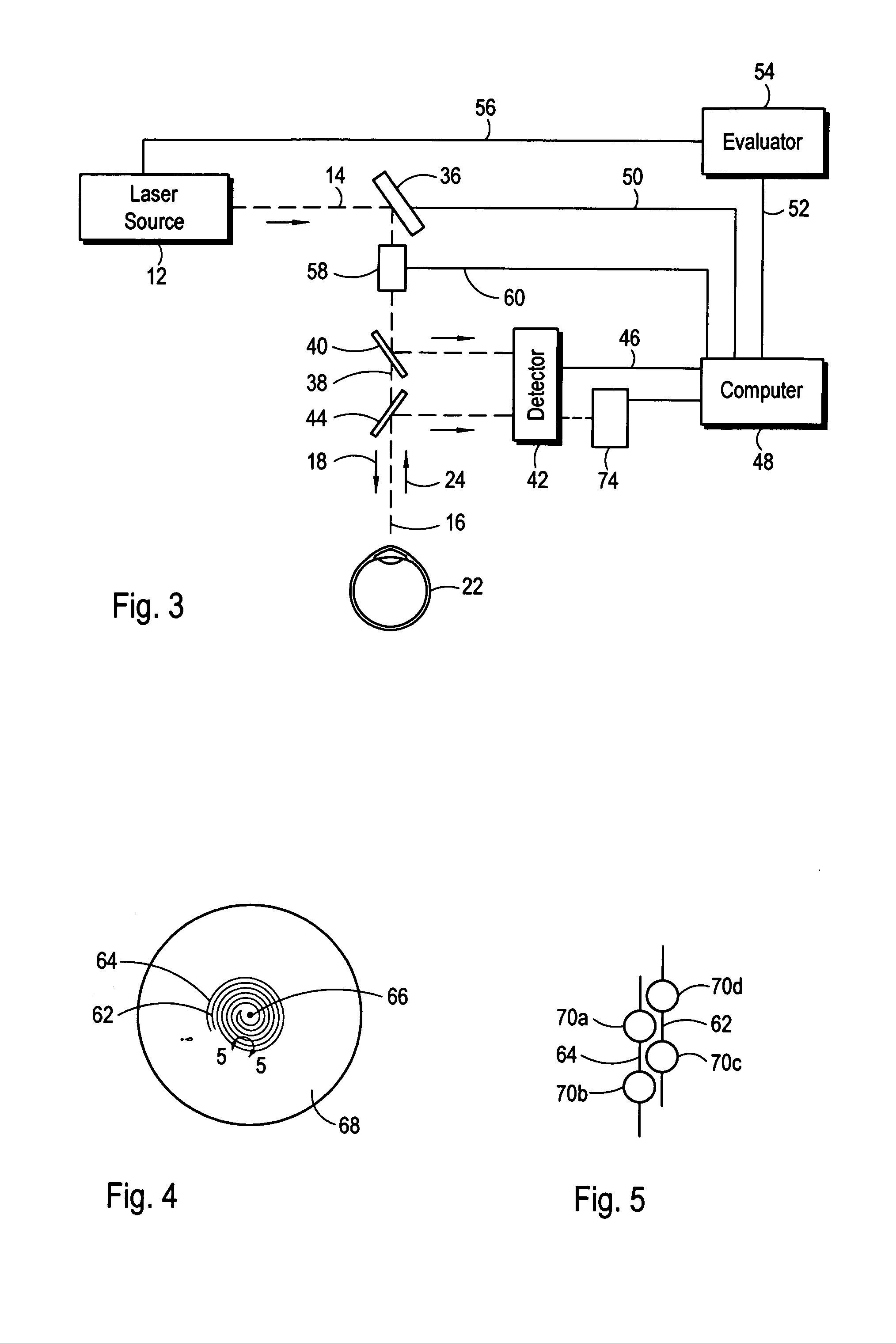
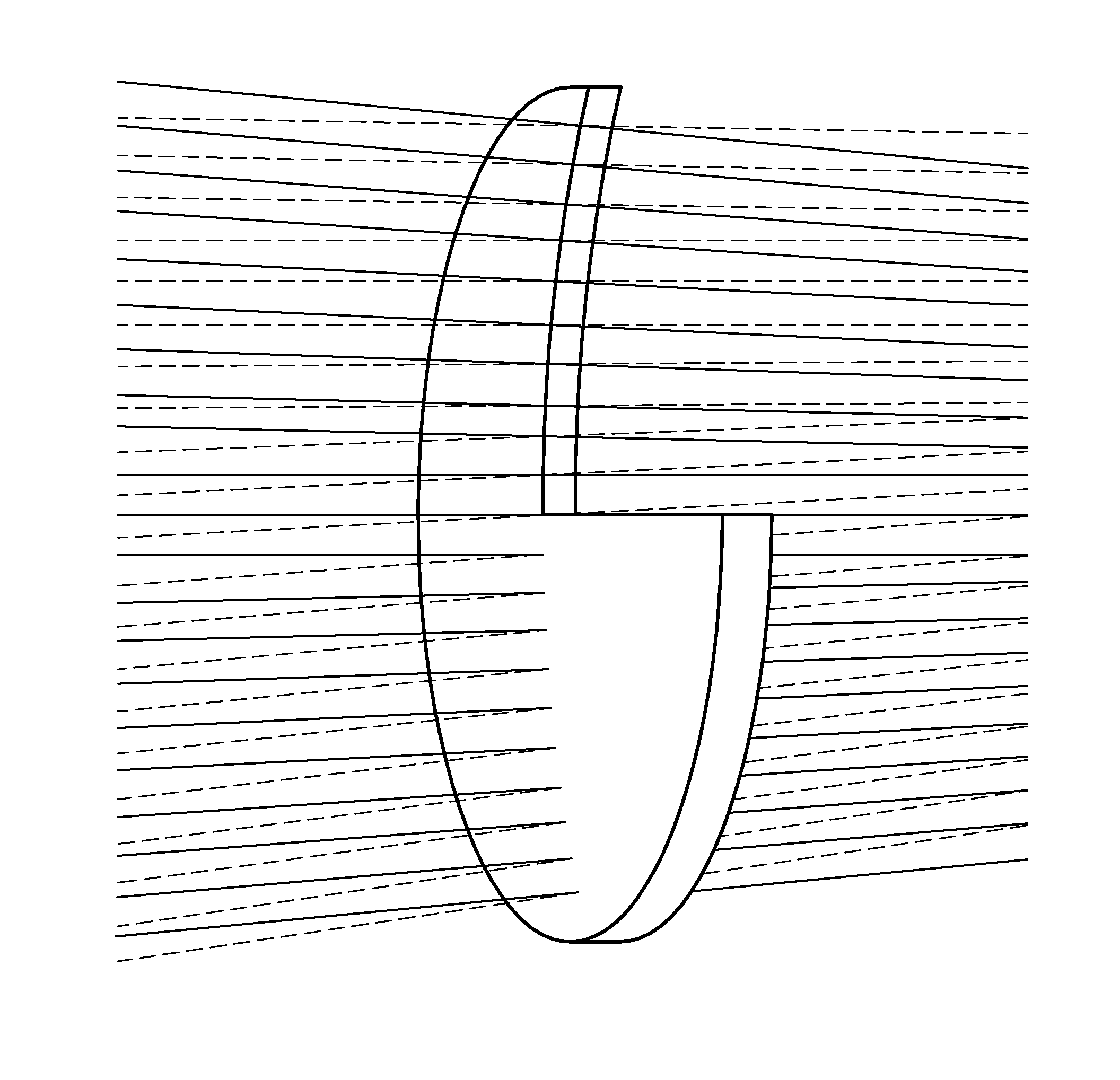
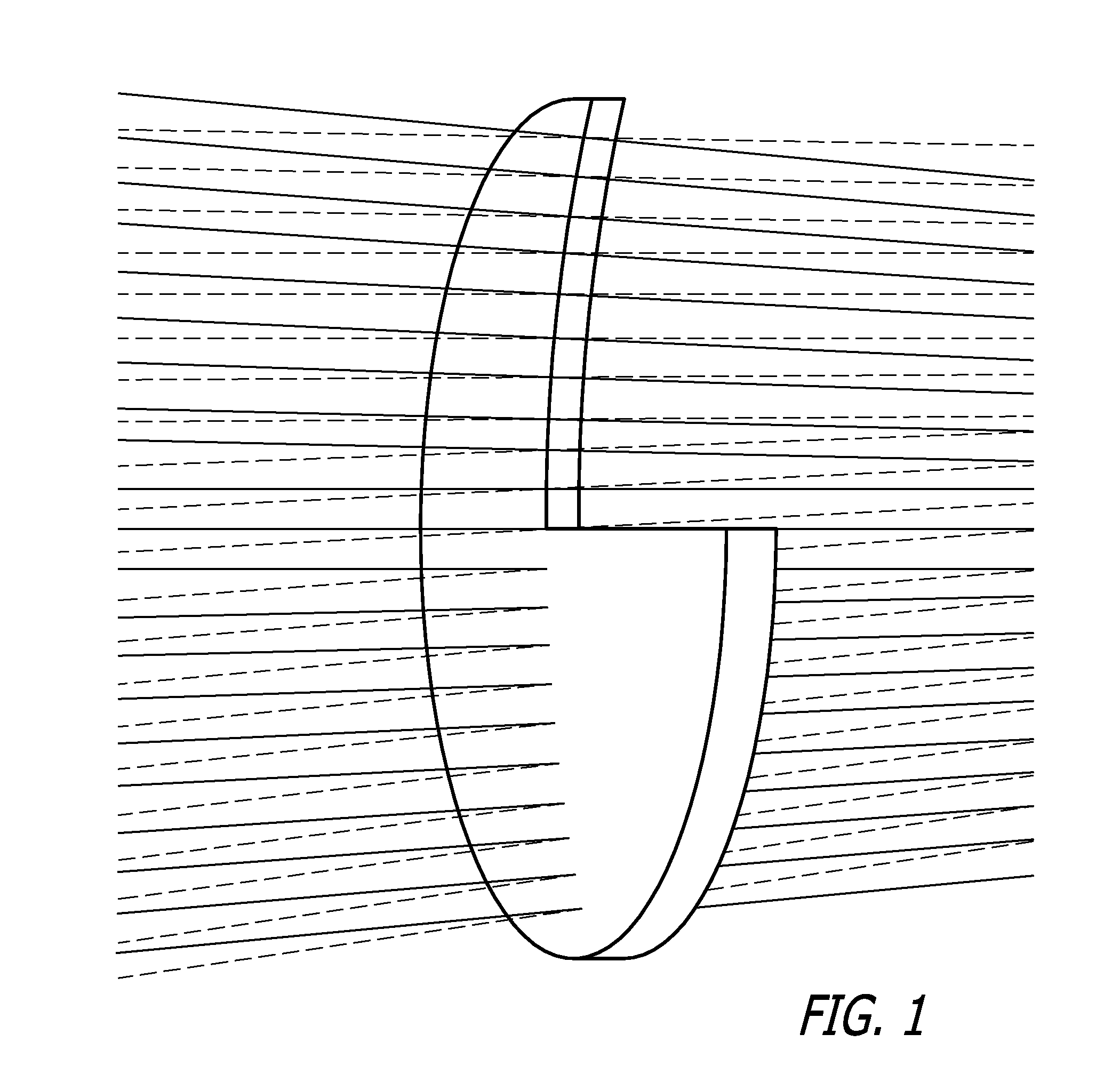
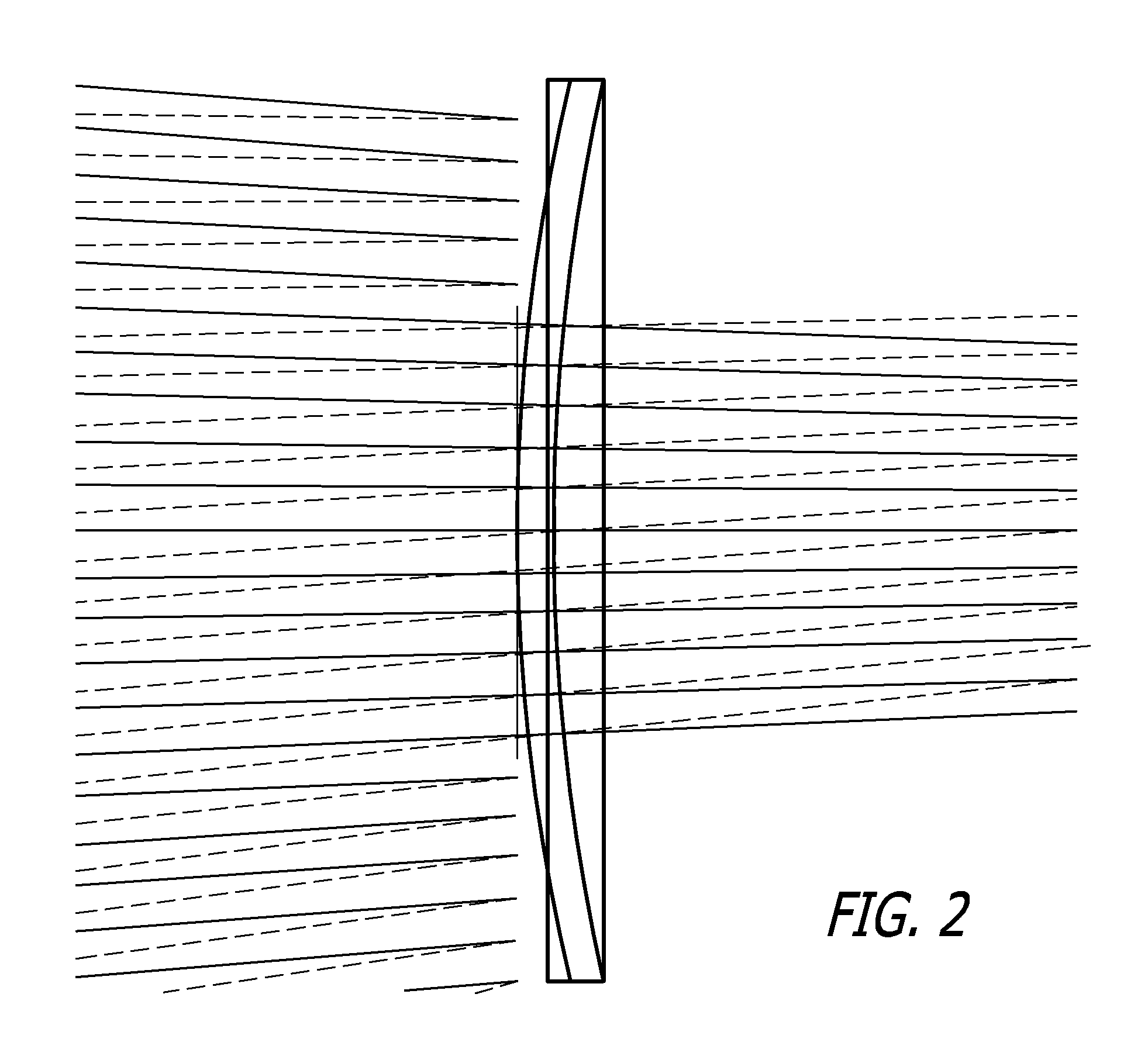
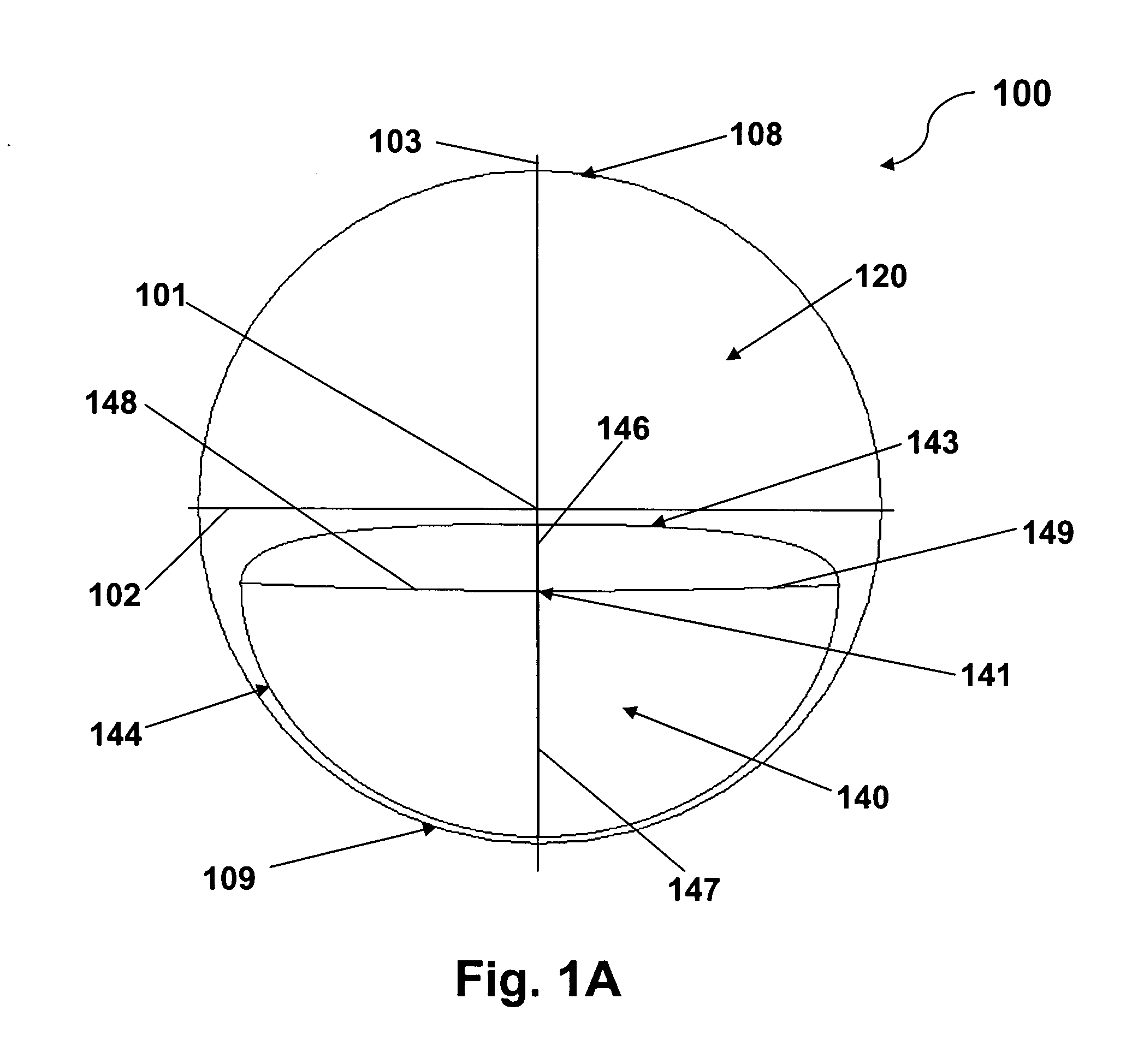
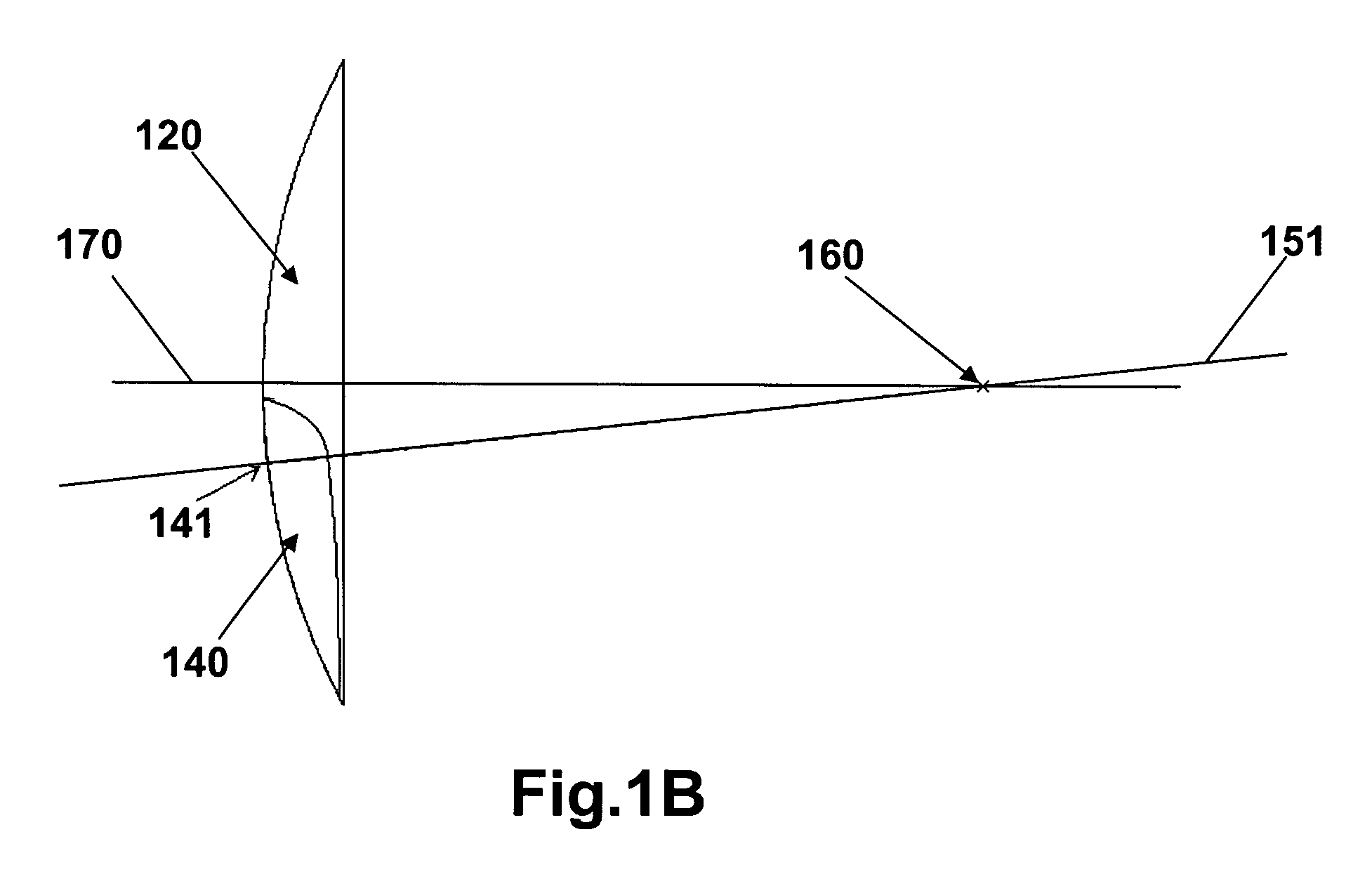
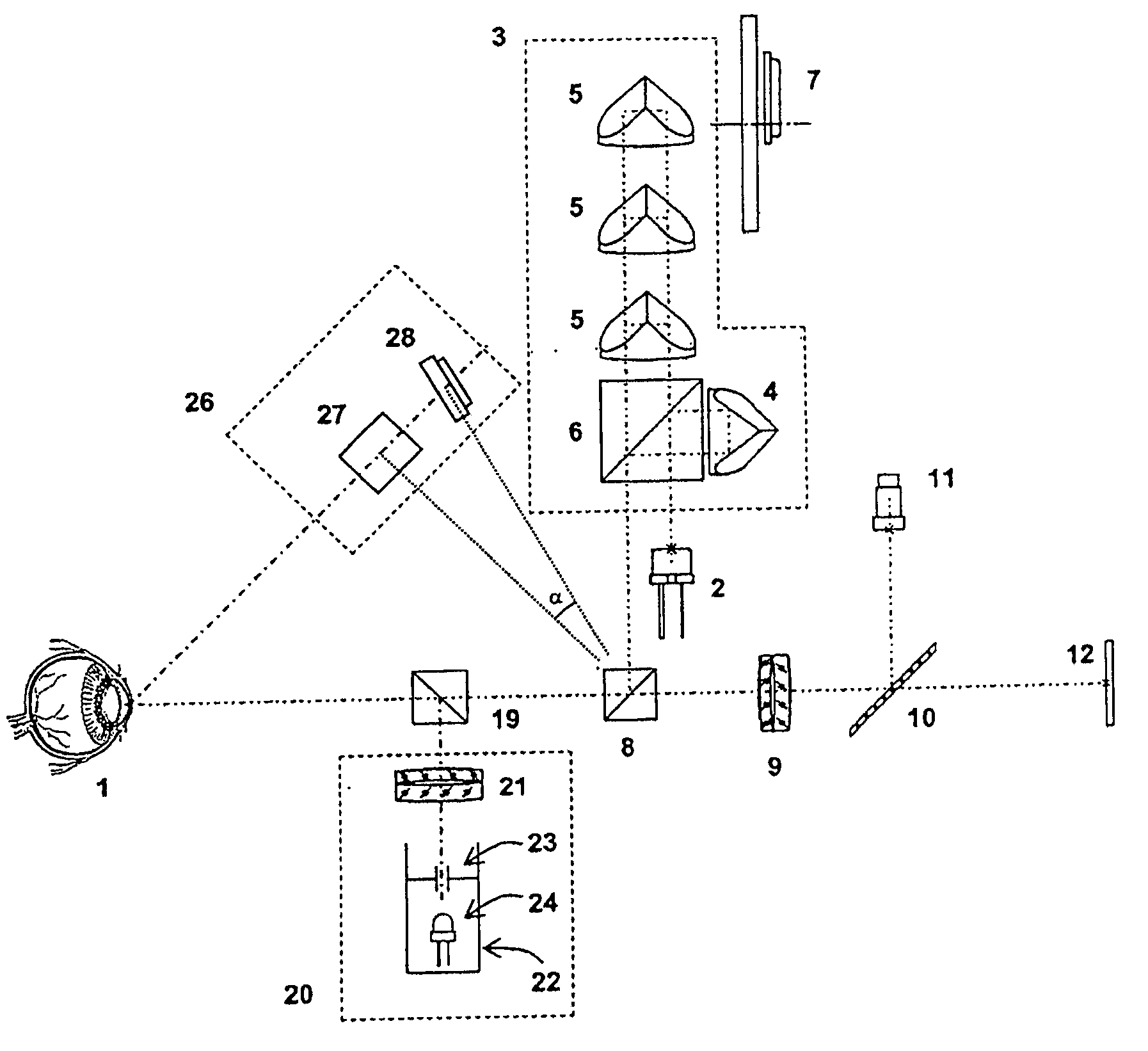
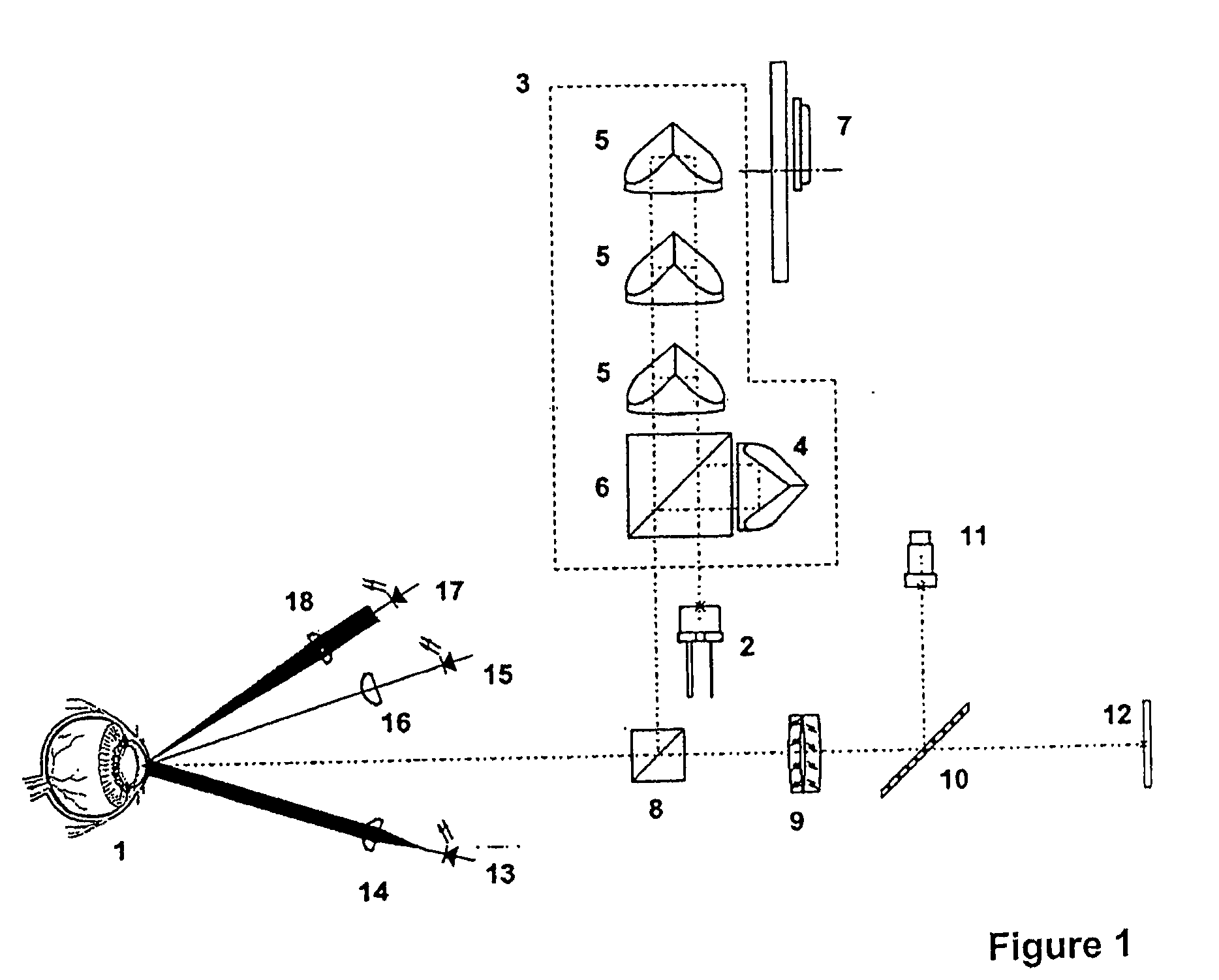
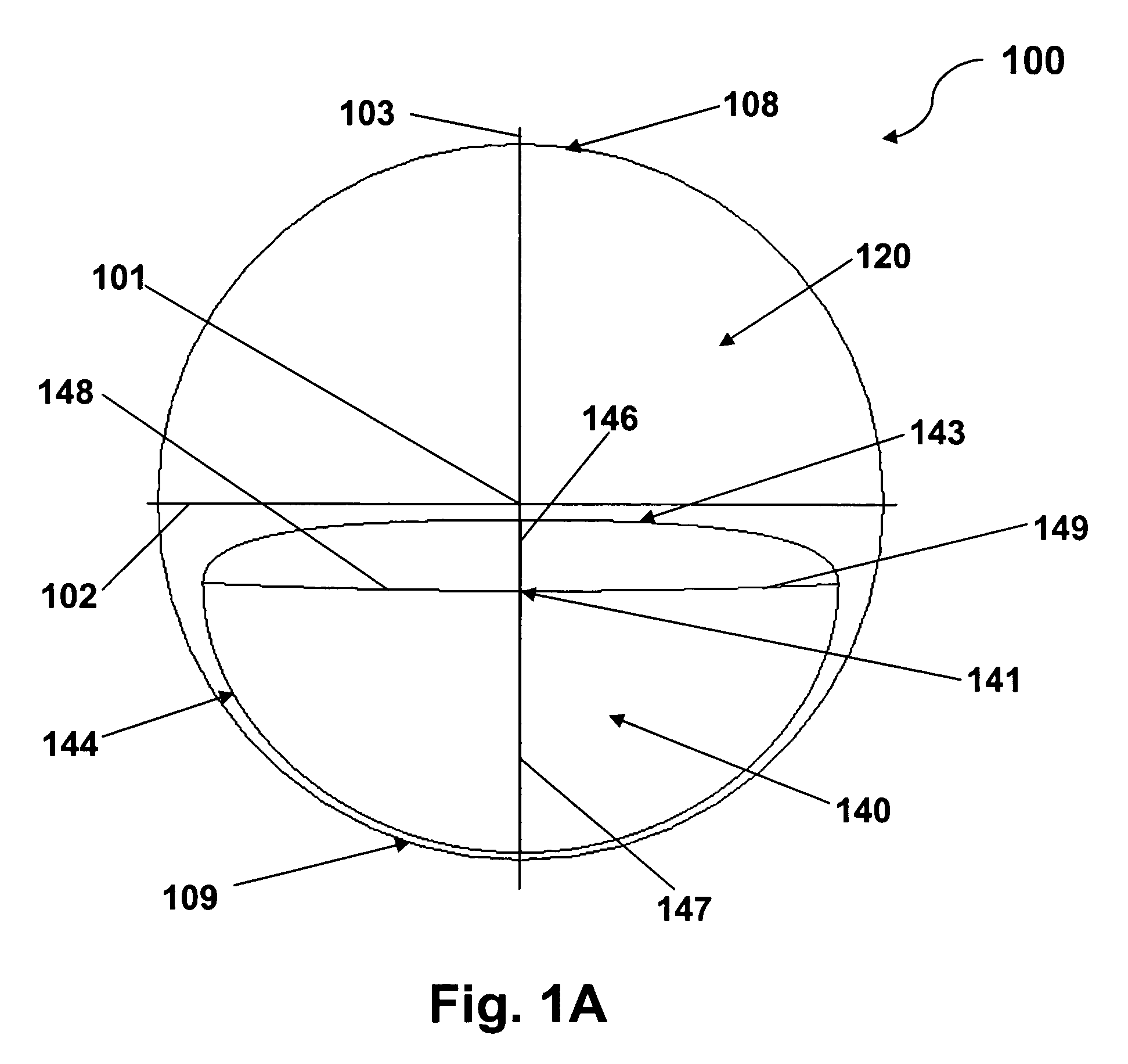
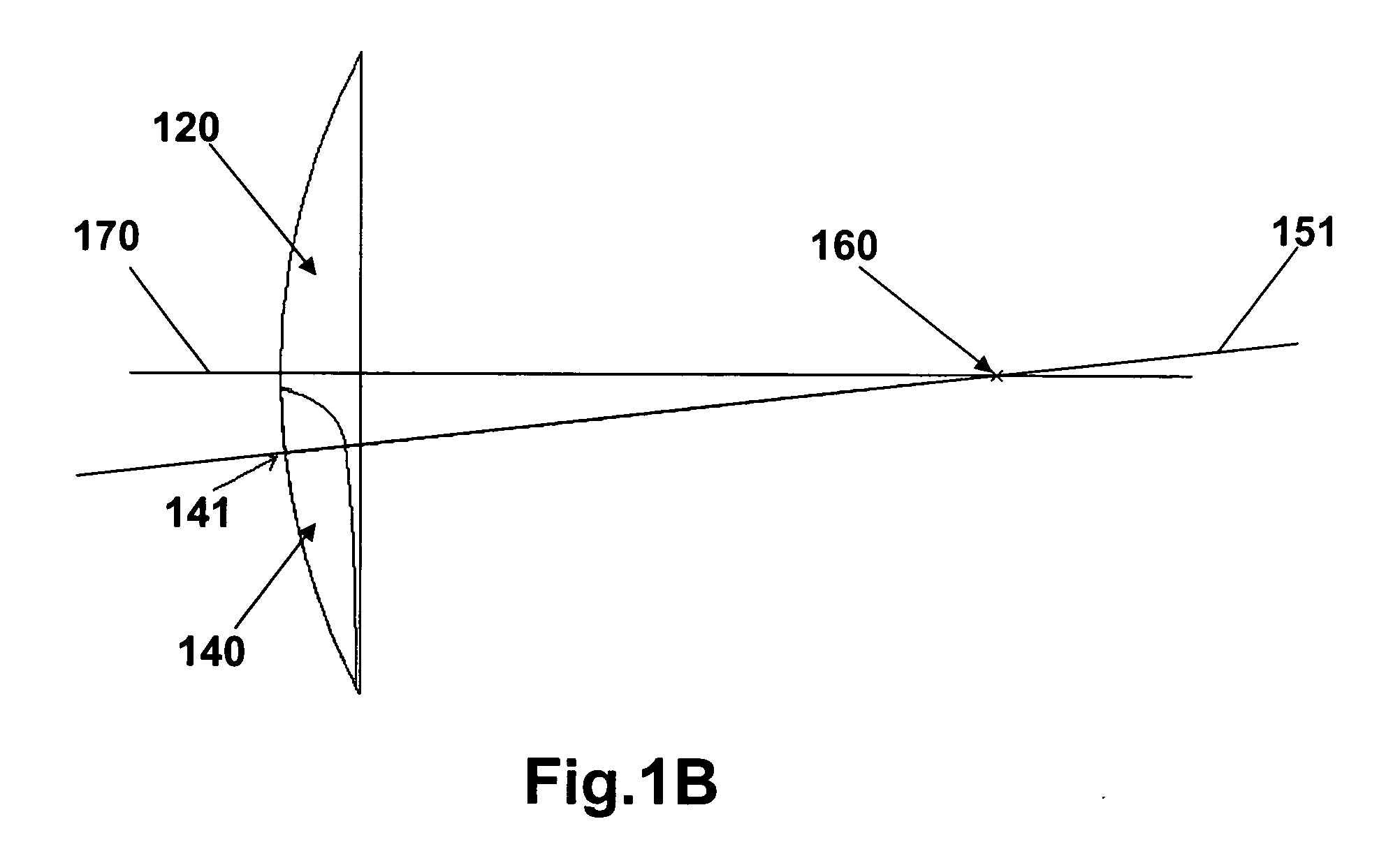
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Keratorefractive surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Keratorefractive surgery. Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus. any procedure in which the shape of the cornea is modified, with the intent of changing the refractive error of the eye; for example, if the cornea is flattened, the eye becomes less myopic.
Presbyopia correction through negative high-order spherical aberration
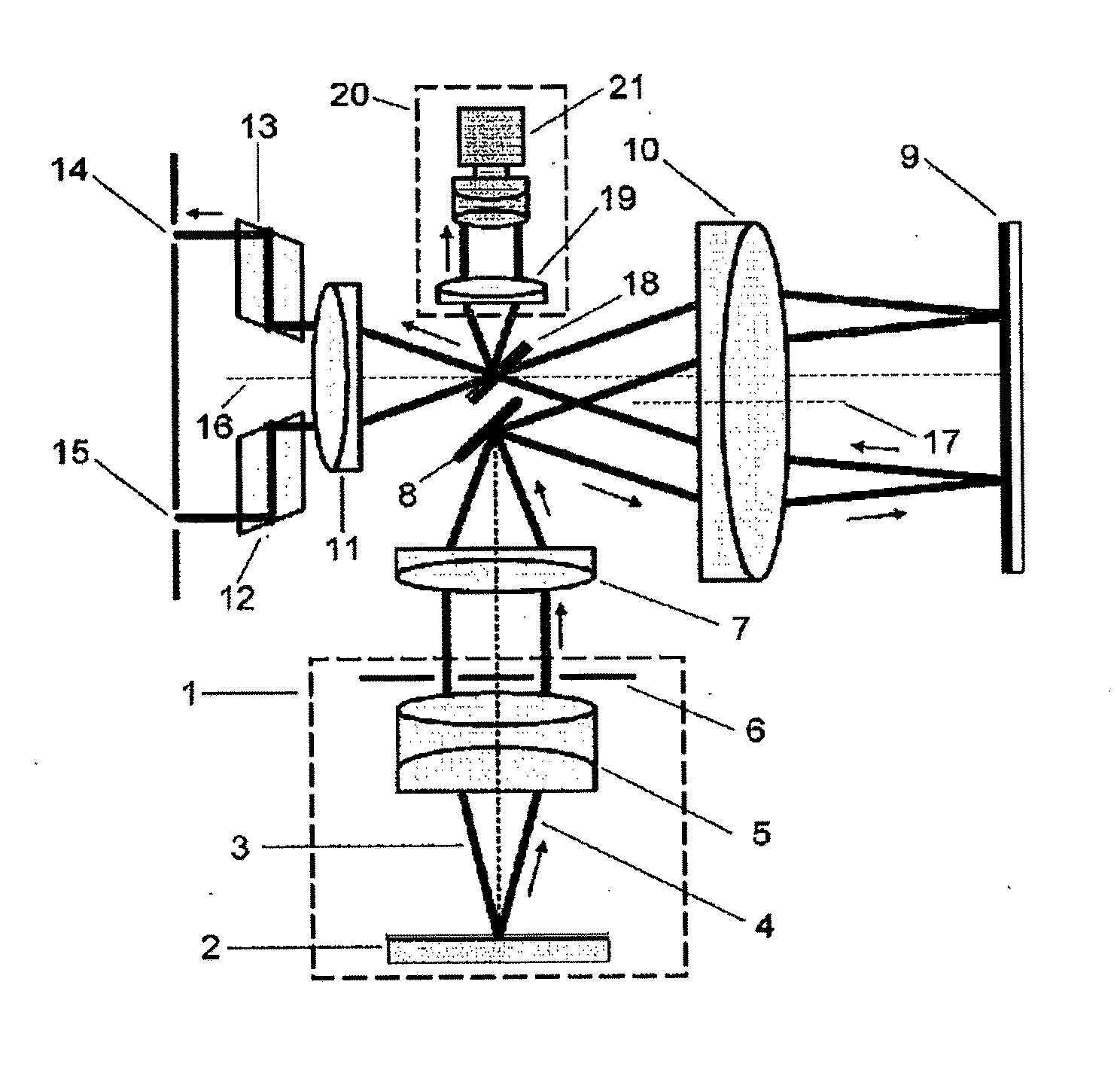
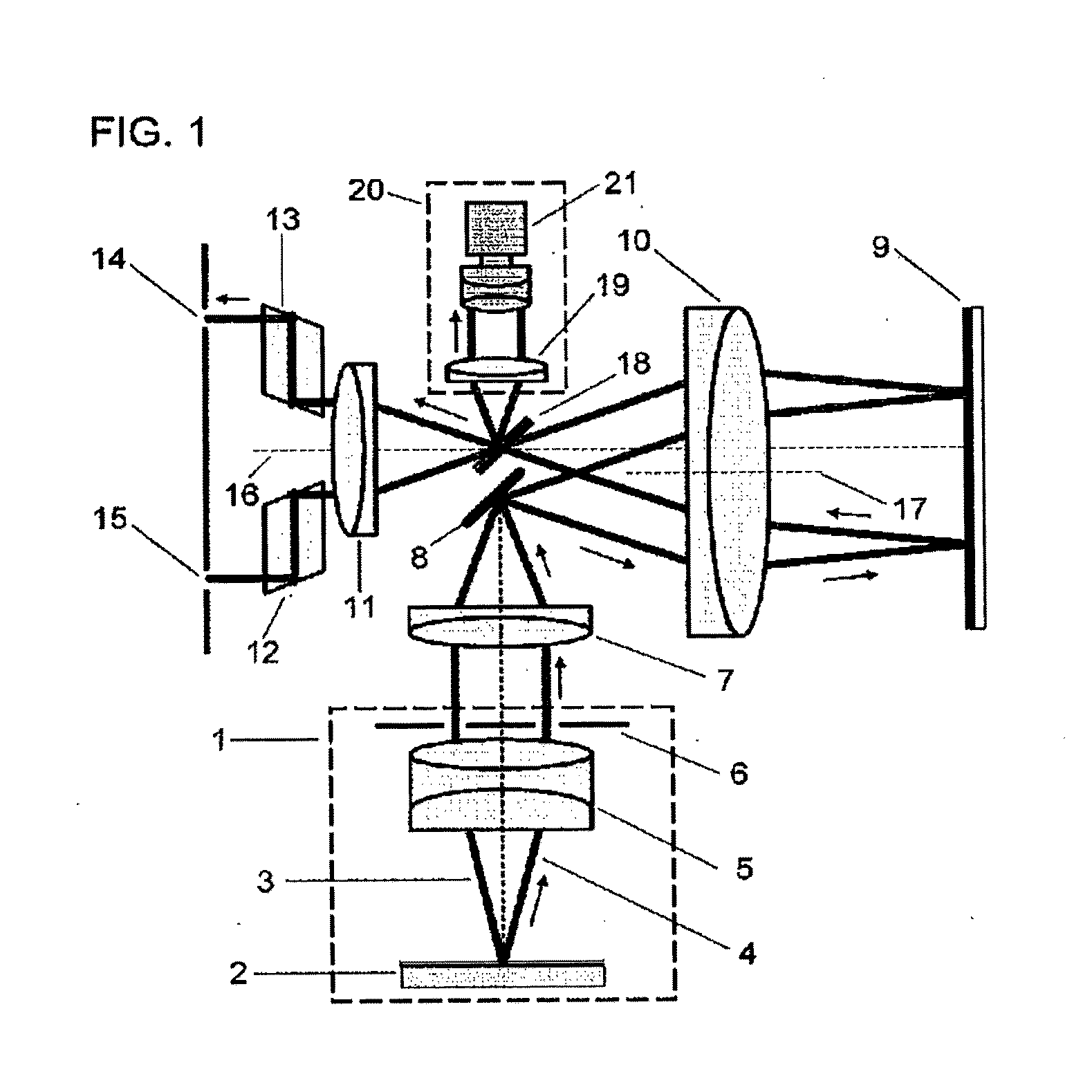
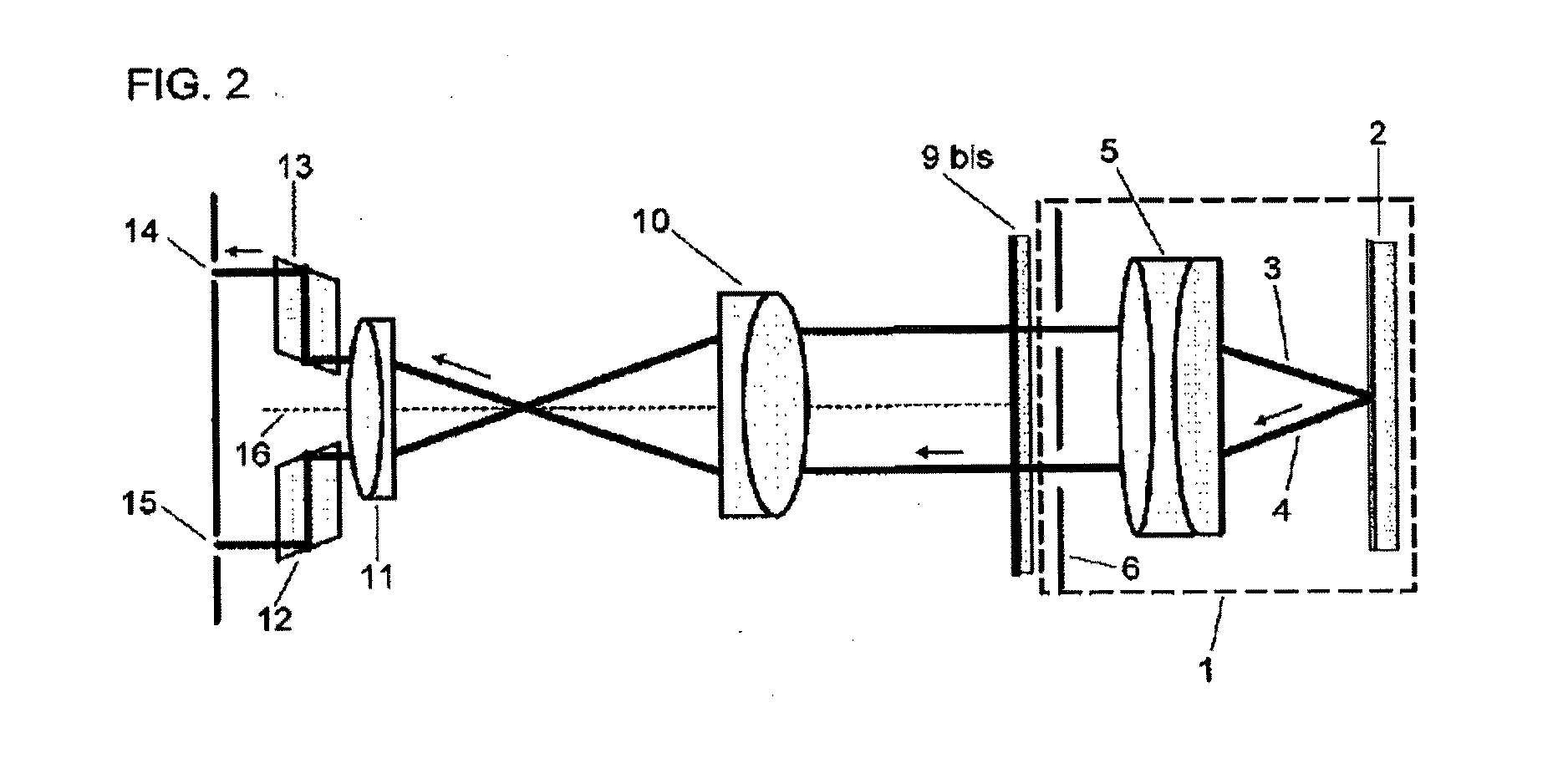
ActiveUS7261412B2Image formed be moreClear imagingSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryKeratorefractive surgeryIntraocular pressure
Devices, systems, and methods for treating and / or determining appropriate prescriptions for one or both eyes of a patient are particularly well-suited for addressing presbyopia, often in combination with concurrent treatments of other vision defects. High-order spherical aberration may be imposed in one or both of a patient's eyes, often as a controlled amount of negative spherical aberration extending across a pupil. A desired presbyopia-mitigating quantity of high-order spherical aberration may be defined by one or more spherical Zernike coefficients, which may be combined with Zernike coefficients generated from a wavefront aberrometer. The resulting prescription can be imposed using refractive surgical techniques such as laser eye surgery, using intraocular lenses and other implanted structures, using contact lenses, using temporary or permanent corneal reshaping techniques, and / or the like.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Shielded intraocular probe for improved illumination or therapeutic application of light
