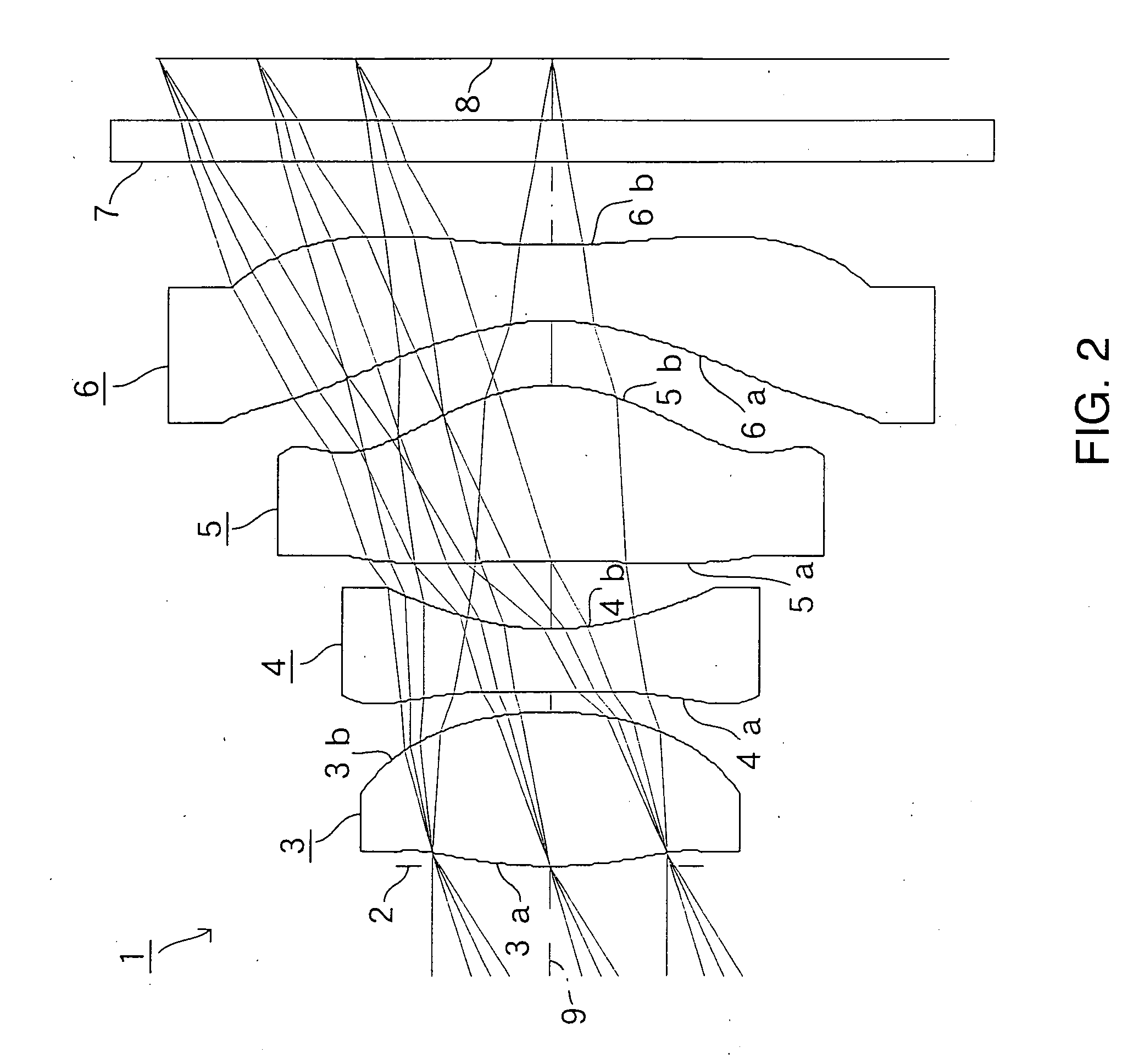
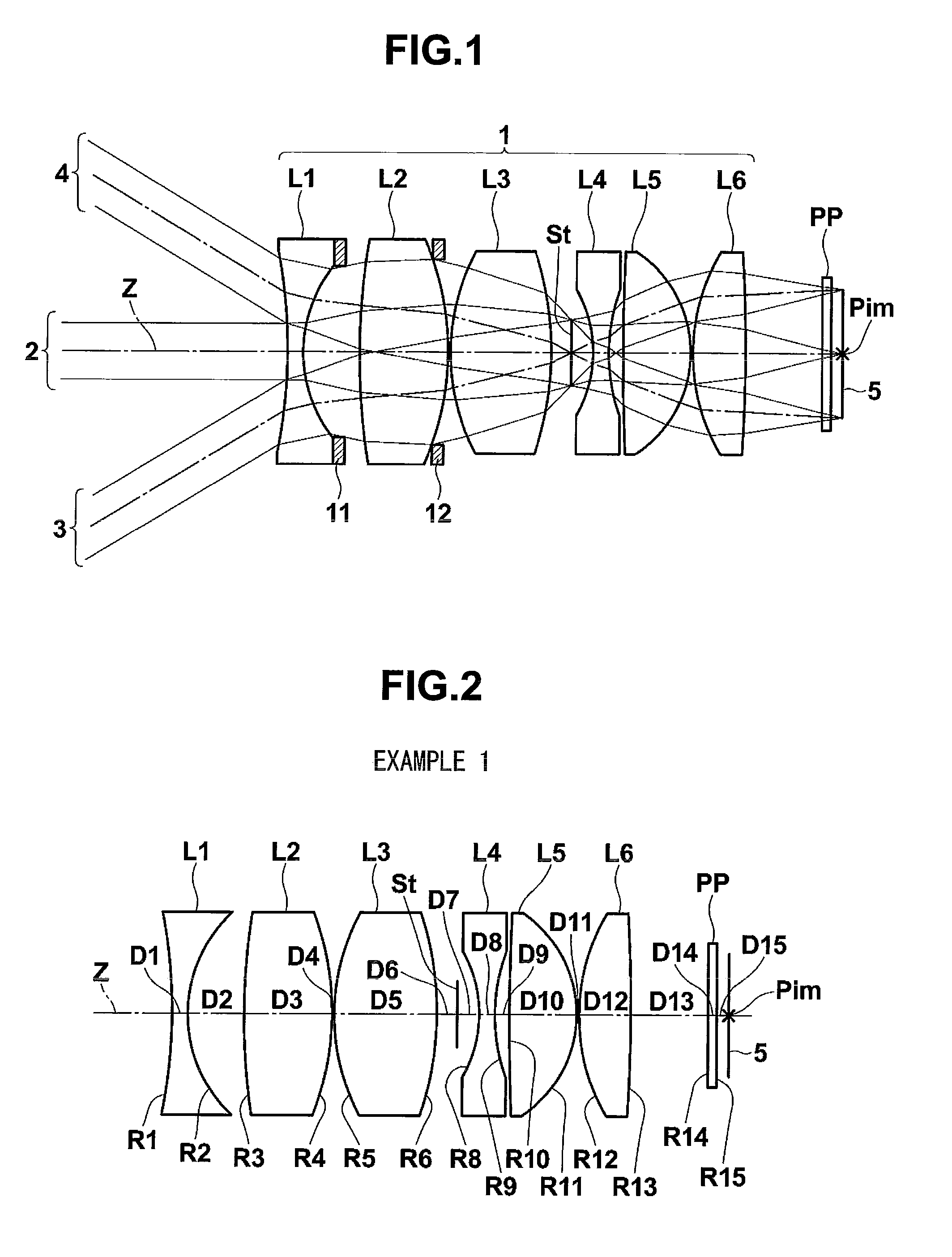
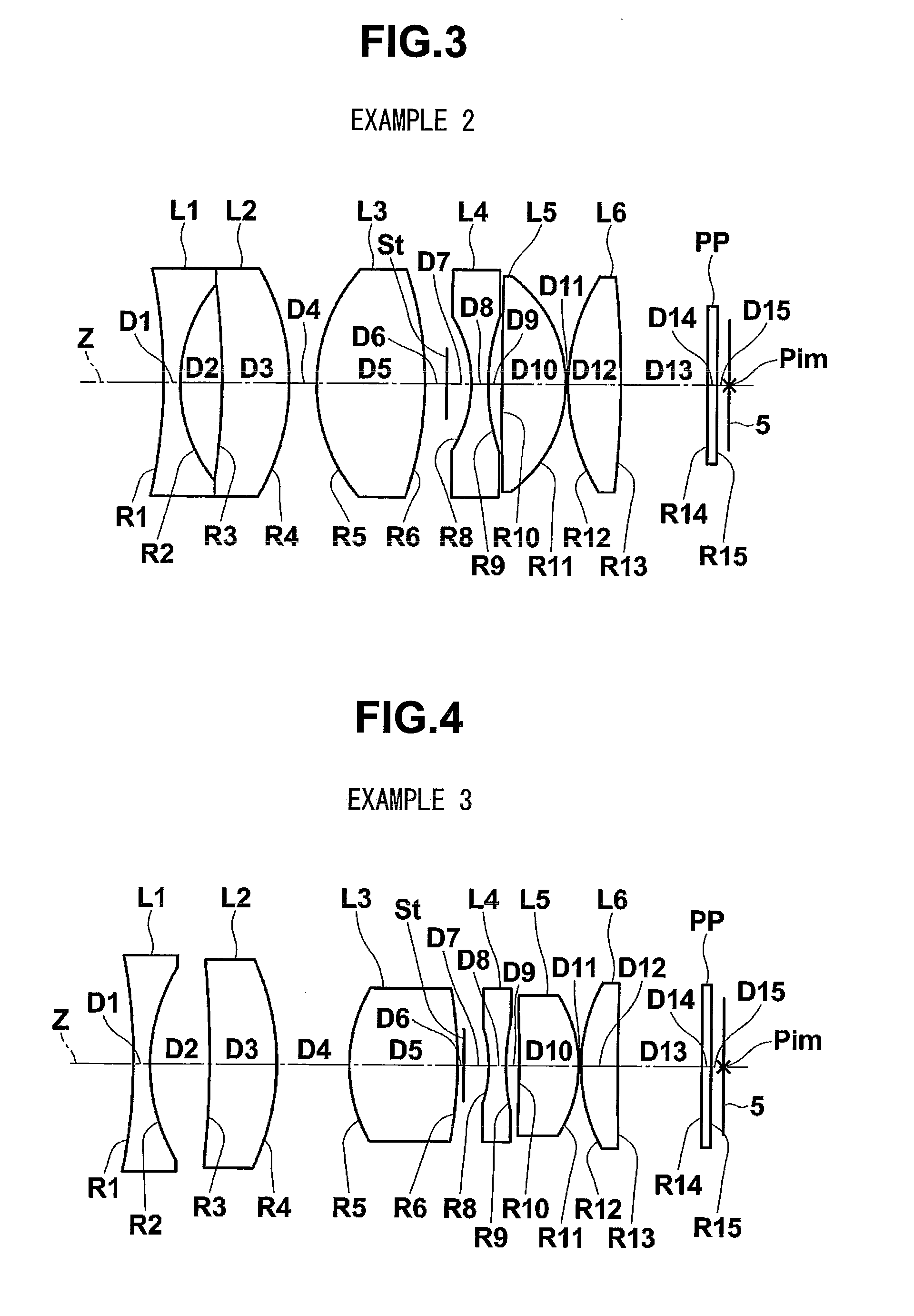
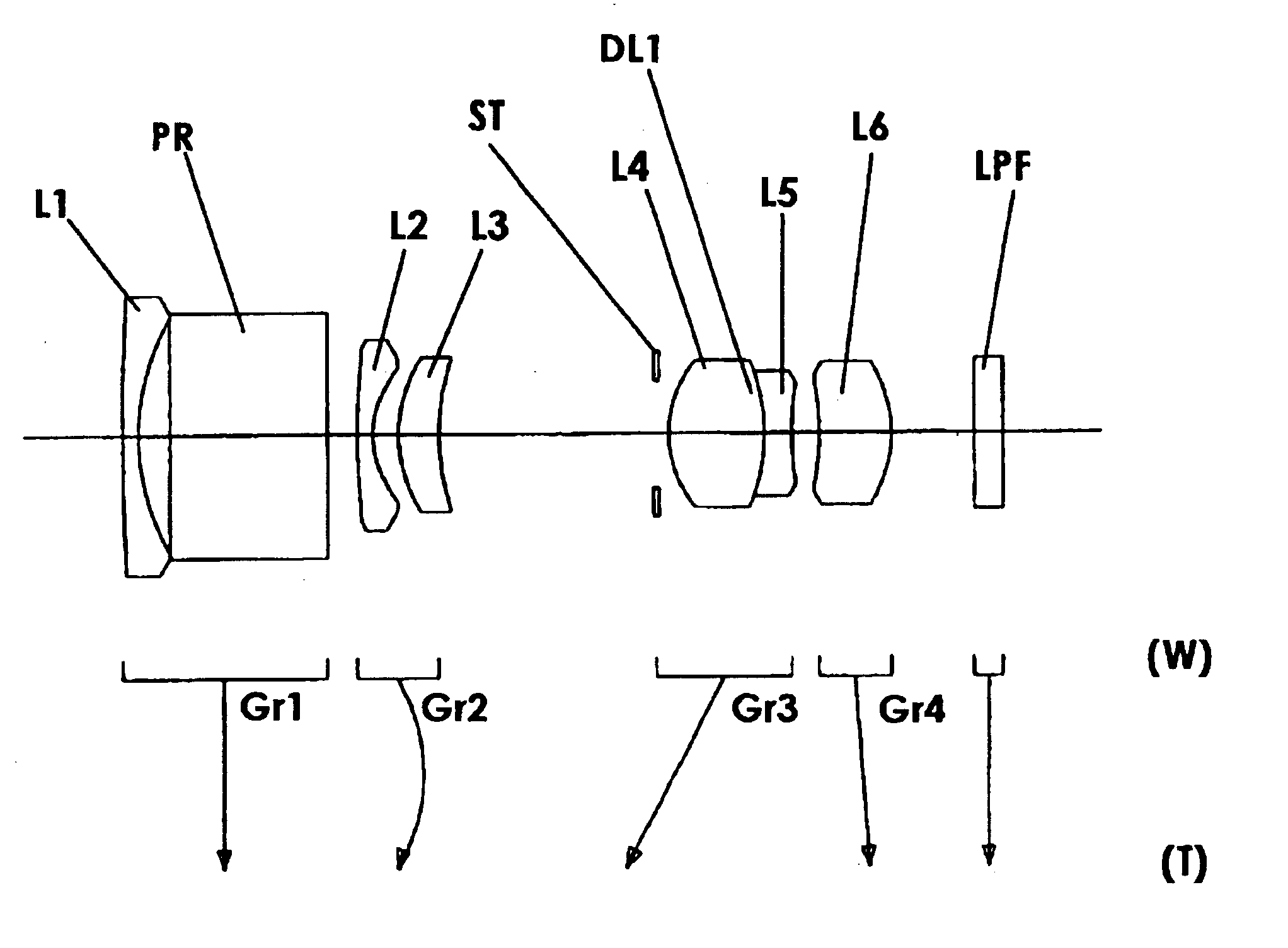
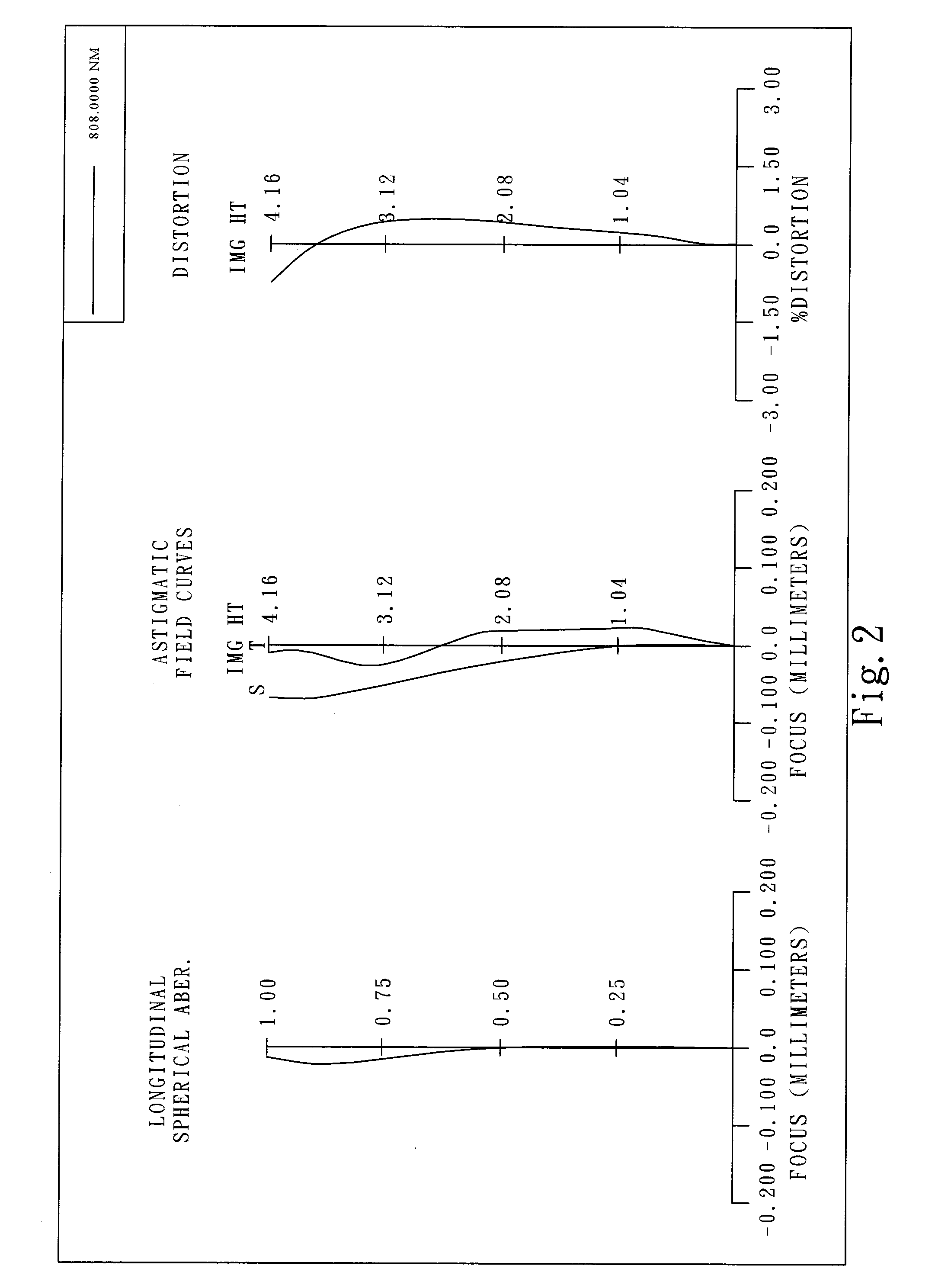
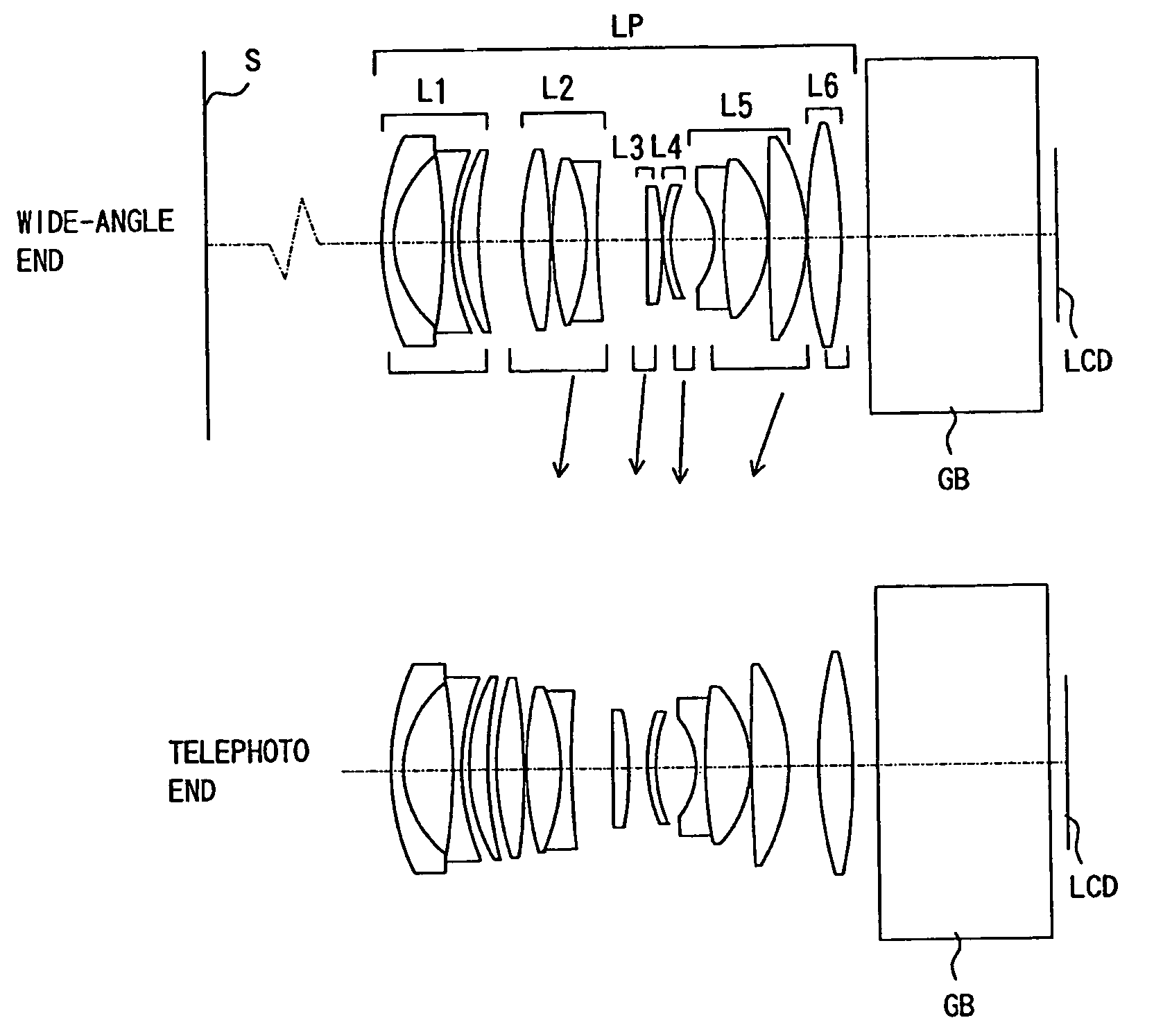
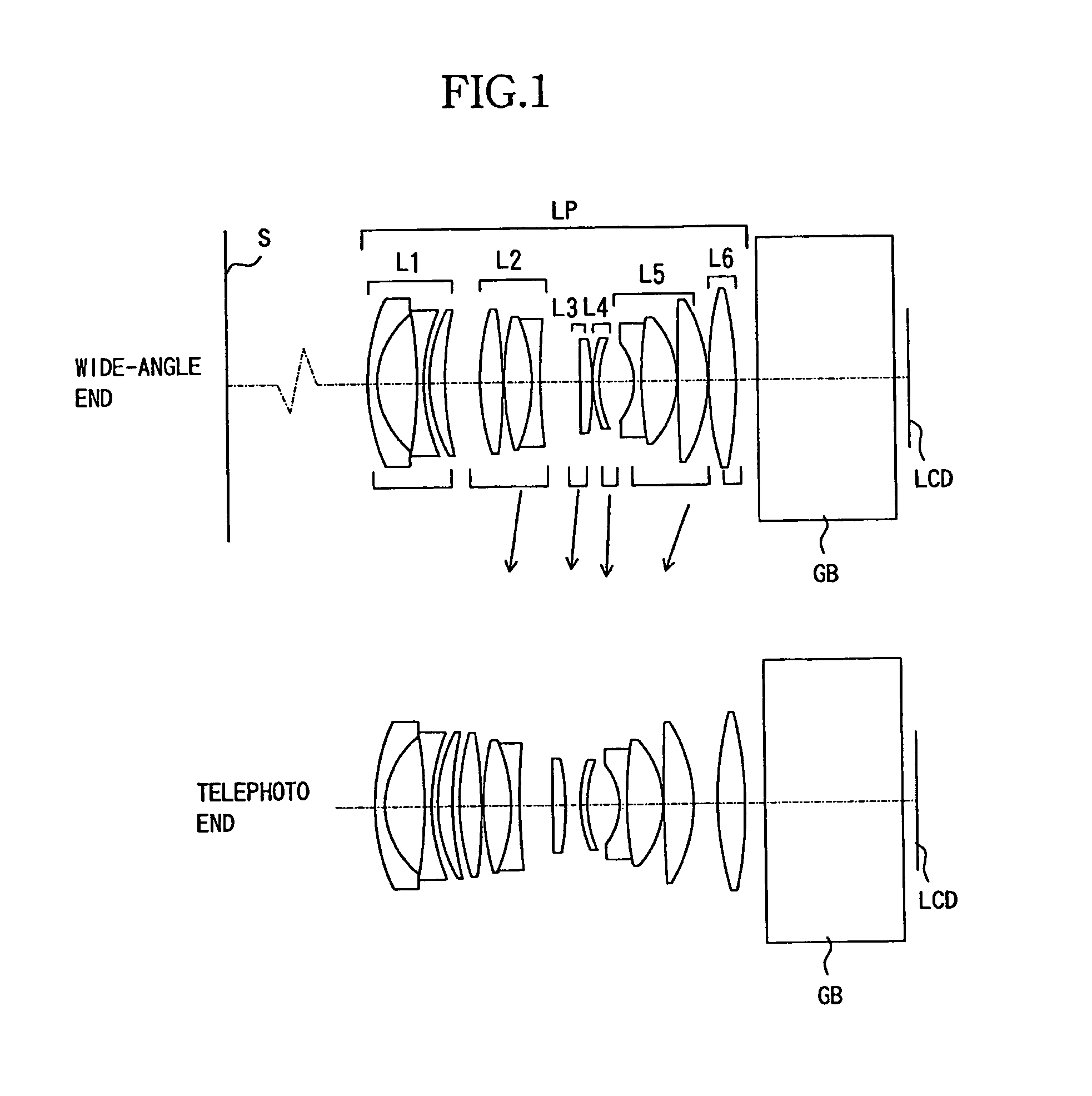
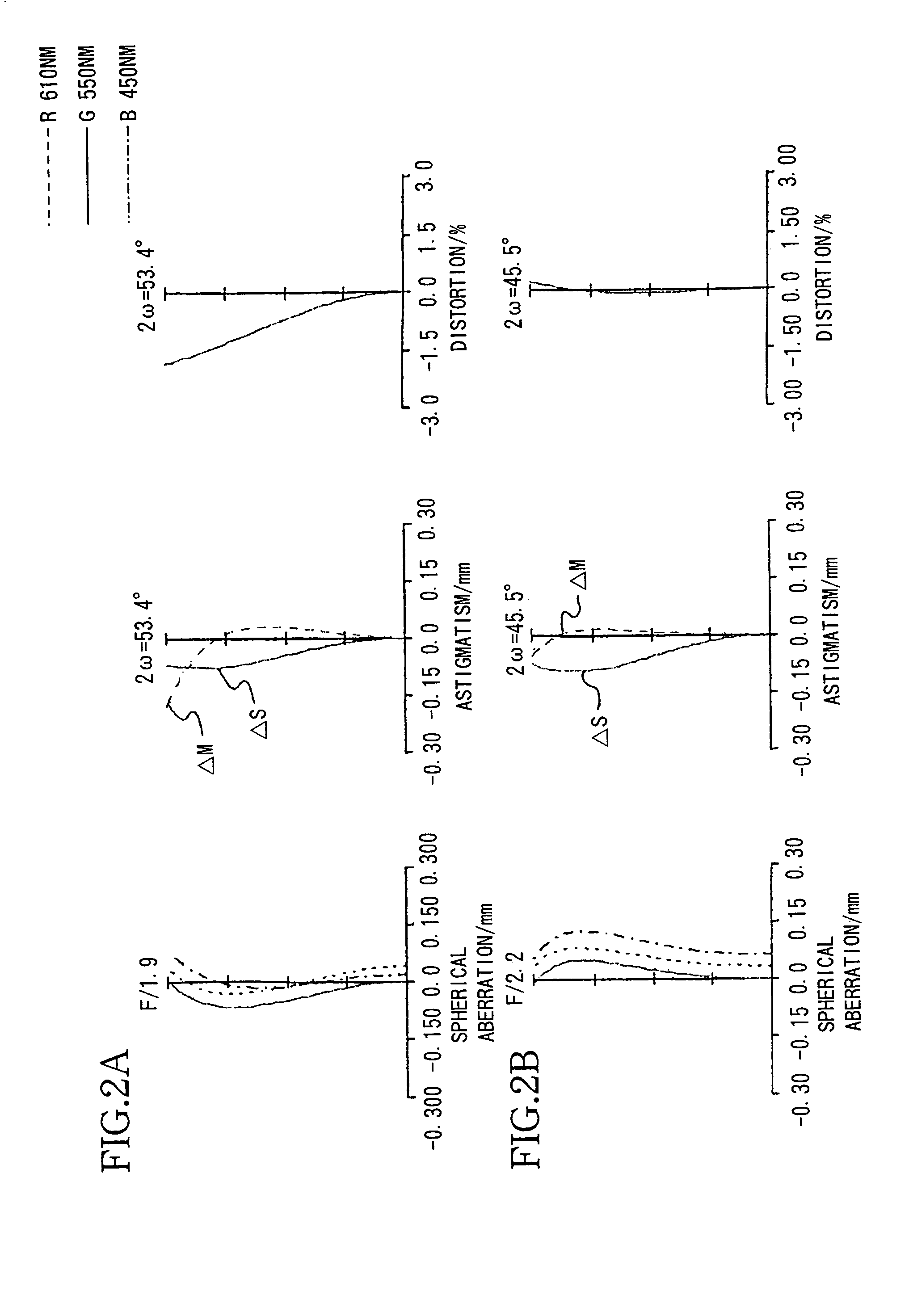
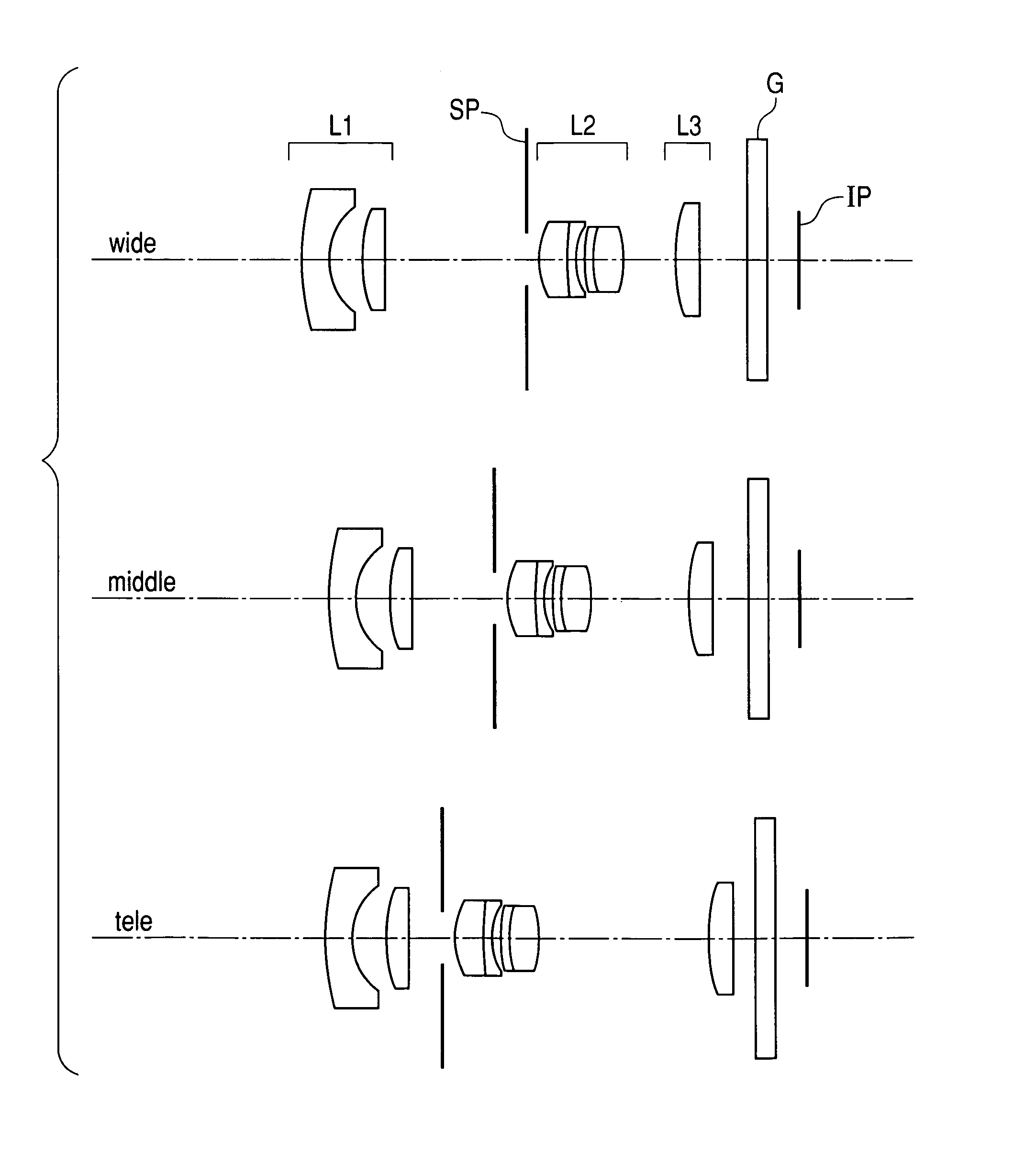
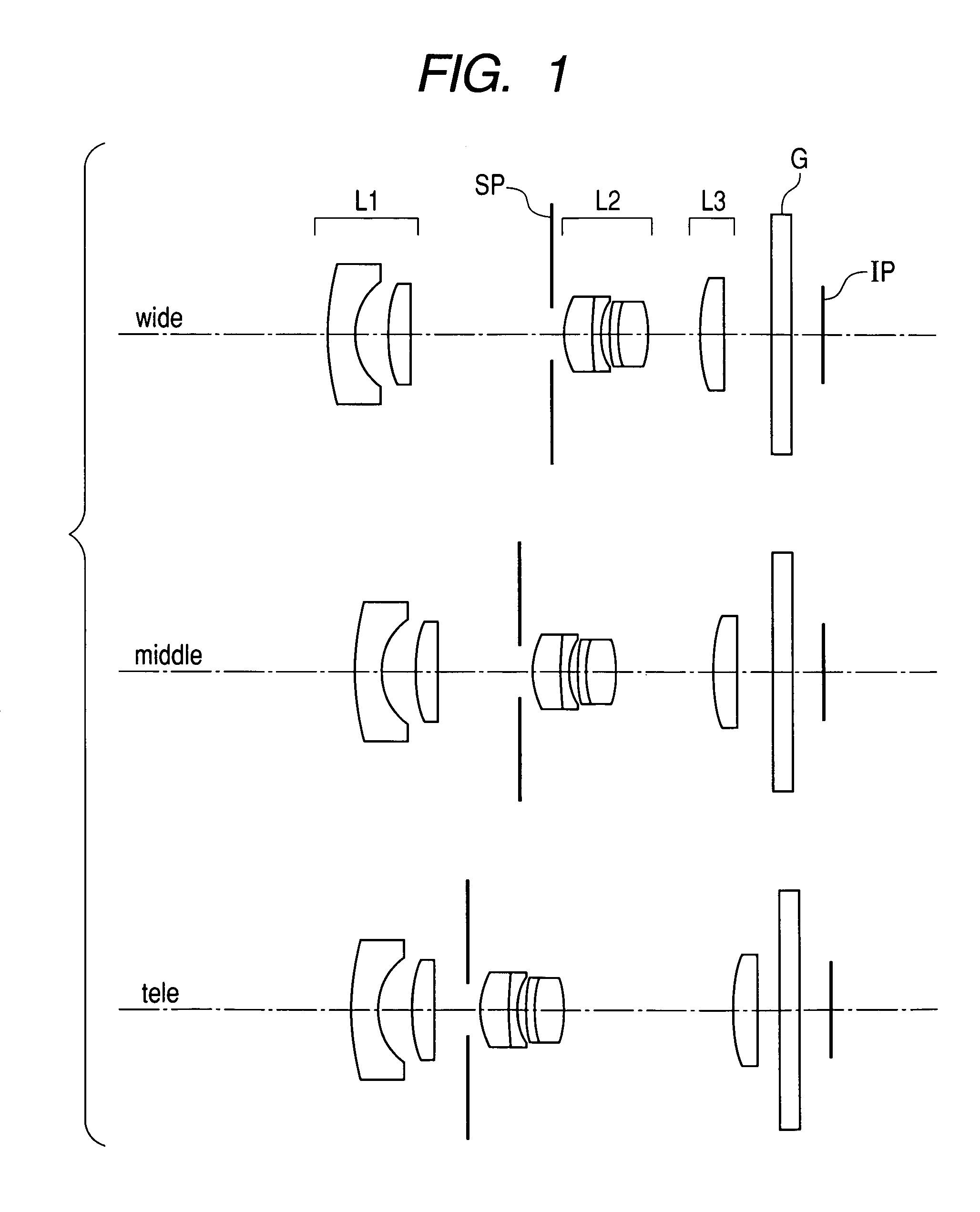
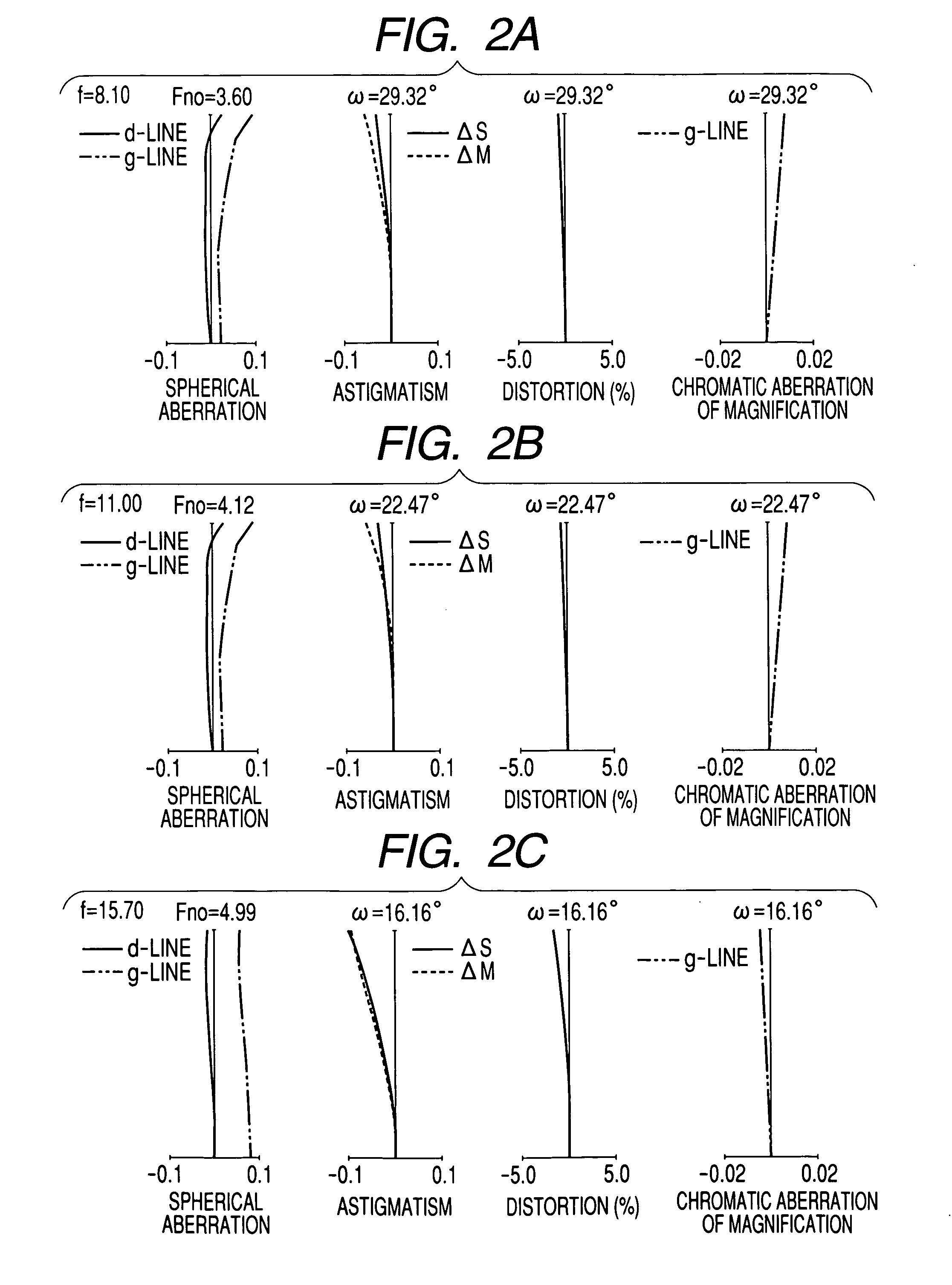
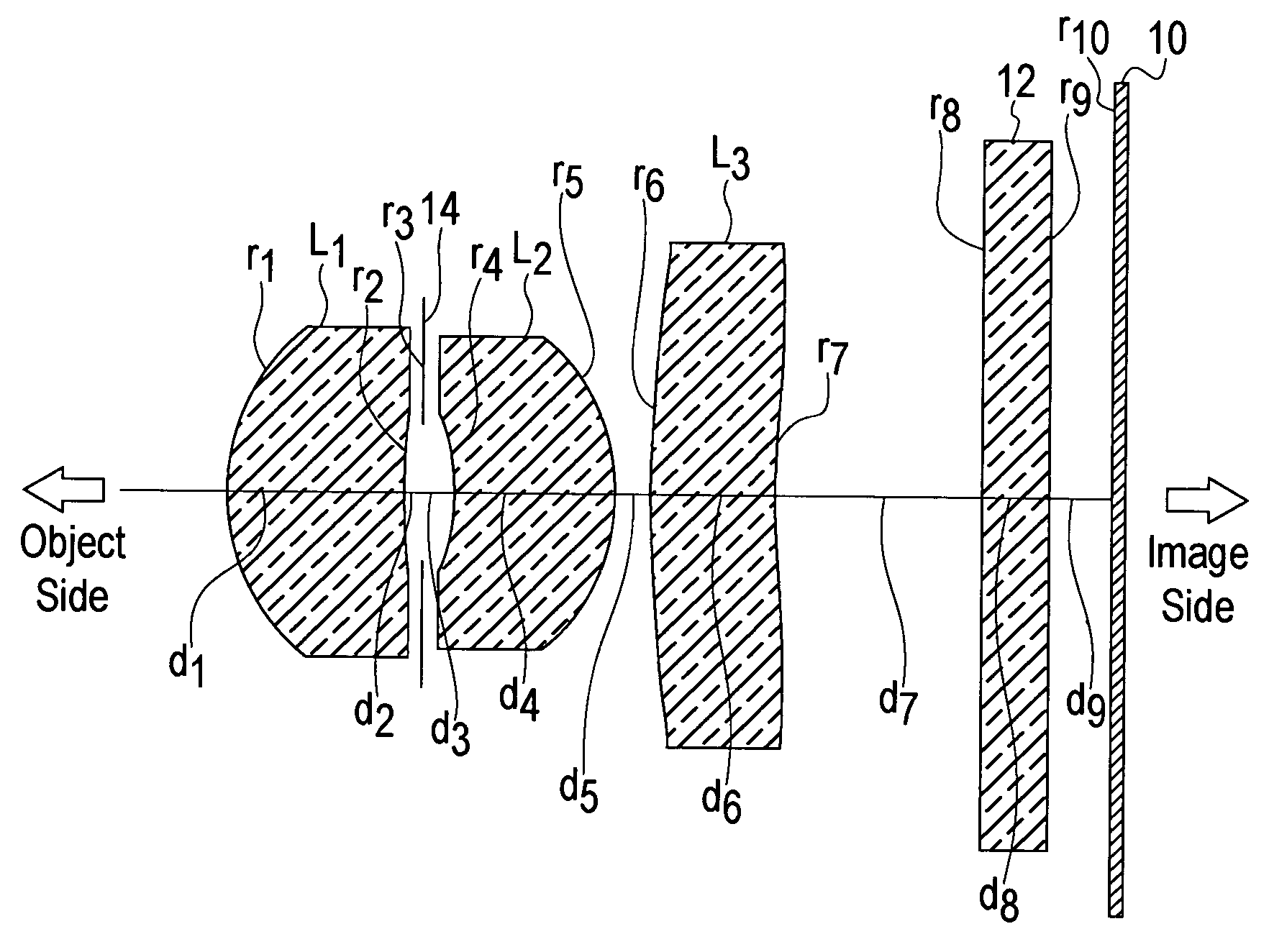
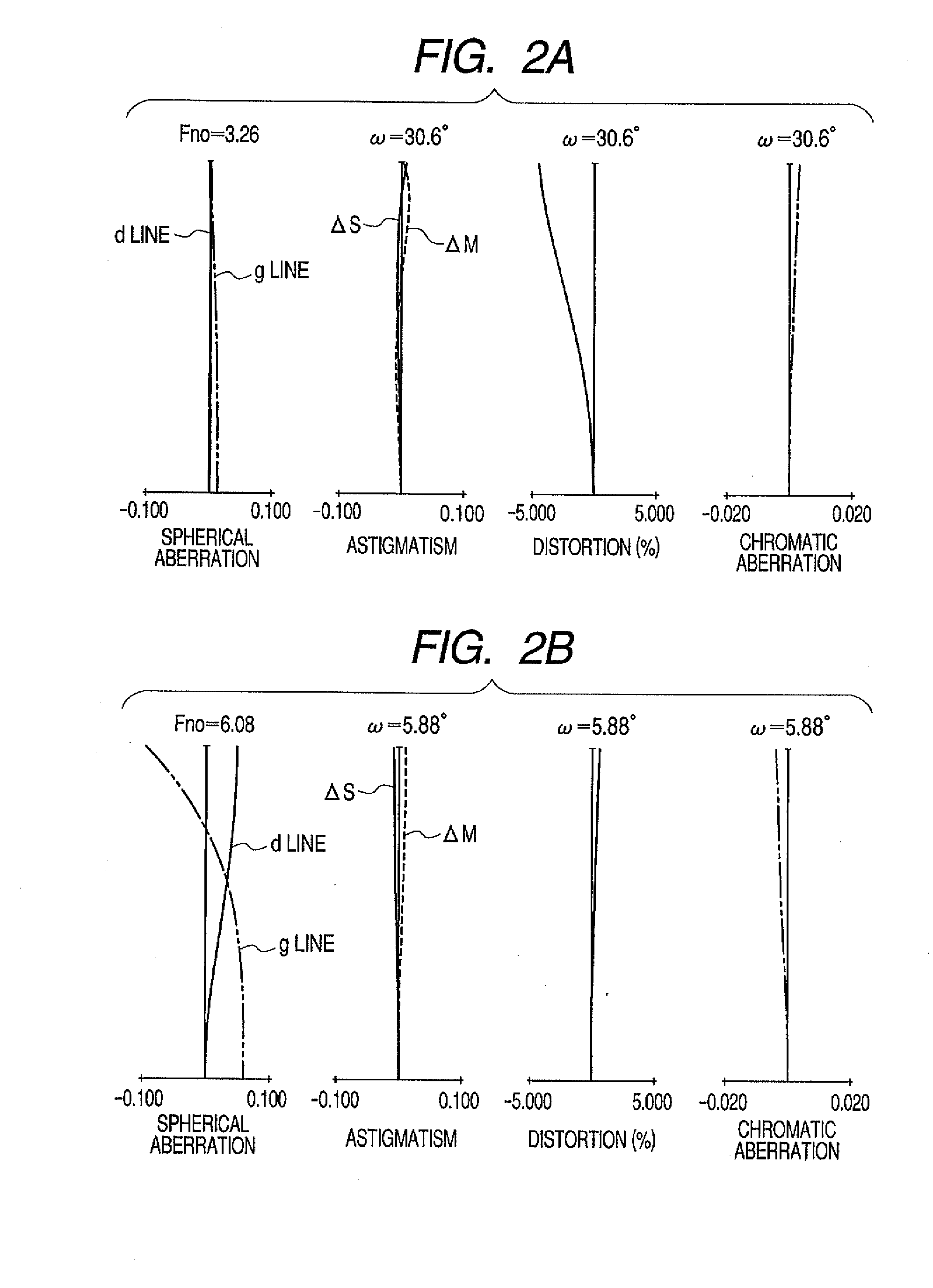
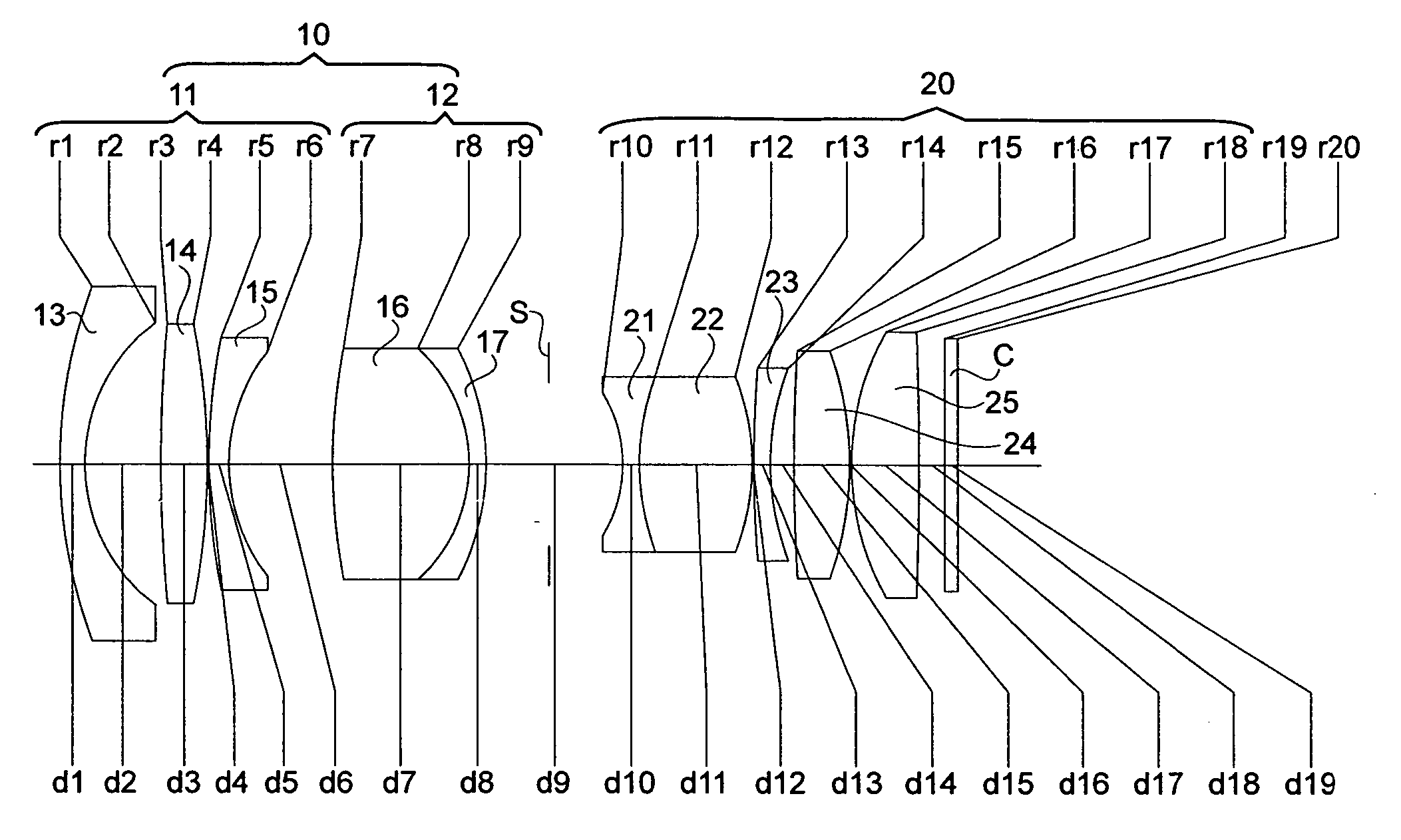
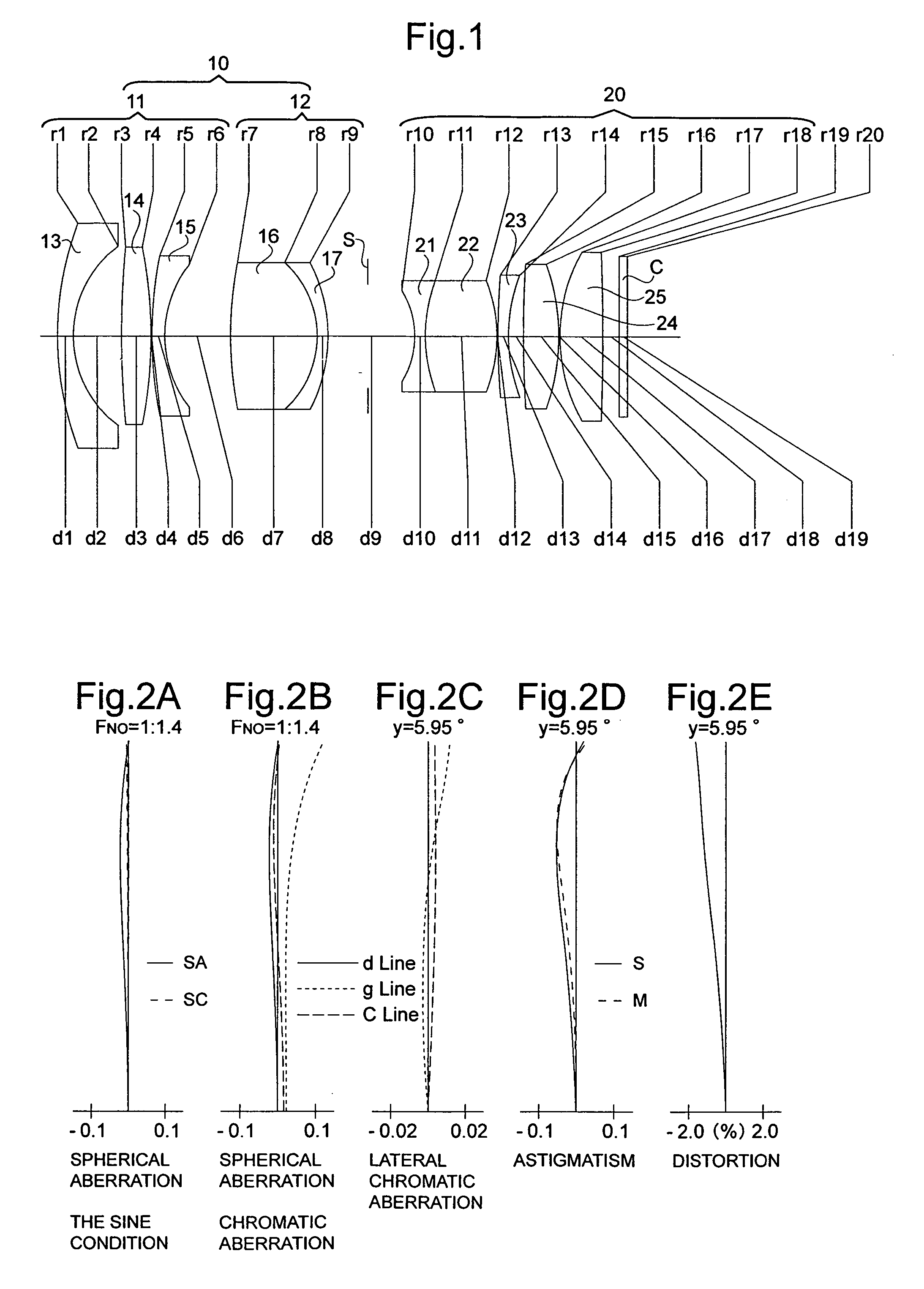
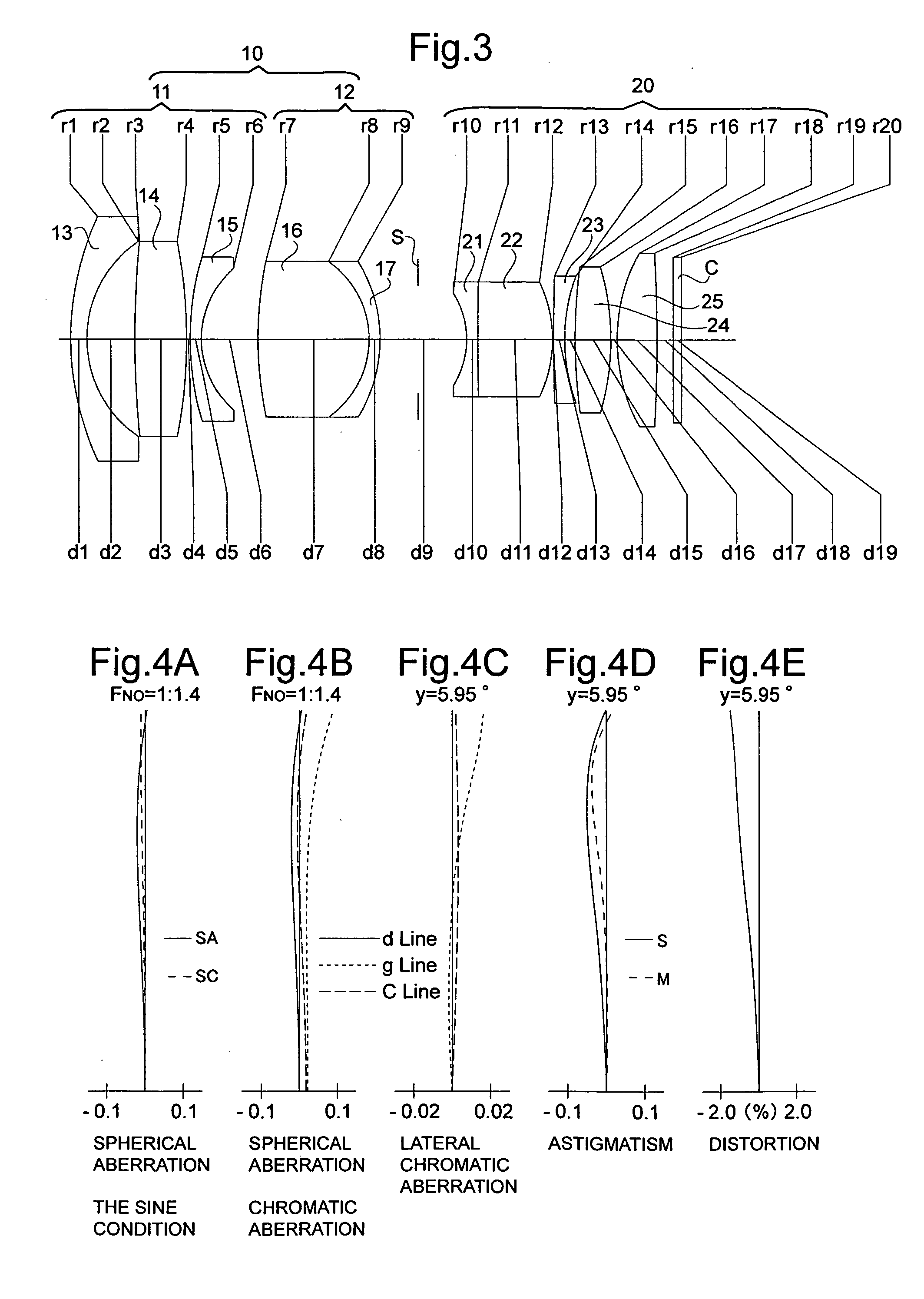
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
255 results about "Entire lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
