Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Zeroth order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
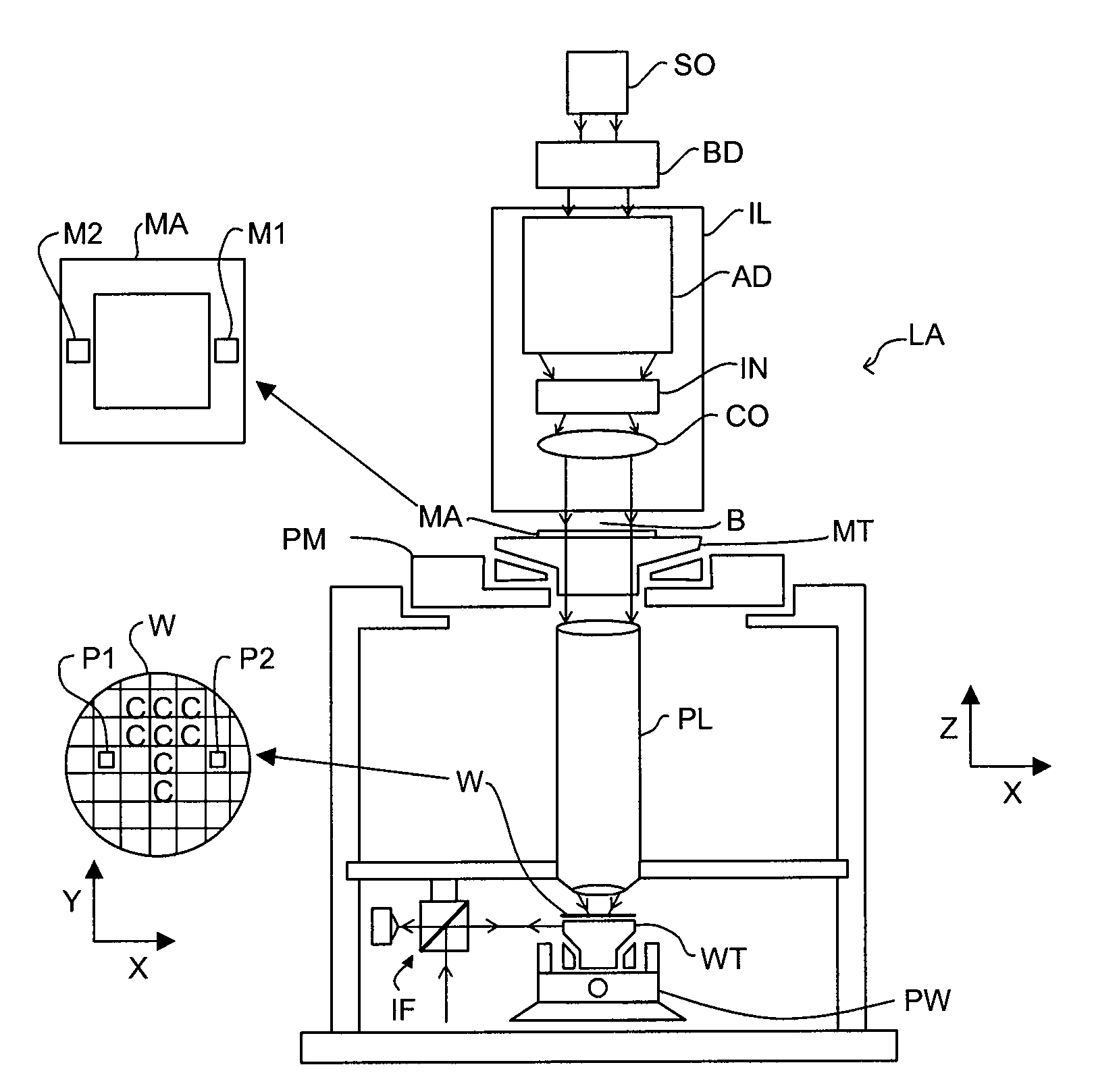
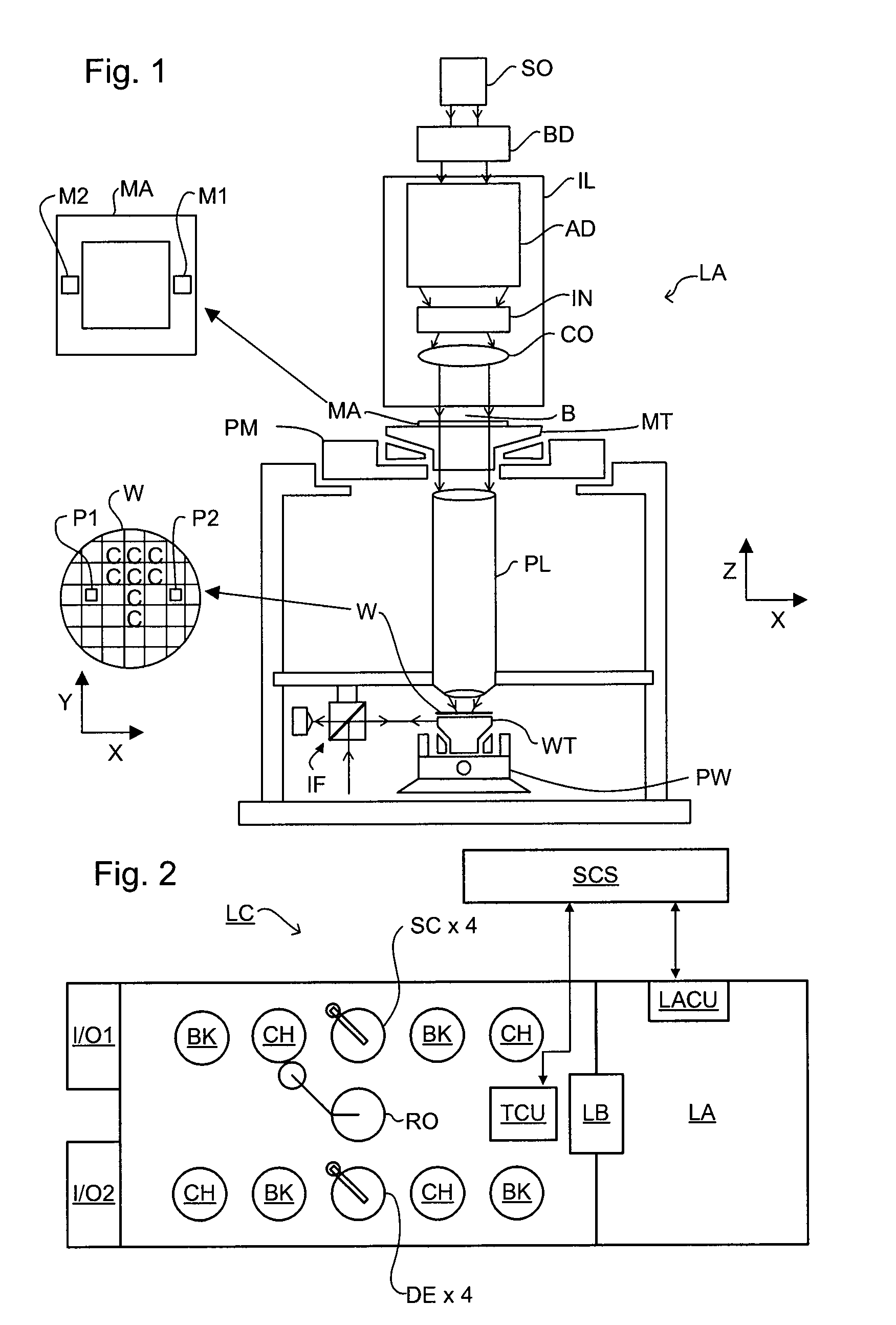
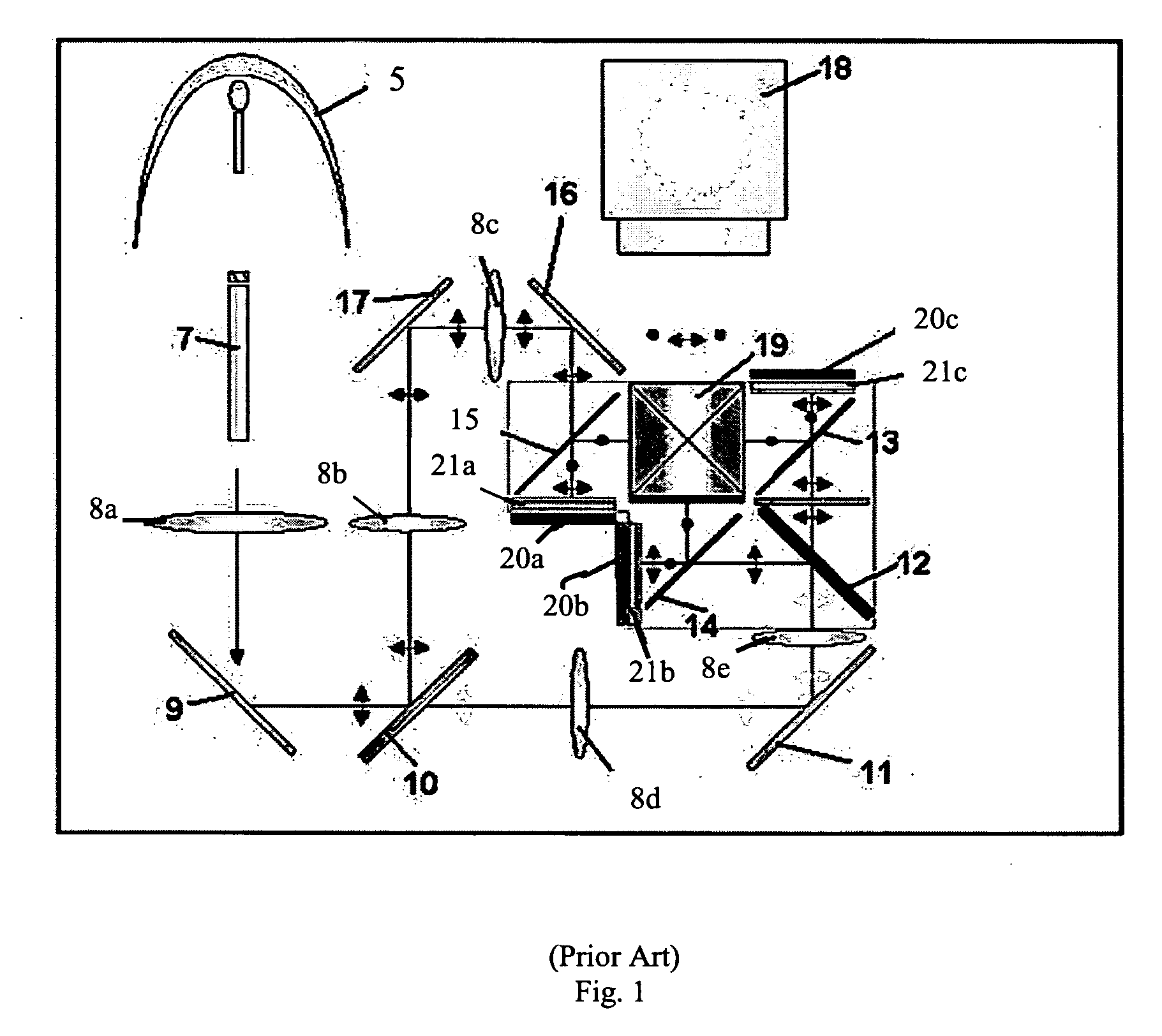
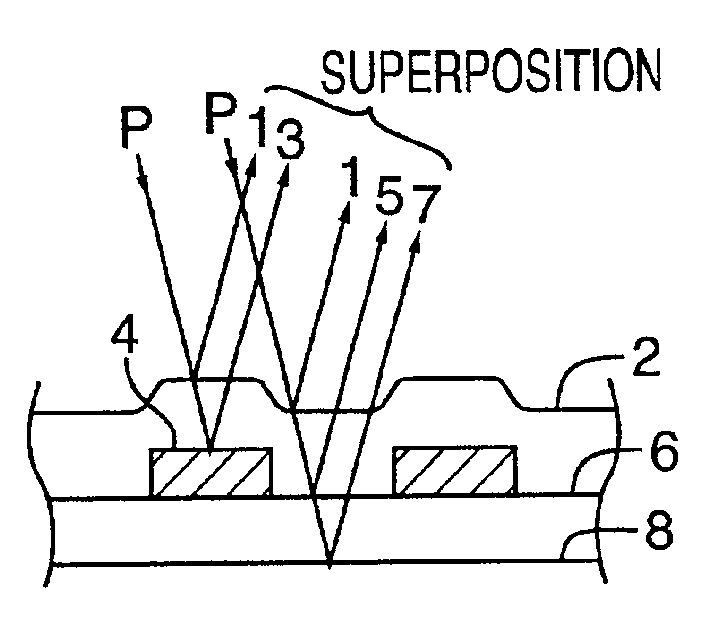
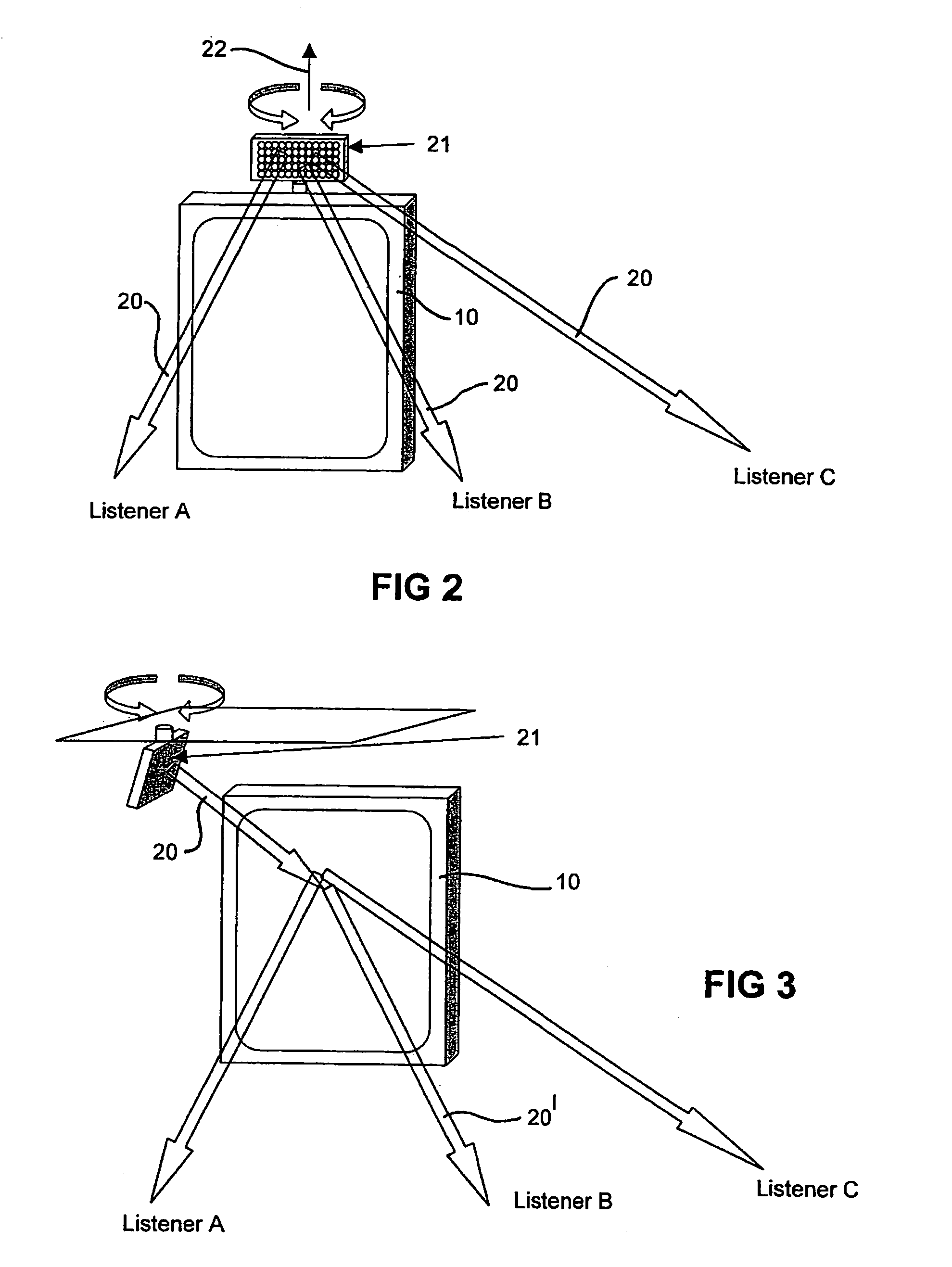
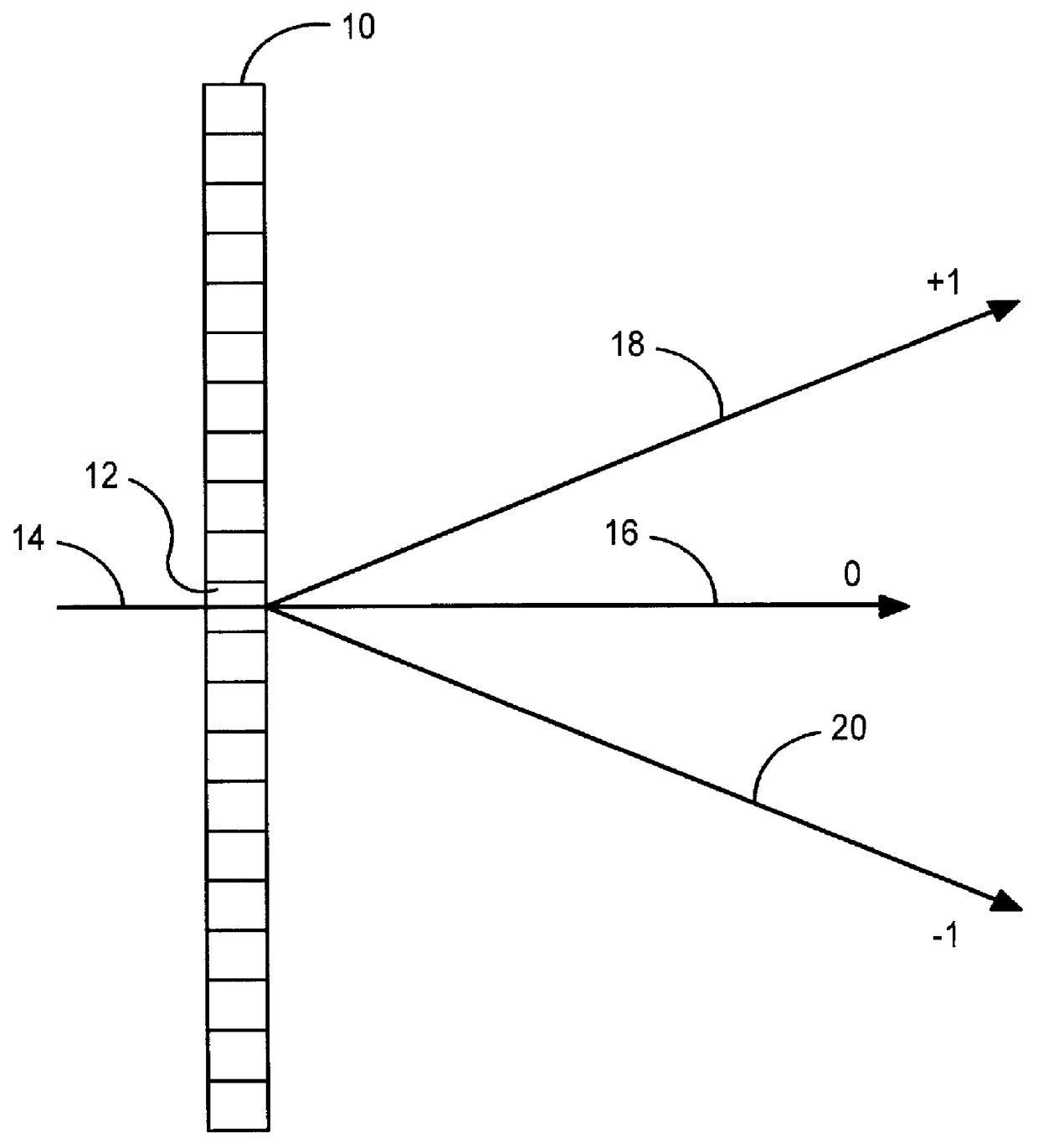
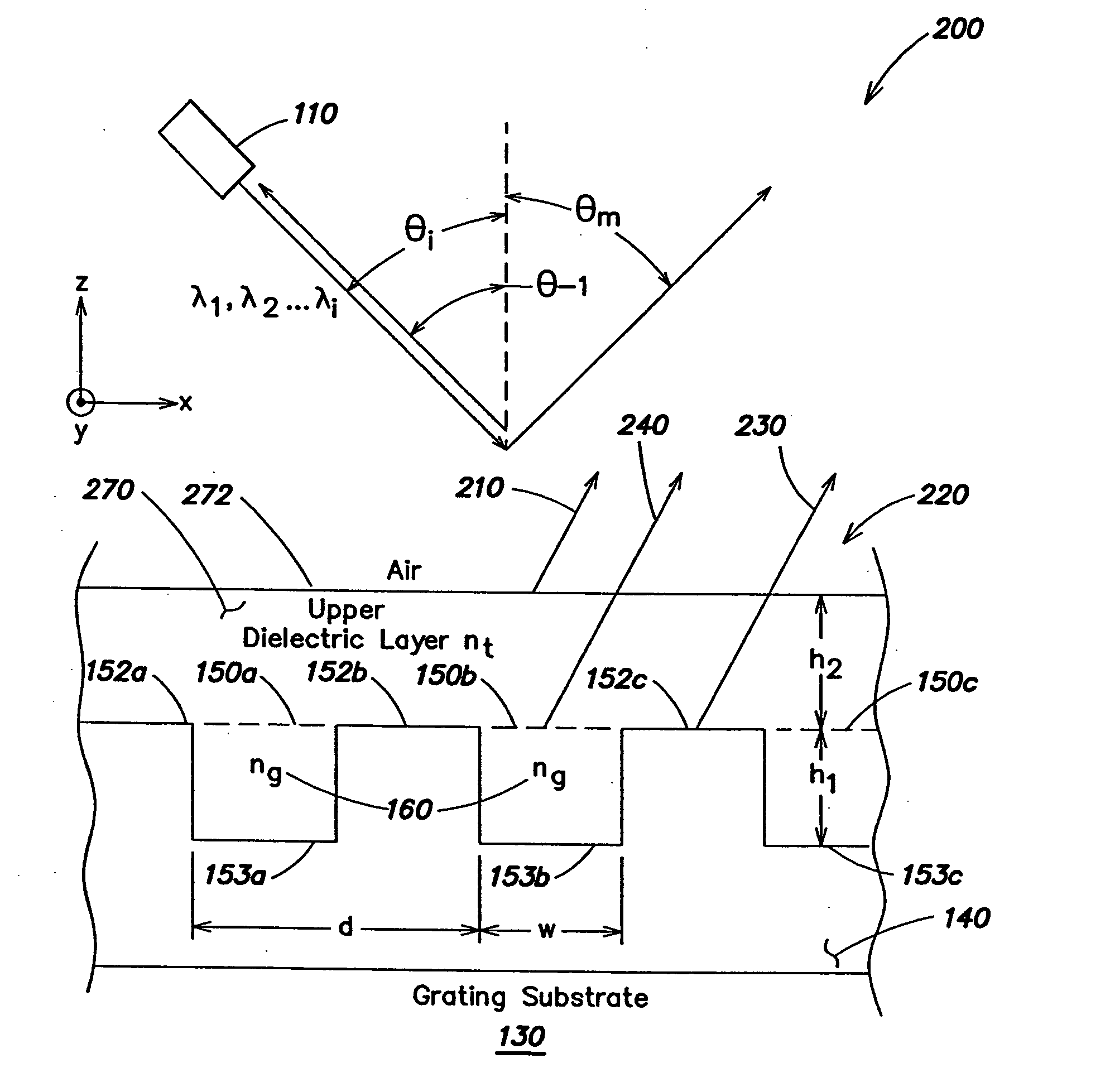
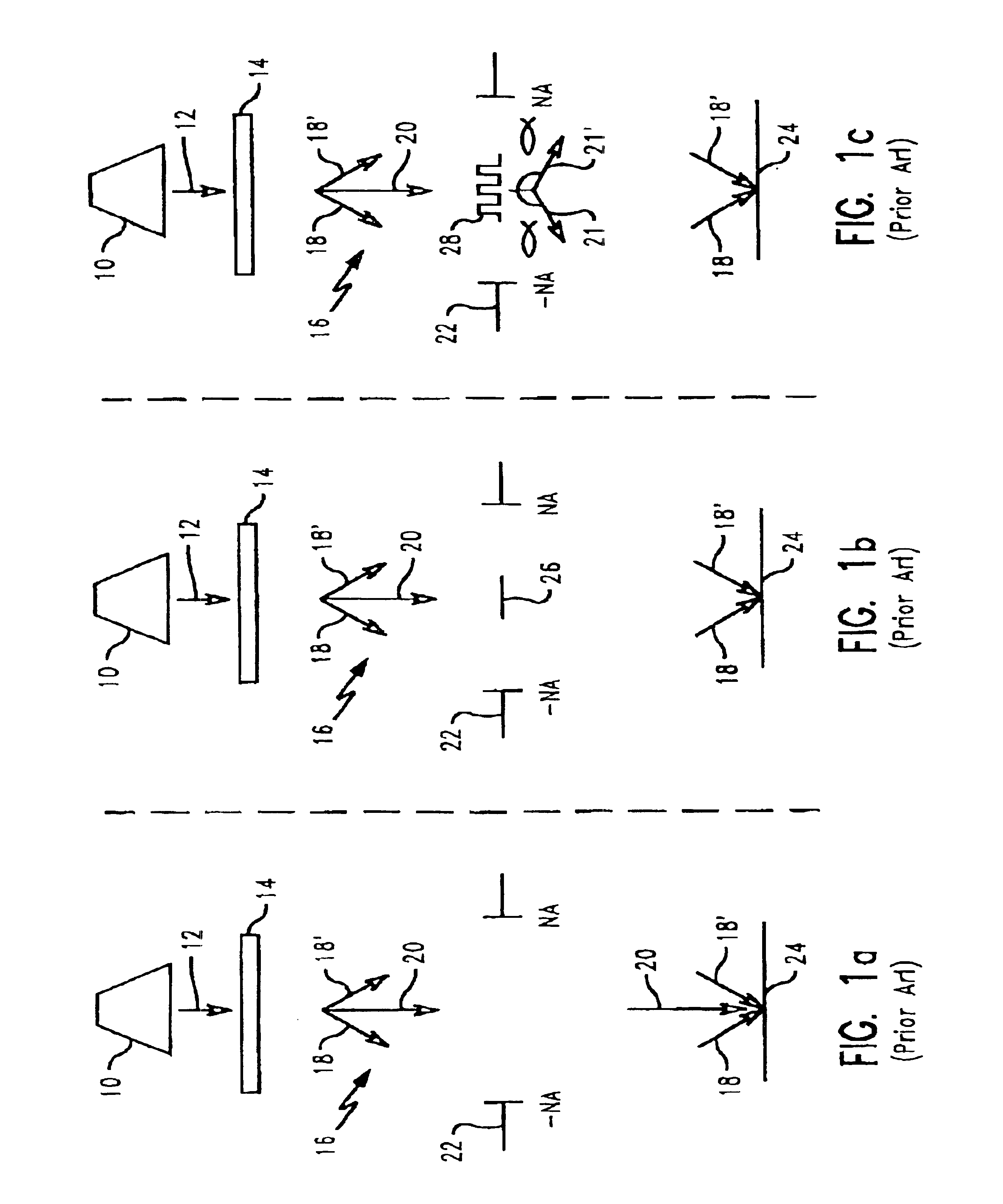
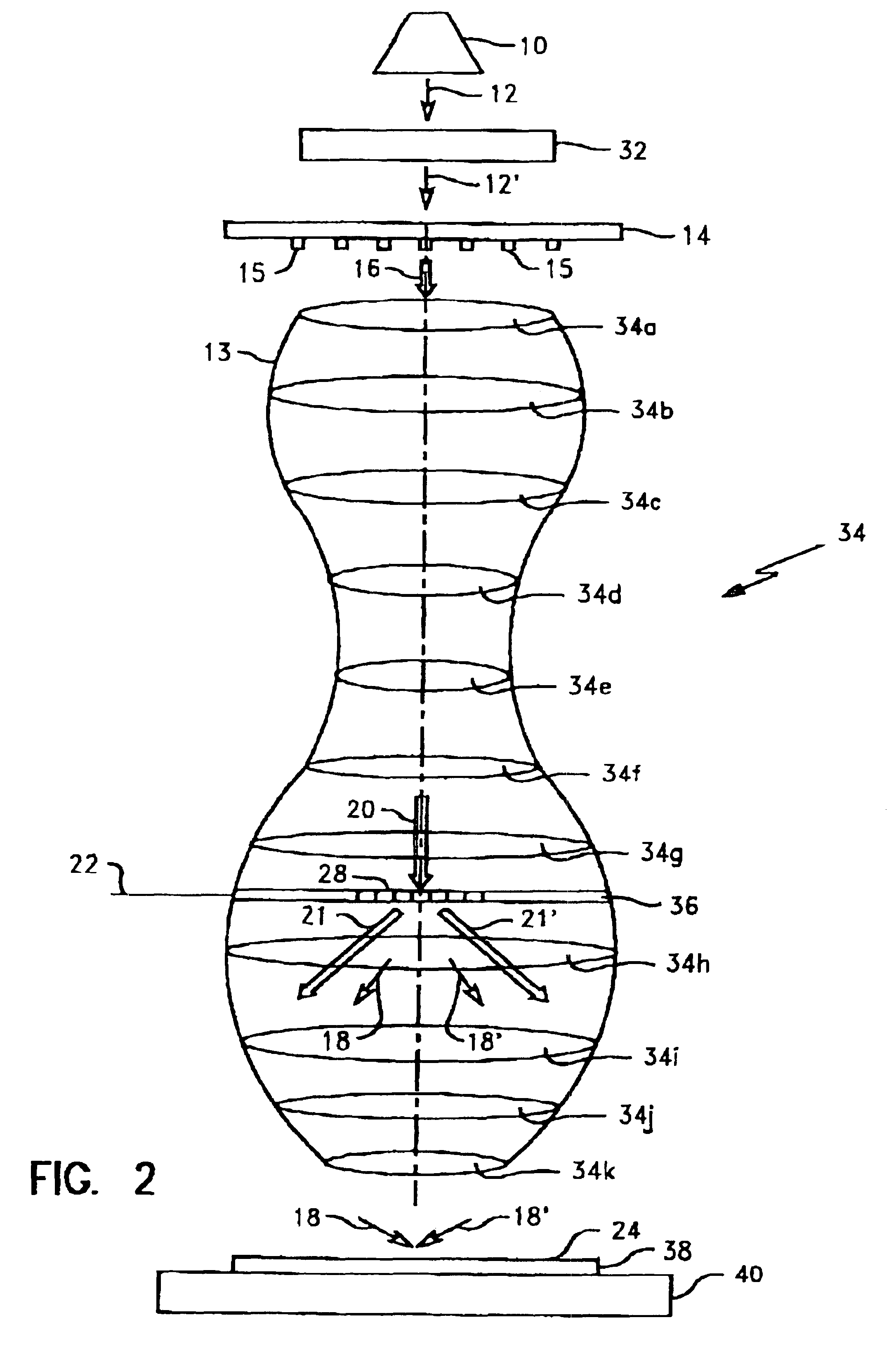
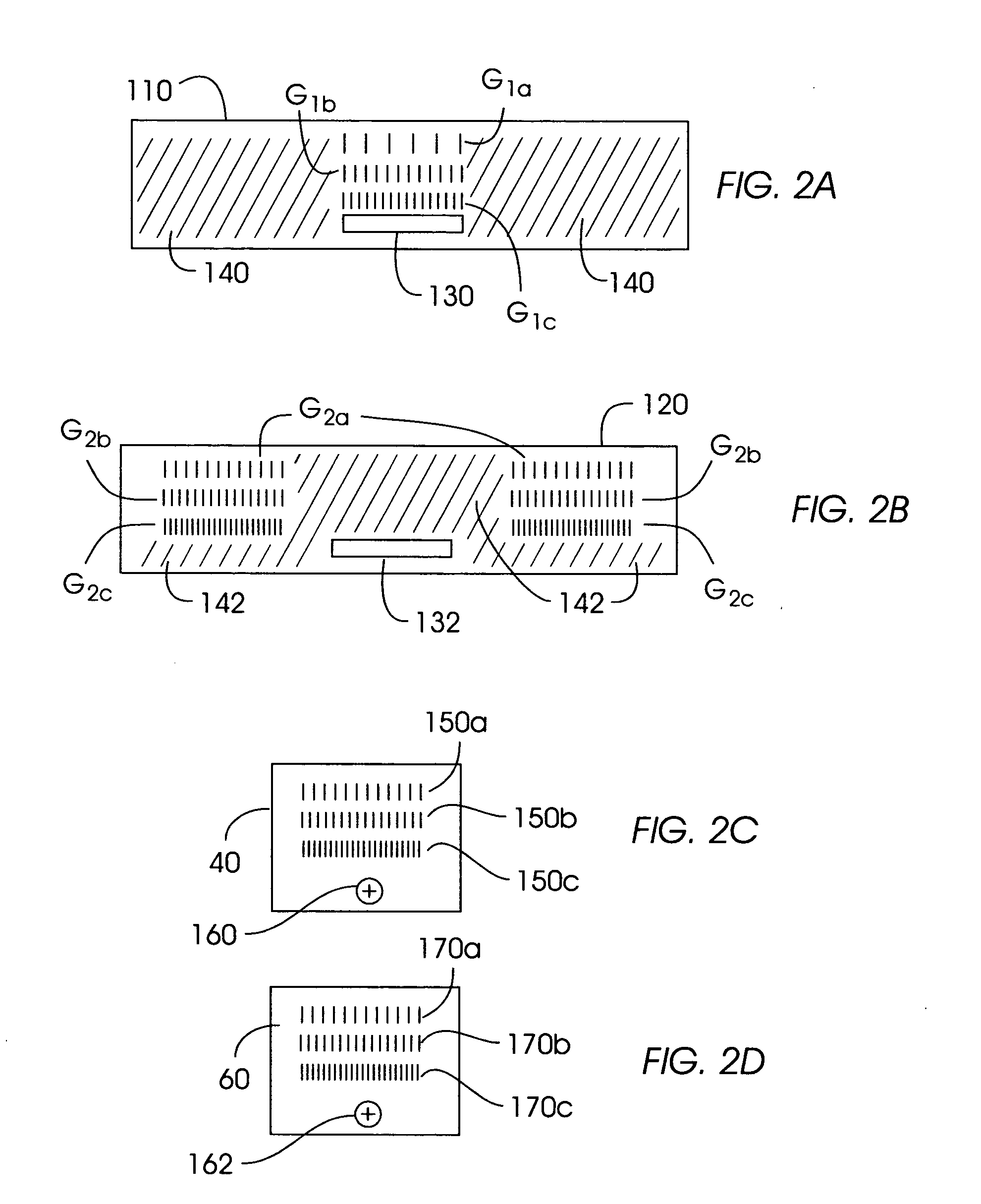
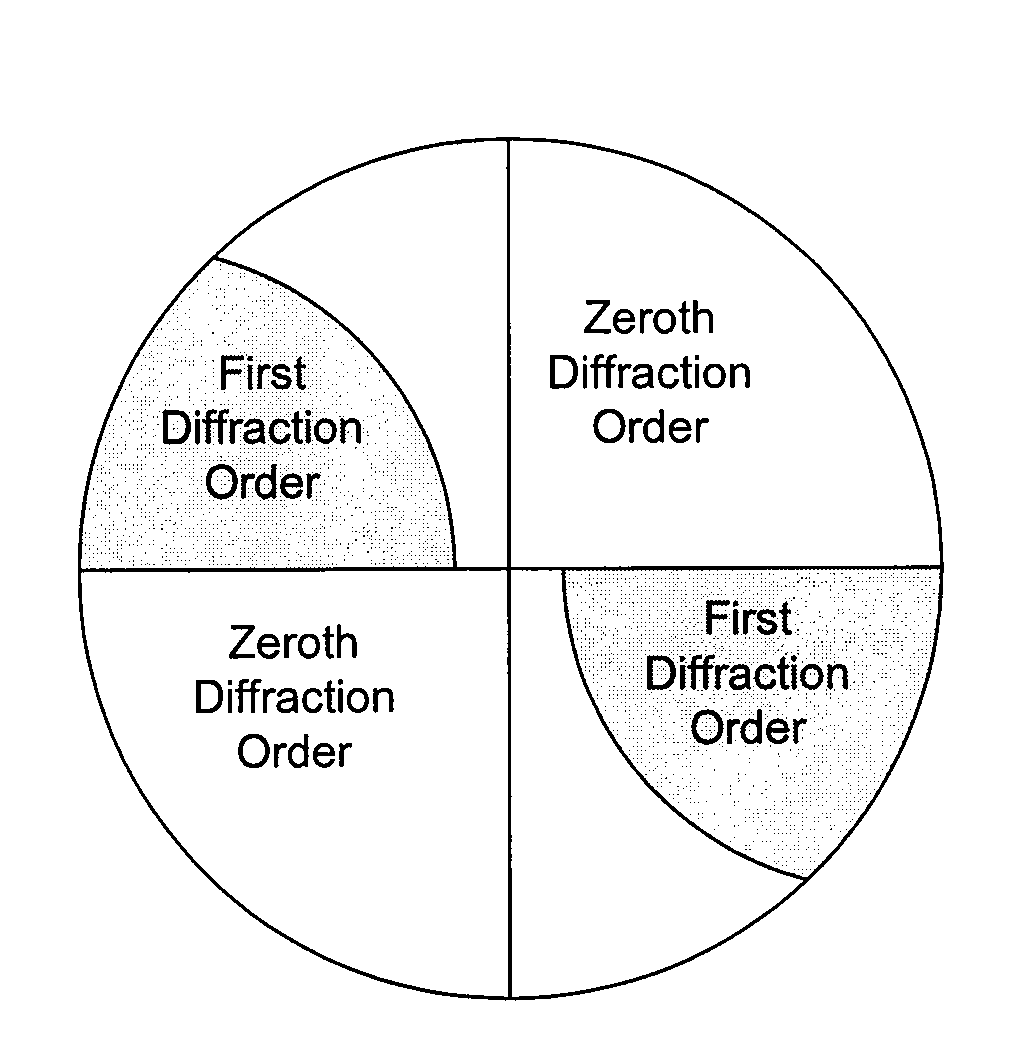
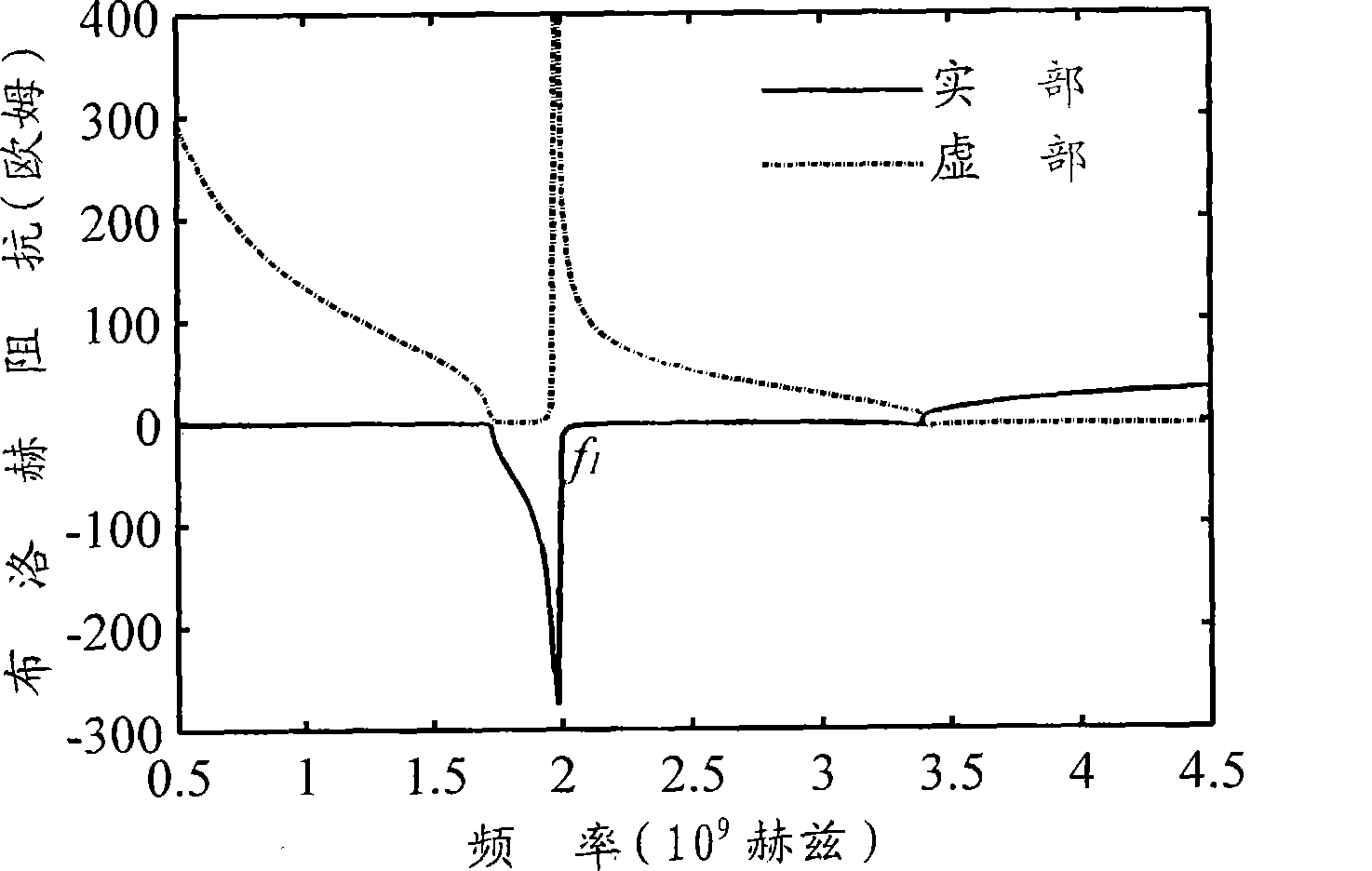
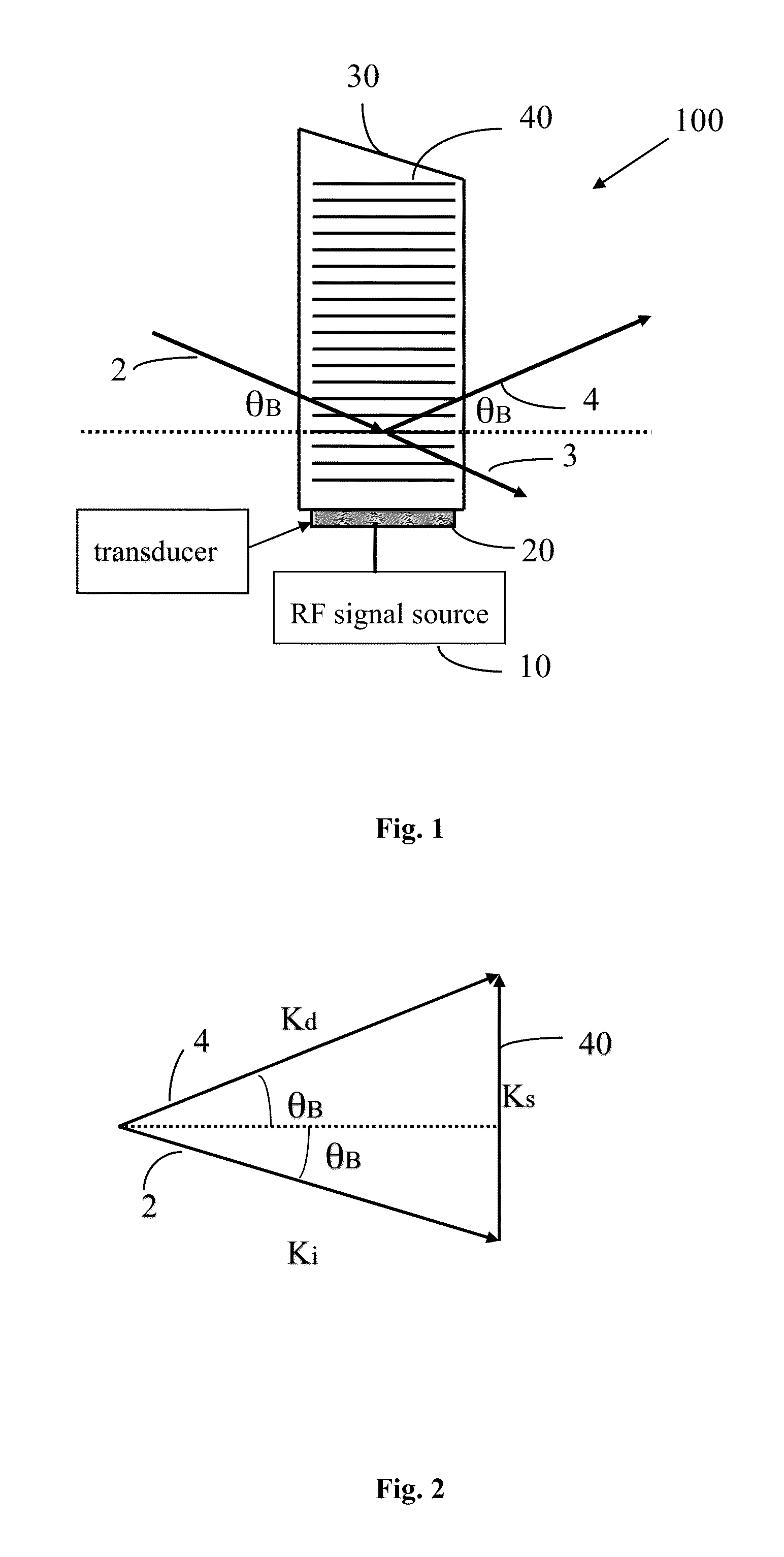
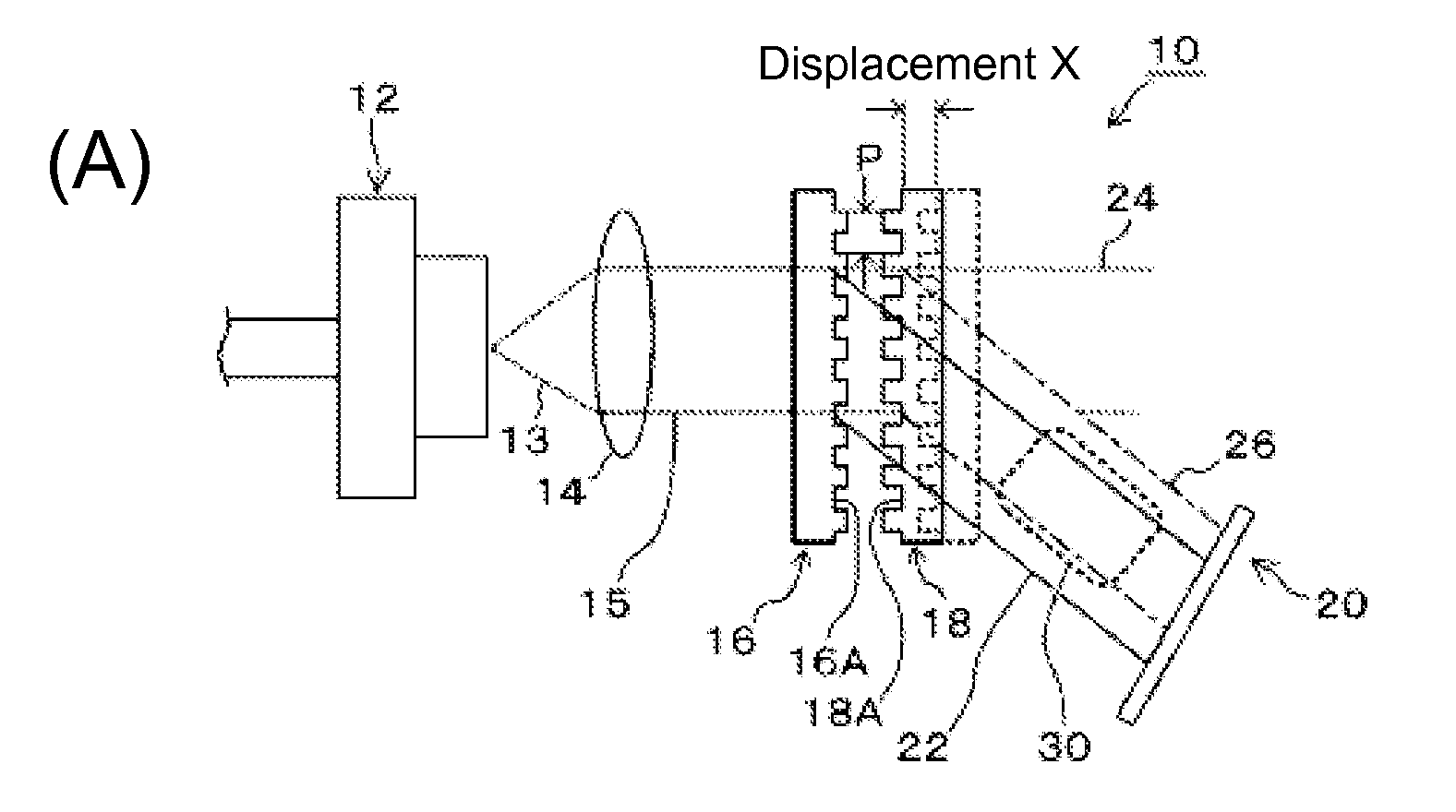
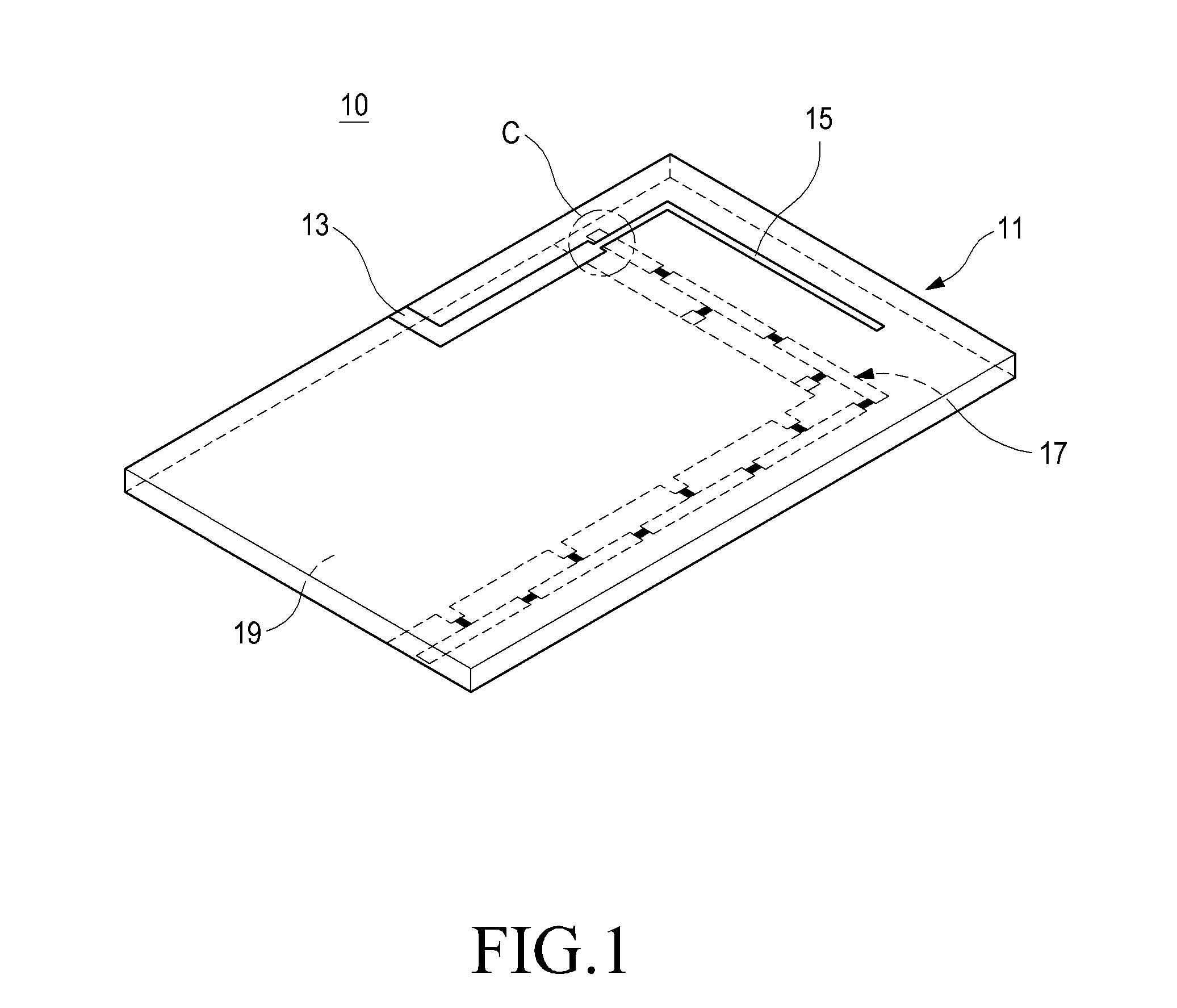
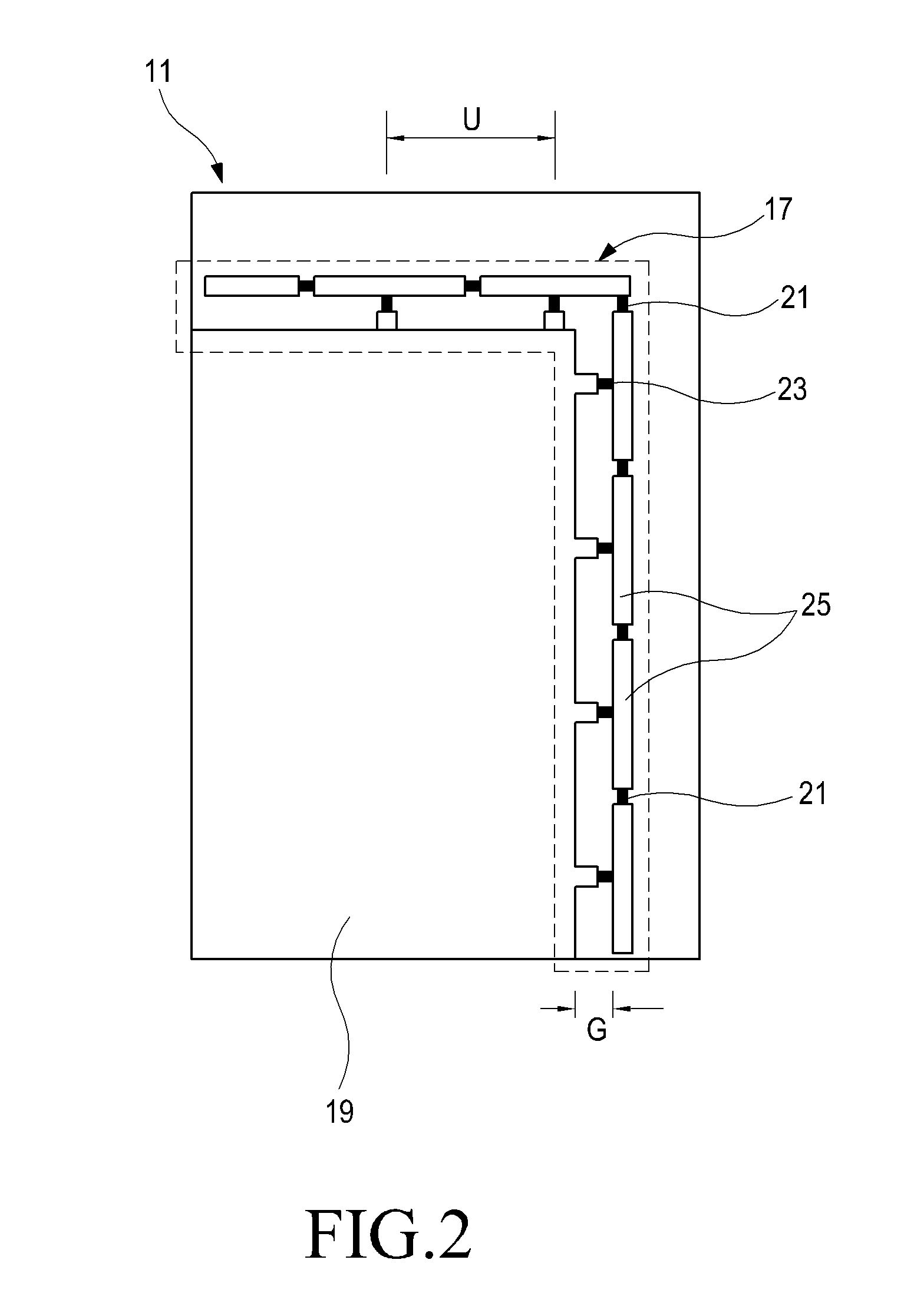
Inspection Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Lithographic Processing Cell and Inspection Method
ActiveUS20100201963A1Increase the number ofPossible to separateRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsFour quadrantsZeroth order
For angular resolved spectrometry a radiation beam is used having an illumination profile having four quadrants is used. The first and third quadrants are illuminated whereas the second and fourth quadrants aren't illuminated. The resulting pupil plane is thus also divided into four quadrants with only the zeroth order diffraction pattern appearing in the first and third quadrants and only the first order diffraction pattern appearing in the second and third quadrants.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Grating trim retarders
InactiveUS20070070276A1Improve image contrastEasily integrated into oneColor television detailsNon-linear opticsIn planeZeroth order
A grating trim retarder fabricated from a form-birefringent multi-layer dielectric stack including at least one anti-reflection coating and supported on a transparent substrate is provided. The form-birefringent dielectric stack includes an axially-inhomogeneous element in the form of a −C-plate grating and a transversely-inhomogeneous element in the form of an A-plate grating. Each of the −C-plate and the A-plate gratings are fabricated with dimensions to form a zeroth order sub-wavelength grating structure. Fabricating the grating trim retarder with anti-reflection coatings and / or a segment where the −C-plate and A-plate grating overlap enables the in-plane and out-of-plane retardances to be tailored independently according to the desired application.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
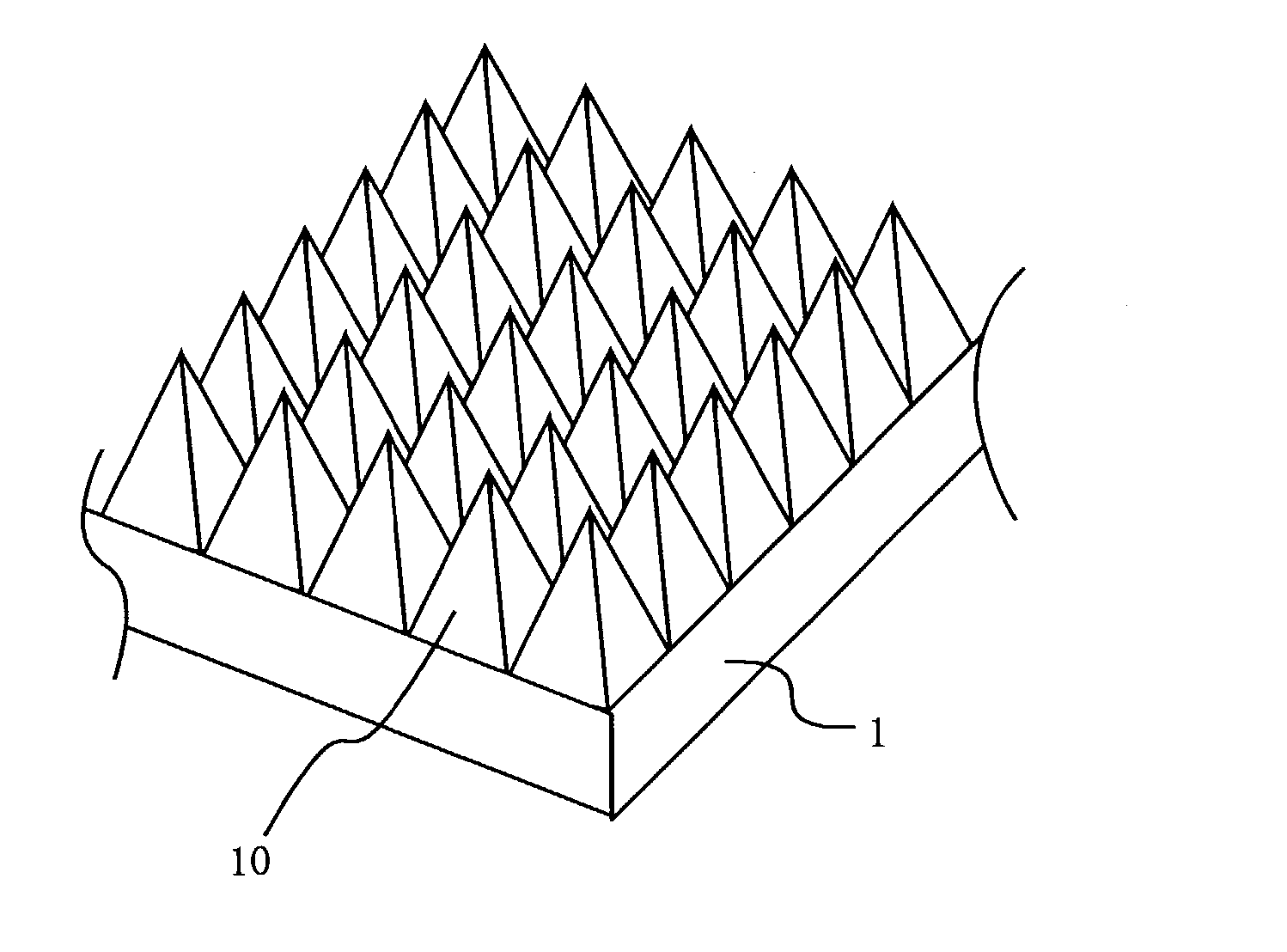
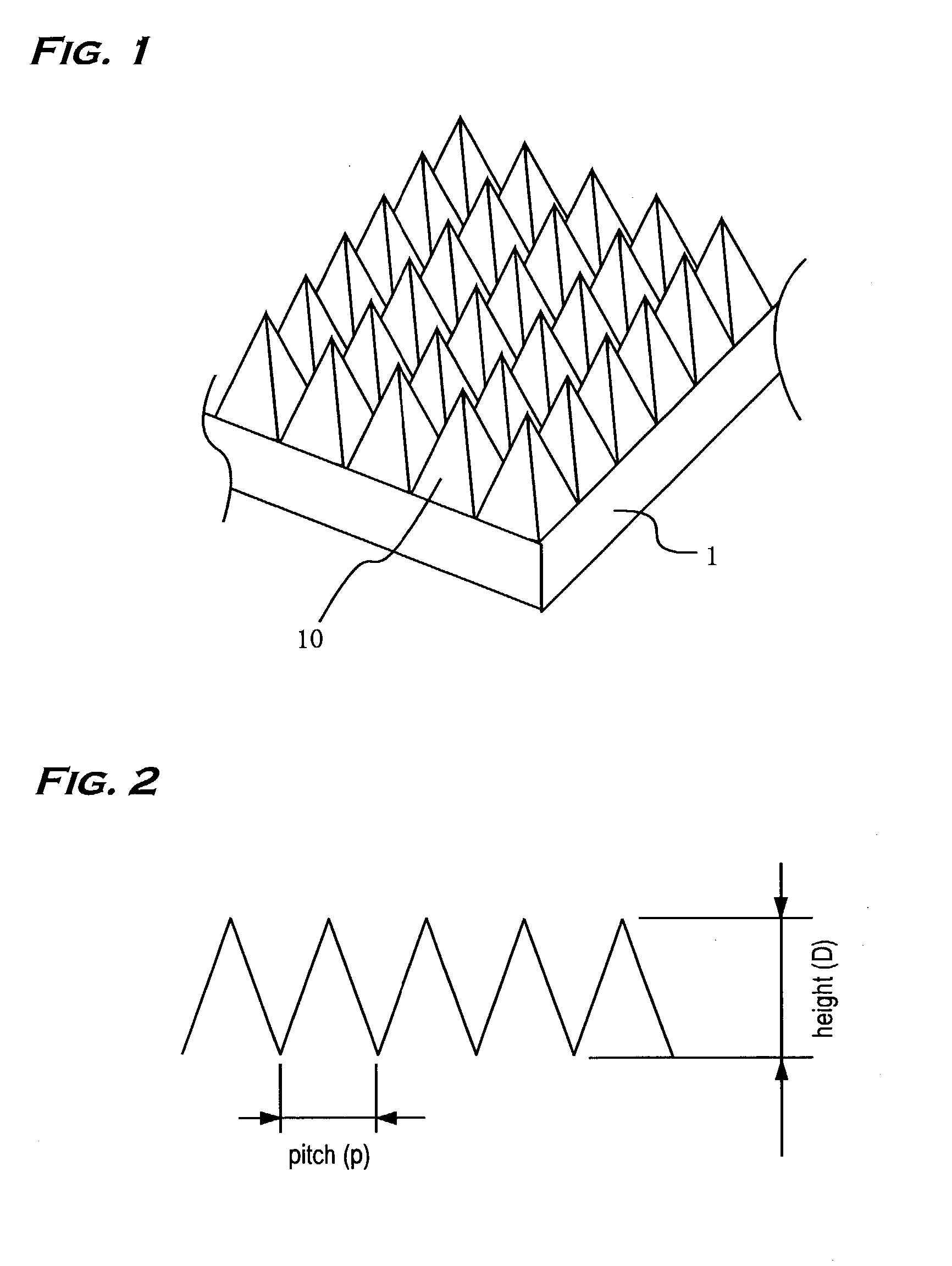
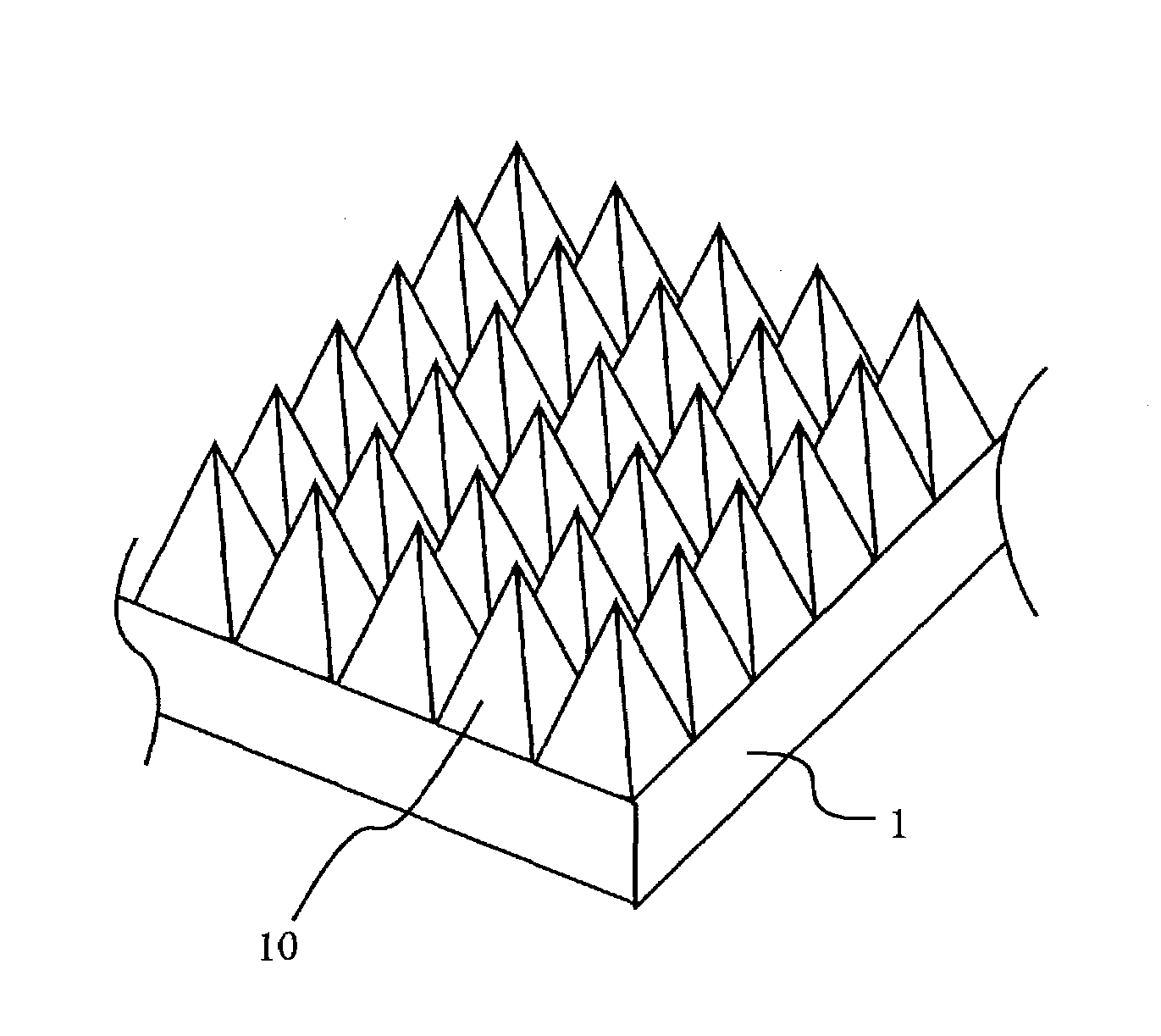
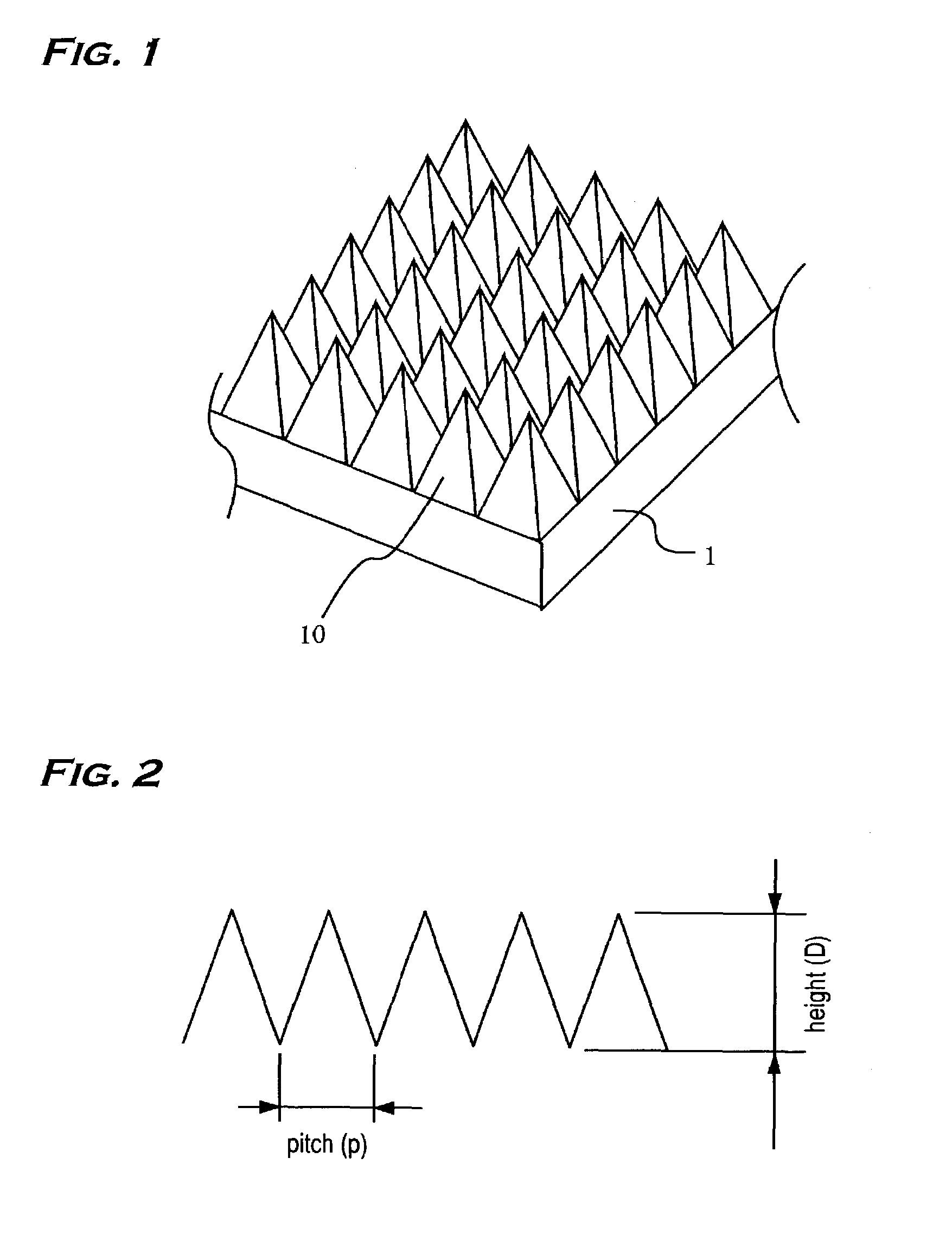
Antireflective member and electronic equipment using same
InactiveUS20030180476A1Stable characteristicsLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsZeroth orderOptoelectronics
