Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
290 results about "Zone plate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A zone plate is a device used to focus light or other things exhibiting wave character. Unlike lenses or curved mirrors however, zone plates use diffraction instead of refraction or reflection. Based on analysis by Augustin-Jean Fresnel, they are sometimes called Fresnel zone plates in his honor. The zone plate's focusing ability is an extension of the Arago spot phenomenon caused by diffraction from an opaque disc.
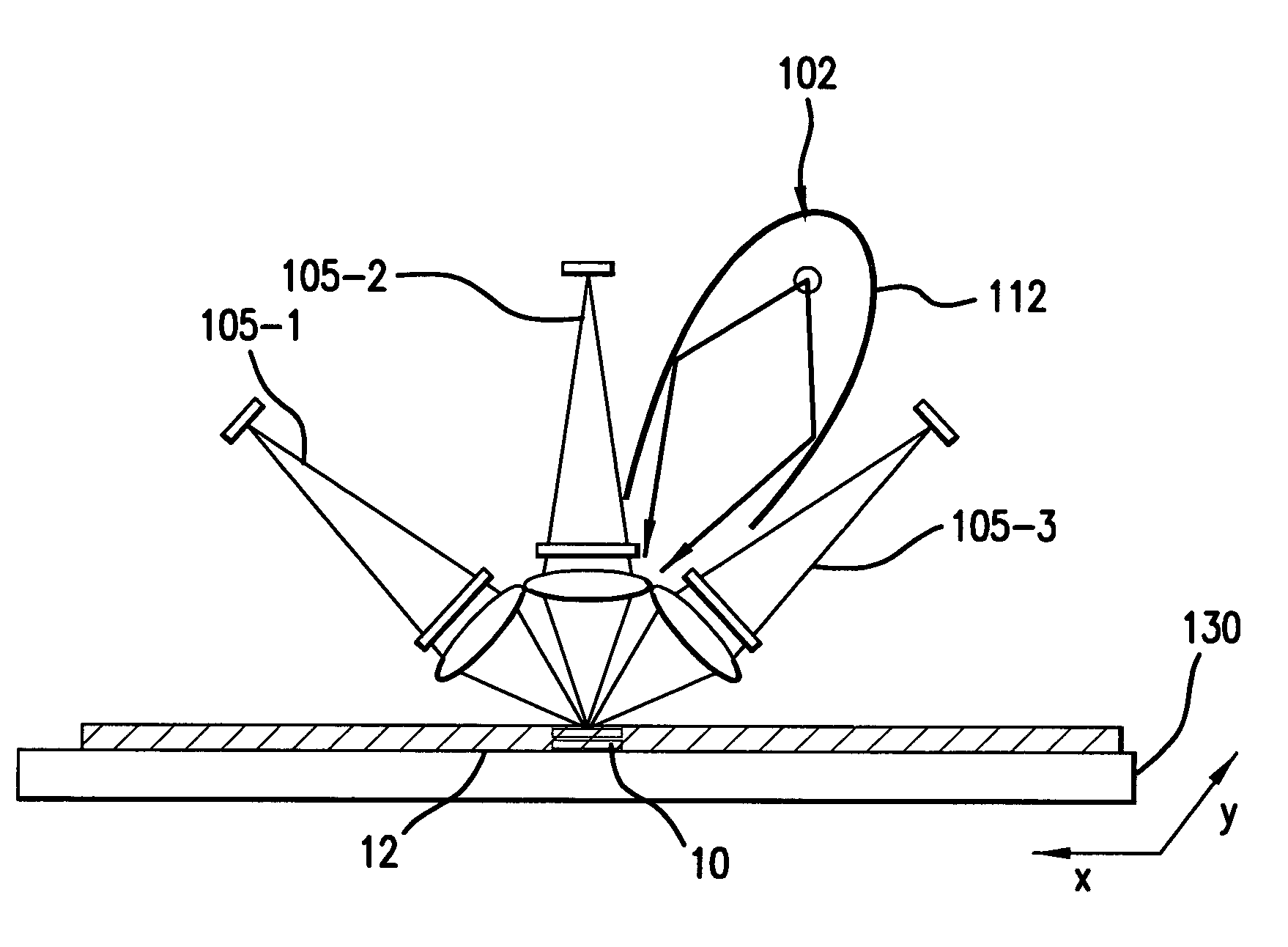
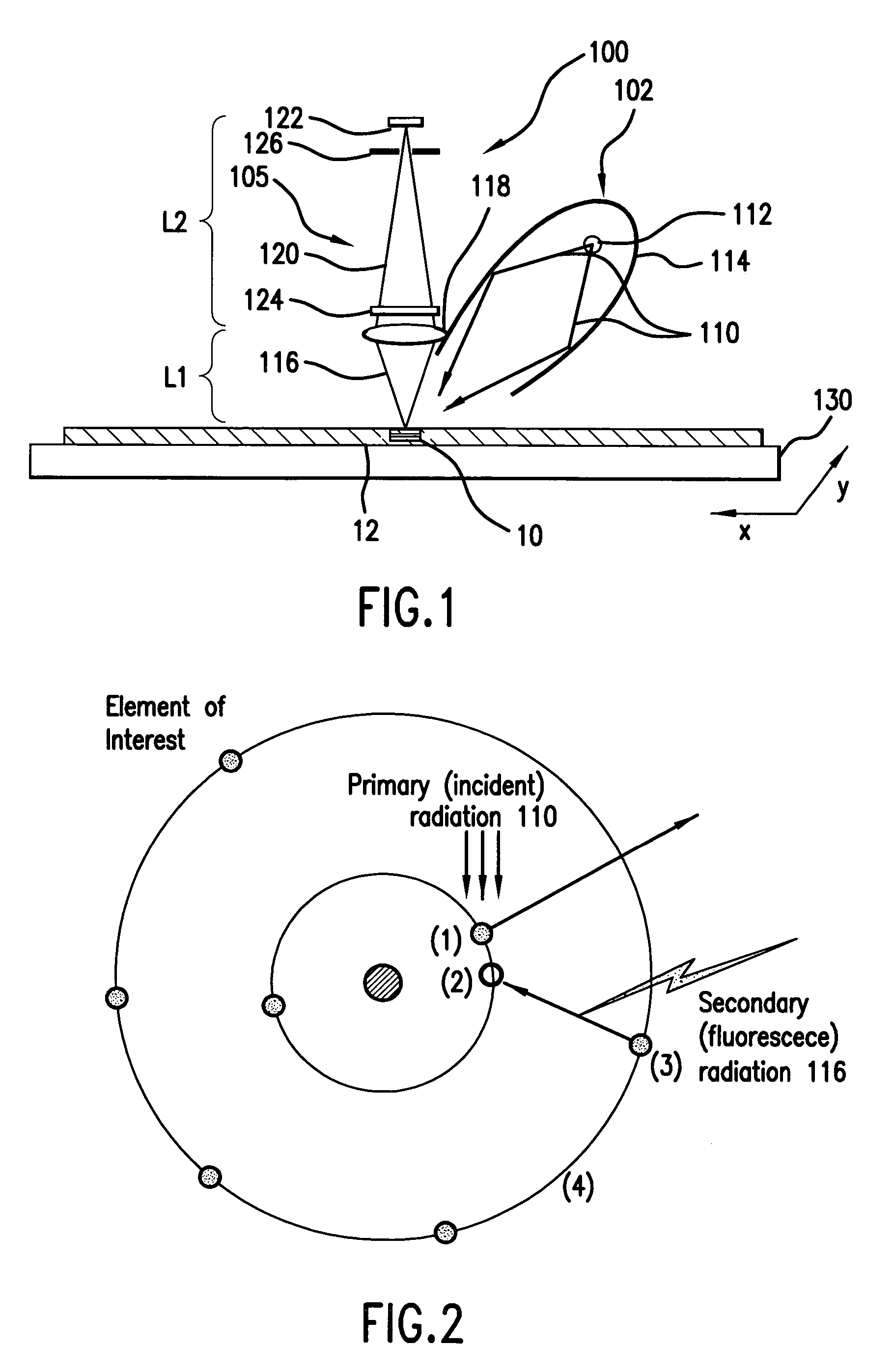
Element-specific X-ray fluorescence microscope and method of operation
InactiveUS7183547B2Enhances preferential imagingEnhance the imageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesConfocalPeak value
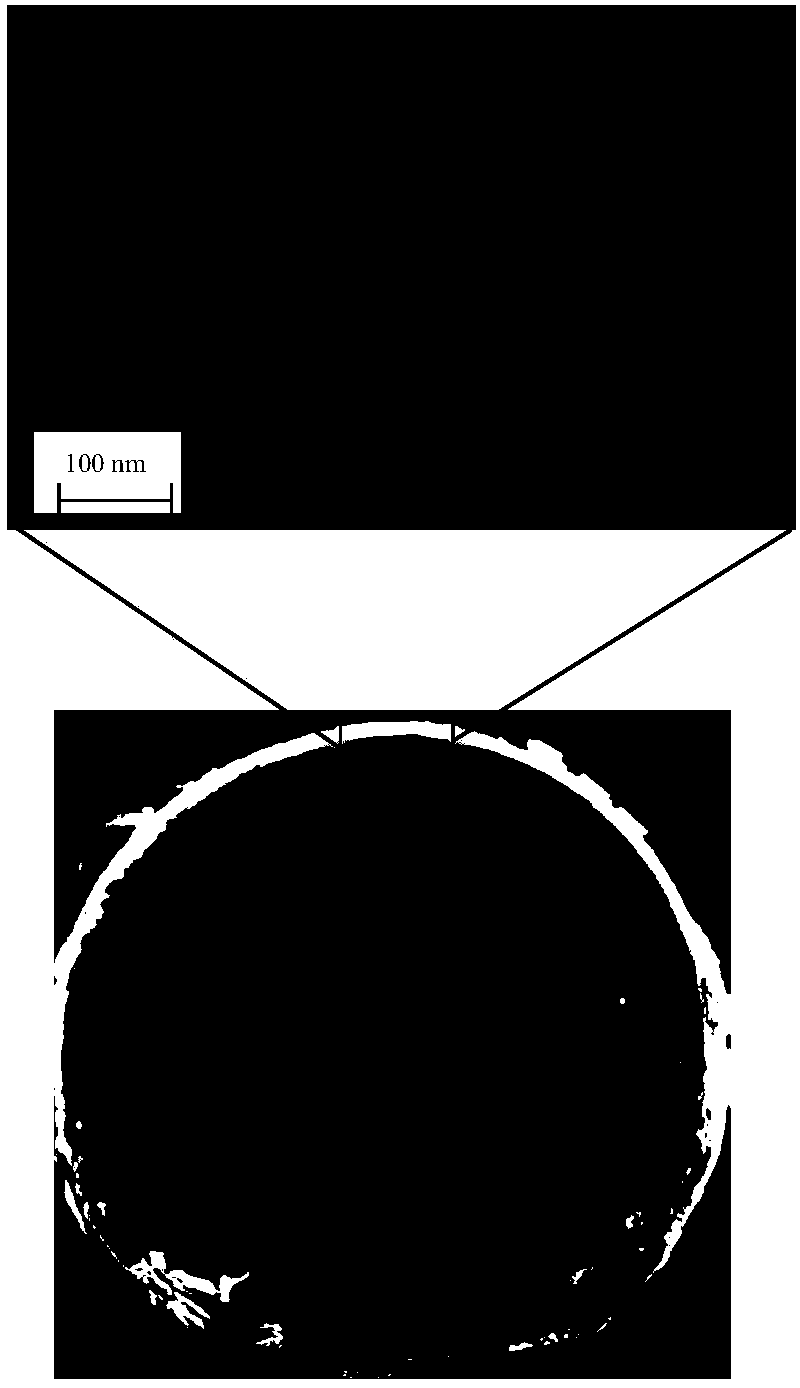
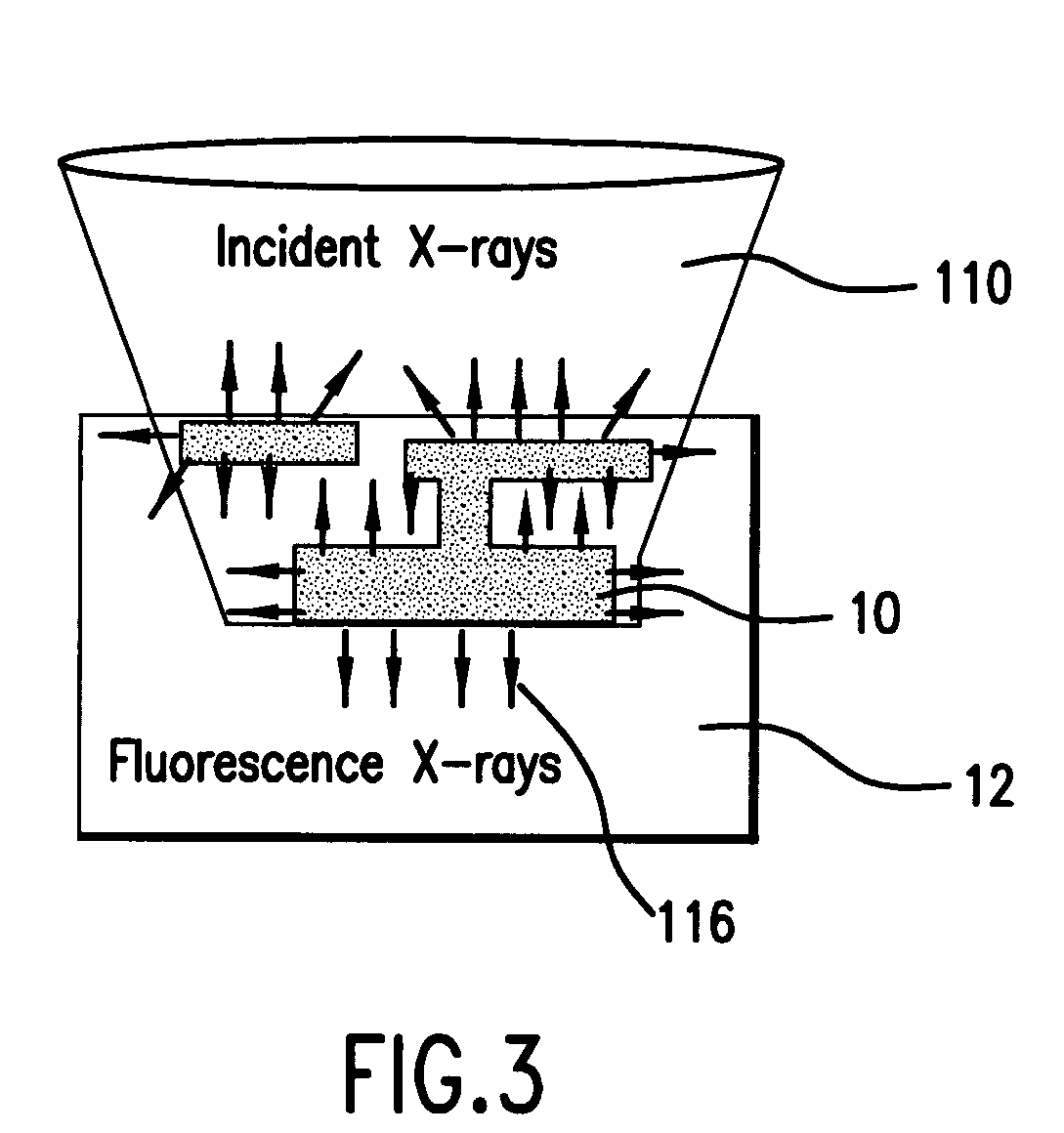
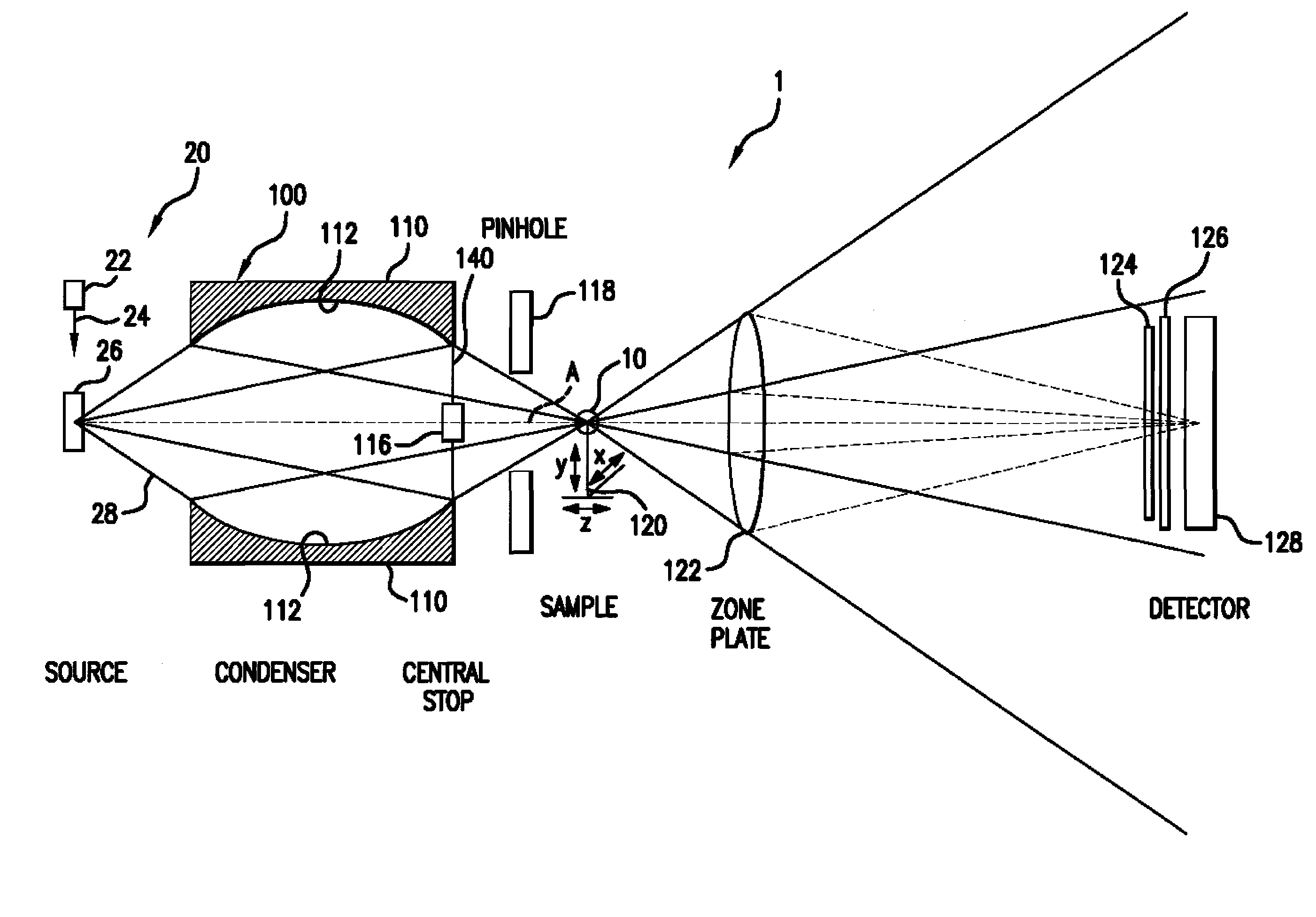
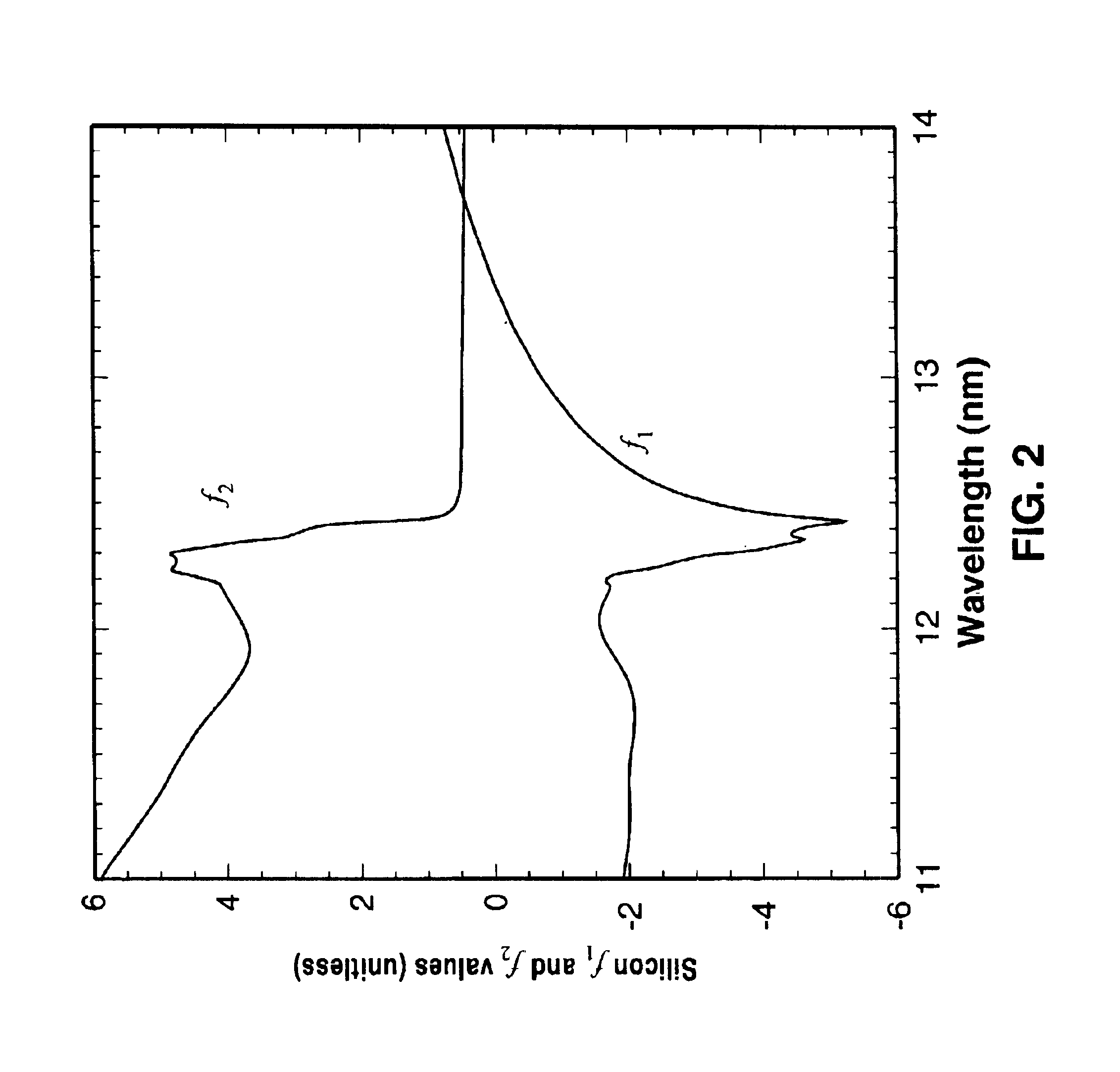
An element-specific imaging technique utilizes the element-specific fluorescence X-rays that are induced by primary ionizing radiation. The fluorescence X-rays from an element of interest are then preferentially imaged onto a detector using an optical train. The preferential imaging of the optical train is achieved using a chromatic lens in a suitably configured imaging system. A zone plate is an example of such a chromatic lens; its focal length is inversely proportional to the X-ray wavelength. Enhancement of preferential imaging of a given element in the test sample can be obtained if the zone plate lens itself is made of a compound containing substantially the same element. For example, when imaging copper using the Cu La spectral line, a copper zone plate lens is used. This enhances the preferential imaging of the zone plate lens because its diffraction efficiency (percent of incident energy diffracted into the focus) changes rapidly near an absorption line and can be made to peak at the X-ray fluorescence line of the element from which it is fabricated. In another embodiment, a spectral filter, such as a multilayer optic or crystal, is used in the optical train to achieve preferential imaging in a fluorescence microscope employing either a chromatic or an achromatic lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Micromirror arry lens with optical surface profiles
