Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2203 results about "Linearly polarized light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
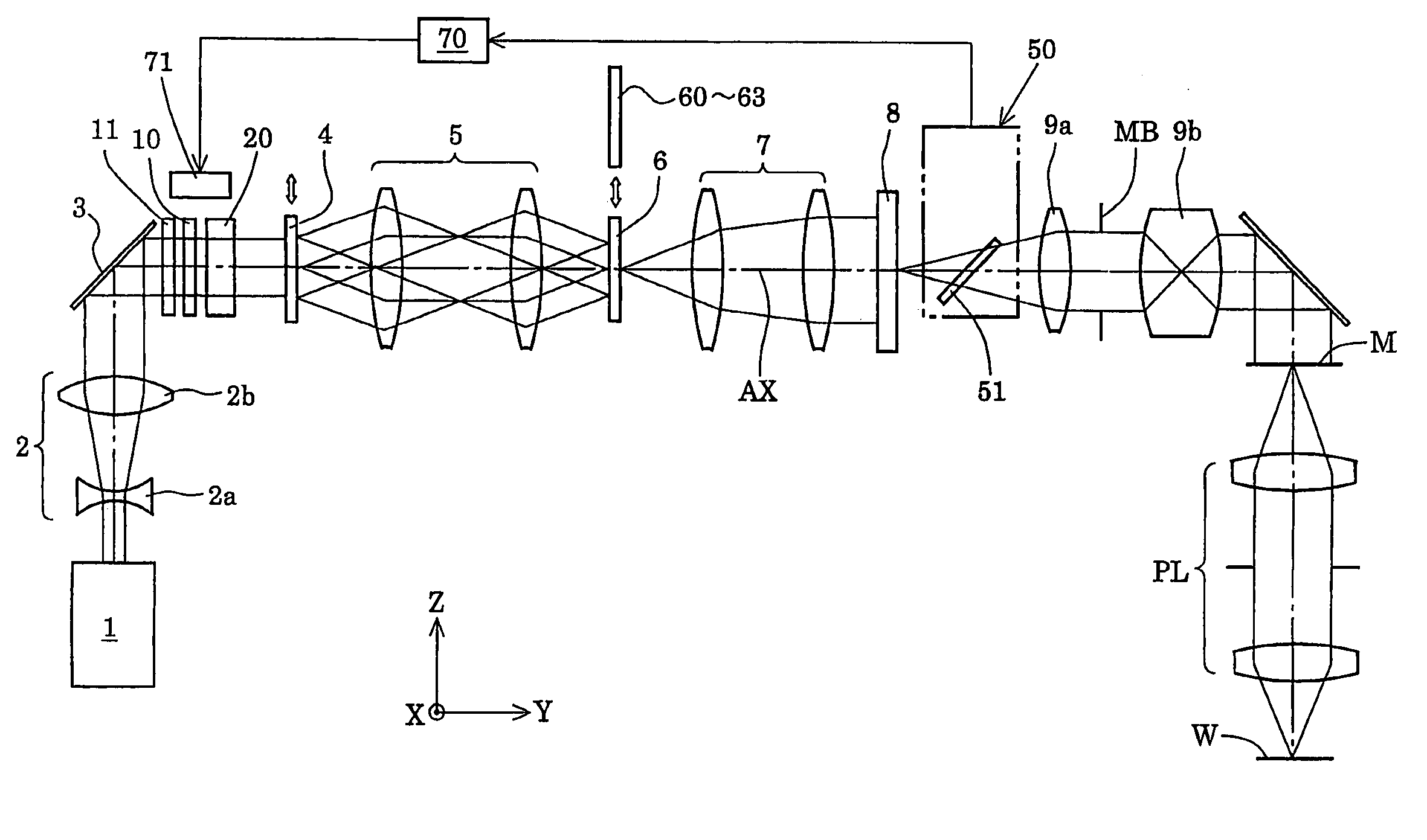
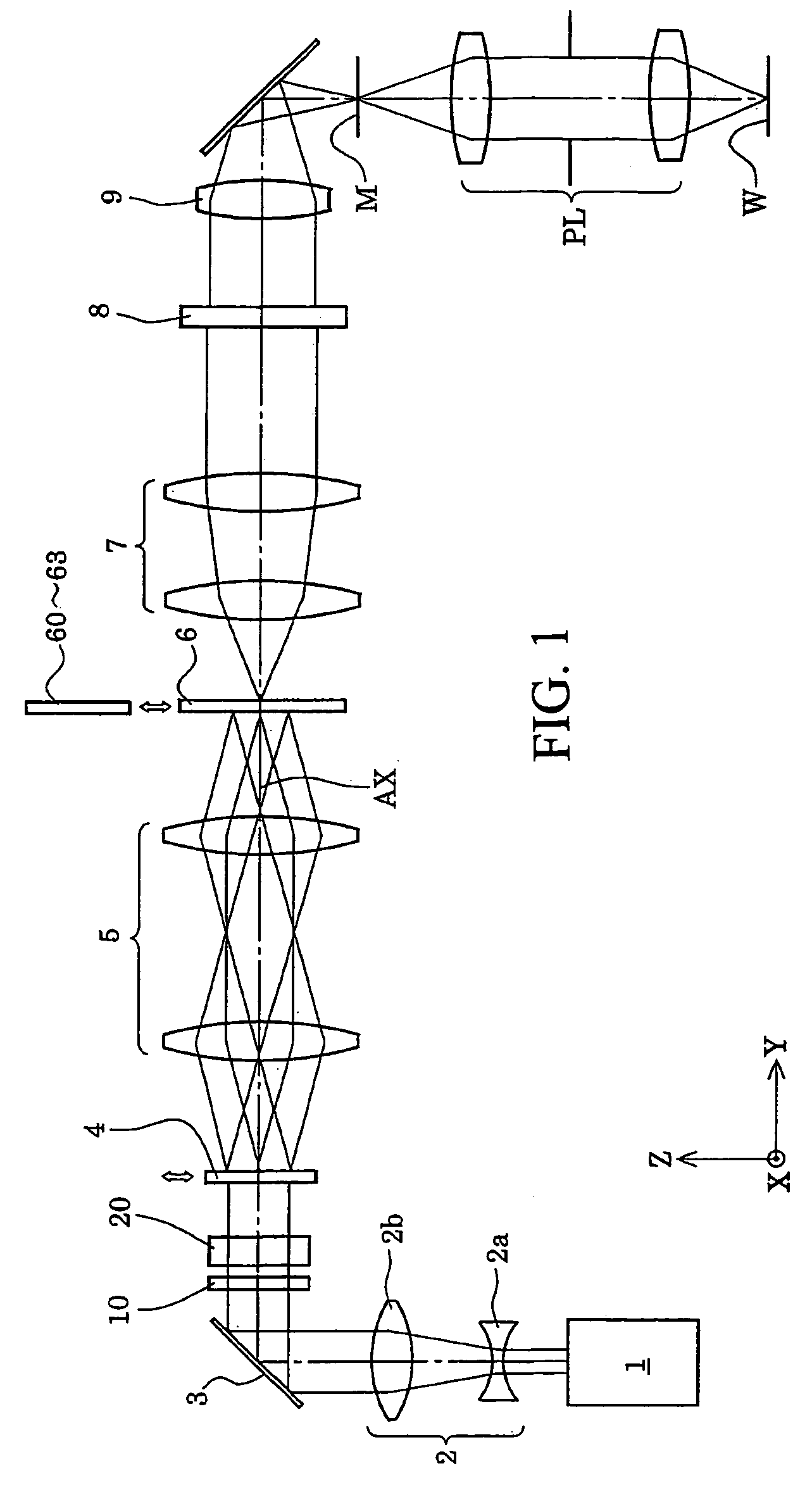
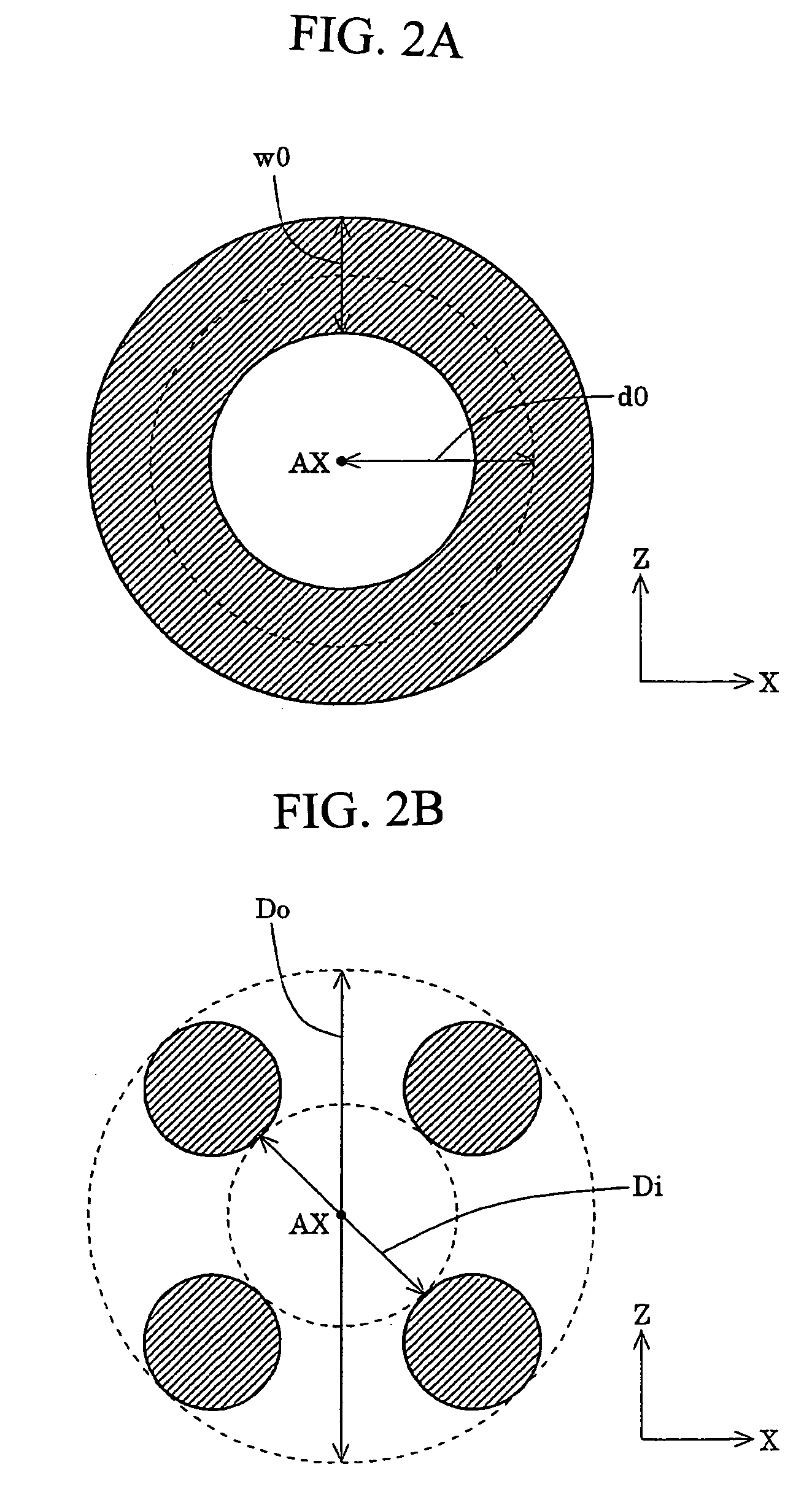
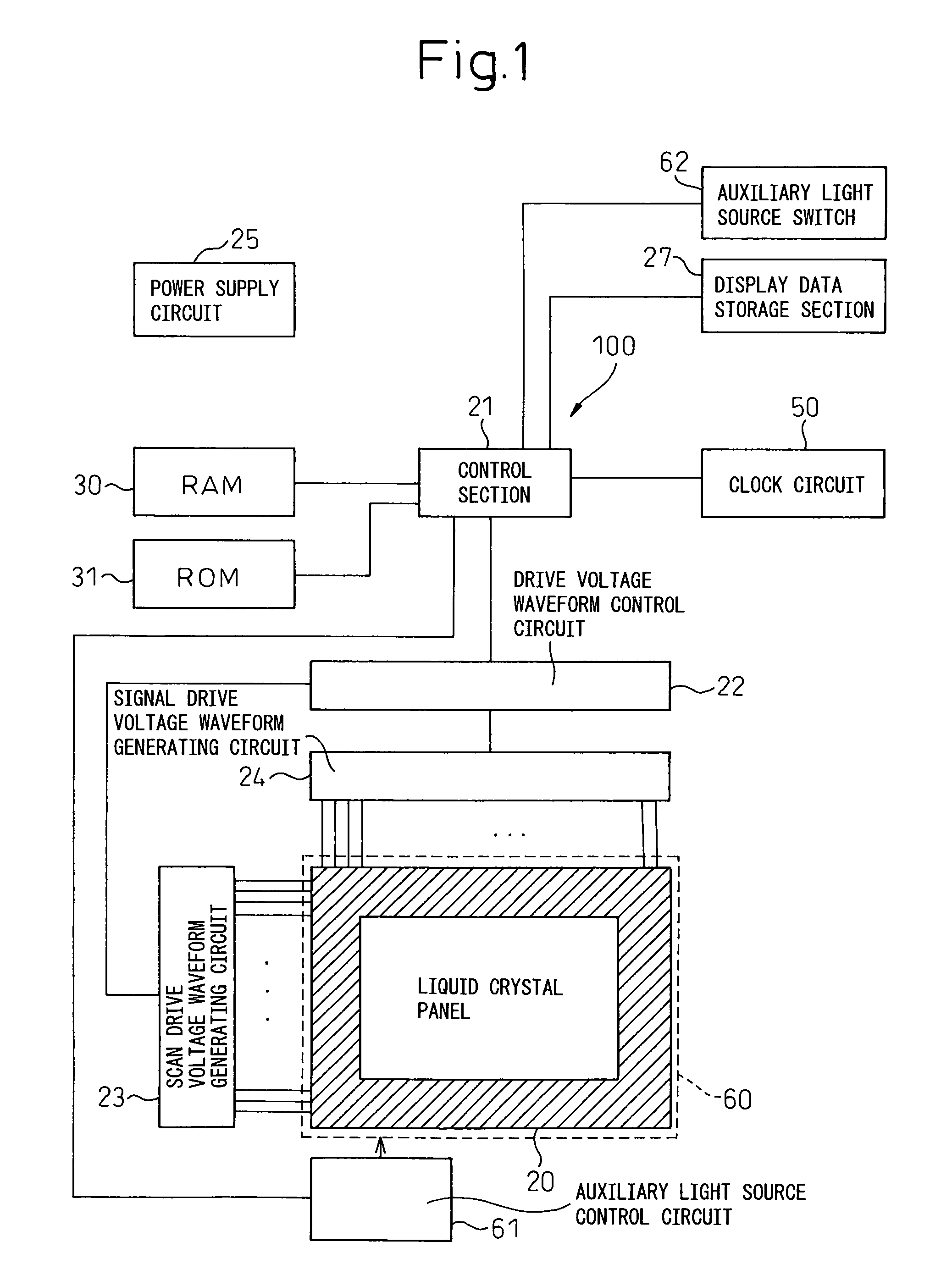
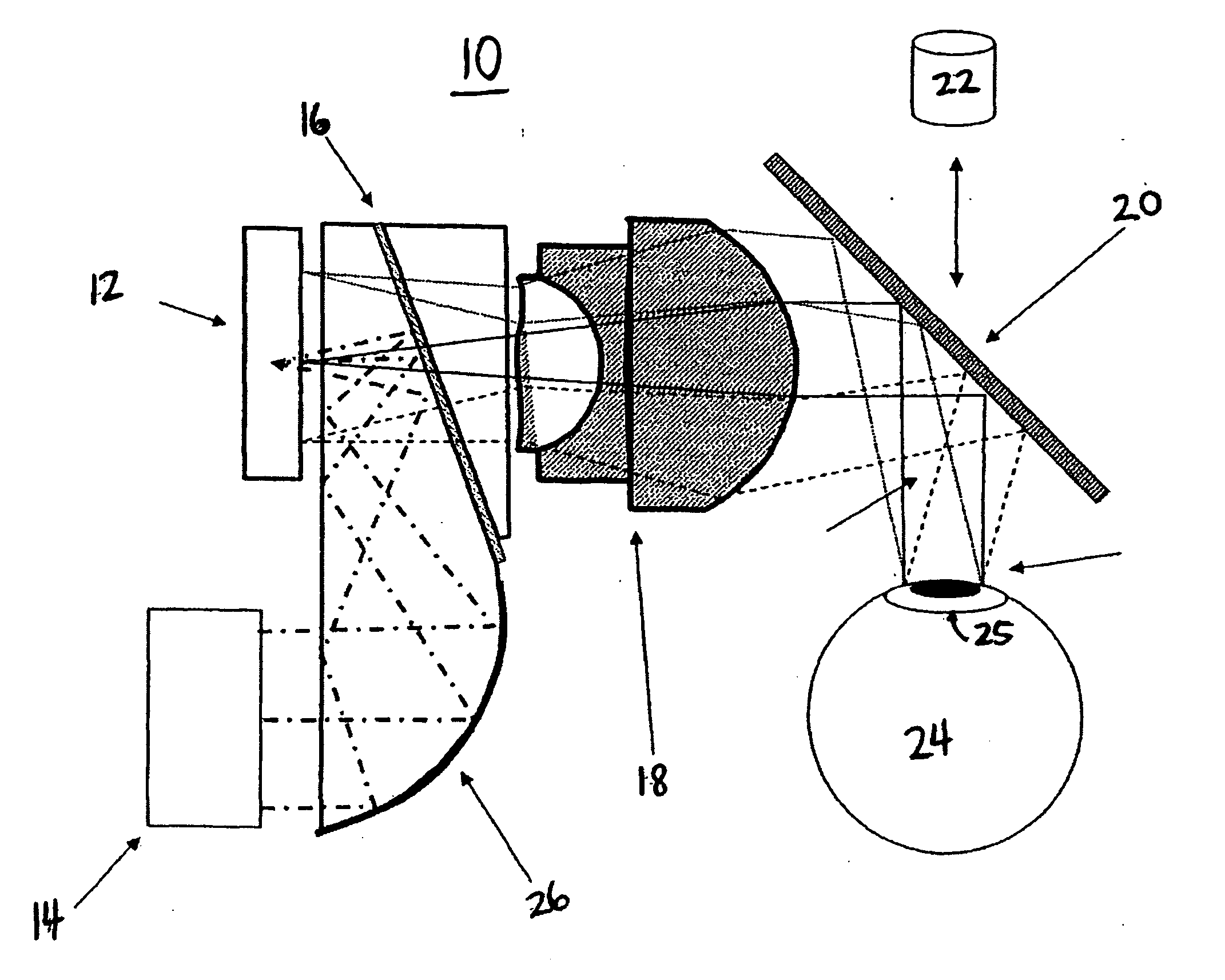
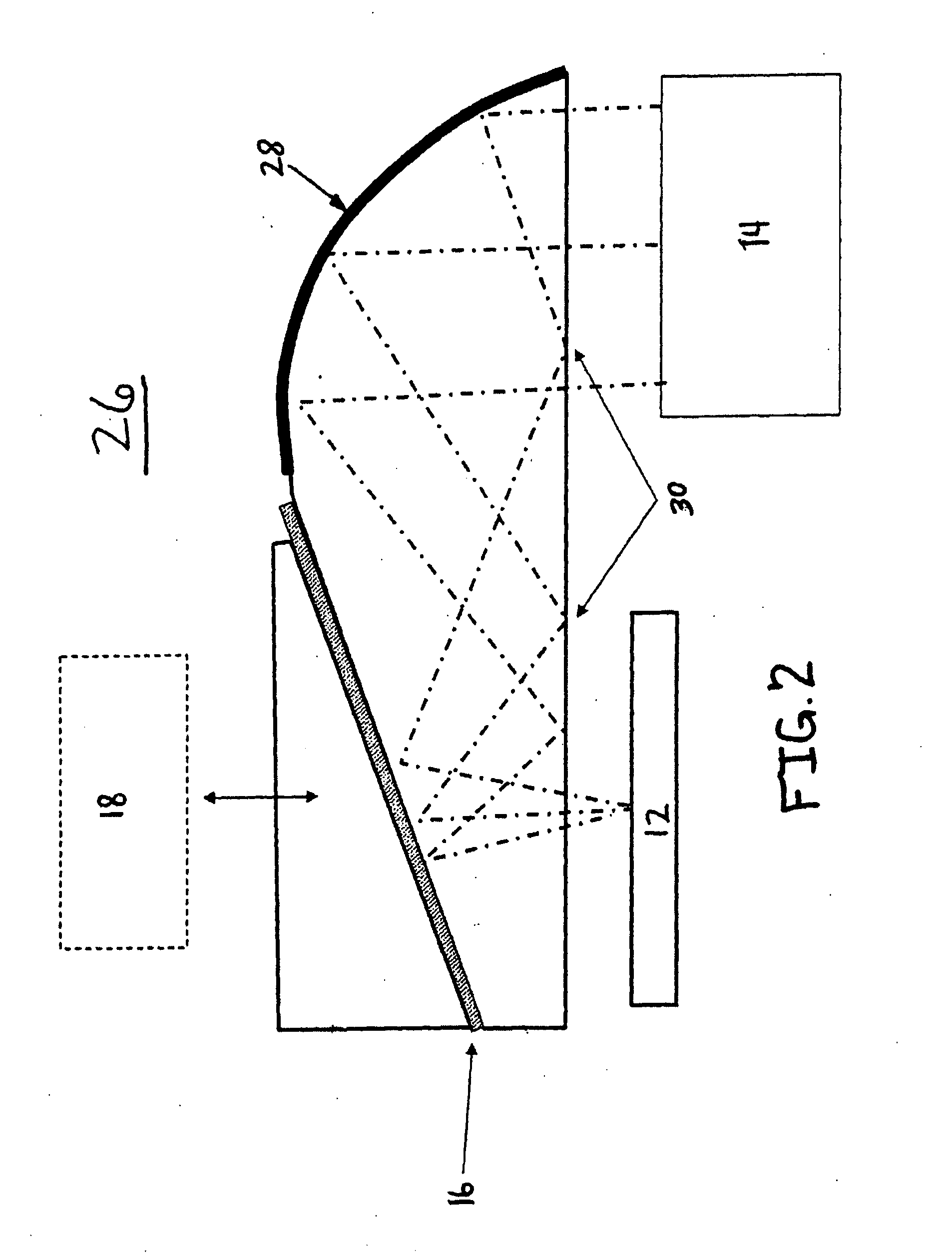
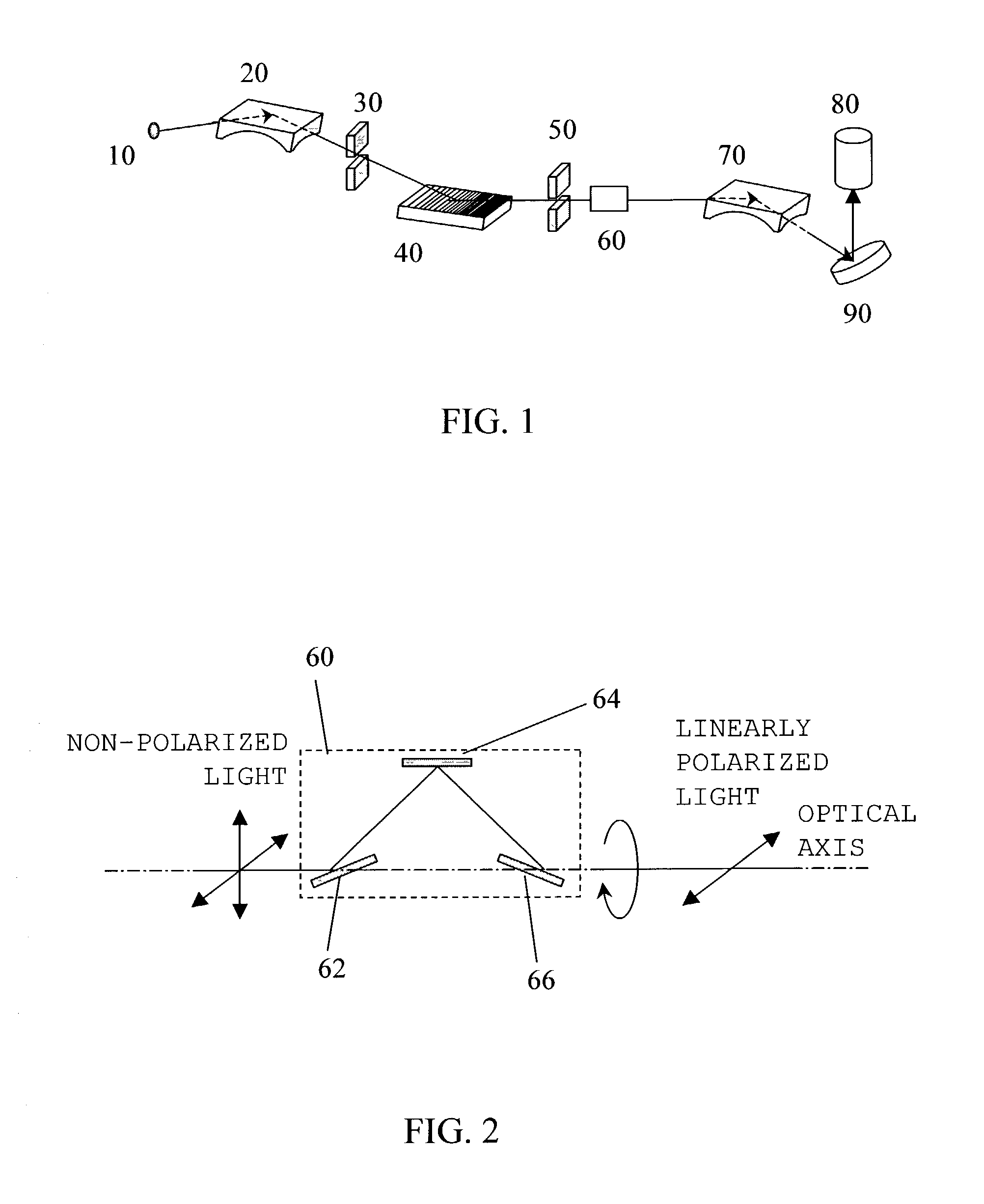
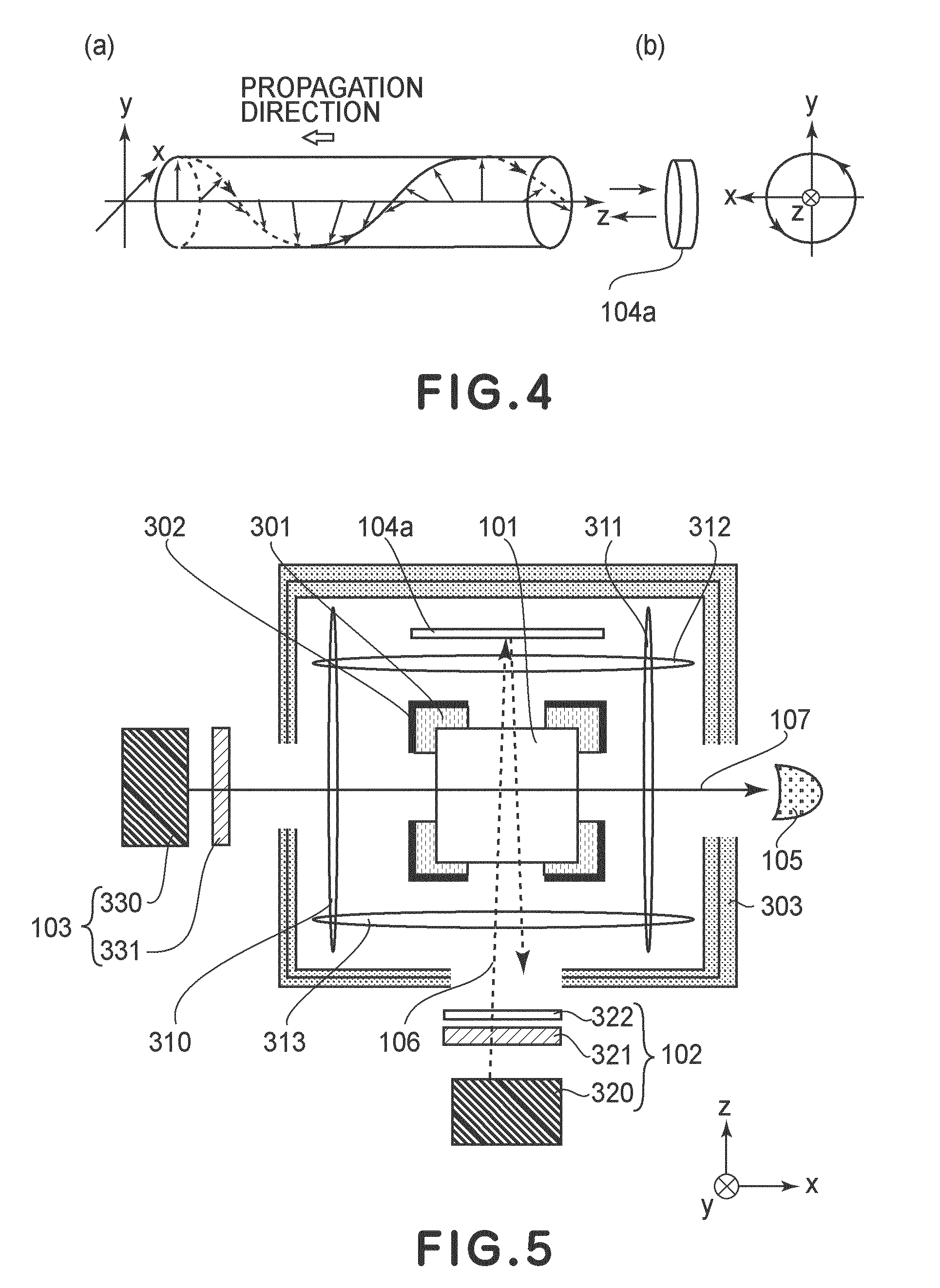
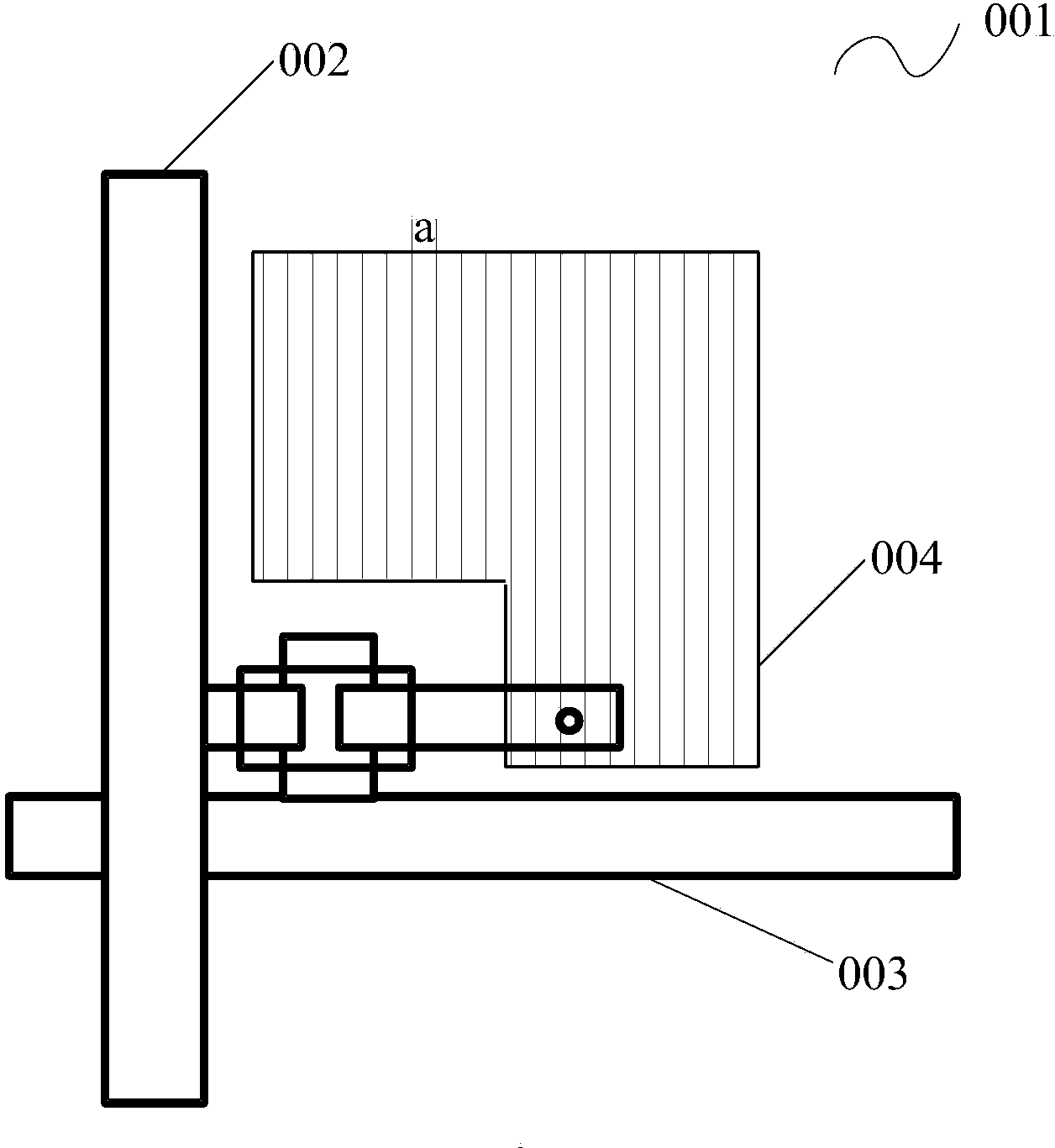
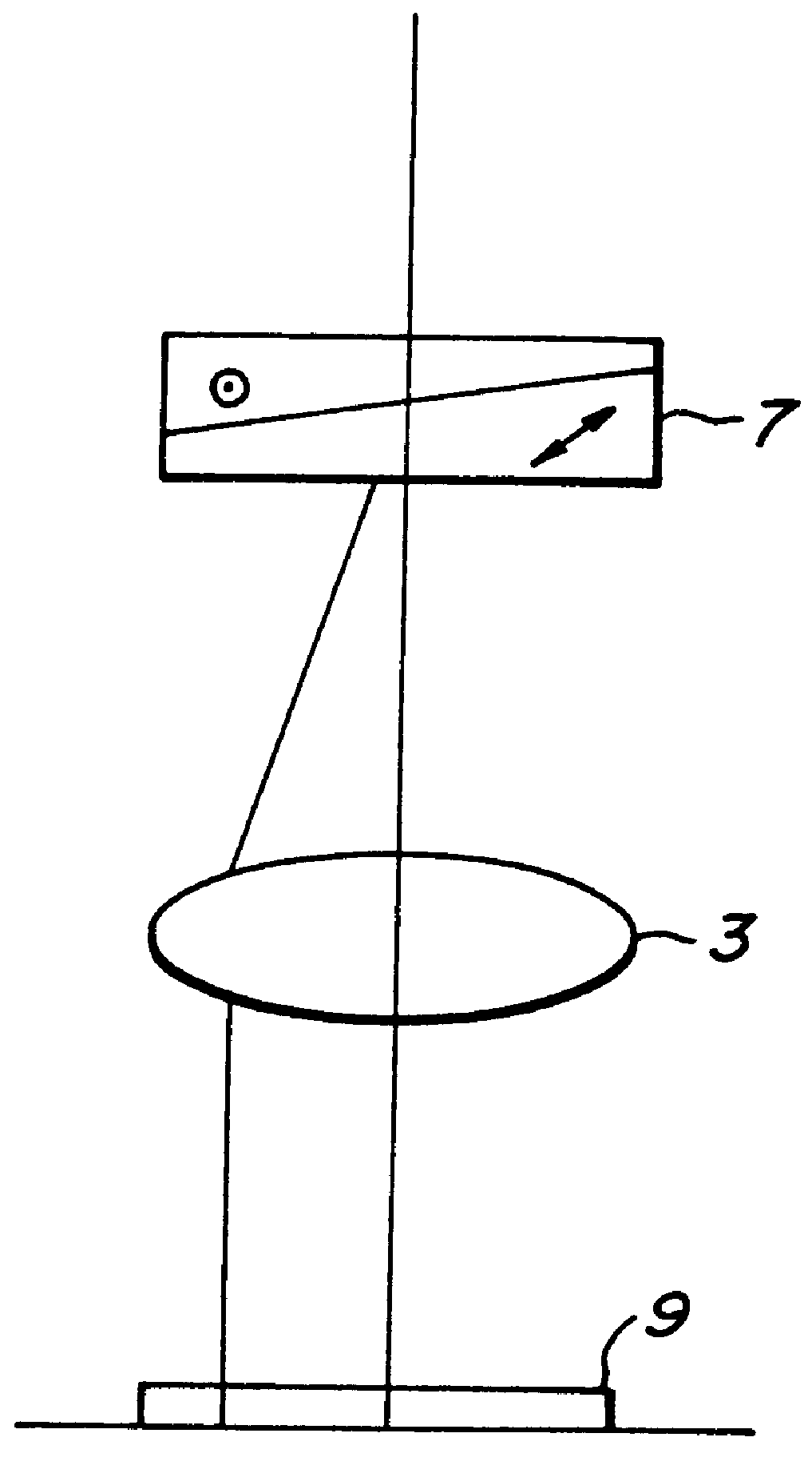
Illumination optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method
InactiveUS20060055834A1Limit lossIncrease exposurePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLinearityOptic system
An illumination optical system for, when installed in an exposure system, realizing a suitable illumination condition by varying the polarized state of the illumination light according to the pattern characteristics of the mask while suppressing the loss of the intensity of the light. The illumination optical system has a light source unit for supplying a linearly polarized light for illuminating surfaces to be illuminated therewith, and a polarized state changing device for changing the polarized state of the illuminating light from a predetermined polarized state to a nonpolarized state and vice versa. The polarized state changing device is arranged in the optical path between the light source unit and the surfaces to be illuminated. The polarized state changing device can be removed from the illumination optical path and has a depolarizer for selectively depolarizing the incident linearly polarized light.
