Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
183results about How to "Reduce light scatter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LED light assembly having heating board
InactiveUS7914162B1Reduce the impactAvoid insufficient heatingPlanar light sourcesFurnace componentsMicrocontrollerEngineering
A light assembly including a housing, a plurality of light emitting diodes (LED) on a circuit board, a lens, a lens cover and a heating board positioned within the housing. The heating board is positioned behind the lens and in front of LEDs within the housing, such that light from the LEDs shines through the heating board. The heating board also includes a sensor and a microcontroller to activate, deactivate and control the heating board in response to an outside air temperature.
Owner:GRAND GENERAL ACCESSORIES LLC
Multi-assay plate cover for elimination of meniscus
InactiveUS6074614AEliminate the problemHigh optical clarityChemical analysis using titrationWithdrawing sample devicesAssayOptical axis
A constant pathlength multi-assay plate cover for multi-assay plates, comprising, a flat top side and a flat bottom side, the bottom side having solid cylindrical projections of equal length extending downwardly from the flat bottom side, wherein each cylindrical projection is centered about the optical axis passing through a corresponding sample well of a multi-assay plate, thereby eliminating the meniscus and evaporation effects.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
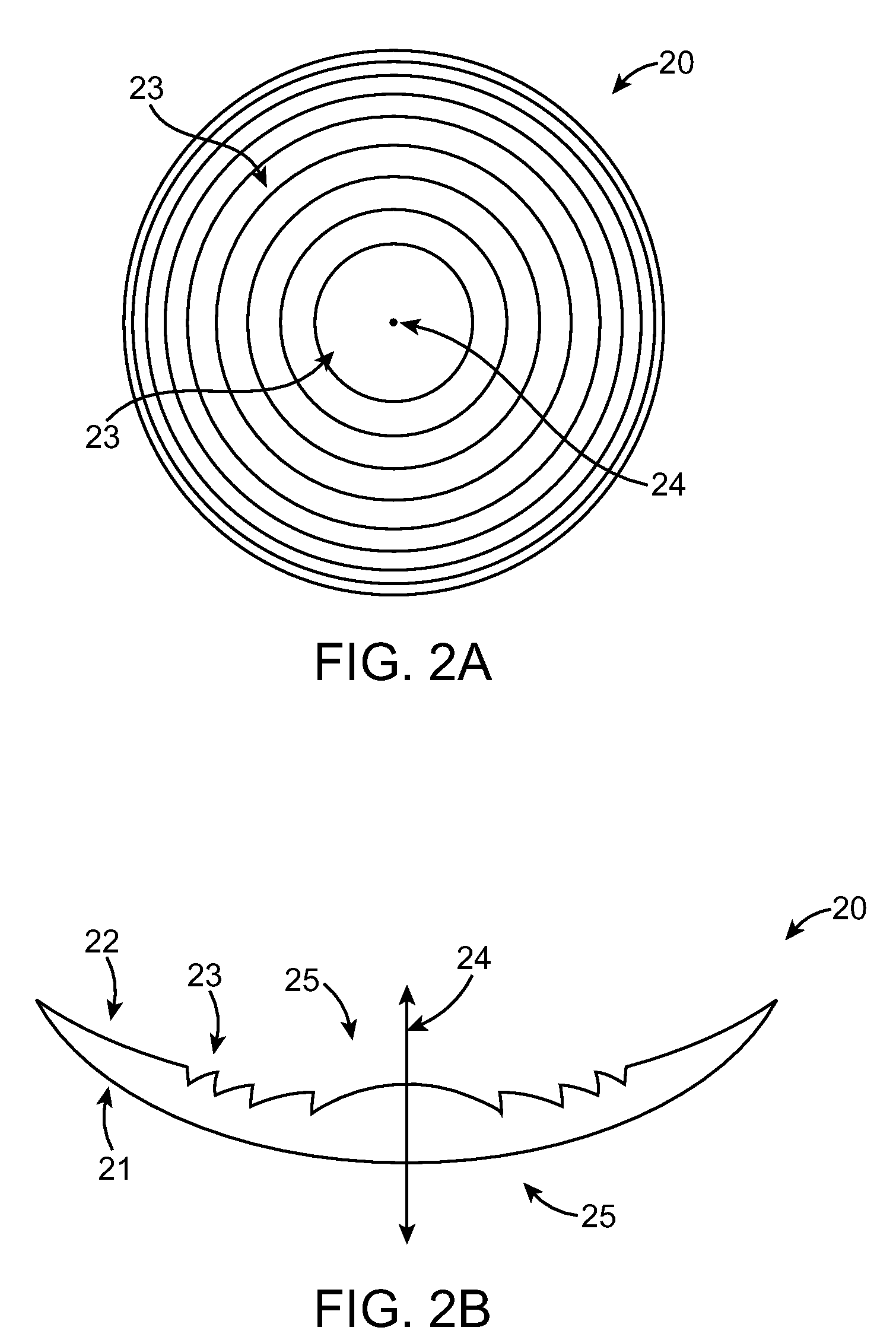
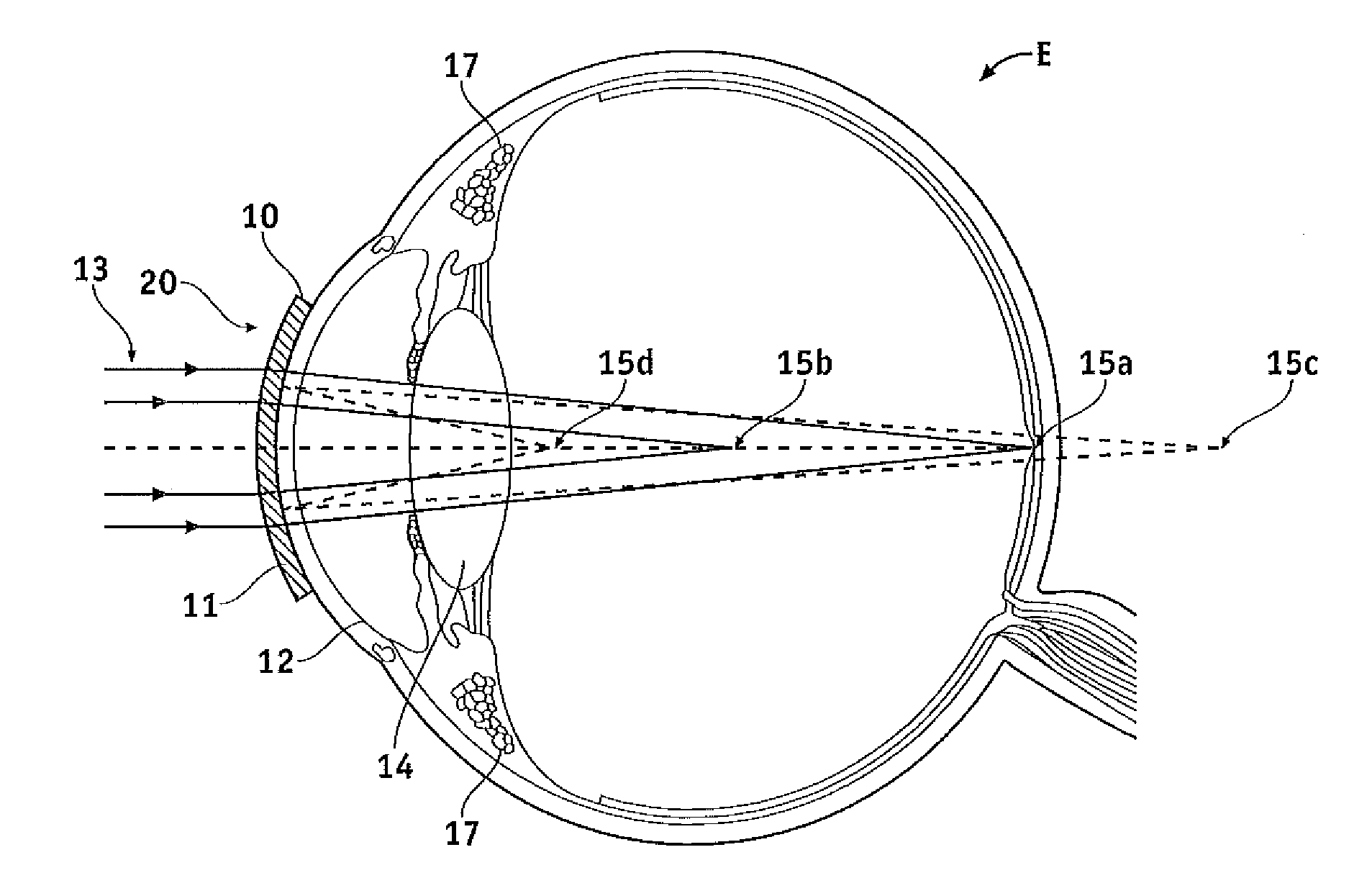
Diffractive multifocal lens having radially varying light distribution
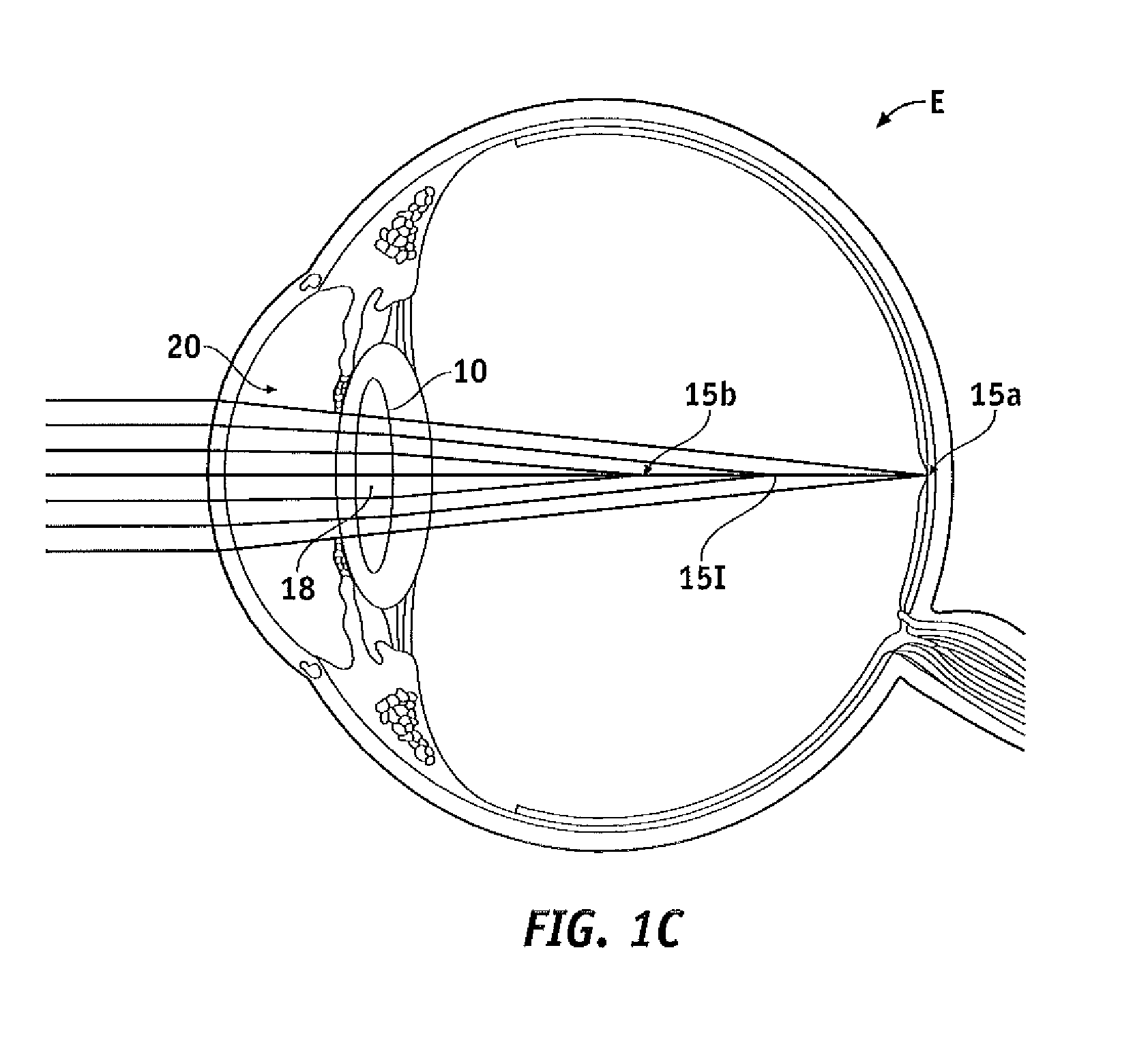
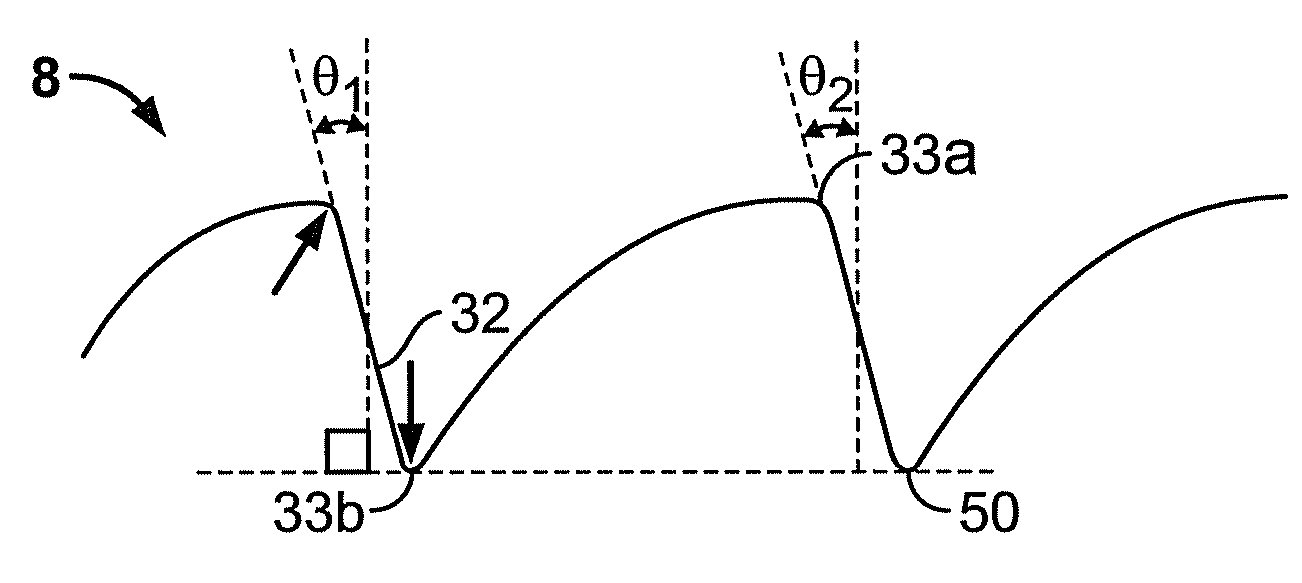
ActiveUS7871162B2Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyEye lens
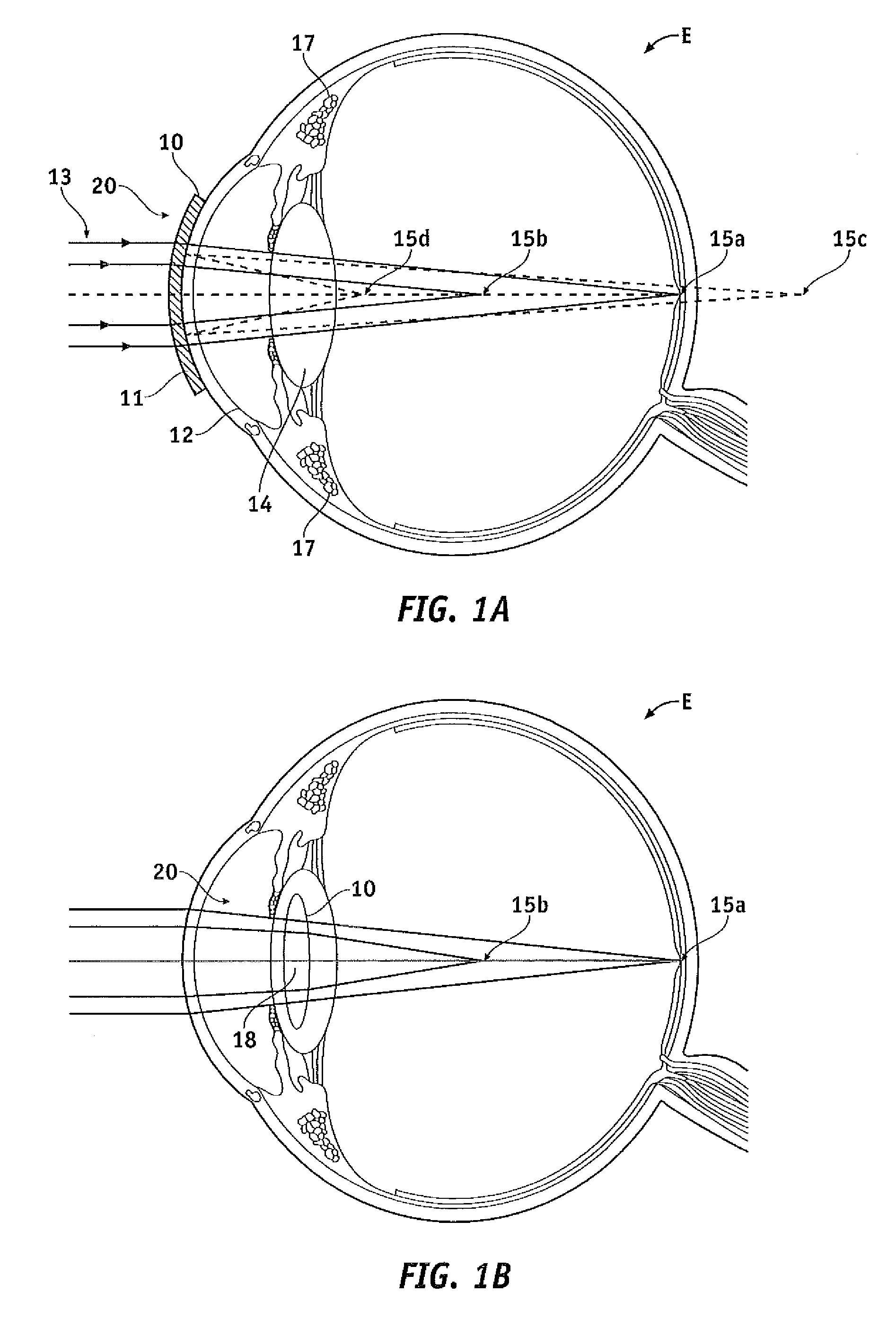
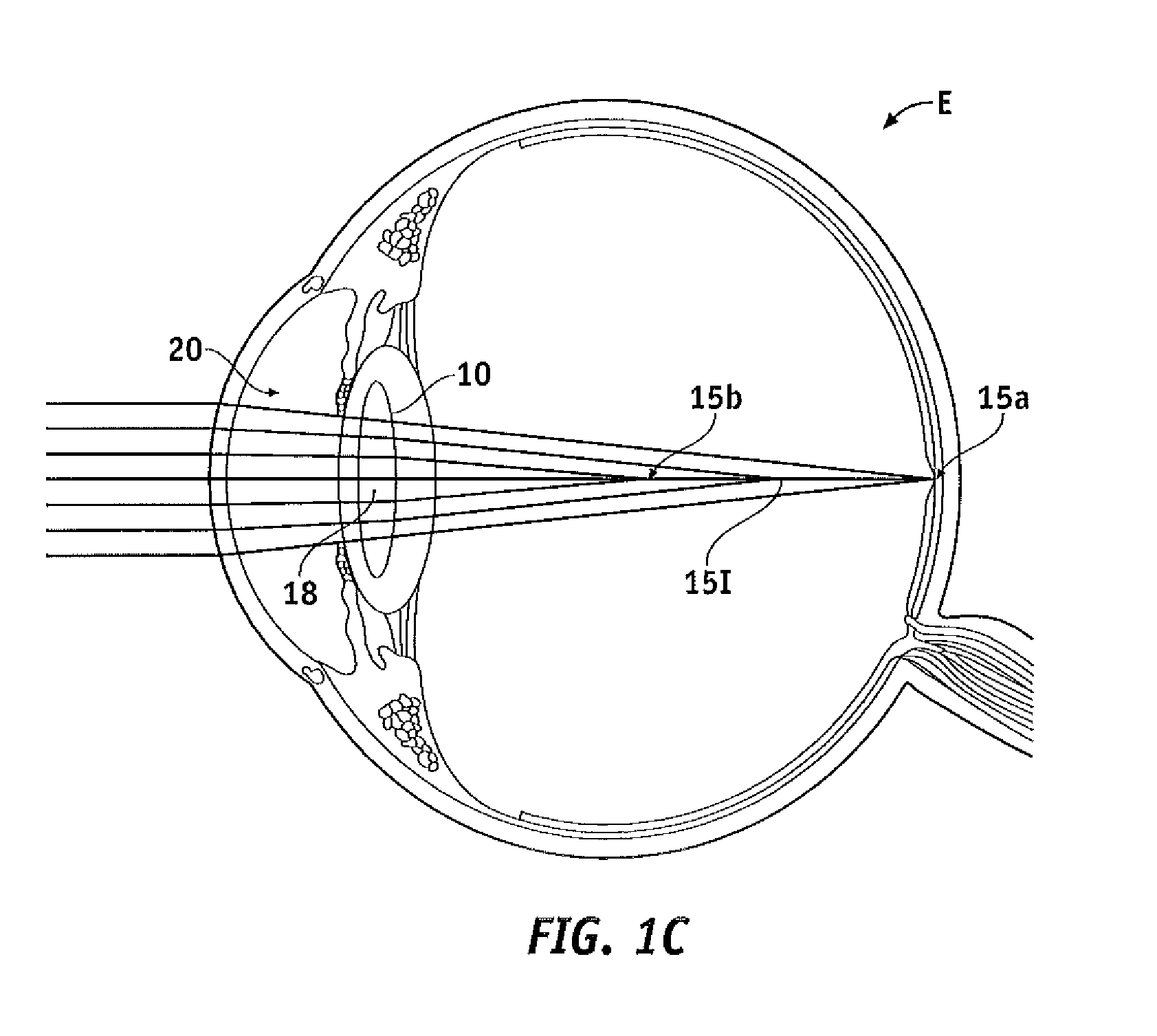
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter and / or improved light energy distribution properties are provided. These properties are provided by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlely shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Light scatter may be generated by the sharp corners associated with vertical steps between adjacent conventional diffractive echelettes. Smooth diffractive profiles of the invention reduce light scatter. Light energy directed towards non-viewing diffractive orders may have a unwanted effects on vision quality. Diffractive profiles of the invention may limit the light energy in certain, selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of the invention can also vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Optical detection system
InactiveUS6759662B1Reduce dispersionReduce light scatterPhotometryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotodetectorOpto electronic
An optical detection system comprising an electromagnetic radiation source, a source radiation focusing and collimating means, a photodetector, an emitted radiation focusing means and a source radiation blocking panel. The radiation source is used to direct source radiation onto a sample which is disposed in a sample platform. The source radiation focusing and collimating means is disposed between the radiation source and the sample for focusing and collimating the source radiation onto the sample. The photodetector is adapted for receiving radiation emitted from the sample which has been focused by the emitted radiation focusing means. The source radiation blocking panel, disposed between the source radiation focusing and collimating means and the sample, is unique in that it is capable of reducing light scattering and interference, such that a clear signal from each individual sample can be obtained by the photodetector.
Owner:CE RESOURCES
Carbon Nanotube Dispersed Polar Organic Solvent and Method for Producing the Same
ActiveUS20070224106A1Effective dispersionAvoid regroupingMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesOrganic solventCarbon nanotube
