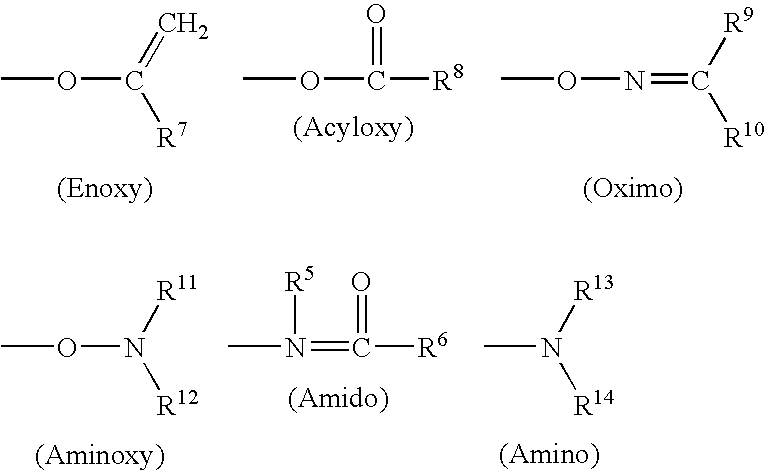
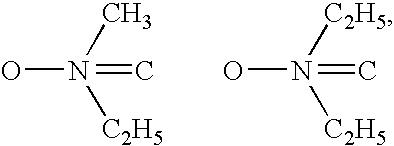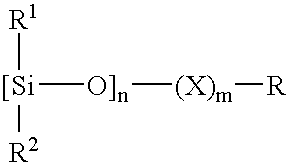Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106results about How to "Modifies its property" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
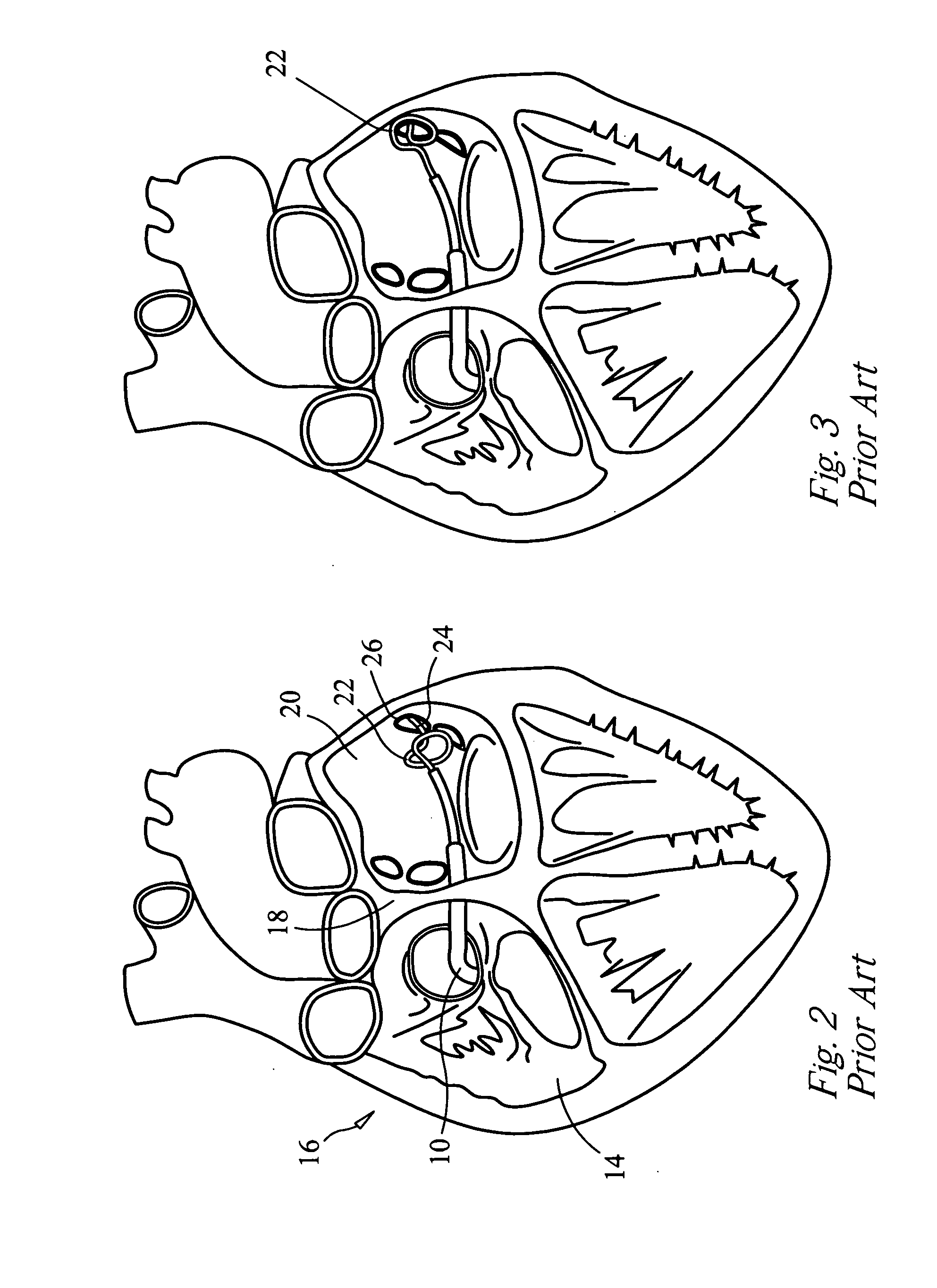
Using Triggers with Video for Interactive Content Identification
InactiveUS20080201736A1Properties for the object can be modifiedModifies its propertyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInteractive contentDisplay device
Access to interactive content at a client device through the use of triggers is disclosed. The client device is coupled to a television communication network and receives an encoded broadcast video stream containing at least one trigger. The client device decodes the encoded broadcast video stream and parses the broadcast video stream for triggers. As the broadcast video stream is parsed, the stream is output to a display device. When a trigger is identified, the client device automatically tunes to an interactive content channel. The client device sends a signal indicative of the trigger through the television communication network to the processing office. The processing office can then use the information contained within the trigger signal to provide content to the client device. The content may be interactive content, static content, or the broadcast program stitched with interactive or static content. The user of the client device can then interact with any interactive content.
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
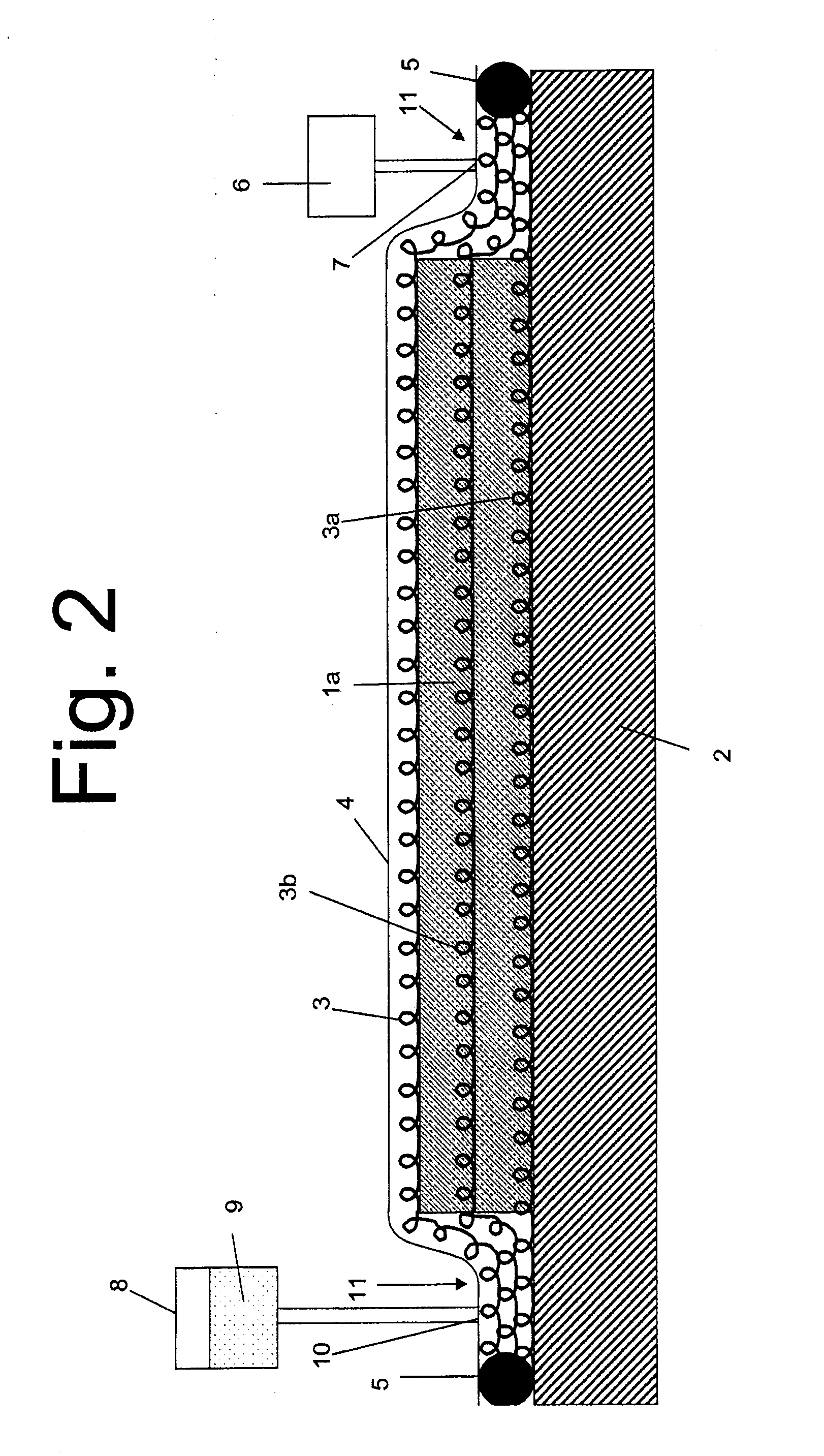
Processes for incorporating inert gas in a cement composition containing spherical beads
ActiveUS20050098317A1High densityModifies its propertySolid waste managementFluid removalAl powderPhysical chemistry
The present invention provides a process for forming cement in a well bore. In this process, a cement composition is formed that comprises a cement and one or more beads mixed with the cement. The cement composition containing the beads is displaced into the well bore, and an inert gas phase is introduced to the cement composition to control a density of the cement composition. The inert gas phase can be introduced by adding a gas generating material to the cement composition and / or a porous material to the cement composition. In