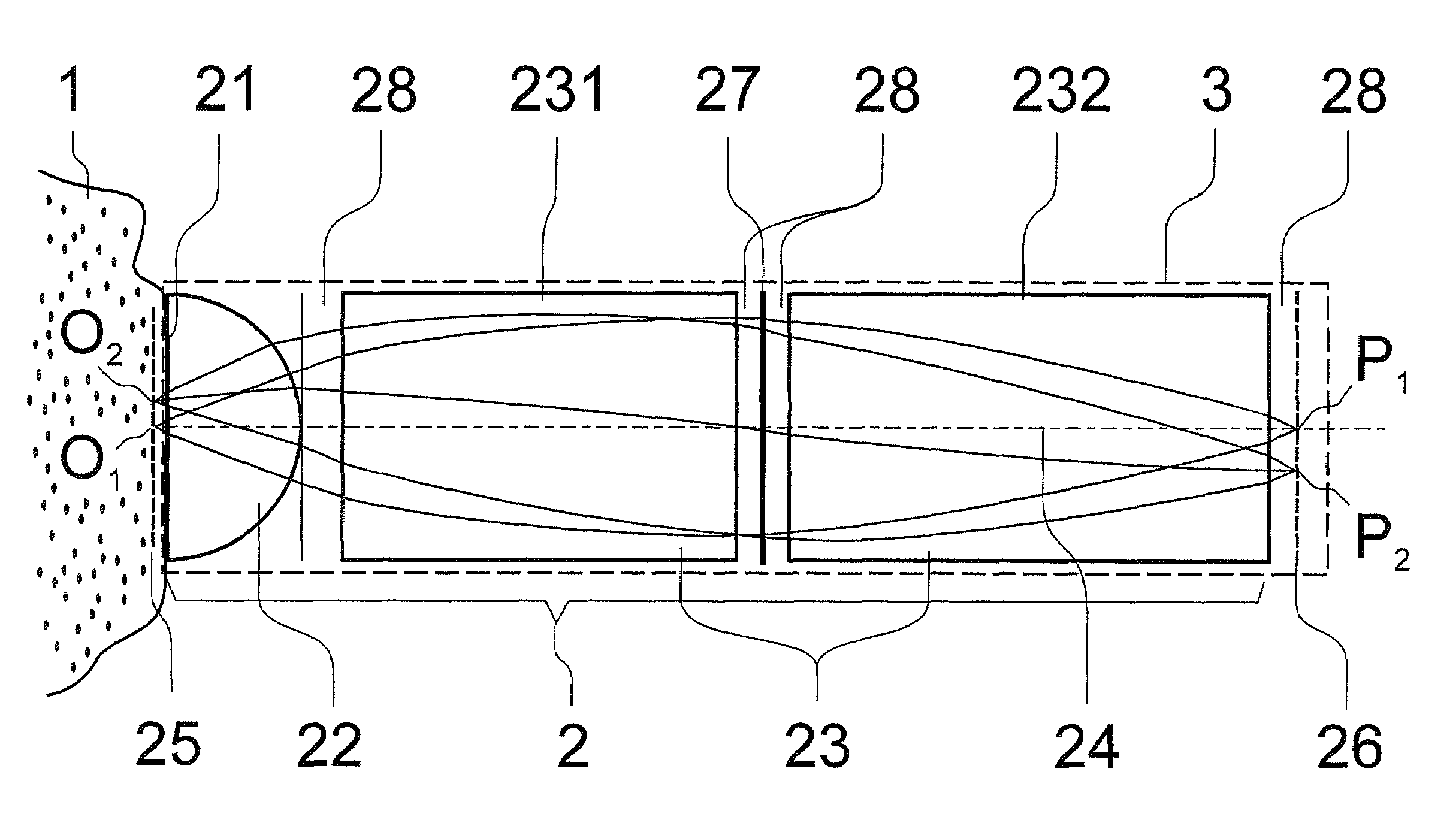
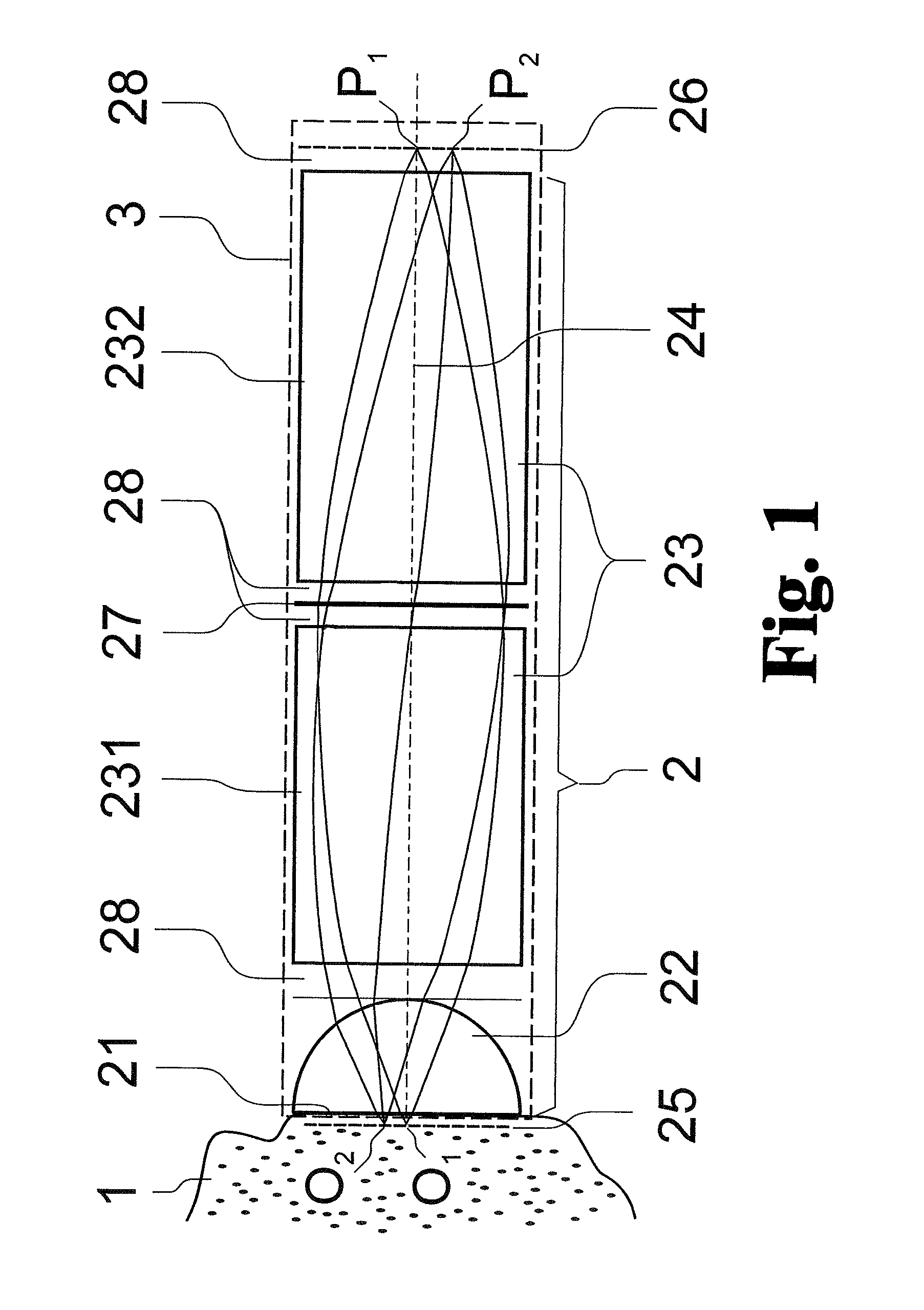
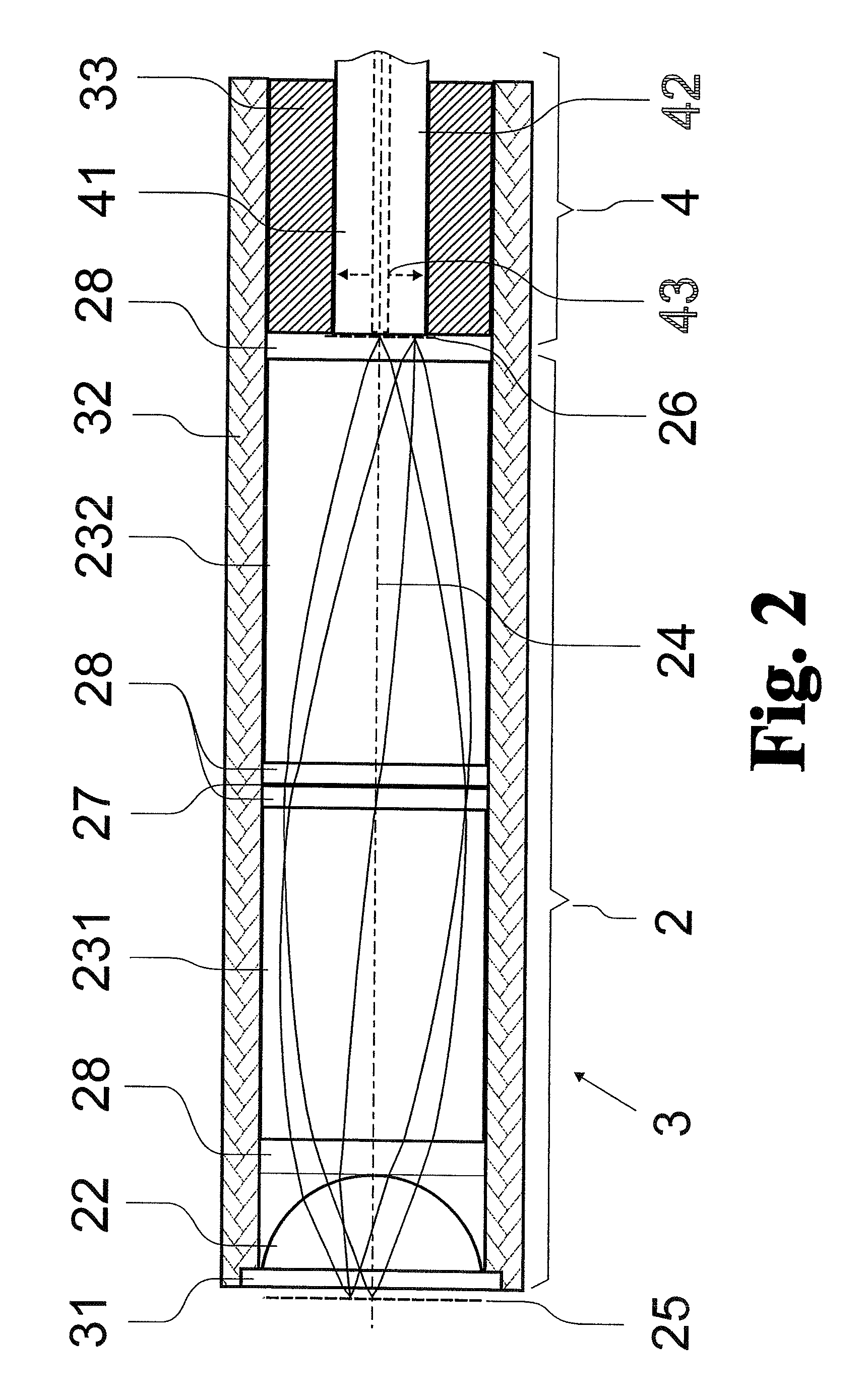
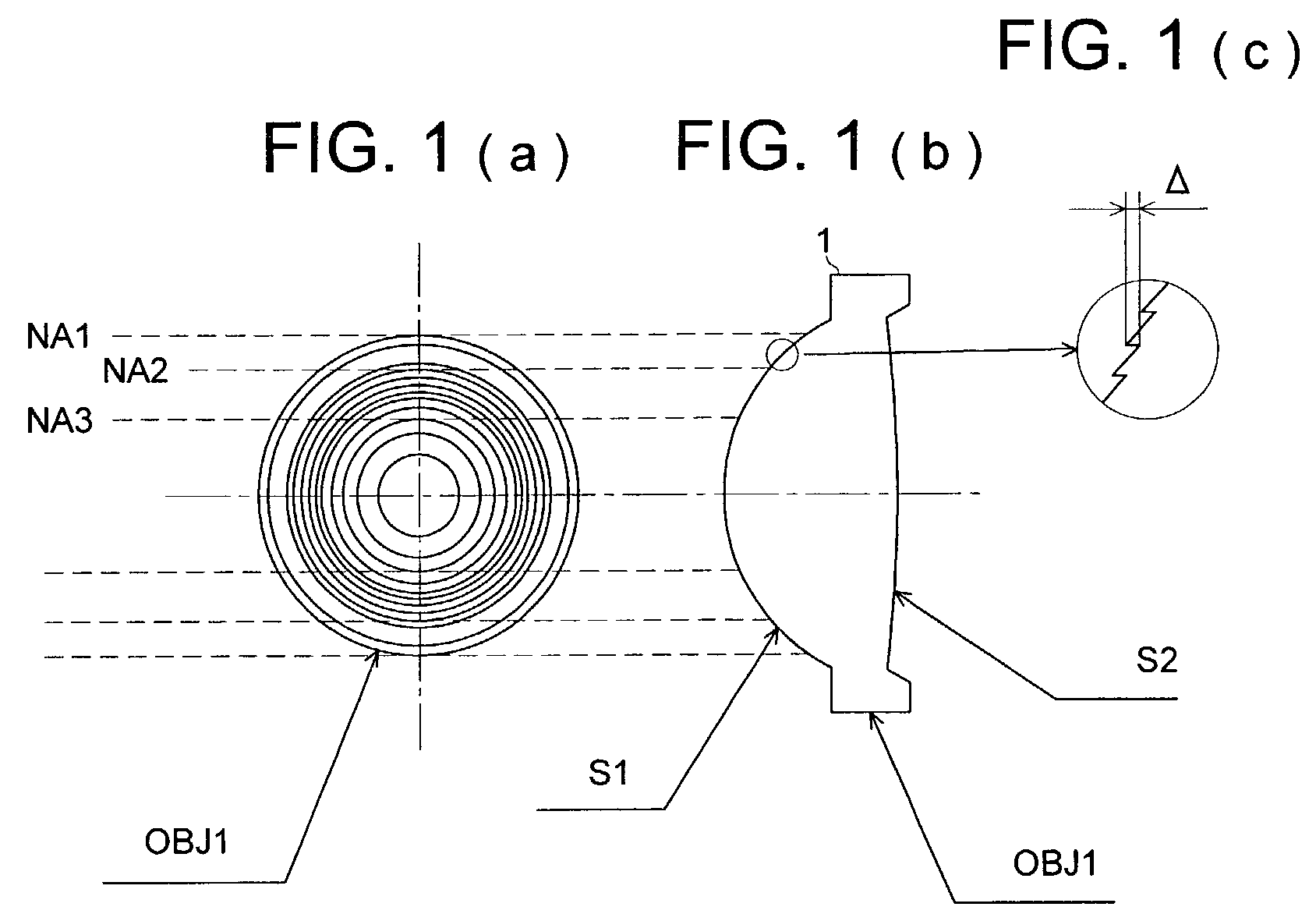
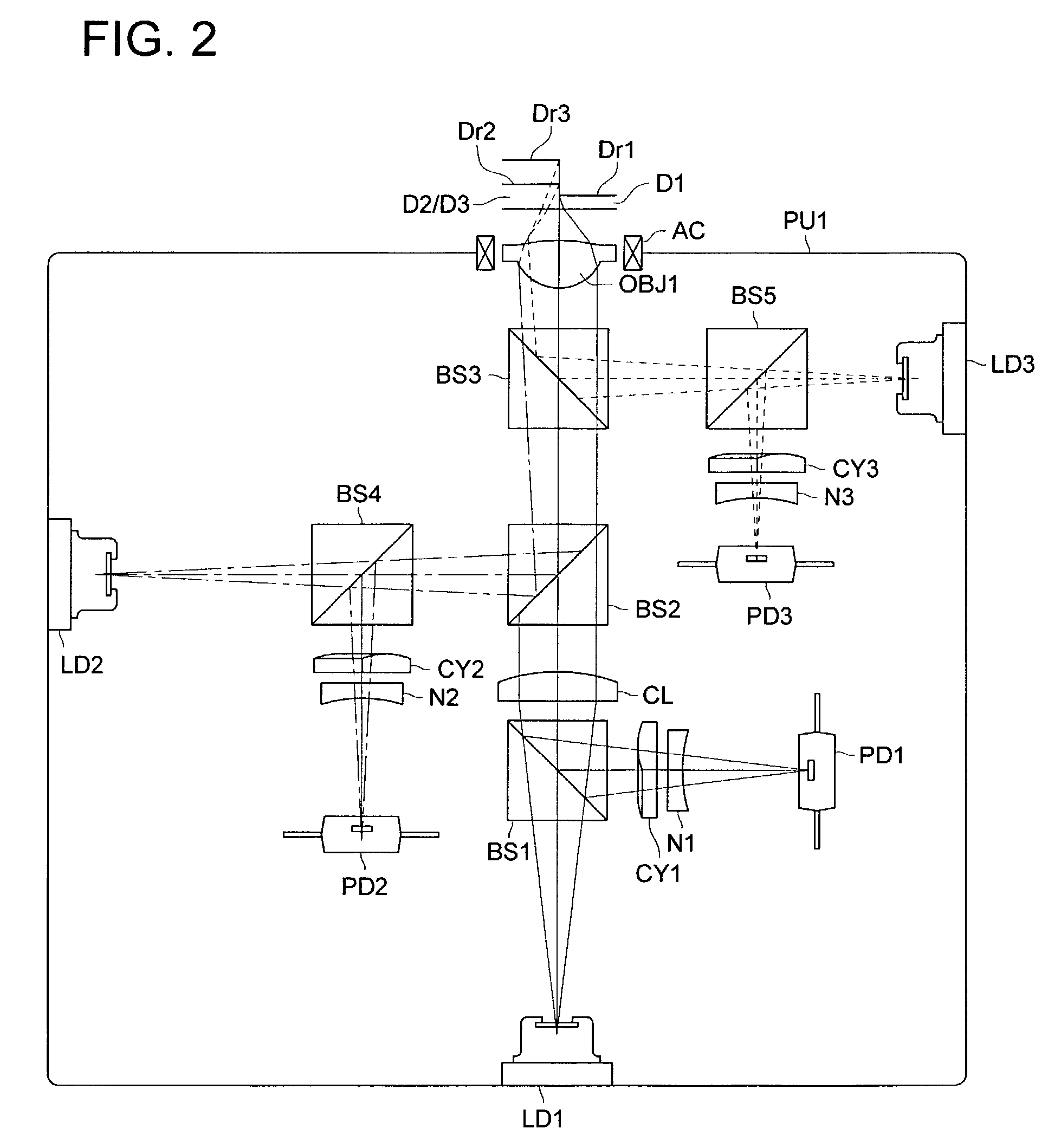
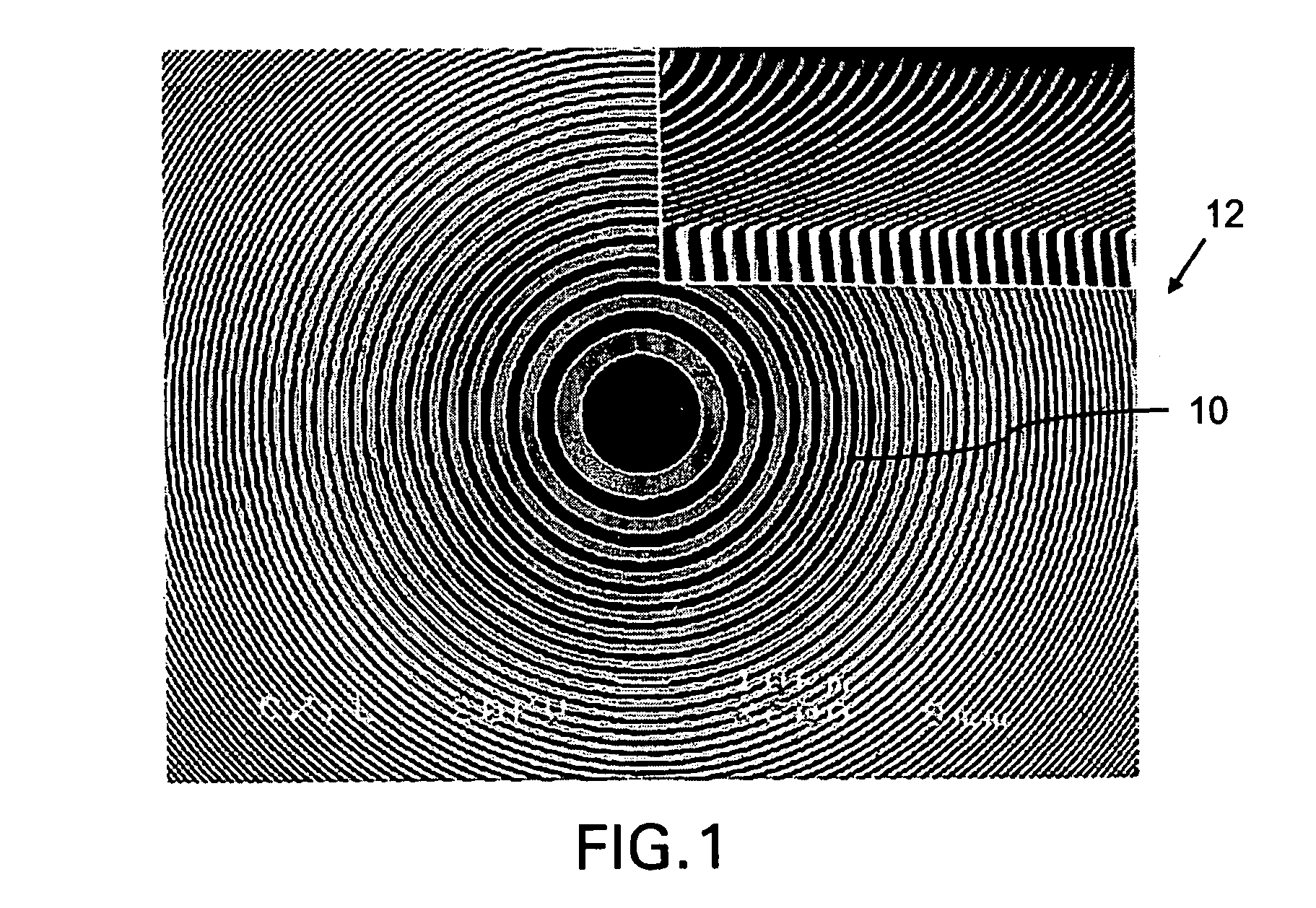
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
255 results about "Refractive lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
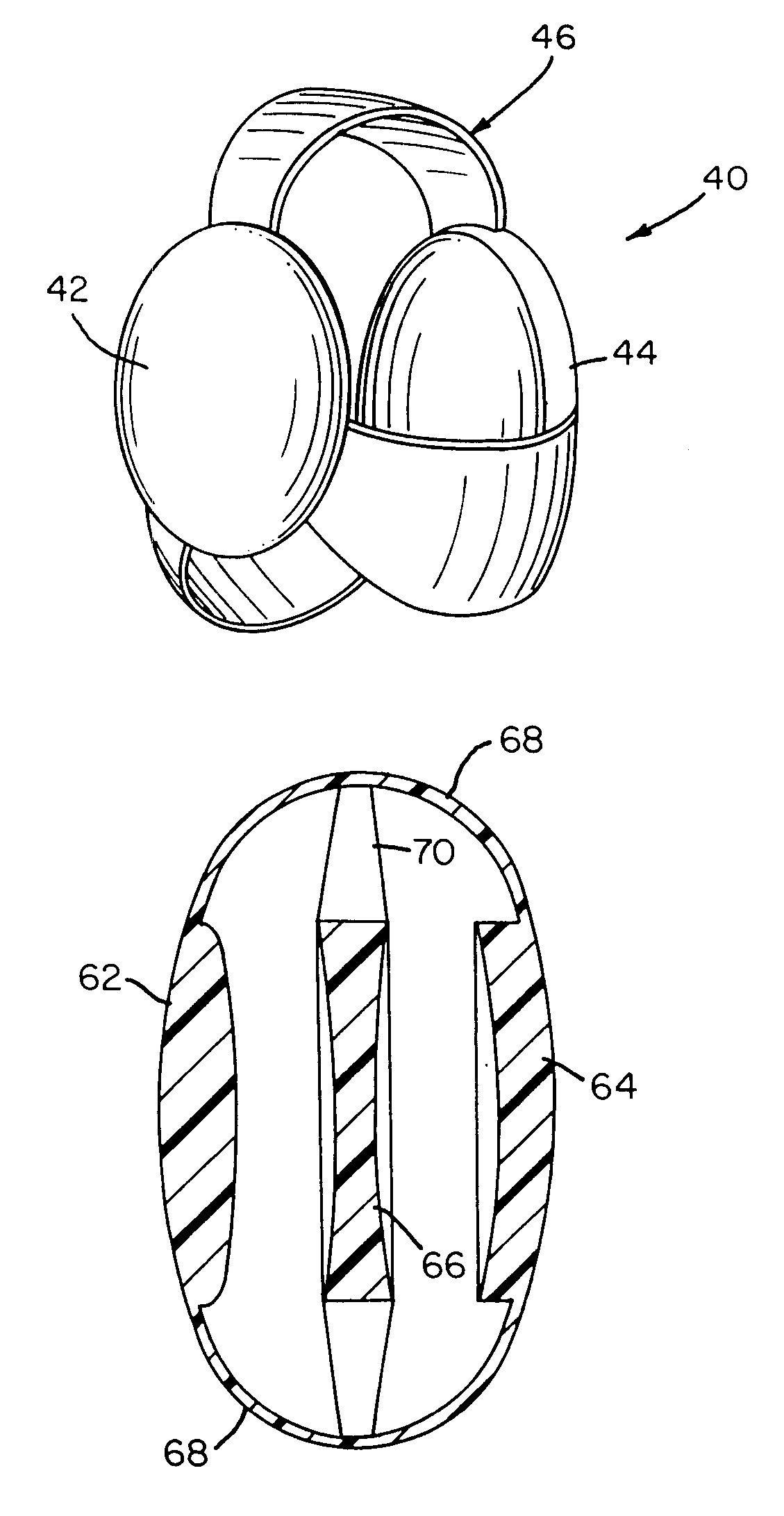
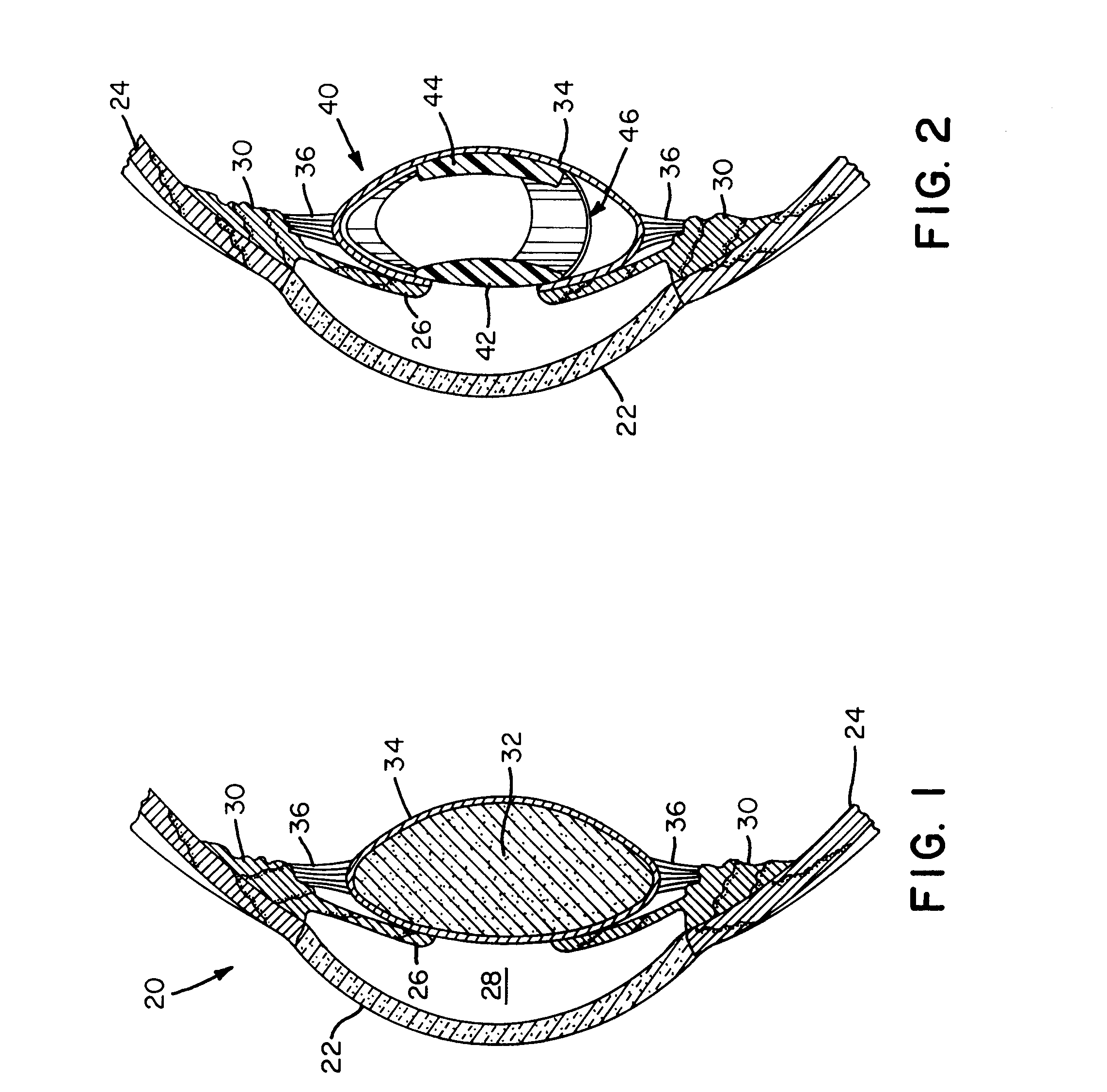
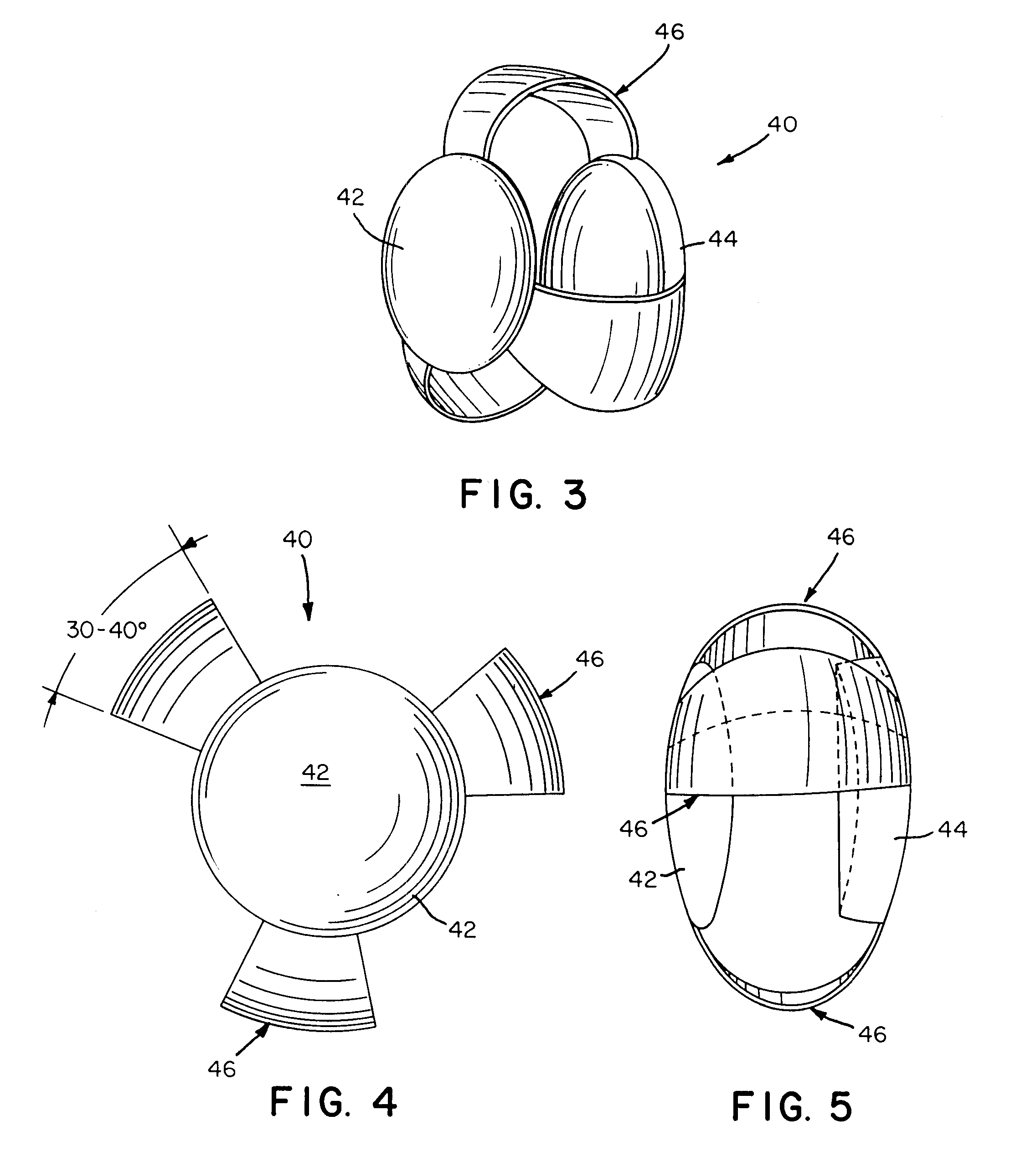
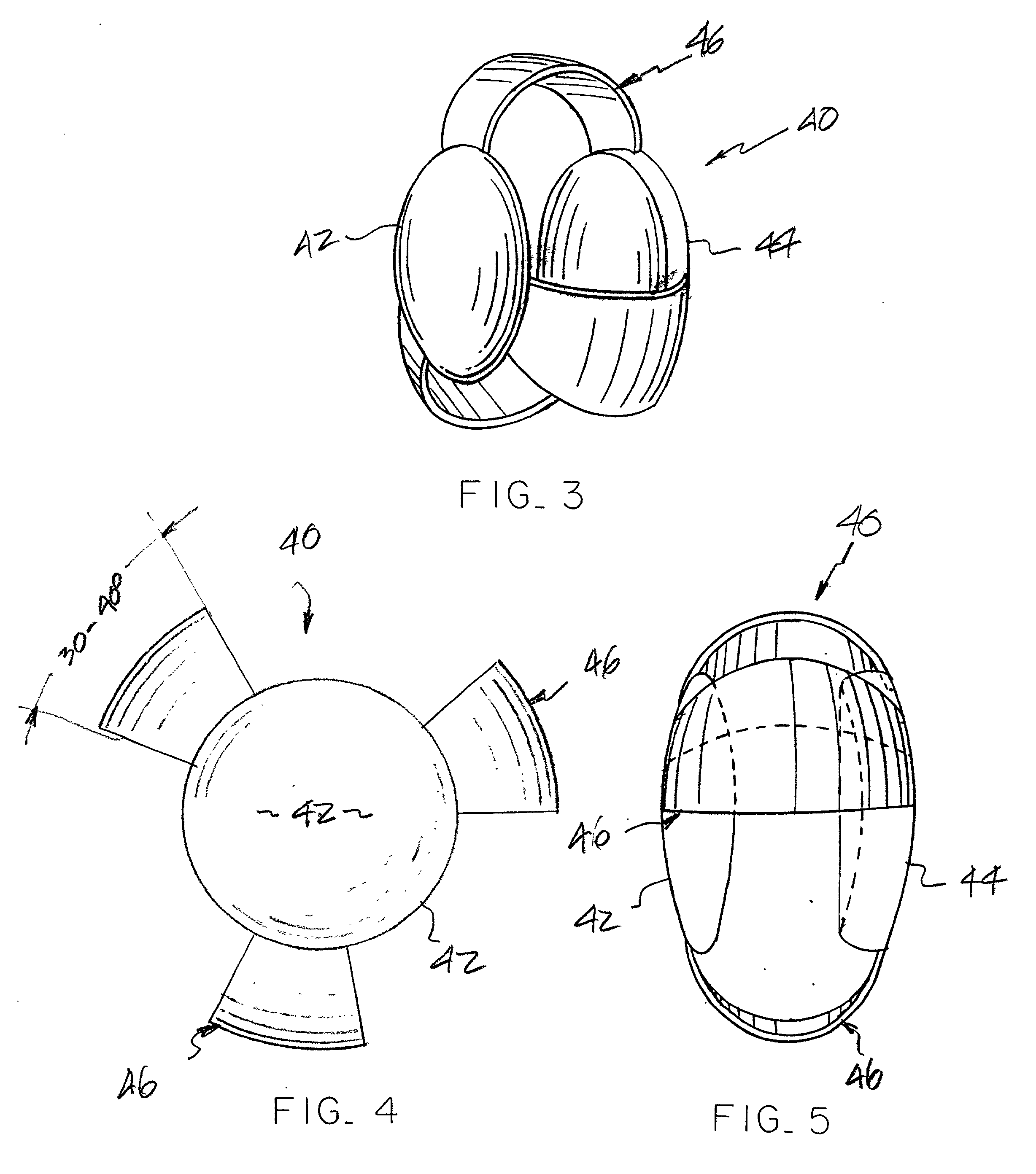
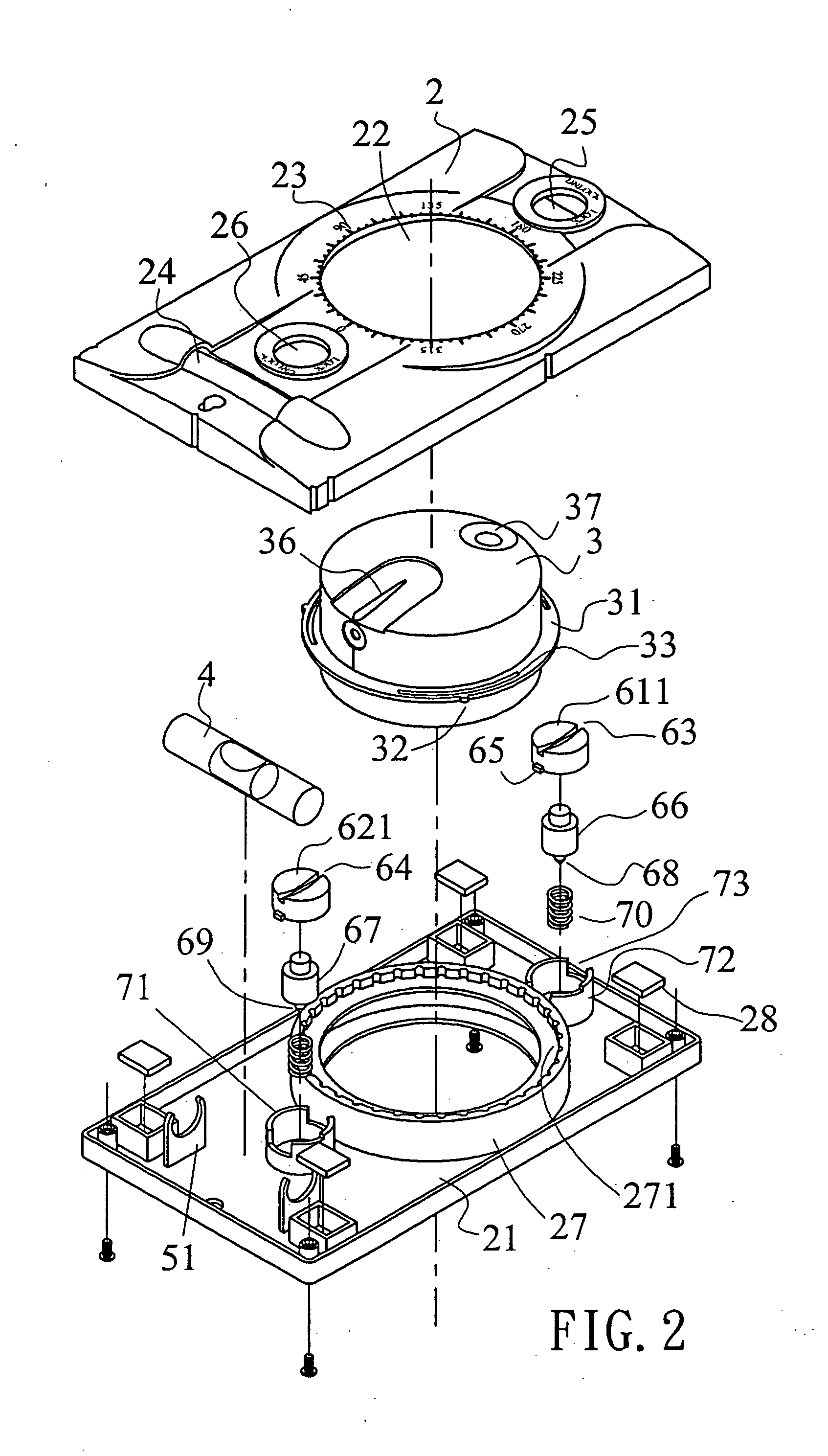
Open chamber, elliptical, accommodative intraocular lens system
InactiveUS6488708B2Restore a patient's accommodative visionRestore visionIntraocular lensRefractive lensCapsular bag
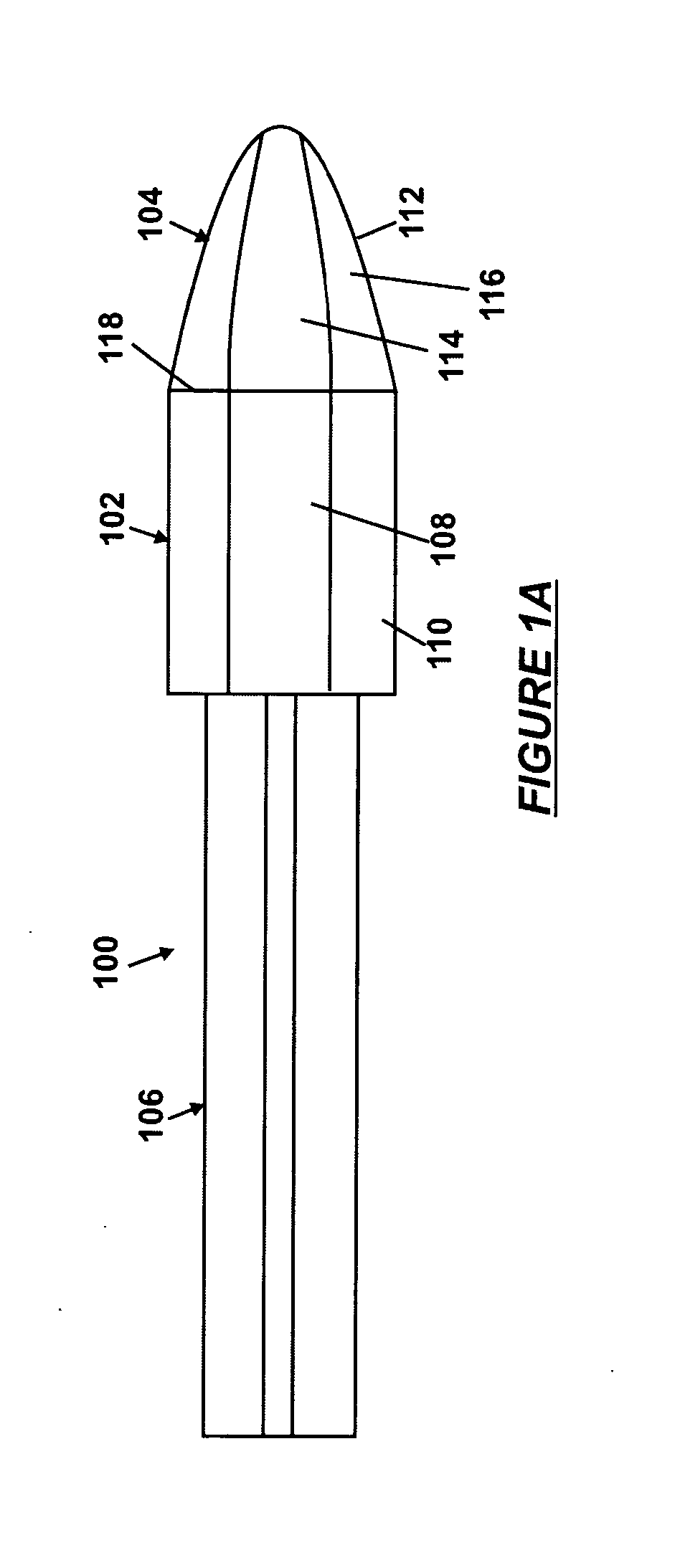
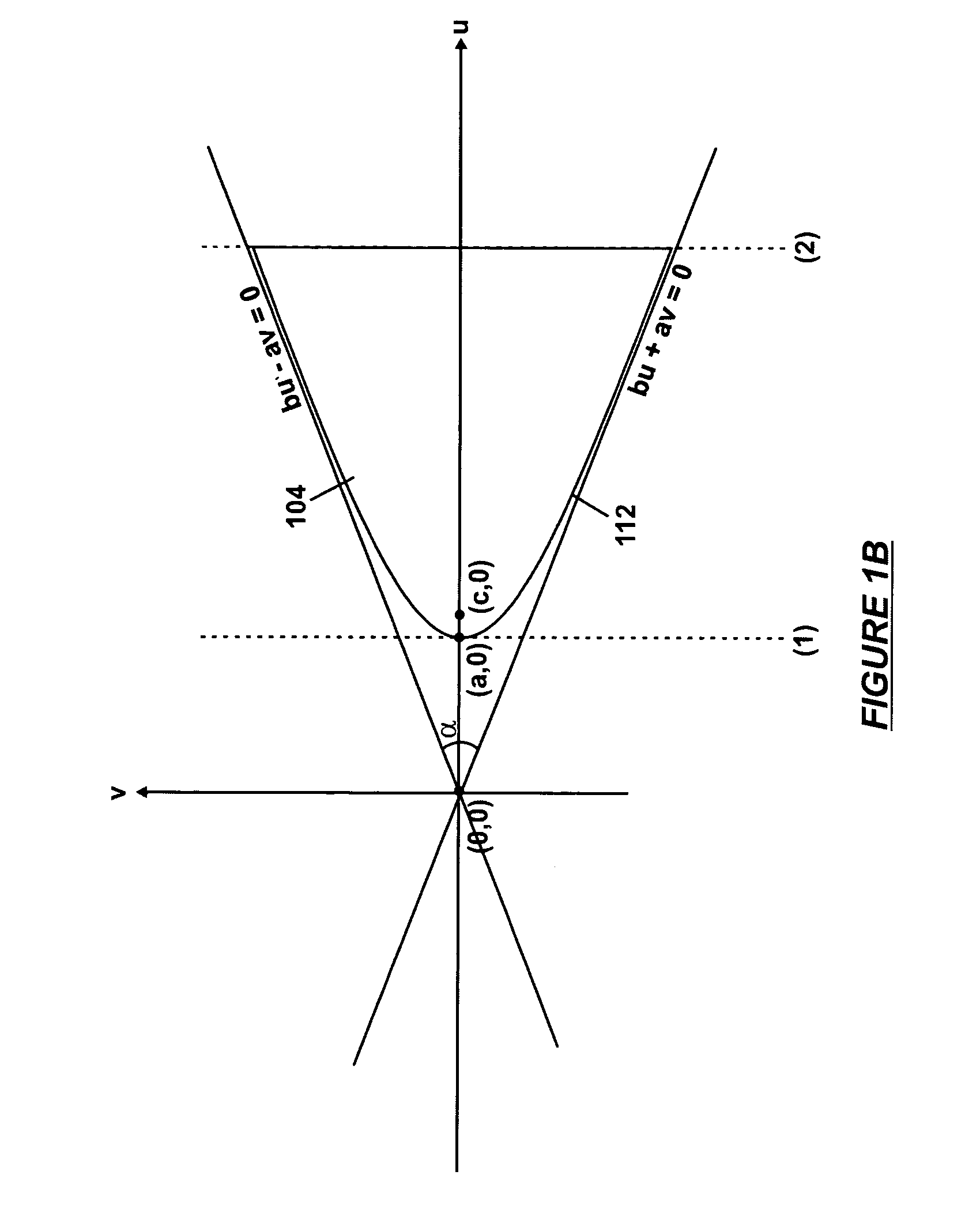
An open chamber, accommodative, intraocular lens method and apparatus operable to be positioned within an evacuated capsular bag of a human eye following extracapsular extraction of a natural crystalline lens is provided having an anterior refractive lens optic, a first haptic segment having a first end and being connected at said first end to a peripheral portion of said anterior lens optic and a second end and said haptic segment extending in an elliptical curve, in longitudinal cross-section, along the the line of sight of the lens and at least a second haptic segment having a first end and being connected at said first end to a peripheral portion of said lens optic and a second end and said at least a second haptic segment extending in an elliptical curve, in longitudinal cross-section, and being operably joined with the second end of said first haptic segment to form an open chamber, elliptical shaped haptic accommodating support for the anterior lens within an evacuated capsular bag of a human eye.
