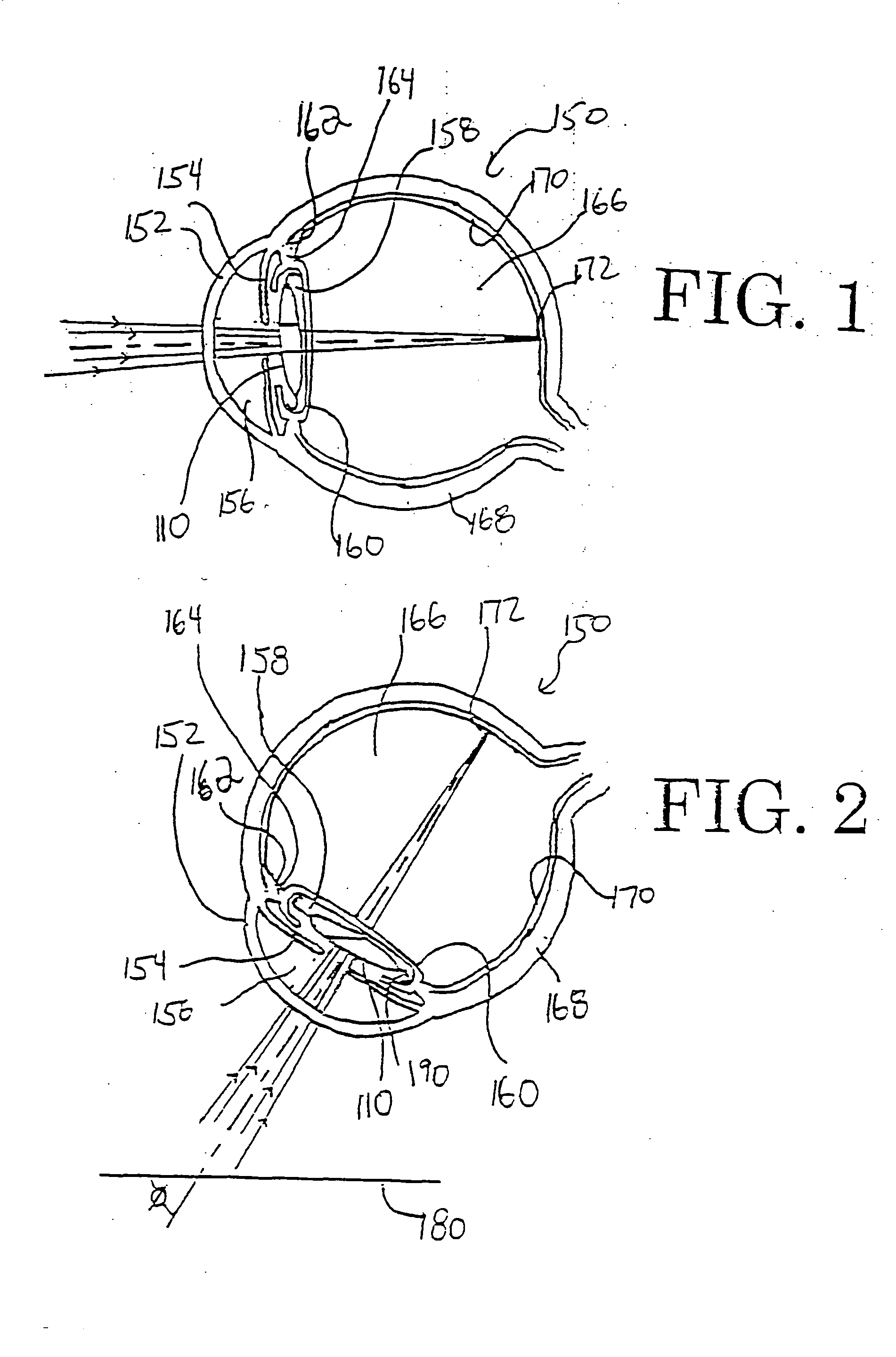
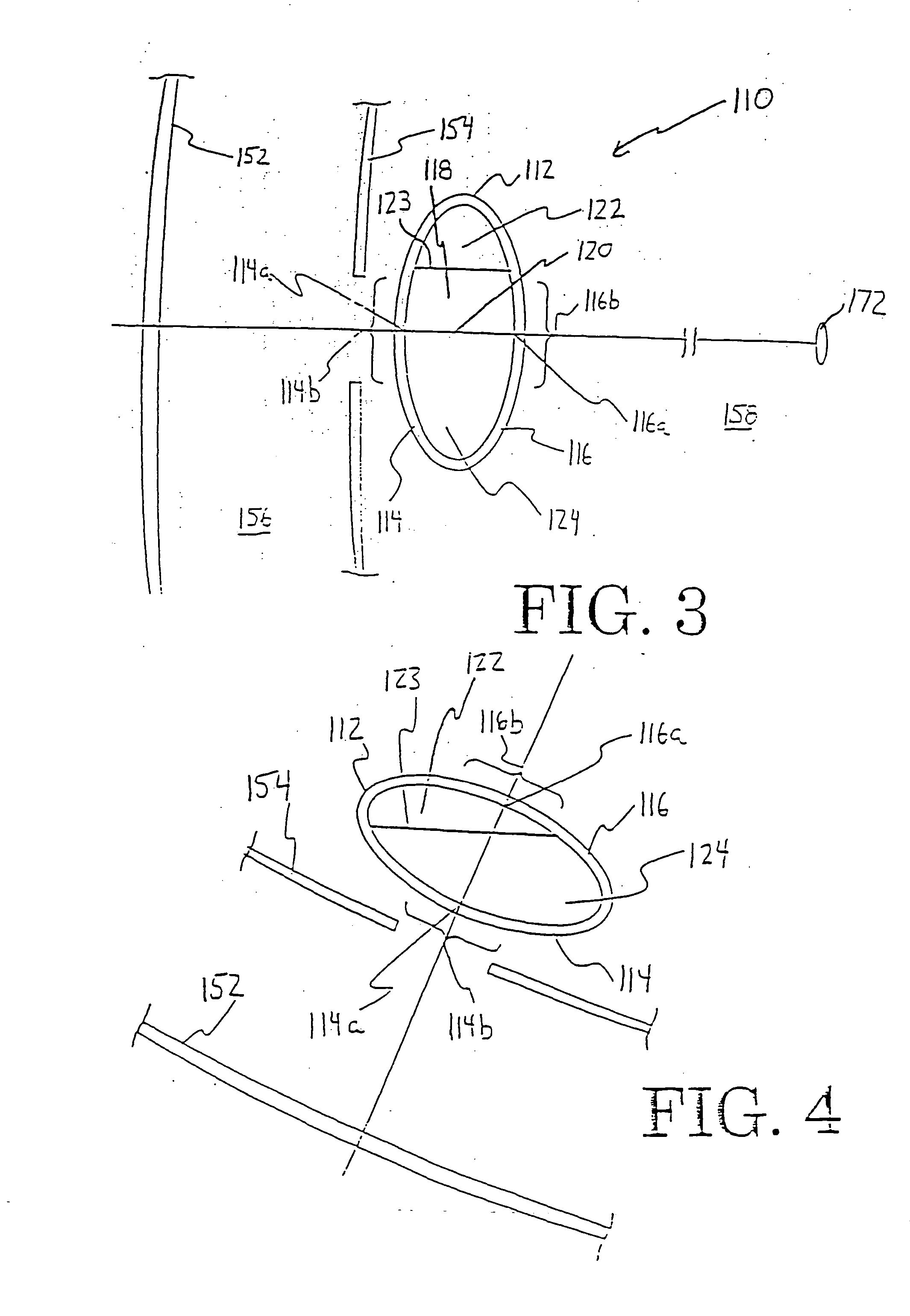
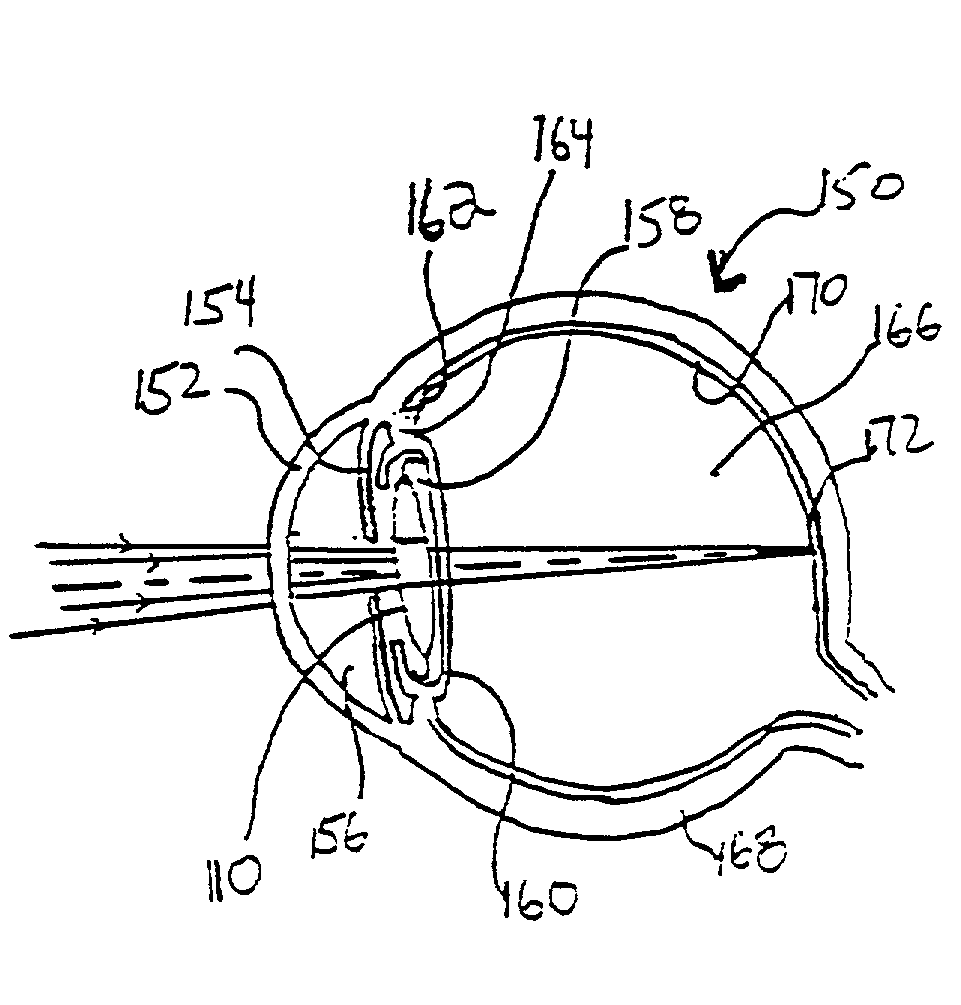
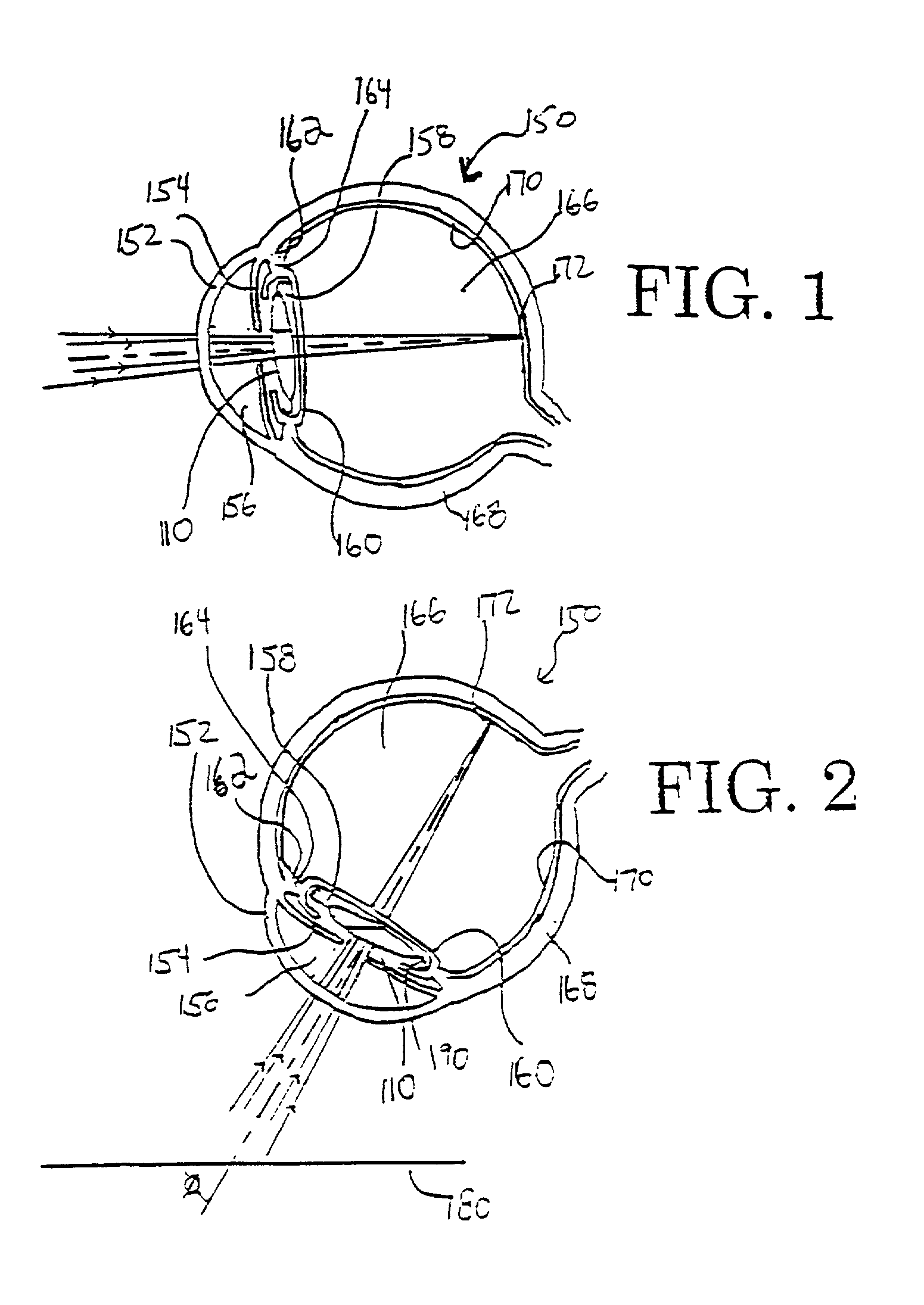
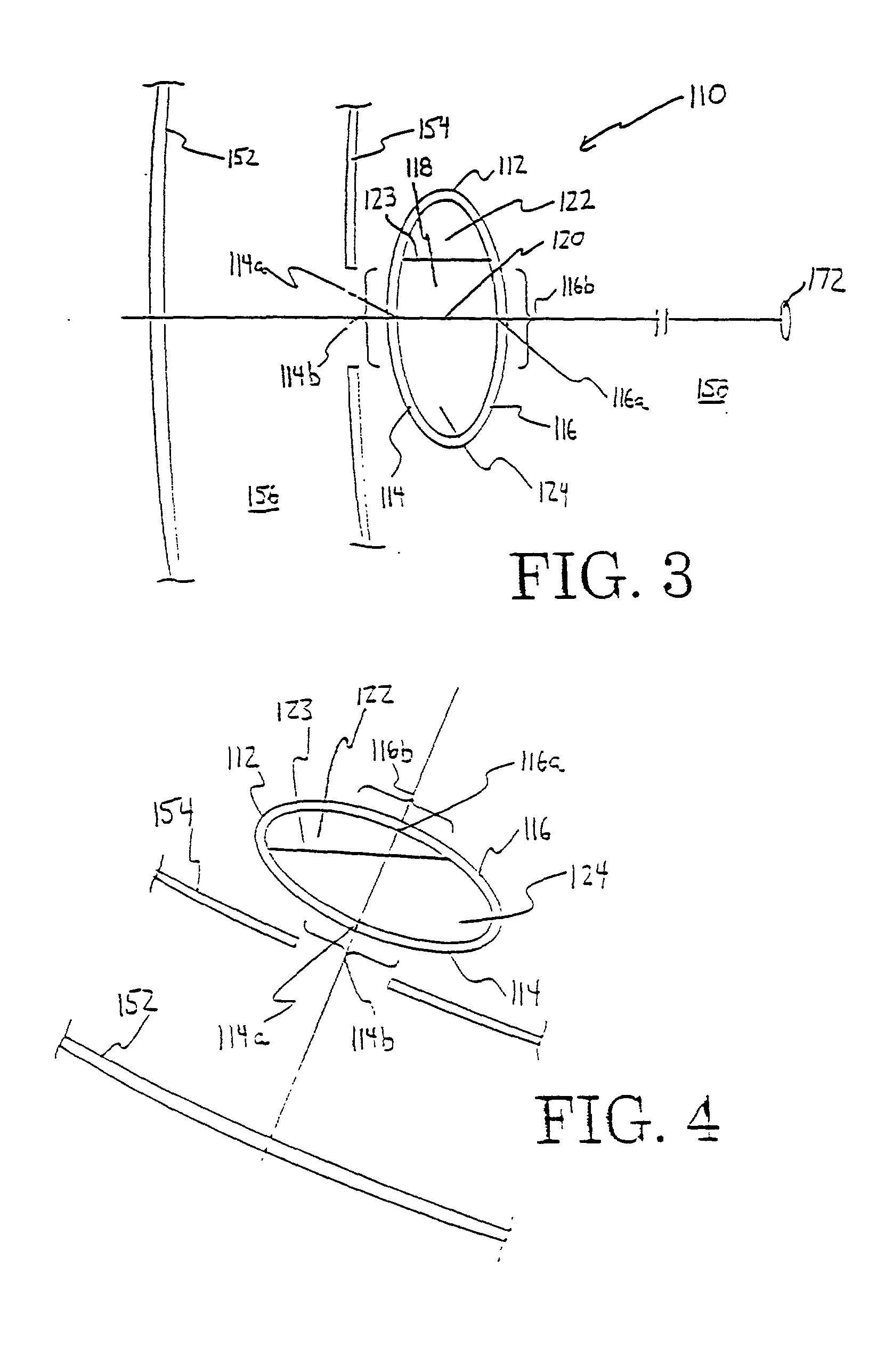
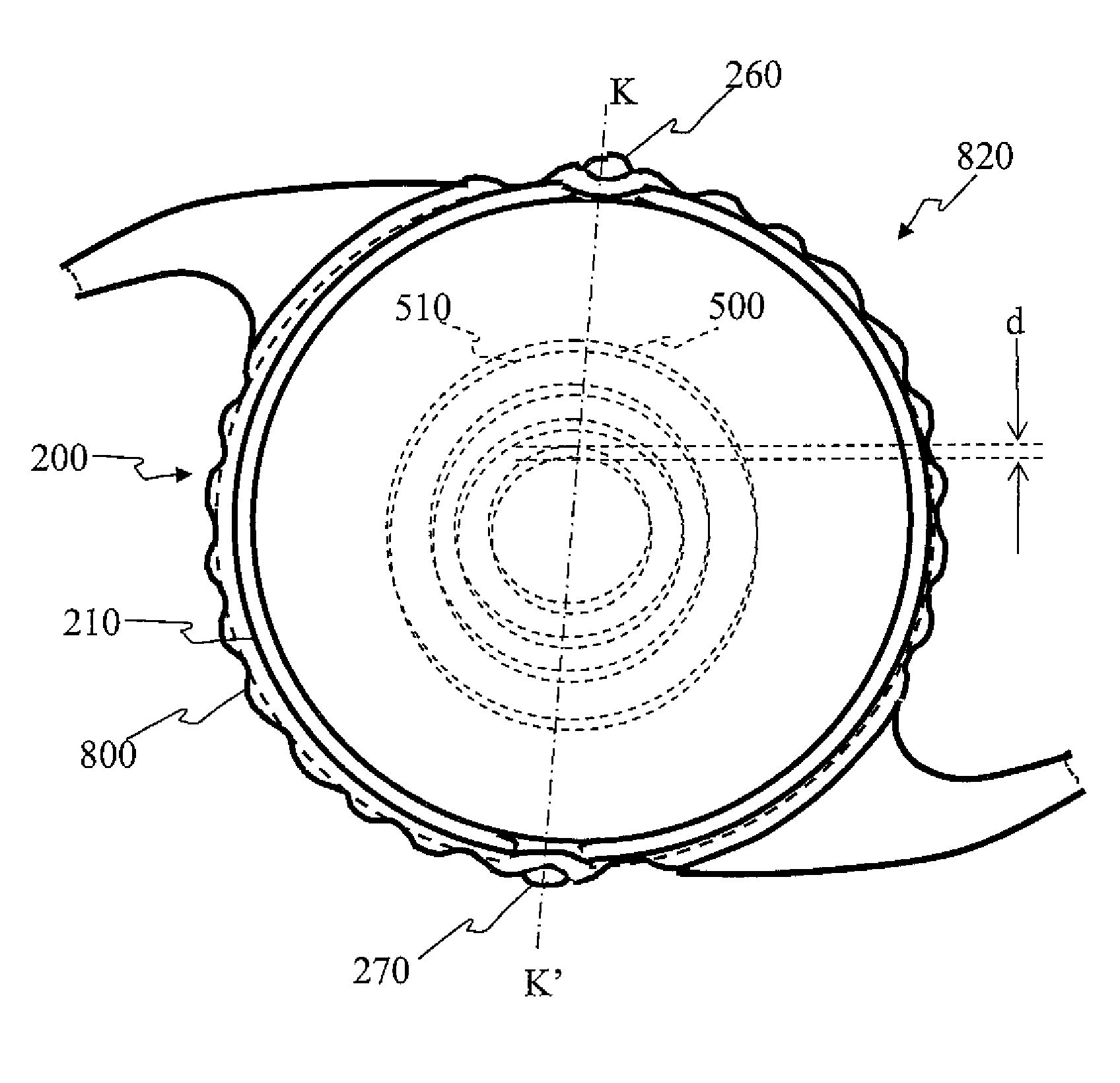
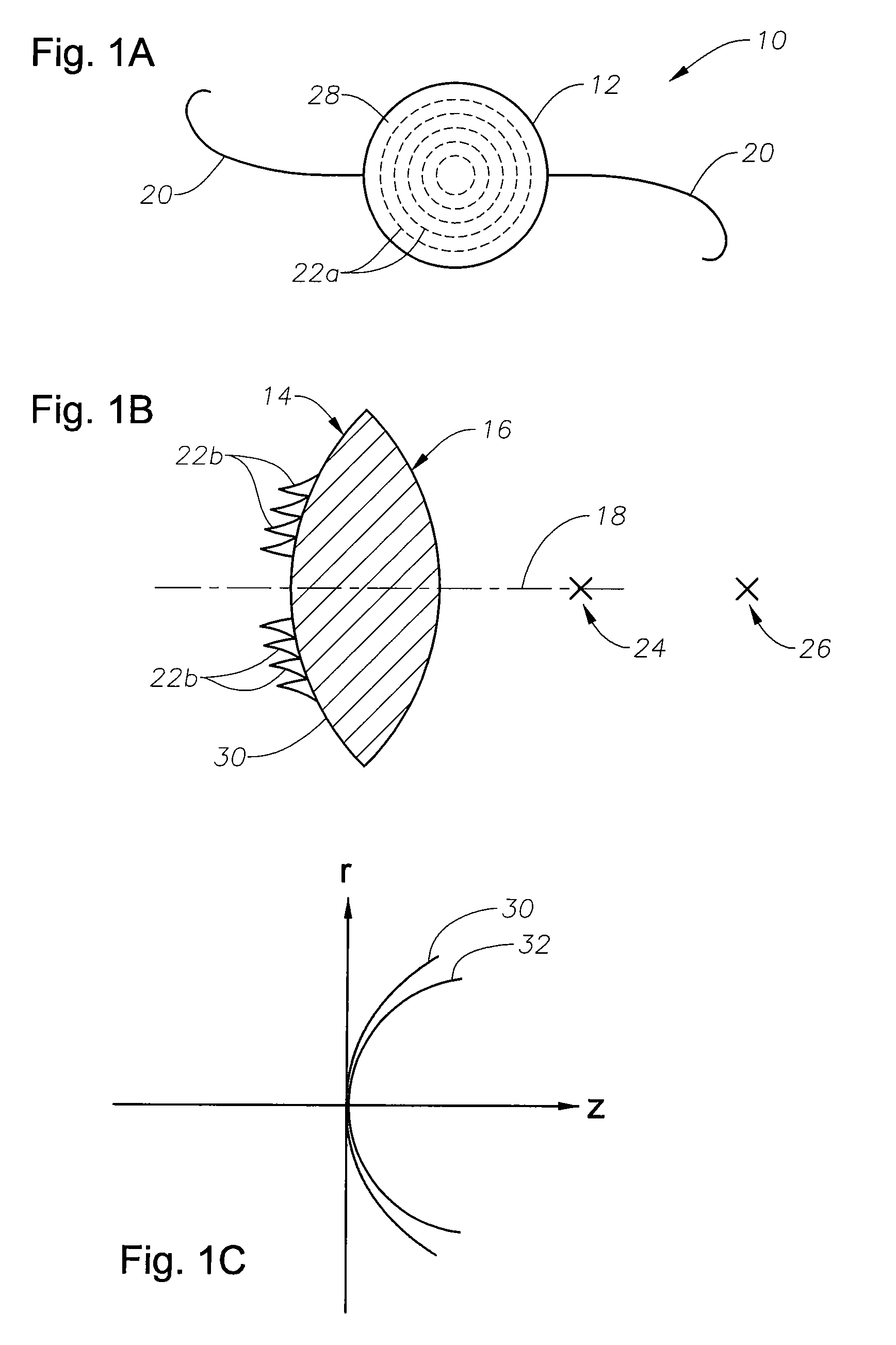
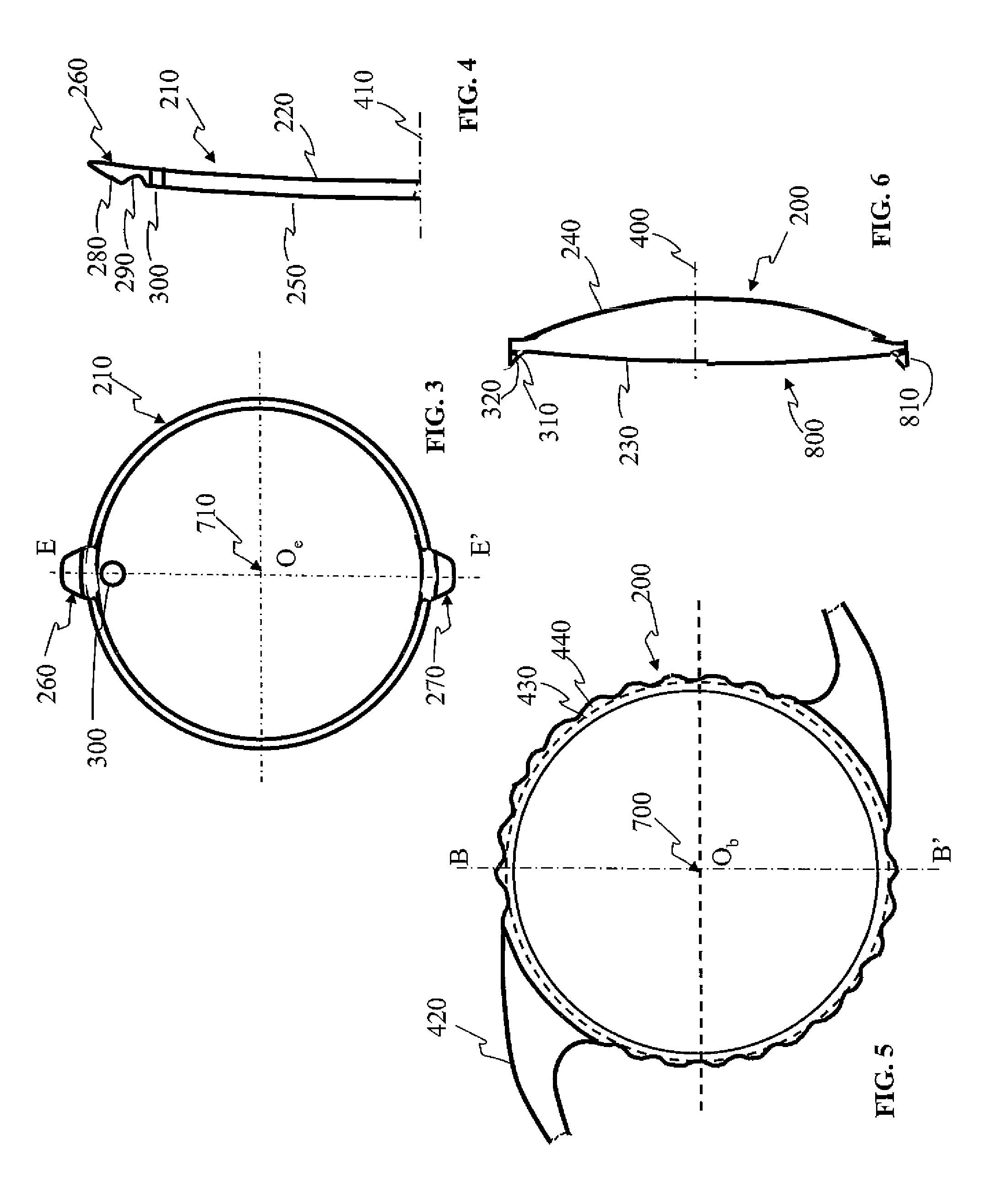
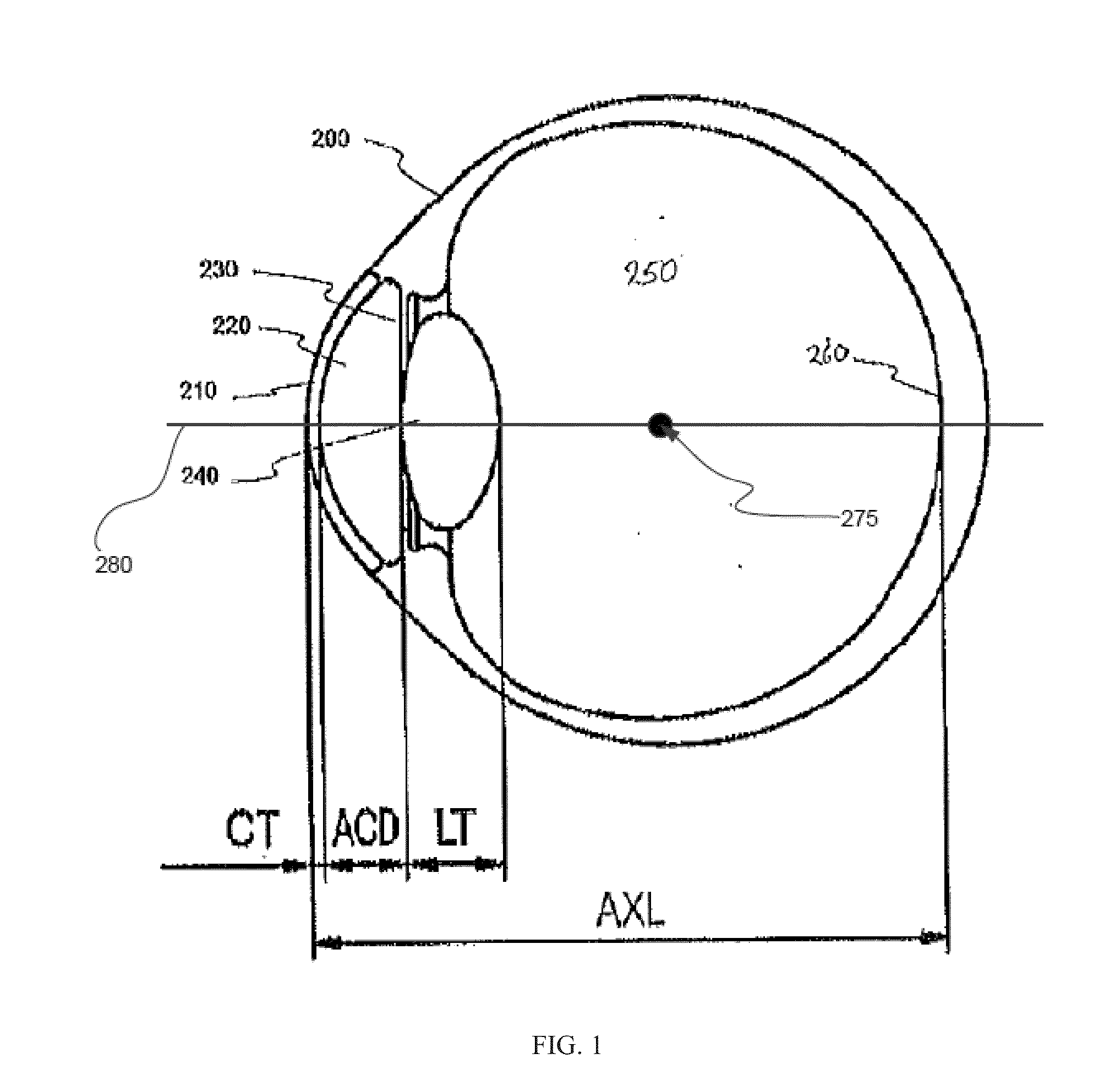
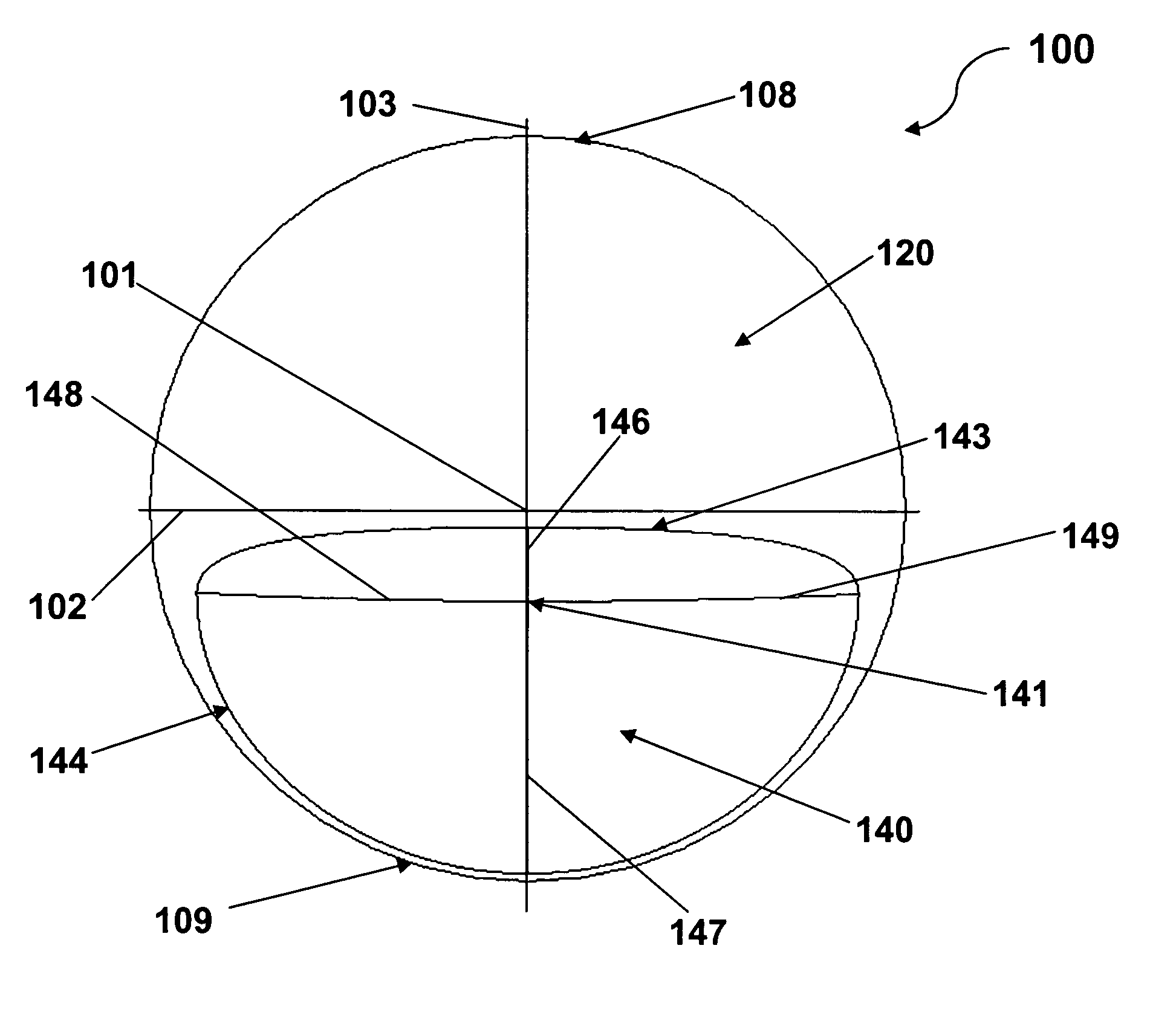
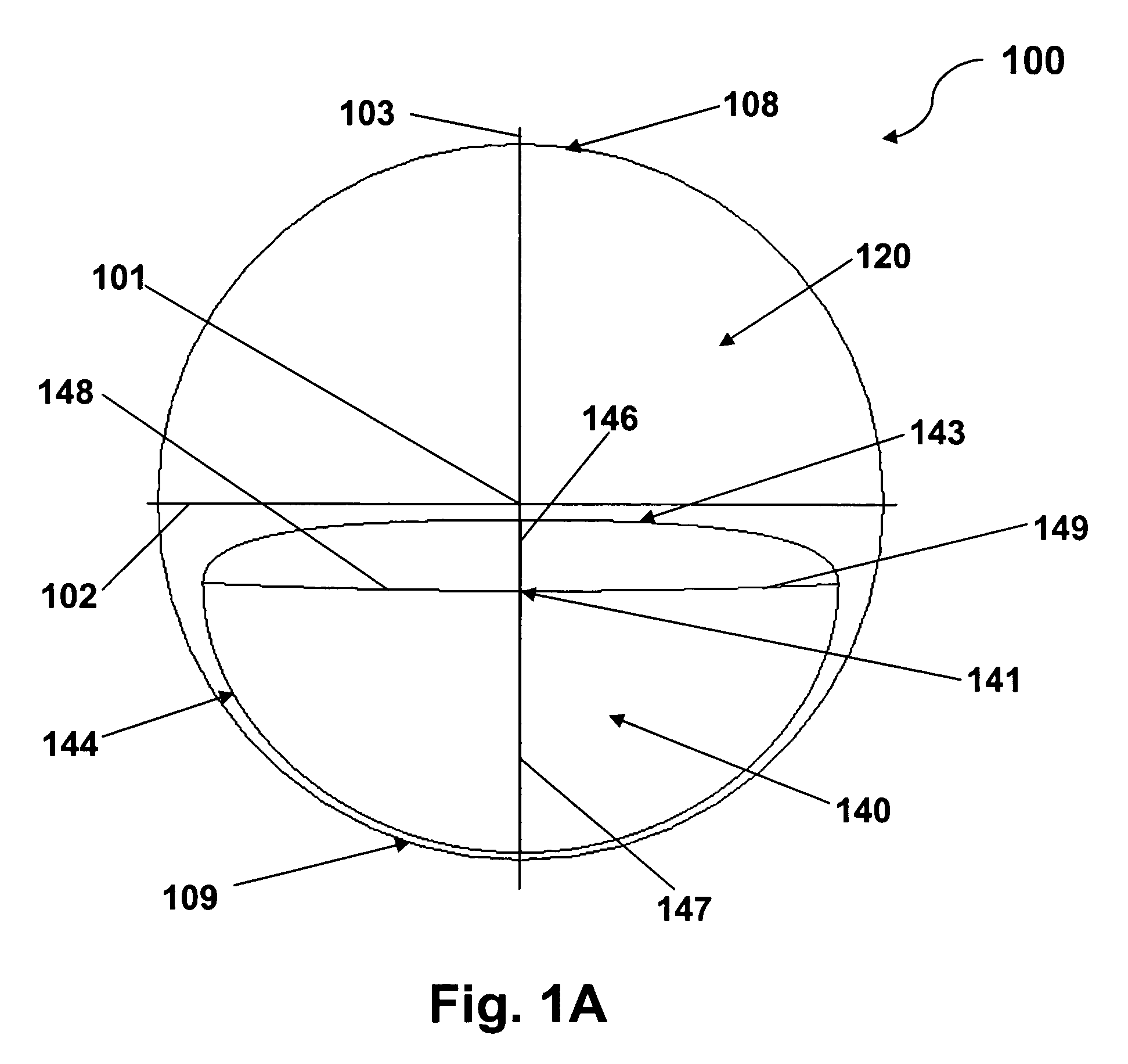
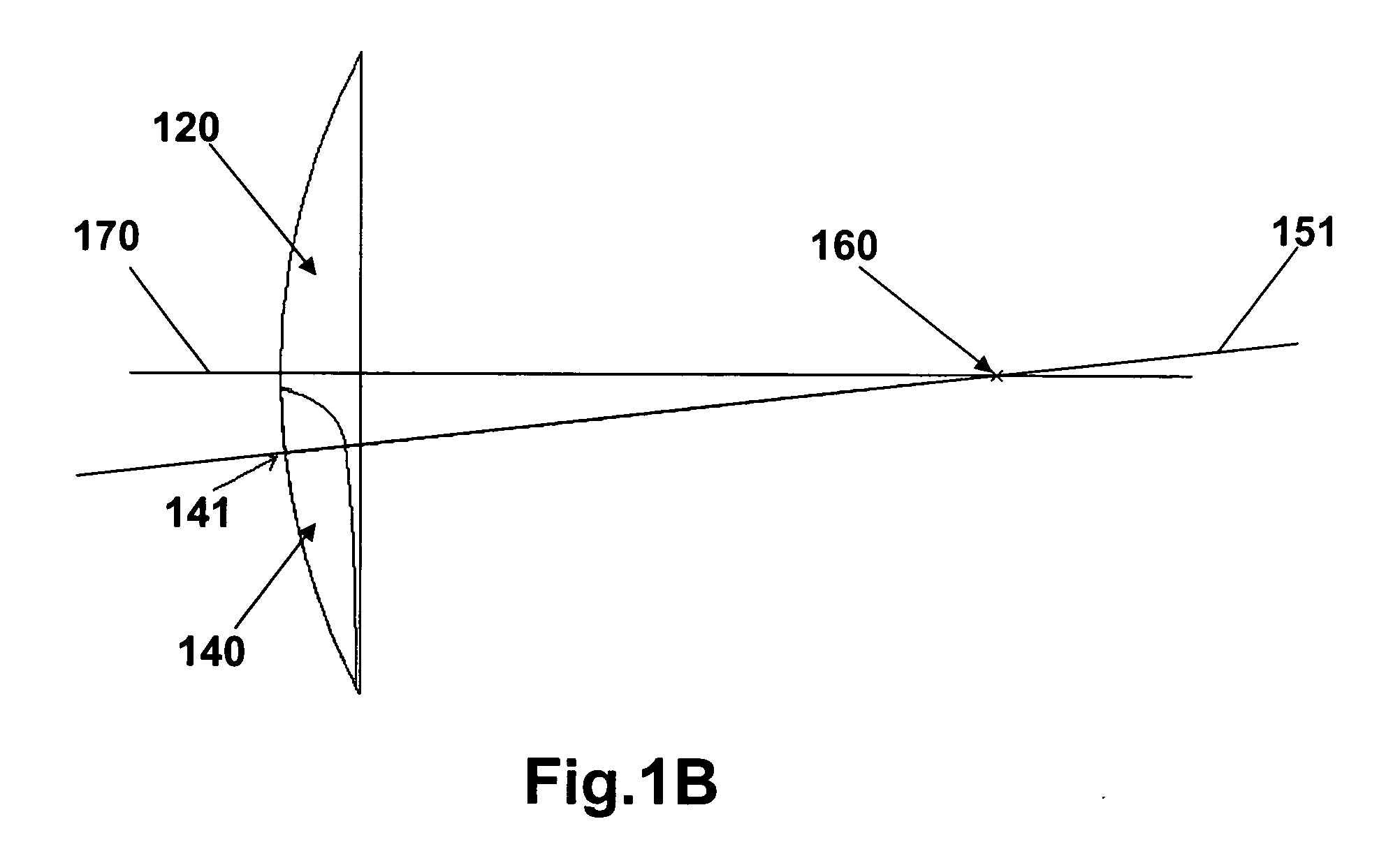
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Multifocal intraocular lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
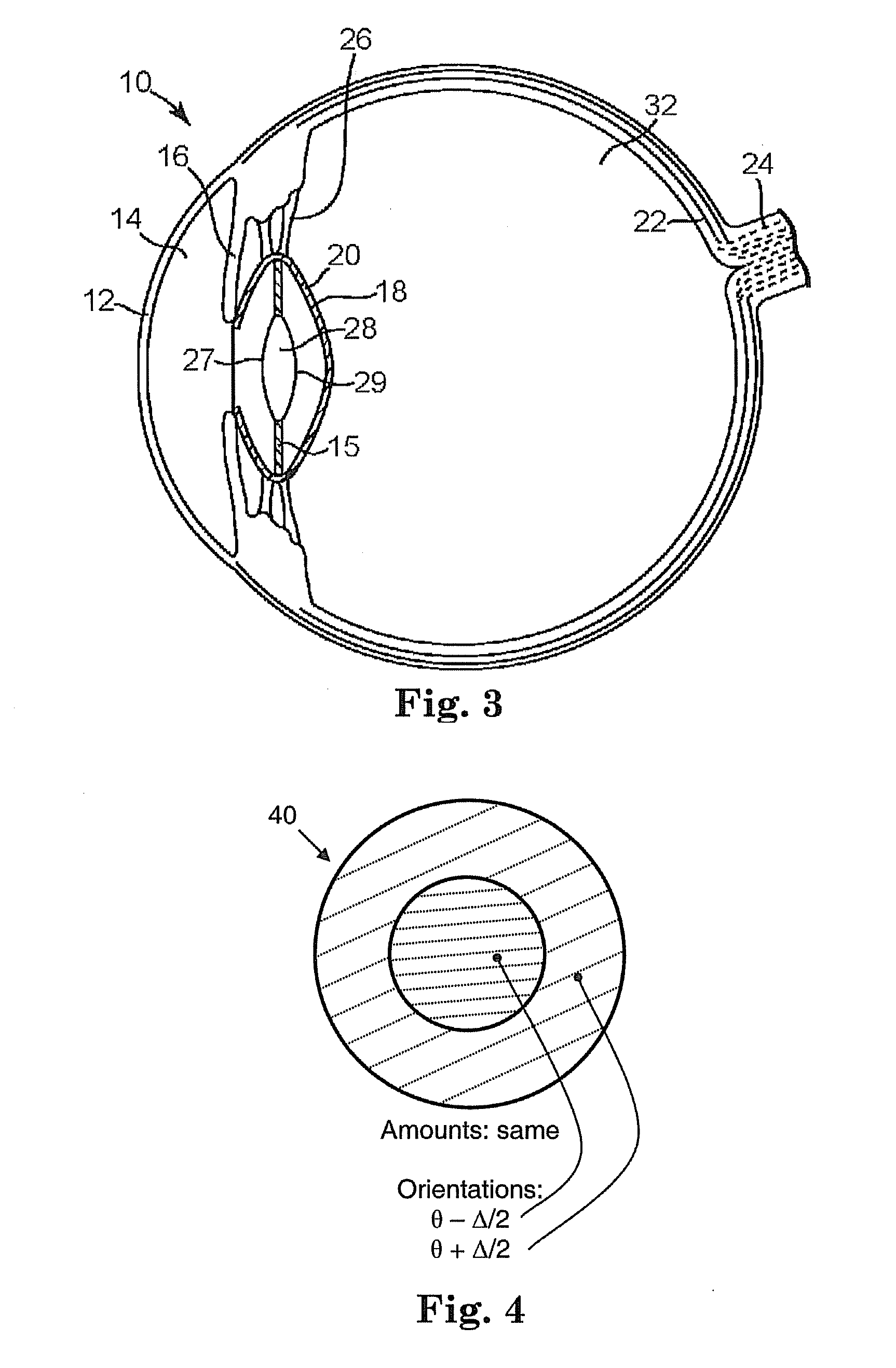
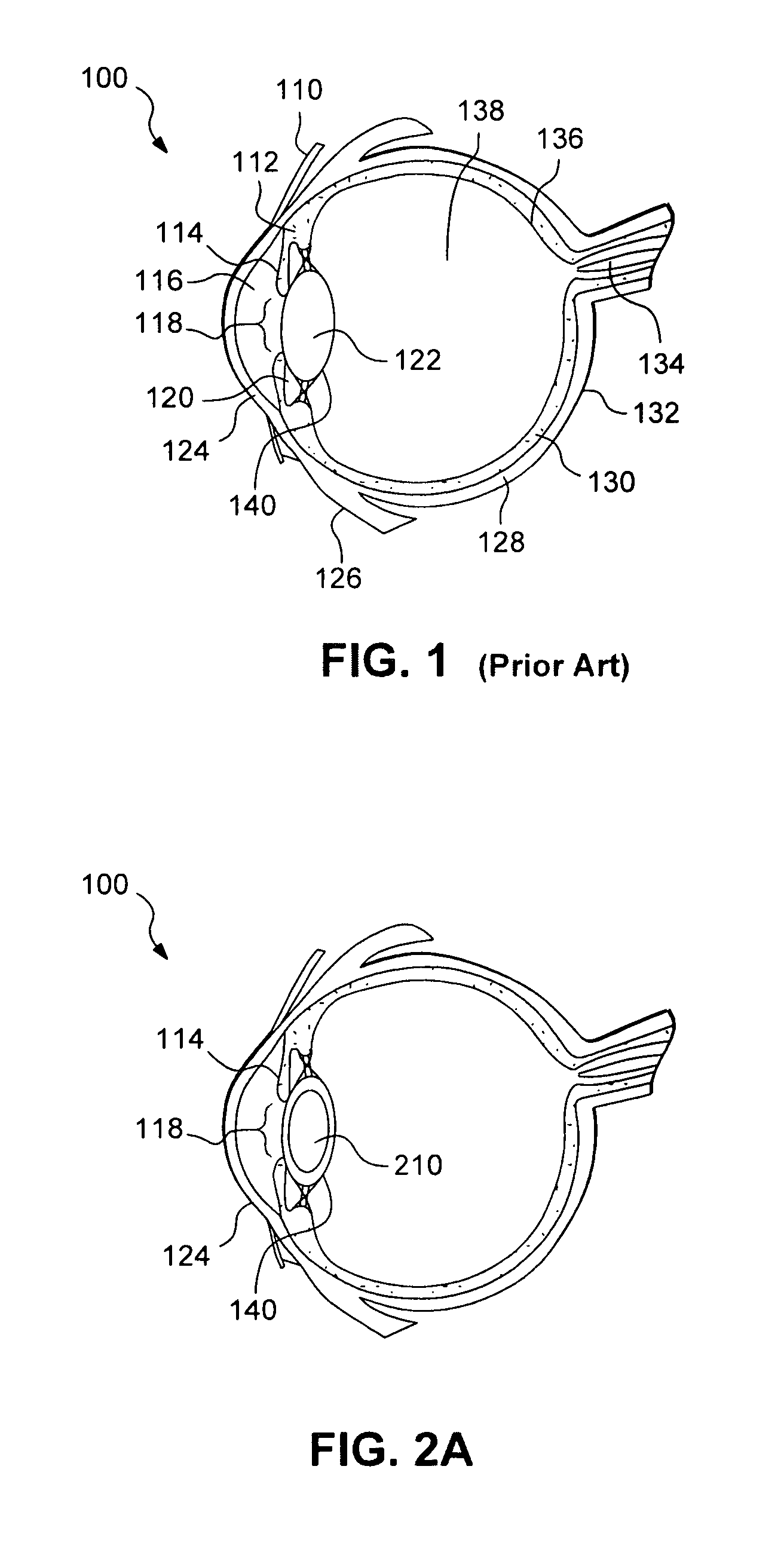
Multifocal and Accommodating intraocular lenses are artificial intraocular lenses (IOLs) that are designed to provide focus of both distance and near objects, in contrast to monofocal intraocular lenses which only have one focal point and correct distance vision. The issue of restoring accommodation following cataract surgery or through refractive lens exchange is becoming an increasingly important topic in ophthalmology.
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20040156014A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
