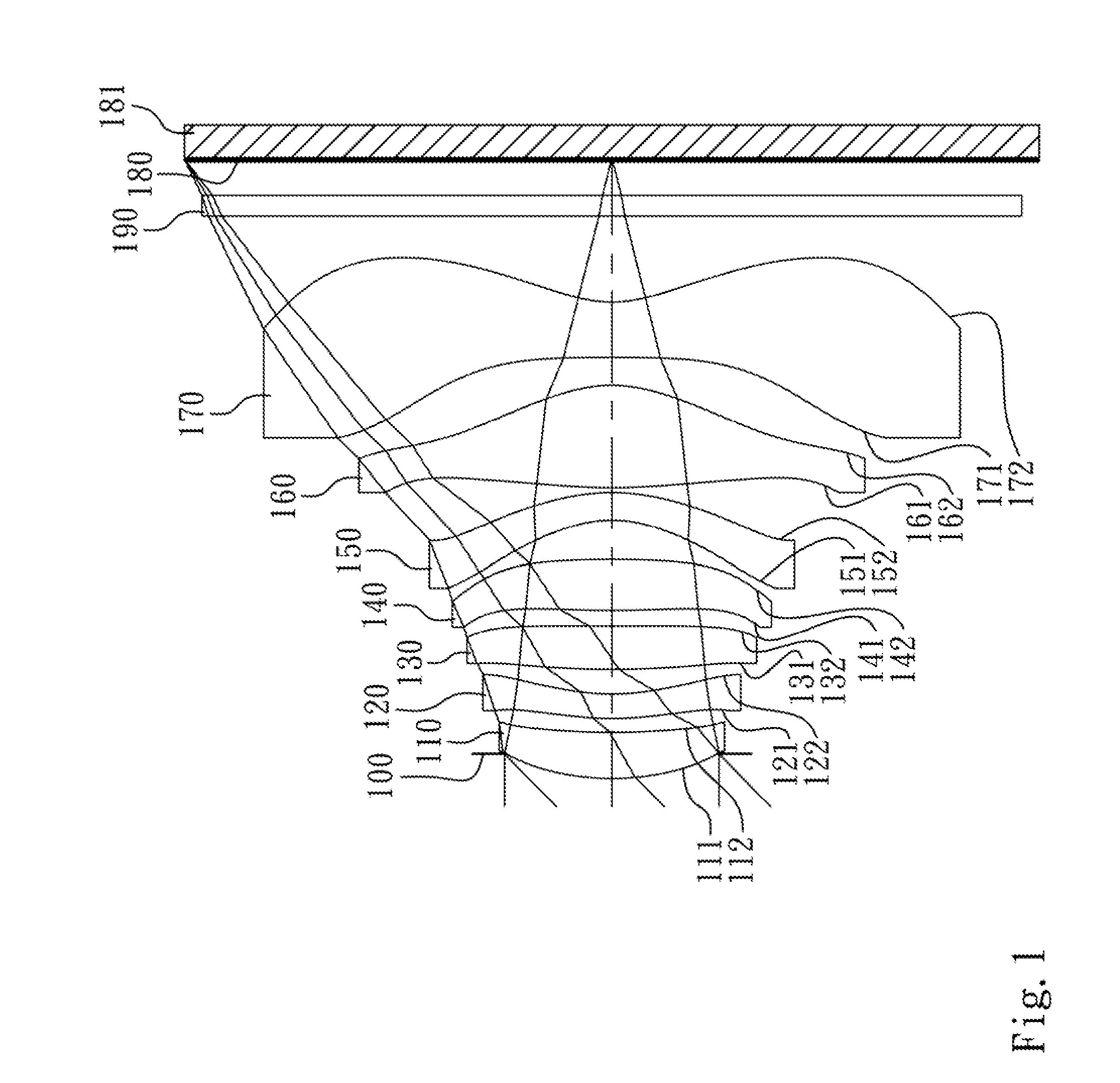
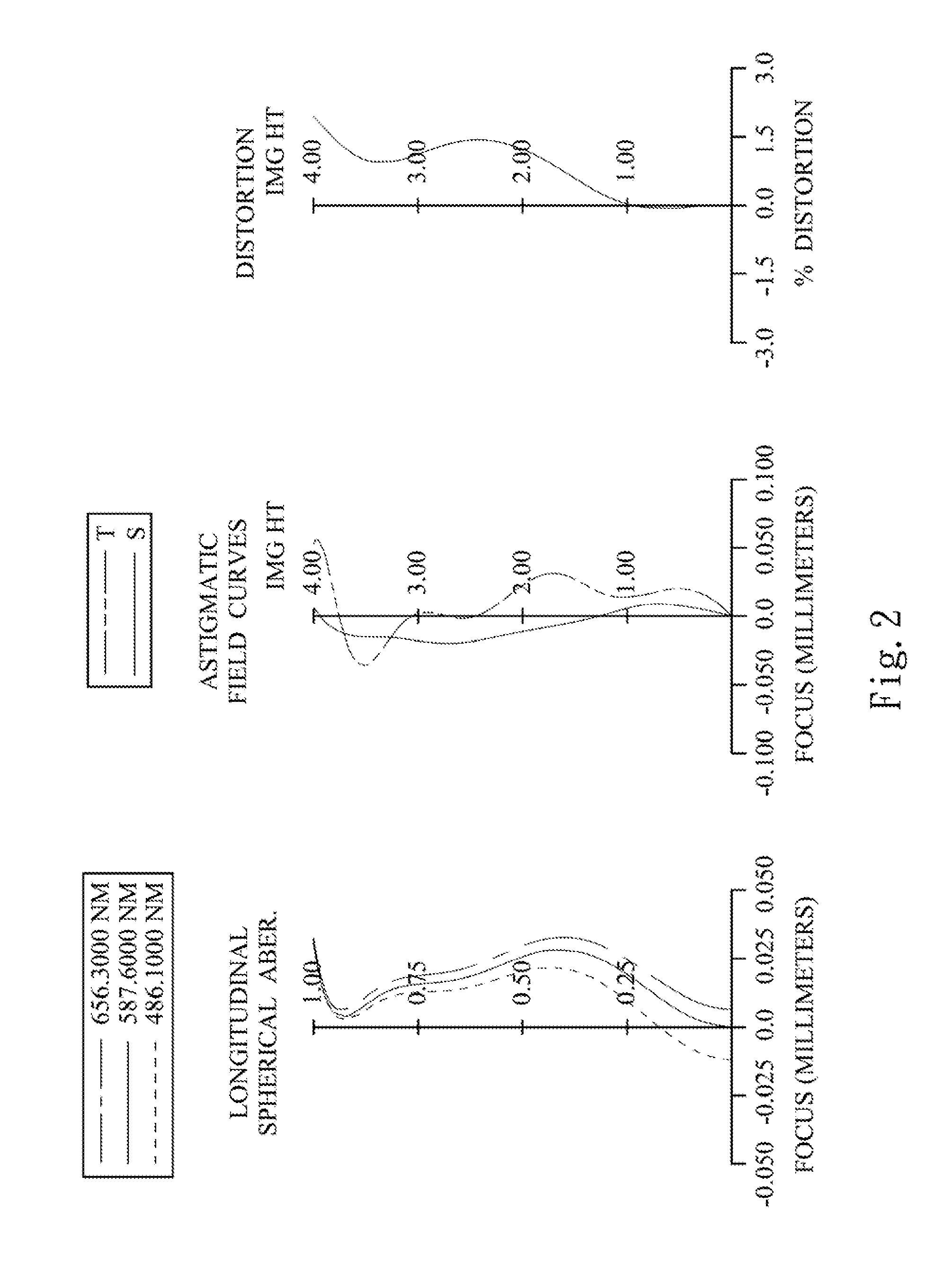
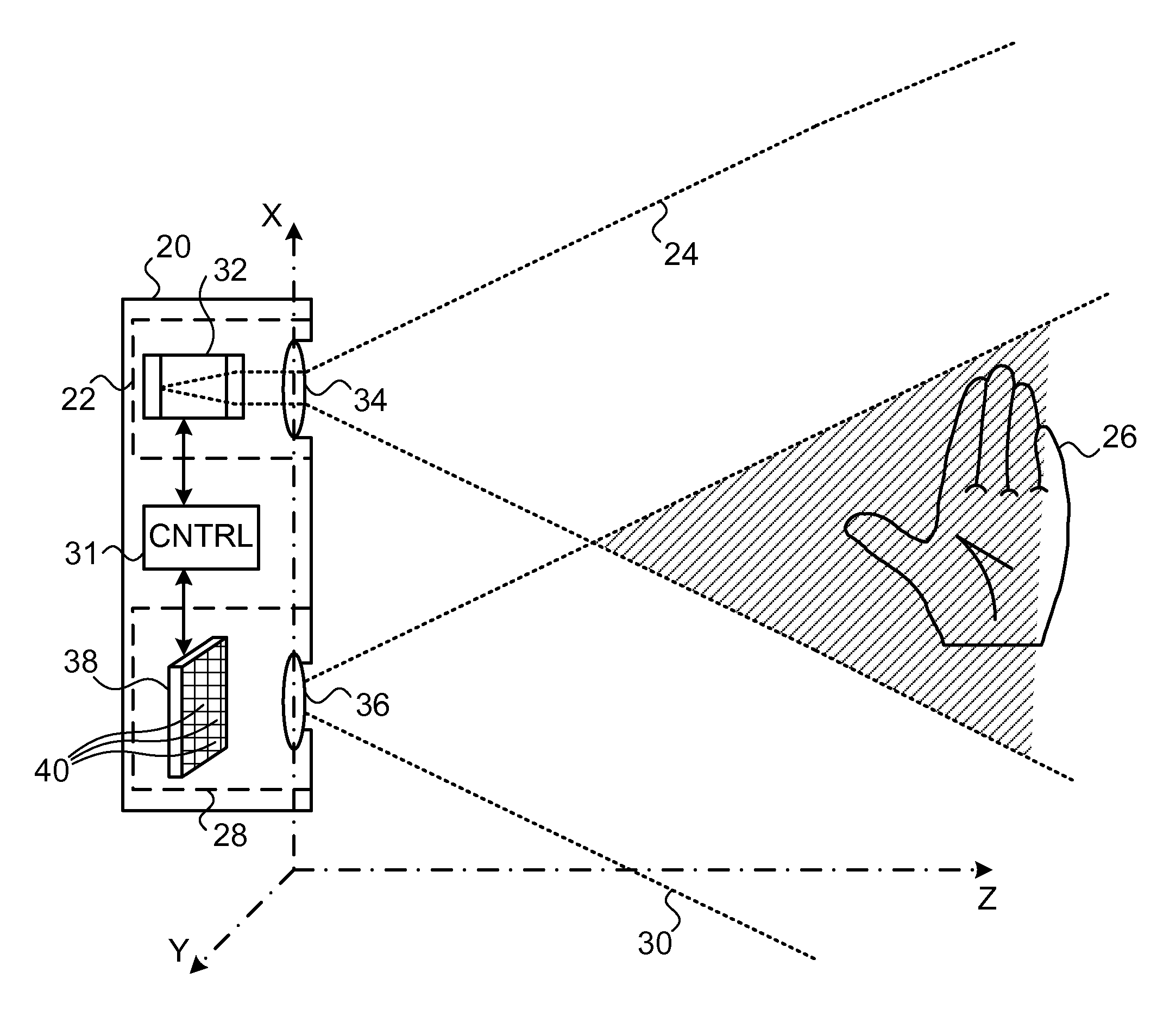
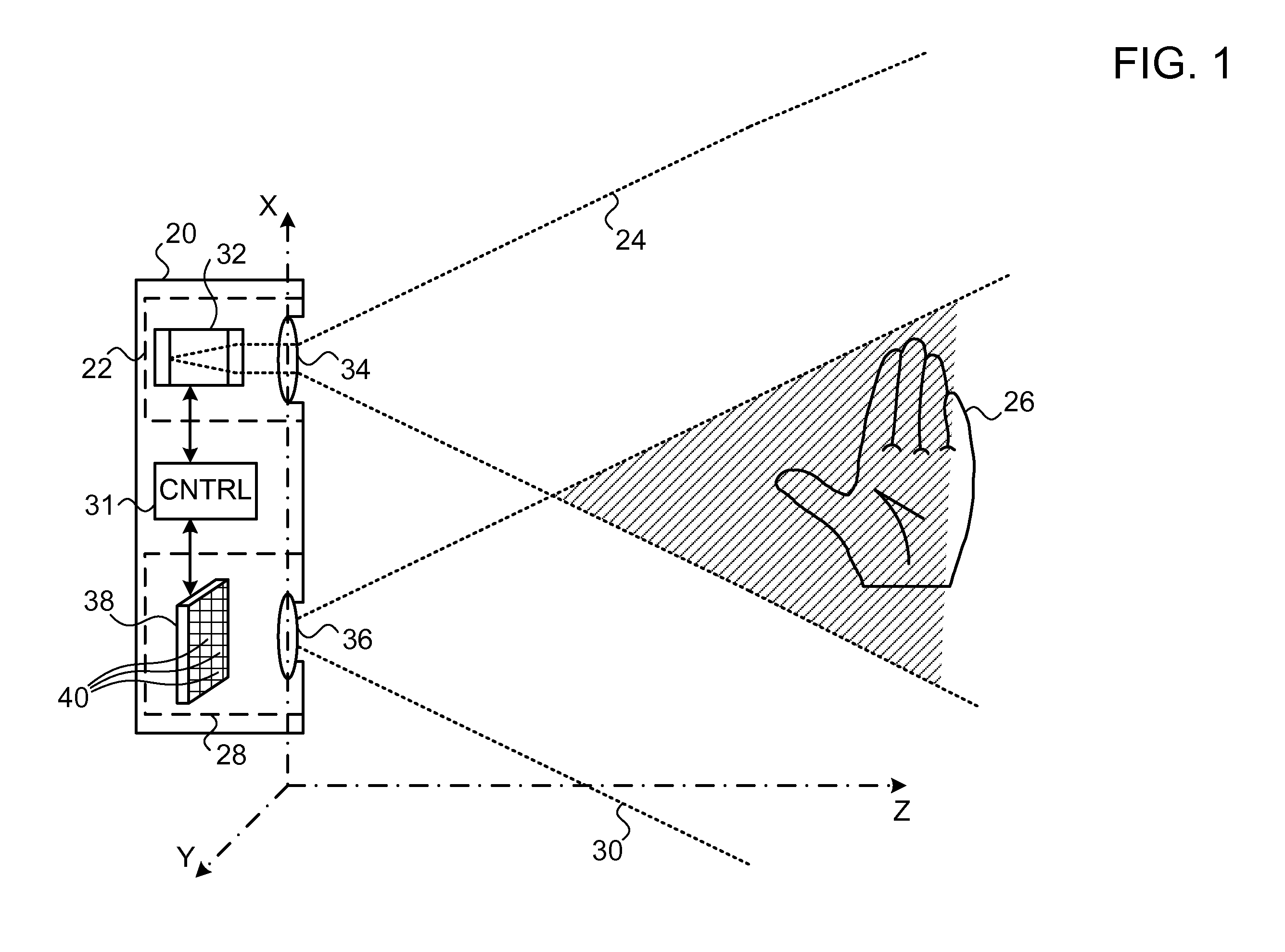
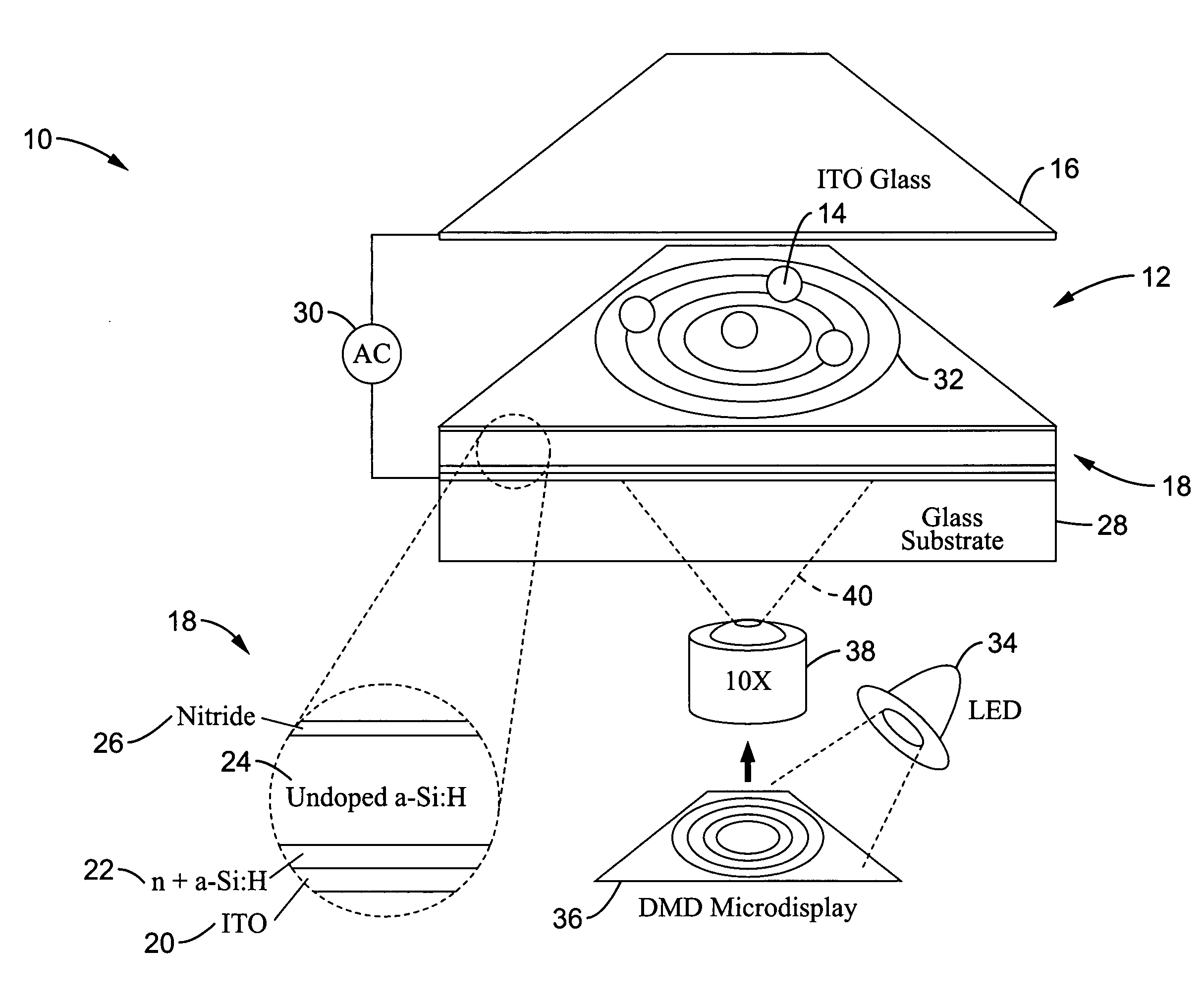
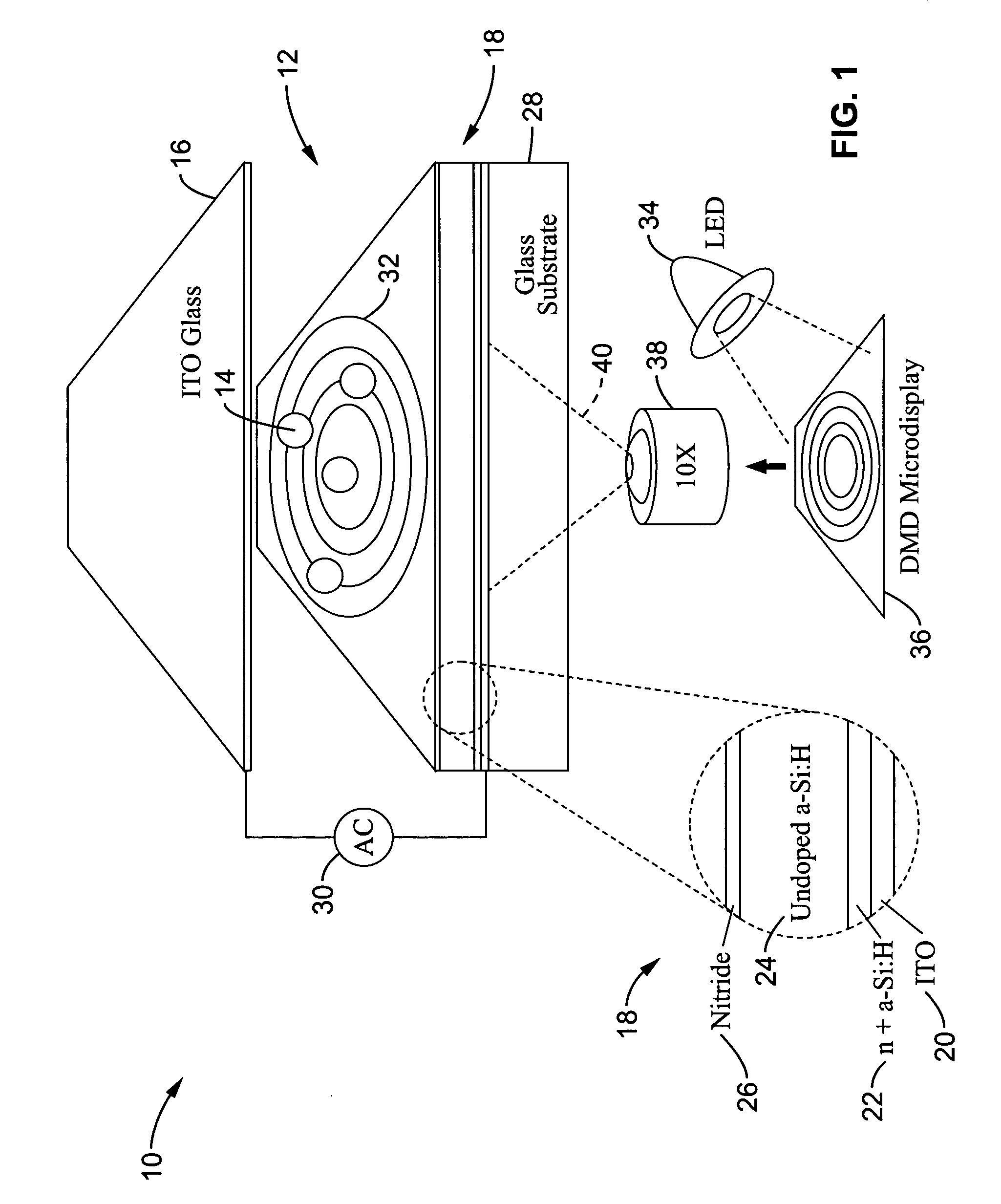
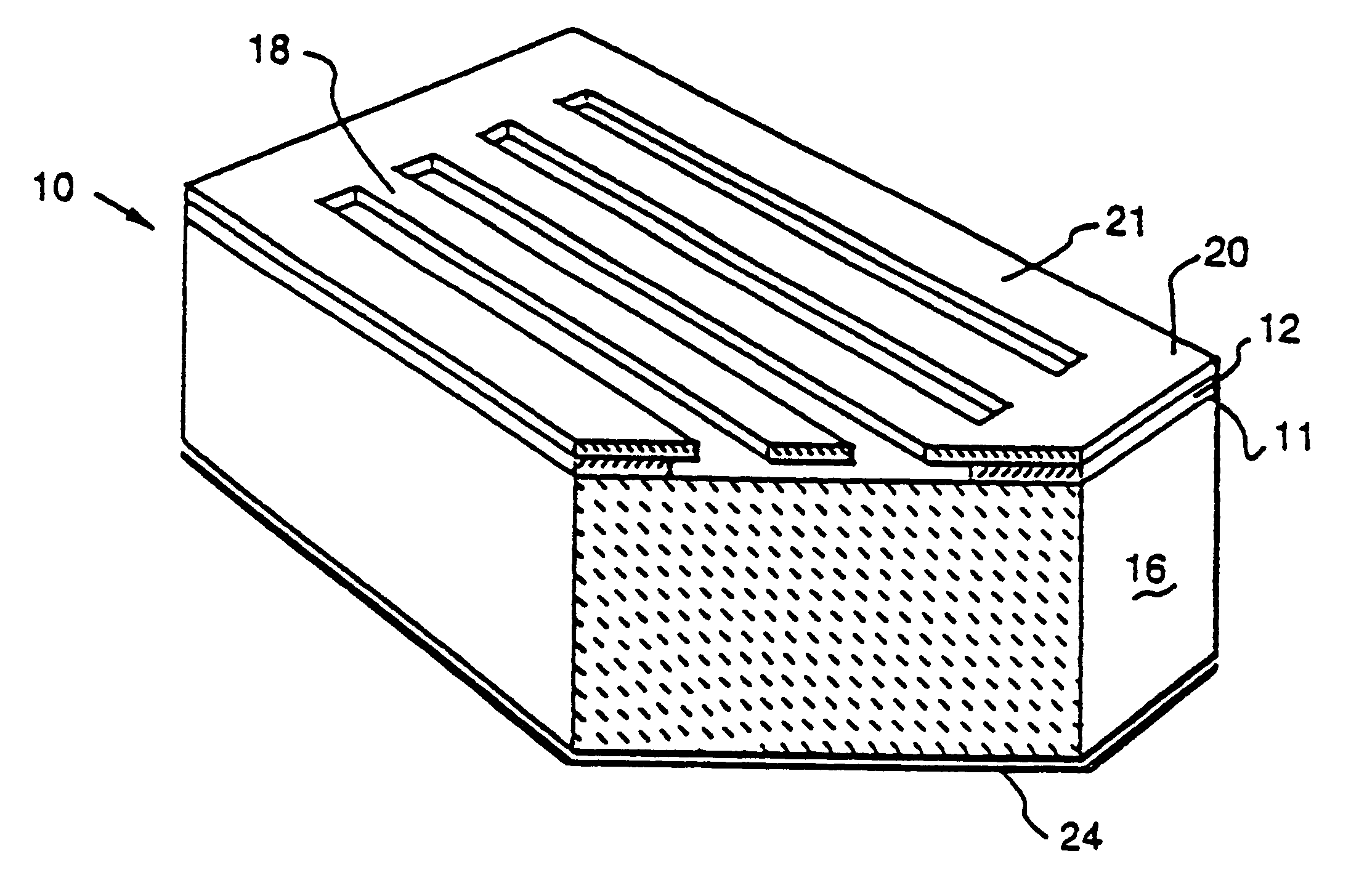
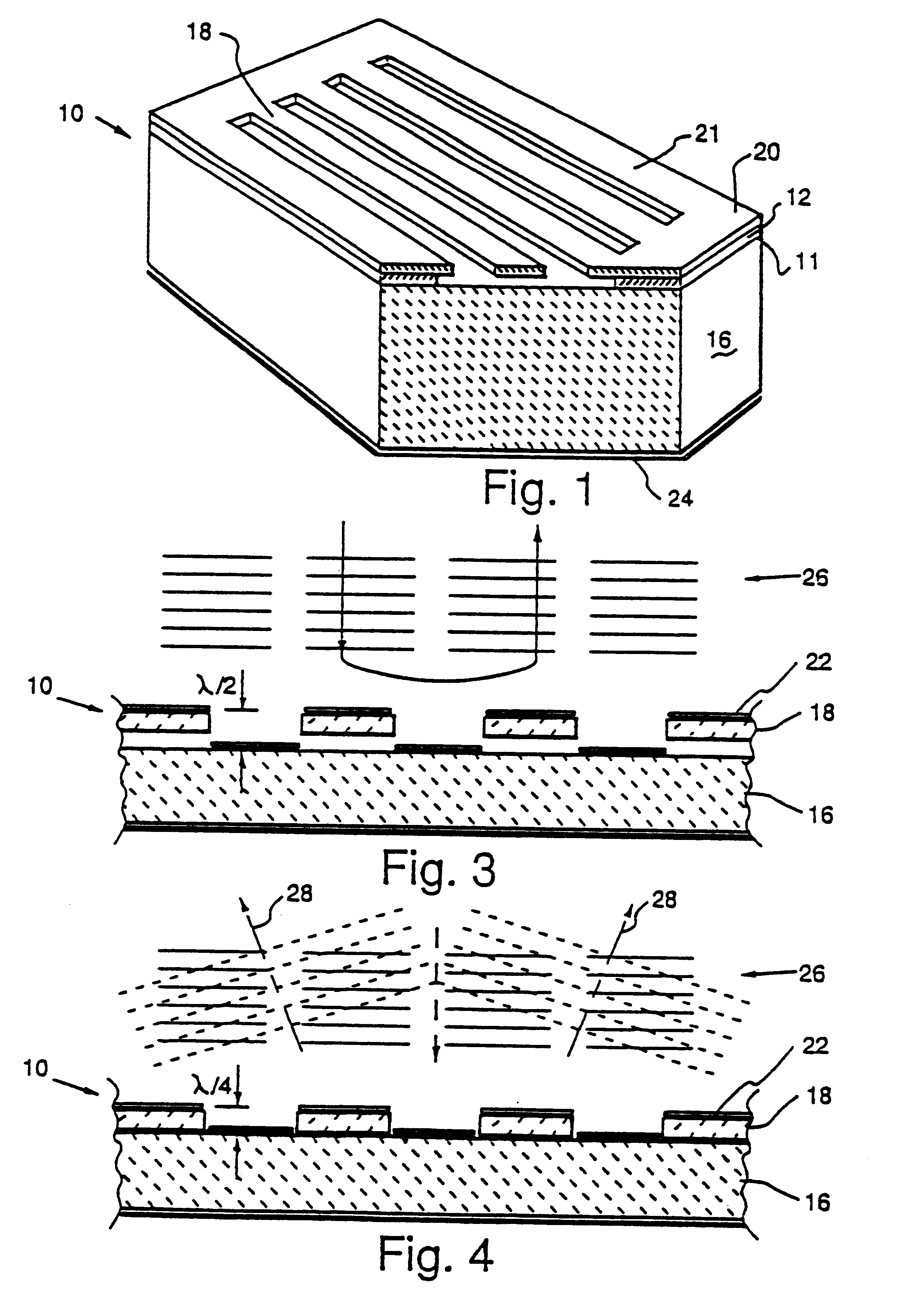
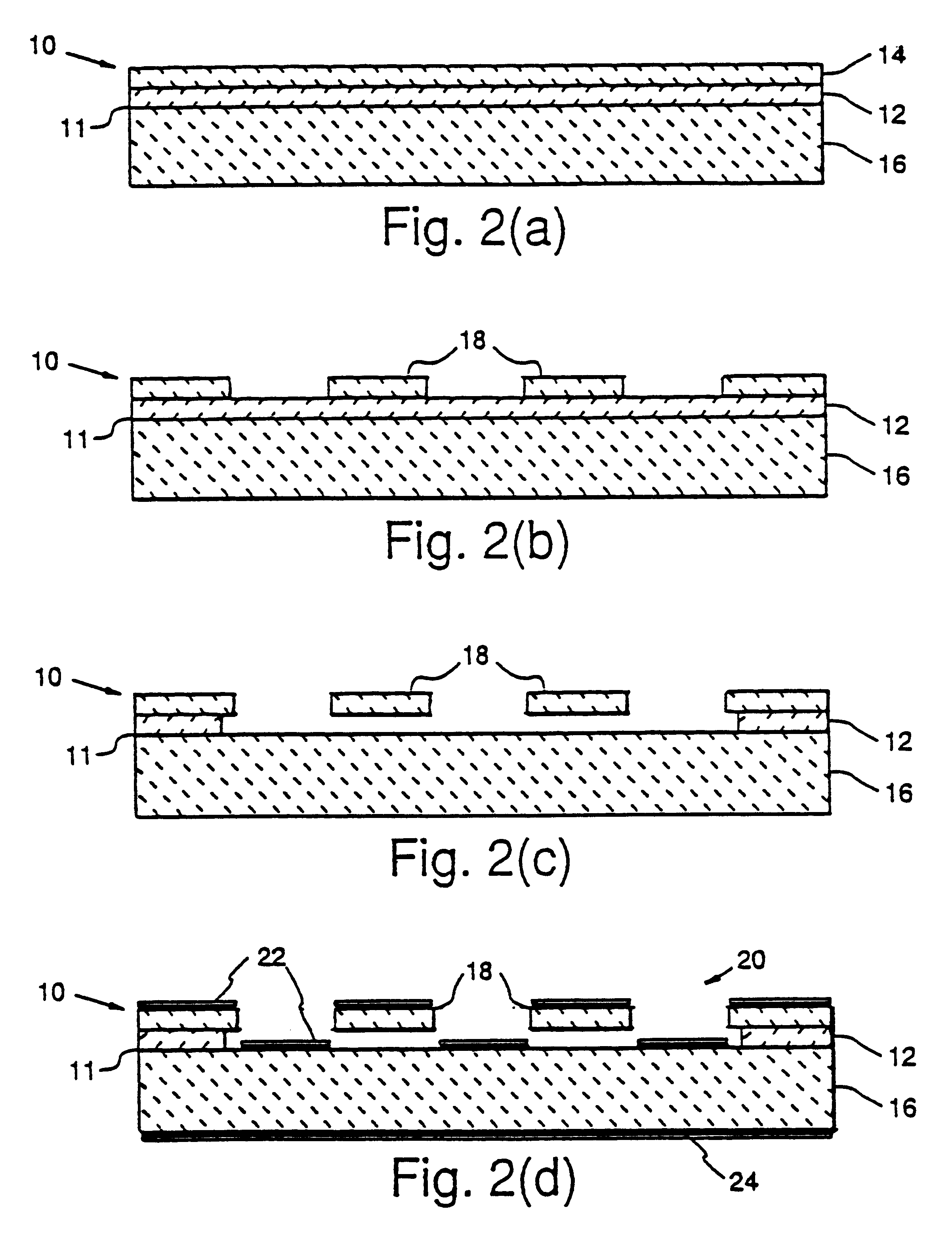
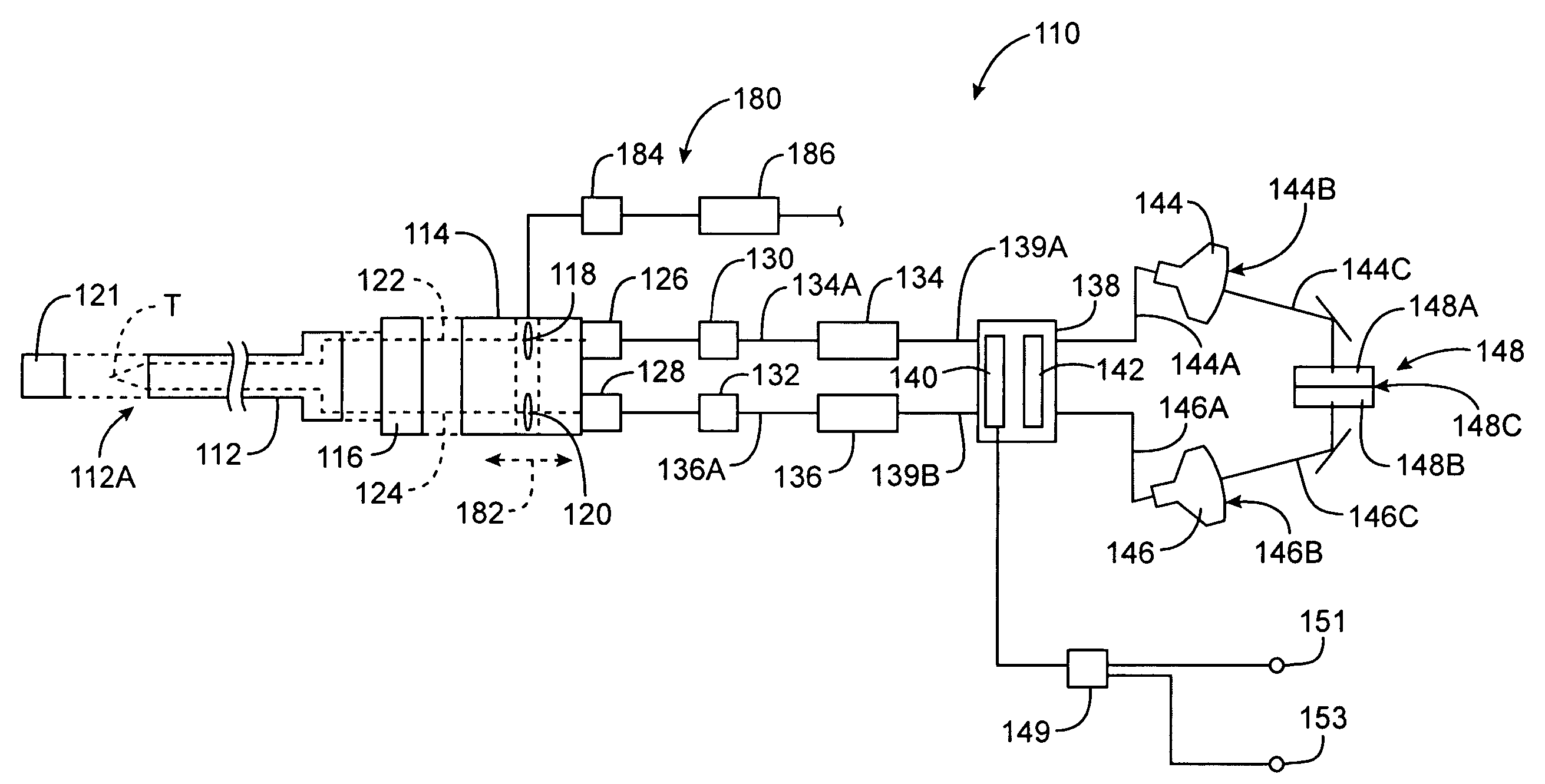
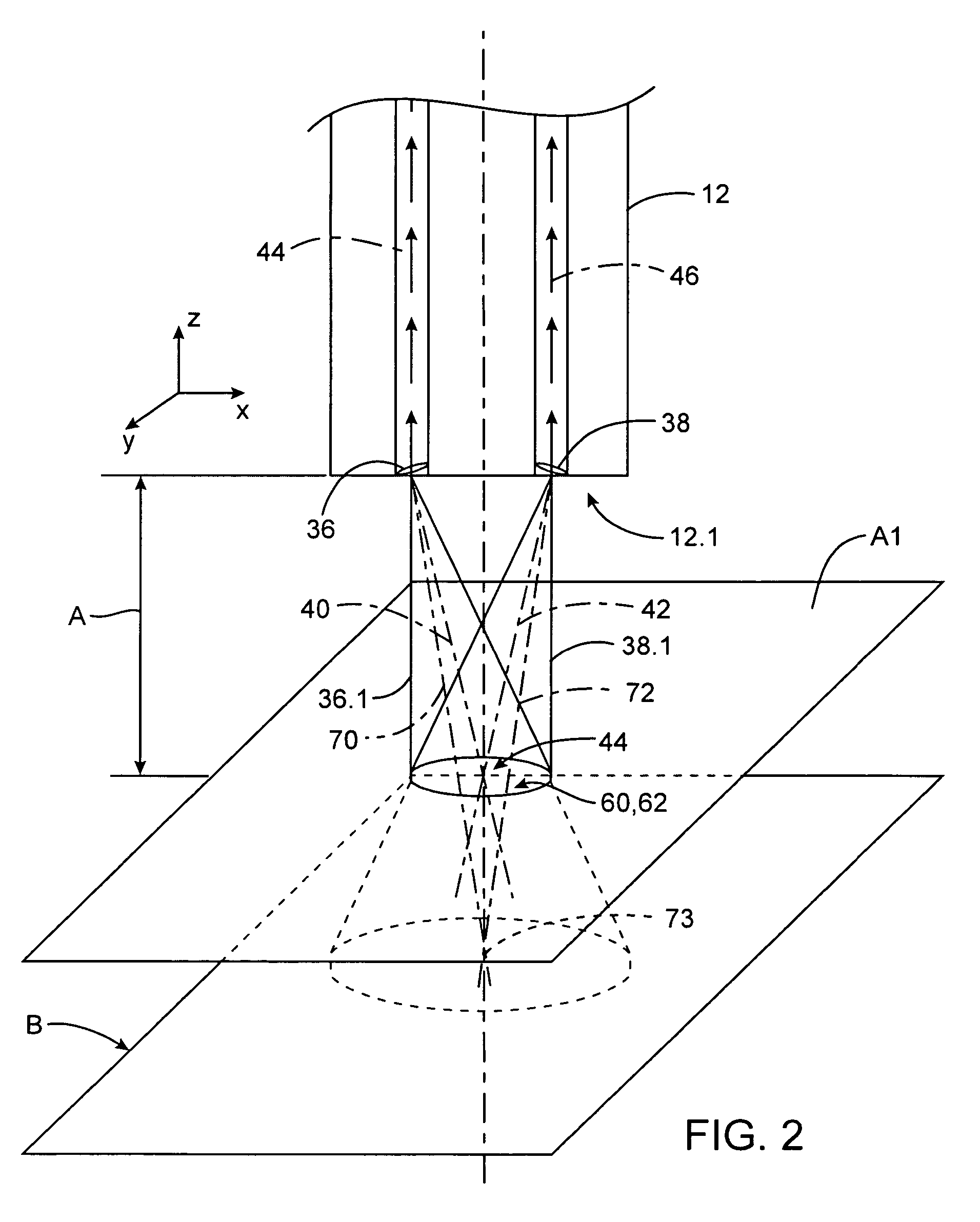
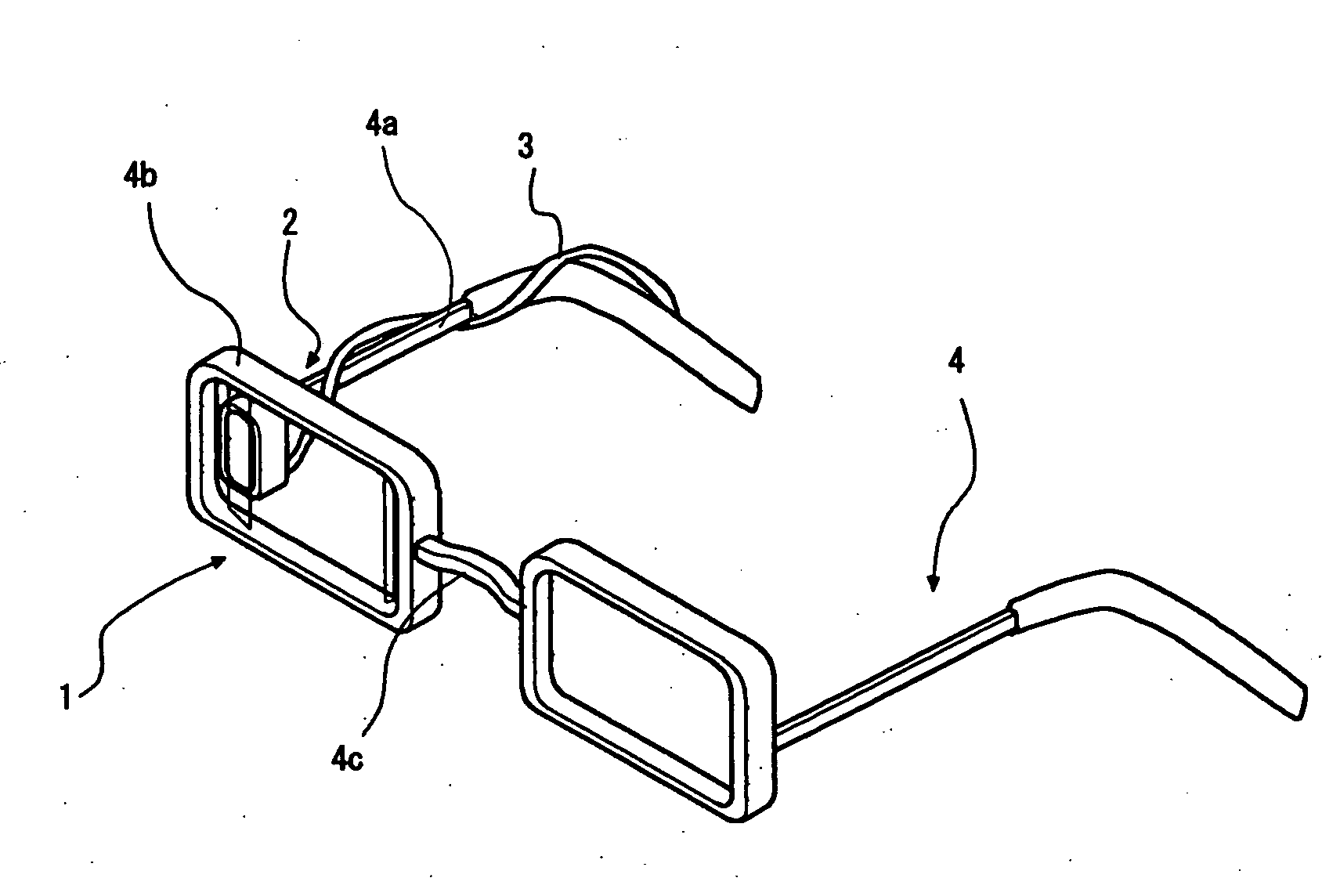
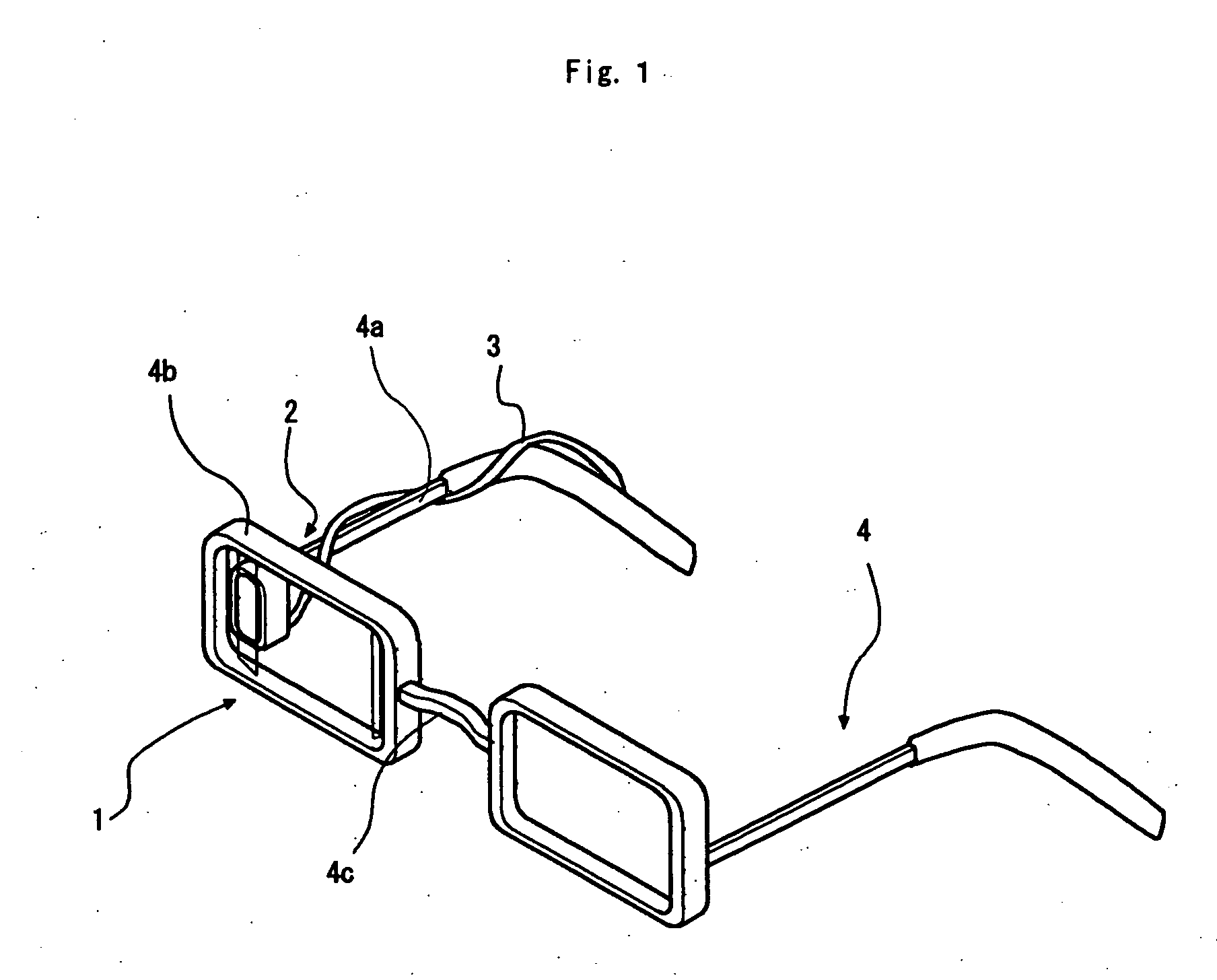
