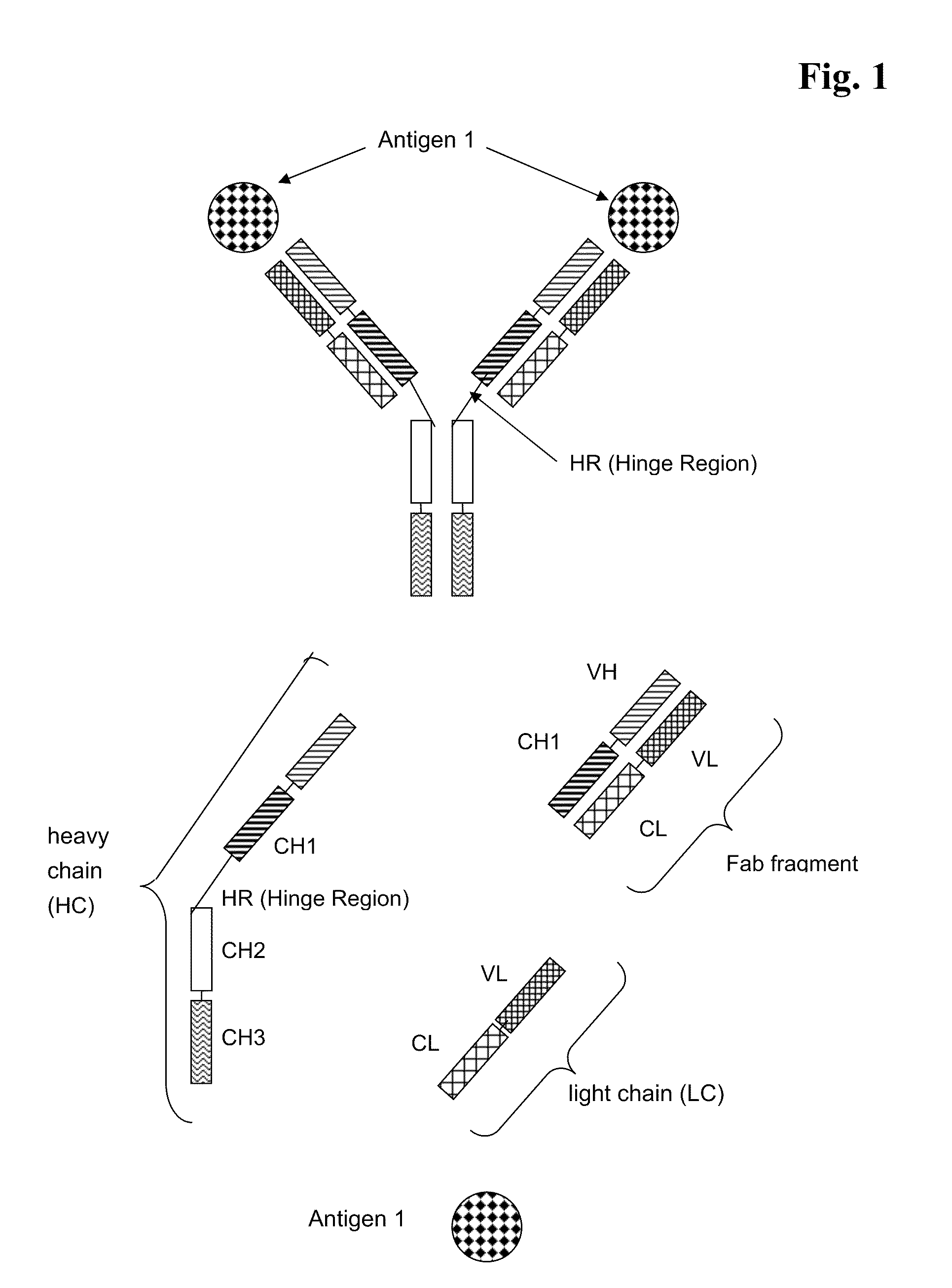Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1901results about How to "Reduce light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
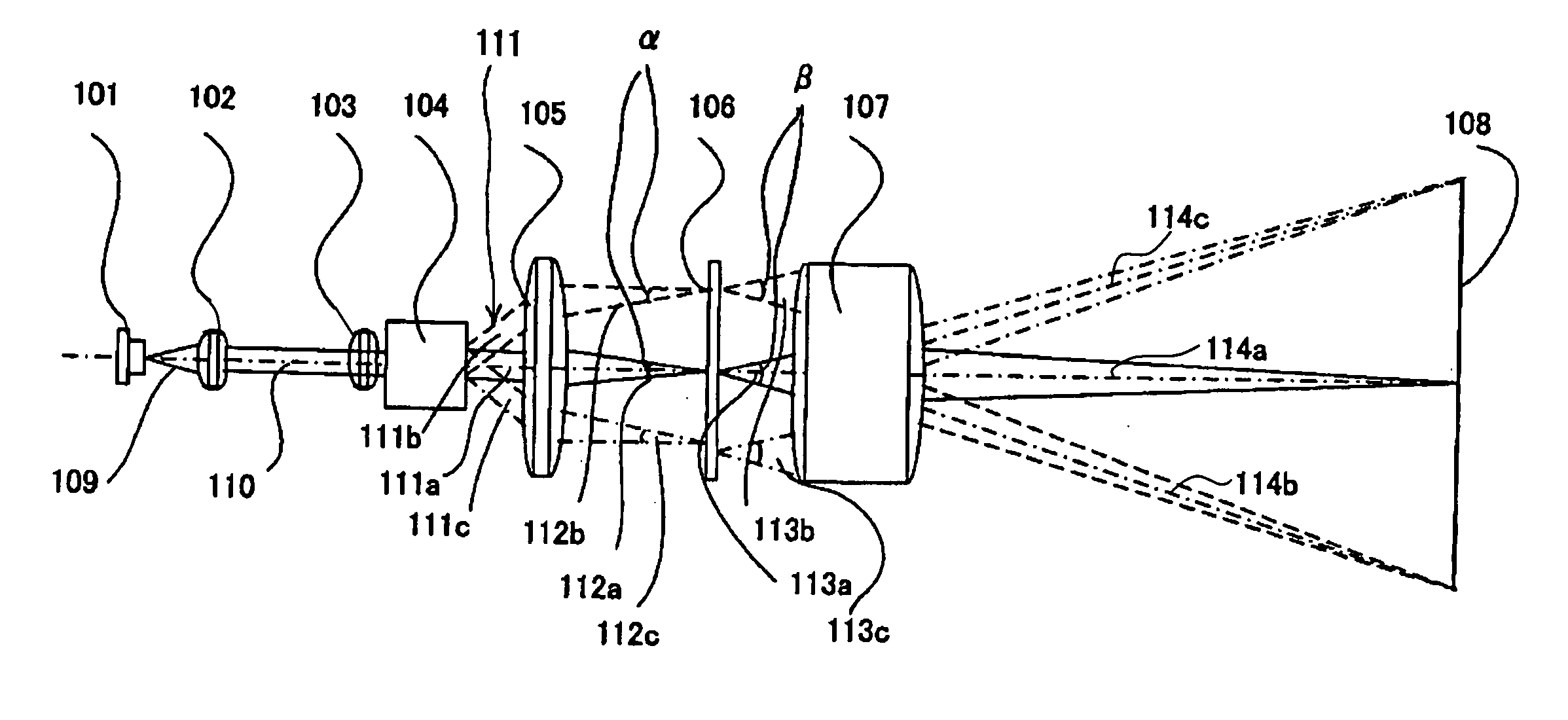
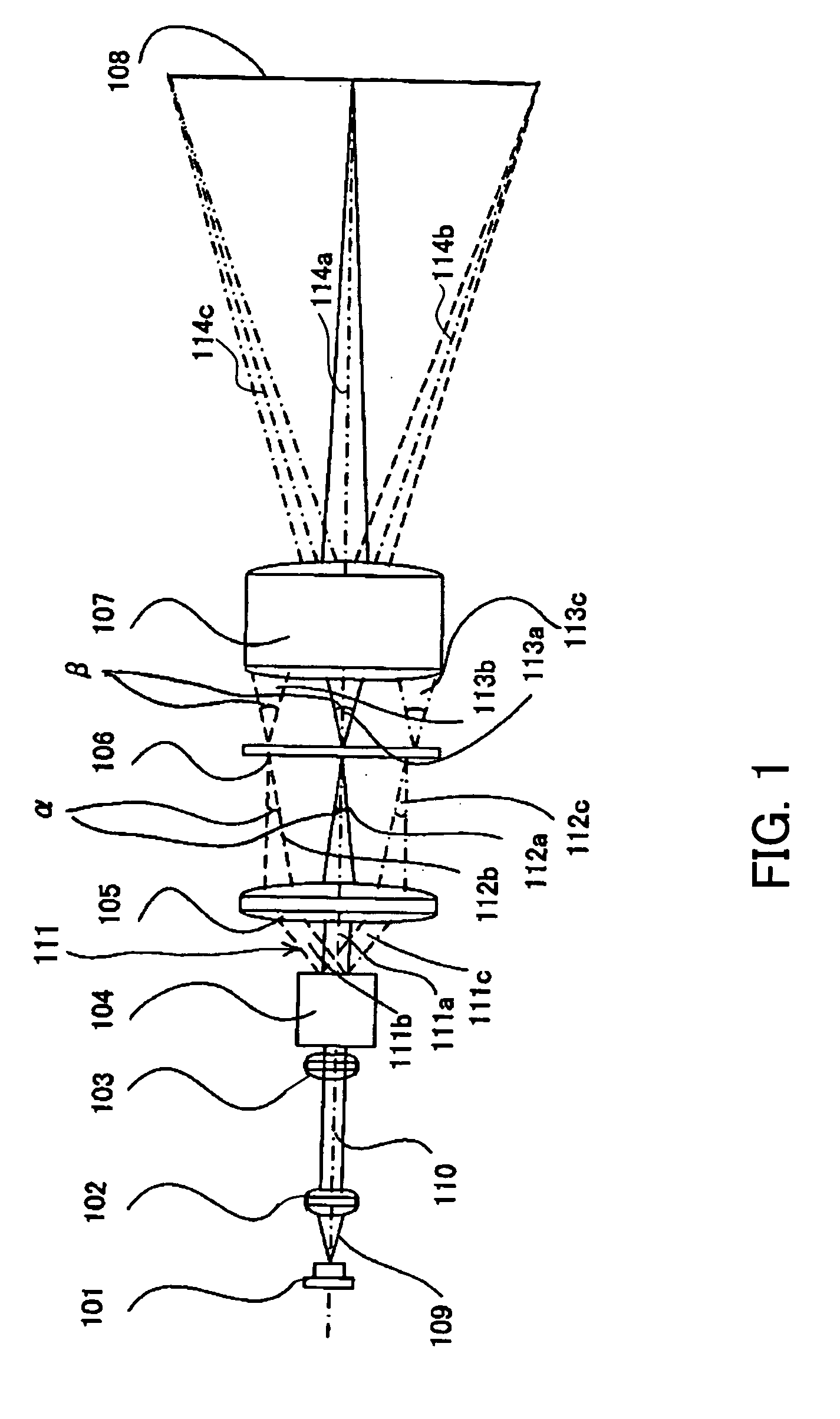
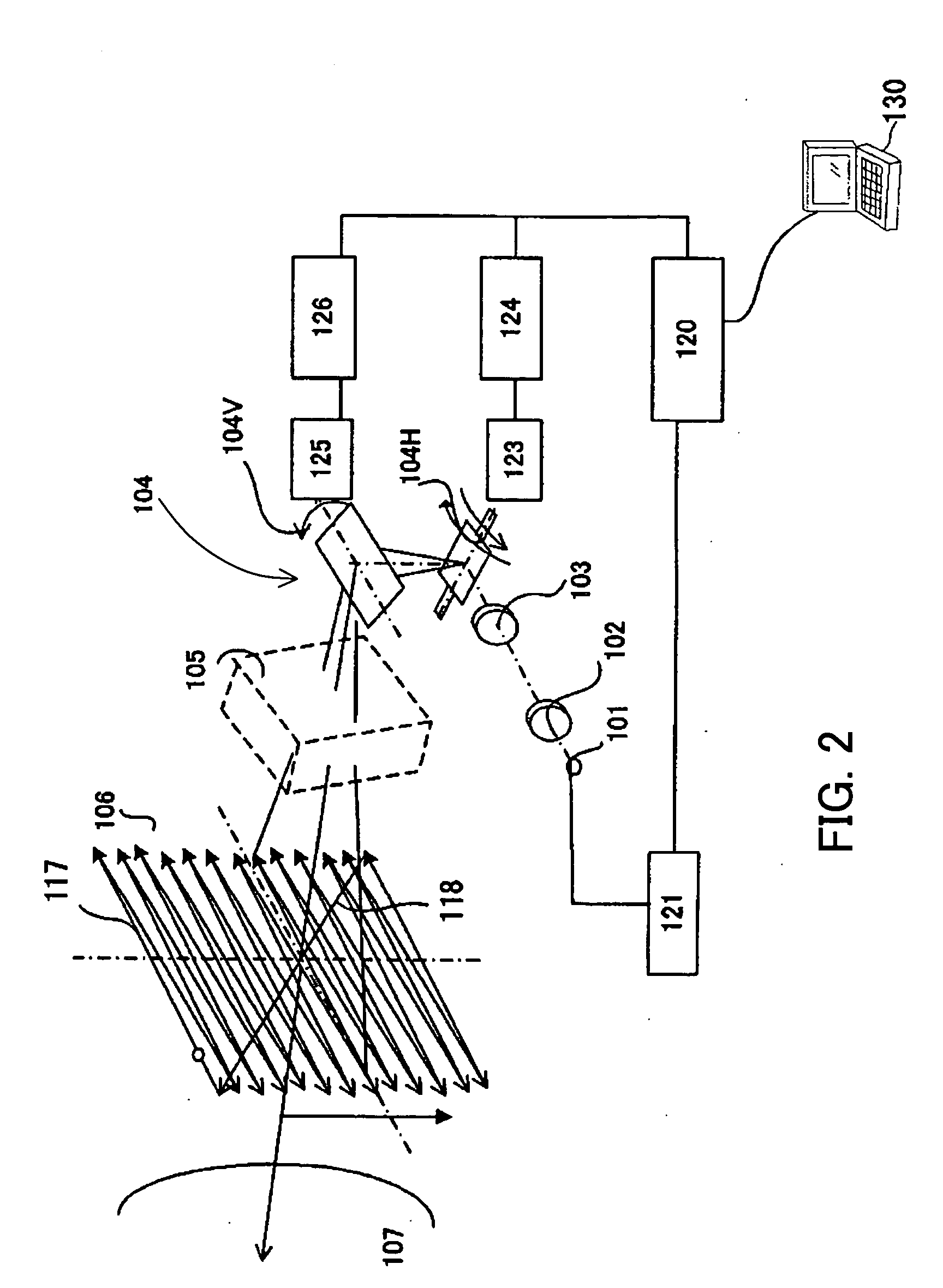
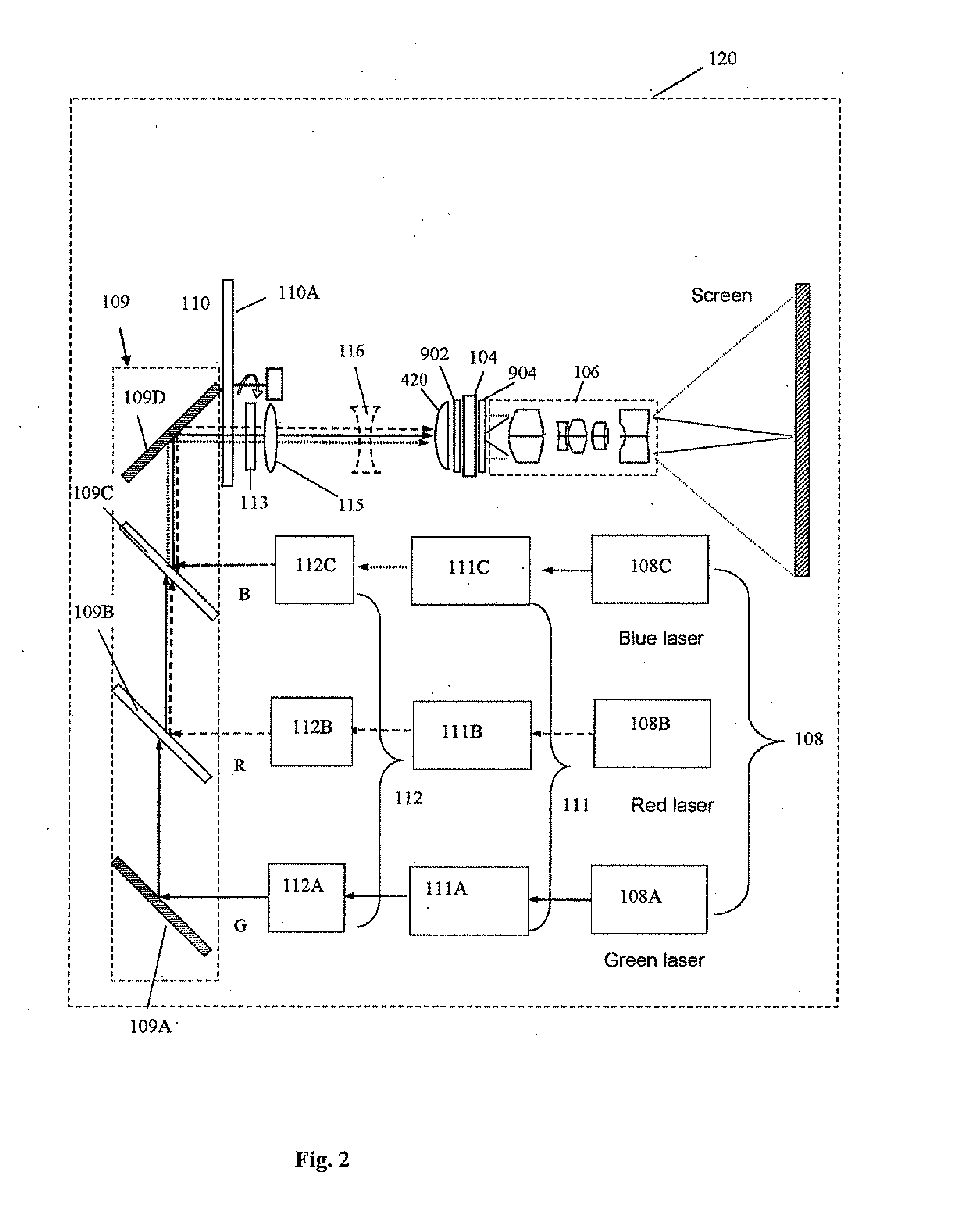
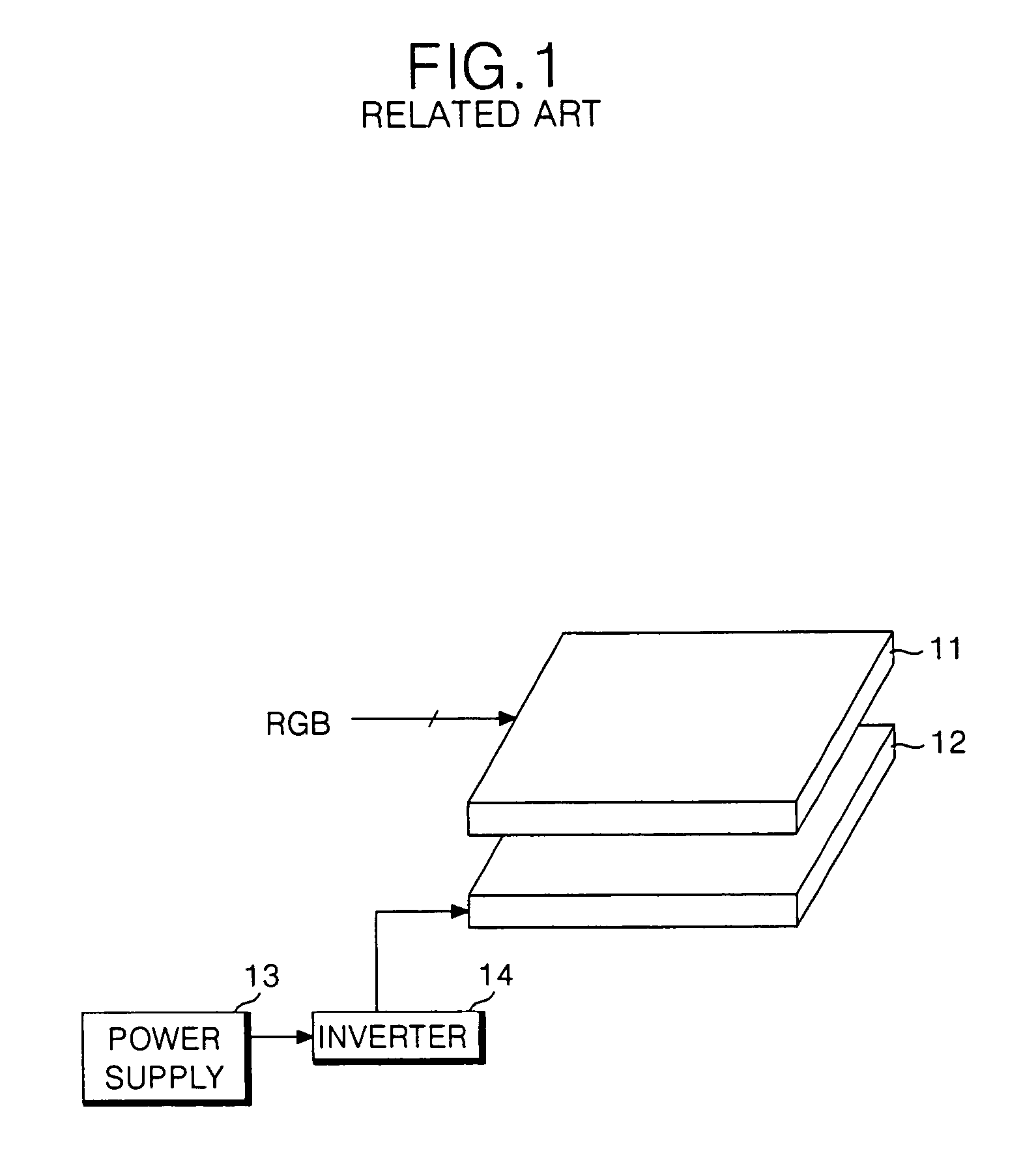
Illuminative light communication device
InactiveUS7583901B2Possible to separateWeaken influenceTransmission/receiving by modifying power source wavePoint-like light sourceMultiplexingSignal on
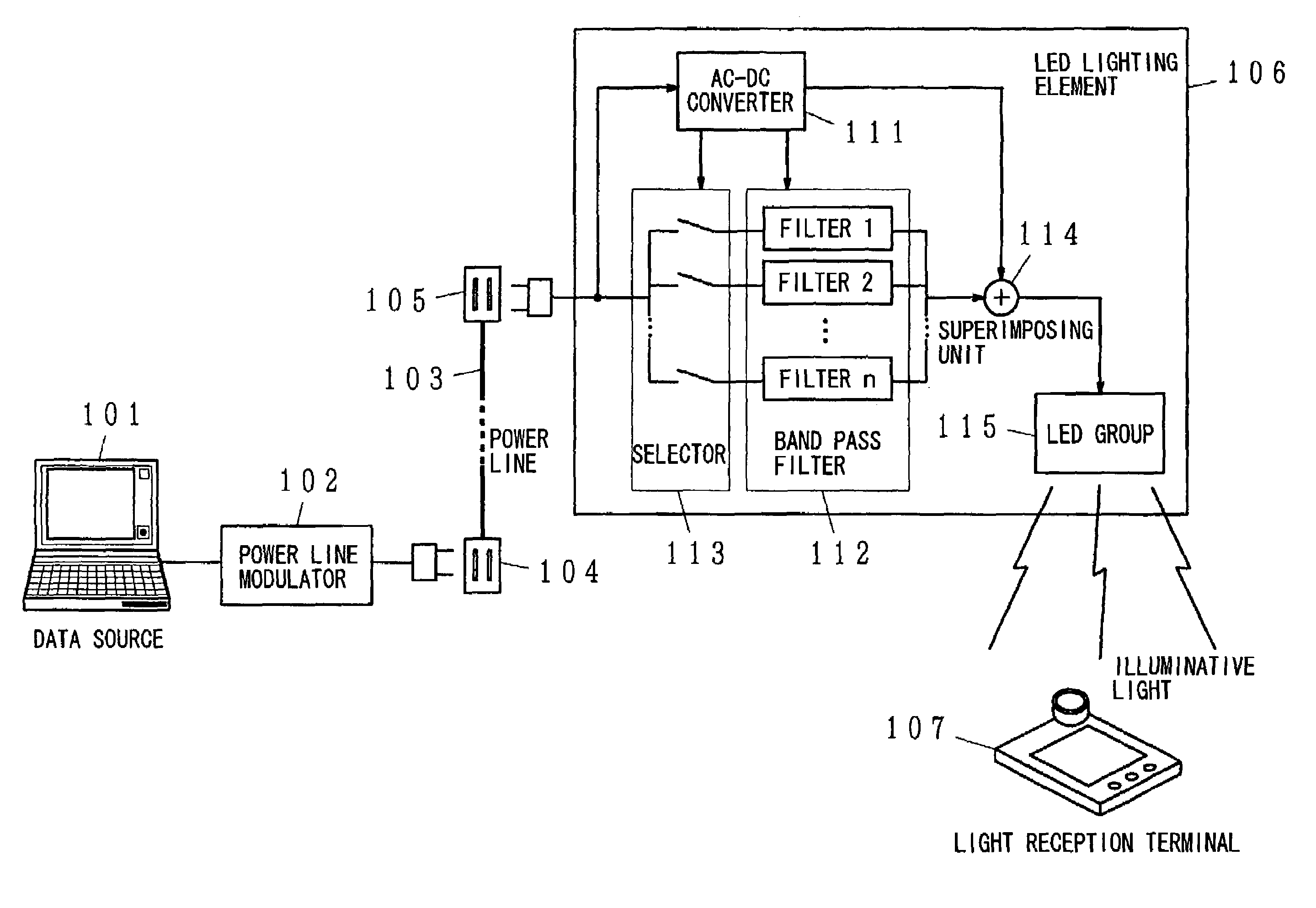
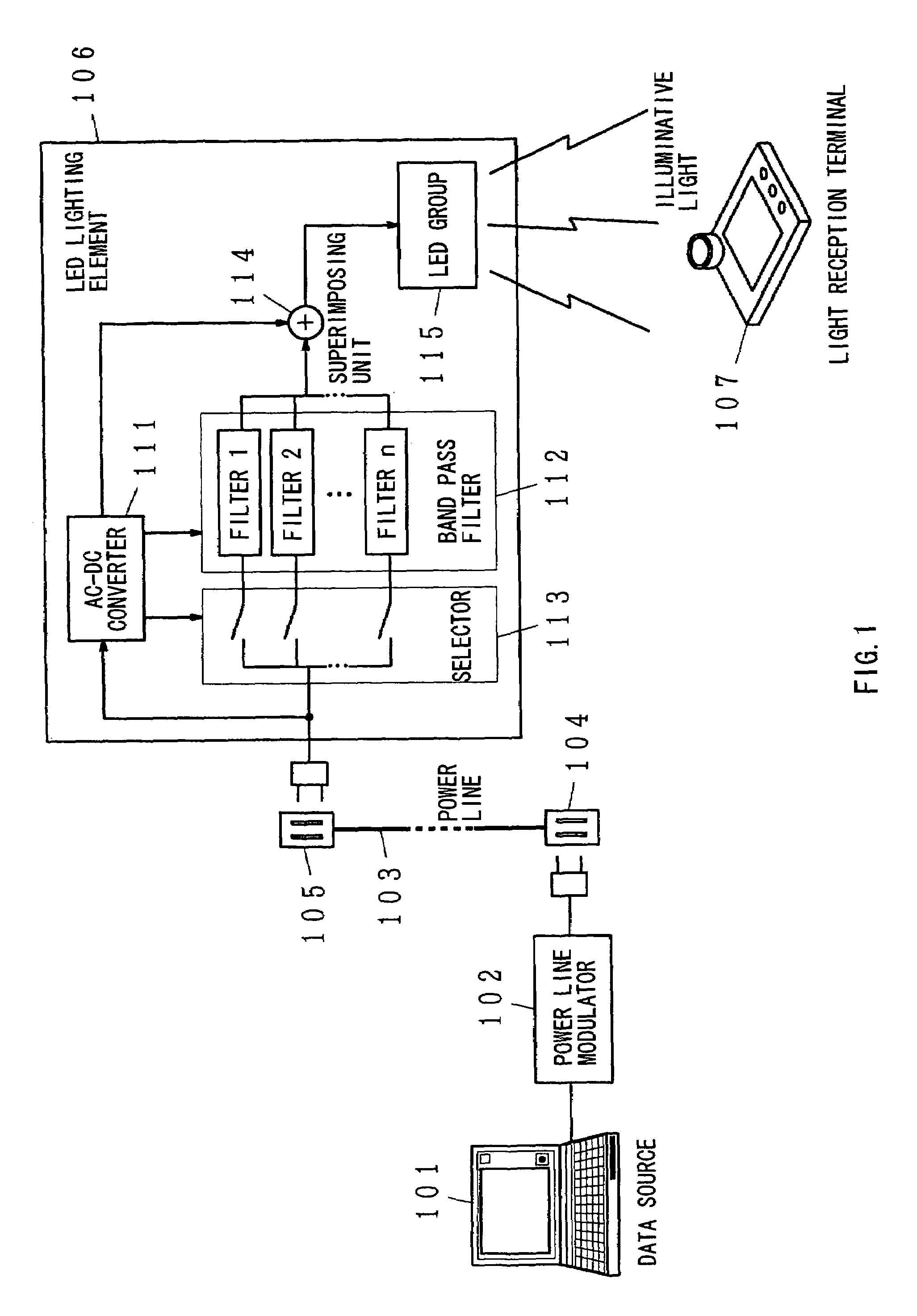
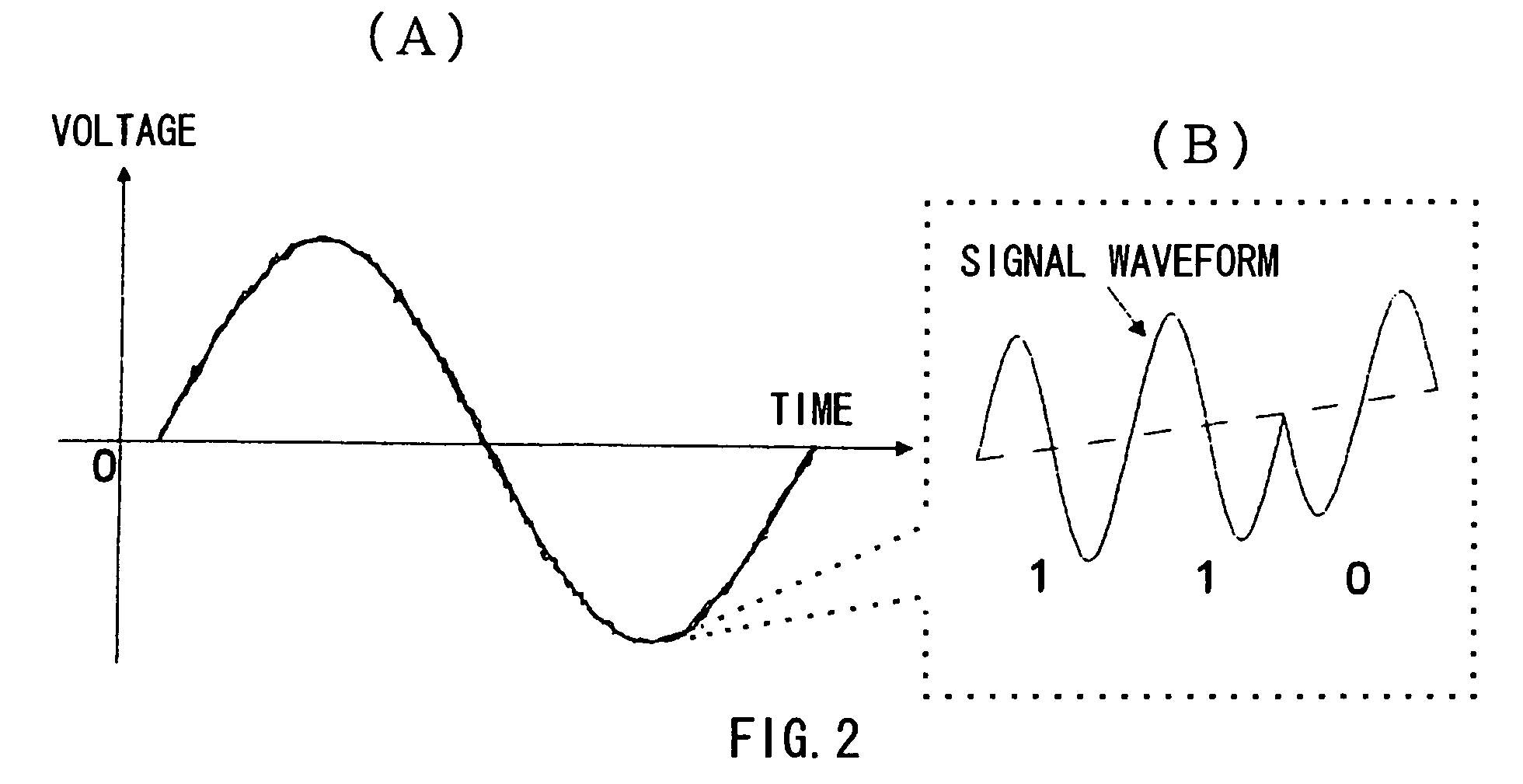
The present invention has been developed considering the above-described problems and aims to provide various structures and applications for illuminative light communication. According to the first aspect of the prevent invention, a broadcast system includes an LED light source 115 for lighting, a power line 103 that supplies electric power to the LED light source 115, a data modulator 102 that modulates and multiplexes a plurality of pieces of data, superimposes the resulting signal on an electric power waveform, and then transmits the resulting superimposed signal waveform to the power line 103, and a filter 112 that selectively separates one or more of a plurality of pieces of modulated data on the power line so as to control light intensity or blinking of the LED light source. Data is transmitted through changes in light intensity or blinking of the LED light source.
Owner:ICHIMARU
Annealing apparatus
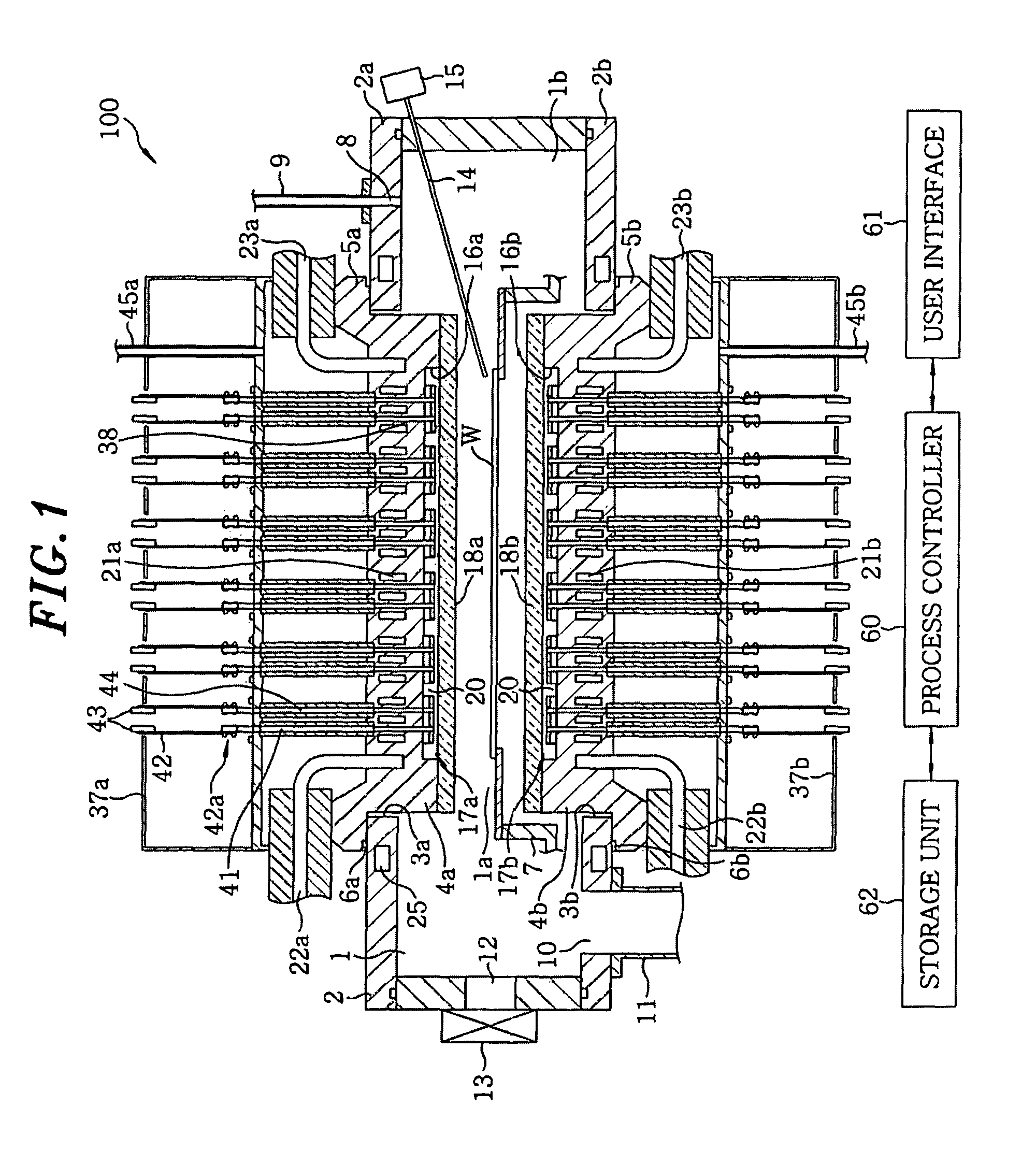
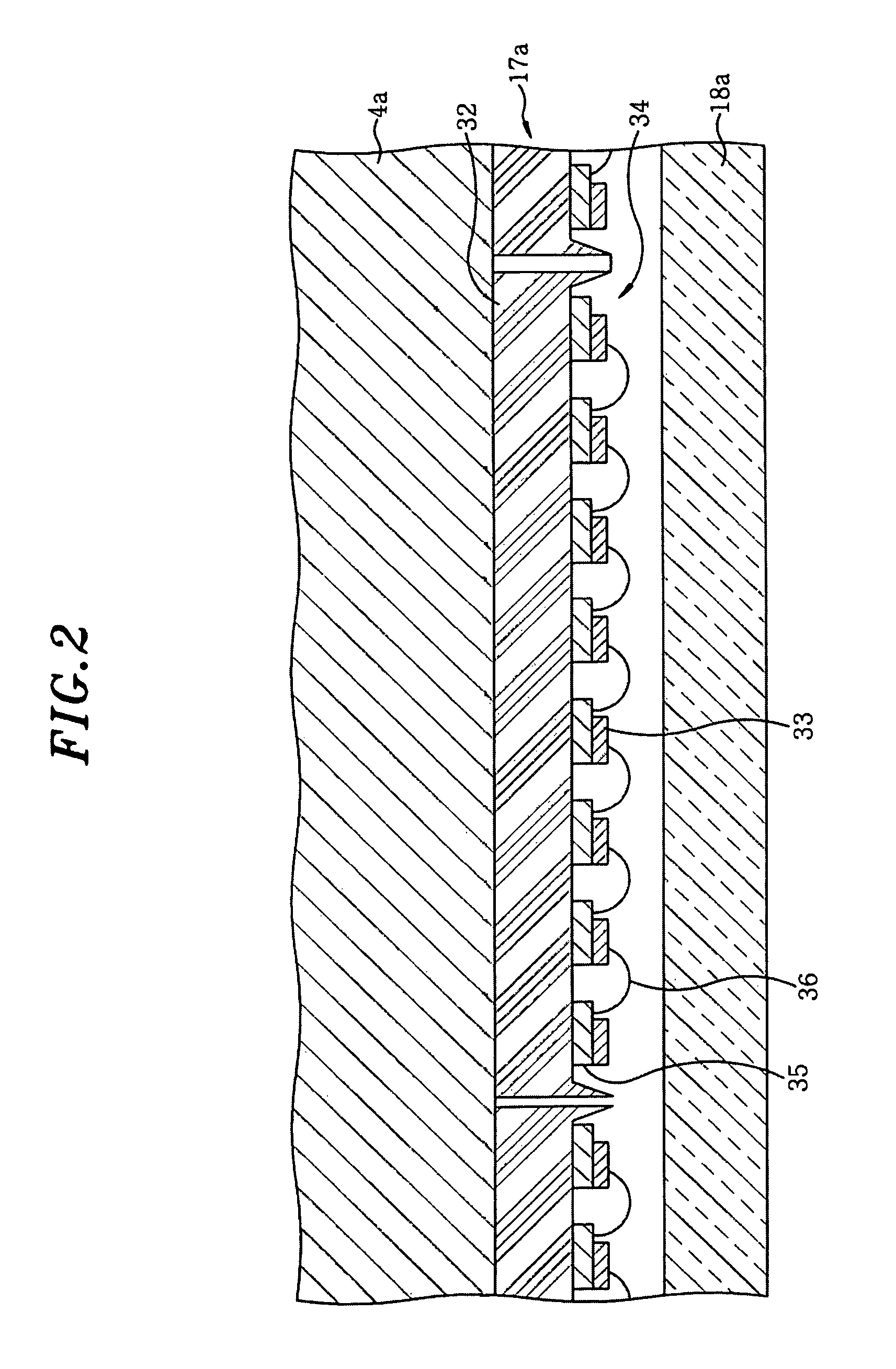
ActiveUS8246900B2Improve performanceLow efficiencyDomestic stoves or rangesDrying solid materials with heatLight energyLight emission
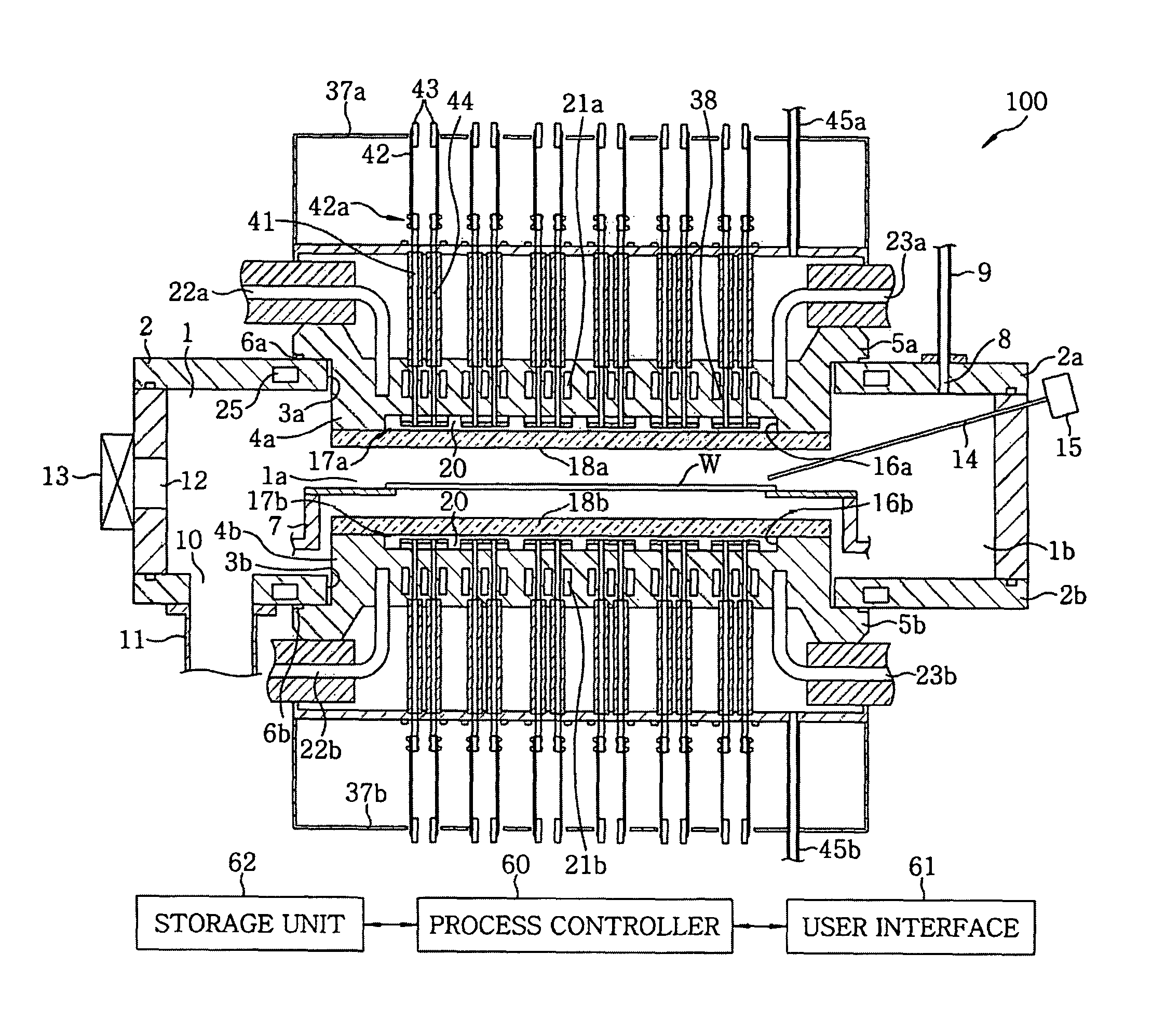
