Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1186 results about "Photon detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High definition lidar system
ActiveUS7969558B2More compactMore ruggedAngle measurementOptical rangefindersHigh definition tvPower coupling
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Medical imaging, diagnosis, and therapy using a scanning single optical fiber system
InactiveUS6975898B2High resolutionEasy to viewEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFlexible endoscopyHigh resolution imaging
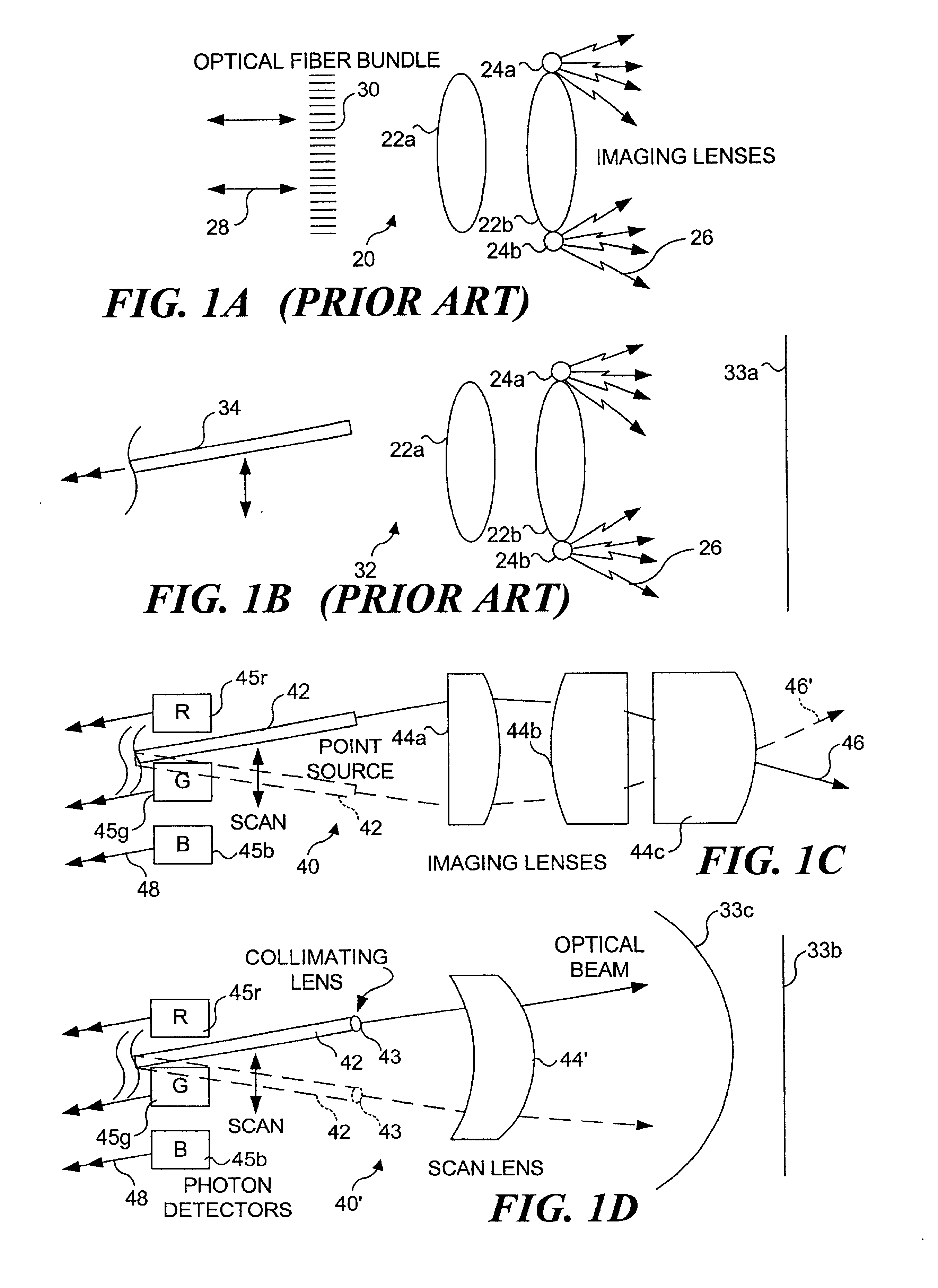
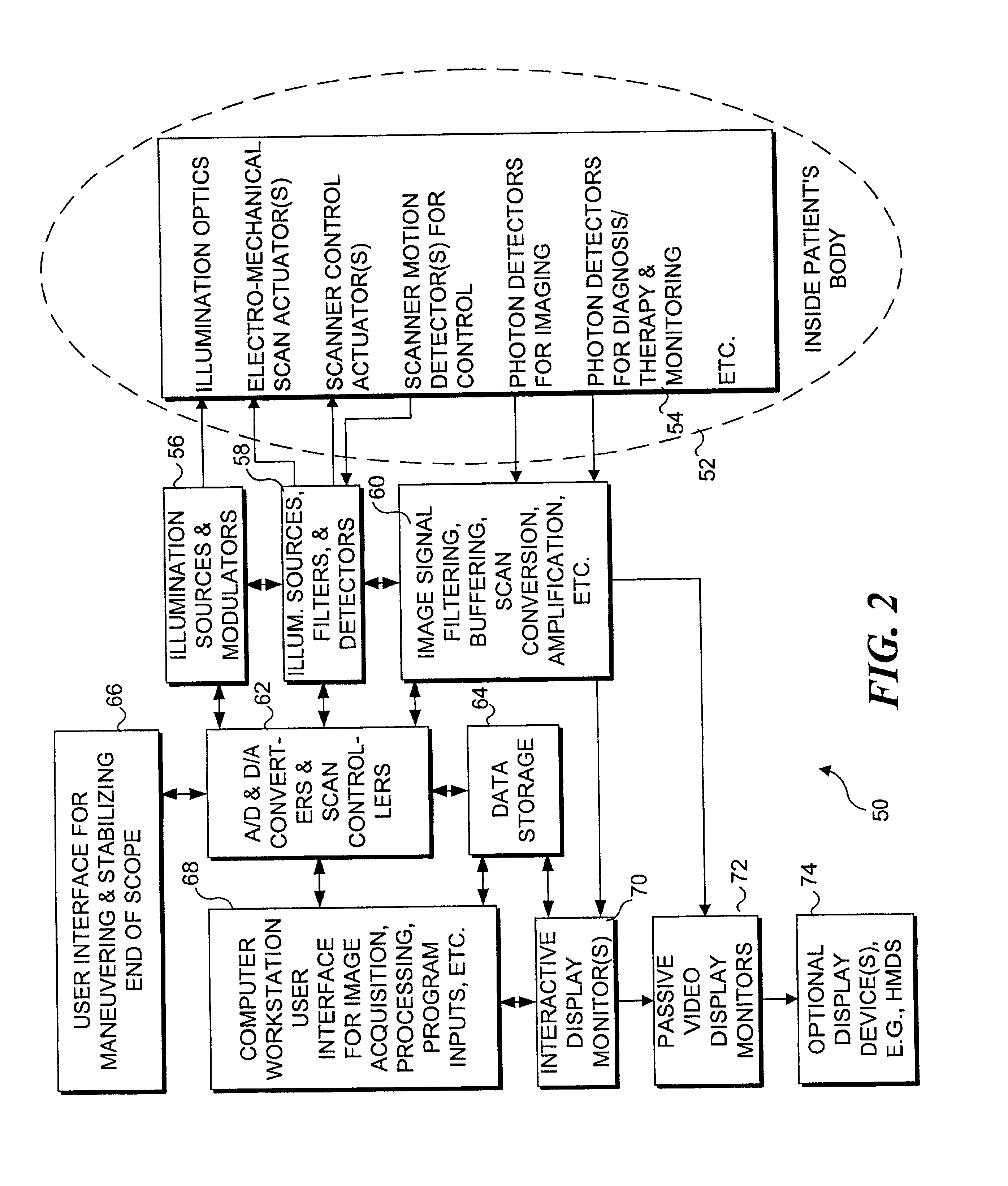
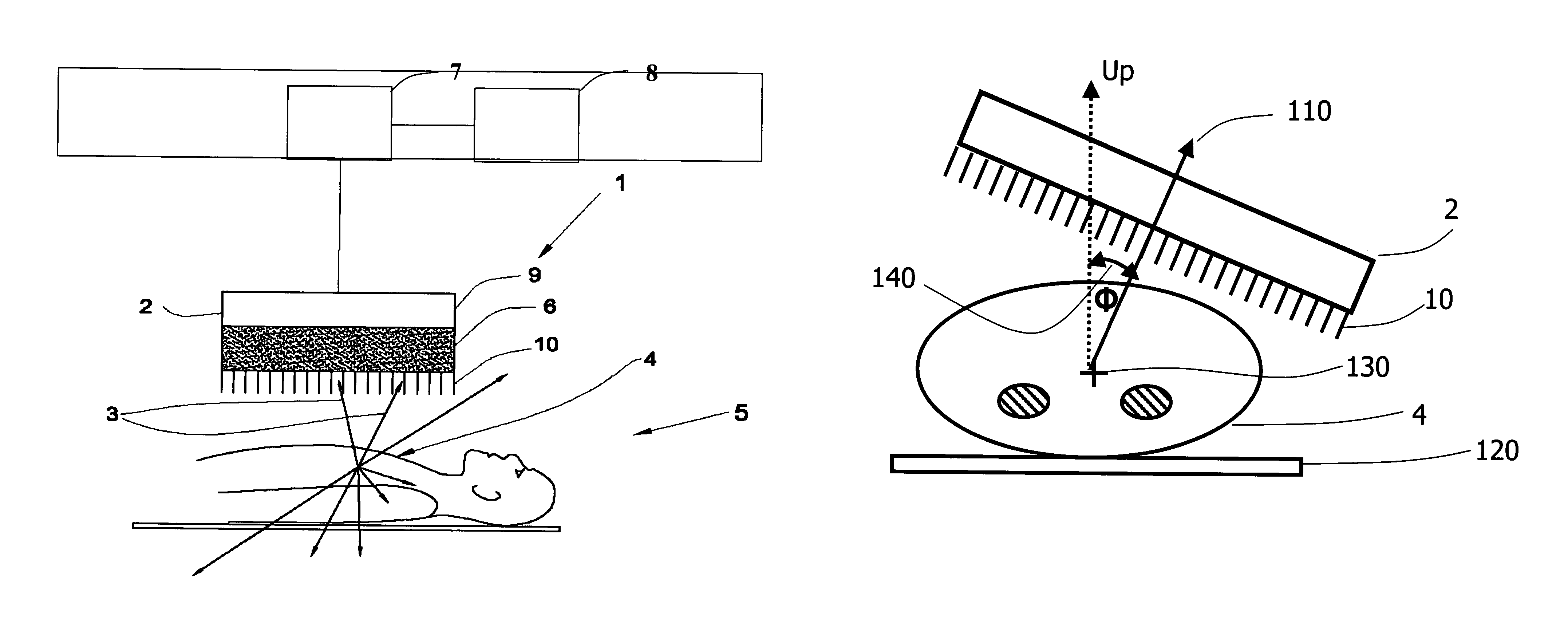
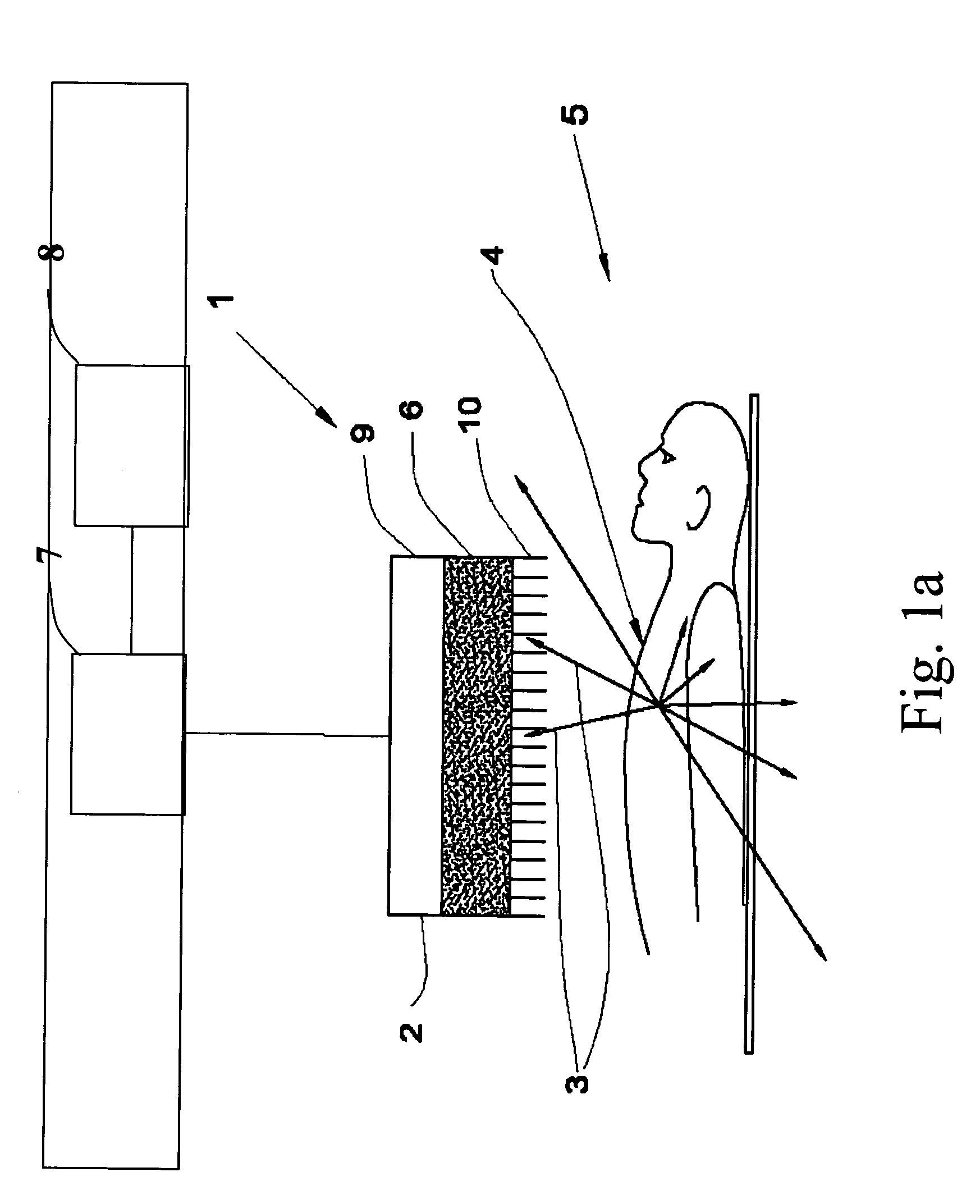
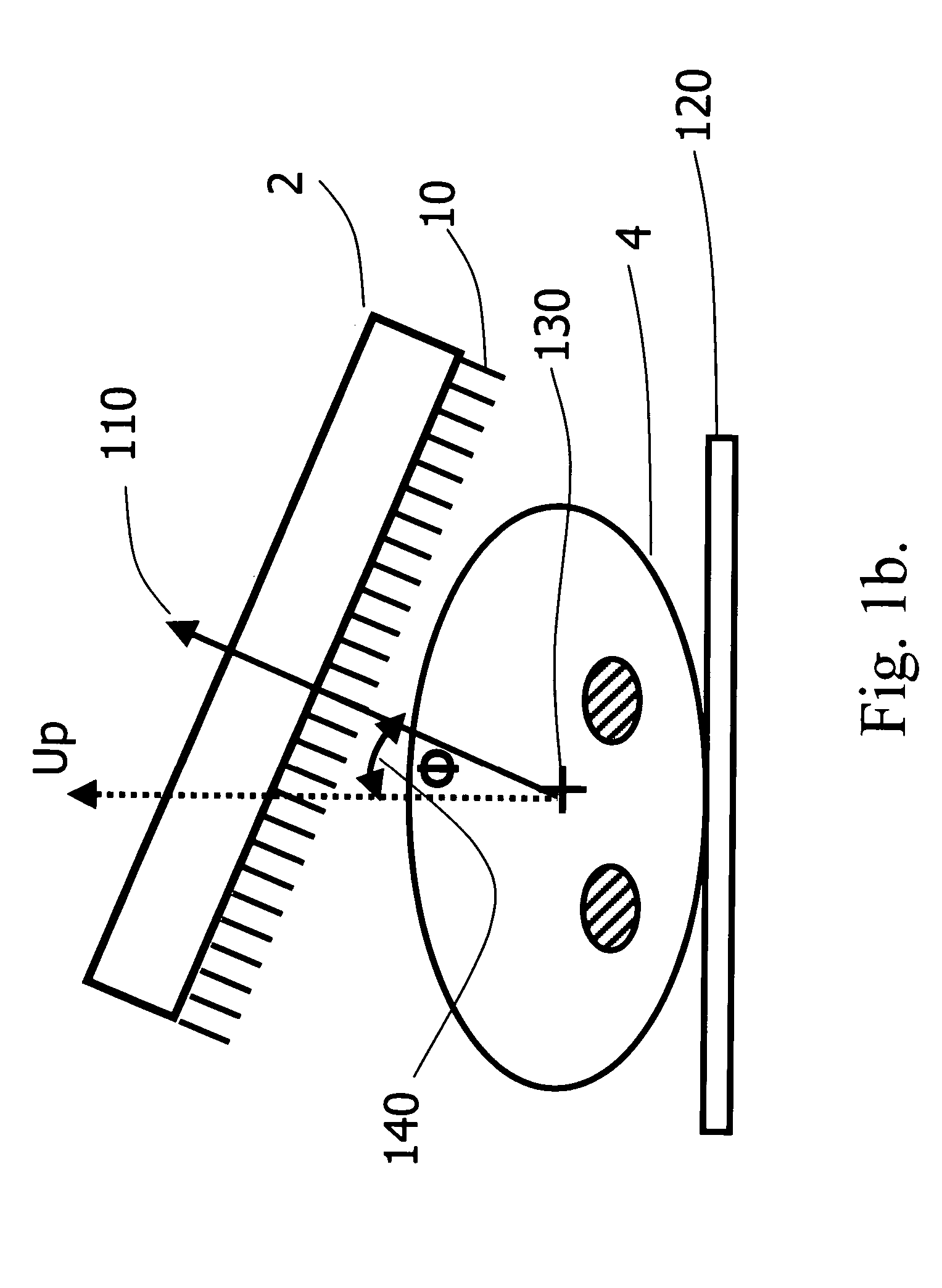
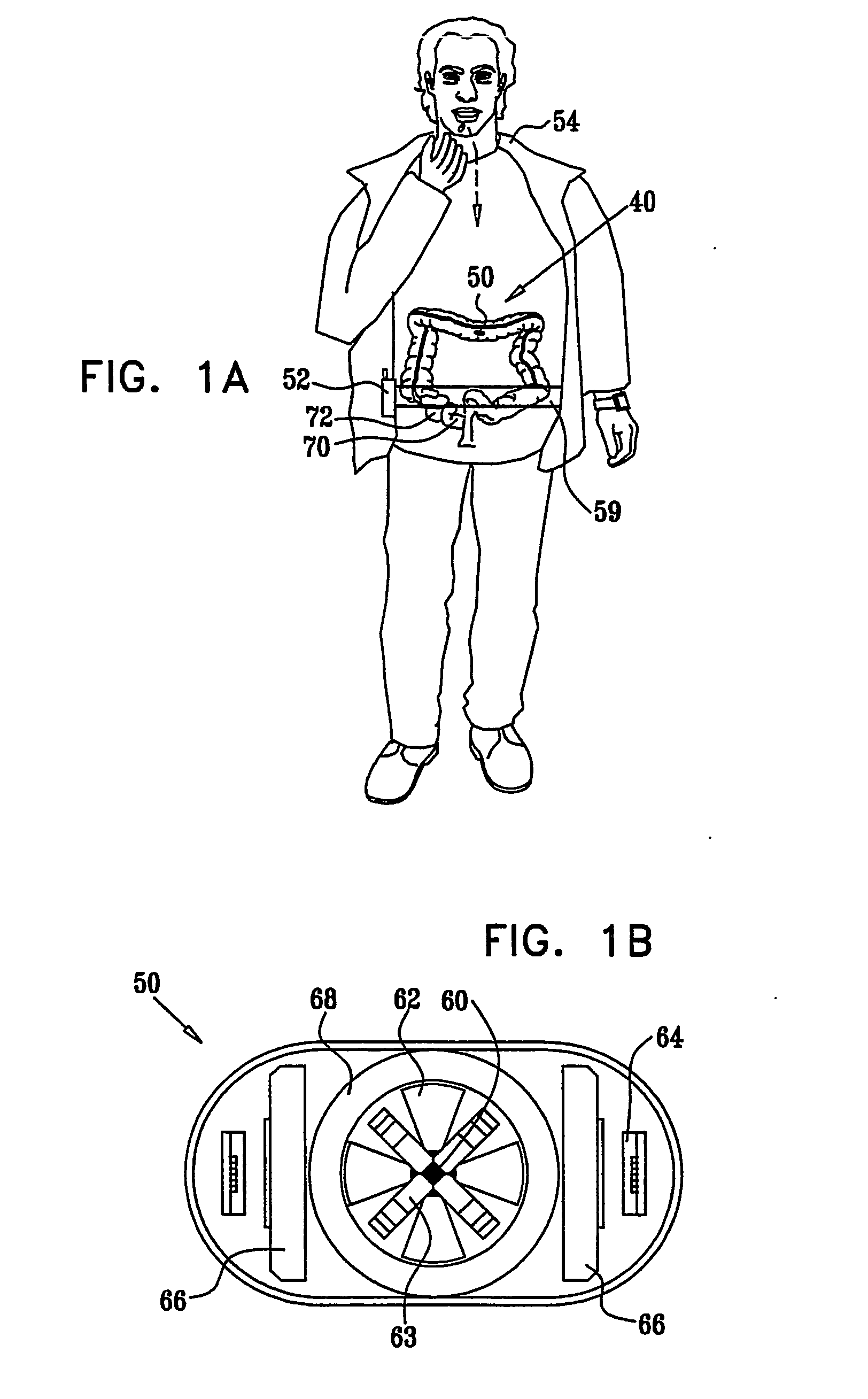
An integrated endoscopic image acquisition and therapeutic delivery system for use in minimally invasive medical procedures (MIMPs). The system uses directed and scanned optical illumination provided by a scanning optical fiber or light waveguide that is driven by a piezoelectric or other electromechanical actuator included at a distal end of an integrated imaging and diagnostic / therapeutic instrument. The directed illumination provides high resolution imaging, at a wide field of view (FOV), and in full color that matches or excels the images produced by conventional flexible endoscopes. When using scanned optical illumination, the size and number of the photon detectors do not limit the resolution and number of pixels of the resulting image. Additional features include enhancement of topographical features, stereoscopic viewing, and accurate measurement of feature sizes of a region of interest in a patient's body that facilitate providing diagnosis, monitoring, and / or therapy with the instrument.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
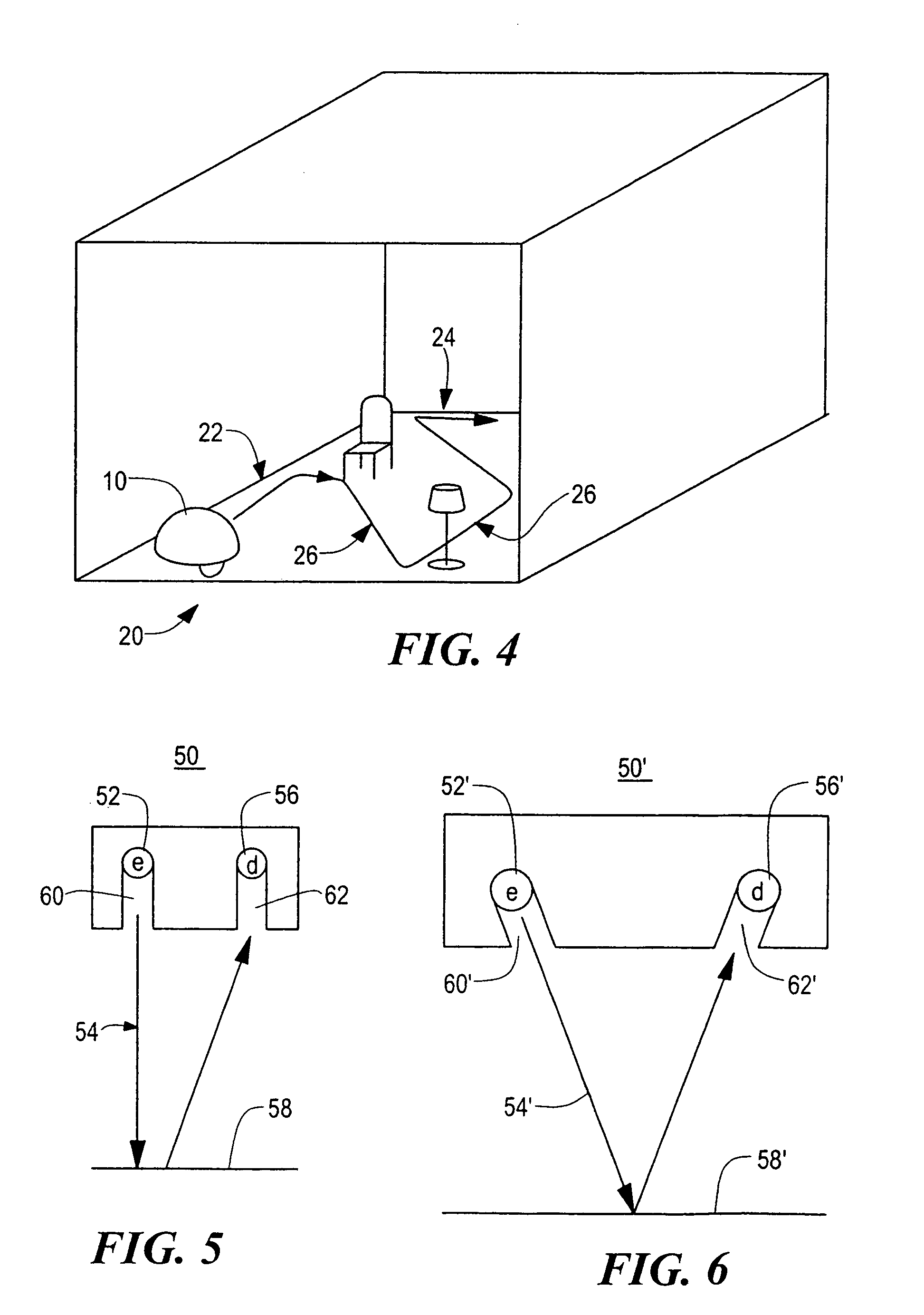
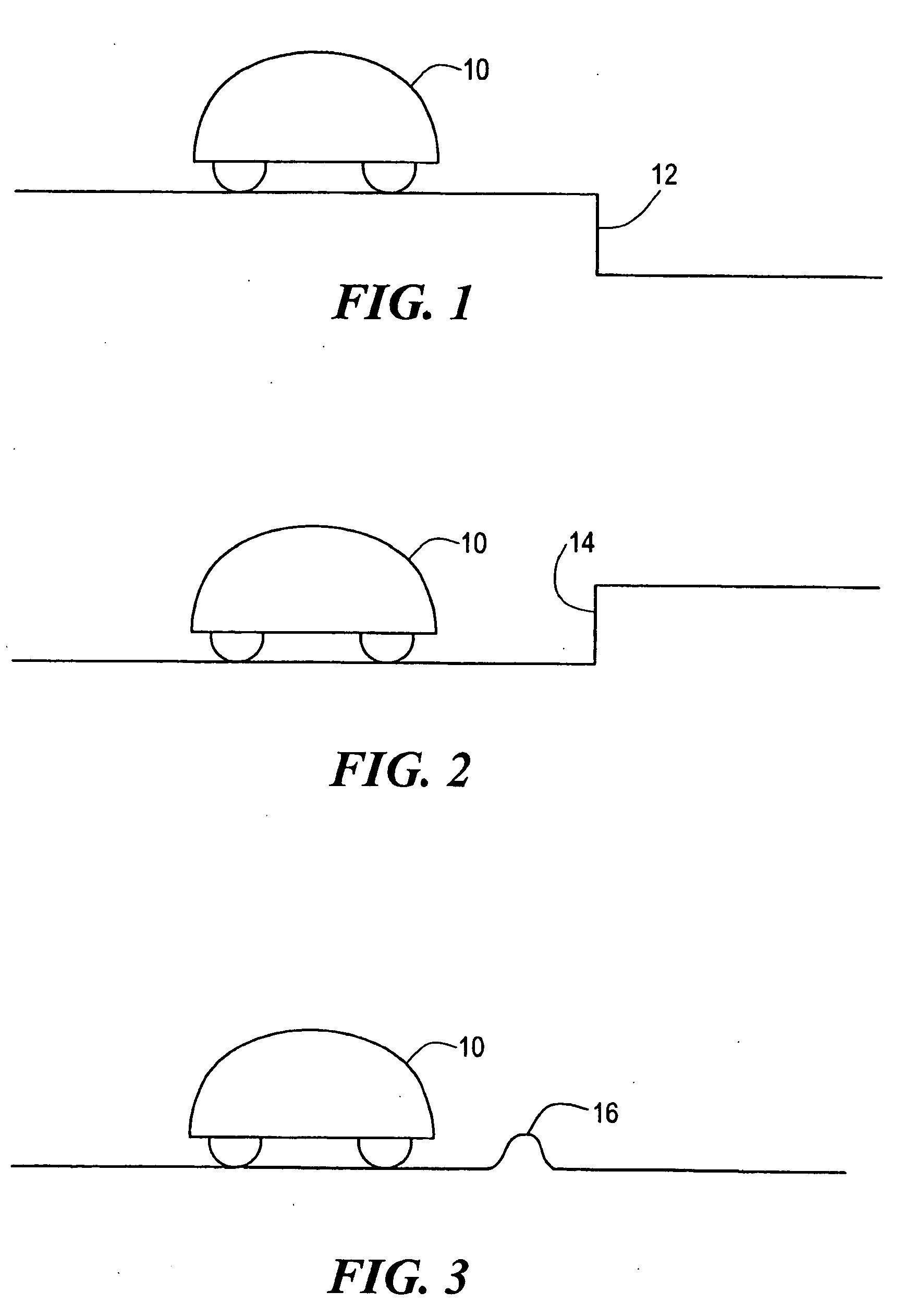
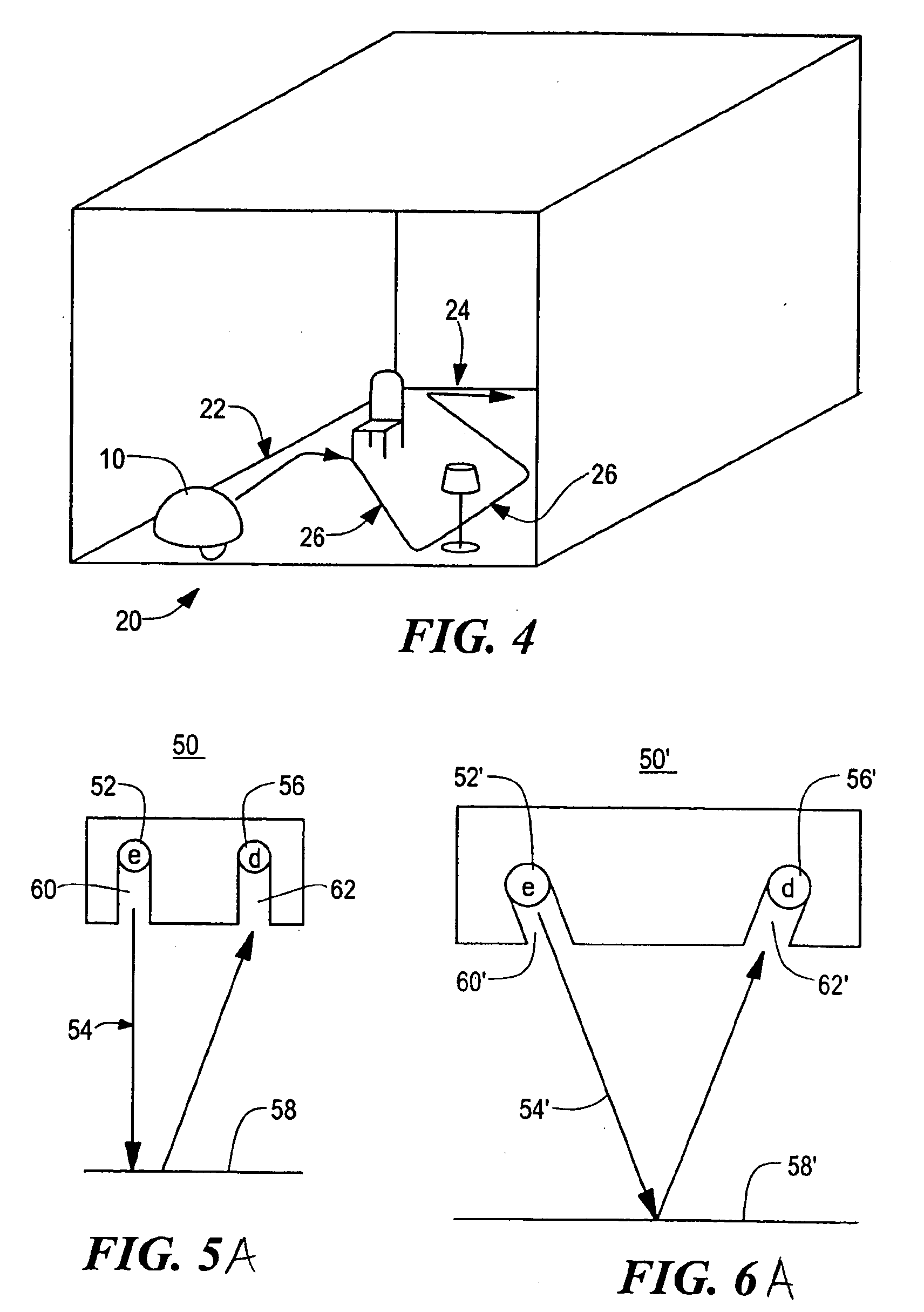
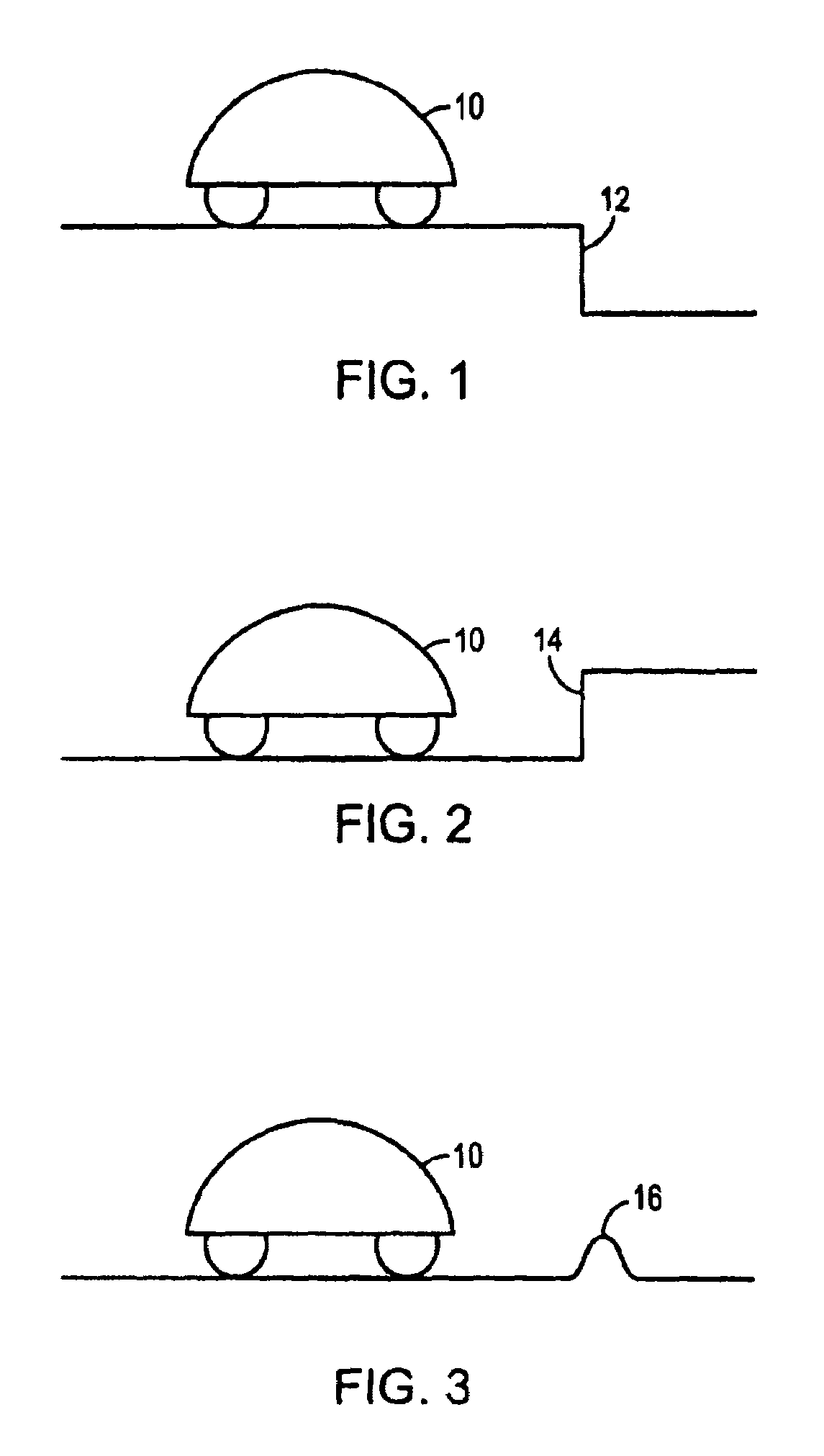
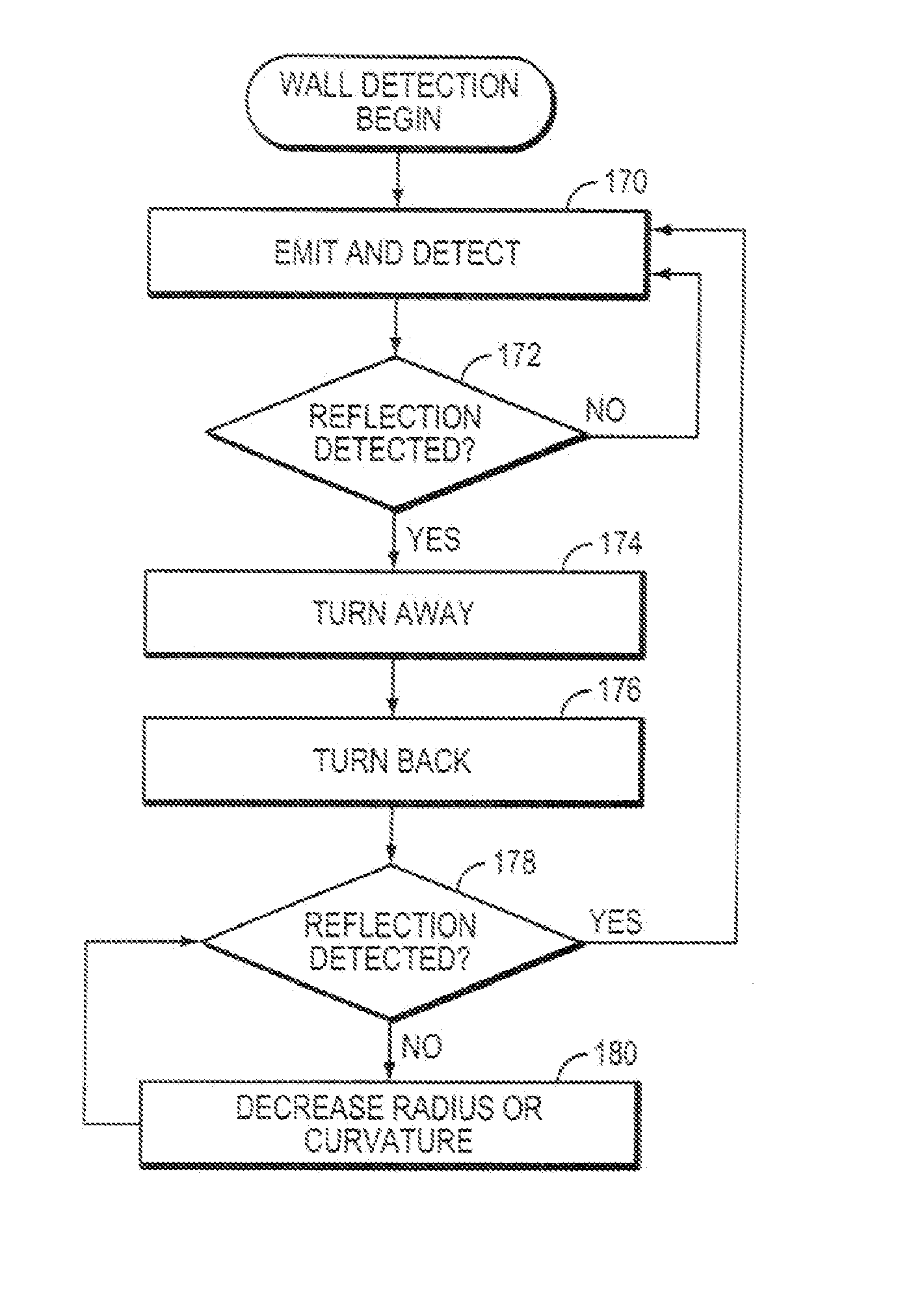
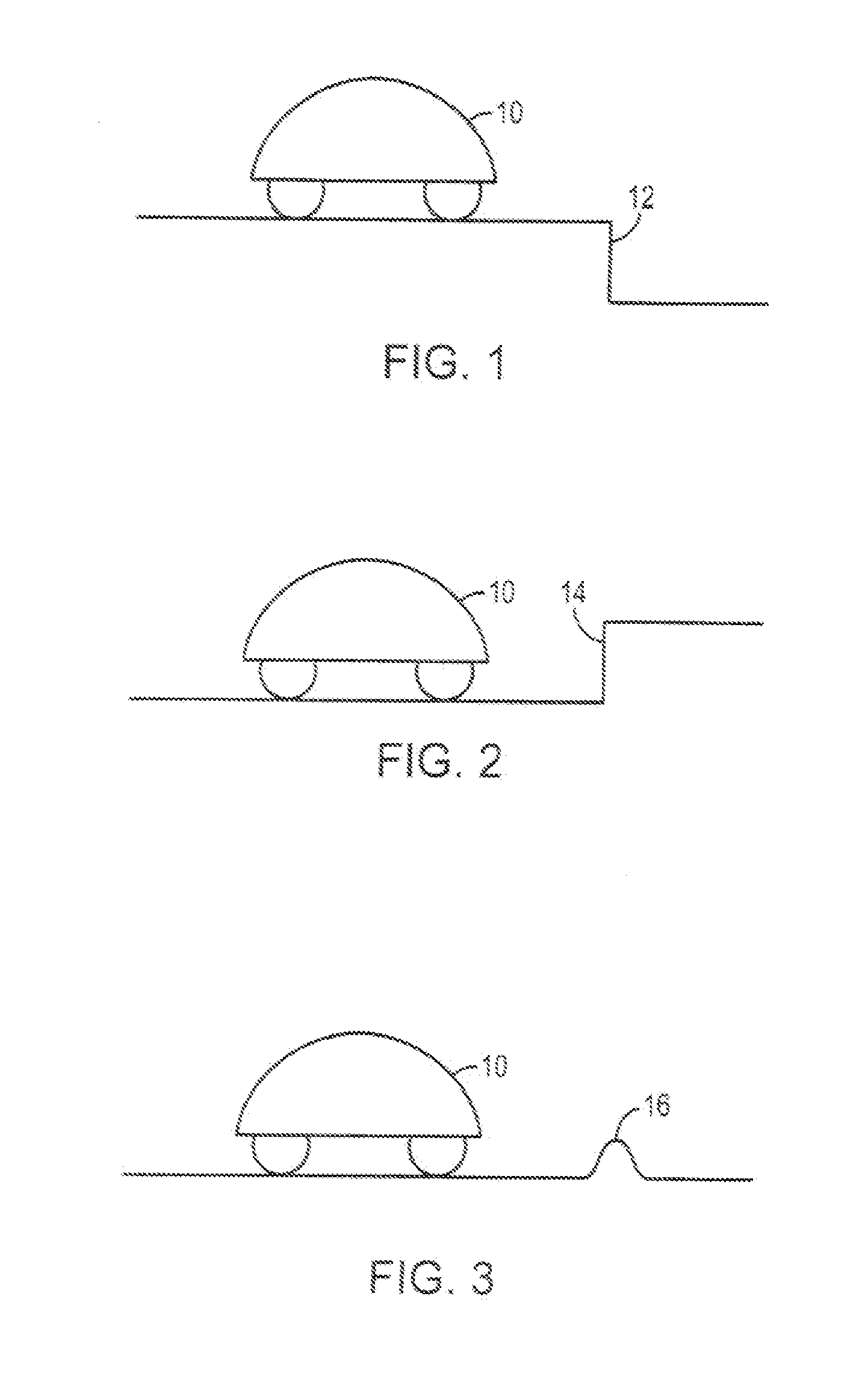
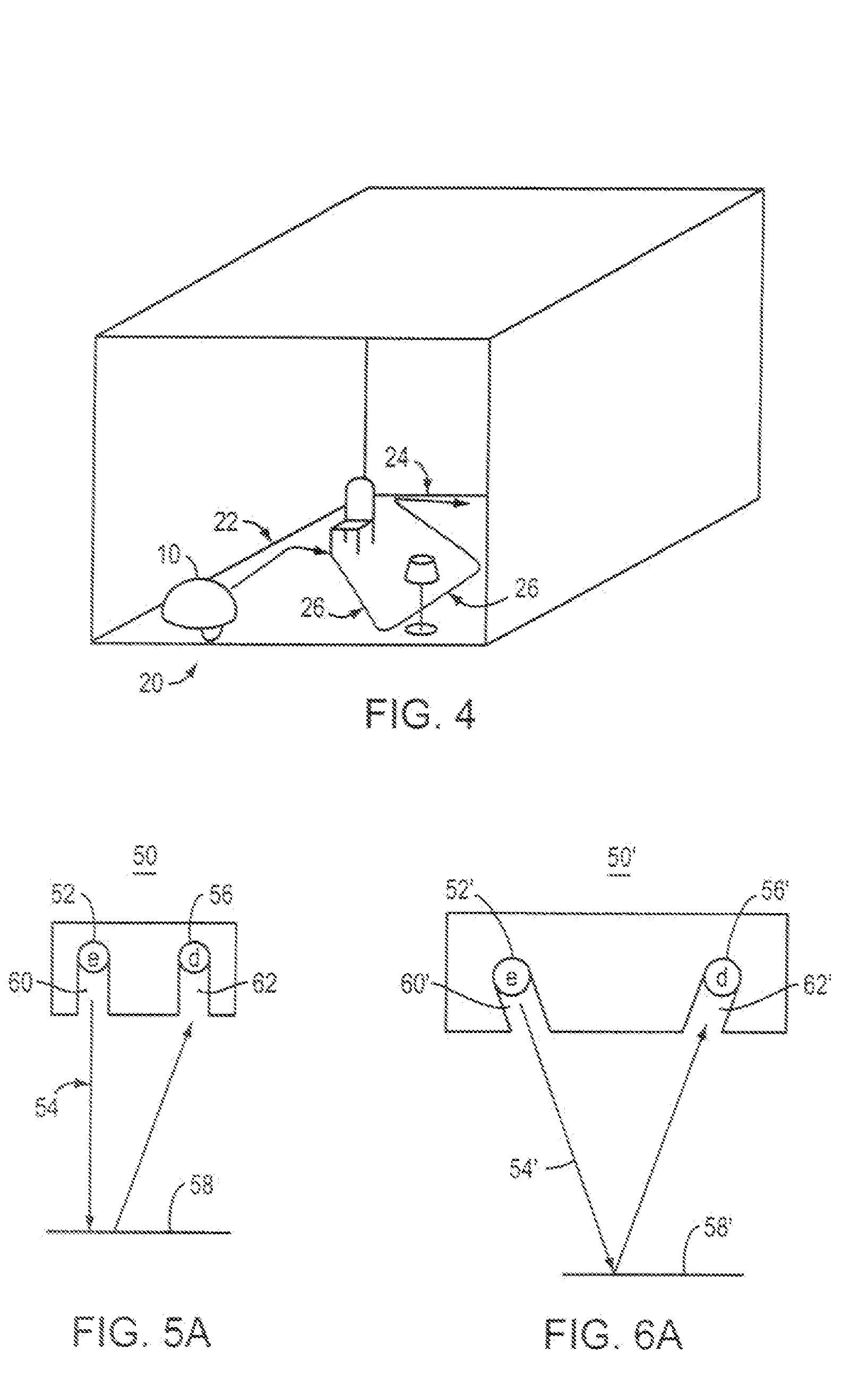
Robot obstacle detection system
InactiveUS7155308B2Simple designLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlLight beamField of view
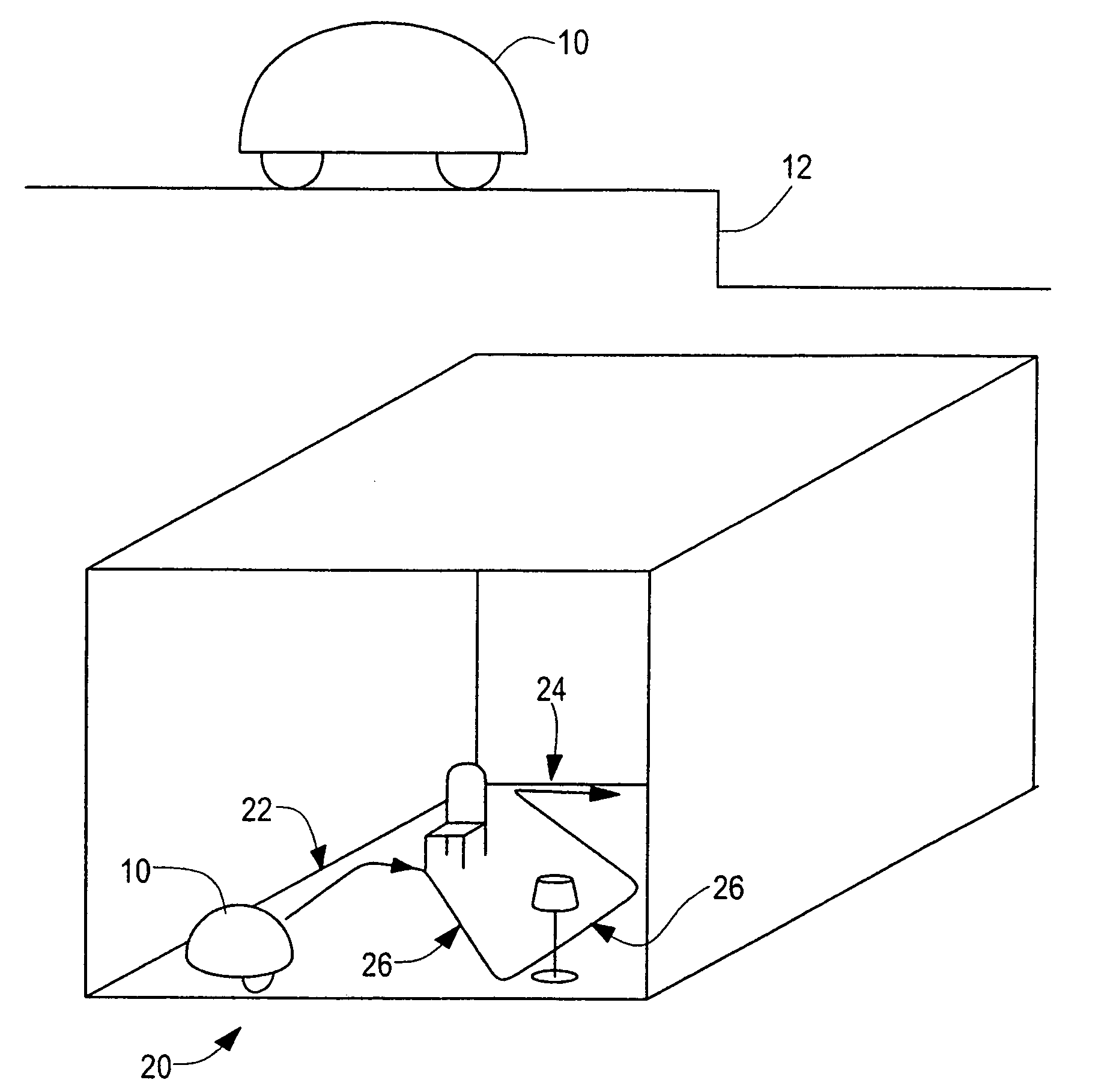
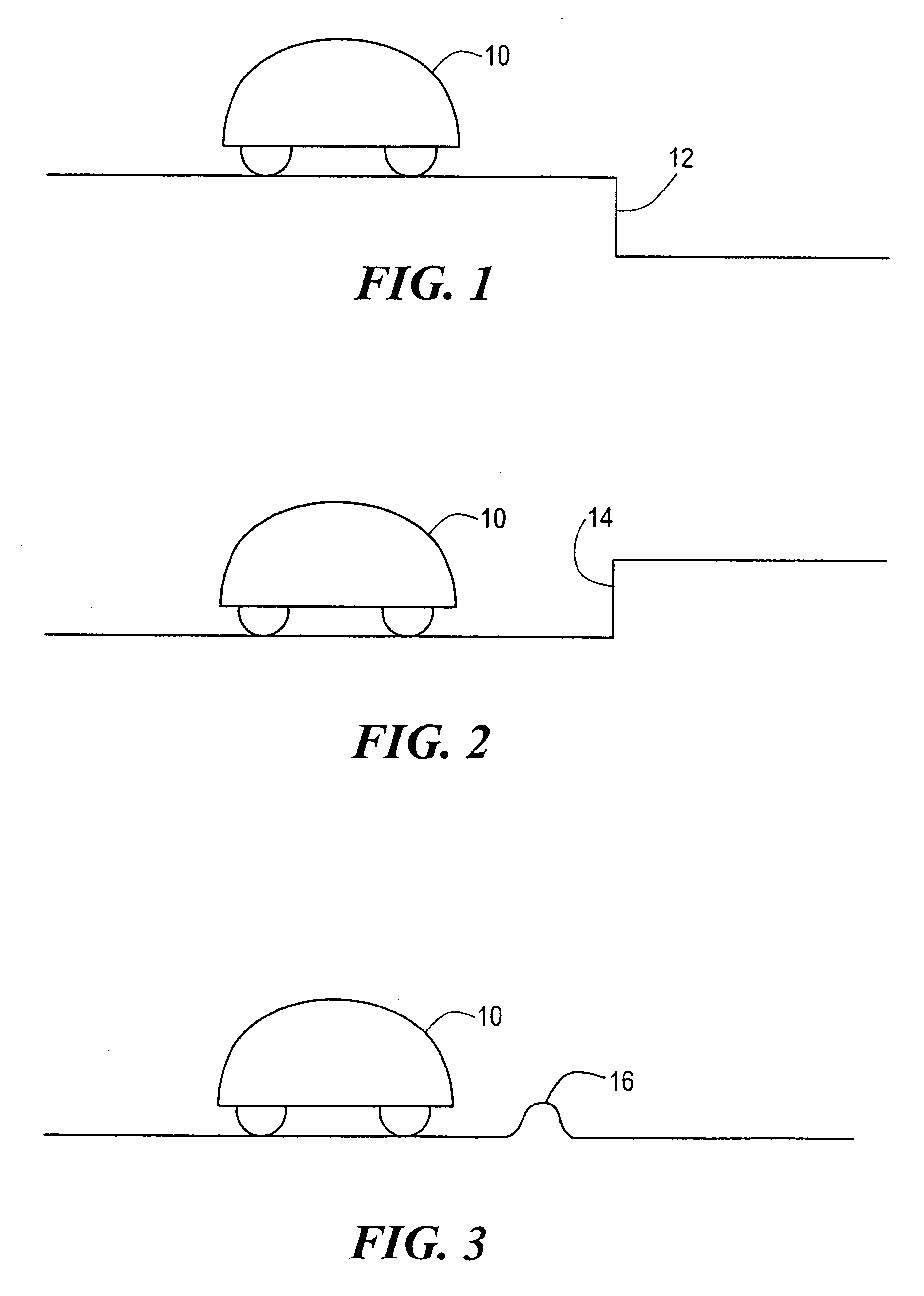
