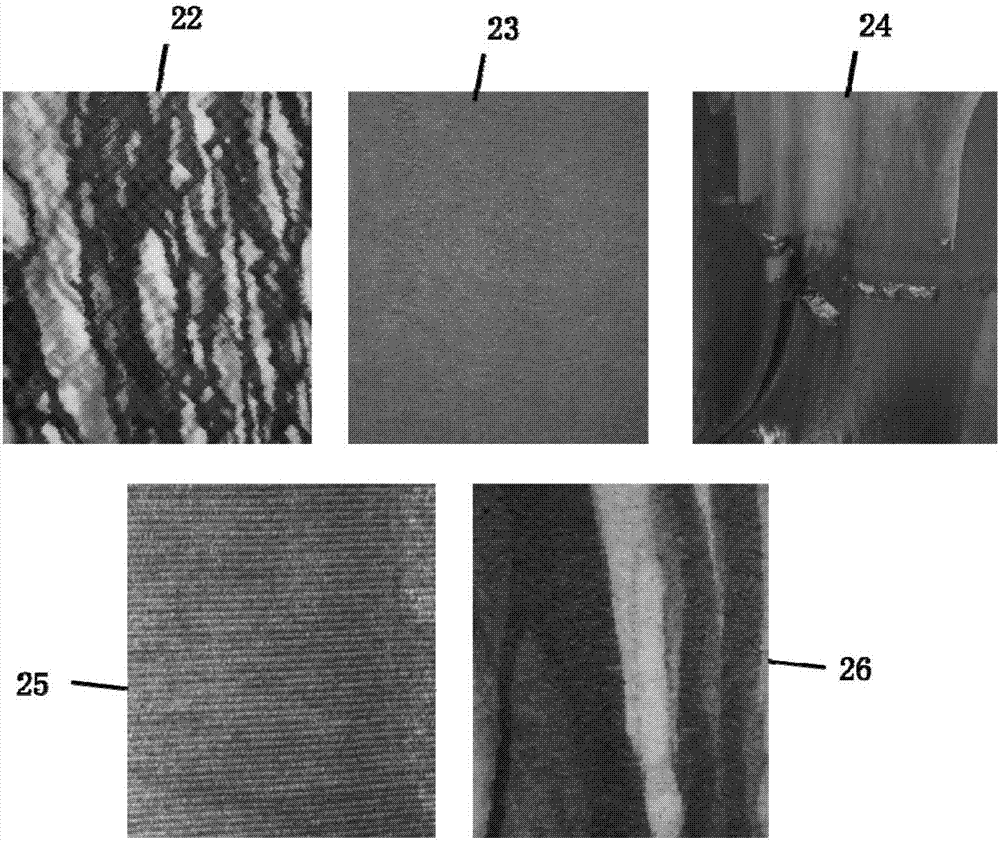
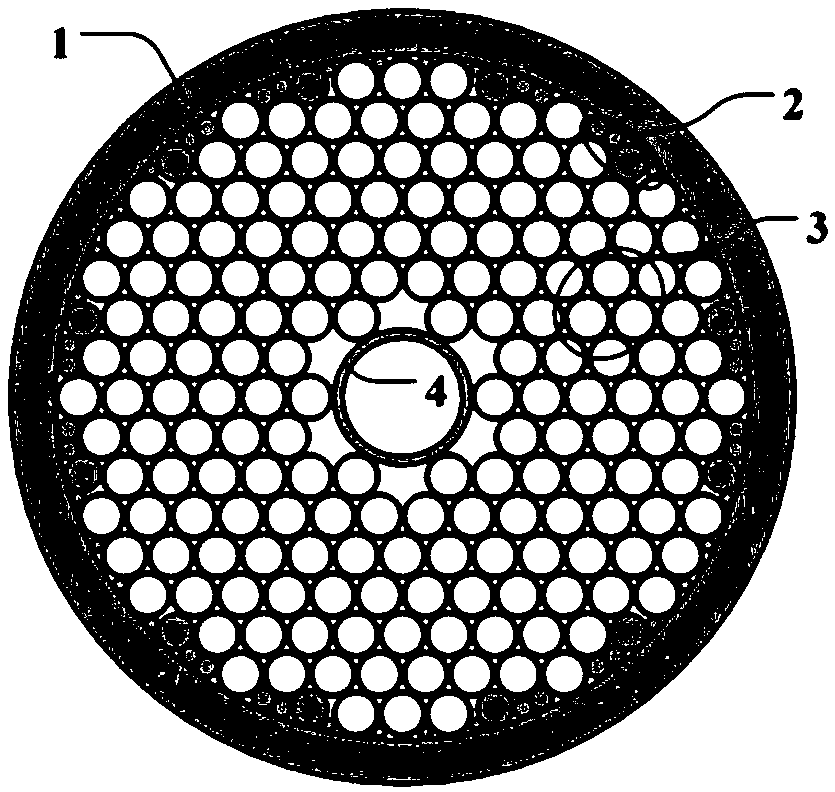