In the present invention, a nonionic surfactant is noticed for a function of dispersing a carbon nanotube, and it is found that a mixture solution of an amide-based organic solvent and a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) or of the amide-based organic solvent, the nonionic surfactant, and the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) has an excellent function as a dispersant for the carbon nanotube. Ultrasonication is required for dispersing a carbon nanotube in the dispersant. The ultrasonication maybe carried out in the step of dispersing the carbon nanotube in the nonionic surfactant and / or the amide-based polar organic solvent, and then the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) may be mixed with the resultant dispersion. Alternatively, a mixture solution of the nonionic surfactant and / or the amide-based polar organic solvent, and the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is prepared, and then the ultrasonication may be carried out in the step of dispersing the carbon nanotube therein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Light-emitting devices utilizing nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050215164A1Improve light extractionReduce light scatterDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesNanoparticleRefractive index
Light-emitting devices are disclosed that comprise a light source emitting first light, a first material substantially transparent to and located to receive at least a portion of the first light, and particles of a second material dispersed in the first material. The second material has an index of refraction greater than an index of refraction of the first material at a wavelength of the first light. The particles of the second material have diameters less than about this wavelength. Particles of a third material may also be dispersed in the first material.
Owner:LUMILEDS
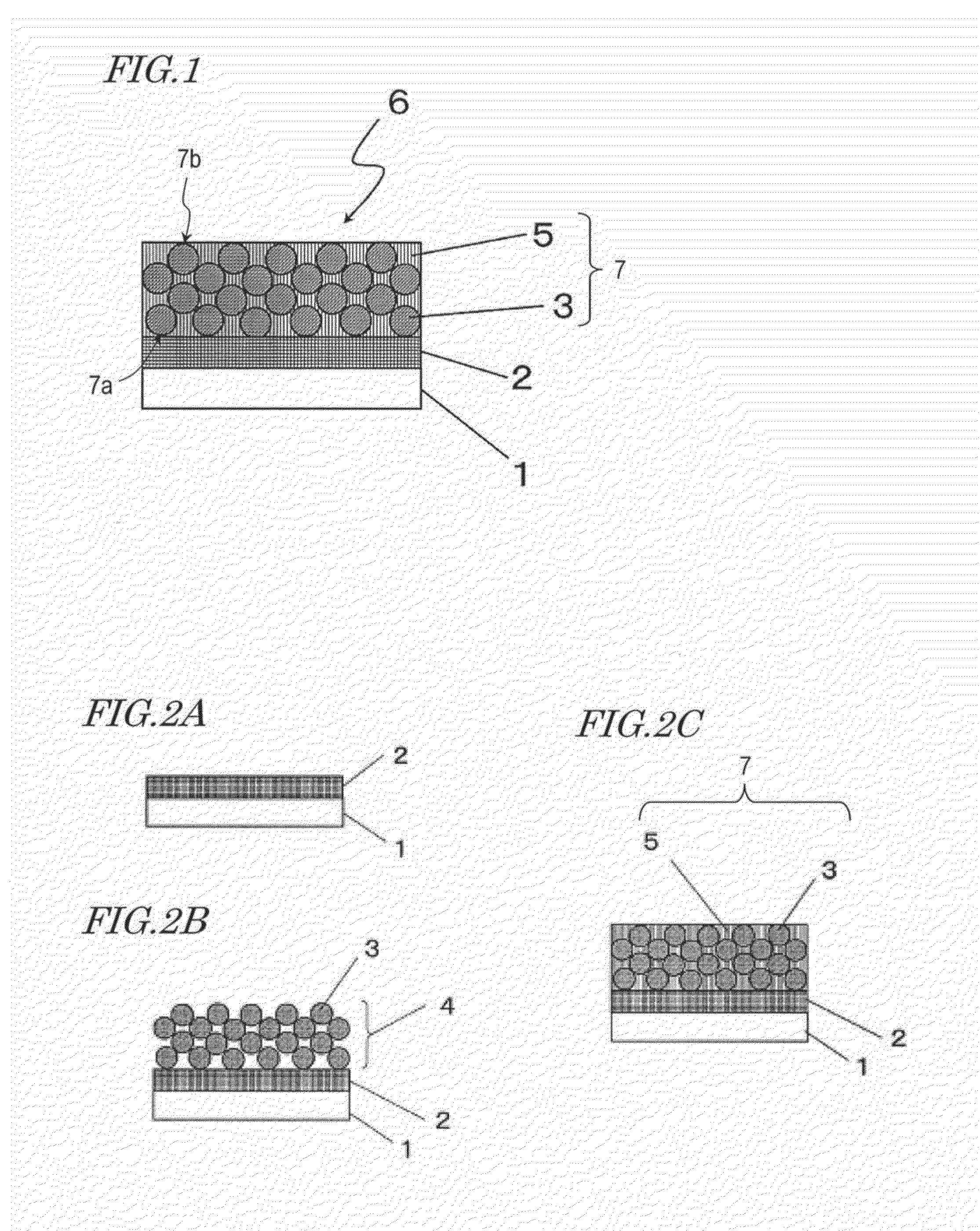
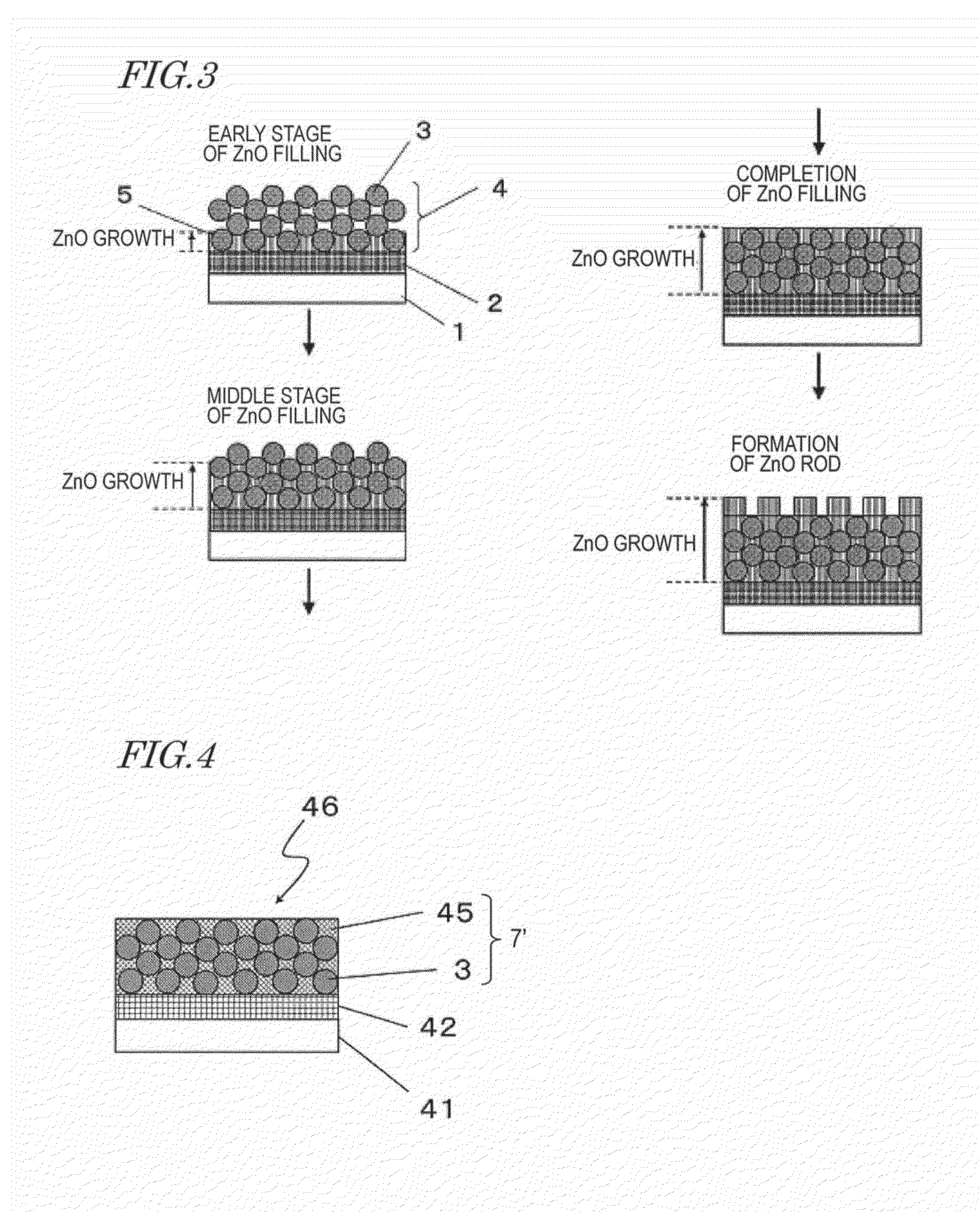
Wavelength conversion element, method of manufacturing the same, and LED element and semiconductor laser light emitting device using wavelength conversion element
ActiveUS20140071683A1Improve light outputImprove heat resistanceSolid-state devicesGlass/slag layered productsPhosphorSingle crystal
A wavelength conversion element disclosed in the present application includes a phosphor layer including a plurality of phosphor particles and a matrix that is located among the plurality of phosphor particles and is formed of zinc oxide. The zinc oxide is columnar crystals or a single crystal in a c-axis orientation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Diffractive Multifocal Lens Having Radially Varying Light Distribution
ActiveUS20090268158A1Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyVisual perception
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter and / or improved light energy distribution properties are provided. These properties are provided by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlely shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Light scatter may be generated by the sharp corners associated with vertical steps between adjacent conventional diffractive echelettes. Smooth diffractive profiles of the invention reduce light scatter. Light energy directed towards non-viewing diffractive orders may have a unwanted effects on vision quality. Diffractive profiles of the invention may limit the light energy in certain, selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of the invention can also vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
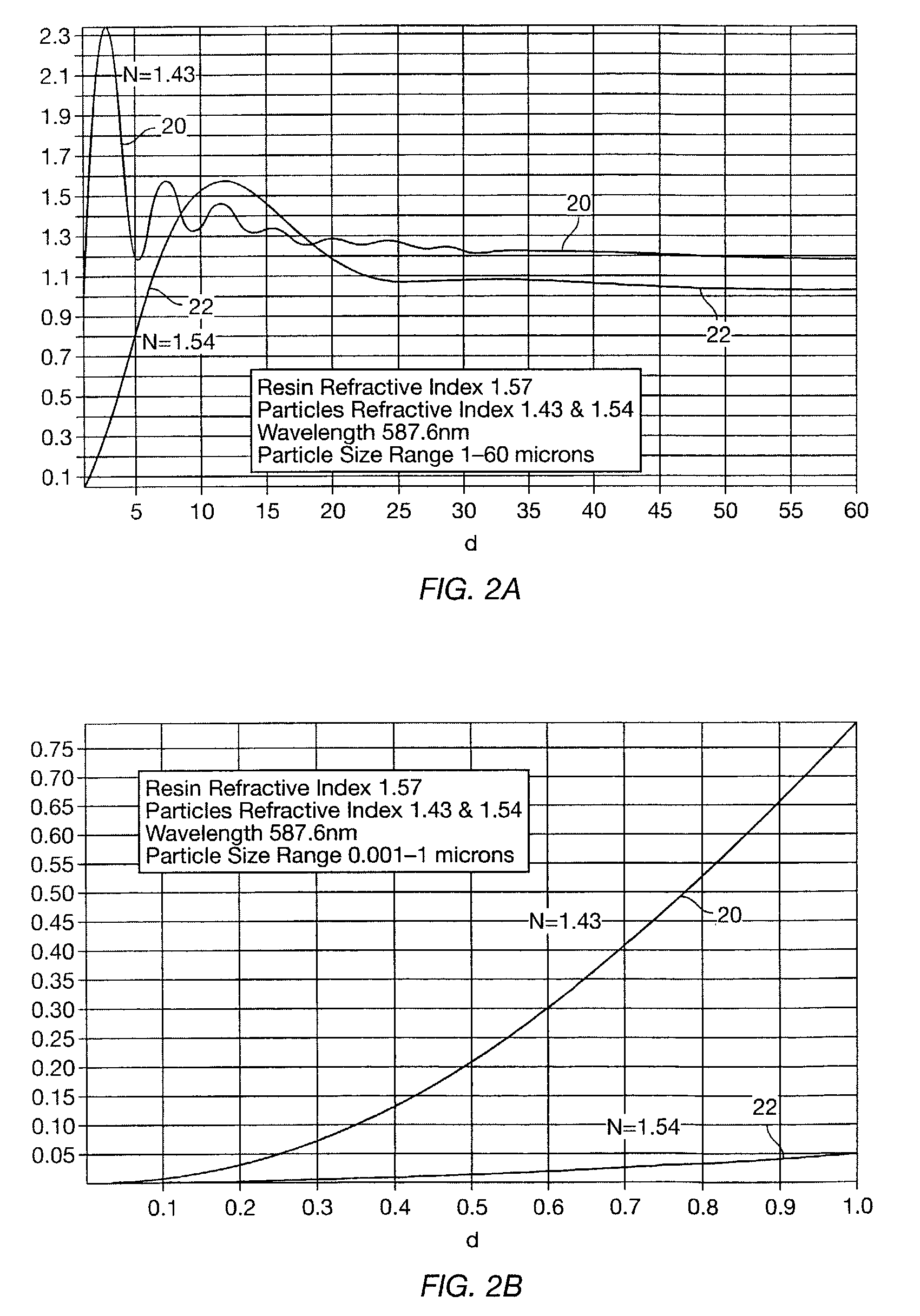
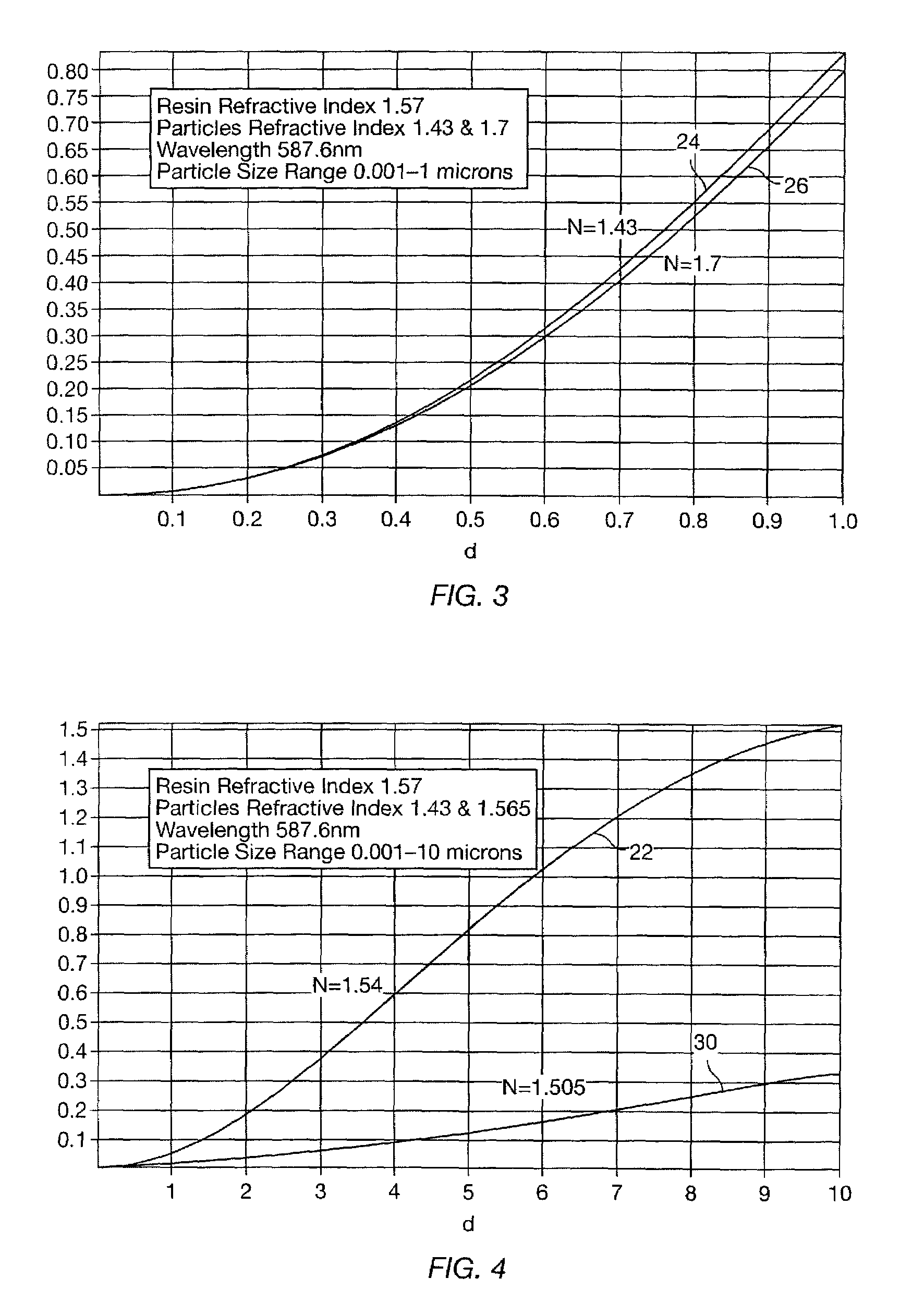
Optical polymer blend with bimodal particle sizes
ActiveUS6979704B1Reduce CTEReduce light scatterMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresAdhesiveOptical polymers
An optical polymer blend includes sub-wavelength particles to modify the refractive index of a polymer to match the refractive index of micro-particles added to adjust the bulk coefficient of thermal expansion of the blend. A relatively large amount of material may be added to the resin to adjust the bulk coefficient of thermal expansion without unduly increasing the viscosity of the blend before setting. In some applications blends are used for molded or extruded optical elements, in other applications, blends are used for optical adhesives with low coefficients of thermal expansion.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Diffractive lens exhibiting enhanced optical performance