A robot obstacle detection system including a robot housing which navigates with respect to a surface and a sensor subsystem having a defined relationship with respect to the housing and aimed at the surface for detecting the surface. The sensor subsystem includes an optical emitter which emits a directed beam having a defined field of emission and a photon detector having a defined field of view which intersects the field of emission of the emitter at a region. A circuit in communication with a detector redirects the robot when the surface does not occupy the region to avoid obstacles. A similar system is employed to detect walls.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Obstacle following sensor scheme for a mobile robot
ActiveUS20050251292A1Simple designLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic obstacle detectionProximateEngineering
A robot obstacle detection system including a robot housing which navigates with respect to a surface and a sensor subsystem aimed at the surface for detecting the surface. The sensor subsystem includes an emitter which emits a signal having a field of emission and a photon detector having a field of view which intersects the field of emission at a region. The subsystem detects the presence of an object proximate the mobile robot and determines a value of a signal corresponding to the object. It compares the value to a predetermined value, moves the mobile robot in response to the comparison, and updates the predetermined value upon the occurrence of an event.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Method and apparatus for photon therapy
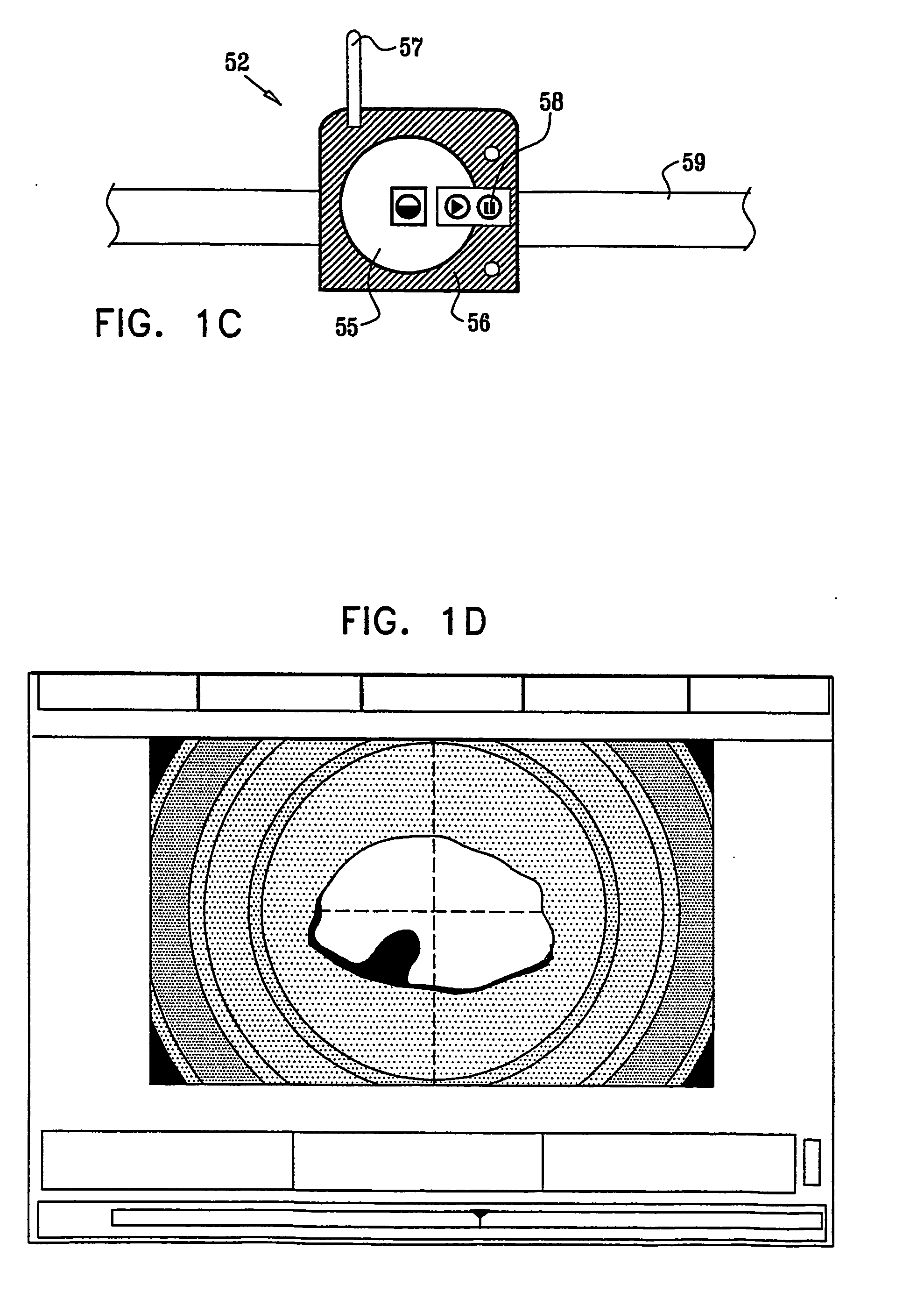
A photon therapy unit implement has a flexible head for conforming to a body part to be treated. The head has a thermally conductive backing to remove heat form the treatment area. The operation of the head is monitored by a photon detector to provide a feedback to the diode drive circuit to maintain the output at the required level. Operation of the head is monitored by a microprocessor which performs a diagnostic function and reports on defects. The treatment protocol is generated by a main control unit that formulates a treatment waveform from a set of treatment protocols. The selection of protocols is performed through a graphical user interface (GUI) which allows selection of treatment areas and customization of treatment as well as maintaining patient history and annotations.
