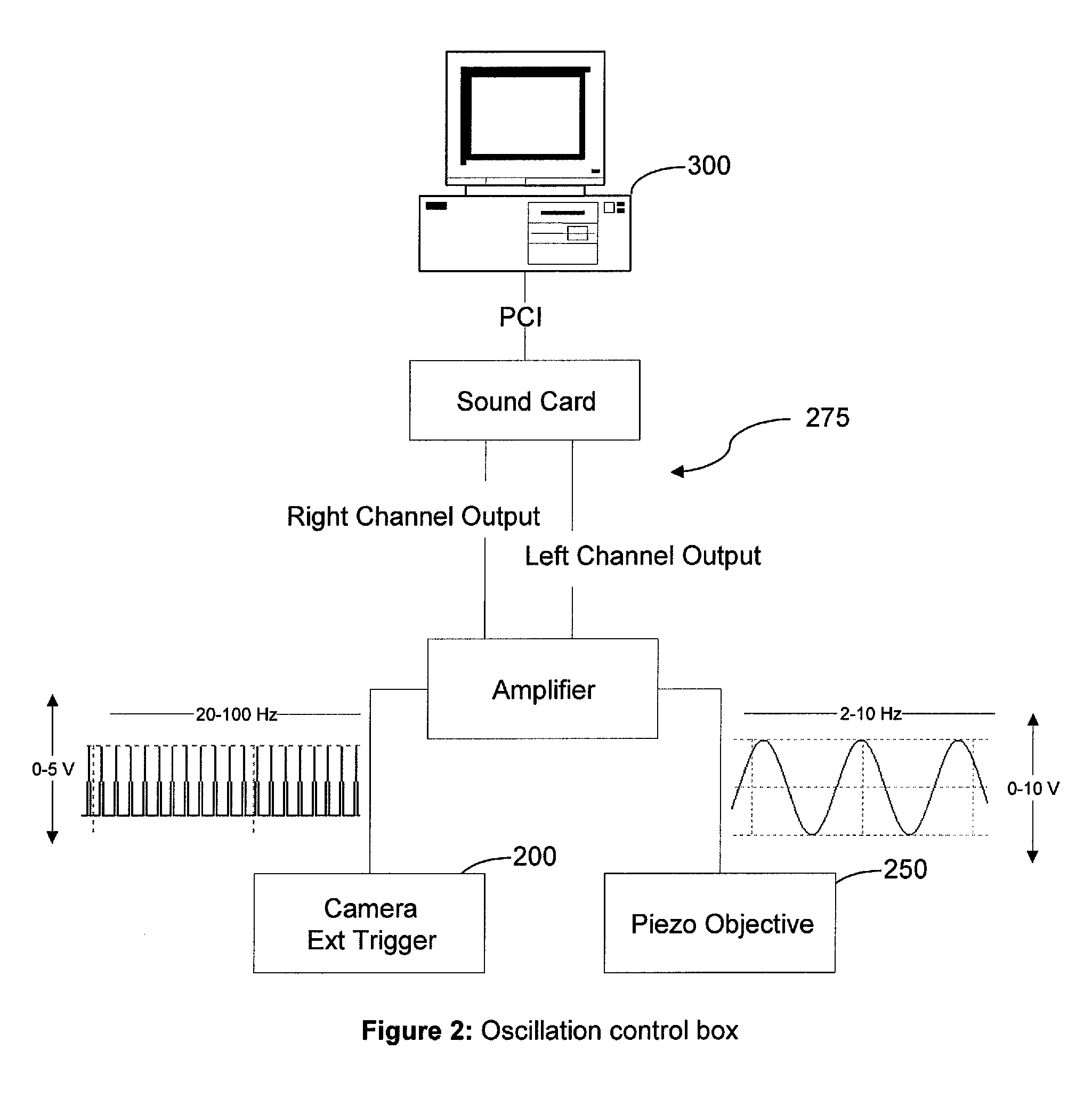
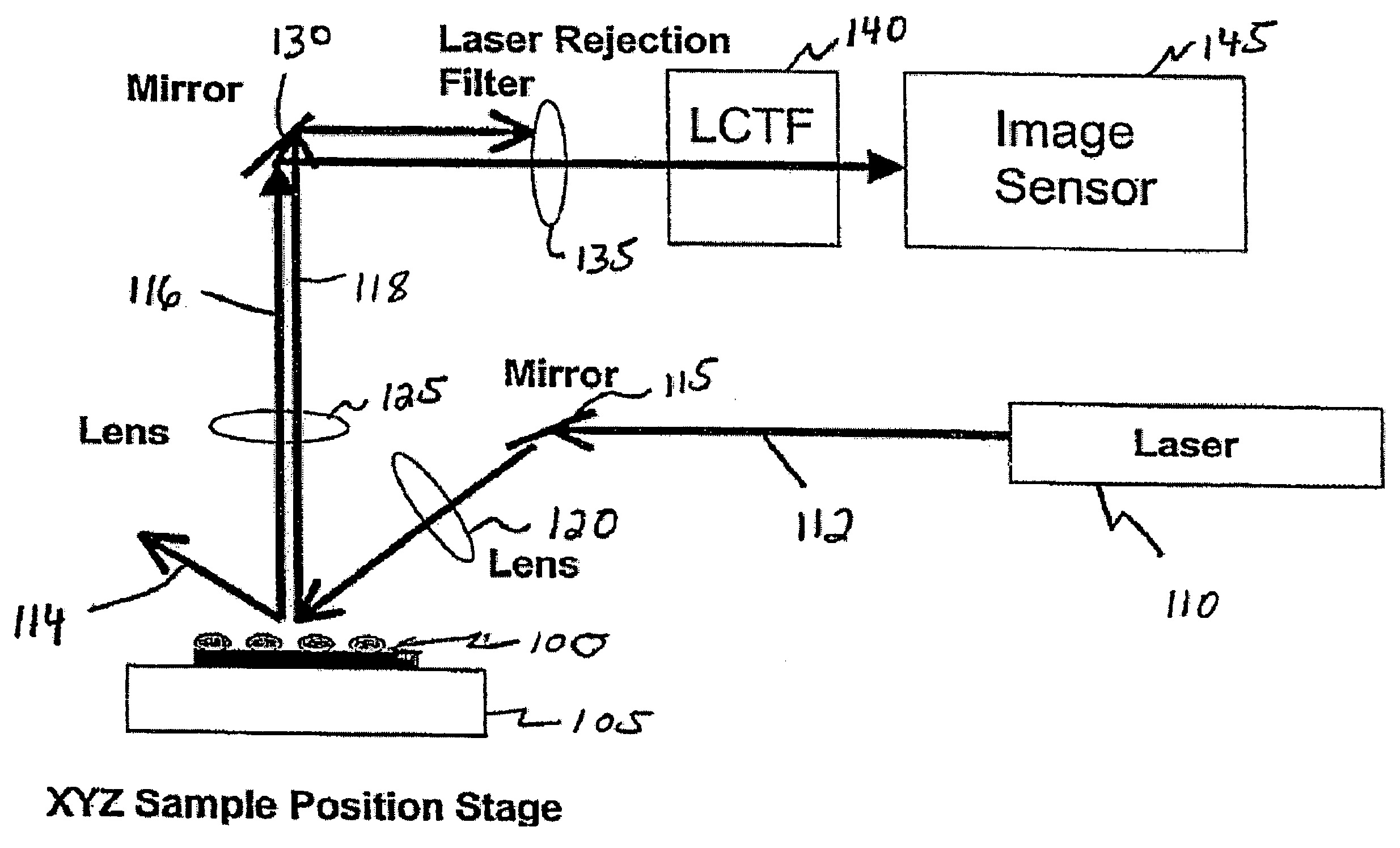
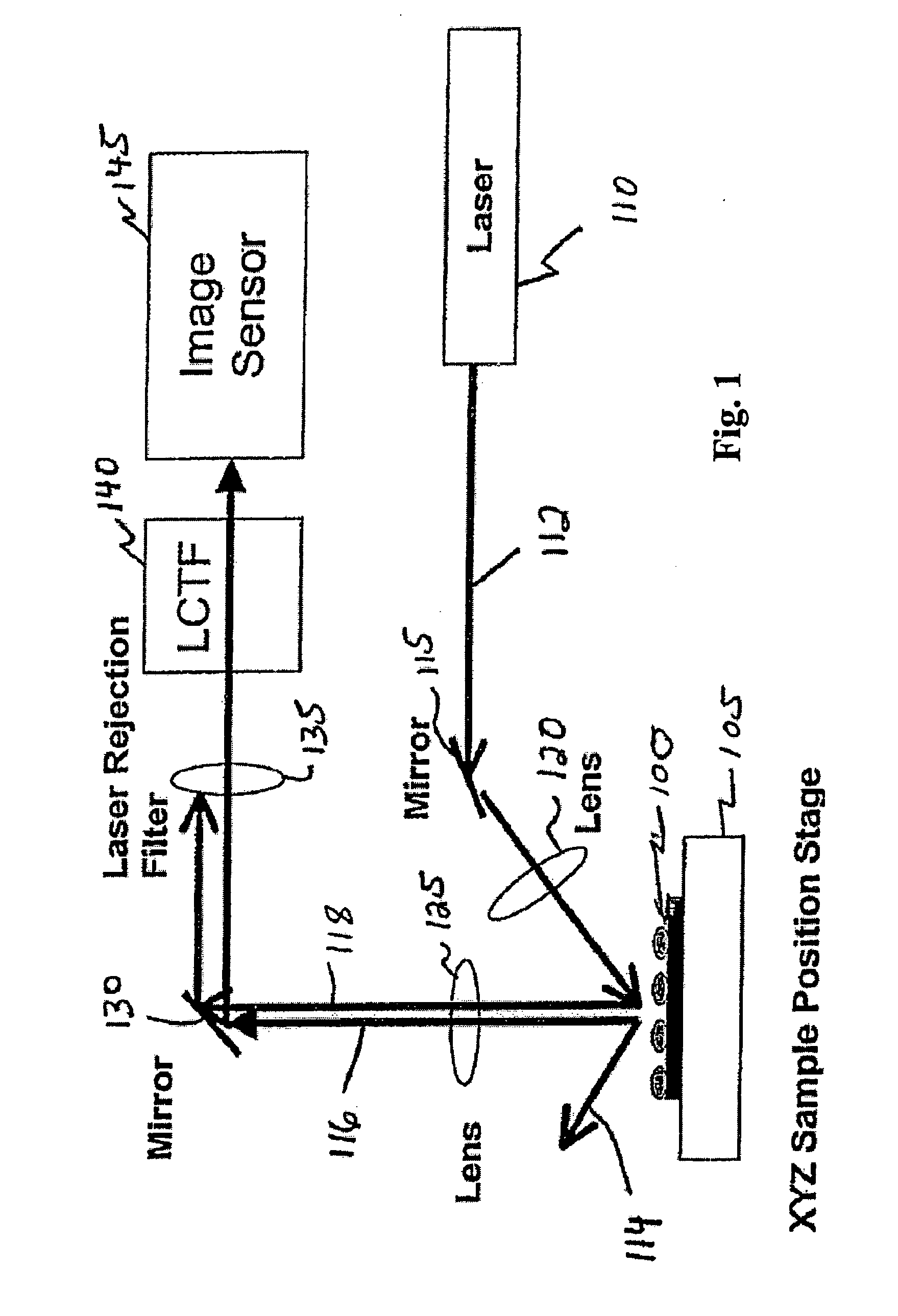
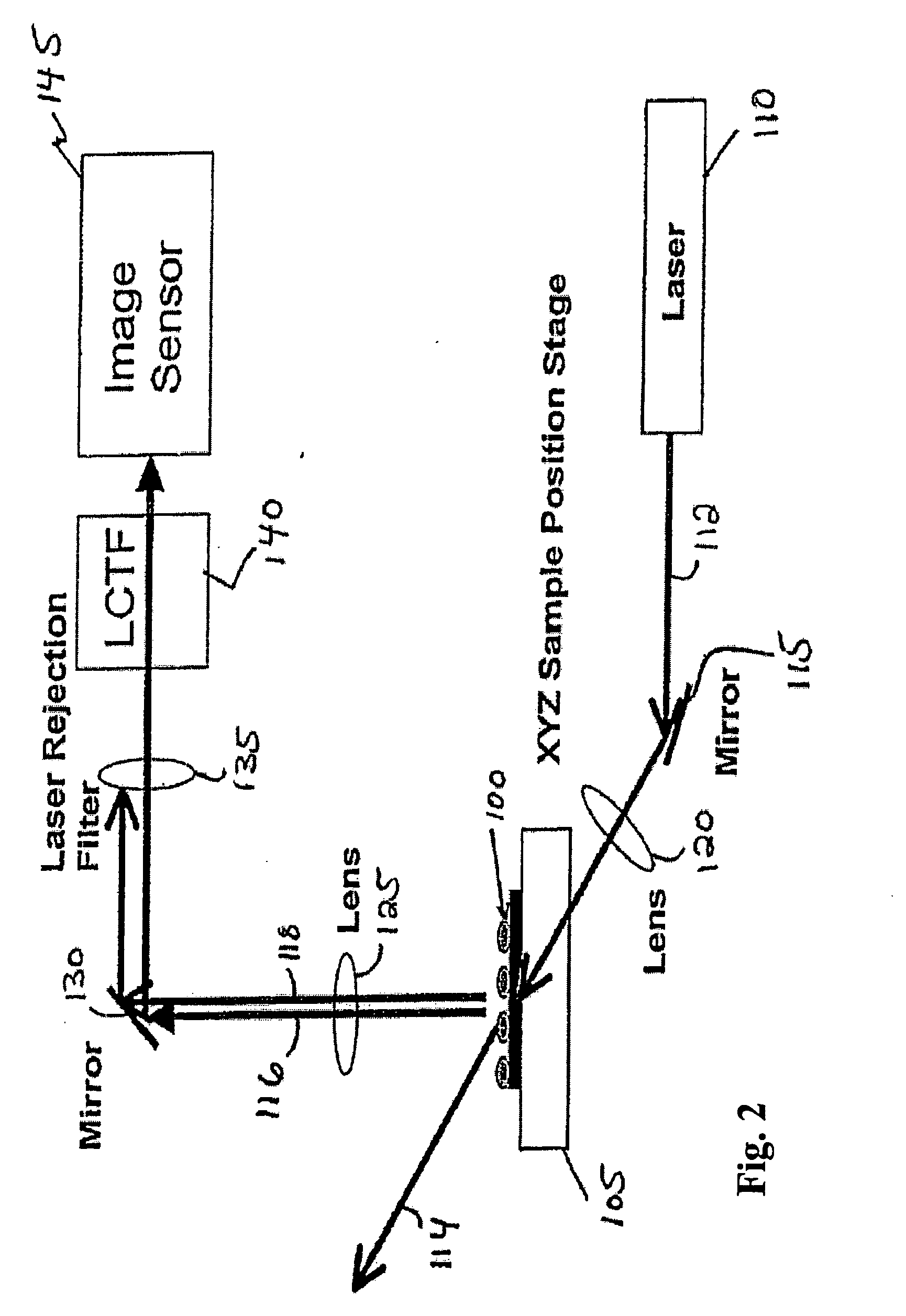
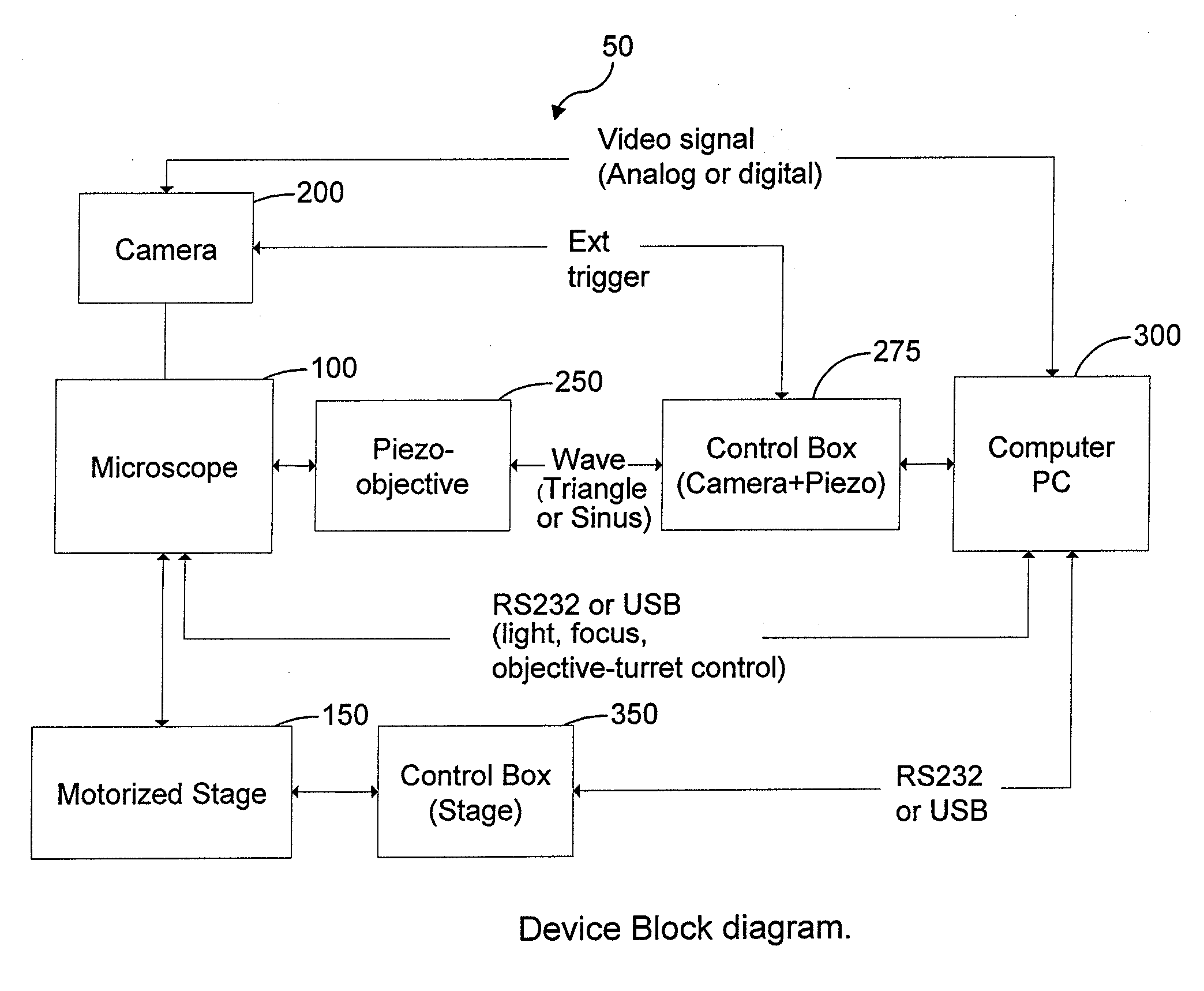
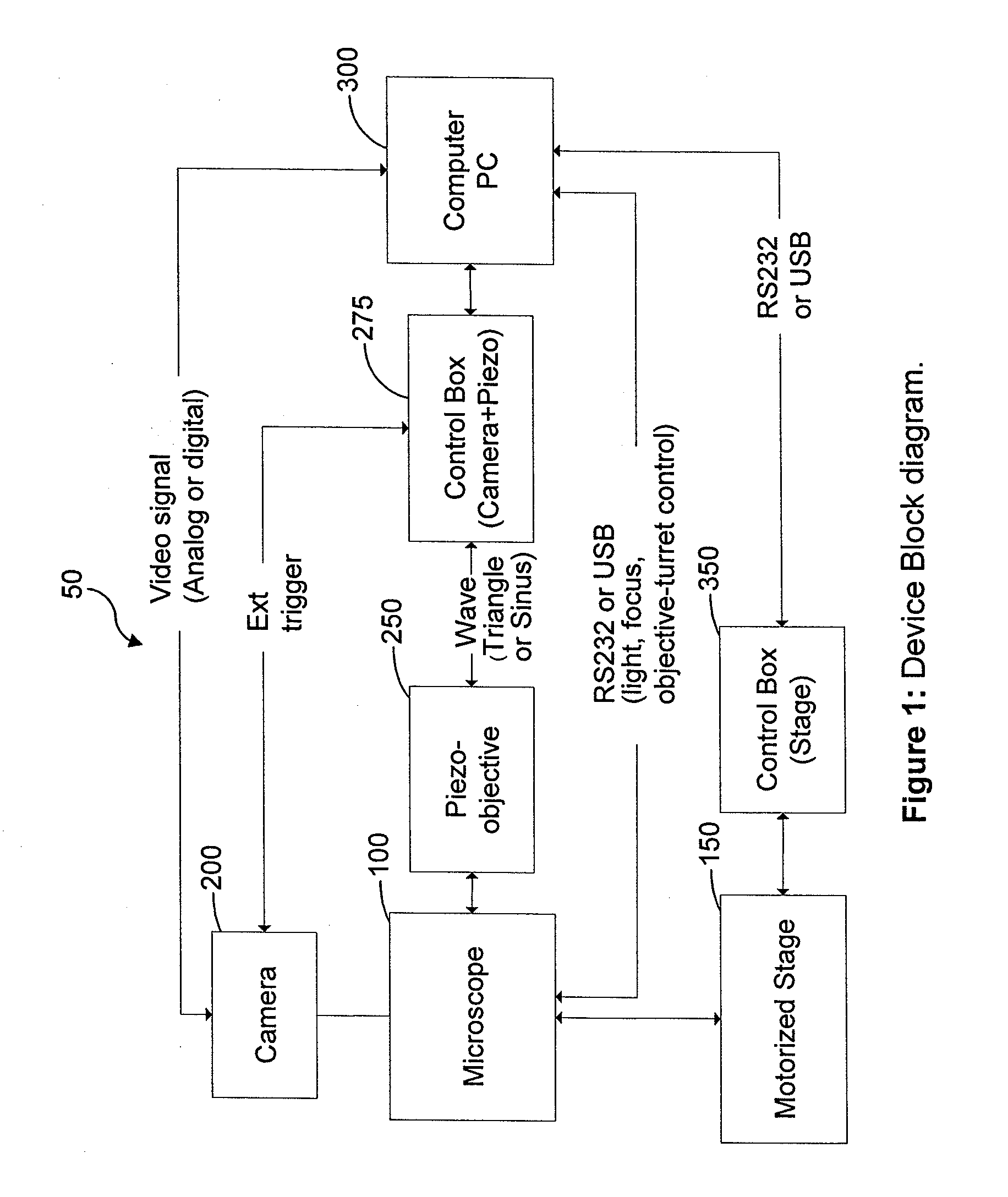
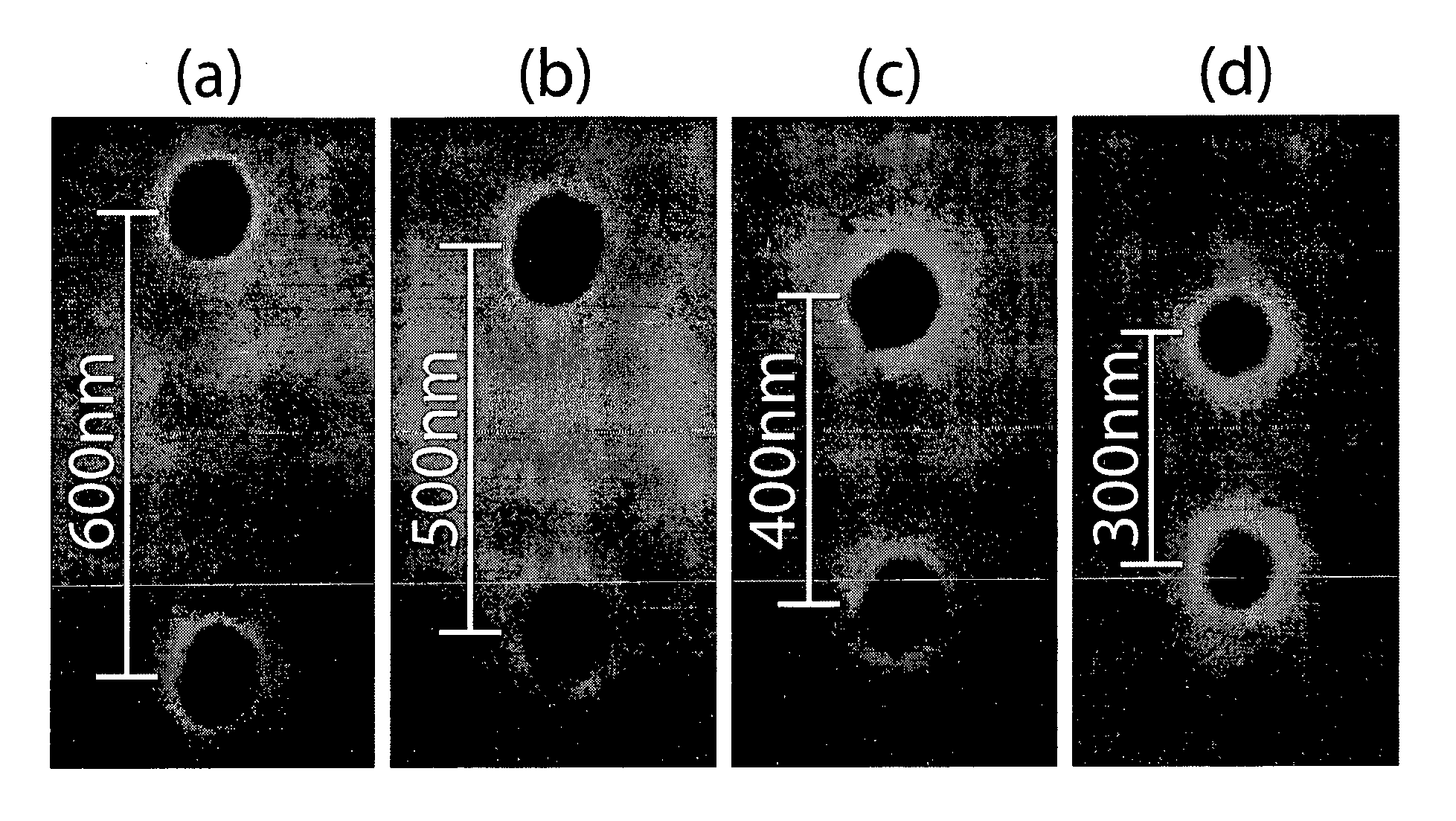
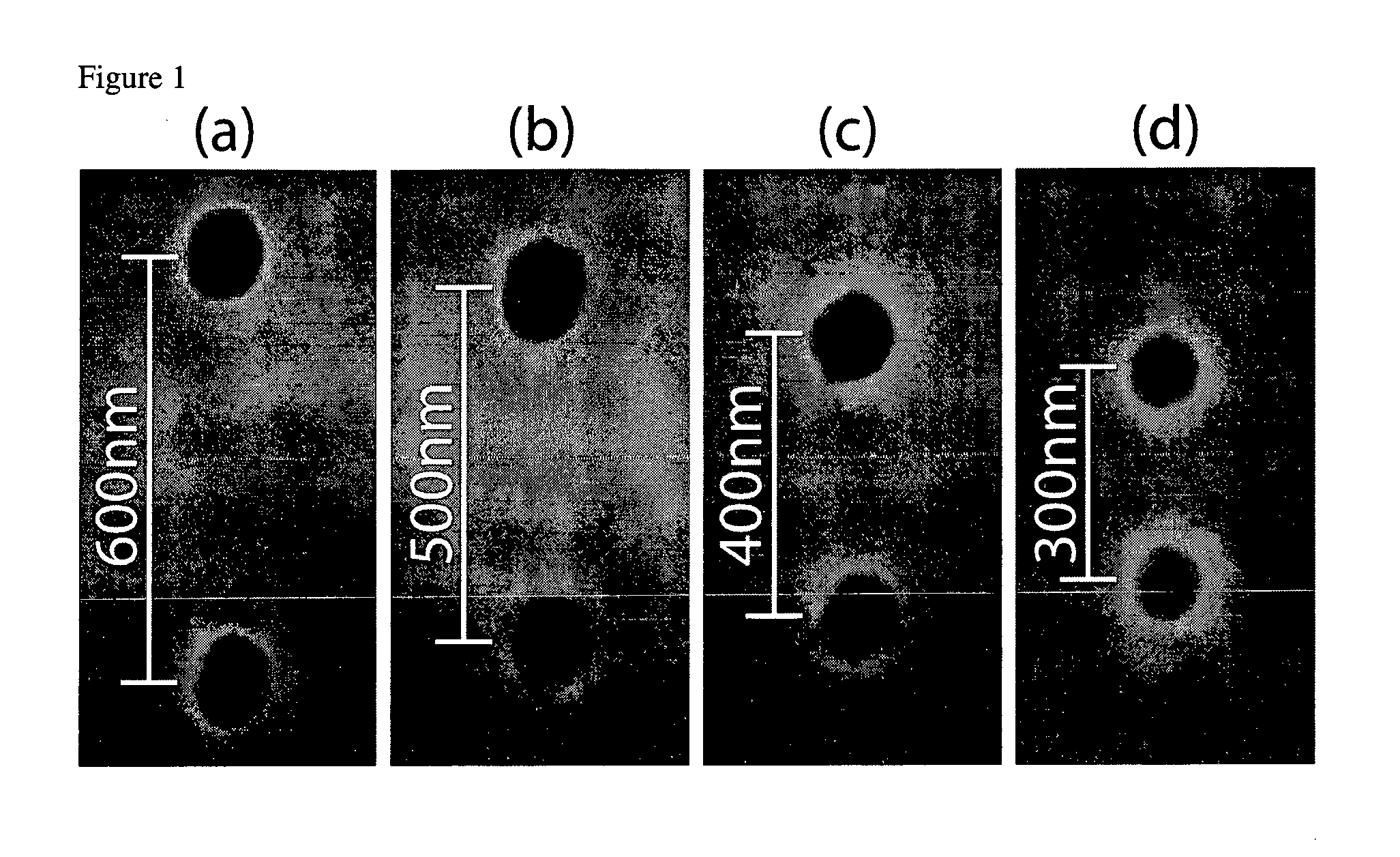
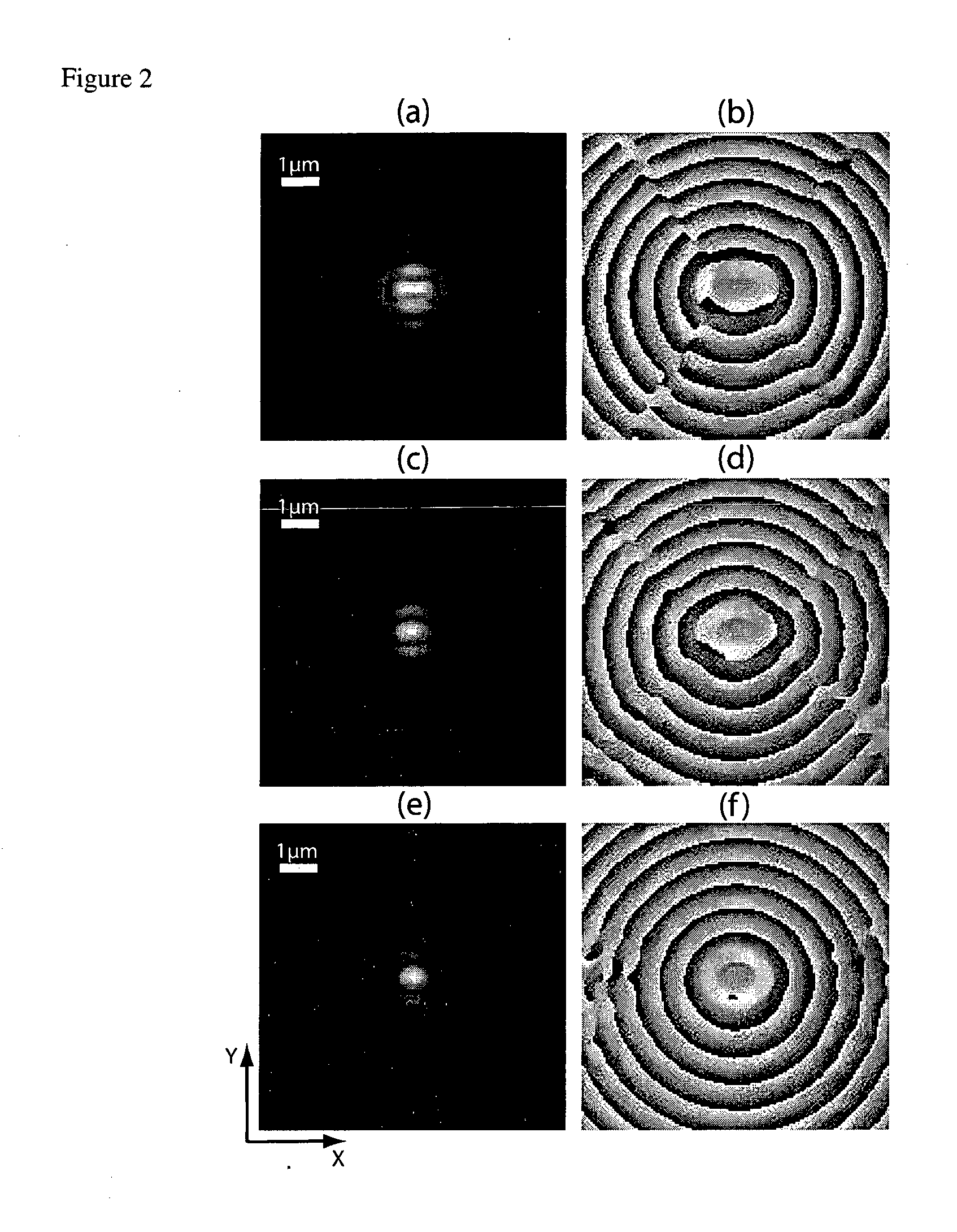
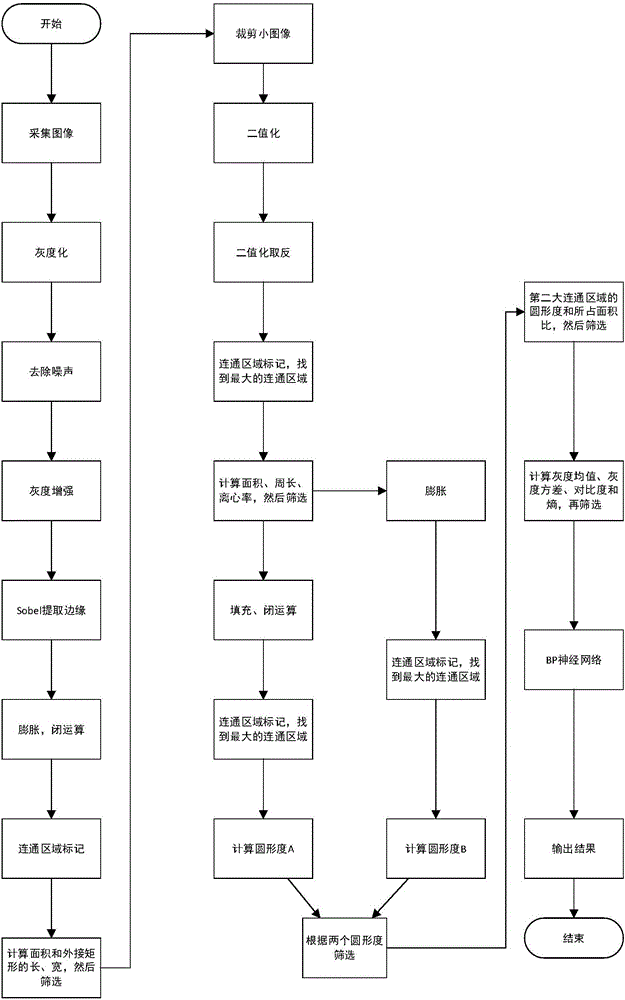
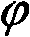Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1600 results about "Microscopic image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
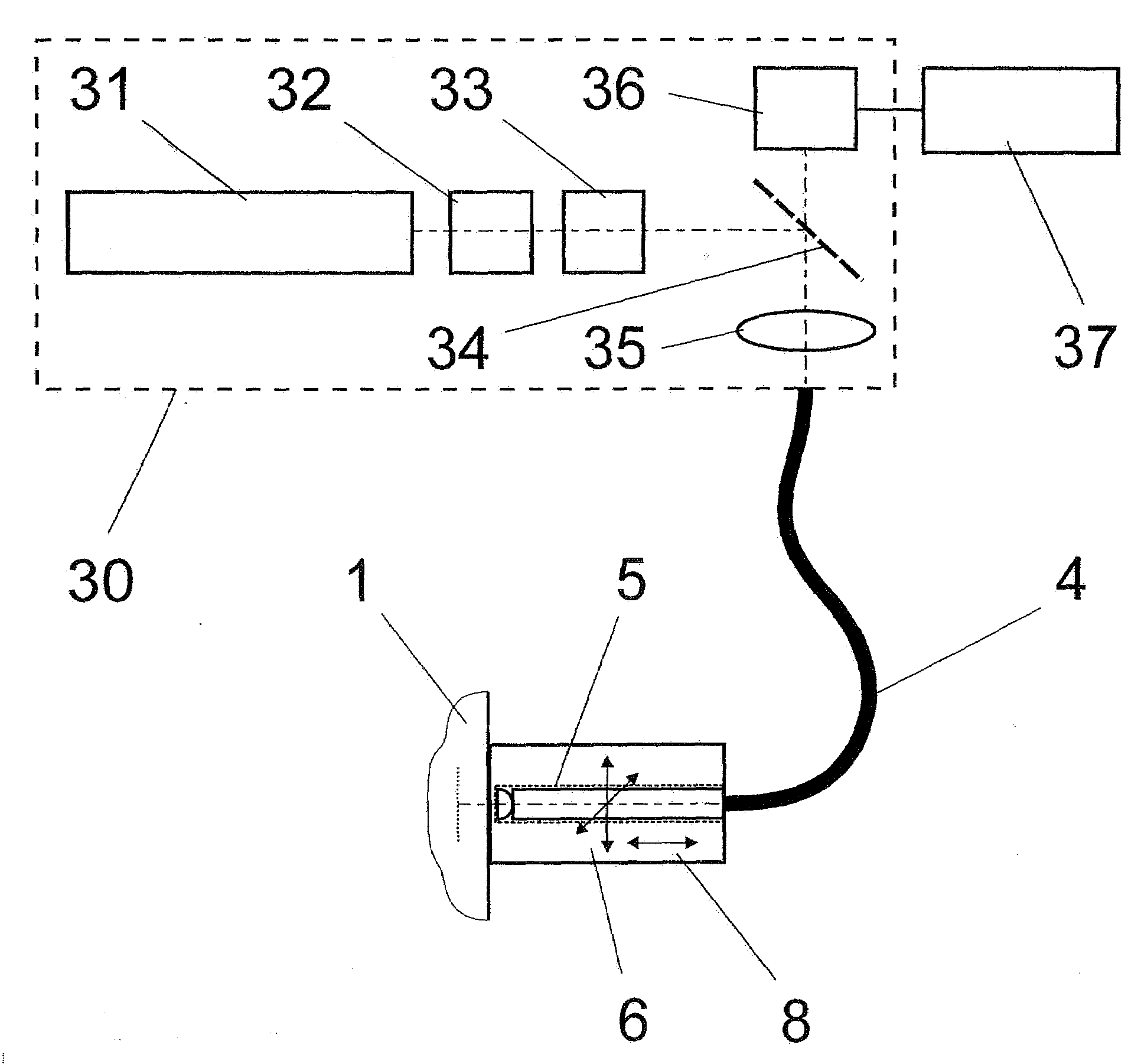
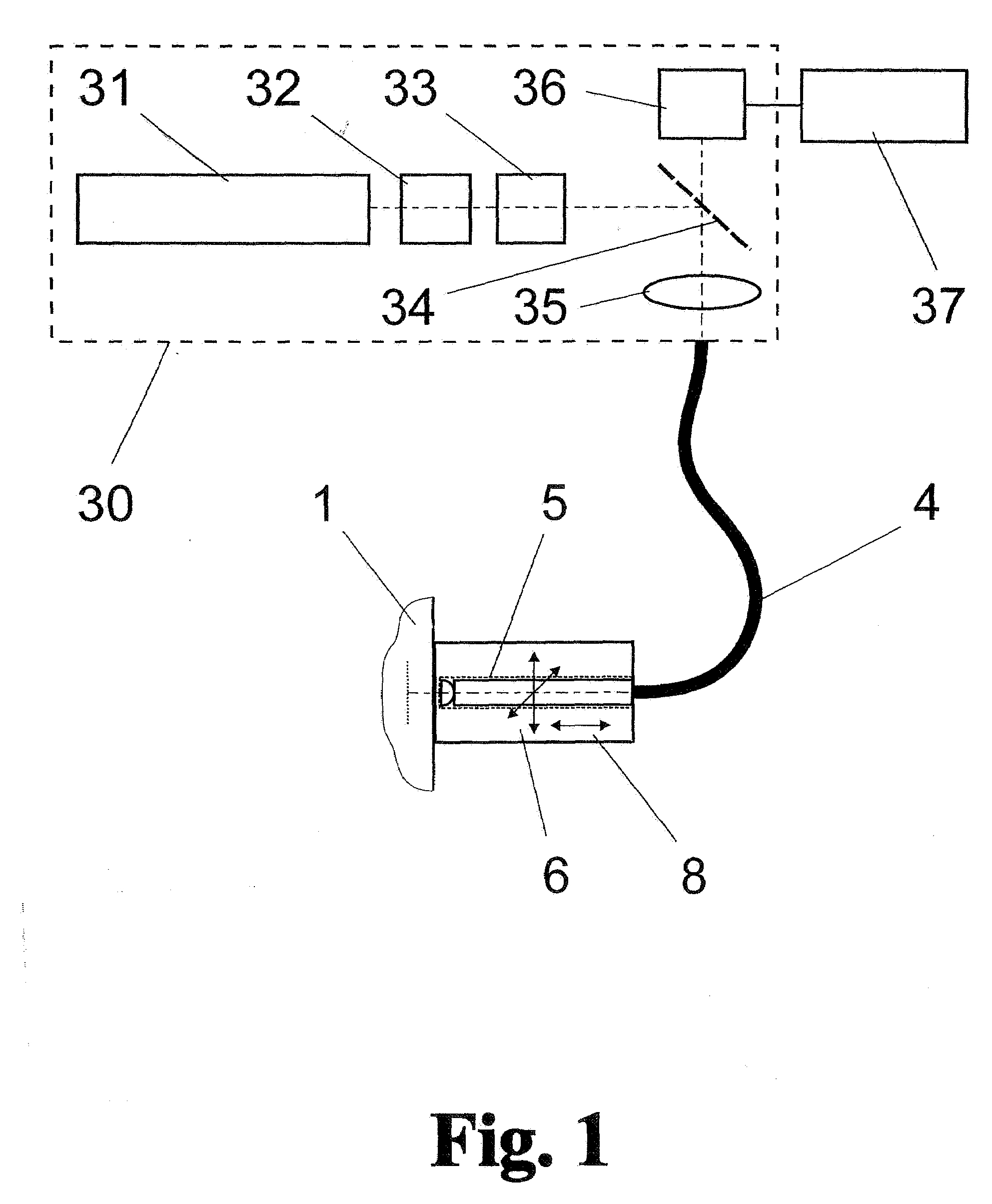
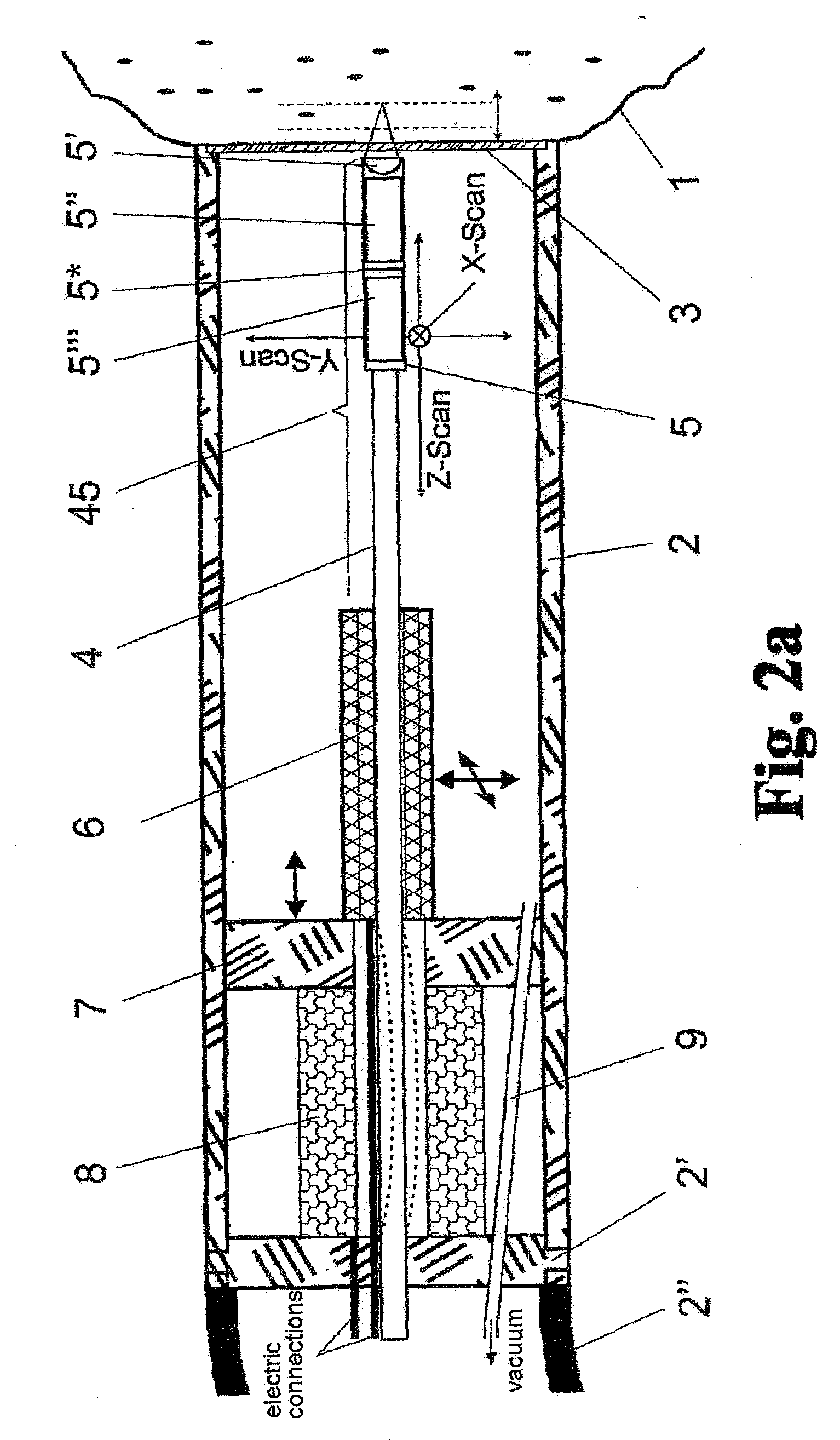
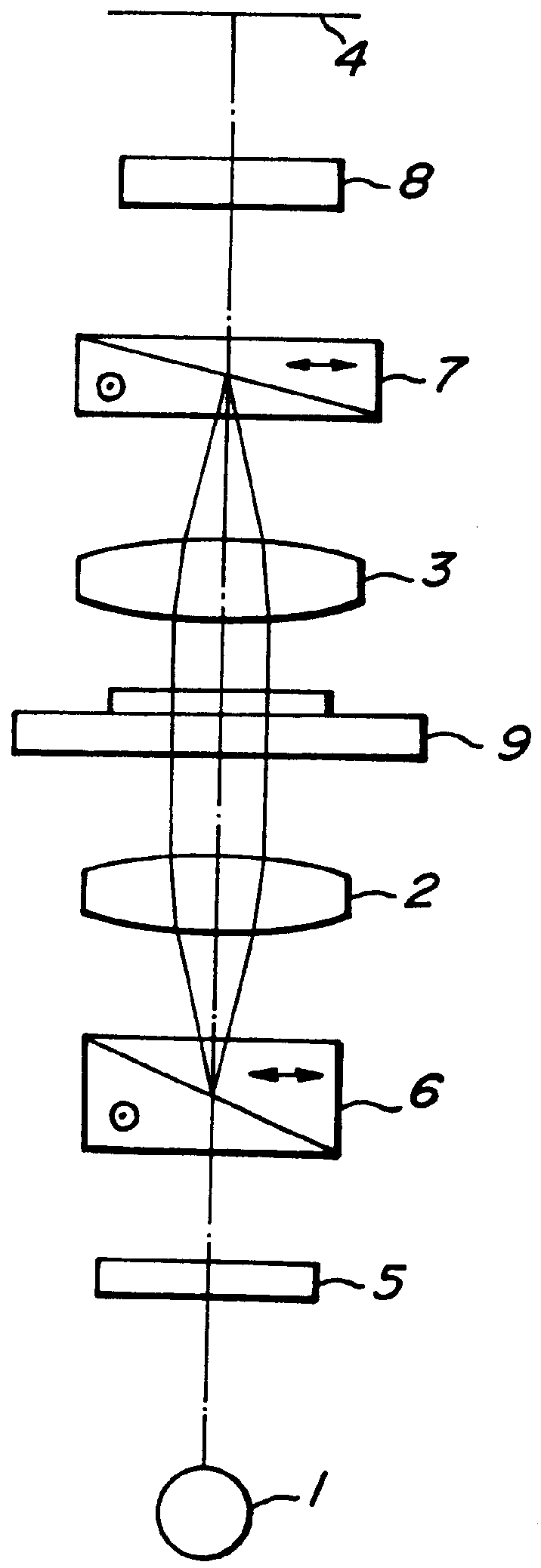
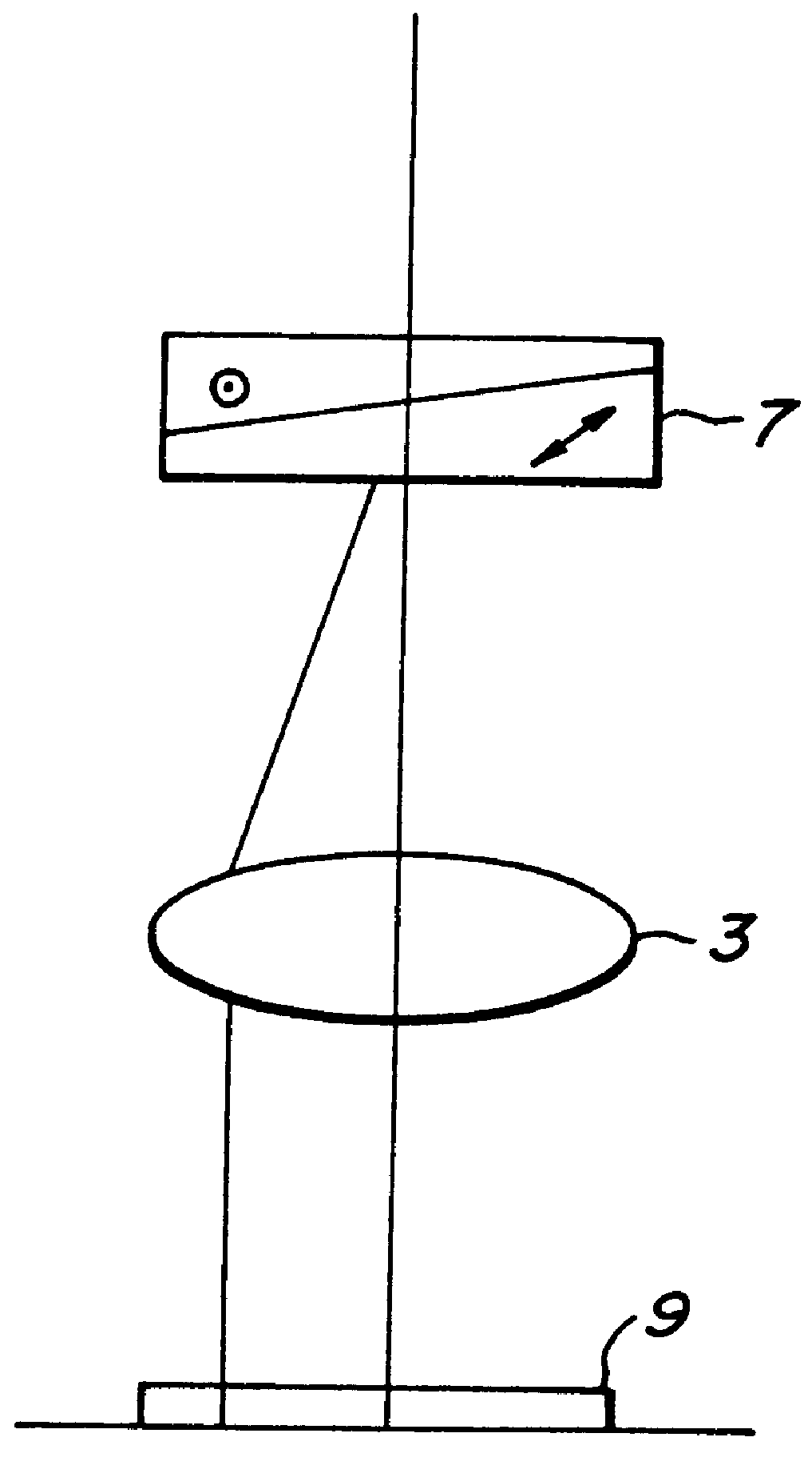
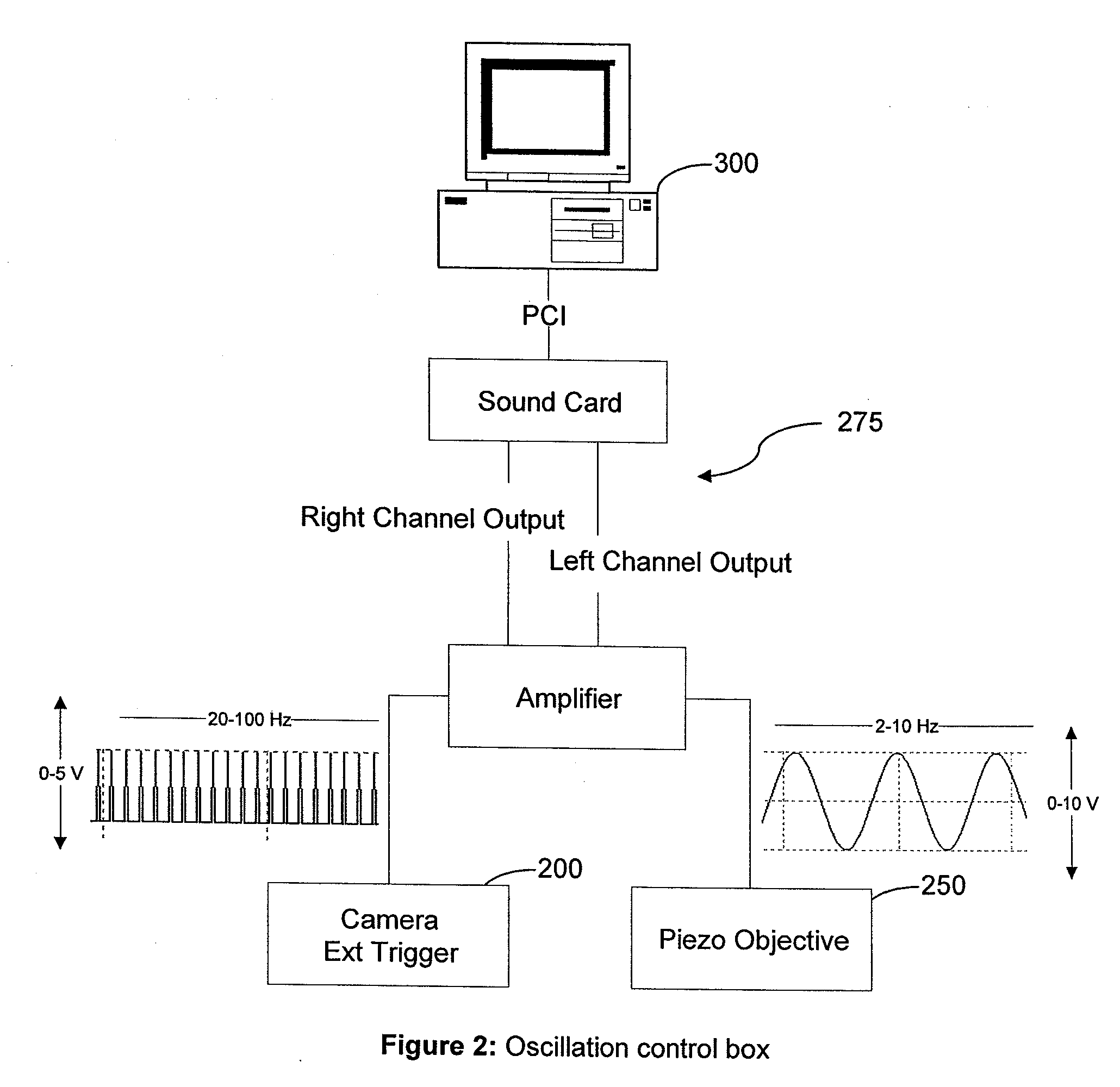
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
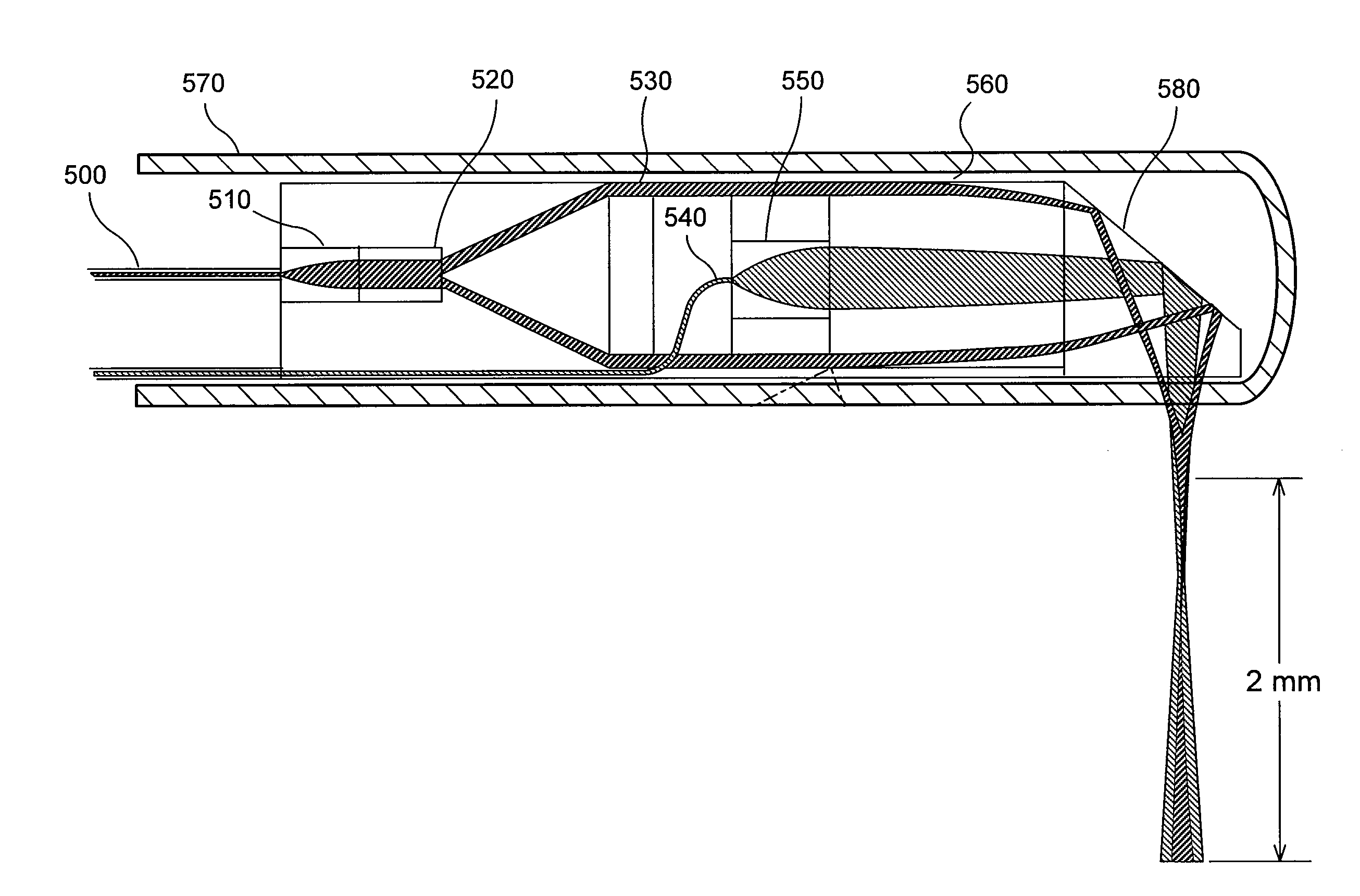
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
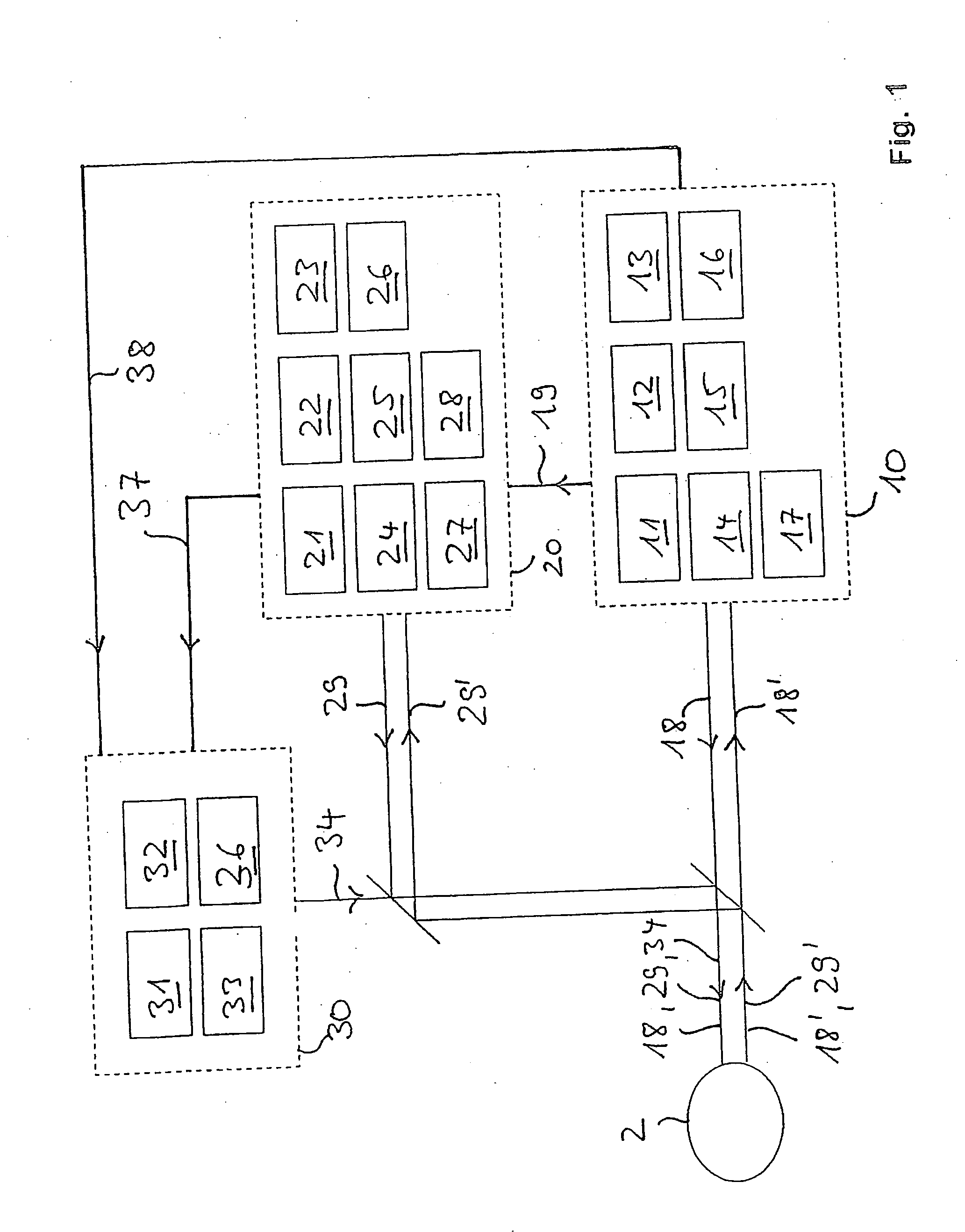
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
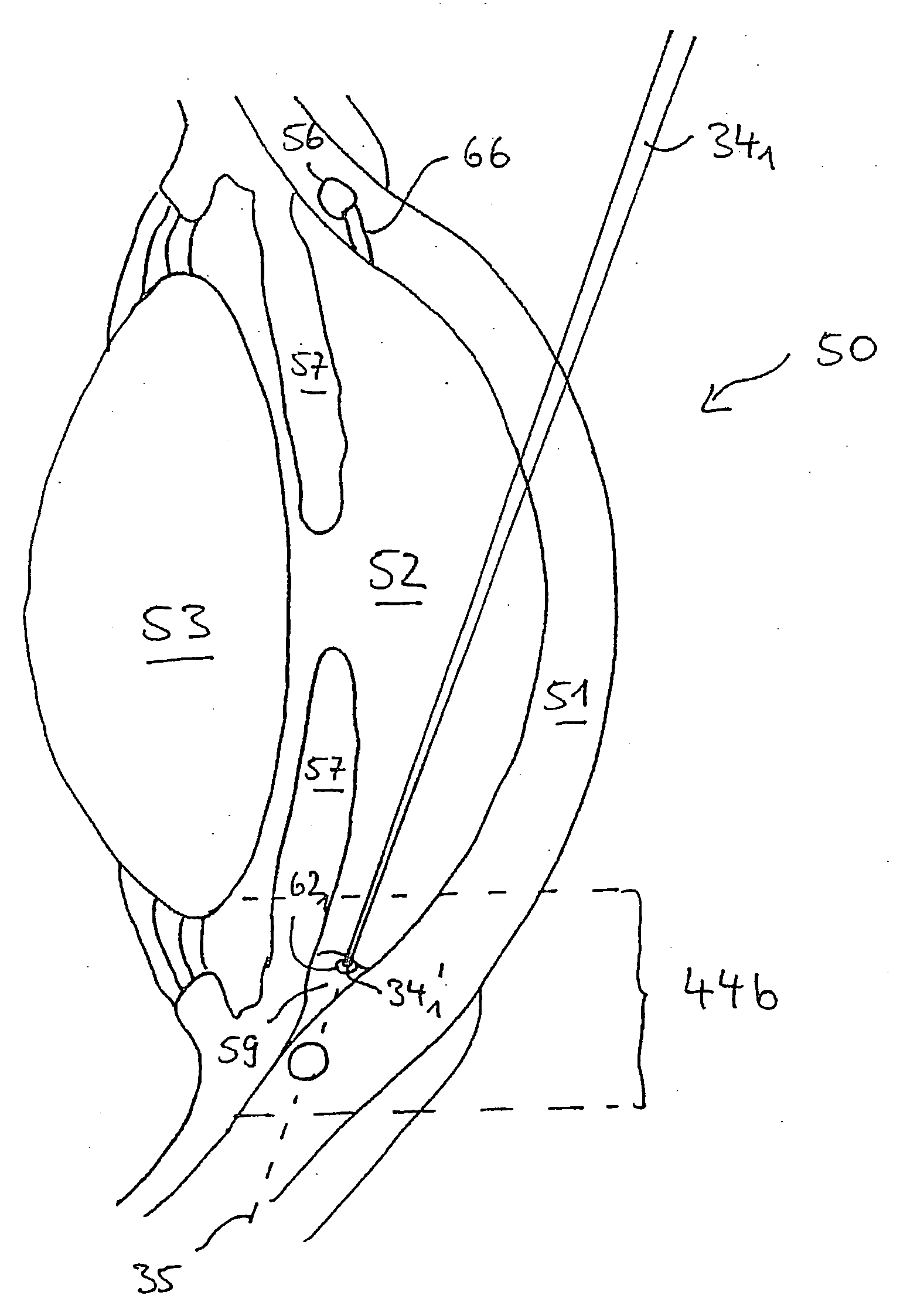
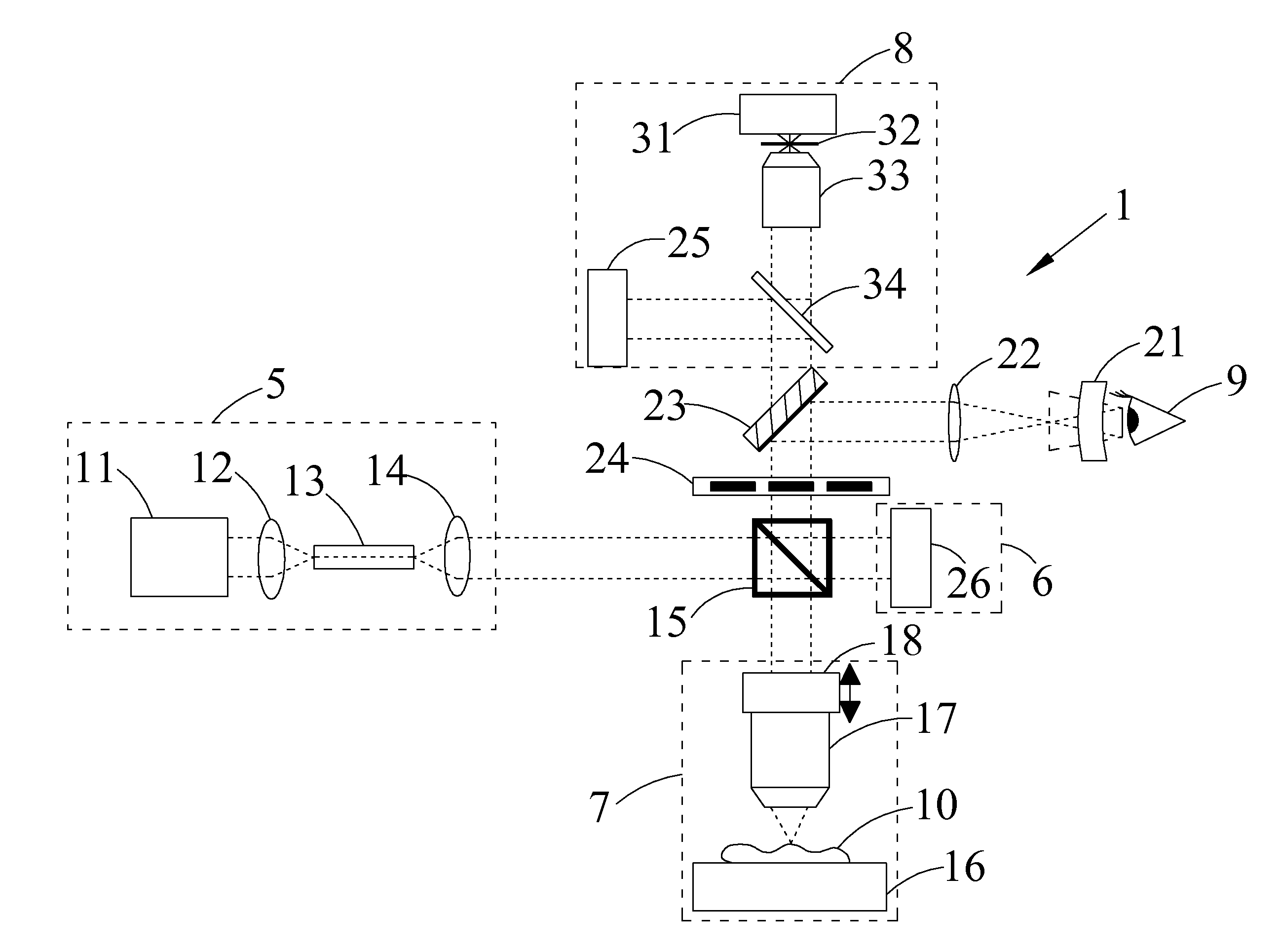
Systems and methods for treating glaucoma and systems and methods for imaging a portion of an eye
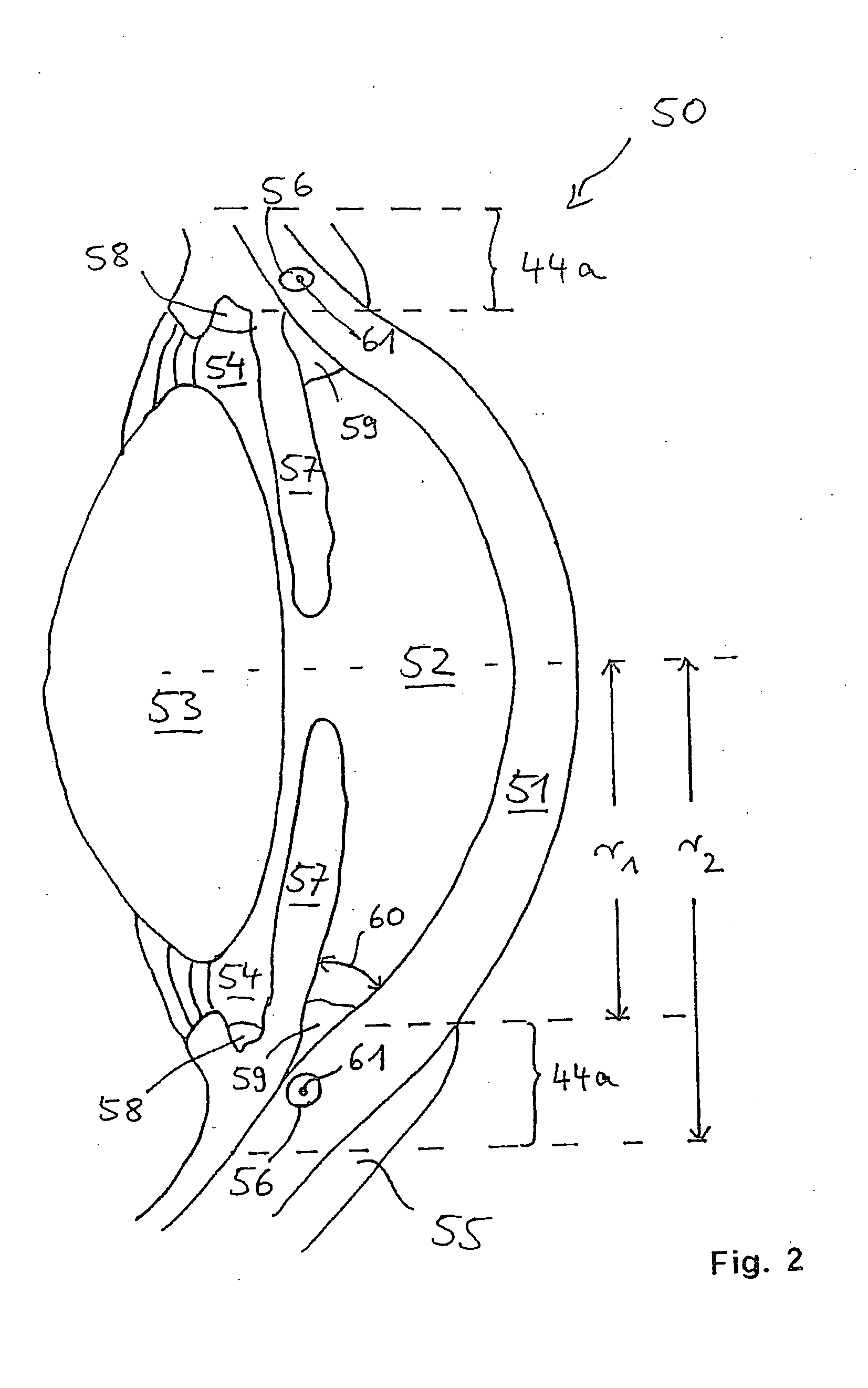
ActiveUS20090157062A1Easy to adaptAvoid damageLaser surgeryWound drainsMicroscopic imageAnatomical structures
Systems and methods are described for imaging an eye portion or for treating glaucoma in an eye of a patient. In a first step an optical microscopic image of a portion of the eye is acquired. In the optical microscopic image a distinguishable anatomical structure is identified to predict a location of a volume portion to be imaged three-dimensionally. Three-dimensional imaging of the located volume portion is performed by acquiring an optical coherence tomography image of the located volume portion. The volume portion is treated by either directing a laser beam to the volume portion or inserting an implant based on the OCT-image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
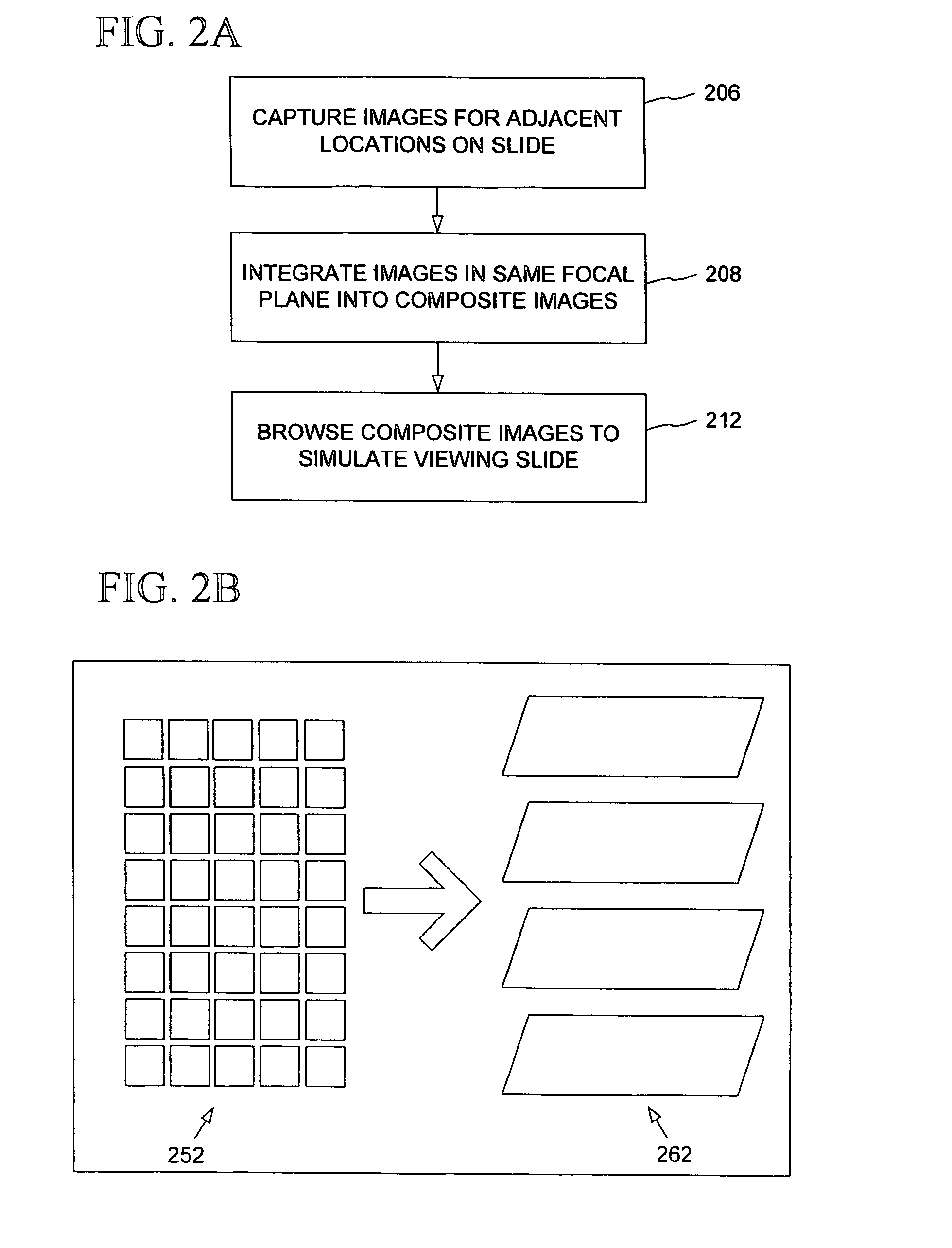
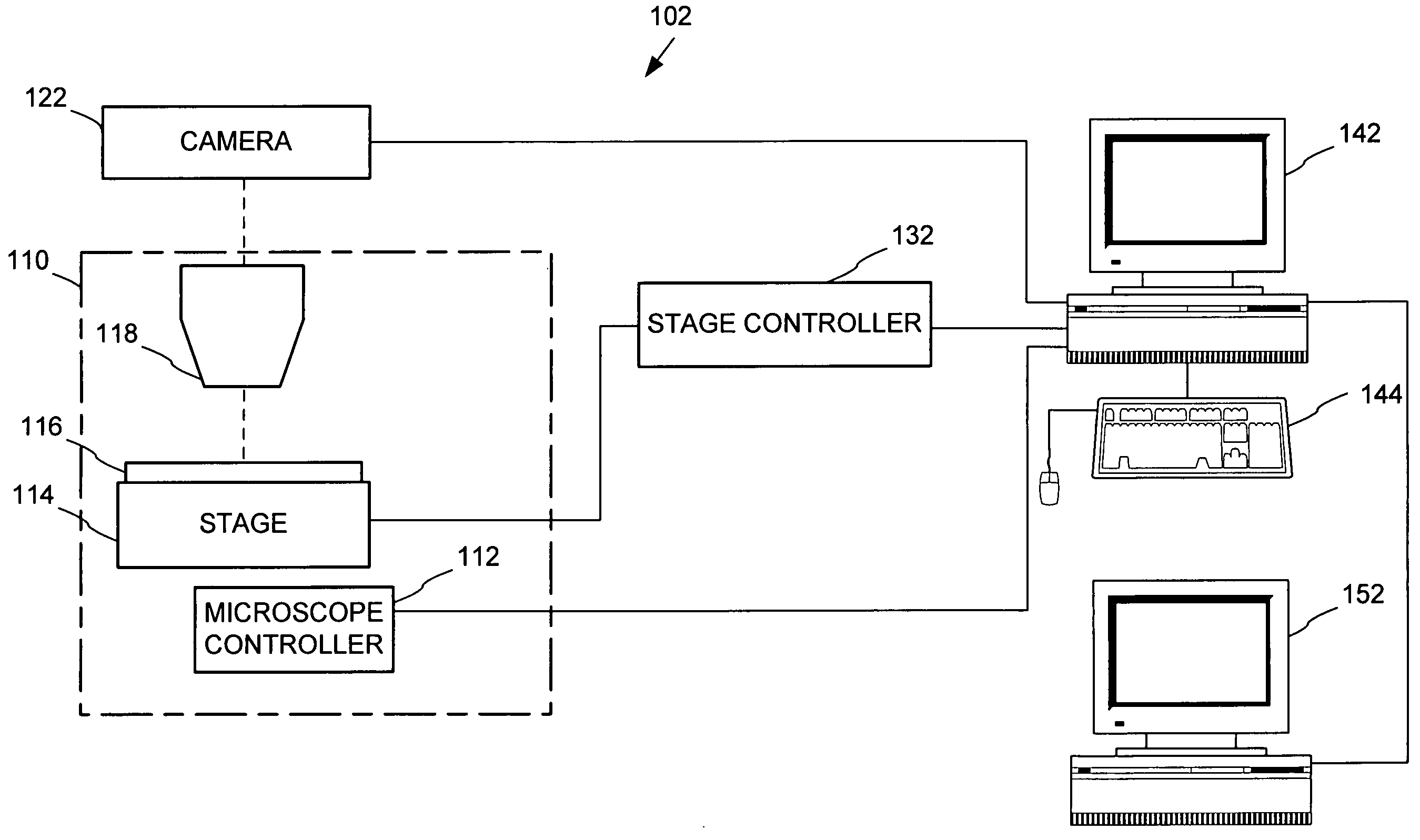
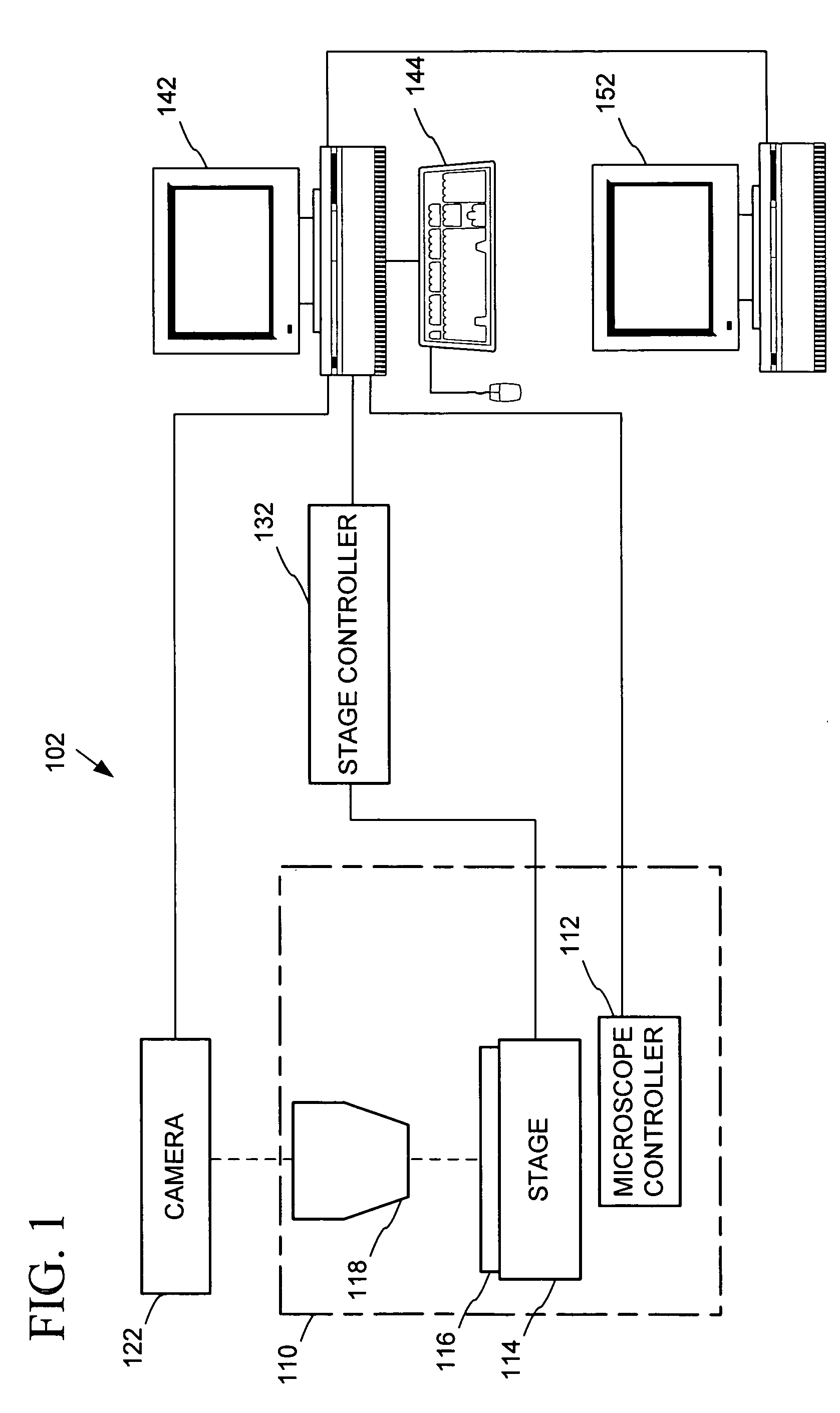
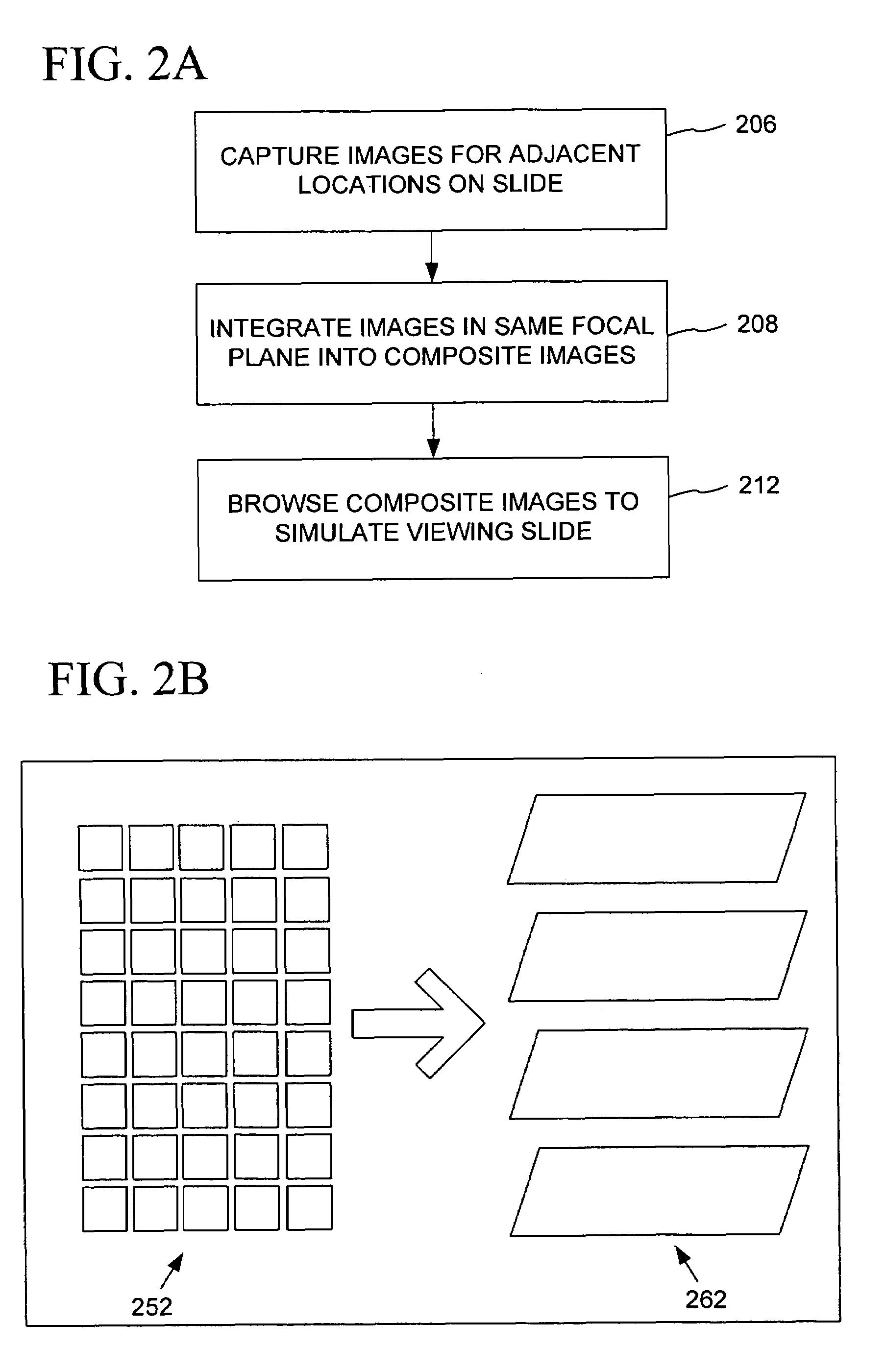
Automated microscopic image acquisition, compositing, and display
InactiveUS7027628B1Inhibition effectSuppress mutationImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageAutomated microscopy
An automated microscope and computer system captures a set of images for a capture area in a plurality of focal planes. The images can then be integrated into composite images for browsing to simulate viewing an item, such as a biological sample, under a microscope. A corrective filter can be constructed from the images to avoid an effect called “tiling.” Before capture, variable focal plane error can be avoided by collecting z locations for a set of points in the capture area. During image browsing, entire composite images can be loaded into memory in compressed form. Compressed image portions can be pre-decompressed to avoid delay as a browsing user navigates throughout the composite images. Pre-decompression can be done by a thread separate from the thread performing navigation operations.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION US SEC THE +1
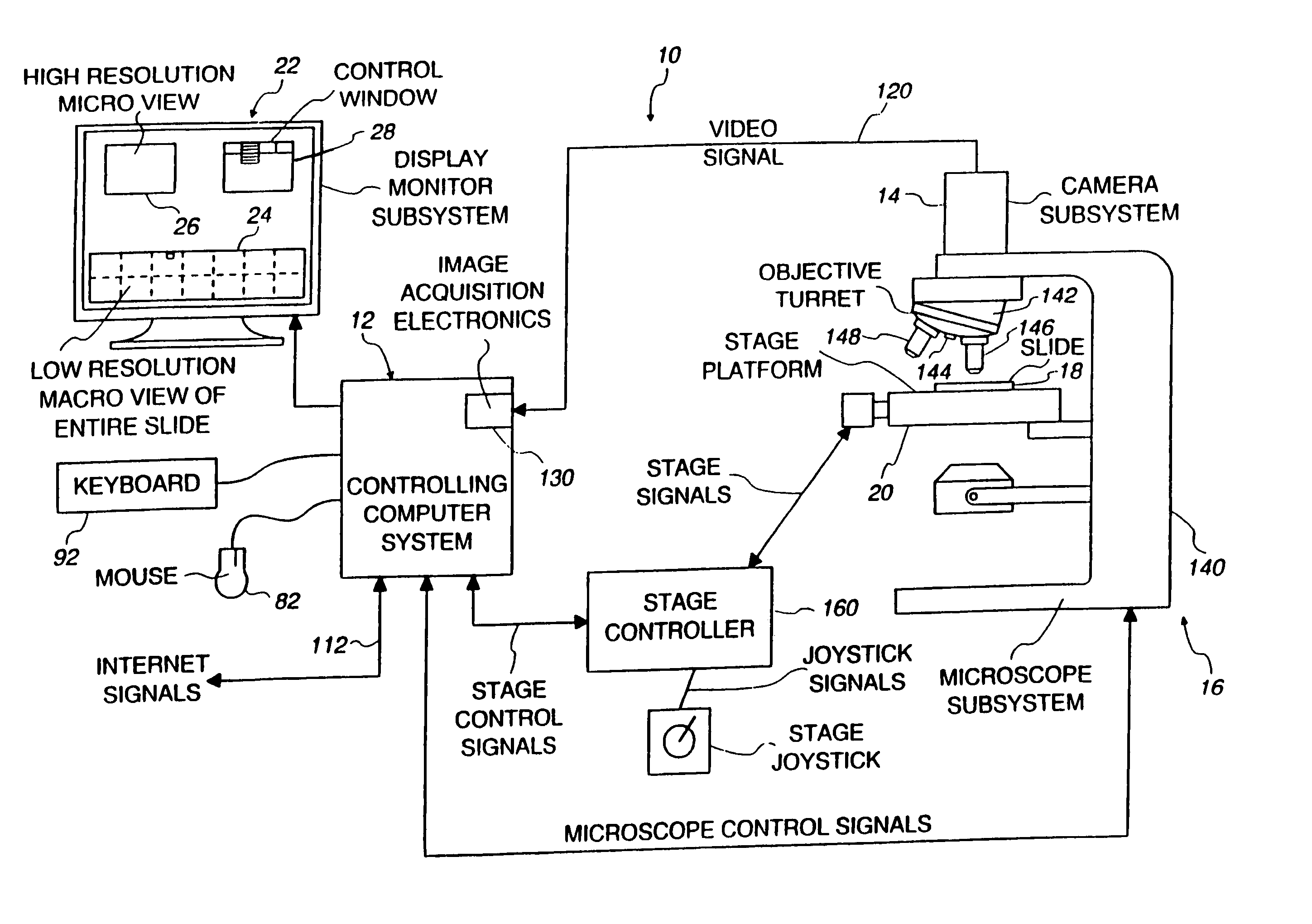
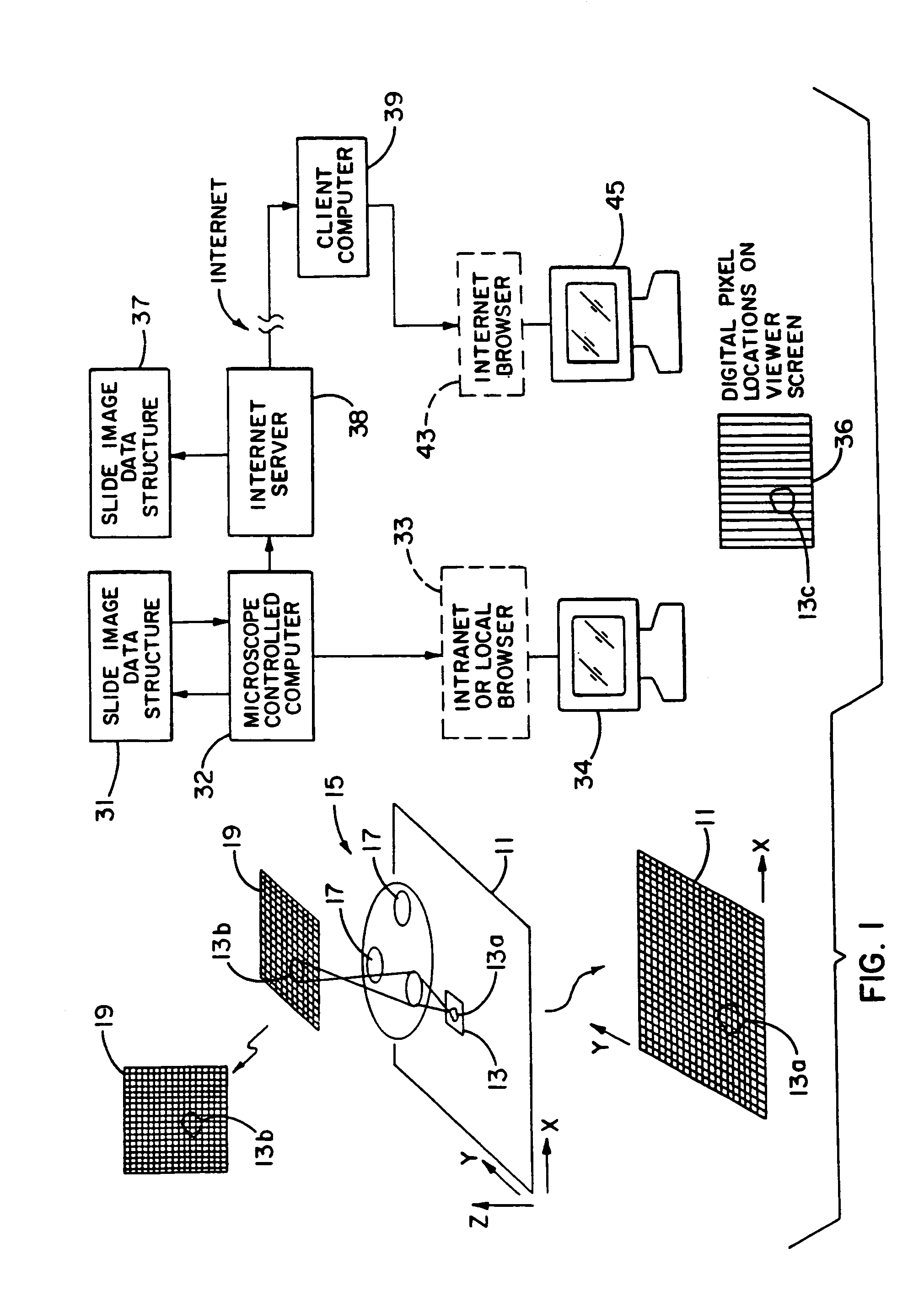
Method and apparatus for internet, intranet, and local viewing of virtual microscope slides
A method of and apparatus for viewing microscopic images include transmitting tiled microscopic images from a server to a client. The client assembles the tiled images into a seamless virtual slide or specimen image and provides tools for manipulating image magnification and viewpoint. The method and apparatus also provides a virtual multi-headed microscope function which allows scattered viewers to simultaneously view and interact with a coherent magnified microscopic image.
Owner:OLYMPUS AMERICA
Systems, methods and computer-accessible medium which provide microscopic images of at least one anatomical structure at a particular resolution
