Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Lens crystalline" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
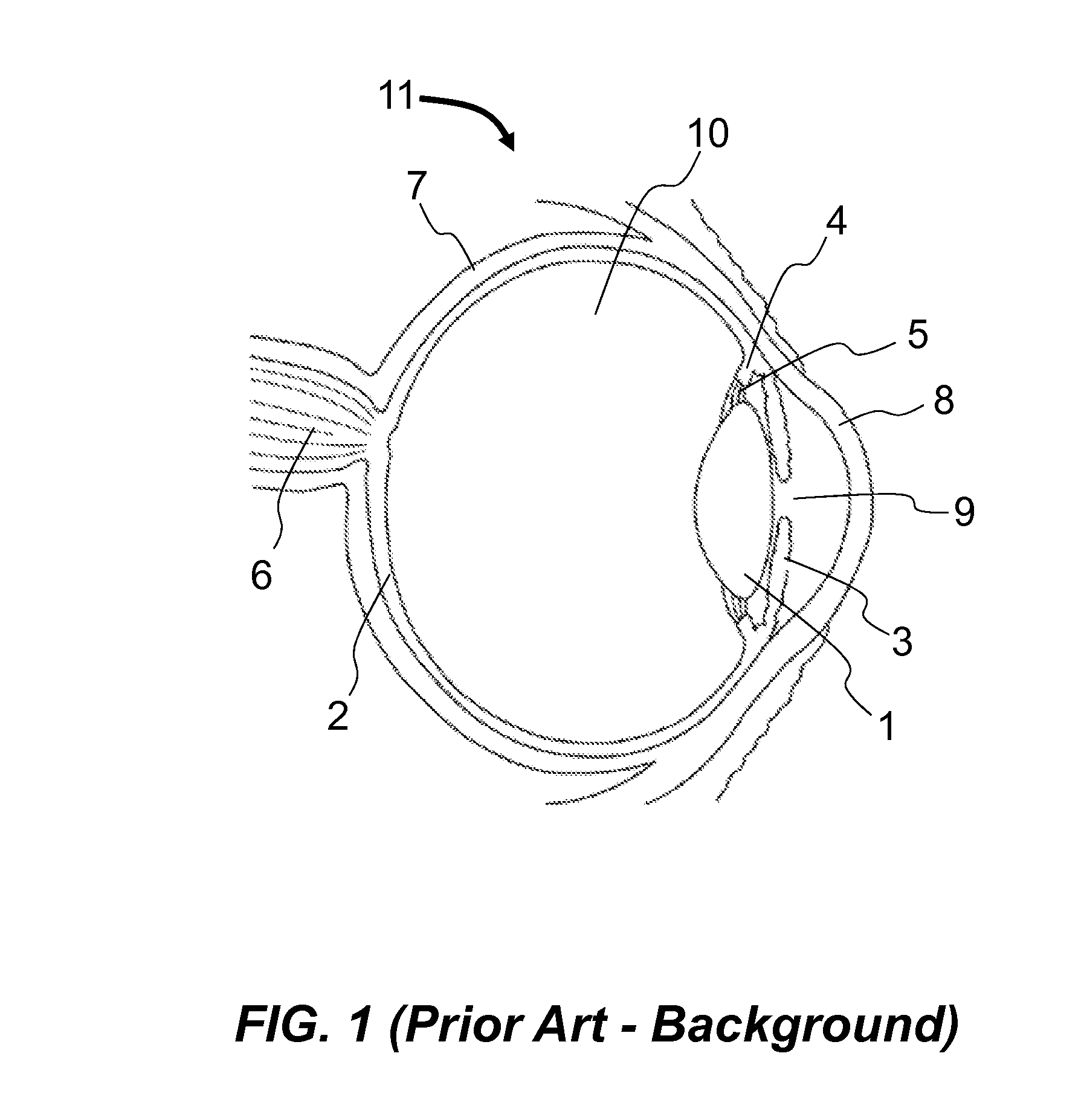
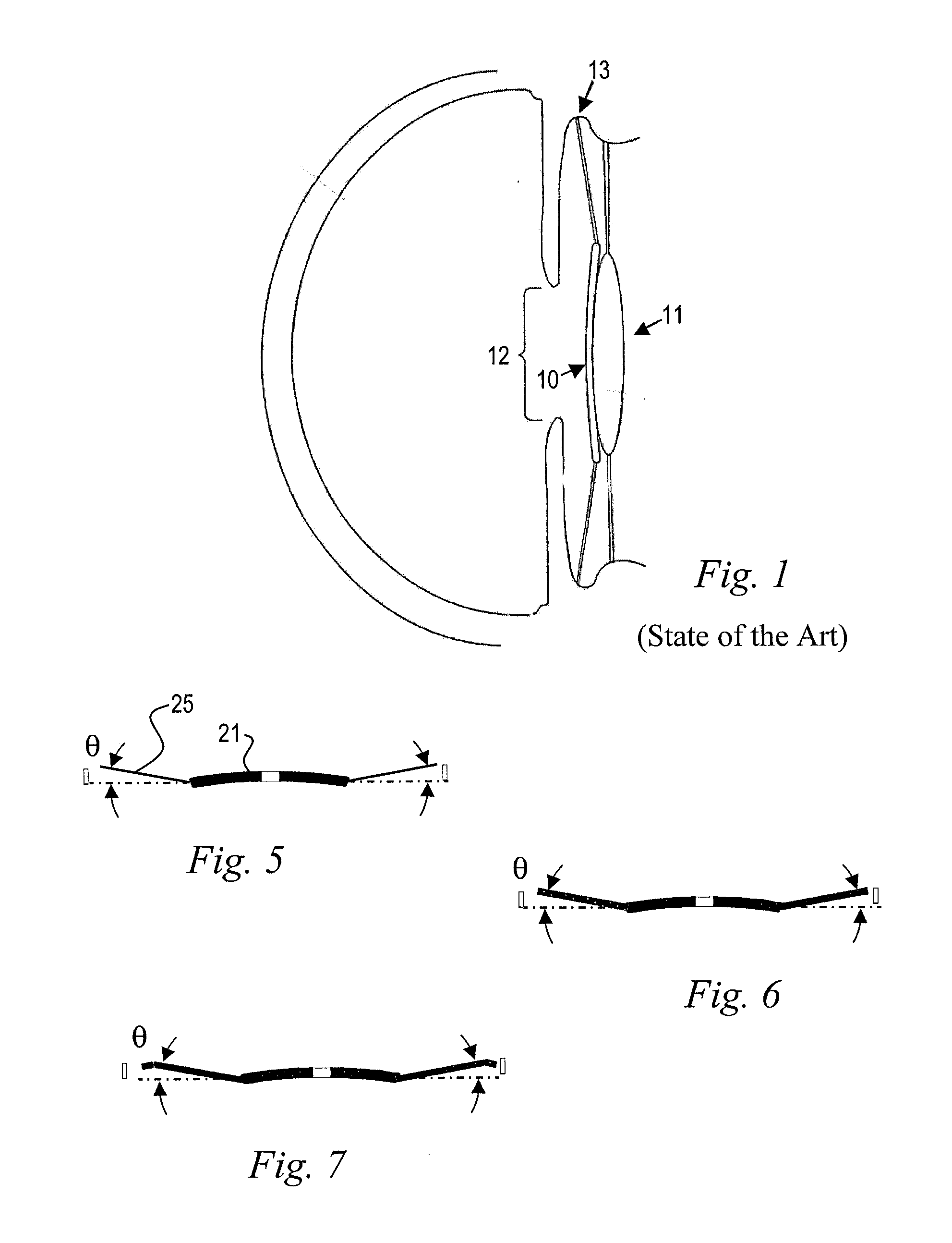
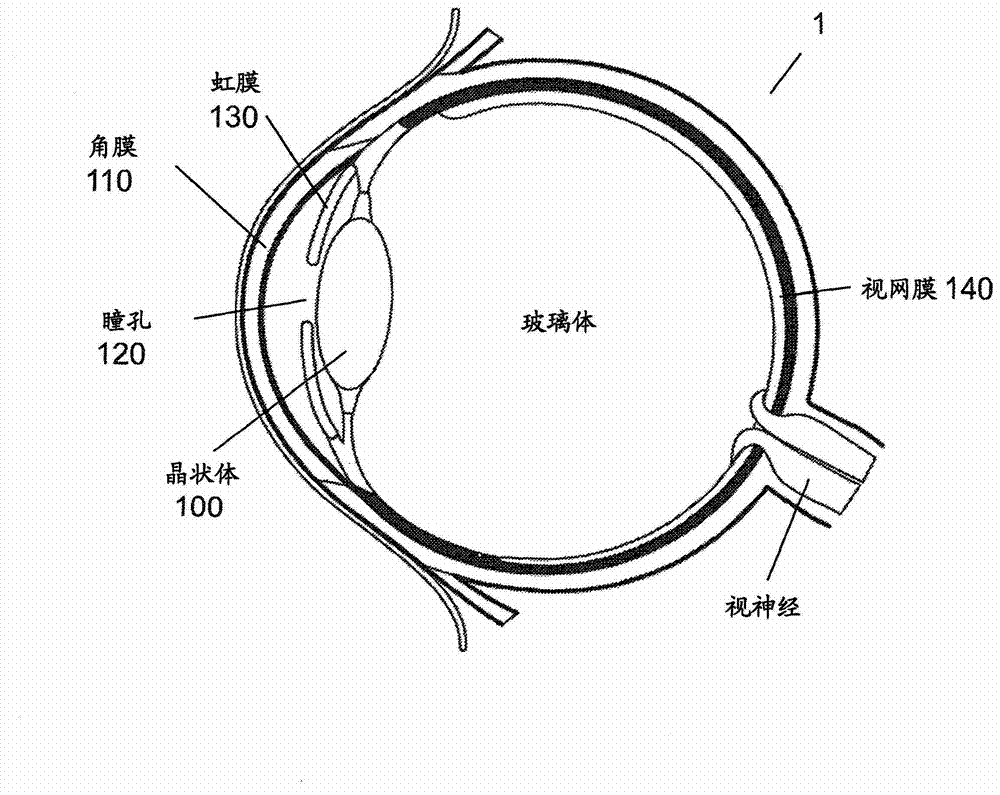
Crystalline lens. a transparent structure of the eye, enclosed in a capsule, situated between the iris and the vitreous humor, and slightly overlapped at its margin by the ciliary processes. It refracts light to focus images on the retina.