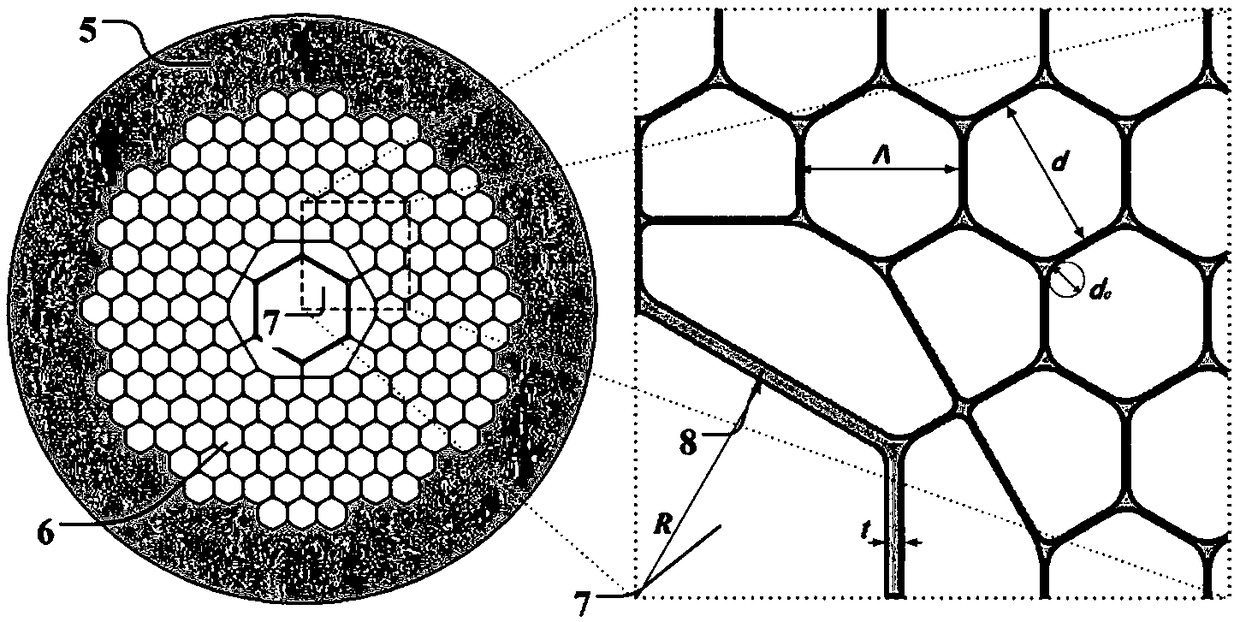
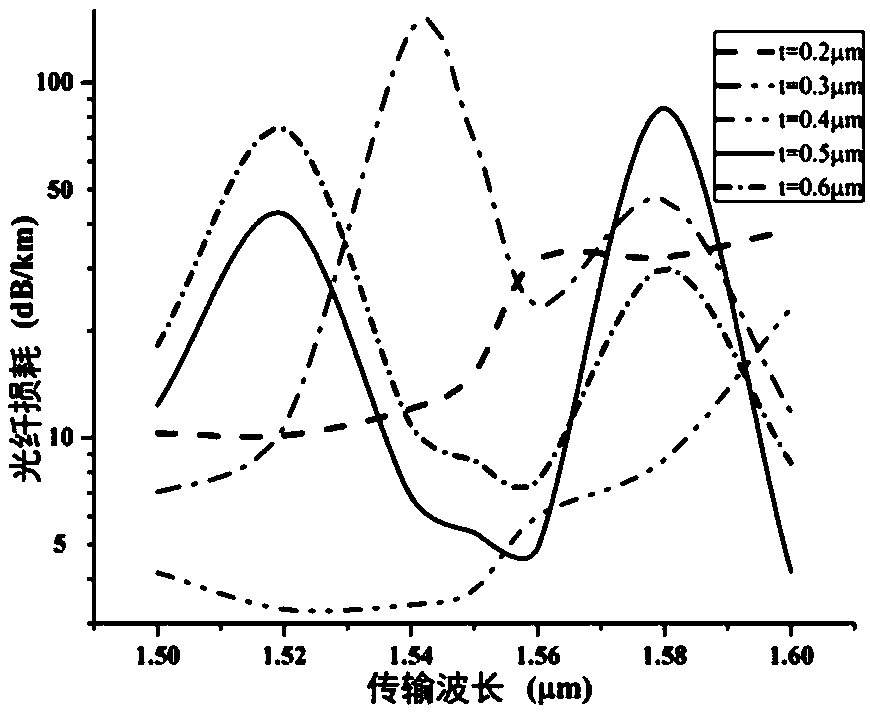