Owner:SARFARAZI FAEZEH
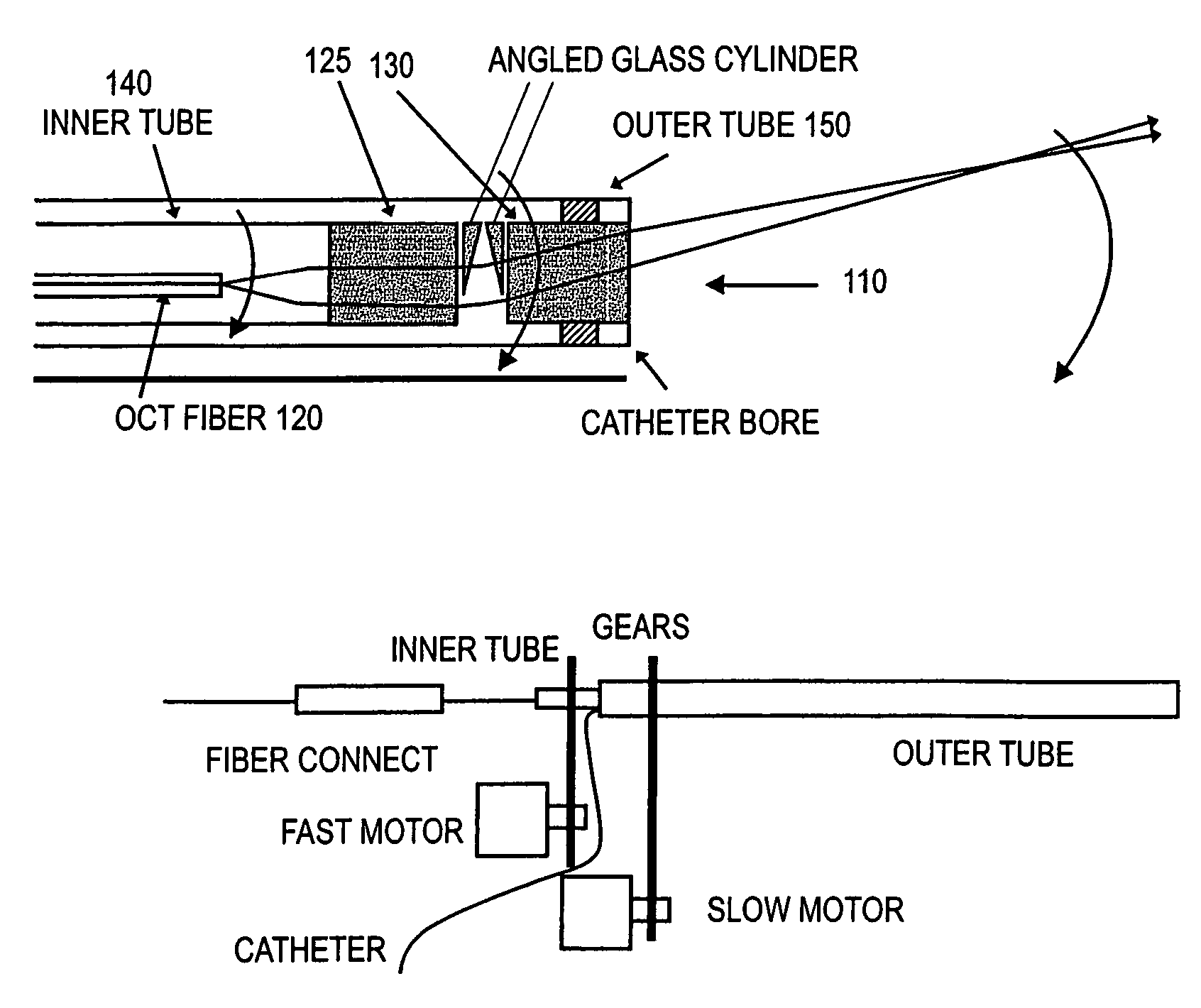
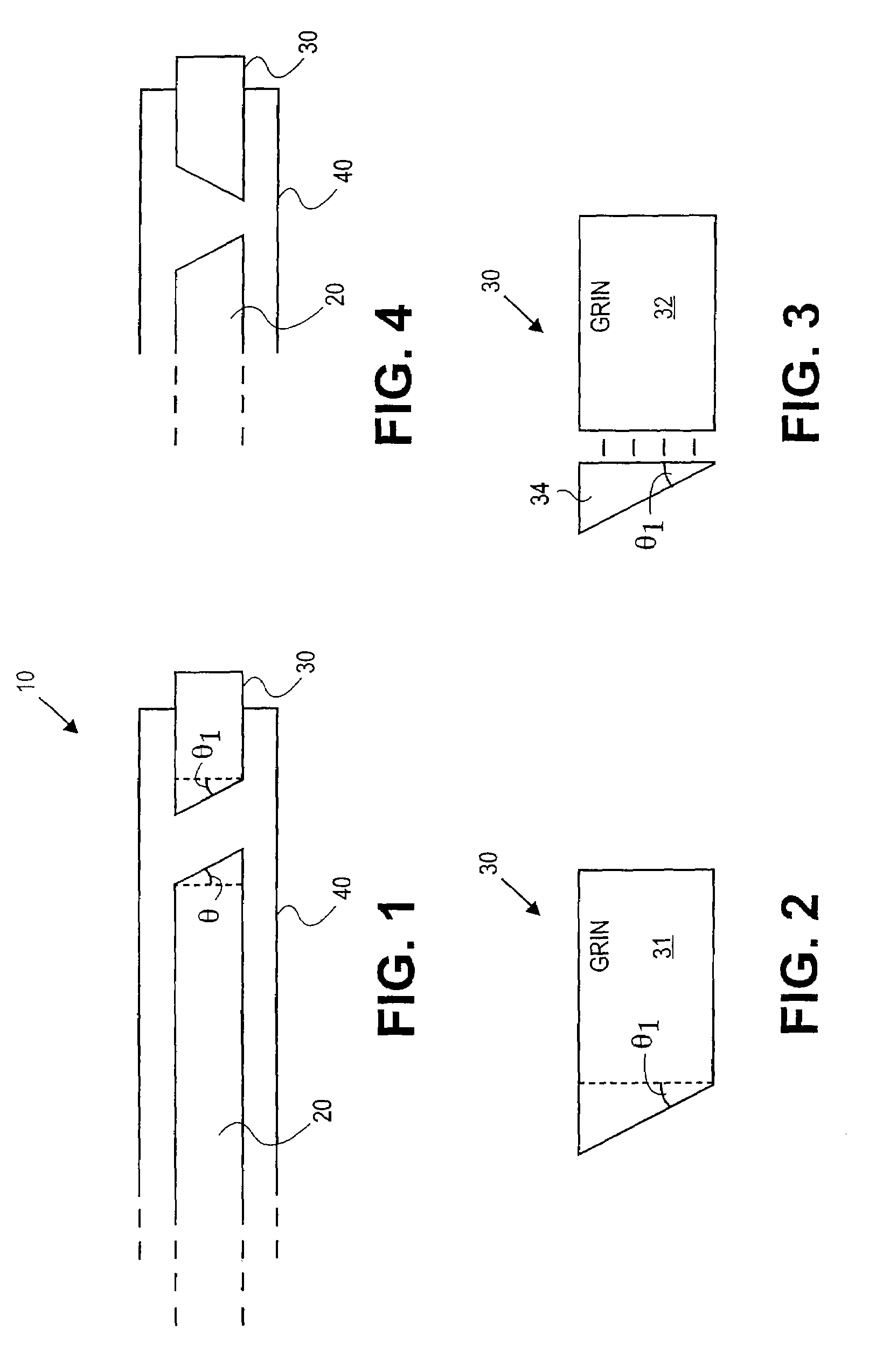
Forward scanning imaging optical fiber probe
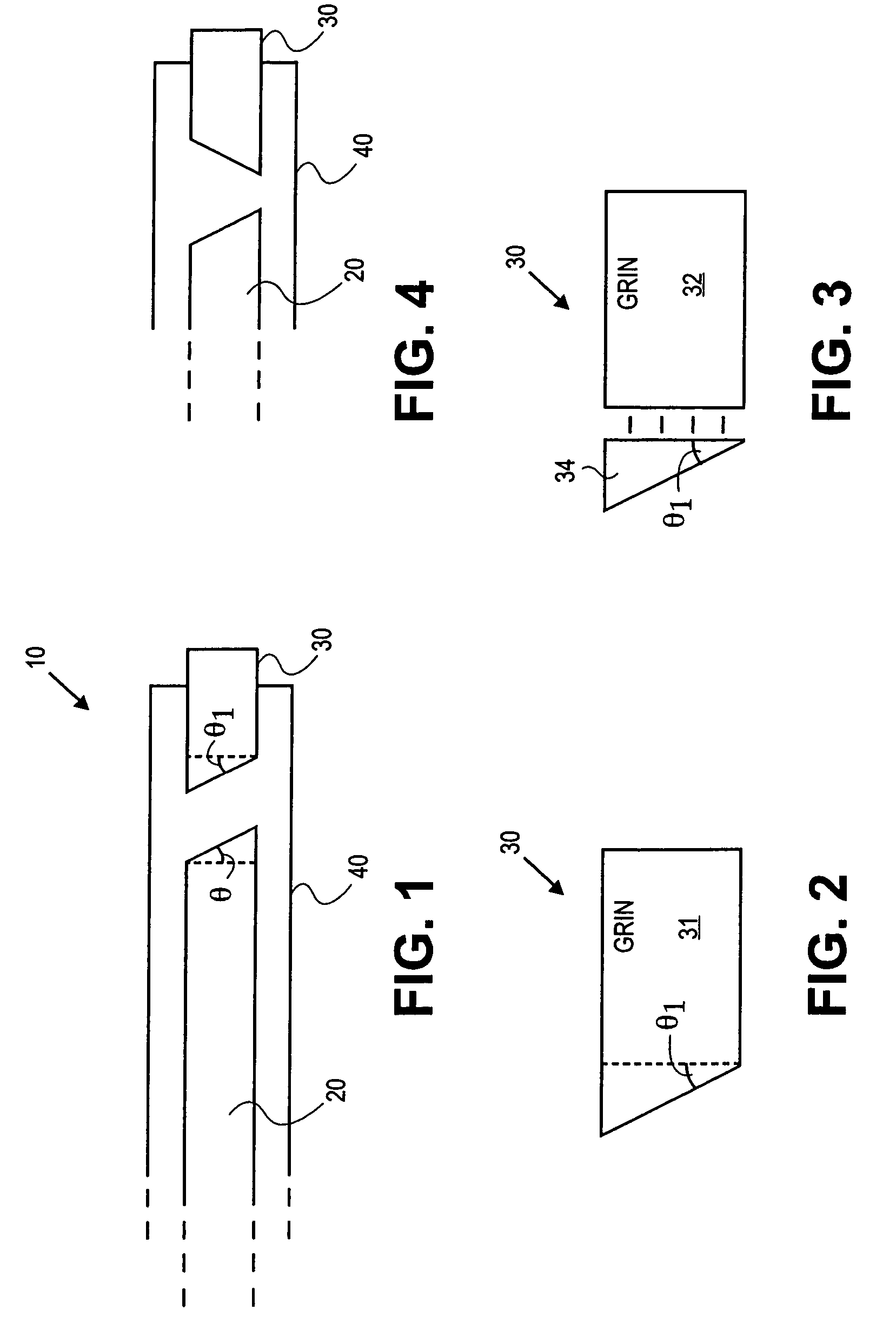
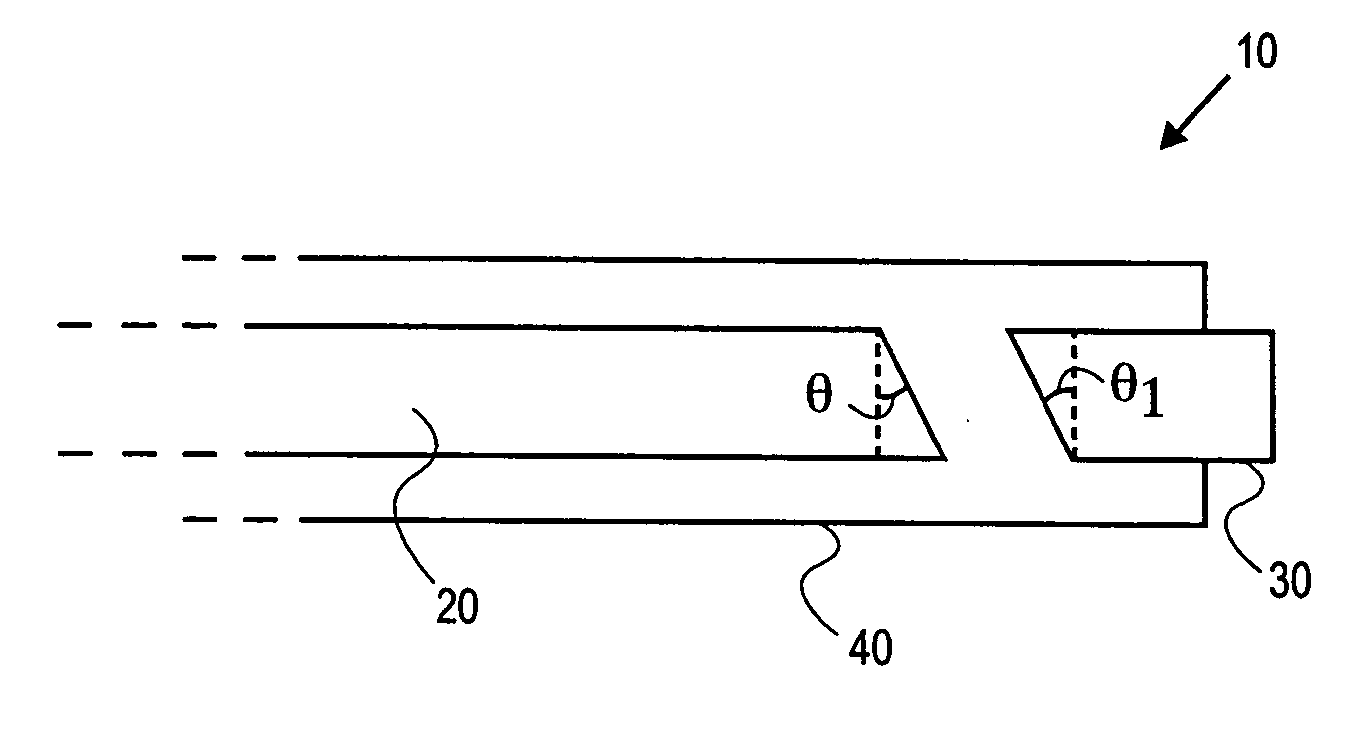
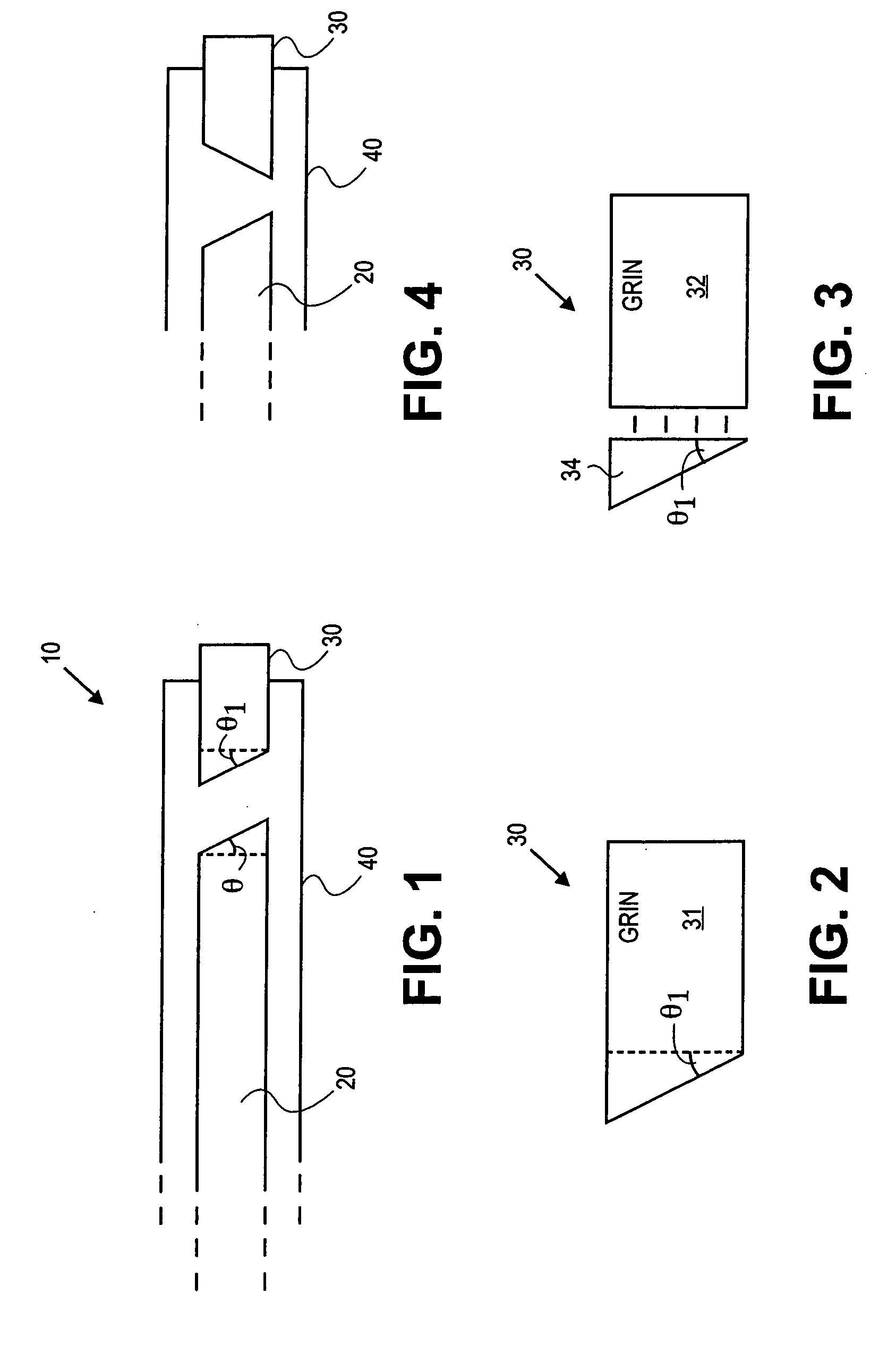
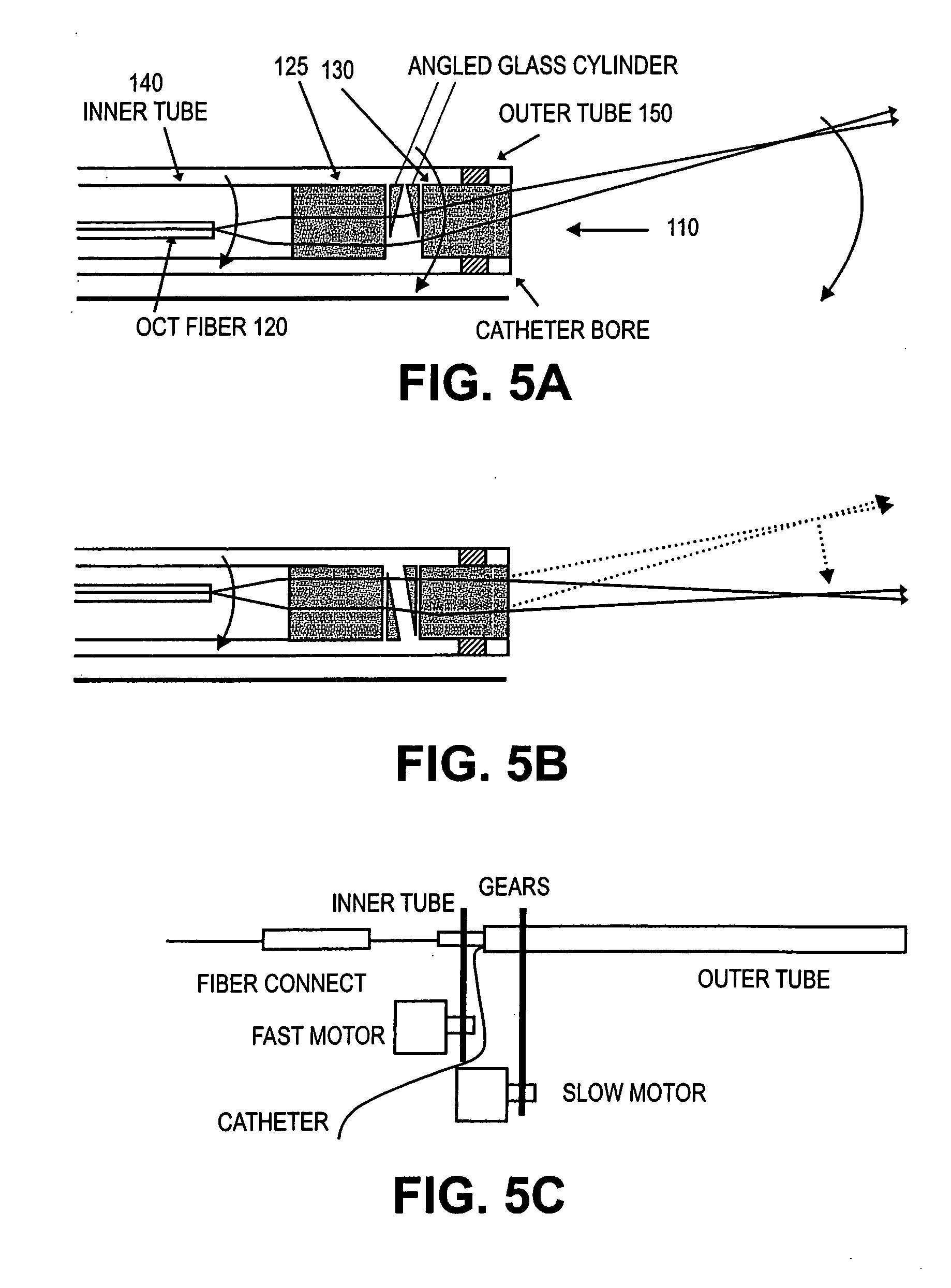
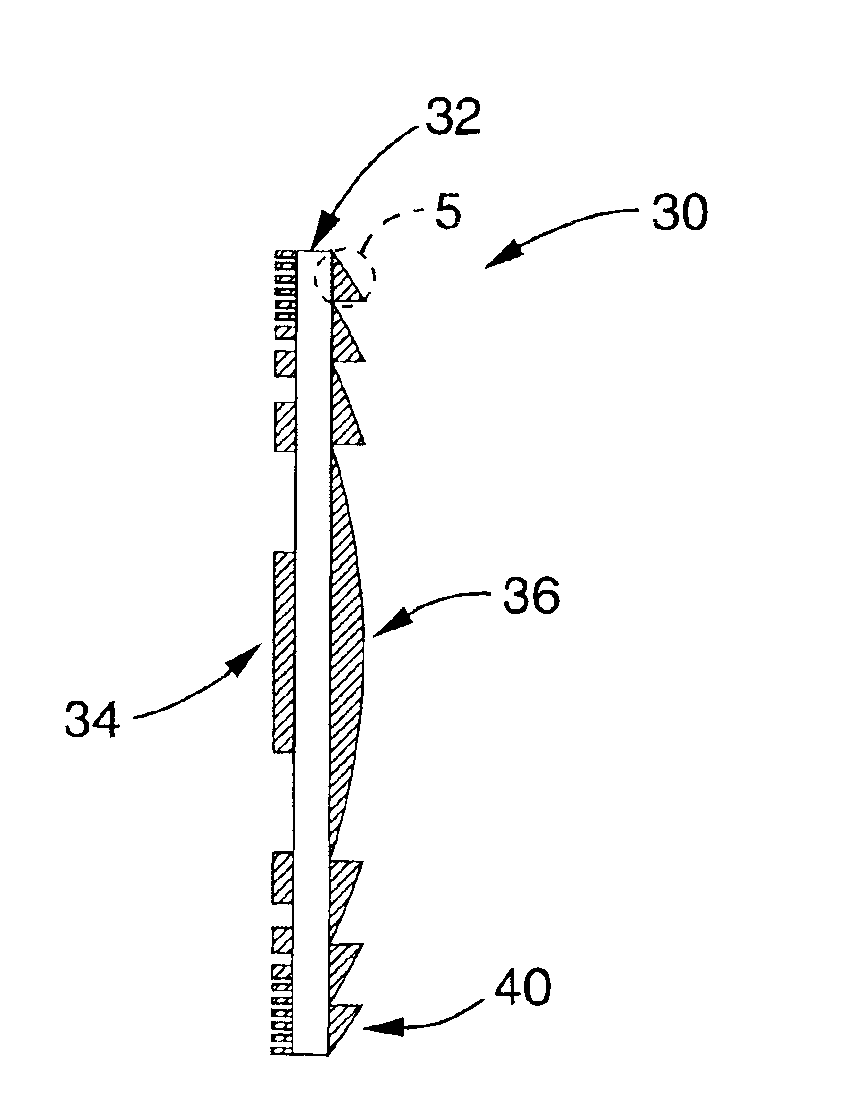
Probes, and systems and methods for optically scanning a conical volume in front of a probe, for use with an imaging modality, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A probe includes an optical fiber having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an axis, with the proximal end of the optical fiber being proximate a light source, and the distal end having a first angled surface. A refractive lens element is positioned proximate the distal end of the optical fiber. The lens element and the fiber end are both configured to separately rotate about the axis so as to image a conical scan volume when light is provided by the source. Reflected light from a sample under investigation is collected by the fiber and analyzed by an imaging system. Such probes may be very compact, e.g., having a diameter 1 mm or less, and are advantageous for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Optical engine and wide angle projection lens module thereof
InactiveUS20100079733A1Space minimizationReduce distanceProjectorsLensRefractive lensProjection lens
A wide-angle projection lens module is provided, including a reflective convex aspheric mirror and a refractive lens group of positive refractive power. The following Conditions (1) to (2) are satisfied:15<|Freflective / F|<25 Condition (1); and1.5<|Frefractive / F|<2.0 Condition (2),wherein, F is a focal length of the wide-angle projection lens module, Freflective is a focal length of the reflective convex mirror, and Frefractive is a focal length of the refractive lens group.
Owner:MEISTREAM INT OPTICAL
Ophthalmic lenses with reduced chromatic blur
The present invention provides single vision and multifocal lenses, as well as methods for their production, having a transverse chromatic aberration enabling provision of a lens the performance of which is equivalent to a refractive lens with a higher Abbe number.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
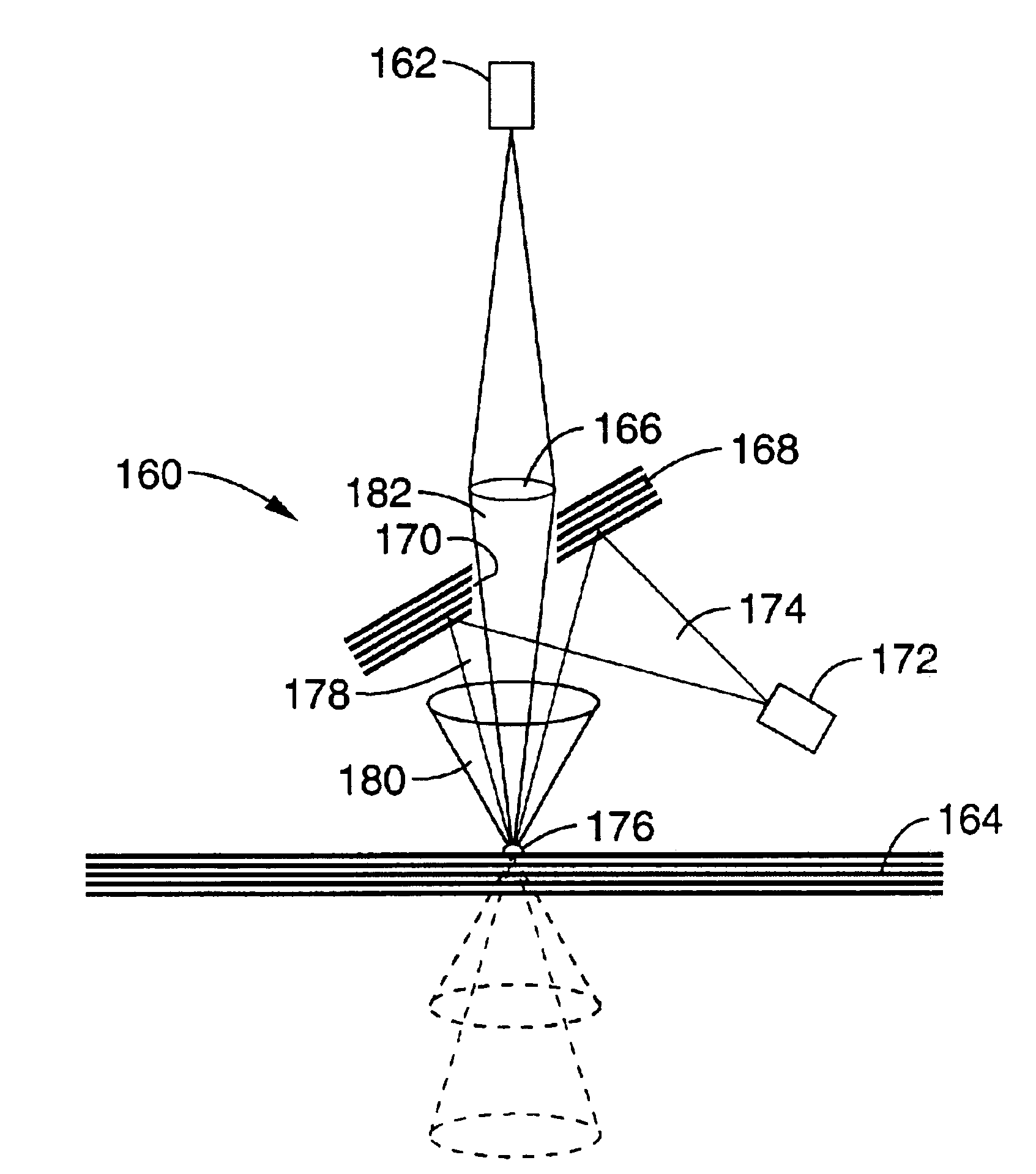
Miniaturized optically imaging system with high lateral and axial resolution
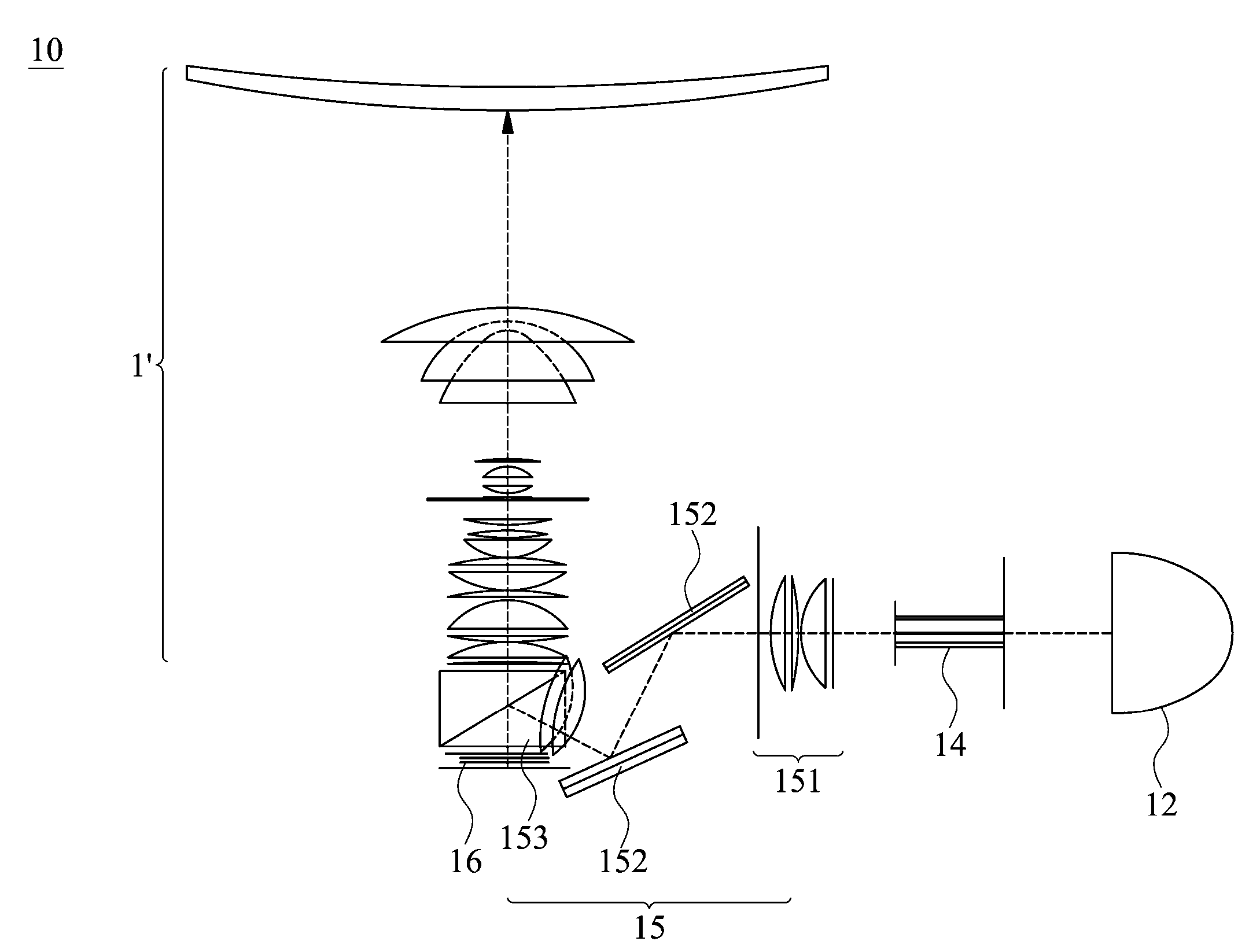
ActiveUS7511891B2Improve efficiencyHigh resolutionPhotometryMicroscopesTransmission systemObject field
The invention is directed to a miniaturized optically imaging system with high lateral and axial resolution for endomicroscopic applications. To provide a miniaturized optical head which permits an appreciable increase in photon efficiency with high lateral and axial spatial resolution compared to conventional GRIN optics the plane side of a refractive, plano-convex, homogeneous lens defines a plane entrance surface of the optical system, and first and second GRIN lenses are arranged along the optical axis orthogonal to the entrance surface, wherein the first GRIN lens being arranged downstream of the refractive lens for reducing the divergence of the highly divergent light bundle transmitted from the object through the refractive lens, and the second GRIN lens being provided for adapting the light bundle transmitted by the first GRIN lens to the aperture and object field size of the downstream transmission system.
Owner:GRINTECH
Open chamber, elliptical, accommodative intraocular lens system