Provided is an annealing apparatus, which is free from a problem of reduced light energy efficiency resulted by the reduction of light emission amount due to a heat generation and capable of maintaining stable performance. The apparatus includes: a processing chamber 1 for accommodating a wafer W; heating sources 17a and 17b including LEDs 33 and facing the surface of the wafer W to irradiate light on the wafer W; light-transmitting members 18a and 18b arranged in alignment with the heating sources 17a and 17b to transmit the light emitted from the LEDs 33; cooling members 4a and 4b supporting the light-transmitting members 18a and 18b at opposite side to the processing chamber 1 to make direct contact with the heating sources 17a and 17b and made of a material of high thermal conductivity; and a cooling mechanism for cooling the cooling members 4a and 4b with a coolant.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
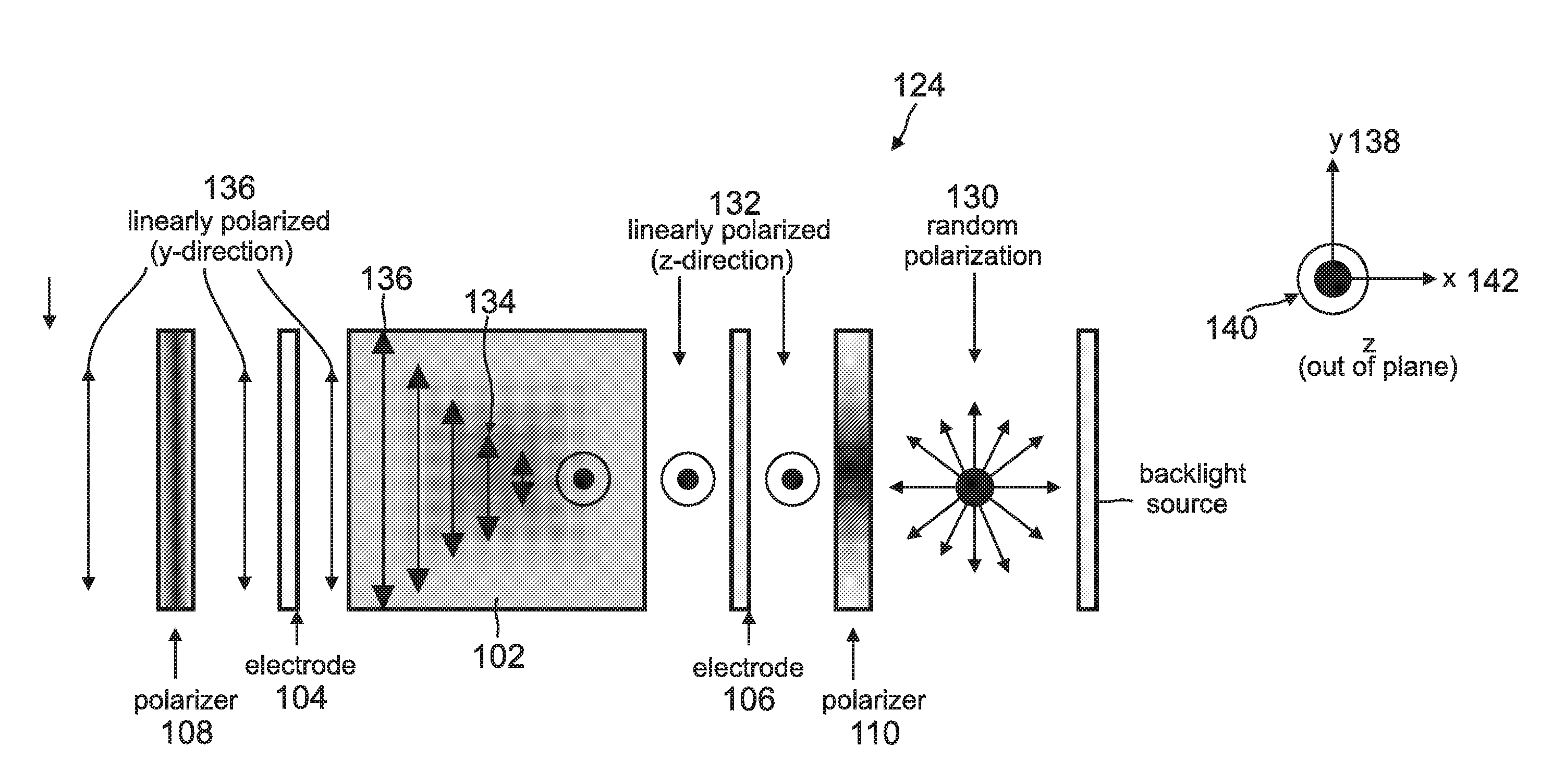
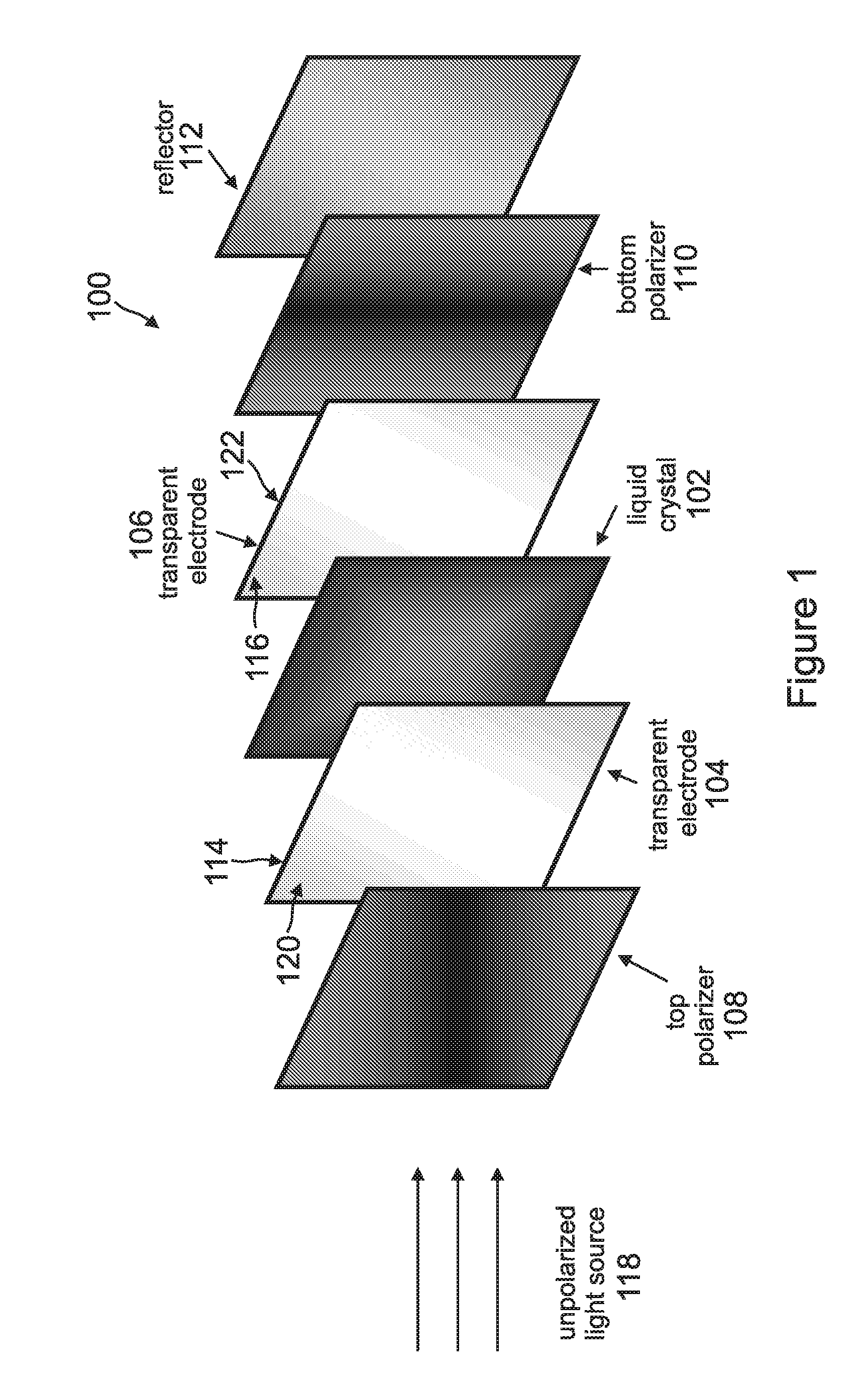
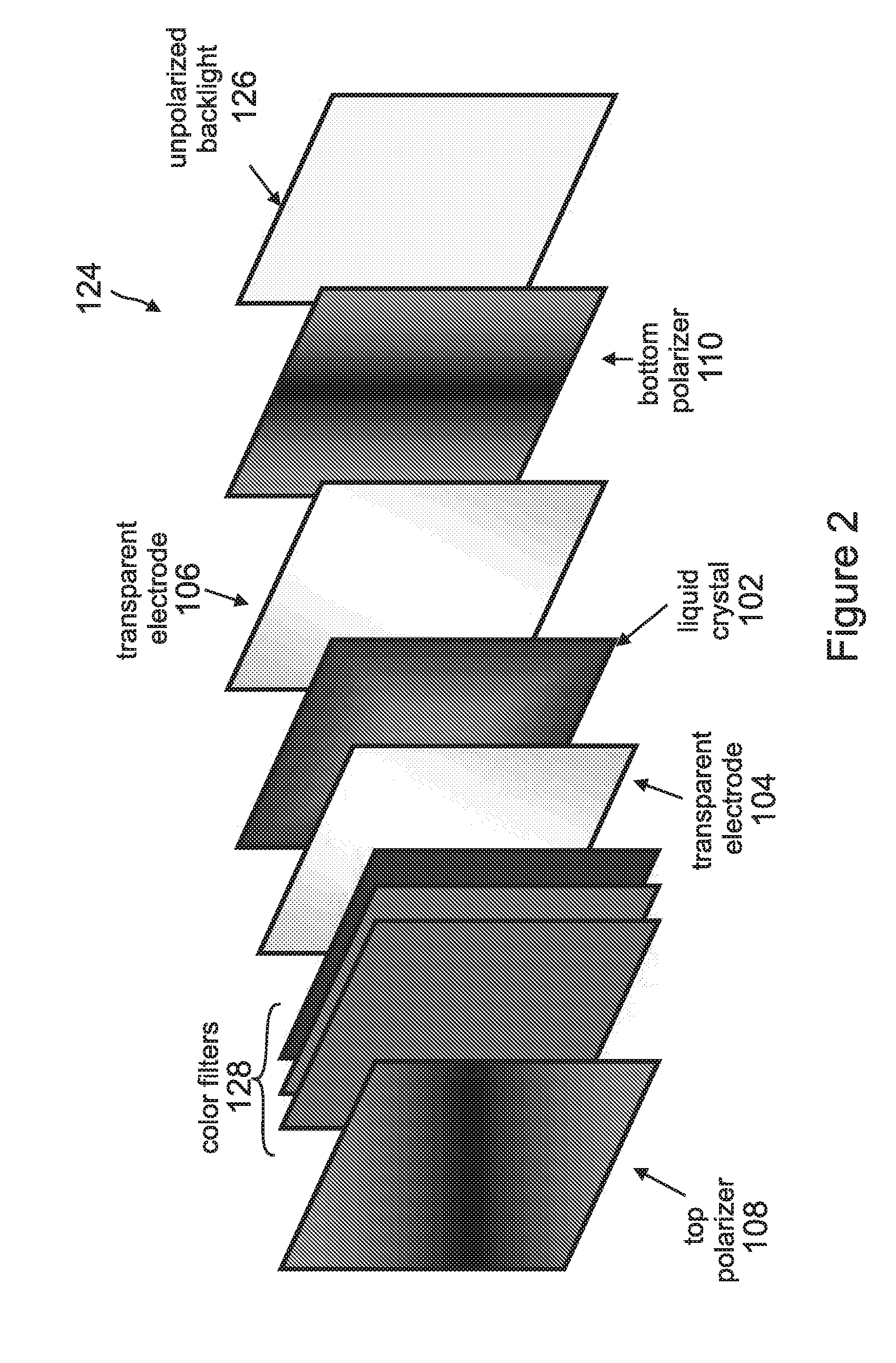
Linearly polarized backlight source in conjunction with polarized phosphor emission screens for use in liquid crystal displays
InactiveUS20100220262A1Improve efficiencyLow efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLuminescent compositionsLiquid-crystal displayPhosphor
A device for displaying images positions a luminescent material between a light source and a liquid crystal display (LCD). The light source, which comprises one or more nonpolar or semipolar III-nitride based light emitting diodes (LEDs), emits a primary light having a specified polarization direction and comprising one or more first wavelengths. This primary light emitted by the light source is a linearly polarized light that eliminates any need for a polarizer. The luminescent material, which comprises one or more phosphors, is optically pumped by the primary light and emits a secondary light having the polarization direction of the primary light, wherein the secondary light is comprised one or more second wavelengths that are different from the first wavelength. This secondary light emitted by the luminescent material is a colored light that eliminates any need for a color filter. The LCD receives the secondary light and displays one or more images in response thereto.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