an embodiment, the gas generating material is a nitrogen generating material that may be activated by an oxidizing agent. In another embodiment, the gas generating material is a hydrogen generating material, e.g., an aluminum powder. The present invention further provides a cement composition comprising a cement, one or more beads combined with the cement, and an inert gas phase created by, e.g., a gas generating material and / or a porous material.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
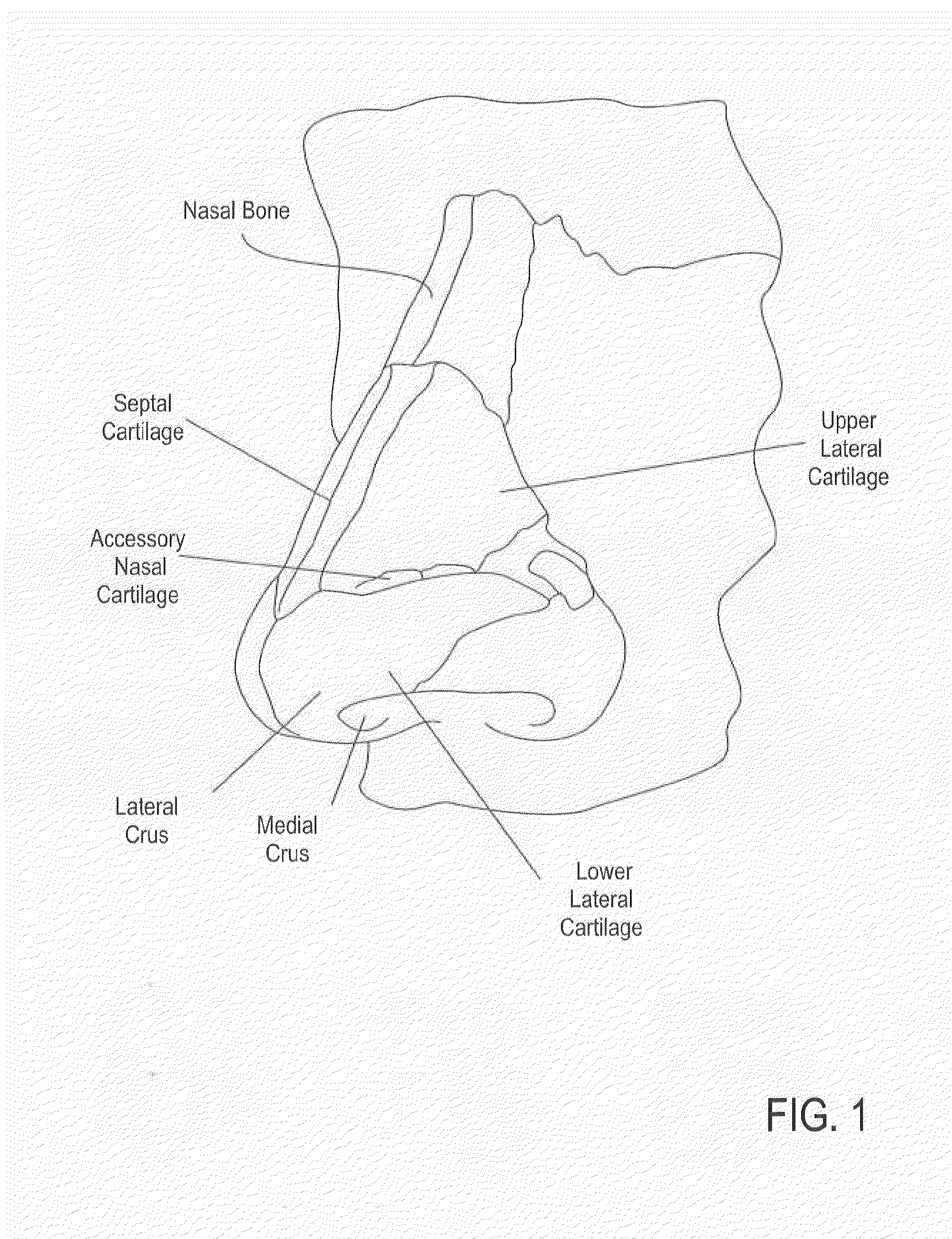
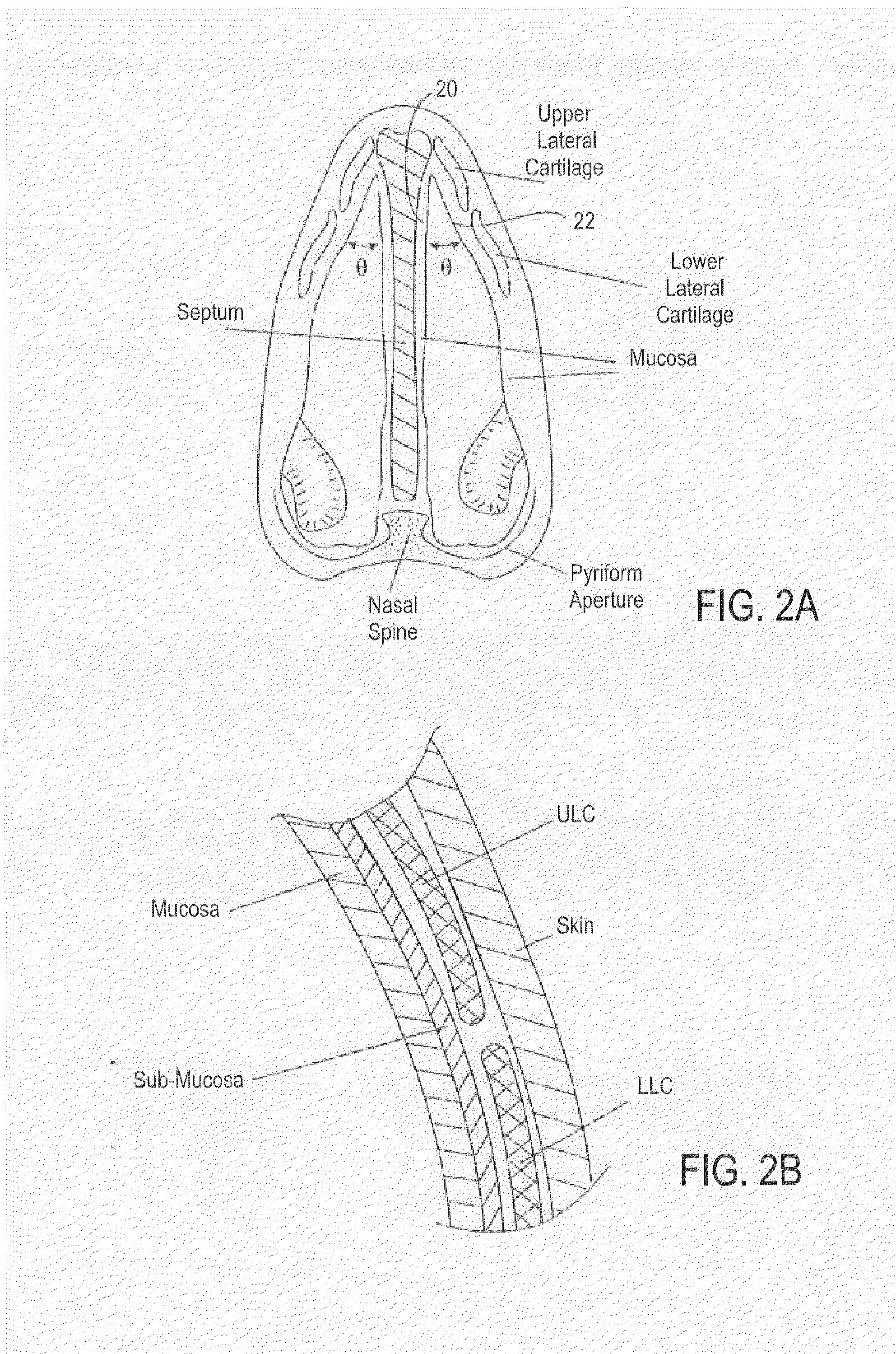
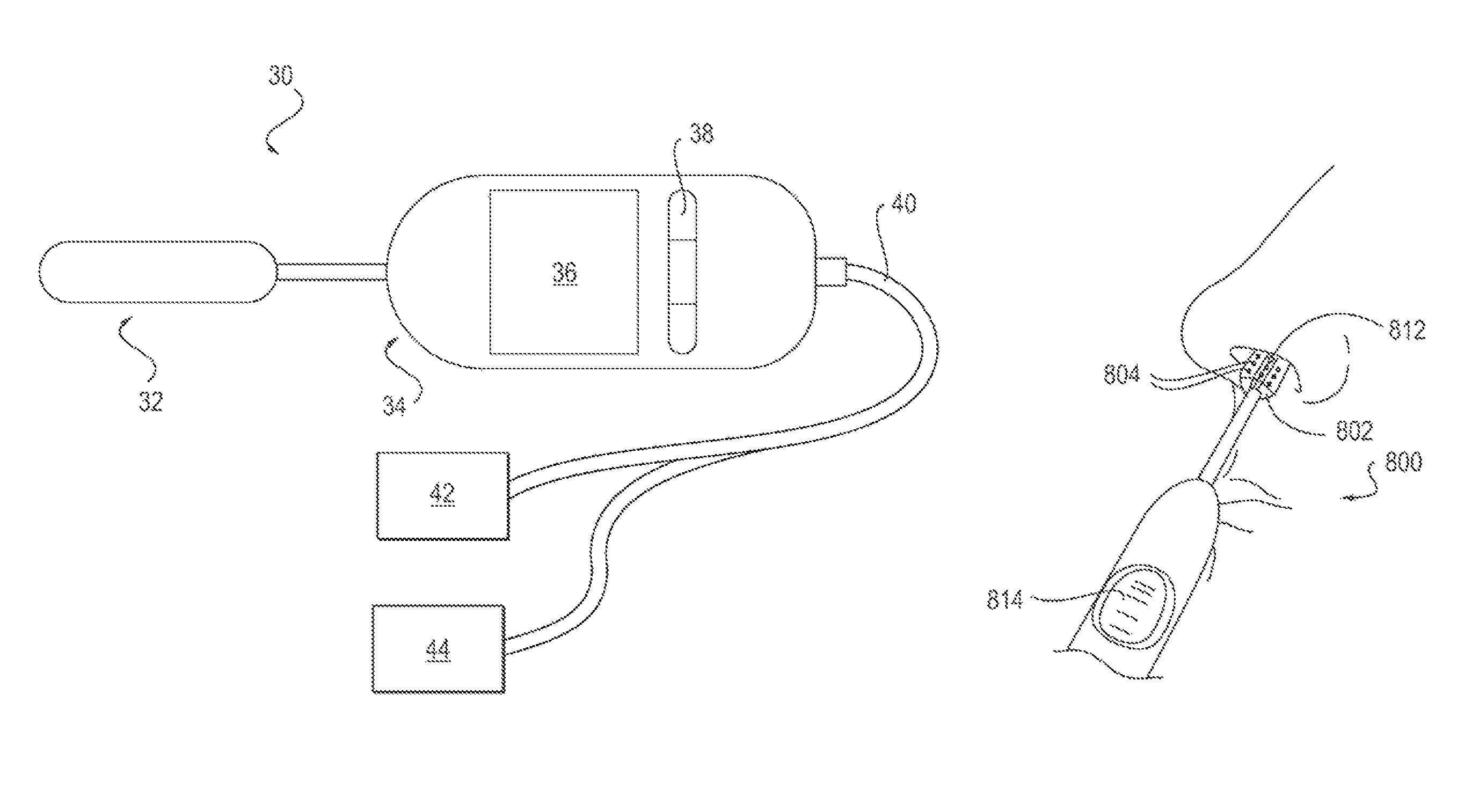
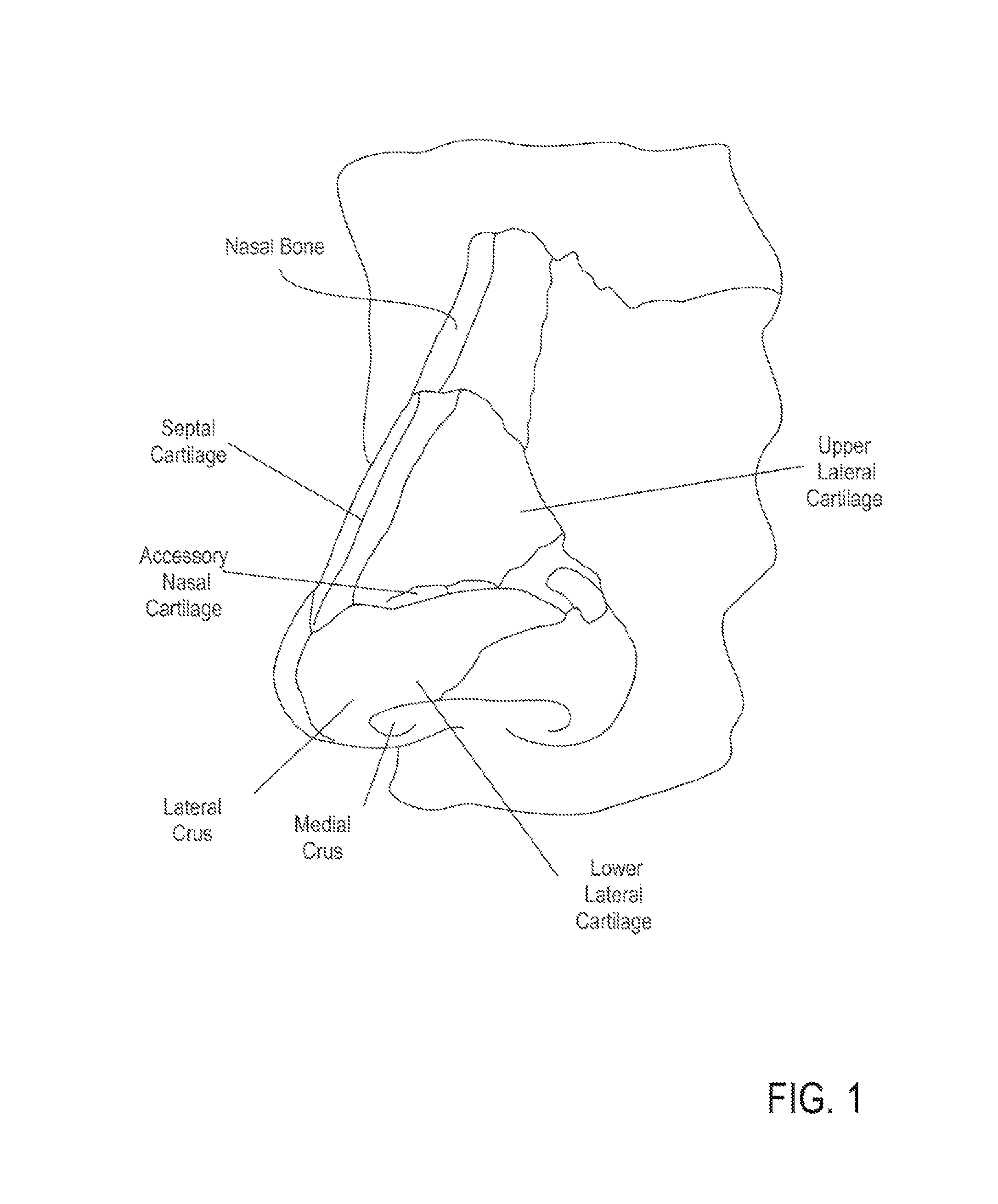
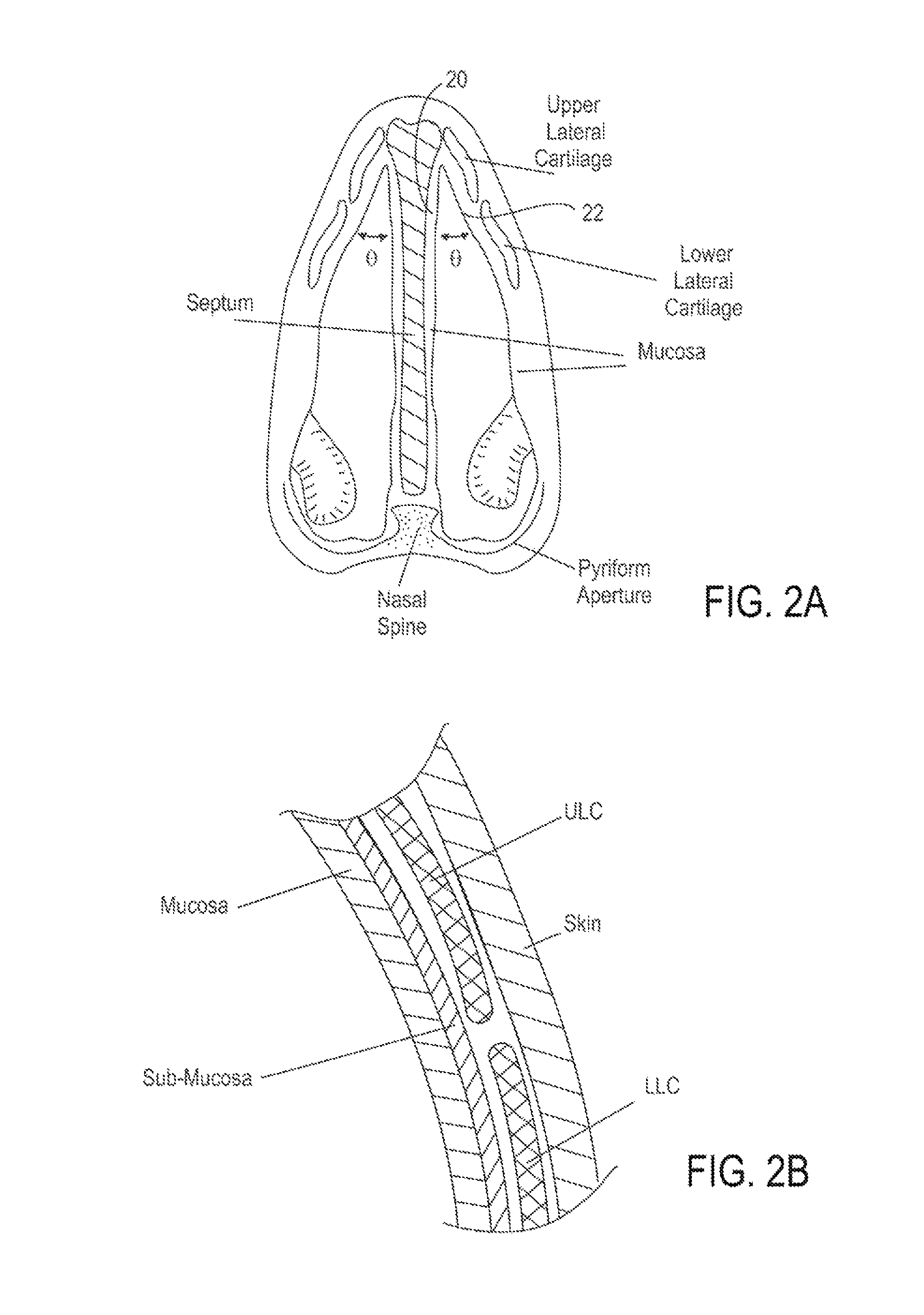
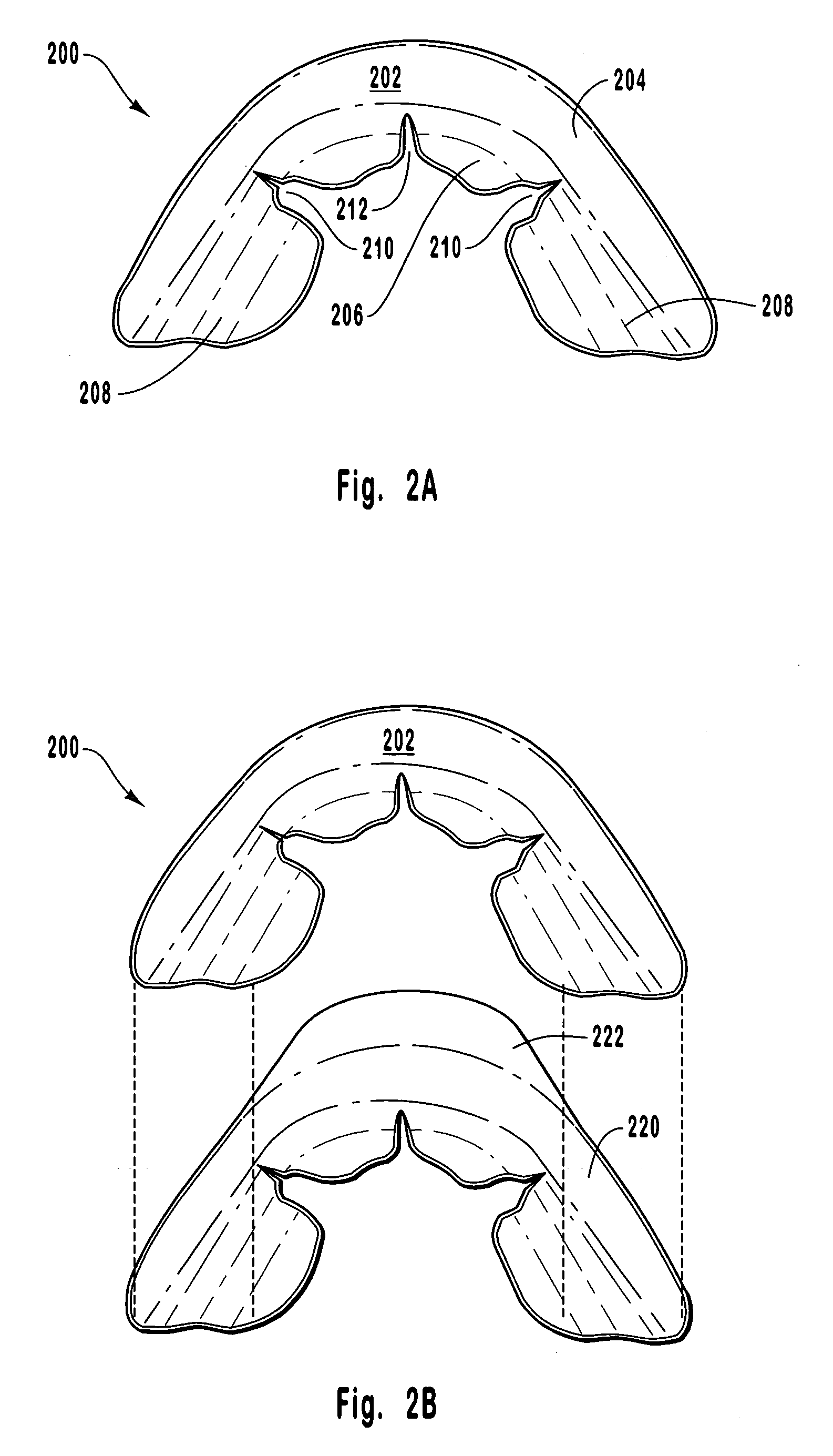
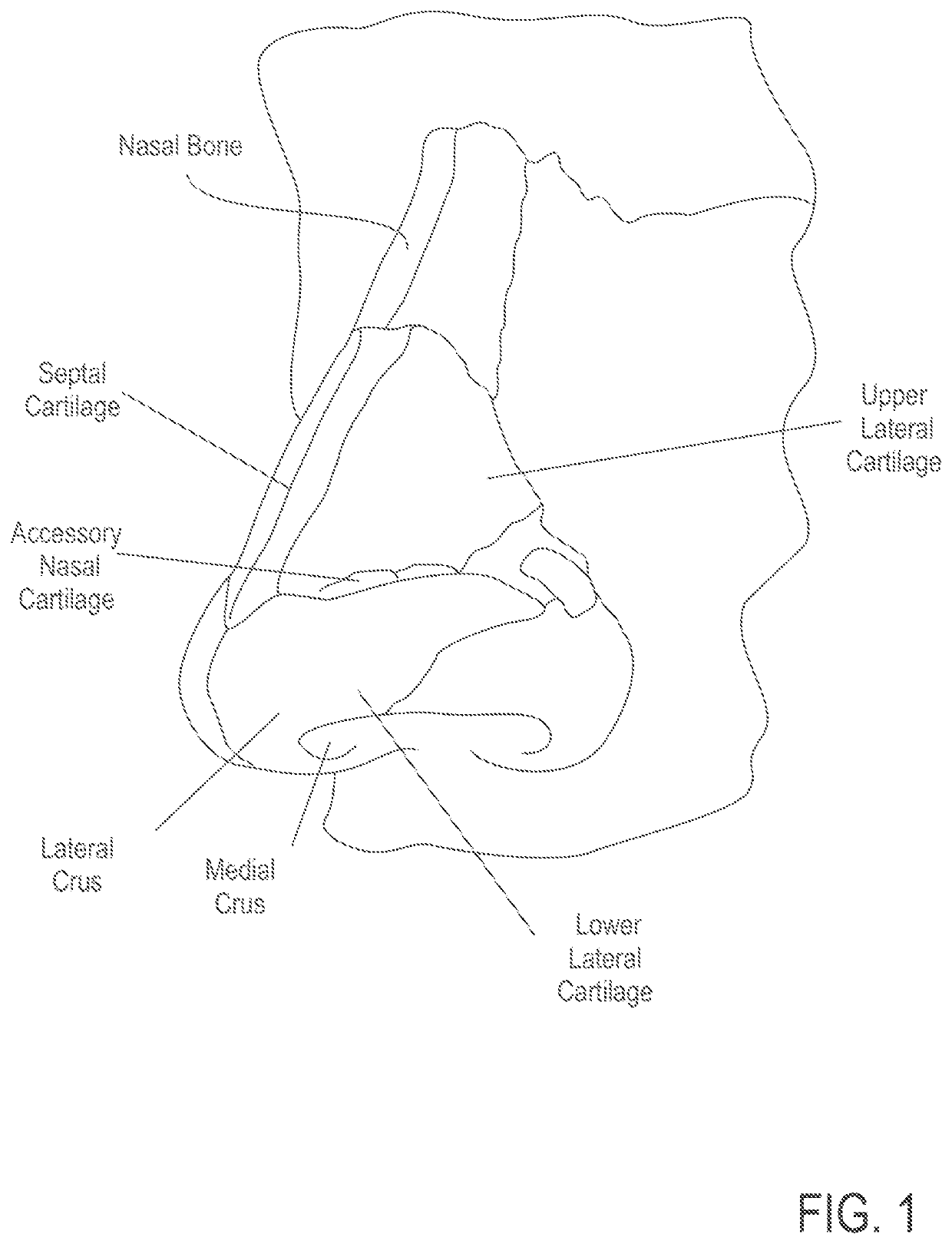
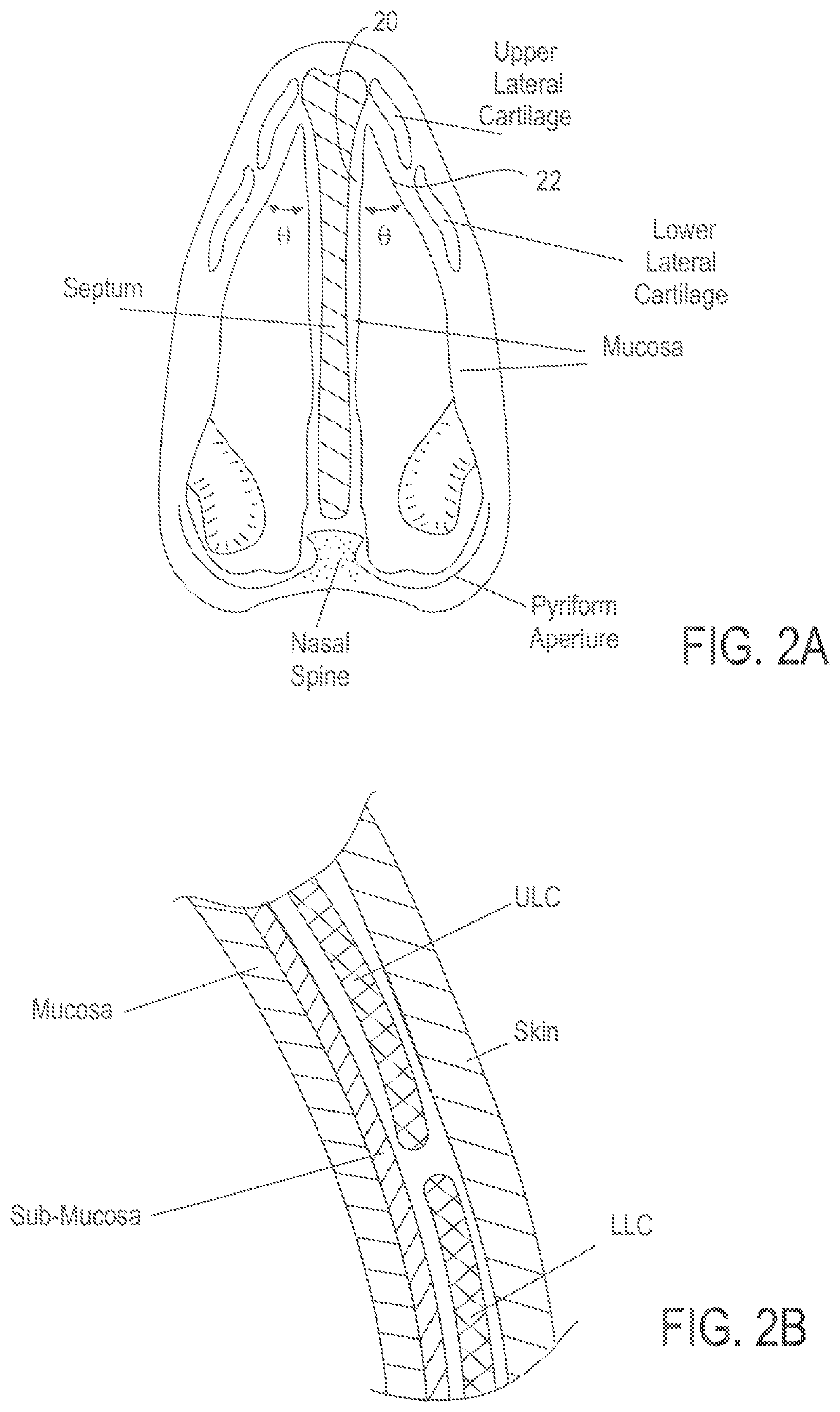
Methods and devices to treat nasal airways
ActiveUS20140088463A1Decrease airflow resistance perceived airflowIncrease ratingsElectrotherapySurgical needlesSmall airwaysNostril
A method is described for modifying at least one property of a tissue of or near a nasal valve of a nose, without using a surgical incision or an implant, to decrease airflow resistance or perceived airflow resistance in a nasal airway. The method may involve contacting a treatment element of a treatment device with the at least one tissue inside the nasal airway, with sufficient force to at least temporarily deform the at least one tissue, applying energy to, or removing energy from, the at least one tissue, using the treatment element, and removing the treatment element from the nostril.
Owner:AERIN MEDICAL
Methods and devices to treat nasal airways
ActiveUS8986301B2Increase ratingsWithout weakeningUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNostrilSurgical incision
Owner:AERIN MEDICAL INC
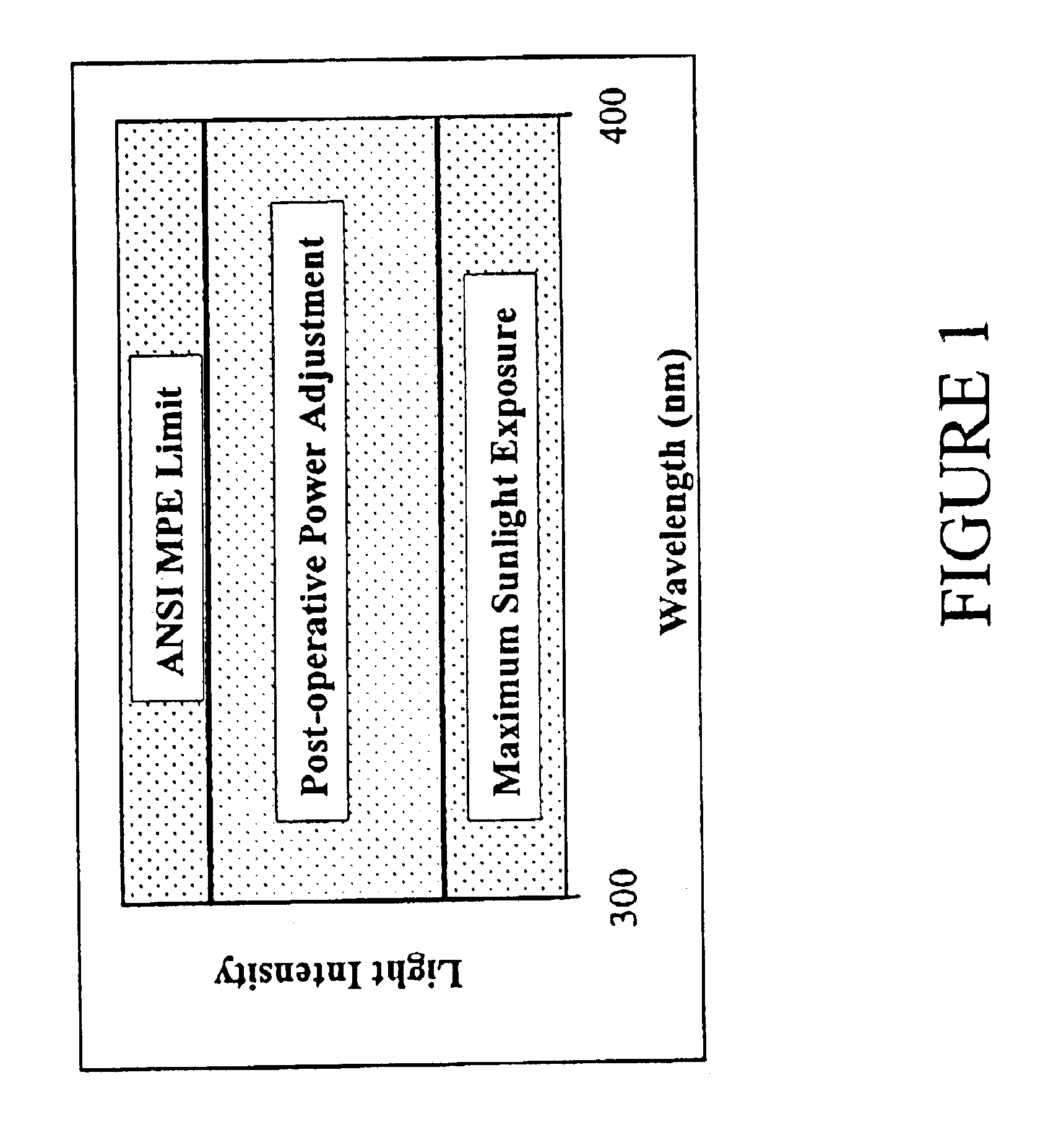
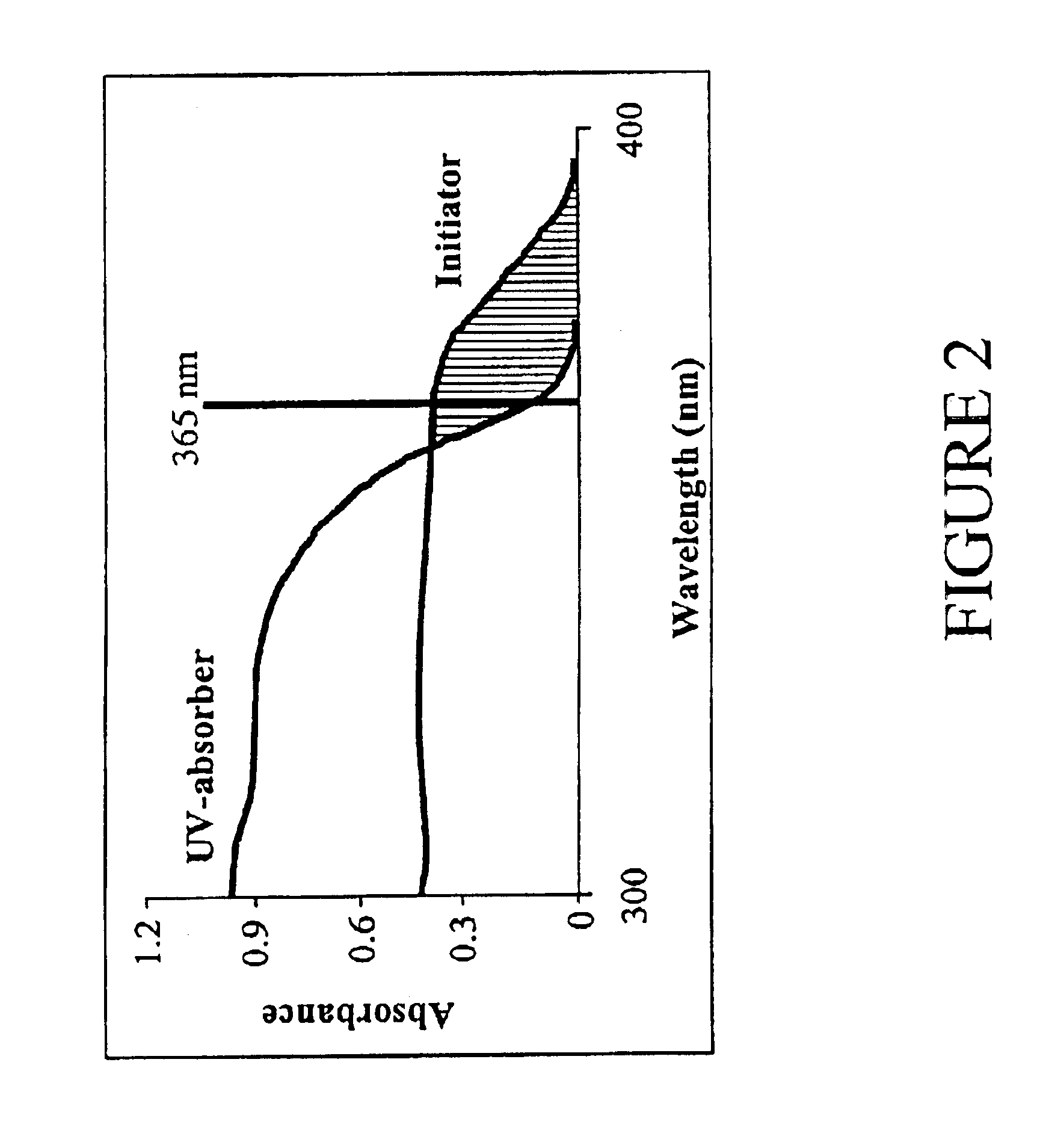
Readjustable optical elements
The invention relates to optical elements whose optical properties can be repeatedly adjusted over time. Through the use of modifying compositions capable of stimulus induced polymerization coupled with a blend of stimulus absorbers and initiators, it is possible to repeatedly adjust the optical properties of the element by exposing the lens to a stimulus which exceeds the absorption capacity of the stimulus absorber.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
