Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Photon scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
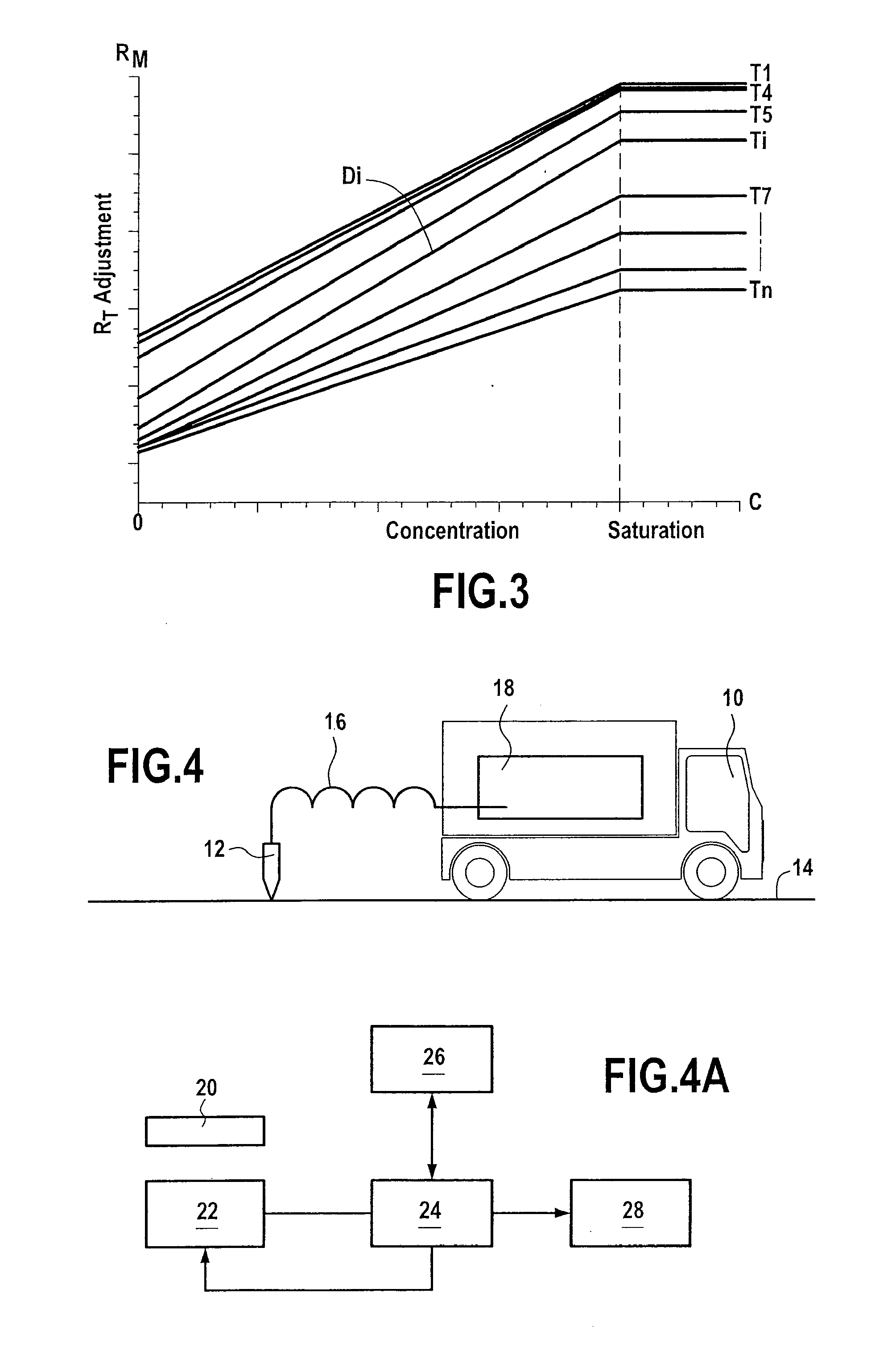
In coherent scattering, an incident photon interacts with matter and excites an atom, causing it to vibrate. The vibration causes the photon to scatter. Also called Thompson scattering, unmodified scattering.
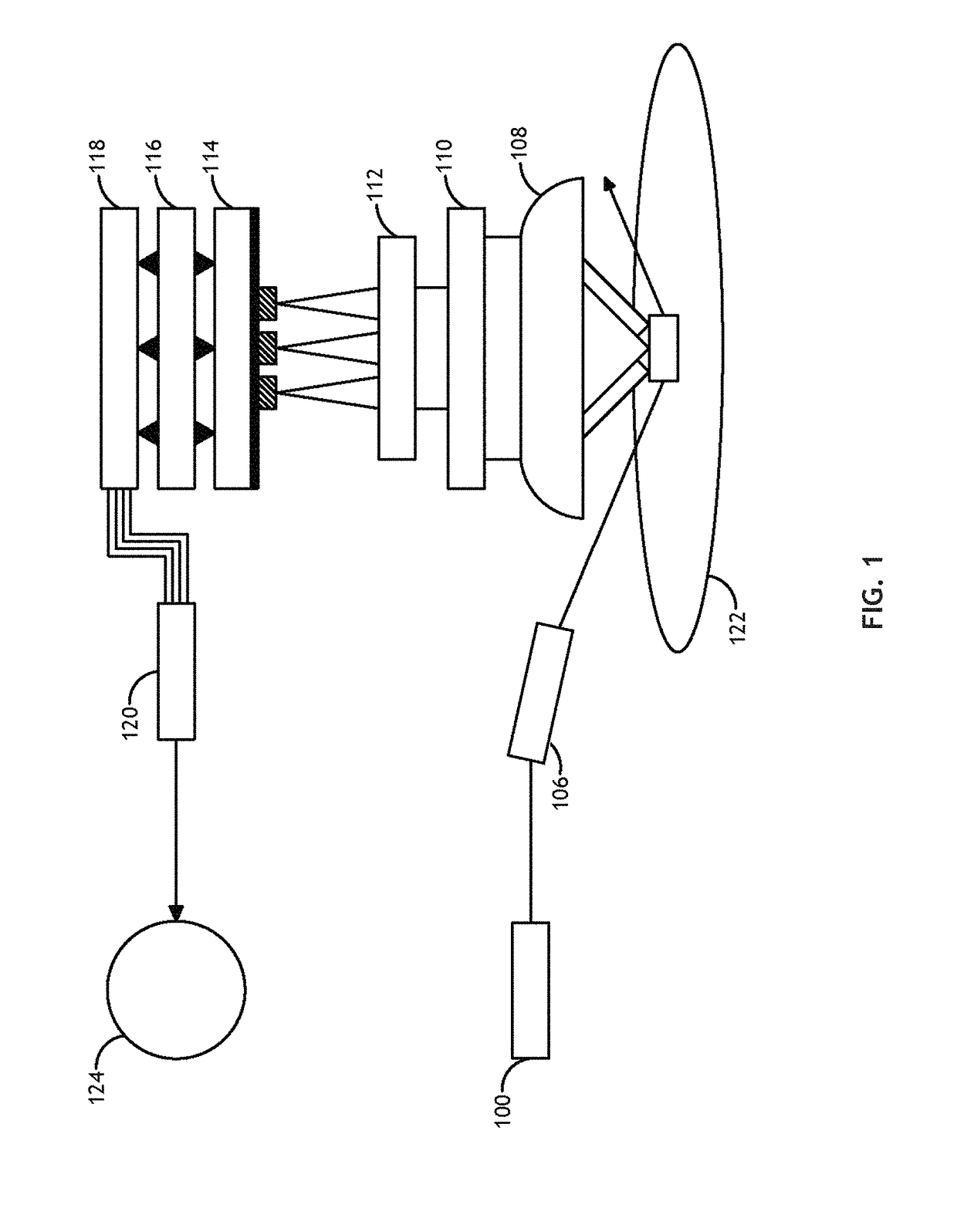
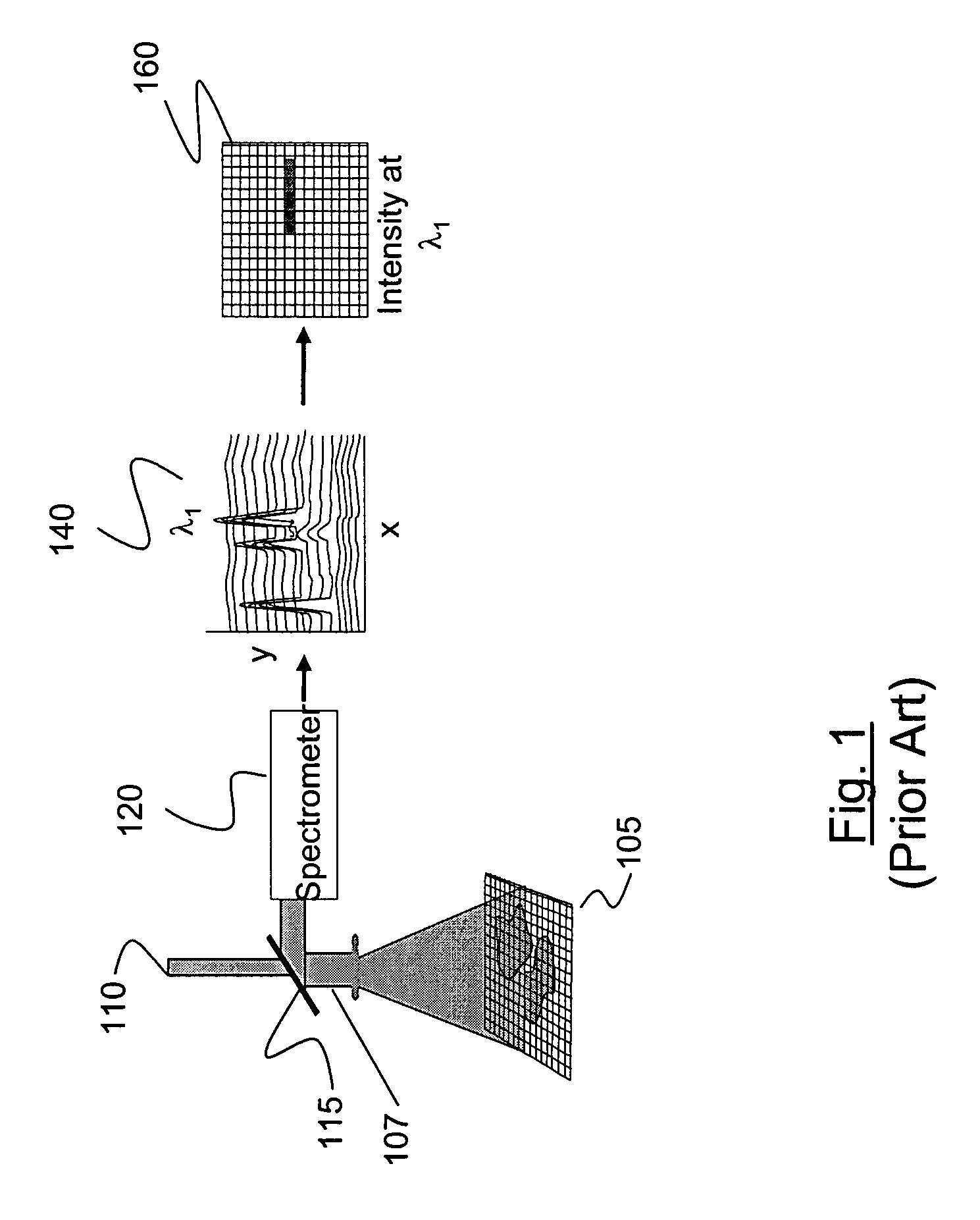
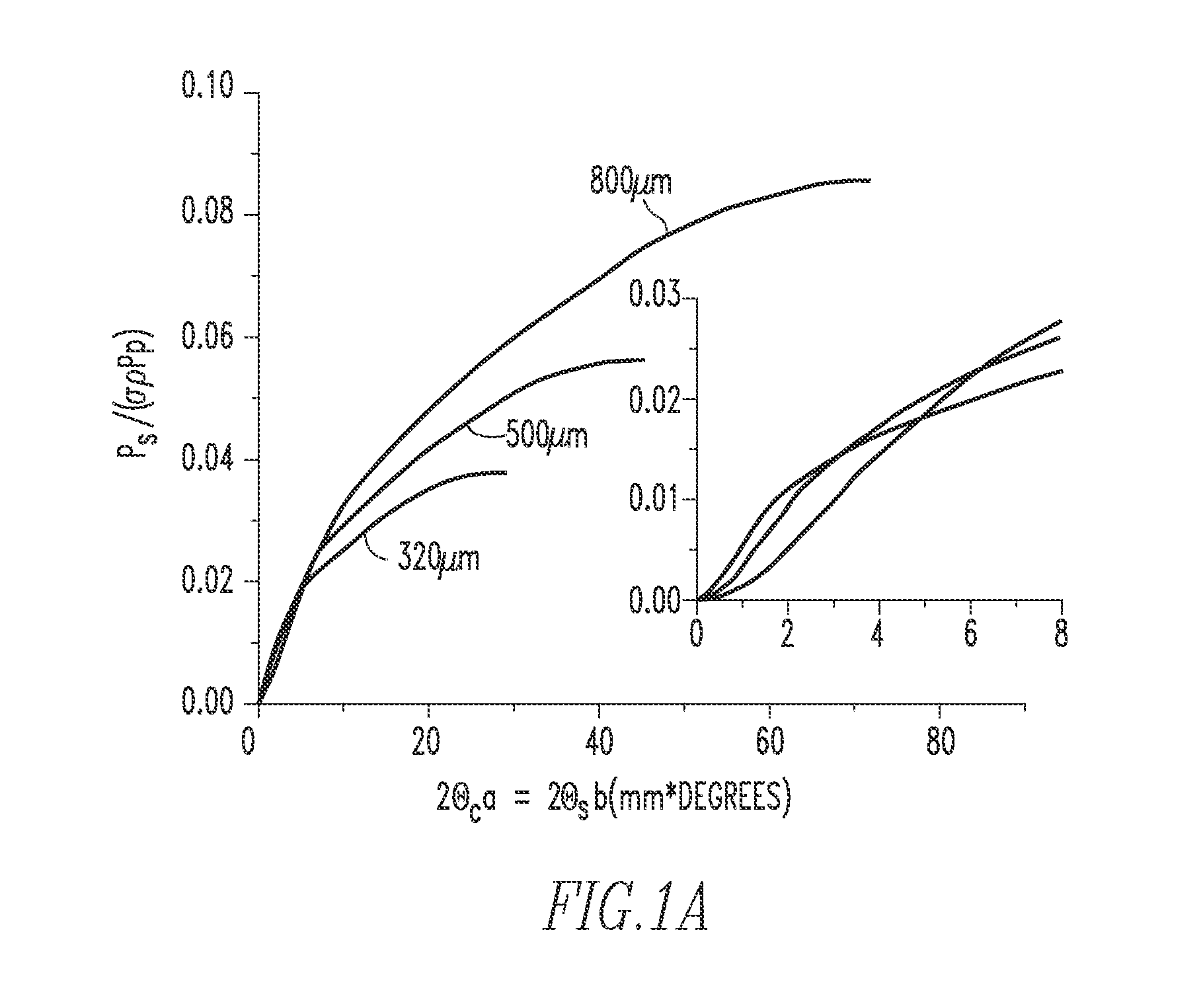
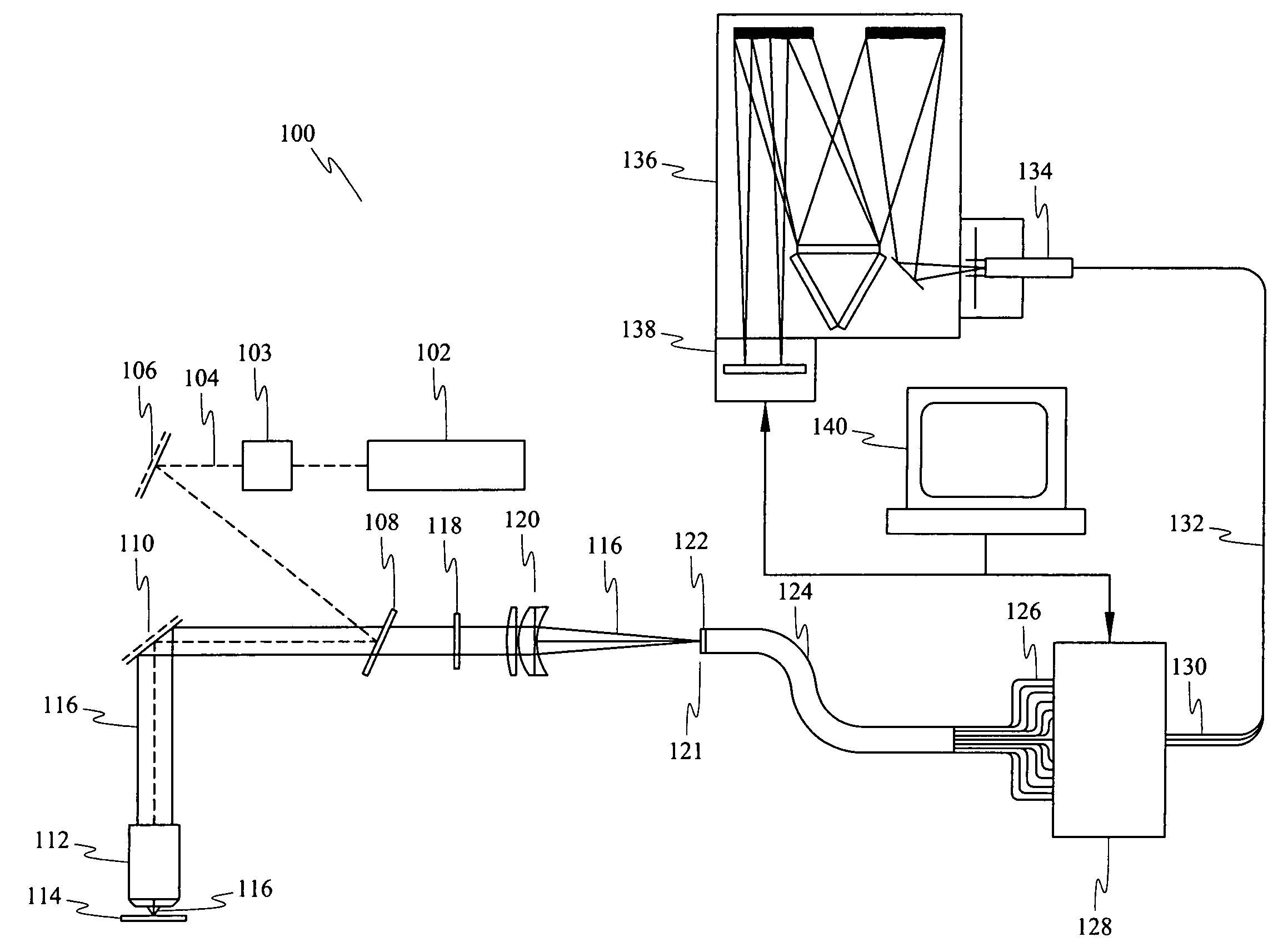
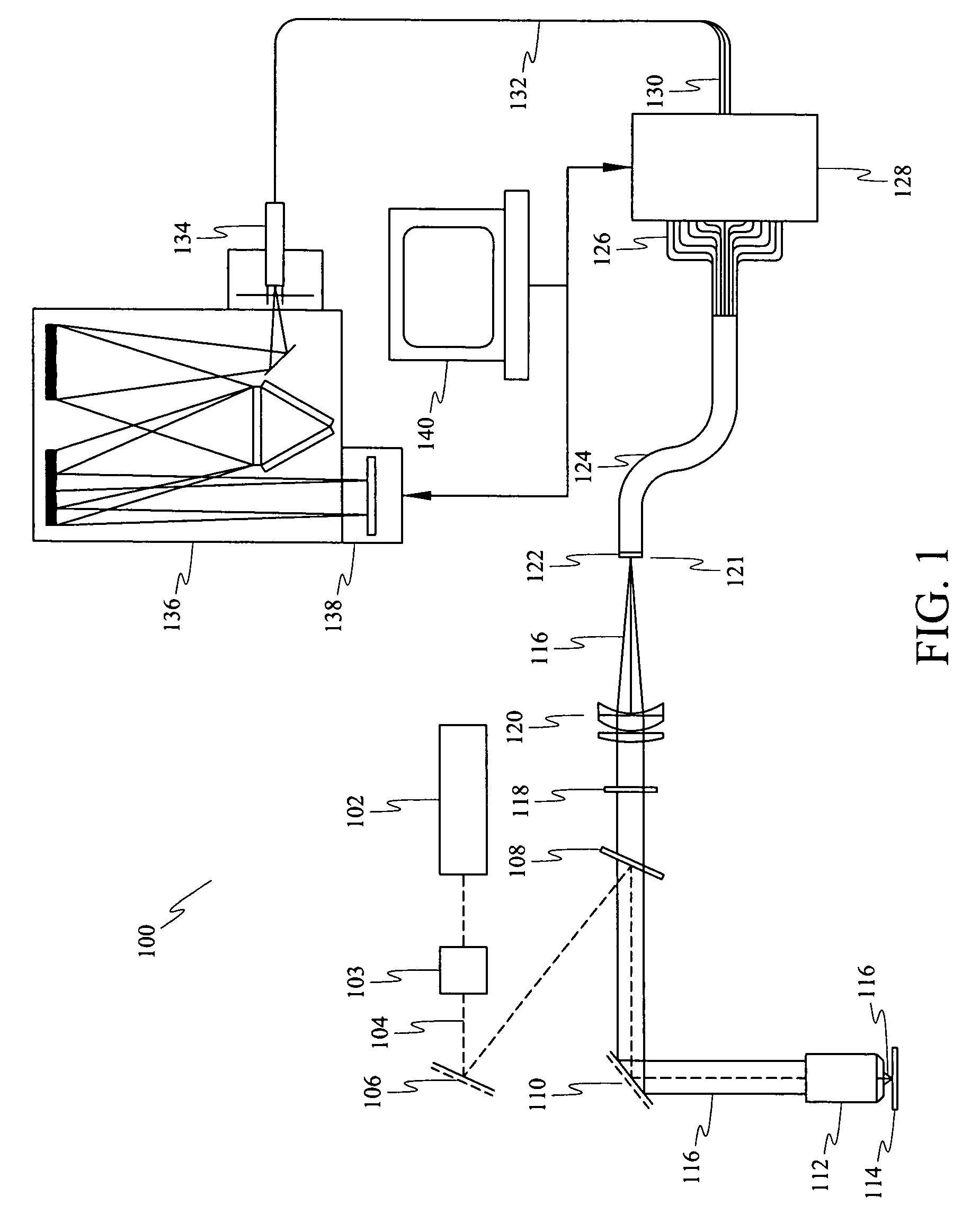
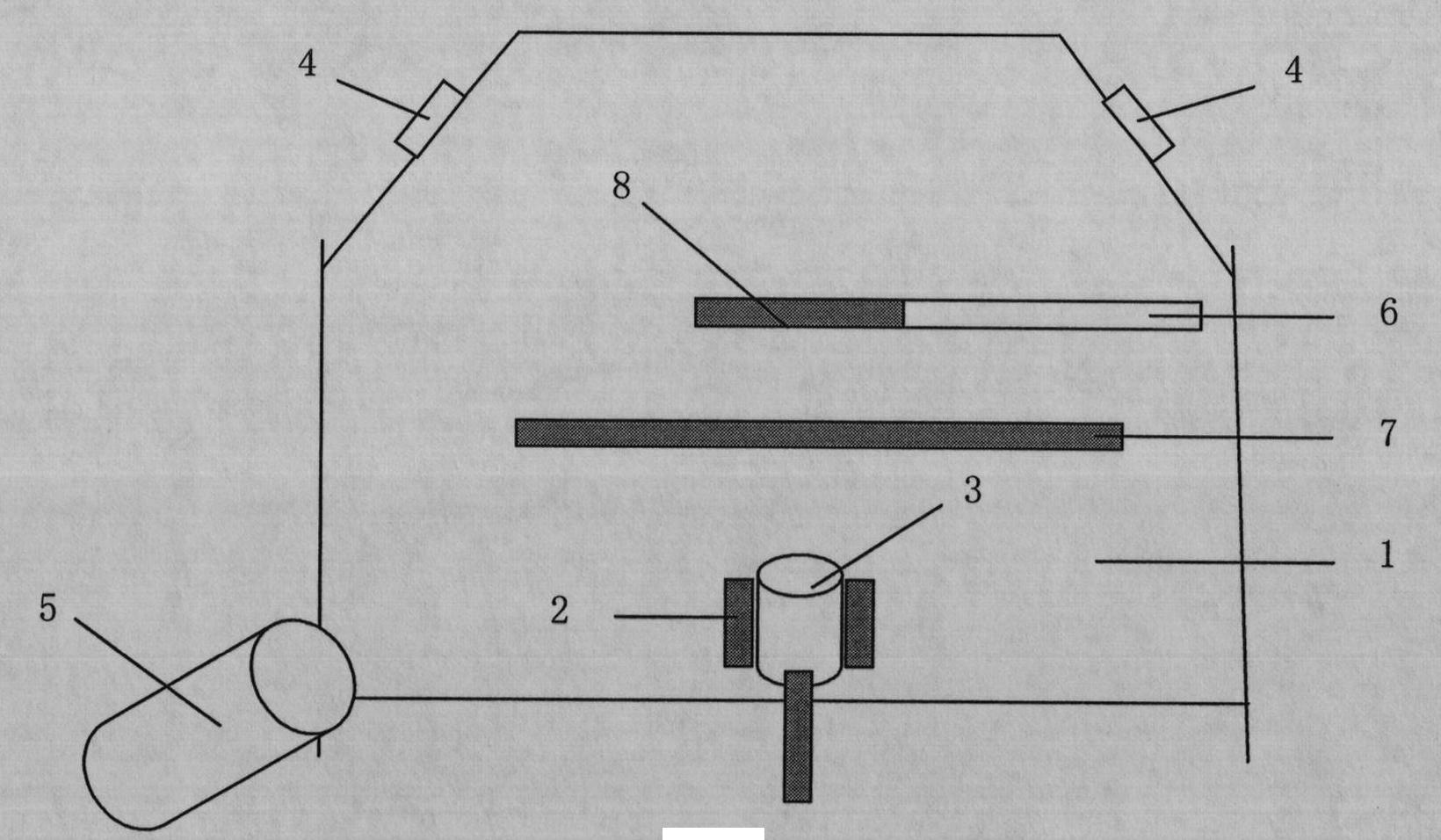
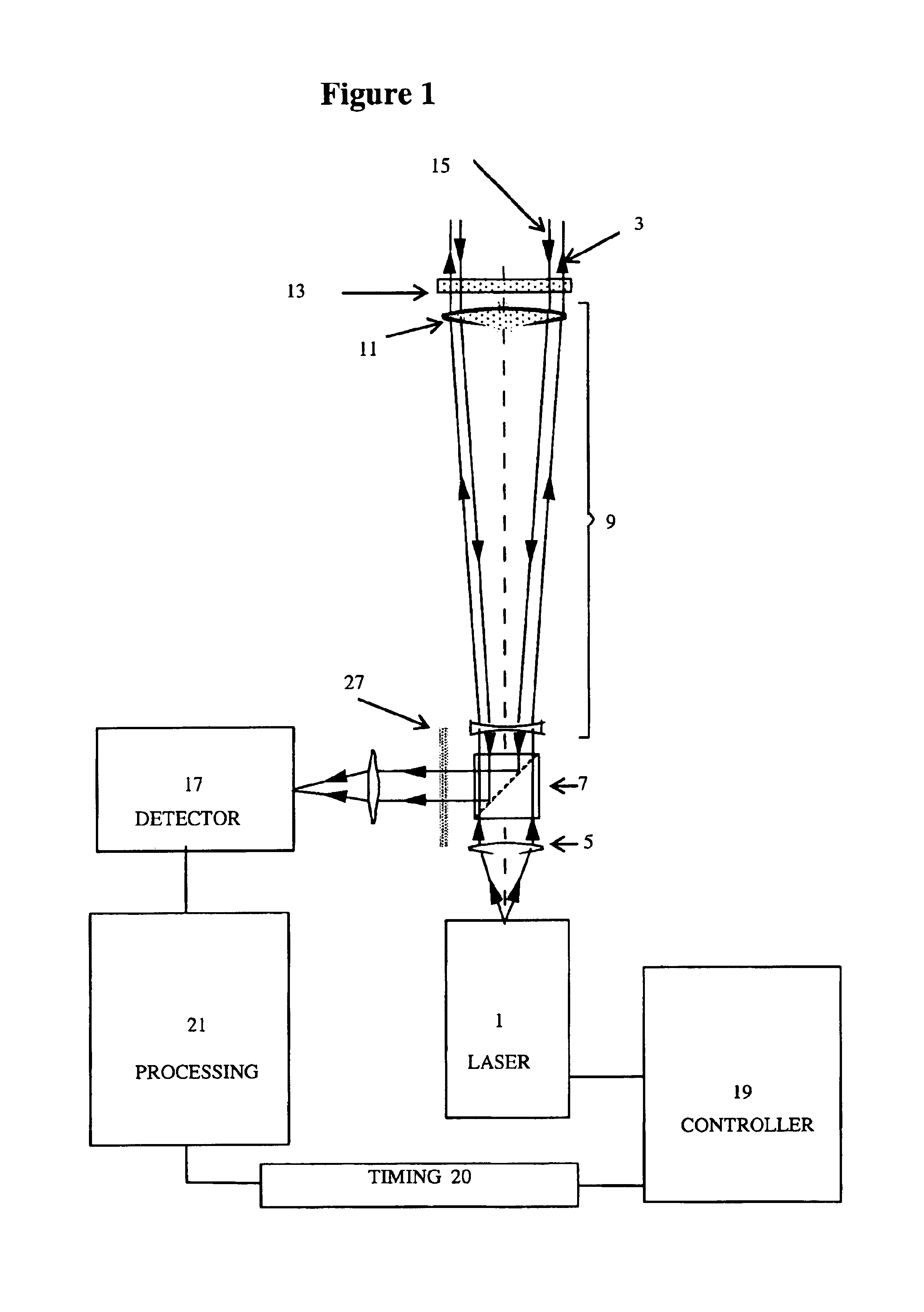
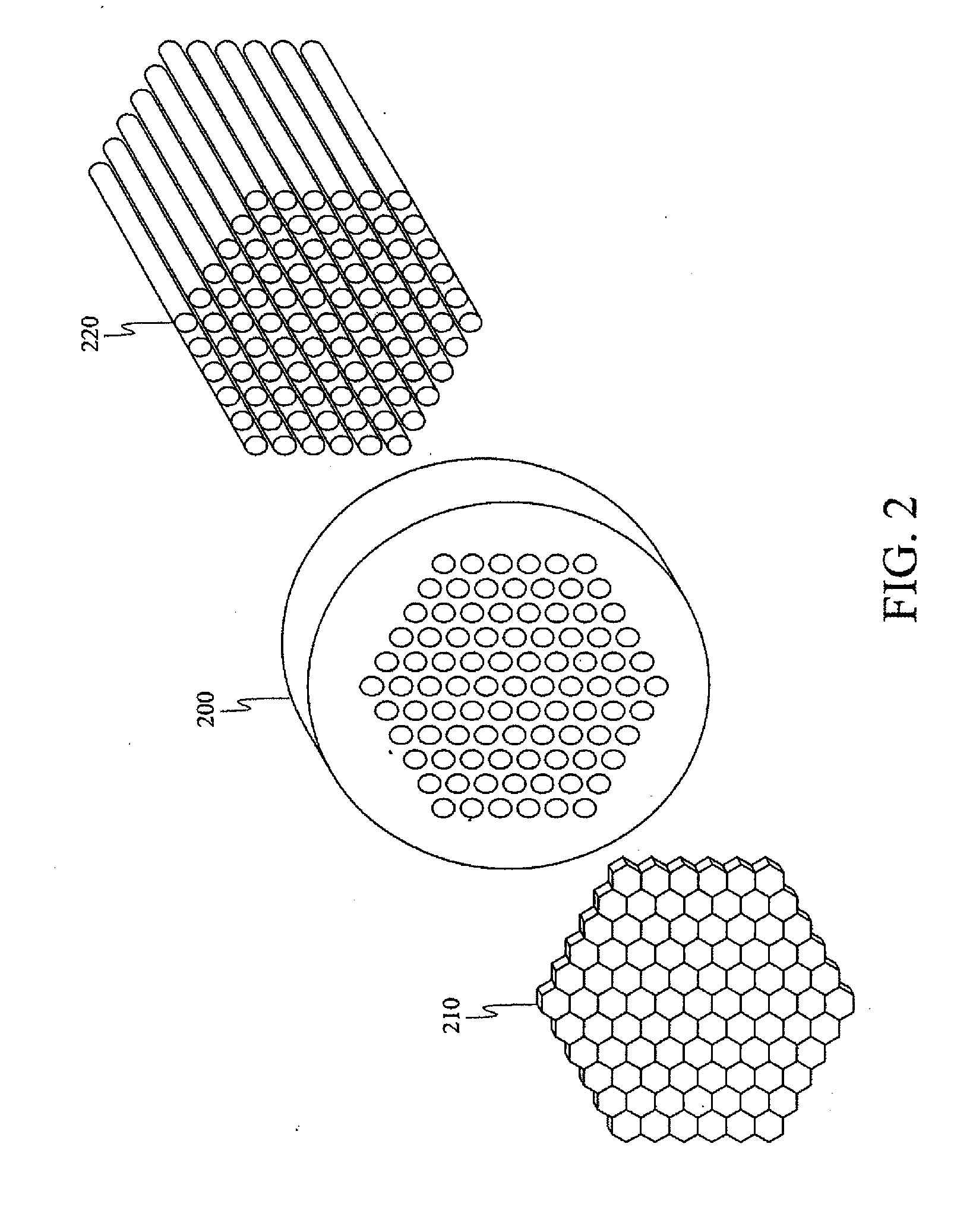
Method and apparatus for compact dispersive imaging spectrometer
ActiveUS20050030533A1Radiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhoton emissionPhoton scattering
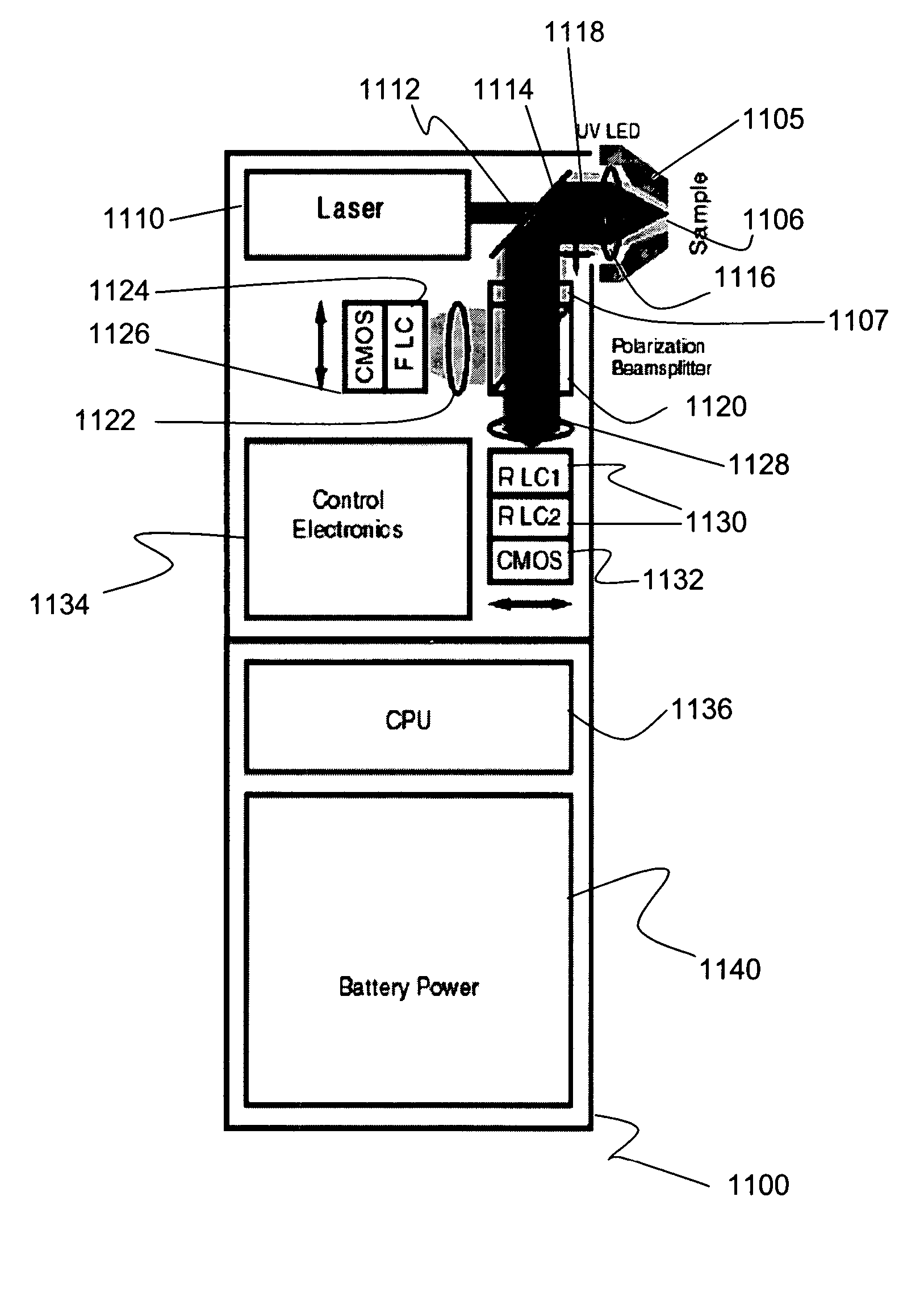
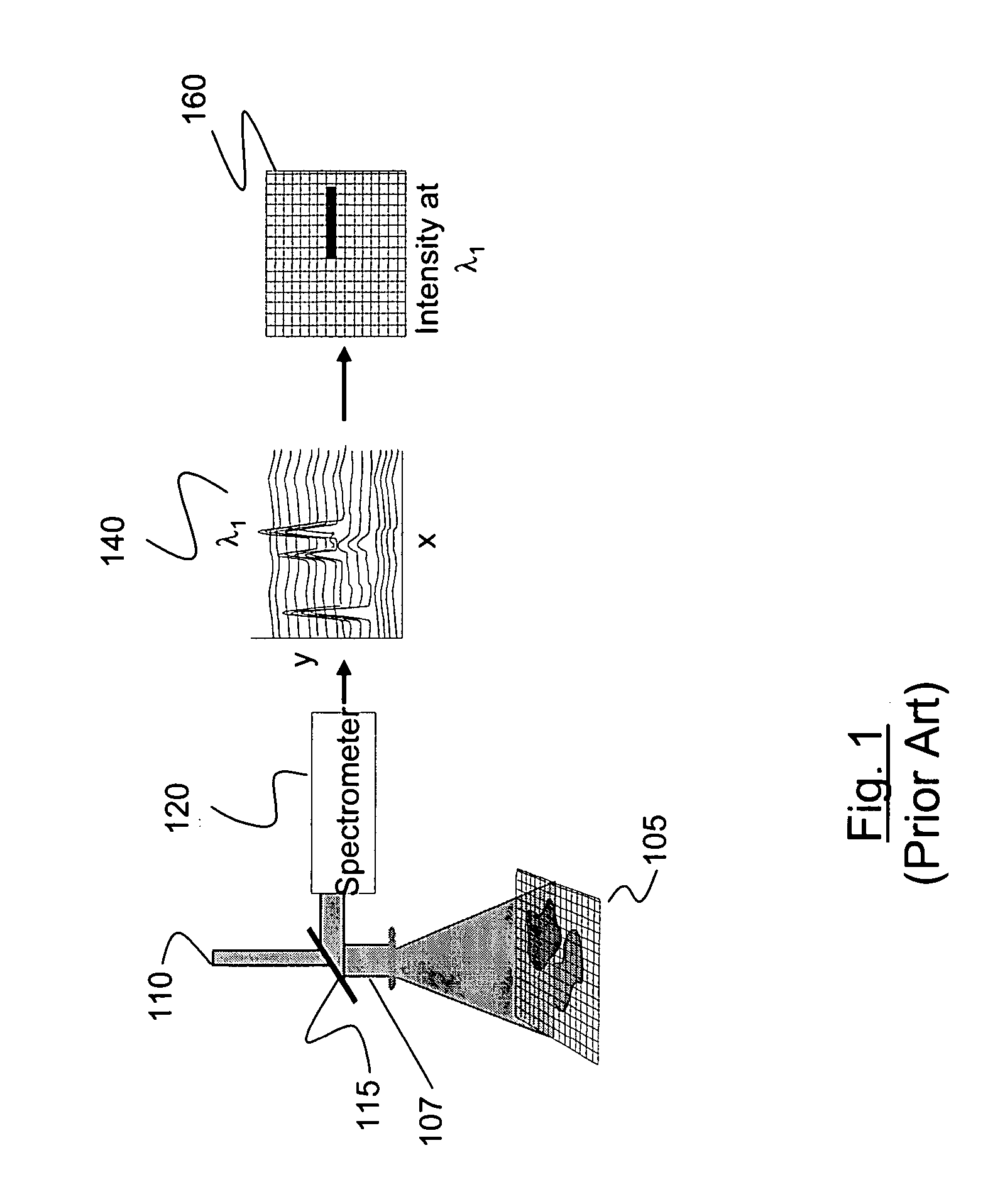
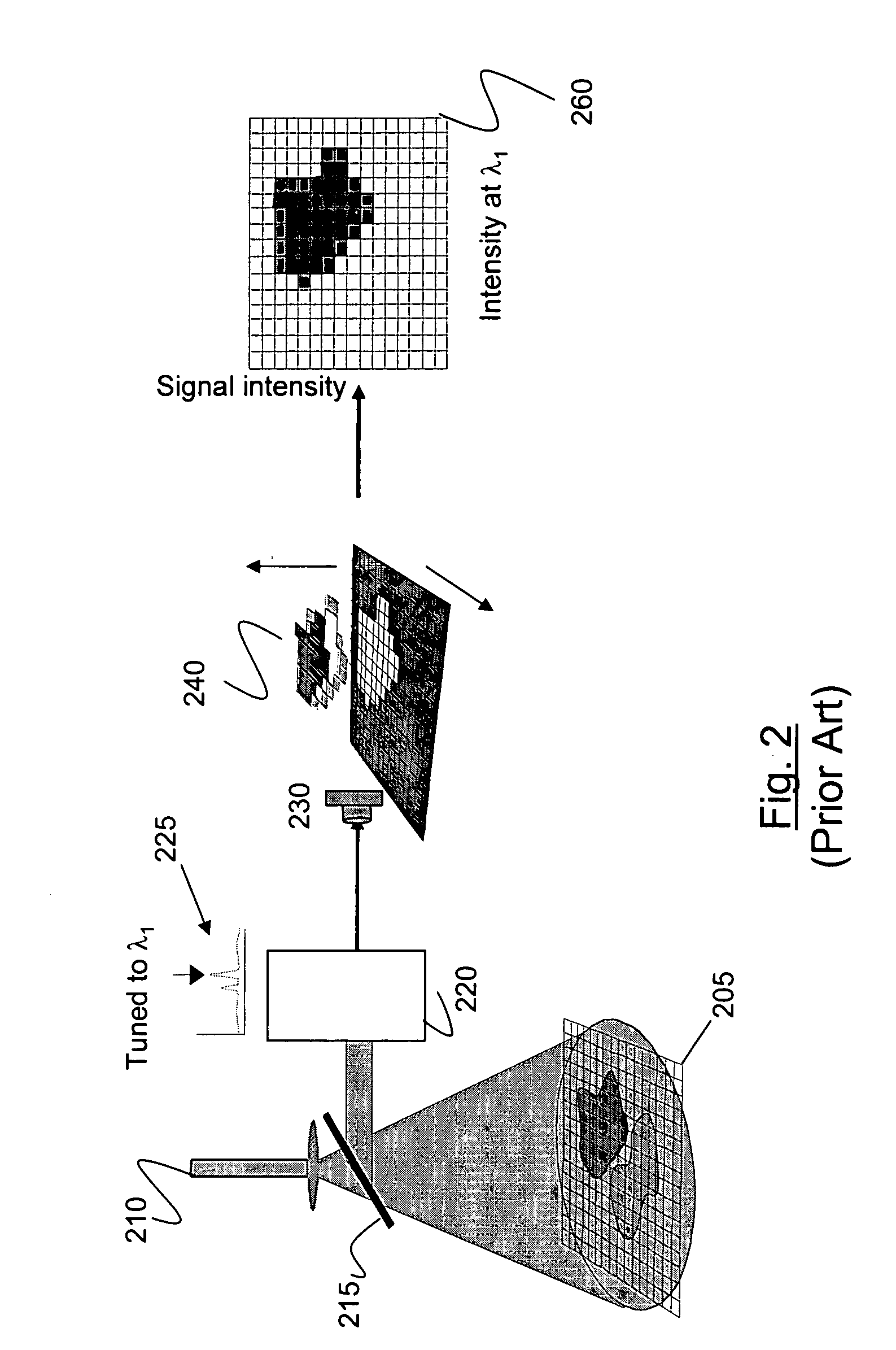
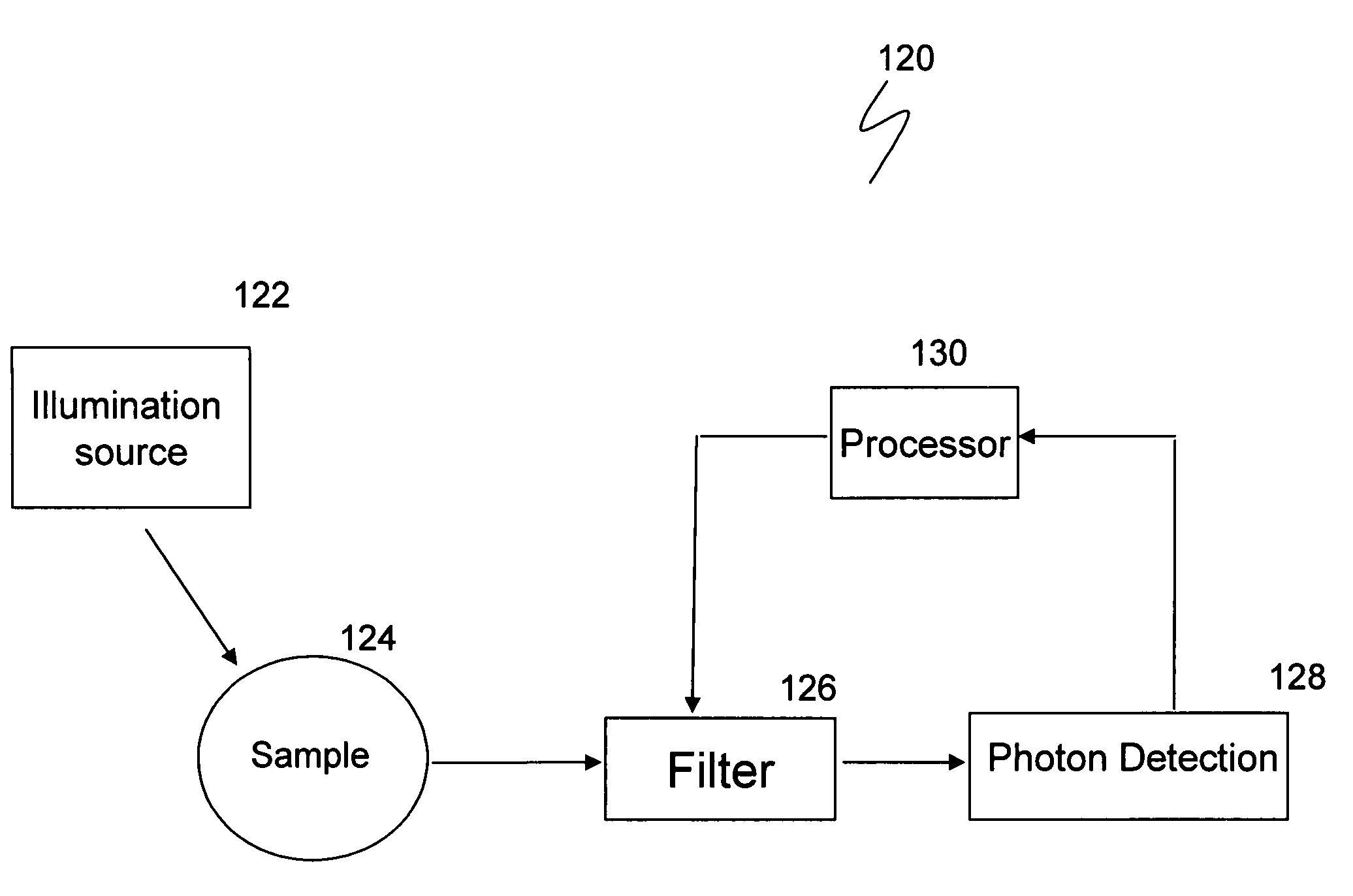
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for compact dispersive imaging spectrometer. More specifically, one embodiment of the disclosure relates to a portable system for obtaining a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample having a first and a second spatial dimension. The portable system can include a photon emission source for sequentially illuminating a plurality of portions of said sample with a plurality of photons to produce photons scattered by the sample. The photon emission source can illuminate the sample along the first spatial dimension for each of plural predetermined positions of the second spatial dimension. The system may also include an optical lens for collecting the scattered photons to produce therefrom filtered photons, a dispersive spectrometer for determining a wavelength of ones of the filtered photons, a photon detector for receiving the filtered photons and obtaining therefrom plural spectra of said sample, and a processor for producing a two dimensional image of said sample from the plural spectra.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
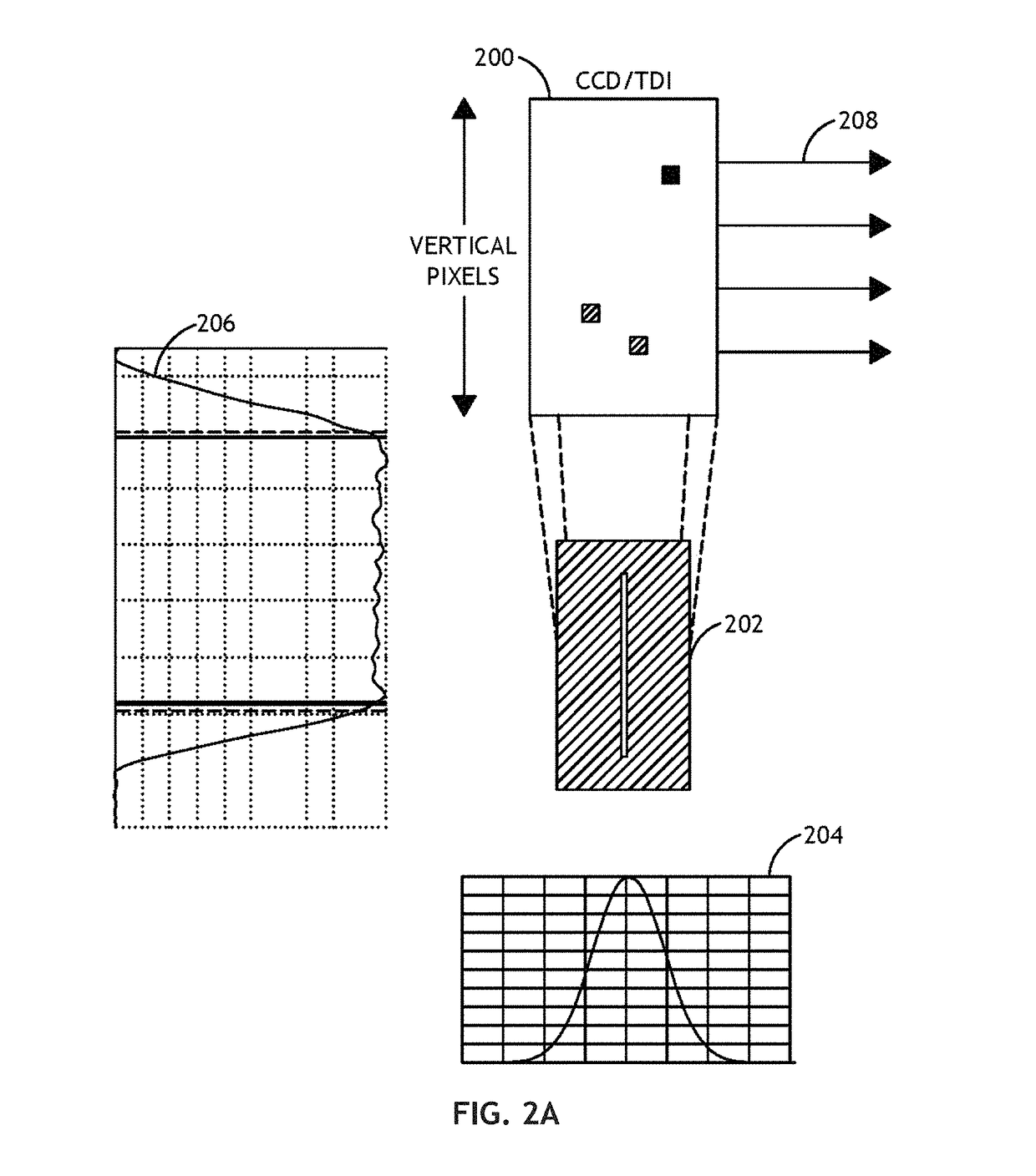
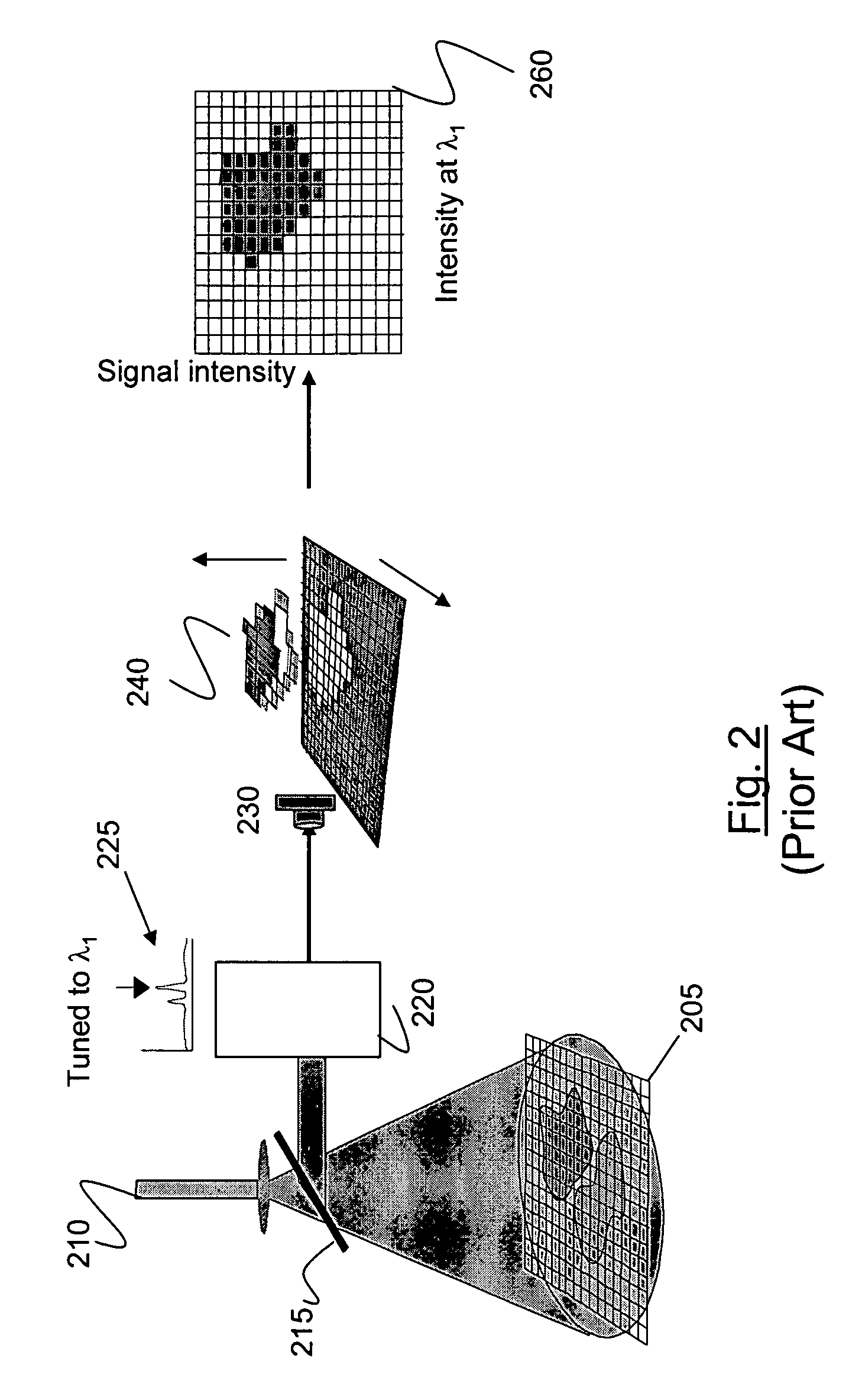
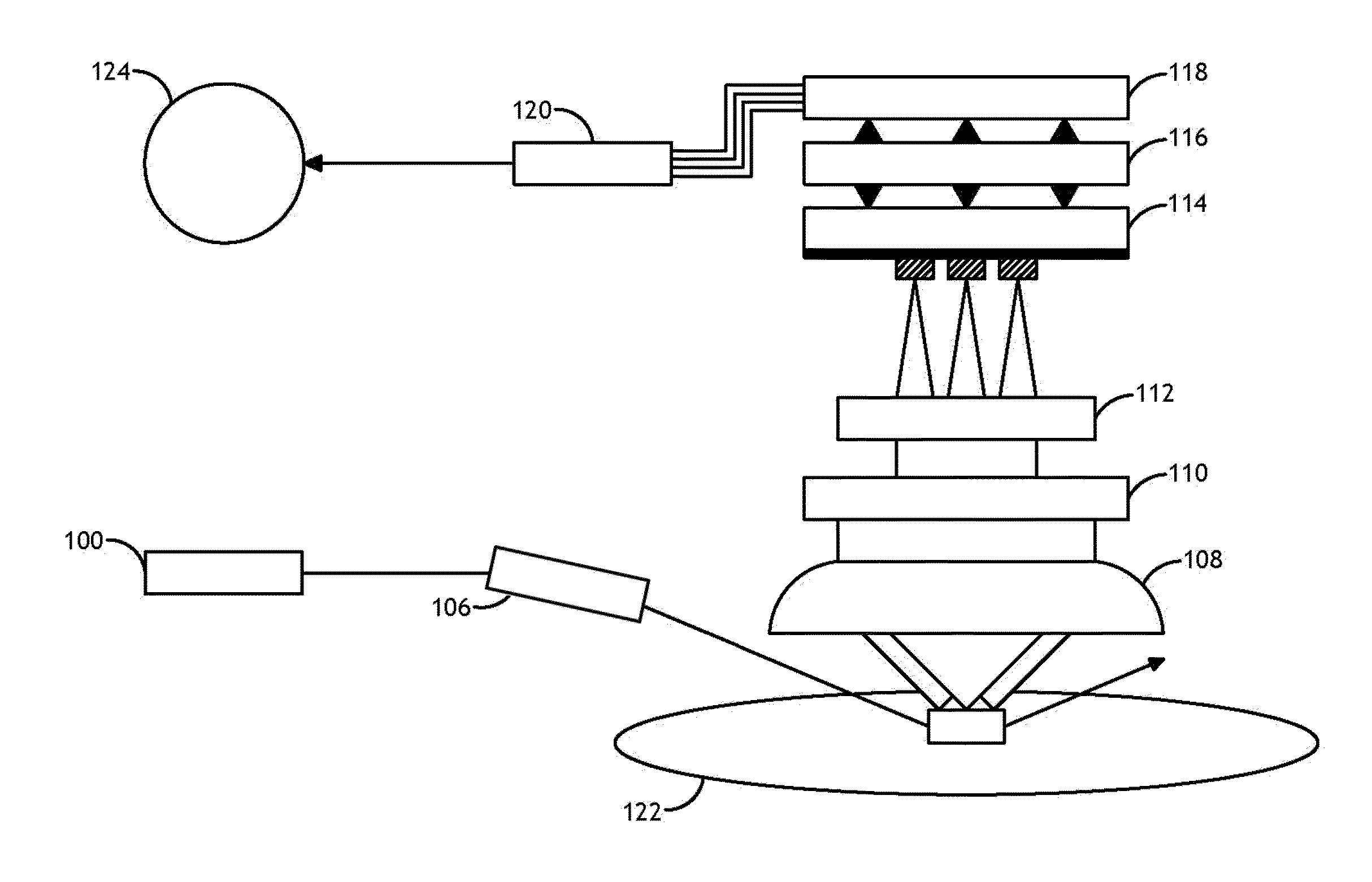
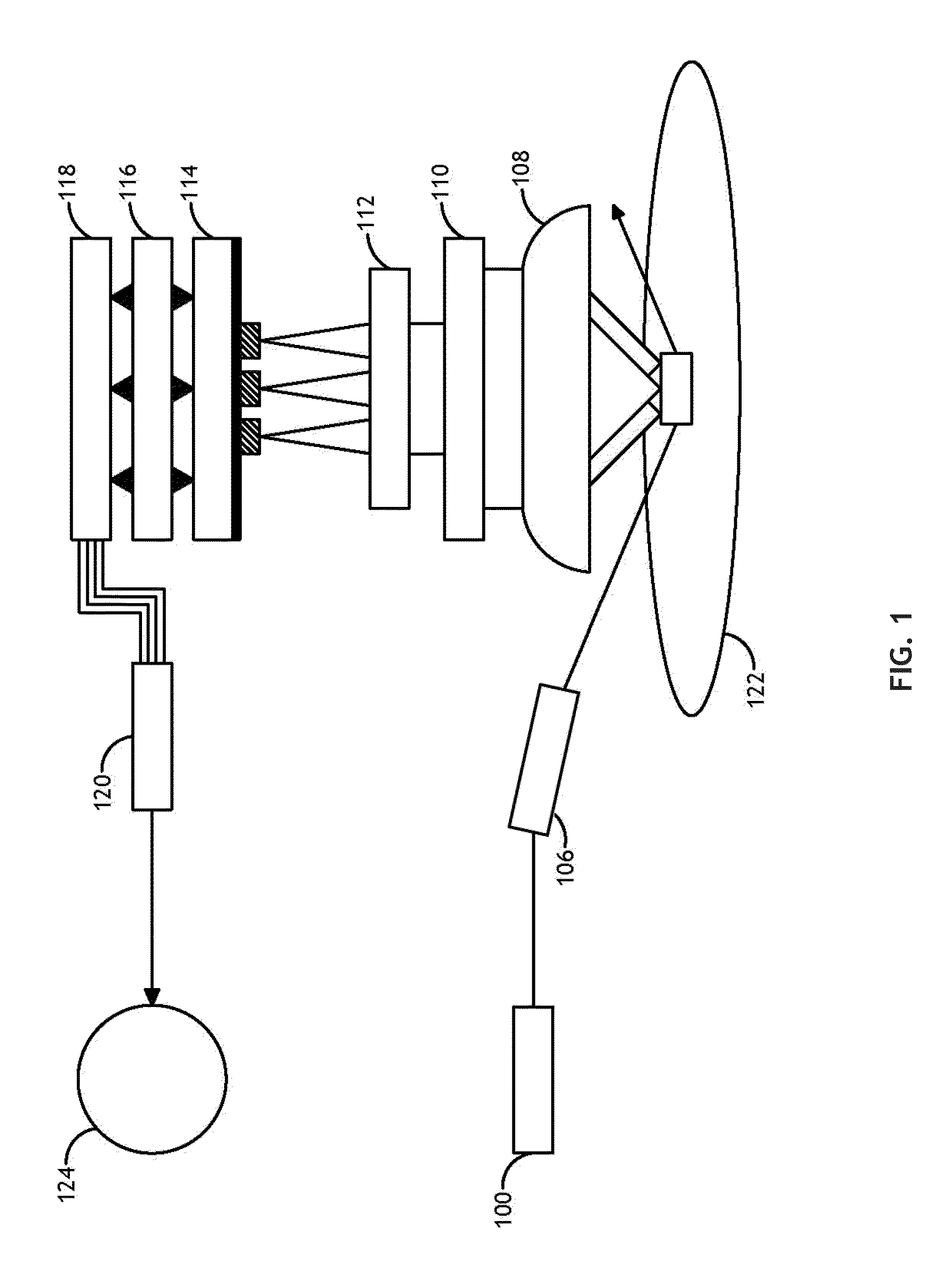
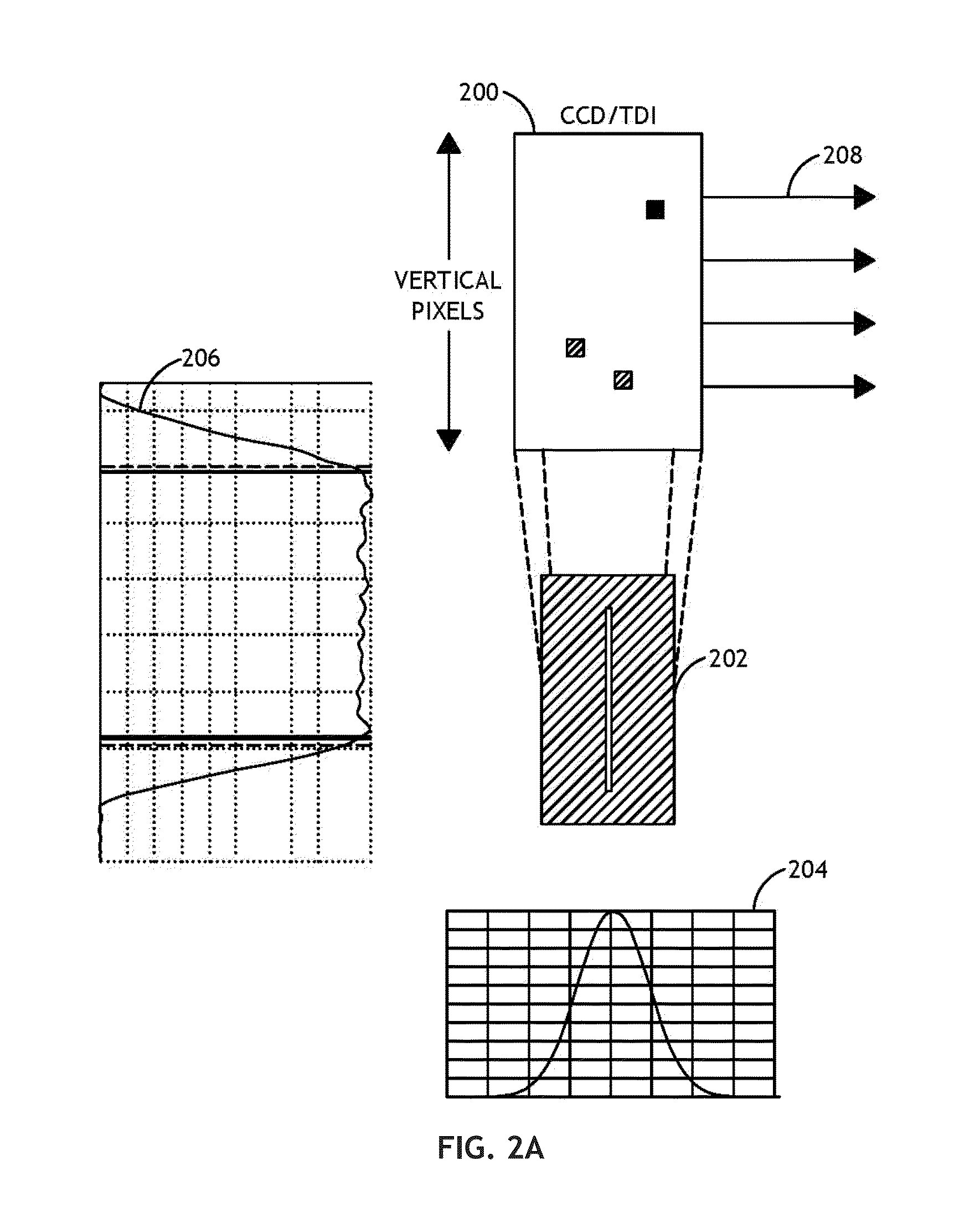
TDI sensor in a darkfield system
ActiveUS9891177B2Increasing signal/background and signal/noise ratioReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisLinear motionOptoelectronics
Owner:KLA CORP
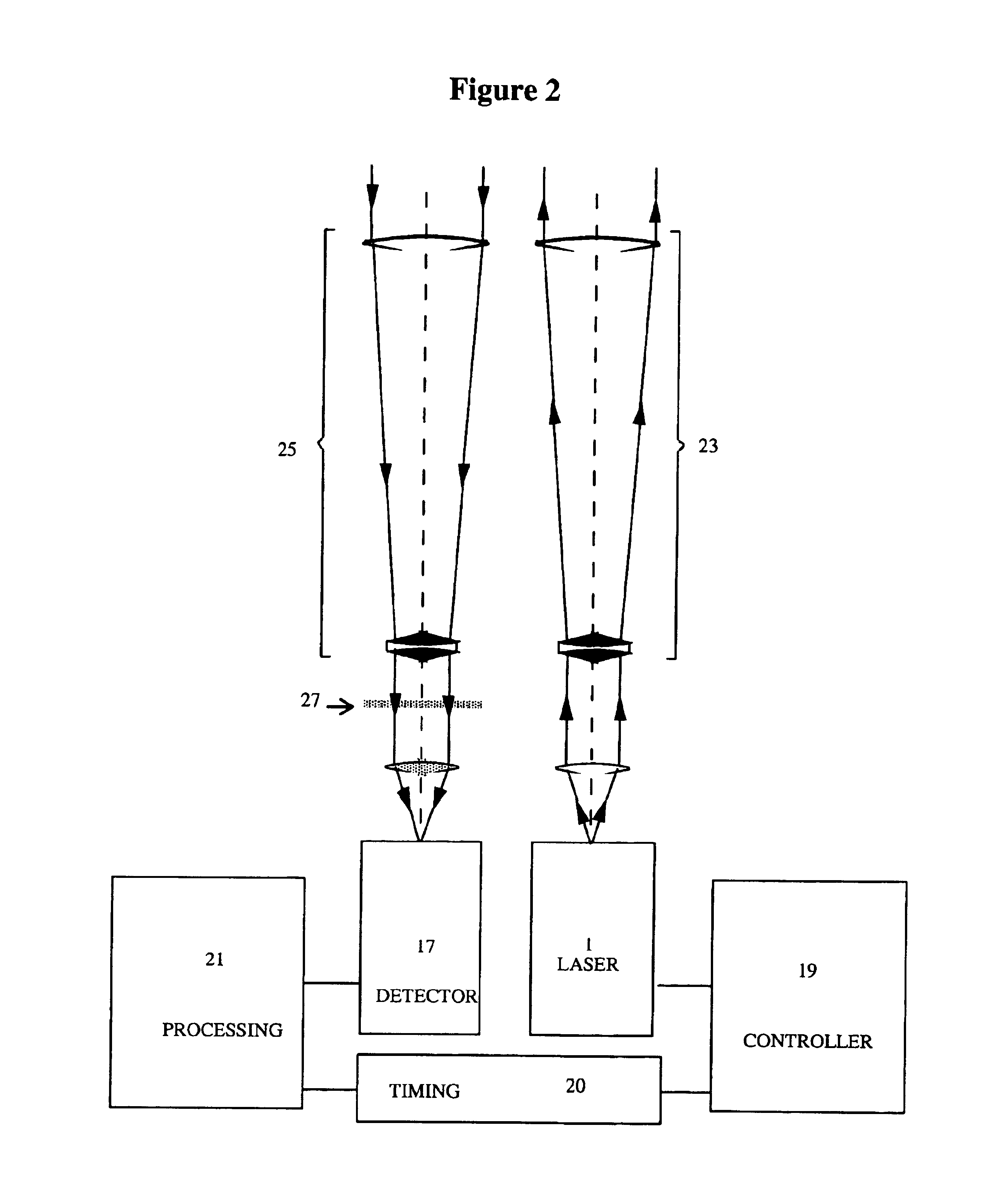
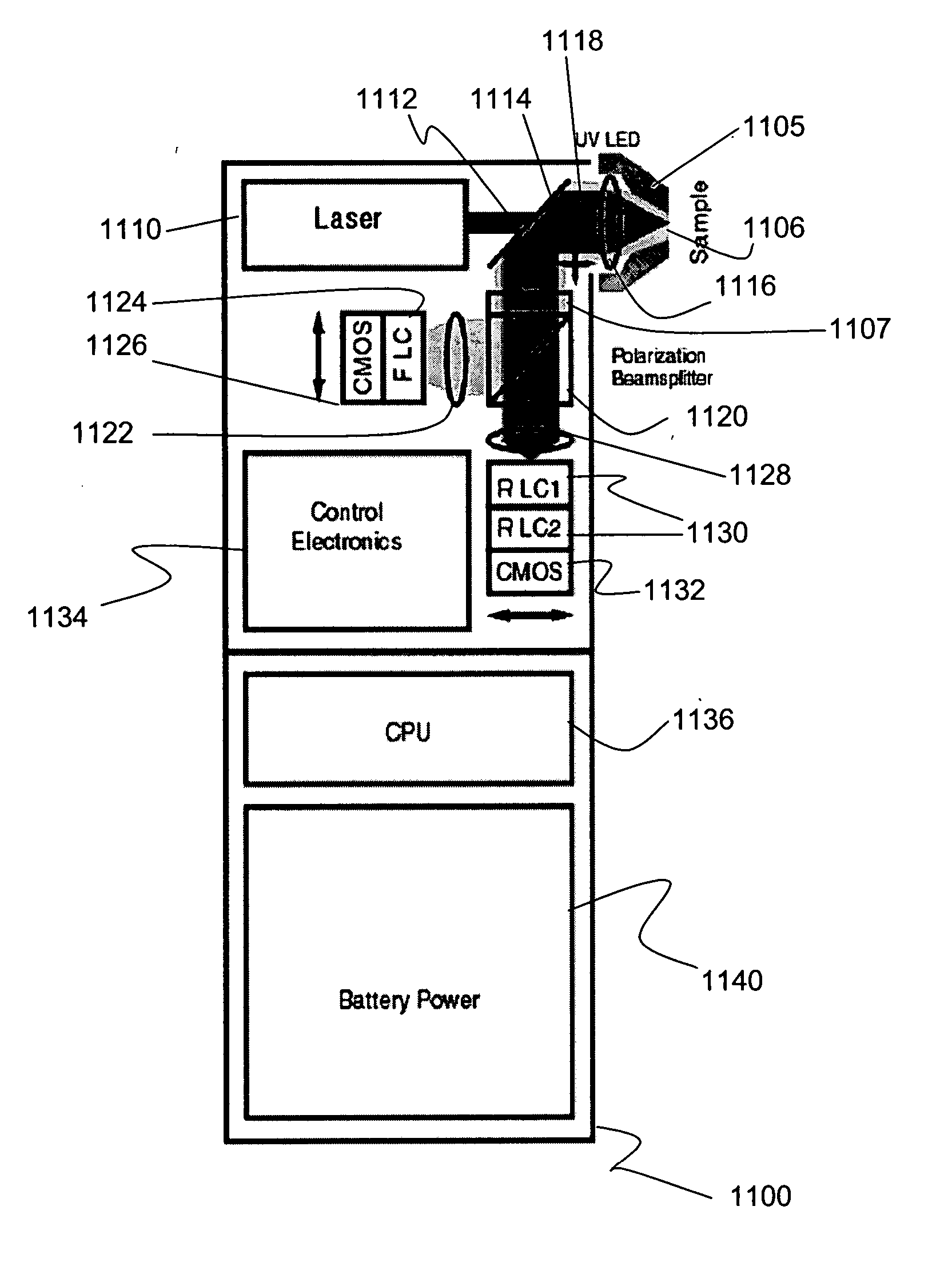
Method and apparatus for compact birefringent interference imaging spectrometer
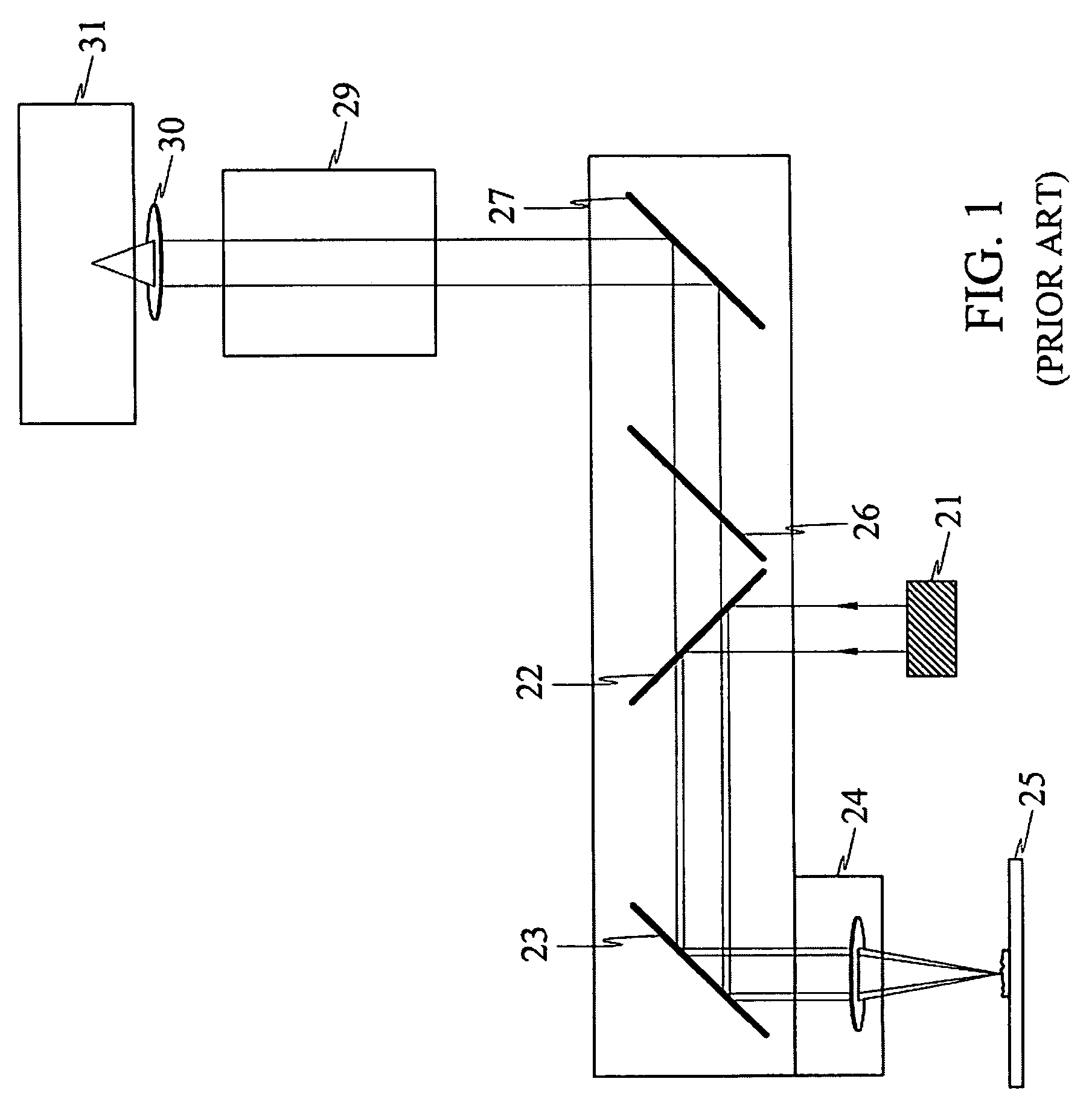
The disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for a compact birefringent interference imaging spectrometer. More specifically, the disclosure relates to a portable system for obtaining a spectrum of a sample. The portable system may include a first photon emission source for illuminating the sample with a first plurality of photons to thereby produce photons scattered by the sample; an optical lens for collecting the scattered photons; a filter for receiving the collected scattered photons and providing therefrom filtered photons; a first photon detector for receiving the filtered photons and obtaining therefrom a spectrum of the sample; and a rejection filter for blocking the photons from said first photon emission source from entering said first photon detector. The disclosure additionally relates to methods of using such portable systems.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
TDI Sensor in a Darkfield System
ActiveUS20160097727A1Increasing signal/backgroundImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisLinear motionOptoelectronics
A wafer scanning system includes imaging collection optics to reduce the effective spot size. Smaller spot size decreases the number of photons scattered by the surface proportionally to the area of the spot. Air scatter is also reduced. TDI is used to produce a wafer image based on a plurality of image signals integrated over the direction of linear motion of the wafer. An illumination system floods the wafer with light, and the task of creating the spot is allocated to the imaging collection optics.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Multi-element co-stabilizing zirconia of heat barrier coat material and preparation method