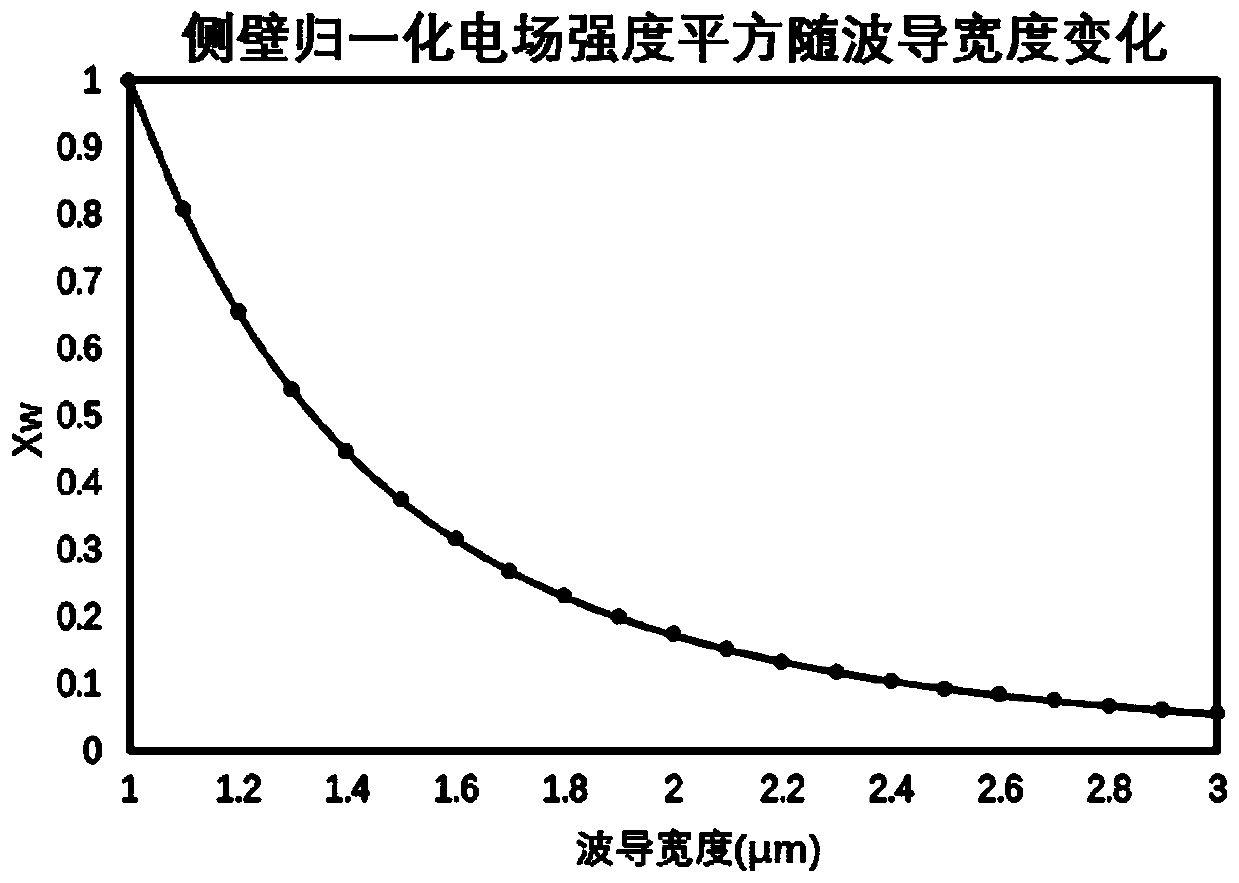
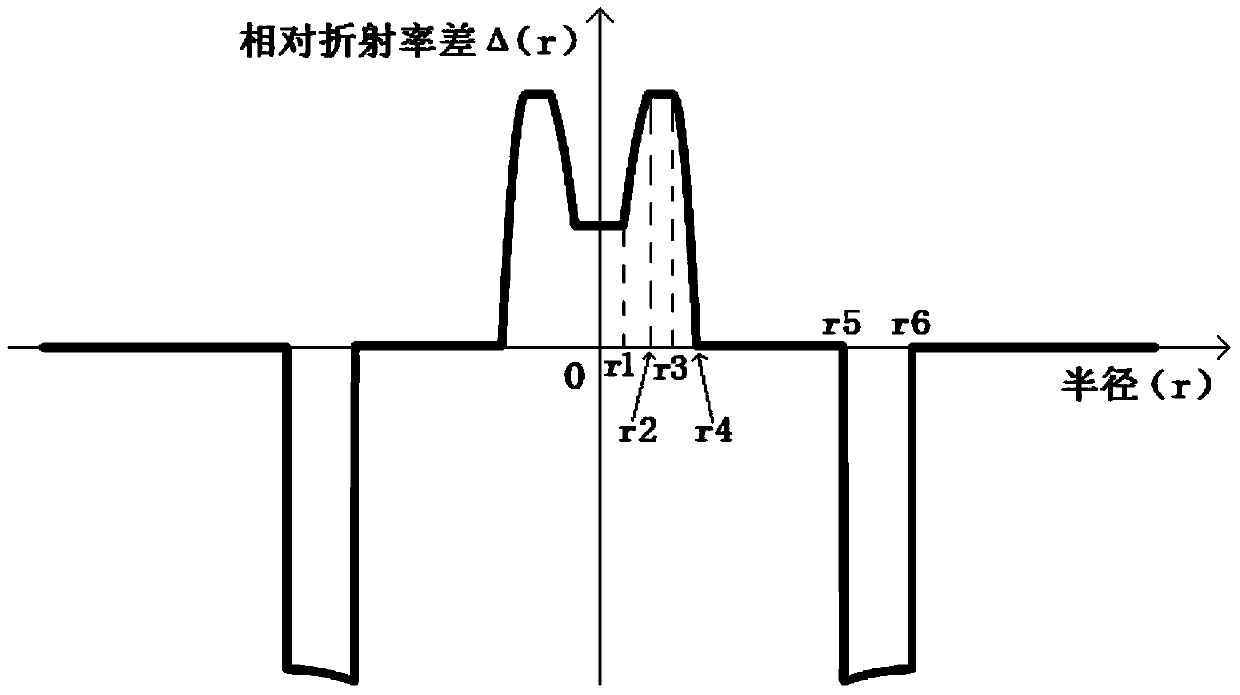