A Micromirror Array Lens comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a flat or a curved surface to reflect incident light. Each micromirror in the Micromirror Array Lens is configured to have at least one motion. The Micromirror Array Lens forms at least one optical surface profile reproducing free surfaces by using the motions of the micromirrors. The free surface can be any two or three-dimensional continuous or discrete reflective surface. The Micromirror Array Lens having the corresponding optical surface profile provides optical focusing properties substantially identical to those of the free surface. The Micromirror Array Lens can forms various optical elements such as a variable focal length lens, a fixed focal length lens, an array of optical switches, a beam steerer, a zone plate, a shutter, an iris, a multiple focal length lens, other multi-function optical elements, and so on.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Fast x-ray lenses and fabrication method therefor
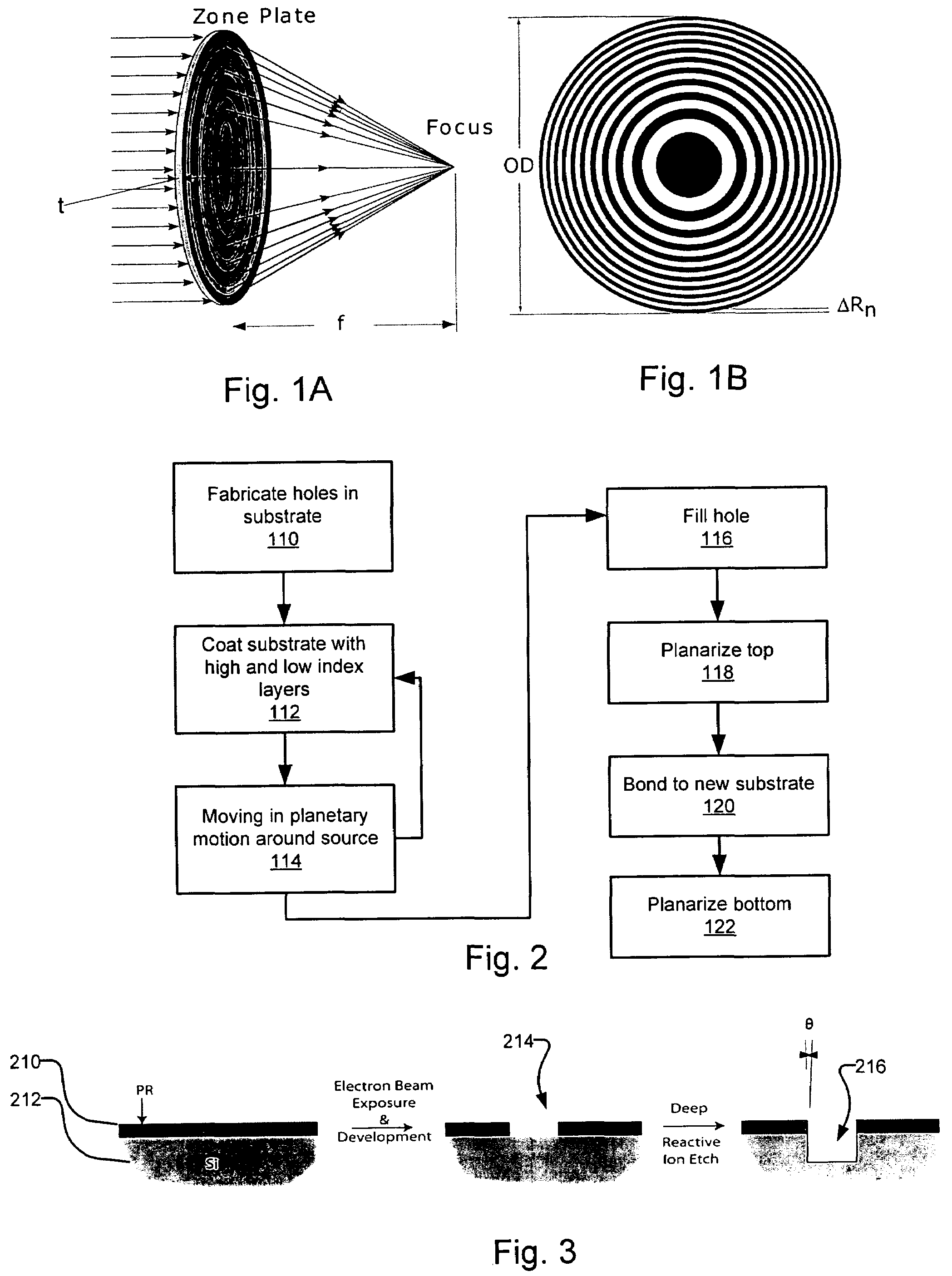
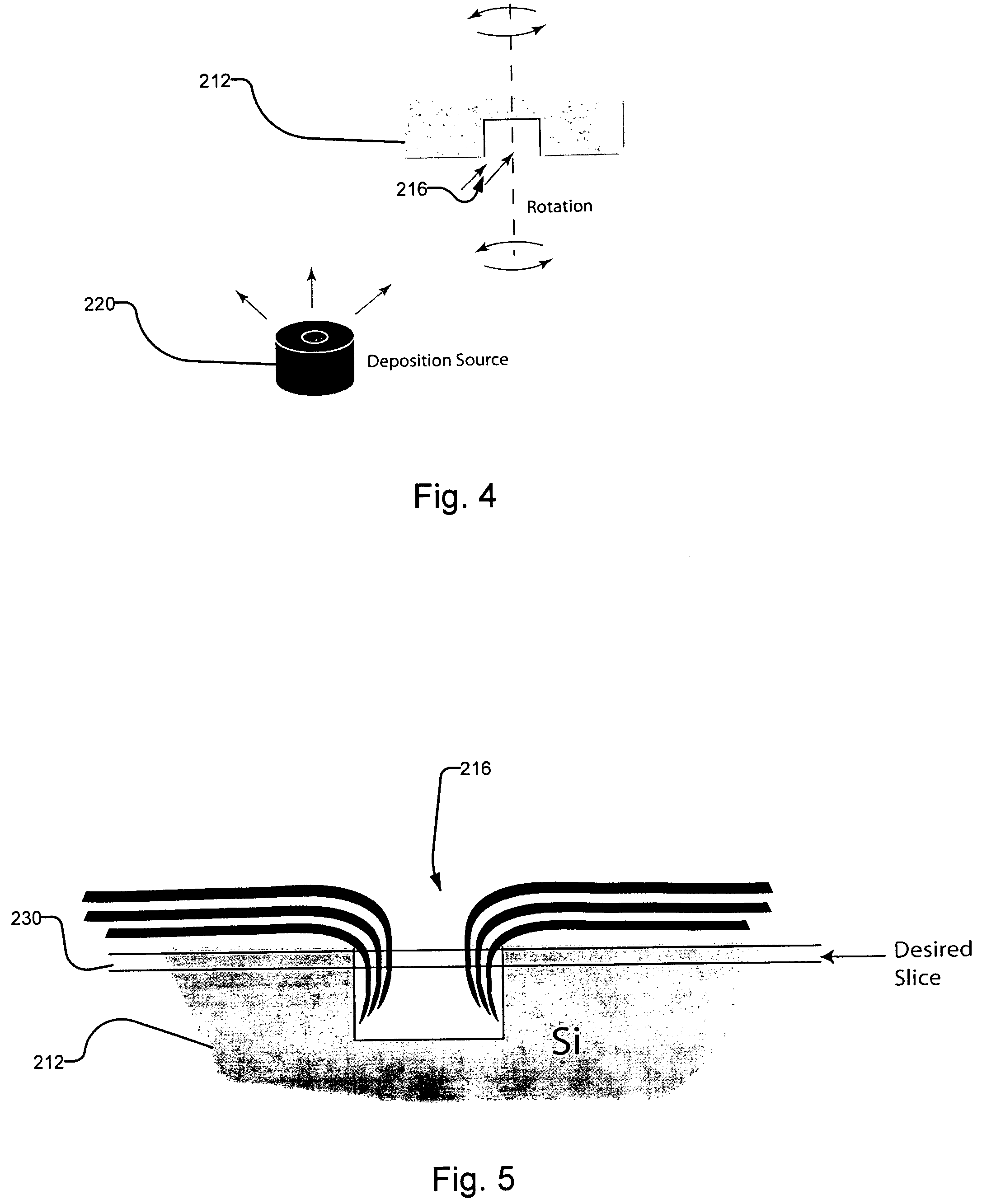
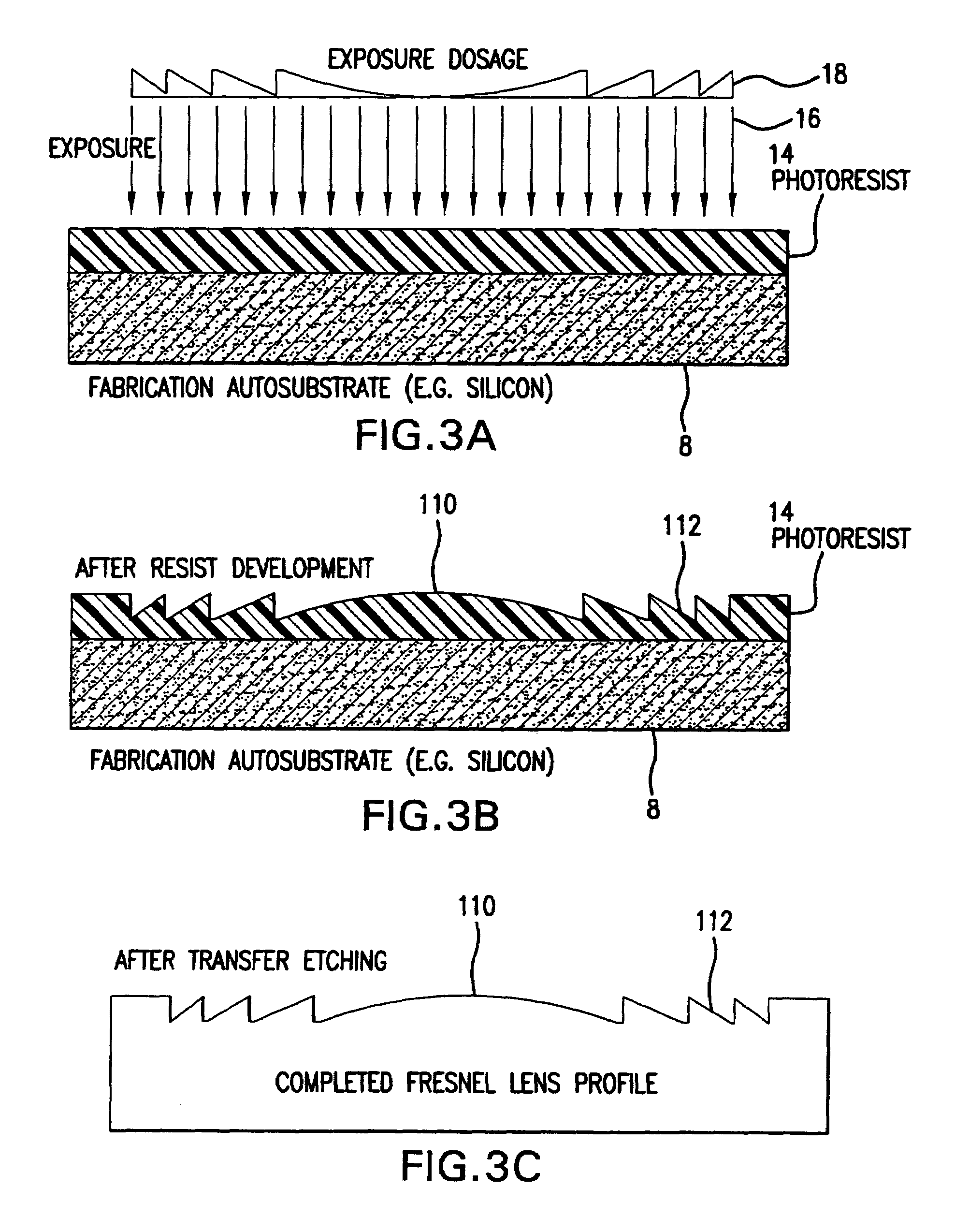
A fabrication process for zone plate lenses is based on controlled thin layer deposition for fabricating structures as small as 2 nanometers (nm) in width, and potentially smaller. The substrate for deposition will take the form of a precision hole, fabricated in a substrate, such as silicon by electron beam lithography and subsequent reactive ion etching. A controlled layer deposition is then used to form the required zone plate structure. A subsequent thinning process is used to section the hole and produce a zone plate with the required layer thicknesses.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Pattern generating systems
InactiveUS7227618B1Increase speedImprove throughputAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusLight spotPattern generation
A pattern generating system for generating two-dimensional images on a surface includes a light source and one or more Zone Plate Modulator (ZPM) arrays. The ZPM arrays comprise diffractive zone plate modulating elements that are capable of either diffracting or reflecting an incident light according to the image data. In a high-resolution pattern generating system, ZPM arrays are used as spot array generators. A complete high-resolution image is formed by scanning individual light spots in the spot array using a subfield scanning means.