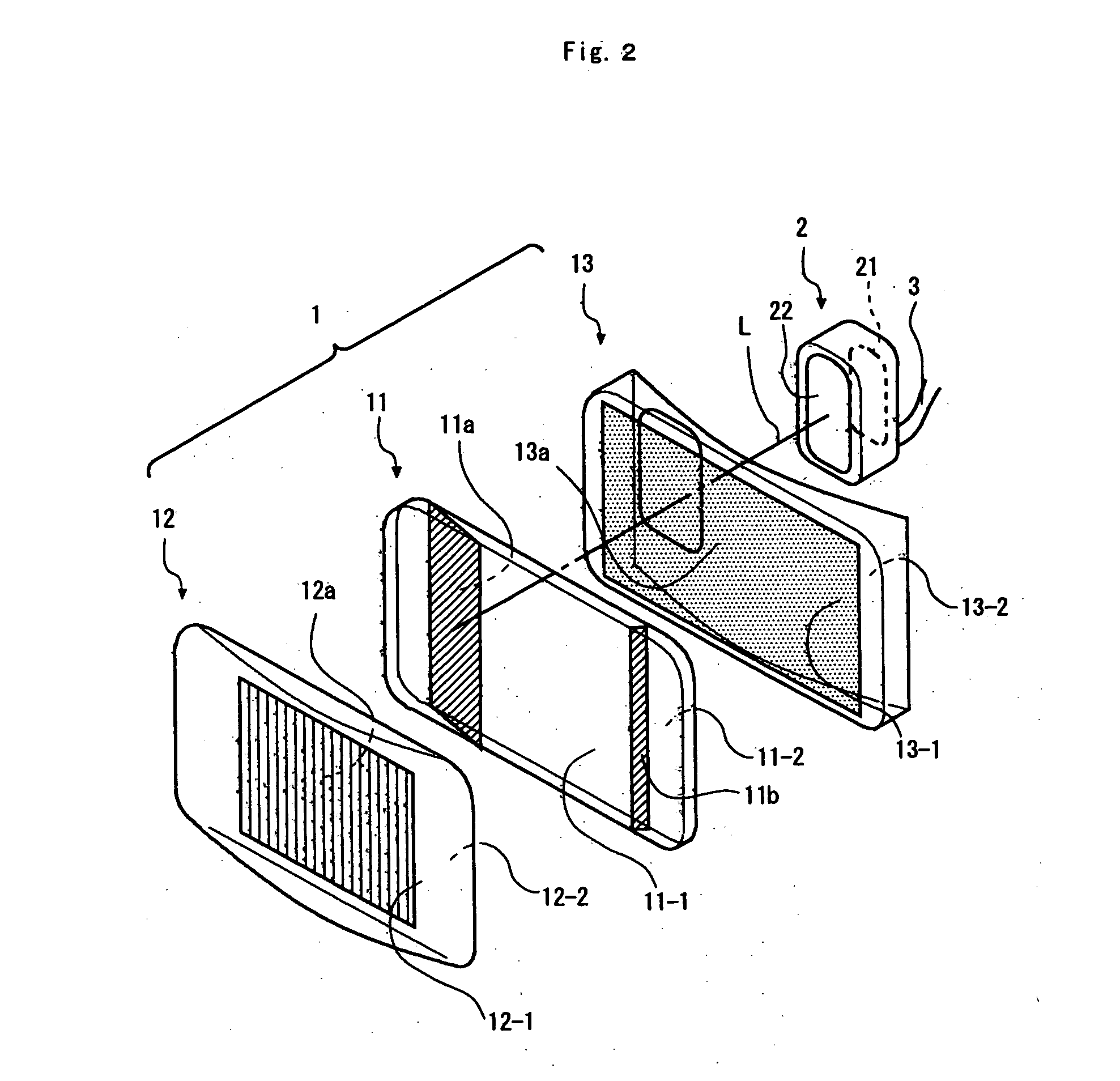
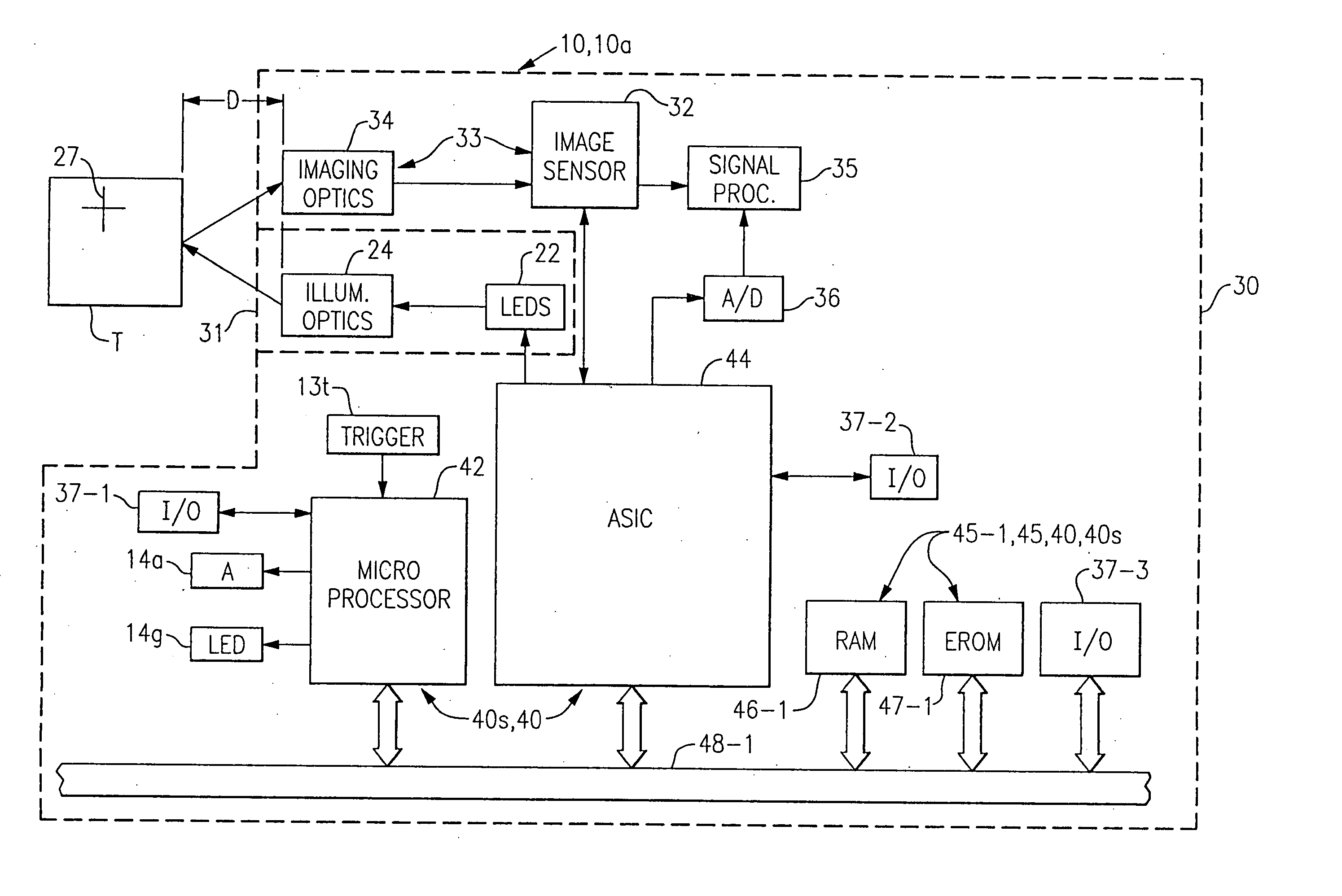
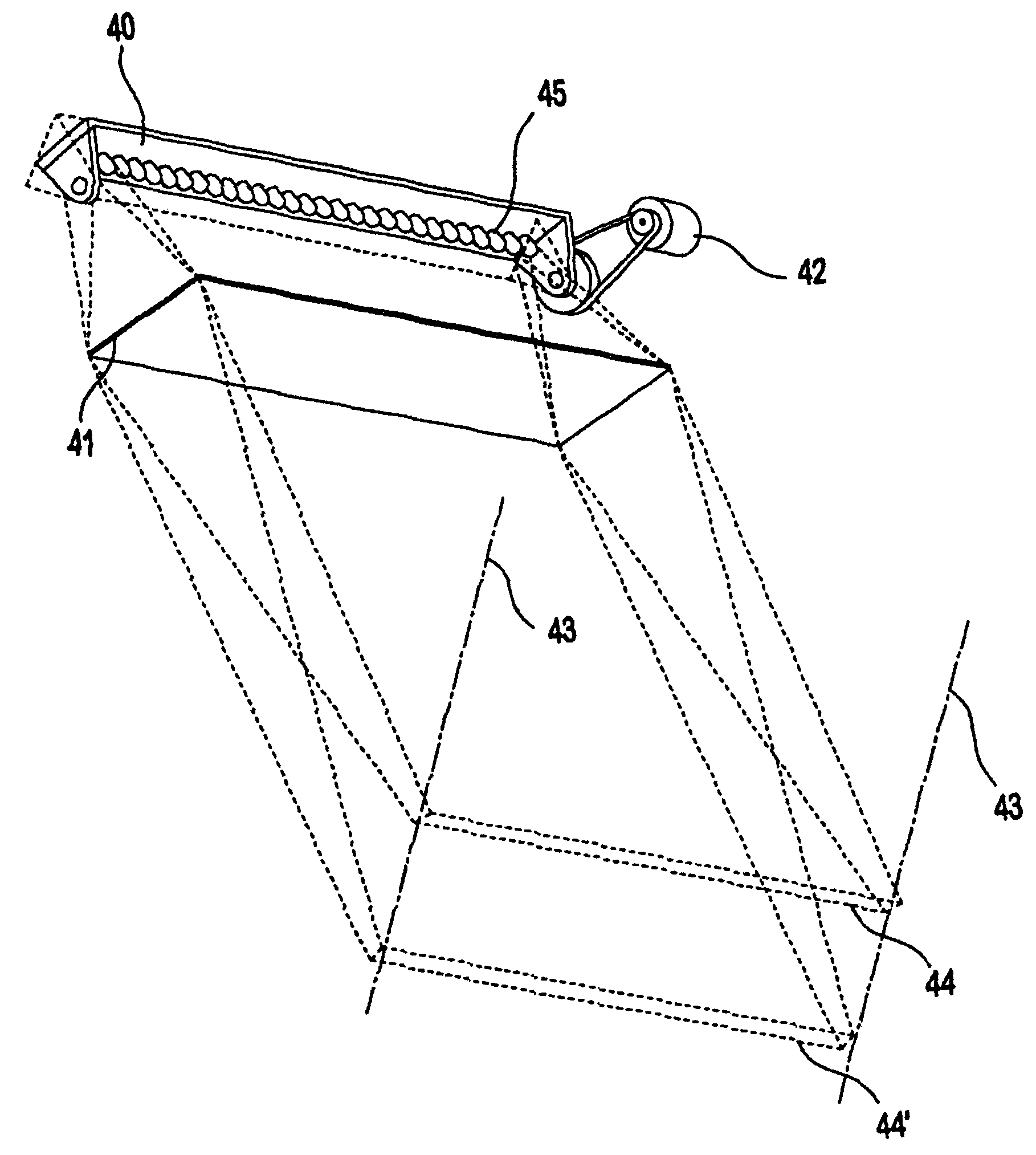
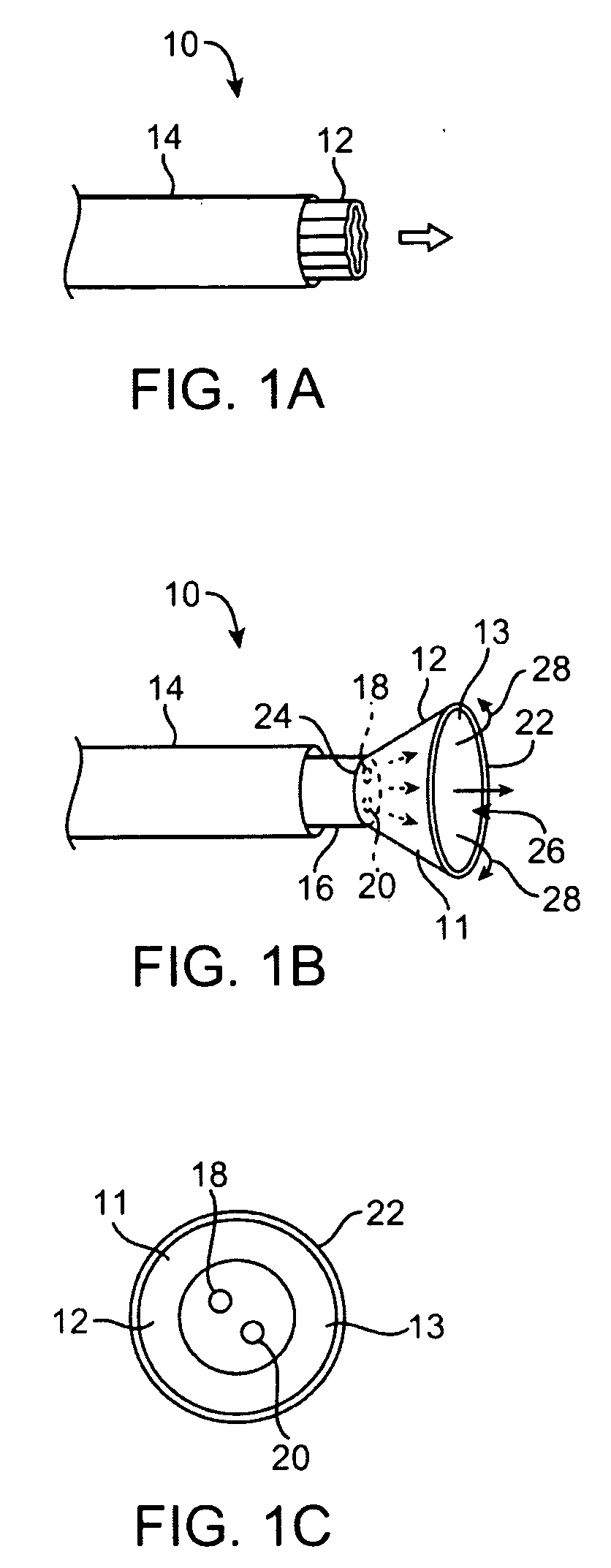
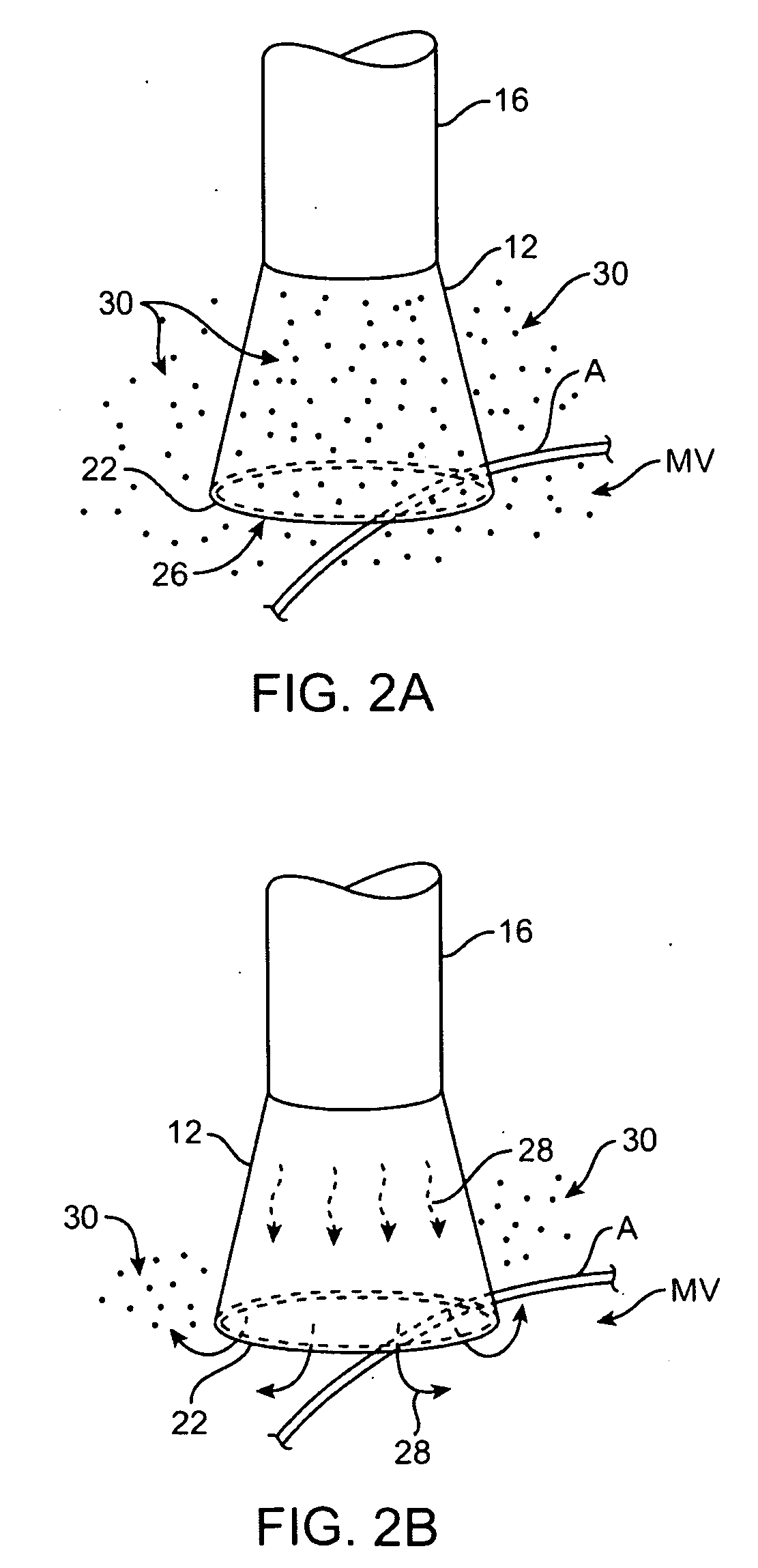
Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]
InactiveUS20120113514A1Unwanted motionReduce quality problemsOptical elementsUnintended MovementImage stabilization
A handheld projector is provided with an image stabilization system that acts to reduce (or even eliminate) unwanted motion of the projected image due to unintended movement of the projector. In certain preferred embodiments, a solid-state motion sensor provides input to an image stabilization system that computes a corrective signal. In embodiments having optical image stabilization, the corrective signal is supplied to a mechanical actuator that moves one or more optical elements within the projector. Other embodiments have electronic image stabilization. In these embodiments, the corrective signal from the image stabilization system is used by the image generator to shift the image so as to compensate for movement of the projector.
