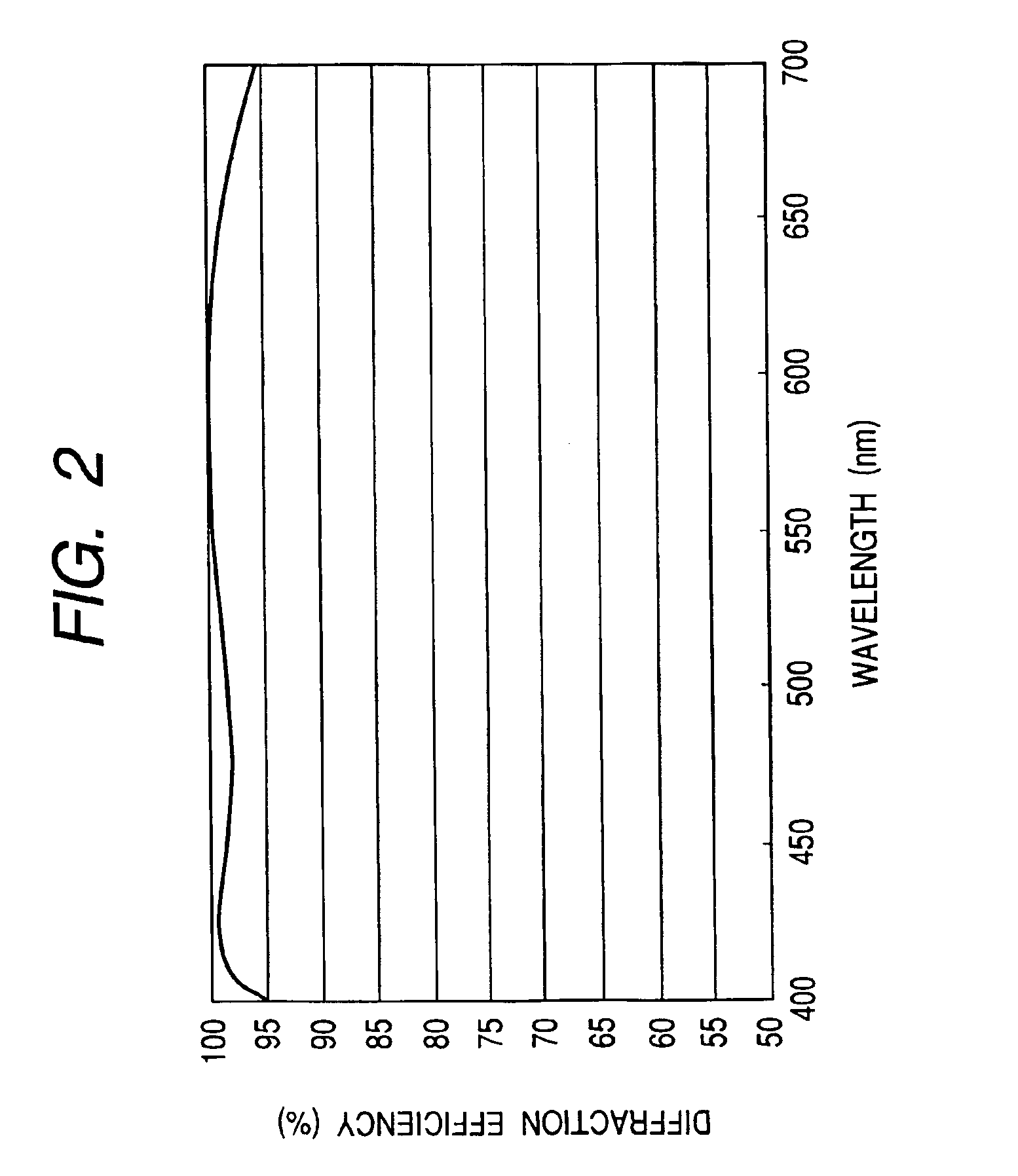
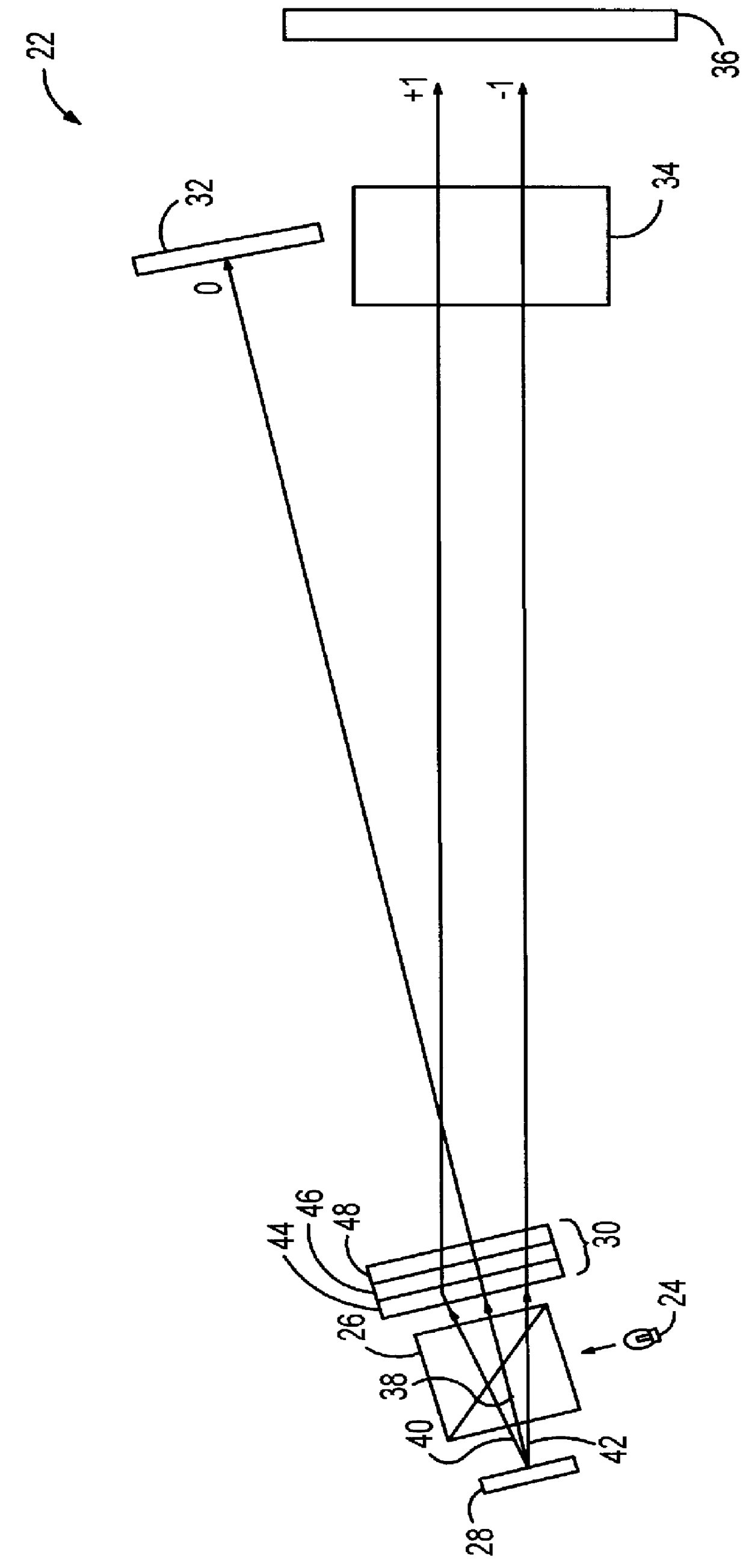
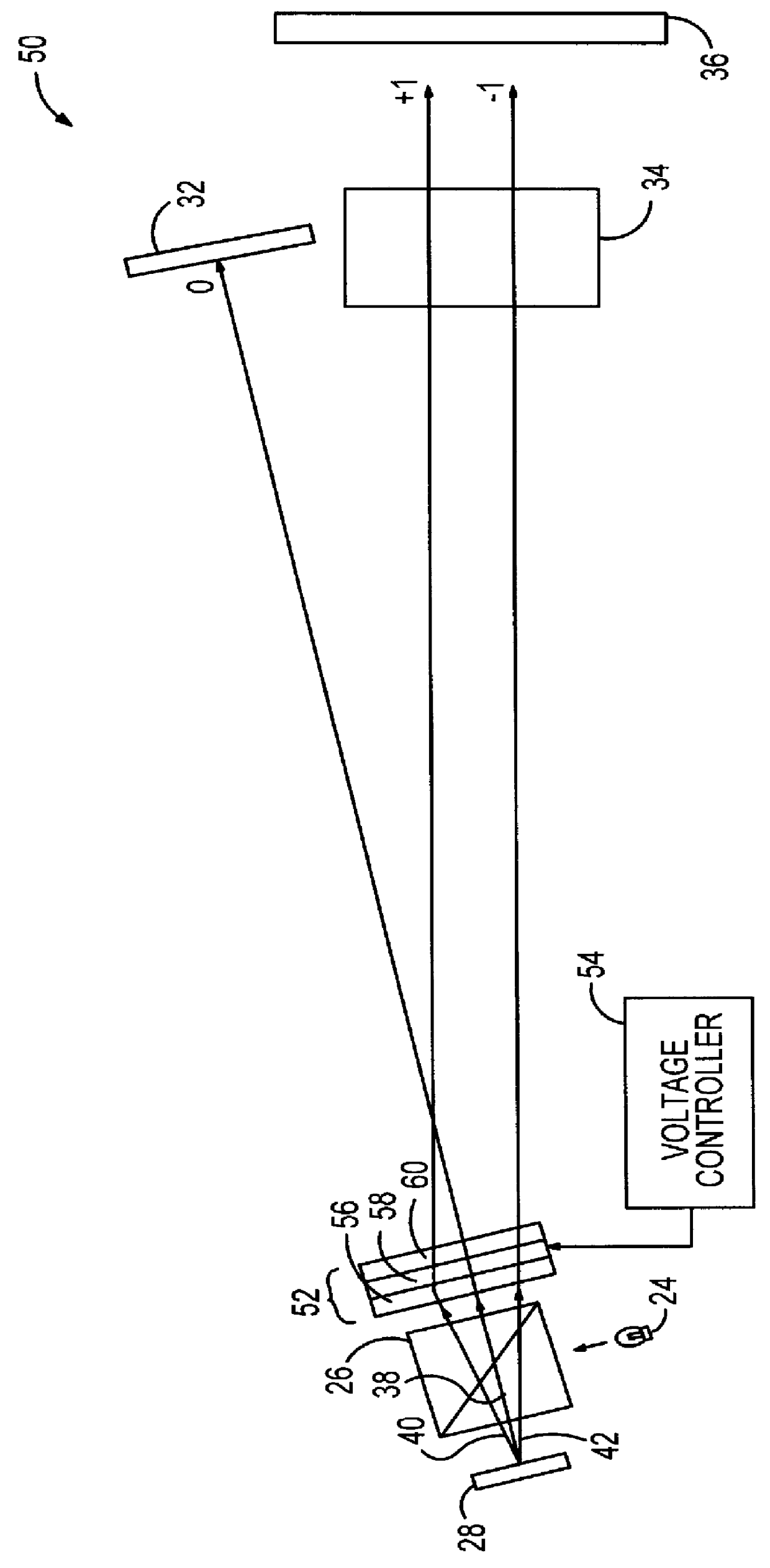
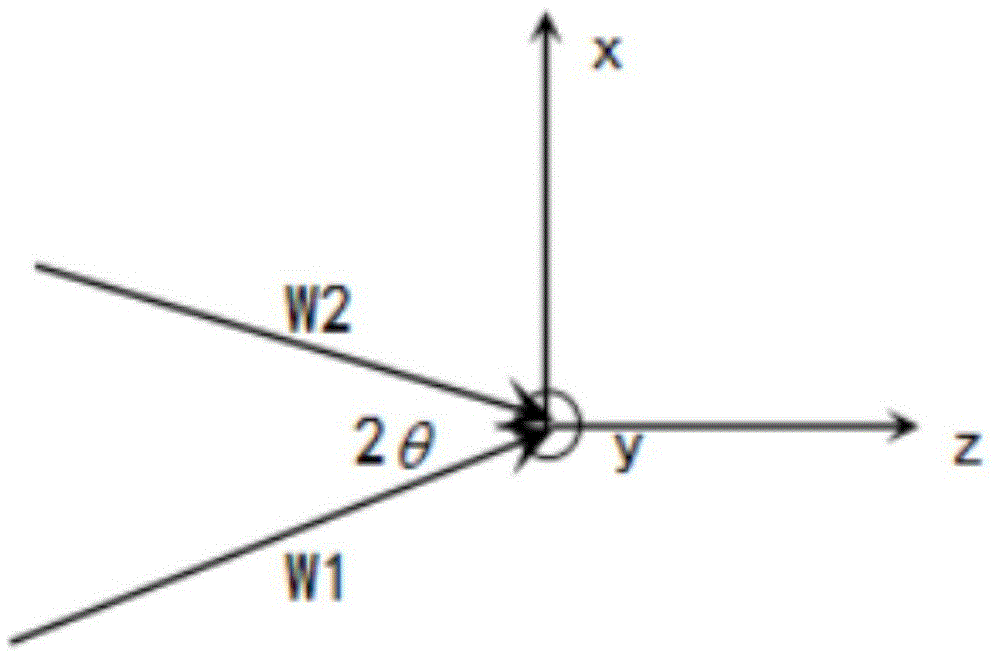
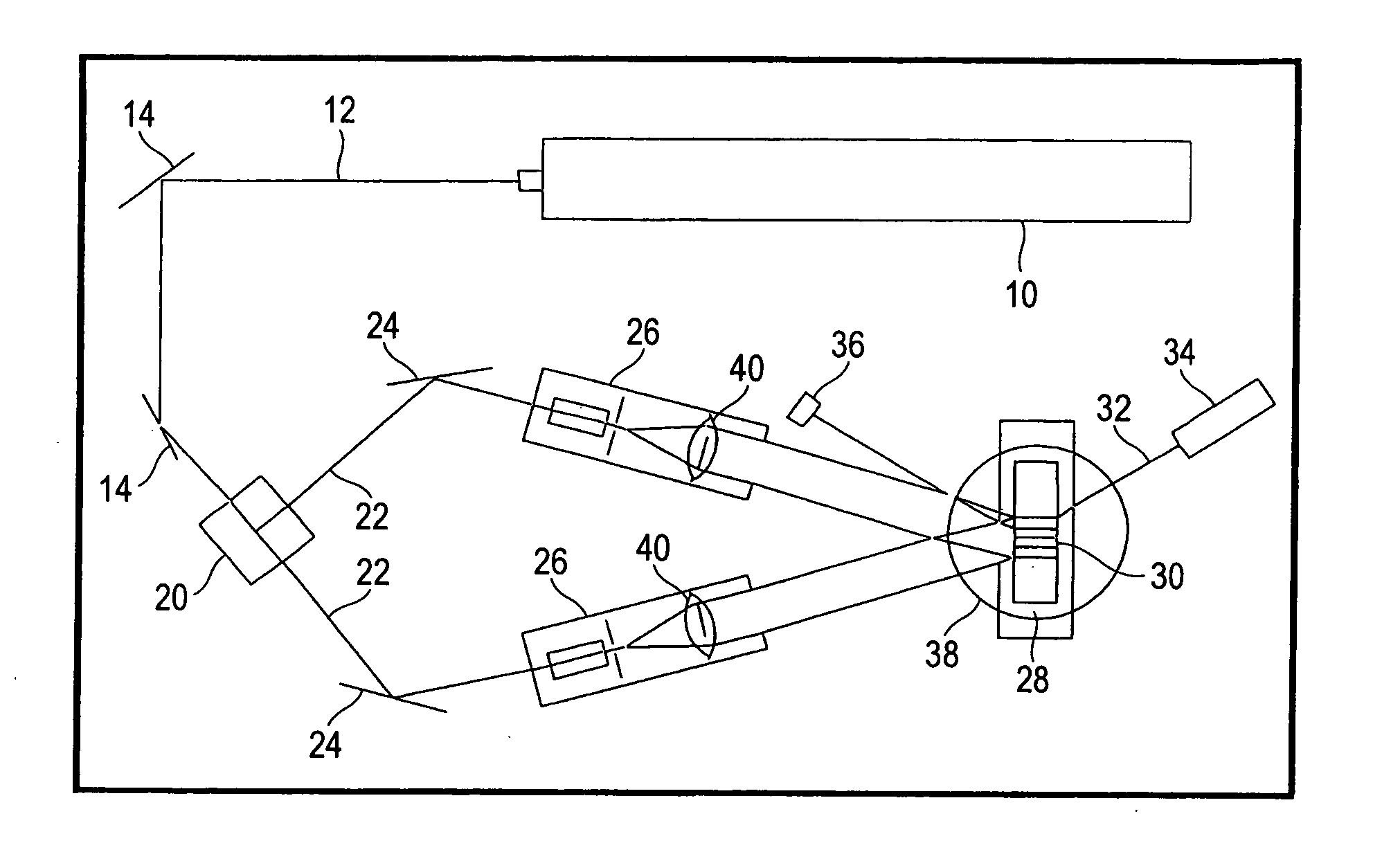
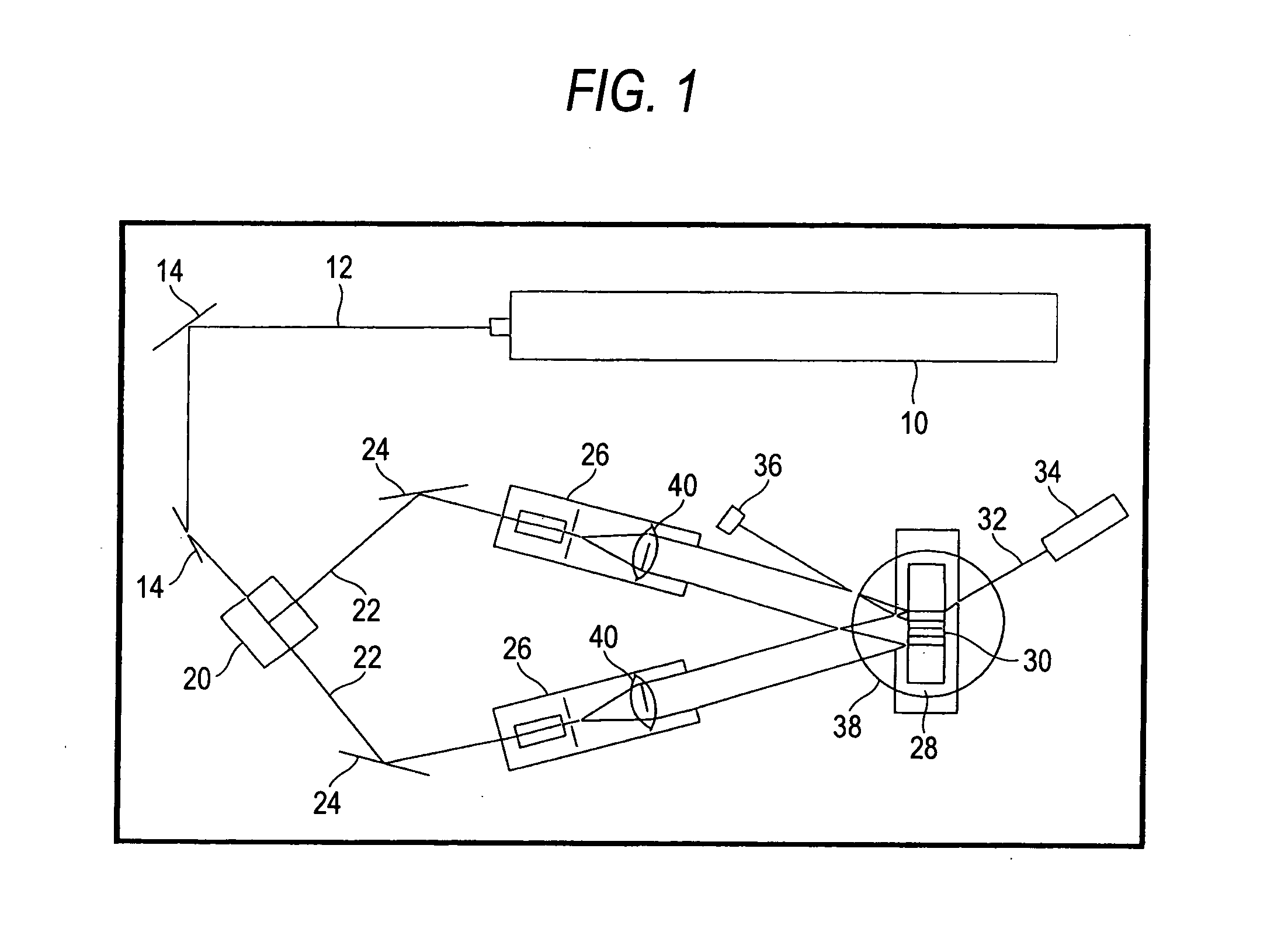
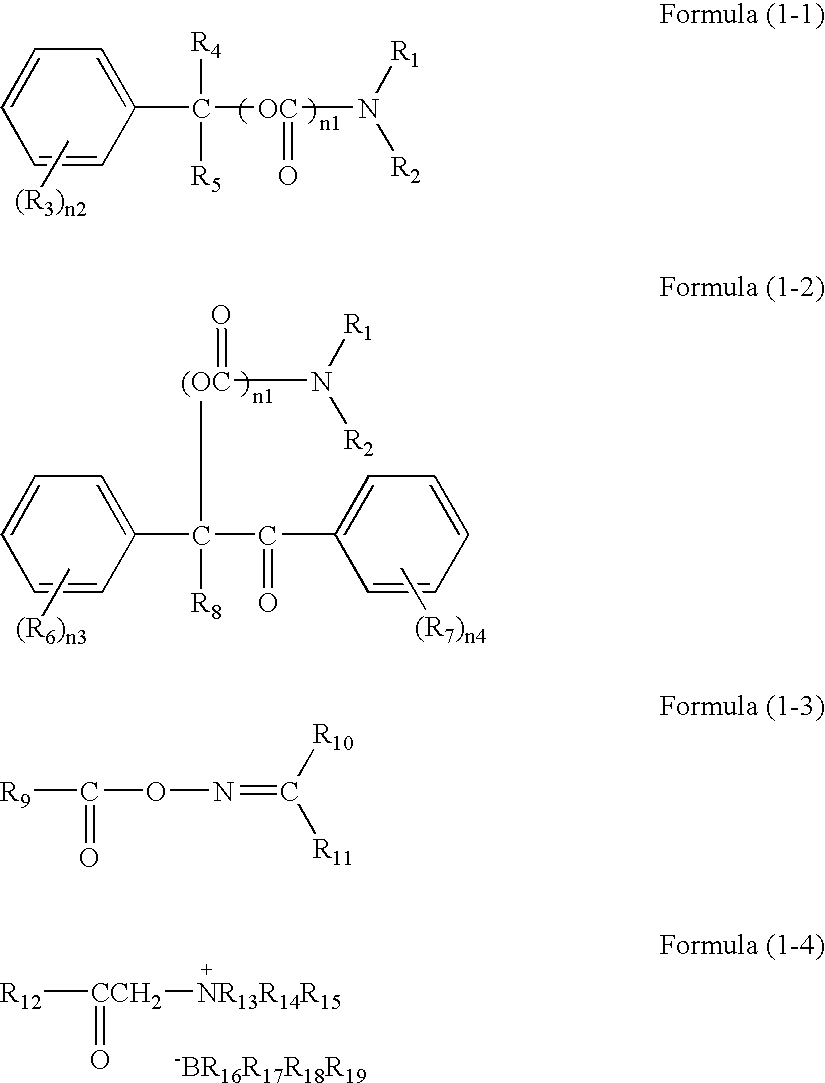
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
690results about How to "High diffraction efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
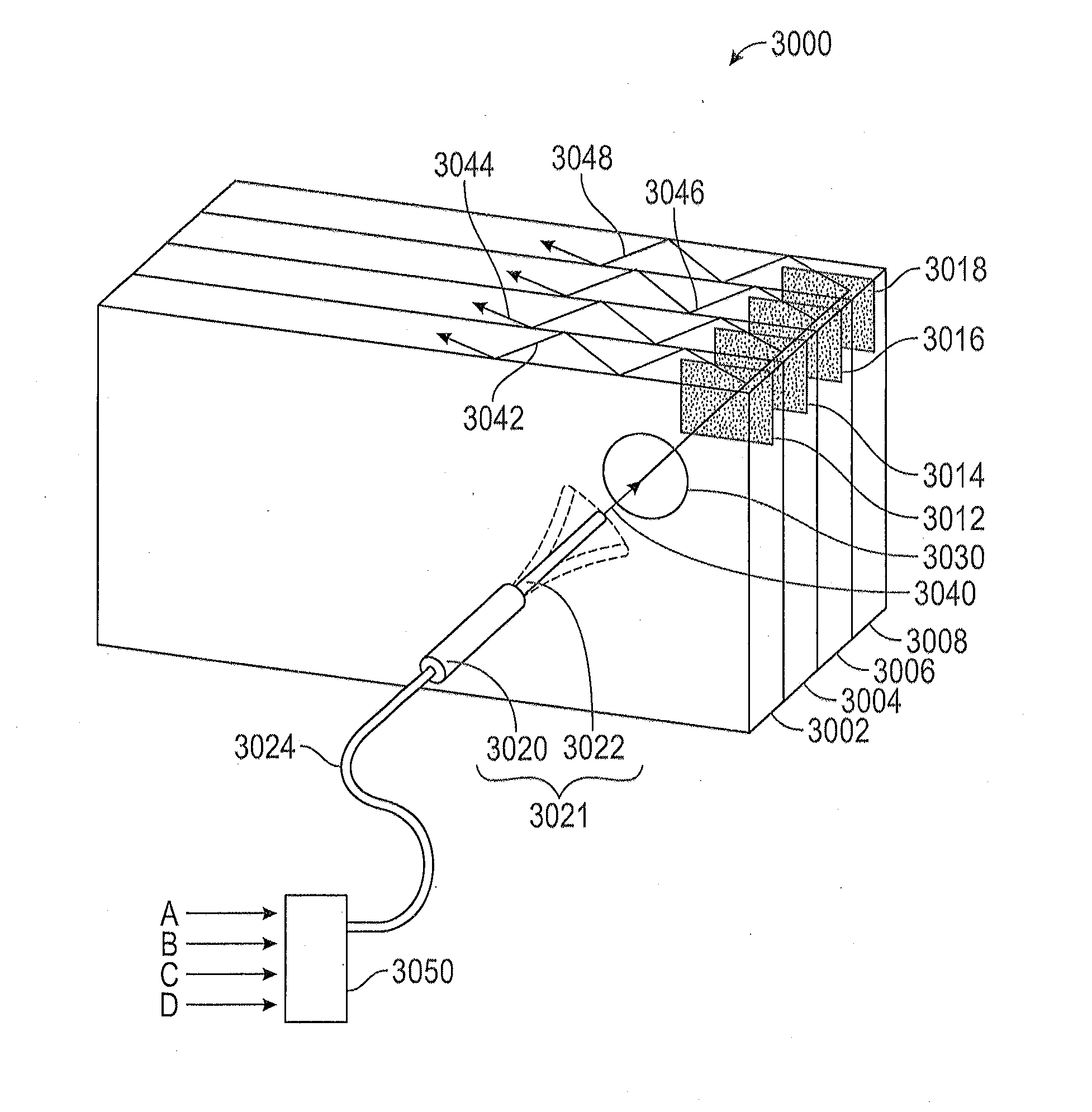
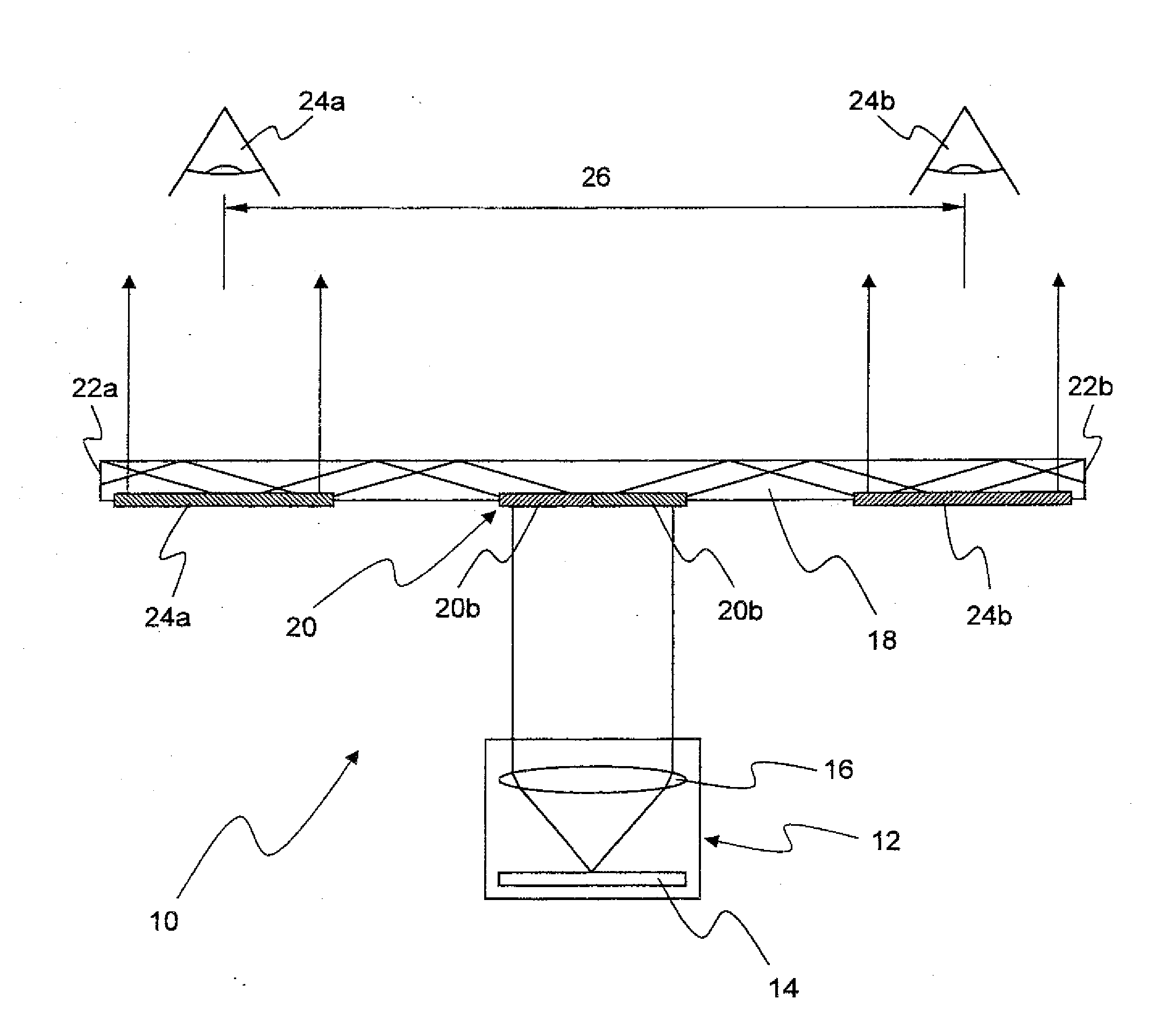
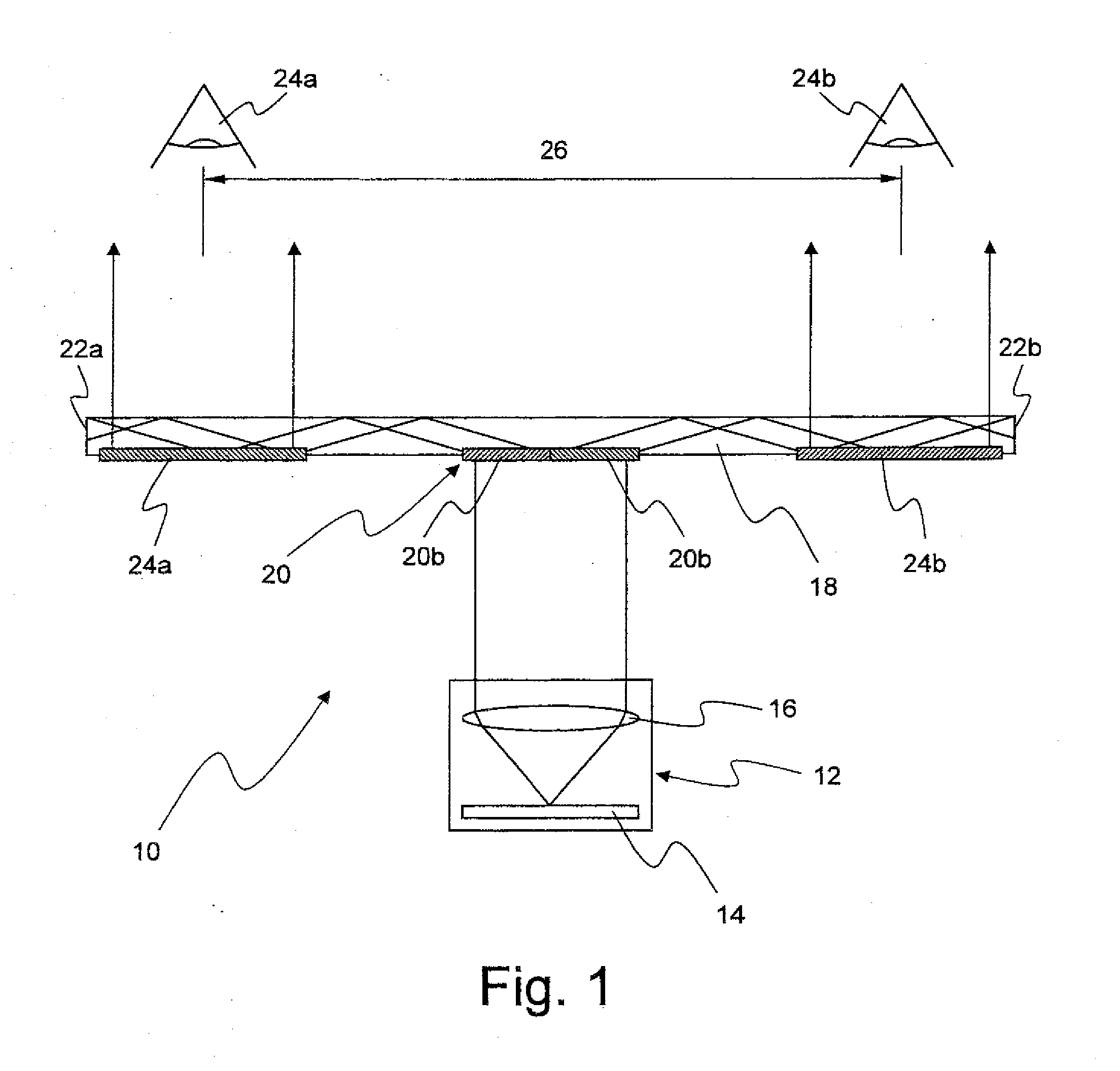
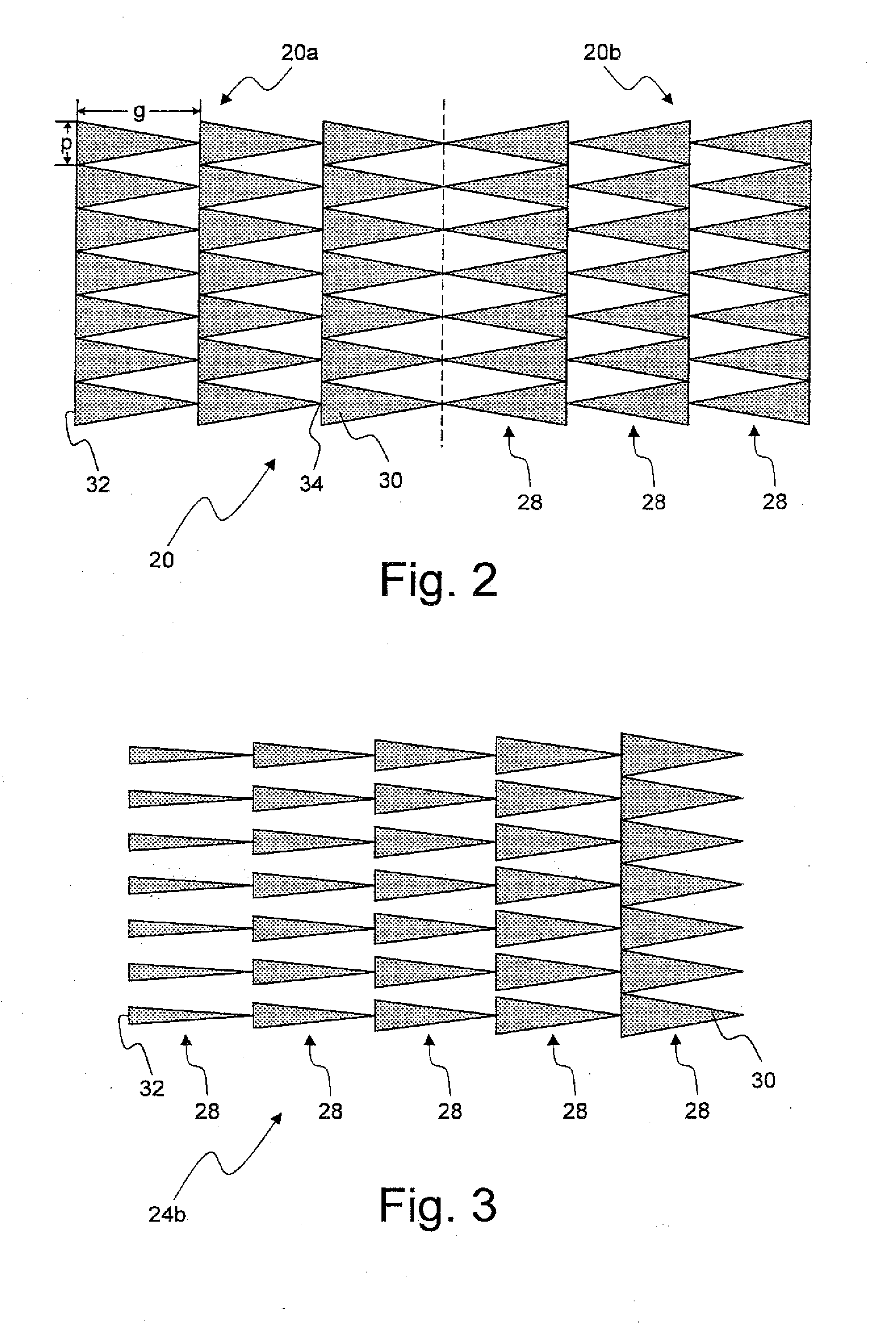
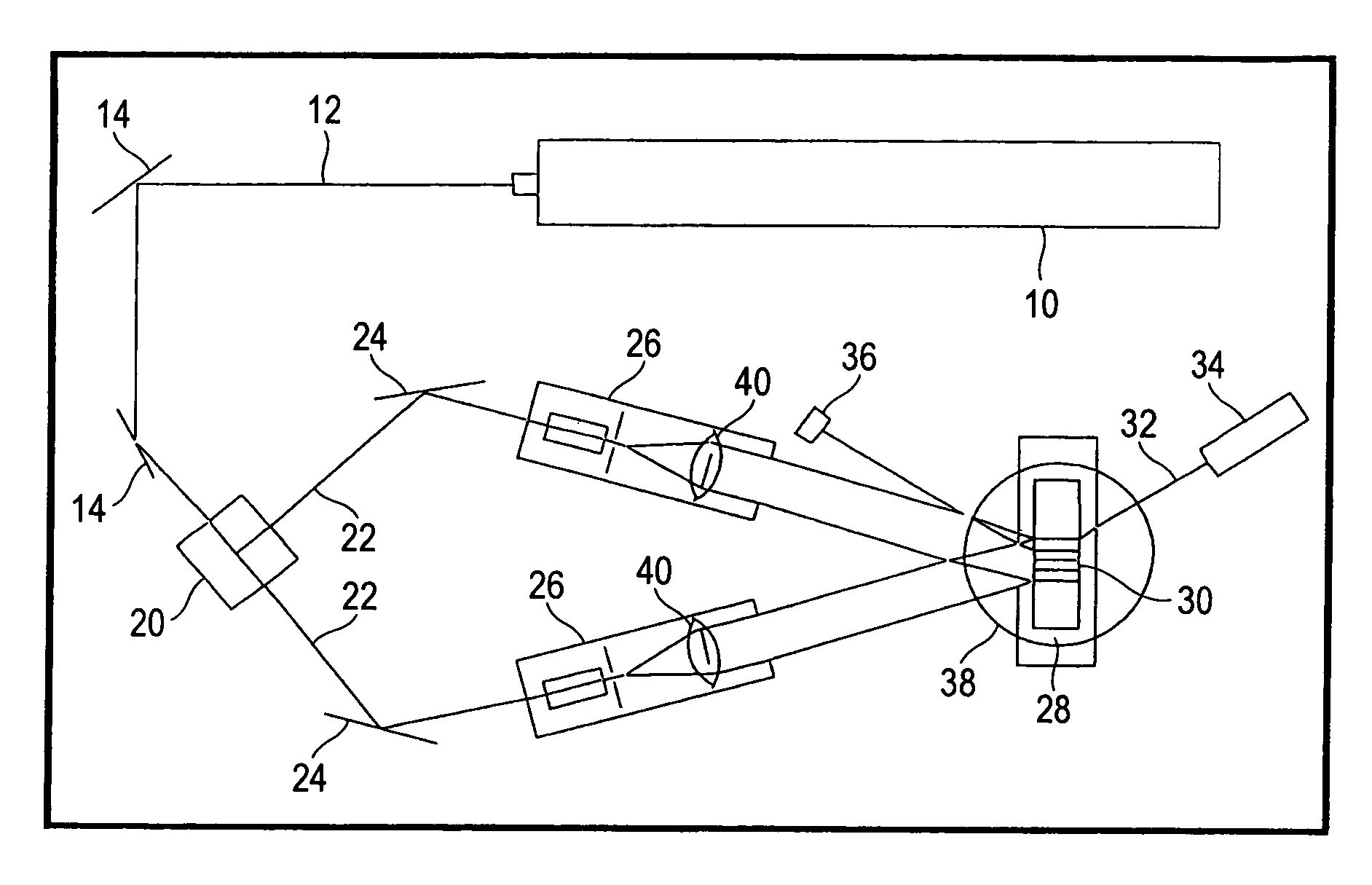
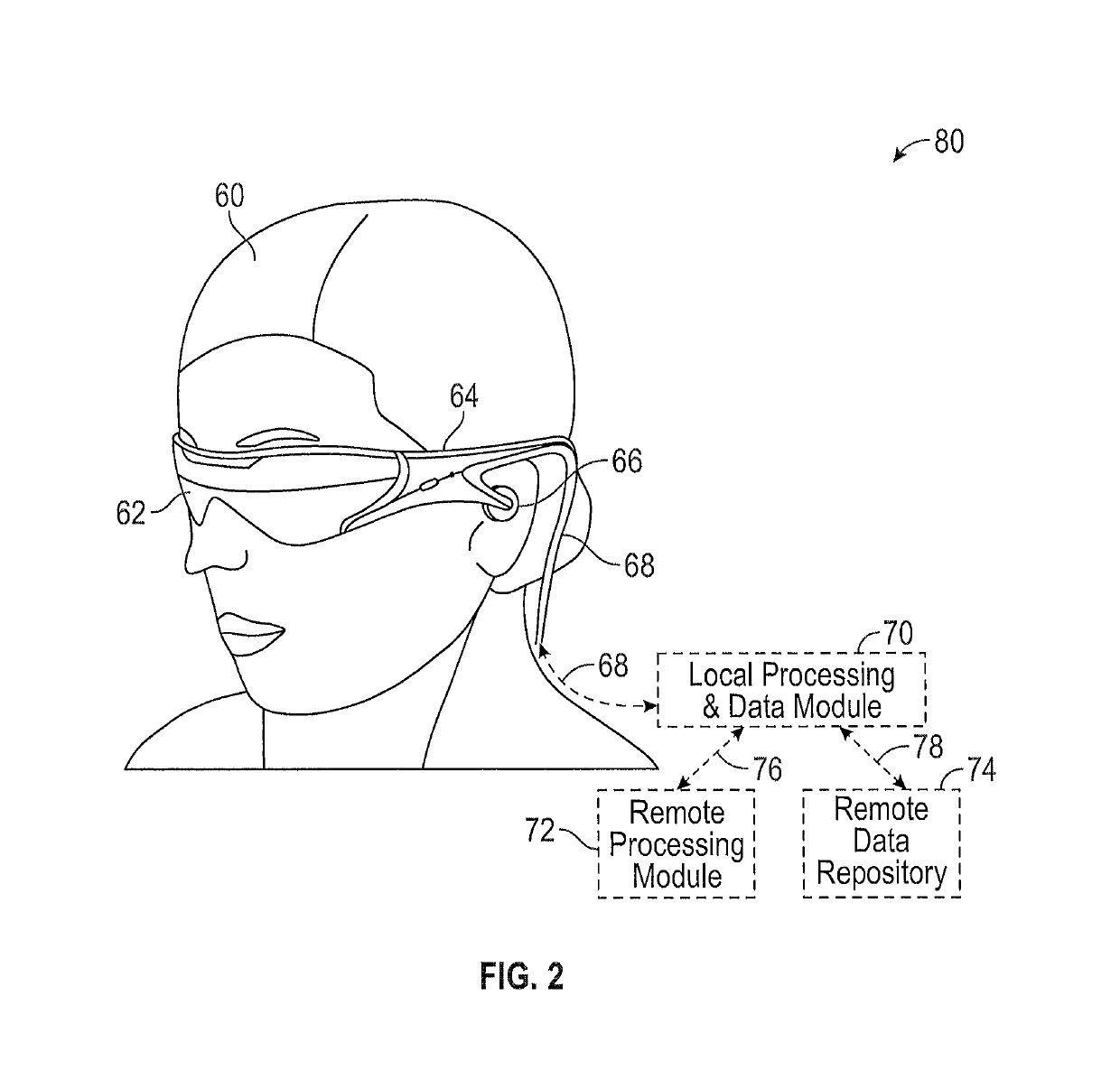
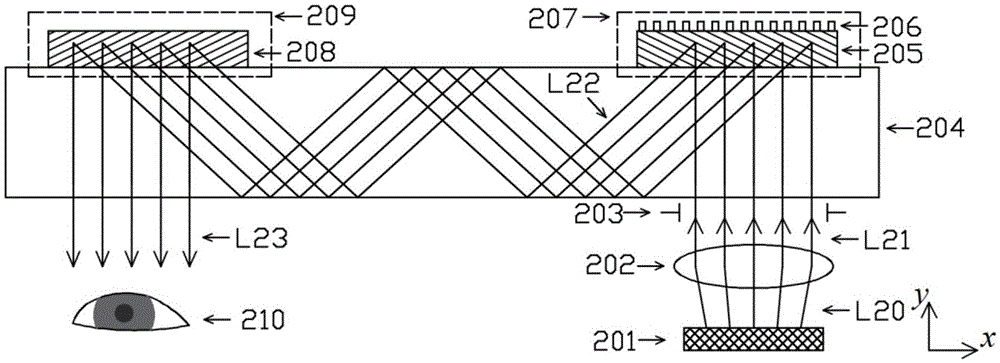
Display system with optical elements for in-coupling multiplexed light streams
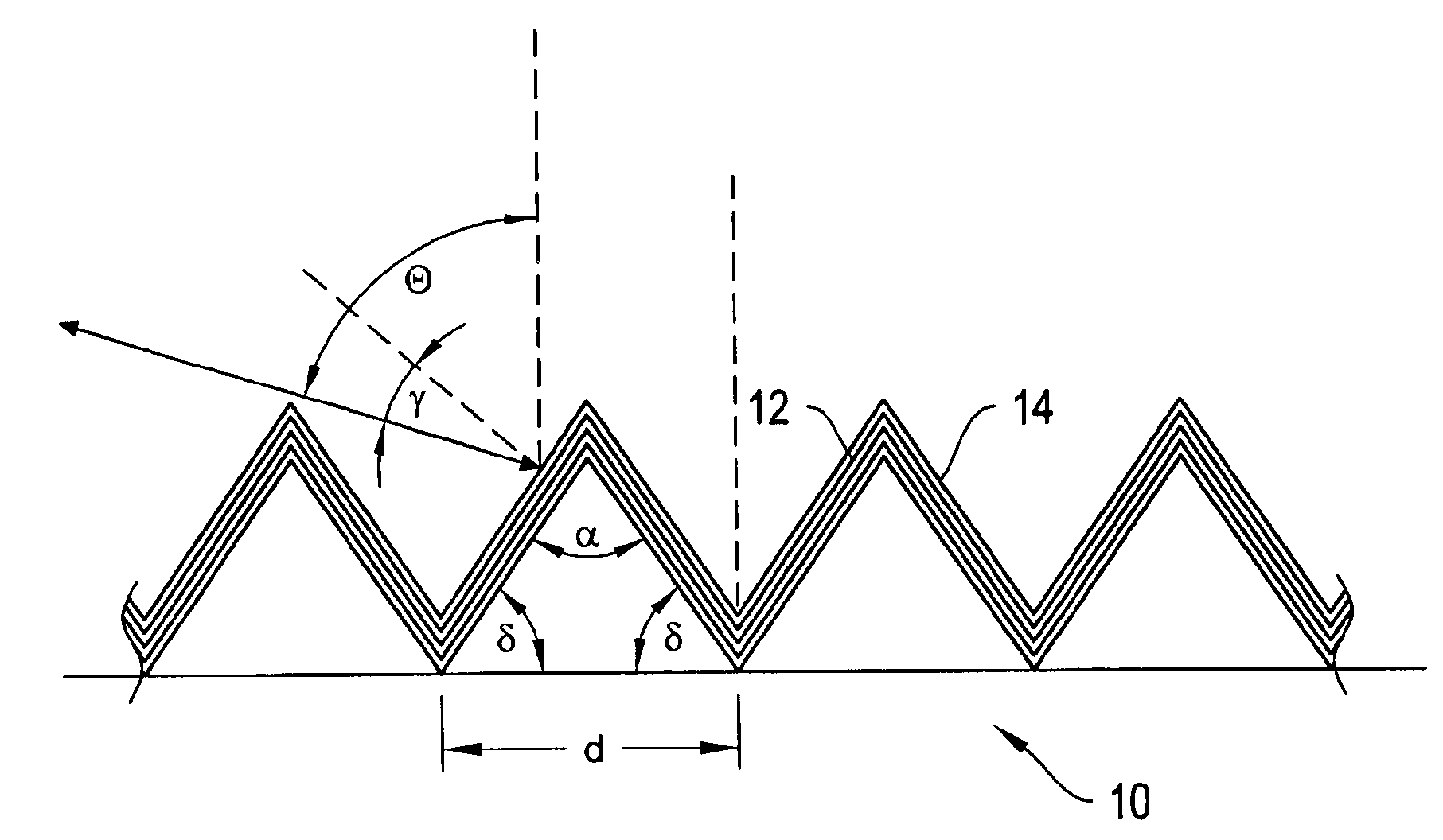
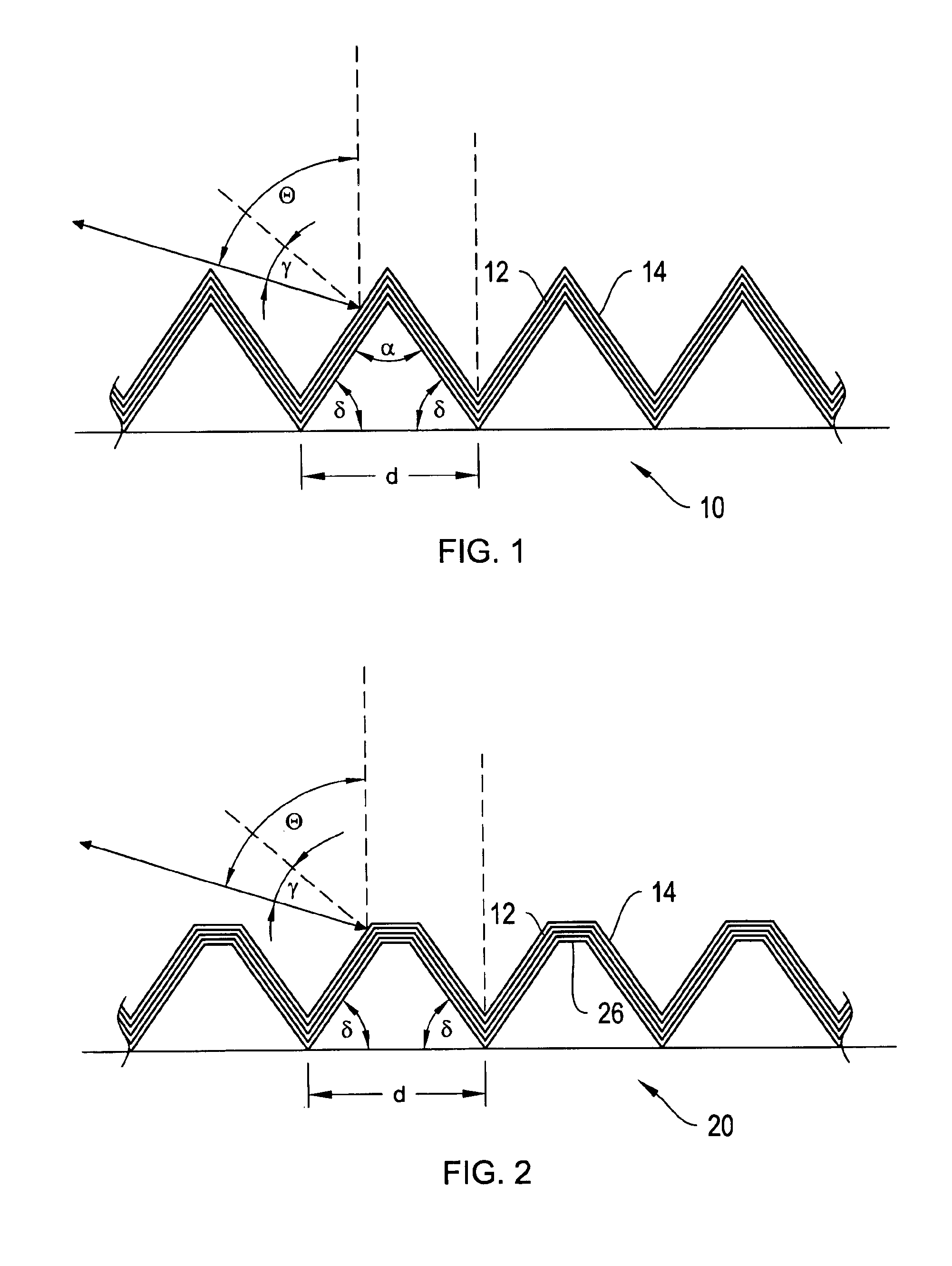
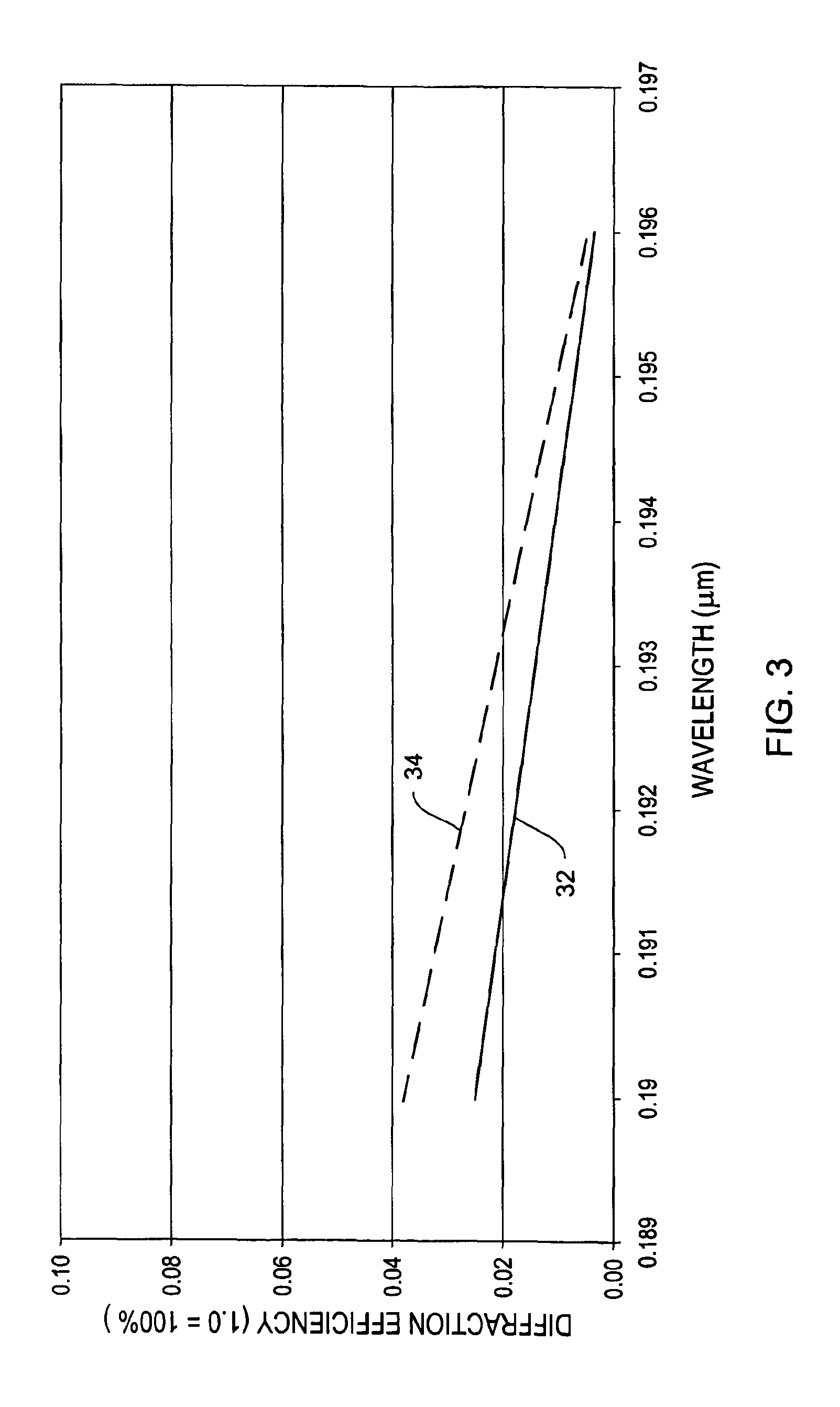
ActiveUS20170010466A1High diffraction efficiencyReduce sensitivityMechanical apparatusPolarising elementsWaveguideLength wave
Architectures are provided for selectively incoupling one or more streams of light from a multiplexed light stream into a waveguide. The multiplexed light stream can have light with different characteristics (e.g., different wavelengths and / or different