ActiveUS20110218403A1Facilitate the μOCT CTFFacilitate a depth-of-field extensionSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresMicroscopic image
Exemplary embodiments of probes, apparatus, systems and methods can be provided which provide at least one electro-magnetic radiation to at least one sample. For example, a plurality of axicon lenses can be provided which are configured to provide the electro-magnetic radiation(s) having at least partially annulus shape. In addition or alternatively, at least one optical arrangement can be provided which is configured to forward at least one radiation to the sample therethrough having at least partially circularly-symmetric pattern. For example, at least one first portion of the radiation transmitted through a circular section of the pattern can have an optical path-length that is different from an optical path-length of at least one second portion of the radiation transmitted through at least one other section of the pattern.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method and device based on tangential polarization
InactiveCN101907766ALow powerReduce bleachingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization, comprising the following steps: carrying out 0-2pi vortex phase coding focus on tangential polarization exciting light, and obtaining an exciting spot below a diffraction limit on a fluorescence sample; adjusting tangential polarization STED laser and the phase coding tangential polarization exciting light to realize confluence and co-axis, focusing on the fluorescence sample to form a circle bread-shaped focusing spot the central point of which coincides with the central point of the exciting spot; adjusting the operating power of the STED laser to cause the area of a luminous point in the exciting spot to reach the super-resolution ratio; and collecting fluorescence emitted from the luminous point and carrying out detection processing to obtain a microimage with the super-resolution ratio. The invention also discloses a device for realizing the super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization. In the invention, on the premise of ensuring the super-resolution ratio, the working power of the STED is reduced greatly, thereby lowering bleaching of the sample and avoiding damage for the sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
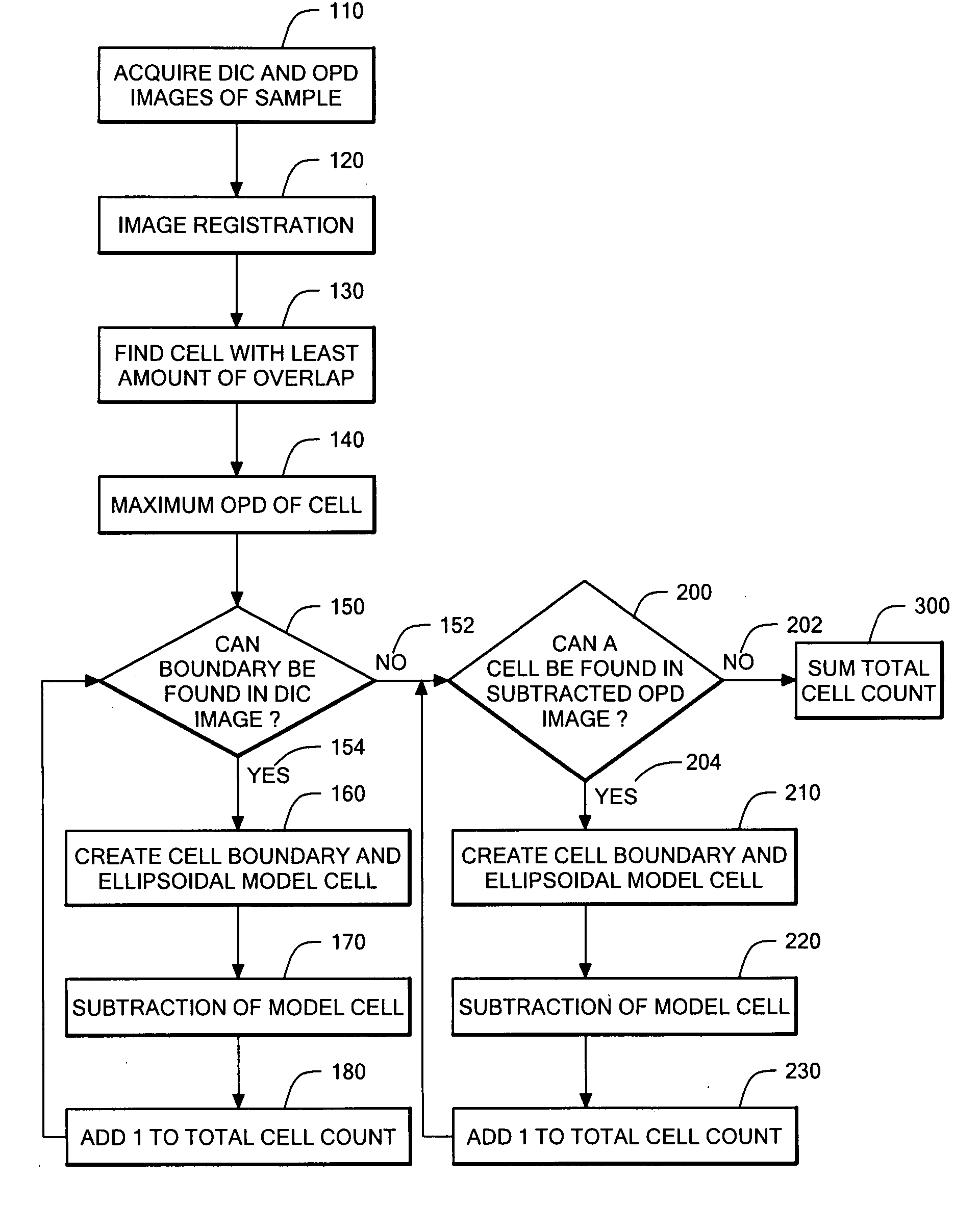
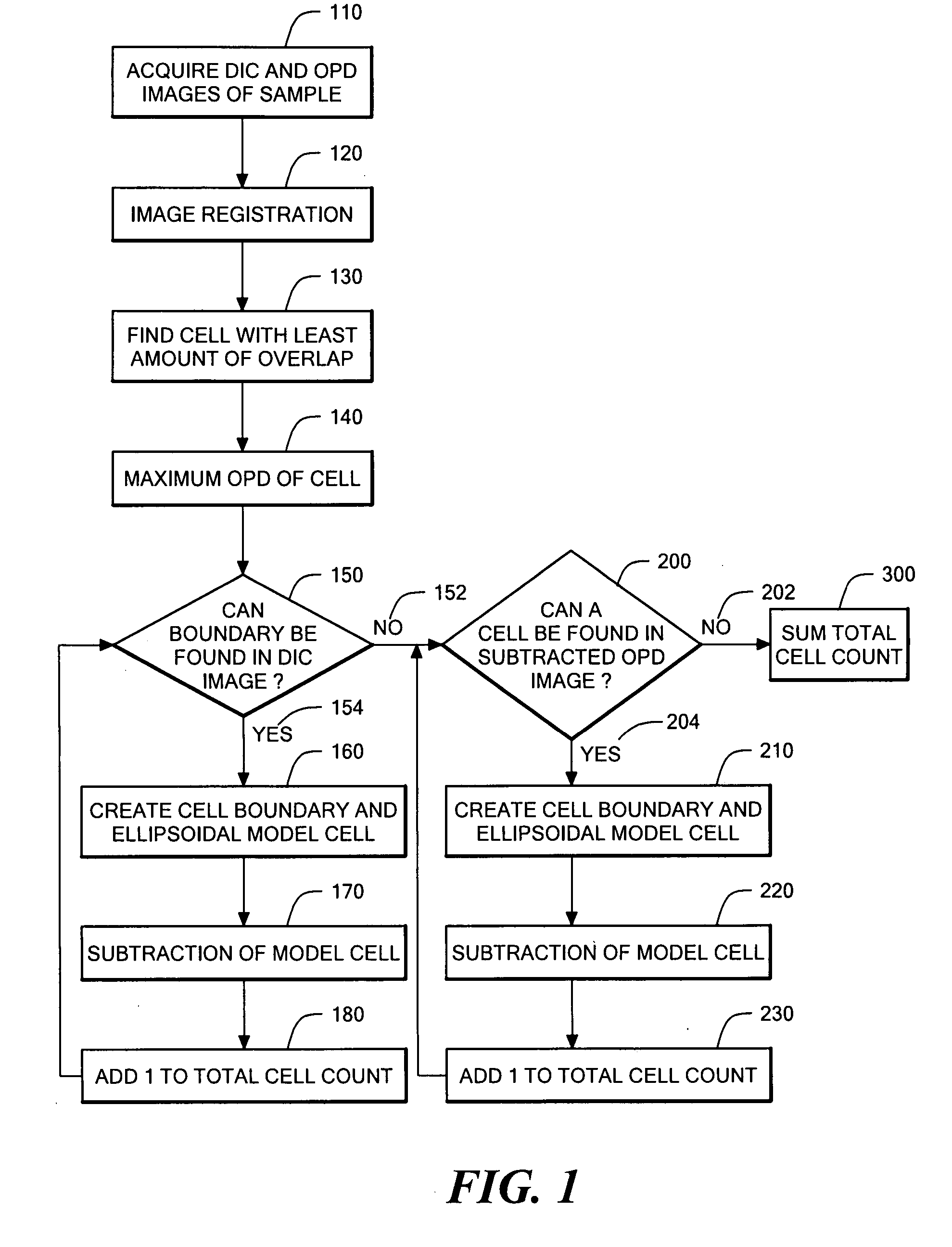
Phase subtraction cell counting method
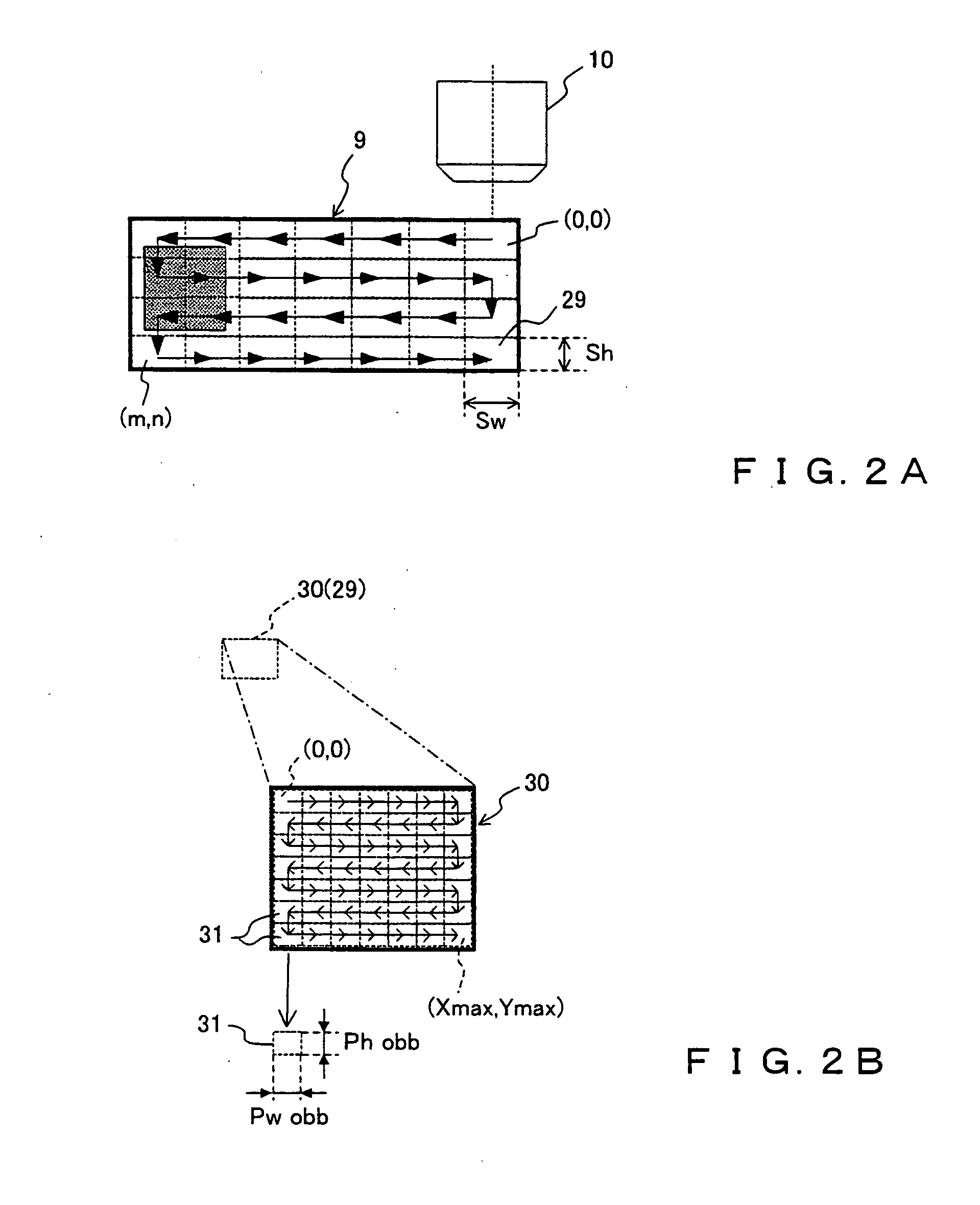
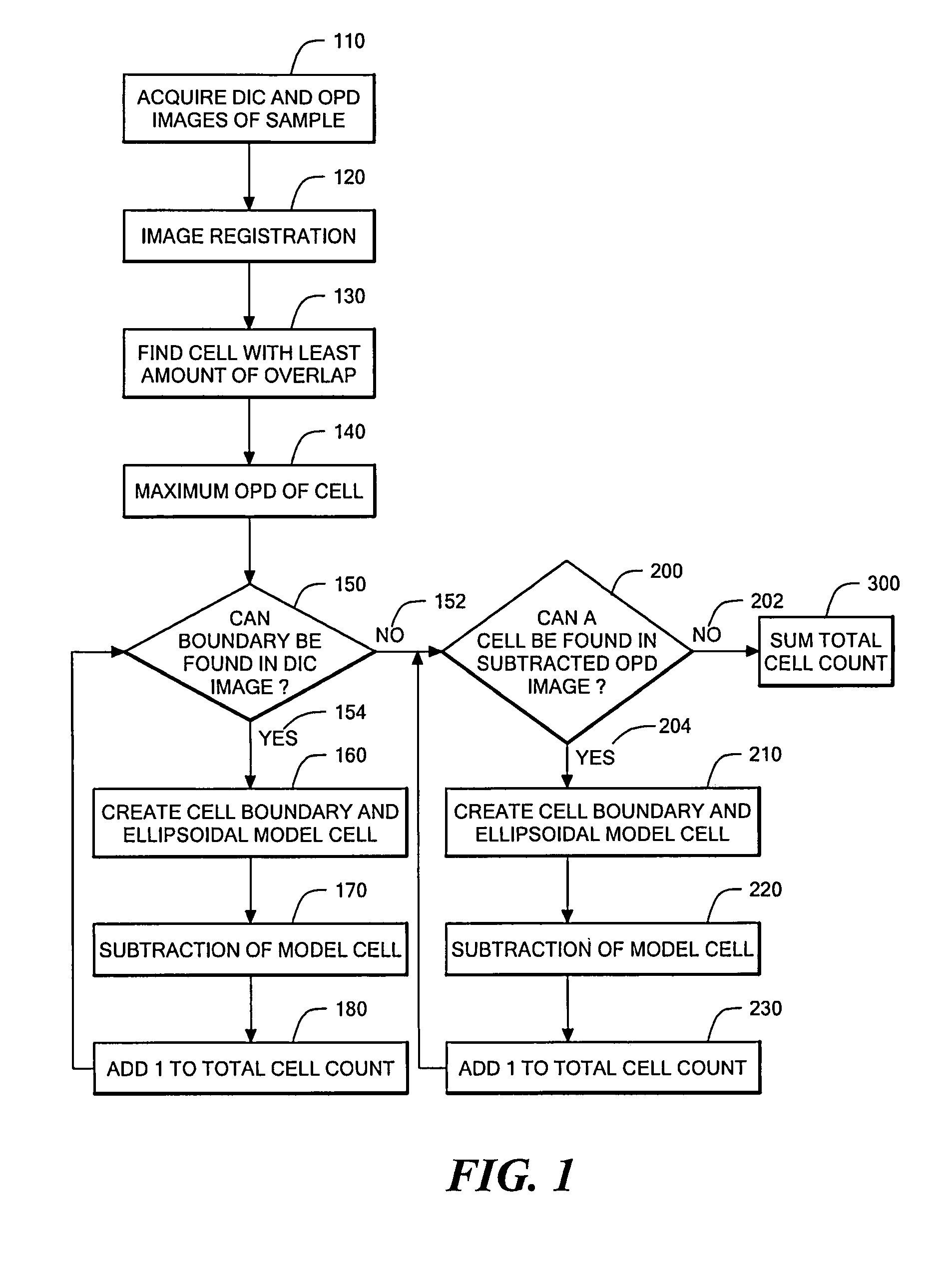
InactiveUS20080032325A1Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageDevelopmental stage
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for analyzing pore structure of solid material based on microscopic image
InactiveCN101639434ACalculated pore sizeCalculate porosityPermeability/surface area analysis3D-image renderingPorosityMicroscopic image
The invention provides a method for analyzing the pore structure of solid material based on microscopic image, belonging to the technical field for analyzing the pore structure of the solid material.The method is characterized of: obtaining the CT single cross section image of the solid material by microscopic CT scanning; using computer language to digitally image process the CT single cross section image; taking the pixel side of the image as the size of hole diameter; computing the hole diameter of the solid material, porosity and change regularity of the hole diameter and the porosity based on the microscopic CT single image; selecting the CT single image after processing a plurality of digital image; generating a CT image sequence; three dimensionally rebuilding the CT single image with a volume rendering algorithm in a visual rebuilding algorithm; generating the three dimensional digital image of the solid material; and computing the hole diameter of the solid material, the porosity and the change regularity of the hole diameter and the porosity based on the microscopic CT single image. The method is widely used for analyzing and computing the hole size and the porosity of the solid material under the various hole sizes of the solid material.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