Owner:MEDITECH INT
Obstacle following sensor scheme for a mobile robot
InactiveUS7430455B2Simple designLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic obstacle detectionEngineeringField of view
A robot obstacle detection system including a robot housing which navigates with respect to a surface and a sensor subsystem aimed at the surface for detecting the surface. The sensor subsystem includes an emitter which emits a signal having a field of emission and a photon detector having a field of view which intersects the field of emission at a region. The subsystem detects the presence of an object proximate the mobile robot and determines a value of a signal corresponding to the object. It compares the value to a predetermined value, moves the mobile robot in response to the comparison, and updates the predetermined value upon the occurrence of an event.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
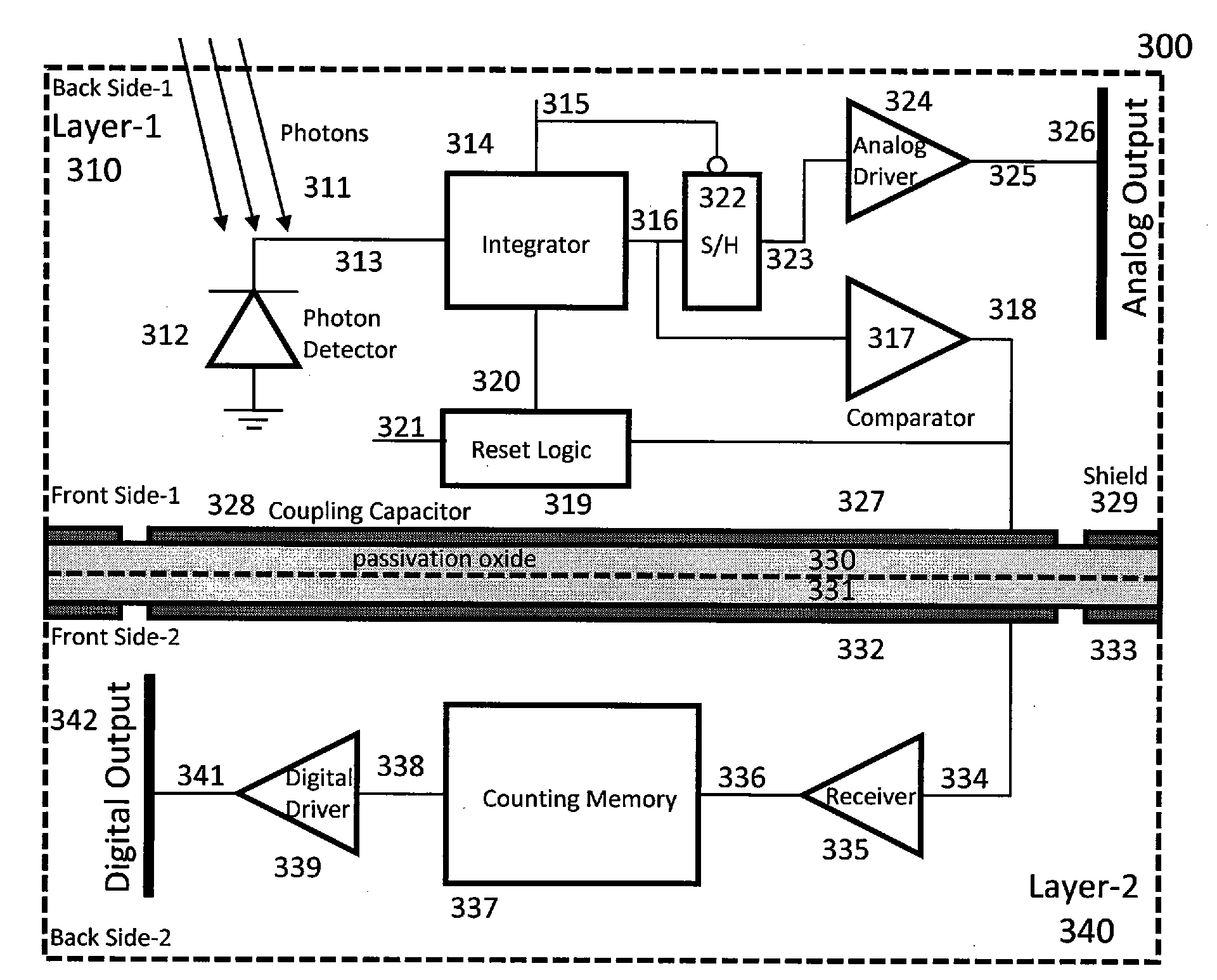
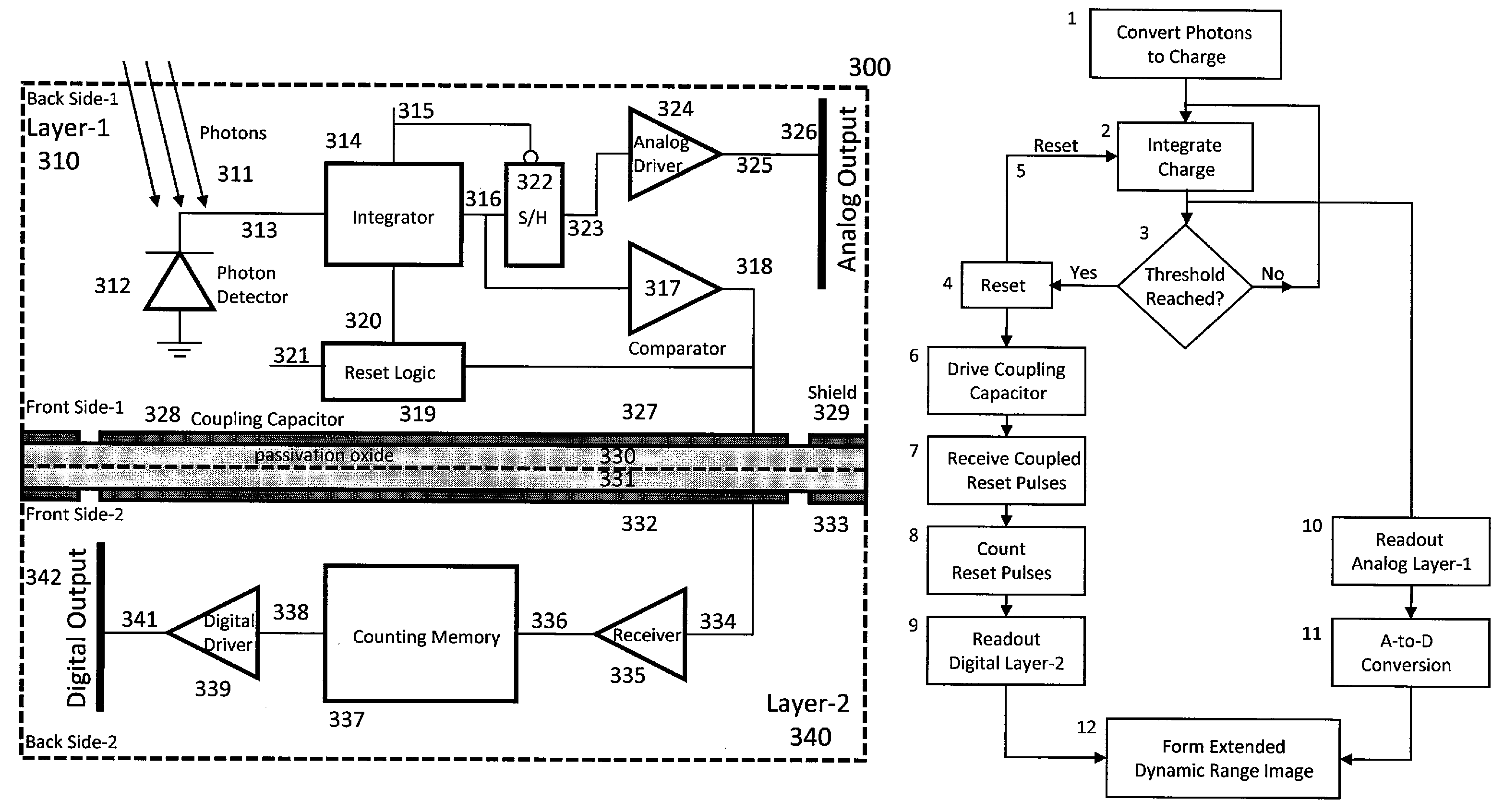
Method and apparatus for backside illuminated image sensors using capacitively coupled readout integrated circuits
InactiveUS20100140732A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove scanning rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIntegrator
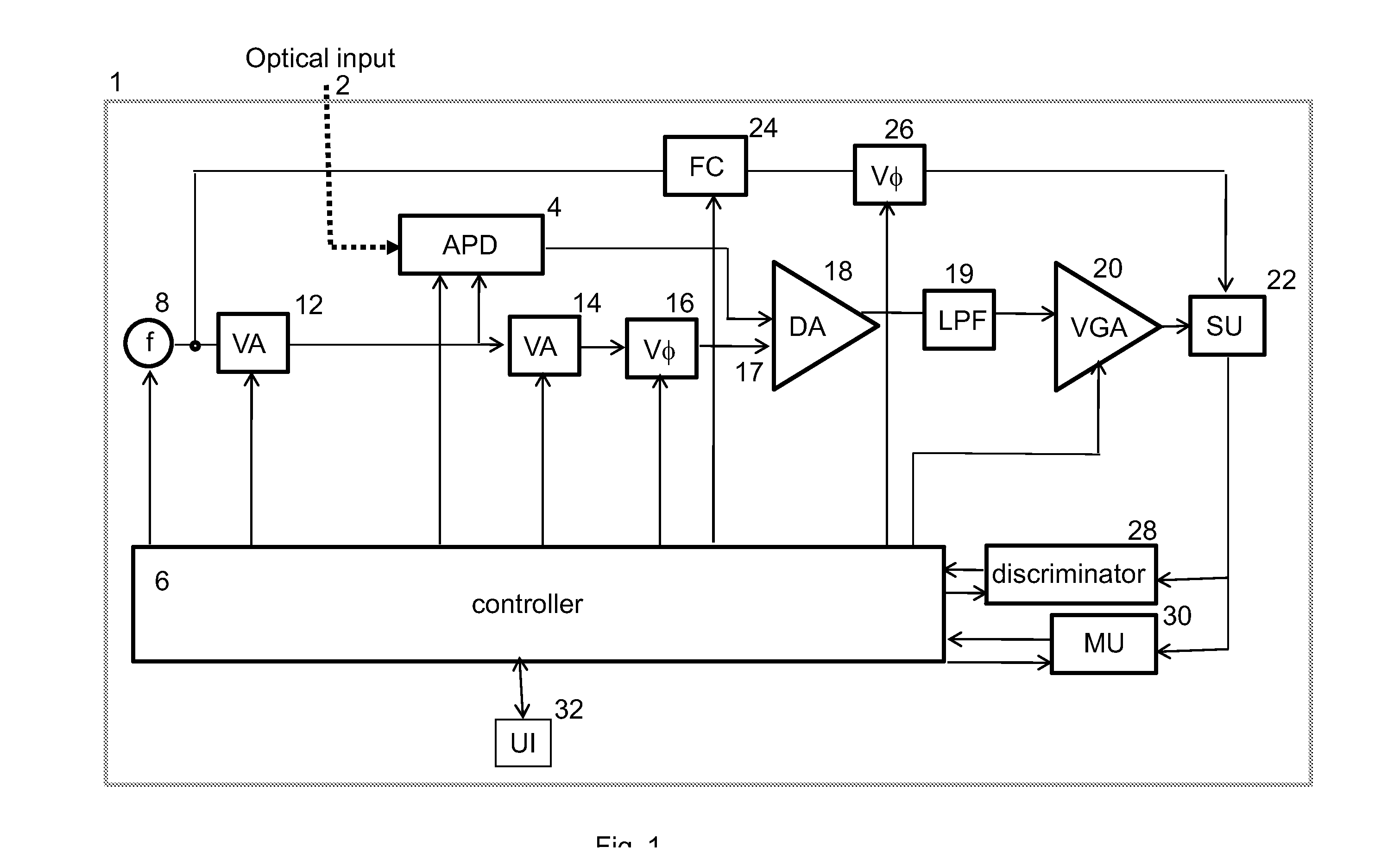
The images sensor includes a readout circuit capacitatively coupled to a memory circuit. The readout circuit includes: (i) a photon detector to receive a plurality of photons and to provide a charge signal corresponding to the received photons, (ii) a resettable integrator that is reset multiple times over a single exposure time and provides an analog representation of the incident photons during the last integration cycle, and (iii) a comparator that monitors the integrator output and generates a reset pulse when the integrator reaches a built-in threshold value. The memory circuit includes: (i) a receiver circuit that detects the output of the digital driver in the front-end readout circuit via capacitive coupling and generates a digital voltage pulse for each received signal, and (ii) a digital counting memory to count the received pulses to provide a coarse digital representation of how many times the integrator is reset.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
LiDAR System Comprising A Single-Photon Detector
ActiveUS20150192676A1Reduce impactHigh operating requirementsOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationWavelengthMulti dimensional
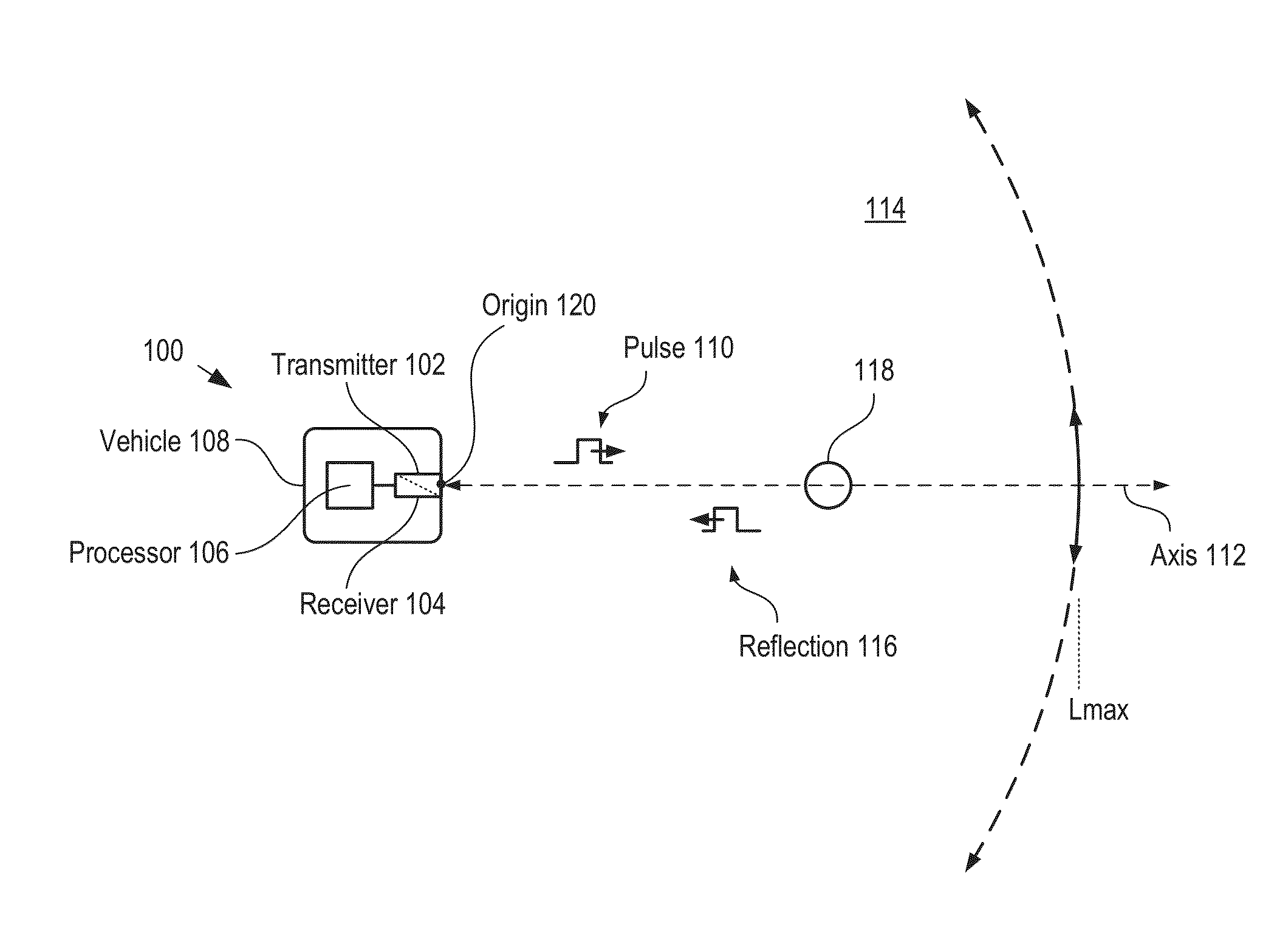
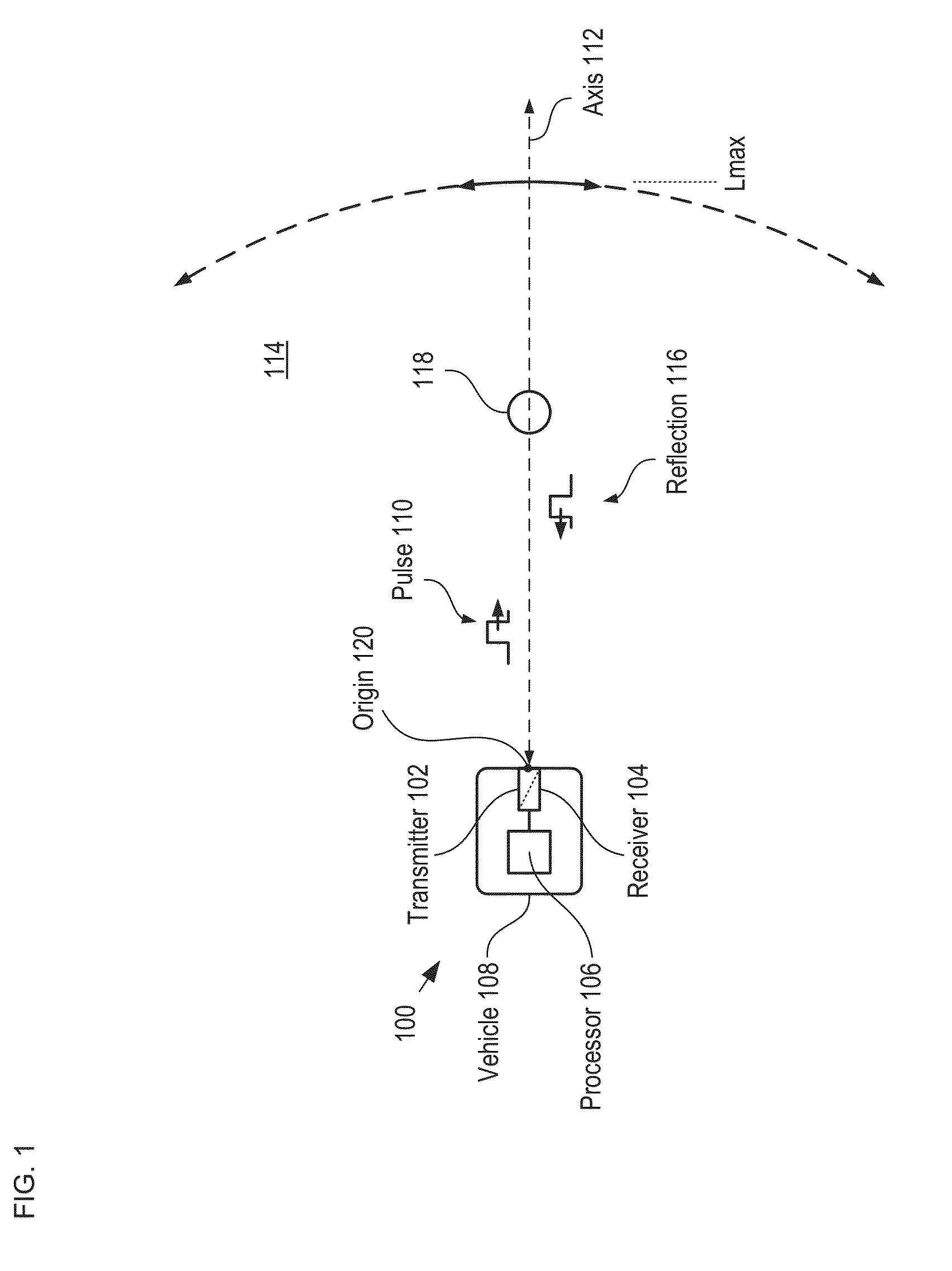
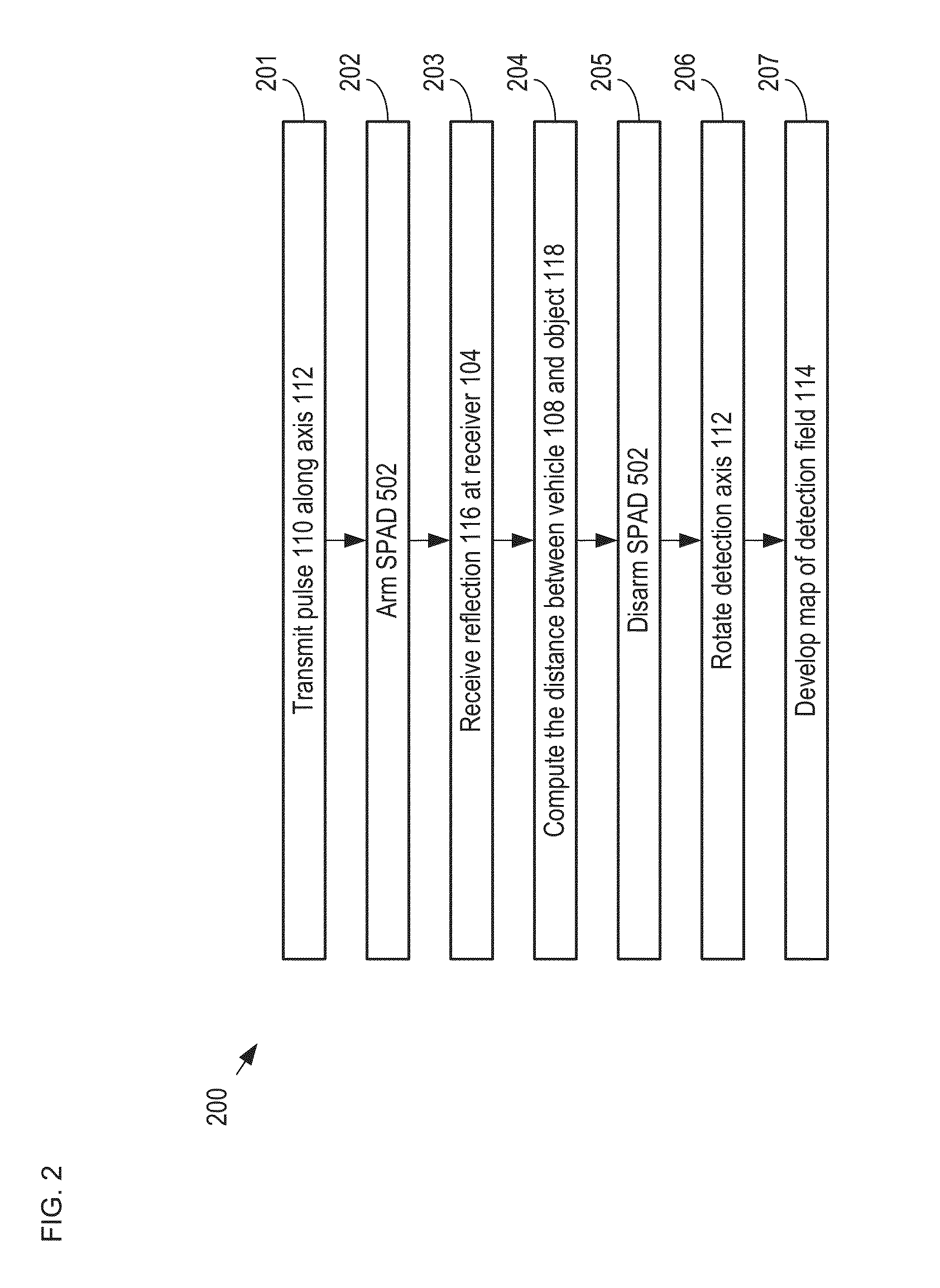
A method for developing a map of objects in a region surrounding a location is disclosed. The method includes interrogating the region along a detection axis with a series of optical pulses and detecting reflections of the optical pulses that originate at objects located along the detection axis. A multi-dimensional map of the region is developed by scanning the detection axis about the location in at least one dimension. The reflections are detected via a single-photon detector that is armed using a sub-gating scheme such that the single-photon detector selectively detects photons of reflections that originate only within each of a plurality of zones that collectively define the detection field. In some embodiments, the optical pulses have a wavelength within the range of 1350 nm to 1390 nm, which is a spectral range having a relatively high eye-safety threshold and a relatively low solar background.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