polarizations). The waveguide can comprise in-coupling elements that can selectively couple one or more streams of light from the multiplexed light stream into the waveguide while transmitting one or more other streams of light from the multiplexed light stream.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Polarization Gratings in Mesogenic Films
ActiveUS20080278675A1Easily produceHigh diffraction efficiencyPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPolarization sensitiveLiquid crystal
A polarization grating comprising a polarization sensitive photo-alignment layer (2) and a liquid crystal composition (3) arranged on said photo-alignment layer is provided. An alignment pattern, corresponding to the polarization pattern of a hologram, is recorded in the photo-alignment layer, and the liquid crystal composition is aligned on the photo-alignment layer. As the origin for the alignment of the liquid crystal composition is a polarization hologram recorded in a photo-alignment layer, an essentially defect-free pattern can be obtained with this approach.
Owner:STICHTING DUTCH POLYMER INST
Optical display device
ActiveUS7751662B2Simple and economical to produceHigh diffraction efficiencyPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesHead-up displayBlazed grating
An optical display device, in particular for use in a head-up display or a head-mounted display, comprises an essentially planar light guide, an image-generating system, a first diffraction grating by which light that comes from the image-generating system can be coupled into the light guide, and a second diffraction grating, by which the light can be coupled out again from the light guide. At least one of the two diffraction gratings is a binary-blazed grating having a multiplicity of diffraction structures, which are composed of a multiplicity of individual substructures that ensure a blaze effect and in plan view have the shape of a closed geometrical surface.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Polarization gratings in mesogenic films
A polarization grating comprising a polarization sensitive photo-alignment layer (2) and a liquid crystal composition (3) arranged on said photo-alignment layer is provided. An alignment pattern, corresponding to the polarization pattern of a hologram, is recorded in the photo-alignment layer, and the liquid crystal composition is aligned on the photo-alignment layer. As the origin for the alignment of the liquid crystal composition is a polarization hologram recorded in a photo-alignment layer, an essentially defect-free pattern can be obtained with this approach.