This invention has an object to provide an antireflective member with stability and a low reflectance at low cost by performing an antireflective treatment to the substrate in the molding process of the substrate. In the invention a roughened surface with a continuous pattern in a fine pyramidal shape 10 is formed on a surface of a transparent substrate 1, the roughened surface is a diffraction surface with zeroth-order diffraction to visible light, and the pattern of the roughened surface is transferred from a mold at a transfer rate of not less than 70%.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Non-Etched Flat Polarization-Selective Diffractive Optical Elements
InactiveUS20090009668A1Well formedLow costPolarising elementsRecord information storageZeroth orderDiffraction optics
A polarization-selective diffractive optical element includes a liquid crystal polymer film supported by a substrate. The liquid crystal polymer film includes an array of pixels, each pixel encoded with a fixed liquid crystal director such that each liquid crystal director is aligned in a common plane perpendicular to the liquid crystal polymer film and provides a predetermined pattern of out-of-plane tilts. A size of the pixels in the array and the predetermined pattern are selected such that the liquid crystal polymer film forms a phase hologram for diffracting light polarized parallel to said common plane and a zeroth order diffraction grating for light polarized perpendicular to the said common plane. The non-etched and flat phase hologram is suitable for a wide range of applications.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Layer-thickness detection methods and apparatus for wafers and the like, and polishing apparatus comprising same
InactiveUS7052920B2Easy to detectHigher diffraction orders is eliminatedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesCorrelation functionSignal light
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for detecting a thickness of a surficial layer (e.g., metal or insulating layer) on a workpiece (e.g., semiconductor wafer) during a process for planarizing the layer, so as to stop the process when a suitable process endpoint is reached. Layer thickness is detected based on a spectral-characteristic signal of reflected or transmitted signal light, obtained by directing a probe light onto the surface of the workpiece. Example spectral characteristics are local maxima and minima of signal-light waveform, differences or quotients of the same, a dispersion of the signal-light waveform, a component of a Fourier transform of the signal waveform, a cross-correlation function of the signal waveform. Alternatively, the zeroth order of signal light is selected for measurement, or a spatial coherence length of the probe light is compared with the degree of fineness of the pattern on the surface illuminated with the probe light. An optical model can be determined based on the comparison, and at least one of the layer thickness and the process endpoint is detected by comparing the measured signal-light intensity with the calculated theoretical signal light intensity.
Owner:NIKON CORP
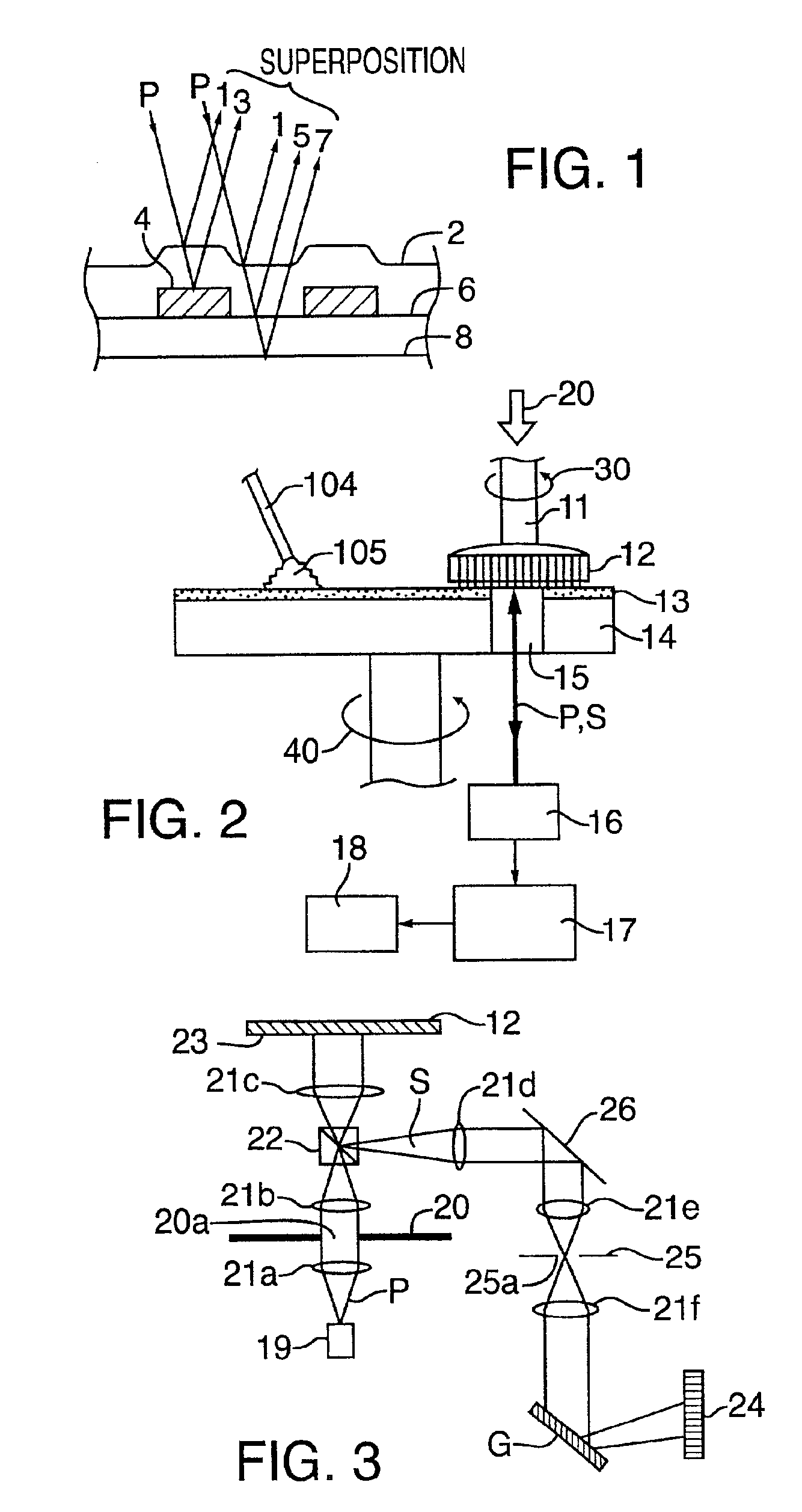
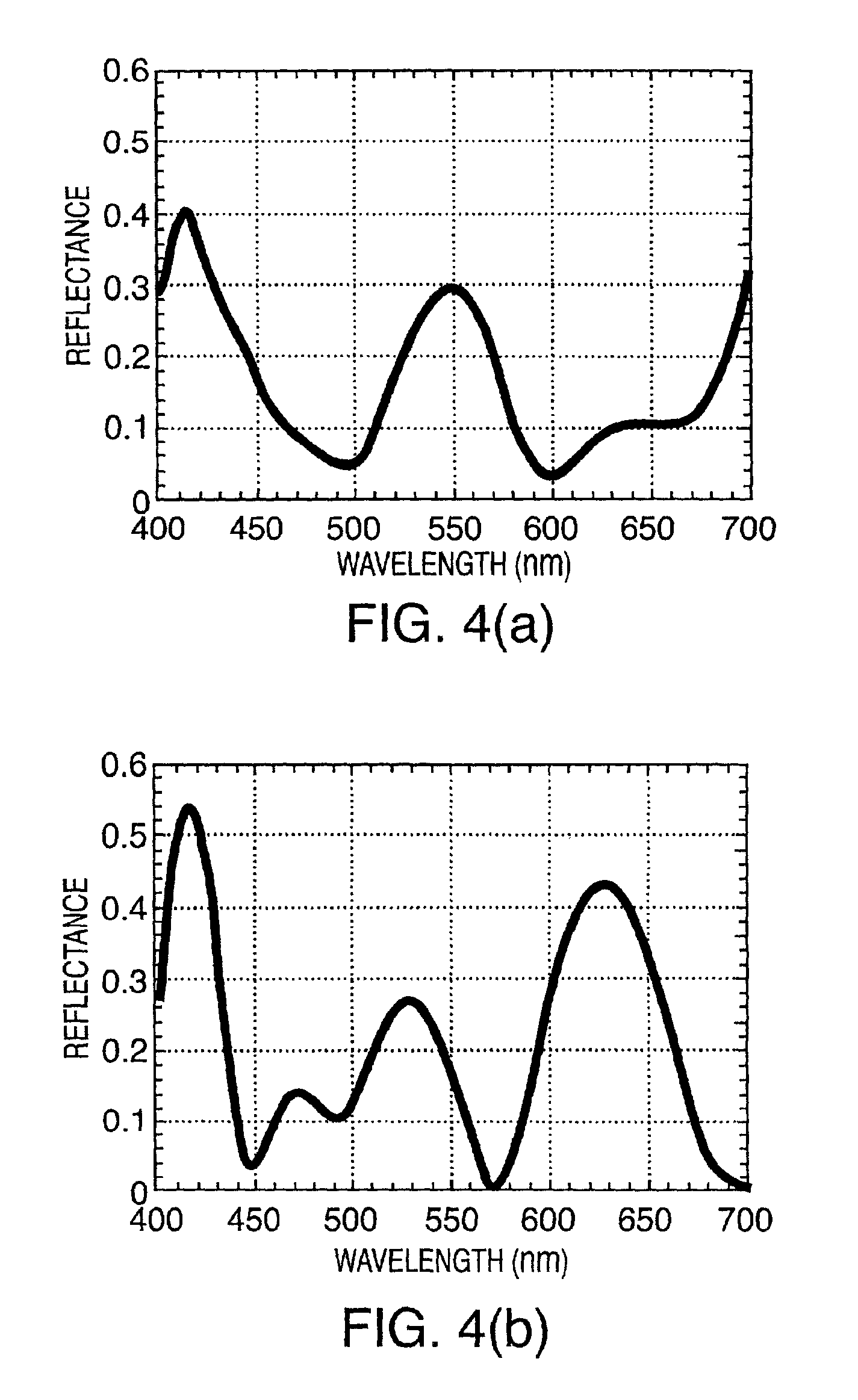
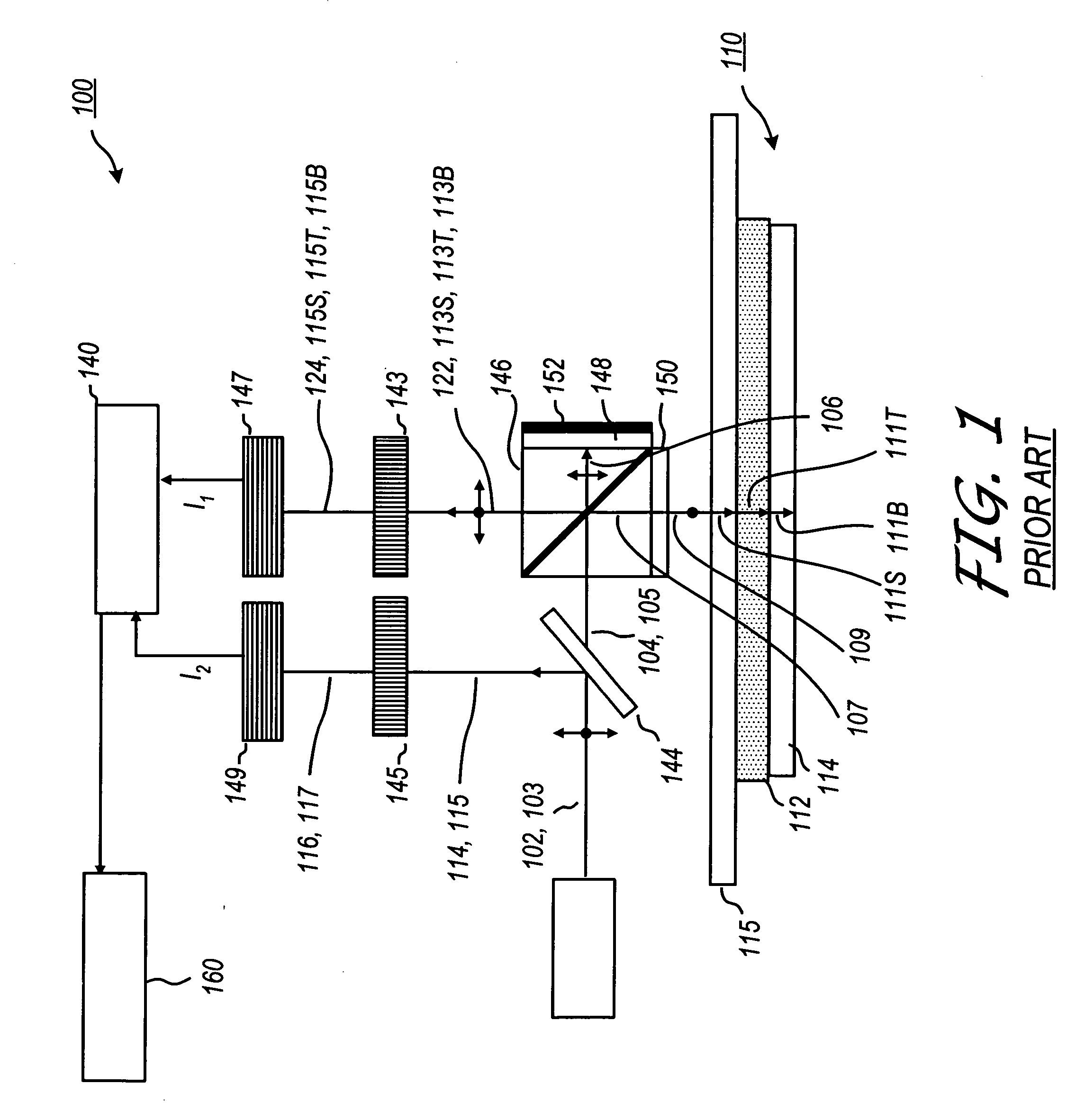