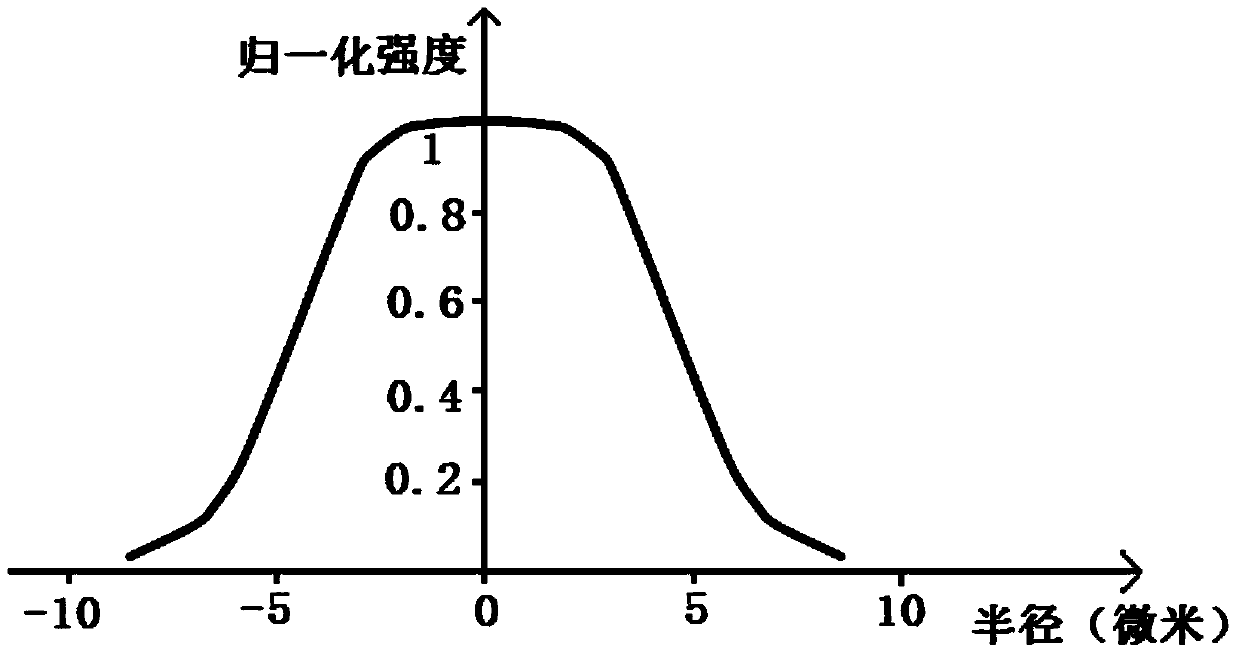
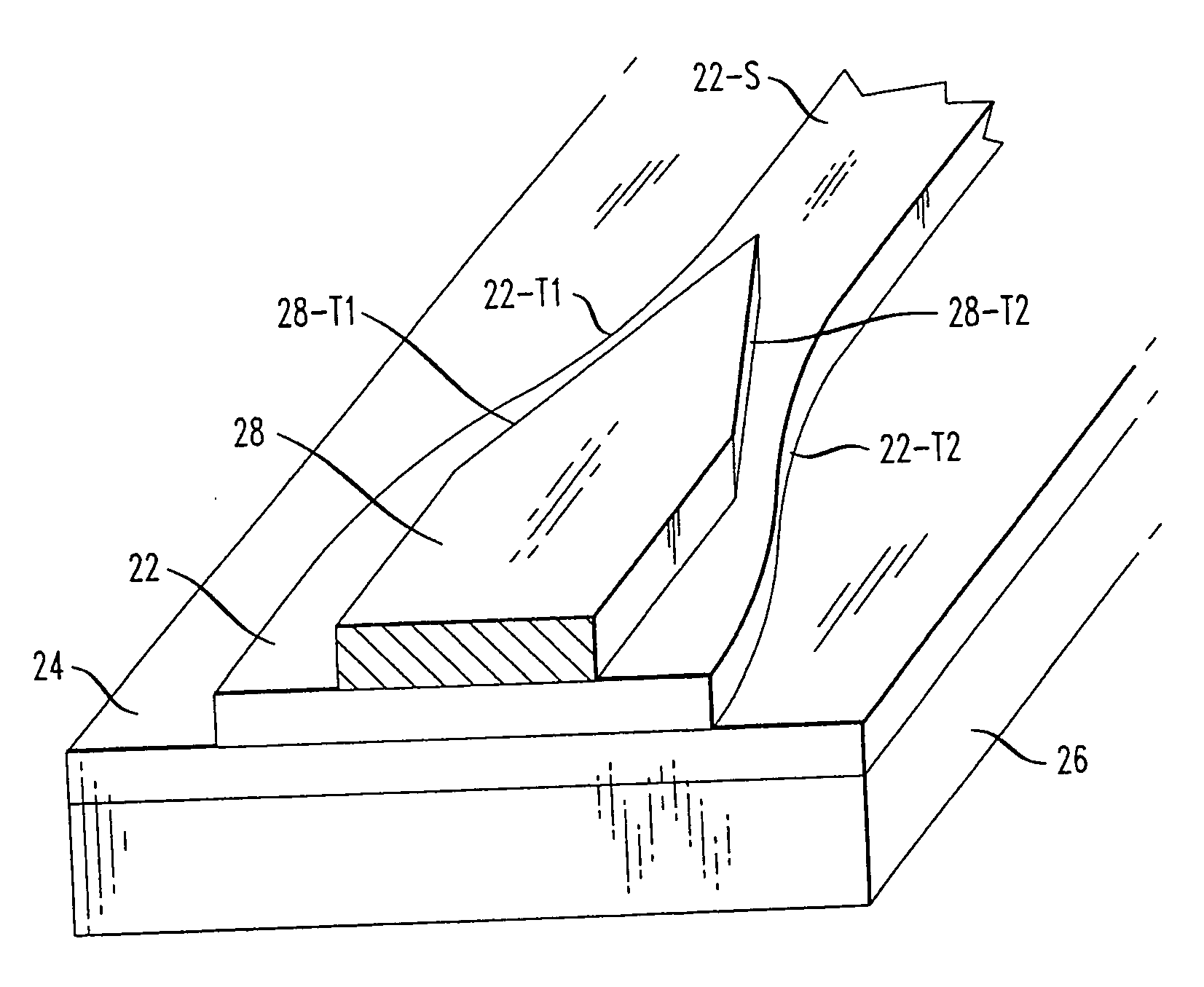