Owner:STICHTING DUTCH POLYMER INST
Optical Display Device
ActiveUS20090245730A1Simple and economical to produceHigh diffraction efficiencyPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesHead-up displayBlazed grating
An optical display device, in particular for use in a head-up display or a head-mounted display, comprises an essentially planar light guide, an image-generating system, a first diffraction grating by which light that comes from the image-generating system can be coupled into the light guide, and a second diffraction grating, by which the light can be coupled out again from the light guide. At least one of the two diffraction gratings is a binary-blazed grating having a multiplicity of diffraction structures, which are composed of a multiplicity of individual substructures that ensure a blaze effect and in plan view have the shape of a closed geometrical surface.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Hologram recording method and hologram recording material
InactiveUS7588863B2High sensitivityHigh diffraction efficiencyPolyhalogenated compound compositionsPhotomechanical apparatusLatent imageCOLORED MATERIAL
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Hologram recording material, hologram recording method and optical recording medium
InactiveUS7572555B2Low shrinkageImprove recording densityPhotomechanical apparatusPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersEnergy transferExcited state
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Wafer scale lens and optical system having the same
InactiveUS20060262416A1High diffraction efficiencyReducing angle of lightMountingsLensMiniaturizationOptoelectronics
Provided are wafer scale lenses having a diffraction surface as well as a refractive surface, and an optical system having the same. The wafer scale lens includes a lens substrate, a first lens element formed on the object side of the lens substrate, having a positive refractive power, a second lens element formed on the image side of the lens substrate, having a diffraction surface, and a third lens element deposited on the diffraction surface of the second lens element, having a negative refractive power. The invention allows miniaturized optical system and efficient calibration of angle of view, reducing the angle of light incident onto the diffractive surface, thereby increasing diffraction efficiency and eliminating high order diffraction light to improve picture quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
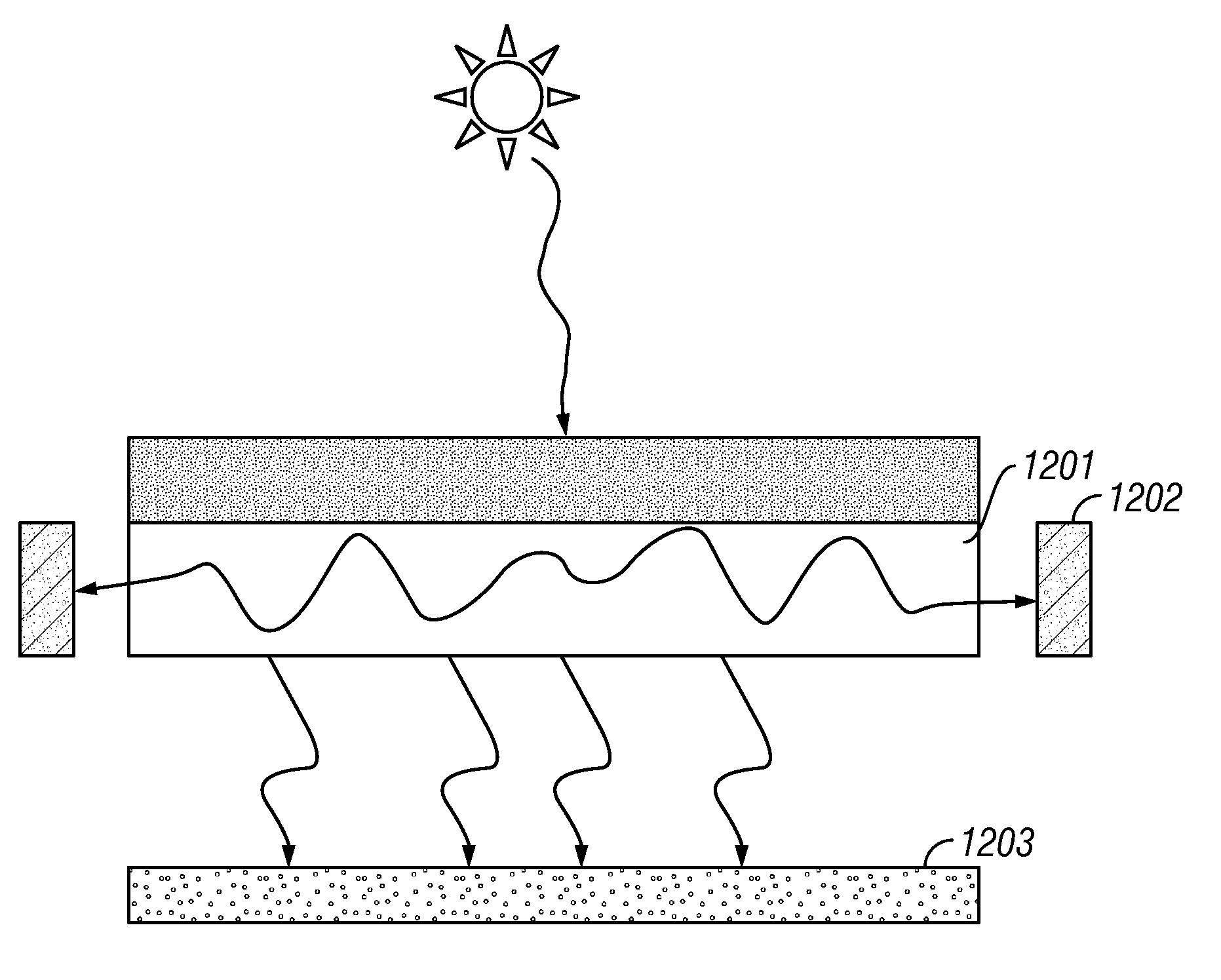
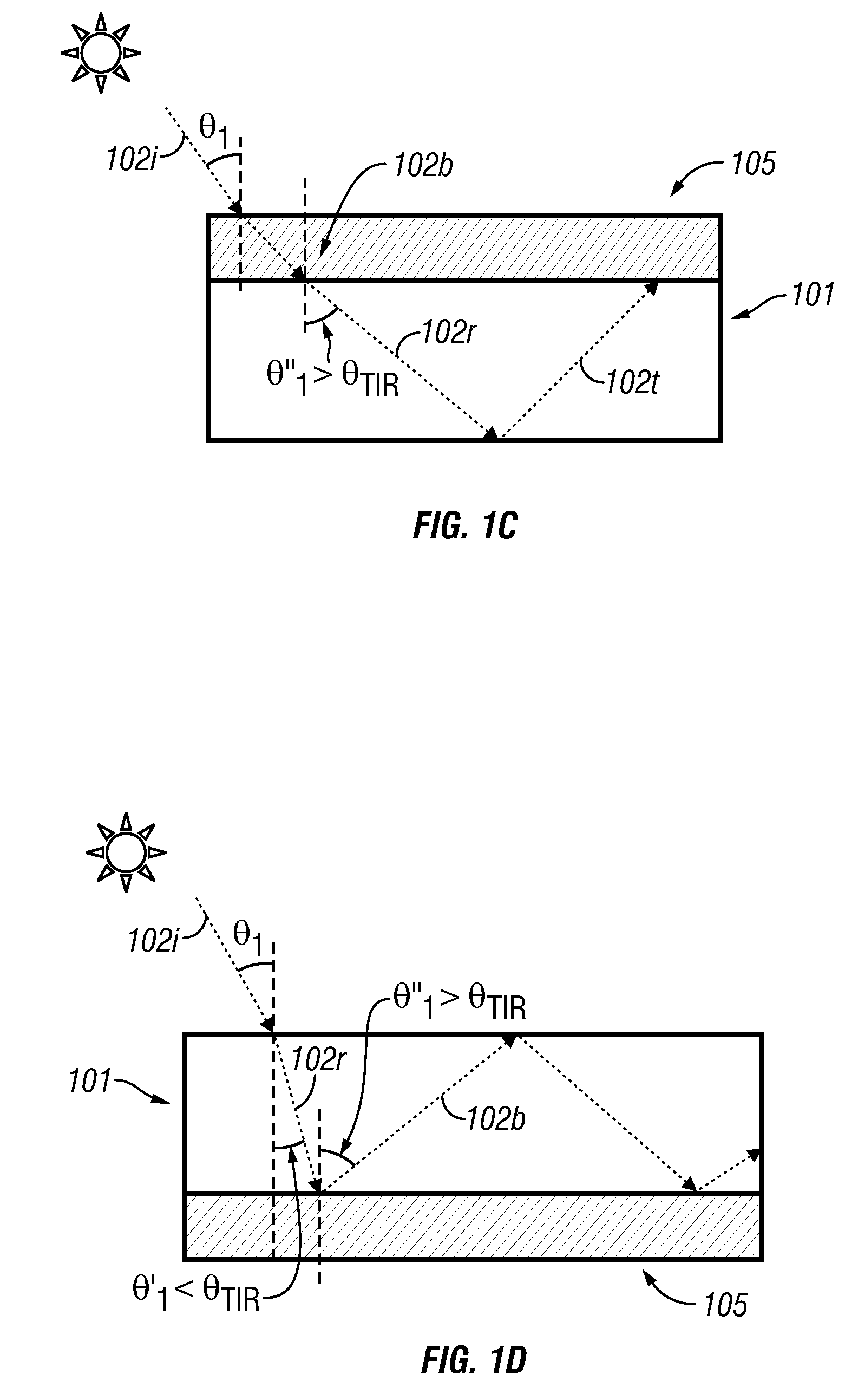
Thin film holographic solar concentrator/collector
InactiveUS20090199893A1High diffraction efficiencyImprove efficiencySolar heating energyPV power plantsTotal internal reflectionLight Cell
In various embodiments described herein, a device comprising a light collector optically coupled to a photocell is described. The device further comprises a light turning film or layer comprising volume or surface diffractive features or holograms. Light incident on the light collector is turned by volume or surface diffractive features or holograms that are reflective or transmissive and guided through the light collector by multiple total internal reflections. The guided light is directed towards a photocell. In various embodiments, the light collector is thin (e.g., less than 1 millimeter) and comprises, for example, a thin film. The light collector may be formed of a flexible material.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
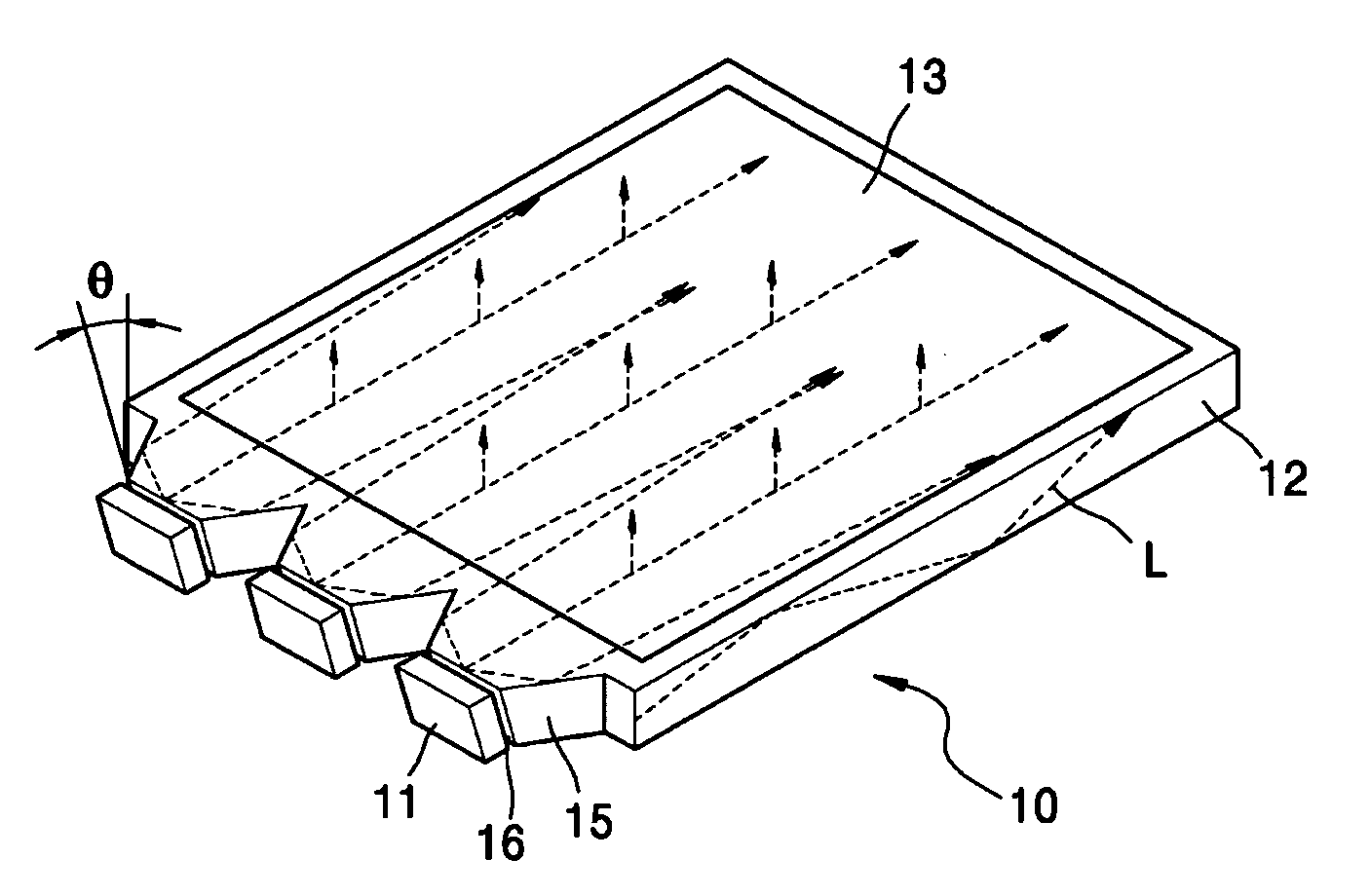
Illumination apparatus for display device using hologram-based light guide plate (LGP)
ActiveUS20060126142A1Improve utilization efficiencyHigh diffraction efficiencyPlanar/plate-like light guidesOptical waveguide light guideLight equipmentLight guide
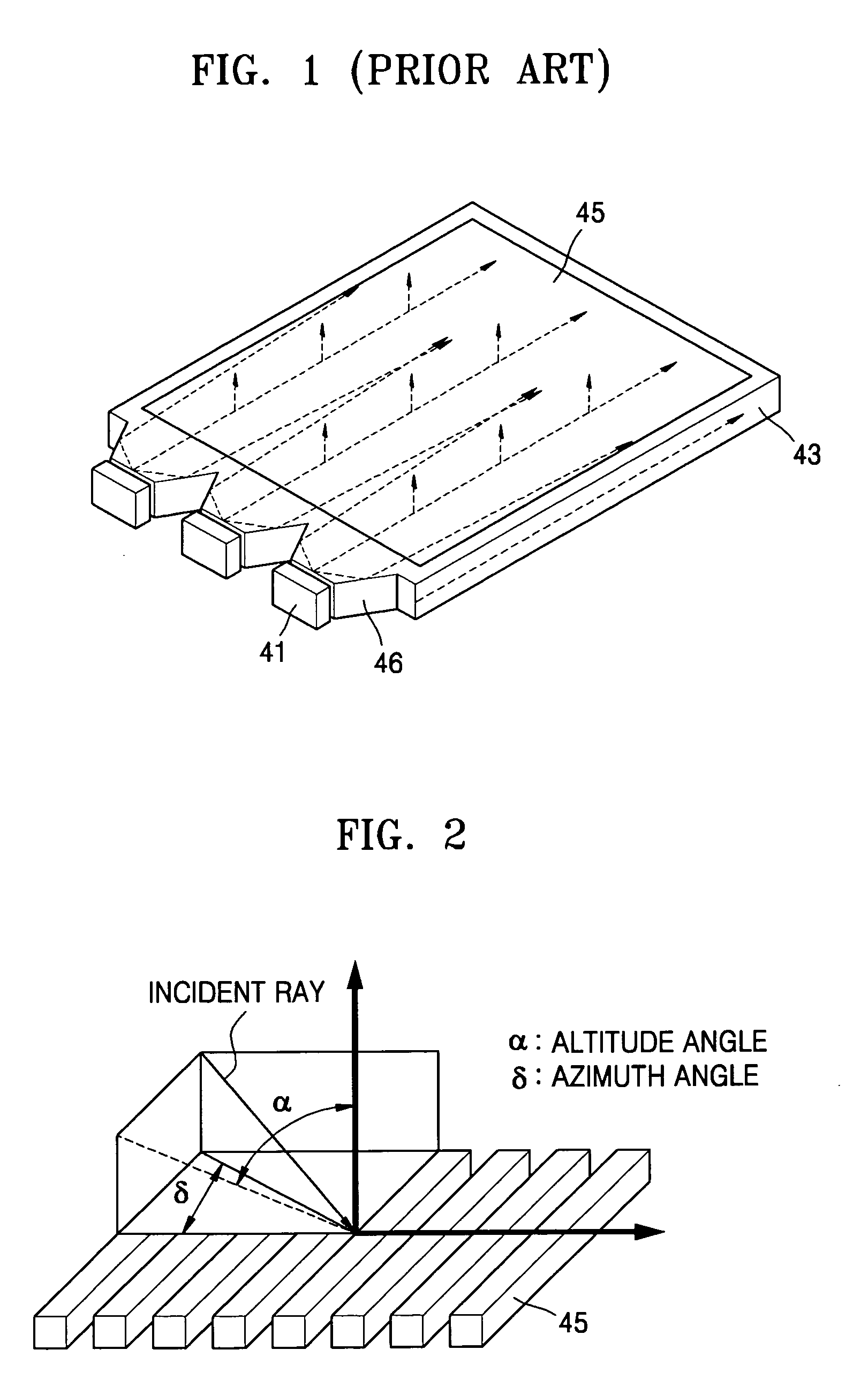
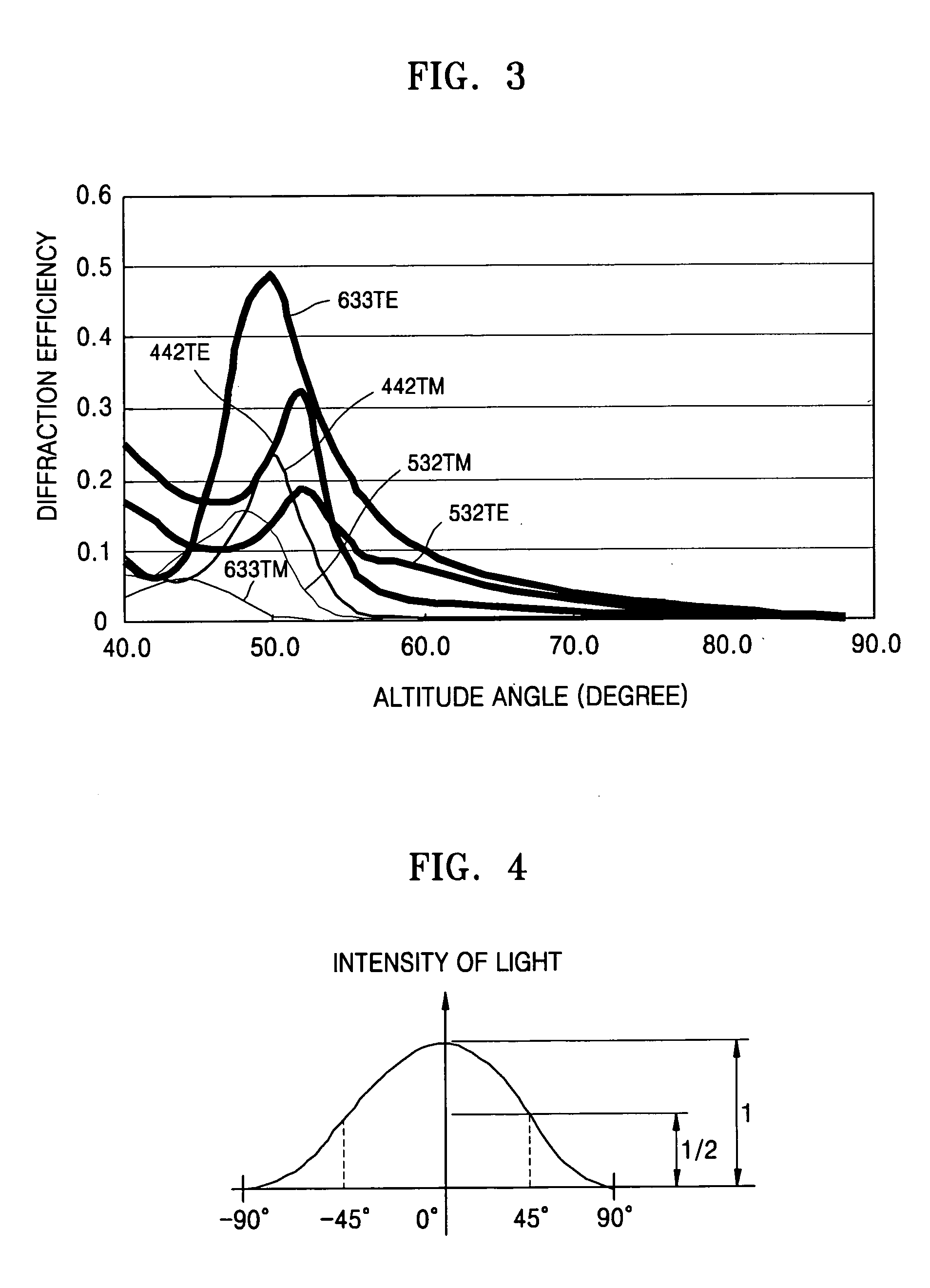
An illumination apparatus and method for a display device designed such that light is incident on a hologram or hologram pattern at an angle for which diffraction efficiency is the highest. The illumination apparatus includes at least one point light source which emits light and a light guide plate (LGP) which has the at least one point light source disposed on a side thereof and a hologram pattern on a top surface which permits the light incident from the point light source to exit from the top surface. The side of the LGP facing the point light source is inclined such that the light is incident obliquely on the hologram pattern at an altitude angle which provides high diffraction efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Dynamic Liquid Crystal Gel Holograms
InactiveUS20080089073A1Easy to manufactureImproved dynamic holographic elementsLiquid crystal compositionsPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamLiquid crystal
A dynamic hologram is formed in anisotropic liquid crystal (LC) gel materials. By applying an electric field, the orientation of part of the liquid crystals can be altered and the hologram can be turned on and off. Using LC gels allows for holographic elements with no diffraction in the voltage off state so that the hologram appears only during application of an electric field. Also, the anisotropic LC gels maintain polarization dependence. The dynamic holograms are suitable in e.g. dynamic holographic optical components whereby an optical function can be included / excluded in a beam path without introducing or removing elements.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Hologram element, production method thereof, and optical header
InactiveUS20060055993A1High film thicknessImprove productivityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesRecord information storageProduction rateLight beam
A method of producing a hologram element is disclosed that is able to prevent spread of a polymerization reaction and light leakage during exposure with interference light, and improve productivity in mass production. The hologram element is for transmitting, reflecting, diffracting, or scattering incident light, and includes a pair of substrates, an isolation member between the substrates that forms an isolated region, and a photo-sensitive recording material sealed in the isolated region. The hologram element includes a periodic structure formed by exposing the recording material to interference light. The interference light is generated by two or more light beams, or by using a master hologram. The recording material is formed from a composite material including a polymerized polymer or a polymerized liquid crystal. The periodic structure is formed by exposing the recording material to the interference light to induce the polymerization reaction and phase separation in the composite material.