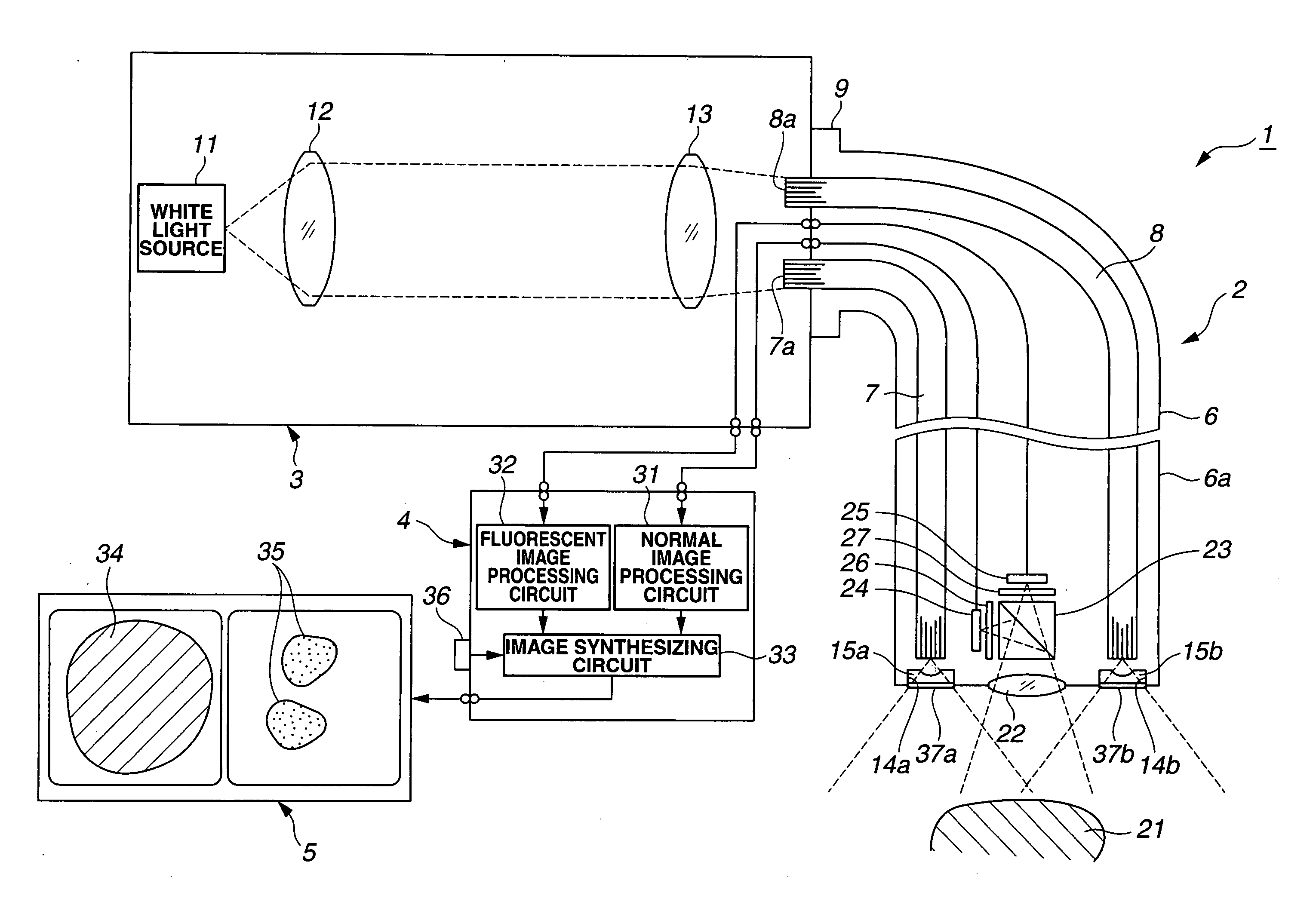
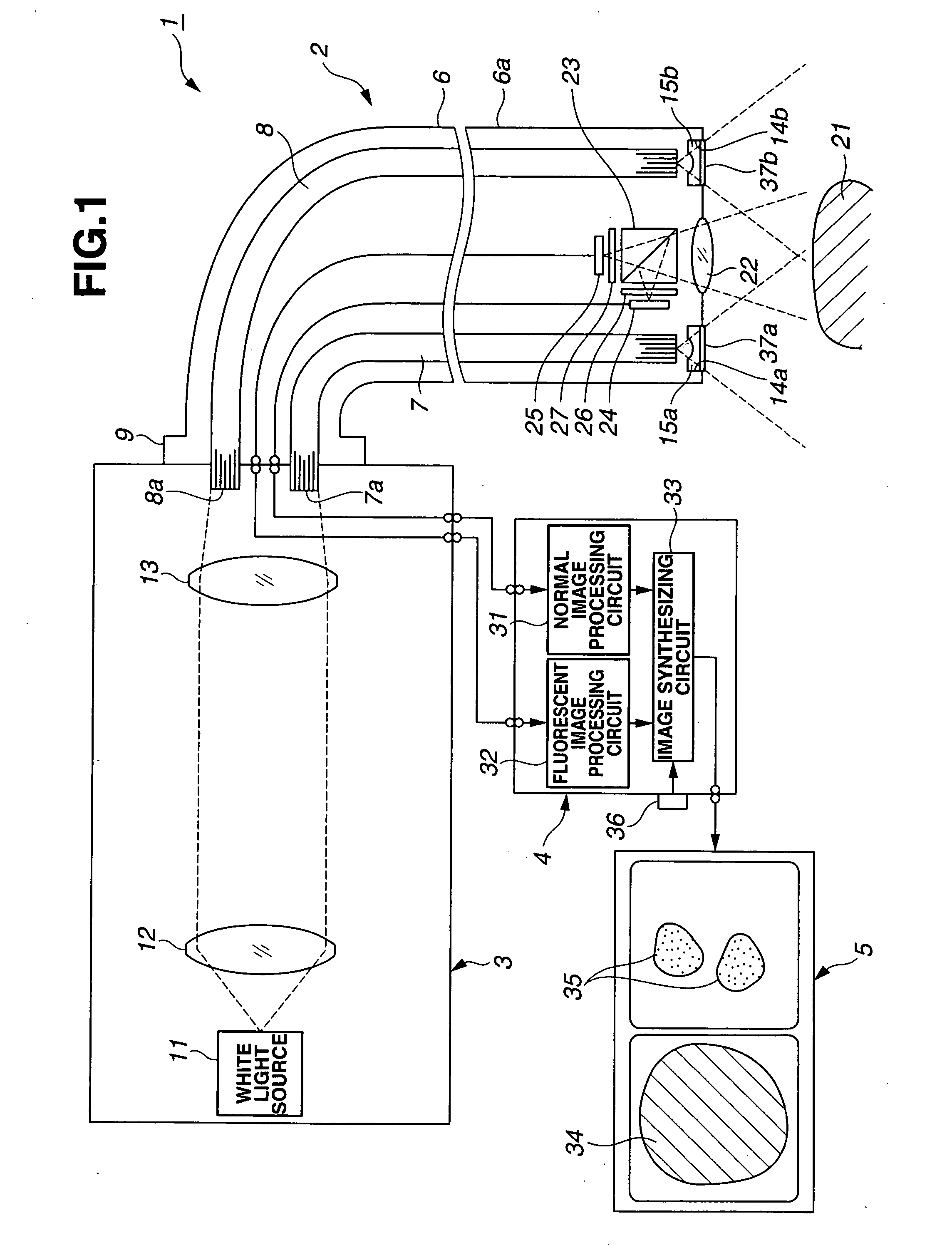
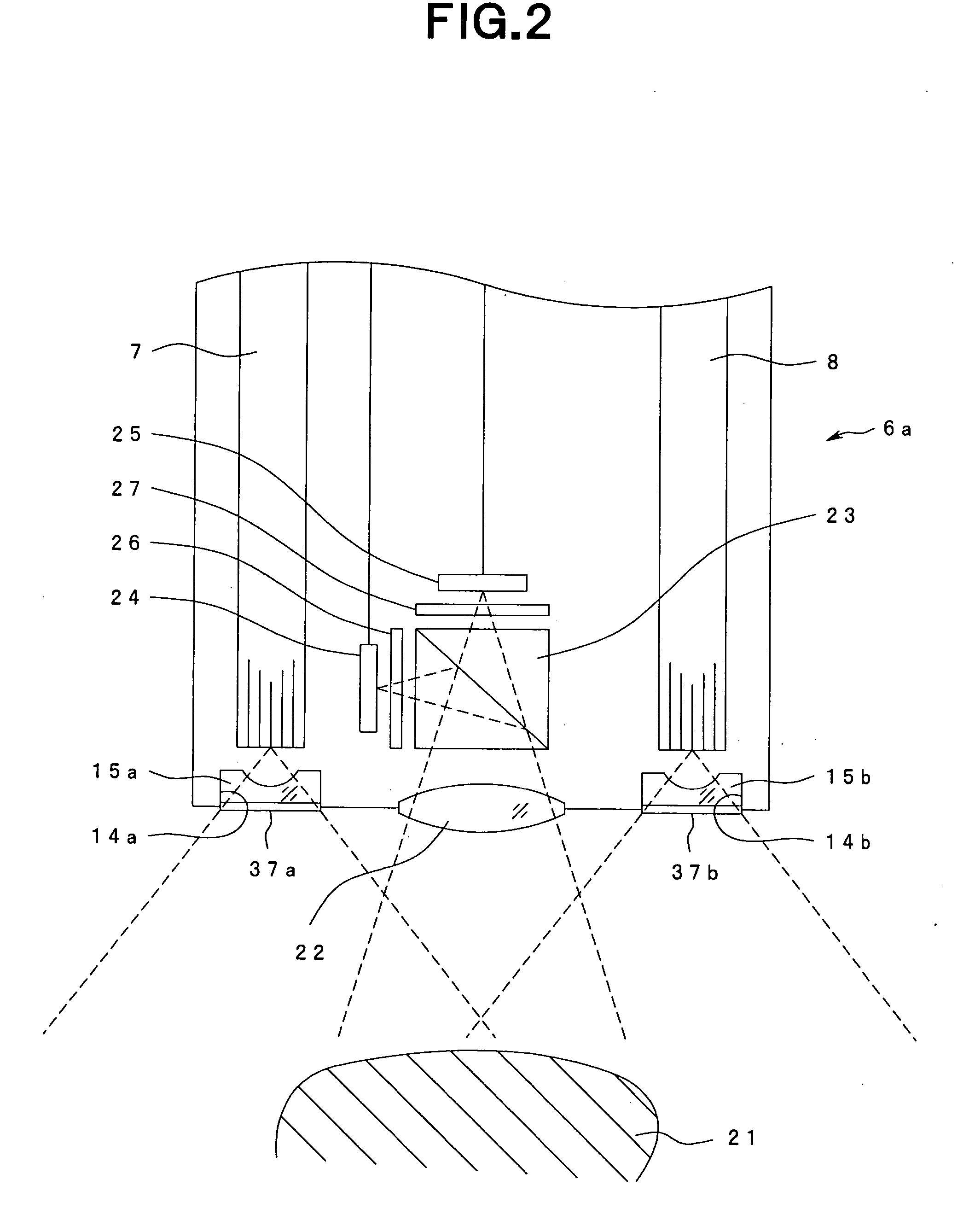
Optical imaging device
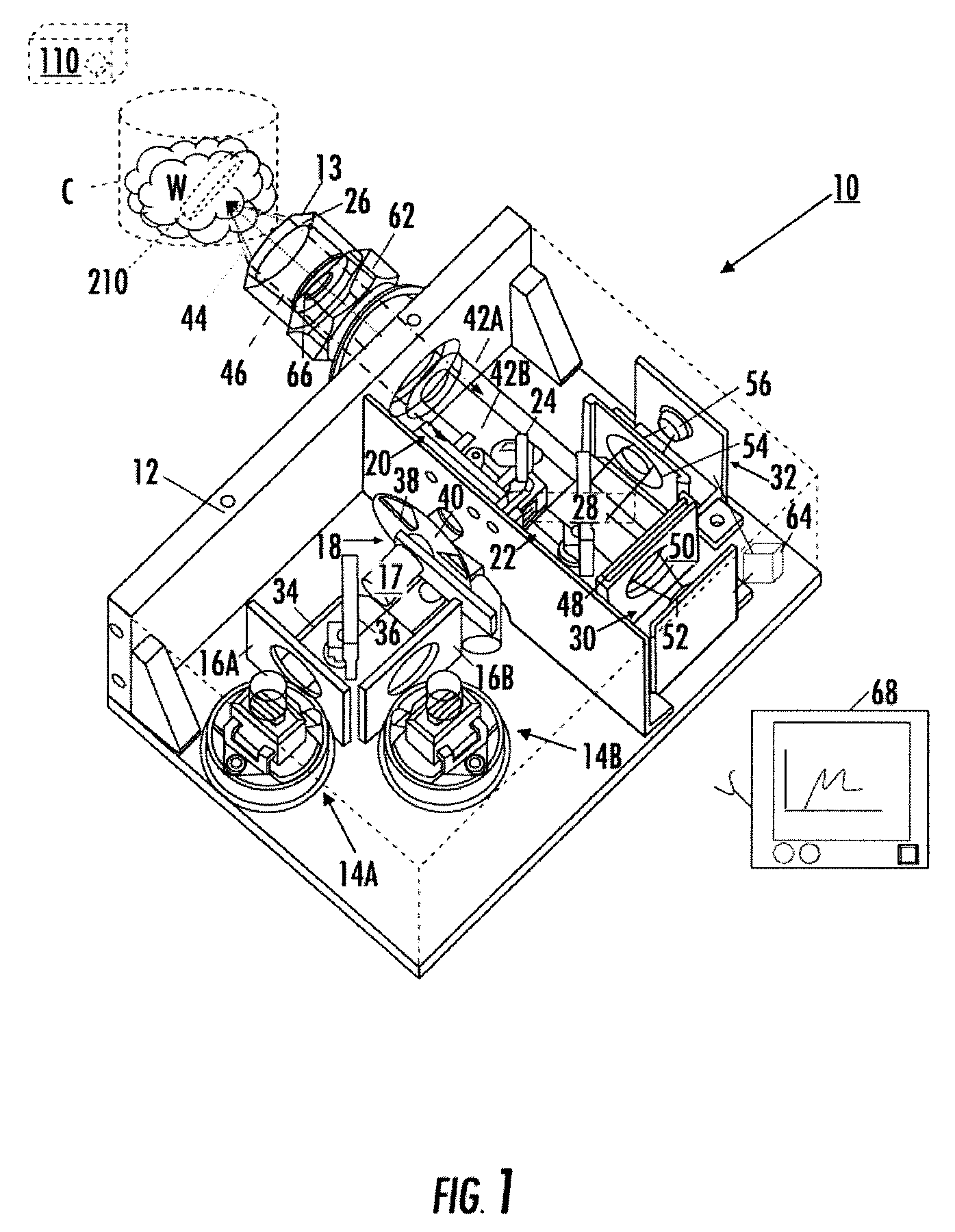
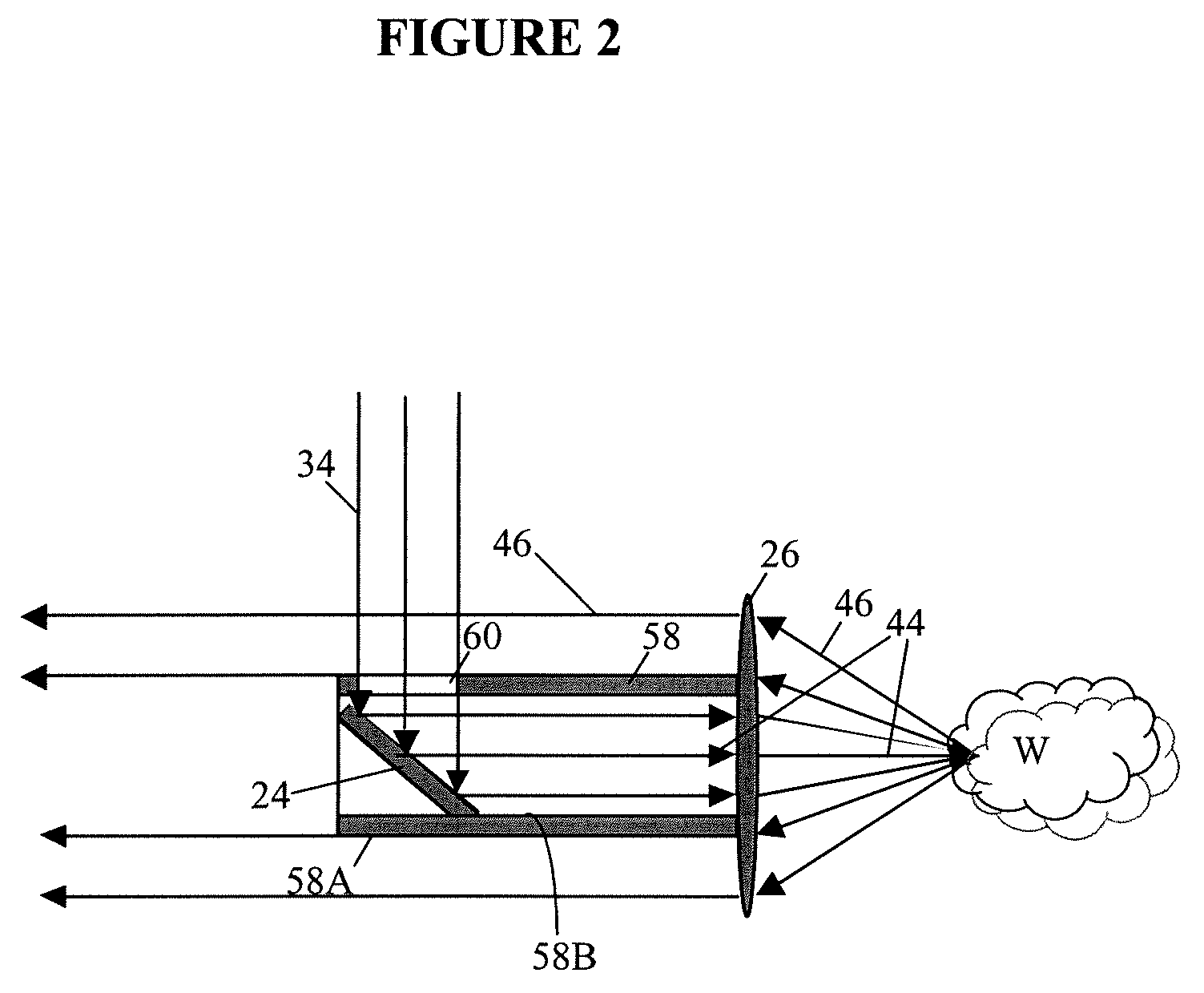
ActiveUS20070046778A1Reduce decreaseReduce lightSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical fluorescenceLight guide
An optical imaging device of the present invention comprises: a light source device; a light guide and illumination lens, provided in an insertion section that can be inserted into a body cavity, for constituting an illumination light path for guiding an illumination light from the light source device to a subject; an objective lens for receiving return lights from the subject; an image capturing section for acquiring a visible light band image from the return light; an excitation light cut filter and image capturing section for acquiring a fluorescent image from the return lights; and an illumination light filter, provided on the illumination light path, for decreasing light in a band overlapping with the band of light of which image is captured by the image capturing section from the illumination light incident on.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Displaying optical system and image projection apparatus
InactiveUS20060033009A1Reduce light lossReduce speckle noiseTelevision system scanning detailsProjectorsIntermediate imageDivergence angle
A displaying optical system is disclosed, which is capable of reducing a speckle noise. The displaying optical system comprises a light source emitting coherent light, a scanning device scanning the light, a first optical system causing the light from the scanning device to form an intermediate image, a second optical system causing the light from the intermediate image to form an image on a real display surface, and an optical element arranged between the first and second optical systems. The optical element widens the divergence angle of the light emerged from the optical element toward the second optical system more than the incident angle of the light on the optical element from the first optical system.