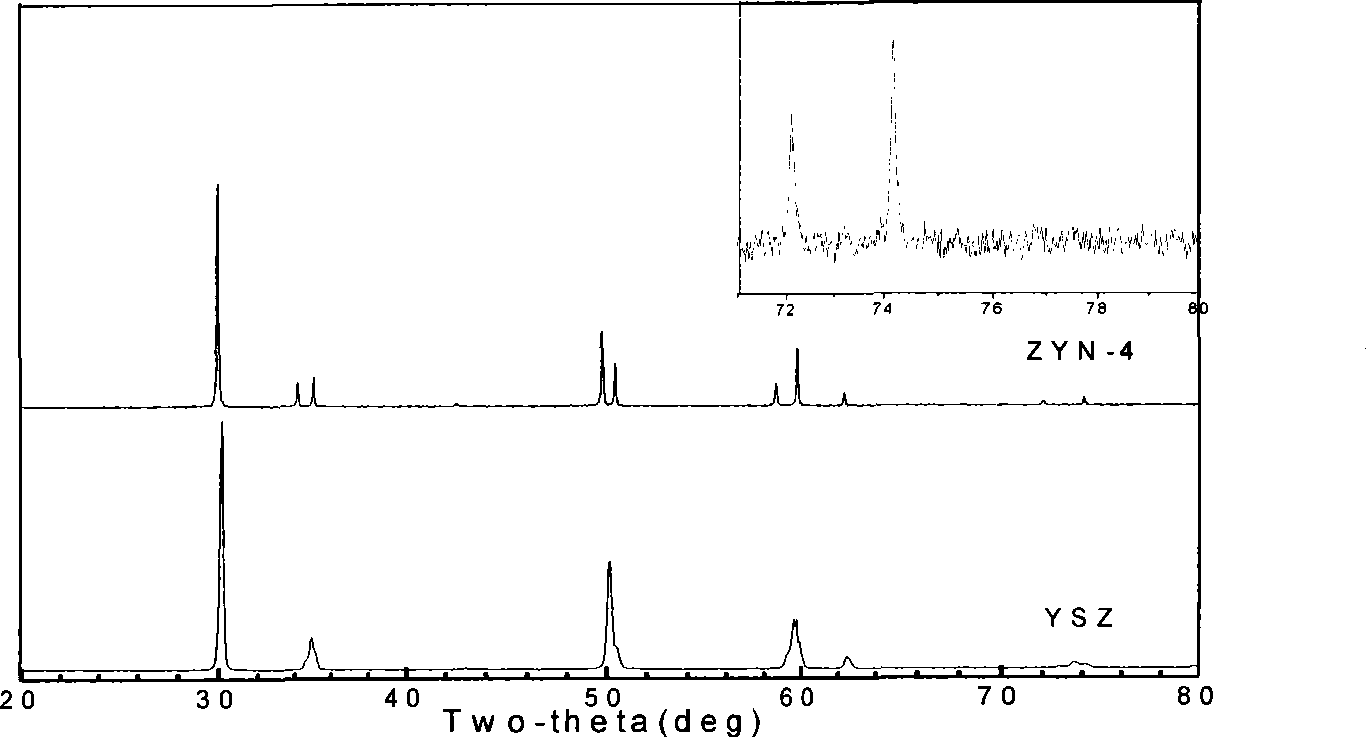
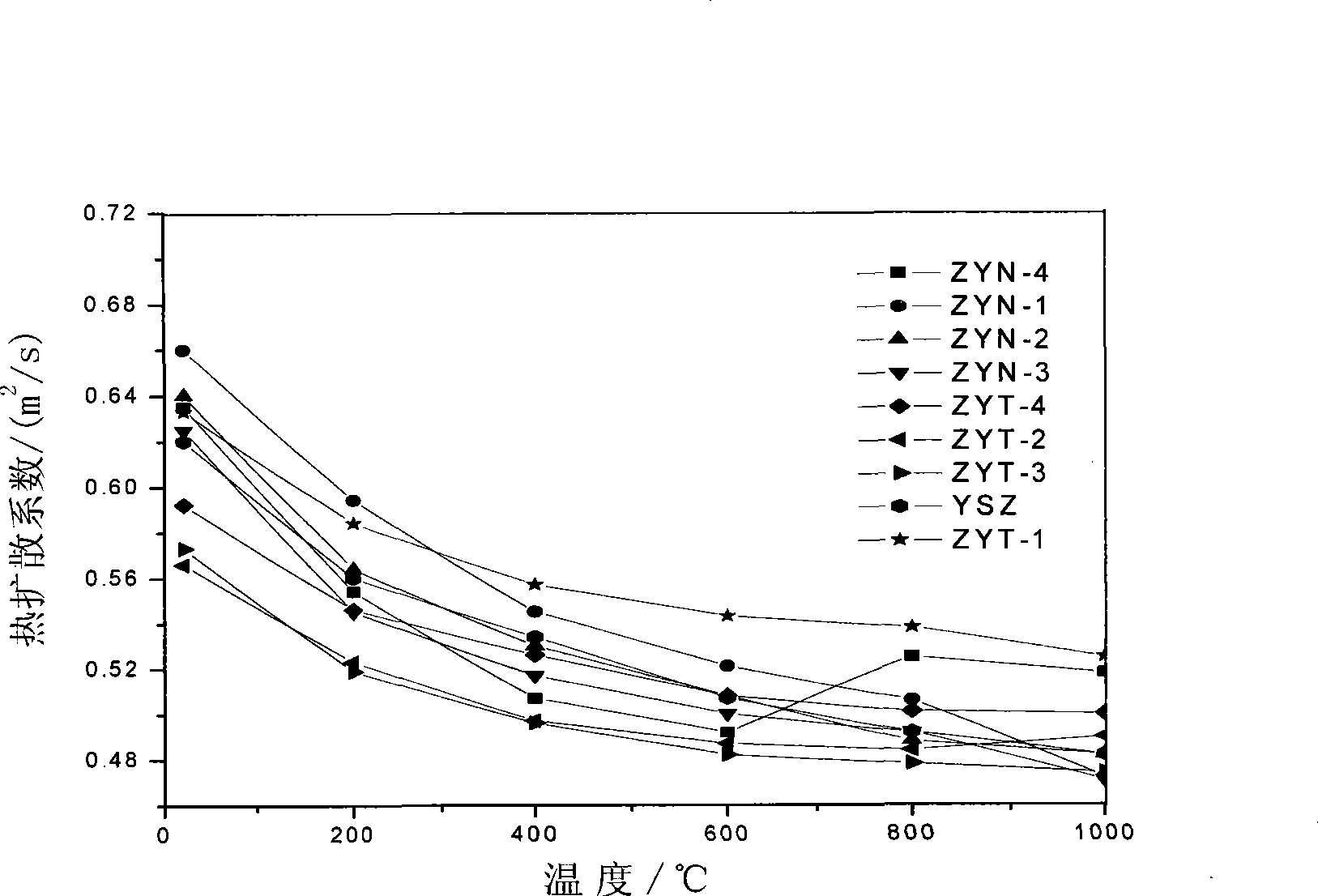
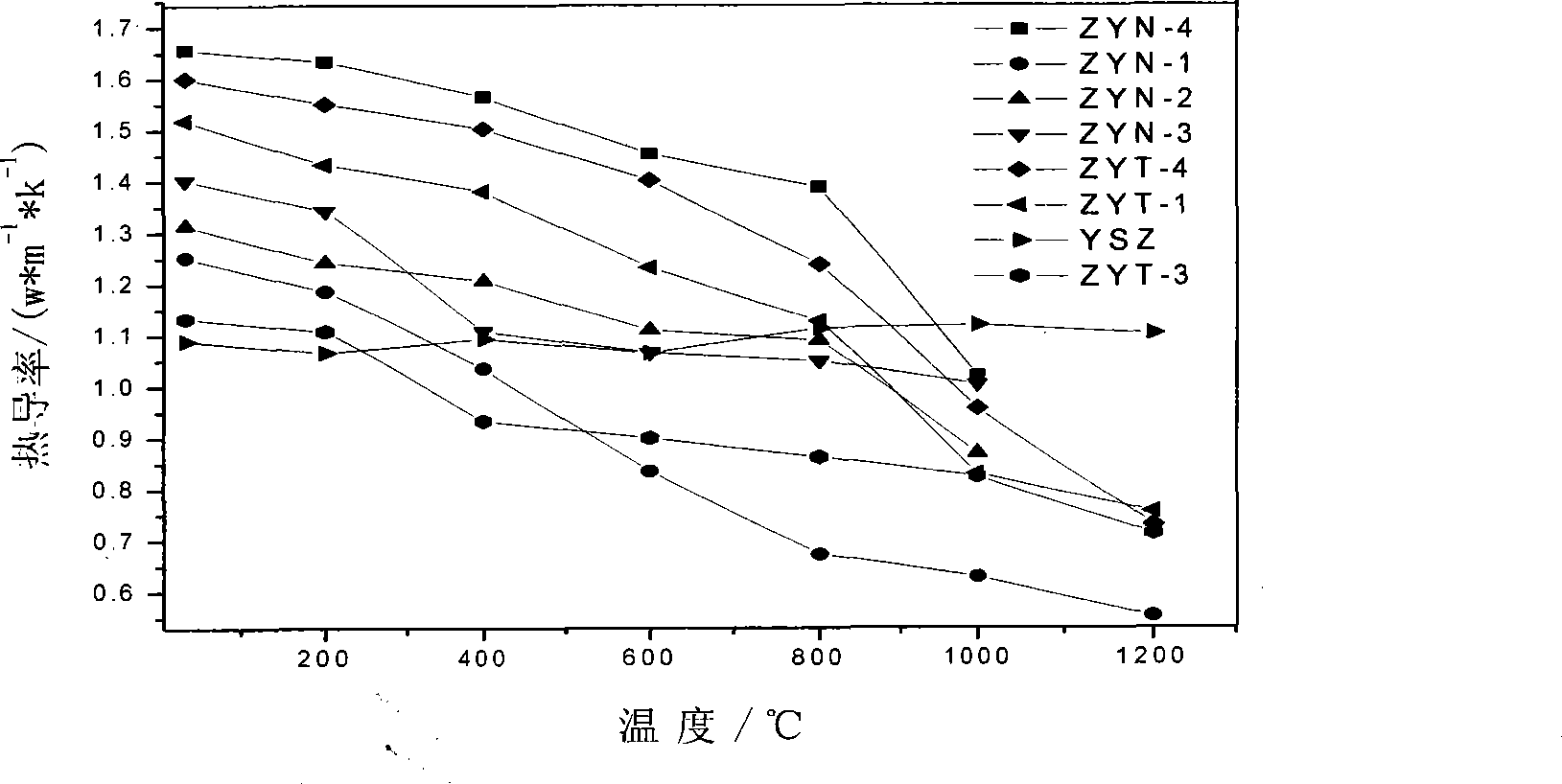
The invention relates to a multivariant co-stable zirconia thermal barrier coating material and a preparation method which belong to the field of materials. The multivariant co-stable zirconia thermal barrier coating material is characterized by consisting of the following materials according to mole fractions: zirconia, yttria, niobium oxide or tantalum oxide and rare earth oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a zirconia ball is ground by wet process, dried and molded; a pre-burnt block is obtained by pre-burning; the pre-burnt block is smashed and further carried out with the wet ball milling to obtain slurry; the slurry is dried, granulated and mould pressed to obtain a green body, the green body is sintered to obtain the multivariant co-stable zirconia thermal barrier coating material; the ceramic material can be used as a target material for preparing a thermal barrier coating by using the EB-PVD method. A third phase of Nb2O5 / Ta2O5 is introduced in YSZ to develop the stable existence interval of t-ZrO2 to further obtain non-transition t'-ZrO2, and the rare earth oxide is added to increase the defects to further improve the phonon or photon scattering on the basis, thereby improving the using temperature of the ZrO2 thermal barrier coating and reducing the thermal conductivity of the material.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
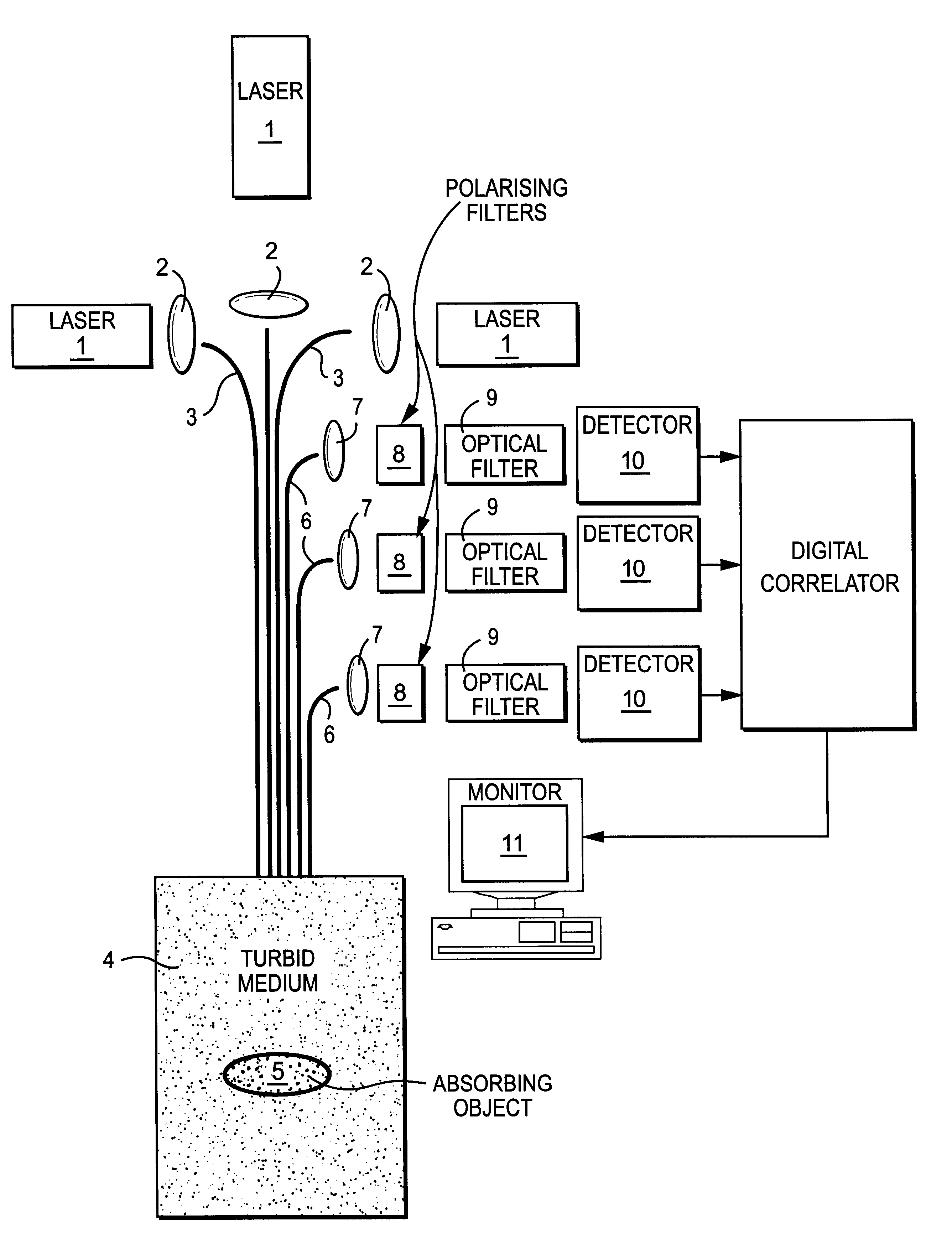
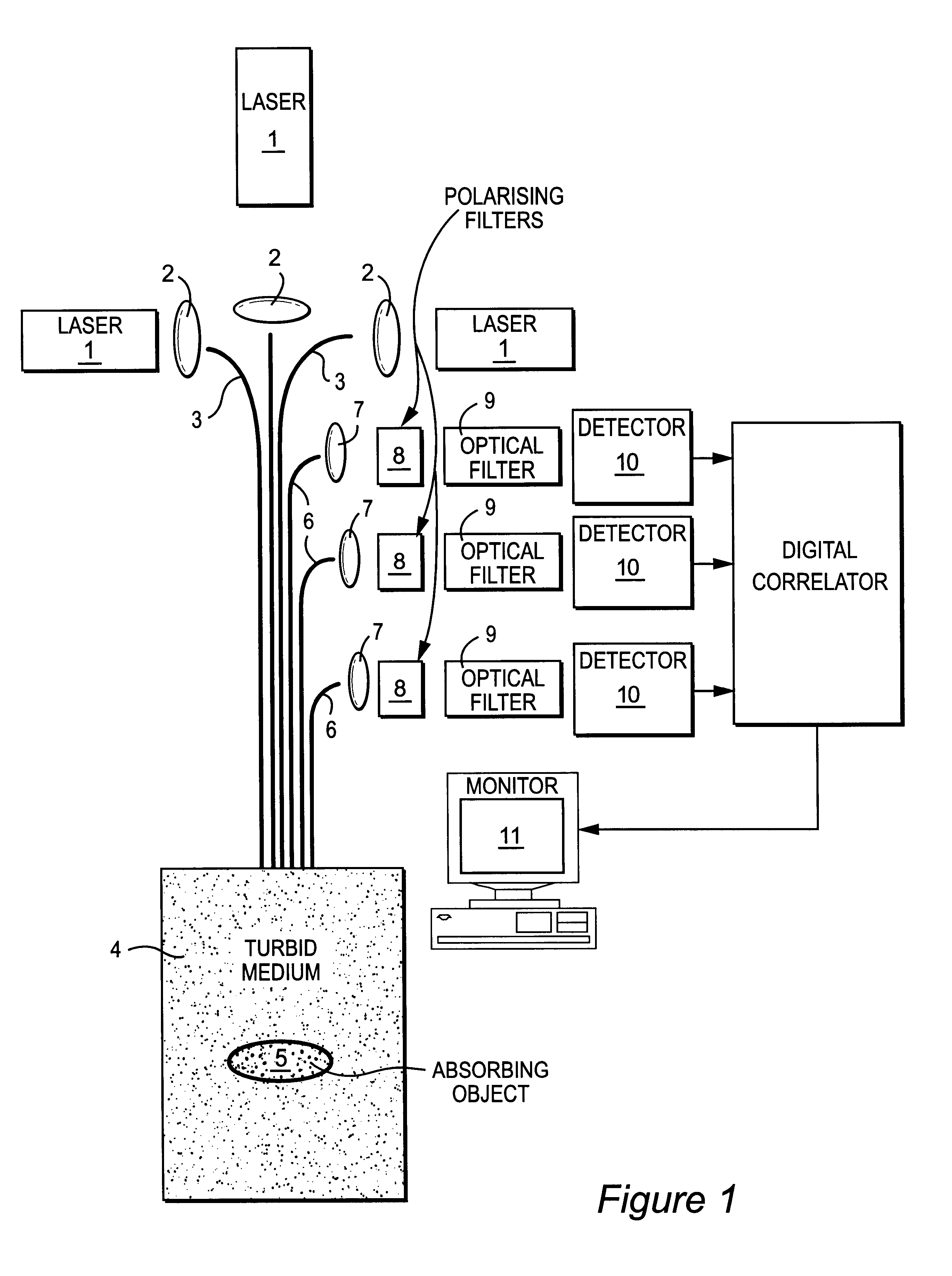
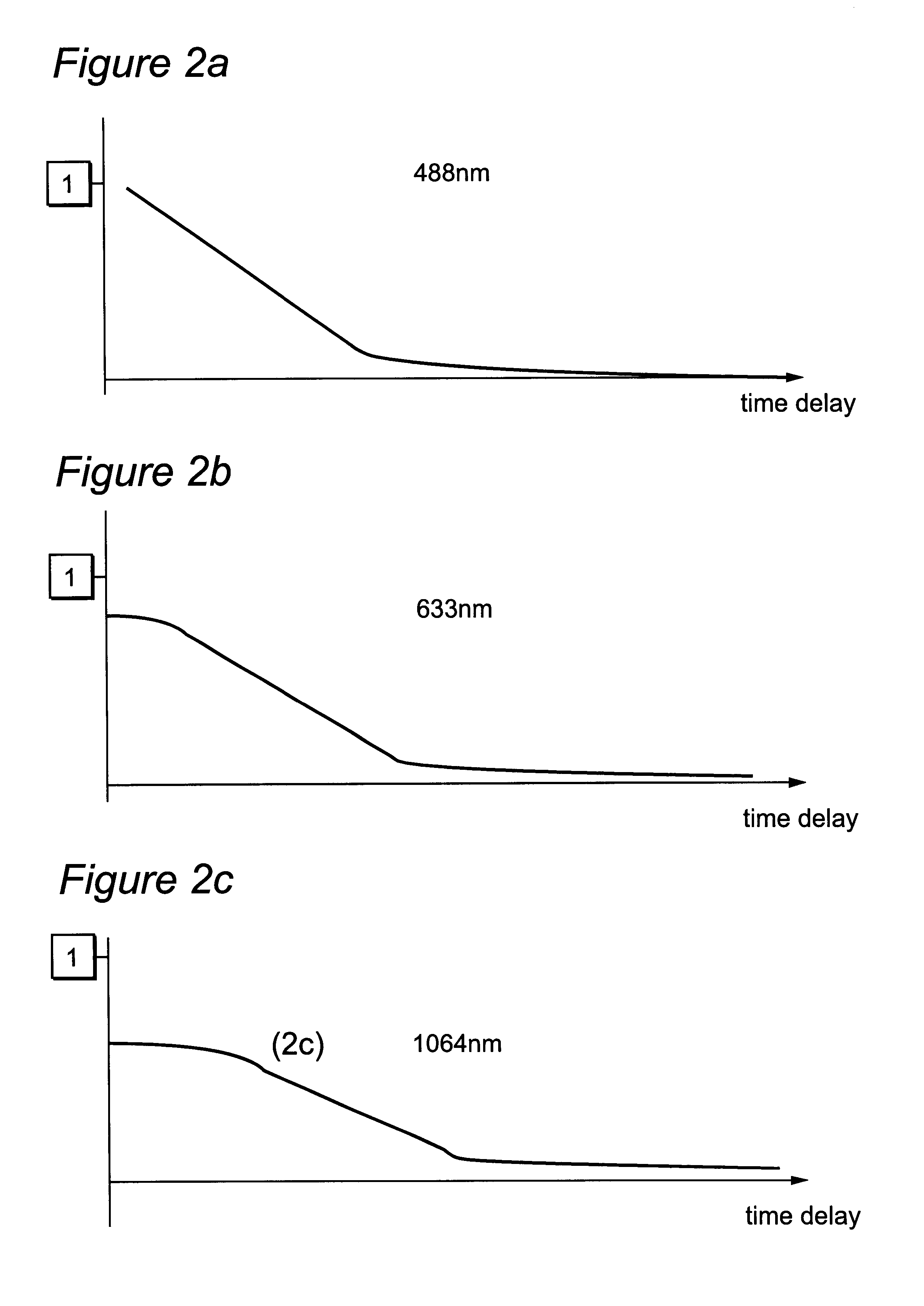
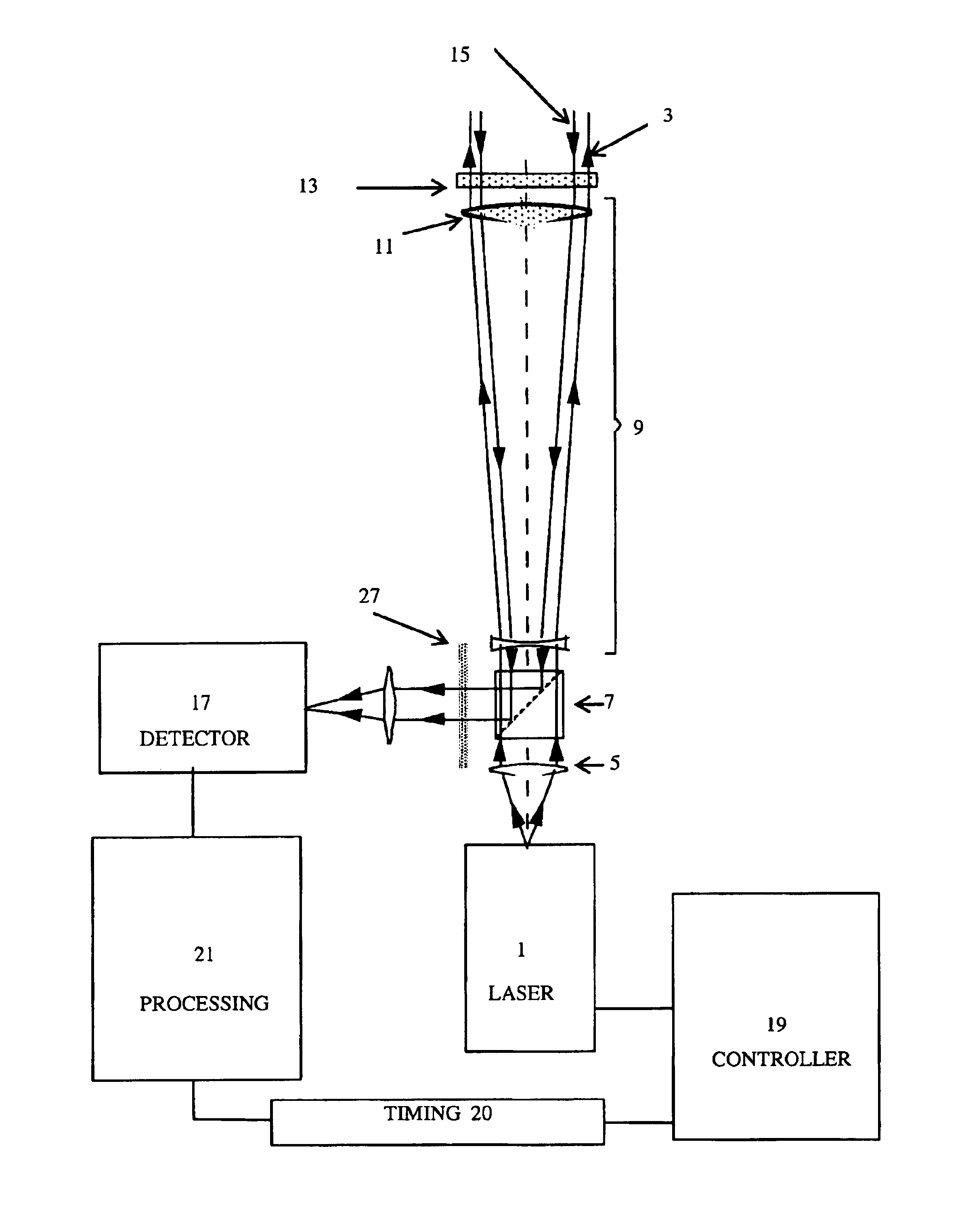
Method and apparatus for detecting an object within a dynamic scattering media
InactiveUS6754518B1Suitable imageIncrease opportunitiesSurgeryScattering properties measurementsTime domainWavelength
A method of detecting an object located within a dynamic scattering media, includes i) directing a continuous coherent light wave of predetermined wavelength into the media; ii) detecting dynamically scattered light emerging from the media; iii) correlating the detected light photons in the time or frequency domain; iv) determining the presence of an object from analysis of differences between the correlation and a correlation which would arise from photons scattered by the media only; and v) determining the approximate position of the object within the media from the analysis of the correlation and knowledge of the mean transport path of the light wave of predetermined wavelength within the media.
Owner:VICTORIA VNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER THE
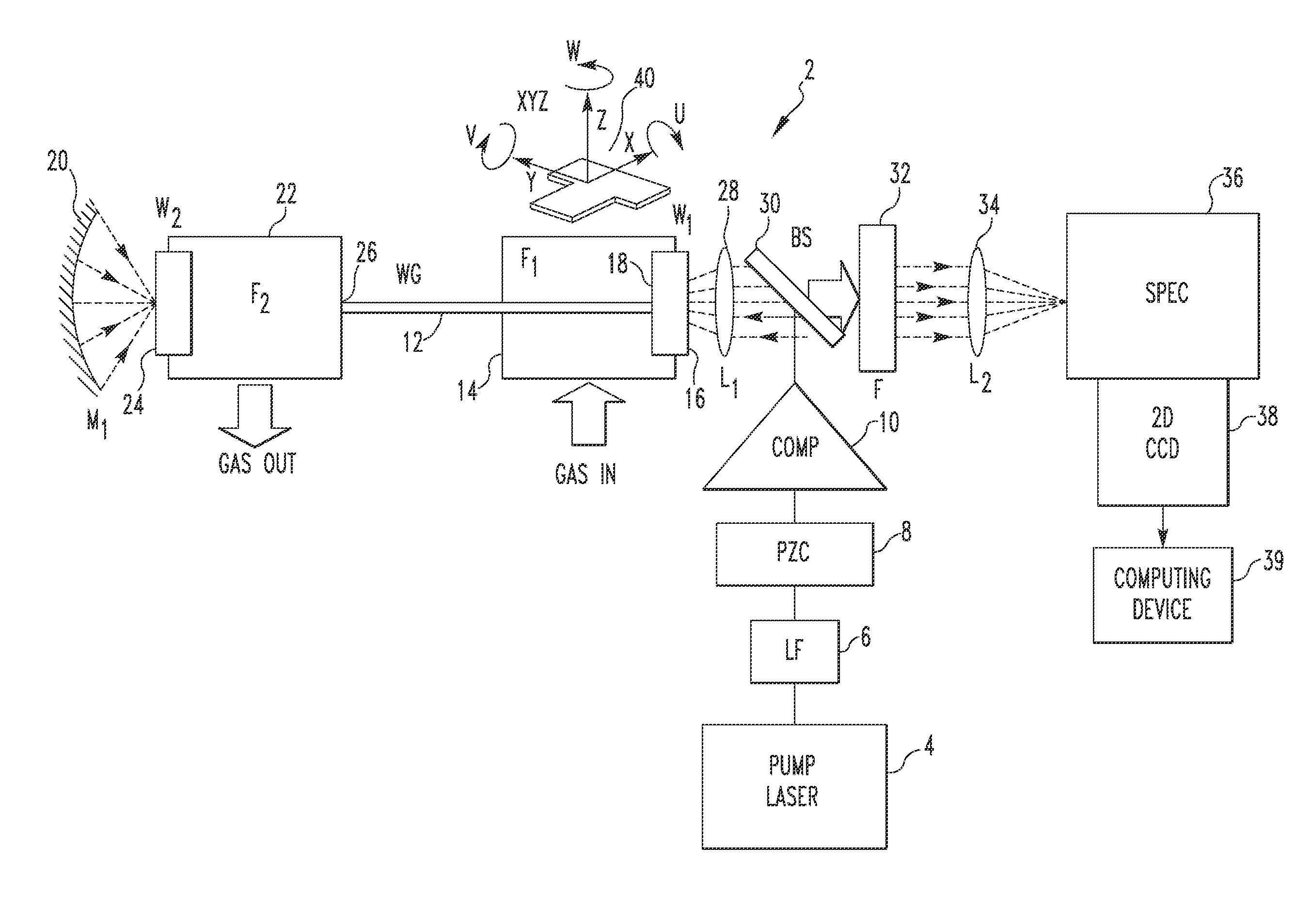
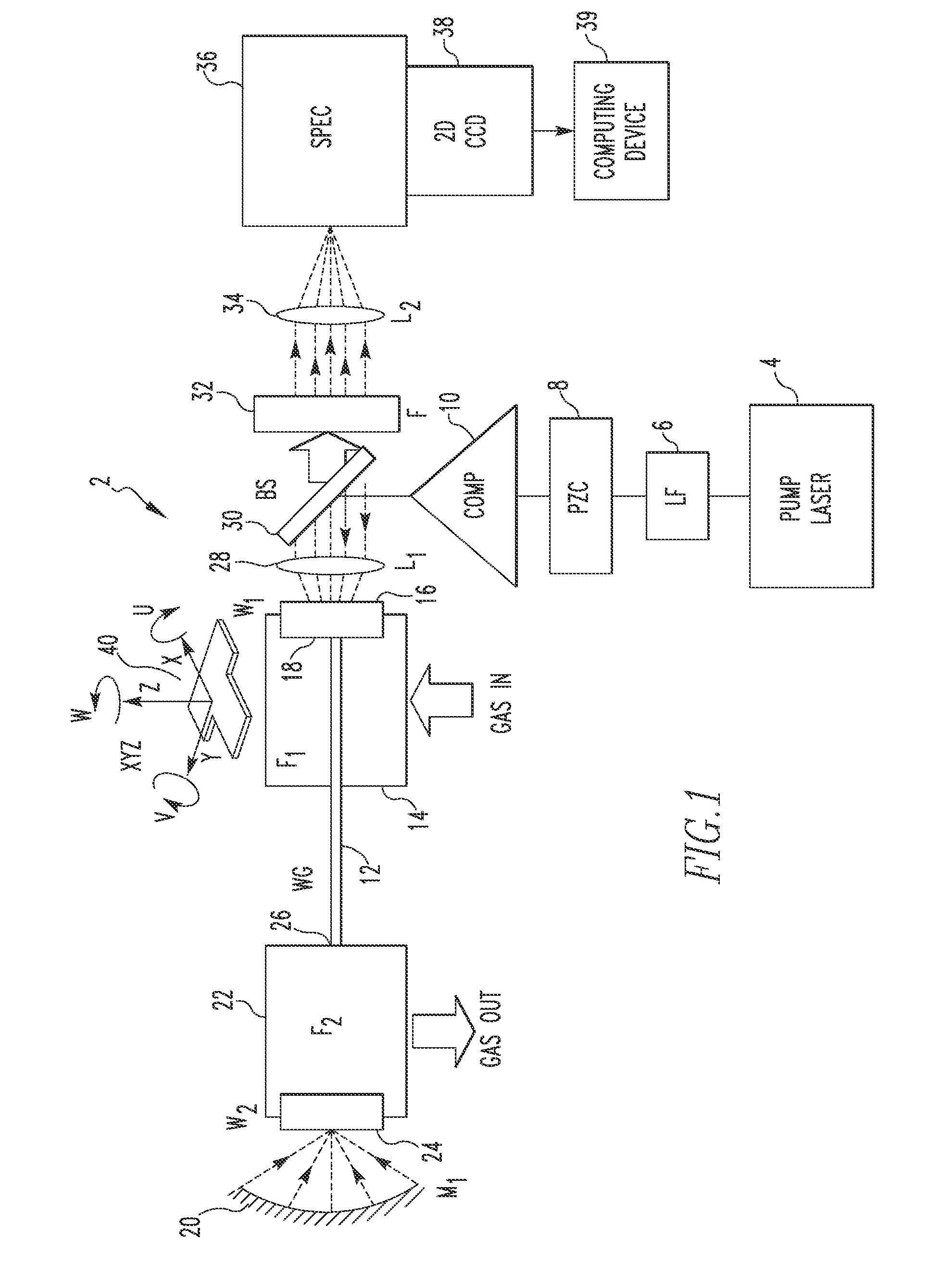
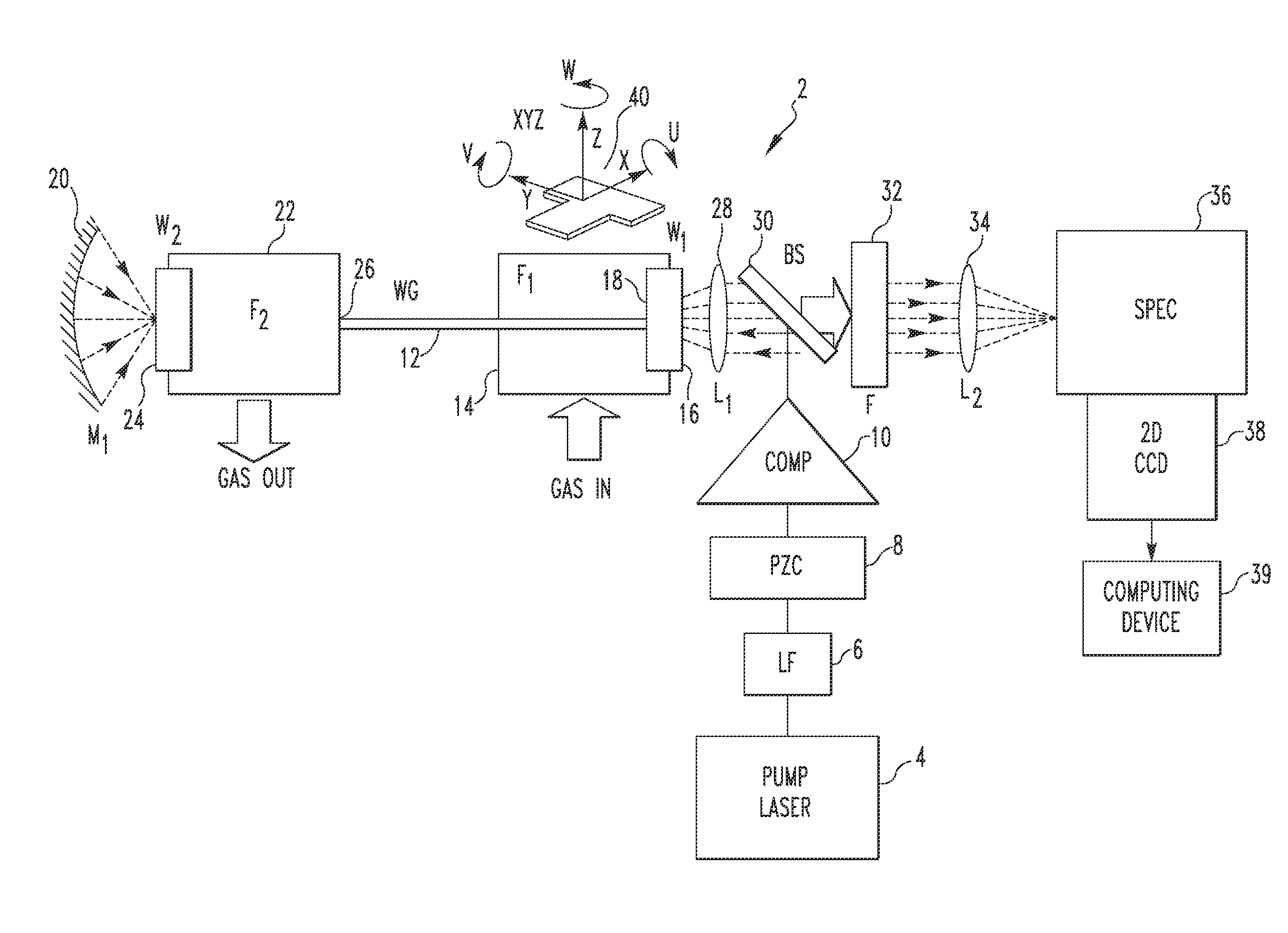
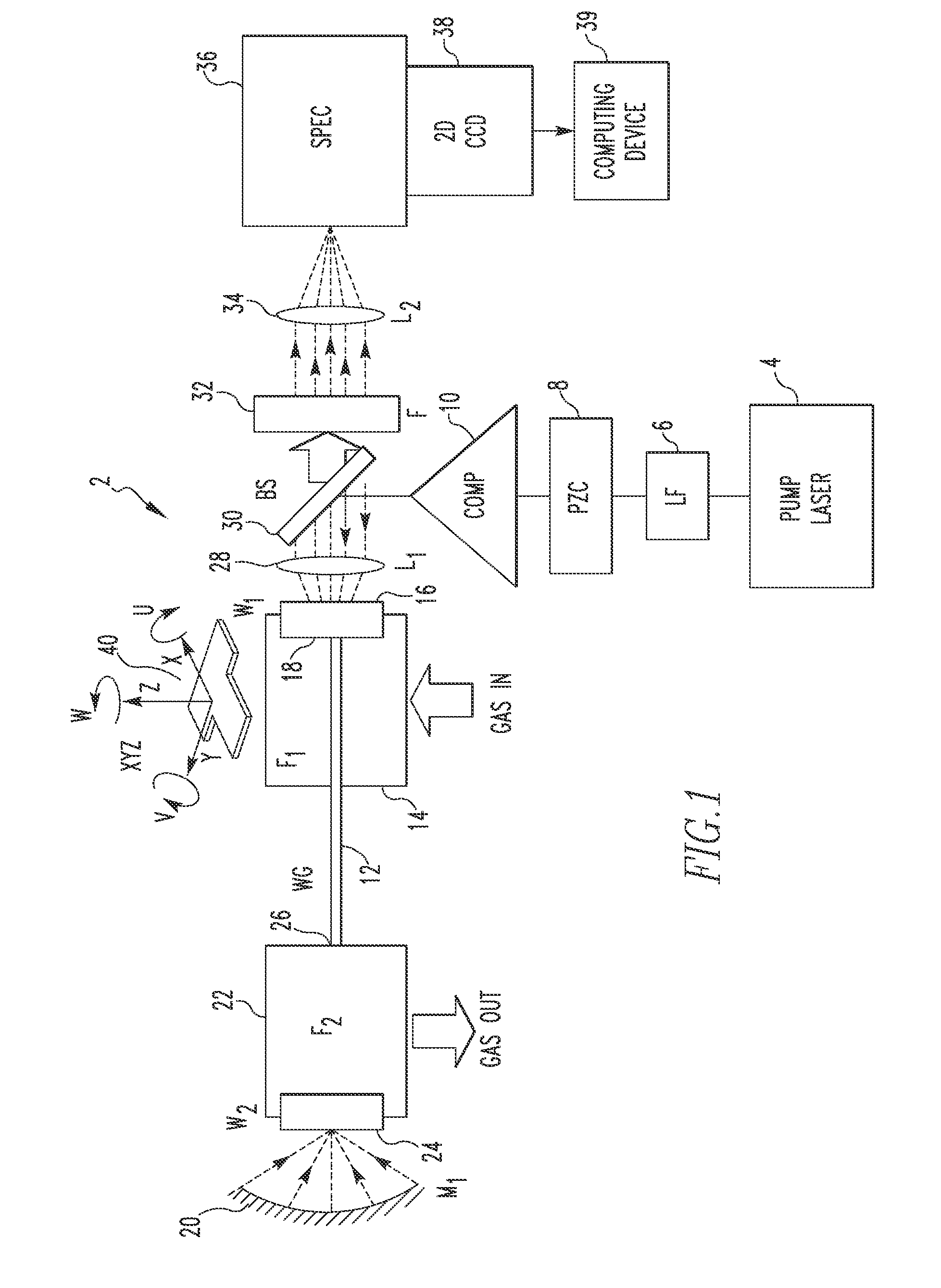
Gas Sensing System Employing Raman Scattering
A gas detection system includes a light detector, a pump laser with spectral emission between UV and IR wavelengths and structured to generate a laser beam, a hollow waveguide structured to receive a sample gas, the hollow waveguide having a bandwidth sufficient to transmit the laser beam and Stokes Raman photons scattered by the sample gas, and an optical system. The optical system is structured to: (i) direct the laser beam into the hollow waveguide such that it propagates in the hollow waveguide in one or more low-order low-loss waveguide modes, and (ii) direct Raman signals generated within the hollow waveguide in response to the laser beam interacting with the sample gas toward the light detector, the Raman signal including the Stokes Raman photons.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
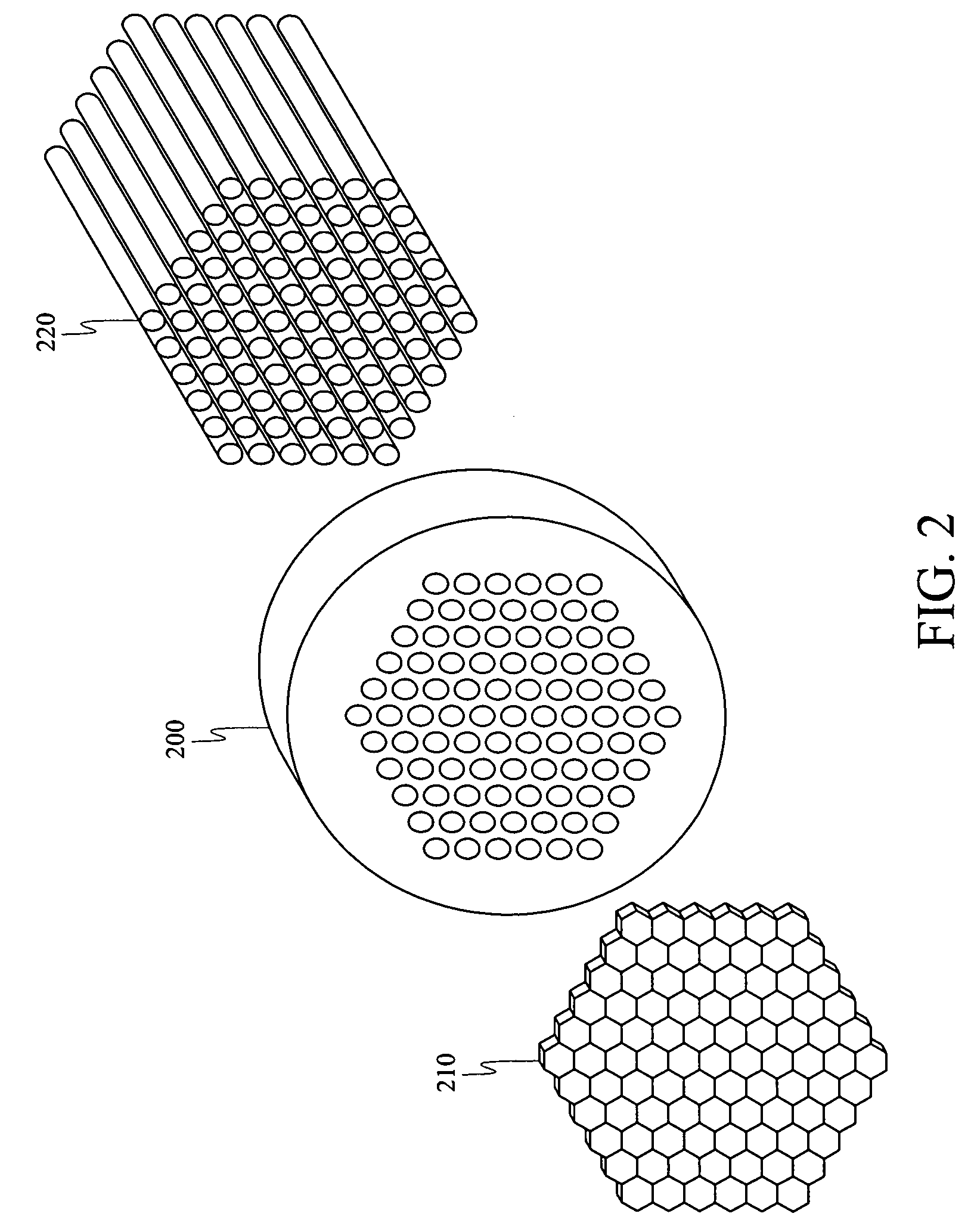
Method and apparatus for microlens array/fiber optics imaging
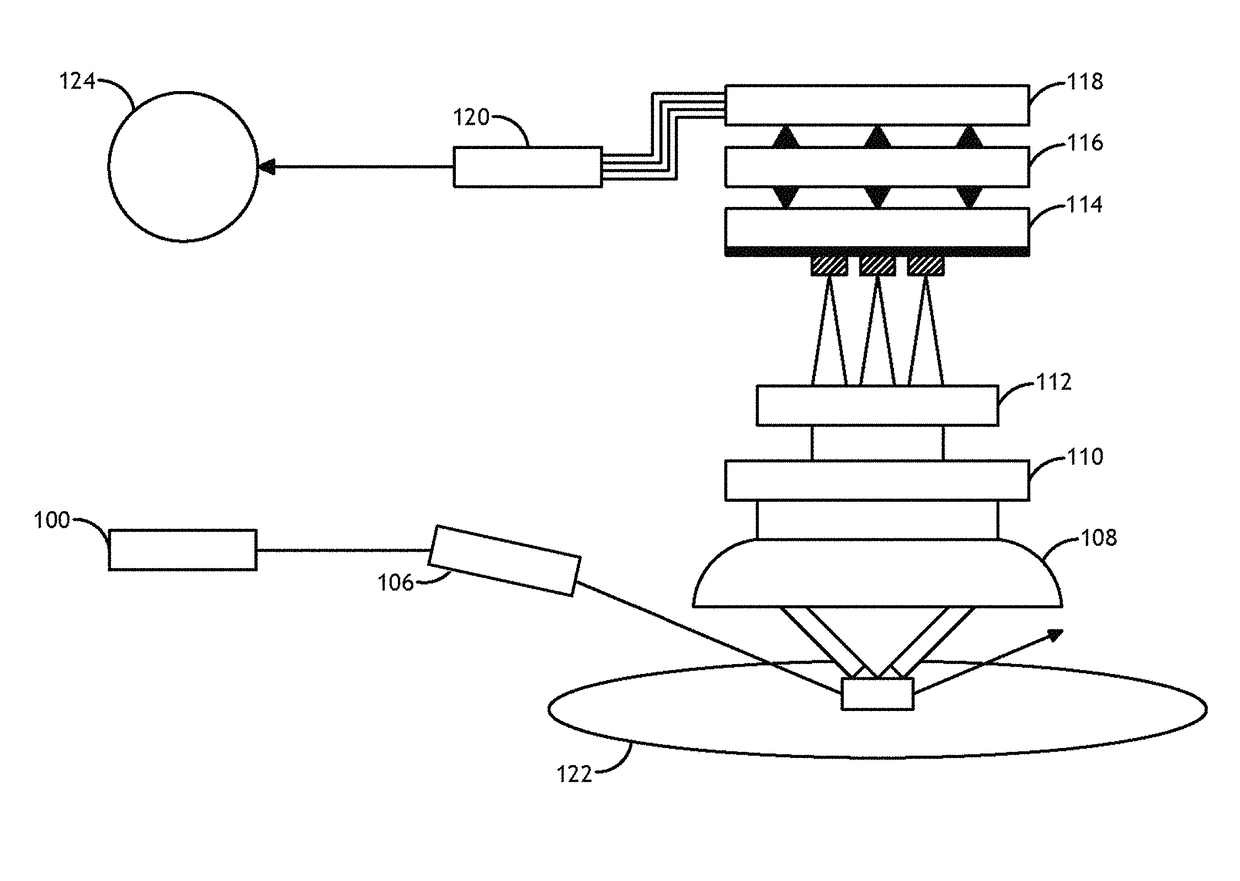
A novel approach for chemical imaging is disclosed. In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a system for producing a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample from photons scattered from the sample, comprising an optical lens; a first optical fiber bundle of M fibers; a second optical fiber bundle of N fibers; an optical fiber switch; and a charge coupled device, wherein the image comprises plural sub-images, and wherein each sub-image is formed from photons scattered from a predetermined two spatial dimension portion of the sample, and wherein the scattered photons forming each sub-image have a predetermined wavelength different from a predetermined wavelength of scattered photons forming the other sub-images, and wherein the scattered photons for each sub-image are collected substantially simultaneously.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Method for preparing thermal barrier coating