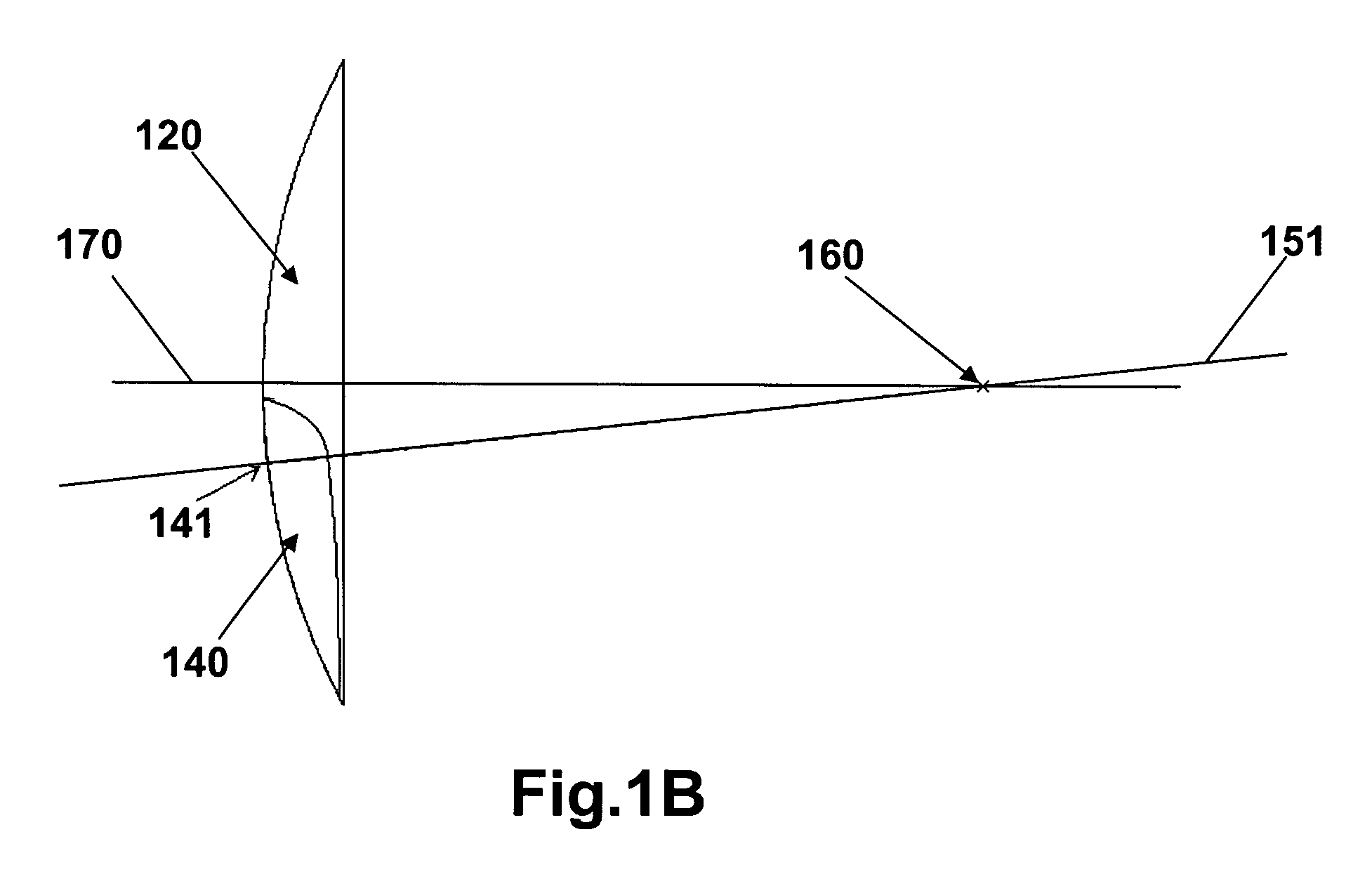
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20060116764A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensImage contrast
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:ALCON INC
Toric intraocular lens with modified power characteristics
An intraocular lens for correcting or reducing the astigmatism of a cornea includes an optical element that has optical properties and characteristics that make it tolerant of rotational misalignment, when compared to a comparable lens having a uniform astigmatism orientation across its entire optical element, leading to more relaxed tolerances for a surgeon that implants the lens. The optical element of the toric ophthalmic lens has meridians associated therewith, including a high power meridian and a low power meridian orthogonal to the high power meridian. The optical element has at least one radially modulated meridian along which power monotonically varies with increasing radial position.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS6855164B2Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensOptical axisRefractive index