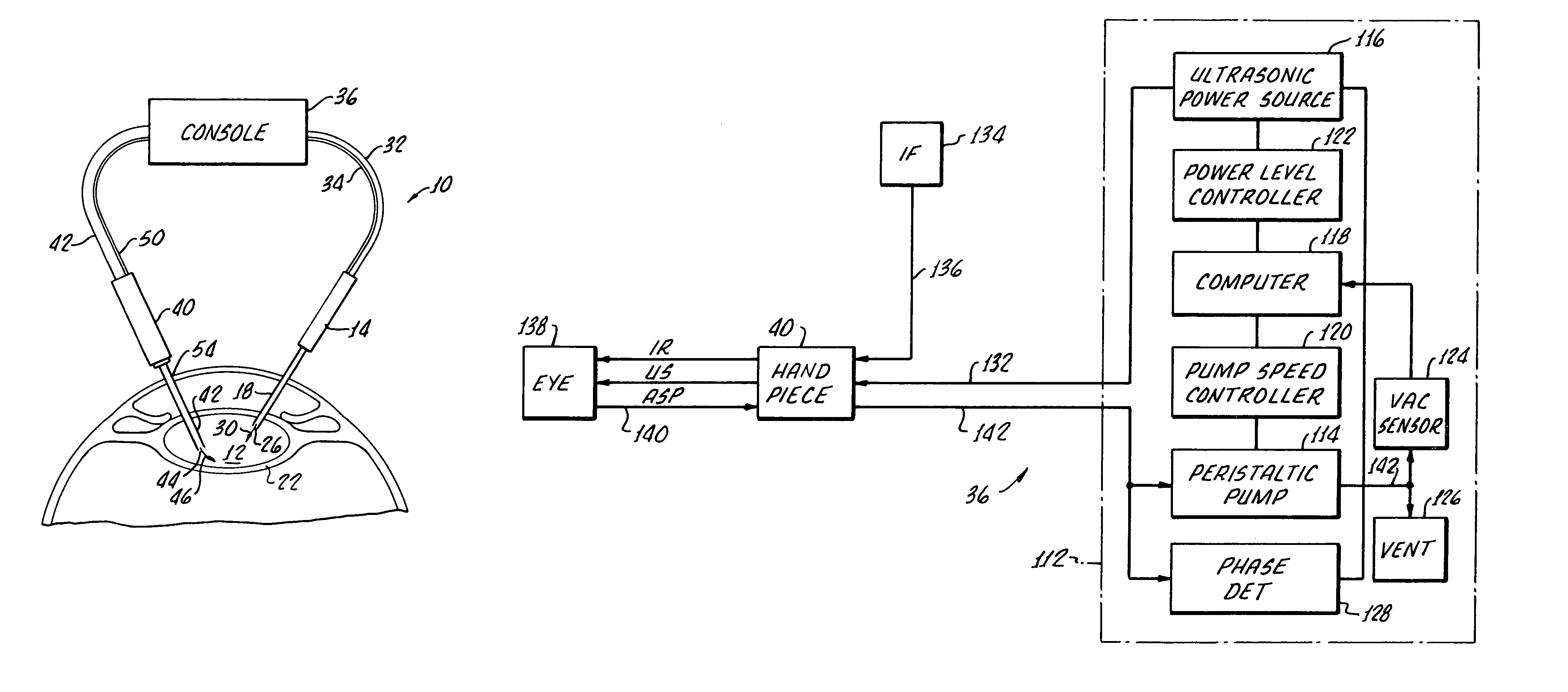
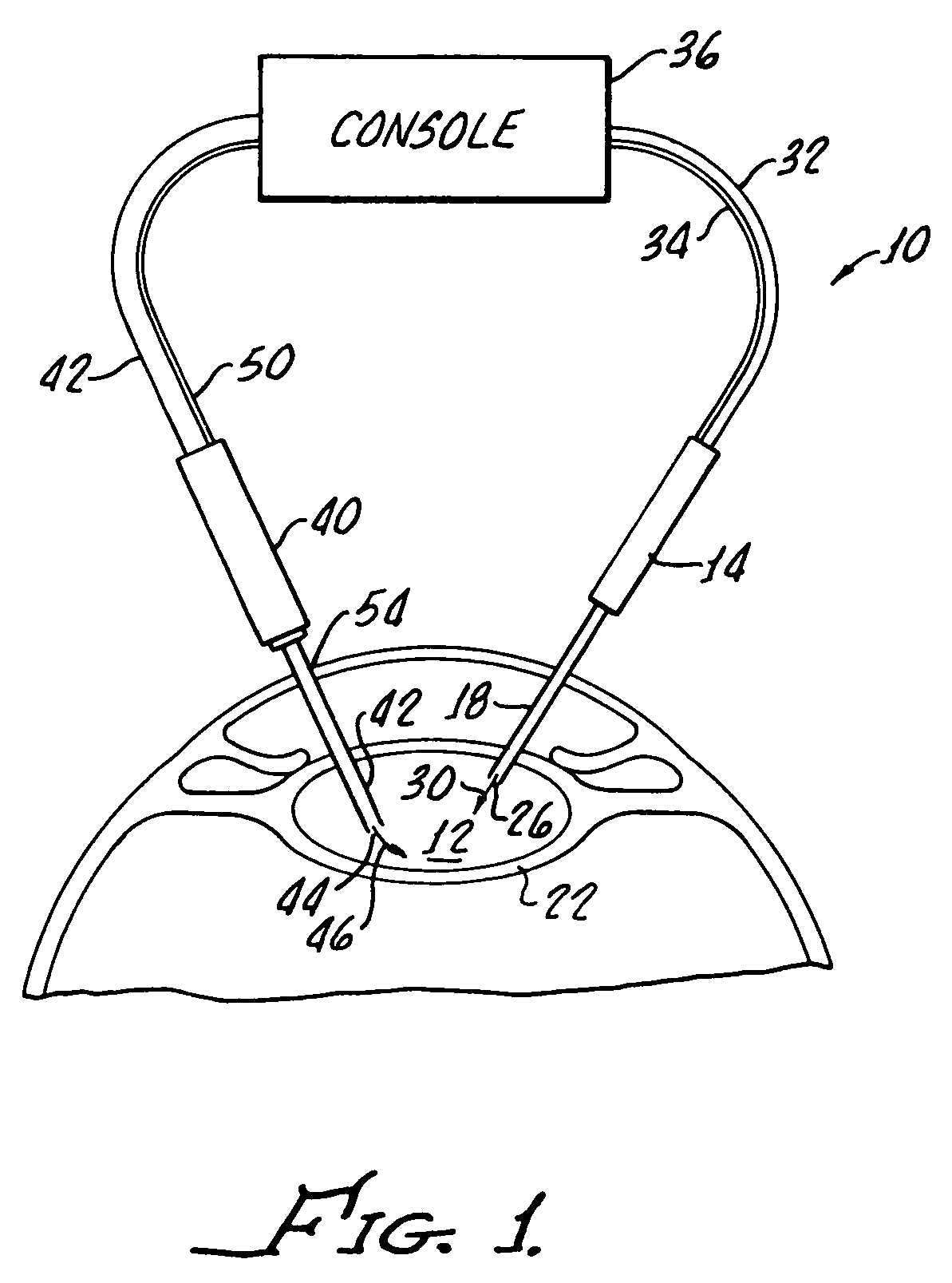
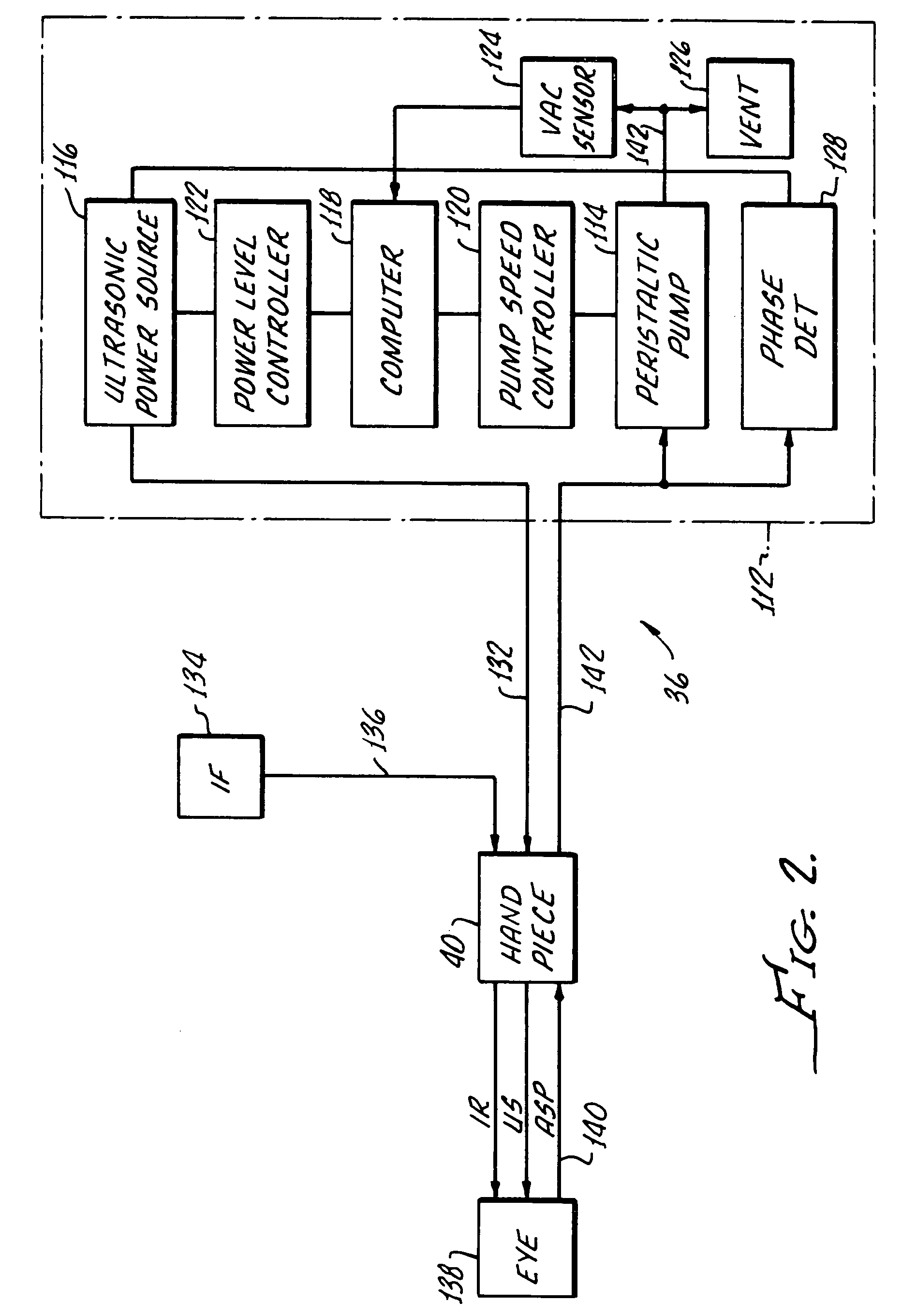
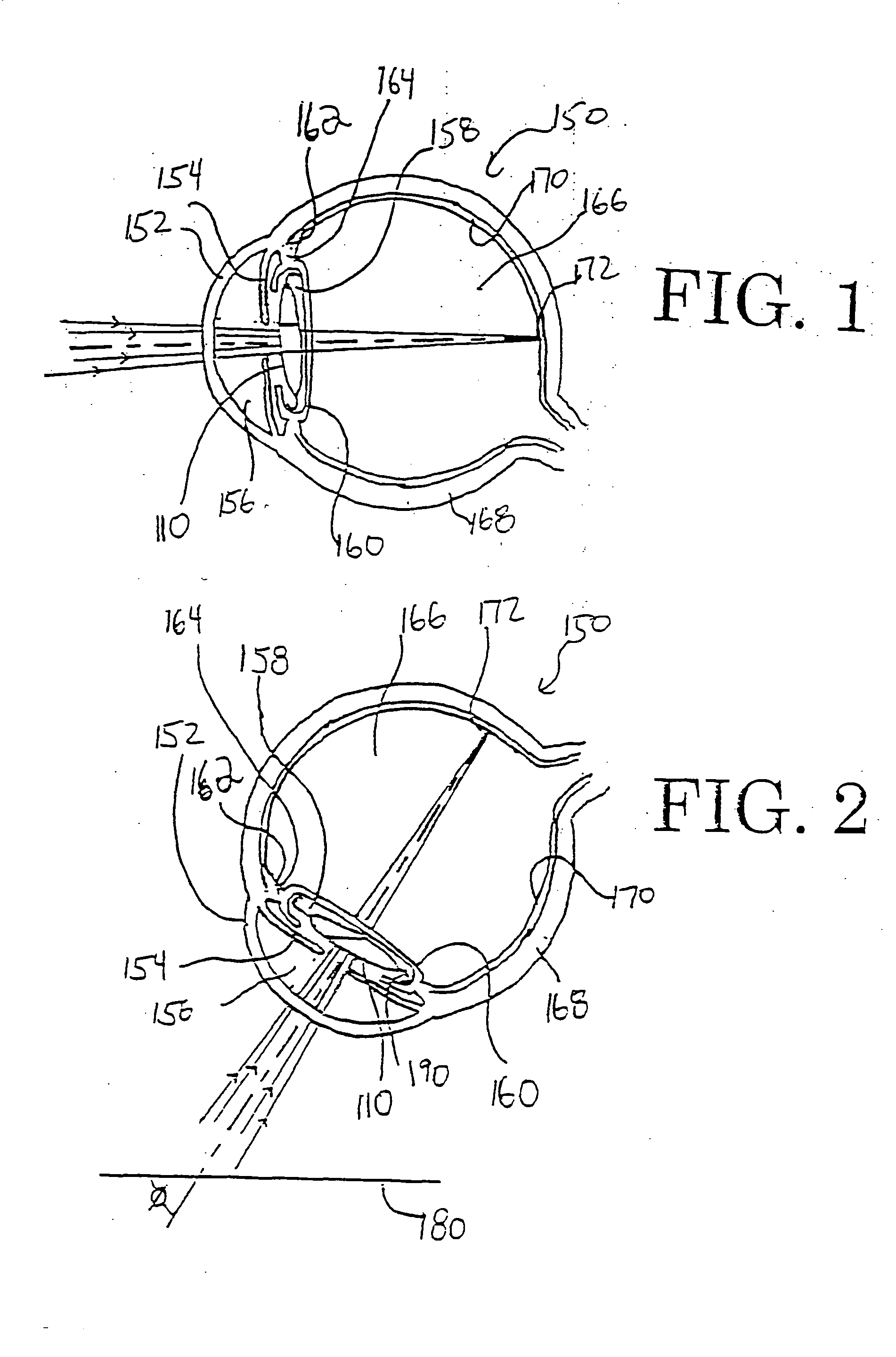
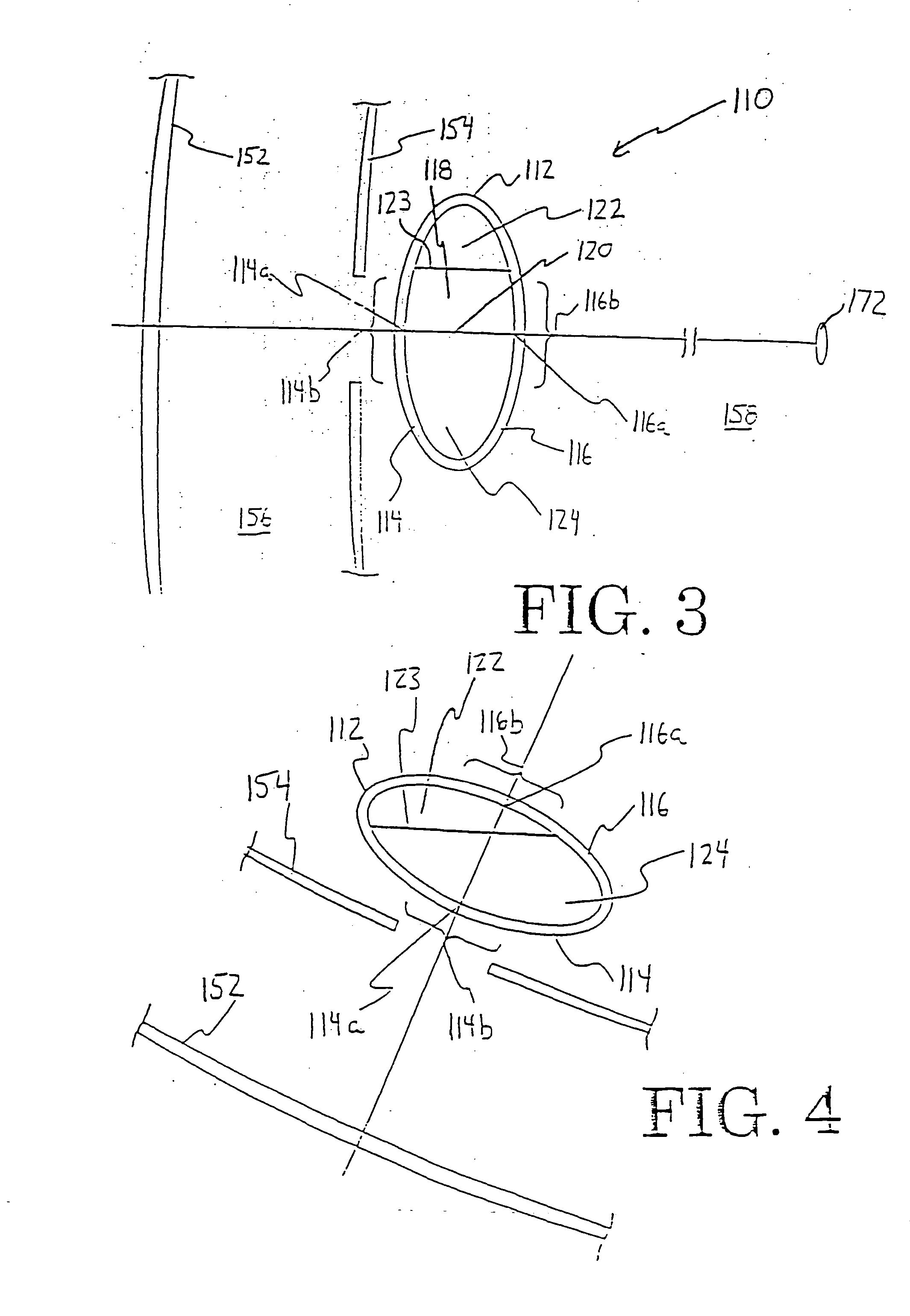
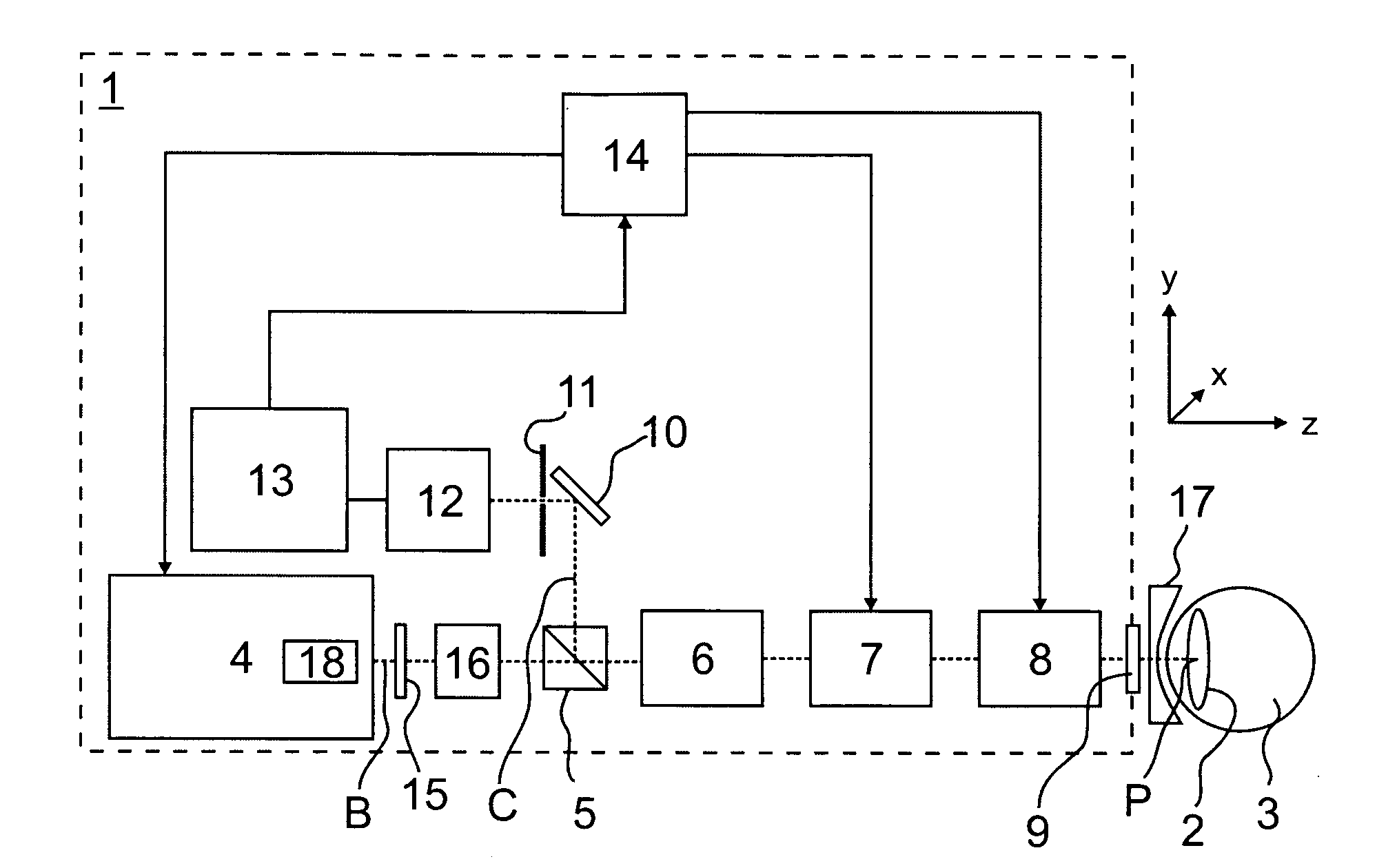
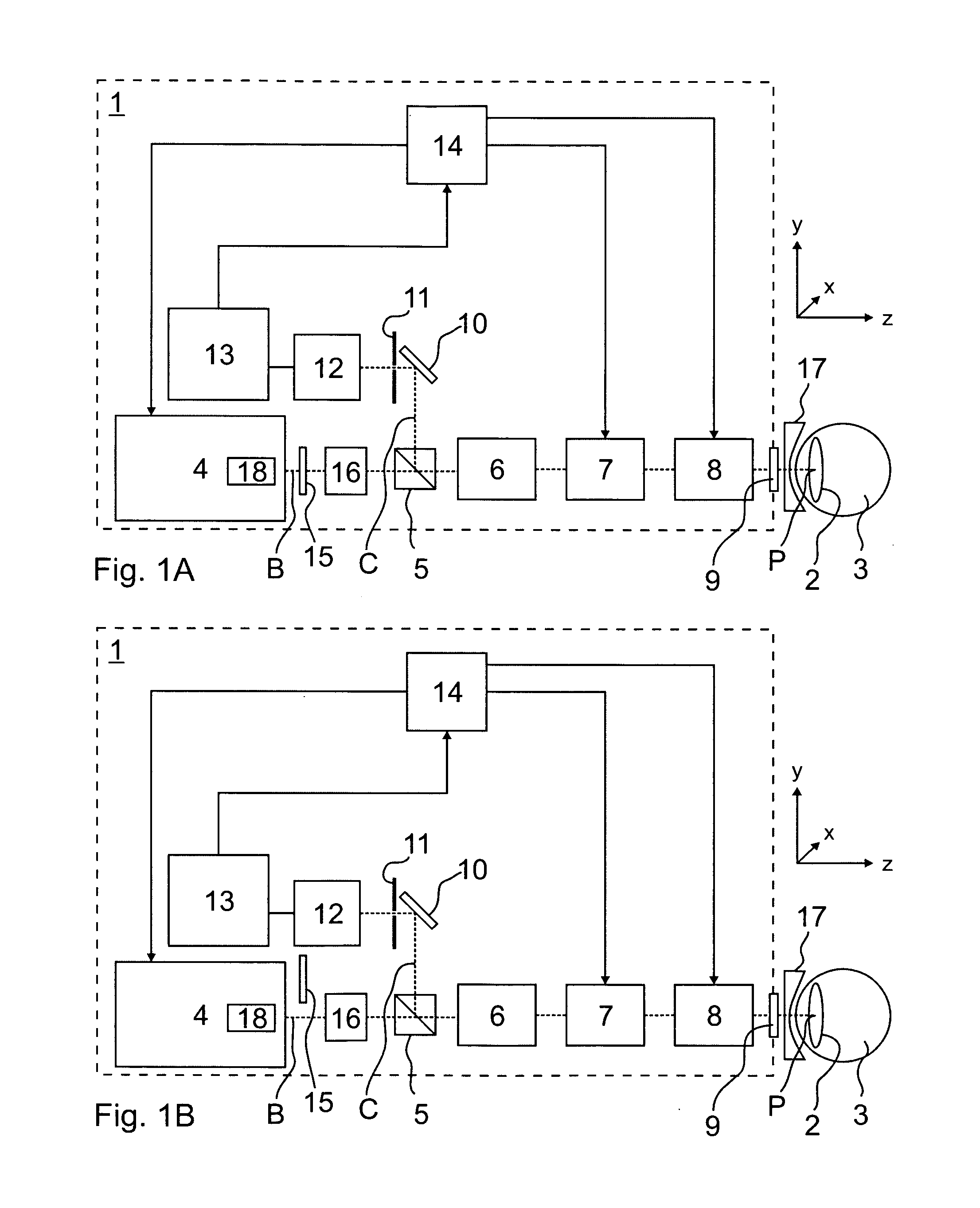
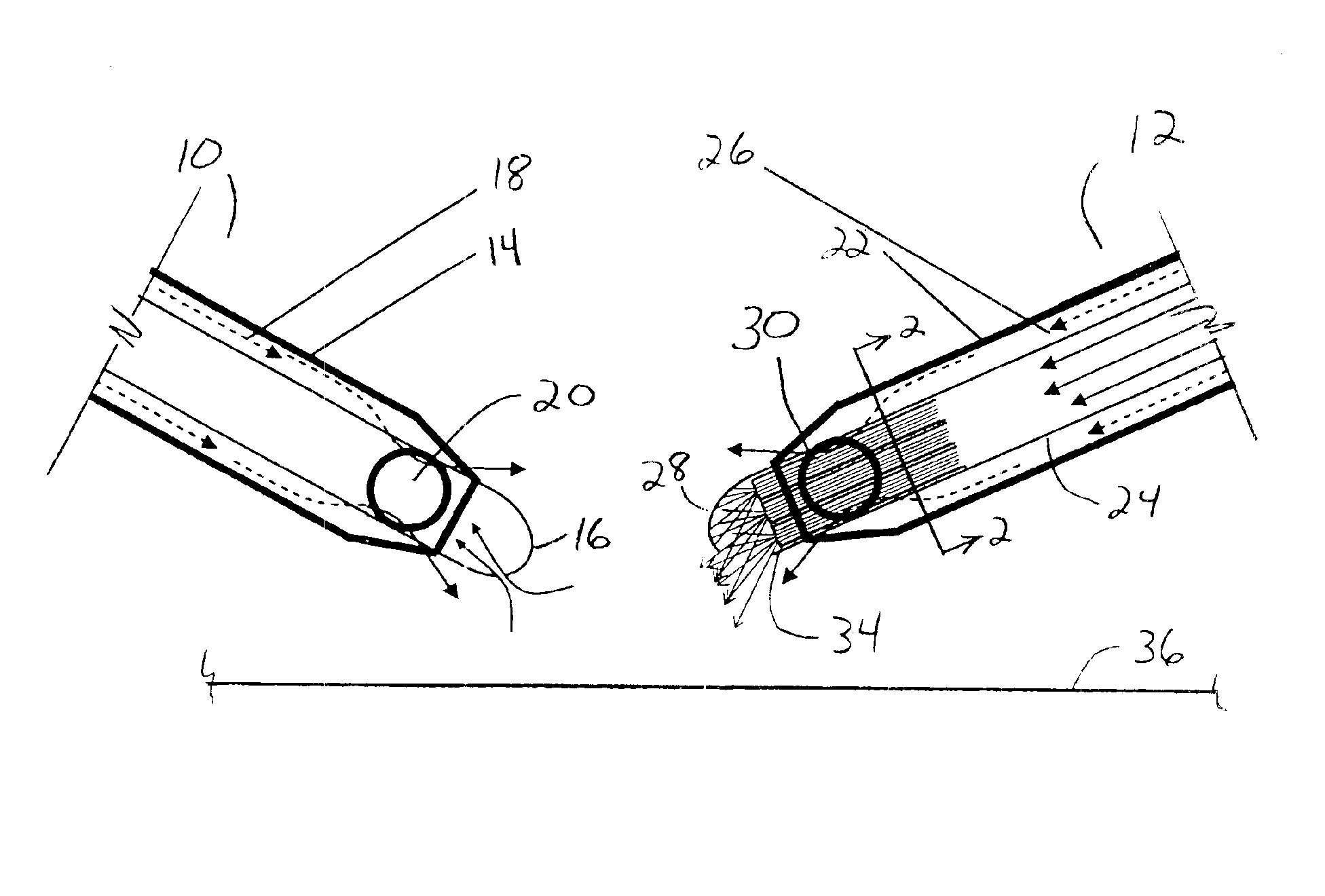
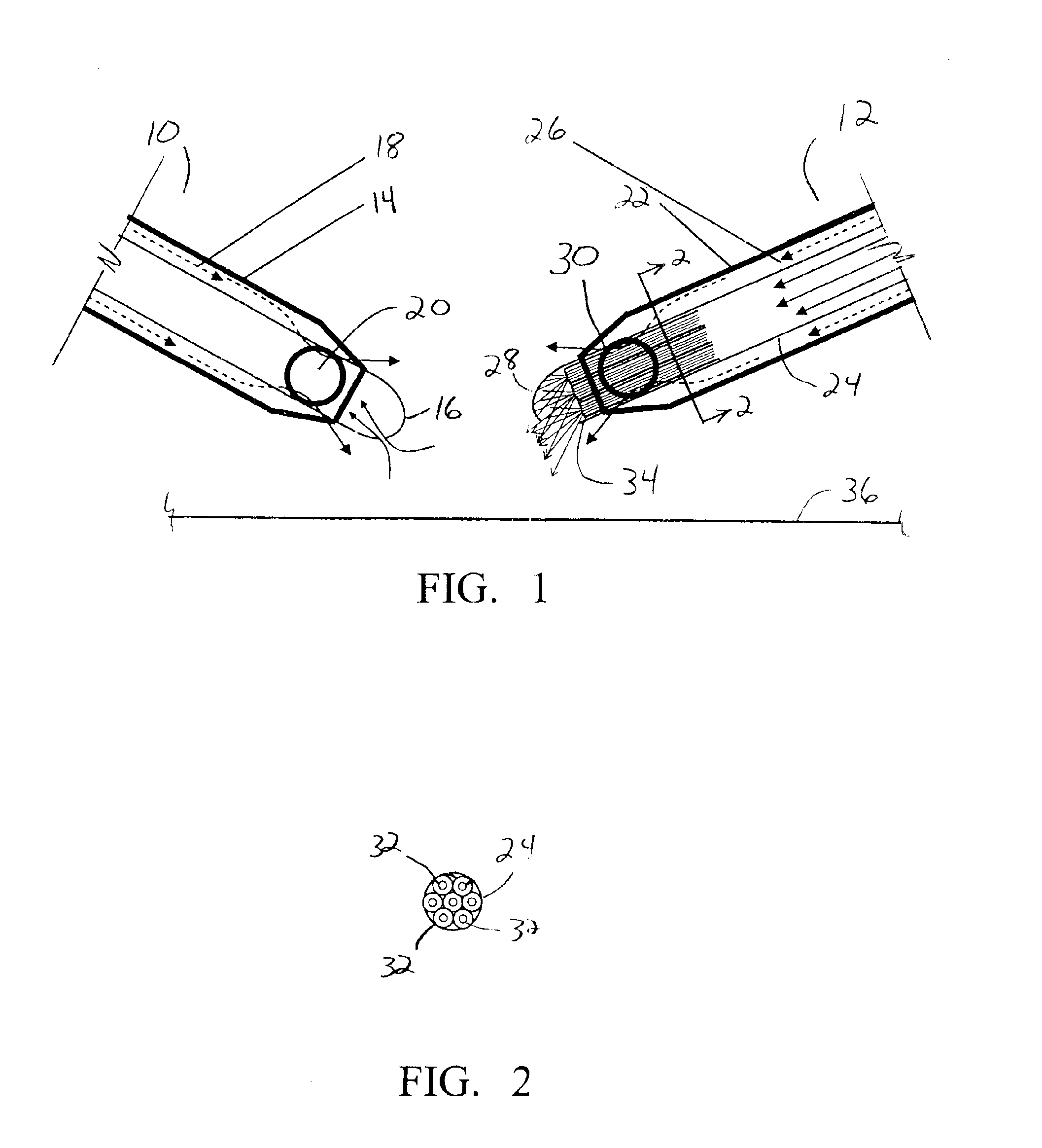
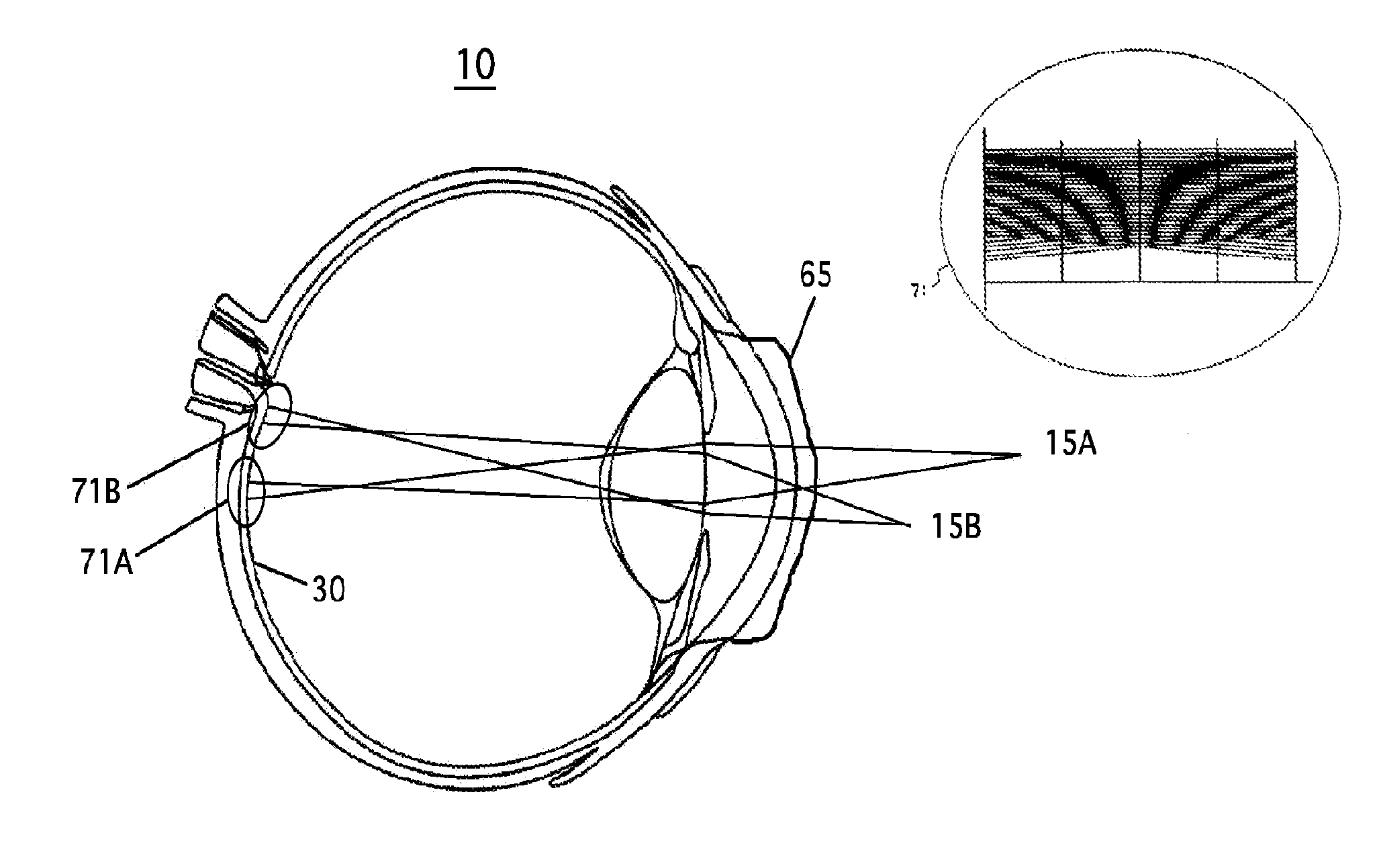
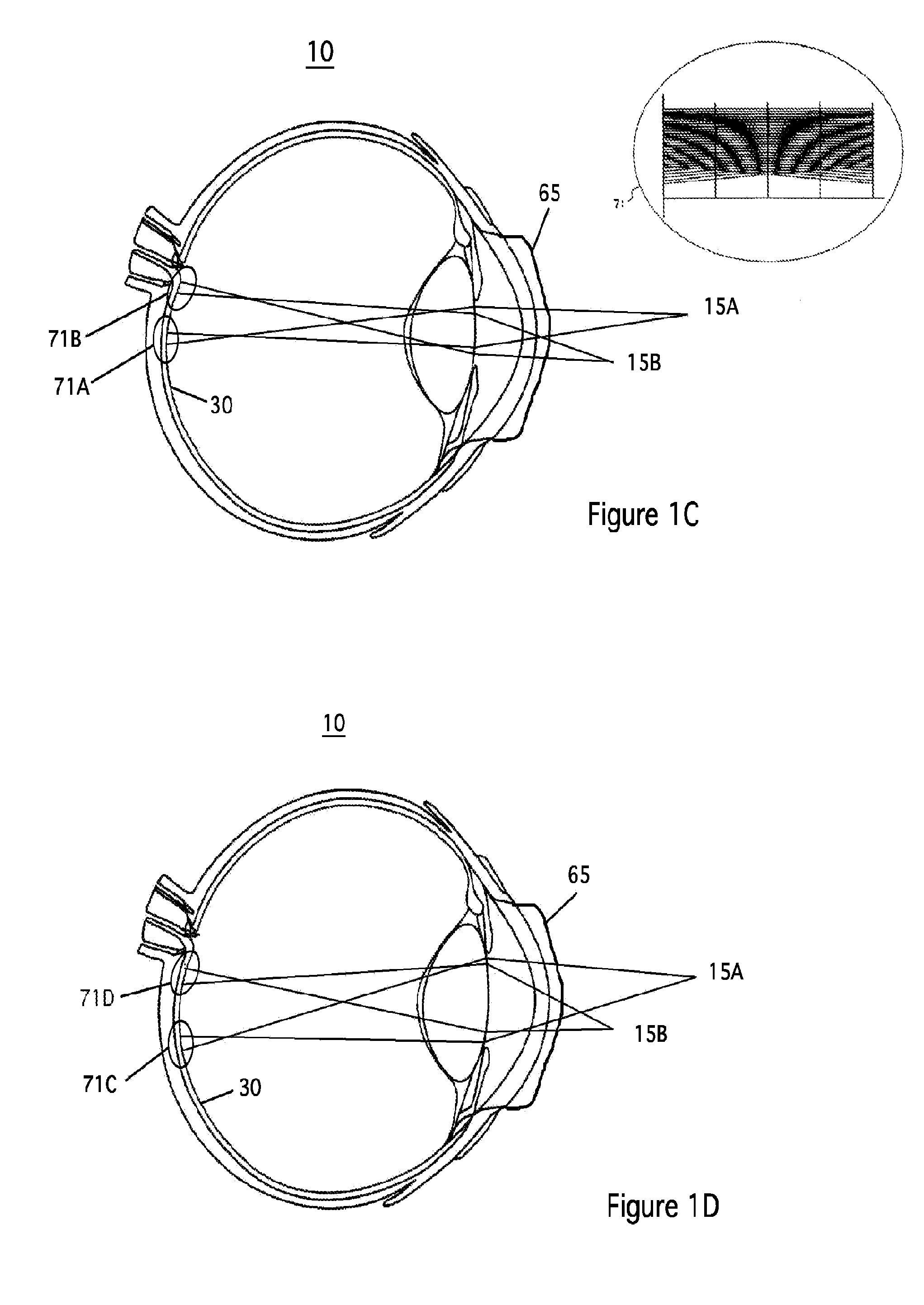
System and apparatus for treating the lens of an eye
A system and apparatus for increasing the amplitude of accommodation and / or changing the refractive power and / or enabling the removal of the clear or cataractous lens material of a natural crystalline lens is provided. Generally, the system comprises a laser, optics for delivering the laser beam and a control system for delivering the laser beam to the lens in a particular pattern. There is further provided apparatus for determining the shape and position of the lens with respect to the laser. There is yet further provided a method and system for delivering a laser beam in the lens of the eye in a predetermined shot pattern.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
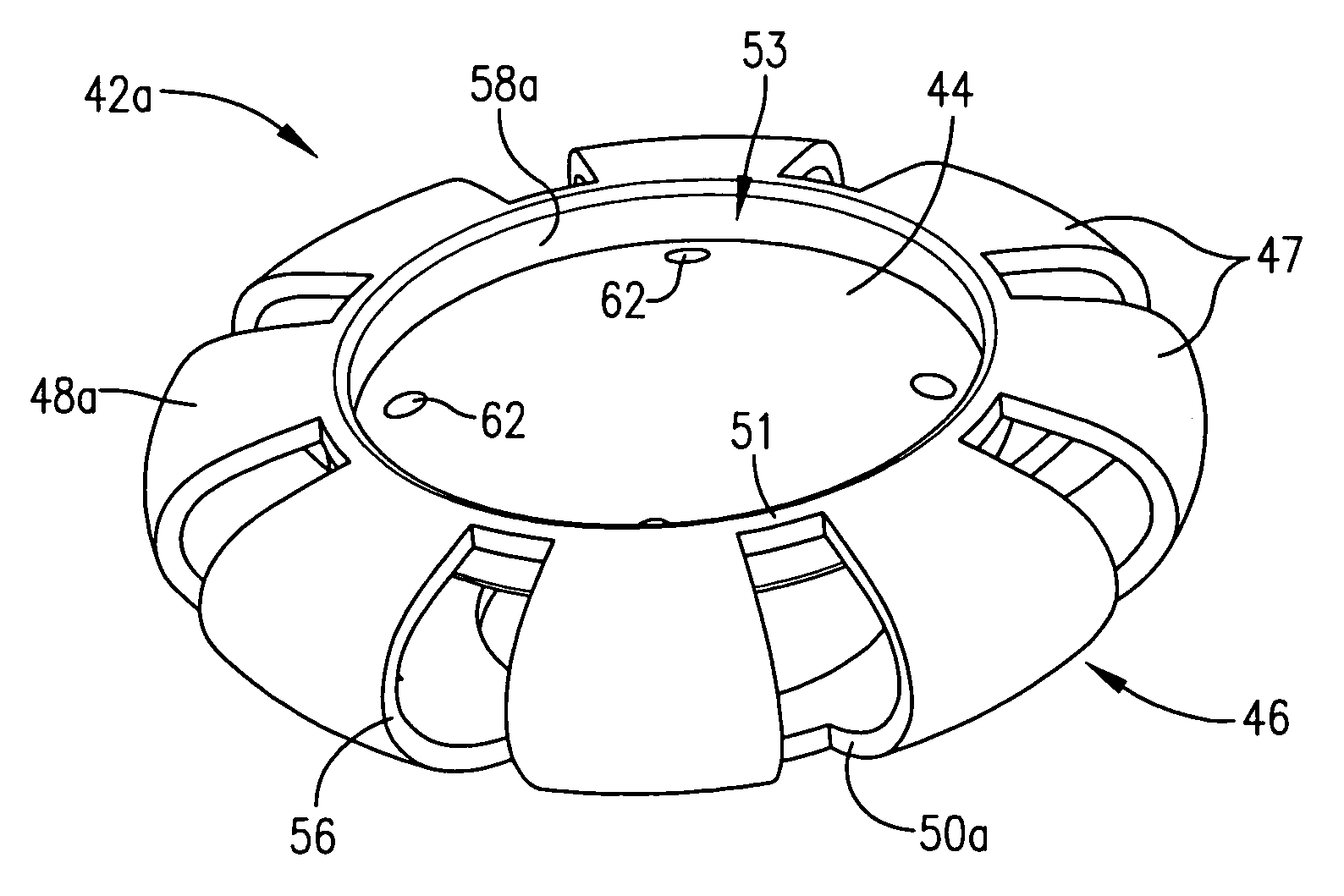
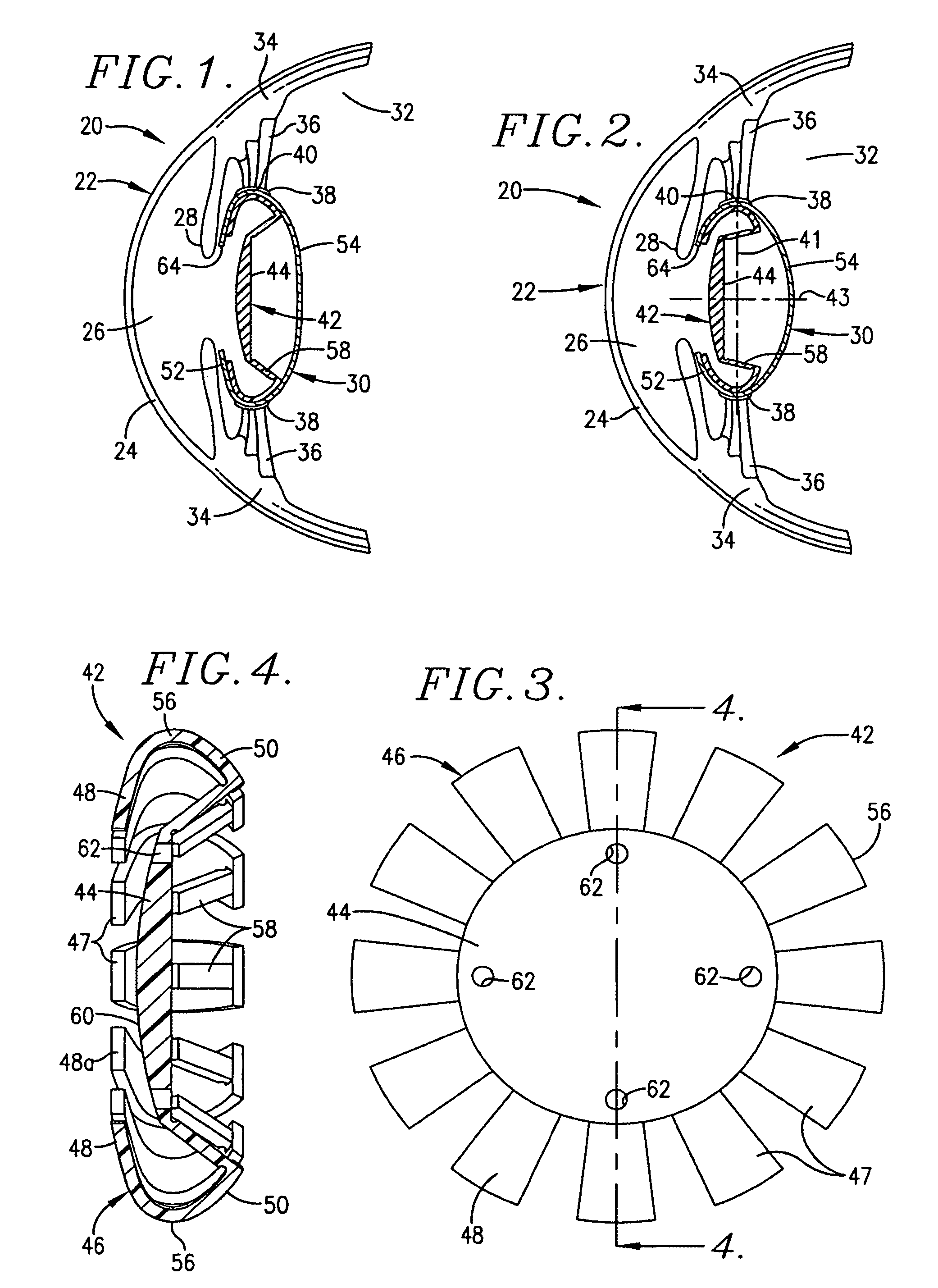
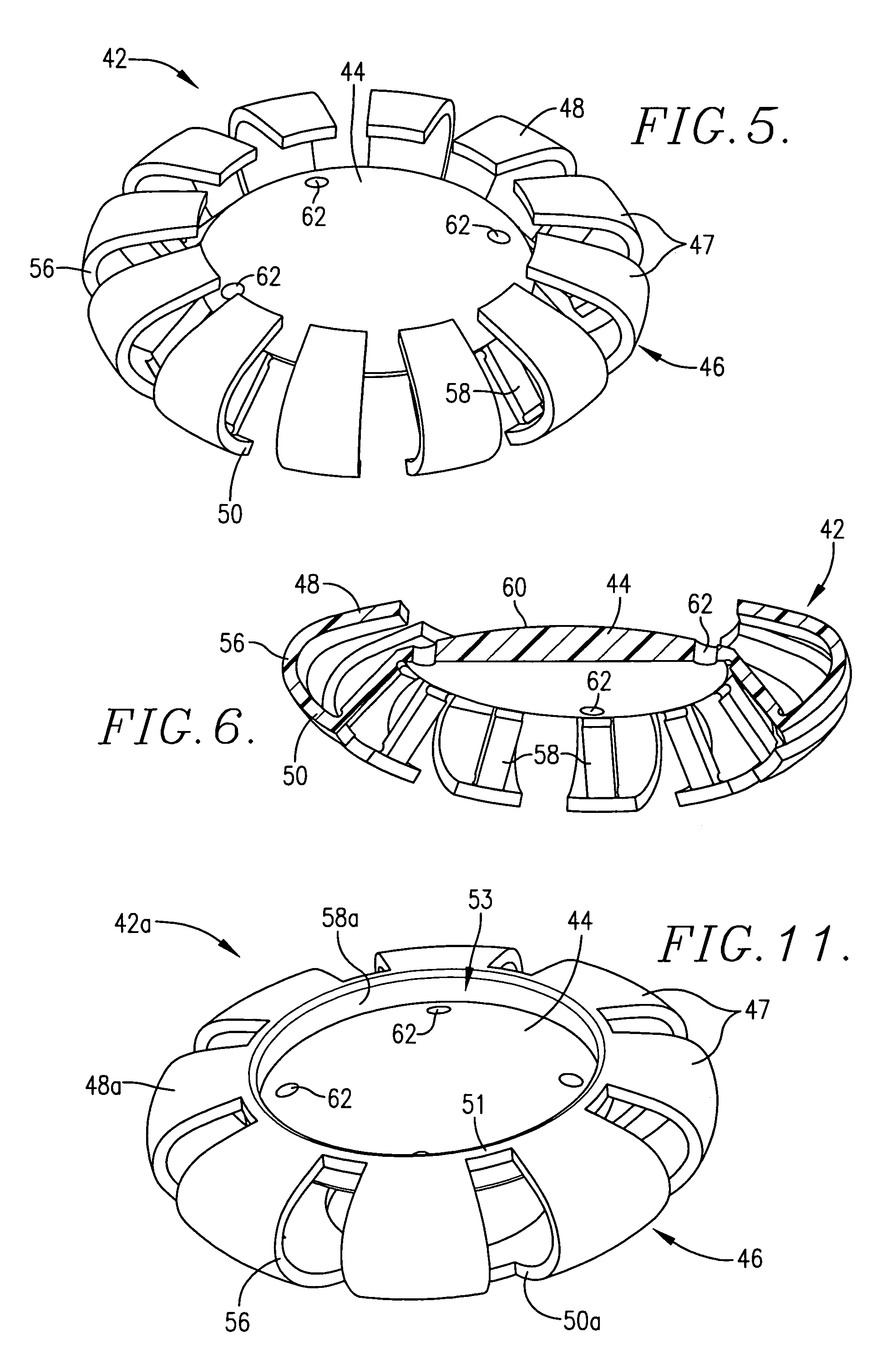
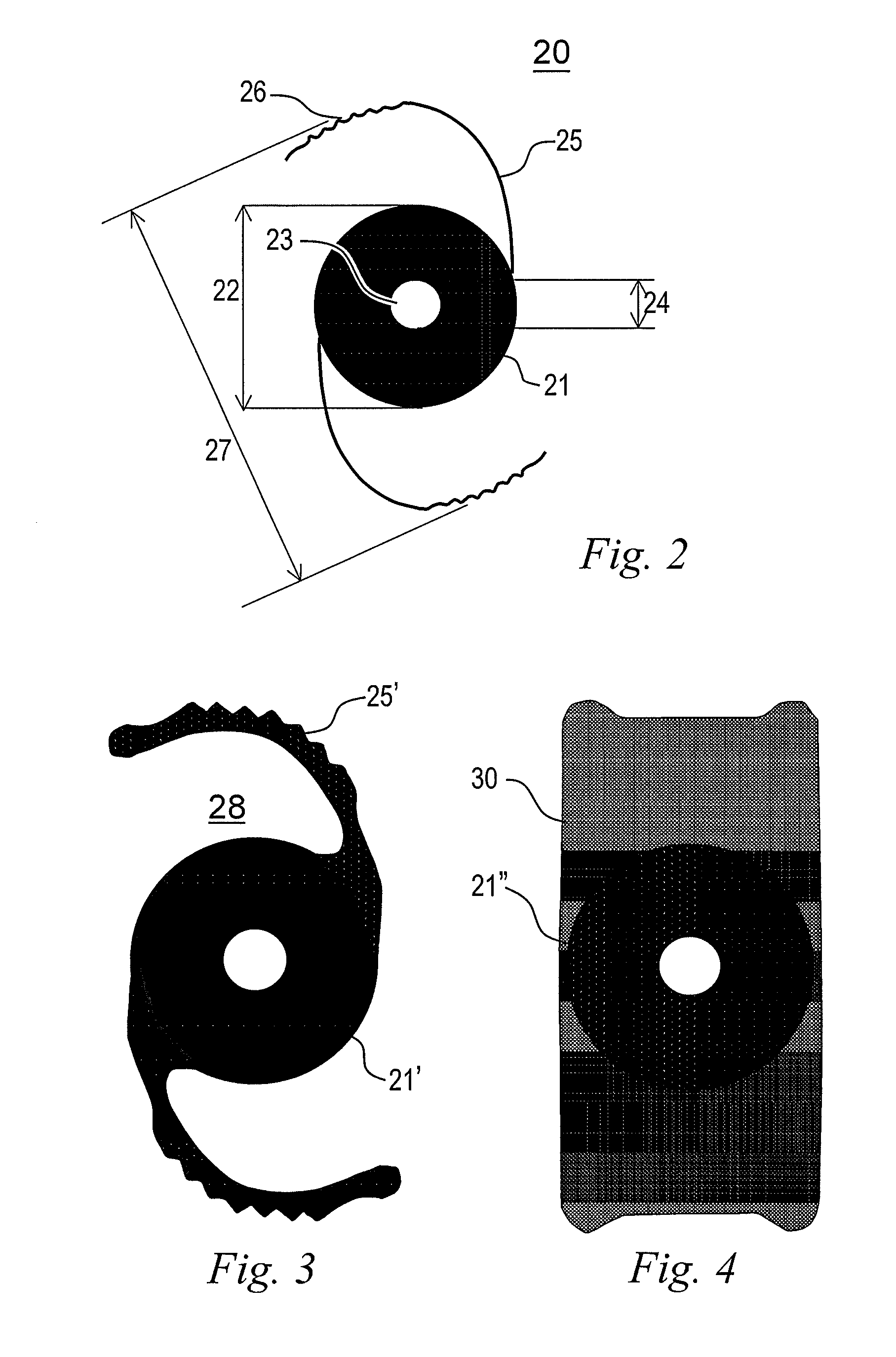
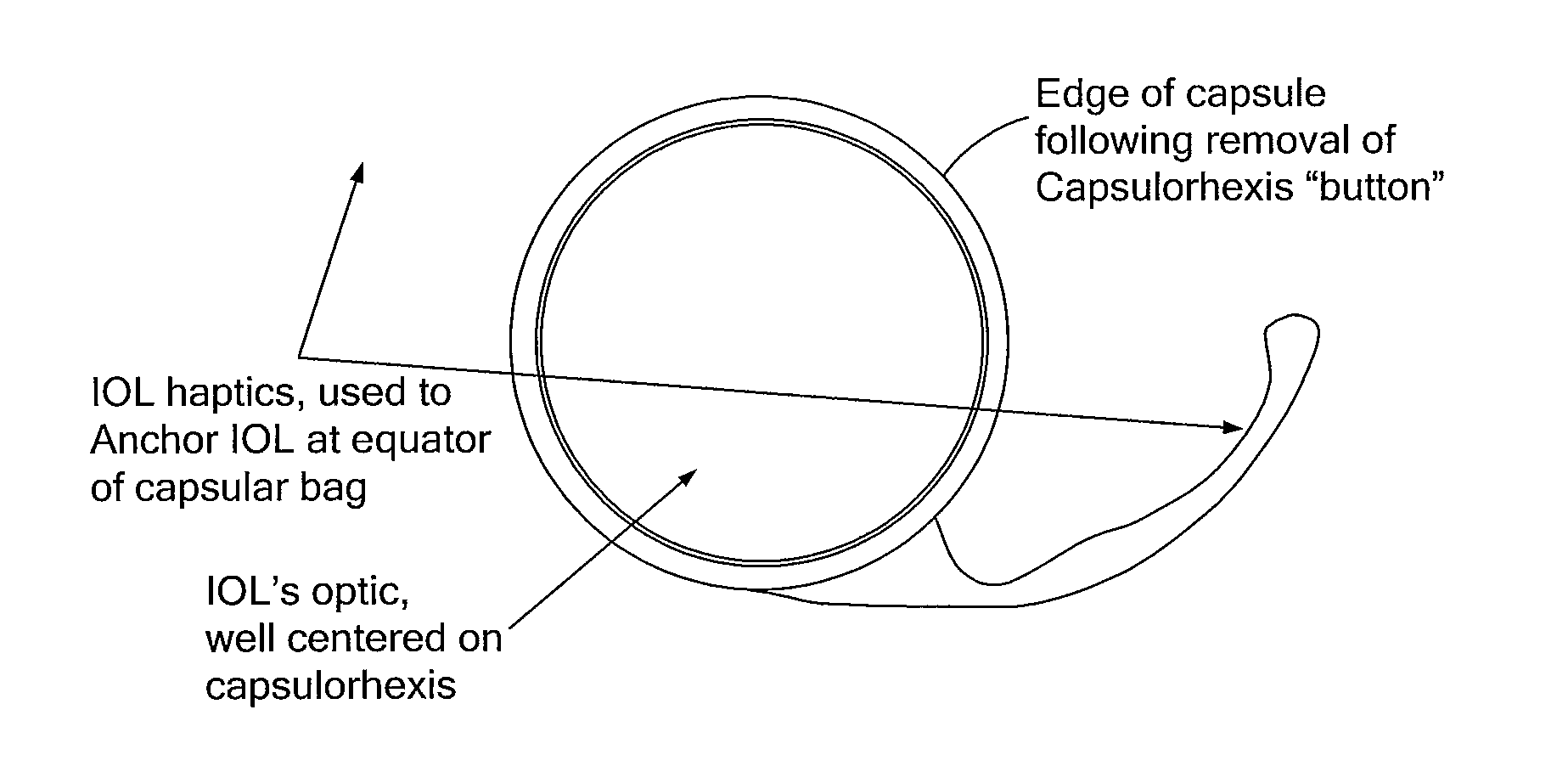
Accommodating intraocular lens implant
InactiveUS7125422B2Easy to insertLong-term useIntraocular lensLens crystallineAccommodating intraocular lens implant