Owner:POLYCOM INC
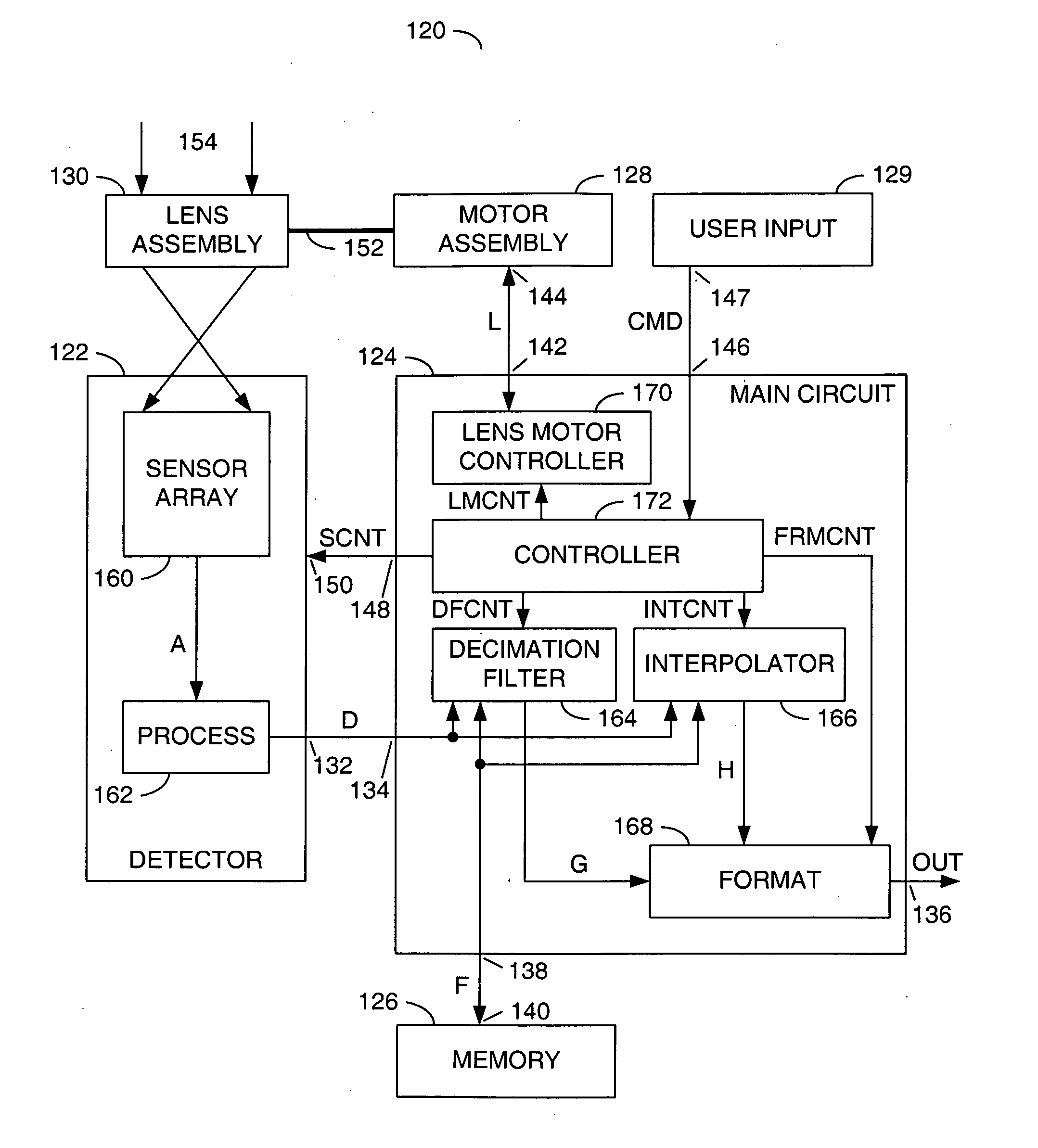
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS20040008271A1Solve the thickerLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical power
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
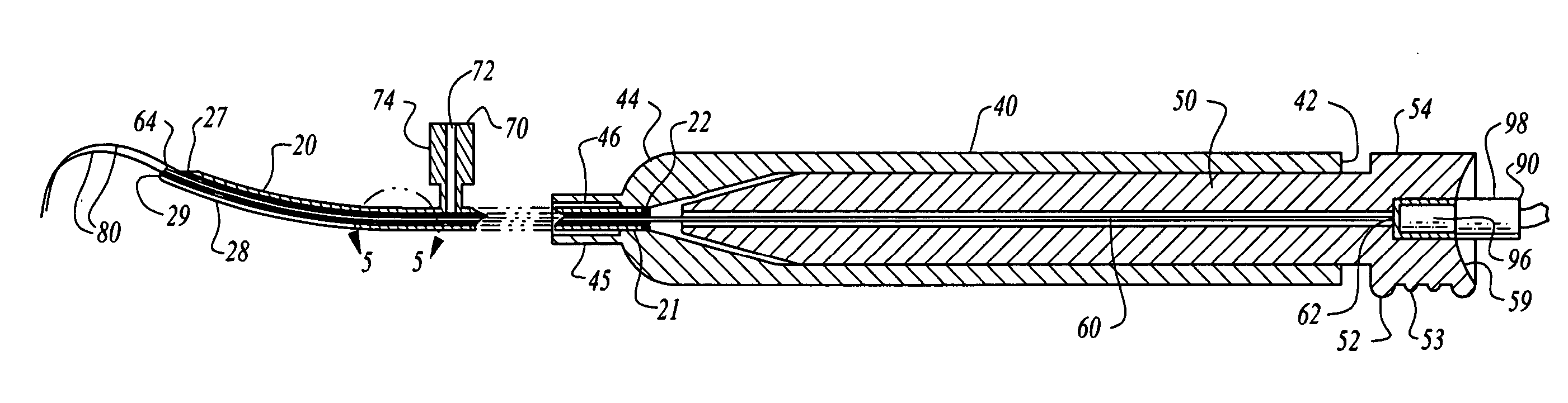
Navigable, multi-positional and variable tissue ablation apparatus and methods
A spinal nerve tissue ablation apparatus includes a stylet needle with a distal end having a rounded blunt tip sufficiently sharp to penetrate tissue but sufficiently blunt to avoid impinging on bony surfaces of spinal vertebra. The apparatus includes an energy delivery device having at least a first electrode and a second electrode. Each electrode has a tissue piercing distal end and is positionable in the stylet as the stylet is advanced through tissue. The first and second electrodes are deployable with curvature from the stylet. The stylet includes rotational means for orienting the first and second electrodes and directing the extension according to the curvature of the electrodes. The stylet further includes an optical imaging module to provide continual progressive feedback of ablation surface development. The apparatus further includes an ultra-wide band radio frequency scanning device capable of accurately determining the location of the electrodes within the spinal structure.
Owner:MOWERY THOMAS M
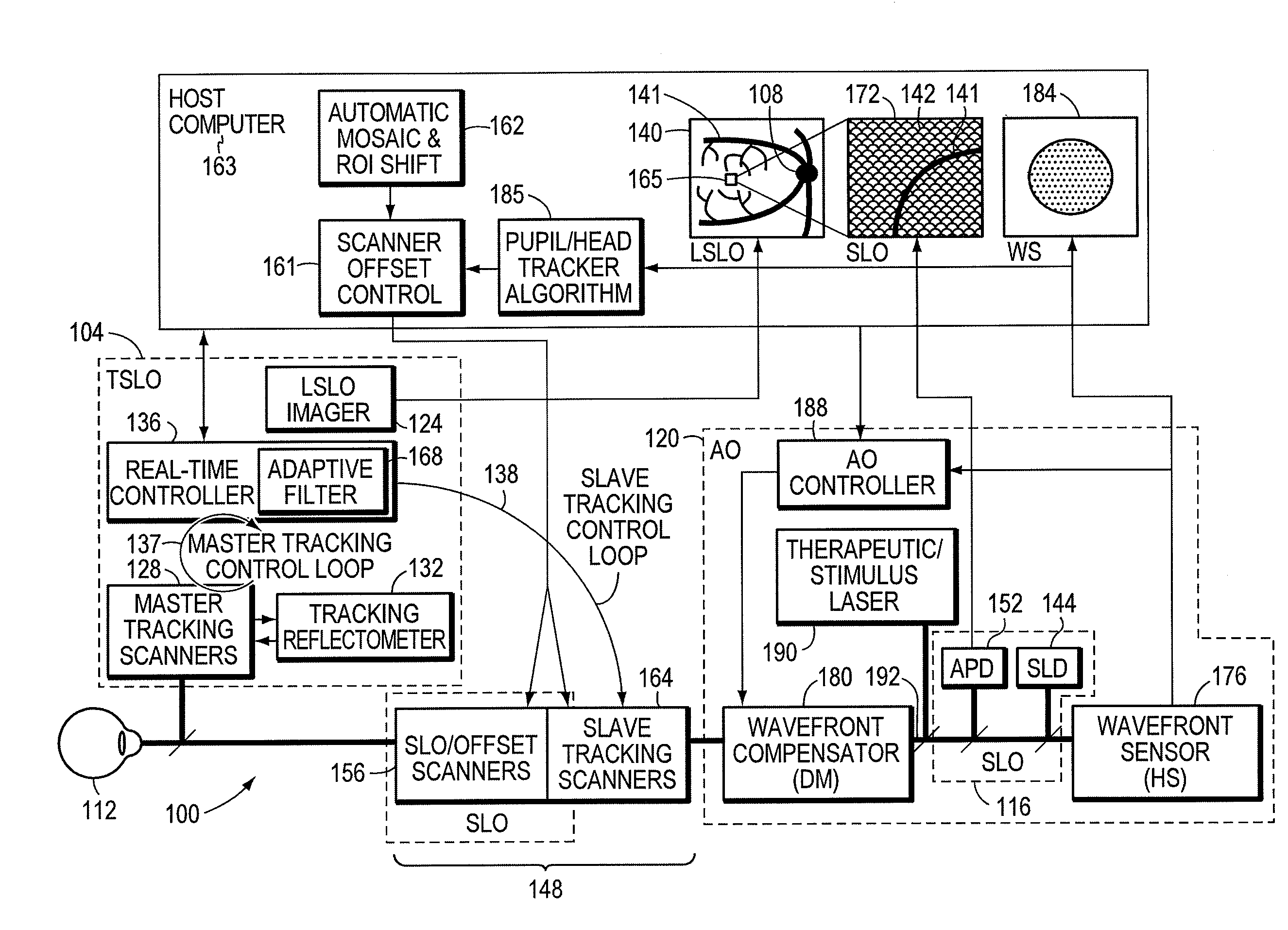
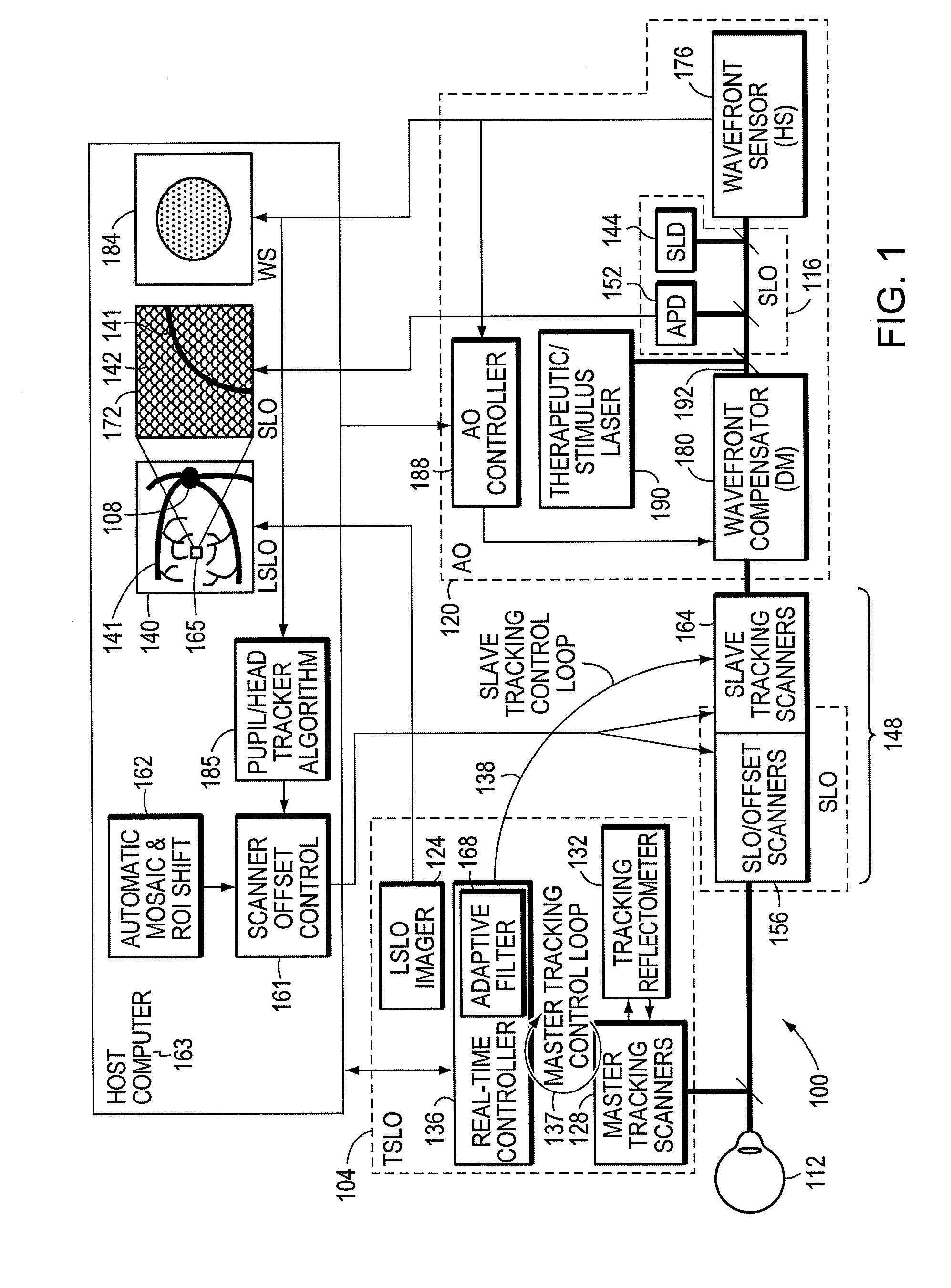
Stabilized retinal imaging with adaptive optics
InactiveUS20070252951A1Improve understandingControl damageLaser surgeryUsing optical meansRetinal imagingLight beam
A system provides an optical image of an object. A first module tracks a reference feature of the object. A second module includes a source for an imaging beam, a scanning device to move the imaging beam along a portion of the object and a detection device receives a signal associated with an image of the portion of the object. The first module controls the position of the imaging beam relative to the reference feature to correct for the motion of the object. A third module detects a distortion of the object and compensates for the distortion.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
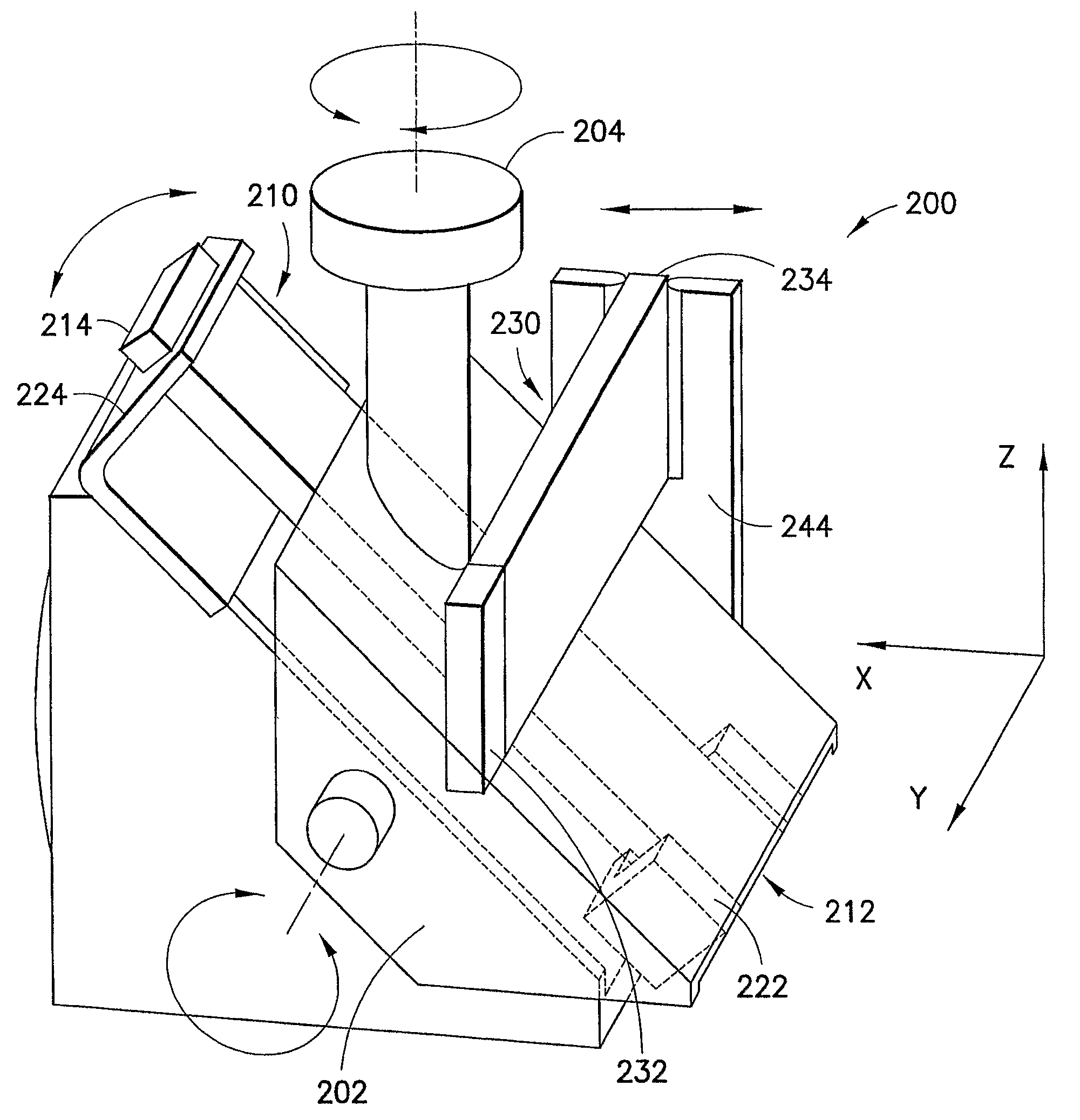
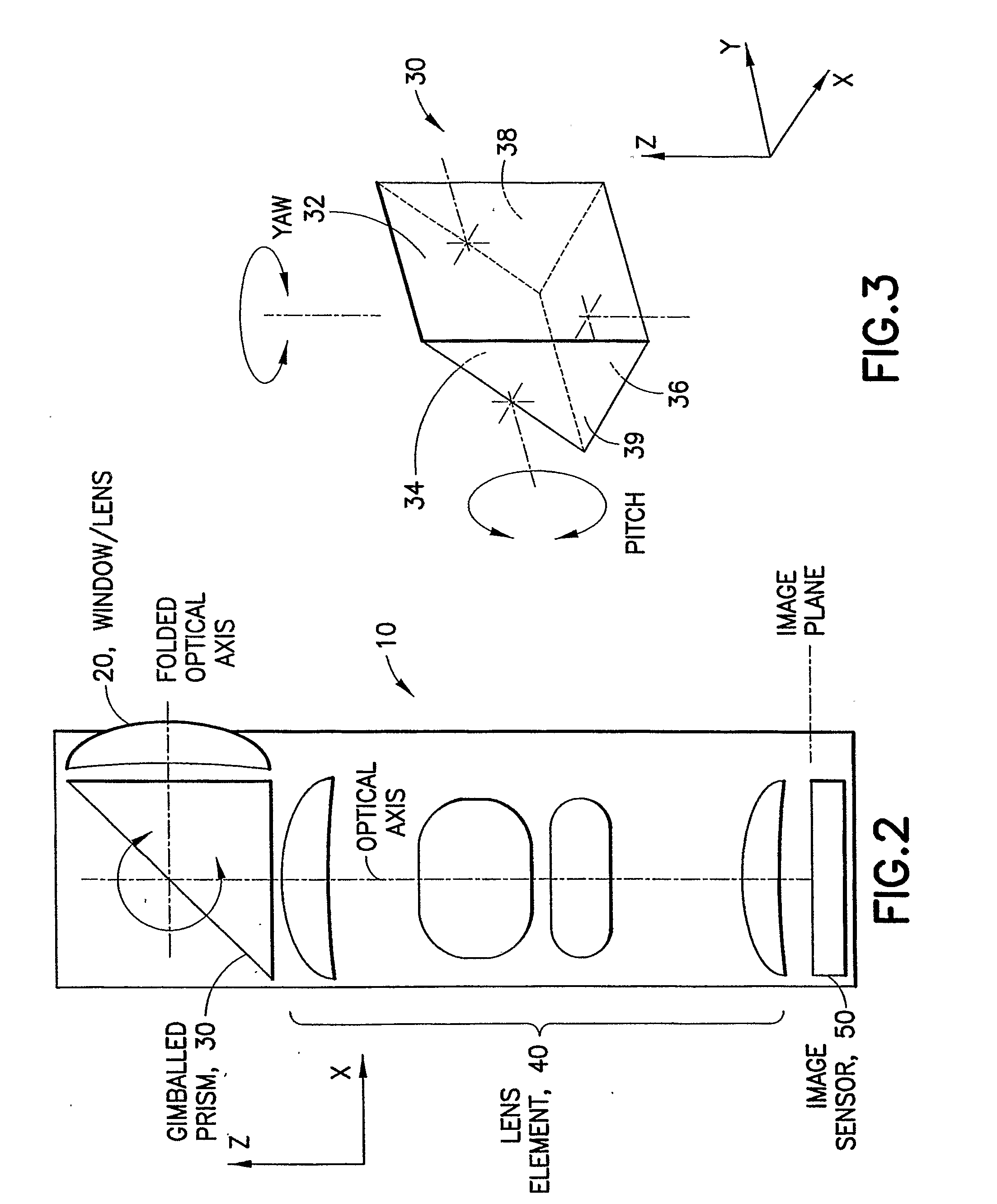
Optical Image Stabilizer Using Gimballed Prism
An optical image stabilizer is used to compensate for an unwanted movement of an imaging system, such as a camera. The camera has a folded optics system using a triangular prism to fold the optical axis. Two actuators are used to rotate the prism around two axes in order to compensate for the yaw motion and pitch motion of the camera. The prism can be mounted on a gimballed system or joint and two actuators are operatively connected to the gimballed system in order to rotate the prism. Alternatively, the folded optics system uses a mirror to fold the optical axis, and two motors are used to rotate the prism.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Optical image capturing system
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Synchronization of projected illumination with rolling shutter of image sensor
Imaging apparatus includes an illumination assembly, including a plurality of radiation sources and projection optics, which are configured to project radiation from the radiation sources onto different, respective regions of a scene. An imaging assembly includes an image sensor and objective optics configured to form an optical image of the scene on the image sensor, which includes an array of sensor elements arranged in multiple groups, which are triggered by a rolling shutter to capture the radiation from the scene in successive, respective exposure periods from different, respective areas of the scene so as to form an electronic image of the scene. A controller is coupled to actuate the radiation sources sequentially in a pulsed mode so that the illumination assembly illuminates the different, respective areas of the scene in synchronization with the rolling shutter.
