Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64results about How to "Highly focused" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
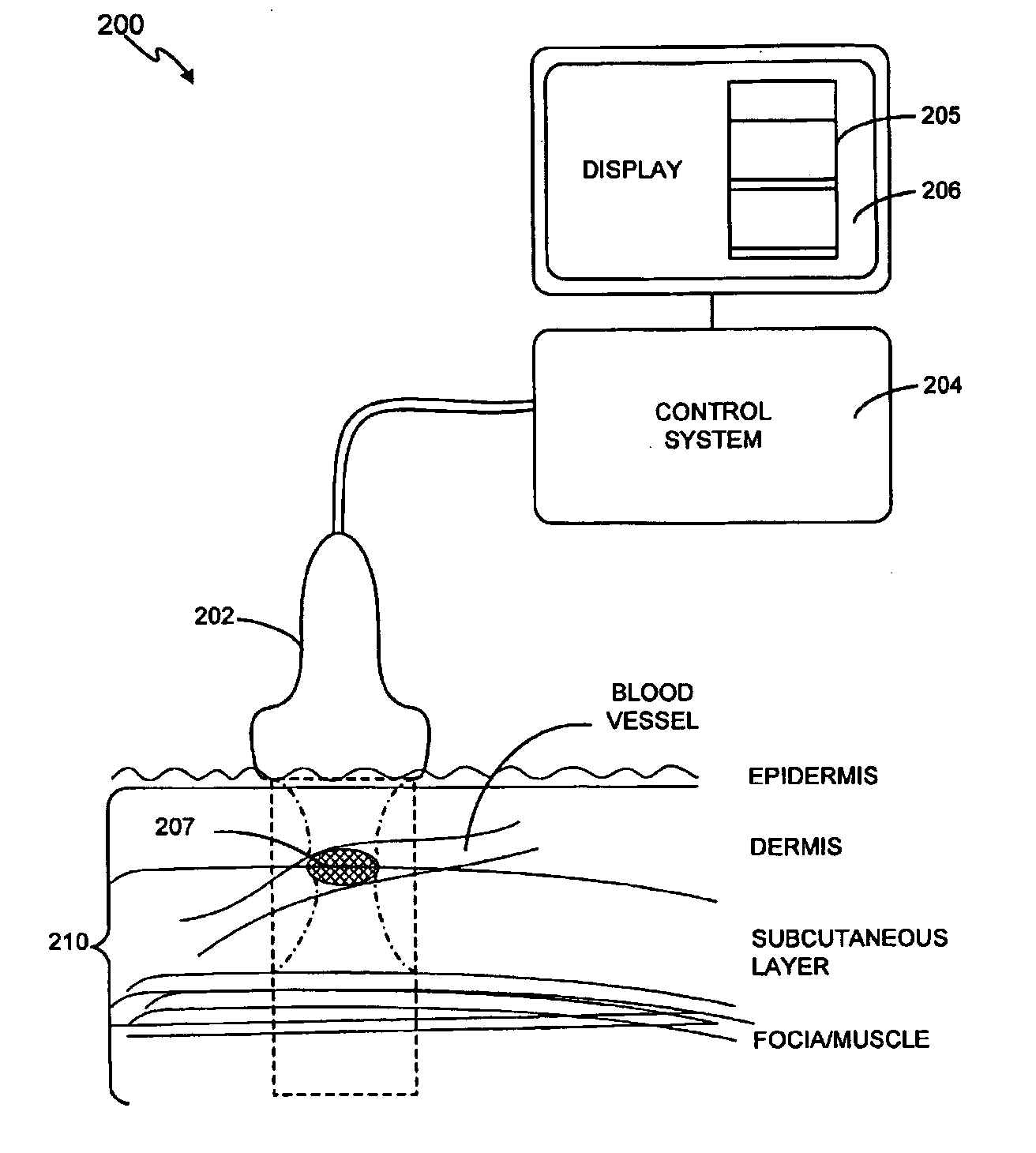
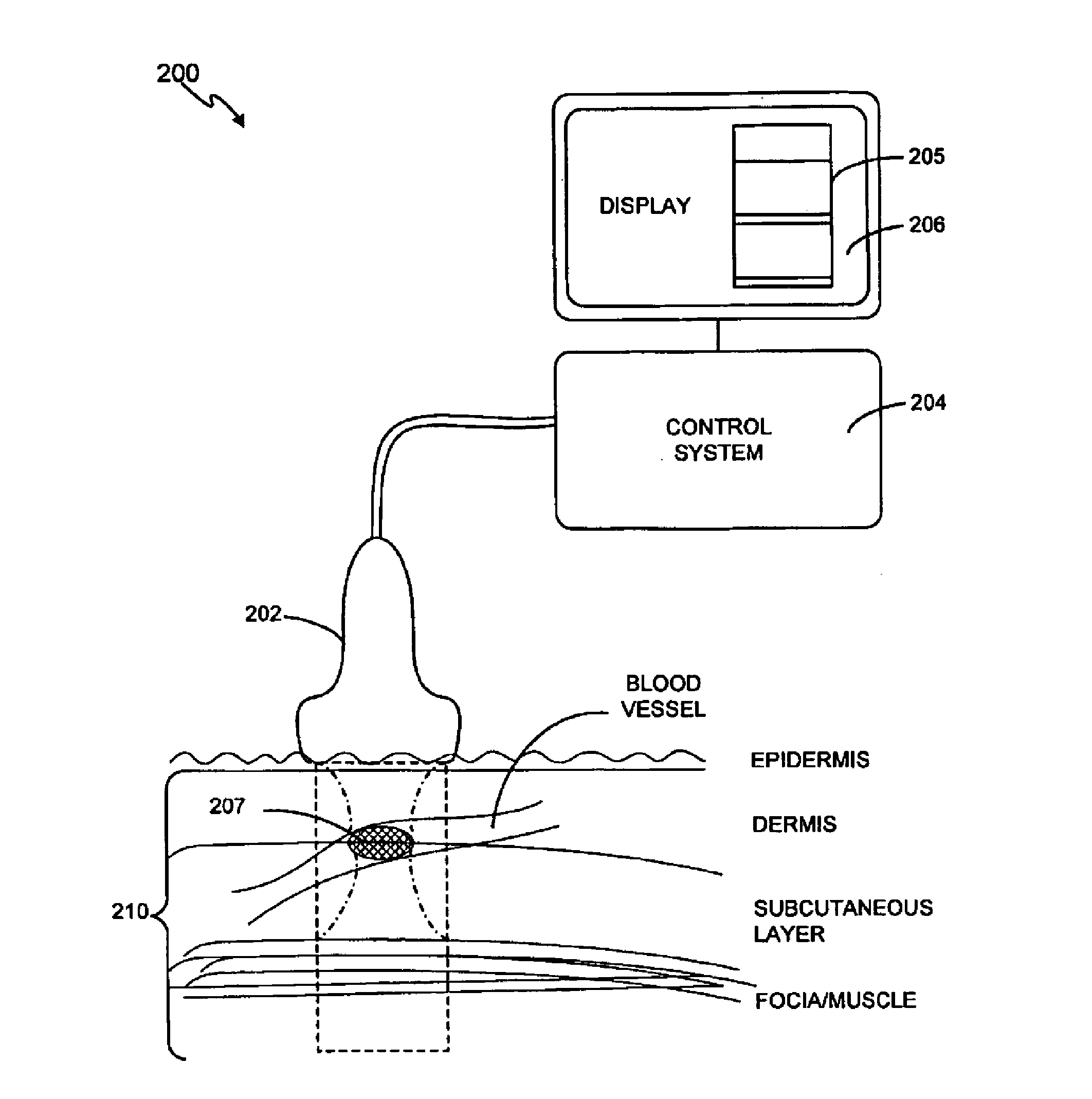
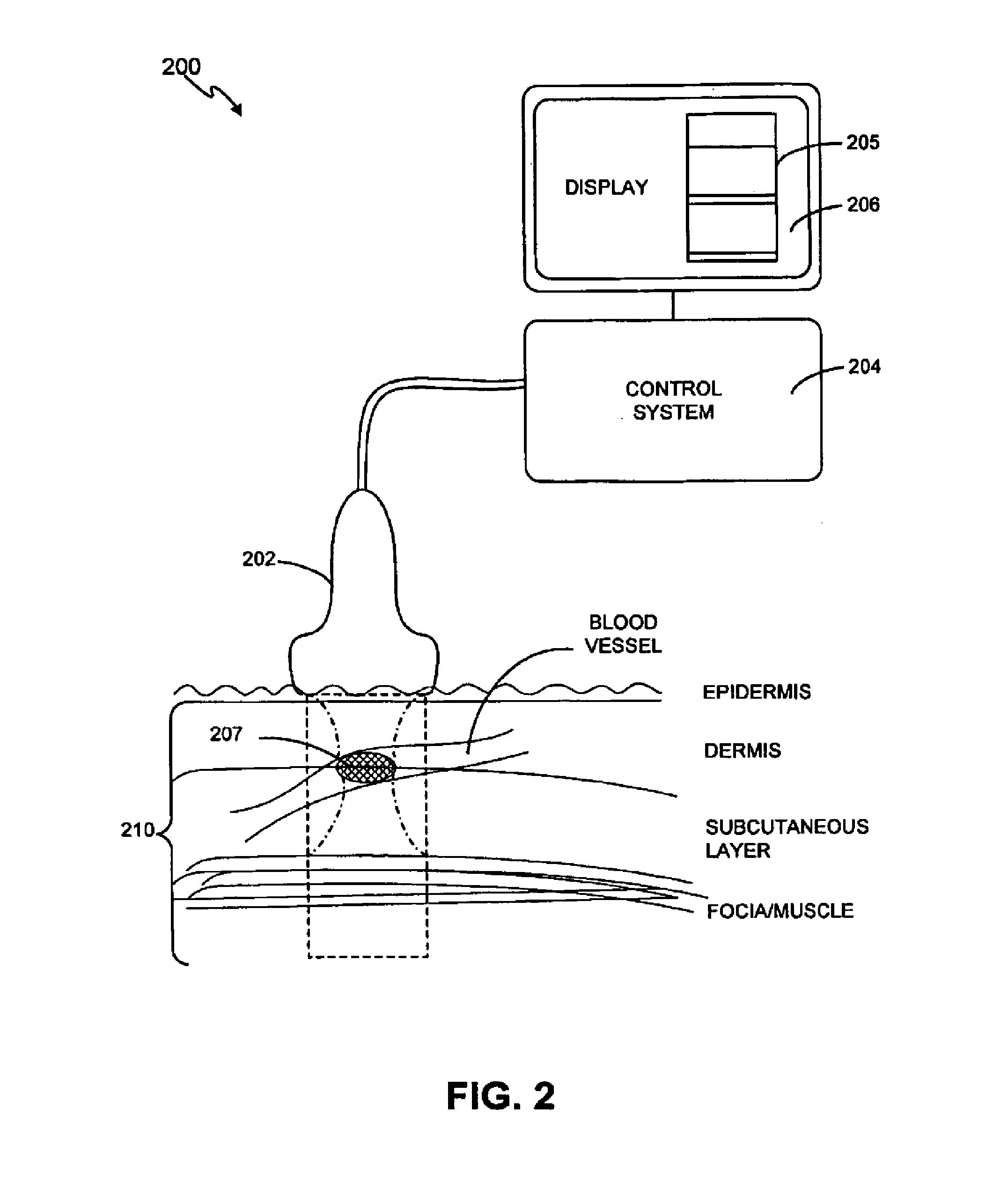
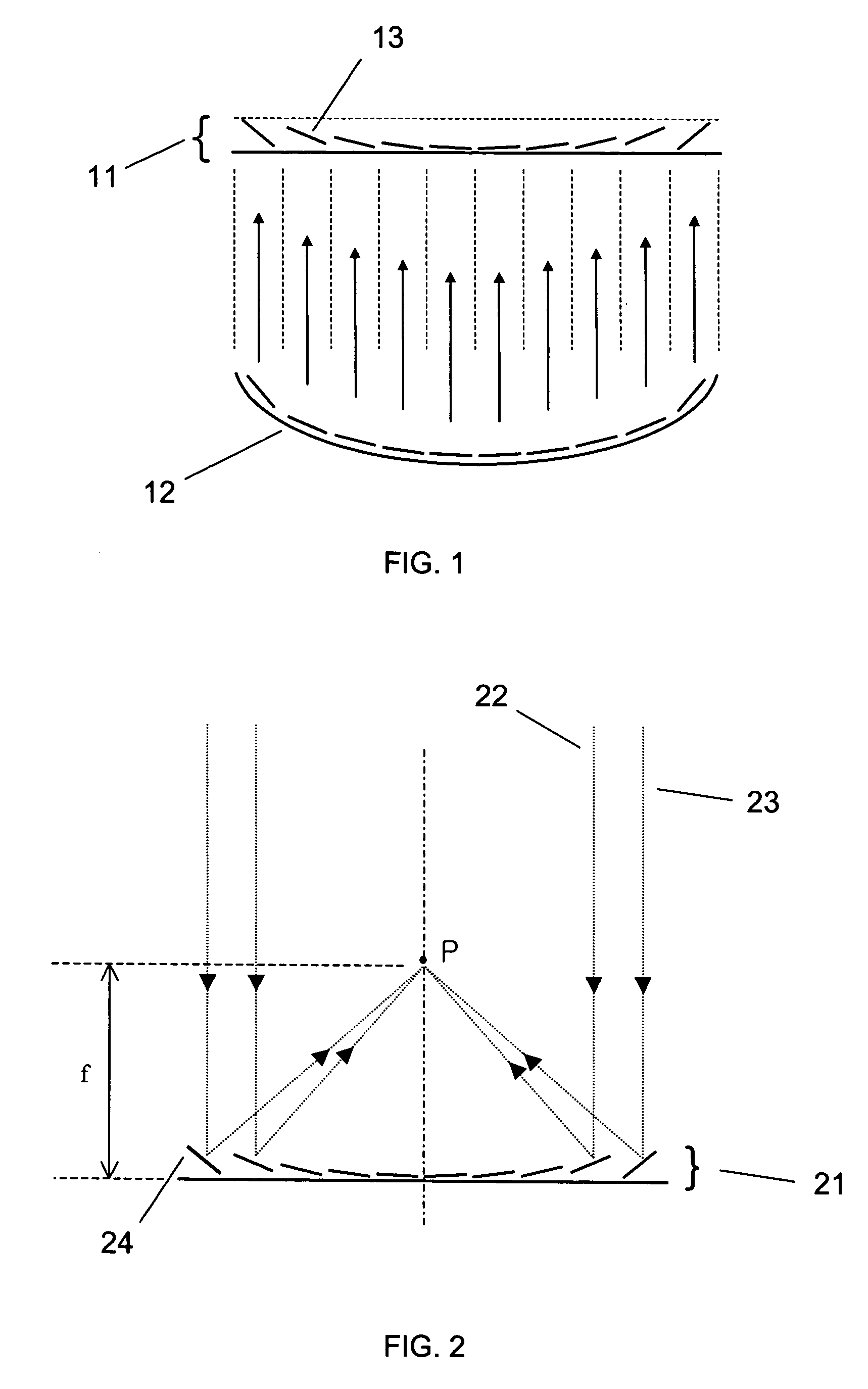
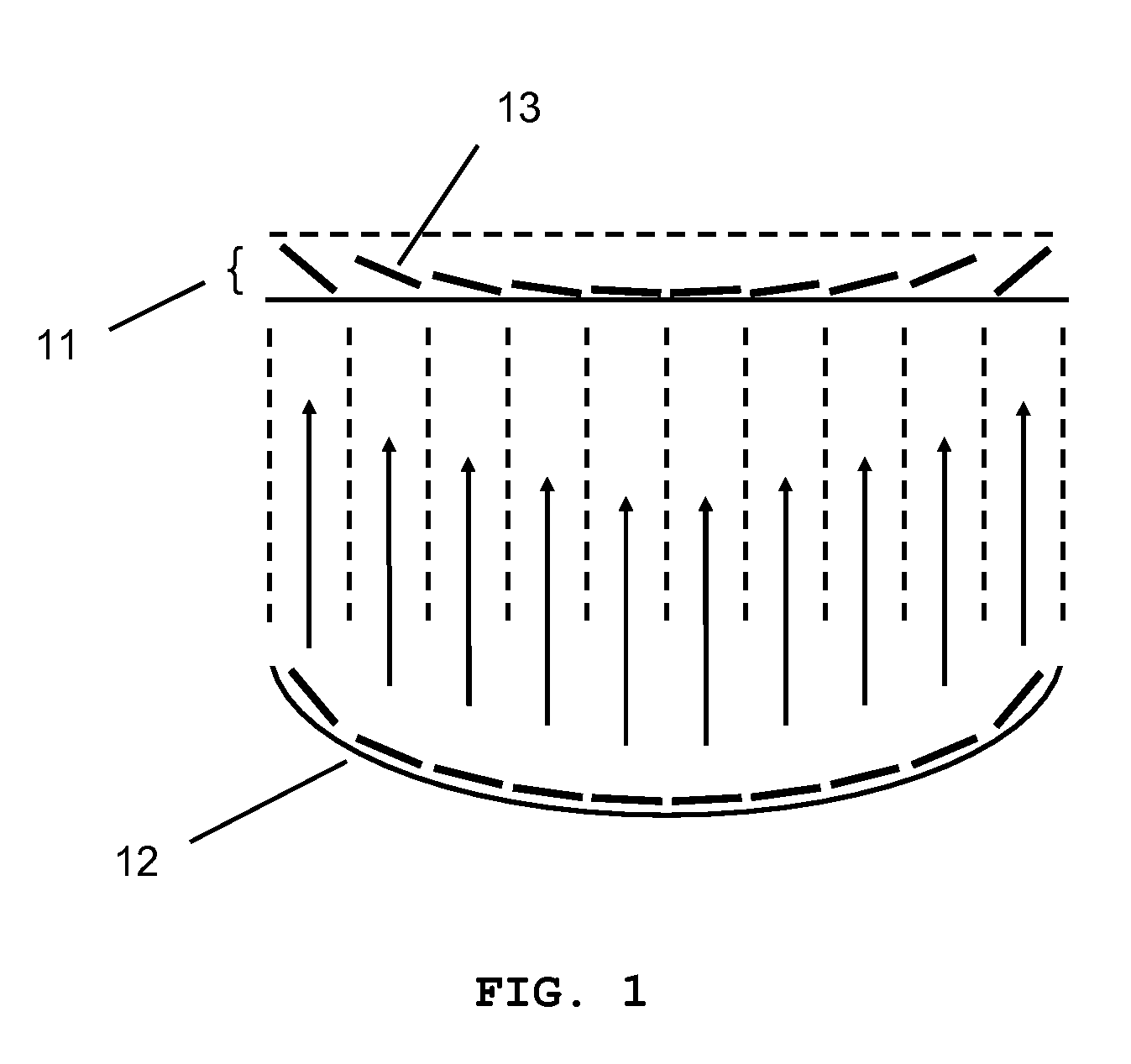
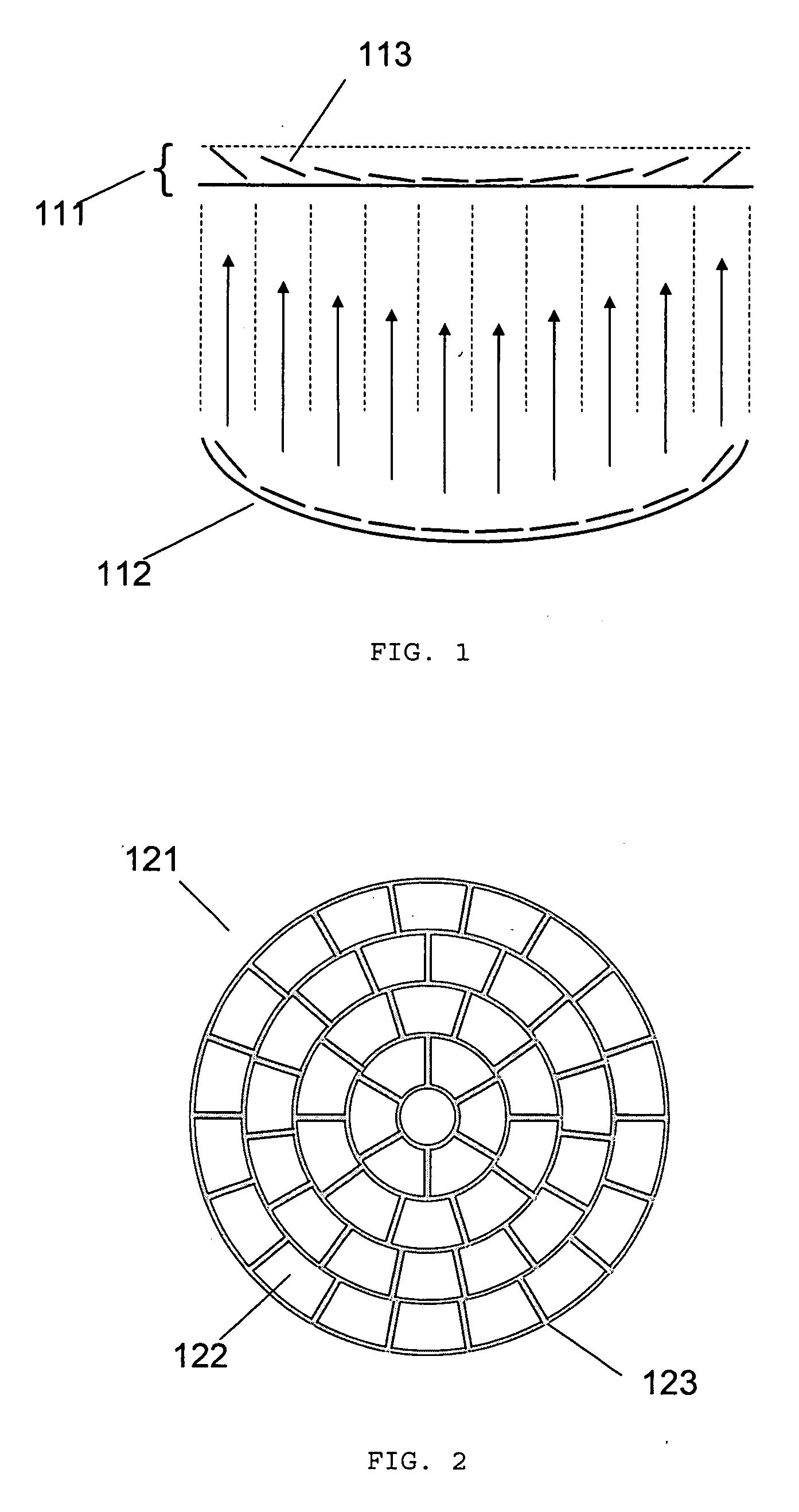
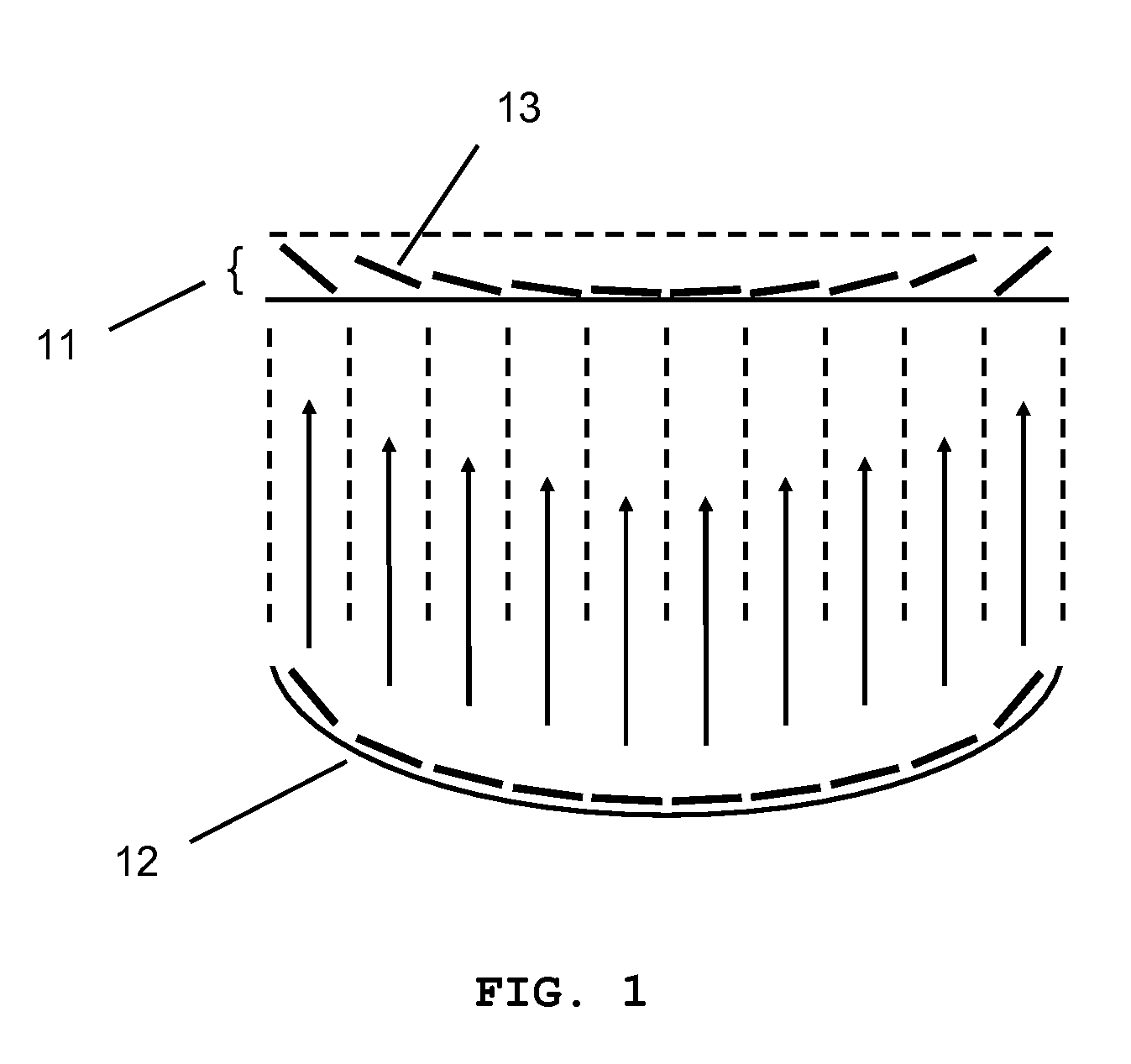
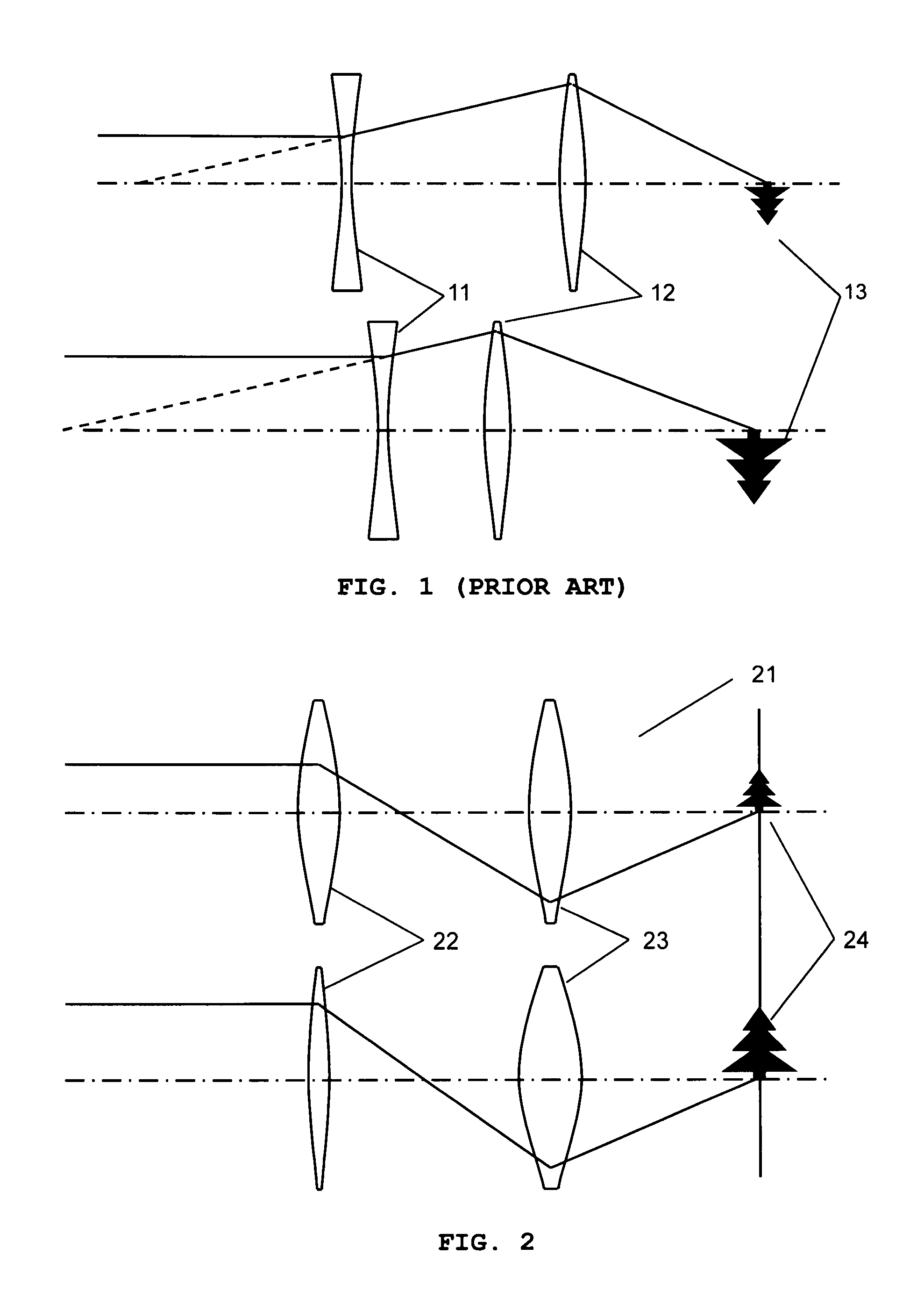
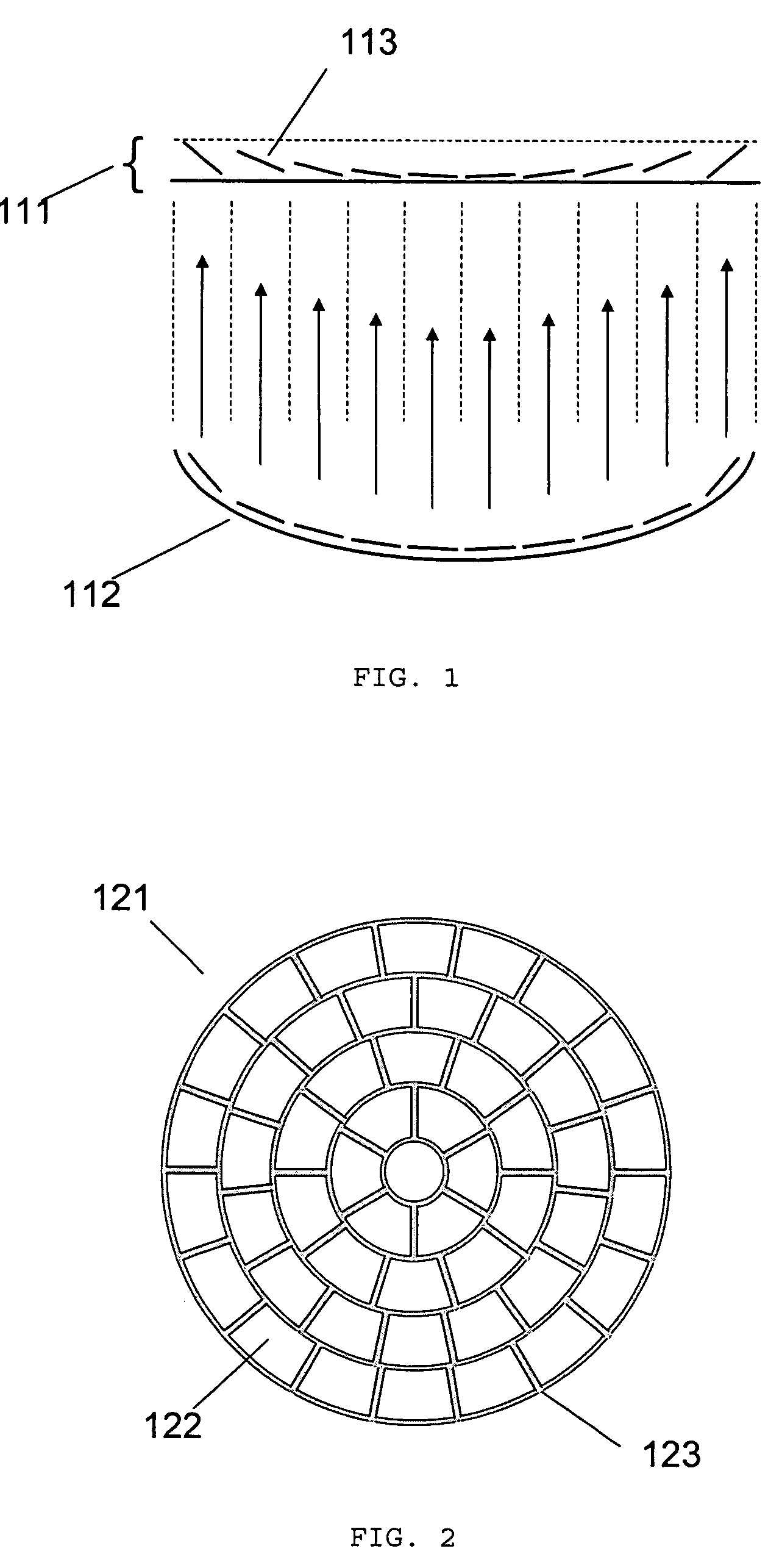
Method and system for treatment of blood vessel disorders
InactiveUS20060079868A1Optimal effectGood effectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyVascular malformationNon invasive
A non-invasive method and system for using ultrasound energy for the treatment of conditions resulting from vascular disorders is provided. In one embodiment, an image-treatment approach can be used to locate the blood vessel to be treated and then to ablate it non-invasively, while also monitoring the progress of the treatment. In another embodiment, a transducer is configured to deliver ultrasound energy to the regions of the superficial tissue (e.g., skin) such that the energy is deposited at the particular depth at which the vascular malformations (such as but not limited to varicose veins) are located below the skin surface. The ultrasound transducer can be driven at a number of different frequency regimes such that the depth and shape of energy concentration can match the region of treatment.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Apparatus
