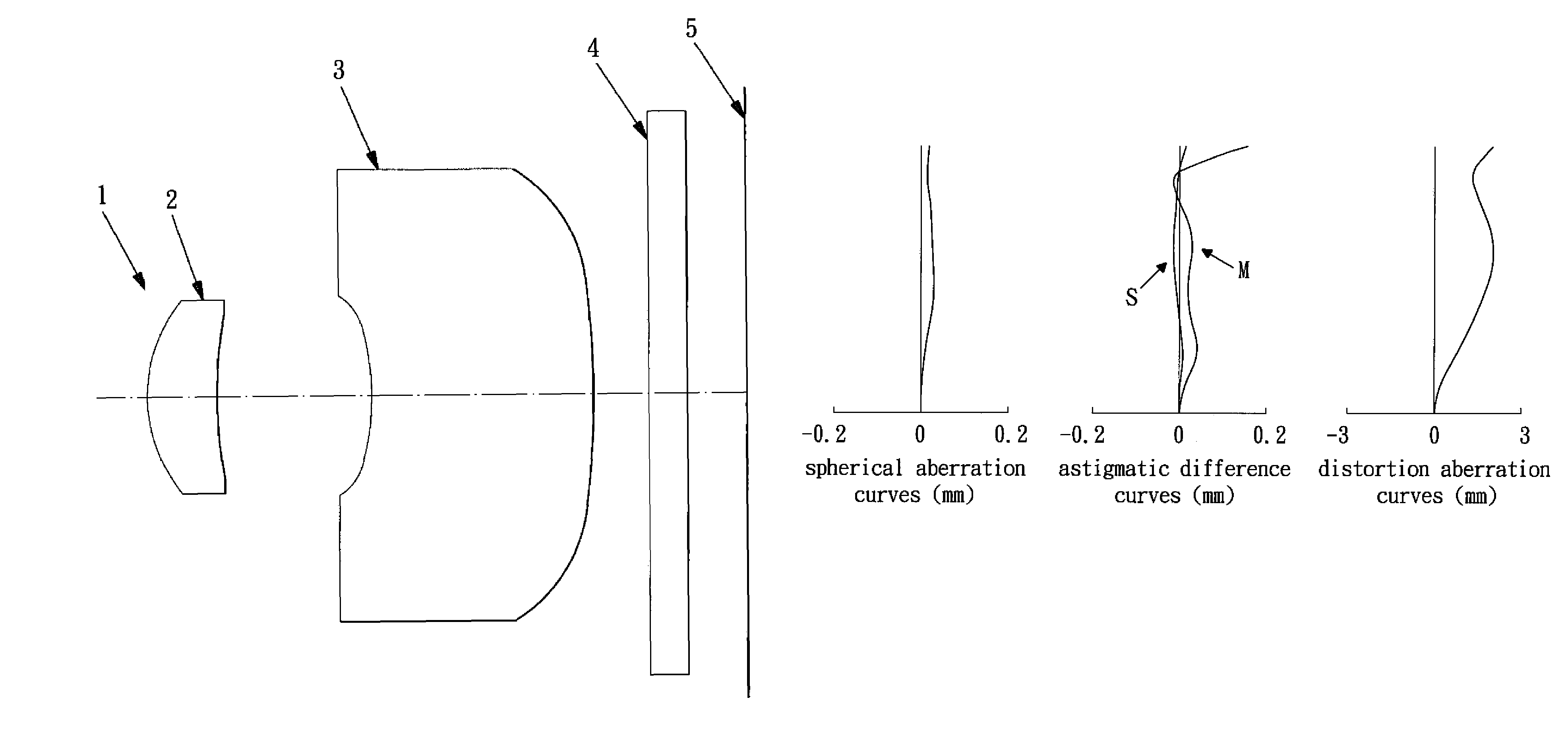
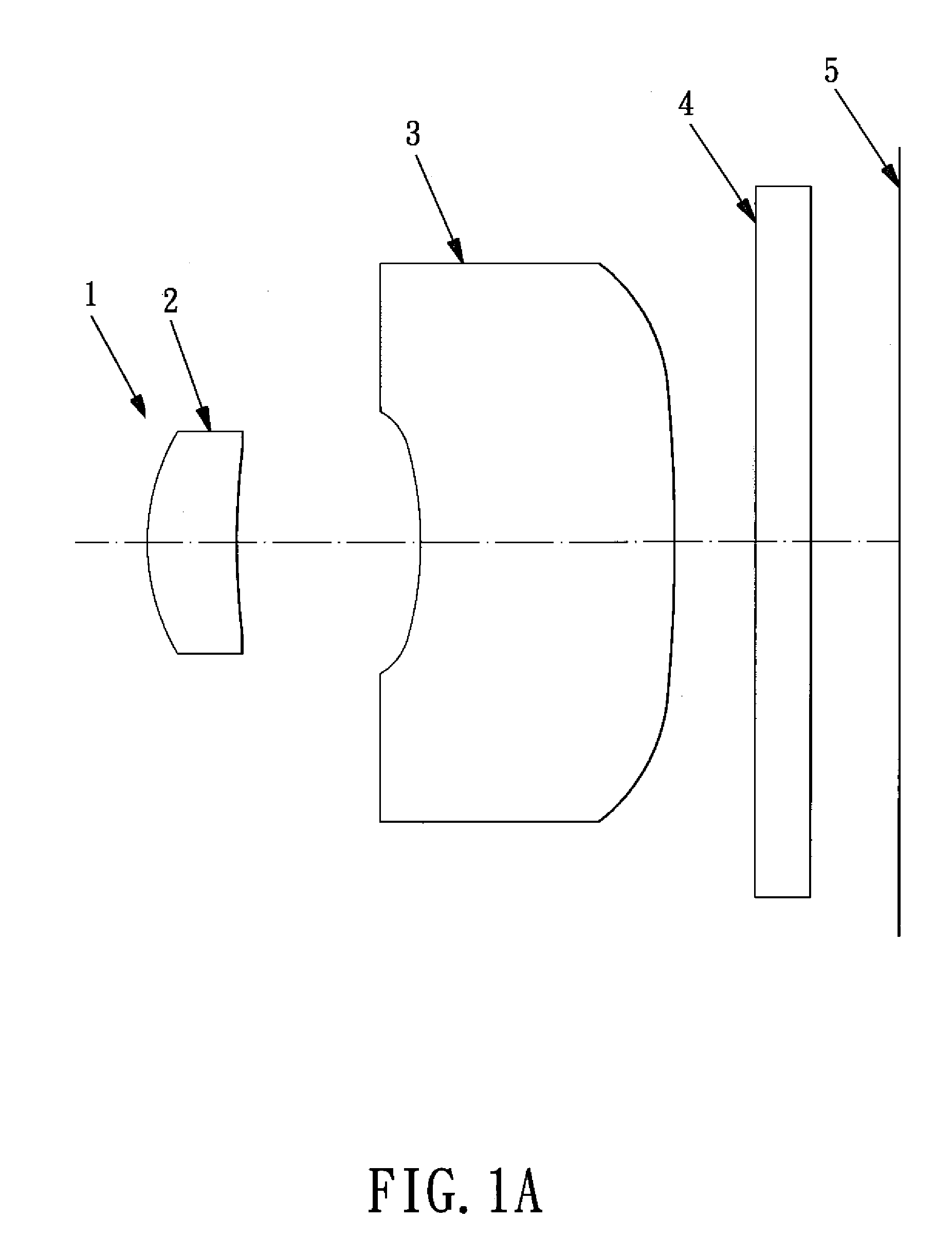
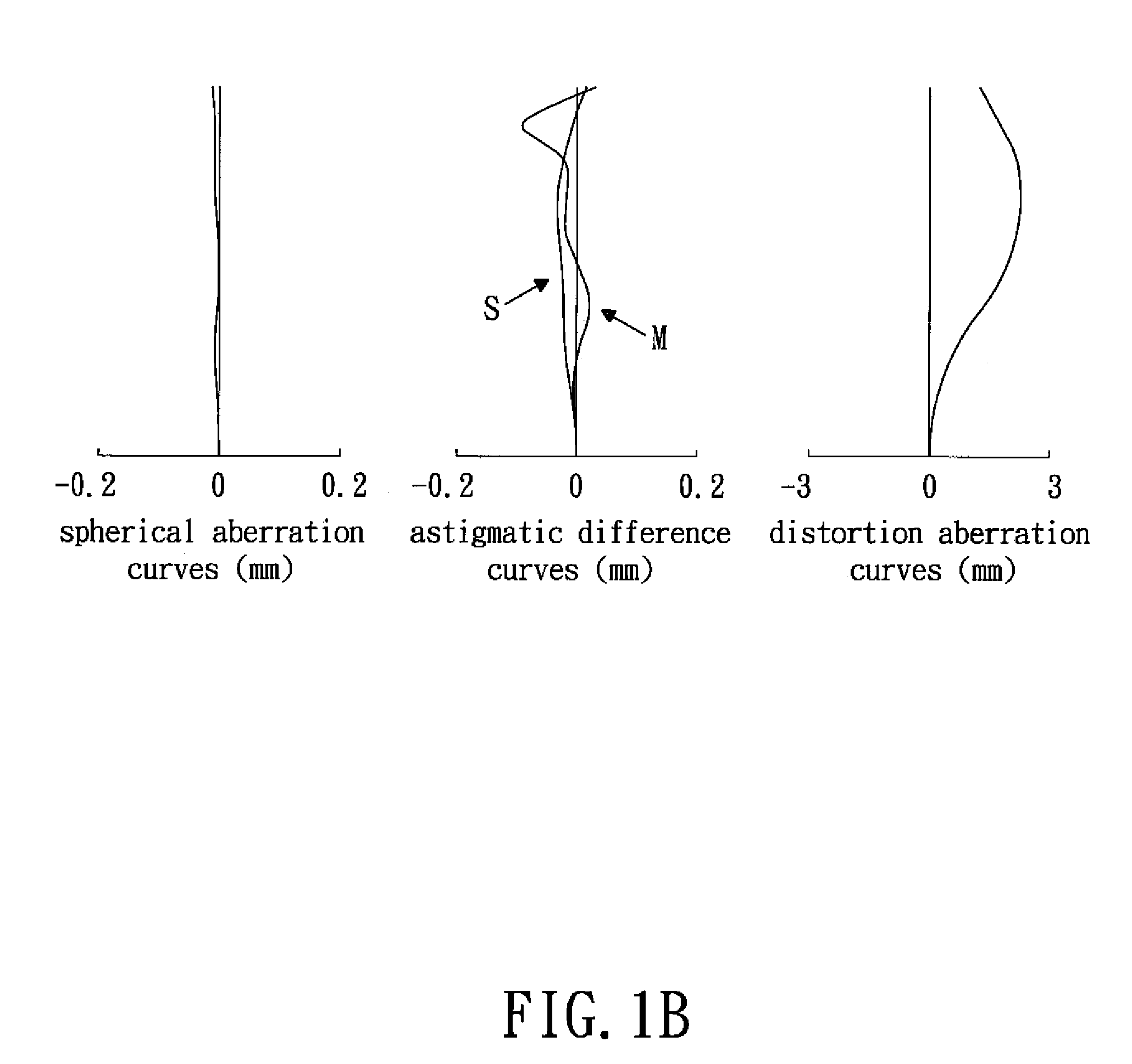
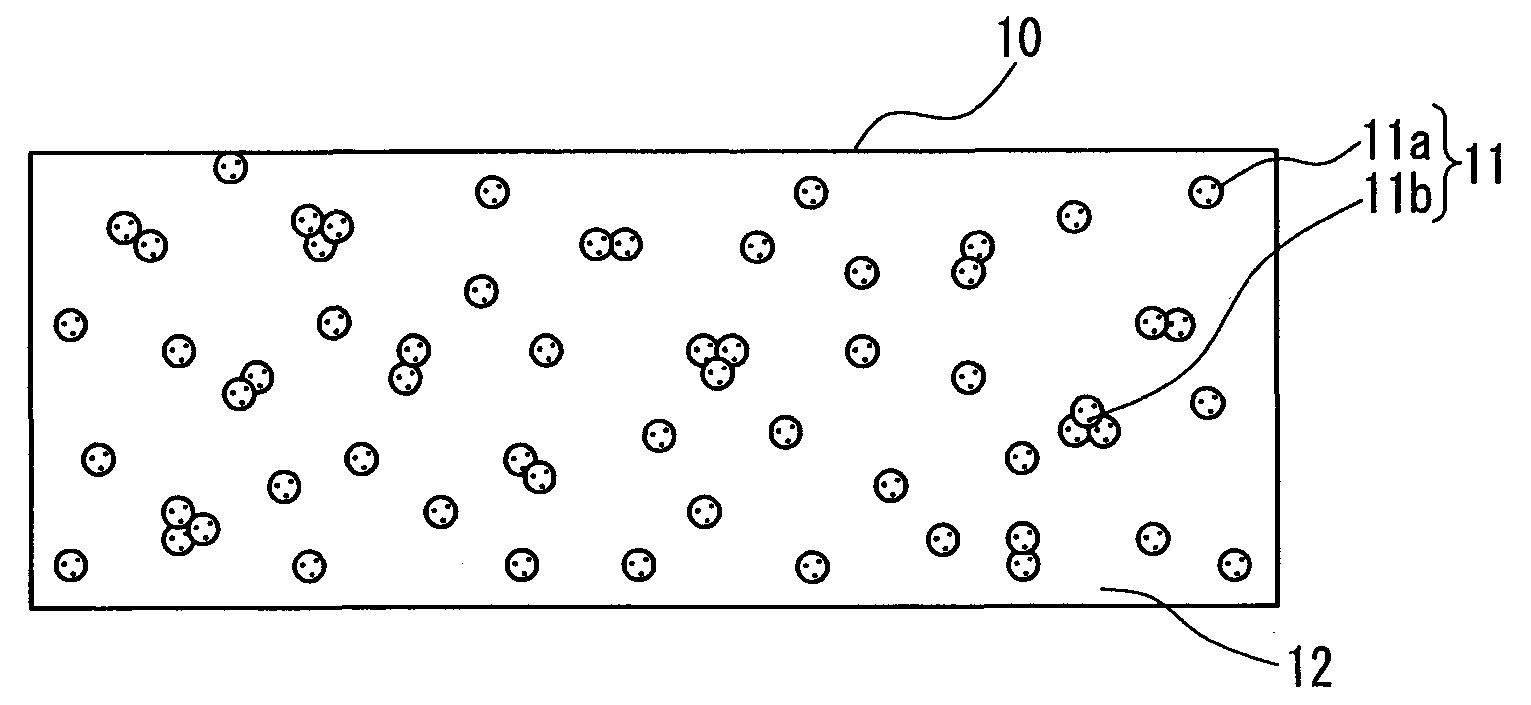
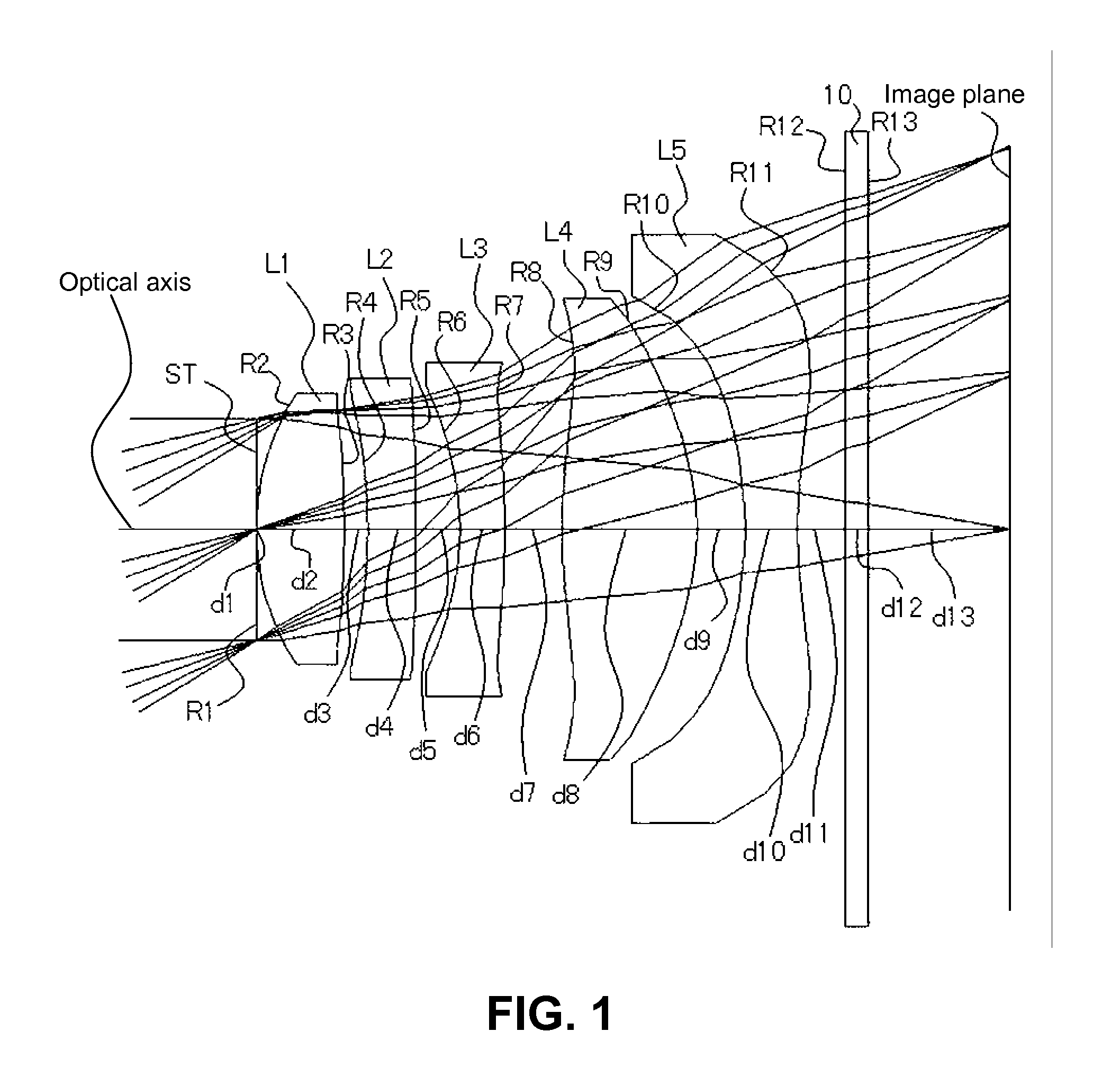
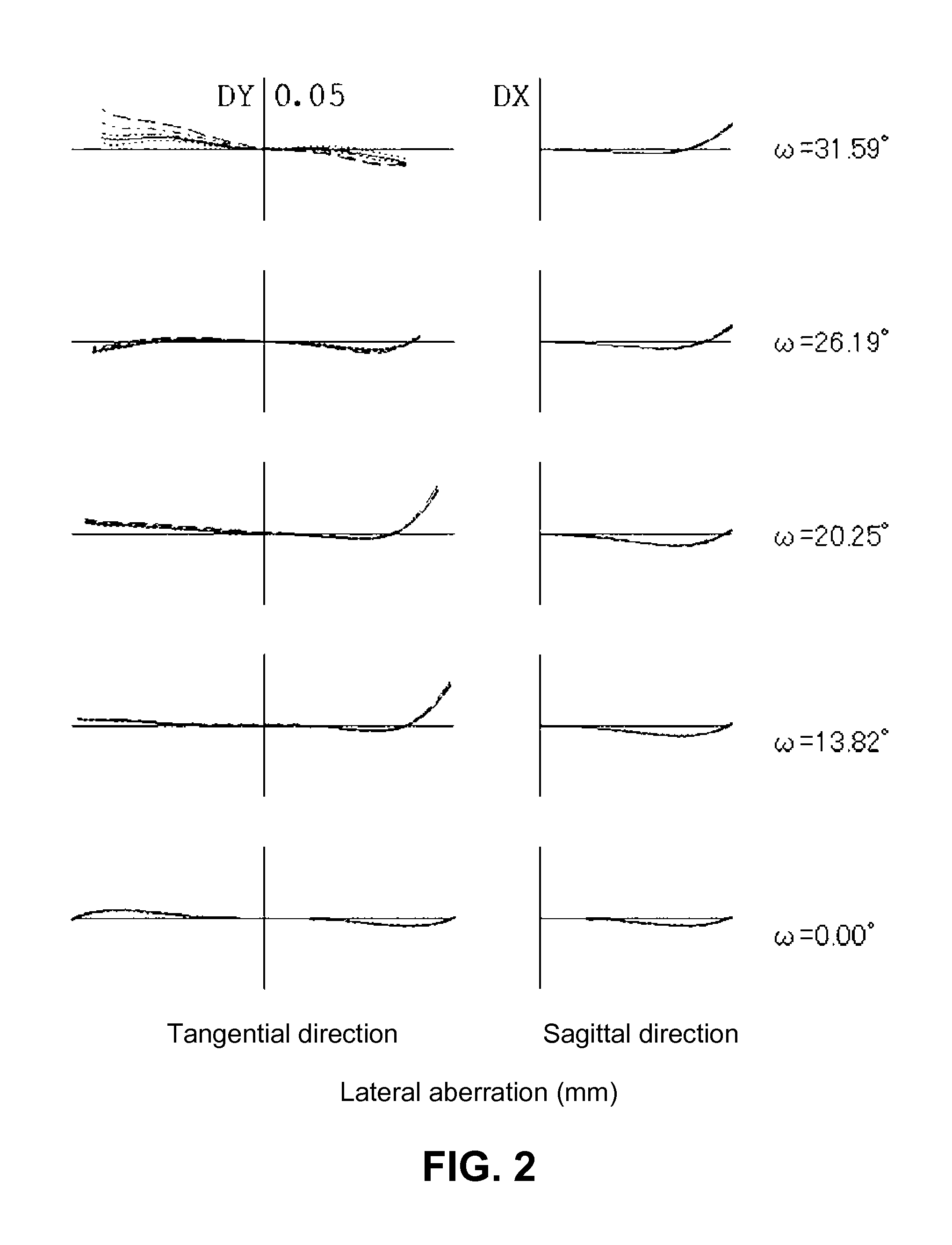
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1788 results about "Abbe number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
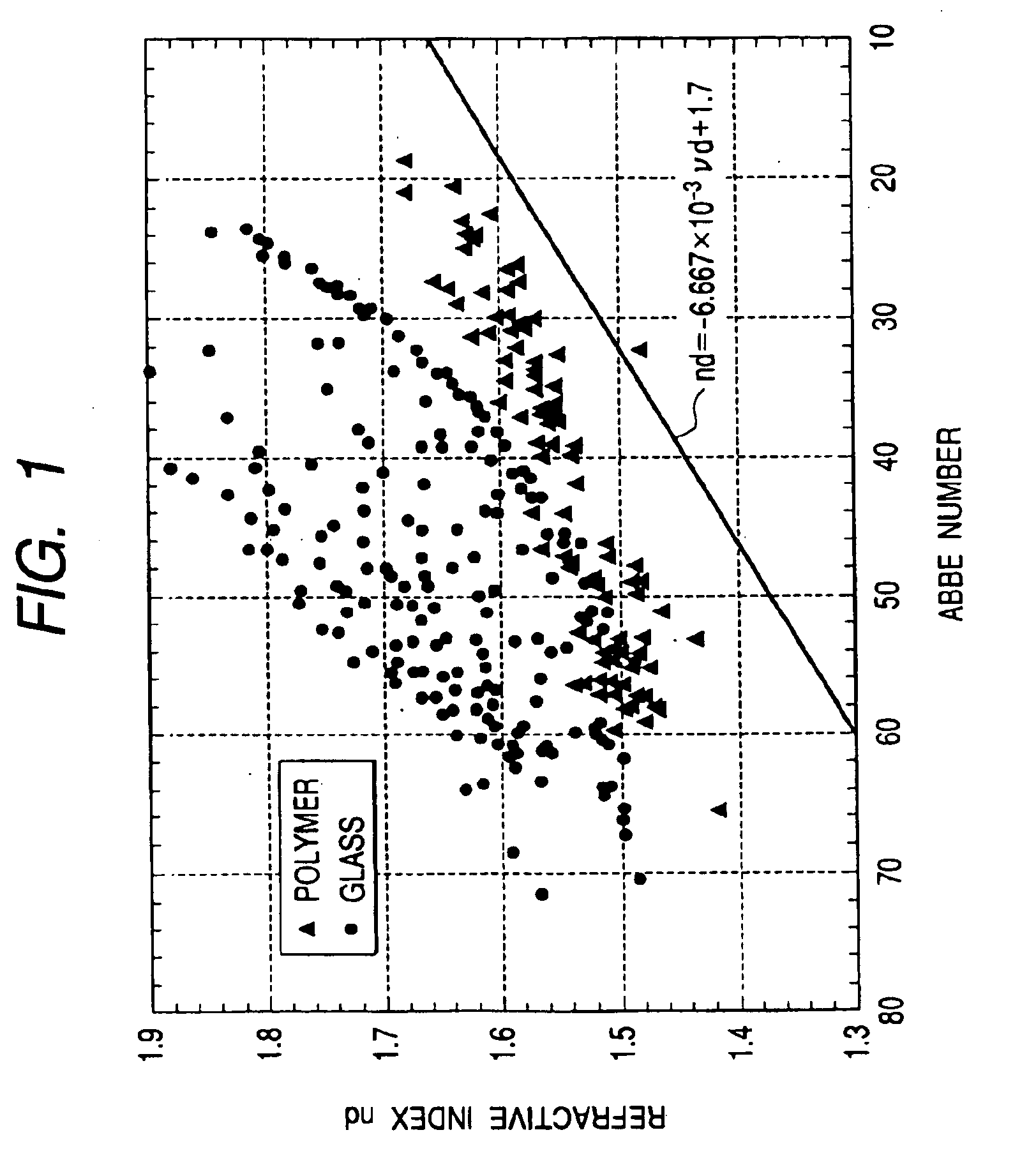
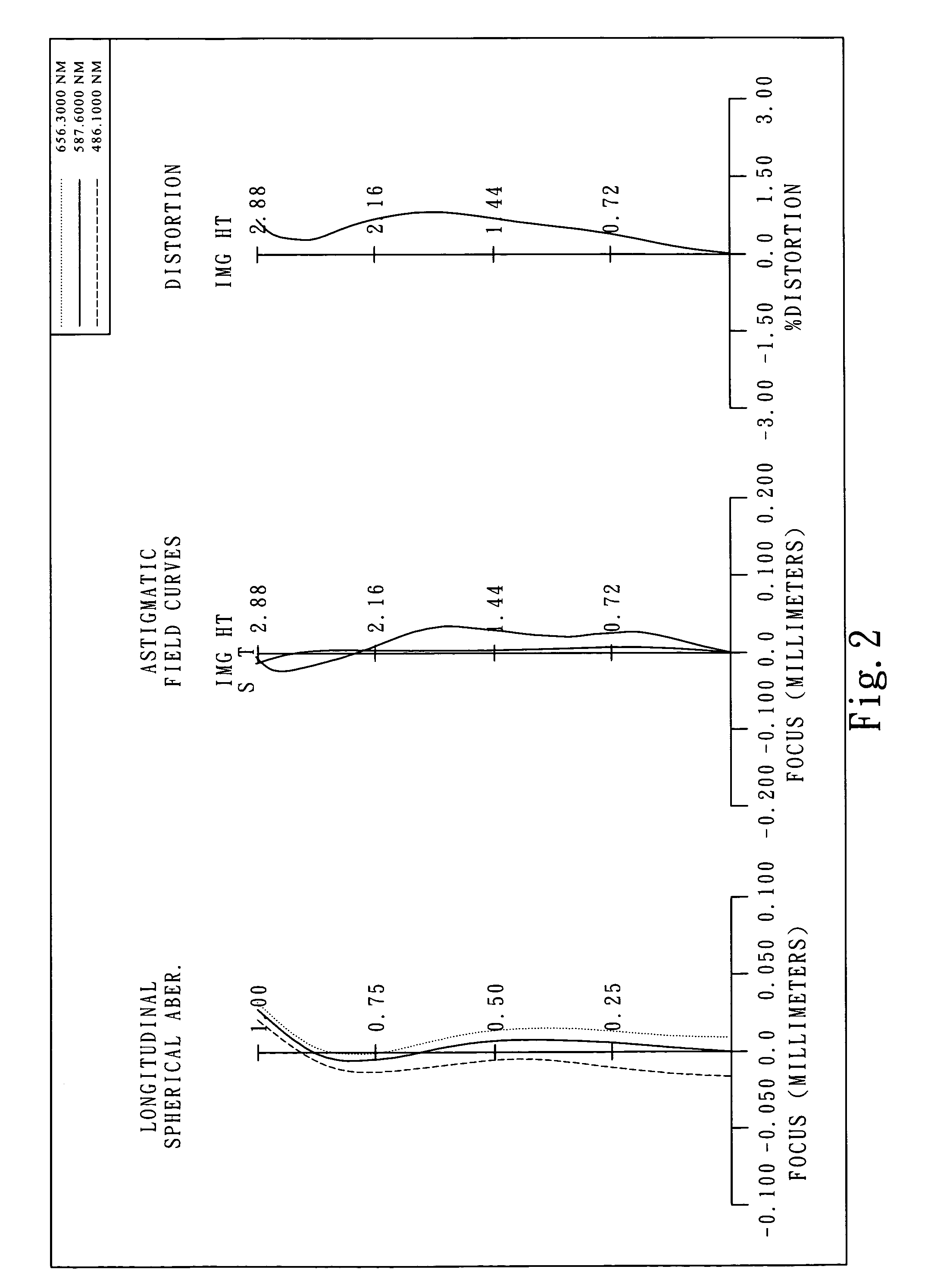
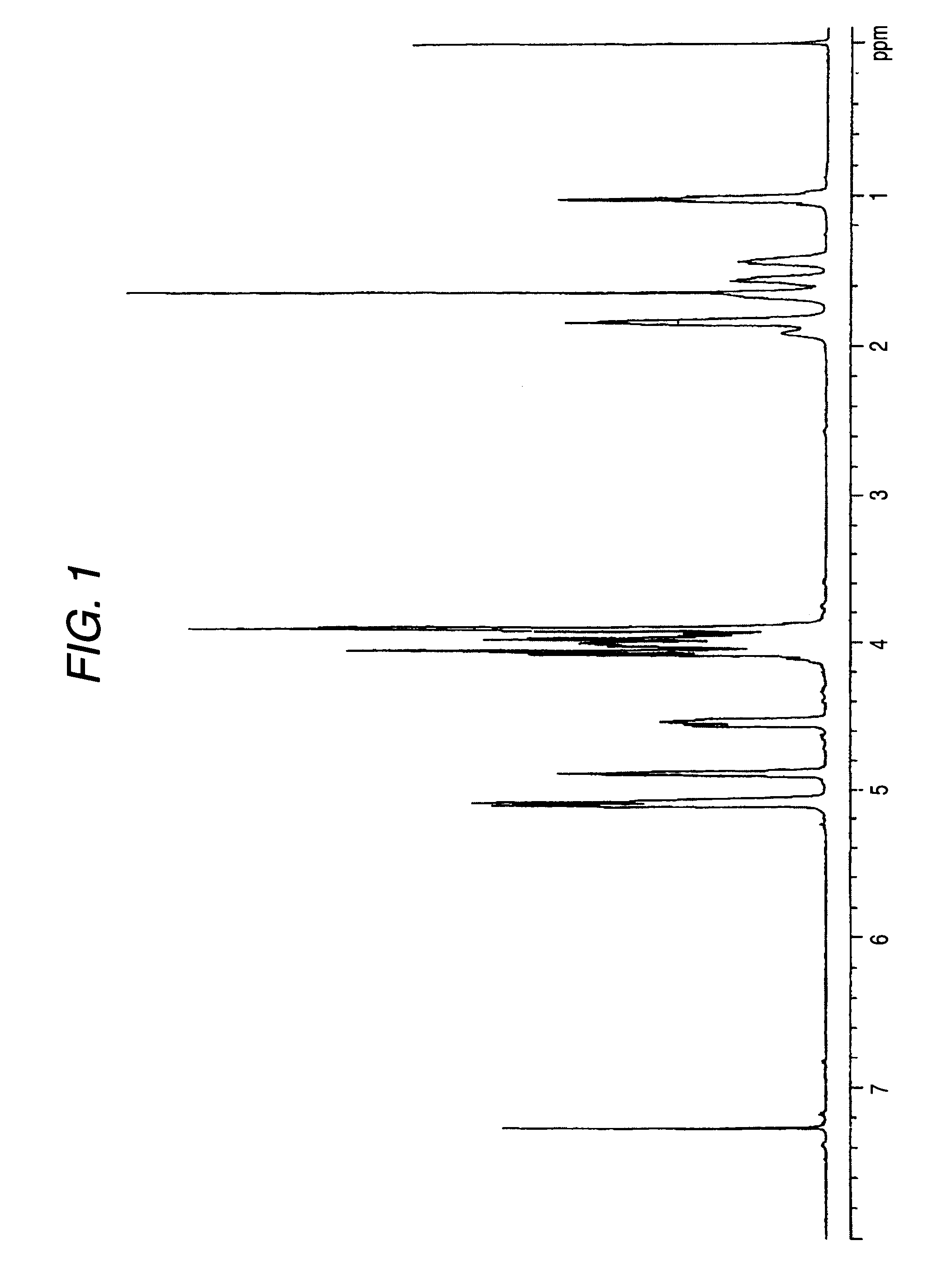
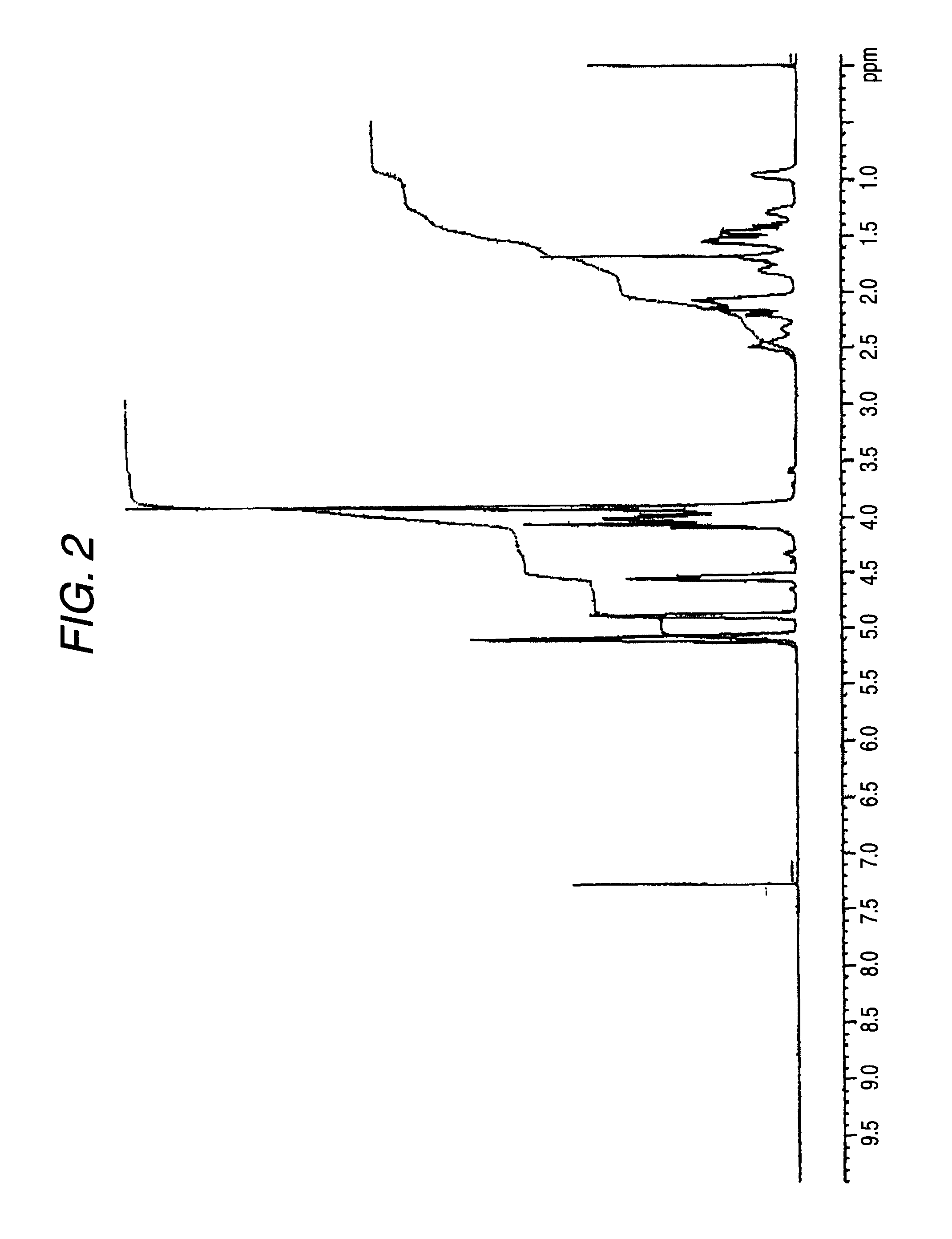
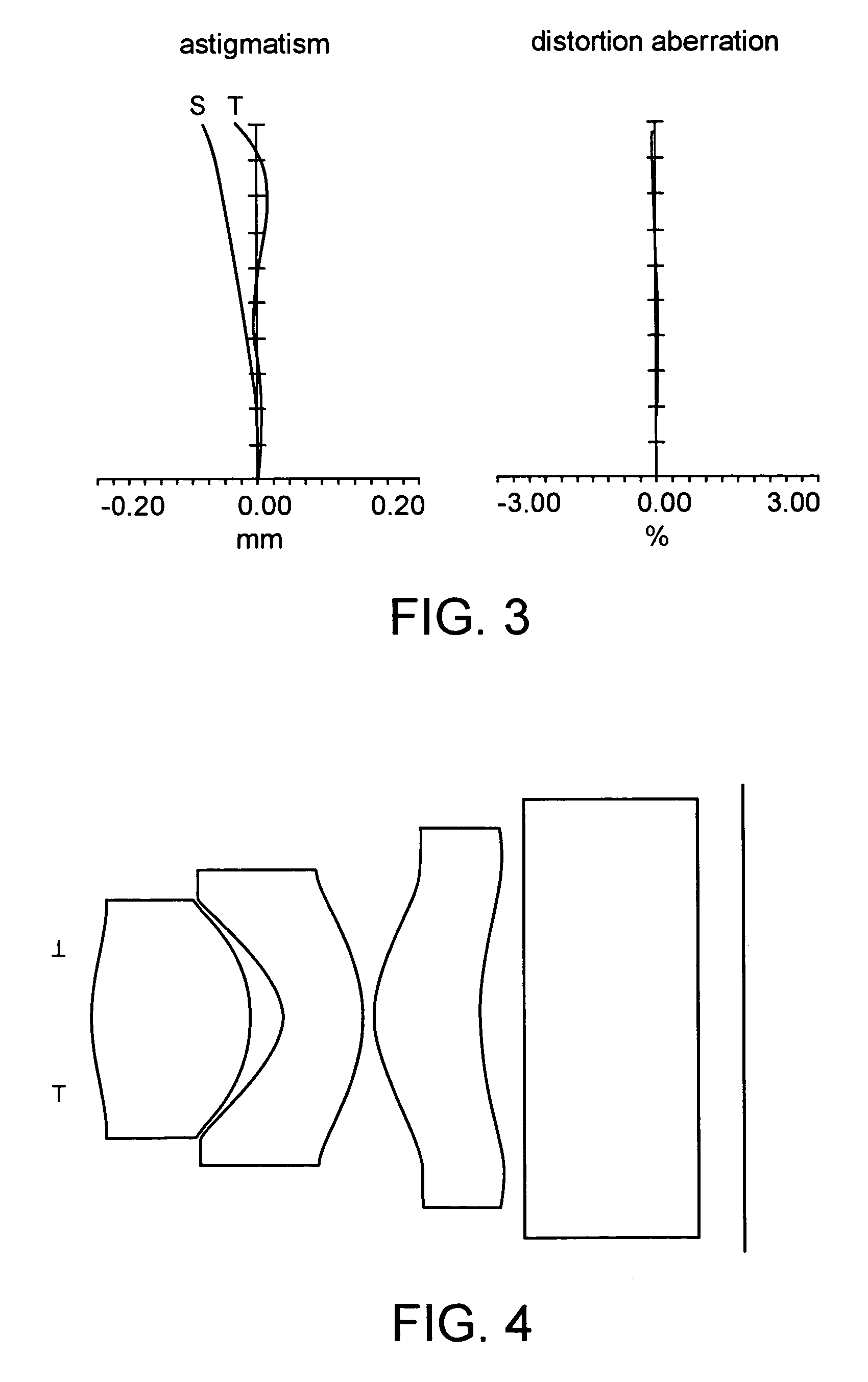
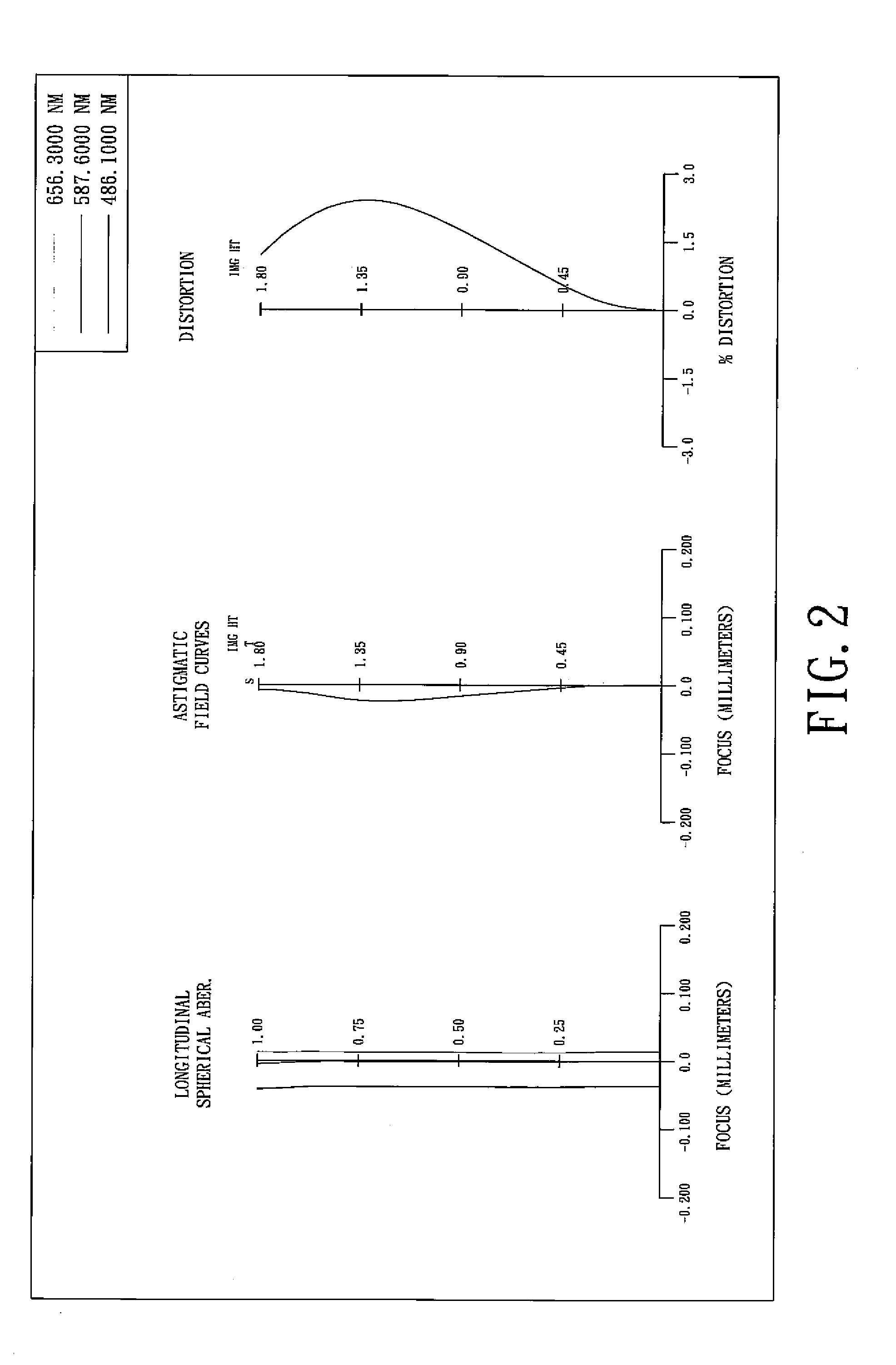
In optics and lens design, the Abbe number, also known as the V-number or constringence of a transparent material, is a measure of the material's dispersion (variation of refractive index versus wavelength), with high values of V indicating low dispersion. It is named after Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), the German physicist who defined it. The Abbe number, VD, of a material is defined as VD=(nD-1)/(nF-nC), where nC, nD and nF are the refractive indices of the material at the wavelengths of the Fraunhofer C, D₁, and F spectral lines (656.3 nm, 589.3 nm, and 486.1 nm respectively).
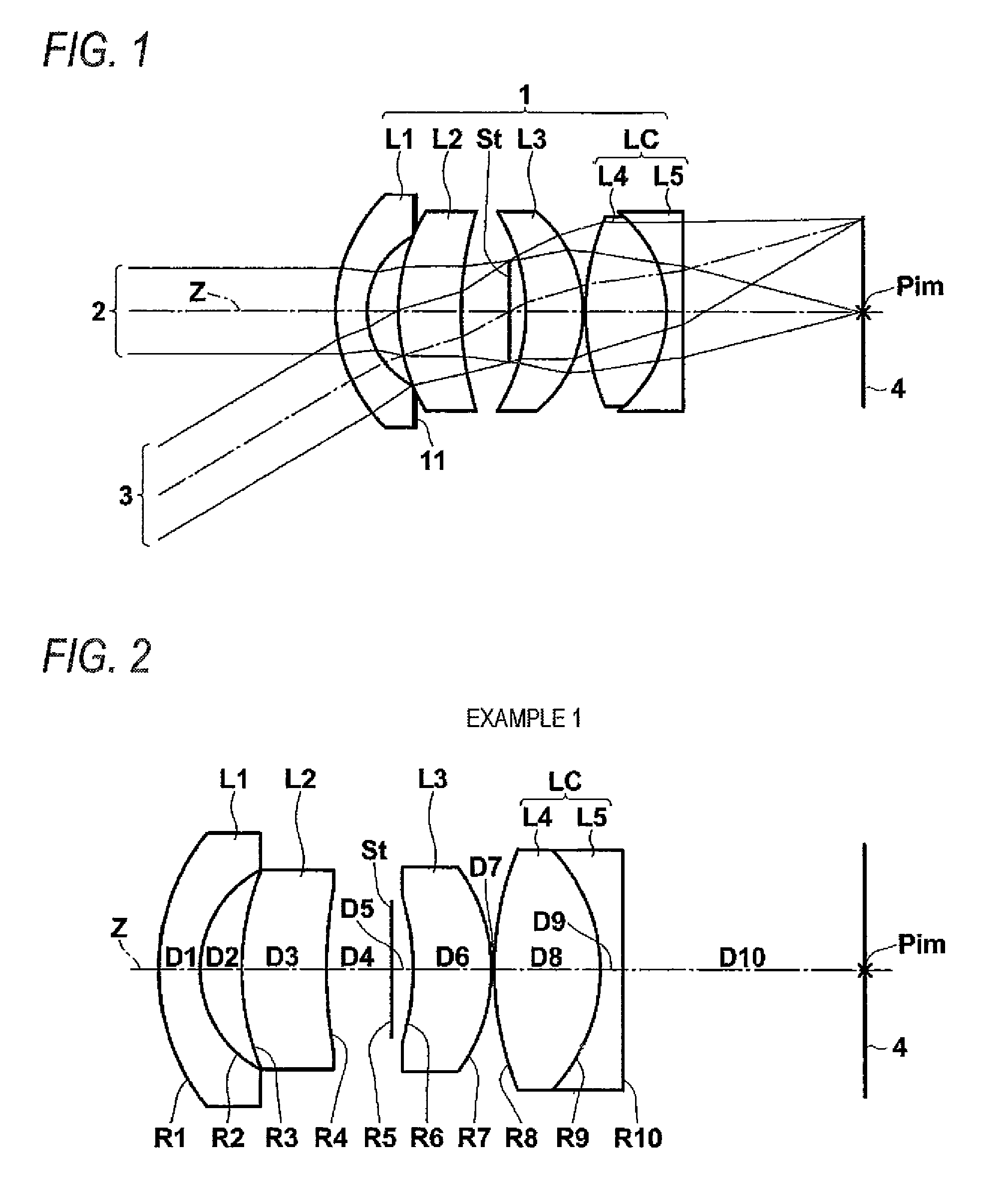
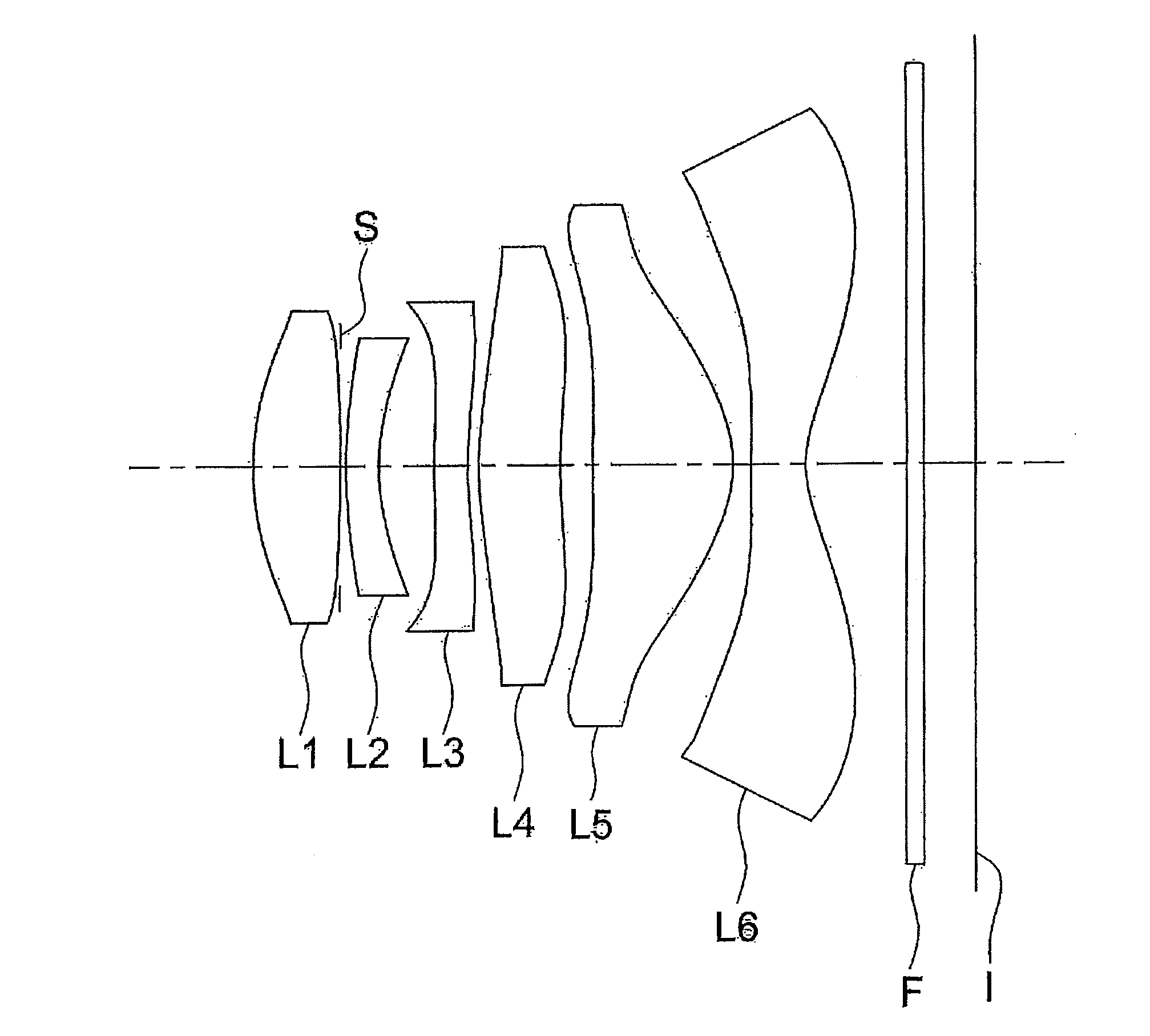
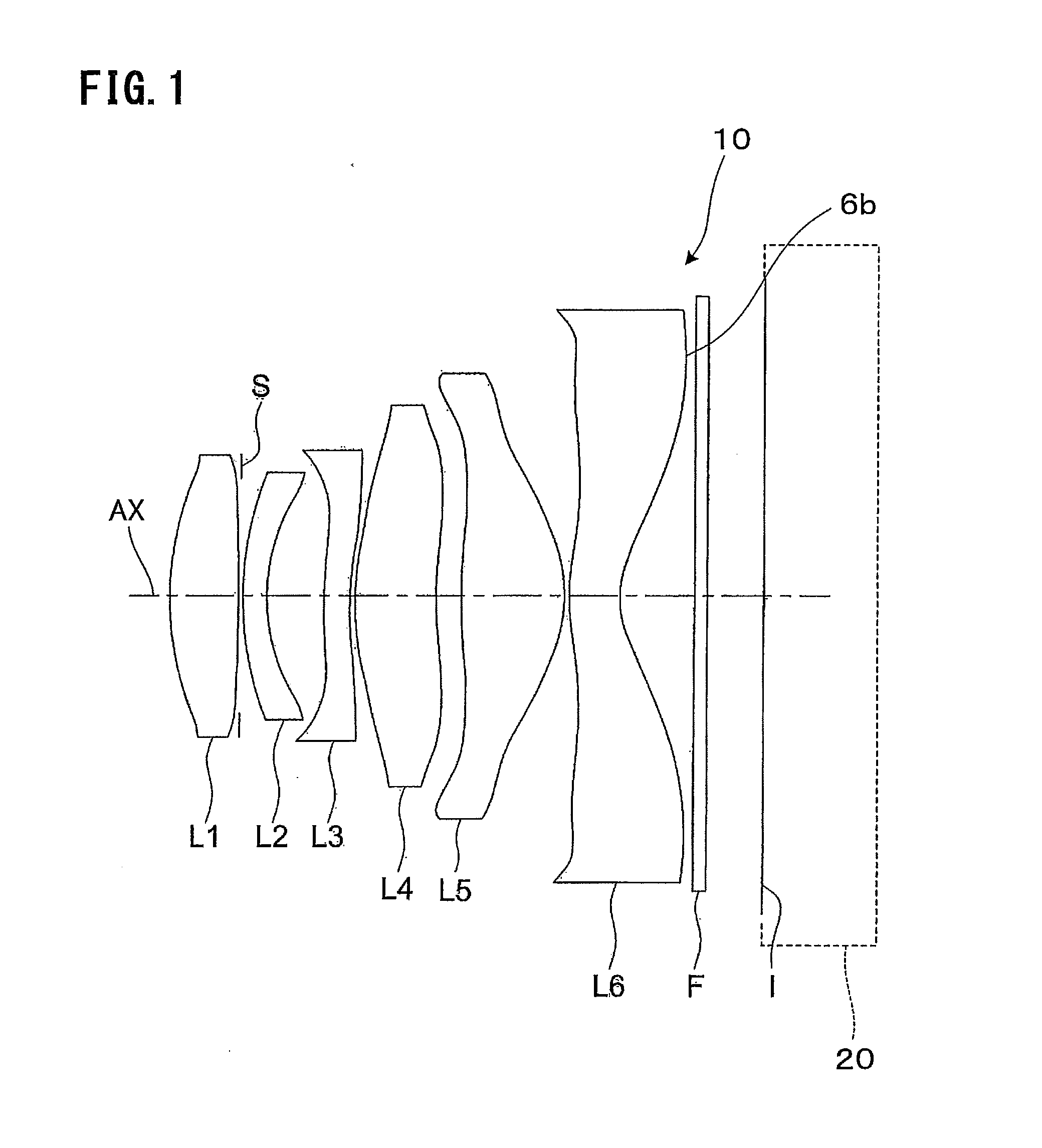
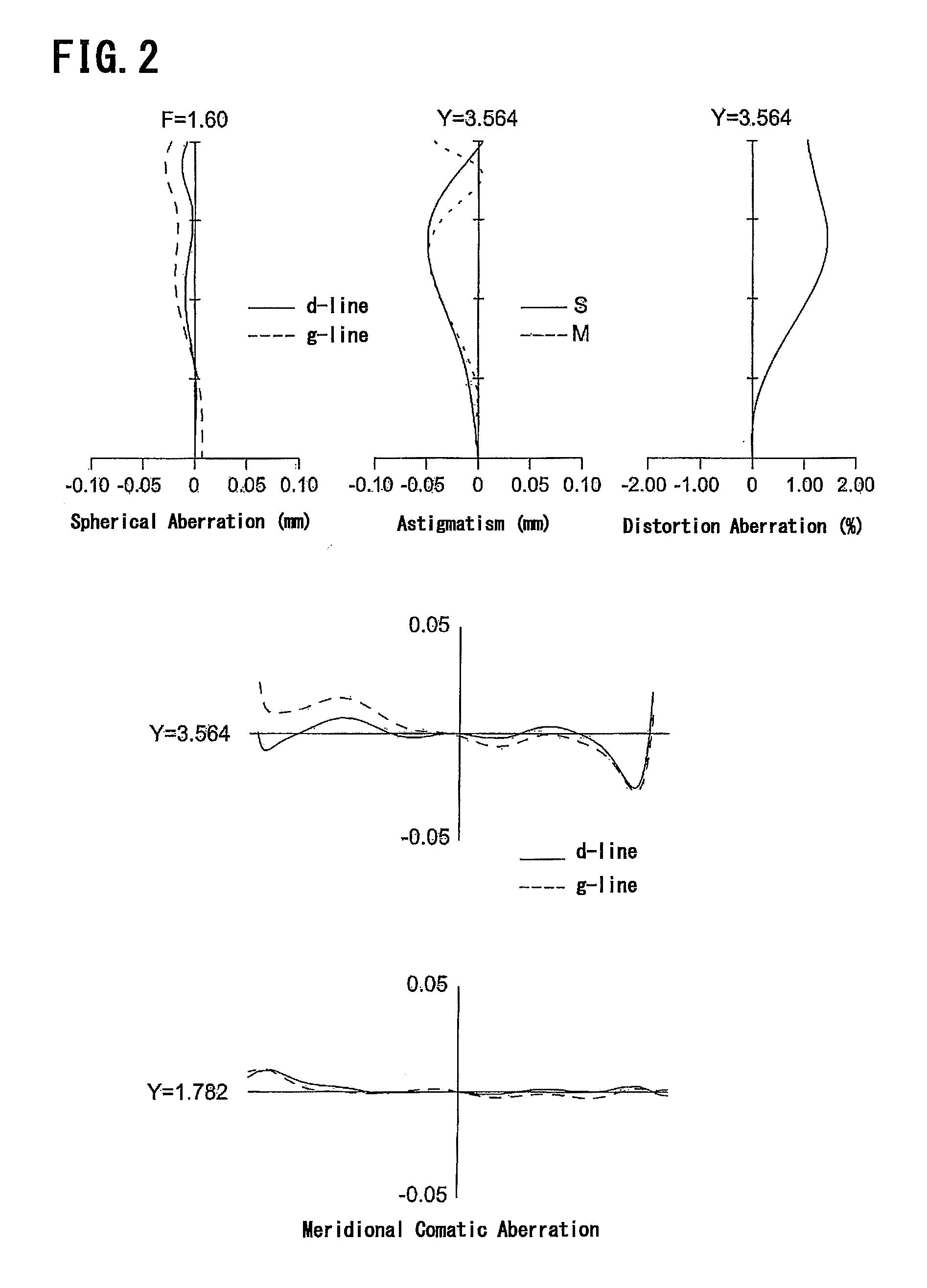
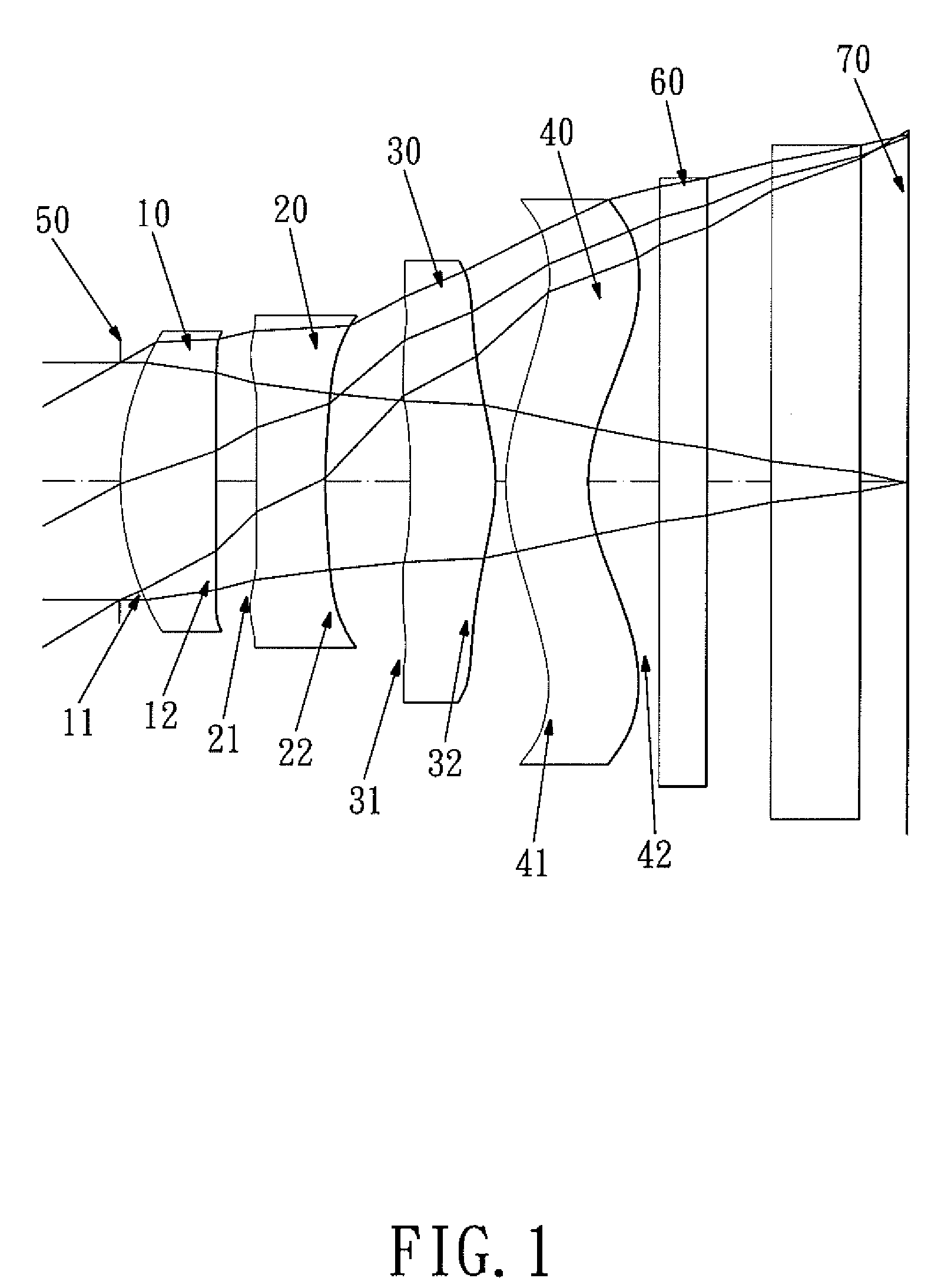
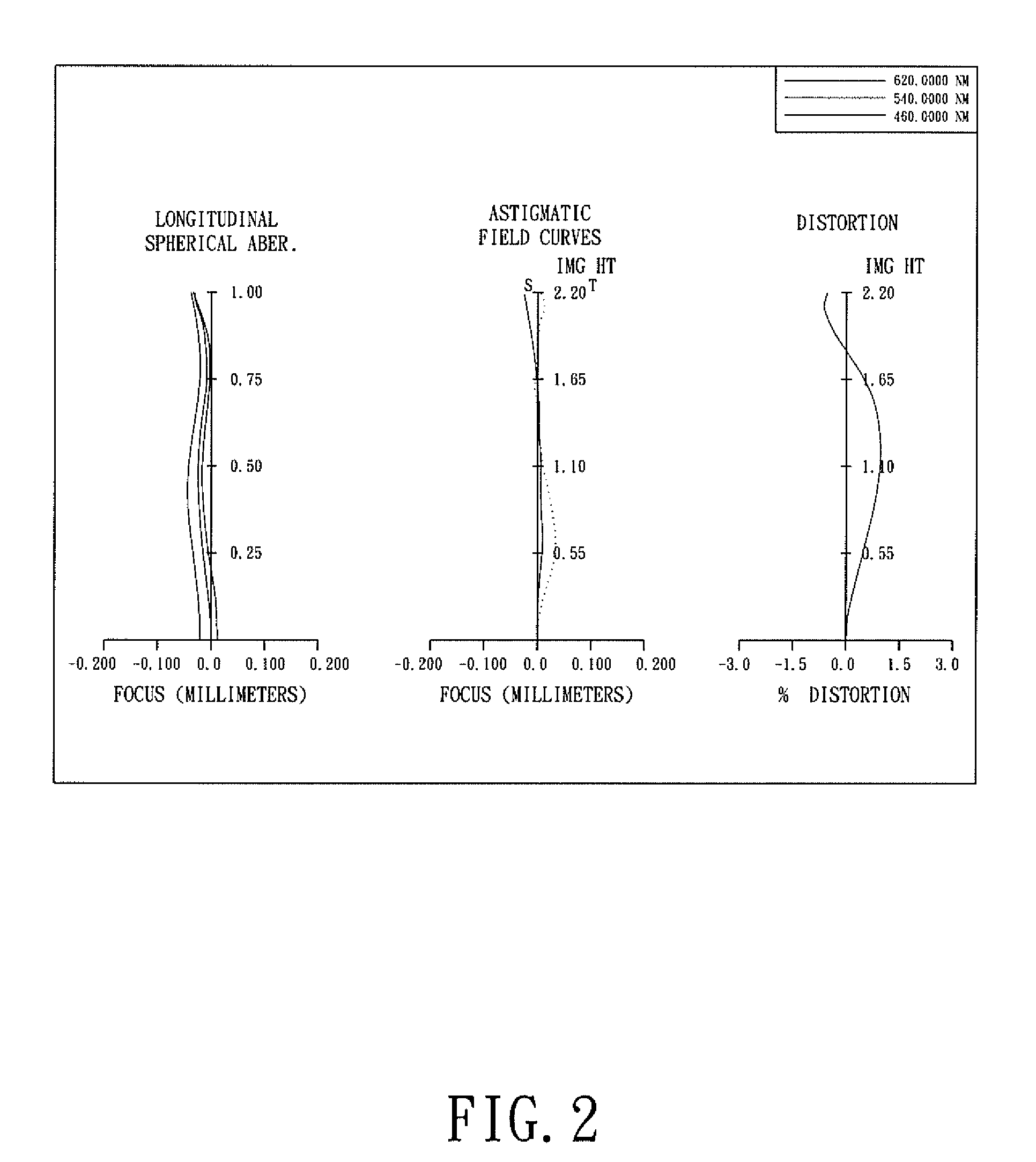
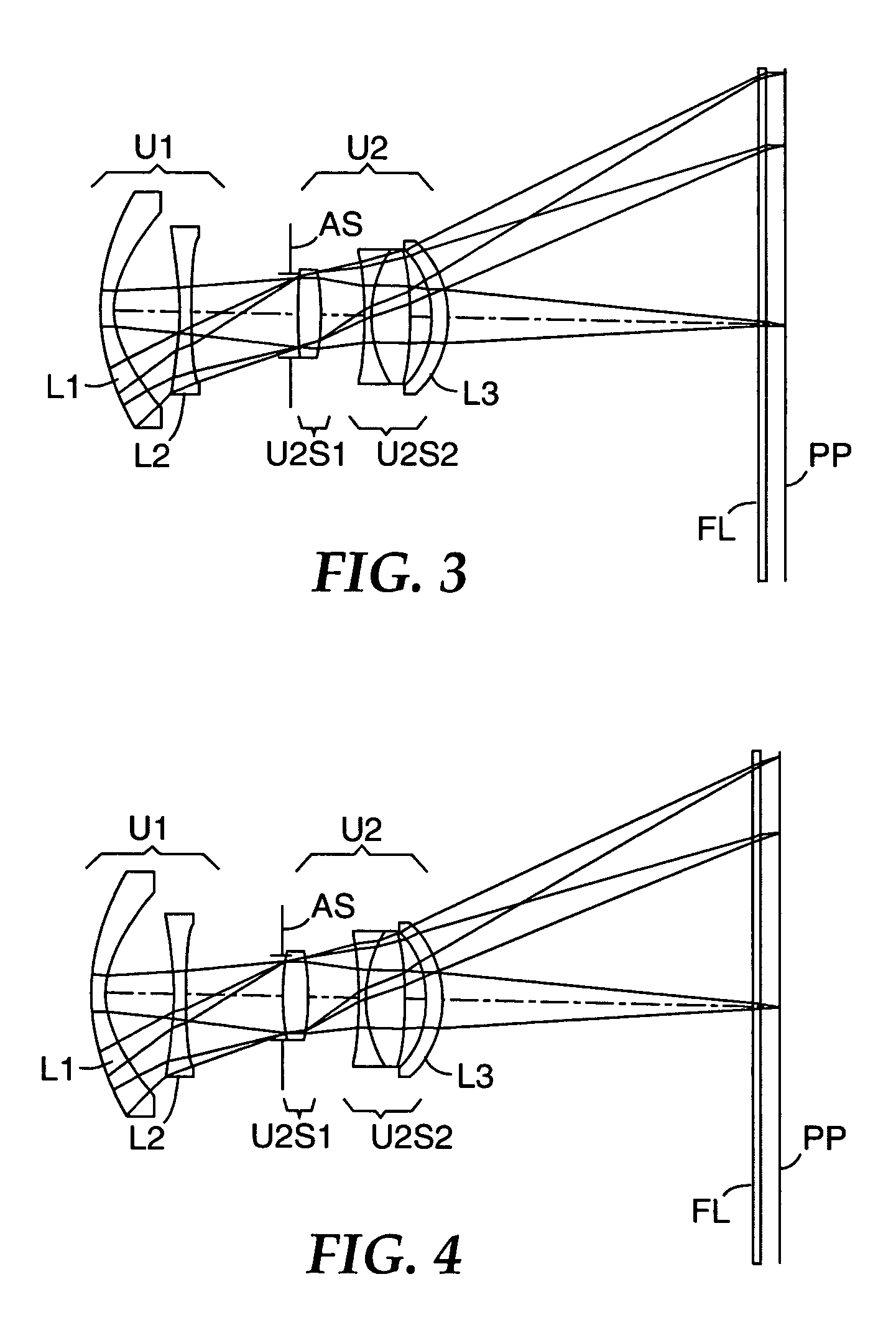
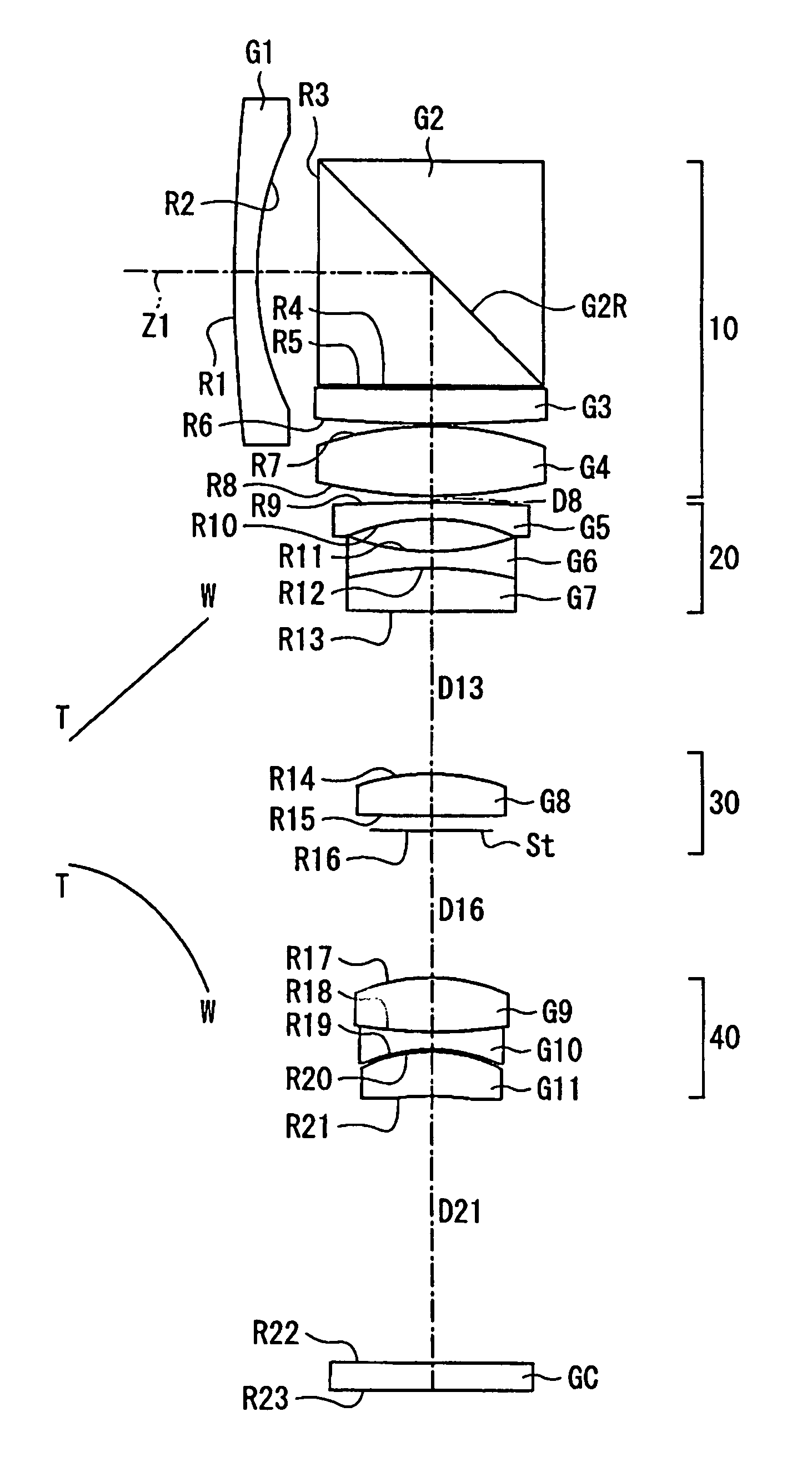
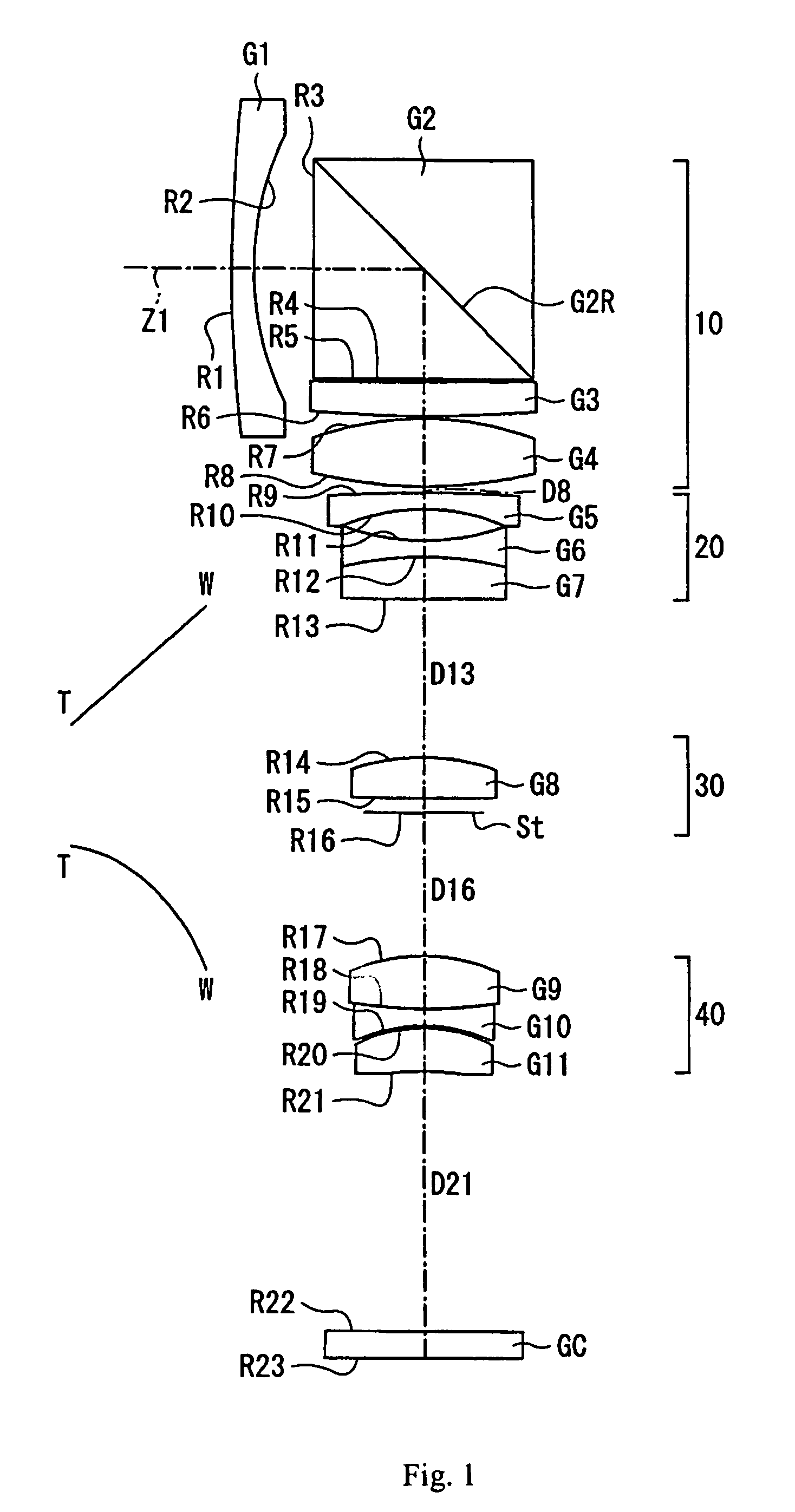
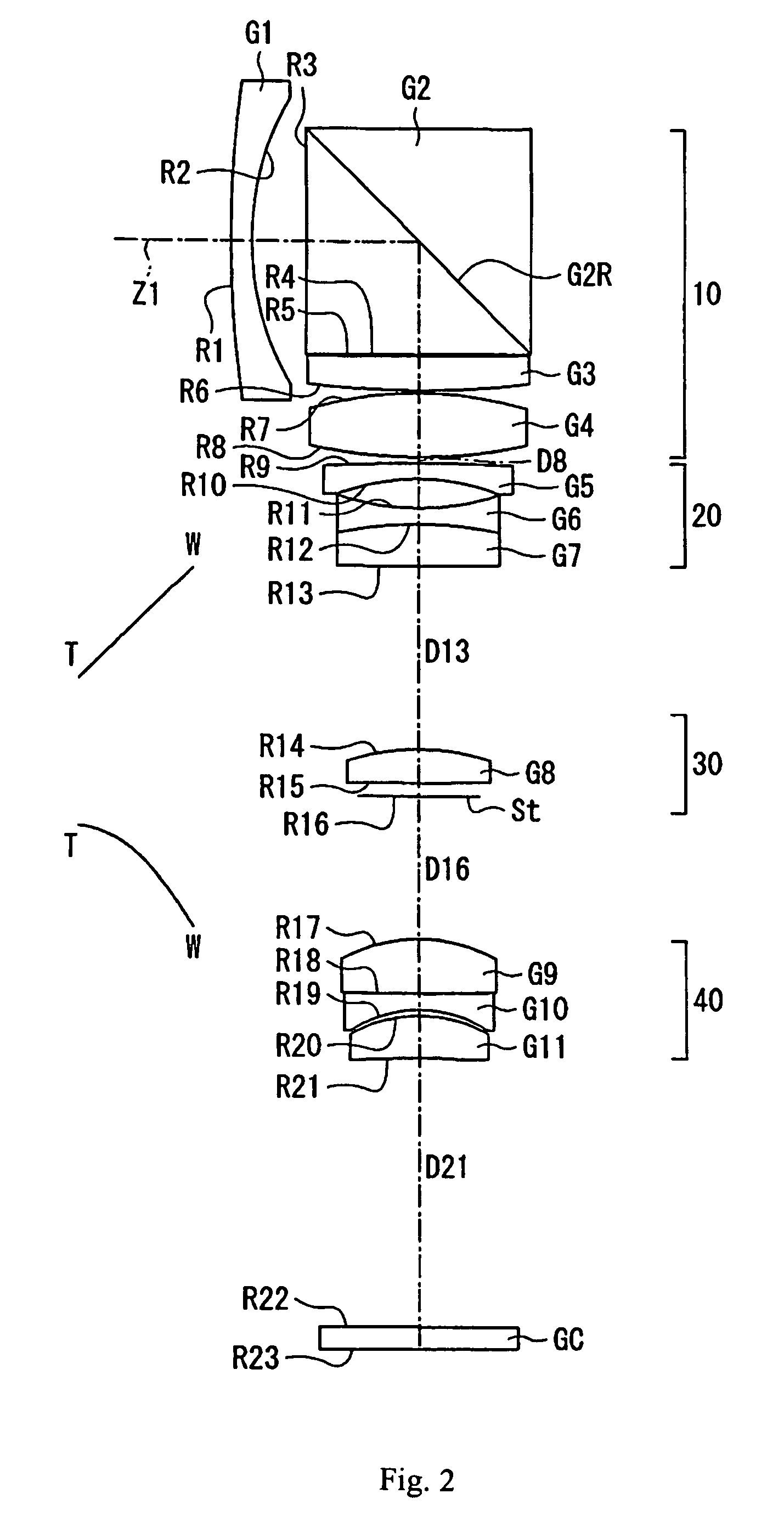
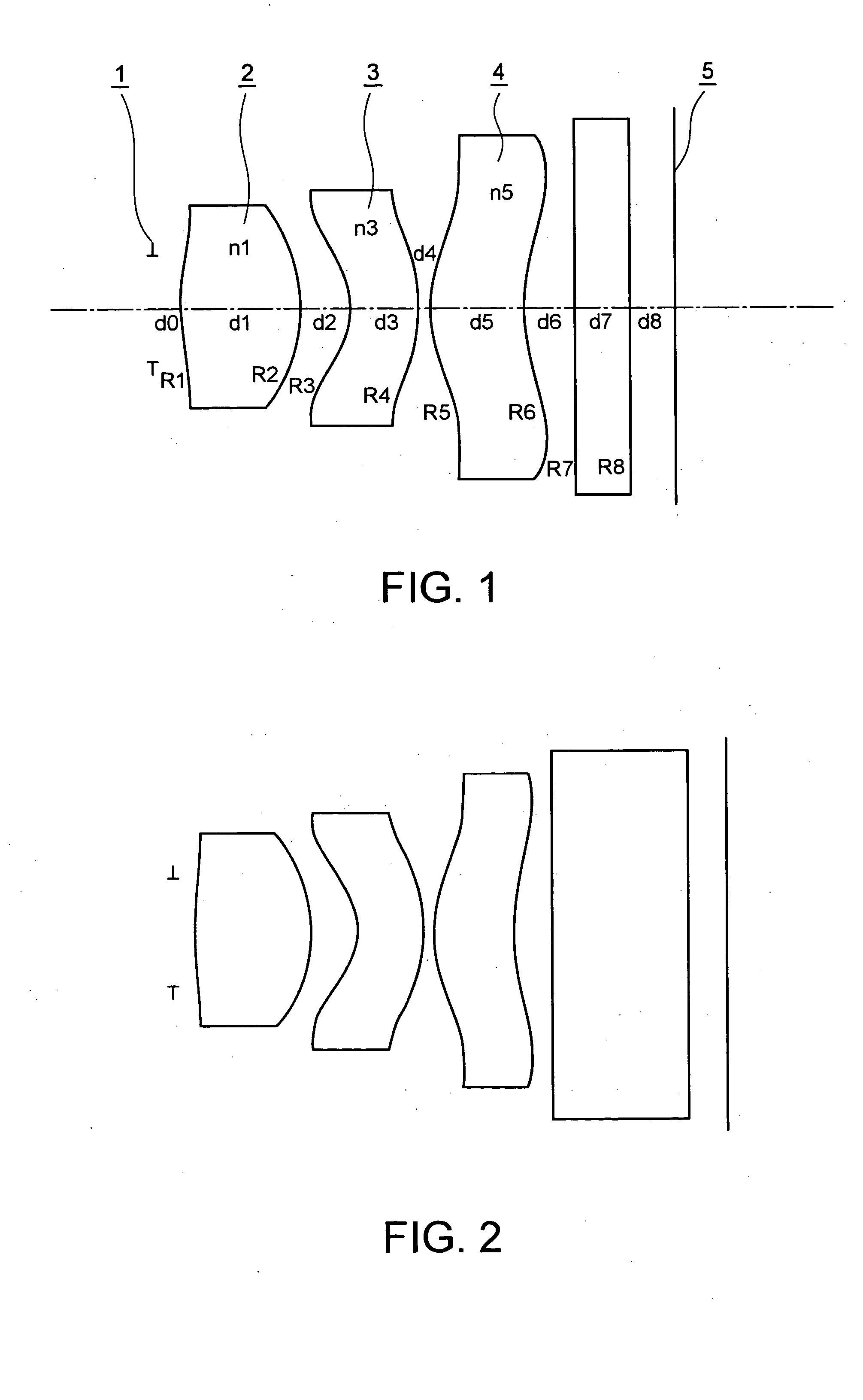
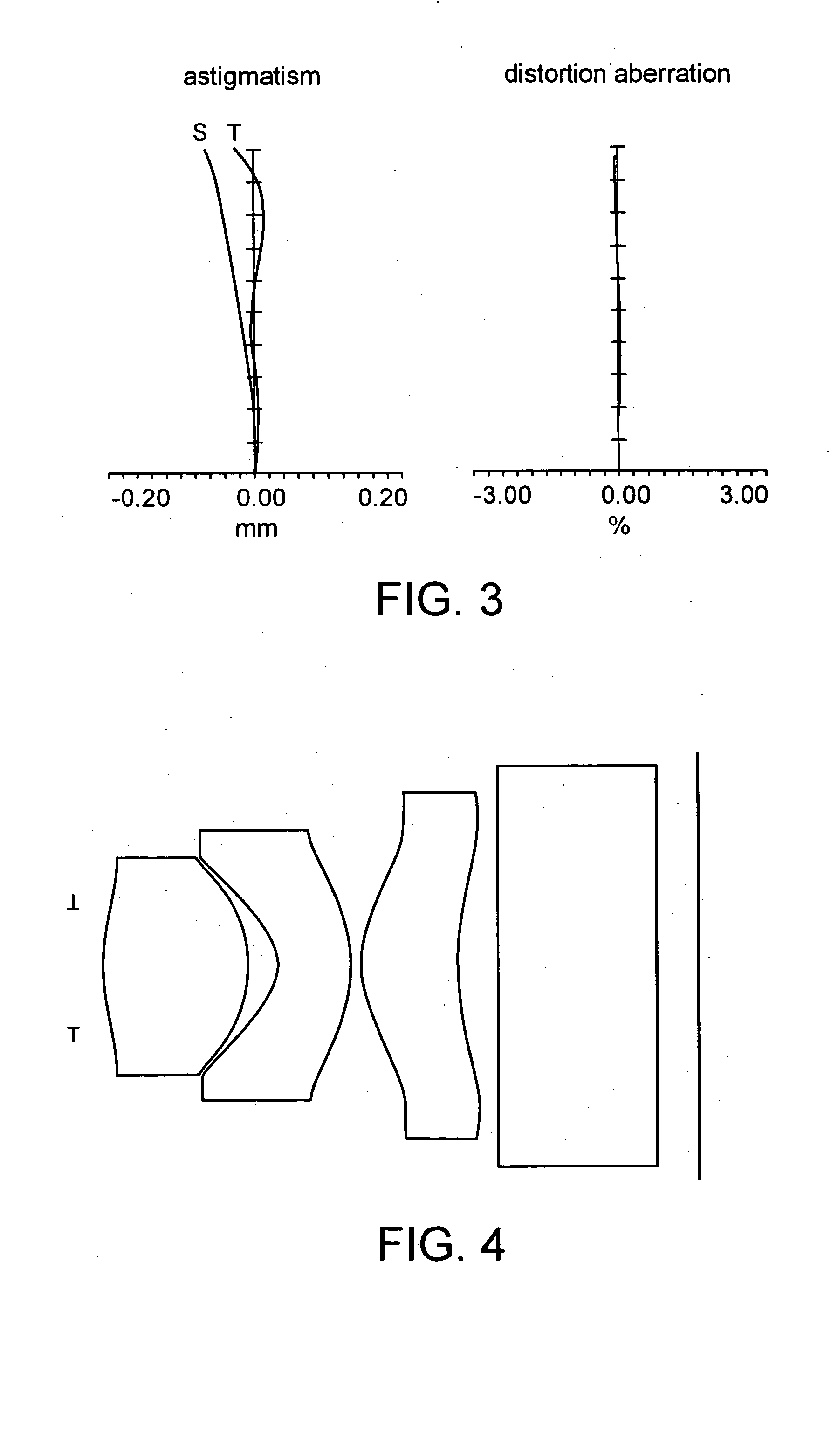
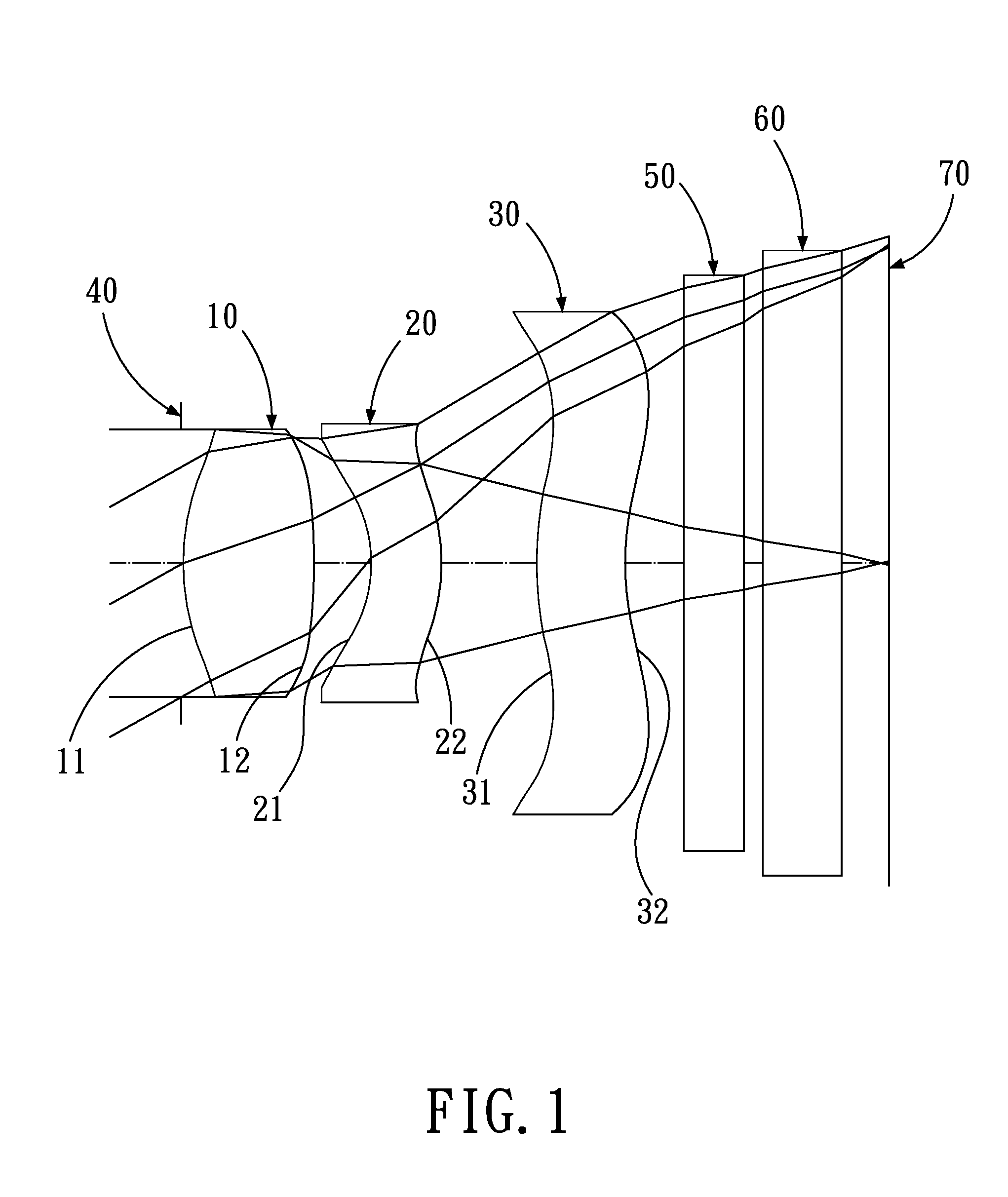
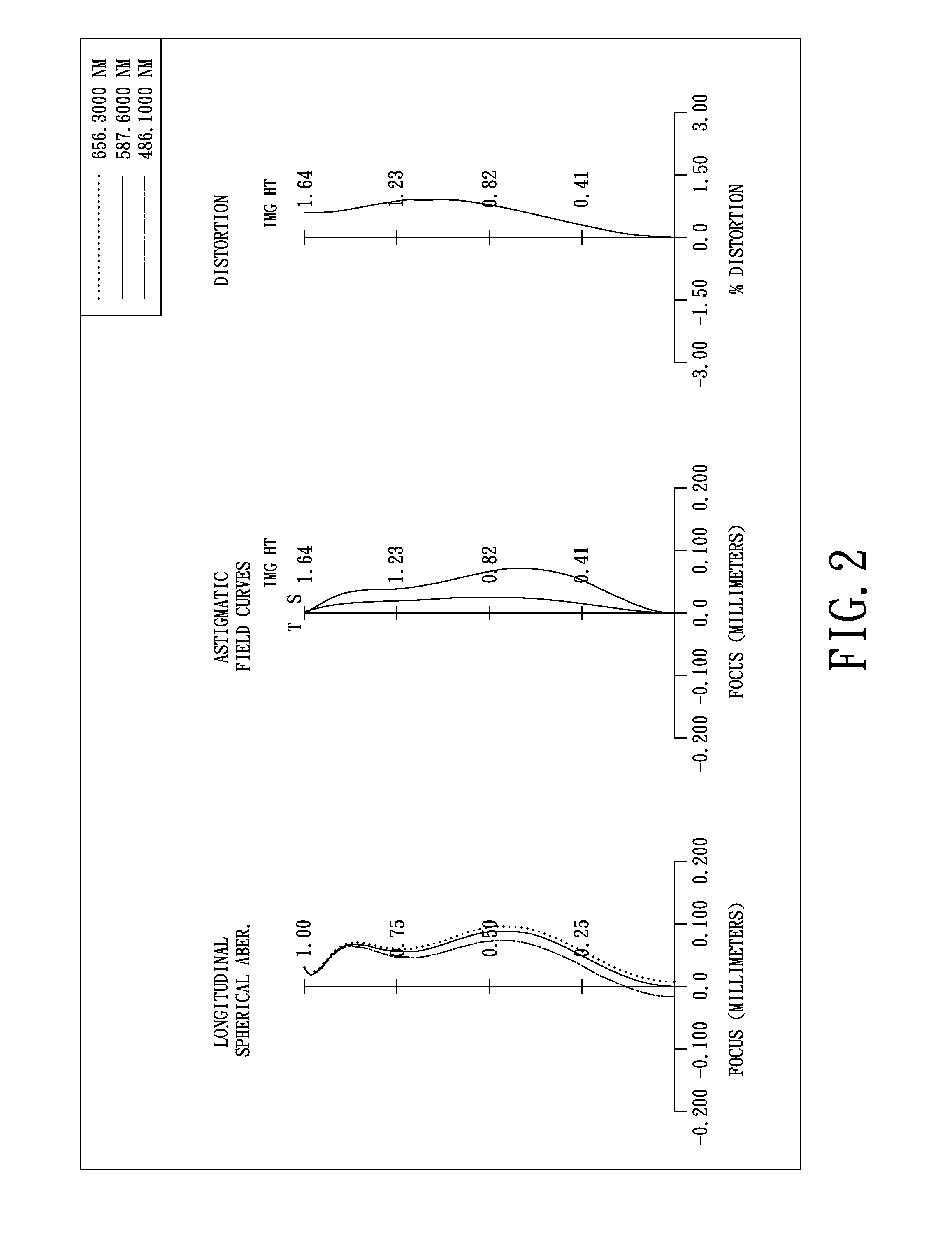
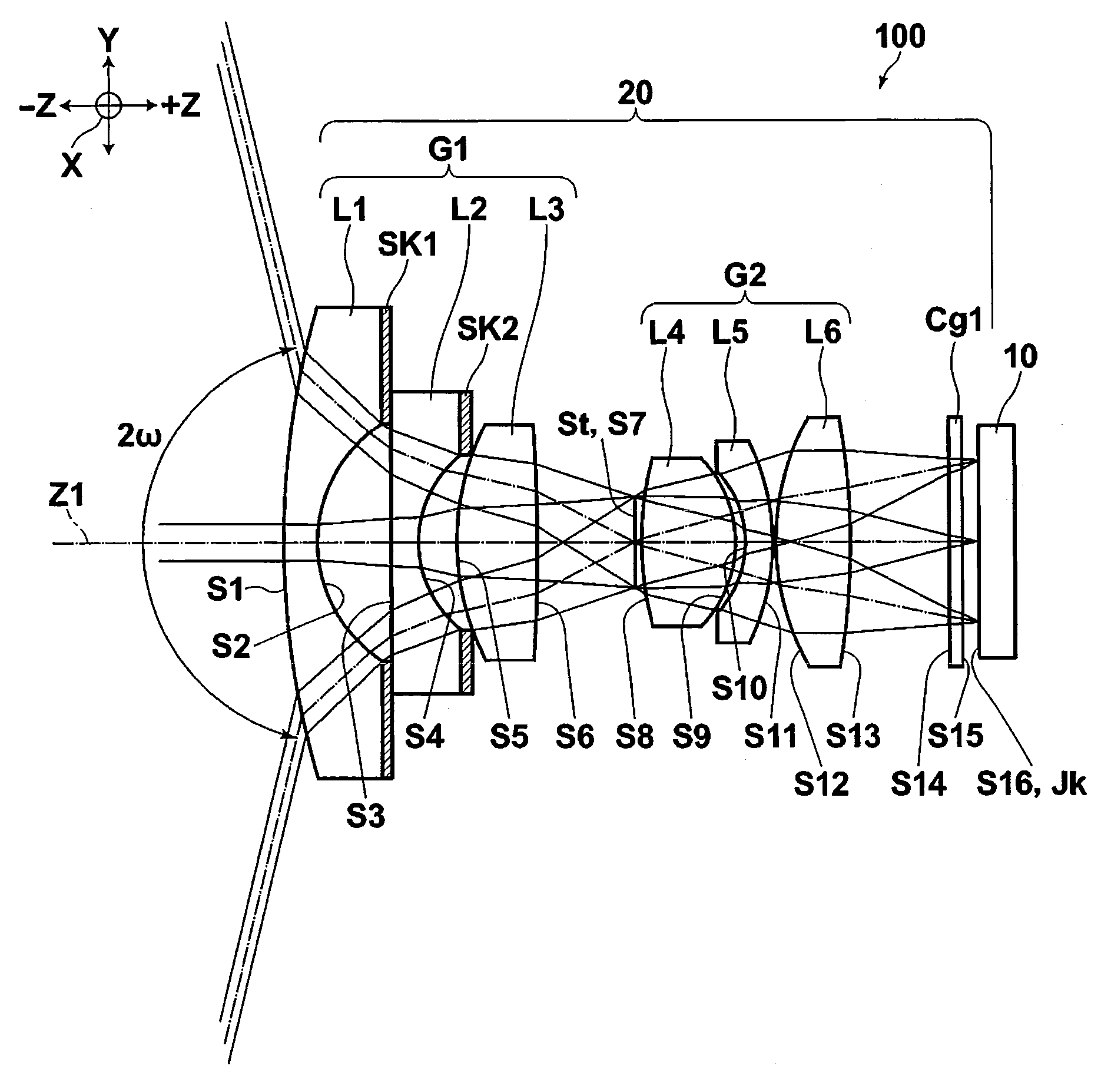
