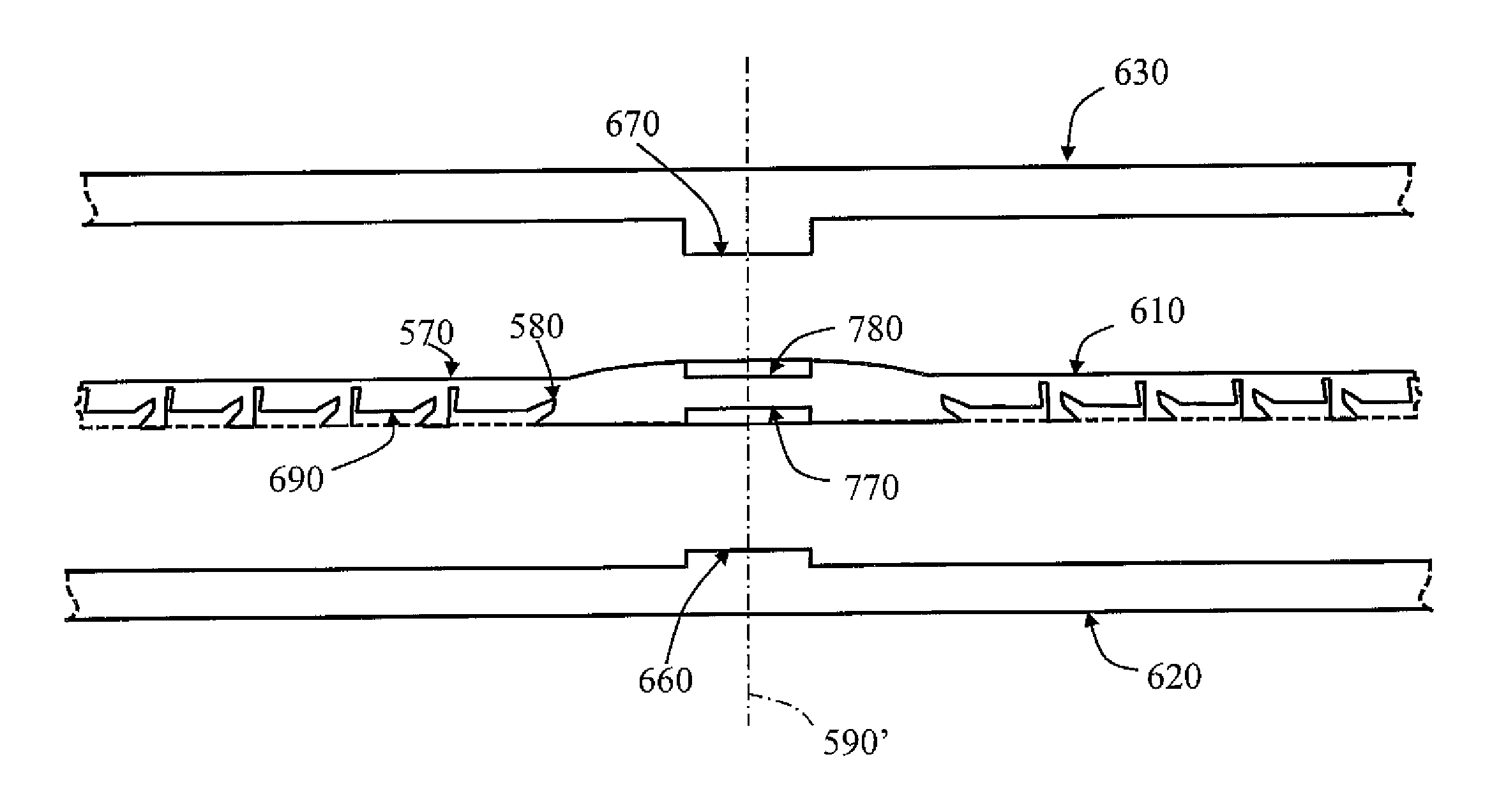
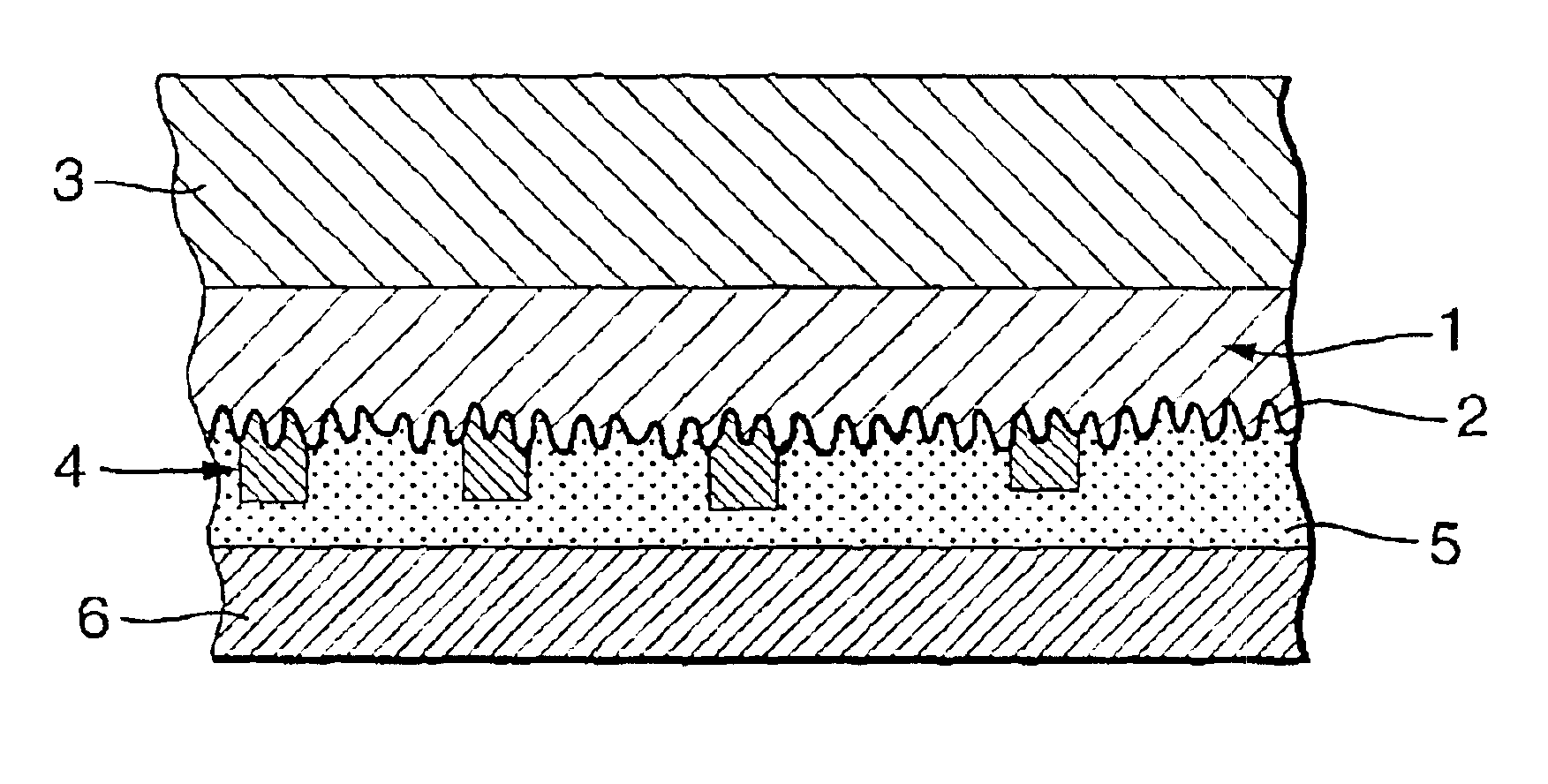
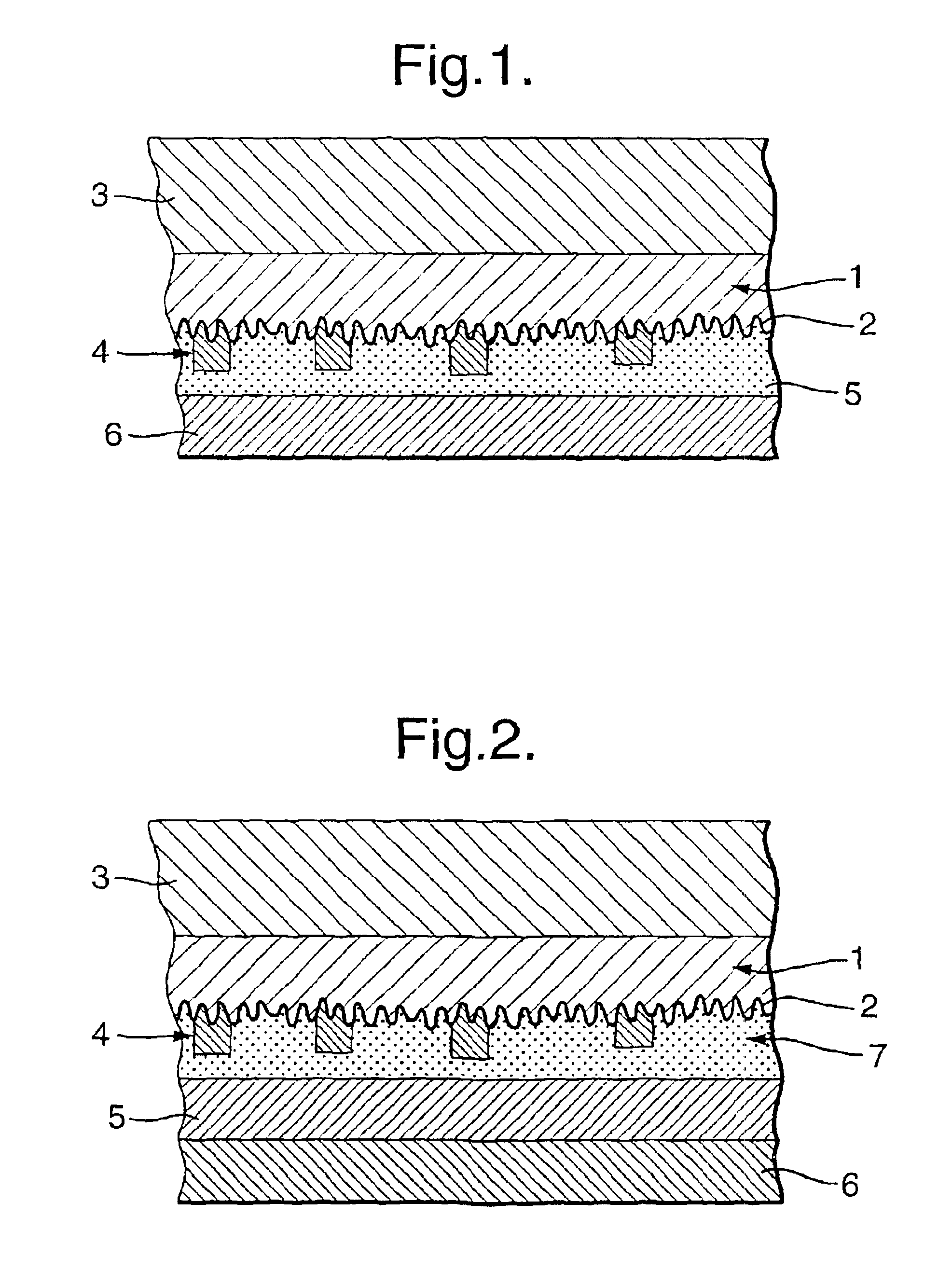
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
373 results about "Surface relief" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
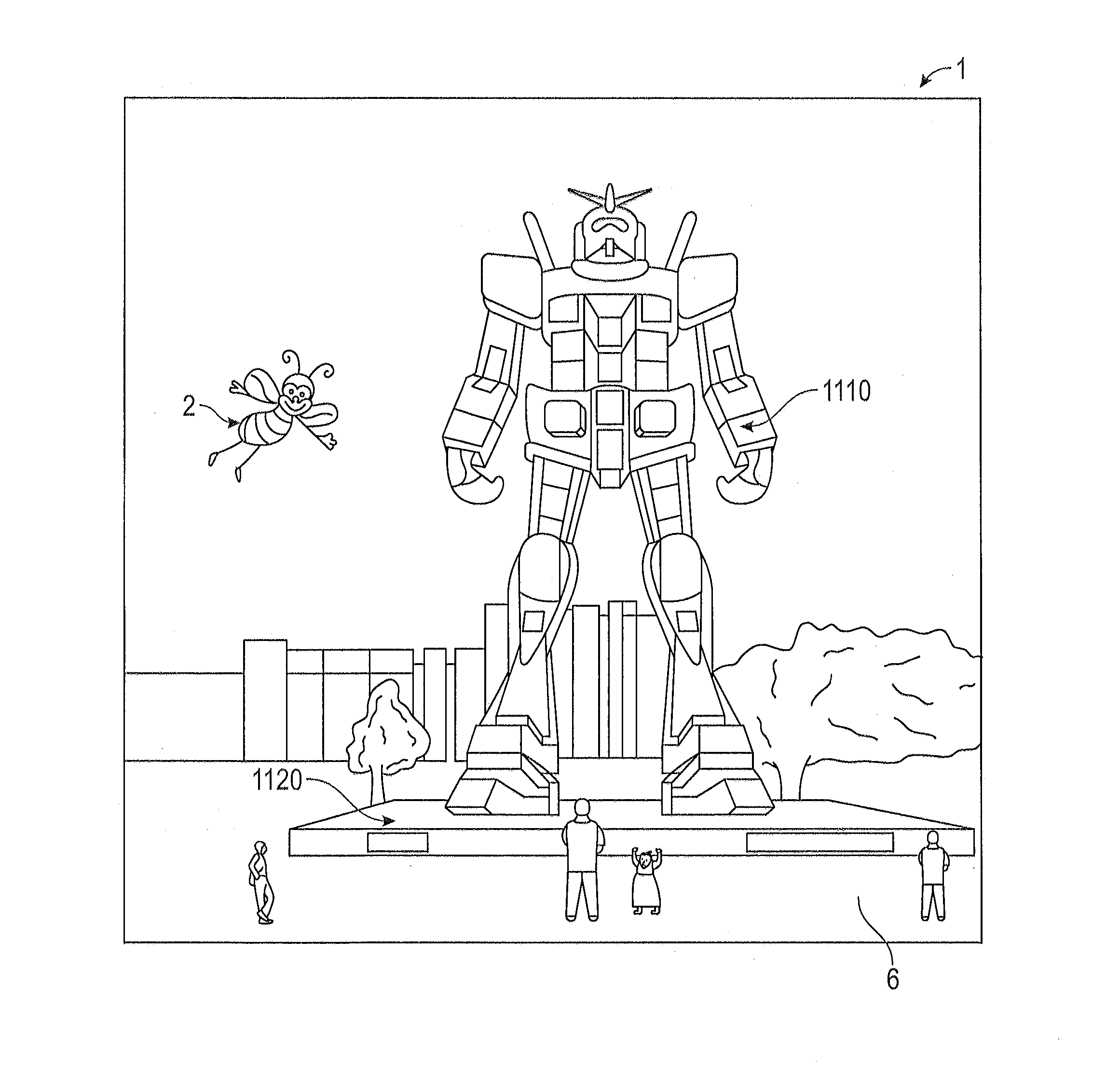
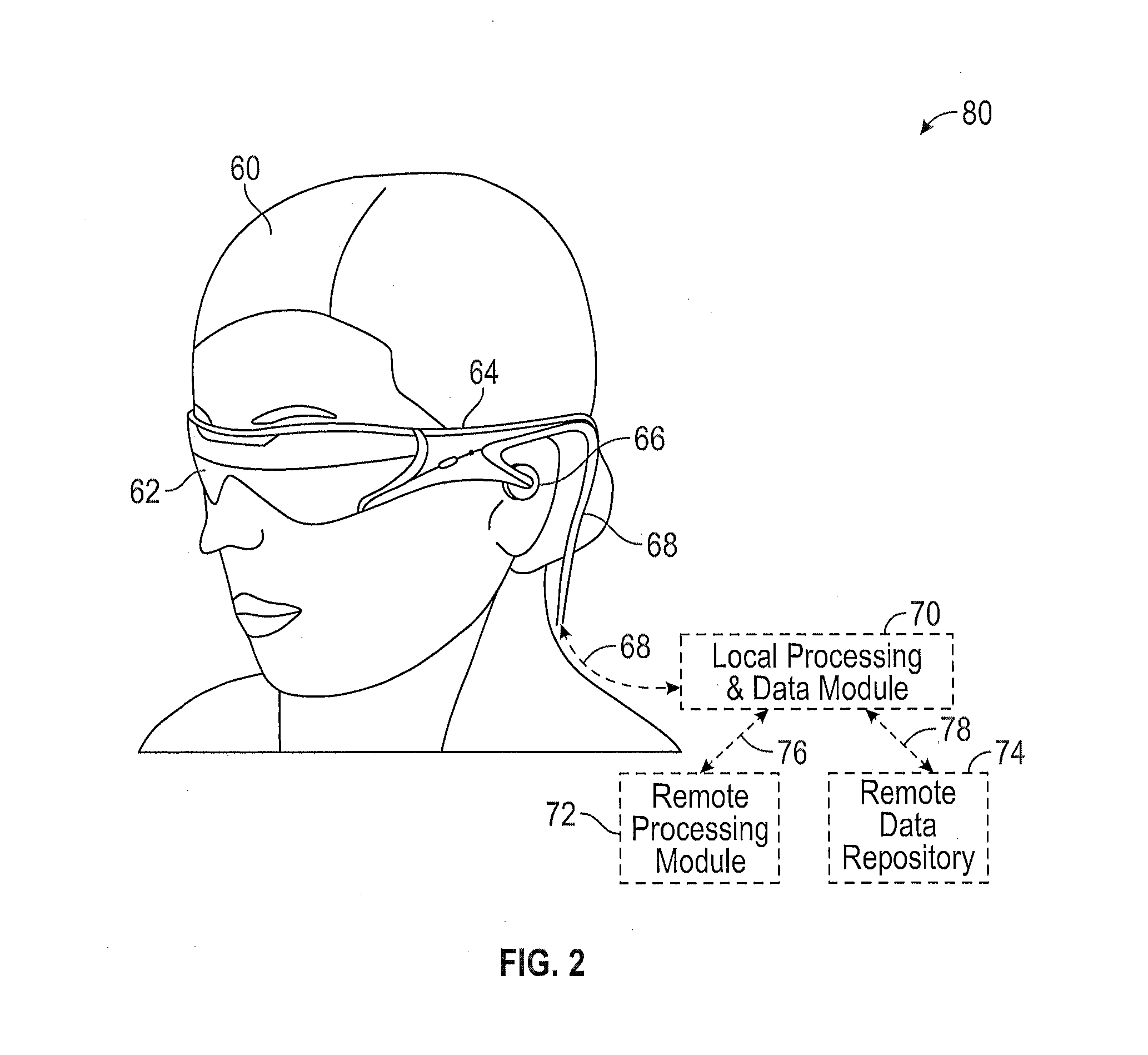
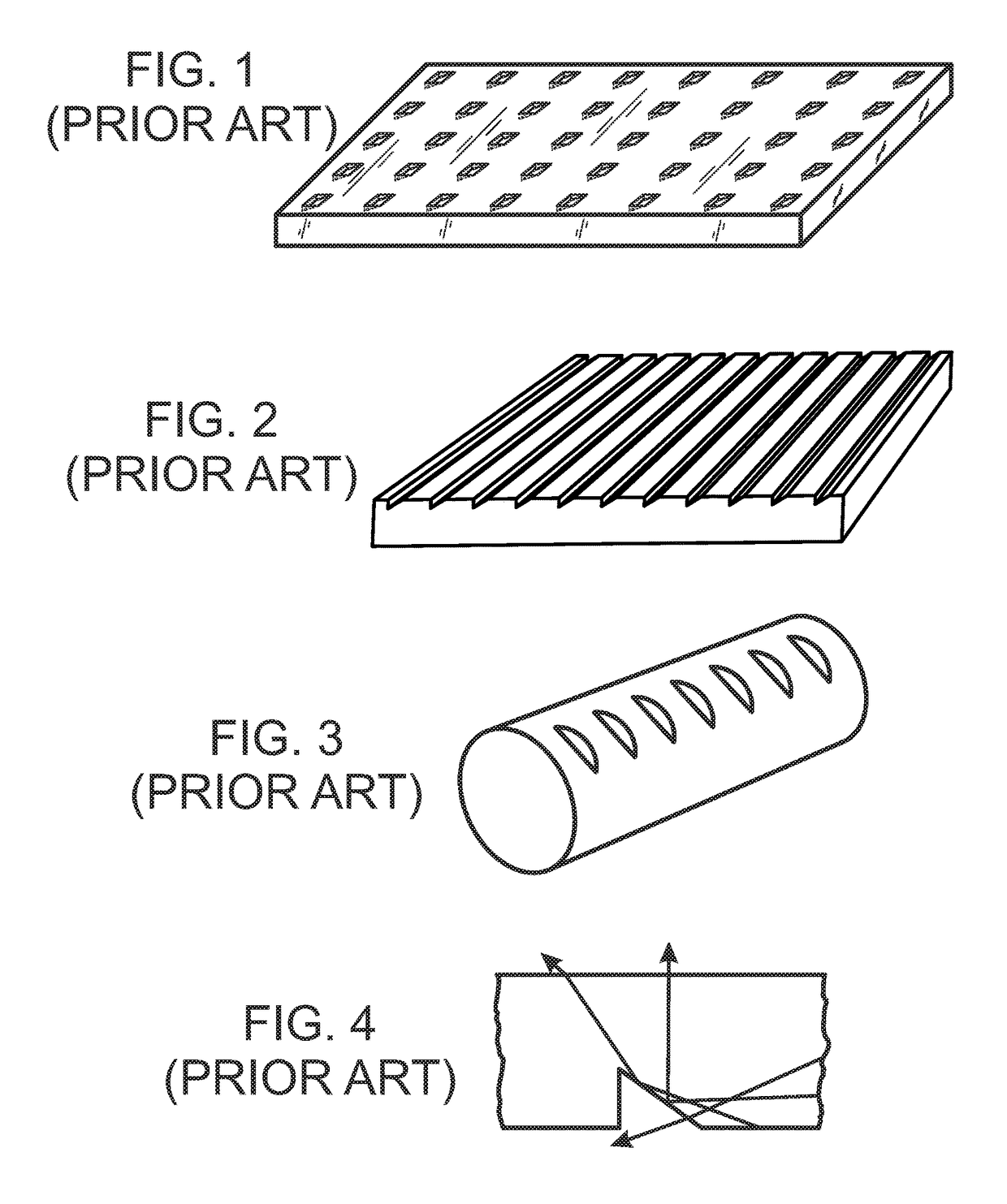
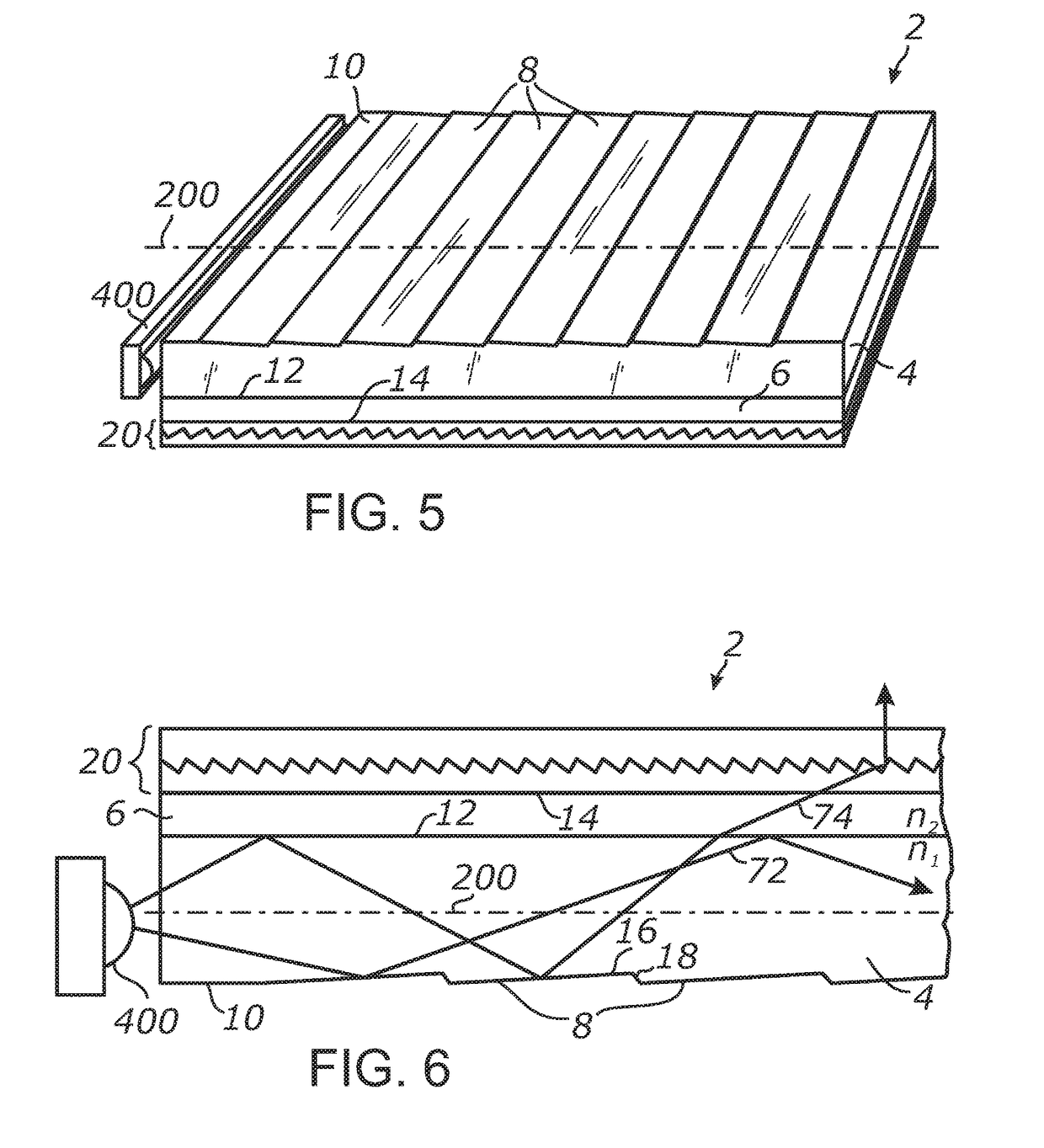
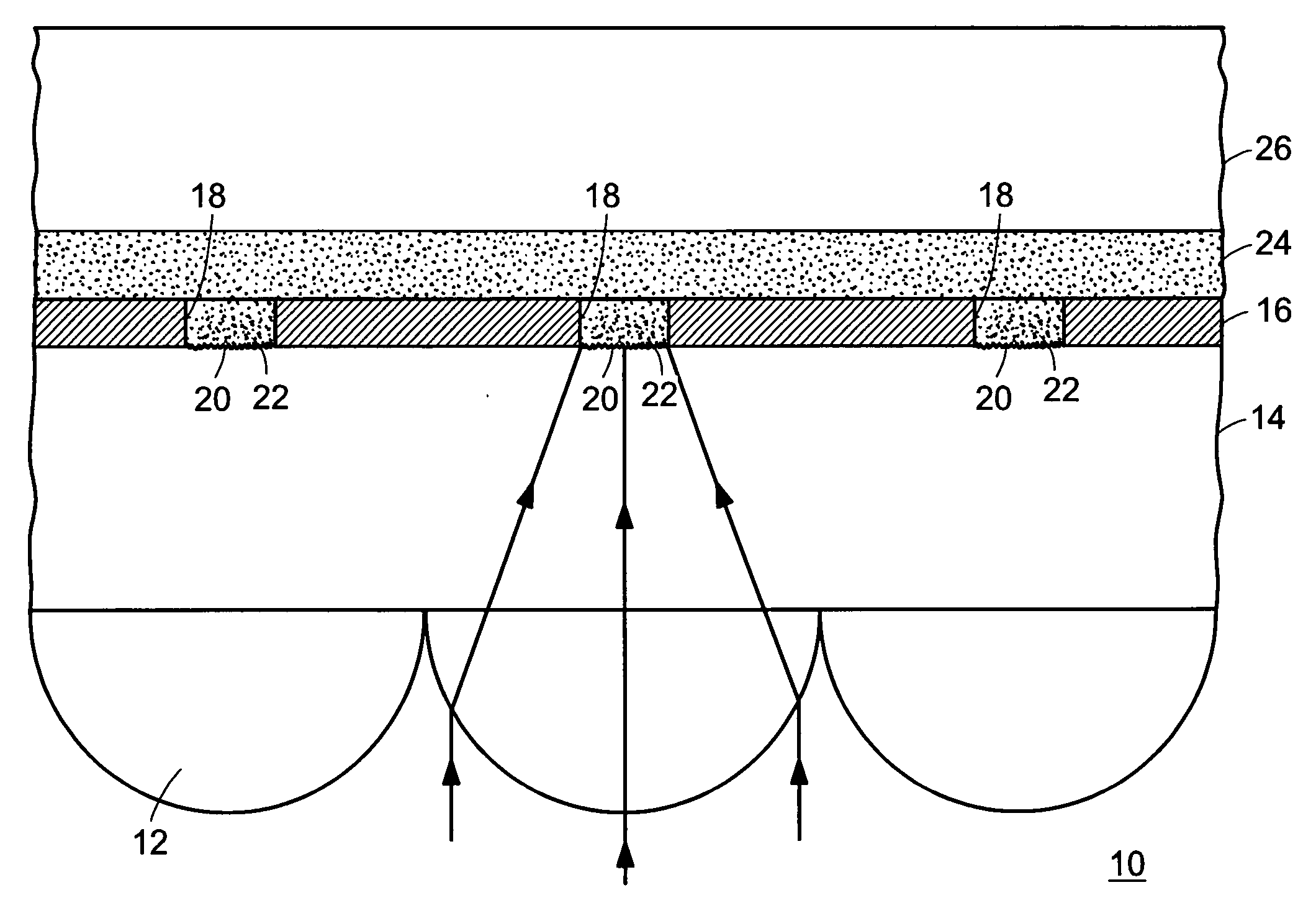
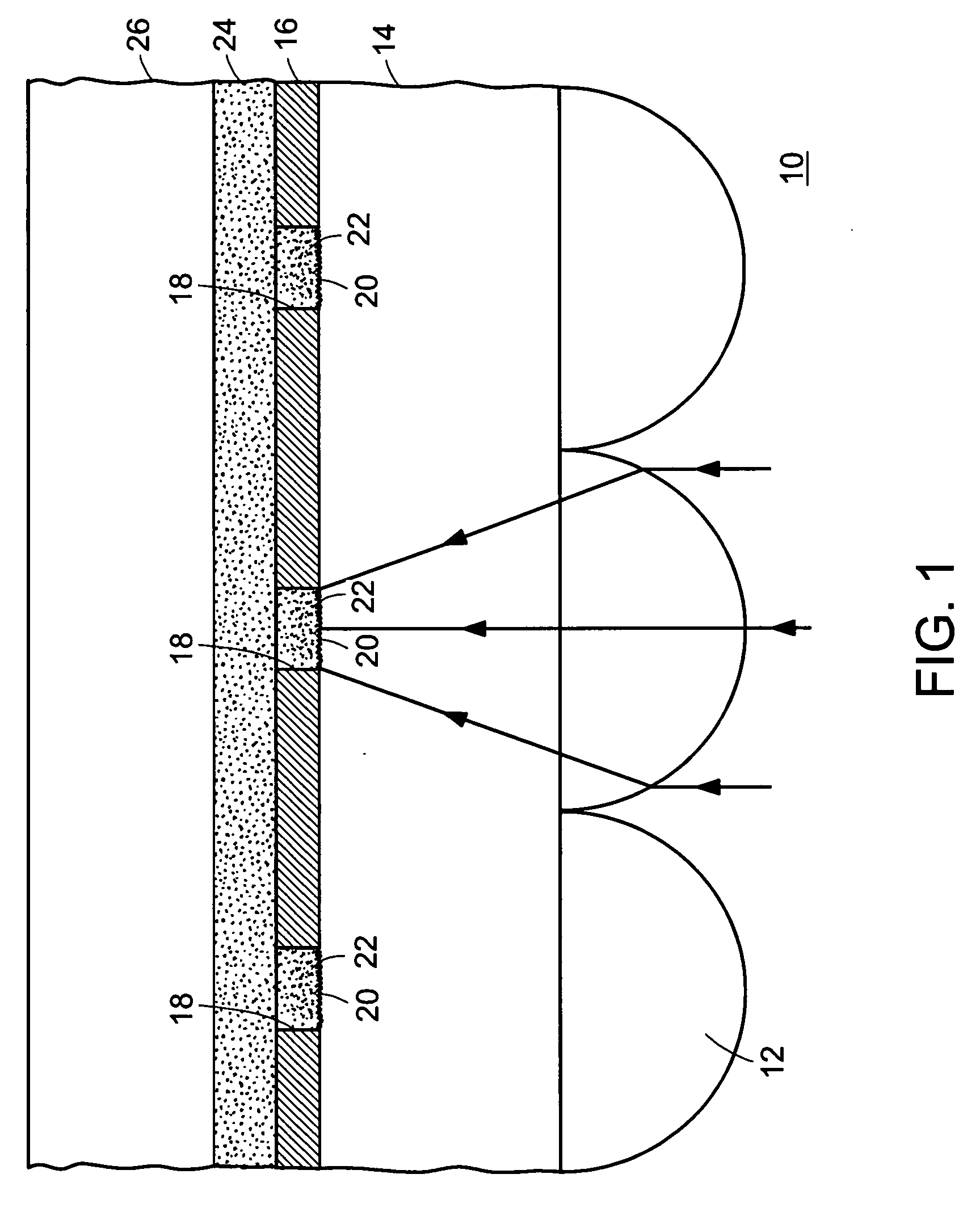
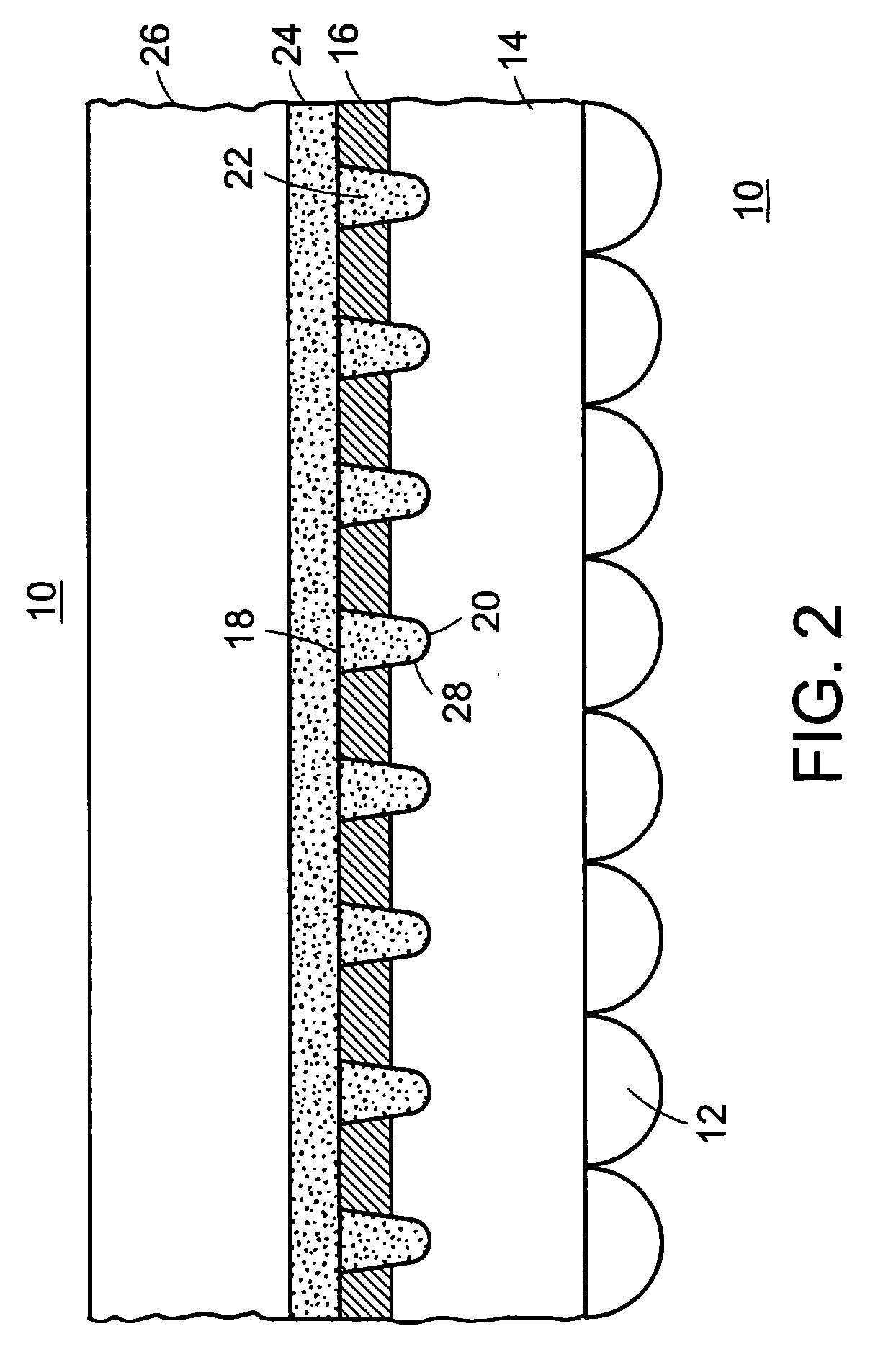
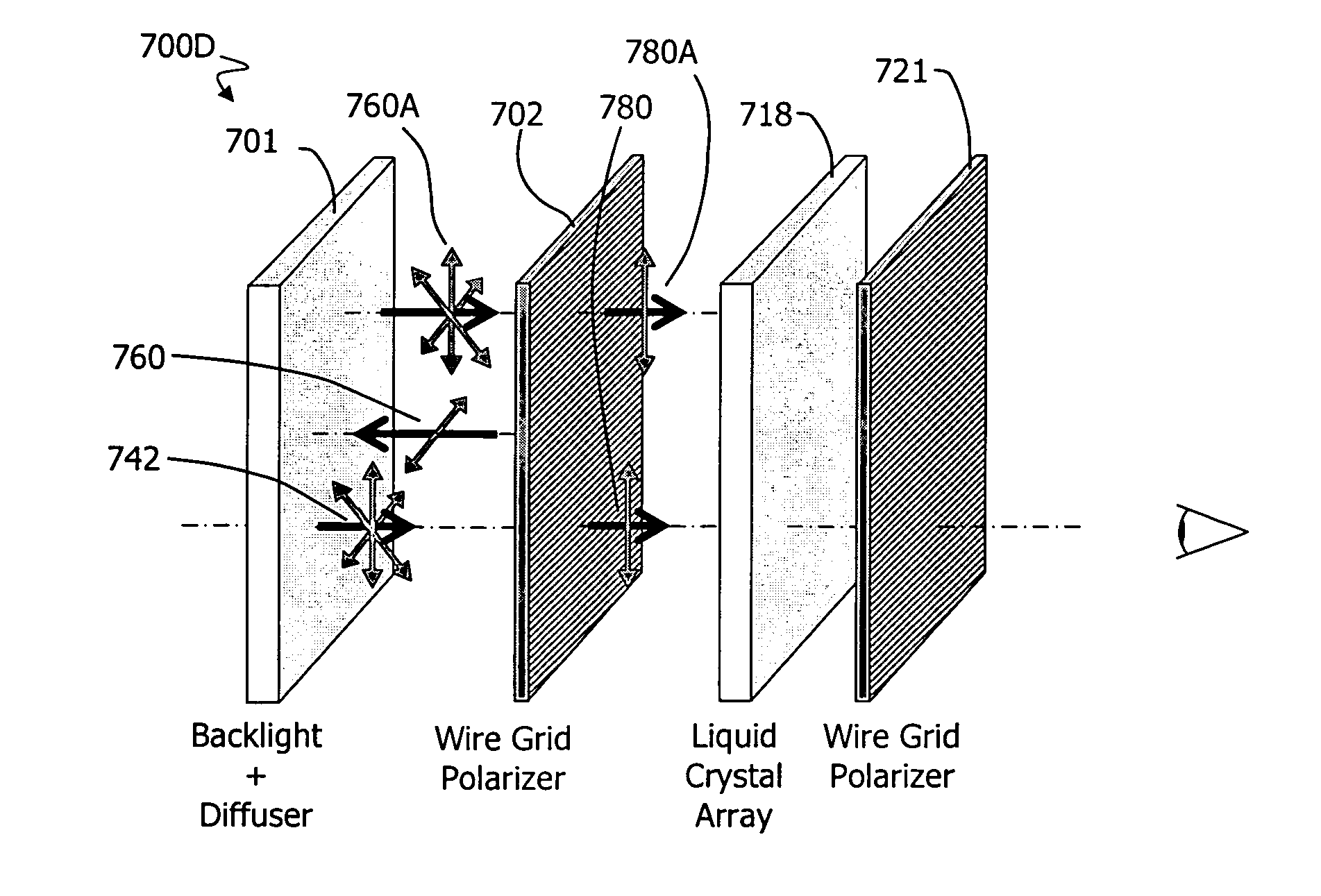
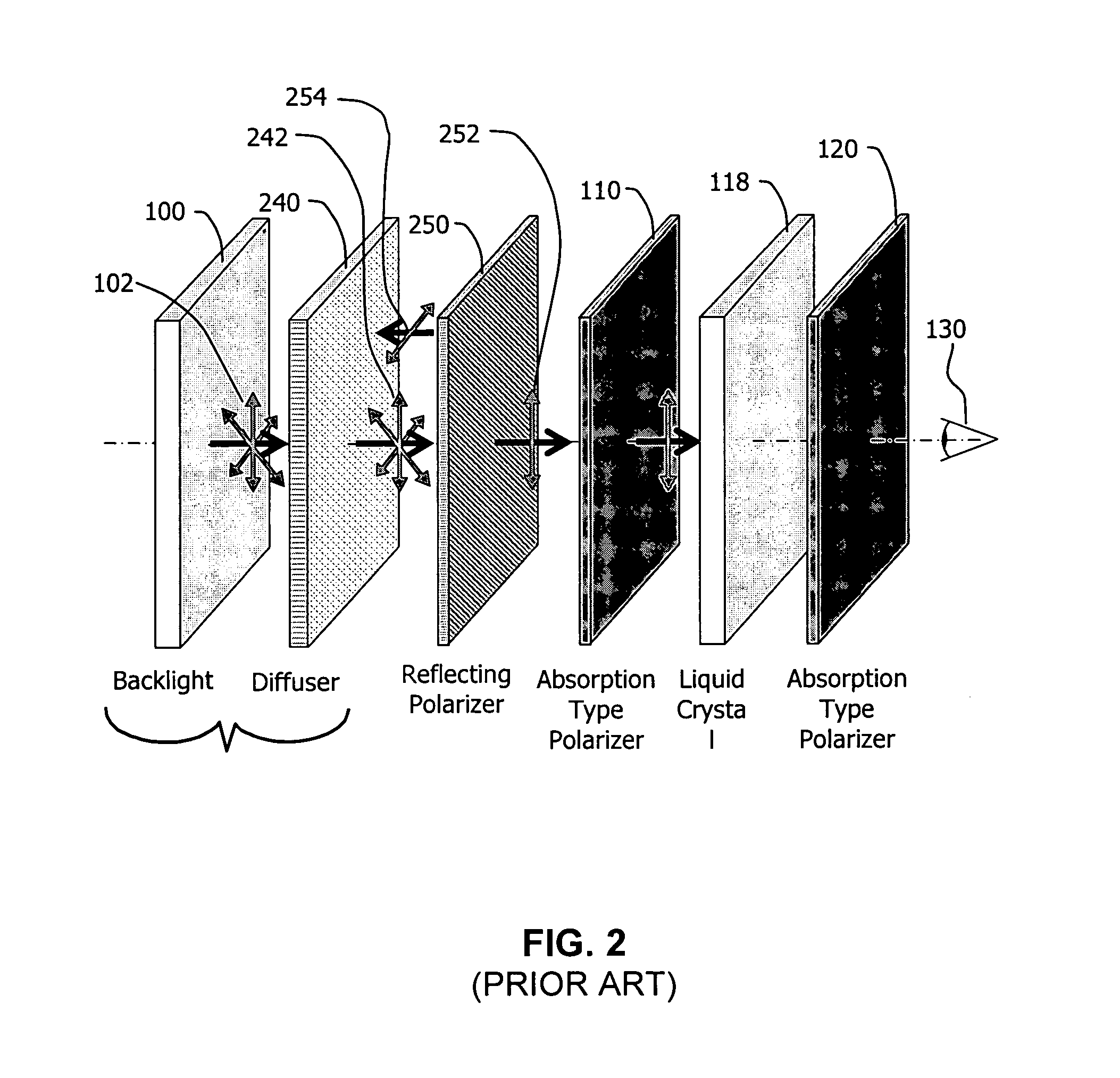
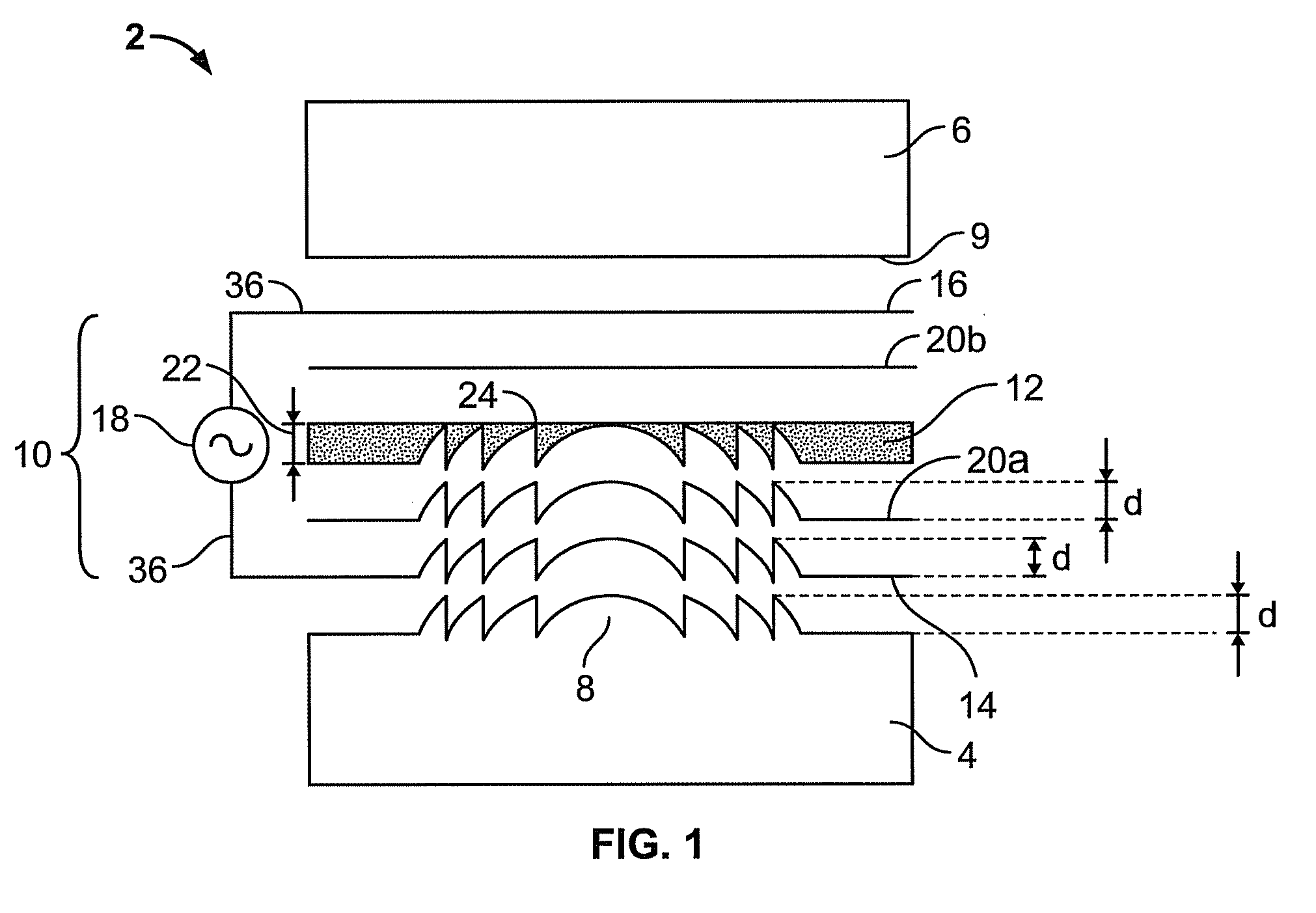
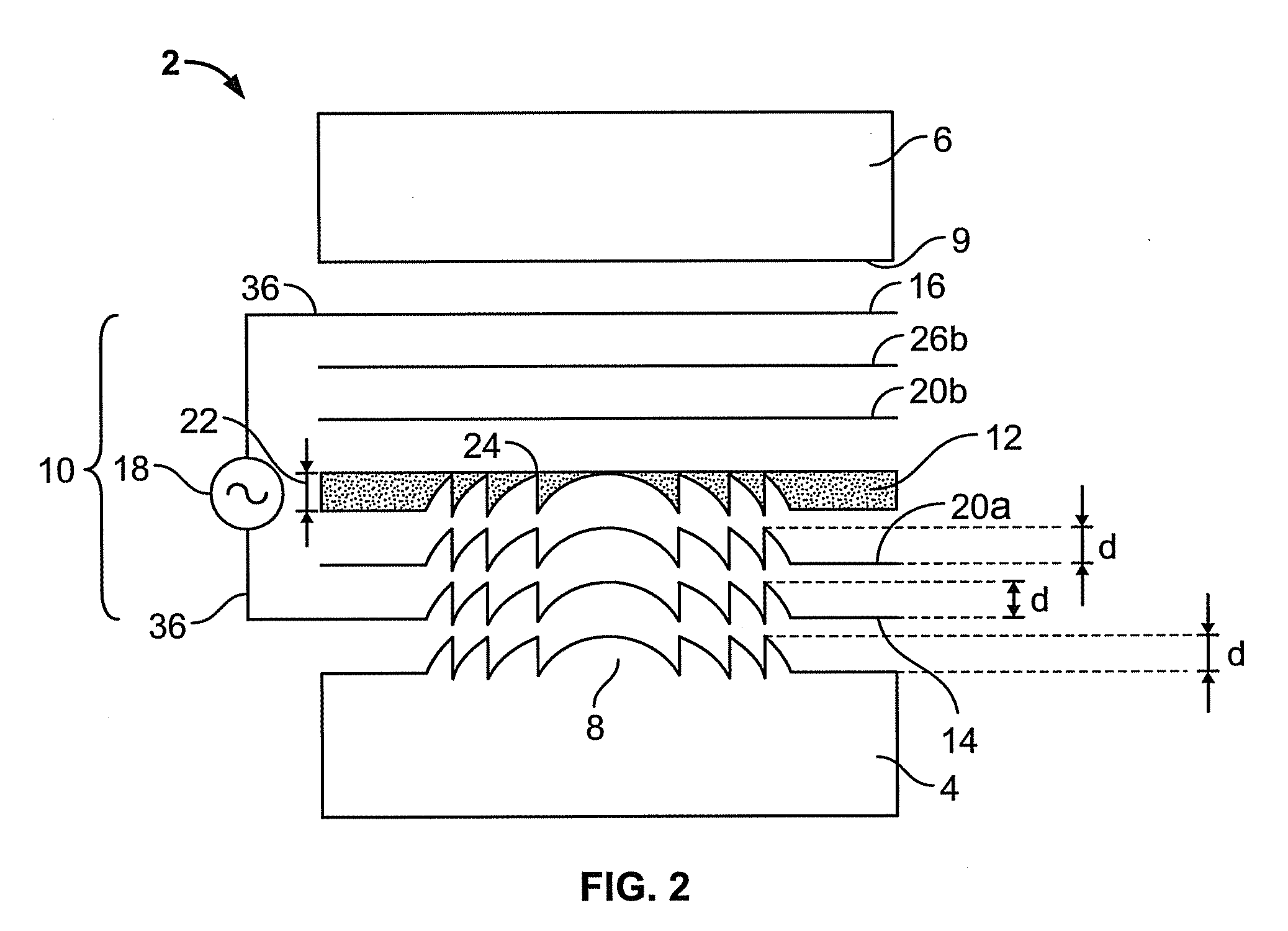
Virtual and augmented reality systems and methods
ActiveUS20170010488A1High diffraction efficiencyReduce sensitivityPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsWavefrontBeam steering