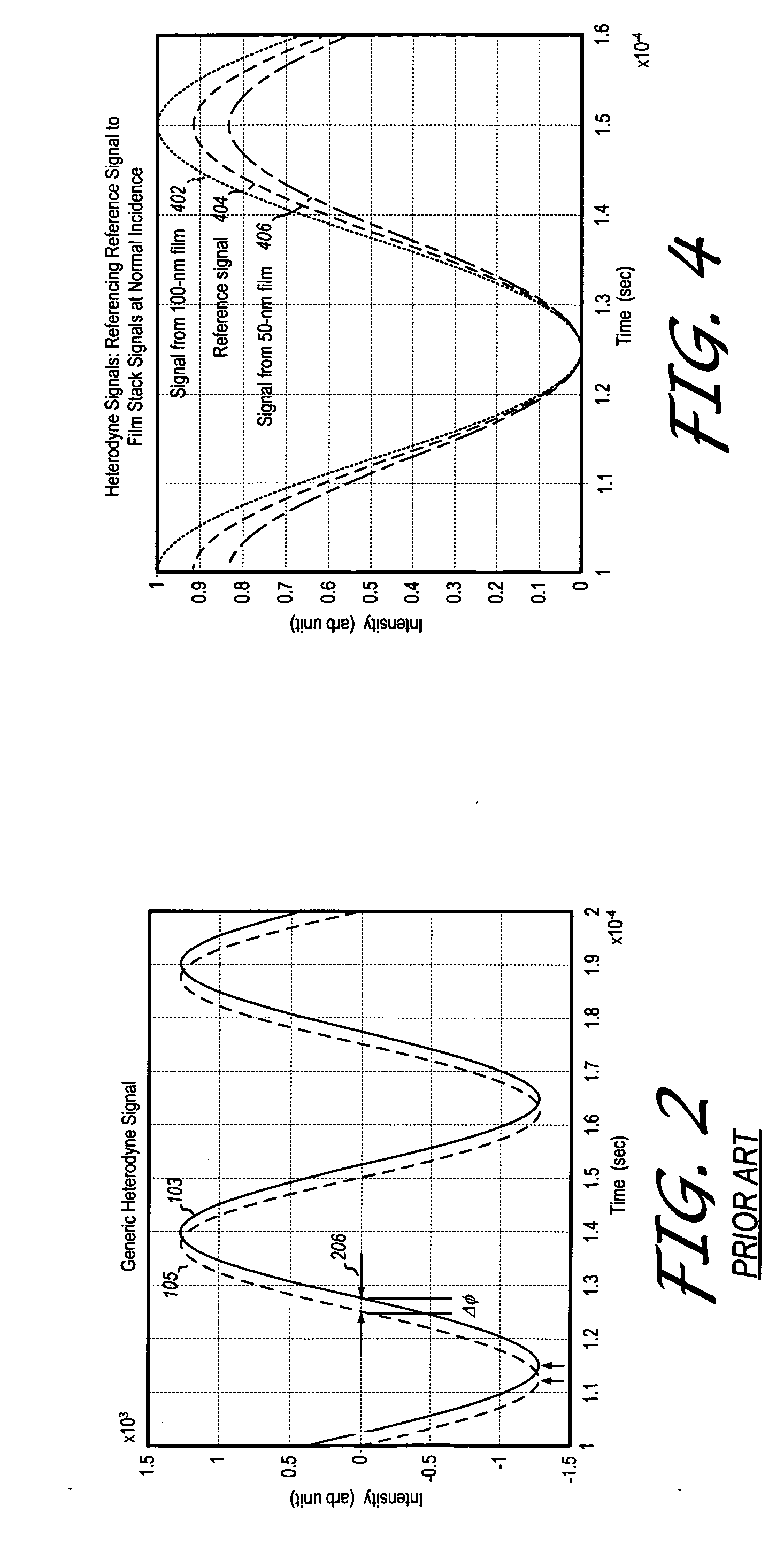
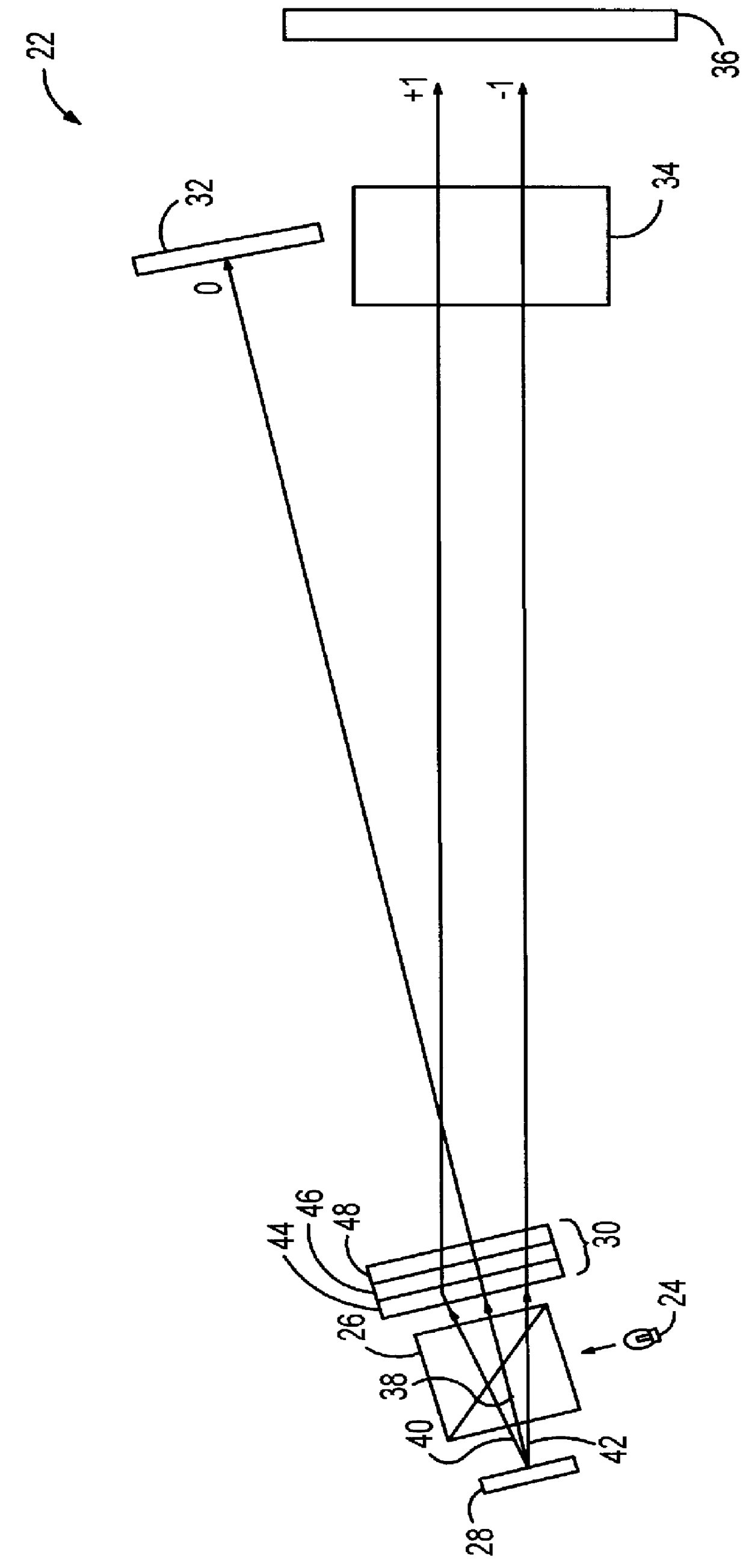
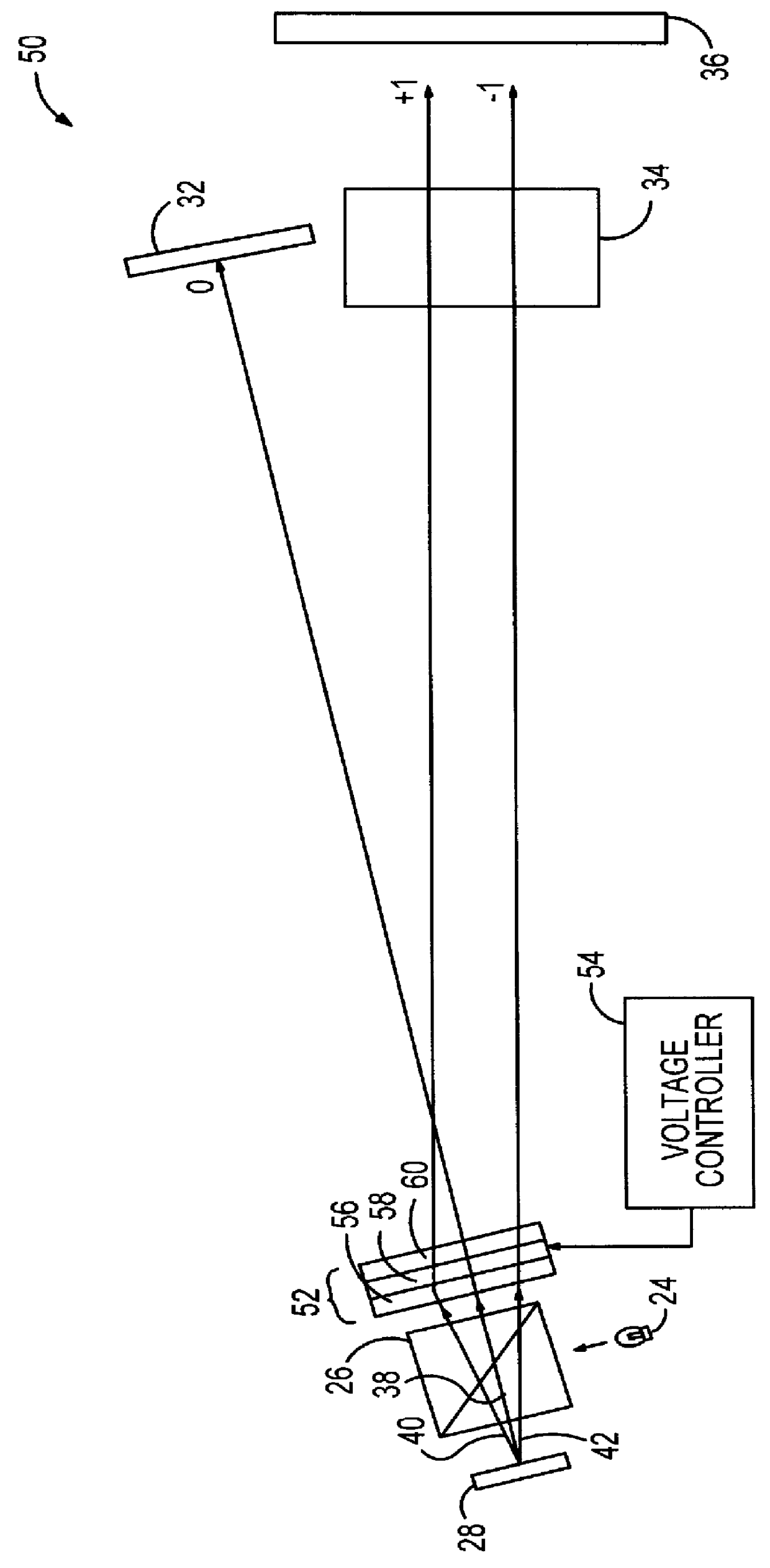
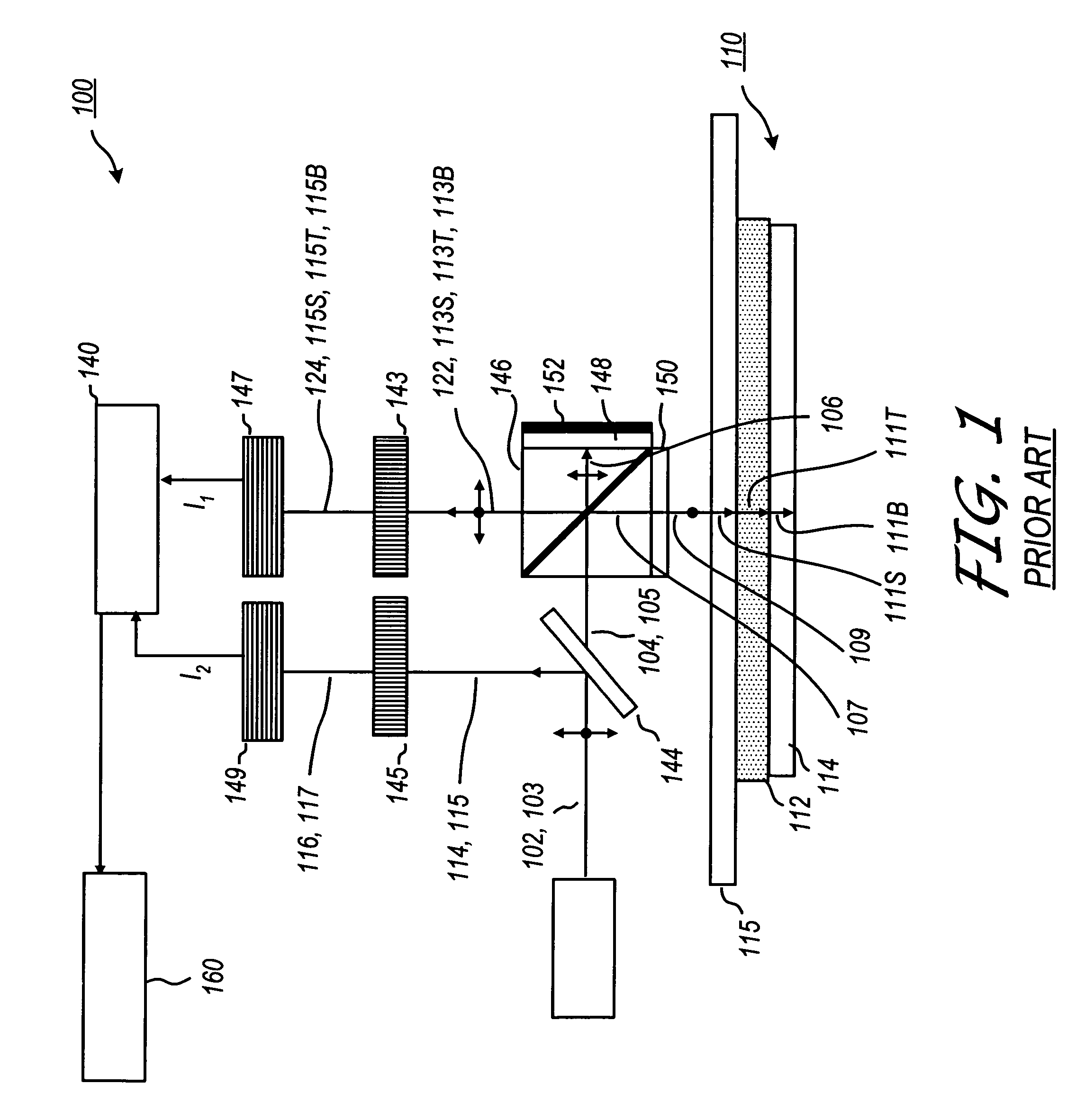
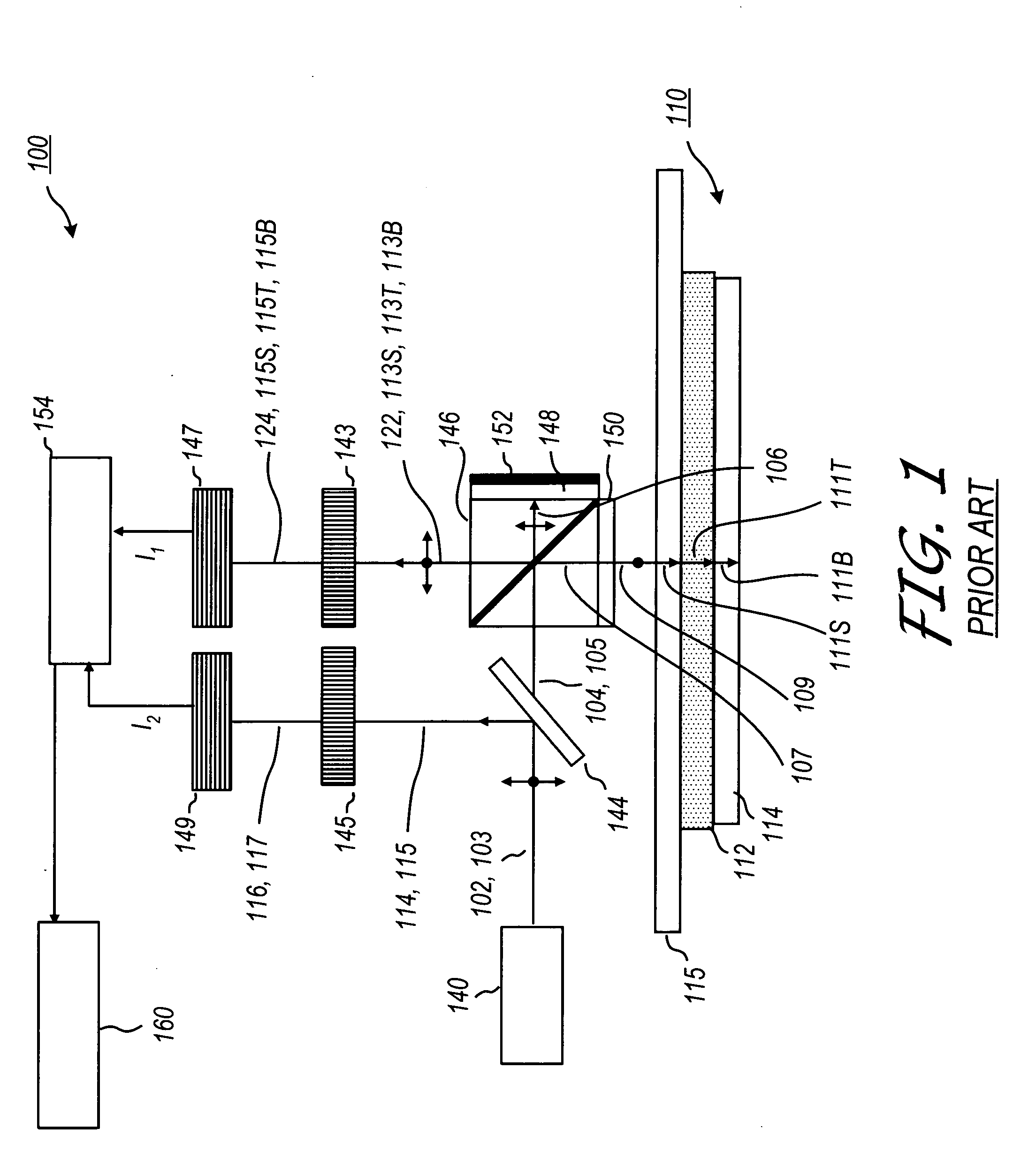
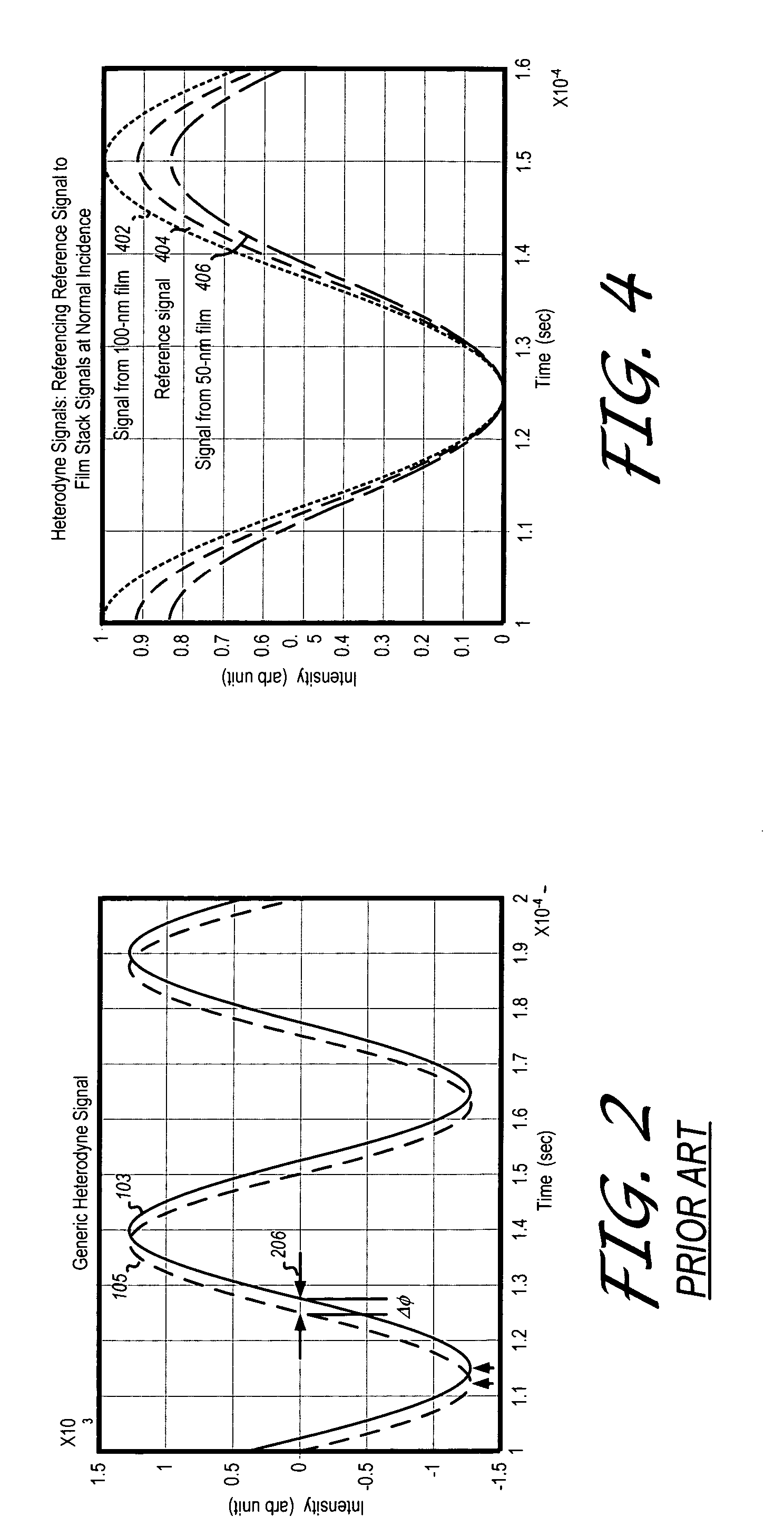
Heterodyne reflectomer for film thickness monitoring and method for implementing
The present invention is directed to a heterodyne reflectometer system and method for obtaining highly accurate phase shift information from heterodyned optical signals, from which extremely accurate film depths can be calculated. A linearly polarized light comprised of two linearly polarized components that are orthogonal to each other, with split optical frequencies, is directed toward a film causing one of the optical polarization components to lag behind the other due to an increase in the optical path in the film for that component. A pair of detectors receives the beam reflected from the film layer and produces a measurement signal, and the beam prior to incidence on the film layer and generates a reference signal, respectively. The measurement signal and reference signal are analyzed by a phase detector for phase shift. The detected phase shift is then fed into a thickness calculator for film thickness results. A grating interferometer may be included with the heterodyne reflectometer system with a grating, which diffracts the reflected beam into zeroth- and first-order bands, which are then detected by separate detectors. A detector receives the zeroth-order beam and generates another measurement signal. Another detector receives the first-order beam and generates a grating signal. The measurement signal from the grating and reference signal may be analyzed by a phase detector for phase shift, which is related to the thickness of the film. Conversely, either measurement signal may be analyzed with the grating signal by a phase detector for detecting a grating phase shift. The refractive index for the film may be calculated from grating phase shift and the heterodyne phase shift. The updated refractive index is then used for calculating thickness.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
Steering of directional sound beams
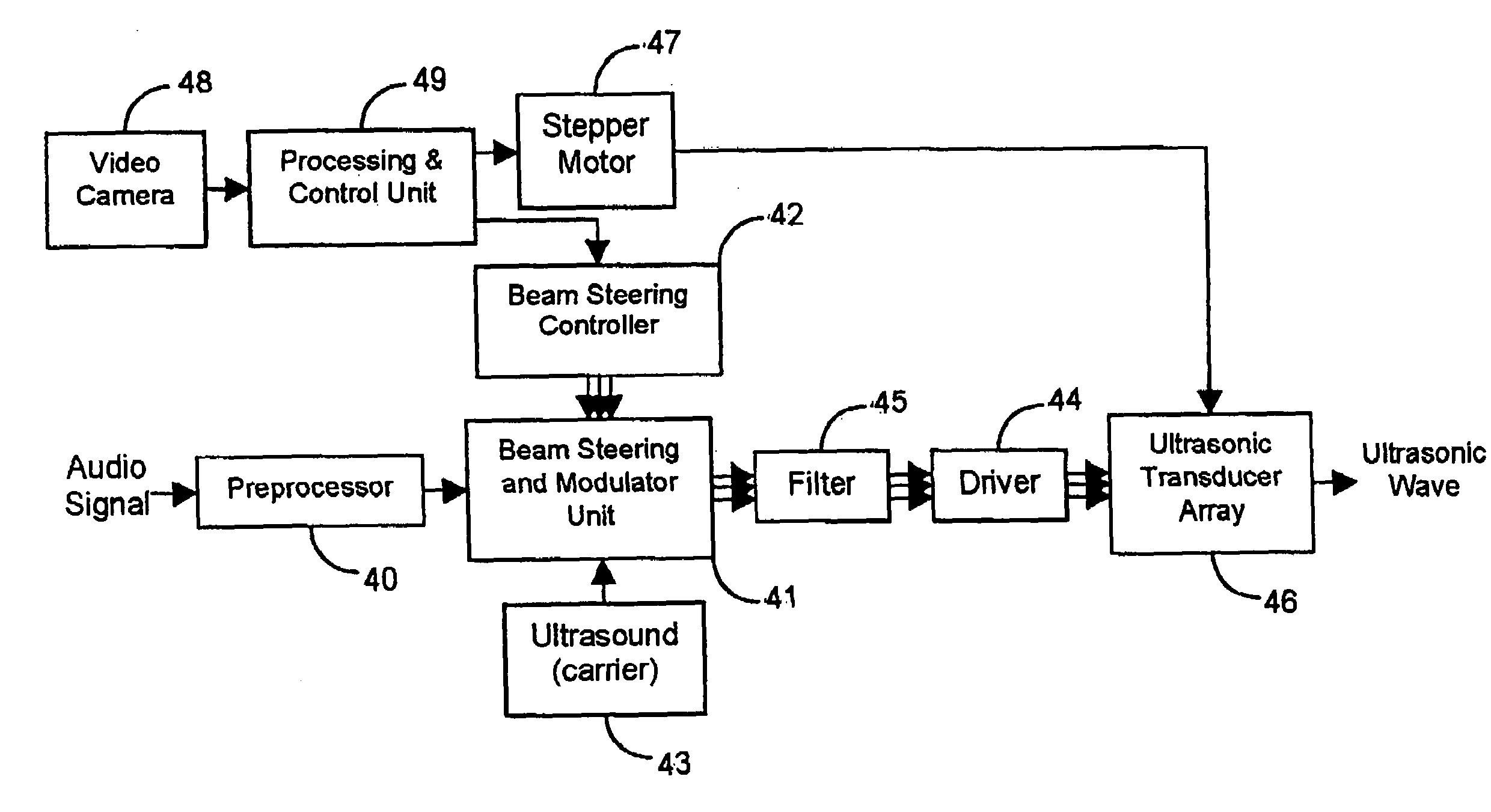
InactiveUS7146011B2Contributing to noise pollutionEasy to adjustNear-field transmissionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersSonificationUltrasonic sensor
Apparatus is disclosed for steering a directional audio beam that is self-demodulated from an ultrasound carrier. The apparatus includes means for modulating a carrier signal with an audio signal and means for adjusting the amplitude and phase of at least one of the audio signal and / or the carrier signal to steer the audio beam to a desired direction. The apparatus also includes means for generating an ultrasound beam in the desired direction driven by the modulated carrier signal. The apparatus may include means for weighting the audio and / or carrier signal by a zeroth order Bessel function to synthesize a Bessel distribution source. A corresponding method for