Owner:BI BAOKANG
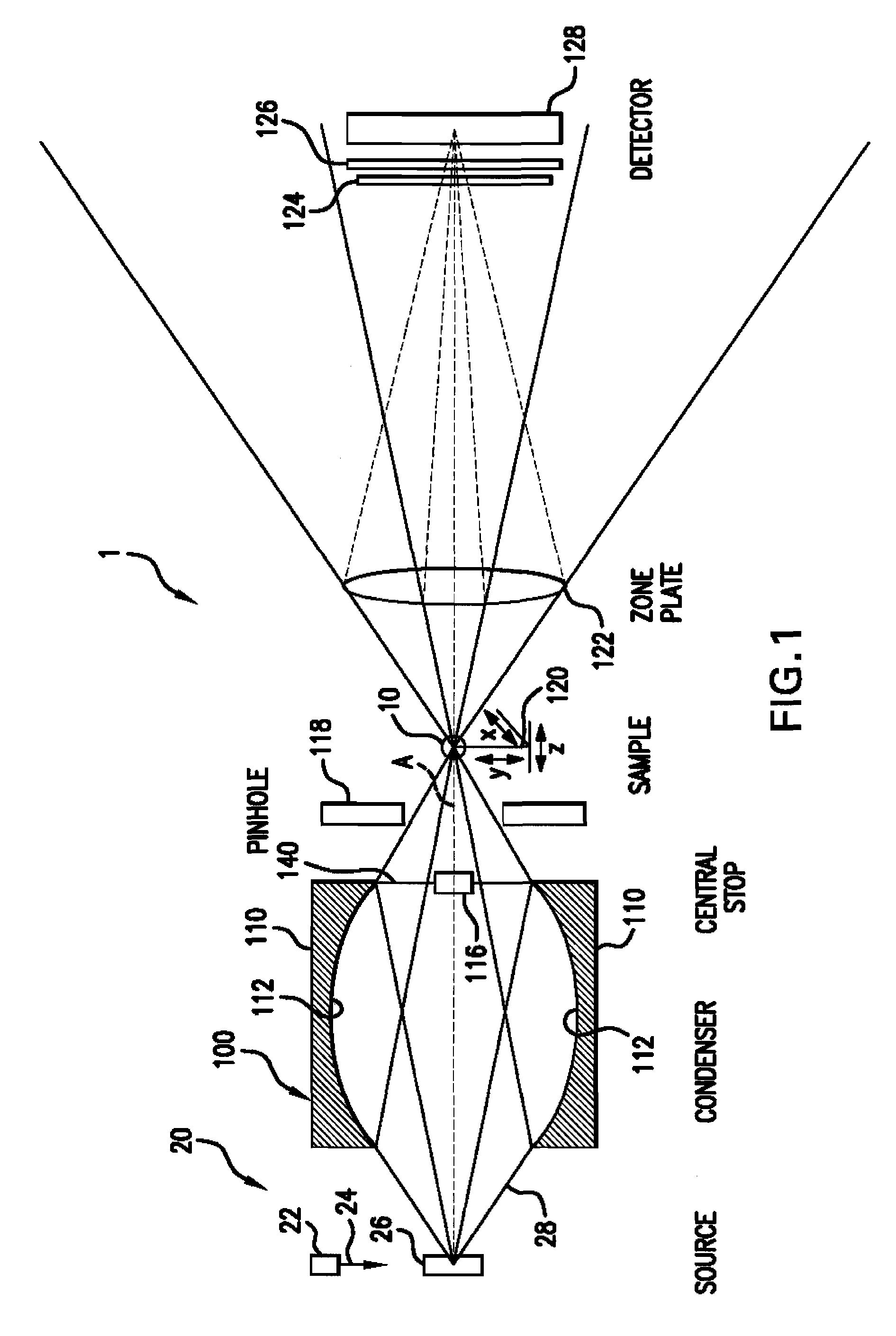
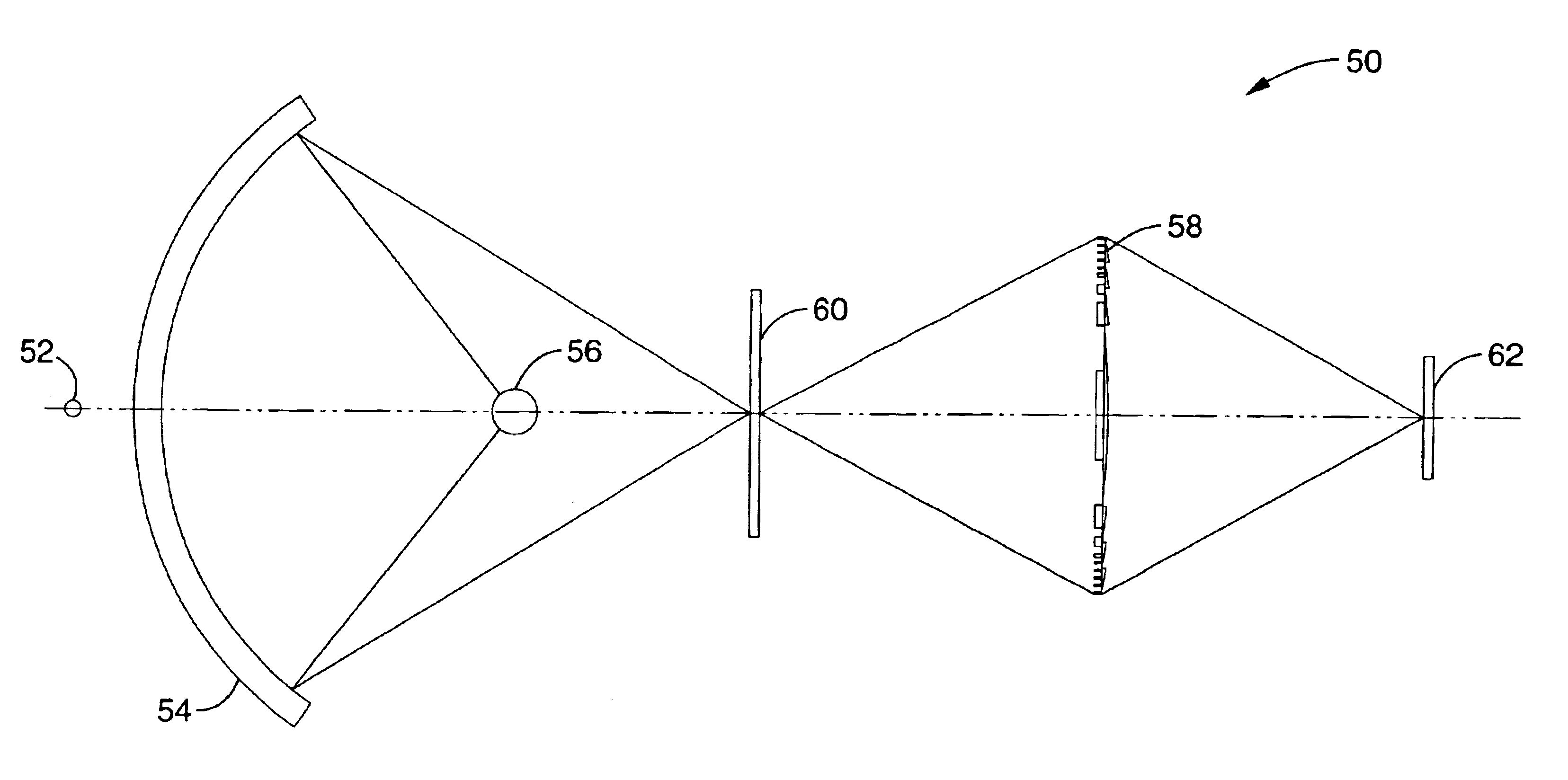
X-ray microscope capillary condenser system
ActiveUS7170969B1Efficient collectionEfficient relayHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGamma-ray/x-ray microscopesZone platePhysics
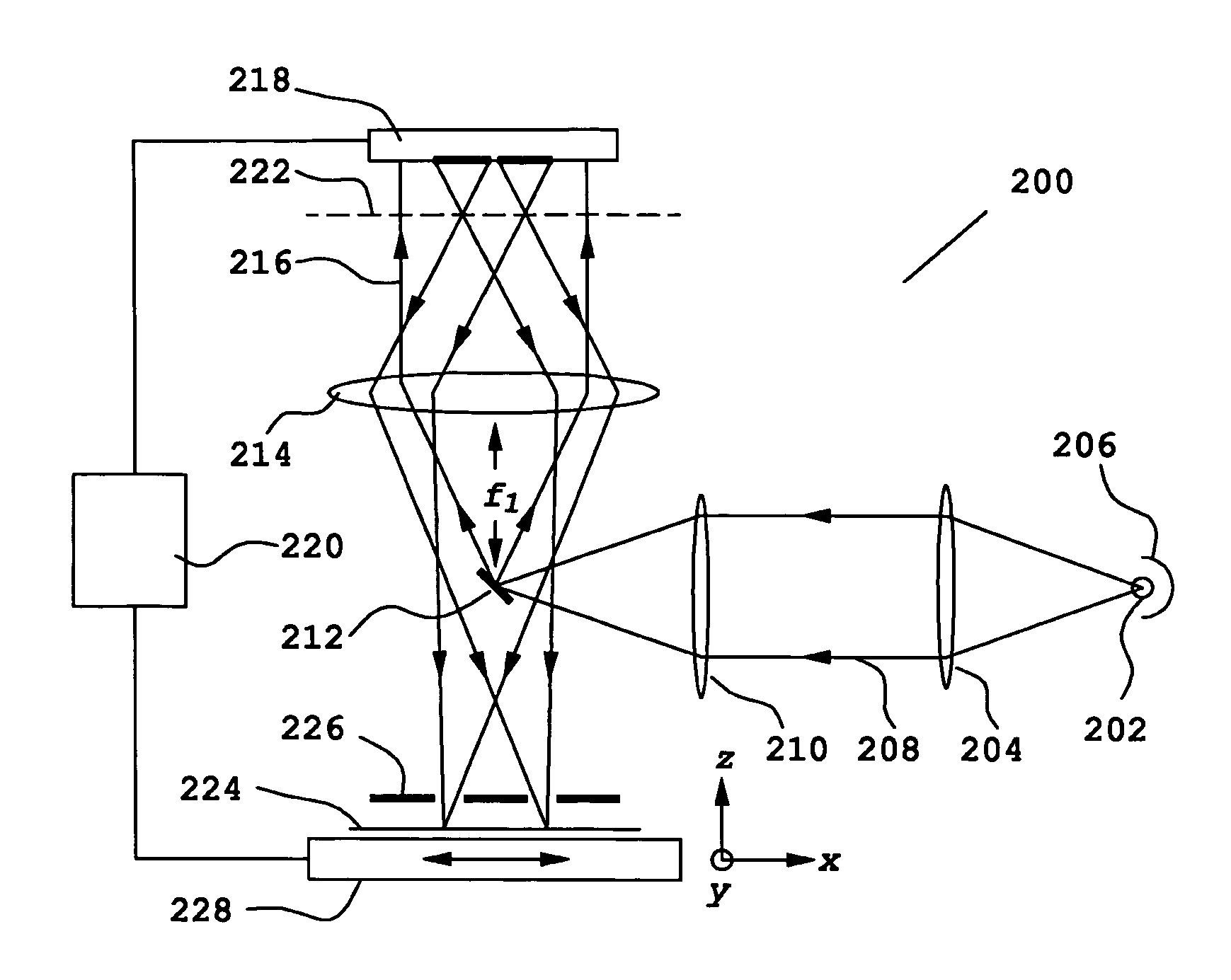
A radiation condenser system for an X-ray microscope allows for the efficient collection and relay of radiation from a source to the sample. It generates a converging hollow cone of radiation that can be used in the imaging of a sample or target using a zone plate lens. This system comprises a capillary tube for receiving and focusing radiation onto a sample. A center stop is provided for blocking radiation being transmitted along an axis of the capillary tube.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
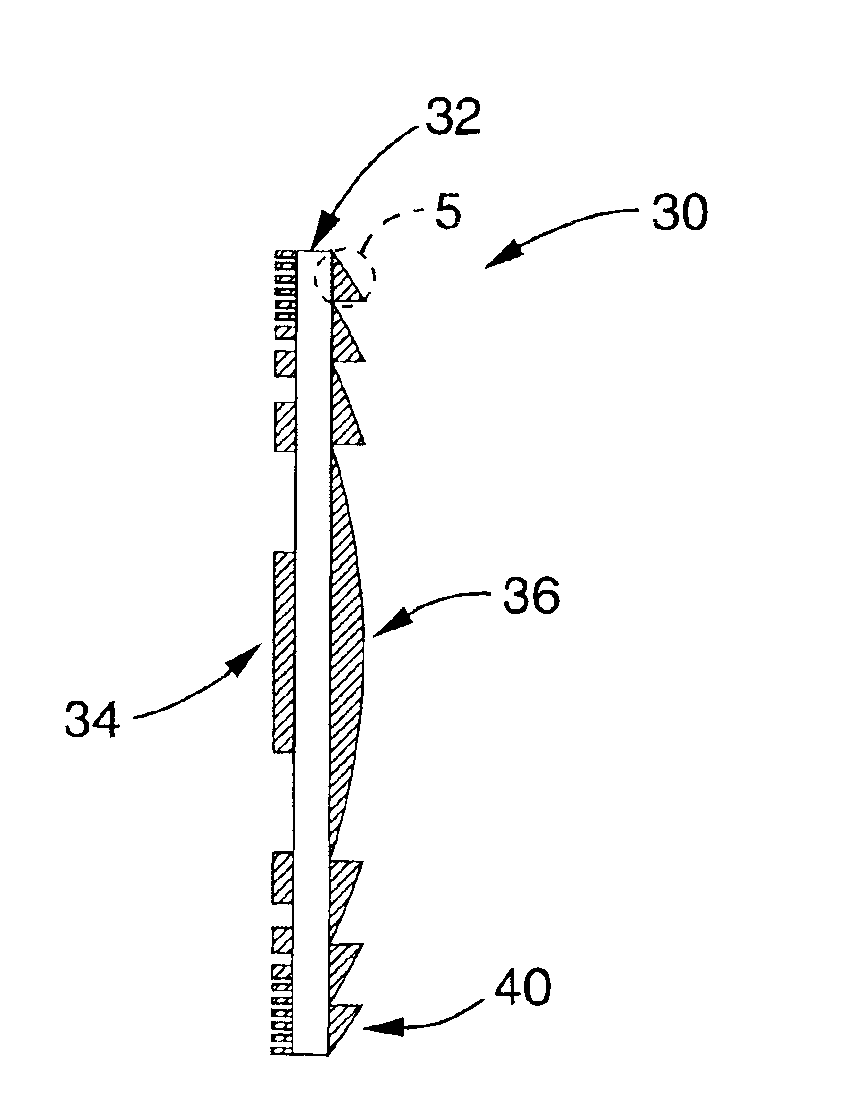
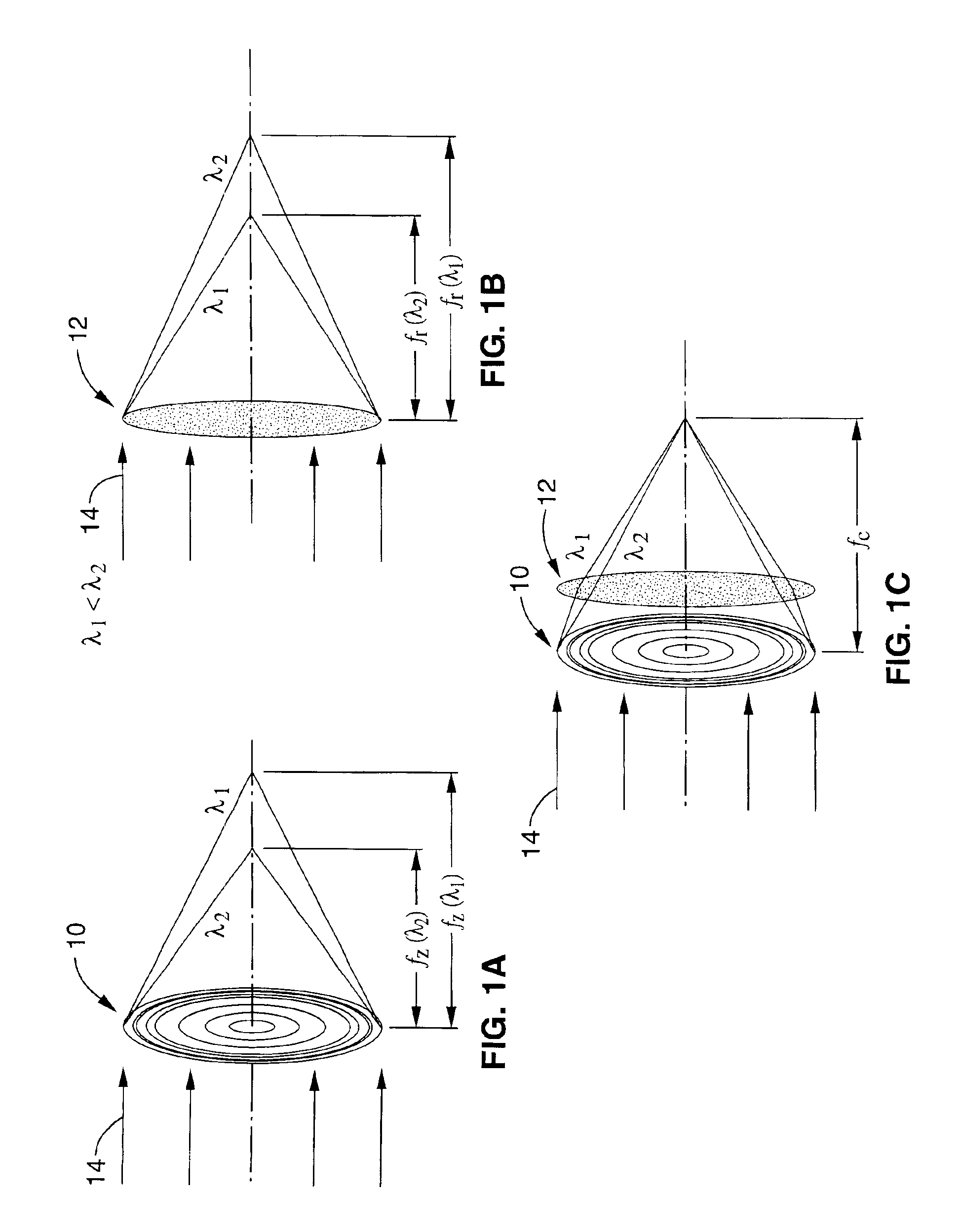
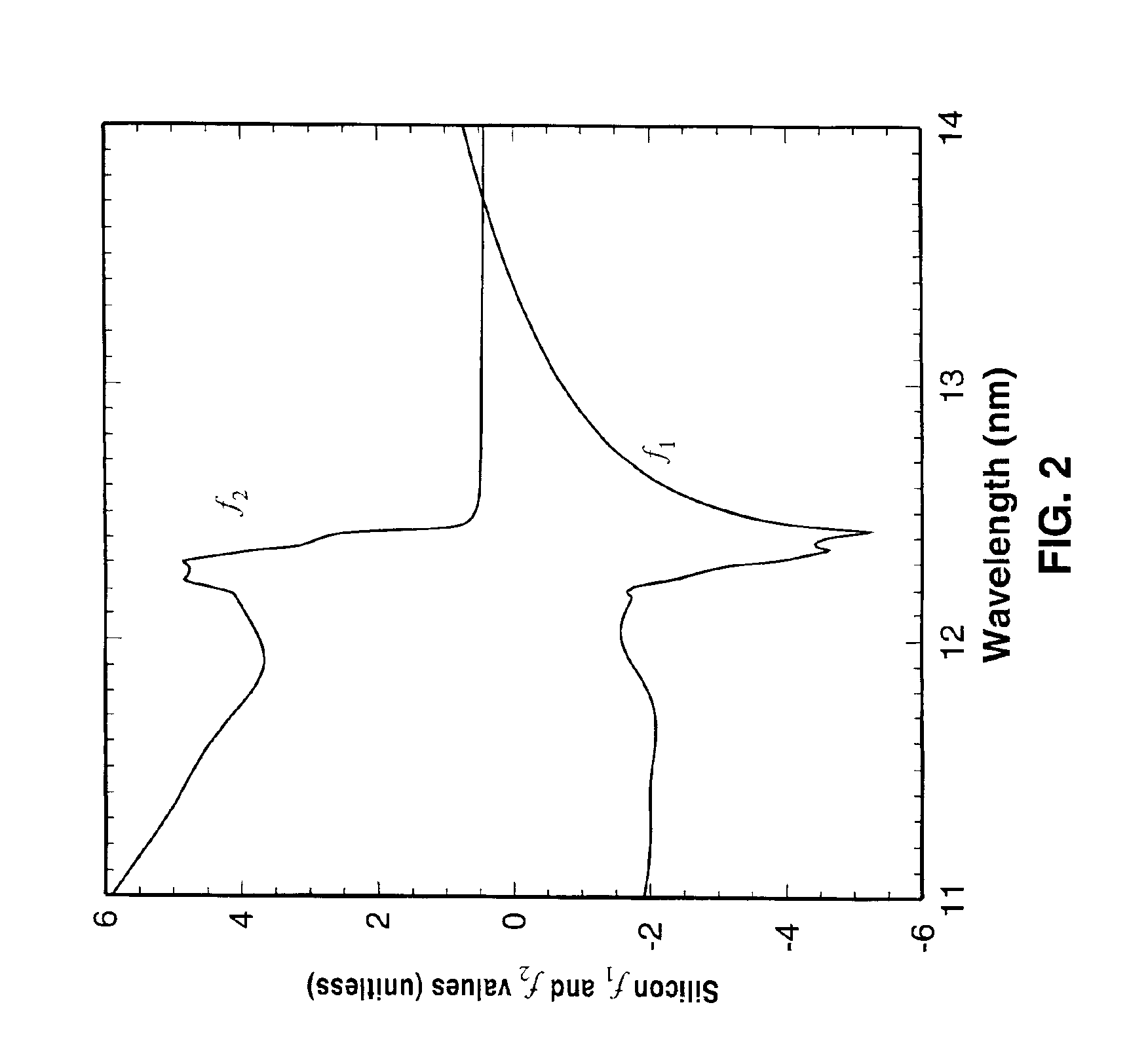
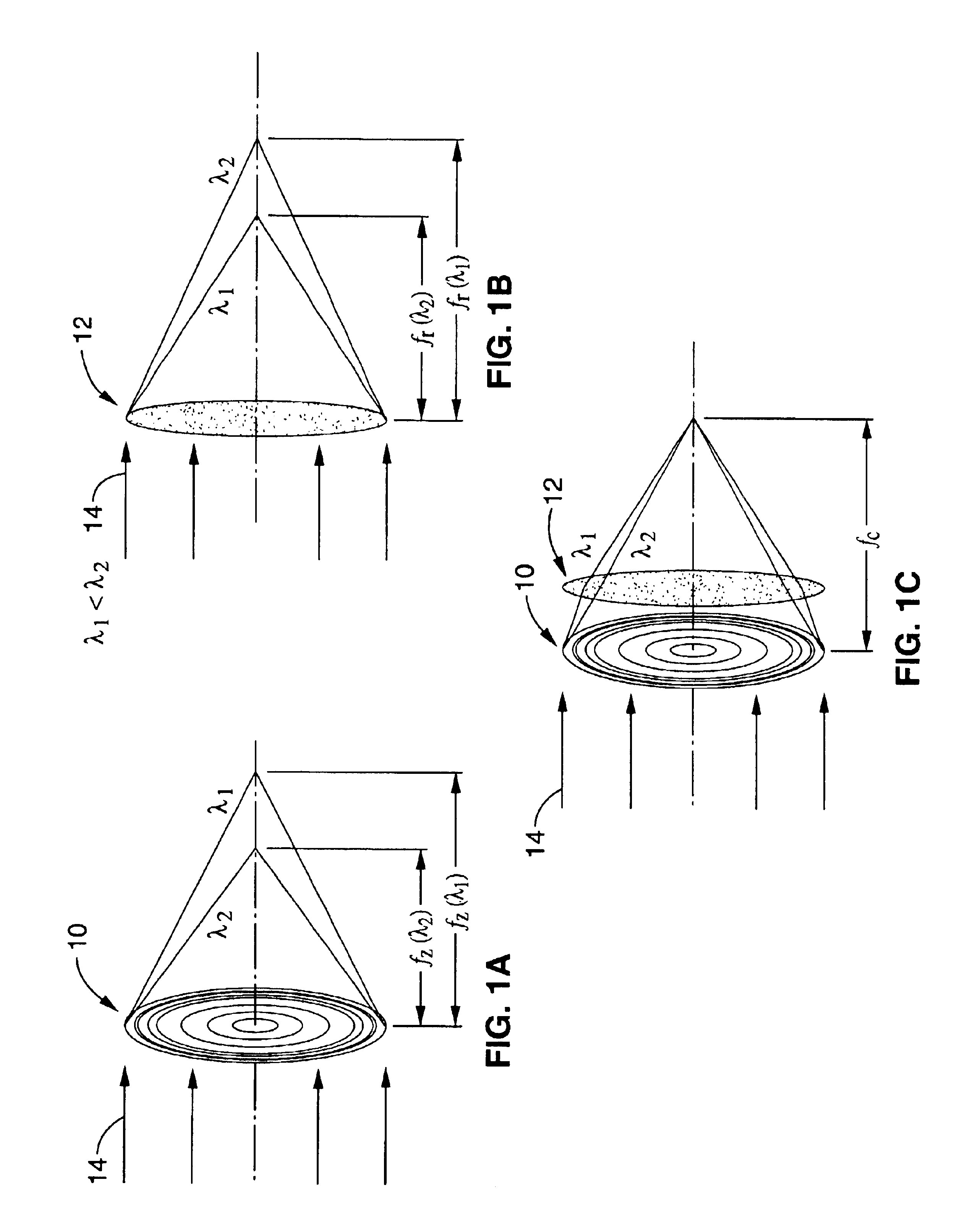
Achromatic fresnel optics for ultraviolet and x-ray radiation
InactiveUS6917472B1Relatively large bandwidthIncrease amplitudeOptical filtersDiffraction gratingsRefractive indexX-ray
An achromatic Fresnel optic that combines a Fresnel zone plate and a refractive Fresnel lens. The zone plate provides high resolution for imaging and focusing, while the refractive lens takes advantage of the refraction index change properties of appropriate elements near absorption edges to recombine the electromagnetic radiation of different energies dispersed by the zone plate. This compound lens effectively solves the high chromatic aberration problem of zone plates. The AFO has a wide range of potential applications in lithography, microimaging with various contrast mechanisms and measurement techniques.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Achromatic fresnel optics based lithography for short wavelength electromagnetic radiations