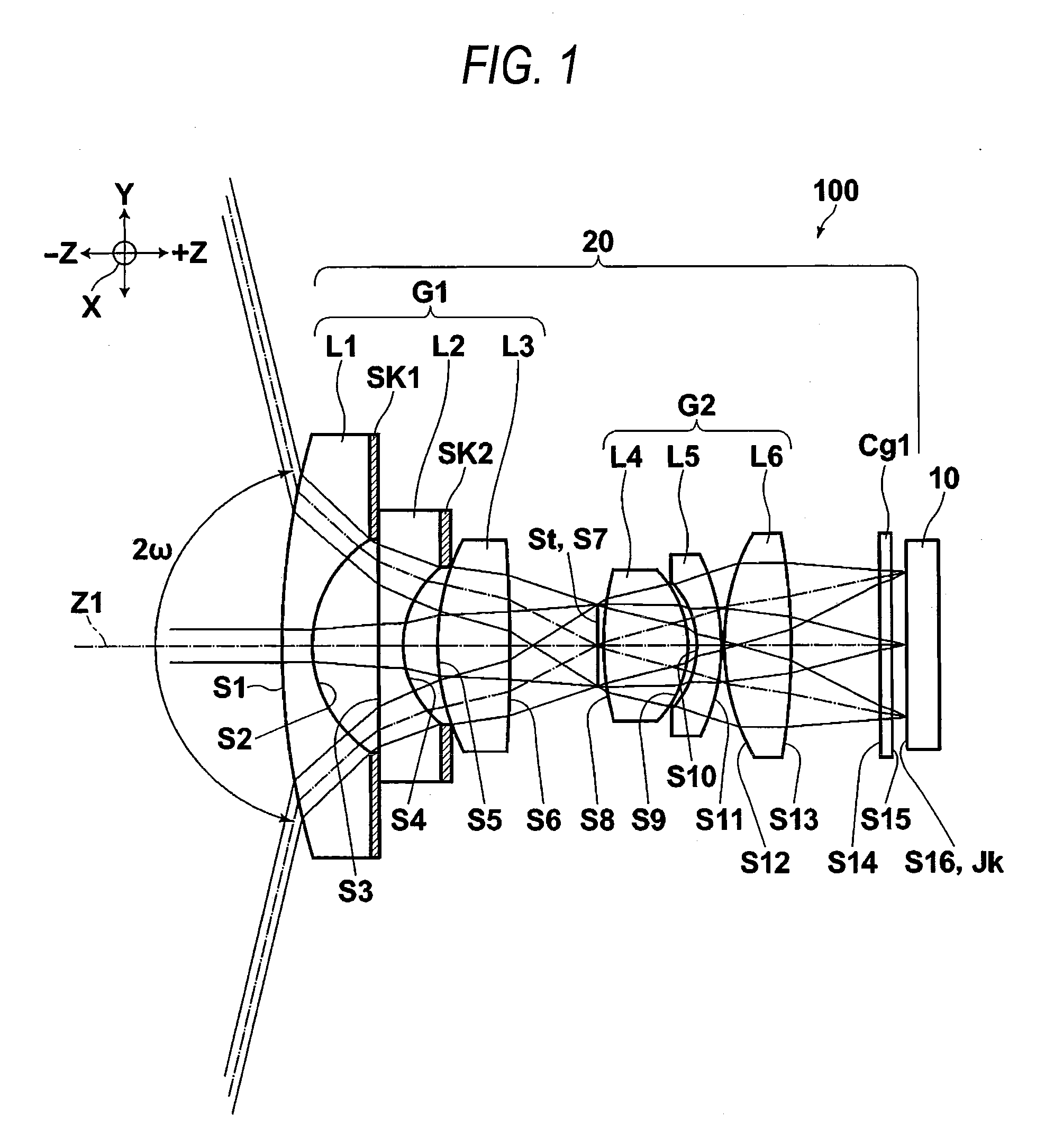
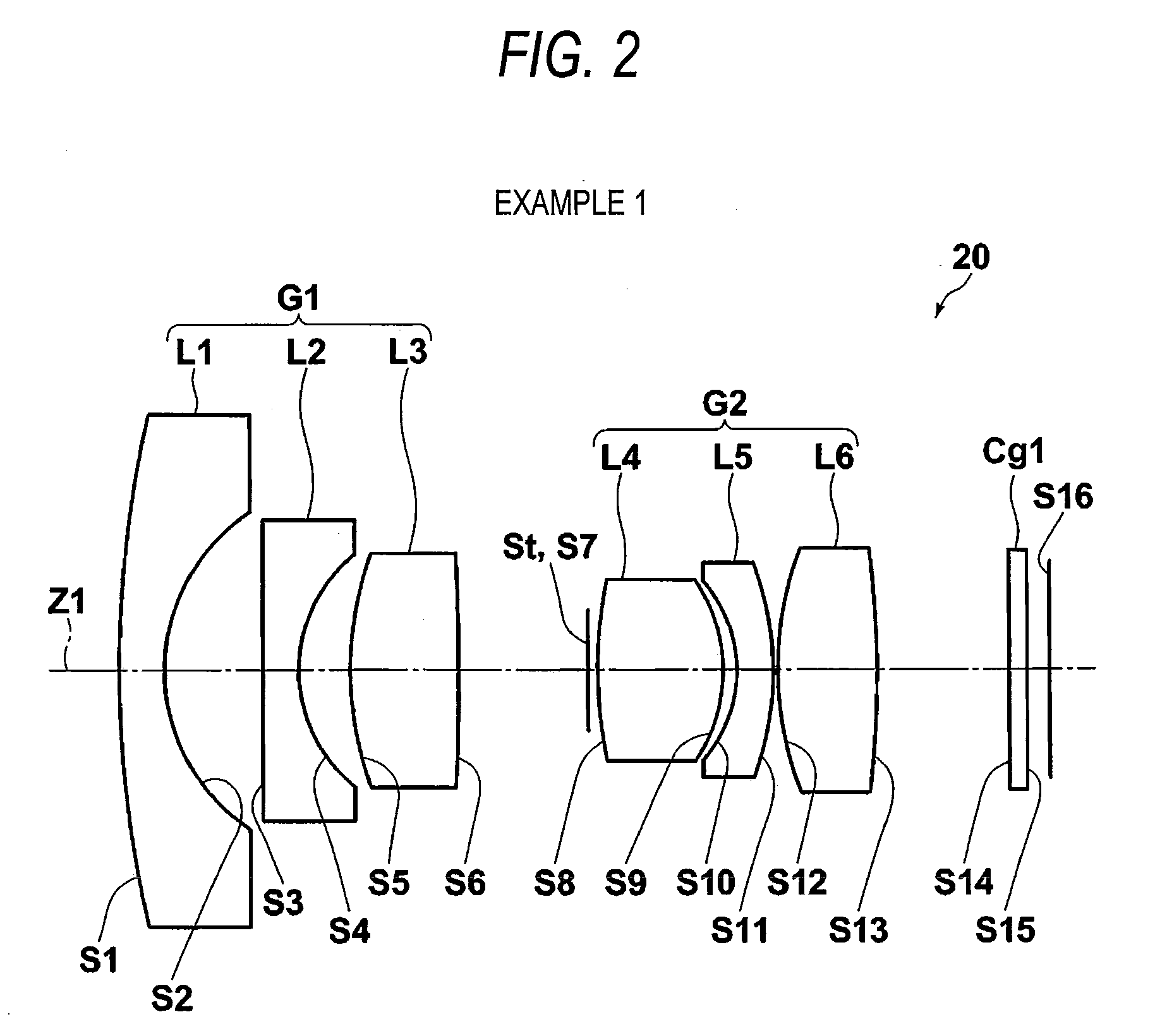
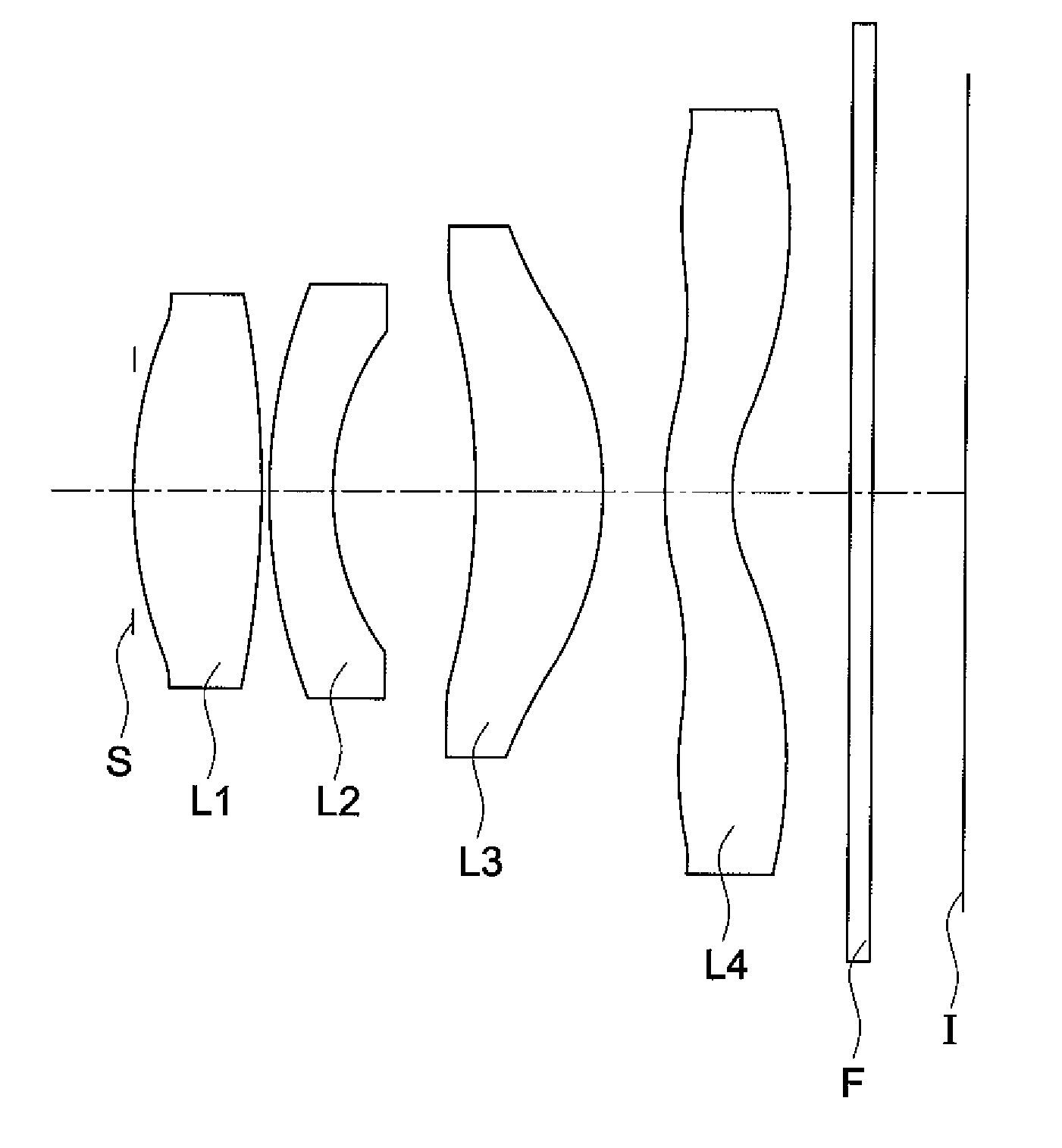
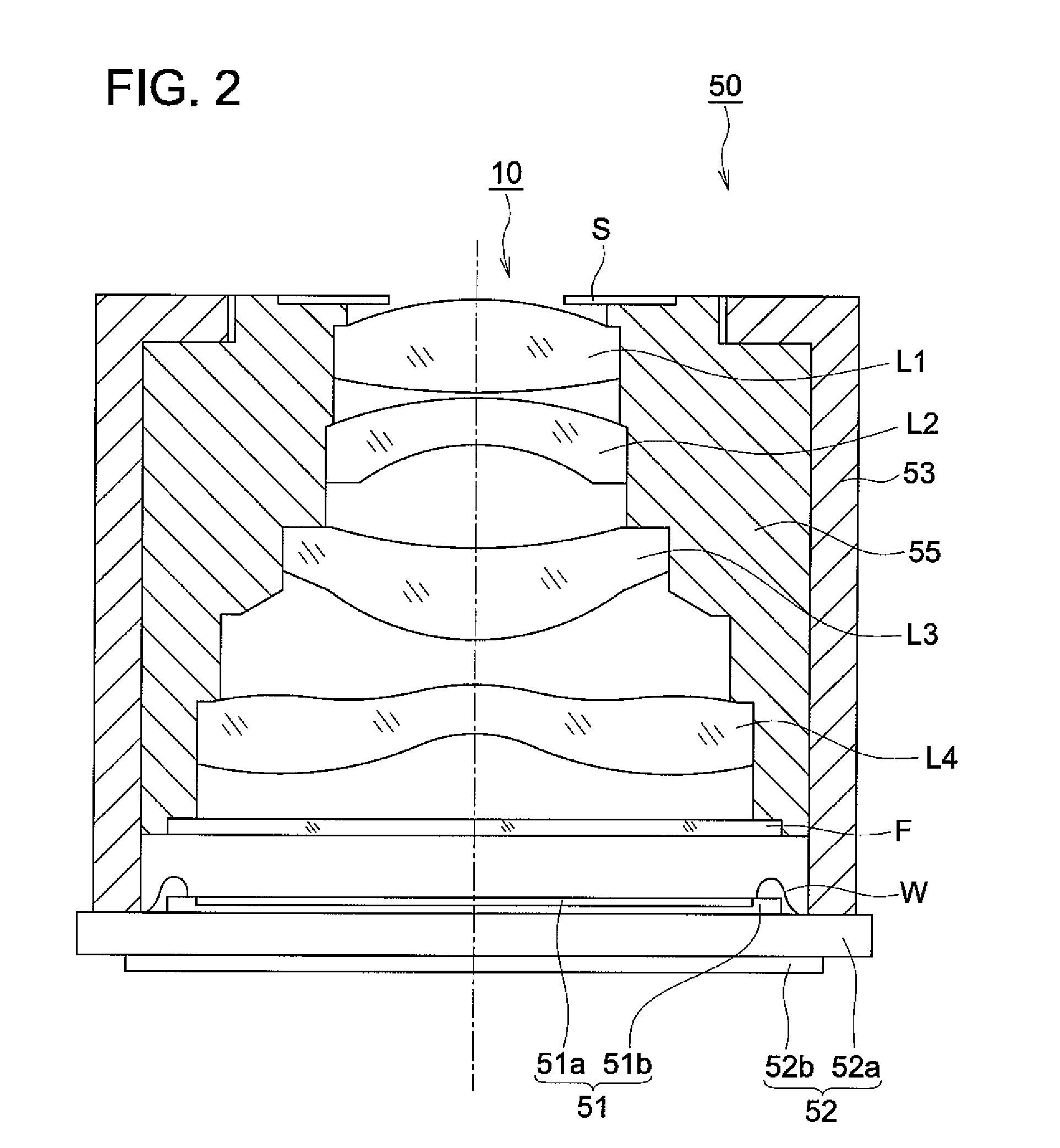
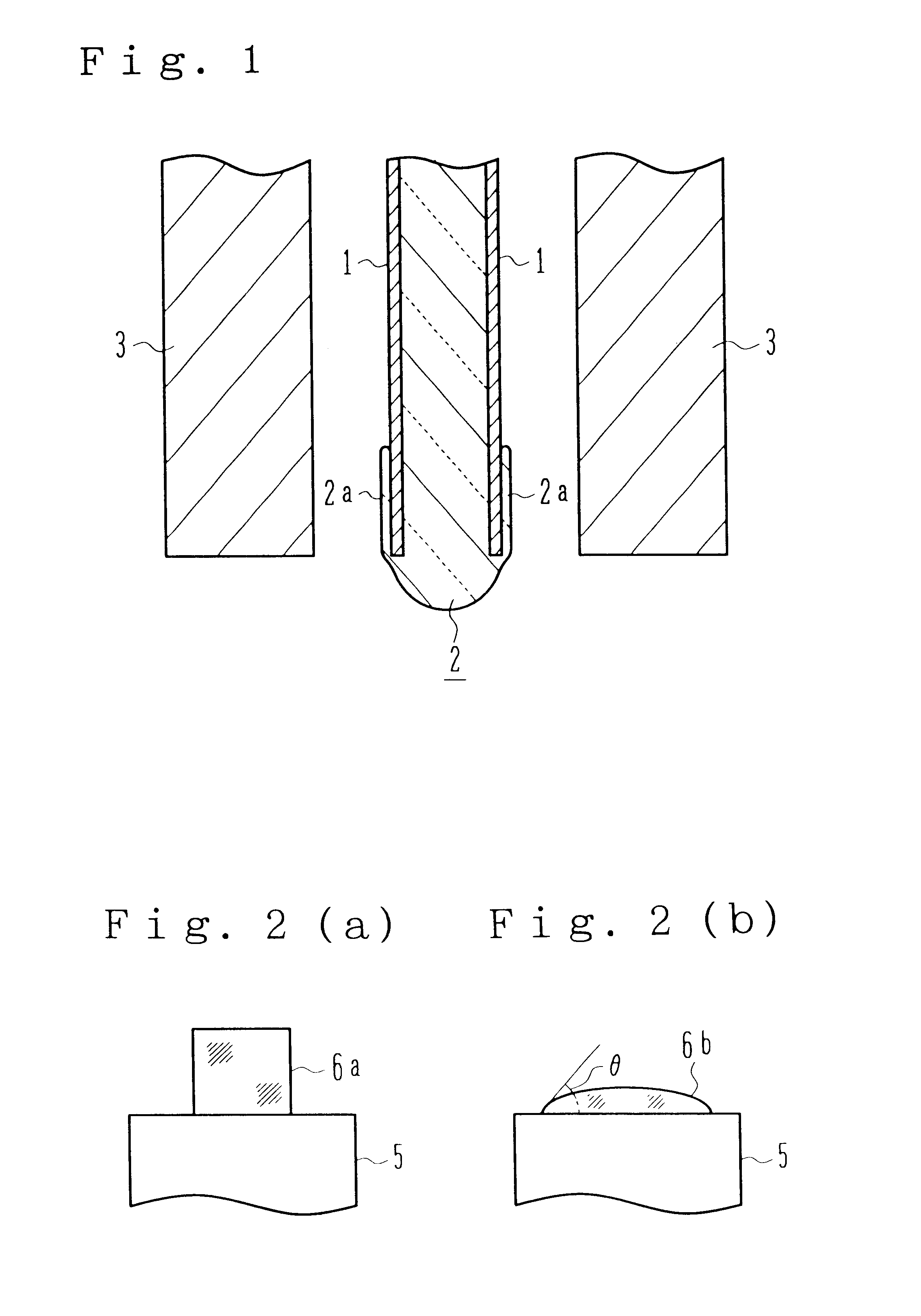
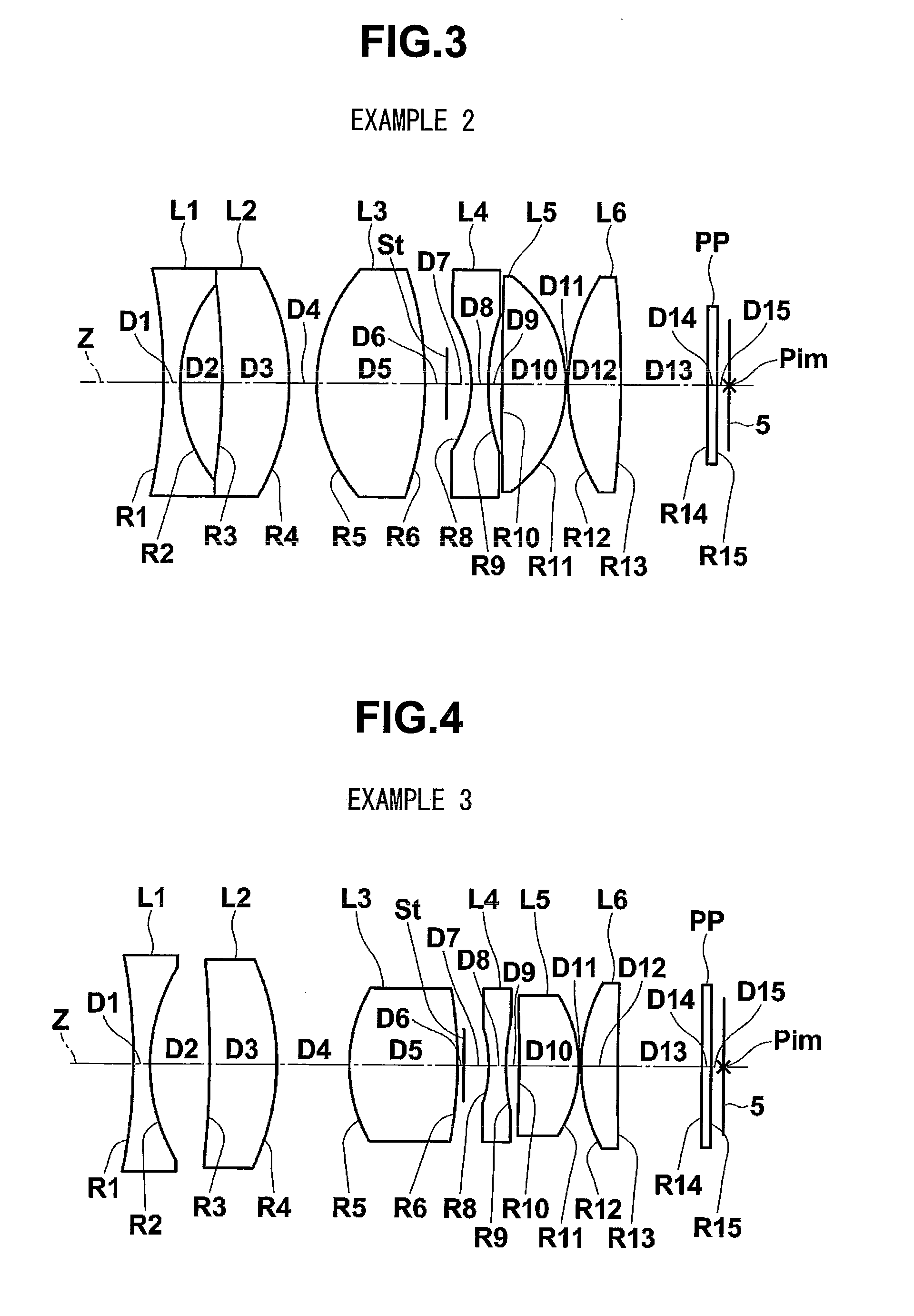
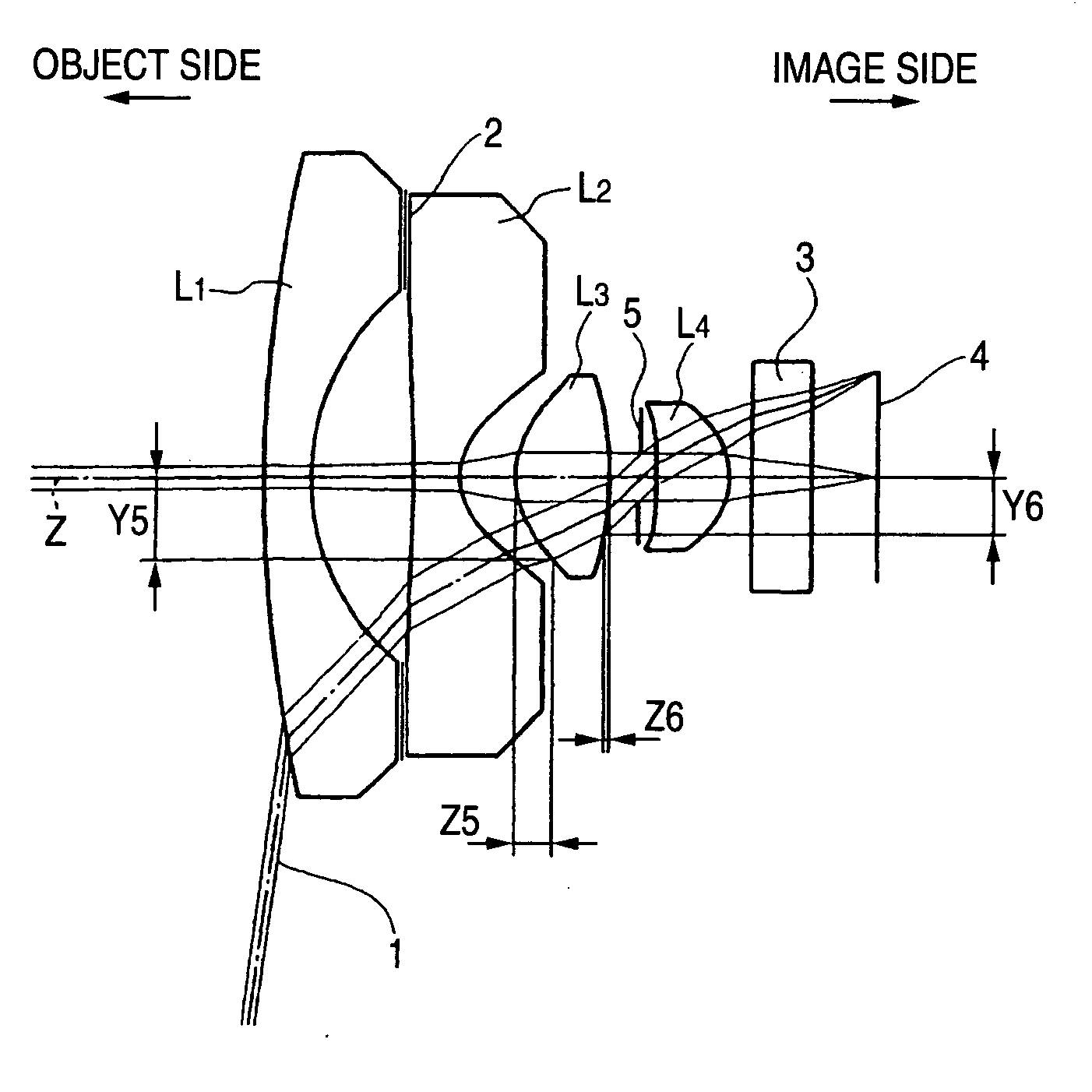
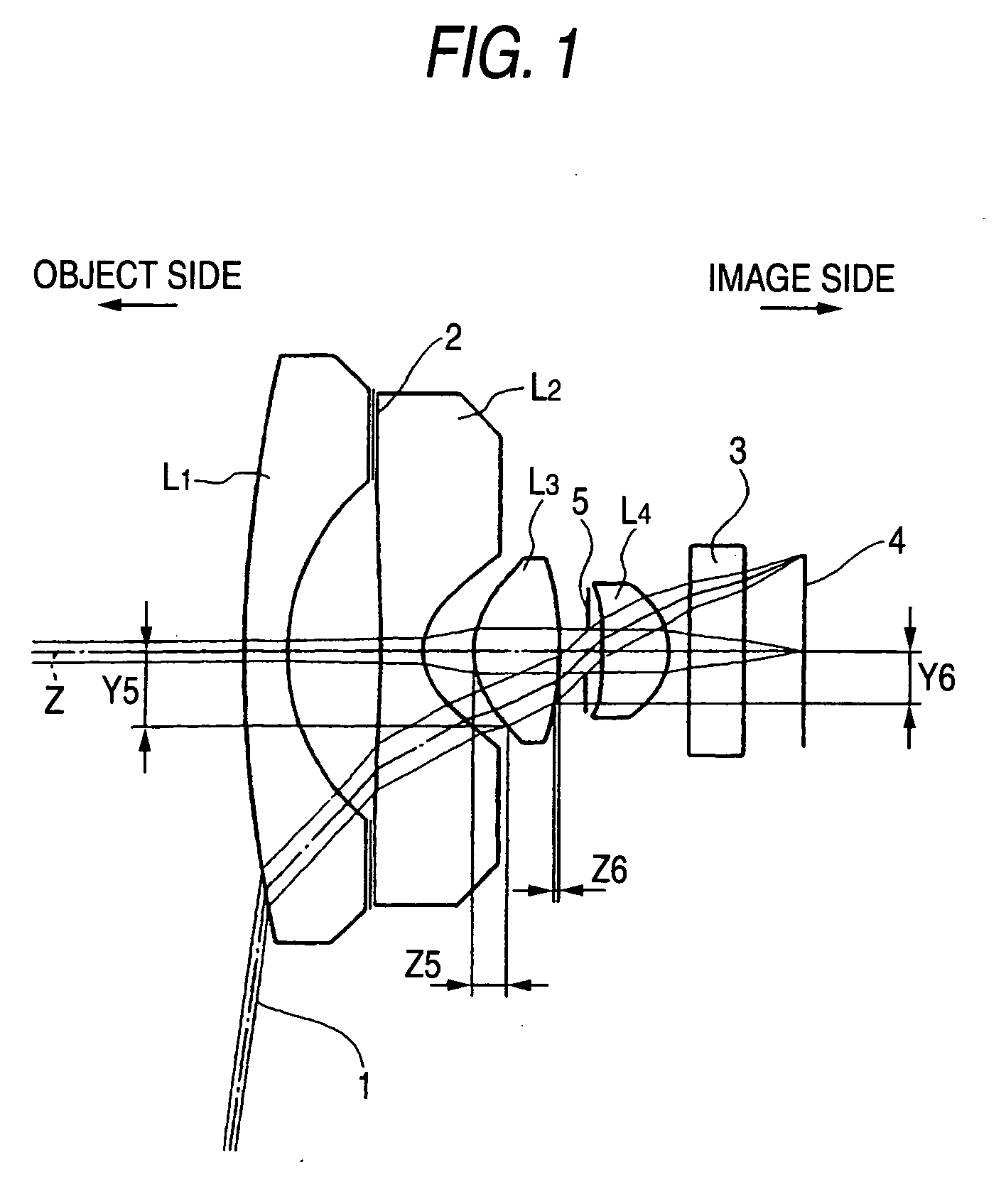
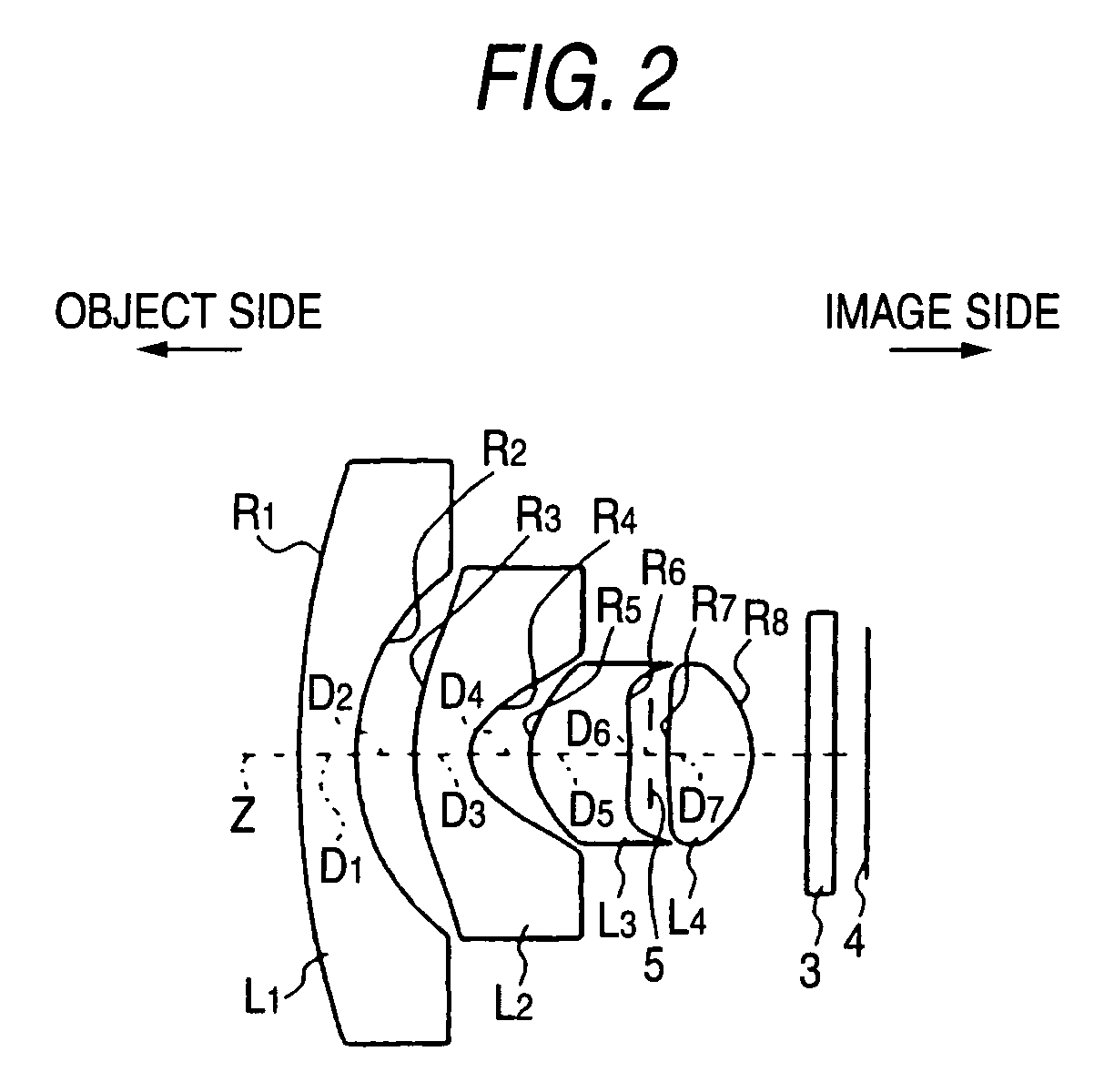
Objective lens for endoscope, and imaging apparatus for endoscope using the same
InactiveUS7486449B2Enhance the imageGood mannersMicroscopesTelescopesRefractive indexConditional expression
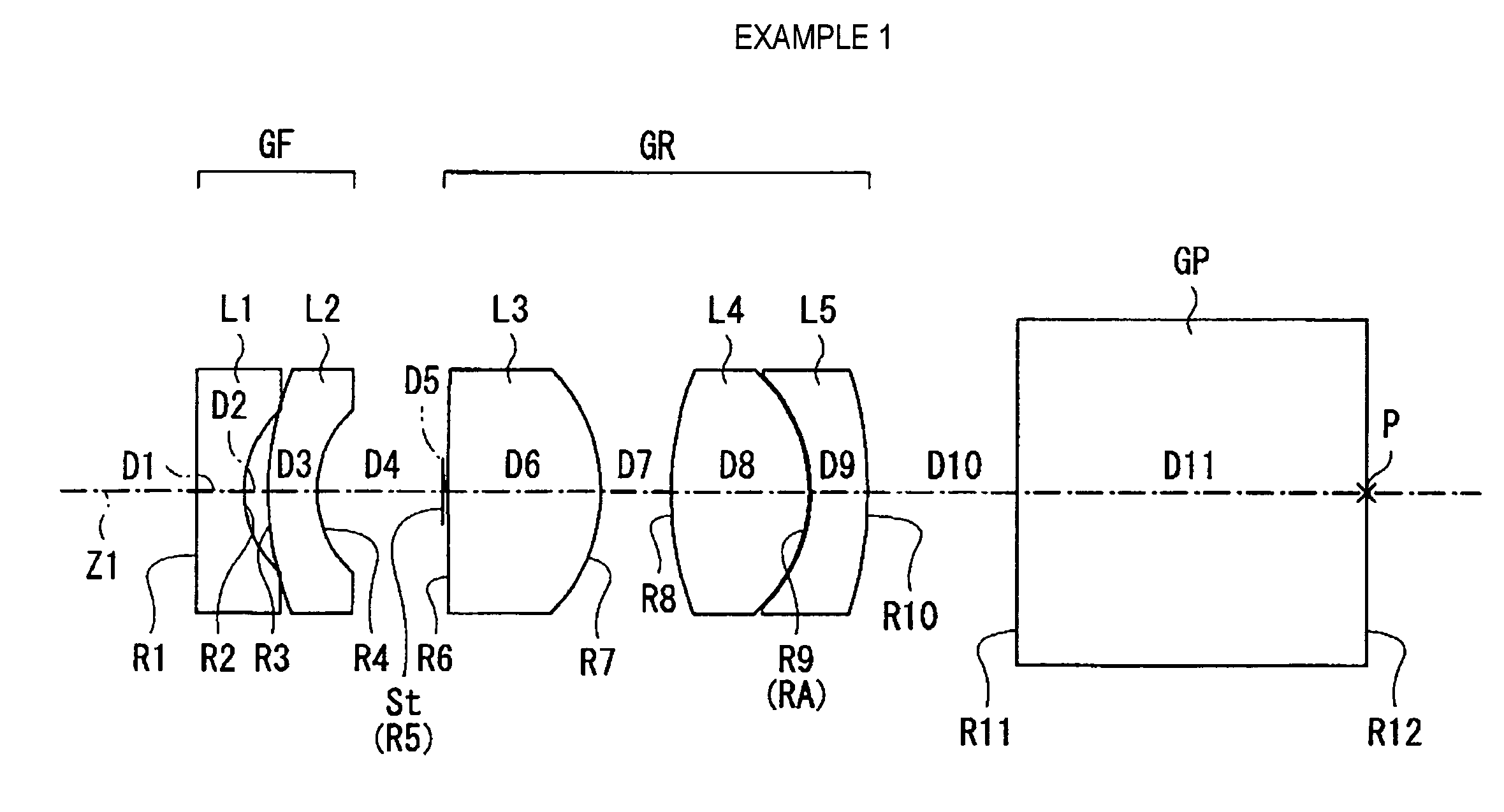
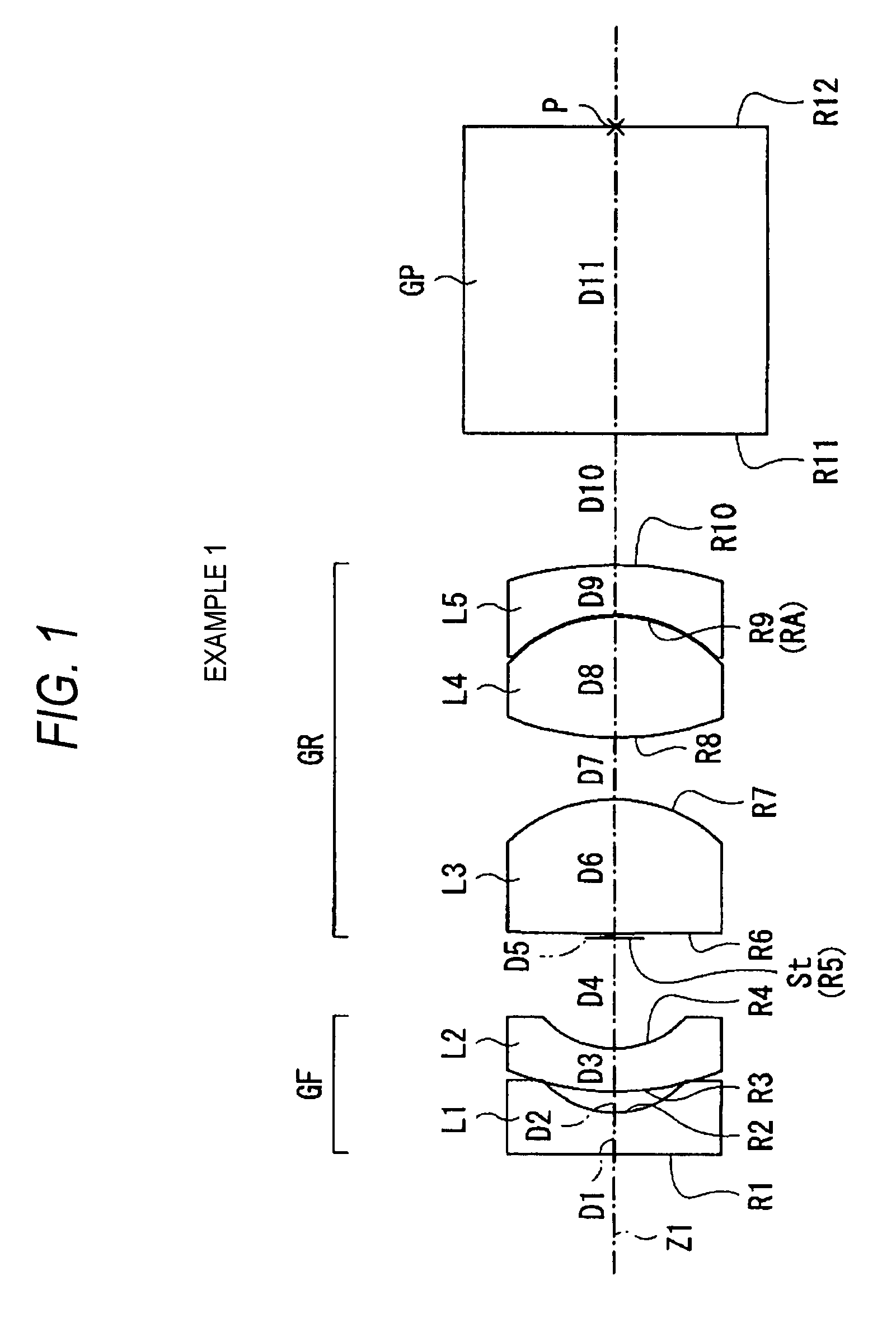
A front group consists of two concave lenses. A rear group consists of: a positive lens in which the object-side surface has a larger radius of curvature; and a cemented lens configured by a positive lens in which the object-side surface has a larger radius of curvature, and a negative