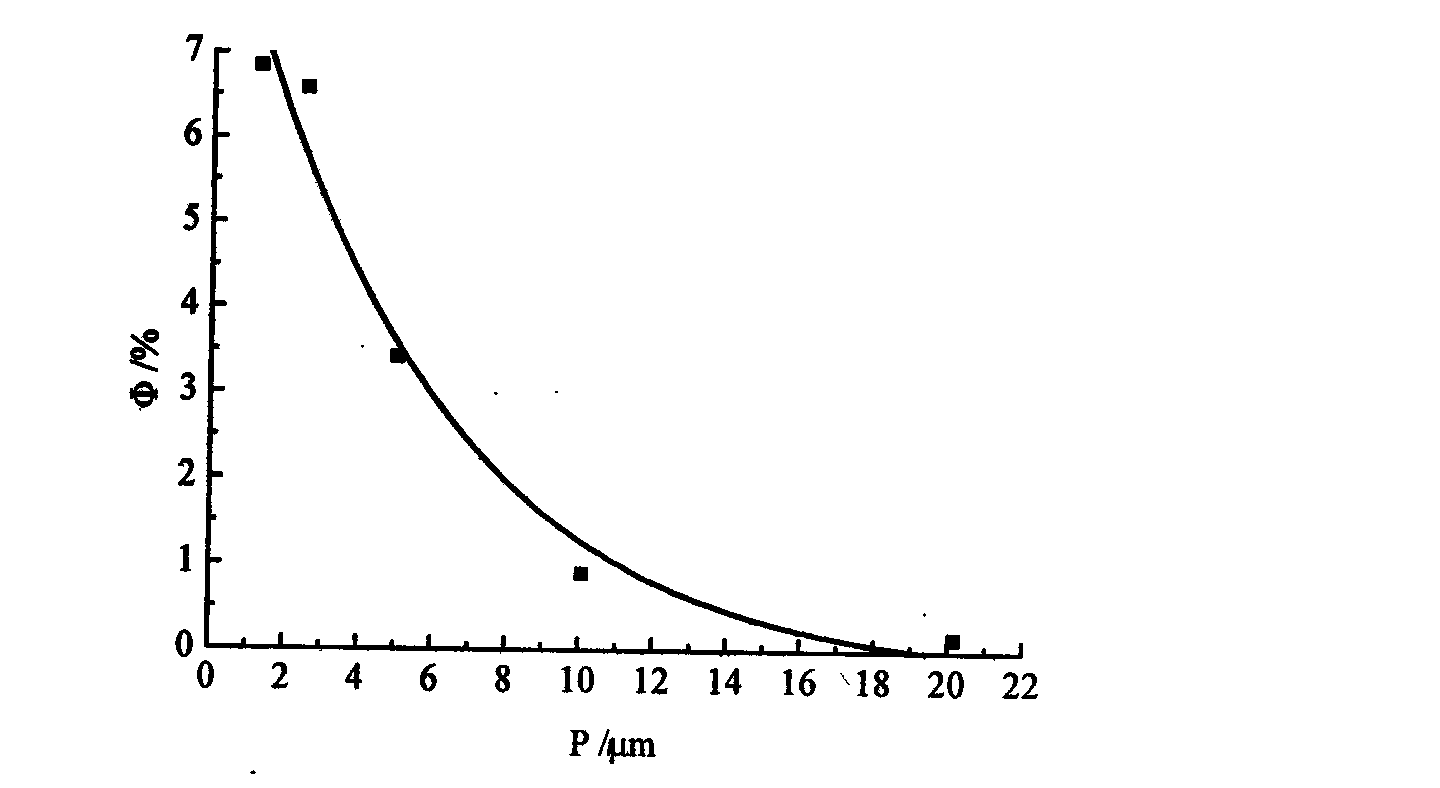
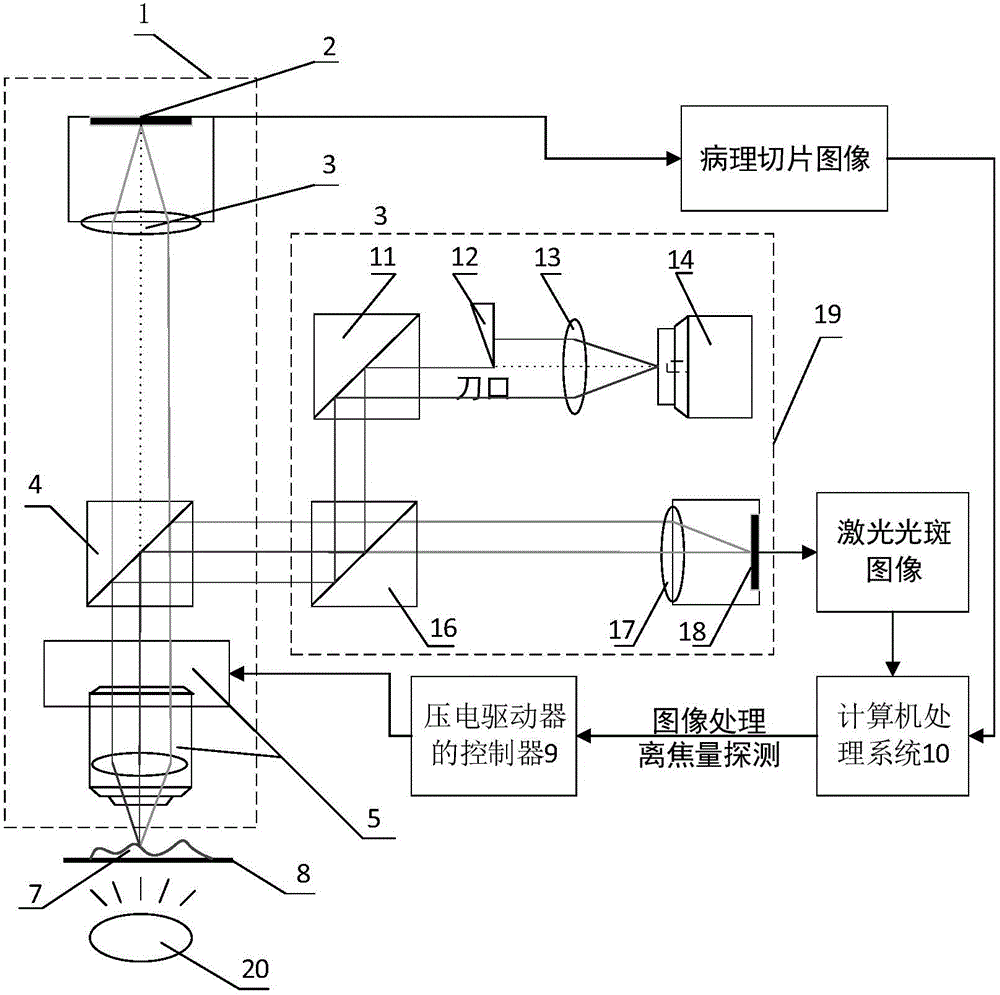
Automatic focusing microscope based on eccentric beam method and focusing method thereof
ActiveCN104932092AImprove noise immunityHigh precisionMicroscopesMicroscopic imageLinear relationship
The invention discloses an automatic focusing microscope based on an eccentric beam method and a focusing method thereof. The hardware comprises an eccentric beam defocus amount detection module, a microscopic imaging module, a piezo lens drive, an XY stage and a computer processing system. The defocus amount detection module transmits a semicircular laser beam to irradiate the surface of a sample and acquire a semicircular spot image formed by sample reflection. The computer processing system uses self-adaptive median filtering, Canny edge detection based on OSTU, the least square fitting and other algorithms to process the grayscaled spot image to acquire spot radius. According to a radius-defocus amount linear relationship model, the sample defocus amount in a field of vision can be calculated. The piezo lens drive drives a lens to compensate the defocus amount. After focusing, the microscopic imaging module acquires a clear sample image. The automatic focusing microscope based on the eccentric beam method and the focusing method thereof, which are provided by the invention, have the advantages of fast focusing speed, high focusing accuracy and large linear range, and can meet the requirement of fast and precise focusing of the microscope under a high power lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
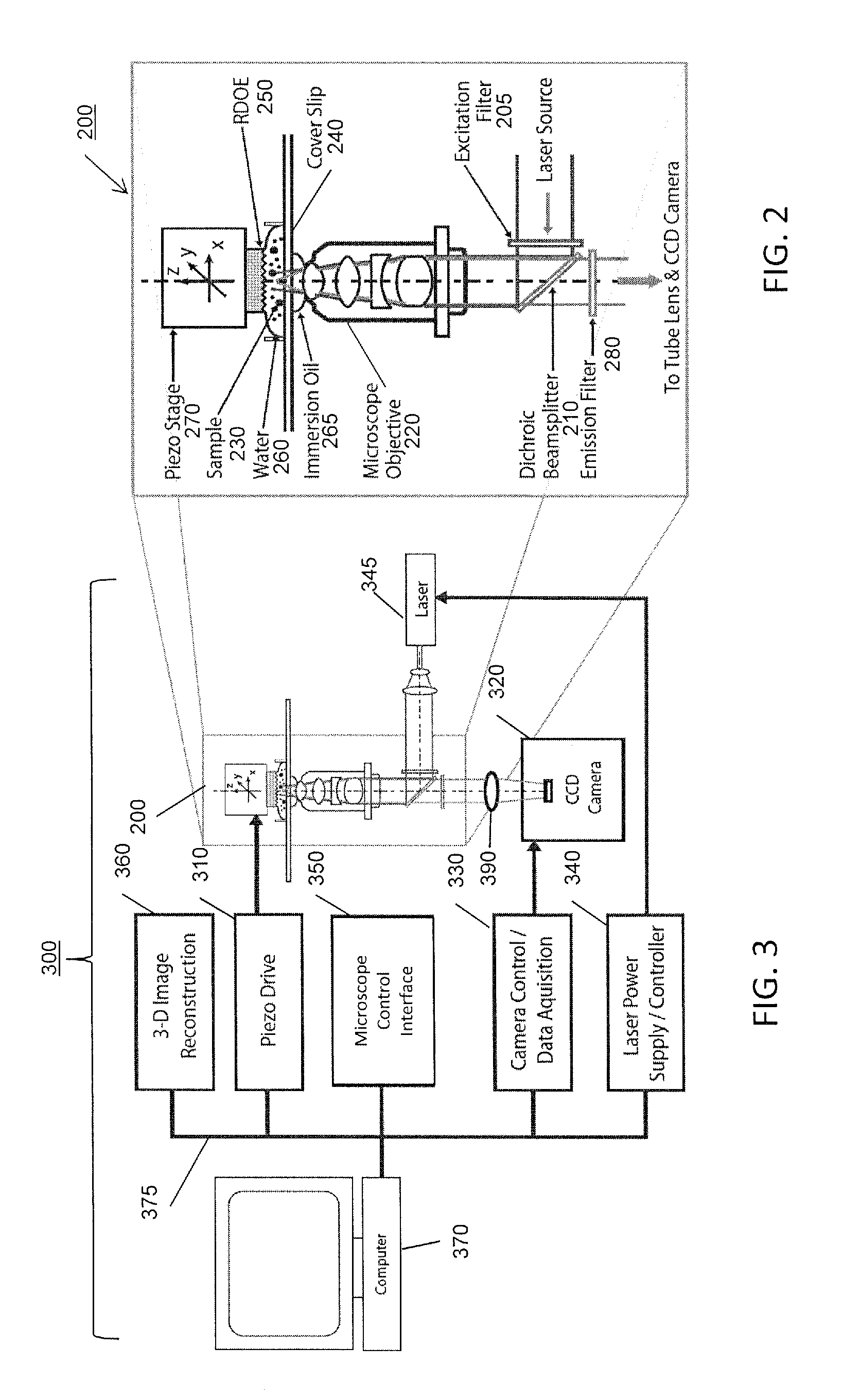
Omnidirectional super-resolution microscopy
InactiveUS20130093871A1Material analysis by optical meansColor television detailsMicroscopic imageImage resolution
A microscopy method and apparatus includes placing a specimen to be observed adjacent to a reflective holographic optical element (RDOE). A beam of light that is at least partially coherent is focused on a region of the specimen. The beam forward propagates through the specimen and is at least partially reflected backward through the specimen. The backward reflected light interferes with the forward propagating light to provide a three dimensional interference pattern that is at least partially within the specimen. A specimen region illuminated by the interference pattern is imaged at an image detector. Computational reconstruction is used to generate a microscopic image in all three spatial dimensions (X,Y,Z), simultaneously with resolution greater than conventional microscopy.
Owner:PHOTONANOSCOPY
Scanning tunnel microscope
PCT No. PCT / JP88 / 00804 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 5, 1990 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 5, 1990 PCT Filed Aug. 12, 1988 PCT Pub. No. WO89 / 01603 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 23, 1989A scanning tunnel microscope is arranged by a combination of an optical microscope and a tunnel scanning unit. The scanning tunnel unit includes a probe held to be spaced apart from a sample placed on a sample table by a predetermined interval in an axial direction, and an actuator for axially moving the sample table and the probe to a tunnel region and relatively and three-dimensionally driving the sample table and the probe. An objective lens and the probe are arranged such that the axis of the probe of the scanning tunnel unit is aligned with an optical axis of the objective lens of the optical microscope. The sample and the probe are axially moved and brought into the tunnel region, and the sample is scanned in its surface direction while the sample and the probe are finely moved in the axial direction and a tunnel current is kept constant, thereby performing an STM observation of an observation surface of the sample. The objective lens of the optical microscope is axially moved to obtain an in-focus state, and the field of the STM observation surface is observed as an optical microscopic image through an eyepiece lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