Owner:CANON KK
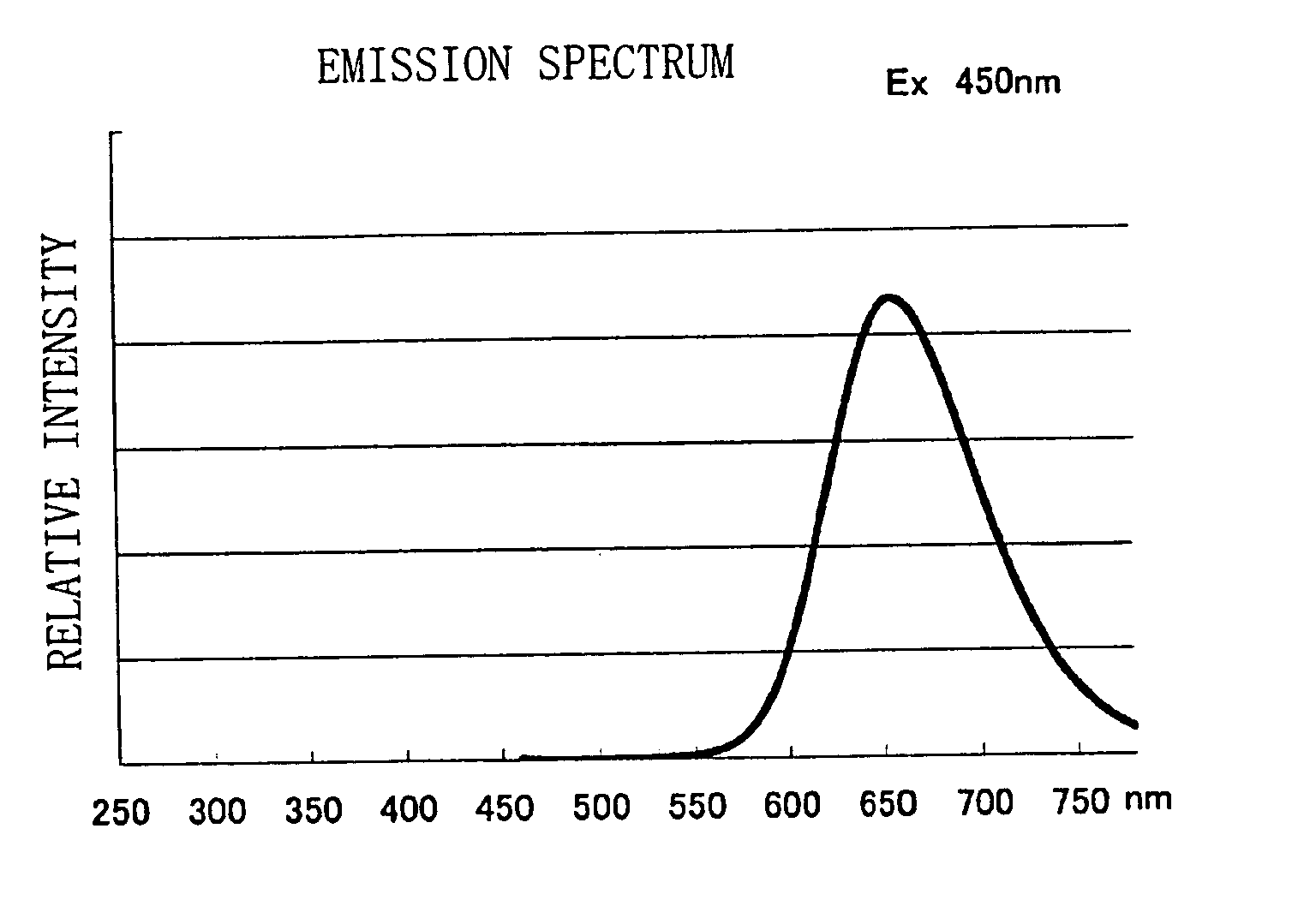
Phosphor, light source and LED
InactiveUS20050189863A1Improve luminance of light lightImprove of visible light lightDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorUltraviolet lights
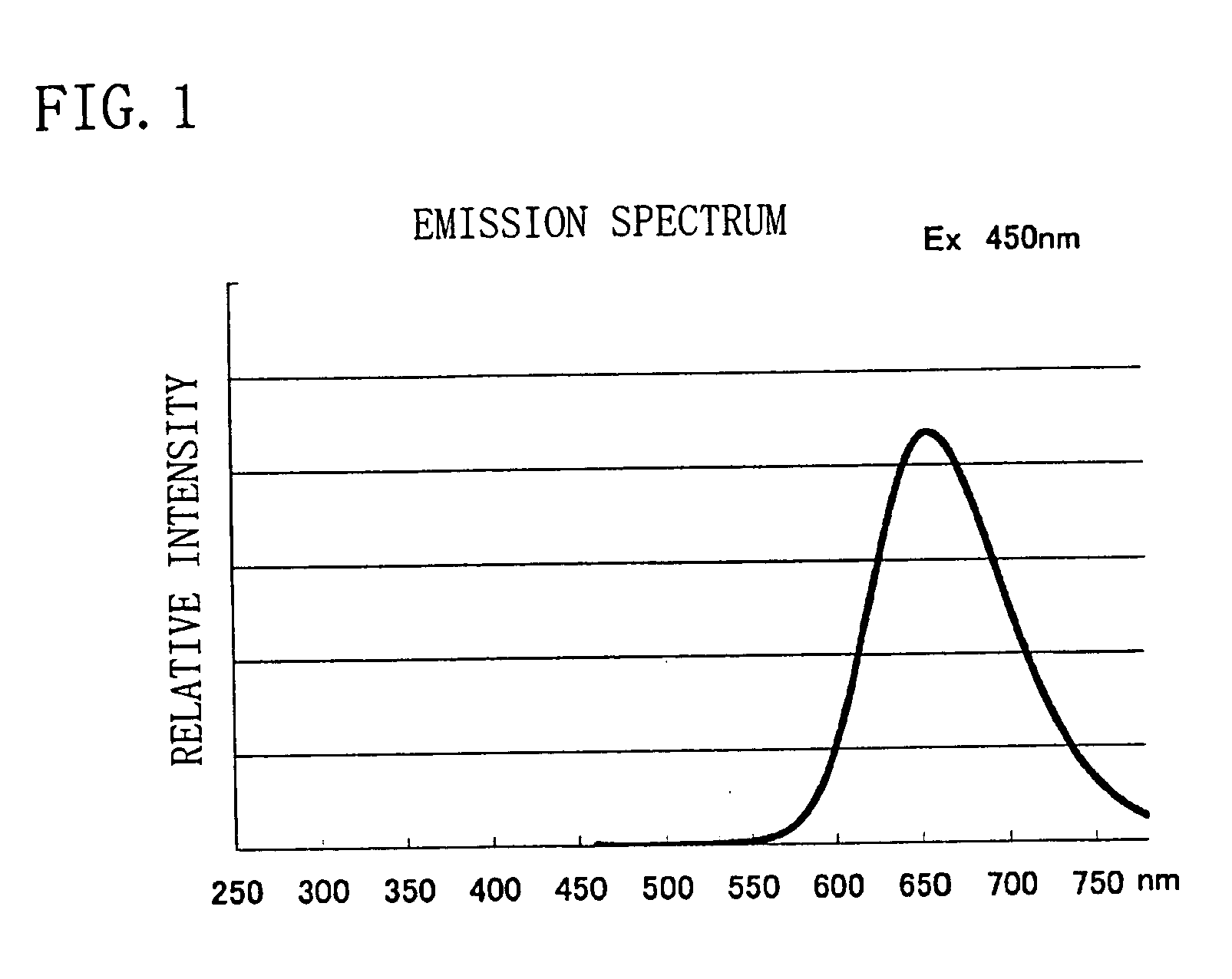
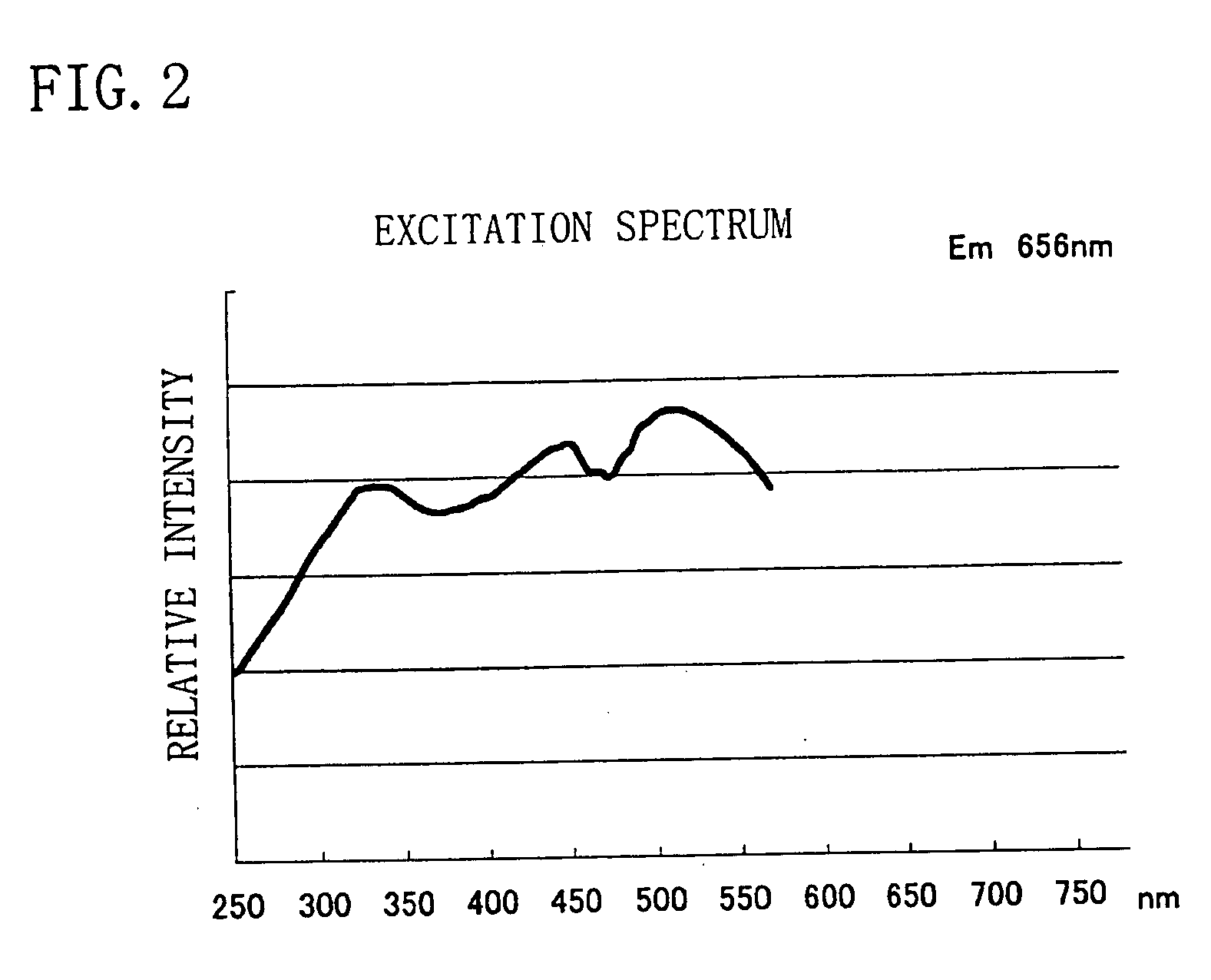
A phosphor with high efficiency having an excitation band corresponding to light of the ultraviolet-visible (300 to 550 nm) wavelength region emitted from a light emitting portion which emits blue or ultraviolet light is provided. A nitride of Ca, a nitride of Al, a nitride QfSi, and an oxide of Eu are prepared, and respective raw materials are weighed so that a mol ratio of respective elements becomes Ca:Al:Si:Eu=0.985:3:1:0.015, mixed under a nitrogen atmosphere, and thereafter fired at 1500° C. in a nitrogen atmosphere to thereby produce a phosphor having a composition formula Ca0.985SiAlN3:Eu0.015.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
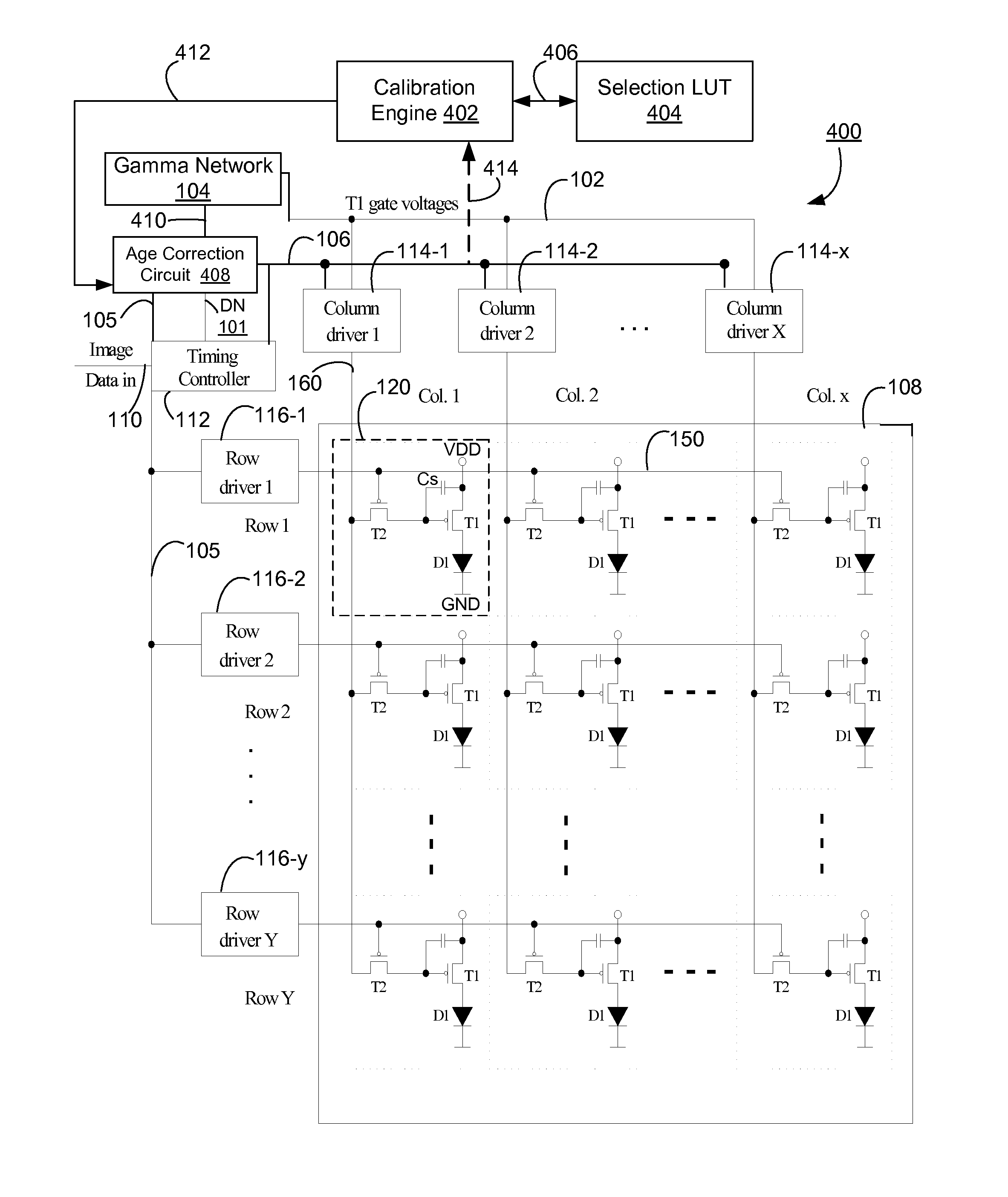
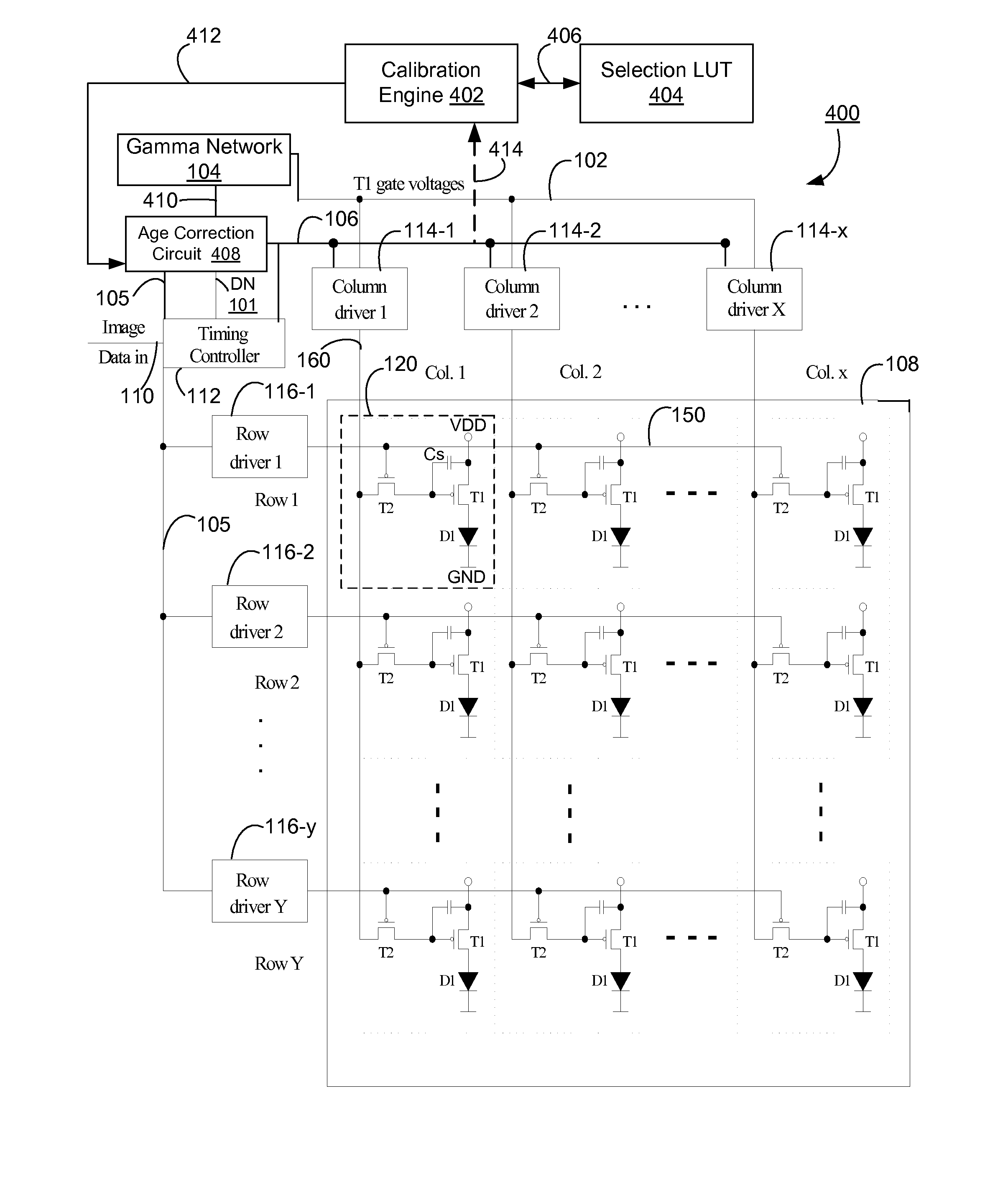
Emission control in aged active matrix OLED display using voltage ratio or current ratio with temperature compensation
InactiveUS20080231558A1Attenuation of lighting efficiencyLow light efficiencyStatic indicating devicesActive matrixVoltage ratio
Compensation needed to be made for reduced light efficiency in aged sub-pixels of an active matrix organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display are determined using a current ratio or a voltage ratio pertaining to an aged sub-pixel relative to un-aged, reference sub-pixels. When the current through the sub-pixels or the voltage across the sub-pixels are measured to determine the age of the sub-pixels, correction is made to the measured current or voltage to account for variations in the ambient temperature in which the OLED display is placed.