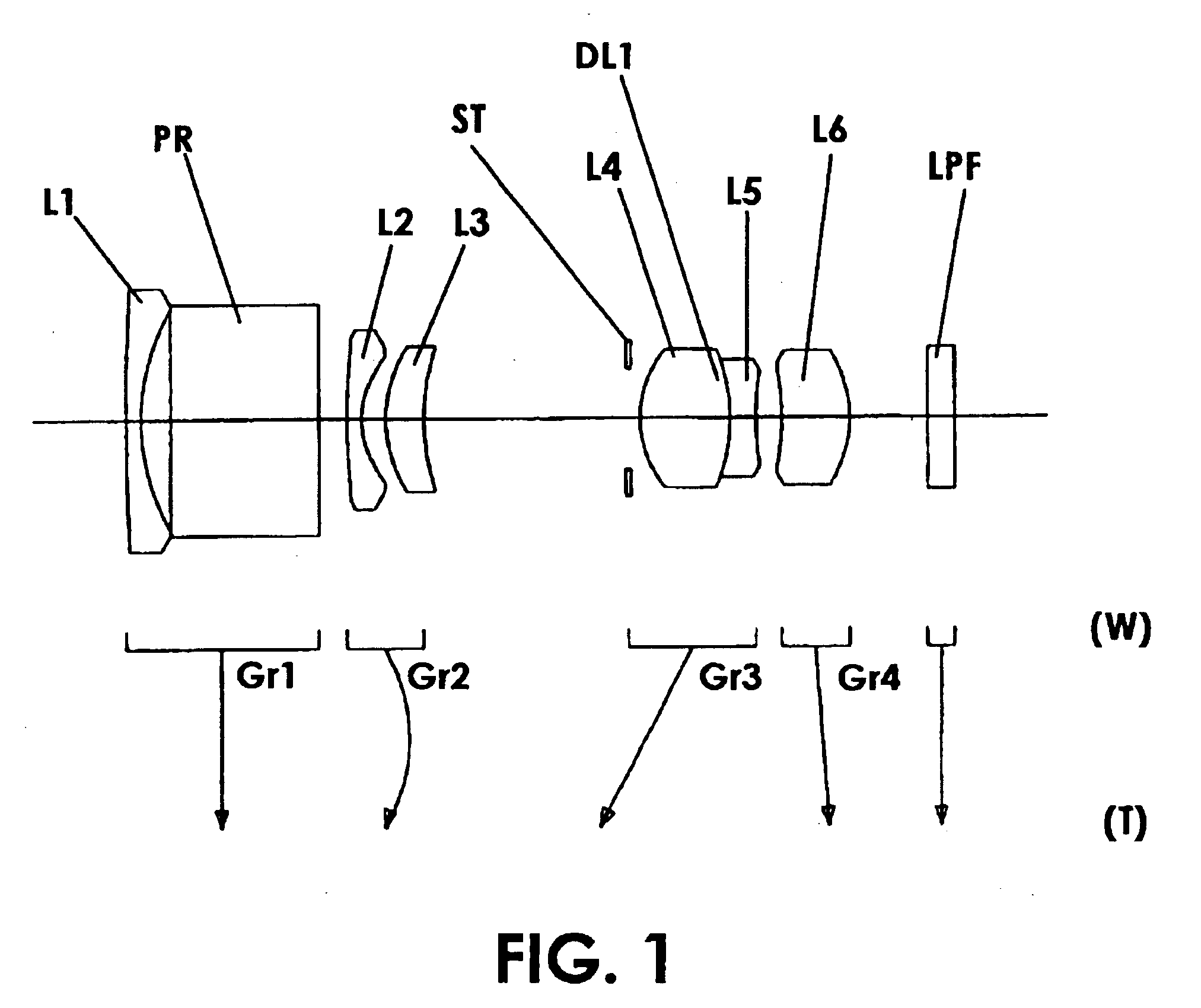
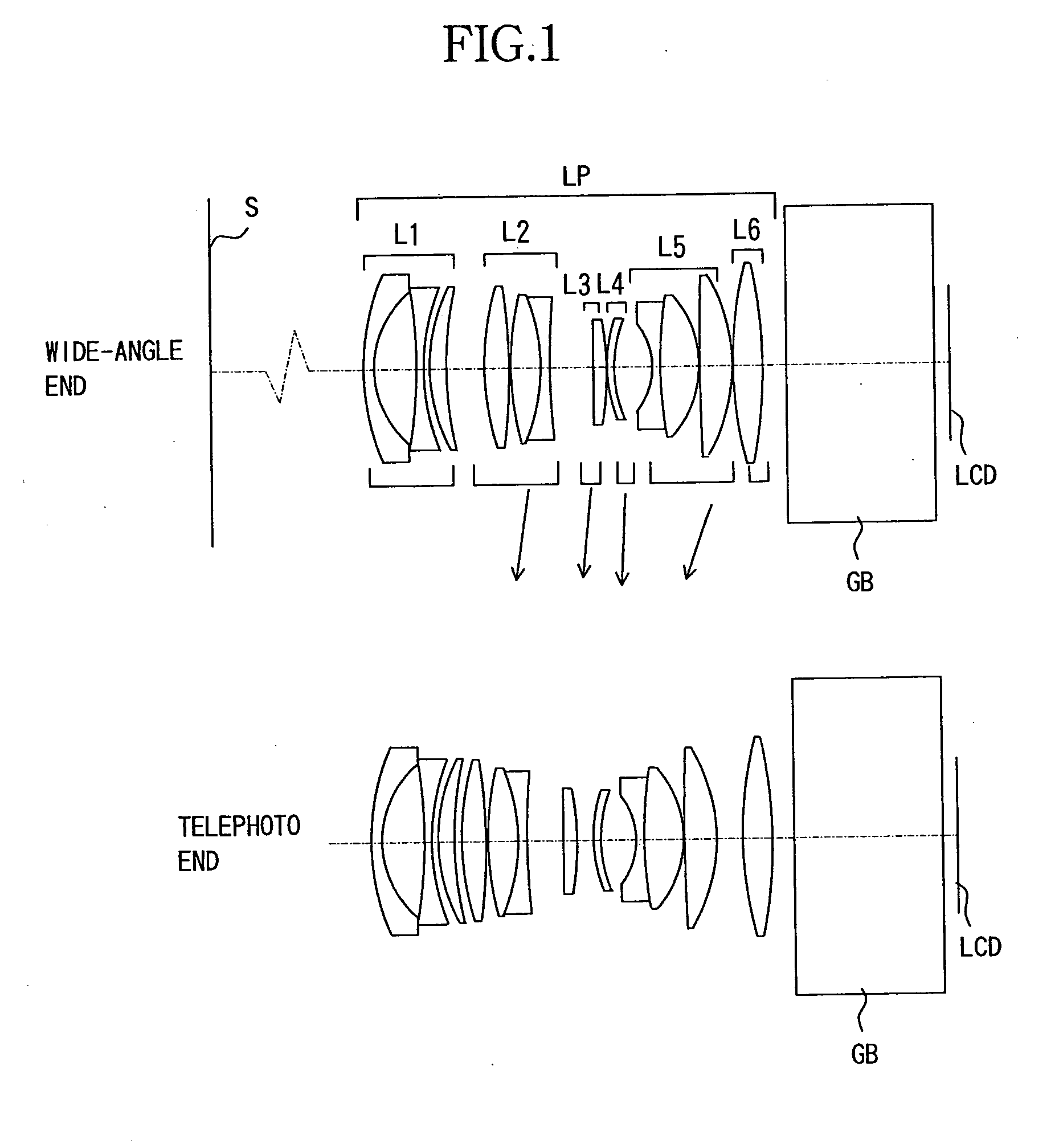
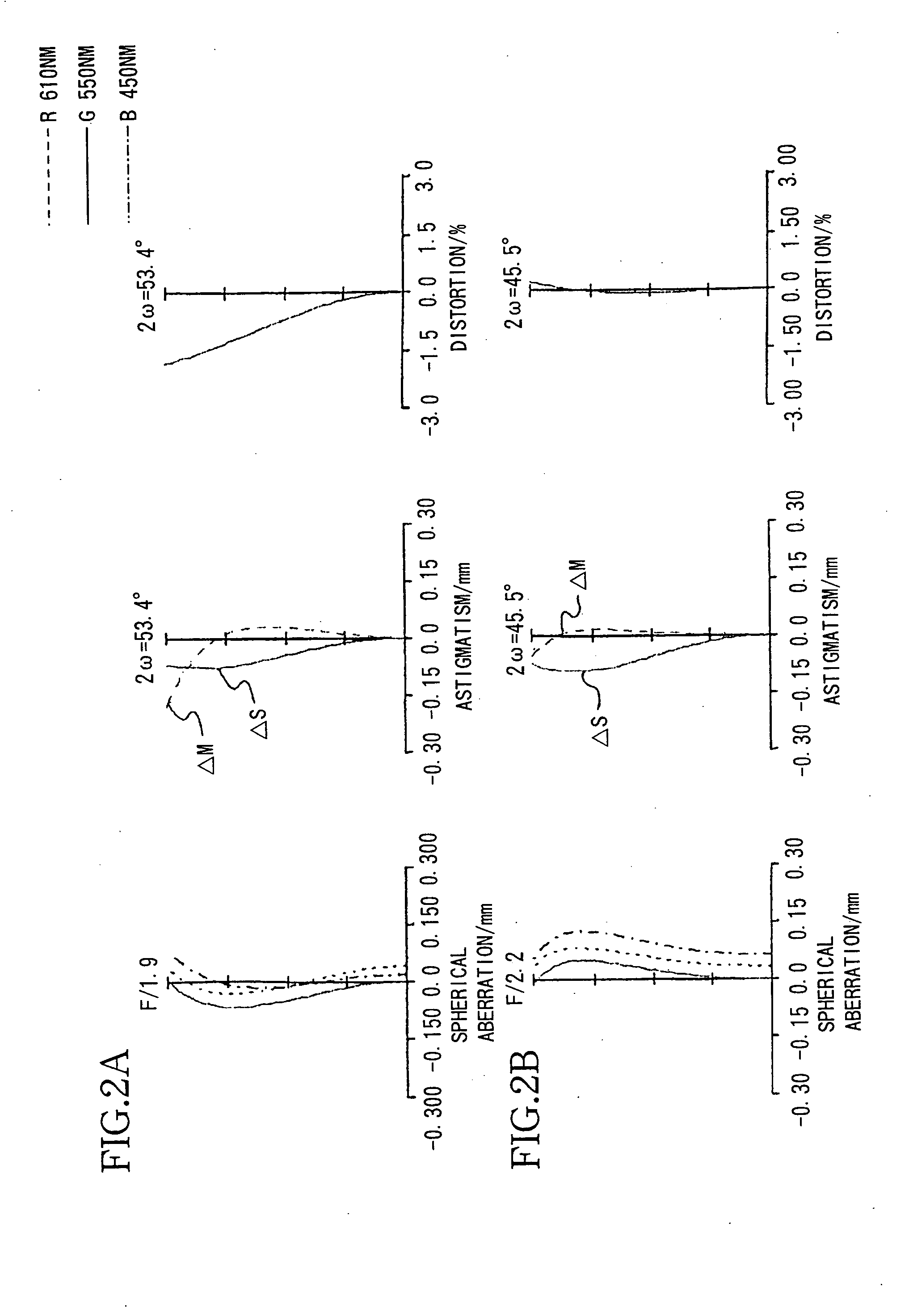
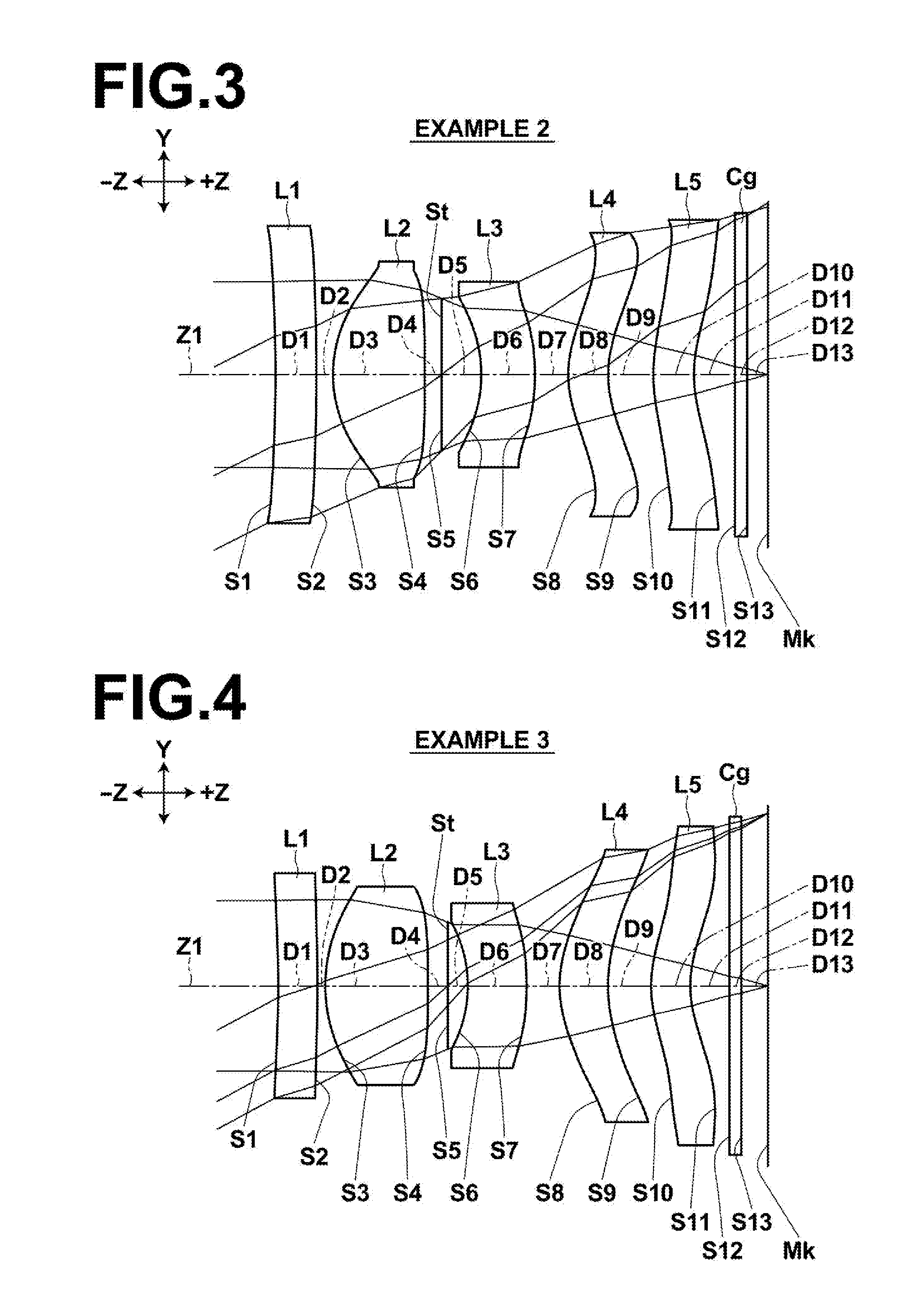
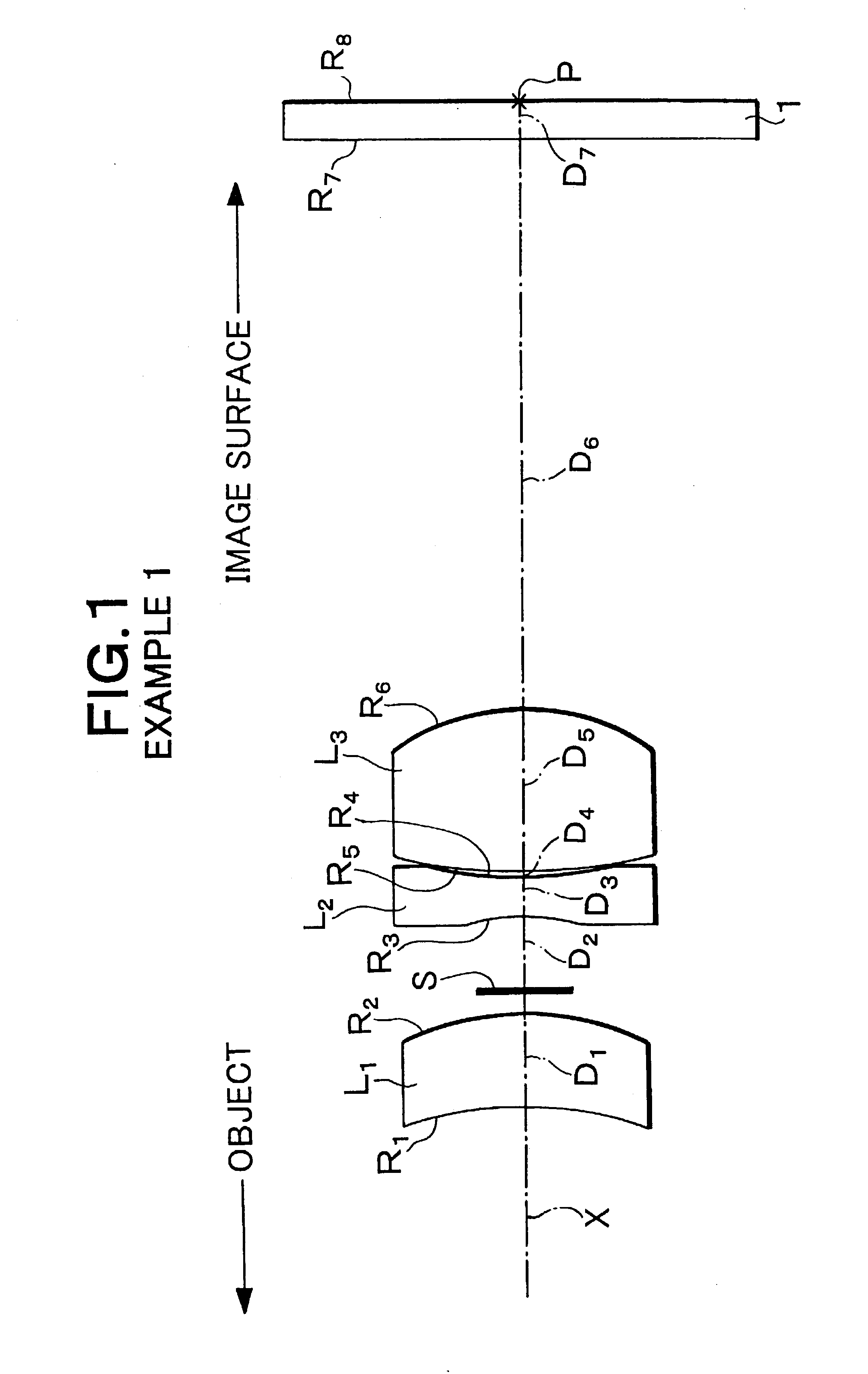
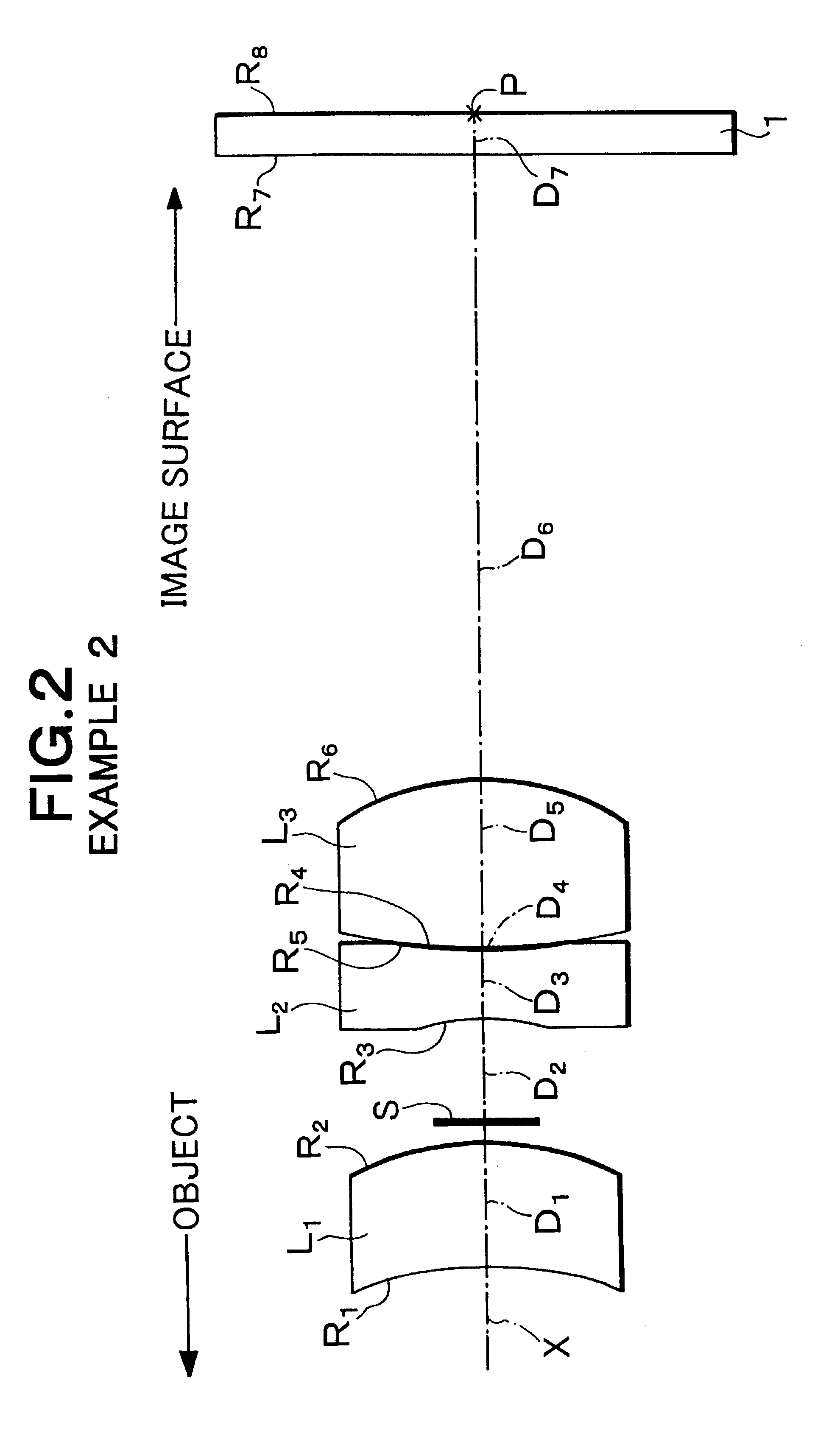
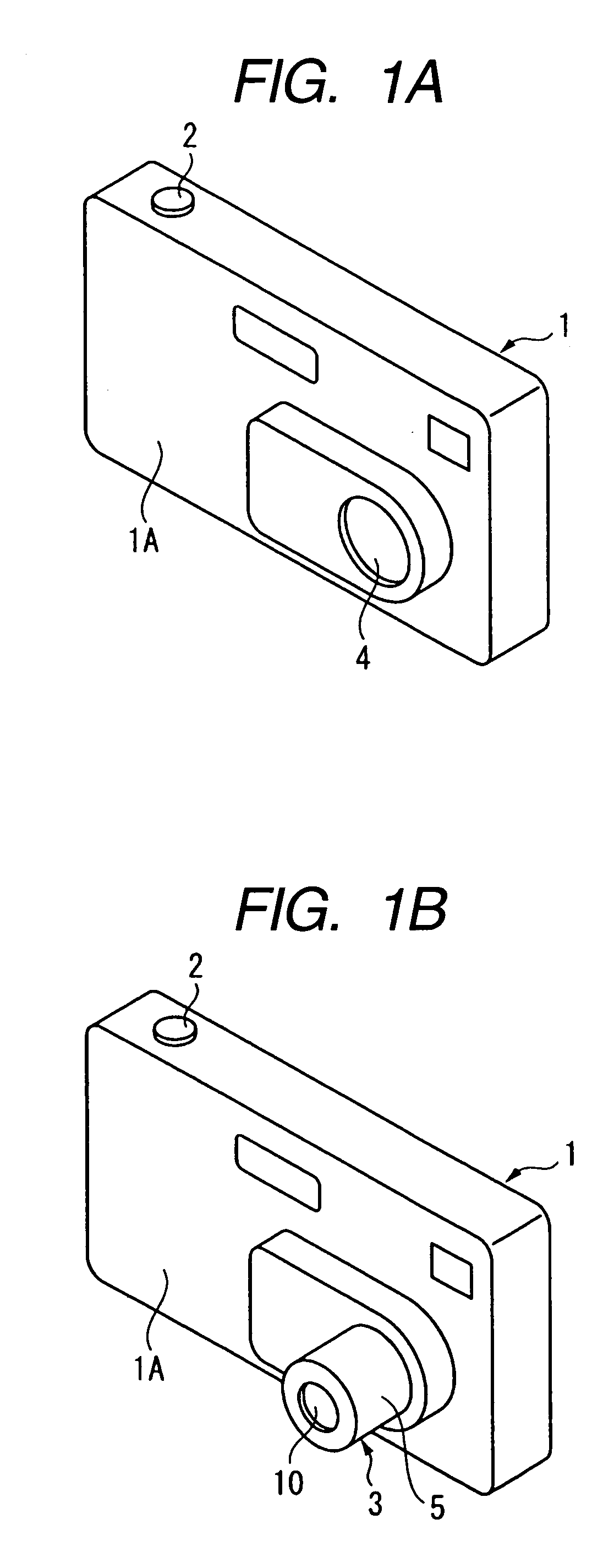
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS20040008271A1Solve the thickerLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical power
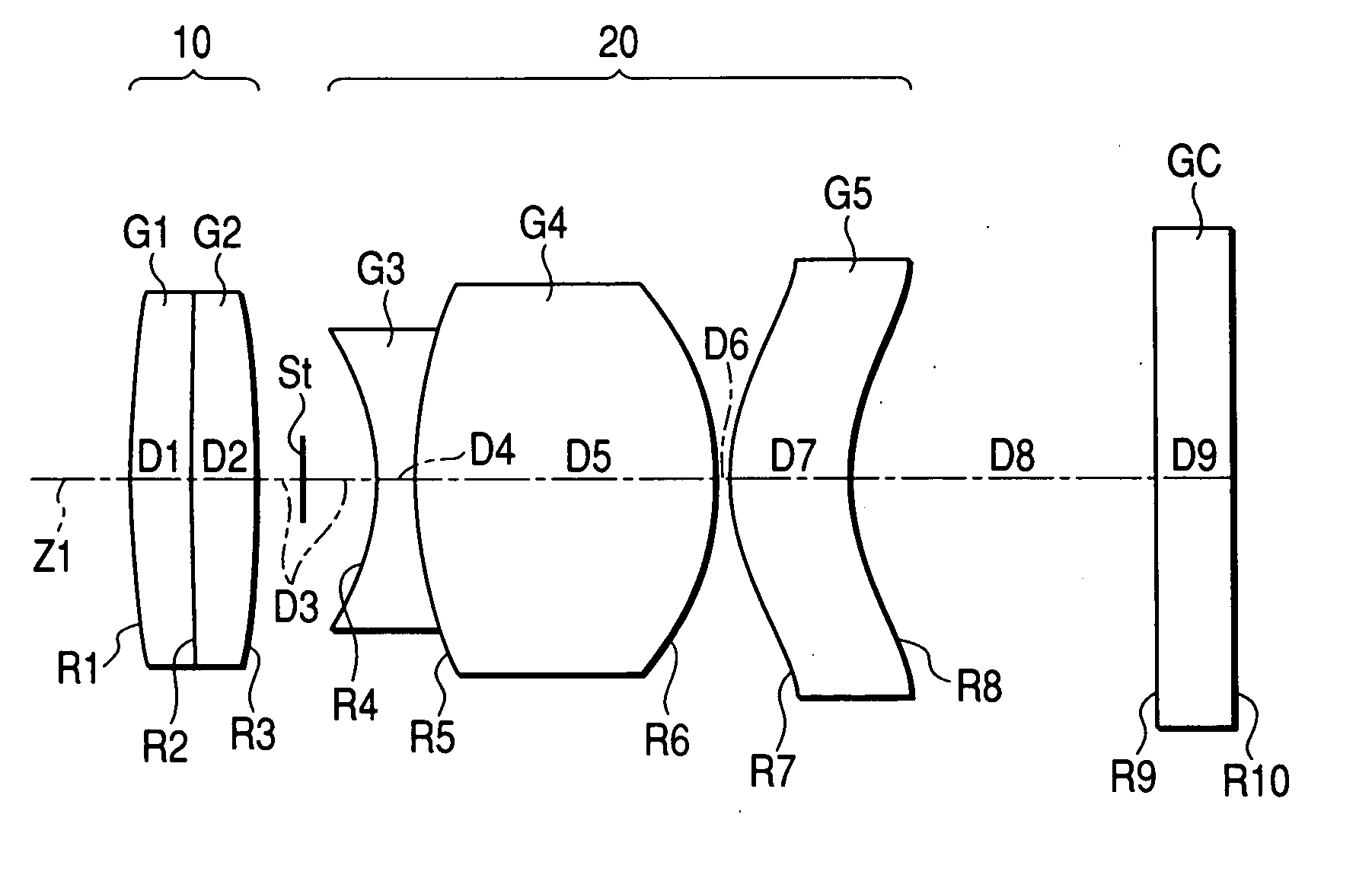
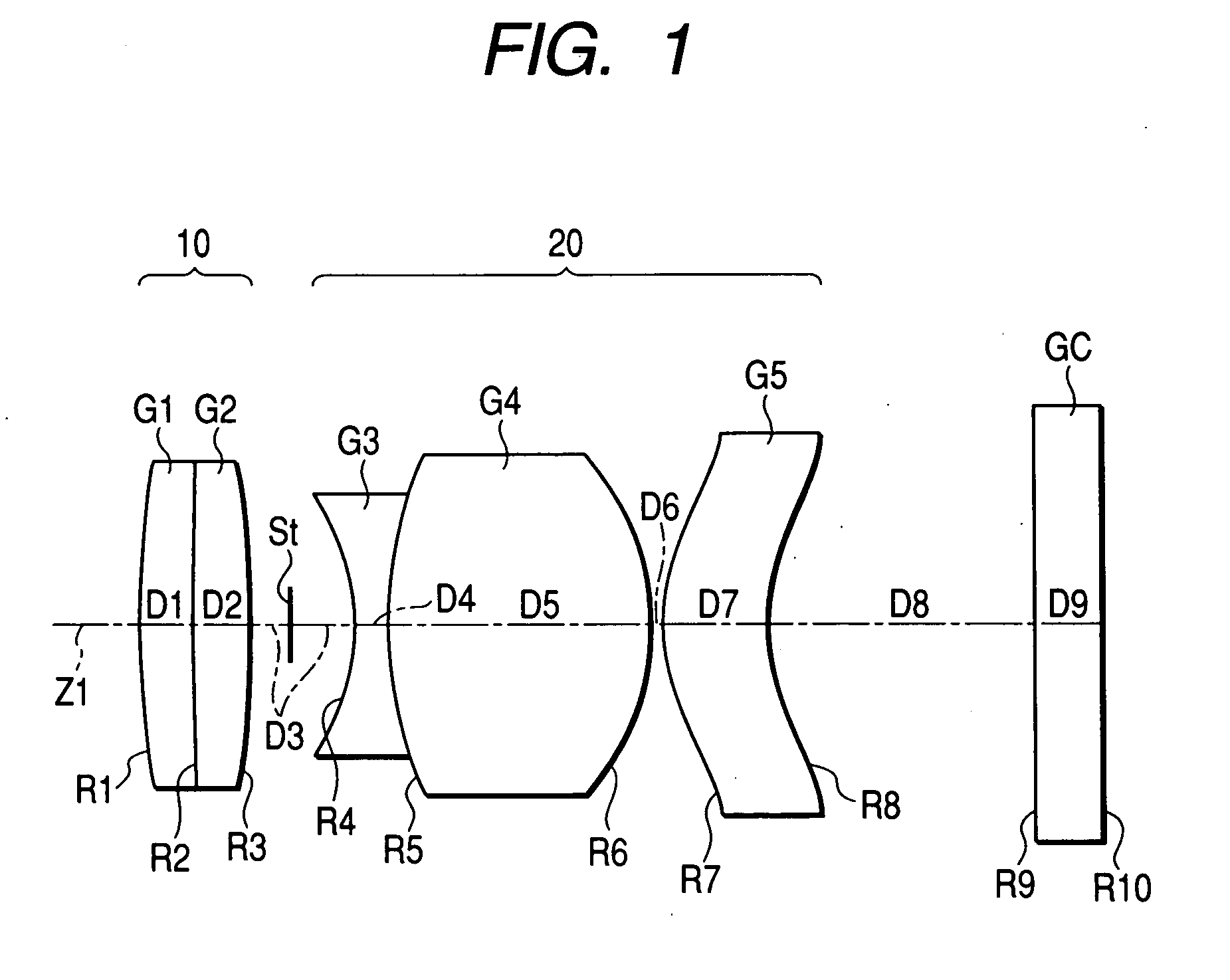
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Ftheta lens
InactiveUS6324015B1Easy to manufactureLow costWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusCamera lensZinc selenide
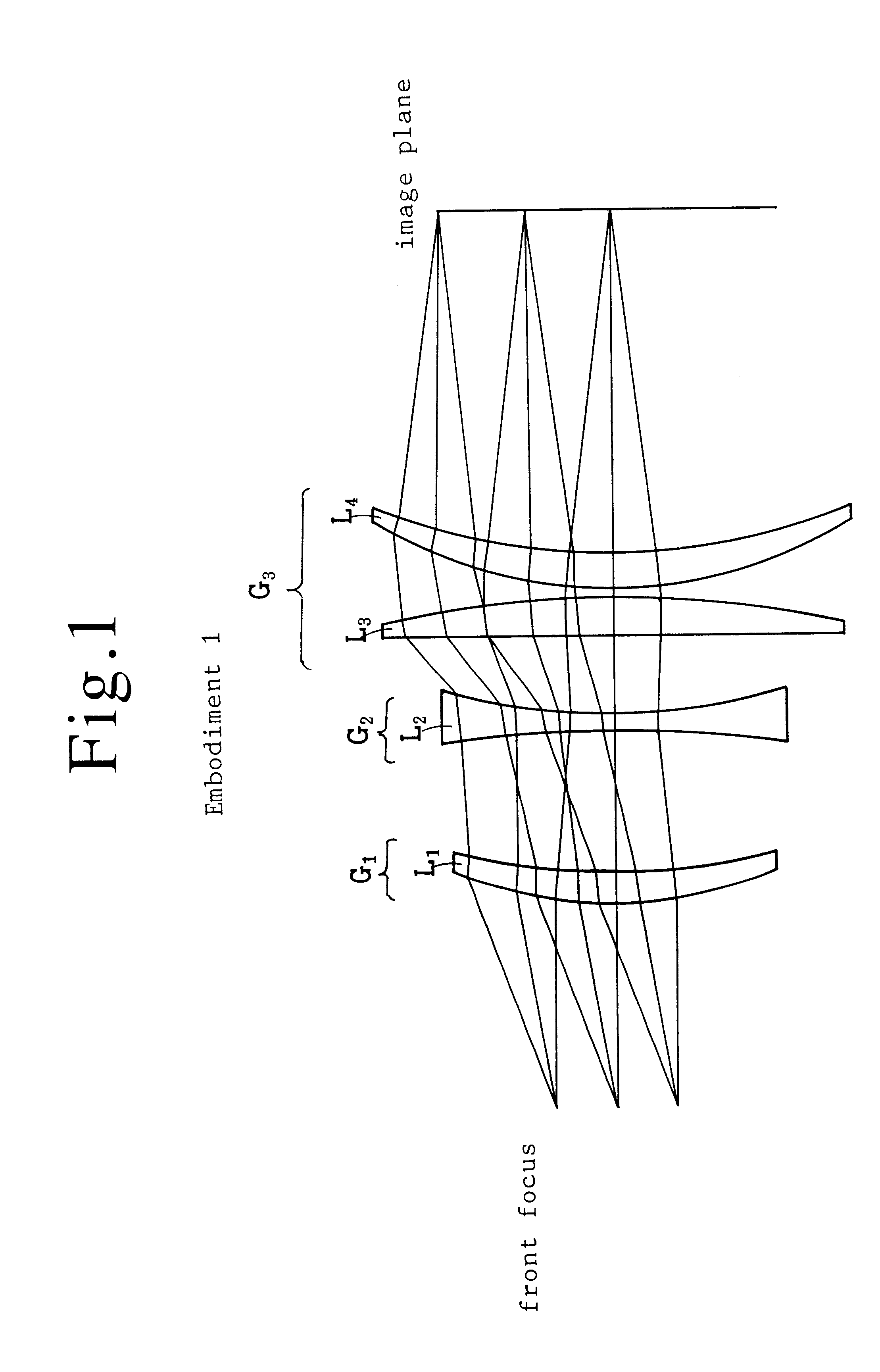
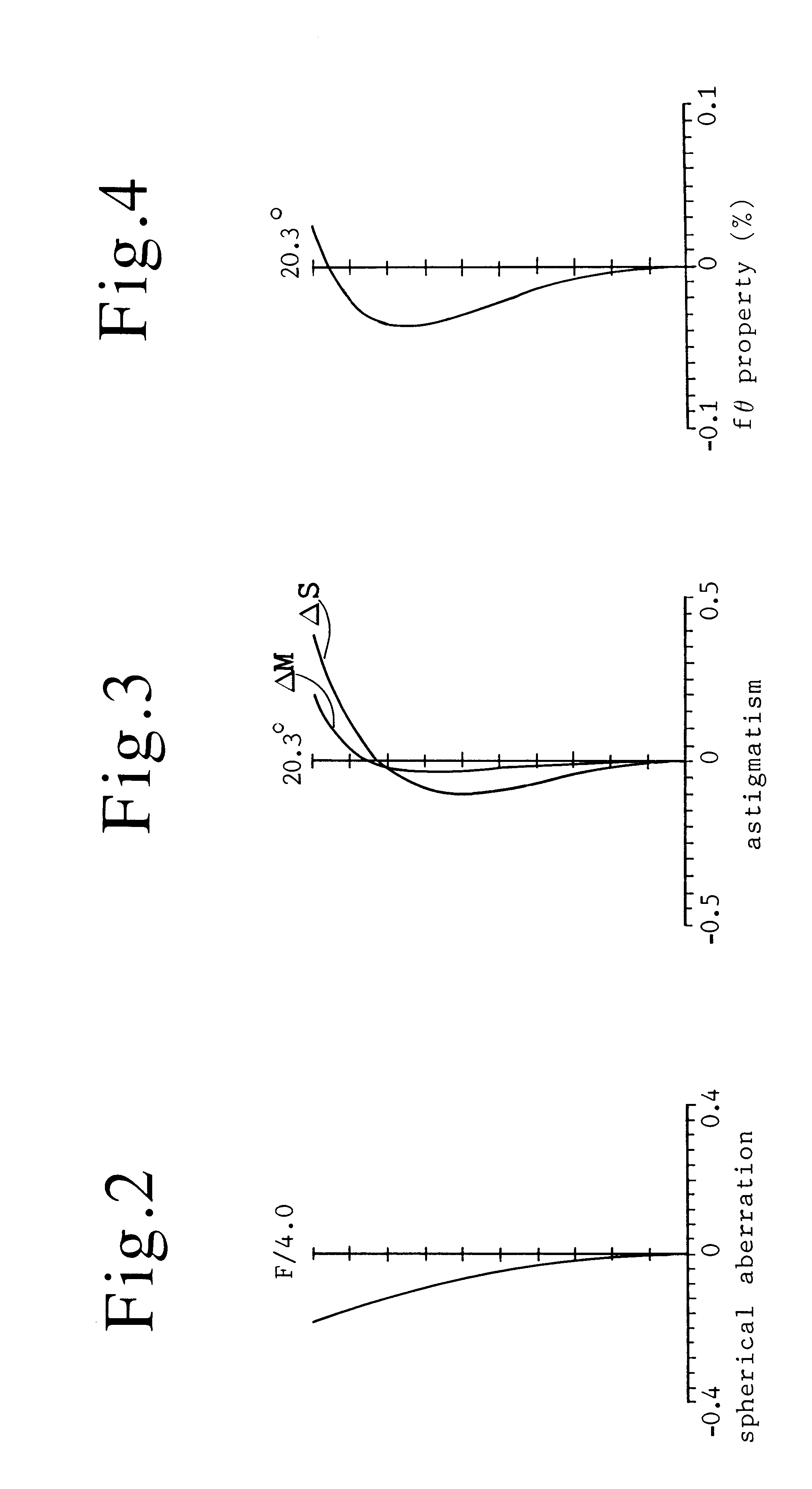
An ftheta lens containing a first lens group having an object-side convex positive lens, a second lens group having an object-side concave negative lens, a third lens group having a positive refractive power, the third lens group being a single positive lens, an assembly of a positive lens and a negative lens or another assembly of a positive lens and another positive lens. The lens components satisfy the conditions (a) to (c);where f2 is the focal length of the second lens group, f3 is the focal length of the third lens group, f is the focal length of the whole lens system and d is the distance from the front focus to the image plane. The material of the lens is zinc selenide (ZnSe) or germanium (Ge). Adoption of an aspherical lens facilitates the design of the ftheta lens.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Imaging lens and imaging device including the imaging lens
It is to provide an imaging lens and an imaging device including the imaging lens in which the imaging lens can maintain excellent optical performance, while achieving sufficient reduction in size and weight.The imaging lens comprises, in order from an object side to an image surface side, a diaphragm, a first lens that is a biconvex lens having a positive power, a second lens having a negative power, a third lens having a positive power, and a fourth lens that is a biconcave lens, wherein a condition expressed by 0.7≦FL / f1≦3.0 (where, FL: focal distance of the entire lens system, and f1: focal distance of the first lens) is to be satisfied.