InactiveUS6885503B2Simplify System DesignImprove system throughputMirrorsDiffraction gratingsRefractive indexElectromagnetic radiation
A lithography apparatus having achromatic Fresnel objective (AFO) that combines a Fresnel zone plate and a refractive Fresnel lens. The zone plate provides high resolution for imaging and focusing, while the refractive lens takes advantage of the refraction index change properties of appropriate elements near absorption edges to recombine the electromagnetic radiation of different energies dispersed by the zone plate. This compound lens effectively solves the high chromatic aberration problem of zone plates. The lithography apparatus allows the use of short wavelength radiation in the 1-15 nm spectral range to print high resolution features as small as 20 nm.
Owner:XRADIA
Fabrication Methods for Micro Compound Optics
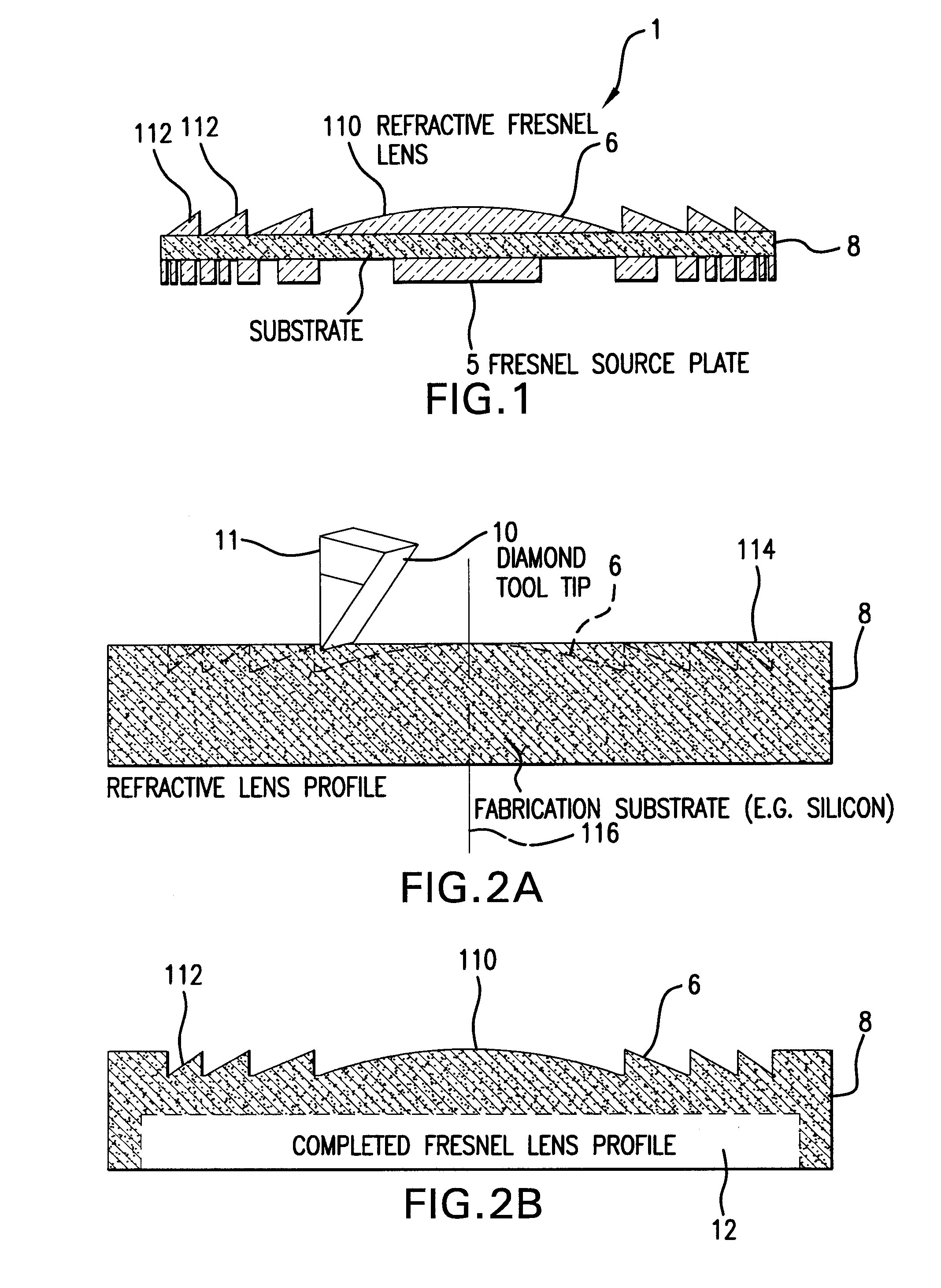
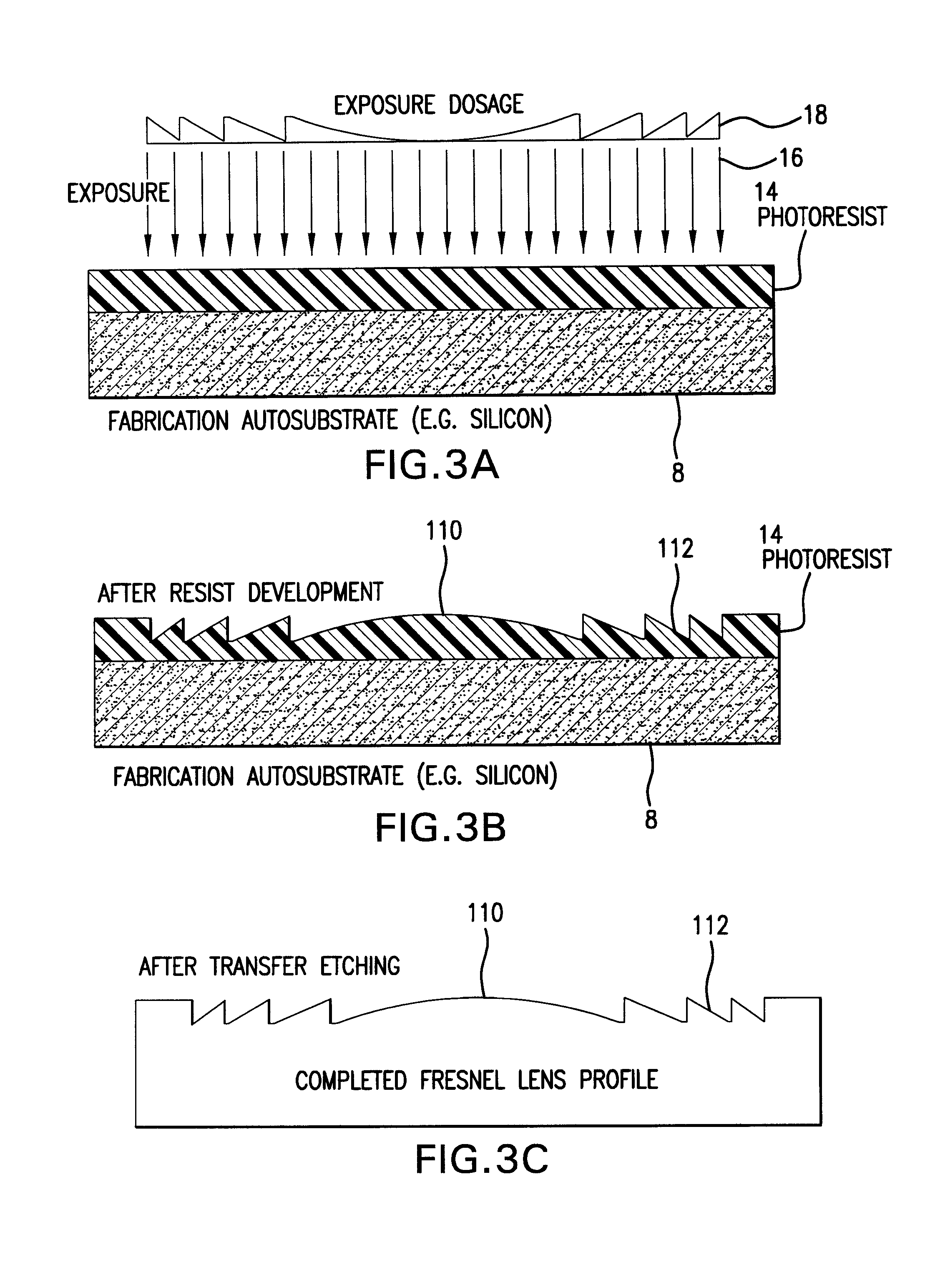
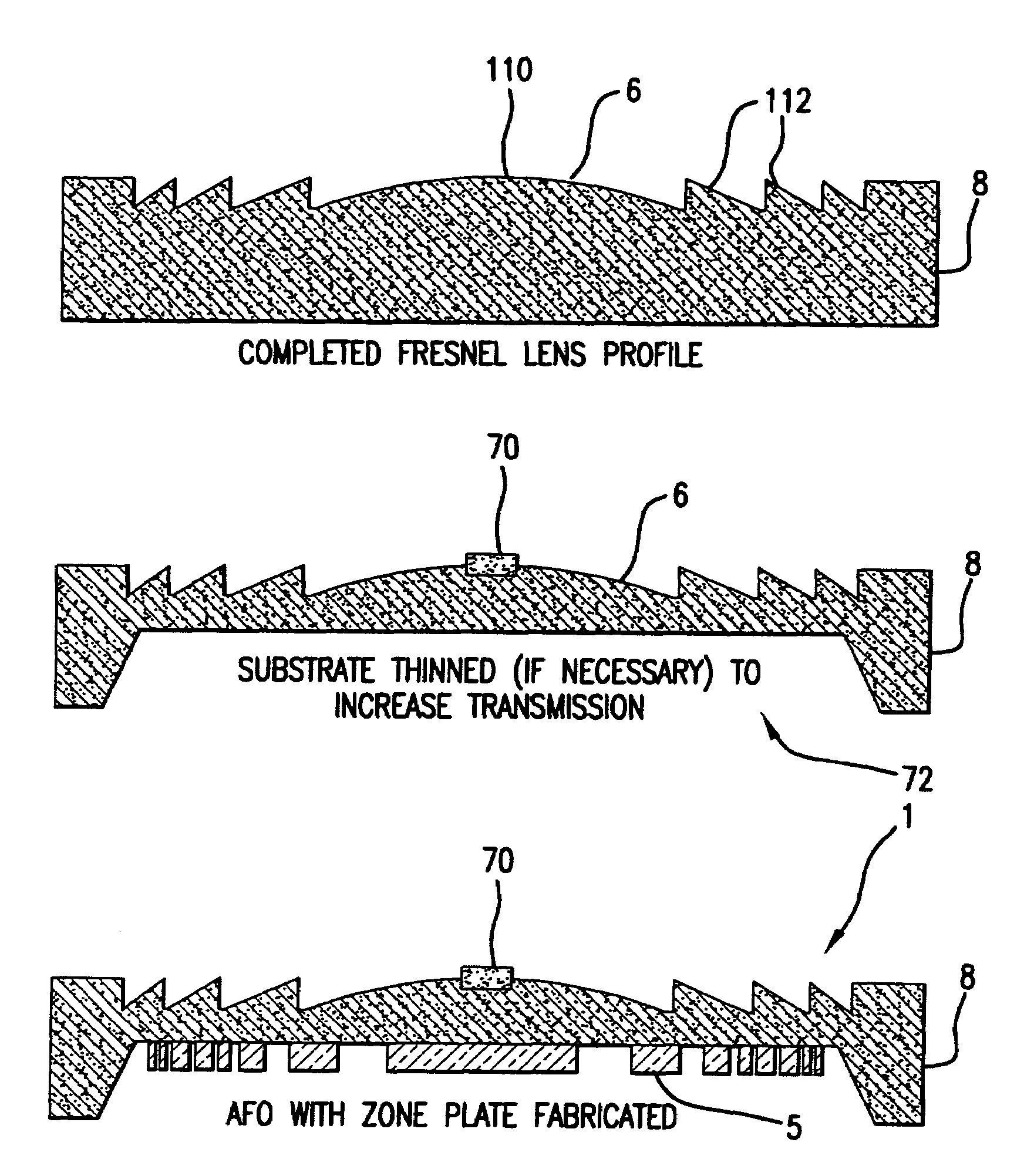
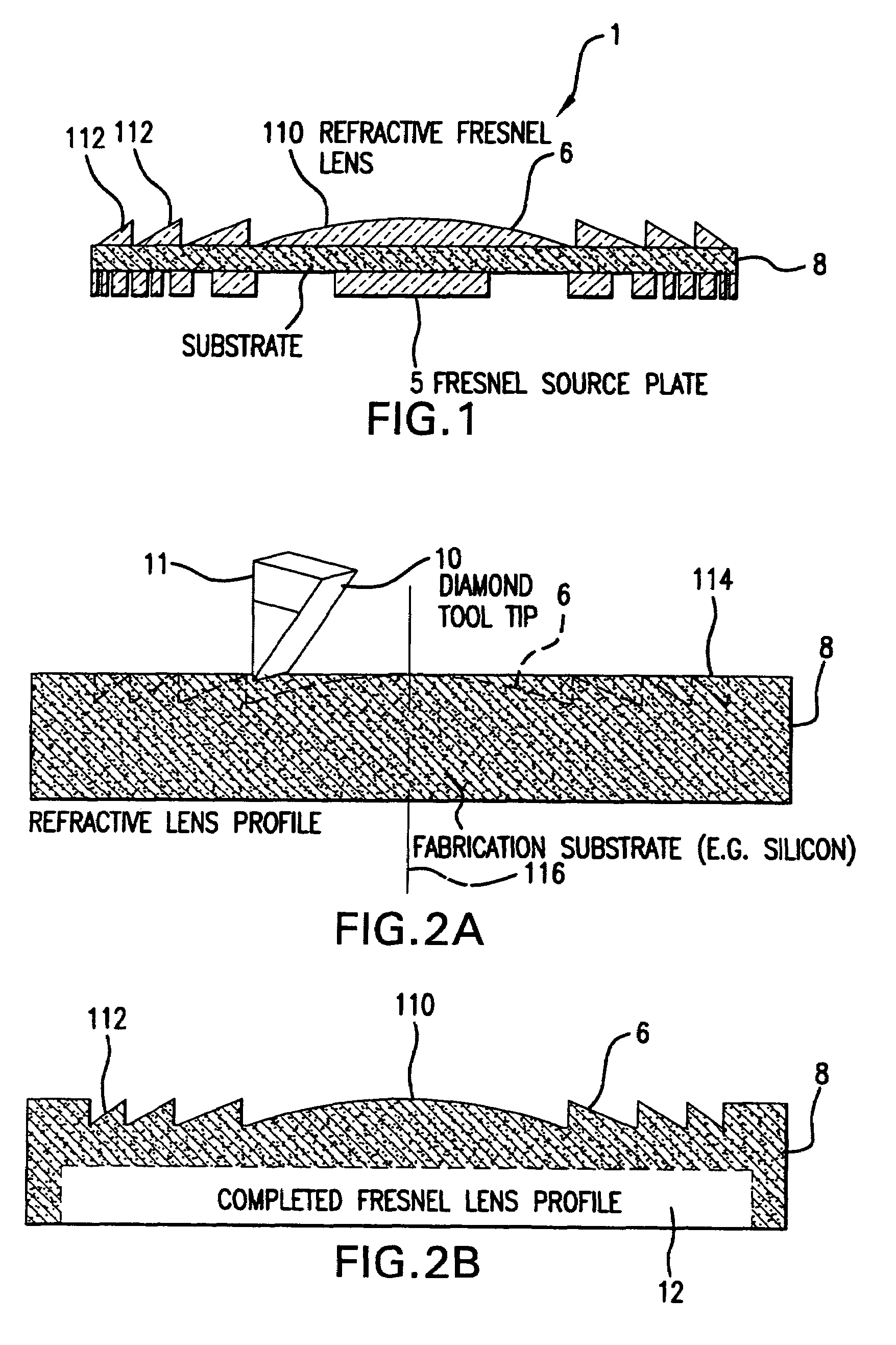
Methods for fabricating refractive element(s) and aligning the elements in a compound optic, typically to a zone plate element. The techniques are used for fabricating micro refractive, such as Fresnel, optics and compound optics including two or more optical elements for short wavelength radiation. One application is the fabrication of the Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). Techniques for fabricating the refractive element generally include: 1) ultra-high precision mechanical machining, e.g,. diamond turning; 2) lithographic techniques including gray-scale lithography and multi-step lithographic processes; 3) high-energy beam machining, such as electron-beam, focused ion beam, laser, and plasma-beam machining; and 4) photo-induced chemical etching techniques. Also addressed are methods of aligning the two optical elements during fabrication and methods of maintaining the alignment during subsequent operation.