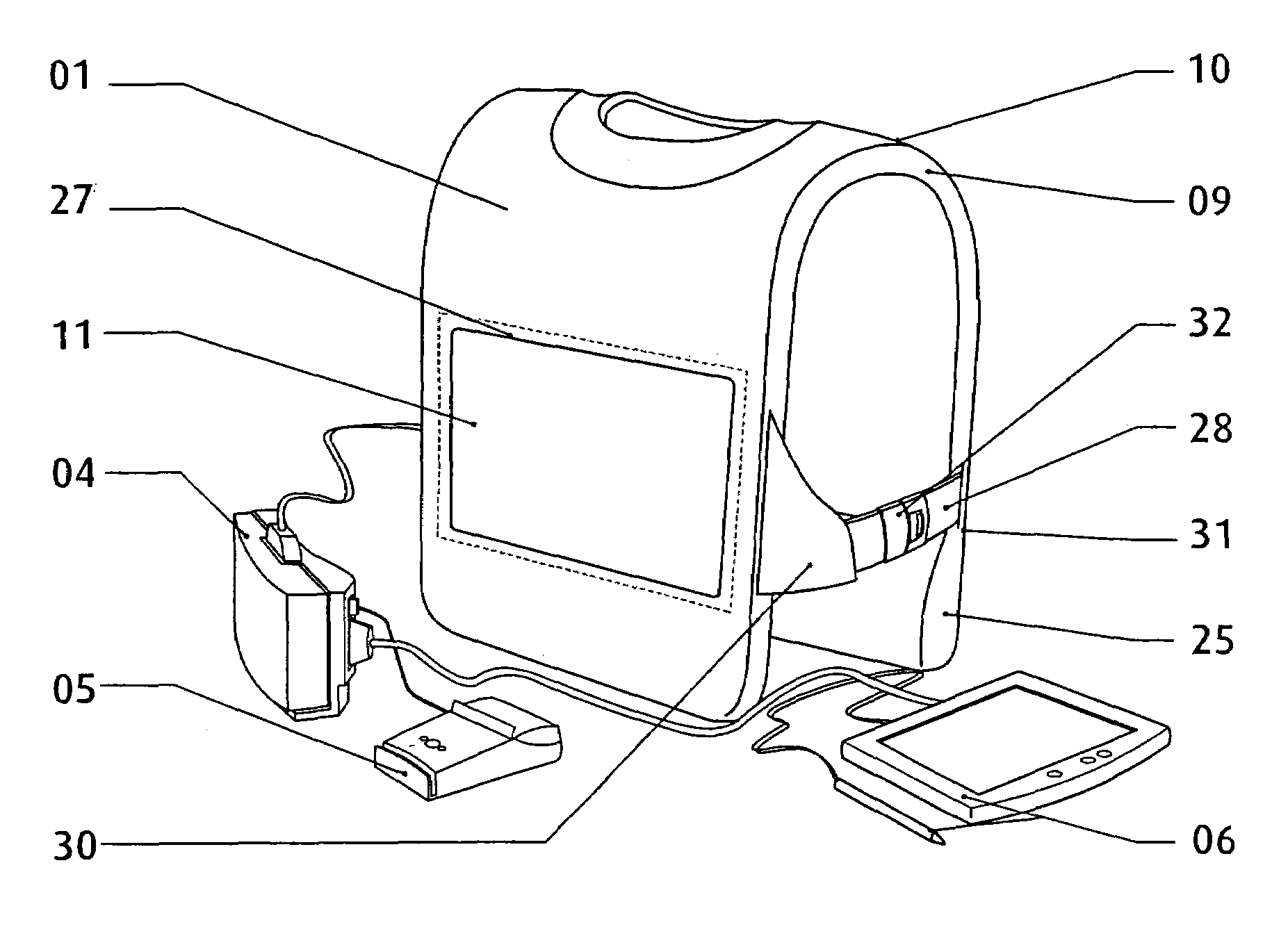
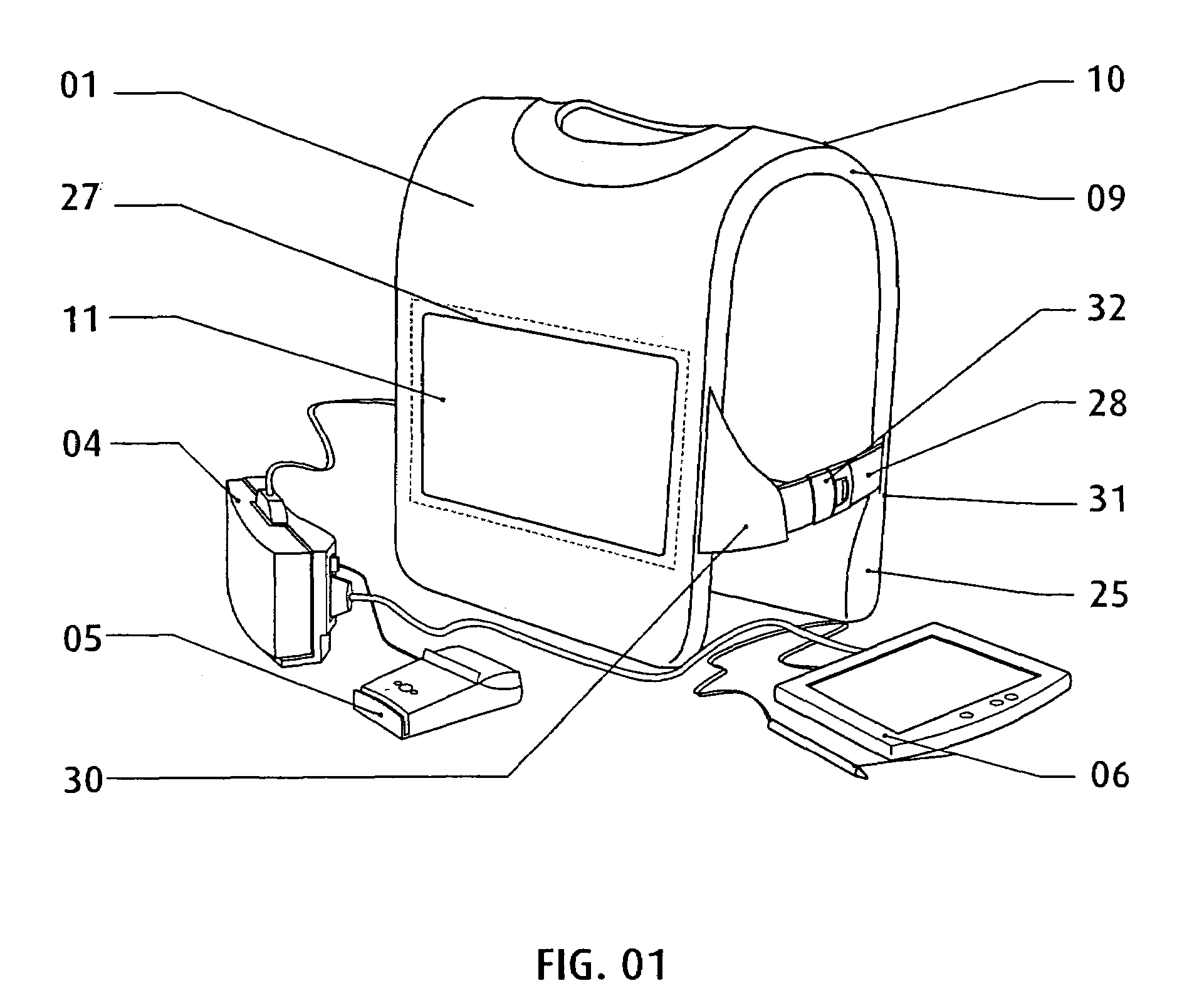
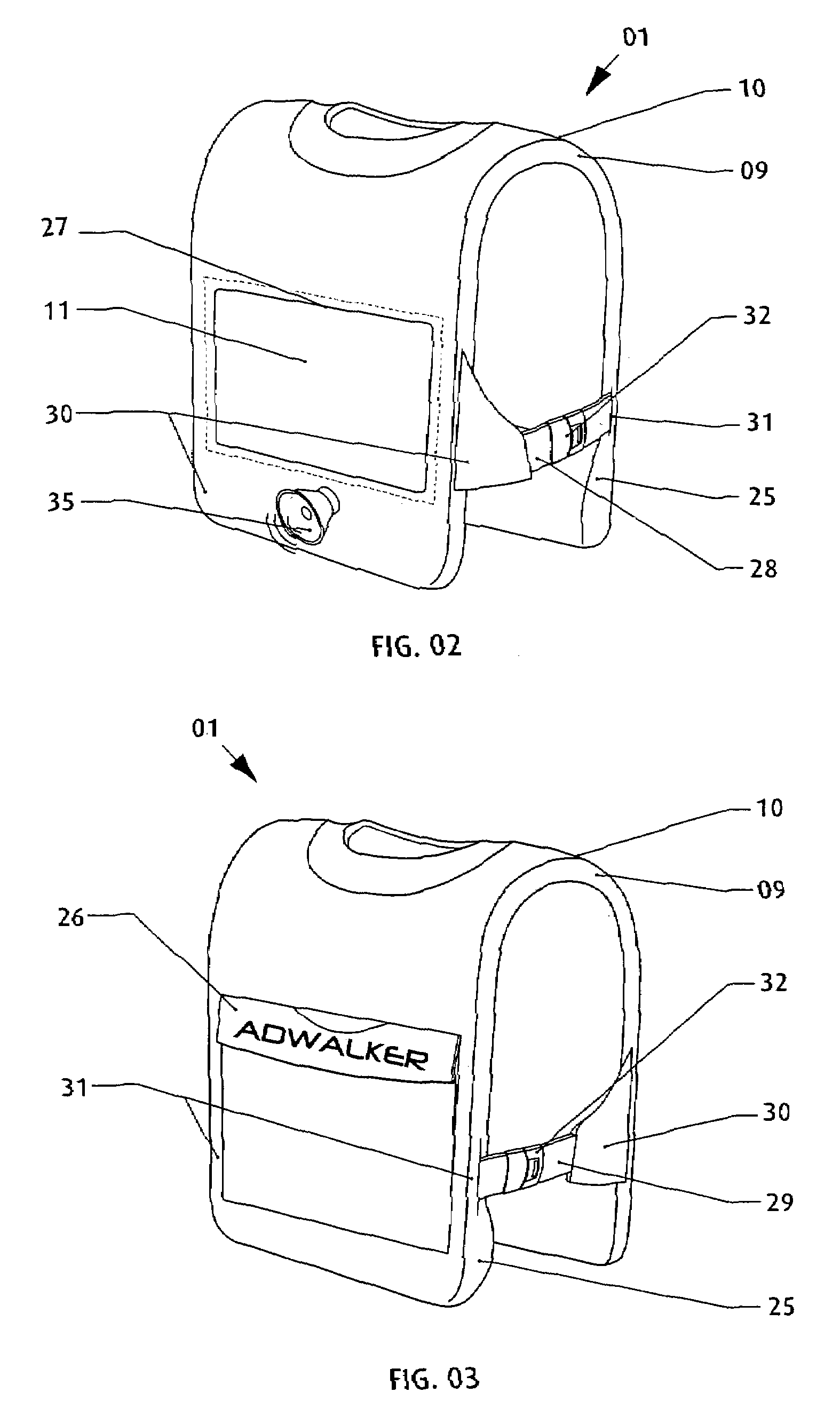
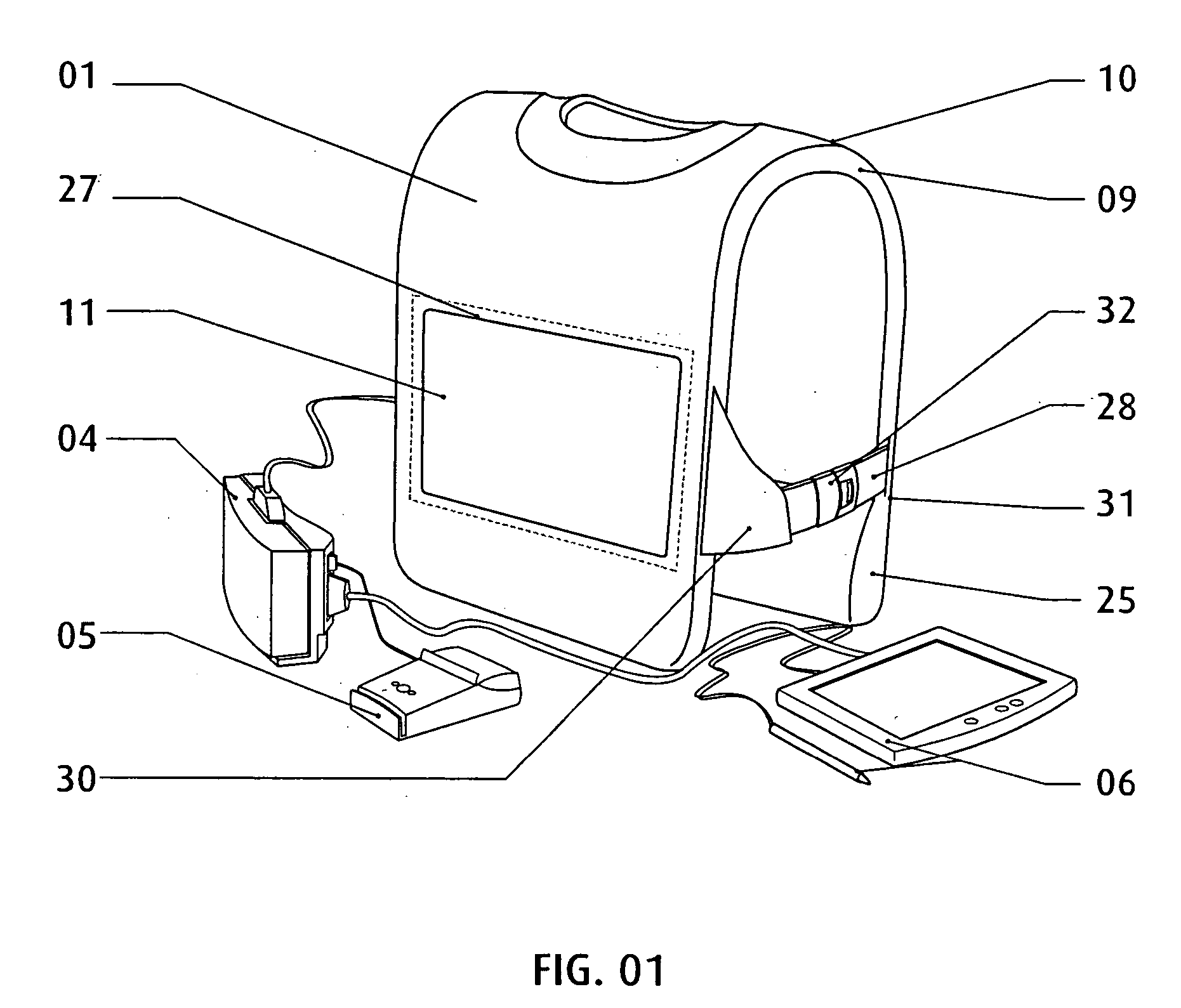
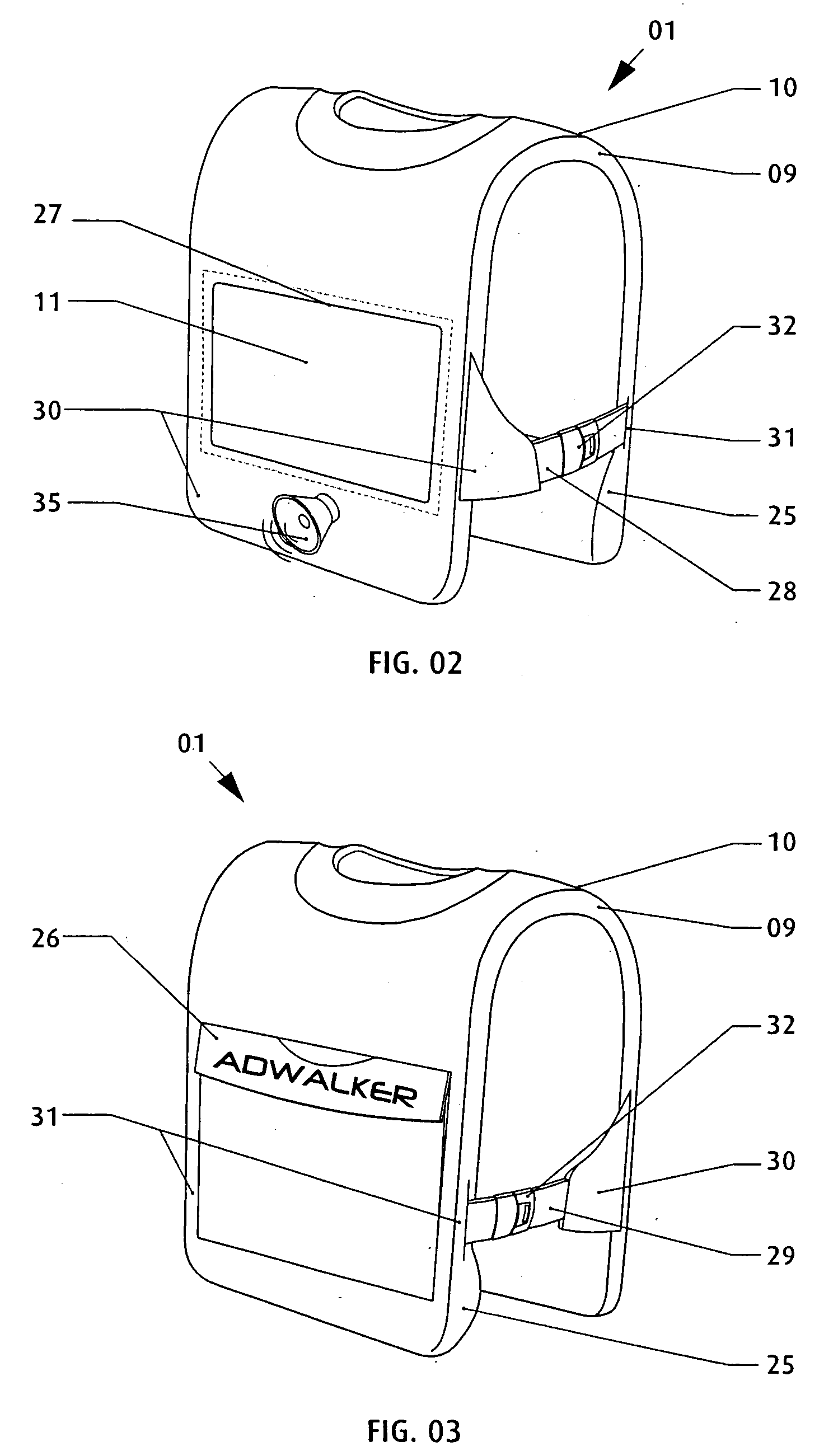
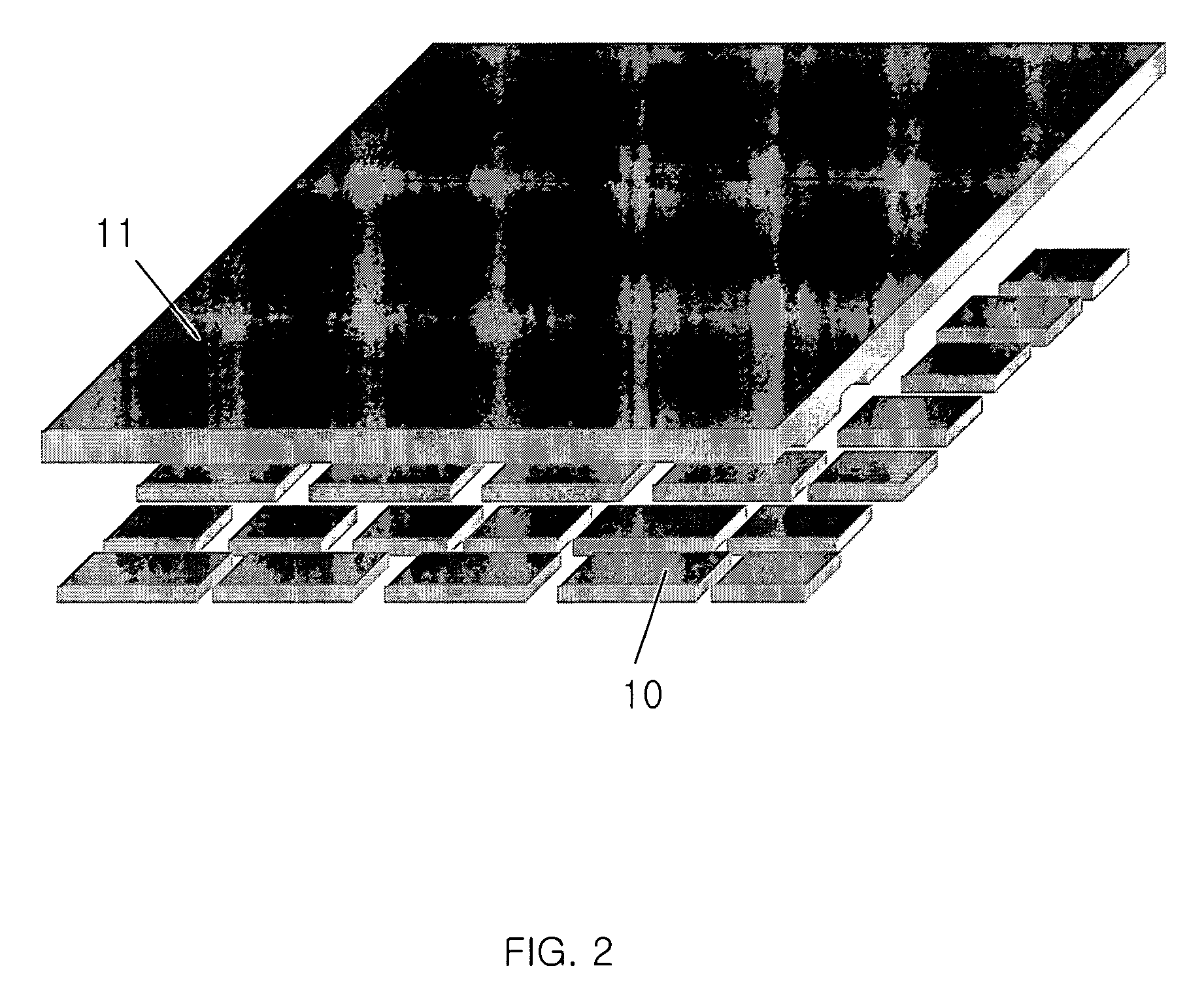
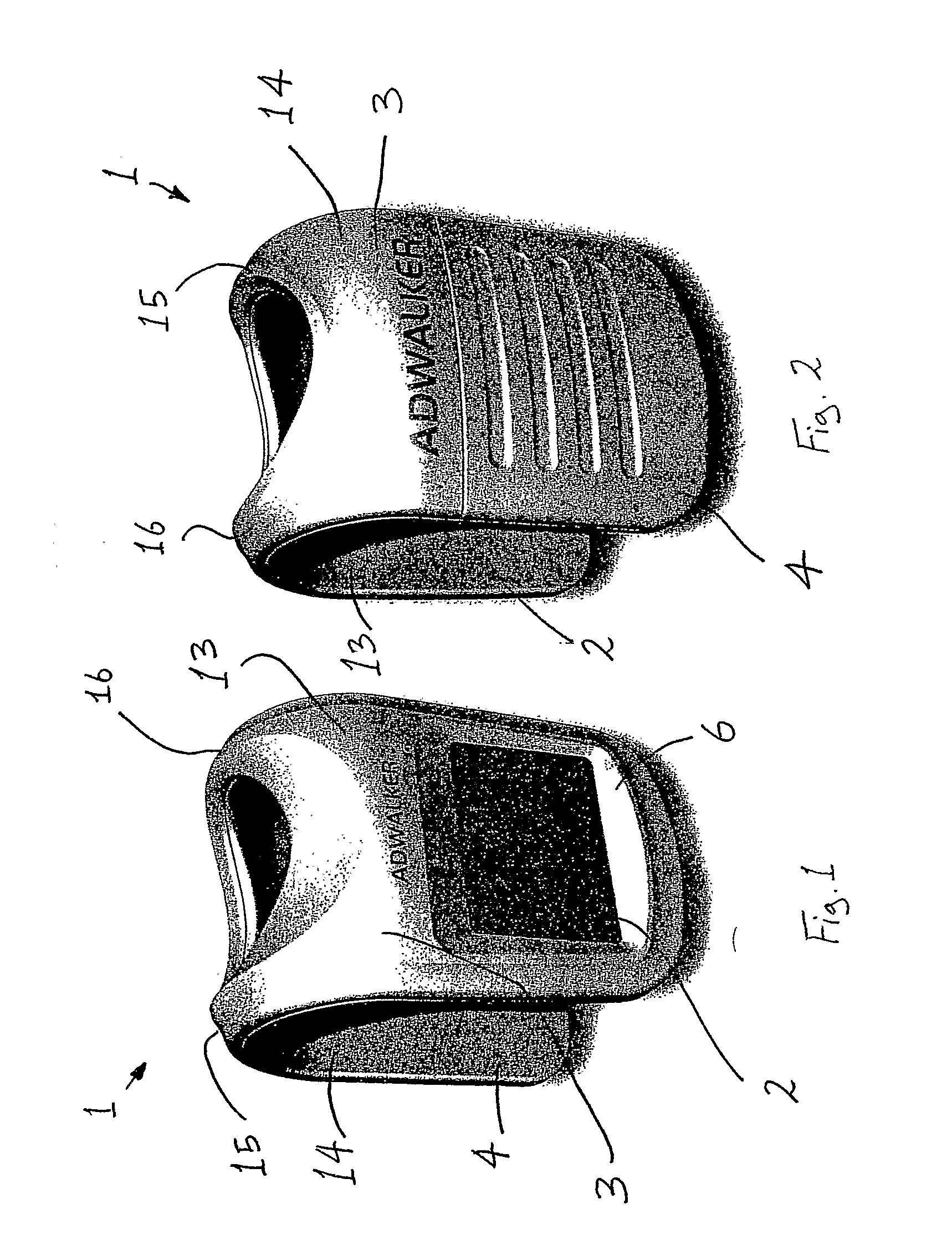
InactiveUS7265970B2Improve comfortImprove liquidityDigital data processing detailsGarmentsEngineeringWearable computer
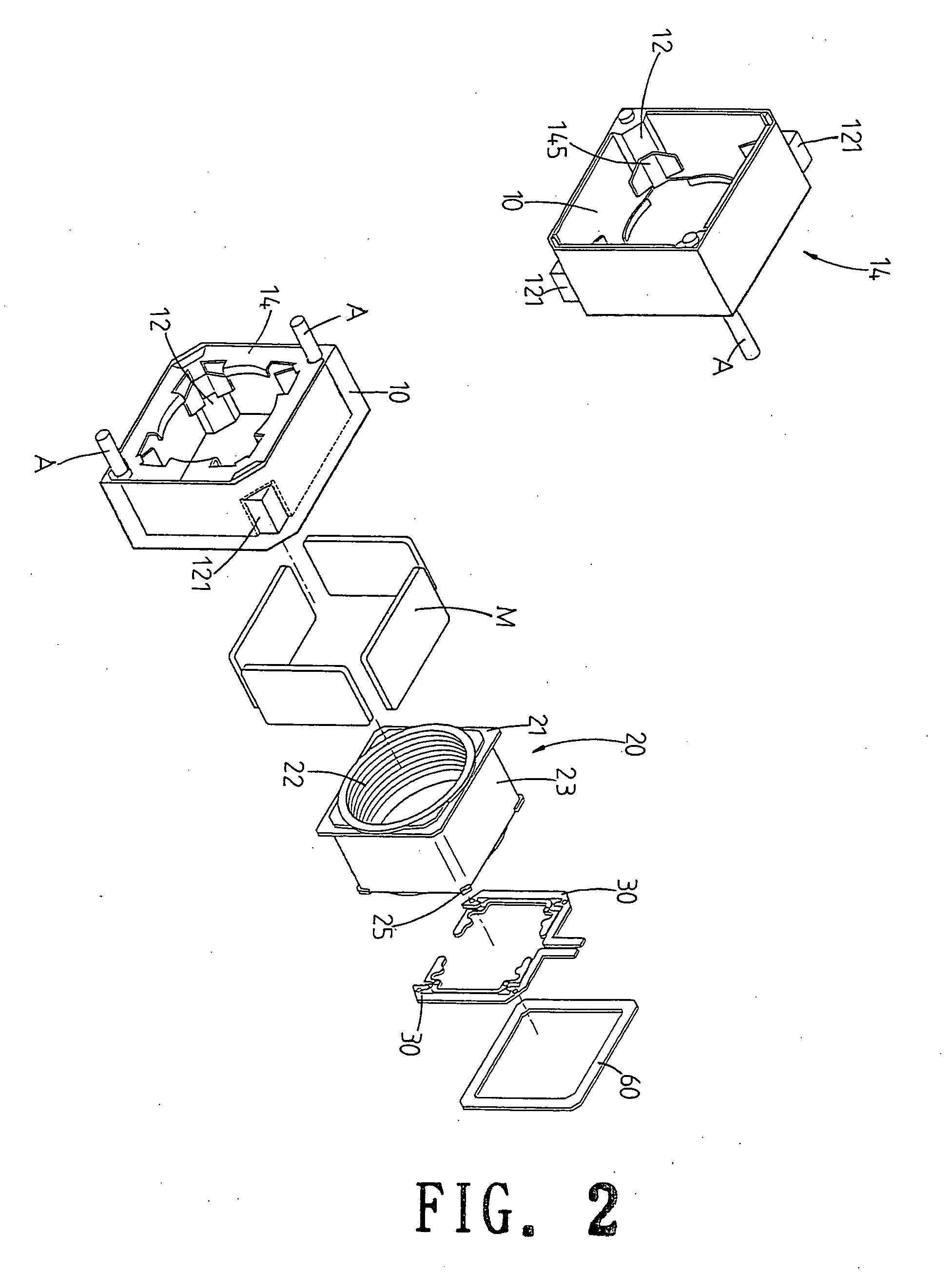
An apparatus (1) for supporting a mobile electronic display system. The mobile electronic display system includes a display element (11) and a power source (12). In use a wearable computer (4) controls operation of the display element (11). The apparatus (1) comprises a relatively rigid support frame (8), a relatively soft cushion member (9), and a cover (10) for the support frame (8). The support frame (8) is suitable for being worn by a person to support the mobile electronic display system. The support frame (8) comprises a front support frame part (13) located at the front of the wearer, a rear support frame part (14) located at the rear of the wearer, a first bearing member (15) extending over a first shoulder of the wearer, and a second bearing member (16) extending over a second shoulder of the wearer.