ActiveUS20050245916A1Diminishes unwanted glareLaser surgeryEndoscopesKeratorefractive surgeryForceps
An intraocular light probe has a mask or shield affixed at its distal end thereof which forms a directed light beam for intraocular illumination of target tissues or intraocular application of therapeutic light. The mask or shield serves to more fully focus, intensify and direct the beam toward the target tissues. The mask or shield also helps direct light away from other tissues and away from the eyes of the surgeon. This lessens unwanted glare. By placing a light probe beneath a surgical instrument such as a phacoemulsifier or vitrector, laser, cutting instrument (e.g., scissors or knife), forceps or probe / manipulator, whether as part of or separate from an infusion sleeve, a mask or shield effect is created. This has the same benefits of directing the beam toward target tissues, away from other tissues and away from the eyes of the surgeon. The mask or shield is opaque or semi-opaque and made of a soft, semi-rigid or rigid material. The shield can be rigid enough to serve as the shaft of an instrument with a probe or manipulator at its distal tip. It may also be reflective on the side adjacent to the fiber bundle to help direct, magnify, and intensify the beam of light. The shape of the shield can be flat, curved or circular with an opening along one side. The mask / shield can be removed from the fiberoptic light for sterilization. The device of the invention is preferably introduced into the eye via the primary or side-port incision to provide intraocular cross-lighting of tissues during surgical procedures such as cataract surgery, corneal surgery, vitrectomy, intraocular lens implantation, refractive surgery, glaucoma surgery and vitreo / retinal surgery.