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Lenses having dispersed metal nanoparticles for optical filtering including sunglasses
InactiveUS20070298242A1Evenly dispersedSpectales/gogglesSynthetic resin layered productsMethylmethacrylatesPoly(methyl methacrylate)
Lenses appropriate for use as sunglasses and other optical filtering devices include one or more composite layers including metal nanoparticles dispensed in a polymer matrix. The entire lens can be a single layer of the composite or the composite can be a coating on one or both faces of the lens. Gold nanoparticles can be dispersed in a poly(methylmethacrylate) or polycarbonate polymer at 0.01 to 1 weight percent.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
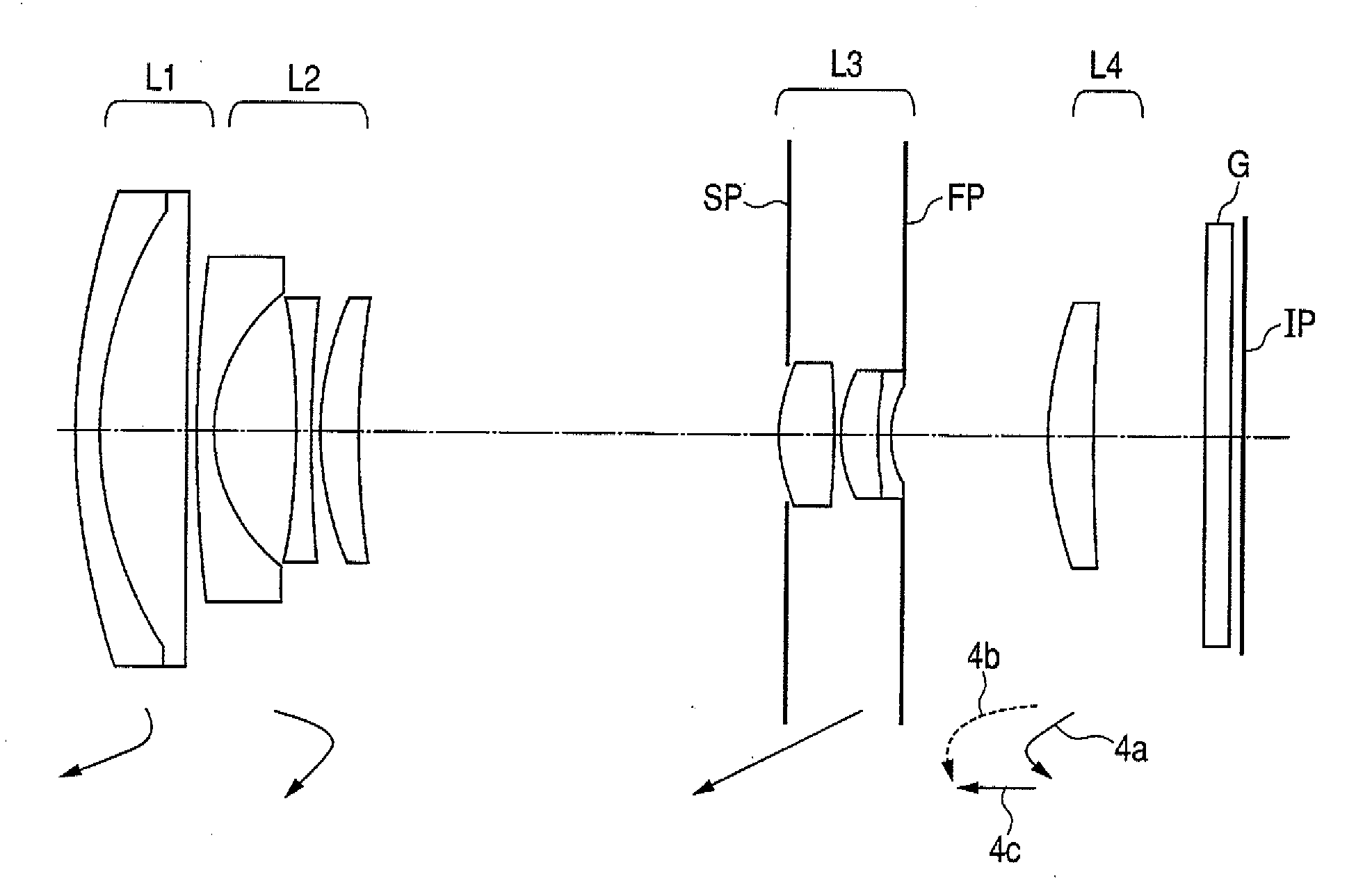
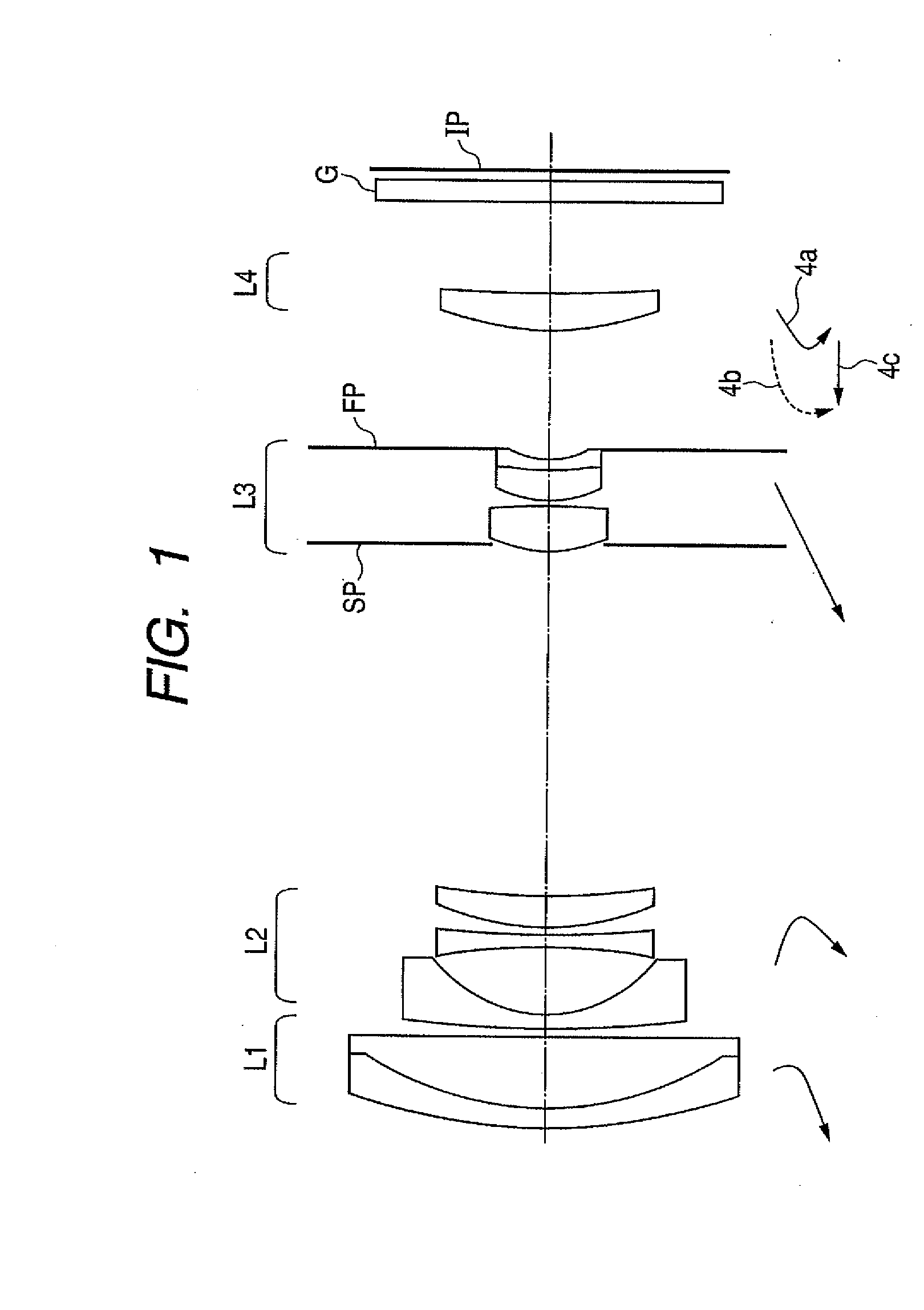
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
An imaging lens includes a first lens having a negative power and including a concave surface facing an image side, a second lens having a positive power, a third lens having a positive power, an aperture diaphragm, a fourth lens, which is a biconvex lens having a negative power, a fifth lens having a positive power and including a convex surface facing the image side, and a sixth lens having a positive power and including a convex surface facing an object side, which are arranged in this order from the object side. The Abbe number of a material forming the fourth lens with respect to the d-line is 30 or less. When the focal length of the entire lens system is f and a composite focal length from the fourth lens to the sixth lens is f456, the imaging lens satisfies following conditional expression:1.00<f456 / f<1.88.
Owner:JIANGXI OFILM OPTICAL CO LTD
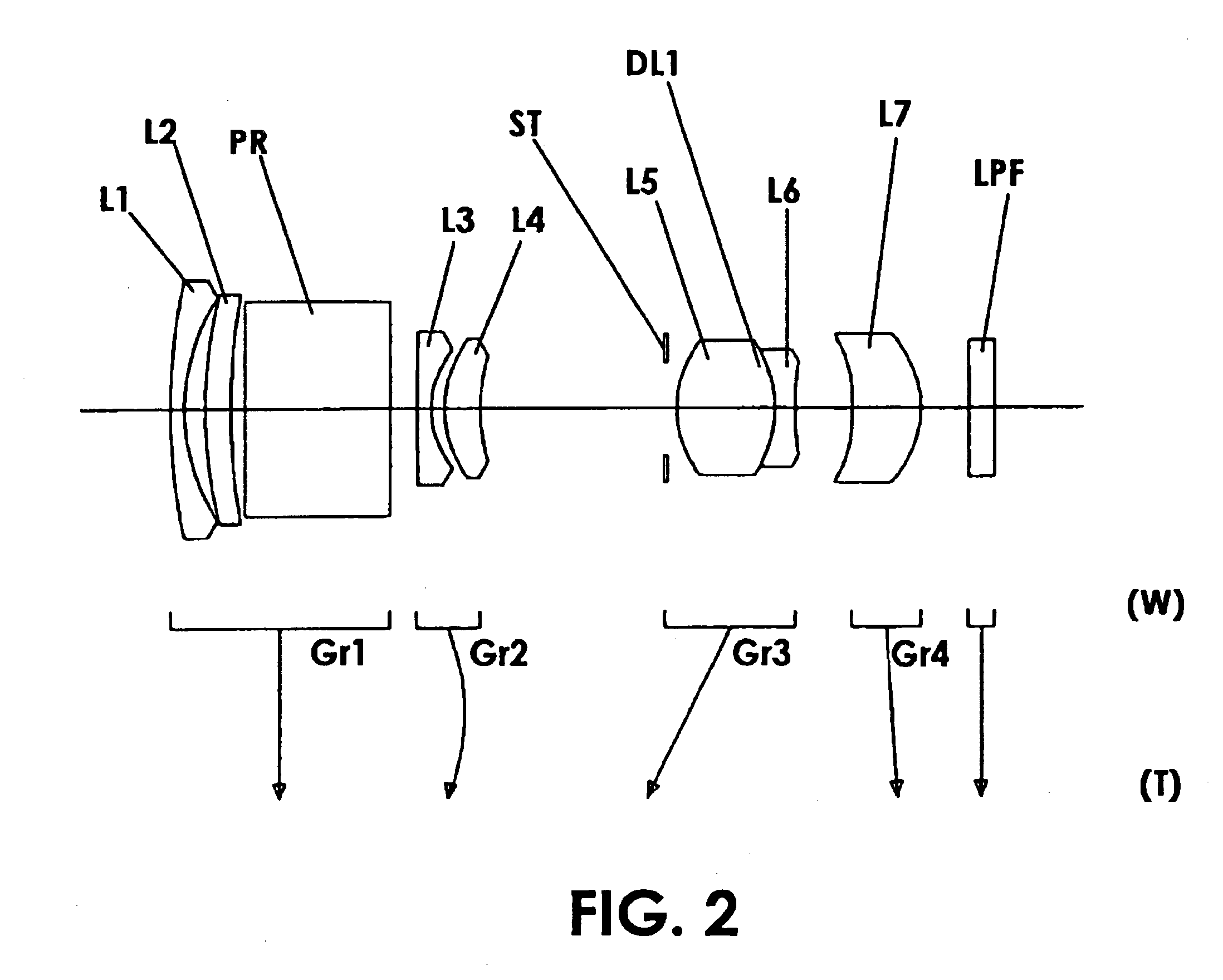
Imaging device and digital camera using the imaging device
InactiveUS6728482B2Reduce manufacturing costLow cost manufacturingTelevision system detailsPrintersCamera lensOptical power
An imaging device has a zoom lens system having a plurality of lens units and forming an optical image of an object so as to continuously optically zoom by varying distances between the lens unit; and an image sensor converting the optical image formed by the zoom lens system to an electric signal. The zoom lens system has from an object side, a first lens unit being overall negative and including a reflecting surface that bends a luminous flux substantially 90 degrees; and a second lens unit disposed with a variable air distance from the first lens unit, and having an optical power, and wherein at least one lens element made of resin is included in the entire lens system.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS7911712B2Small and fast and inexpensiveSufficient optical performanceOptical elementsOptical axisNegative power
An imaging lens includes, in order from an object side, a first lens having a negative power and including a concave image-side surface, a second lens having a positive power, a stop, a third negative lens, which is a biconcave lens, a fourth lens having a positive power, and a fifth lens having a positive power and including a convex image-side surface. The imaging lens satisfies the following conditional expressions:0.18<(D4+D5) / f<0.44, and0.18<D1 / f where f denotes a focal length of an entire lens system, D1 denotes a thickness of a center of the first lens, D4 denotes a distance from an image-side surface of the second lens to the stop on an optical axis, and D5 denotes a distance from the stop to an object-side surface of the third lens on the optical axis.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Zoom lens and image projection apparatus having the same
The present invention discloses a zoom lens which reduces the size of an entire lens system, effectively corrects various types of aberration accompanying zooming and has good optical performance over the entire screen. The zoom lens comprises, in order from a front side to a front side, a first lens unit having a negative refractive power, a second lens unit having a positive refractive power, a third lens unit having a positive refractive power, a fourth lens unit having a negative refractive power, a fifth lens unit having a positive or negative refractive power and a sixth lens unit having a positive refractive power and satisfies the following conditions; at least four lens units move during zooming from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end, o1 represents a distance from a surface vertex on the most front side of the first lens unit to a position of a principal plane on the front side and L1 is an overall length of the first lens unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Serially controllable LED lighting systems
ActiveUS7494244B1Deter damageDeter to breakageCoupling device connectionsMechanical apparatusSurface mountingEffect light
Owner:HAYWARD IND INC
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
An imaging lens includes a first lens having a negative power and including a concave surface facing an image side, a second lens having a positive power, a third lens having a positive power, an aperture diaphragm, a fourth lens, which is a biconvex lens having a negative power, a fifth lens having a positive power and including a convex surface facing the image side, and a sixth lens having a positive power and including a convex surface facing an object side, which are arranged in this order from the object side. The Abbe number of a material forming the fourth lens with respect to the d-line is 30 or less. When the focal length of the entire lens system is f and a composite focal length from the fourth lens to the sixth lens is f456, the imaging lens satisfies following conditional expression:1.00<f456 / f<1.88.
Owner:JIANGXI OFILM OPTICAL CO LTD
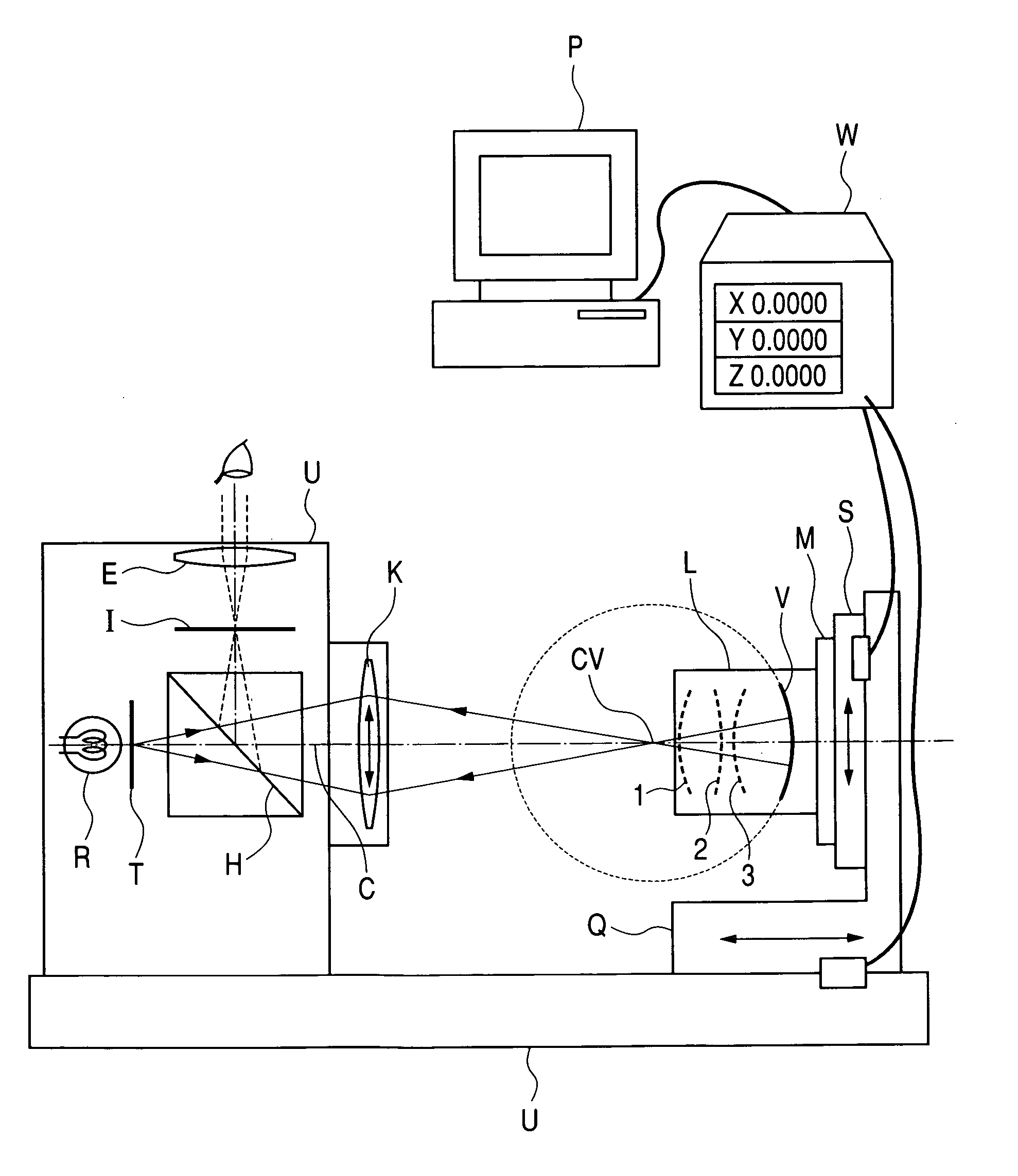
Eccentricity measuring method and eccentricity measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20050128468A1Accurate quantityReduce measurementUsing optical meansOptical axis determinationMeasurement deviceEntire lens
A surface to be tested and an optical system for projecting an index to an apparent spherical center position of the surface to be tested are moved relative to each other and an eccentric quantity of the surface to be tested is calculated from an movement quantity. A focal distance of an optical system is changed according to an apparent radius of curvature of each surface to be tested, which is calculated in advance. A reflection image on a surface to be tested, which is to be measured, is determined from the apparent radius of curvature of each surface to be tested, which is calculated in advance. Thus, an eccentric quantity of the entire lens system is accurately measured.
Owner:CANON KK
Near Infra-red Imaging Lens Assembly
ActiveUS20110069378A1Reducing interference and influenceImprove imaging resolutionOptical elementsImage resolutionImaging lens
This invention provides an NIR imaging lens assembly comprising a lens element with refractive power made of a visible-light-absorbable material, and a filter or a filter film formed on one lens element with refractive power for filtering out infrared light, wherein the number of lens elements with refractive power in the NIR imaging lens assembly is N, and wherein N≧2. The above lens arrangement allows light in a specific NIR wavelength range to pass through the lens assembly, thereby reducing interferences or influences from light in the other wavelength ranges. As a result, the resolution of the imaging lens assembly is improved, and its total track length is reduced effectively so that the entire lens system can be compact.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Zoom lens and image projection apparatus having the same
The present invention discloses a zoom lens which reduces the size of an entire lens system, effectively corrects various types of aberration accompanying zooming and has good optical performance over the entire screen. The zoom lens comprises, in order from a front side to a rear side, a first lens unit having a negative refractive power, a second lens unit having a positive refractive power, a third lens unit having a positive refractive power, a fourth lens unit having a negative refractive power, a fifth lens unit having a positive or negative refractive power and a sixth lens unit having a positive refractive power and satisfies the set forth conditions.
Owner:CANON KK
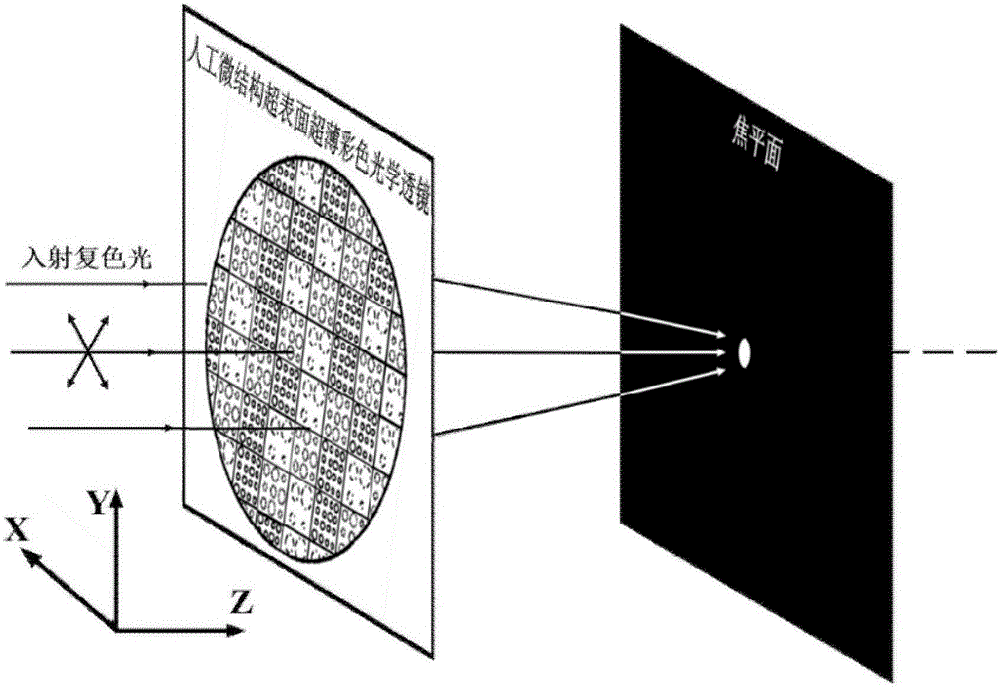
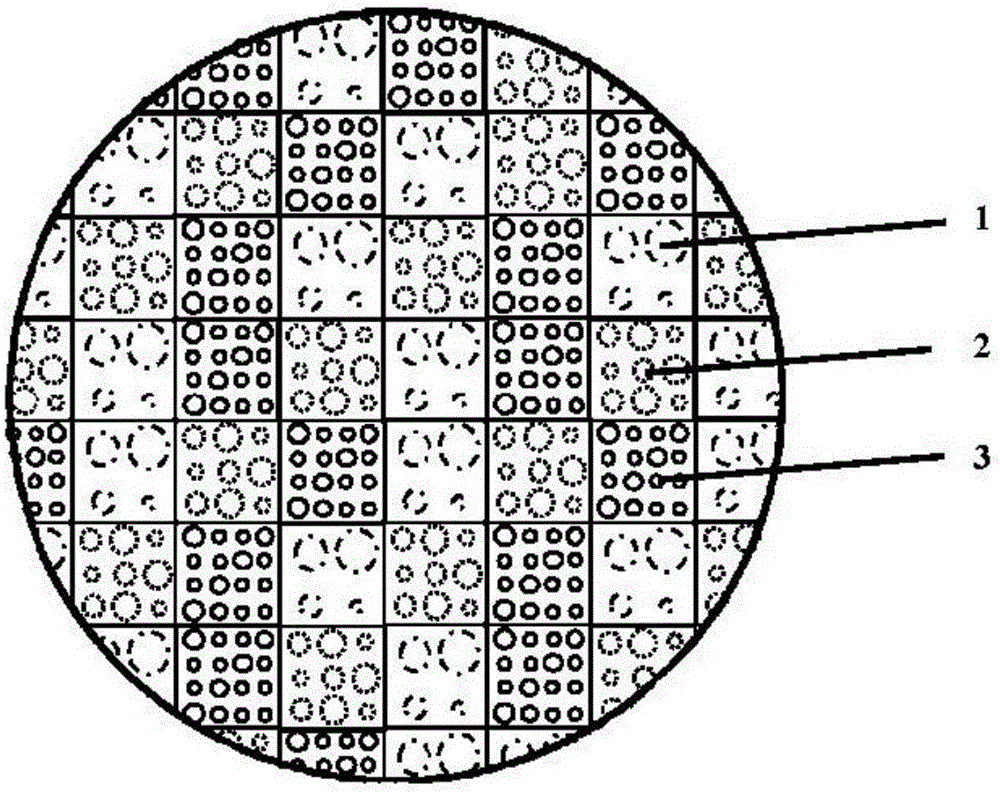
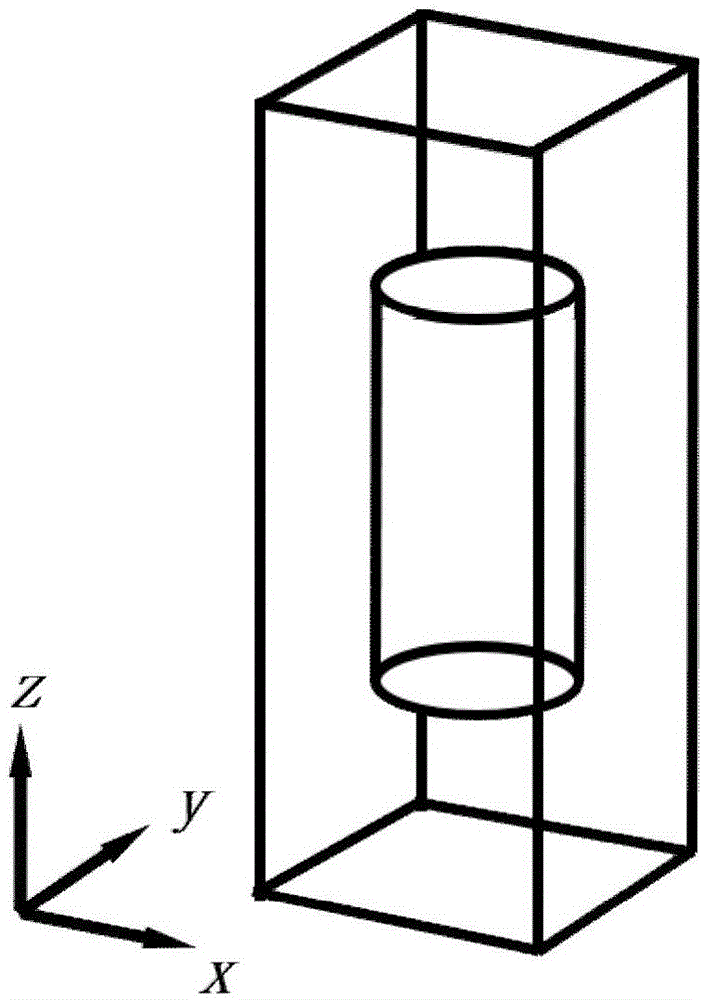
Method of constructing ultrathin color optical lens based on artificial microstructure super surface
The invention discloses a method of constructing an ultrathin color optical lens based on an artificial microstructure super surface, comprising the following steps: (1) calculating the phase distribution on an artificial microstructure super surface according to the position of a focus point needing emergence; (2) designing a rotational symmetry periodic structure for each center wavelength, and determining a specific phase value based on the phase gradient distribution; (3) designing a columnar structure of determined height as a basic unit of the artificial microstructure super surface, and designing a corresponding specific implementation structure; (4) randomly dividing the N regions of an entire lens into m parts, and ensuring that the number of regions in each part is roughly the same according to the need or ensuring that a certain ratio is achieved according to the specific need; (5) taking m selected regions to m corresponding lenses in step (3) to form new lenses; and (6) forming a filter array based on filters of corresponding working wavelengths on the lenses according to the specific wavelength of each region. A color optical lens constructed using the method has the advantages of being ultra-thin, bi-planar and easy to integrate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
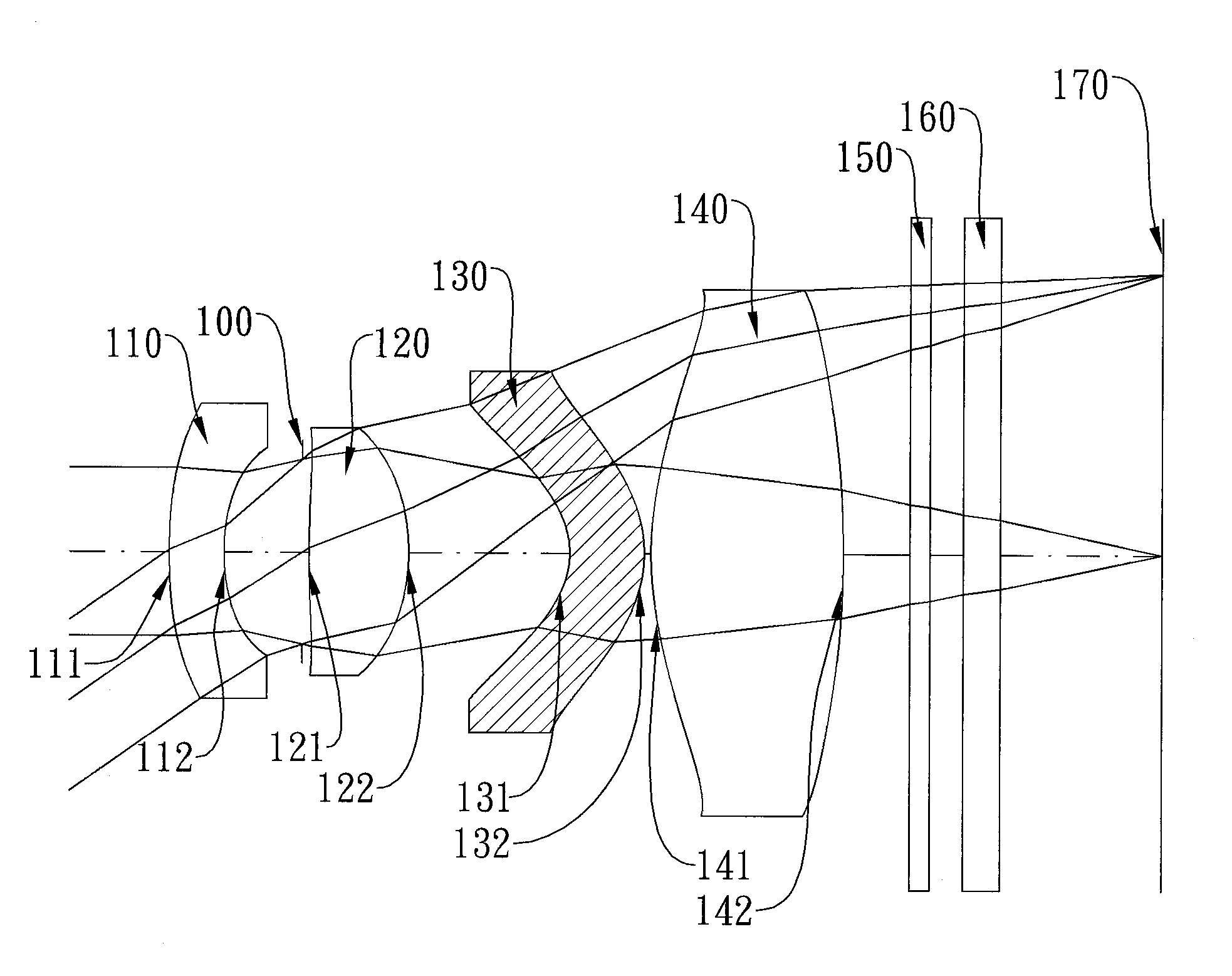
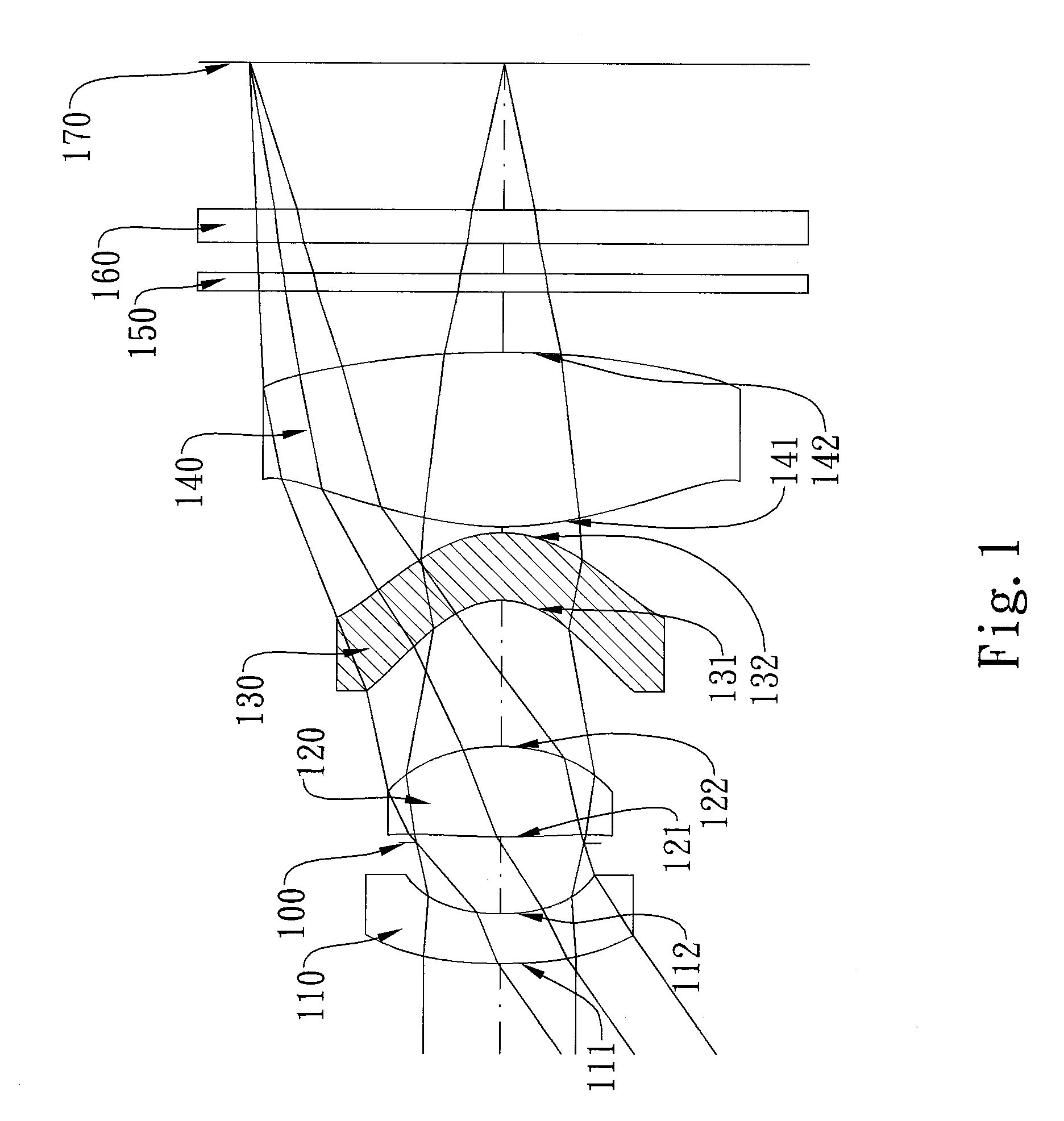
Image capturing lens and image capturing apparatus
InactiveUS20140029117A1Appropriate back focusAvoid distortionLensOphthalmologyConditional expression
Arranging a negative first lens, a positive second lens, a negative third lens, a positive fourth lens, and a negative fifth lens from the object side, in which the image side surface of the fifth lens has an aspherical shape with one or more inflection points and a concave shape toward the image side in a paraxial region, and, when the focal length of the entire lens system, radius of curvature of the image side surface of the first lens, radius of curvature of the image side surface of the second lens, overall optical length, focal length of jth lens, and Abbe number of jth lens are taken as f, R2, R4, TL, fj, and vj respectively, the image capturing lens is configured to simultaneously satisfy conditional expressions (1a): −1.5<f / R2<1.6, (2a): −1.6<f / R4<0.05, (3a): 0.95≦f4 / f≦4.3, (5a): 1.0≦TL / f≦2.2, and (12b): −2.0<Σ(fj / νj) / f<0.5.