Owner:ADWALKER PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY
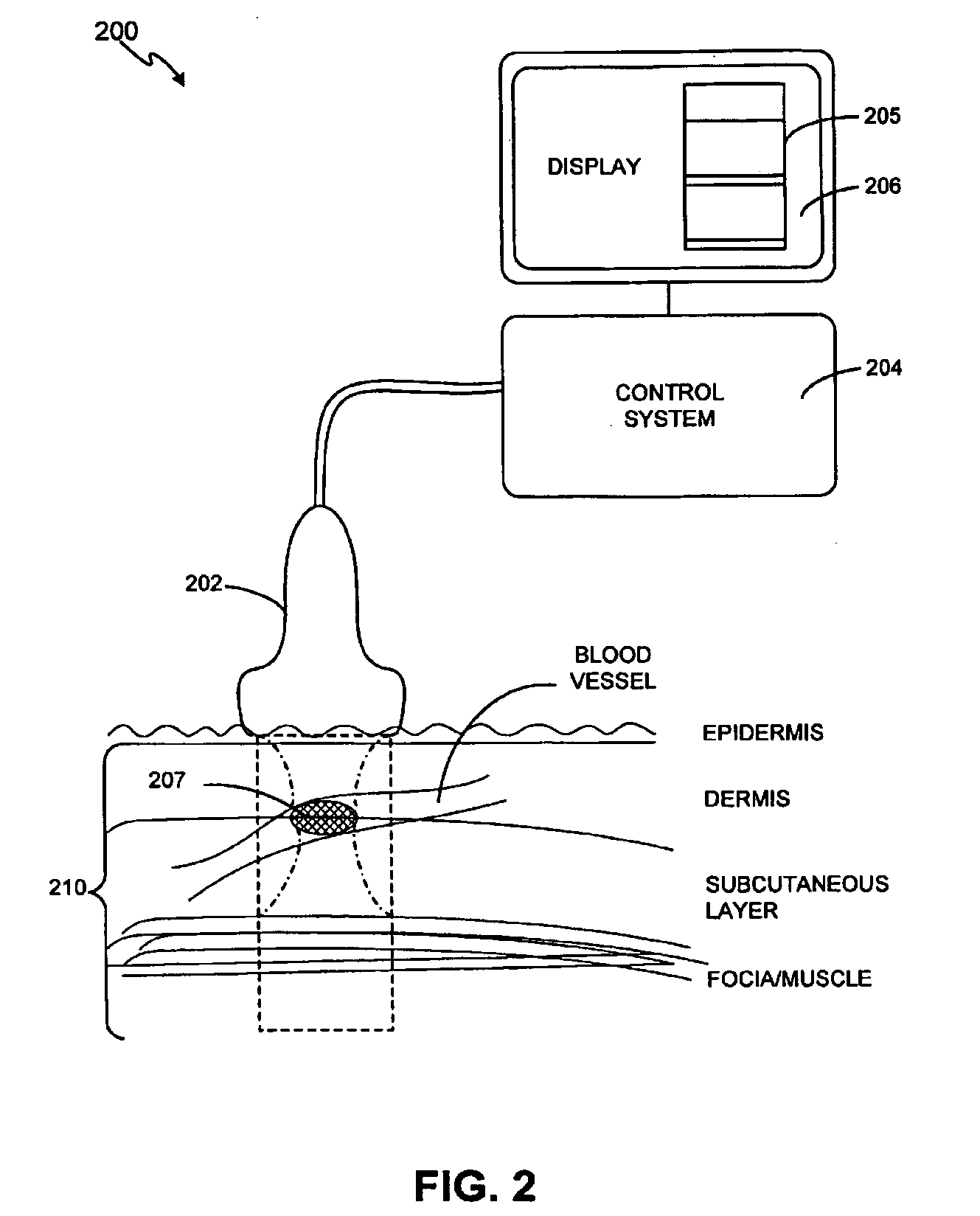
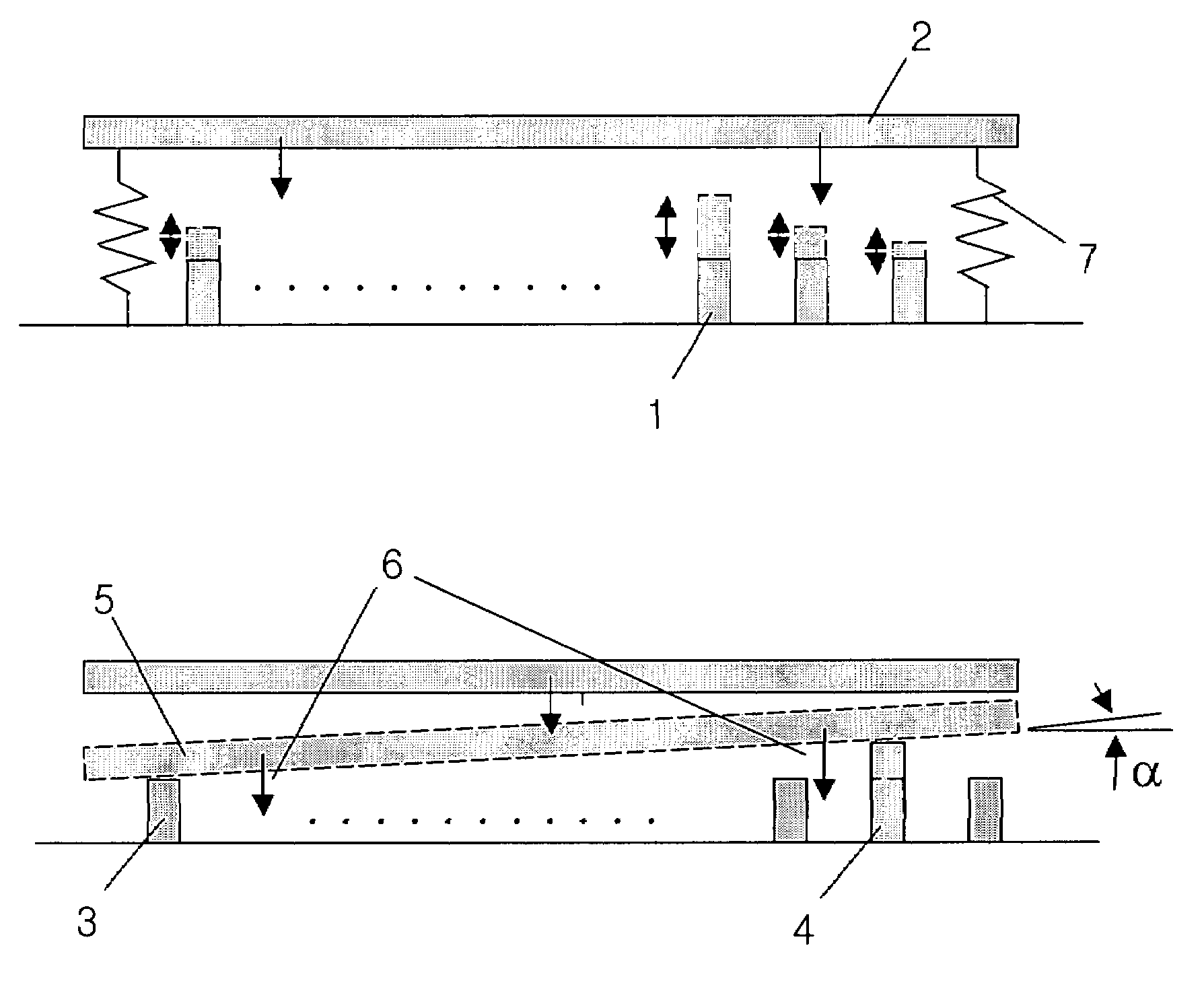
Noninvasive treatment of blood vessels
InactiveUS20120330197A1Good effectHighly focusedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyVascular diseaseBlood vessel spasm
A non-invasive method and system for using ultrasound energy for the treatment of conditions resulting from vascular disorders is provided. In one embodiment, an image-treatment approach can be used to locate the blood vessel to be treated and then to ablate it non-invasively, while also monitoring the progress of the treatment. In another embodiment, a transducer is configured to deliver ultrasound energy to the regions of the superficial tissue (e.g., skin) such that the energy is deposited at the particular depth at which the vascular malformations are located below the skin surface. The ultrasound transducer can be driven at a number of different frequency regimes such that the depth and shape of energy concentration can match the region of treatment.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
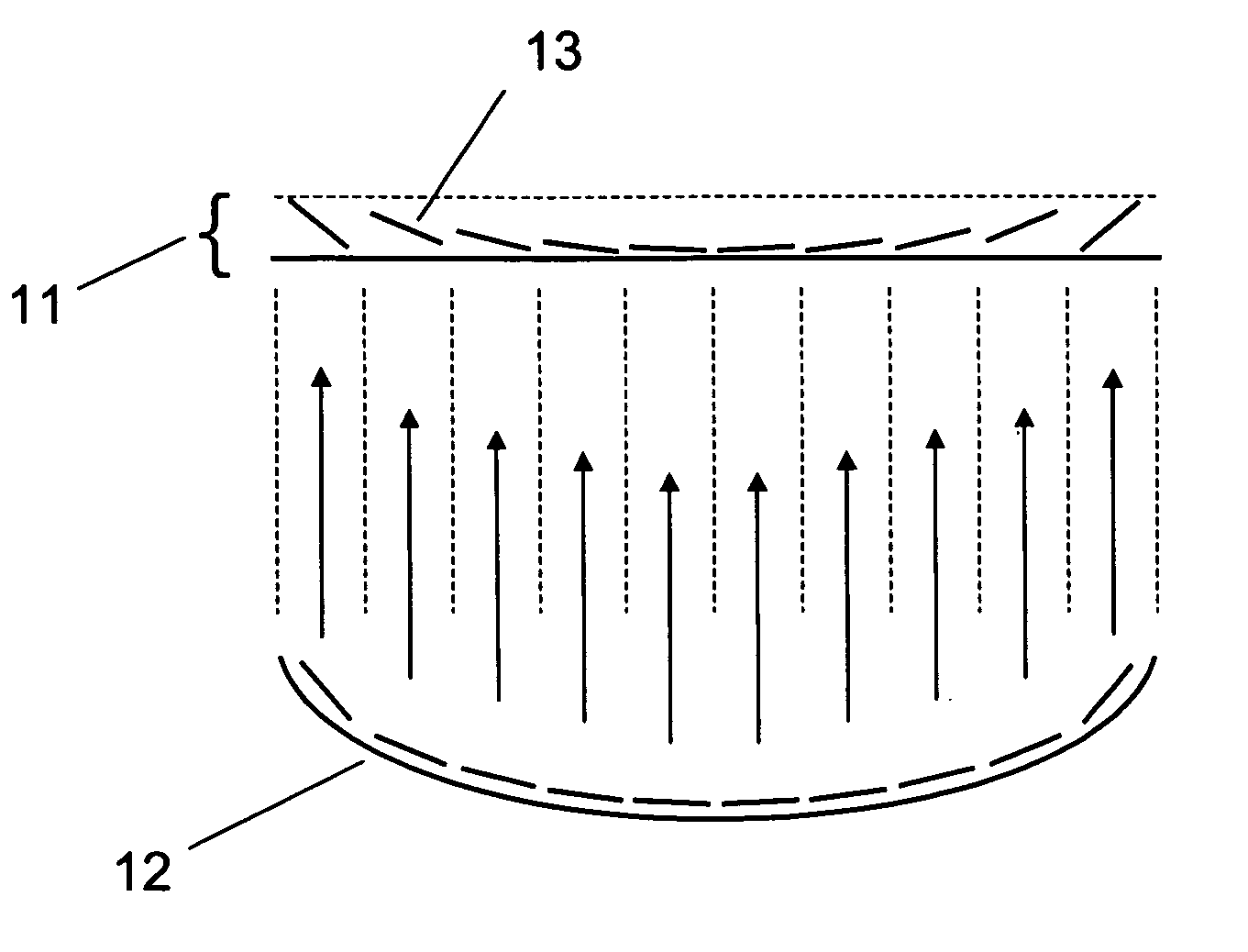
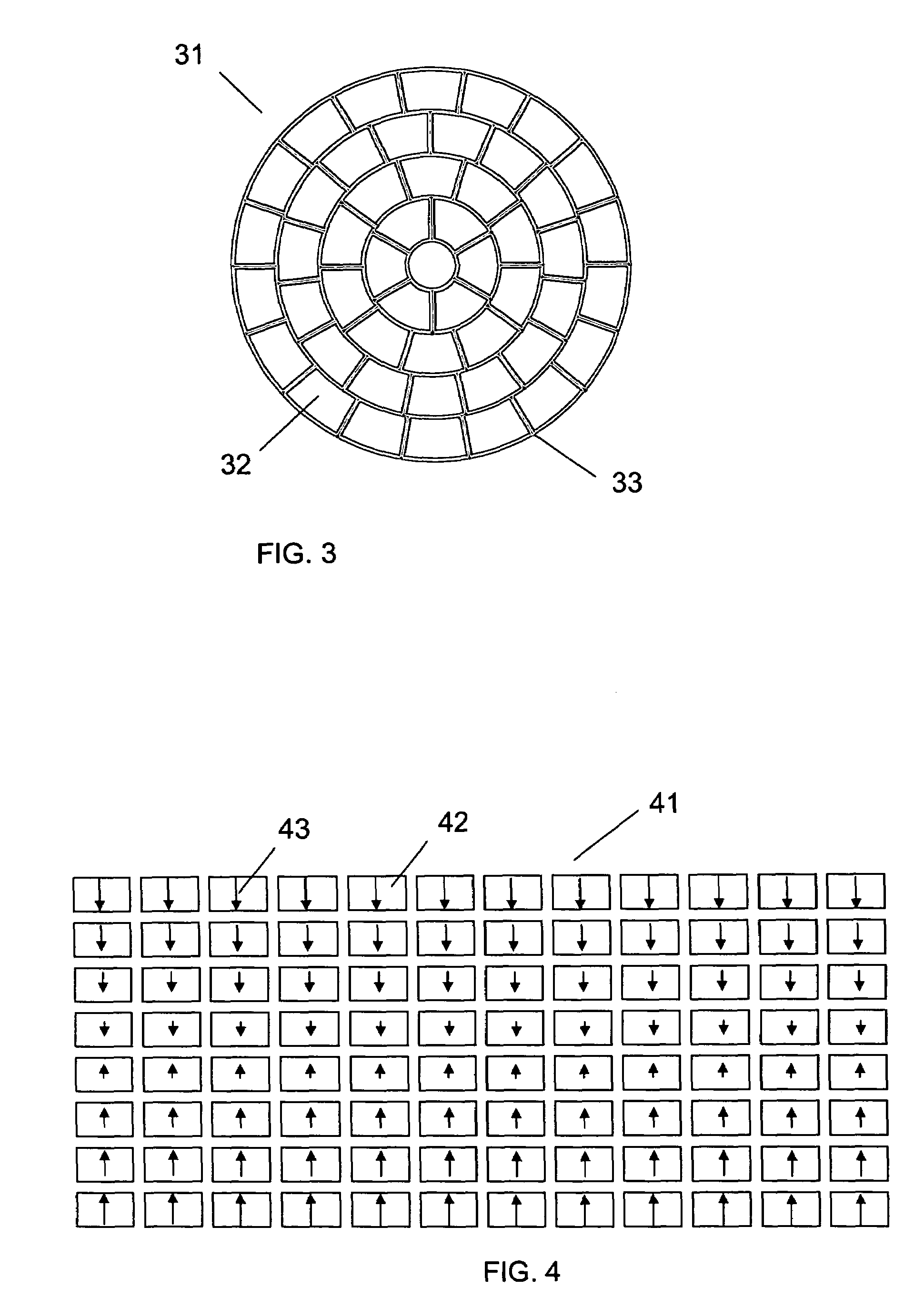
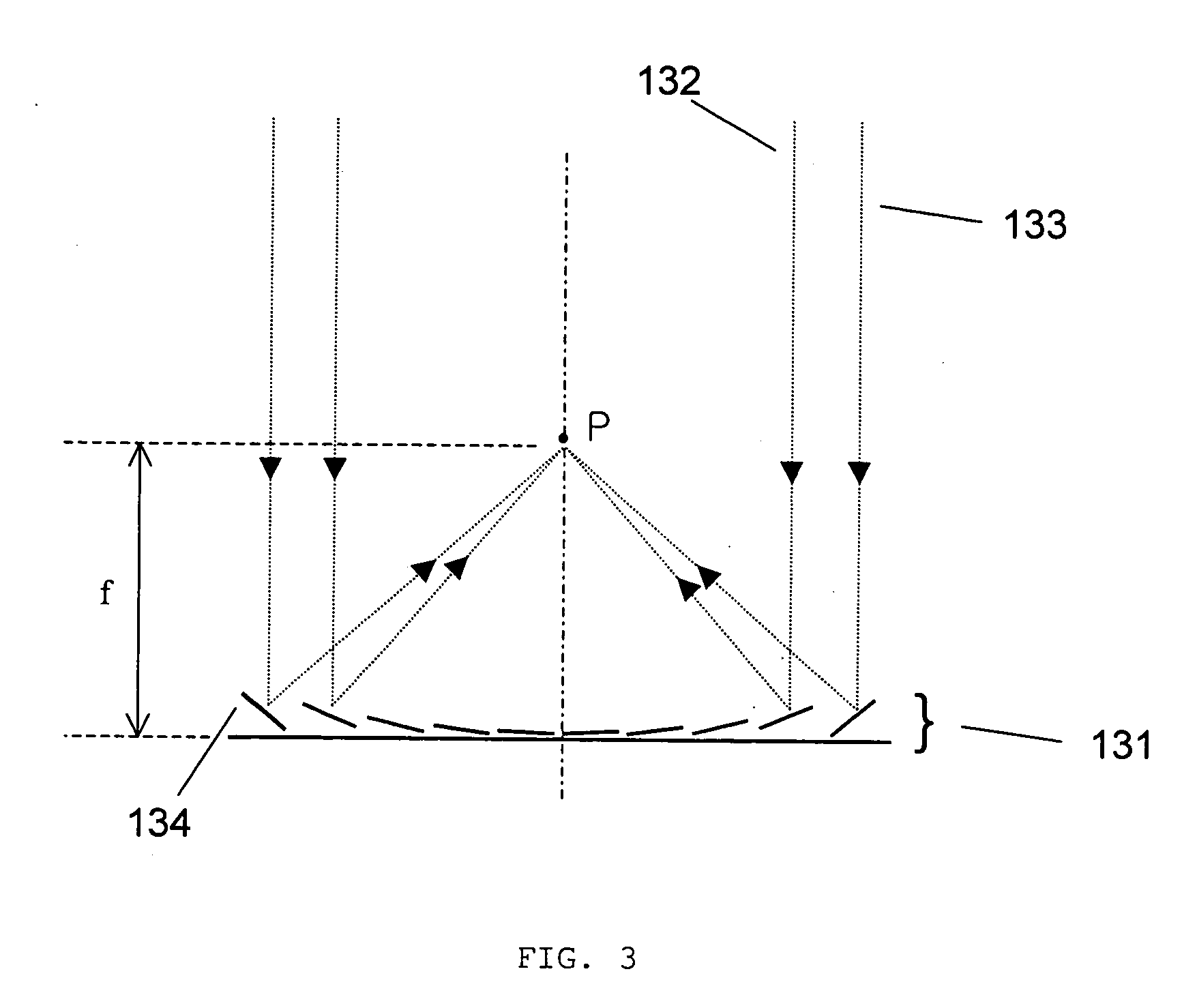
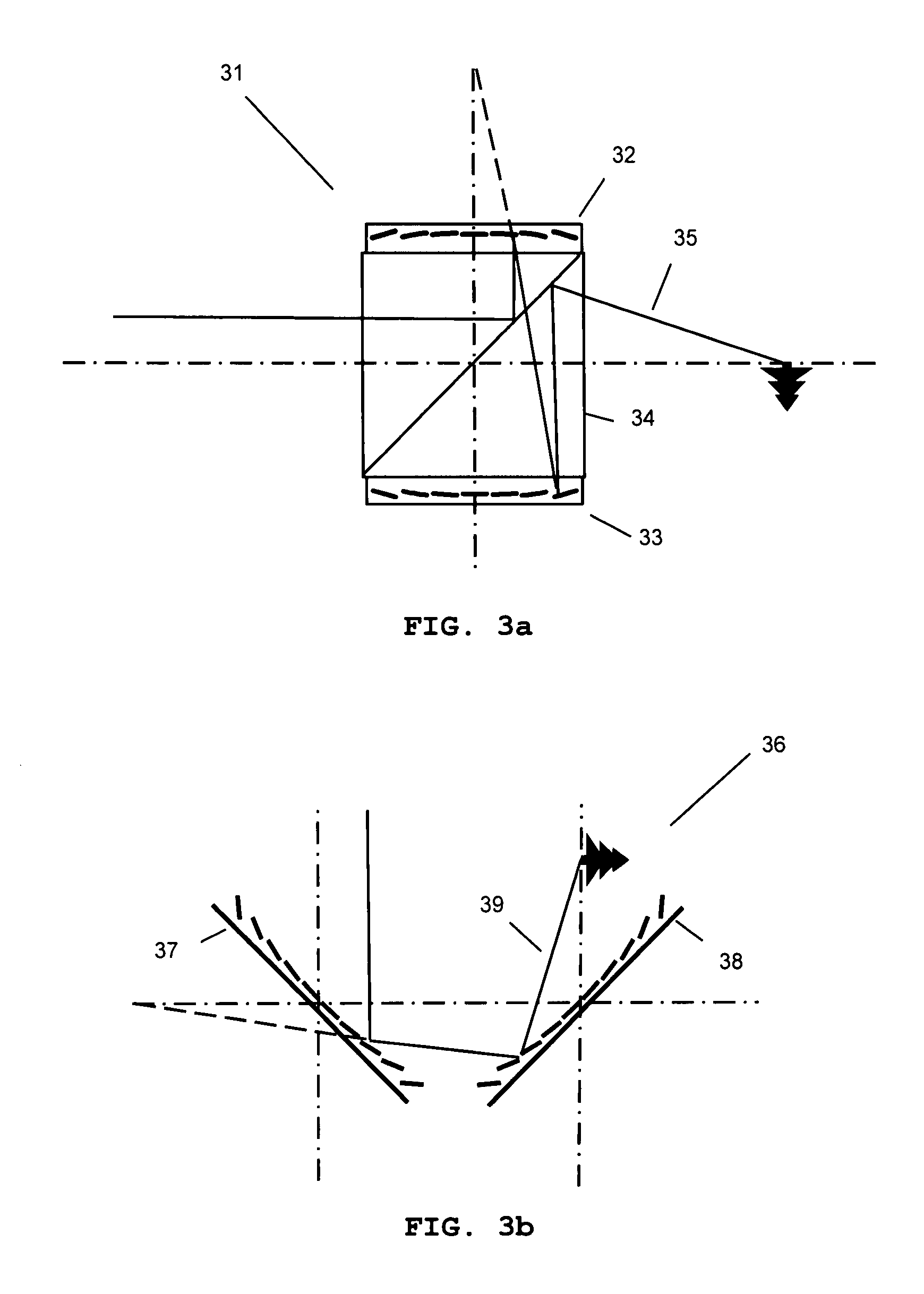
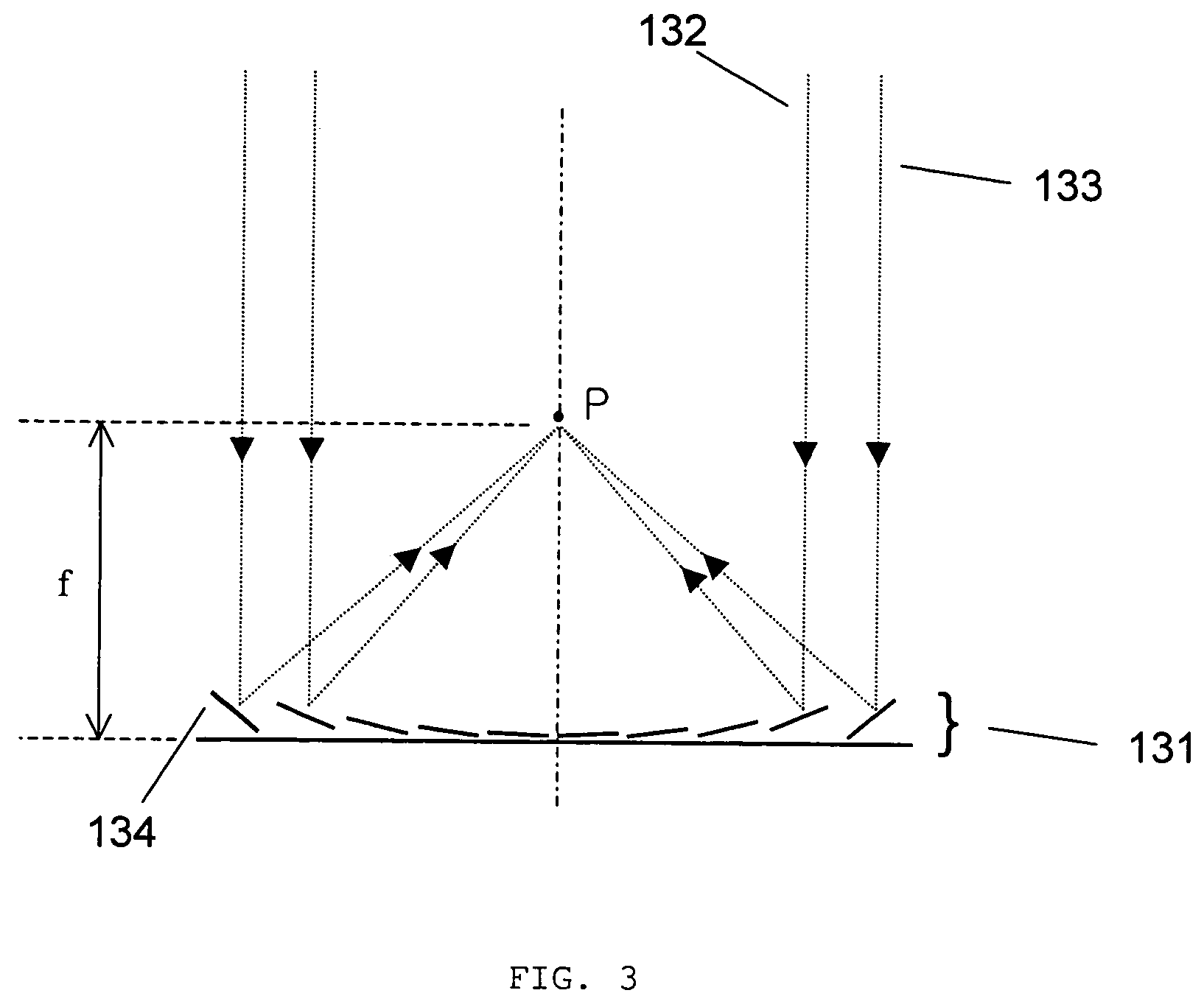
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with two degrees of freedom rotation and one degree of freedom translation
ActiveUS6934072B1Fast response timeLarge length variationNon-linear opticsOptical elementsSemiconductorImage plane
A micromirror array lens consists of many micromirrors with two degrees of freedom rotation and one degree of freedom translation and actuating components. As a reflective variable focal length lens, the array of micromirrors makes all lights scattered from one point of an object have the same periodic phase and converge at one point of image plane. As operating methods for the lens, the actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. Semiconductor microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. Independent control of each micromirror is possible by known semiconductor microelectronics technologies. The micromirror array can also form a lens with desired arbitrary shape and / or size.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with one degrees of freedom rotation and one degree of freedom translation
ActiveUS6934073B1Improve reflectivityIncrease the effective reflection areaNon-linear opticsOptical elementsCamera lensDegrees of freedom
A micromirror array lens consists of many micromirrors with one degree of freedom rotation and one degree of freedom translation and actuating components. As a reflective variable focal length lens, the array of micromirrors makes all lights scattered from one point of an object have the same periodic phase and converge at one point of image plane. As operational methods for the lens, the actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The known semiconductor microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. Independent control of each micromirror is possible by known semiconductor microelectronics technologies.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Three-dimensional imaging system
A new three-dimensional imaging system has been needed to overcome the problems of the prior arts using conventional variable focal length lenses, which have slow response time, small focal length variation, and low focusing efficiency, and require a complex mechanism to control it. The three-dimensional imaging system of the present invention uses the variable focal length micromirror array lens. Since the micromirror array lens has many advantages such as very fast response time, large focal length variation, high optical focusing efficiency, large size aperture, low cost, simple mechanism, and so on, the three-dimensional imaging system can get a real-time three-dimensional image with large depth range and high depth resolution.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Method and System for Providing Discounted Services to Customers
InactiveUS20090094109A1Efficient and economicalHigh focusFinanceAdvertisementsService providerService provision
ServiceClub provides an efficient and economic way to connect sellers of services with potential buyers of their services. Discounts, coupons, and special promotions can be provided potential customers based on geographic considerations, so a potential customer can receive services of a specific type either around where he lives or works, or currently is located. Since the system provides geographic filtering, a national or international system can provide discounts and promotions local to a user. Customers benefit because of the national system, and service providers benefit through highly focused advertising.