Owner:SILICONFILE TECH INC
Three dimensional structure producing device and producing method
An apparatus for making a three-dimensional object includes a powdery layer-forming unit for forming a powdery layer on a table and an optical beam-irradiating unit for irradiating an optical beam on a predetermined region of the powdery layer to sinter the predetermined region. The optical beam-irradiating unit is disposed at a position spaced from immediately above an optical beam-irradiating range to obliquely irradiate the optical beam on the powdery layer. Because fumes generated by irradiating and heating the powdery layer with the optical beam rise towards a position immediately above them, the optical beam is irradiated from the position spaced from immediately above the optical beam-irradiating range, thereby reducing a cloud of the optical beam-irradiating unit that may be caused by the fumes.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
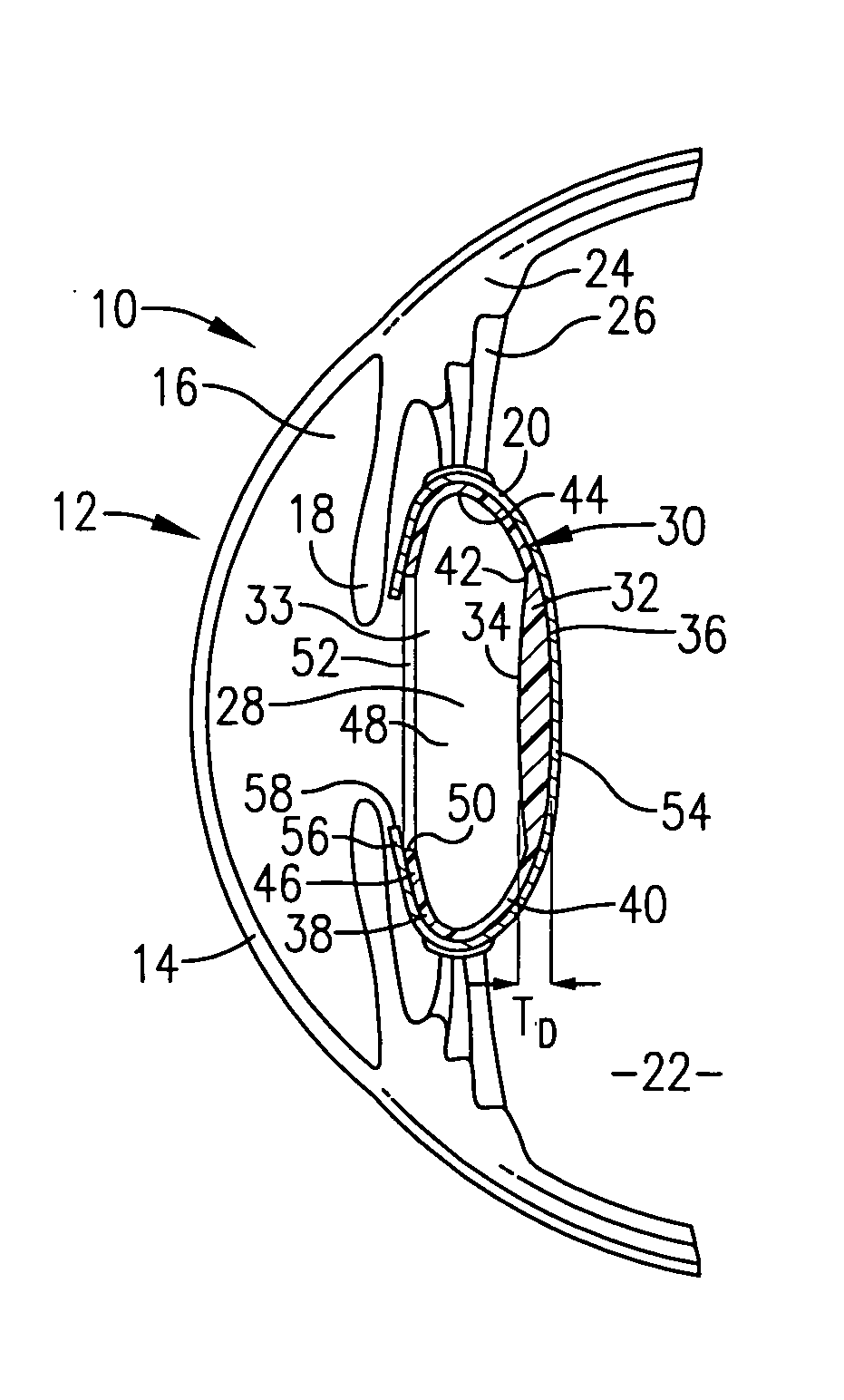
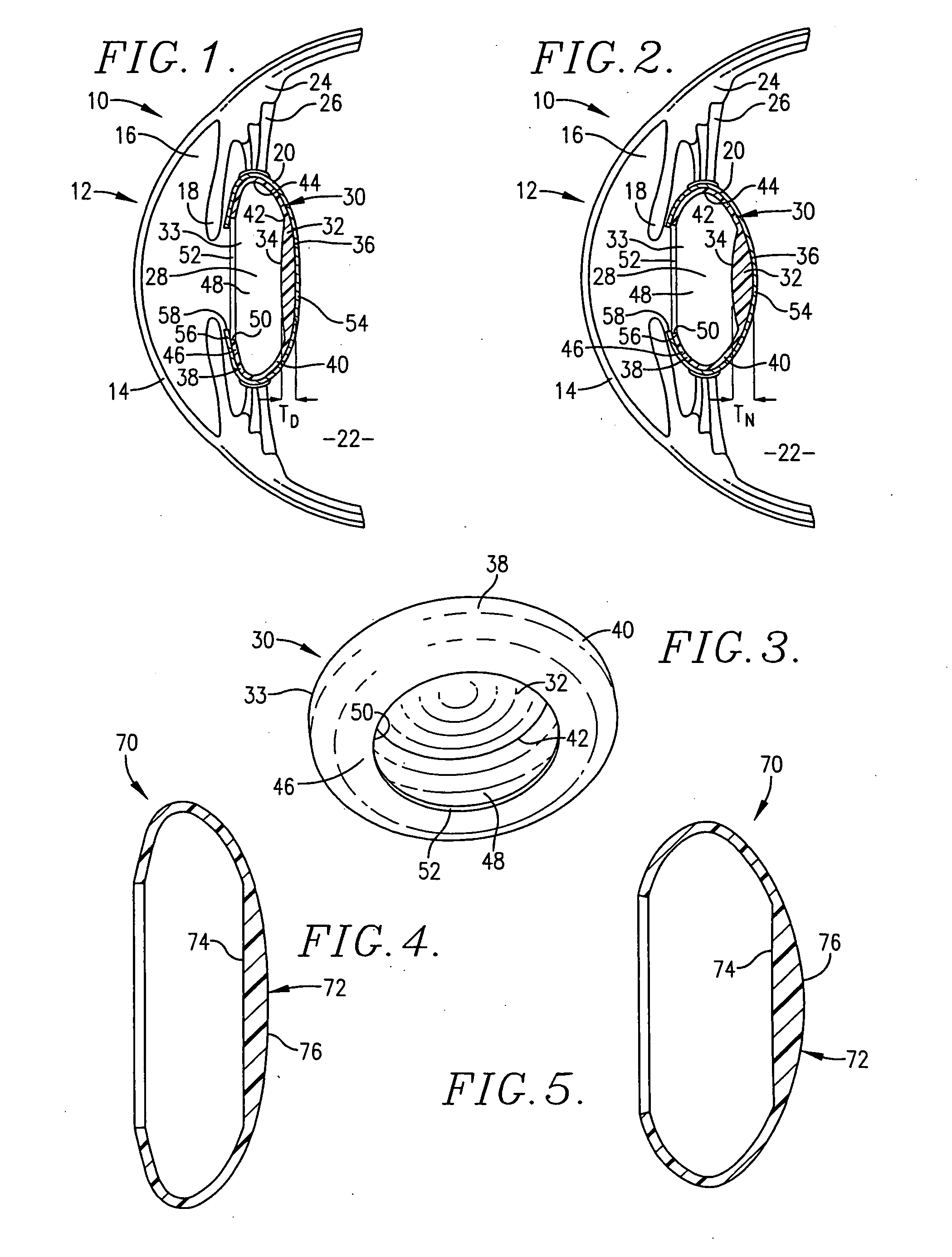
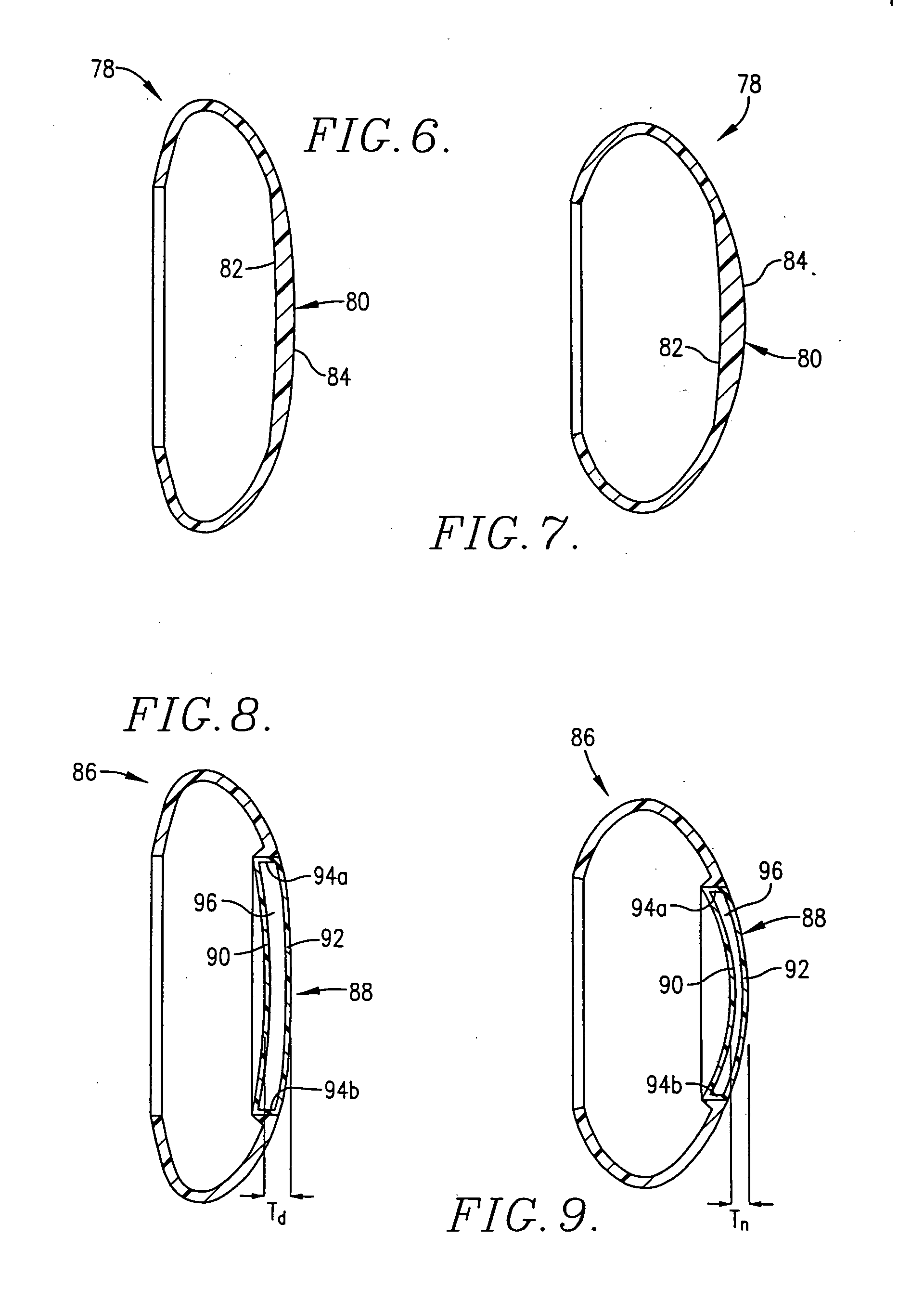
Intraocular lens implant having posterior bendable optic
InactiveUS20050131535A1Safe for long-term use in eyeReduce lightIntraocular lensCiliary epitheliumThinning
An intraocular lens (30) having focusing capabilities permitting focusing movement of the lens (30) in response to normal ciliary body (24) movement incident to changes in the distance between the eye and an object under observation is provided. The lens (30) is designed for surgical implantation within the capsule (20) of an eye (10) and includes an optic (32) and an optic positioning element (33) which cooperate to form the lens (30). Accommodation is achieved by relying upon the thickening and thinning of the optic (32) as a result of the normal retracting and contracting of the ciliary body (24) in response to the distance of an object from the viewer.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
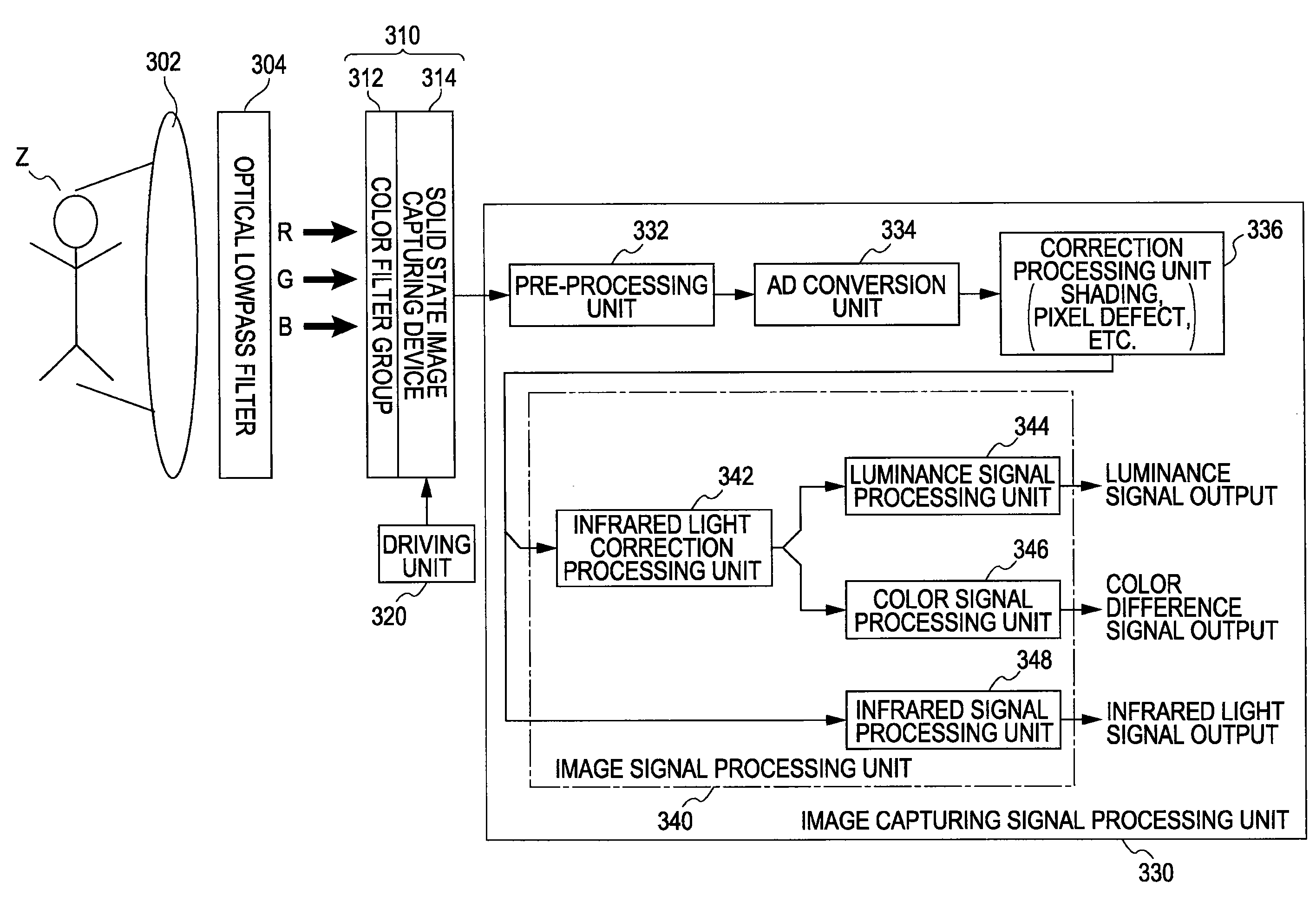
Physical information acquisition method, physical information acquisition device, and semiconductor device
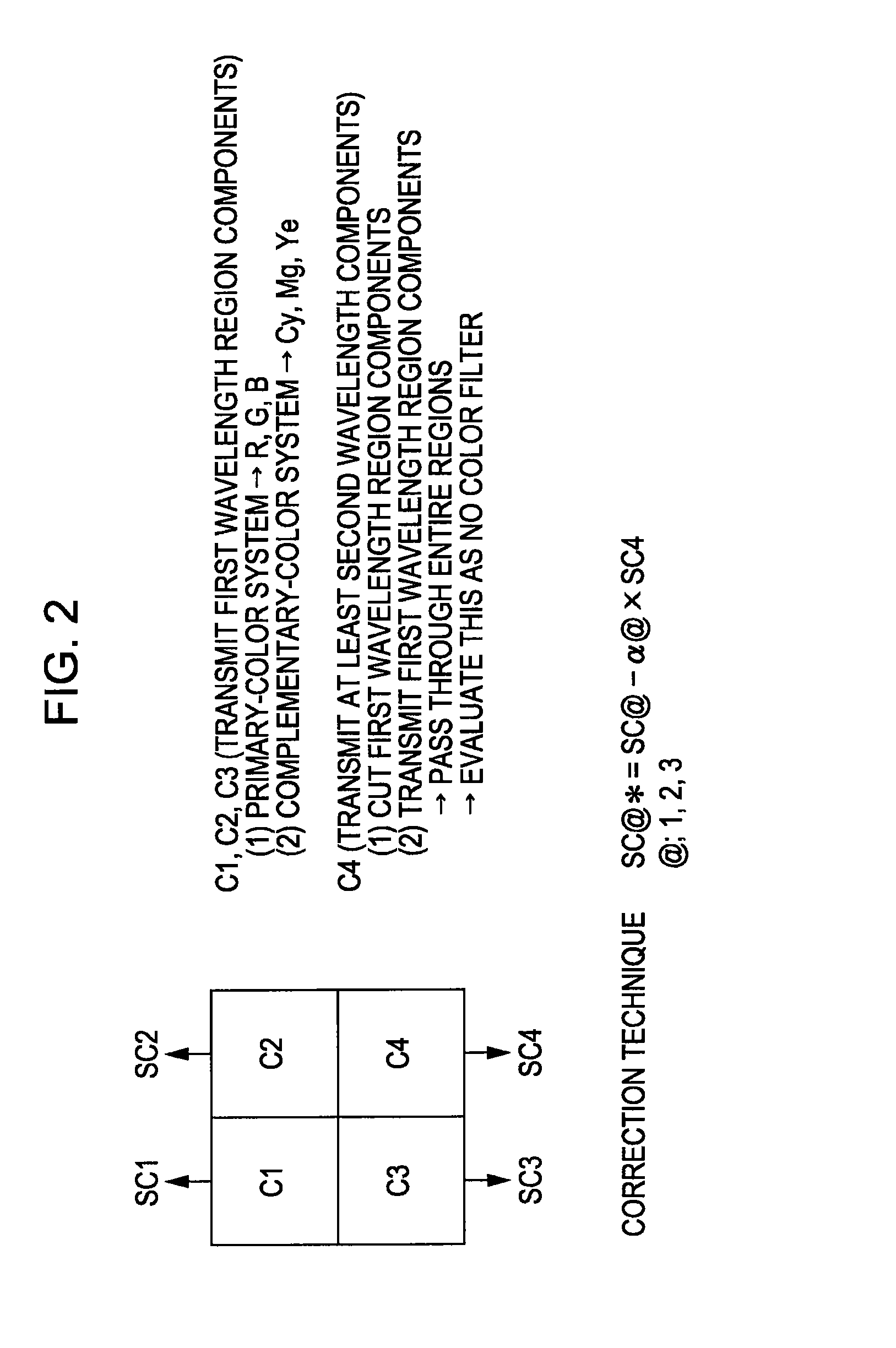
ActiveUS20070201738A1Exclude influenceReduce lightTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCell basedGenerating unit
A physical information acquisition device uses a device including a detection unit for detecting electromagnetic waves, and a unit signal generating unit for generating and outputting the corresponding unit signal based on the amount of electromagnetic waves detected by the detection unit for detecting a physical quantity distribution in which the unit components are disposed on the same substrate in a predetermined sequence, for acquiring physical information for a predetermined application based on the unit signal. The physical information acquisition device includes a first detection unit which detects first wavelength region components following second wavelength region components different from the first wavelength region components being separated from the first wavelength region components beforehand; a second detection unit which detects wavelength region components for correction including at least the second wavelength region components; and a signal processing unit for obtaining physical information relating to the first wavelength region components from which at least a part of influence of the second wavelength region components is eliminated using the unit signal detected by the first detection unit, and the unit signal detected by the second detection unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Micro-projector
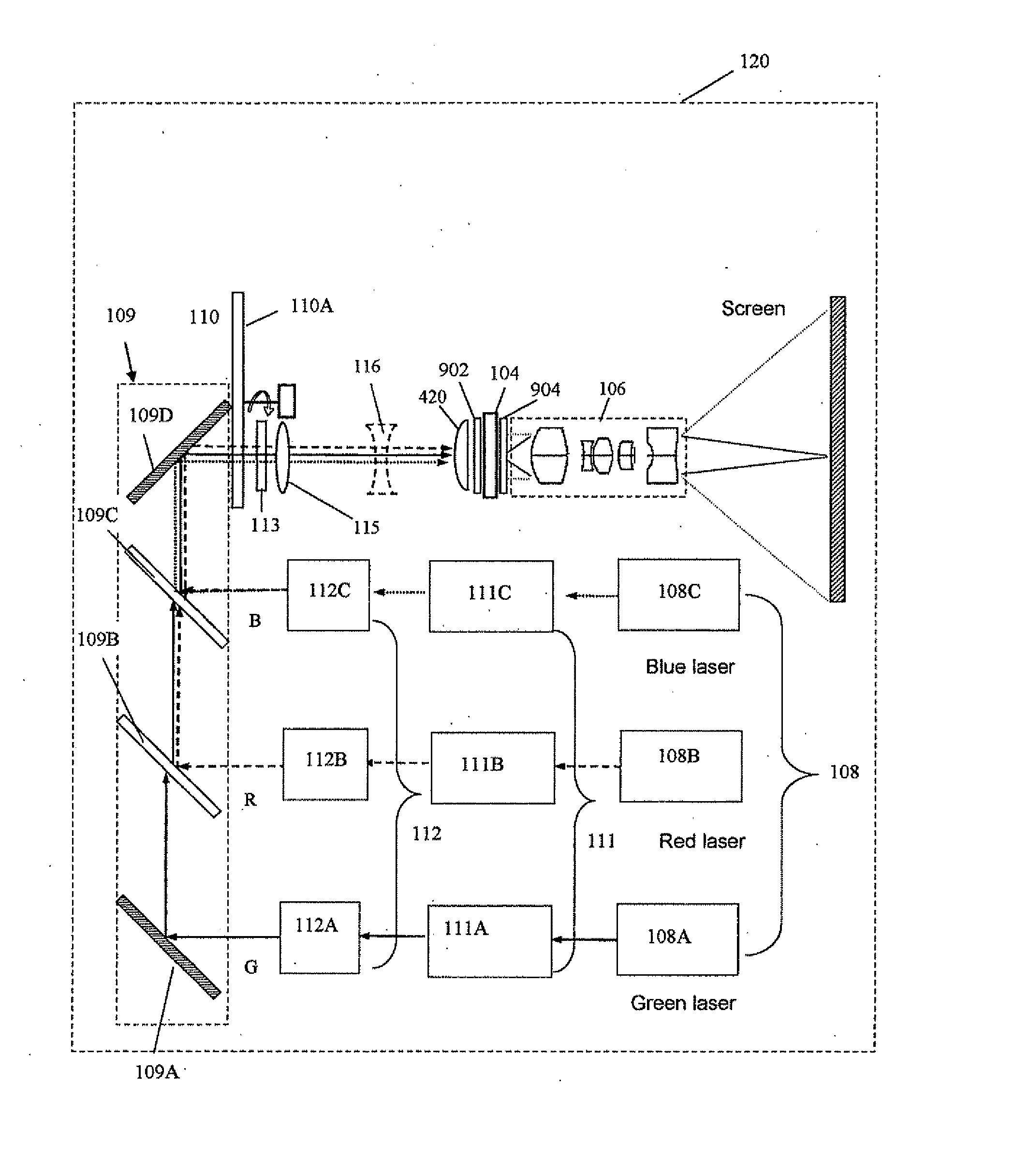
InactiveUS20110037953A1Increase brightnessQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceLaser source
The present invention provides a projection display comprising an illumination system comprising at least one laser source unit and configured and operable for producing one or more light beams; a spatial light modulating (SLM) system accommodated at output of the illumination system and comprising one or more SLM units for modulating light incident thereon in accordance with image data; and a light projection optics for imaging modulated light onto a projection surface. The illumination system comprises at least one beam shaping unit comprising a Dual Micro-lens Array (DMLA) arrangement formed by front and rear micro-lens arrays (MLA) located in front and rear parallel planes spaced-apart along an optical path of light propagating towards the SLM unit, the DMLA arrangement being configured such that each lenslet of the DMLA directs light incident thereon onto the entire active surface of the SLM unit, each lenslet having a geometrical aspect ratio corresponding to an aspect ratio of said active surface of the SLM unit.
Owner:EXPLAY
Light source device, illumination device liquid crystal device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6883934B2Improve incident efficiencyEasy to seeTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusLight guideLight emitting device
A light source device 41A, 41B or 41C comprising a lens 44A, 44B or 44C which receives light from a light emitting device 43 such as LED. The lens 44A is a lens having the property that the directivity of exiting light in the Y direction is higher than the directivity in the X direction perpendicular to the Y direction. Namely, the light emitted from the light emitting device 43 is condensed in a narrow angular range in the Y direction, and is scattered in a wide angular range in the X direction. When the light source device 41A is used as a light source of an illumination device of a liquid crystal device, the height direction of a light guide in which the dimension is small coincides with the Y direction, and the width direction of the light guide in which the dimension is large coincides with the X direction.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
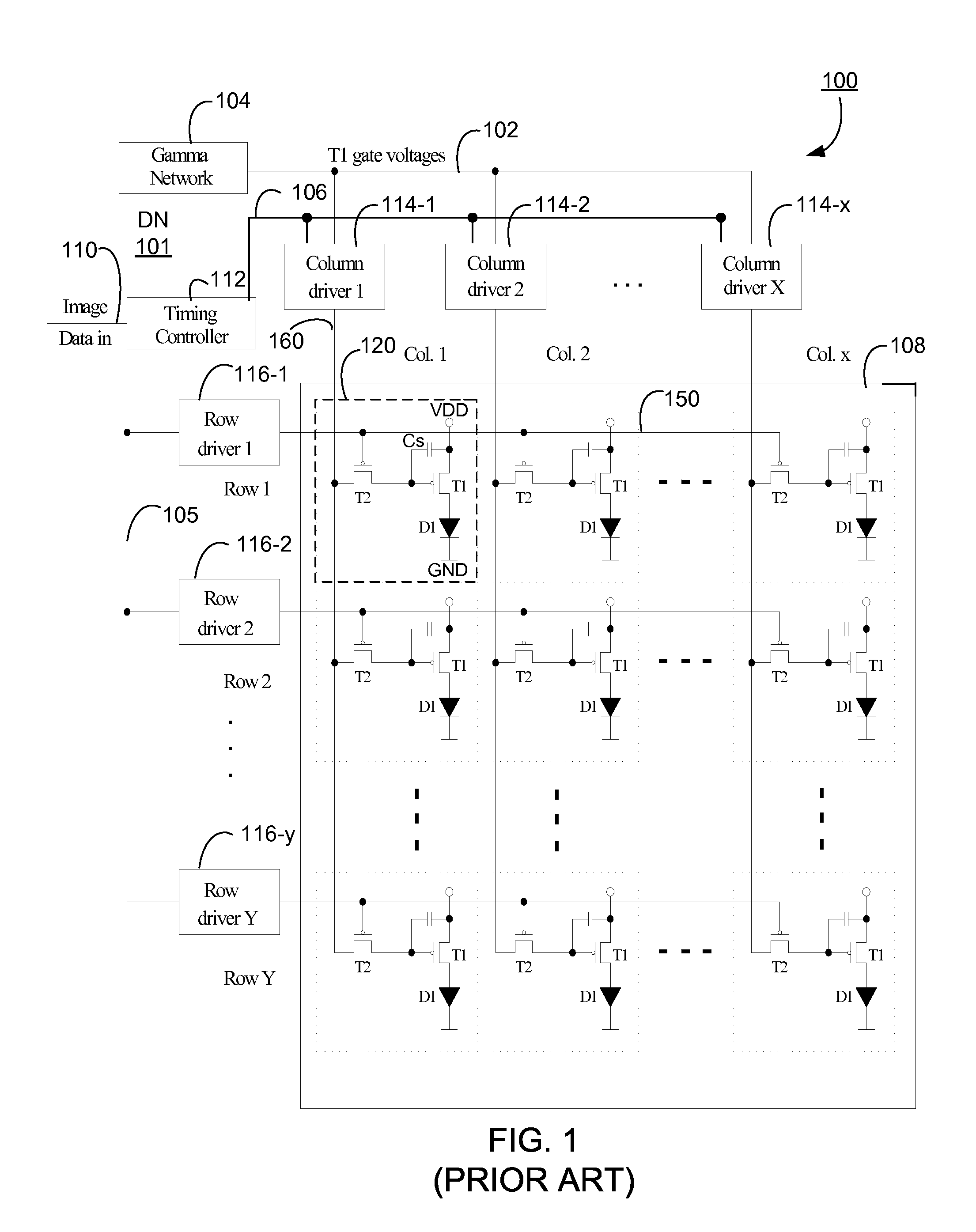
Emission control in aged active matrix OLED display using voltage ratio or current ratio with temperature compensation
Compensation needed to be made for reduced light efficiency in aged sub-pixels of an active matrix organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display are determined using a current ratio or a voltage ratio pertaining to an aged sub-pixel relative to un-aged, reference sub-pixels. When the current through the sub-pixels or the voltage across the sub-pixels are measured to determine the age of the sub-pixels, correction is made to the measured current or voltage to account for variations in the ambient temperature in which the OLED display is placed.