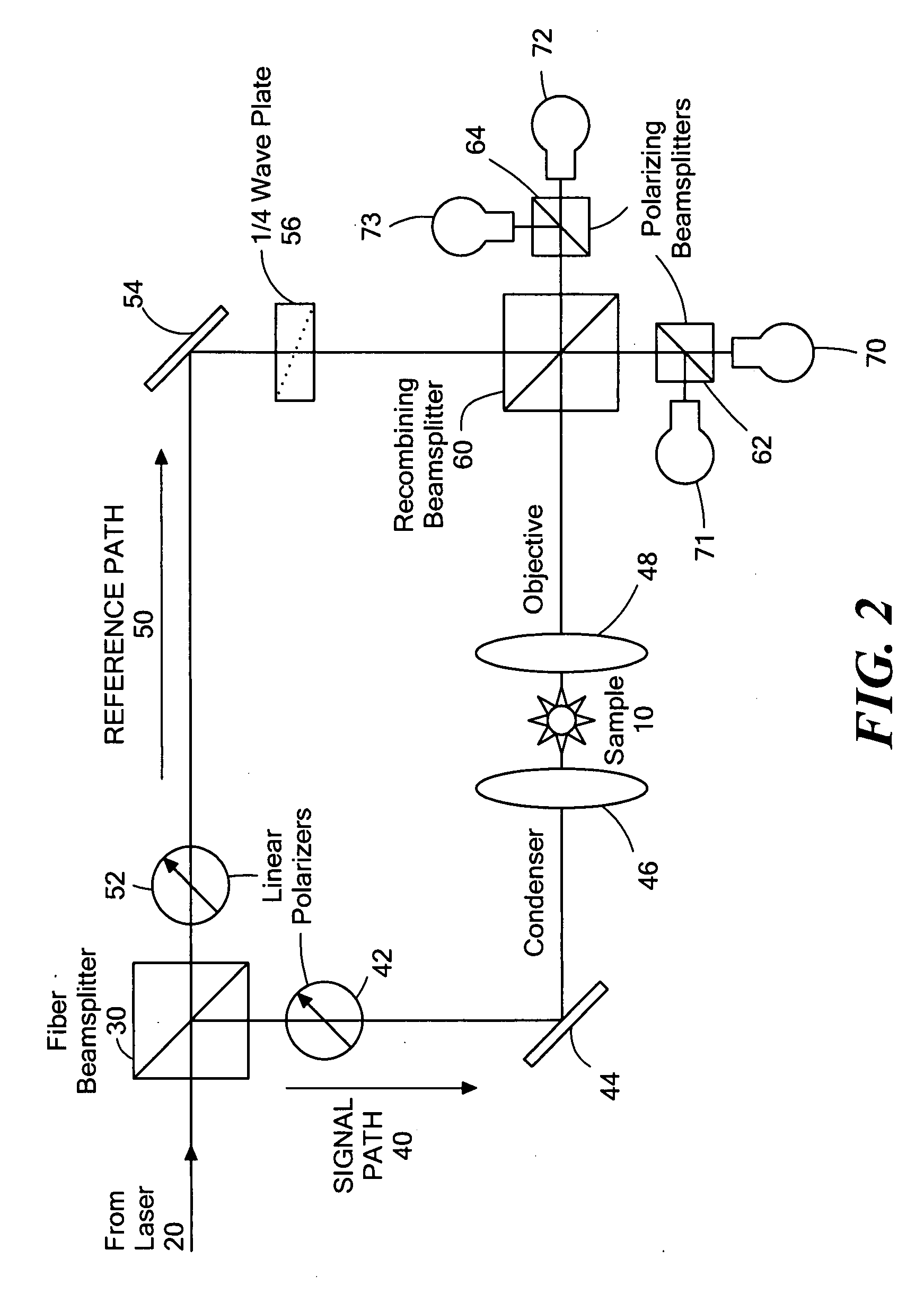
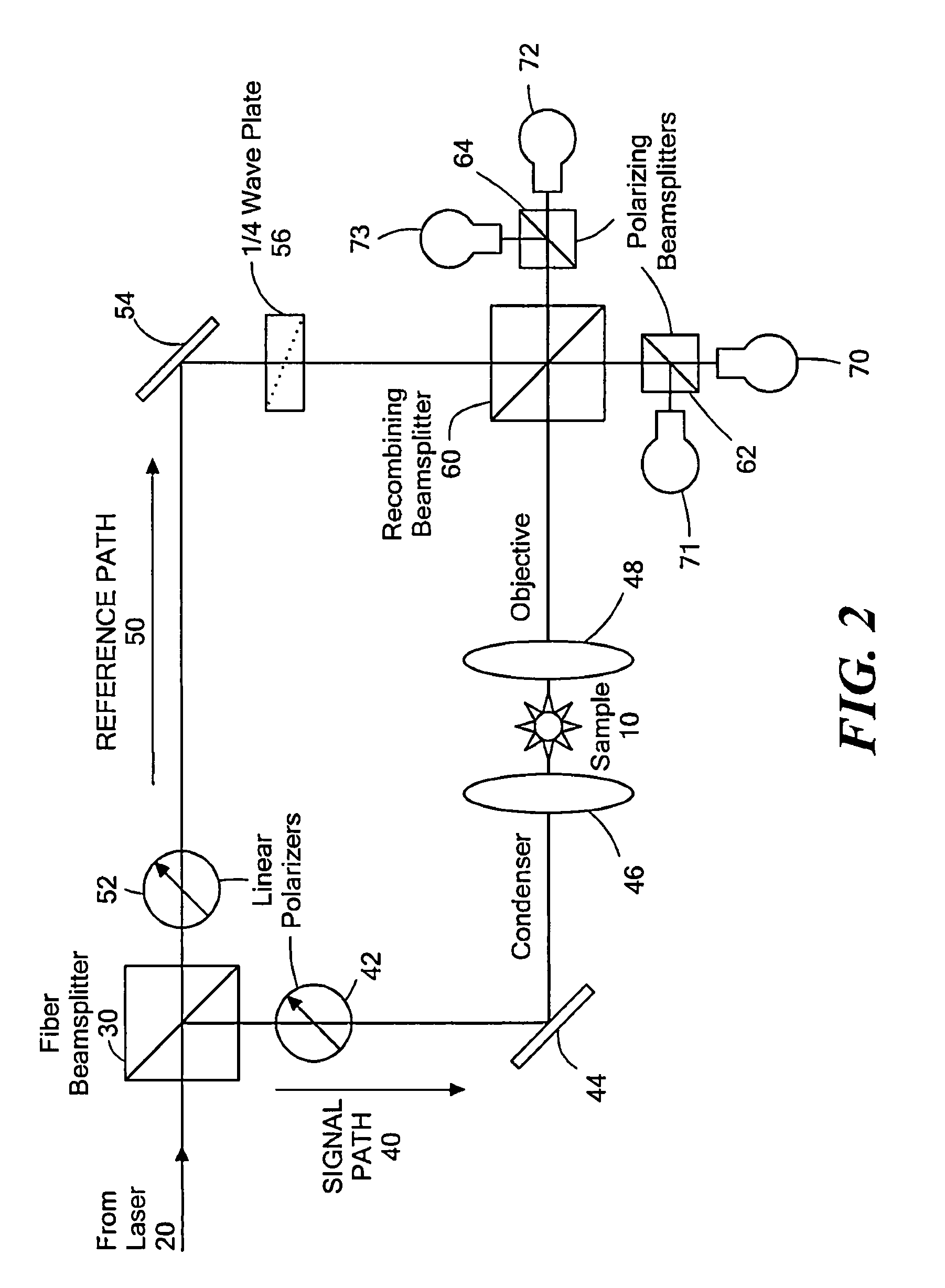
Differential interference contrast microscope and microscopic image processing system using the same
InactiveUS6128127AEasy constructionLess expensiveMicroscopesUsing optical meansMicroscopic imageWavefront
A differential interference contrast microscope including an illuminating light source, a polarizer for converting an illumination light ray into a linearly polarized light, a polarized light separating unit for dividing the linearly polarized light ray into two linearly polarized light rays having mutually orthogonal vibrating directions, an illuminating optical system, for projecting the two linearly polarized light rays onto an object under inspection, a polarized light combining unit for combining the two linearly polarized light rays on a same optical path via an inspecting optical system, an analyzer for forming a differential interference contrast image on an imaging plane. The polarized light separating unit is constructed such that an amount of wavefront shear between the two linearly polarized light rays on the object can be changed, and the polarized light combining unit is arranged between the object and the analyzer at such a position that the two linearly polarized light rays propagate in parallel with each other and is constructed such that the two linearly polarized light rays can be combined with each other in accordance with the shear amount of wavefront introduced by the polarized light separating unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
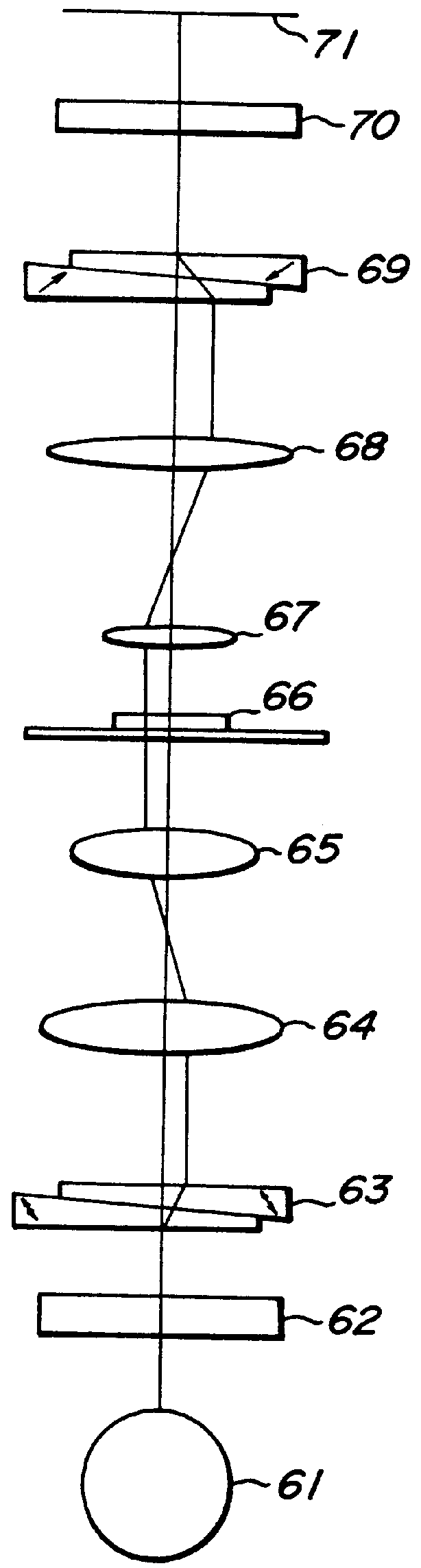
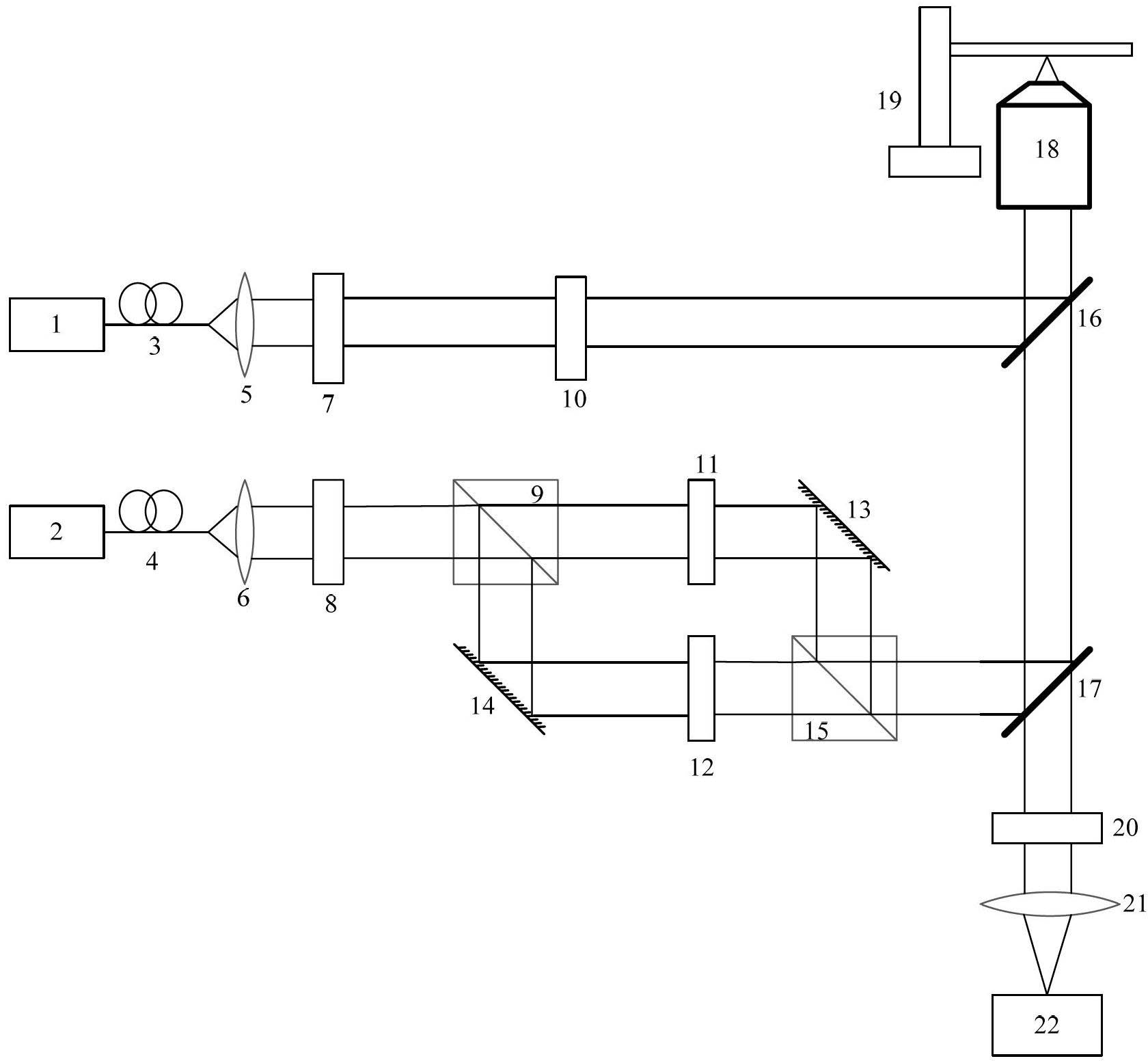
Three-dimensional optical coherence tomography confocal imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110310395A1Easy to useInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansCamera lensMicroscopic image
A 3D OCT confocal imaging apparatus includes a light source module for providing an illumination beam with wider bandwidth from a crystal fiber; a reference source module; a pickup module; a beam splitter; an optical filter; and a sensor module. When the illumination beam illuminates a sample, a pickup objective lens and a piezoelectric actuator of the pickup module together provide an image beam scanning the sample in depth direction. The image beam and a reference beam from the reference source module together form an interference image beam, which is converted by a photosensor into a coherence image electric signal. Meanwhile, the interference image beam passes through a pinhole to form a confocal image, which is converted by an excited light photometer into a confocal image electric signal. With an image processing system, a 3D OCT confocal microscopic image of the sample can be produced from these image electric signals.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for rapid microscopic image focusing having a movable objective
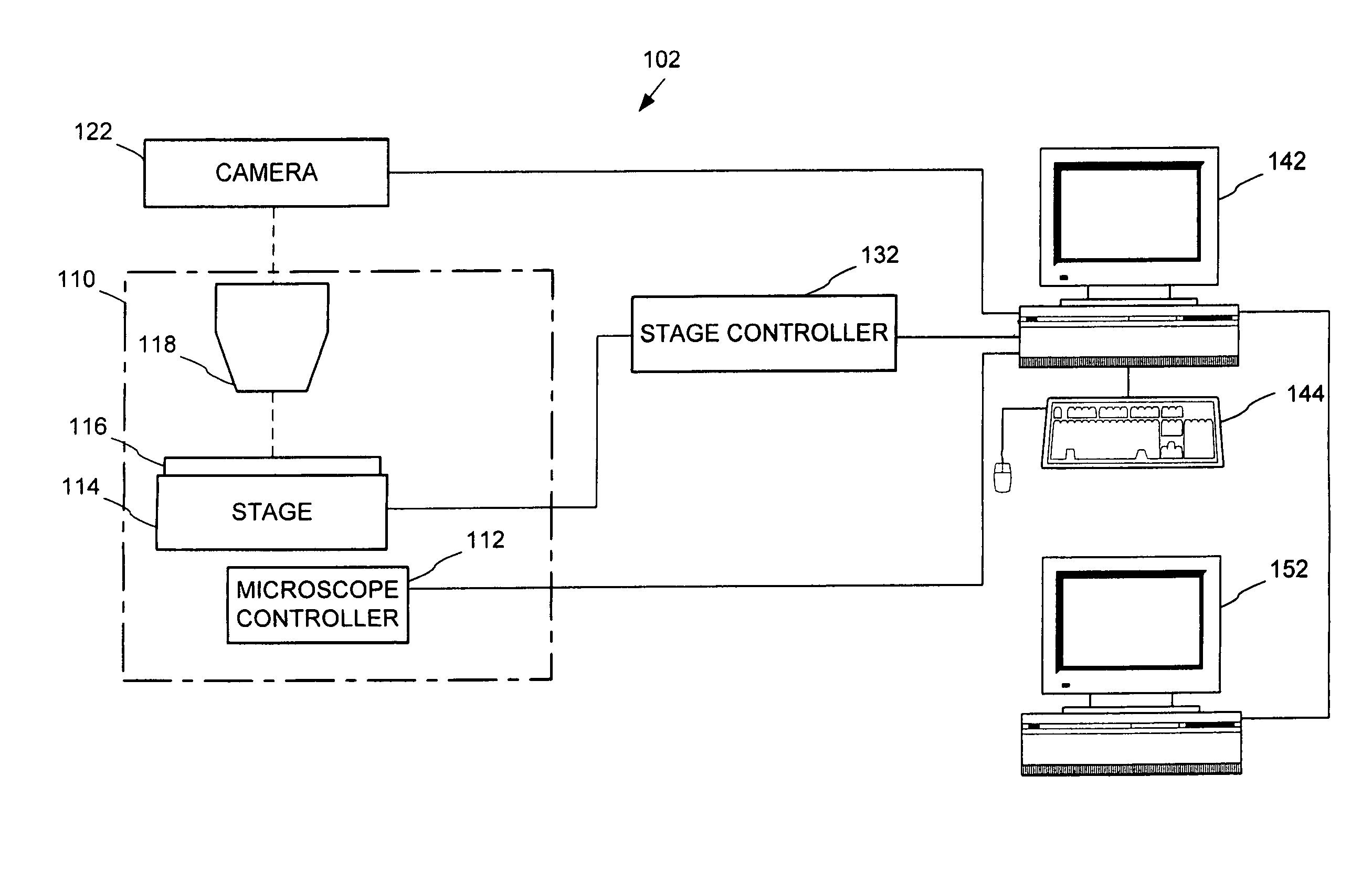
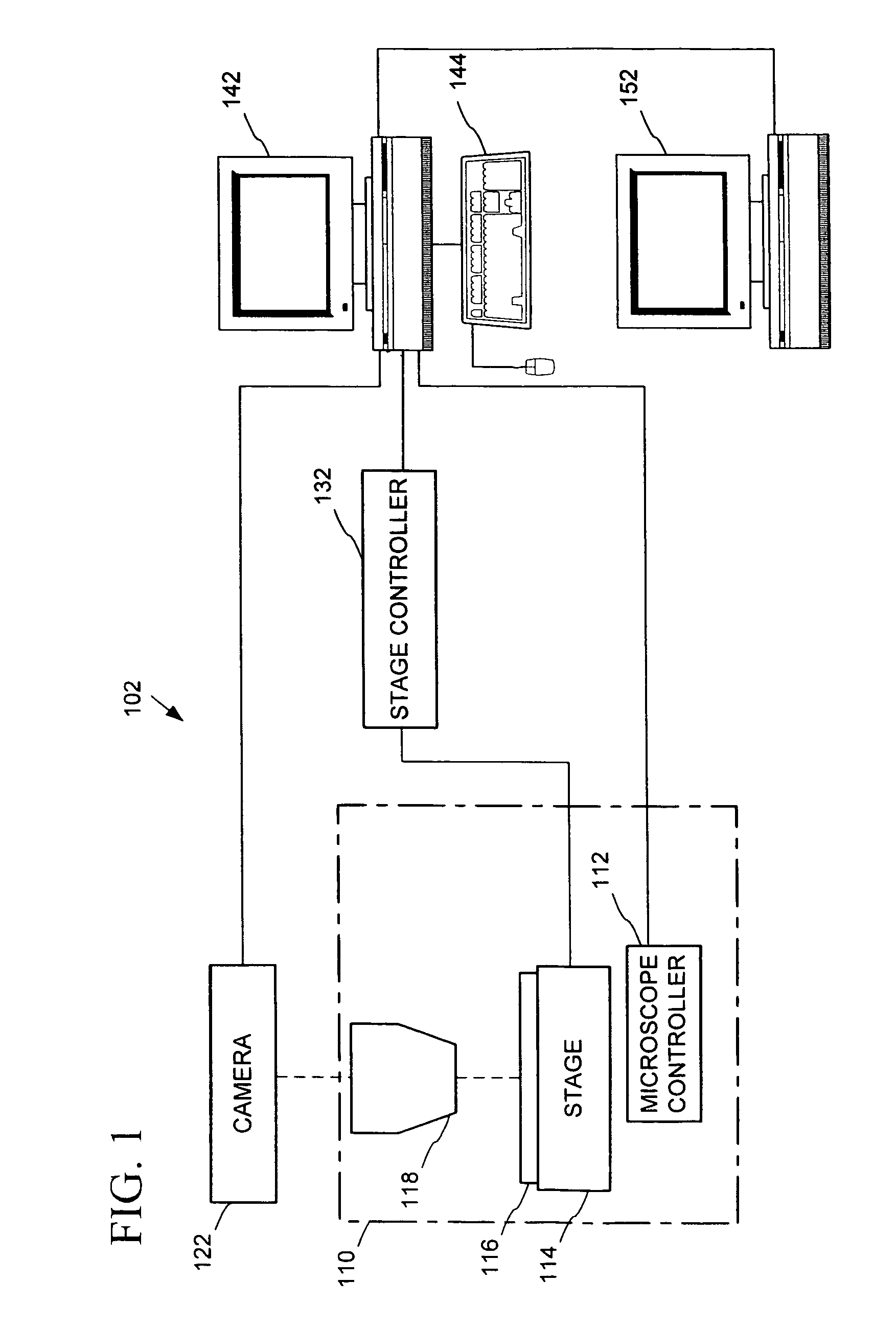
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Dynamic imaging of biological cells and other subjects
ActiveUS20070182959A1Quick observationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscopic imageMultivariate analysis
The invention relates to methods of dynamic chemical imaging, including methods of cellular imaging. The method comprises illuminating at least a portion of a cell with substantially monochromatic light and assessing Raman-shifted light scattered from the illuminated portion at a plurality of discrete times. The Raman-shifted light can be assessed at a plurality of Raman shift (RS) values at each of the discrete times, and the RS values can be selected to be characteristic of a pre-selected component at each of the discrete times. Multivariate analysis of Raman spectral features of the images thus obtained can yield the location and chemical identity of components in the field of view. This information can be combined or overlaid with other spectral data (e.g., a visible microscopic image) obtained from the field of view.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