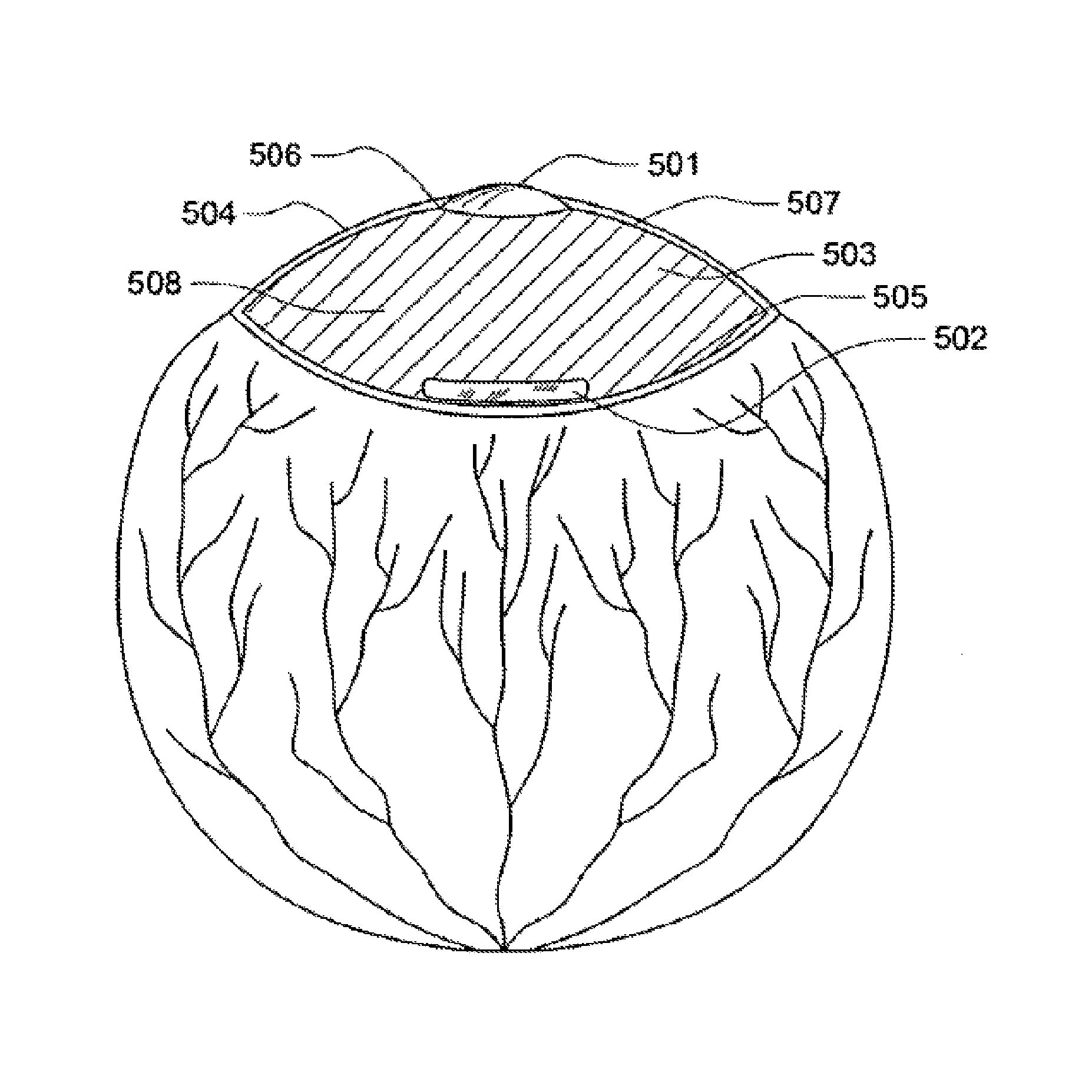
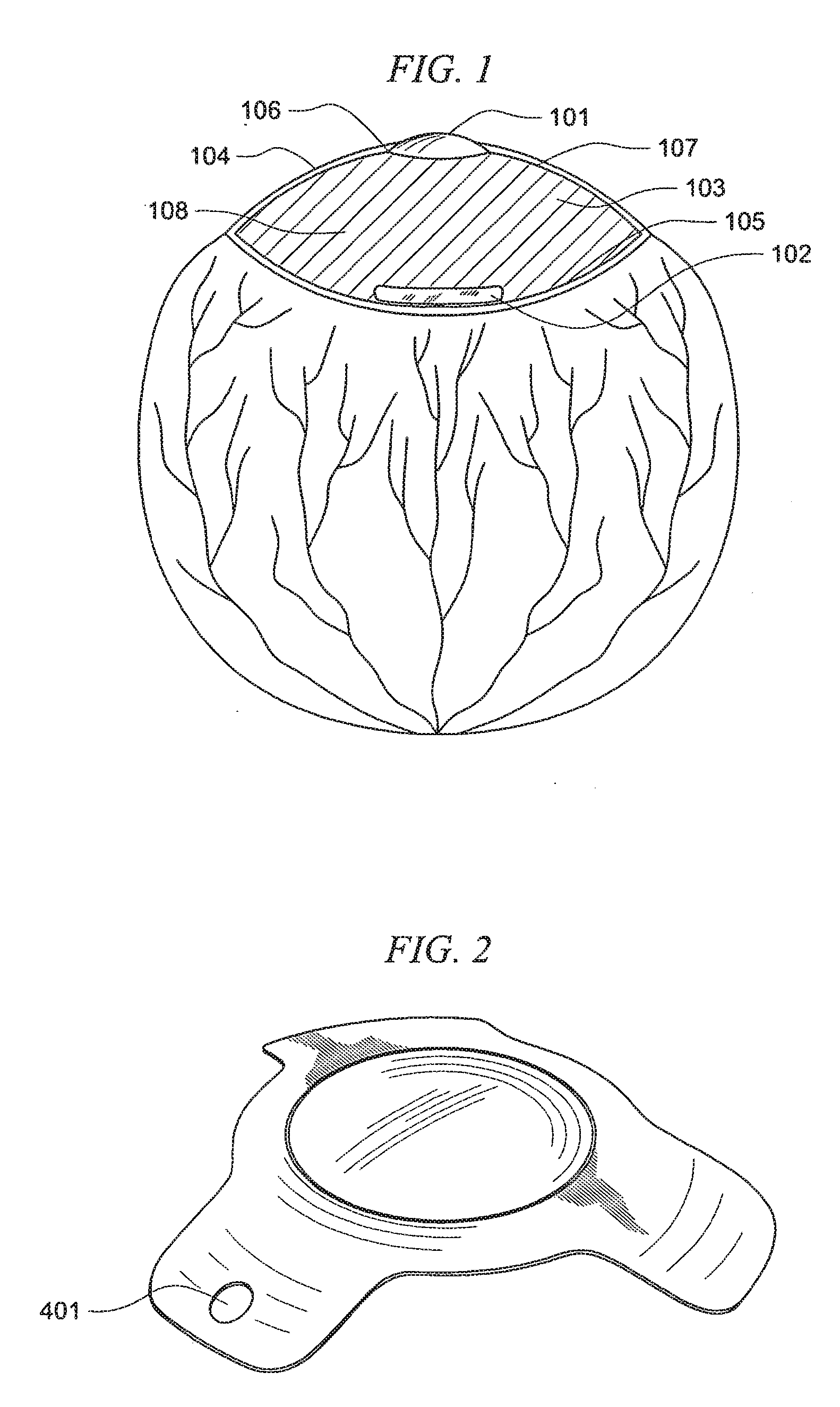
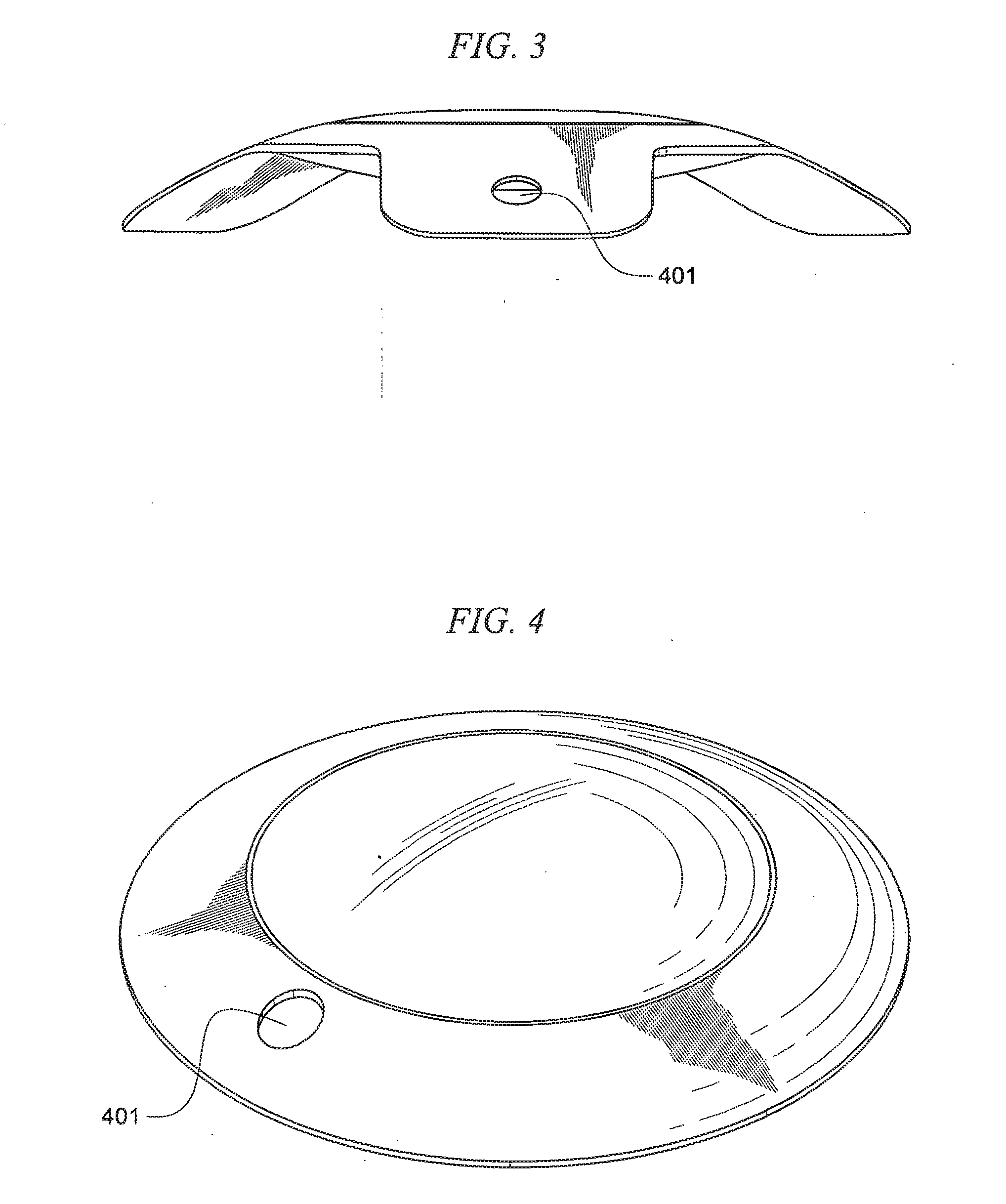
Intraocular lens system with injectable accommodation material
ActiveUS9005282B2Modulus of accommodationModifies its propertyIntraocular lensIntraocular lensLens placode
The invention relates to a intraocular lens system having a flexible anterior lens accommodation material behind the lens. The accommodation material may comprise of one or more macromers, which, when polymerized, adjust the properties of the accommodation material. The anterior lens is flexible such that the curvature of the lens changes during accommodation. The anterior lens may be used alone or in combination with a posterior lens.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Multilens Intraocular System with Injectable Accommodation Material
ActiveUS20160113761A1Modulus of accommodationModifies its propertyEye surgeryTissue regenerationOptical propertyAnterior surface
The invention relates to a multi-lens intraocular lens system having an accommodation material between the lenses. The system comprises an posterior lens attached to the posterior surface of the capsular bag and an anterior lens attached to the anterior surface of the capsular bag. The anterior and posterior lenses have different optical properties providing different degrees and types of correction. An accommodation material is place between the anterior and posterior lenses. The accommodation material may comprise of one or more macromers, which, when polymerized, adjust the properties of the accommodation material.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
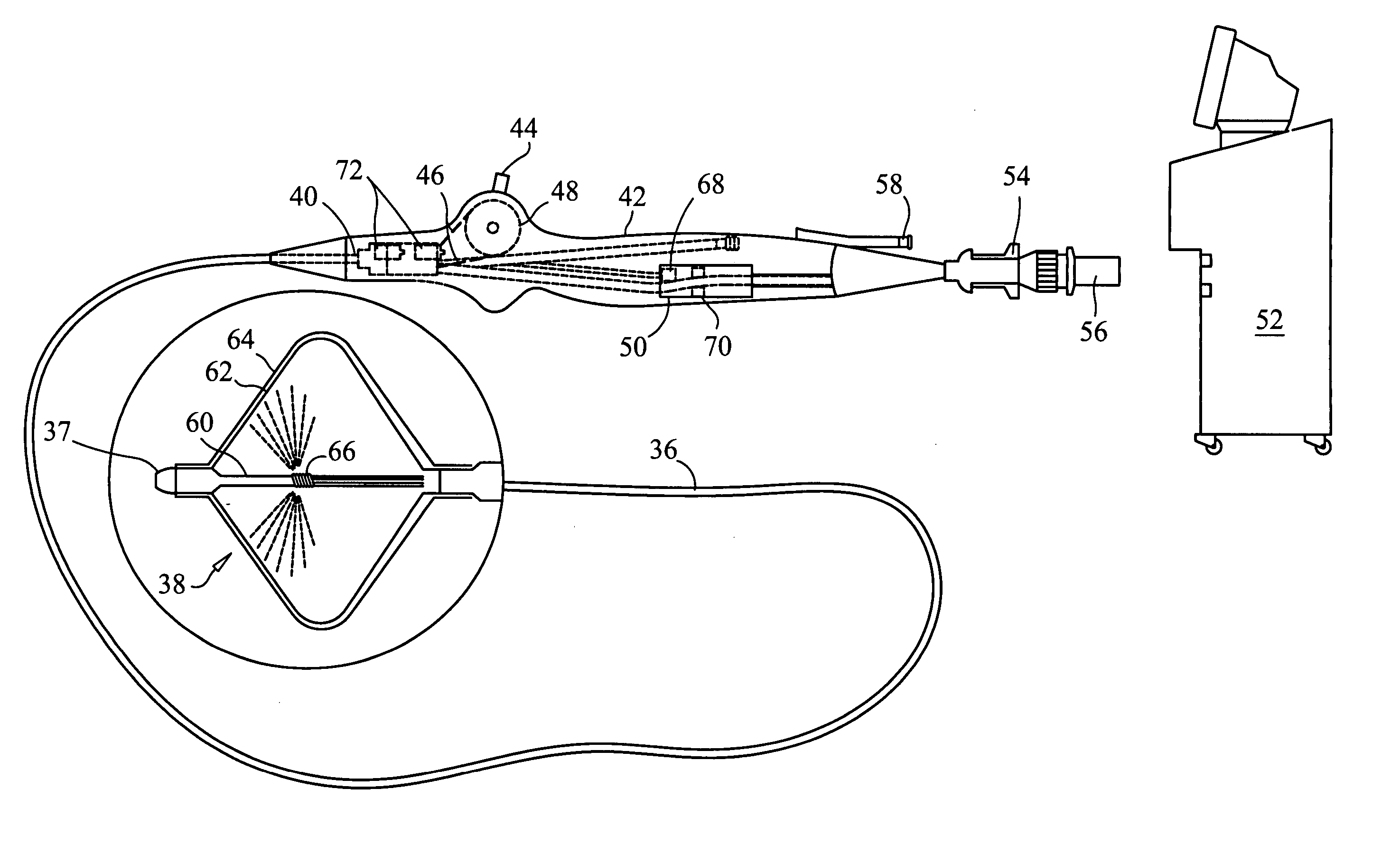
Wide area ablation of myocardial tissue
ActiveUS20060247611A1Modifies its propertyCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingWide areaCardiac muscle
The present invention advantageously provides a method and system for cryogenically ablating large areas of tissue within the left atrium. In an exemplary embodiment a cryotherapy device includes a catheter body having a substantially fixed diameter, a proximal end and a distal end; a first lumen for permitting passage of a cooling fluid from the proximal end to the distal end; a second lumen permitting return of the cooling fluid from the distal end to the proximal end; and an ablation element expandable