Owner:XRADIA
Fabrication methods for micro compounds optics
InactiveUS7365909B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDiamond turningLithographic artist
Methods for fabricating refractive element(s) and aligning the elements in a compound optic, typically to a zone plate element. The techniques are used for fabricating micro refractive, such as Fresnel, optics and compound optics including two or more optical elements for short wavelength radiation. One application is the fabrication of the Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). Techniques for fabricating the refractive element generally include: 1) ultra-high precision mechanical machining, e.g,. diamond turning; 2) lithographic techniques including gray-scale lithography and multi-step lithographic processes; 3) high-energy beam machining, such as electron-beam, focused ion beam, laser, and plasma-beam machining; and 4) photo-induced chemical etching techniques. Also addressed are methods of aligning the two optical elements during fabrication and methods of maintaining the alignment during subsequent operation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
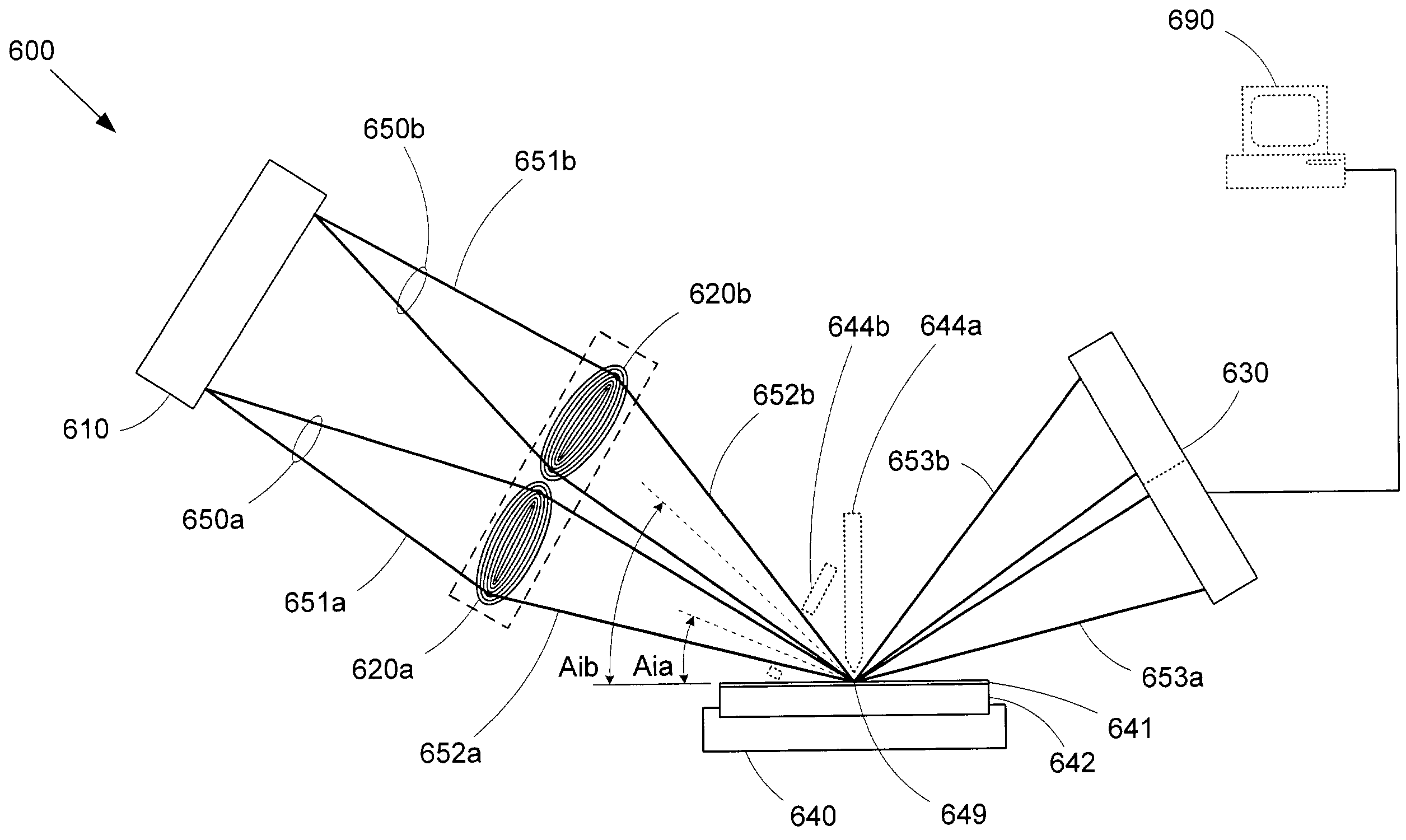
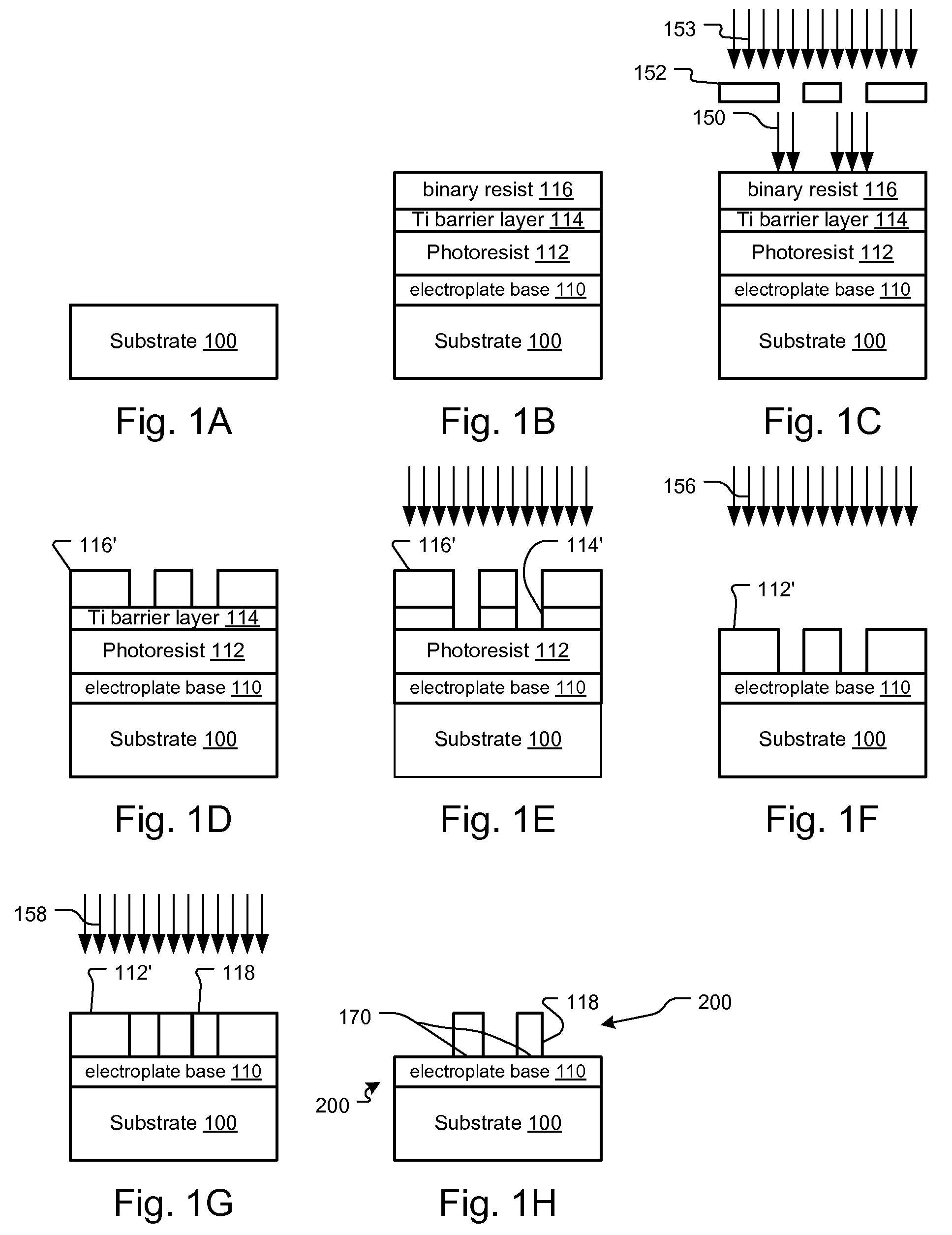
X-ray metrology using a transmissive x-ray optical element
InactiveUS7072442B1Eliminate needStable supportHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMetrologyTest sample
An x-ray metrology system includes one or more transmissive x-ray optical elements, such as zone plates or compound refractive x-ray lenses, to shape the x-ray beams used in the measurement operations. Each transmissive x-ray optical element can focus or collimate a source x-ray beam onto a test sample. Another transmissive x-ray optical element can be used to focus reflected or scattered x-rays onto a detector to enhance the resolving capabilities of the system. The compact geometry of transmissive x-ray optical element allows for more flexible placement and positioning than would be feasible with conventional curved crystal reflectors. For example, multiple x-ray beams can be focused onto a test sample using a transmissive x-ray optical element array. Robust zone plates can be efficiently produced using a damascene process.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
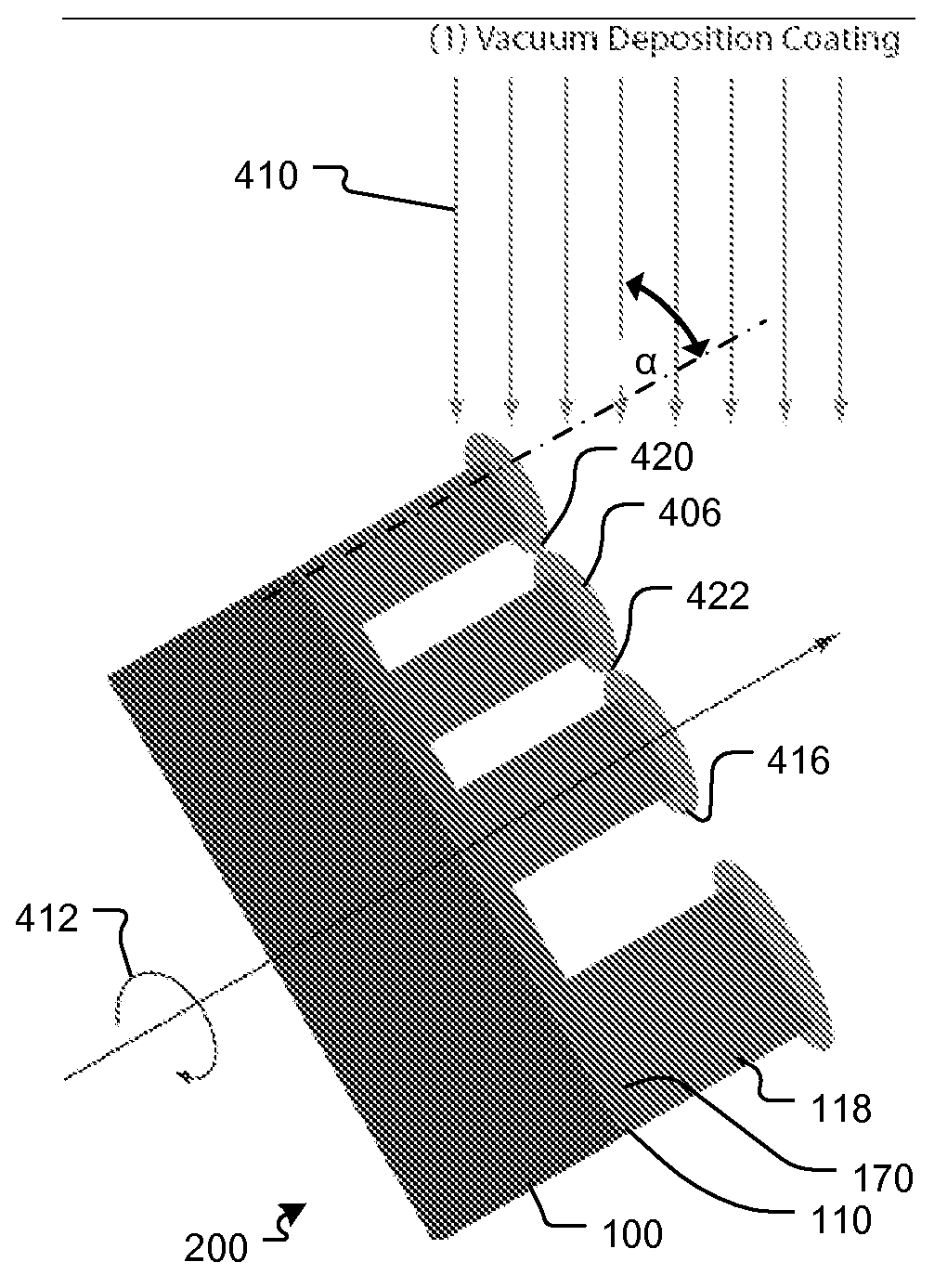
High aspect-ratio X-ray diffractive structure stabilization methods and systems
ActiveUS7864426B2Reduced stabilityReduce gradientHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionDiffraction gratingsGratingX-ray
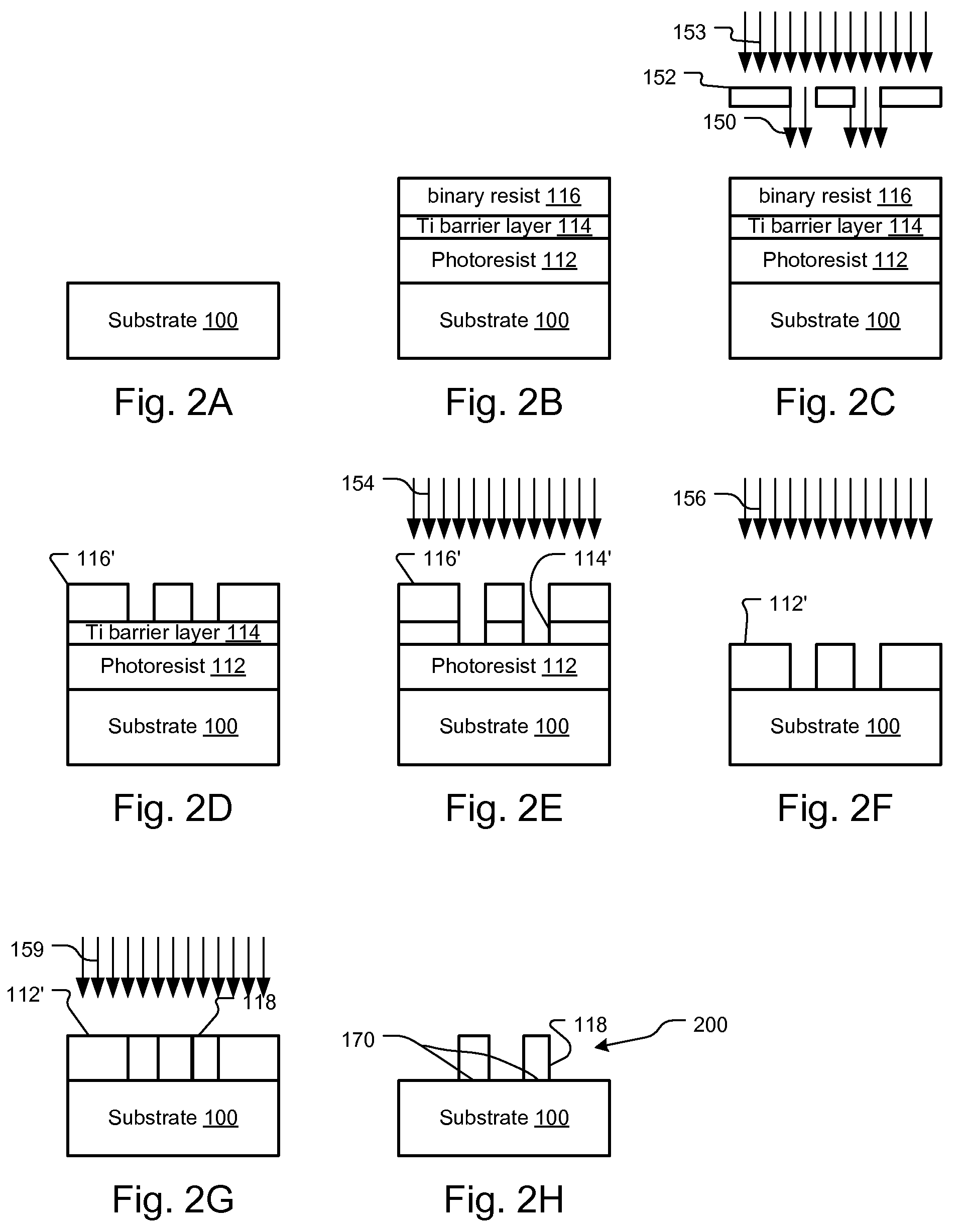
A method to stabilize planar nanostructures, for example grating and zone plate lenses that are typically used for directing or focusing x-ray radiation, includes the deposition of a top, stabilizing layer. The structures are typically made on a flat substrate, and therefore are only fixed at the bottom. At high aspect ratio, the stability can be poor since small forces such as electrostatic forces and van de Waals forces that are often present can alter the structure. The top coating of a metallic material such as titanium constrains the nanostructures at the top and at the same time eliminates electrostatic forces and reduces any thermal gradient that may be present across the device.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
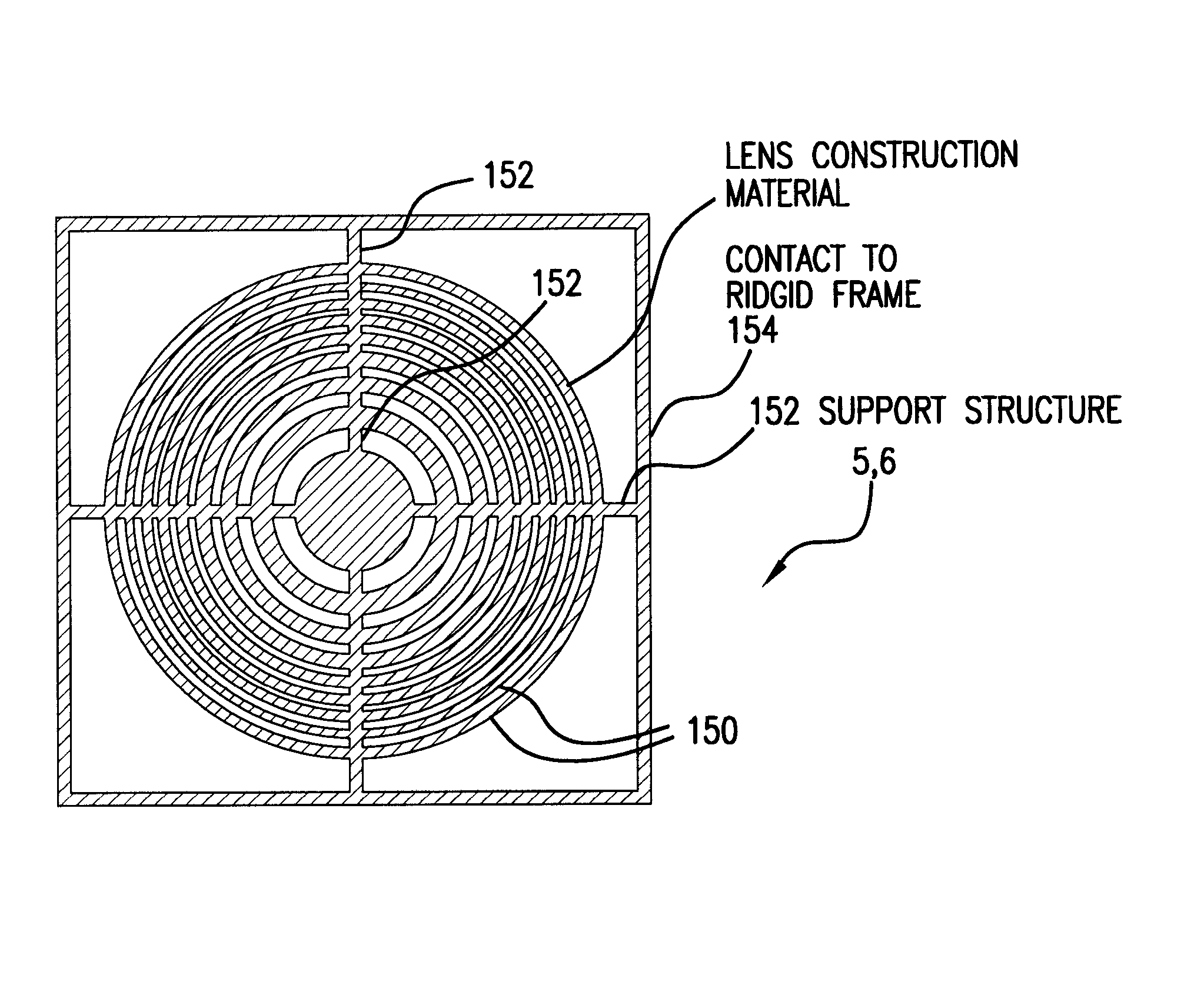
Compound x-ray lens having multiple aligned zone plates
ActiveUS8737565B1Improve focusing efficiencyX-ray spectral distribution measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionAdhesiveX-ray
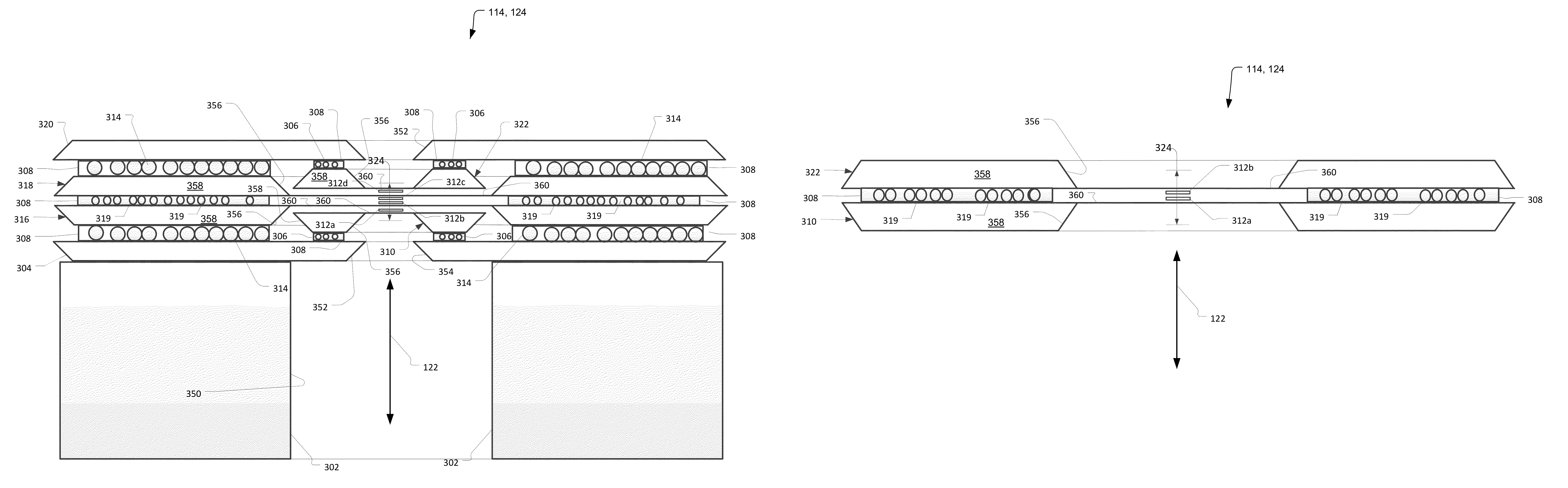
A compound zone plate comprising a first zone plate frame including a first zone plate, a second zone plate frame including a second zone plate, and a base frame to which the first zone plate frame and the second zone plate frame are bonded. In examples, two more zone plates are added to make a four element optic. In the assembly process, the microbeads are used to ensure the parallelism, dial in the distance precisely between the zone plates by selecting the microbead size, possibly in response to the width of the frames, and ensure low friction lateral movement enabling nanometer precision alignment of the zone plates with respect to each other prior to being fixed by the adhesive. That is, when the frames are pressed together to ensure parallelism, it is still possible to align them to each other since the microbead layer facilitates the inplane movement of the alignment process.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Micromirror array lens with optical surface profiles
A Micromirror Array Lens comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a flat or a curved surface to reflect incident light. Each micromirror in the Micromirror Array Lens is configured to have at least one motion. The Micromirror Array Lens forms at least one optical surface profile reproducing free surfaces by using the motions of the micromirrors. The free surface can be any two or three-dimensional continuous or discrete reflective surface. The Micromirror Array Lens having the corresponding optical surface profile provides optical focusing properties substantially identical to those of the free surface. The Micromirror Array Lens can forms various optical elements such as a variable focal length lens, a fixed focal length lens, an array of optical switches, a beam steerer, a zone plate, a shutter, an iris, a multiple focal length lens, other multi-function optical elements, and so on.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
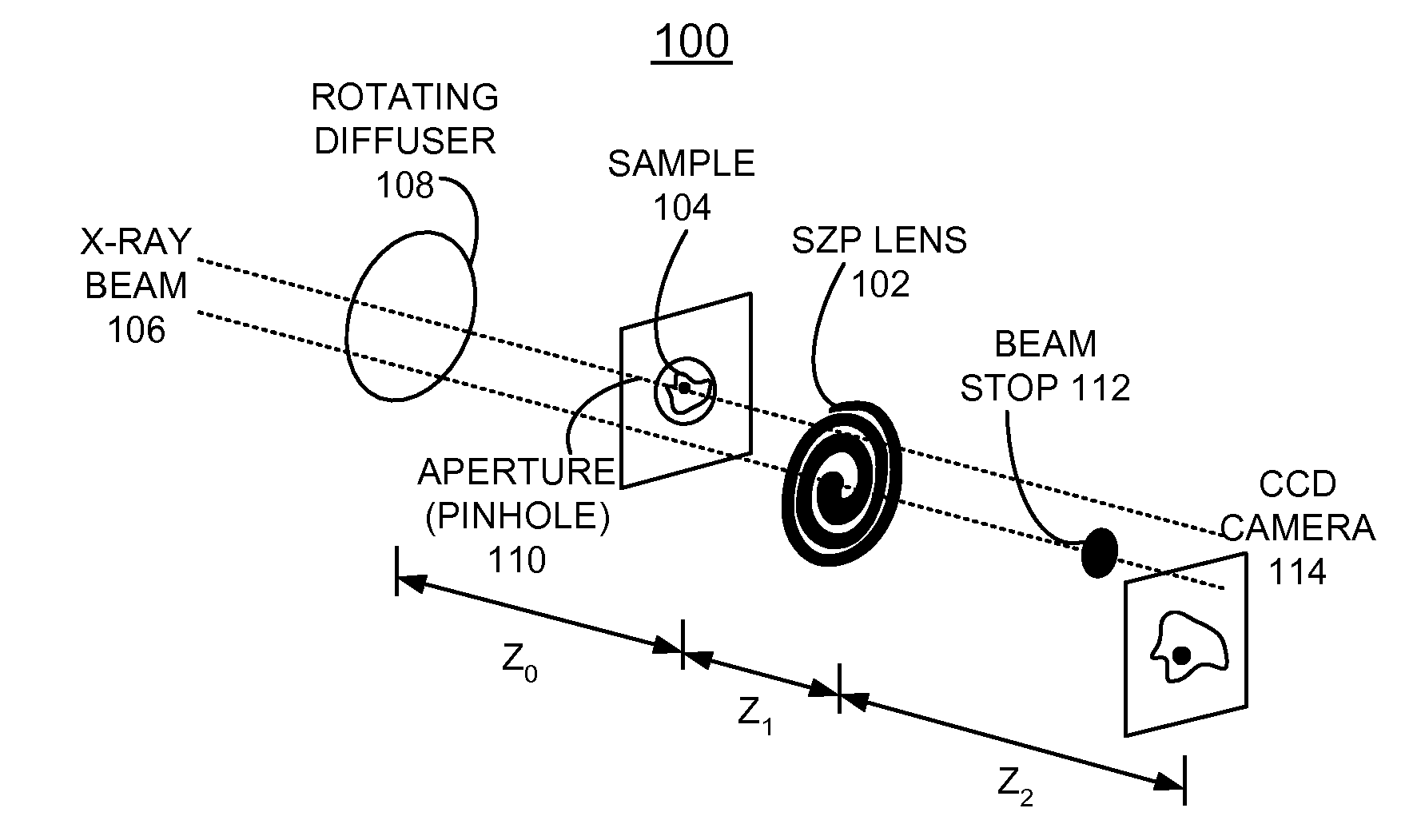
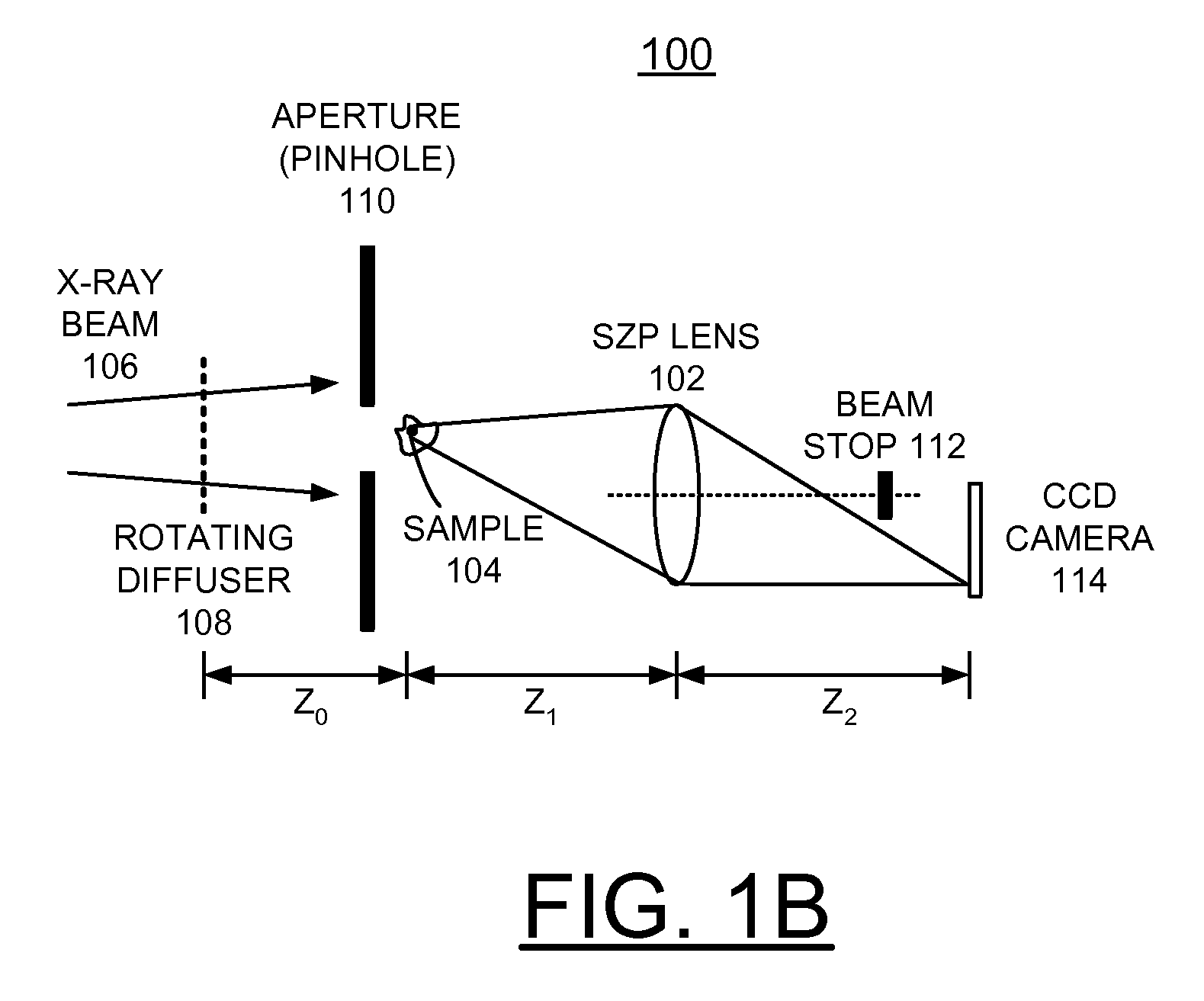
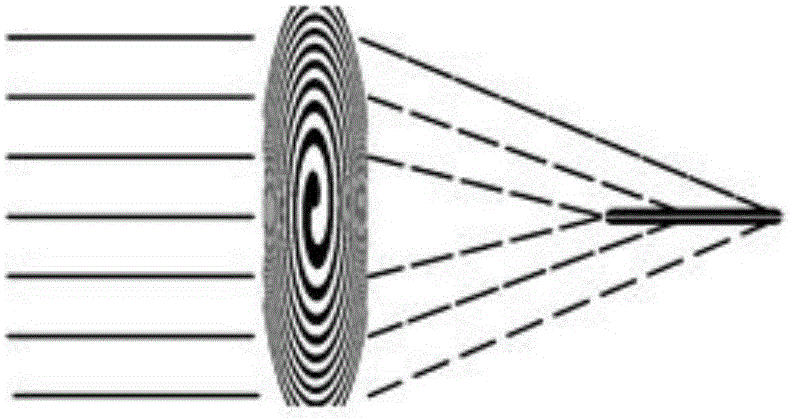
Use of a focusing vortex lens as the objective in spiral phase contrast microscopy