Owner:CONNOR CHRISTOPHER S
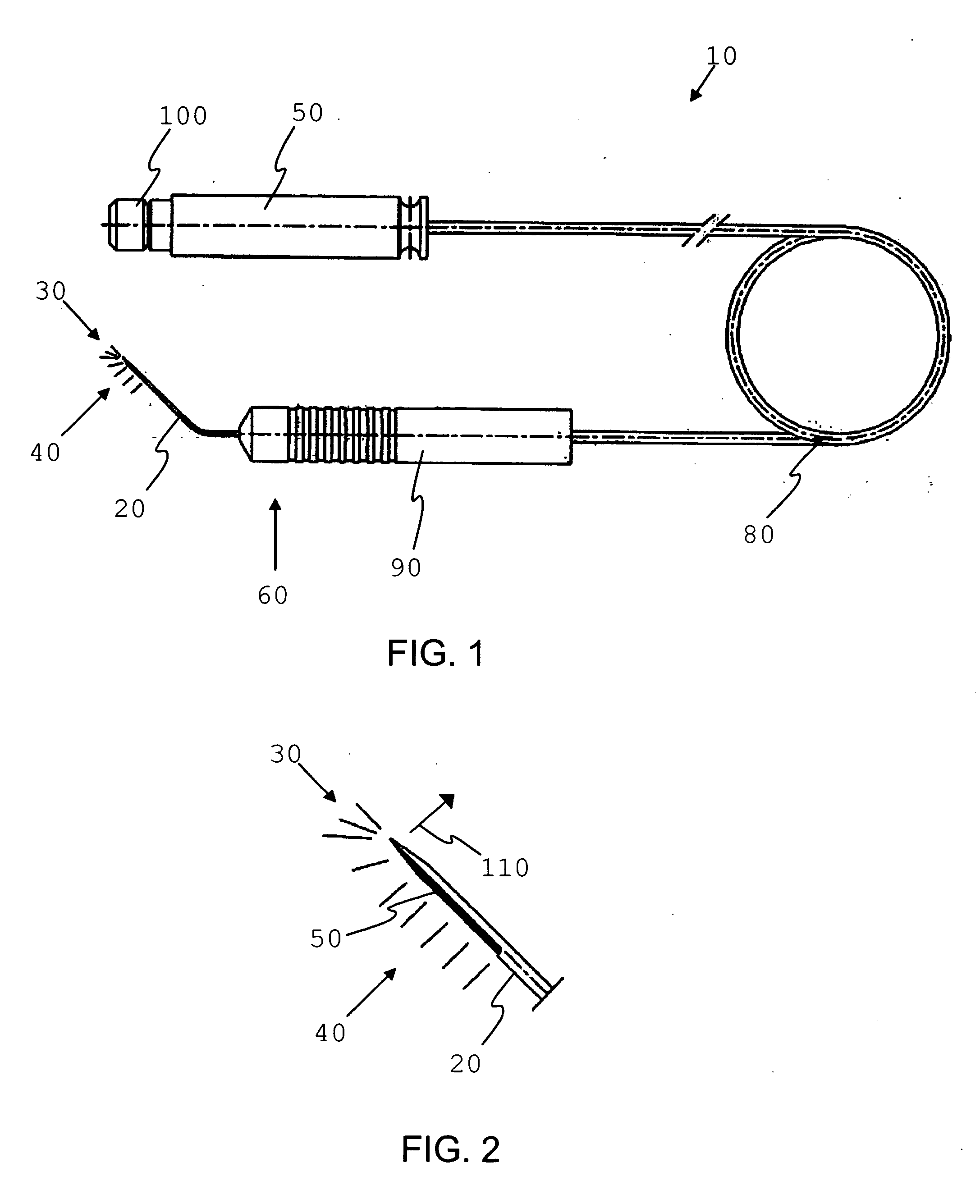
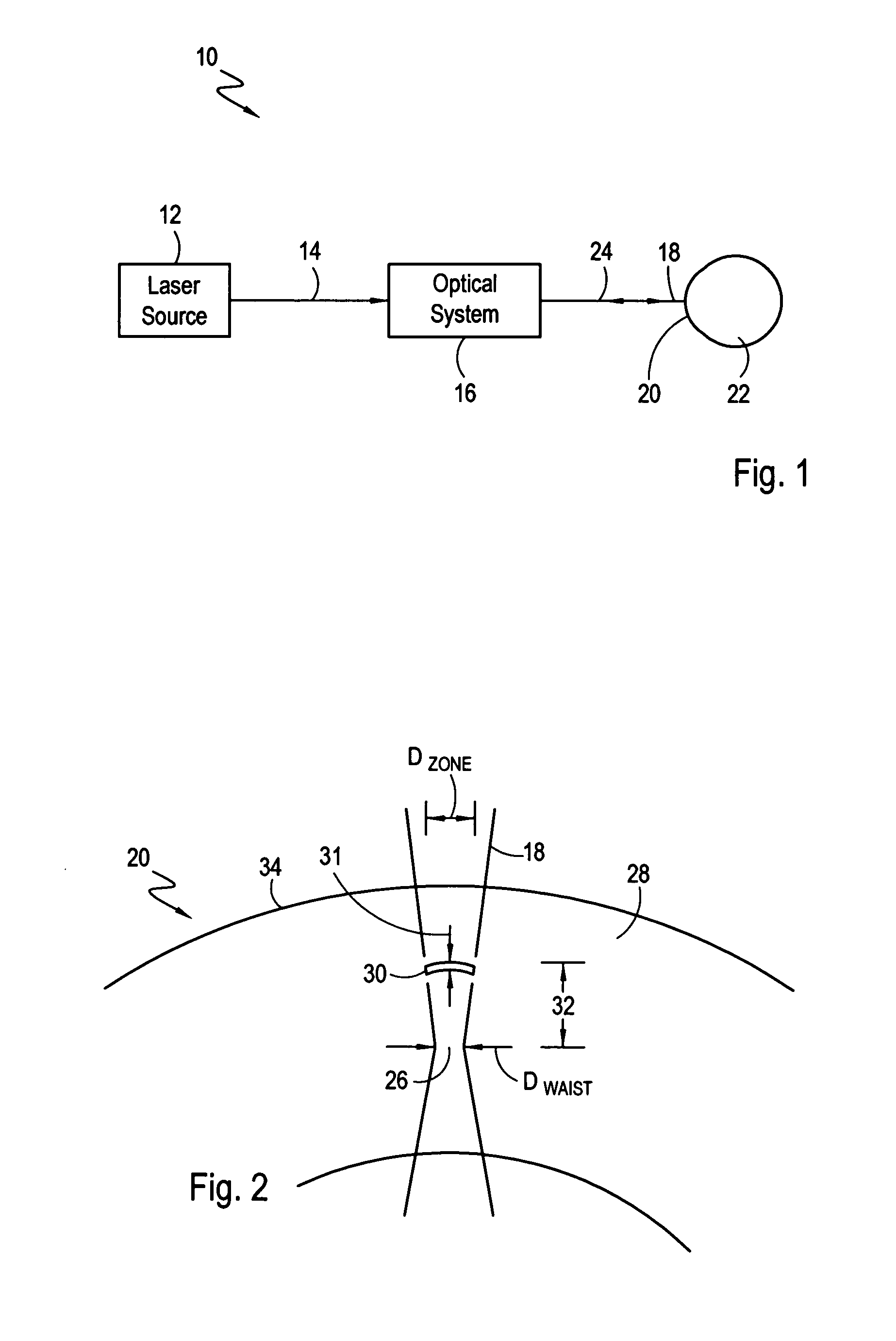
Method and apparatus for intrastromal refractive surgery
InactiveUS7101364B2Minimize heat damageFast ablationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsKeratorefractive surgeryPulse energy
A method and apparatus for intrastromal refractive surgery is disclosed wherein tissue at selected locations within the stroma of the cornea is photoablated using a pulsed laser beam. The apparatus includes an optical system for forming a shaped laser beam having a waist at a predetermined distance from the optical system. The pulse duration and pulse energy of the laser beam are selected to cause ablation to occur in front of the waist (i.e. between the waist and the optical system). To achieve this, a pulse energy is used that exceeds the minimum pulse energy required for ablation at the waist. By ablating in front of the waist, a relatively large ablation zone (per pulse) is created (compared to ablation at the waist). Furthermore, while the laser is scanned through the cornea to effectuate a refractive change, the optical system maintains a uniform waist for the laser beam.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Free-form progressive multifocal refractive lens for cataract and refractive surgery
InactiveUS20140135919A1Improve acuityIncrease distanceIntraocular lensOptical partsPresent dayKeratorefractive surgery
A new type of multi-focal lens that has a free-form progressive multifocal front surface consisting of a 16th order polynomial superimposed on a standard conic base surface is described. The center region of the lens is optimized for distance vision, while simultaneously optimizing the rest of the lens for near vision. The resulting free-form even asphere polynomial surface is smooth, unlike present day diffractive multifocal designs. Additionally, this lens design is suitable for both refractive and cataract surgeries.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
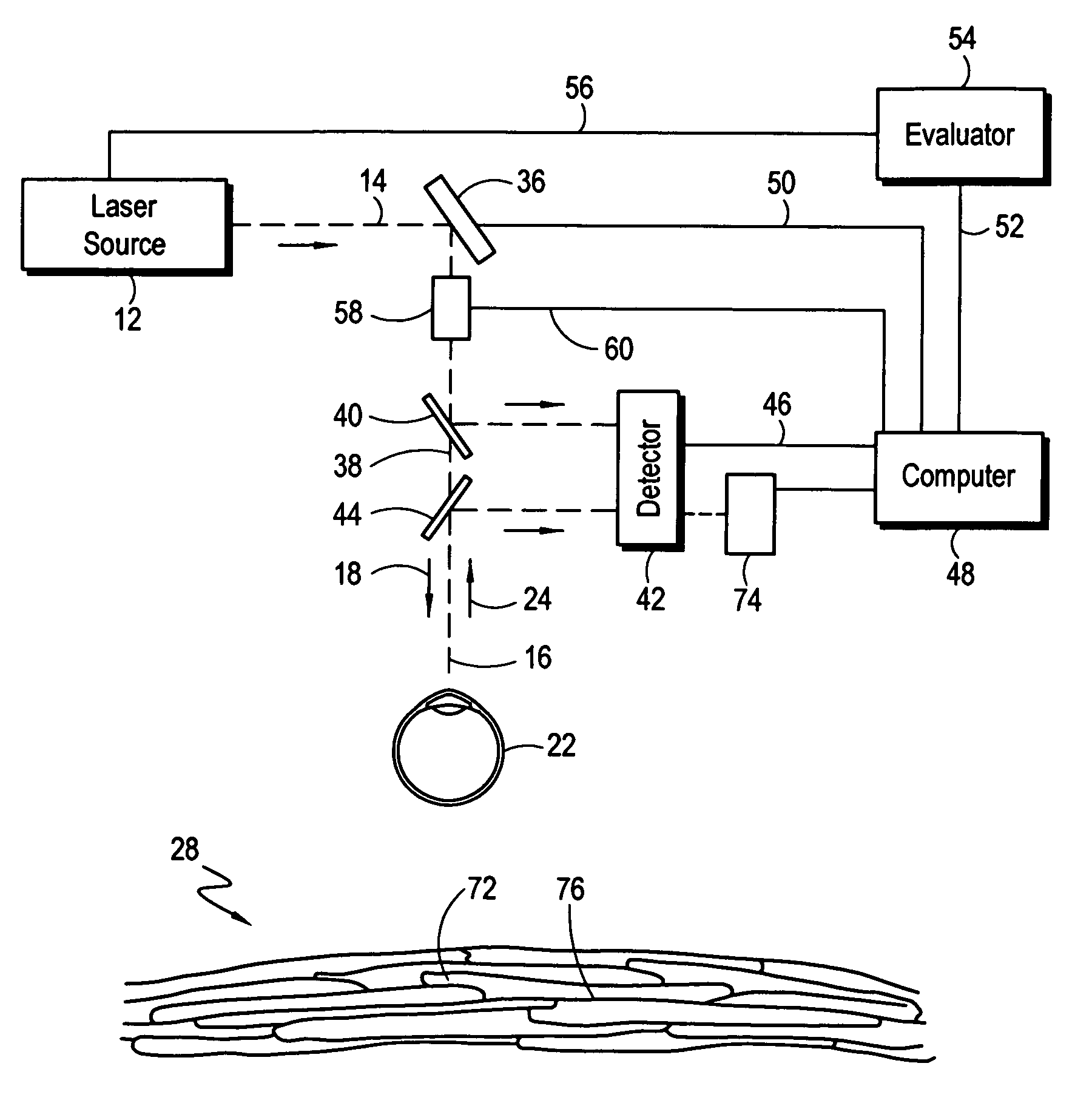
Method and apparatus for correcting off-center laser ablations in refractive surgery
InactiveUS6951556B2Uniform optical correctionAccurate centerLaser surgeryDiagnosticsKeratorefractive surgeryLaser beams
A novel method and apparatus are provided for correcting an off-center laser ablation in the cornea, in which the original ablated area has a center that is offset from the correct center of the optical cornea. The method comprises the steps of determining the correct optical center of the cornea and the offset location of the ablation; performing a supplemental laser ablation on the cornea with the laser beam covering generally the original ablated area, and with the energy of the supplemental laser increasing in a direction from the offset center toward the correct center; introducing a laser shield to cover the entire original ablated area; and performing another laser ablation with the correct optical center as the center of the ablated area.
Owner:EPSTEIN ROBERT L
Multifocal opthalmic lens
This invention is generally related to vision corrections by means of multifocal ophthalmic lenses or by means of corneal refractive surgery. In particular, the present invention provides a multifocal contact lens, a multifocal intraocular lens, a method for making a multifocal ophthalmic lens (contact lens and intraocular lens), and a method of correcting presbyopia by reshaping the cornea of an eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Device and Method for Axial Length Measurement Having Expanded Measuring Function in the Anterior Eye Segment
InactiveUS20100271594A1Accurate calculationImprove accuracyUsing optical meansGonioscopesKeratorefractive surgeryCorneal surface
The present invention is directed to a solution for measuring geometric parameters in the eye which are required for calculating the refractive power of intraocular lenses. The device according to the invention for axial length measurement which acquires axial length, anterior corneal radii, anterior chamber depth, and other parameters in the anterior eye segment includes a control unit, a first measuring device for determining axial length, and an additional measuring device which acquires a plurality of structures in the anterior segment (such as the cornea, anterior chamber, and lens) and which has at least one illumination unit and at least one image recording unit. By determining additional partial-distance parameters of the anterior eye segments, the IOL can be calculated with high precision even after refractive surgery in which the natural relationship between the radii of the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces is extensively altered by corneal surgery.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Electronic eye marking/registration
InactiveUS20140125949A1Improve astigmatism correction/neutralization outcomePromote resultsRefractometersSkiascopesRefractive errorKeratorefractive surgery
One embodiment is a method for finding, calculating and electronically marking a reference axis for astigmatism correction / neutralization of a patient eye during a refractive surgery.The reference axis for astigmatism correction / neutralization can be determined intra-operatively based on one or more eye property measurements together with simultaneous recording a live eye image. The determined reference axis of astigmatism correction / neutralization can be updated and registered with one or more land mark(s) of the recorded eye image(s); and overlaid onto a live image of the eye. Another embodiment is a method of calculating and displaying in real time compensated refractive errors of the eye under operation with refractive components due to temporary surgically induced factors removed and refractive components due to surgeon-induced factors added.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Intrastromal refractive surgery by inducing shape change of the cornea
InactiveUS8409177B1Reduce the valueHigh viscosityLaser surgeryEye implantsRefractive errorKeratorefractive surgery
A shape change is induced in a cornea for treating a keratoconus condition, and / or correcting a refractive error and / or a high order aberration. A beam of laser pulses is focused to a stromal layer of a patient's eye, and an intrastromal pocket is ablated. An injection port is cut between the intrastromal pocket and a cornea surface of the eye. A polymerizable fluid is flowed into the intrastromal pocket through the injection port. The fluid is cured to form a polymeric insert, and thereby inducing a cornea shape change.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
This invention is generally related to vision corrections by means of multifocal ophthalmic lenses or by means of corneal refractive surgery. In particular, the present invention provides a multifocal contact lens, a multifocal intraocular lens, a method for making a multifocal ophthalmic lens (contact lens and intraocular lens), and a method of correcting presbyopia by reshaping the cornea of an eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Refractive surgery and presbyopia correction using infrared and ultraviolet lasers
InactiveUSRE40184E1Avoid smooth surfaceImprove distributionLaser surgeryLaser detailsKeratorefractive surgeryFiber
A method and surgical technique for corneal reshaping and for presbyopia correction are provided. The preferred embodiments of the system consists of a scanner, a beam spot controller and coupling fibers and the basic laser having a wavelength of (190-310) nm, (0.5-3.2) microns and (5.6-6.2) microns and a pulse duration of about (10-150) nanoseconds, (10-500) microseconds and true continuous wave. New mid-infrared gas lasers are provided for the corneal reshaping procedures. Presbyopia is treated by a method which uses ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue and increase the accommodation of the ciliary body. The tissue bleeding is prevented by a dual-beam system having ablative and coagulation lasers. The preferred embodiments include short pulse ablative lasers (pulse duration less than 200 microseconds) with wavelength range of (0.15-3.2) microns and the long pulse (longer than 200 microseconds) coagulative lasers at (0.5-10.6) microns. Compact diode lasers of (980-2100) nm and diode-pumped solid state laser at about 2.9 microns for radial ablation patterns on the sclera ciliary body of a cornea are also disclosed for presbyopia correction using the mechanism of sclera expansion.
Owner:SURGILIGHT
Method of Refraction Surgery of the Eye and a Tool for Implanting Intraocular Refractive Lens
InactiveUS20100057095A1Avoiding lens damage dangerLower Level RequirementsEye surgeryIntraocular lensKeratorefractive surgeryEllipse
A reduction of eye trauma is achieved during opthalmolic surgery branch for implanting the intraocular refractive lens to the anterior chamber of the eye. The pupil is extended by mydriatic compounds and after anesthesia the cornea cut is made (clear cornea—3 mm). Thereafter, the anterior chamber of the eye is filled with viscoelastic compound with low molecular weight and then the refractive lens is implanted with the help of said cannula, the working face of the cannula at the middle between the lens edge and the border of the optic area, with the edge bent on the cannula face. The end by the top of the bending the refractive lens is introduced into the cornea cut and set in the posterior chamber of the eye. Thereafter, vacuum is removed and the cannula is detached from the refractive lens, and taken off the anterior chamber of the eye by the reverse movement. The refractive lens cannula is made as a tube with round or oval cross-section with inner diameter 0.5-2.5 mm and wall thickness not less than 0.05 mm. The tube is bent at 110-160, supplied with limiter, and working end that has diameter of the round cross-section of 1.0-2.0 mm or ellipse-shaped cross-section with small and big axes 0.6-0.9 mm and 1.5-2.5 mm, respectively.
Owner:LEONID ORBACHEVSKY
Device for dissecting an eye for the introduction of photosensitizer and method of refractive surgery
InactiveUS20130310728A1High densityLow densityLaser surgeryElectrotherapyKeratorefractive surgeryPhotosensitizer
A device for dissecting an eye for the introduction of photosensitizer into the cornea where laser radiation is focused in the interior of the cornea to create cavitation bubbles, whereby channels are created in the cornea through which the photosensitizer can be introduced into the cornea. Furthermore, a method for refractive surgery includes utilizing a sensitizer for hardening corneal tissue by cross-linking.