Owner:APPLE INC
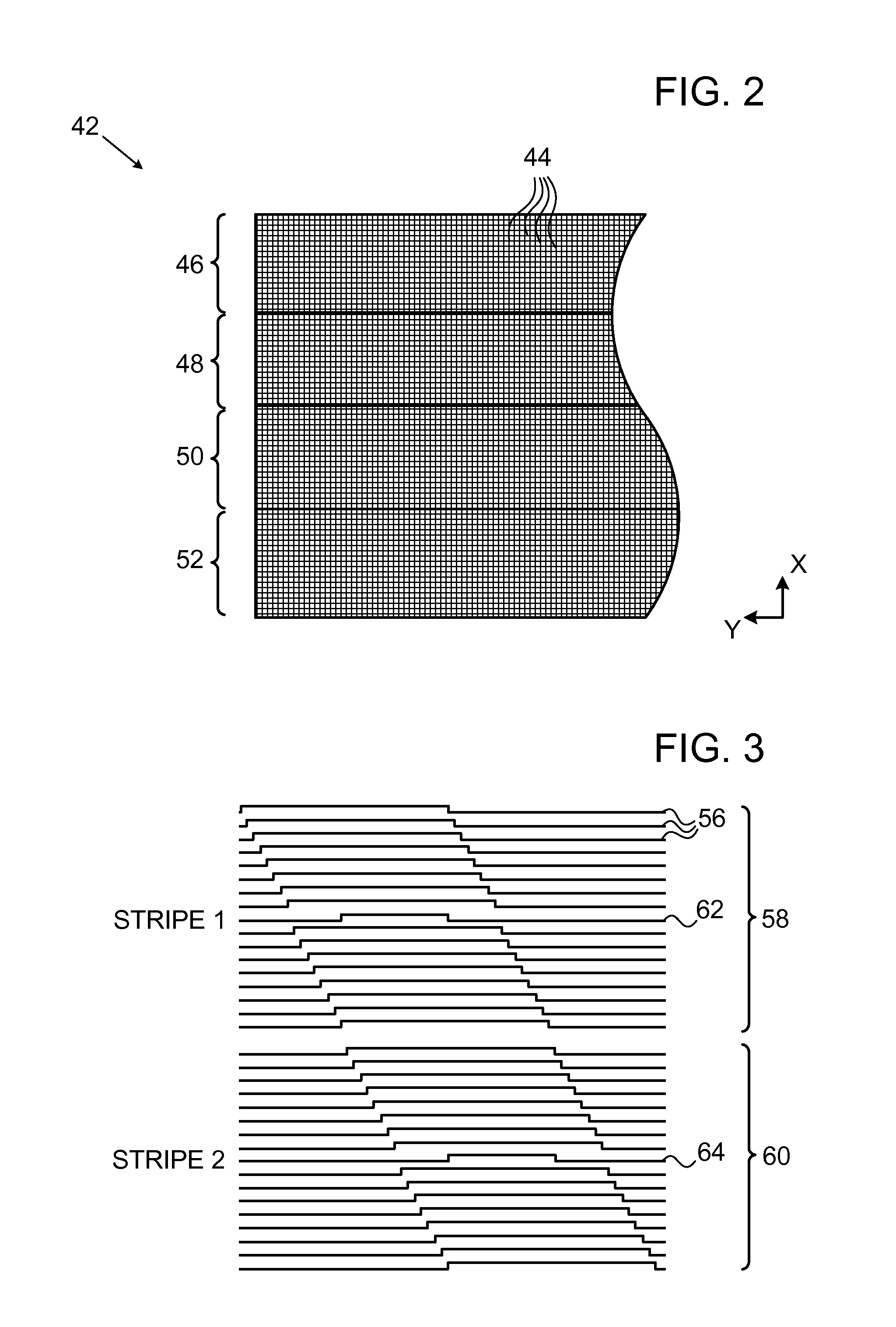
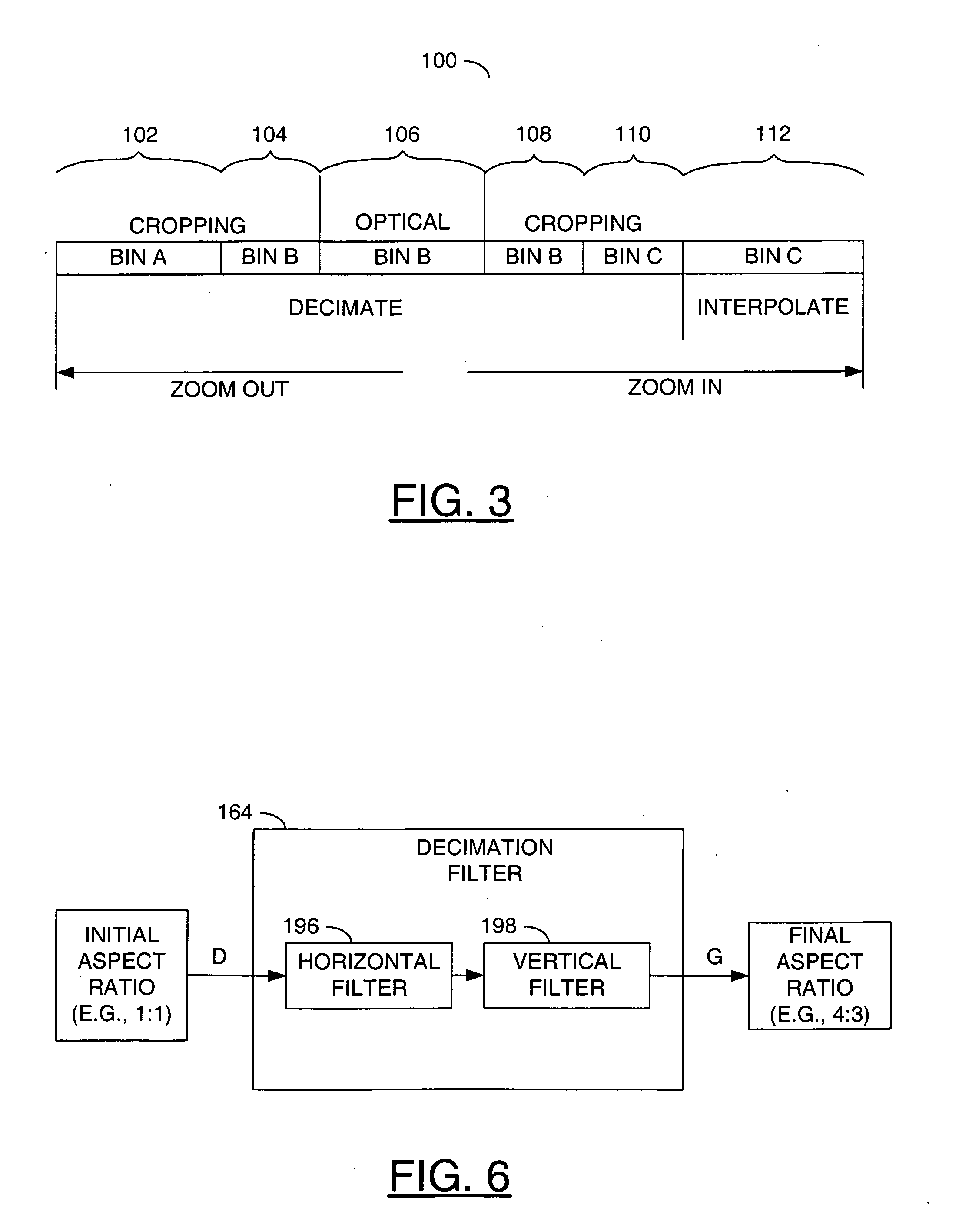
High resolution zoom: a novel digital zoom for digital video camera
ActiveUS20060125937A1Improve abilitiesConstant output image resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoDigital zoom
A camera system and a method for zooming the camera system is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) generating an electronic image by sensing an optical image received by the camera, the sensing including electronic cropping to a window size to establish an initial resolution for the electronic image, (B) generating a final image by decimating the electronic image by a decimation factor to a final resolution smaller than the initial resolution and (C) changing a zoom factor for the final image by adjusting both of the decimation factor and the window size.
Owner:AMBARELLA INT LP
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS20090170186A1Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleDielectrophoresis
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
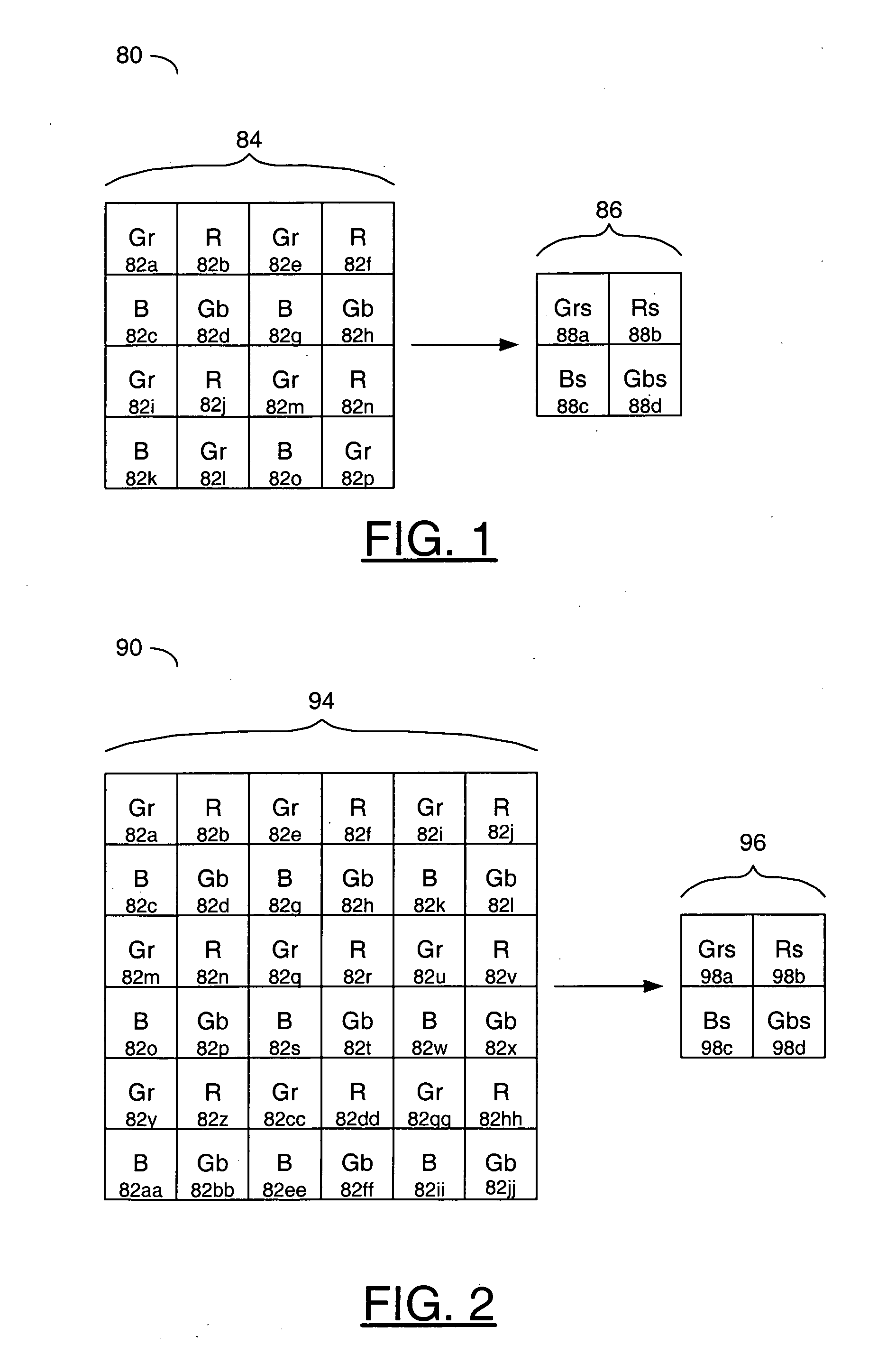
Method and apparatus for using an array of grating light valves to produce multicolor optical images
InactiveUS6219015B1Improve accuracyMade smallStatic indicating devicesDiffraction gratingsPlane mirrorColored light
A multicolor optical image-generating device comprised of an array of grating light valves (GLVs) organized to form light-modulating pixel units for spatially modulating incident rays of light. The pixel units are comprised of three subpixel components each including a plurality of elongated, equally spaced apart reflective grating elements arranged parallel to each other with their light-reflective surfaces also parallel to each other. Each subpixel component includes means for supporting the grating elements in relation to one another, and means for moving alternate elements relative to the other elements and between a first configuration wherein the component acts to reflect incident rays of light as a plane mirror, and a second configuration wherein the component diffracts the incident rays of light as they are reflected from the grating elements. The three subpixel components of each pixel unit are designed such that when red, green and blue light sources are trained on the array, colored light diffracted by particular subpixel components operating in the second configuration will be directed through a viewing aperture, and light simply reflected from particular subpixel components operating in the first configuration will not be directed through the viewing aperture.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
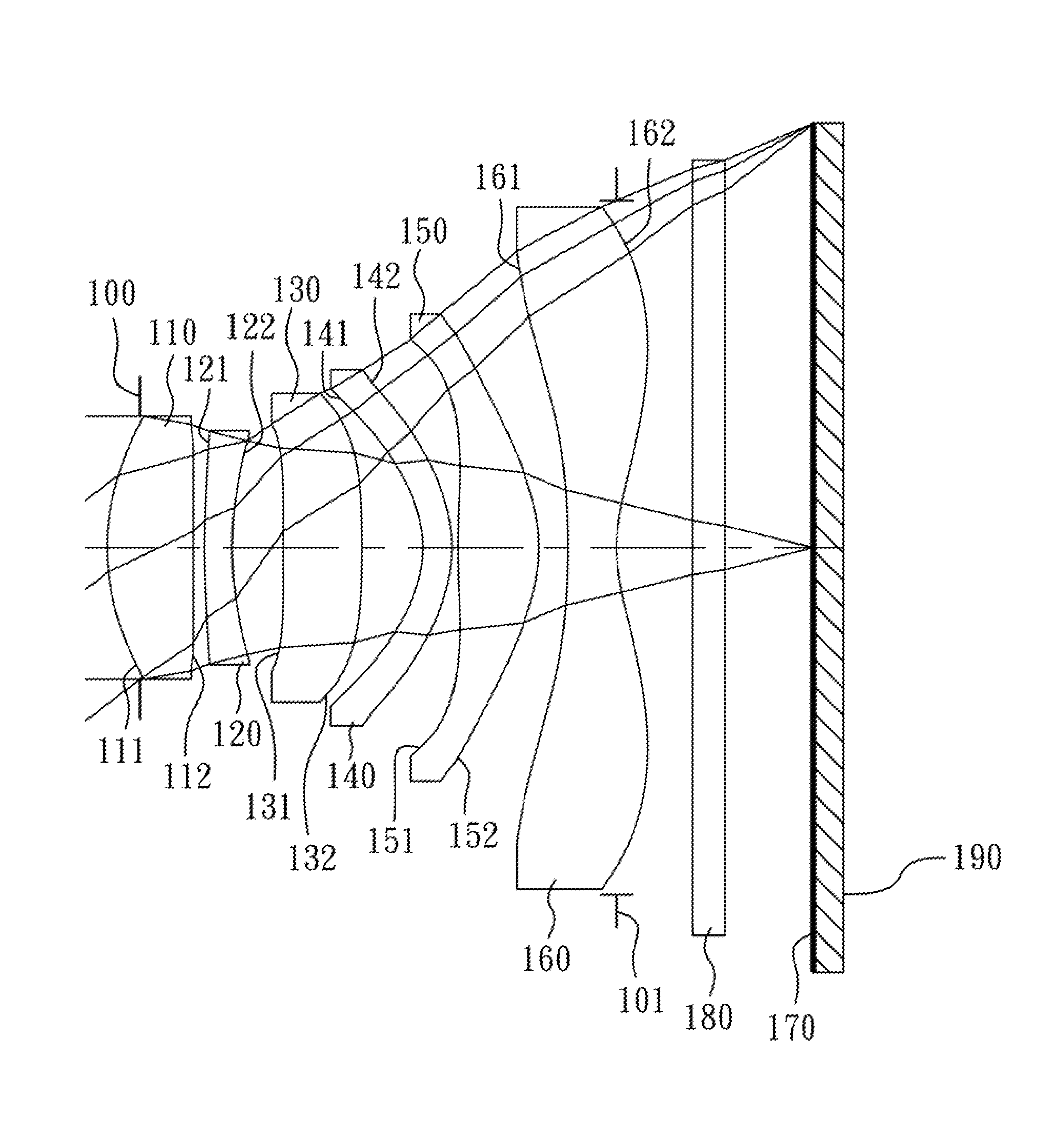
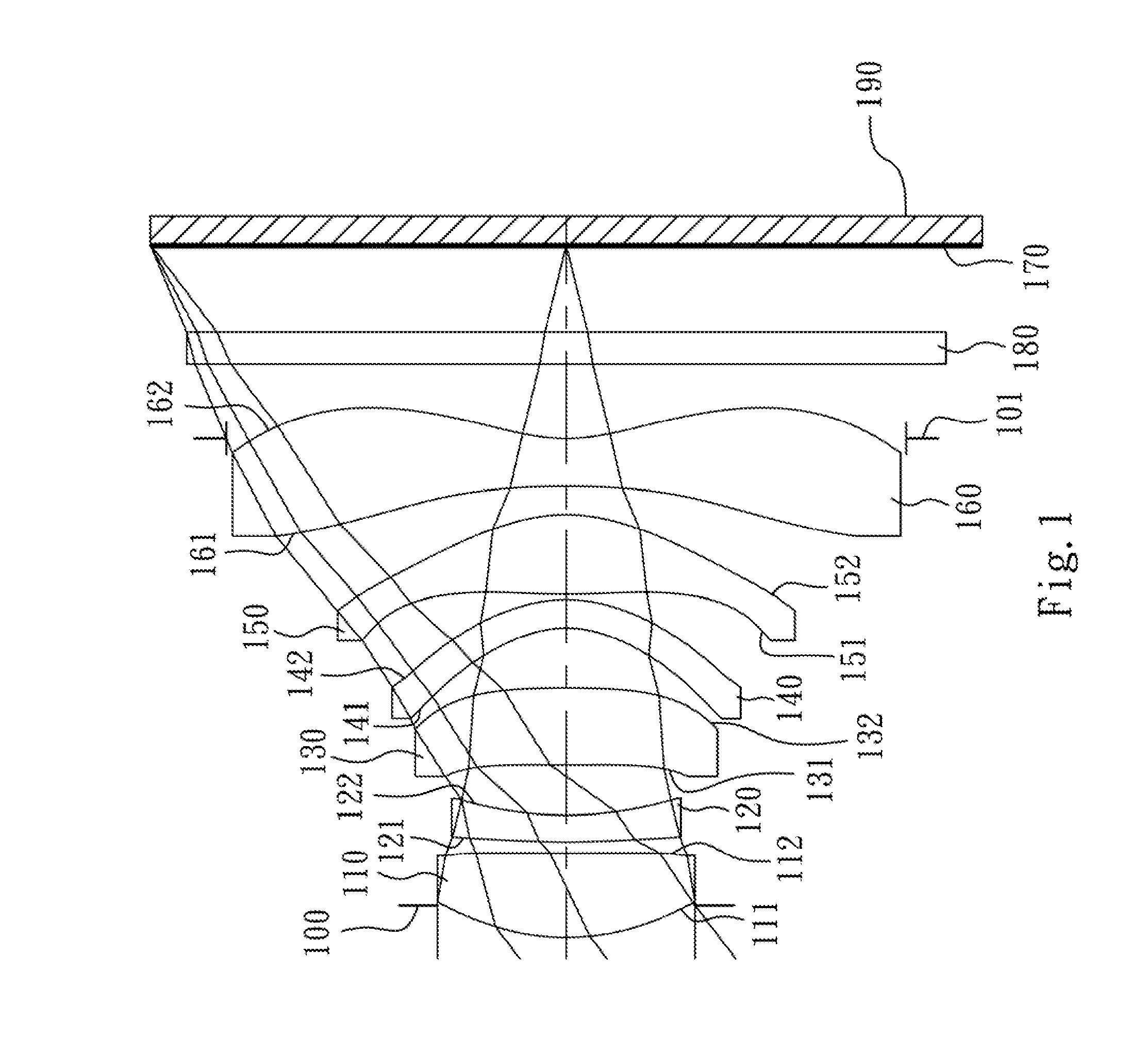
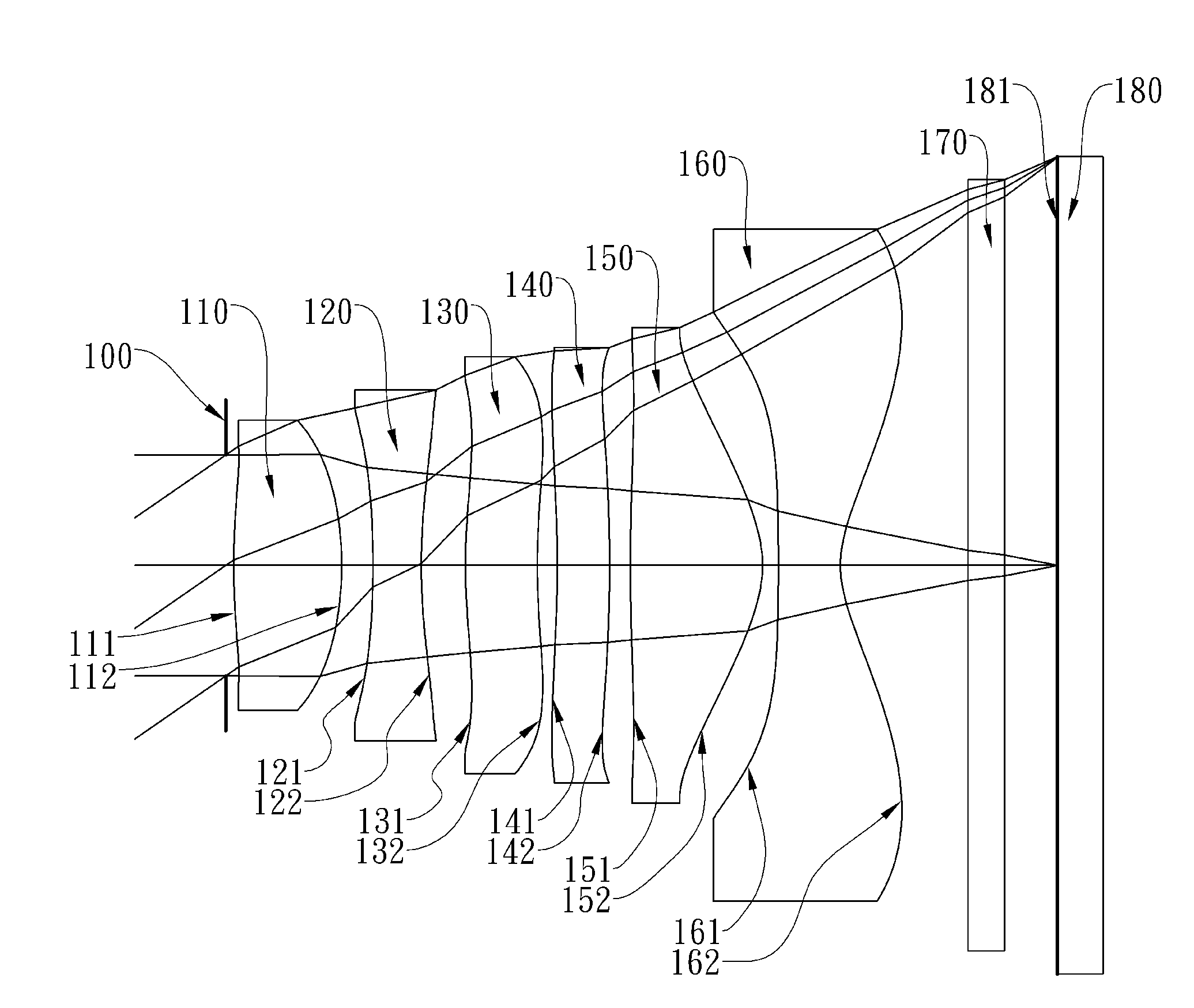
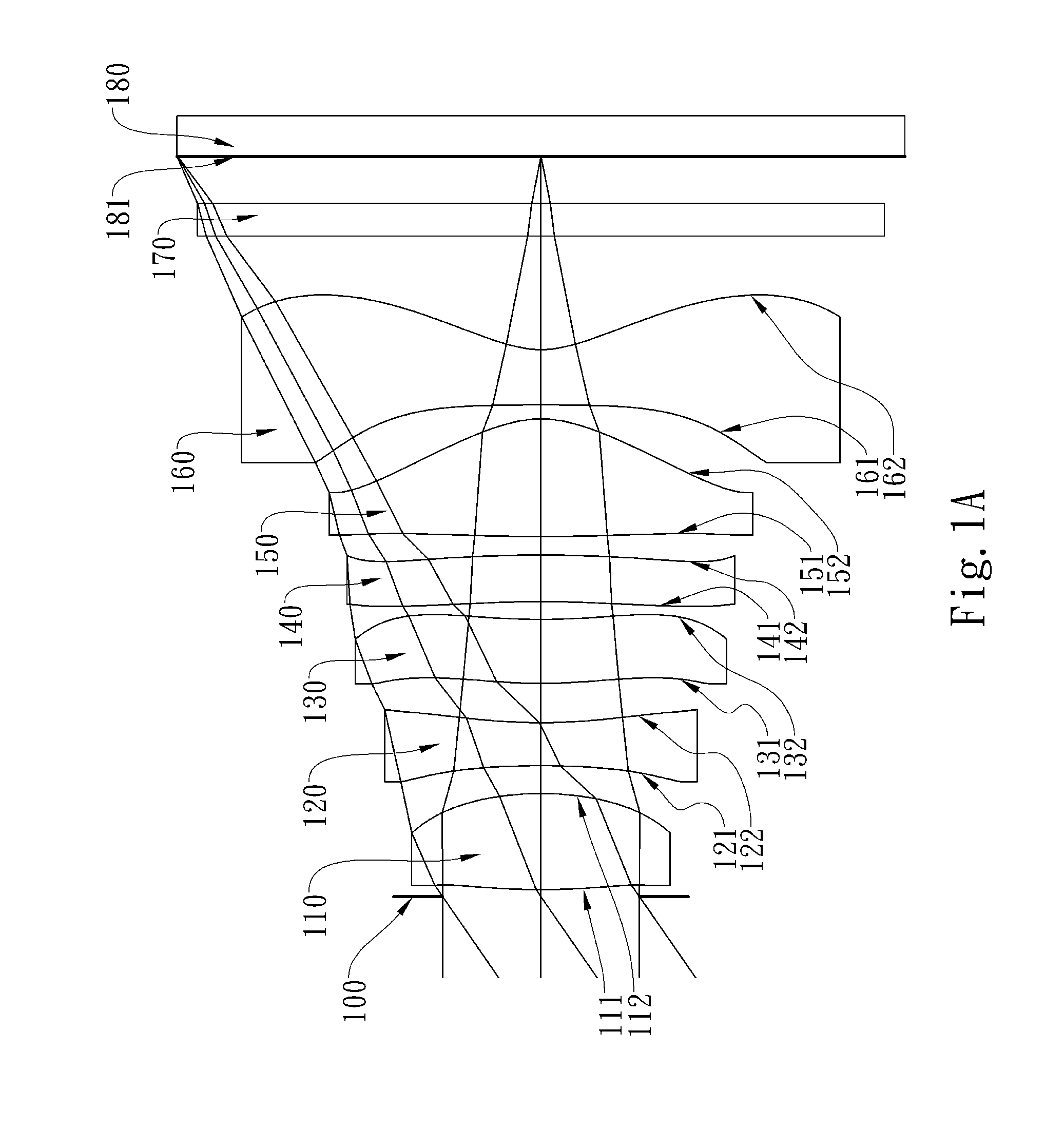
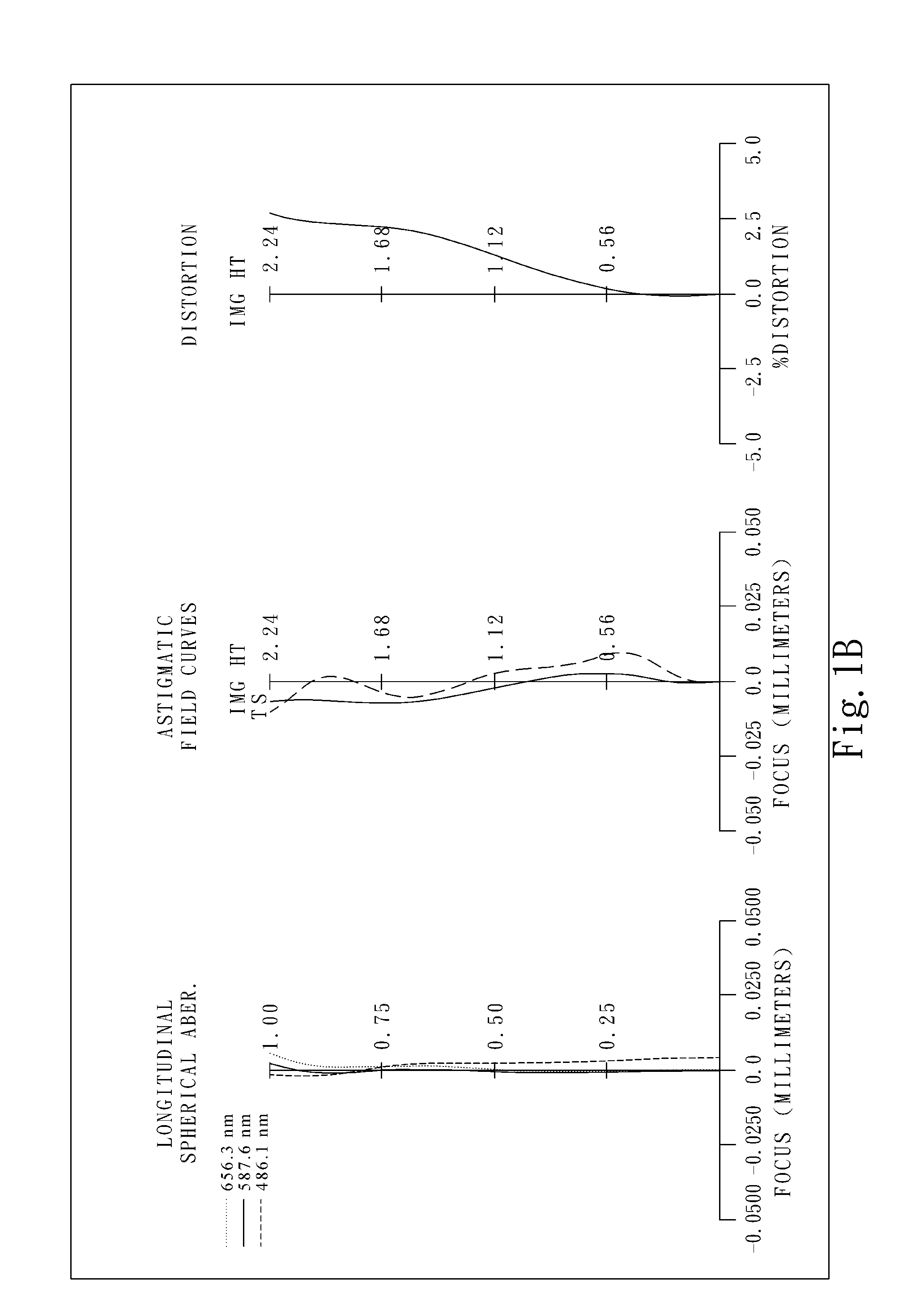
Optical image capturing lens assembly