Owner:SILICONFILE TECH INC
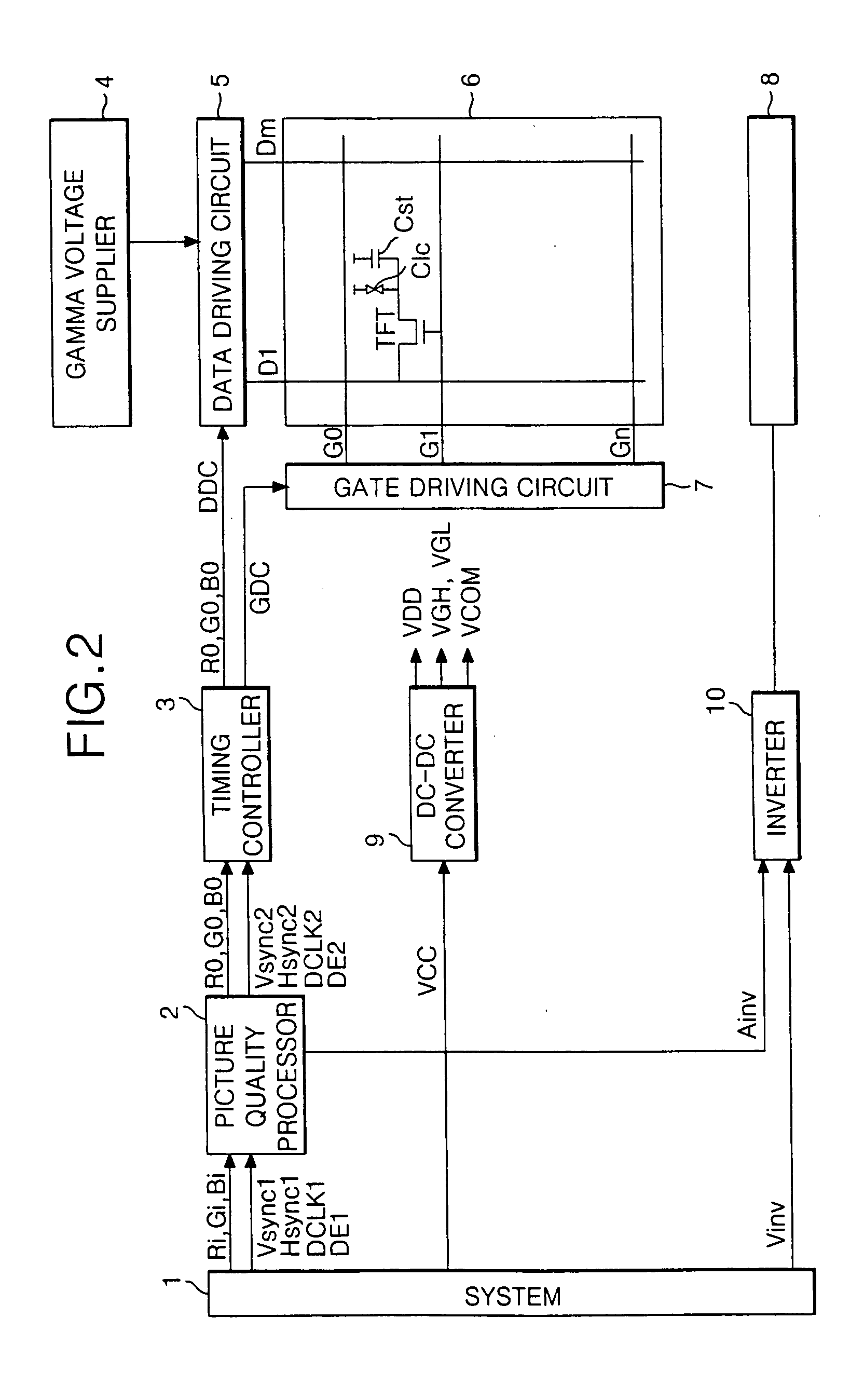
Liquid crystal display device and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20050140640A1Brightness ratio be increaseImprove qualityTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesNormal modeLiquid-crystal display
The liquid crystal display device includes a histogram analyzer analyzing a histogram of an input image and determining the input image as being in one of a low brightness mode, a normal mode, and a high brightness mode based on the histogram analysis, a back light controller controlling a maximum brightness of a back light unit based on the mode determination, and a data modulator enlarging the histogram of the input image to modulate data of the input image. The histogram analyzer detects a most frequent value of gray scale occurring most frequently in the input image of one frame, compares the most frequent value with a predetermined low reference gray value and a predetermined high reference gray value, and determines the input image as in one of the low brightness mode, the normal mode, and the high brightness mode based on the compared result.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Intraocular lens implant having posterior bendable optic
ActiveUS20060253196A1Safe for long-term use in eyeReduce lightIntraocular lensCiliary epitheliumThinning
An intraocular lens (30) having focusing capabilities permitting focusing movement of the lens (30) in response to normal ciliary body (24) movement incident to changes in the distance between the eye and an object under observation is provided. The lens (30) is designed for surgical implantation within the capsule (20) of an eye (10) and includes an optic (32) and an optic positioning element (33) which cooperate to form the lens (30). Accommodation is achieved by relying upon the thickening and thinning of the optic (32) as a result of the normal retracting and contracting of the ciliary body (24) in response to the distance of an object from the viewer.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
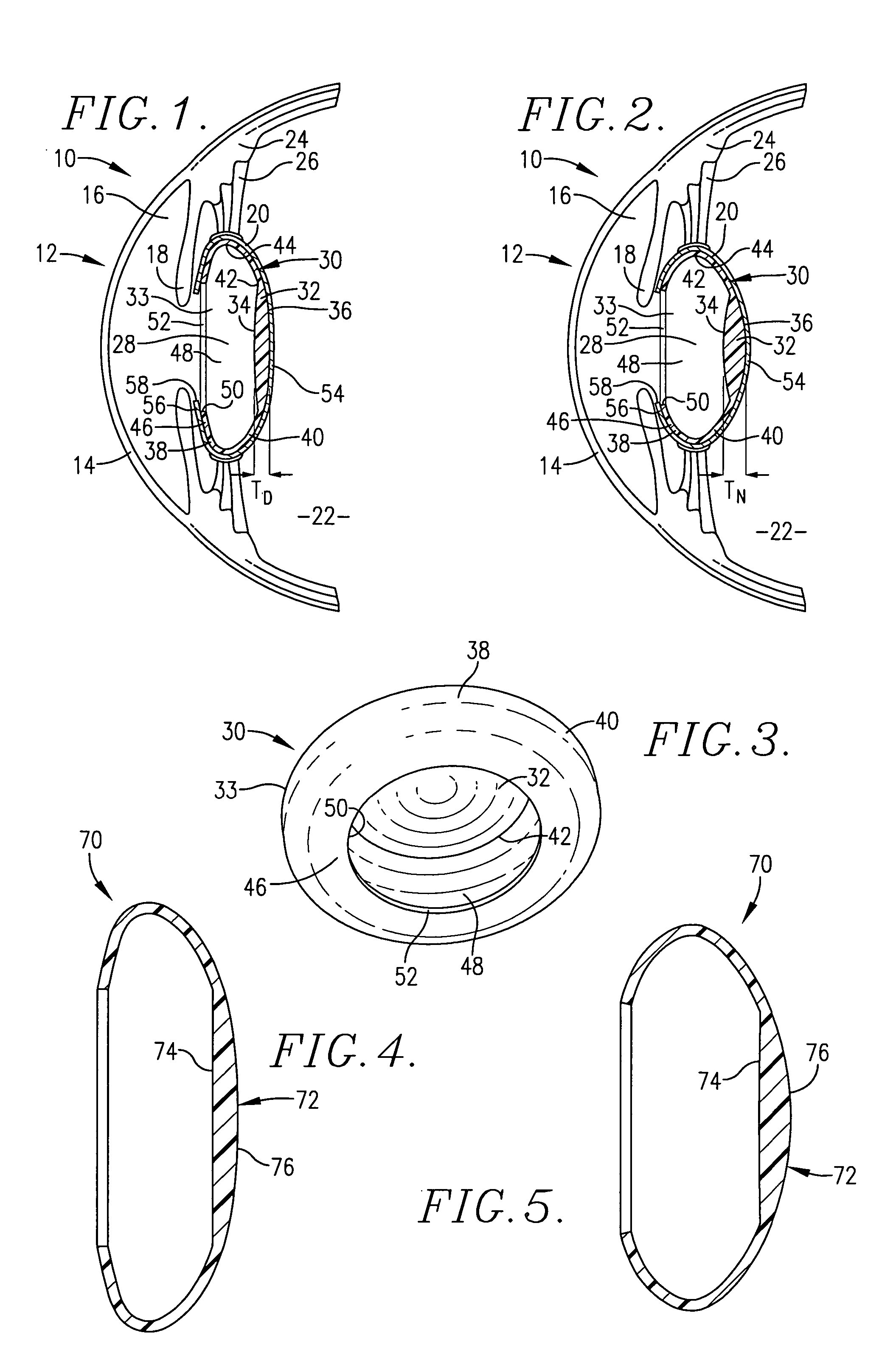
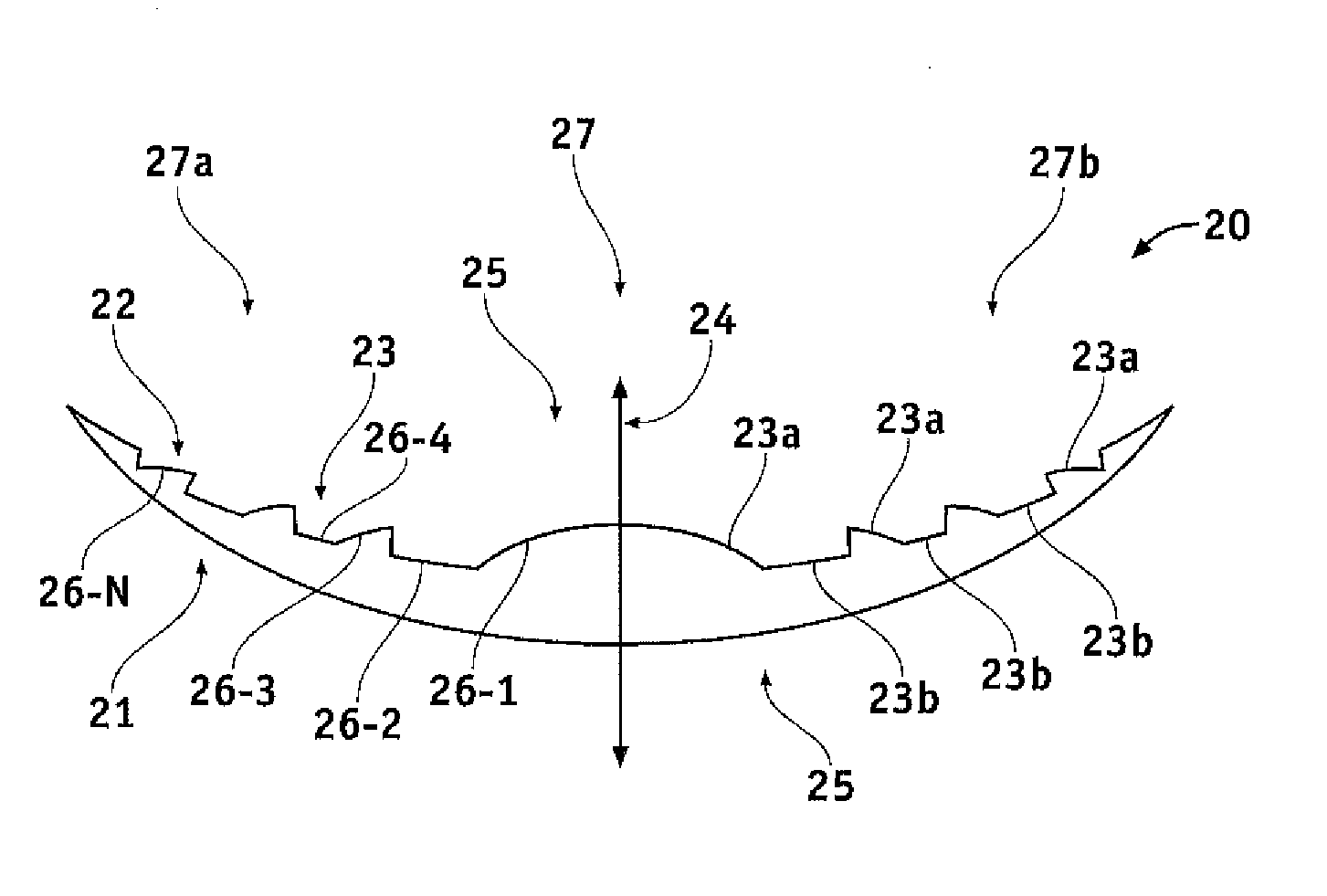
Pupil dependent diffractive lens for near, intermediate, and far vision
InactiveUS20120140166A1Reduce light scatterImproved patient visionSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensMultifocal diffractive lensOptical power
A multifocal diffractive lens comprises a multifocal diffractive structure coupled to a refractive component. The refractive component comprises at least one curved surface. The multifocal diffractive structure comprises a first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having a first optical power for near vision correction and a second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes for far vision correction. The first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes combined with the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes can provide a multifocal diffractive profile having decreased light scatter, chromatic aberration, and diffraction to non-viewing orders such that dysphotopsia is substantially inhibited. A third plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having an intermediate optical power can be combined with the first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes and the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
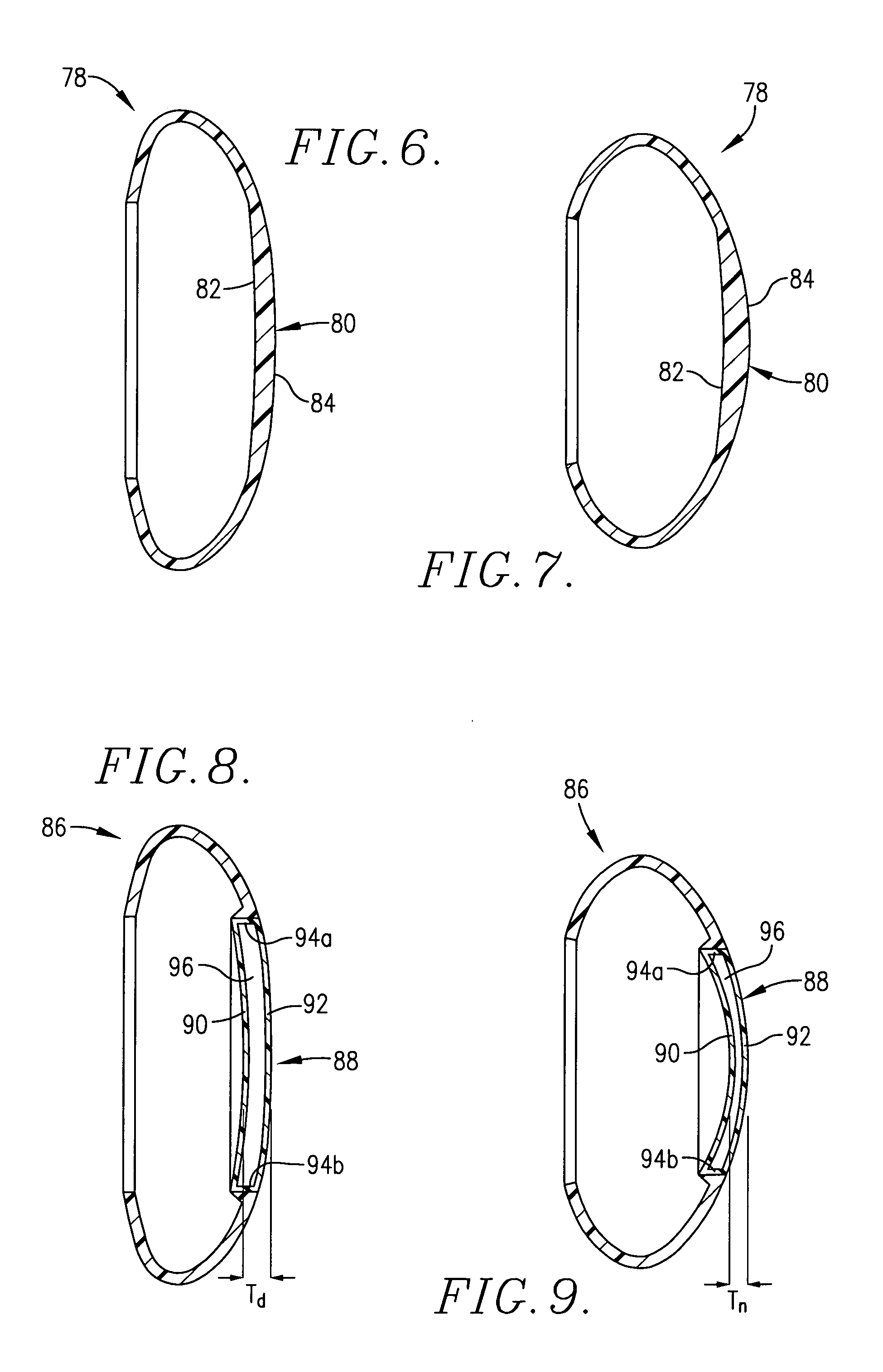
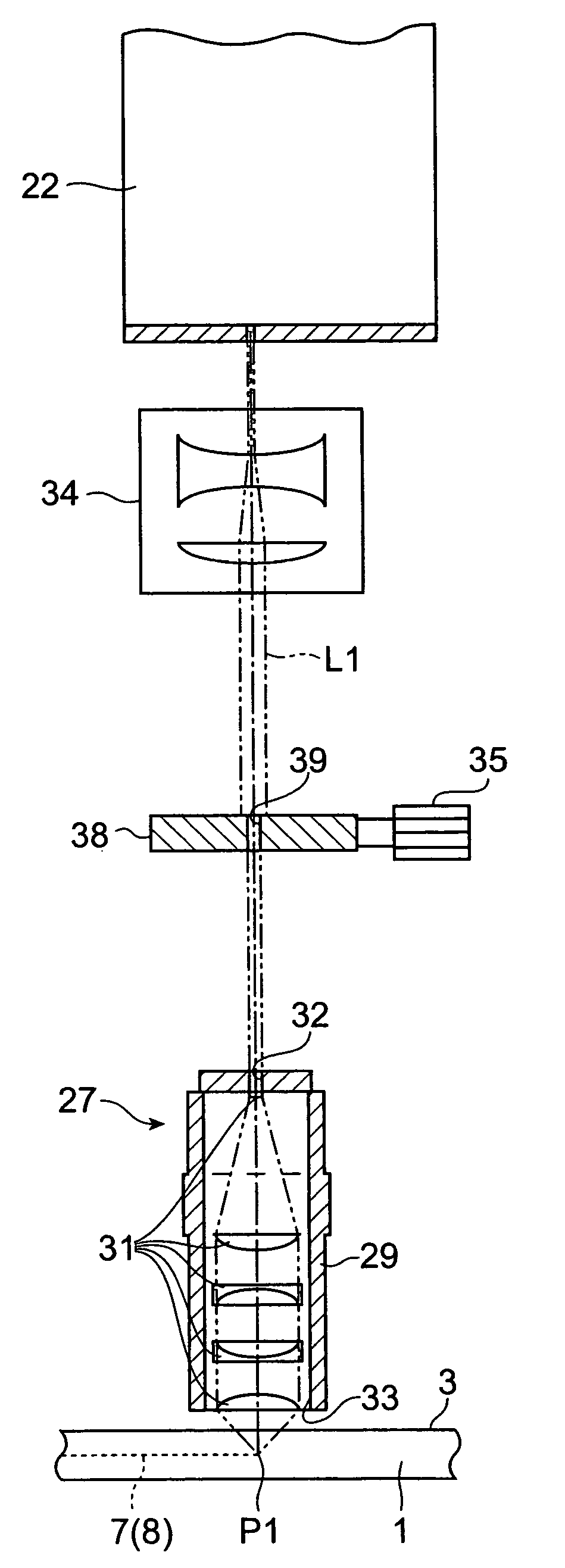
Laser processing device
ActiveUS7489454B2Suppress positional fluctuationReduce lightLaser detailsFine working devicesBeam expanderLaser processing
A laser processing apparatus which can suppress the positional fluctuation in light-converging point of laser light during laser processing is provided. On an optical path of laser light L1 connecting a beam expander 34 and a first light-transmitting hole 32 of a lens holder 29 to each other in a laser processing apparatus 20, a stop member 38 including a second light-transmitting hole 39 having the same diameter as that of the first light-transmitting hole 32 is disposed. Hence, the amount of laser light L1 cut by the surrounding part of the first light-transmitting hole 32 can substantially be eliminated, whereby the lens holder 29 can be prevented from being heated upon irradiation with the laser light L1. Also, even when the stop member 38 is heated by the laser light L1 cut by the surrounding part of the second light-transmitting hole 39, heat is prevented from being transmitted from the stop member 38 to the lens holder 29, since the stop member 38 is separated from the lens holder 29. Therefore, the positional fluctuation in light-converging point P1 of the laser light L1 during laser processing can be suppressed to a low level.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Nanocomposite photonic structures for solid state lighting
InactiveUS7259400B1Quality improvementHigh color rendering indexDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesPhosphorNanoparticle
A photonic structure for “white” light generation by phosphors under the excitation of a LED. The photonic structure mounts the LED and an optically transparent nanocomposite matrix having dispersed therein phosphors which will emit light under the excitation of the radiation of the LED. The phosphors dispersed in the matrix may be nanocrystalline, or larger sized with the addition of non light emitting, non light scattering nanoparticles dispersed within the matrix material so as to match the index of refraction of the matrix material to that of the phosphors. The nanocomposite matrix material may be readily formed by molding and formed into a variety of shapes including lenses for focusing the emitted light. A large number of the photonic structures may be arranged on a substrate to provide even illumination or other purposes.
Owner:NANOCRYSTAL LIGHTING
Photosensitive paste, a plasma display, and a method for the production thereof
InactiveUS6197480B1Reduce processDeformation MinimizationPhotography auxillary processesCoatingsInorganic particleDisplay device
To provide a photosensitive paste that permits pattern formation with a high aspect ratio and a high accuracy and to provide a plasma display including the photosensitive paste, by using a photosensitive paste that includes, as essential components, an inorganic particles and an organic component that contains a photosensitive compound with the difference between the average refractive index of the organic component and the average refractive index of the inorganic particles being 0.1 or less.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
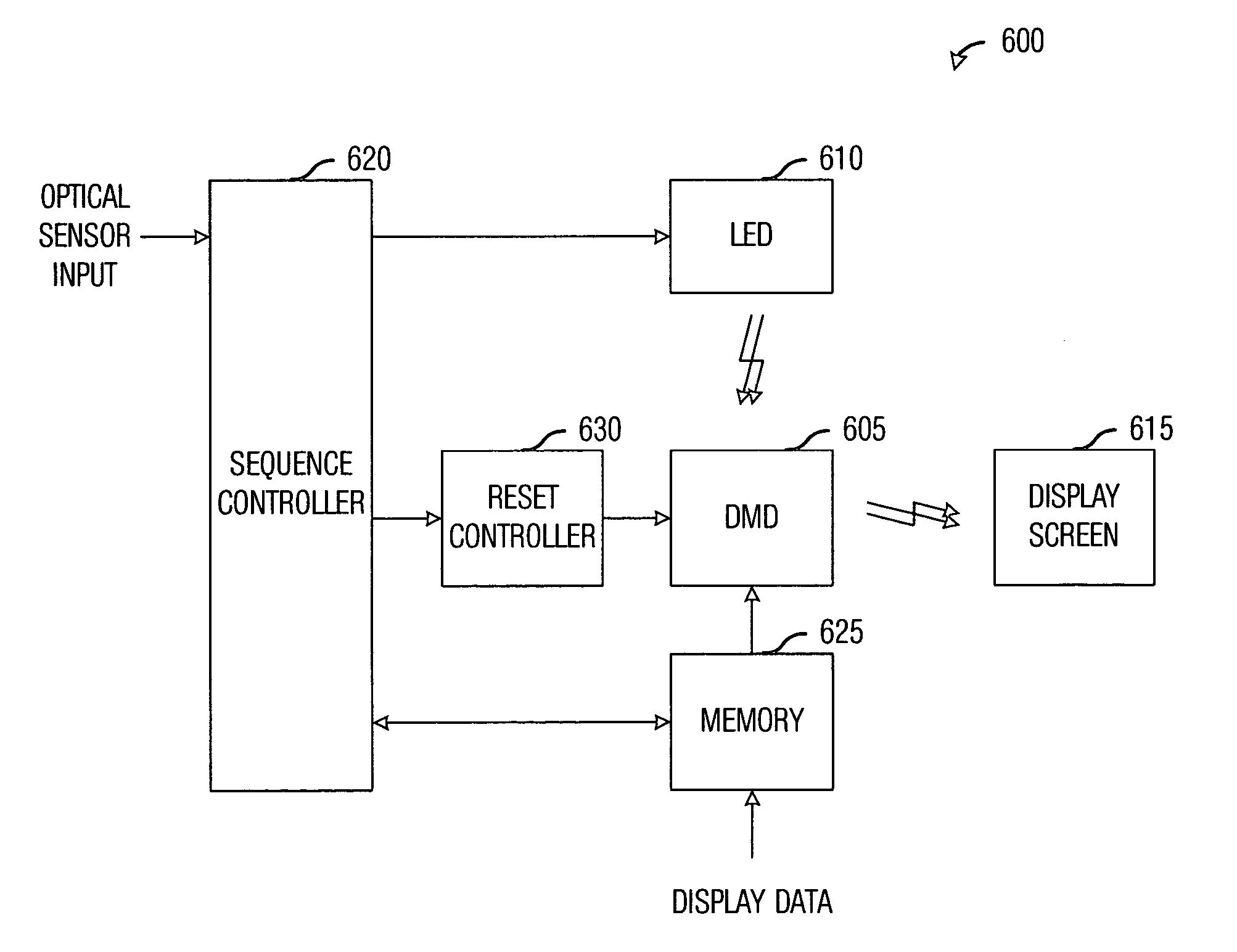
Light-emitting diode (LED) illumination in display systems using spatial light modulators (SLM)
InactiveUS20070013871A1Quick switchEasy to adjustProjectorsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorImage quality
System and method for enhancing performance in an SLM display system using LED illumination. A preferred embodiment comprises computing a set of spectral characteristics, analyzing the set of spectral characteristics, and modulating a light produced by a light source of a display system based upon the analysis, wherein the light source comprises one or more light-emitting diodes. The spectral characteristics can provide information regarding either the images being displayed by the display system or an operating environment of the display system. Either can have an impact upon the quality of the images being displayed on the display system and can be used to make adjustments to the light source.