Owner:WAVELIGHT AG
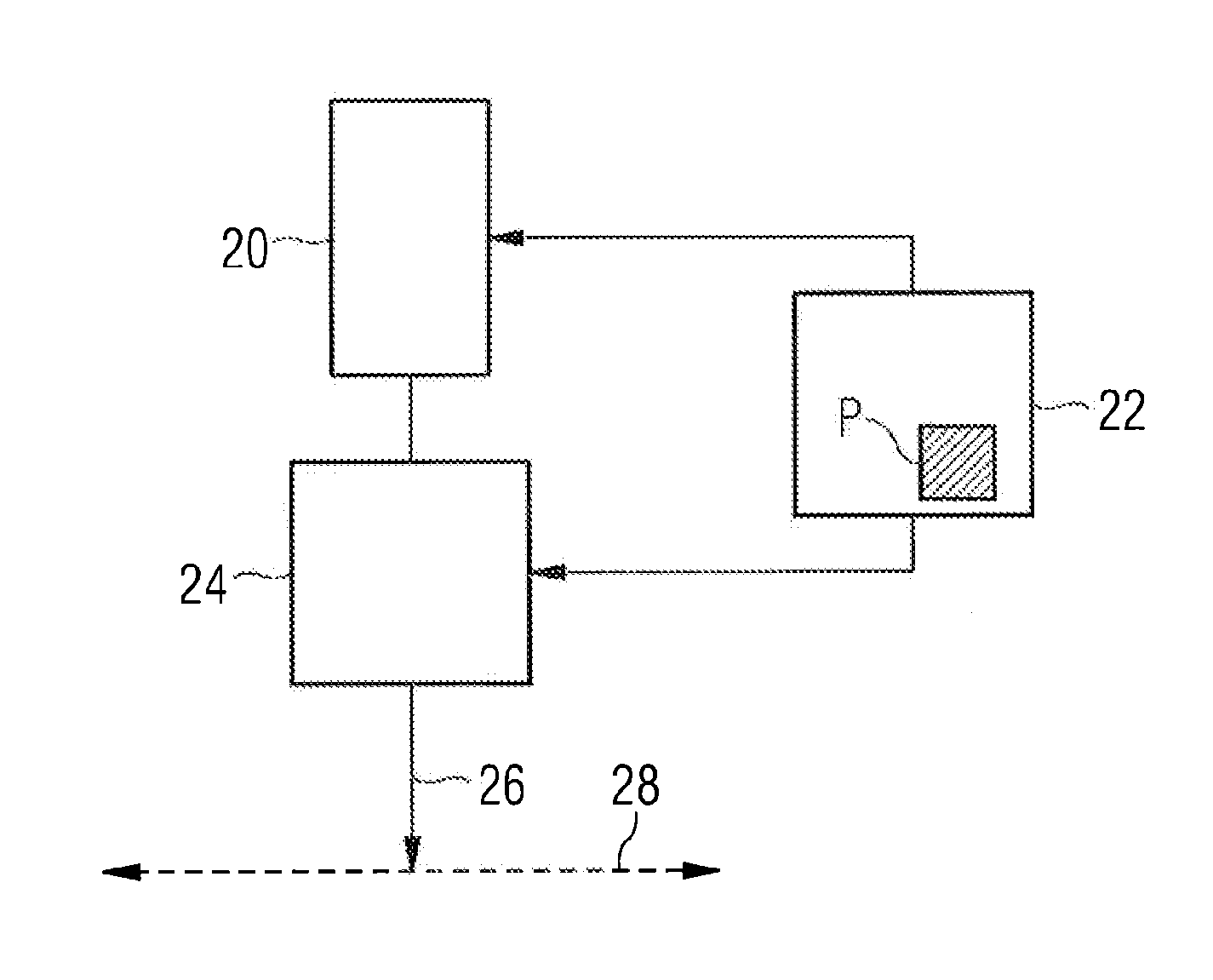
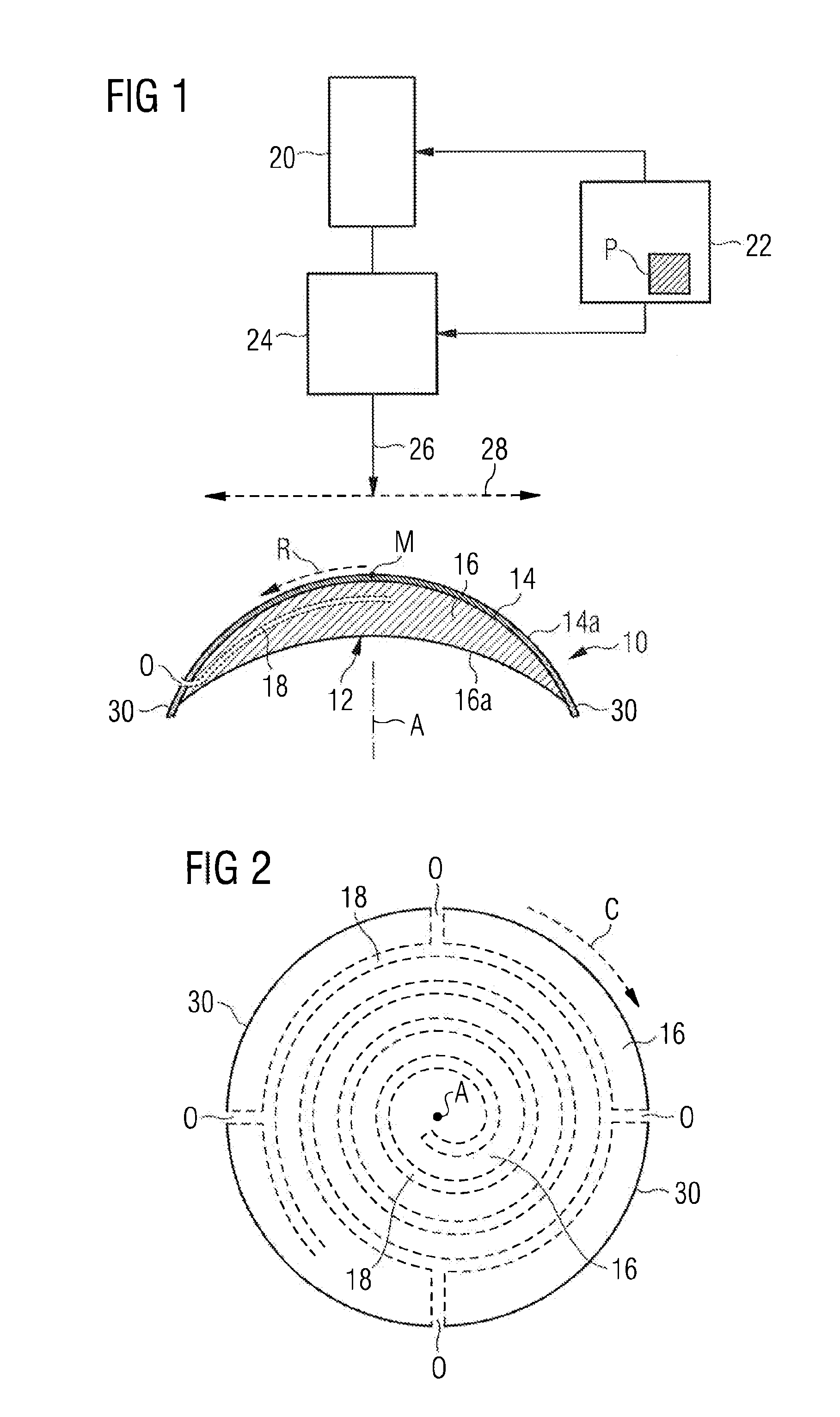
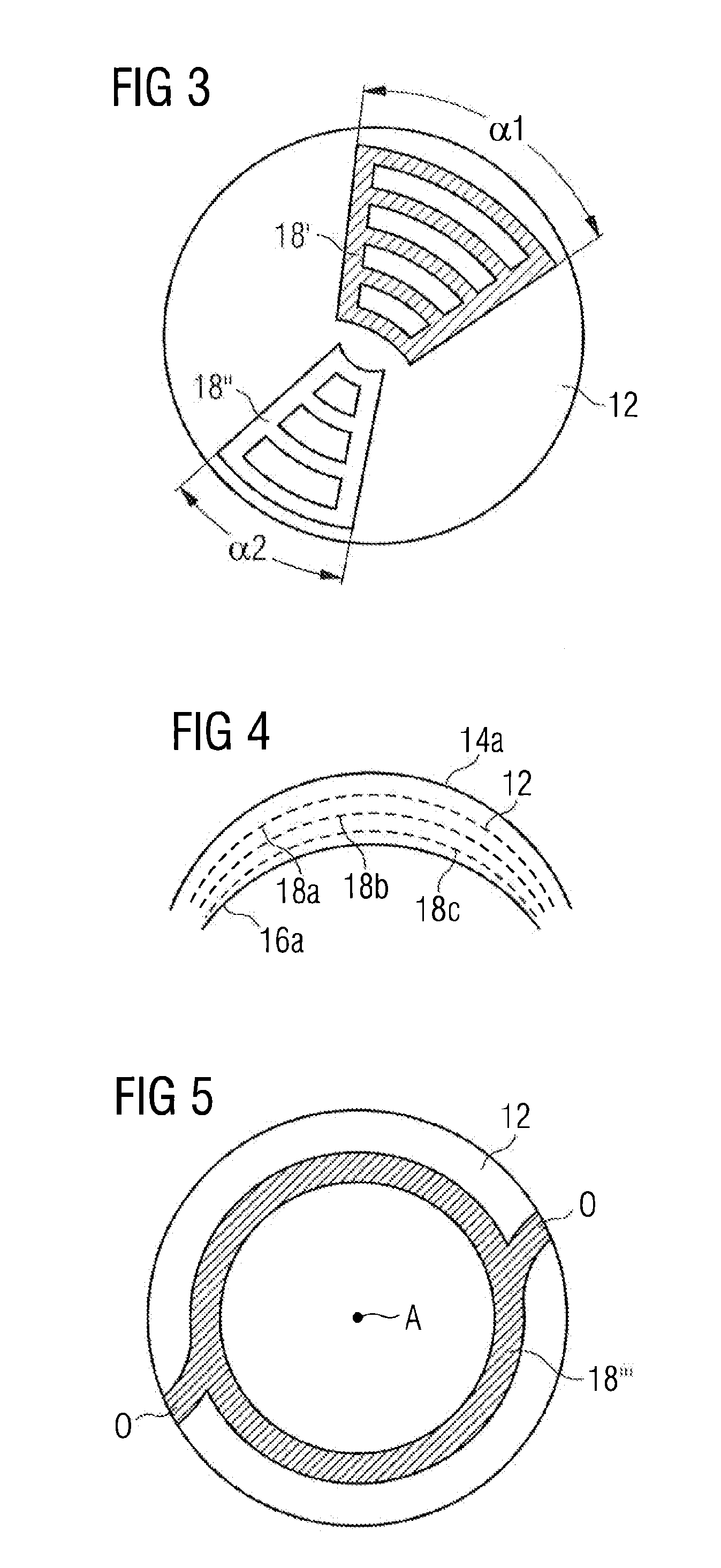
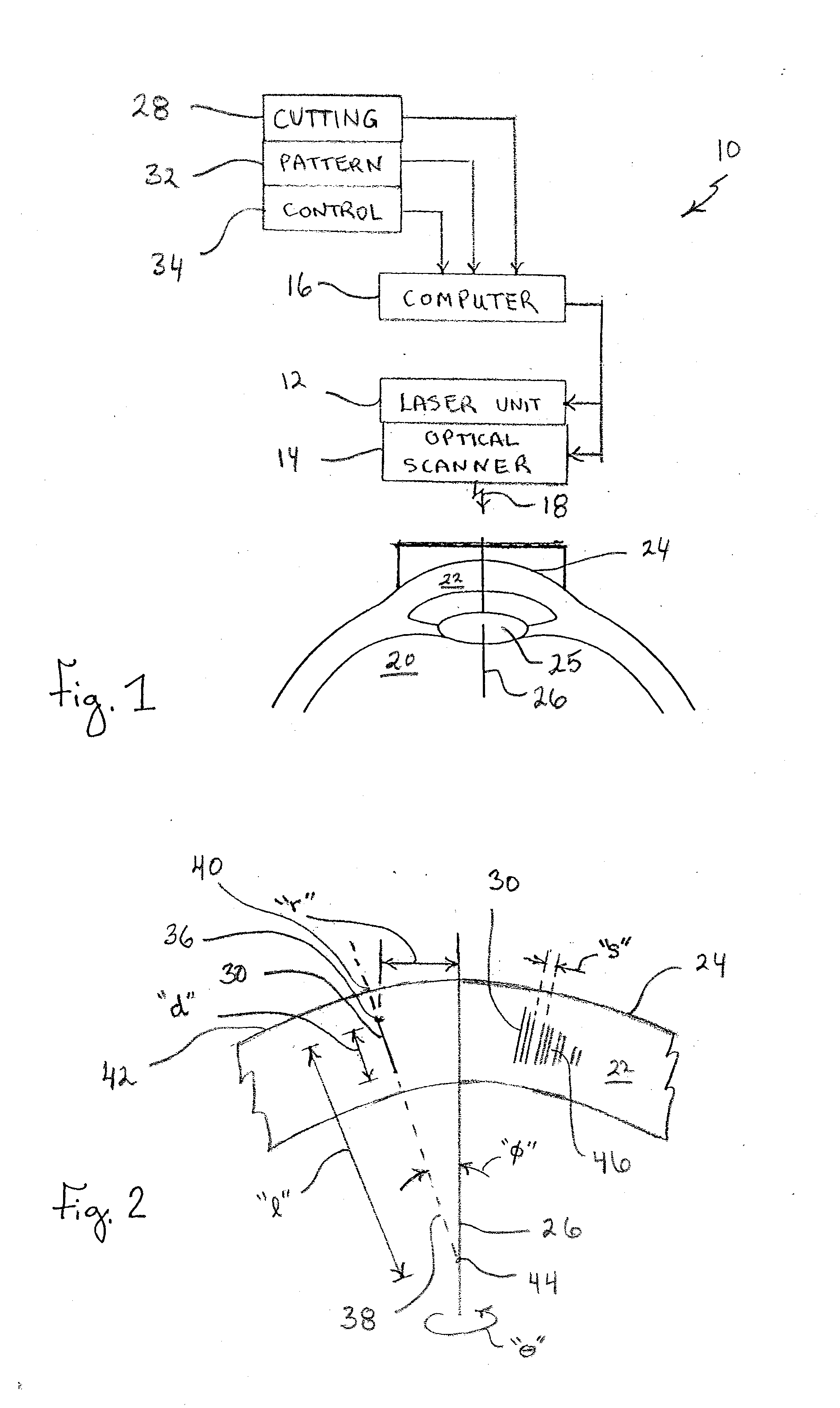
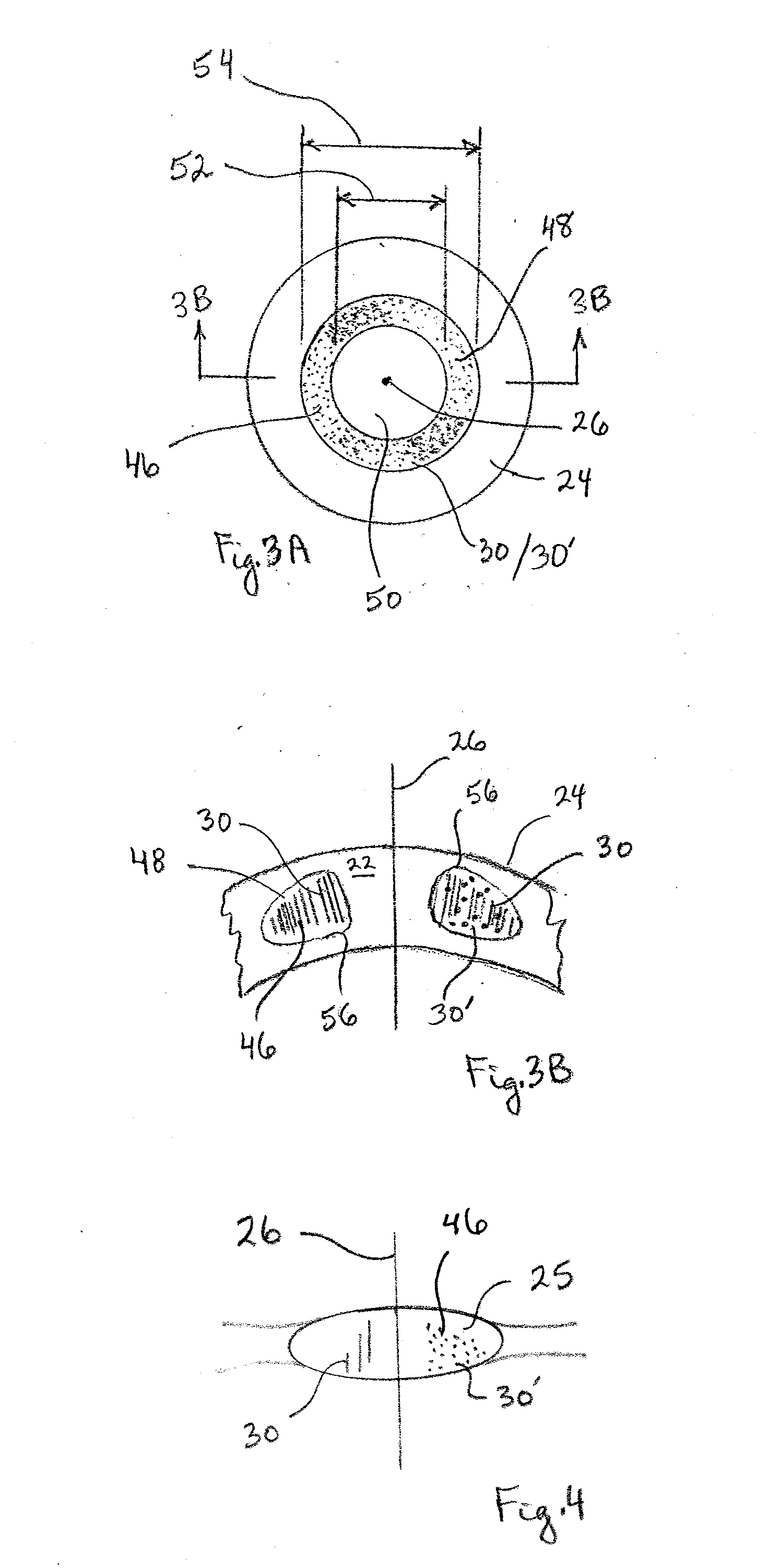
System and Method for Minimizing the Side Effects of Refractive Corrections Using Line or Dot Cuts for Incisions
InactiveUS20110022037A1Weaken biomechanical stress distributionCorrected visionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsKeratorefractive surgerySide effect
A system and method for performing refractive surgery in an eye requires creating a plurality of cuts in the stroma or the lens that are randomly positioned relative to a reference axis. The geometry for each cut is unique and includes a start point in the stroma that is identified by a distance “r” from the axis, and an azimuthal angle “θ” that is measured around the axis. A computer provides concerted control for a laser unit and an optical scanner to randomly vary the start point for each cut, to create a pattern of cuts that will implement the desired refractive surgery, yet be visually illusive.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
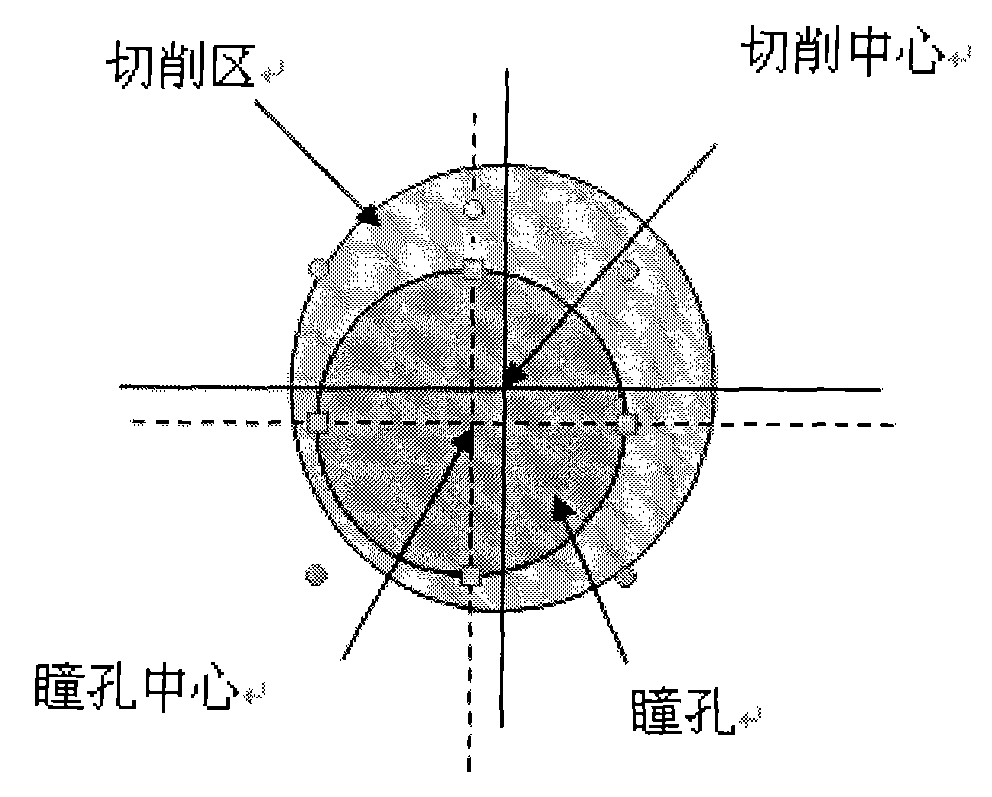
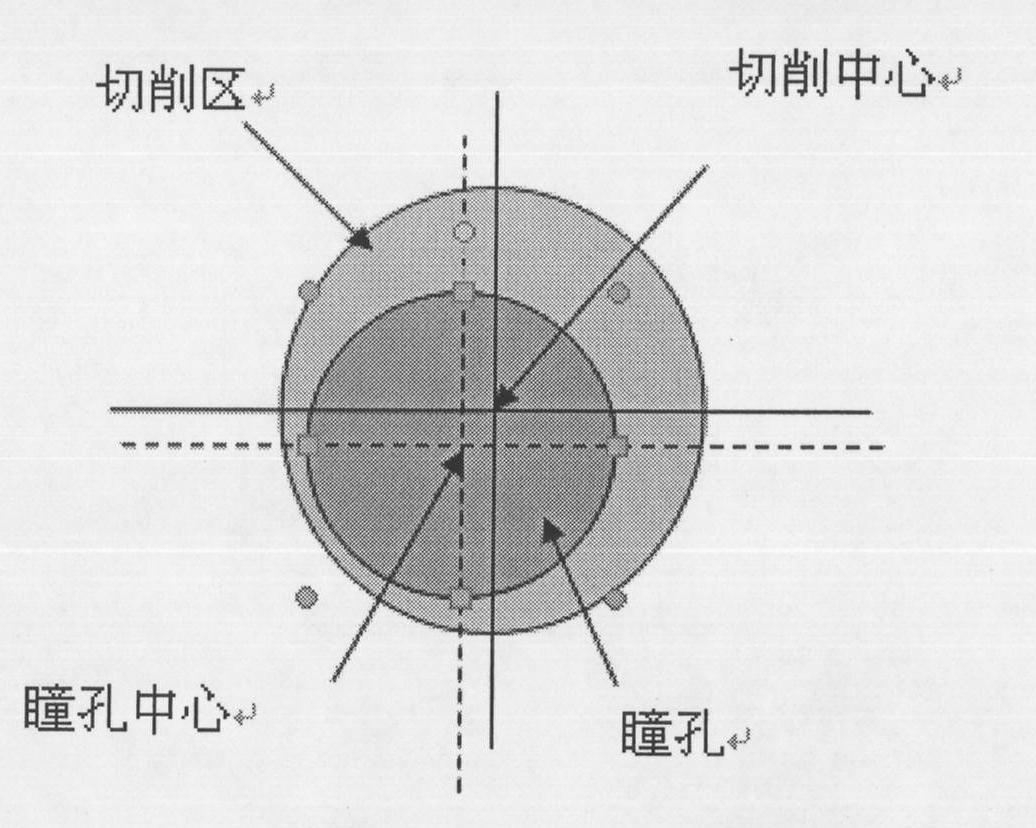
Cornea center positioning method for excimer laser cornea refractive surgery
InactiveCN101810528ARealize dynamic trackingReduce mistakesLaser surgeryKeratorefractive surgeryPupil diameter
The invention relates to a cornea center positioning method for excimer laser cornea refractive surgery. In the method, a horizontal offset model and a vertical offset model are established by measuring the pupillary diameter and the offset of the pupillary center relative to the center of the corneal vertex under different luminance brightness, and the data of the established models is input into a laser cornea refractive surgery machine with an eye tracking system, so the pupil in the laser cornea refractive surgery is dynamically tracked, the error of the tracking system is reduced, and the visual quality after the laser cornea refractive surgery is obviously improved.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +1