Owner:RICOH KK
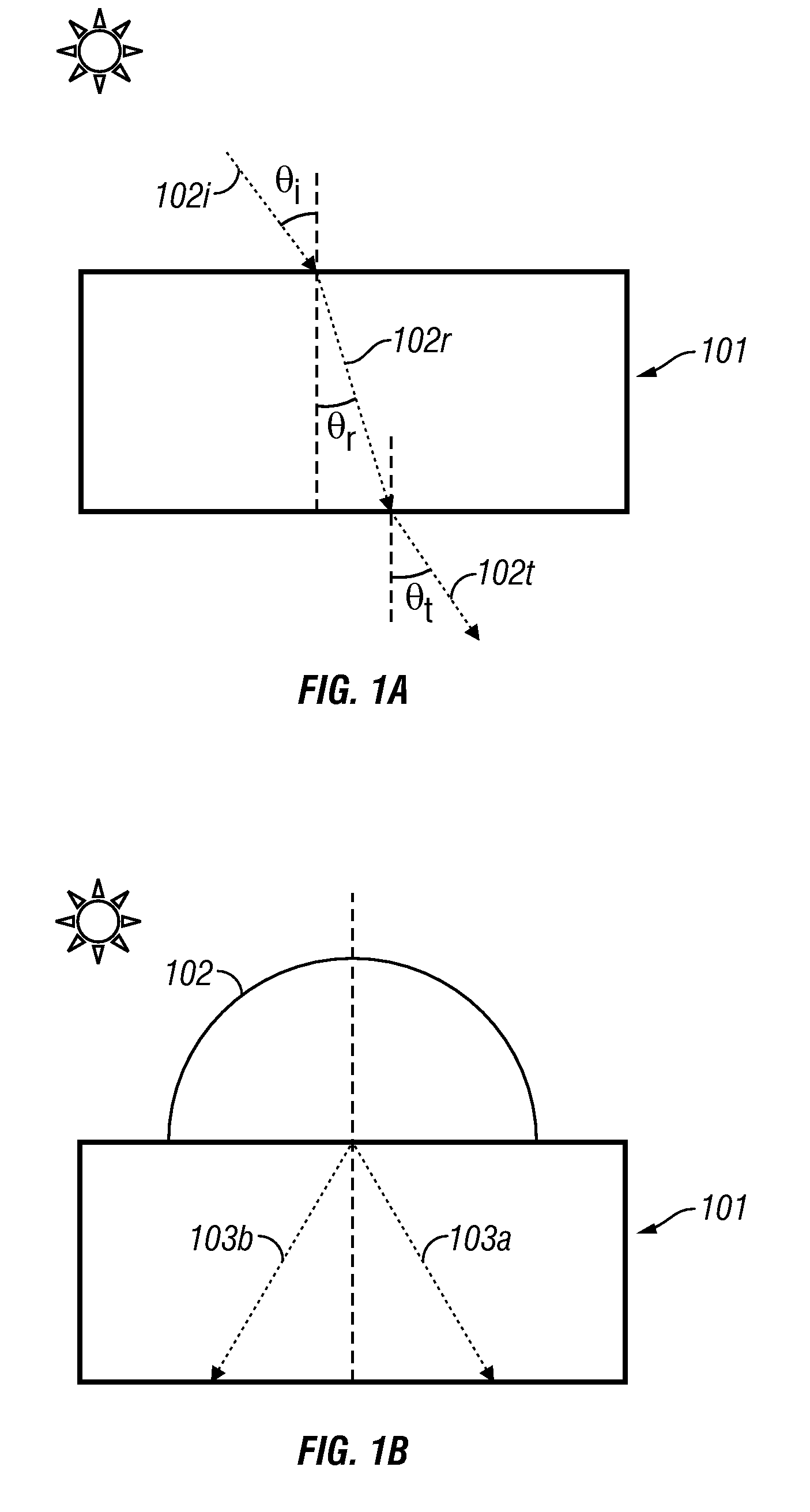
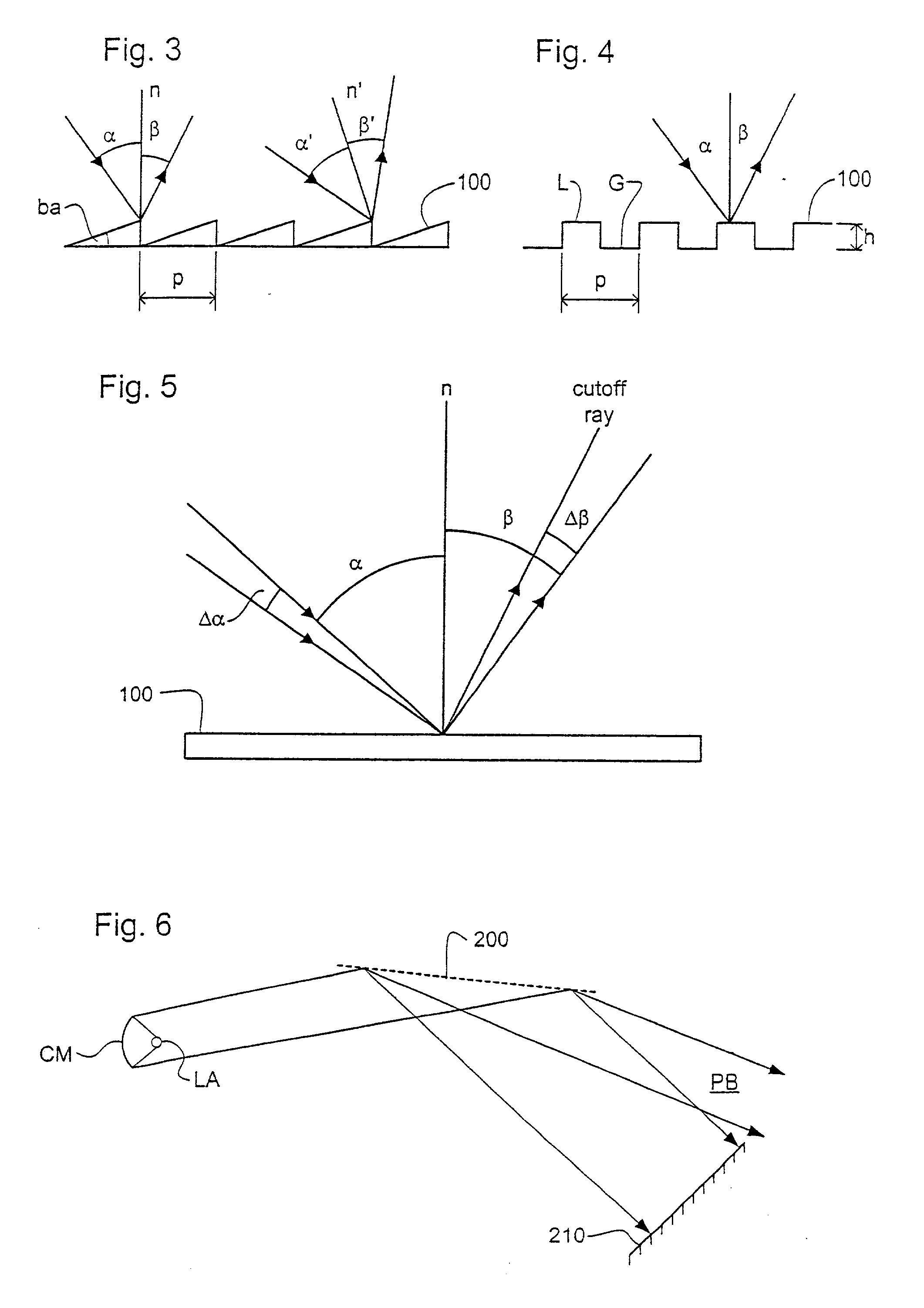
Grating device with high diffraction efficiency
InactiveUS6958859B2High diffraction efficiencyHigh wavelength dispersionDiffraction gratingsElectricityLength wave
A grating structure with a dielectric coating is disclosed that operates efficiently away from the blaze angle in low order with a high diffraction efficiency and high wavelength dispersion. Such grating structure can be employed in Littrow configuration to provide, for example, cavity feedback in excimer lasers.
Owner:LUMELLA
Display system with optical elements for in-coupling multiplexed light streams
ActiveUS10254454B2High diffraction efficiencyReduce sensitivityMechanical apparatusPolarising elementsMultiplexingLength wave
Architectures are provided for selectively incoupling one or more streams of light from a multiplexed light stream into a waveguide. The multiplexed light stream can have light with different characteristics (e.g., different wavelengths and / or different polarizations). The waveguide can comprise in-coupling elements that can selectively couple one or more streams of light from the multiplexed light stream into the waveguide while transmitting one or more other streams of light from the multiplexed light stream.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
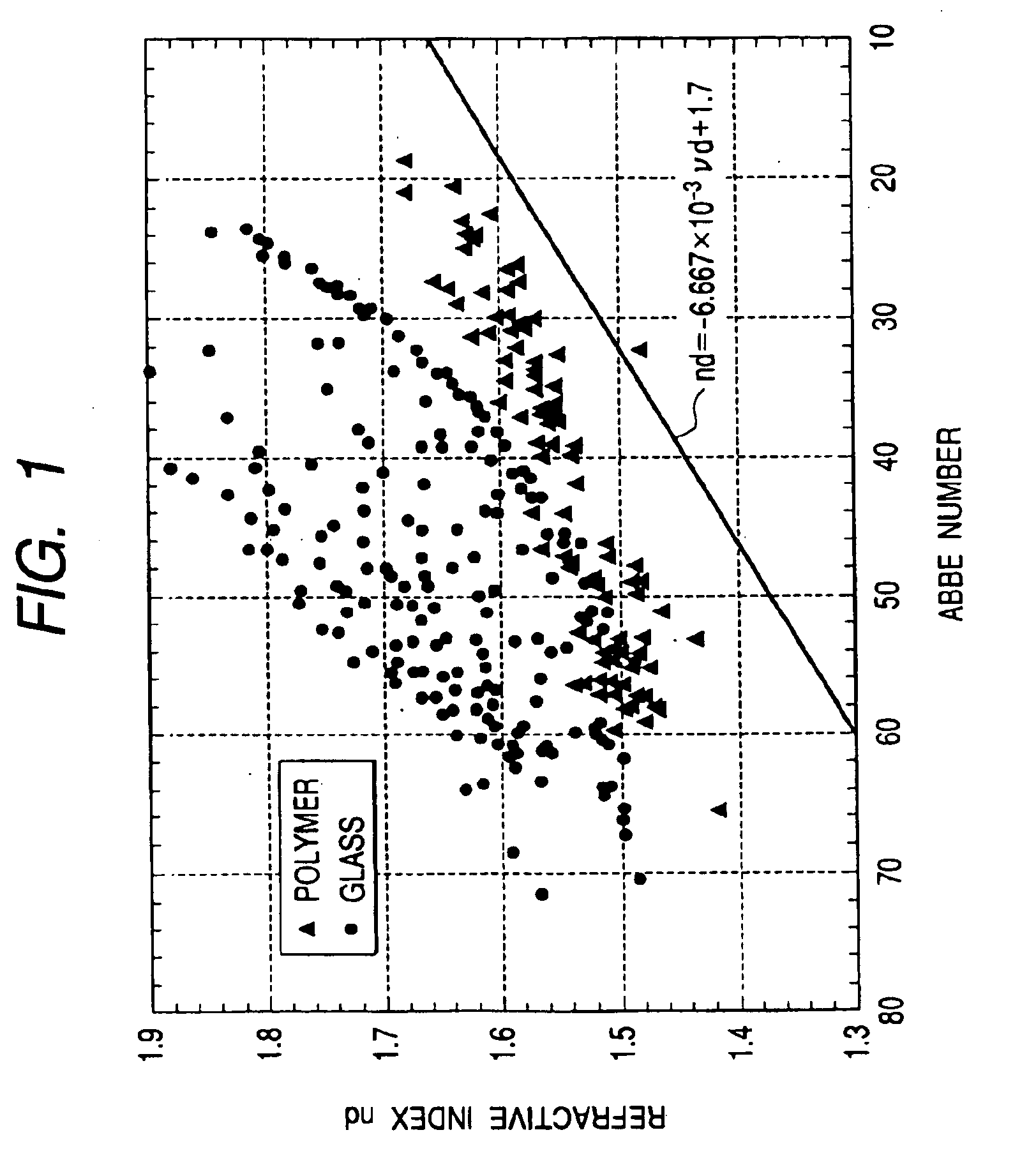
Optical material, and, optical element, optical system and laminated diffractive optical element using it
InactiveUS6912092B2High diffraction efficiencyReduction of diffraction efficiencyLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractive indexLength wave
An optical element of which diffraction efficiency hardly varies with wavelength is provided by using an optical material satisfying the conditions that nd>−6.667×10−3vd+1.70 and θg,F≦−2×10−3νd+0.59 where nd is a refractive index at d-line, νd is an Abbe number at the d-line, and θg,F is a second order dispersion at d-line, whereby diffraction efficiency is improved in any working visible wavelength region and more precise chromatic aberration correction is obtained.
Owner:CANON KK
Light collection from diffractive displays
InactiveUS6091521AHigh diffraction efficiencyGuaranteed normal transmissionProjectorsNon-linear opticsZeroth orderLight beam
A diffractive display system and a method of collecting first order light beams from a diffractive display of the system utilize holographic optical elements (HOEs) to deflect one of two first order diffracted light beams that emerge from each diffracting pixel of the diffractive display, so that the first order diffracted light beams can be separated from the zeroth order light beams. The utilization of the HOEs allows the system to be implemented in a compact optical configuration, without sacrificing any portion of the first order diffracted light. In a first embodiment, the system includes three HOEs that have static diffracting properties that are optimized for red, green and blue lights. For each set of light beams from a diffracting pixel of the diffractive display, the HOEs are holographically configured to deflect only one of the two first order diffracted light beams, such that the deflected first order light beam propagates in the same direction as the other non-deflected first order light beam. In a second embodiment, the system includes three HOEs that have reconfigurable diffracting properties that are also optimized for red, green and blue lights. In a third embodiment, the system further includes a holographic color filter that is comprised of three reconfigurable HOEs to sequentially illuminate the diffractive display with each of the tristimulus color lights.