ActiveUS8231219B2Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsLight energyEye lens
The present invention provides improved ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use. Monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses having reduced light scatter, improved light energy distribution properties, and / or other improvements in optical performance are provided. These properties are provided, at least in part, by the diffractive profiles of the invention, often having subtlety shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Smooth diffractive profiles may be used reduce light scatter. Diffractive profiles may be configured to limit the light energy in certain selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles of may additionally or alternatively vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Absorbent article with indicator
An absorbent article such as a disposable diaper is provided with an indicator adapted to become visible as soon as bodily fluid is discharged. The indicator is formed from a composite nonwoven fabric composed of a hydrophilic melt blown nonwoven fabric layer and a hydrophilic spun bond nonwoven fabric layer on which a display element is depicted and laminated on one surface of the hydrophilic melt blown nonwoven fabric layer. A first surface of the composite nonwoven fabric facing an absorbent core of the diaper is held together with the display element and a second surface of the composite nonwoven fabric facing a backsheet of the diaper is held in close contact with the inner surface of the backsheet. The display element is covered up by the composite nonwoven fabric in its dry state covers up and the display elements become visible from the outside of the backsheet through the nonwoven fabric as soon as the nonwoven fabric is wetted with bodily fluids.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Reflection barrier for panoramic display
ActiveUS7012669B2Good colorNo seamsTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsProjection screenPartial reflection
Owner:EVANS & SUTHERLAND COMP
Optical fiber and production method thereof
ActiveUS20060010921A1Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyCladded optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical fiber, which has a zero-material dispersion wavelength equal to or greater than 2 μm, and a high nonlinear susceptibility χ3 equal to or greater than 1×10−12 esu, and uses tellurite glass having sufficient thermal stability for processing into a low loss fiber, employs a PCF structure or HF structure having strong confinement into a core region. This enables light to propagate at a low loss. The size and geometry of air holes formed in the core region, and the spacing between adjacent air holes make it possible to control the zero dispersion wavelength within an optical telecommunication window (1.2-1.7 μm), and to achieve large nonlinearity with a nonlinear coefficient γ equal to or greater than 500 W−1 km−1.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
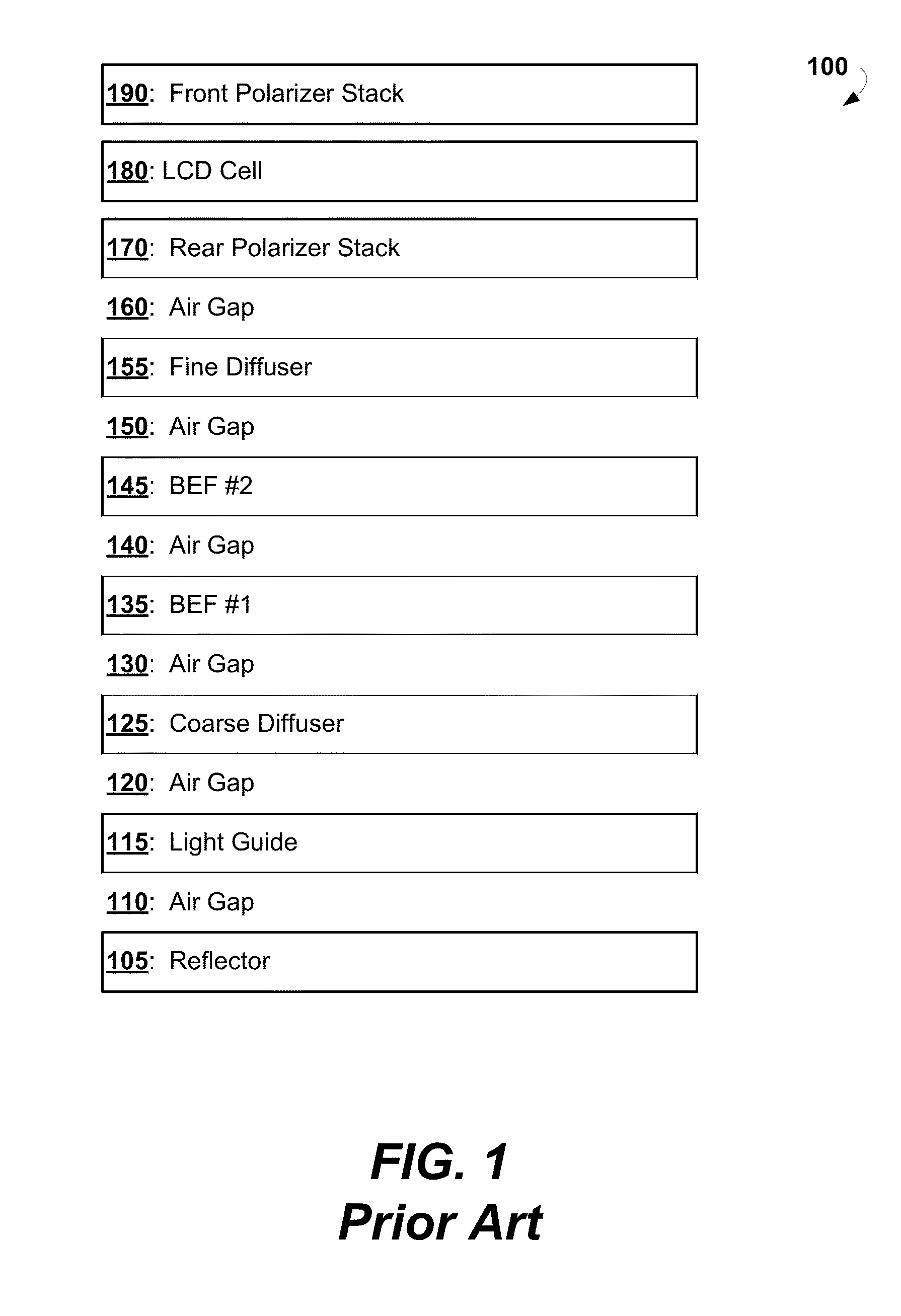
LCD backlight component coatings for reducing light losses and improving in-stack light collimation
InactiveUS20140133177A1Low costEfficient backlightMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesCross-linkSolubility
Provided are multilayer stacks for backlight units in LCD panels and methods for forming thereof. The stacks include refractive index matching layers and pressure sensitive adhesives to minimize light losses. More particularly, the stacks comprise a reflector, a light guide, a course diffuser, one or more brightness enhancing films, and a fine diffuser. A refractive index matching layer is deposited onto at least one surface of the backlight components. A pressure sensitive adhesive is deposited onto the refractive index matching layers. Alternatively, the stacks comprise two or more refractive index matching layers on each surface of the backlight components and retain an air gap between the backlight components. The refractive index matching interlayers are based on a polymer solution having about 0.1%-30% by weight of specific rigid rod-like polymer molecules. The molecules may include various cores, spacers, and sides groups to ensure their solubility, viscosity, and cross-linking ability.