Indices for management of dry eye syndrome, corneal ectasia, keratoplasty graft rejection and failure and fuchs' dystrophy
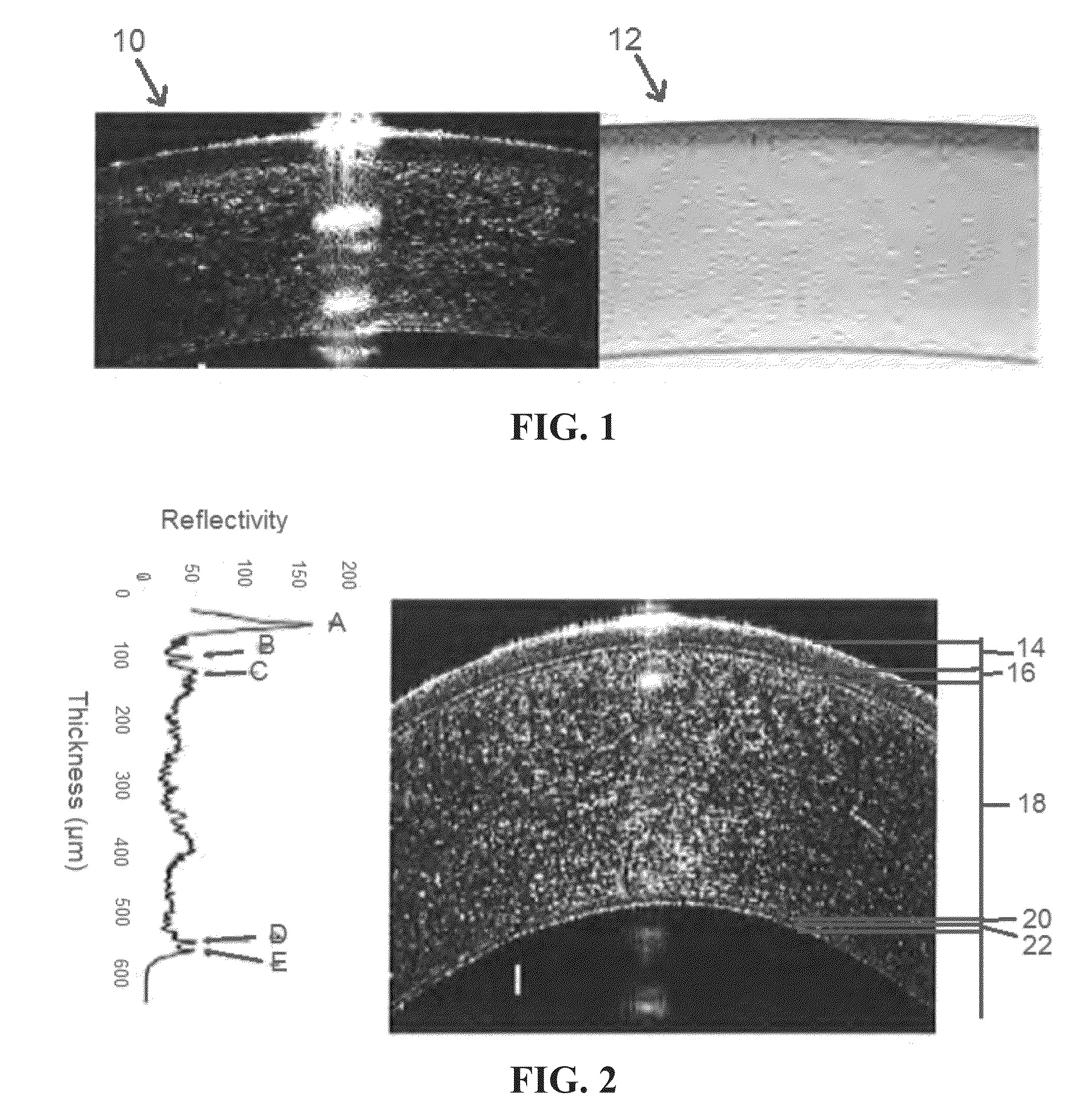
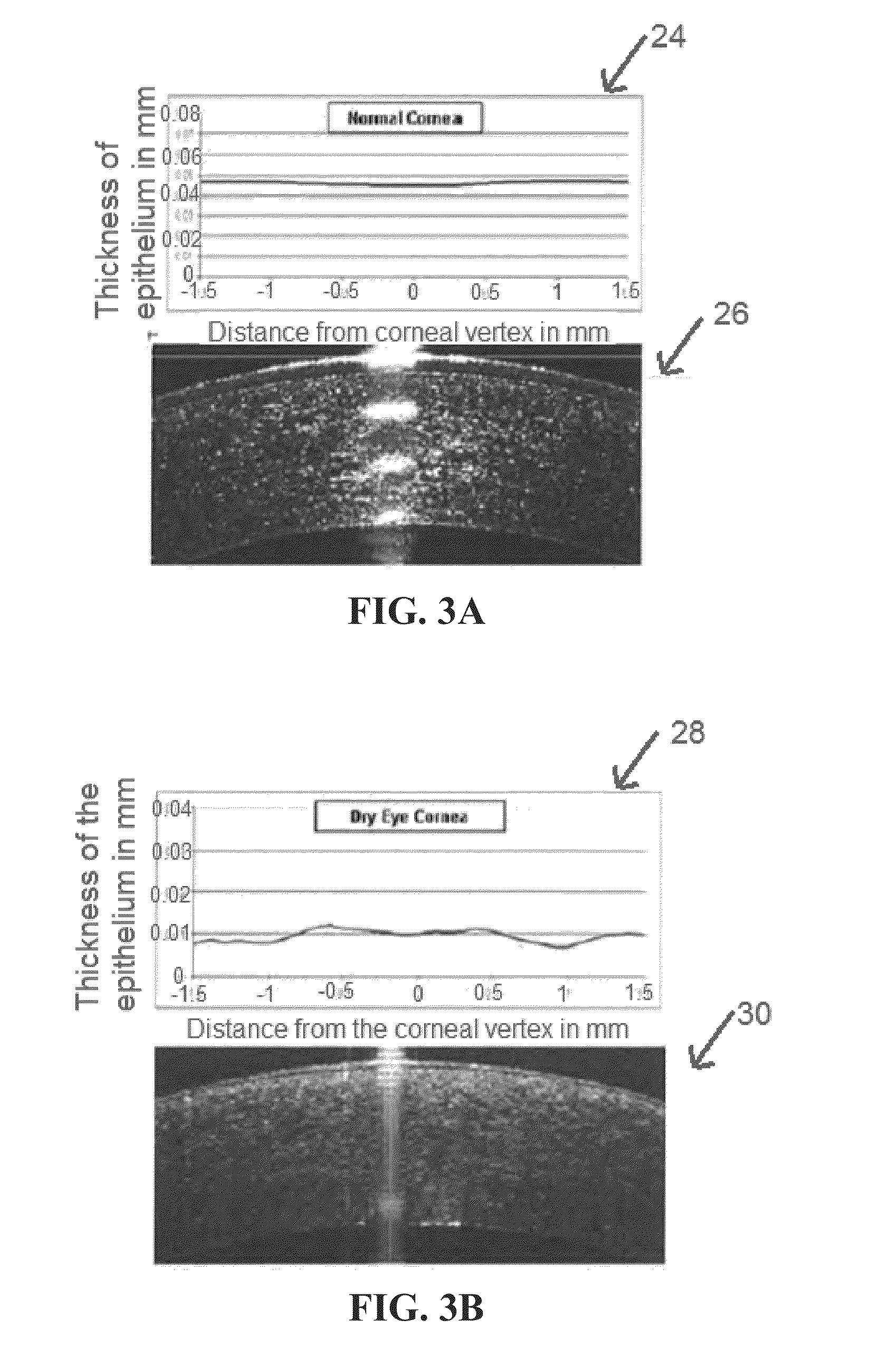
InactiveUS20140300862A1Easy diagnosisImprove treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisKeratorefractive surgeryHigh resolution image
Improved indices for the diagnosis and evaluation of conditions affecting the eye. Specifically, the indices include an Enhanced Epithelial Irregularity Factor (eEIF) for the diagnosis and evaluation of conditions such as dry eye syndrome (DES), Bowman's Ectasia Index (BEI), including enhanced BEI (eBEI) and BEI-Max, and Bowman's Relative Thinning (BRT) Index for the diagnosis and evaluation of ectatic conditions such as keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration, post-refractive surgery ectasia, and keratoglobus, and Descemet's Membrane Thickening Index (DMT), Descemet's Rejection Index (DRI), and Descemet's Membrane Irregularity Factor (DIF) for the diagnosis and evaluation of conditions such as keratoplasty rejection and failure and Fuchs' dystrophy. These improved indices may be incorporated into optical coherence tomography systems, or any other imaging device capable of capturing high resolution images of the cornea, for more sensitive and specific diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of certain corneal conditions, in addition to the evaluation of new treatments.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
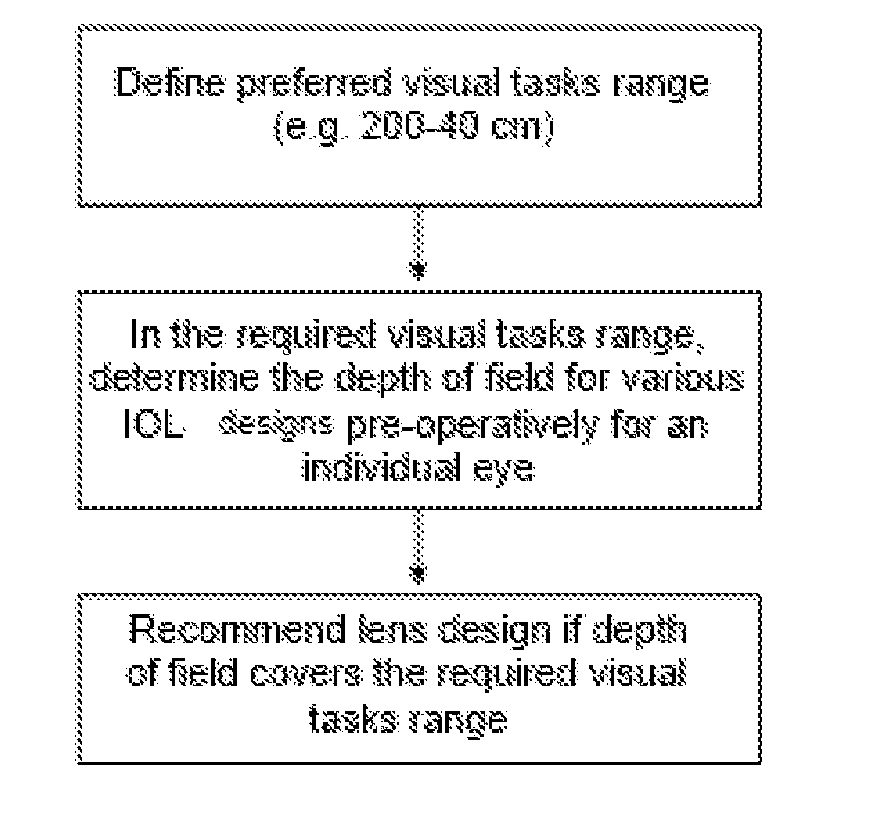
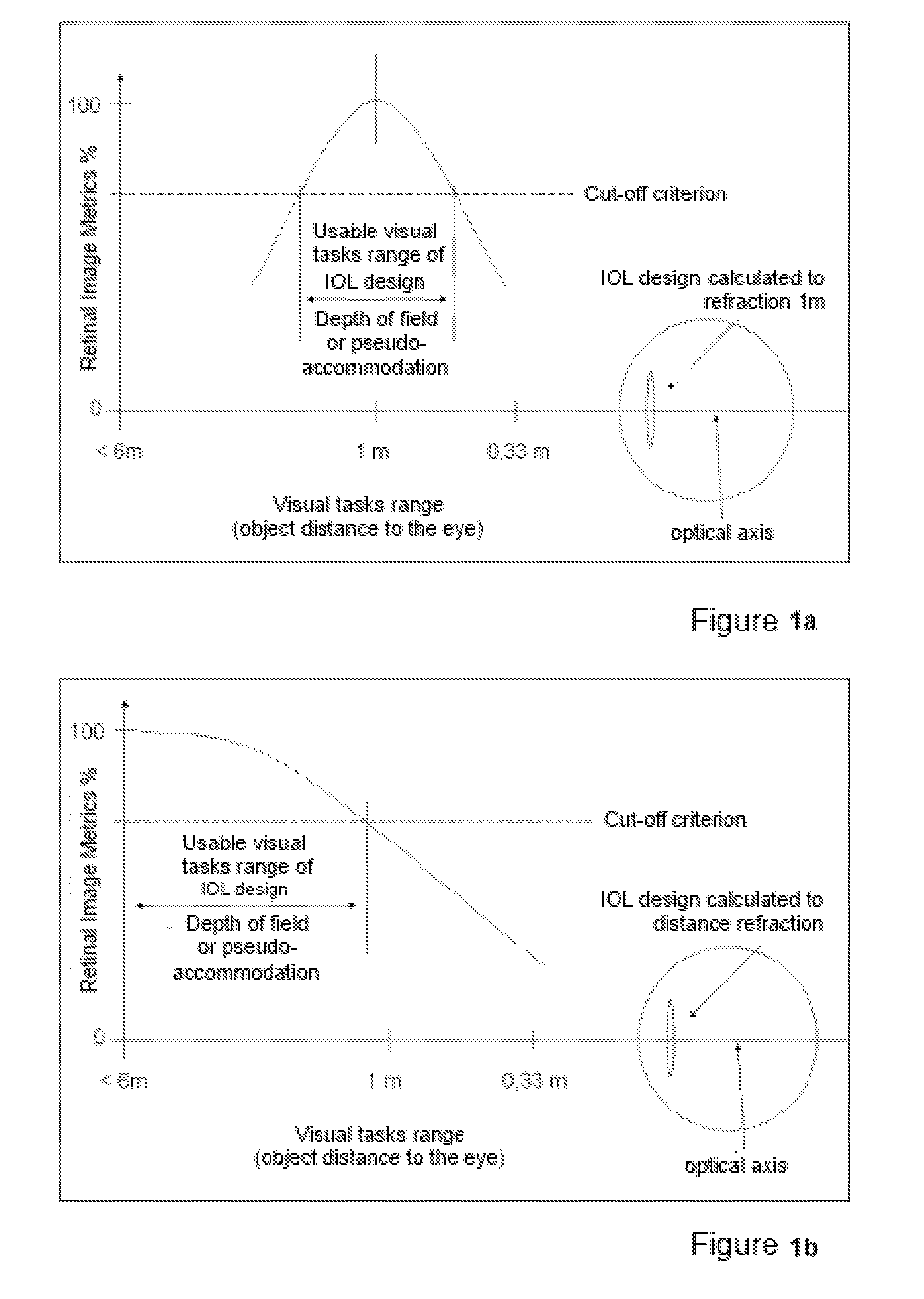
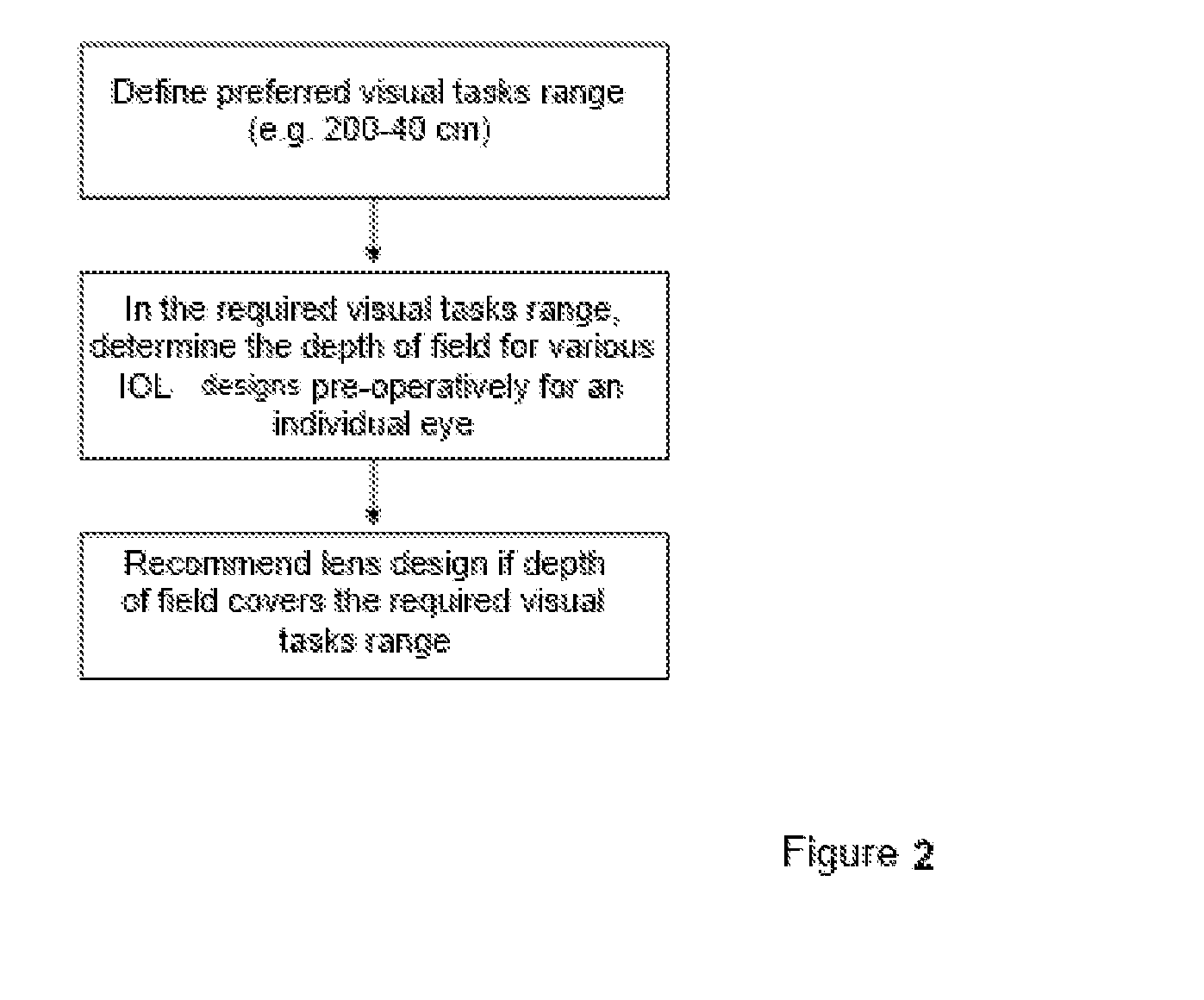
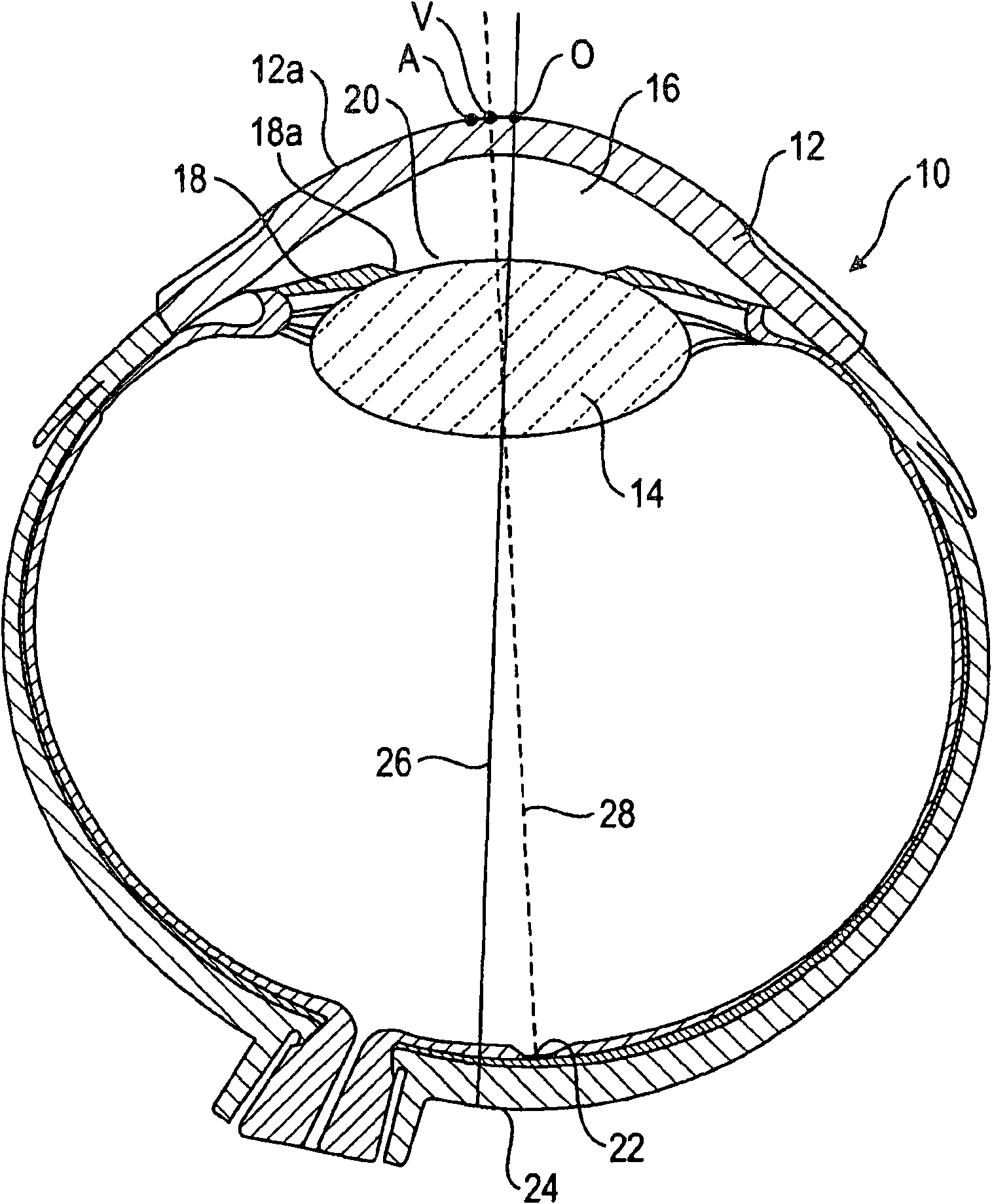
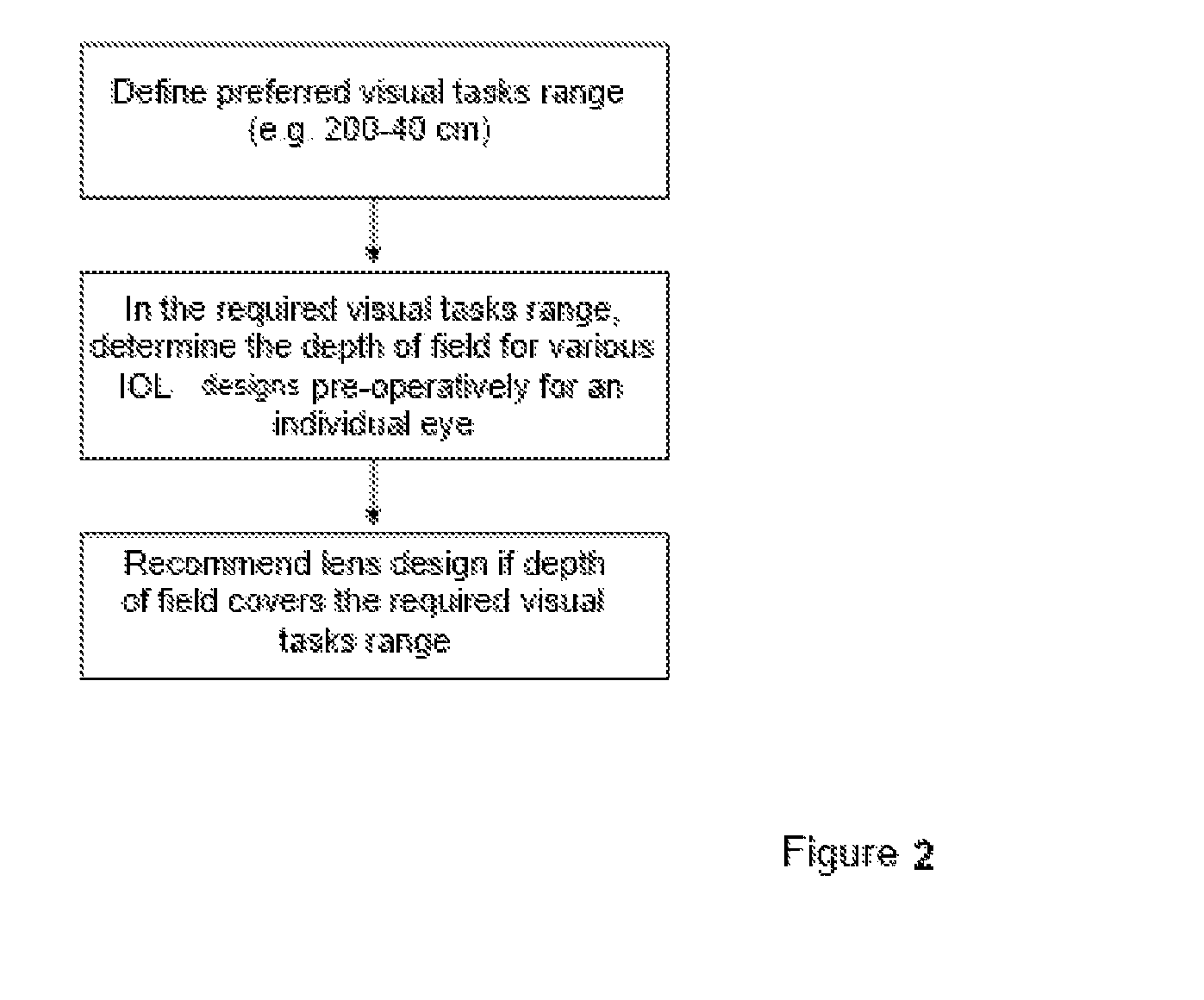
Method for the pre-operative selection of an intraocular lens to be implanted in an eye
ActiveUS20140192317A1Promote resultsSimplify the selection processEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensKeratorefractive surgeryIntraocular lens
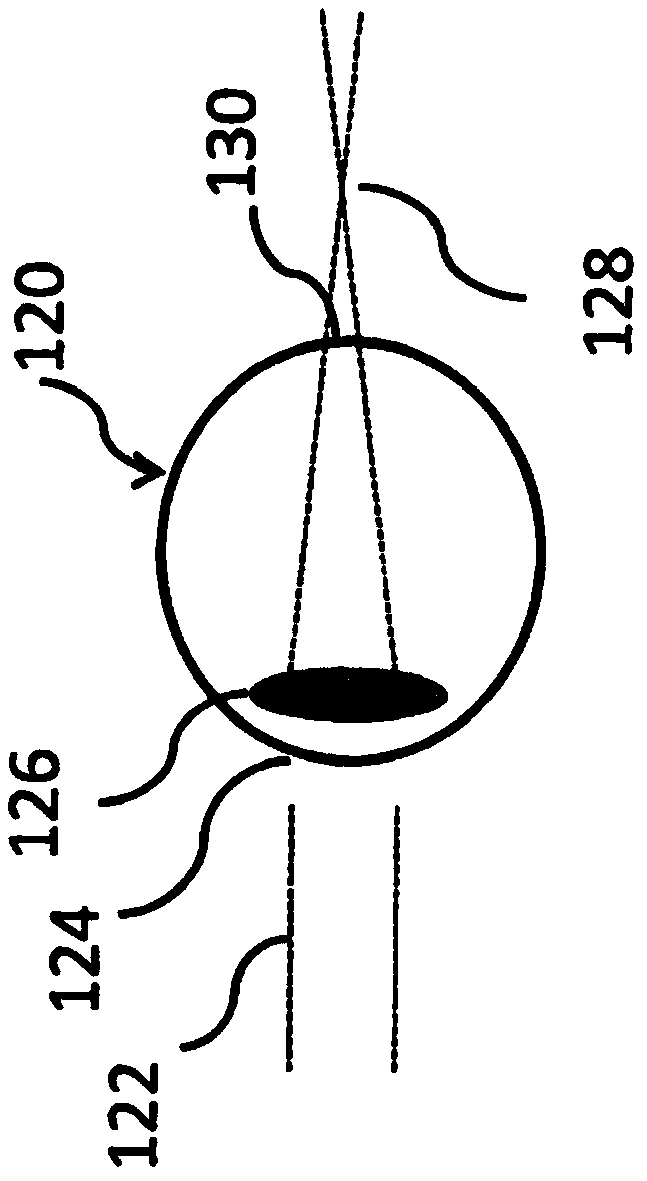
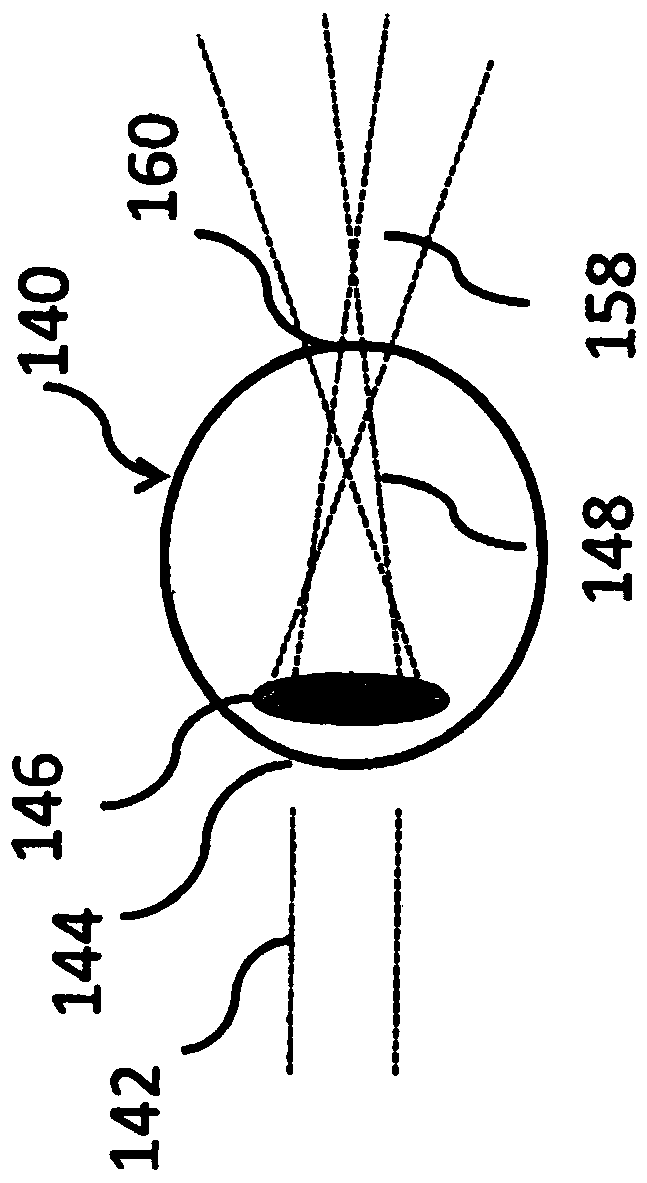
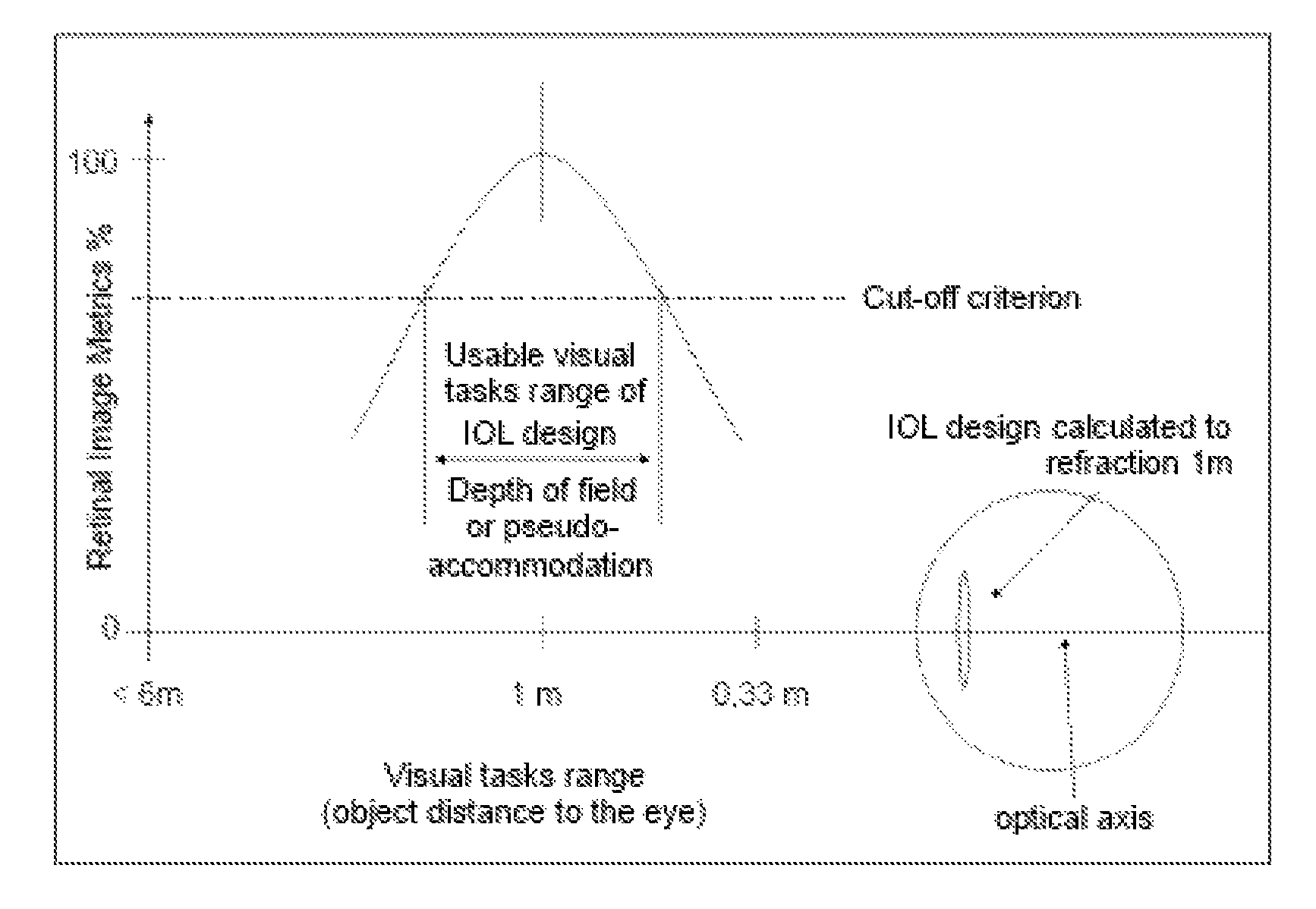
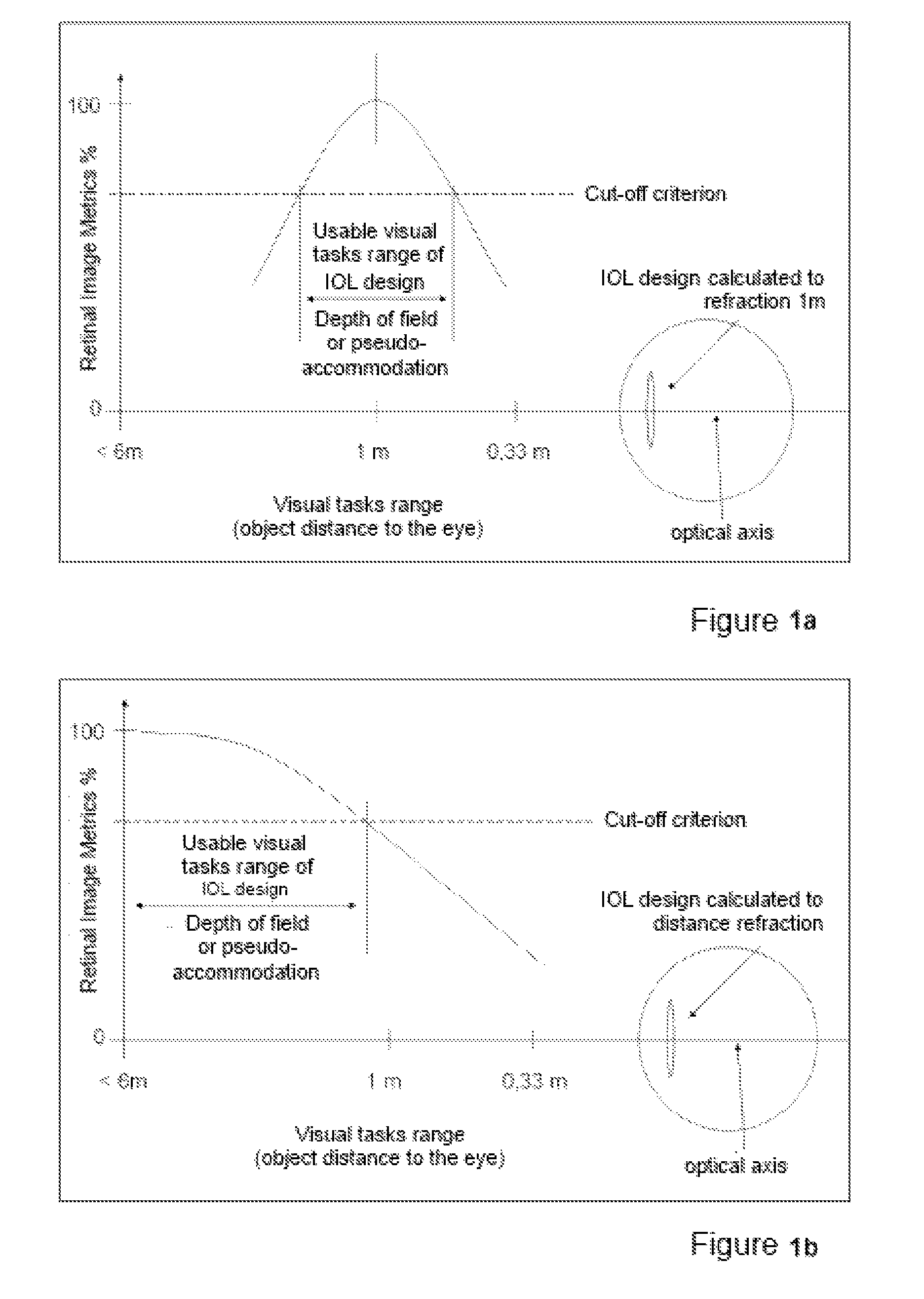