An improved intraocular lens (42) is provided which more closely mimics the accommodation and focusing of the eye's natural lens. The lens (42) comprises an optic (44) and a flexible, resilient optic positioning element (46) which includes an anterior section (48), a posterior section (50), a bight (56), in cross-section, joining the anterior and posterior sections, and a haptic arm (58) extending between the optic (44) and the optic positioning element (46). The lens (42) may optionally include a posterior optic (44a) coupled to the optic positioning element (46). The optic positioning element (46) is formed of unitary construction. The anterior (48) and posterior (50) sections are configured for yieldable engagement with the anterior (52) and posterior (54) walls of the eye capsule (30), respectively.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Method and apparatus for creating incisions to improve intraocular lens placement
ActiveUS20080281413A1Precisely and accurately seatLaser surgeryLight therapyLens crystallineMedicine
A system and method for inserting an intraocular lens in a patient's eye includes a light source for generating a light beam, a scanner for deflecting the light beam to form an enclosed treatment pattern that includes a registration feature, and a delivery system for delivering the enclosed treatment pattern to target tissue in the patient's eye to form an enclosed incision therein having the registration feature. An intraocular lens is placed within the enclosed incision, wherein the intraocular lens has a registration feature that engages with the registration feature of the enclosed incision. Alternately, the scanner can make a separate registration incision for a post that is connected to the intraocular lens via a strut member.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Fluidic intraocular lens systems and methods