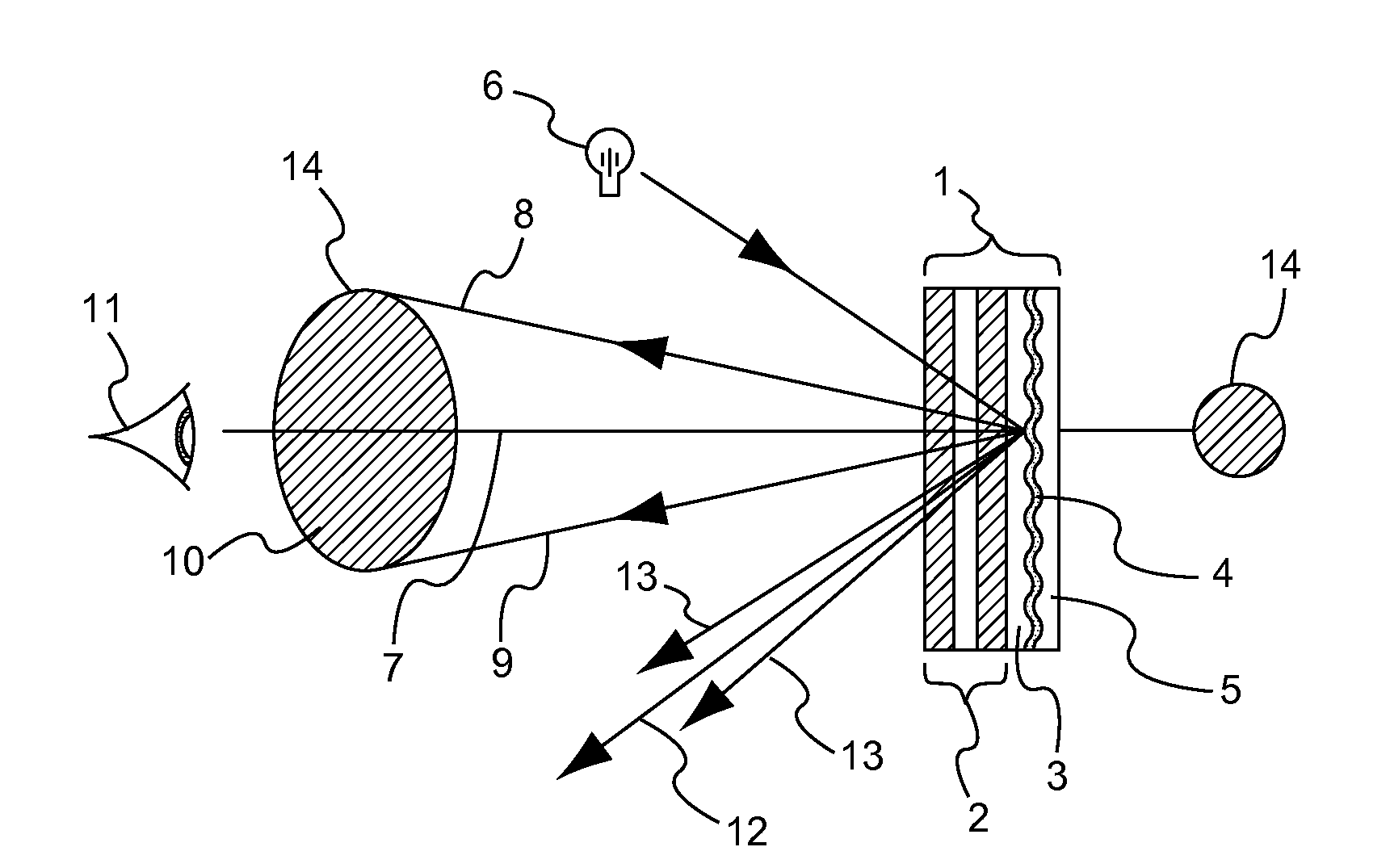
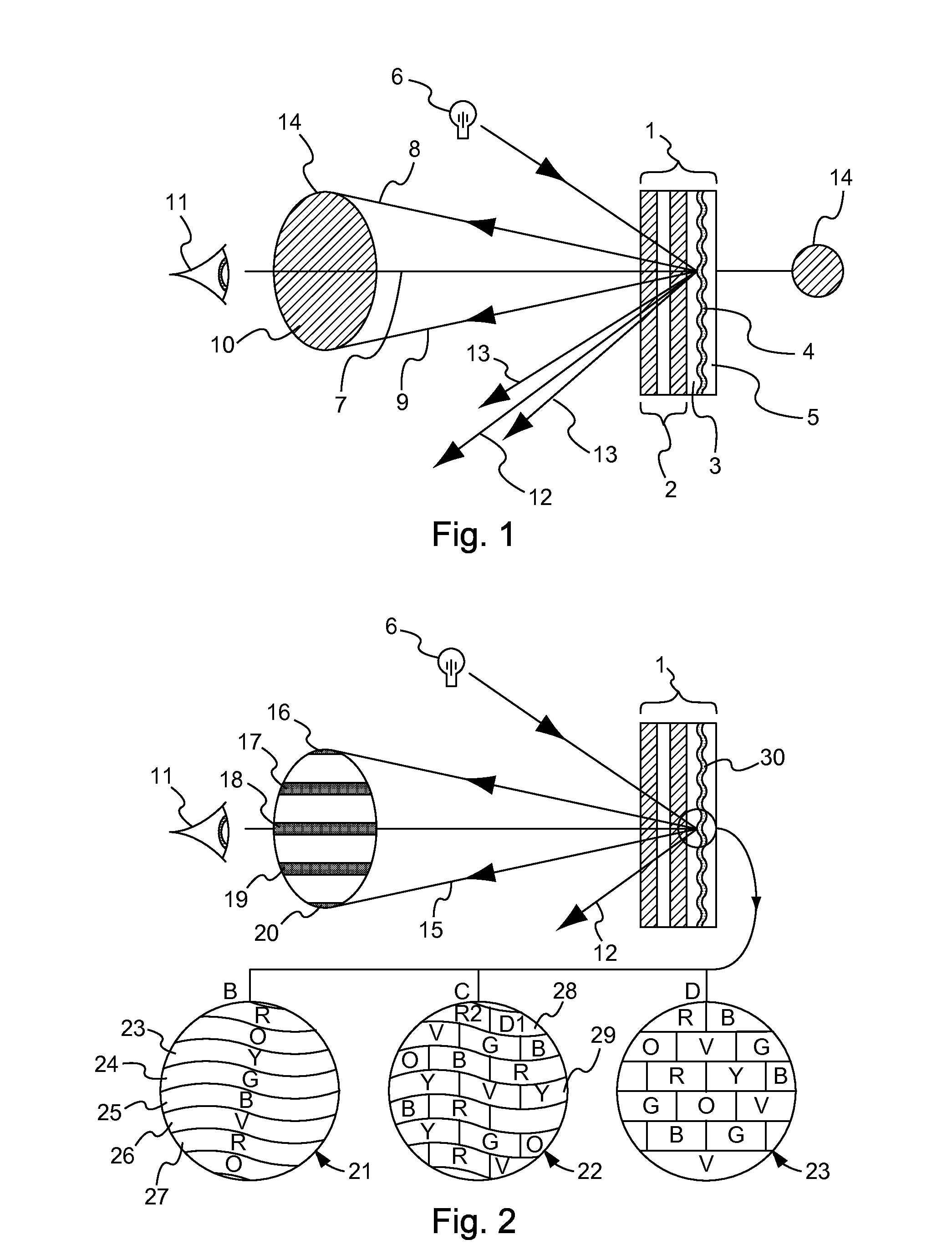
Methods of manufacturing a liquid crystal device including depositing a layer of liquid crystal material on a substrate and imprinting a pattern on the layer of liquid crystal material using an imprint template are disclosed. The liquid crystal material can be jet deposited. The imprint template can include surface relief features, Pancharatnam-Berry Phase Effect (PBPE) structures or diffractive structures. The liquid crystal device manufactured by the methods described herein can be used to manipulate light, such as for beam steering, wavefront shaping, separating wavelengths and / or polarizations, and combining different wavelengths and / or polarizations.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
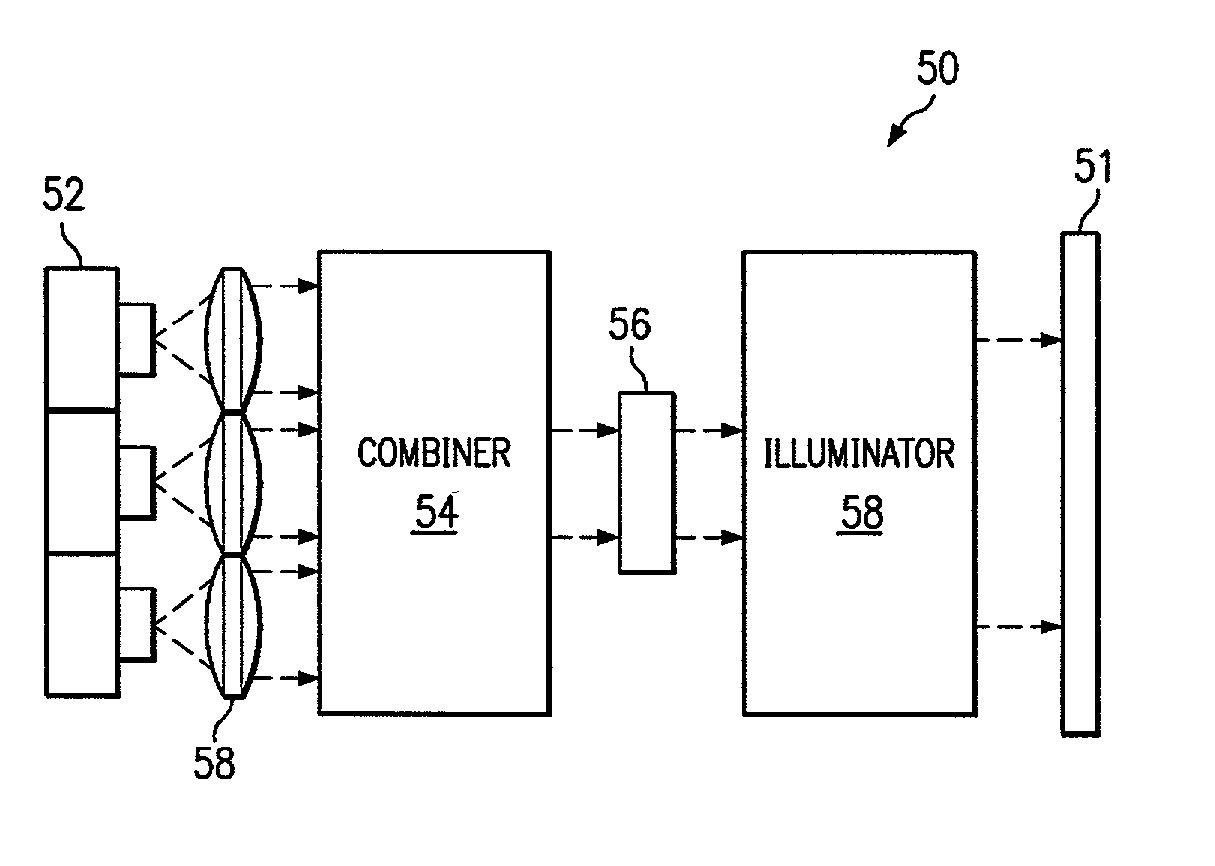
High power incoherent light source with laser array
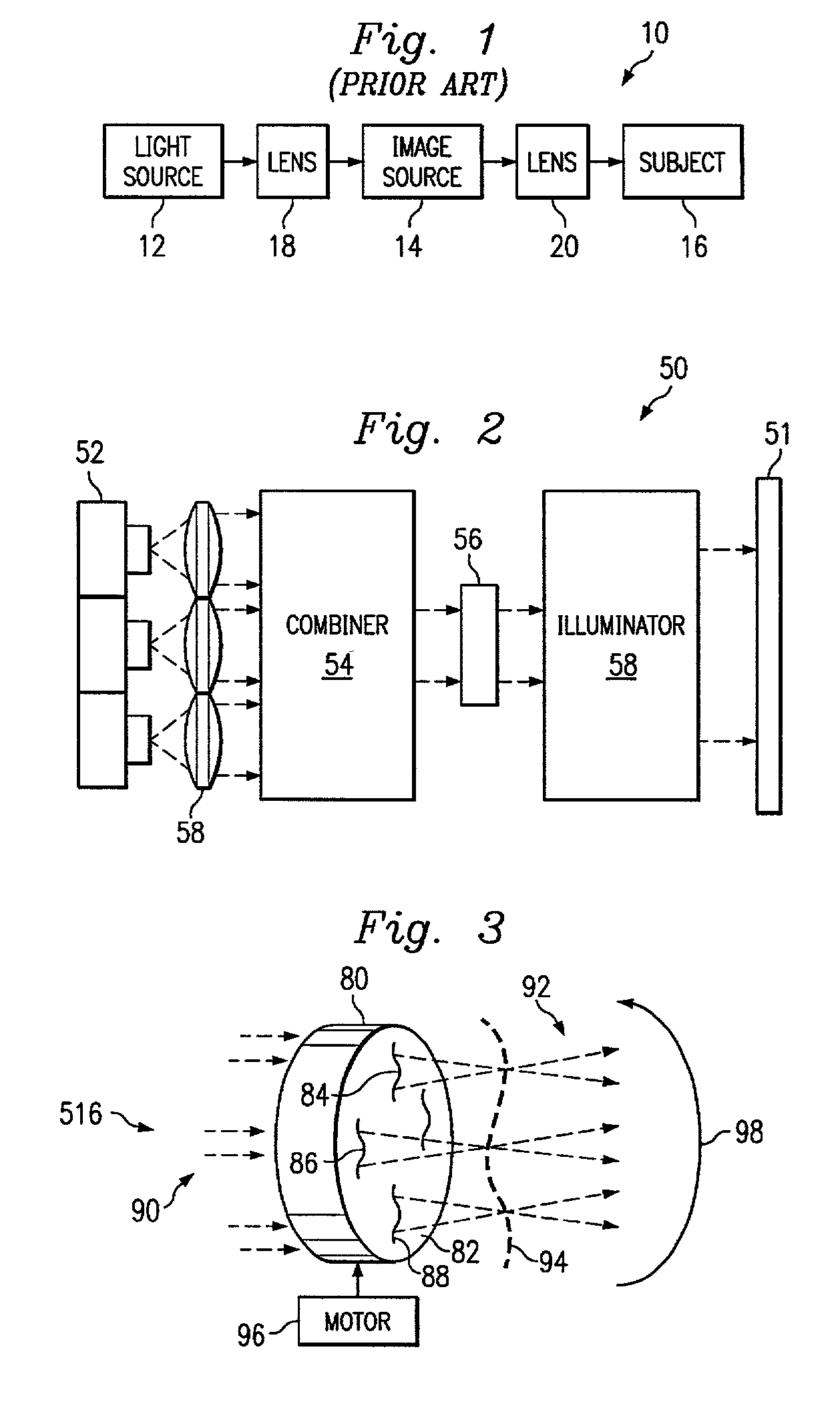