A method for the preoperative selection of an intraocular lens to optimise the results of refractive surgery on the eye. On the basis of an eye model comprising the individual biometric parameters of the eye, potentially suitable IOLs are selected on the basis of their optical parameters such as optical power, asphericity and toricity, and the residual refraction of potentially suitable IOLs is calculated using ray tracing. Various metrics, preferably retinal image metrics, are used to calculate the residual refraction and in order to improve the selection, at least one additional parameter is taken into consideration for the calculation, said calculation taking the postoperative effects of the selected IOL and / or of the surgical technique used into account.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
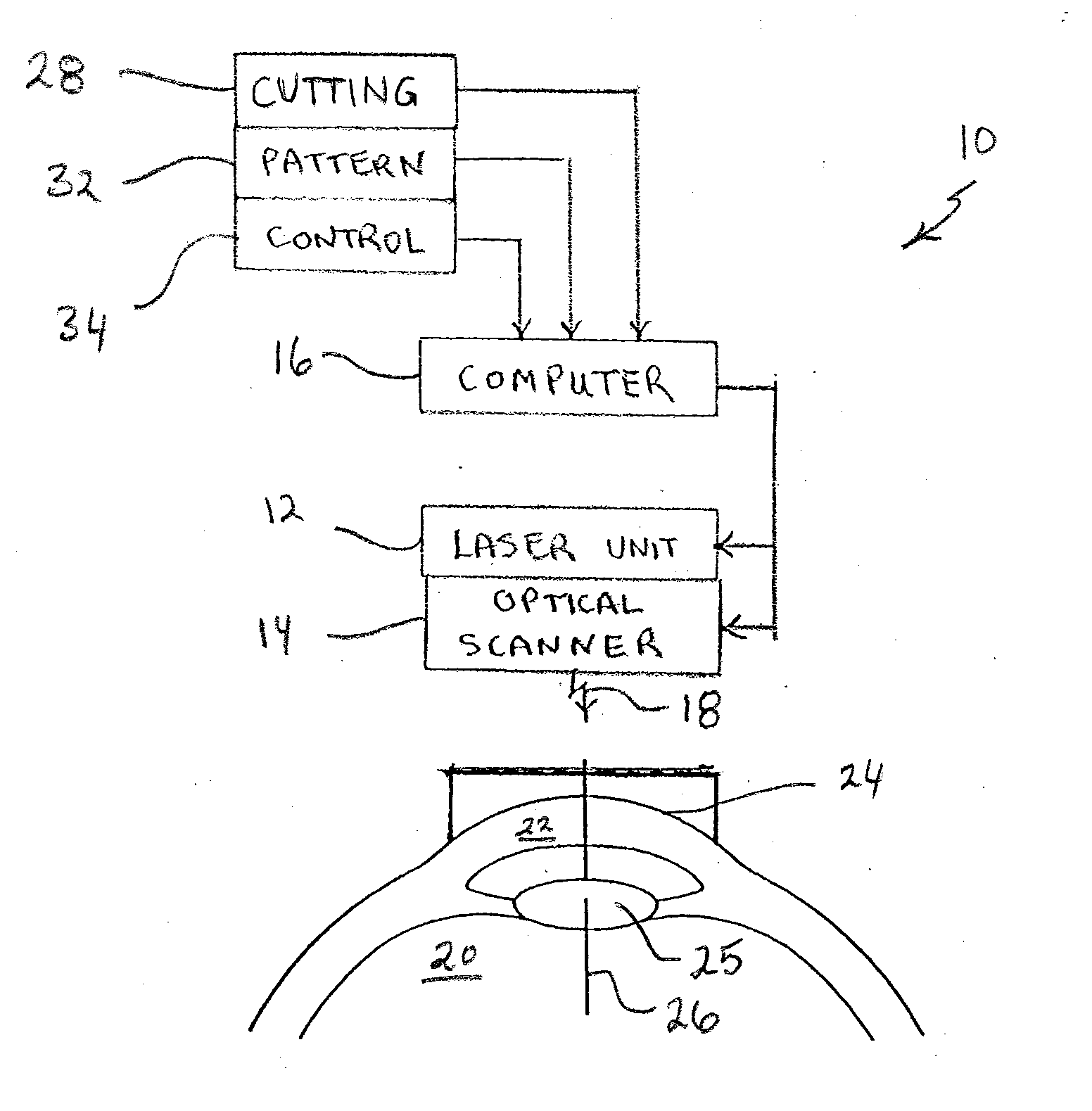
Device, method, and control program for refractive surgery
ActiveCN101677875AImproved refractive resultsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsKeratorefractive surgeryPupil
The invention relates to a device and a method for refractive surgery, particularly LASIK, provide that the apex of the cornea is the basis for the ablation center for the refractive procedure. To this end, the dependency of the position of the apex on properties of the pupil is determined in the eye to be treated, and the position of the ablation center for the refractive surgery is computed fromthis dependency by means of the properties of the pupil measured.
Owner:ALCON INC
Ultrasonic microkeratome
The invention relates to medical instruments and methods for performing eye surgery to correct focusing deficiencies of the cornea. More particularly, the present invention relates to mechanical instruments known as microkeratomes, and related surgical methods for performing lamellar keratotomies and refractive surgery. The device is designed to create a flap of epithelium, or stroma and epithelial flap as is done now with LASIK. This will enable a new technique, ELF, or Epithelial Laser Flap, which will combine the advantages of LASIK and PRK, an older, but easier technique.