from a first diameter that is substantially the same as the diameter of the catheter body to a second diameter that is at least twice the diameter of the catheter body, the ablation element having a surface portion that conforms to the uneven surface topography of the cardiac tissue. The ablation element can include one or more balloon and / or a flexible element that is deformed by moving the distal end of the catheter toward the proximal end of the catheter. The surface of the balloon can further be shaped by regulation of pressure within the one or more balloons. In an exemplary method a tissue ablation device is provided and tissue in the antrum of the left atrium is ablated with the device. In an exemplary method, only tissue in the antrum is ablated, and the ablation is created by freezing tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Self-leveling cementitious composition with controlled rate of strength development and ultra-high compressive strength upon hardening and articles made from same
ActiveUS20090239977A1High strengthImprove the immunitySolid waste managementTriethanolamineFiber reinforcement
A self-leveling cementitious mixture with excellent flow properties and which hardens with a controlled rate of strength development to an ultra-high compressive strength composite composition for use in making articles such as cementitious armor panel with ballistic and blast resistant properties including: a continuous phase resulting from the curing of an aqueous mixture, in the absence of silica flour, of inorganic cement binder, inorganic mineral filler having a particle size of about 150-450 microns, pozzolanic mineral filler, polycarboxylate based self-leveling agent and water. The cementitious mixture may include alkanolamine, such as triethanolamine, and acid or acid salt, such as tartaric acid. The cementitious composition may be reinforced with reinforcing fibers, e.g. glass fibers, in an amount of about 0.5-6.0% by volume of the overall cementitious composition. The fibers are uniformly dispersed in the cementitious composition before it is cured to form a final cementitious armor panel.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO +1
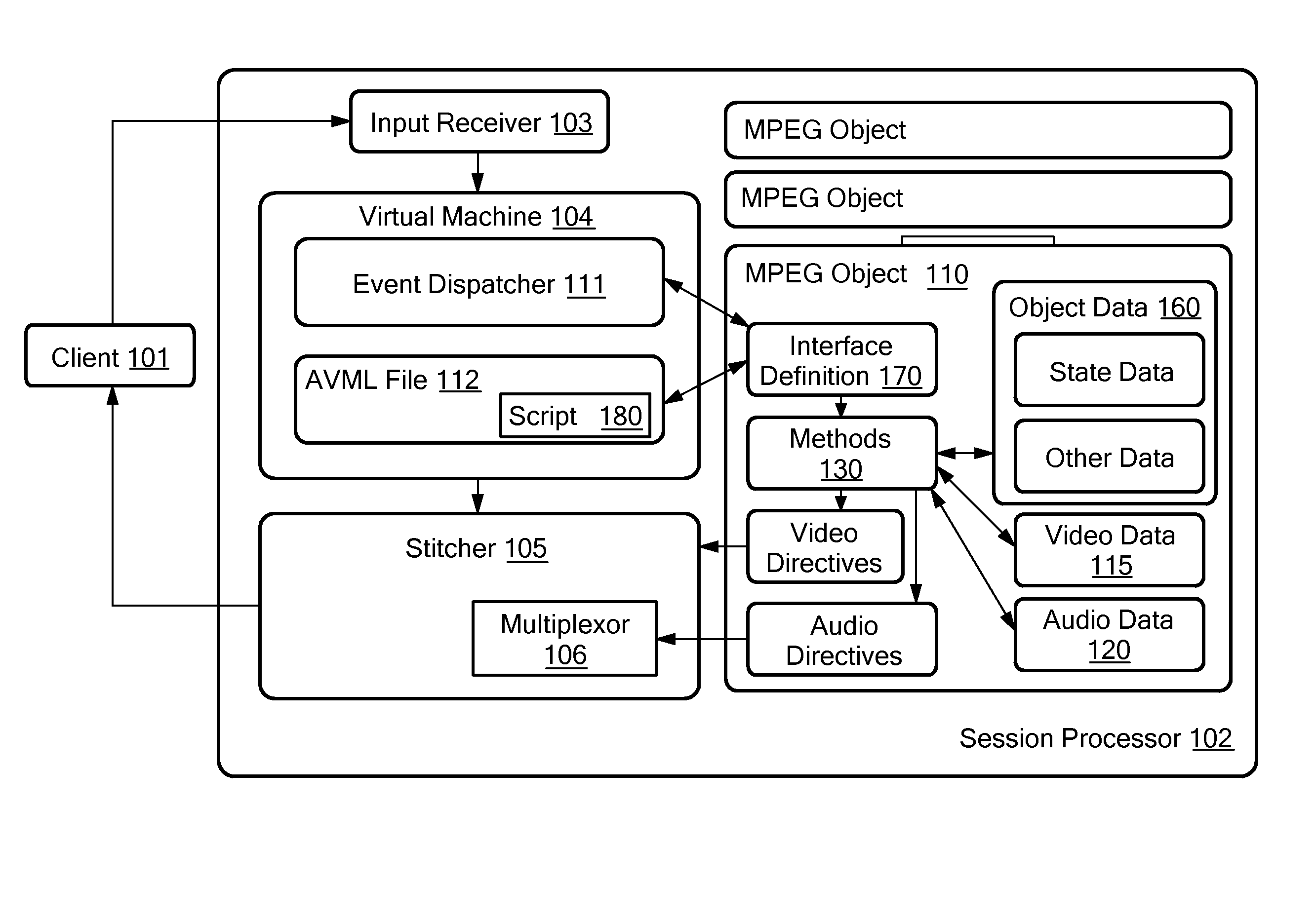
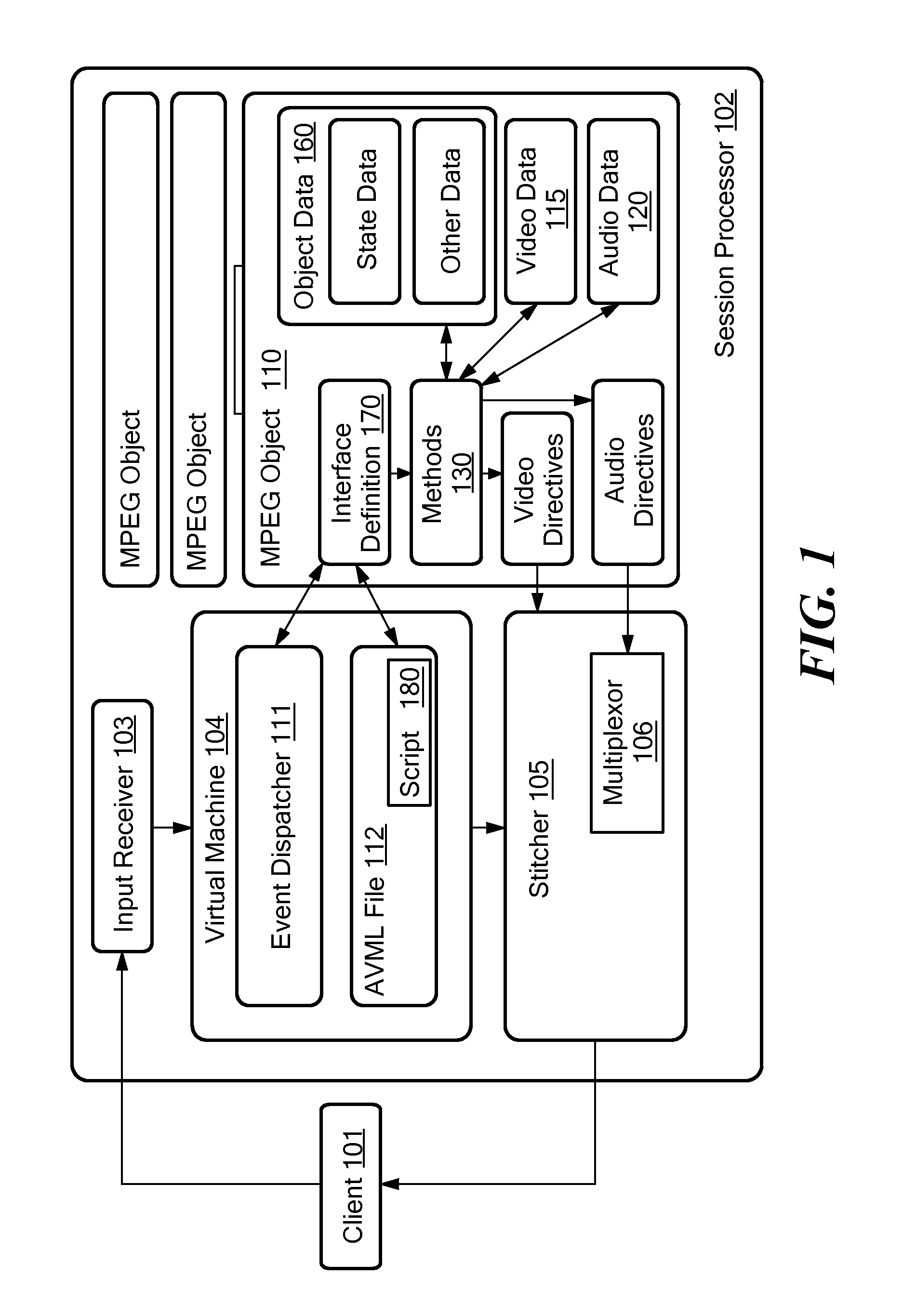
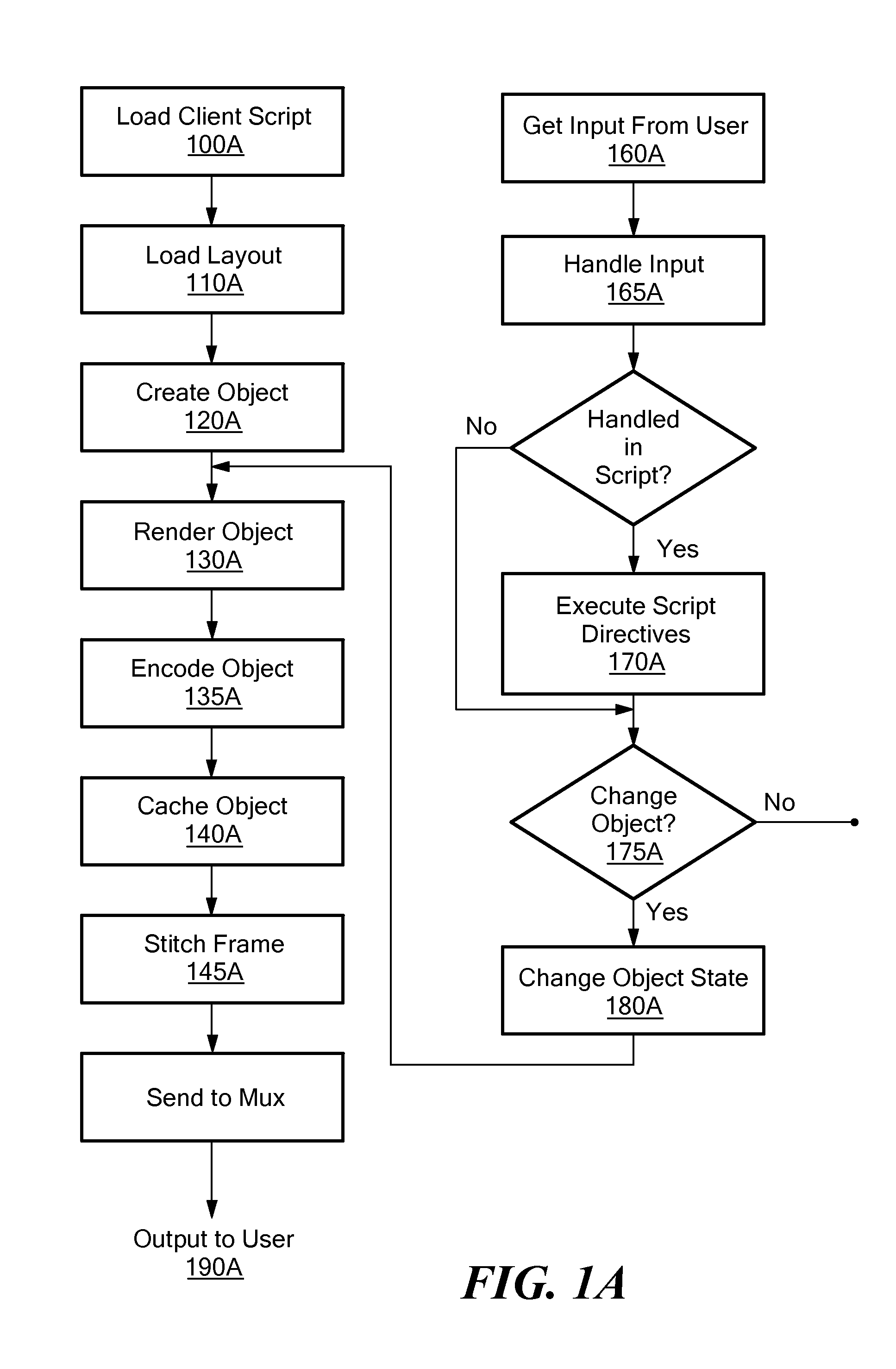
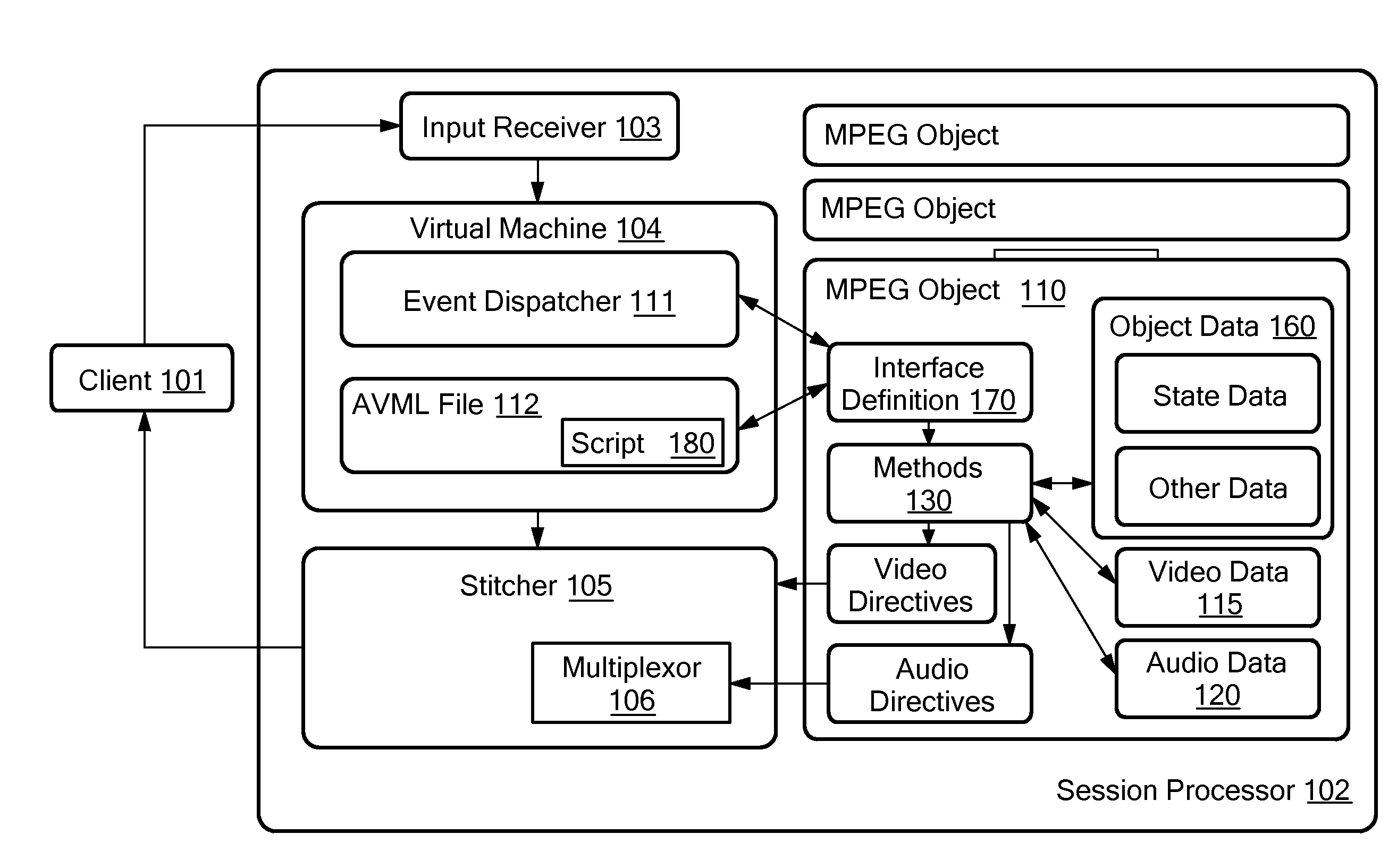