meniscus lens, the cemented lens having being positive as a whole. An objective lens satisfies the following conditional expressions:|dx / fF|≧3.0 (1)(f / f3)×ν3<23 (2)f2×(ν5−ν4) / {RA×(Bf+d5 / n5)}>7 (3)where dx is the distance between the groups, f, fF, and f3 are the focal lengths of the objective lens, the front group, and the lens, respectively, ν3, ν4, and ν5 are the Abbe numbers of the lenses, RA is the radius of curvature of the cementing surface between the lenses, Bf is the back focus, and d5 and n5 are the center thickness and refractive index with respect to the d-line of the lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
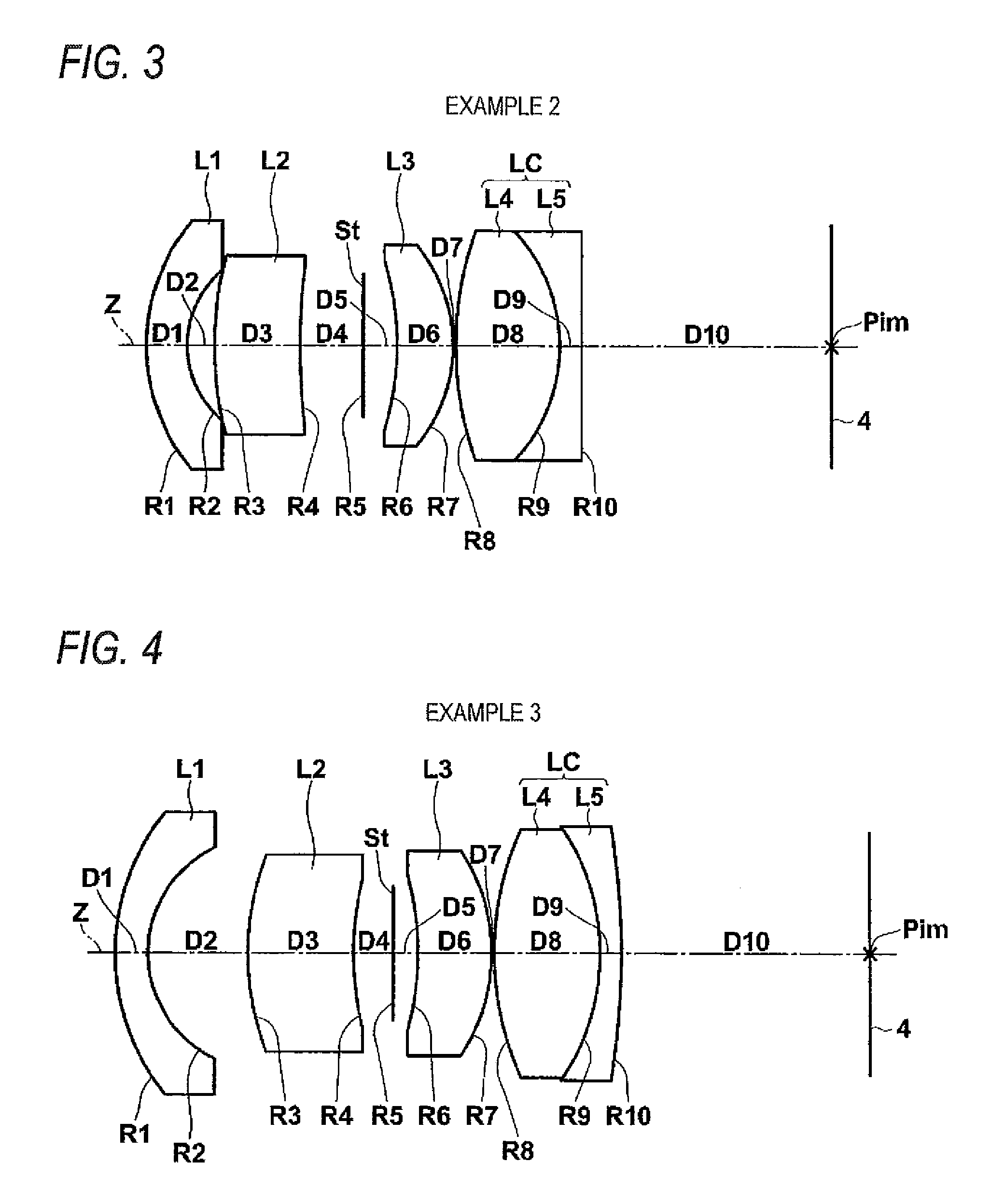
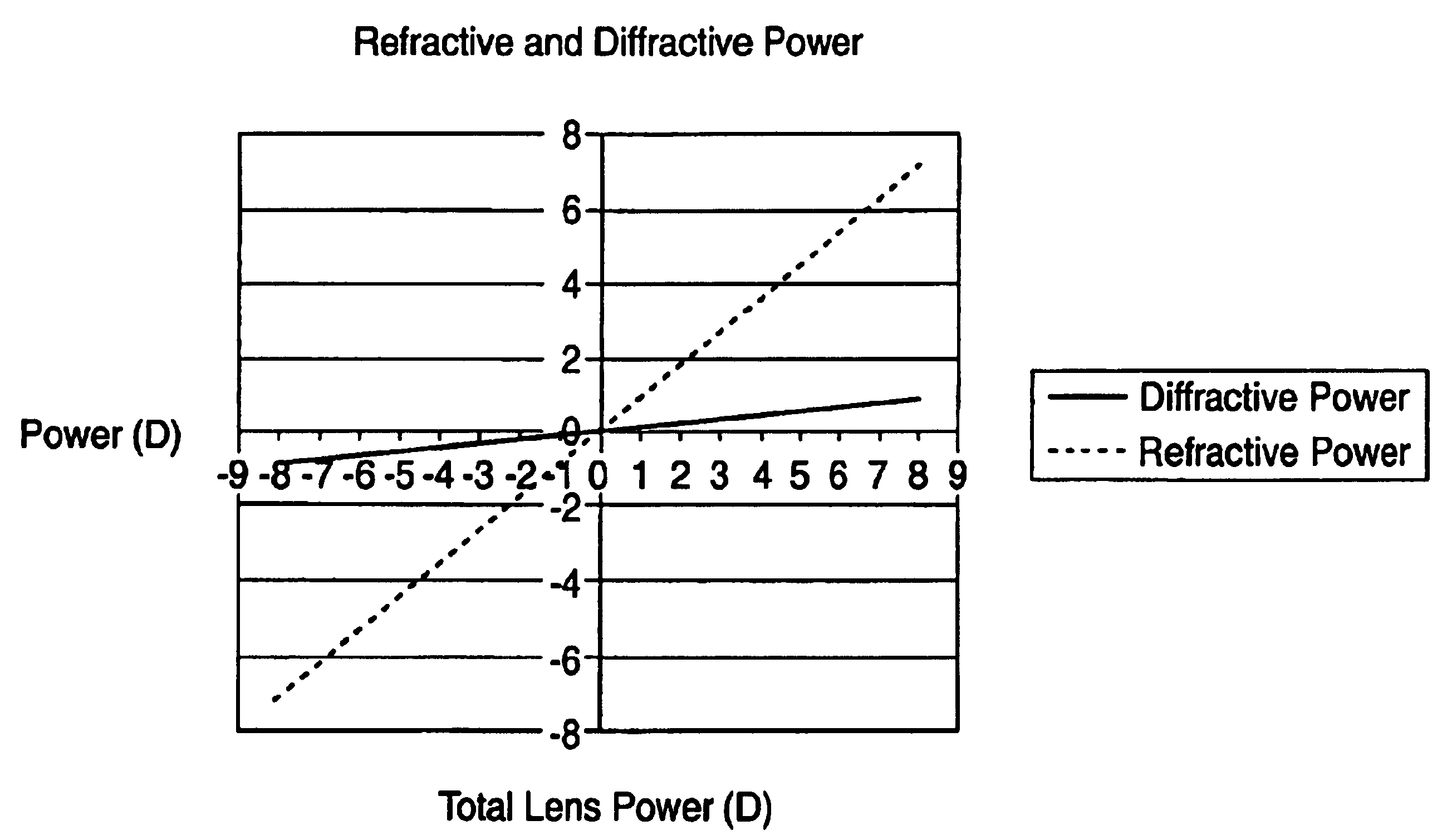
Imaging lens and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS7746572B2Corrected spherical aberrationAberration correctionOptical elementsOptical axisConditional expression