Owner:HOYA CORP +1
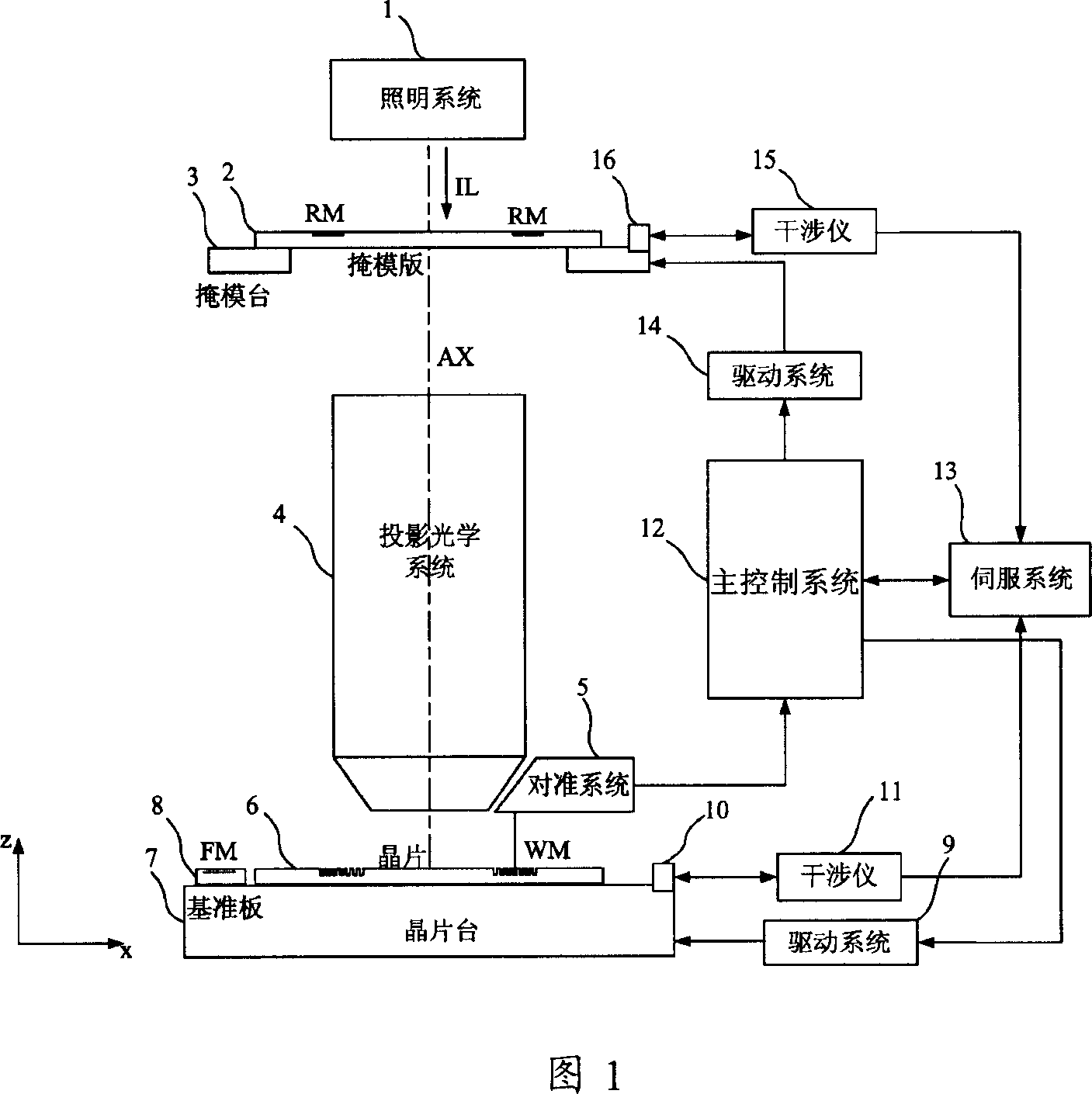
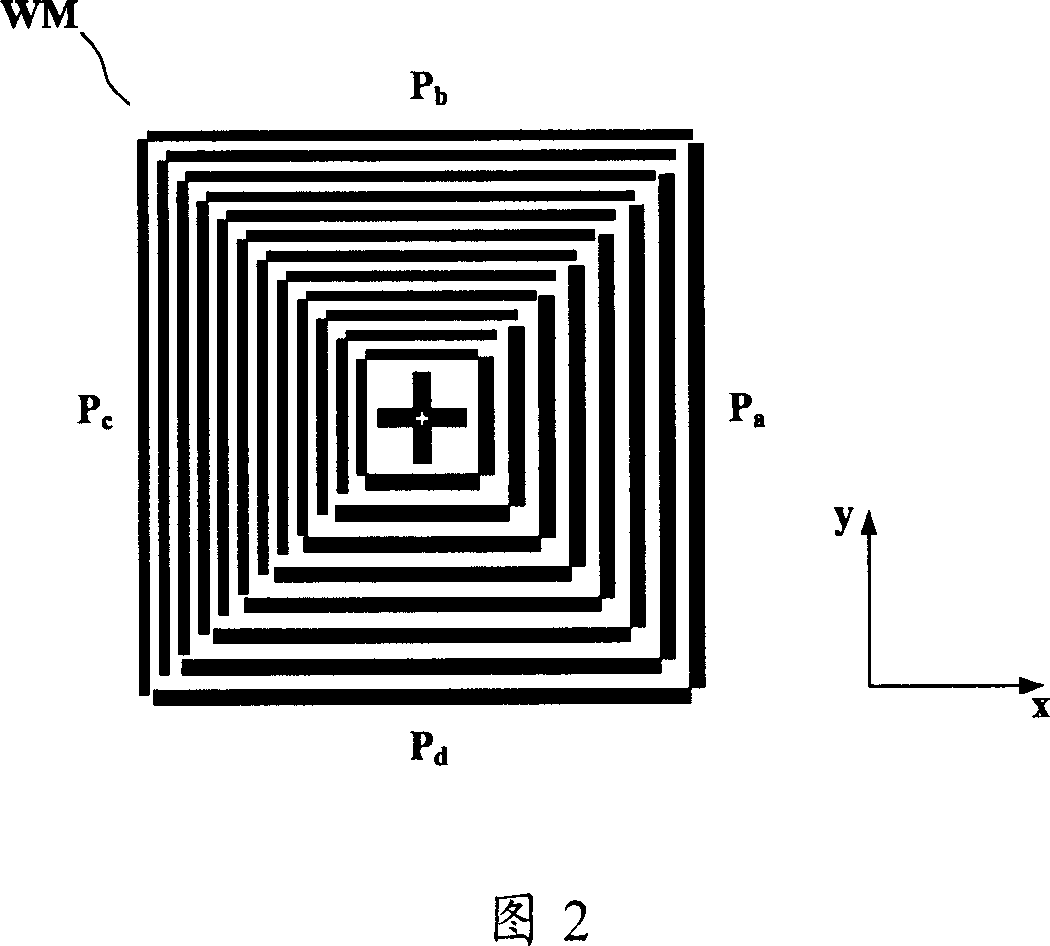
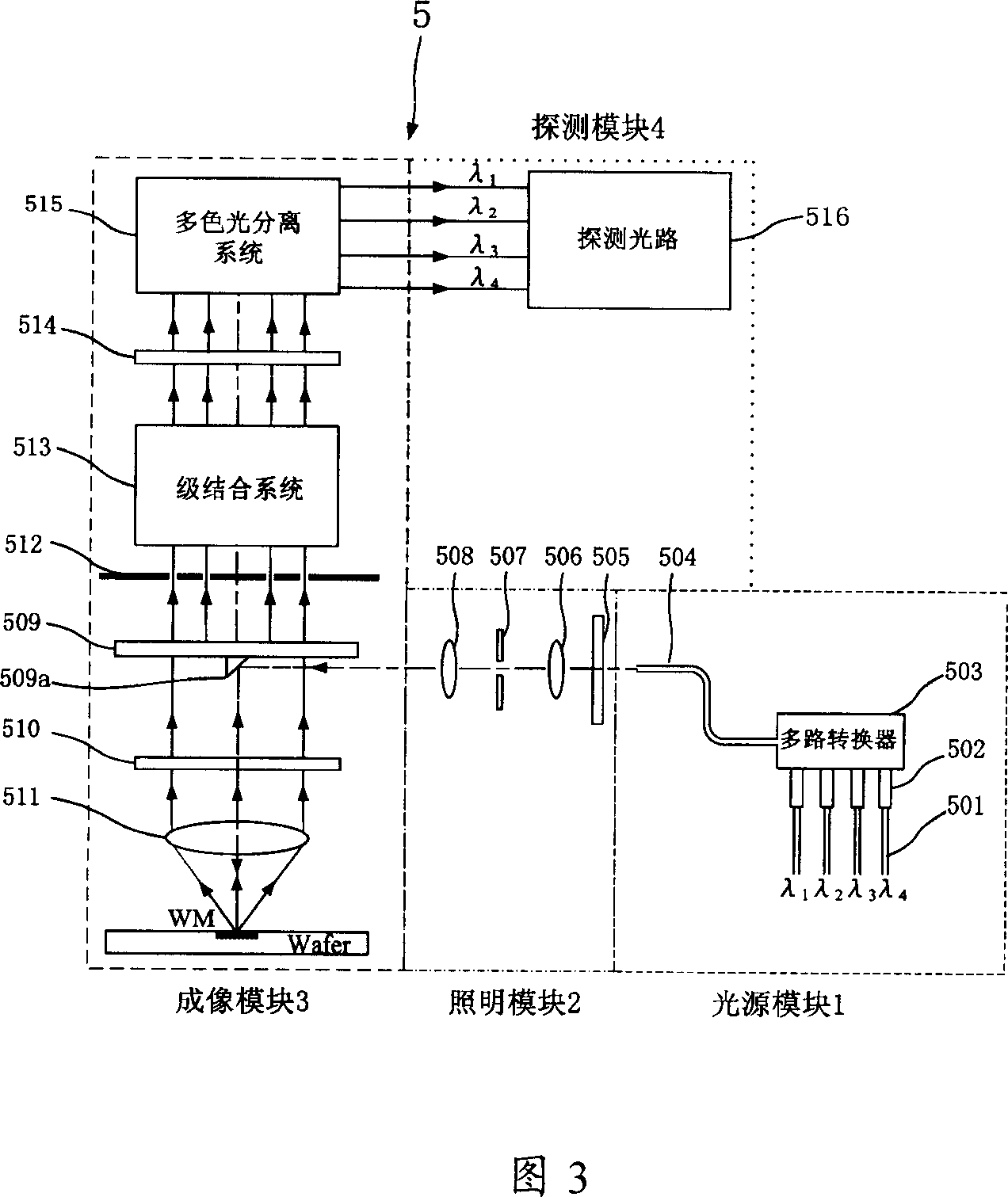
Aligning system of photoetching apparatus and steping combined system of said aligning system thereof
ActiveCN1949087ASolve absorptionSuppresses the effects of interference destructive effectsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusFrequency spectrumLight beam
The invention discloses mask-alignment aligning system and its grade combining system. The aligning system includes light source module, illumination module, imaging module, and detecting module. The grade combining system makes positive negative grade frequency spectrum facula of the alignment mark diffraction spectrum process corresponding overlap coherent, uses polychromatic light separating system to separate multiple wavelength light signal, measures light intensity or phase change at the corresponding position of the multiple wavelength multistage secondary diffracted facula to gain alignment mark position information. The invention has high alignment precision and stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Holographic waveguide display device
ActiveCN105549150AHigh diffraction efficiencyReduce light energy lossOptical light guidesStray lightWavelength
The invention discloses a holographic waveguide display device and belongs to the technical field of wearable display. The holographic waveguide display device comprises a micro displayer, a collimating lens, a diaphragm, a waveguide, an inlet coupling diffraction optical element and an outlet coupling diffraction optical element. The inlet coupling diffraction optical element comprises a reflection body holographic grating and a sub-wavelength one-dimensional metal nanometer grating. One side of the reflection body holographic grating is closely connected to the waveguide, and the sub-wavelength one-dimensional metal nanometer grating is arranged on the surface of the other side of the reflection body holographic grating. Photons penetrating through the reflection body holographic grating can be coupled into a surface plasma mode through the sub-wavelength one-dimensional metal nanometer grating, and thus the photons can enter the reflection body holographic grating again to be diffracted and enter the waveguide. Compared with the prior art, by means of the holographic waveguide display device, the diffraction efficiency of TM light can be improved on the premise of ensuring the high diffraction efficiency of the TE light, so that the total light energy utilization rate of the holographic waveguide display device is increased, and meanwhile stray light in transmission is effectively suppressed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for eliminating image speckles in scanning laser image projection
InactiveUS6367935B1Eliminate speckleHigh diffraction efficiencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsLight beamSpeckle pattern
A method for the elimination of image speckles in a scanning laser projection is suggested, in which a phase hologram is used for dividing the illumination beam of the projector into partial beams. The partial beams are heterodyned again on the image screen within the image element (pixels) to be projected in such a way that differing speckle patterns are formed which average each other out in the eye of the viewer over time and / or space. Thus, a device is provided especially for the laser projection which substantially eliminates or reduces the speckles at the viewer. However, the beam form and the beam density are hardly or not changed.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Diffractive optical element, and optical system and optical apparatus provided with the same
A diffractive optical element of the blazed-binary grating type is disclosed, with which a high diffraction efficiency can be achieved over substantially the entire used wavelength region. The diffractive optical element has a periodic structure taking a grating unit including a plurality of grating portions with different grating width and grating interval as one period. The diffraction element further includes a plurality of first grating portions made of a first material and a plurality of second grating portions made of a second material having a different refractive index than the first material that are arranged between the first grating portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Hologram recording material and optical recording medium
InactiveUS20060194122A1High sensitivityHigh diffraction efficiencyPhotomechanical apparatusHologram recording materialLatent imageCompound (substance)
A hologram recording material is provided and has: an optical refractive index-modulating component; and a curable polymer. The optical refractive index-modulating component performs at least one of: (1) a color development reaction; (2) a color development reaction amplified by a self-sensitization with a coloring material of a latent image; (3) a color development reaction amplified by a self-sensitization with a coloring material of a latent image; (4) an alignment change in a compound having a birefringence; (5) a dye discoloration reaction; and (6) a latent image-sensitized polymerization reaction sensitized by a latent image of a residual of a discolorable dye, to record interference fringes providing a refractive index modulation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Optical apparatus and image production apparatus
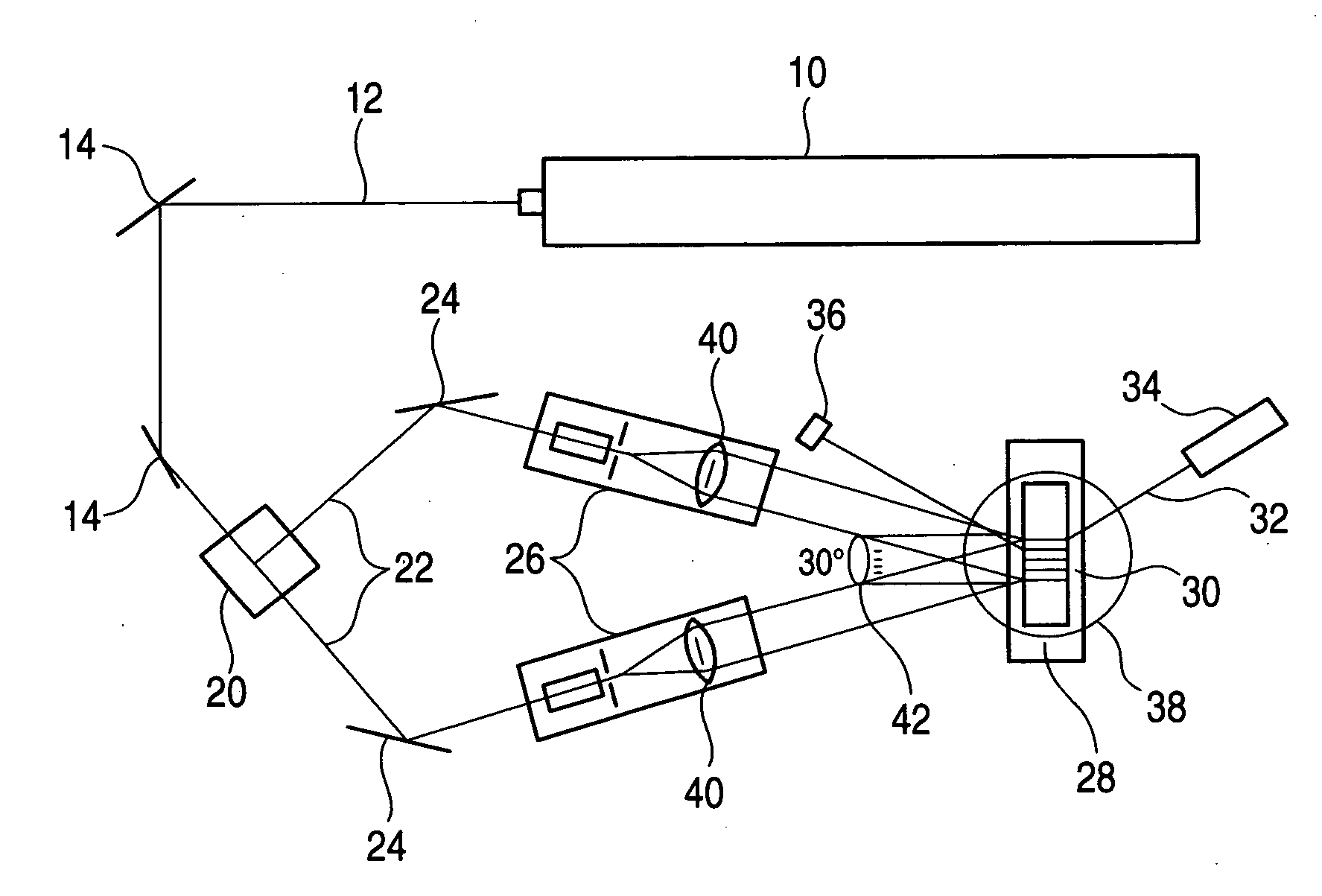
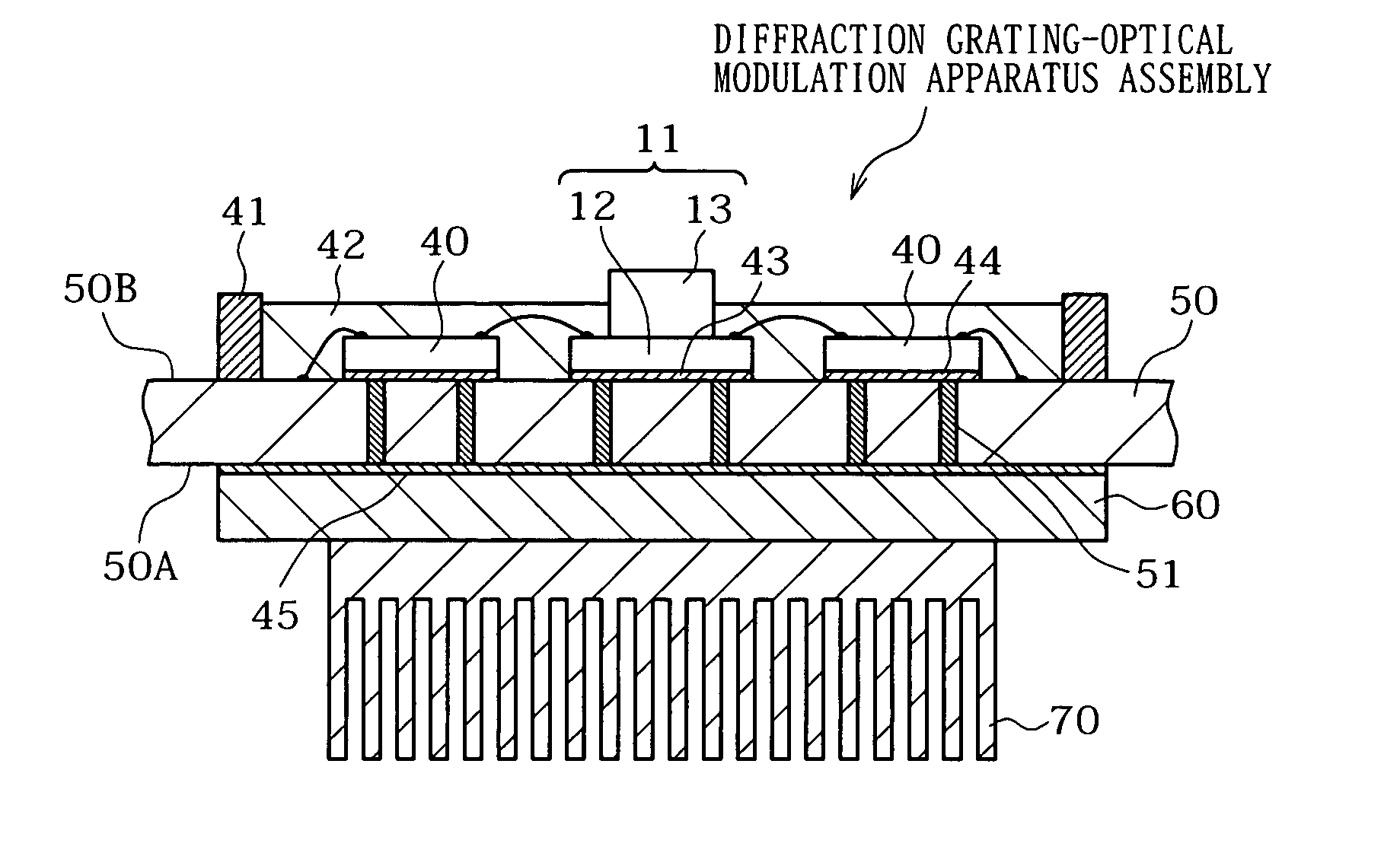
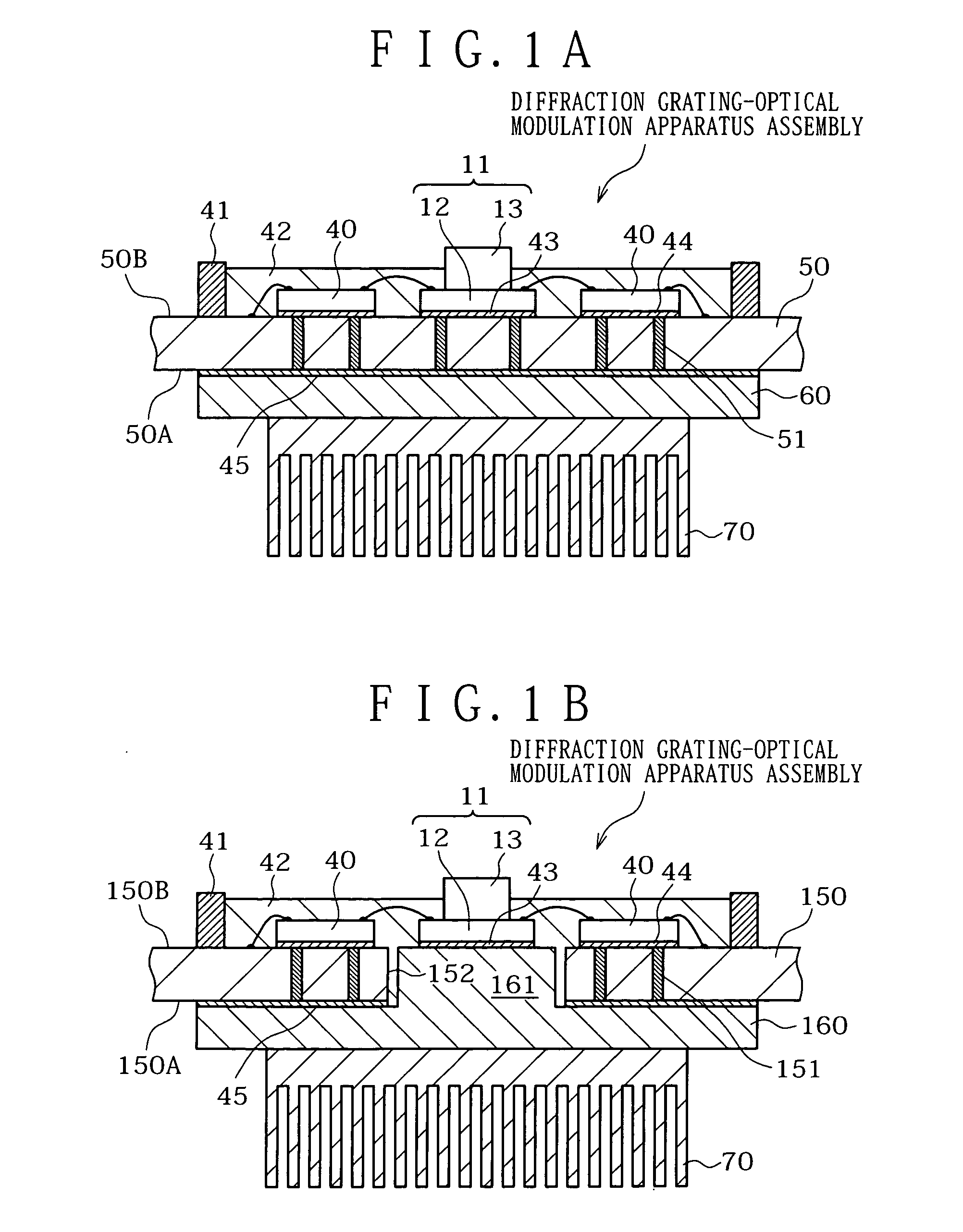
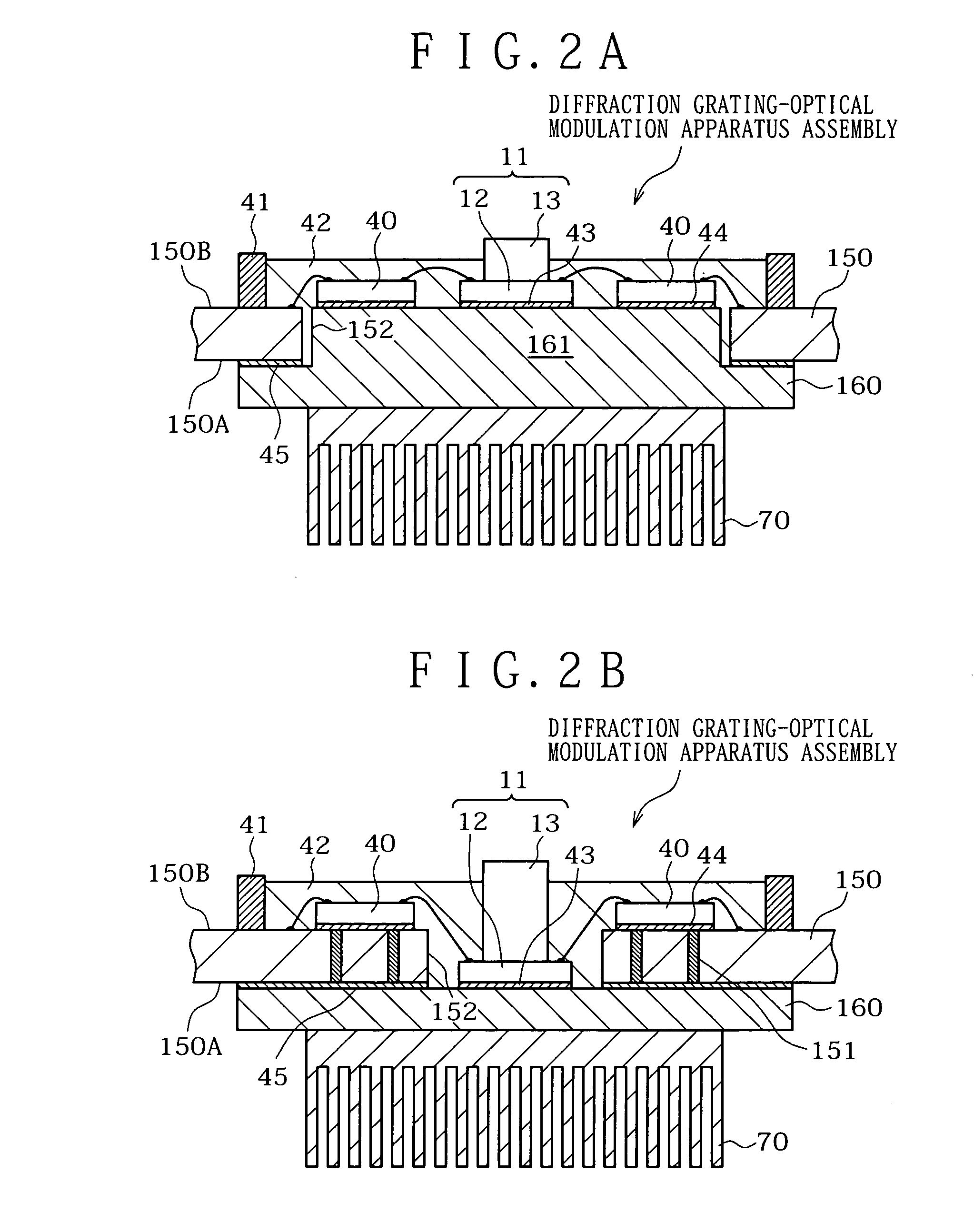
InactiveUS20050133698A1High diffraction efficiencyDisplay imageSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHeat transmissionEngineering
An optical apparatus is disclosed by which, even if heat is generated with optical elements in a diffraction grating-optical modulation apparatus, lights emitted from the optical elements is less likely to suffer from displacement therebetween. The optical apparatus includes an optical element, a mounting substrate, a support member, and a cooling / heat radiating member. The support member is attached to a first face of the mounting substrate while the optical element is attached to a second face of the mounting substrate. The cooling / heat radiating member is attached to the support member. The optical element and the support member are thermally connected to each other by a heat transmission element provided in the inside of the mounting substrate. The support member is made of a material having a thermal conductivity of 230 W / m·K or more.