Owner:WORLDWIDE SERVICECLUB A MASSACHUSETTS CORP
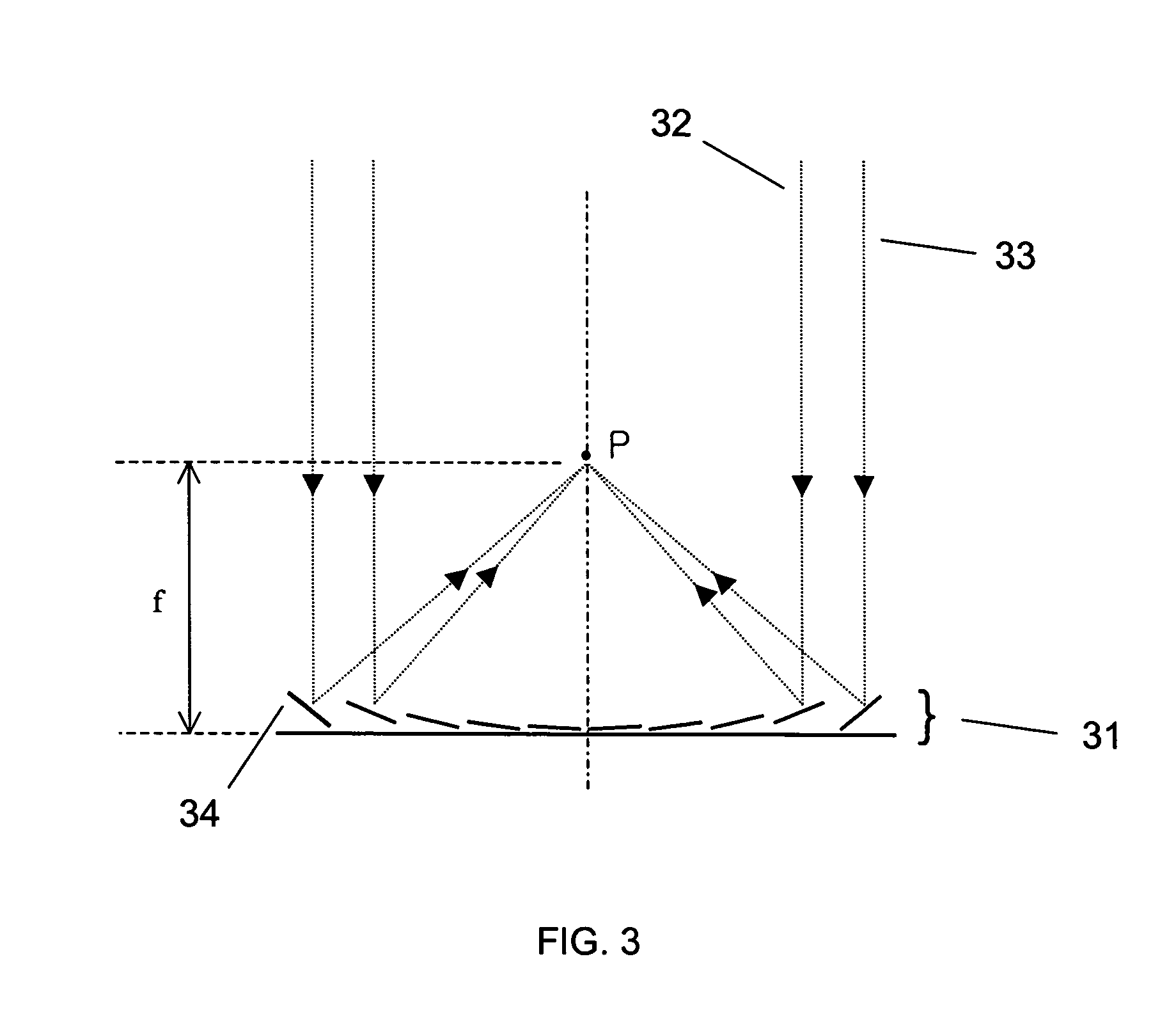
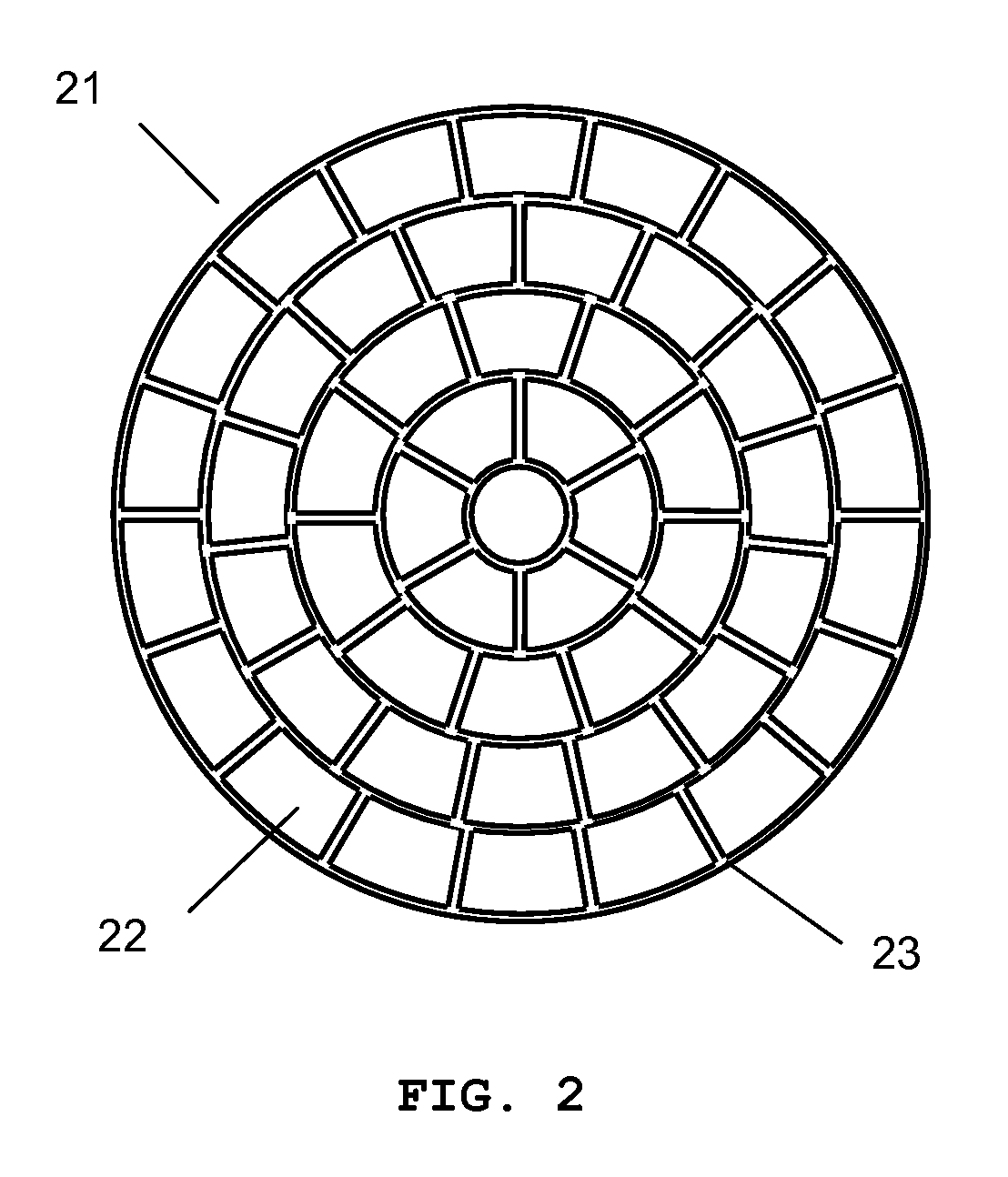
Microlens arrays having high focusing efficiency
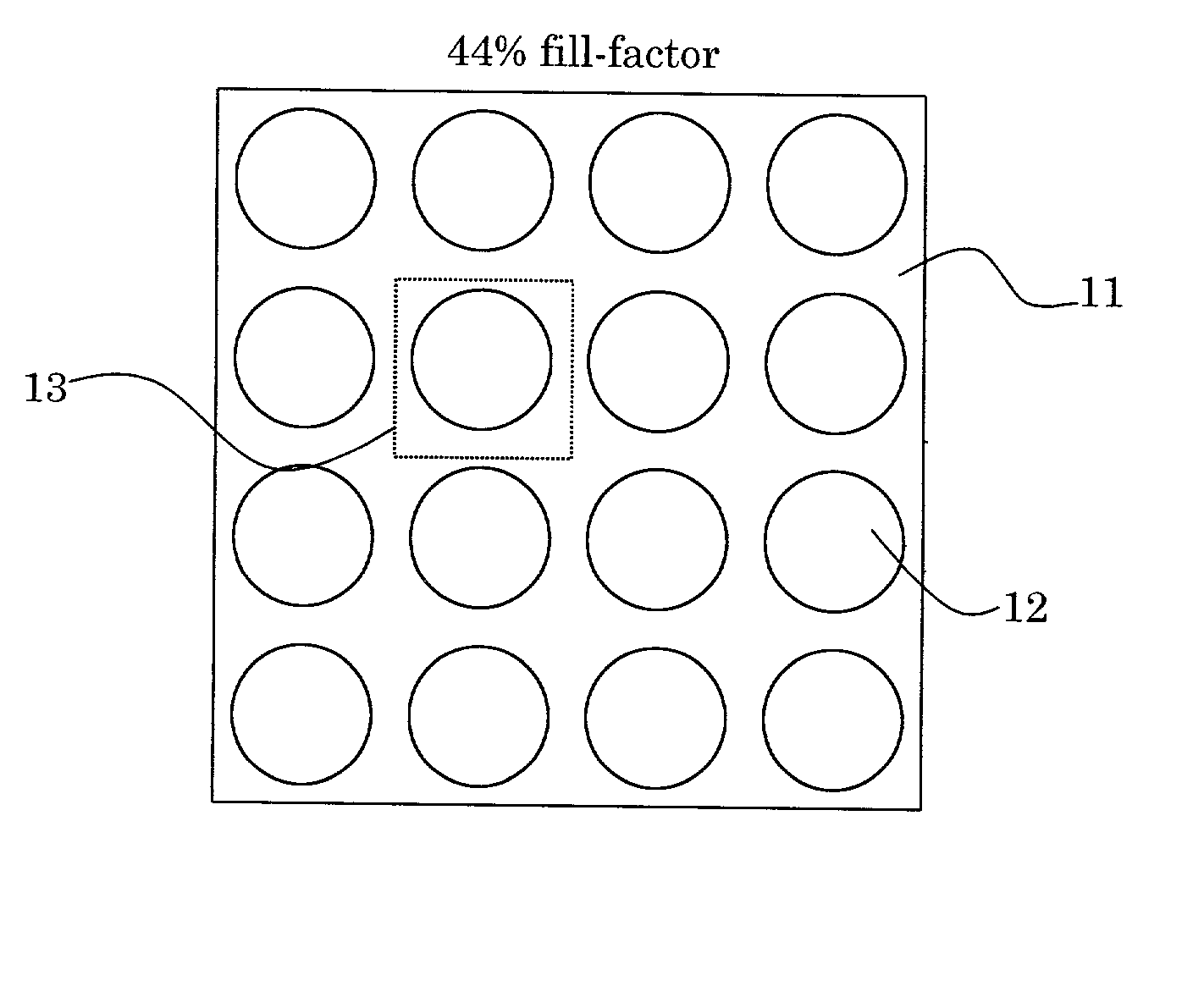
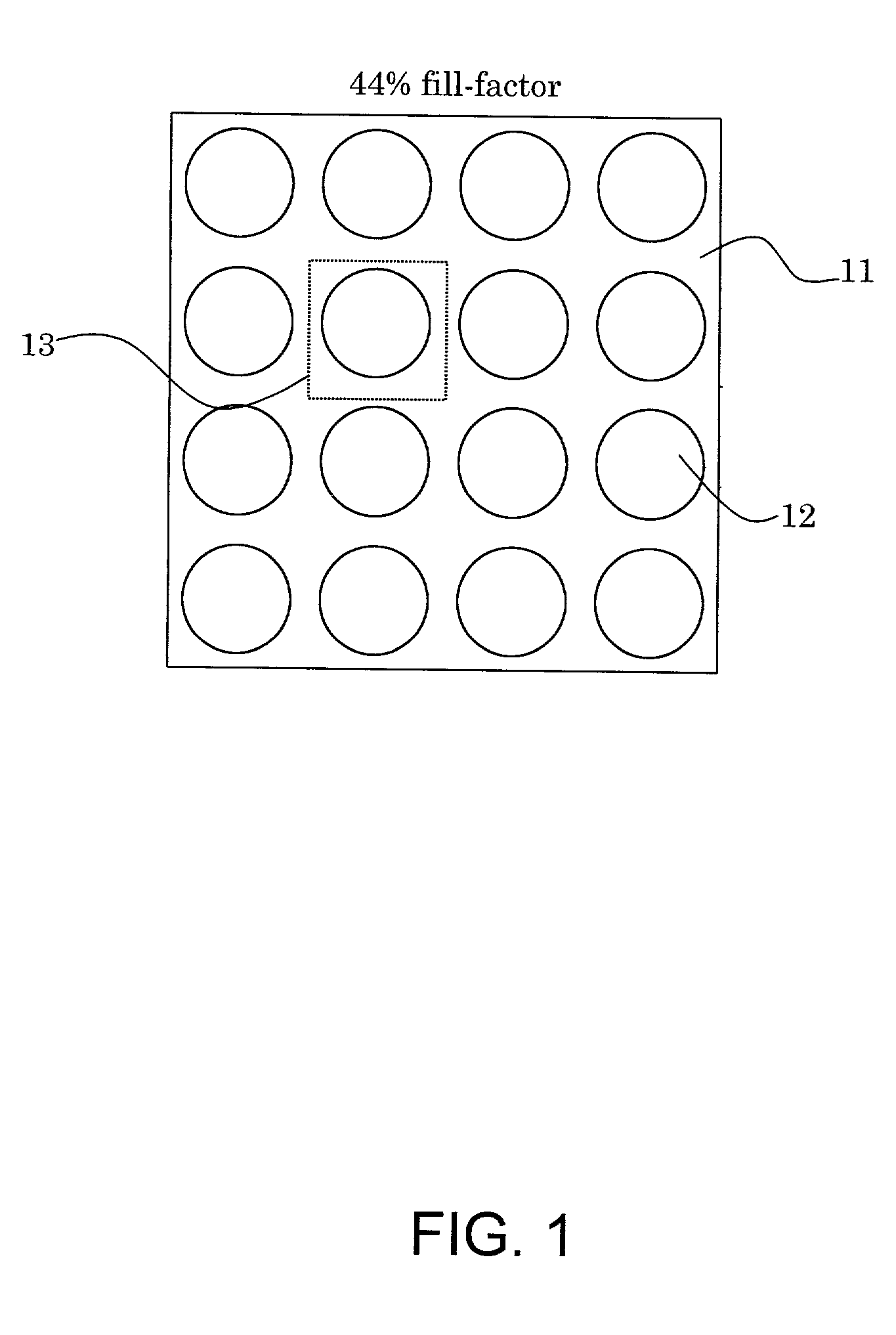
InactiveUS20020034014A1Improve fill factorHighly focusedRadiation applicationsSolid-state devicesFill factorMicro lens array
Microlens arrays (105) having high focusing efficiencies are provided. The high focusing efficiencies are achieved by accurately producing the individual microlenses making up the array at high fill factors. Arrays of positive microlenses are produced by forming a master having a concave surface-relief pattern (101) in a positive photoresist (21) using direct laser writing. Through this approach, the problems associated with the convolution of a finite laser beam with a desired profile for a microlens are overcome. The microlens arrays of the invention have focusing efficiencies of at least 75%.