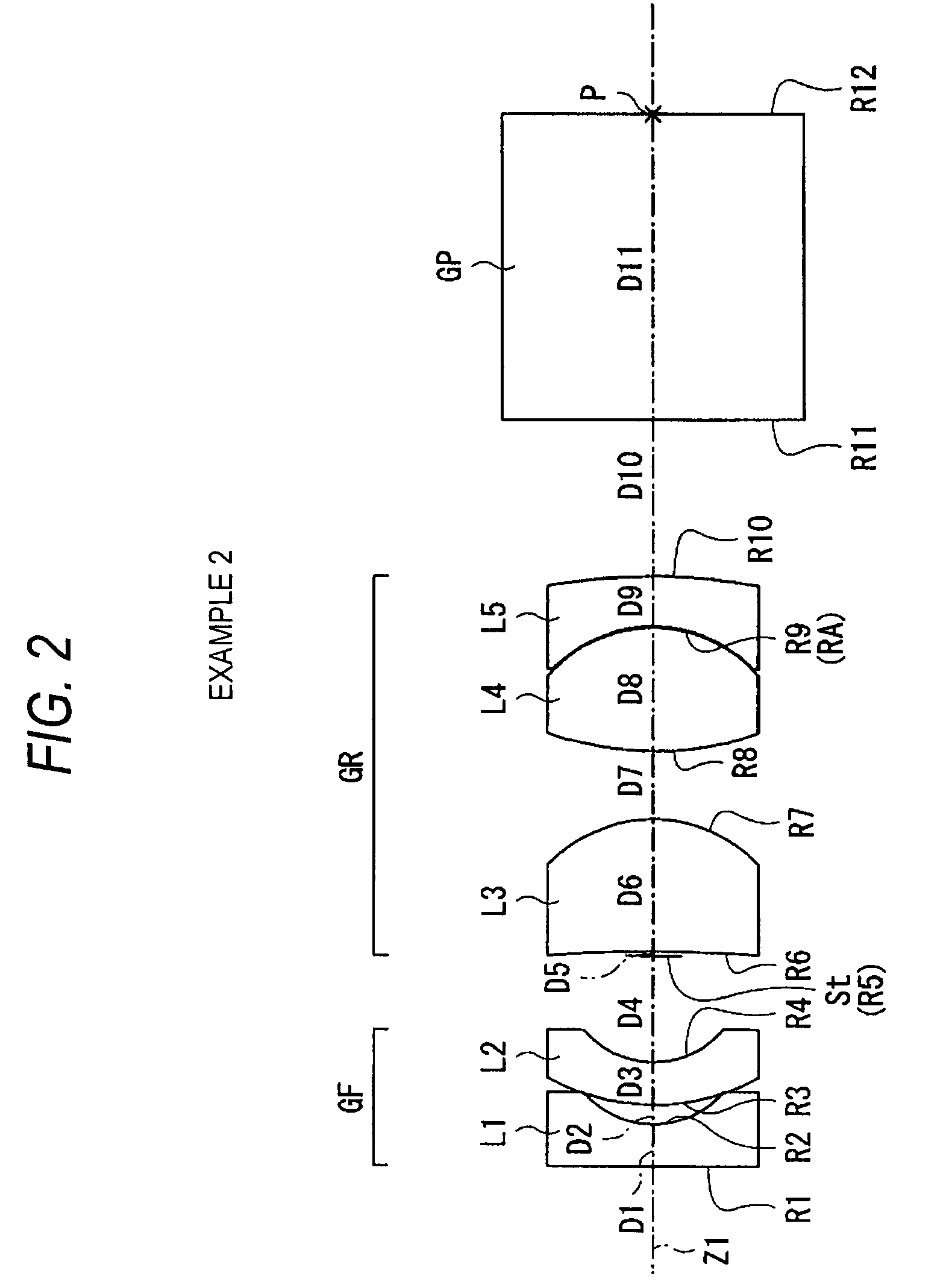
An imaging lens comprises, in order from an object side: a first lens that has a negative refractive power and is convex toward the object side; a second lens that has a positive refractive power and is a meniscus lens convex toward the object side; a stop; a third lens that has a positive refractive power and is convex toward an image side; and a cemented lens that has a positive refractive power as a whole and is formed by cementing a fourth lens and a fifth lens, wherein assuming that an Abbe number of the second lens with respect to d-line is ν2, a distance on an optical axis from a vertex of a surface of the first lens facing toward the object side to an image plane of the imaging lens is L, a focal length of the imaging lens is f, and a back focus of the imaging lens is Bf, the following conditional expressions (1) to (3) are satisfied:ν2>30 (1),2.5<L / f<4.0 (2), and0.5<Bf / f<1.3 (3).