Owner:NIKON CORP
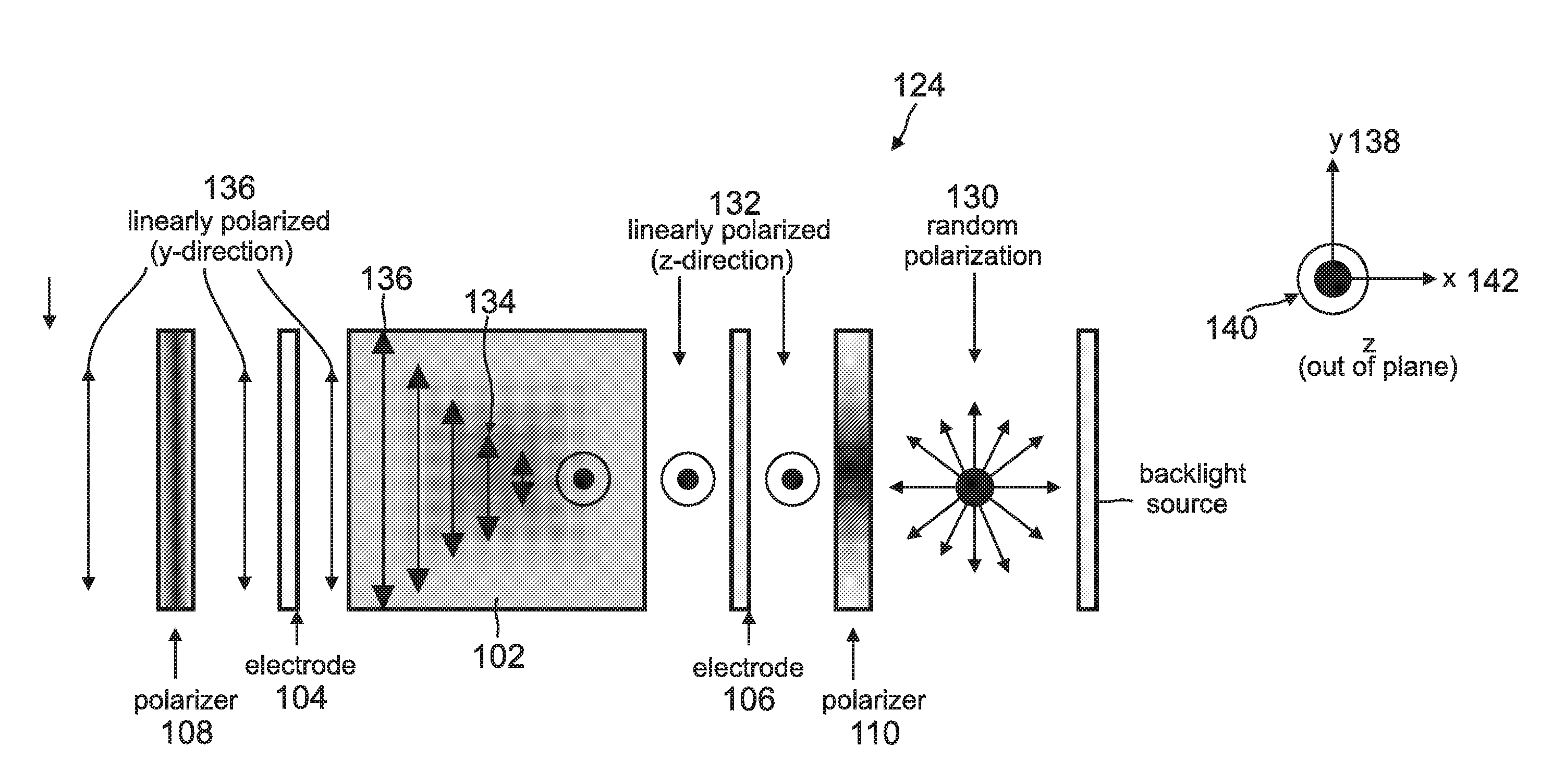
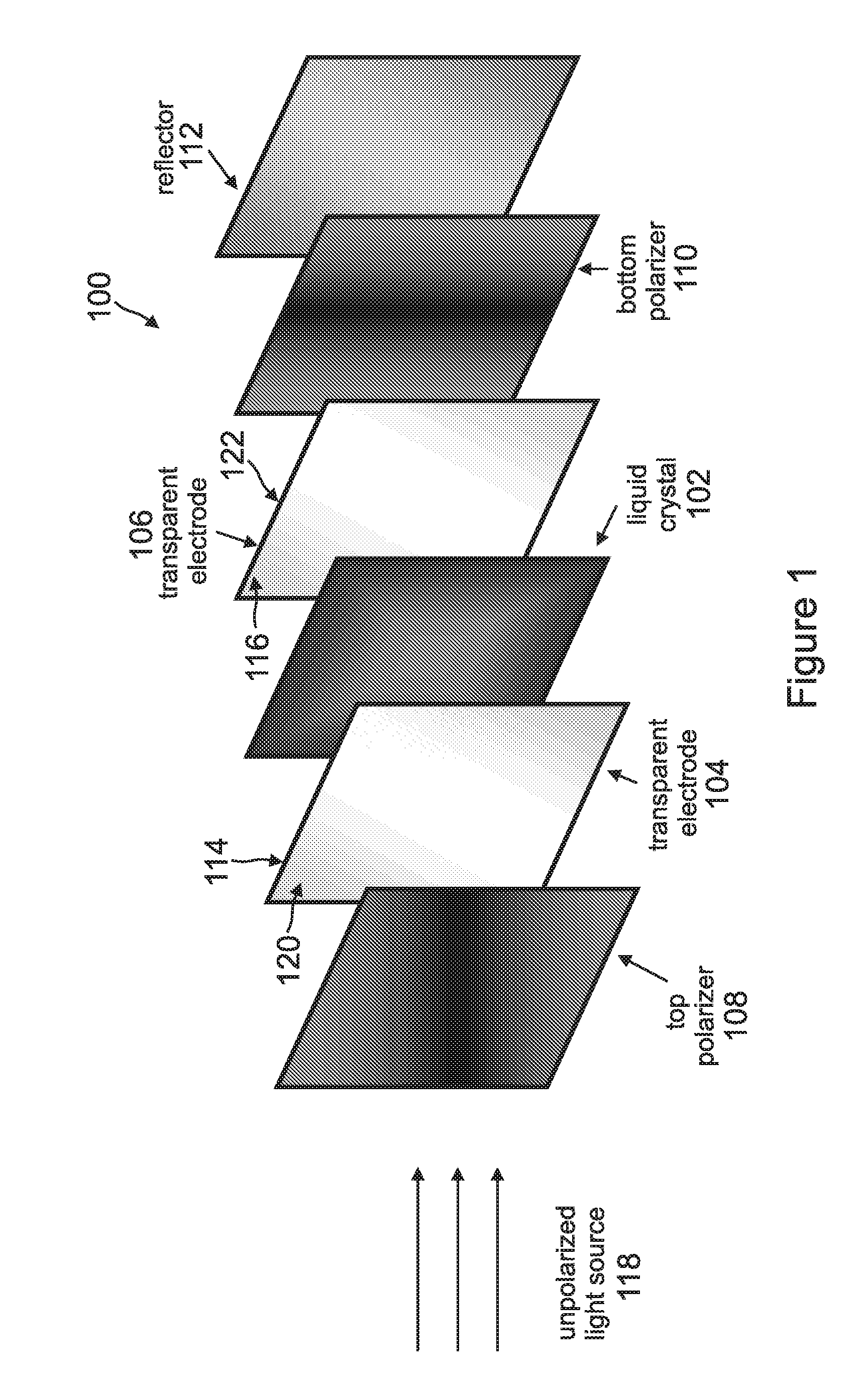
Linearly polarized backlight source in conjunction with polarized phosphor emission screens for use in liquid crystal displays
InactiveUS20100220262A1Improve efficiencyLow efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLuminescent compositionsLiquid-crystal displayPhosphor
A device for displaying images positions a luminescent material between a light source and a liquid crystal display (LCD). The light source, which comprises one or more nonpolar or semipolar III-nitride based light emitting diodes (LEDs), emits a primary light having a specified polarization direction and comprising one or more first wavelengths. This primary light emitted by the light source is a linearly polarized light that eliminates any need for a polarizer. The luminescent material, which comprises one or more phosphors, is optically pumped by the primary light and emits a secondary light having the polarization direction of the primary light, wherein the secondary light is comprised one or more second wavelengths that are different from the first wavelength. This secondary light emitted by the luminescent material is a colored light that eliminates any need for a color filter. The LCD receives the secondary light and displays one or more images in response thereto.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
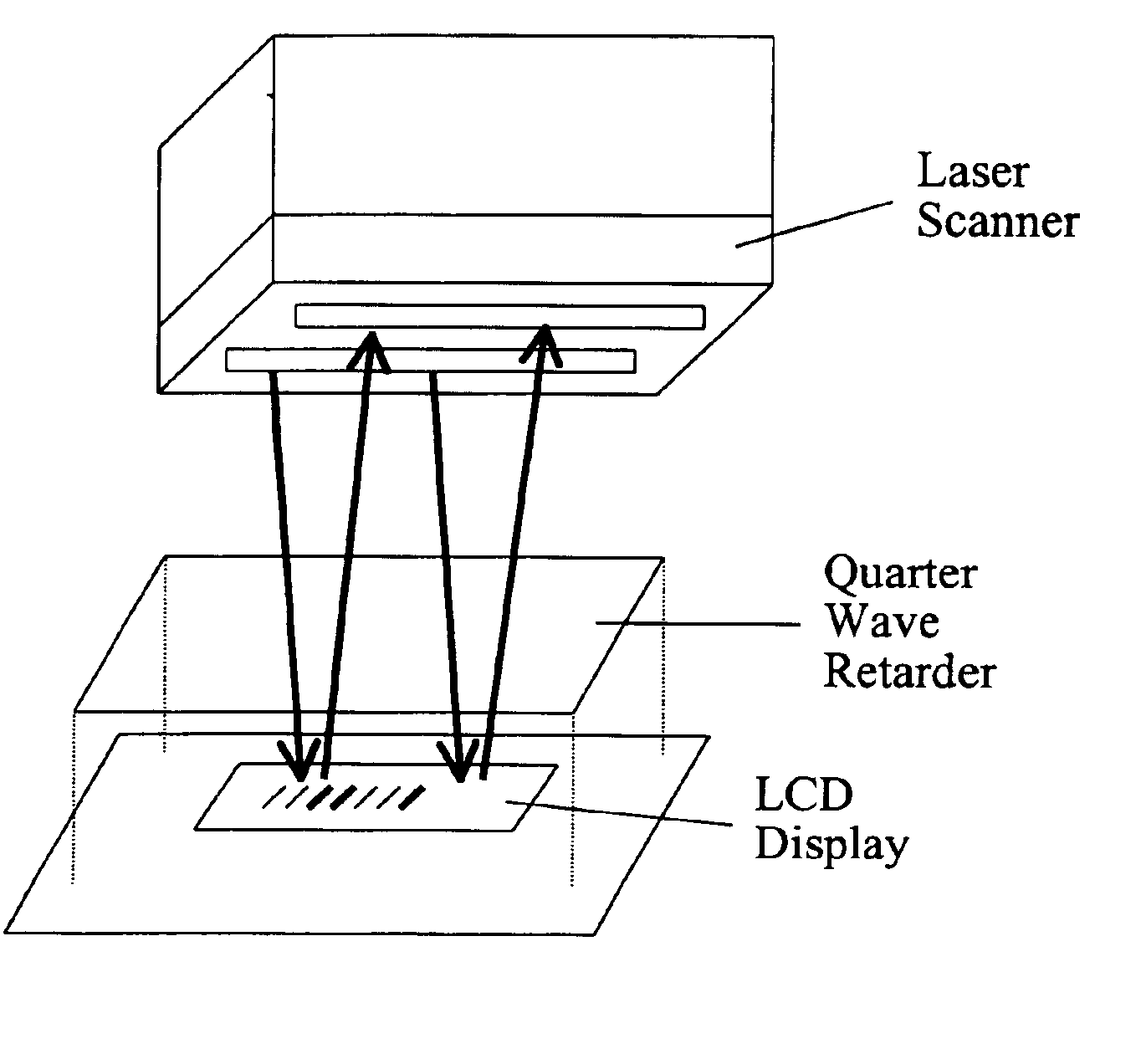
Scannable barcode display and methods for using the same
InactiveUS6877661B2Facilitates redemptionClear wellCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesData centerData acquisition
A system and method for implementing a wireless data transmission scheme through the use of a display capable of displaying symbolic information, a data acquisition device capable of identifying and capturing said displayed information and a mitigation device adapted to allow the data acquisition device to capture the symbolic information. The symbolic information may be a barcode displayed on an LCD outputting linearly polarized light. The data acquisition device may be a laser scanner, and the mitigation device may be a quarter wave retarder located between the display and the scanner. A larger system may utilize this wireless system or a different front end in a more generalized backend information transfer system. The backend system may include a centralized data center adapted to be used with retail couponing, ticketing, digital receipts, or a plurality of other information systems in which data is used separately from its storage location.
Owner:WEBB RICHARD M +4
Device capable of switching between an image display status and a mirror status, and an instrument disposed therewith
InactiveUS7495719B2Efficient processImprove usabilityNon-linear opticsBeam polarizationComputer science
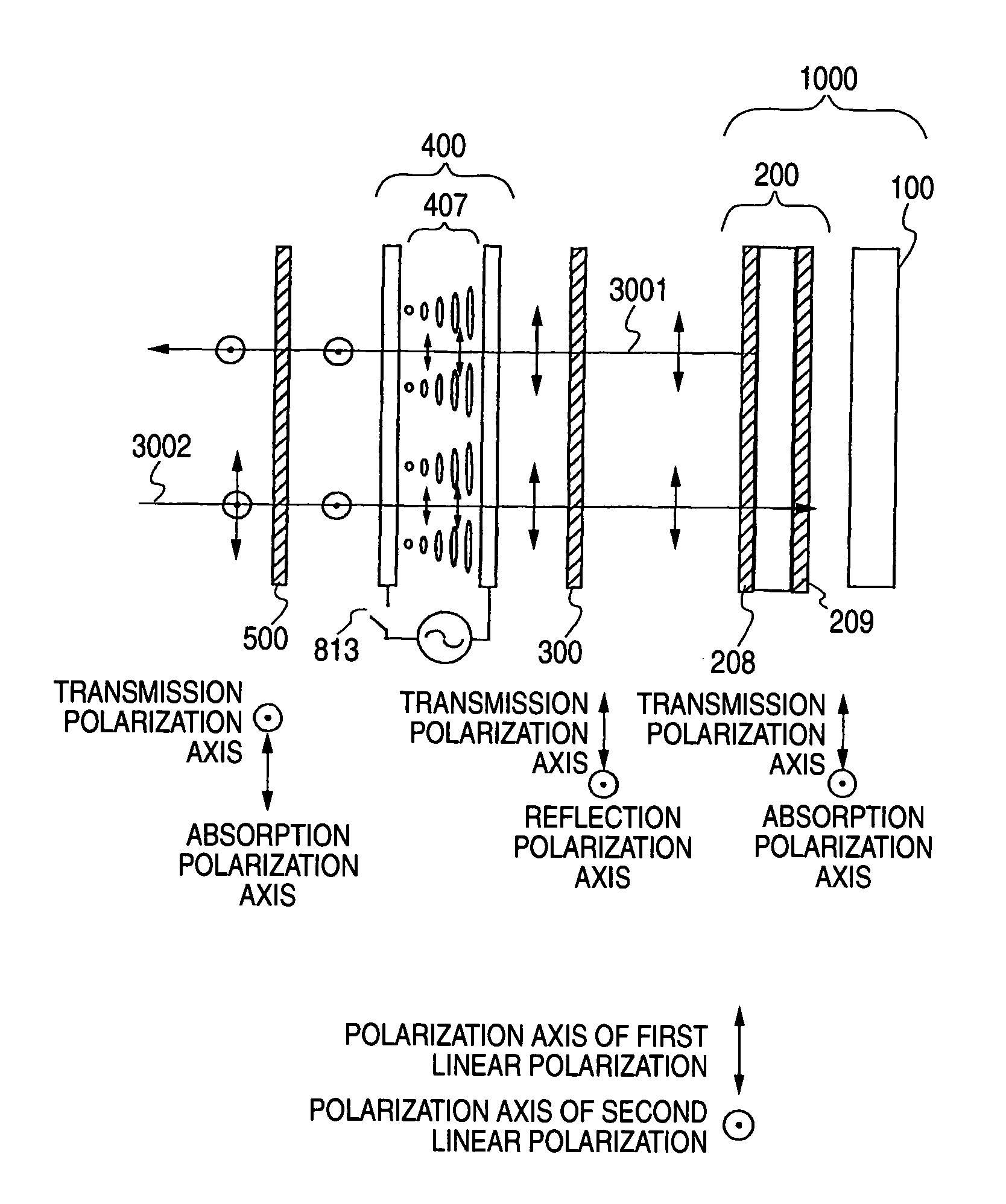
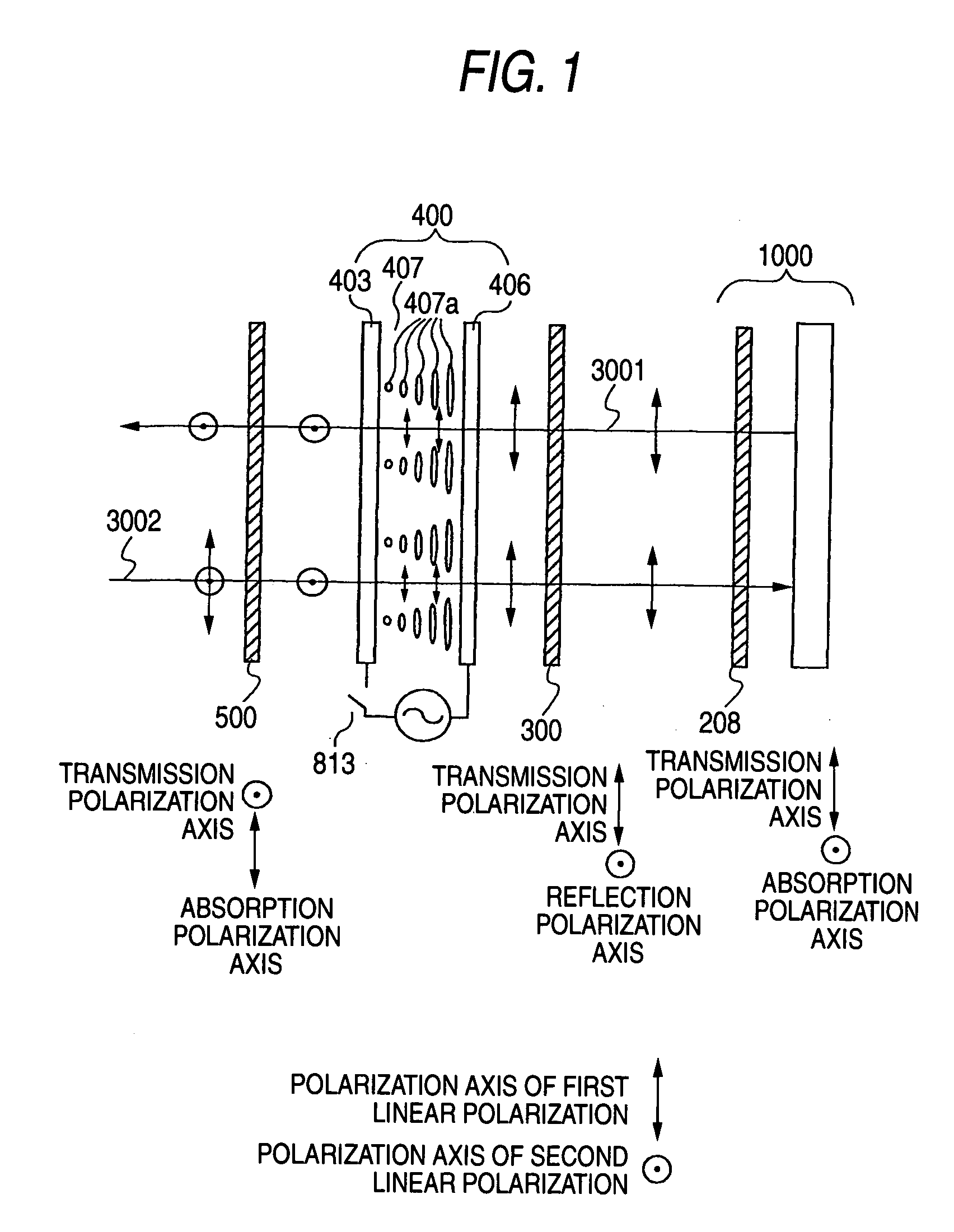
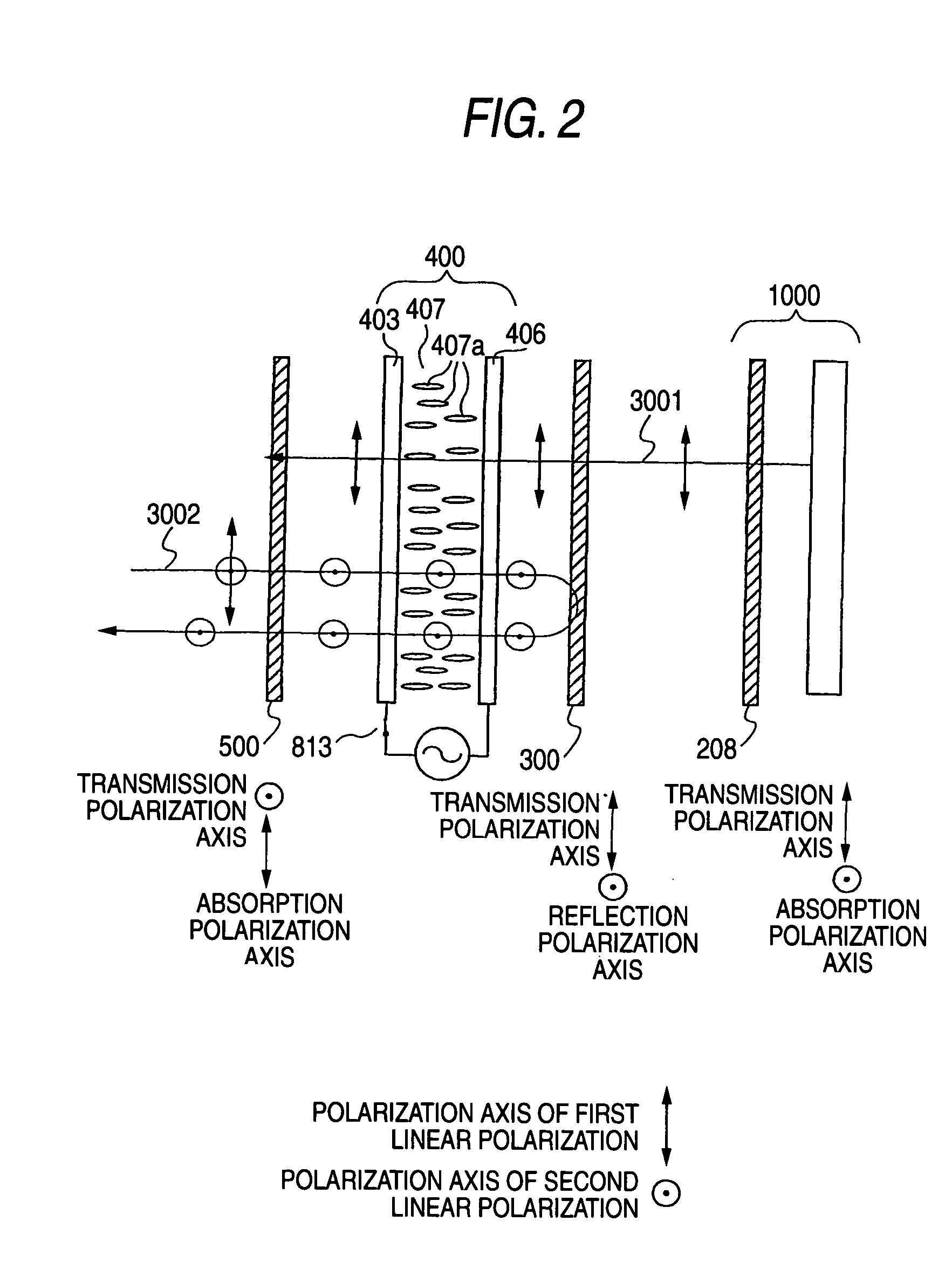
There is provided a device capable of switching between a state that displays a high-quality image and a mirror status in which is obtained an easy-to-view reflection image suitable for a person to view his / her own face or figure. An image display portion 1000 that emits image light 3001, reflective polarization selection means 300 that transmits a first linear polarization component emitted from the image display portion 1000 and reflects a second linear polarization component, whose polarization axis is orthogonal to that of the first linear polarization component, a transmission polarization axis variable portion 400 capable of selecting between one of a state that changes the polarization axis of incident linearly polarized light and a state that does not change the polarization axis of incident linearly polarized light, and a polarization selection member 500 which, of the incident light, absorbs the first linear polarization component and transmits the second linear polarization component, whose polarization axis is orthogonal to that of the first linear polarization component, are disposed in this order. In this case, absorbing polarization selection means 208 is disposed at the image display portion 1000, and the first linear polarization is emitted as the image light.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Liquid crystal display device having particular reflective polarizer
InactiveUS7006173B1Wide viewing angleReduce power consumptionNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
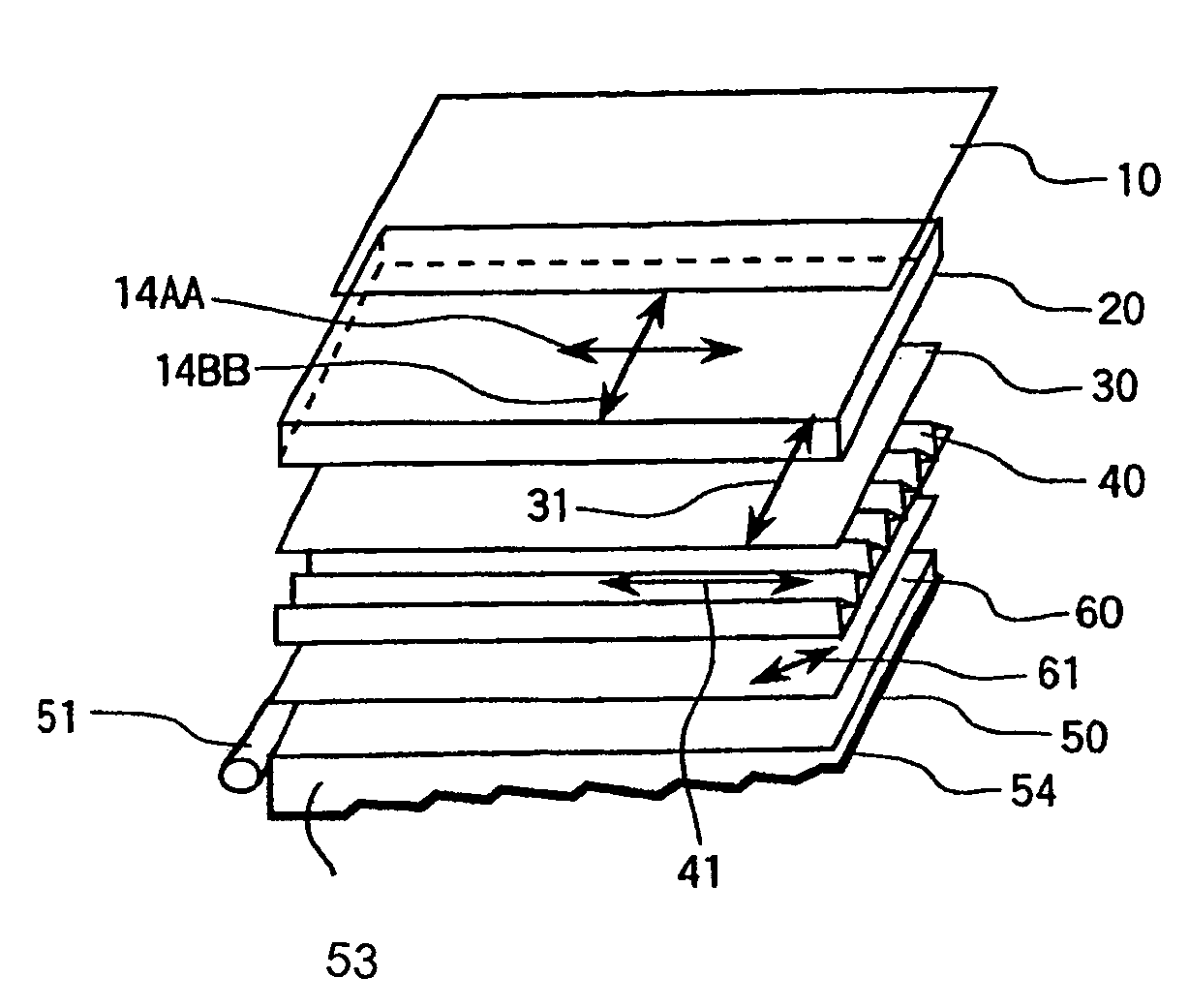
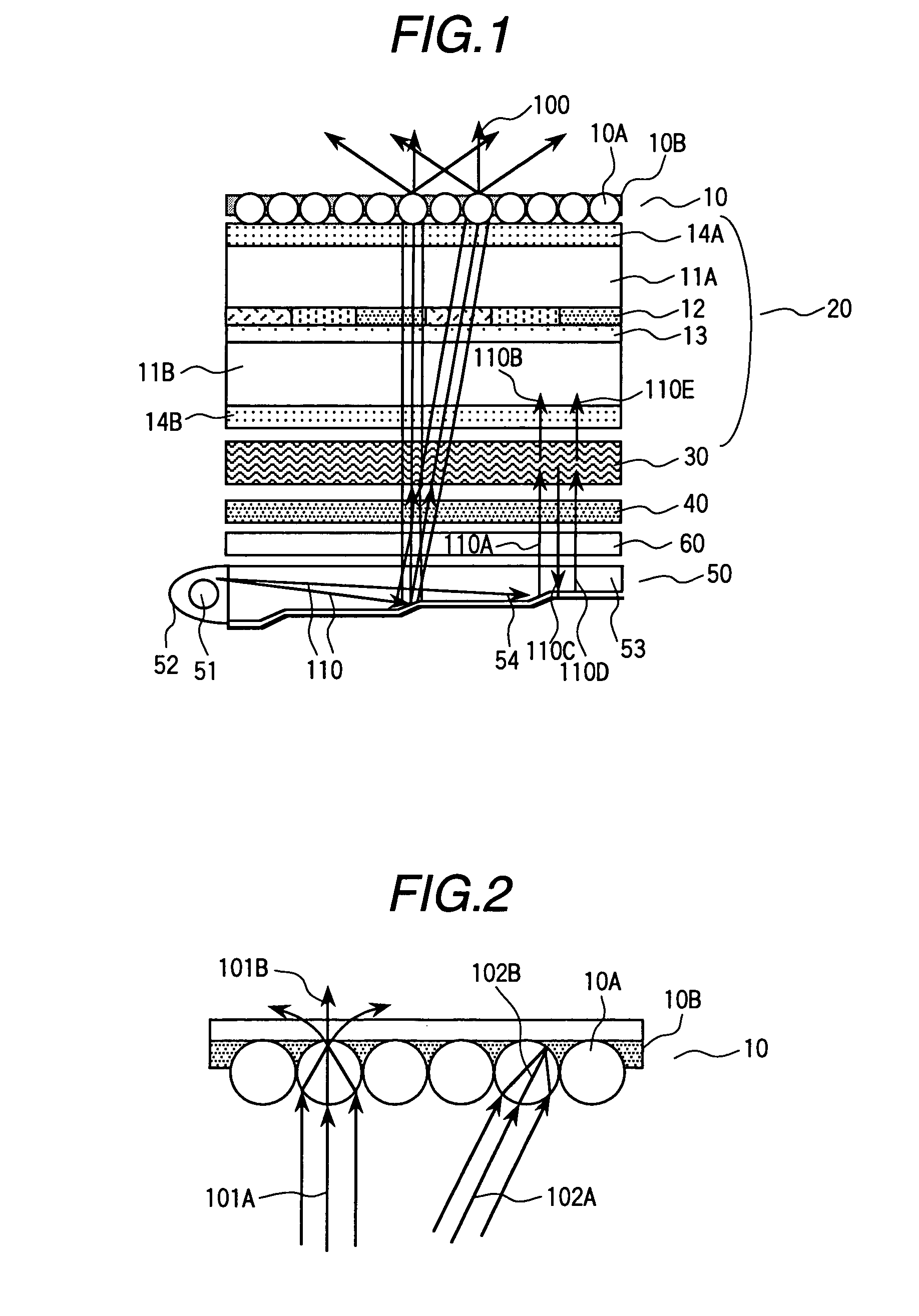