Owner:CORNING INC
Variable focusing lens comprising micromirrors with one degree of freedom rotation
ActiveUS6970284B1Simple mechanical structure and actuating componentLarge aberrationMirrorsMountingsCMOSSoi cmos technology
A variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors with one degree of freedom rotation is invented. The lens consists of many micromirrors and actuating components. The array of micromirrors with one degree of freedom rotation makes all lights scattered from one point of an object converge at one point of image plane by using rotation of micromirror. The micromirror has the same function as a mirror. Therefore, the reflective surface of the micromirror is made of metal, metal compound, multi-layered dielectric material, or other materials with high reflectivity. The actuating components control the rotational displacements of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the micromirror array lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The known CMOS technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
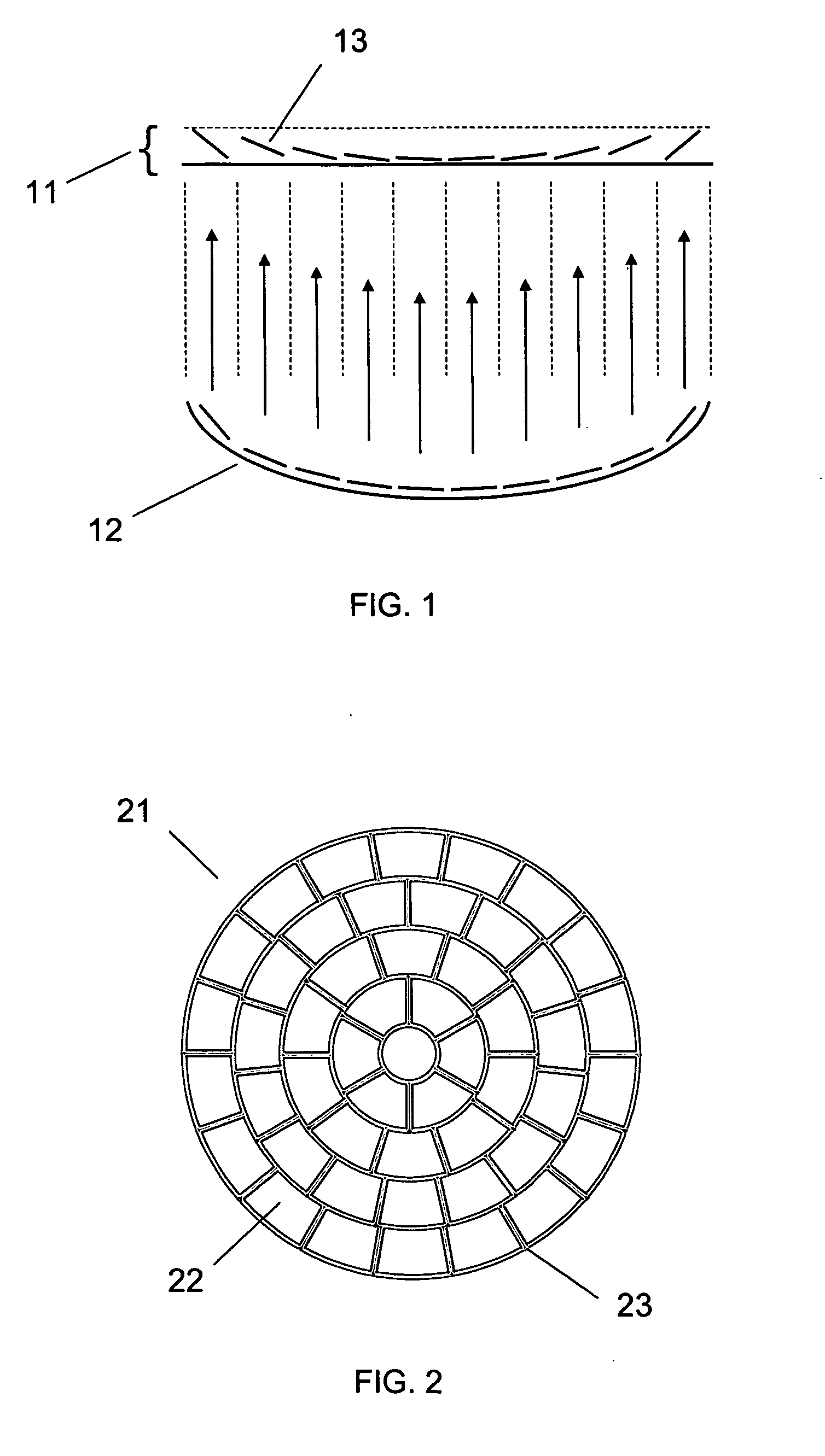
Micromirror arry lens with optical surface profiles
A Micromirror Array Lens comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a flat or a curved surface to reflect incident light. Each micromirror in the Micromirror Array Lens is configured to have at least one motion. The Micromirror Array Lens forms at least one optical surface profile reproducing free surfaces by using the motions of the micromirrors. The free surface can be any two or three-dimensional continuous or discrete reflective surface. The Micromirror Array Lens having the corresponding optical surface profile provides optical focusing properties substantially identical to those of the free surface. The Micromirror Array Lens can forms various optical elements such as a variable focal length lens, a fixed focal length lens, an array of optical switches, a beam steerer, a zone plate, a shutter, an iris, a multiple focal length lens, other multi-function optical elements, and so on.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Variable focal length lens and lens array comprising discretely controlled micromirrors
ActiveUS20060012852A1Large length variationFast response timeMirrorsMountingsCamera lensMicroelectronics
A discretely controlled micromirror array lens (DCMAL) consists of many discretely controlled micromirrors (DCMs) and actuating components. The actuating components control the positions of DCMs electrostatically. The optical efficiency of the DCMAL is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding DCMs and the actuating components under DCMs to increase an effective reflective area. The known microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberrations by controlling DCMs independently. Independent control of each DCM is possible by known microelectronics technologies. The DCM array can also form a lens with arbitrary shape and / or size, or a lens array comprising the lenses with arbitrary shape and / or size.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors
ActiveUS20050264870A1Increase the number ofLower resistanceMirrorsMountingsDegrees of freedomRotational degrees of freedom
A variable focal length lens consists of many micromirrors with degrees of freedom rotation and / or degrees of freedom translation and actuating components. As operating methods for the lens, the actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the variable focal length lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. The lens can also be of a desired arbitrary shape and / or size. The micromirrors are arranged in a flat plane or in a curved plane with a predetermined curvature. The electrodes determining the position of the micromirrors can be made of material with high electrical conductivity, preferably metal. The surface material of the micromirror is made of a material with high reflectivity such as aluminum, silver, and gold, which are coated with multi-layer dielectric material or antioxidant.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
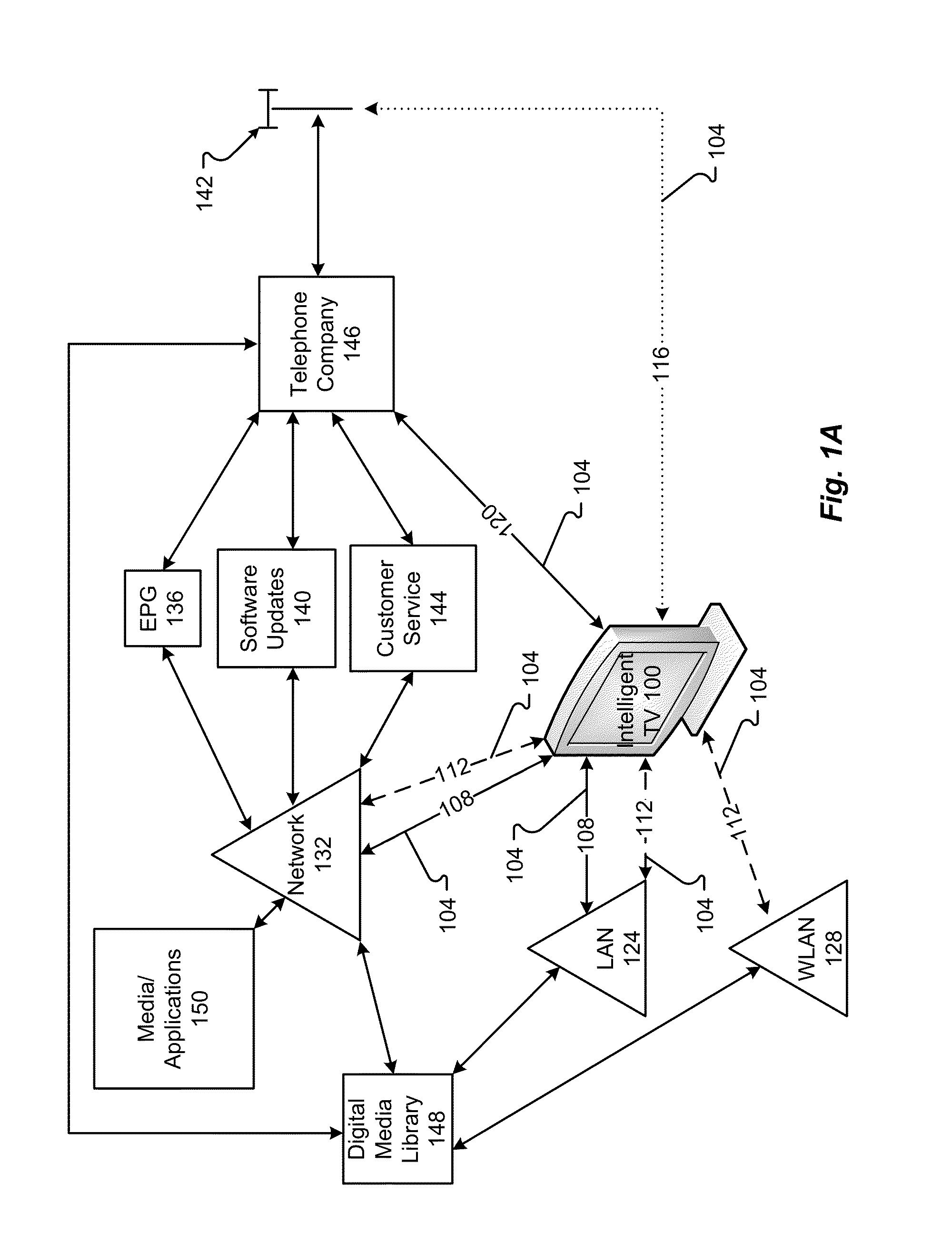
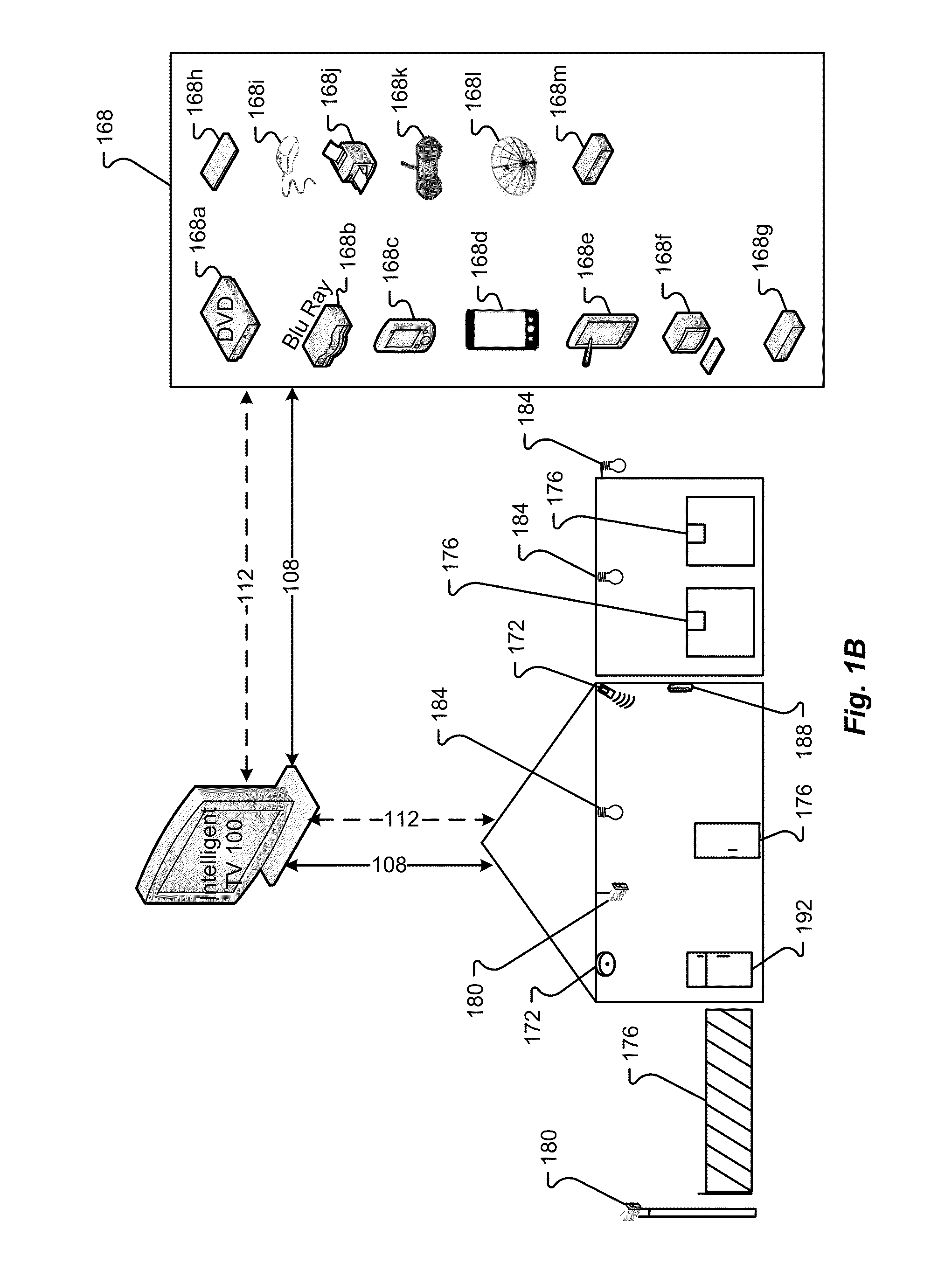
Systems and methods for providing user interfaces in an intelligent television
ActiveUS20140075477A1Easy to learnEasy to navigateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisual perceptionUser interface
An intelligent television can provide various interfaces for navigating processes associated with providing content. The user interfaces include unique visual representations and organizations that allow the user to utilize the intelligent television more easily and more effectively. Particularly, the user interfaces pertain to the display of media content, electronic programming guide information, television content, and other content. Further, the user interfaces provide unique process of transitioning between the content.
Owner:MULTIMEDIA TECH PTE LTD
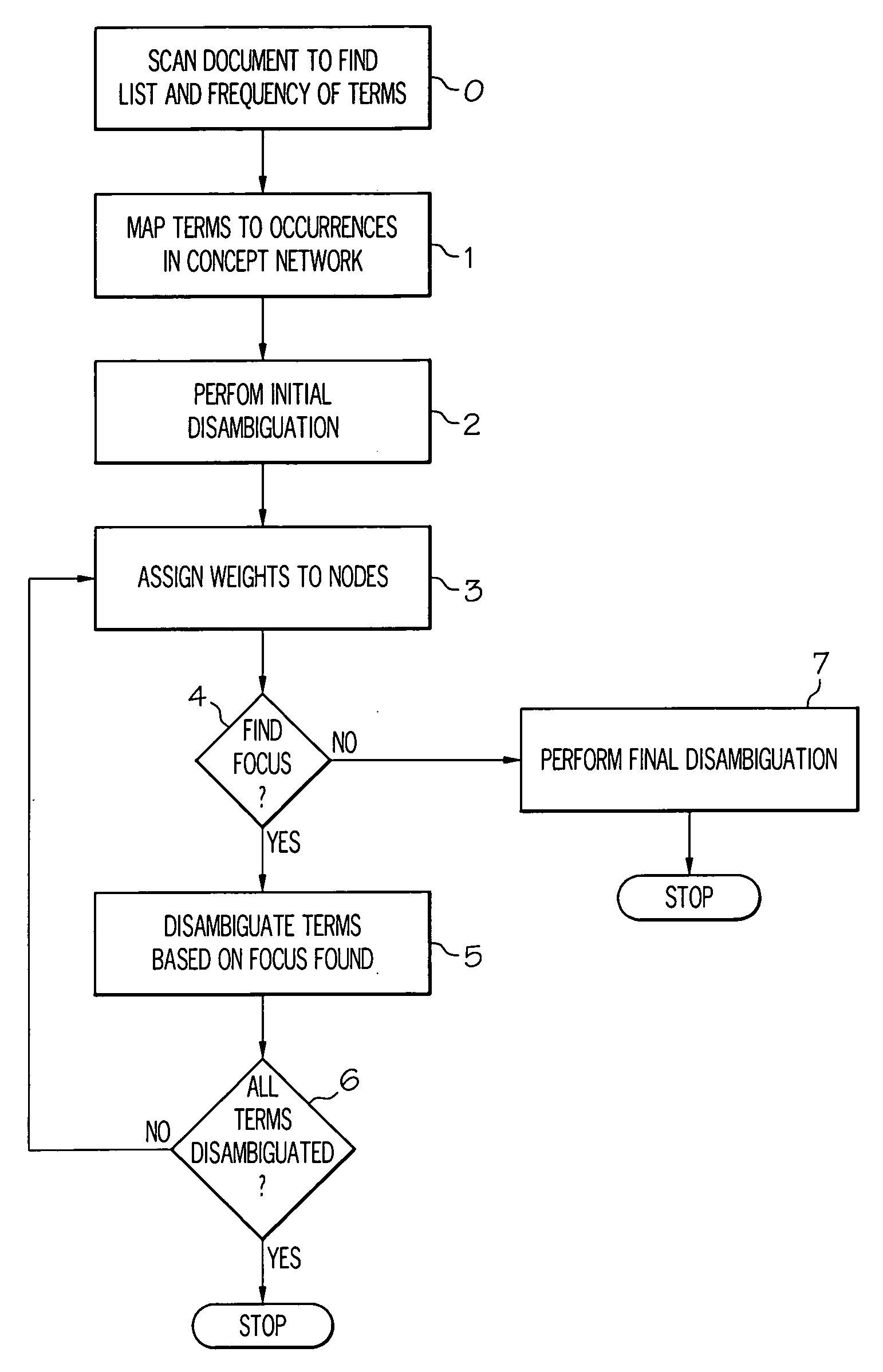
Method and system for finding a focus of a document
InactiveUS20080263038A1Highly focusedReduce impactDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingSemantic networkDocumentation
Method and apparatus for finding the focus of a document. A semantic network includes a plurality of nodes, each representing a concept, and links, connecting the nodes, representing relations between the concepts is used. The method including: providing a list of terms in an input document which match concepts represented by the semantic network, and a frequency value for each matched term indicating the number of times the term appears in the document; mapping each matched term to a referent node or to a plurality of possible referent nodes in the semantic network, and assigning weights to nodes.
Owner:IBM CORP
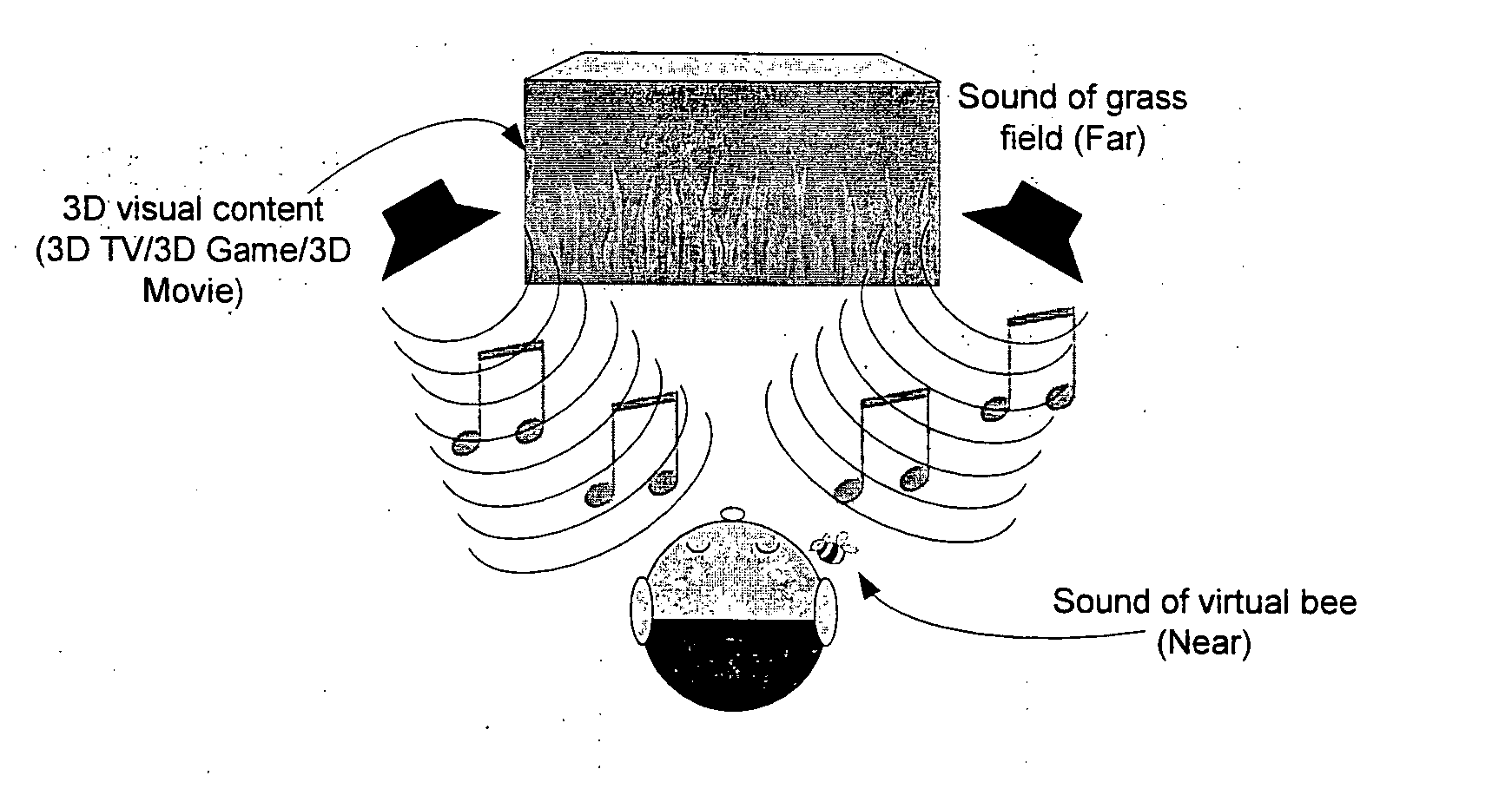
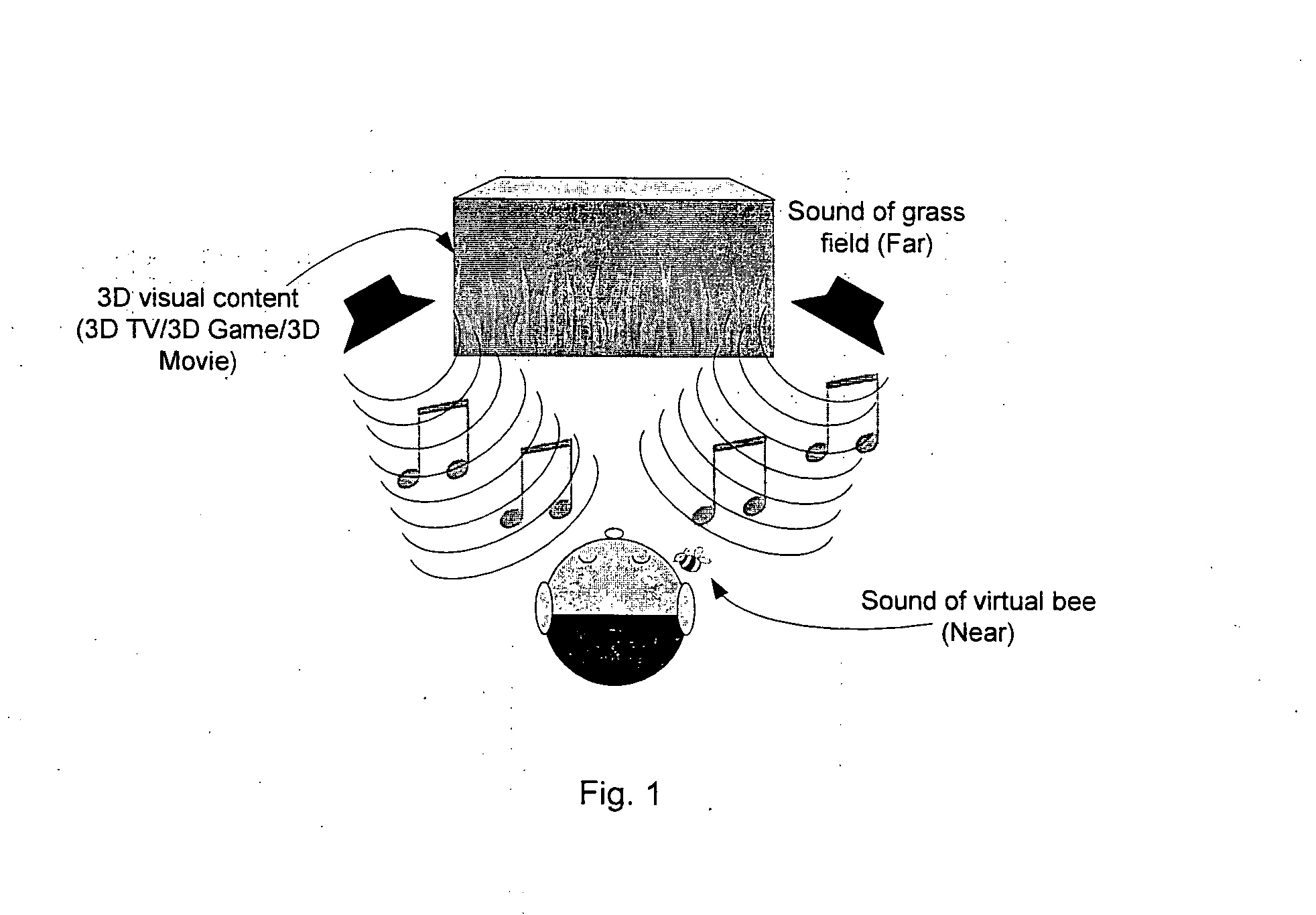
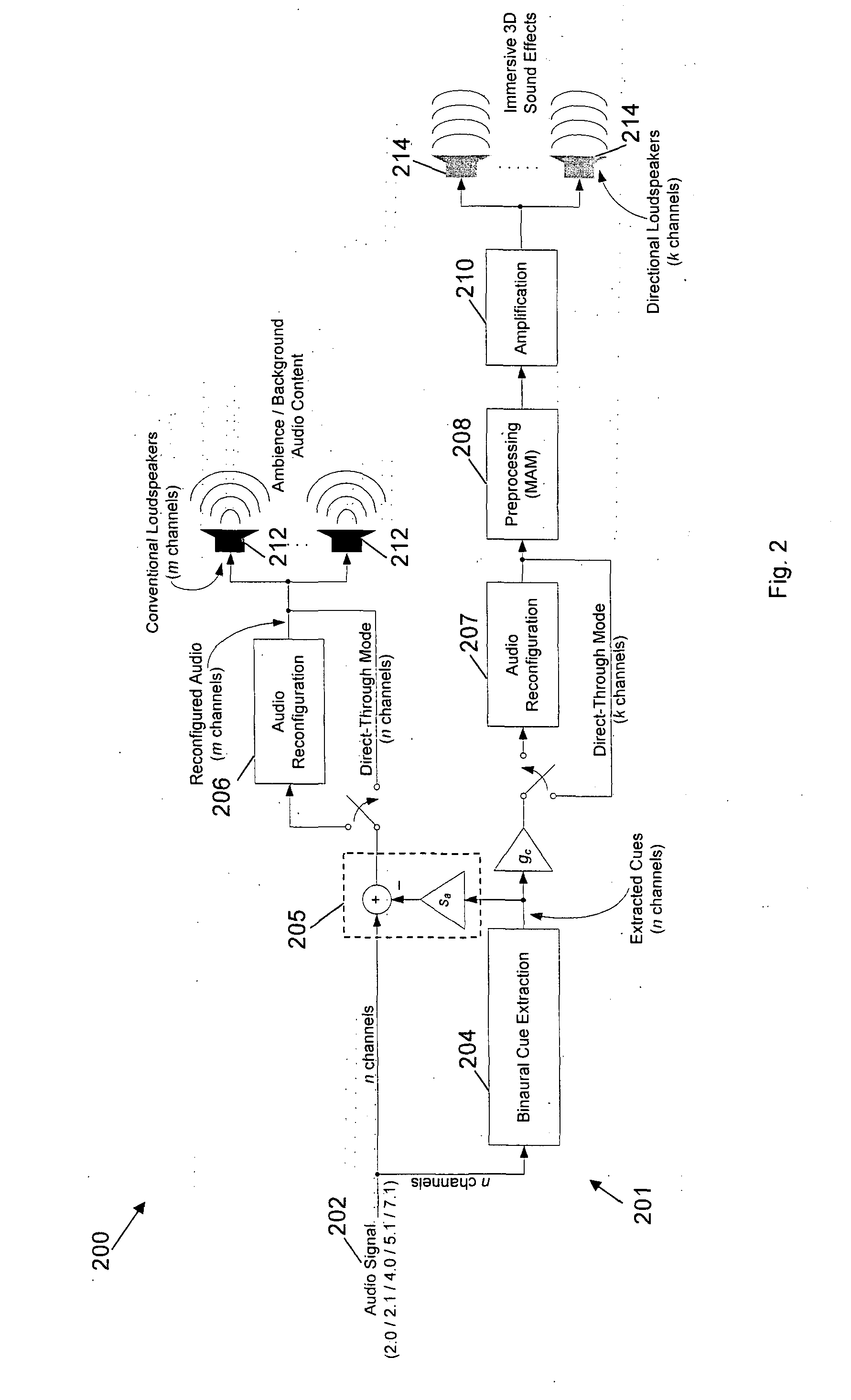
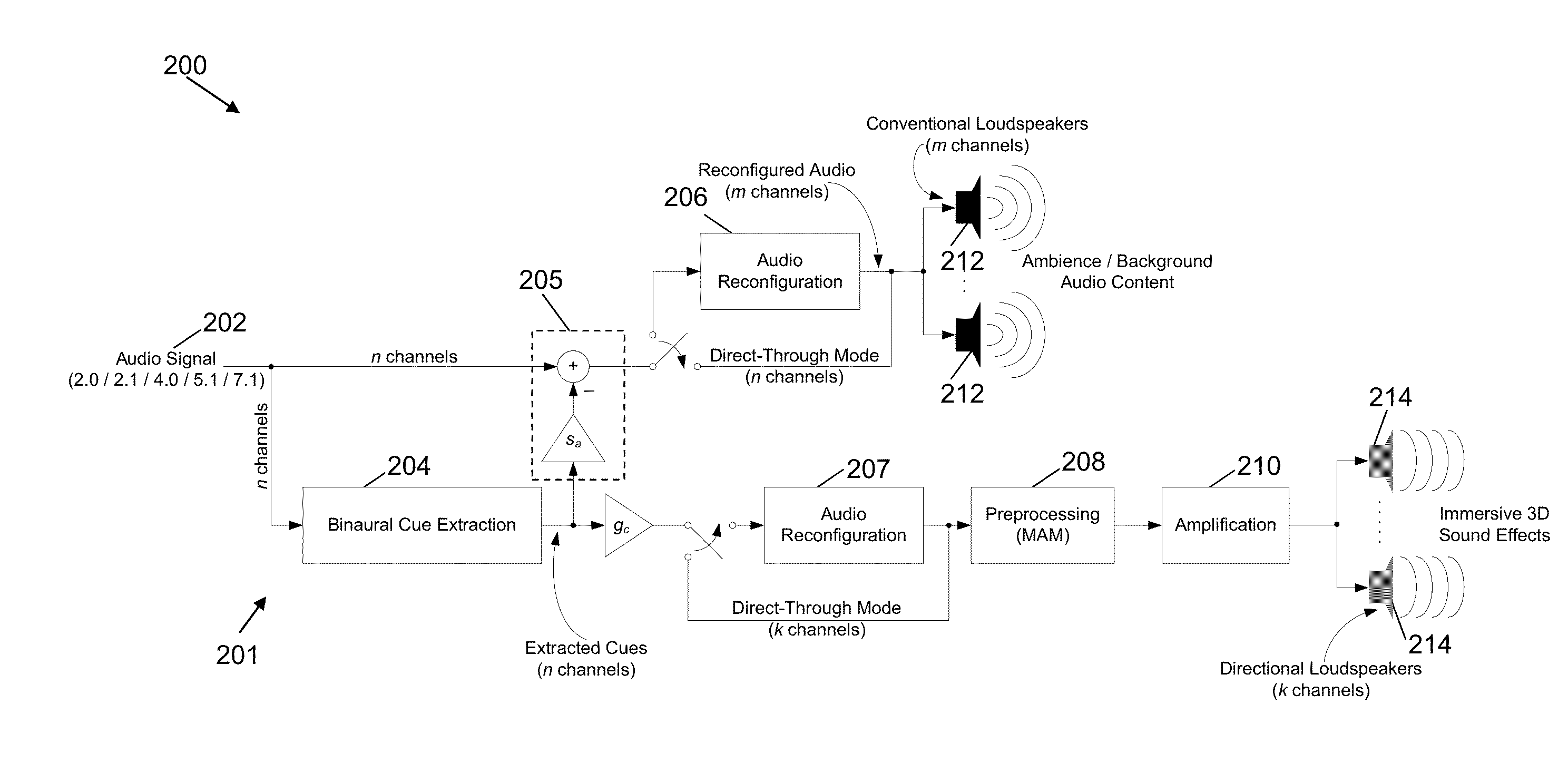
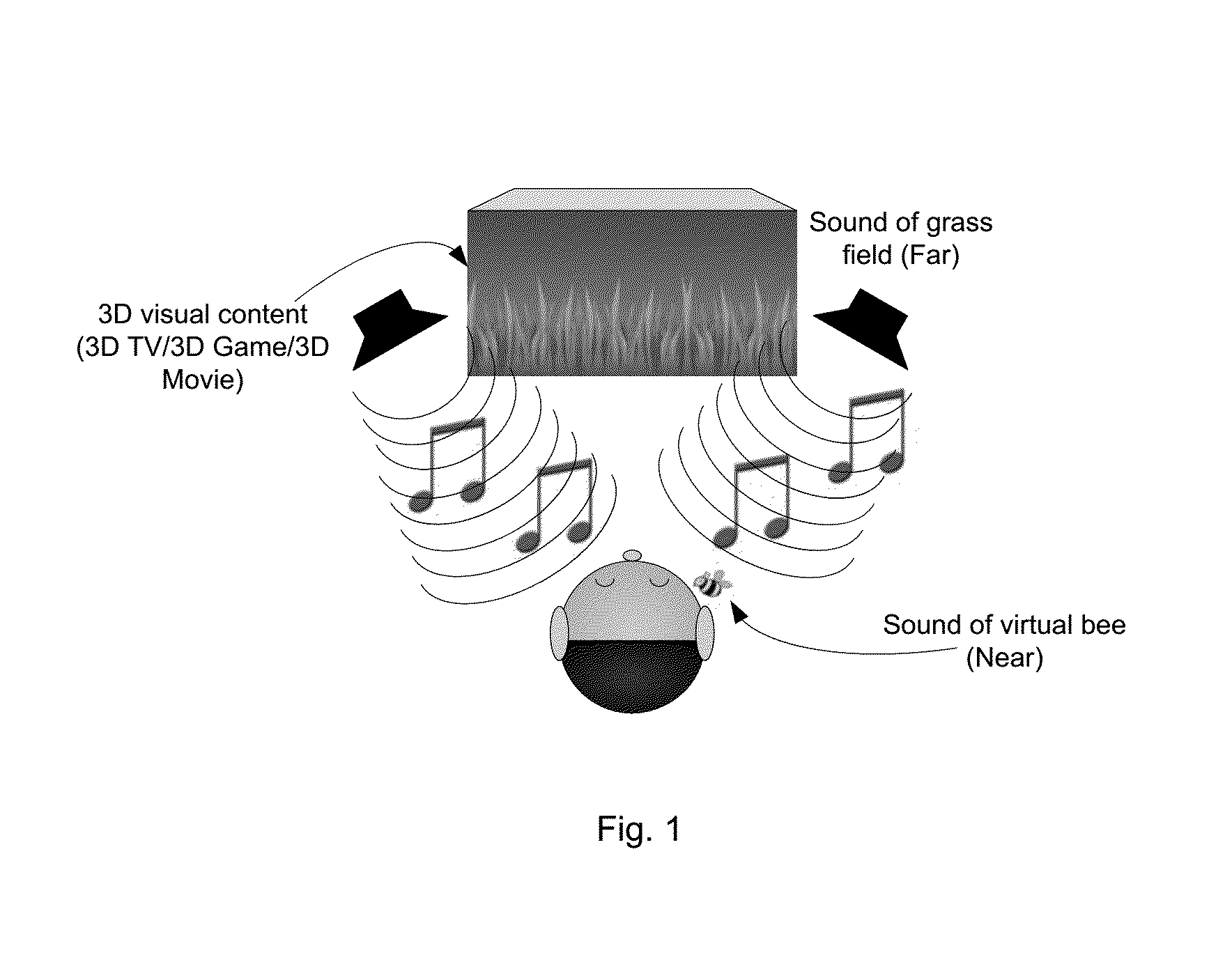
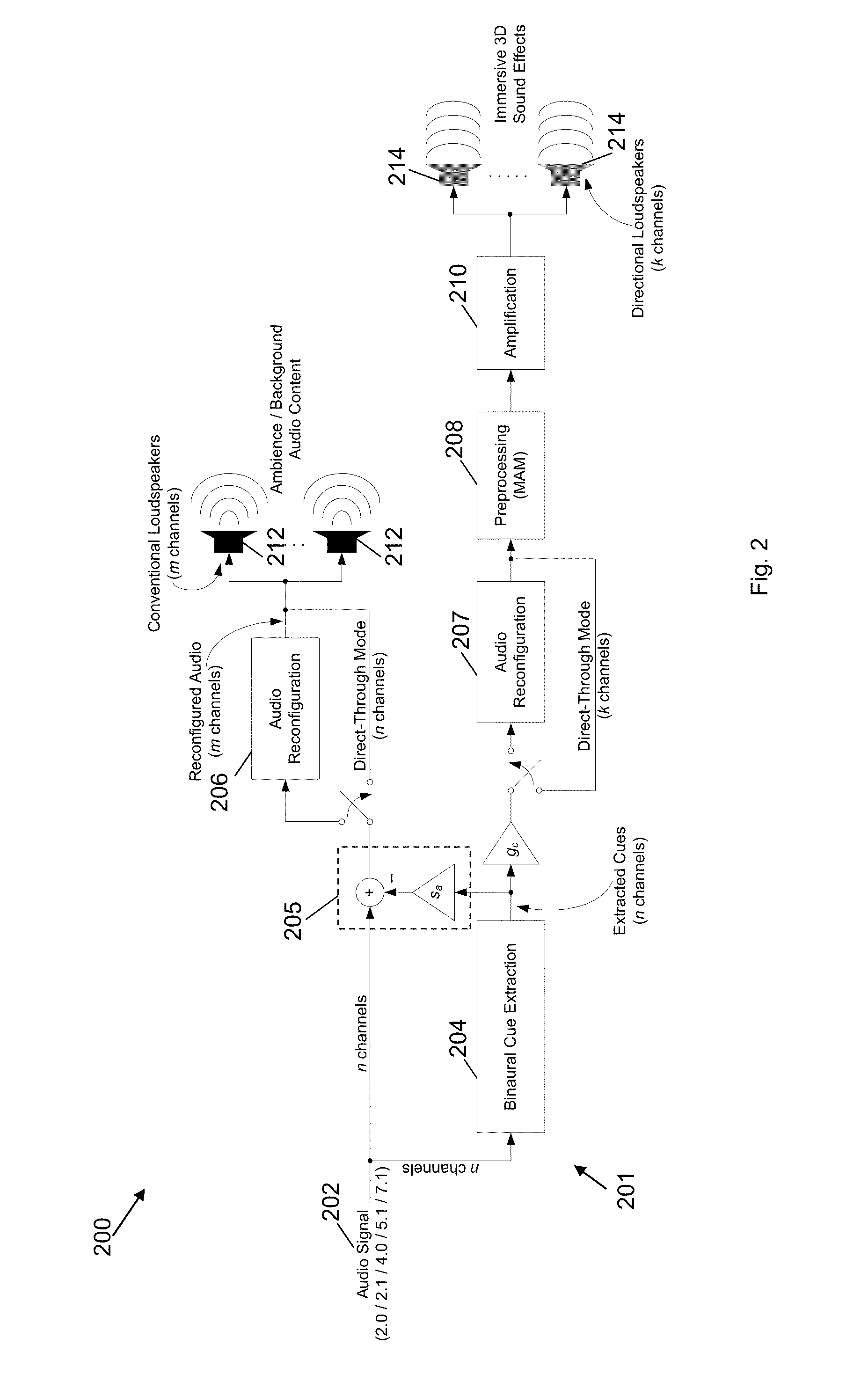
System and method for processing an input signal to produce 3D audio effects
InactiveUS20120314872A1Wide dispersionWidely distributedTelevision system detailsMicrophonesVIT signalsLoudspeaker
A processing system for processing an input signal to produce three-dimensional audio effects is disclosed. The processing system comprises: a cue sending path configured to extract a set of binaural cues from the input signal and further configured to send at least a portion of the extracted set of binaural cues to at least one directional loudspeaker for transmission; and an ambience sending path configured to send at least a part of the input signal comprising ambience sounds to at least one conventional loudspeaker for transmission.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
High performance focusing actuator of a voice coil motor
InactiveUS20080036304A1Improve performanceStable structureMountingsPropulsion systemsFixed frameEngineering
A high performance focusing actuator of a voice coil motor comprises a retaining unit having a plastic retaining frame; a center portion of the plastic retaining frame being a receiving space; two opposite corners of the receiving space being chamfered; an inner side of each chamfered side being formed with a slide portion; and a metal rear cover plate having a shape corresponding to that of the plastic retaining frame; the metal rear cover plate having an open space coaxial with the receiving space of the plastic retaining frame; an outer side of the metal rear cover plate having four outer plates; each of two opposite corners of each outer plate being formed with an inclined guide surface corresponding to the slide portion of the plastic retaining frame; an iron receiving gap being formed between an inclined guide surface and outer plate; and each iron receiving gap receiving a magnet.