ActiveCN102212786AImprove thermal shock resistanceExtend your lifeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingBiological activationPhonon
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thermal barrier coating. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a deposition matrix is bombarded by ion beams while a deposition coating is evaporated by electron beams, the steam energy of the electron beams is about 0.1-1 electron volts, and the energy is not enough to well migrate atoms in the process of depositing the coating; and the energy of the ion beams can reach thousands of electron volts, and the energy is enough to interfere growth of columnar crystals to increase crystal boundaries and crystal sub-boundaries and enlarge or increase microscopic holes so as to reduce phonon and photon scattering mean free path and reduce the thermal conductivity of the thermal barrier coating. The energy of vaporous clouds can be increased through activation ionization effects of ions; and compared with the conventional EB-PVD (Electron Beam Physical Vapour Deposition), the method can ensure that same performances can be achieved at low deposition temperature; furthermore, forms, structures and stresses of the columnar crystals can be also adjusted and controlled through ion assisted deposition, and thus, the service life ofthe thermal barrier coating can be prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Apparatus for and method of optical detection and analysis of an object
InactiveUS6943868B2Conveniently separatedSolve the detection speed is slowWave based measurement systemsOptical rangefindersQuality controlOptical instrument
An apparatus for detection and analysis of optical systems. Prior art systems exploit the phenomenon of photon scattering in order to range the distance of objects from the ranging apparatus. However, no information other than the distance of the target object is obtained from such systems. There is therefore provided an apparatus that exploits the technique of single photon counting and the phenomenon of retro reflection to provide information about a target optical system. Such information can be analysed and compared against known optical systems to provide a means of identification. Alternatively such information can be used as a method of quality control when constructing precision optical instruments such as telescopes or microscopes.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Method and apparatus for microlens array/fiber optic imaging
A novel approach for chemical imaging is disclosed. In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a system for producing a spatially accurate wavelength-resolved image of a sample from photons scattered from the sample, comprising an optical lens; a first optical fiber bundle of M fibers; a second optical fiber bundle of N fibers; an optical fiber switch; and a charge coupled device, wherein the image comprises plural sub-images, and wherein each sub-image is formed from photons scattered from a predetermined two spatial dimension portion of the sample, and wherein the scattered photons forming each sub-image have a predetermined wavelength different from a predetermined wavelength of scattered photons forming the other sub-images, and wherein the scattered photons for each sub-image are collected substantially simultaneously.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for compact birefringent interference imaging spectrometer
InactiveUS20050041244A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryPhoton emissionPhoton scattering
The disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for a compact birefringent interference imaging spectrometer. More specifically, the disclosure relates to a portable system for obtaining a spectrum of a sample. The portable system may include a first photon emission source for illuminating the sample with a first plurality of photons to thereby produce photons scattered by the sample; an optical lens for collecting the scattered photons; a filter for receiving the collected scattered photons and providing therefrom filtered photons; a first photon detector for receiving the filtered photons and obtaining therefrom a spectrum of the sample; and a rejection filter for blocking the photons from said first photon emission source from entering said first photon detector. The disclosure additionally relates to methods of using such portable systems.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for scatter correction
InactiveCN102037495APrecise scatter correctionReduced risk of visible scatter artifactsReconstruction from projectionPhysical modelPhoton scattering
A method and apparatus of image reconstruction correcting for photon scatter is provided. A direct physical measurement of scattered photons is used in conjunction with a physical model of the photon scattering process to make the corrections.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High-speed VCSEL laser epitaxial structure and preparation method therefor
PendingCN107171181AIncrease modulation bandwidthReduce intrinsic parasitic capacitanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersModulation bandwidthPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a high-speed VCSEL laser epitaxial structure. The laser epitaxial structure comprises a GaAs substrate; a GaAs buffer layer, an N type doped DBR, an active layer, an oxidization limiting layer, a P type doped DBR and an ohmic contact layer are deposited on the GaAs substrate by adopting MOCVD in sequence; and the oxidization limiting layer is formed by multiple Al<1-x>Ga<x>As epitaxial layers with freely adjustable Ga components, wherein X is the Ga element component. According to the laser epitaxial structure, the multiple layers of Al<1-x>Ga<x>As with certain thickness and jumping components are adopted to form the oxidization limiting layer; and the front-end shape of the oxidization limiting layer can be changed by adjusting the components in each layer of Al<1-x>Ga<x>As, so that a lens structure can be formed at the front end of the oxidization limiting layer, and photon scattering loss can be lowered, thereby improving the modulation bandwidth of the VCSEL. The laser epitaxial structure has the following advantages: 1) by adjusting the ratio of Ga in the oxidization limiting layer, the oxidization rate of the oxidization limiting layer is lowered, the oxidization can be controlled easily, and the product yield of the VCSEL chip is improved; and 2) the oxidization limiting layer is high in thickness and low in intrinsic stray capacitance.
Owner:全磊光电股份有限公司
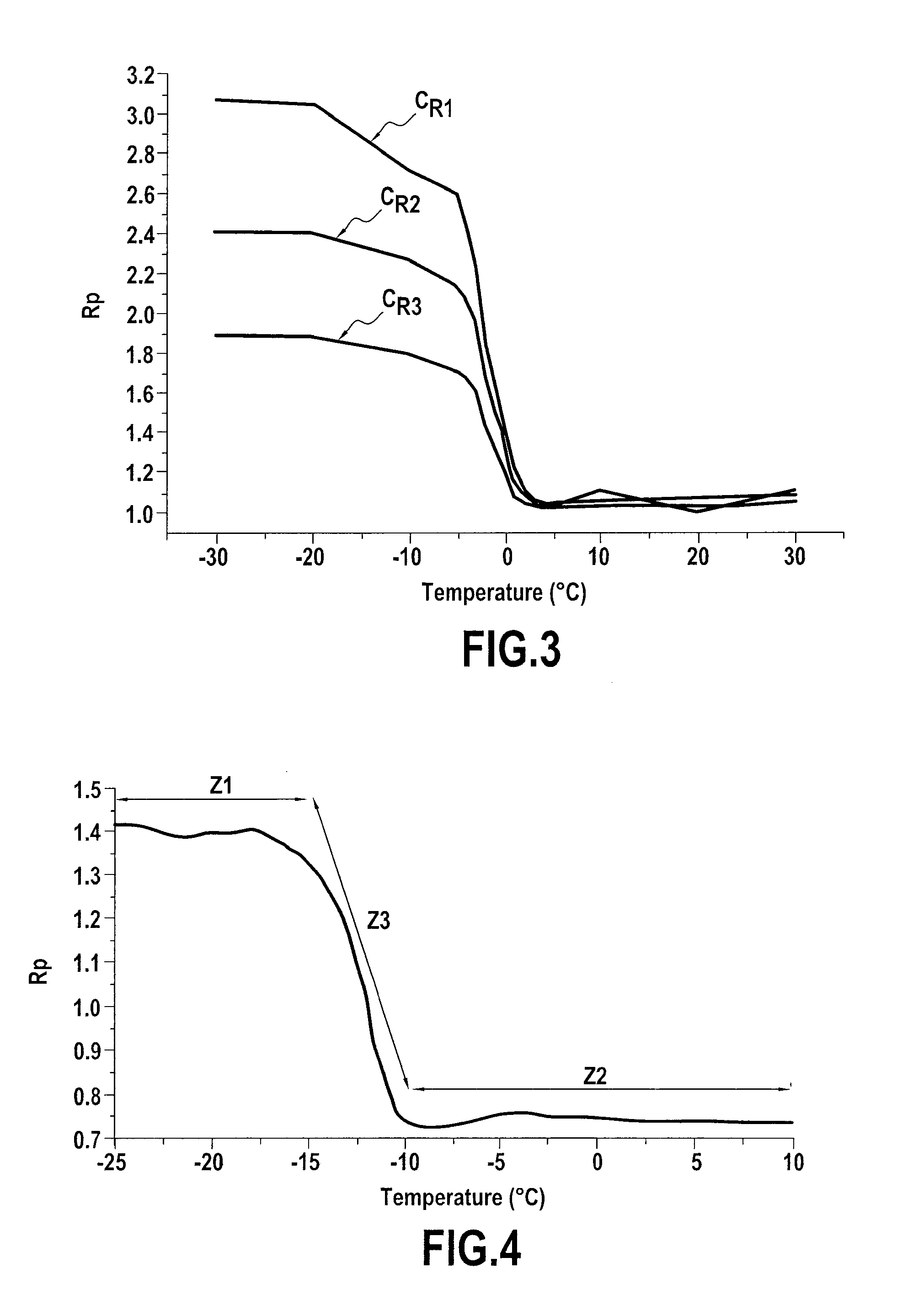
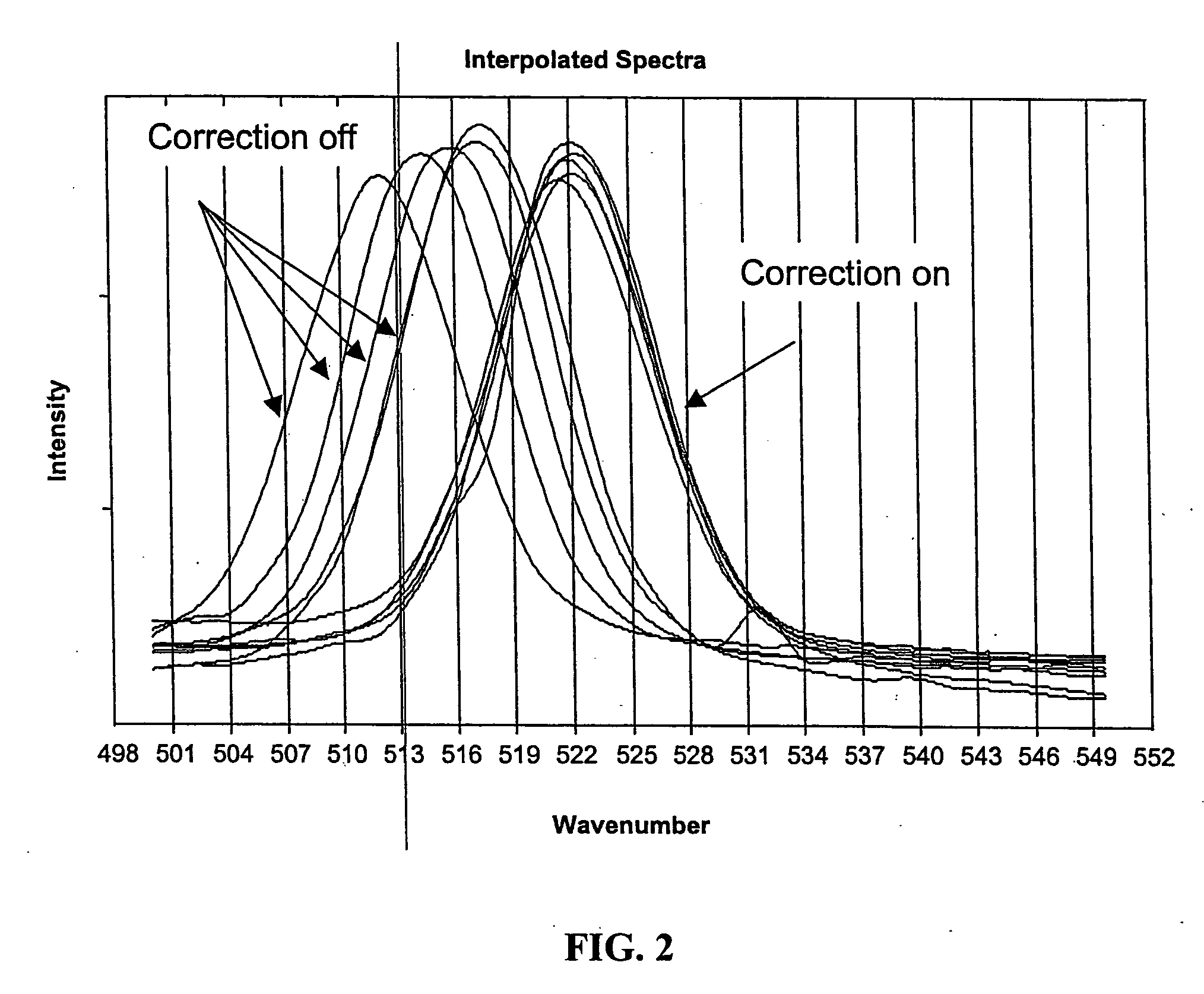
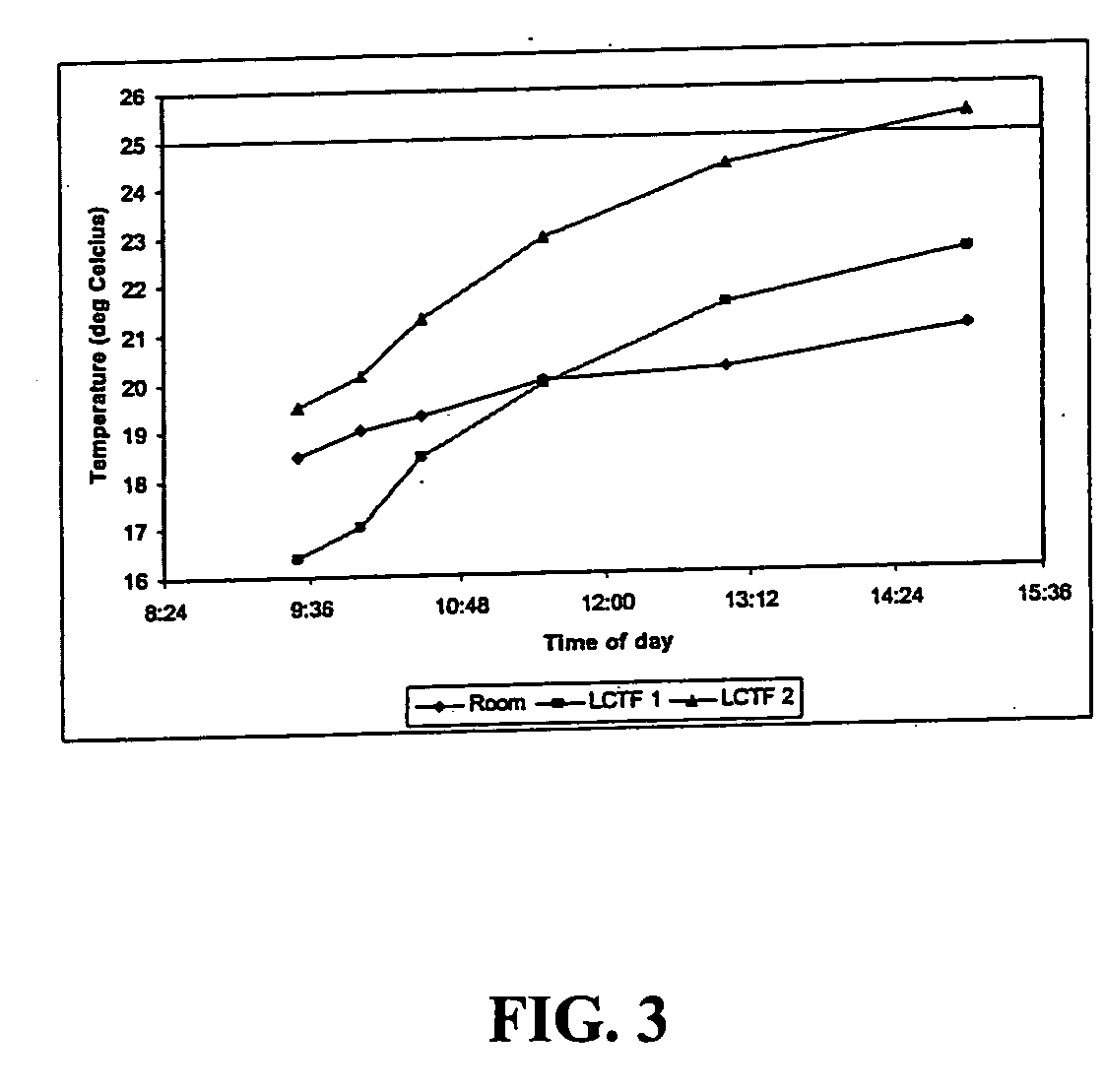
Method and apparatus for peak compensation in an optical filter
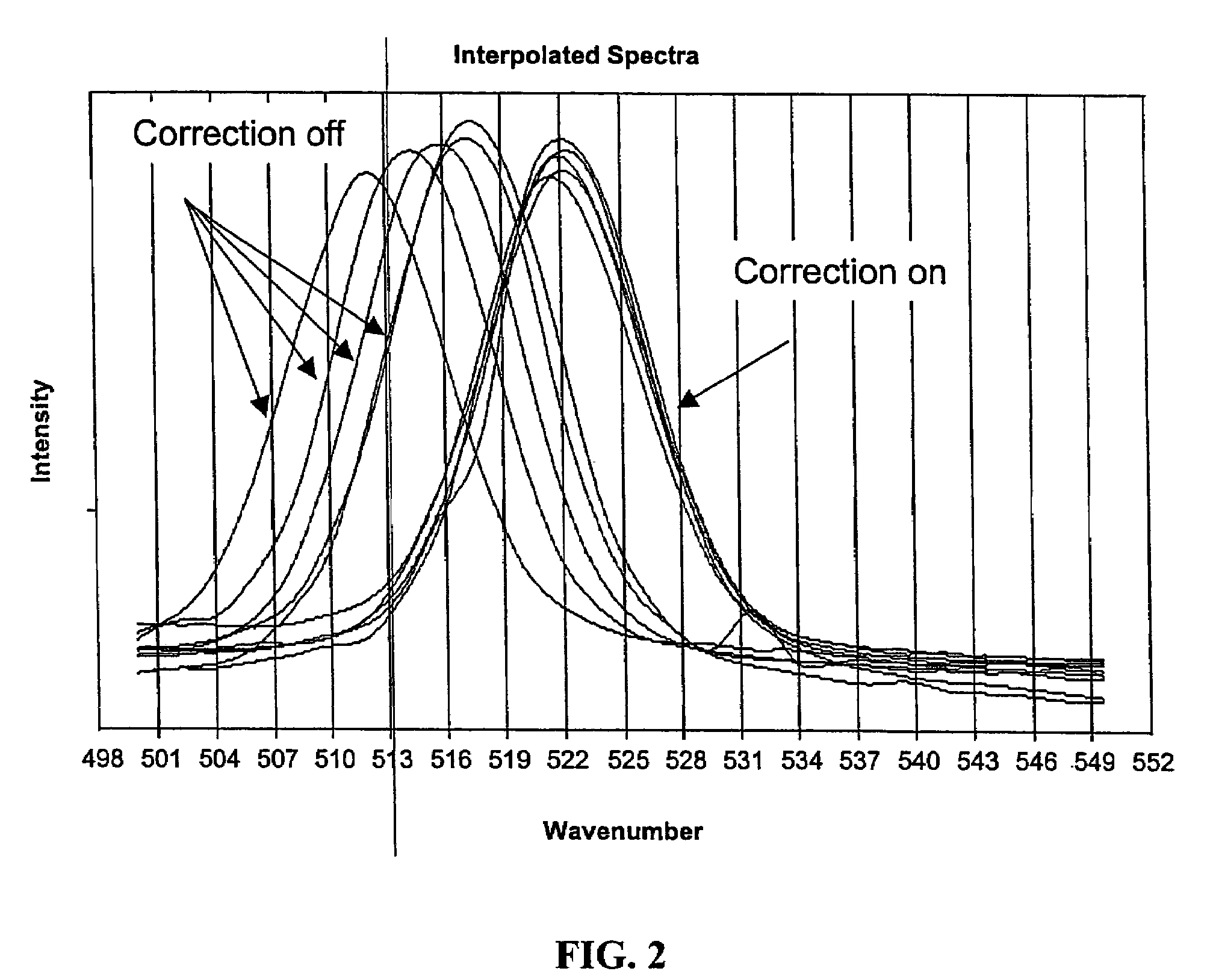
In one embodiment the disclosure relates to a method and a system for determining the corrected wavelength of a photon scattered by a sample. The method includes the steps of determining a wavelength of a photon scattered from a sample exposed to illuminating photons and passed through a tunable filter and correcting the determined wavelength of the photon as a function of the temperature of the tunable filter and as a function of the bandpass set point of the tunable filter. The step of correcting the determined wavelength can further include determining an offset and adding the offset to the determined wavelength of the photon.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Gas sensing system employing raman scattering
A gas detection system includes a light detector, a pump laser with spectral emission between UV and IR wavelengths and structured to generate a laser beam, a hollow waveguide structured to receive a sample gas, the hollow waveguide having a bandwidth sufficient to transmit the laser beam and Stokes Raman photons scattered by the sample gas, and an optical system. The optical system is structured to: (i) direct the laser beam into the hollow waveguide such that it propagates in the hollow waveguide in one or more low-order low-loss waveguide modes, and (ii) direct Raman signals generated within the hollow waveguide in response to the laser beam interacting with the sample gas toward the light detector, the Raman signal including the Stokes Raman photons.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
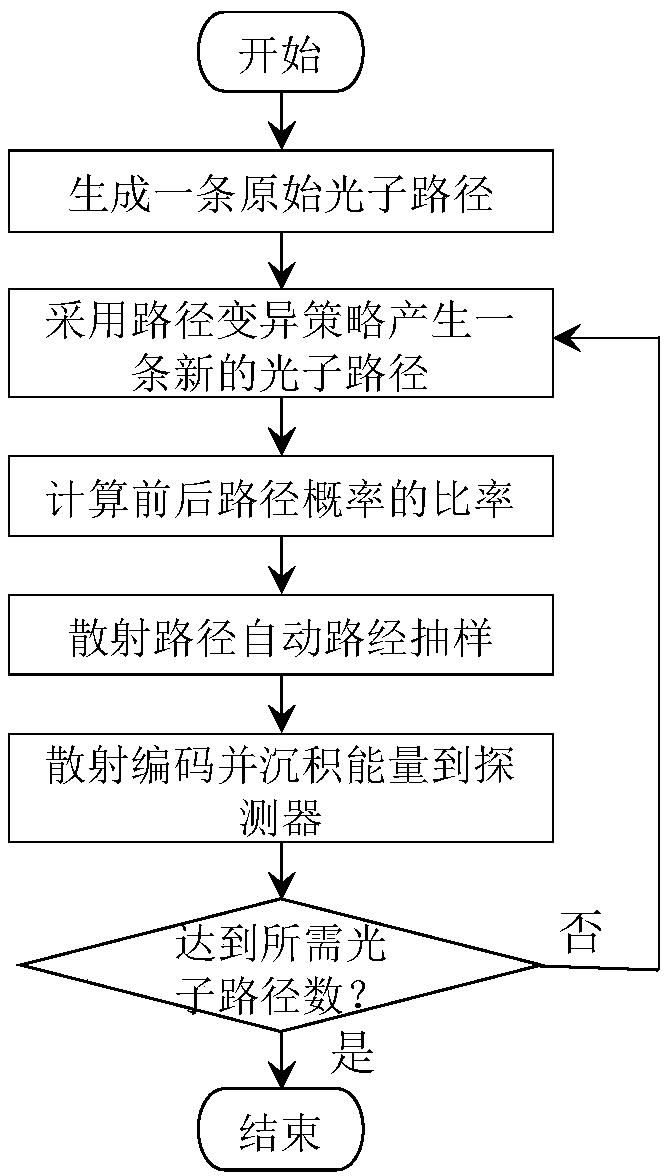