InactiveUS20020002404A1Limited visionImprove eyesightIntraocular lensIntraocular lensRefractive lens
An open chamber, accommodative, intraocular lens system operable to be positioned within an evacuated capsular bag of a human eye following extracapsular extraction of a natural crystalline lens is provided having an anterior refractive lens optic, a first haptic segment having a first end and being connected at said first end to a peripheral portion of said anterior lens optic and a second end and said haptic segment extending in an elliptical curve, in longitudinal cross-section, and at least a second haptic segment having a first end and being connected at said first end to a peripheral portion of said lens optic and a second end and said at least a second haptic segment extending in an elliptical curve, in longitudinal cross-section, and being operably joined with the second end of said first haptic segment to form an open chamber, elliptical shaped haptic accommodating support for the anterior lens within an evacuated capsular bag of a human eye.
Owner:SARFARAZI FAEZEH
Apparatus and method for an improved lens structure for polymer wave guides which maximizes free space light coupling
InactiveUS7369724B2Reduce sensitivityMinimizes problemCoupling light guidesInput/output processes for data processingRefractive lensWaveguide
A polymer waveguide assembly. The assembly includes a polymer waveguide have a plurality of waveguide cores and an associated plurality of lenses respectively. The assembly also includes a molded lens structure having a support region, a primary refractive surface and a secondary refractive lens. The polymer waveguide is positioned onto the support surface of the molded lens structure so that the waveguide lenses are in optical alignment with the primary refractive lens and the secondary refractive lens of the molded waveguide structure. The lenses of the polymer waveguide are capable of collimating in the X and Y directions respectively. The primary refractive lens and the secondary refractive lens are both capable of collimating light in the Z direction. With this arrangement, a substantial; portion of the light passing through the secondary lens toward the waveguide cores is within the acceptance angle of the plurality of waveguides lenses respectively. The secondary lens thus creates a shallow angle of convergence relative to the input of the plurality of lenses of the waveguide. As a result, issues caused by misalignment are minimized and optical coupling is improved.
Owner:POA SANA LIQUIDATING TRUST
Refrigerated led illumination system
InactiveUS20100097780A1Good dispersionGood removal effectMechanical apparatusFurnace componentsSystems designRefractive lens
A self-contained LED lighting assembly for use in a refrigerated cabinet contains a plurality of LEDs mounted upon a substrate, each using a refractive lens designed to evenly disperse the light emitted from each LED into a flat, wide pattern suitable for lighting the contents of the cabinet. Heat is effectively removed from each LED and transported to an interior air space within the LED lighting assembly housing. The system is designed to replace current lighting systems and is sized fit within the space provided for current lighting systems, without the need for substantial modification, cutting, or removal of the current lighting systems. The assembly may be composed of individual LED lighting modules wired end-to-end to provide a desired length of strip lighting. Upon complete installation, the system provides the same or better lighting using only a fraction of the power required by the system replaced.