The present invention relates to a fluidic intraocular lens inserted into a capsular bag of an eye to replace a crystalline lens. The fluidic intraocular lens may be shaped by elastic membranes bonded to a support ring. The space inside the device may be filled with optically transparent fluid or gel having an index of refraction greater than the index of vitreous humor. The device may be such designed so that the focusing power of the lens can be changed by the deformation of the capsular bag, which may be subsequently controlled by a ciliary muscle.
Owner:RHEVISION TECH
Method of crystalline lens replacement
InactiveUS6413262B2Easy injectionSuitable refractive powerEye surgerySurgical instrument detailsLens crystallineLens substance
A method of crystalline lens replacement for eyes comprises the steps of forming a small hole that penetrates through the lens capsule, removing a part of the crystalline lens substance through the hole, refilling the lens capsule by injecting a composition comprising a hydrophilic polymer directly into the lens capsule, and closing the hole. The method of crystalline lens replacement may be performed on animals or humans. Furthermore, the method of crystalline lens replacement may be performed on a patient suffering from cataract, where the opaque crystalline lens substance in the lens capsule is removed.
Owner:SAISHIN MOTOTSUGU +3
Accommodating intraocular lens and methods of use
The present invention relates to an accommodating intraocular lens, which is suitable for replacement of the natural crystalline lens of the eye within the capsular bag. The intraocular lens can include a retainer plate with an annular region surrounding a central opening, and an optical lens. The retainer plate acts as a foundation for the optical