Task-driven Monte Carlo scattered photon simulation method
InactiveCN108618796AImproving Scattering Simulation EfficiencyImplementing Automatic Importance SamplingReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsPhoton scatteringComputer science
The invention discloses a task-driven Monte Carlo scattered photon simulation method. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: presetting and initializing photon scattering parameters,so that original photon paths are generated; conducting position sampling on scattering points via a uniform sampling algorithm and a random walk sampling algorithm, so that simulation photon paths are generated; comparing probabilities of the original photon paths and the simulation photon paths; automatically sampling the simulation photon paths via a path sampling algorithm, and judging whetherthe quantity of photon paths of deposition satisfies a preset photon path quantity; if so, ending operations; otherwise, returning to the second step. According to the method, the efficiency of photon scattering simulation is improved from the level of a sampling principle, and a simulation task demand is actively included into a controllable path variable space; the photon paths are subjected variation sampling via an automatic sampling model, then the importance of front and rear sampling paths is taken into comparison and paths, which are relatively important to a simulation task, are selected as current energy deposition paths, so that automatic importance sampling of the photon paths is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Process for the determination of the solid/liquid phase
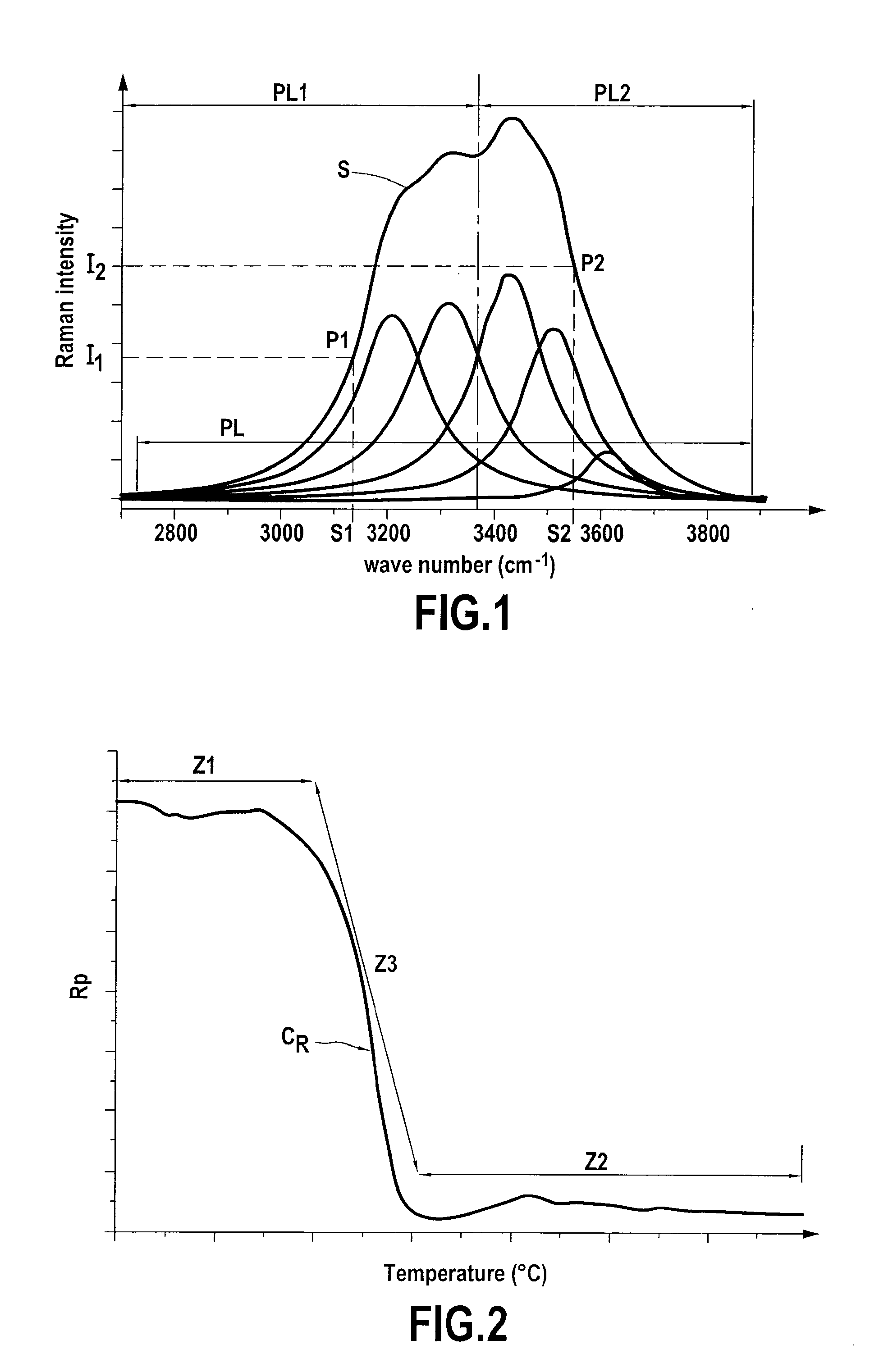
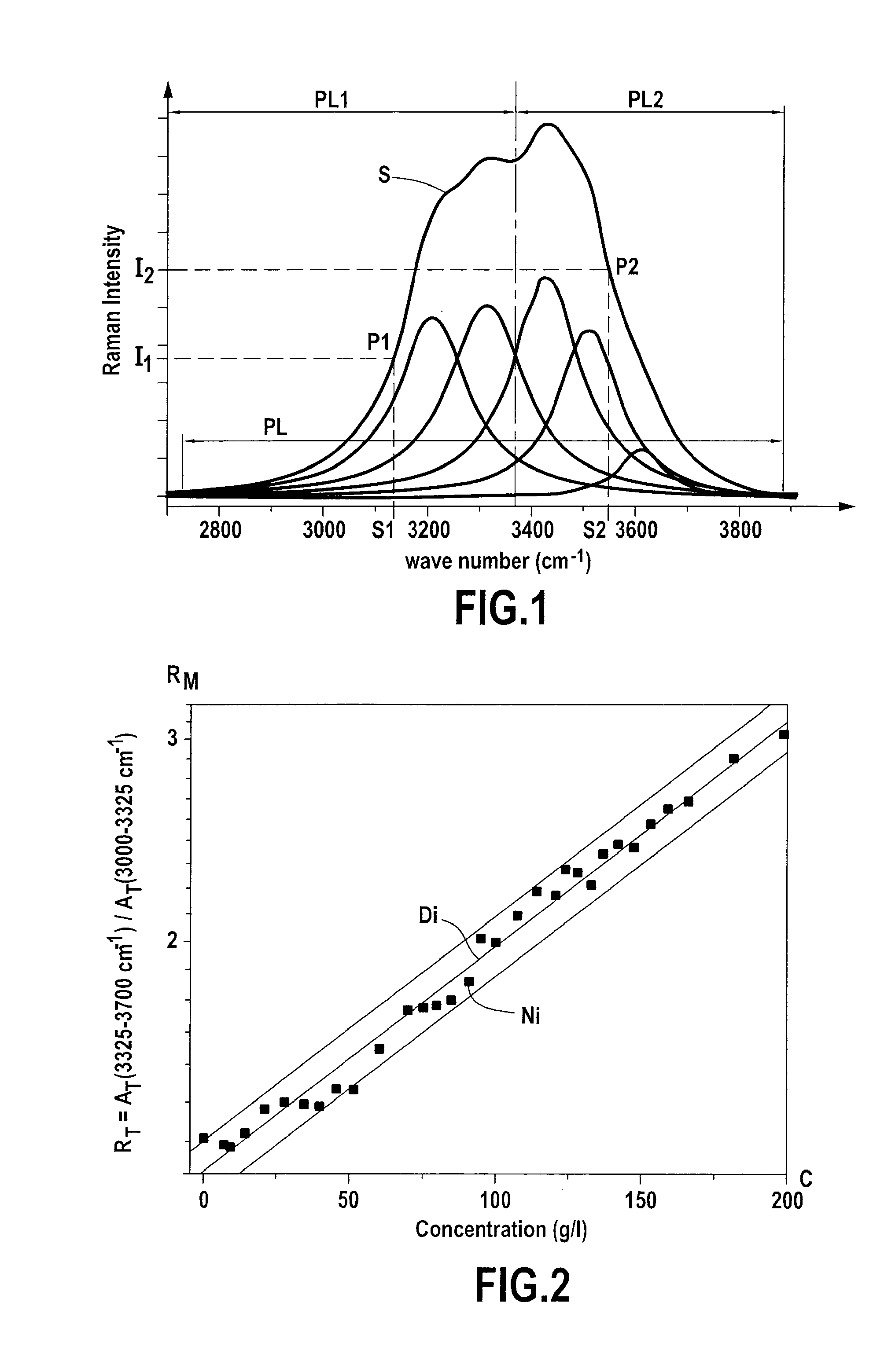
A method of determining the solid / liquid phase of an aqueous solution, characterized in that it comprises the following steps: a) subjecting said aqueous solution to a beam of photons; b) recording the Raman spectrum of the photons scattered by said solution in the wave number range between 2500 cm−1 to 4000 cm−1; and c) processing said recording in order to deduce therefrom the solid / liquid phase of said aqueous solution.
Owner:UNIV DE METZ PAUL VERLAINE
Method and apparatus for peak compensation in an optical filter
In one embodiment the disclosure relates to a method and a system for determining the corrected wavelength of a photon scattered by a sample. The method includes the steps of determining a wavelength of a photon scattered from a sample exposed to illuminating photons and passed through a tunable filter and correcting the determined wavelength of the photon as a function of the temperature of the tunable filter and as a function of the bandpass set point of the tunable filter. The step of correcting the determined wavelength can further include determining an offset and adding the offset to the determined wavelength of the photon.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
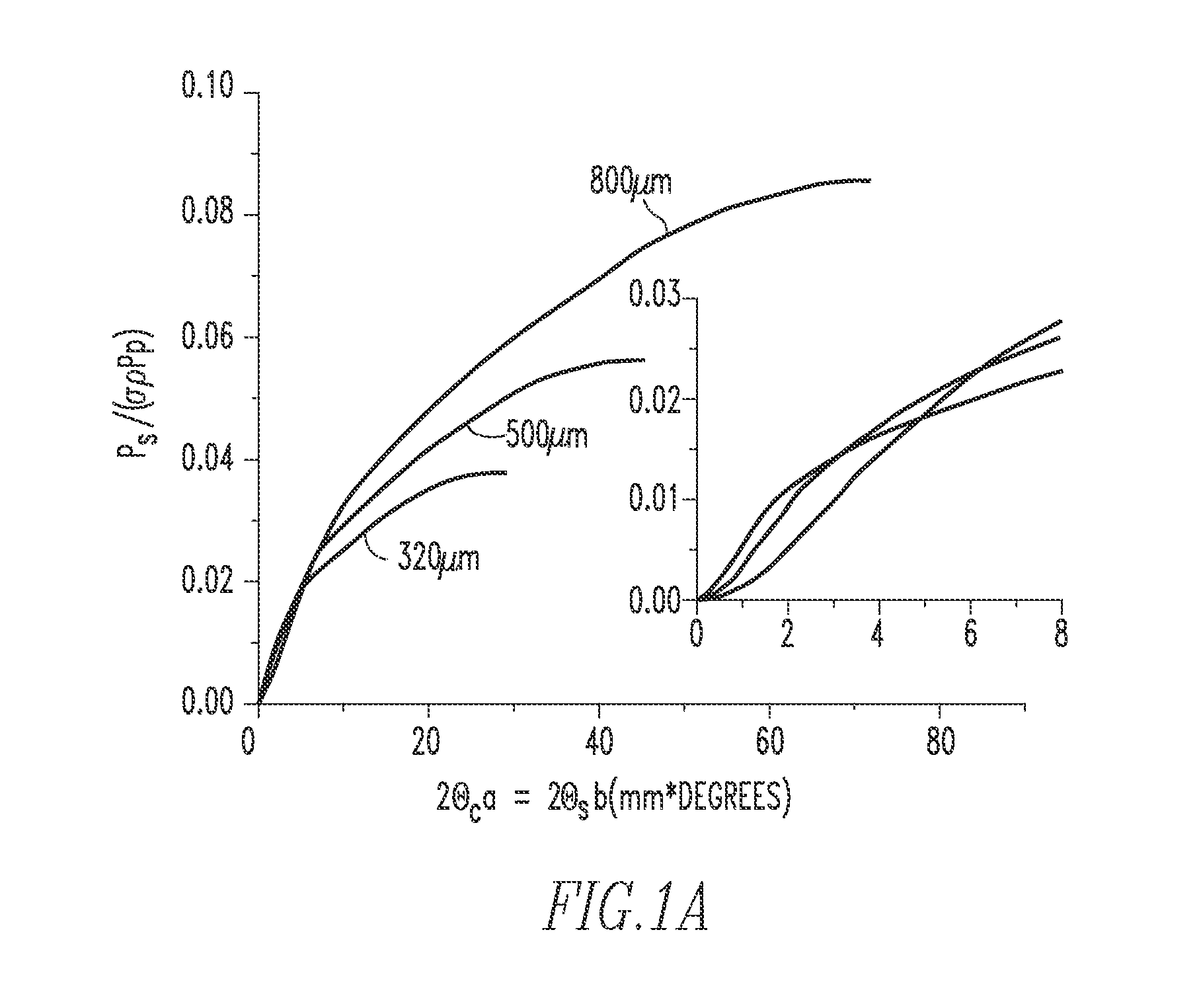
Wireless ultraviolet light communication scattering channel simulation method in mobile scene
ActiveCN112187358AReduce lossImprove signal-to-noise ratioClose-range type systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsUltraviolet lightsEngineering
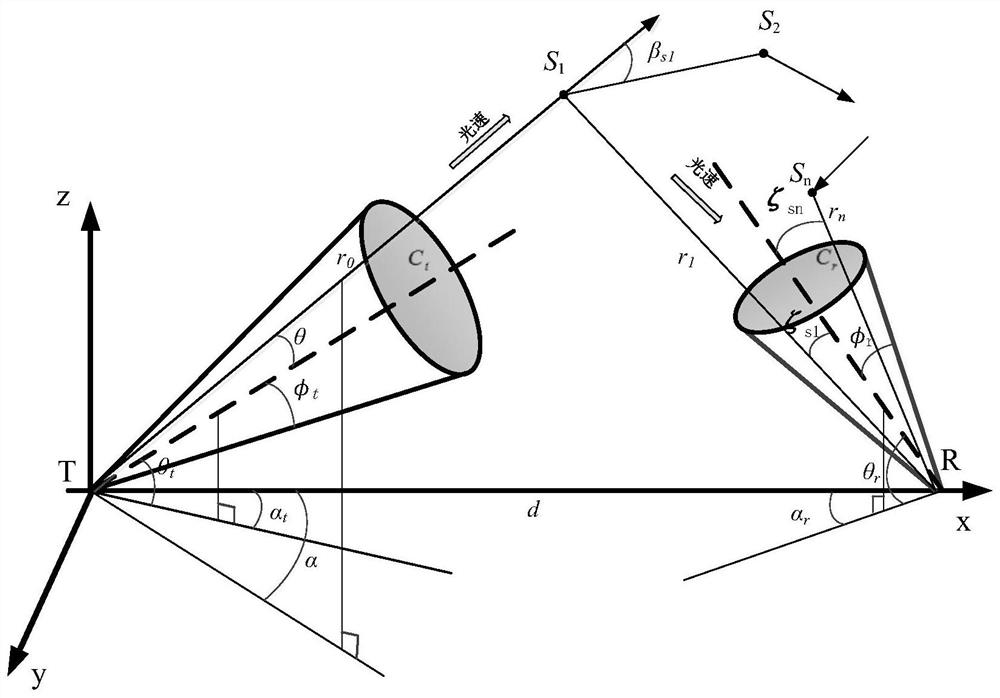
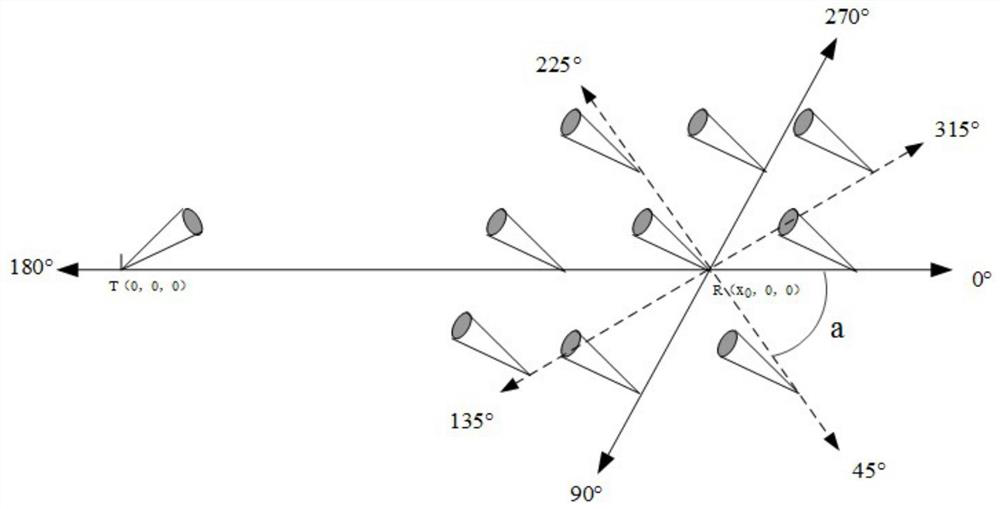
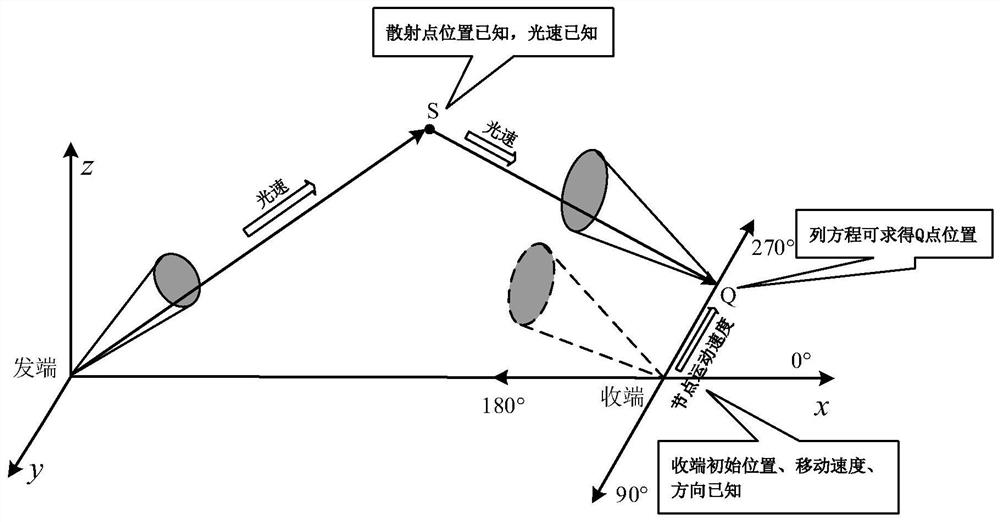
The invention discloses a wireless ultraviolet light communication scattering channel simulation method in a mobile scene, which is specifically implemented according to the following steps of: 1, establishing a wireless ultraviolet light communication scattering channel transmission model, and determining a scattering position of emitted photons; 2, determining the moving direction and speed of the receiving end; 3, determining the position of a receiving light cone vertex Q in the moving scene; 4, calculating the probability that the photons scattered by the scattering point Sn can reach theQ point; and 5, drawing an impulse response and path loss graph in the moving direction. By means of the method, the relation between the relative movement speed and movement direction of the wireless ultraviolet light communication nodes and scattering channel characteristics in a moving scene is studied, an impulse response and path loss graph is drawn, and a theoretical basis is provided for reducing the path loss of a receiving end and improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the receiving end.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method of restoring gamma photon scattering coincidence to true coincidence