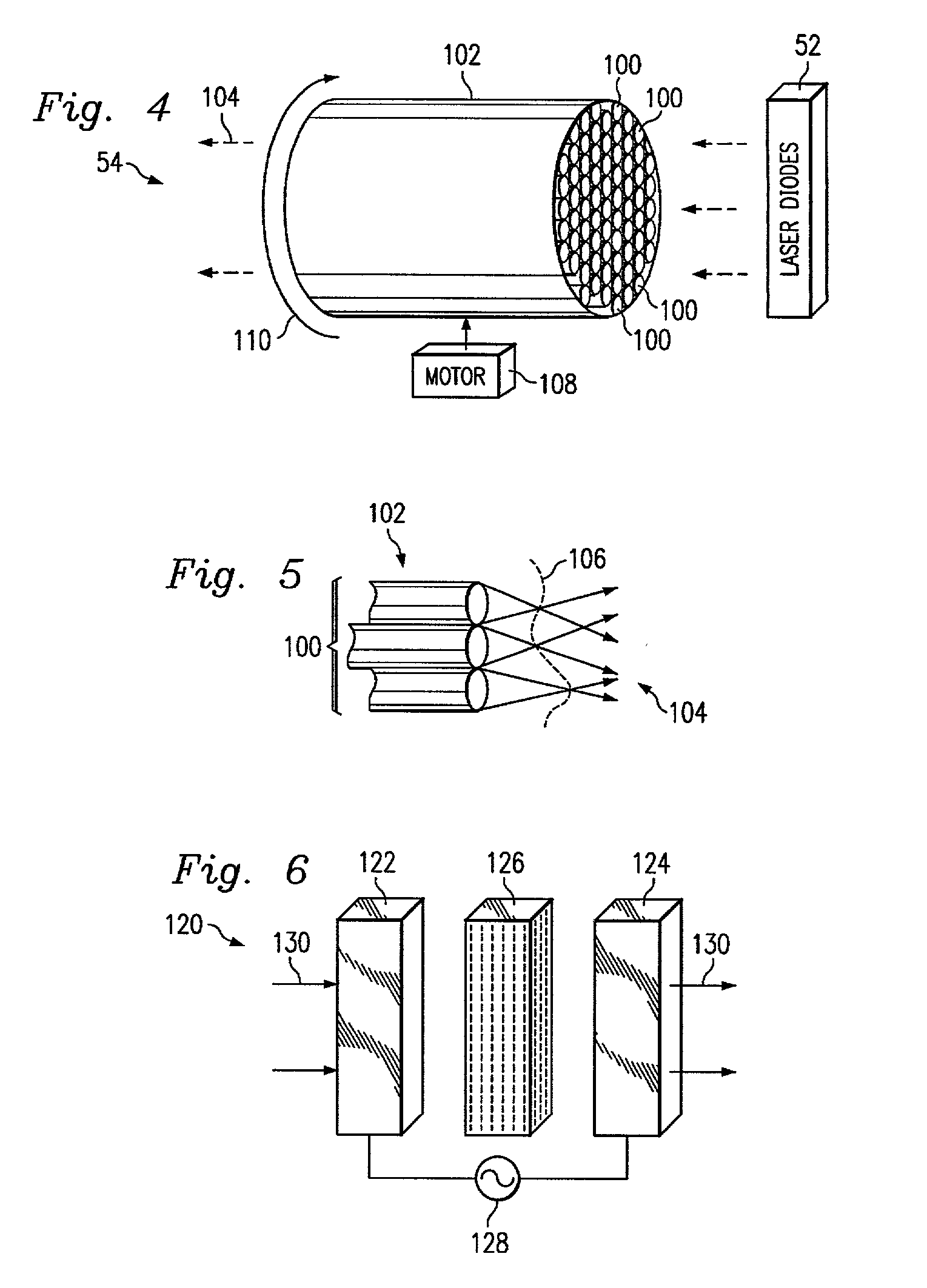
A high power light source is provided. The light source includes one or more diodes that may produce relatively coherent light of a desired intensity. The diodes may be pulsed to provide light as desired. The light projected by the diodes passes through a combiner, which combines the light from the different diodes and passes the combined light to an incoherence apparatus. The incoherence apparatus may include a rotating surface relief phase device such as an optical hologram, a computer generated hologram, or a diffractive optical element with random phase modulation. The incoherence apparatus may include a rotating fiber conduit comprising a plurality of multifiber cores. The incoherence apparatus renders the combined light incoherent and passes it to an illuminator apparatus that focuses the incoherent combined light onto an image plane.