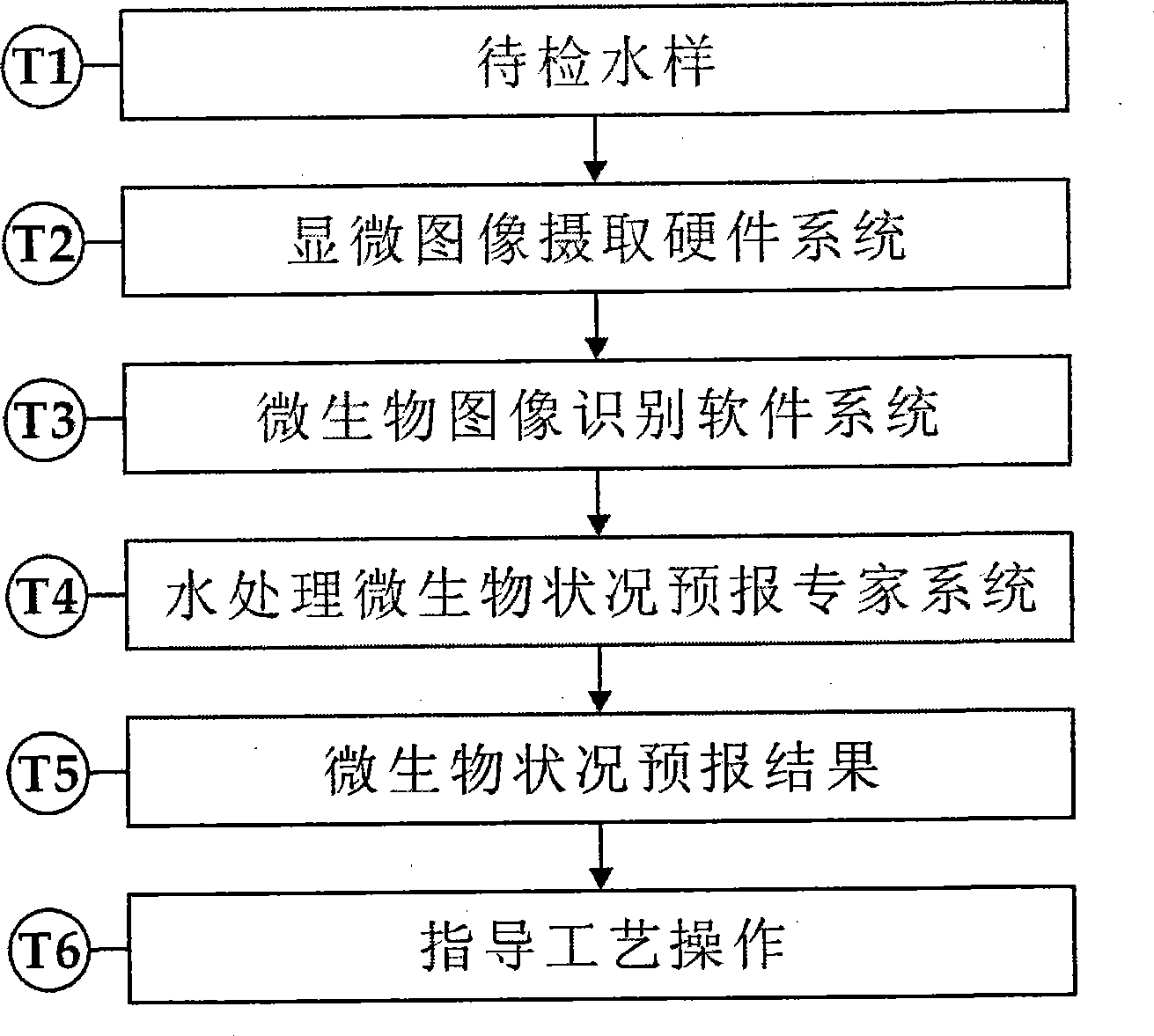
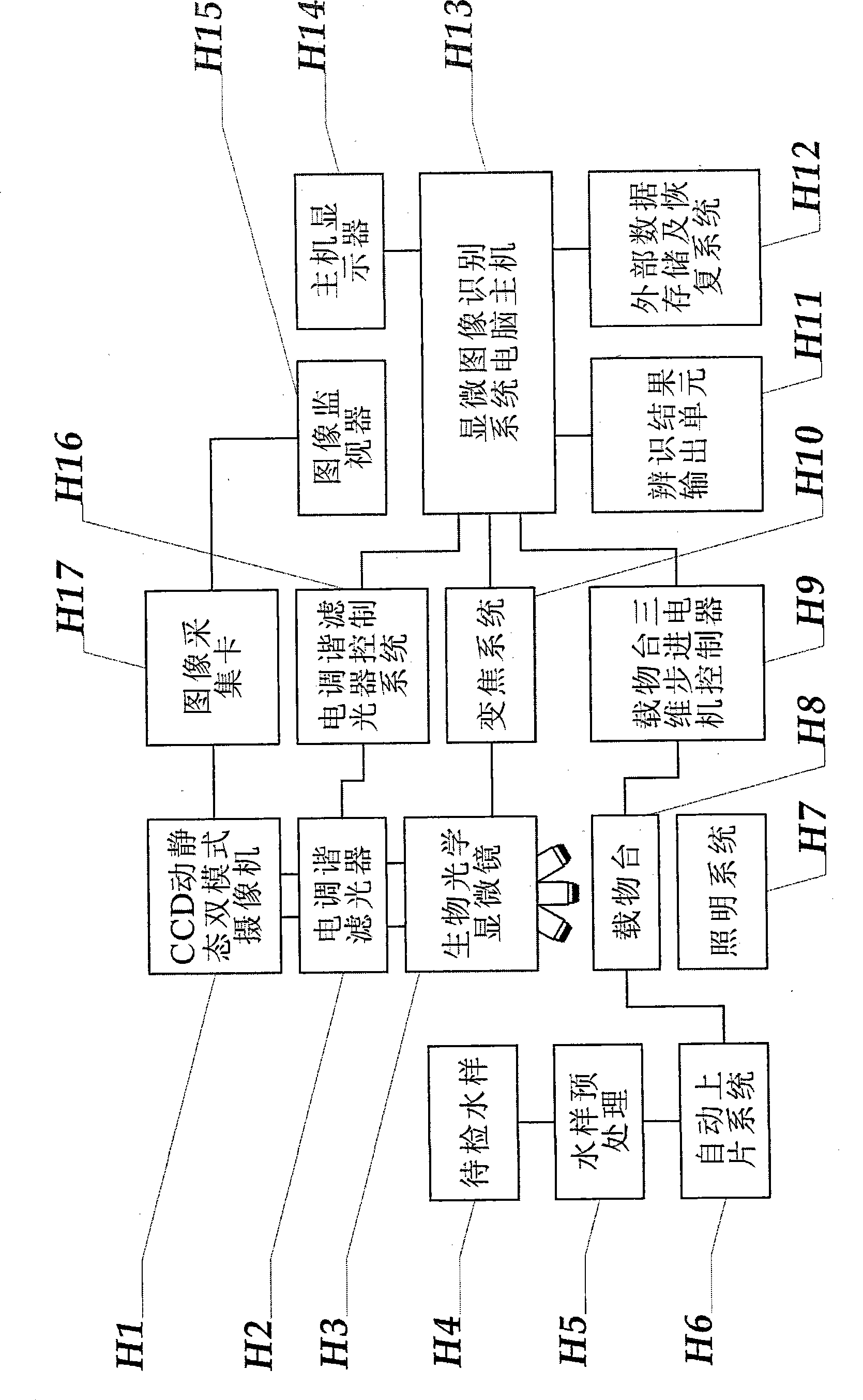
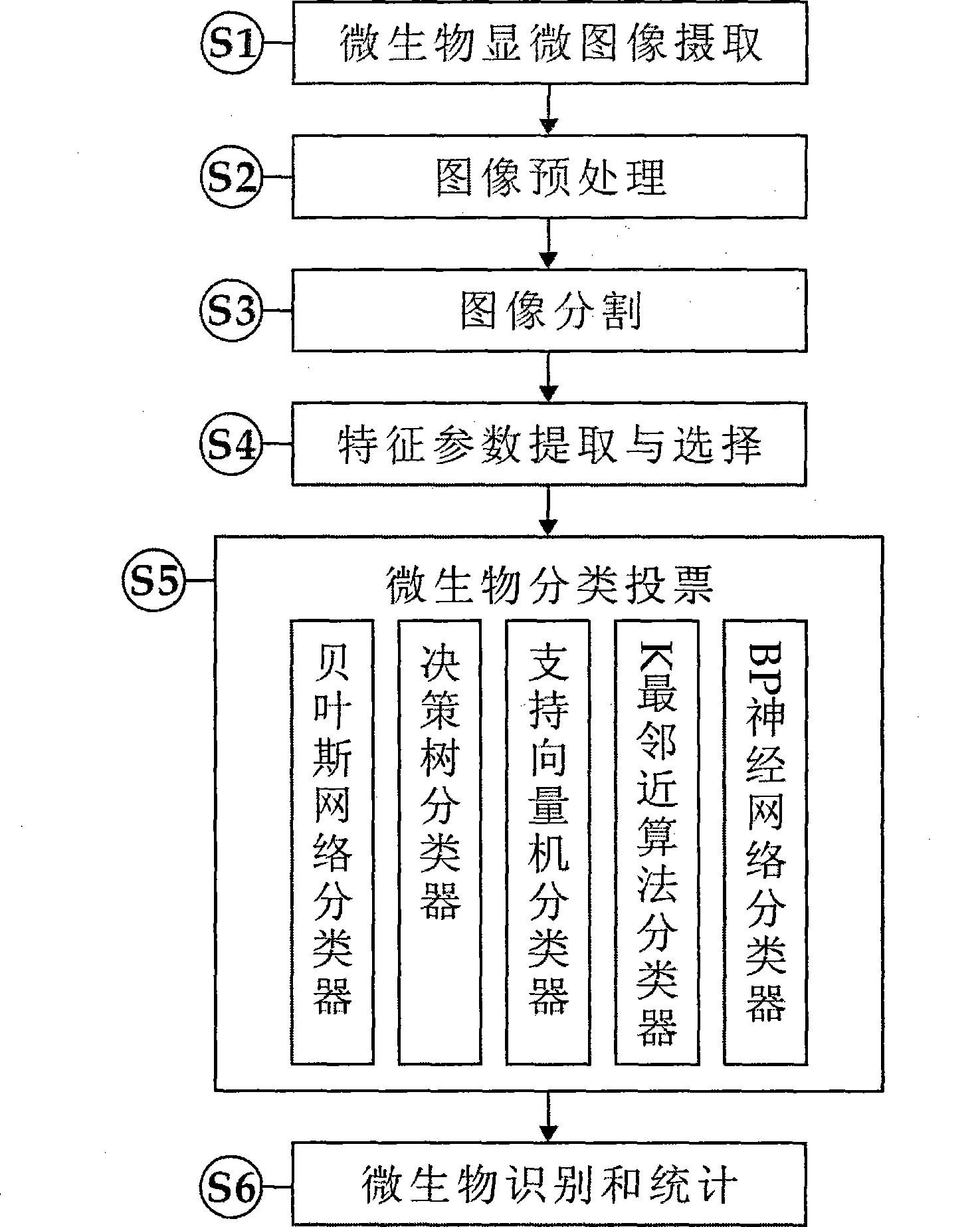
System and method for intelligent water treatment micro-organism machine vision identification
InactiveCN101477630AEasy to detectSimple dataTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageImage segmentation algorithm
The invention provides an intelligent water-treatment microorganism machine vision identification system and a method. By using artificial intelligent technology, the system and the method can real-timely shoot microscopic images of microorganism in water and carry out the steps of automatic image pre-treatment, image segmentation, microorganism characteristic parameter extraction and selection, and microorganism classification and identification. The system and the method have the advantages that optimal segmentation threshold value can be searched automatically in HIS color space by using self-adaptive image segmentation algorithm; and the classifier is designed in a voting manner to obviate the low classification accuracy by using single classifier so as to effectively improve the entire classification accuracy and accurately identify microorganisms in drinking water and urban domestic sewage. The implementation of the method can further shorten the microorganism detection period in the water treatment process and accurately predict the condition of the water-treatment microorganisms to allow the operators to take measures in time. Accordingly, the method and the system can powerfully ensure the safety of drinking water and the normal operation of urban domestic sewage treatment facility so as to achieve considerable economic and social benefits.
Owner:吴俊 +2
Method and device of stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy based on tangential polarized light
InactiveCN102661938AHigh resolutionSmall light emitting areaMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageFluorescence
The invention discloses a stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy method based on tangential polarized light. The stimulated emission depletion microscopy method comprises the following steps of: respectively converting a first laser beam and a second laser beam into first tangential polarized light and second tangential polarized light; projecting the first tangential polarized light onto a fluorescence sample to form an exciting light spot after phase modulation; decomposing the second tangential polarized light into a first working beam and a second working beam, and carrying out phase modulation on the first working beam and the second working beam to form a first STED beam and a second STED beam; projecting the first STED beam and the second STED beam onto the fluorescence sample to form a corresponding STED light spot through incoherence addition, wherein the central point of the STED light spot coincide with the central point of the exciting light spot to obtain a focusing light spot; and collecting fluorescence emitted by the fluorescence sample under the action of the focusing light spot, and obtaining a microscopic image after processing. The invention also discloses an STED microscopy device based on the STED microscopy method. According to the STED microscopy method and the STED microscopy device, a higher resolution can be realized under the same working light intensity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Apparatus and Method for Rapid Microscopic Image Focusing