In order to realize liquid crystal display devices having a wide viewing angle and reduce the absorption loss by polarizers and color filters, and arrangement of reflective color selective means, reflective polarizing selective means, a light control element, and others are specified. The liquid crystal display device able to produce a display of high performance and improved brightness is formed of liquid crystal display elements 20 for controlling polarizing light so that the major axis direction of a pixel is arranged approximately in parallel with a direction wherein the linearly polarized light component of the projected light projected from said illumination device is high; an illumination device 50 arranged at a rear plane of the liquid crystal display element; a reflector 54 arranged at a rear plane of the illumination device; light control elements 40 and reflective polarizing selective means 30 arranged between the liquid crystal display element and the illumination device; and a screen arranged at an opposite side relative to the illumination device of the liquid crystal display element.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS7787077B2Good bright display state free from unevennessStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPolarizer
The liquid crystal display apparatus according to the present invention includes a first substrate, a second substrate, a reflective polarizer, mounted on the first substrate and having a first transmission axis and a first reflection axis at right angles to each other, for transmitting linearly polarized light vibrating in a plane parallel to the first transmission axis and for reflecting linearly polarized light vibrating in a plane parallel to the first reflection axis, a polarizer, mounted on the second substrate and having a second transmission axis, for transmitting linearly polarized light vibrating in a plane parallel to the second transmission axis, and a liquid crystal layer, provided between the first and second substrates, having a first mode which causes the direction of polarization of incident light to change by utilizing birefringence and a second mode which does not utilize birefringence and therefore does not cause the direction of polarization of incident light to change, wherein a display state is switched between a bright display state and a dark display state by applying a voltage to the liquid crystal layer, and the bright display state is produced by driving the liquid crystal layer in the second mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High recording density magnetic recording medium and recording/reproduction mechanism for the same
ActiveUS20180350398A1Improve recording densityMaintain good propertiesRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsUltrasound attenuationRefractive index
A refractive index nL and an attenuation rate kL of a magnetic layer are obtained by irradiating linearly polarized light at an irradiation angle of 70° from a lengthwise direction of the magnetic layer to the surface of the magnetic layer, and a vertical reflectance RL during vertical incidence of the linearly polarized light in the lengthwise direction is obtained based on nL and kL. A refractive index nT and an attenuation rate kT of the magnetic layer are obtained by irradiating linearly polarized light at an irradiation angle of 70° from a width direction of the magnetic layer to the surface of the magnetic layer, and a vertical reflectance RT during vertical incidence of the linearly polarized light in the width direction is obtained from nT and kT. If a variation rate A (%) of RL and RT is A=|RL / RT−1|×100, the relationship A≤10% is established.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
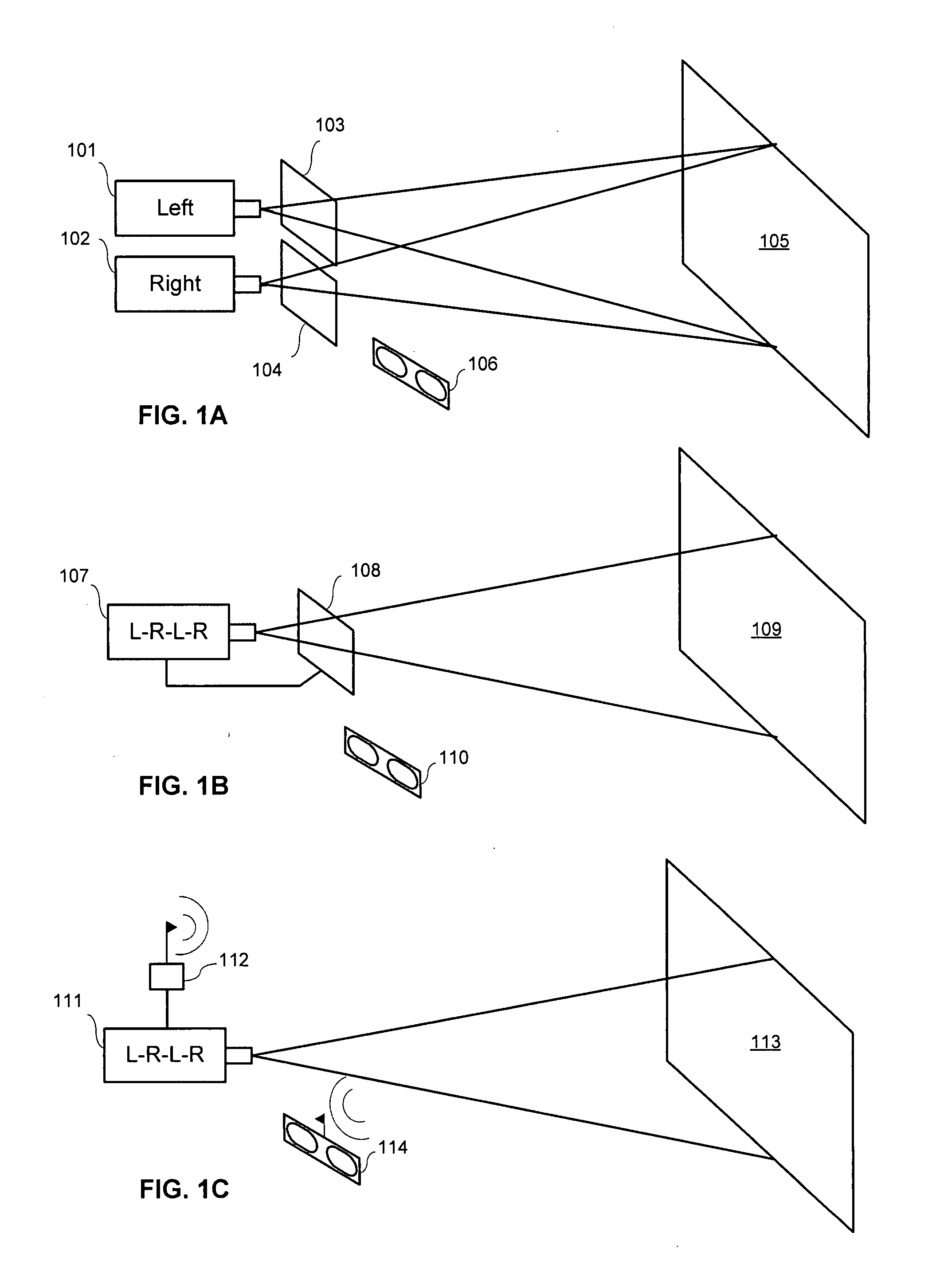
Projection of stereoscopic images using linearly polarized light
InactiveUS20070188602A1Reduce crosstalkImprove abilitiesStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Eyewear
A method and system for projecting linearly polarized stereoscopic images to a viewer that results in increased viewer head-tipping capabilities is provided. The design includes projecting linearly polarized light energy toward a screen and providing the viewer with a set of linearly polarized eyewear configured to receive the linearly polarized light energy projected to the screen and transmit a right perspective view to a right eye of the viewer and a left perspective view to a left eye of the viewer. Projecting comprises performing a noise reduction technique to reduce crosstalk in linearly polarized light energy images projected.