Owner:BALL SEMICON
Electrically tunable diffractive grating element
ActiveUS7184615B2Improve color uniformityImprove image qualityDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesElectricityExit pupil
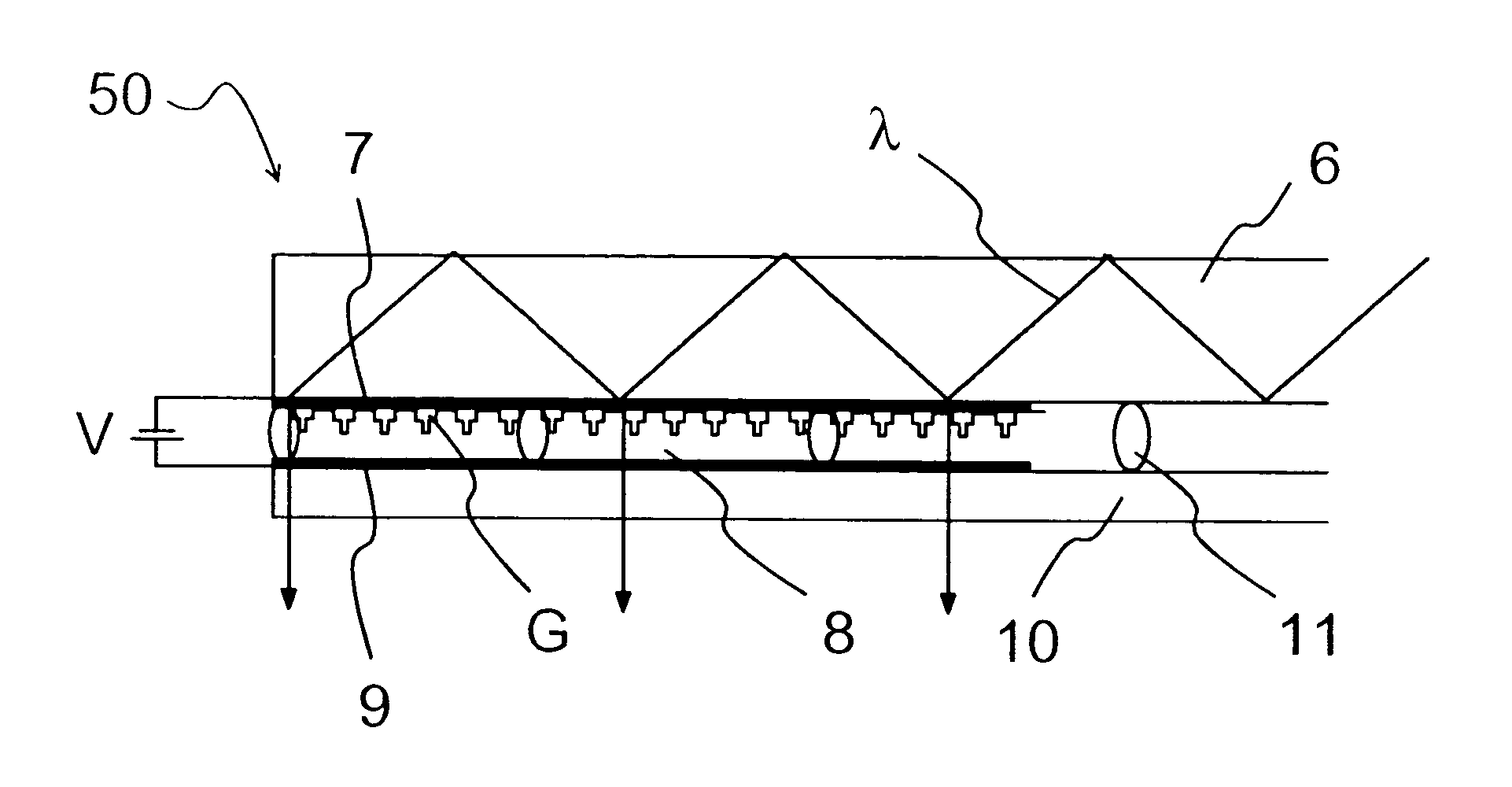
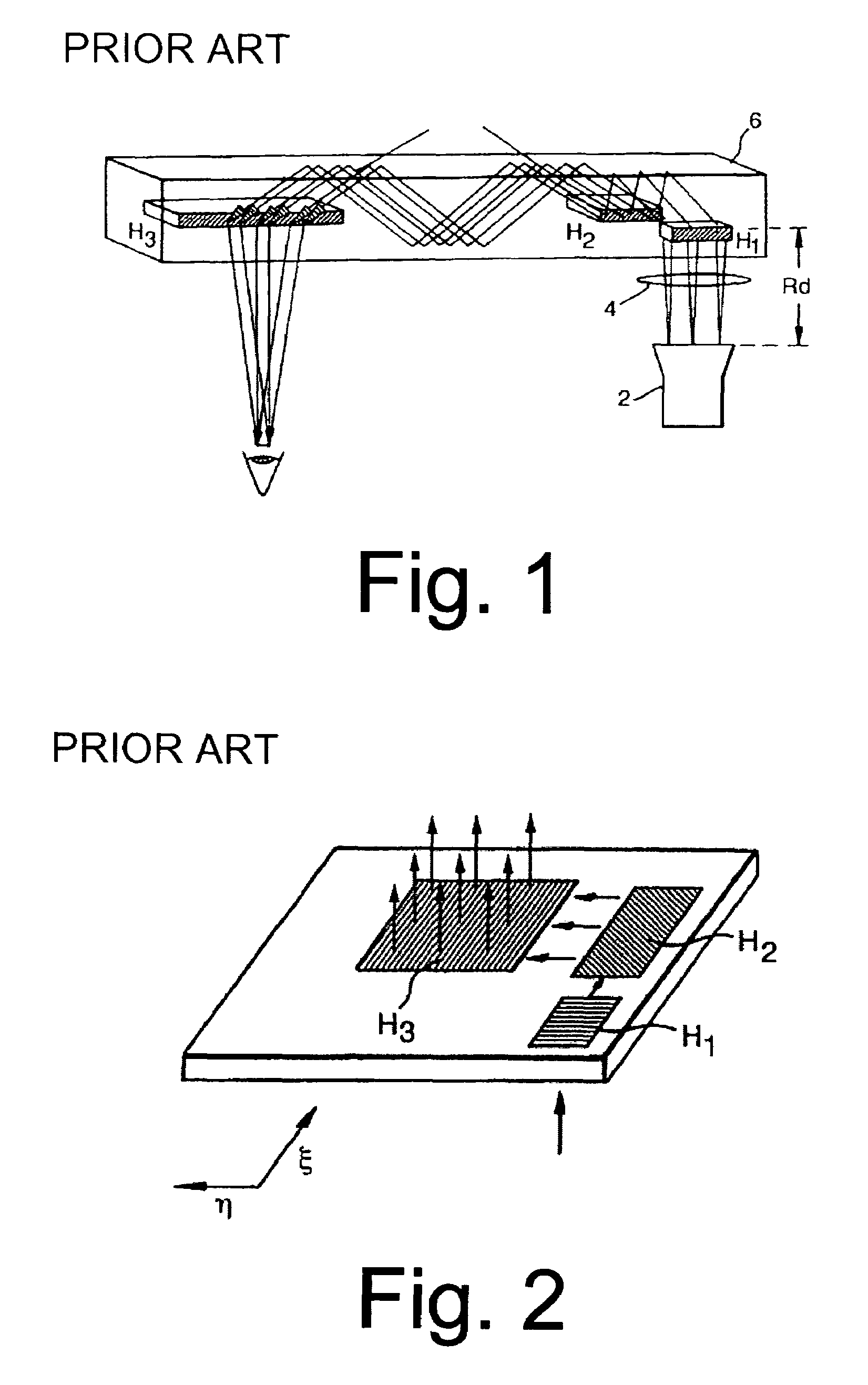
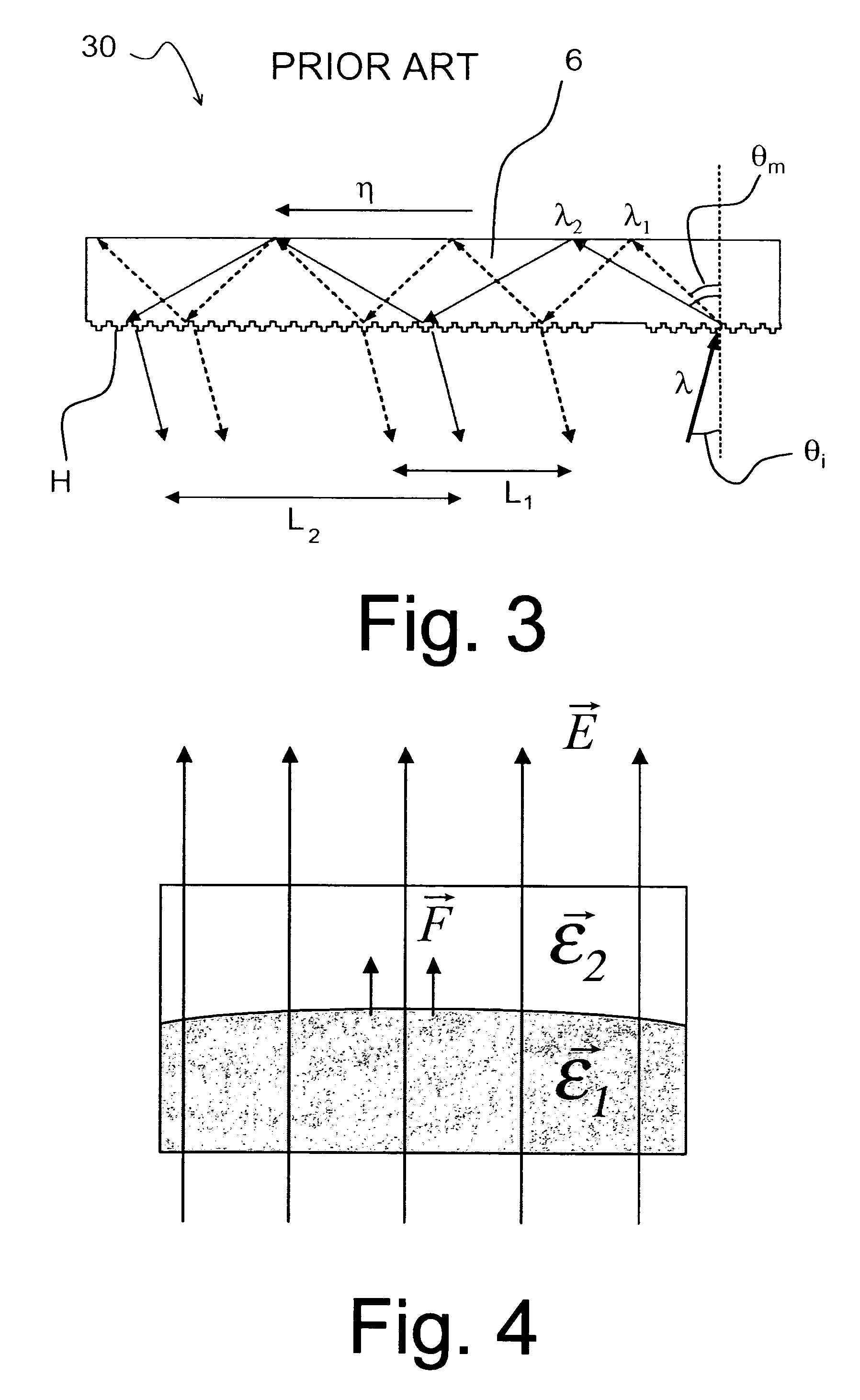
The invention relates to an optical device (50) for manipulating a light wave (λ) using a diffractive grating structure (G). According to the basic idea behind the invention a prior art type diffractive grating structure having a permanently shaped surface relief is substituted with an electrically deformable diffractive grating structure (G), where a preformed, basic surface relief of the grating is composed of dielectric and deformable viscoelastic material, which can be electrically and sequentially fine tuned in shape to adjust the diffraction properties of said grating individually for different wavelengths. The invention permits manufacture of virtual display devices with a significantly larger exit pupil diameter than prior art solutions without degrading the color uniformity of the display device.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20120018764A1Improve efficiencyLight extraction efficiencyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDielectricElectrical connector
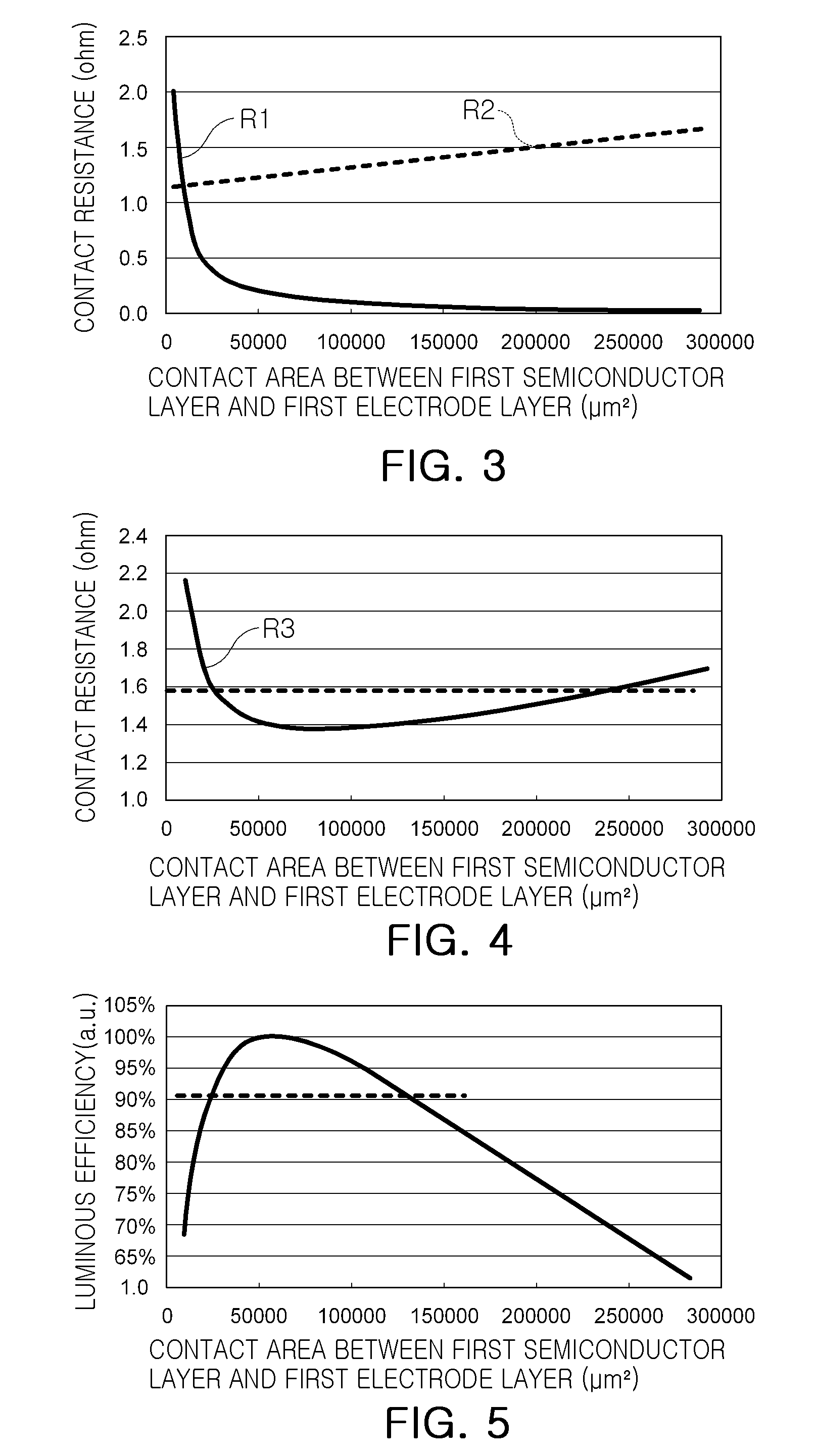
The present invention relates to a vertical / horizontal light-emitting diode for a semiconductor. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a semiconductor light-emitting diode comprising: a conductive substrate; a light-emitting structure including a first conductive semiconductor layer, an active layer and a second conductive semiconductor layer sequentially formed over the conductive substrate; a second conductive electrode including a conductive via that passes through the first conductive semiconductor and active layers to be connected with the second conductive semiconductor layer therein, and an electrical connector that extends from the conductive via and is exposed outside the light-emitting structure; a passivation layer for covering a dielectric and at least the side surface of the active layer of the light-emitting structure, the dielectric serving to electrically isolate the second conductive electrode from the conductive substrate, the first conductive semiconductor layer and the active layer; and a surface relief structure formed on the pathway of light emitted from the active layer. According to the present invention, a semiconductor light-emitting diode exhibiting enhanced external light extraction efficiency, especially the diode's side light extraction efficiency, can be obtained.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
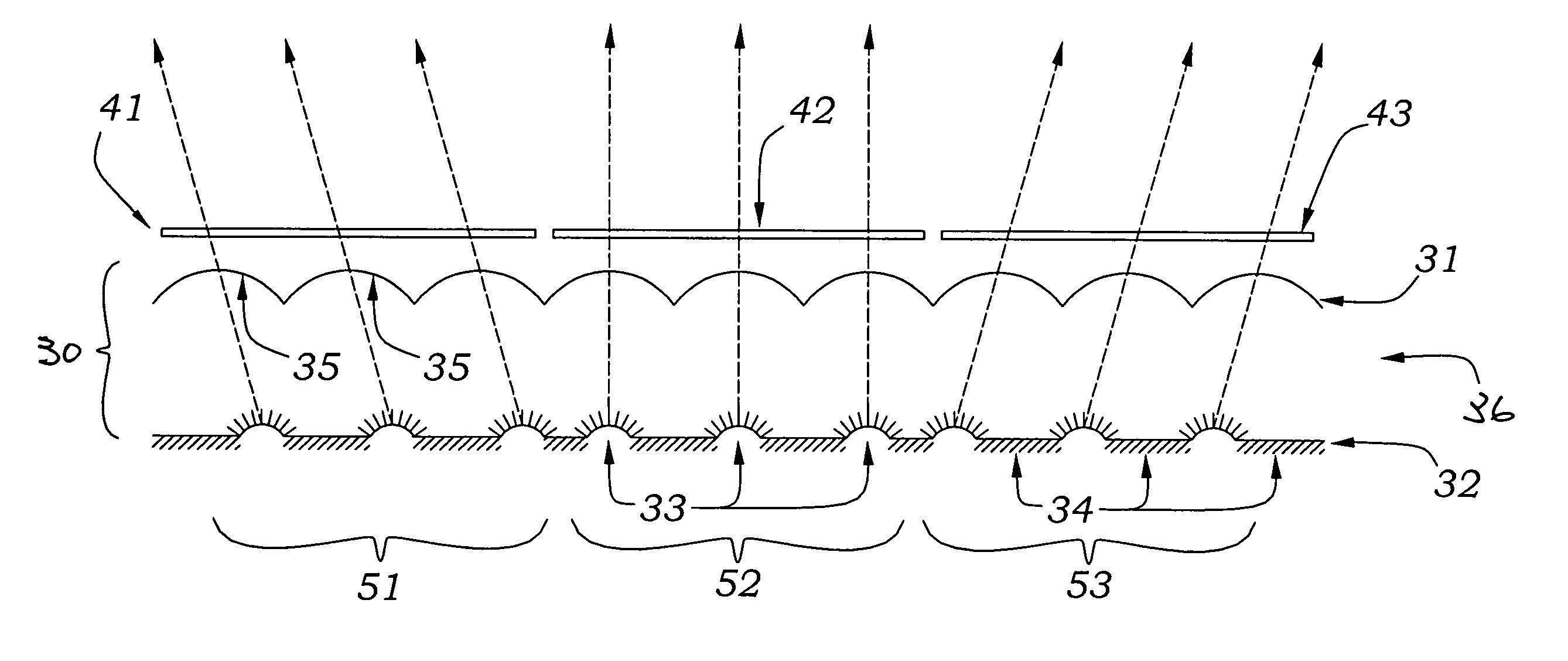
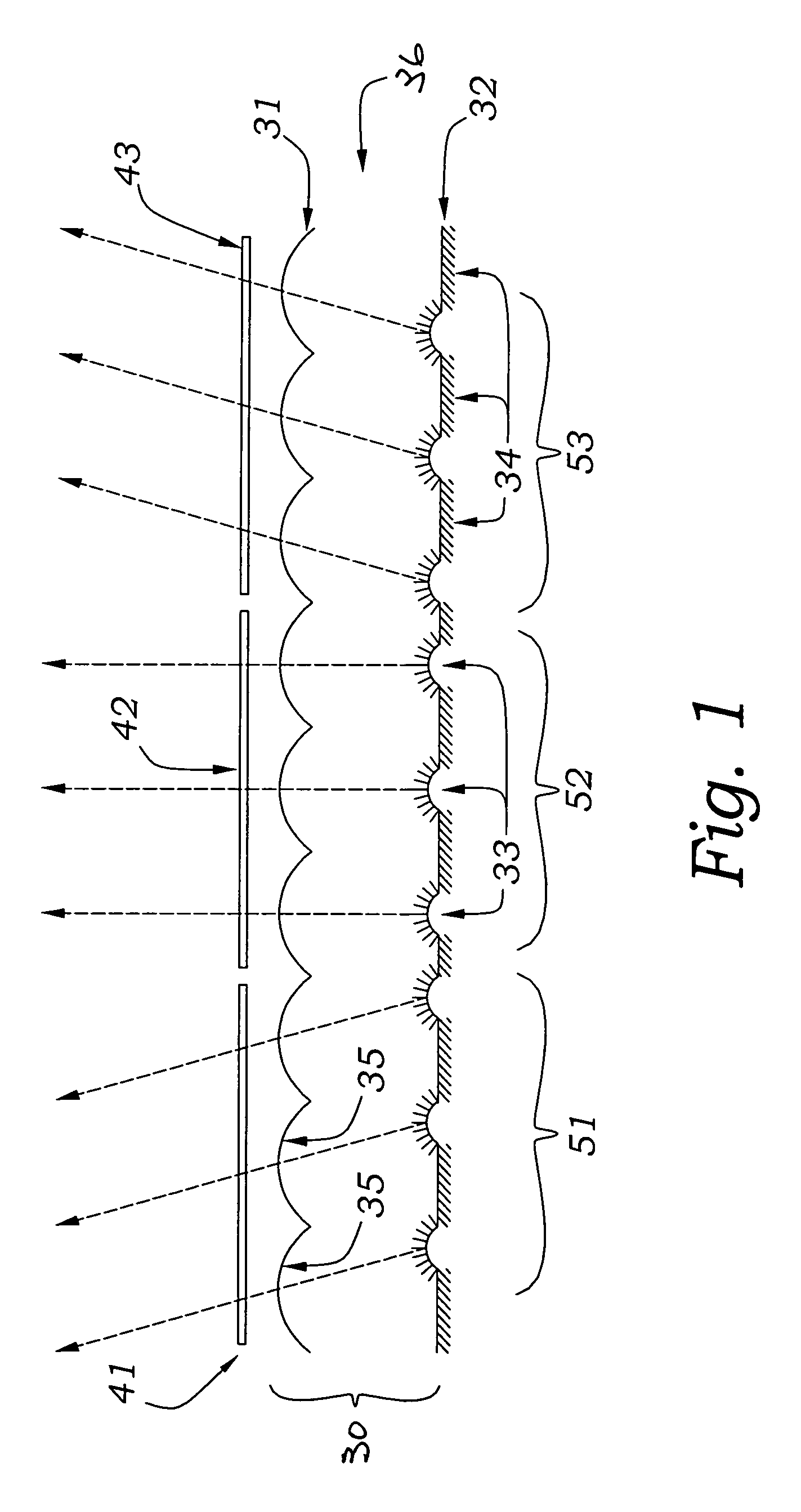
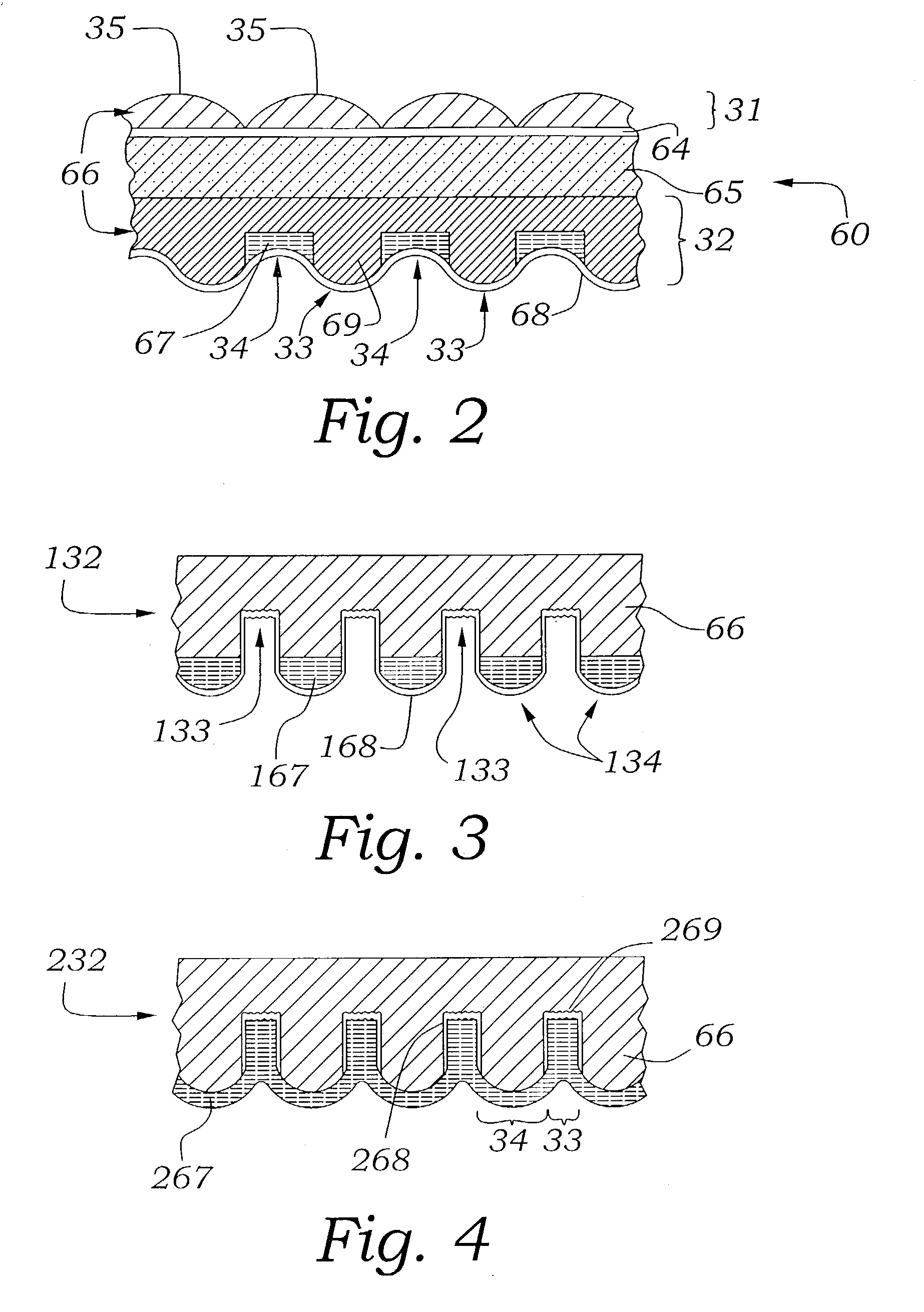
Waveguide illumination system
InactiveUS20140140091A1Reduce light lossMinimizes lightMechanical apparatusElectric lightingForward scatterTotal internal reflection
An illumination system employing a waveguide. Light received from an edge or an end of a waveguide is propagated in response to transmission and total internal reflection. Light deflecting elements distributed along the propagation path of light continuously change the out-of-plane propagation angle of light rays and cause decoupling of portions of the propagated light from the core of the waveguide at different distances from the light input edge or end. Light escapes from the waveguide into an intermediate layer at low out-of-plane angles and is further redirected by light extraction features out of the system. In one embodiment, the illumination system is configured to emit collimated light. In one embodiment, the illumination system includes shallow surface relief features. In one embodiment, the light deflecting elements include forward-scattering particles distributed throughout the volume of the waveguide. Additional collimating and non-collimating illumination units and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:VASYLYEV SERGIY VICTOROVICH
Tissue dressing assemblies, systems, and methods formed from hydrophilic polymer sponge structures such as chitosan
InactiveUS20050147656A1Imparts complianceImparts flexibilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideInlet channelHydrophilic polymers
Tissue dressing assemblies are formed from hydrophilic polymer sponge structures. The tissue dressing assemblies can be used, e.g., (i) stanch, seal, or stabilize a site of tissue injury, tissue trauma, or tissue access; or (ii) form an anti-microbial barrier; or (iii) form an antiviral patch; or (iv) intervene in a bleeding disorder; or (v) release a therapeutic agent; or (vi) treat a mucosal surface; or (vii) combinations thereof. The tissue dressing structures are made compliant, e.g., by (i) micro-fracturing of a substantial portion of the sponge structure by mechanical manipulation prior to use, or (ii) a surface relief pattern formed on a substantial portion of the sponge structure prior to use, or (iii) a pattern of fluid inlet channels formed in a substantial portion of the sponge structure prior to use, or (iv) the impregnation of a sheet material within the sponge structure.