Owner:TRICORE CORP
System and method for imaging a patient user's body part
InactiveUS20140350379A1Vastly increasedQuality improvementDiagnostics using lightSurgeryData setImaging processing
A system and method for imaging a patient user's body part is disclosed. The system may include a patient user body part imaging non-transitory storage media to image a patient user body part. The method may include selecting an optical imaging device to image the patient user's body part, acquiring one or more data sets with the optical imaging device, the acquiring is performed with focus at multiple axial positions and exposure control or deliberate focus at specified image locations and exposure control, registering the acquired data sets, performing image processing on the acquired data sets and recombining good data from the image processed data sets into a single image of the patient user's body part.
Owner:NEUROVISION IMAGING INC
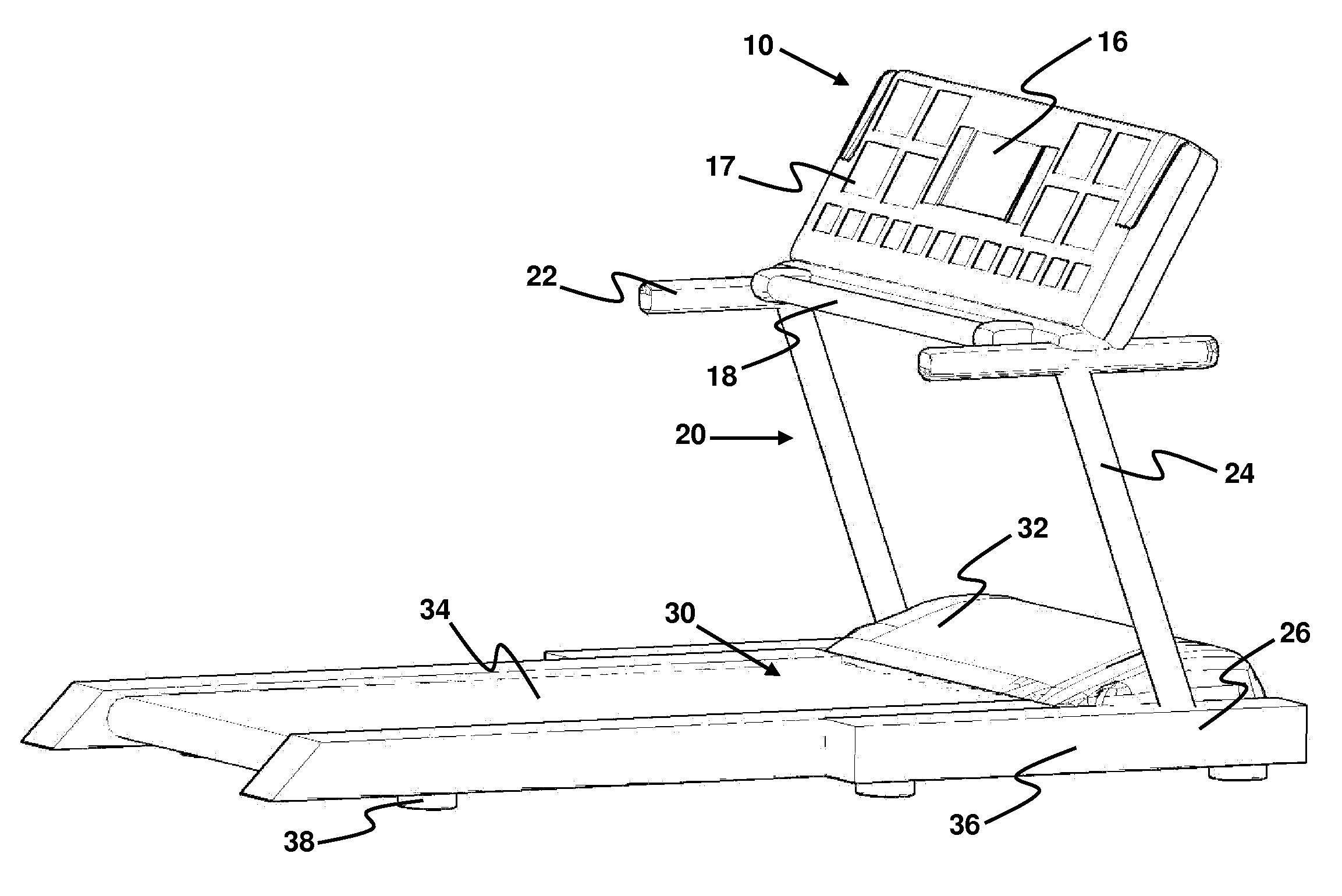
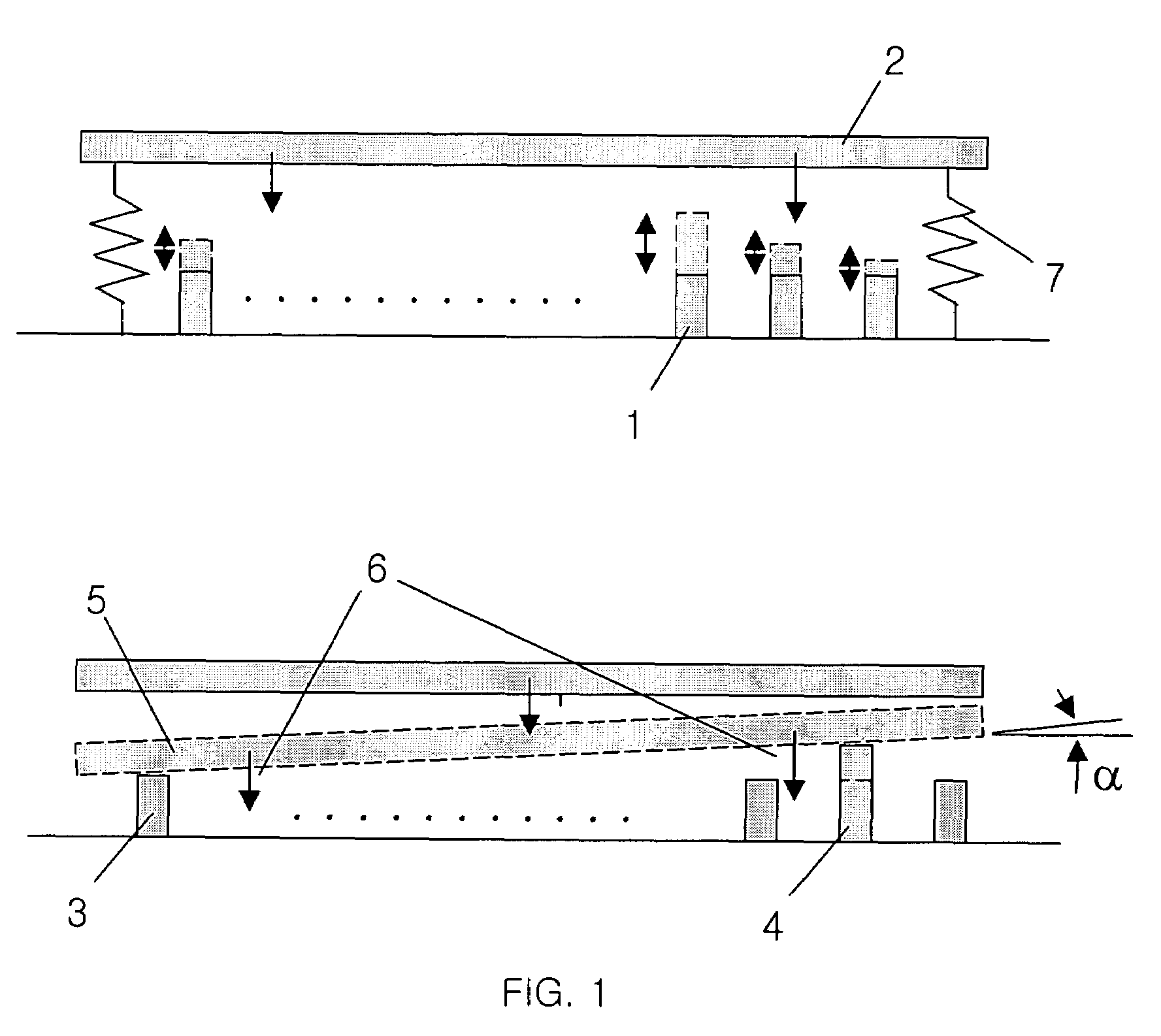
Multi-functional motivating exercise equipment
InactiveUS8876661B2Guaranteed to workHighly focusedClubsMovement coordination devicesDistractionFunctional exercises
A multi-functional exercise machine, whose console has a transformation bearing and can be converted between a central control panel and an exercise workstation, so that the exercise machine can be used not only for intensive exercise but also for moderate exercise while working or entertaining at the same time. The exercise workstation has an arm support and a computer desk for a user to efficiently work with a personal computer free of distractions while doing exercise. The arm support is specially designed to minimize upper body movements. A supporting assembly for the console is specially designed to minimize vibration and shaking during exercise. The equipment can further comprise a force adjustable body support to decrease load by supporting predetermined amount of weight, so that a user can do exercise longer while working with a computer.
Owner:LU ZHENYU
Micromirror array lens with optical surface profiles
A Micromirror Array Lens comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a flat or a curved surface to reflect incident light. Each micromirror in the Micromirror Array Lens is configured to have at least one motion. The Micromirror Array Lens forms at least one optical surface profile reproducing free surfaces by using the motions of the micromirrors. The free surface can be any two or three-dimensional continuous or discrete reflective surface. The Micromirror Array Lens having the corresponding optical surface profile provides optical focusing properties substantially identical to those of the free surface. The Micromirror Array Lens can forms various optical elements such as a variable focal length lens, a fixed focal length lens, an array of optical switches, a beam steerer, a zone plate, a shutter, an iris, a multiple focal length lens, other multi-function optical elements, and so on.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
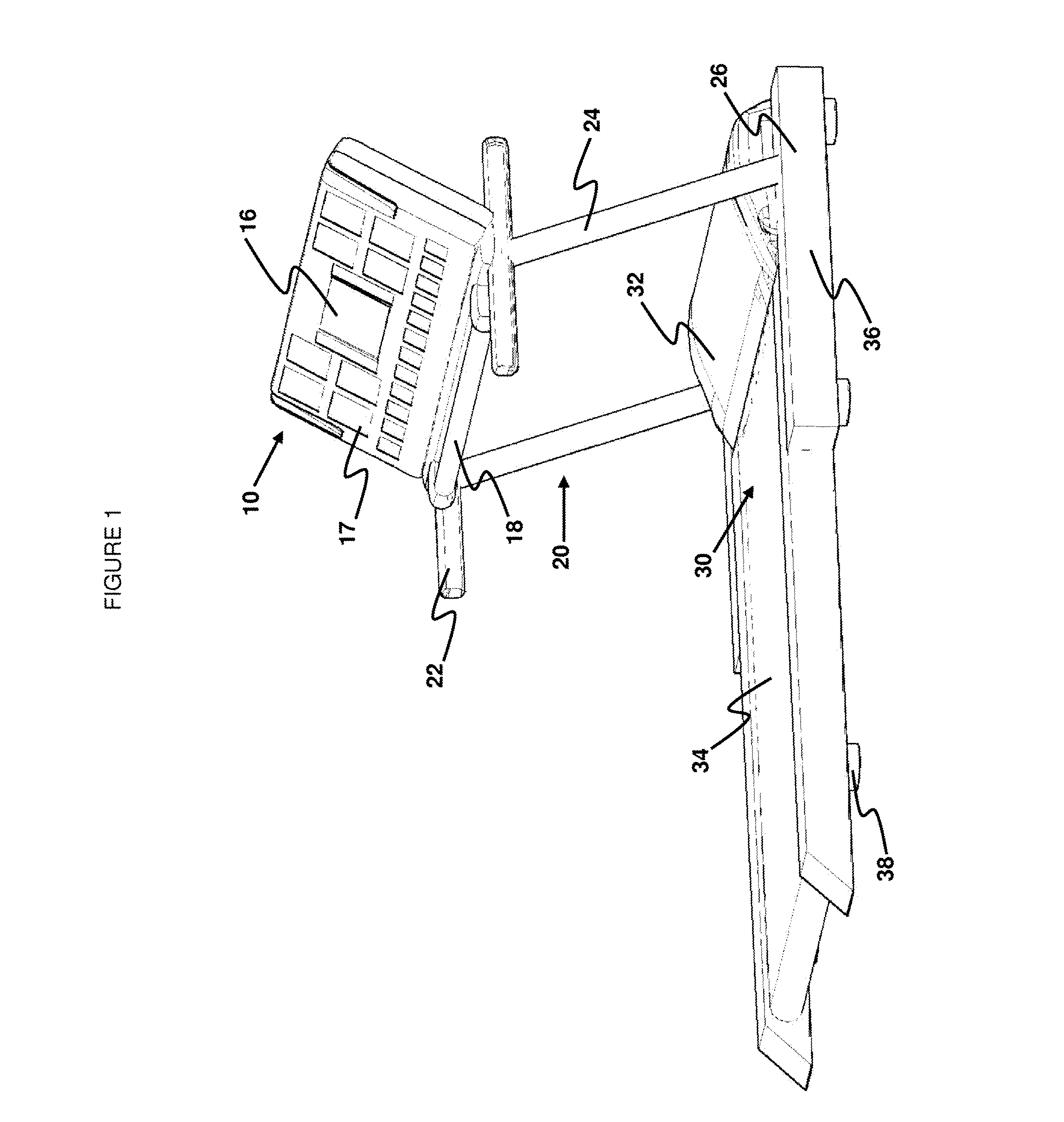
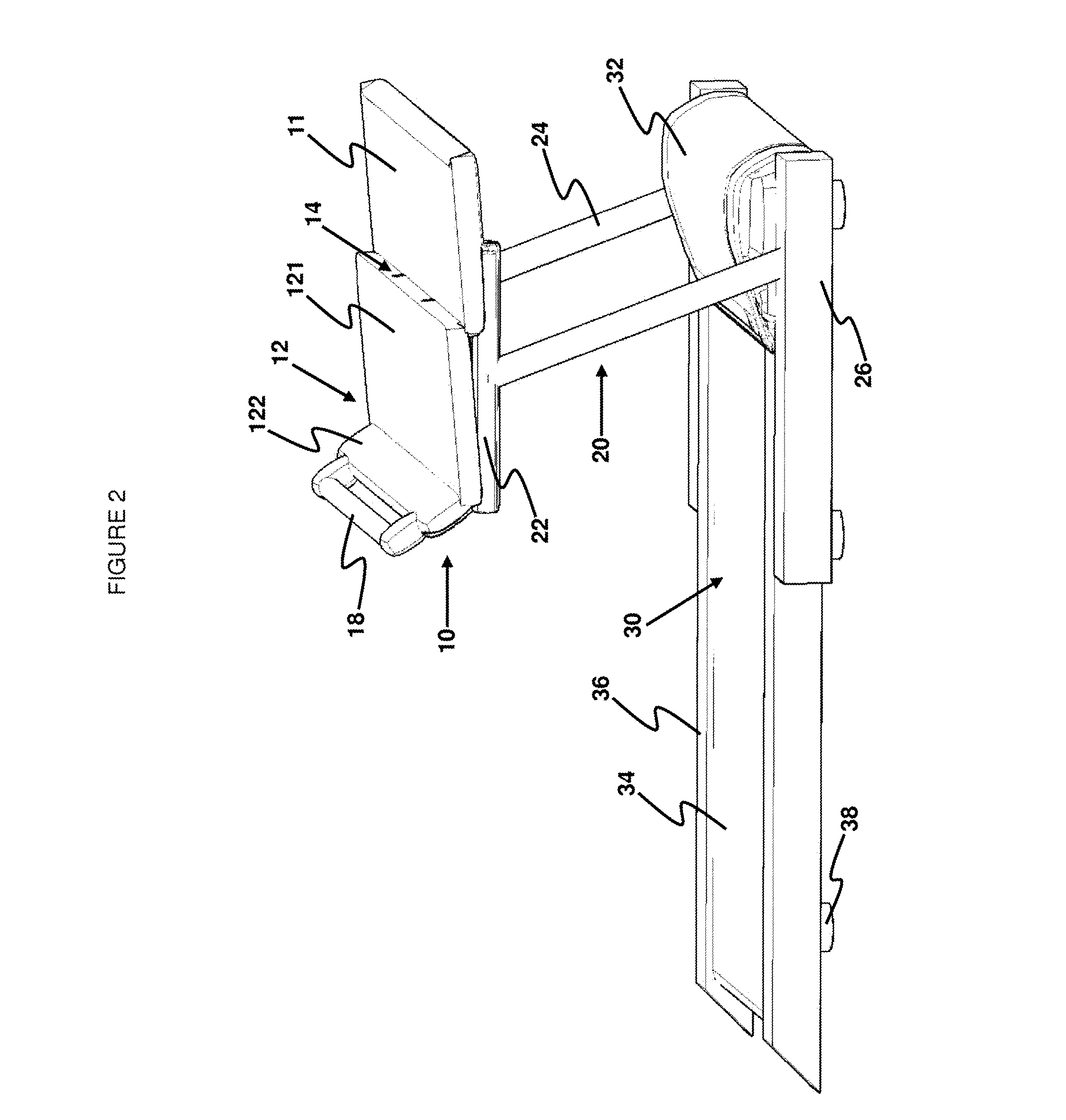
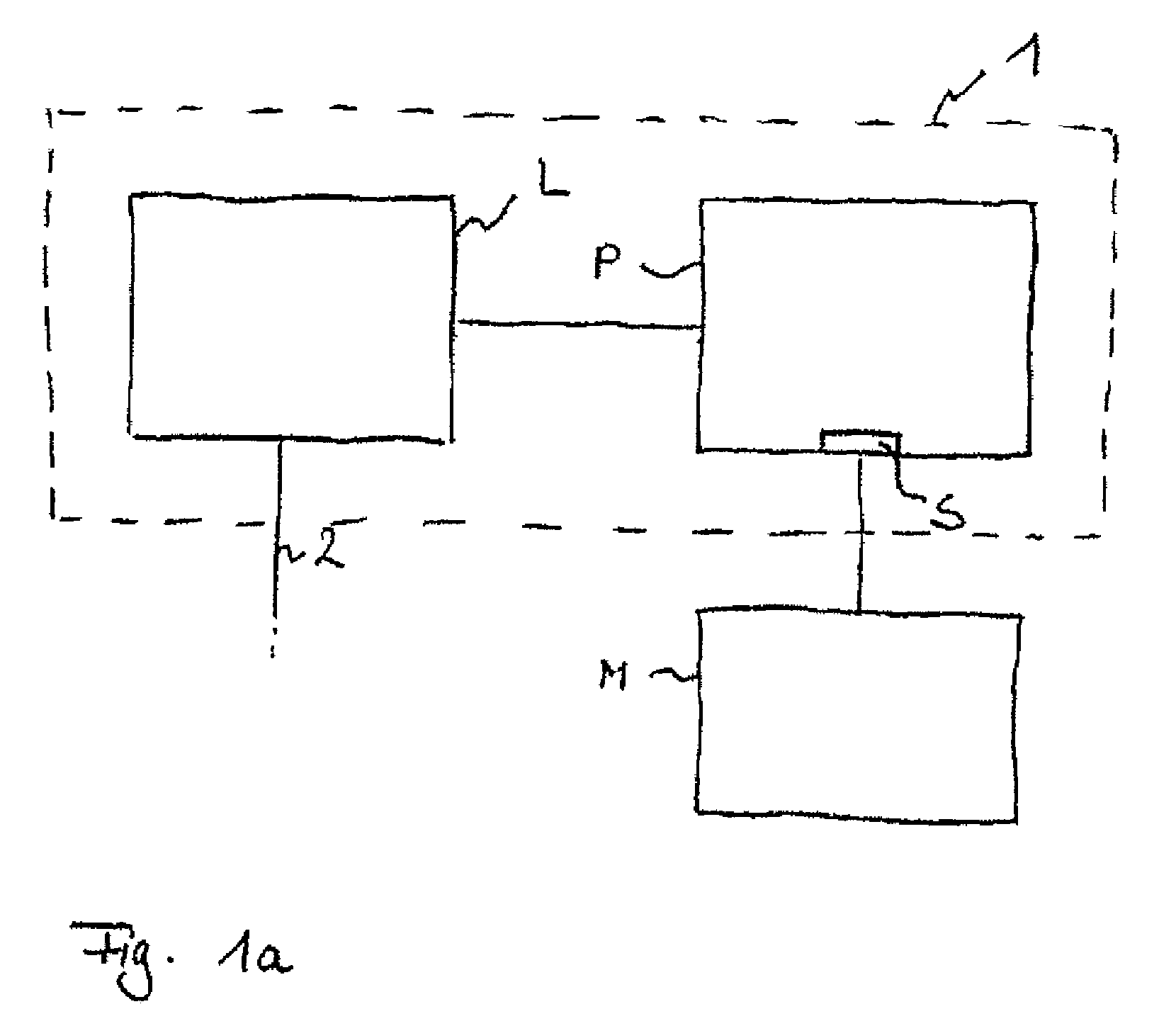
Apparatus
InactiveUS20050111174A1Improve comfortImprove liquidityDigital data processing detailsGarmentsEngineeringWearable computer
An apparatus (1) for supporting a mobile electronic display system. The mobile electronic display system includes a display element (11) and a power source (12). In use a wearable computer (4) controls operation of the display element (11). The apparatus (1) comprises a relatively rigid support frame (8), a relatively soft cushion member (9), and a cover (10) for the support frame (8). The support frame (8) is suitable for being worn by a person to support the mobile electronic display system. The support frame (8) comprises a front support frame part (13) located at the front of the wearer, a rear support frame part (14) located at the rear of the wearer, a first bearing member (15) extending over a first shoulder of the wearer, and a second bearing member (16) extending over a second shoulder of the wearer.