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ophthalmic lenses with reduced chromatic blur
The present invention provides single vision and multifocal lenses, as well as methods for their production, having a transverse chromatic aberration enabling provision of a lens the performance of which is equivalent to a refractive lens with a higher Abbe number.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Lens module with low chromatic aberration
InactiveUS20130044378A1Poor chromatic aberration correction propertyHigh chromatic aberration correction propertyMountingsLensNegative refractionCamera lens
Provided is a lens module for imaging an object on an image plane. In the order from the object side to the image side of the lens module, the lens module includes a first lens made of glass and having positive refraction power, a second lens made of plastic and having negative refraction power, a aperture stopper, a third lens having positive refraction power, and a fourth lens having negative refraction power. The lens module satisfies the following formula: Vd1−Vd2≧35; wherein, Vd1 is the Abbe number of the first lens in d light and Vd2 is the Abbe number of the second lens in the d light.
Owner:FOSHAN PREMIER SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Two-piece optical lens system for taking image
A two-piece optical lens system for taking image comprises, from the object side: a first lens element and a second lens element. The first lens element is a positive meniscus lens element has a convex object-side surface. The second lens element is a negative meniscus lens element has a convex image-side surface. Both the object-side surface and the image-side surface of the first and second lens elements are aspheric, the first and second lens elements are made of plastic material, and they satisfy the relations: 0.55<f1 / f<0.95, −2.0<f2 / f<−1.0, 27.0<ν1−ν2. The focal length of the optical lens system is f, the focal length of the first lens element is f1, the focal length of the second lens element is f2, the Abbe number of the first lens element is ν1, and the Abbe number of the second lens element is ν2.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Composite material and optical component using the same
ActiveUS20090128912A1Good dispersionHigh refractive indexDiffraction gratingsEpoxy resin coatingsInorganic particleRefractive index
A composite material (10) includes a resin (12), and first inorganic particles (11) dispersed in the resin and containing at least zirconium oxide. The composite material has a refractive index at the d line nCOMd of not less than 1.60 and an Abbe's number νCOM of not less than 20, and satisfies a relationship nCOMd≧1.8−0.005 νCOM. This composite material exhibits both a high refractive index and low dispersion in good balance, and has excellent workability. Accordingly, using this composite material makes it possible to realize a small optical component having favorable wavelength characteristics.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical glass for precision press molding, preform for precision press molding, and process for the production thereof
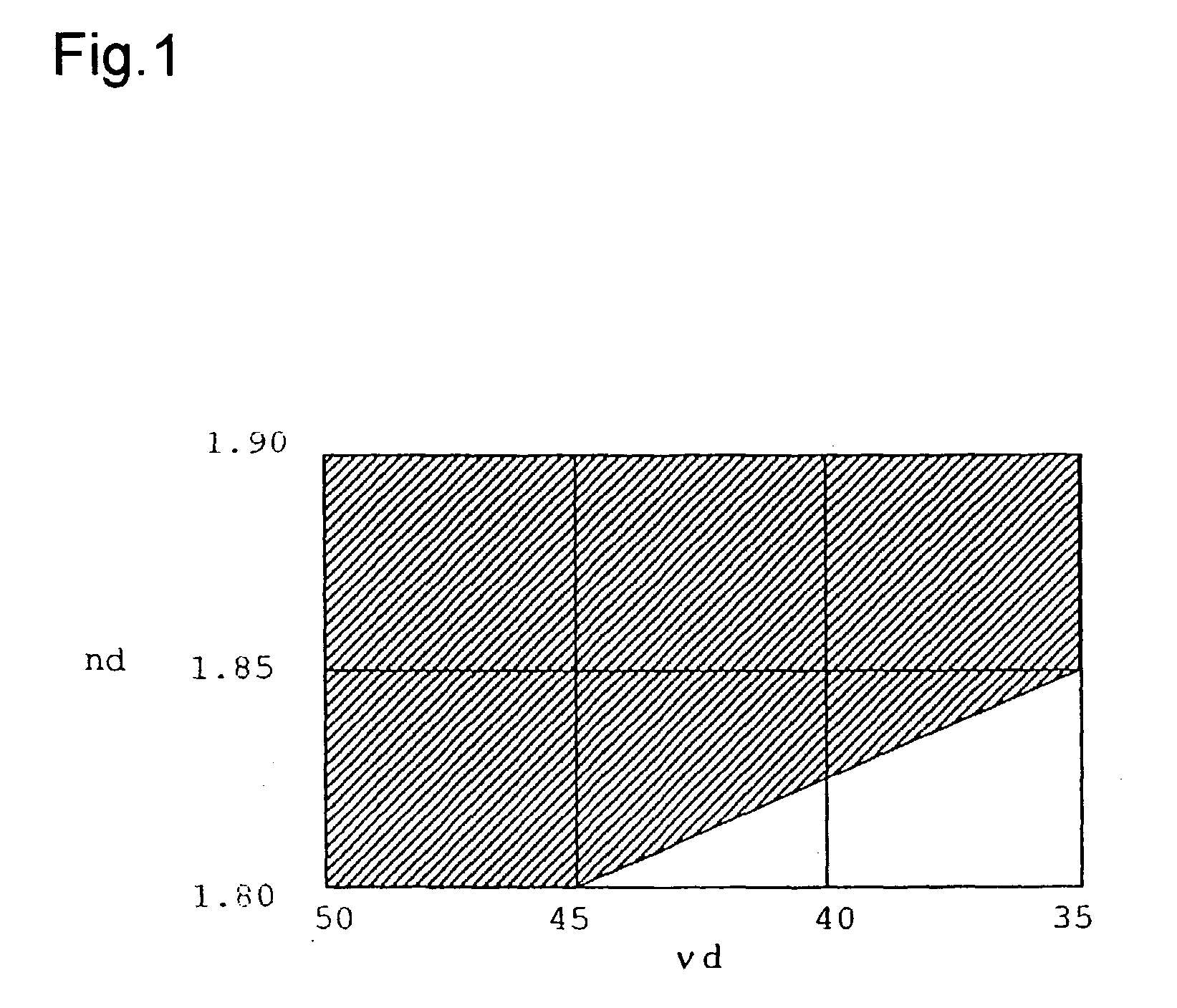
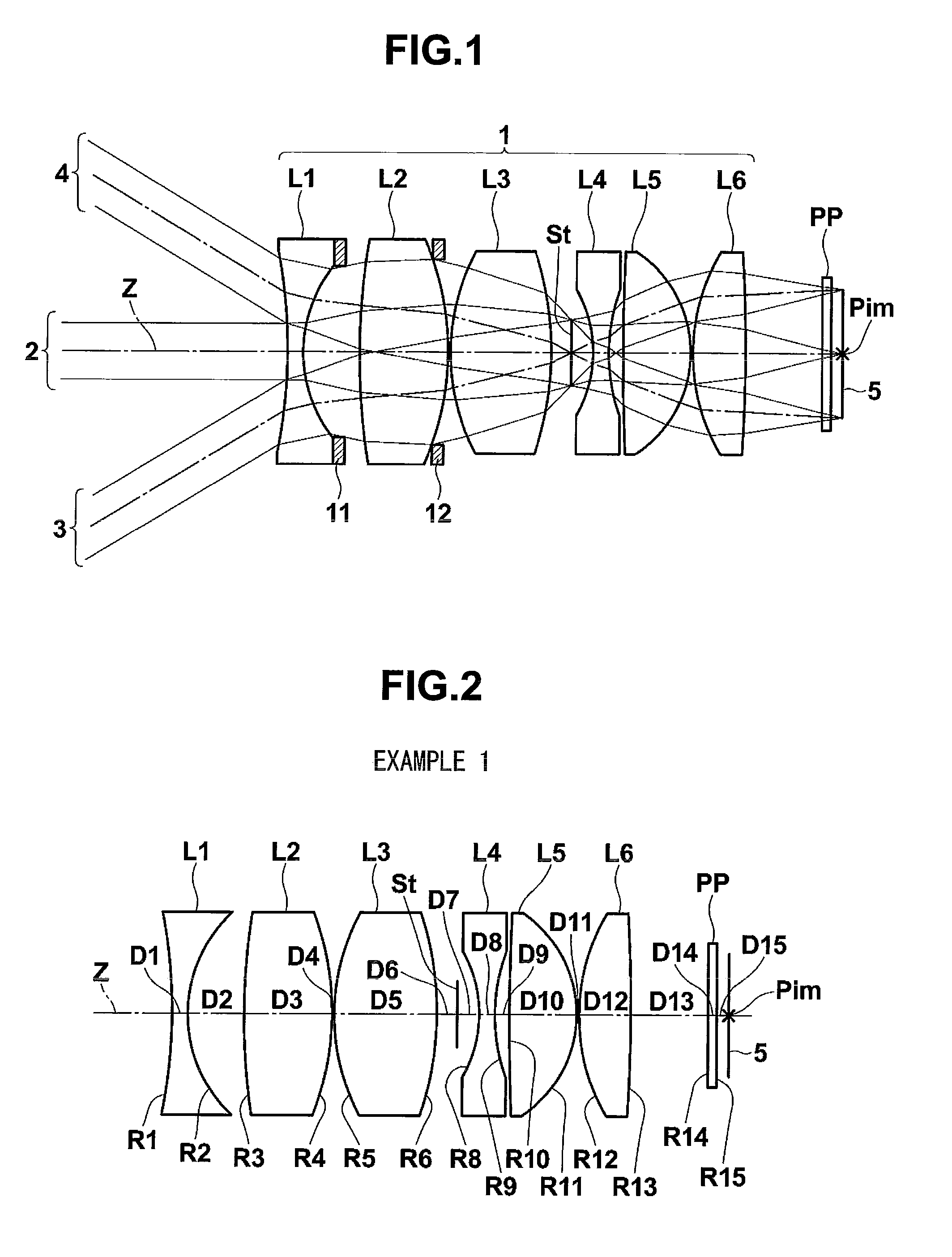
A high-refractivity high-dispersion optical glass for producing an optical element, which requires no machining, such as polishing or lapping, of an optical-function surface after precision press molding, containing B2O3, SiO2, La2O3, Gd2O3, ZnO, Li2O, ZrO2 and Ta2O5 as essential components, containing 0 to 1 mol % of Sb2O3 as an optional component, substantially containing none of PbO and Lu2O3, having a glass transition temperature of 630° C. or lower, and (1) having a refractive index nd and an Abbe's number nud which satisfy all of the following relational expressions, 1.80<nd<=1.90, 35<nud<=50, and nd>=2.025-(0.005xnud) or (2) having an nd of greater than 1.85 and a nud of greater than 35.
Owner:HOYA CORP
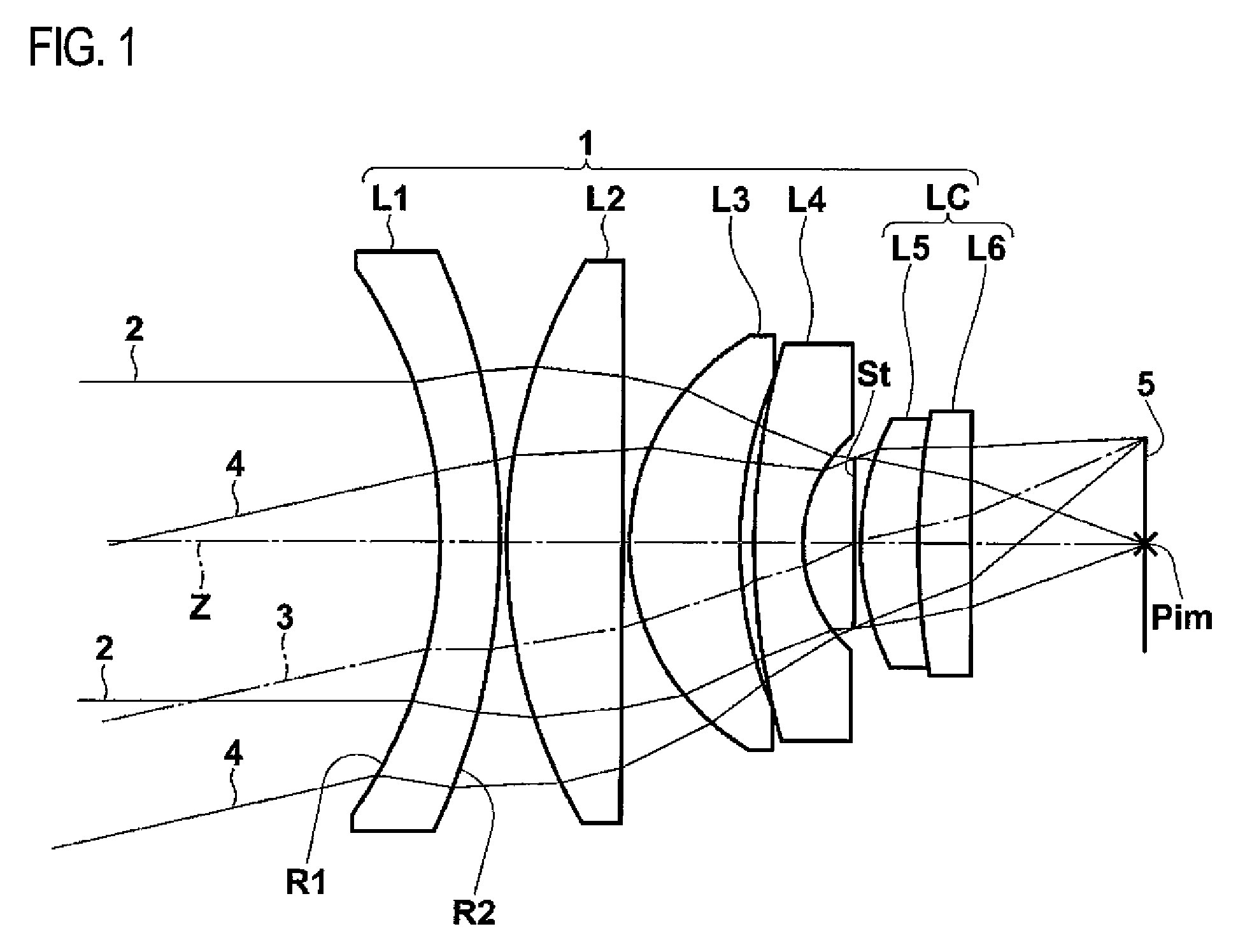
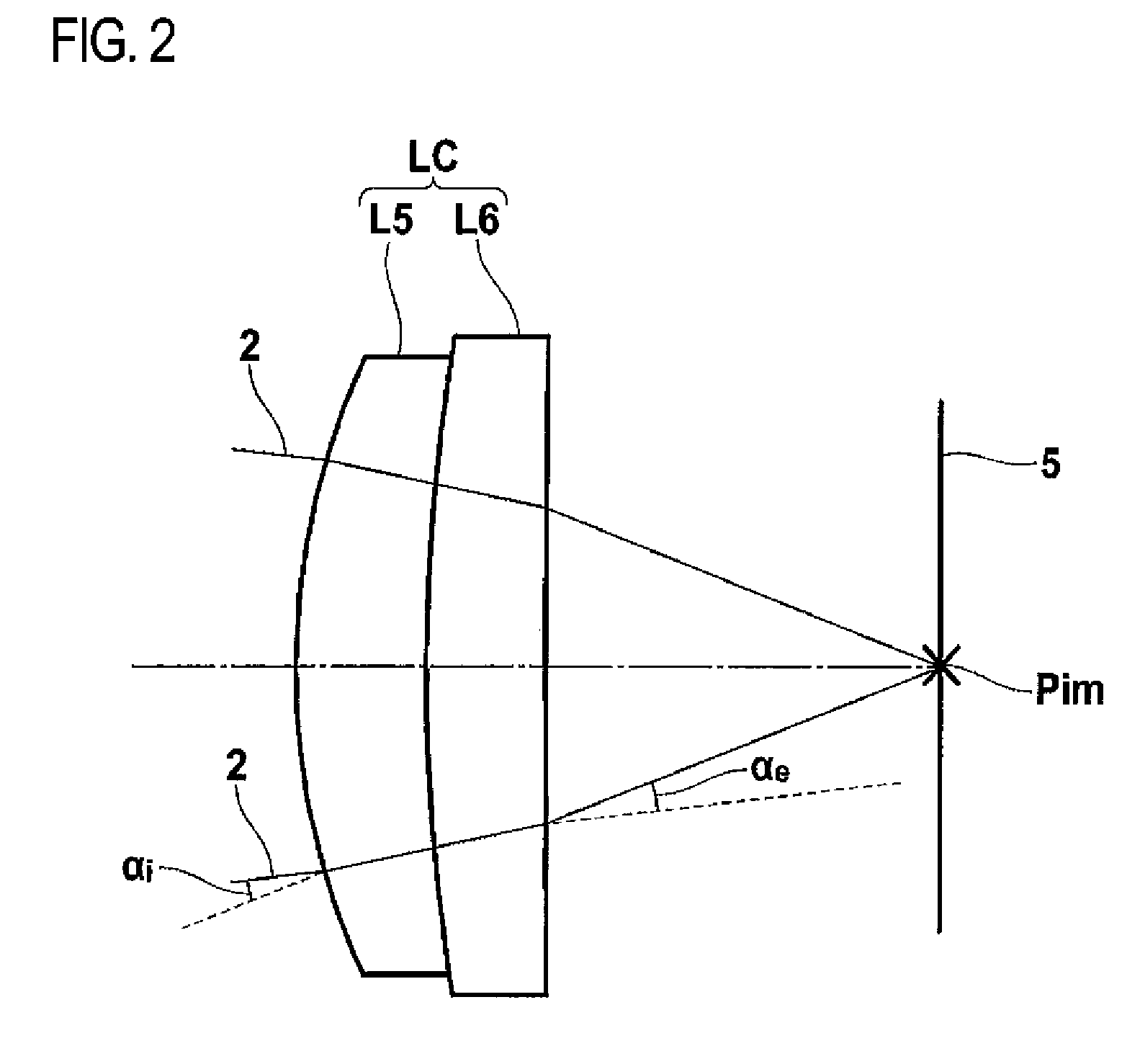
Image Capture Lens
There is provided an image pickup lens having a 6-element structure which has a small size and a sufficiently lens speed of F / 2 or less and in which various aberrations are corrected favorably. This image pickup lens includes a first lens having a positive refractive power and comprising a convex surface directed to the object side; a second lens having a negative refractive power and comprising a concave surface directed to the image side; a third lens having a positive or negative refractive power; a fourth lens having a positive refractive power; a fifth lens having a positive refractive power and comprising a convex surface directed to the image side; and a sixth lens having a negative refractive power and comprising a concave surface directed to the image side, in this order from the object side, wherein the image side surface of the sixth lens has an aspherical shape and an inflection point at a position other than an intersection point with the optical axis, and the image pickup lens satisfies the following conditional expressions.ν1>50ν2≦30where,ν1 is an Abbe number of the first lens, andν2 is an Abbe number of the second lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Optical system for taking image