This intraocular lens includes an optic body having anterior and posterior walls, a chamber, and optically transmissive primary and secondary fluids, and method for making and using the same. The secondary fluid is substantially immiscible with the primary fluid and has a different density and a different refractive index than the primary fluid. The primary fluid is present in a sufficient amount that orienting optical body optical axis horizontally for far vision positions the optical axis through the primary fluid, thereby immersing the anterior and posterior optical centers in the primary fluid. The secondary fluid is contained in the optic body in a sufficient amount that orienting the optical axis at a range of effective downward angles relative to the horizontal for near vision positions the optical axis to extend through the primary fluid and the secondary fluid, thus changing the focus of the intraocular lens.
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal design for ocular implant
ActiveUS20100161048A1Reduce step heightIncrease depth of focusIntraocular lensMedicineOptical energy
A radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL for ocular implant is provided. The ocular implant can comprise a radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal intraocular lens optic and a number of haptics. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL may pass optical energy in both photopic and mesopic conditions. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL includes a number of radially segmented apodization zones, each radially segmented apodization zones having a unique focal length. The haptics mechanically couple to the apodized diffractive multifocal IOL optic in order to position and secure the apodized diffractive multifocal IOL within the eye. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL may include both a diffractive region and a refractive region.
Owner:ALCON INC
Intraocular multifocal lens
In accordance with the present invention, a multifocal intraocular lens provides greater or lesser refraction in relation to the position of the head and eyes of a user. A multifocal intraocular lens body for insertion into a fluid-filled enucleated natural lens capsule of an eye is provided wherein the lens body encompasses the optical axis of the eye and provides different greater or lesser refraction depending upon the position of the eye. In a second embodiment, the lens body can be used with an artificial lens capsule implanted within an eye.
Owner:MCDONALD & CO
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS7377641B2Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20050071002A1Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensLens crystallineOptical axis
An intraocular lens is provided that includes an optic body having anterior and posterior walls, a chamber, and optically transmissive primary and secondary fluids, and method for making and using the same. The secondary fluid is substantially immiscible with the primary fluid and has a different density and a different refractive index than the primary fluid. The primary fluid is present in a sufficient amount that orienting optical body optical axis horizontally for far vision positions the optical axis through the primary fluid, thereby immersing the anterior and posterior optical centers in the primary fluid. The secondary fluid is contained in the optic body in a sufficient amount that orienting the optical axis over a range of effective downward angles relative to the horizontal for near vision positions the optical axis to extend through the primary fluid and the secondary fluid, thus changing the focus of the intraocular lens.