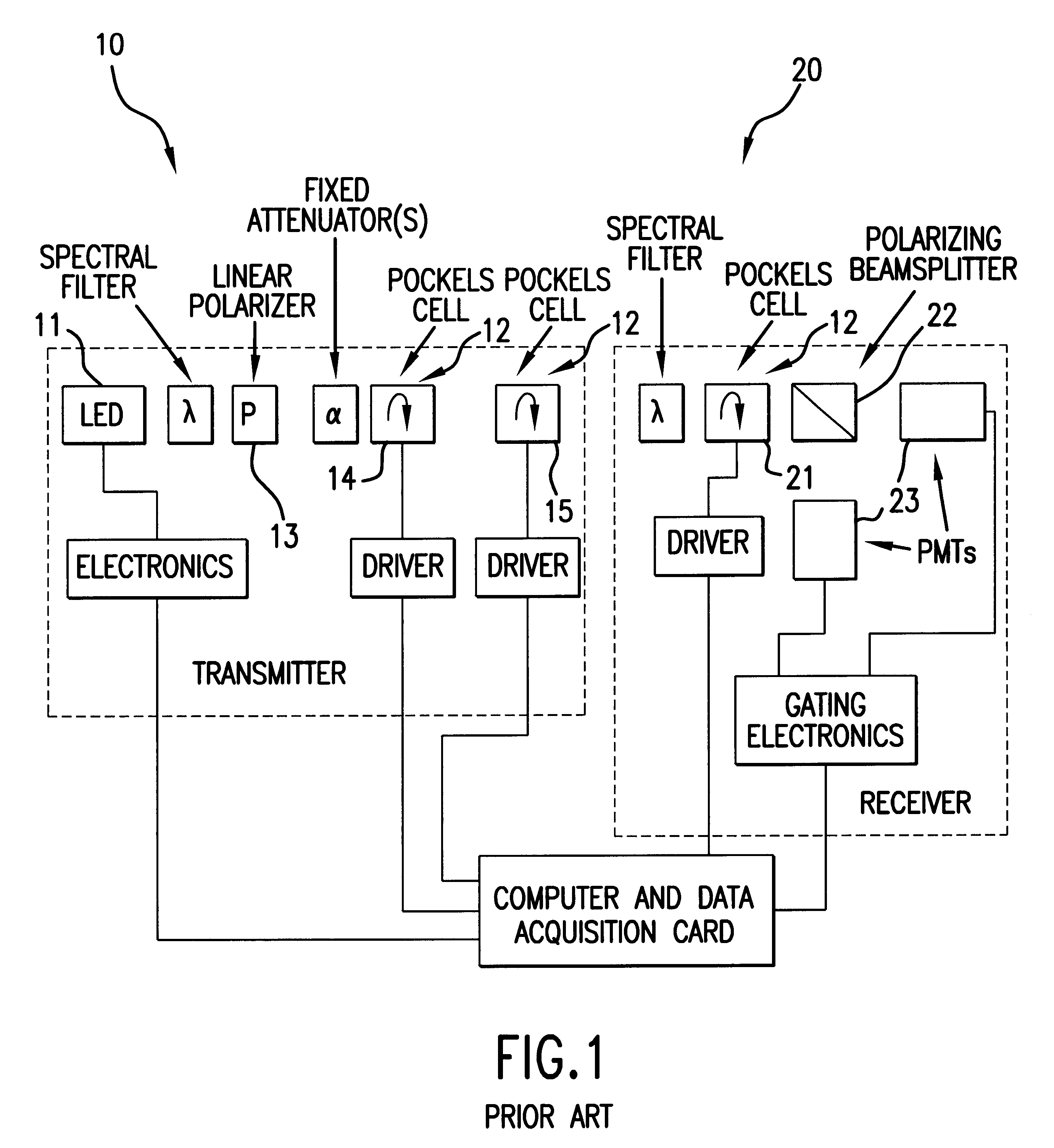
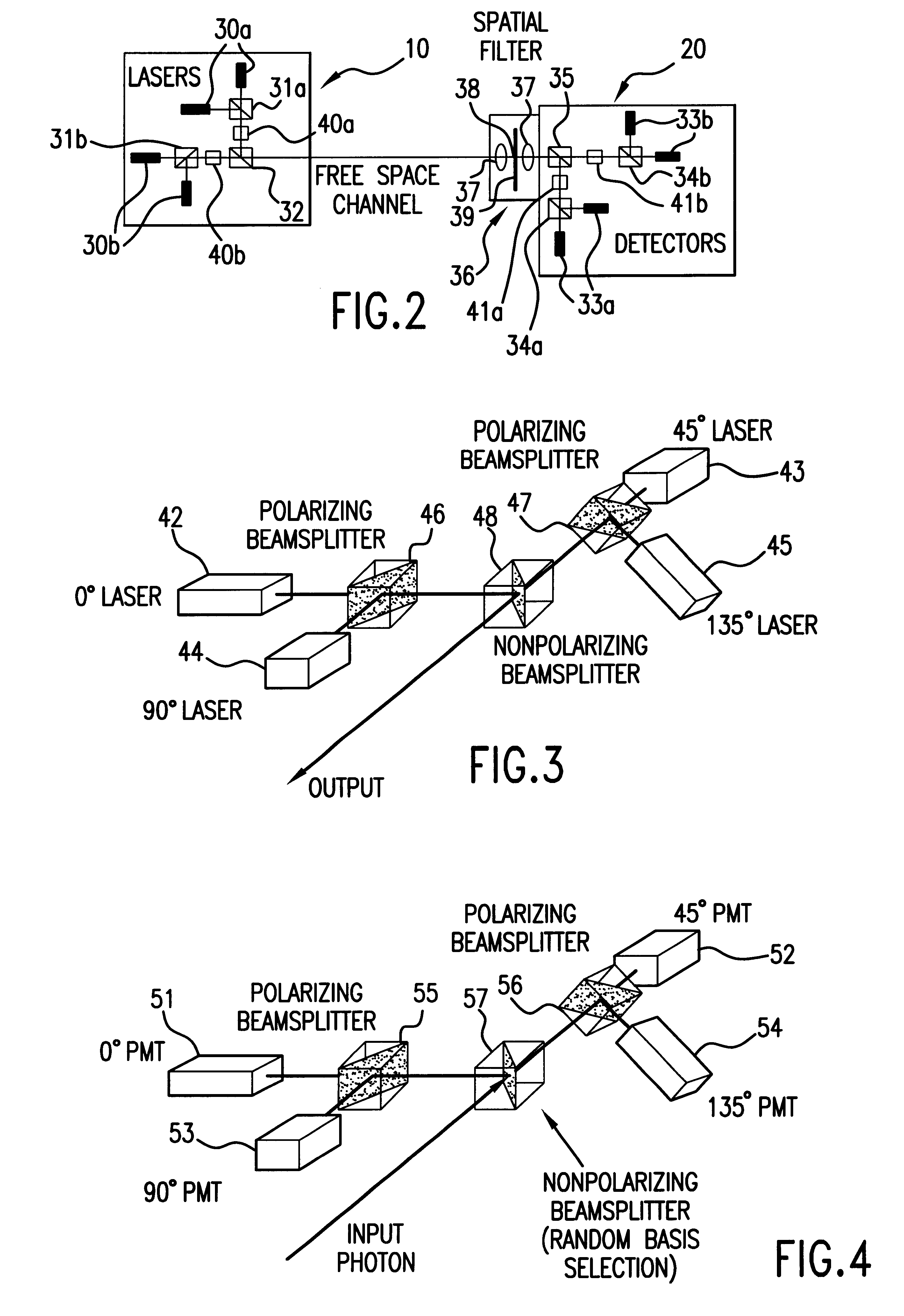
Free-space quantum cryptography system
InactiveUS6289104B1Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationOptoelectronicsPolarization beam splitter
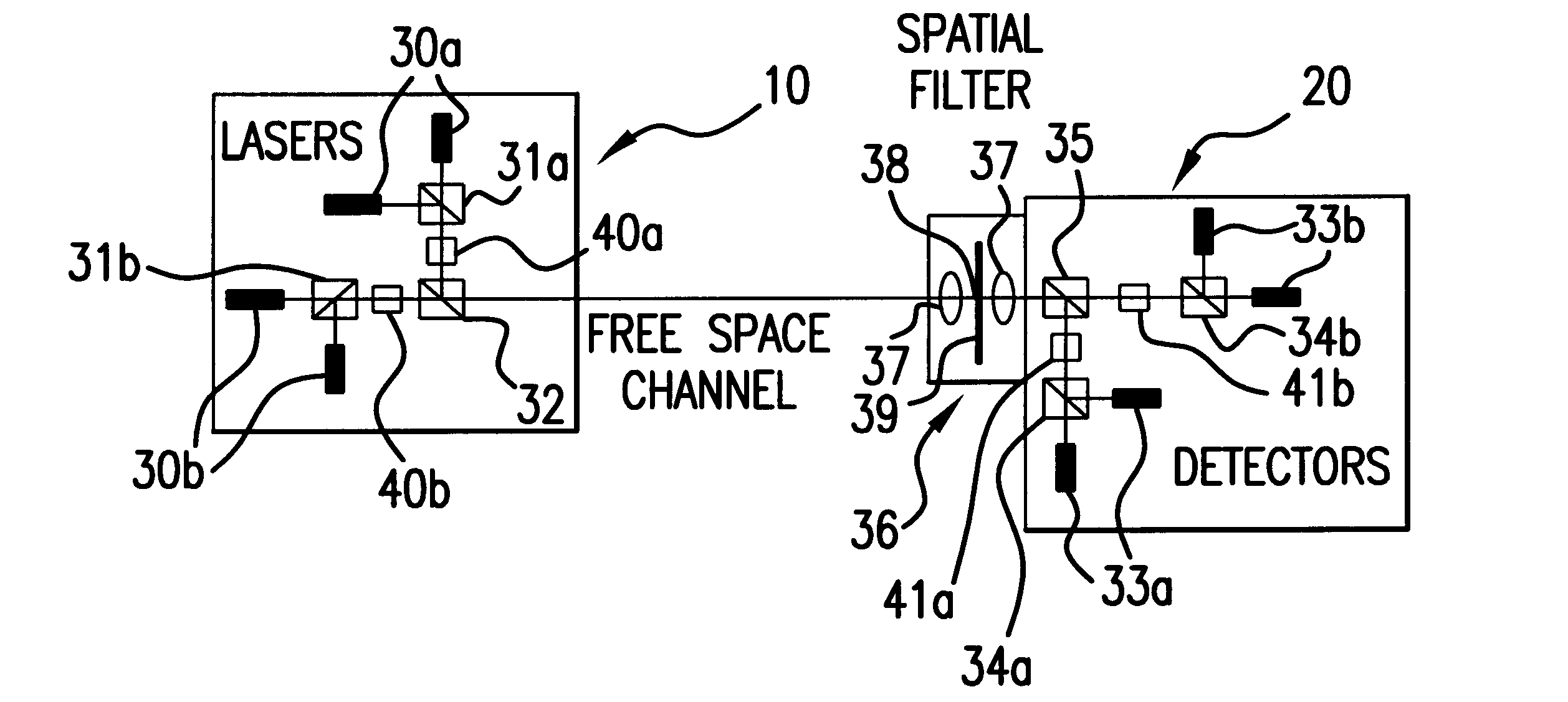
A system and method for quantum key delivery in a single-photon, free-space cryptography scheme including a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter includes two pairs of photon sources, each of which represents a specific photon polarization direction. The first pair of photon sources represents a first polarization basis while the remaining pair of photon sources represents a second polarization basis. The first and second polarization basis are rotated with respect to each other so as to produce non-orthogonal polarization eigenstates. A transmitter polarizing beamsplitter corresponding to each of the pairs of the photon sources is provided whereby the polarizations of each of the photon sources of each pair of photon sources are recombined. A transmitter non-polarizing beamsplitter is provided whereby the recombined polarizations are combined for output to the receiver. The receiver includes a set of optics inversely disposed with respect to the optics of the transmitter and two pairs of photon detectors.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Time-of-flight based imaging system using a display as illumination source
InactiveUS20110037849A1Easy to implementLow cost configurationColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsElectronic systemsPhoton emission
The present invention concerns a time-of-flight based imaging system comprising a photon emitter used as an illumination source; a photon sensor (6); an electronic system for delivering a signal depending on the reception time of photons by said photon detector, characterized in that an electronic display (2) is used as said photonic source.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
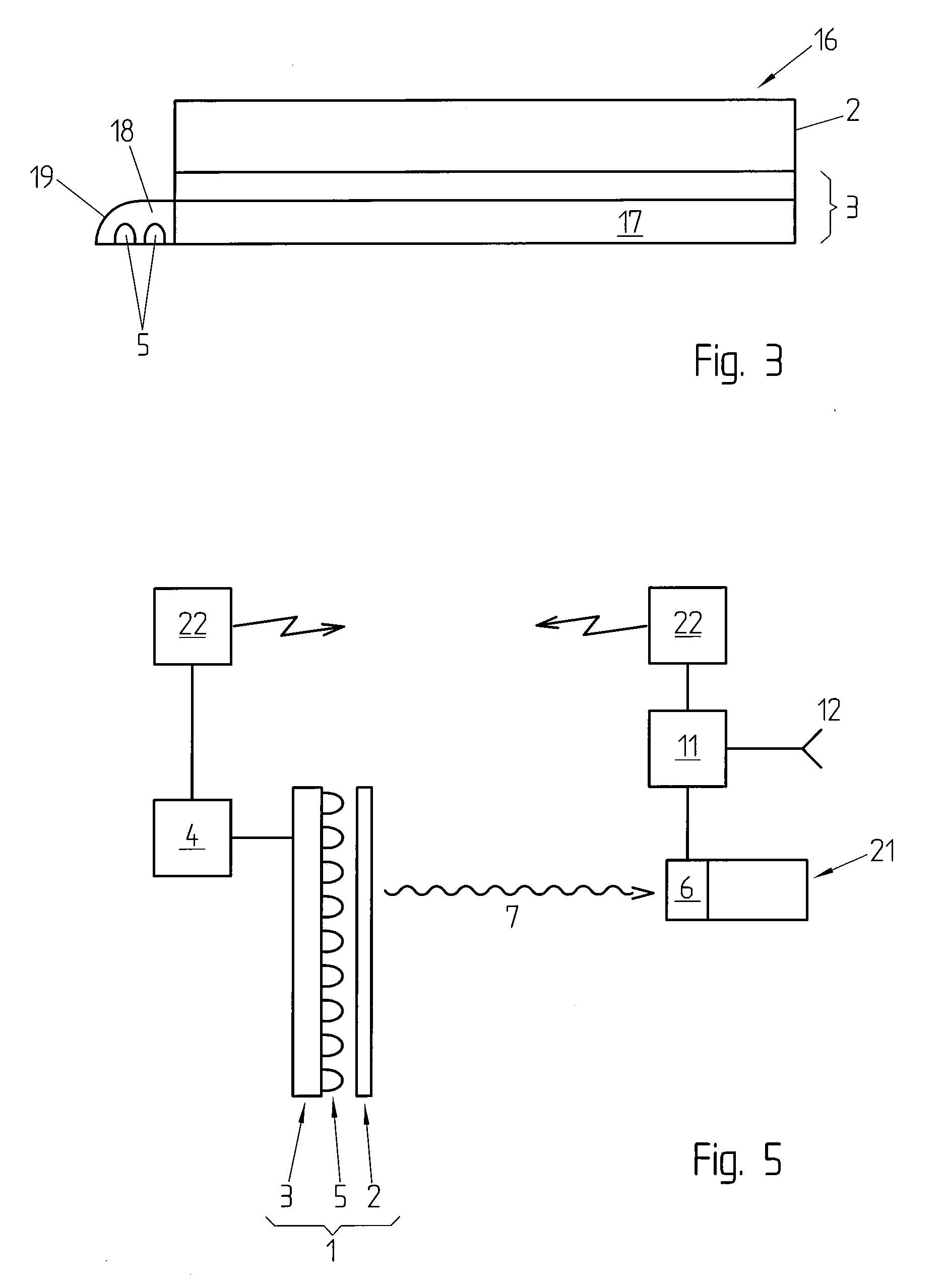
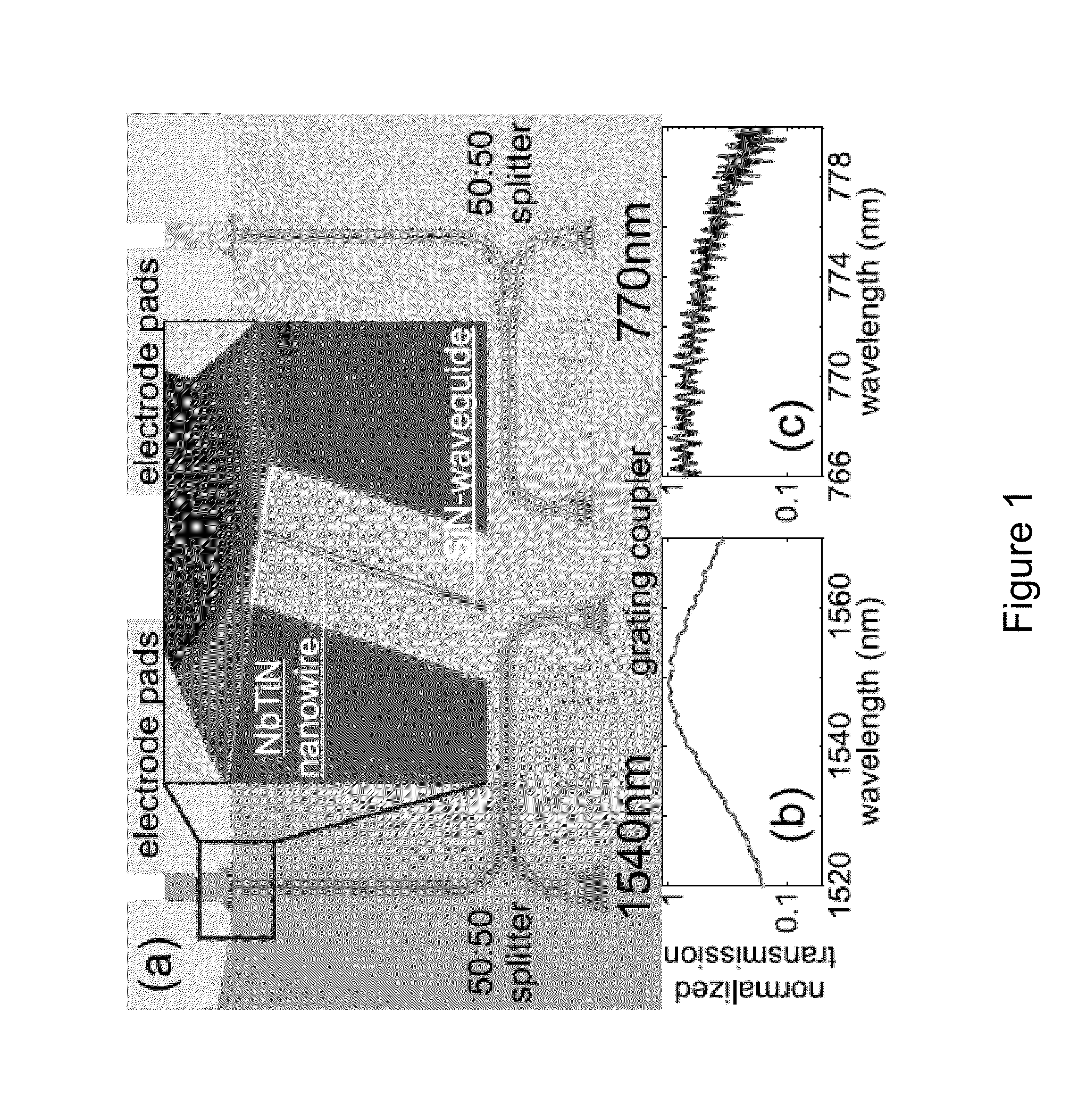
Superconducting Single Photon Detector
The present invention provides a device and system for high-efficiency and low-noise detection of single photons within the visible and infrared spectrum. In certain embodiments, the device of the invention can be integrated within photonic circuits to provide on-chip photon detection. The device comprises a traveling wave design comprising a waveguide layer and a superconducting nanowire atop of the waveguide.
Owner:YALE UNIV
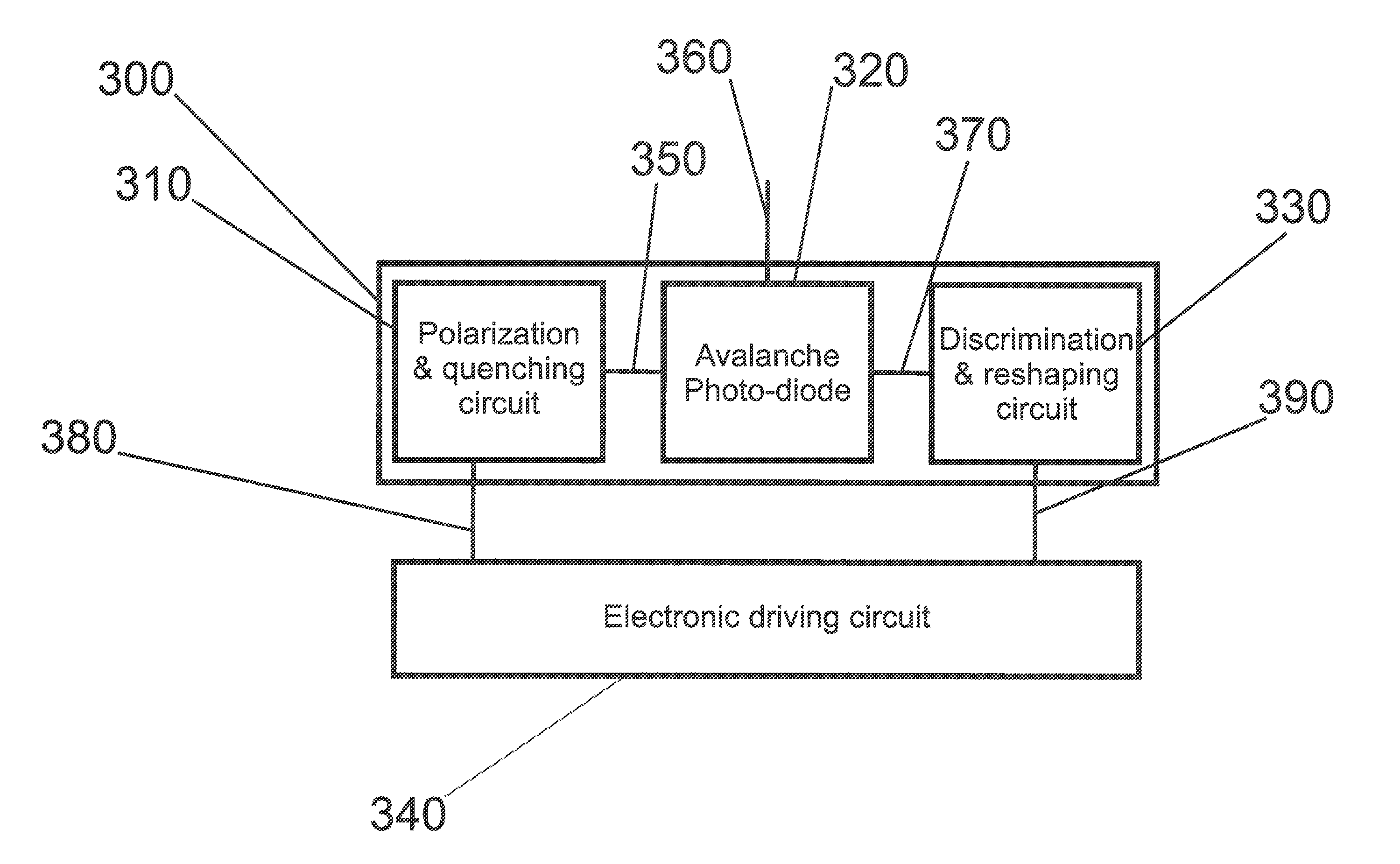
Apparatus and method for allowing avalanche photodiode based single-photon detectors to be driven by the same electrical circuit in gated and in free-running modes
An apparatus and method for allowing avalanche photodiode based single-photon detectors to be driven by the same electrical circuit in gated and in free-running modes is proposed. The high-performance working of all the running modes relies on the capability of tuning the rise-time value of the electrical pulse driver which activates the avalanche photodiode in Geiger mode.