Owner:LIGHT POLYMERS HLDG
High efficiency optic
ActiveUS20140009736A1Reduce light scatterOptimize light energy distributionSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsMedicineLight energy
Ophthalmic lenses and methods for their design and use involve displacement functions based on the sum of a continuous cosine function and a continuous sine function, optionally over a plurality of echelettes. Exemplary monofocal and multifocal diffractive ophthalmic lenses provide reduced light scatter and / or improved light energy distribution properties. Such properties can be provided by diffractive profiles, often having subtlety shaped echelettes with appropriately curving profiles. Light scatter may be generated by the sharp corners associated with vertical steps between adjacent conventional diffractive echelettes. Smooth diffractive profiles of the invention reduce light scatter. Light energy directed toward non-viewing diffractive orders may have a unwanted effects on vision quality. Diffractive profiles as described herein may limit the light energy in certain, selected orders, thereby improving viewing quality and mitigating unwanted effects such as dysphotopsia. Diffractive profiles may also vary the light energy distributed between individual echelettes, providing additional advantages in various viewing situations.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Light assembly for automotive lighting applications
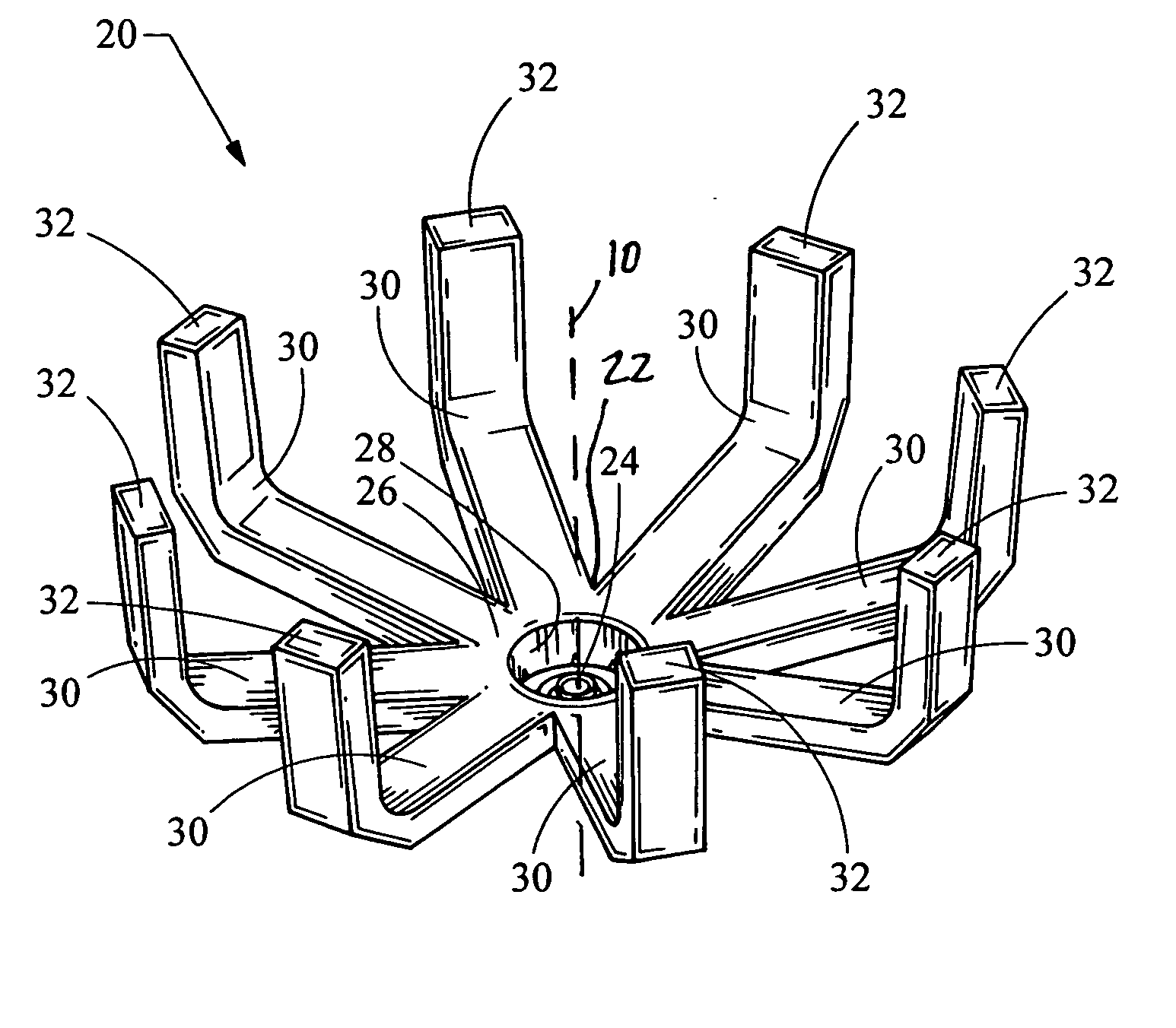
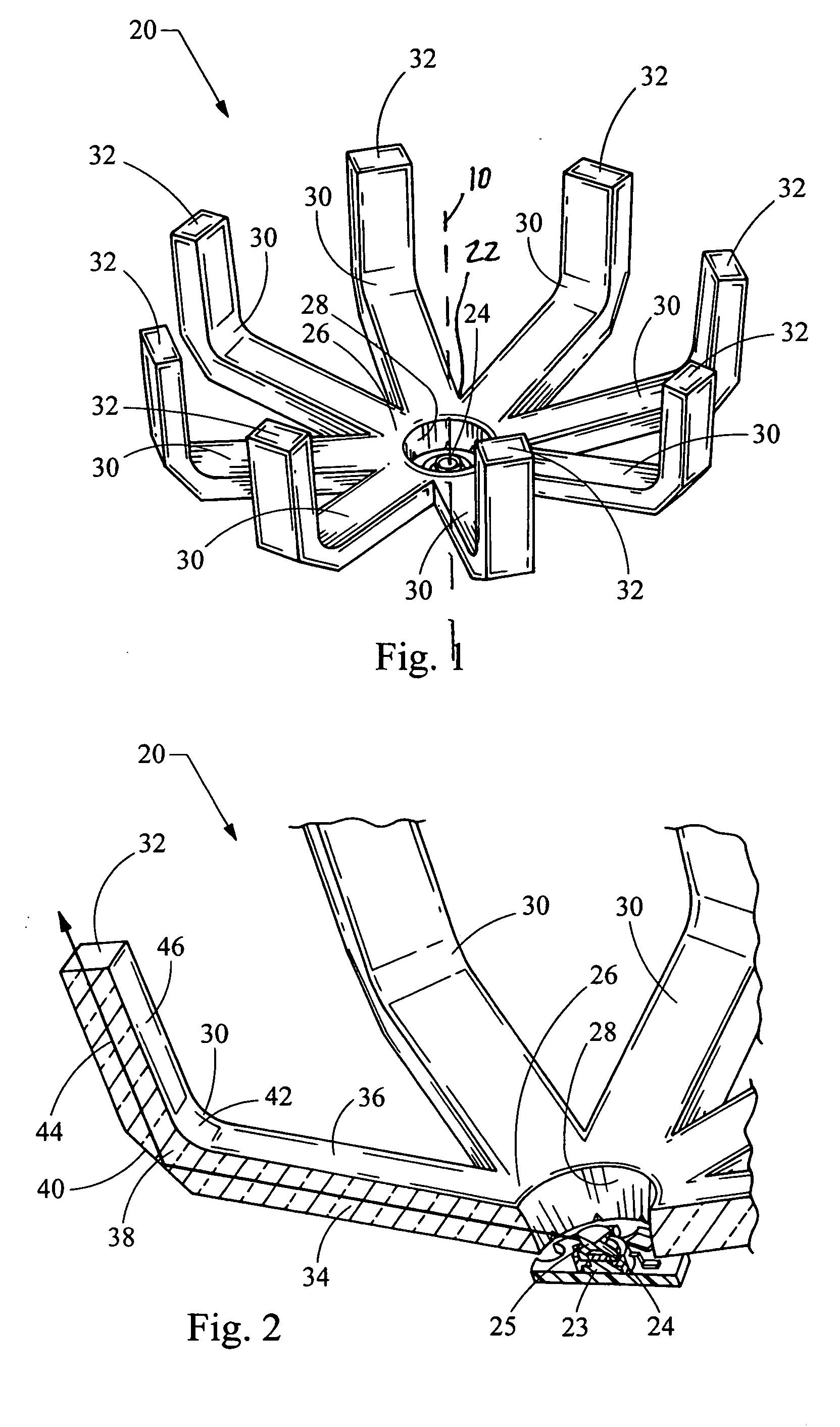
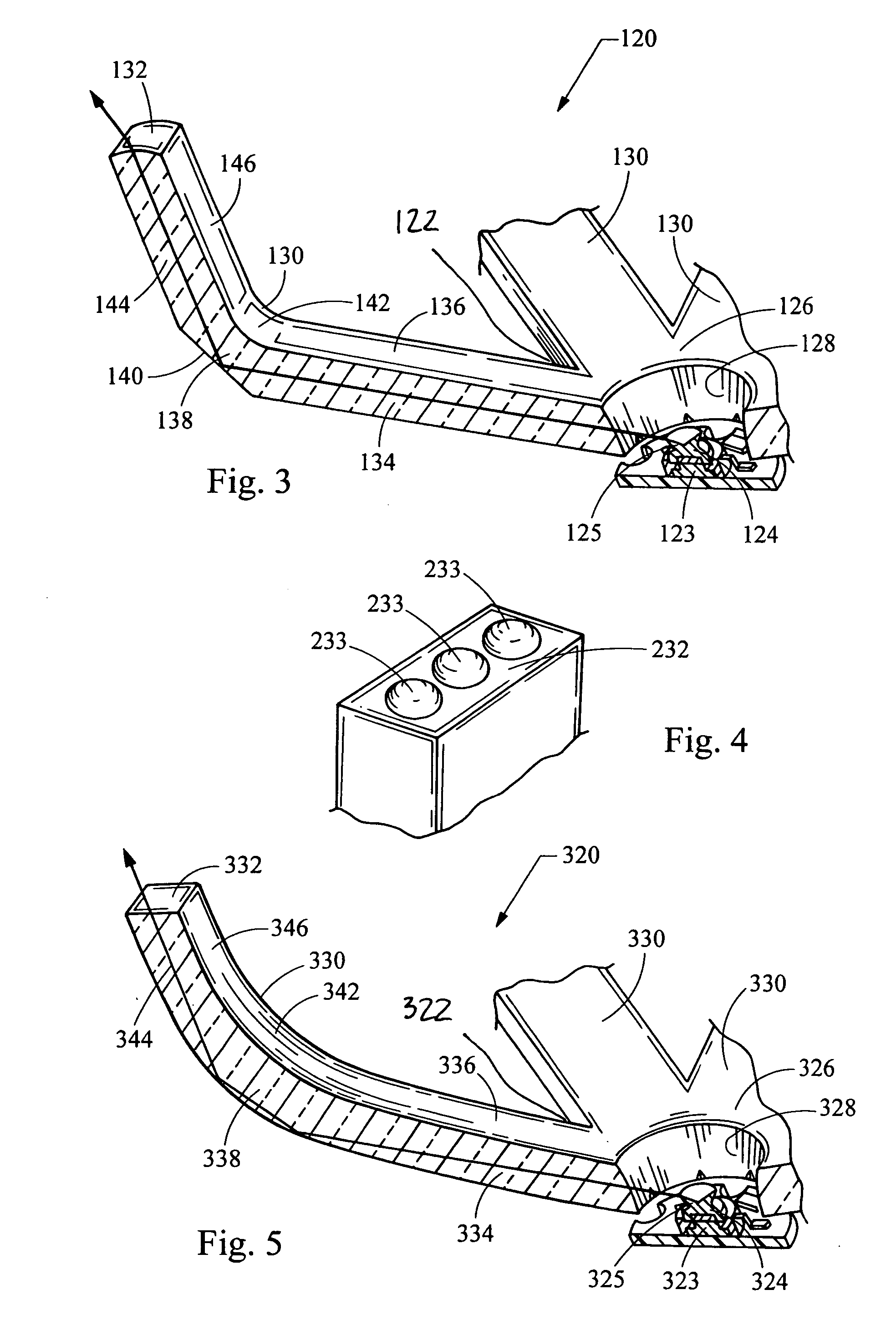
InactiveUS7438454B2Efficient collectionReduce light scatterPoint-like light sourceLight guidesLight pipeLight beam
An automotive light assembly produces numerous beam patterns meeting automotive requirements through the reduction of light scatter and collection and redirection in efficiencies. A light source projects light laterally, which is collected by a light conducting body having a hub and a plurality of fingers extending from the hub. By using a plurality of small individual fingers, large and bulky light pipes are eliminated and the light collection and redirection efficiency is improved.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
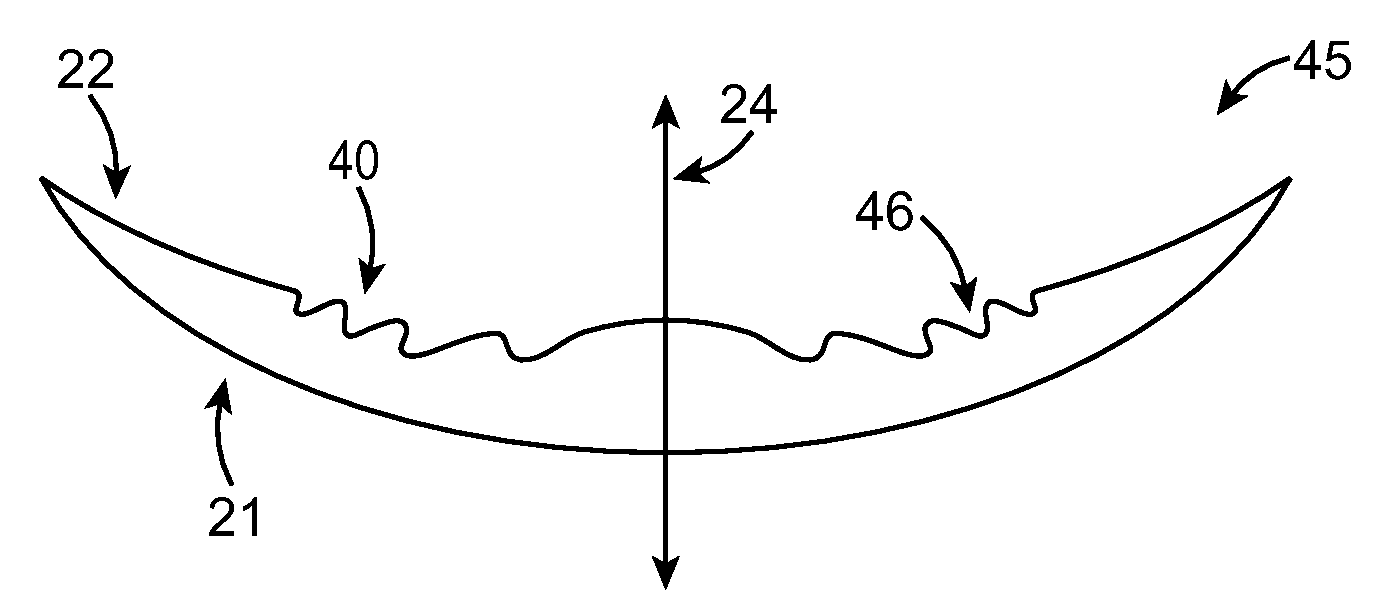
Pupil dependent diffractive lens for near, intermediate, and far vision
ActiveUS20130278891A1Reduce light scatterReduce overall chromatic aberrationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsMultifocal diffractive lensOptical power
A multifocal diffractive lens comprises a multifocal diffractive structure coupled to a refractive component. The refractive component comprises at least one curved surface. The multifocal diffractive structure comprises a first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having a first optical power for near vision correction and a second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes for far vision correction. The first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes combined with the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes can provide a multifocal diffractive profile having decreased light scatter, chromatic aberration, and diffraction to non-viewing orders such that dysphotopsia is substantially inhibited. A third plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having an intermediate optical power can be combined with the first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes and the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
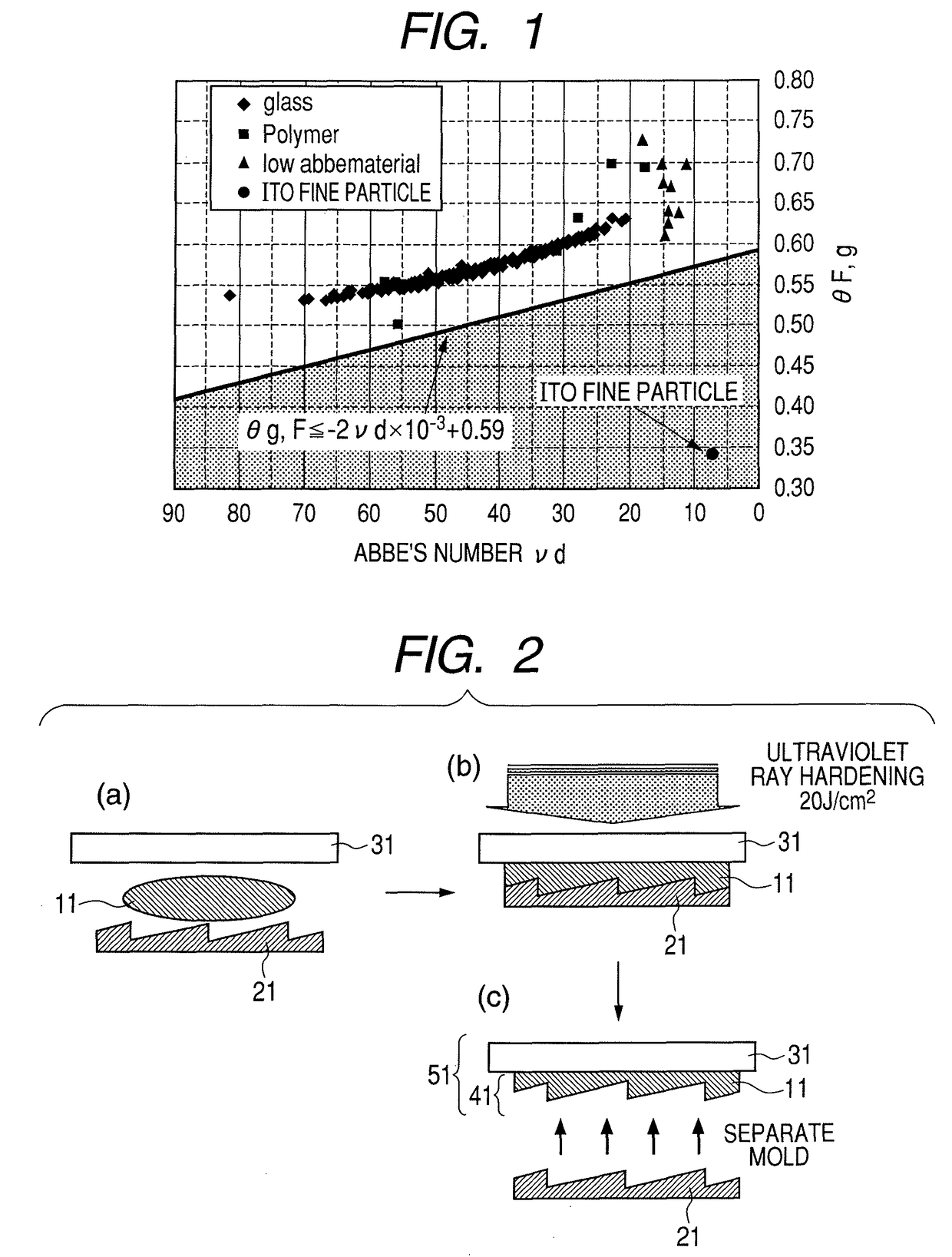
Optical material and optical element, diffraction optical element, and stacked type diffraction optical element molded thereof
InactiveUS8120851B2Reduce light scatterLow dispersion characteristicDiffraction gratingsMetalDiffraction
Use of an organic optical material whose Abbe's number (νd) and secondary dispersion (θg,F) satisfy the relationship θg,F≦−2νd×10−3+0.59 provides an optical material which causes reduced optical scattering, the optical material having excellent optical scattering characteristics and secondary dispersion characteristics equivalent to those of a compound in which fine particles of conductive metal oxides such as ITO are dispersed in an organic resin.