Owner:EFFICIENTLIGHTS
Objective lens, optical element, optical pick-up apparatus and optical information recording and/or reproducing apparatus equipped therewith
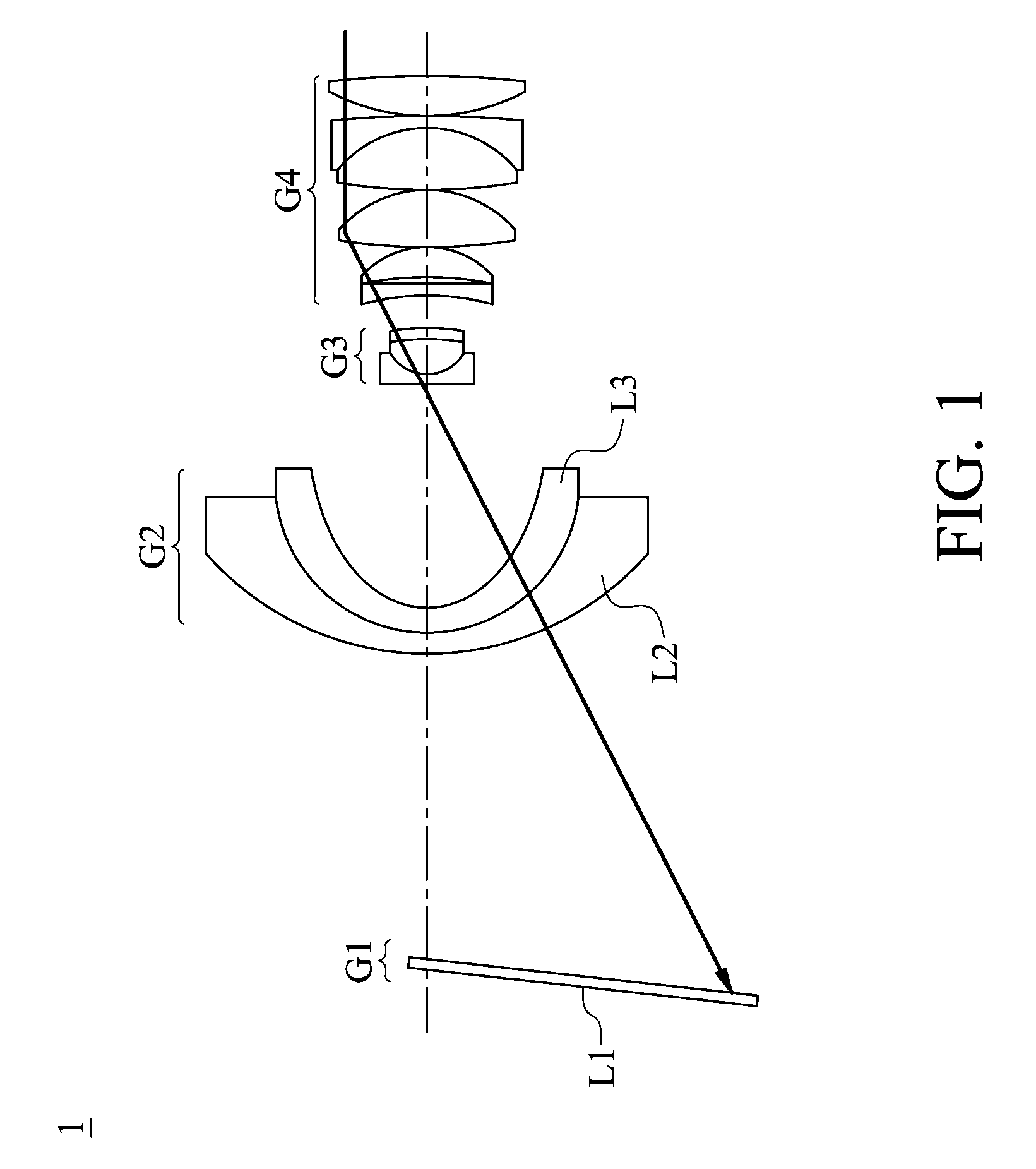
ActiveUS7206276B2Compact structureReduce the number of partsOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageDiffraction orderWavefront
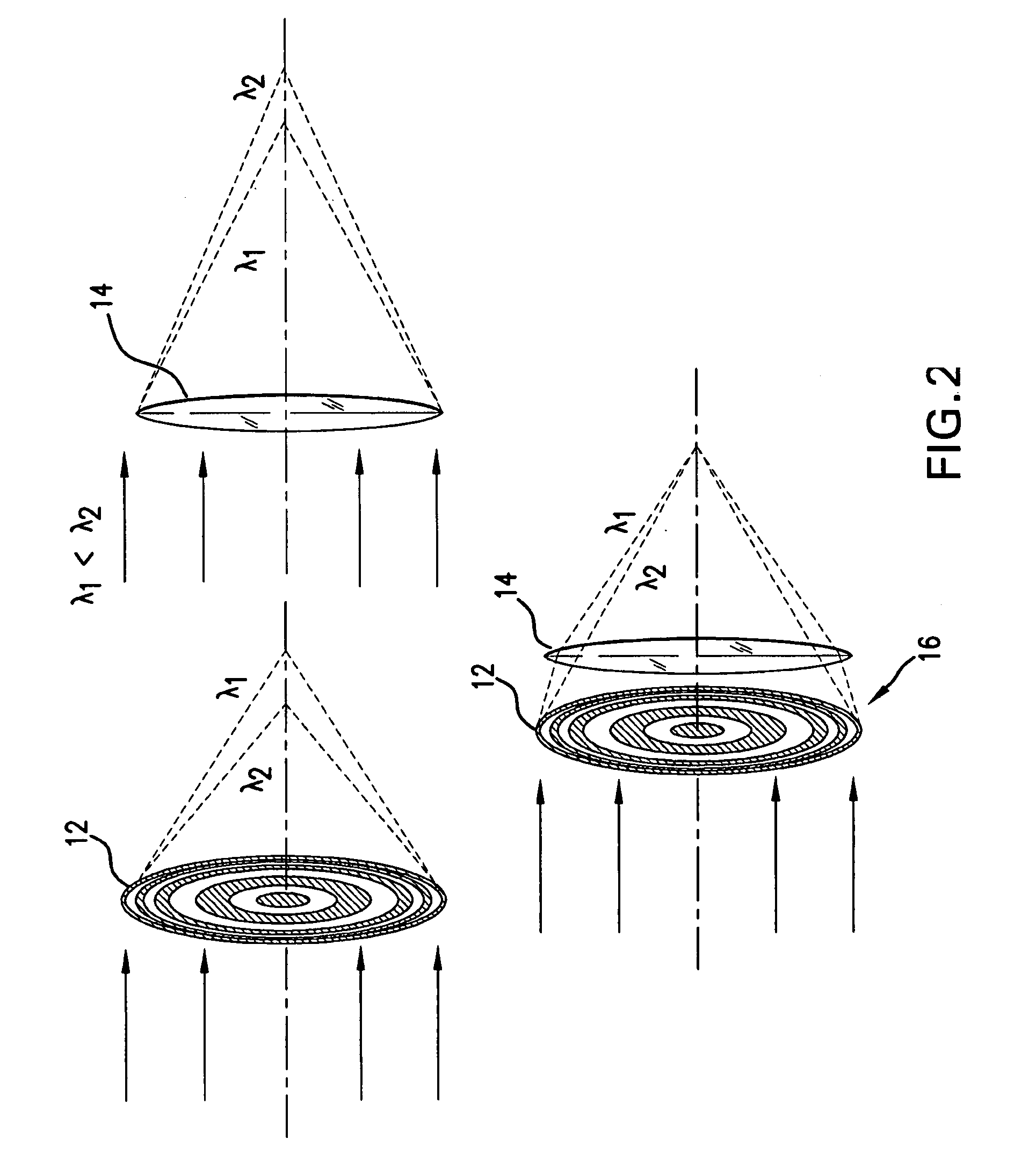
A hybrid objective lens has a refractive lens and a diffractive optical element constructed by plural coaxial ring-shaped zones on at least one optical surface thereof. When n1, n2 and n3 each is a diffraction order of a diffracted ray having a maximum light amount among diffracted rays of each of first, second and third light flux having wavelength λ1, λ2 and λ3 when respective light flux comes to be incident into the diffractive structure respectively, the following formulas are satisfied:|n1|>|n2|, and |n1|>|n3|, andthe hybrid objective lens converges a n1-th, n2-th and n3-th order diffracted ray of the first, second and third light flux onto an information recording plane of each of the first, second ant third optical information recording medium respectively so as to form an appropriate wavefront within respective prescribed necessary image side numerical apertures.
Owner:KONICA CORP
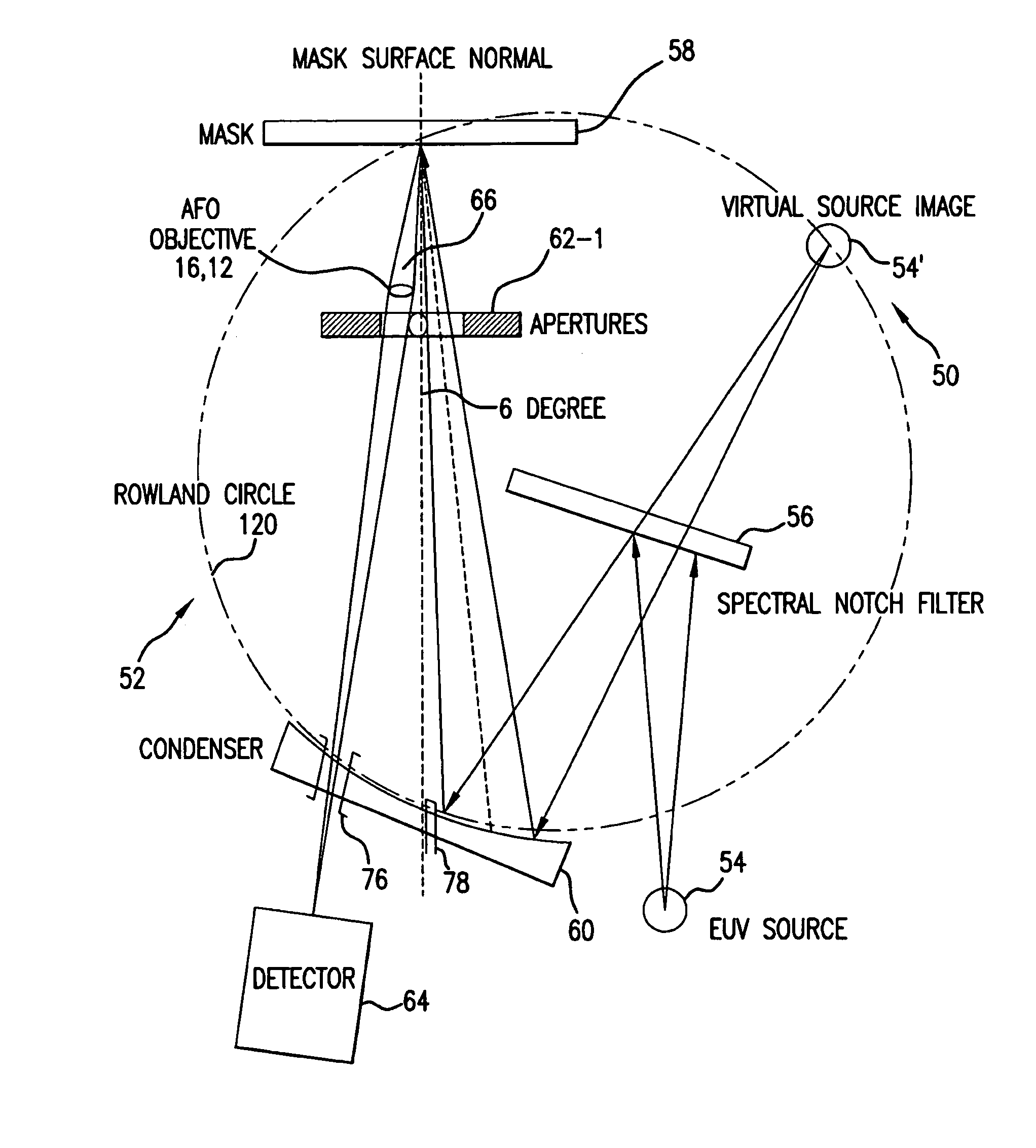
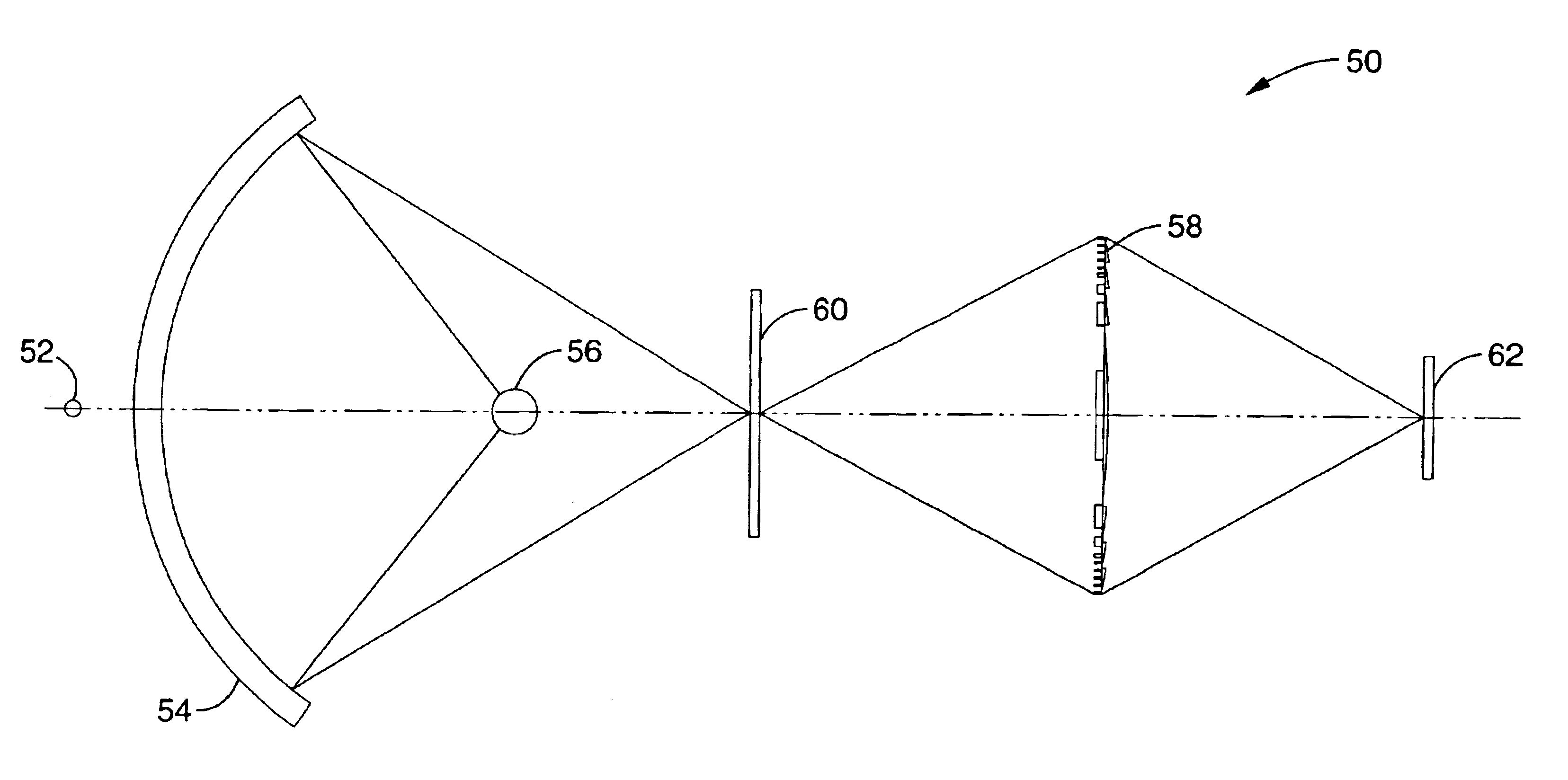
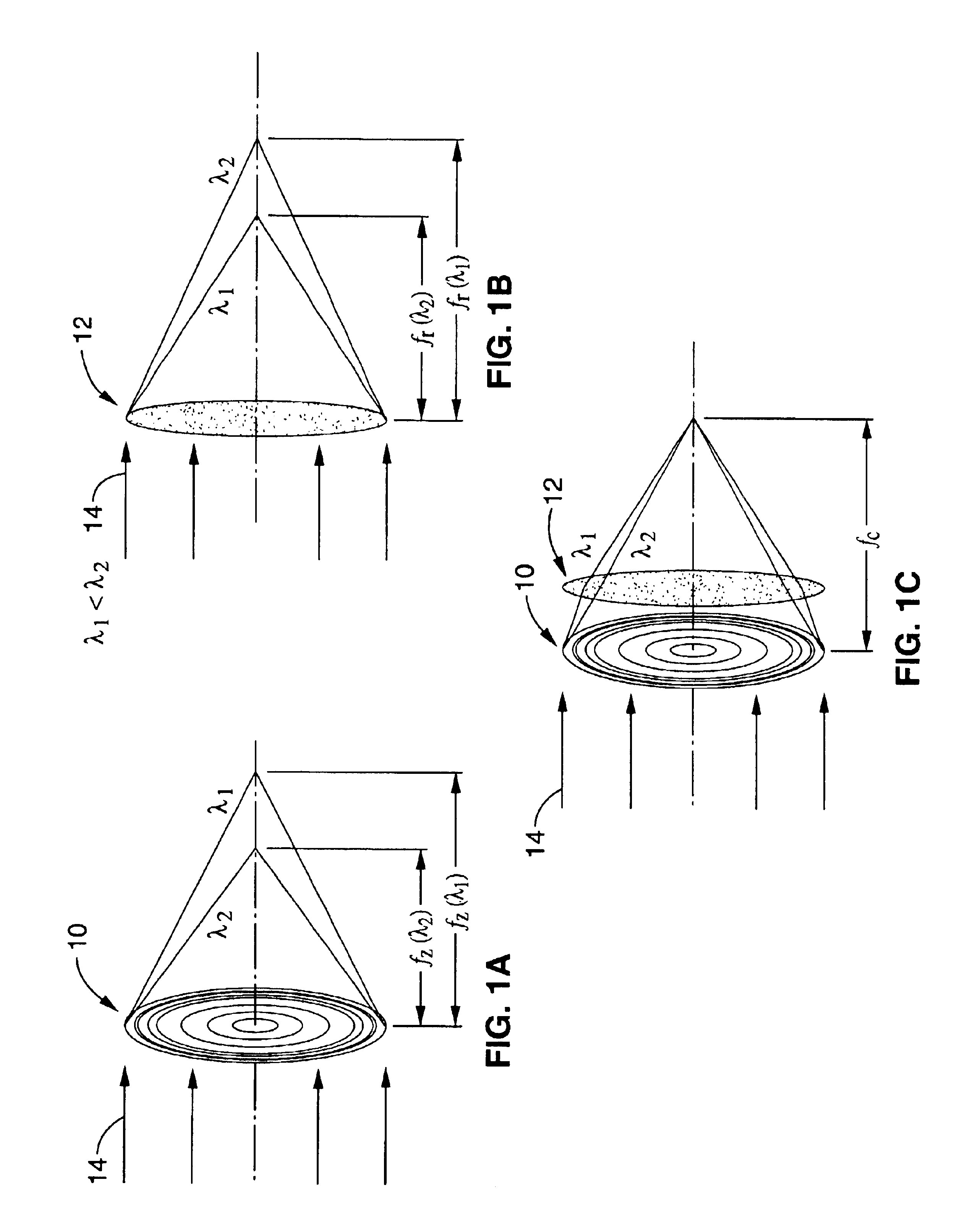
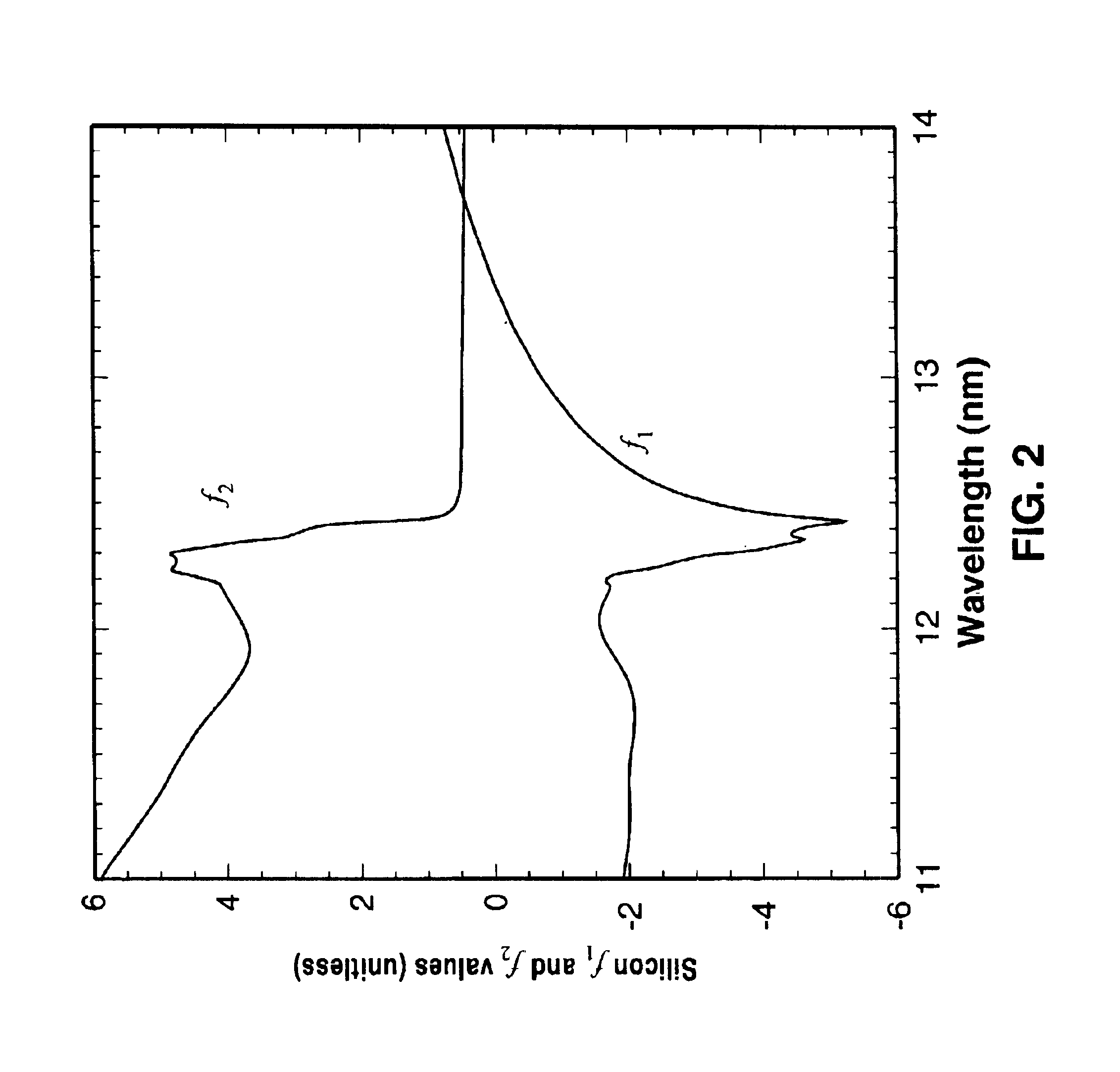
Short wavelength metrology imaging system
ActiveUS7268945B2Easy to implementEasy to switchImaging devicesNanoinformaticsHigh resolution imagingSystems design
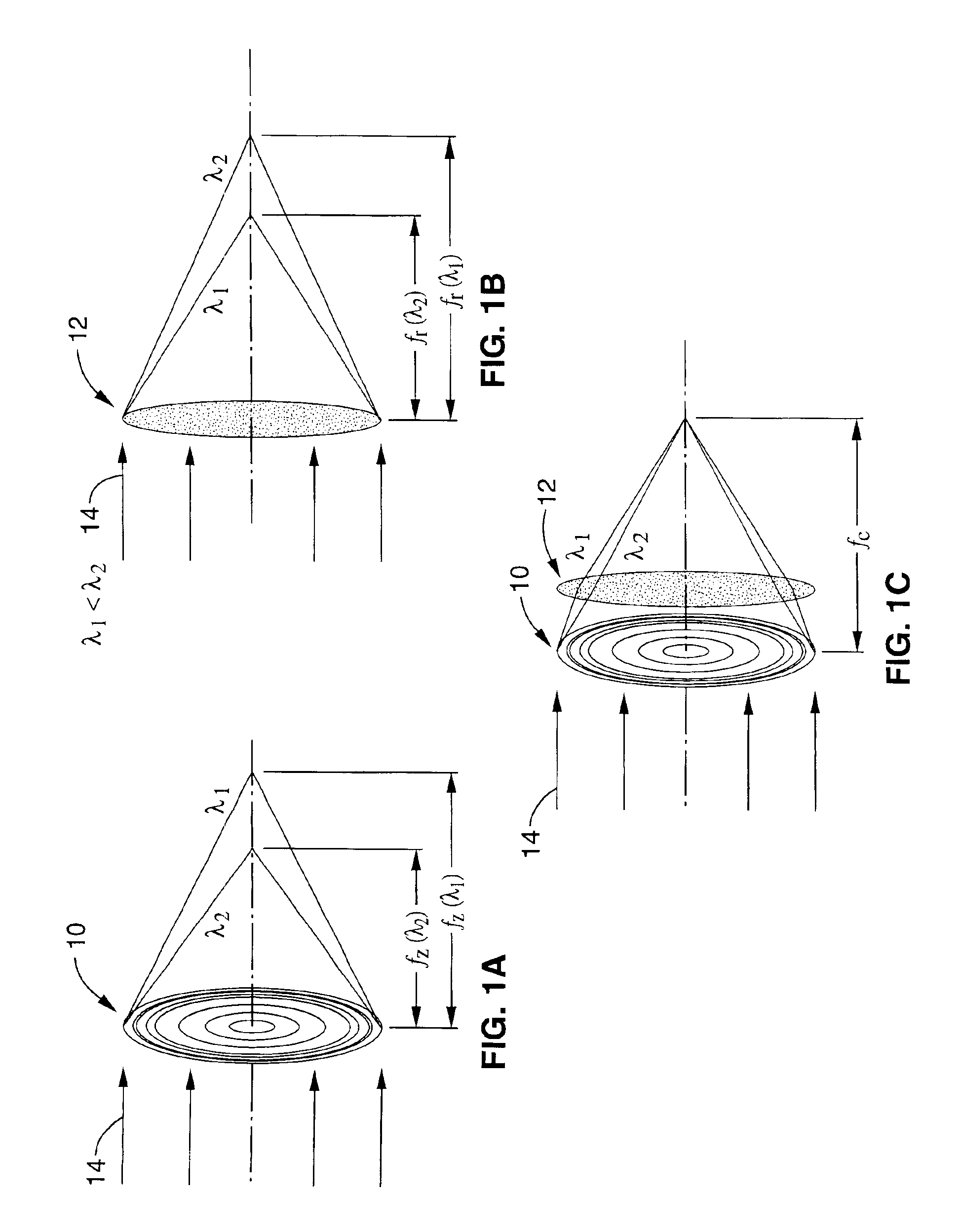
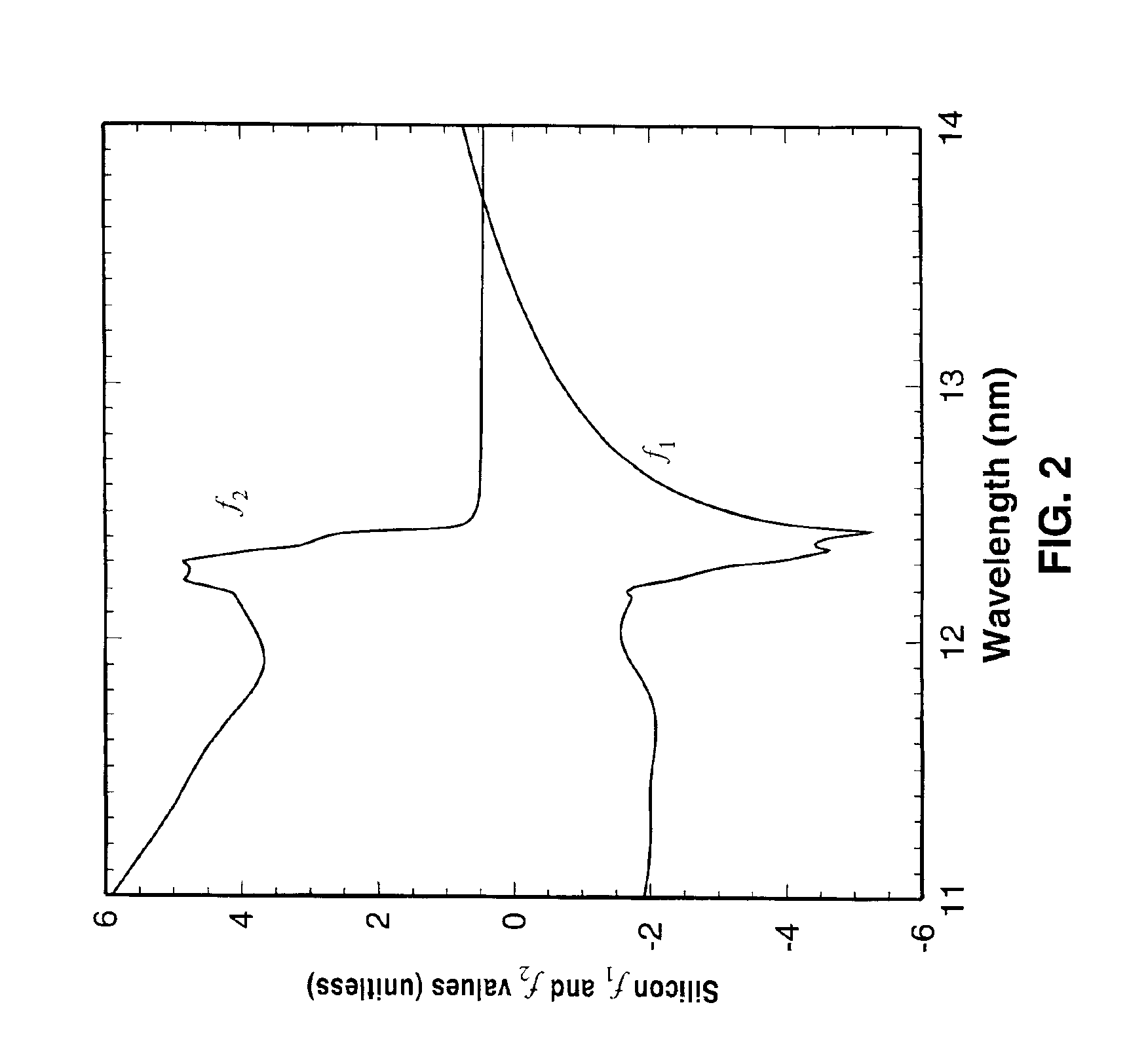
An extreme ultraviolet (EUV) AIM tool for both the EUV actinic lithography and high-resolution imaging or inspection is described. This tool can be extended to lithography nodes beyond the 32 nanometer (nm) node covering other short wavelength radiation such as soft X-rays. The metrology tool is preferably based on an imaging optic referred to as an Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). The AFO is a transmissive optic that includes a diffractive Fresnel zone plate lens component and a dispersion-correcting refractive lens component. It retains all of the imaging properties of a Fresnel zone plate lens, including a demonstrated resolution capability of better than 25 nanometers and freedom from image distortion. It overcomes the chromatic aberration of the Fresnel zone plate lens and has a larger usable spectral bandwidth. These optical properties and optical system designs enable the development of the AFO-based AIM tool with improved performance that has advantages compared with an AIM tool based on multilayer reflective mirror optics in both performance and cost.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Bionic eye lens
ActiveUS20130218270A1Restore and improve qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field sensorsOphthalmology departmentQuality of vision
The present invention relates generally to the restoration or improvement of the quality of human vision and, more particularly to a self-adapting system and method for achieving automatic sharp vision by the human eye of objects for instance at distances between 25 cm and more than 10 meters away. The invention can be situated in at least four technological domains: 1. ophthalmology, in particular the implantation of intraocular lenses. 2. Non-contact biometric signal recording and processing. 3. Electro-optic control of refractive lens power. 4. Wireless energy transfer.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Forward scanning imaging optical fiber probe
Probes, and systems and methods for optically scanning a conical volume in front of a probe, for use with an imaging modality, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A probe includes an optical fiber having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an axis, with the proximal end of the optical fiber being proximate a light source, and the distal end having a first angled surface. A refractive lens element is positioned proximate the distal end of the optical fiber. The lens element and the fiber end are both configured to separately rotate about the axis so as to image a conical scan volume when light is provided by the source. Reflected light from a sample under investigation is collected by the fiber and analyzed by an imaging system. Such probes may be very compact, e.g., having a diameter 1 mm or less, and are advantageous for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Reflective lithography mask inspection tool based on achromatic Fresnel optics
InactiveUS6914723B2High resolutionEfficient use ofOptical filtersMaterial analysis by optical meansFresnel lensMask inspection