Owner:ID QUANTIQUE SA
Density detection using real time discrete photon counting for fast moving targets
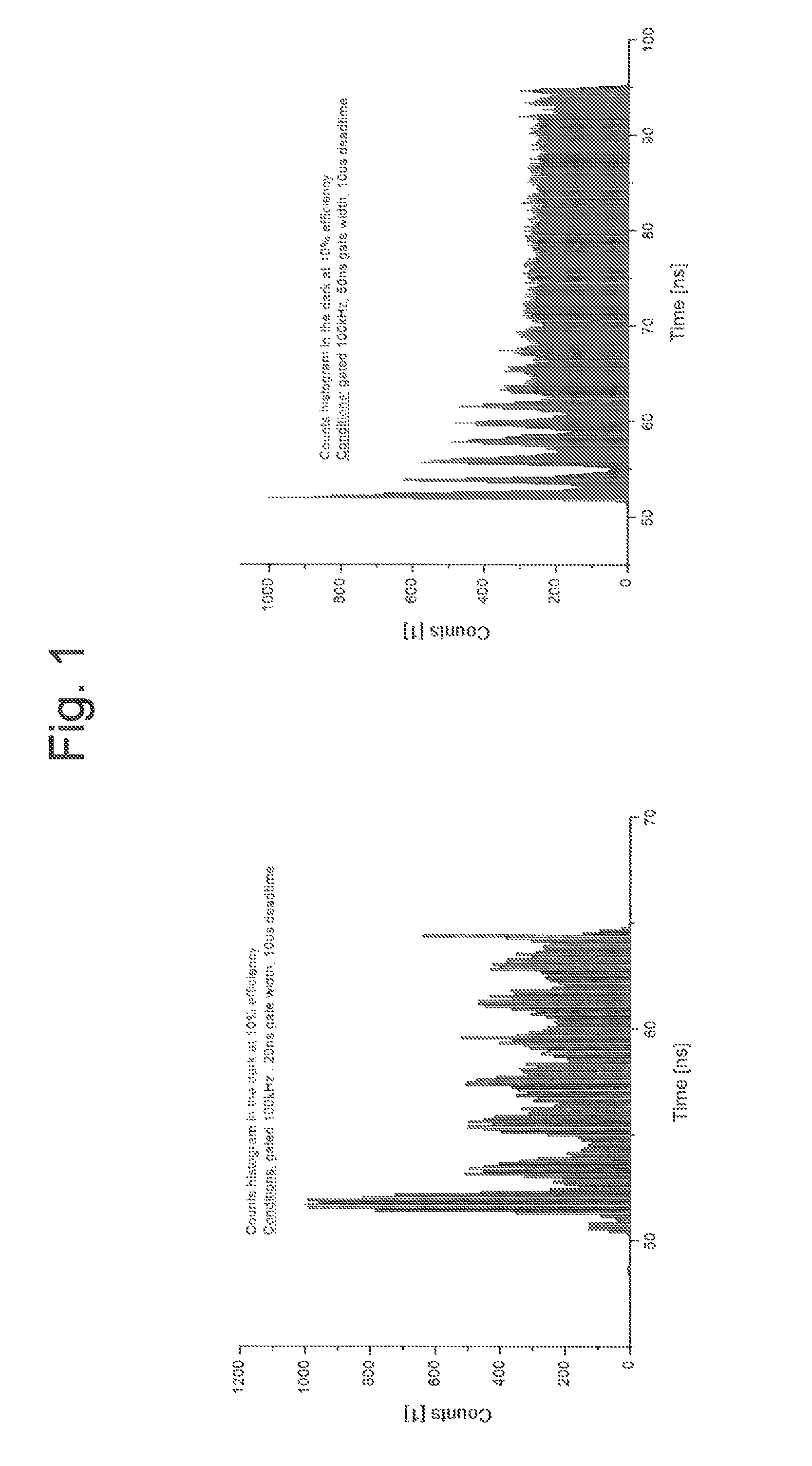
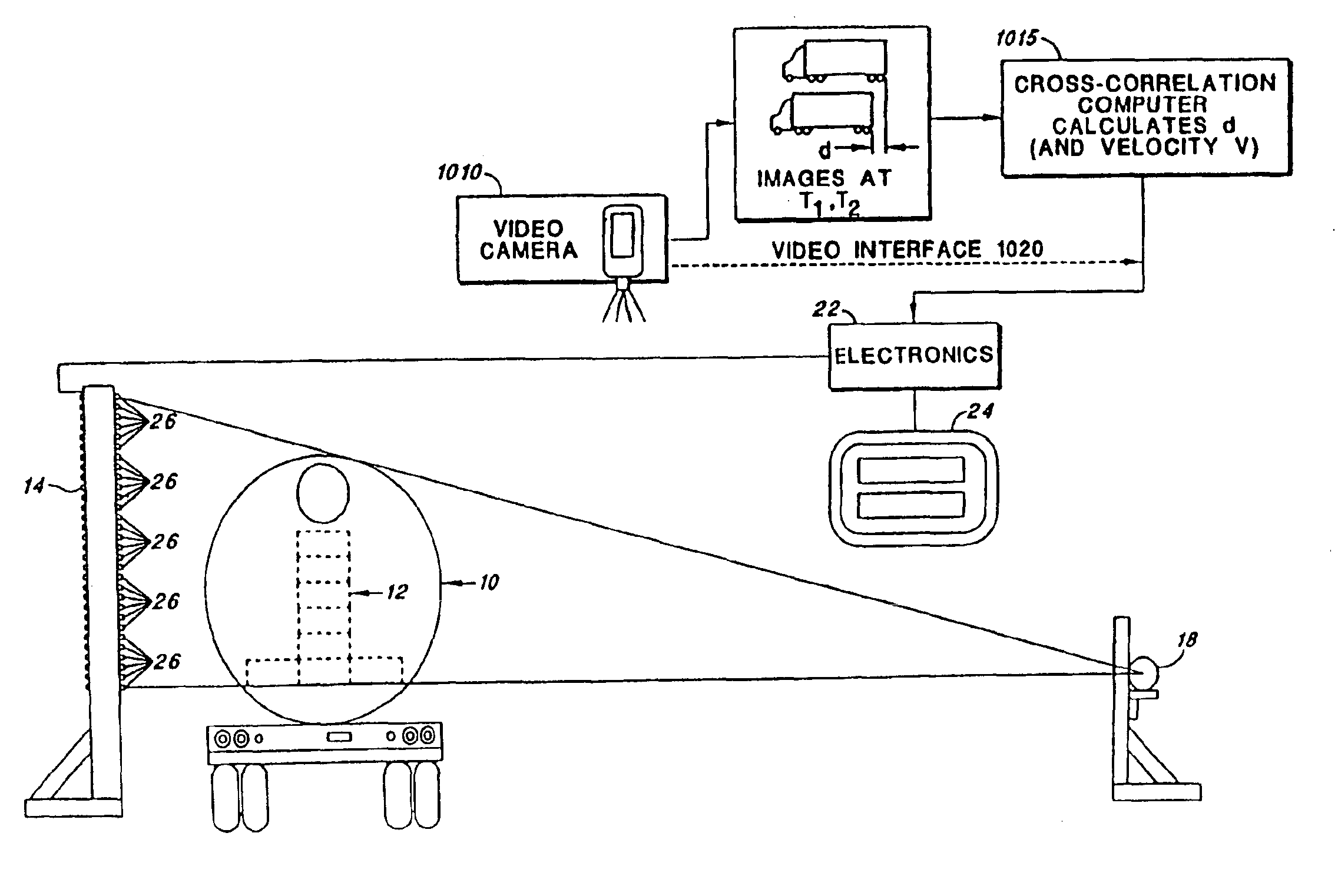
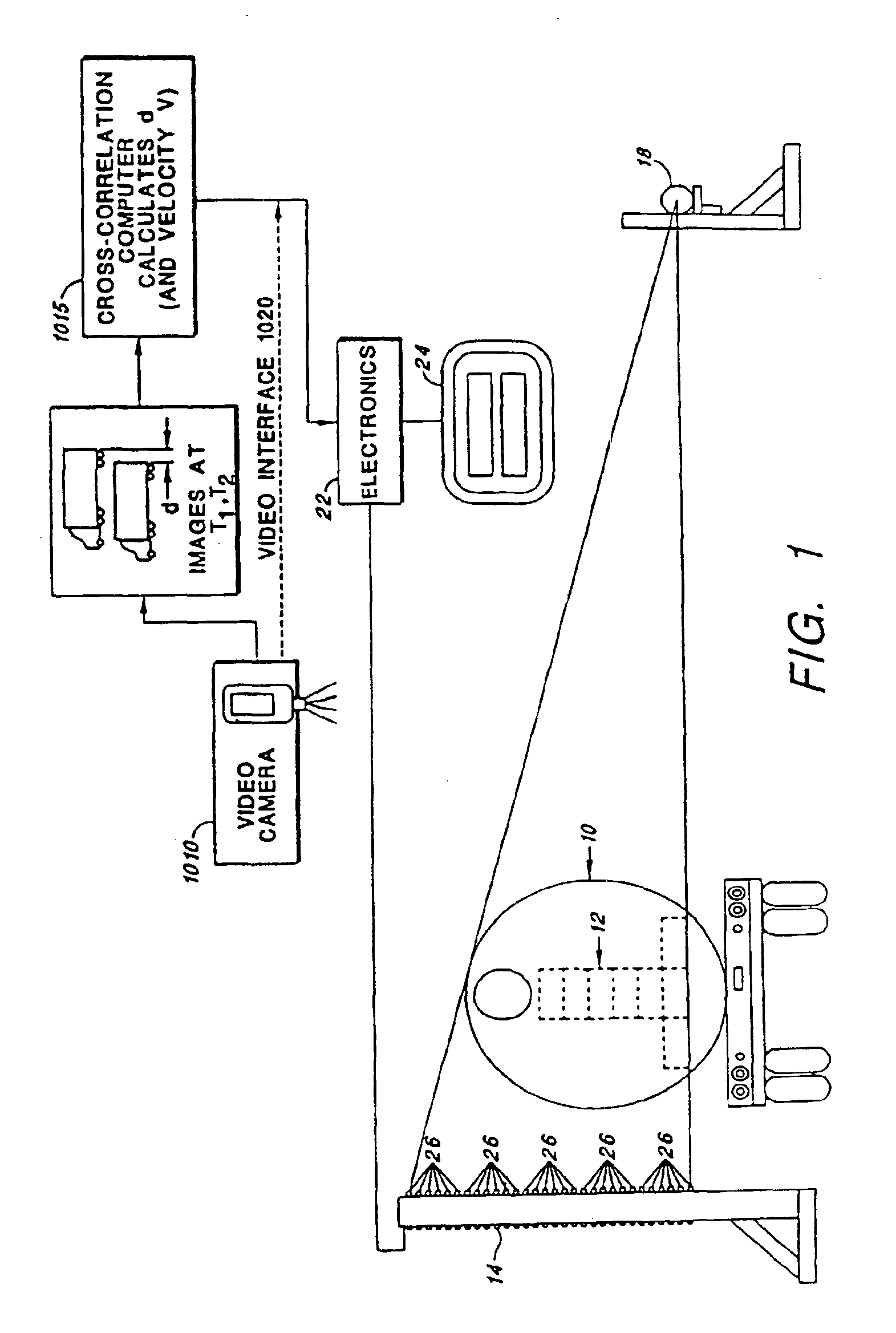
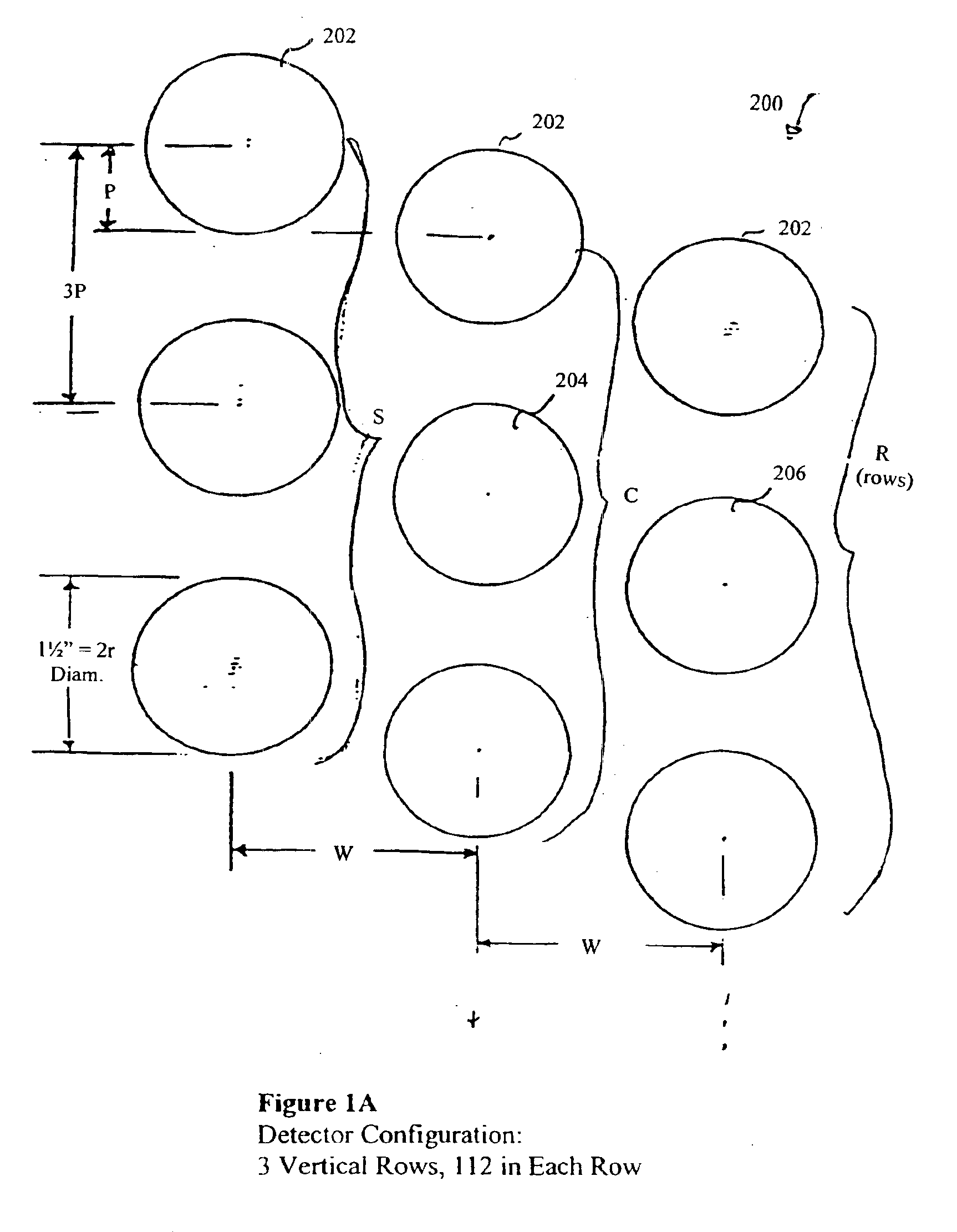
A system for detecting and graphically displaying a contents of a fast-moving target object comprises: a radiation source, having a position such that at least a portion of radiation emitted from the radiation source passes through the fast-moving target object, the fast-moving target object having a variable velocity and acceleration while maintaining a substantially constant distance from the radiation source and being selected from the group consisting of: a vehicle, a cargo container and a railroad car; a velocity measuring device configured to measure the variable velocity of the fast-moving target object; a detector array comprising a plurality of photon detectors, having a position such that at least some of the at least a portion of the radiation passing through the target object is received thereby, the detector array having a variable count time according to the variable velocity and a grid unit size; a counter circuit coupled to the detector array for discretely counting a number of photons entering individual photon detectors, the counter circuit measuring a count rate according to a contents within the fast-moving target object; a high baud-rate interface coupled to the counter circuit for sending count information from the counter circuit at a rate fast enough to support real-time data transfer therethrough; and a processor coupled to the velocity measuring device and to the high-baud-rate interface, receiving count information from the high baud-rate interface and generating distortion-free image data in real time as a function of the count information and the variable velocity. A method for using the system is also disclosed.
Owner:LEIDOS
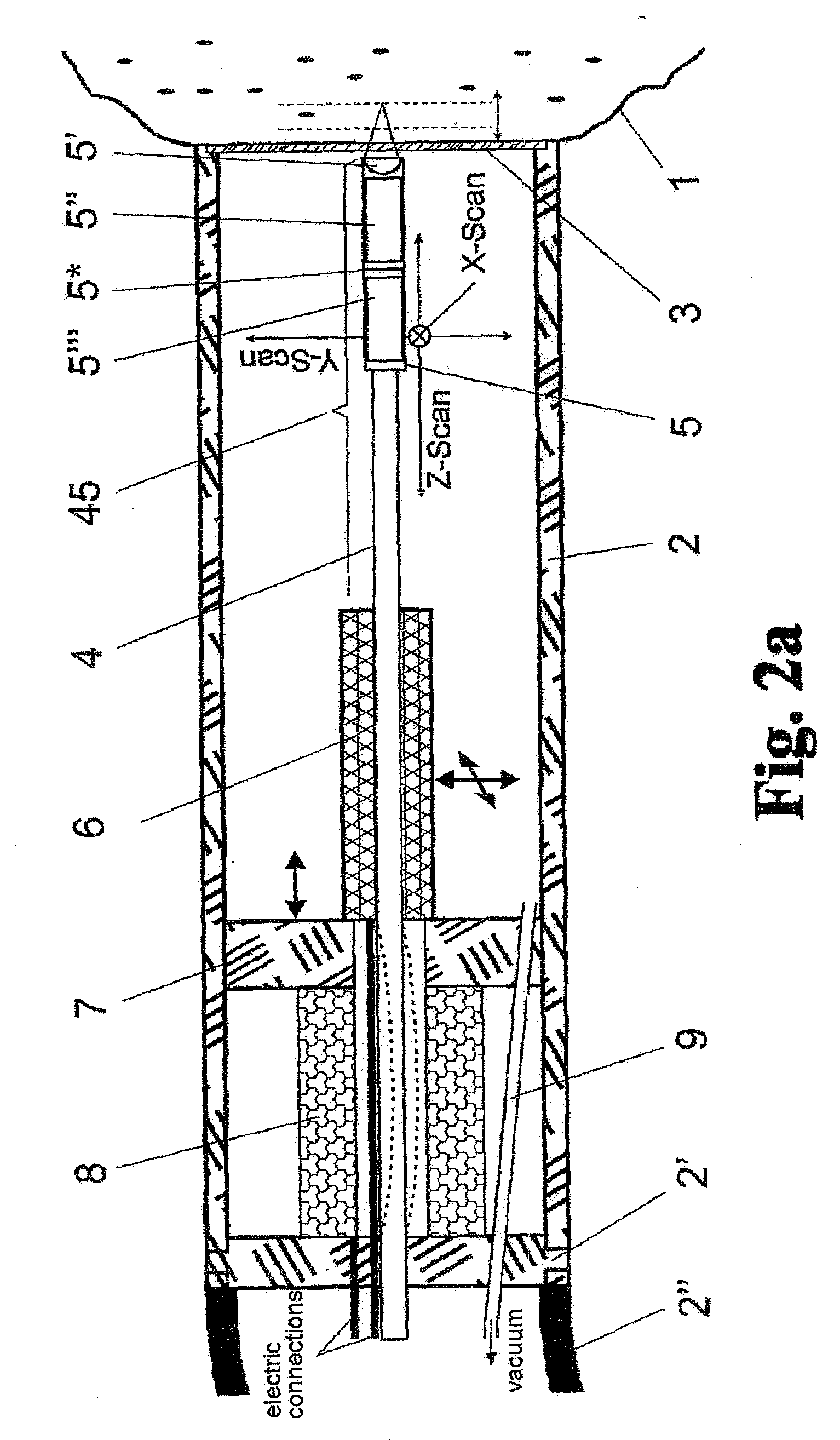
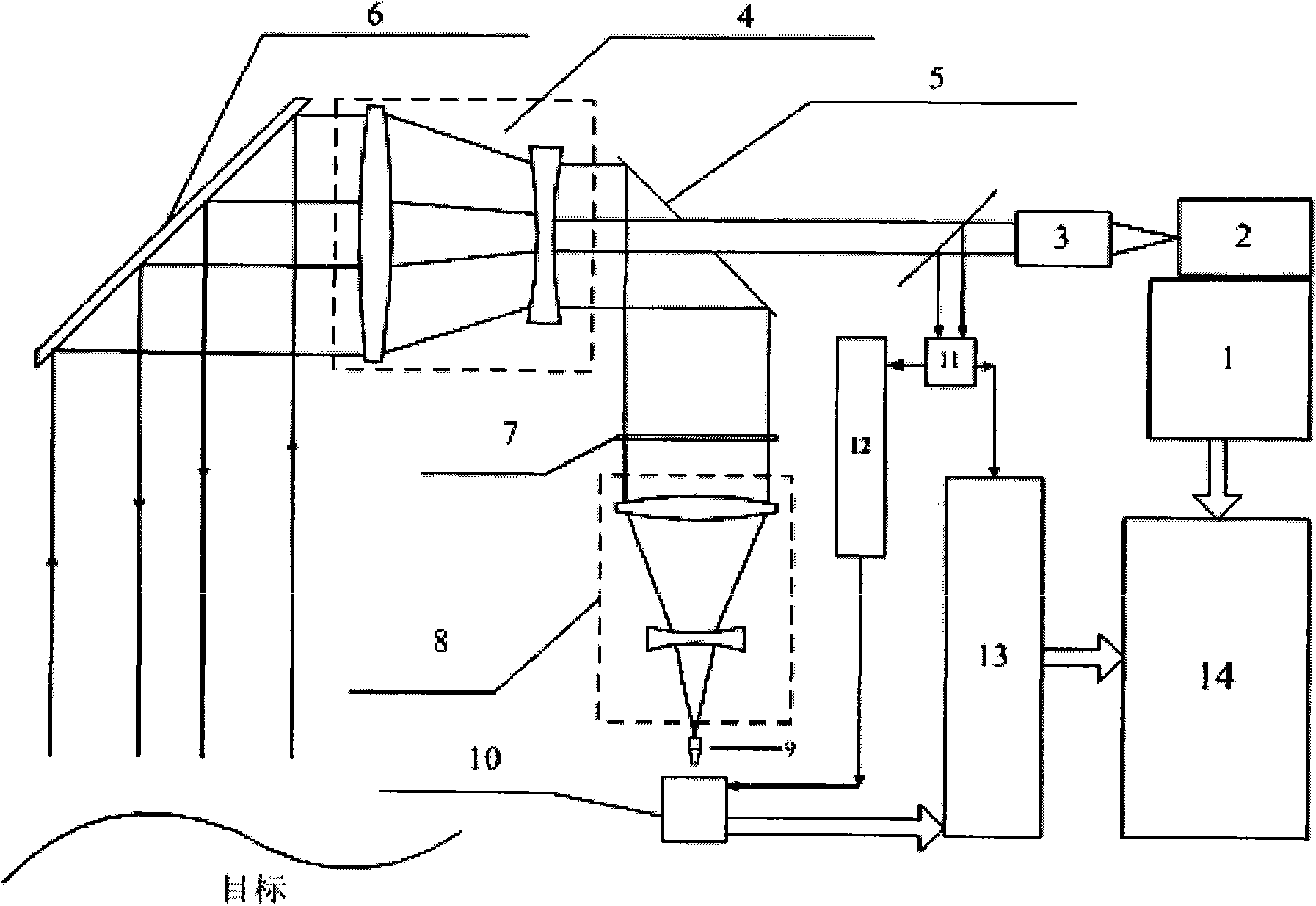
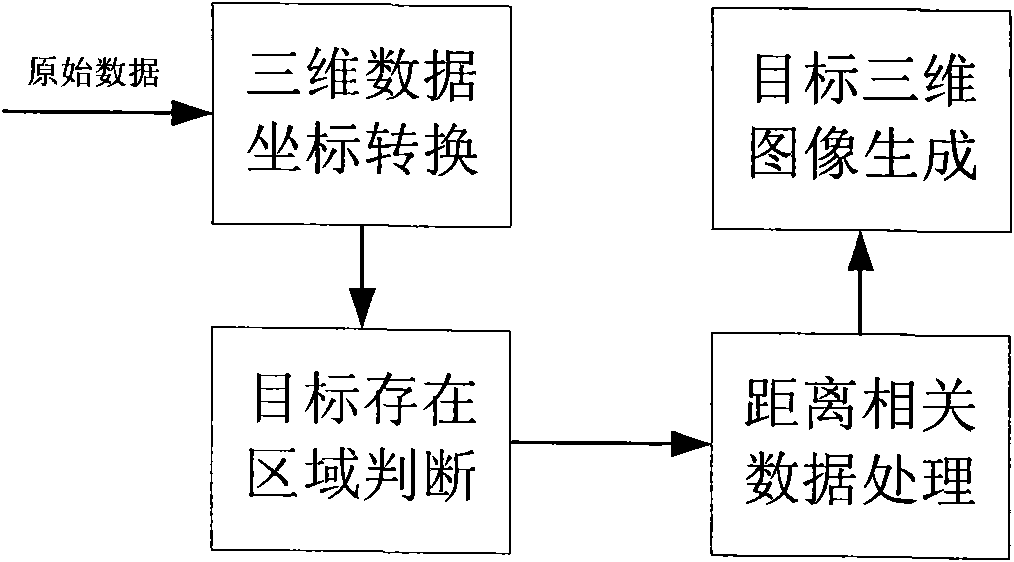
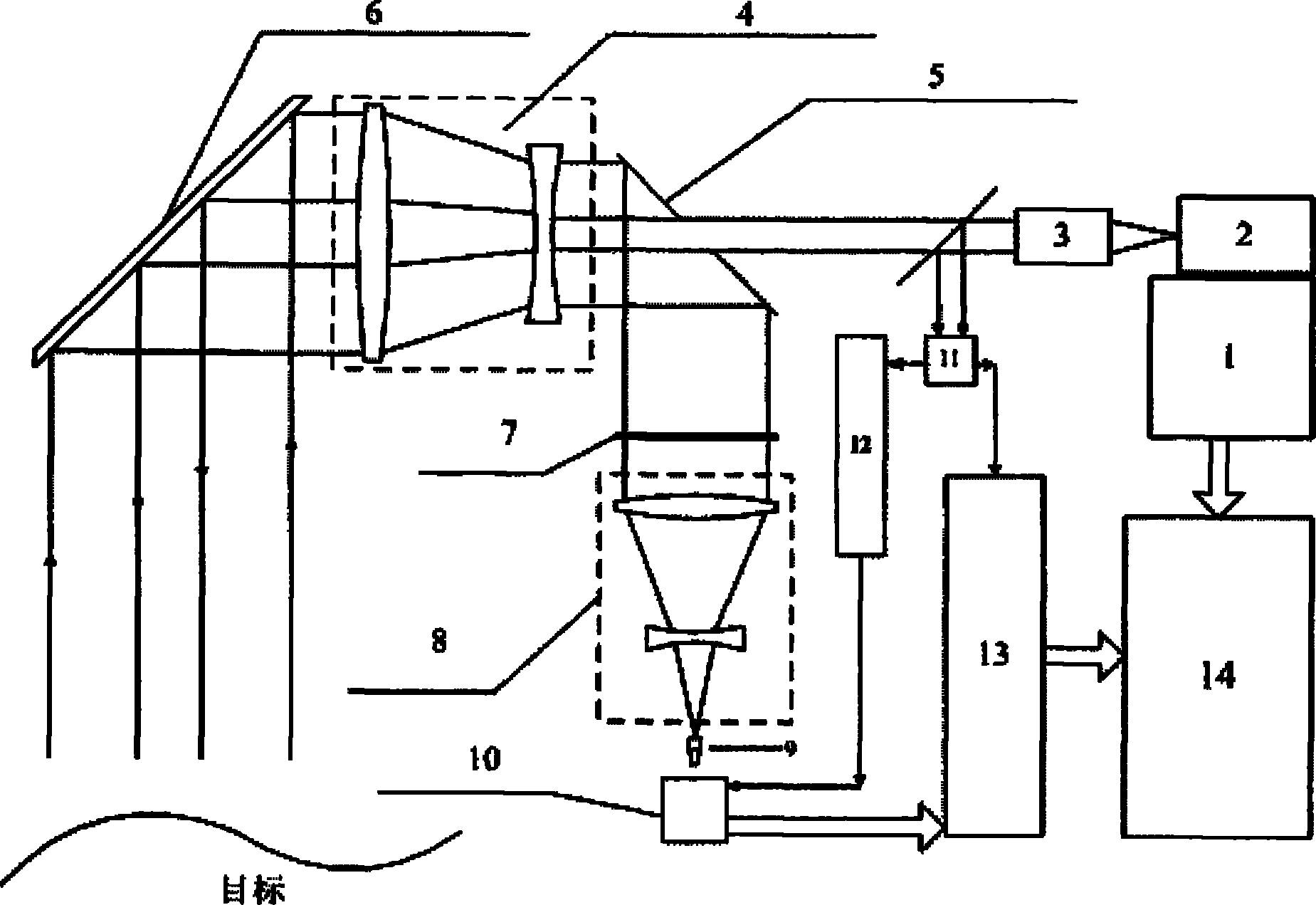
Laser three-dimensional imaging device based on single-photon detector
InactiveCN101776760AHigh sensitivityMiniaturizationElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical elementsMeasurement pointFlight time
The invention discloses a laser three-dimensional imaging device based on a single-photon detector, belonging to the technical field of photoelectric instruments. A target to be detected is irradiated by the laser pulse emitted by a pulsed laser via a scanning system; the returning photons are received by a receiving / emitting co-axial optical system, i.e., the returning photons are received by a double-gating single-photon detecting module via a spectral filter and a spatial filter and an arriving pulse is outputted, so that the photon flight time of the target measuring point can be measured by combining the laser emission detection and the multi-photon arriving pulse time; and a data processing unit