Owner:ADWALKER PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY
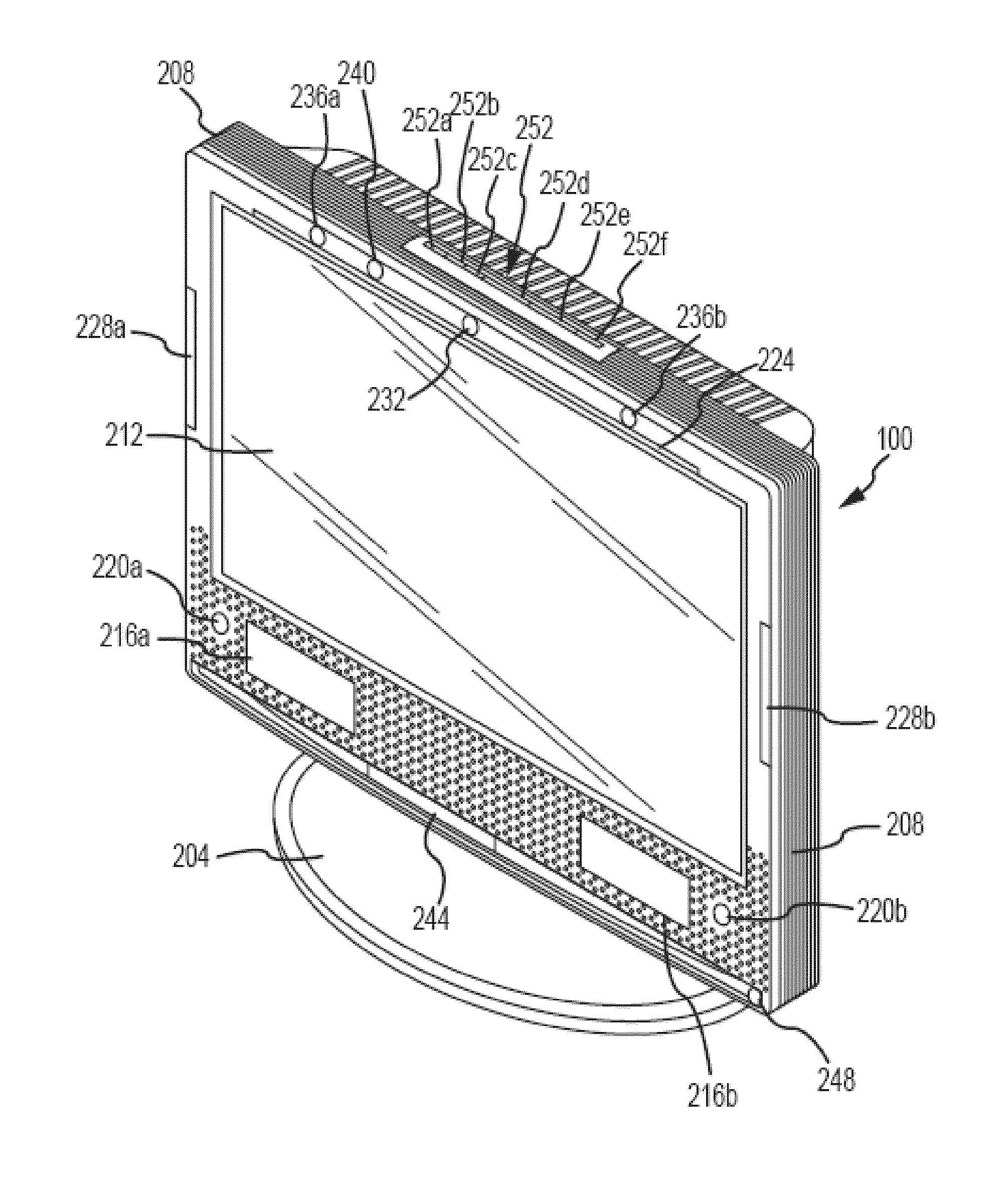
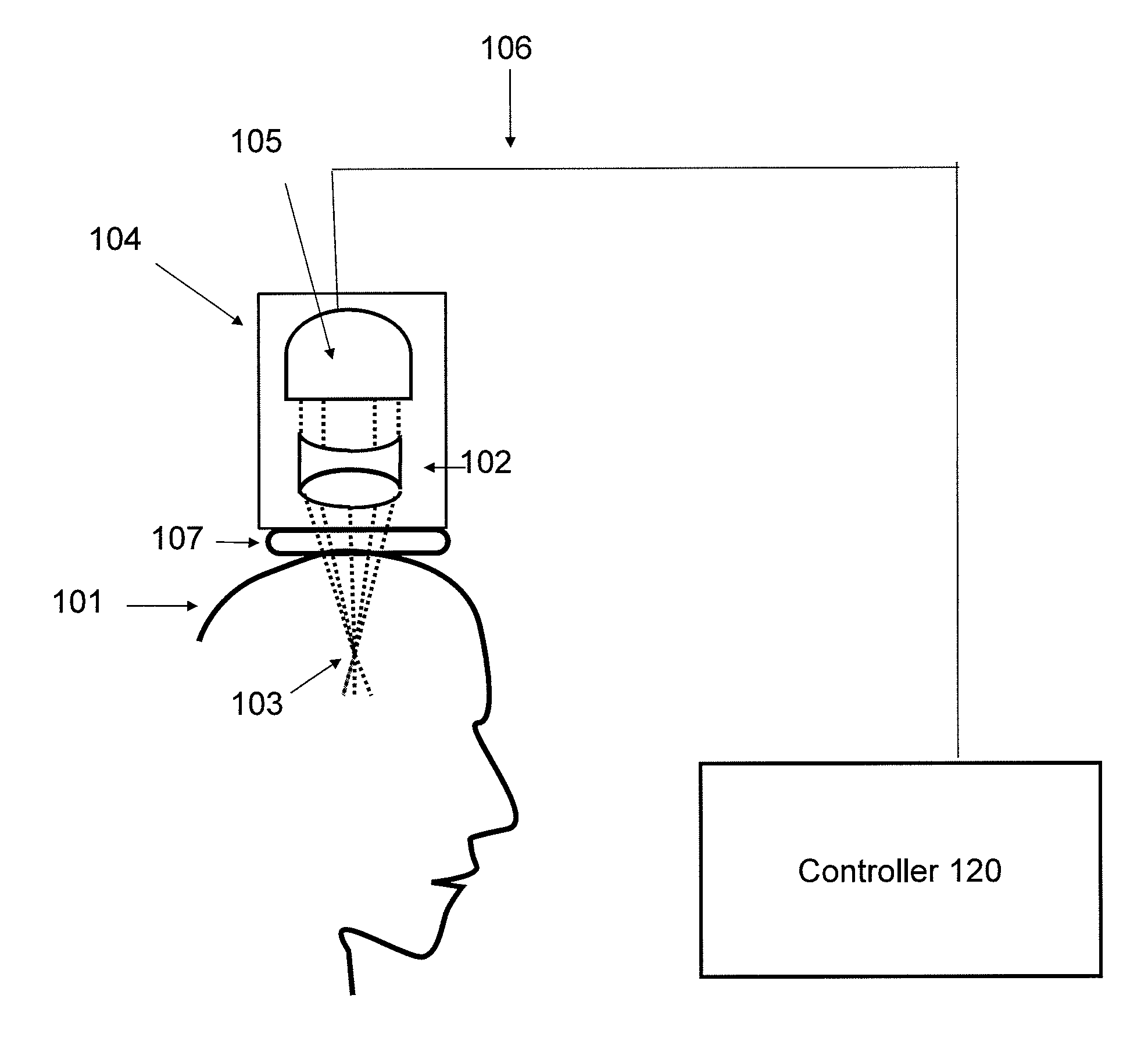
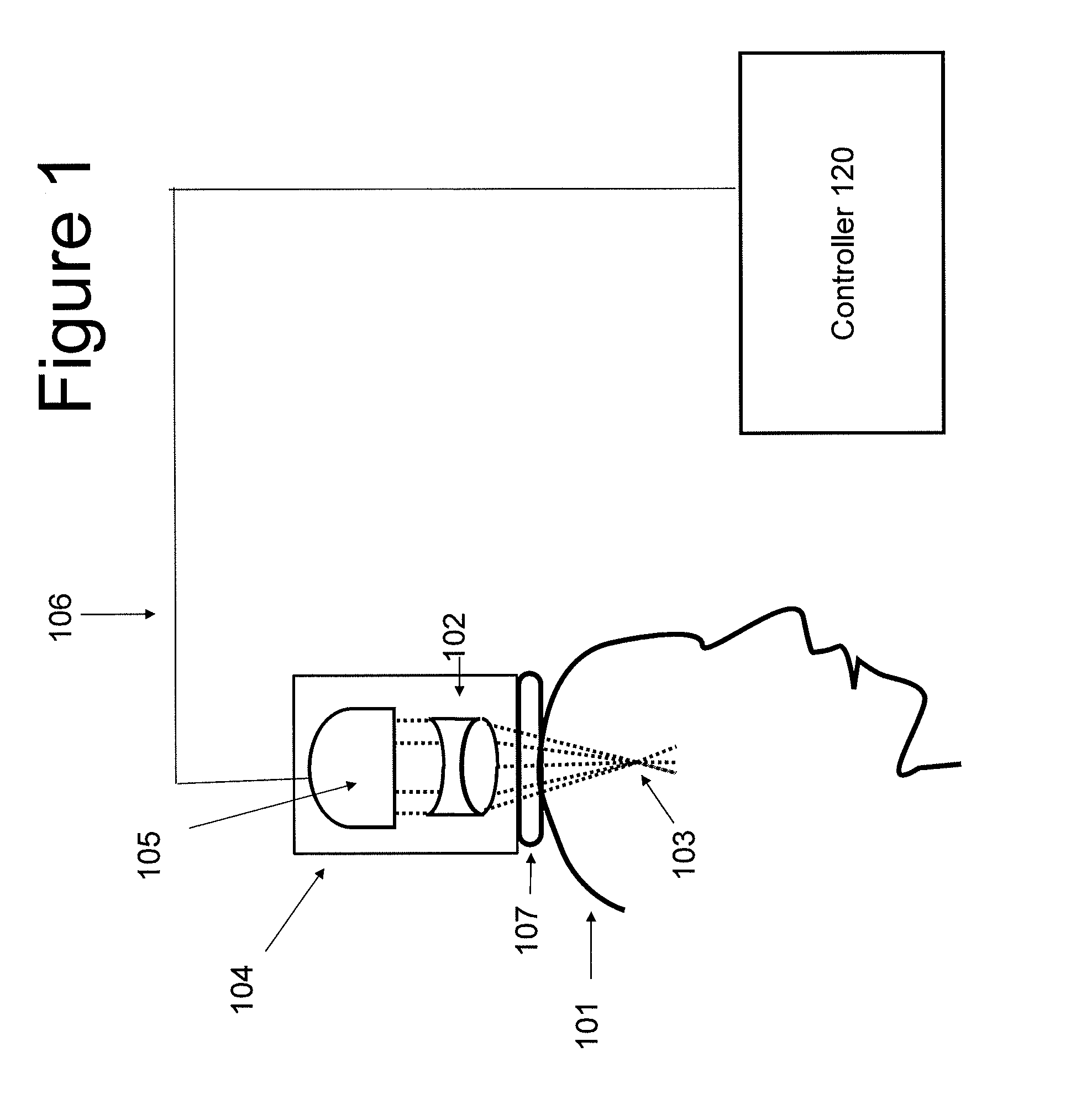
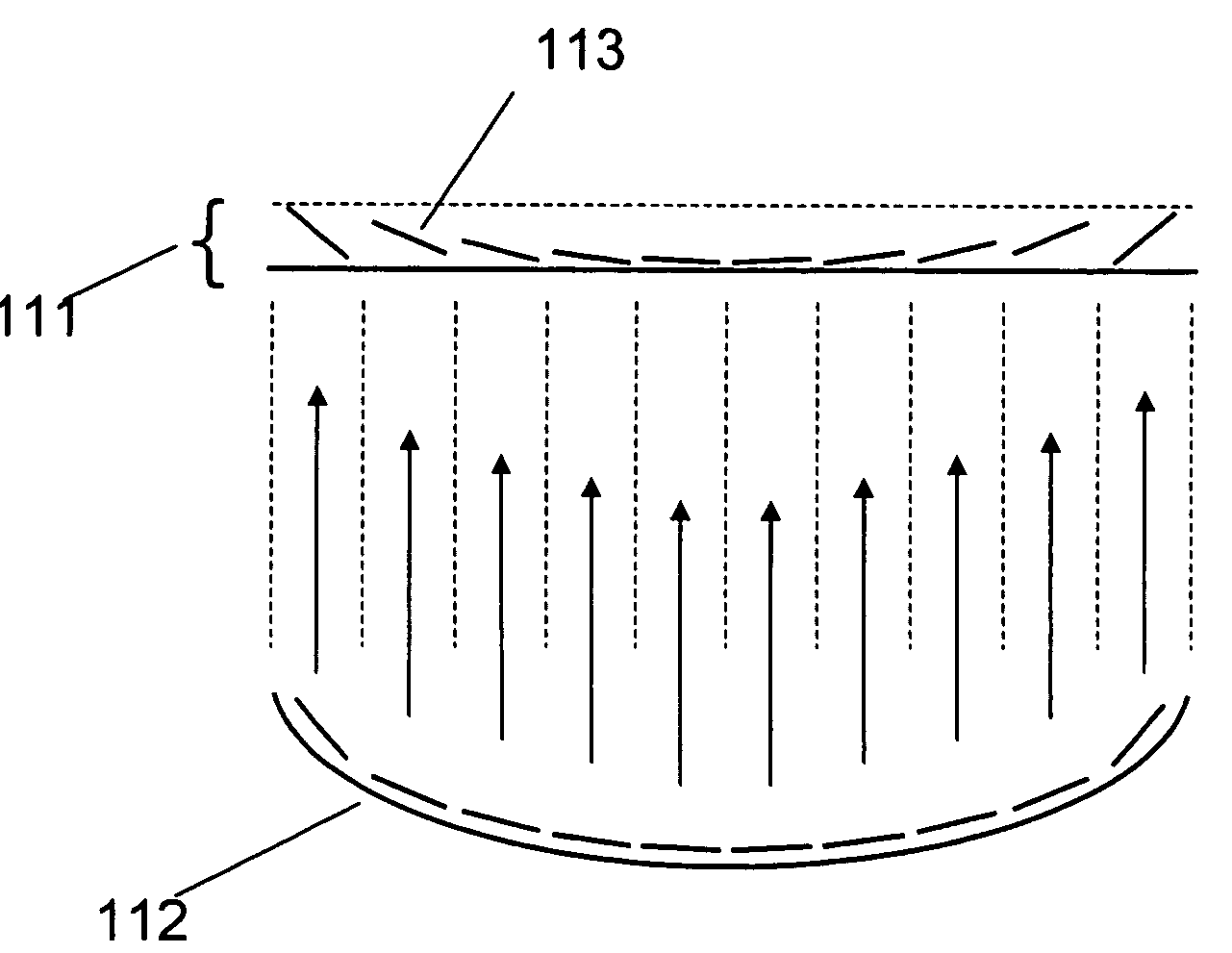
Focused transcranial ultrasound systems and methods for using them
InactiveUS20160038770A1Highly focused ultrasoundMinimizing standing waveUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesAcoustic energyMedicine
Apparatus and methods for focusing transcranial ultrasound. The systems described herein are advantageous for noninvasive neuromodulation and other transcranial ultrasound applications such as high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). In particular, described herein are compound acoustic lens apparatus having a short focal length for use with a transcranial ultrasound system, systems including methods of using them. These compound lens assemblies allow transcranial stimulation of even superficial cortical regions of the brain for ultrasound neuromodulation with a compact, single transducer element system at low (e.g., 0.2 to 1 MHz) frequencies with relatively large diameter (e.g., >15 mm) transducers applying 1 to 10 watts / cm2 of acoustic energy (spatial-peak, temporal-average intensity at the target brain region), and short focal length (e.g., between 15 and 35 mm).
Owner:CEREVAST MEDICAL
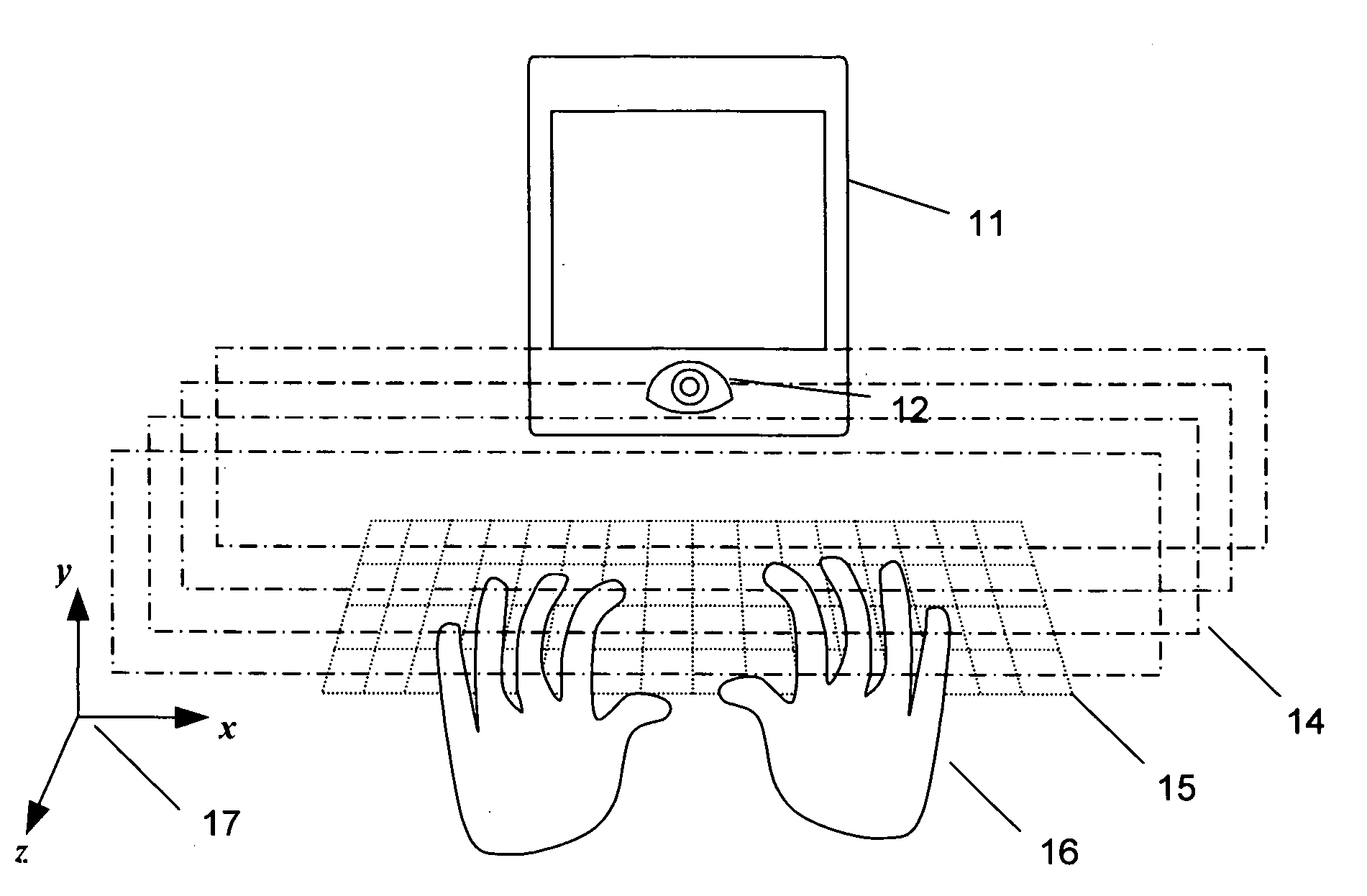
Small and fast zoom system using micromirror array lens
The present invention provides a small and fast zoom system using micromirror array lens (MMAL). Thanks to the fast response and compactness of the MMAL as well as absence of the macroscopic mechanical movements of lenses, the zoom system of the present invention fastens the speed of the zooming and reduces the space and weight for the zoom system. Also the present invention provides magnifying the area not on the optical axis and can compensate the aberration of the zoom system.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
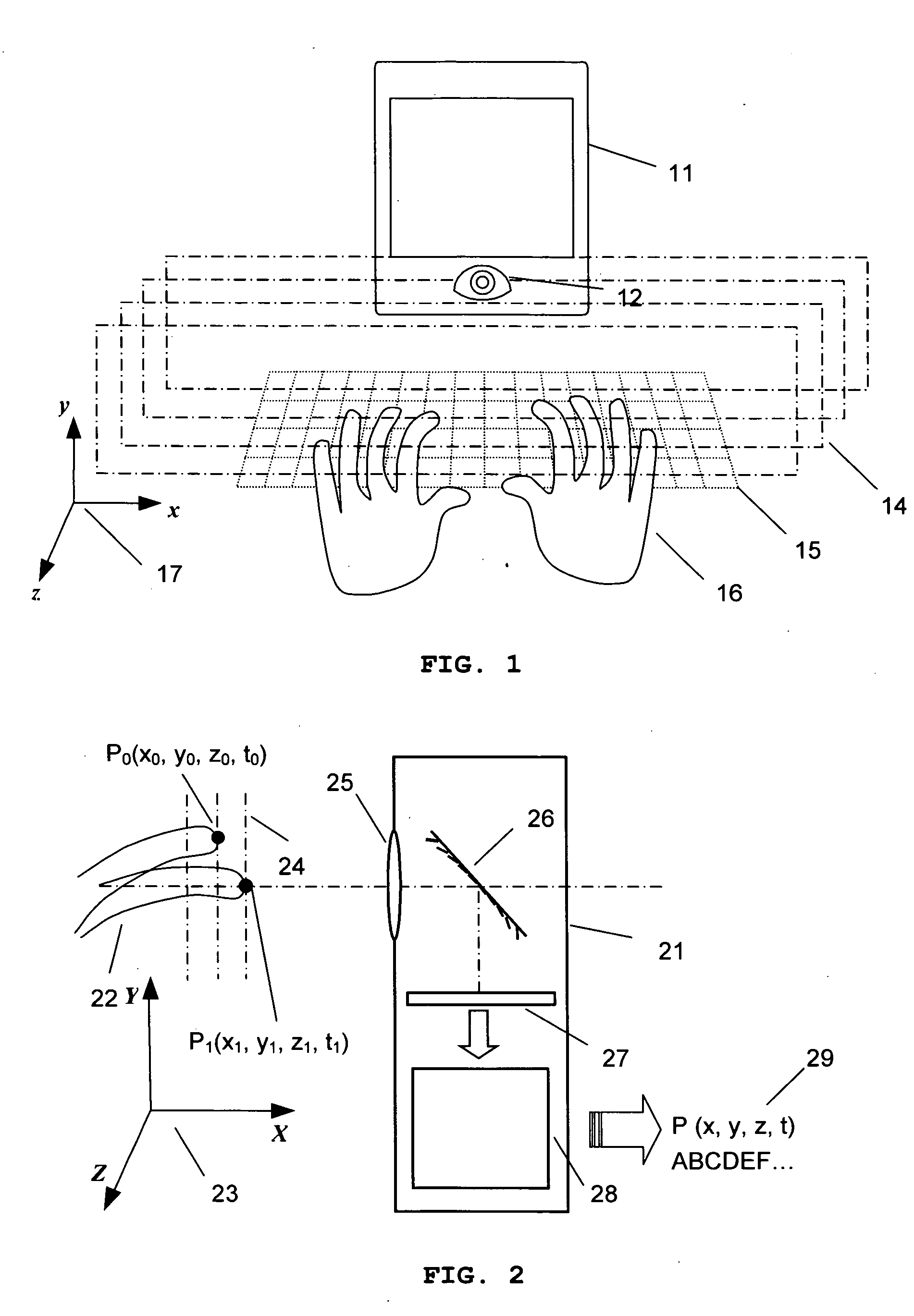
Virtual Keyboard input system using three-dimensional motion detection by variable focal length lens
InactiveUS20070115261A1Large focal length variationGreat depth resolutionInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsSystem usageComputer science
A virtual keyboard input system using three-dimensional motion detecting by variable focal length MMAL is provided. The compactness of the virtual keyboard input system is accomplished by the variable focal length MMAL performing three-dimensional imaging function. Since the three-dimensional imaging process occurs in a very short time scale, the system can determine the motion of the input by the user and track the motion of the user in real-time based response. Image processor can determine which input is occurred at the moment and the time-dependent profile of the motion itself. The input system gives an output just like a conventional keyboard and a mouse system.
Owner:ANGSTROM INC +1
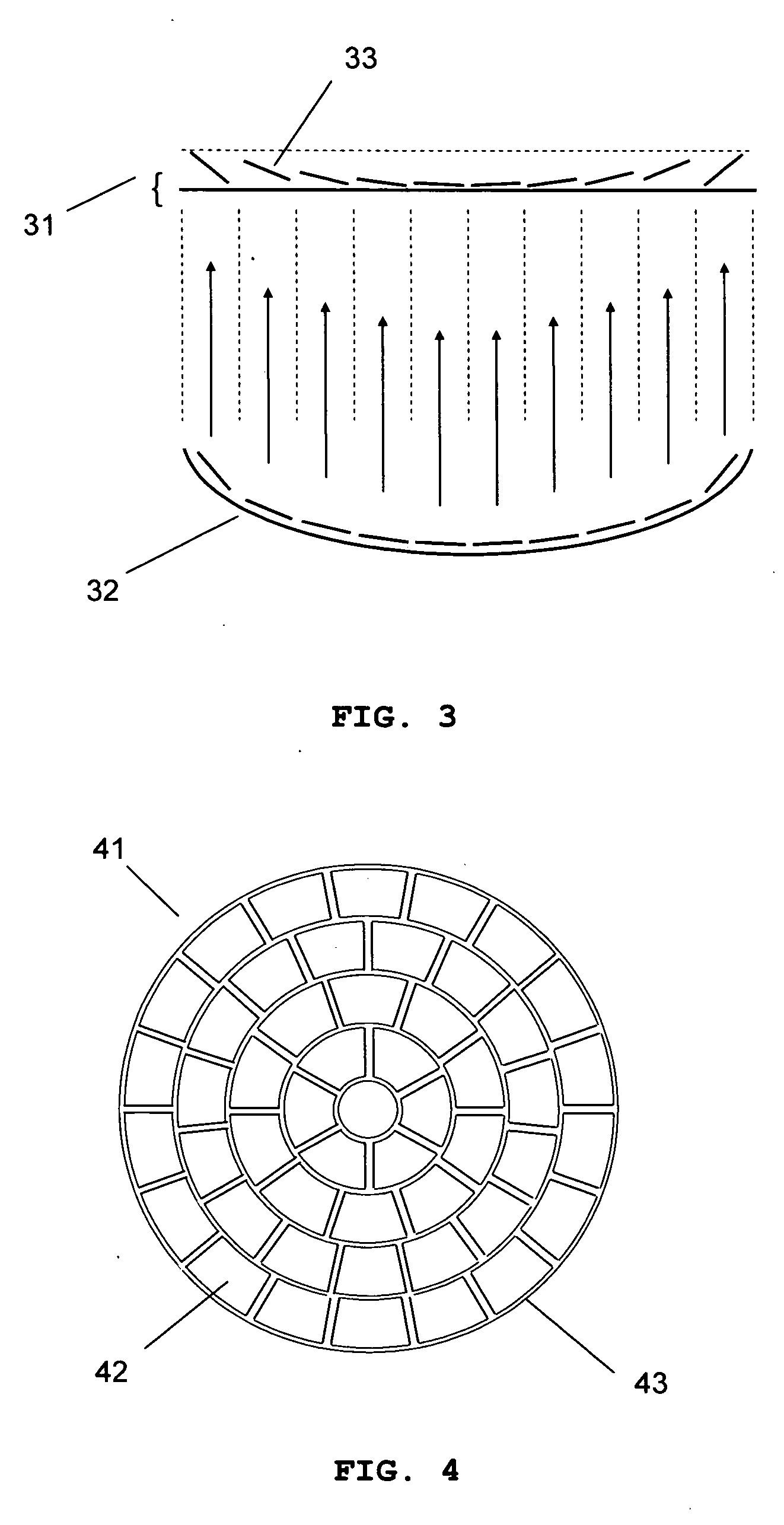
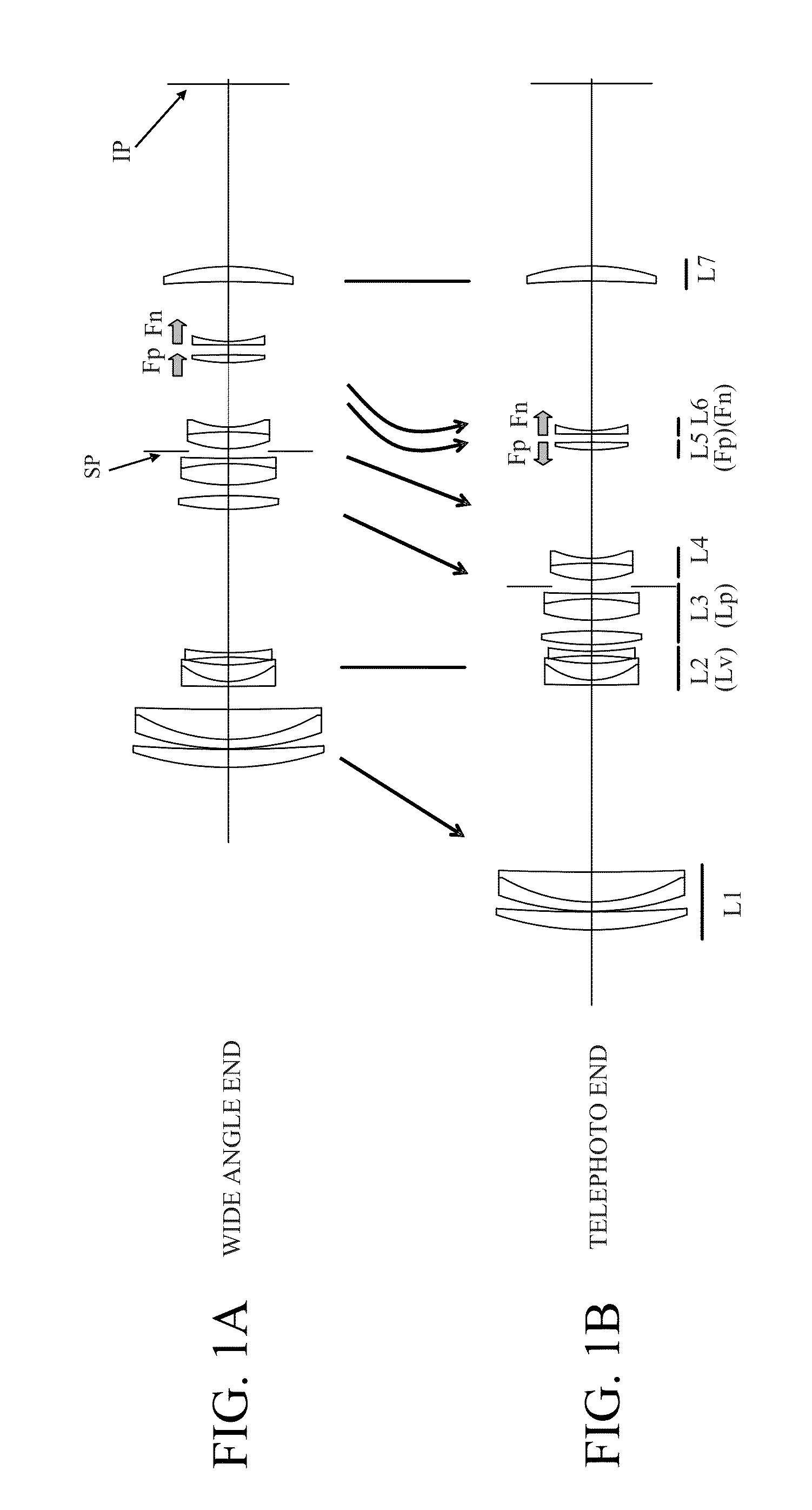
Zoom lens and image-pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20140139722A1Good optical performanceHighly focusedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensZoom lens
A zoom lens includes a lens unit Lv positioned at the most object side of a plurality of lens units having the negative refractive power, a lens unit Lp positioned at the most object side of lens units having a positive refractive power, the lens units being positioned at an image side of the lens unit Lv, and lens units Fp and Fn respectively having a positive and a negative refractive power positioned at an image side of the lens unit Lp, the lens units Fp and Fn being configured to move during focusing. During focusing from infinity to minimum object distance, the lens unit Fp and the lens unit Fn move in the same direction in a wide angle range, and the lens unit Fp moves to an object side and the lens unit Fn moves to an image side in a telephoto range.