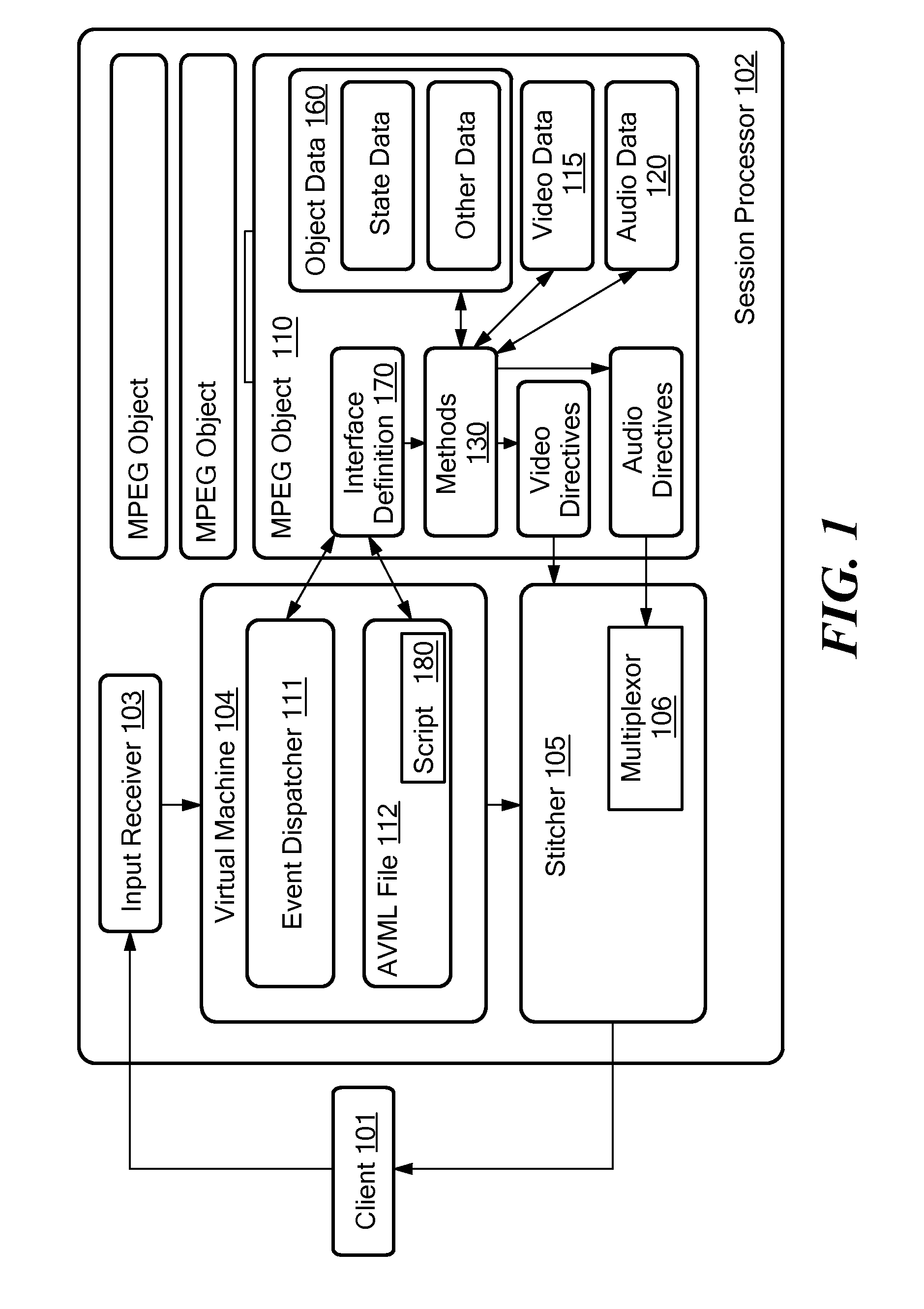
MPEG objects and systems and methods for using MPEG objects
InactiveUS20080178249A1Properties for the object can be modifiedModifies its propertyInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsComputer graphics (images)Data structure
Owner:ACTIVE VIDEO NETWORKS INC
Flow-through cavitation-assisted rapid modification of beverage fluids
ActiveUS20100104705A1Smooth tasteReduced adverse after-effectsMilk preparationMilk preservationFlavorCavitation
A method and device for manipulating alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages to obtain desirable changes in the beverages, comprising subjecting said beverages to a flow-through hydrodynamic cavitation process and continuing the application of such process for a period of time sufficient to produce a consumable product. In the case of wine, the method includes altering the composition and accelerating the conversion of ingredients to obtain wine with a superior homogeny, an extended shelf life and a mouth feel, flavor, bouquet, color and body resembling those of wine that was subjected to a traditional oak barrel maturation. The system provided implements the described method.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
Self-leveling cementitious composition with controlled rate of strength development and ultra-high compressive strength upon hardening and articles made from same
ActiveUS8030377B2Reduce the amount requiredModifies its propertySolid waste managementGlass fiberPolymer science
A self-leveling cementitious mixture with excellent flow properties and which hardens with a controlled rate of strength development to an ultra-high compressive strength composite composition for use in making articles such as cementitious armor panel with ballistic and blast resistant properties including: a continuous phase resulting from the curing of an aqueous mixture, in the absence of silica flour, of inorganic cement binder, inorganic mineral filler having a particle size of about 150-450 microns, pozzolanic mineral filler, polycarboxylate based self-leveling agent and water. The cementitious mixture may include alkanolamine, such as triethanolamine, and acid or acid salt, such as tartaric acid. The cementitious composition may be reinforced with reinforcing fibers, e.g. glass fibers, in an amount of about 0.5-6.0% by volume of the overall cementitious composition. The fibers are uniformly dispersed in the cementitious composition before it is cured to form a final cementitious armor panel.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO +1