InactiveCN109115809AReduce in quantityHigh densityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGamma photonPhoton scattering
The invention discloses a method for restoring gamma photon scattering coincidence to true coincidence. The method comprises the following steps: step one, classifying single-time scattering responselines obtained by detecting through a detection device; step two, calculating an actual positions of scattering of gamma photons in each single-time scattering response line according to positions ofa detector pair through relations between energy and scattering angles of the gamma photons; step three, obtaining a detector with detected gamma photon energy of 511KeV and a detector on which an extension line of a connection line between the actual positions of scattering of the gamma photons passes, and taking a connection line between the two detectors as a true coincidence line; step four, repeating the step two and the step three and restoring all single-time scattering response lines on the pair of detectors to true coincidence lines; and step five, repeating the step four and restoring all the single-time scattering response lines on the detectors to the true coincidence response lines. The method is capable of eliminating scattering and reducing the number of the response lines,so that higher image reconstruction quality is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Determination of the salt concentration of an aqueous solution
Owner:UNIV DE METZ PAUL VERLAINE
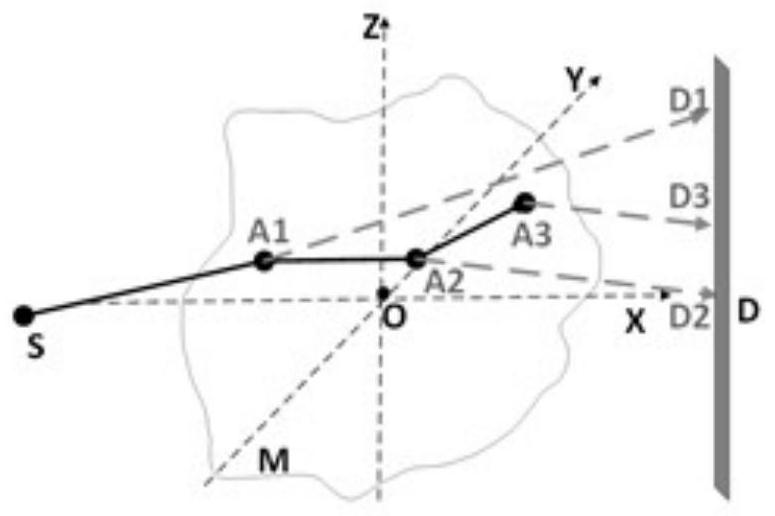
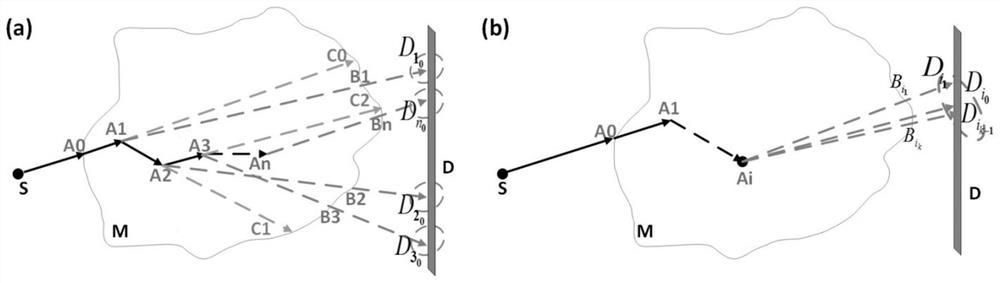
Method for simulating photon scattering by using quasi Monte Carlo method
ActiveCN112763519AReduce computing timeHigh precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation diagnosticsQuasi-Monte Carlo methodParticle physics
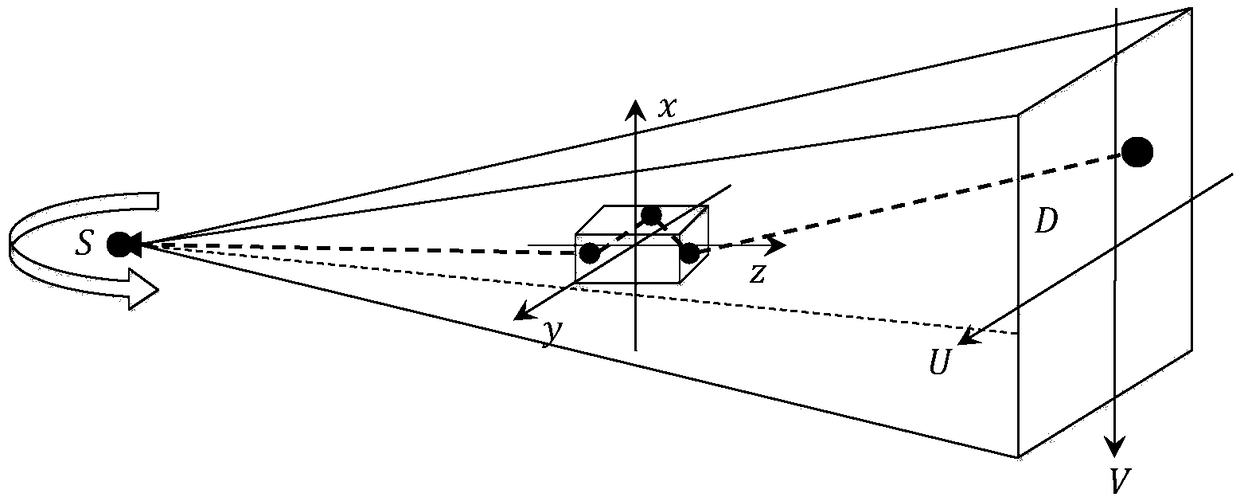
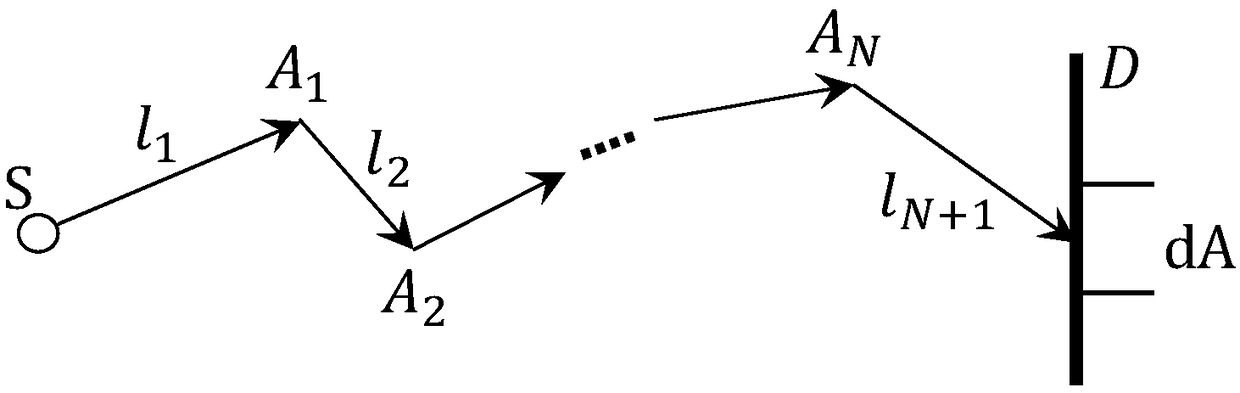
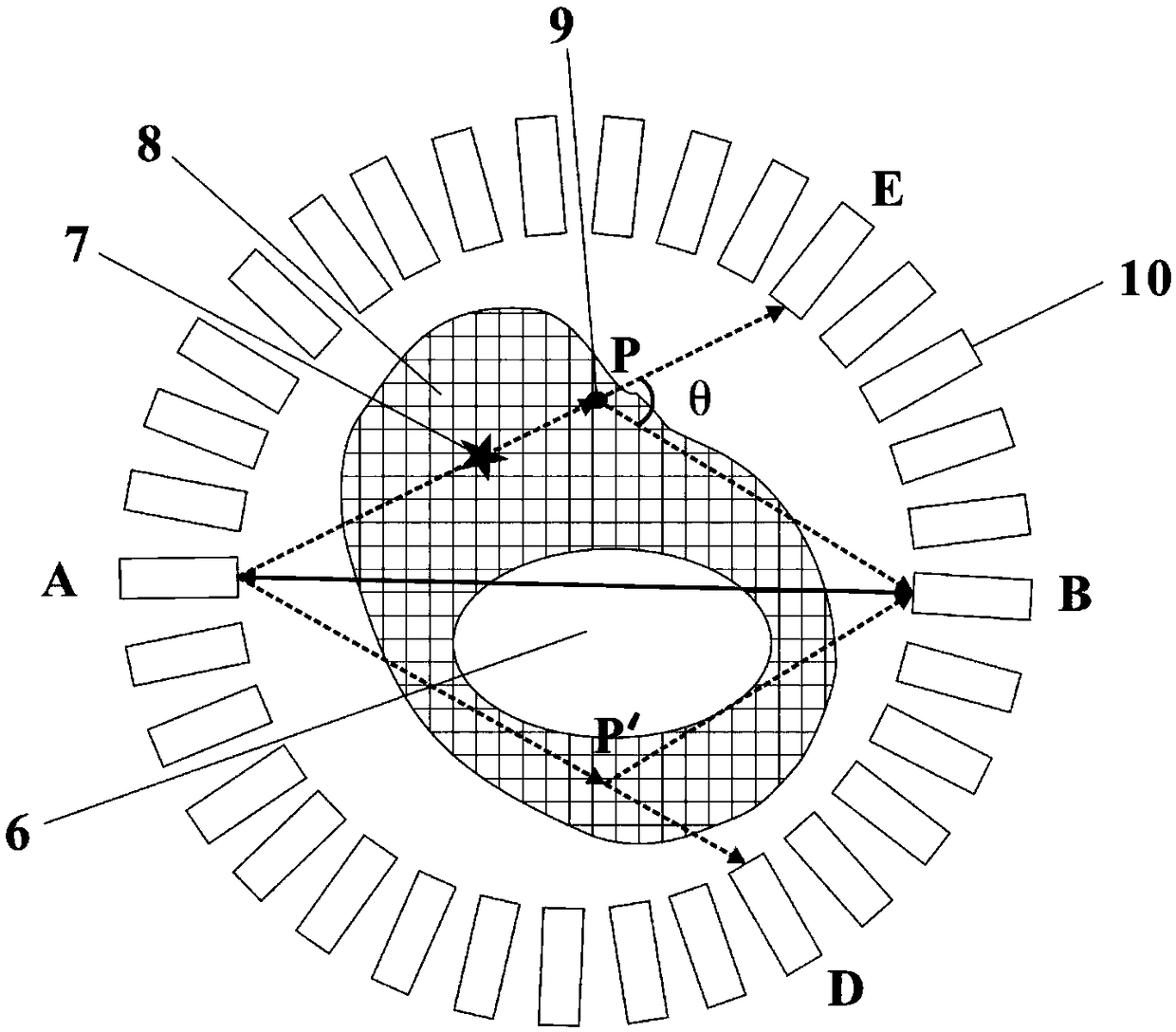
The invention discloses a method for simulating photon scattering by using a quasi Monte Carlo method, which is applied to a system comprising a light source S, a motif M and a detector D. Photons are preset to be emitted from the light source S, initially enter the motif M at an intersection point A0, and are subjected to i-order scattering at an interaction point Ai, (i = 1,..., n), and the method tracks distribution of the photons reaching the measured motif M from the light source S. The scattering path of photons in the motif M is simulated, and detector pixels corresponding to interaction points are forcibly selected, so that the simulation of the photon scattering process is realized, and by adopting the method, the precision of photon scattering simulation is high, and the calculation time of scattered photons is shortened.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
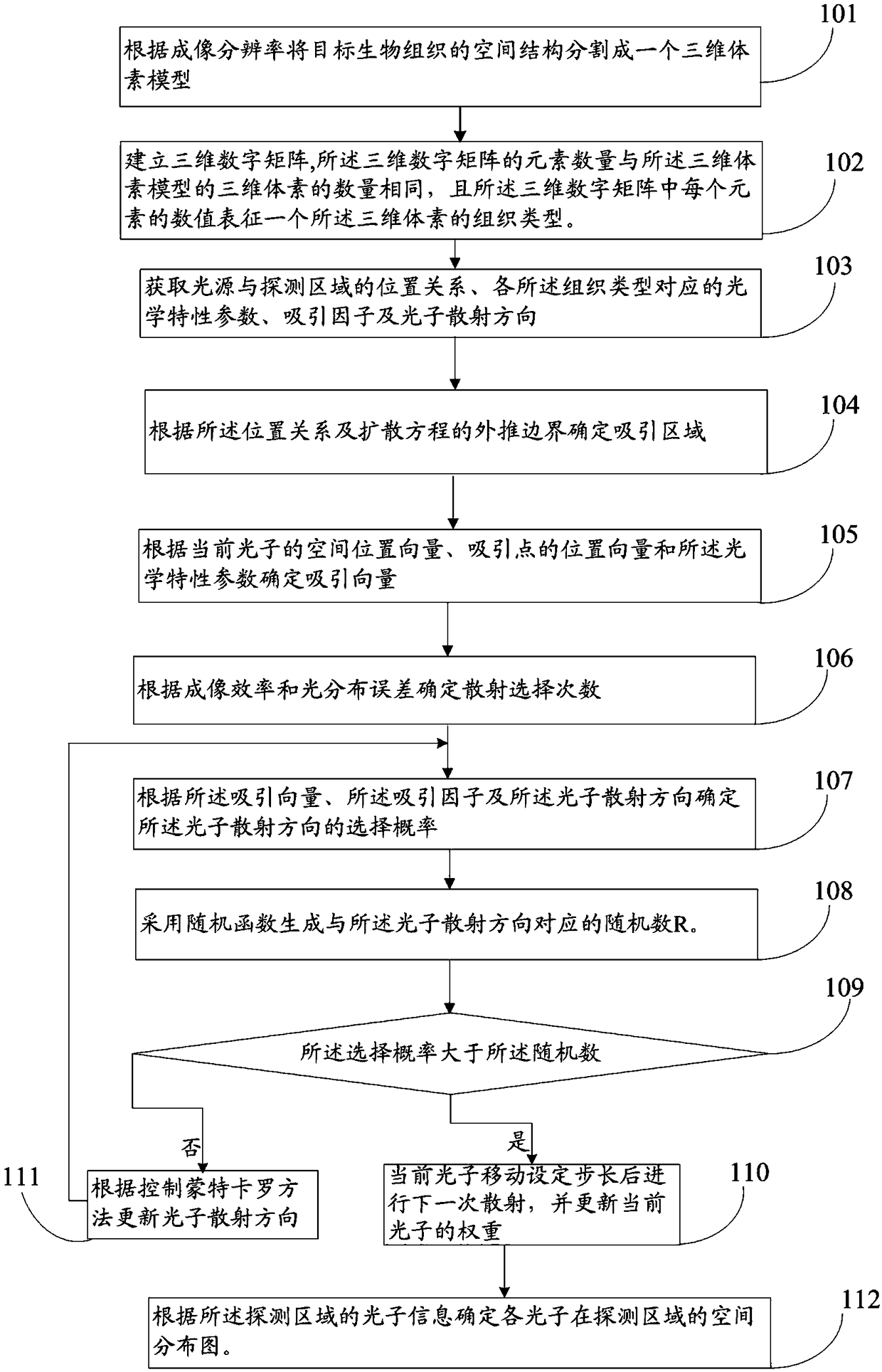
Diffusion optical imaging method and system based on controlled Monte Carlo method
ActiveCN109342367AIncrease the number ofSolve the problem of unstable distribution accuracyScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiffusionImaging quality
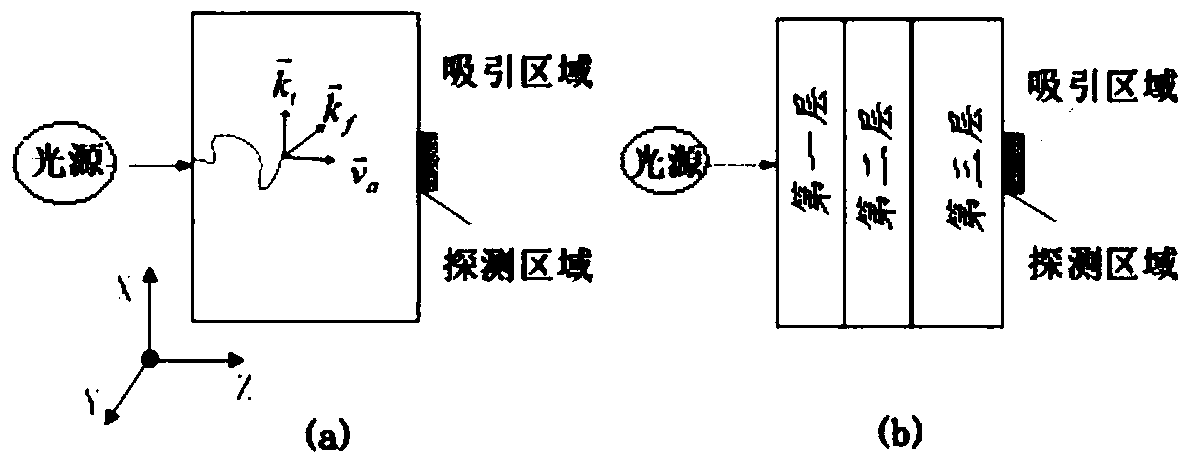
The invention discloses a diffusion optical imaging method and system based on a controlled Monte Carlo method. The method comprises: determining an attracting area according to the position relationship between the light source and the detection area and the extrapolated boundary; determining an attracting vector according to a spatial position vector, a attracting point position vector and an optical characteristic parameter of a current photon; determining the selection probability of a photon scattering direction according to a attracting vector, a attracting factor, and a photon scattering direction; and finally, determining whether the photon performs the next scattering and whether to update the photon weight according to the size relationship between the selection probability and the random number. According to the diffusion optical imaging method and system based on the controlled Monte Carlo method, photons scattered by the next time are selected through the attracting area,and the weight of the selected photons is updated in real time. On the premise of emitting the same number of photon, the number of photons and the accuracy of light distribution in the detection areacan be effectively improved, and the imaging quality and the imaging efficiency are guaranteed. Meanwhile, the problem that the light distribution precision is unstable caused by different scatteringcoefficients of the target biological tissue or the distance between the light source and the detection area can be solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