A method of capturing a focused image of a continuously moving slide / objective arrangement is provided. A frame grabber device is triggered to capture an image of the slide through an objective at a first focus level as the slide continuously moves laterally relative to the objective. Alternatingly with triggering the frame grabber device, the objective is triggered to move to a second focus level after capture of the image of the slide. The objective moves in discrete steps, oscillating between minimum and maximum focus levels. The frame grabber device is triggered at a frequency as the slide continuously moves laterally relative to the objective so multiple images at different focus levels overlap, whereby a slide portion is common to each. The image having the maximum contrast value within overlapping images represents an optimum focus level for the slide portion, and thus the focused image. Associated apparatuses and methods are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Automated microscopic image acquisition compositing, and display
InactiveUS7305109B1Suppress mutationImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageAutomated microscopy
An automated microscope and computer system captures a set of images for a capture area in a plurality of focal planes. The images can then be integrated into composite images for browsing to simulate viewing an item, such as a biological sample, under a microscope. A corrective filter can be constructed from the images to avoid an effect called “tiling.” Before capture, variable focal plane error can be avoided by collecting z locations for a set of points in the capture area. During image browsing, entire composite images can be loaded into memory in compressed form. Compressed image portions can be pre-decompressed to avoid delay as a browsing user navigates throughout the composite images. Pre-decompression can be done by a thread separate from the thread performing navigation operations.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
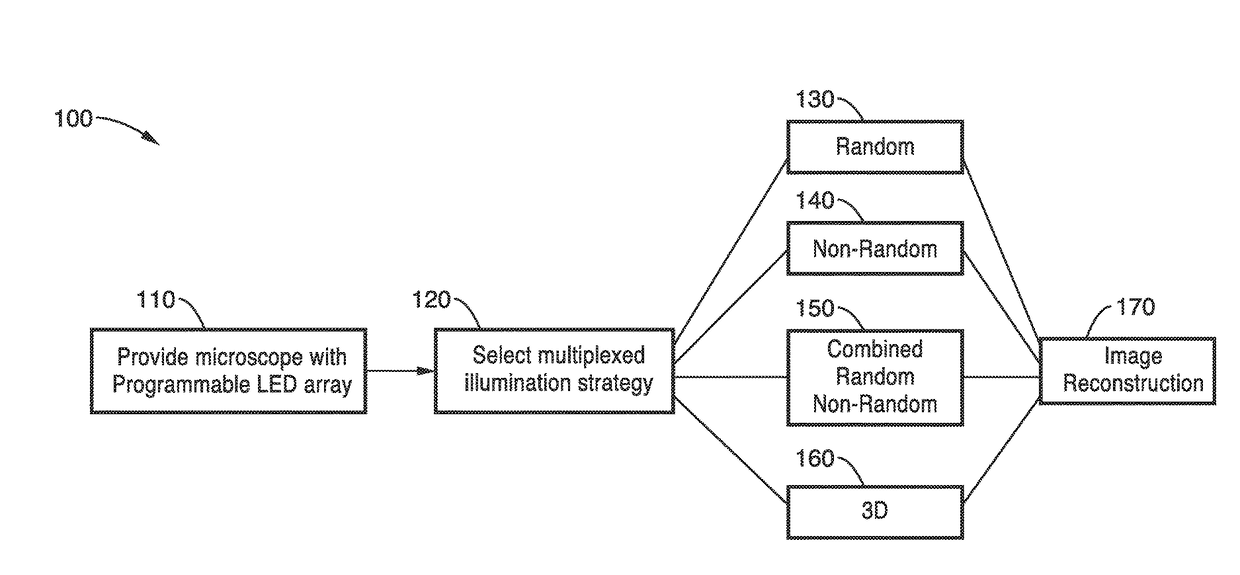
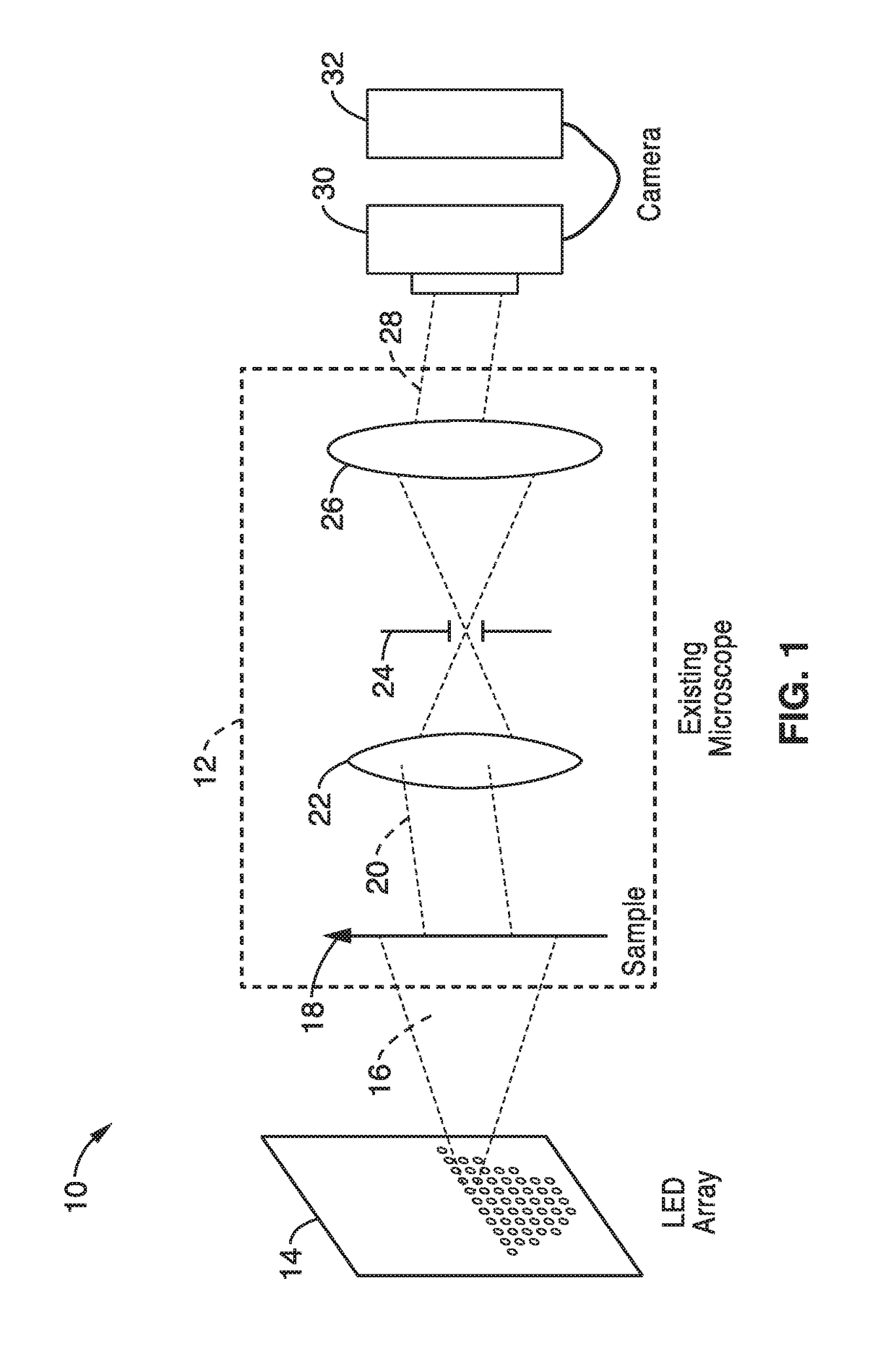
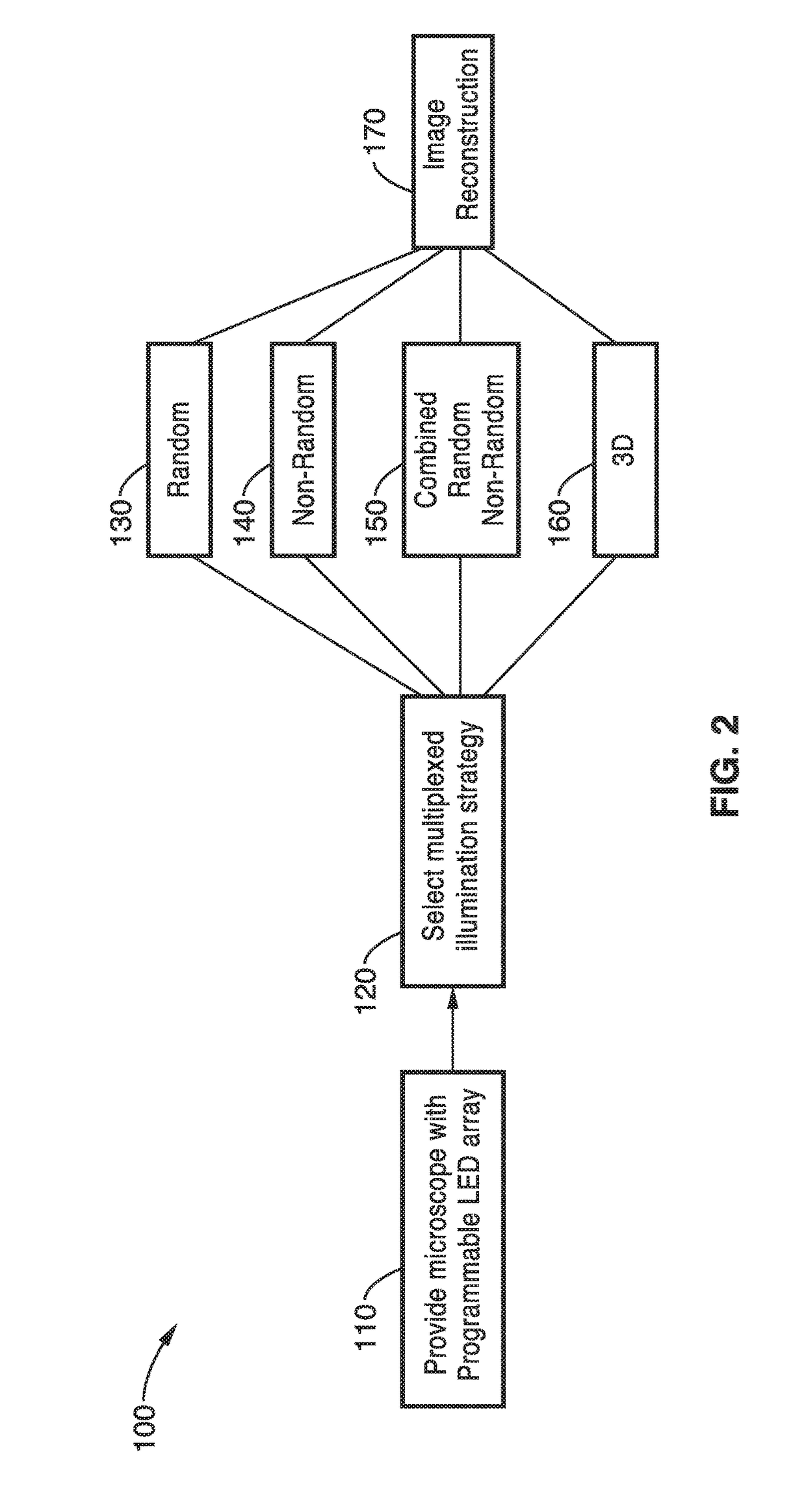
Fourier ptychographic microscopy with multiplexed illumination
InactiveUS20170146788A1Exploits redundancyFaster sample dynamicImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMicroscopic imageWide field
A system and methods for wide field of view, high resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopic imaging with a programmable LED array light source. The individual lights in the LED array can be actuated according to random, non-random and hybrid random and non-random illumination strategies to produce high resolution images with fast acquisition speeds. The methods greatly reduce the acquisition time and number of images captured compared to conventional sequential scans. The methods also provide for fast, wide field 3D imaging of thick biological samples.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
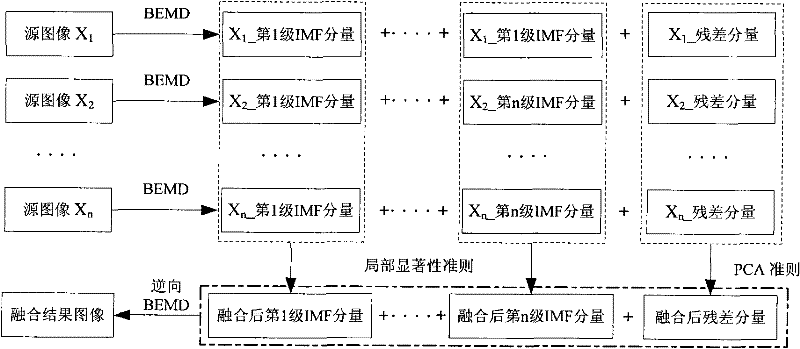
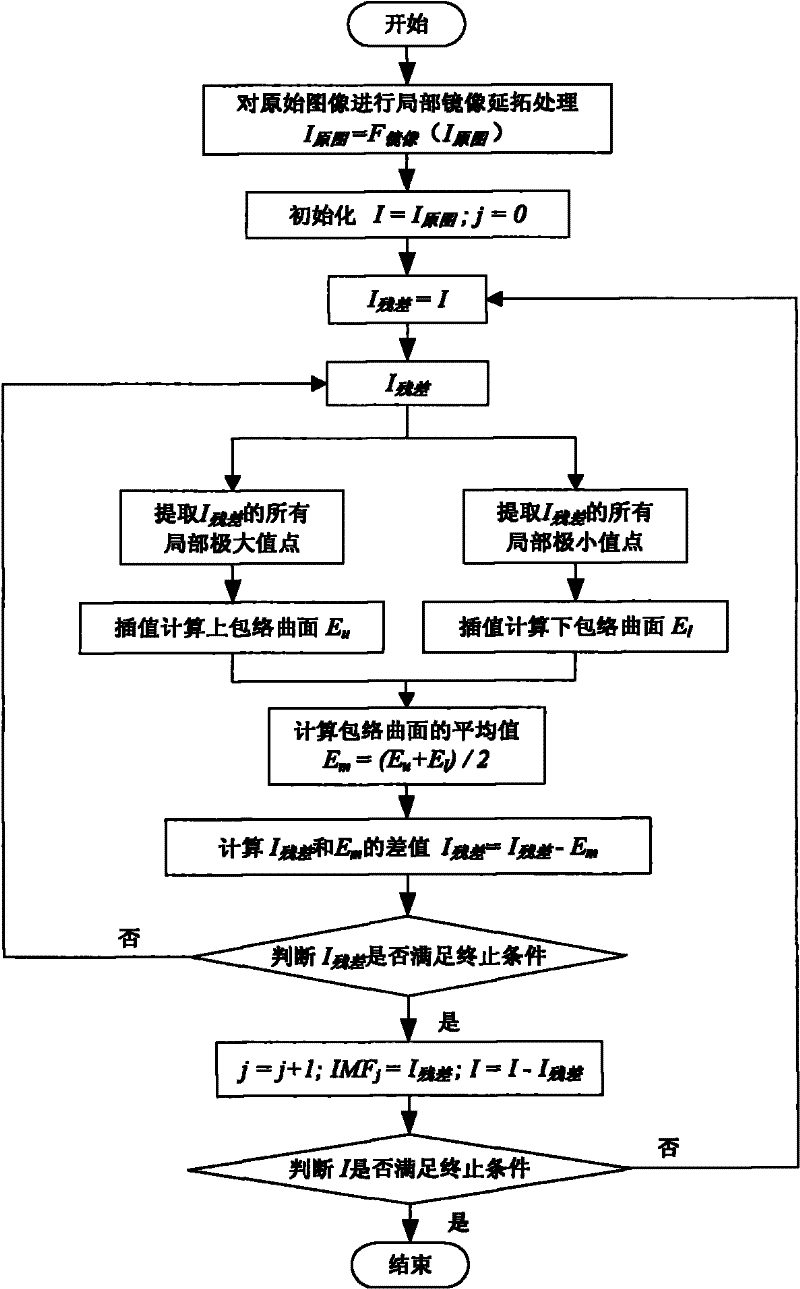
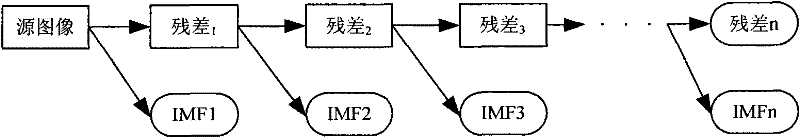
Microscopic image fusing method based on two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition
InactiveCN102129676AIncrease contrastImprove visual interpretationImage enhancementMicroscopic imageMultiscale decomposition
The invention relates to a microscopic image fusing method based on two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition, which comprises the following steps: performing multi-scale decomposition on the acquired ordered microscopic original images by using a two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition method, thereby acquiring the multi-scale high-frequency components of original images; fusing the multi-scale high-frequency components according to local obvious standard; fusing the low-frequency components of the original images by using a principal component analysis method; and finally reversely recomposing to acquire a merged image. By using the method provided by the invention, the multi-scale decomposition is performed on the acquired ordered microscopic original images by using the two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition method and the decomposition process is adaptive; high-frequency fusing treatment is performed according to the local obvious standard based on a big area value and the relevance between adjacent coefficients is considered, so the detail information clearly focused of each original image can be supplied; and the low-frequency fusing treatment is performed by using the principal component analysis method, so the relevant information of original image pixel is utilized and the visual decoding effect of the merged image is increased, thereby increasing the quality of the fused image.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