Removable floor
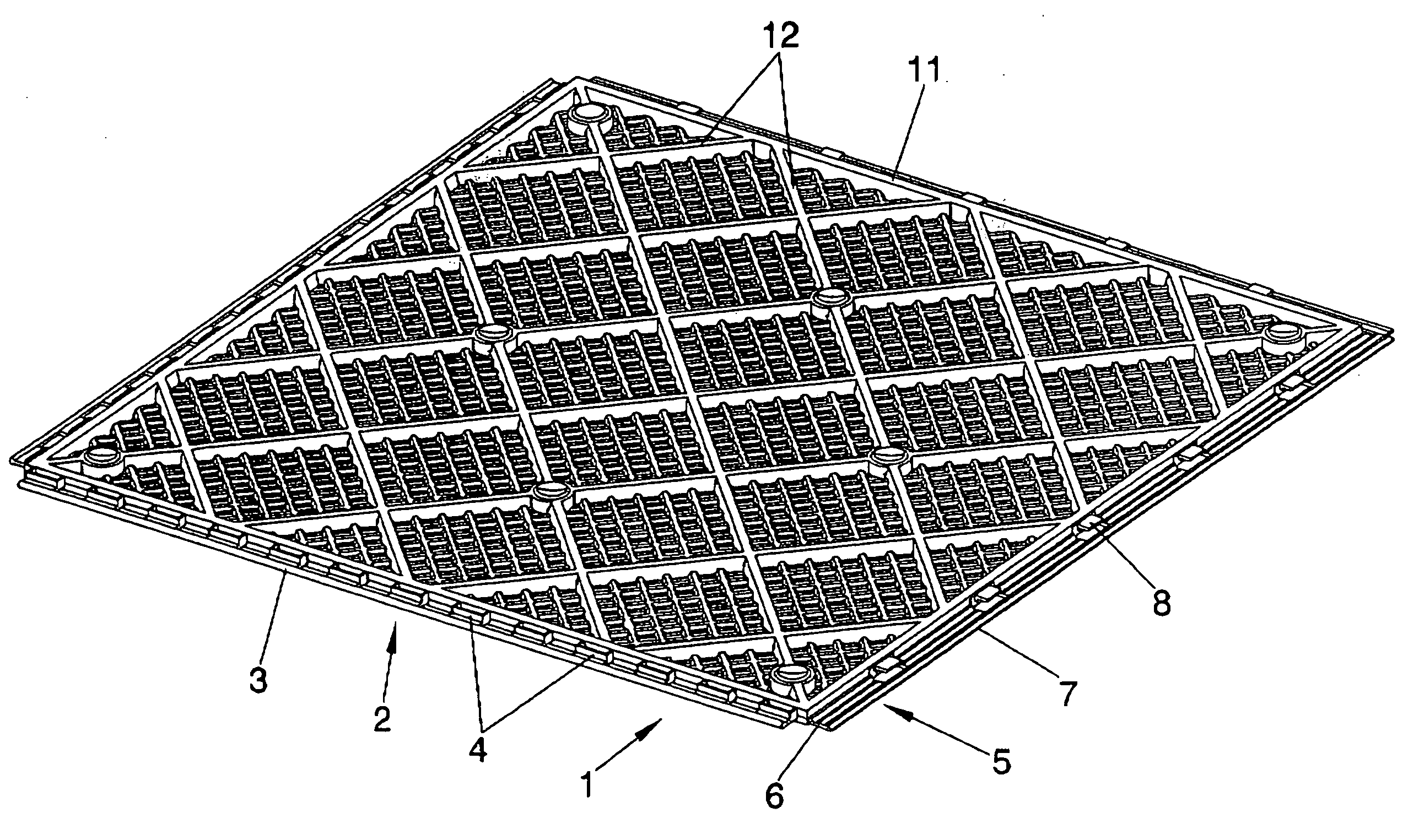
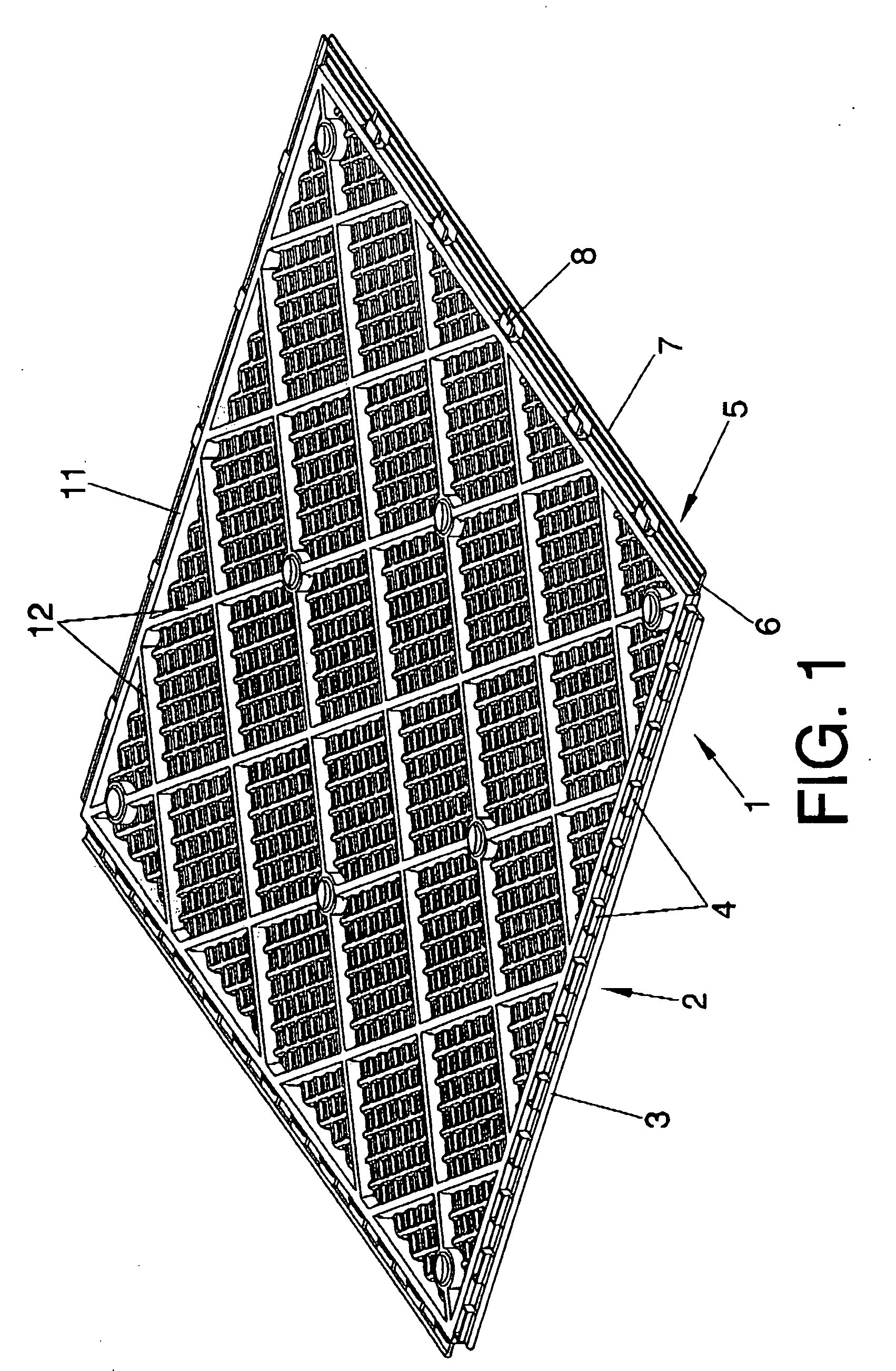
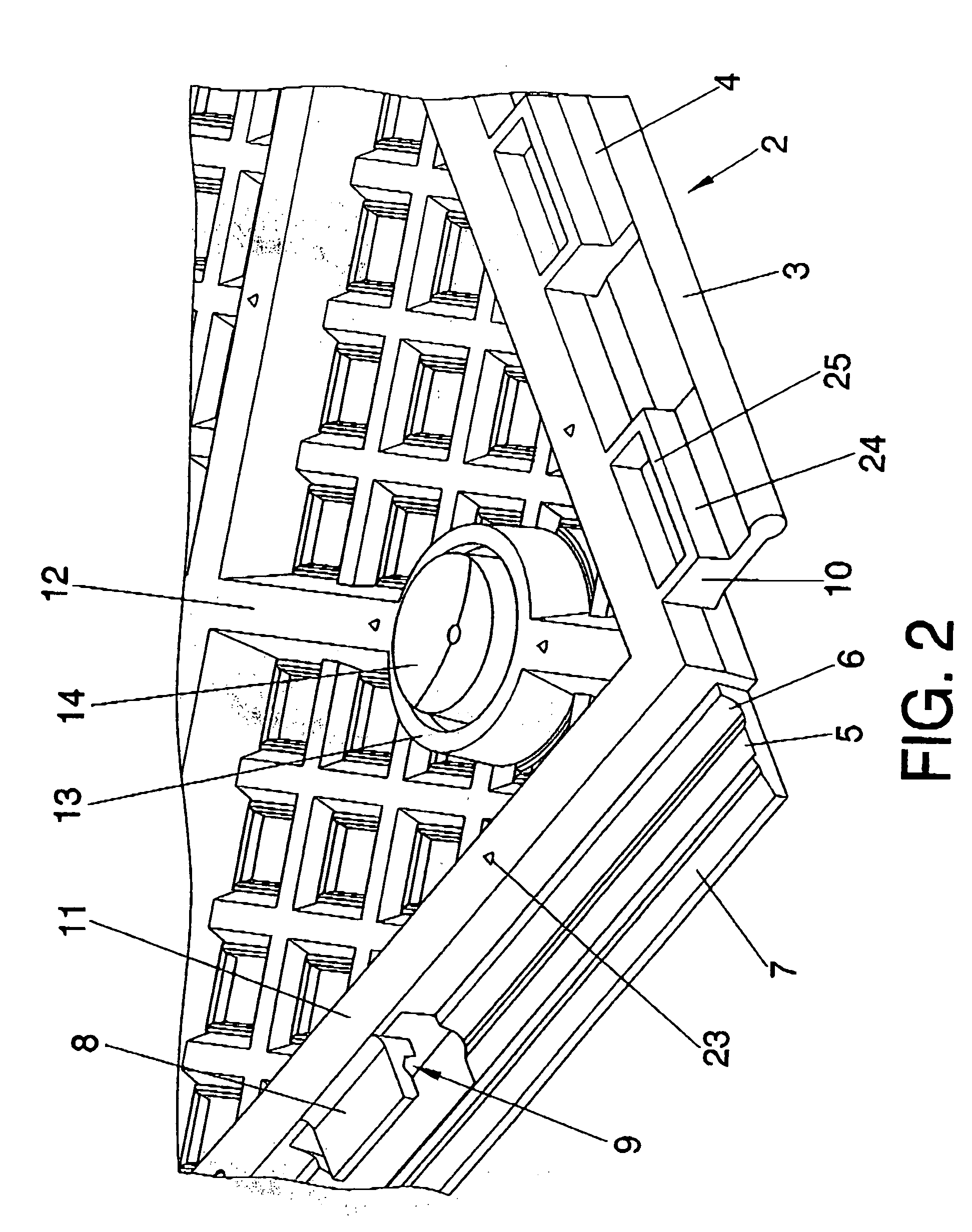
InactiveUS7757449B2Modifies its propertyFacilitates laying/removingCeilingsTreadsMechanical engineeringOut of phase
A removable floor includes a support piece (1) having a floor tile (15) affixed to the upper surface thereof, with the support piece being equipped to be secured to other support pieces, in order to facilitate the installation and removal of the floor by the user and to enable the supports to be installed in an aligned and / or out of phase manner such as to produce different decorative patterns.
Owner:TAULELL +1
Method and apparatus for use of beam control prisms with diode laser arrays
InactiveUS6975465B1Shorten physical lengthHigh densityPrismsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser arrayPrism
The subject invention relates to beam control prisms and the use of a beam control prism to modify the beam properties of light emitted from an edge emitting diode laser. The subject invention can utilize a beam control prism placed next to a diode laser bar. The subject beam control prism can have, for example, a curved surface and / or a high reflective coated surface for a diode laser wavelength. The curved surface can collimate the fast axis divergence and the mirror surface can change the beam direction. The subject curved surface beam control prisms can incorporate one or more features, such as parabolic reflecting surface, elliptical exit surface with flat reflecting surface, and a hyperbolic entrance surface with flat reflecting surface.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Highly elastomeric and paintable silicone compositions
InactiveUS20050288415A1Good paintabilityGood weather resistanceSpecial tyresCoatingsSealantPolymer chemistry
Highly elastomeric, curable, paintable silicone compositions are provided. The paintable silicone compositions comprise an organopolysiloxane, a silicone functional crosslinker, and an organic polymer. The highly elastomeric, curable, paintable silicone compositions have an elongation of at least 150% and are useful as paintable sealants and caulks.