Owner:SONY CORP
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20020097385A1High proportionEasy to providePhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingLight beam
In a lithographic projection apparatus, a grating spectral filter is used to filter an EUV projection beam. The grating spectral filter is preferably a blazed, grazing incidence, reflective grating. Cooling channels may be provided in or on the rear of the grating spectral filter. The grating spectral filter may be formed of a material effectively invisible to the desired radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
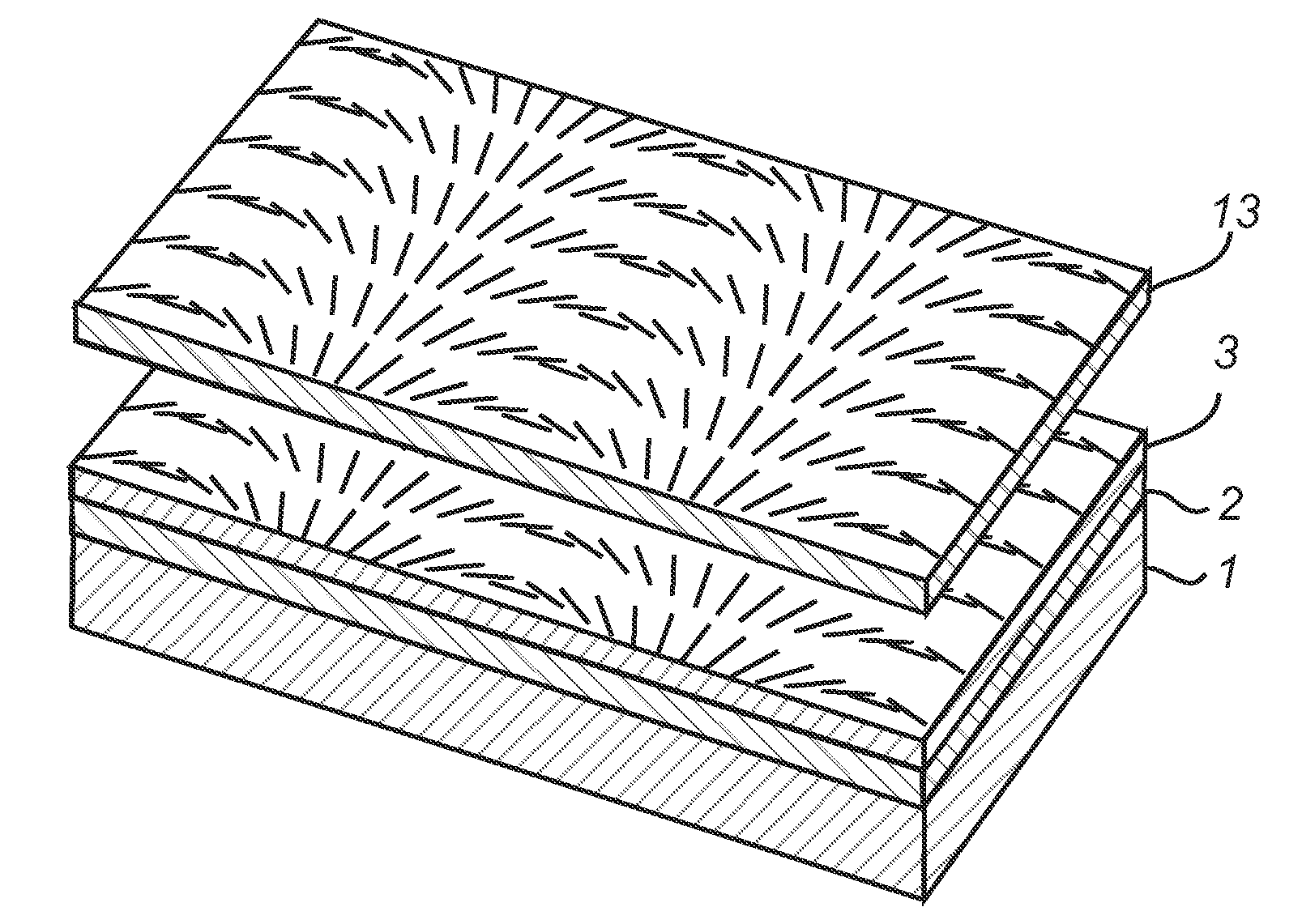
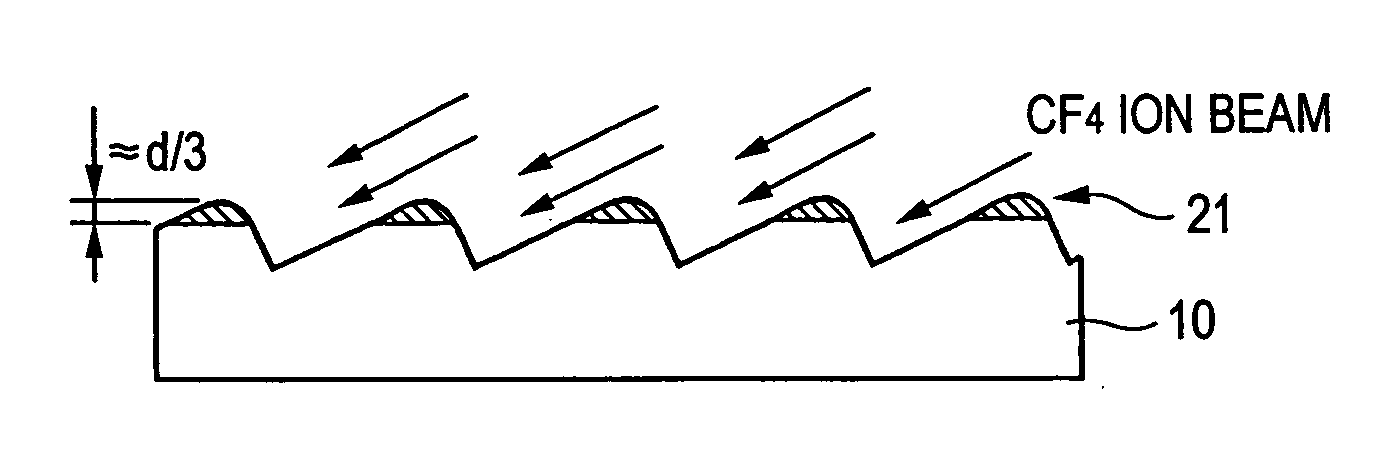
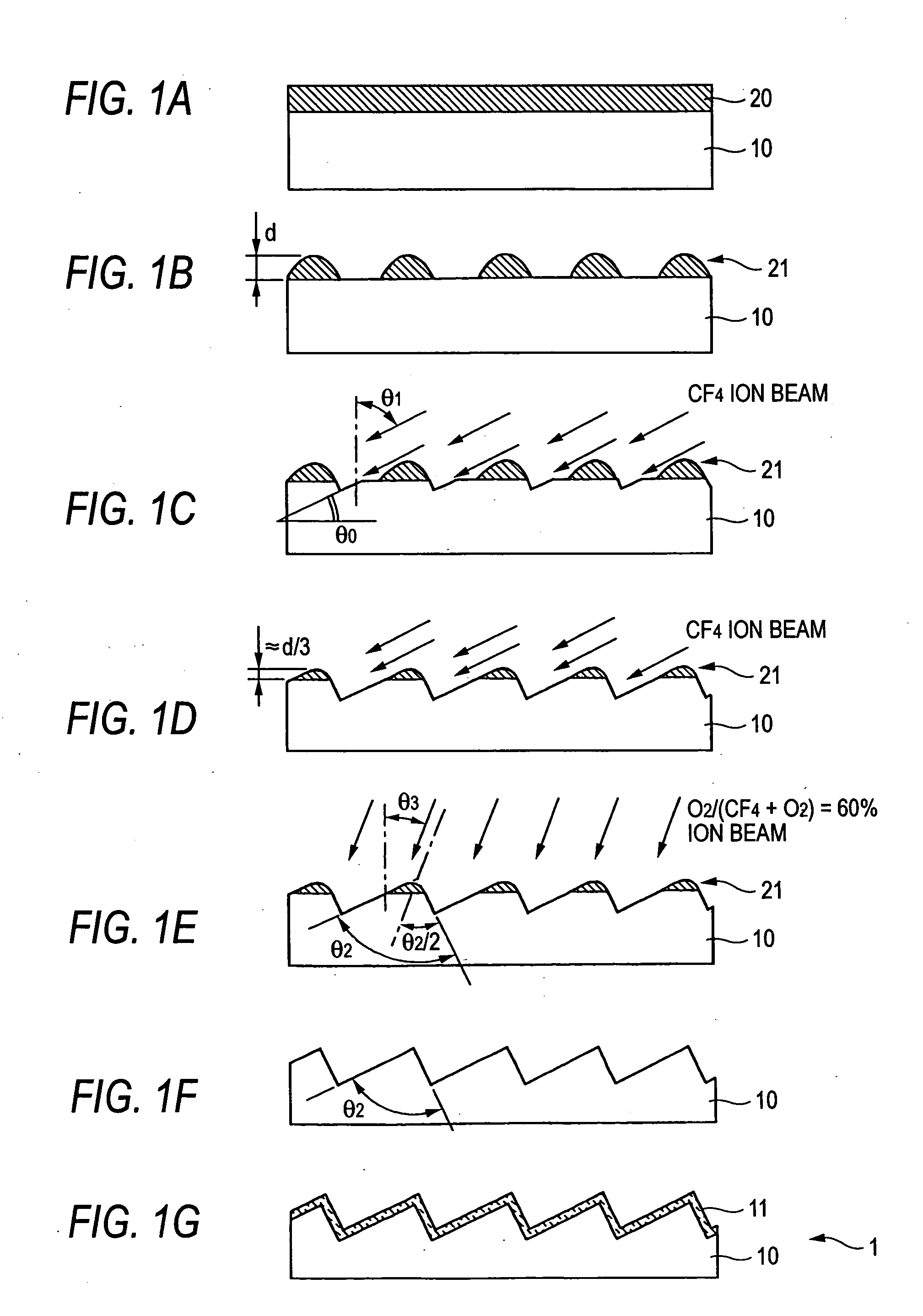
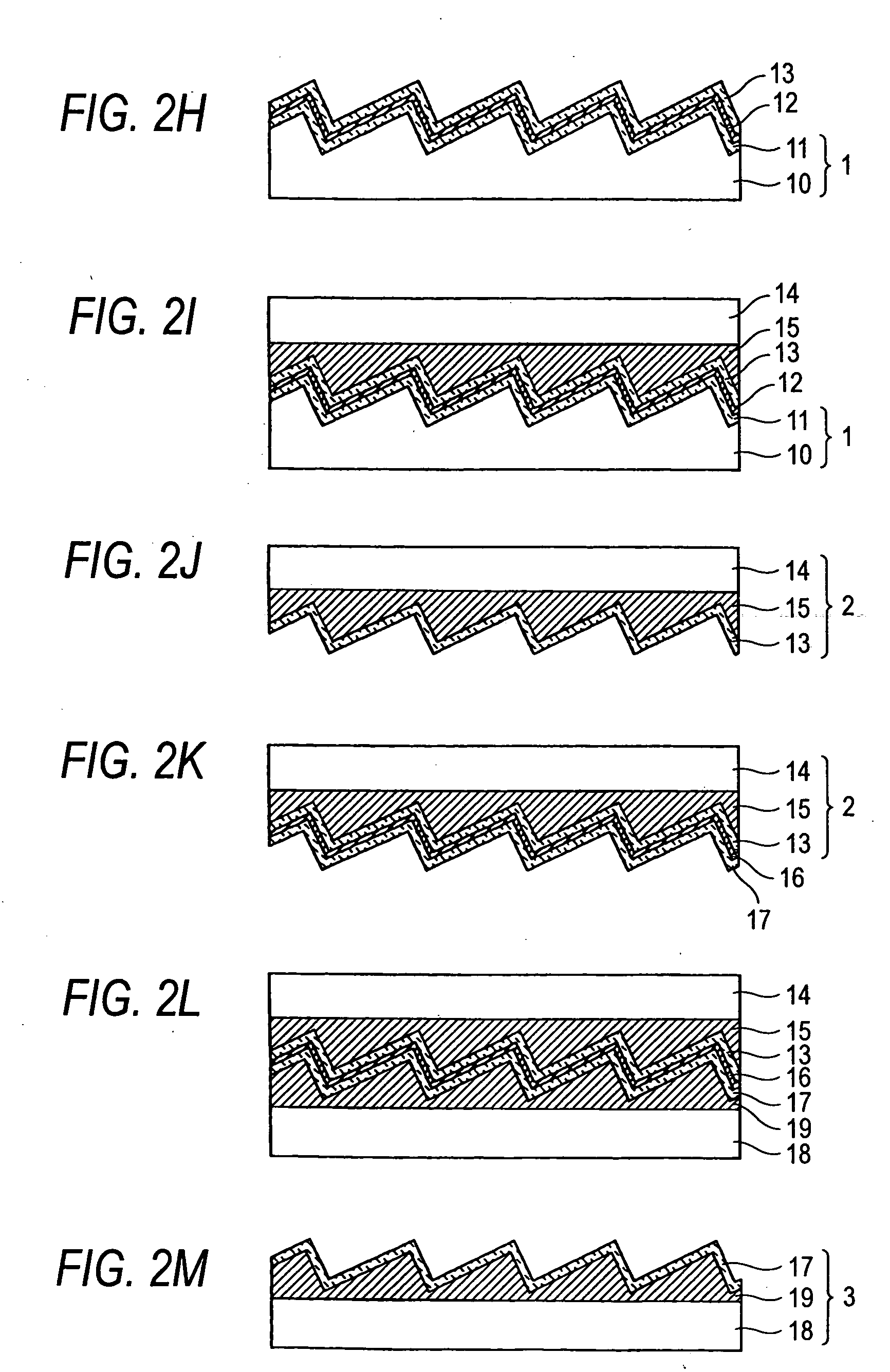
Blazed holographic grating, method for producing the same and replica grating
InactiveUS20050130072A1High diffraction efficiencyImprove linearityOptical articlesDiffraction gratingsResistIon beam irradiation
A substrate is subjected to holographic exposure to a sinusoidal or half-sinusoidal resist pattern corresponding to grating groove thereon. Thereafter, the substrate and the resist pattern are subjected to a first etching step at which they are irradiated with an ion beam obliquely at an angle that is identical to the blaze angle in the presence of CF4 as an etching gas, whereby they are cut until the height of the resist is about ⅓ of the initial value. Thereafter, the substrate is subjected to a second etching step at which the substrate is irradiated with an ion beam in the direction corresponding to the bisector of the vertex in the presence of a mixture of CF4 and O2 as an etching gas, whereby the substrate is cut until the resist disappears completely to an extent such that some overetching occurs.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
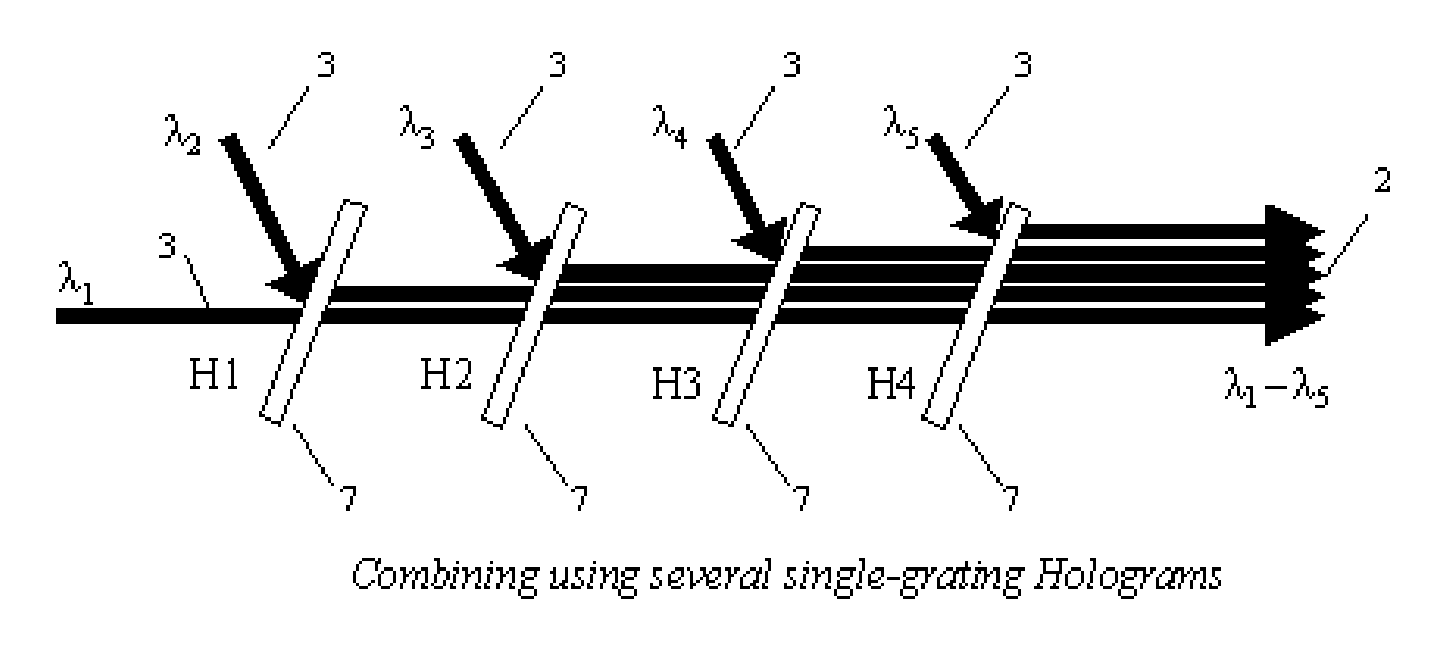
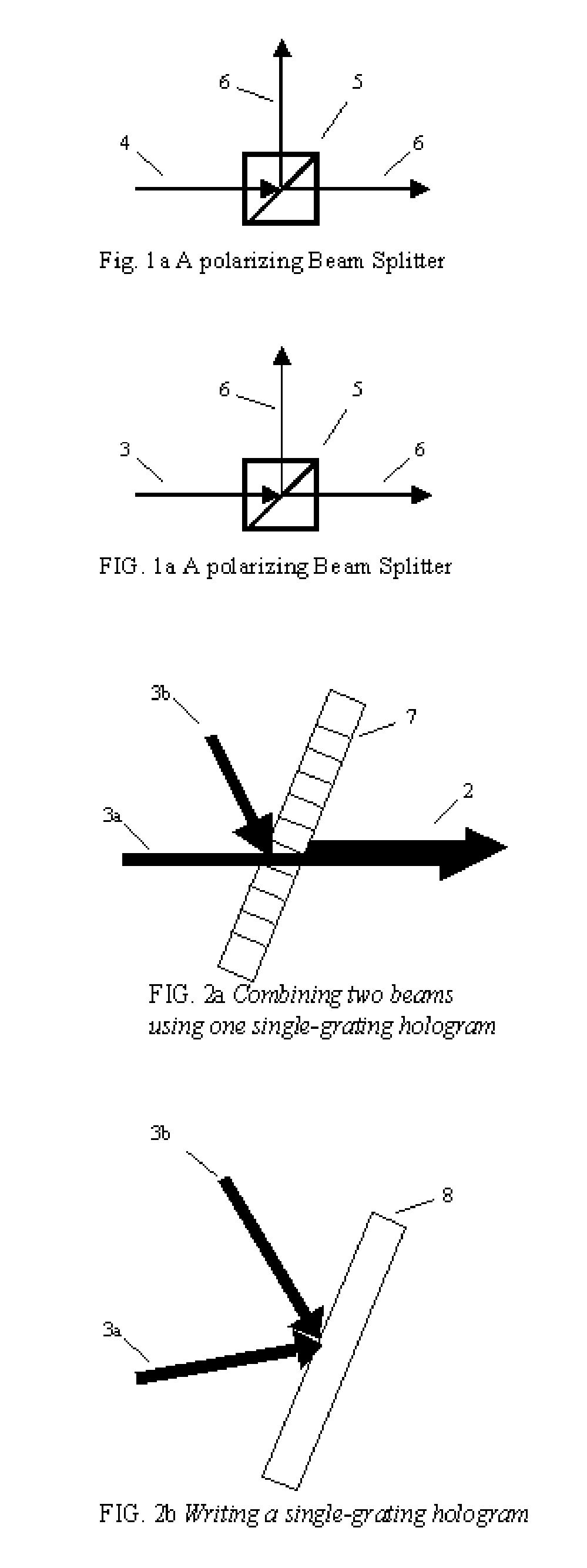
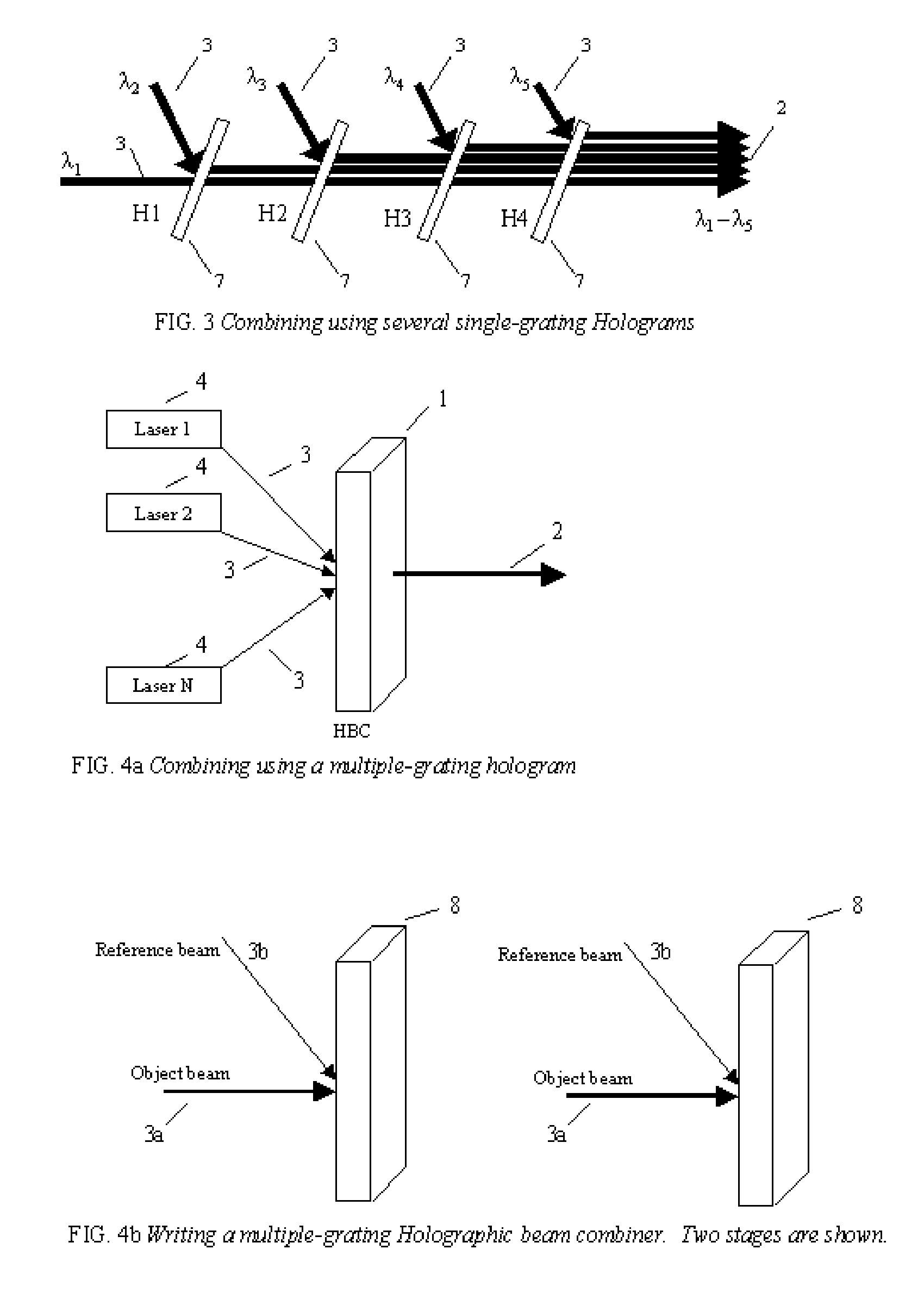
Method and system for combining multiple laser beams using transmission holographic methodologies
InactiveUS20060109876A1Low costGood techniqueOptical resonator shape and constructionCondensersQuinonePhotopolymer
The Holographic Beam Combiner, (HBC), is used to combine the output from many lasers into a single-aperture, diffraction-limited beam. The HBC is based on the storage of multiple holographic gratings in the same spatial location. By using a photopolymer material such as quinone-doped polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) that uses a novel principle of “polymer with diffusion amplification” (PDA), it is possible to combine a large number (N) of diode lasers, with an output intensity and brightness 0.9 N times as much as those of the combined outputs of individual N lasers. The HBC will be a small, inexpensive to manufacture, and lightweight optical element. The basic idea of the HBC is to construct multiple holograms onto a recording material, with each hologram using a reference beam incident at a different angle, but keeping the object beam at a fixed position. When illuminated by a single read beam at an angle matching one of the reference beams, a diffracted beam is produced in the fixed direction of the object beam. When multiple read beams, matching the multiple reference beams are used simultaneously, all the beams can be made to diffract in the same direction, under certain conditions that depend on the degree of mutual coherence between the input beams.
Owner:SHAHRIAR SELIMM
Backlight using planar hologram for flat display device
InactiveUS7253799B2Reduce degree of color separationAmount of output also increasesShow cabinetsMechanical apparatusGratingLight guide
The backlight for a flat display device including a light source, a light guide plate and a surface hologram is provided. The light guide plate is installed at one side of the light source, and light from the light source travels in the light guide plate while being totally reflected. The surface hologram is formed on at least one surface of the light guide plate. The surface hologram has a pattern of a predetermined grating interval and a predetermined grating depth in order to diffract light at a predetermined angle toward the light guide plate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Holographic optical waveguide and holographic optical waveguide display device
InactiveCN105487170ASolving Off-Axis Transmission IssuesSolve the problems of large thickness, uncompact structure and large volumeOptical light guidesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