InactiveUS20090135486A1Simple and efficient and inexpensiveImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhase contrast microscopyPhase gradient
A method and objective apparatus are provided for implementing an enhanced phase contrast microscope. A focusing vortex lens, defined by a diffractive spiral zone plate (SZP) lens, is used for the objective for the phase contrast microscope. The SZP lens focuses and imparts a helical phase to incident illumination to image the specimen with spiral phase contrast. The spiral phase contrast microscope is sensitive to phase gradients in all sample axes. Replacing the objective of a microscope with the diffractive SZP lens of the invention immediately provides existing instruments with spiral phase contrast capability.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof and display used this light emitting device
InactiveUS6900457B2Simple processAvoid light leakageElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceOrganic electroluminescence
A light emitting device and a manufacturing method thereof and a display used the light emitting device, in which fine patterning for the light emitting device is realized by a simple process and the light leakage is prevented and the efficiency at extracting light is increased, are provided. The light emitting device provides an organic electroluminescent (EL) device in which electrodes and a luminescent layer are formed, a diffraction grating or a zone plate, and a filter. Light emitted from the luminescent layer transmits through the diffraction grating or the zone plate, which is formed with a designated grating pitch, or is reflected at the diffraction grating or the zone plate. With this, the transmitting or reflecting light is controlled to be in a designated angle region. And when the light is transmitted through the filter, light having different color tone and chromaticity from those of the light emitted from the luminescent layer is extracted.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Charged-particle exposure apparatus with electrostatic zone plate
ActiveUS8304749B2Reduce various aberration effectSimple and efficientThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsComposite electrodeParticle beam
In a particle-beam projection processing apparatus for irradiating a target by a beam of energetic electrically charged particles, including an illumination system, a pattern definition system for positioning an aperture arrangement composed of apertures transparent to the energetic particles in the path of the illuminating beam, and a projection system to project the beam onto a target, there is provided at least one plate electrode device, which has openings corresponding to the apertures of the pattern definition system and including a composite electrode composed of a number of partial electrodes being arranged non-overlapping and adjoining to each other, the total lateral dimensions of the composite electrode covering the aperture arrangement of the pattern definition system. The partial electrodes can be applied different electrostatic potentials.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Alignment or overlay marks for semiconductor processing
InactiveUS6888260B2Enhanced signalSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Semiconductor
An alignment or overlay mark with improved signal to noise ratio is disclosed. Improved signal-to-noise ratio results in greater depth of focus, thus improving the performance of the alignment mark. The alignment mark comprises a zone plate having n concentric alternating opaque and non-opaque rings. Light diffracted by either the odd or even rings are cancelled while light diffracted by the other of the odd or even rings are added.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Integrating method of three-dimensional spatial distribution vortex arrays
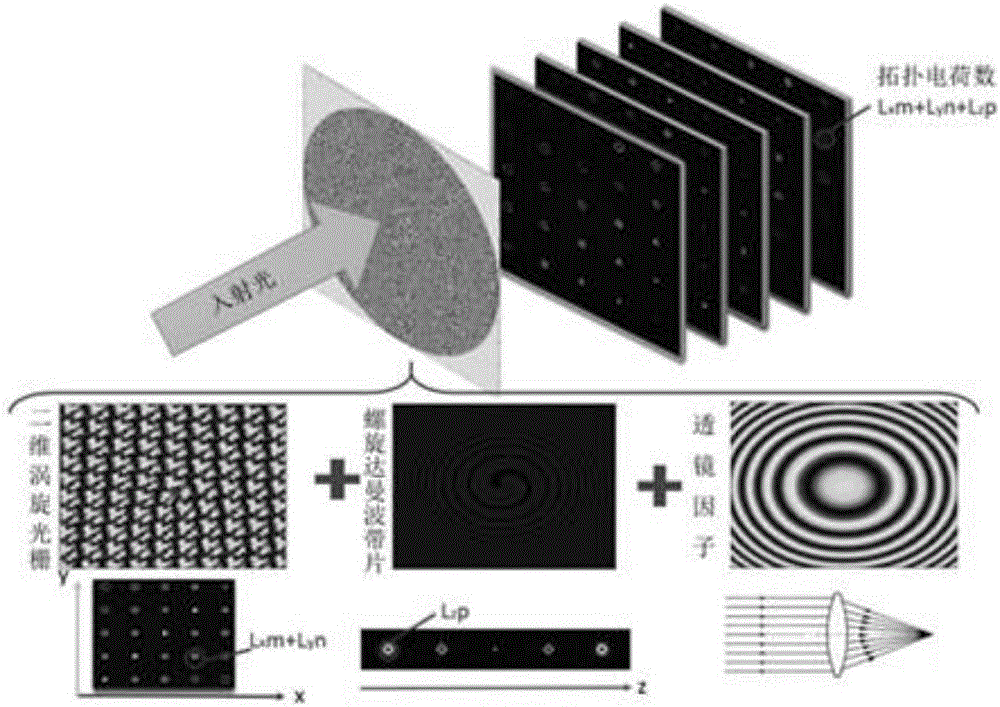
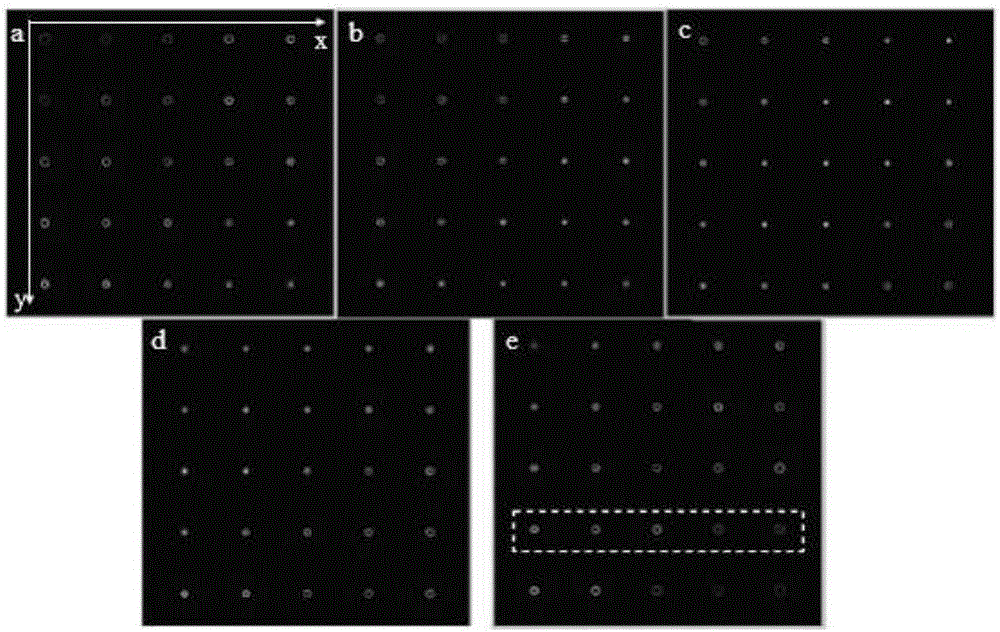
ActiveCN106199800AEqual light intensityReduce complexityDiffraction gratingsSpatial light modulatorGrating
The invention relates to an integrating method of three-dimensional spatial distribution vortex arrays, and belongs to the field of diffraction optics. A pure-phase code of a two-dimensional uniform-strength vortex optical grating and a pure-phase code of a spiral Dammam wave zone plate are obtained through analytic operation and an optimization algorithm respectively, phase information of the pure-phase codes is overlaid, a lens factor is introduced, discretized phase values are loaded to a spatial light modulator according to the pixel number and the pixel size of the spatial light modulator, and then the corresponding three-dimensional vortex arrays can be obtained. According to the method, the equal-strength and regular-distribution three-dimensional vortex arrays can be obtained, and each vortex beam in the arrays has the specific topological charge number.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof and display used this light emitting device
InactiveUS20050026530A1Exquisite patternSimple processDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceHue
A light emitting device and a manufacturing method thereof and a display used the light emitting device, in which fine patterning for the light emitting device is realized by a simple process and the light leakage is prevented and the efficiency at extracting light is increased, are provided. The light emitting device provides an organic electroluminescent (EL) device in which electrodes and a luminescent layer are formed, a diffraction grating or a zone plate, and a filter. Light emitted from the luminescent layer transmits through the diffraction grating or the zone plate, which is formed with a designated grating pitch, or is reflected at the diffraction grating or the zone plate. With this, the transmitting or reflecting light is controlled to be in a designated angle region. And when the light is transmitted through the filter, light having different color tone and chromaticity from those of the light emitted from the luminescent layer is extracted.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Adaptive focusing using liquid crystal zone plates in electro-optical readers