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Imaging lens system
InactiveUS20070195432A1Shorten the lengthEasy to correctApparel holdersPicture framesOrder formConvex side
Owner:ENPLAS CORP
Imaging device
InactiveCN1745337ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensConditional expression
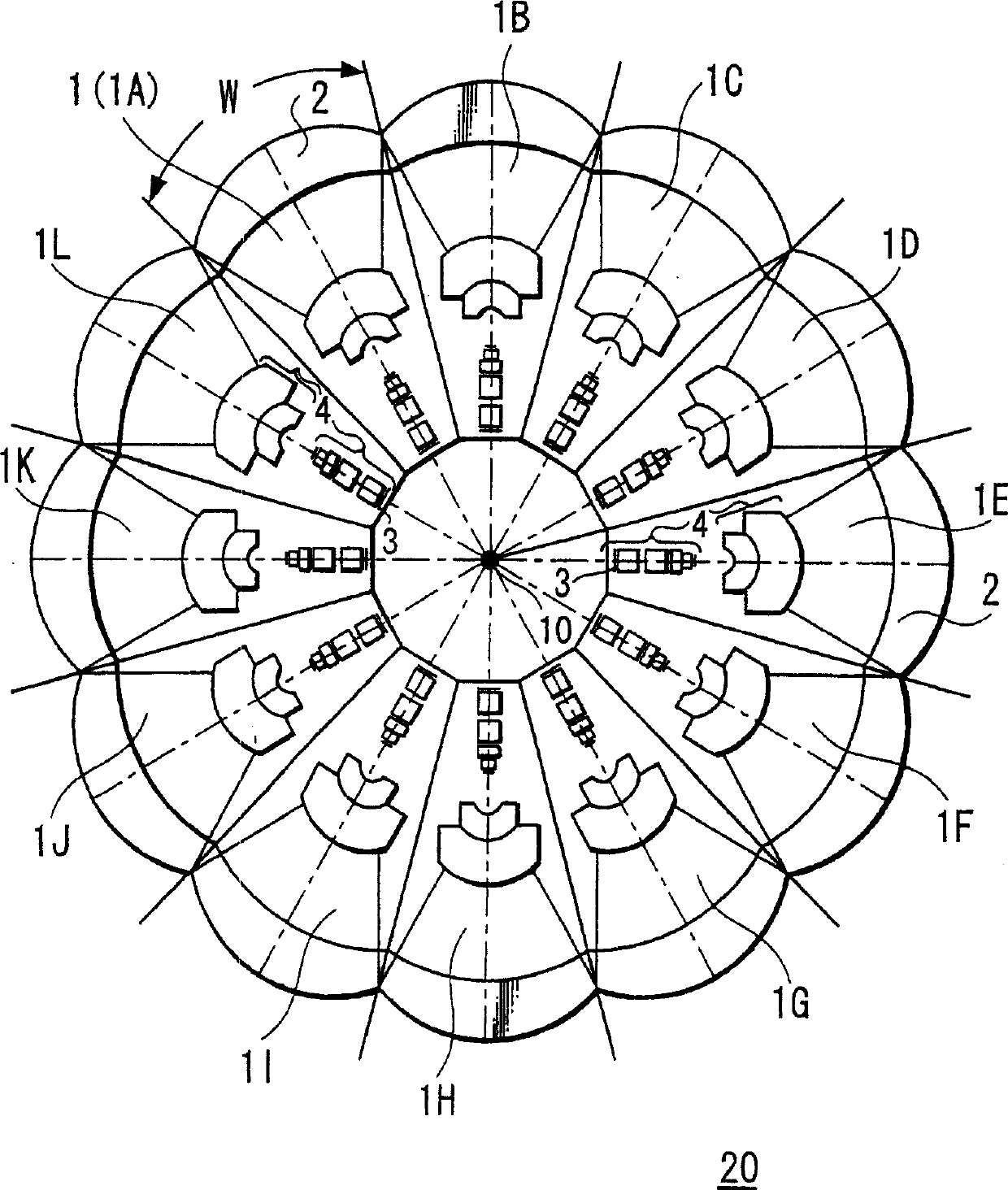
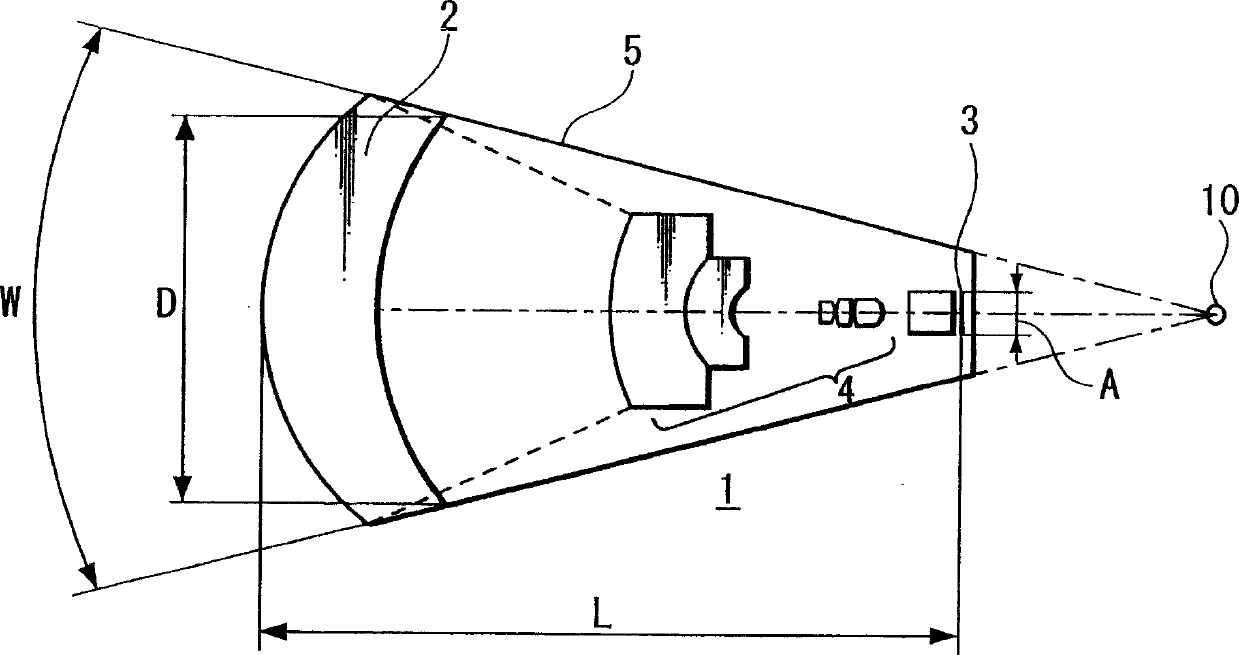
An imaging device capable of picking up a wide range from a plurality of imaging units, providing a good image quality, and being downsized. The imaging device (20) comprises a plurality of imaging units (1) each provided with an imaging element (3) and a lens front cell (2), wherein adjacent imaging units (1) are so disposed as to allow their imaging areas to be overlapped, and, when a section passing through a view point center, an imaging element (3), and a lens front cell (2) in this overlapping direction is assumed, a conditional expression, AL < fD (1), is satisfied and the view point center of each imaging unit (1) is disposed within a 20-mm sphere; where the section length of the imaging element (3) is A, the section length of the lens front cell (2) D, the distance from the lens front cell (2) to the imaging element (3) L, a focal distance obtained by combining the entire lens in the imaging unit (1) including the lens front cell (2) f.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Lens unit and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050219717A1Satisfactory workabilitySatisfactory assembly workabilityOptical articlesMountingsInfraredOptoelectronics
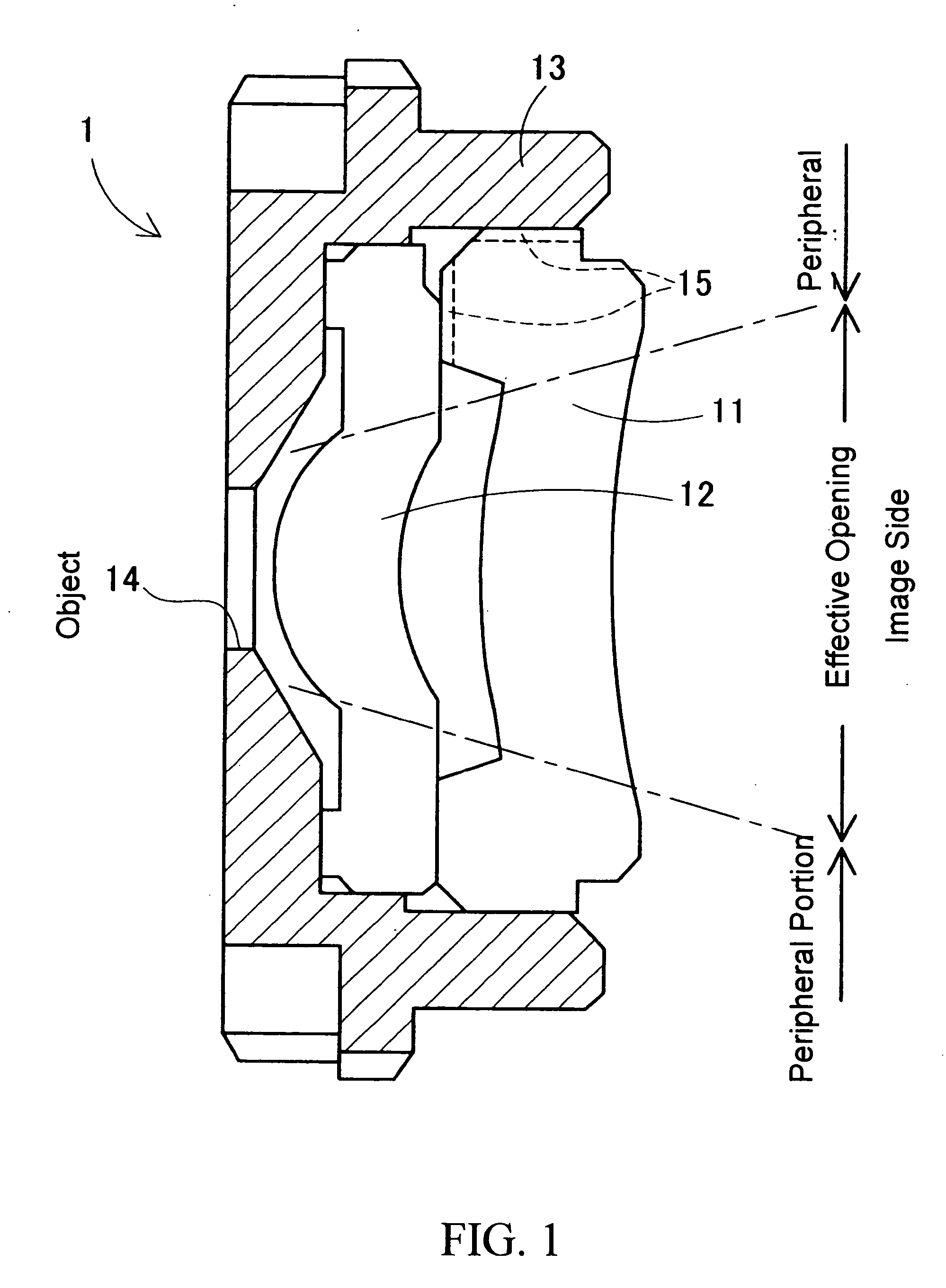
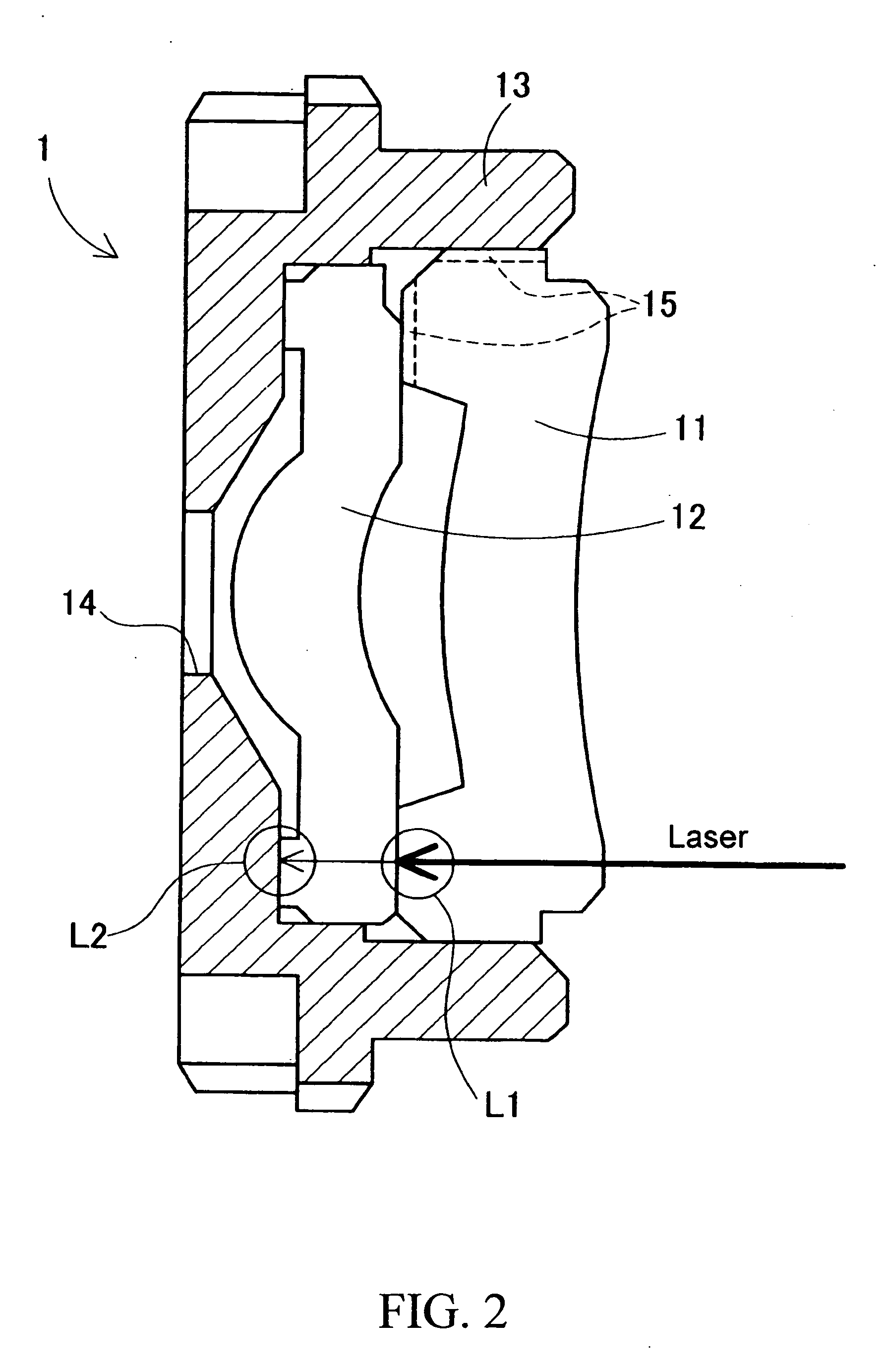
In the case where a lens unit where two ore more transparent resin lenses are combined is constituted, at least one transparent resin lens contains infrared absorbent. When the lens unit is assembled, an infrared laser is emitted to a joined portion between the transparent resin lens and the other transparent resin lens. As a result, the emitted infrared ray is absorbed by the infrared absorbent, so that the transparent resin lenses are welded to each other. An opaque lens barrel which holds the entire lens unit and the transparent resin lenses are joined by welding.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Zoom lens and image projection apparatus having same
A zoom lens telecentric on a reduction side includes a first negative lens, a second negative lens and a first positive lens arranged from the enlargement side to the reduction side. At least one of the first and second negative lenses has an aspherical surface. The zoom lens satisfies −f12 / fw<1.4, −f12 / (Hwpn−f12)<0.6 and |dn / dt|<1.0×10−5, where f12 is the focal length of the combined optical system composed of the first and second negative lenses, Hwpn is the distance from the rear principal point of the combined optical system composed of the first and second negative lenses to the front principal point of the first positive lens, dn / dt is a change in the refractive index of the material of which said one negative lens is made relative to a change in its temperature from 25° C., and fw is the focal length of the entire lens system at the wide angle end.