is used for carrying out the coordinate conversion based on the position and attitude data, scanning mirror targeting data, and photon flight time of the three-dimensional imaging device, de-noising and three-dimensional image construction and correction, so as to output the reliable target three-dimensional range image. The invention solves the problems that the existing laser three-dimensional imaging device is incapable of penetrating vegetation and camouflage and being miniaturized when conducting long-distance operations.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
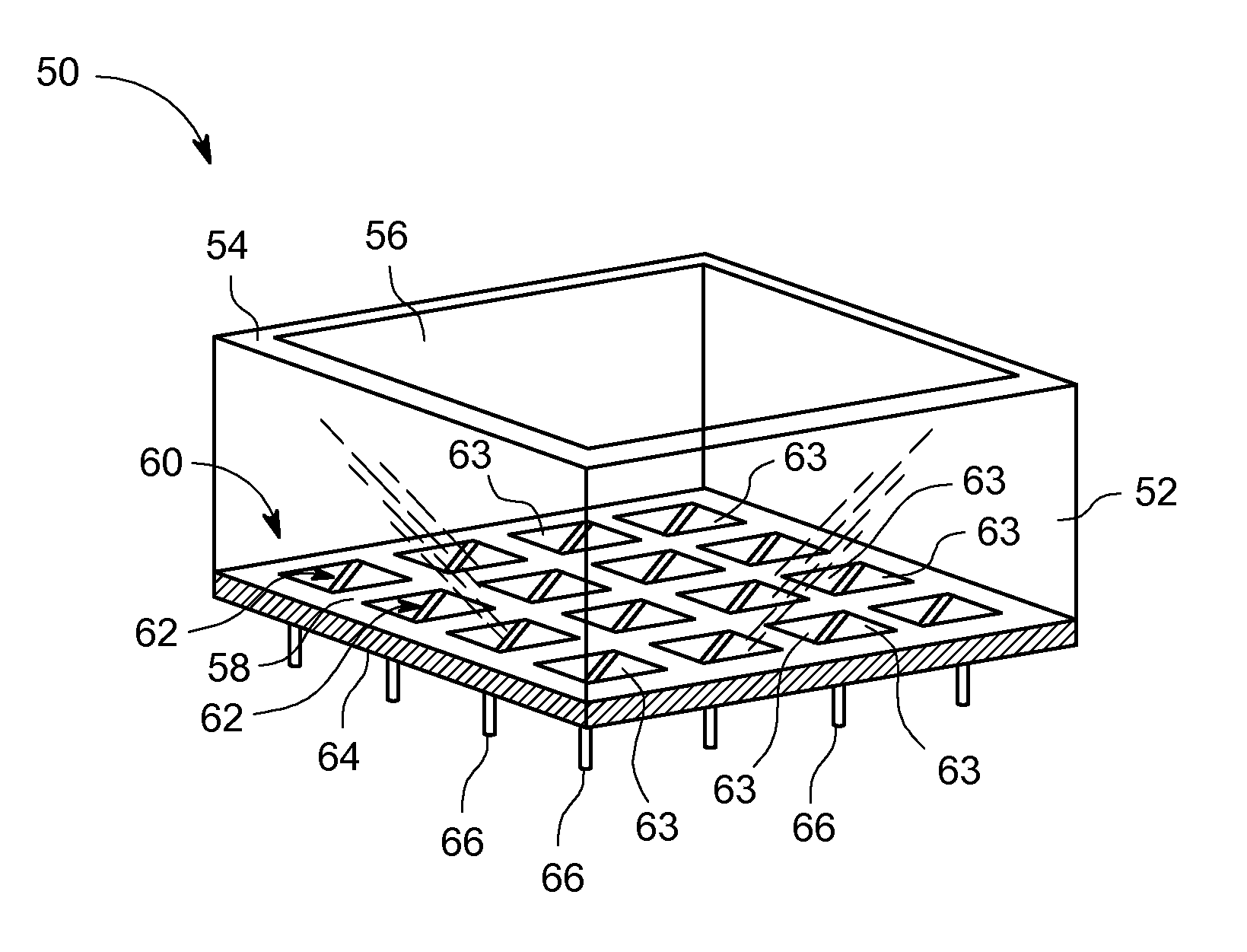
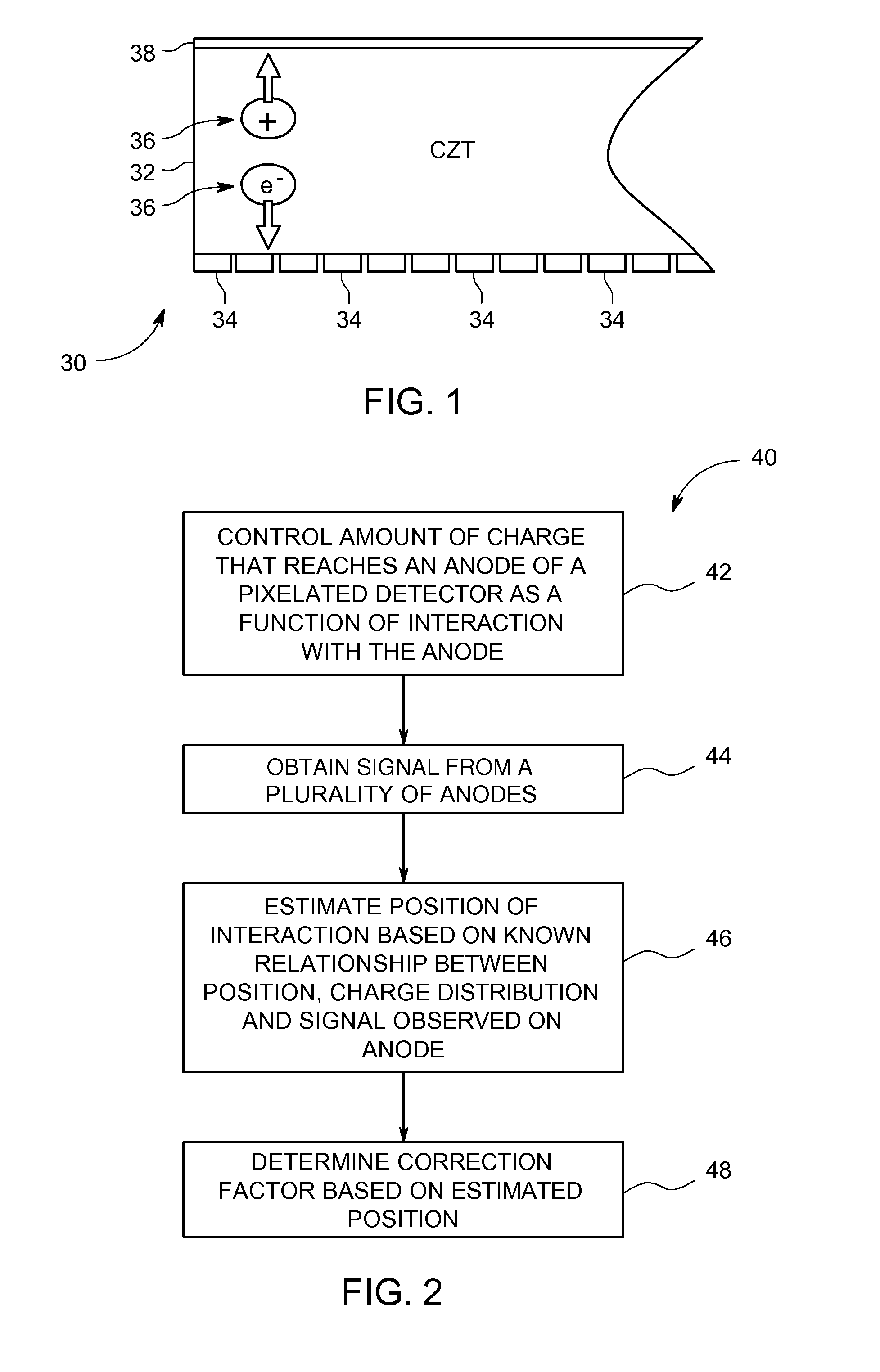
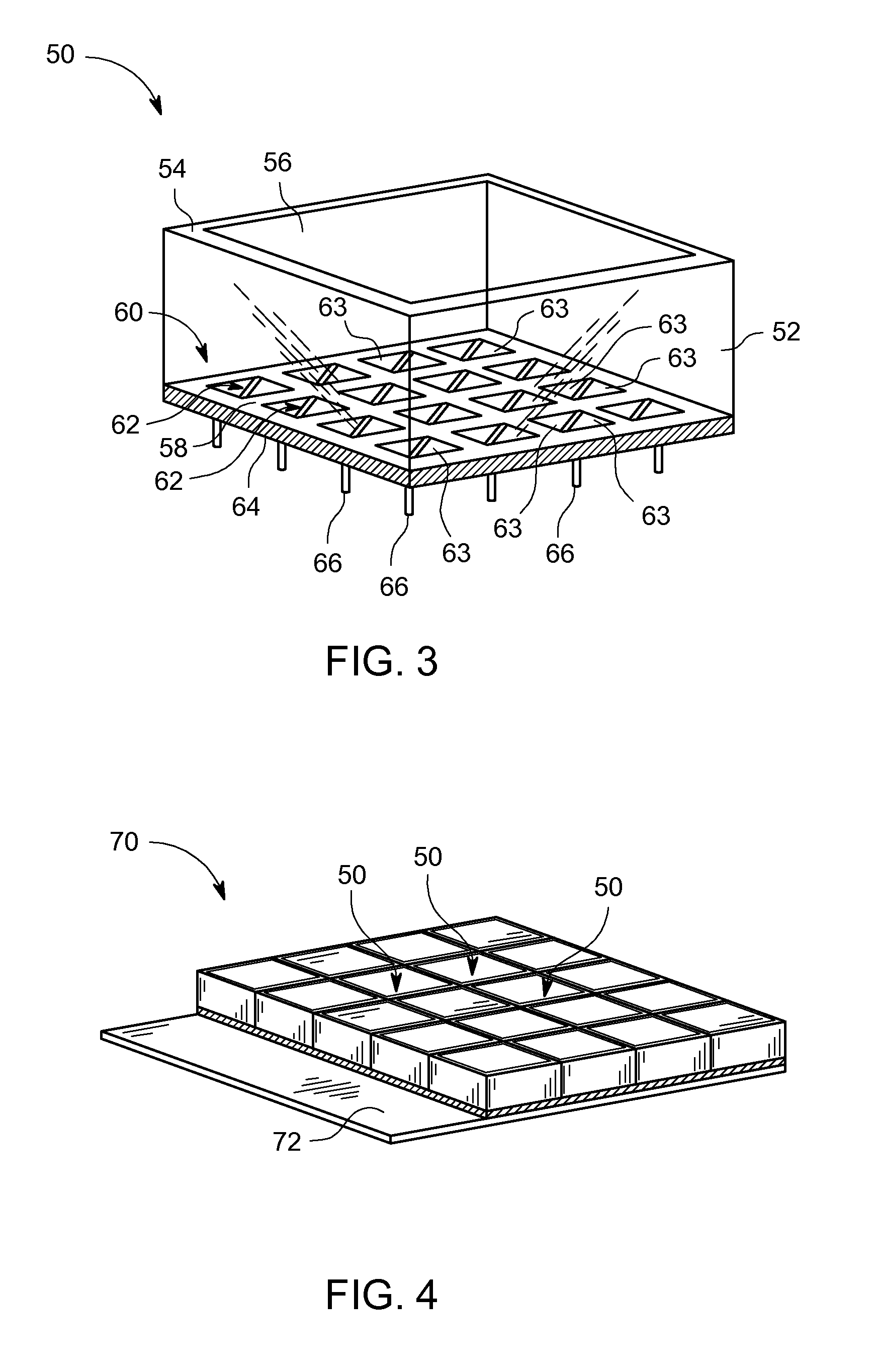
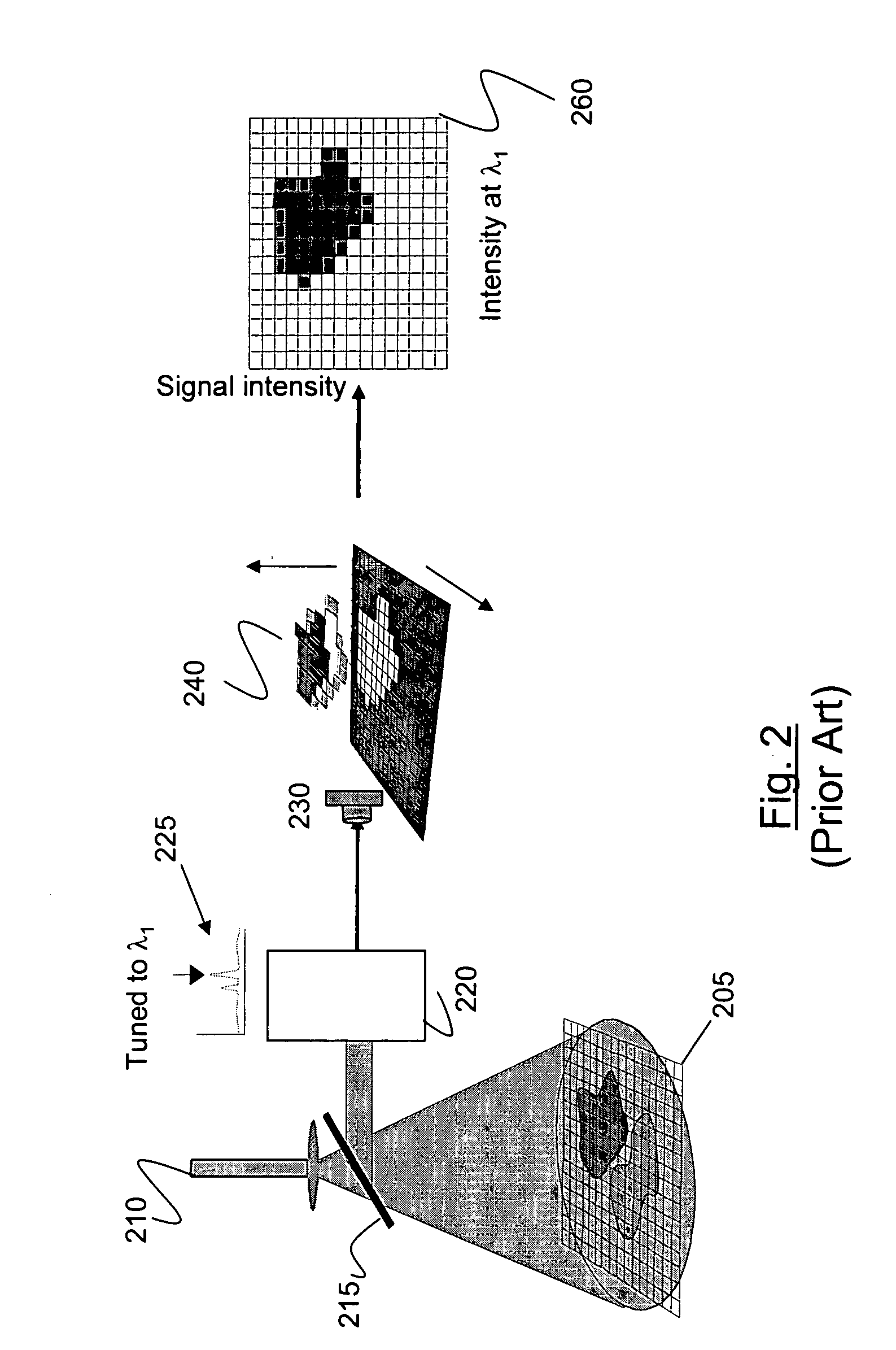
Systems and methods for providing a shared charge in pixelated image detectors
InactiveUS20110155918A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPixel basedComputer science
Systems and methods for providing a shared charge in pixelated image detectors are provided. One method includes providing a plurality of pixels for a pixelated solid state photon detector in a configuration such that a charge distribution is detected by at least two pixels and obtaining charge information from the at least two pixels. The method further includes determining a position of an interaction of the charge distribution with the plurality of pixels based on the obtained charge information.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST ISRAEL
Obstacle Following Sensor Scheme for a mobile robot
InactiveUS20080015738A1Simple designLow costProgramme controlComputer controlEngineeringField of view
A robot obstacle detection system including a robot housing which navigates with respect to a surface and a sensor subsystem aimed at the surface for detecting the surface. The sensor subsystem includes an emitter which emits a signal having a field of emission and a photon detector having a field of view which intersects the field of emission at a region. The subsystem detects the presence of an object proximate the mobile robot and determines a value of a signal corresponding to the object. It compares the value to a predetermined value, moves the mobile robot in response to the comparison, and updates the predetermined value upon the occurrence of an event.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Cryptographic receiver
InactiveUS6028935AKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesFiber couplerPhoton detector
PCT No. PCT / GB94 / 02067 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 10, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 10, 1996 PCT Filed Sep. 23, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 10907 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 20, 1995A cryptographic receiver (10) includes photon detectors (52, 54, 56, 58) arranged to detect photons arriving from filters (22) and (24). A fiber coupler (14) randomly distributes each received photon (16) from an optical fiber toone of two photon channels (18, 20). The filters (22, 24) are each unbalanced Mach-Zehner interferometers with a phase modulator (34, 44) in one arm (28, 38). The filters (22, 24) impose non-orthogonal measurement bases on photons within the respective channels (18, 20). A signal processor (60) derives a cryptographic key-code by analysis of signals received from the photon detectors (52, 54, 46, 58).