steering a directional audio beam is also disclosed. A harmonic generator may be used to generate harmonics of low frequencies in the audio signal. The harmonics may provide (upon demodulation) a psycho-acoustic impression of improved perception of low frequencies. Further, a modulated ultrasonic signal or an unmodulated audio signal may be band-passed into two or more different band-limited signals. The band-limited signals may be amplified and transmitted by ultrasonic transducers having mechanical resonance frequencies substantially equal to a characteristic frequency of the band-limited signals. Ultrasonic processing of the audio signal may include square root methods without generating large numbers of harmonics.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Antireflective member and electronic equipment using same
InactiveUS7094452B2Stable characteristicsLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsZeroth orderOptoelectronics
An antireflective member with stability and a low reflectance at low cost may be provided by performing an antireflective treatment to a substrate in a molding process of the substrate. A roughened surface with a continuous pattern in a fine pyramidal shape is formed on a surface of a transparent substrate, the roughened surface is a diffraction surface with zeroth-order diffraction to visible light, and the pattern of the roughened surface is transferred from a mold at a transfer rate of not less than 70%.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Light collection from diffractive displays
InactiveUS6091521AHigh diffraction efficiencyGuaranteed normal transmissionProjectorsNon-linear opticsZeroth orderLight beam
A diffractive display system and a method of collecting first order light beams from a diffractive display of the system utilize holographic optical elements (HOEs) to deflect one of two first order diffracted light beams that emerge from each diffracting pixel of the diffractive display, so that the first order diffracted light beams can be separated from the zeroth order light beams. The utilization of the HOEs allows the system to be implemented in a compact optical configuration, without sacrificing any portion of the first order diffracted light. In a first embodiment, the system includes three HOEs that have static diffracting properties that are optimized for red, green and blue lights. For each set of light beams from a diffracting pixel of the diffractive display, the HOEs are holographically configured to deflect only one of the two first order diffracted light beams, such that the deflected first order light beam propagates in the same direction as the other non-deflected first order light beam. In a second embodiment, the system includes three HOEs that have reconfigurable diffracting properties that are also optimized for red, green and blue lights. In a third embodiment, the system further includes a holographic color filter that is comprised of three reconfigurable HOEs to sequentially illuminate the diffractive display with each of the tristimulus color lights.