Owner:CANON KK
Surface relief diffractive optical elements providing reduced optical losses in electro-active lenses comprising liquid crystalline materials
InactiveUS20080273167A1Diffraction efficiency is loweredReduce light scatterDiffraction gratingsOptical partsSurface contourLiquid crystal
An electro-active lens has a first substrate with a surface relief diffractive topological profile and a second substrate positioned opposite to the first substrate having a substantially smooth topological profile. A first electrode is positioned along the surface relief diffractive topological profile of the first substrate, and a second electrode is positioned between the first electrode and second substrates. An electro-active material is positioned between the first and second electrodes. The surface relief diffractive topological profile of the first substrate has been modified to eliminate nearly vertical side walls and / or sharp, nearly discontinuous changes in the surface profile, to instead be characterized by sloped side walls and smooth changes in the surface profile, i.e., rounded corners. The radius of curvature of the rounded corners may be, by way of example only, between 1 μm and 100 μm, the slope of the side walls may be at some angle θ, or the shape of the surface profile may be determined by a mathematical smoothing function.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
Pupil dependent diffractive lens for near, intermediate, and far vision
ActiveUS9304329B2Reduce light scatterReduce overall chromatic aberrationSpectales/gogglesDiffraction gratingsMultifocal diffractive lensOptical power
A multifocal diffractive lens comprises a multifocal diffractive structure coupled to a refractive component. The refractive component comprises at least one curved surface. The multifocal diffractive structure comprises a first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having a first optical power for near vision correction and a second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes for far vision correction. The first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes combined with the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes can provide a multifocal diffractive profile having decreased light scatter, chromatic aberration, and diffraction to non-viewing orders such that dysphotopsia is substantially inhibited. A third plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes having an intermediate optical power can be combined with the first plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes and the second plurality of substantially monofocal echellettes.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Holographic recording material composition
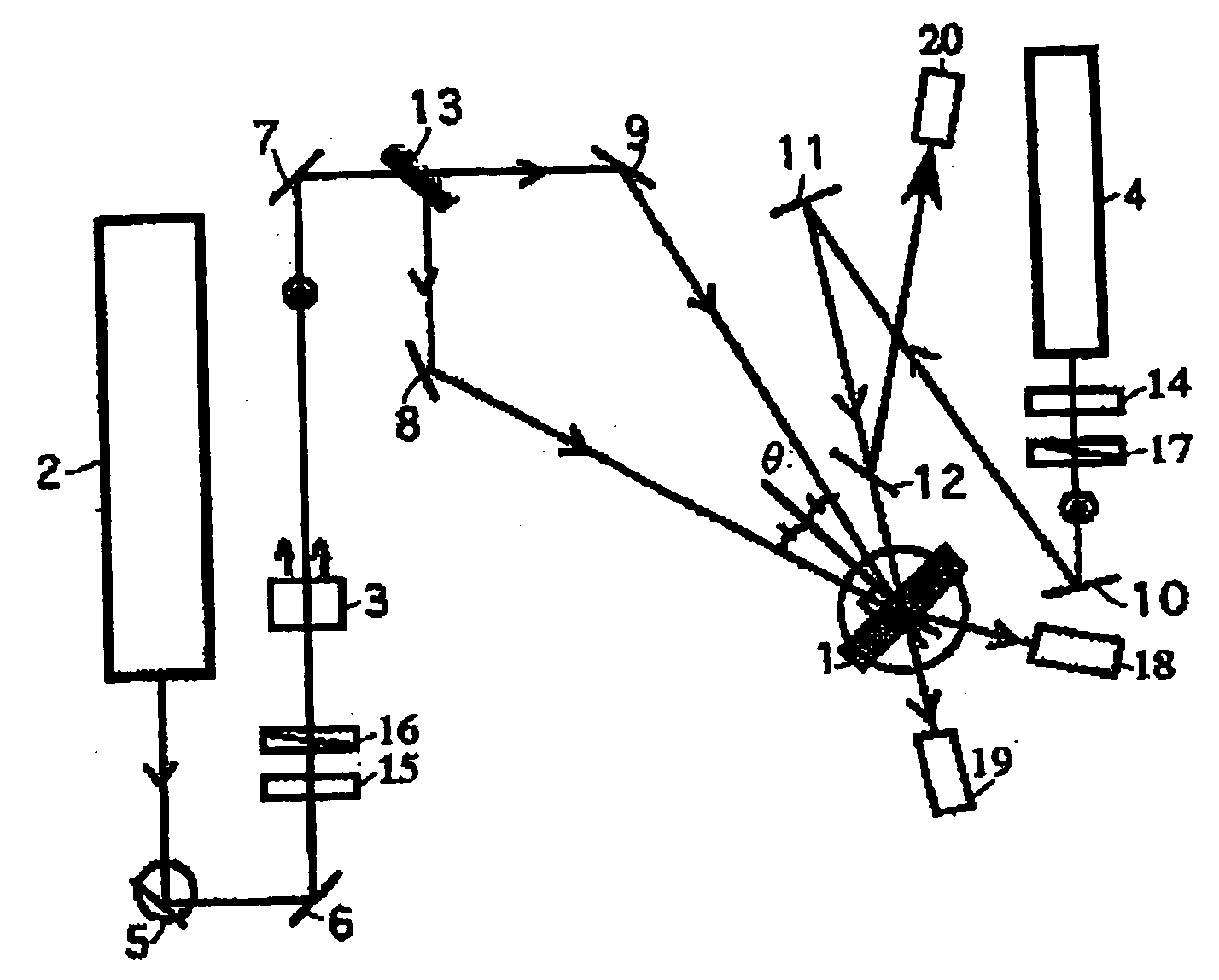
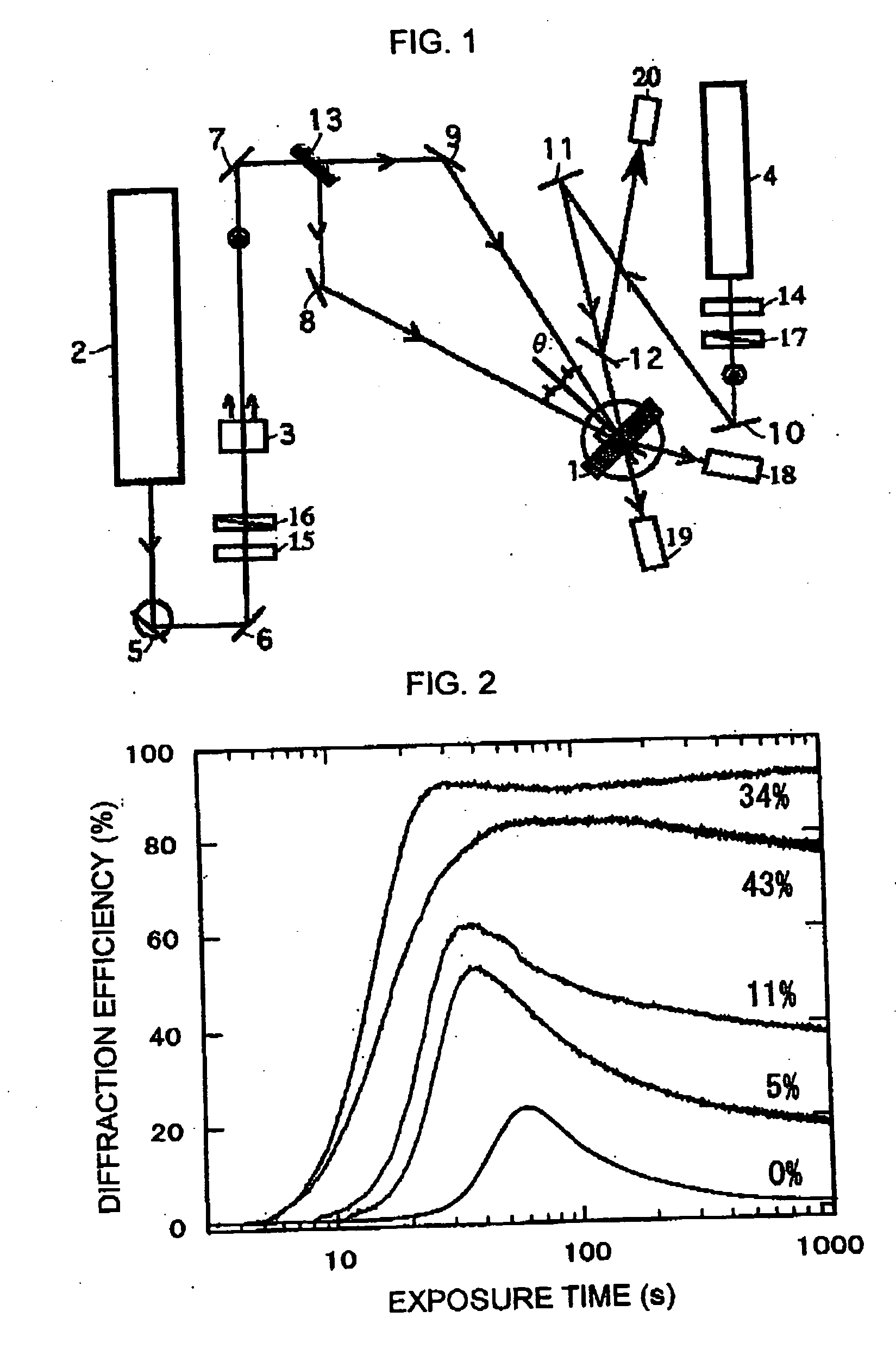
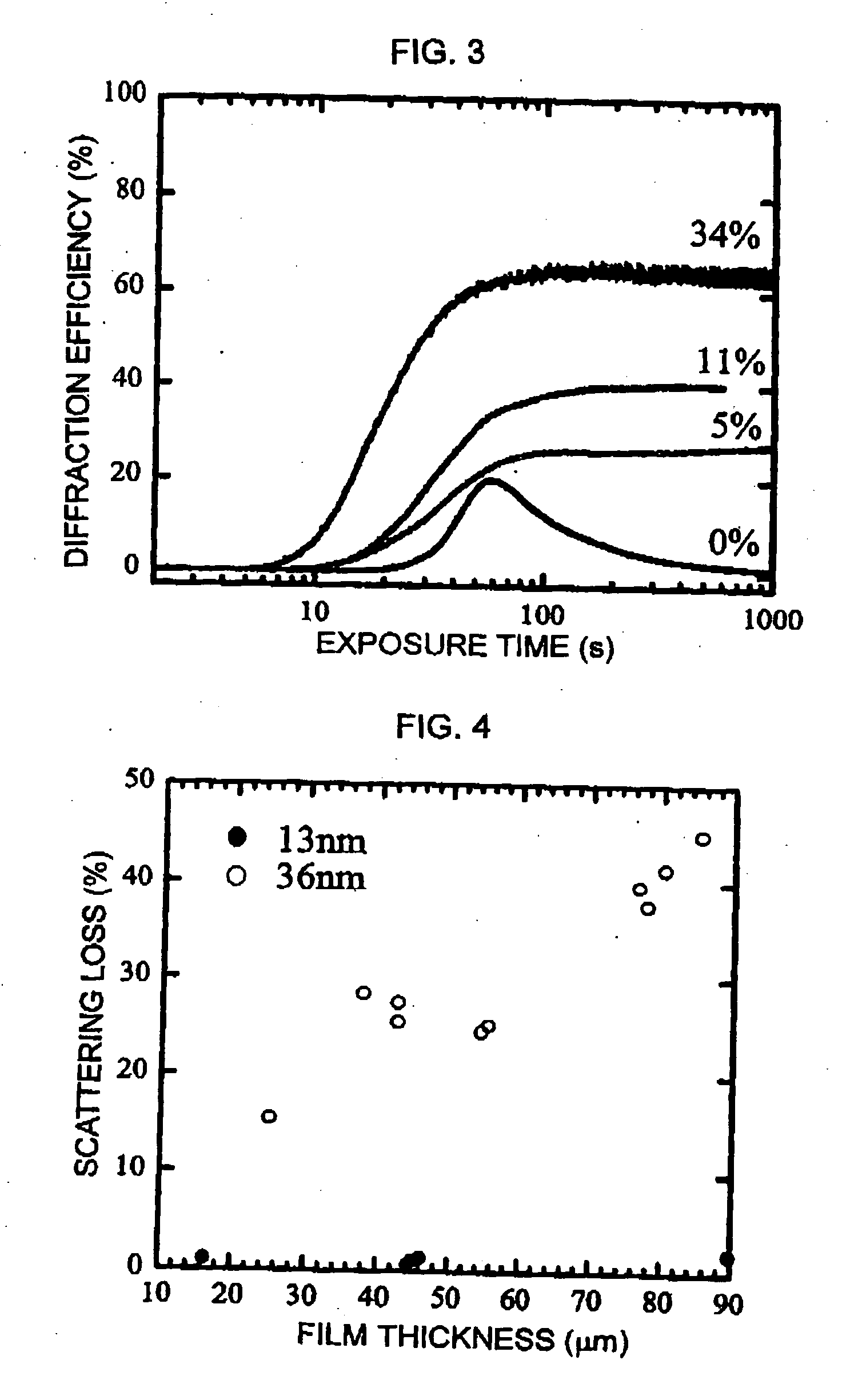
ActiveUS20050068594A1Low light scattering lossHigh diffraction efficiencyPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusHologram nature/propertiesColloidal silicaRefractive index
The present invention provides a holographic recording material composition used for storing optical information as a spatial variation of refractive index, comprising: (a) a compound having at least one polymerizable functional group; (b) a photopolymerization initiator, and (c) colloidal silica particles having an average particle diameter of from 4 to 30 nm.