Owner:HEMCON MEDICAL TECH
Luminance enhancement apparatus and method
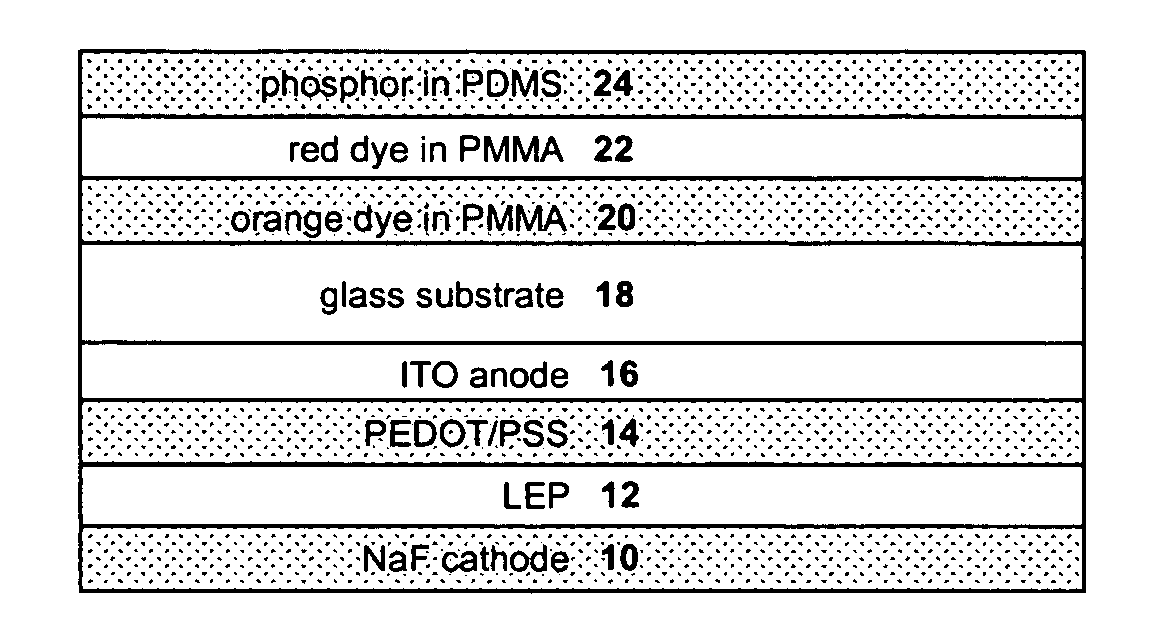
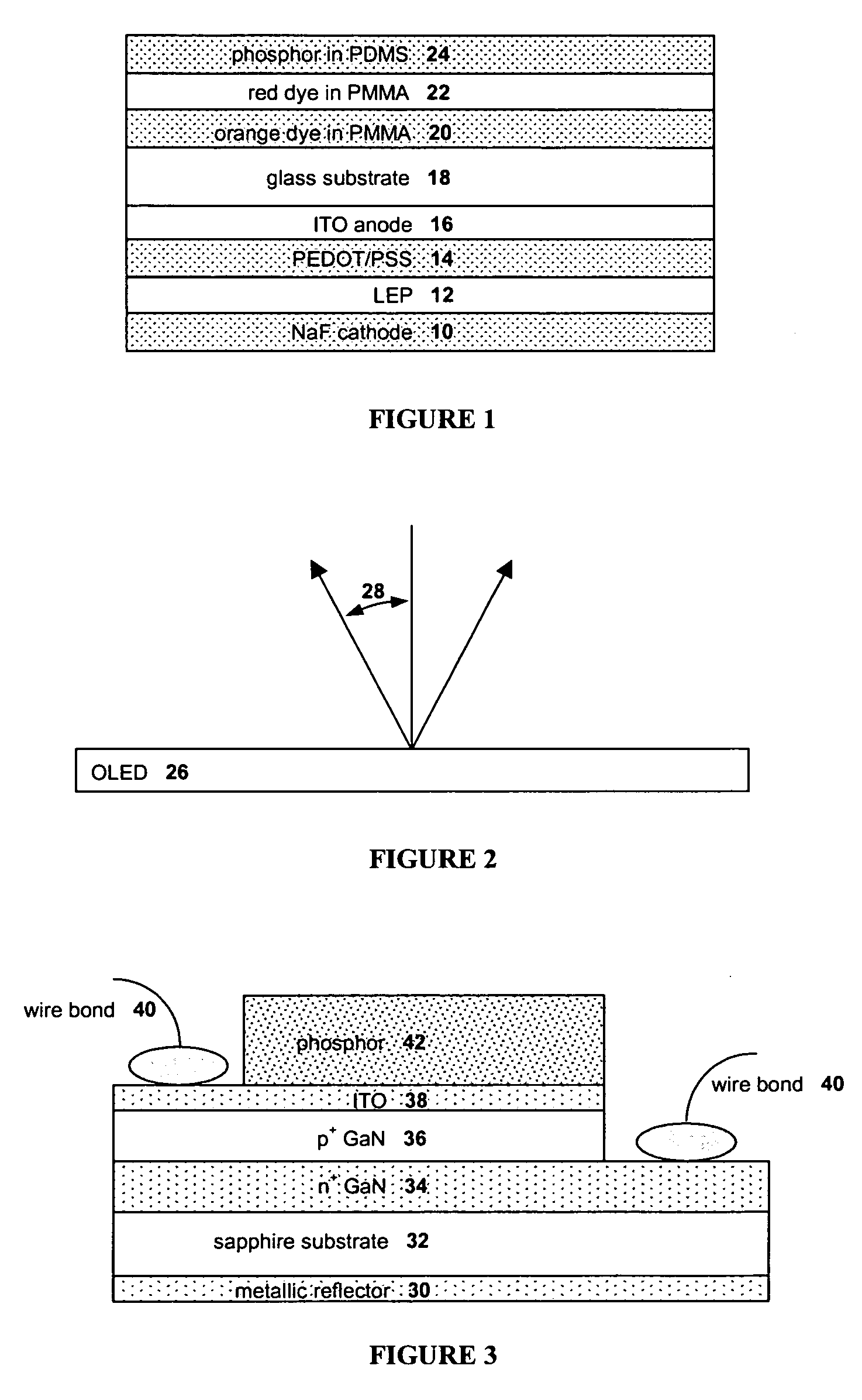
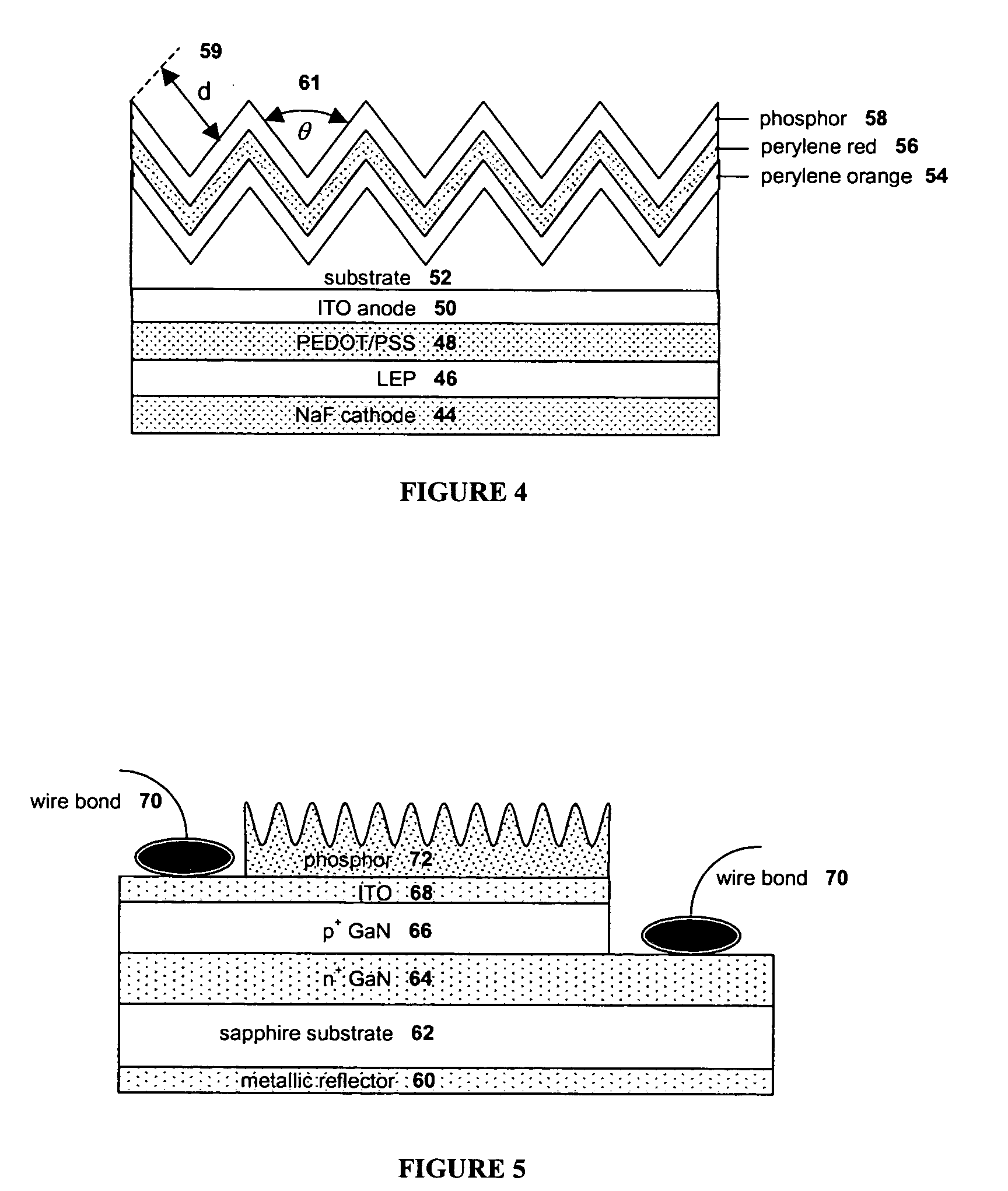
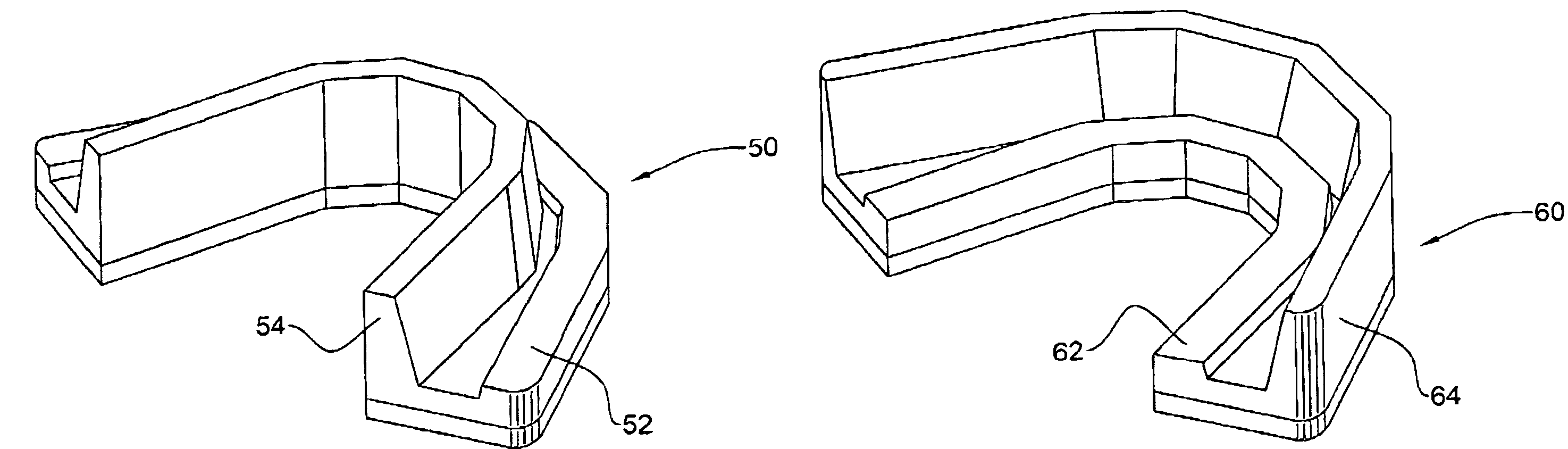
The present invention provides a luminance enhancement apparatus and method for use with light-emitting elements comprising a conversion system adjacent the light-emitting element for converting electromagnetic radiation of one or more wavelengths to alternate wavelengths. This conversion process can be enabled by the absorption of the one or more wavelengths by the conversion system and emission of the alternate wavelengths thereby. The conversion system comprises a predetermined surface relief pattern on the face opposite the light-emitting element to provide a means for reducing absorption of the emitted alternate wavelengths in addition to providing a means for reflection of the emitted alternate wavelengths from the conversion system with a reduced number of reflections, thereby enhancing the illumination provided by the light-emitting element. As the present invention operates on principles of increased surface area and self-excitation of the conversion materials through the use of a predetermined surface relief pattern, the present invention may be applied to both organic LEDs, phosphor-coated semiconductor LEDs, and light-emitting elements coated with a population of quantum dots embedded in a host matrix.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
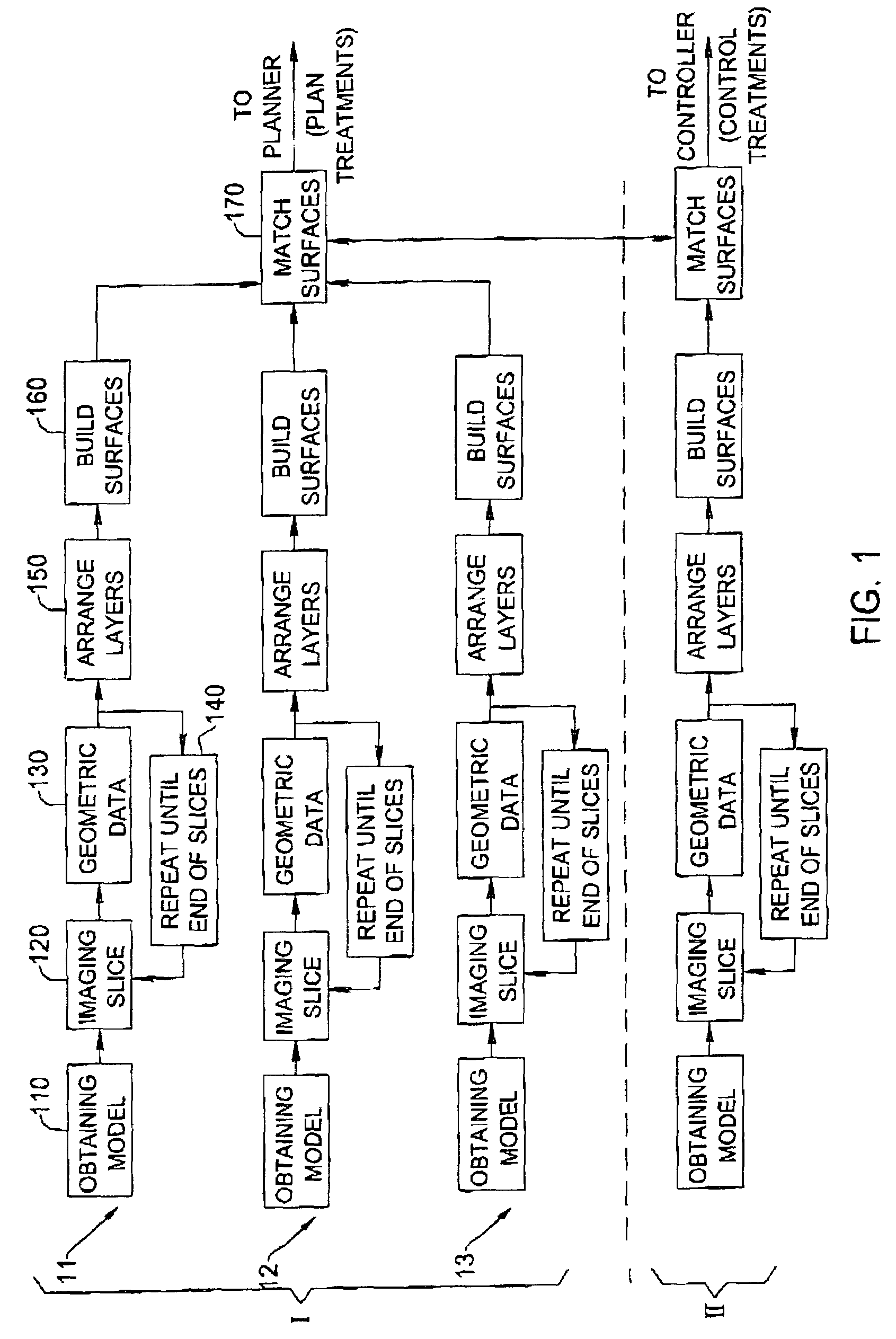
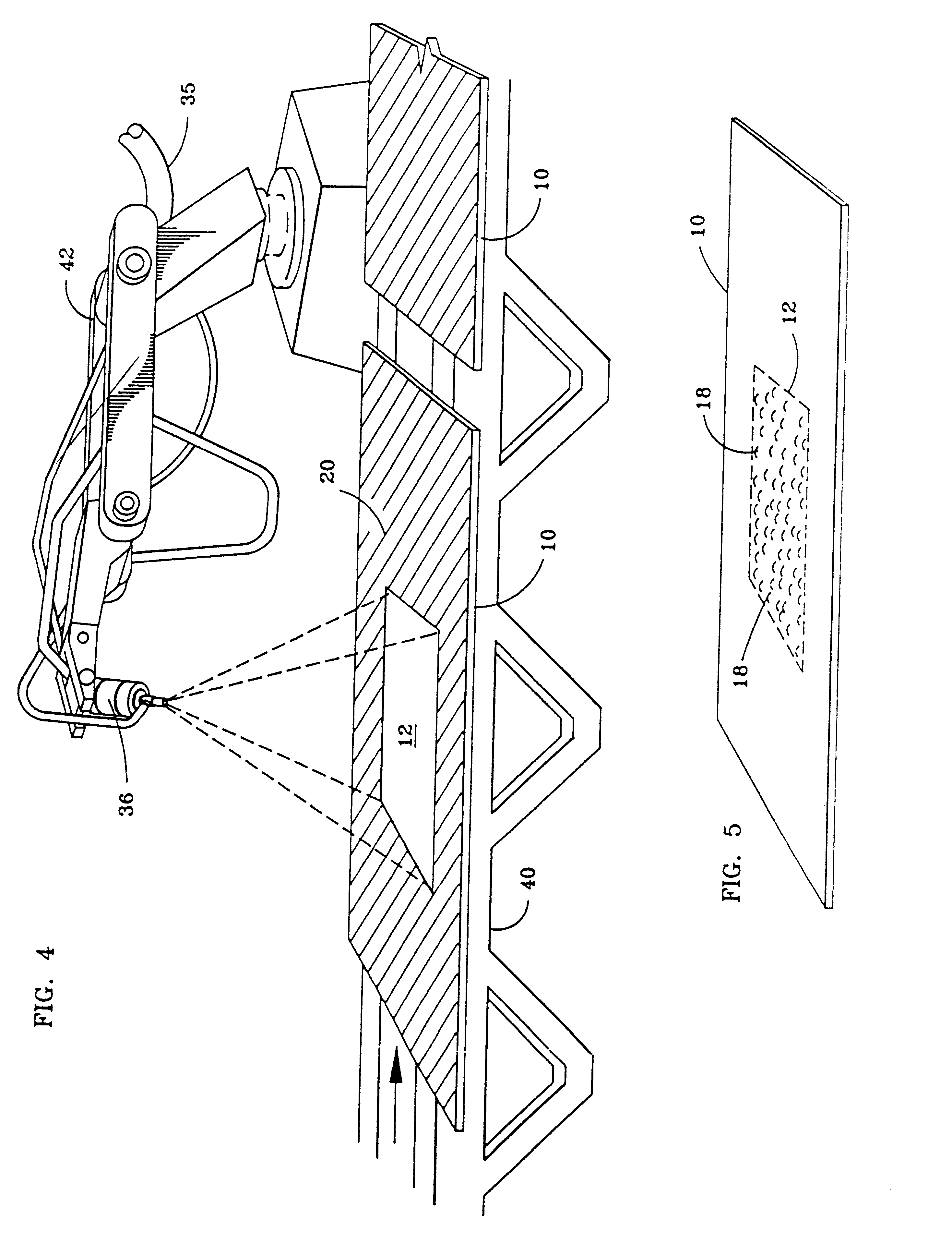
Method and system for imaging a patient's teeth arrangement
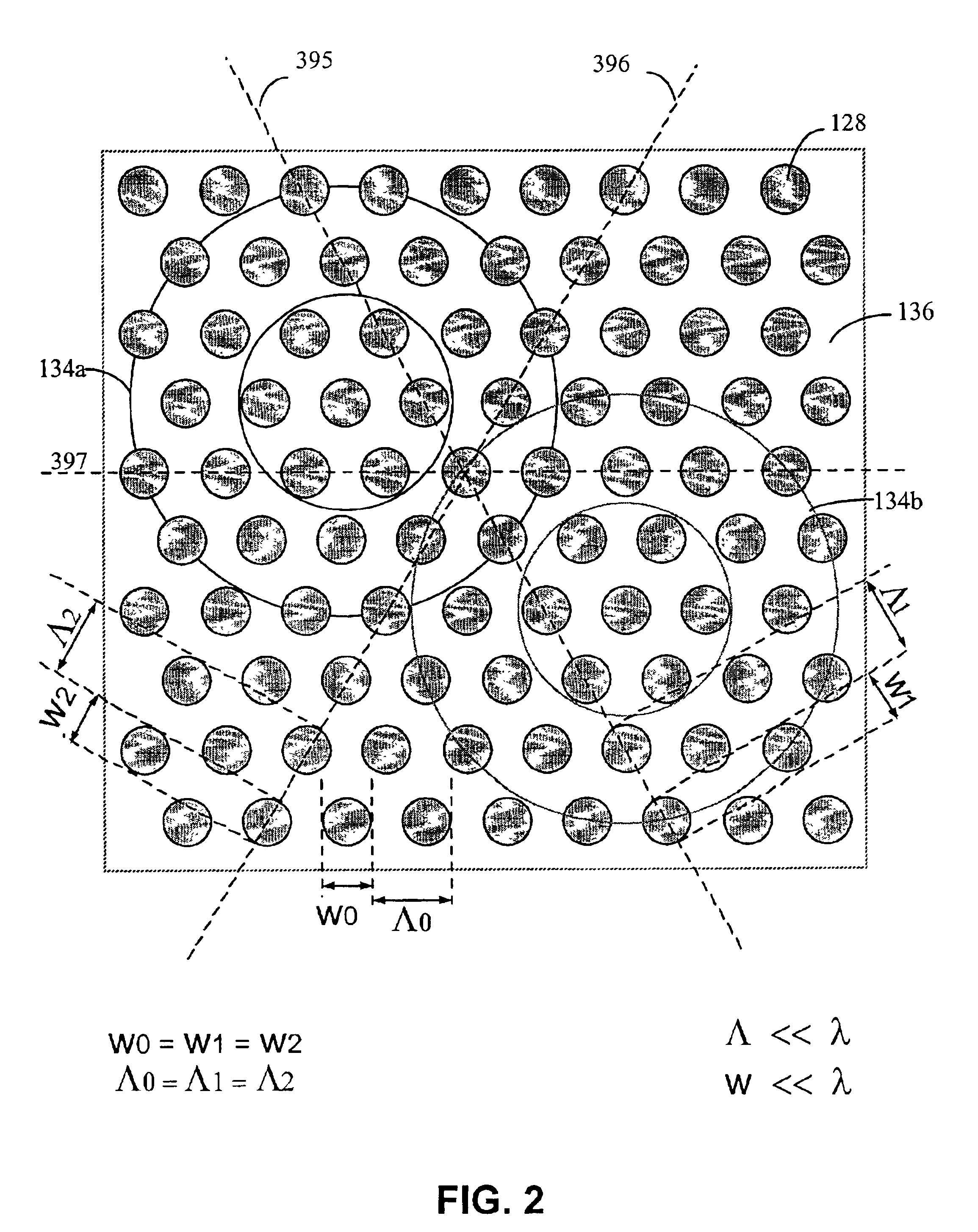
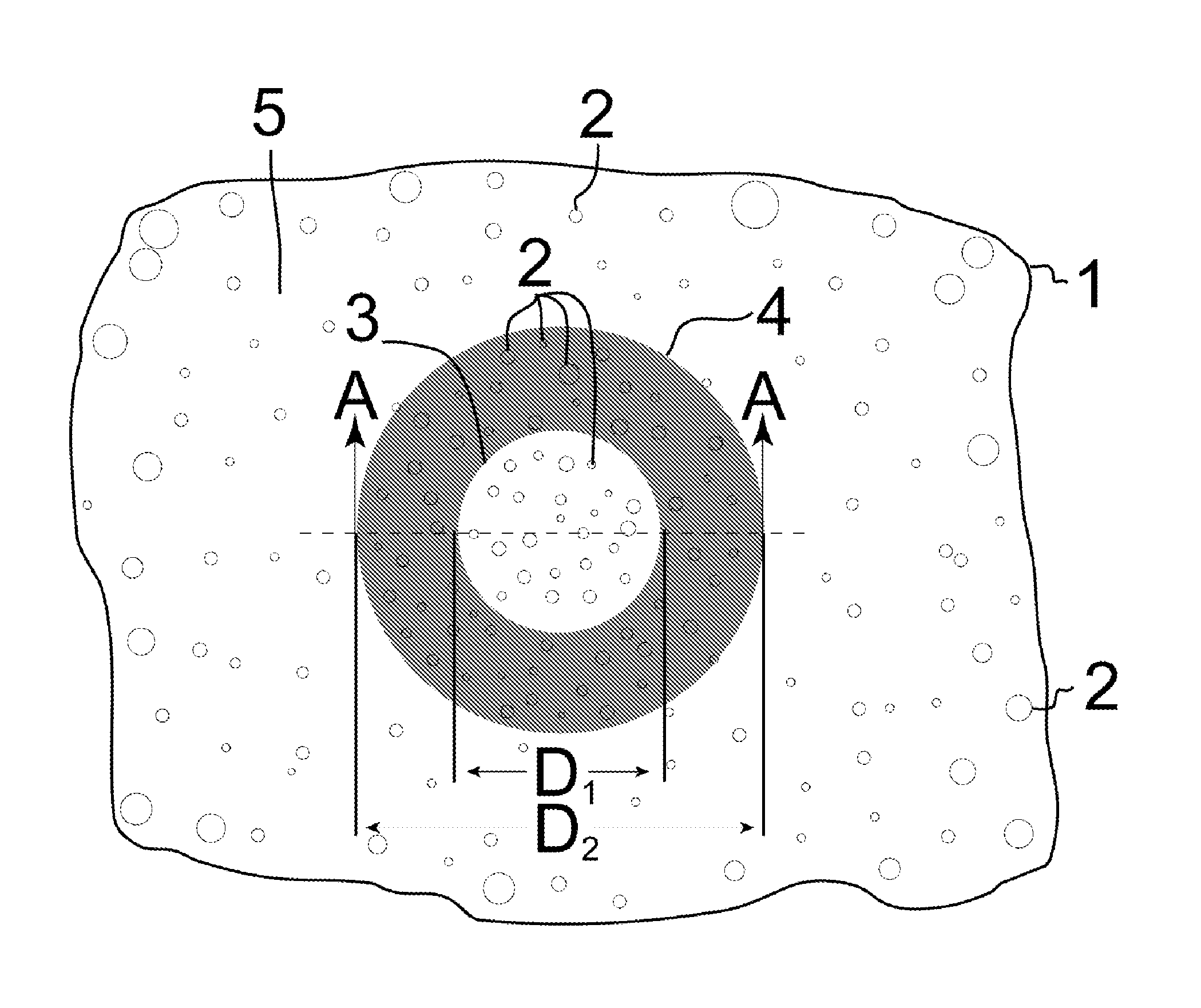
The invention provides a method and system for obtaining a three-dimensional representation of a patient's teeth arrangement. A three-dimensional physical teeth model is provided, having a surface relief corresponding to the patient's teeth arrangement. Computerized tomography (CT) is applied to the three-dimensional physical teeth model, to thereby acquire data of multiple slices of at least a portion of the teeth model. The data is analyzed to produce a virtual three-dimensional representation of the teeth model or a portion thereof.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Diffractive optical element and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20060121358A1Liquid crystal compositionsPhotomechanical apparatusRefractive indexDiffraction optics
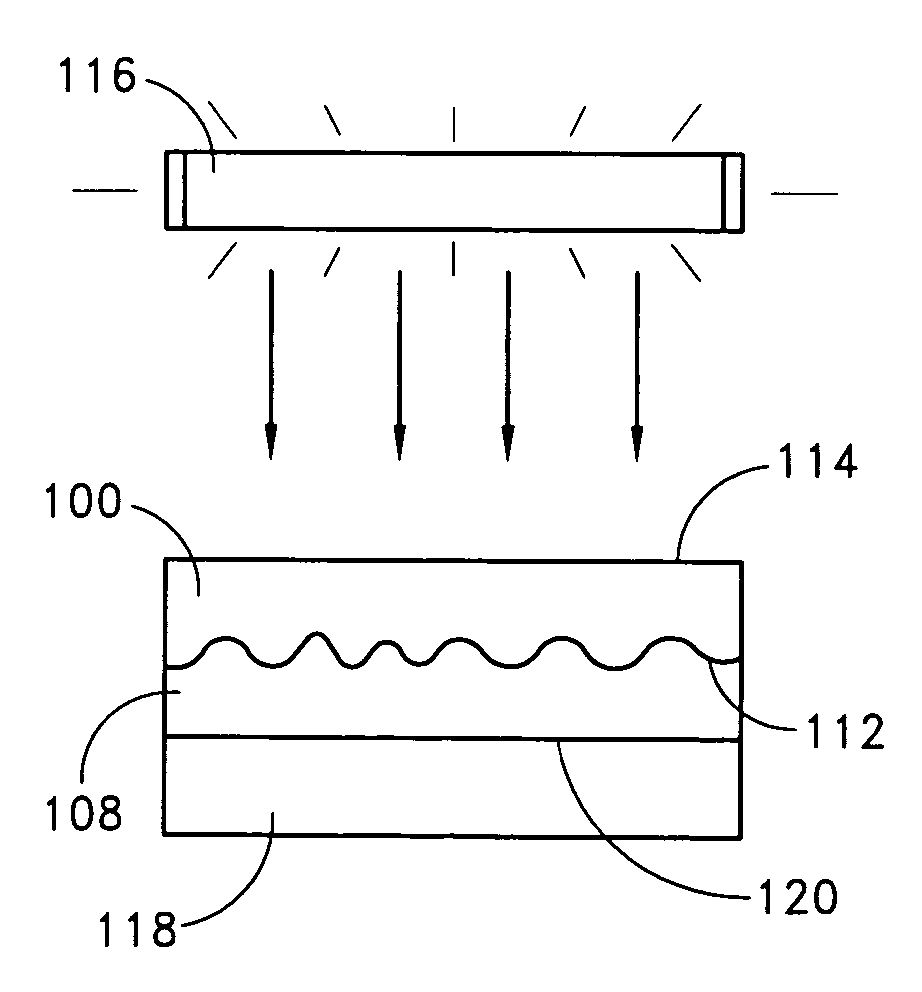
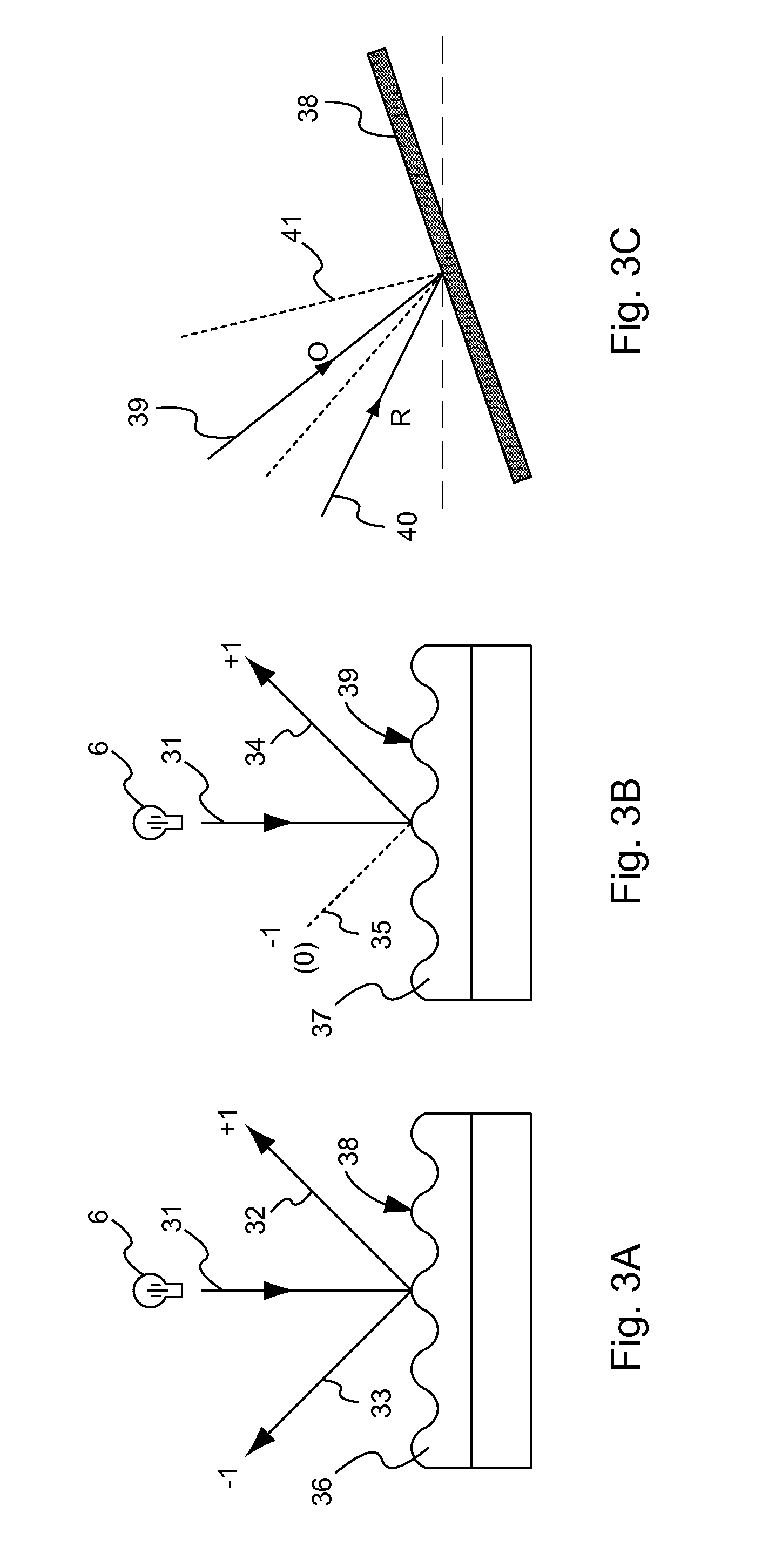
A diffractive optical element such as a diffuser, diffraction grating, and / or hologram, can be manufactured by using a surface relief pattern on a surface of a surface relief tool. A layer of curable material is physically contacted with the surface relief pattern on the surface of the surface relief tool to thereby imprint the pattern on a surface of the layer. Diffractive features are formed in the layer by propagating energy through the surface relief tool and into the layer such that refractive index variations corresponding to the pattern are created in the layer. The resultant product is a diffractive optical element comprising a layer of material having diffractive features formed by a predetermined pattern of refractive index variations. The diffractive features originate at an undulating boundary and extend only from one side of the boundary into the material. The undulating boundary has an undulating pattern that corresponds to the predetermined pattern of refractive index variations.
Owner:WAVEFRONT TECH INC
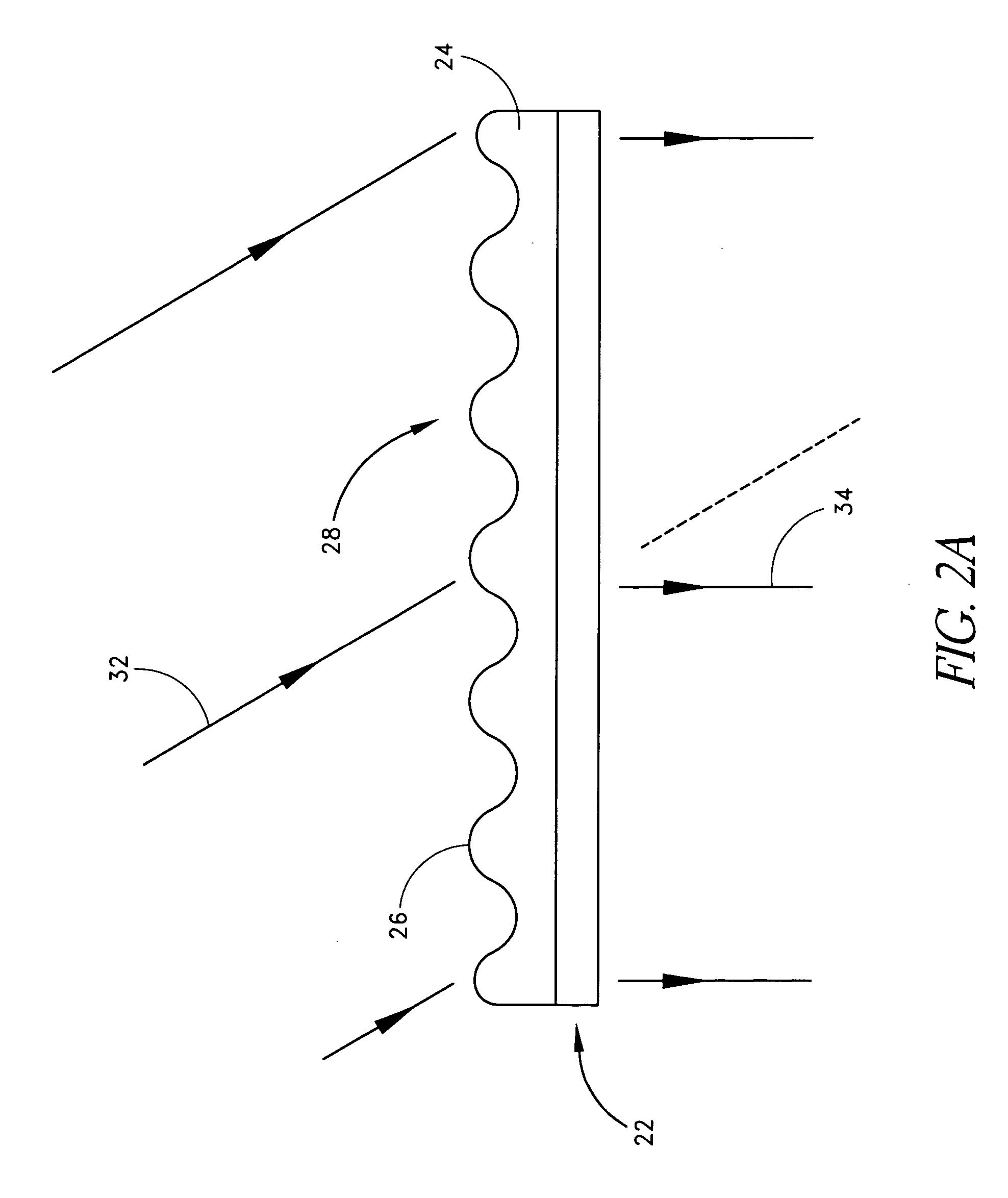
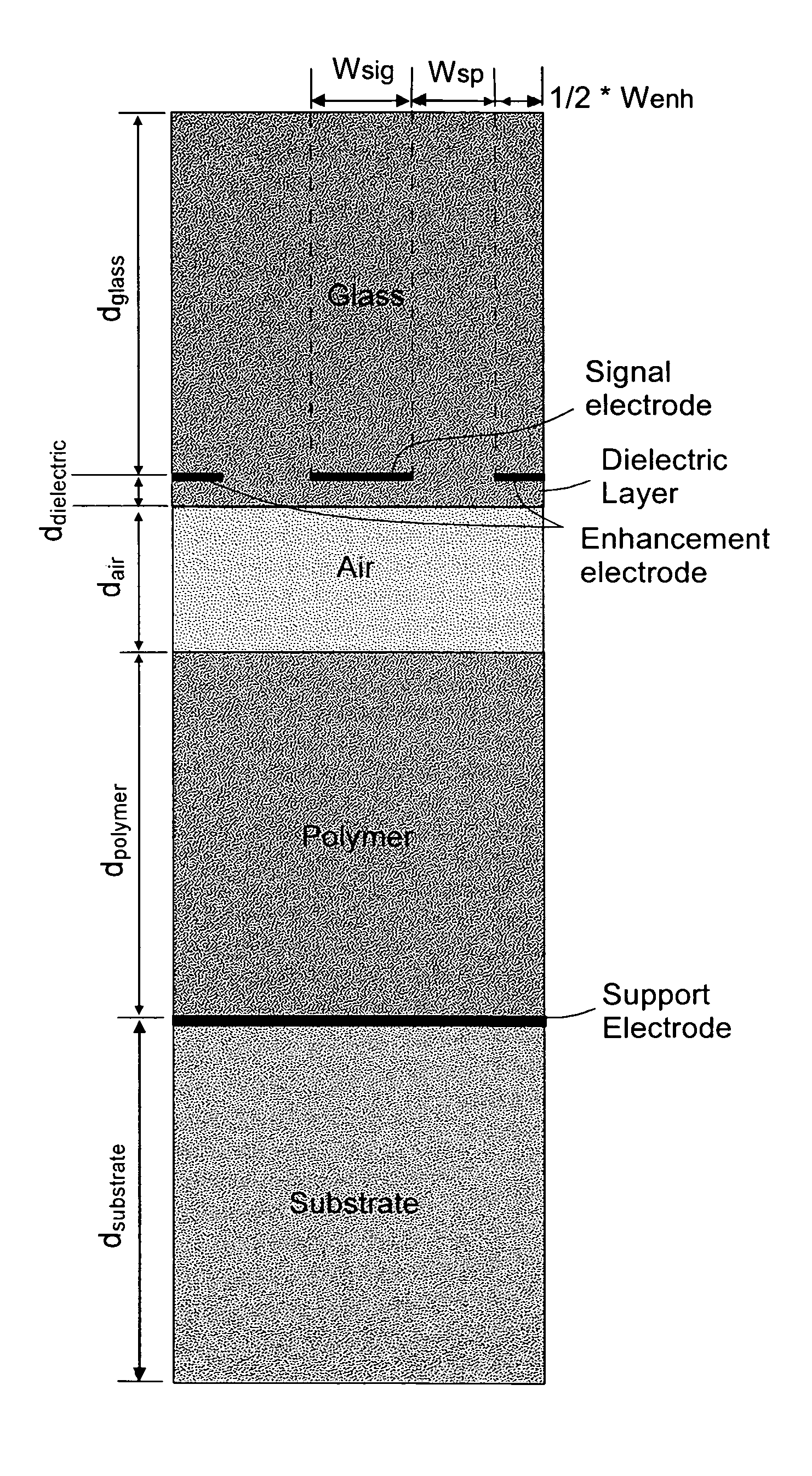
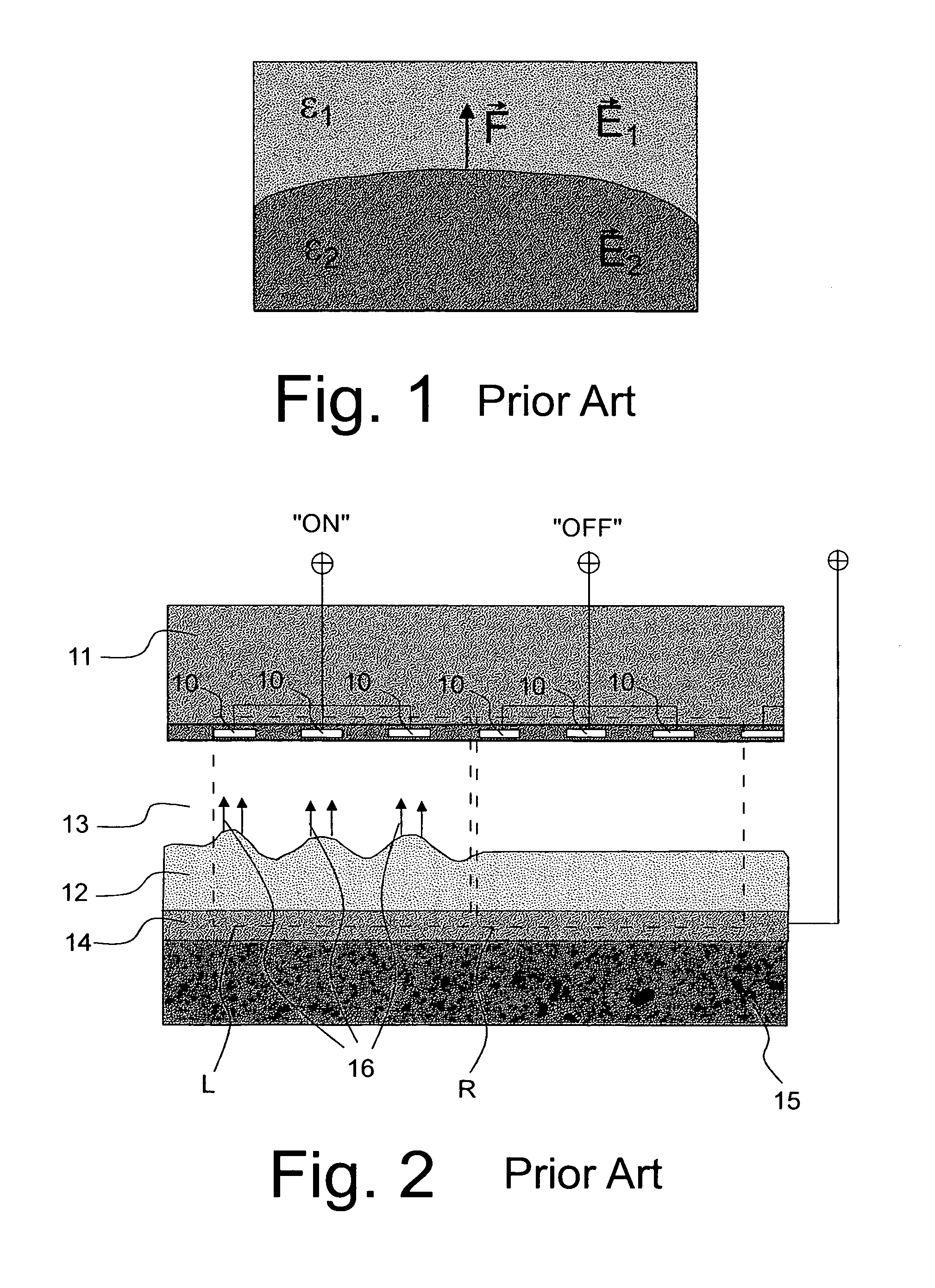
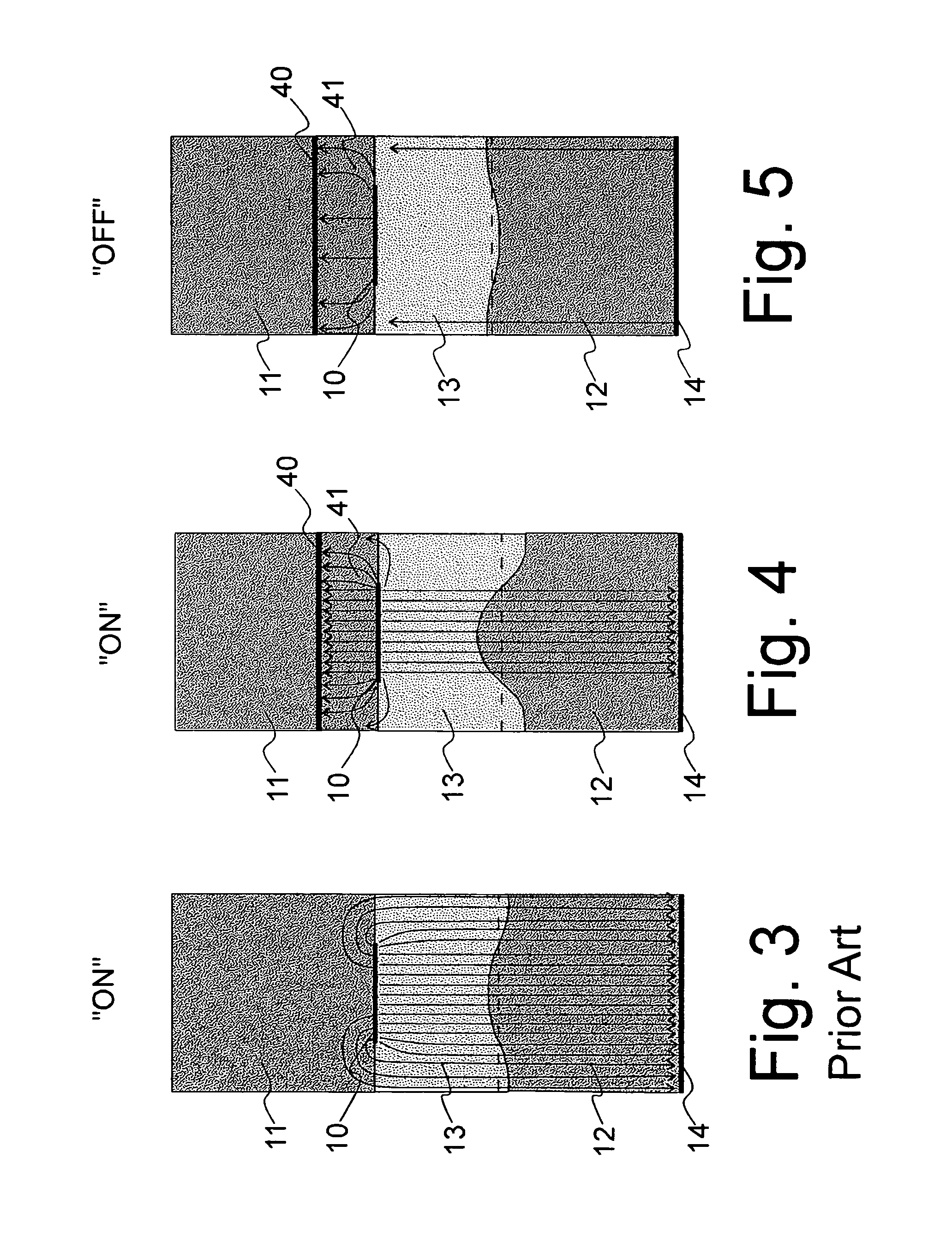
Enhancement electrode configuration for electrically controlled light modulators
InactiveUS7375870B2Improve efficiencyGood optical contrastActive addressable light modulatorNon-linear opticsElectrical batteryDielectric layer
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Switchable diffractive accommodating lens
InactiveUS20130035760A1Improve image contrastReduces halo and glareSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensPressure differenceRefractive index matching