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
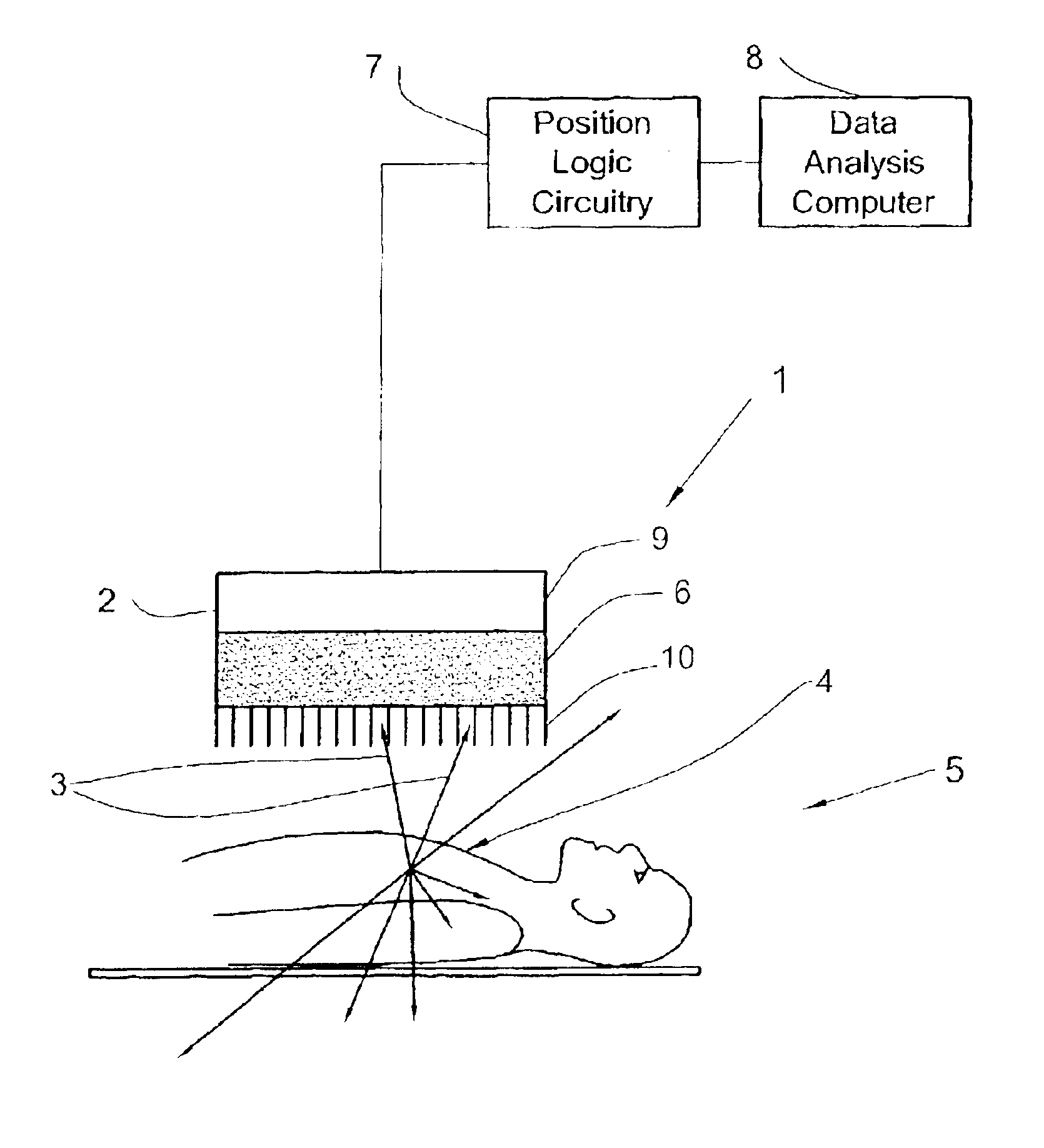
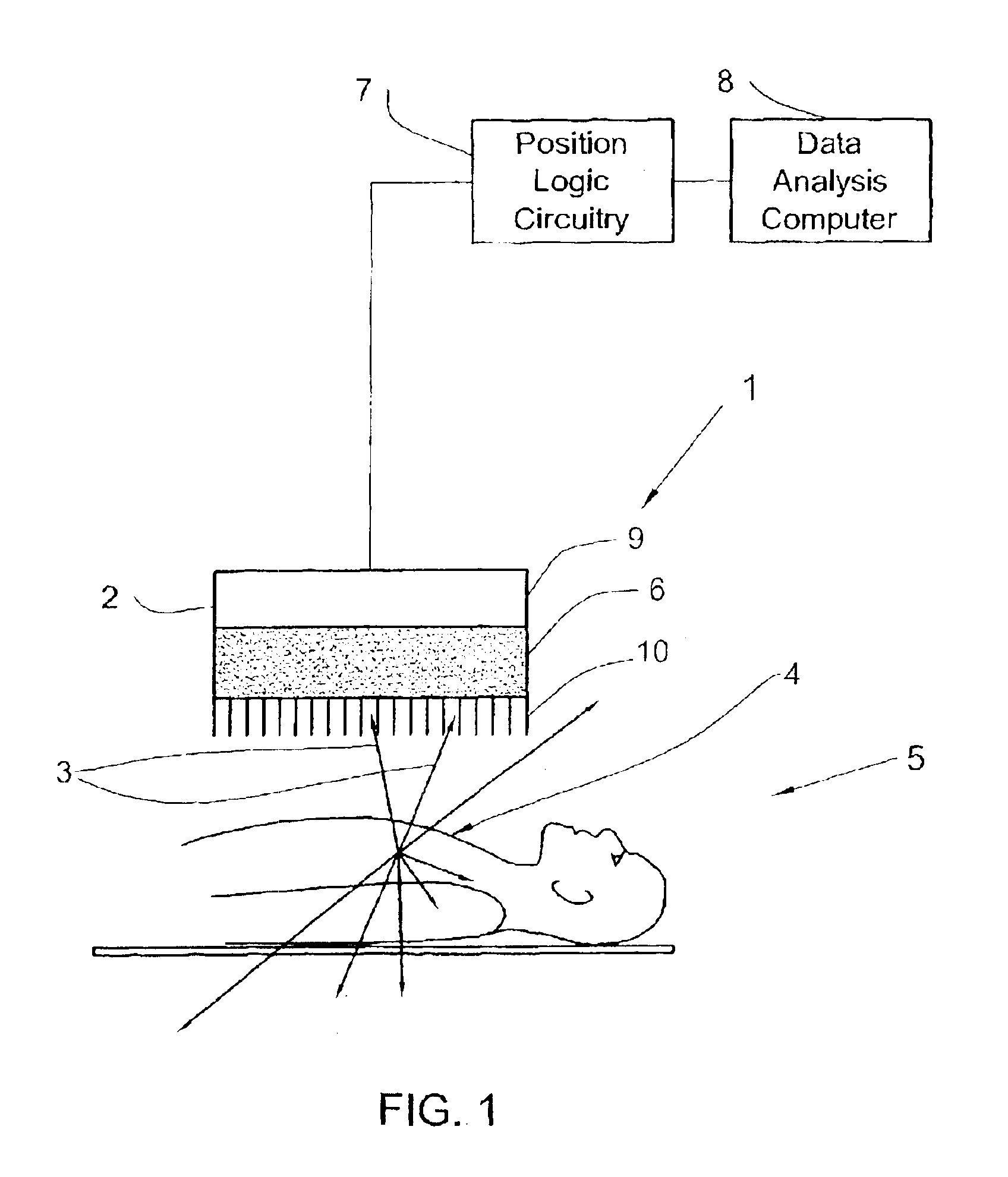
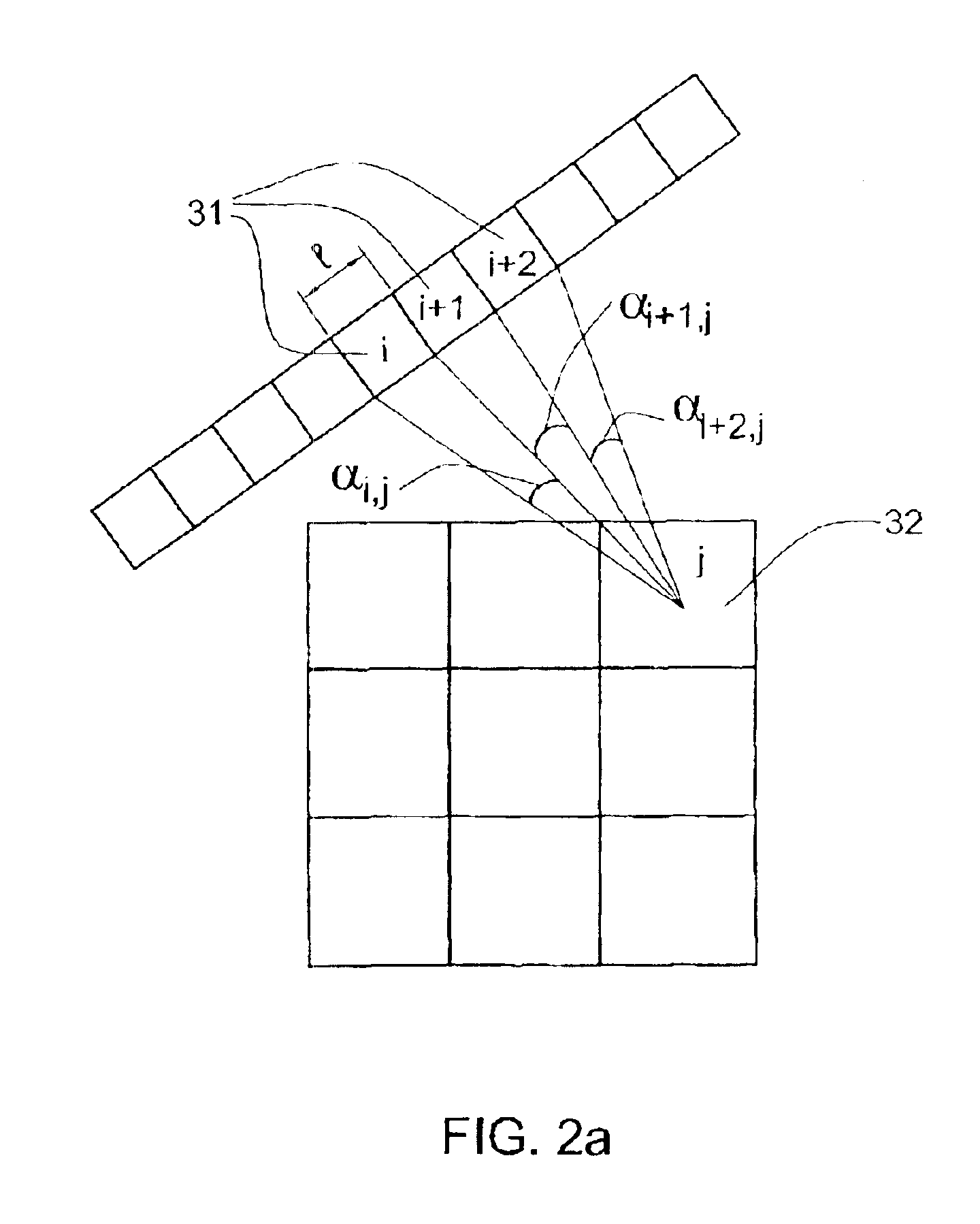
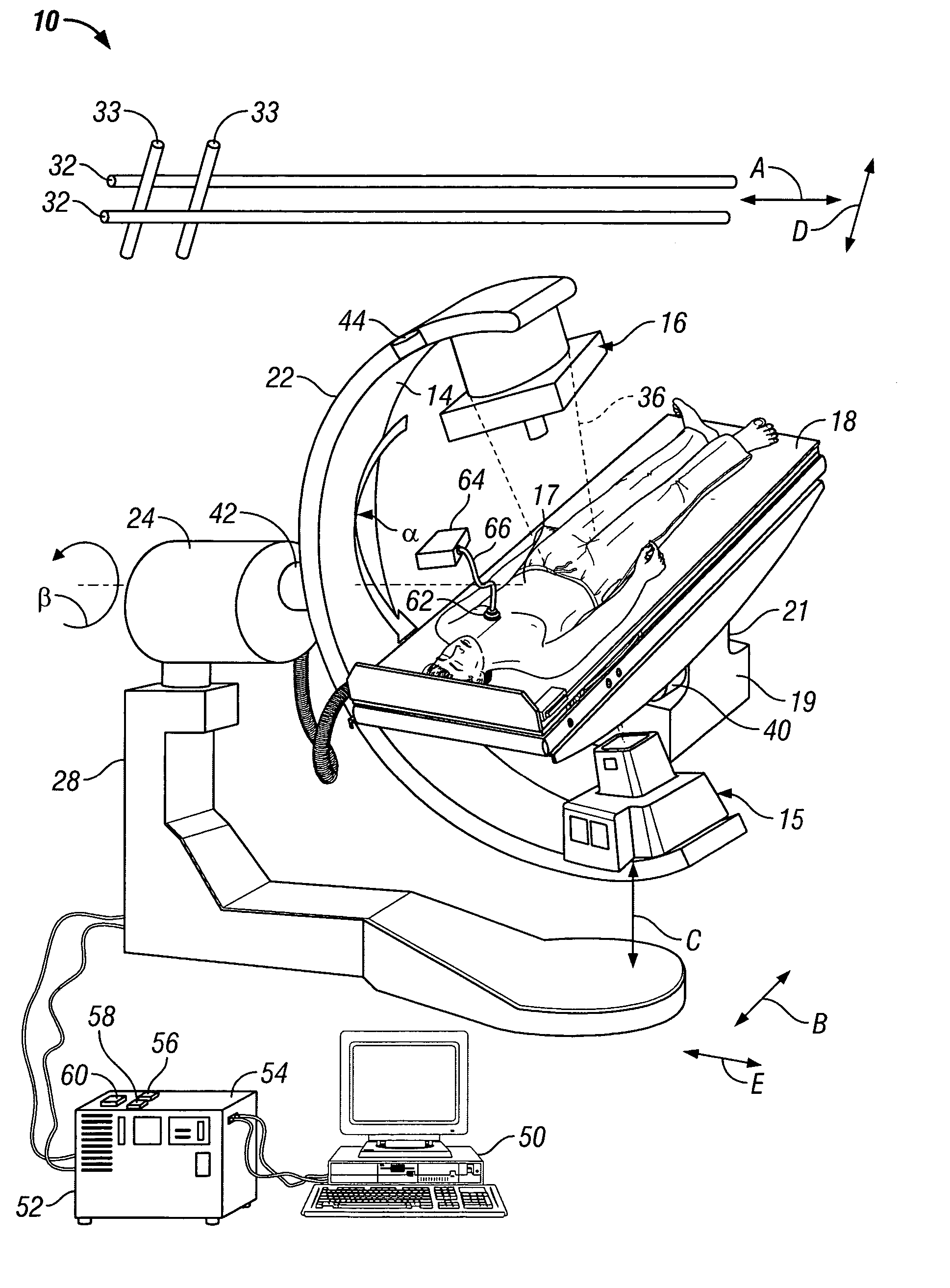
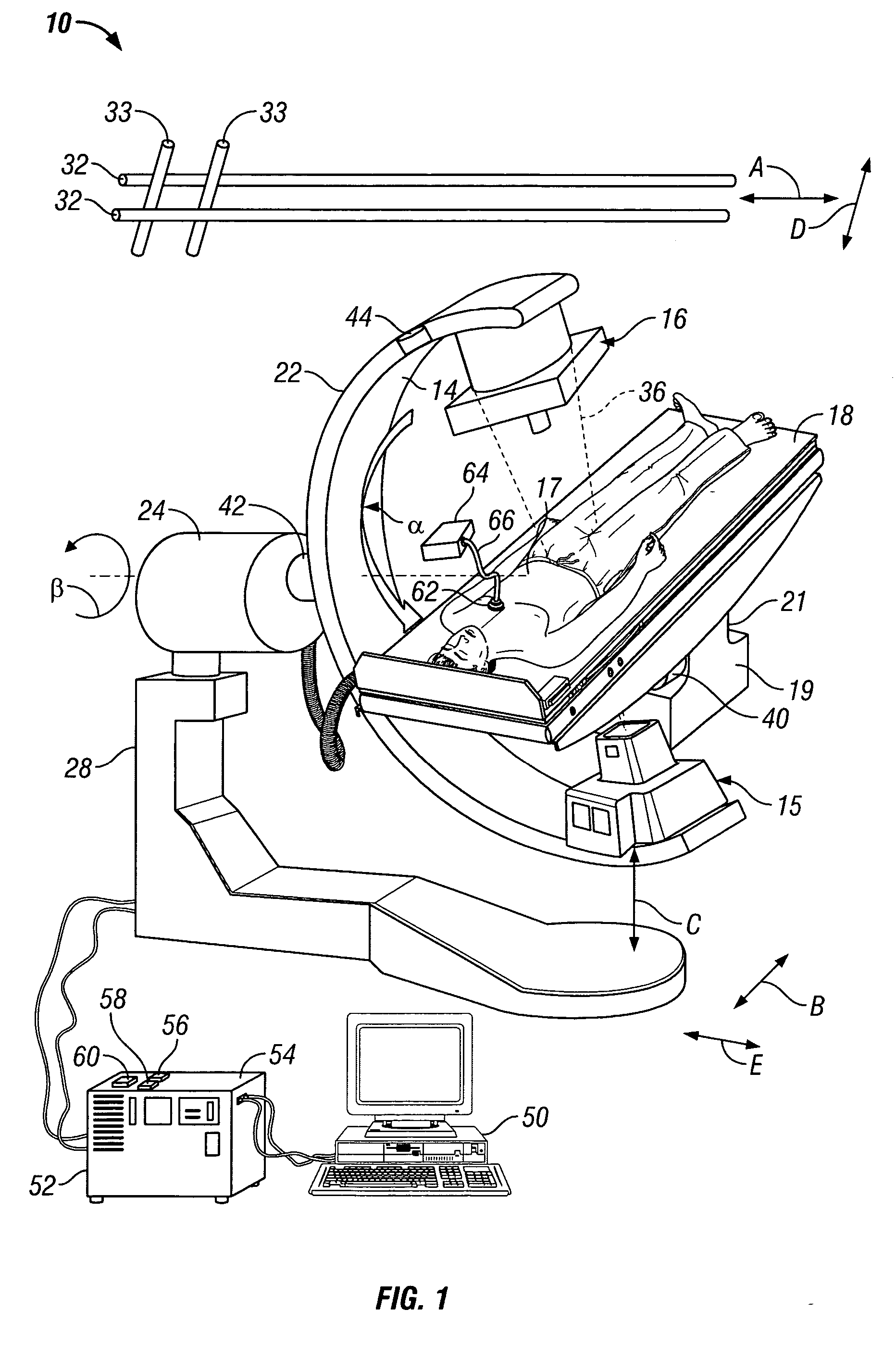
SPECT gamma camera
InactiveUS6943355B2Improve imaging resolutionEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSingle photon emission computerized tomographyGamma ray
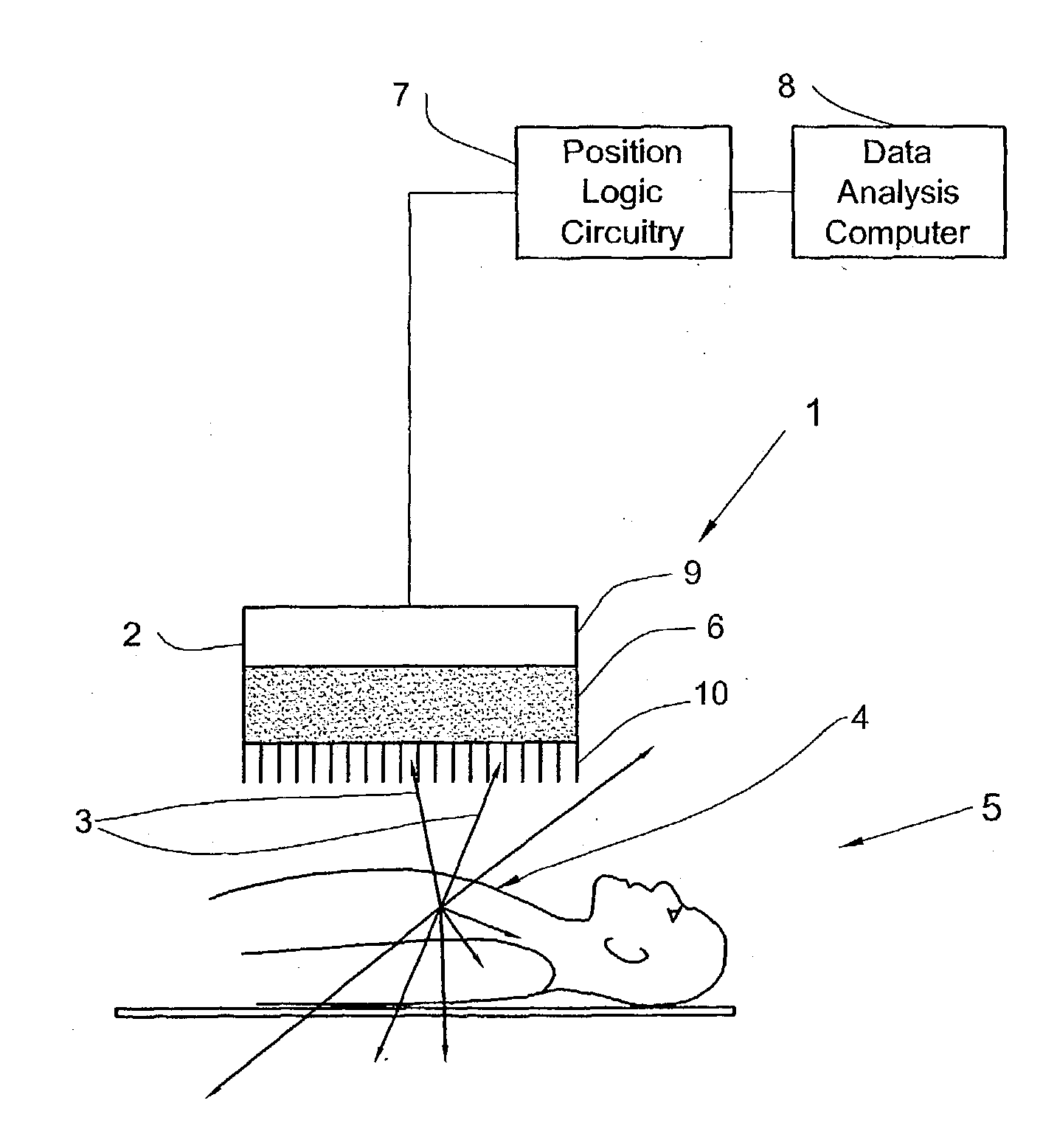
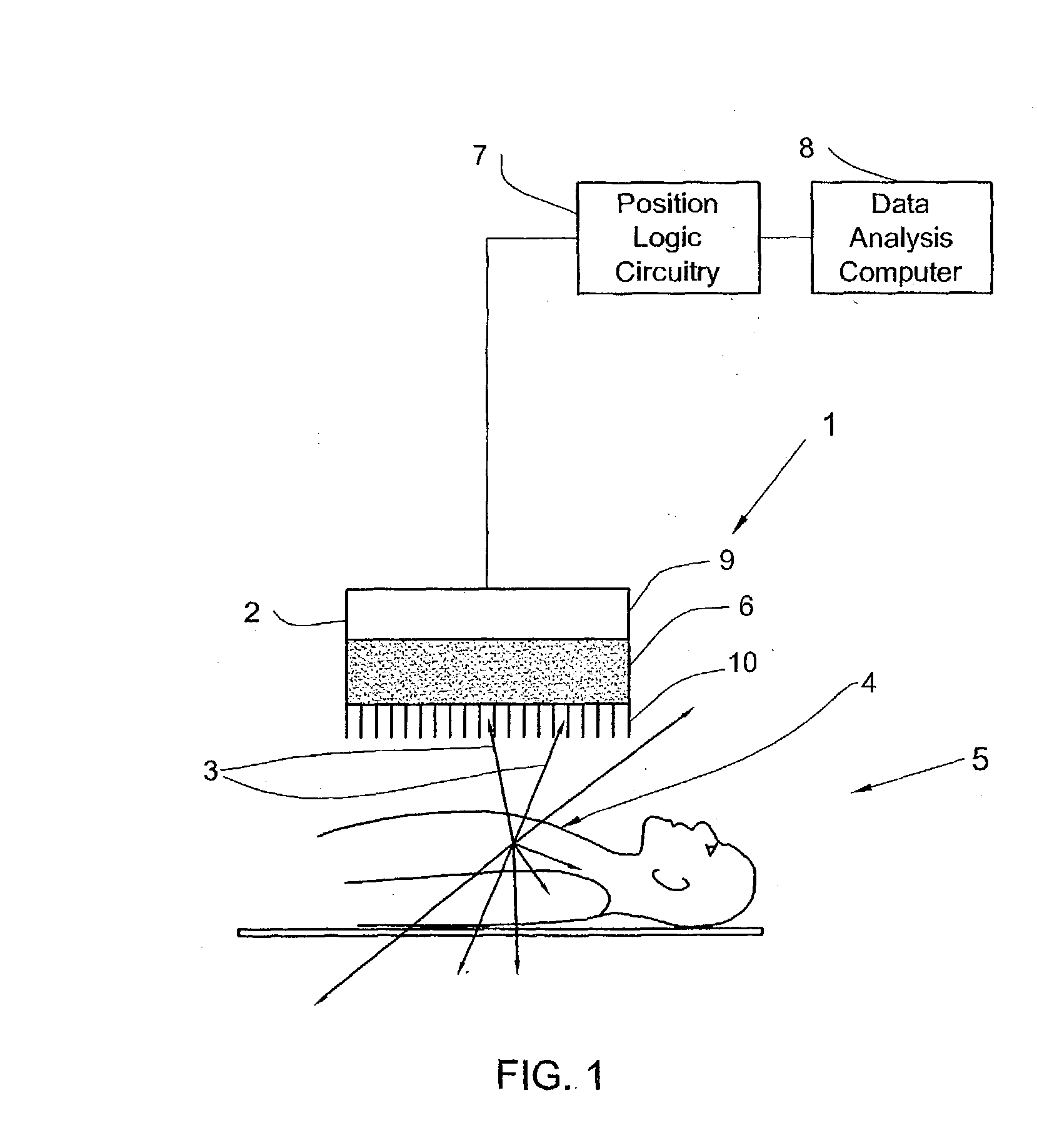
A method and apparatus of obtaining and reconstructing an image of a portion of a body, administered by a radiopharmaceutical substance, by using Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) for determination of functional information thereon. The method comprises (a) acquiring gamma ray photons emitted from said portion by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, the detector having at least one crystal and allowing said gamma rays having incident angles essentially exceeding 5 degrees and, preferably, exceeding 10 degrees to be detected; (b) processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby transforming them into data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and (c) reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by processing said data and taking into consideration weight values which are functions of angles and, possibly, distances between different elements of the portion of the body and corresponding elements of this position's projection on the detector.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
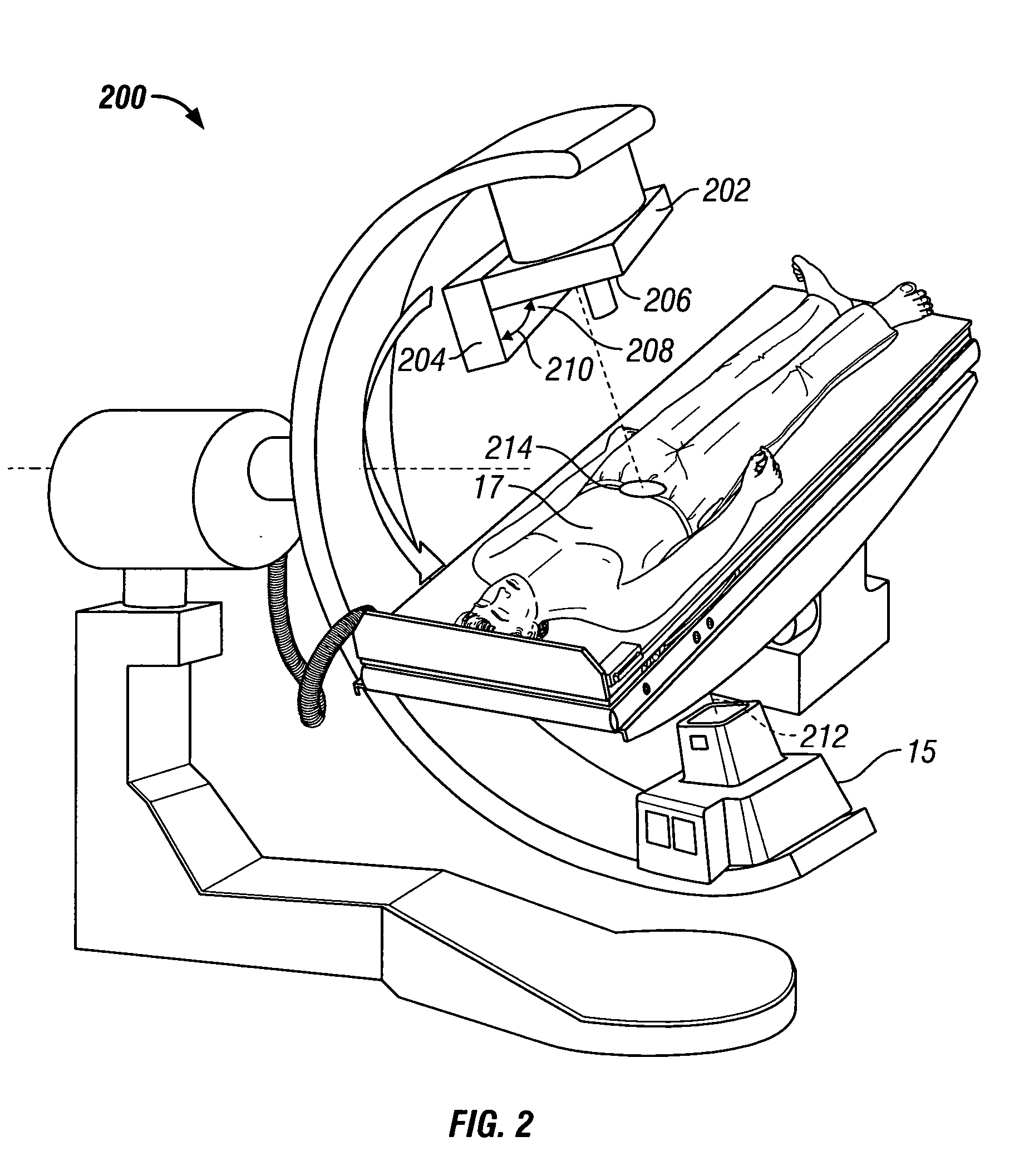
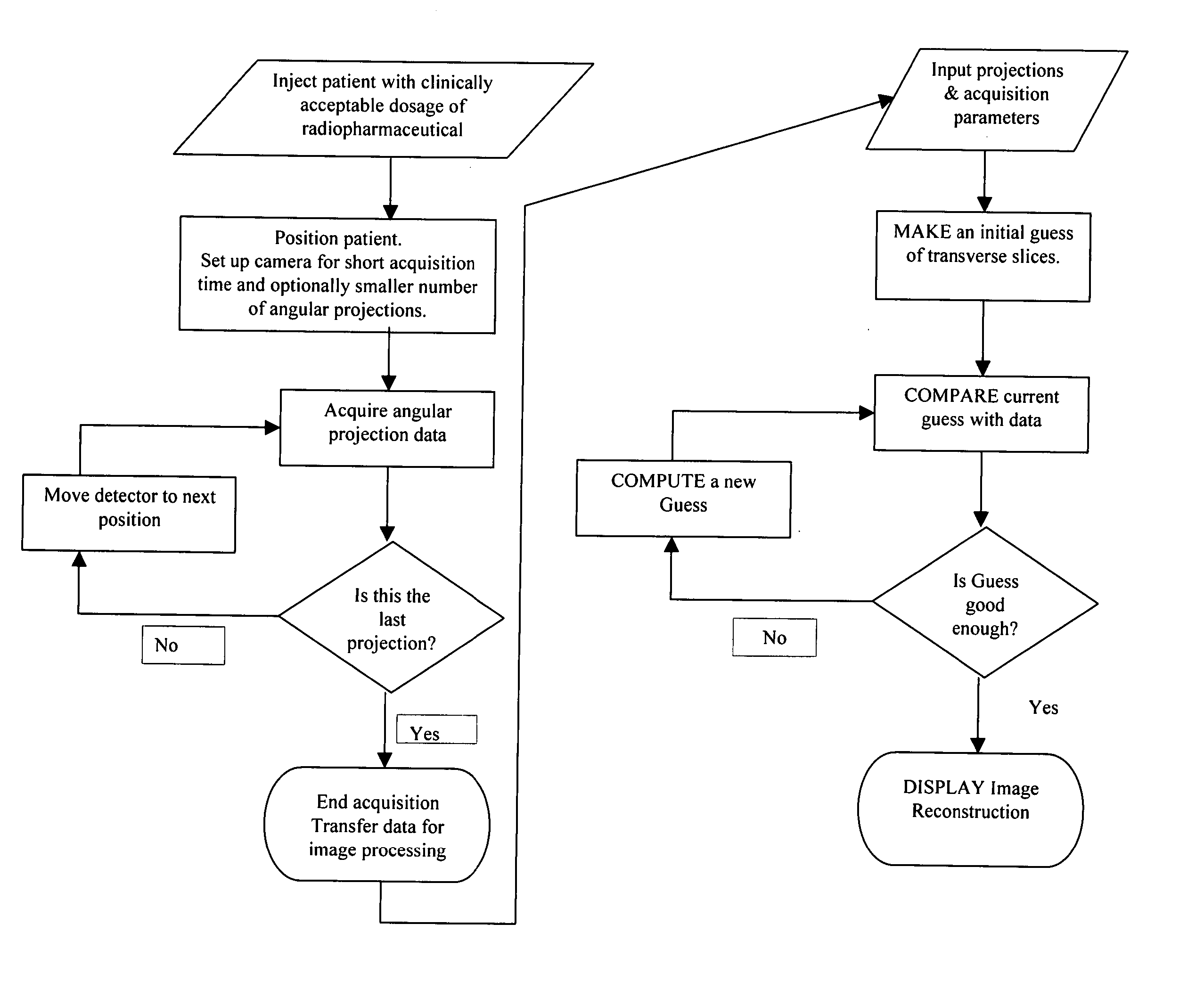
Efficient single photon emission imaging
InactiveUS7026623B2Shorten the timeImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive drugRadiology
Owner:ULTRASPECT
Method and apparatus for photon therapy
A photon therapy unit implement has a flexible head for conforming to a body part to be treated. The head has a thermally conductive backing to remove heat from the treatment area. The operation of the head is monitored by a photon detector to provide a feedback to the diode drive circuit to maintain the output at the required level. Operation of the head is monitored by a microprocessor which performs a diagnostic function and reports on defects. The treatment protocol is generated by a main control unit that formulates a treatment waveform from a set of treatment protocols. The selection of protocols is performed through a graphical user interface (GUI) which allows selection of treatment areas and customization of treatment as well as maintaining patient history and annotations.