Owner:HOYA CORP +1
Heterodyne reflectometer for film thickness monitoring and method for implementing
Owner:VERITY INSTR
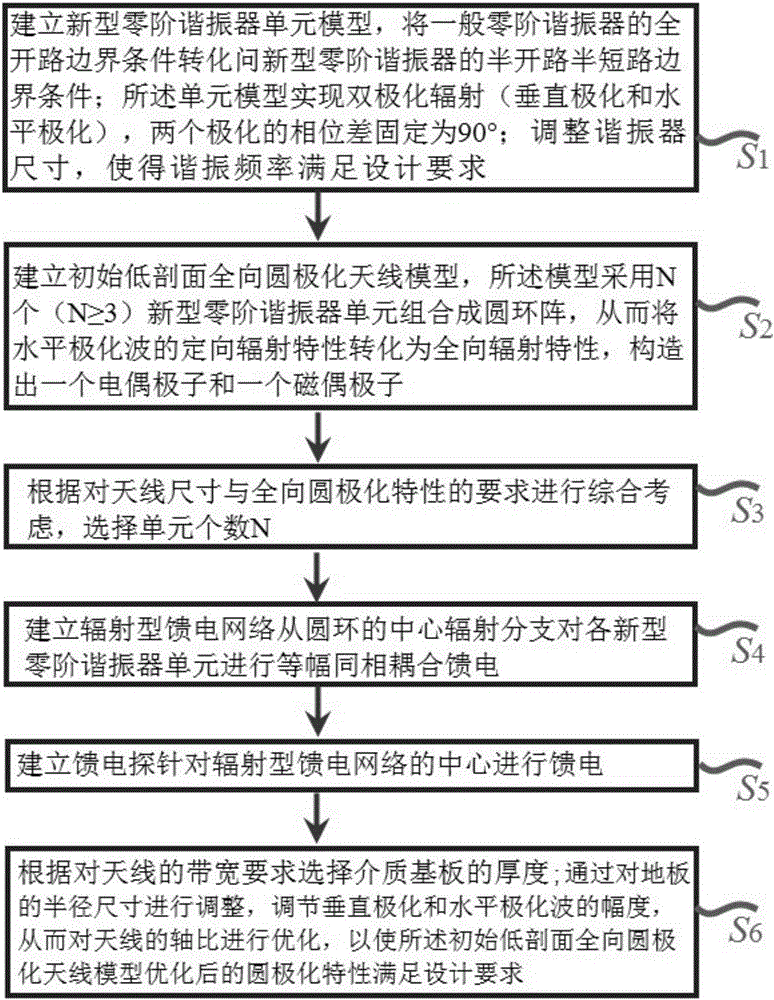
Zeroth-order resonator and low-profile zeroth-order resonator omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna
InactiveCN105206911AImprove optimization efficiencyLow profileAntennas earthing switches associationResonatorsPhase differenceDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a zeroth-order resonator and a low-profile zeroth-order resonator omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna. The zero-order resonator is composed of a dielectric substrate, a metal patch, a metal floor and a short-circuit pin. The metal patch and the metal floor are respectively adhered on the two relatively parallel surfaces of the dielectric substrate. One end of the short-circuit pin is connected with the metal patch, and the other end is connected with the metal floor. The zeroth-order resonators are arranged at the external side of the radiation type feed network of the antenna in a surrounding way. Phase difference between two polarizations is enabled to be fixed at 90 degrees by the zeroth-order resonators, electric dipoles and magnetic dipoles are constructed by using a mode of circular ring group arrays, and the design of the zeroth-order resonator units and optimization of the circular ring array circularly polarized antenna are separated without considering the phase problem of two mutually perpendicular linear polarization components so that optimization efficiency can be enhanced, system resources can be saved and design efficiency can be enhanced. Besides, the designed omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna has the low-profile characteristic and can be applied to systems with the requirement for the antenna profile.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
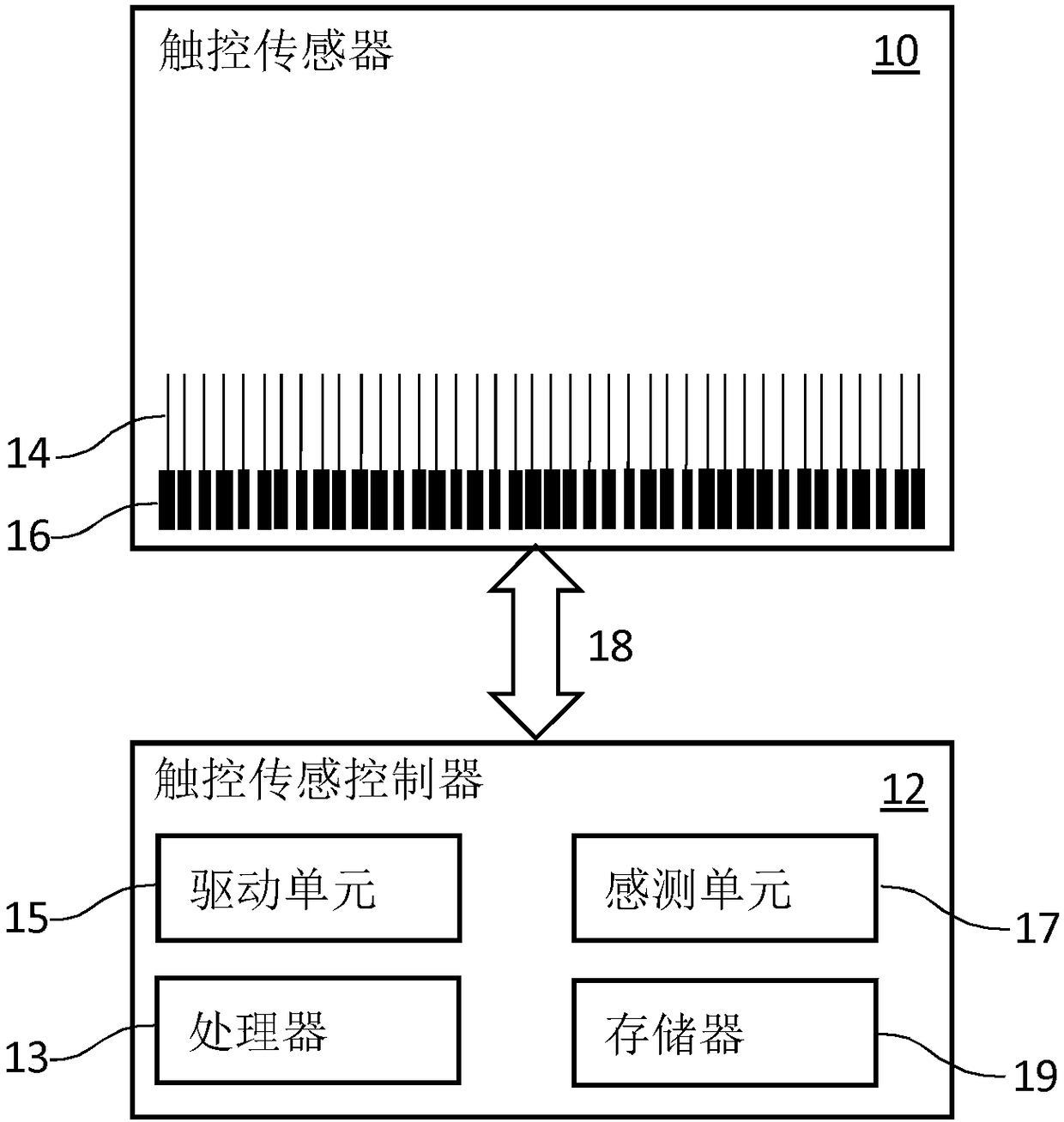
Touch Sensor
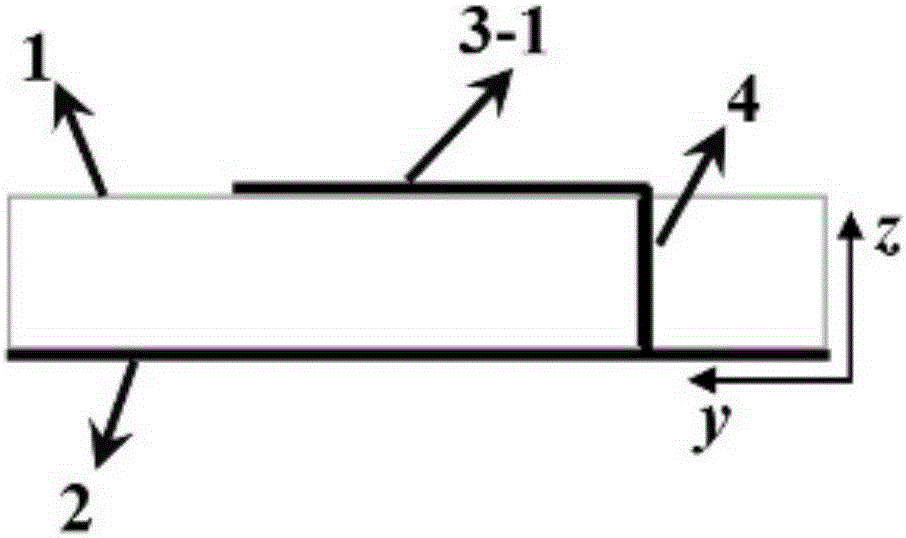
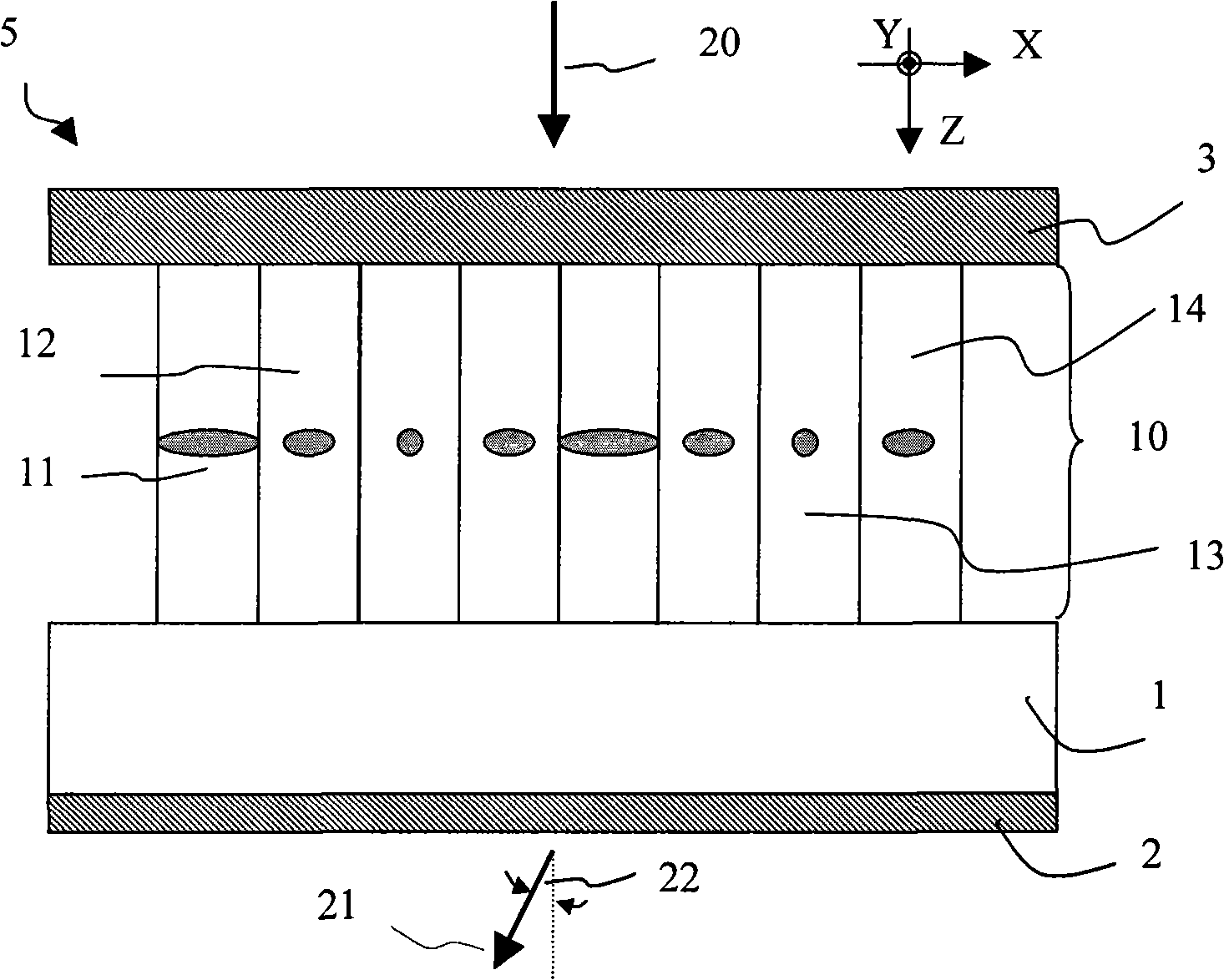
InactiveUS20180224968A1Reduce coverageImprove Noise PerformanceNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingZeroth orderConductive materials
A capacitive touch sensor device comprising set of crossing X and Y electrodes whose crossing points form a two-dimensional array of nodes which define a touch sensitive area made up of rectilinear sub-areas bounded by adjacent pairs of X and Y electrodes. The main electrode branches are referred to as zeroth order branches, since, in each sub-area, there are also higher order branches arranged such that some higher order X branches interdigitate with some higher order Y branches separated by a gap suitable for making a mutual capacitance measurement. The electrode branches are implemented as a fine mesh. The fine mesh comprises criss-crossing lines of conductive material which have gaps in between that are free of conductive material. Some of the criss-crossing lines include breaks formed by absence of individual length portions of the criss-crossing lines that form the mesh.
Owner:SOLOMON SYSTECH
Diffraction grating having high throughput efficiency
A reflective diffraction grating having grooves and ridges and providing high throughput efficiency in the minus-first diffraction order. All but the zeroth diffraction order and the minus-first diffraction order may be prevented from existence by directing the radiation onto the grating at an appropriate angle. The radiation having a TM polarization is eliminated from the zeroth order by destructive interference by appropriate selection of a the groove width of the grating, and radiation having a TE polarization is eliminated from the zeroth order by destructive interference by depositing an overcoat of an appropriate thickness. A dielectric material may be deposited in the grooves.
Owner:AHURA SCI
Method and apparatus for amplitude filtering in the frequency plane of a lithographic projection system
InactiveUS6940583B2Improve imaging resolutionPhoto-taking processesPhotomechanical apparatusZeroth orderLight beam
A method of projecting a pattern from a mask onto a substrate comprises providing an energy source, a substrate, and a mask containing a pattern of features to be projected onto the substrate, and projecting an energy beam from the energy source though the mask toward the substrate to create a projected mask pattern image. The projected mask pattern image is created by zeroth and higher orders of the energy beam. The method then includes diffracting zeroth order beams of the projected mask pattern image to an extent that prevents the zeroth order beams from reaching the substrate, while permitting higher order beams of the projected mask pattern image to reach the substrate. Preferably, the zeroth order beams of the projected mask pattern image are diffracted at an obtuse angle.
Owner:QIMONDA +1
Apparatus for characterization of photoresist resolution, and method of use
InactiveUS20050168717A1Effective characterizationFacilitate automated evaluationRadiation applicationsUsing optical meansResistSinusoidal grating
An optical apparatus used for the efficient characterization of photoresist material includes at least one grating interferometer having at least two gratings that together define an optical recombination plane. An optical stop blocks any zeroth order beam from propagating through the apparatus. A reticle positioned at the recombination plane has at least one fiducial marking therein. A lithographic imaging optical tool is positioned so that its input optical plane is substantially coincident with the optical recombination plane and its output imaging plane is substantially coincident with photoresist on a wafer. The apparatus writes in the photoresist latent, sinusoidal grating patterns, preferably of different spatial frequencies, as well as at least one fiducial mark whose pattern is determined by the marking in the reticle. After the photoresist is developed, its intrinsic spatial resolution may be determined by automated means.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Non-etched flat polarization-selective diffractive optical elements
The invention relates to a polarization-selective diffractive optical element that includes a liquid crystal polymer film supported by a substrate. The liquid crystal polymer film includes an array of pixels, each pixel encoded with a fixed liquid crystal director such that each liquid crystal director is aligned in a common plane perpendicular to the liquid crystal polymer film and provides a predetermined pattern of out-of-plane tilts. A size of the pixels in the array and the predetermined pattern are selected such that the liquid crystal polymer film forms a phase hologram for diffracting light polarized parallel to said common plane and a zeroth order diffraction grating for light polarized perpendicular to the said common plane. The non-etched and flat phase hologram is suitable for a wide range of applications.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Inspection apparatus, lithographic apparatus, lithographic processing cell and inspection method
ActiveUS8705007B2Raman/scattering spectroscopySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsZeroth orderFour quadrants
For angular resolved spectrometry a radiation beam is used having an illumination profile having four quadrants is used. The first and third quadrants are illuminated whereas the second and fourth quadrants aren't illuminated. The resulting pupil plane is thus also divided into four quadrants with only the zeroth order diffraction pattern appearing in the first and third quadrants and only the first order diffraction pattern appearing in the second and third quadrants.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