A lens in accordance with the present invention includes an accommodating cell having two chambers with at least one chamber filled with optical fluid with the refractive index matching the refractive index of the accommodating element separating them. The accommodating element has a diffractive surface with surface relief structure that maintains its period but changes its height due a pressure difference between the chambers to redirect most of light that passes through the lens between different foci of far and near vision. The invention also includes a sensor cell that directly interacts with the ciliary muscle contraction and relaxation to create changes in pressure between the accommodating cell chambers that results in changing surface relief structure height and the lens accommodation.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
Security device
InactiveUS6903850B2High technological barrierNovel attractive appearanceOther printing matterPhotomechanical apparatusSurface relief
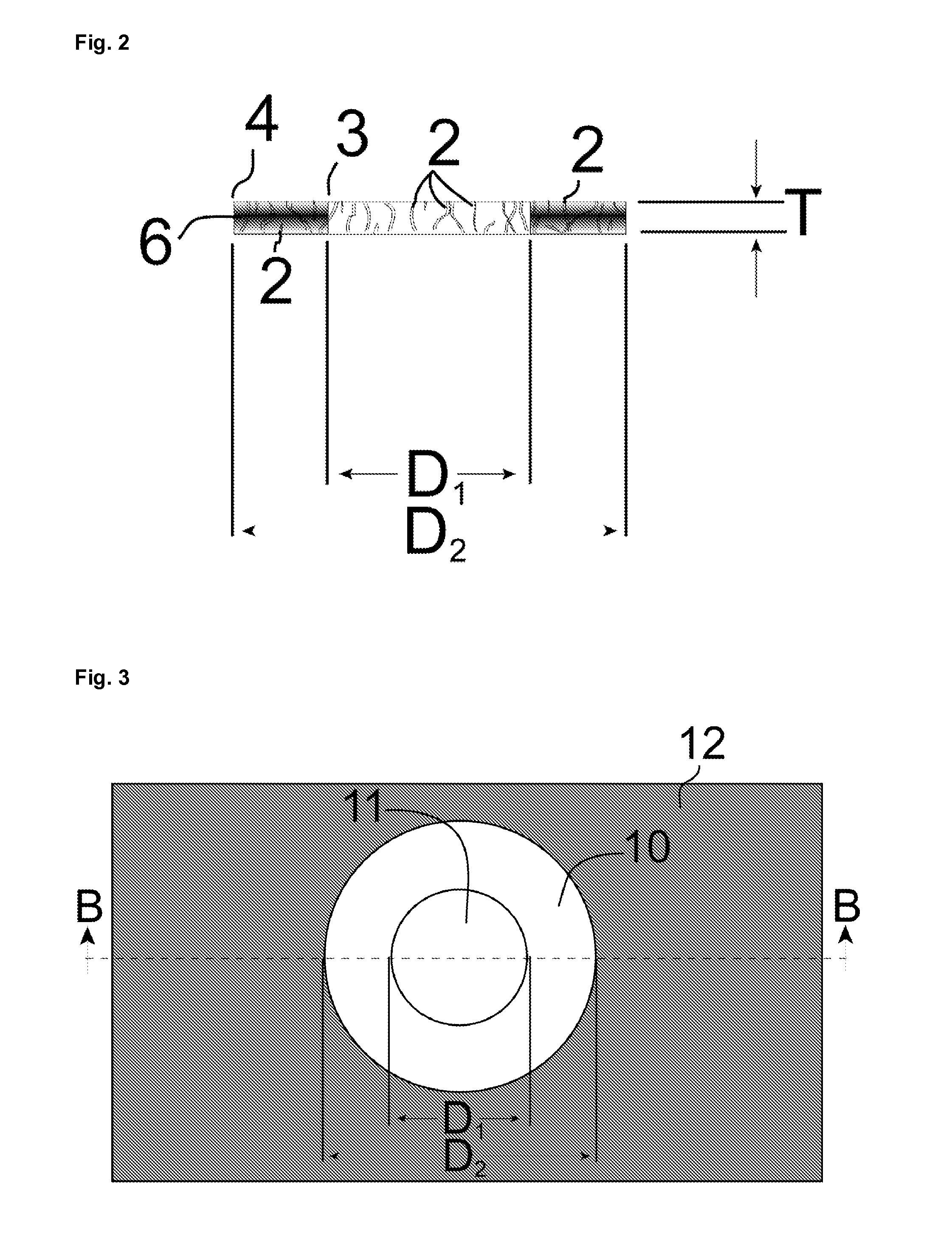
A security device has a substrate formed with a surface relief defining an optically variable effect generating structure. At least two different reflection enhancing materials are provided on, or on the same side of, substrate with respect to the surface relief, whereby the optically variable effect can be viewed against a background defined by the reflection enhancing materials.
Owner:DE LA RUE INT LTD
Micro-optics for article identification
InactiveUS7006294B2Deteriorates reproduction qualityQuality improvementOther printing matterMirrorsGratingPhotonic crystal
The present invention provides methods and compositions for authentication of articles and counterfeit deterrence using non-holographic micro-optics and microstructures having a surface relief greater than a few microns. Embodiments of the present invention disclose a range of distinctive optical effects obtained from micro-optic systems incorporating micro lenses, non-imaging collectors, prisms, wave guides, mirrors, gratings, structural interference filters, and photonic crystal microstructures.
Owner:PRINTPACK ILLINOIS
Optical wavelength resonant device for chemical sensing
InactiveUS20030210396A1Minimal lossHigh degreeOptical filtersDiffraction gratingsLength waveDielectric body
An apparatus for filtering electromagnetic waves, the apparatus comprising a substrate having a surface relief structure containing at least one dielectric body with physical dimensions smaller than the wavelength of the filtered electromagnetic waves, such structures repeated in a two dimensional array covering at least a portion of the surface of the first substrate. Also disclosed is a material sensor utilizing this apparatus.
Owner:X BODY
Ultra-compact HUD utilizing waveguide pupil expander with surface relief gratings in high refractive index materials
ActiveUS9715067B1High refractive index modulationHigh refractive indexCoupling light guidesHead-up displayRefractive index
A head up display include an image source, and a waveguide. The waveguide has a first diffraction grating and a first end and a second diffraction grating at a second end. The waveguide is positioned as a combiner and allows viewing of an outside scene and information from the image source. The first and second diffraction gratings are surface relief gratings having a high index of modulation.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
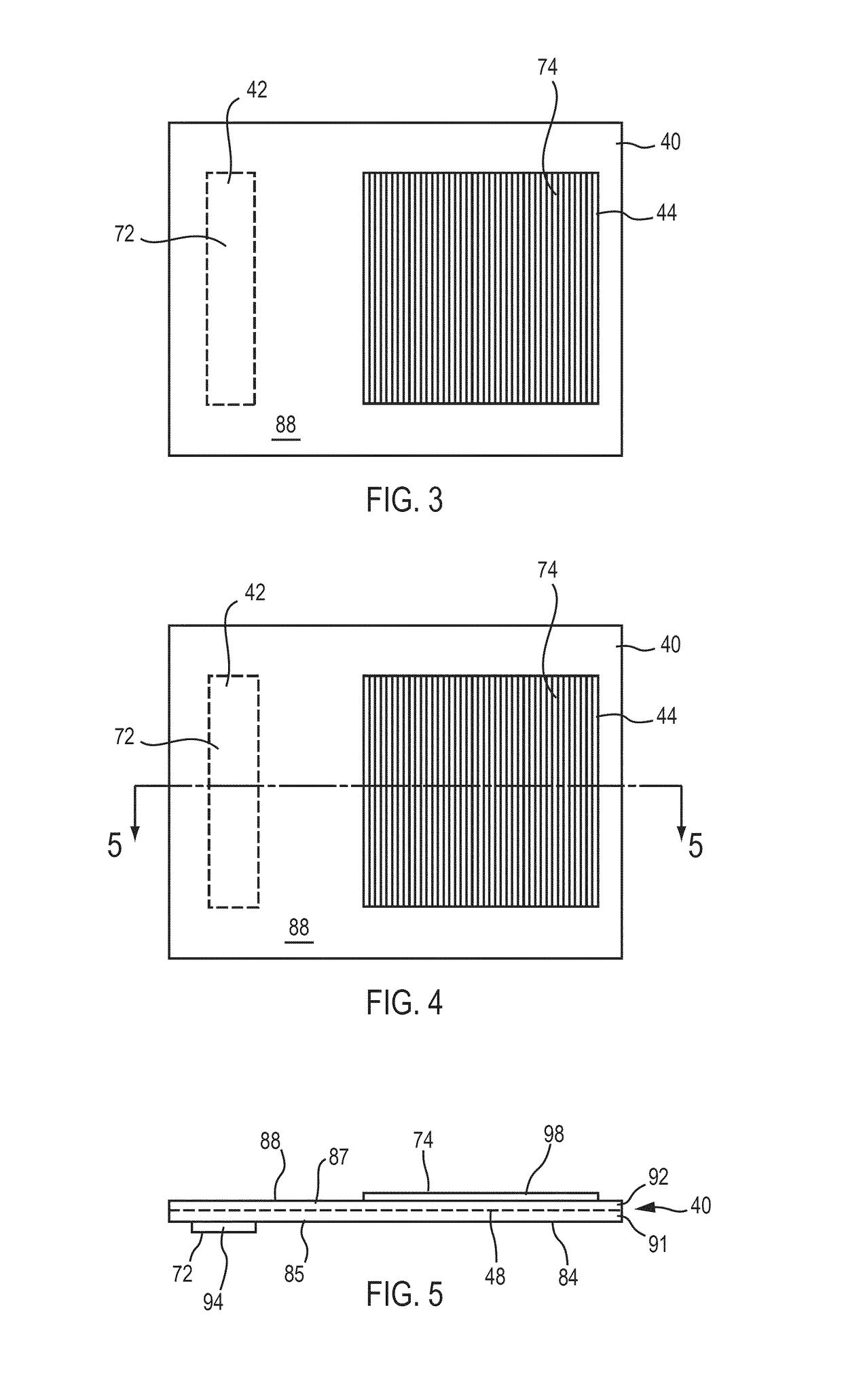
Method of manufacturing a diffuser master using a blasting agent
InactiveUS20010001459A1Enhance etching reactionImprove permeabilityDiffusing elementsDecorative surface effectsOptoelectronicsMetal
A diffuser master is provided which is manufactured mechanically instead of holographically. The master can be made from a suitable substrate including relatively hard materials such as plastic, glass or metal. A substrate having a first side is worked to form a diffuser surface relief structure thereon. The substrate can be buffed using a buffing agent of a selected grit in order to form surface scratches in the first side of the substrate. The substrate can also be blasted with shot particles in order to form indentations and depressions in the first side. The substrate can alternatively be acid or alkali etched in order to form surface irregularities in the first side. The scratches, depressions or irregularities can be formed in order to create a desired surface relief and hence desired diffuser output characteristics.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Waveguide illumination system
ActiveUS20170212295A1Reduce light lossMinimizes lightMechanical apparatusElectric lightingForward scatterTotal internal reflection