Owner:REAID INC
Polarization-modulating optical element
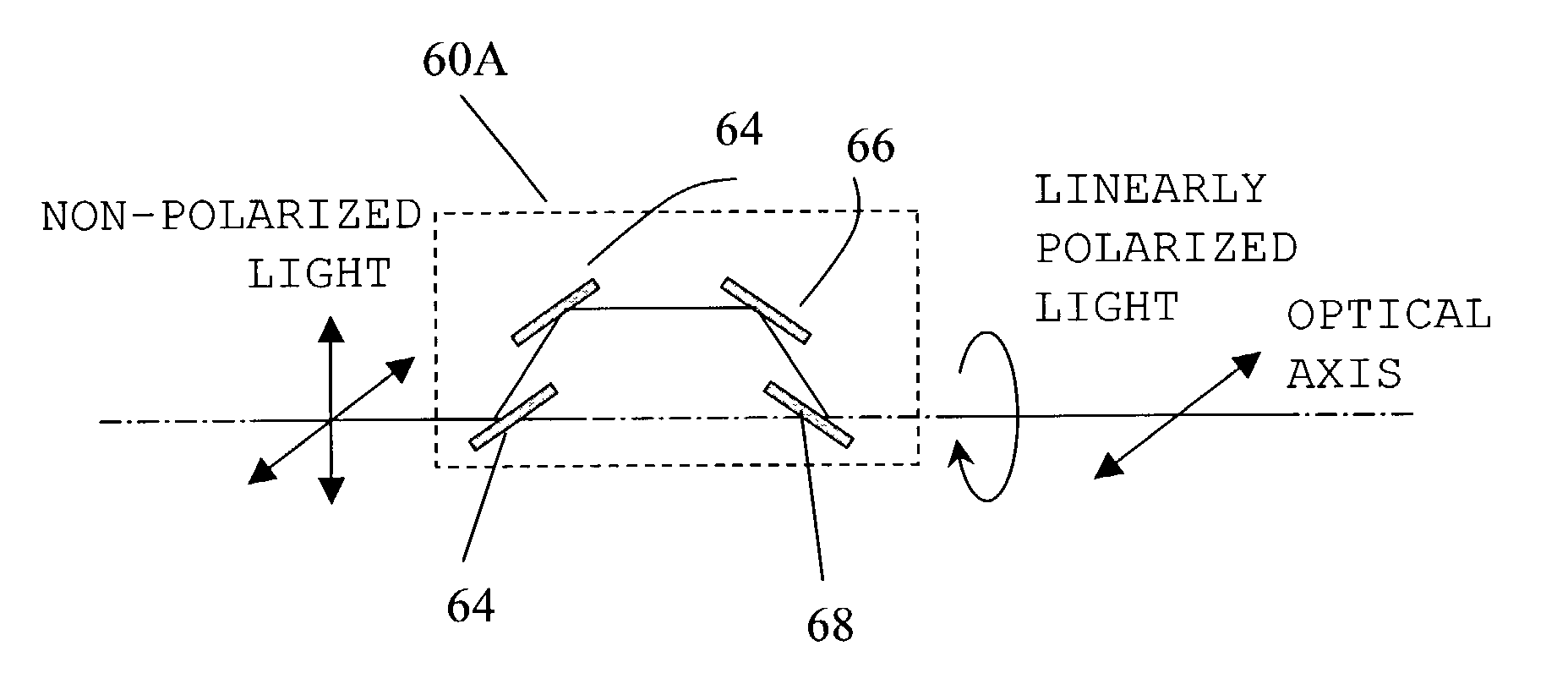
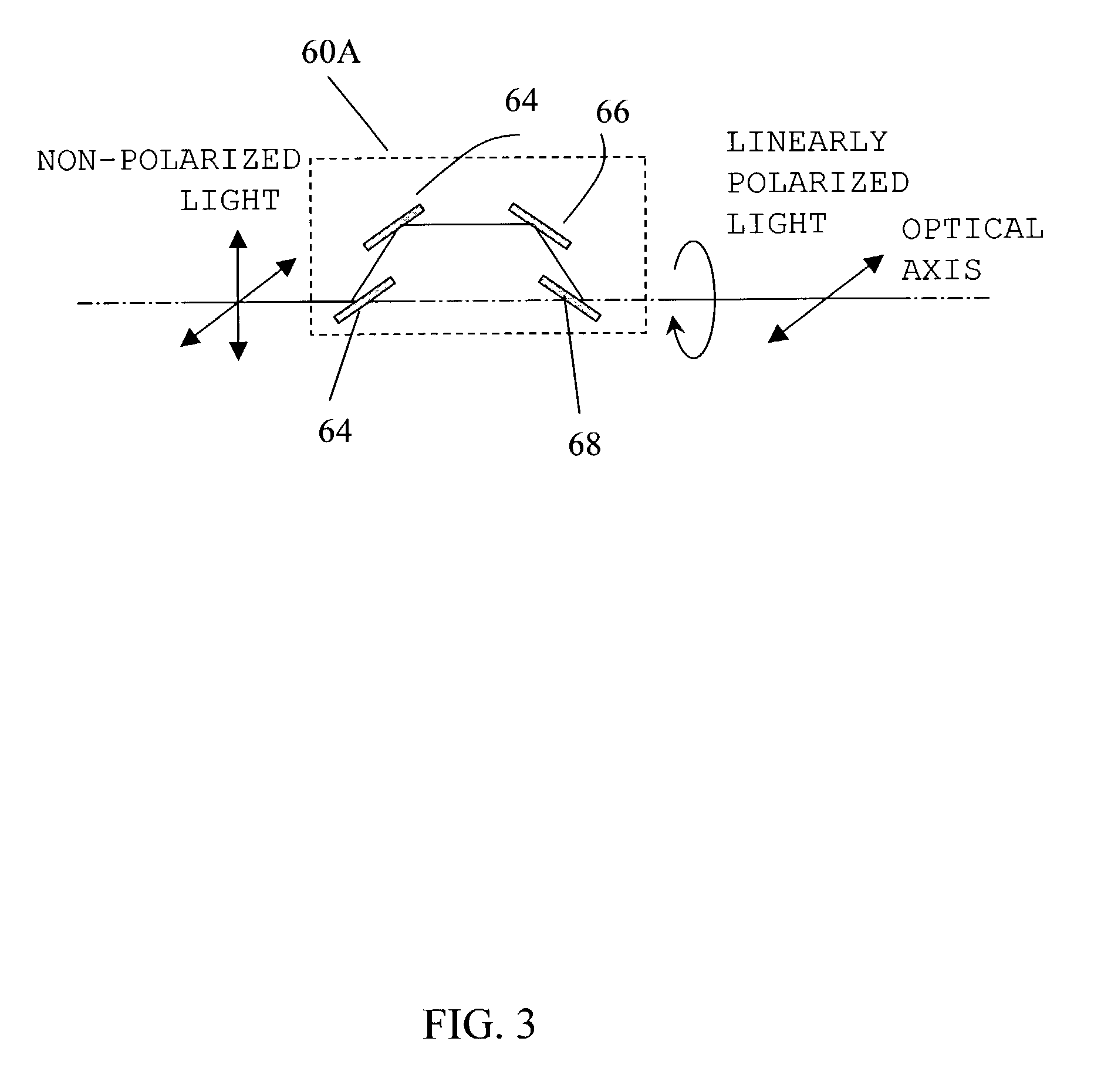
InactiveUS20070081114A1Improve propertiesMinimize impactPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisAngle of rotation
A polarization-modulating optical element (1) consisting of an optically active crystal material has a thickness profile where the thickness, as measured in the direction of the optical axis, varies over the area of the optical element. The polarization-modulating optical element (1) has the effect that the plane of oscillation of a first linearly polarized light ray and the plane of oscillation of a second linearly polarized light ray are rotated, respectively, by a first angle of rotation and a second angle of rotation, with the first angle of rotation and the second angle of rotation being different from each other.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
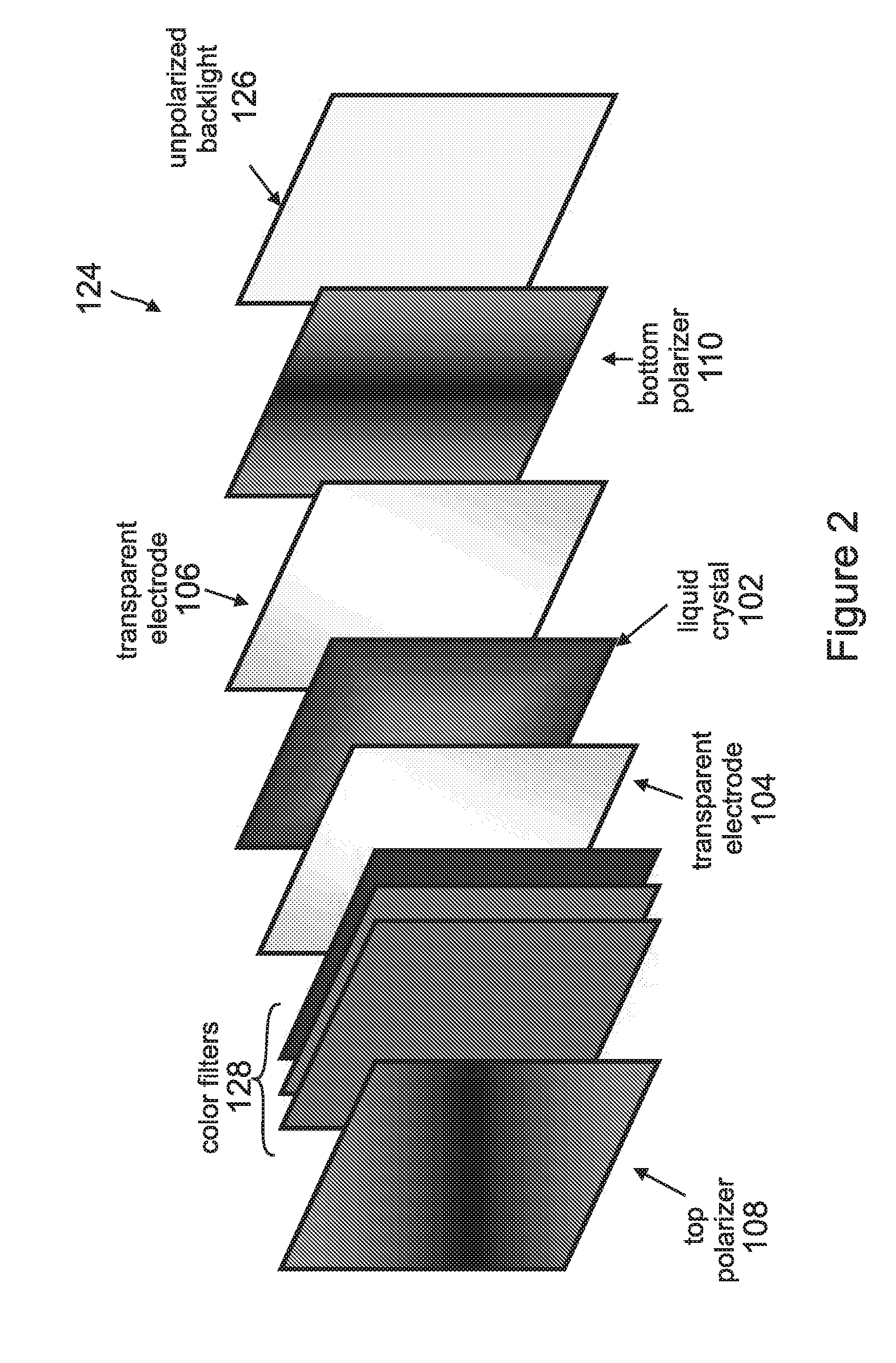
Display panel and display device
InactiveCN104330918AHigh light conversion efficiencyNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
The invention discloses a display panel and a display device, capable of improving light conversion efficiency of the display panel. The display panel comprises an array substrate and a color film substrate which are oppositely arranged as well as a liquid crystal layer between the array substrate and the color film substrate, wherein a quantum dot excitation layer is arranged on the color film substrate; an upper polarizing layer is arranged between the color film substrate and the liquid crystal layer; a lower polarizing layer is arranged on one surface, not adjacent to the liquid crystal layer, of the array substrate; and through the upper polarizing layer, linearly polarized light transmitted from the lower polarizing layer can reach the quantum dot excitation layer by keeping the state of the linearly polarized light.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060092356A1Reduce image qualityReduce the differenceNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPhase difference
The present invention provides a transmission-type, partial-transmission-type or a semi-transmission-reflection-type lateral electric field driving liquid crystal display device which can obtain the favorable transmissivity even when a circulatory polarized light is incident on a liquid crystal layer from a back surface side. In a liquid crystal display device which includes a first substrate which has a pixel electrode and a counter electrode, a second substrate which is arranged to face the first substrate in an opposed manner, a liquid crystal layer which is sandwiched between the first substrate and the second substrate, an upper polarizer which is arranged at a front surface side than the liquid crystal layer, and a lower polarizer which is arranged at a back surface side than the liquid crystal layer, the liquid crystal display device further includes a lower phase difference film which is arranged between the liquid crystal layer and the lower polarizer and converts a linearly polarized light to a circularly polarized light and an upper phase difference film which is arranged between the liquid crystal layer and the upper polarizer, the liquid crystal layer is driven by an electric field which is generated between the pixel electrode of the first substrate and the counter electrode of the first substrate, and a twist angle of the liquid crystal layer is within a range of 50° to 120° to perform a black display when a voltage is not applied.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
3D stereo OLED display
ActiveUS7221332B2Effectively produce and alter handednessLarge color gamutStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devices3d imageDisplay device
A switchable stereoscopic display system, wherein the switchable stereoscopic display system can display two-dimensional and three-dimensional images, includes: an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display device; Electronics that rapidly updates individual OLEDs; and a linearly polarizer for the OLED display device. Additionally, a circular polarizing layer changes light from linearly polarized light to circular polarized light. A polarization layer, on top of the circular polarization layer, switches a polarization direction of emitted light within the OLED display device. Other electronics switches the polarization direction within independent segments of the polarization layer. Refreshed OLEDs are synched with the independent segments of the polarization layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Wearable display system
InactiveUS7545571B2Large field of viewBrighter imagePolarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWire gridOptical power
A wearable display system, such as a Head Mounted Display, having a display engine producing light, preferably linearly polarized light, which defines a synthetic image that is relayed to a wire grid polarizing combiner which overlays the synthetic image onto a real image of an object of the outside world, and wherein the real image is contemporaneously viewed through the wire grid polarizing combiner by the wearer of the system. The wire grid polarizing combiner can be curved in at least one axis, and preferably two axis such that optical power is added to the wire grid polarizing combiner.