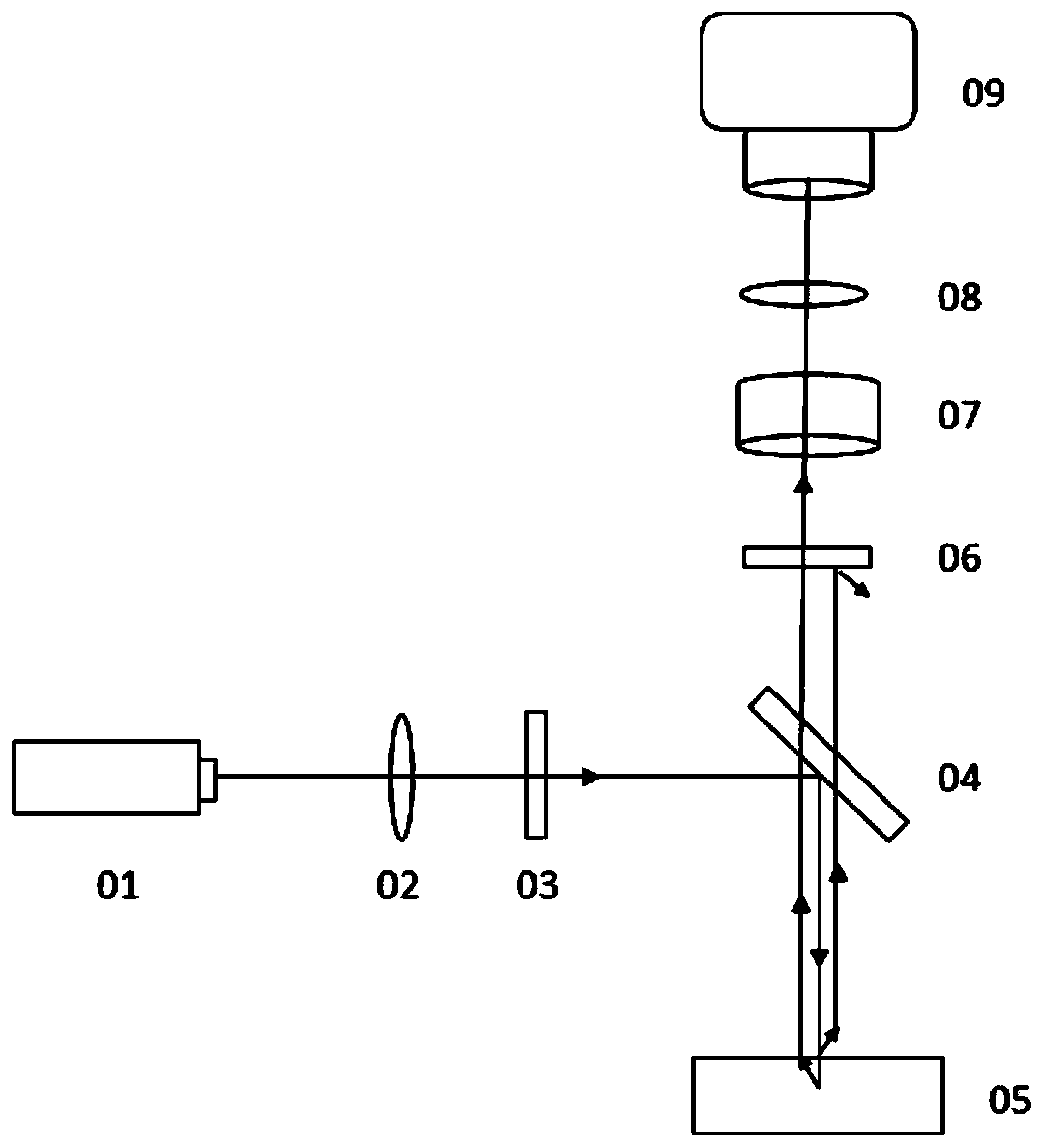
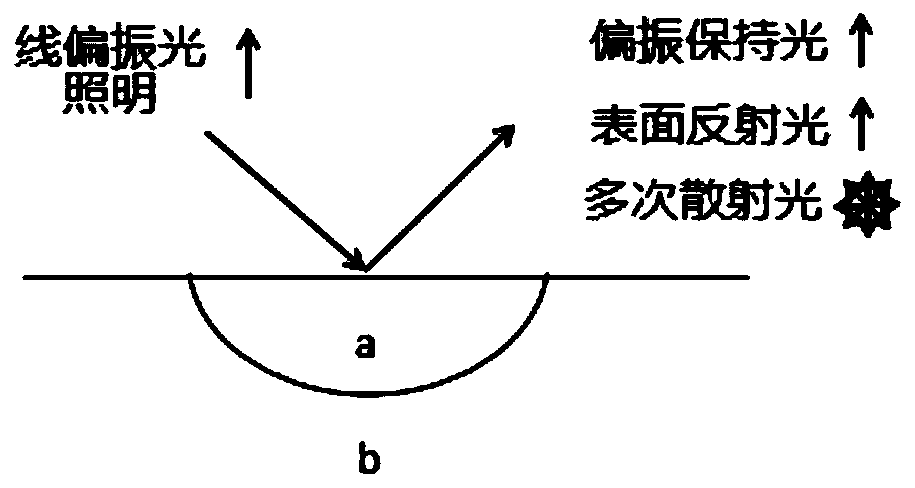
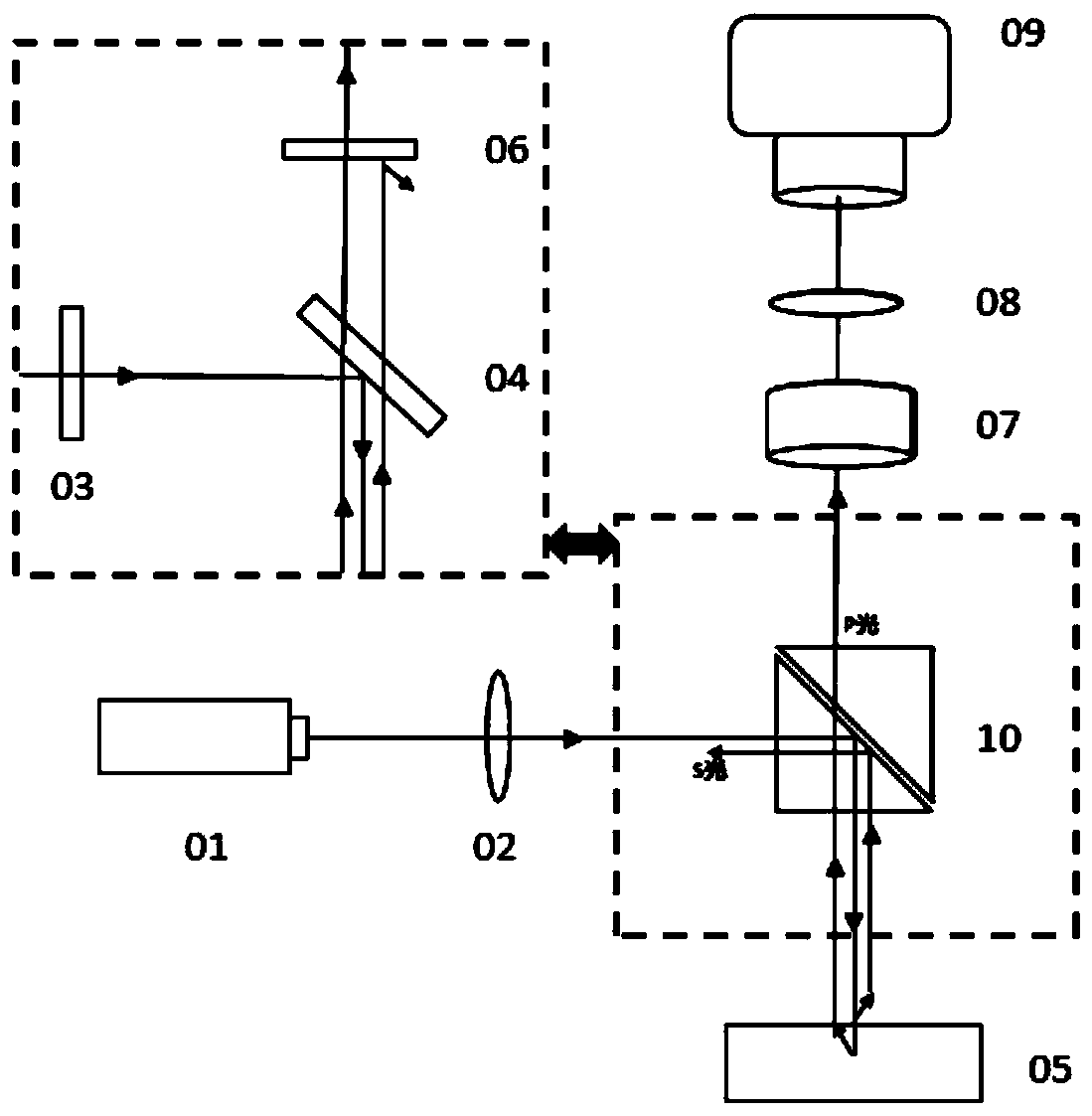
Laser speckle contrast imaging device and laser speckle contrast imaging method for realizing deep tissue detection
PendingCN110954509AReduce distractionsImprove contrastScattering properties measurementsLight-field cameraLaser light
The invention discloses a laser speckle contrast imaging device and method for realizing deep tissue detection, and the device comprises a laser light source which is used for irradiating a to-be-detected sample; a beam expander which is used for expanding an irradiation area of laser and making irradiation more uniform; a polarizer which is a linear polarizer; to-be-detected samples which are biological tissues, scattering media, turbid liquid and the like; a semi-transmitting and semi-reflecting mirror which is used for reflecting the light emitted by a laser light source and transmitting the back-scattered light of the to-be-detected samples; a polarization analyzer which is a linear polaroid, the vibration transmission direction of the polarization analyzer being perpendicular to the vibration transmission direction of the polarizer, and the polarization analyzer being used for filtering photons scattered and depolarized from the sample to be detected; an objective lens; a relay lens; a light field camera which is used for collecting and imaging the scattered light to realize depth-of-field expansion of the image. According to the technical scheme, light scattered on the surface and the shallow surface of tissues can be filtered out, the influence of mutual superposition of information of light from different depth levels of the tissues on imaging is eliminated, the contrast ratio degree and the signal-to-noise ratio of a speckle image of the tissue are improved, and deep tissue detection is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Continuous time-of-flight scatter simulation method and device
InactiveCN102439626BReconstruction from projectionImage data processing detailsPet imagingComputational physics
The present invention provides a continuous time-of-flight scattering simulation method and related methods for correcting PET imaging data to compensate for photon scattering. The scatter contribution from each imaging pixel in the field of view can be calculated without binning data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray anti-scattering grating based on orthogonal structure
PendingCN112089428AIncrease the amount of direct radiationStrong penetrating powerComputerised tomographsTomographyDirect radiationImaging equipment
The invention relates to optical imaging equipment, and particularly relates to an X-ray anti-scattering grating based on an orthogonal structure. The X-ray anti-scattering grating is used for improving the quality of an X-ray image and is applied to X-ray machines and CT detection equipment in the fields of medical image diagnosis and treatment, industrial nondestructive testing, security detection and the like. The X-ray anti-scattering grating is used for filtering photons scattered by a researched detected human body, organs and articles and only retaining photons emitted by a source to improve an X-ray photographic image. The X-ray anti-scattering grating based on the orthogonal structure not only reduces the influence of X-ray scattering radiation on the resolution ratio of the quality of the detected image, but also can reduce the influence of X-ray direct radiation on the quality degradation of the detected image, effectively solves the problems of low resolution ratio, large error and the like of the X-ray detected image in the prior art, obviously improves the quality of the X-ray image detected image, or can reduce the radiation damage to a detected patient or object exposed to a high dose under the condition of obtaining the same quality of the detected image.