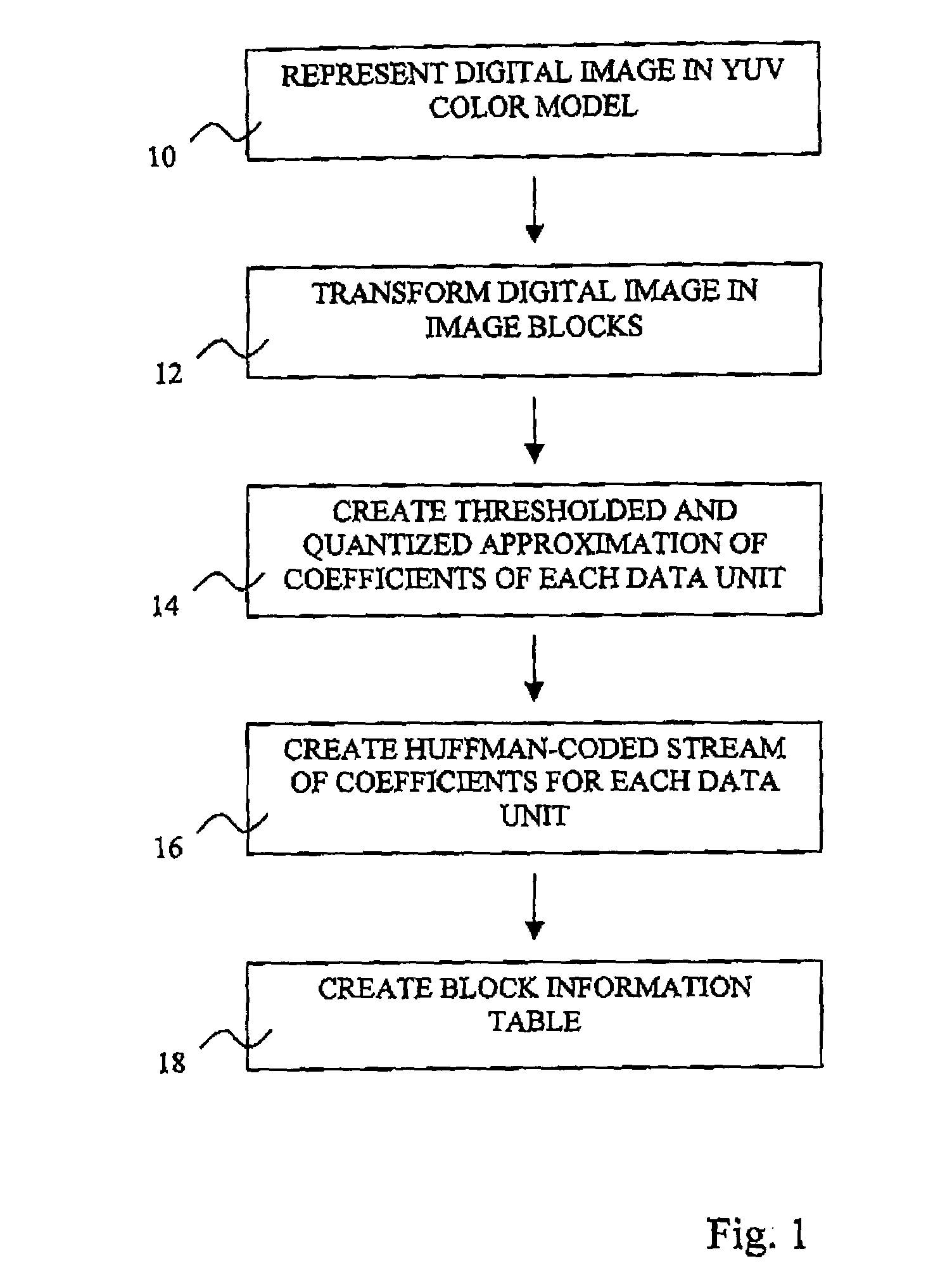
Method for processing a digital image and image representation format
InactiveUS7480418B2Easy to analyzeEasily be manipulatedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionZeroth orderDigital image
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
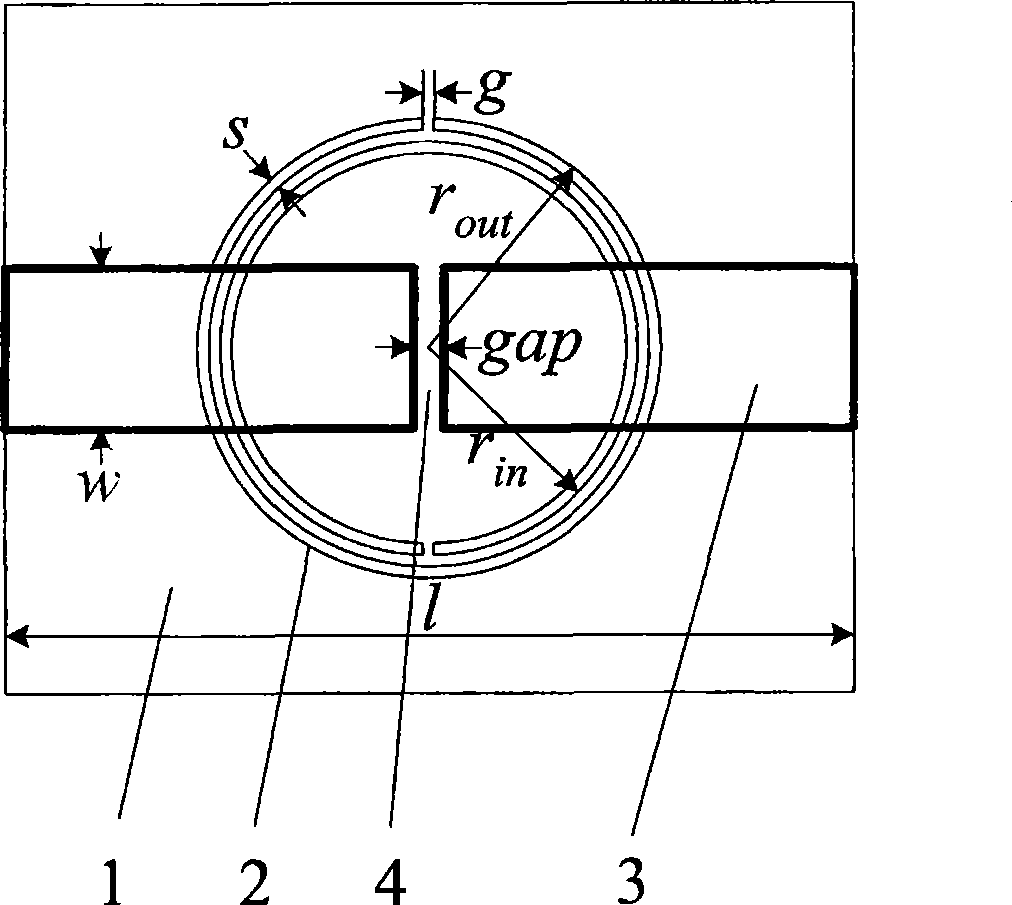
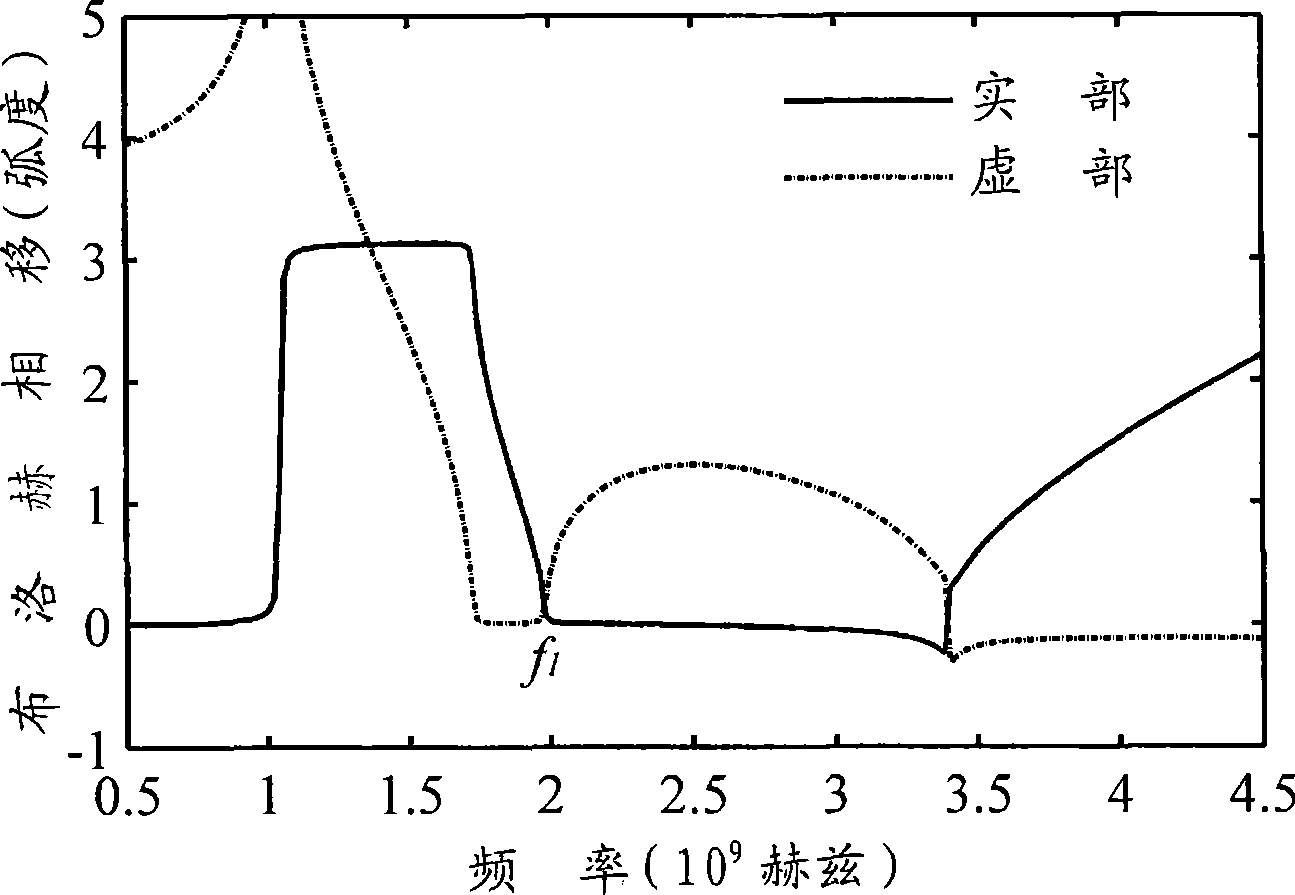
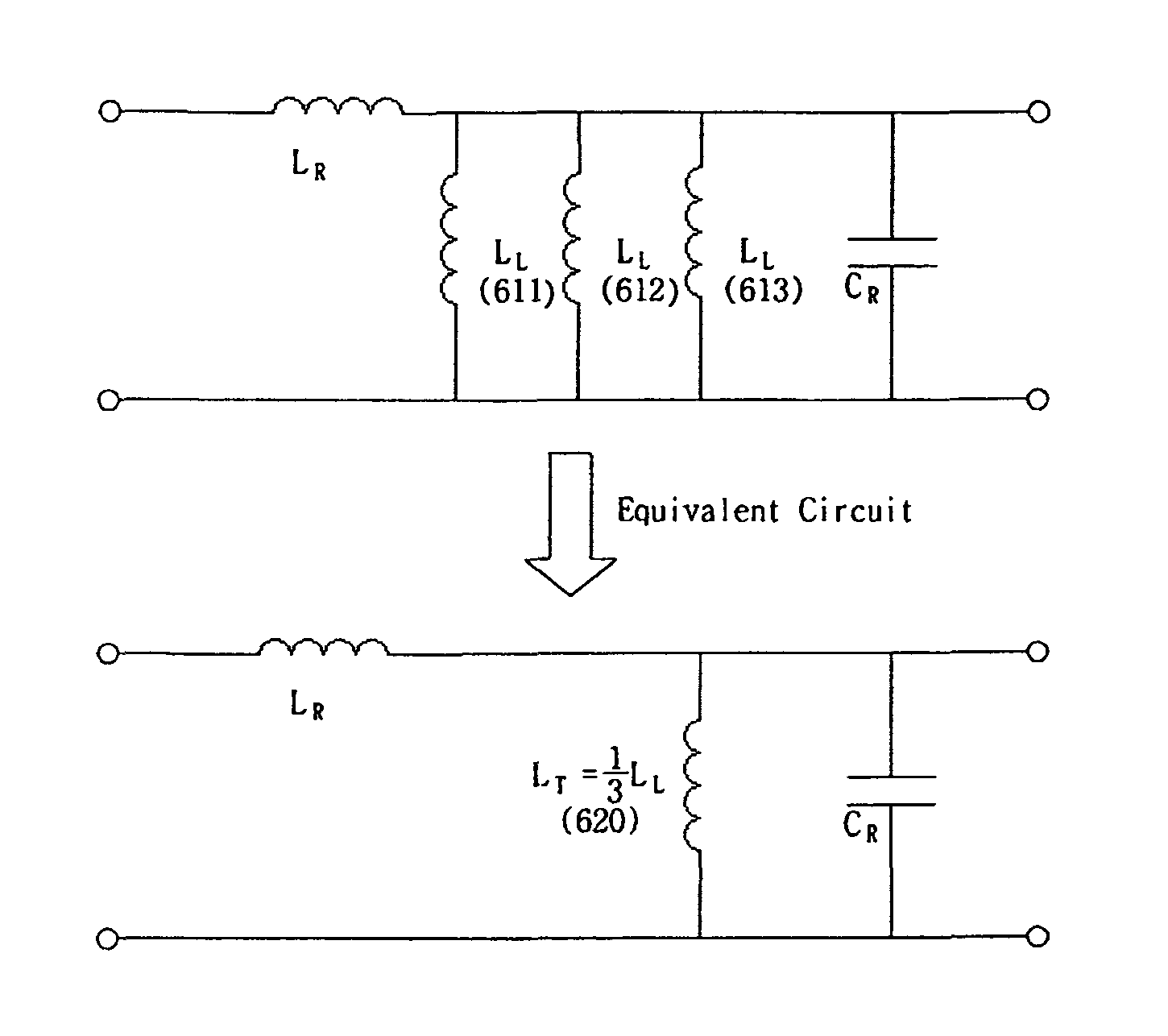
Zero order resonator, narrow band filter and optimum design method
InactiveCN101471479ALarge susceptance slope parameterNarrow bandwidthResonatorsCapacitanceBand-pass filter
A zeroth-order resonator is characterized in that a complementary split ring resonator is etched on a grounding layer; and a slit capacitor is etched on a microstrip signal line and is located above the complementary split ring resonator. The method comprises the following steps: setting an initial value for each parameter of the zeroth-order resonator; subjecting the zeroth-order resonator to Bloch analysis according to the initial values to obtain a resonant frequency f1; adjusting the parameter until f1 is equal to f0; and calculating input admittance near the resonant frequency f0 to obtain admittance slope parameter of the zeroth-order resonator. A narrow-band filter has a complementary split ring resonator and includes a plurality of zeroth-order resonators and a plurality of J-converters in alternated arrangement. By adopting the complementary split ring resonator, the zeroth-order resonator has large susceptance slope parameter, and the filter using the zeroth-order resonator has narrower bandwidth. The narrow-band filter can be used for separating signals among different channels in a communication system, and a medium-frequency narrow-band filter used for RF / microwave measurement instruments can acquire high frequency resolution.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
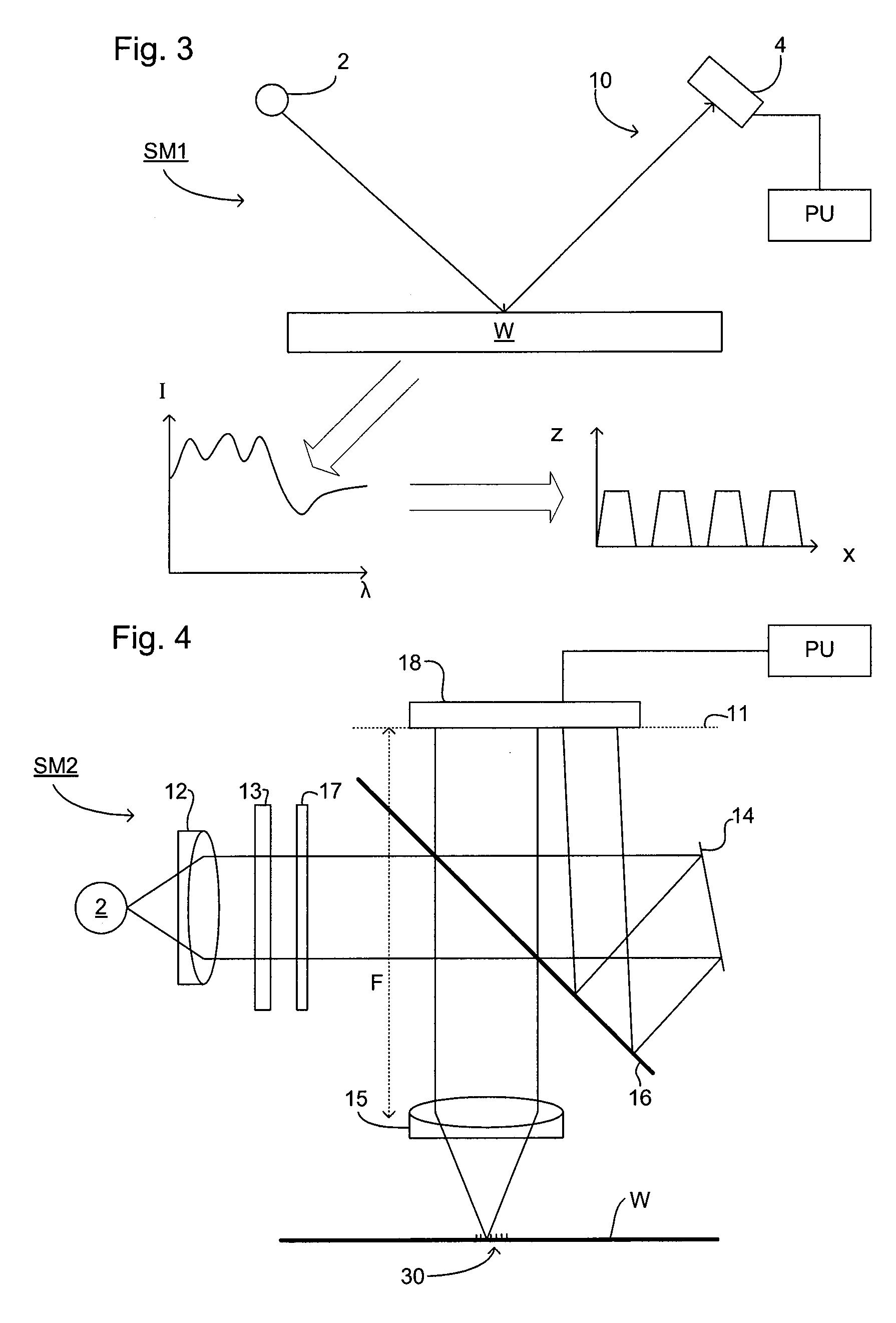
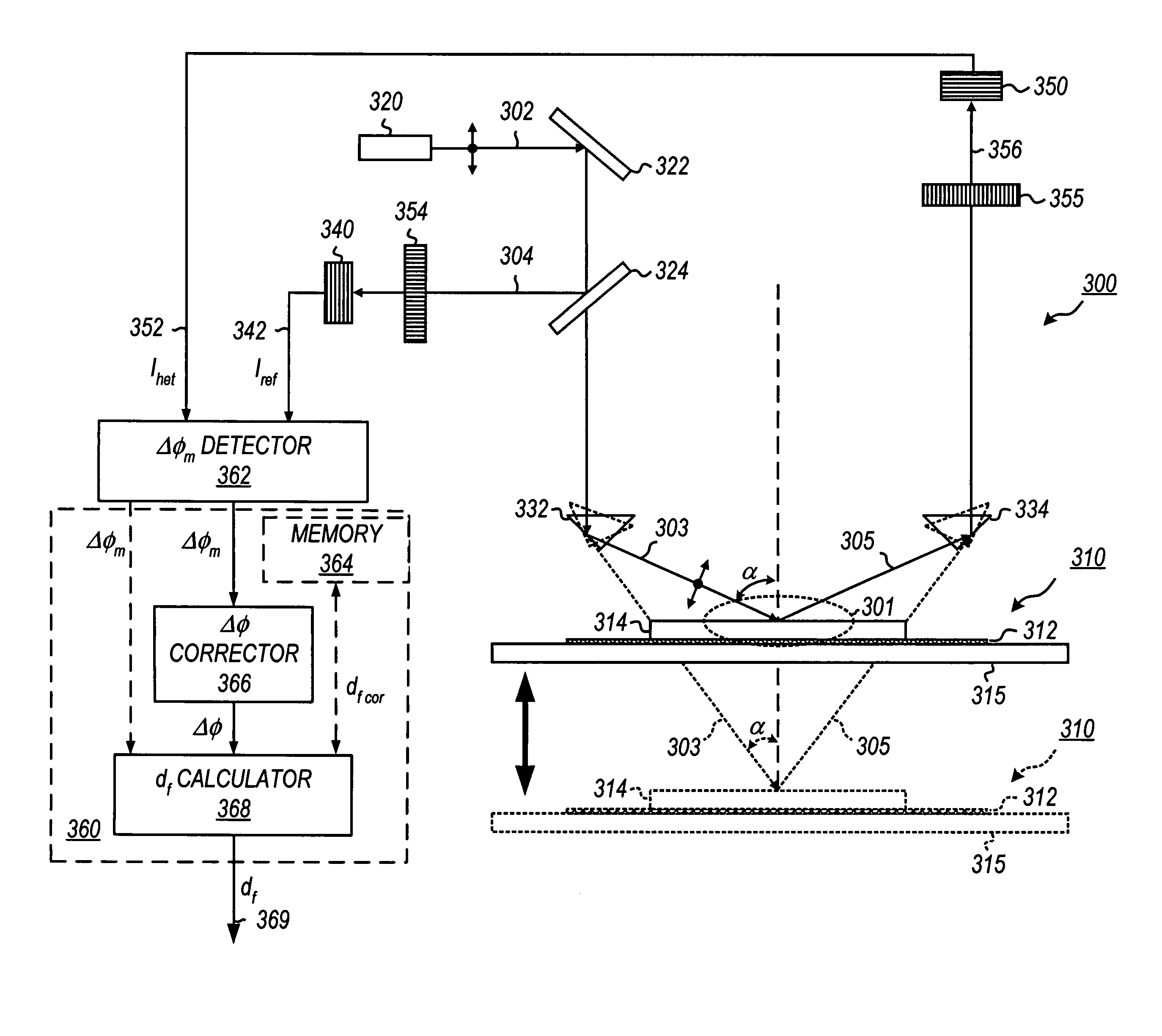
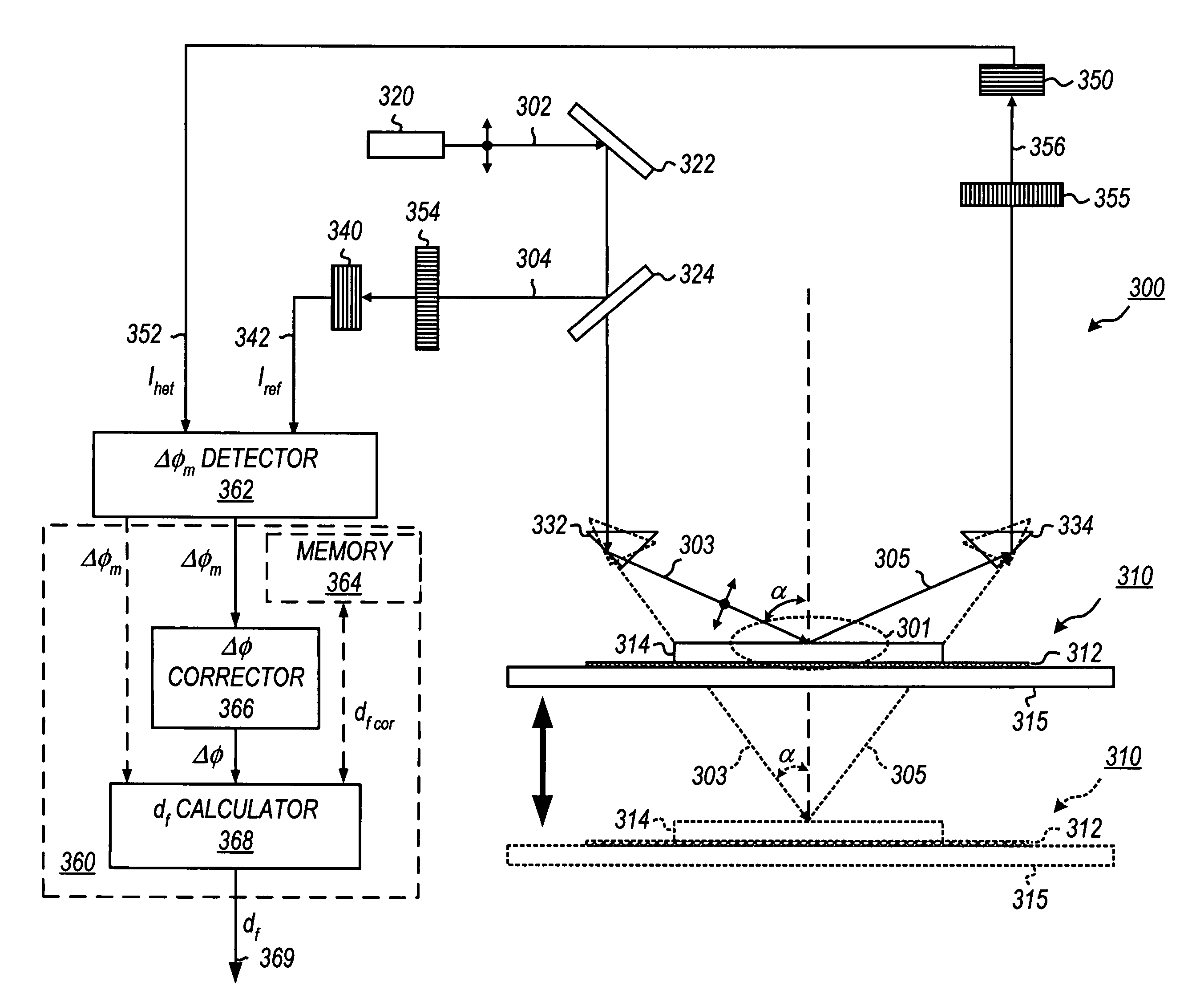
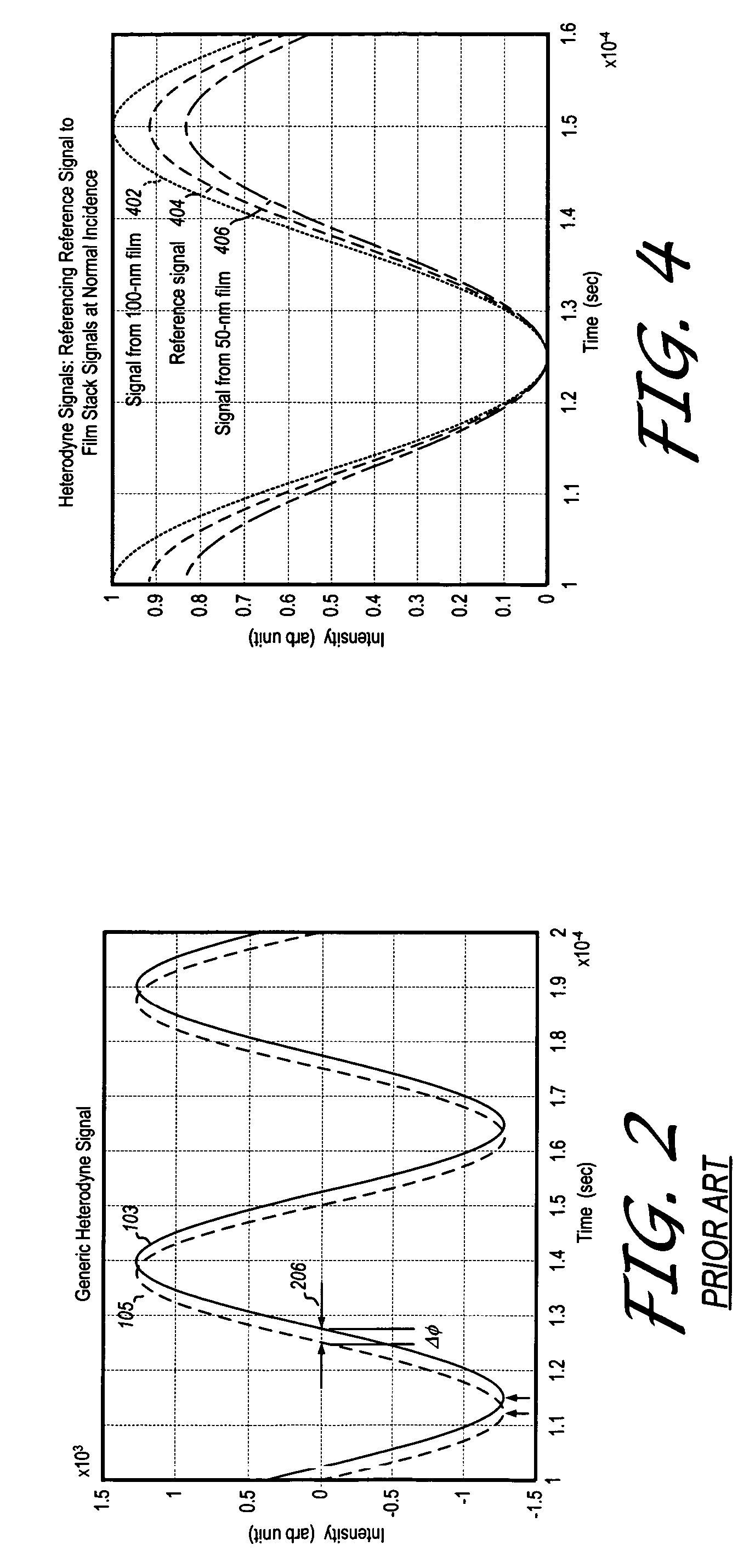
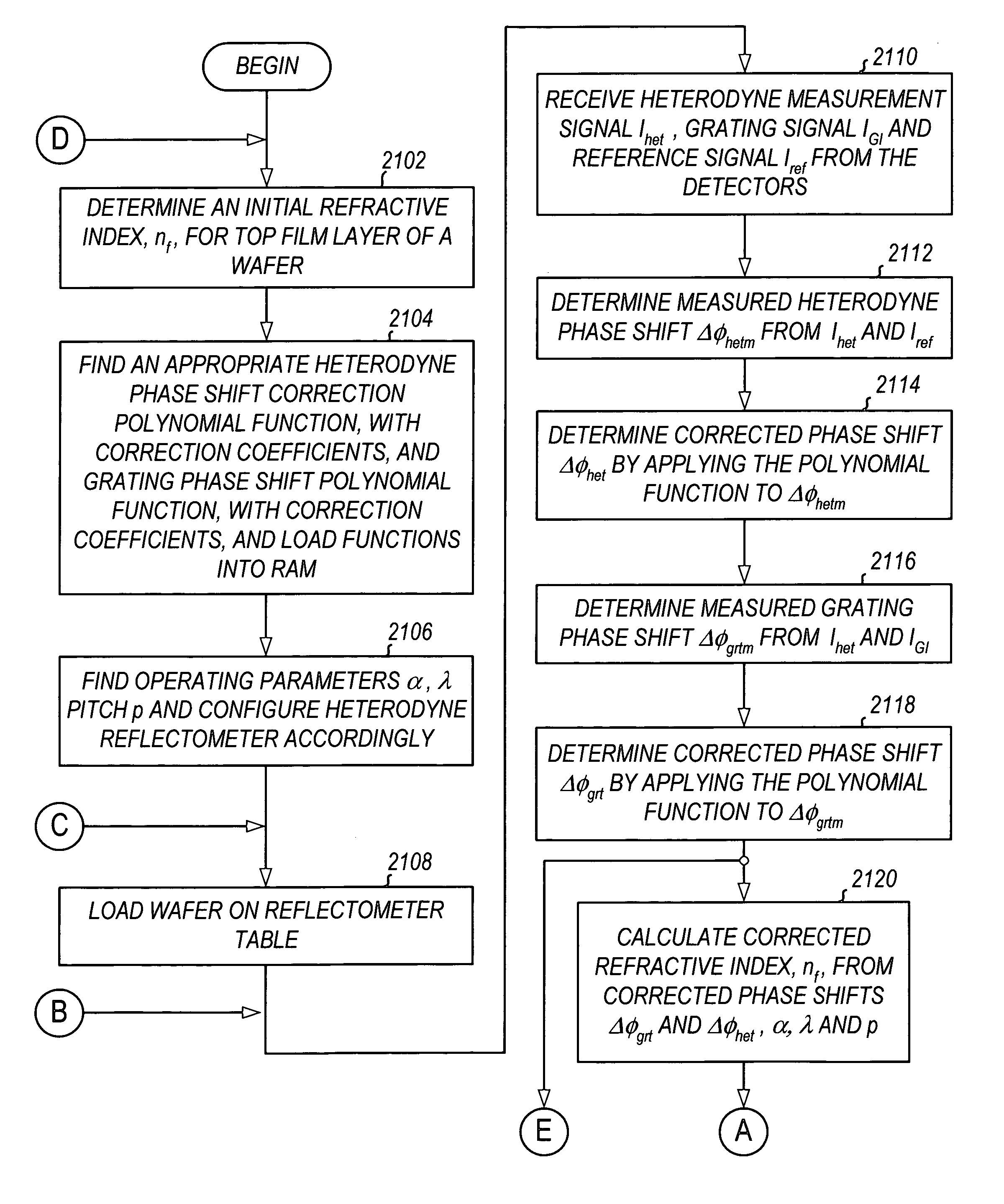
Method for monitoring film thickness using heterodyne reflectometry and grating interferometry
InactiveUS20060285120A1The result is accurateInterferometersUsing optical meansOptical frequenciesRefractive index
A linearly polarized light comprised of two linearly polarized components, orthogonal to each other and with split optical frequencies, is directed toward a film. A detector receives the beam prior to incidence on the film layer and generates a reference signal. The reflected beam is diffracted into zeroth- and first-order bands, which are then detected by separate detectors; a measurement signal is generated from the zeroth-order beam and a grating signal from the first-order beam. The zeroth-order beam's measurement signal and reference signal are analyzed by a phase detector for a heterodyne phase shift, and an accurate film thickness calculated from this phase shift by knowing a refractive index for the film. Additionally, the zeroth-order beam measurement signal is analyzed with the grating signal by a phase detector for detecting a grating phase shift induced by the grating. The refractive index for the film can then be calculated directly from grating phase shift and the heterodyne phase shift for the grating pitch, and the beam's wavelength and incidence angle on the film of the measurement apparatus. Using the refractive index and heterodyne phase shift, the film's thickness is determined for the apparatus. Conversely, the thickness of the film can be calculated independent of the refractive index, and without knowing the film's refractive index, directly from the grating phase shift and the heterodyne phase shift for the apparatus.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
Touch Sensor
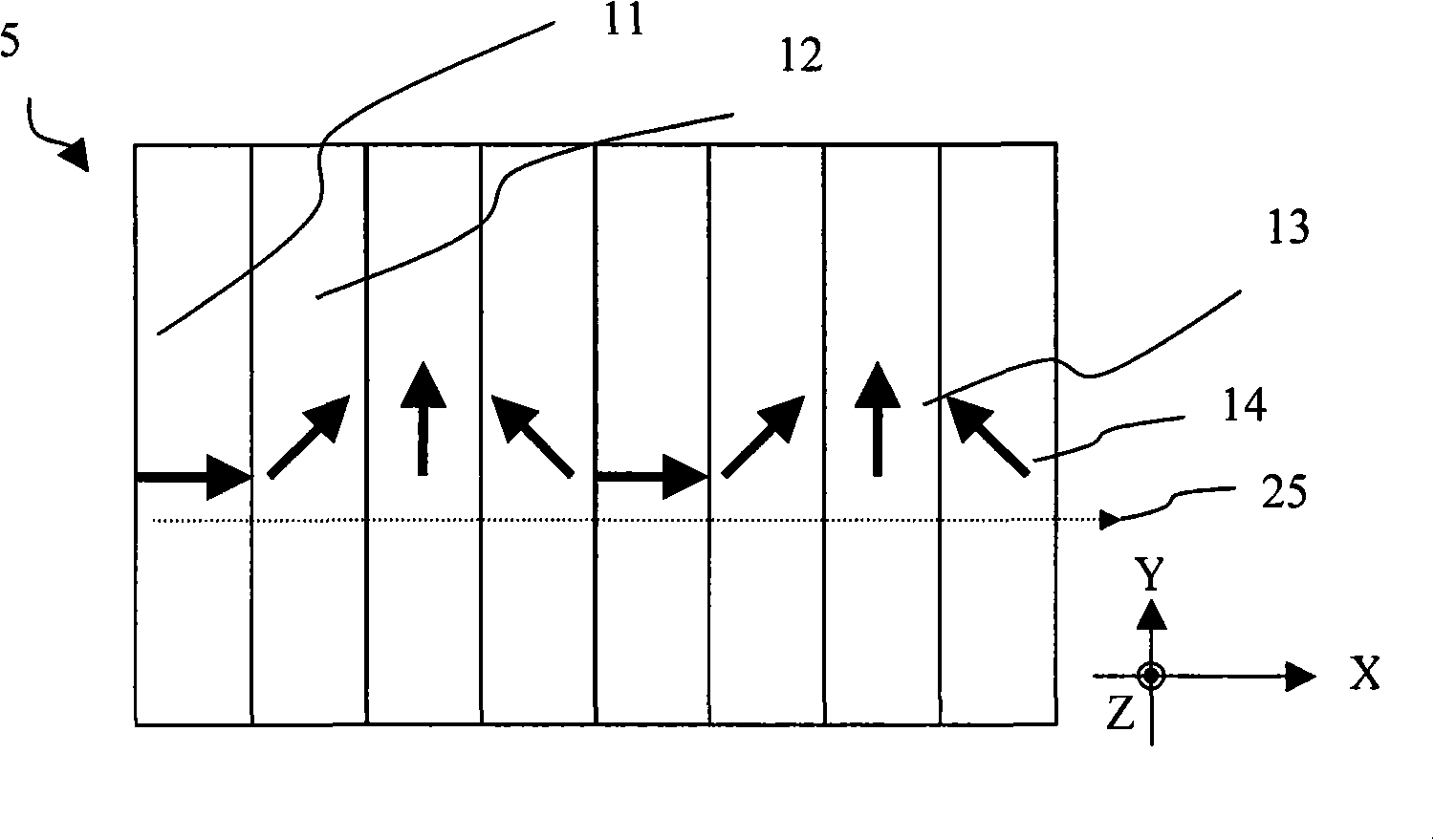
InactiveUS20180224967A1Reduce coverageImprove Noise PerformanceSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsZeroth orderFill factor
A capacitive touch sensor device comprising set of crossing X and Y electrodes whose crossing points form a two-dimensional array of nodes which define a touch sensitive area made up of rectilinear sub-areas bounded by adjacent pairs of X and Y electrodes. The main electrode branches are referred to as zeroth order branches, since, in each sub-area, there are also higher order branches arranged such that some higher order X branches interdigitate with some higher order Y branches separated by a gap suitable for making a mutual capacitance measurement. The X and Y electrodes are designed so that they fill the touch sensitive area relatively sparsely, which reduces the electrodes' self capacitance, so that charge time can be kept low. The low fill factor also lends itself to a high degree of interdigitation of the higher order electrode branches.
Owner:SOLOMON SYSTECH
External cavity tunable laser with dual beam outputs
The invention relates to an external cavity tunable laser with dual beam outputs. The first laser cavity of the tunable laser comprises a first laser cavity mirror, a laser gain medium, an intracavity collimating lens, an active optical phase modulator, a tunable acousto-optic filter, a tunable Fabry-Perot tunable filter, a second reflection mirror all disposed inside a laser cavity sequentially, and a laser driver and control system. The laser cavity beam reflected by the first laser cavity mirror enters the tunable acousto-optic filter to generate a zeroth order diffracted beam as the first laser output beam. The laser cavity beam reflected by the second laser cavity mirror enters the tunable acousto-optic filter to generate a zeroth order diffracted beam as the second laser output beam. The tunable laser further comprises a wavelength locker outside the laser cavity. The second laser cavity of the tunable laser has a Fabry-Perot etalon disposed in the first laser cavity to further compress the spectrum width of the laser output beams. The invention is compact with high performance without mechanical moving parts, stable laser output, low cost for volume production and installation.
Owner:GP PHOTONICS INC
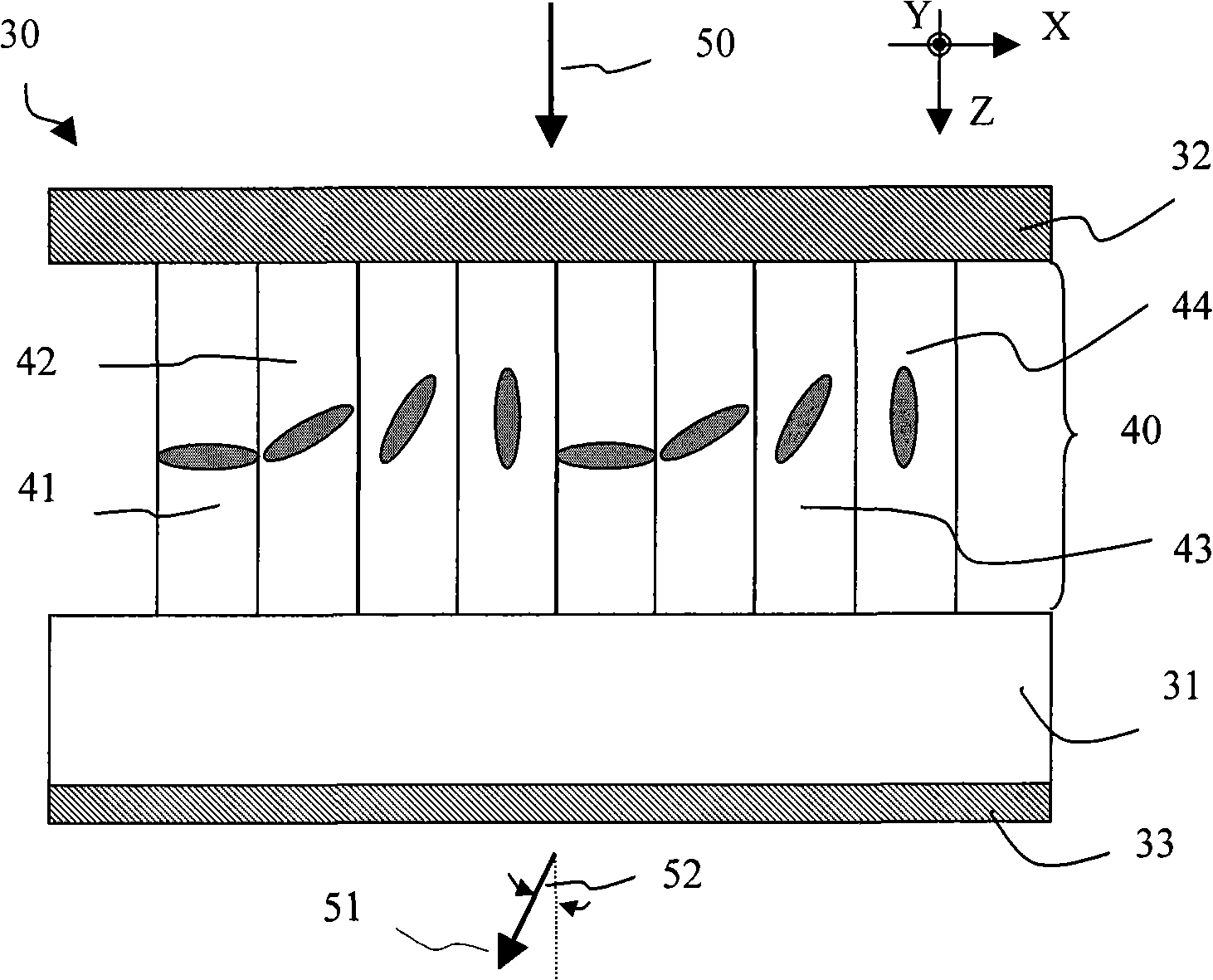
Device combined with capacitive touch sensor, and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides a device combined with a capacitive touch sensor, and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the device comprises a set of crossing X and Y electrodes whose crossing points form a two-dimensional array of nodes which define a touch sensitive area. As well as the main electrode spines which cross, referred to as zeroth order electrode branches, the electrodes have higher order branches, some of which interdigitate. By varying the dimensions of the electrode branches, such as width and length, the overall area of the X and Y electrodes can be varied relatively independently of each other. It is therefore possible to produce an electrode pattern in which the self capacitances of the X and Y electrodes have a certain ratio, e.g. unity, and thereby compensate for the aspect ratio of the touch sensitive area, and / or to have a certain absolute value, e.g. in order not to overload a touch-sensor controller to which the sensor is to be connected.