An optical system comprises from the object side: a positive first lens element, a negative second lens element, a positive third lens element, a fourth lens element, and an aperture stop located between the object side of the optical system and the second lens element for controlling the brightness of the optical system. A radius of curvature R3 of a front surface of the second lens element satisfies the relation: −0.02 [1 / mm]<1 / R3<0.22 [1 / mm], an Abbe number V2 of the second lens element is less than 40. A focal length of the fourth lens element is f4, a focal length of the optical system is f, they satisfy the relation: f / f4<0.1, at least one inflection point is formed on the rear surface of the fourth lens element.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Color-corrected projection lenses for use with pixelized panels
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
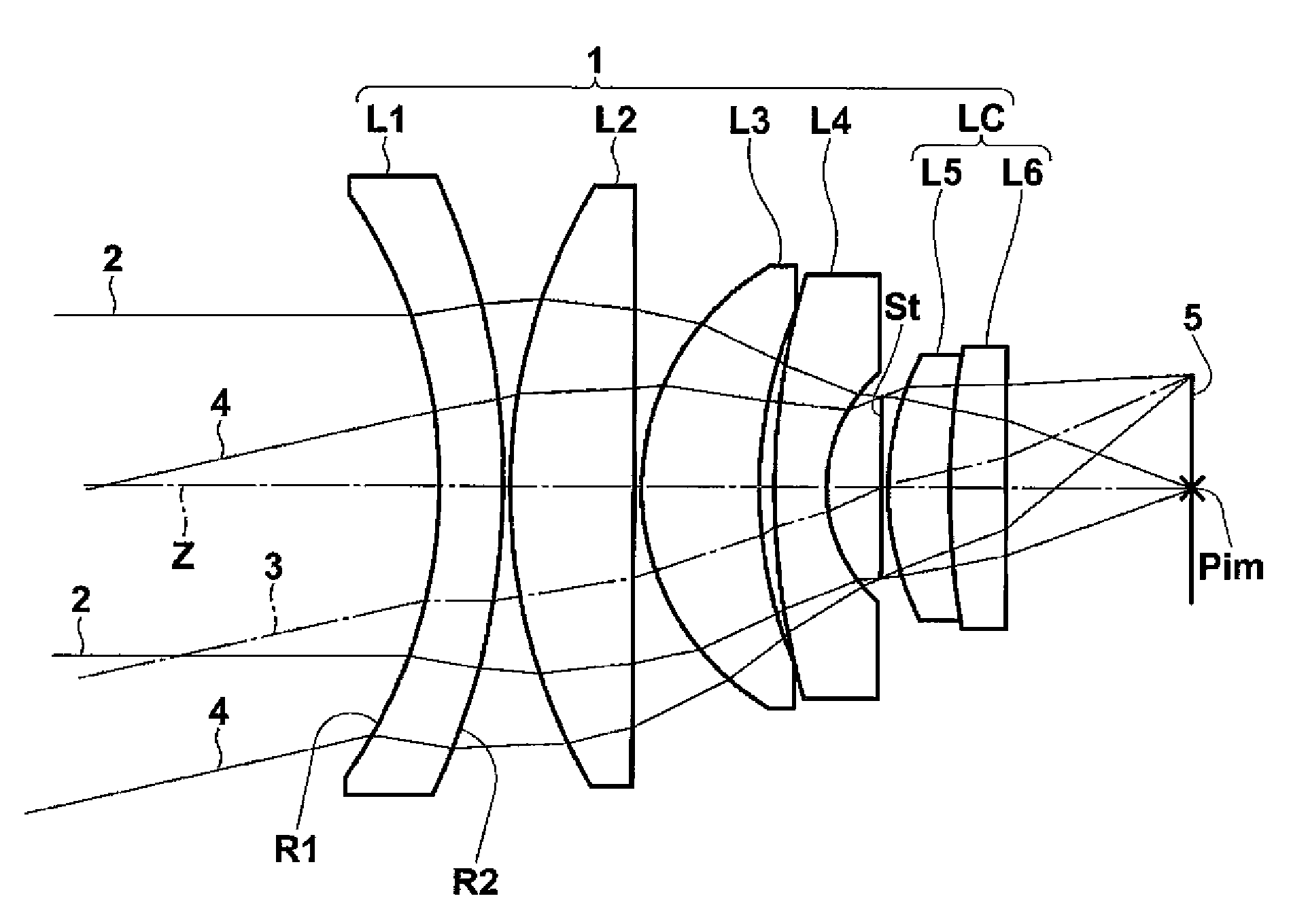
Imaging lens system and imaging apparatus
ActiveUS7663814B2Long back focusGood optical performanceOptical elementsConditional expressionImaging lens
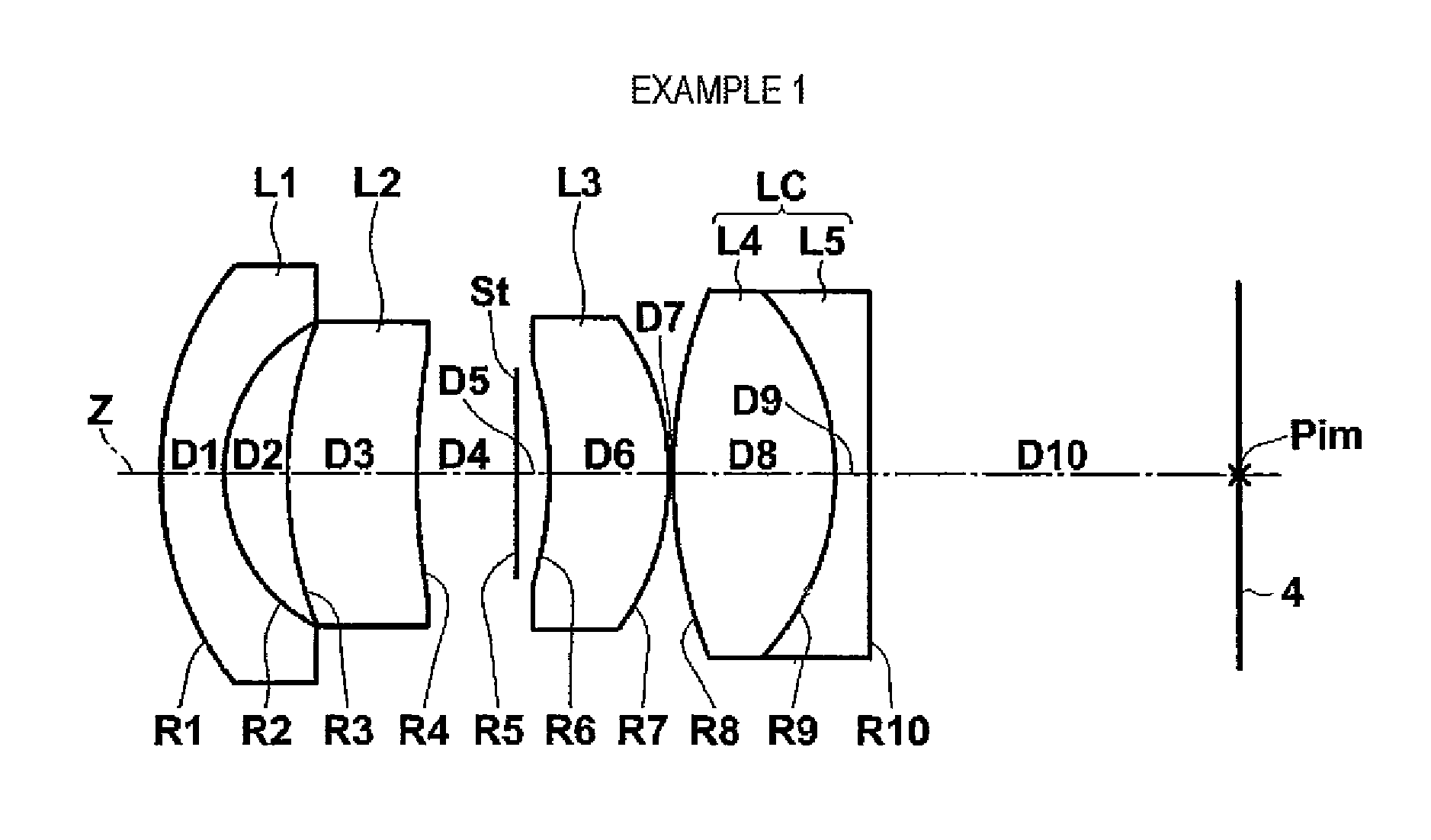
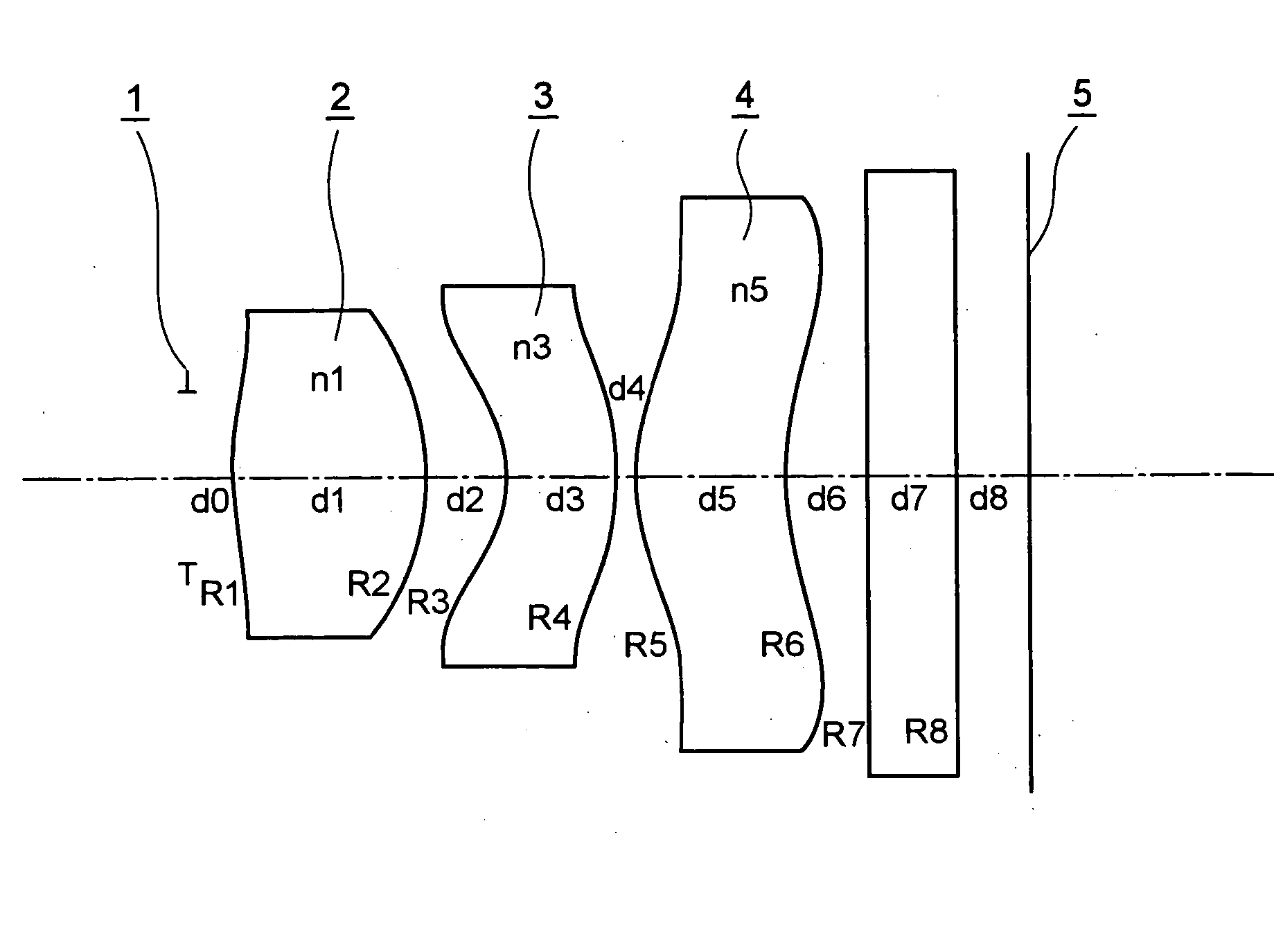
The imaging lens system includes a negative first lens disposed on a most object side, having a concave surface directed toward the object side and having a meniscus shape, a cemented lens LC disposed on a most image side and having a convex surface on its most object side, and an aperture diaphragm disposed just in front of the object side of the cemented lens. The system satisfies the following conditional expressions:0.05<(R2−R1) / (R1+R2)<0.25vd1 −vd2 >15whereR1 and R2 denote radius of curvatures of object side and image side surfaces of the first lens, respectively, andvd1 and vd2 denote Abbe numbers of lenses, which are located on the most object side and on the most image side among lenses constituting the cemented lens, at the d-line, respectively.
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Zoom lens including four lens groups
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
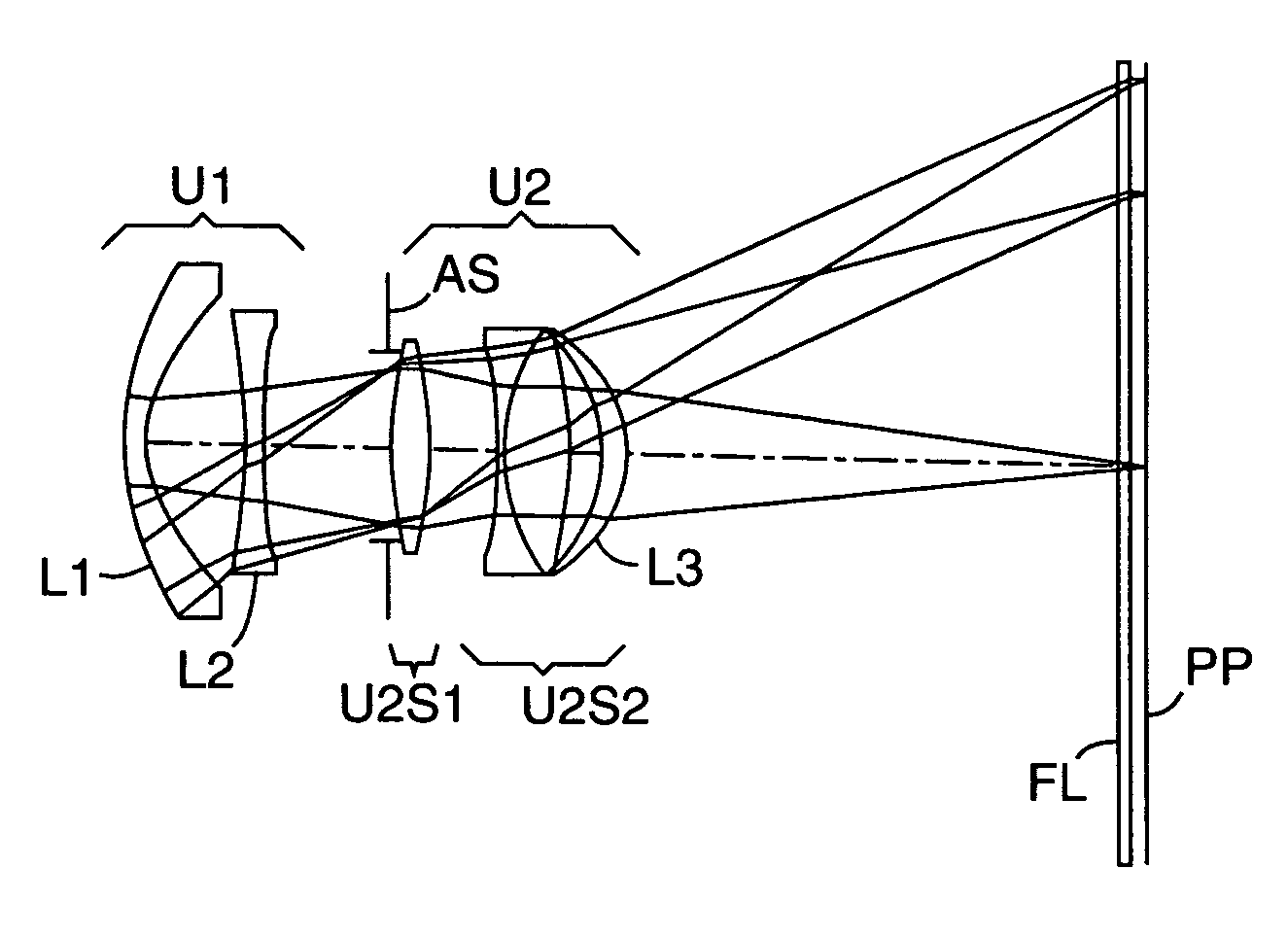
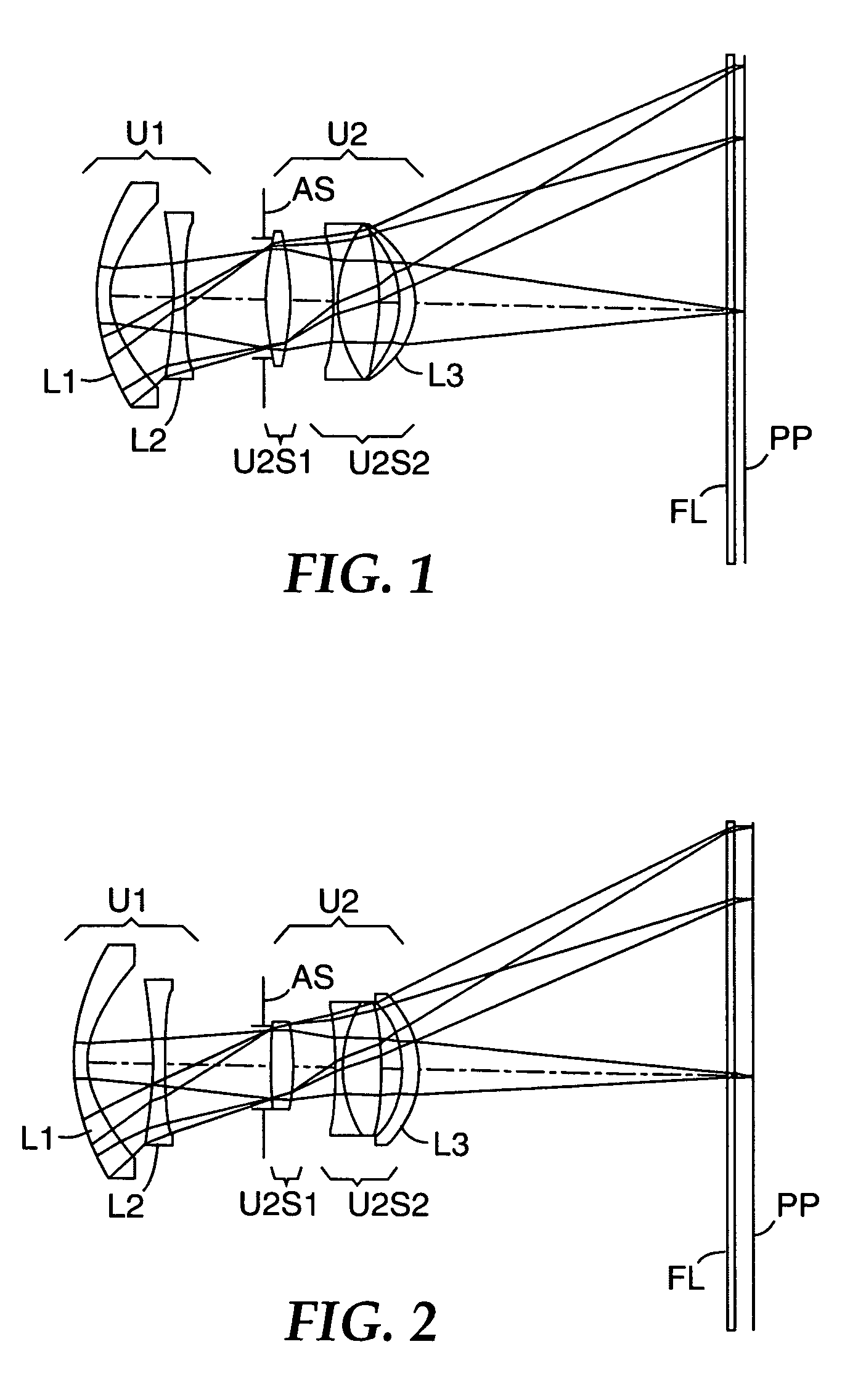
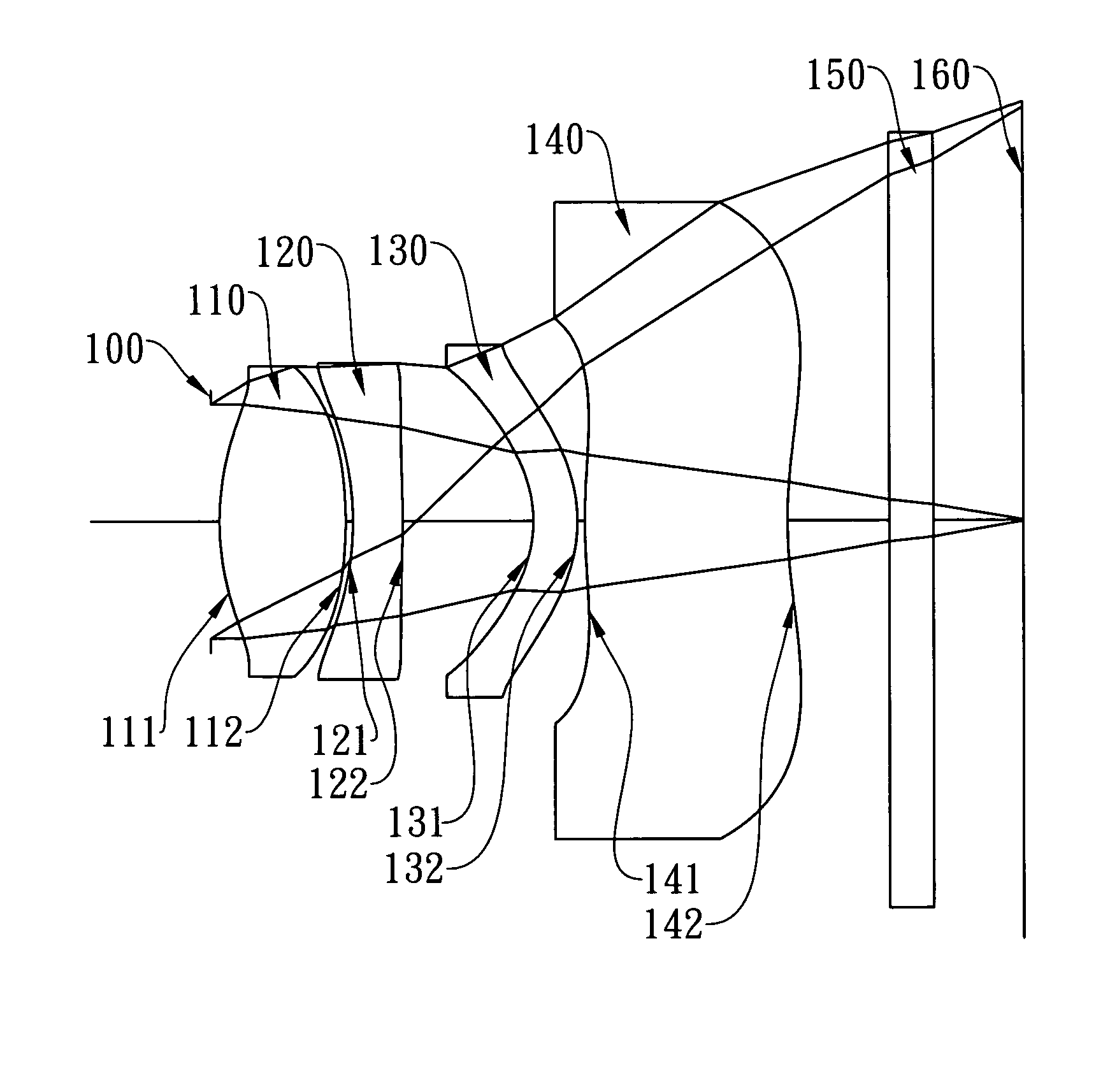
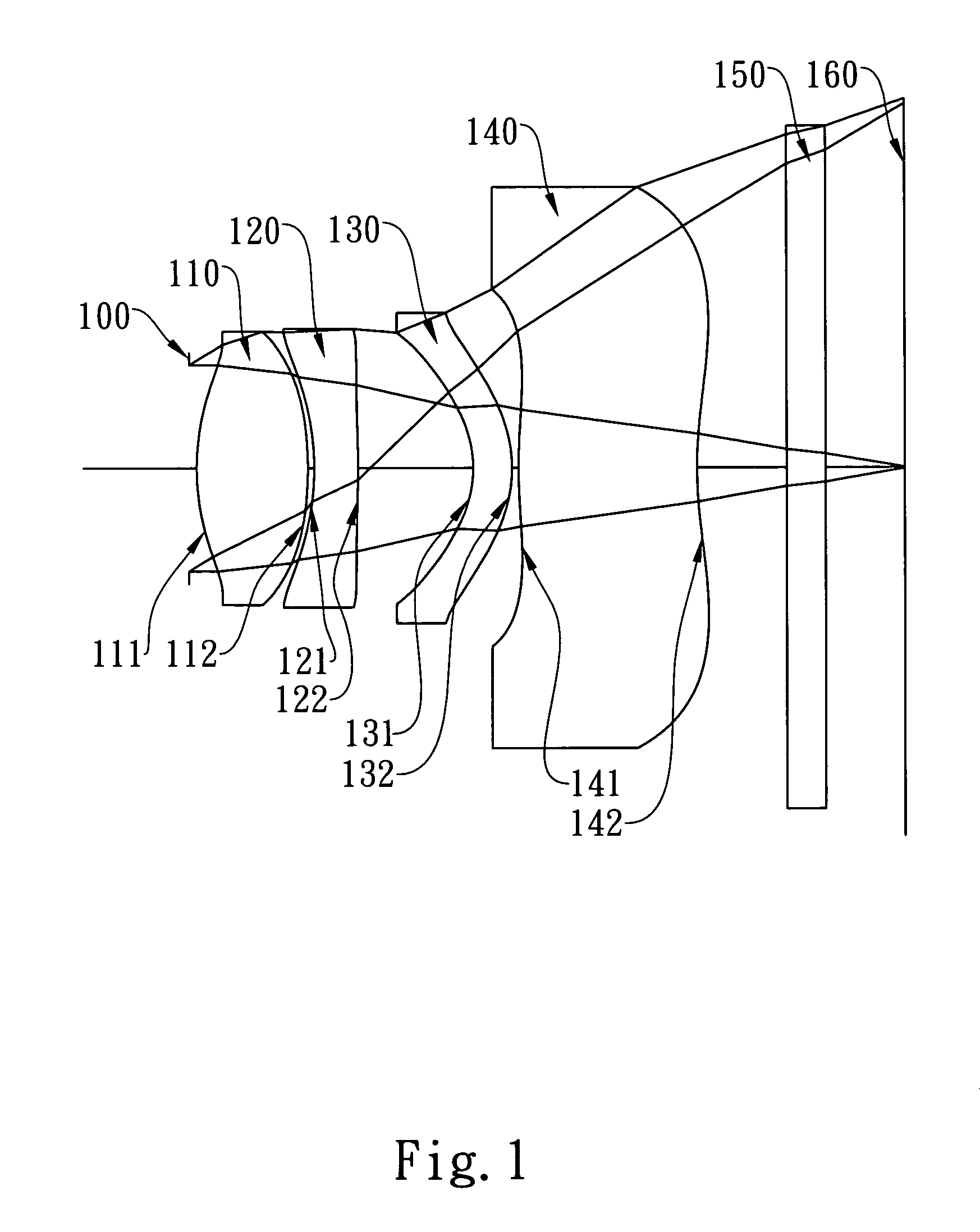
Imaging lens
A bright, small, and inexpensive imaging lens system is provided with a short total length that can provide more than a 30 degree viewing angle and whose aberrations are excellently corrected. The imaging lens includes, in order from an object side, a positive first lens with a convex surface facing the object side, an aperture stop provided on the object side or an image side of the first lens, a meniscus second lens with a concave surface facing the object side, and a meniscus third lens with a convex surface facing the object side. Furthermore, at least one of the first lens and the second lens includes an aspheric surface, and the third lens is a biaspheric lens. In addition, the second lens and the third lens have paraxial focal lengths whose signs are different. When v max and v min are the maximum Abbe number and the minimum Abbe number among the lenses, respectively, the condition, 1.25<v max / v min, is satisfied.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical lens system for taking image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises: a first lens element with positive refractive power, an Abbe Number of the first lens element being V1, and it satisfying the relation: 50<V1<60; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a third lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and the image-side surfaces of the third lens element being aspheric; a fourth lens element having at least one aspheric surface; and an aperture stop being located in front of the second lens element.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
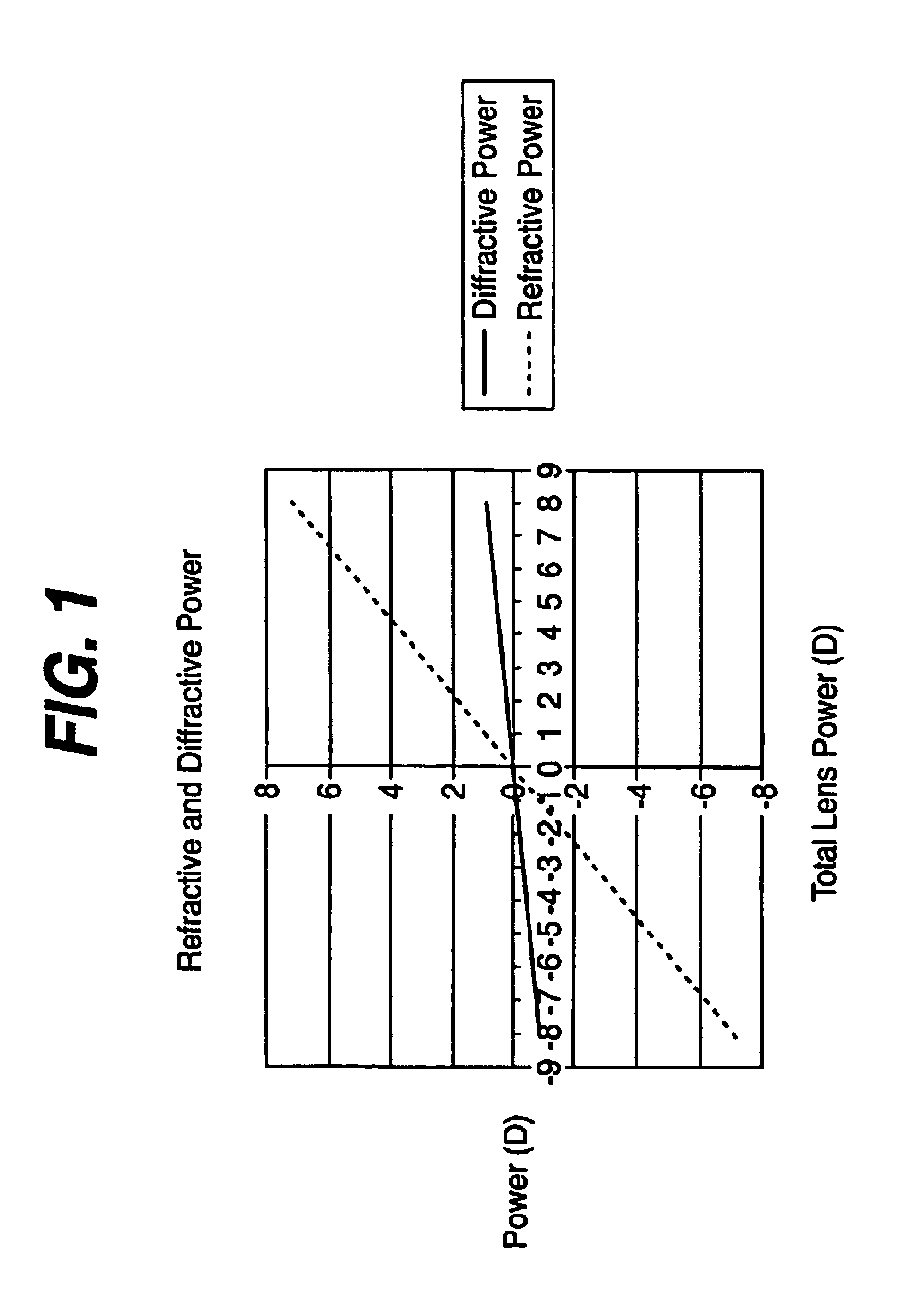
Optical material, and, optical element, optical system and laminated diffractive optical element using it
InactiveUS6912092B2High diffraction efficiencyReduction of diffraction efficiencyLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexLength wave
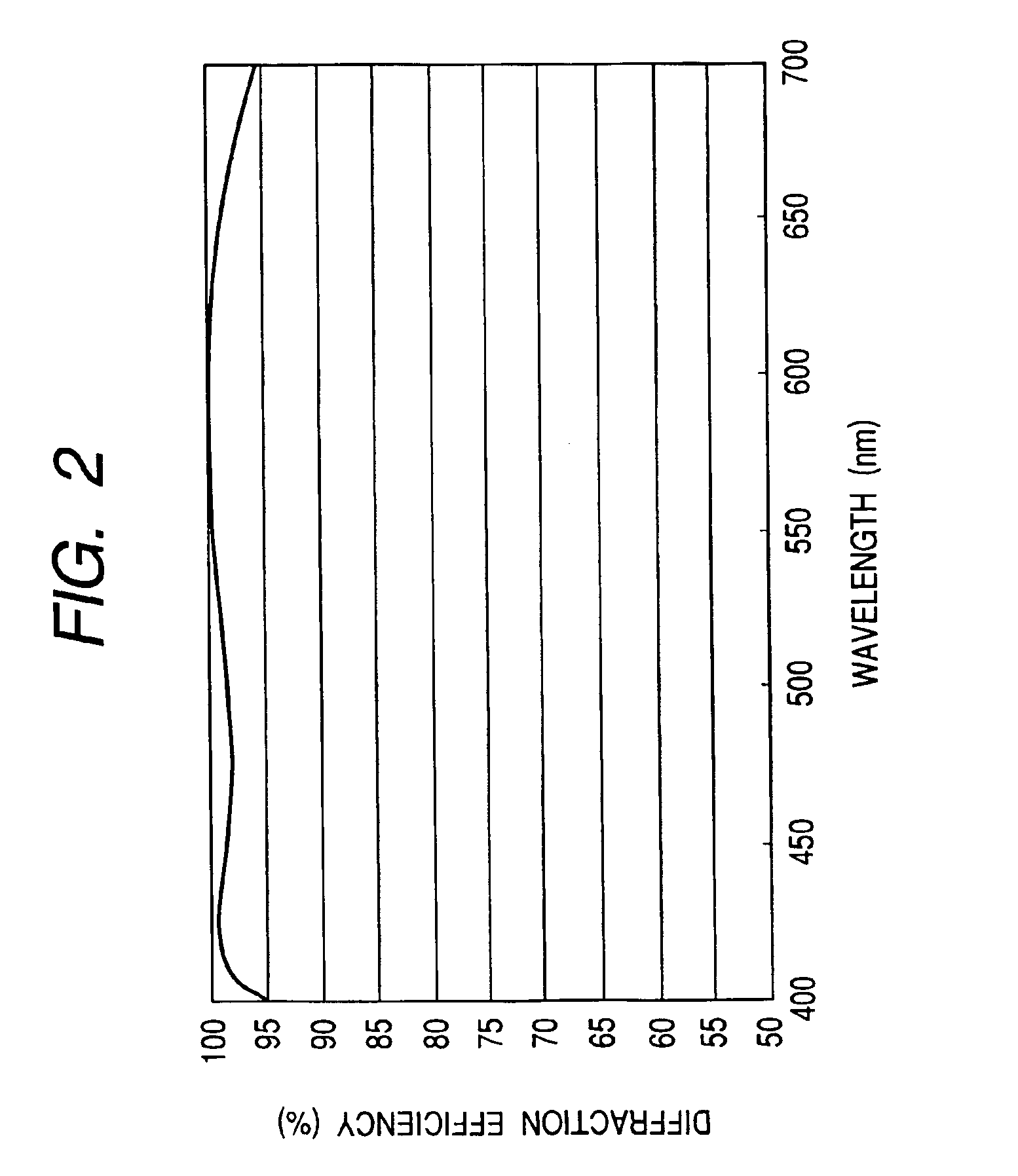
An optical element of which diffraction efficiency hardly varies with wavelength is provided by using an optical material satisfying the conditions that nd>−6.667×10−3vd+1.70 and θg,F≦−2×10−3νd+0.59 where nd is a refractive index at d-line, νd is an Abbe number at the d-line, and θg,F is a second order dispersion at d-line, whereby diffraction efficiency is improved in any working visible wavelength region and more precise chromatic aberration correction is obtained.