Owner:CANON KK
Variable focal length lens comprising micromirrors
ActiveUS7267447B2Increase the effective reflection areaImprove optical efficiencyMirrorsMountingsCamera lensDegrees of freedom
A variable focal length lens consists of many micromirrors with degrees of freedom rotation and / or degrees of freedom translation and actuating components. As operating methods for the lens, the actuating components control the positions of micromirrors electrostatically and / or electromagnetically. The optical efficiency of the variable focal length lens is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding micromirrors and the actuating components under micromirrors. The lens can correct aberration by controlling each micromirror independently. The lens can also be of a desired arbitrary shape and / or size. The micromirrors are arranged in a flat plane or in a curved plane with a predetermined curvature. The electrodes determining the position of the micromirrors can be made of material with high electrical conductivity, preferably metal. The surface material of the micromirror is made of a material with high reflectivity such as aluminum, silver, and gold, which are coated with multi-layer dielectric material or antioxidant.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Variable focal length lens and lens array comprising discretely controlled micromirrors
ActiveUS7239438B2Increase the effective reflection areaImprove optical efficiencyMirrorsMountingsCamera lensMicromirror array
A discretely controlled micromirror array lens (DCMAL) consists of many discretely controlled micromirrors (DCMs) and actuating components. The actuating components control the positions of DCMs electrostatically. The optical efficiency of the DCMAL is increased by locating a mechanical structure upholding DCMs and the actuating components under DCMs to increase an effective reflective area. The known microelectronics technologies can remove the loss in effective reflective area due to electrode pads and wires. The lens can correct aberrations by controlling DCMs independently. Independent control of each DCM is possible by known microelectronics technologies. The DCM array can also form a lens with arbitrary shape and / or size, or a lens array comprising the lenses with arbitrary shape and / or size.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Mobile Display
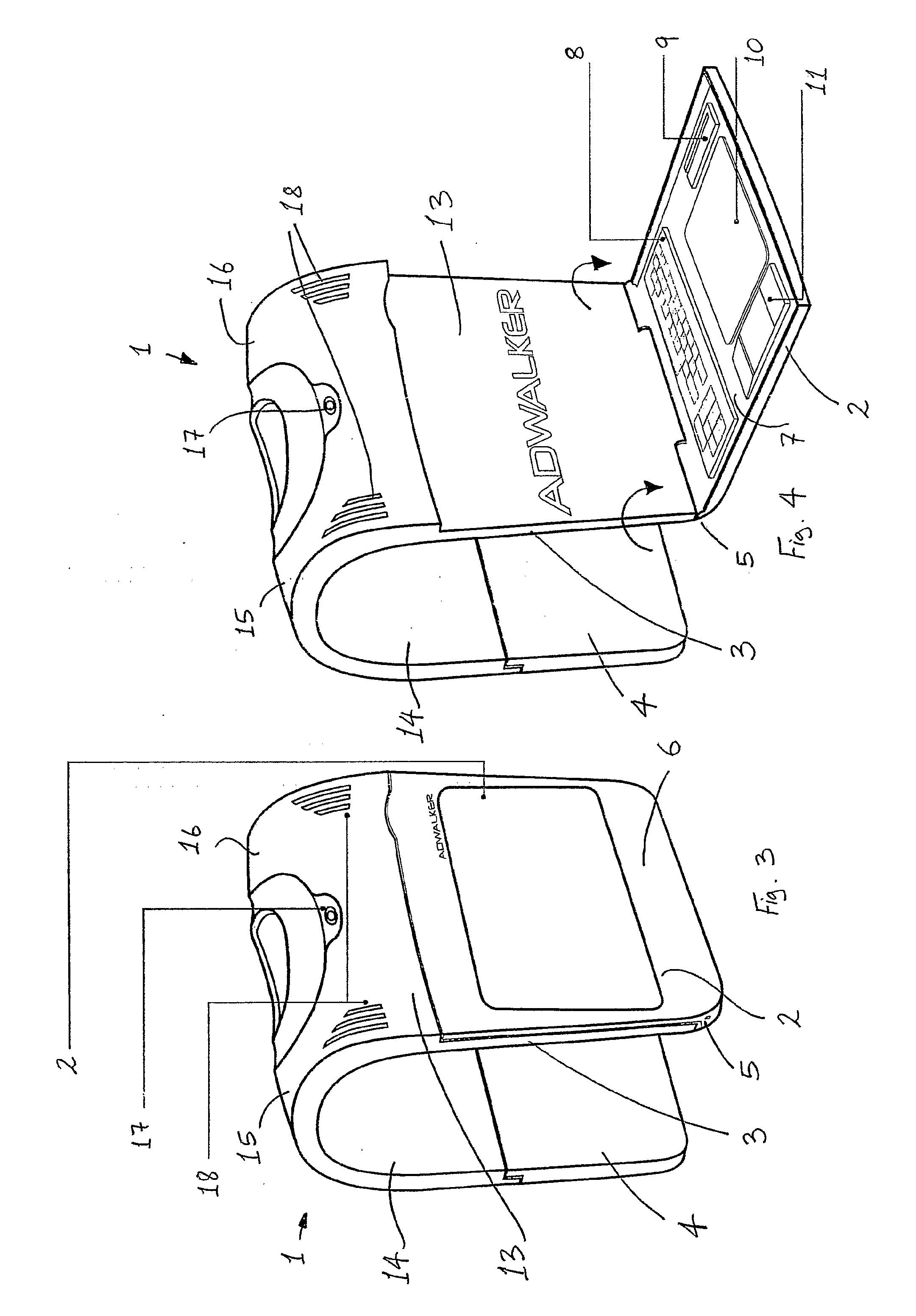
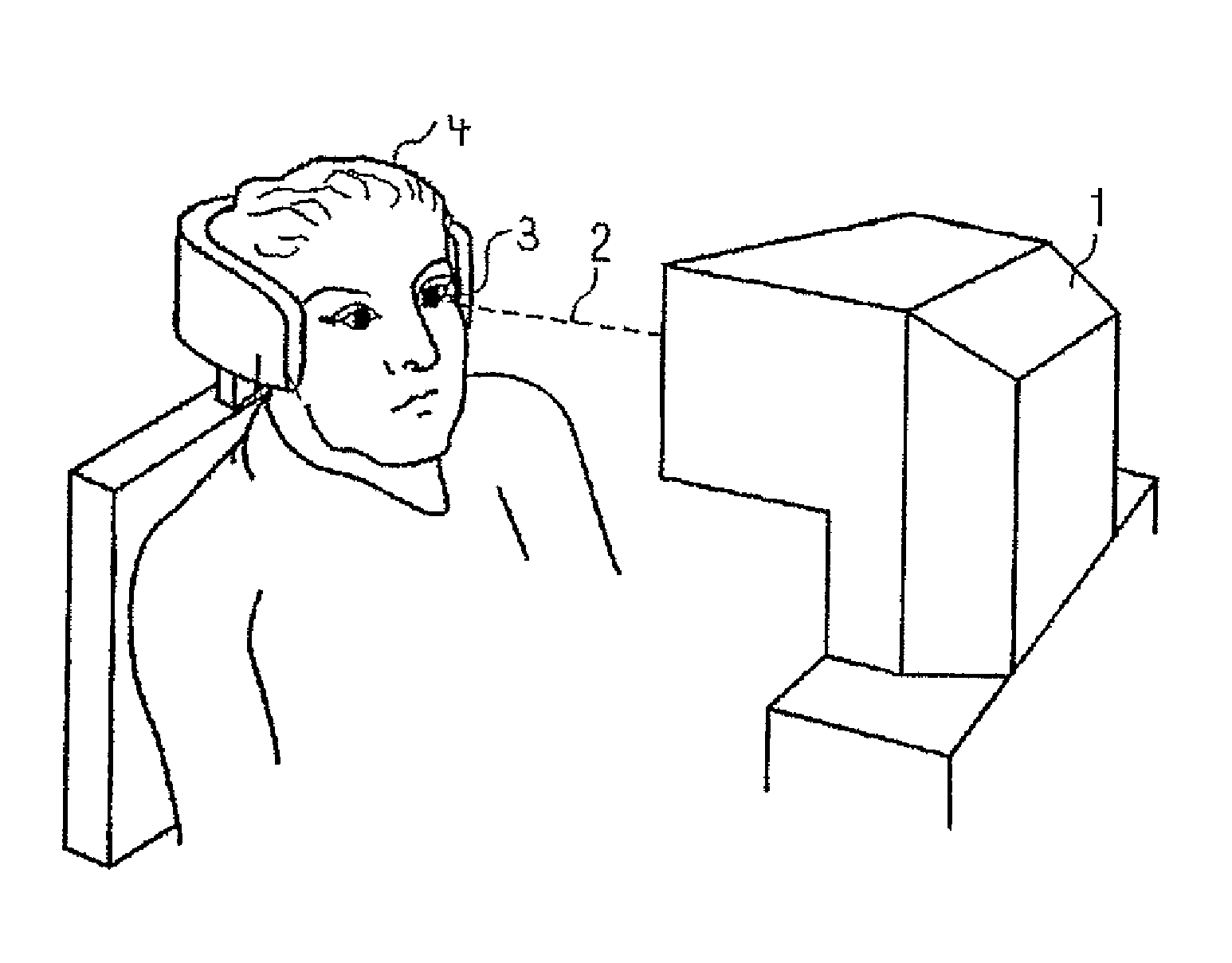
InactiveUS20080040960A1Improve comfortImprove stabilityDetails for portable computersMobile visual advertisingDisplay deviceEngineering
A mobile display (1) comprises an electronic display element (2), a power source (4), and an apparatus (3) suitable for being worn by a person to support the display element (2) and the power source (4). A wearable computer for controlling operation of the display element (2) is housed within the apparatus (3). The apparatus (3) comprises a front part (13) configured to be located at the front of the wearer, and a rear part (14) configured to be located at the rear of the wearer. The front part (13) and the rear part (14) are formed integrally from a fibre reinforced composite material. The display element (2) is attached to the front part (13) at a hinge region (5). This hinged attachment facilitates hinging movement of the display element (2) relative to the front part (13) between a display configuration and an interface configuration. The display element (2) has a front side (6) for displaying and a rear side (7). User interface means are supported on the rear side (7) of the display element (2). The power source (4) is detachably coupled to the lower end of the rear part (14) by abutting an end of the power source (4) with an end of the rear part (14). In this manner, the power source (4) forms a continuous, smooth, planar extension of the rear part (14).
Owner:ADWALKER PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY
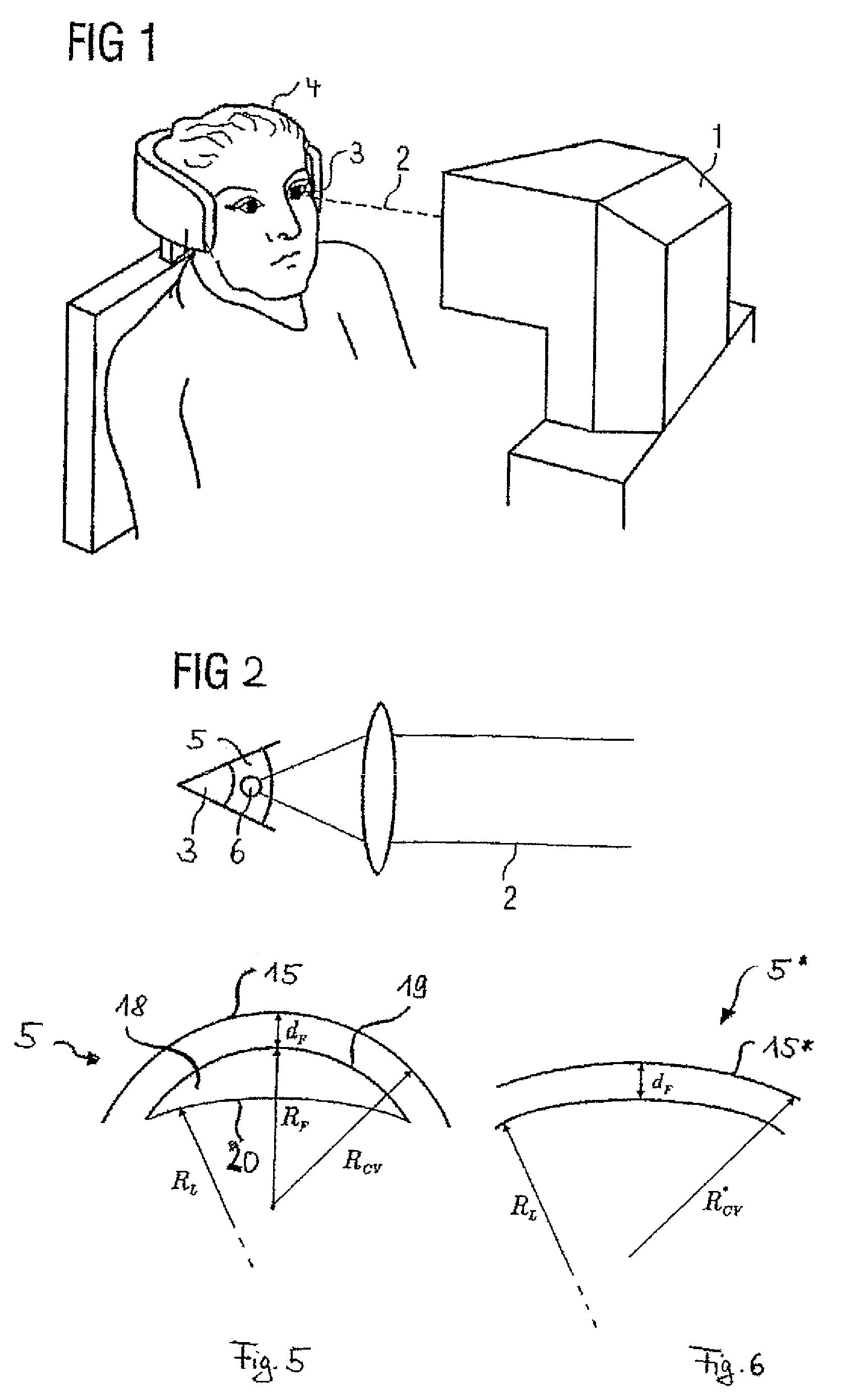
Treatment apparatus for surgical correction of defective eyesight, method of generating control data therefore, and method for surgical correction of defective eyesight
ActiveUS8685006B2Highly focusedReduce datasetLaser surgeryDiagnosticsControl dataSurgical correction
A treatment method and apparatus for surgical correction of defective-eyesight in an eye of a patient, wherein a laser device is controlled by a control device, said laser device separating corneal tissue by irradiation of laser radiation to isolate a volume located within a cornea, wherein the control device controls the laser device to focus the laser radiation, by providing target points located within the cornea, into the cornea, wherein the control device, when providing the target points, allows for focus position errors which lead to a deviation between the predetermined position and the actual position of the target points when focusing the laser radiation, by pre-offsets depending on the positions of the respective target points to compensate for said focus position errors.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
System and method for processing an input signal to produce 3D audio effects
InactiveUS20160174012A1Widely distributedSharper and more vivid auditory spatial imagesTelevision system detailsMicrophones3D audio effectLoudspeaker
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
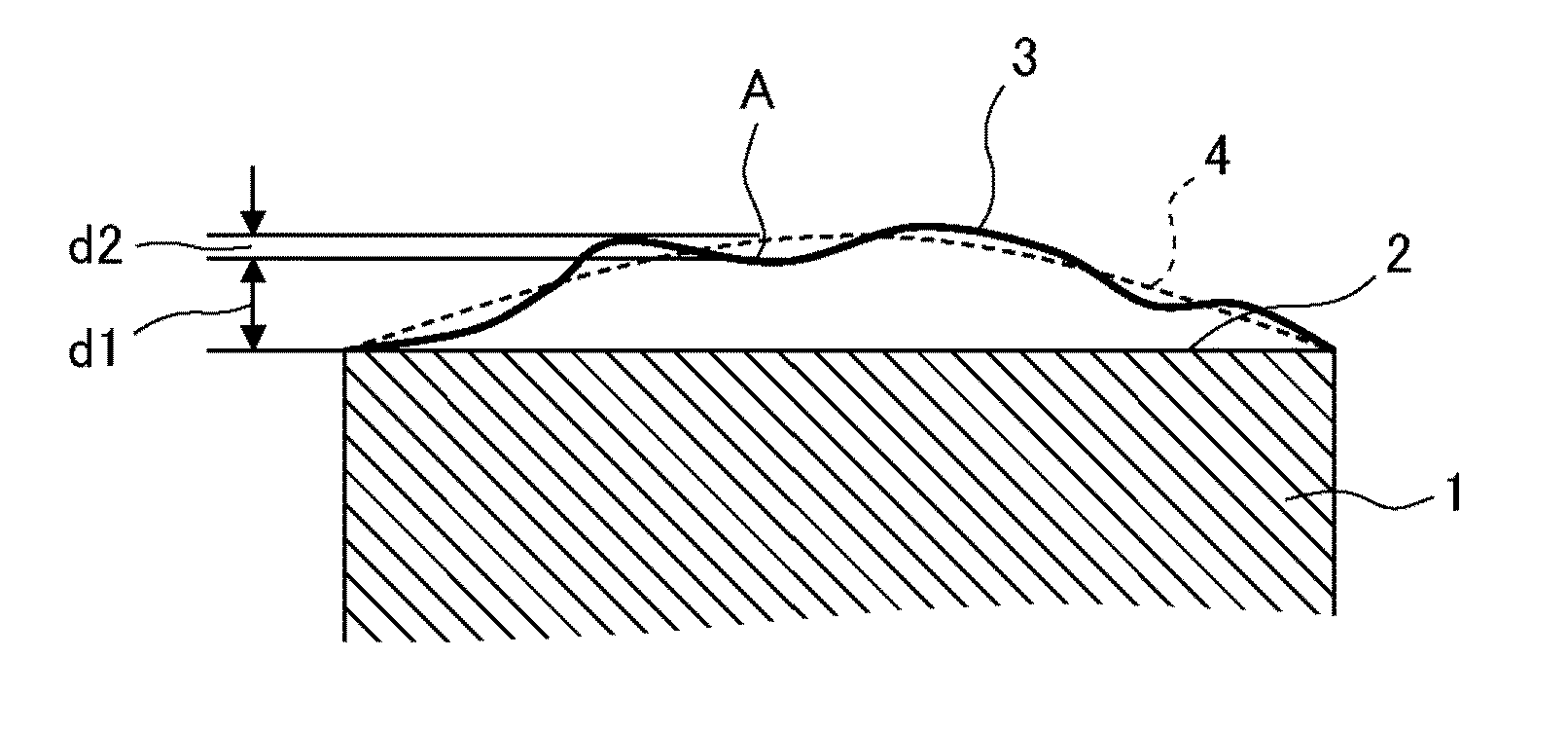
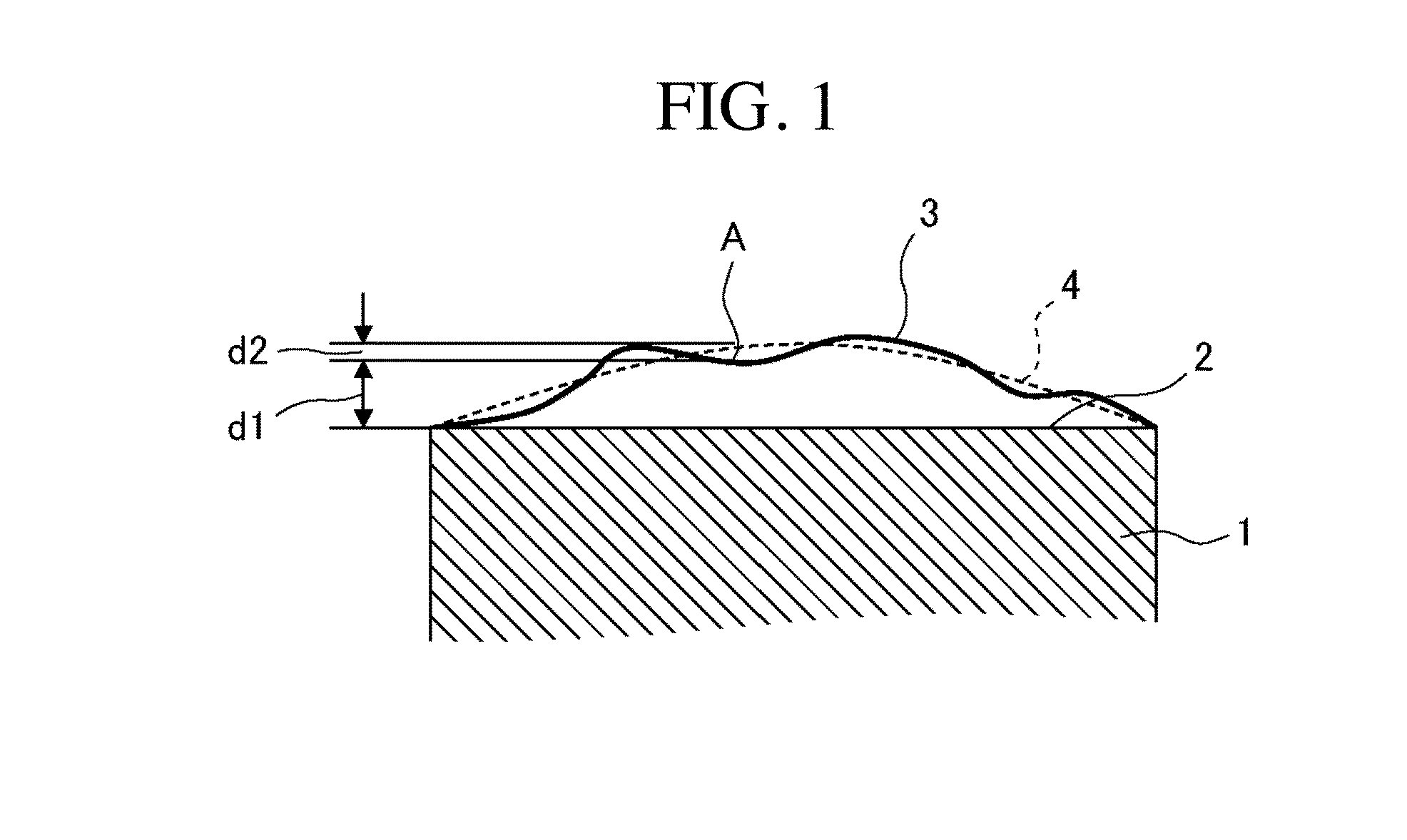
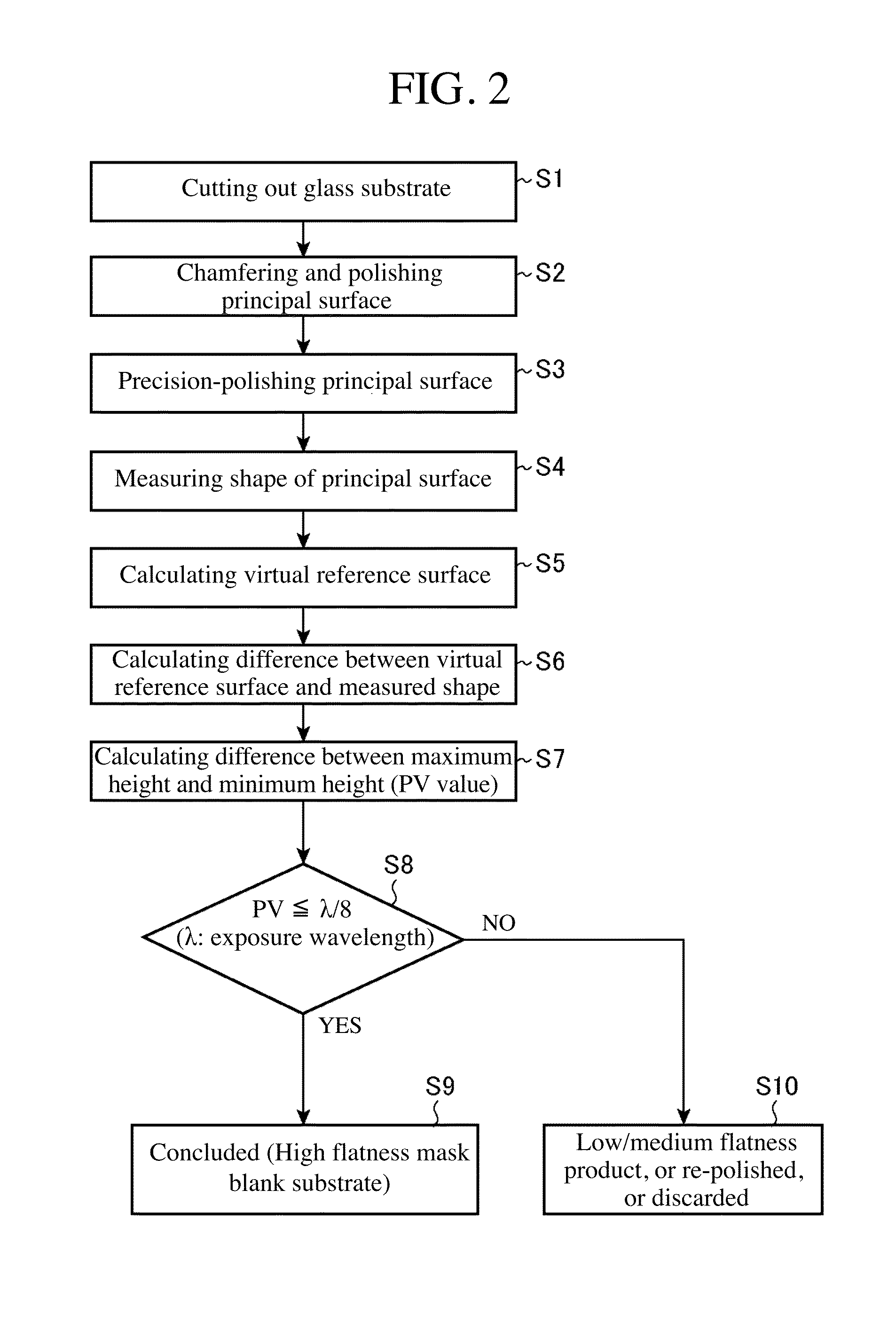
Mask blank substrate, mask blank, transfer mask, and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20160109797A1Reducing manufacturing throughputMaximum flatnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringLength wave
Provided are a mask blank substrate which has effectively and extremely high principal surface flatness while a reduction in the manufacturing throughput of the mask blank substrate is suppressed, a mask blank, and a transfer mask. Also provided are manufacturing methods therefor.A virtual reference surface that becomes an optically effective flat reference surface defined by a Zernike polynomial which is composed of only terms in which the order of a variable related to a radius is the second or lower order, and includes one or more terms in which the order of the variable related to the radius is the second order is set, and a mask blank substrate satisfying the condition that data (PV value) relating to the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the difference data between the reference surface and the measured shape of the mask blank substrate is one-eighth or less of an exposure wavelength (A) is selected.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com