Owner:CONCURRENT TECH
Optically pumped atomic magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
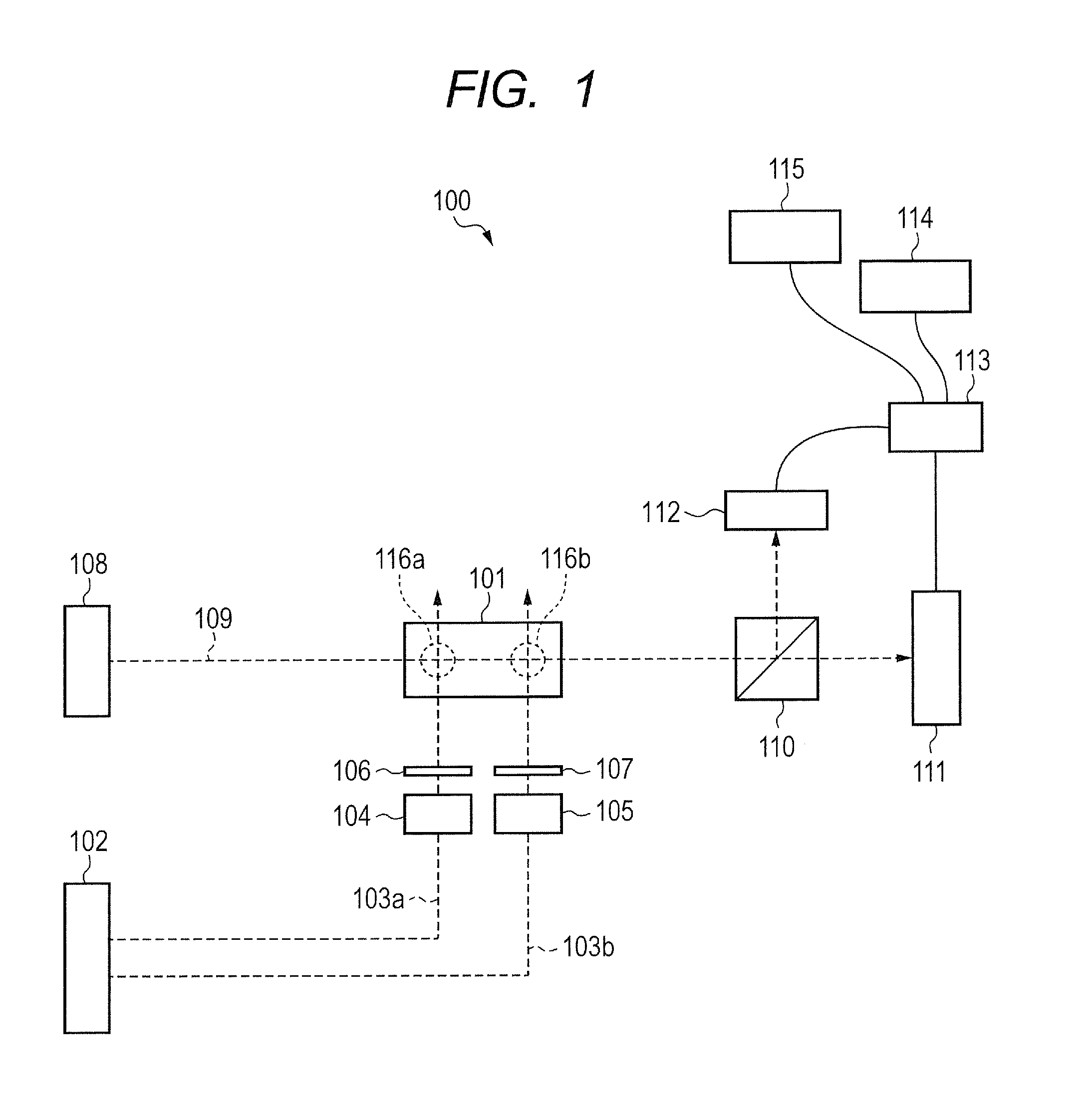
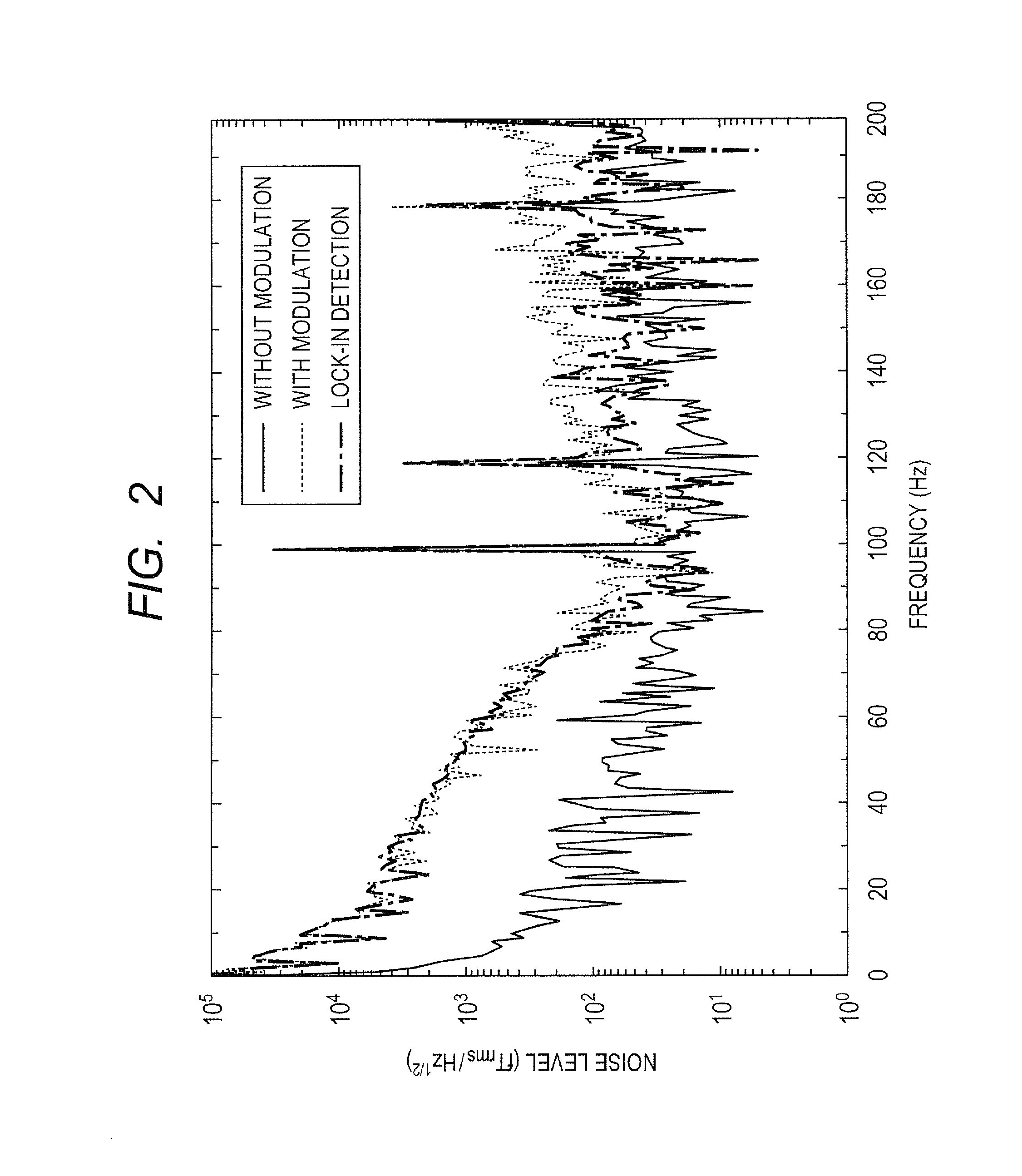
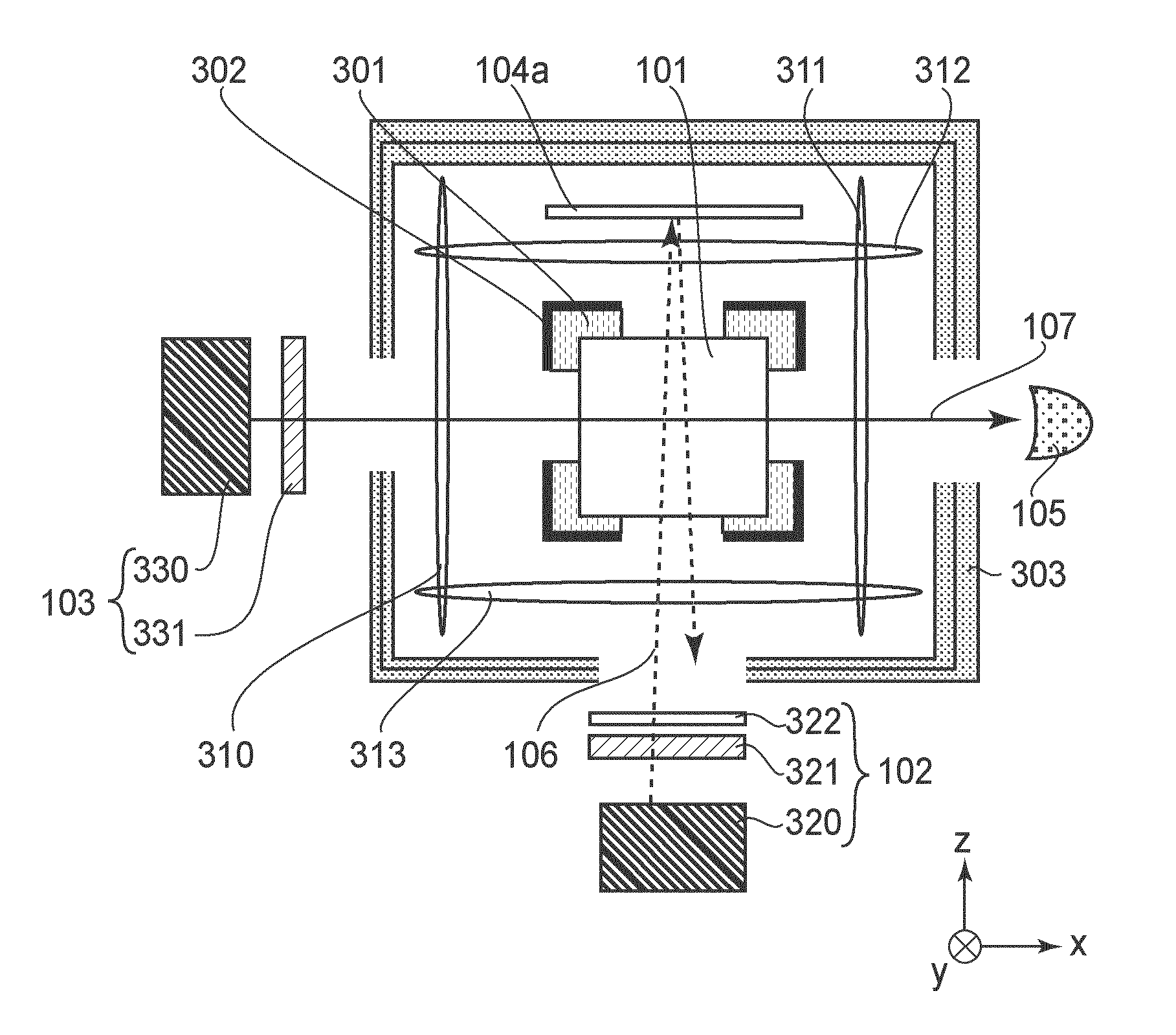
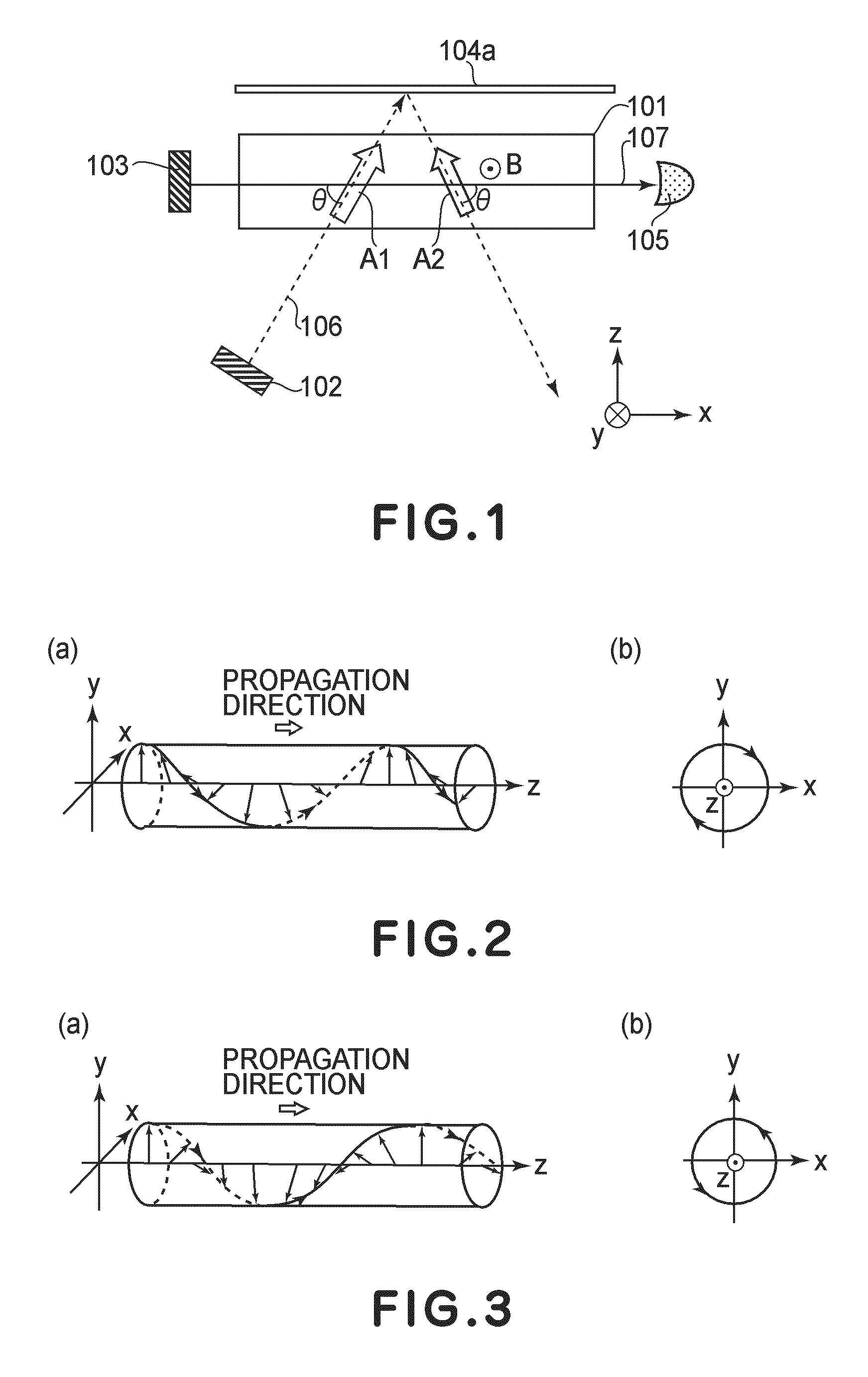
ActiveUS20160061913A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceLight beamOptic system
Provided is an optically pumped atomic magnetometer that can separate and acquire magnetic information of spatially different places at the same time by one probe beam. The optically pumped atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing alkali metal atoms, a pump beam optical system introducing pump beams including circularly polarized light component to different locations of the cell, a probe beam optical system introducing a probe beam including linearly polarized light component to the cell, a detection unit detecting a signal reflecting a rotation angle of a plane of polarization of the probe beam after intersecting with the pump beams, and an information acquisition unit acquiring information related to a magnetic field intensity of each of the different locations from the detected signal. The pump beam optical system includes a modulation unit modulating the pump beams so that one of frequencies and phases of the pump beams is different.
Owner:CANON KK
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic force measuring method
ActiveUS8054074B2High sensitivityNanomagnetismElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic tension forceAtomic group
An atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing an atomic group, a pump light source, a probe light source, a mirror, and a detector. The cell is disposed between the pump light source and the mirror and between the probe light source and the detector. A pump beam emitted from the pump light source is circularly polarized light. The pump beam passes through the cell and is reflected by the mirror and then passes through the cell again. The probe beam emitted from the probe light source is linearly polarized light. An optical path of the probe beam is parallel to the plane of incidence of the pump beam and is also parallel to the surface of the mirror. The optical path of the probe beam crosses the optical path of the pump beam in the cell. The probe beam which has passed through the cell enters the detector.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS8587304B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSelf-oscillationLight beam
An optical atomic magnetometers is provided operating on the principles of nonlinear magneto-optical rotation. An atomic vapor is optically pumped using linearly polarized modulated light. The vapor is then probed using a non-modulated linearly polarized light beam. The resulting modulation in polarization angle of the probe light is detected and used in a feedback loop to induce self-oscillation at the resonant frequency.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Generation device of random polarization distributing vector light beam
InactiveCN101178484AGenerate real-time newsReduce the impactNon-linear opticsOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorGrating
The invention provides a generation device of an arbitrary polarization distribution vector light beam, and is in turns provided with a spatial light modulator controlled by a computer, a first lens, a wave filter, two quarter wave plates, a second lens and a Rochi grating along the light direction of the light source producing linearly polarized light. The spatial light modulator is positioned on a front focal plane of the first lens, a back focal plane is provided with the wave filter, and the wave filter is synchronously positioned on a front focal plane of the second lens. Rochi grating is positioned on a back focal plane of the second lens. Two quarter wave plates are placed by closely depending on the backlight source surface of the wave filter. The invention has the advantage of producing arbitrary vector light beam, and to be important, the device of the invention can produce the vector light beam in real time and dynamic manner. Moreover, the device greatly reduces the effect to the light beam quality caused by coherent noise, and can produce the high-quality vector light beam, and the producing manner is real time and dynamic.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Phase correction element and optical head device
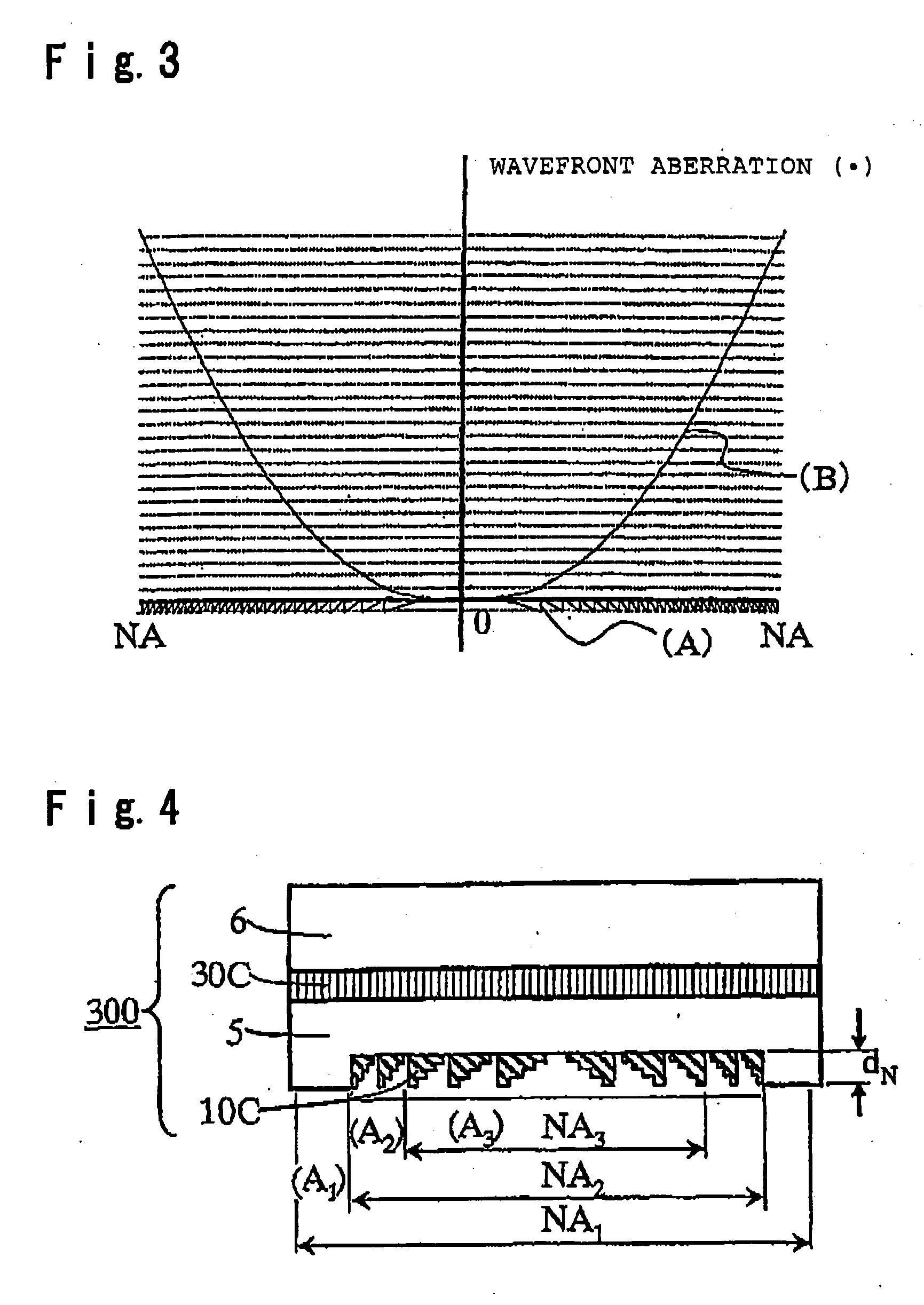
InactiveUS20050226122A1Polarising elementsRecord information storagePhase differenceNumerical aperture
The present invention provides a phase correction element which can be used for recording and / or reproducing an information of three types of optical disks for HD, DVD and CD by employing a single objective lens for HD, and an optical head device. The phase correction element 100 of present invention comprises a first phase correction layer 10A formed in a region of numerical aperture NA2, and a first phase plate 30A integrally formed; the first phase correction layer 10A comprising a concavo-convex portion having a rotational symmetry with respect to the optical axis of incident light and having a cross-sectional shape of a saw-tooth-form or a saw-tooth-form whose convex portions are each approximated by a step form; the first phase plate 30A generating a birefringent phase difference of about an odd number times of π / 2 for linearly polarized light having a wavelength of λ1; and the phase correction element 100 having a function of not changing a transmitted wavefront of the wavelength of λ1 and changing a transmitted wavefront of the wavelength of λ2 or transmitted wavefront of both wavelengths of λ2 and λ3 when three types of incident light in a λ1=410 nm wavelength band, a λ2=650 nm wavelength band and a λ3=780 nm wavelength band respectively, are incident.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
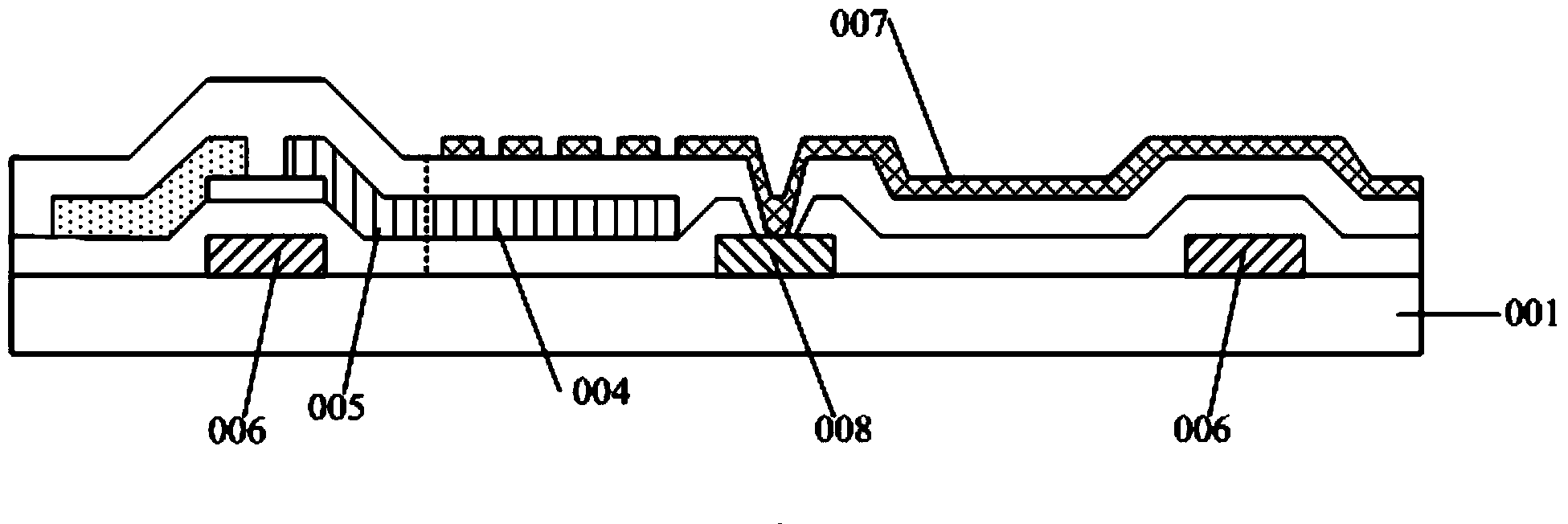
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050271833A1Promoting and stabilizing capacityImprove responseLiquid crystal compositionsPhotosensitive materialsLiquid-crystal displayHigh volume manufacturing
It is an object to provide a liquid crystal display which reduces unsatisfactory display caused by distorted initial alignment direction in a liquid crystal alignment layer for IPS type displays, realizes stable liquid crystal alignment, is high in mass-productivity, and produces high-quality images of increased contrast ratio. The liquid crystal display contains alignment layers 109 placed between a pair of substrates 101 and 102, at least one of which is transparent, liquid crystal layer 110′ sealed between the alignment layers, common electrode 103 and source electrode 105 for applying an electrical field to the liquid crystal layer, thin-film transistors connected to each of these electrodes, polarizer plate 114 provided on at least one of the substrates, wherein at least one of the alignment layers 109 is composed of a photo-reactive polyimide and / or polyamic acid which can be provided with a liquid crystal alignment capacity by being irradiated with essentially linearly polarized light.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Method of combining images in a wearable display system
InactiveUS20080013185A1Large field of viewBrighter imagePolarising elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsWire gridDisplay device
A wearable display system, such as a Head Mounted Display, having a display engine producing light, preferably linearly polarized light, which defines a synthetic image that is relayed to a wire grid polarizing combiner which overlays the synthetic image onto a real image of an object of the outside world, and wherein the real image is contemporaneously viewed through the wire grid polarizing combiner by the wearer of the system. The wire grid polarizing combiner can be curved in at least one axis, and preferably two axis such that optical power is added to the wire grid polarizing combiner.