Owner:TREMCO INC
Method of synthesising carbon nano tubes
InactiveUS7033647B2Increase flexibilityImprove propertiesCarbon compoundsVacuum evaporation coatingIon beamCarbon nanotube
Owner:ELECTROVAC FABATION ELEKTRO TECHNR SPEZIALARTIKEL GES +1
Molding of Thermoplastic Polyesters
InactiveUS20070224377A1Improve clarityIncrease flexibilityLayered productsBottlesPolyesterPolymer science
Disclosed are processes for rotational molding of thermoplastic polyesters and for hollow articles produced therefrom. The thermoplastic polyesters have a crystallization half time of at least 10 minutes and an inherent viscosity of 0.55 to 0.70 dL / g. Additional thermoplastic polymers may be used to produce multilayered articles.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Process for manufacturing a multilayer structure made from semiconducting materials
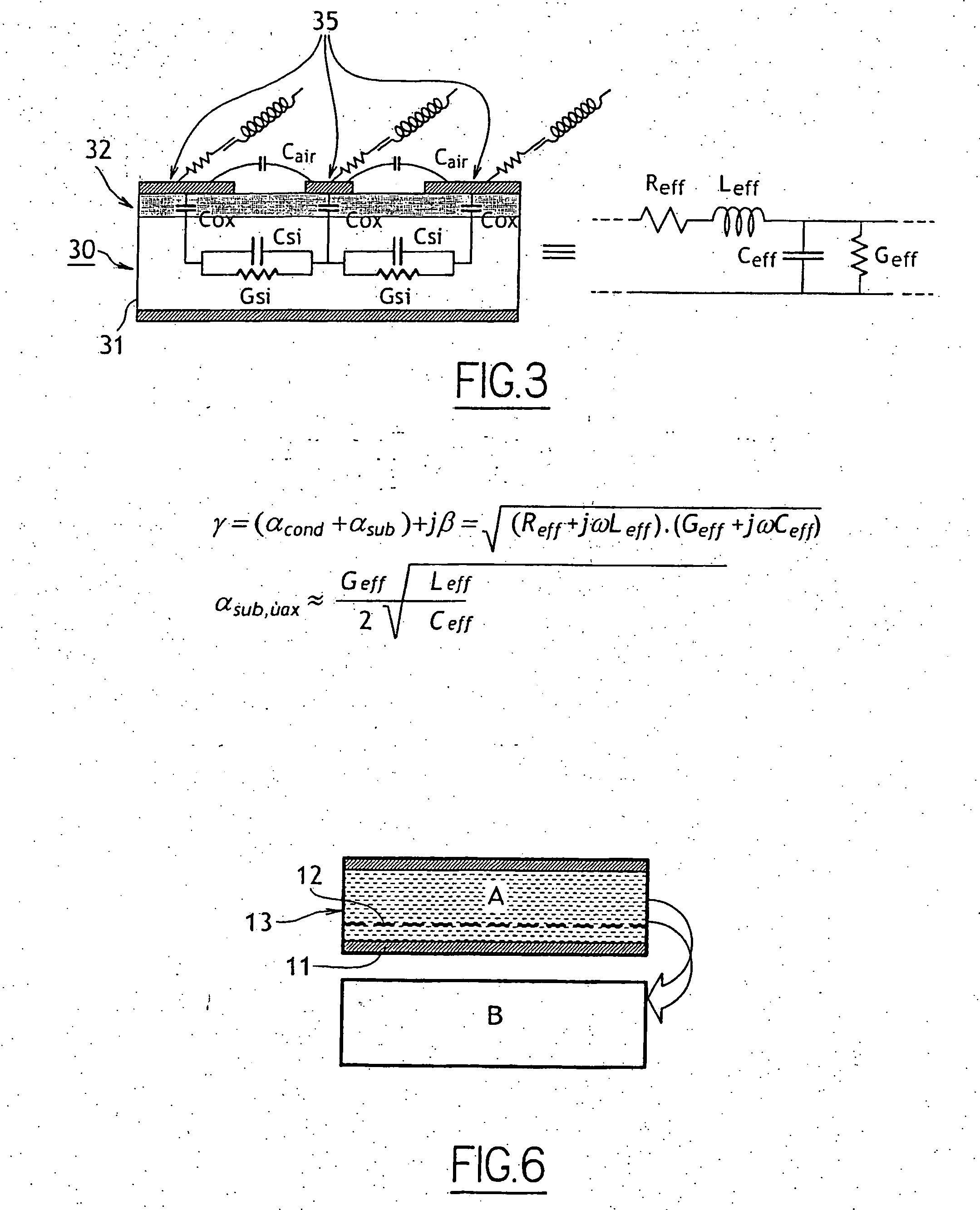
ActiveUS20060166451A1Minimize lossReduce power lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
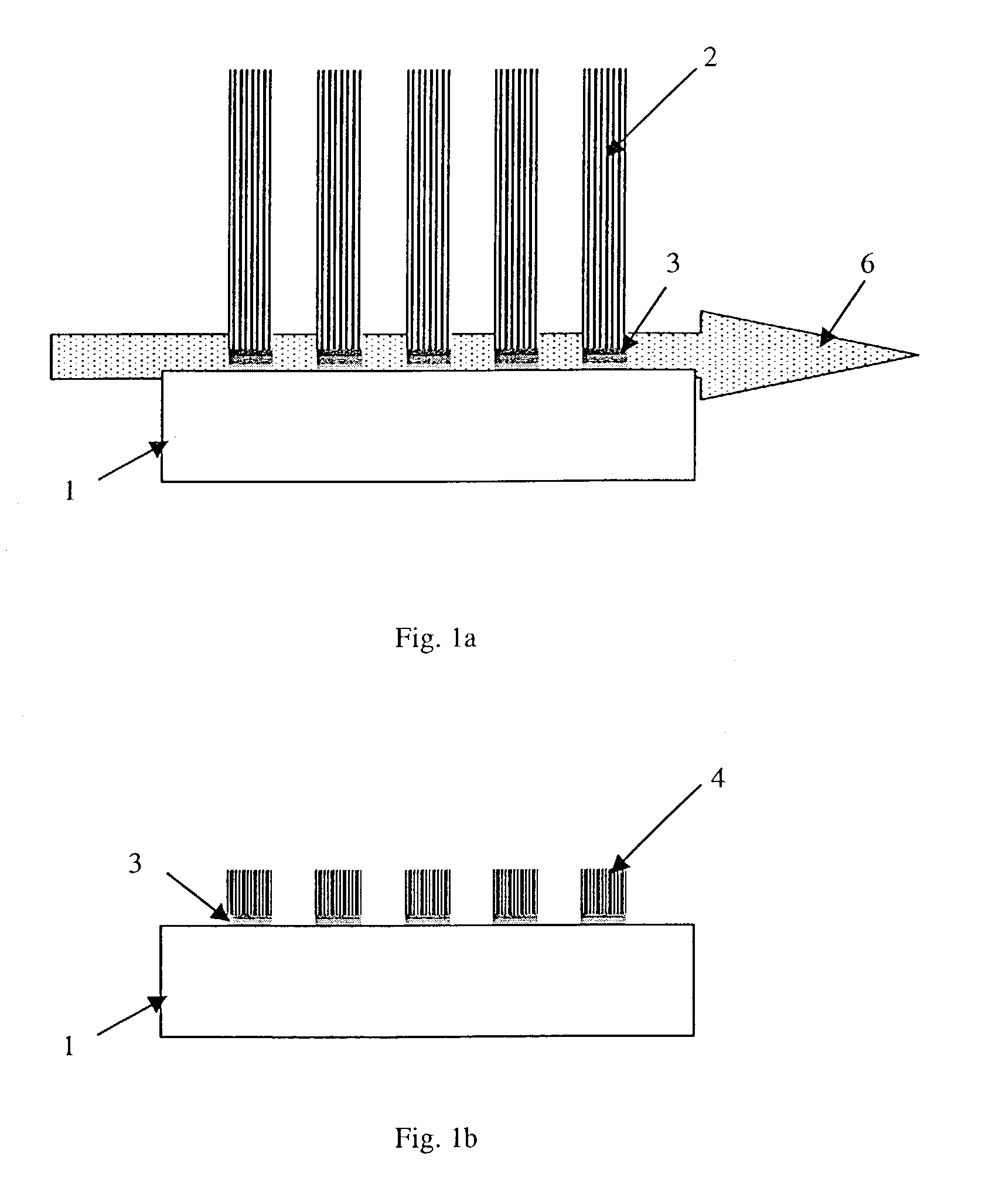
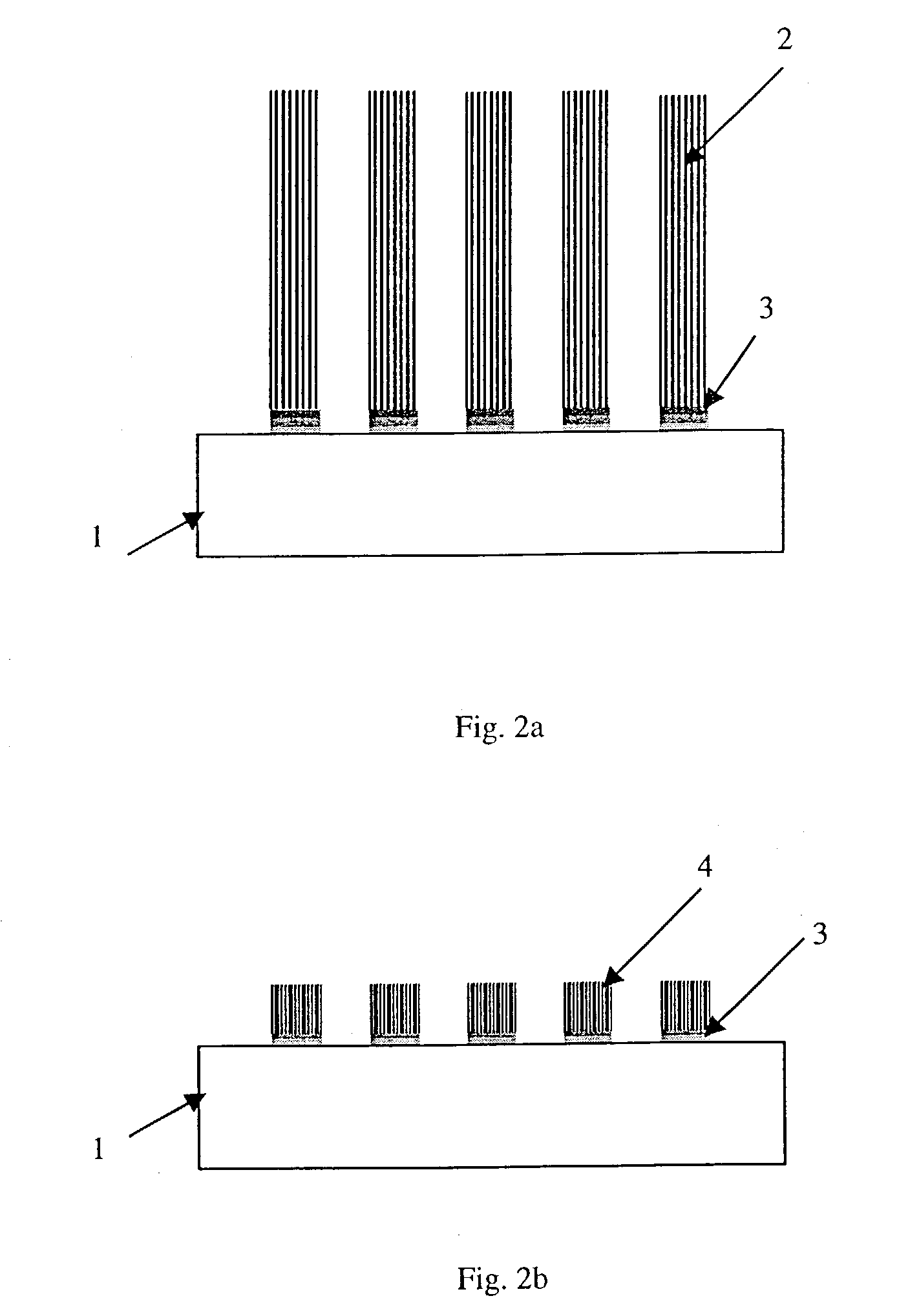
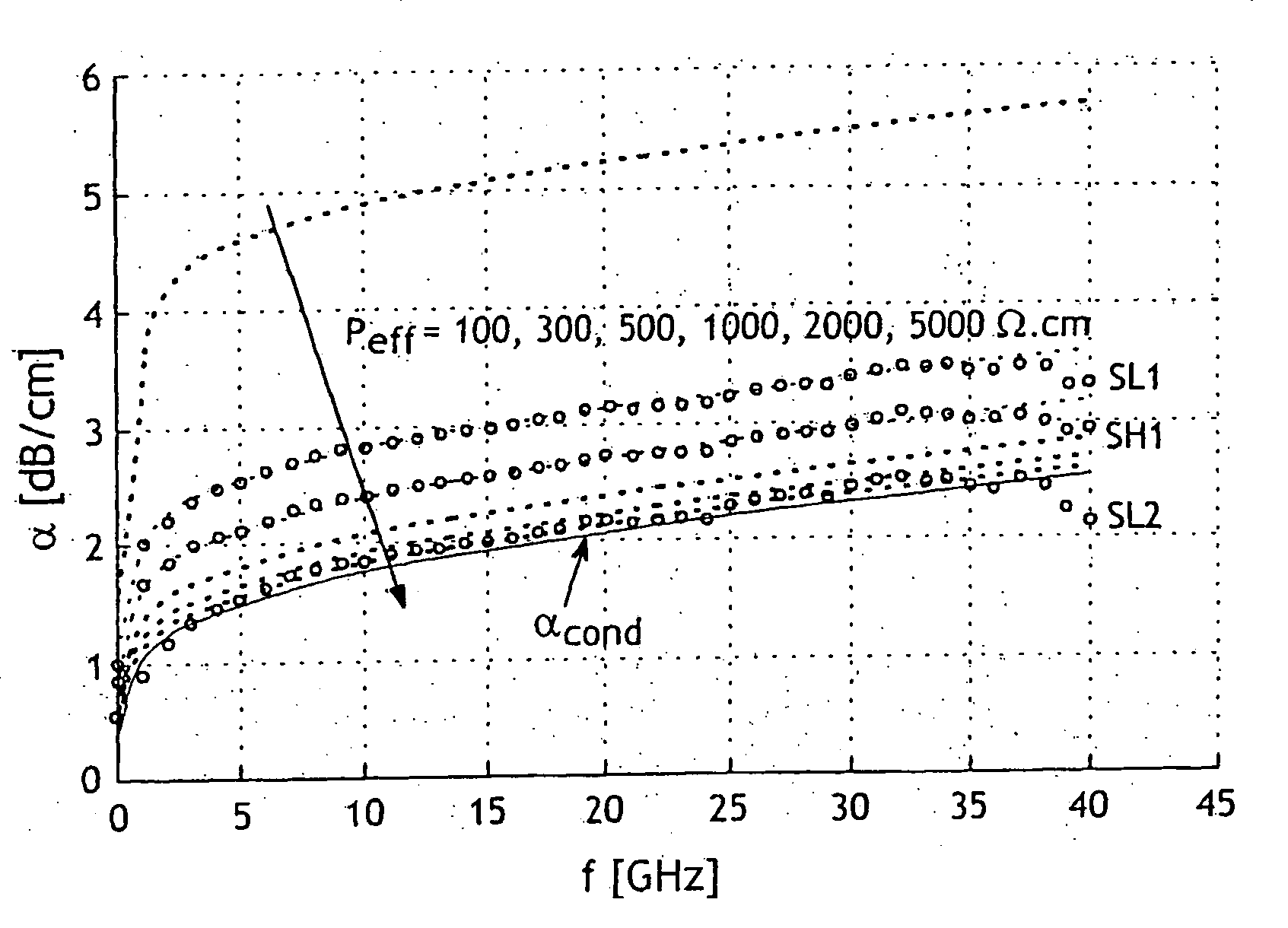
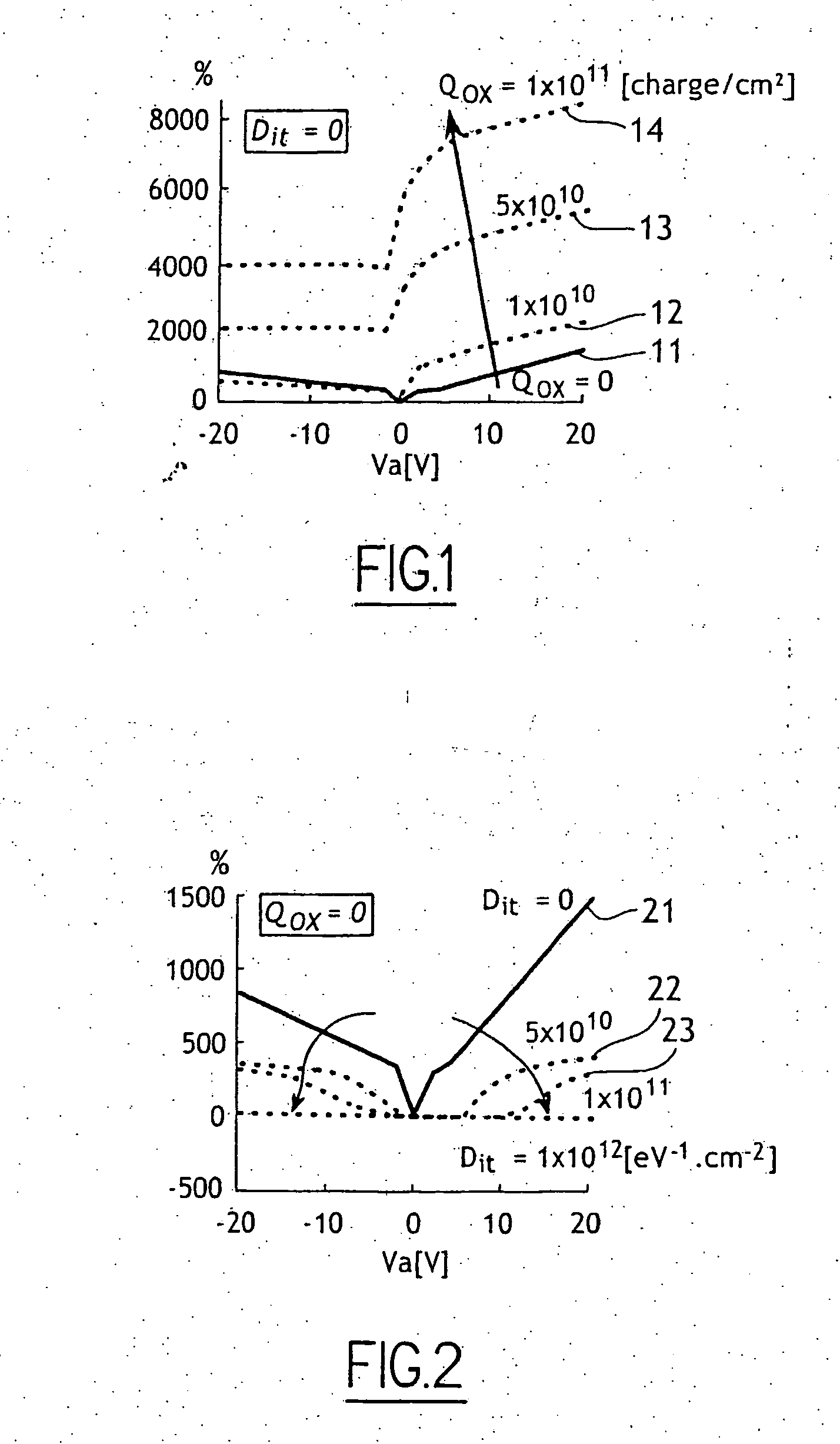
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing a multilayer structure made from semiconducting materials that include an active layer, a support layer and an electrically insulating layer between the active layer and the support layer. The process includes the step of modifying the density of carrier traps or the electrical charge within the electrically insulating layer in order to minimize electrical losses in the structure support layer.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN +1
Construction of playing surfaces
A playing surface structure includes a resin impregnated textile layer (1) having a resin bonded layer of particulate rubber (7) adherent to its undersurface and overlying a fibrous random pile mat (8) incorporating a random pile layer (9) and a relatively compact, resin impregnated backing layer (10).