Owner:MARSHALL STEPHEN WESLEY +1
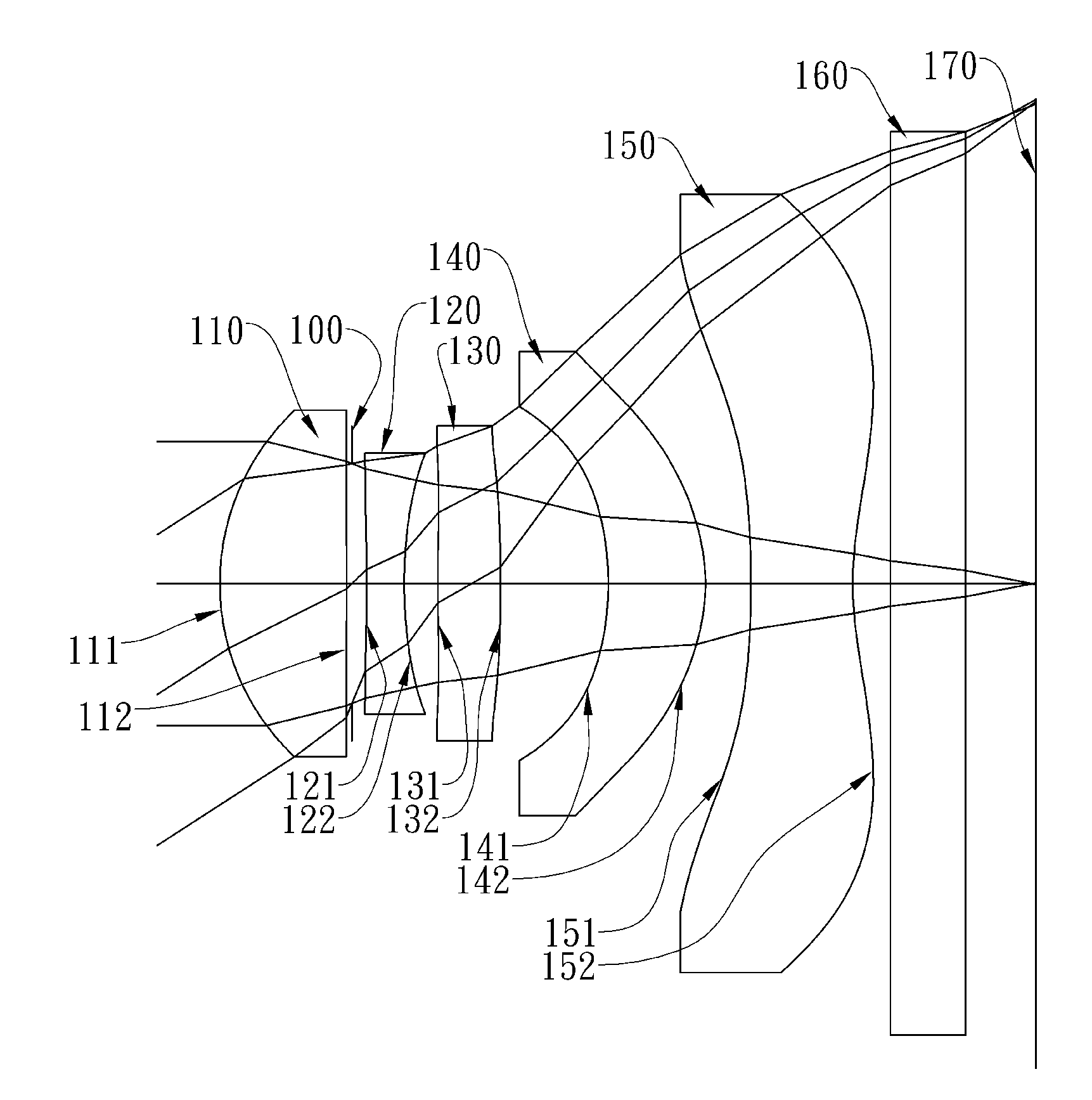
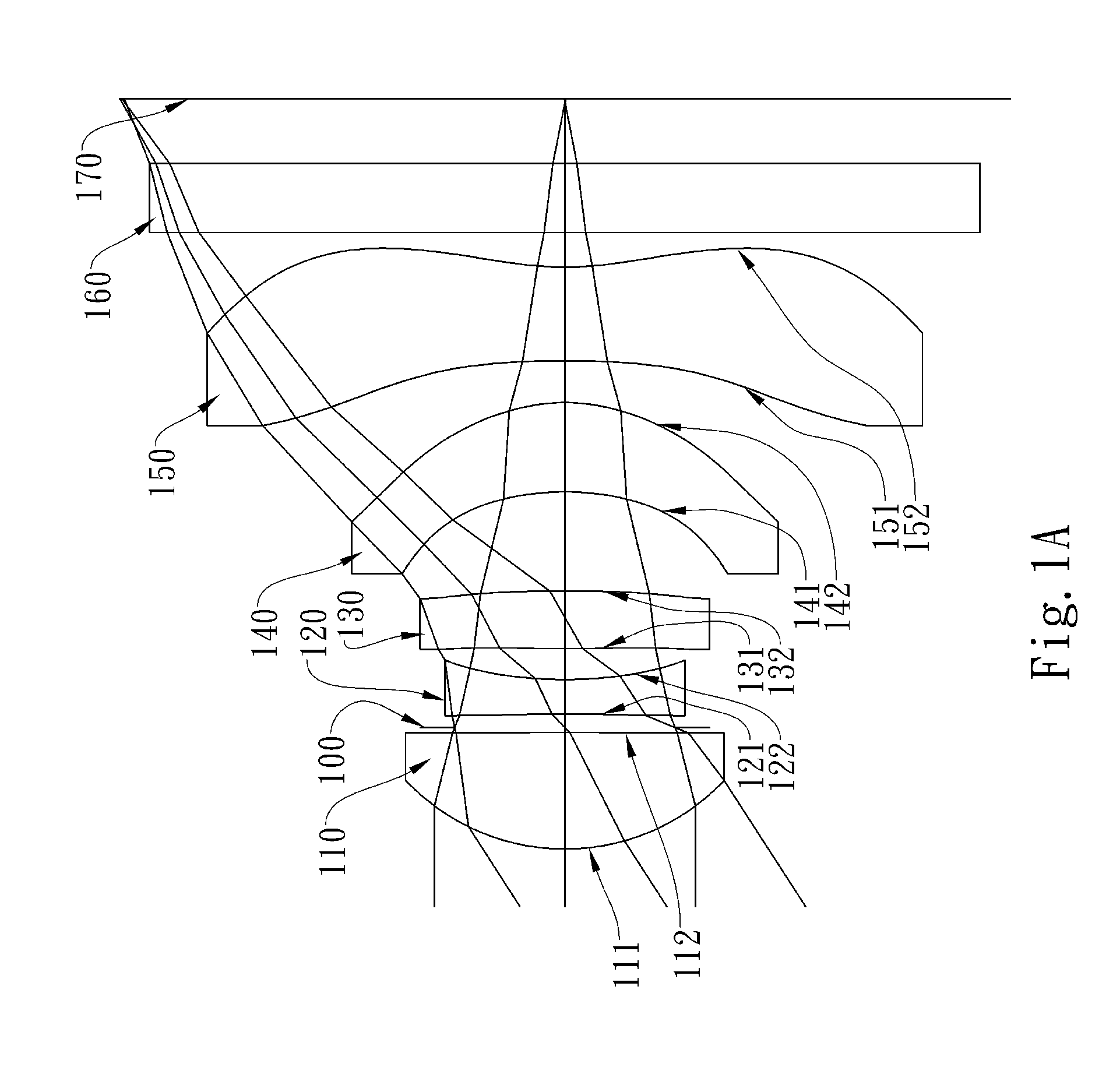
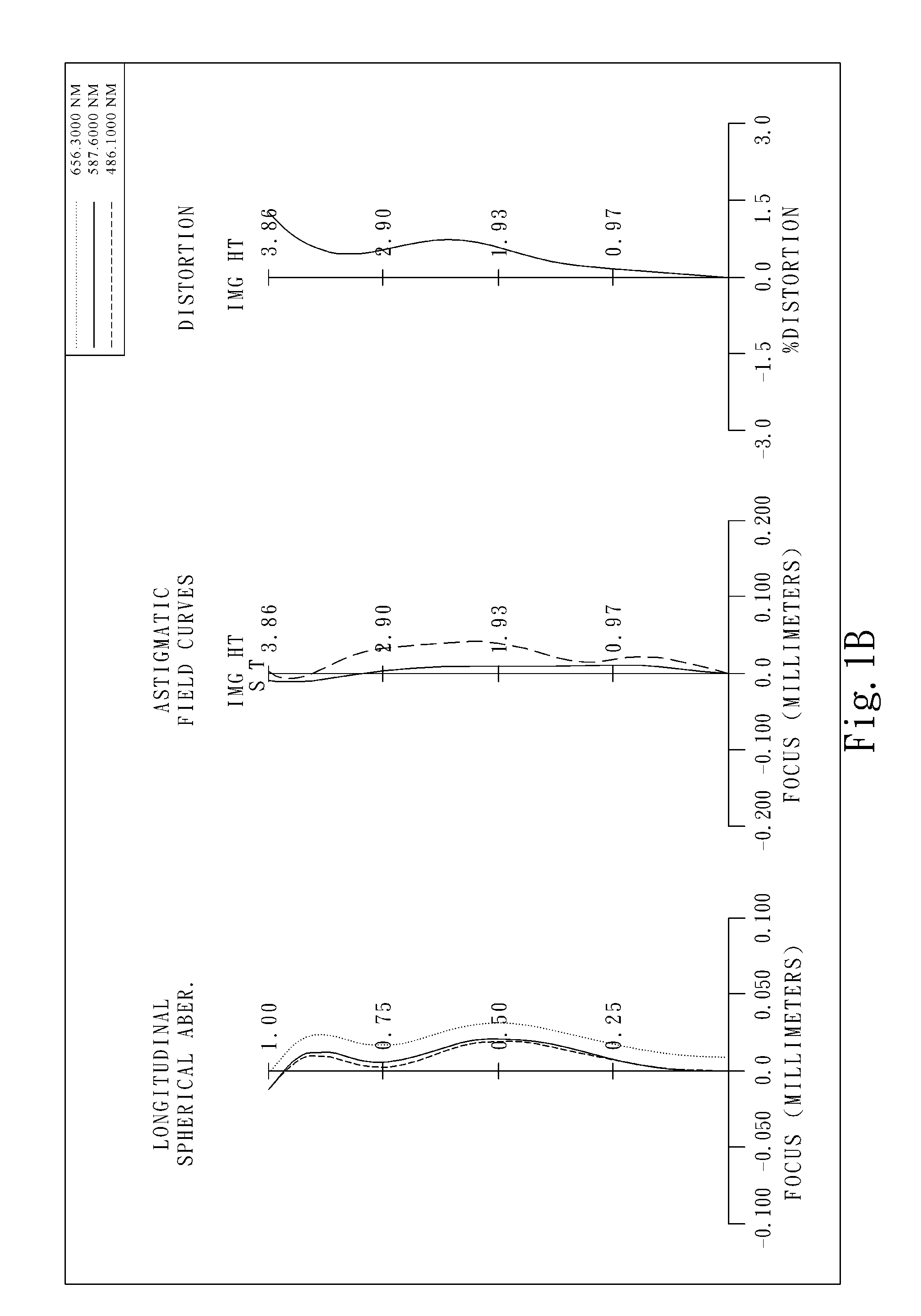
Optical lens system
The present invention provides an optical lens system comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element; and a fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric and at least one inflection point being formed on the image-side surface. Such arrangement of optical elements can effectively minimize the size of the optical lens system, lower the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Wavelength conversion chip for use with light emitting diodes and method for making same
InactiveUS20080042153A1Improve conversion efficiencyShorten the counting processElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotometryOptical coatingElectrical connection
A wavelength conversion chip is formed by depositing a wavelength conversion material on a substrate to form a layer, removing the resulting wavelength conversion layer from the substrate and then segmenting the wavelength conversion layer into a plurality of wavelength conversion chips. The wavelength conversion material can be annealed by thermal annealing or radiation annealing to increase the wavelength conversion efficiency of the chips or to sinter the wavelength conversion material to form a ceramic material. Optical coatings, vias, light extraction elements, electrical connections or electrical bond pads can be fabricated on the wavelength conversion chips.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Blade insert illuminator
ActiveUS8088066B2Maximize light transferReduce light lossEndoscopesSurgical field illuminationPlastic materialsEngineering
An air gap retractor illumination system includes any suitable retractor such as a McCulloch with a channel in the blade to accommodate an air gap illuminator. The illuminator is preferably made from a suitable light conducting plastic material such as acrylic or polycarbonate or silicone. The illuminator has active portions in which light passes and inactive or dead zones in which light does not pass as a result of the configuration and orientation of the input, output and surfaces of the illuminator. The illuminator is formed to have an air gap surrounding any active portion of the illuminator extending from the light input to the light output portion. The dead zones may include elements to allow the illuminator to securely engage the retractor. The light output portion of the illuminator contains from two to eight output zones, each zone having specially designed output optical structures that control and direct light to escape the illuminator to shine onto a predetermined area of interest or to form one or more predetermined shapes or footprints.
Owner:INVUITY
Compact optical fingerprint capturing and recognition system
InactiveUS6870946B1Solve bulkyImprove simplicityCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansRecognition systemFingerprint
An apparatus and method for acquiring an image of a patterned object such as a fingerprint including a light refracting device, a focusing lens, a light source, and a biometric circuit for detecting the presence of a patterned object such as a fingerprint at the light refracting device. Incident light from the light source is projected through a light receiving surface of the light refracting device and is directly reflected off an imaging surface. The resulting image is projected through the focusing lens. The focusing lens has a diameter which is larger than the projection of the patterned object through the light refracting device.
Owner:SECUGEN CORP
Optical analysis systems and methods for dynamic, high-speed detection and real-time multivariate optical computing
ActiveUS7623233B2Simple and economical to manufacture and assemble and useReduce noiseRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsOptic lensOptical computing
Multivariate optical analysis systems employ multivariate optical elements and utilize multivariate optical computing methods to determine information about a product carried by light reflected from or transmitted through the product. One method of processing and monitoring the product includes introducing the product at an inspection point; illuminating the product with a spectral-specific light though an optic lens; directing the light that has passed through at least a section of the product through at least one multivariate optical element to produce a first signal, the directed light carrying information about the product; detecting the first signal at a first detector; deflecting a portion of the directed light to produce a second signal in a direction of a second detector, the second detector configured to detect the second signal; and determining at least one property of the product at a rate of about one section of the product per second to about five sections of the product per second based upon the detector outputs.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Patterned color conversion film and display device using the same