The invention discloses a holographic optical waveguide, and belongs to the technical field of augmented reality and virtual reality. The holographic optical waveguide comprises a planar optical waveguide, and an optical coupling in end and an optical coupling out end which are respectively arranged at the two ends of the planar optical waveguide. The optical coupling in end reflects received light rays so that the reflected light rays are enabled to meet the total reflection conditions to be transmitted to the optical coupling out end through multiple times of total reflection between the two reflecting surfaces of the planar optical waveguide. The received light rays are diffractively emergent out of the optical coupling out end. The optical coupling out end is a holographic grating. The holographic grating is a polarization holographic liquid crystal grating comprising a transparent substrate, a light orientation layer and a liquid crystal layer which are arranged in turn, wherein polarization holographic patterns having periodic structures are recorded on the light orientation layer. The invention also discloses a holographic optical waveguide display device. The polarization holographic liquid crystal grating is used as the optical coupling out end of the holographic optical waveguide so that 100% of diffraction efficiency can be achieved theoretically, and zero order waves can be suppressed and conjugate images can be eliminated.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Hologram recording method and hologram recording material
InactiveUS20050058910A1High sensitivityHigh efficiencyPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusRefractive index modulationPhotochemistry
To provide a hologram recording method capable of satisfying high sensitivity and at the same time, satisfying high diffraction efficiency, good preservability, low shrinkage percentage, dry processing and multiplex recording properties, a hologram recording method comprises a first step of producing a latent image upon holographic exposure, and a second step of causing a polymerization reaction due to the latent image, to form a interference fringe providing a refractive index modulation, wherein the first and second steps are dry process; particularly, the first step is a step of producing a colored material to form the latent image and the second step is a step of causing the polymerization reaction upon irradiating the colored material with a light having a wavelength different from that of the holographic exposure, to form the interference fringe providing the refractive index modulation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS6678037B2High proportionEasy to providePhoto-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingLight beam
In a lithographic projection apparatus, a grating spectral filter is used to filter an EUV projection beam. The grating spectral filter is preferably a blazed, grazing incidence, reflective grating. Cooling channels may be provided in or on the rear of the grating spectral filter. The grating spectral filter may be formed of a material effectively invisible to the desired radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
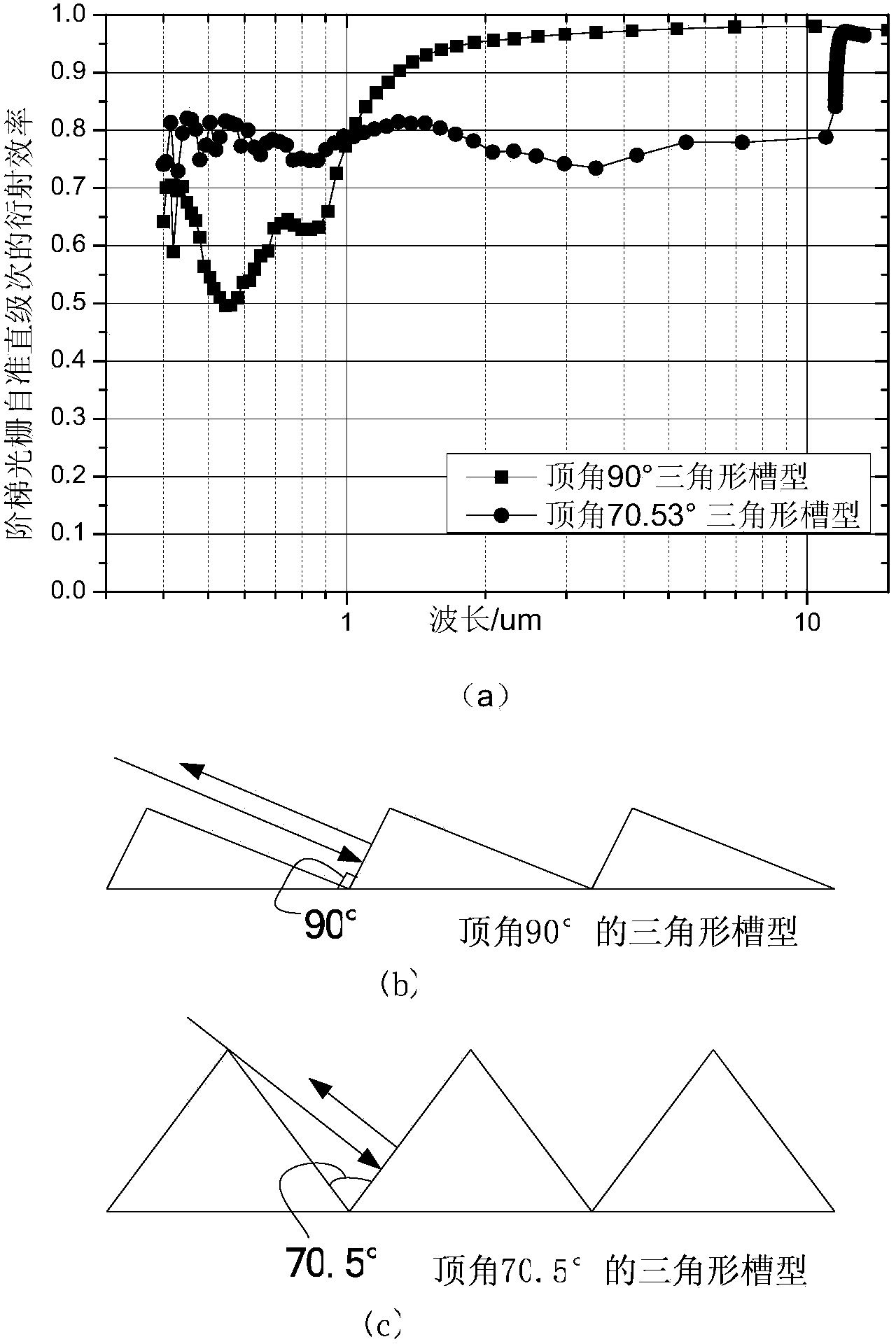
Method for manufacturing triangular groove echelon gratings with 90-degree vertex angles
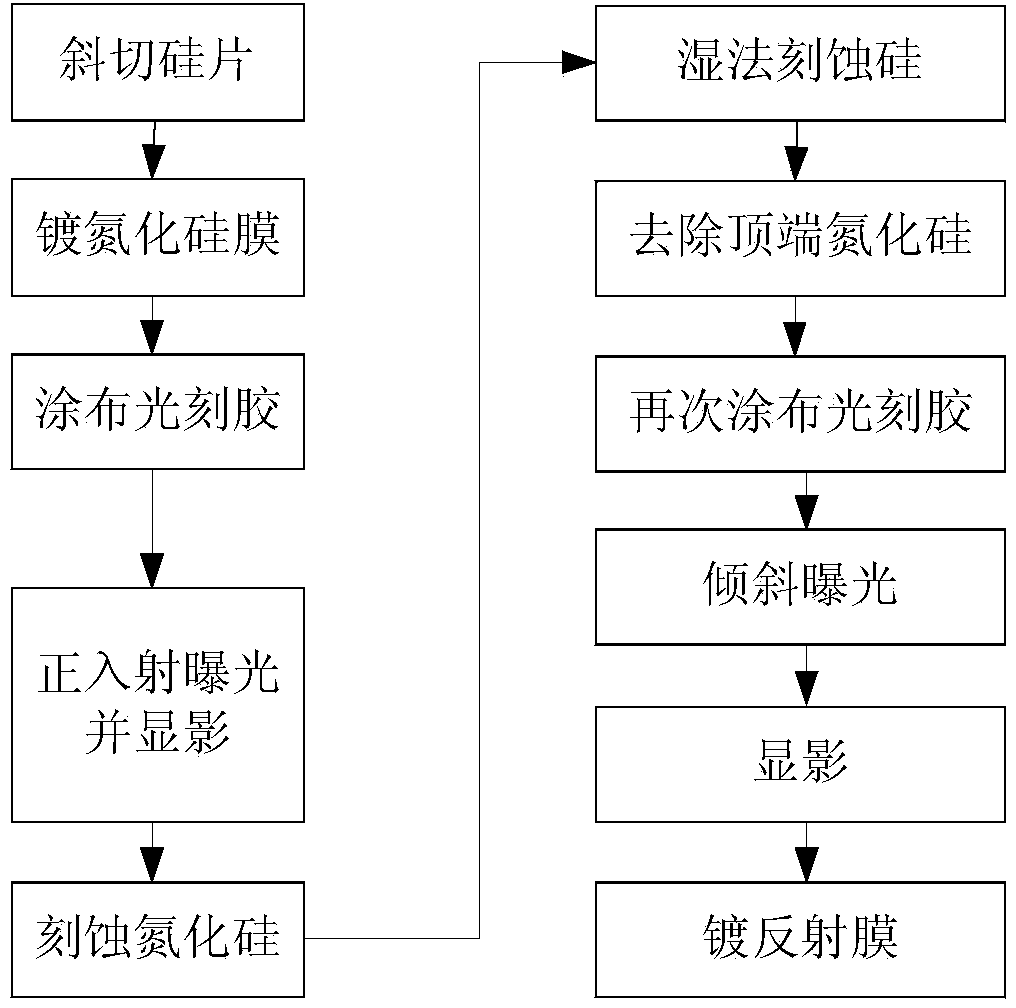
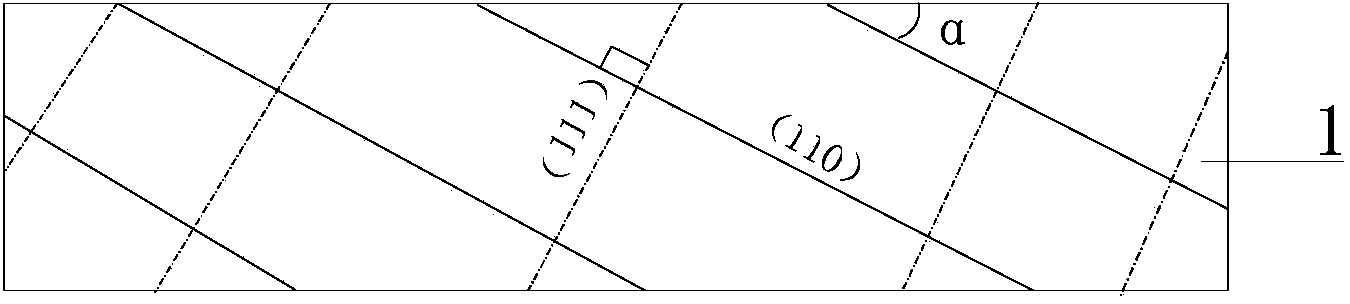
ActiveCN103901520AMake anyMeet the conditions for perfect sparkleDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusBroadbandWave band
The invention provides a method for manufacturing triangular groove echelon gratings with 90-degree vertex angles. Each triangular groove echelon grating is composed of a silicon grating structure (1), photoresist (3) and a metal film (4). A manufactured grating groove is a triangle with the vertex angle being 90 degrees, so that the diffraction efficiency higher than that of an echelon grating with the vertex angle being not 90 degrees can be achieved. Each grating structure is produced in an obliquely-cut monocrystalline wafer, the shining angles of the gratings are determined by an obliquely-cut angle for cutting each silicon wafer, and gratings with any blazing angles can be manufactured; according to the 90-degree vertex angles, grooves of silicon gratings with the vertex angles being not 90 degrees are filled with photoresist, then photoetching is conducted again, and the original silicon gratings with the vertex angles being not 90 degrees are converted into the triangular groove gratings with the vertex angles being 90 degrees. According to the manufactured grating structure, the shining face of each grating is a smooth monocrystal silicon <111> grate plane, scattering can be effectively lowered, and the diffraction efficiency of each grating is improved. The purpose that all the gratings have high diffraction efficiency on a broadband is achieved according to the fact that using wave bands can choose to be coated with various different reflecting film layers on the surfaces of the gratings.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com