Owner:NOTTINGHAMSHIRE SPORTS & SAFETY SYST
Processes for incorporating inert gas in a cement composition containing spherical beads
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
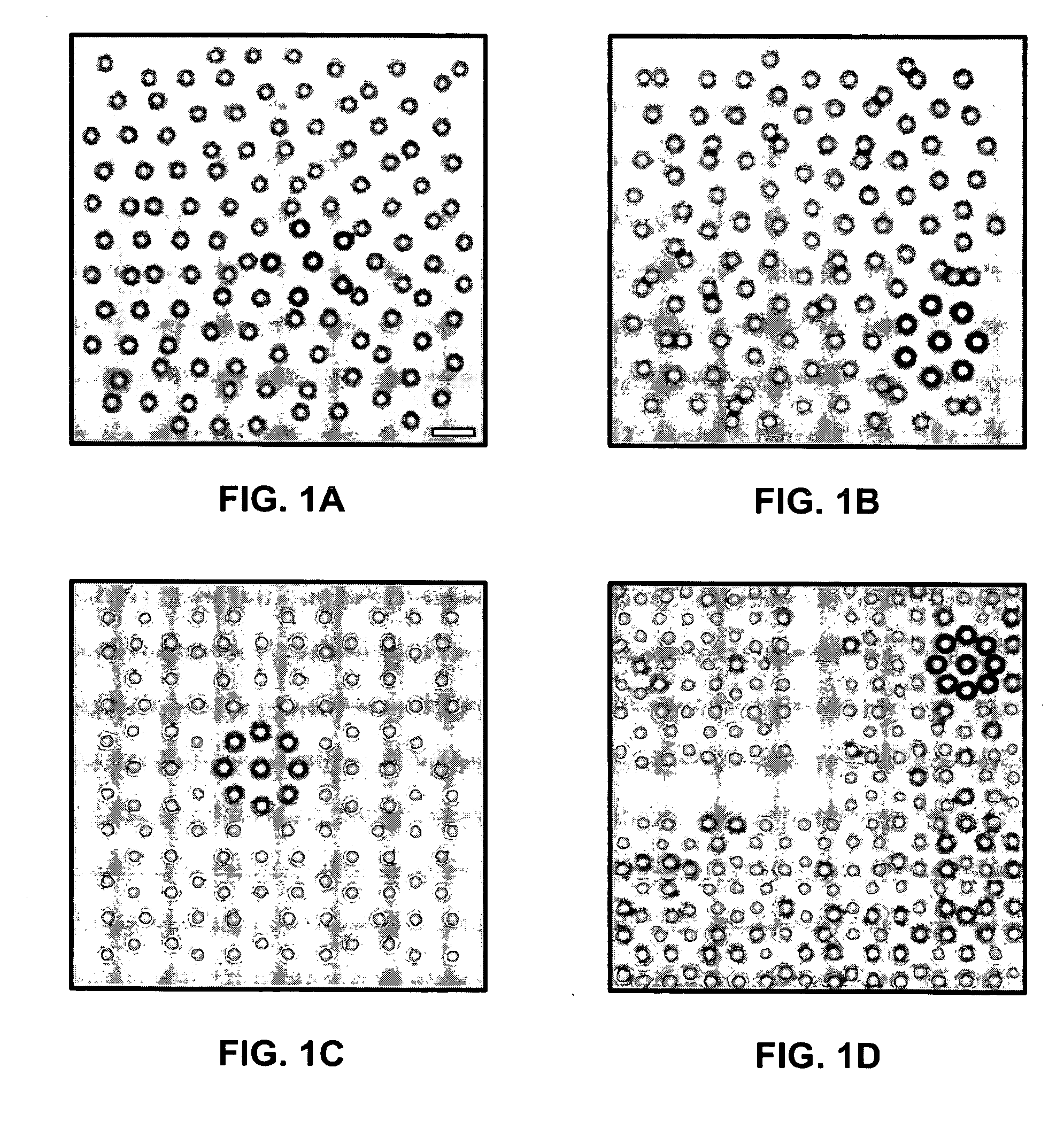
Assembly of quasicrystalline photonic heterostructures
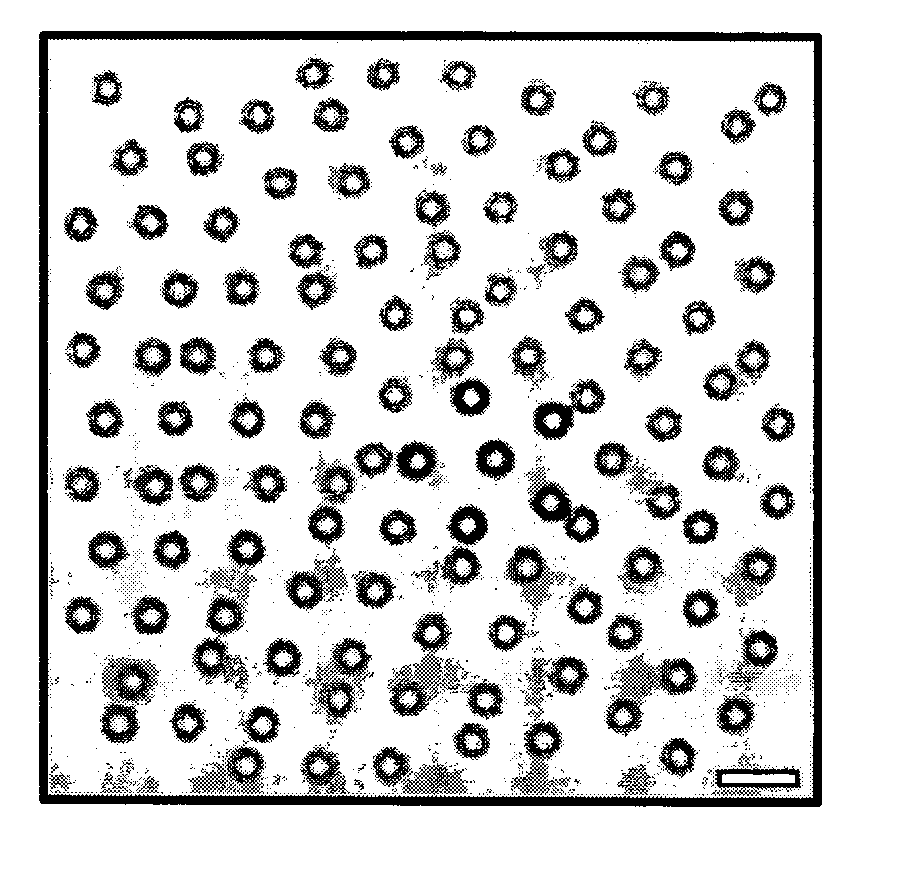
InactiveUS20070119522A1Modifies its propertySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPhotonicsEngineering
A method and system for assembling a quasicrystalline heterostructure. A plurality of particles is provided with desirable predetermined character. The particles are suspended in a medium, and holographic optical traps are used to position the particles in a way to achieve an arrangement which provides a desired property.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
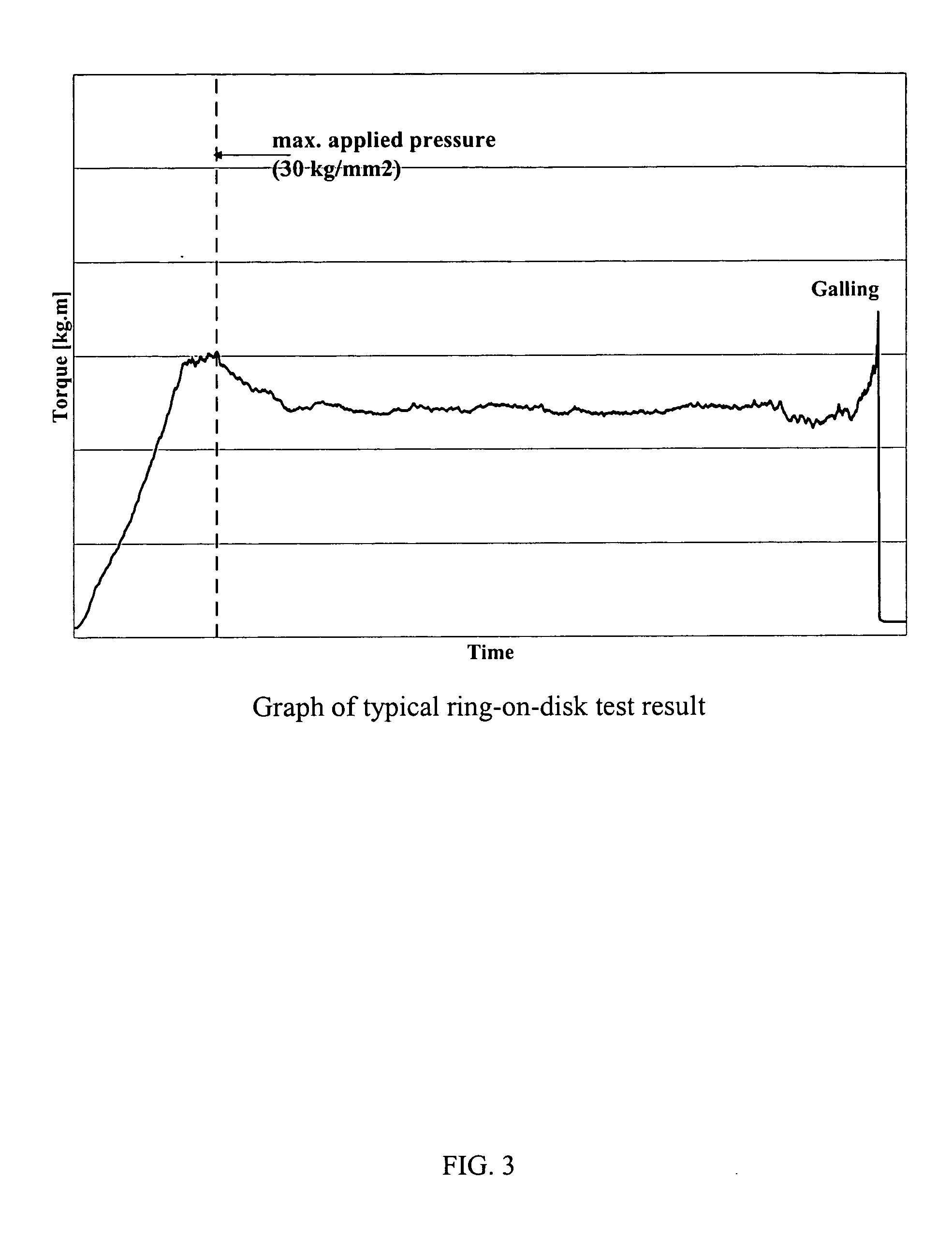
Method of using intrinsically conductive polymers with inherent lubricating properties, and a composition having an intrinsically conductive polymer, for protecting metal surfaces from galling and corrosion
InactiveUS20050176592A1Increase pressureIncrease frictionLiquid surface applicatorsOrganic chemistryGallingConductive polymer
A method for protecting a metal surface from galling and corrosion includes a step of providing a protective dry film on the metal surface. The film includes a solid lubricant and a conducting polymer, the conducting polymer having lubricant properties and being capable of binding the solid lubricant to the metal surface. Threaded metal joint surfaces coated with the film are capable of resisting galling under high pressure and high torque conditions, even after several fastening and unfastening operations or over a long period of time. Protection from corrosion is also provided by the film. The method and film are economical in that only a single layer of protective compound need be applied in order to provide metal surfaces with both lubrication and protection against corrosion, and problems such as removal or leakage, which are associated with protective compounds that use oils, are avoided. Additionally, the dry film is advantageous because it does not contain heavy metals that are harmful to the environment.
Owner:TENARIS CONNECTIONS
Surface coating for microfluidic devices that incorporate a biopolymer resistant moiety
InactiveUS6841193B1Stable and reproducible electroosmotic flowModifies its propertyElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementBiopolymerSilylation
Methods of coating the surfaces of the microchannels of a microfluidic device are provided. These methods include silylating a first portion of the surfaces of the microchannels with a first silylating reagent to produce a first silylated surface, and silylating a second portion of the surfaces of the microchannels with a second silylating reagent to produce a second silylated surface.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Intraocular lens system with injectable accommodation material
ActiveUS20080033547A1Modifies its propertyShape adjustableIntraocular lensPosterior lensAnterior lens
The invention relates to a intraocular lens system having a flexible anterior lens accommodation material behind the lens. The accommodation material may comprise of one or more macromers, which, when polymerized, adjust the properties of the accommodation material. The anterior lens is flexible such that the curvature of the lens changes during accommodation. The anterior lens may be used alone or in combination with a posterior lens.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Dental treatment tray comprising a plasticized resin for improved moldability and conformability
A dental treatment tray used to provide a desired treatment is injection molded from a composition that includes at least one thermoplastic resin and at least plasticizer. The plasticized thermoplastic resin permits the dental treatment tray to be injection molded even while having a wall thickness less than about 0.015 inch. The plasticizer increases the melt flow index of the thermoplastic resin while in a molten state, which facilitates complete filling of the mold cavity by the thermoplastic resin. The plasticizer also softens the thermoplastic polymer while in a solidified state in order to yield a dental tray that is even more flexible and comfortable for the user to wear.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Highly elastomeric and paintable silicone compositions
ActiveUS20080312369A1Good paintabilityGood weather resistanceDyeing processCoatingsSealantPolymer chemistry
Highly elastomeric, curable, paintable silicone compositions are provided. The paintable silicone compositions comprise an organopolysiloxane, a silicone functional crosslinker, and an organic polymer. The highly elastomeric, curable, paintable silicone compositions have an elongation of at least 150% and are useful as paintable sealants and caulks.
Owner:TREMCO CPG INC
Removable Floor
InactiveUS20080313987A1Modifies its propertyFacilitates laying/removingCeilingsTreadsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a removable floor. The invention comprises a support piece (1) having a floor tile (15) affixed to the upper surface thereof, said support piece being equipped with means for securing same to other support pieces. The invention aims to improve the securing means in order to facilitate the installation and removal of the floor by the user and to enable the supports to be installed in an aligned and / or out of phase manner such as to produce different decorative patterns.
Owner:TAULELL +1
Method of processing a composite material
InactiveUS20100086765A1StrengthToughnessNatural cellulose pulp/paperSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperPorous layerMatrix diffusion
A method of processing a composite material comprising heating a porous layer in contact with the composite material above its melting point whereby it melts and becomes incorporated into the composite material. The material may be formed by a matrix diffusion process. In this case the porous layer acts as a distribution layer. Alternatively the material may be formed as a stack of prepregs. In this case the porous layer acts as a breather layer. The porous layer may comprise a polysulphone or polyethersulphone which increases the toughness of the material.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
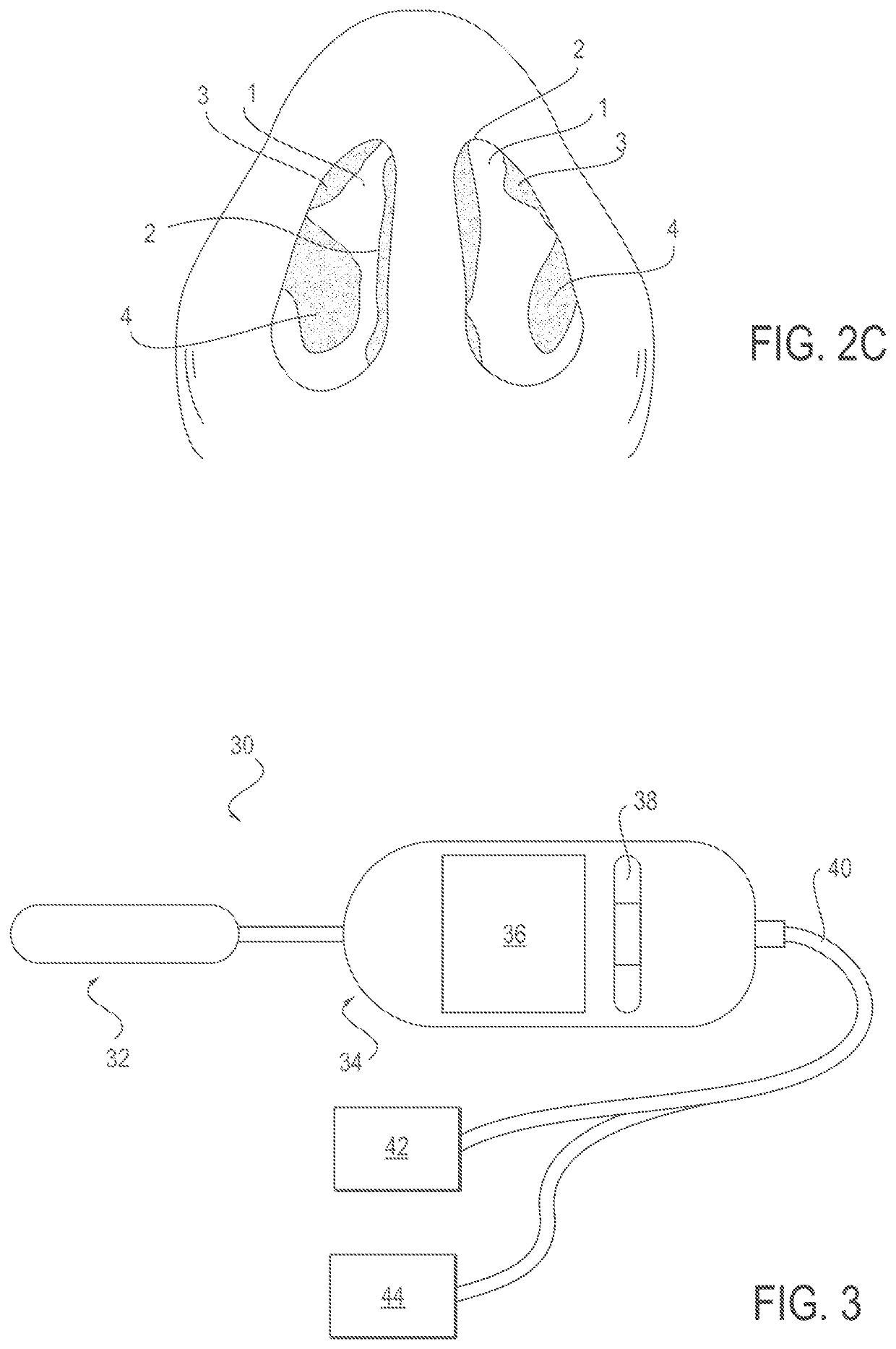
Methods of treating nasal airways
ActiveUS20190336196A1Decrease airflow resistance perceived airflowIncrease ratingsElectrotherapySurgical needlesSurgical incisionNasal valve
A device is described for treating a nasal airway by modifying a property of a nasal tissue of or near a nasal valve of the airway, without using a surgical incision or an implant, to decrease airflow resistance or perceived airflow resistance in the nasal airway. Various embodiments include an elongate shaft, a bipolar radiofrequency delivery member extending from one end of the shaft, and a handle attached to the elongate shaft at an opposite end from the radiofrequency delivery member. The radiofrequency delivery member is sized to be inserted into a nose and configured to at least temporarily deform the nasal tissue and deliver radiofrequency energy. The radiofrequency delivery member includes two rows of protruding electrodes disposed on a tissue contact surface, and the device is configured to deliver radiofrequency energy from one row of electrodes to the other row of electrodes.
Owner:AERIN MEDICAL
Quasicrystalline structures and uses thereof
ActiveUS8064127B2Modifies its propertyMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusSpinsCrystal structure
This invention relates generally to the field of quasicrystalline structures. In preferred embodiments, the stopgap structure is more spherically symmetric than periodic structures facilitating the formation of stopgaps in nearly all directions because of higher rotational symmetries. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of quasicrystalline structures for optical, mechanical, electrical and magnetic purposes. In some embodiments, the invention relates to manipulating, controlling, modulating and directing waves including electromagnetic, sound, spin, and surface waves, for a pre-selected range of wavelengths propagating in multiple directions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com