Owner:CONCURRENT TECH
Achromatic retarder array for polarization imaging
In addition to having color, light waves have the attribute of polarization. An apparatus and method to convert circular polarized light into linearly polarized light over a wide range of wavelengths is provided by utilizing a first surface-relief grating functioning as a quarter-wave waveplate and a second surface-relief grating functioning as a half-wave waveplate. A plurality of such devices are arranged in a two-dimensional array and combined with an array of linear polarizers and an array of photodetectors to form a polarization imaging sensor. Such a sensor could have applications in automobiles to alert drivers of the presence of other vehicles, especially at night, in fog, or in rain. Military applications include the detection of vehicles placed among trees and shrubs. Another advantage of using circular polarization images is that the sign and magnitude of the circular polarization can potentially be used to reveal the spatial orientation, material, and surface roughness of the object's surface.
Owner:CHUN CORNELL SEU LUN
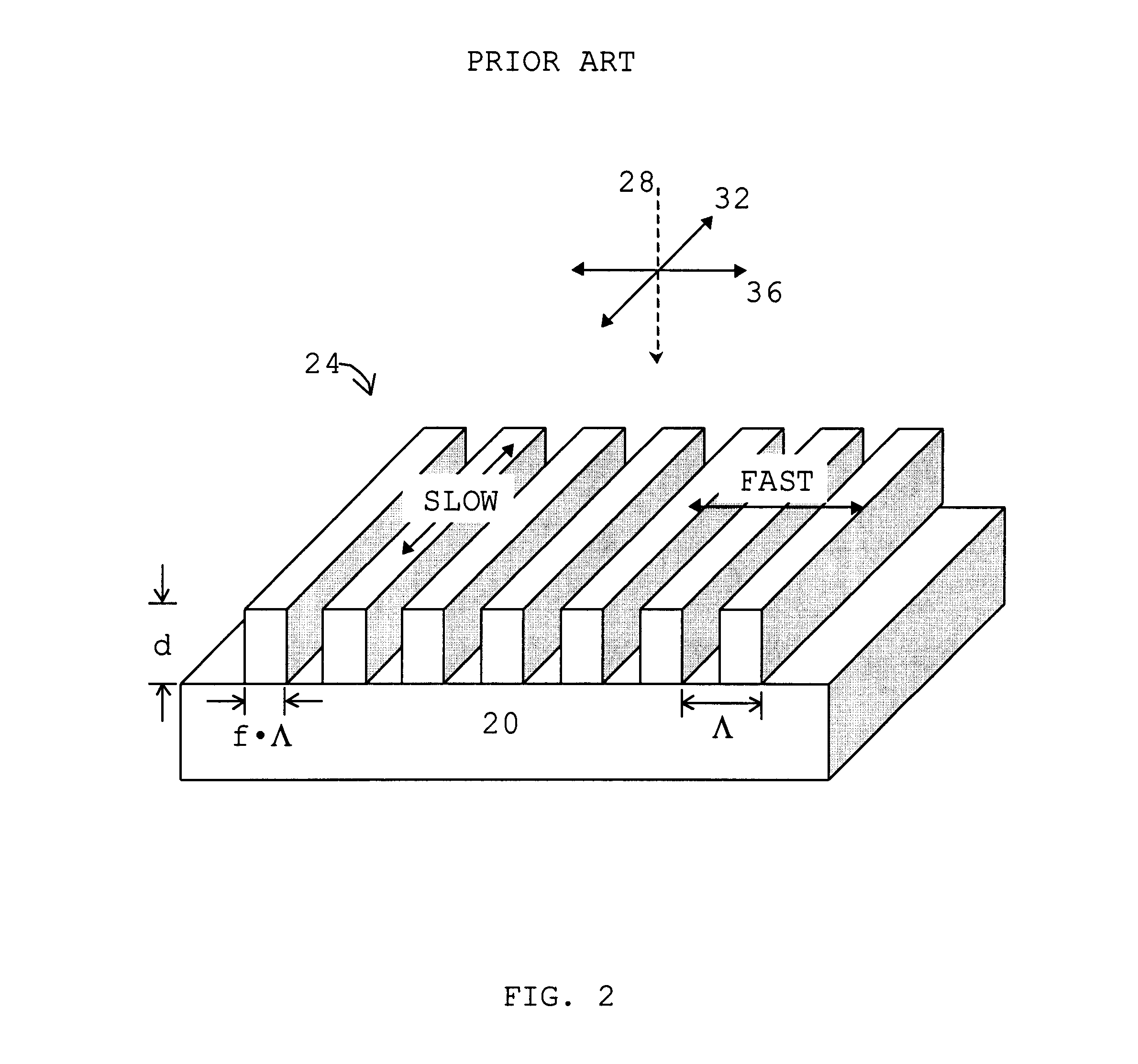
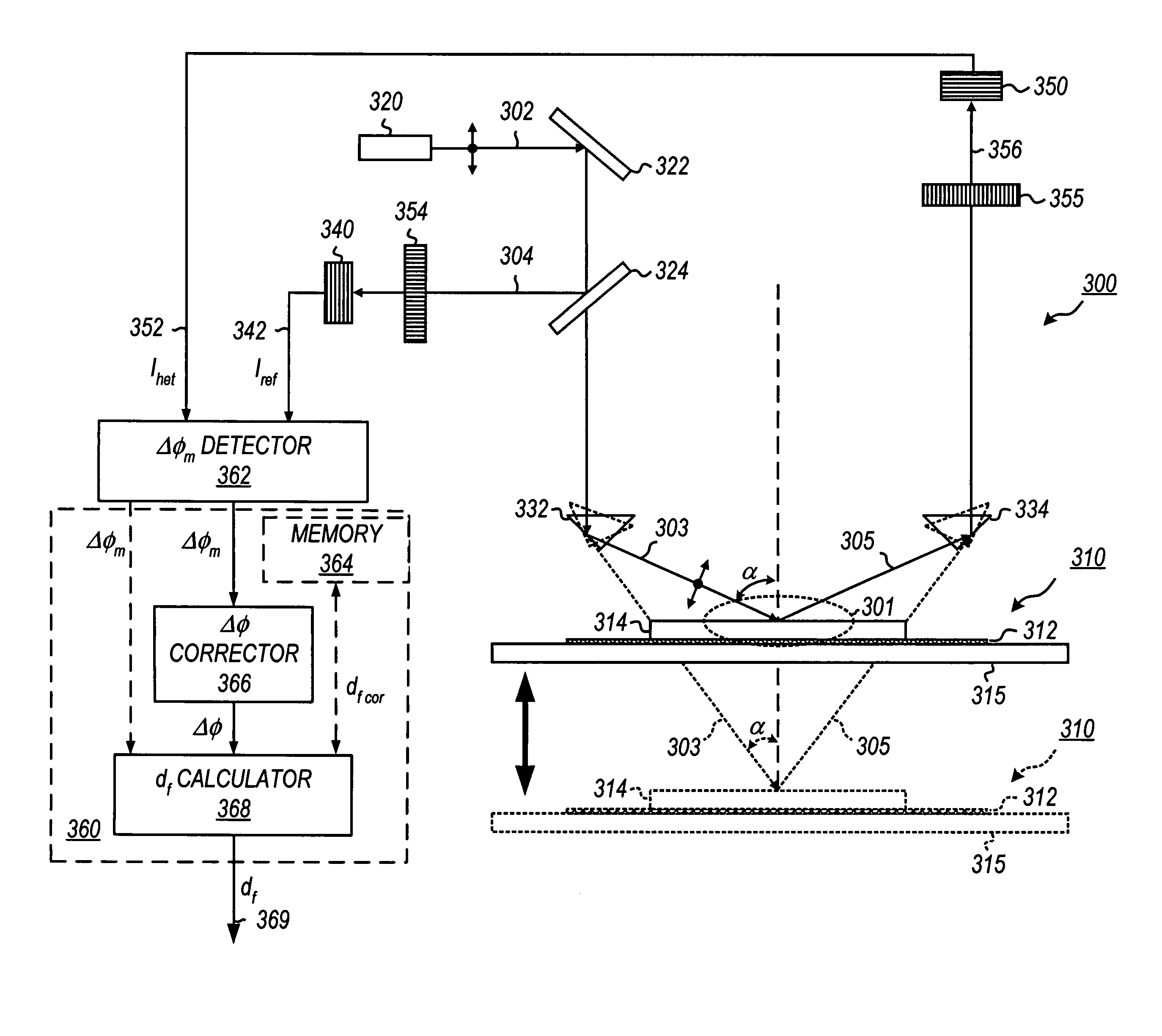
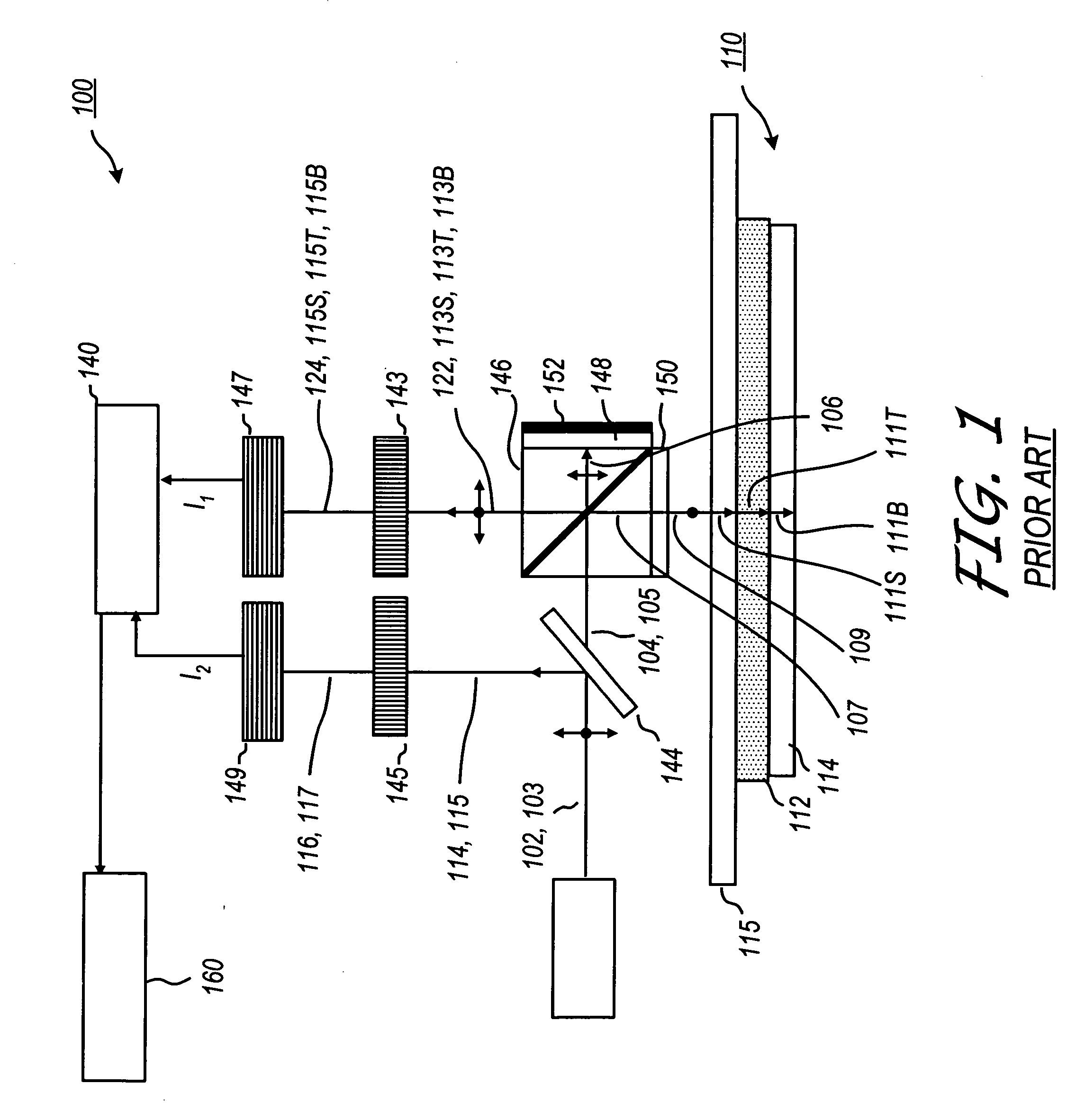
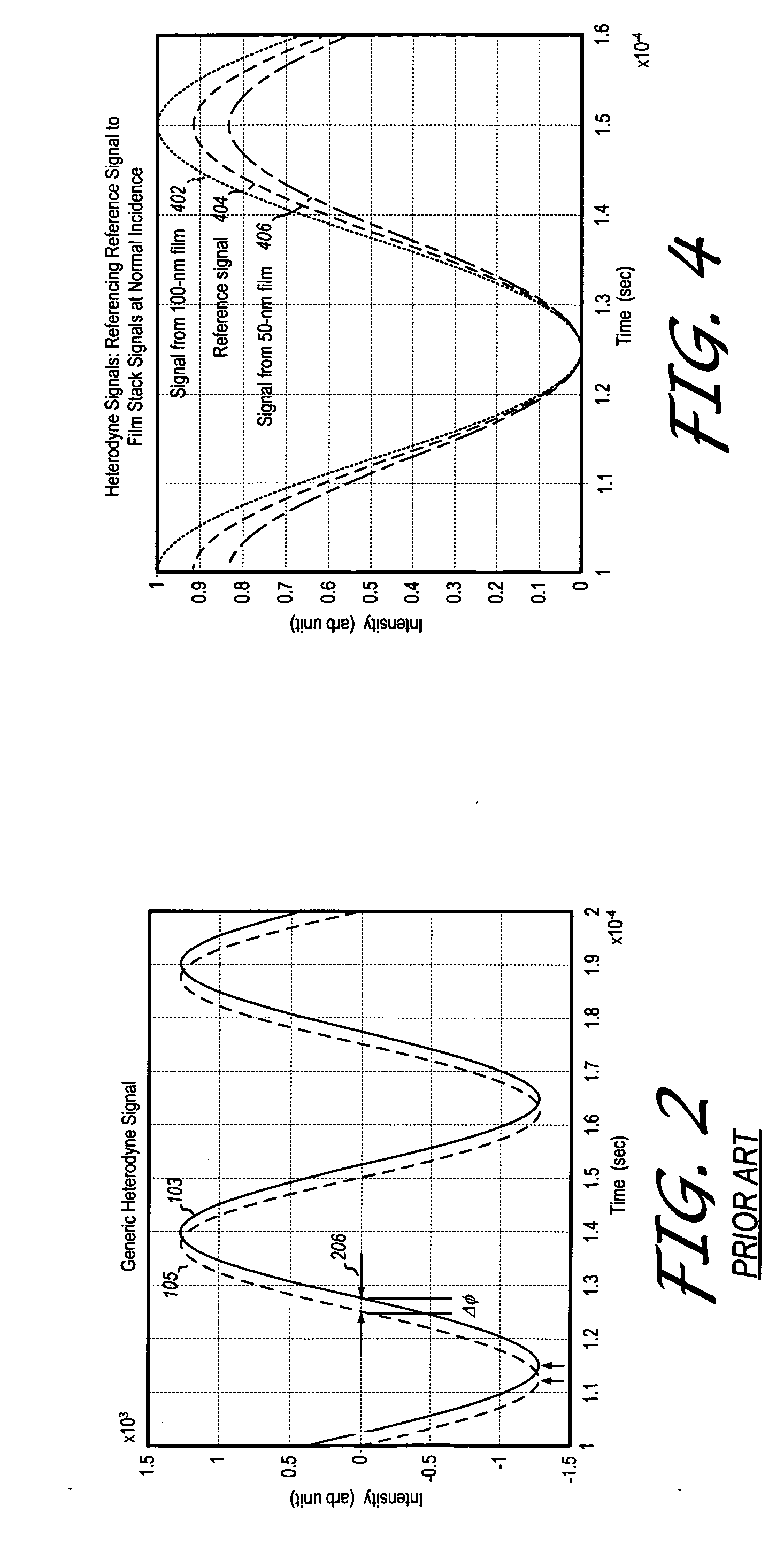
Heterodyne reflectomer for film thickness monitoring and method for implementing
The present invention is directed to a heterodyne reflectometer system and method for obtaining highly accurate phase shift information from heterodyned optical signals, from which extremely accurate film depths can be calculated. A linearly polarized light comprised of two linearly polarized components that are orthogonal to each other, with split optical frequencies, is directed toward a film causing one of the optical polarization components to lag behind the other due to an increase in the optical path in the film for that component. A pair of detectors receives the beam reflected from the film layer and produces a measurement signal, and the beam prior to incidence on the film layer and generates a reference signal, respectively. The measurement signal and reference signal are analyzed by a phase detector for phase shift. The detected phase shift is then fed into a thickness calculator for film thickness results. A grating interferometer may be included with the heterodyne reflectometer system with a grating, which diffracts the reflected beam into zeroth- and first-order bands, which are then detected by separate detectors. A detector receives the zeroth-order beam and generates another measurement signal. Another detector receives the first-order beam and generates a grating signal. The measurement signal from the grating and reference signal may be analyzed by a phase detector for phase shift, which is related to the thickness of the film. Conversely, either measurement signal may be analyzed with the grating signal by a phase detector for detecting a grating phase shift. The refractive index for the film may be calculated from grating phase shift and the heterodyne phase shift. The updated refractive index is then used for calculating thickness.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
Optical apparatus
InactiveUS6999172B2Easily polarization planeImprove polarizationPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsOptical axisX-ray
Owner:CANON KK
Polarization-modulating optical element
ActiveUS20080316598A1Improve propertiesMinimize impactPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisAngle of rotation
A polarization-modulating optical element consisting of an optically active crystal material has a thickness profile where the thickness, as measured in the direction of the optical axis, varies over the area of the optical element. The polarization-modulating optical element has the effect that the plane of oscillation of a first linearly polarized light ray and the plane of oscillation of a second line early polarized light ray are rotated, respectively, by a first angle of rotation and a second angle of rotation, with the first angle of rotation and the second angle of rotation being different from each other.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic force measuring method
ActiveUS20090243610A1High sensitivityNanomagnetismElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic tension forceAtomic group
An atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing an atomic group, a pump light source, a probe light source, a mirror, and a detector. The cell is disposed between the pump light source and the mirror and between the probe light source and the detector. A pump beam emitted from the pump light source is circularly polarized light. The pump beam passes through the cell and is reflected by the mirror and then passes through the cell again. The probe beam emitted from the probe light source is linearly polarized light. An optical path of the probe beam is parallel to a plane of incidence of the pump beam and is also parallel to a surface of the mirror. The optical path of the probe beam crosses an optical path of the pump beam in the cell. The probe beam which has passed through the cell enters the detector.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS20110025323A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSelf-oscillationLight beam