A mask blank inspection tool includes an AFO having a diffractive lens and a refractive lens formed on a common substrate. The diffractive lens is a Fresnel zone plate and the refractive lens is a refractive Fresnel lens. The AFO is used to image light from a defect particle on a multilayer mask blank or the surface of the multilayer mask blank to a detector.
Owner:XRADIA
Achromatic fresnel optics for ultraviolet and x-ray radiation
InactiveUS6917472B1Relatively large bandwidthIncrease amplitudeOptical filtersDiffraction gratingsRefractive indexX-ray
An achromatic Fresnel optic that combines a Fresnel zone plate and a refractive Fresnel lens. The zone plate provides high resolution for imaging and focusing, while the refractive lens takes advantage of the refraction index change properties of appropriate elements near absorption edges to recombine the electromagnetic radiation of different energies dispersed by the zone plate. This compound lens effectively solves the high chromatic aberration problem of zone plates. The AFO has a wide range of potential applications in lithography, microimaging with various contrast mechanisms and measurement techniques.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Optic positioning device
ActiveUS20090103299A1Insertion and removal of the opticEasy to insertNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceRefractive lensEngineering
A device for holding and positioning an optic, such as a refractive lens, over a light source such as a light emitting diode. The refractive lens is frustum-shaped with an upper light-exiting end having an upper rim, a lower light-entering end, and a conical sidewall that tapers from the upper rim to the lower end. The device has a channel including a base and first and second sidewalls extending from the opposed side edges of the base, and further having one or more optic holding positions. The optic holding position includes an aperture formed in the base that is configured to receive the conical sidewall of the optic, and an aperture formed in a portion of each sidewall, adjacent the aperture in the base, for retaining a portion of the upper rim of the optic lens. The aperture can include a slot opening through which a portion of the upper rim of the optic lens at least partially extends.
Owner:LSI INDS
Achromatic fresnel optics based lithography for short wavelength electromagnetic radiations
InactiveUS6885503B2Simplify System DesignImprove system throughputMirrorsDiffraction gratingsRefractive indexElectromagnetic radiation
A lithography apparatus having achromatic Fresnel objective (AFO) that combines a Fresnel zone plate and a refractive Fresnel lens. The zone plate provides high resolution for imaging and focusing, while the refractive lens takes advantage of the refraction index change properties of appropriate elements near absorption edges to recombine the electromagnetic radiation of different energies dispersed by the zone plate. This compound lens effectively solves the high chromatic aberration problem of zone plates. The lithography apparatus allows the use of short wavelength radiation in the 1-15 nm spectral range to print high resolution features as small as 20 nm.
Owner:XRADIA
Free-form progressive multifocal refractive lens for cataract and refractive surgery
InactiveUS20140135919A1Improve acuityIncrease distanceIntraocular lensOptical partsPresent dayKeratorefractive surgery
A new type of multi-focal lens that has a free-form progressive multifocal front surface consisting of a 16th order polynomial superimposed on a standard conic base surface is described. The center region of the lens is optimized for distance vision, while simultaneously optimizing the rest of the lens for near vision. The resulting free-form even asphere polynomial surface is smooth, unlike present day diffractive multifocal designs. Additionally, this lens design is suitable for both refractive and cataract surgeries.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
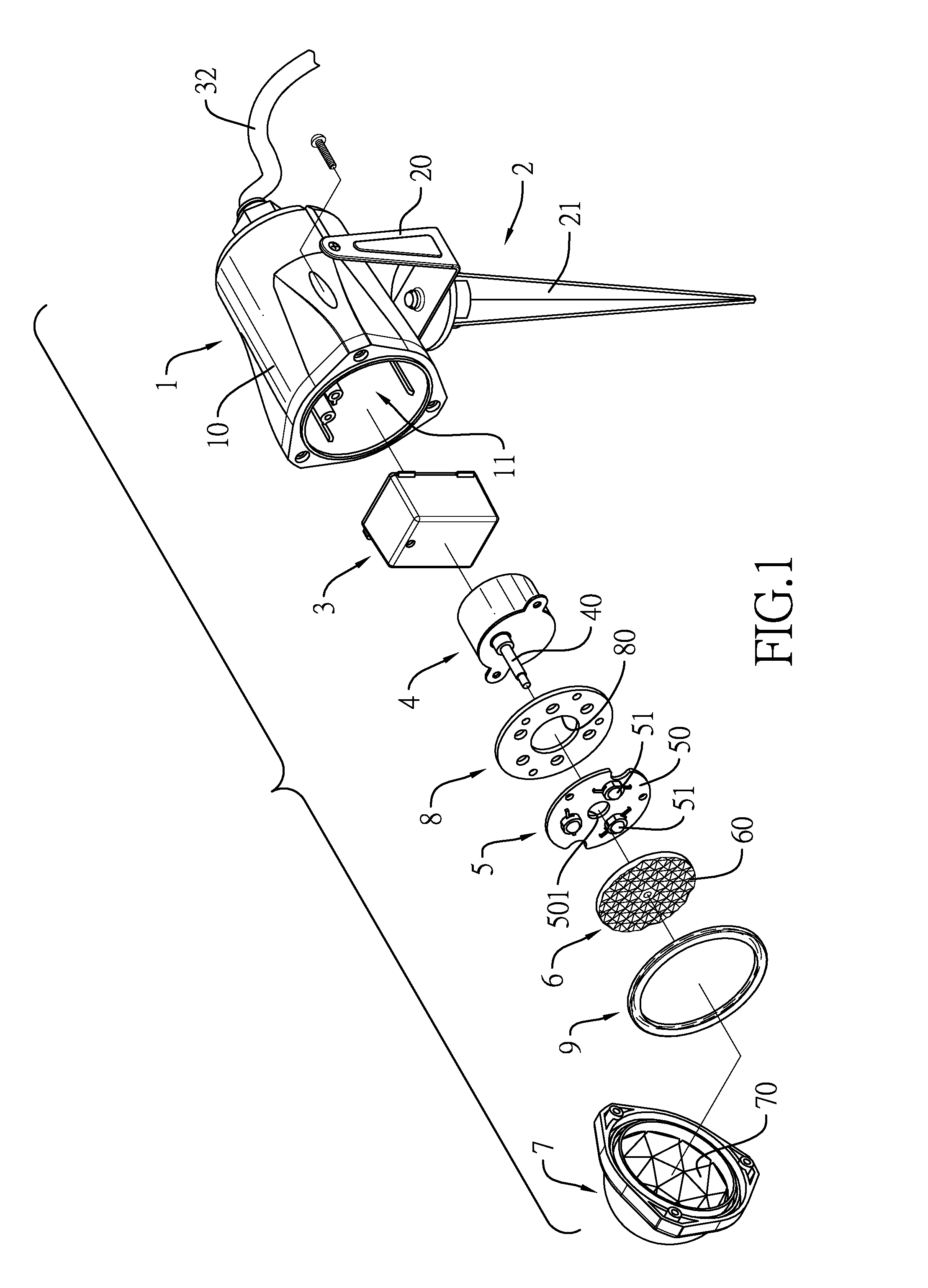
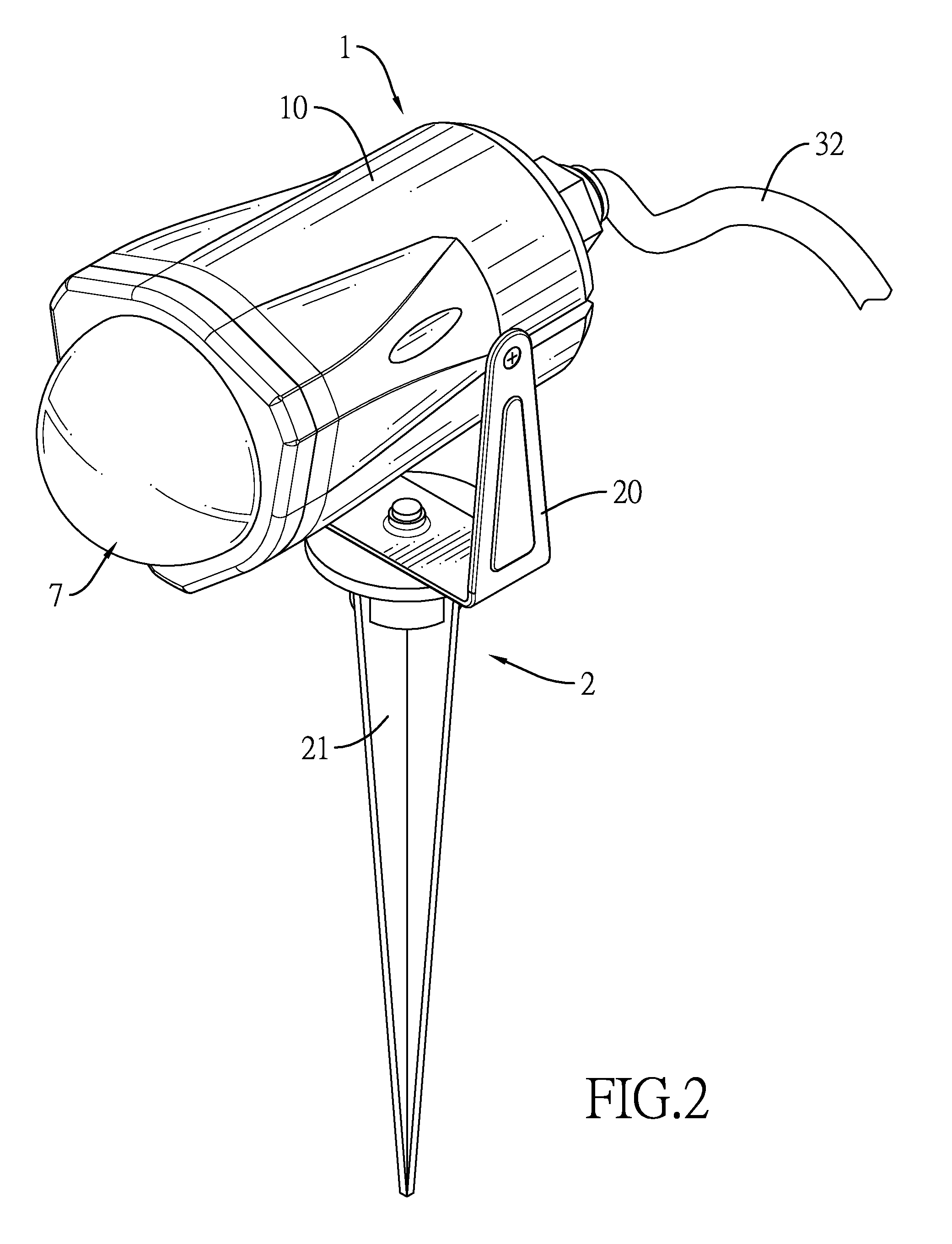
Spotlight
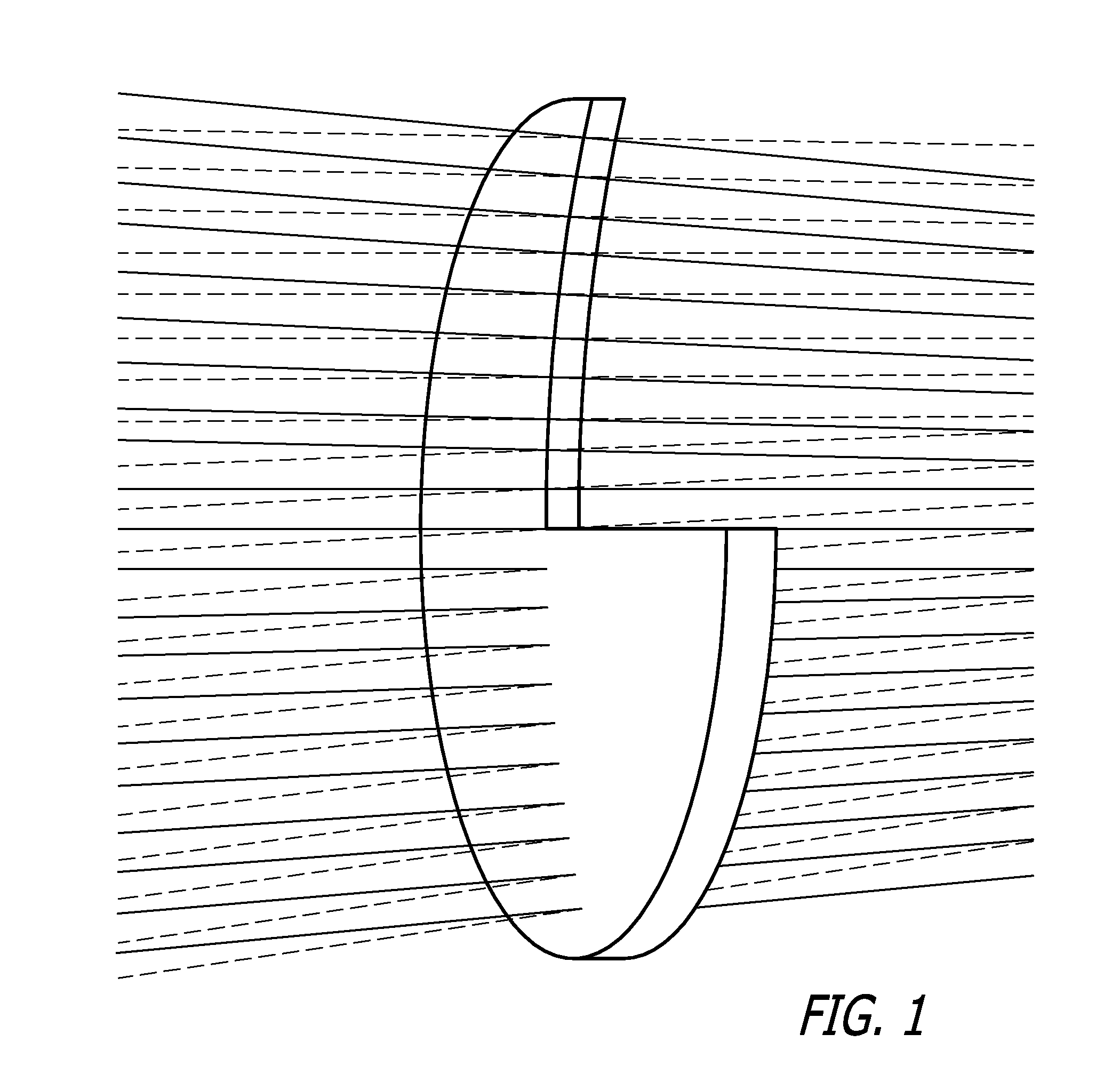
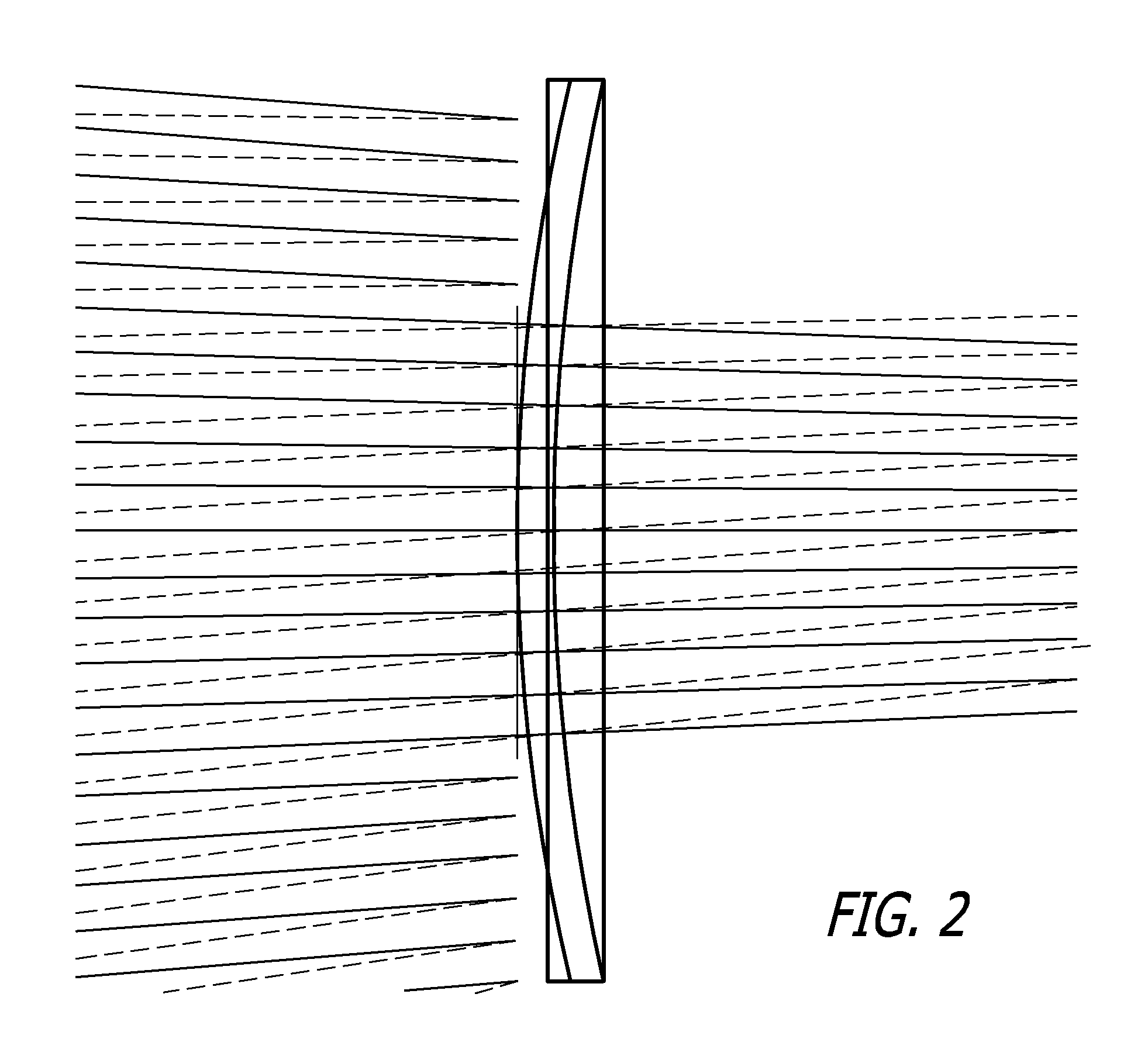
A spotlight has a light base, a supporting base, a power supply, a motor, a lighting module, a multi-surface refractive lens and a beam-splitter lens light shade. The supporting base is connected with the light base. The power supply, the motor, the lighting module, and the multi-surface refractive lens are mounted in the light base. The lighting module has multiple light emitting diode units facing the multi-surface refractive lens. The multi-surface refractive lens is mounted around a motor shaft of the motor. The beam-splitter lens light shade is mounted on the light base and has multiple multi-angle refractive convex-lens bodies facing the multi-surface refractive lens.