Owner:CANON KK
Lens unit, image capturing lens, image capturing device and portable terminal
InactiveUS20110013070A1Suppress defocusDeterioration of performance can be immunizedTelevision system detailsOptical articlesOphthalmologyRefractive index
A lens unit LU in which a lens portion L is formed at least on either a light-receiving surface or a light-emitting surface of a lens holding plate P, wherein a difference in coefficients of linear expansion of the lens holding plate P and the lens portion L is used to suppress mis-focusing by causing changes in a paraxial image point position of the entire lens system due to changes in the surface shape of the lens portion L which accompany temperature changes, and changes in the paraxial image point position of the entire lens system due to changes in the refraction index to cancel each other out. Furthermore, deterioration of performance of the entire lens system caused by rising temperature is suppressed by satisfying a predetermined conditional expression.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Imaging lens
InactiveUS20050128334A1Conveniently implementedImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisImaging lens
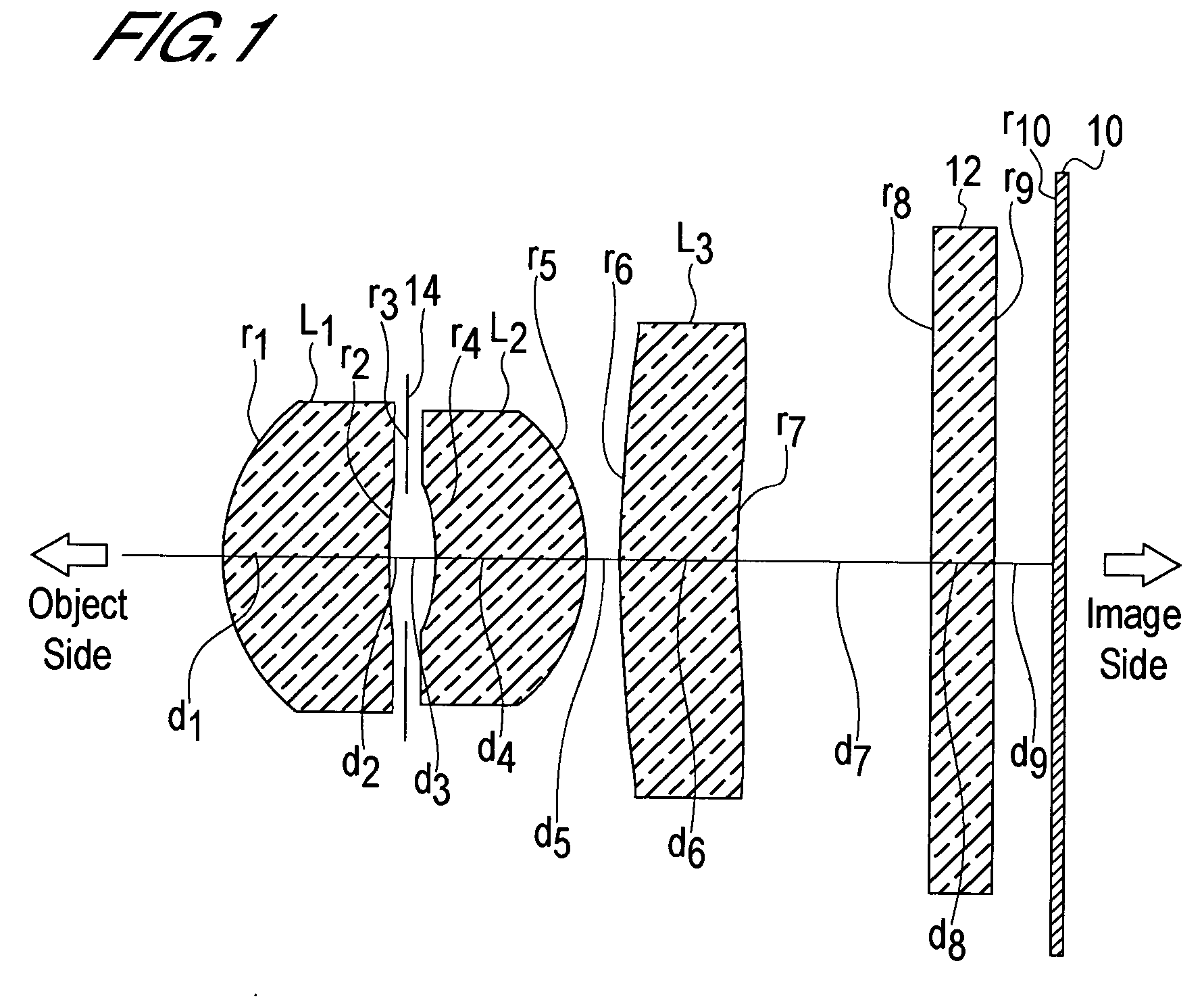
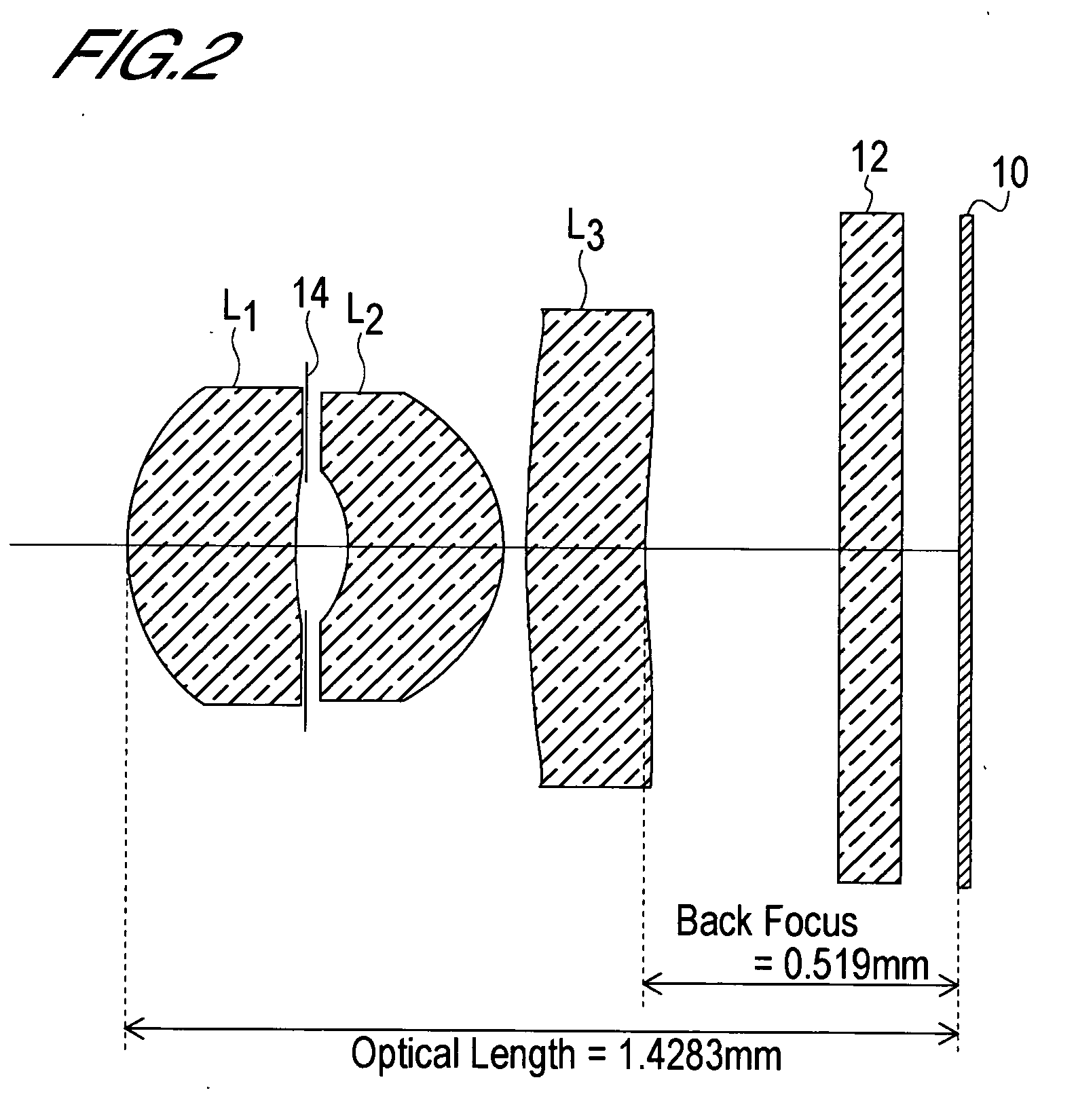
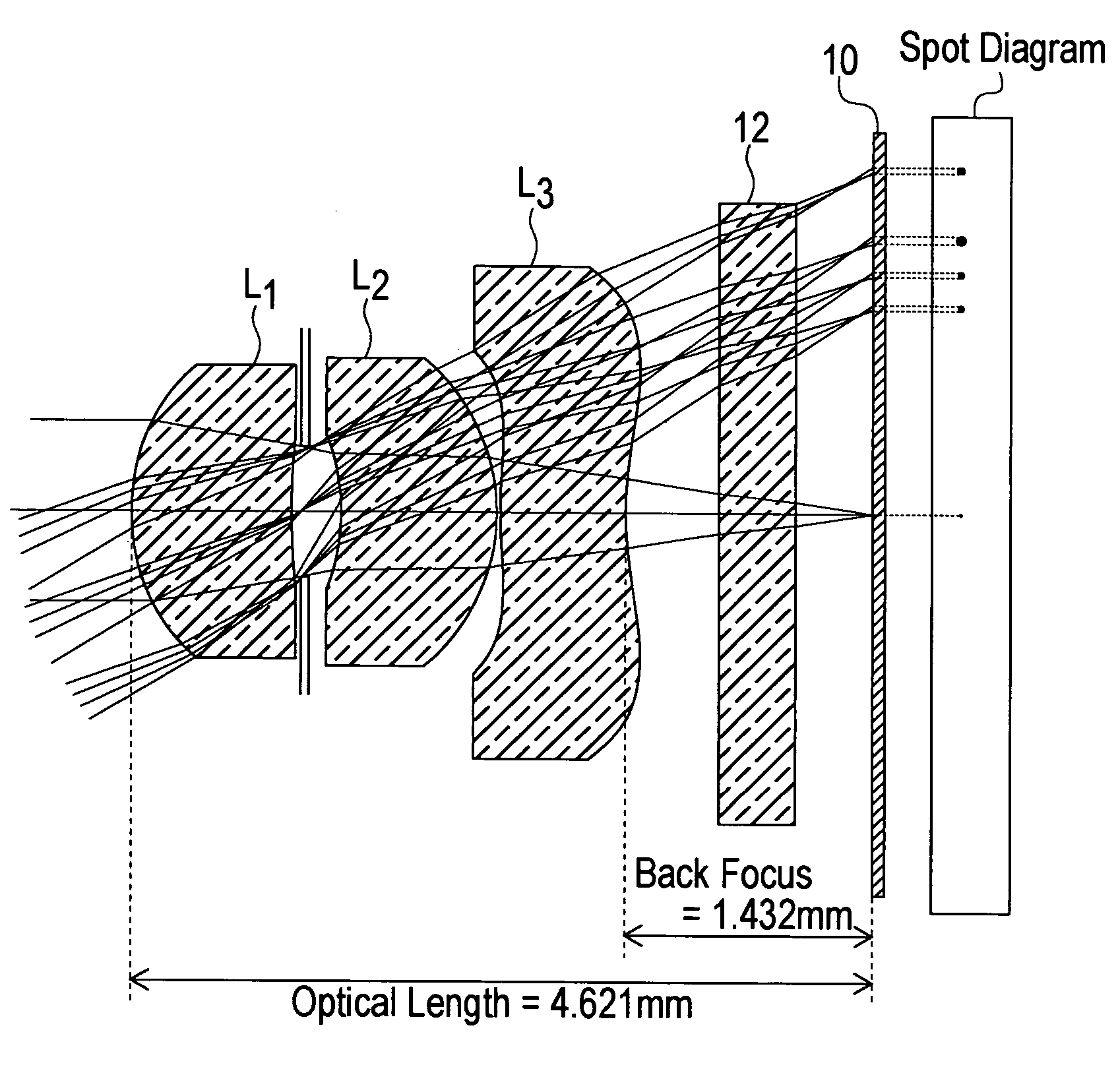
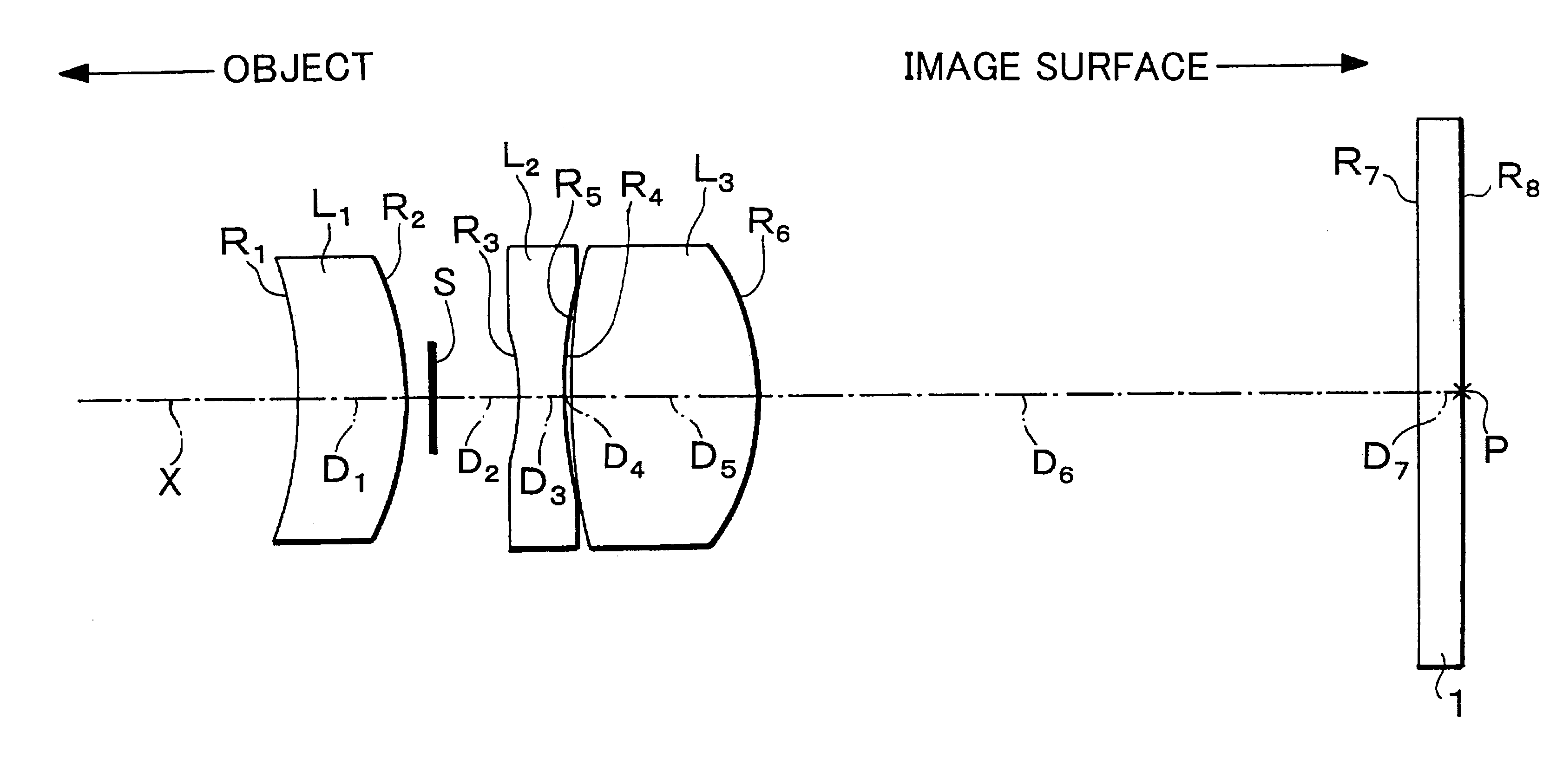
The present invention is an imaging lens in which various aberrations are satisfactorily corrected, the optical length is short, and a sufficient back focus is secured. The imaging lens is constituted by arranging a first lens L1, an aperture diaphragm S1, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in succession from the object side to the image side, and thus satisfies the following conditions. 0.40<r1 / r2<0.65 (1) 0.08<D2 / f<0.1 (2) 0.2<D3 / f<0.3 (3) 1.0<d / f<1.5 (4) 0.4<bf / f<0.6 (5) where f is the focal length of the entire lens system, [0001]r1 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the object-side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, [0002]r2 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the image-side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, [0003]D2 is the interval between the first lens L1 and second lens L2, [0004]D3 is the thickness at the center of the second lens L2, [0005]d is the distance(in air) from the object-side surface of the first lens L1 to the imaging surface, and [0006]bf is the back focus (in air).
Owner:DO CORP LTD +1
Imaging lens
InactiveUS20050030645A1Not impair compactnessDistortion can be sufficientlyLensOptical elementsOptical axisOptoelectronics
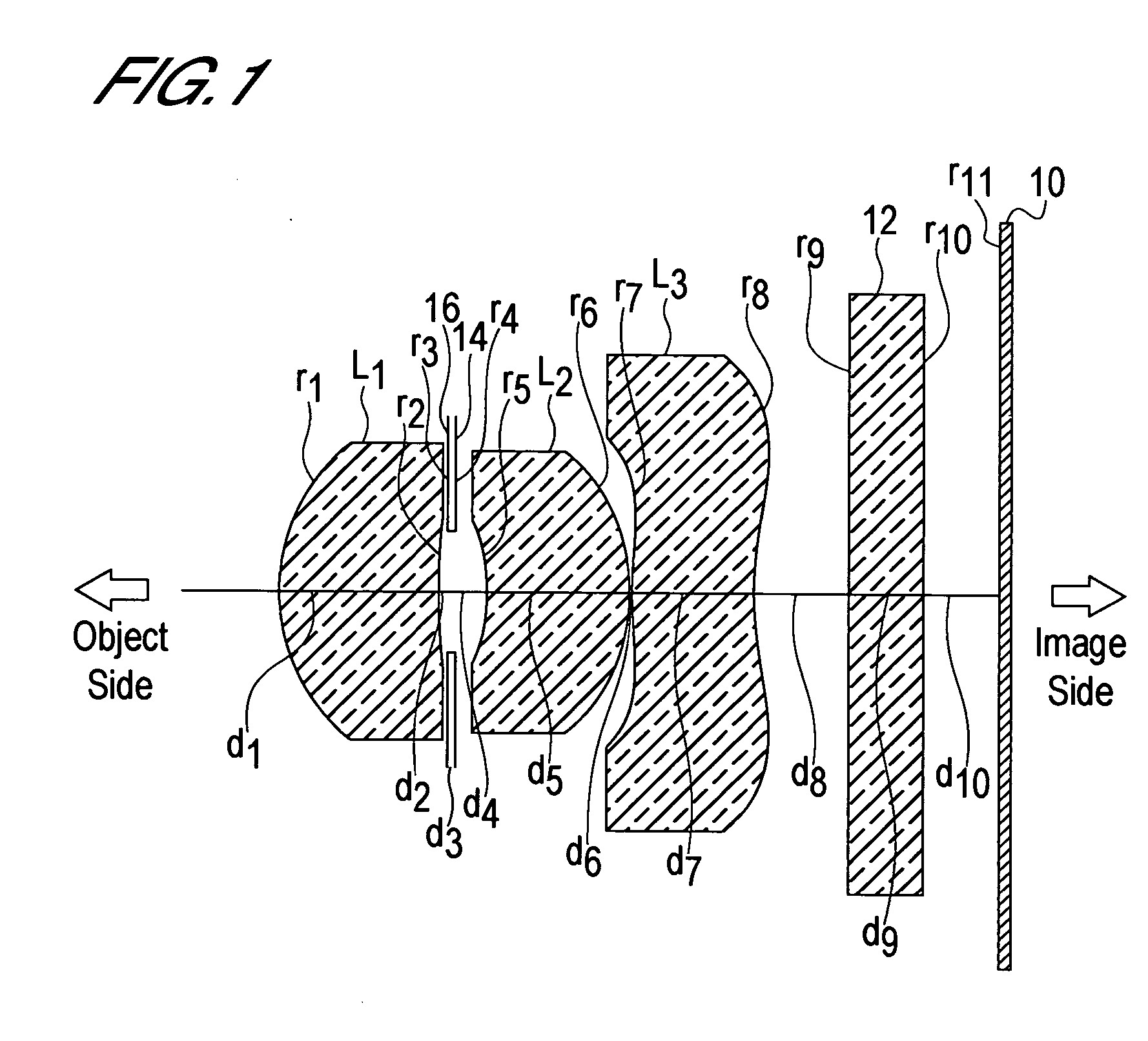
In an imaging lens of the present invention, aberration is satisfactorily corrected, the optical length is short, and a sufficient back focus is secured. The imaging lens of the present invention is constituted by arranging a first lens L1, an aperture diaphragm S1, a second lens L2, and a third lens L3 in succession from the object side to the image side, and thus satisfies the following conditions.0.24<r1 / r2<0.34 (1)0.08<D2 / f<0.1 (2)0.24<D3 / f<0.29 (3)1.0<d / f<1.5 (4)where f is the focal length of the entire lens system, r1 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the object side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, r2 is the radius of curvature (axial curvature radius) of the image side surface of the first lens L1 in the vicinity of the optical axis, D2 is the distance between the first lens L1 and second lens L2, D3 is the thickness at the center of the second lens L2, and d is the distance(in air) from the object side surface of the first lens L1 to the image surface.
Owner:MILESTONE CO LTD +1
Customized Z-Lens Design Program
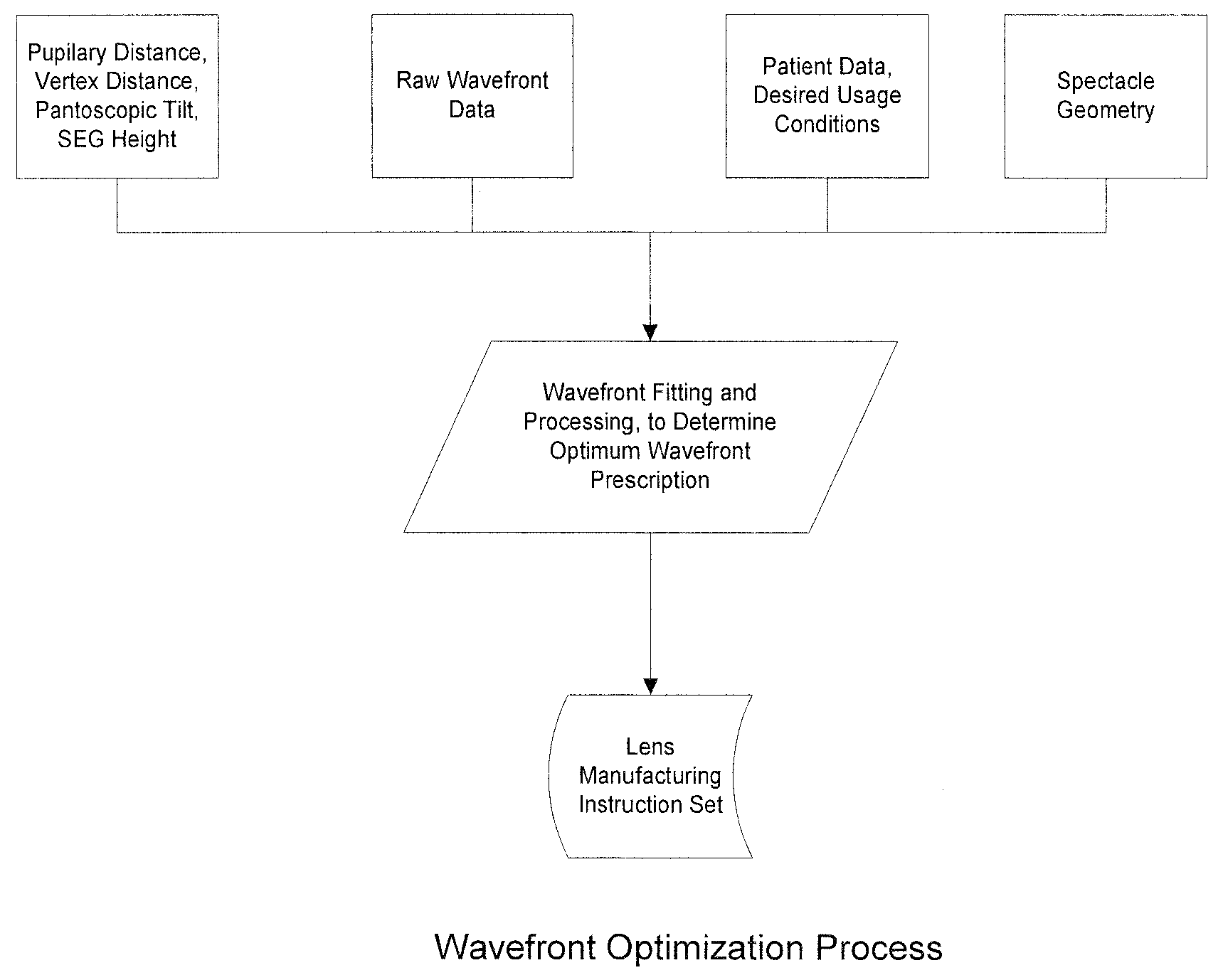
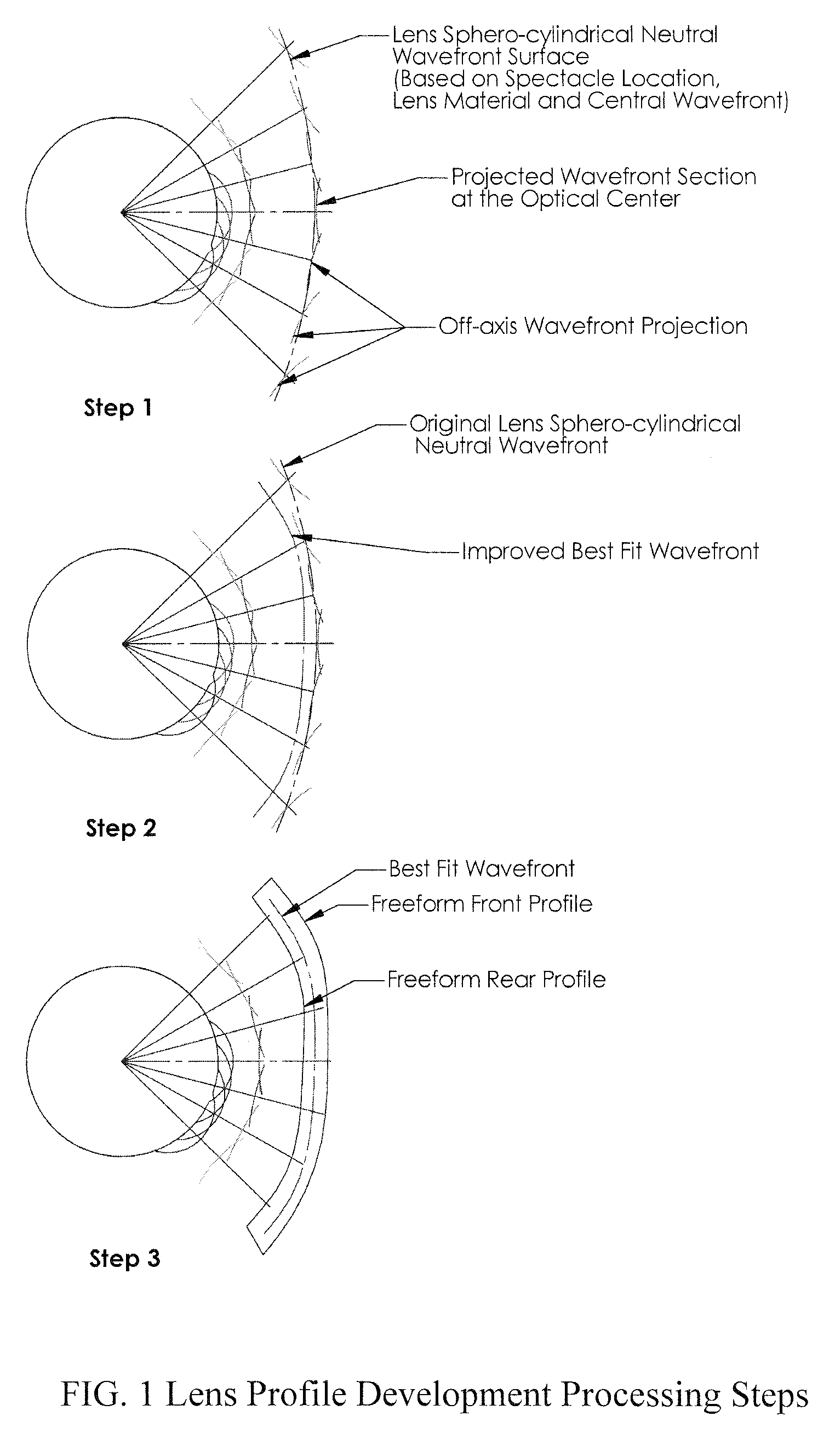
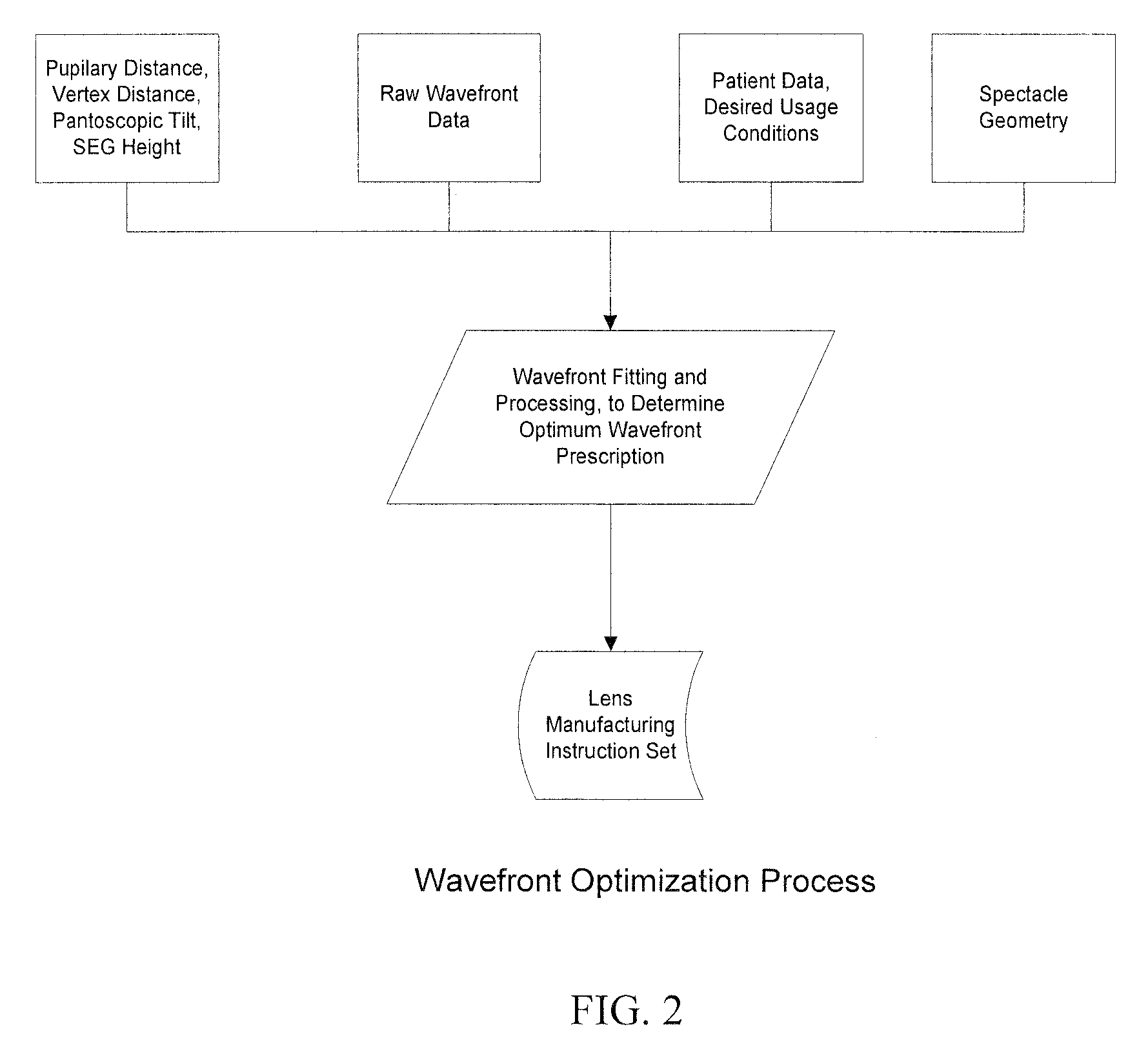
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method for producing a spectacle lens with optimal correction across the entire lens taking into account the patient's complete measured wavefront. Specific embodiments can also take into account one or more additional factors such as vertex distance, SEG height, pantoscopic tilt, and use conditions. The lens wavefront can be achieved by optimizing a corrected wavefront, where the corrected wavefront is the combined effect of the patient's measured wavefront and the lens wavefront. The optimization of the corrected wavefront can involve representing the measured wavefront and the lens wavefront on a grid. In an embodiment, the grid can lie in a plane. During the optimization, a subset of the grid can be used for the representation of the measured wavefront at a point on the grid so as to take into account the portions of the measured wavefront that contribute to the corrected wavefront at that point on the grid.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Imaging optical system with focusing function
InactiveUS20060103947A1Great easeEfficient preparationTelevision system detailsLensImage-forming optical systemRefractive index
An imaging optical system is provided and has a focusing section including a cemented lens (first and second lenses), which includes first and second fluid materials having different refractive indices from each other; and whose cemented surface shape can be electrically controlled. A refractive index Nd1 of the first fluid material, a refractive index Nd2 of the second fluid material, a minimum value RA of a radius of curvature of the cemented surface of the cemented lens, a focal length fa of the whole cemented lens, and a focal length f of the whole lens system satisfy the conditions specified in the specification.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Single-focus lens
A single-focus lens includes from the object side, a first lens with a positive refracting power having at least one aspheric surface, a stop, a second lens with a negative refracting power, and a third lens with a positive refracting power having at least one aspheric surface. This single-focus lens further satisfies the conditional expression of 0.3<f / f2'3<0.8, where f is the focal length of the lens as a whole, and f23 is the composite focal length of the second and third lenses.