An optical image capturing lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, the first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, the second lens element with refractive power, the third lens element with refractive power, the fourth lens element with refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, the fifth lens element with refractive power having a convex image-side surface, the object-side surface and the image side surface of the fifth lens element being aspheric, and the sixth lens element with negative refractive power made of plastic material and having a concave image-side surface. The object-side surface and the image-side surface of the sixth lens element are aspheric, and at least one surface thereof has at least one inflection point.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Stereo imaging system and method for use in telerobotic systems
This invention relates to a stereo imaging system for use in telerobotic systems. A method of imaging a target site in a stereo imaging system is provided. The method typically includes capturing a right and a left optical image of the target site and transforming the right and the left optical images preferably into digital information. The method further includes converting the digital information into opposed images of the target site displayed on a stereo display of the stereo imaging system, one of the opposed images being associated with the right optical image and the other of the opposed images being associated with the left optical image. The method further includes regulating the digital information to cause the positions of the target site displayed on the opposed images to change relative to each other. The invention further provides for a method of aligning the opposed images, to a method of adjusting the stereo working distance of an image capture device, such as an endoscope and to a stereo imaging system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
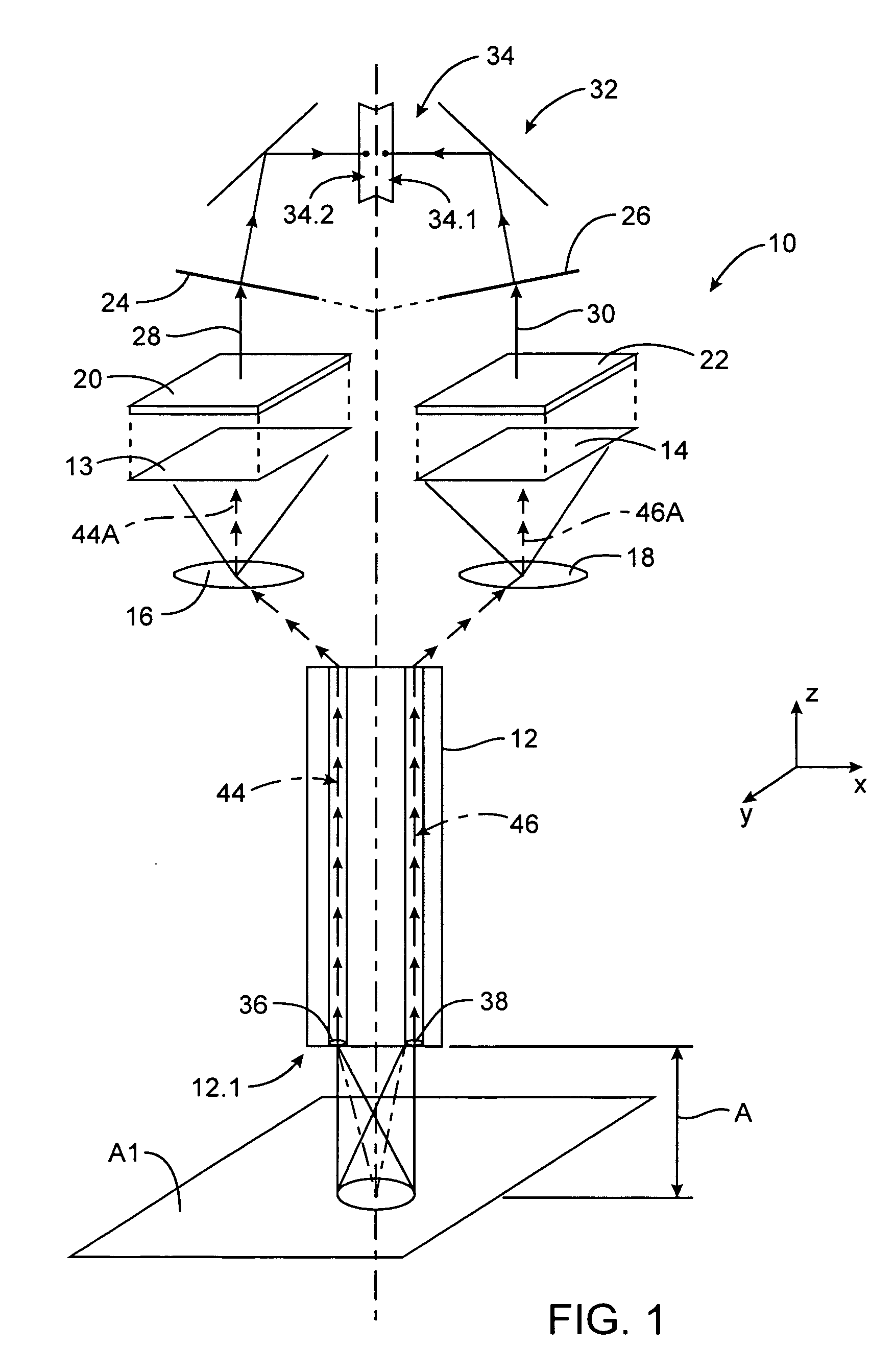
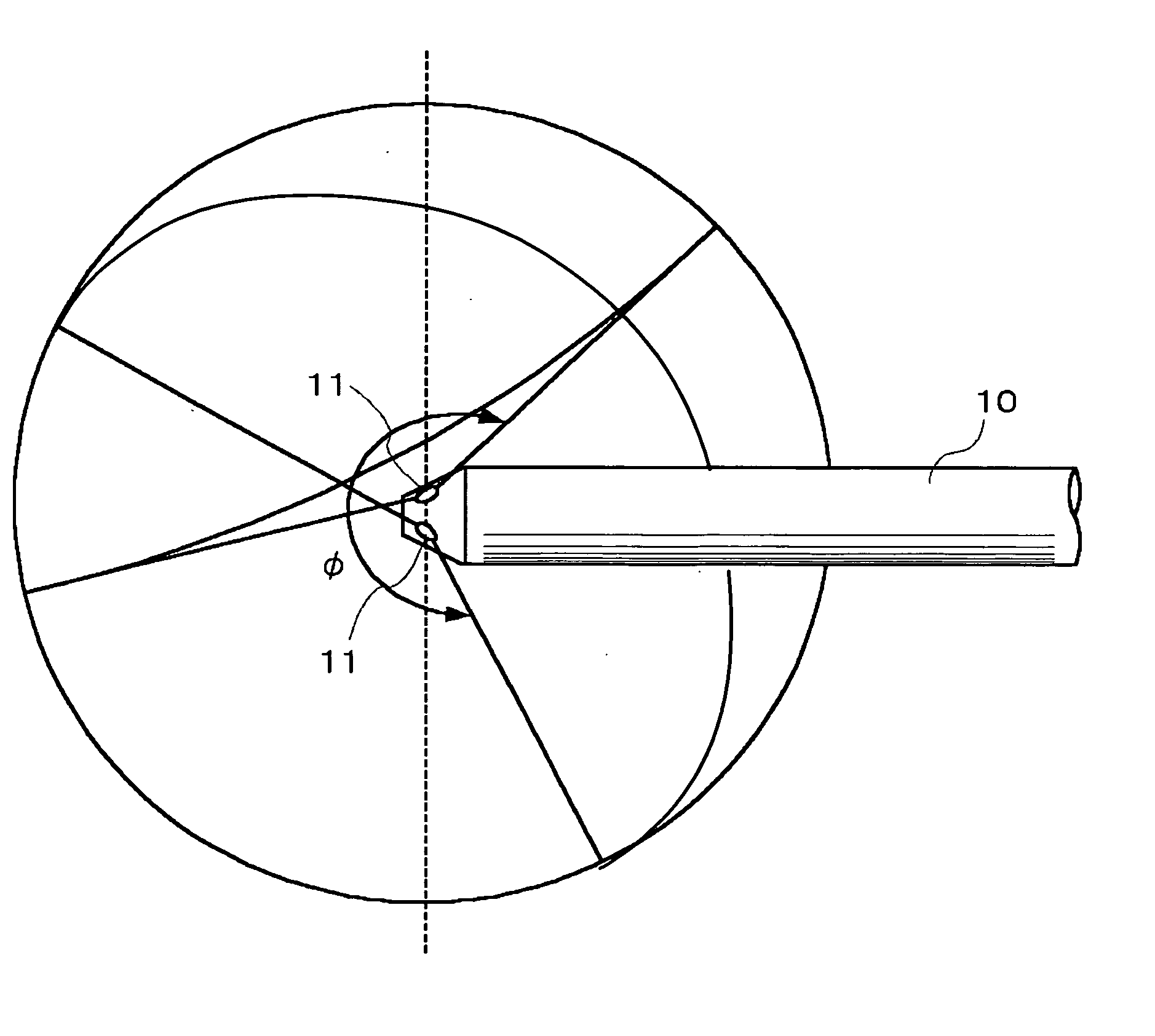
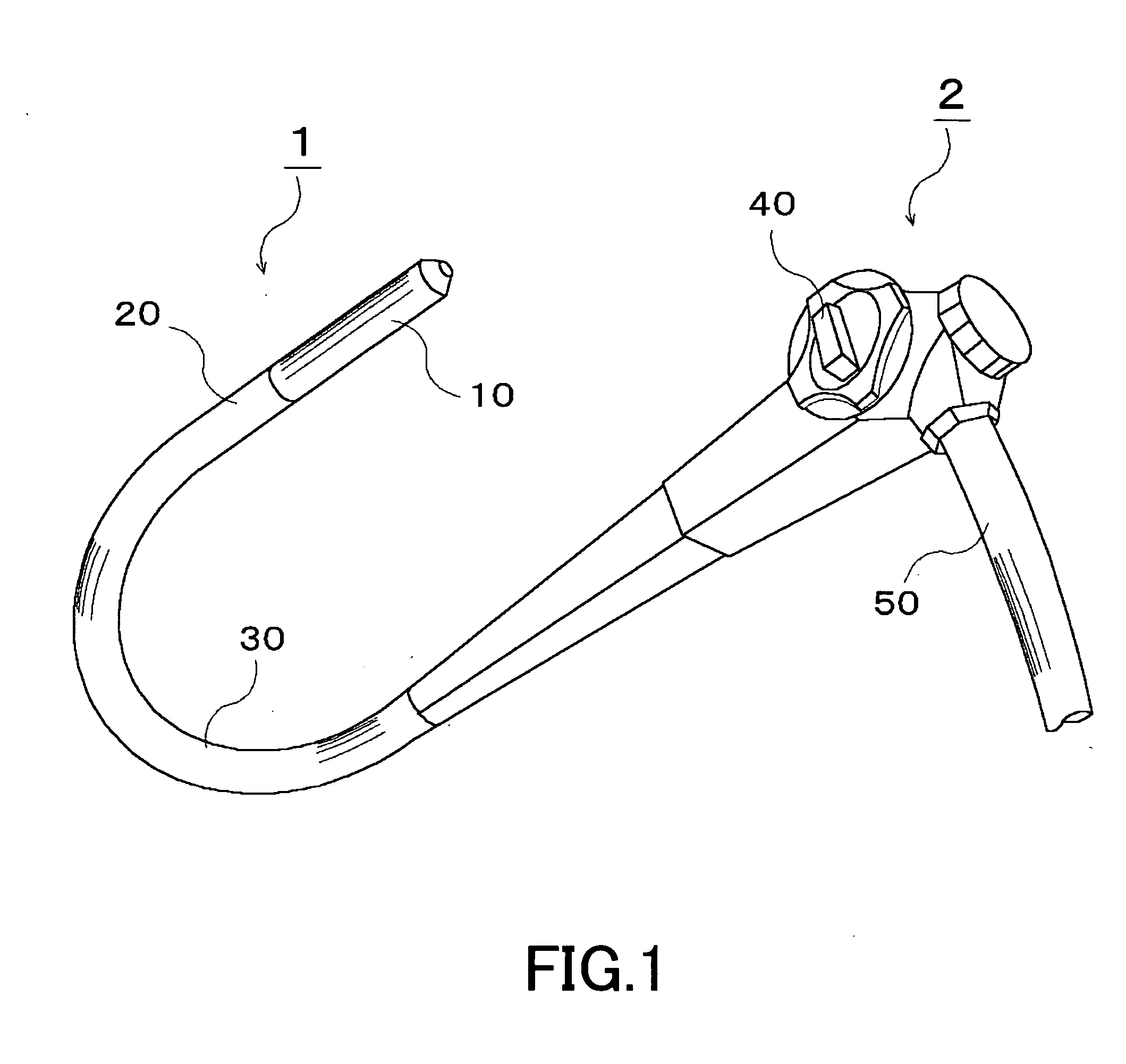
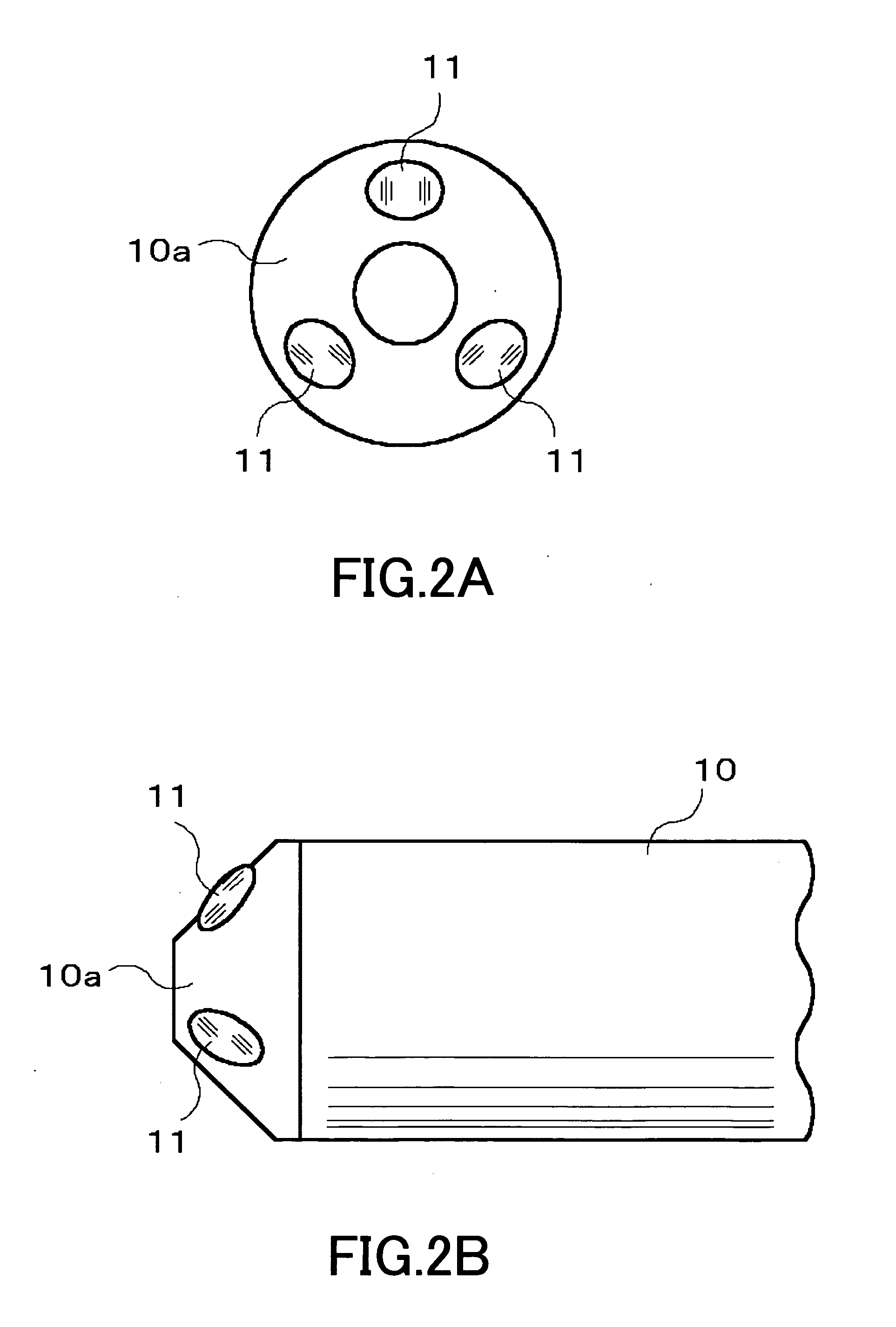
Endoscope device and imaging method using the same
Three objective lenses (11) having optical axes L oriented to different directions are mounted on a head portion (10) of an endoscope device. The objective lens (11) has a predetermined view angle θ centered by the optical axes L. Each objective lens (11) is disposed so as to have the peripheral portions of its viewing field overlap with the peripheral portions of the viewing fields of adjoining other objective lenses (11). Hence, the three objective lenses (11) causes the head portion (10) as a whole to have a view angle φ extending over a wider range than the view angle θ of the objective lens (11) with no discontinuation. Each optical image of a testing target part captured within this view angle φ is imaged by an imaging element.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER +1
Optical image display system and image display unit
InactiveUS20070008624A1Simple structureLarge exit pupilTelevision system detailsPolarising elementsExit pupilLight beam
Optical-image display systems are disclosed having simple structure and a large exit pupil. An exemplary system includes a transmissive plate having inside an optical path of light flux from a display at each angular field of view of an image-display element. The light flux is internally reflected repeatedly in the transmissive plate. An optical-deflection member is provided in close contact with a predetermined region of one surface of the plate used for internal reflection. The optical-deflection member emits to the outside of the plate a portion of each of the light fluxes from the display having reached the predetermined region, and deflects a portion of each light flux in a predetermined direction by reflection. Thus, a virtual image is formed of the display screen of the image-display element.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Adaptive optical image reader