Owner:SLADE STEPHEN G
After-cornea refractive surgery artificial lens design
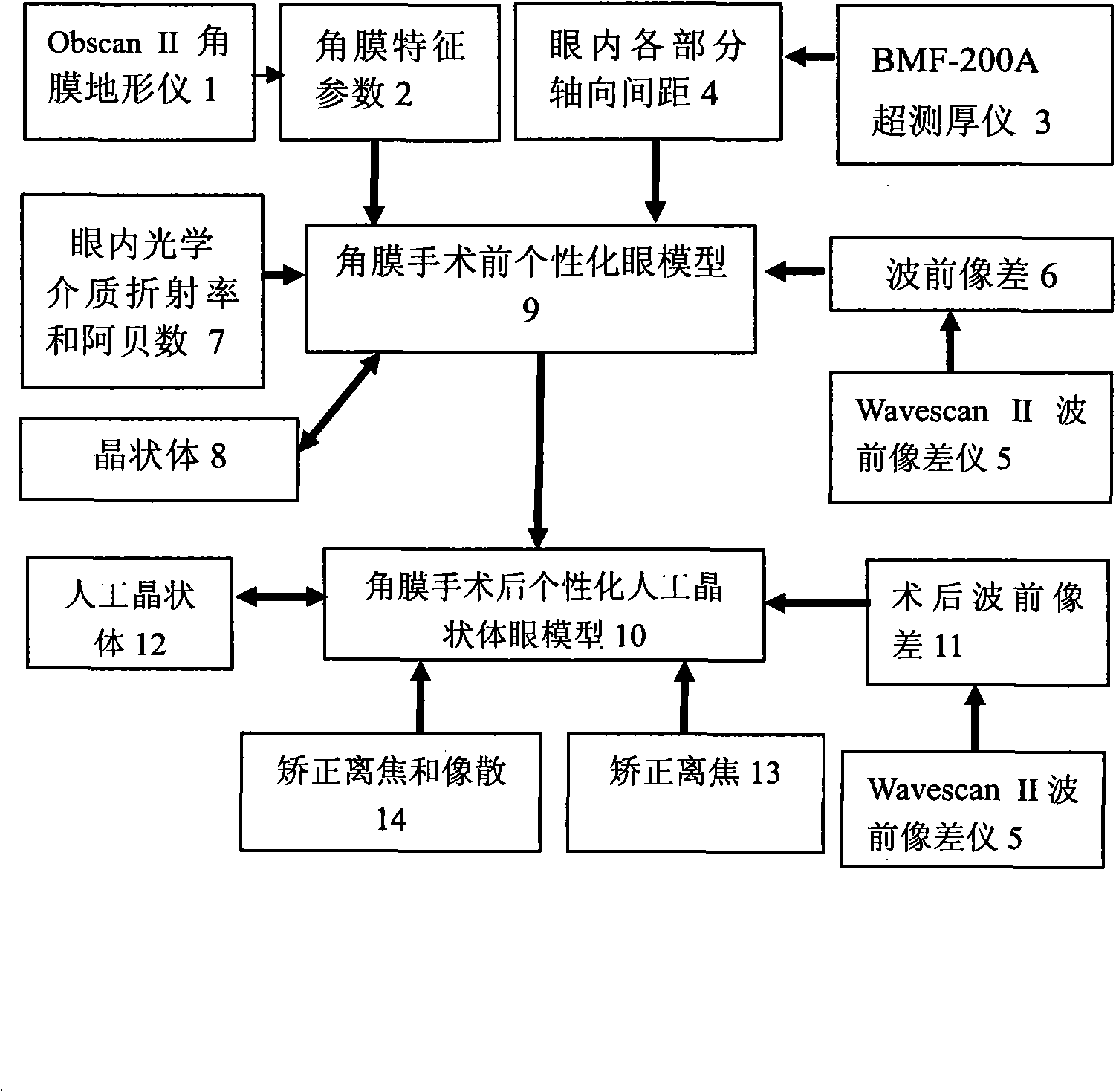
The invention belongs to the technical field of vision correction and cataract vision therapy. A before-refractive surgery individualized eye model is built by using ZEMAX optical design software according to a corneal topography, an axial distance between components in an eye and a wavefront aberration which are obtained before the cornea refractive surgery; an after-refractive surgery individualized eye model is built by combining an wavefront aberration actually measured after the cornea refractive surgery; and, finally, a bispherical artificial lens for correcting defocusing and a spherical column-shaped artificial lens for correcting a defocusing and astigmation are designed by using the model.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
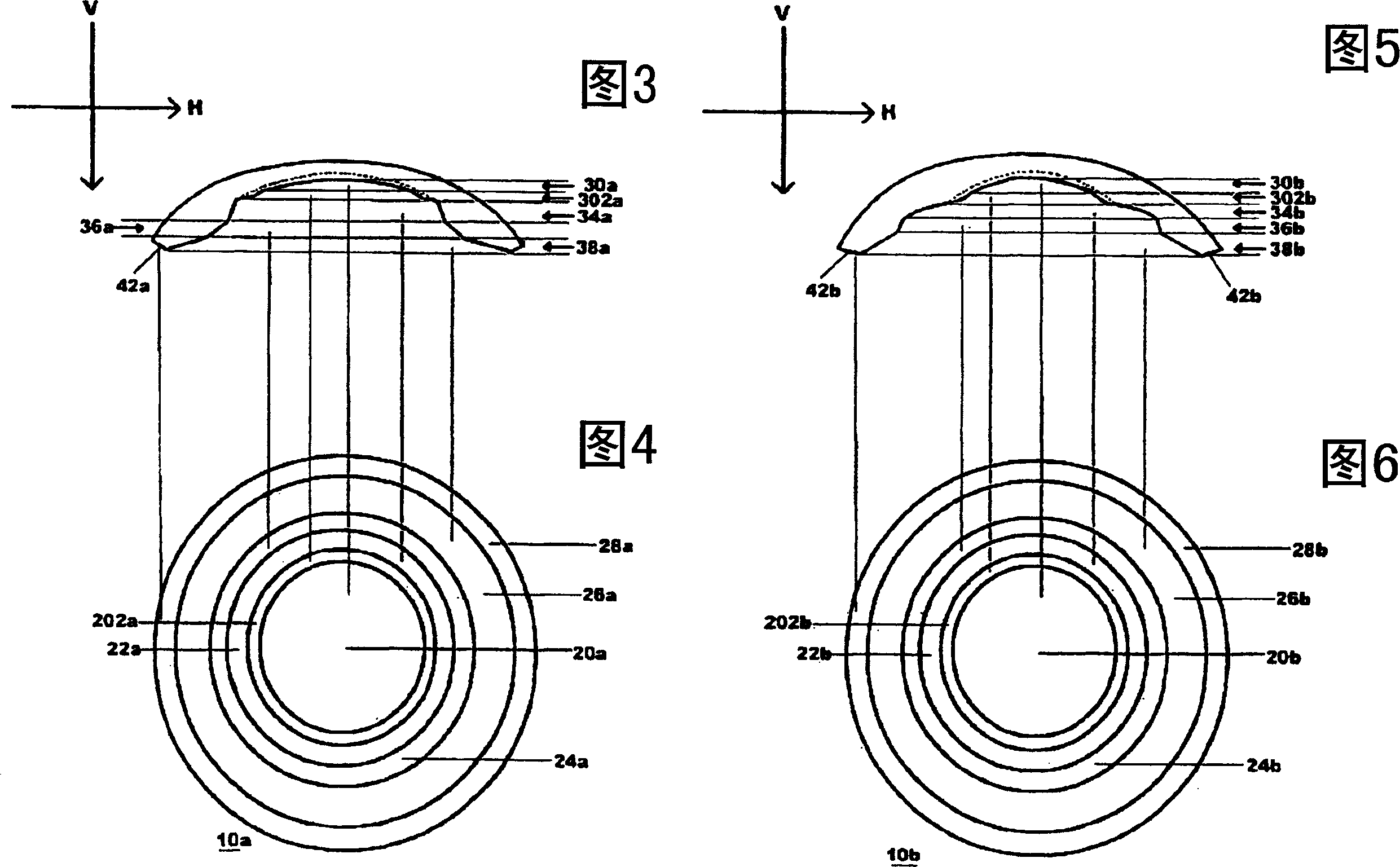
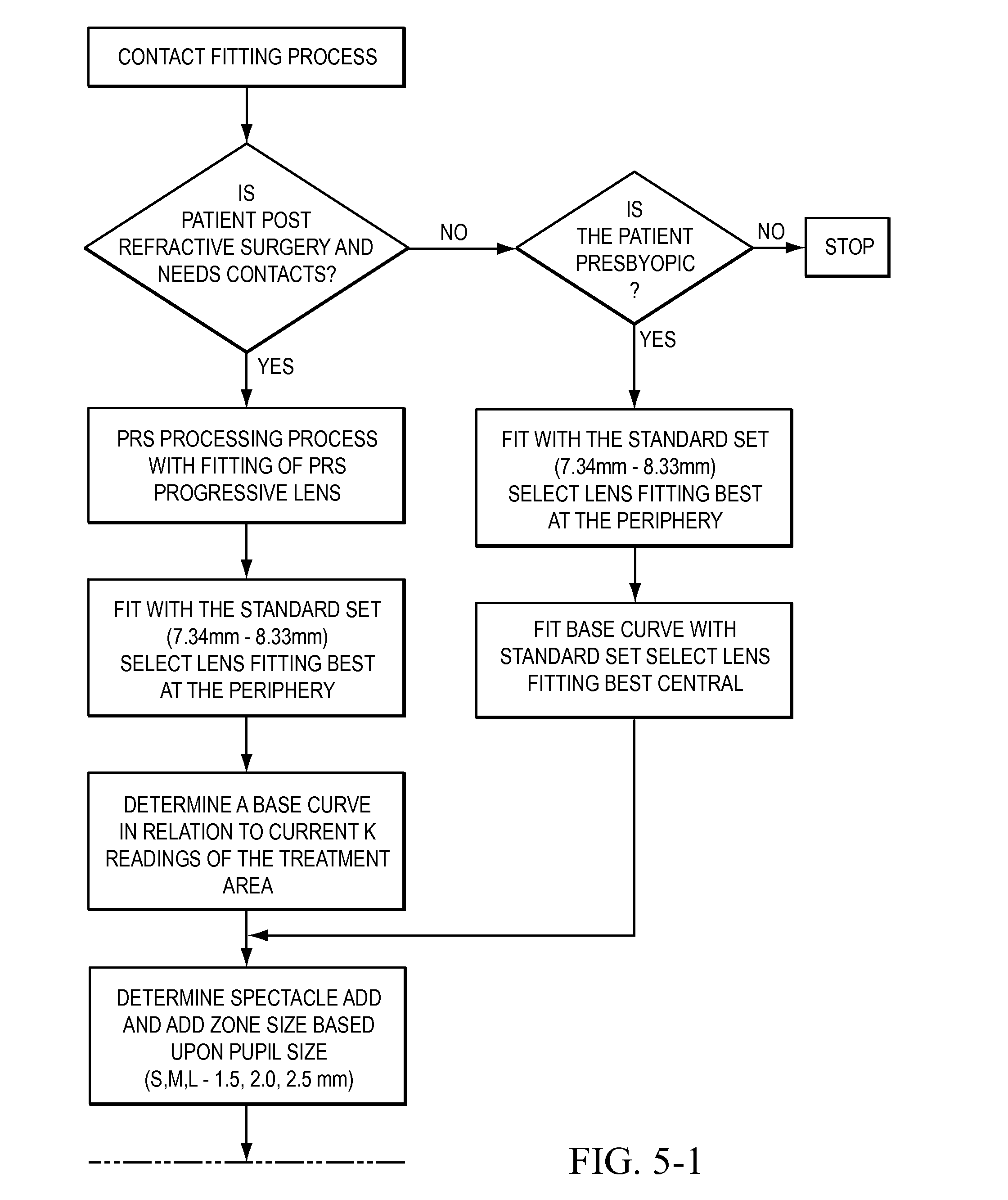
Contact lens for reshaping the altered corneas of post refractive surgery, post ortho-k or keratoconus
ActiveCN101002132AEffective remodelingImprove or rebuild visionEye treatmentOptical partsKeratorefractive surgeryRefractive error
A contact lens is fitted to a cornea of a patient's eye to gradually alter the patient's cornea during continued wear to reshape the altered cornea conditions such as the corneas of post refractive surgery, post previous Ortho-K. and keratoconus. The contact lens has a plurality of zones that comprise one optical zone, at least one conformation zone, a connecting zones complex, an alignment zone and a peripheral zone. The one or more conformation zones are utilized to conform the angle of the central optical zone, as well as the alignment zone, to compress on the central and mid-peripheral portion of the altered cornea for redistribute cornea tissue to reduce the residual refractive errors, after refractive surgery, or to smooth out the central cornea surface of the keratoconus for better bare or spectacle vision after contact lens are removed.
Owner:董晓青
Progressive multifocal rigid gas permeable contact lens
ActiveUS8857982B2Comfortable to wearEye diagnosticsOptical partsKeratorefractive surgeryRigid gas permeable lens
A contact lens is provided. It is a rigid gas permeable, corneal-scleral progressive, multifocal, vision lens that covers the cornea and a portion of the sclera of an eye. It is particularly beneficial for use on patients who have undergone refractive surgery and / or on patients experiencing presbyopia. The lens is designed to have dual touch contact with an eye. One contact point is the central portion of the cornea and the other contact point is a portion of the sclera.
Owner:DAKOTA SCI
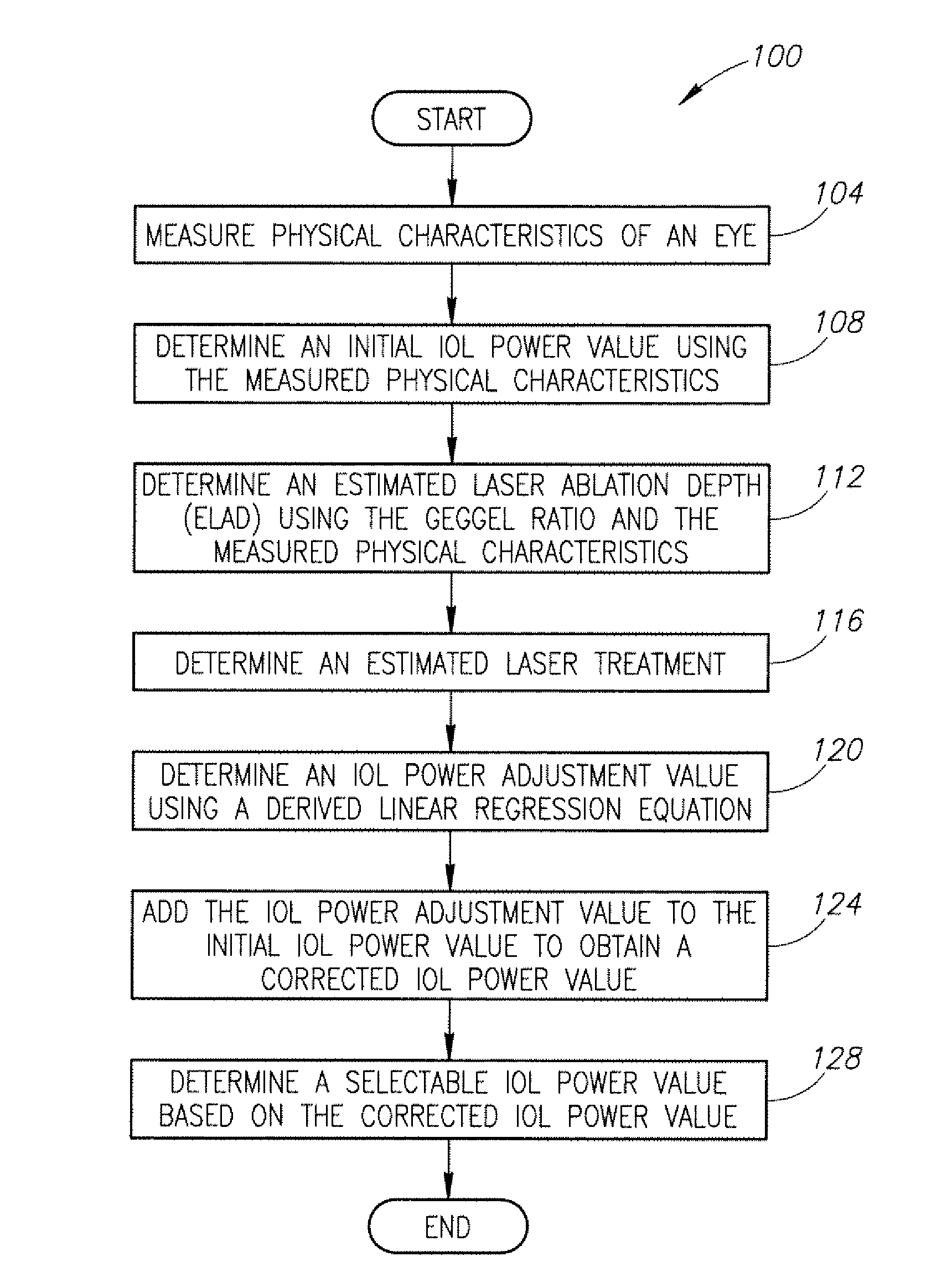
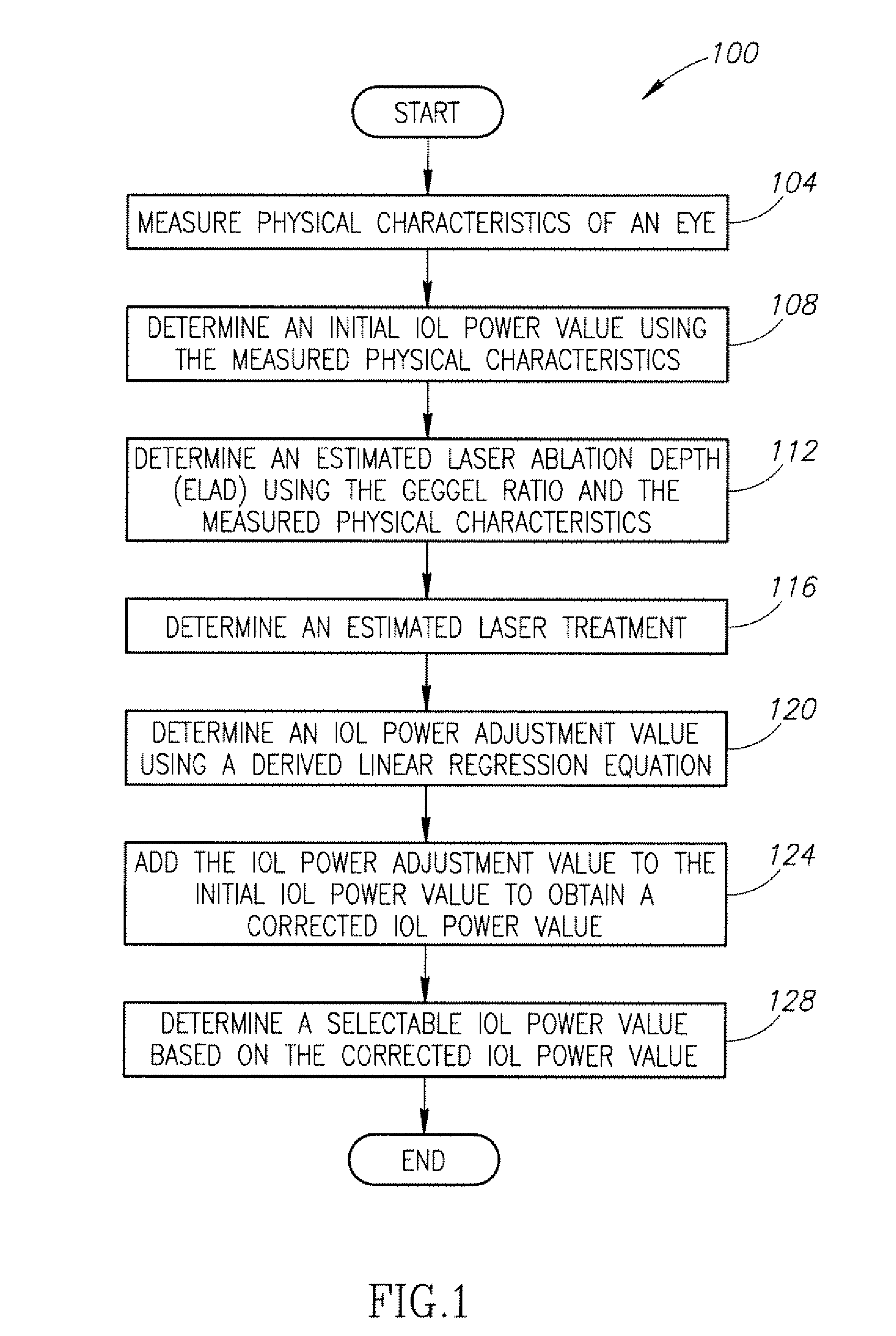
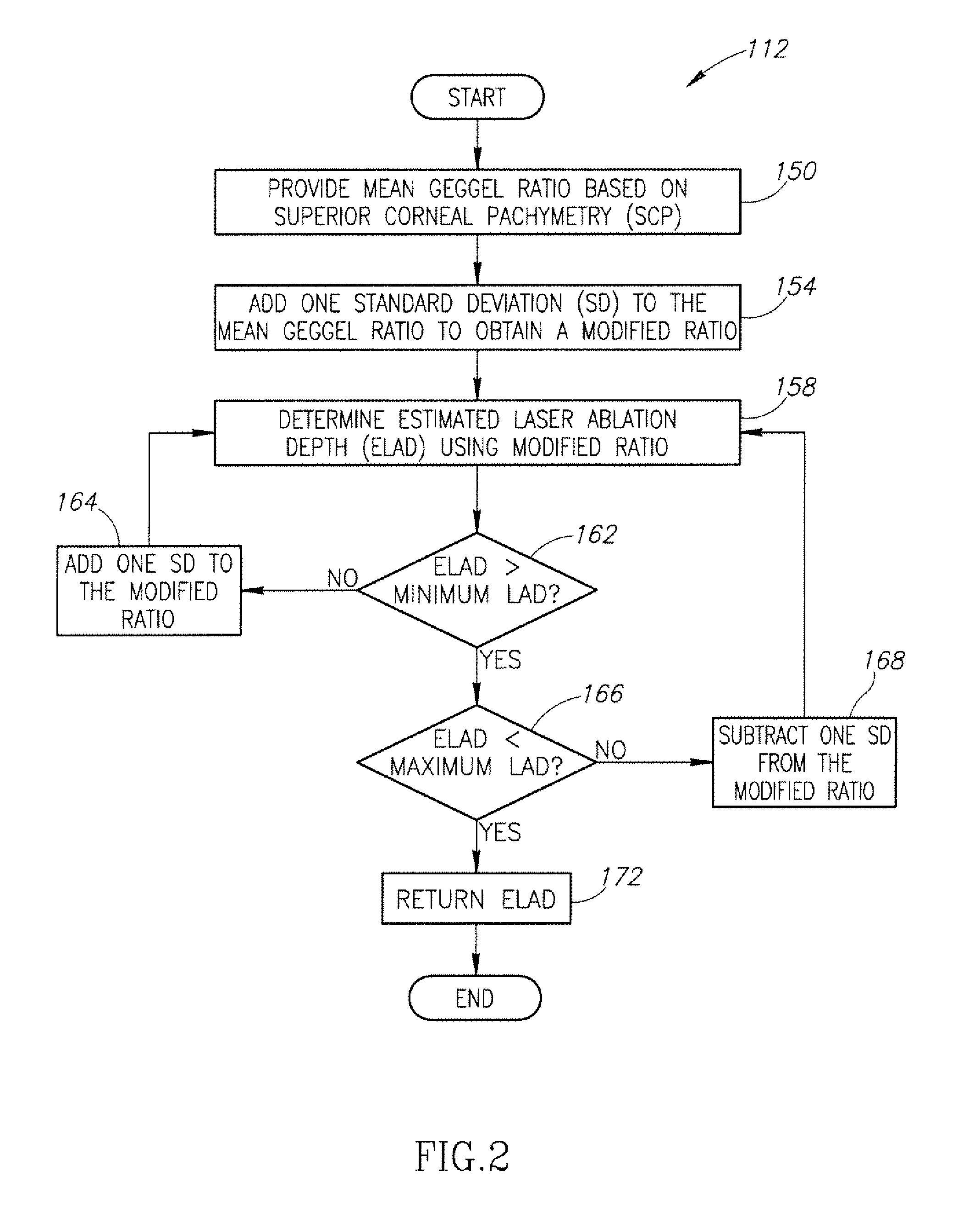
No-history method for intraocular lens power adjustment after excimer laser refractive surgery
InactiveUS20110051083A1Laser surgeryEye diagnosticsKeratorefractive surgeryIntraocular lens power calculation
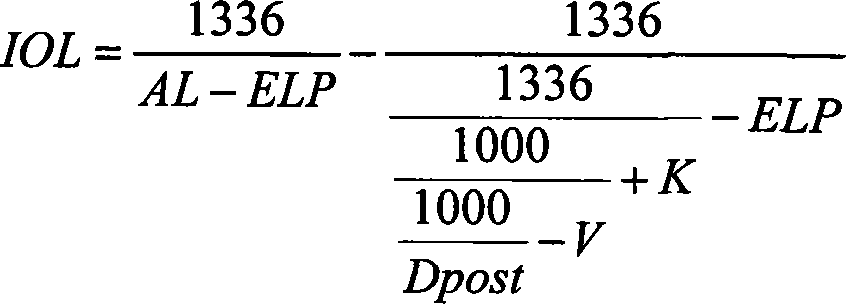
Systems and methods for using a new corneal ratio, referred to as the Geggel ratio, to estimate how much treatment a patient received at an original myopic or mixed astigmatism excimer laser refractive surgery. The Geggel ratio represents the ratio of the measure of a pre-IOL central pachymetry to a measure of a pre-IOL superior pachymetry. The estimated laser ablation depth (ELAD) is used in a derived linear regression equation to determine an IOL power adjustment that is added to the standard SRK / T formula used to determine IOL power.