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20030093149A1Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensOptical axisRefractive index
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Adjustable multifocal intraocular lens system
InactiveUS20110125261A1Overcomes the issues of ocular trauma of the lens exchangeEasy to measureMetal working apparatusIntraocular lensIntraocular lensAnterior surface
An adjustable multifocal intraocular lens system for an individual's eye, includes a base multifocal intraocular lens having an optic with an optical axis, a peripheral edge, a multifocal optical power anterior surface and a posterior surface along with an attachment for maintaining said base multifocal lens in the individual's eye with the optical axis centered along an eye optical axis. An enhanced multifocal intraocular lens is provided with an optic with a peripheral edge, an anterior surface and a reverse multifocal optical power posterior surface, and a coupling enables assembly of the base lens and enhance lens with the enhance lens posterior surface overlaying the base lens anterior surface in order that the enhance intraocular lens reverse multifocal surface adjust multifocal powers of the base IOL by substantially masking near power of the base multifocal intraocular lens.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
Apodized aspheric diffractive lenses
InactiveUS20100087921A1Improve image contrastSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryCamera lensAnterior surface
Aspheric diffractive lenses are disclosed for ophthalmic applications. For example, multifocal intraocular lens (IOLs) are disclosed that include an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface, at least one of which surfaces includes an aspherical base profile on a portion of which a plurality of diffractive zones are disposed so as to generate a far focus and a near focus. The aspherical base profile enhances image contrast at the far focus of the lens relative to that obtained by a substantially identical IOL in which the respective base profile is spherical.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Adjustable multifocal intraocular lens system
InactiveUS8287593B2Overcomes the issues of ocular trauma of the lens exchangeEasy to measureMetal working apparatusIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
An adjustable multifocal intraocular lens system for an individual's eye, includes a base multifocal intraocular lens having an optic with an optical axis, a peripheral edge, a multifocal optical power anterior surface and a posterior surface along with an attachment for maintaining the base multifocal lens in the individual's eye with the optical axis centered along an eye optical axis. An enhanced multifocal intraocular lens is provided with an optic with a peripheral edge, an anterior surface and a reverse multifocal optical power posterior surface, and a coupling enables assembly of the base lens and enhance lens with the enhance lens posterior surface overlaying the base lens anterior surface in order that the enhance intraocular lens reverse multifocal surface adjust multifocal powers of the base IOL by substantially masking near power of the base multifocal intraocular lens.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
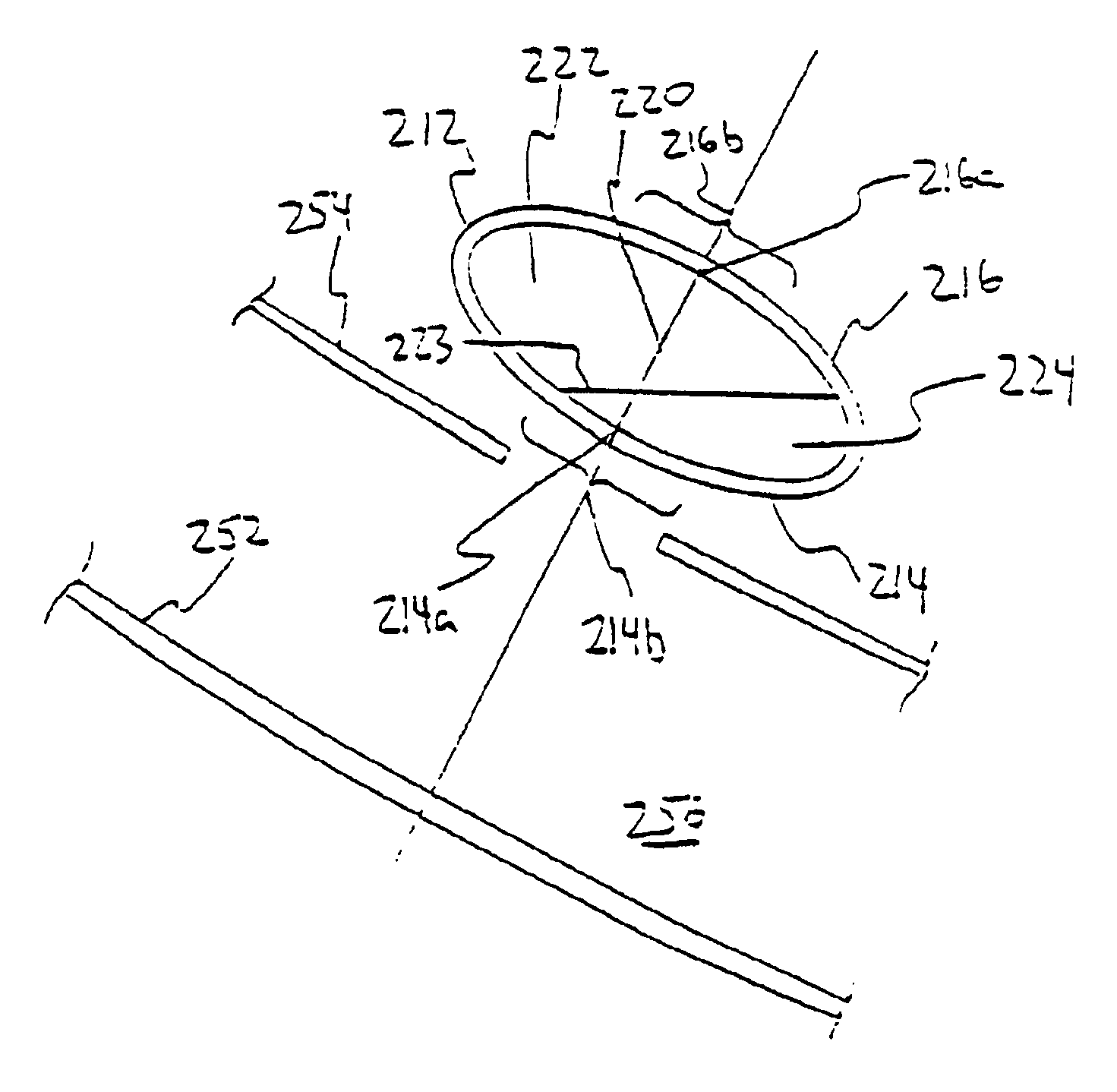
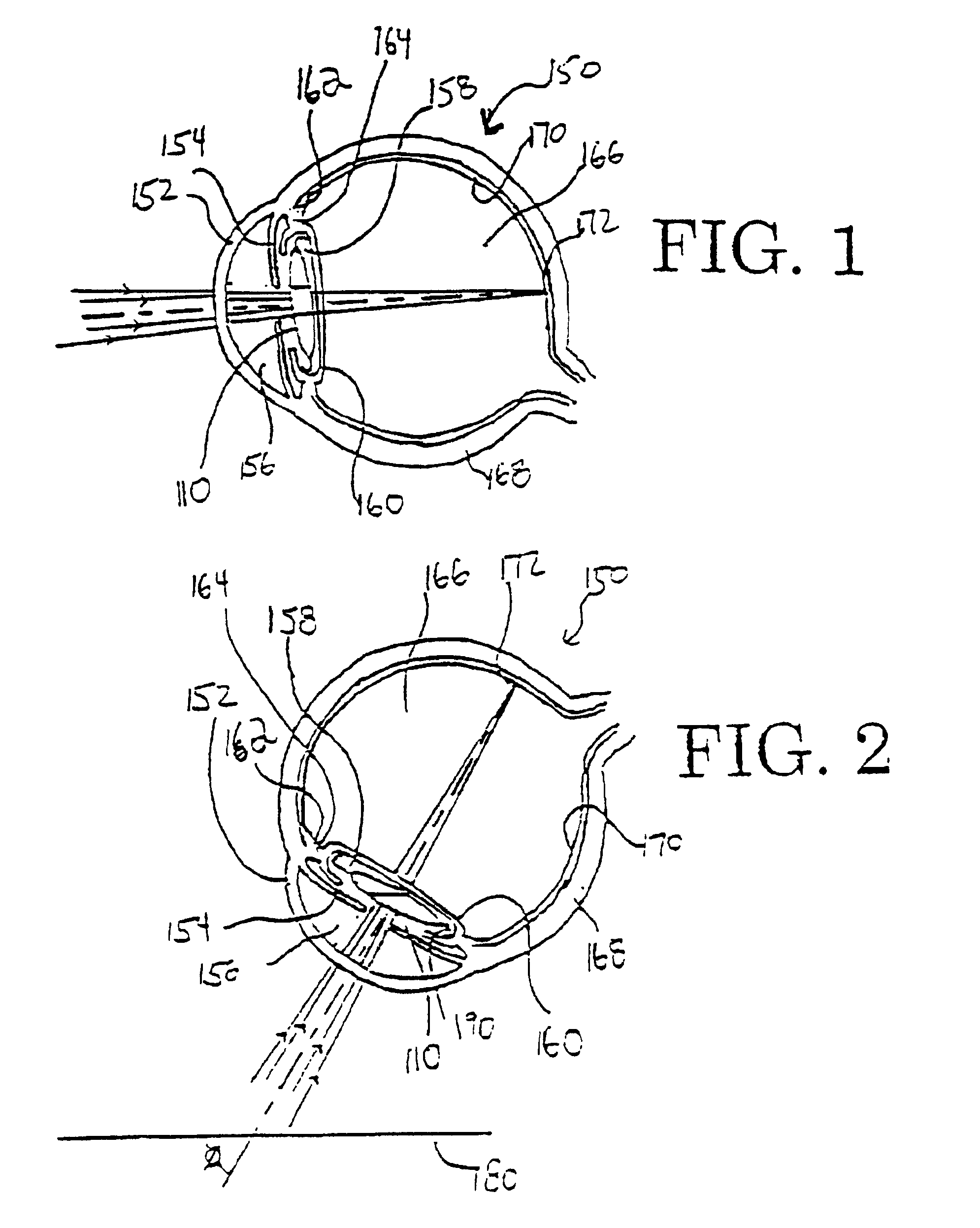
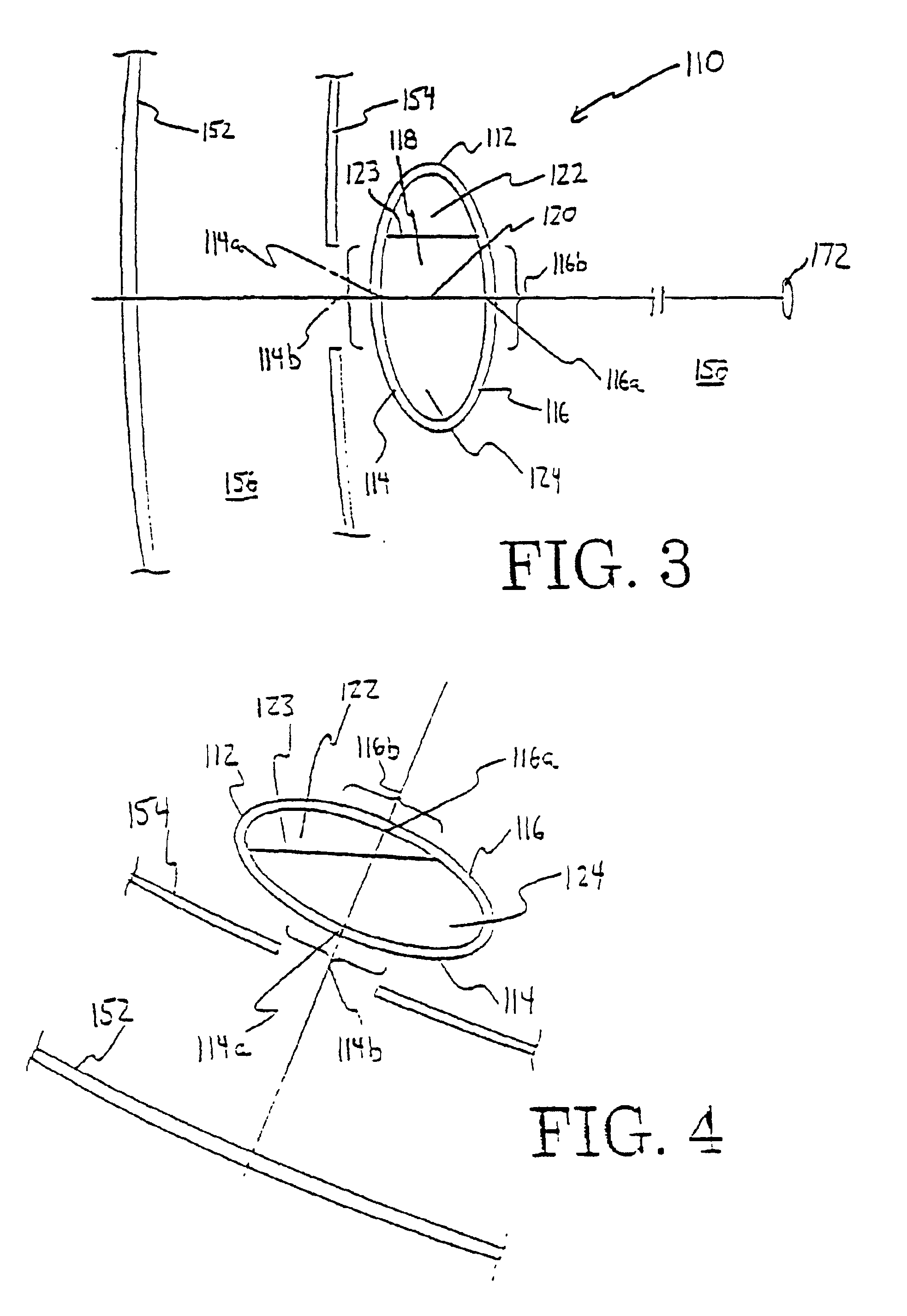
Optical angular measurement system for ophthalmic applications and method for positioning of a toric intraocular lens with increased accuracy
An ophthalmic system for use in performing angular measurements in relation to a patient's eye. The ophthalmic system can include an optical angular measurement device that can provide angular indicia by, for example, projecting an image of an angular measurement reticle onto a patient's eye or by superimposing an image of an angular measurement reticle onto an image of the patient's eye. The ophthalmic system can include an optical refractive power measurement device for providing desired angular orientations for ocular implants or for incisions. The ophthalmic system can be used, for example, to align a toric intraocular lens to a desired angular orientation.