An illumination system employing a waveguide that receives and propagates light in response to transmission and total internal reflection. Light deflecting elements distributed along the propagation path incrementally change the out-of-plane angles of light rays and cause decoupling of portions of light from the waveguide at different distances from the light input edge or end. Light may escape from the waveguide into an intermediate layer at low out-of-plane angles and can be further redirected by light extraction features out of the system. In one embodiment, the illumination system is configured to emit collimated light. In one embodiment, the illumination system includes shallow surface relief features. In one embodiment, the light deflecting elements include forward-scattering particles distributed throughout the volume of the waveguide.
Owner:S V V TECH INNOVATIONS
Microlens arrays having high focusing efficiency
InactiveUS20020034014A1Improve fill factorHighly focusedRadiation applicationsSolid-state devicesFill factorMicro lens array
Microlens arrays (105) having high focusing efficiencies are provided. The high focusing efficiencies are achieved by accurately producing the individual microlenses making up the array at high fill factors. Arrays of positive microlenses are produced by forming a master having a concave surface-relief pattern (101) in a positive photoresist (21) using direct laser writing. Through this approach, the problems associated with the convolution of a finite laser beam with a desired profile for a microlens are overcome. The microlens arrays of the invention have focusing efficiencies of at least 75%.
Owner:CORNING INC
Applications and fabrication techniques for large scale wire grid polarizers
InactiveUS20060118514A1Enable formationMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsWire gridElectrical conductor
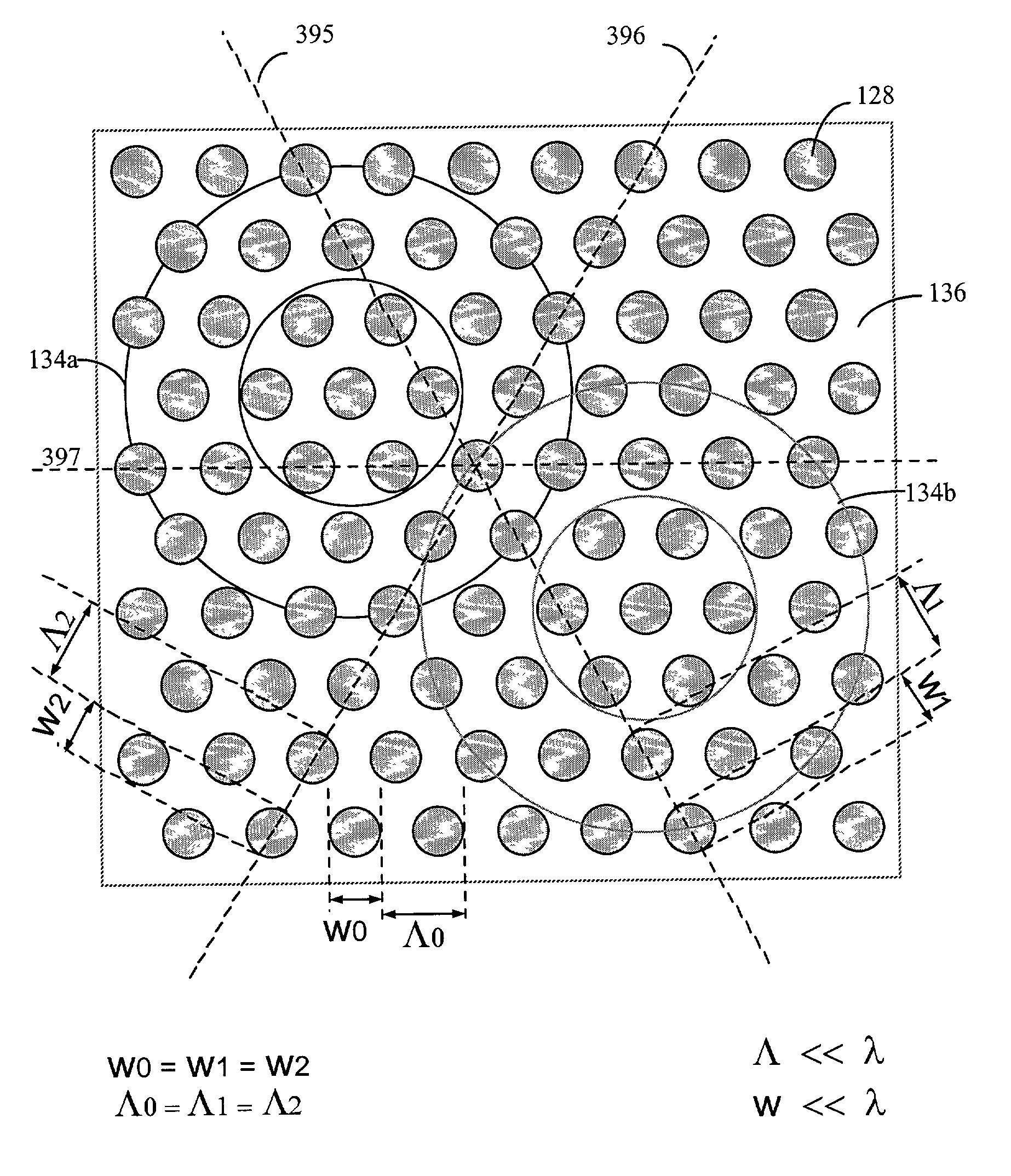
A wire grid polarizer may be fabricated by forming plurality of substantially-straight metallic lines of predetermined periodicity Λ on a thin film substrate A plurality of substantially straight nanometer-scale periodic surface relief structures is created on a surface of the substrate. The periodic surface relief structures cover a region greater than about 4 centimeters in length and greater than about 4 centimeters in width, wherein the periodicity Λ is between about 10 nanometers and about 500 nanometers. One or more layers of material are formed on the periodic relief structures. The one or more layers include one or more conductor materials that form the plurality of substantially straight metallic lines over a region of the substrate greater than about 4 centimeters in length and greater than about 4 centimeters in width.
Owner:AGOURA TECH
High performance rear-projection screen
A rear-projection screen and a method for forming same are provided. The screen can include a substrate including a first side and a second side, apertures disposed on the first side of the substrate, and an opaque layer disposed on the second side of the substrate. In a particular embodiment, the opaque layer includes a plurality of apertures therethrough. A surface relief diffuser can be provided in the substrate at the plurality of apertures. A bulk diffuser can be provided at the plurality of apertures to diffuse the projected image. A cover can be attached to the opaque layer, for example, with an adhesive. An overlayer can be provided on the opaque layer for providing deep apertures that can be filled with bulk diffuser to further diffuse the projected image. The overlayer disposed on the opaque layer can include a light-absorbing material in and / or on the overlayer.
Owner:REFLEXITE
Applications and fabrication techniques for large scale wire grid polarizers
InactiveUS7561332B2Material nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsManufacturing technologyElectrical conductor
A wire grid polarizer may be fabricated by forming plurality of substantially-straight metallic lines of predetermined periodicity Λ on a thin film substrate A plurality of substantially straight nanometer-scale periodic surface relief structures is created on a surface of the substrate. The periodic surface relief structures cover a region greater than about 4 centimeters in length and greater than about 4 centimeters in width, wherein the periodicity Λ is between about 10 nanometers and about 500 nanometers. One or more layers of material are formed on the periodic relief structures. The one or more layers include one or more conductor materials that form the plurality of substantially straight metallic lines over a region of the substrate greater than about 4 centimeters in length and greater than about 4 centimeters in width.