Owner:CANON KK
Photographing optical lens assembly
The present invention provides a photographing optical lens assembly comprising, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located in front of the first lens element; wherein an Abbe number of the first lens element is V1, an Abbe number of the second lens element is V2, and they satisfy the relation: |V1−V2|<15; and wherein the number of the lens elements of the photographing optical lens assembly is limited to two. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively reduce the volume of the lens assembly and the sensitivity of the optical system and enable the lens assembly to obtain a higher resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical lens system for taking image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: an aperture stop; a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a plastic second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface, a convex image-side surface and at least one aspheric surface; a plastic third lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface, a concave image-side surface and at least one aspheric surface. The number of the lens elements with refractive power being limited to three. Focal lengths of the optical lens system, the first lens element, the second lens element and the third lens element are f, f1, f2, f3 respectively; Abbe numbers of the first and second lens elements are V1, V2 respectively, an on-axis distance between second and third lens elements is T23, and they satisfy the relations: 0.8<f / f1<1.8; 0<|f / f2|<0.8; 0<|f / f3|<0.7; 20<V1−V2<38; 0.13<T23 / f<0.21.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens assembly
ActiveUS8089704B2Improve image qualityAberration correctionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging lensPhysics
This invention provides an imaging lens assembly including, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens with negative refractive power having a convex image-side surface; a third lens having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, at least one of both surfaces thereof being aspheric; a fourth lens having a concave image-side surface, at least one of both surfaces thereof having at least one inflection point; and an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the second lens; the on-axis spacing between the first lens and second lens is T12, the focal length of the imaging lens assembly is f, the Abbe number of the first lens and third lens is, V1 and V3, respectively, they satisfy the relations: 0.5<(T12 / f)*100<20, 23<V1−V3.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
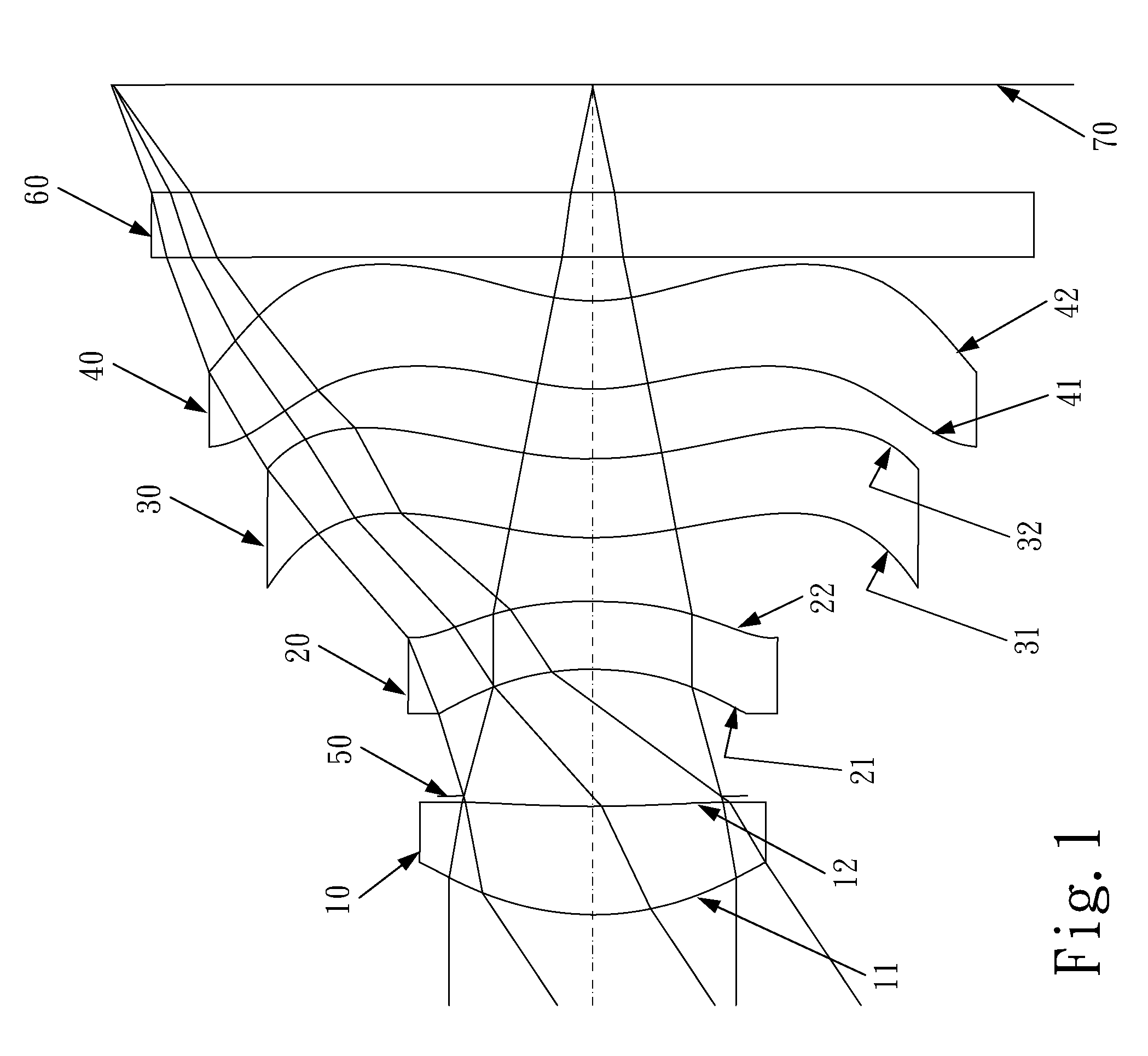
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus using imaging lens
ActiveUS20100142062A1Improve environmental resistanceIncrease manufacturing costOptical elementsNegative powerImaging lens
An imaging lens is provided and includes, in order from the object side, a front group having a negative power, a stop, and a rear group having a positive power. The front group includes, in order from the object side, a first negative lens having a meniscus shape with a concave surface on an image side, a second negative lens, and a third positive lens. The rear group includes, in order from the object side, a fourth positive lens, a fifth negative lens having a meniscus shape with a concave surface on the object side, and a sixth positive lens. An Abbe number of each of the first lens, the second lens, the fourth lens, and the sixth lens at the d-line is equal to or larger than 40, and an Abbe number of each of the third lens and the fifth lens at the d-line is equal to or smaller than 40. Each lens constituting the front group and the rear group is a single lens.
Owner:JIANGXI OFILM OPTICAL CO LTD
Polycarbonate copolymer and method of producing the same
The object is to provide a polycarbonate copolymer having excellent mechanical strength, good heat resistance, a low refractive index, a large Abbe number, a low berefringence and excellent transparency and containing a plant-derived raw material. Disclosed is a polycarbonate copolymer which comprises a constituent unit derived from a dihydroxy compound represented by the general formula (1) and a constituent unit derived from an alicyclic dihydroxy compound and has an Abbe number of 50 or greater and “a 5% heating weight loss temperature” (a temperature at which the 5% weight loss under heating is observed) of 340° C. or higher. Also disclosed is a process for producing the polycarbonate copolymer by reacting a dihydroxy compound represented by the general formula (1) and an alicyclic dihydroxy compound with a carbonate diester in the presence of a polymerization catalyst.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Image pickup lens, image pickup apparatus and mobile terminal
An image pickup lens relating to the present invention is a lens for forming an image of a subject onto a photoelectric converter of a solid-state image pickup element. The image pickup lens includes, in order from an object side thereof: an aperture stop; a first lens with a positive refractive power; a second lens in a meniscus shape with a negative refractive power, whose object side surface is a convex surface; a third lens with a positive refractive power; and a fourth lens with a negative refractive power. The image pickup lens satisfies a predetermined conditions relating to a curvature radius of the object side surface of the second lens and an Abbe number of the second lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Imaging lens
To obtain a high-performance imaging lens coping with a larger number of pixels. The imaging lens includes a first positive lens G1 whose surface on an object side is convex, a second lens G2 which is a negative meniscus turning its concave surface to an image surface side, a third lens G3 which is a positive meniscus turning its convex surface to the image surface side, a fourth negative lens G4 whose both surfaces are aspherical and whose surface on the image surface side is concave near an optical axis, and a fifth positive or negative lens G5 whose both surfaces are aspherical in order from the object side. The imaging lens satisfies following conditions; (1) [nu]d1>50, (2) [nu]d2<30 and (3) [nu]d4<30 concerning the Abbe numbers of the first and the second lenses G1 and G2 are [nu]d1 and [nu]d2, and the Abbe number of the fourth lens G4 is [nu]d4.
Owner:JIANGXI JINGCHAO OPTICAL CO LTD
Optical glass and optical product
When a glass melt of an optical glass having a refractive index (nd) of at least 1.7 and an Abbe number (νd) of 28 to 41 is flowed down from a flow pipe made of Pt or a Pt alloy to form glass gobs continuously, there is caused a problem that the glass gobs have striae or that the weight variability among the glass gobs is large, and the problem can be overcome by the use of an optical glass comprising silicon oxide and boron oxide, the ratio of a content of the silicon oxide to a content of the boron oxide being greater than 0.78, the optical glass having a contact angle of at least 40° to Pt or a Pt alloy at a predetermined temperature equivalent to, or higher than, its liquidus temperature or in a predetermined temperature range whose lower limit is equivalent to, or higher than, the liquidus temperature and having a sag temperature Ts of 580° C. or lower.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Imaging lens
A bright, small, and inexpensive imaging lens system is provided with a short total length that can provide more than a 30 degree viewing angle and whose aberrations are excellently corrected. The imaging lens includes, in order from an object side, a positive first lens with a convex surface facing the object side, an aperture stop provided on the object side or an image side of the first lens, a meniscus second lens with a concave surface facing the object side, and a meniscus third lens with a convex surface facing the object side. Furthermore, at least one of the first lens and the second lens includes an aspheric surface, and the third lens is a biaspheric lens. In addition, the second lens and the third lens have paraxial focal lengths whose signs are different. When v max and v min are the maximum Abbe number and the minimum Abbe number among the lenses, respectively, the condition, 1.25<v max / v min, is satisfied.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical lens system for taking image
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
High refraction and low dispersion optical glass
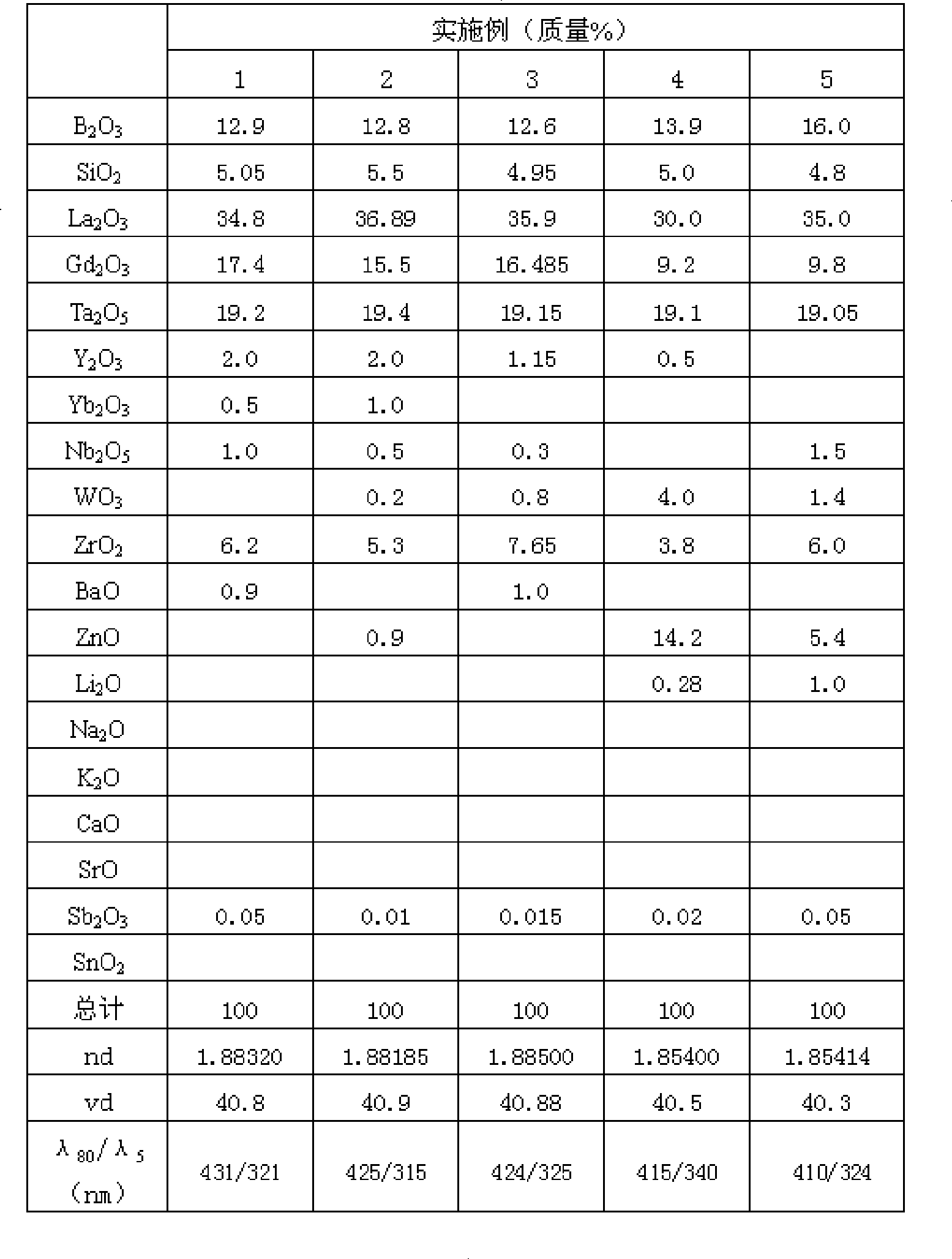
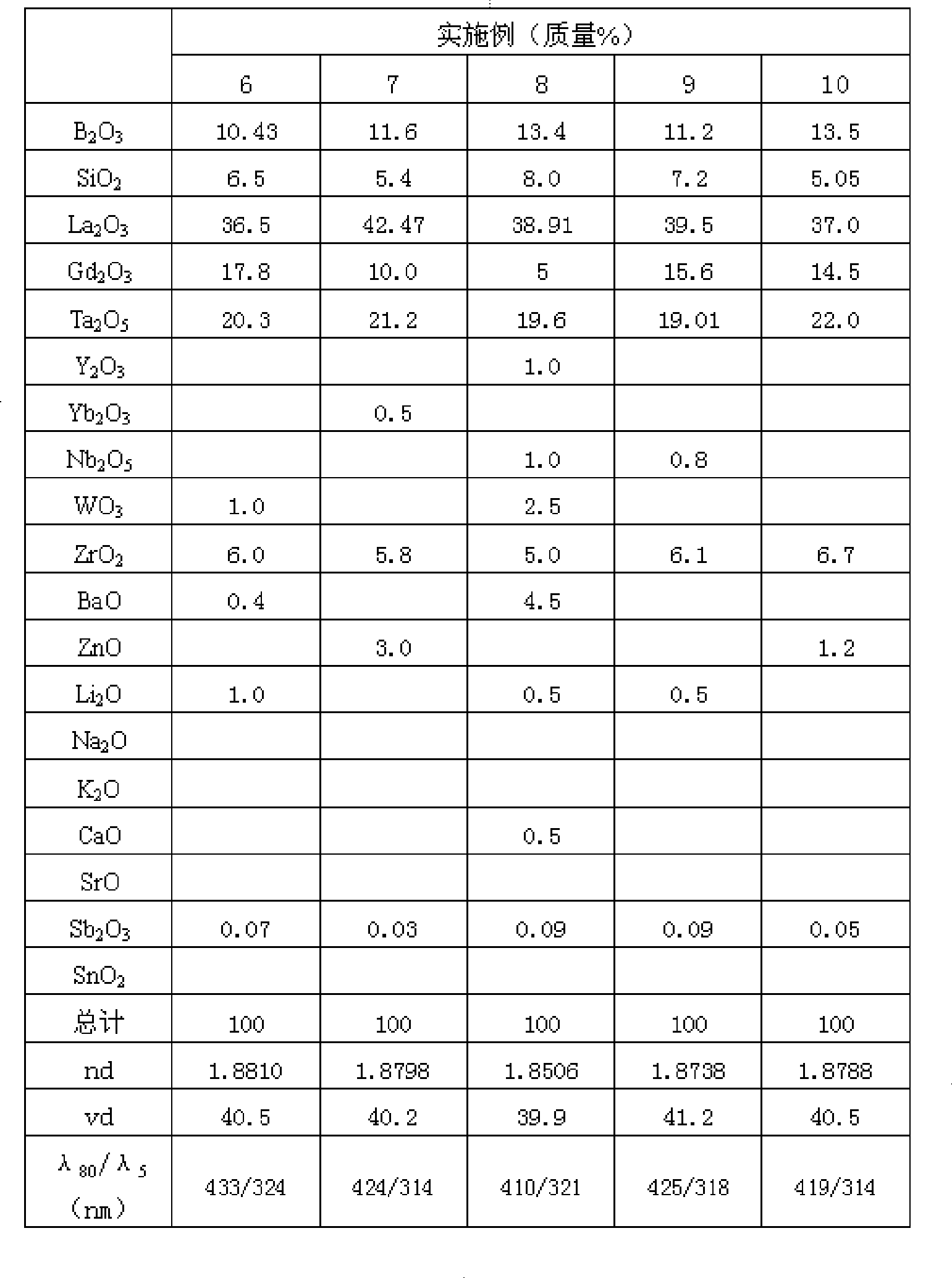
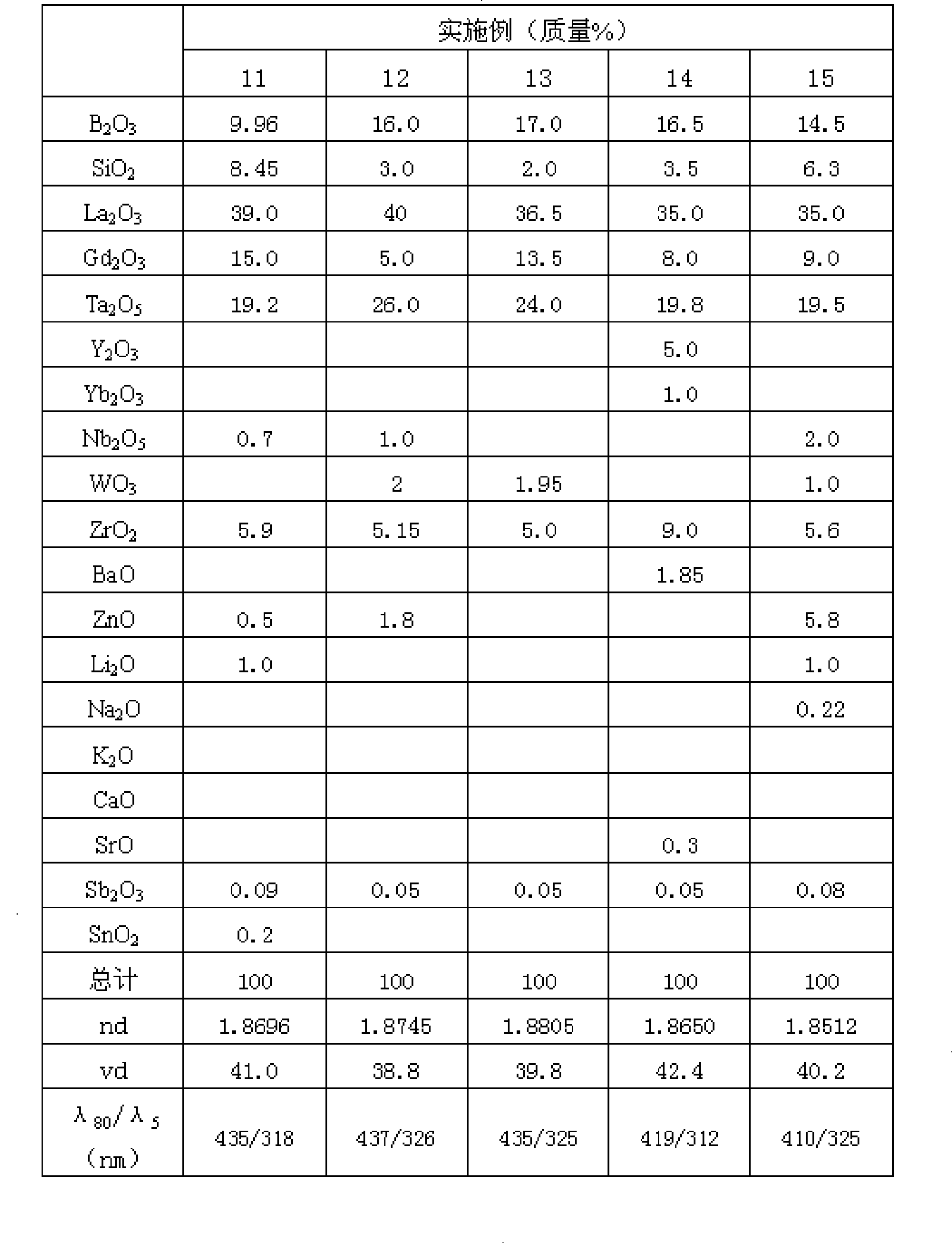
The invention provides an environment-friendly optical glass with high refractive index, low dispersion and high light transmittance, which has components according to weight percentage: B2O3: 6 percent to 17 percent, SiO2: 2 percent to 10 percent, La2O3: more than 25 percent but less than 45 percent, Gd2O3: 5 percent to 25 percent, Nb2O5: 0 to 3 percent, Ta2O5: more than 19 percent but less than 27 percent, ZnO: 0 percent to 16 percent, BaO: 0 percent to 5 percent, CaO: 0 percent to 5 percent, SrO: 0 percent to 5 percent, ZrO2: 0 percent to 9 percent, Y2O3: 0 percent to 8 percent, Yb2O3: 0 percent to 8 percent, WO3: 0 percent to 5 percent, Li2O, Na2O and K2O: the total content of 0 percent to 2 percent, Sb2O: equal to 0.01 percent or less than 0.1 percent, SnO2: 0 percent to 1 percent. GeO2 is not included in the components of the environment-friendly optical glass and the refractive index is 1.85 to 1.90, while the Abbe number is 35 to 45. Meanwhile, the corresponding wavelength is below 440nm when the transmittance thereof is up to 80 percent, and the environment-friendly optical glass has high light transmittance.
Owner:CDGM OPTICAL GLASS
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
An imaging lens includes a first lens having a negative power and including a concave surface facing an image side, a second lens having a positive power, a third lens having a positive power, an aperture diaphragm, a fourth lens, which is a biconvex lens having a negative power, a fifth lens having a positive power and including a convex surface facing the image side, and a sixth lens having a positive power and including a convex surface facing an object side, which are arranged in this order from the object side. The Abbe number of a material forming the fourth lens with respect to the d-line is 30 or less. When the focal length of the entire lens system is f and a composite focal length from the fourth lens to the sixth lens is f456, the imaging lens satisfies following conditional expression:1.00<f456 / f<1.88.
Owner:JIANGXI OFILM OPTICAL CO LTD
Projection optical system and projection display device using the same
ActiveUS20060193036A1Small distortionEasy to assembleTelevision system detailsProjectorsIntermediate imageRefractive index
A projection optical system having a magnification side and a reduction side for forming a magnified image on a magnification side image surface conjugate with a reduction side conjugate image surface includes, arranged in order from the reduction side, a first imaging system including a plurality of lens elements and lens components and a second imaging system including a mirror having a concave, aspheric reflecting surface. An intermediate image is formed between the first imaging system and the second imaging system. The projection optical system satisfies specified conditions related to the travel of principal rays through the projection optical system and related to the Abbe number of a lens element having positive refractive power of the first imaging system. A projection display device includes the projection optical system and may include a light valve for modulating a light beam for projection on a screen.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Wide angle imaging lens
ActiveUS20060187557A1Excellently correcting lateral colorFunction increaseLensImaging lensAbbe number
A wide angle imaging lens is provided and includes, in order from an object side, four lenses of a first lens of a negative meniscus lens having a convex surface on the object side, a negative second lens having a concave surface on an image side and constituting at least one of both surfaces by an aspherical surface, a positive third lens having a convex surface on the object side and constituting at least one of both surfaces by an aspherical surface, and a fourth lens having a convex surface on the image side and constituting at least one of both surfaces by an aspherical surface. Further, Abbe numbers of the respective first to fourth lenses with respect to d line are respectively set to be equal to or larger than 40, equal to or larger than 50, equal to or smaller than 40 and equal to or larger than 50, and an aperture diaphragm is arranged between the third lens and the fourth lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20110249347A1Degradation worsensSet the refractive power of the first lens relatively strongLensConditional expressionImaging lens
An imaging lens includes an aperture stop, a positive first lens with a biconvex shape, a negative second lens; a negative third lens, a positive fourth lens, and a negative fifth lens arranged in this order from an object side. When the whole lens system has a focal length f, focal lengths and Abbe's numbers of the first and the second lenses are f1, νd1, f2, and νd2, focal lengths of the fourth and fifth lenses are f4 and f5, a composite focal length of the first lens L1 and the second lens L2 is f12, and a distance from a surface of the first lens L1 on the object side to a surface of the fifth lens L5 on the image side is Σd, the imaging lens satisfies the following conditional expressions:0.7<f12 / f<1.40.2<|f1 / f2|<0.615<νd1−νd20.4<f4 / f<1.0Σd / f<1.2|f5 / f|<1.0
Owner:KANTATSU CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com