InactiveUS20050056699A1Data augmentationExtension of timeCharacter and pattern recognitionExposure controlDigital imageDigital converter
A digital image reading system including an image sensor and a computer that is programmed to adjust the frame rate of the image sensor, and to obtain a maximum frame rate of the image sensor for obtaining an acceptable image. An algorithm for adjusting the frame rate evaluates image parameters and calculates new exposure times, gain values, and exposure settings to support a maximum frame rate of the image sensor. A process for obtaining an acceptable image with an image reader evaluates an image signal level and adjusts the frame rate if the signal level is outside of a predetermined range. The process adjusts the image sensor to run at a maximum operational frame rate. A digital image reading system including multiple separate digitizers for use in various read environments and under various read conditions.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
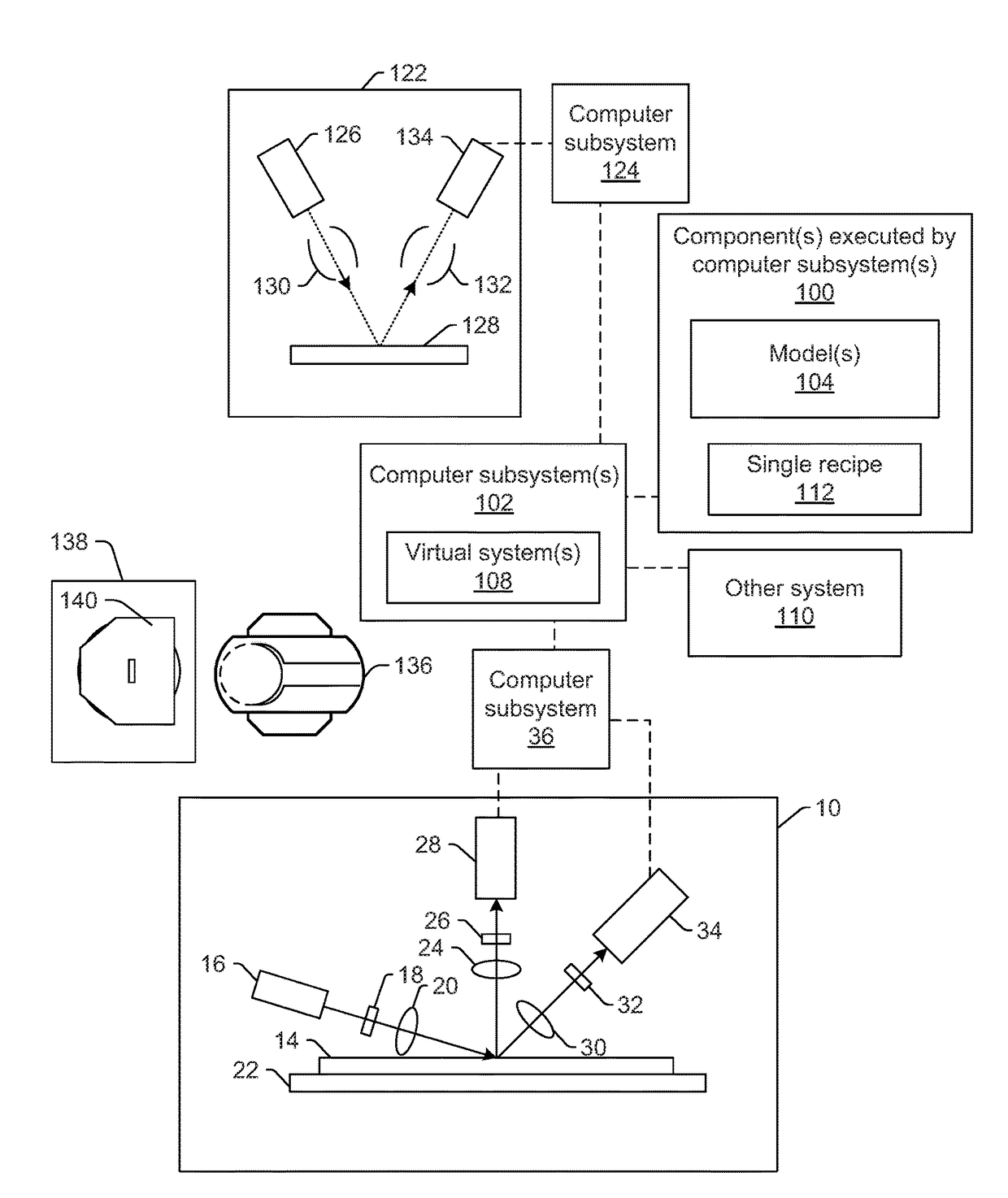
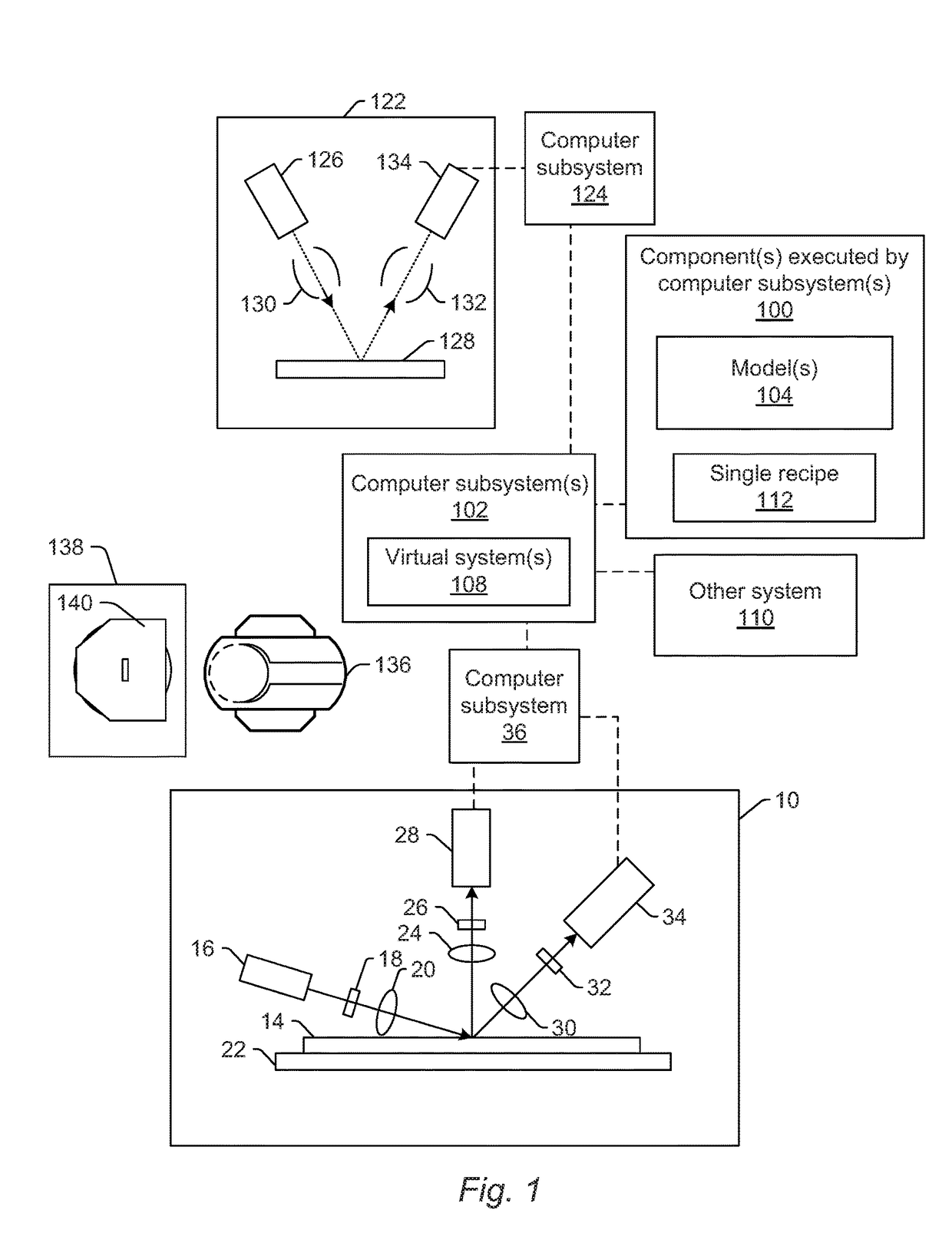
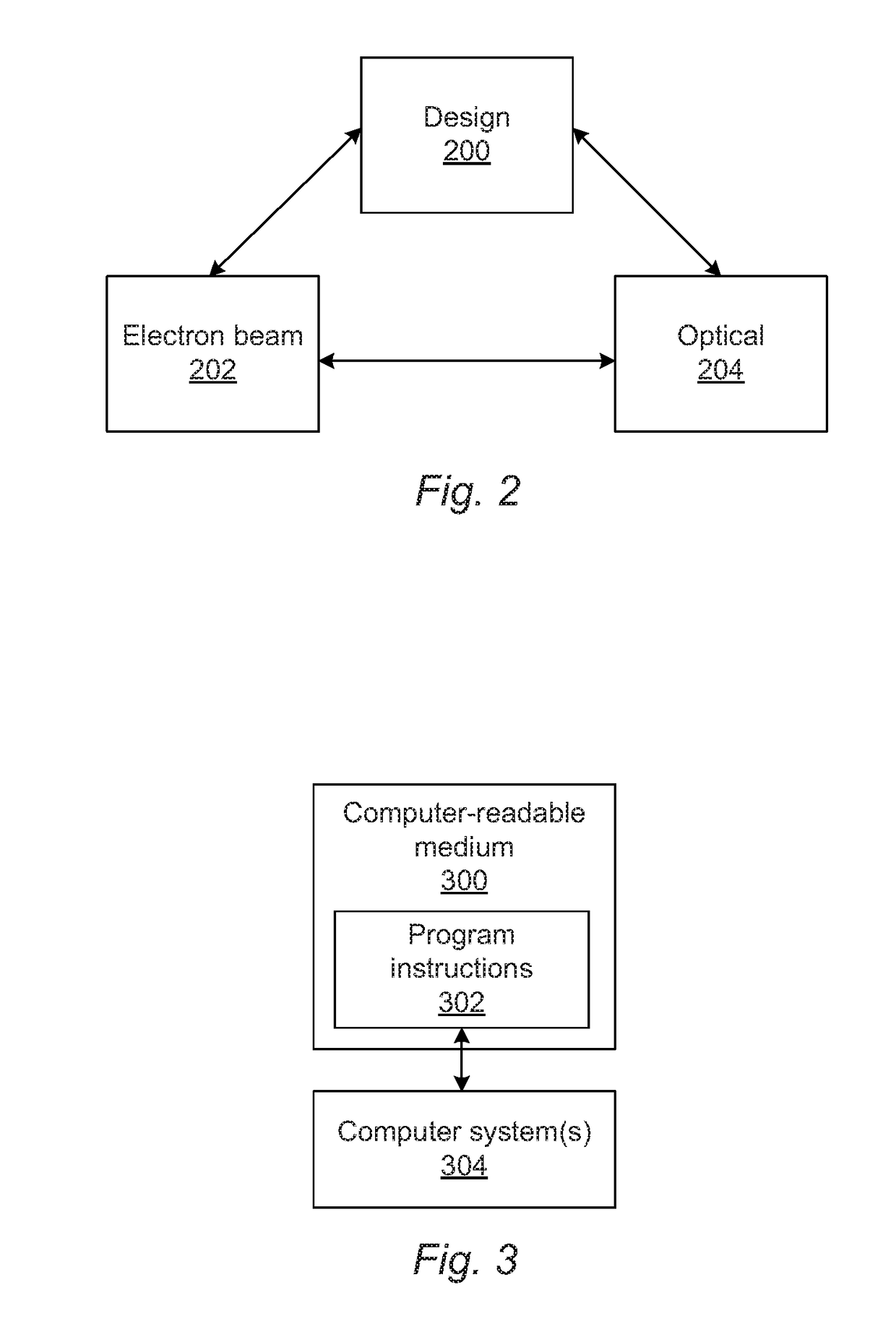
Generating simulated output for a specimen
Methods and systems for generating simulated output for a specimen are provided. One method includes acquiring information for a specimen with one or more computer systems. The information includes at least one of an actual optical image of the specimen, an actual electron beam image of the specimen, and design data for the specimen. The method also includes inputting the information for the specimen into a learning based model. The learning based model is included in one or more components executed by the one or more computer systems. The learning based model is configured for mapping a triangular relationship between optical images, electron beam images, and design data, and the learning based model applies the triangular relationship to the input to thereby generate simulated images for the specimen.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
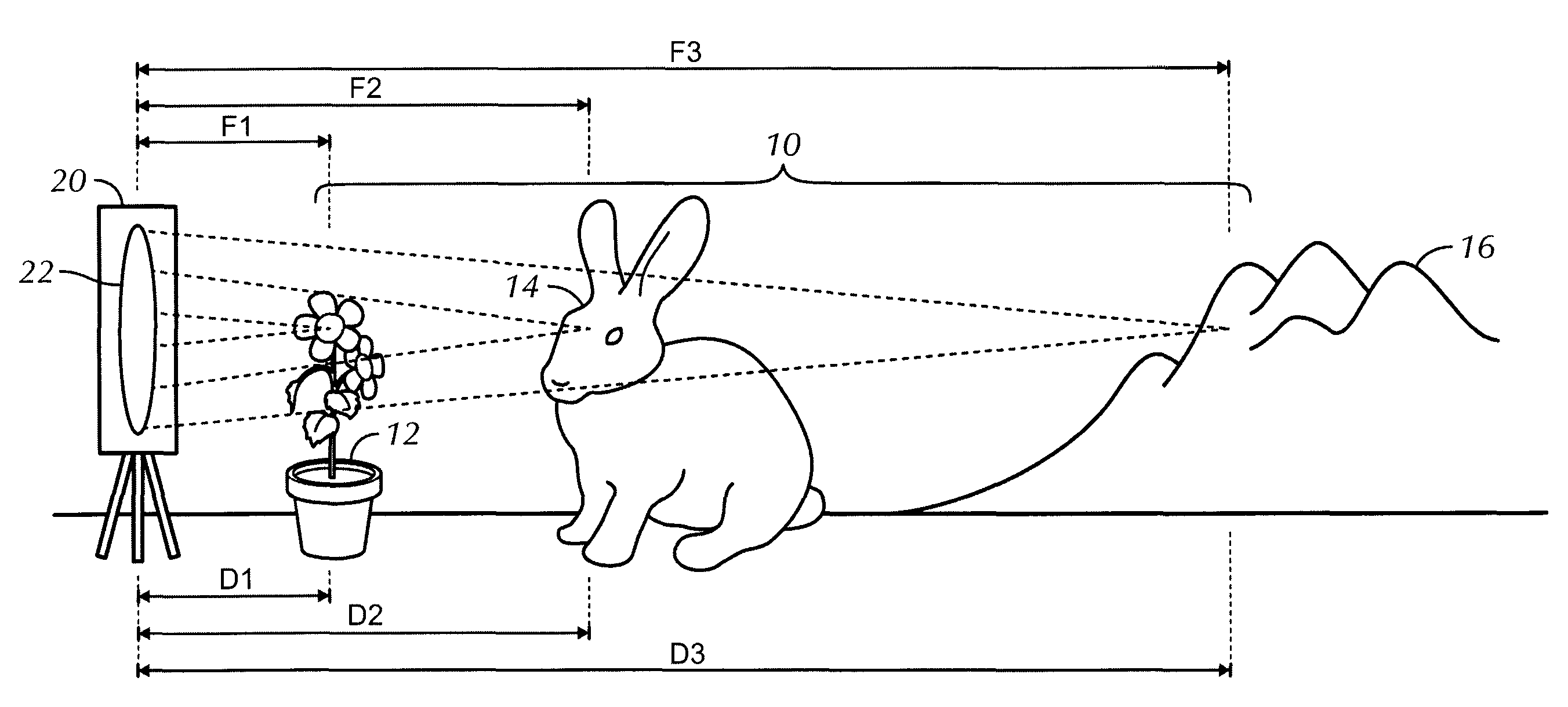
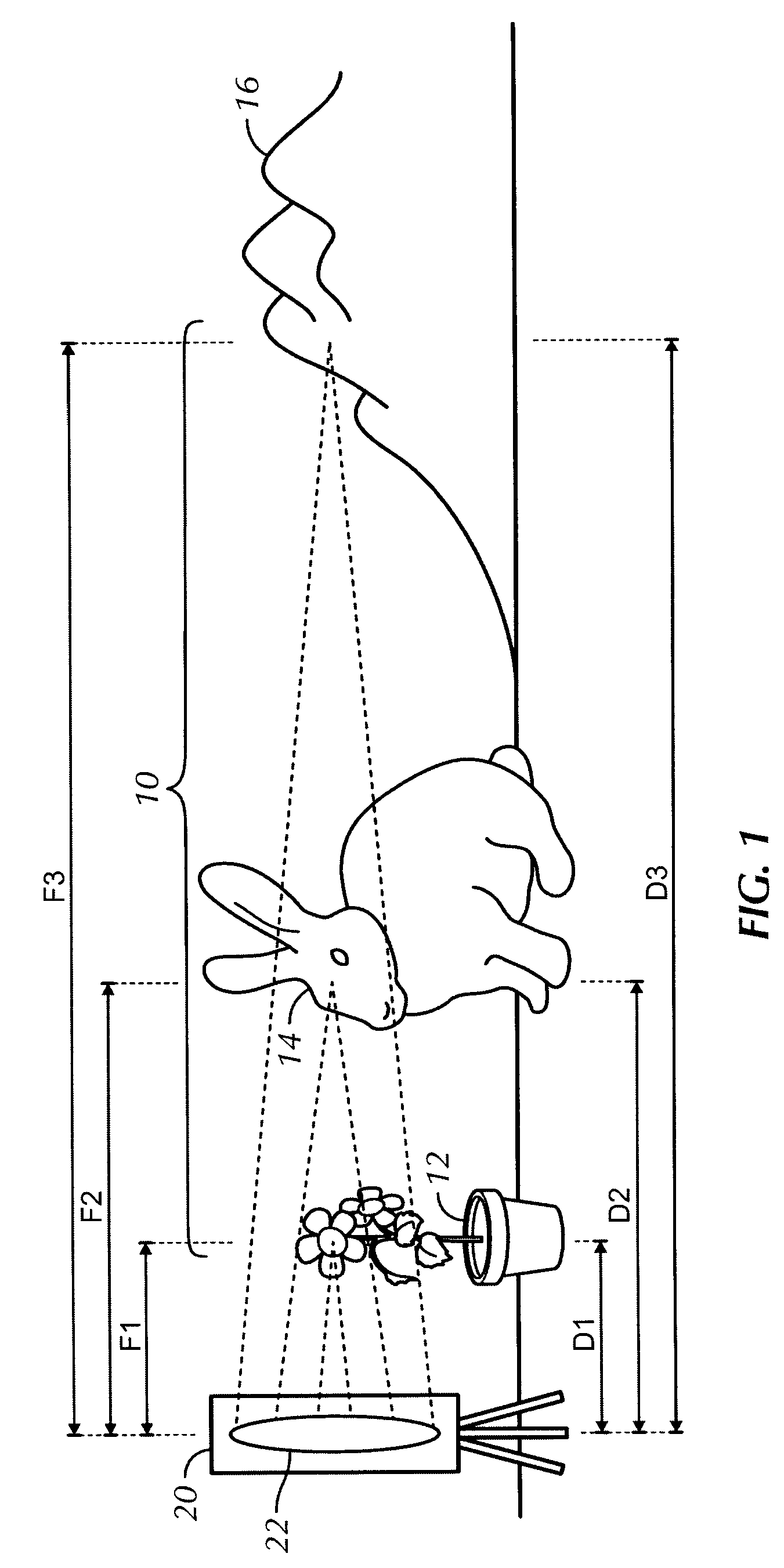
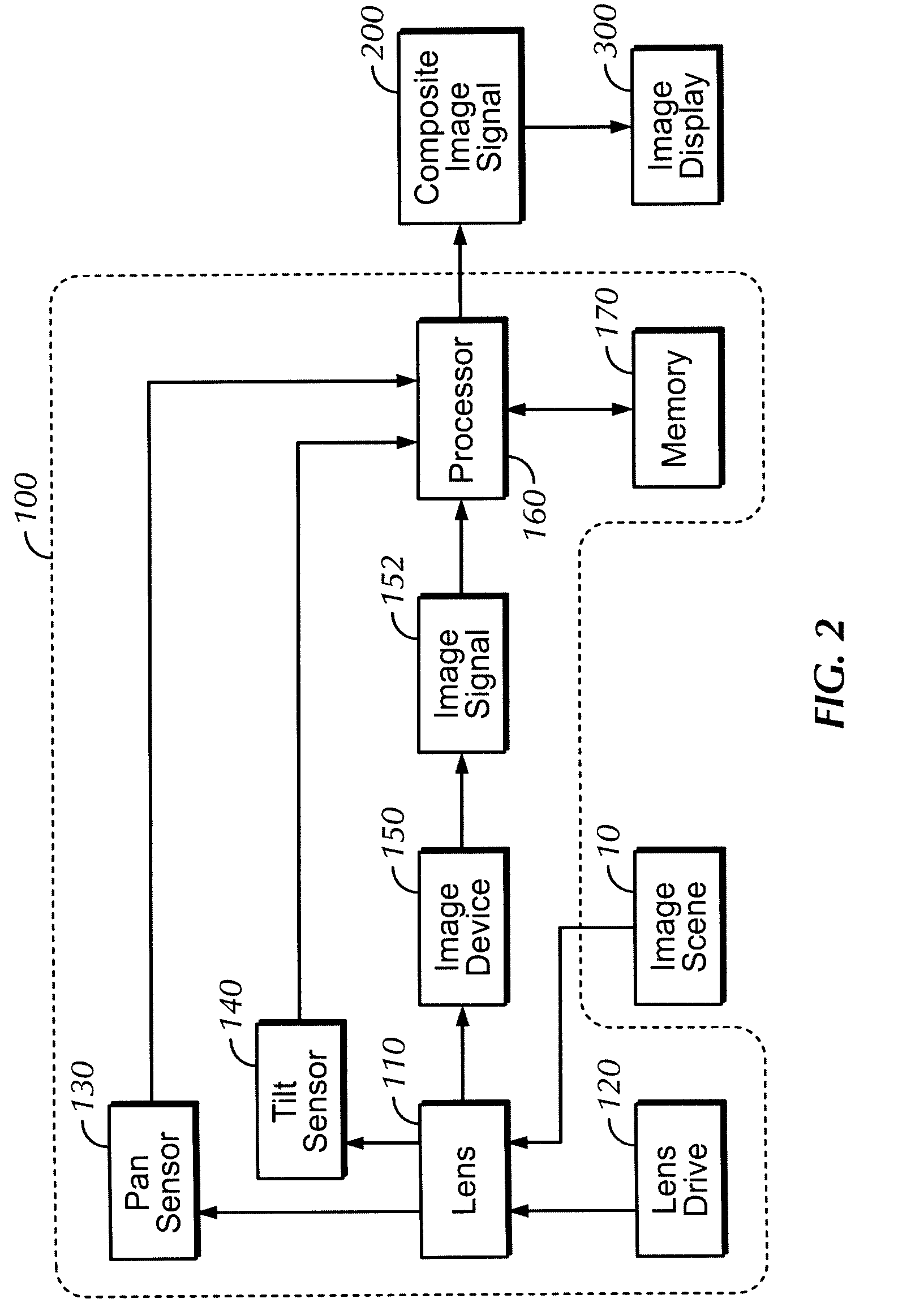
Method and apparatus for providing a video image having multiple focal lengths
A method and apparatus for providing a video image having multiple focal lengths includes a multi-focal lens system and a drive mechanism capable of moving the multi-focal lens system through a cyclic path. A plurality of optical images are formed as the multi-focal lens system moves through the cyclic path. An image pickup device is capable of converting each of the plurality of optical images into a corresponding image signal. An image processor is operative to preferably form a composite image signal wherein individual elements of the optical images are selected to provide preferred focus characteristics.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Optical image capturing lens assembly
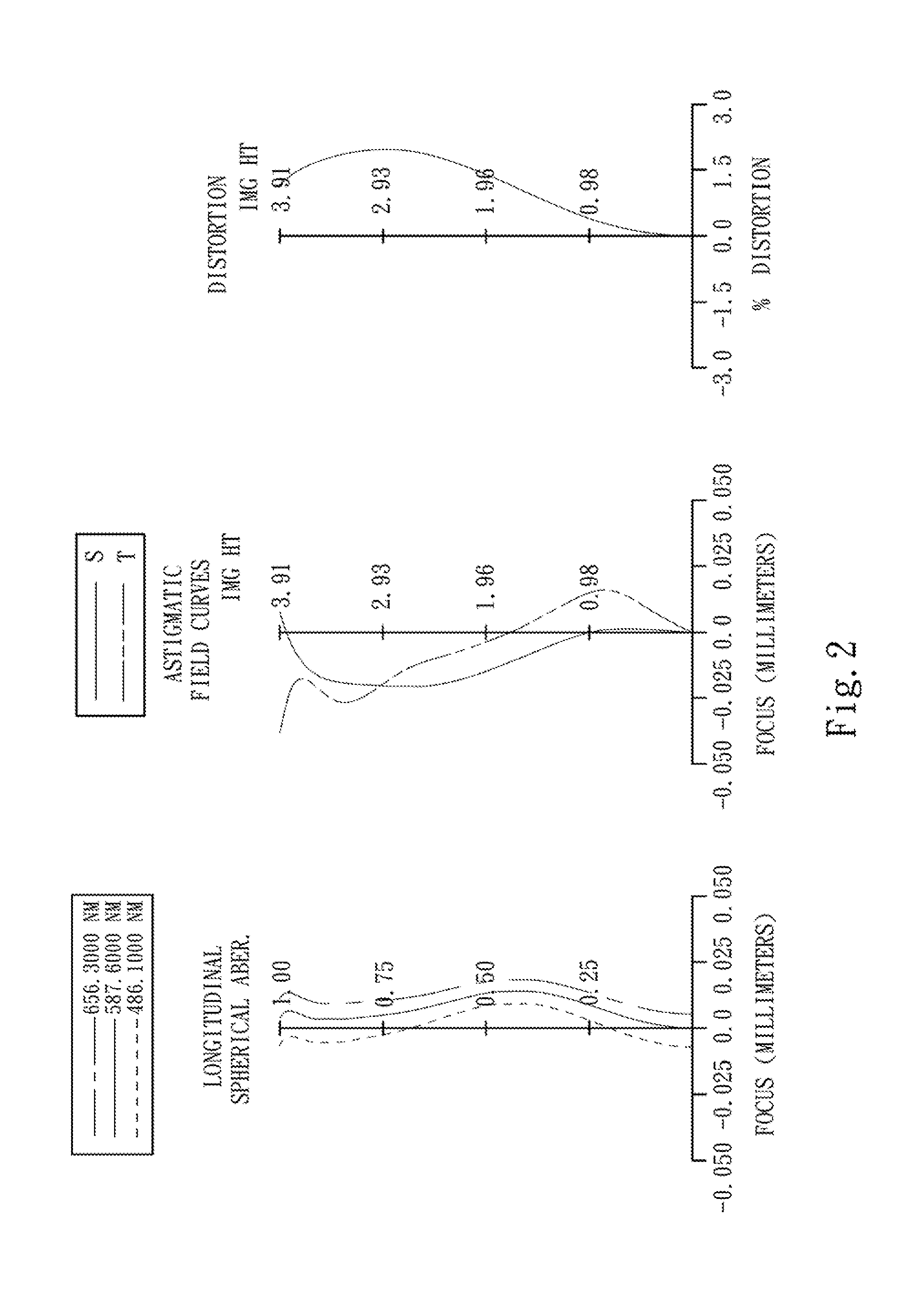