ActiveUS20090237575A1Decreasing noise and vibration and dustSize and weight and power and volume requirementLiquid crystal compositionsProjector focusing arrangementRefractive indexLight beam
Working range and beam cross-section are adjusted in an electro-optical reader for reading indicia by applying voltages to electrodes in one or more liquid crystal zone plates in which the index of refraction is changed in different regions of each zone plate.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
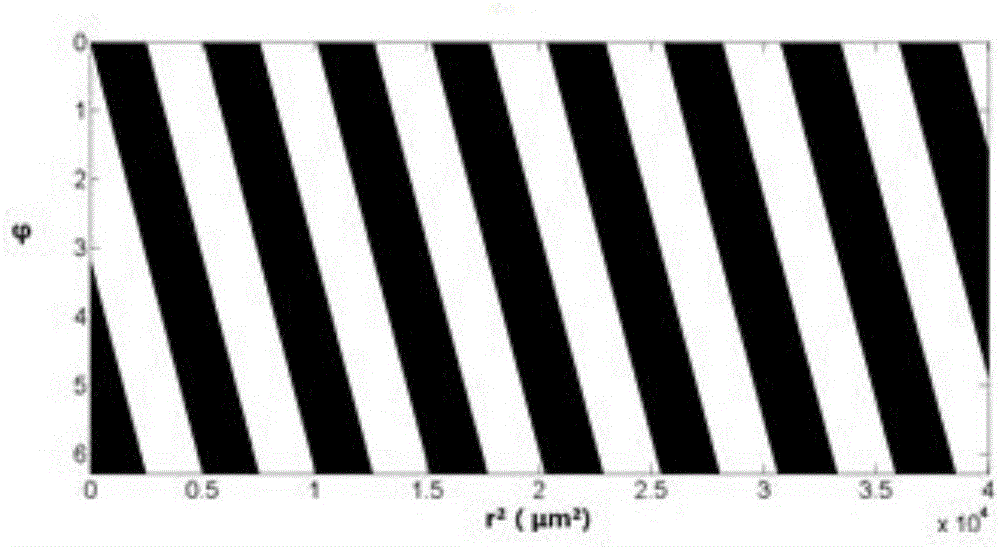
Damman wave zone plate
The invention relates to a damman wave zone plate which is characterized in that a phase modulation detail is added in each period of the traditional binary phase-only type (0, pi) zone wave plate structure relative to the square of the radial coordinate so as to generate axial constant-strength distribution of focal spots with any numbers within a certain range. The distribution of a plurality of constant-strength focal spots along the optical axis direction can be widely applied to imaging systems (optical microscopes), optical tweezers, implantable contact lens, and the like with large depth of field-. Besides, the damman wave zone plate in binary phase-only distribution is a series of concentric circle structures intuitively and is easy to process and duplicate. Therefore, the damman wave zone plate has important application prospect in the fields of optical imaging systems and biomedicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Volume Fresnel zone plates fabricated by laser direct writing
ActiveUS7969654B1High diffraction efficiencyOptical articlesOptical elementsDirect writingNumerical aperture
A volume Fresnel zone plate and a method of producing such a device using a femtosecond laser for direct writing of zone plates. A volume zone plate has a number of Fresnel zone plate layers designed to focus light coherently to a single spot. Embodiments include both low numerical aperture (NA) and high NA zone plates, and provide a significant increase in overall diffraction efficiency over a single Fresnel zone plate.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Axial line focusing spiral zone plate
ActiveCN105158834AEasy to design and makeIncreased axial focus sizeDiffraction gratingsParticulatesElectric power system
The invention discloses an axial line focusing spiral zone plate. The zone plate is formed by alternately arranging a series of discontinuous spiral light transmitting ring bands and light shielding ring bands. The coordinates of the spiral ring bands in different cycles are adjusted in a certain distributing mode, so that incident light passes through the ring bands in the different cycles to be focused at different focal points, and a hollow-column-shaped line focal point is formed. Compared with a common spiral zone plate with same numerical apertures, the size of the focal point on an optical axis is effectively lengthened; designing and manufacturing are convenient and rapid, and only a production formula of the spiral ring bands and focal distances corresponding to the cycles need to be designed according to requirements; practical application and practical popularization are easy, and particularly practical application to and practical popularization for the vacuum-ultraviolet-ray waveband to the soft-X-ray waveband are easy; the axial line focusing spiral zone plate has broad application prospects in the researching fields such as particulate control, extreme ultra-violet lithography, astronomy, microscopes and micro power systems.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Systems and methods for achieving a required spot says for nanoscale surface analysis using soft x-rays
InactiveUS20070019789A1Small spot sizeX-ray tube with very high currentCondensersSoft x rayLength wave
A nano-scale surface analysis system is configured to reduce a laser-produced plasma spot size, while maintaining flux levels at target. The system comprises a condenser zone plate operable to receive short wavelength radiation and focus the short wavelength radiation into a spot on the target. The target is positioned such it is located at an order of diffraction of the condenser zone plate that is greater than the first diffractive order of the condenser zone plate and sufficient to demagnify the spot to a diameter less than one micron. In addition, the target is still positioned such that a flux created at the target by the spot is sufficient to produce a nanoplasma.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
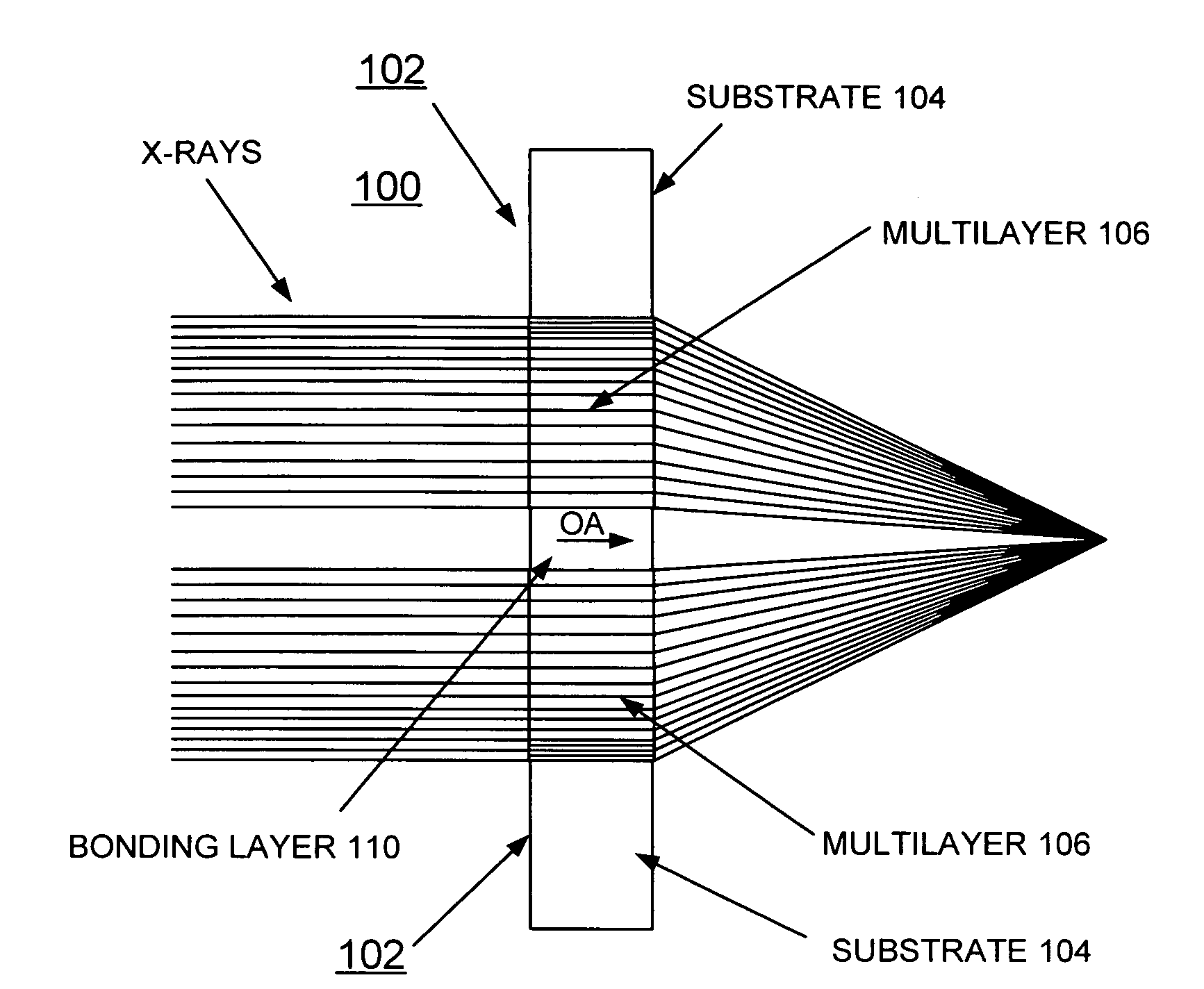
Method of making and structure of Multilayer Laue Lens for focusing hard x-rays
InactiveUS20080137810A1High diffraction efficiencyImprove efficiencyNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysTransmission geometry
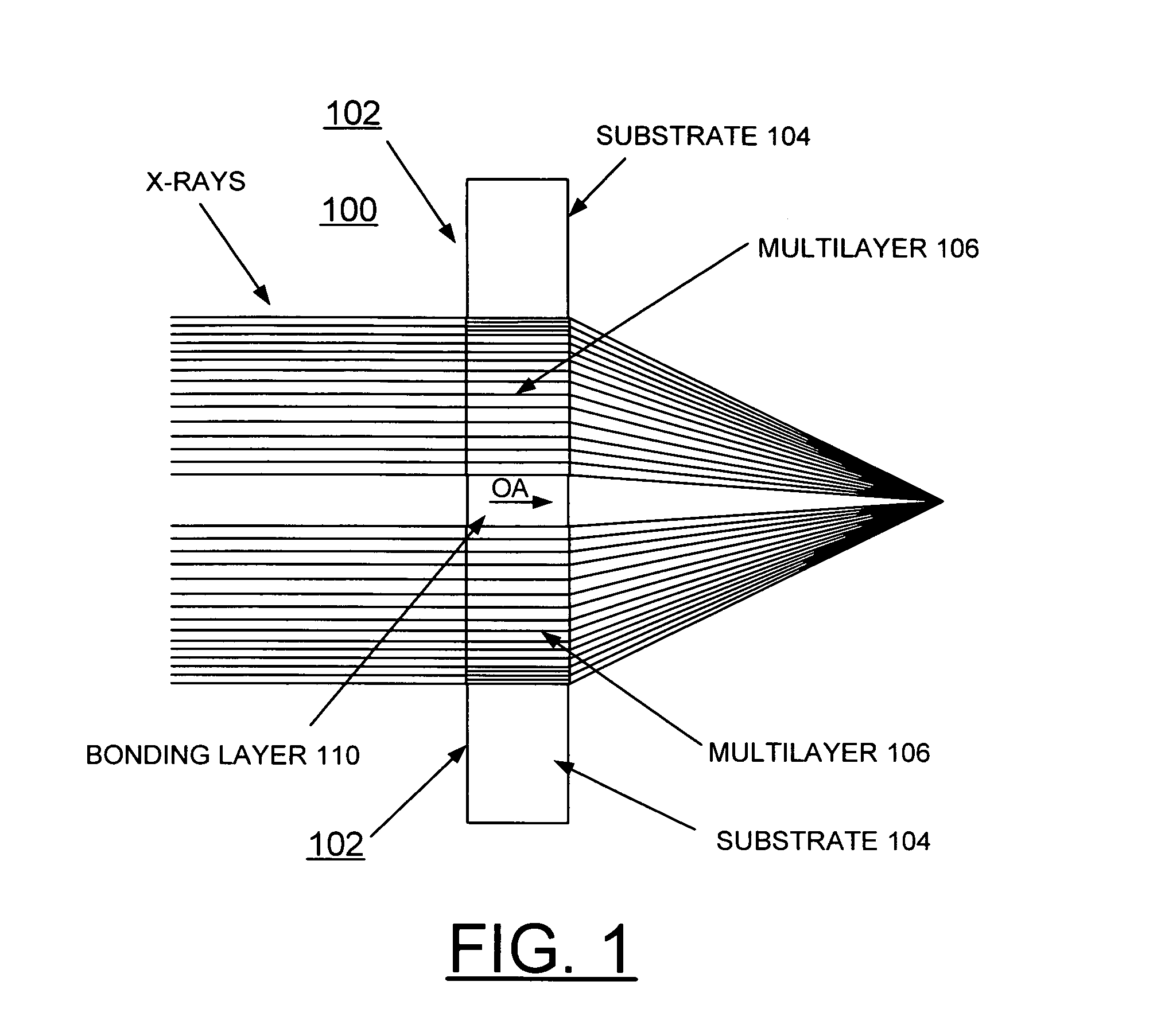
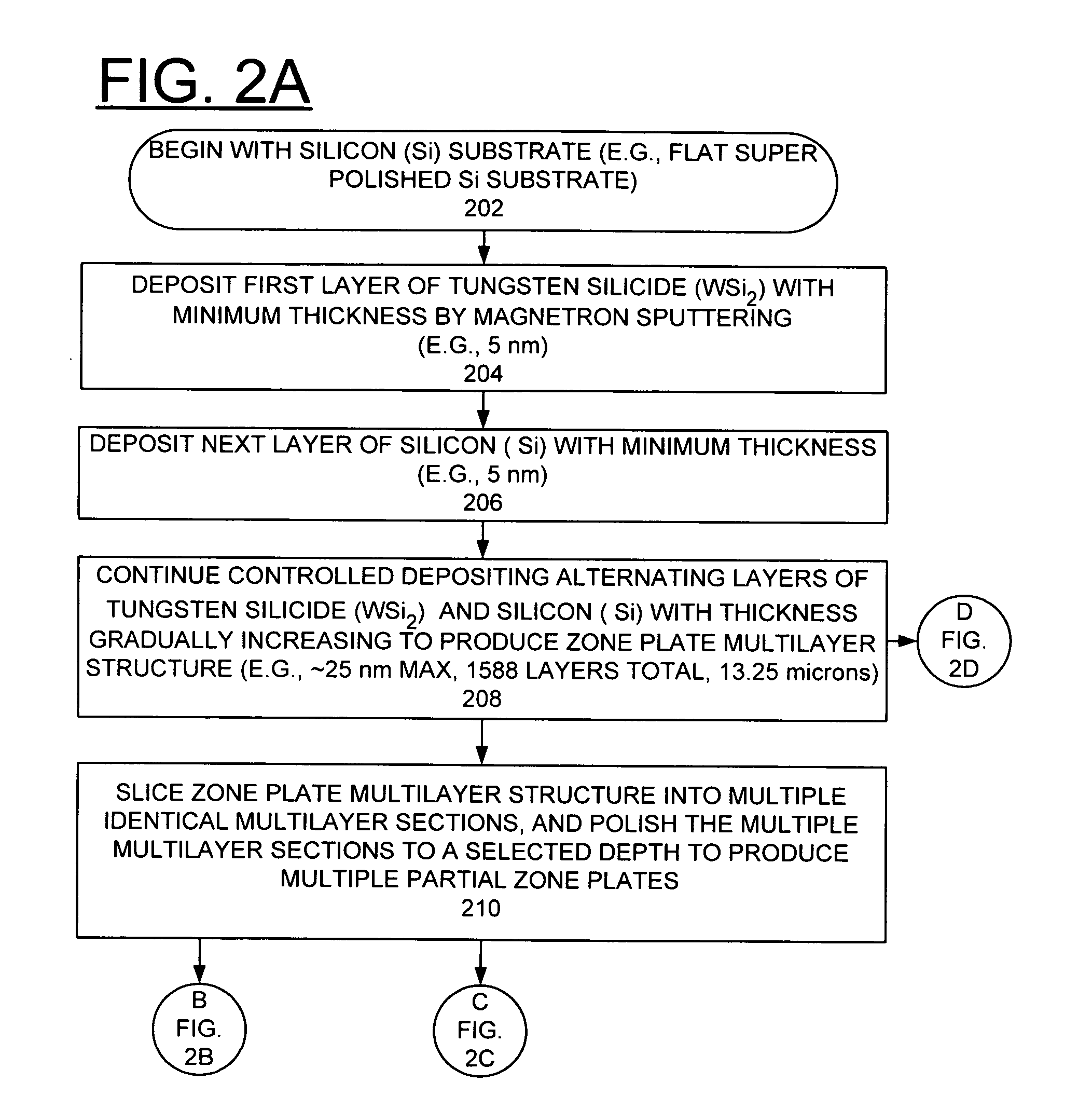
A zone plate multilayer structure includes a substrate carrying a plurality of alternating layers respectively formed of tungsten silicide (WSi2) and silicon (Si). The alternating layers are sequentially deposited precisely controlling a thickness of each layer from a minimum thickness of a first deposited layer adjacent the substrate to a maximum thickness of a last deposited layer. The first minimum thickness layer has a selected thickness of less than or equal to 5 nm with the thickness of the alternating layers monotonically increasing to provide a zone plate multilayer structure having a thickness of greater than 12 μm (microns). The x-rays are diffracted in Laue transmission geometry by the specific arrangement of silicon and tungsten silicide.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Preparation method of X-ray zone plate