Owner:AGOURA TECH
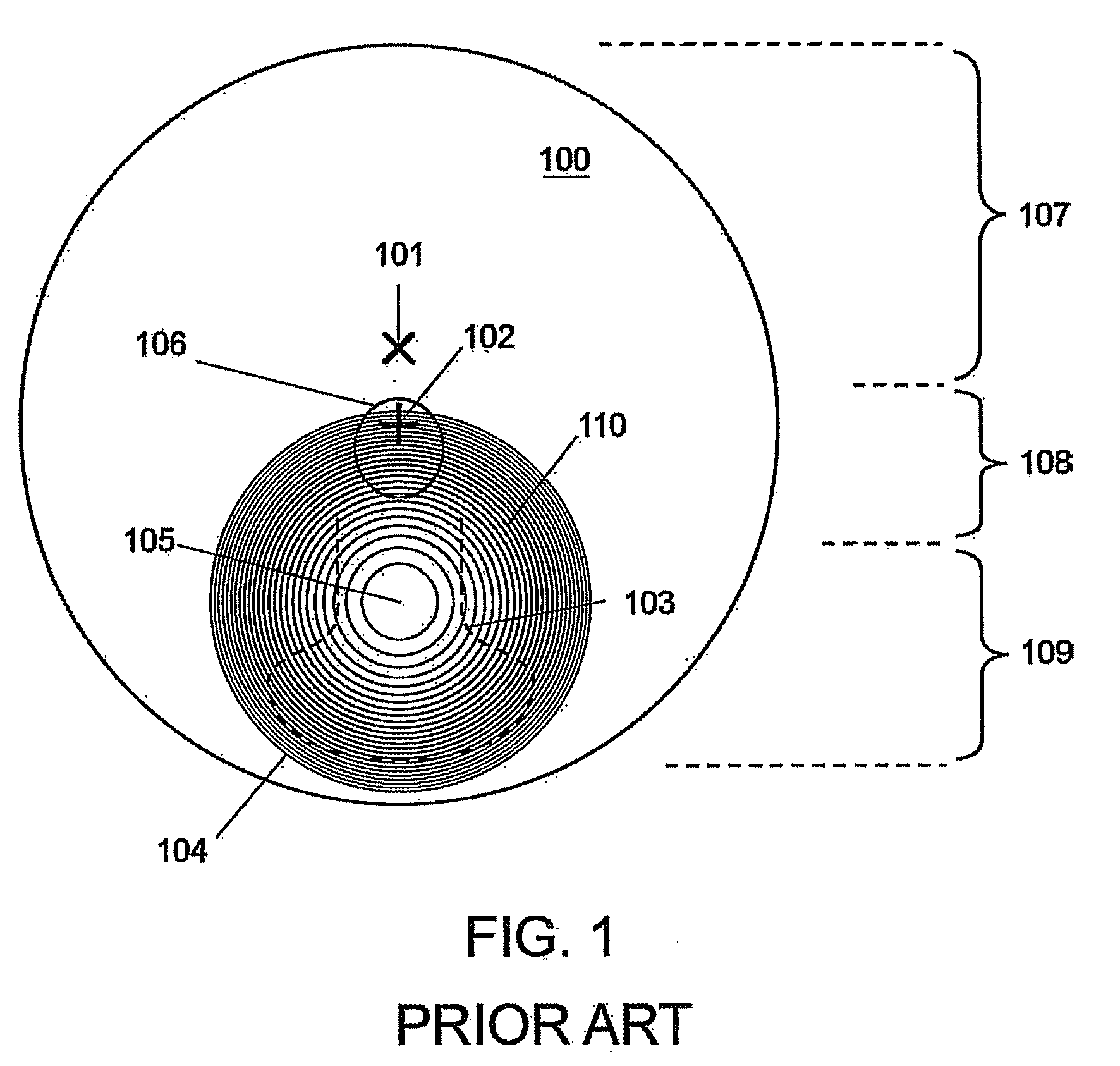
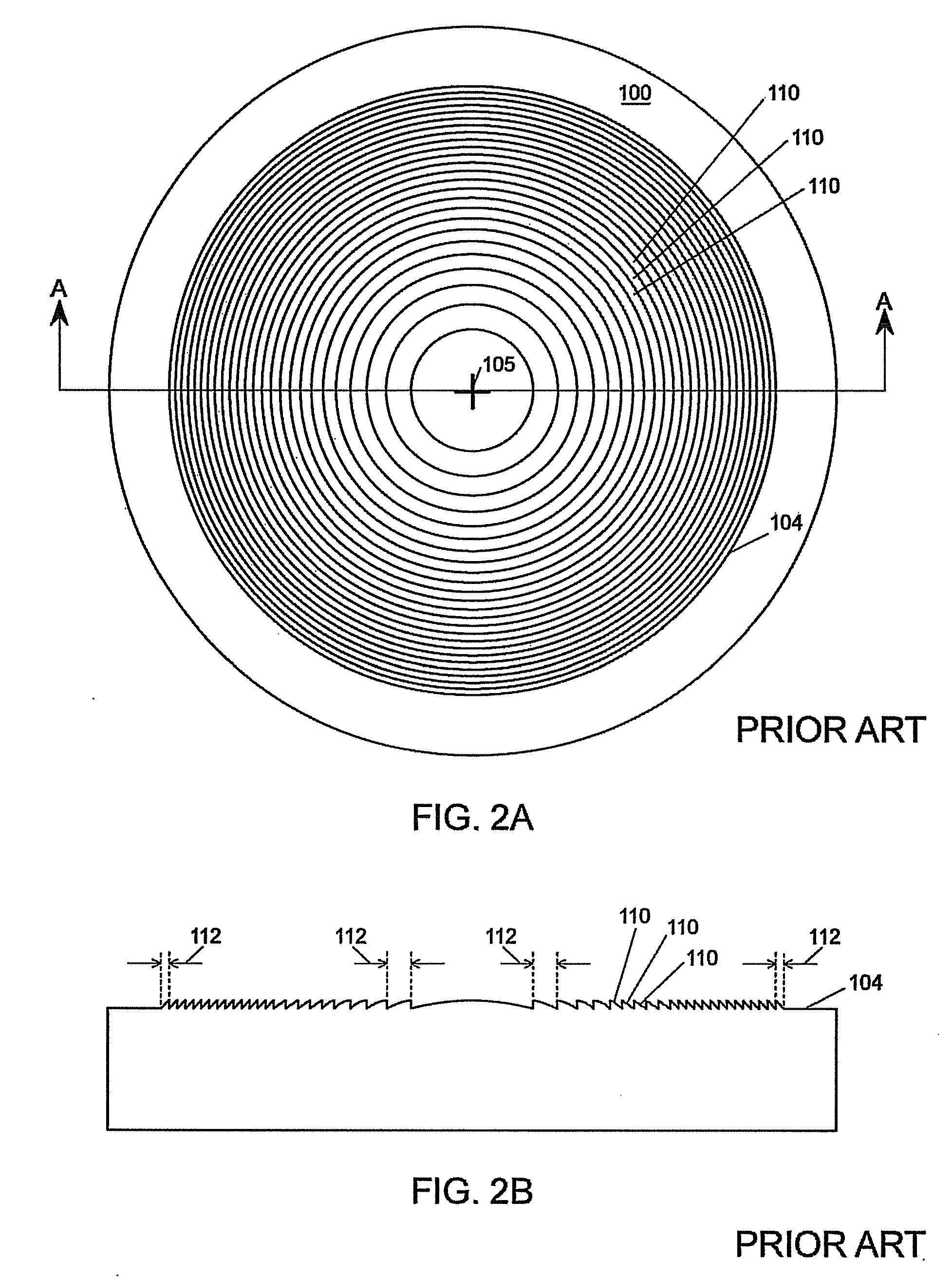
Multifocal lens with a diffractive optical power region
A lens system is presented having a diffractive optical power region. The diffractive optical power region has a plurality of concentric surface relief diffractive structures. A greater portion of light incident on a diffractive structure near the center point contributes to the optical power than light incident on a diffractive structure peripherally spaced therefrom.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Calibration of Holographic Data Storage Systems Using Holographic Media Calibration Features
InactiveUS20080008076A1Easy to readEasy to operateRecord information storageAuxillary data arrangementGratingHolographic Data Storage System
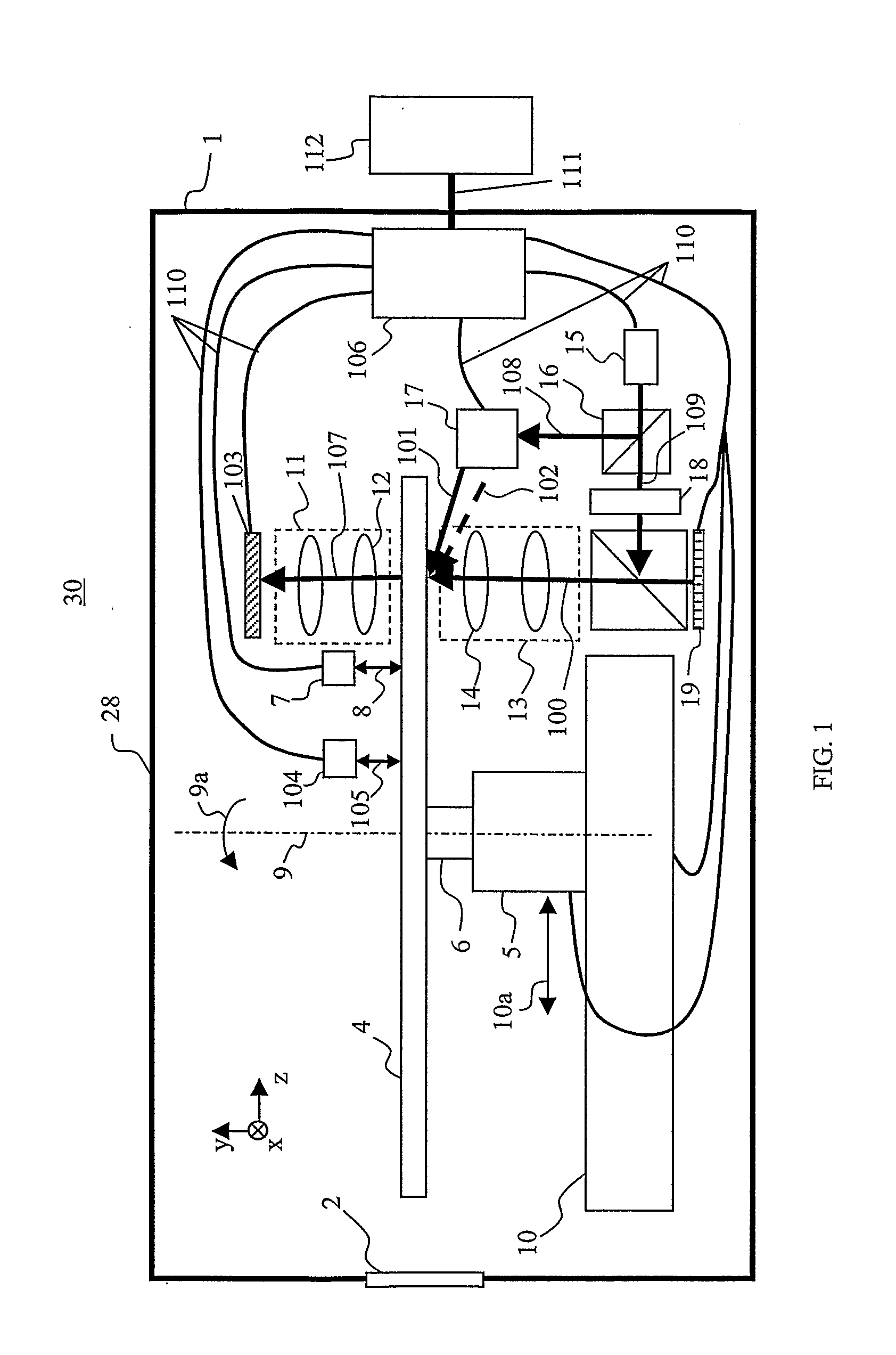
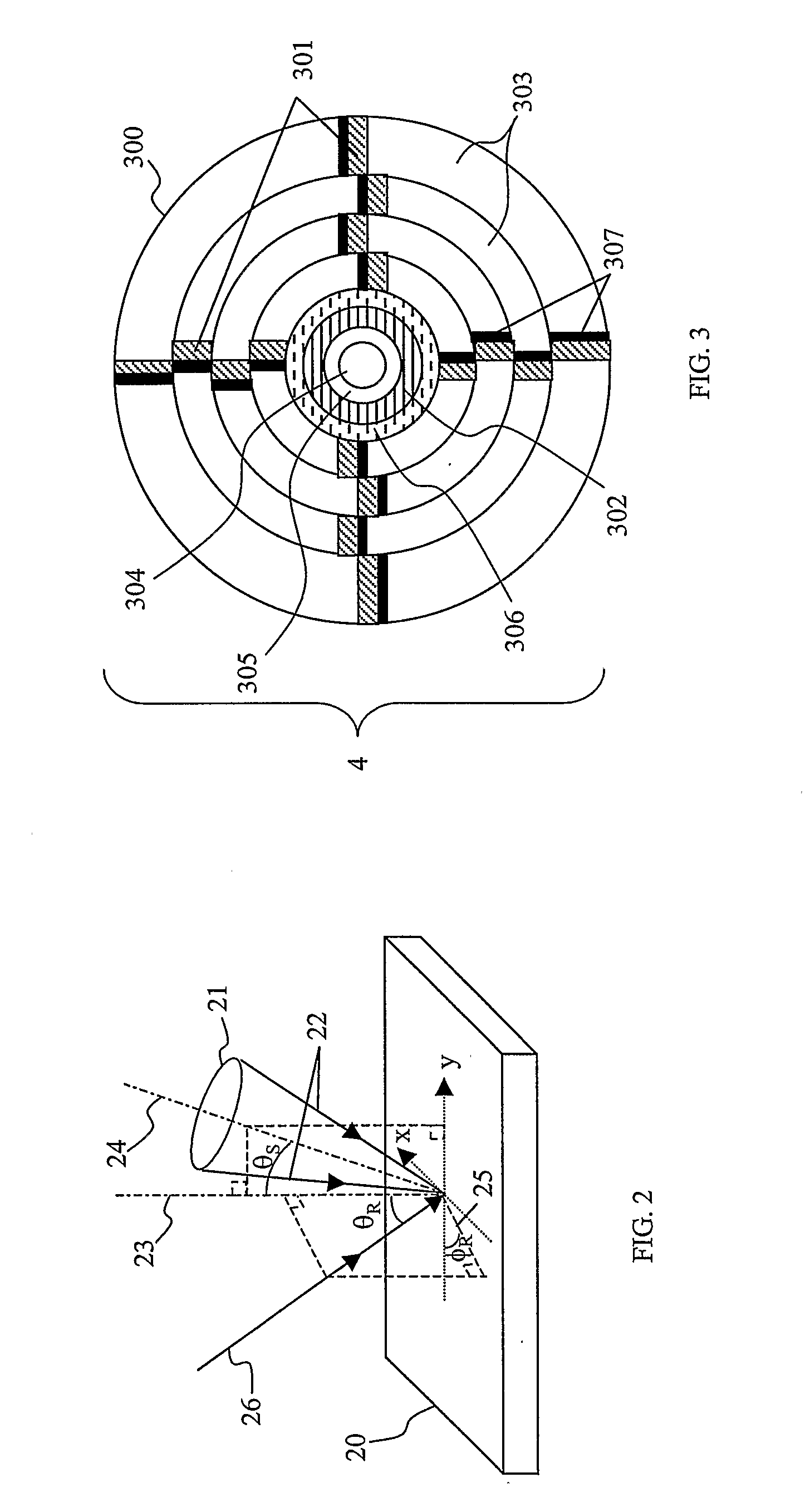
Calibration of holographic data storage systems (HDSS) is provided by utilizing holographic media (4) having calibration features which can be read, written, or read and written by a HDSS (30). Calibration features may represent for example, surface-relief gratings, holographic recordings, amplitude varying regions, or magnetic regions, or a combination thereof, at locations on or within the media. One or more of the calibration features along media region (302) are media calibration features with media and format information, and other calibration features along region (301) are system calibration features for optically and mechanically aligning HDSS optics. The media (4) may have performance calibration features along region (307) which can be recorded by a HDSS and then read back to determine characteristics of the media. Different HDSS systems can read the calibration features of the media (4) when installed in each HDSS to obtain information about the media, and to optically and mechanically align the media for optimal operation with the media.
Owner:POSTECH CO LTD
Thermoplastic products having antislip surfaces
InactiveUS6509084B2Effective antislip surface propertyGood adhesion and durability and wearabilityKitchenware cleanersCleaning machinesEngineeringVolcano
Thermoplastic products such as vehicle cargo area liners, floor mats, recreational and playground equipment, cargo pallets, and wet area walking surfaces are provided with an antislip surface treatment. The antislip surface is made up of individual non-interconnected asperities of an antislip polymer material, which do not form a continuous film over the surface of the thermoplastic product. The thermoplastic product is especially made of high density polyethylene. The antislip polymer is preferably a thermoset polymer, and most particularly is a polyurea / isocyanate polymer. The antislip polymer is preferably applied by spraying, and then the product is heat treated at a temperature in the range from 100 to 200° F., or is thermoformed at a temperature in the range from 250 to 550° F. The antislip asperities are durably bonded onto the thermoplastic base material, and provide a significantly increased coefficient of friction. The asperity size, height, and hardness can be controlled by adjusting the processing conditions. The asperities may have an increased surface relief due to a so-called "moth effect" and an increased surface roughness due to cratering as a result of a so-called "volcano effect" in the process using thermoforming.
Owner:CUSTOM PLASTICS MOLDING
Diffractive device
InactiveUS20100085642A1Good for observationDiffusing elementsLighting elementsDiffraction effectNon symmetric
The invention provides in particular for an achromatic diffractive diffuser comprising a surface relief diffractive device arranged such that, under illumination by ambient light, the diffractive effect serves to provide a uniform achromatic diffuser reflection into a defined viewing zone for observation by an observer, and also such that the achromatic diffractive replay of the device has a non-symmetric distribution of diffractive light intensity between positive and negative diffractive order such that the diffractive efficiency in the desired diffractive order is enhanced over that of the undesired order to provide an enhanced brightness achromatic device.
Owner:OPTAGLIO
Lightguide arrangement and related applications
ActiveUS20080186736A1Reduces optical efficiencyImprove optical efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency actuatorsCouplingEngineering
A lightguide arrangement including a substantially thin, lightguide for transporting and coupling light. At least one light source is coupled to the lightguide. A plurality of micro-optic surface relief forms are arranged on the lightguide. The lightguide is configured to produce one or more active indicative and / or decorative illumination effects via interaction between the one or more light sources and the plurality of micro-optic surface relief forms. A keypad assembly including the lightguide and uses of lightguide constructions.
Owner:MODILIS HLDG LLC
Diffractive optical element and method of manufacture
InactiveUS6998196B2Liquid crystal compositionsPhotomechanical apparatusRefractive indexDiffraction optics
A diffractive optical element such as a diffuser, diffraction grating, and / or hologram, can be manufactured by using a surface relief pattern on a surface of a surface relief tool. A layer of curable material is physically contacted with the surface relief pattern on the surface of the surface relief tool to thereby imprint the pattern on a surface of the layer. Diffractive features are formed in the layer by propagating energy through the surface relief tool and into the layer such that refractive index variations corresponding to the pattern are created in the layer. The resultant product is a diffractive optical element comprising a layer of material having diffractive features formed by a predetermined pattern of refractive index variations. The diffractive features originate at an undulating boundary and extend only from one side of the boundary into the material. The undulating boundary has an undulating pattern that corresponds to the predetermined pattern of refractive index variations.
Owner:WAVEFRONT TECH INC
Optical wavelength resonant device for chemical sensing
InactiveUS6870624B2Minimal lossEffective filteringOptical filtersScattering properties measurementsLength waveDielectric body
An apparatus for filtering electromagnetic waves, the apparatus comprising a substrate having a surface relief structure containing at least one dielectric body with physical dimensions smaller than the wavelength of the filtered electromagnetic waves, such structures repeated in a two dimensional array covering at least a portion of the surface of the first substrate. Also disclosed is a material sensor utilizing this apparatus.
Owner:X BODY
Corneal implants produced by irradiation of polymer films
The corneal implant of the current invention takes the general form of a thin, transparent, flexible, porous, biocompatible film of suitable polymer material. The implant is sufficiently porous, the porosity being imparted by the film being irradiated to produce tracks and the material in those tracks being subsequently removed through an etching process, to allow the adequate flow of gaseous and tissue fluid components through the film. Specific embodiments of the invention are achieved by the addition of features to the general form. The embodiment applicable to corneal reshaping features a surface relief pattern in the implant. The artificial iris embodiment features an imprinted partly to fully opaque or partially reflective annular iris pattern of selected inner and outer diameters.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTICAL TECH
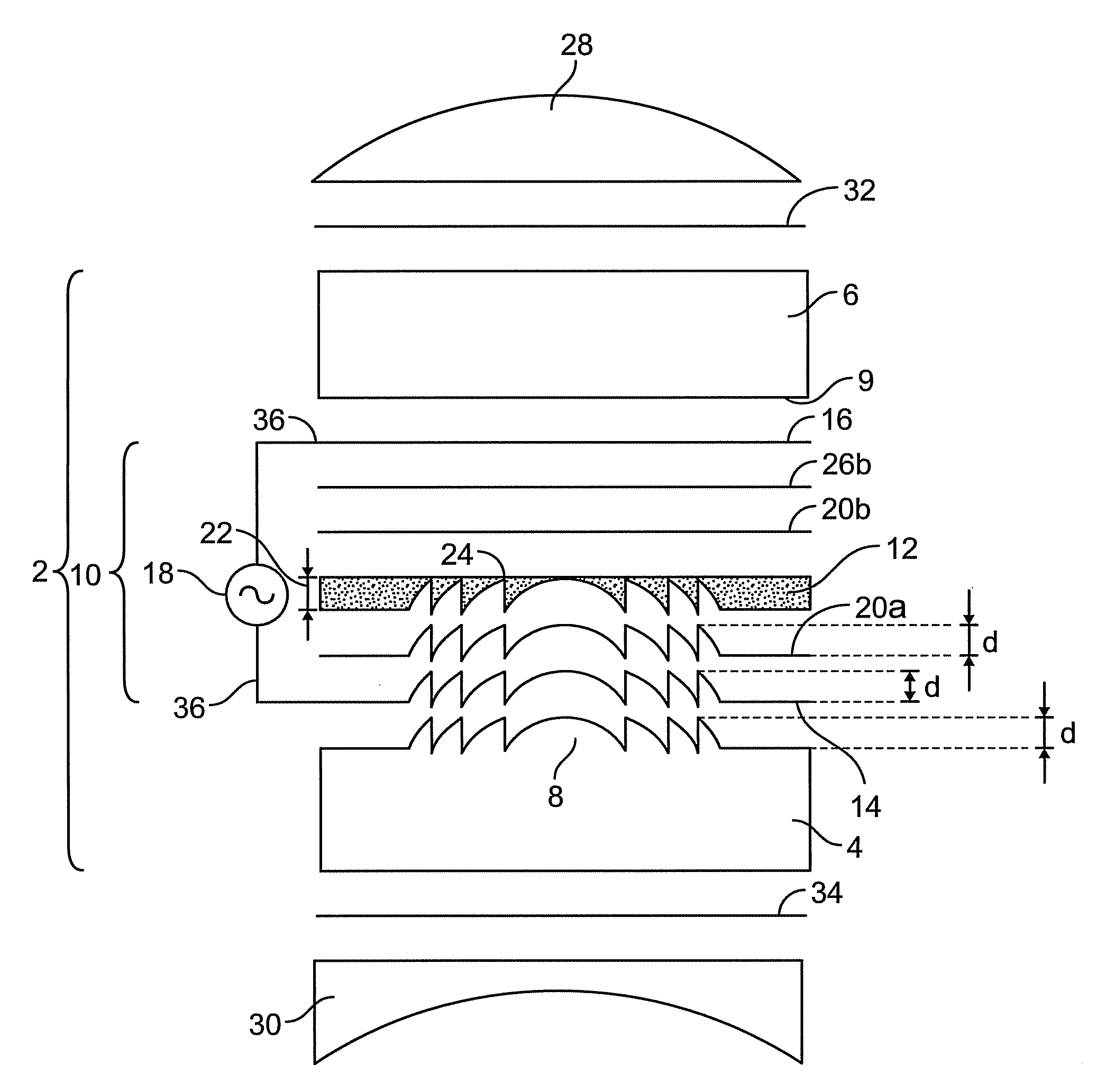
Electrical insulating layers, UV protection, and voltage spiking for electro-active diffractive optics
InactiveUS20100002190A1Avoid conducting electricitySufficient impedanceNon-linear opticsOptical partsElectricityUv protection
An electro-active lens has a first substrate with a surface relief diffractive topological profile and a second substrate positioned opposite to the first substrate having a substantially smooth topological profile. A first electrode is positioned along the surface relief diffractive topological profile of the first substrate and a second electrode is positioned between the first electrode and the second substrate. The smallest distance between the electrodes is less than or equal to about 1 micron An electro-active material is positioned between the first and second electrodes and a first insulating layer is positioned between the first and second electrodes.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com