Owner:GEMMY IND CORP
Apparatus and method for an improved lens structure for polymer wave guides which maximizes free space light coupling
InactiveUS20080080811A1Reduce sensitivityMinimizes problemCoupling light guidesInput/output processes for data processingRefractive lensWaveguide
A polymer waveguide assembly. The assembly includes a polymer waveguide have a plurality of waveguide cores and an associated plurality of lenses respectively. The assembly also includes a molded lens structure having a support region, a primary refractive surface and a secondary refractive lens. The polymer waveguide is positioned onto the support surface of the molded lens structure so that the waveguide lenses are in optical alignment with the primary refractive lens and the secondary refractive lens of the molded waveguide structure. The lenses of the polymer waveguide are capable of collimating in the X and Y directions respectively. The primary refractive lens and the secondary refractive lens are both capable of collimating light in the Z direction. With this arrangement, a substantial; portion of the light passing through the secondary lens toward the waveguide cores is within the acceptance angle of the plurality of waveguides lenses respectively. The secondary lens thus creates a shallow angle of convergence relative to the input of the plurality of lenses of the waveguide. As a result, issues caused by misalignment are minimized and optical coupling is improved.
Owner:POA SANA LIQUIDATING TRUST
Level laser indicator
A level laser indicator comprising a housing, a laser-indicating means and a bubble leveler; wherein one position of the housing is equipped with a laser-indicating means that can rotate freely, which makes the emitting laser light closing to the housing and the measuring surface as the visible light by a refractive lens installed in the front of it; the other position of the housing is equipped with a bubble leveler, which provides a set of holding arms. In addition, there are two nails passes through a base and a magnet is installed on it, so that the whole is conveniently fixed to the wall or the metal surface on a datum plane of measure. Furthermore, two sides of the housing are installed with several vertical grooves / marks, and the angle scale is drawn around said laser-indicating means to conveniently provide with precise measurement of plane.
Owner:INDEX MEASURING TAPE
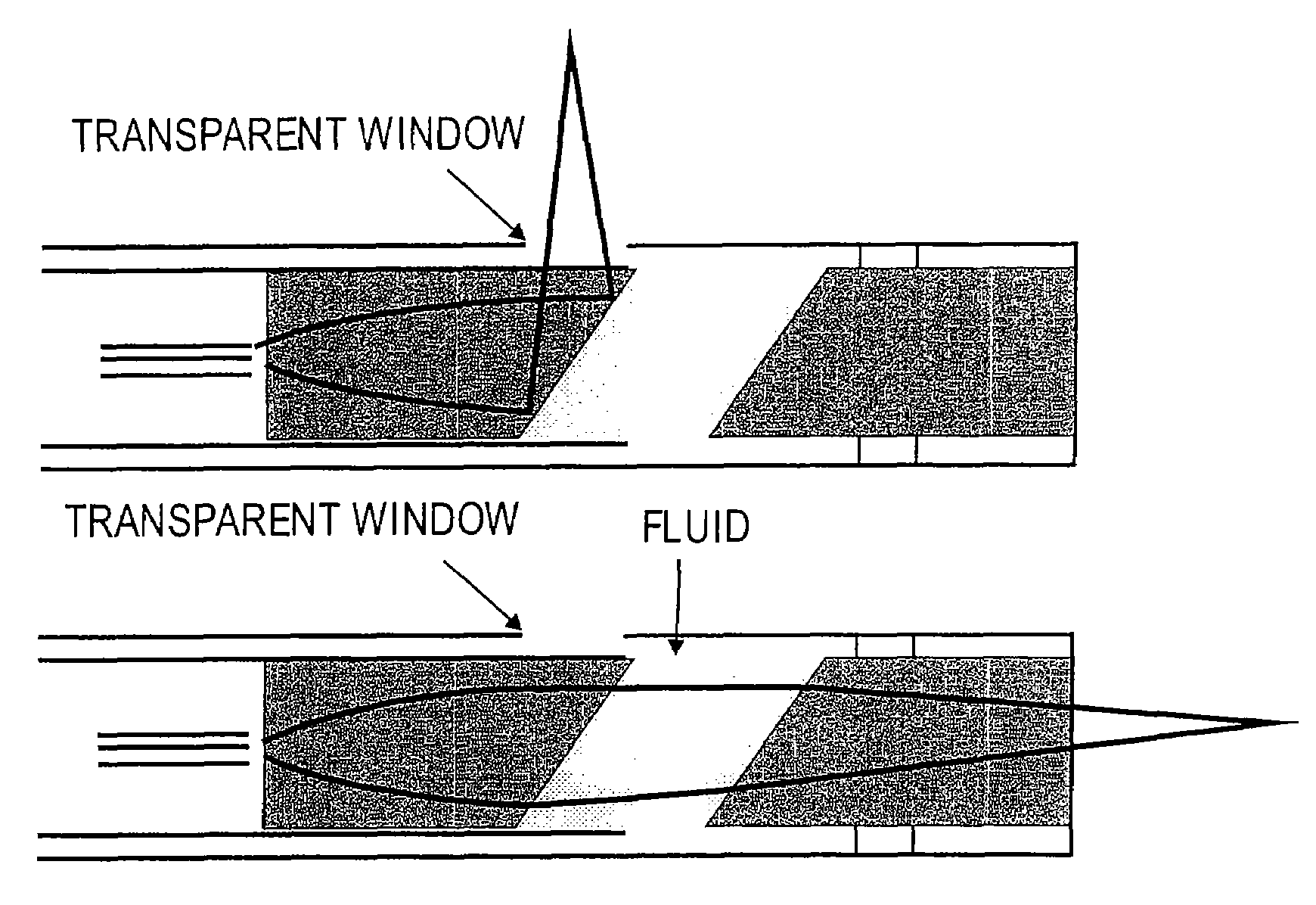
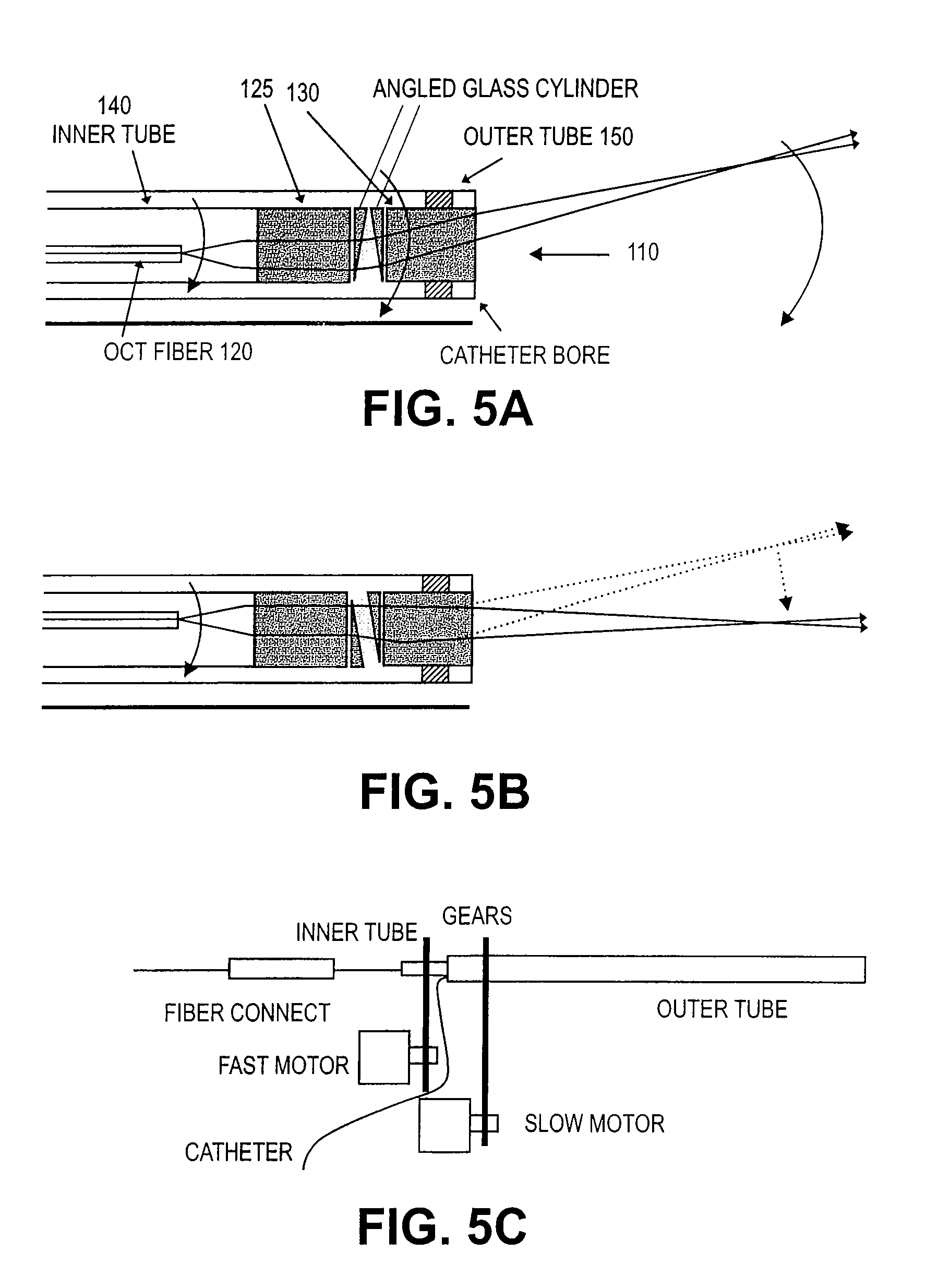
Paired angled rotation scanning probes and methods of use
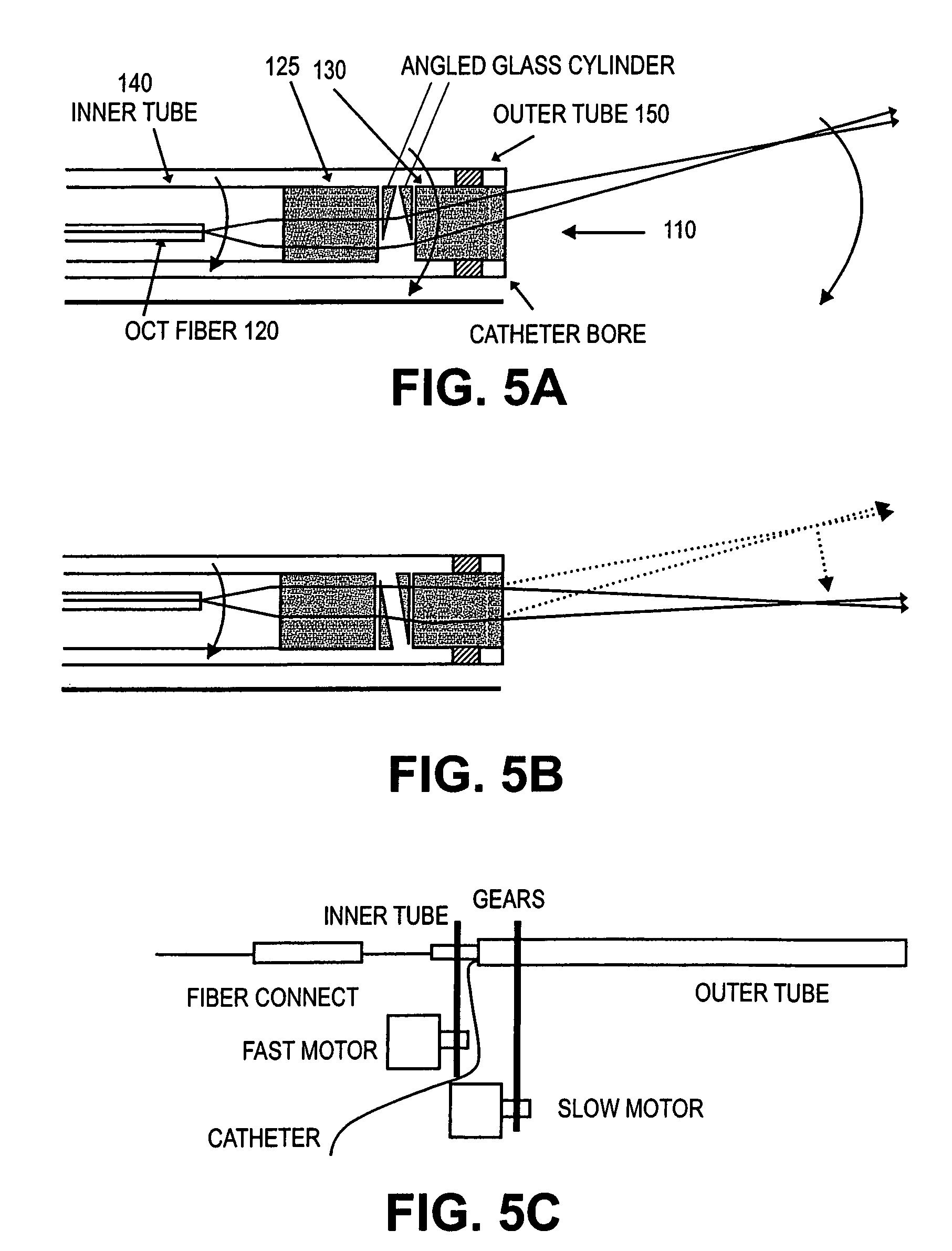
InactiveUS7364543B2Enhance the imageApplied imageRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFiberProximate
Probes, and systems and methods for optically scanning a conical volume in front of a probe, for use with an imaging modality, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A probe includes an optical fiber having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an axis, with the proximal end of the optical fiber being proximate a light source, and the distal end having a first angled surface. A refractive lens element is positioned proximate the distal end of the optical fiber. The lens element and the fiber end are both configured to separately rotate about the axis so as to image a conical scan volume when light is provided by the source. Reflected light from a sample under investigation is collected by the fiber and analyzed by an imaging system. Such probes may be very compact, e.g., having a diameter 1 mm or less, and are advantageous for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures. A fluid medium can be introduced between two lens elements at the distal end of the probe to switch a mode from side viewing to forward viewing.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Micro-lens array and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050074702A1Large numerical apertureSimple processPhotomechanical apparatusOptical articlesUltravioletRefractive lens
A micro-lens array and manufacturing method. A hybrid micro-lens in which a refractive lens and a diffraction lens are formed includes: a refractive lens; a first ultraviolet hardening material which is bonded on a curved surface of the refractive lens to form an aspheric surface; a support substrate including a concave portion into which the refractive lens is inserted and supported; and a diffraction lens which is formed at a position corresponding to the refractive lens disposed on the support substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for illuminating blood
An apparatus including a light-emitting device configured to illuminate blood is described. The light-emitting device may include a red light source configured to emit red light. The light-emitting device may also include a green light source configured to emit green light. The light-emitting device may additionally include a first refractive lens and a reflector having a concave surface to reflect a portion of red light emitted by the red light source and a portion of green light emitted by the green light source toward the first refractive lens. The first refractive lens may be configured to direct red light emitted by the red light source to form a red light beam and to direct green light emitted by the green light source to form a green light beam. Additionally, the light-emitting device may include an optical adjuster configured to adjust a separation distance between the first refractive lens and at least one of the green light source and the red light source. The optical adjuster may further be configured to move the first refractive lens with respect to at least one of the red light source and the green light source. A method for illuminating blood is additionally disclosed.
Owner:BUSHNELL HLDG
Projection Type Image Display Apparatus
ActiveUS20070291236A1Wide viewing angleEasy to manufactureProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementRefractive lensComputer science
A projection-type image display apparatus for projecting an image, enlargedly, onto a projection surface, comprises: an image display element; a lens group, being disposed behind the image display element, comprising therein, a front lens group made up with a plural number of lenses, including, at least, a refractive lens, having a positive power and being rotationally symmetric in a surface configuration thereof, and a rear lens group made up with a plural number of lenses, including, at least, a lens having a free curved surface configuration and being rotationally asymmetric, thereby emitting the image displayed on the image display element; a reflection mirror for reflecting the light from the lens group, thereby projection onto the projection surface, obliquely; a first mounting base, on which the rear lens group is mounted; and a rod member, which is provided on the mounting base for moving the mounting base.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Off-axis reflective transmit telescope for a directed infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) system
ActiveUS20110084195A1Improve aberrationAberration correctionDefence devicesPhotometry using reference valueAxis of symmetryCatoptrics
An off-axis reflective transmit telescope for a DIRCM system is mounted on the gimbal along a transmit-axis offset laterally from the optical axis of the receive telescope but nominally aligned with the line-of-sight of the receive telescope to transmit a laser beam. The telescope comprises an optical port optically coupled to a laser to receive and direct the laser beam away from the dome and a reflective optical assembly that reflects the laser beam through the dome. The reflective optical assembly comprises an off-axis mirror segment and a second optical element that together precompensate the laser beam for dome aberrations induced by the lateral offset of the transmit telescope's transmit axis from the optical axis. The off-axis mirror segment comprises a segment of a parent mirror having an aspheric curvature (e.g. parabolic, elliptical or higher-order asphere) about an axis of symmetry. The segment is offset so that it is not centered on the axis of symmetry of the parent mirror. The use of the off-axis mirror segment allows the optical port and any folding mirror to be positioned so that they do not obscure the reflected laser beam. The second optical element may be a segment of a dome corrector parent lens, a prism or a refractive lens formed on the front surface of the off-axis minor segment.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Small mode-field fiber lens
InactiveUS7099535B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingCoupling light guidesCamera lensLight beam
A fiber lens includes a graded-index lens, a single-mode fiber disposed at a first end of the graded-index lens, and a refractive lens having a hyperbolic or near-hyperbolic shape disposed at a second end of the graded-index lens to focus a beam from the single-mode fiber to a diffraction-limited spot.