Owner:TOMITA YASUO +1
Light assembly for automotive lighting applications
InactiveUS20070121331A1Reduce light scatterEfficient collectionPoint-like light sourceLight guidesLight pipeEffect light
An automotive light assembly produces numerous beam patterns meeting automotive requirements through the reduction of light scatter and collection and redirection in efficiencies. A light source projects light laterally, which is collected by a light conducting body having a hub and a plurality of fingers extending from the hub. By using a plurality of small individual fingers, large and bulky light pipes are eliminated and the light collection and redirection efficiency is improved.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
System, devices, and methods for optically clearing tissue
ActiveUS20130178916A1Reduce light scatterReduce the scattering intensityDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionOptical clearingOptical property
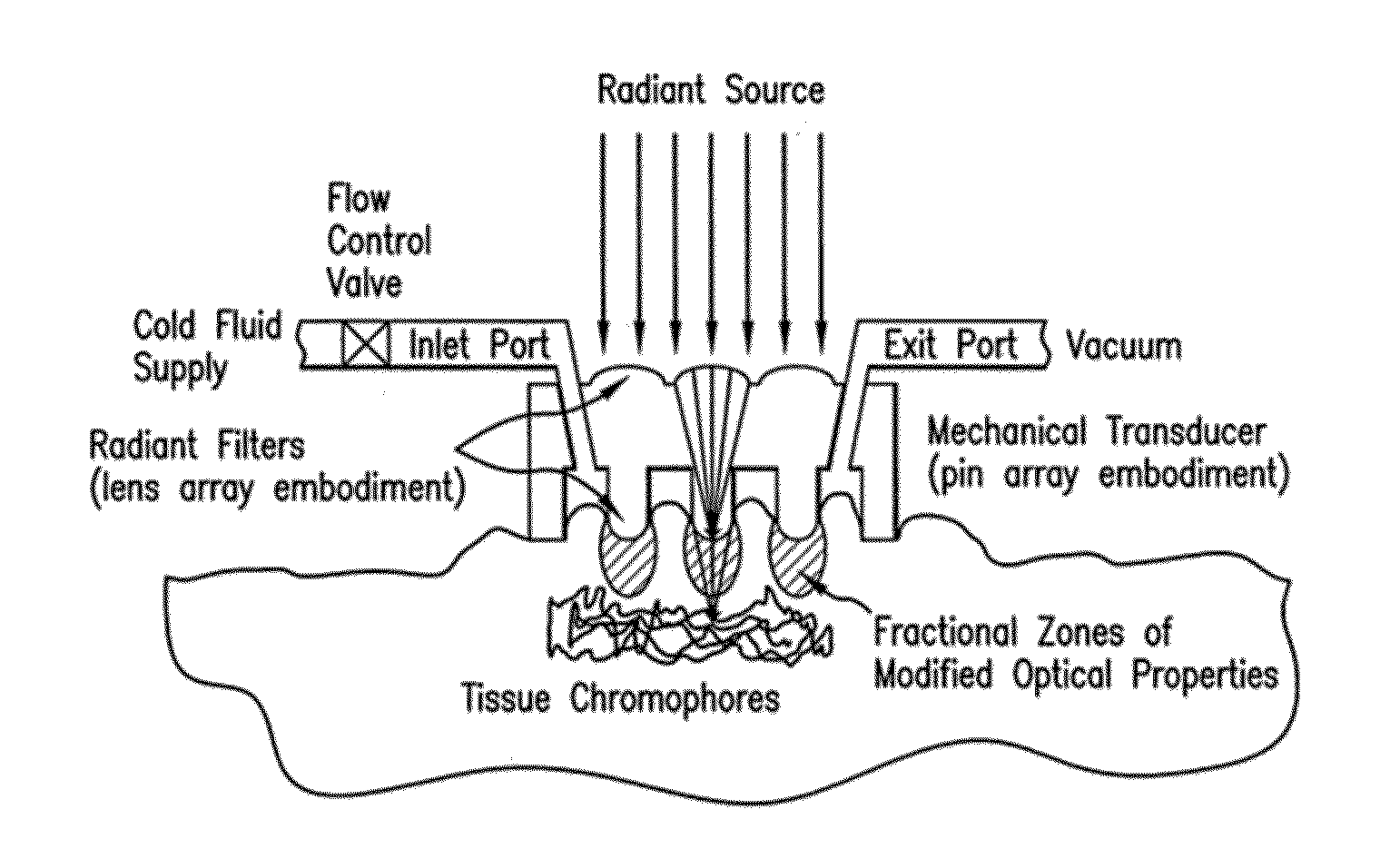
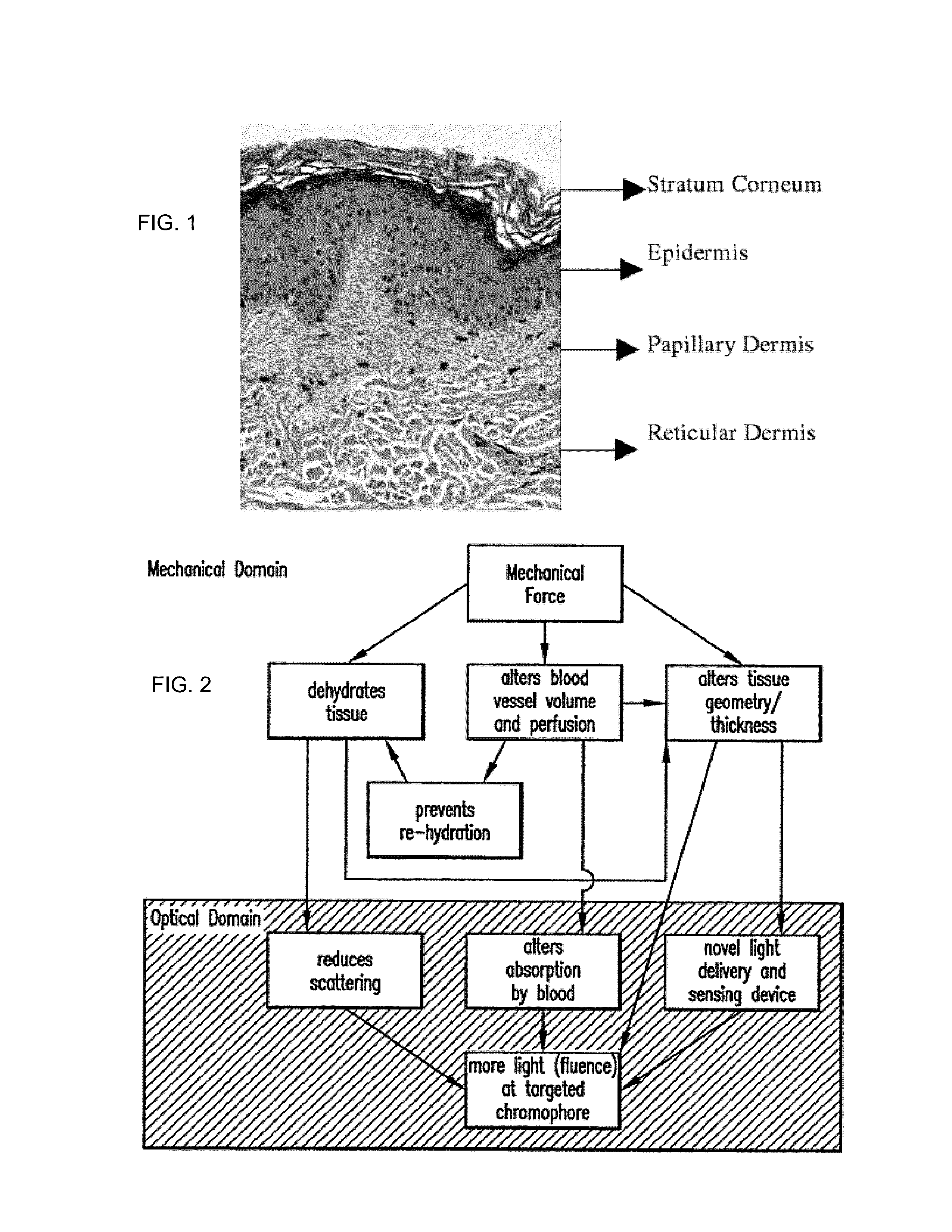
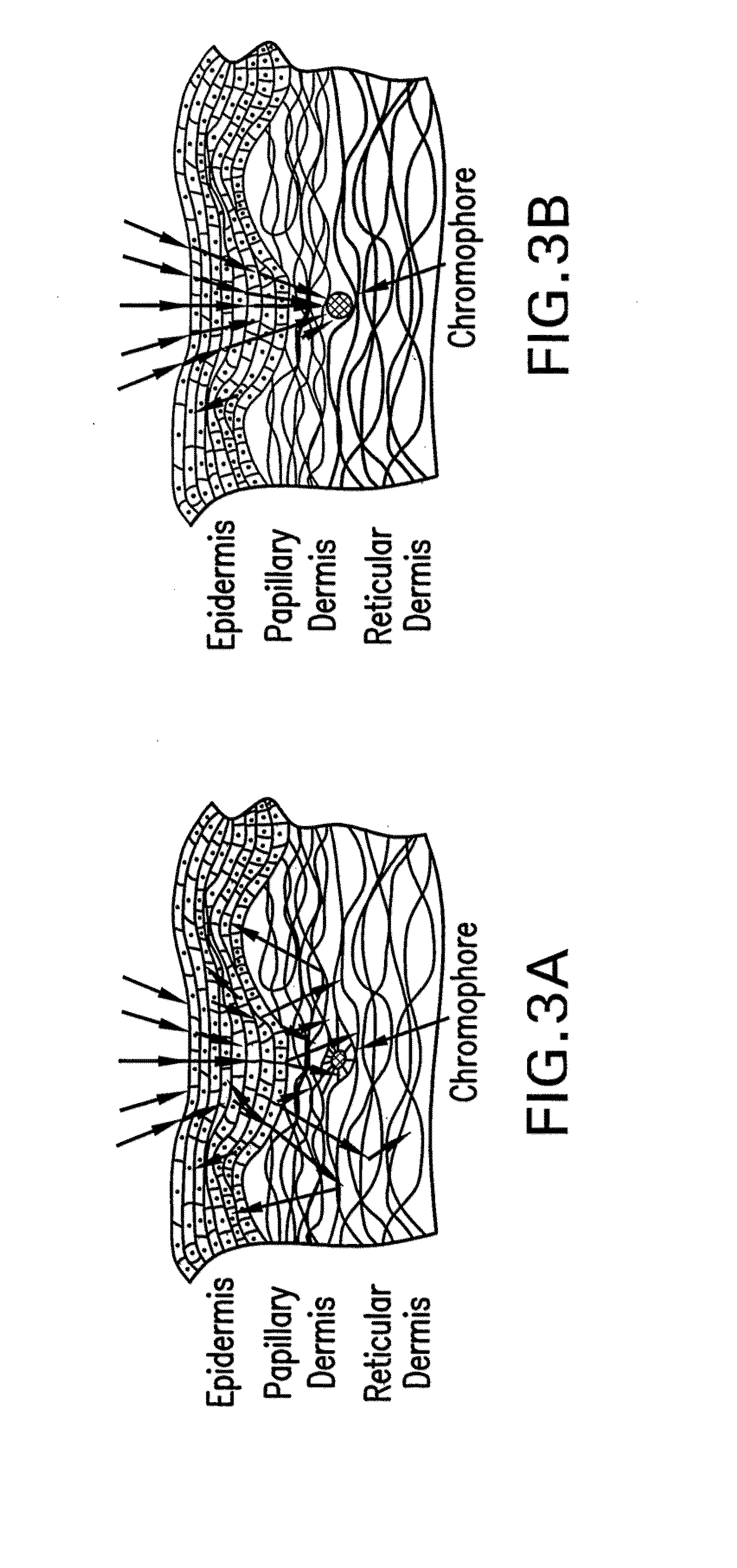
Embodiments of the present disclosure provides systems, devices, and methods for non-invasively modifying, maintaining, or controlling local tissue optical properties. Methods and devices of the disclosure may be used for optically clearing tissue, for example, for diagnostic and / or therapeutic purposes. A method of optically clearing a tissue may comprise contacting the tissue with an optical clearing device having a base, an array of pins fixed to one side of the base, a brim fixed to the base, an inlet port in the base, an exit port in the base, and a handpiece interface tab fixed to the side of the base opposite the array of pins, applying a mechanical force to the tissue, and illuminating said tissue with at least one wavelength of light through the optical clearing device. A method may further comprise controlling the temperature of the tissue illuminated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Objective-type dark-field illumination device for microfluidic channel
InactiveUS20110157692A1Conveniently and rapidly adjustedReduce image contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesFluorescenceImage contrast
An objective-type dark-field illumination device for a microfluidic channel is provided and includes an optical stop having a pair of symmetric curved slits used to adjust the optical path and inner numerical aperture of a dark-field light source generated by the device. The dark-field illumination can focus on a smaller spot to illuminate a sample in the microfluidic channel by matching a pin-hole combined with a transmitter objective lens. The optical path and smaller spot is advantageous to solve the problem of a traditional dark-field illumination that may generate background light noise scattered from inner walls of the microfluidic channel to lower the image contrast. Therefore, the signal or image resolution of capturing the scattered light and / or emitted fluorescent light emitted from the sample in the microfluidic channel can be enhanced. Meanwhile, the device can simultaneously excite and detect multiple fluorescent samples with different excited wavelengths in the microfluidic channel.