An optical atomic magnetometers is provided operating on the principles of nonlinear magneto-optical rotation. An atomic vapor is optically pumped using linearly polarized modulated light. The vapor is then probed using a non-modulated linearly polarized light beam. The resulting modulation in polarization angle of the probe light is detected and used in a feedback loop to induce self-oscillation at the resonant frequency.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Array substrate, liquid crystal display panel and display device
The invention discloses an array substrate, a liquid crystal display panel and a display device. Wire grating polarizing films manufactured in each pixel region in the array substrate are adopted for replacing existing polaroids attached to the outer side of the array substrate, and are of a grating structure with the grating space being less than half of the minimum wavelength in visible lights, so an effect of changing passing natural lights into linearly polarized lights is achieved. On the premise of ensuring that the liquid crystal display panel can display normally, the wire grating polarizing films with effects of the polaroids are formed in the process of manufacturing the array substrate, so that a working process of independently laminating the polaroids after box aligning box can be omitted, the production efficiency, the manufacturing cost is saved, and the whole thickness of the display panel can be favorably thinned.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
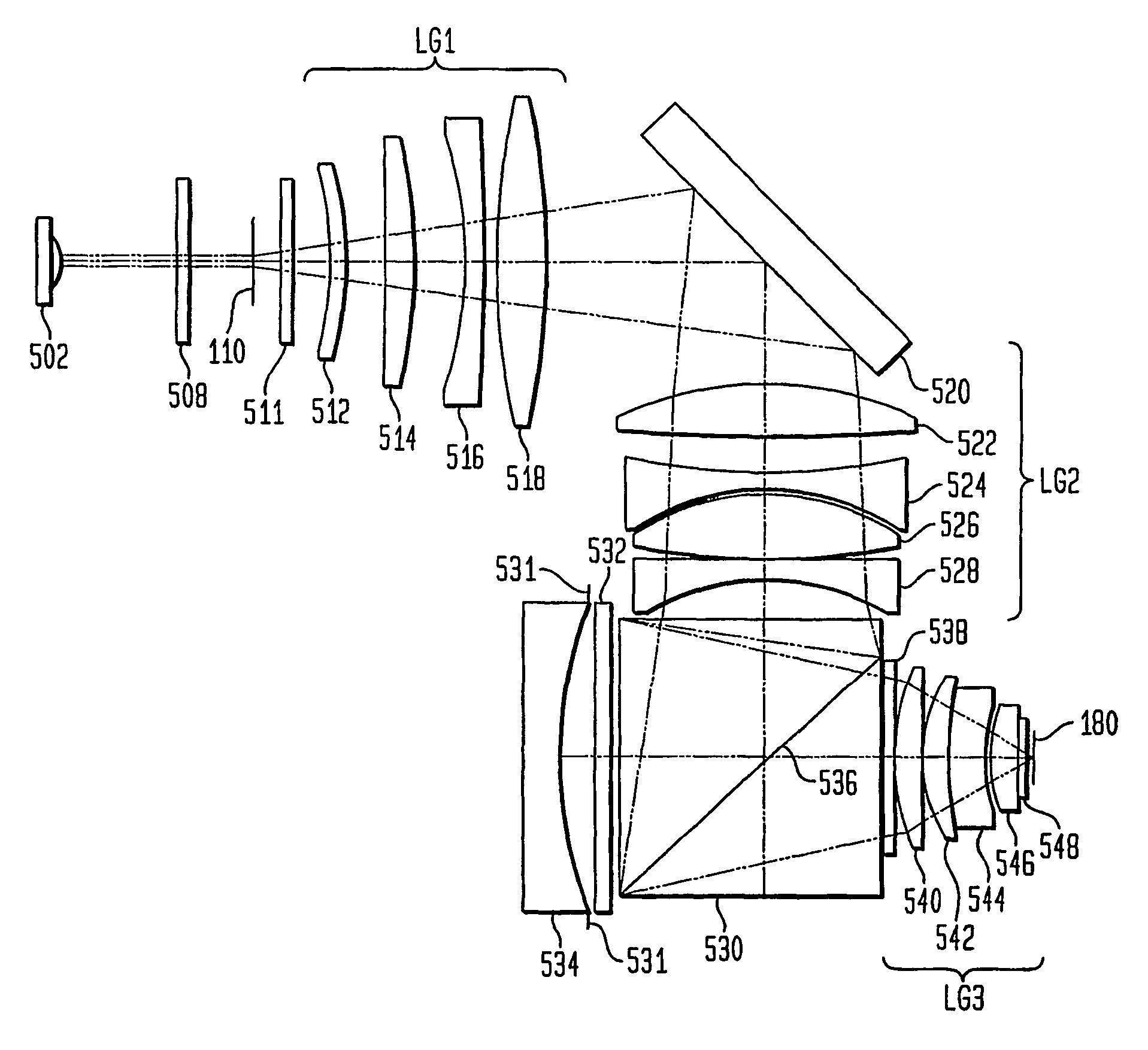
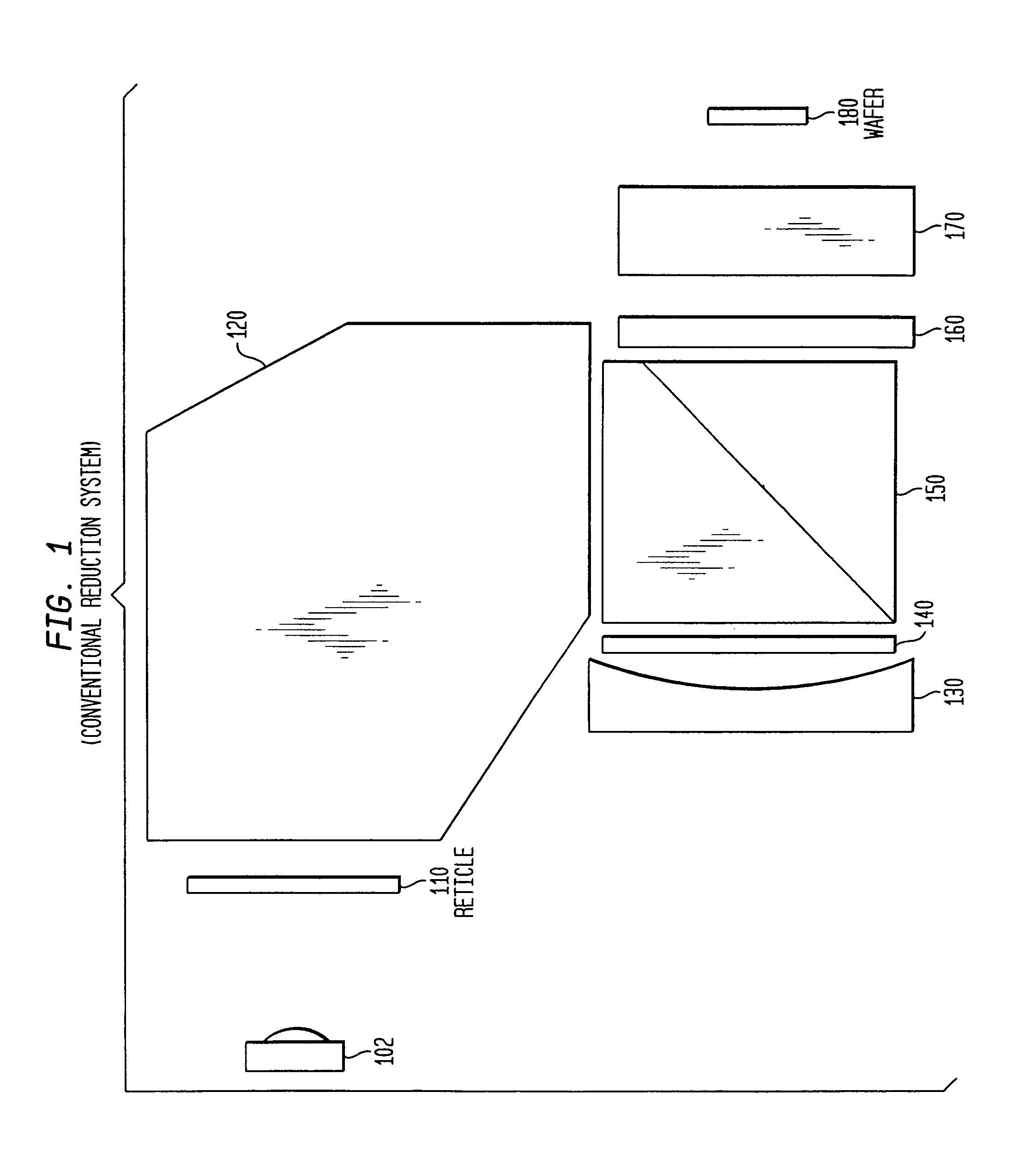
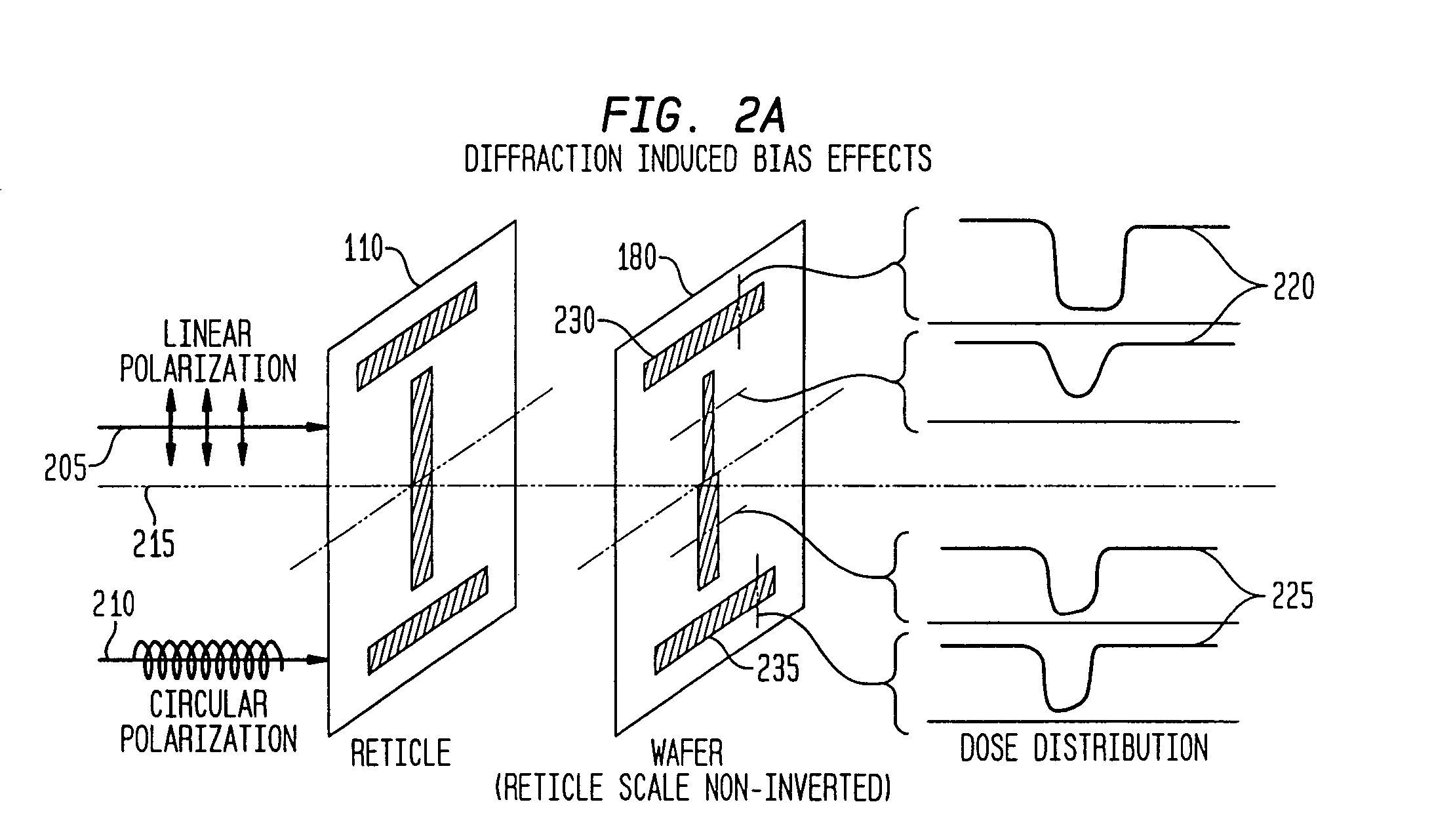
Optical reduction method with elimination of reticle diffraction induced bias
InactiveUS7031077B2Acceptable system performanceImprove system performancePolarising elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh numerical apertureTransmission loss
An optical reduction system for use in the photolithographic manufacture of semiconductor devices having one or more quarter-wave plates operating near the long conjugate end. A quarter-wave plate after the reticle provides linearly polarized light at or near the beamsplitter. A quarter-wave plate before the reticle provides circularly polarized or generally unpolarized light at or near the reticle. Additional quarter-wave plates are used to further reduce transmission loss and asymmetries from feature orientation. The optical reduction system provides a relatively high numerical aperture of 0.7 capable of patterning features smaller than 0.25 microns over a 26 mm×5 mm field. The optical reduction system is thereby well adapted to a step and scan microlithographic exposure tool as used in semiconductor manufacturing. Several other embodiments combine elements of different refracting power to widen the spectral bandwidth which can be achieved.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY GRP INC
Optical spectrum analyzer
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
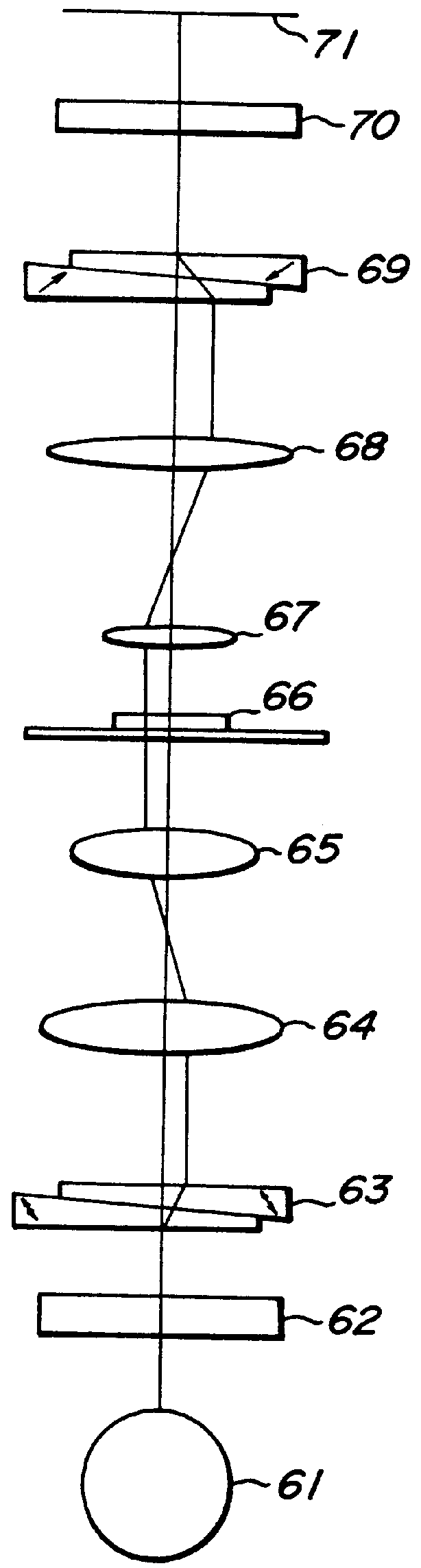
Differential interference contrast microscope and microscopic image processing system using the same
InactiveUS6128127AEasy constructionLess expensiveMicroscopesUsing optical meansMicroscopic imageWavefront
A differential interference contrast microscope including an illuminating light source, a polarizer for converting an illumination light ray into a linearly polarized light, a polarized light separating unit for dividing the linearly polarized light ray into two linearly polarized light rays having mutually orthogonal vibrating directions, an illuminating optical system, for projecting the two linearly polarized light rays onto an object under inspection, a polarized light combining unit for combining the two linearly polarized light rays on a same optical path via an inspecting optical system, an analyzer for forming a differential interference contrast image on an imaging plane. The polarized light separating unit is constructed such that an amount of wavefront shear between the two linearly polarized light rays on the object can be changed, and the polarized light combining unit is arranged between the object and the analyzer at such a position that the two linearly polarized light rays propagate in parallel with each other and is constructed such that the two linearly polarized light rays can be combined with each other in accordance with the shear amount of wavefront introduced by the polarized light separating unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com