Owner:CORNING INC
Hybrid lens array and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050174643A1Large numerical apertureReduce overall chromatic aberrationBathsDouchesRoom temperatureRefractive lens
Provided are a hybrid lens and method of fabricating the same. A hybrid lens designed as a combination of a refractive lens and a diffractive lens includes a refractive lens including a first spherical surface and a second planar surface, a diffractive lens that is bonded onto the first surface of the refractive lens and includes a refractive portion for correcting spherical aberration, and a lens holder attached to an outer perimeter of the first surface of the refractive lens. The method eliminates the need for high temperature heating or cooling or a high pressure process while allowing rapid and simple processing at room temperature under low pressure and thus high volume production.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High resolution objective lens assembly
InactiveUS20060087725A1High resolutionEffective correctionPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesImage resolutionHigh numerical aperture
A high resolution objective lens assembly (20, 120, 220, 320) is implemented with refractive lens elements made of modified fused silica for operation at deep ultraviolet (DUV) wavelengths to reduce birefringence-caused image aberrations. The high resolution is achieved by an optical design that is characterized by a very high numerical aperture (NA) and short wavelength operation.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Projection unit for a head-up display
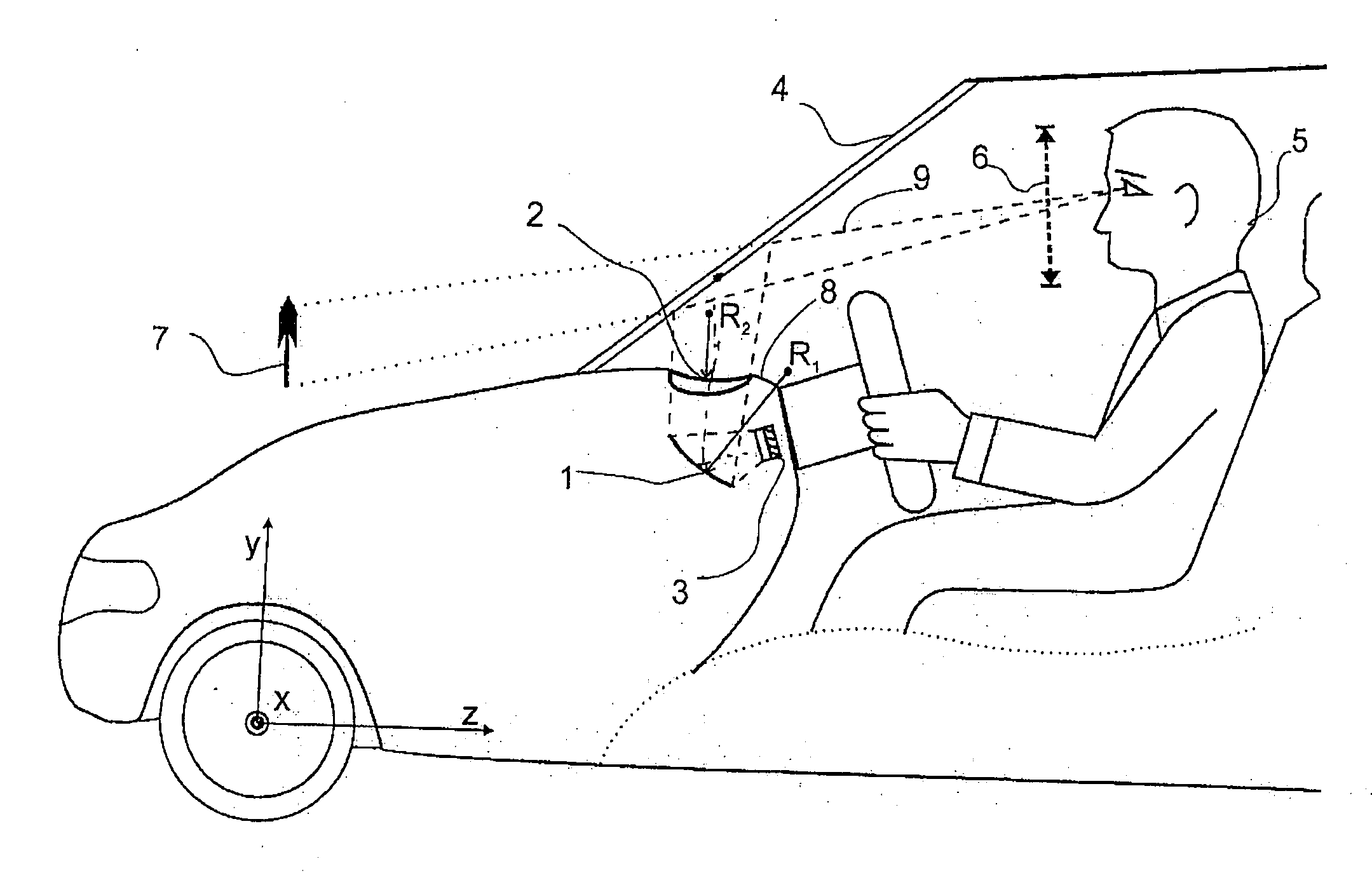
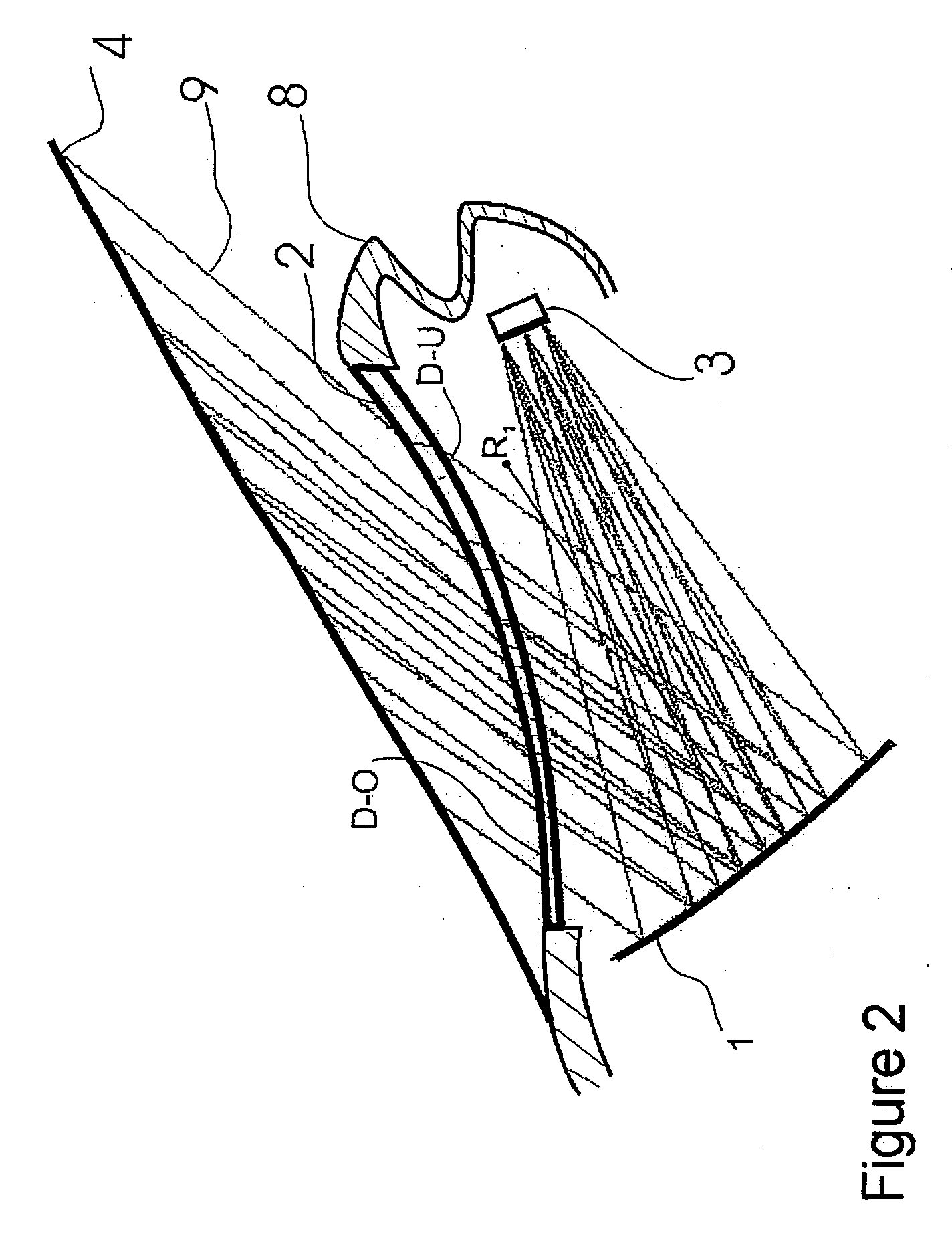
ActiveUS20060209419A1Reduce disadvantagesSimple meansCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsHead-up displayLight beam
The invention is directed to a projection unit for a head-up display comprising an image generator, a mirror and a refractive lens which are arranged in a housing one behind the other in the light propagation direction. The beam path is directed to a windshield. The invention is characterized in that the mirror has a concave reflection surface, and the lens has a free-form surface at least on one of the optically active surfaces (D-U and / or D-O).
Owner:SYPRO OPTICS
Method of Refraction Surgery of the Eye and a Tool for Implanting Intraocular Refractive Lens
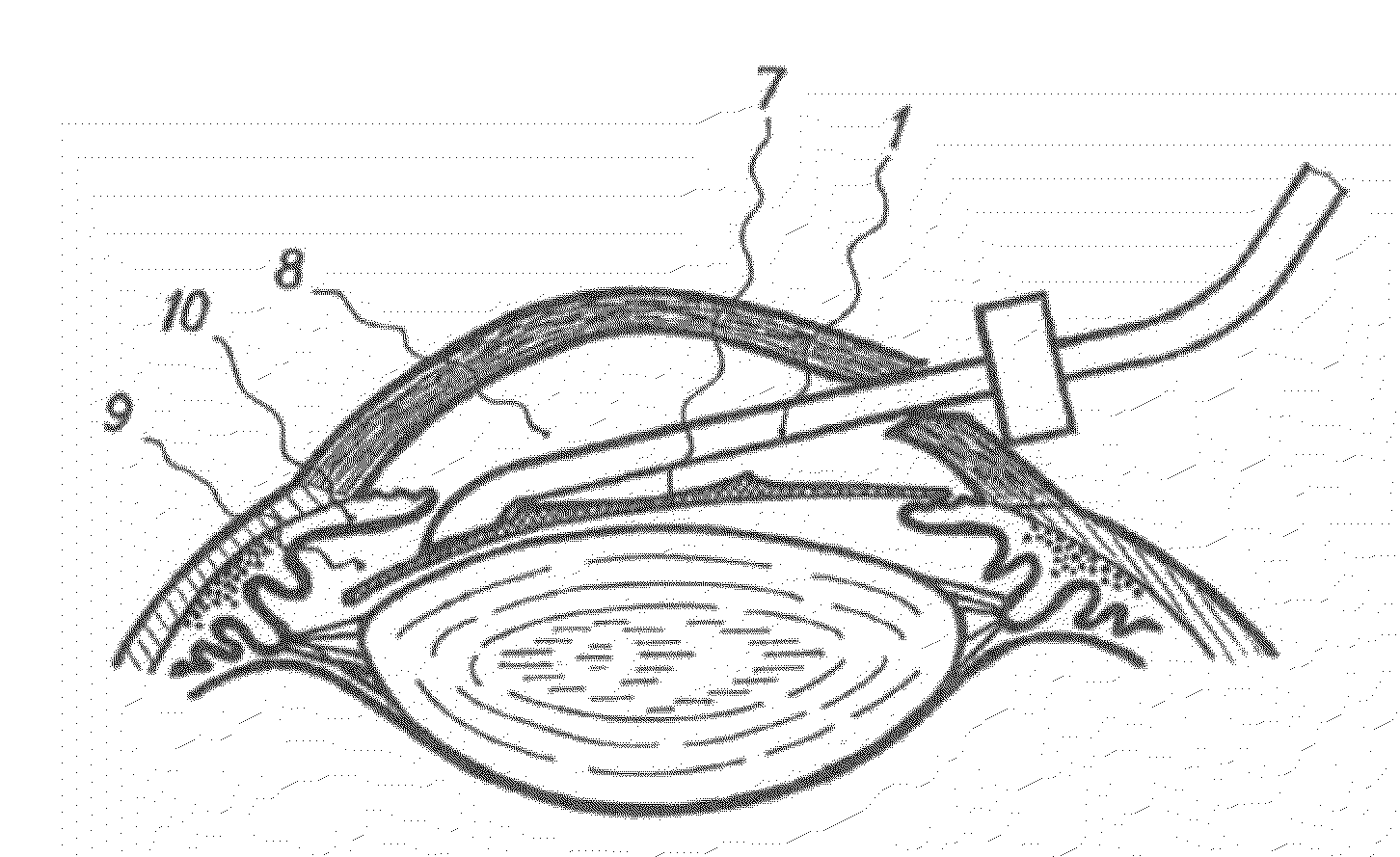
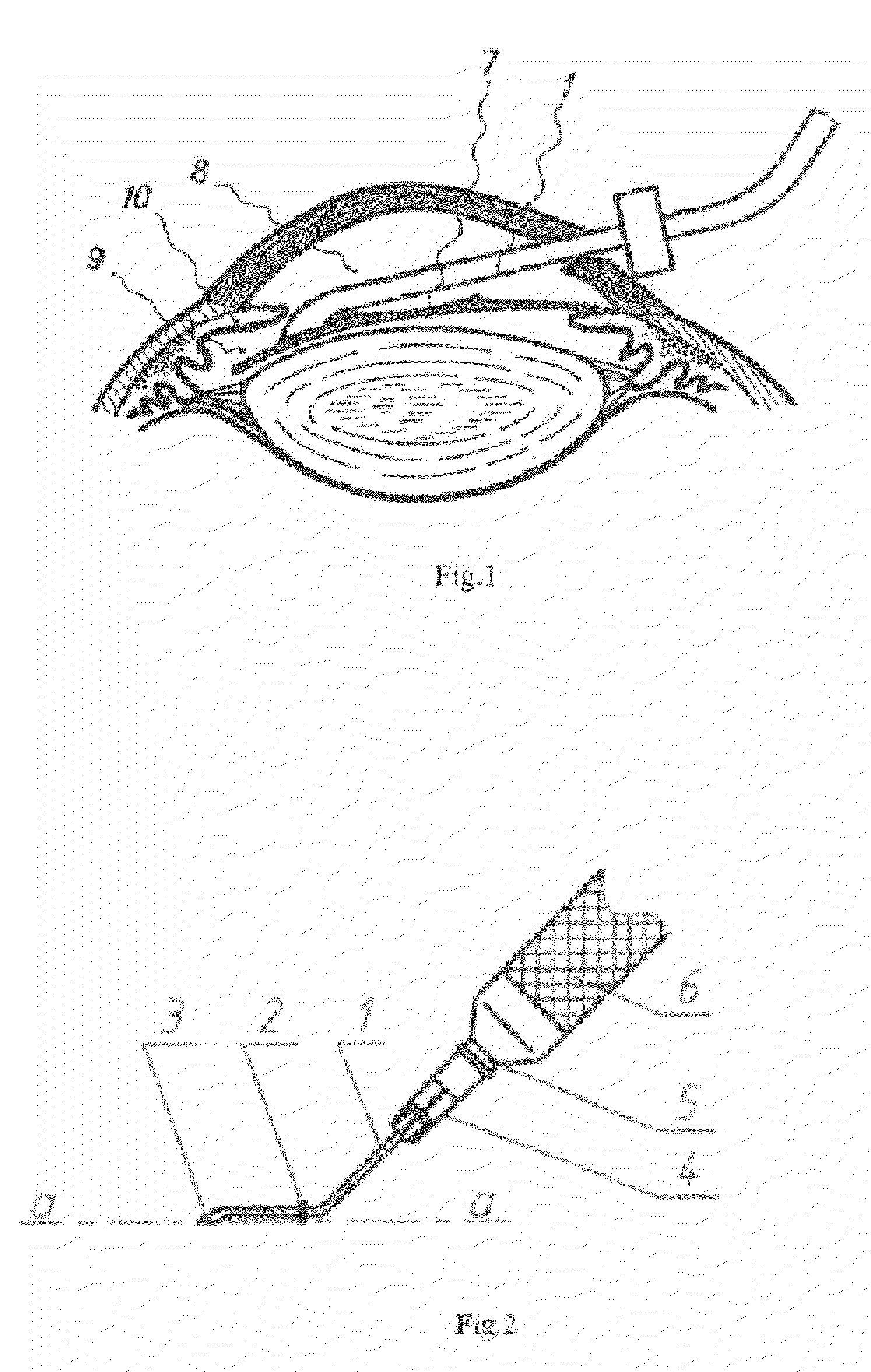
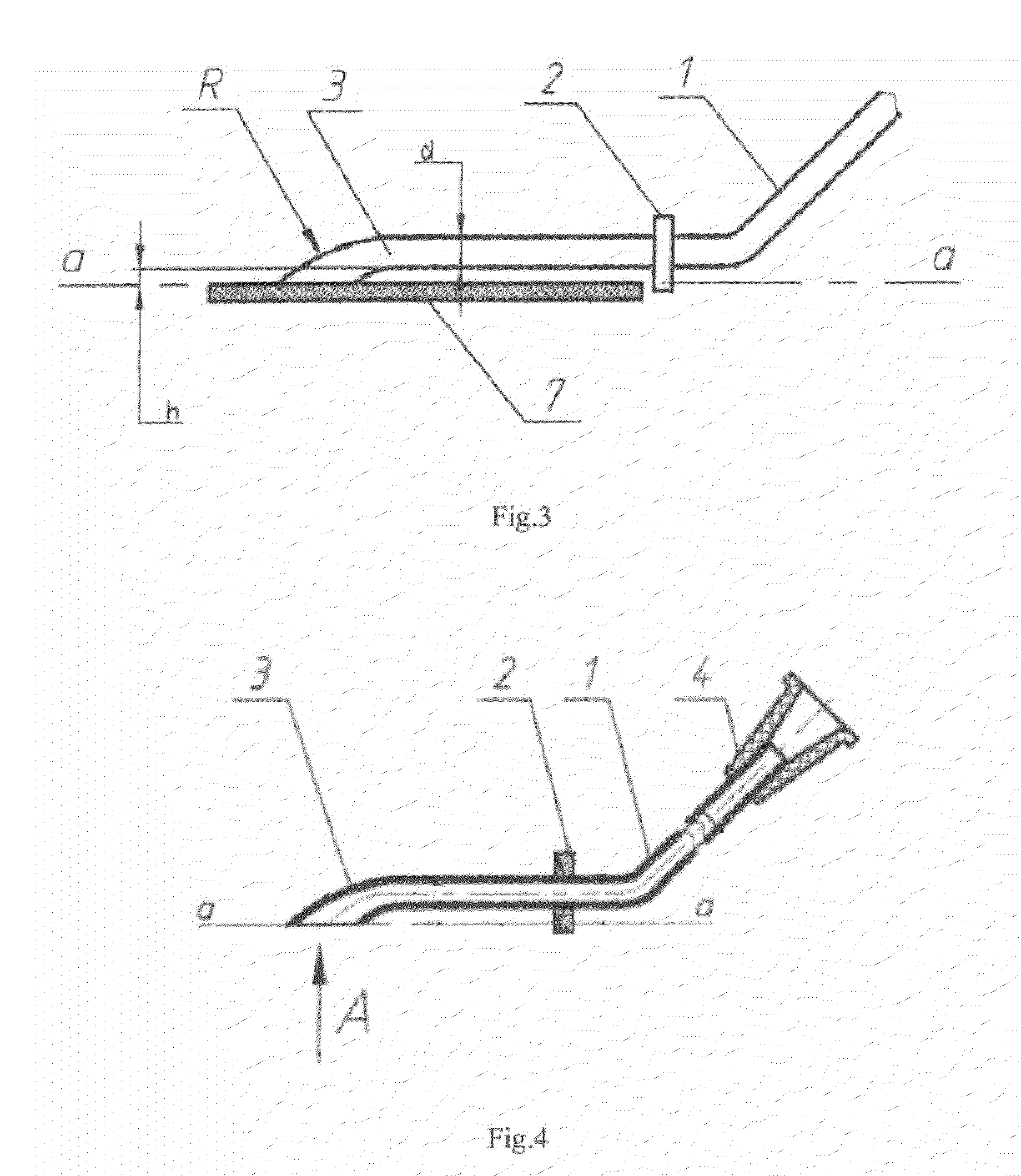
InactiveUS20100057095A1Avoiding lens damage dangerLower Level RequirementsEye surgeryIntraocular lensKeratorefractive surgeryEllipse
A reduction of eye trauma is achieved during opthalmolic surgery branch for implanting the intraocular refractive lens to the anterior chamber of the eye. The pupil is extended by mydriatic compounds and after anesthesia the cornea cut is made (clear cornea—3 mm). Thereafter, the anterior chamber of the eye is filled with viscoelastic compound with low molecular weight and then the refractive lens is implanted with the help of said cannula, the working face of the cannula at the middle between the lens edge and the border of the optic area, with the edge bent on the cannula face. The end by the top of the bending the refractive lens is introduced into the cornea cut and set in the posterior chamber of the eye. Thereafter, vacuum is removed and the cannula is detached from the refractive lens, and taken off the anterior chamber of the eye by the reverse movement. The refractive lens cannula is made as a tube with round or oval cross-section with inner diameter 0.5-2.5 mm and wall thickness not less than 0.05 mm. The tube is bent at 110-160, supplied with limiter, and working end that has diameter of the round cross-section of 1.0-2.0 mm or ellipse-shaped cross-section with small and big axes 0.6-0.9 mm and 1.5-2.5 mm, respectively.
Owner:LEONID ORBACHEVSKY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com