Owner:VAN ZUYLEN JEFFREY +2
Method and apparatus for backside illuminated image sensors using capacitively coupled readout integrated circuits
InactiveUS7795650B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove scanning rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceIntegrator
The images sensor includes a readout circuit capacitatively coupled to a memory circuit. The readout circuit includes: (i) a photon detector to receive a plurality of photons and to provide a charge signal corresponding to the received photons, (ii) a resettable integrator that is reset multiple times over a single exposure time and provides an analog representation of the incident photons during the last integration cycle, and (iii) a comparator that monitors the integrator output and generates a reset pulse when the integrator reaches a built-in threshold value. The memory circuit includes: (i) a receiver circuit that detects the output of the digital driver in the front-end readout circuit via capacitive coupling and generates a digital voltage pulse for each received signal, and (ii) a digital counting memory to count the received pulses to provide a coarse digital representation of how many times the integrator is reset.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Methods and systems for multi-modality imaging
ActiveUS20050207526A1Radiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityX-ray
A method of examining a patient is provided. The method includes aligning a patient table in an opening of a gantry unit that includes a CZT photon detector and an x-ray source, imaging a patient utilizing a first imaging modality during a first portion of a scan using the CZT detector, and imaging a patient utilizing a second imaging modality during a second portion of the scan using the CZT detector wherein the second imaging modality is different than the first imaging modality.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Efficient single photon emission imaging
InactiveUS20050145797A1Data acquisition time can be shortenedImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansAcquisition timeGamma ray
A method of diagnostic imaging in a shortened acquisition time for obtaining a reconstructed diagnostic image of a portion of a body of a human patient who was administered with dosage of radiopharmaceutical substance radiating gamma rays, using SPECT. The method comprises acquiring photons emitted from said portion of the body, by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, wherein the total time of photon acquiring is substantially shorter than the clinically acceptable acquisition time; processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby deriving data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by iteratively processing said data.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
Method and apparatus for compact dispersive imaging spectrometer
ActiveUS20050030533A1Radiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhoton emissionPhoton scattering
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for compact dispersive imaging spectrometer. More specifically, one embodiment of the disclosure relates to a portable system for obtaining a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample having a first and a second spatial dimension. The portable system can include a photon emission source for sequentially illuminating a plurality of portions of said sample with a plurality of photons to produce photons scattered by the sample. The photon emission source can illuminate the sample along the first spatial dimension for each of plural predetermined positions of the second spatial dimension. The system may also include an optical lens for collecting the scattered photons to produce therefrom filtered photons, a dispersive spectrometer for determining a wavelength of ones of the filtered photons, a photon detector for receiving the filtered photons and obtaining therefrom plural spectra of said sample, and a processor for producing a two dimensional image of said sample from the plural spectra.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
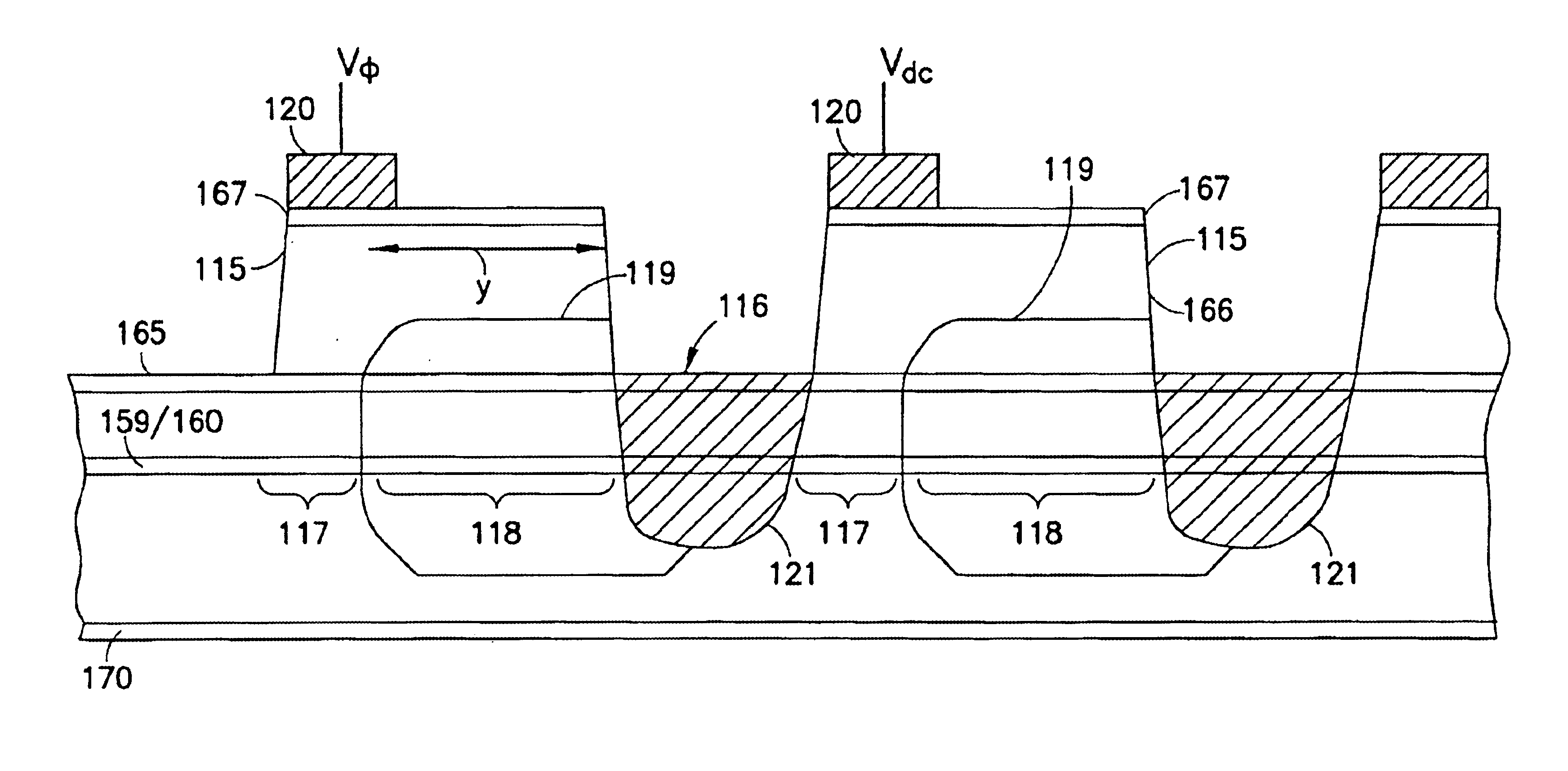
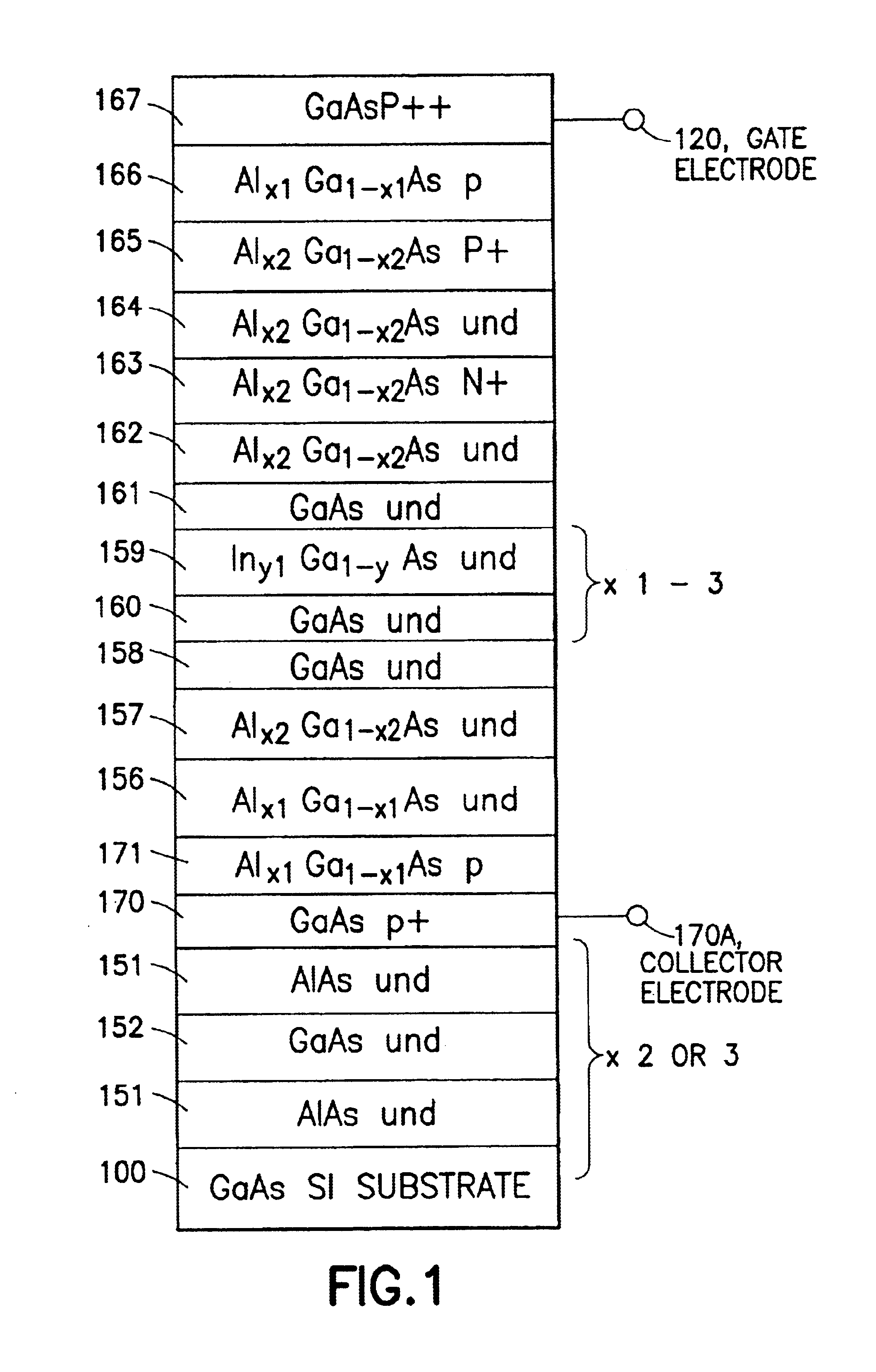
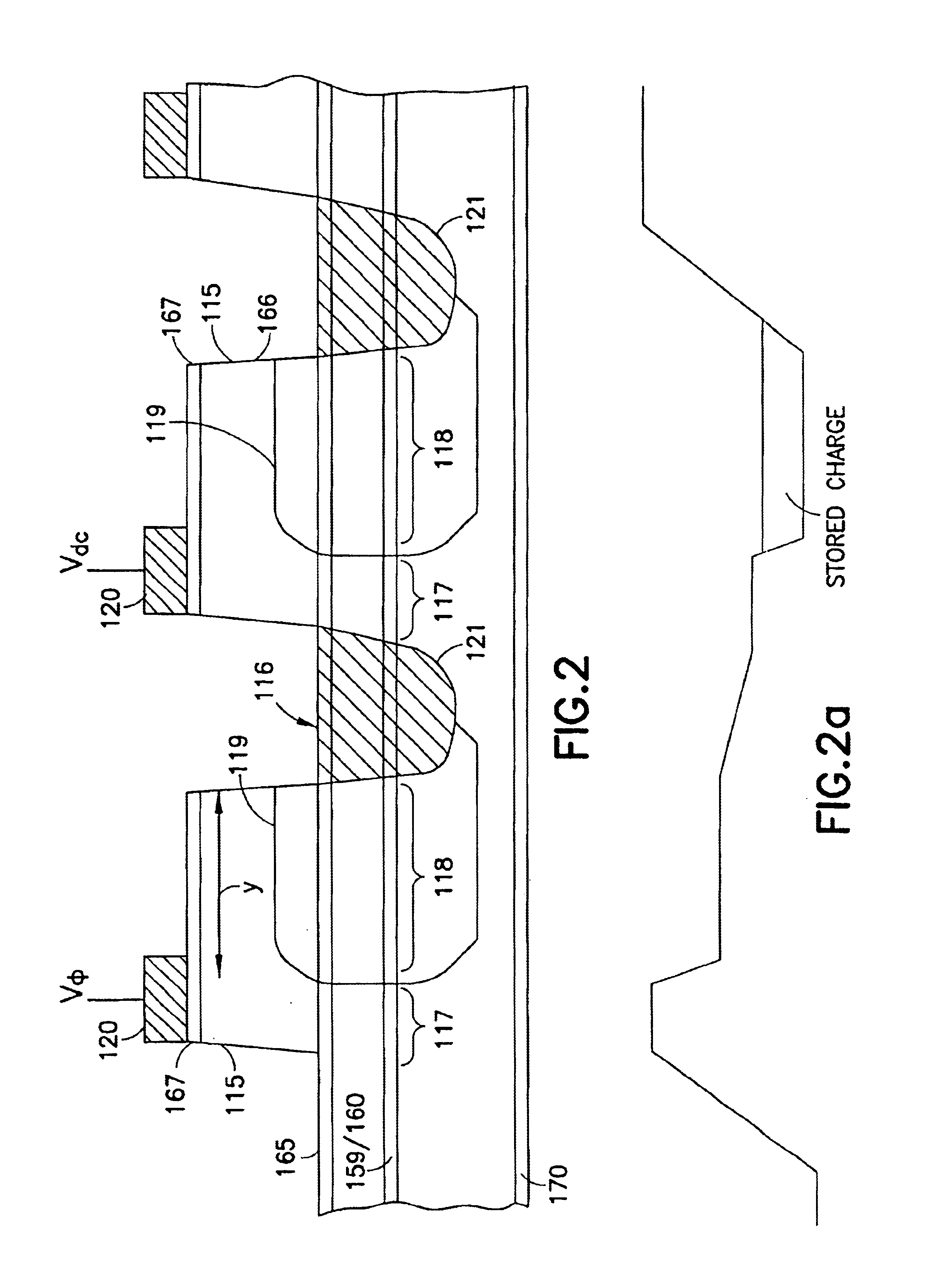
III-V charge coupled device suitable for visible, near and far infra-red detection
InactiveUS6870207B2Optimized drift velocityLower resistanceSolid-state devicesNanoopticsFar infraredElectron
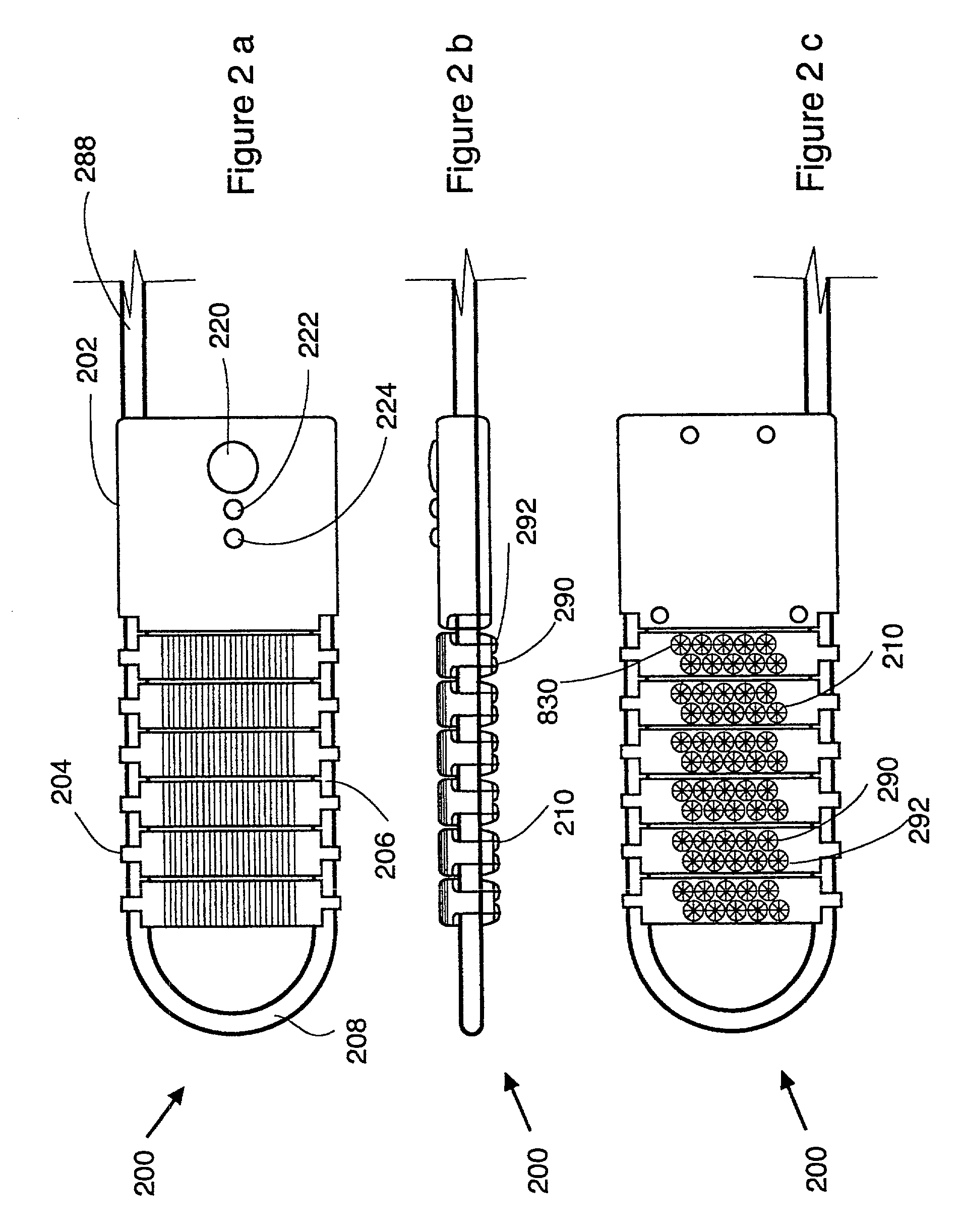
A photon detector is obtained by using the intersubband absorption mechanism in a modulation doped quantum well(s). The modulation doping creates a very high electric field in the well which enables absorption of input TE polarized light and also conducts the carriers emitted from the well into the modulation doped layer from where they may recombine with carriers from the gate contact. Carriers are resupplied to the well by the generation of electrons across the energy gap of the quantum well material. The absorption is enhanced by the use of a resonant cavity in which the quantum well(s) are placed. The absorption and emission from the well creates a deficiency of charge in the quantum well proportional to the intensity of the input photon signal. The quantity of charge in the quantum well of each detector is converted to an output voltage by transferring the charge to the gate of an output amplifier. The detectors are arranged in the form of a 2D array with an output amplifier associated with the entire array or a row of the array as in the known charge coupled devices, or a separate amplifier could be dedicated to each pixel as in the known architecture of the active pixel device. This detector has the unique advantage of near room temperature operation because the dark current is limited to the generation across the semiconductor bandgap and not the emission over the quantum well barrier. The detector also has the advantage that the readout circuitry is implemented monolithically by the HFETs formed in the GaAs substrate simultaneously, with the detecting elements.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Spect gamma camera
InactiveUS20030208117A1Improve imaging resolutionShort acquisition timeDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographySingle photon emission computerized tomographyGamma ray
A method and apparatus of obtaining and reconstructing an image of a portion of a body, administered by a radiopharmaceutical substance, by using Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) for determination of functional information thereon. The method comprises (a) acquiring gamma ray photons emitted from said portion by means of a detector capable of converting the photons into electric signals, the detector having at least one crystal and allowing said gamma rays having incident angles essentially exceeding 5 degrees and, preferably, exceeding 10 degrees to be detected; (b) processing said electric signals by a position logic circuitry and thereby transforming them into data indicative of positions on said photon detector crystal, where the photons have impinged the detector; and (c) reconstructing an image of a spatial distribution of the pharmaceutical substance within the portion of the body by processing said data and taking into consideration weight values which are functions of angles and, possibly, distances between different elements of the portion of the body and corresponding elements of this position's projection on the detector.
Owner:ULTRASPECT
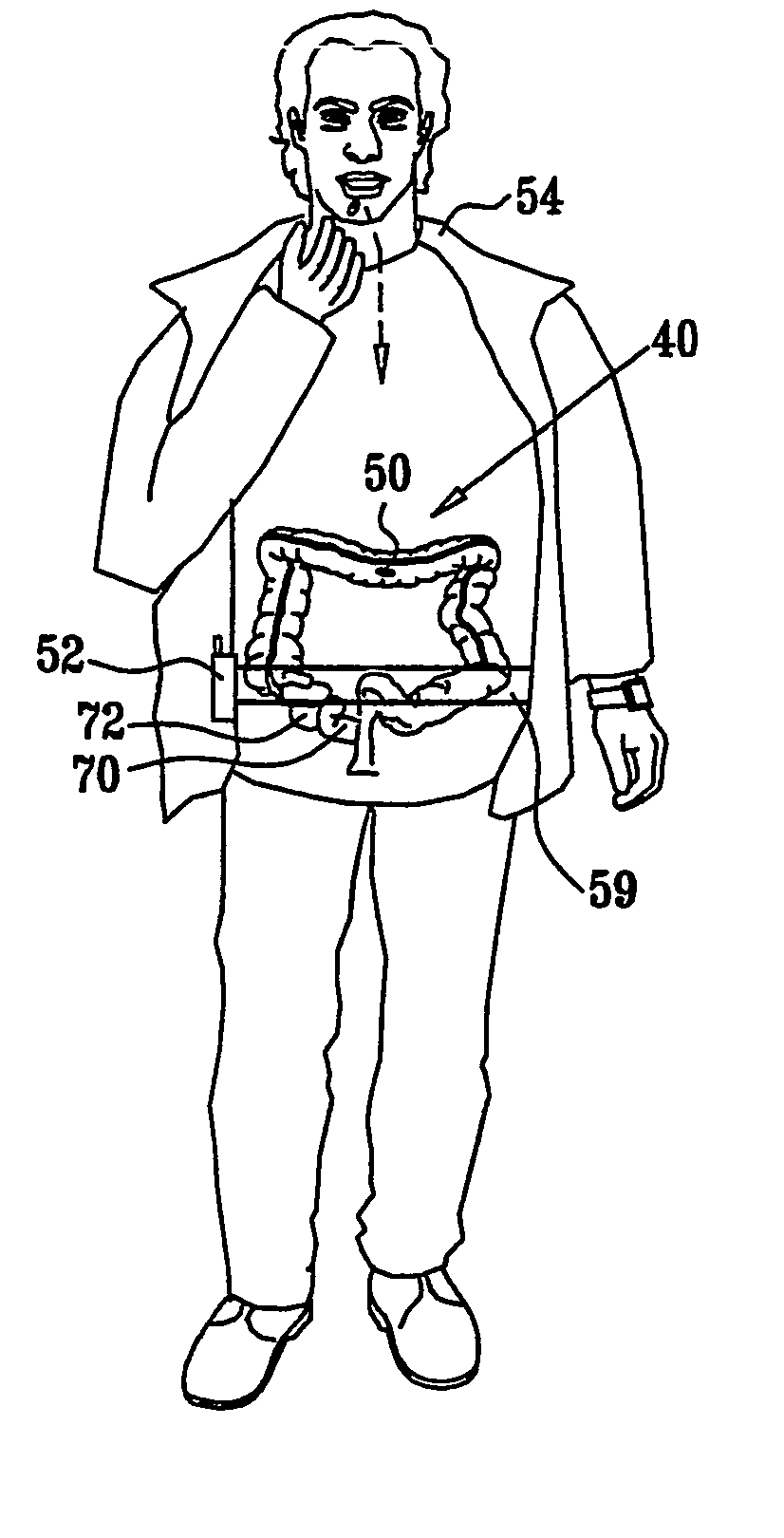
Intra-lumen polyp detection
Apparatus (40) is provided, including a capsule (50), adapted to be swallowed by a subject (54), the capsule (50) including (a) at least one radiation source (60), adapted to emit radiation having an energy of at least 10 keV, and (b) at least one photon detector (62), adapted to detect photons generated responsively to the emitted radiation, the photons having an energy of at least 10 keV. The apparatus (40) additionally includes a control unit (64), adapted to analyze data regarding the photons in order to generate information useful for identifying a clinically-relevant feature of a gastrointestinal (GI) tract (72) of the subject (54).
Owner:CHECK CAP
System for controling and calibrating single photon detection devices
ActiveUS20110127415A1Minimizing measurement timeOptimal measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCalibration apparatusElectricityDark count rate
A single photon detection system and method are disclosed which have a control block for helping to monitor and optimize performance, especially at high detection rates. The system is based on photon detectors constructed with avalanche photodiodes (APD) gated in time to operate in the Geiger mode. An electrical reference frequency is generated which is subtracted from the APD output in order to better isolate the breakdown event. The resulting signal is sampled and analyzed to allow the control unit to optimize the magnitude and phase of the electrical reference frequency. The control unit may also change the gate pulse shape and phase, including by the use of a digital-to-analog converter. The gate pulse can be shifted off an input optical pulse so as to estimate dark count rate, or shifted to measure a reference input signal to estimate detection efficiency.
Owner:NUCRYPT
STED super-resolution microscope based on first-order Bessel beams and adjustment method thereof
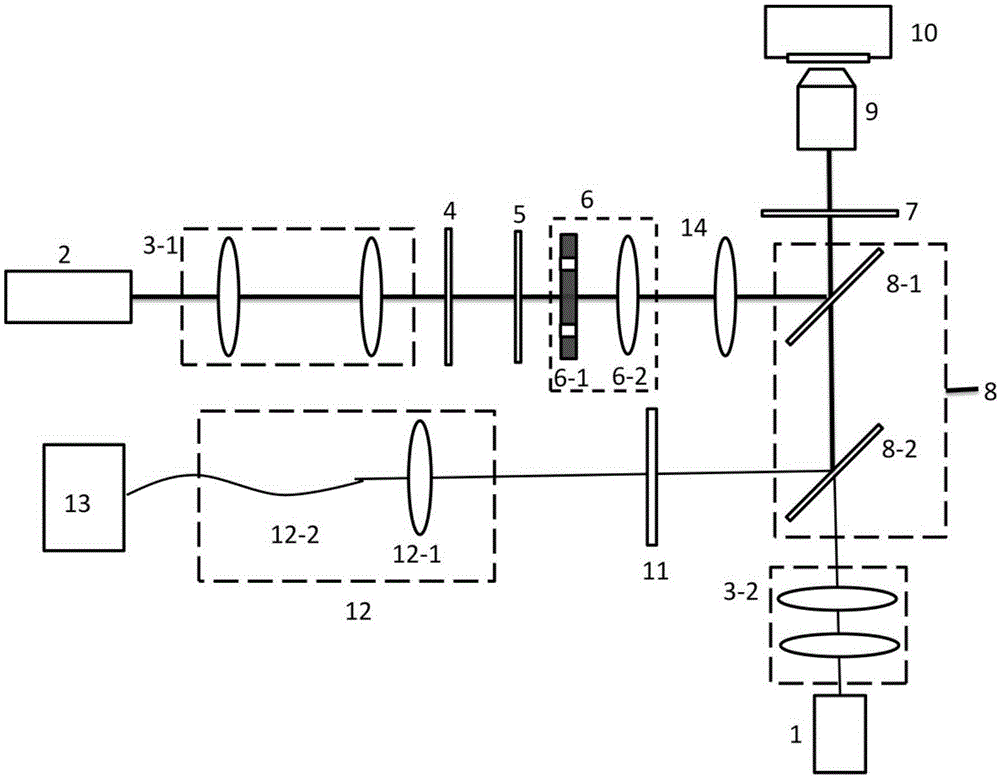
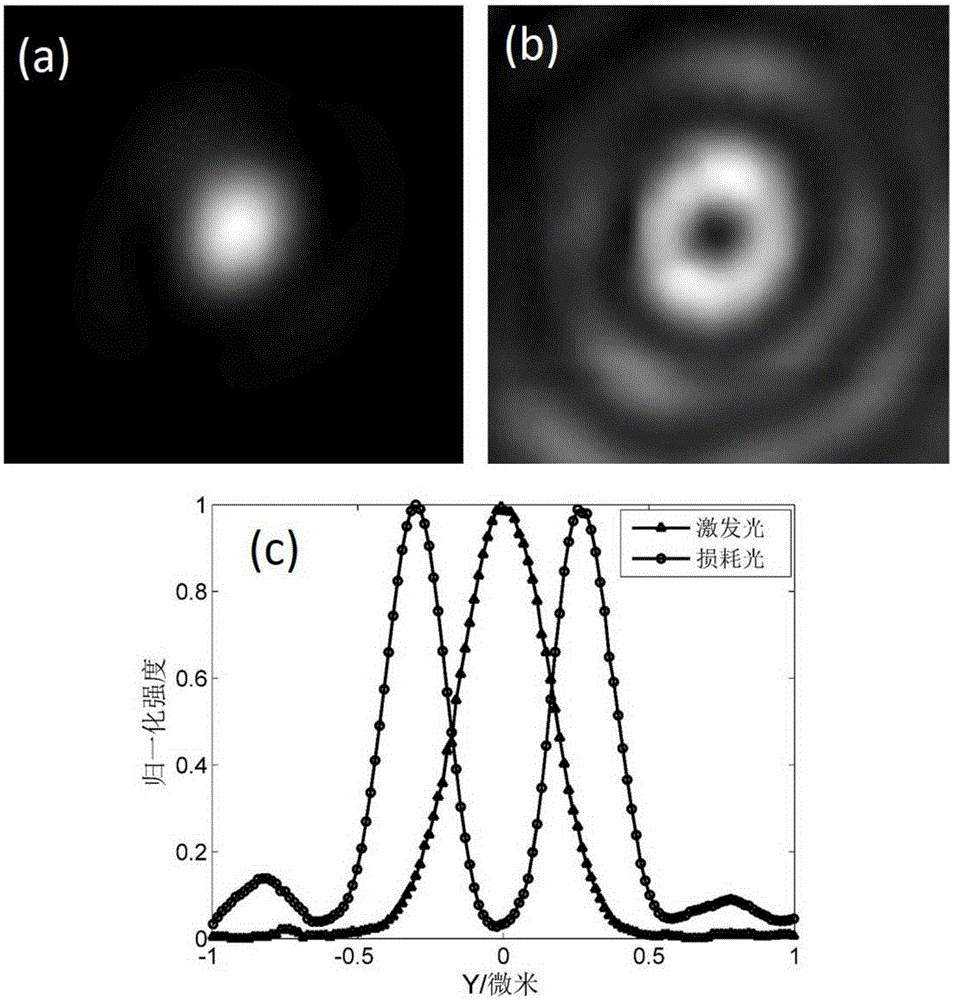
ActiveCN105182523AHigh-resolutionGood spot shapeMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesSelf-healingCollection system
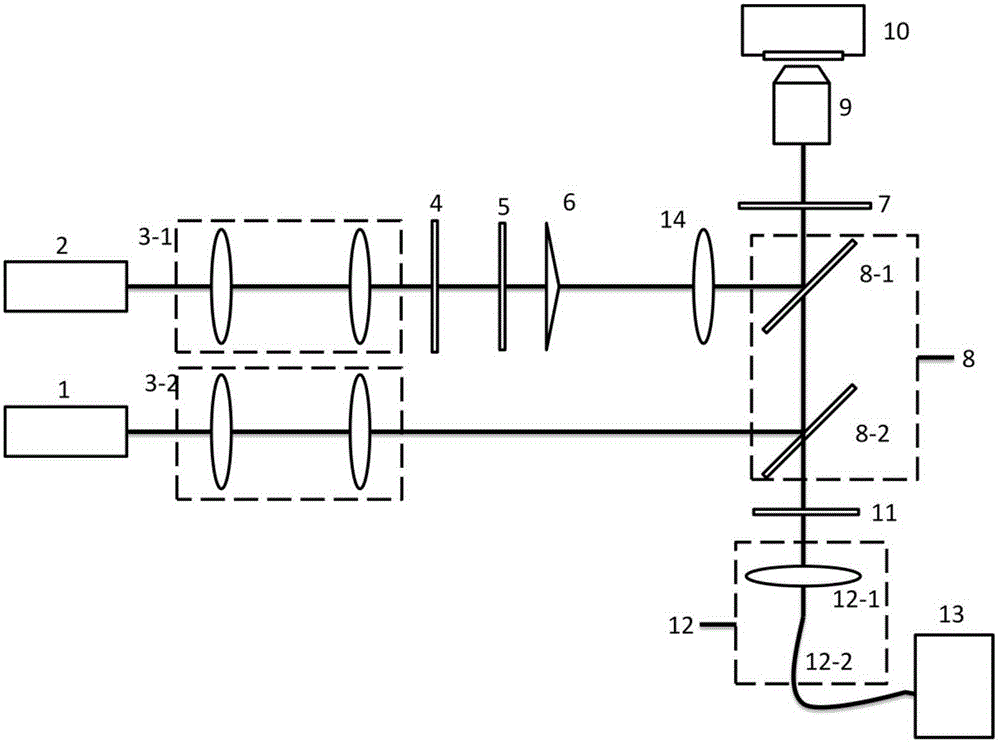
The invention discloses an STED super-resolution microscope based on first-order Bessel beams and an adjustment method thereof. The STED microscope comprises an excitation light source, a loss light source, an excitation light beam expanding and collimation system, a loss light beam expanding and collimation system, a spiral phase plate, a Bessel beam generation system, a loss light focusing lens, a beam combining system, an object lens, a piezoelectric scanning system, a filter plate, a signal collection system and a single-photon detector. Loss light is the first-order Bessel beams and has scattering-resistant and self-healing characteristics, and great light spot form of the deep position of a sample can be maintained so that resolution of the deep area of the sample can be enhanced. Compared with a method of realizing STED super-resolution microscope deep imaging through adjusting an object lens correction ring, the method is relatively simple in experiment operation without active adjustment. Compared with a method of using a self-adaptive optical system, the experiment device is relatively simple and cheap.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com