lens, as the retainer plate can be positioned near or at the posterior portion of the lens capsule. The optical lens can sit on the retainer plate, but is otherwise not attached to the retainer plate. The optical lens can overlap or fit within the central opening of the retainer plate. The retainer plate can include a lip portion integrally disposed on a region of the retainer plate, wherein the lip provides a surface for holding at least a portion of an intraocular lens.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Cataract extraction apparatus and method with rapid pulse phaco power
InactiveUS7182759B2Prevent crashAvoid heat damageLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPulse controlLens crystalline
Apparatus for the removal of lens tissue includes a first handpiece having a laser emitting probe sized for insertion into a lens capsule and radiating a lens therein. The laser emitting probe includes a lumen for introducing irrigation fluid into the lens capsule. A second handpiece includes a pulsed controlled vibrated needle for insertion into the lens capsule and emulsifying laser eradiated lens tissue. The vibrated needle includes a lumen therethrough for aspiration of emulsified lens tissue and irrigation fluid.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Cataract extraction apparatus and method with rapid pulse phaco power
InactiveUS6962583B2Prevent crashAvoid heat damageLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPulse controlLens crystalline
Apparatus and method for the removal of lens tissue includes a first handpiece having a laser emitting probe sized for insertion into a lens capsule and radiating a lens therein. The laser emitting probe includes a lumen for introducing irrigation fluid into the lens capsule. A second handpiece includes a pulsed controlled vibrated needle for insertion into the lens capsule and emulsifying laser eradiated lens tissue. The vibrated needle includes a lumen therethrough for aspiration of emulsified lens tissue and irrigation fluid.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Laser instrument for eye therapy
ActiveUS20140046308A1Reduce decreaseSwivelling speed can be increasedLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLens crystallineTherapeutic Area
A laser instrument for therapy on the human eye, designed for surgery of the cornea, the sclera, the vitreous body or the crystalline lens, especially suitable for use in immediate succession with other instruments for eye diagnosis or eye therapy, in such a way that during the alternating use of the various instruments, the eye or at least the patient preferably remains in a predetermined position and alignment within one and the same treatment area.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Accommodative intraocular lens system
InactiveUS20090198326A1Efficiently accommodatedLarge separationDiagnosticsSurgeryIntraocular lensLens crystalline
An accommodative intraocular lens system for treating presbyopic is disclosed. The system includes a first lens having negative optic power adapted for placement in the posterior chamber of the eye and capable of moving forward and back along the optic axis; and a second lens having a positive optic power which is implanted within the capsular bag. The second lens can be the natural crystalline lens of the eye. The position of the first lens, forward or back relative to the second lens, focuses the eye for seeing distant or close-in objects.