Owner:ALCON INC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS20060244906A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Multifocal opthalmic lens
This invention is generally related to vision corrections by means of multifocal ophthalmic lenses or by means of corneal refractive surgery. In particular, the present invention provides a multifocal contact lens, a multifocal intraocular lens, a method for making a multifocal ophthalmic lens (contact lens and intraocular lens), and a method of correcting presbyopia by reshaping the cornea of an eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Phase-shifted center-distance diffractive design for ocular implant
ActiveUS20110098811A1Improved diffractive multifocal designImprove eyesightIntraocular lensPhase shiftedMedicine
A diffractive multifocal design for ocular implant is provided. This ocular implant includes a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) and a number of haptics. The diffractive multifocal IOL passes optical energy to distance, intermediate and near foci. The haptics mechanically couple to the diffractive multifocal IOL in order to position and secure the diffractive multifocal IOL within the eye. The diffractive multifocal IOL may include both a diffractive region and a refractive region, the diffractive multifocal IOL operable to phase shift optical energy such that constructive interference occurs within the diffractive region and the refractive region.
Owner:ALCON INC
Multi-focal intraocular lens with asymmetric point spread function
The present invention describes a multi-focal intraocular lens for the human eye. The intraocular lens of the present invention provides improved vision quality over a range of object distances without producing glare or halos. It also provides non-symmetric, or nearly symmetric, optical zones about the lens optical axis.
Owner:SARVER EDWIN J +1
Multifocal intraocular lens
InactiveUS20090240328A1Reduce eye traumatismShorten post-surgical time periodIntraocular lensIntraocular lensVisual acuity
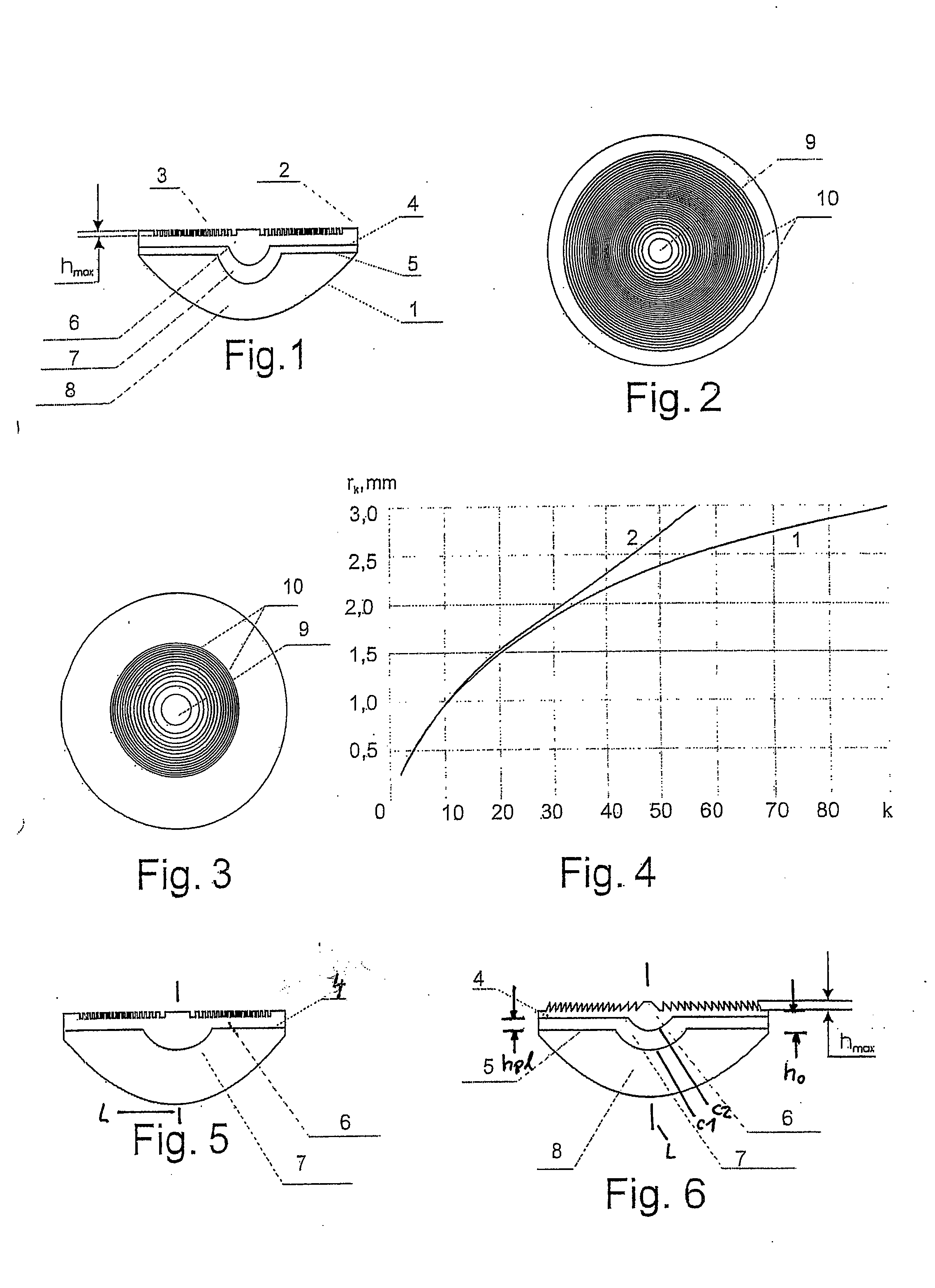
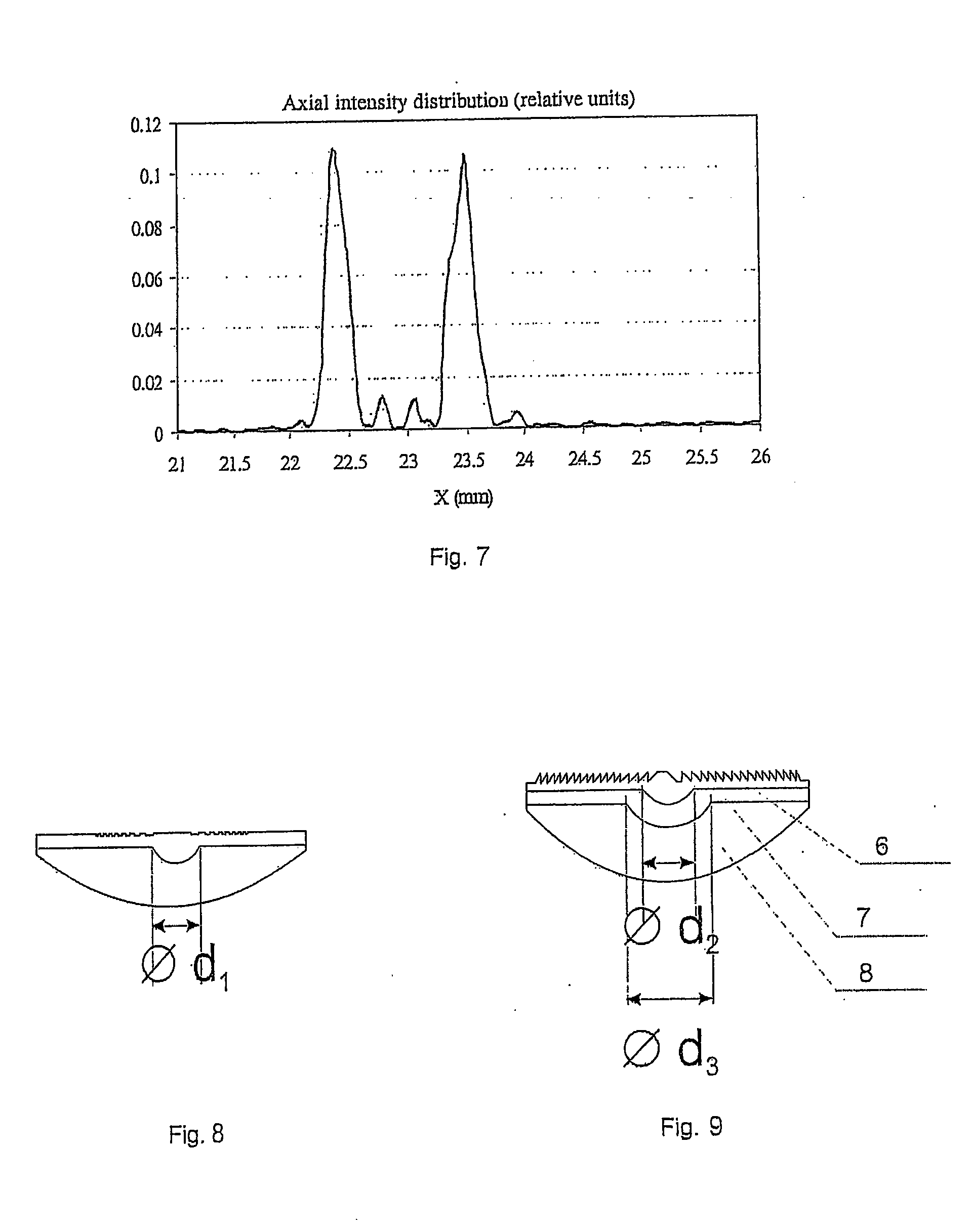
A multifocal intraocular lens is provided having two external refractive surfaces and a longitudinal axis, and a diffractive structure superimposed on one of the surfaces in the form of a Fresnel zone. To reduce eye traumatism during surgery, to shorten post-surgical time period, to increase visual acuity, and to ensure a constant quality image at any distance from an object, a multifocal intraocular lens is proposed in which at least one additional refractive surface is inserted between the two external refractive surfaces, wherein the at least one additional refractive surface divides the lens volume into zones made of materials having different refraction coefficients.
Owner:ICON LAB
Phase-shifted center-distance diffractive design for ocular implant
ActiveUS8652205B2Improved diffractive multifocal designImprove eyesightIntraocular lensPhase shiftedMedicine
A diffractive multifocal design for ocular implant is provided. This ocular implant includes a diffractive multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) and a number of haptics. The diffractive multifocal IOL passes optical energy to distance, intermediate and near foci. The haptics mechanically couple to the diffractive multifocal IOL in order to position and secure the diffractive multifocal IOL within the eye. The diffractive multifocal IOL may include both a diffractive region and a refractive region, the diffractive multifocal IOL operable to phase shift optical energy such that constructive interference occurs within the diffractive region and the refractive region.