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Carbon nanotube dispersed polar organic solvent and method for producing the same
ActiveUS7682590B2Effective dispersionAvoid regroupingMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesOrganic solventCarbon nanotube
In the present invention, a nonionic surfactant is noticed for a function of dispersing a carbon nanotube, and it is found that a mixture solution of an amide-based organic solvent and a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) or of the amide-based organic solvent, the nonionic surfactant, and the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) has an excellent function as a dispersant for the carbon nanotube. Ultrasonication is required for dispersing a carbon nanotube in the dispersant. The ultrasonication may be carried out in the step of dispersing the carbon nanotube in the nonionic surfactant and / or the amide-based polar organic solvent, and then the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) may be mixed with the resultant dispersion. Alternatively, a mixture solution of the nonionic surfactant and / or the amide-based polar organic solvent, and the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is prepared, and then the ultrasonication may be carried out in the step of dispersing the carbon nanotube therein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
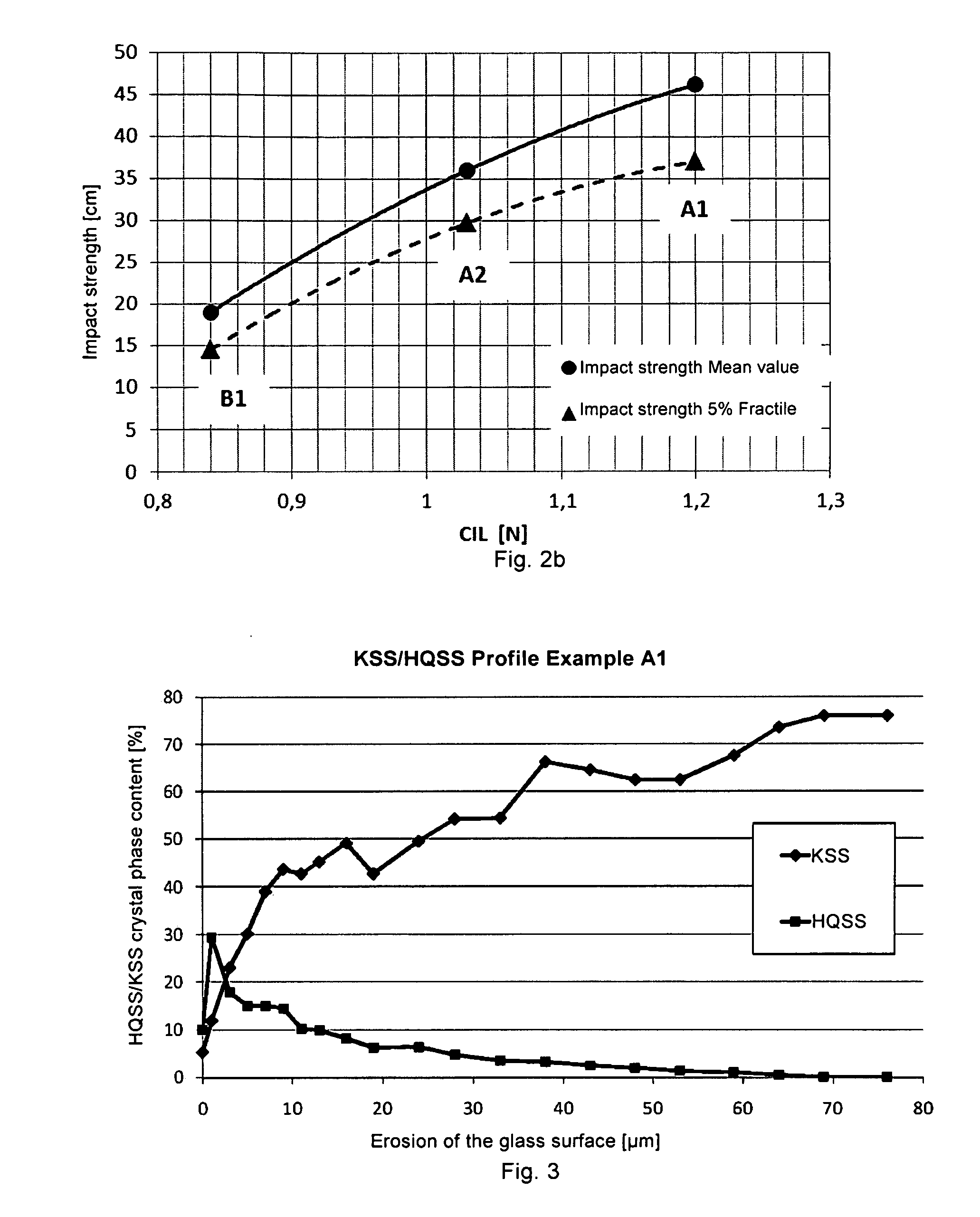
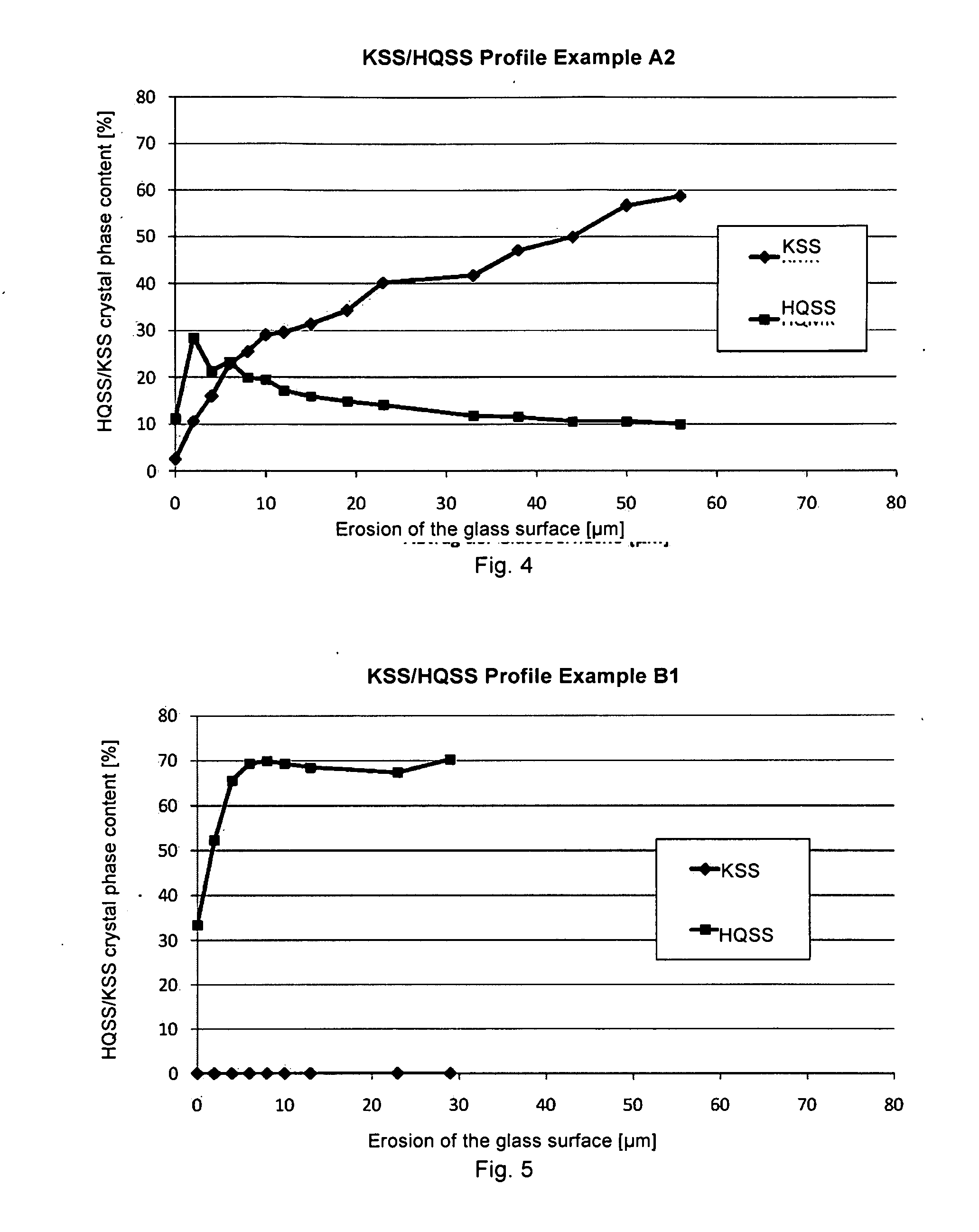
Glass ceramic substrate made of a transparent, colored LAS glass ceramic and method for producing it
A glass ceramic substrate made of a transparent, colored LAS glass ceramic is provided. The glass ceramic has a gradient layer with keatite solid solution and an underlying core with high-quartz solid solution as predominant crystal phase. The keatite solid solution in a depth of 10 μm or greater exceeds 50% of the sum of the high-quartz solid solution proportion and keatite solid solution proportion. The ceramization includes a crystal transformation step, in which the high-quartz solid solution is transformed at a maximum temperature in the range of 910° to 980° and a time period of between 1 and 25 minutes in part into the keatite solid solution.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
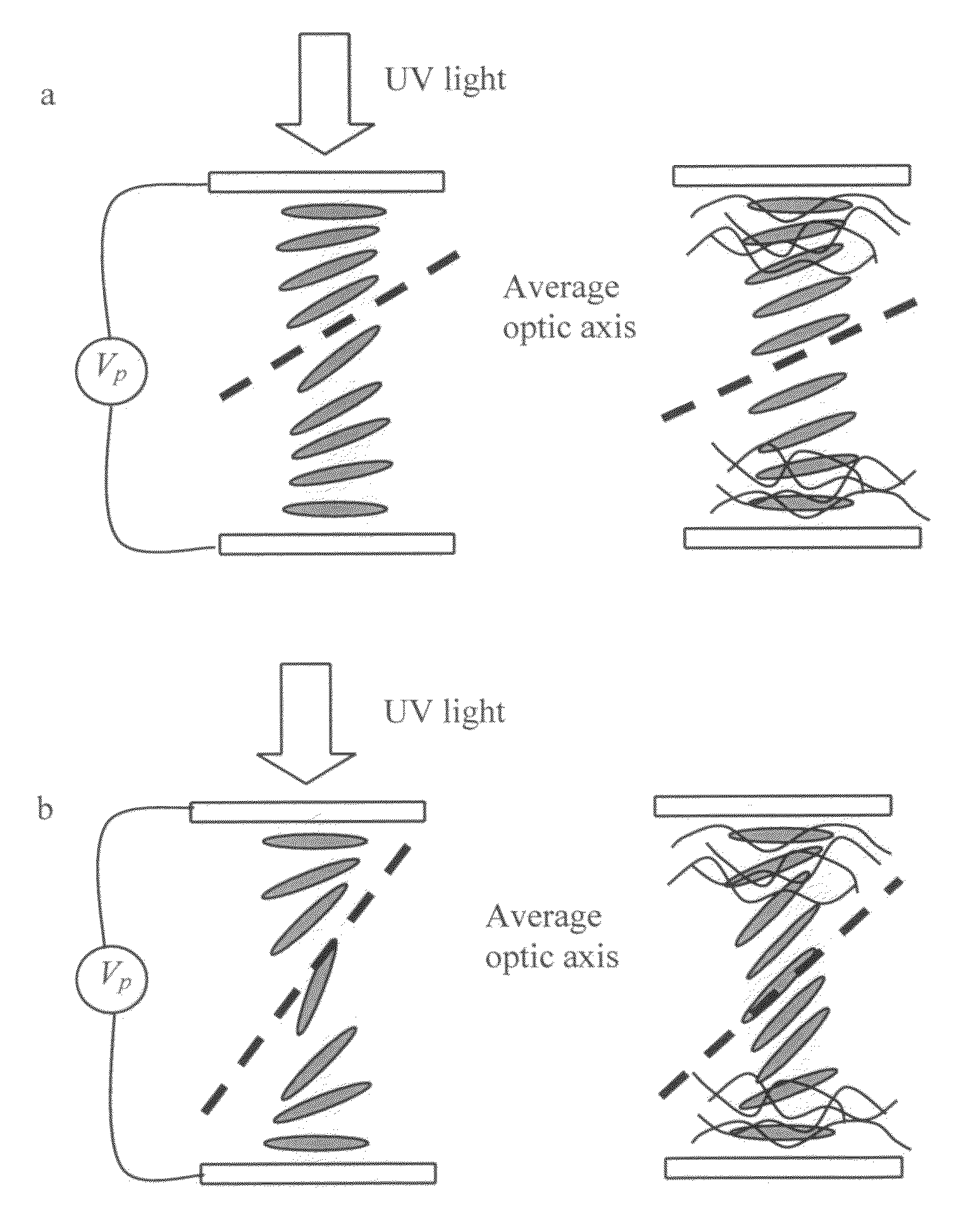
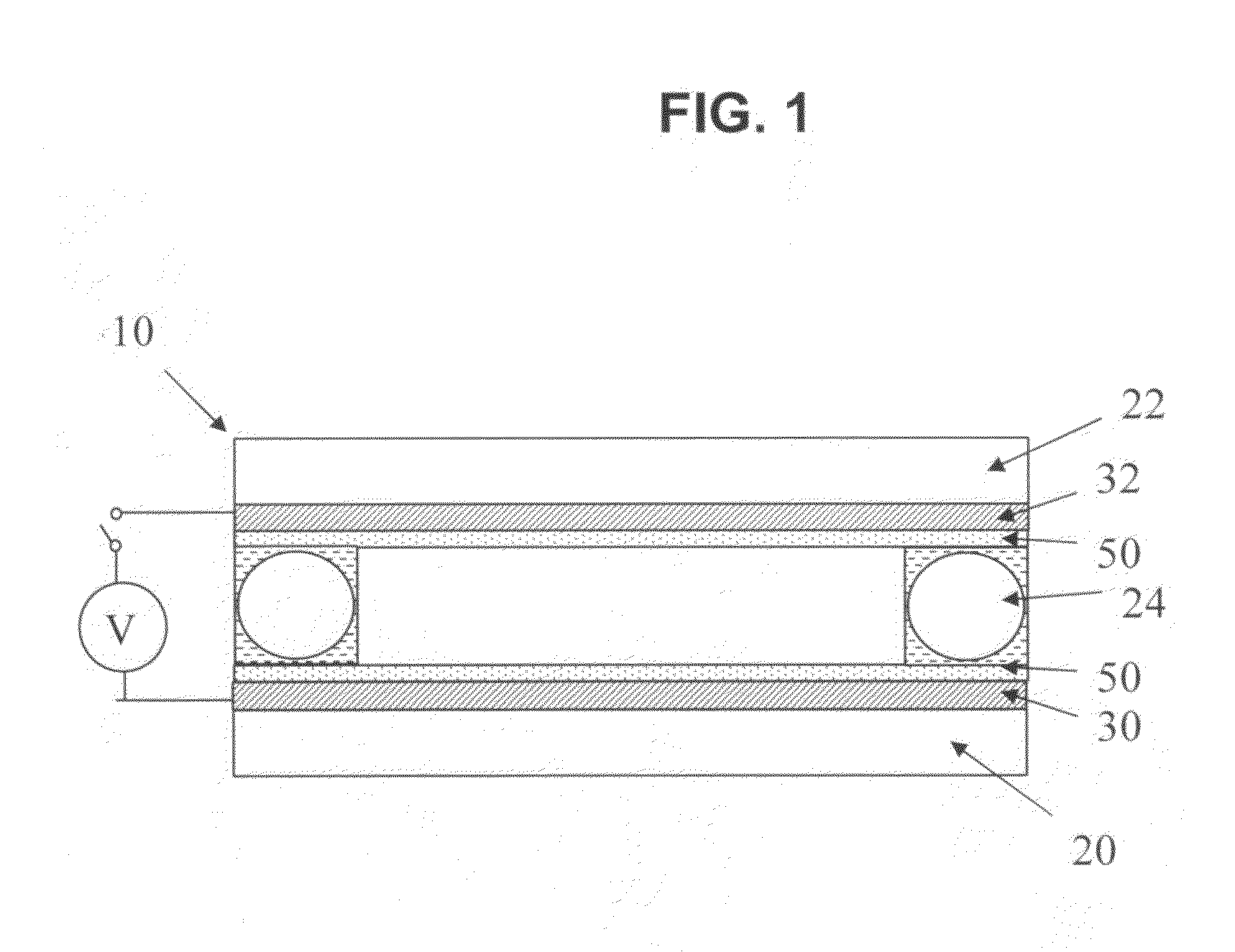
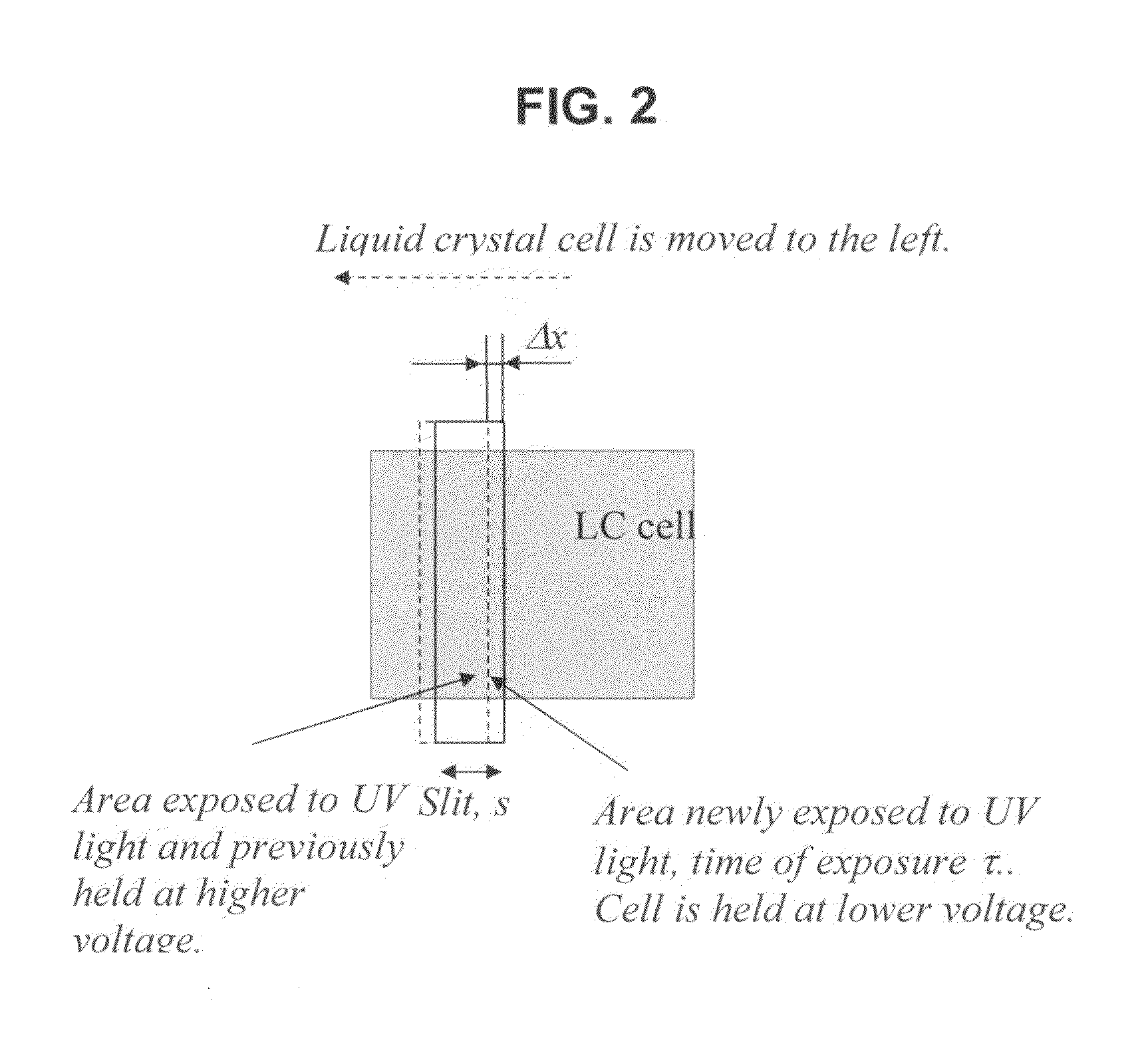
Photo-patterned pre-tilt liquid crystal cells, lenses and methods
ActiveUS20110170039A1Different overall resultReduce light scatterLamination ancillary operationsHollow inflatable ballsLiquid crystallineCrystallography
Liquid crystal cells and lenses having a variable resulting pre-tilt across two or more areas of the cell, and in particular, cells and lenses are provided wherein a resulting pre-tilt is varied across the cell according to any desired birefringence profile that can be utilized in liquid crystalline optical elements and liquid crystal displays. Methods of fabrication of the liquid crystal cells with variable resulting pre-tilt are disclosed.