Owner:MEDENNIUM
Multi-focal intraocular lens, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20050071002A1Without significant disruptionRestores focus mechanismEye surgeryIntraocular lensLens crystallineOptical axis
An intraocular lens is provided that includes an optic body having anterior and posterior walls, a chamber, and optically transmissive primary and secondary fluids, and method for making and using the same. The secondary fluid is substantially immiscible with the primary fluid and has a different density and a different refractive index than the primary fluid. The primary fluid is present in a sufficient amount that orienting optical body optical axis horizontally for far vision positions the optical axis through the primary fluid, thereby immersing the anterior and posterior optical centers in the primary fluid. The secondary fluid is contained in the optic body in a sufficient amount that orienting the optical axis over a range of effective downward angles relative to the horizontal for near vision positions the optical axis to extend through the primary fluid and the secondary fluid, thus changing the focus of the intraocular lens.
Owner:VISION SOLUTION TECH LLC
Device for use in eye surgery
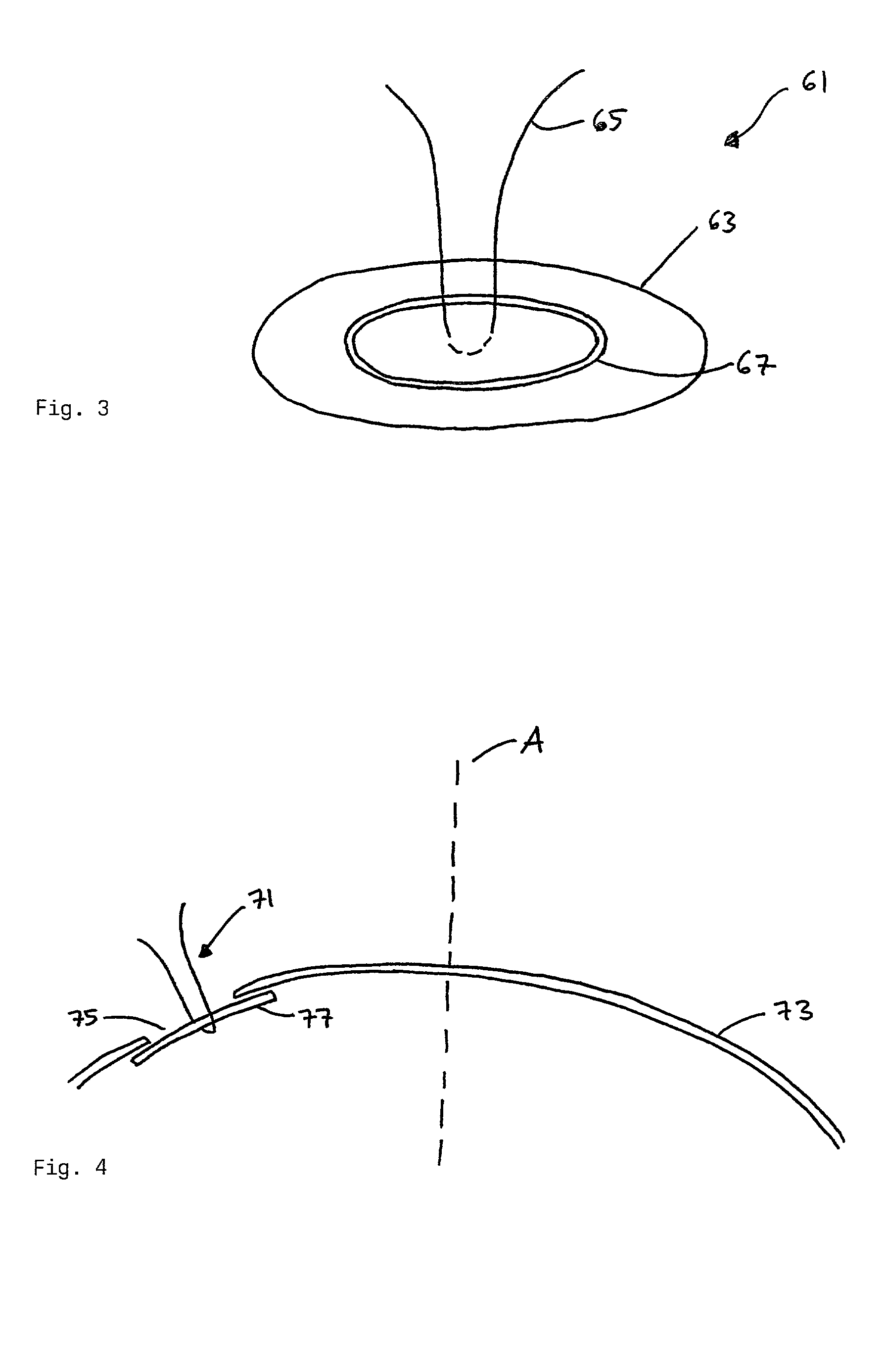
A method of manufacturing an intraocular lens inside a capsular bag after the natural lens has been removed employs a sealing device comprising a plug part adapted to seal a rhexis in a capsular bag, thus preventing displacement through the rhexis of a lens-forming liquid material injected through the rhexis and adapted to replace the natural lens and form an intraocular lens implant. The plug part has a slightly larger area than the capsulorhexis and is made of a deformable polymer. The sealing device further comprises an adjusting means connected to the plug part and adapted to position the plug part to a desired location.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Intraocular and intracorneal refractive lenses
ActiveUS7455691B2Improve rigidityHigh retention rateIntraocular lensLens crystallineIntraocular lens
An intraocular and intracorneal lens includes an optical portion and a corrugated haptic portion. Corrugations of the haptic portion may be linear or arcuate, and such corrugations may be present on both anterior and posterior surfaces of the haptic portion. The intraocular lens may be deformed before or during insertion in an eye of a patient, and may be positioned in the posterior chamber of the eye such that the optical portion is spaced anteriorly from the crystalline lens of the eye. In alternative embodiments, an intraocular or intracorneal lens of the invention may be inserted in the anterior chamber, or within the cornea, of an eye of a patient. An alternative intraocular lens includes an optical portion having a peripheral optic zone and an inner non-optic zone. Methods for correcting visual deficiencies of a patient, by insertion of an intraocular or intracorneal lens of the invention in an eye of the patient, are also disclosed.
Owner:PRESBIA IRELAND LTD
Intraocular lenses
InactiveUS7048759B2Efficient use ofGreat freedom of designingIntraocular lensLens crystallineOptical axis
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Accommodative intraocular lens system
ActiveUS20100204787A1Add depthStable relative fixationIntraocular lensLens crystallineNegative power
A two-optic accommodative lens system is disclosed. Two coupled lenses are located within the capsular bag to extend depth of focus and / or restore accommodation following extraction of a natural lens. The first lens comprises a spring-like structure attaching an optic to a ring-like support structure. The optic can be a monofocal or multifocal optical element having a positive or negative power. The first lens further comprises features designed to couple the ring-like structure to a second lens. The first lens can be located anteriorly within the capsular bag. The second lens is located posteriorly to the first lens within the capsular bag and can have an opposite or supplementary power to that of the first lens. The second lens can also be a monofocal or multifocal lens and comprises a plurality of haptics which can be used to size the lens system over a range of capsular bag sizes. The second lens further comprises features for coupling the second lens to the ring-like structure of the first lens. The haptics of the second lens are relatively firm, yet still flexible and can be configured to interlock with features of the ring-like structure.
Owner:ALCON INC
Spatial focal field type glasses display
ActiveUS20150015814A1Size of display is limitedEasy to manufactureNon-optical adjunctsPolarising elementsVirtual imageLens crystalline
A spatial focal field type glasses display product can present virtual images at different distances simultaneously. The product is a frame type glasses or corneal contact lens and comprises a projection component and a display control device. The projection component comprises a plurality of projection units, each projection unit projects a plurality of elementary beams. The elementary beams projected by the same projection unit diverge and do not intercept with each other. The elementary beams projected by different projection units intersect near the retina after passing through the crystalline lens. The intersection point is a cluster focus. All cluster focuses form a spatial focal field which envelop the retina. When the diopter of the crystalline lens changes, the spatial focal field displaces and deforms accordingly, so different cluster focuses fall on the retina to be seen clearly, while the other cluster focuses tend to disperse and cannot be seen clearly.
Owner:BEIJING ANTVR TECH
Adjustable intraocular lens system
The present invention is related to an adjustable intraocular lens system comprised of a lens body having an adjustable refractive index and a shield for protecting the lens body from degradation that might otherwise be caused by exposure to particular electromagnetic radiation. More preferably, the present invention is directed to an adjustable intraocular lens system comprised of a lens body and a shield wherein the lens body is formed of a material with a refractive index that can be adjusted by exposure to adjusting electromagnetic radiation (e.g., multiple photon energy) and wherein the shield protects the lens body from degradation that might otherwise be caused by exposure to degrading electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Lens delivery system
A lens delivery system having a two folding mechanisms. The first mechanism is structured to fold an intraocular lens stabilizing ring, and the second mechanism is designed to fold an intraocular lens.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method and apparatus to project image on retina at various focal depths utilizing flexible substrate containing optical array
The current invention relates to the method to achieve artificial vision with using flexible substrate based light emitting arrays, or optical passage arrays, to project image upon the retina of a human eye. Further, it relates to the method to detect the real-time focal length change of the eye-lens and modify the flexible substrate curvature and distance from the eye to vary global angle configurations of light beams that go into the eye to produce images on the retina at various focus depth of the eye to achieve re-focusable artificial vision.
Owner:ZHOU YUCHEN
Ophthalmologic laser system
ActiveUS20120016352A1Interference minimizationReduce radiation exposureLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLens crystallineUltra short pulse
An ophthalmological laser system for photodisruptive irradiation of ocular tissue, including a crystalline lens or a cornea. The system includes an ultra-short pulse laser, the radiation of which is focusable as illumination light via an illumination beam path including a scanner unit and focusing optics. A control unit is programmed to execute determining irradiation control data for photodisruptions at irradiation points in an interior of the ocular tissue distributed three-dimensionally and non-equidistantly to create at least one predetermined target incision. The laser system then irradiates the ocular tissue according to the determined irradiation control data.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Methods for producing epithelial flaps on the cornea and for placement of ocular devices and lenses beneath an epithelial flap or membrane, epithelial delaminating devices, and structures of epithelium and ocular devices and lenses
InactiveUS7497866B2Enhances delamination processSpeed up the processEye surgerySurgeryCorneal surfaceLens crystalline
These methods, devices, and structures are useful in the field of ophthalmology; the devices and methods relate variously to separating or lifting corneal epithelium from the eye preferably in a substantially continuous layer, placing a lens or other suitable ocular or medical device beneath the epithelial membrane, and to the resulting structures formed by those procedures. The de-epilthelialization devices generally utilize a non-cutting separator or dissector that is configured to separate the epithelium at a naturally occurring cleavage surface in the eye between the epithelium and the corneal stroma (Bowman's membrane), specifically separating in the region of the lamina lucida. The separator or dissector may have a structure that rolls or vibrates (or both) at that cleavage surface or interface during the dissection step. The separated epithelium may be lifted or peeled from the surface of the eye to form an epithelial flap or a pocket. The epithelium may then be replaced on the cornea after a refractive procedure or after placement of an ocular lens (or other subepithelial device) on the eye. The subepithelial device may comprise a wide variety of synthetic, natural, or composite polymeric materials. The step of replacing epithelial tissue upon the subepithelial device or upon the anterior corneal surface promotes epithelial healing.
Owner:TISSUE ENG REFRACTION
System and apparatus for treating the lens of an eye
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Small aperture (pinhole) intraocular implant to increase depth of focus
InactiveUS20140379078A1Increase depth of focusMinimize impactIntraocular lensLighting spectrumLens implant
Small aperture (pinhole) intraocular implant to increase depth of focus comprising a diaphragm juxtaposed to the front surface of a lens implanted previously, having its anterior surface convex and its posterior surface concave. The diaphragm is held in position by inserting engaging means in the ciliary sulcus.It is proposed that said diaphragm is opaque to a visible light spectrum and transparent to light in the infrared range and is equipped with passage means of visible light in its central region, such as a through hole whose diameter is between 1 mm and 2.5 mm.The constriction of the incident light rays increases the depth of focus, featuring a pinhole effect. The engagement means may be provided by two handles shaped with curved proximal ends joined to the peripheral edge of said diaphragm and having substantially circular section with a diameter between 80 μm and 800 μm or two handles of the same material as the diaphragm and constituting an extension of this edge, or even one elongated platform whose center is located in the small-diameter circular opening.