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Zoom lens and image pickup apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20090296230A1High zoom ratioGood optical performanceDiffraction gratingsOptical axisEntire lens
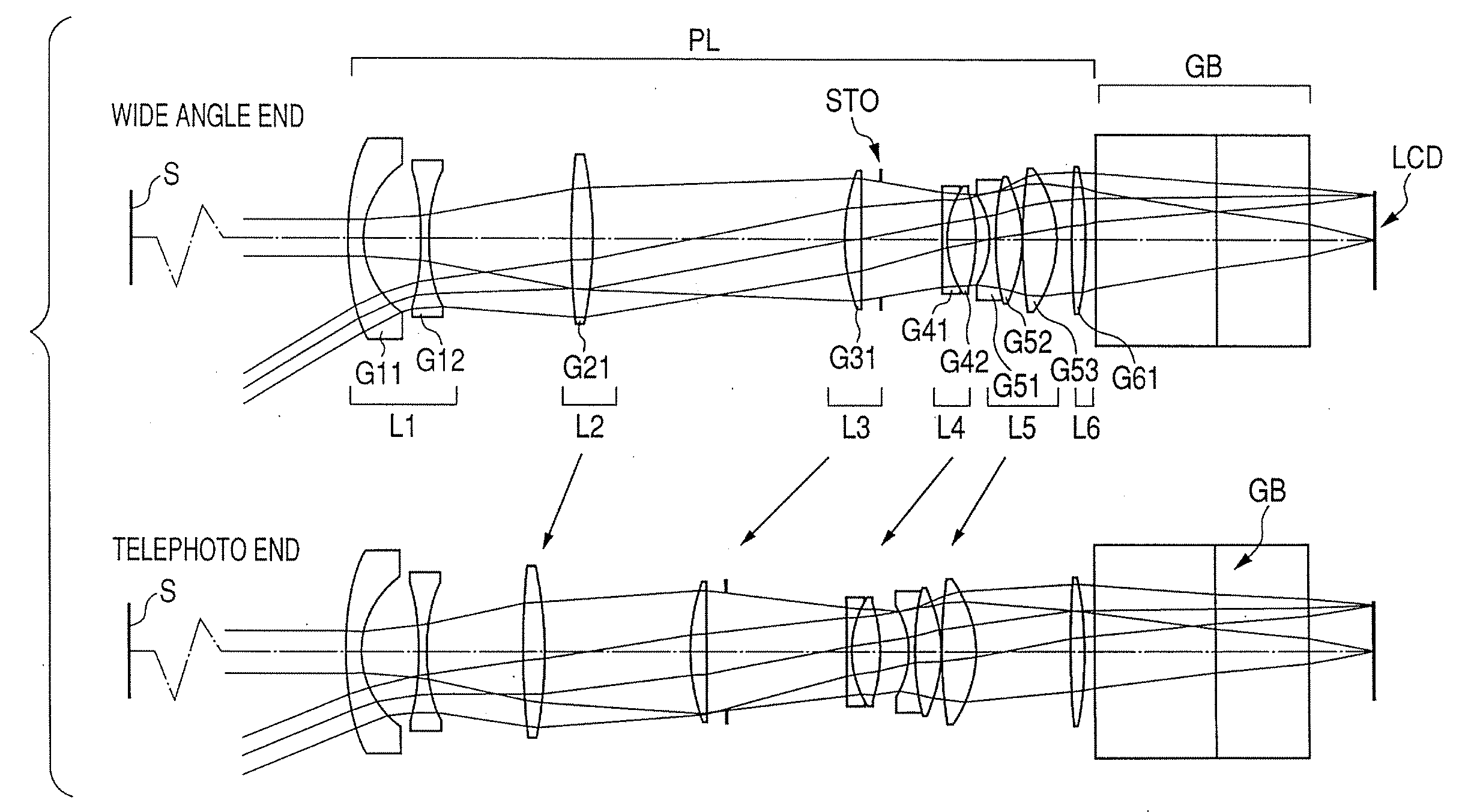
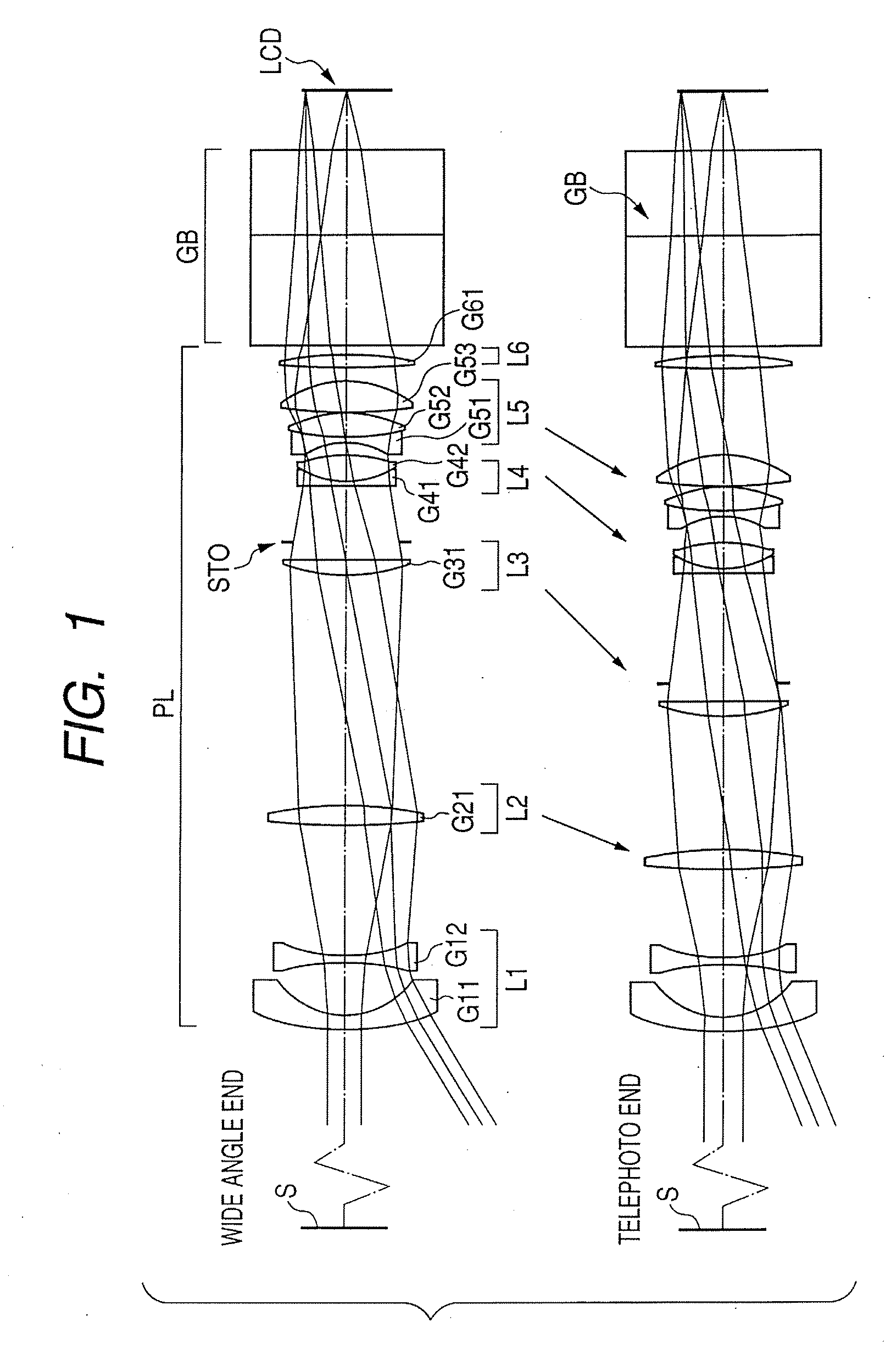
Provided is a zoom lens including in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens unit having a positive refractive power; a second lens unit having a negative refractive power; a third lens unit having a positive refractive power; and a fourth lens unit having a positive refractive power, each of the first lens unit, the second lens unit, the third lens unit, and fourth lens unit moving to perform zooming, in which M3 representing a moving amount of the third lens unit on an optical axis during zooming from a wide angle end to a telephoto end, Lt representing a total lens length on the telephoto end, f3 representing a focal length of the third lens unit, and ft representing a focal length of an entire lens system on the telephoto end are each appropriately set.
Owner:CANON KK
Wide-angle lens system
A wide-angle lens system includes a positive front lens group, a diaphragm, and a positive rear lens group. The front lens group includes a negative first-sub-lens group and a positive second-sub-lens group. The negative first-sub-lens group includes a negative lens element, a positive lens element, and a negative lens element. The front lens group satisfies the following conditions: 0.5<f / |f1a|<0.75 . . . (1) 0.5<|f1a| / f1b<1.0 . . . (2) 0.35<f / f1bi<0.6 . . . (3) wherein f: the focal length of the entire lens system; f1a: the focal length of the negative first-sub-lens group ; f1b:the focal length of the positive second-sub-lens group ; f1bi: the focal length of the most image-side surface of the positive second-sub-lens group; r1bi: the radius of curvature of the most image-side surface of the positive second-sub-lens group; and N1bi: a refractive index of the most image-side lens element of the positive second-sub-lens group.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Vehicle-mounted camera lens
ActiveCN108681050AHigh image qualityImprove distortionVehicle componentsMountingsCamera lensEntire lens
The invention discloses a vehicle-mounted camera lens, which comprises, in order from the object side to the image side, a first lens having a negative focal power, a convex object side surface and aconcave image side surface; a second lens having a negative focal power, a concave object side surface and a convex object side surface; a third lens having a positive focal power and double convex surfaces; a diaphragm; a fourth lens having a positive focal power and double convex surfaces; a fifth lens having a negative focal power and a concave object side surface, and forming a cemented lens with the fourth lens; a sixth lens having a positive focal power and a convex object side surface; and a filter. The second lens, the third lens, the fourth lens, and the fifth lenses are all glass spherical lenses, and the first lens and the sixth lens are glass aspherical lenses. The vehicle-mounted camera lens significantly increases the distortion of the lens in a small angle of view to meet the special algorithm requirements of the vehicle system; and the lens size and length of the lens are effectively controlled while improving the resolution of the entire lens.
Owner:JIANGXI LIANCHUANG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical lens adjusting device and adjusting method thereof
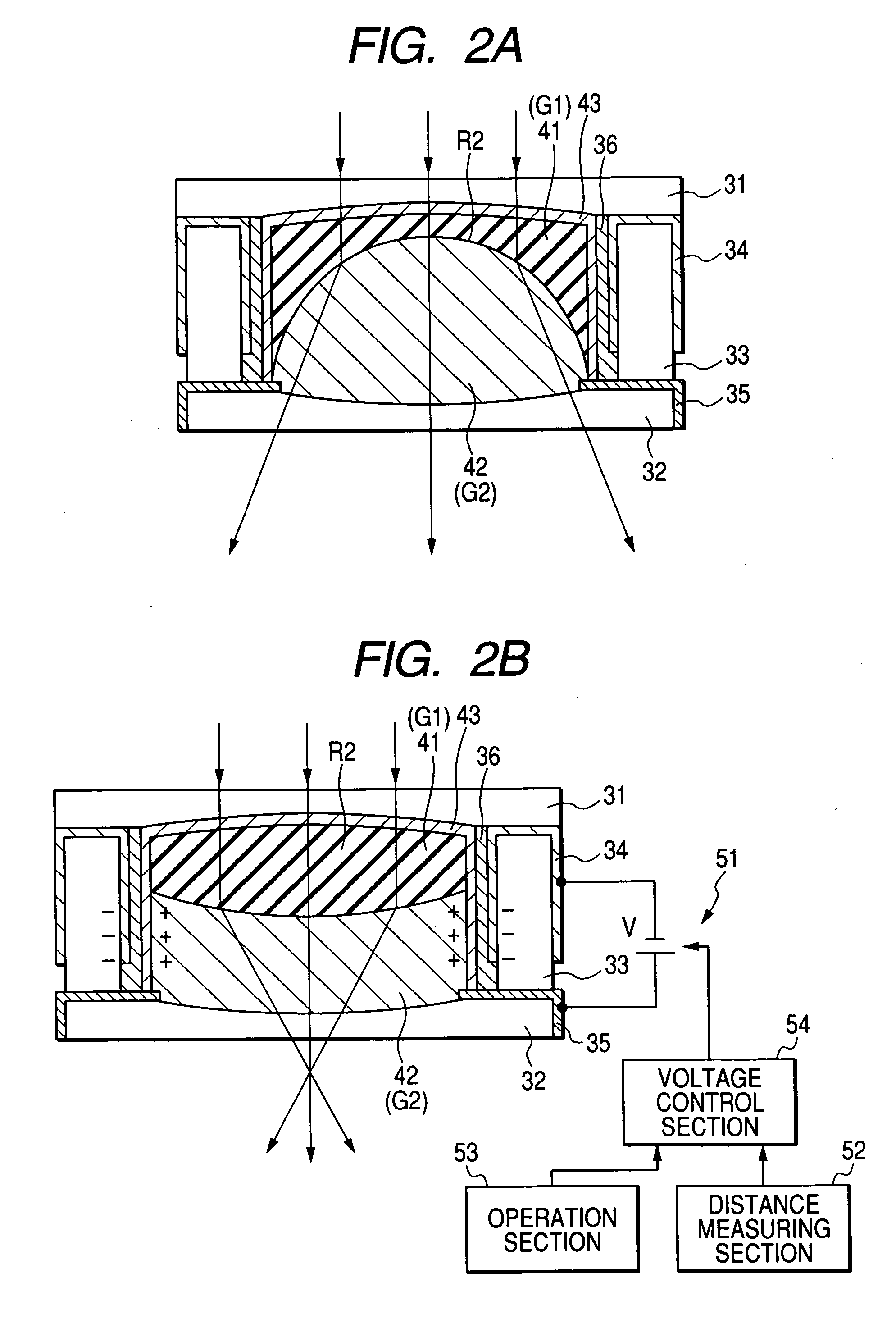
InactiveUS20060028742A1Optical axis alignment optical axis be efficientlyImprove performanceProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementOptical axisEngineering
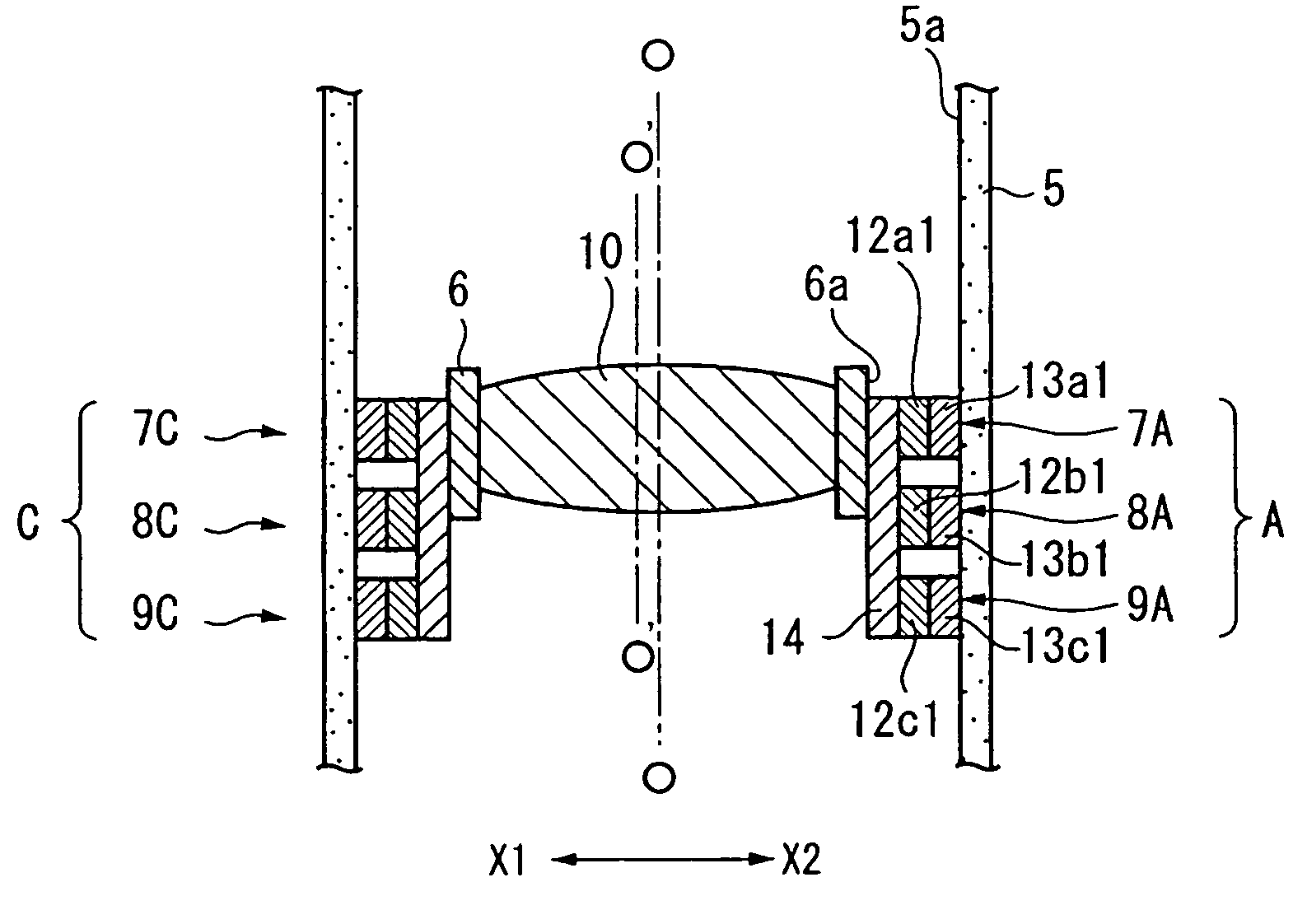
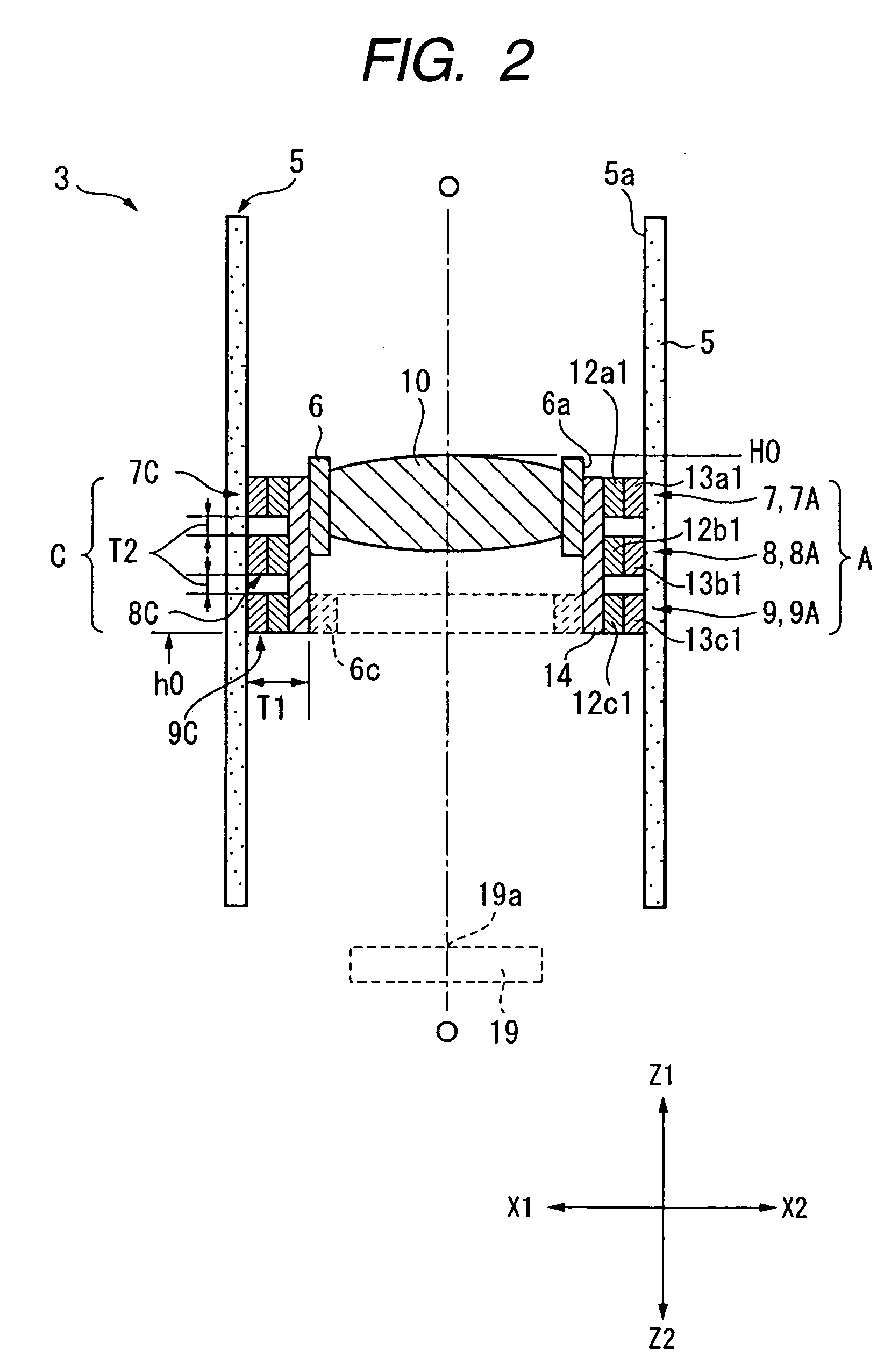
When a voltage is applied between outside electrodes and a common electrode that constitute driving parts of a driving unit provided between a holder holding a lens and a lens barrel, as shown in FIG. 9, respective dielectric elastomers provided in the driving parts are slightly deformed in a direction that is crushed in an X1-X2 direction. Thus, the entire lens can be slightly moved in the direction of an arrow (X2-direction). This enables an optical axis O′-O′ of the lens to coincide with or get closer to a reference optical axis.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com