Owner:CALIFORNIA STATE UNIV SACRAMENTO +1
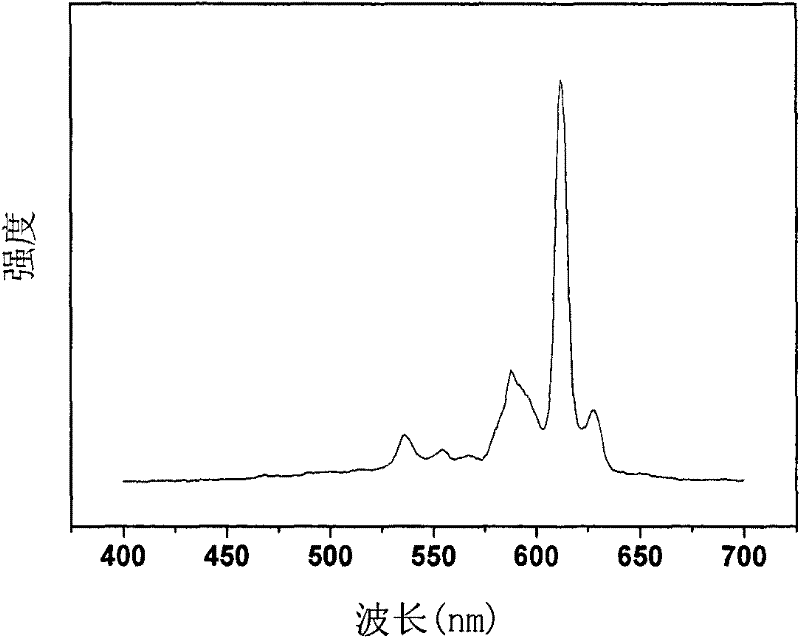
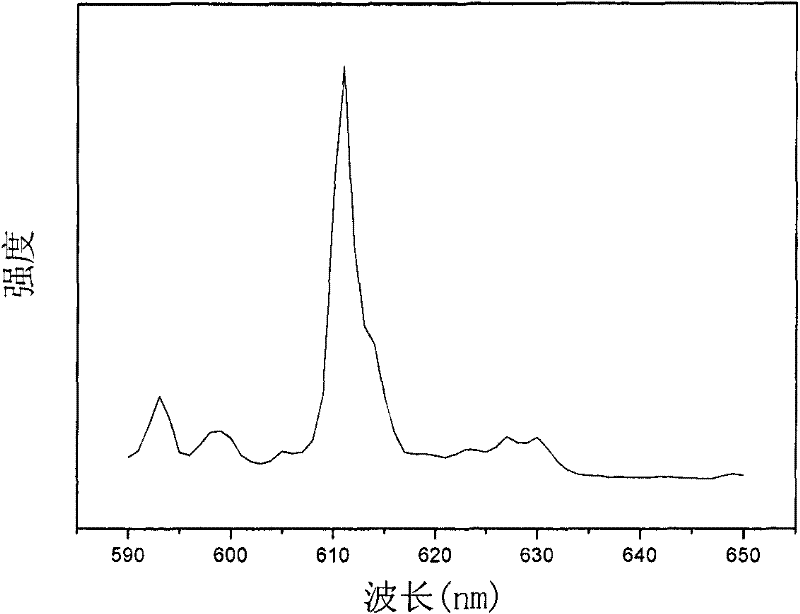
Fluorescent material with core-shell structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102191033ASimple preparation processLow equipment requirementsLuminescent compositionsLuminous intensityMicrosphere
The invention provides a fluorescent material with a core-shell structure. The structural formula of the fluorescent material is SiO2@ fluorescent powder, wherein @ means SiO2 serving as a core is covered by fluorescent powder serving as a shell. The preparation method of the fluorescent material comprises the following steps: preparation of SiO2 micro-suspension, preparation of SiO2@oxalate and preparation of SiO2@ fluorescent powder. In the invention, silicon dioxide microspheres serve as cores and a precipitator is dripped to coat a fluorescent powder layer on the surface of silicon dioxide; and thus, the preparation process of the fluorescent material is simple, the requirement on the equipment is low, the preparation period is short, and the cost is low. Meanwhile, the fluorescent material preparation by the invention is uniform in particle size and shape; and thus, the bulk density of the particles is high, the luminous intensity, luminous efficiency and resolution of the particles are improved, and the light scattering of the fluorescent powder is reduced.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Apparatus for reading signals generated from resonance light scattered particle labels
InactiveUS20090190129A1Convenient and efficient detectionEasy to analyzeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsResonanceCcd camera
Owner:INVITROGEN
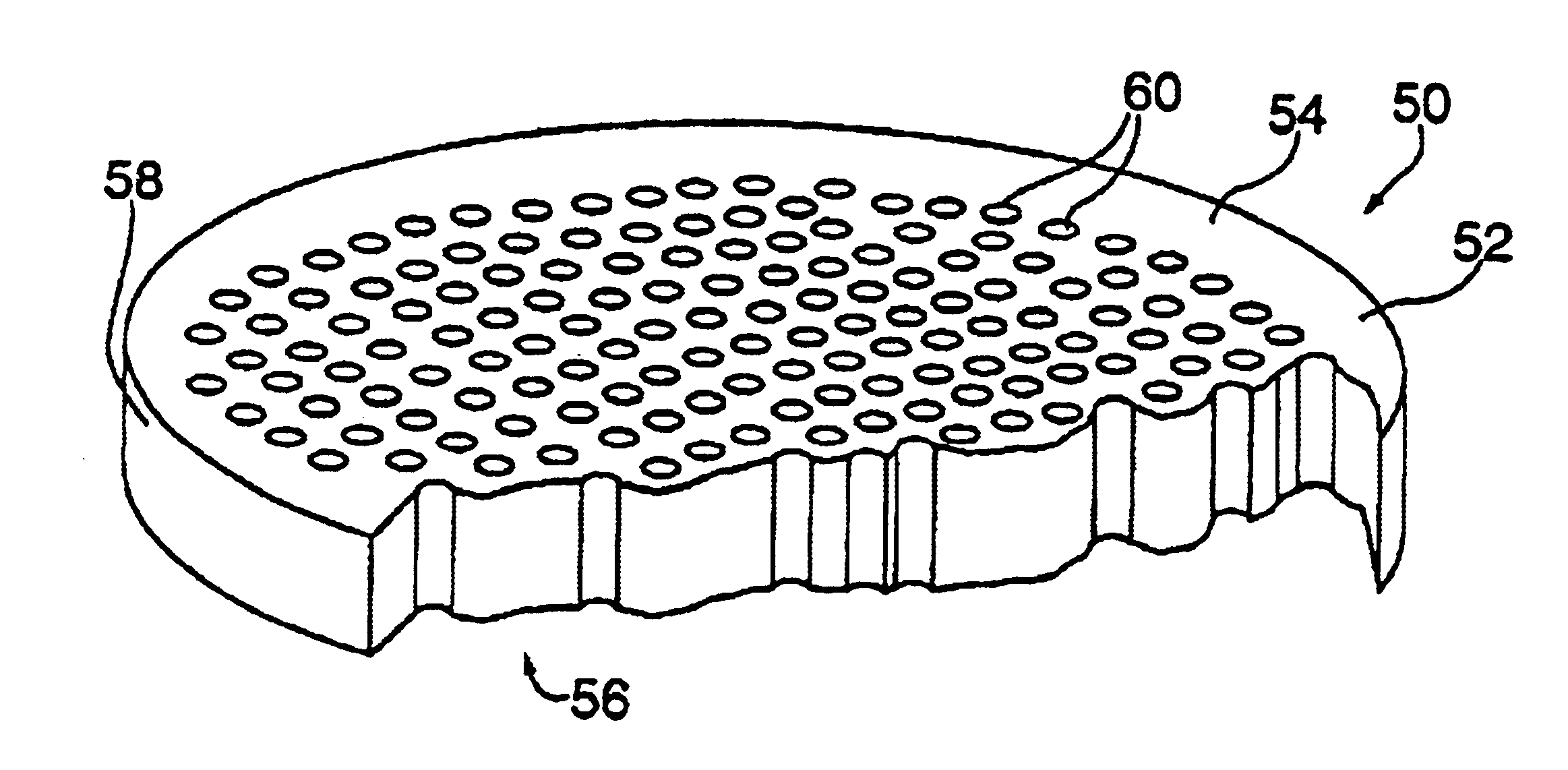
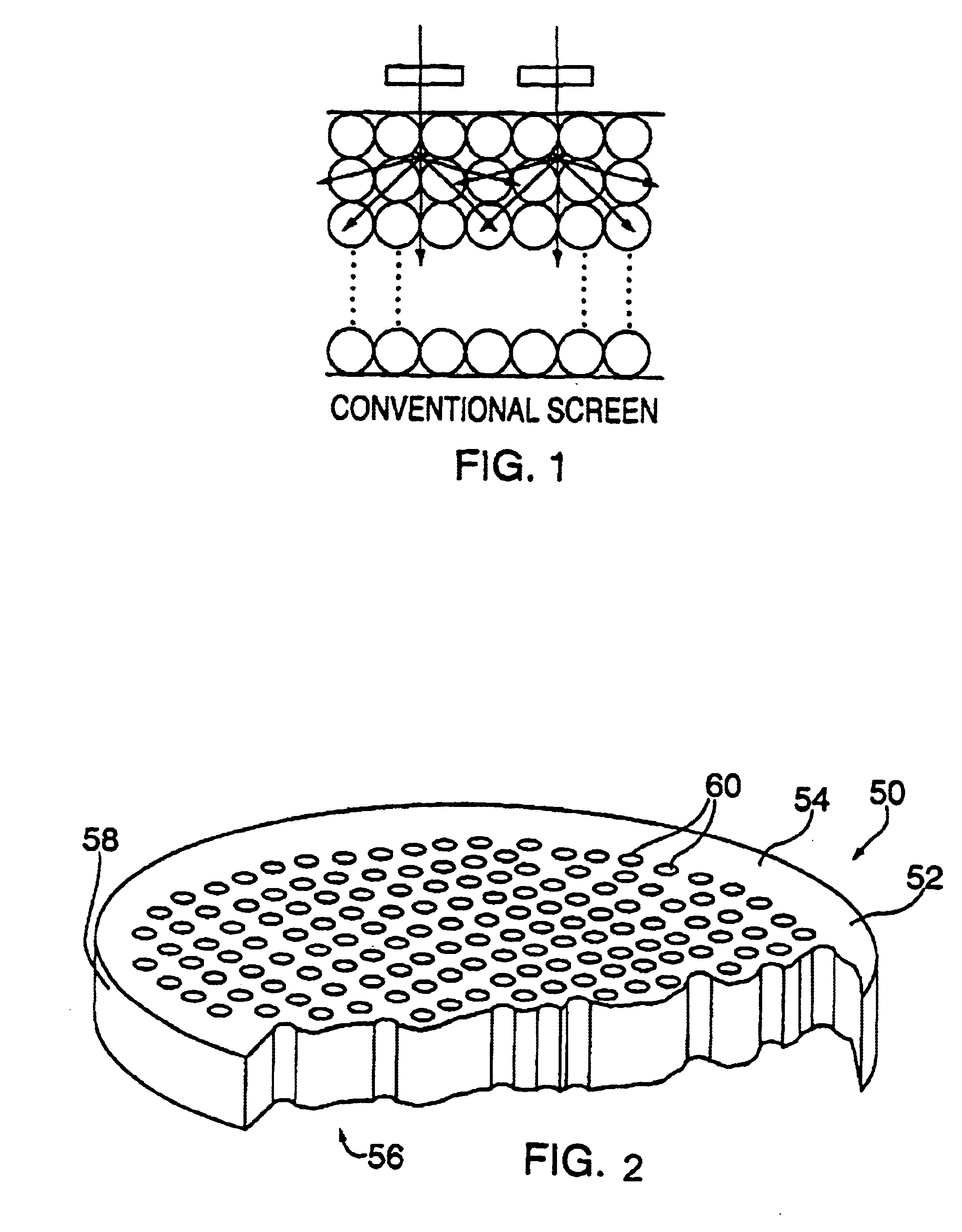
High resolution tiled microchannel storage phosphor based radiation sensor
InactiveUS6885004B2Easy to produceSmall sizeX-ray/infra-red processesCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesImage resolutionX-ray
X-ray imaging screens utilizing phosphors disposed in microchannels disposed in a plate. This application relates to the “tiling” of such microchannel plates to form a larger imaging area and to the use of “storage phosphors” in the microchannel plates which enables the phosphors to be read out after exposure and from the side exposed to the X-rays. The storage phosphor screens of the present invention provide significantly increased resolution than the prior art storage phosphor screens.
Owner:NANOCRYSTAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com