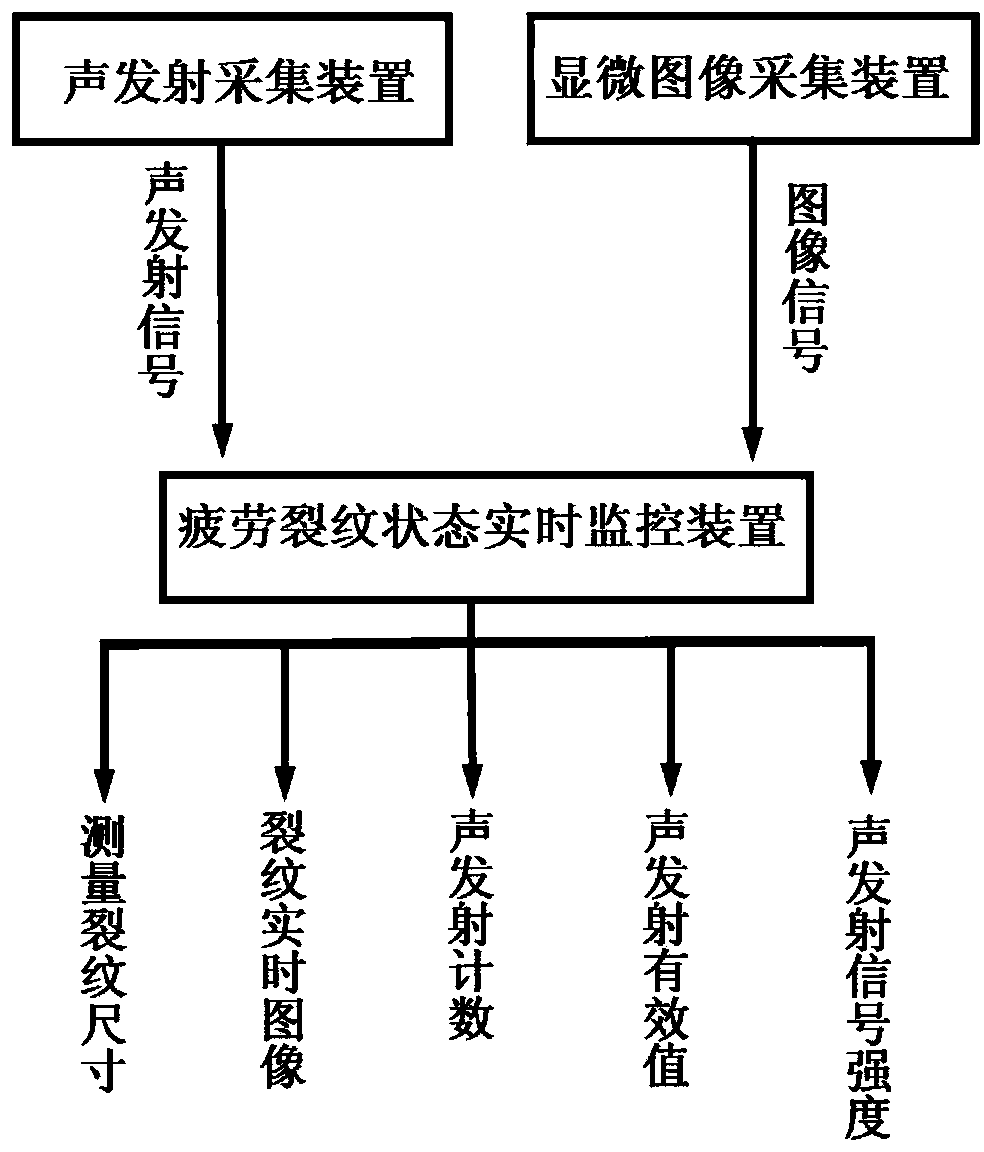
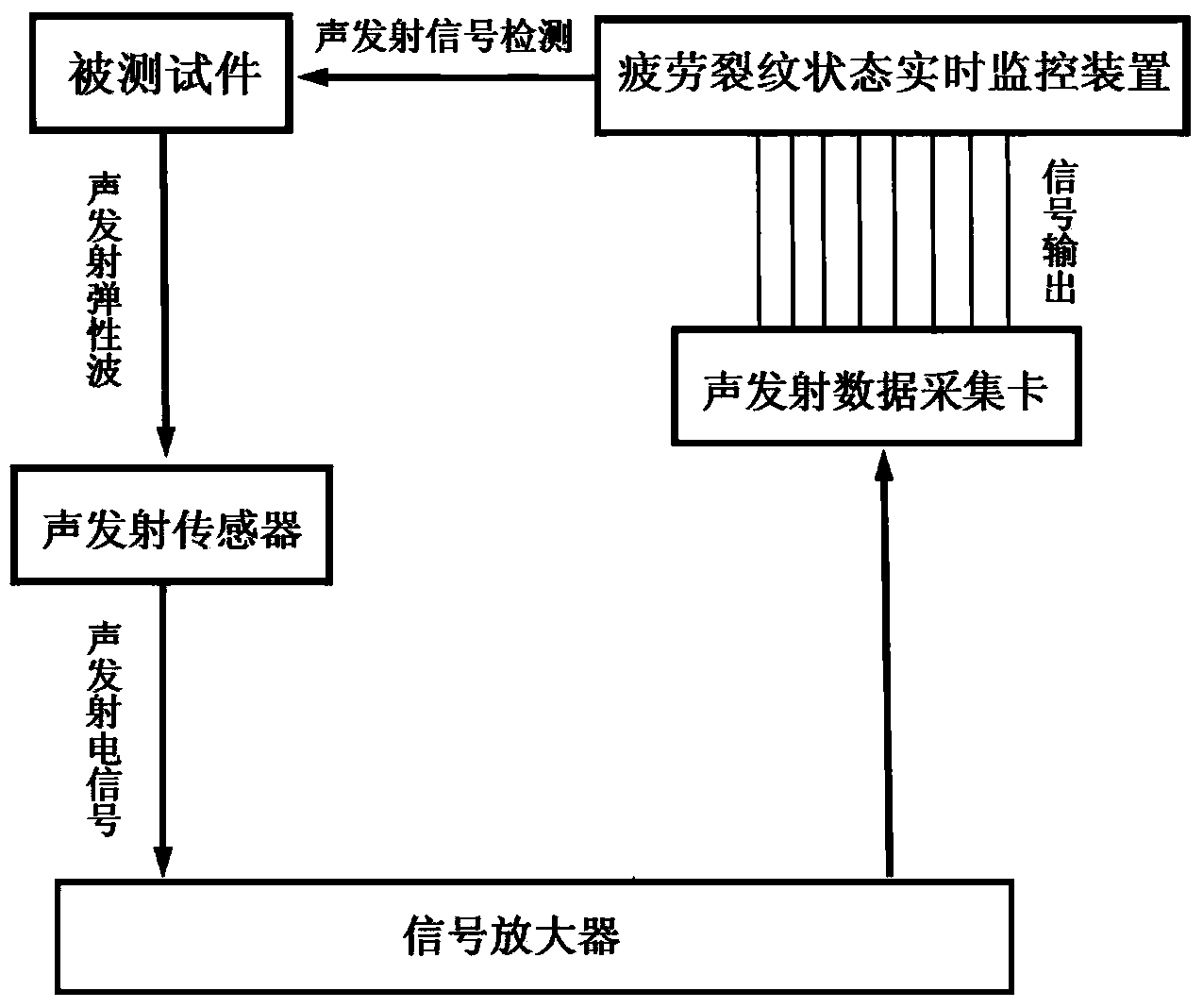
On-line fatigue crack detecting system and on-line fatigue crack detecting method
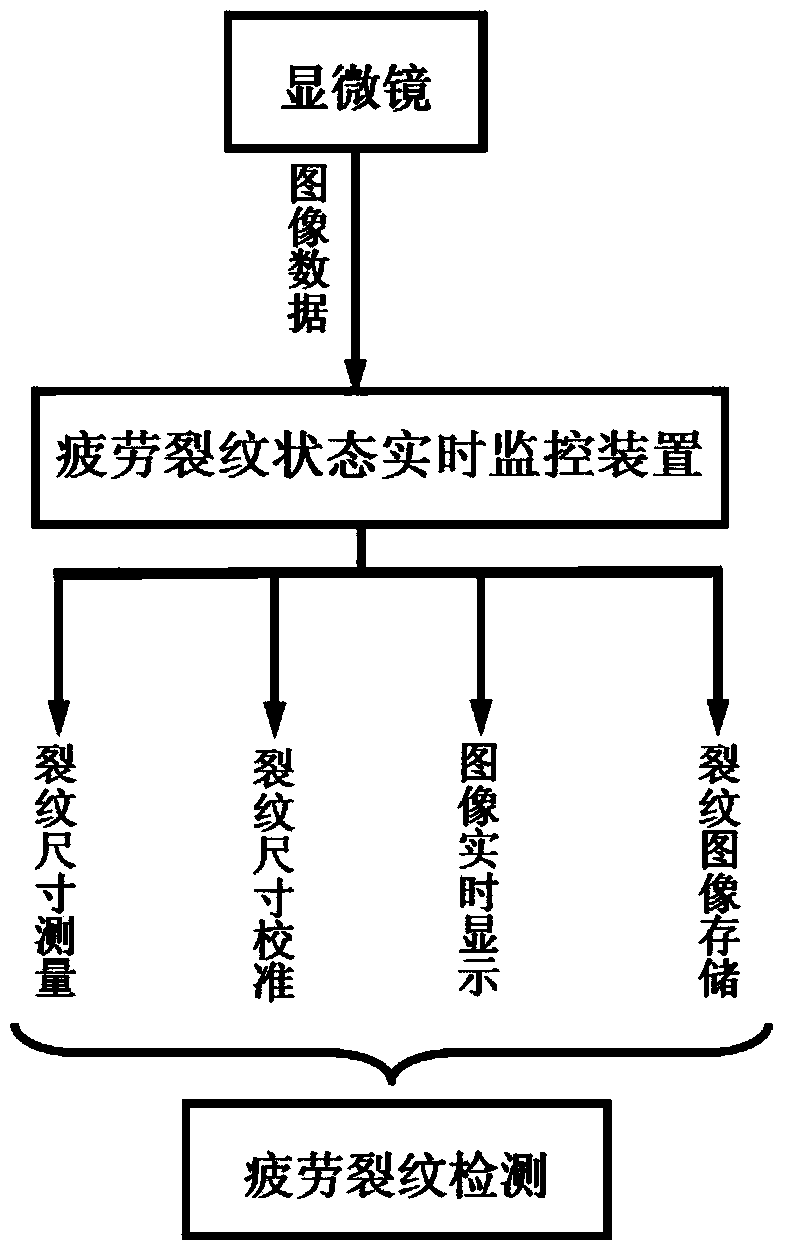
ActiveCN103529128ADetection of germination in real timeReal-time detection of scalabilityMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopic imageAcoustic emission
The invention discloses an on-line fatigue crack detecting system. The detecting system comprises an acoustic emission collecting device, a microscopic-image collecting device and a real-time fatigue crack state monitoring device. The acoustic emission collecting device collects acoustic emission signals of fatigue crack initiation and extension and release in real time. The microscopic-image collecting device collects image signals of fatigue crack states in real time. The real-time fatigue crack state monitoring device receives the signals from the acoustic emission collecting device and signals from the microscopic-image collecting device. A real-time fatigue crack state monitoring software, which is used to process the received signals and generates acoustic emission characteristic parameters, images and crack dimension data of a fatigue crack changing process, is disposed in the real-time fatigue crack state monitoring device. The invention also provides an on-line fatigue crack detecting method. The detecting system and the detecting method can achieve on-line dynamic real-time detection of fatigue crack initiation and extension.
Owner:TIANJIN ENG MACHINERY INST
Five-dimensional fluorescent microscope imaging technique
InactiveCN1737536AMeasurable fluorescence lifetimeImprove spatial resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageFluorescence
This invention relates to one method to acquire biology spectrum information and life information and to realize three-dimensional imaging. The invention is characterized by the following: getting multi-photon or single photon triggering of five-dimensional fluorescent microscope imaging information, that is three-dimensional space, one dimensional time and spectrum. This multi-parameter compound measurement and technique, which can satisfy the needs of different layers in study and can realize the flexible made three-dimensional spectrum for measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Digital interactive laboratory
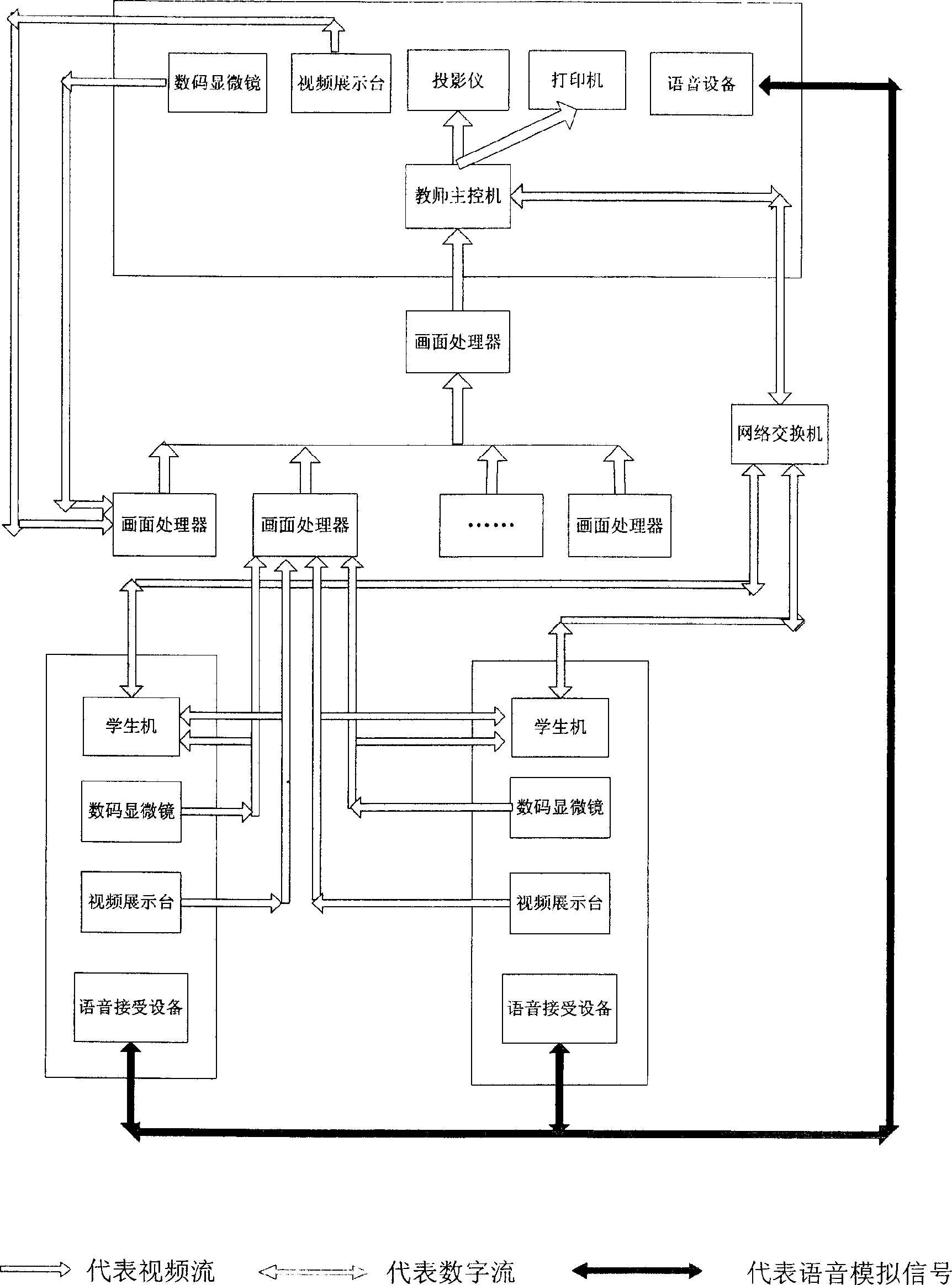
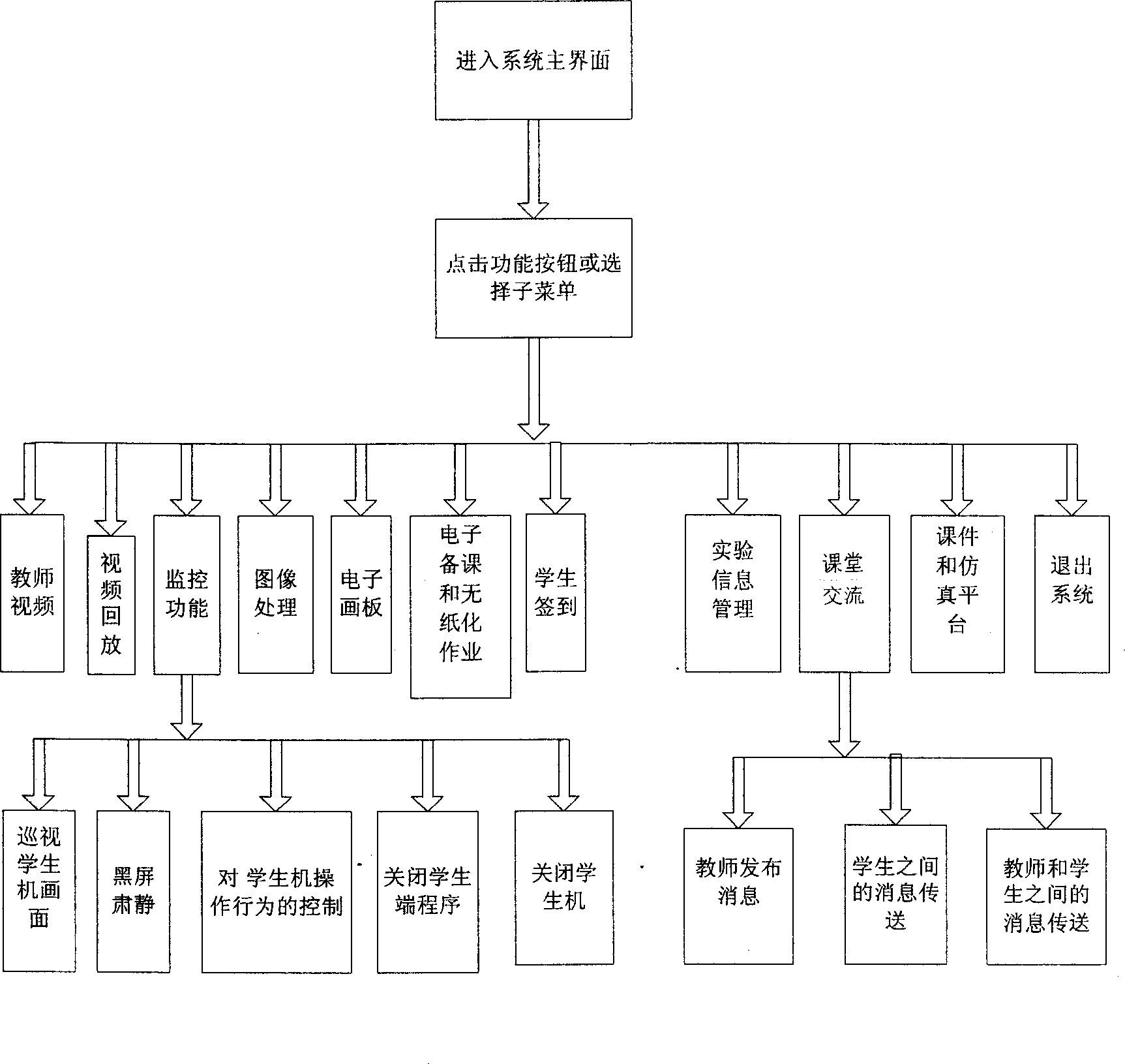
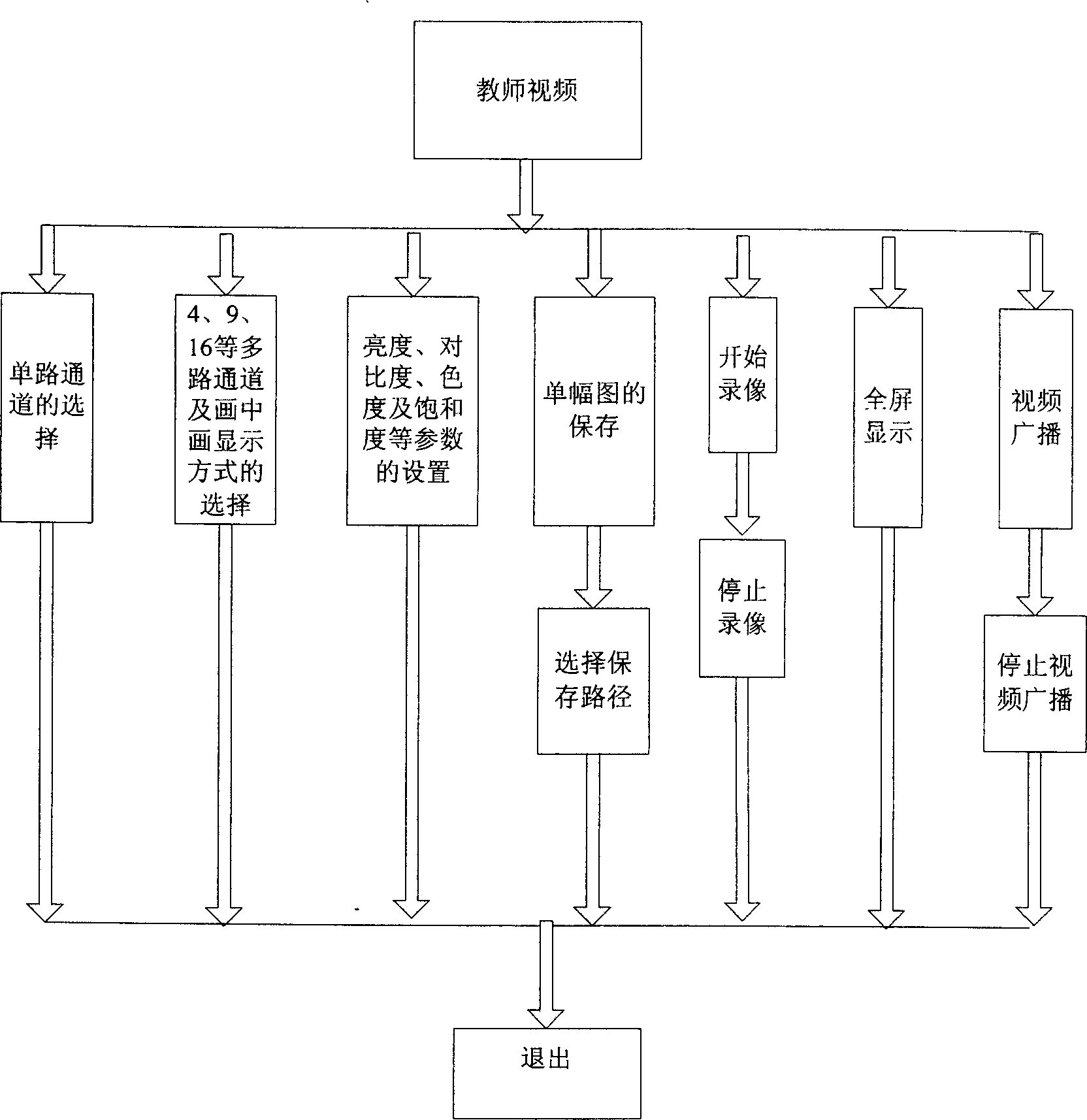
InactiveCN1598893AReduce workloadExercise thinkingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicroscopic imageSystems management
The invention relates to a digital interaction laboratory which is made up with teacher controlling station, student controlled station, network switch and more than one menu processors. The teacher controlling station includes teacher controlling computer, image collection device, image output device and voice equipments. The student controlled station includes student computer, image collection device and voice equipments. Adopting the invention, interaction experiments teach of biology, physics and chemistry can be made. The invention can transfer and broadcast real-time active images of each kind of imaging equipments and memorize these images. Also it can supervise images displayed in students' terminal image collection equipment, running state of student computer and students' action. Using the invention, teacher can instruct students to observe microscopic images and kinds of science experiments process, communicate with students using voice, words and images. The teacher can conduct multiple analysis and treatment to realize teacher's electronic preparation and lessons and students' no-paper work. The system can conduct system manage to kinds of information in laboratory and self define format of experiment report.