Owner:SOLOMON SYSTECH CHINA LTD
Silicon-based electro-optic device
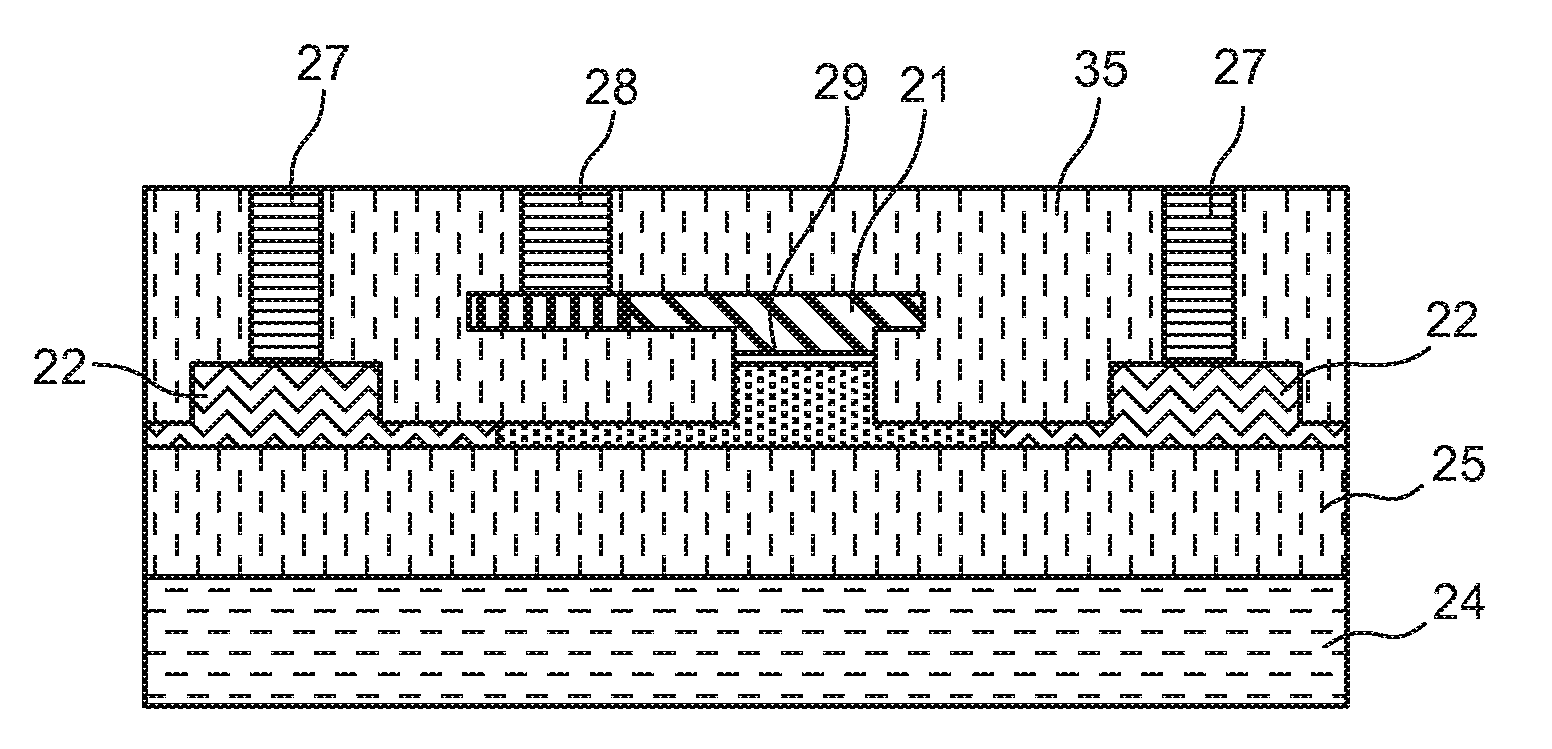
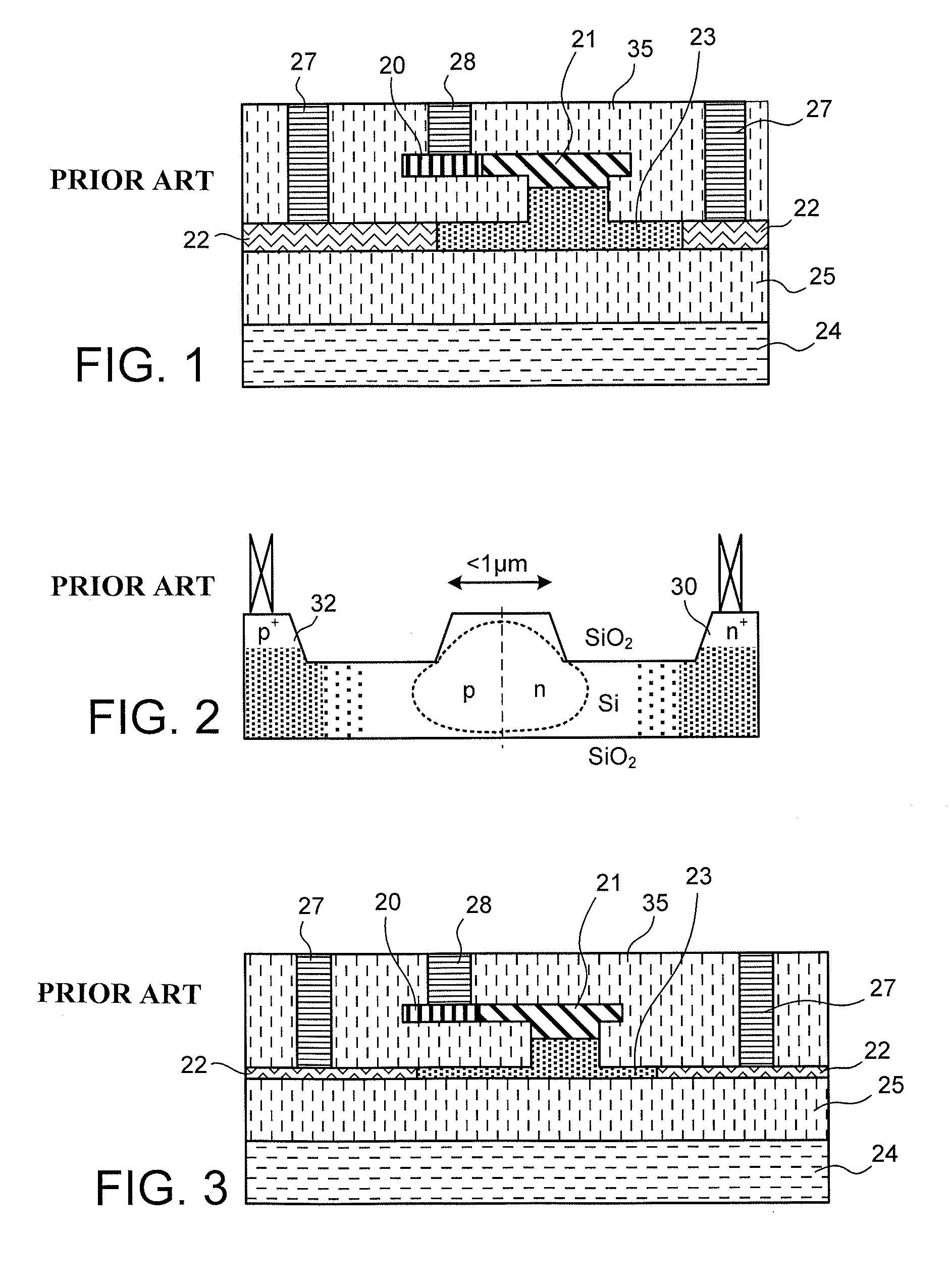
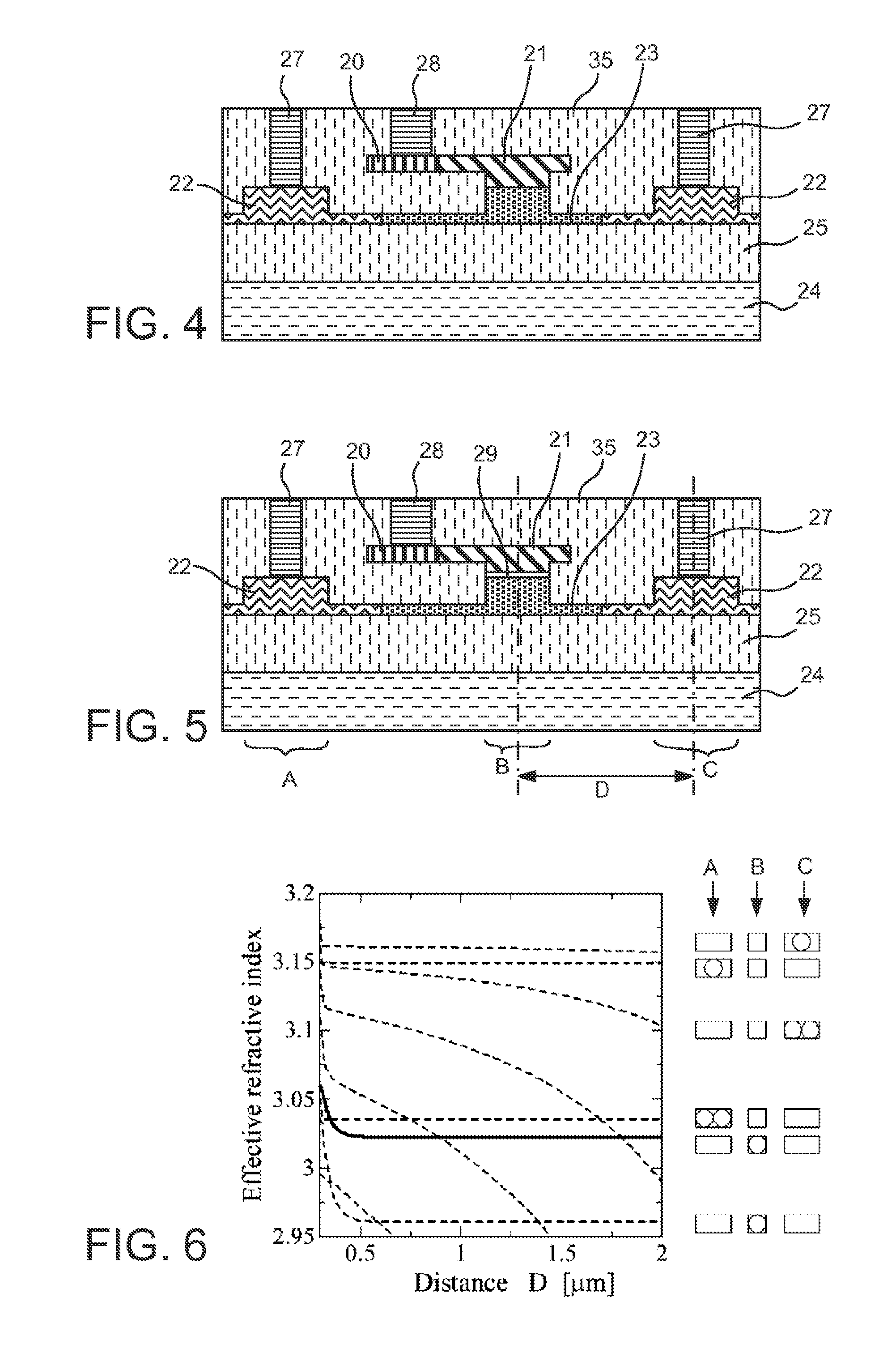
ActiveUS8532440B2Efficient connectionReduced propagation lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsZeroth orderMetal electrodes
In an electro-optic device, a stack structure including a first silicon layer of a first conductivity type and a second silicon layer of a second conductivity type has a rib waveguide shape so as to form an optical confinement area, and a slab portion of a rib waveguide includes an area to which a metal electrode is connected. The slab portion in the area to which the metal electrode is connected is thicker than a surrounding slab portion. The area to which the metal electrode is connected is set so that a range of a distance from the rib waveguide to the area to which the metal electrode is connected is such that when the distance is changed, an effective refractive index of the rib waveguide in a zeroth-order mode does not change.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FOUNDRY PTE LTD +1
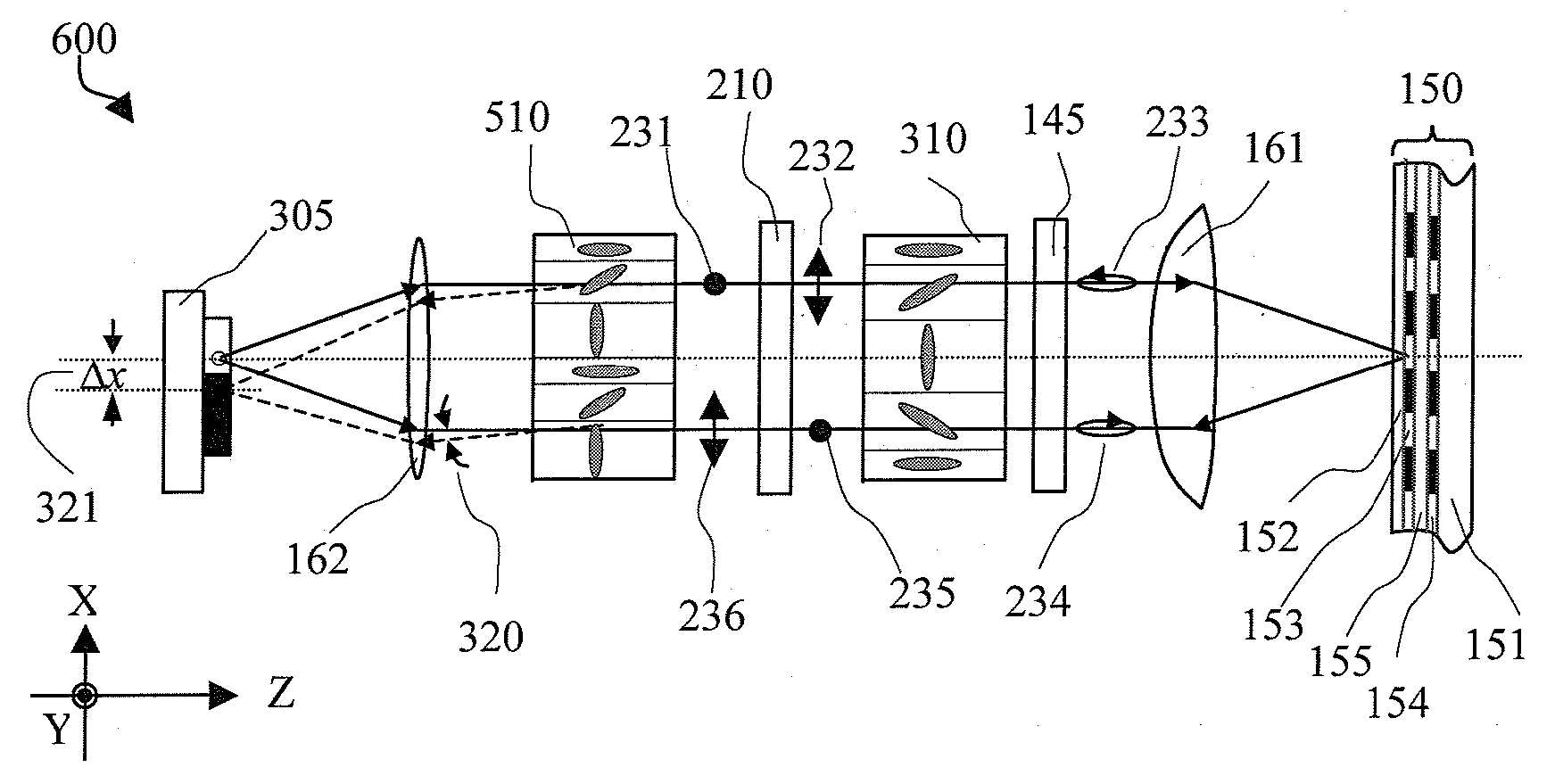
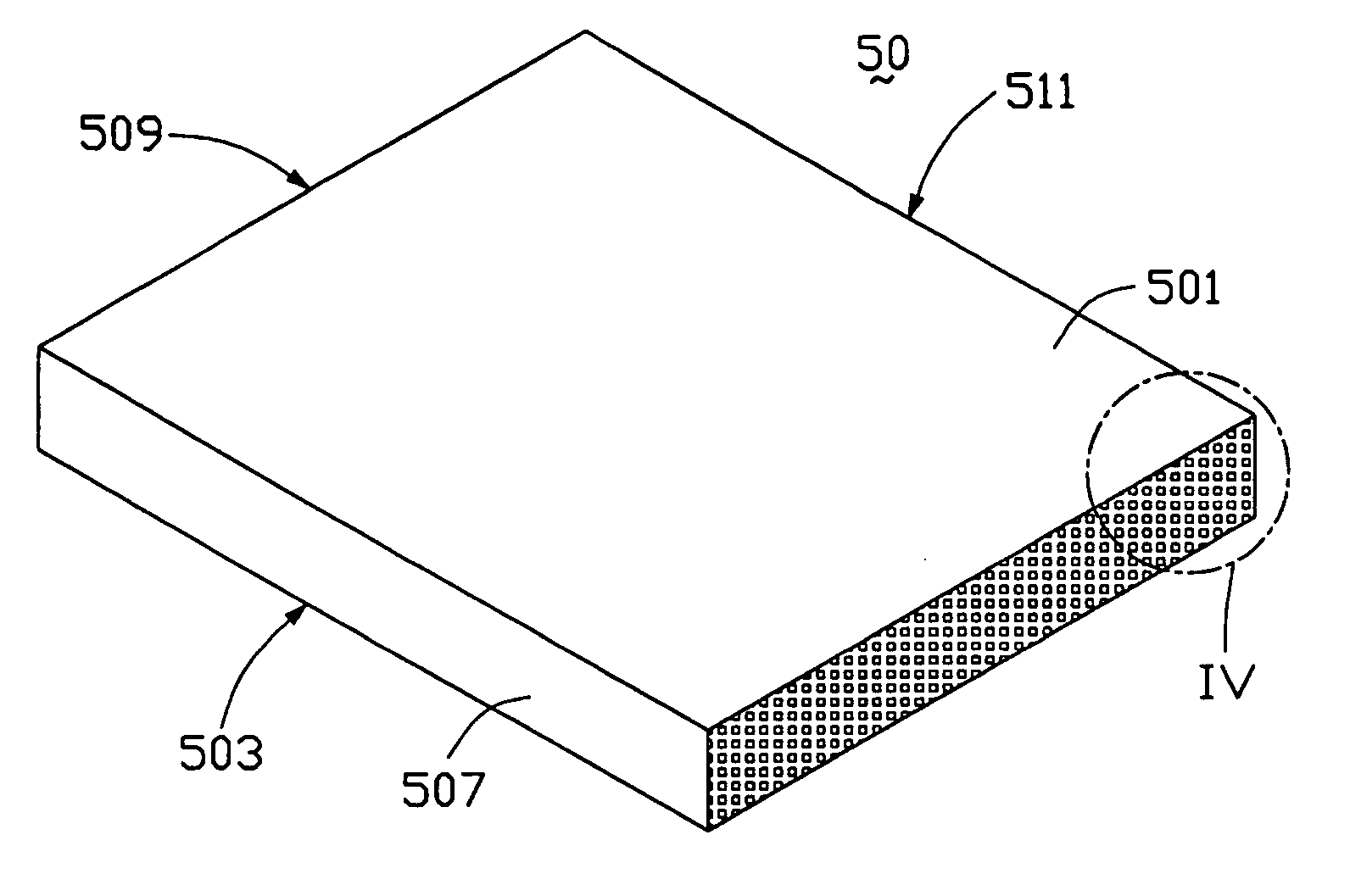
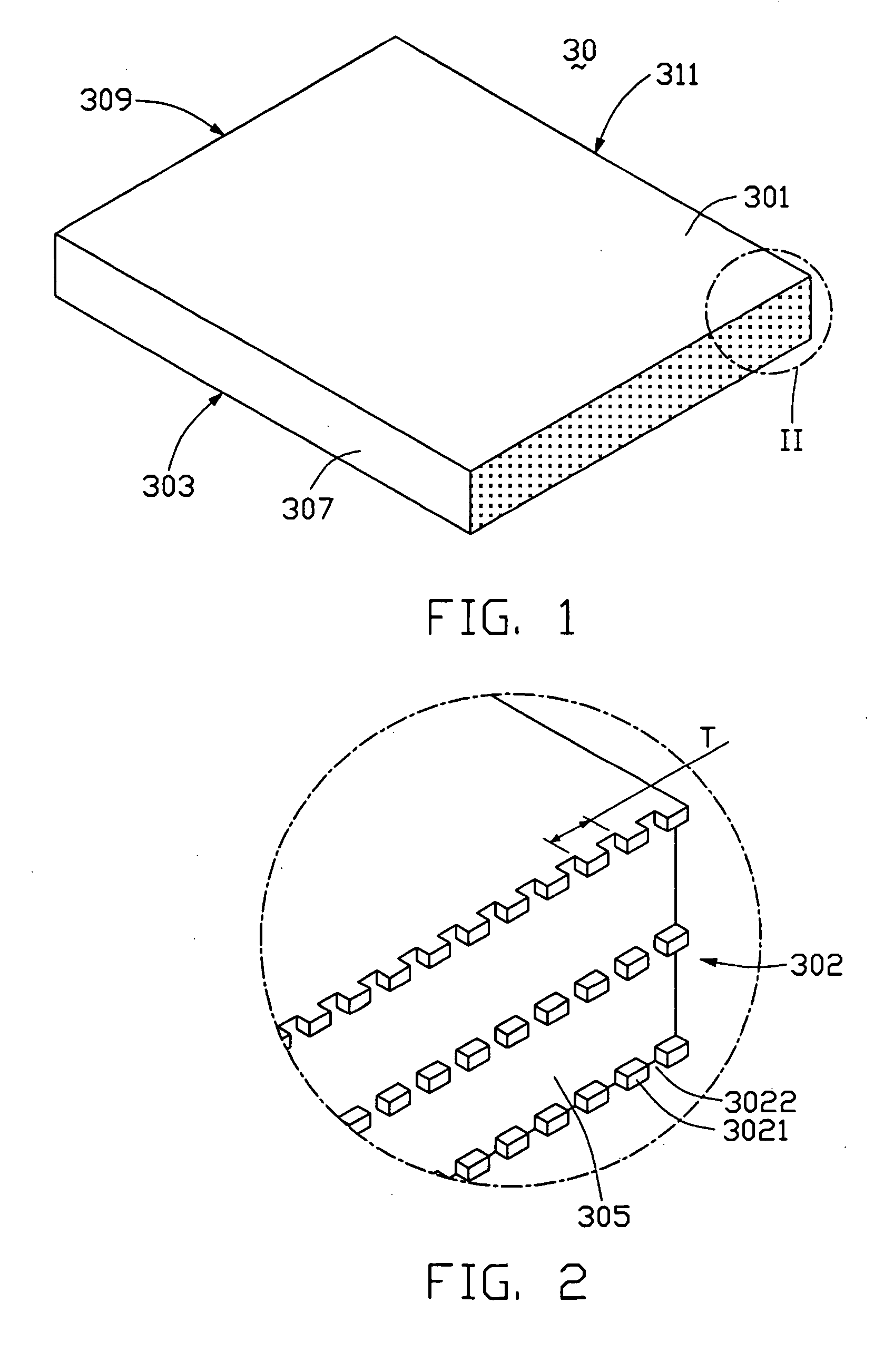
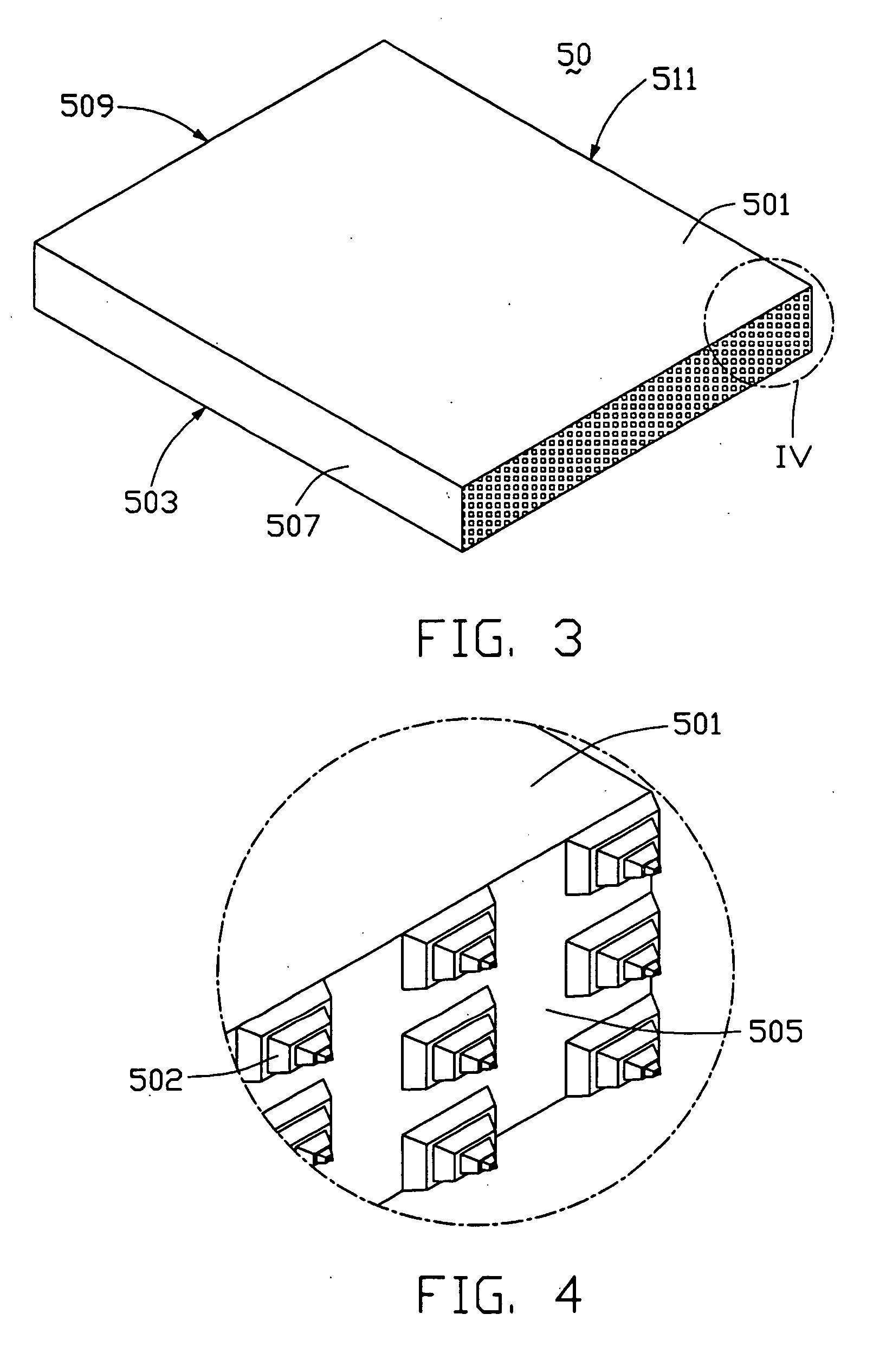
Light guide plate with subwavelength grating and backlight module using the same
InactiveUS20050185915A1Improve utilization efficiencyUniform lightMechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsZeroth orderGrating
A light guide plate (30) has a light incident surface (305) for receiving light, a light emitting surface (301) for emitting light, a bottom surface (303) opposite to the light emitting surface, and side surfaces (307, 309, 311). A subwavelength grating (302) is formed on the light incident surface for diffracting the light. The subwavelength grating is a zeroth-order grating which covers a wide wavelength band and diffracts the light into zeroth-order waves. So that the light guide plate has a high light utilization efficiency and yields high uniformity of outgoing light.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
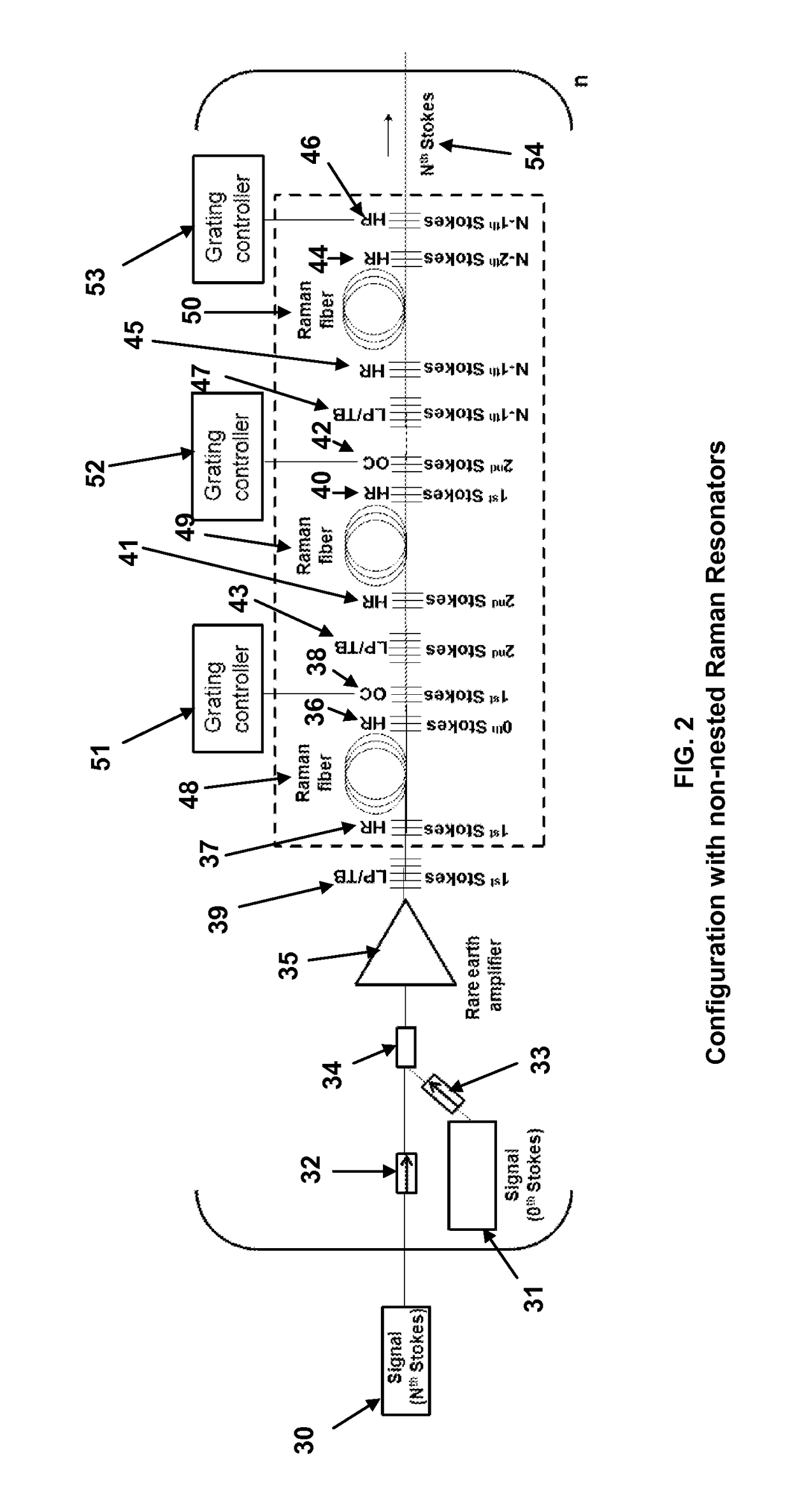
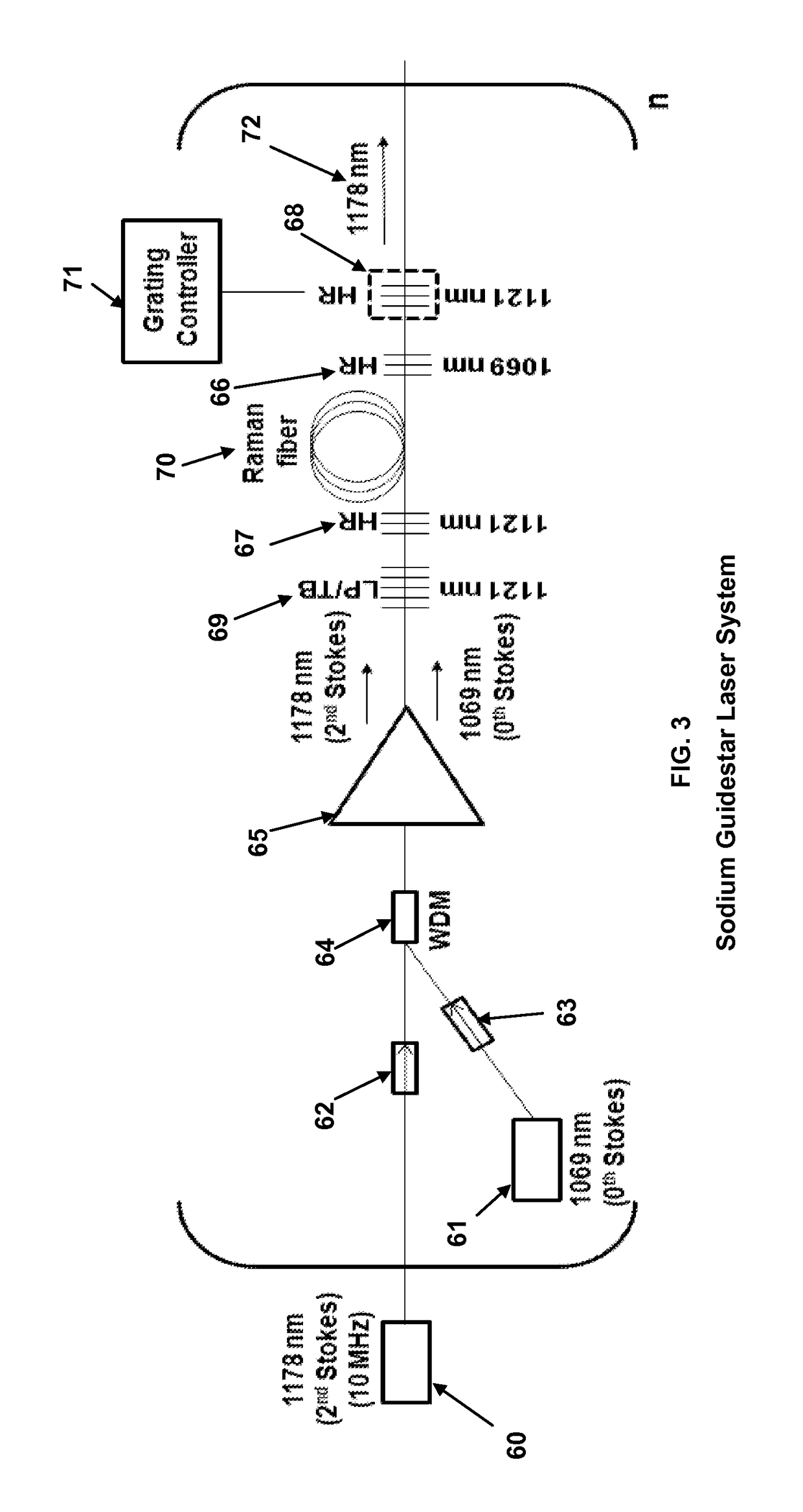
Seeded raman amplifier for applications in the 1100-1500 nm spectral region
ActiveUS8472486B1Increase output powerImprove conversion efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor lasersHigh power lasersZeroth order
A method of generating high-power laser output in the 1100 to 1500 um spectral region having a controllable linewidth. A Raman amplifier comprised of one or more nested pairs of fiber Bragg grating cavities tuned to the 1st, 2nd, . . . N−1st order Stokes wavelengths is seeded with both the desired Nth order Stokes output wavelength and the corresponding zeroth-order Stokes pump wavelength. As the pump wavelength propagates through the apparatus, it is sequentially converted to the 1st, 2nd, . . . N−1st order Stokes wavelengths in the nested fiber Bragg grating cavities. The desired Nth order Stokes output wavelength is then amplified by the N−1st Stokes order as it propagates through the nested fiber Bragg grating cavities. The linewidths of various Stokes orders can be controlled through adjusting resonant bandwidths of the fiber Bragg grating cavities by offsetting, through heating, the reflectivity bandwidths of each pair of cavity gratings.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
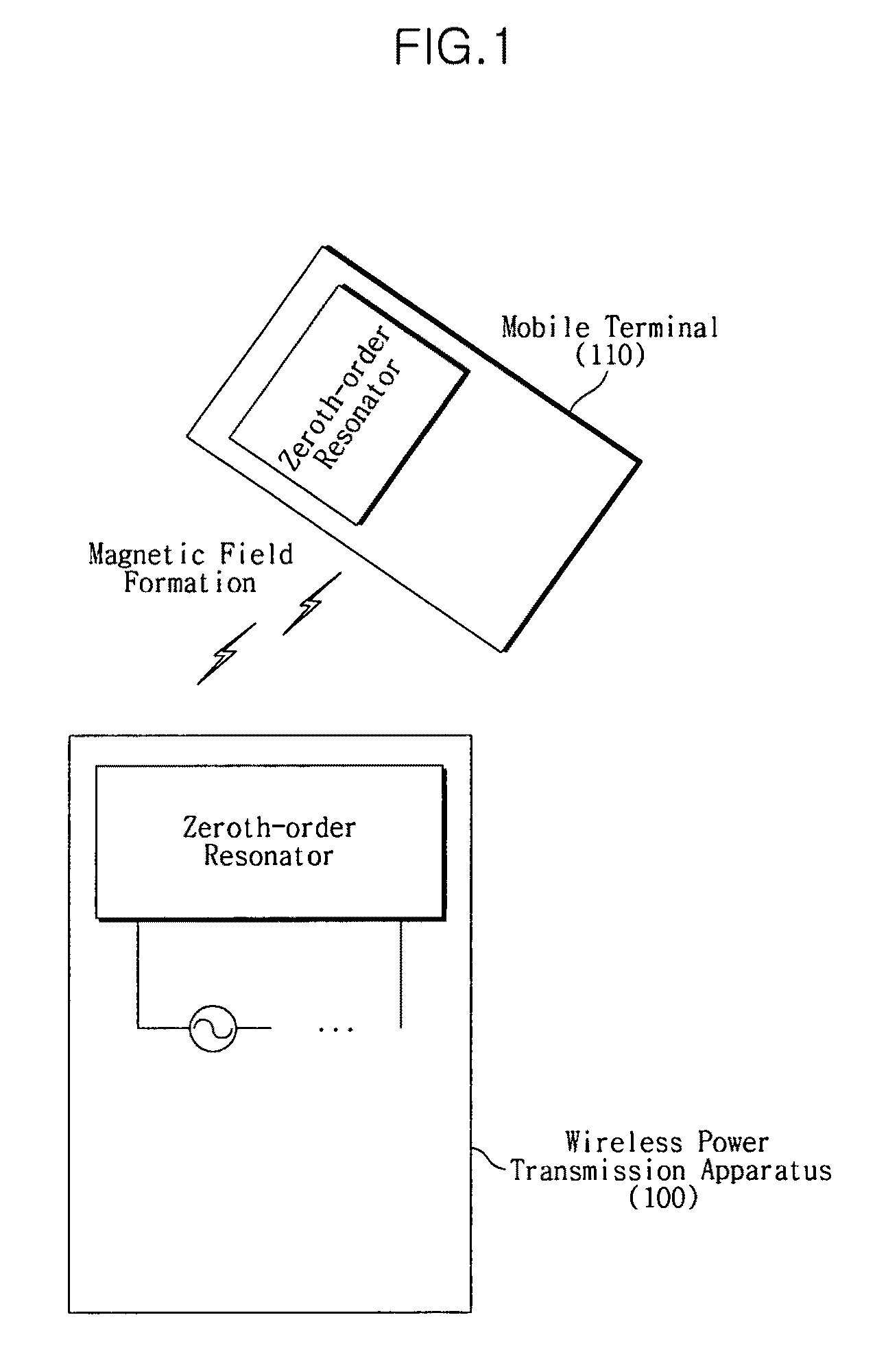
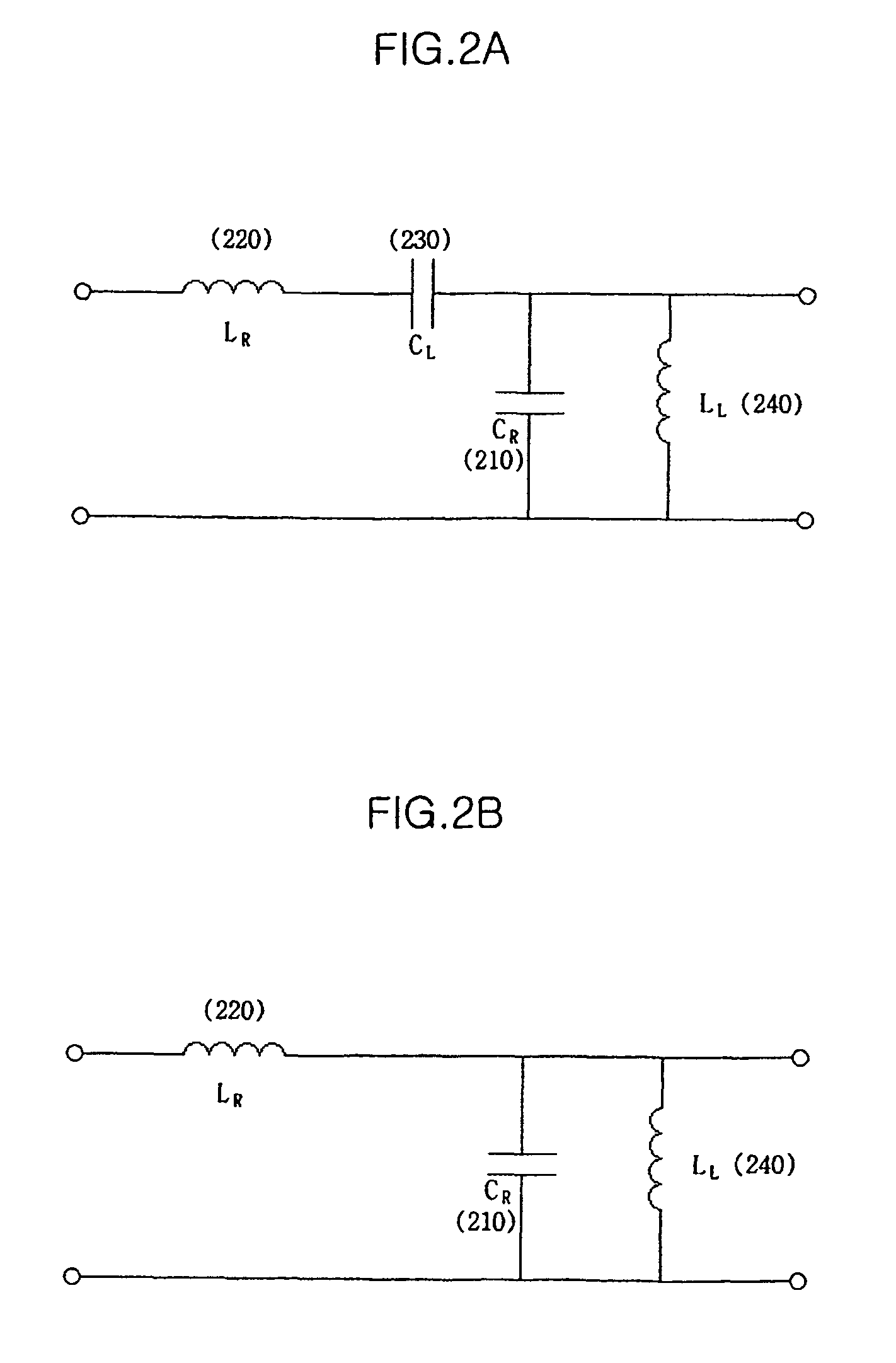
Apparatus for wireless power transmission using high Q low frequency near magnetic field resonator