ActiveUS20140192294A1Increase utilization ratePoor view angleSpectral modifiersNon-linear opticsQuantum dotQuantum
A patterned color conversion film and a display device using the same are disclosed. The patterned color conversion film of the present invention comprises: a separator with plural openings; and plural pixel units disposed in the openings respectively, each pixel unit respectively comprising: a medium and scattering particles dispersed therein. Herein, at least one of the plural pixel units comprises quantum dots having the scattering particles sized of between 0.05 and 1 μm when a volume concentration of the quantum dots is in a range more than or equal to 5% and less than or equal to 80%, or having the scattering particles sized of between 0.2 and 2 μm when the volume concentration of the quantum dots is in a range less than 5% and more than or equal to 0%.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
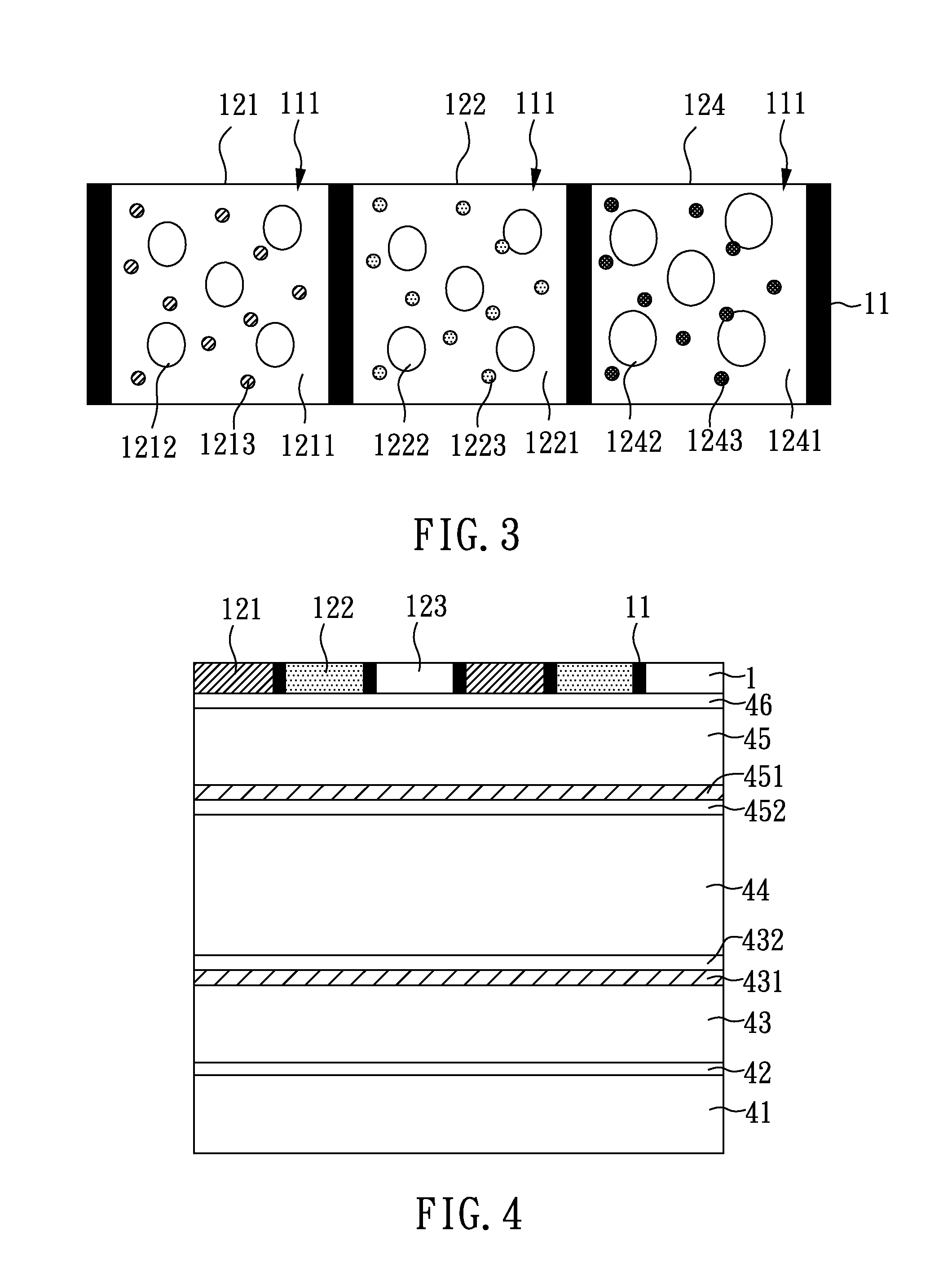
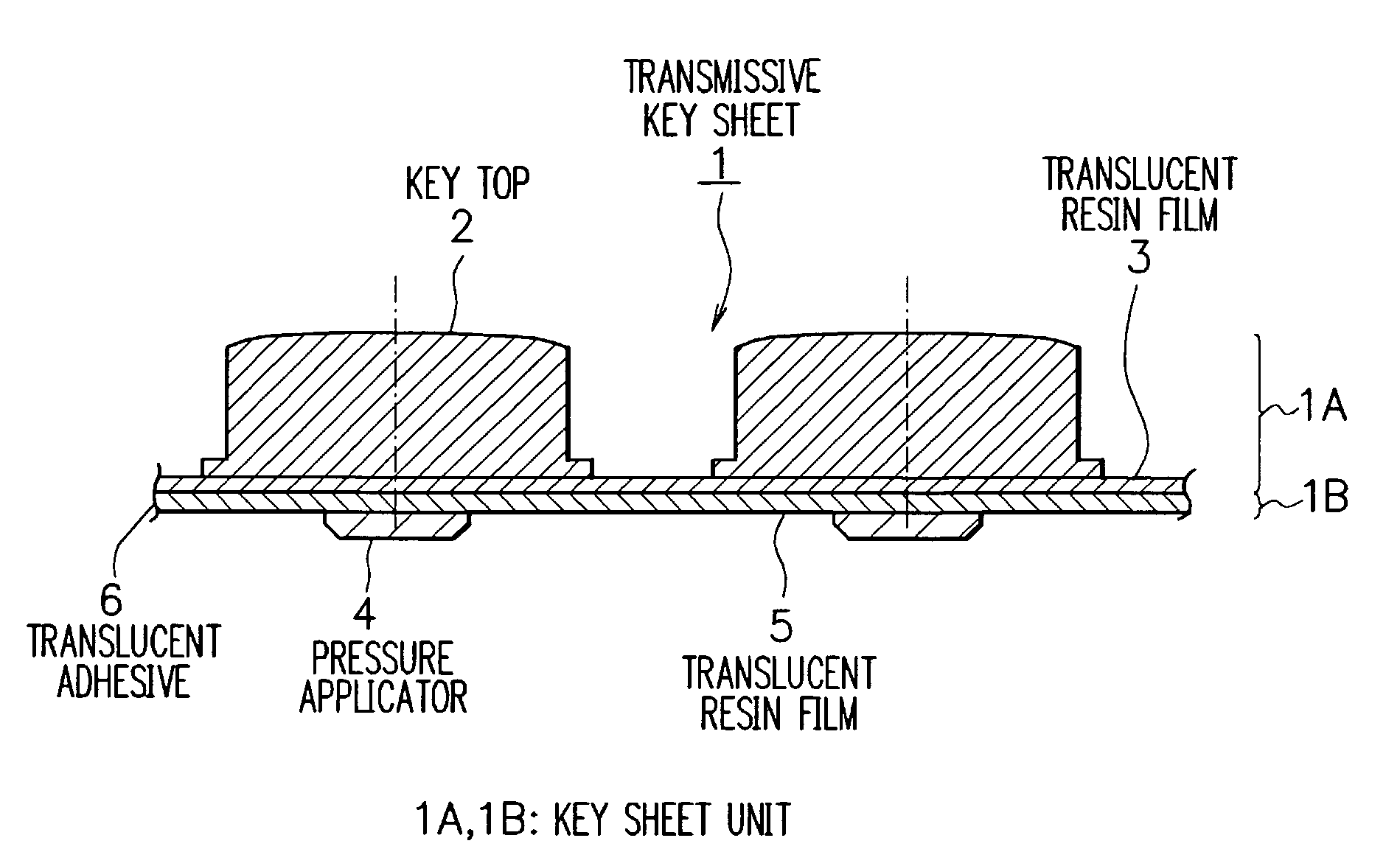
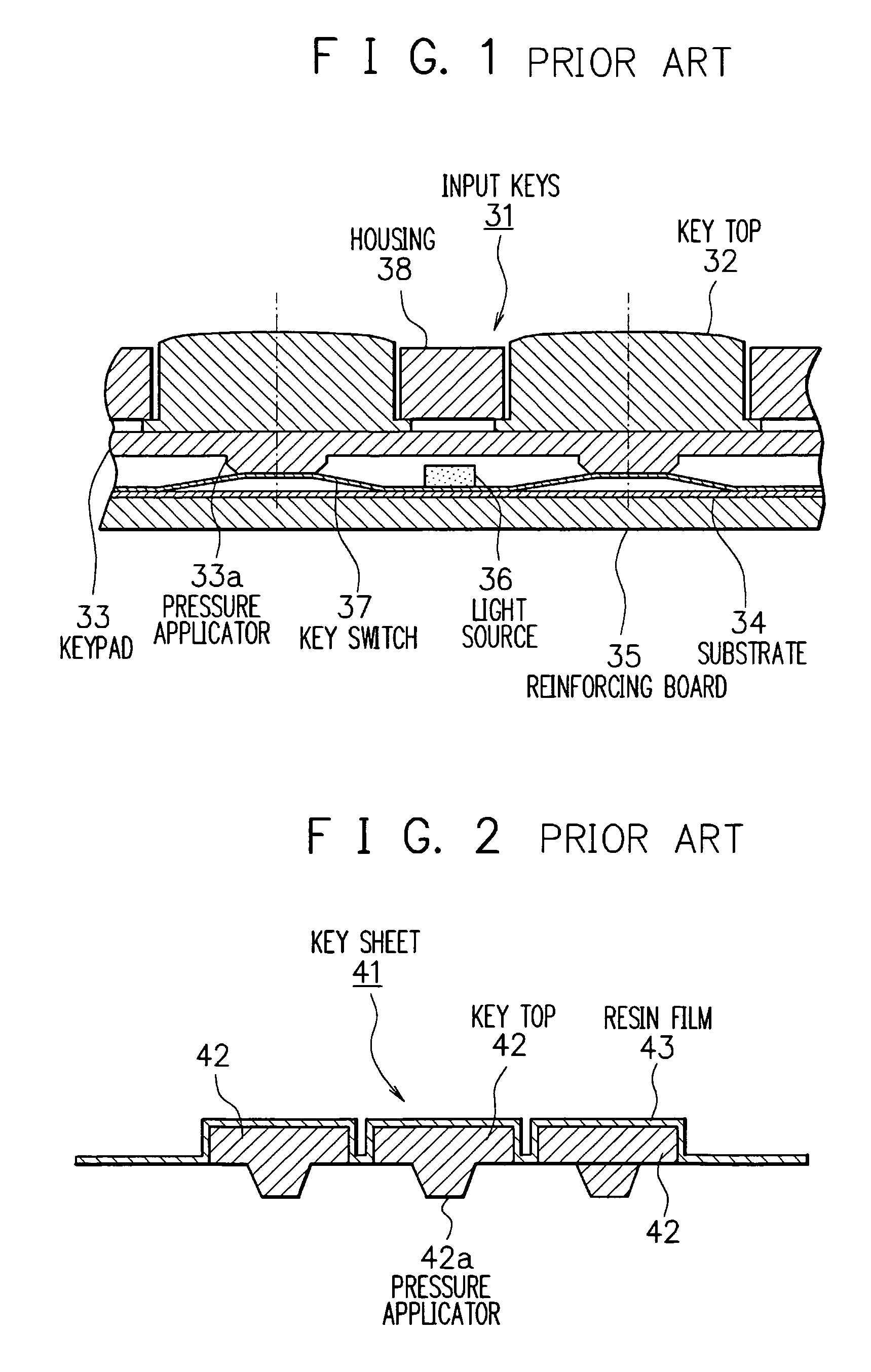
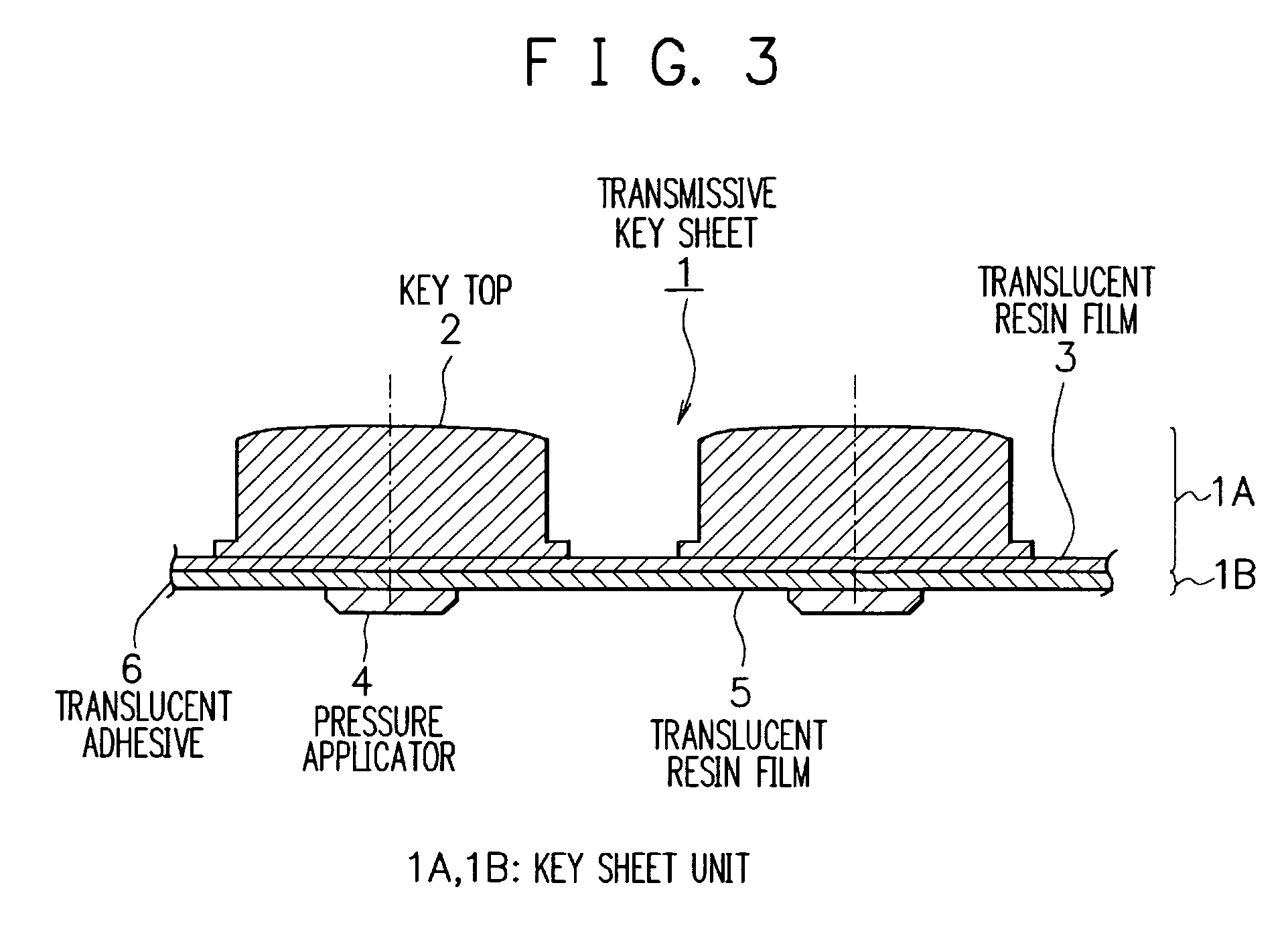
Transmissive key sheet, input keys using transmissive key sheet and electronic equipment with input keys
InactiveUS6977352B2Reduce lightEfficient illuminationEmergency actuatorsContact surface shape/structureAdhesiveEngineering
A transmissive key sheet using translucent resin, which is capable of effective illumination while ensuring the thinness of the entire key sheet as well as suppressing a decrease in light transmission, input keys using the transmissive key sheet, and electronic equipment with the input keys. A transmissive key sheet of input keys comprises a first key sheet unit and a second key sheet unit, the opposite side of the first key sheet unit from key tops and the opposite side of the second key sheet unit from pressure applicators being bonded together with a translucent adhesive. The key tops made of translucent resin are molded integral with a translucent resin film having letters on its under surface to provide the first key sheet unit. The pressure applicators made of translucent resin are molded integral with a translucent resin film to provide the second key sheet unit. The light from a light source on a substrate illuminates keys so that the letters printed on the under surface of the translucent resin film become visible form outside. The pressing of each key top presses a corresponding key switch through the pressure applicator, and the key switch is concavely curved to make a contact with an electrode on the substrate. Thus, key input is provided.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Gas-discharge lamp replacement
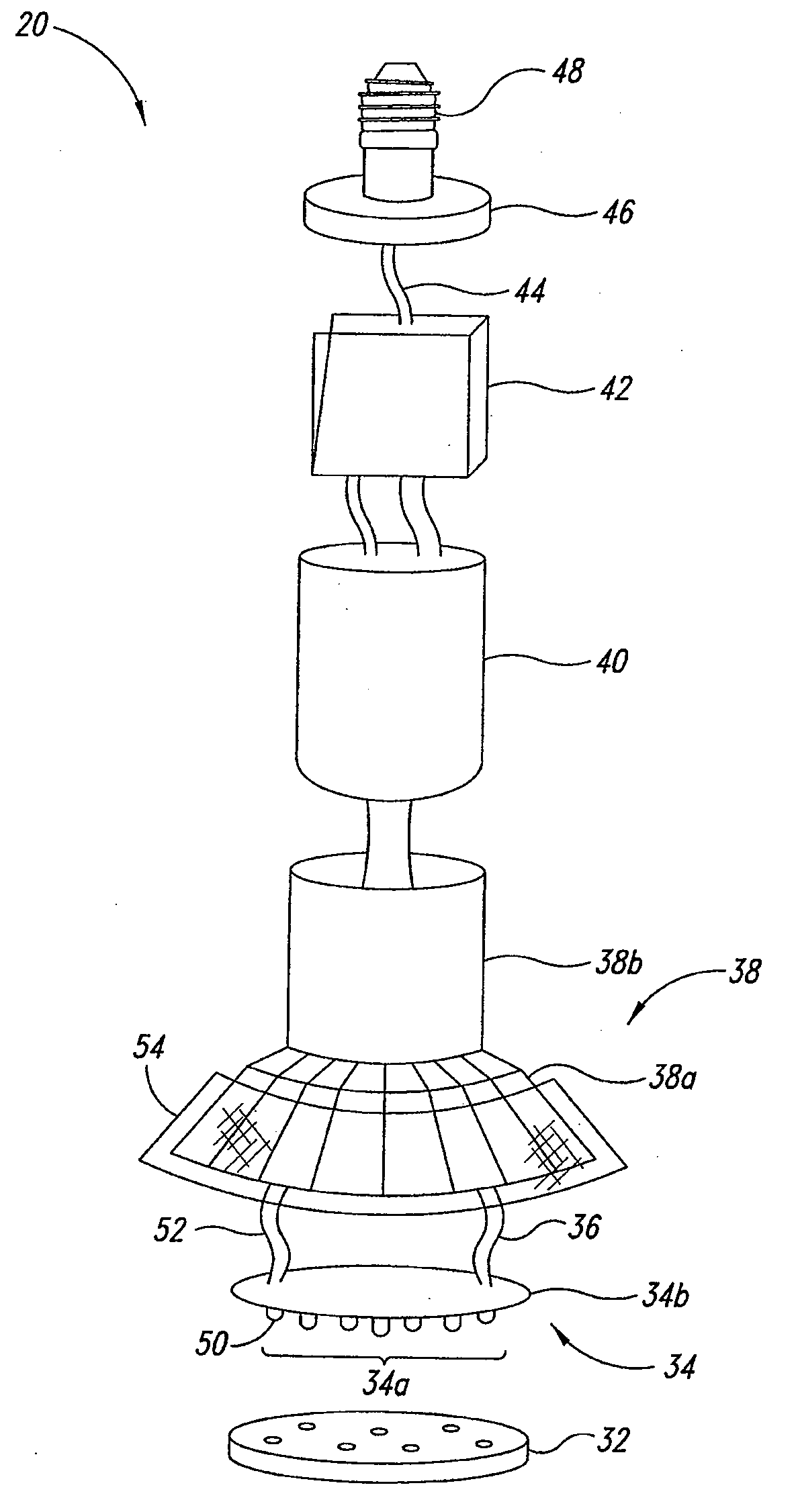
ActiveUS20090284155A1Reduce reflection lossReduce lightPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsGas-discharge lampColor rendering index
An illumination device comprising a housing fixture, a light source, and an active heat transfer device is provided. The housing fixture includes a base adapted to be receivable in a light fixture receptacle configured to receive a gas-discharge lamp. The light source emits light with a color rendering index higher than a respective color rendering index of at least a type of gas-discharge lamp. The active heat transfer device is physically coupled to the light source and mounted to the housing fixture. The active heat transfer device receives power from a power supply to remove thermal energy from the light source.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
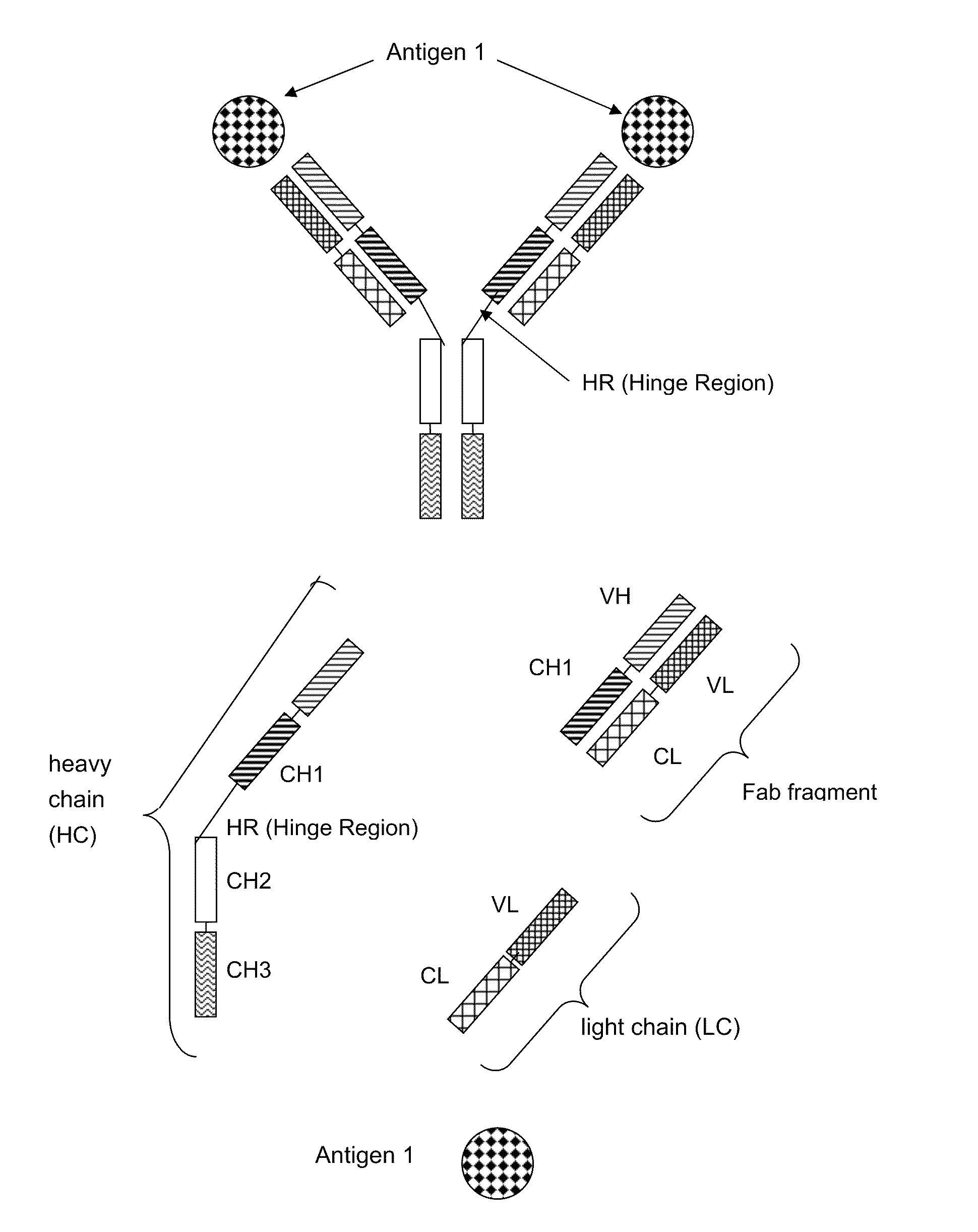
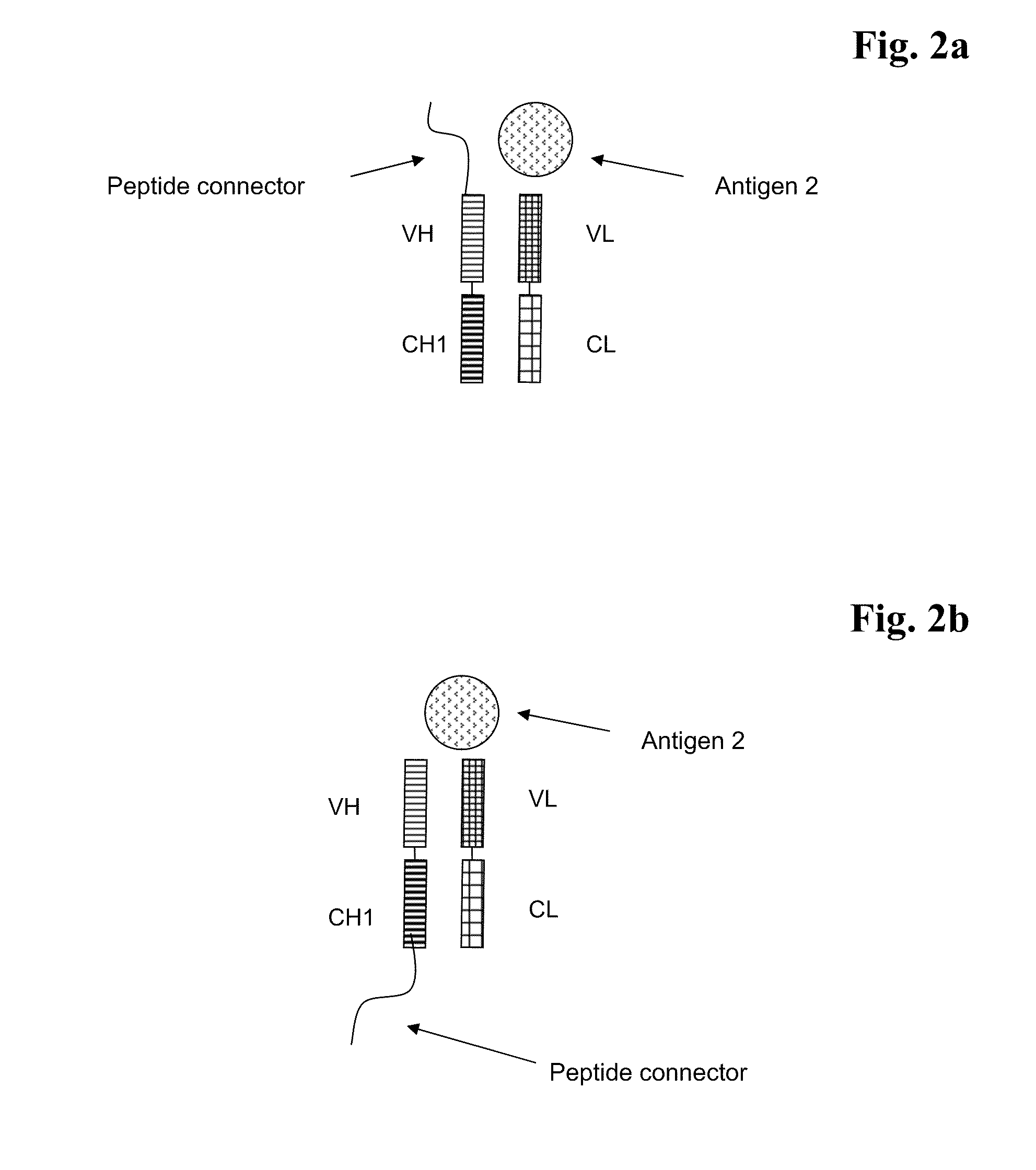
Bispecific Antigen Binding Proteins
ActiveUS20100316645A1Raise the ratioReduce lightAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntigen bindingCancer research
The present invention relates to bispecific antigen binding proteins, methods for their production, pharmaceutical compositions containing said antibodies, and uses thereof.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
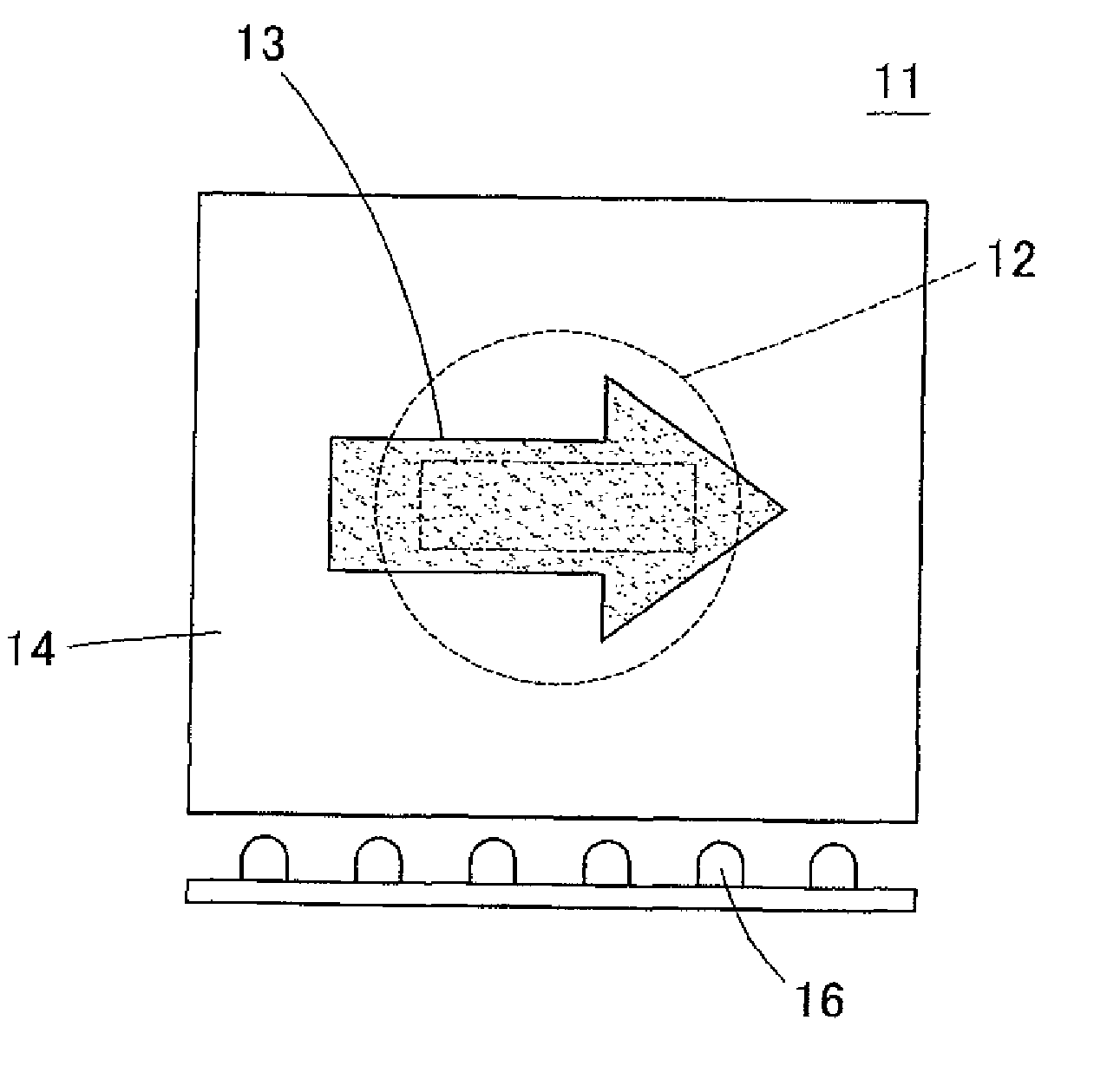
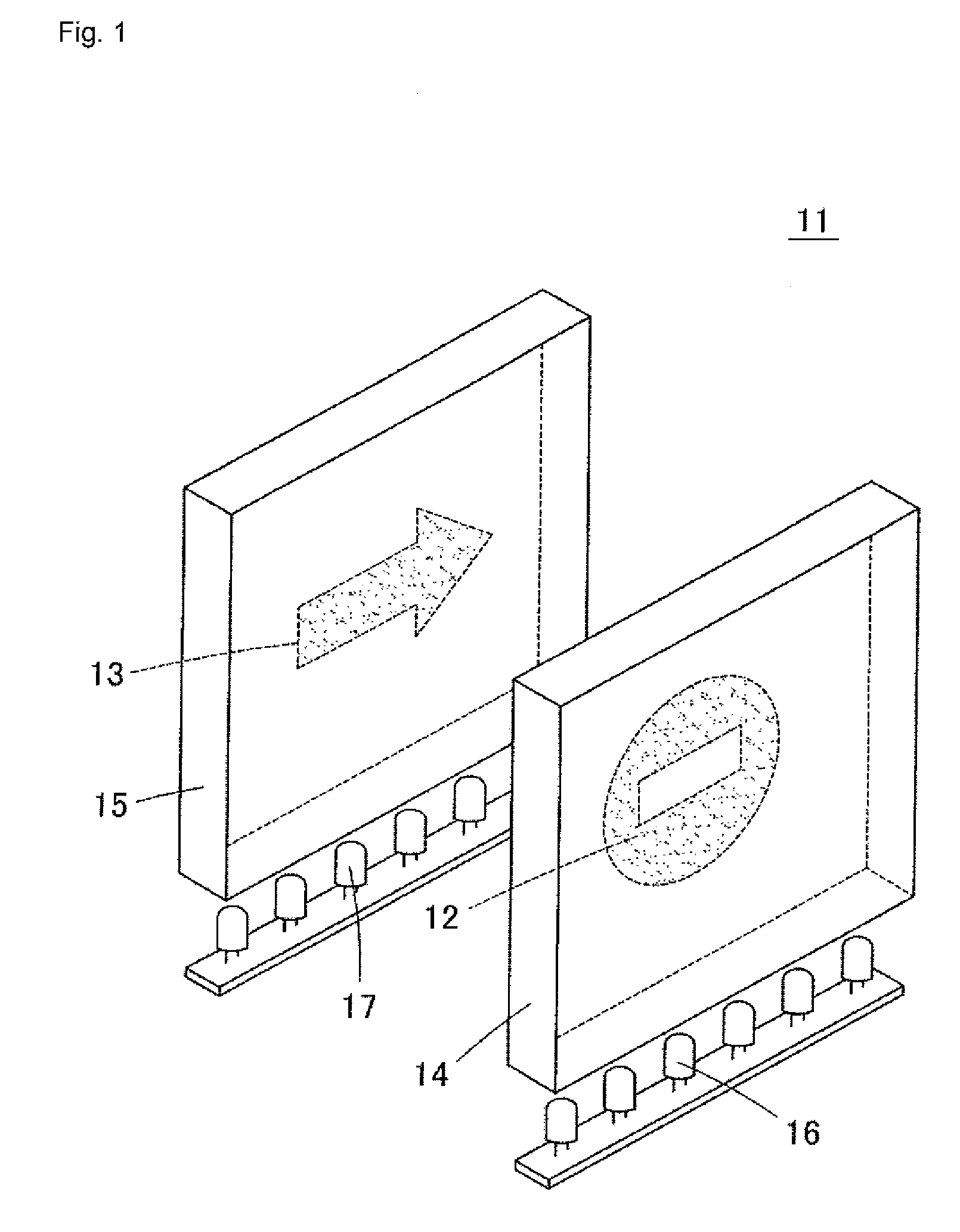
Display device
InactiveUS20090219734A1Big spaceReduce lightPlanar/plate-like light guidesIlluminated signsLight guideDisplay device
A display device has a light guide plate formed with a display pattern by a plurality of diffusion dots having translucency in a display pattern formed region, a light shielding layer, and a light source. A plurality of the light guide plates are arranged facing each other, and the light shielding layer is sandwiched between the light guide plates. Light from the light source is selectively introduced to one of the light guide plates to display the display pattern of the light guide plate. The light shielding layer has a surface facing an observer's side formed by a low reflectivity material and a surface facing a side opposite to the observer's side formed by a high reflectivity material. A region facing the display pattern of the light guide plate positioned on the side opposite to the observer's side than the light shielding layer is cut out.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com