Owner:TRINDADE CLAUDIO
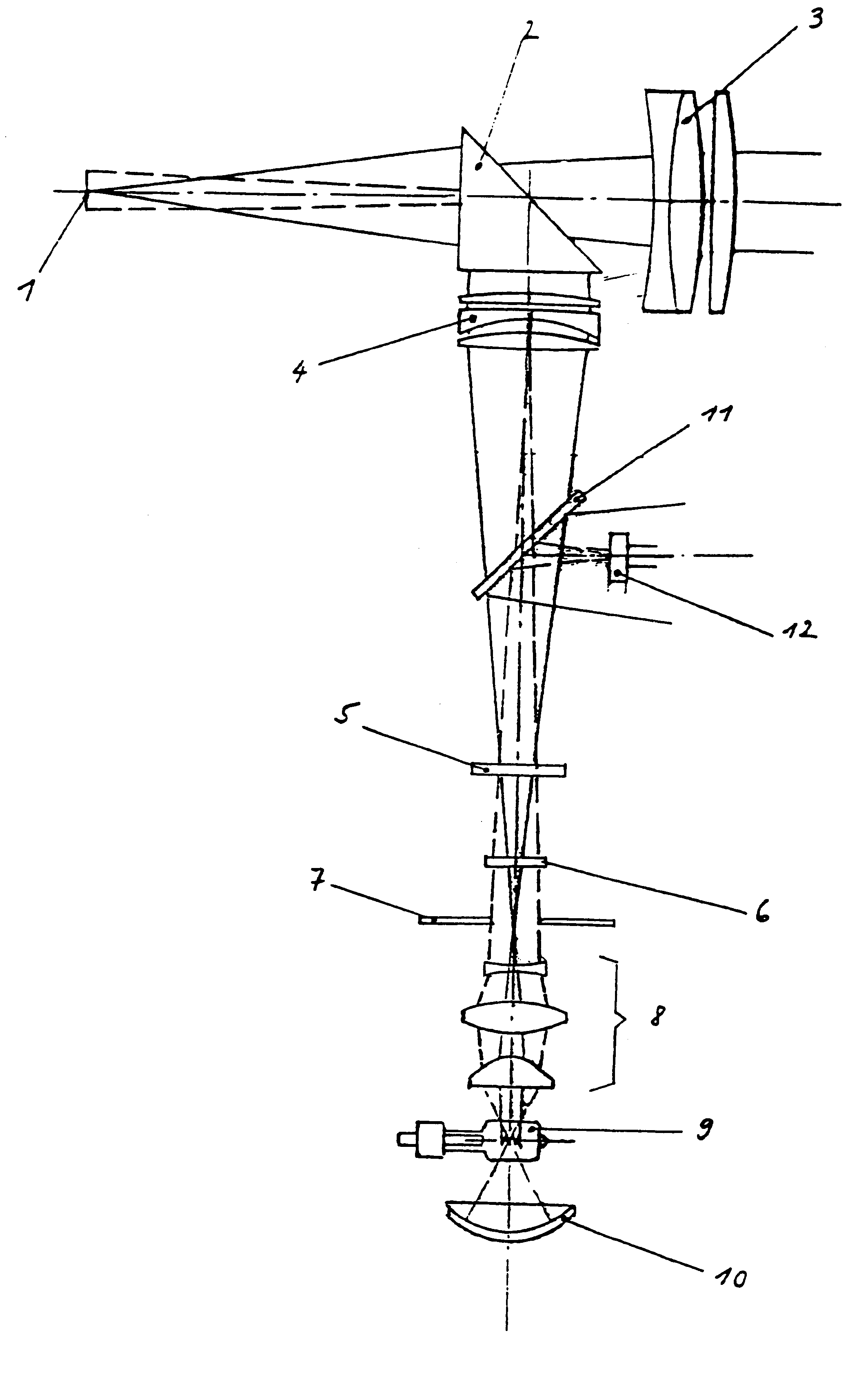
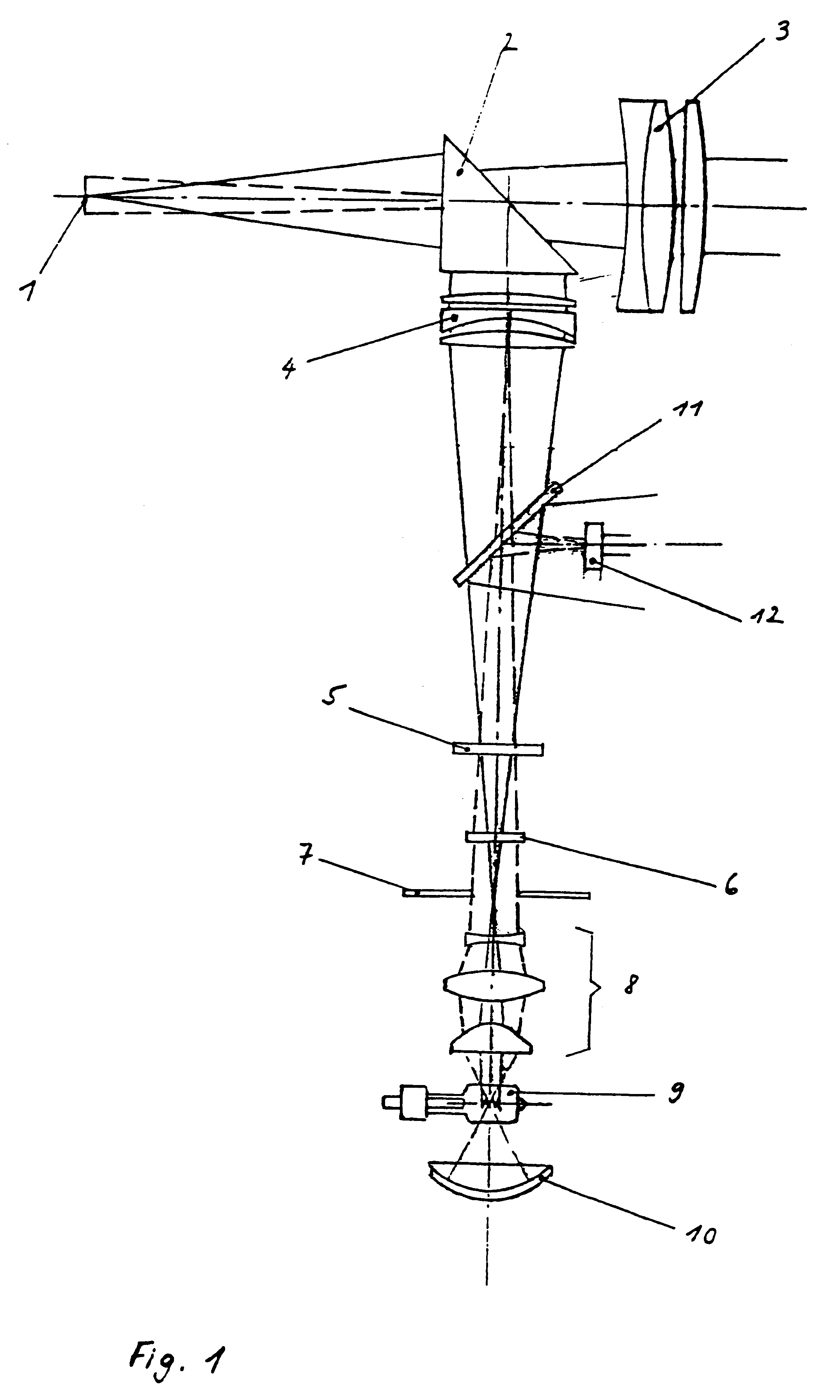
Luminous intensity detection and control system for slit lamps and slit lamp projections
The invention is characterised by the provision that in a slit lamp or a slit lamp projector an oblique thin glass flat with a partial reflection of the light is disposed at a defined angle relative to the optical path above the filter assembly between the latter and the "slit projector" lens (4), and in the configuration with an achromatic doublet lens between the lens assemblies in the parallel optical path, in such a way that as a result one part of the incident rays is incident as deflected light cone on a detector assembly which is arranged laterally in the housing at an angle dependent on the angle of the thin glass flat in the housing, which detector assembly measures the respectively existing luminous intensity, transmits the detected values to an evaluation and control means which compares the values so received against a predetermined maximum value, calculates the irradiation dose for the phakic or aphakic eye and, when the value is exceeded, signals this situation on an indicating alarm means and / or reduces the luminous intensity automatically to the predetermined maximum value in a controlled manner.
Owner:G RODENSTOCK INSTR
Surgical method and apparatus
ActiveUS6852093B1Good removal effectSimple materialEye surgeryCannulasLens crystallineLens epithelial cell
A method and apparatus for directing relatively gentle pulses of heated surgical fluid against the capsular bag to assist in the removal of lens epithelial cells and cortical material adhered to the capsular bag.
Owner:ALCON INC
Method to guide a cataract procedure by corneal imaging
A method of performing a cataract procedure may include the steps of: imaging one or more corneal marks created by a corneal procedure, determining corneal location information regarding a location of a treatment region of the corneal procedure based on the imaged corneal marks, and placing laser pulses for a cataract surgery using the corneal location information. A corresponding ophthalmic laser system may include an imaging system to image a corneal region of an eye, an image analyzer to facilitate a determination of corneal location information based on one or more image provided by the imaging system, and a surgical laser system to place laser pulses into a lens of the eye using the corneal location information. The imaging system may include an ophthalmic coherence tomographic (OCT) system.
Owner:ALCON LENSX
System and method for measuring tilt in the crystalline lens for laser phaco fragmentation
A method of generating three dimensional shapes for a cornea and lens, the method including illuminating an eye with multiple sections of light and obtaining multiple sectional images of the eye based on the multiple sections of light. For each obtained multiple sectional image, the following processes are performed:a) automatically identifying arcs corresponding to anterior and posterior corneal and lens surfaces of the eye by image analysis and curve fitting of the obtained multiple sectional images; andb) determining an intersection of lines ray traced back from the identified arcs with a known position of a section of space containing the section of light that generated the obtained multiple sectional images, wherein the intersection defines a three-dimensional arc curve. The method further including reconstructing three-dimensional shapes of the cornea surfaces and the lens surfaces based on fitting the three-dimensional arc curve to a three-dimensional shape.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Extended Depth Field Optics With Variable Pupil Diameter
ActiveUS20130308186A1Increase depth of focusAdd depthPolarising elementsMicroscopesPupil diameterRefractive index
Apparatus and methods to increase the depth of field in human vision in order to correct for loss in refocusing ability. Optics variations, such as changes in thickness, shape, or index of refraction of contact lenses, intraocular implants, or the shape of the cornea or eye lens, affect the phase, or wavefront, of the light perceived by the eye. The optics variations are chosen such that the resulting optical transfer function remains relatively constant over a desired range of object distances and pupil diameters.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Intraocular lens
An intraocular lens to be fixed in an eyeball has an optical pupil to provide a pinhole effect at the front center of the lens. The optical pupil is constituted by a limitative pattern that is partly formed in the front peripheral center of the lens to limit part of an optical path.
Owner:MIKAWA YOICHI
Eye ground retina OCT image correction method
The invention discloses an eye ground retina OCT image correction method. The method comprises the steps that scanning beams scan an anterior segment and a posterior segment, and meanwhile a human anterior segment OCT image and an eye ground retina OCT image are obtained, wherein the human anterior segment OCT image contains a corneal OCT image, a crystalline lens anterior surface OCT image and a crystalline lens posterior surface OCT image, and the human anterior segment OCT image and the eye ground retina OCT image are processed by a computer without correction; the OCT images are corrected and restored to images with a true form to obtain the corneal anterior surface curvature radius, the corneal posterior surface curvature radius, the crystalline lens anterior surface curvature radius, the crystalline lens posterior surface curvature radius, the corneal thickness, the anterior chamber depth and the crystalline lens thickness; a rendezvous point (O45) of center lines of the scanning beams which are refracted by the posterior surface of a crystalline lens is determined, and the circle center of the sector scanning region and the scanning angle (uO45) are calculated; the uncorrected eye ground retina OCT image is restored to an image with a true form, and finally a true sectional image of an eye ground retina is obtained through restoration and the curvature of the eye ground retina is measured according to a measured anterior segment OCT image and a measured posterior segment OCT image.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com