ActiveCN107833649AStable outer ring widthImprove performanceHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionIridiumIon beam
The invention relates to a preparation method of an X-ray zone plate. An atomic layer deposition (ALD) method is used to depose alumina / hafnium oxide or alumina / iridium films of different density andthickness alternatively at the surface of a metal wire whose diameter is of a micron order, namely, a first deposed alumina film layer and a second deposed hafnium oxide film or iridium film layer arearranged alternatively and cyclically to form a series of concentric circular rings. The film plated metal wire is cut and polished by focusing ion beams after film plating, and the zone plate of therequired thickness and precision is obtained. The method is suitable for preparing different types of zone plates.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
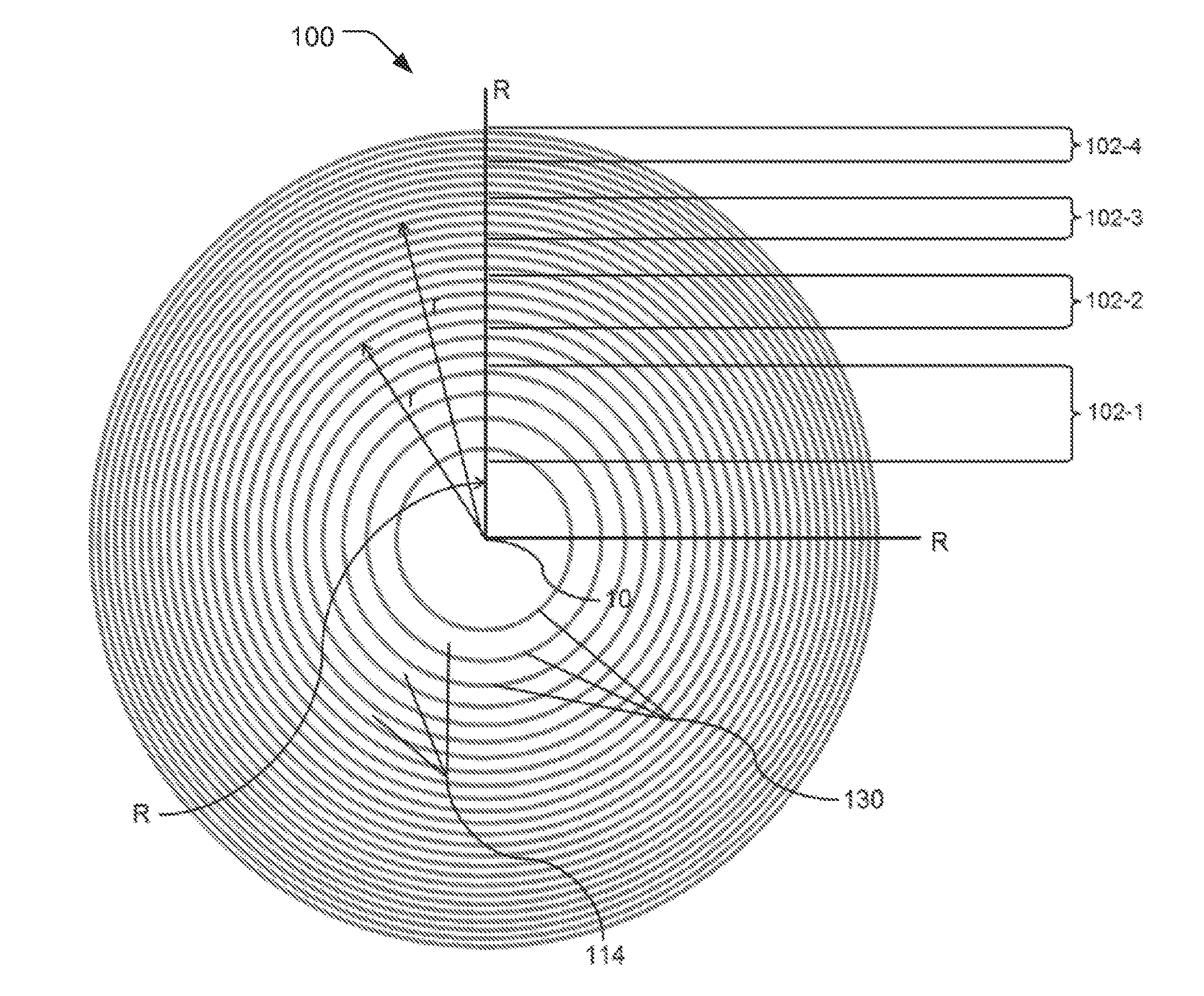
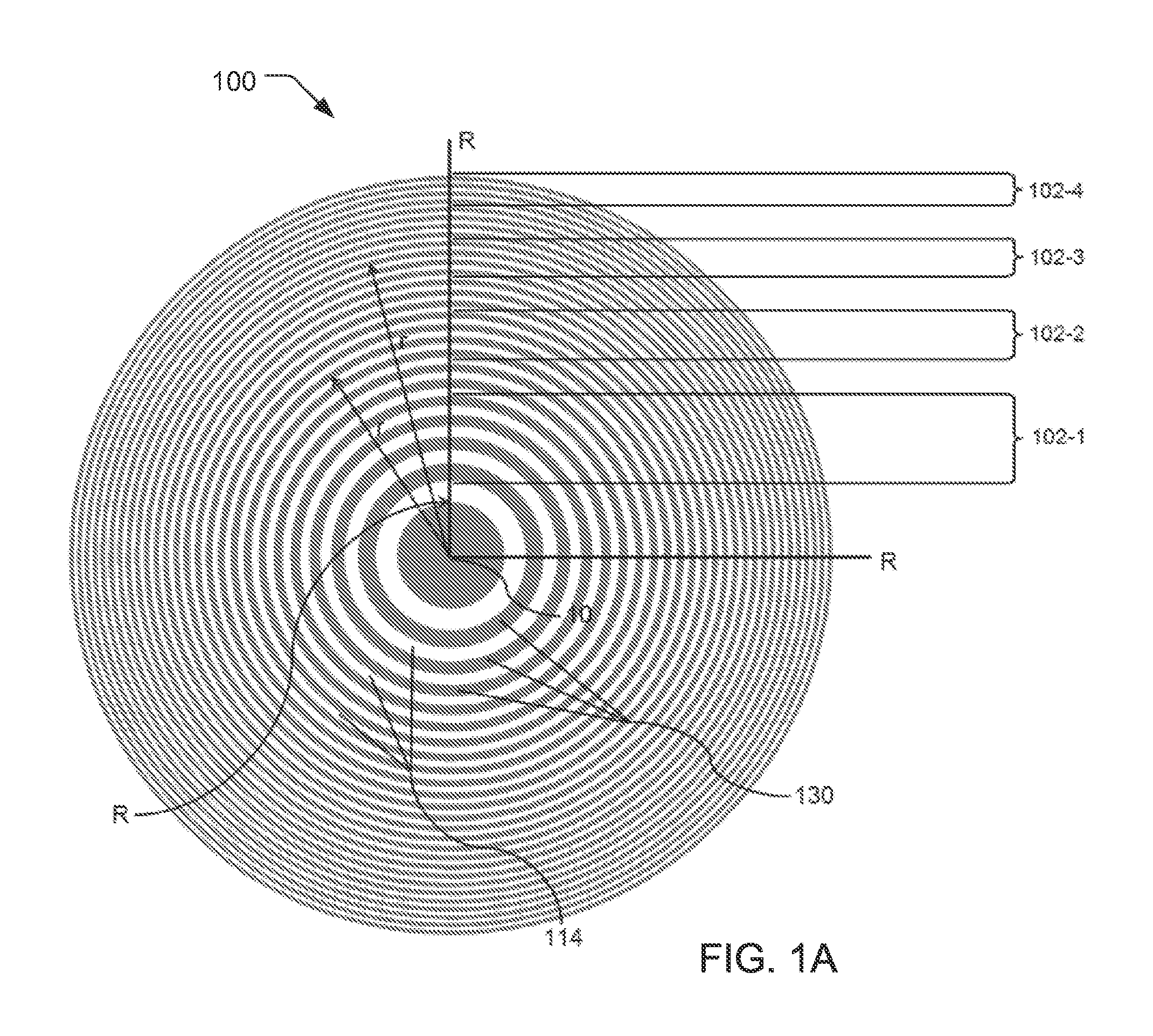
Zone Plate and Method for Fabricating Same Using Conformal Coating
InactiveUS20160086681A1Improve efficiencySpatial frequency is enlargedHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionElectrostatic spraying apparatusConformal coatingZone plate
A system and method for improving efficiency of zone plates fabricated by conformal layer coatings is disclosed. In embodiments, the inventive conformal layer coating zone plates provide increased zone widths from one times a deposited conformal layer coating thickness up to and including two times the conformal layer coating thickness. By designing a template that increases a mark-to-space ratio of the annular rings of the template, coating sidewalls of the annular rings with an conformal layer coating to form the zones, and then substantially filling annular channels defined by the annular rings with the conformal layer coating to form wider zones, significant efficiency increases can be achieved over conventional conformal layer coating zone plates, especially for innermost zones.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Wavefront detection method based on Fresnel zone plate
ActiveCN106338343AShorten the lengthOvercoming the problem of imprecise detectionOptical measurementsOptical elementsWavefrontLight spot
The invention provides a wavefront detection method based on a Fresnel zone plate. Distortion wavefront passes the Fresnel zone plate, images are collected at position near the focal plane and far from the focal plane of the zone plate respectively, and an input waveform can be recovered accurately by utilizing the two images as well as the relative defocusing amount therebetween. The Fresnel zone plate belongs to a light and thin focusing element, the length of an optical path can be shortened greatly by utilizing the short focus of the Fresnel zone plate, and the problem that information detection for light spots in the focal plane is not accurate enough under large apertures can be overcome by utilizing the characteristic that the size of light spots near the focal plane is strict and the size of light spots in the focal plane is larger. The method of the invention is suitable for wide-aperture and super-wide-aperture wavefront detection, and has significance in lightweight wavefront inversion.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High intensity refiner plate with inner fiberizing zone
InactiveUS20060006265A1Easy to produceReduce energy consumptionPretreatment with water/steamReed/straw treatmentFiberHigh intensity
Plate elements, a plate configuration, and associated system for thermomechanical refining of wood chips wherein destructured and partially defibrated chips are fed to a rotating disc primary refiner, where opposed discs each have an inner band pattern of bars and grooves and outer band pattern of bars and grooves, such that substantially complete fiberization (defibration) of the chips is achieved in the inner band and the resulting fibers are fibrillated in the outer band. One embodiment is directed to a pair of opposed co-operating refining plate elements for a flat disc refiner wherein the bars and grooves on each of the inner bands form an inner feed region followed by an outer working region, the bars and groove on each of the outer bands form an inner feed region followed by an outer working region, and the gap and / or material flow area formed when the plates are placed in front of each other increases between the inner working region and the outer feed region.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Vacuum laser dam deformation measuring method
InactiveCN1546942ARequirements for reduced reception rangeSmall diameterUsing optical meansLight spotOptoelectronics
The invention is a measuring method for vacuum laser dam deformation, which belongs to optical, photo-sensing and geometric position measurement field. The character lies in: there sets a two-dimension position adjusting mechanism between the measuring base and the wave zone plate, when measuring, the invention adjusts the position of wave zone board relative to the measuring base through the adjusting mechanism, makes the laser focus around the centre of the laser receiver, the invention calculates the shift of the measuring point according to the shift of the wave zone plate relative to the measuring point base and the bias of the light-spot on the laser receiver. The invention reduces the diameter of the vacuum channel on the receiving end, at the same time; it also reduces the demands of the receiving range of the laser receiver, thus reduces the vacuum channel diameter, and reduces the system cost.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com