Owner:VIRGINIA MASON MEDICAL CENT
Lenses, devices, methods and systems for refractive error
ActiveCN108714063ALess ghostingImprove visual effectsSpectales/gogglesEye treatmentKeratorefractive surgeryRefractive error
The present disclosure is directed to lenses, devices, methods and / or systems for addressing refractive error. Certain embodiments are directed to changing or controlling the wavefront of the light entering a human eye. The lenses, devices, methods and / or systems can be used for correcting, addressing, mitigating or treating refractive errors and provide excellent vision at distances encompassingfar to near without significant ghosting. The refractive error may for example arise from myopia, hyperopia, or presbyopia with or without astigmatism. Certain disclosed embodiments of lenses, devicesand / or methods include embodiments that address foveal and / or peripheral vision. Exemplary of lenses in the fields of certain embodiments include contact lenses, corneal onlays, corneal inlays, and lenses for intraocular devices both anterior and posterior chamber, accommodating intraocular lenses, electro-active spectacle lenses and / or refractive surgery.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Method for the pre-operative selection of an intraocular lens to be implanted in an eye
ActiveUS9271829B2Promote resultsSimplify the selection processEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensKeratorefractive surgeryIntraocular lens
A method for the preoperative selection of an intraocular lens to optimise the results of refractive surgery on the eye. On the basis of an eye model comprising the individual biometric parameters of the eye, potentially suitable IOLs are selected on the basis of their optical parameters such as optical power, asphericity and toricity, and the residual refraction of potentially suitable IOLs is calculated using ray tracing. Various metrics, preferably retinal image metrics, are used to calculate the residual refraction and in order to improve the selection, at least one additional parameter is taken into consideration for the calculation, said calculation taking the postoperative effects of the selected IOL and / or of the surgical technique used into account.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
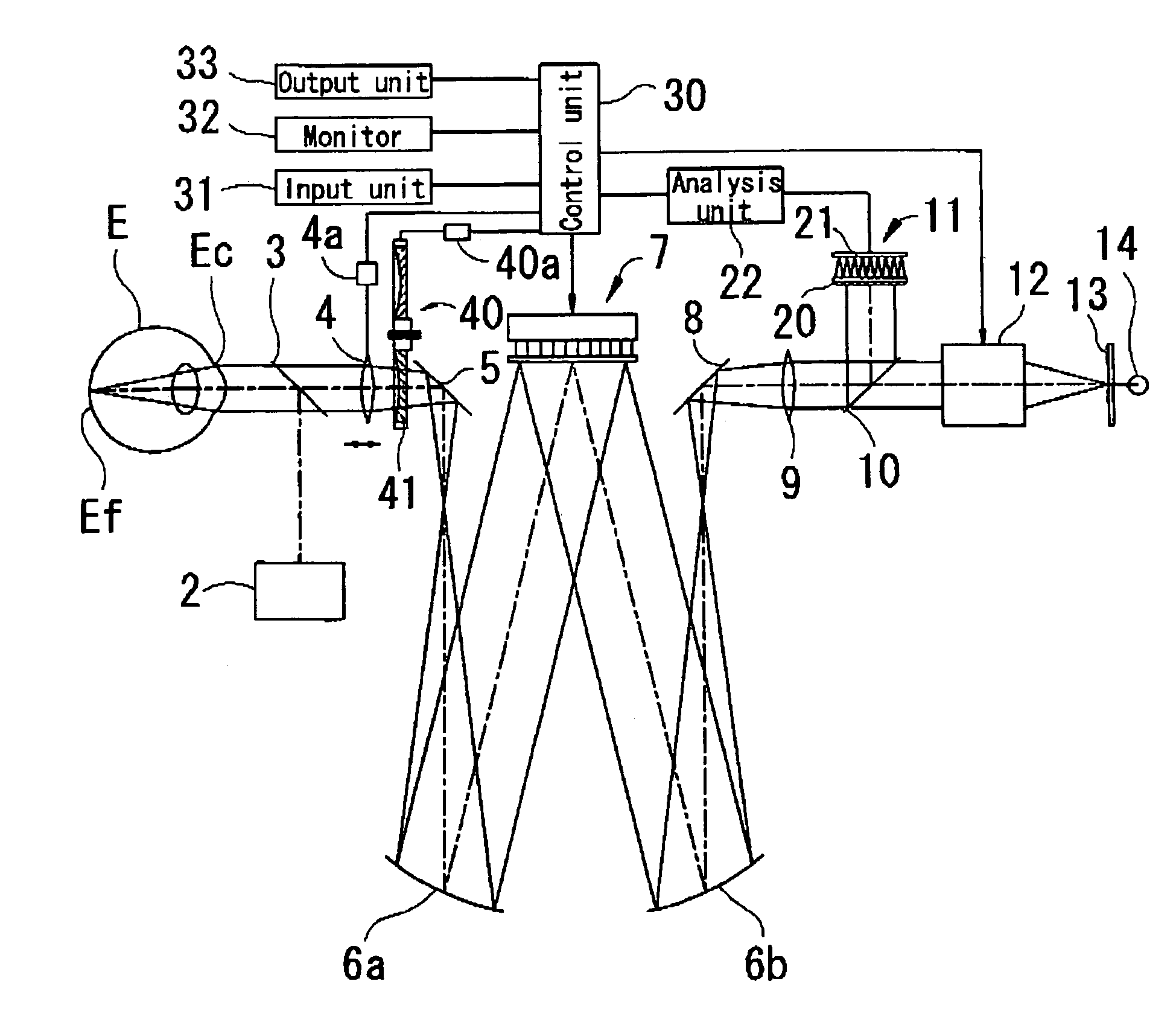
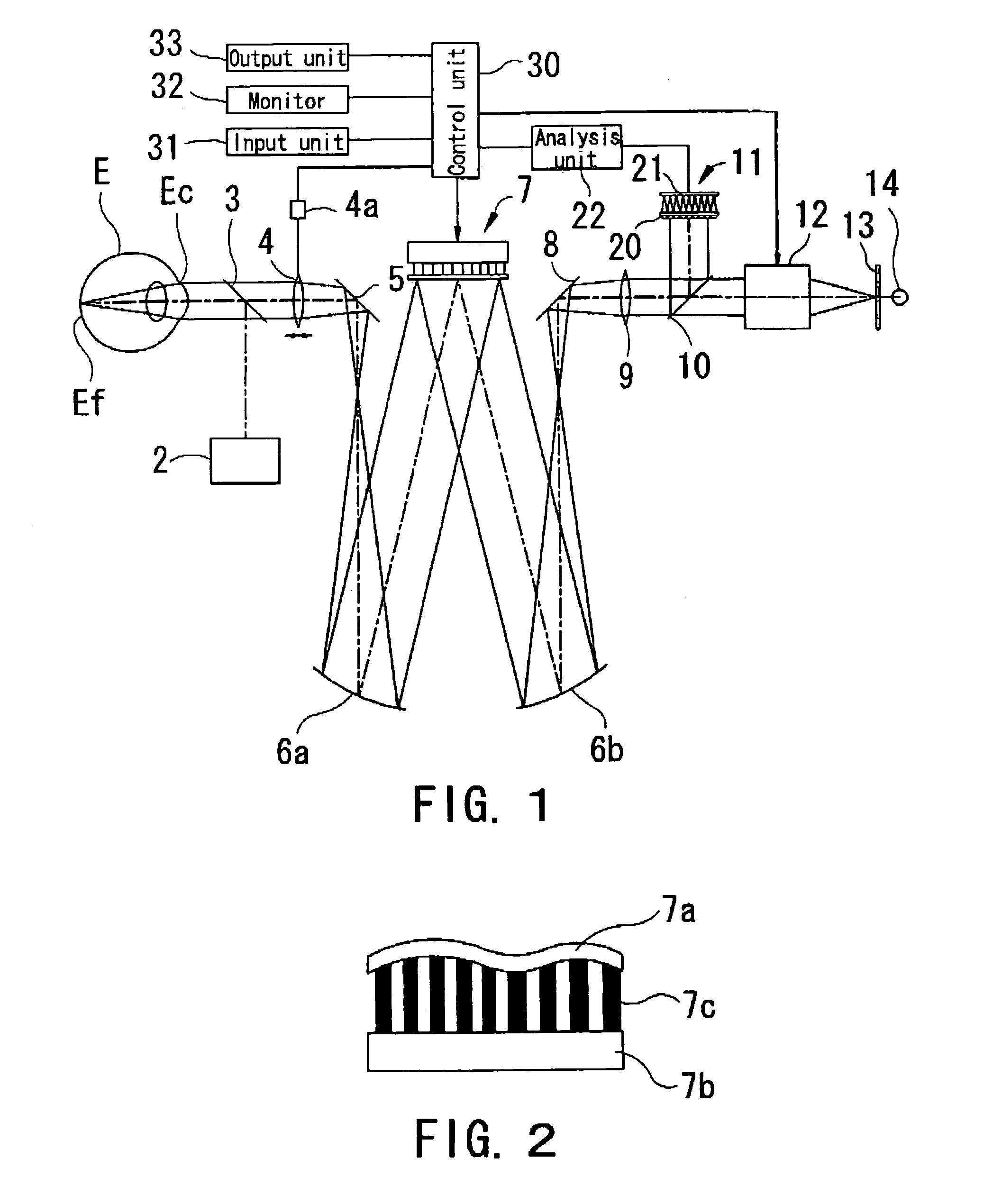
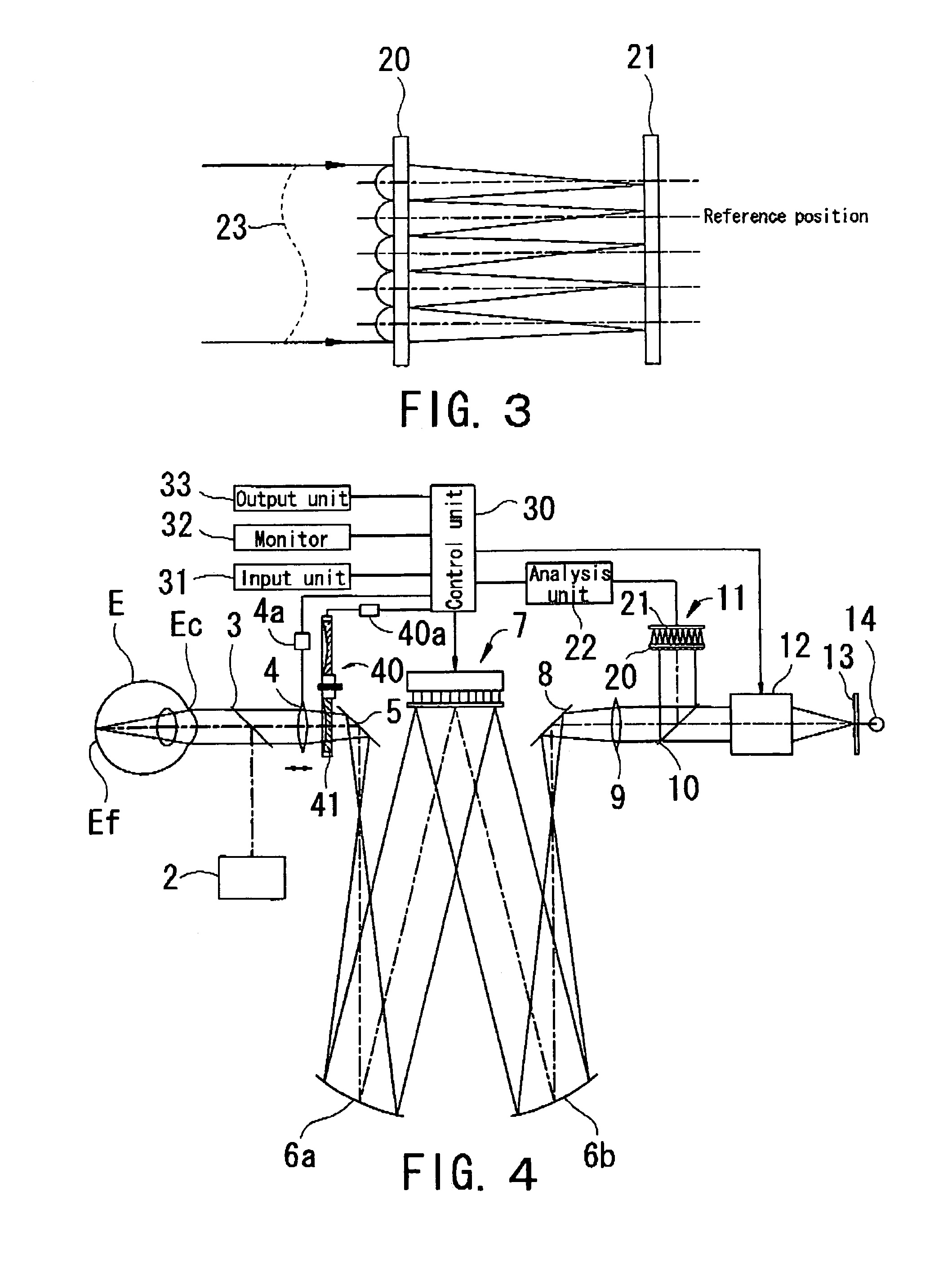
Ophthalmic apparatus
An ophthalmic apparatus which allows a patient to experience a manner of view after surgery (after correction) prior to surgery (prior to correction) and is capable of obtaining information required for performing refractive surgery suitable for the patient. The apparatus, which allows a patient to experience a manner of view after correction of optical aberration of a patient's eye, includes a target presenting optical system for presenting a target which the patient's eye is made to visually recognize, an aberration correcting optical system, which is arranged within an optical path of the target presenting optical system and has a light shaping optical unit which performs light shaping, for correcting the optical aberration of the patient's eye, an input unit which inputs data for correcting the optical aberration of the patient's eye, and a control unit which controls driving of the aberration correcting optical system based on the inputted correction data.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Ophthalmic instrument for the measurement of ocular refraction and visual simulation, and associated methods of measurement of ocular refraction, simulation of ophthalmic elements, visual simulation and for obtaining optical parameters
An ophthalmic instrument for measurement of ocular refraction and visual simulation and a method of measurement obtaining the ocular refraction in a binocular manner, which incorporates a digitally controlled phase modulator for generating best ophthalmic correction in each subject. The instrument enables measuring refraction, not only associated with blurring and astigmatism, but also optical aberration of any order. The phoropter can simulate vision by any phase profile, including those of a diffractive or discontinuous type. The instrument also incorporates a subsystem for presentation of stimuli that produces stereoscopic vision of the same, enabling the subject to enjoy a three dimensional perception during the process, and two output pupils. The instrument, by its electro-optical features, enables simulation of vision as it would be modified after submitting an eye to different surgical techniques, such as refractive surgery or interocular lens implantation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MURCIA
Indices for management of dry eye syndrome, corneal ectasia, keratoplasty graft rejection and failure and Fuchs' dystrophy
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
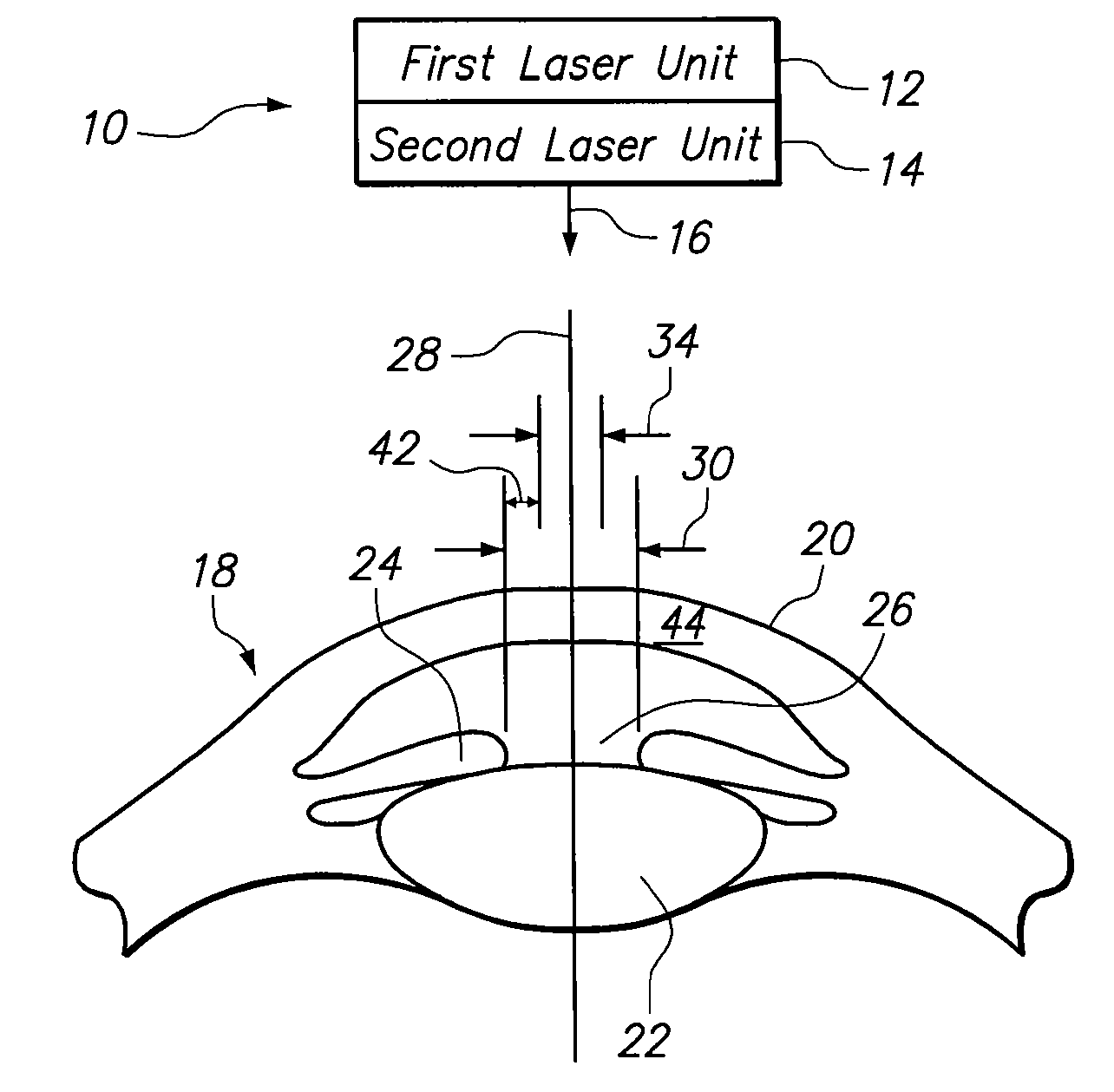
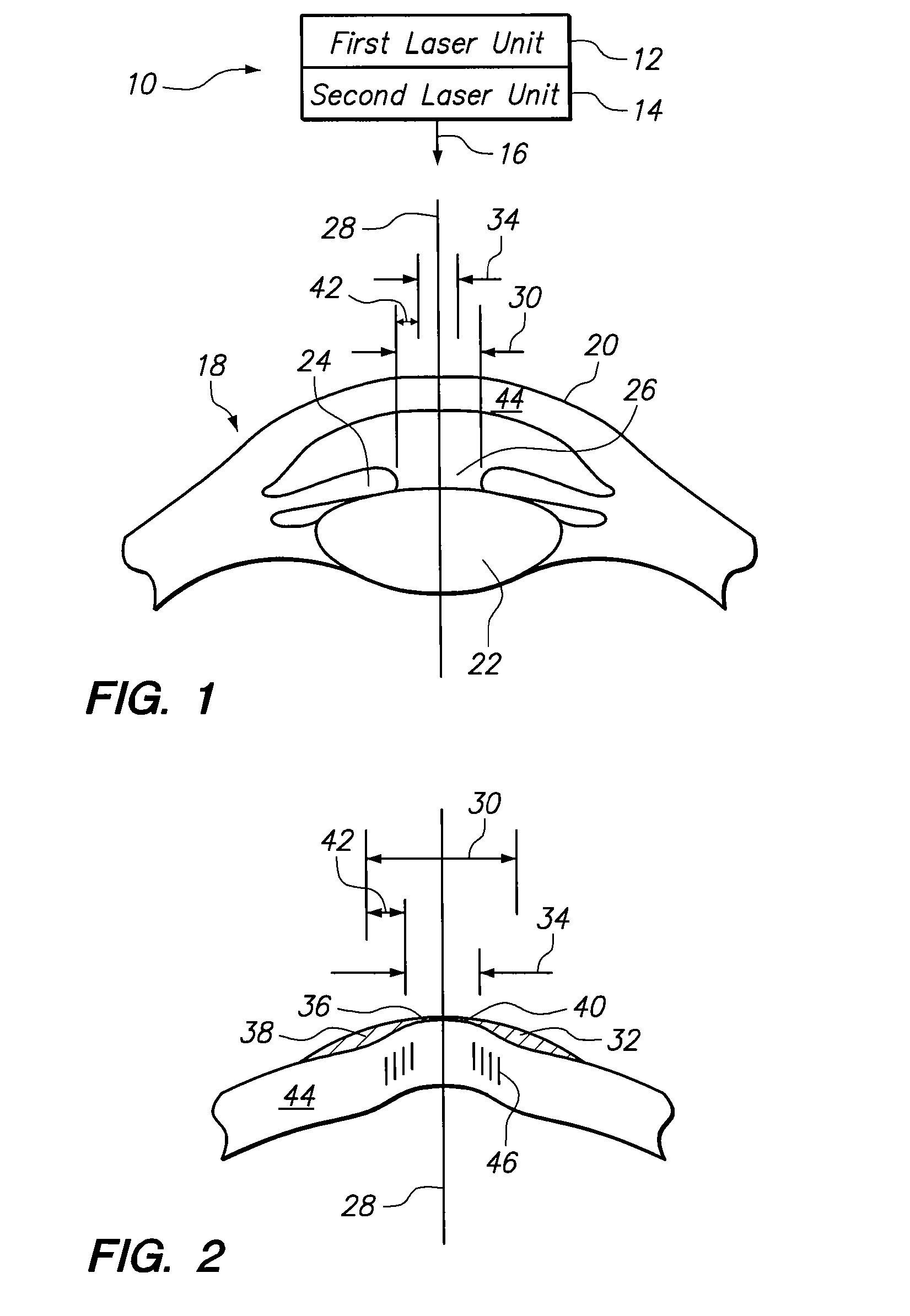
Methods for Employing Intrastromal Corrections in Combination with Surface Refractive Surgery to Correct Myopic/Hyperopic Presbyopia
InactiveUS20100191229A1Reduced accommodationCorrected visionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsKeratorefractive surgeryLaser
A system and method for correcting a vision defect (i.e. presbyopia) of a patient requires two laser units. A first laser unit is used to photoablate (i.e. remove) tissue from the cornea for the creation of a multi-focal cornea that simultaneously provides for both near and distance vision capabilities. A second laser unit can also be used to refine the shape of the cornea by weakening selected portions with LIOB. Together, the removal and weakening of corneal tissue are regulated to optimize the resultant near vision and distant vision capabilities of the patient.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Contact lens for reshaping the altered corneas of post refractive surgery, post ortho-k or keratoconus
ActiveCN100507639CEffective remodelingImprove or rebuild visionEye treatmentOptical partsKeratorefractive surgeryPre operative
A kit for determining a hypothetical cornea for use with post-LASIK and post myopia Ortho-K amendment. The kit has a reference table for determining conformation data by using at least one of following data: pre-treatment KM readings, post-treatment KM readings, power reduced from before- to after-treatment, and post-treatment cornea optical zone. The kit further comprises a plurality of conformed lenses based on the conformation data in predetermined increments from the reference table. The pre-treatment KM readings comprise pre-operative or pre-ortho-K readings. The post-treatment KM readings comprise post-operative or post ortho-K readings. The post-treatment cornea optical zone comprises post-operative or post-ortho-K cornea optical zone. Also, a method of determining a hypothetical cornea for use with post-LASIK and post myopia Ortho-K amendment is disclosed. The method has inputting pre-treatment KM readings, inputting post-treatment KM readings, inputting power reduced from before- to after treatment, inputting post-treatment cornea optical zone, calculating conformation data, which is adapted to be used to generate specification for conformed lenses. Another kit for determining a hypothetical cornea for use with Keratoconus and post-hyperopia Ortho-K amendment can be constructed using at least one of following data: pre-altered KM readings, post-altered KM readings, pre-altered refraction error, and post altered specifications. The kit further comprises a plurality of conformed lenses based on the conformation data in predetermined increments from the reference table. The pre-altered KM readings comprise pre-keratoconus or pre-hyperopia ortho-K readings. The pre-altered refraction errors comprise refraction errors from a set of normal corneas. The post-altered specifications comprise cone widths of Keratoconus or steepened cornea zone of hyperopic Ortho-K and also magnitude of off centering of the cone apex.
Owner:董晓青
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com