An apparatus for wireless power transmission is disclosed. According to an exemplary aspect, the wireless power transmission apparatus includes a high Q low frequency near magnetic field resonator having characteristics of a metamaterial. Accordingly, manufacturing of a compact power supply capable of wirelessly supplying power to mobile communication terminals or multimedia terminals is possible. By using a zeroth-order resonator with a DNG or ENG structure, a small-sized power supply with a simple configuration may be manufactured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Displacement measurement method and displacement measurement device
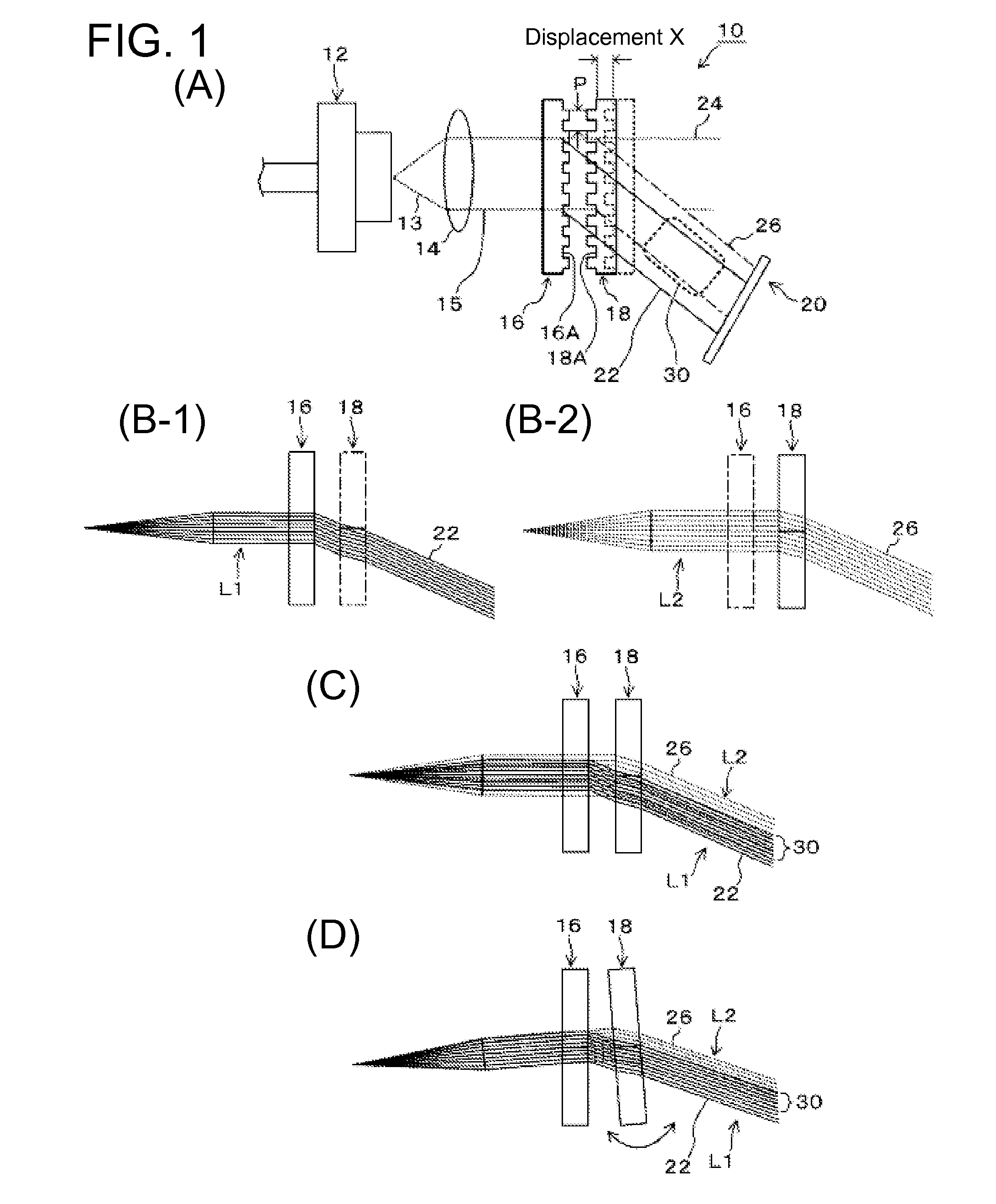
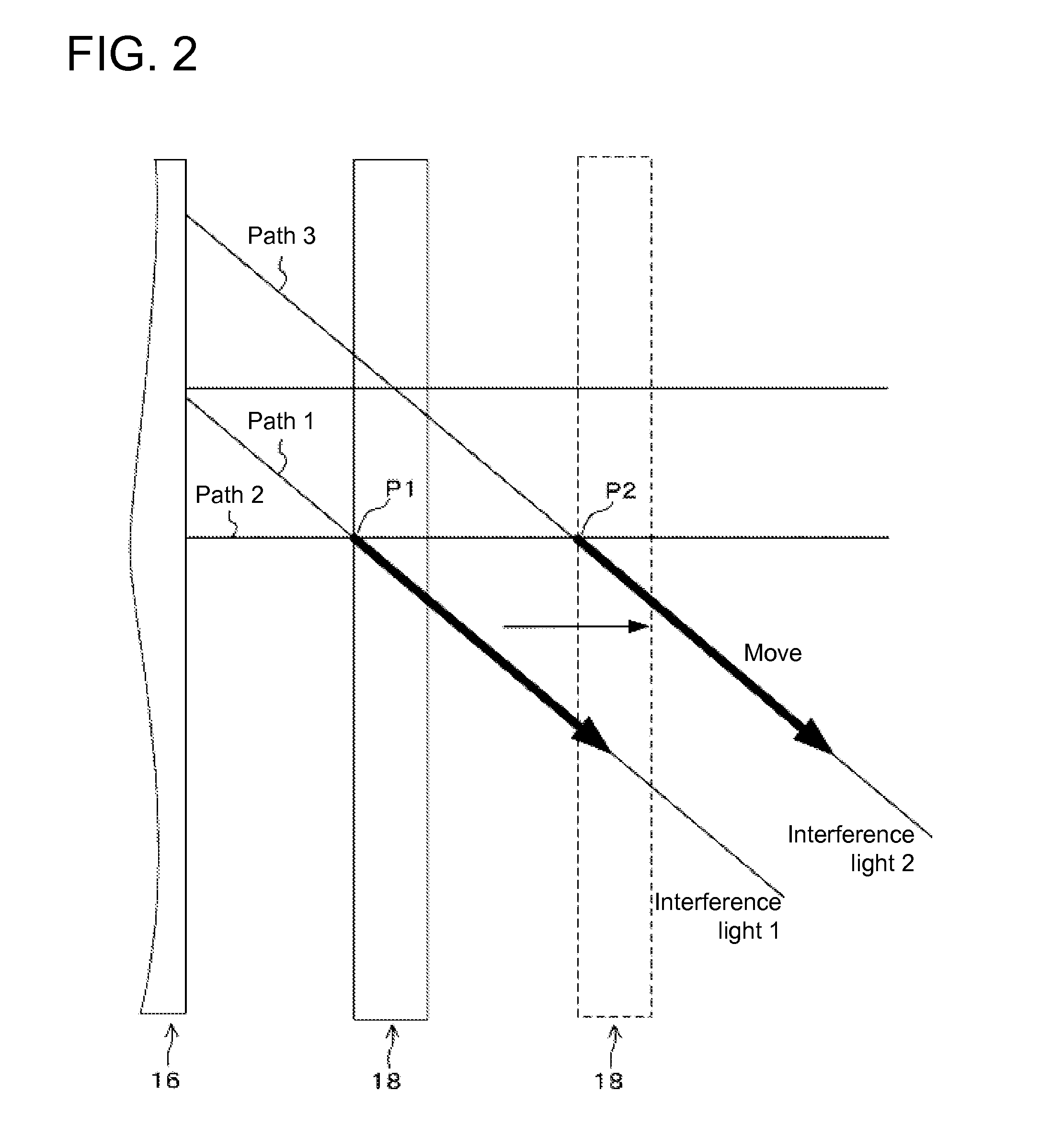
InactiveUS20120250031A1Resolve adjustmentsSimple configurationUsing optical meansRider propulsionZeroth orderMeasurement device
A displacement measurement device includes a first diffraction grating that generates first diffraction light of a prescribed order; a second diffraction grating movable relative to the first diffraction grating, the second diffraction grating dividing the zeroth-order light that has passed through the first diffraction grating into zeroth-order light and a second diffraction light of a prescribed order; and a first optical sensor that detects interfering light beams formed by the first diffraction light from the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction light from the second diffraction grating to determine an amount of a displacement of the second diffraction grating relative to the first diffraction grating.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Antenna device for a portable terminal
ActiveUS20110210897A1Easy to operateWell formedSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsZeroth orderMiniaturization
An antenna device for a portable terminal includes: a ground pattern provided on one surface of a circuit board; a first antenna pattern configured to resonate at a first frequency band and provided on an opposite surface of the circuit board; and a second antenna pattern configured to resonate at a second frequency band different from the first frequency band and arranged along a periphery of the ground pattern. The second antenna pattern is a zeroth order mode resonator including a plurality of capacitors and a plurality of inductors. The antenna device easily secures the operation characteristics of different operation frequency bands and contributes to miniaturization of the portable terminal. Thus, a user can conveniently carry and use the portable terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
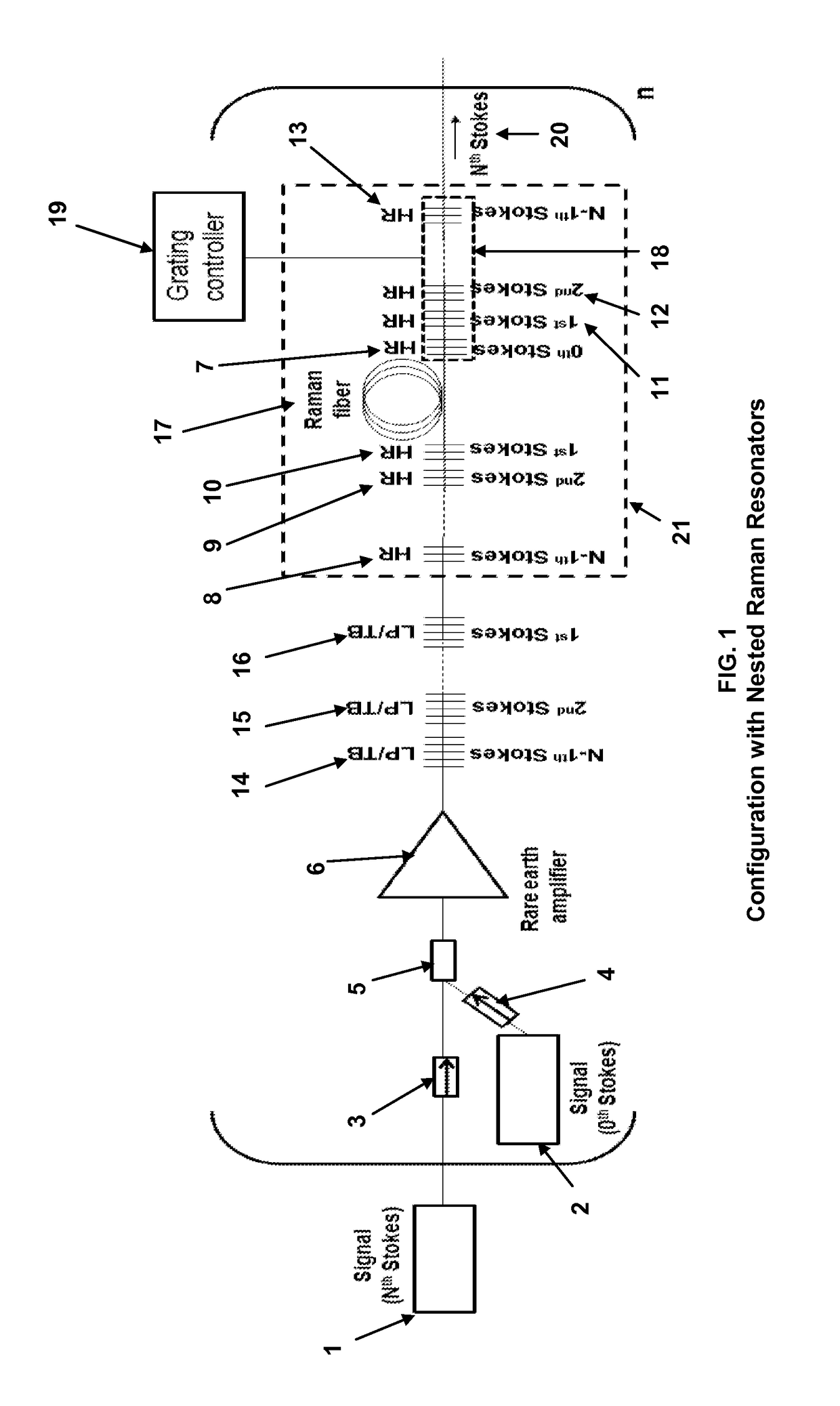
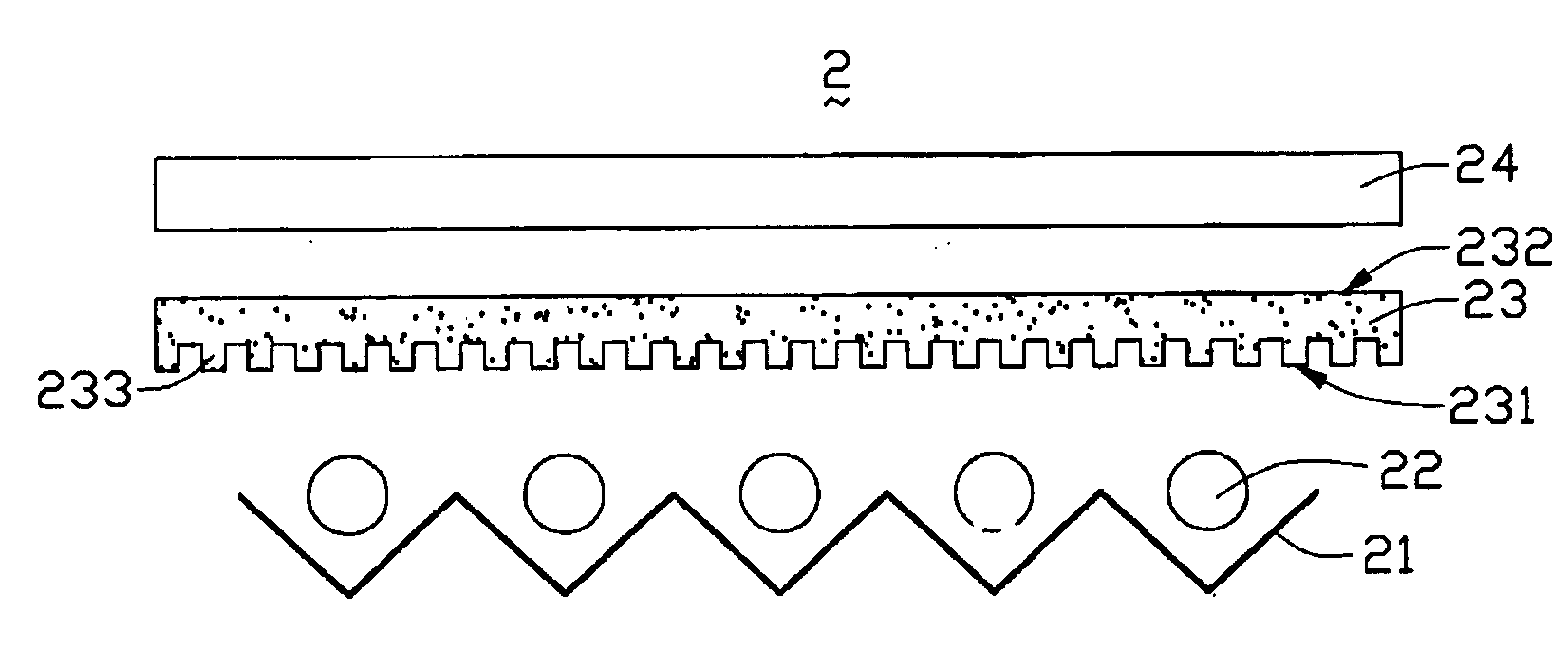
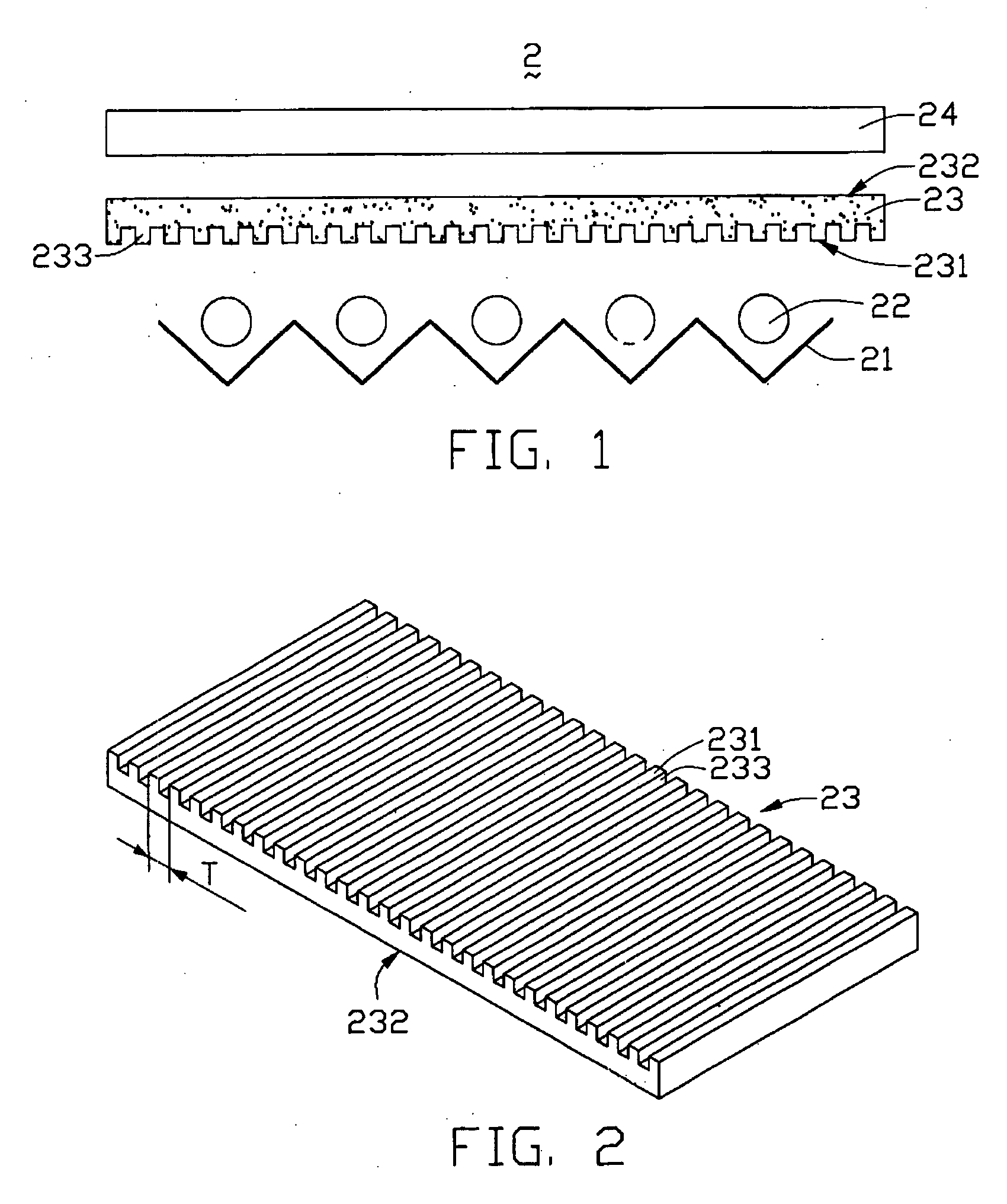
Backlight module with diffusion sheet having a subwavelength grating
InactiveUS20050195487A1Improve utilization efficiencyUniform lightDiffusing elementsNon-linear opticsZeroth orderGrating
A diffusion sheet (23) of the present invention includes a light incident surface (231) having a subwavelength grating (233) formed thereat, and a light emitting surface (232) opposite to the light incident surface. When light beams propagate through the subwavelength grating, they are diffracted forward and backward, to form front diffraction waves and back diffraction waves. Because the subwavelength grating is a zeroth-order grating, it only propagates the zeroth-order diffraction waves. Therefore, based on diffraction theory, the back diffraction waves can be eliminated by adjusting the period T and the shape of the subwavelength grating. If this is done, almost all the incident light beams are transmitted through the incident surface. Thereby, the efficiency of light utilization is enhanced. Moreover, the light beams are diffracted and distributed uniformly. Accordingly, the diffusion sheet yields high uniformity of outgoing light emitted from the emitting surface.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com