Owner:上海创投机电工程有限公司
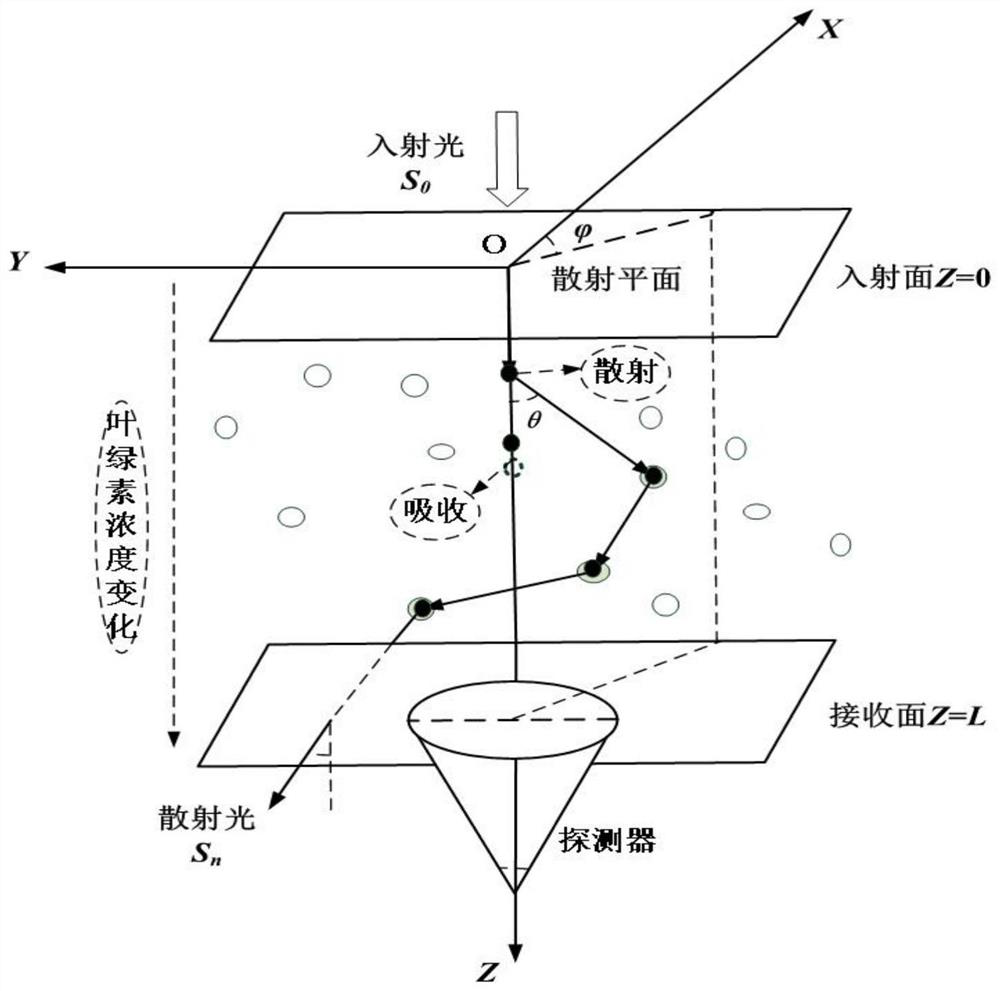
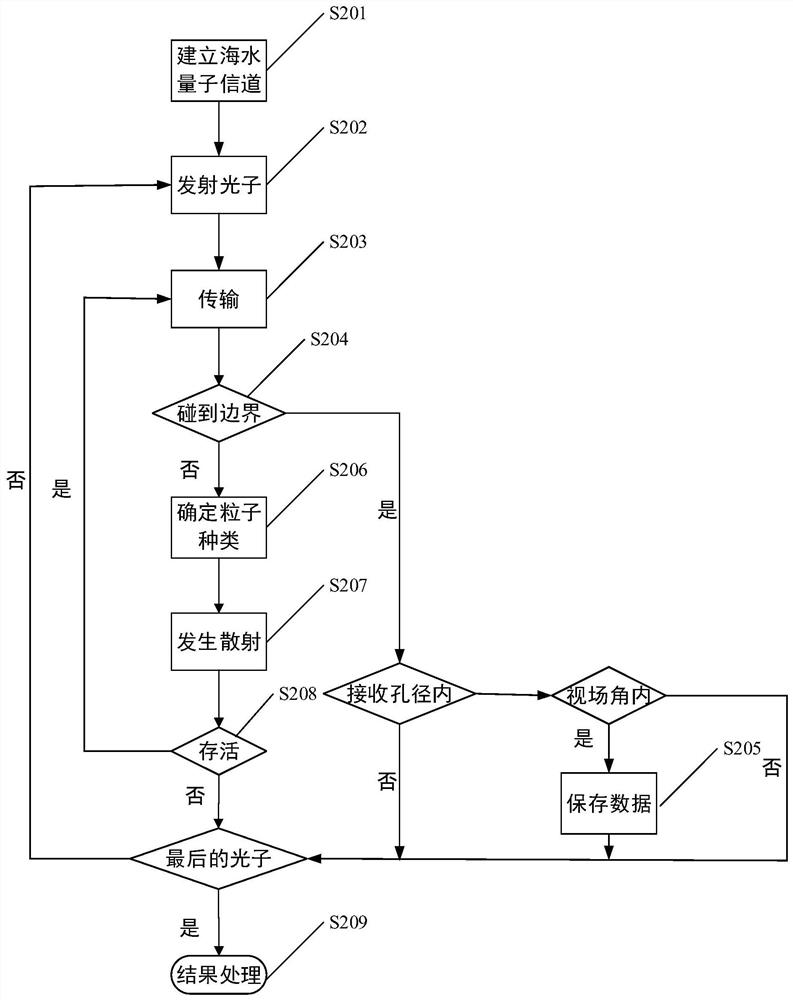
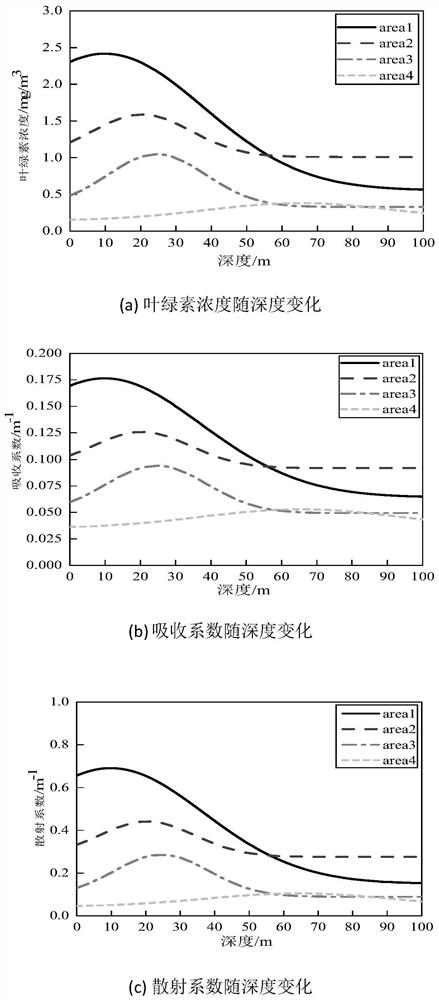
Underwater photon transmission simulation method based on vertical chlorophyll concentration distribution
PendingCN113810137AAvoid measuringSimulation results are in line with realityPhotonic quantum communicationTransmission monitoringPhoton transmissionSurface layer
The invention relates to an underwater photon transmission simulation method based on vertical chlorophyll concentration distribution, and the method comprises the steps: building an underwater quantum channel vertical transmission model, dividing a sea area according to different chlorophyll concentrations of a seawater surface layer, and carrying out the analysis to obtain a change condition of a deep seawater attenuation coefficient; and then using a Monte Carlo method to simulate the underwater transmission characteristic change trend of polarized photons, and realizing the uncertainty of the photon scattering process through random sampling. According to the simulation method, measurement of deep seawater parameters is avoided, and compared with a traditional method for describing seawater attenuation characteristics through a single parameter, the method is closer to reality, description of the seawater characteristics is more specific, practicability is high, and the method is universally applicable to multiple sea areas. Calculation is simple, physical images are visual, and the photon transmission characteristics obtained through analysis can provide theoretical reference for application of underwater communication, detection and positioning technologies and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
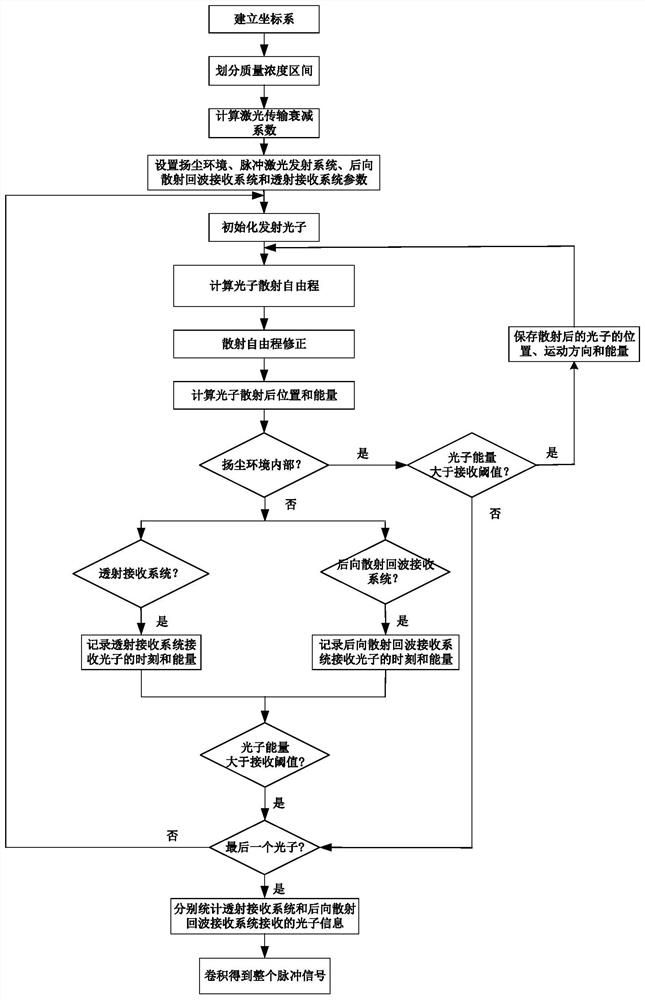
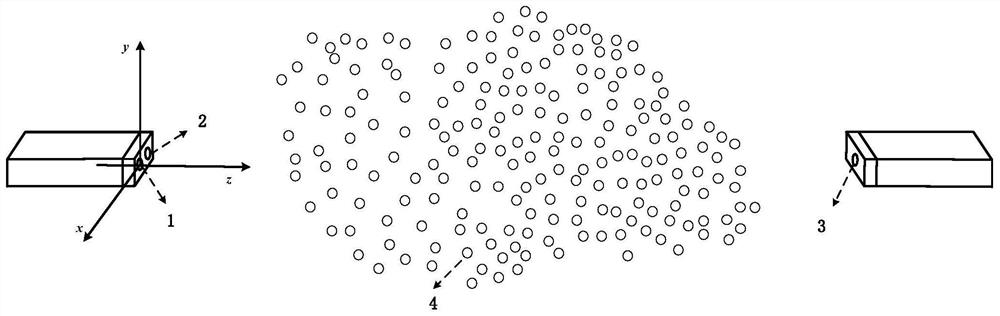
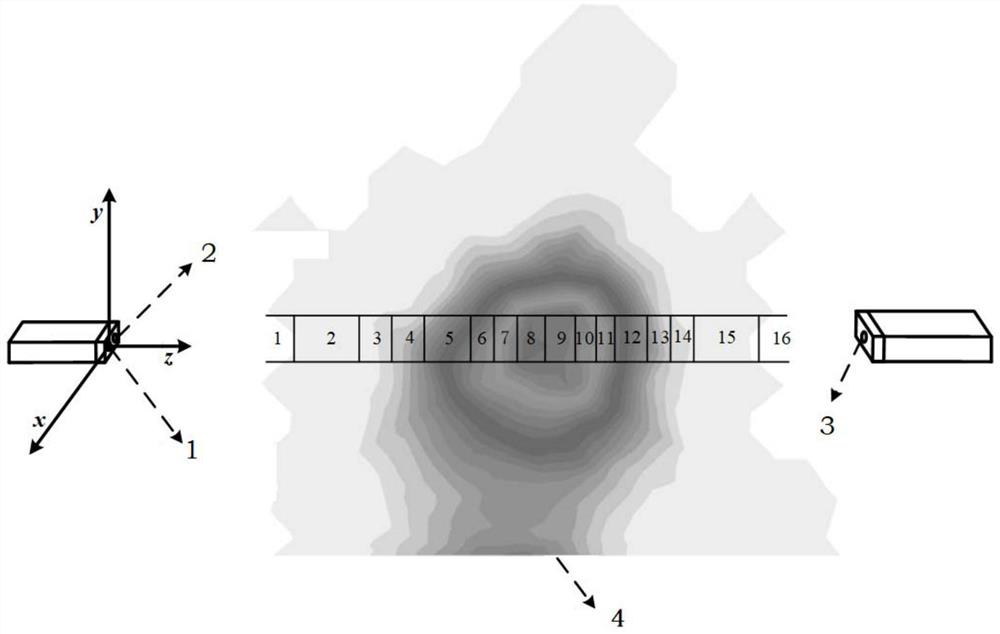
Pulse laser transmission characteristic simulation method in flying dust environment
PendingCN113626997AAchieving precise characterizationSolve the problem that the scattering free path will changeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPhoton scatteringLaser
The invention discloses a pulse laser transmission characteristic simulation method in a flying dust environment, and belongs to the technical field of numerical simulation. The simulation method comprises the following implementation steps: establishing a coordinate system, dividing flying dust mass concentration intervals, calculating corresponding laser attenuation coefficients of laser in different mass concentration intervals, setting flying dust environment parameters, pulse laser emission system parameters, back scattering echo receiving system parameters and transmission receiving system parameters, initializing emitted photons, calculating the free scattering path of the photons, correcting the free scattering path, and calculating the positions and energy of the photons after scattering; and judging the position of the photon in the coordinate system, counting photon information received by the transmission receiving system and the back scattering echo receiving system, and finally shaping the photon information into a pulse signal. According to the method, the detection characteristics of the pulse laser fuze in the complex battlefield dust raising environment can be effectively simulated, and a theoretical basis is provided for improving the detection performance of the pulse laser fuze.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Devices, systems, and methods using wearable time domain-based activity tracker
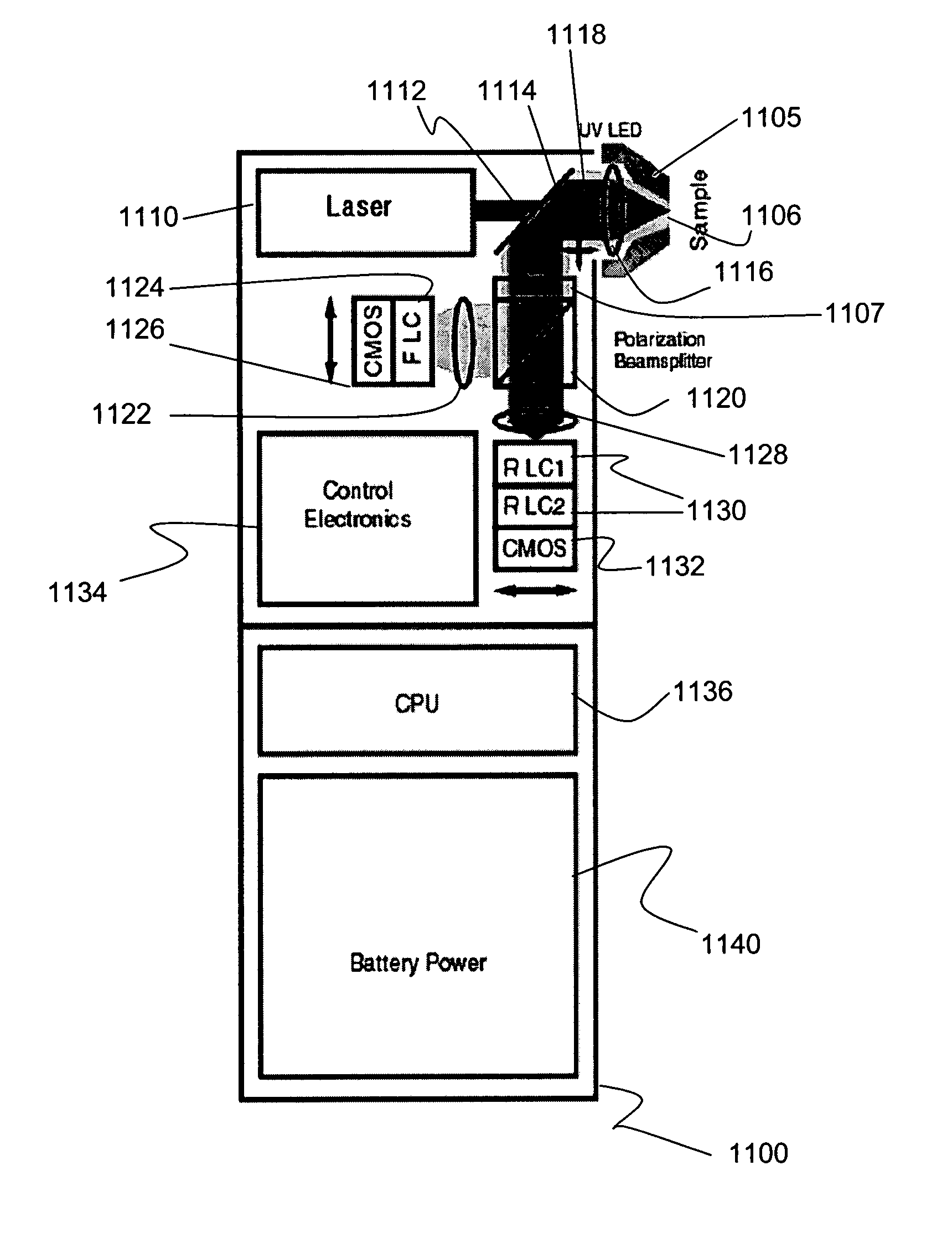
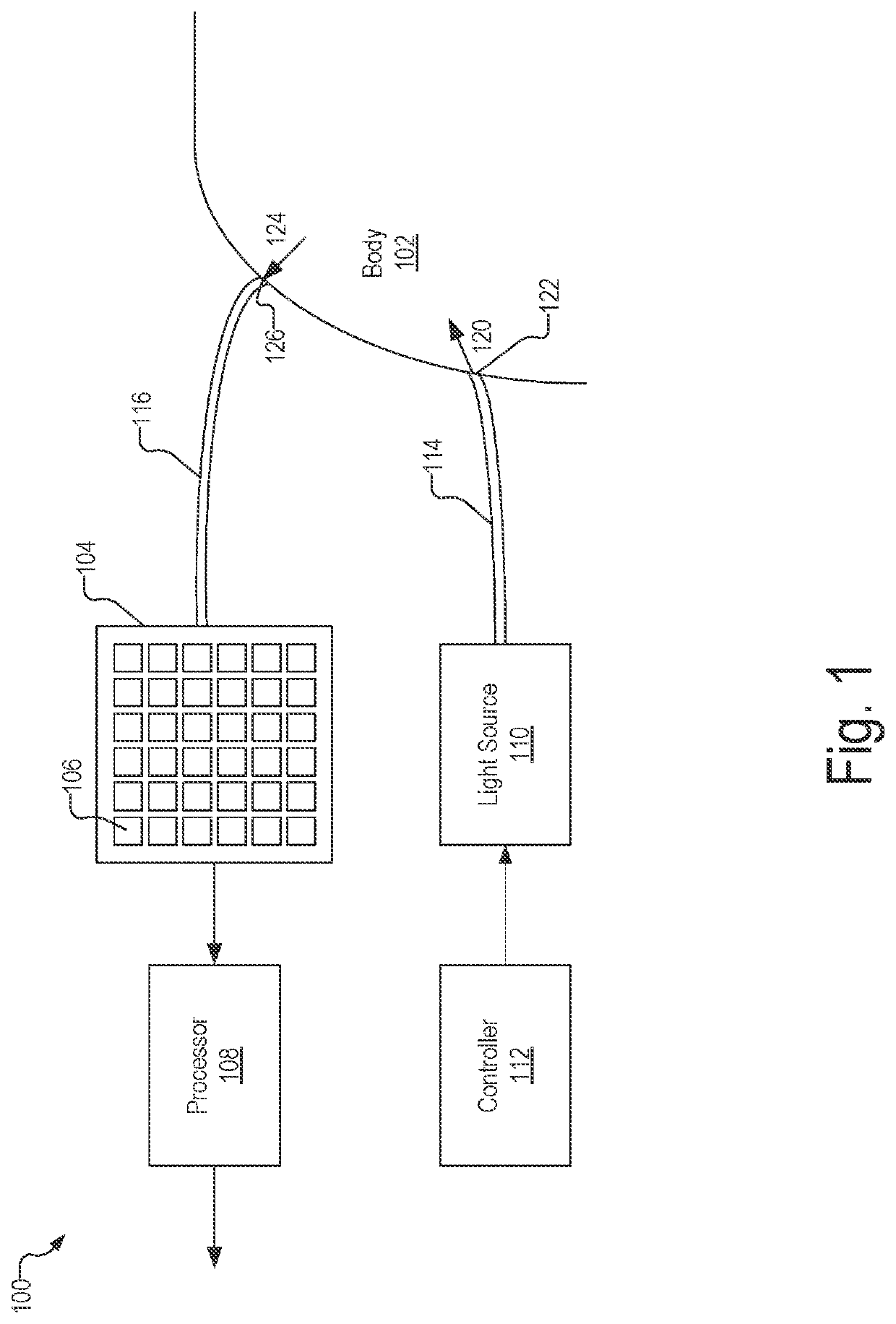
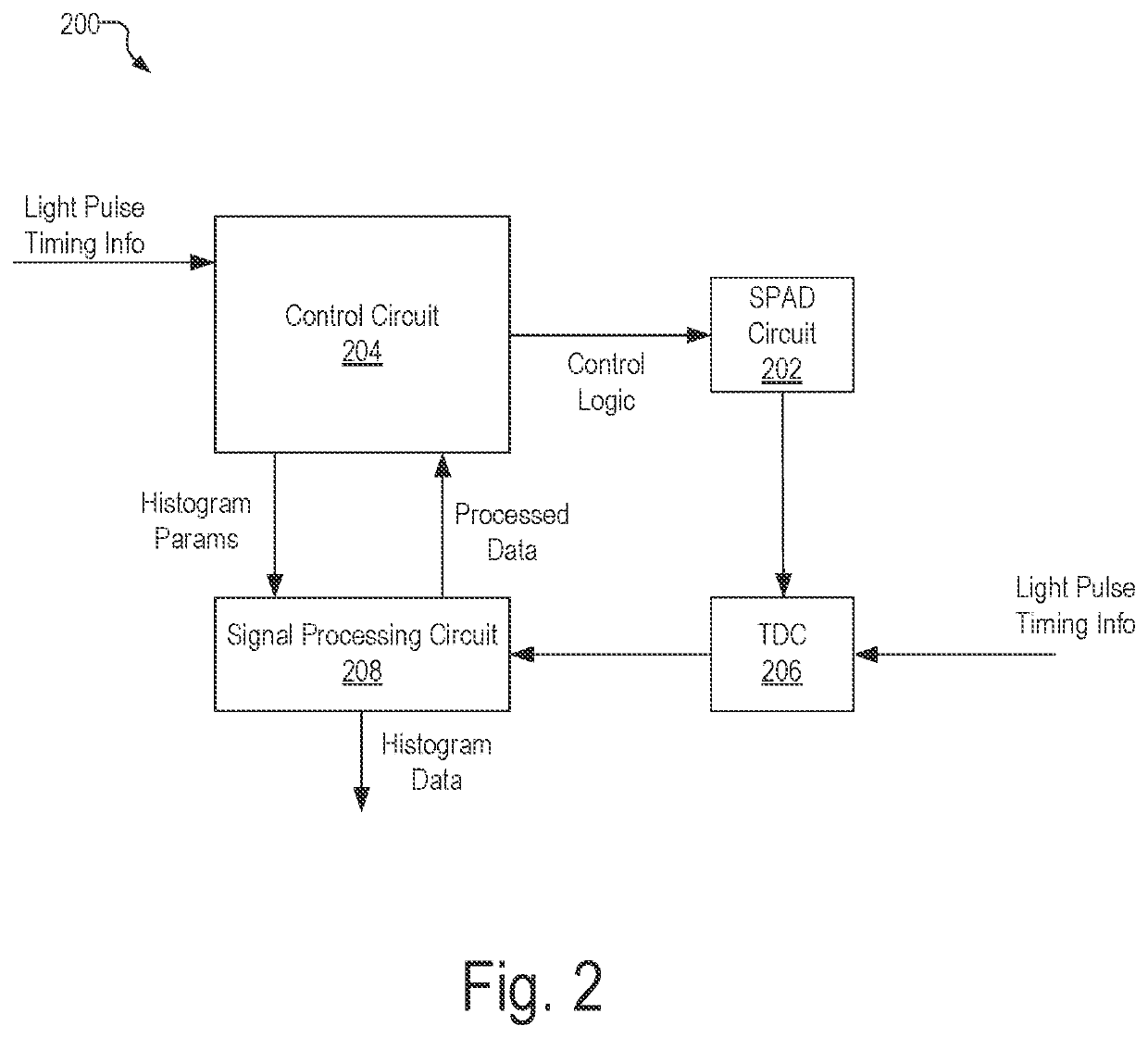
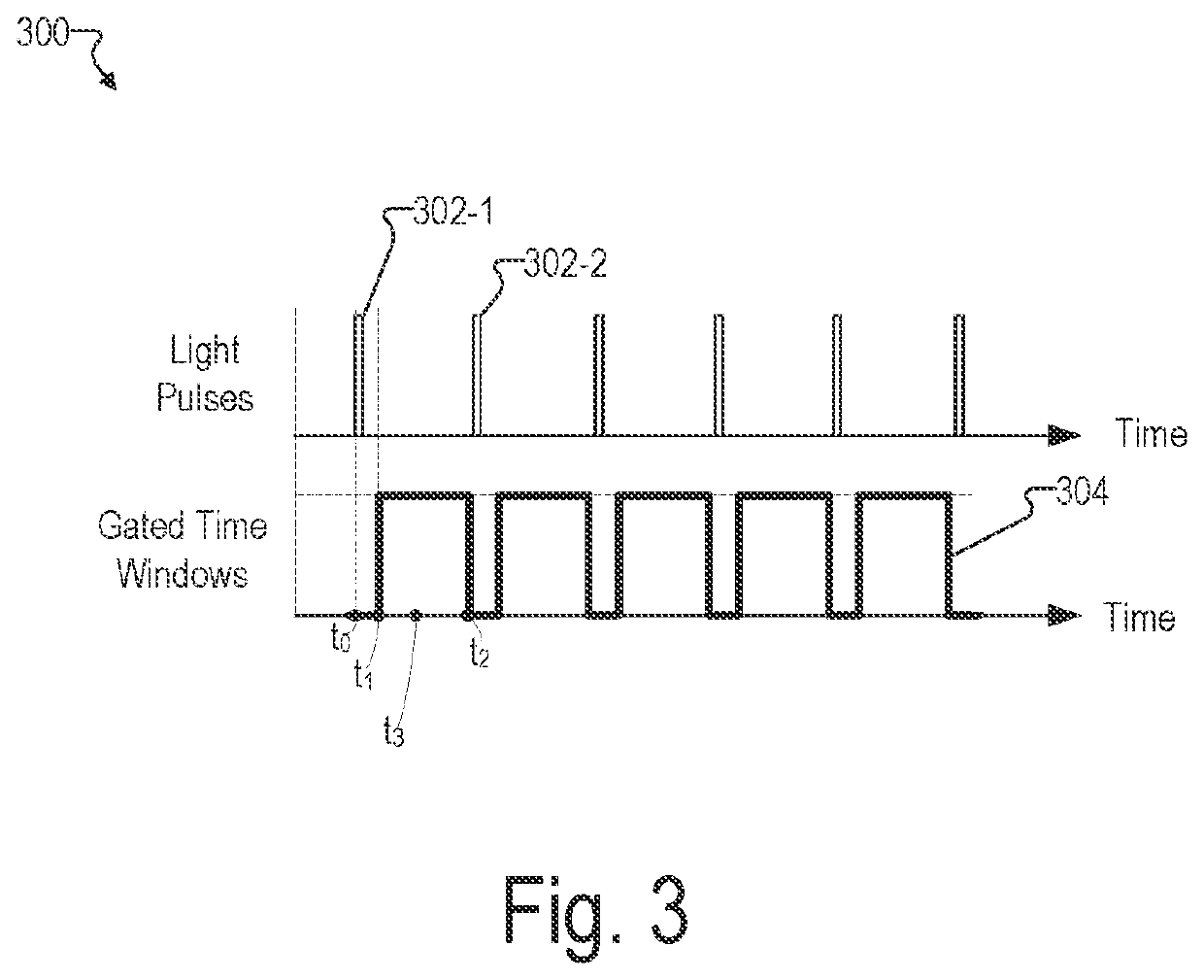
An illustrative optical measurement device includes a light source configured to emit light pulses directed at a target. The optical measurement device further includes a detector configured to detect arrival times for photons of the light pulses after the photons are scattered by the target. The optical measurement device further includes a processing unit configured to generate, based on the arrival times of the photons at the detector, histogram data associated with the target. The processing unit is further configured to determine, based on the histogram data, an absolute optical property associated with the target. The processing unit is further configured to determine, based on the absolute optical property, a blood oxygenation level of the user, and perform an operation based on the blood oxygenation level.
Owner:HI LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com