Owner:北京清大德人科技有限公司
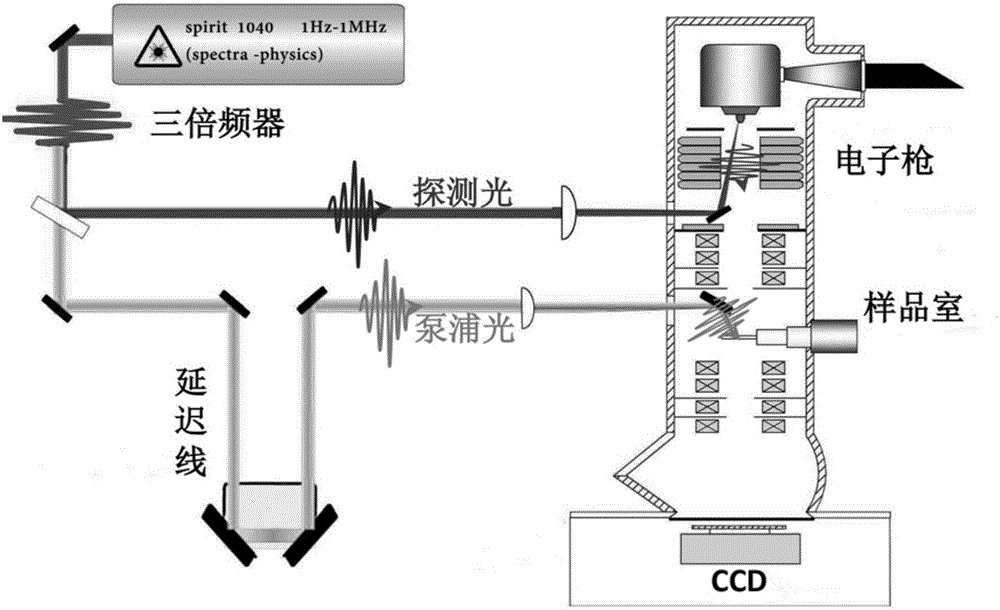
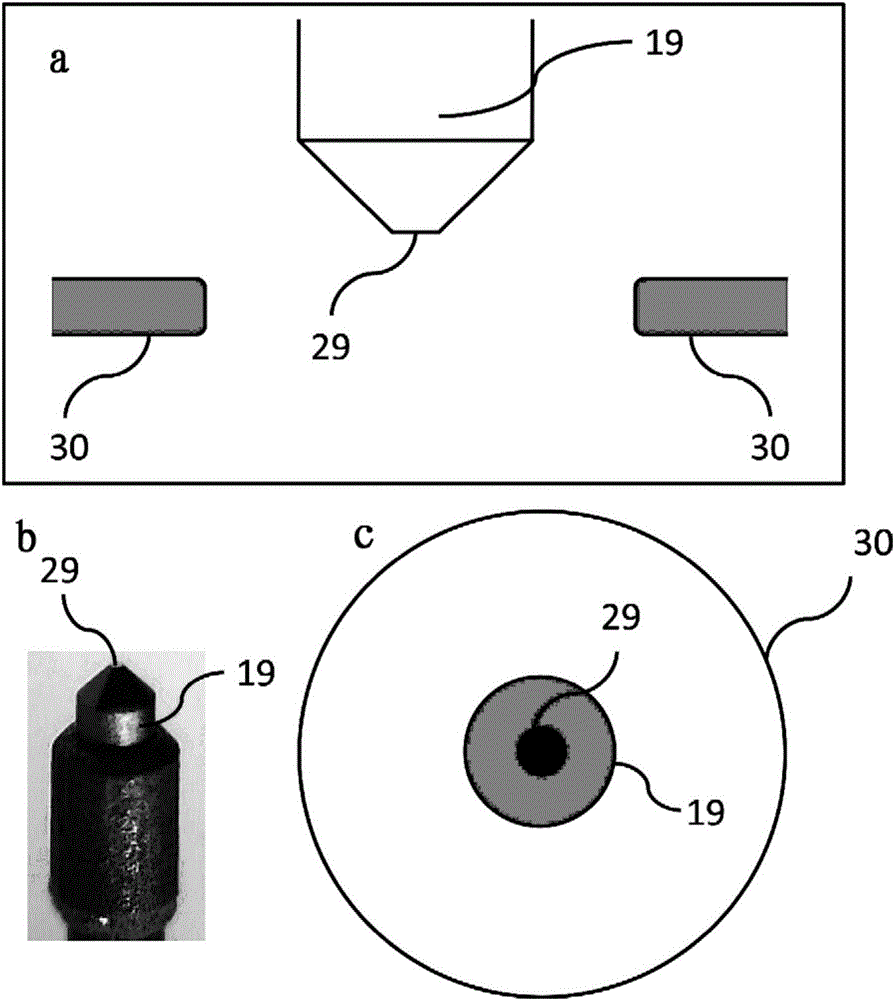
Ultra-fast transmission electron microscope system and use method thereof
ActiveCN106645236AMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionConventional transmission electron microscopeMicroscopic image
The invention provides an ultra-fast transmission electron microscope system which comprises an ultra-fast laser system, an electronic gun, an illuminating system, an imaging system, a sample chamber, a detector and a vacuum device, the ultra-fast transmission electron microscope system can particularly test ultra-fast structure change processes of samples under different laser parameters and environmental temperature, the different laser parameters include different excitation wavelengths, pulse width, laser power, repetitive frequency, sample temperature and the like, acquired signals comprise diffraction, microscopic images, energy loss spectroscopy and the like, and the ultra-fast structure change processes are analyzed by analyzing position and strength of diffraction peaks, image contrast change and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
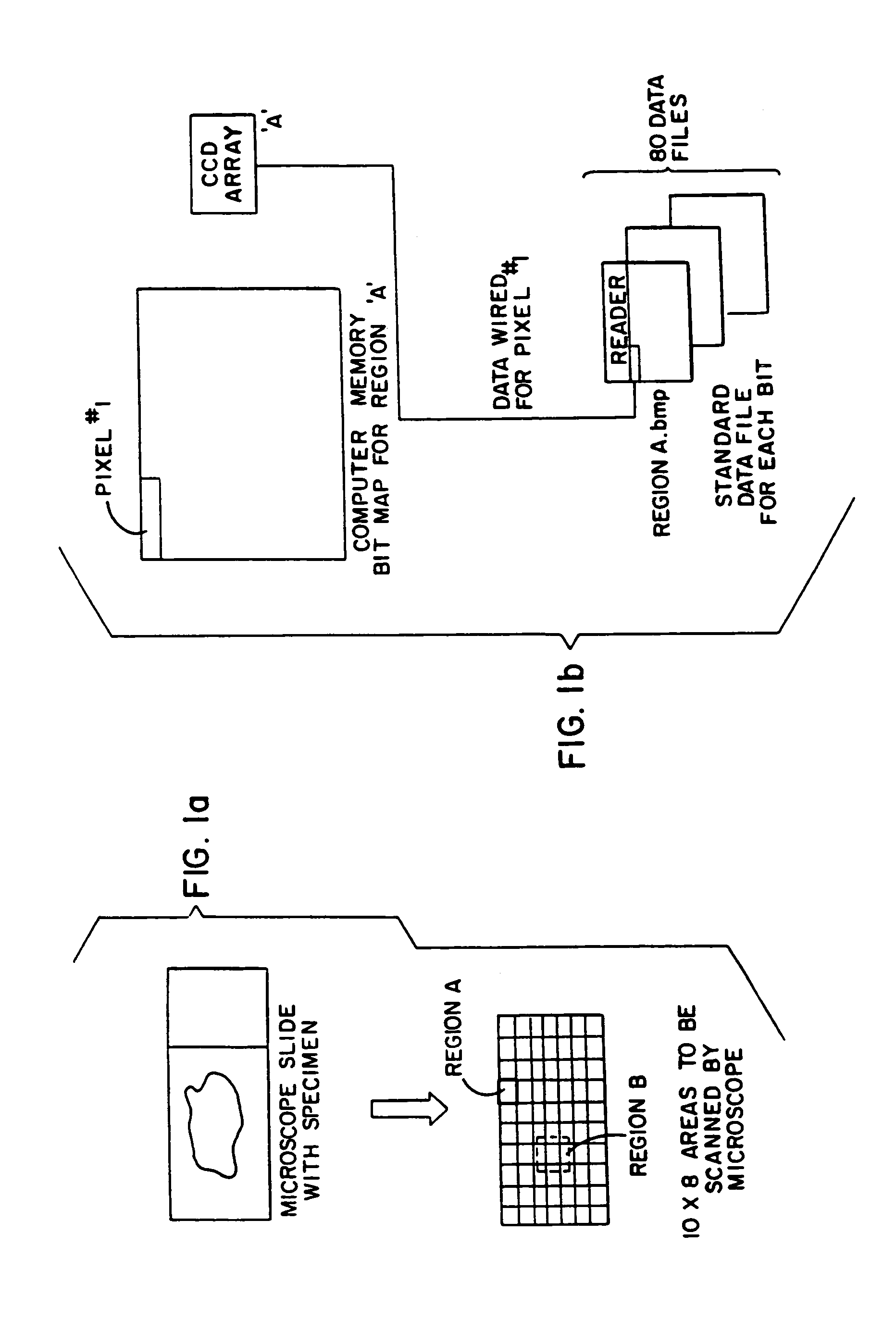
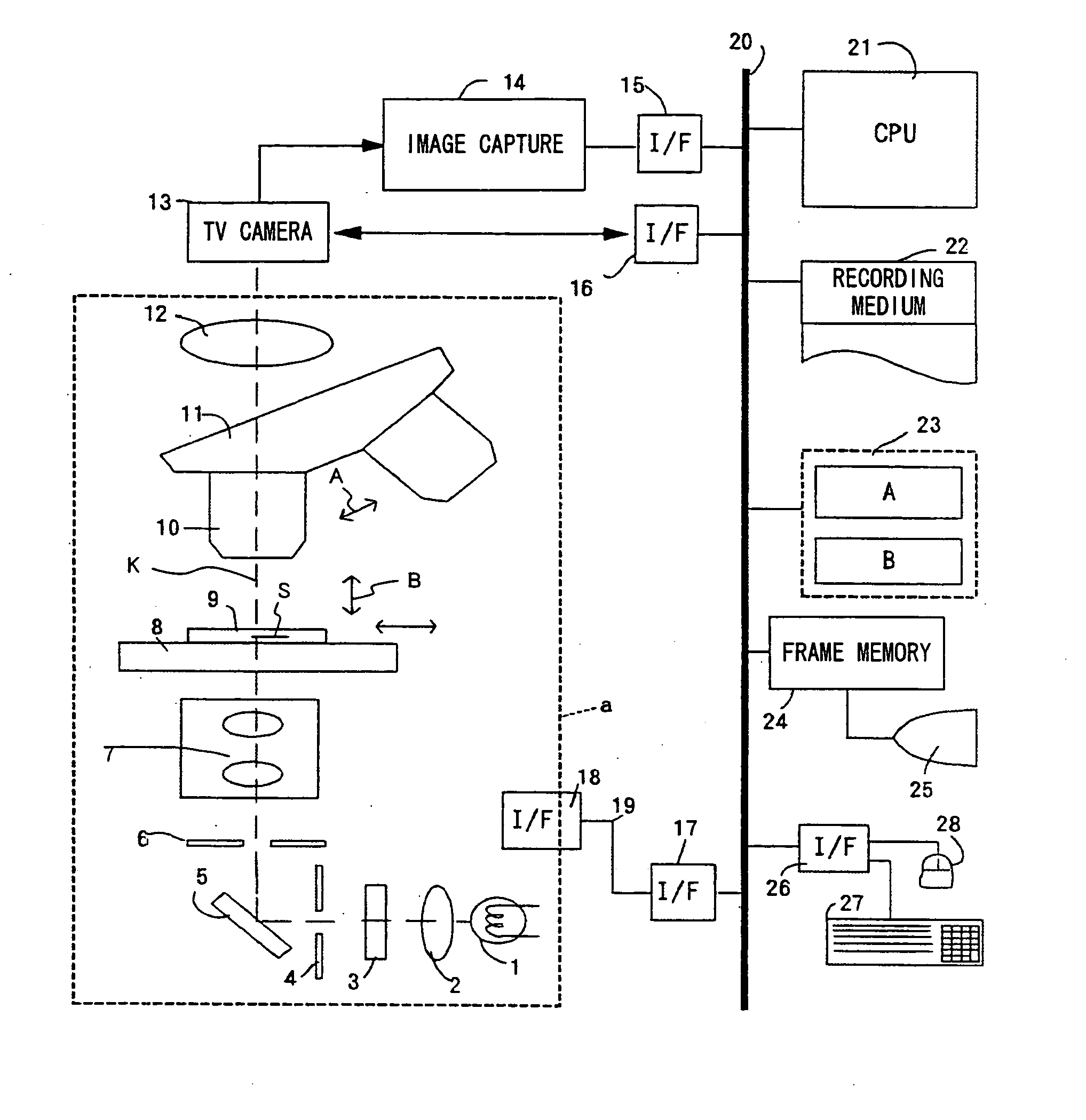
Microscopic image capture apparatus and microscopic image capturing method
ActiveUS20050190437A1High precision imagingLong is wastedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageField size
A microscopic image capture apparatus and a microscopic image capturing method allow a wide-angle field and high-precision microscope digital image to be efficiently captured. First, the entire area of a slide glass on a stage is divided into field size sections (low-magnification sections) of a low-powered objective lens, the stage is sequentially transferred perpendicular to an optical axis, image information is obtained for each low-magnification section of the entire area, each low-magnification section is divided into high-magnification size sections (high-magnification sections), a high-magnification image is captured using a high-powered objective lens only on a high-magnification section including simultaneously in the high-magnification sections, a high-magnification image is generated by correctly maintaining the relative position between the obtained image information and the area of a high-magnification section which is not captured, and a high-magnification composite image information about a sample on the slide glass is generated.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Phase subtraction cell counting method
InactiveUS8428331B2Enough timeAccurate countMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionDevelopmental stageMicroscopic image
A method and device are provided for counting cells in a sample of living tissue, such as an embryo. The method involves obtaining a microscopic image of the unstained tissue that reveals cell boundaries, such as a differential interference contrast (DIC) image, and an optical quadrature microscopy (OQM) image which is used to prepare an image of optical path length deviation (OPD) across the cell cluster. The boundaries of individual cells in the cell cluster are modeled as ellipses and used, together with the maximum optical path length deviation of a cell, to calculate ellipsoidal model cells that are subtracted from the OPD image. The process is repeated until the OPD image is depleted of phase signal attributable to cells of the cell cluster, and the cell count is obtained from the number of cells subtracted. The method is capable of accurately and non-invasively counting the number of cells in a living embryo at the 2-30 cell stage, and can be employed to assess the developmental stage and health of human embryos for fertility treatments.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Complex index refraction tomography with sub lambda/6-resolution
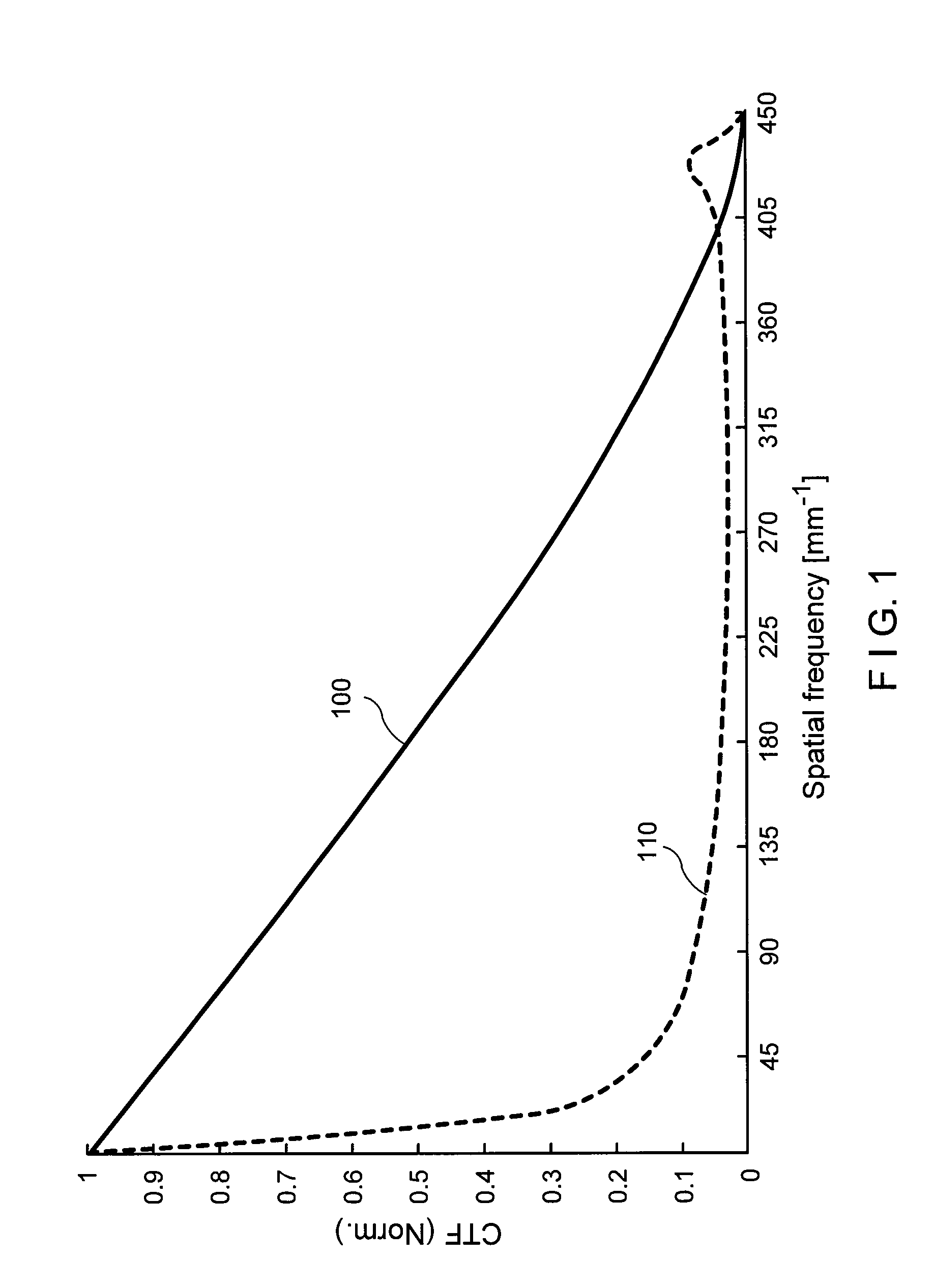
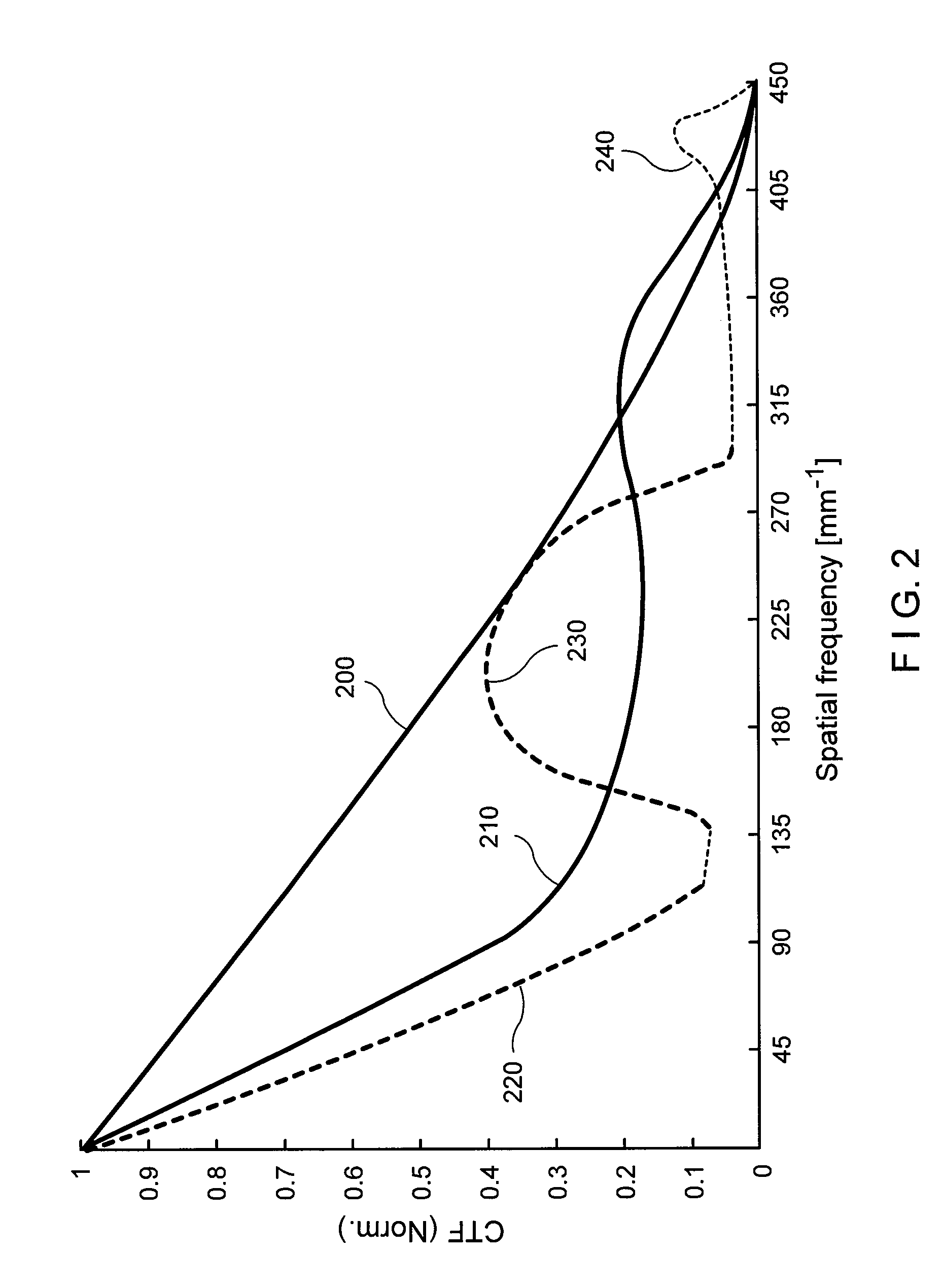
The present invention discloses a method to improve the image resolution of a microscope. This improvement is based on the mathematical processing of the complex field computed from the measurements with a microscope of the wave emitted or scattered by the specimen. This wave is, in a preferred embodiment, electromagnetic or optical for an optical microscope, but can be also of different kind like acoustical or matter waves. The disclosed invention makes use of the quantitative phase microscopy techniques known in the sate of the art or to be invented. In a preferred embodiment, the complex field provided by Digital Holographic Microscopy (DHM), but any kind of microscopy derived from quantitative phase microscopy: modified DIC, Shack-Hartmann wavefront analyzer or any analyzer derived from a similar principle, such as multi-level lateral shearing interferometers or common-path interferometers, or devices that convert stacks of intensity images (transport if intensity techniques: TIT) into quantitative phase image can be used, provided that they deliver a comprehensive measure of the complex scattered wavefield. The hereby-disclosed method delivers superresolution microscopic images of the specimen, i.e. images with a resolution beyond the Rayleigh limit of the microscope. It is shown that the limit of resolution with coherent illumination can be improved by a factor of 6 at least. It is taught that the gain in resolution arises from the mathematical digital processing of the phase as well as of the amplitude of the complex field scattered by the observed specimen. In a first embodiment, the invention teaches how the experimental observation of systematically occurring phase singularities in phase imaging of sub-Rayleigh distanced objects can be exploited to relate the locus of the phase singularities to the sub-Rayleigh distance of point sources, not resolved in usual diffraction limited microscopy. In a second, preferred embodiment, the disclosed method teaches how the image resolution is improved by complex deconvolution. Accessing the object's scattered complex field—containing the information coded in the phase—and deconvolving it with the reconstructed complex transfer function (CTF) is at the basis of the disclosed method. In a third, preferred embodiment, it is taught how the concept of “Synthetic Coherent Transfer Function” (SCTF), based on Debye scalar or Vector model includes experimental parameters of MO and how the experimental Amplitude Point Spread Functions (APSF) are used for the SCTF determination. It is also taught how to derive APSF from the measurement of the complex field scattered by a nanohole in a metallic film. In a fourth embodiment, the invention teaches how the limit of resolution can be extended to a limit of λ / 6 or smaller based angular scanning. In a fifth embodiment, the invention teaches how the presented method can generalized to a tomographic approach that ultimately results in super-resolved 3D refractive index reconstruction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method for automatically identifying leukocytes in leucorrhea microscopic image
ActiveCN106295588ASave time at workImprove work efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageWhite blood cell
The invention discloses a method for automatically identifying leukocytes in a leucorrhea microscopic image, and belongs to the field of medical digital image processing, particularly an algorithm for automatically identifying leukocytes in a leucorrhea microscopic image. According to the method, the microscopic image is subjected to gray-scale processing, then communication regions in the image are searched, the communication regions in the image are sequentially screened according to actual morphologies of the leukocytes, and finally, a leukocyte image in leucorrhea is identified, so that working time of a worker and personal errors are greatly reduced, and working efficiency is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
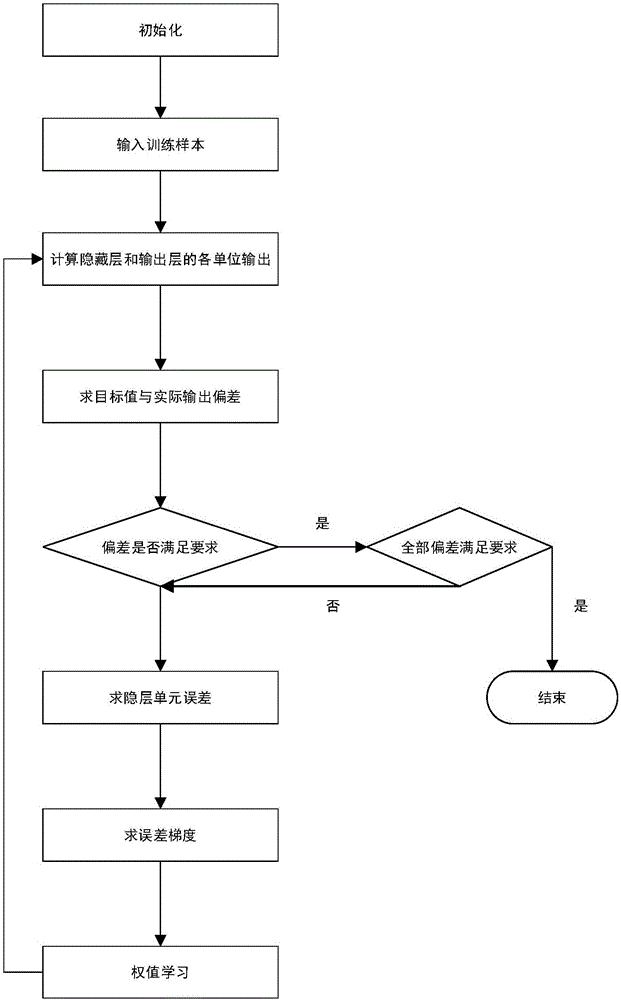
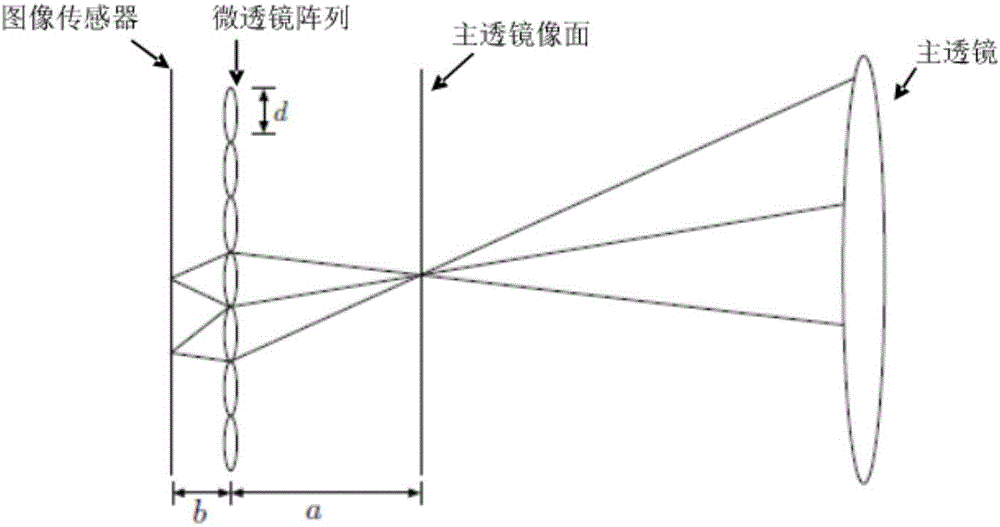
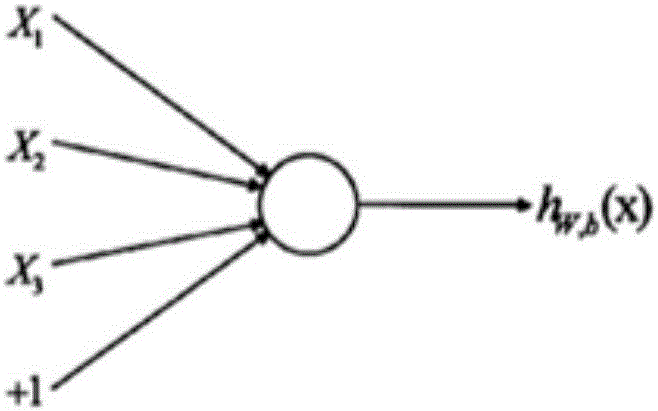
Deep learning neural network-based microscopic image three-dimensional reconstruction method and system
ActiveCN106846463ALow data requirementsHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageImage resolution
The invention provides a deep learning neural network-based microscopic image three-dimensional reconstruction method and system. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a neural network; obtaining a training set of the neural network; training the neural network according to the training set, thereby obtaining network parameters; and according to the network parameters, performing three-dimensional reconstruction on a to-be-reconstructed object to obtain a reconstructed image. According to the method and the system, an image recovery reconstruction network is obtained through learning of an optical field image and different layers of focus images, so that the three-dimensional reconstruction speed and resolution are increased, and the longitudinal resolution is greatly increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com