The present disclosure provides an optical image capturing lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface; a second lens element; a third lens element; a fourth lens element, at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; a fifth lens element, at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; and a sixth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, at least one inflection point being formed on at least one of the surfaces thereof. With the aforementioned arrangements, the sensitivity of the optical system can be attenuated while the aberration and astigmatism can be effectively corrected to improve the image quality.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Coplanar camera scanning system
InactiveUS6856440B2Sufficient lightingReduce intensityMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionMechanical engineeringLinear arrays
A system for scanning objects having a linear array sensor, adapted to detect light input signals, is provided. A lens is optically connected to the linear array sensor, and is adapted to receive and transmit an optical image located in a field of view along a lens axis to the linear array sensor. A light source which generates an illumination stripe in general linear alignment with the lens axis is provided. A cylindrical lens is positioned between the light source and an object to be scanned. The cylindrical lens adapted to collect, transmit and focus light from the light source to form the illumination stripe.
Owner:DATALOGIC AUTOMATION
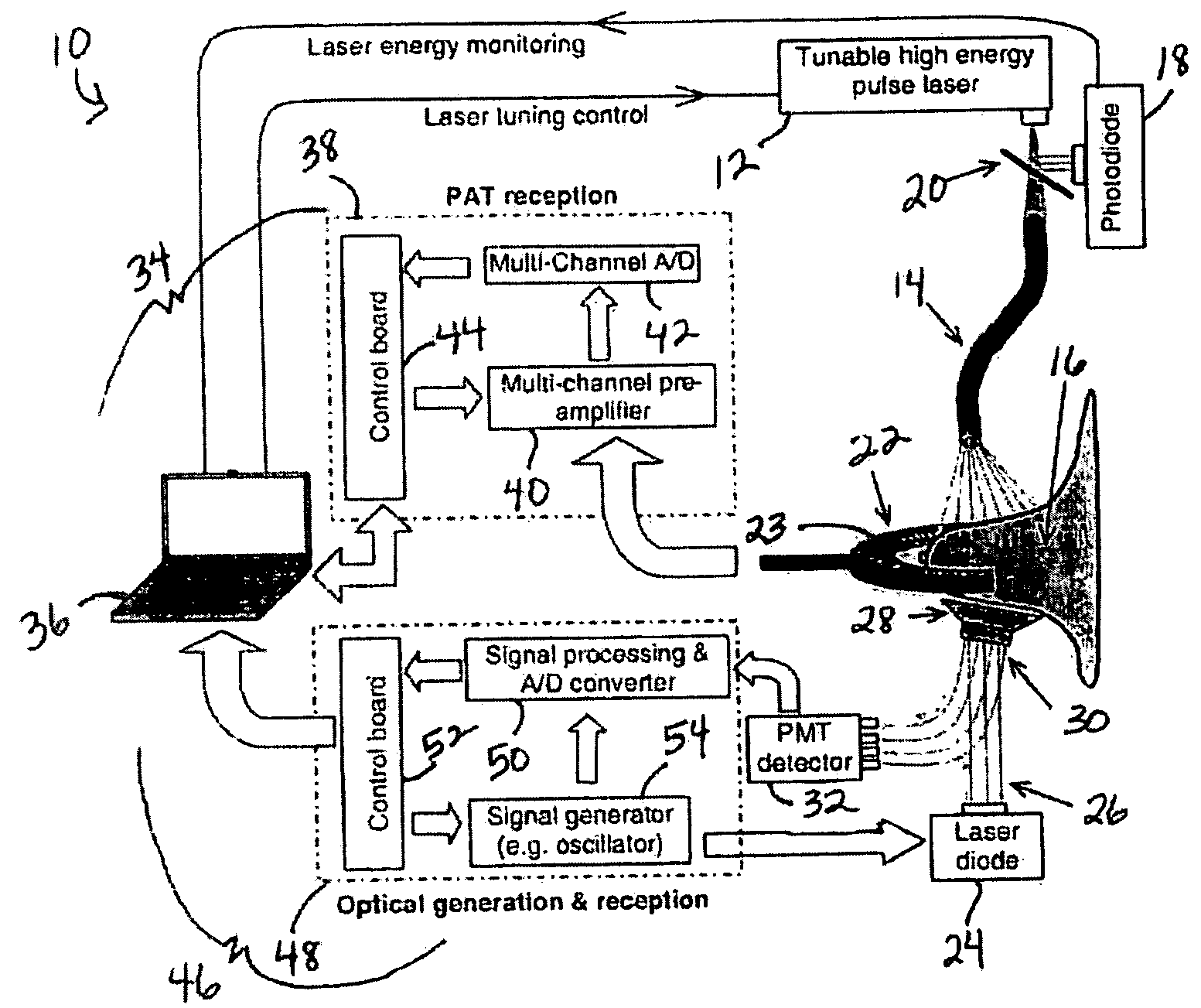
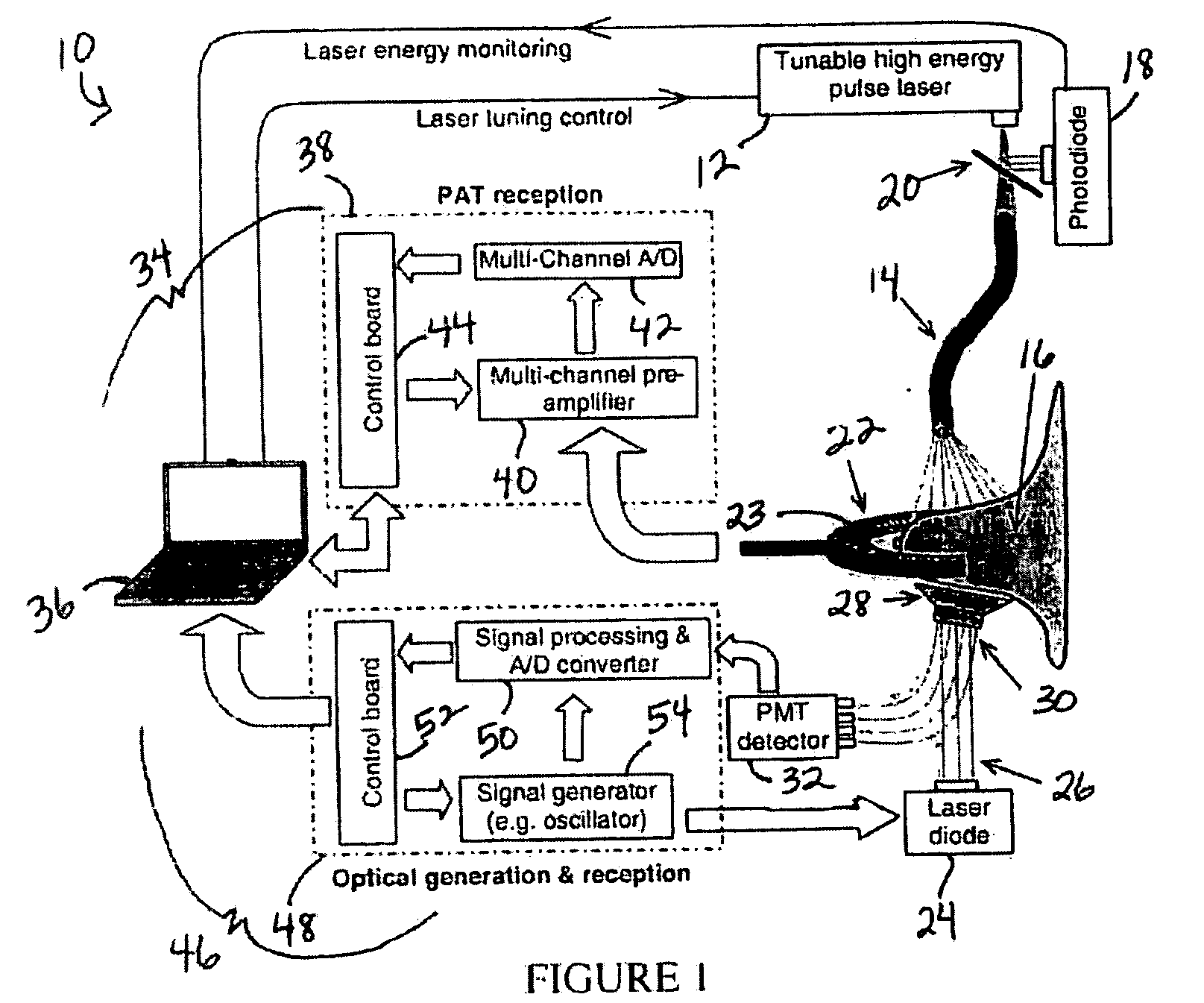
System and Method for Photoacoustic Guided Diffuse Optical Imaging
InactiveUS20080123083A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsScattering properties measurementsSonificationUltrasonic sensor
A system and method for photoacoustic guided diffuse optical imaging of a sample include at least one light source configured to deliver light to the sample, at least one ultrasonic transducer disposed adjacent to the sample for receiving photoacoustic signals generated due to optical absorption of the light by the sample, and at least one optical detector for receiving optical signals generated due to light scattered by the sample. A control system is provided in communication with the at least one light source, the ultrasonic transducer, and the optical detector for reconstructing photoacoustic images of the sample from the received photoacoustic signals and reconstructing optical images of the sample from the received optical signals. The priori anatomical information and spatially distributed optical parameters of biological tissues from the photoacoustic images employed in diffuse optical imaging may improve the accuracy of measurements and the reconstruction speed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector] Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/69908f5d-c70f-43ec-b137-dbc7e98ba54d/US20120113514A1-20120510-D00000.png)
![Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector] Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/69908f5d-c70f-43ec-b137-dbc7e98ba54d/US20120113514A1-20120510-D00001.png)
![Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector] Picoprojector with Image Stabilization [Image-Stabilized Projector]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/69908f5d-c70f-43ec-b137-dbc7e98ba54d/US20120113514A1-20120510-D00002.png)