Owner:ALCON INC
Dual-optic intraocular lens that improves overall vision where there is a local loss of retinal function
ActiveUS20150265399A1Improve eyesightReduce sensitivityRefractometersSkiascopesCentral visionPeripheral retina
Systems and methods are provided for improving overall vision in patients suffering from a loss of vision in a portion of the retina (e.g., loss of central vision) by providing a dual optic intraocular lens which redirects and / or focuses light incident on the eye at oblique angles onto a peripheral retinal location. The intraocular lens can include a redirection element (e.g., a prism, a diffractive element, or an optical component with a decentered GRIN profile) configured to direct incident light along a deflected optical axis and to focus an image at a location on the peripheral retina. Optical properties of the intraocular lens can be configured to improve or reduce peripheral errors at the location on the peripheral retina. One or more surfaces of the intraocular lens can be a toric surface, a higher order aspheric surface, an aspheric Zernike surface or a Biconic Zernike surface to reduce optical errors in an image produced at a peripheral retinal location by light incident at oblique angles.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Multi-focal intraocular lens system and methods
InactiveUS20090032679A1Accurately determine changeAccurately determineOptical rangefindersInvestigating moving sheetsIntraocular lensVisual perception
The invention pertains to methods, components, and operations of multi-focal intraocular lens systems, including range finding for driving same and for discriminating between multiple objects and varying brightness conditions. The invention also pertains to intraocular photosensors and range-finding methods to be used with intra-ocular lens systems, and components, that provide multi-focal IOL capabilities in dynamic visual environments.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
This invention is generally related to vision corrections by means of multifocal ophthalmic lenses or by means of corneal refractive surgery. In particular, the present invention provides a multifocal contact lens, a multifocal intraocular lens, a method for making a multifocal ophthalmic lens (contact lens and intraocular lens), and a method of correcting presbyopia by reshaping the cornea of an eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
Multi-focus intraocular lens
ActiveCN107212949AEliminate chromatic aberrationLarge depth of focusIntraocular lensIntraocular lensPlastic injection molding
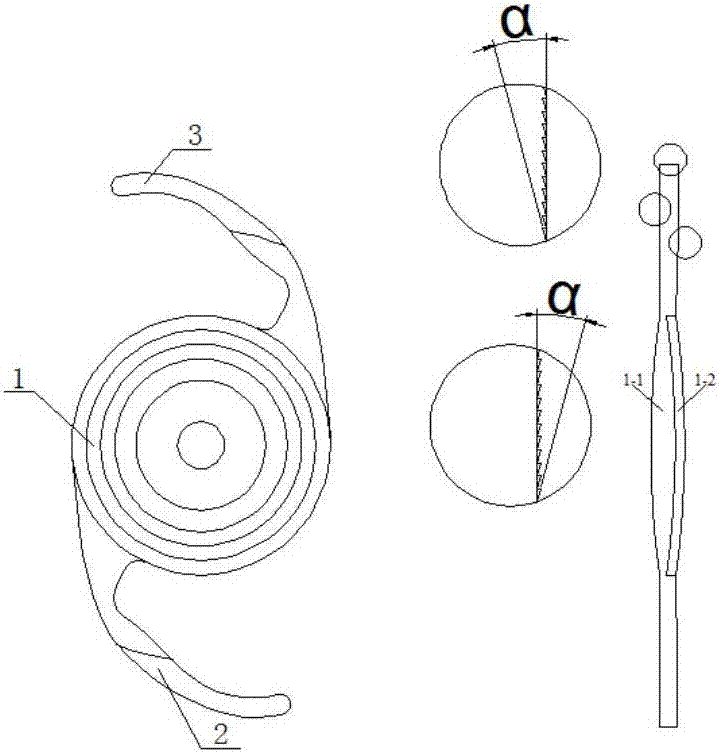
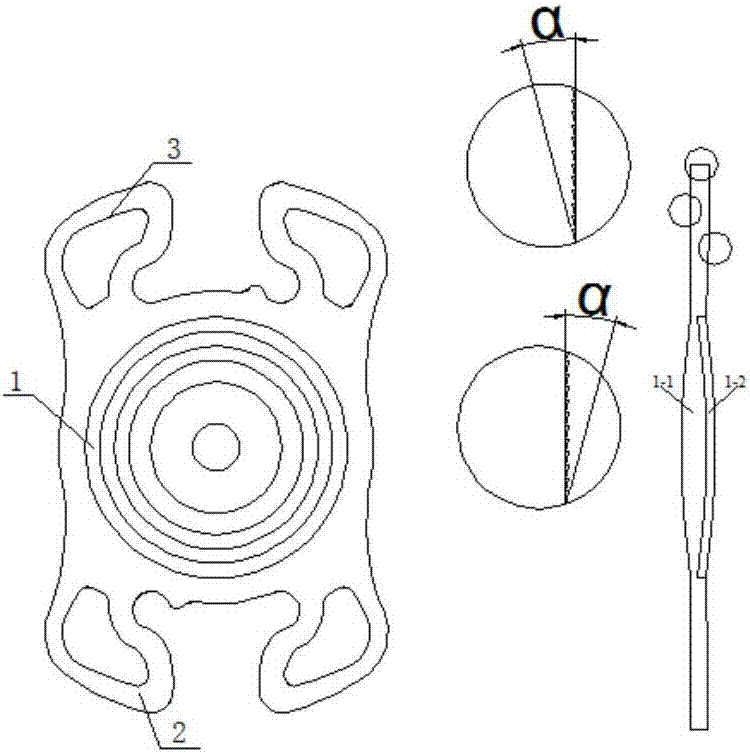
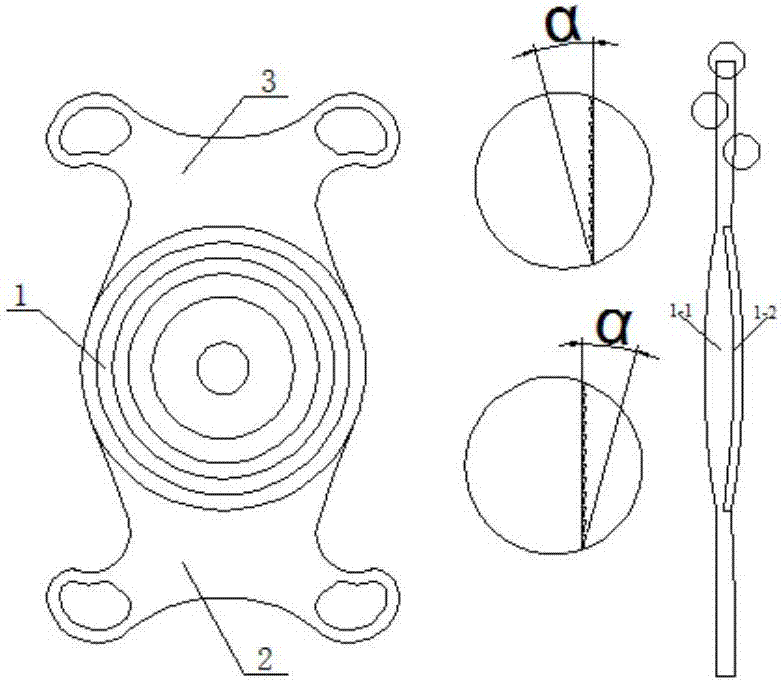
The invention discloses a multi-focus intraocular lens. The intraocular lens comprises an optical body (1), a first supporting loop (2) and a second supporting loop (3). The optical body (1) consists of a substrate layer (1-1) and a coating layer (1-2); the substrate layer (1-1), the first supporting loop (2) and the second supporting loop (3) are in an integral structure and integrally made of a same material; the coating layer (1-2) is adhered to the substrate layer (1-1) by means of plastic injection molding; the substrate layer (1-1) and the coating layer (1-2) are made of different materials. The optical body is a multi-focus optical area with double gluing structures, and by multiple binary faces (in a quantity of 2-4) and non-spherical faces in the optical area, secondary spectral chromatic aberration can be effectively corrected, image quality is improved, an additional focal power range is expanded, and full vision is realized.
Owner:WUXI VISION PRO
Multifocal ophthalmic lens
ActiveUS20060244905A1Improve visual qualitySpectales/gogglesOptical measurementsAberrations of the eyeCorneal surface
A method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens with one base focus and at least one additional focus, capable of reducing aberrations of the eye for at least one of the foci after its implantation, comprising the steps of: (i) characterizing at least one corneal surface as a mathematical model; (ii) calculating the resulting aberrations of said corneal surface(s) by employing said mathematical model; (iii) modelling the multifocal ophthalmic lens such that a wavefront arriving from an optical system comprising said lens and said at least one corneal surface obtains reduced aberrations for at least one of the foci. There is also disclosed a method of selecting a multifocal intraocular lens, a method of designing a multifocal ophthalmic lens based on corneal data from a group of patients, and a multifocal ophthalmic lens.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Multifocal intraocular lens simulator and method of simulating multifocal intraocular lens
A multifocal intraocular lens simulator includes an optical system enabling an object to be observed therethrough, and a test lens holder which holds a prescribed test intraocular lens. The intraocular lens holder is installed at a position optically conjugate with a position at which an eye of an observer is to be placed. The present invention also teaches a method of simulating a multifocal intraocular lens.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Zonal diffractive multifocal intraocular lens with central monofocal diffractive region
InactiveCN102460274AEliminate aberration effectsSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensAnterior surfaceChromatic aberration
An ophthalmic lens includes an optic having an anterior surface and a posterior surface. The lens also includes a monofocal diffractive structure disposed on one of said surfaces for providing a diffractive focusing power. The lens further includes at least one multifocal diffractive structure disposed on one of said surfaces for providing a plurality of diffractive focusing powers. The multifocal diffractive structure is adapted to provide chromatic aberration compensation for near vision.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Multi-focal intraocular lens system and methods
InactiveUS7964833B2Accurately determineOptical rangefindersInvestigating moving sheetsIntraocular lensComputer science
The invention pertains to methods, components, and operations of multi-focal intraocular lens systems, including range finding for driving same and for discriminating between multiple objects and varying brightness conditions. The invention also pertains to intraocular photosensors and range-finding methods to be used with intra-ocular lens systems, and components, that provide multi-focal IOL capabilities in dynamic visual environments.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC
Multilens intraocular lens system with injectable accommodation material
ActiveUS9713527B2Modulus of accommodationModifies its propertyEye surgeryJoint implantsOptical propertyIntraocular lens
The invention relates to a multi-lens intraocular lens system having an accommodation material between the lenses. The system comprises an posterior lens attached to the posterior surface of the capsular bag and an anterior lens attached to the anterior surface of the capsular bag. The anterior and posterior lenses have different optical properties providing different degrees and types of correction. An accommodation material is place between the anterior and posterior lenses. The accommodation material may comprise of one or more macromers, which, when polymerized, adjust the properties of the accommodation material.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20070067030A1Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensLens crystallineOptical axis
An intraocular lens is provided that includes an optic body having anterior and posterior walls, a chamber, and optically transmissive primary and secondary fluids, and method for making and using the same. One of the fluids is a gas. The secondary fluid is substantially immiscible with the primary fluid and has a different density and a different refractive index than the primary fluid. The primary fluid is present in a sufficient amount that orienting optical body optical axis horizontally for far vision positions the optical axis through the primary fluid, thereby immersing the anterior and posterior optical centers in the primary fluid. The secondary fluid is contained in the optic body in a sufficient amount that orienting the optical axis over a range of effective downward angles relative to the horizontal for near vision positions the optical axis to extend through the primary fluid and the secondary fluid, thus changing the focus of the intraocular lens.
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Multi-focus artificial lens
ActiveCN104127263AImprove image qualityImprove tilt resistanceIntraocular lensImaging qualityOptical axis
The invention relates to a multi-focus artificial lens which comprises an optical part formed by an optical portion and an optical part edge. 6-35 diffraction slope rings are arranged on the front surface and / or the rear surface of the optical portion in a mirror symmetry manner according to the optical axis of the multi-focus artificial lens, a starting border position of the first diffraction slope ring is 0.580-0.520mm while a finishing border position of the same is 0.815-0.735mm, and feature size of the first diffraction slope ring is 0.125-0.048, so that color difference of the multi-focus artificial lens is enabled to be zero. Imaging quality of the multi-focus artificial lens under the condition of polychromatic light is improved, and characteristics of resisting inclination and decentration are enhanced, so that acquiring of super sight is facilitated.
Owner:EYEBRIGHT MEDICAL TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com