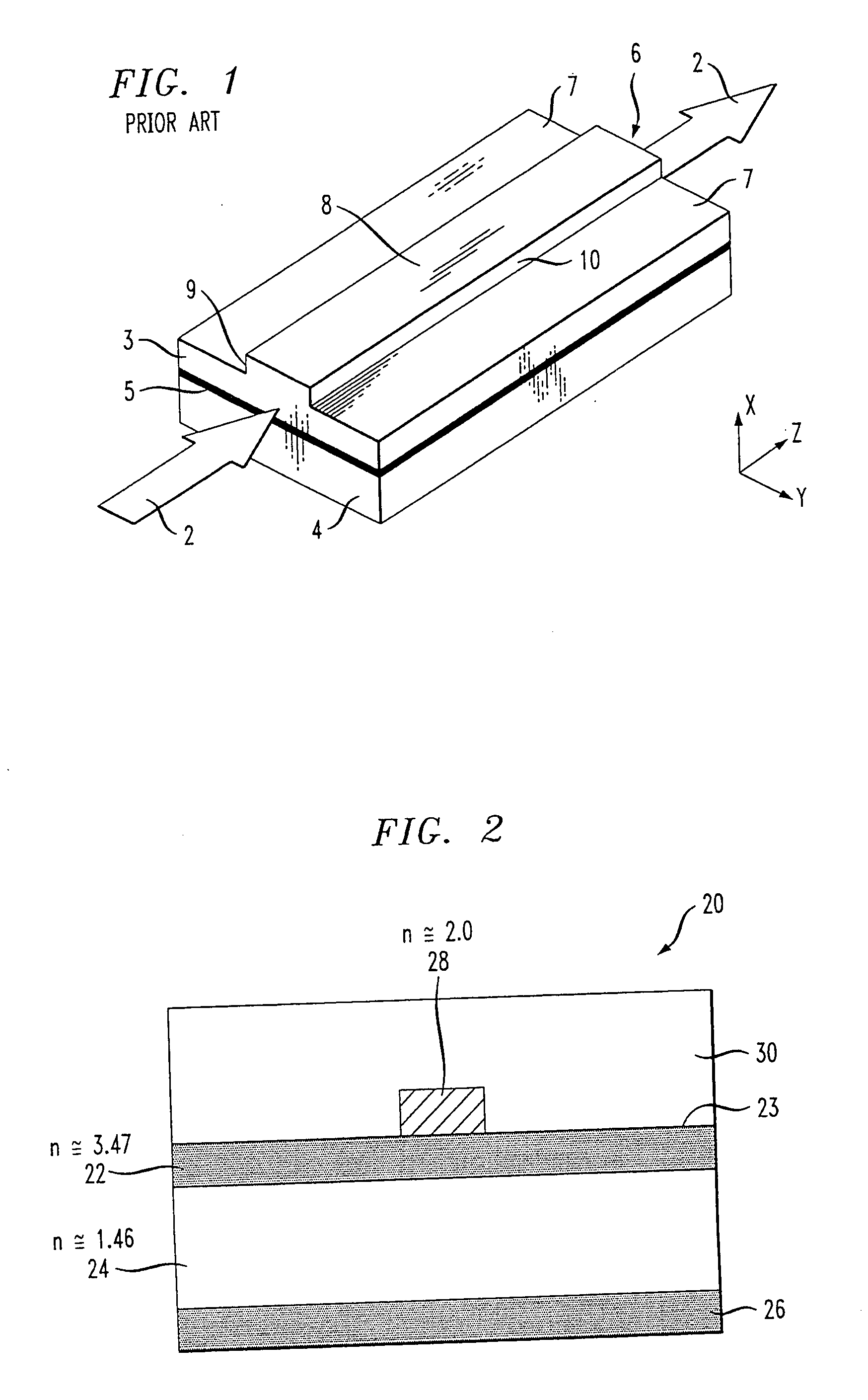
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
173 results about "Scattering loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
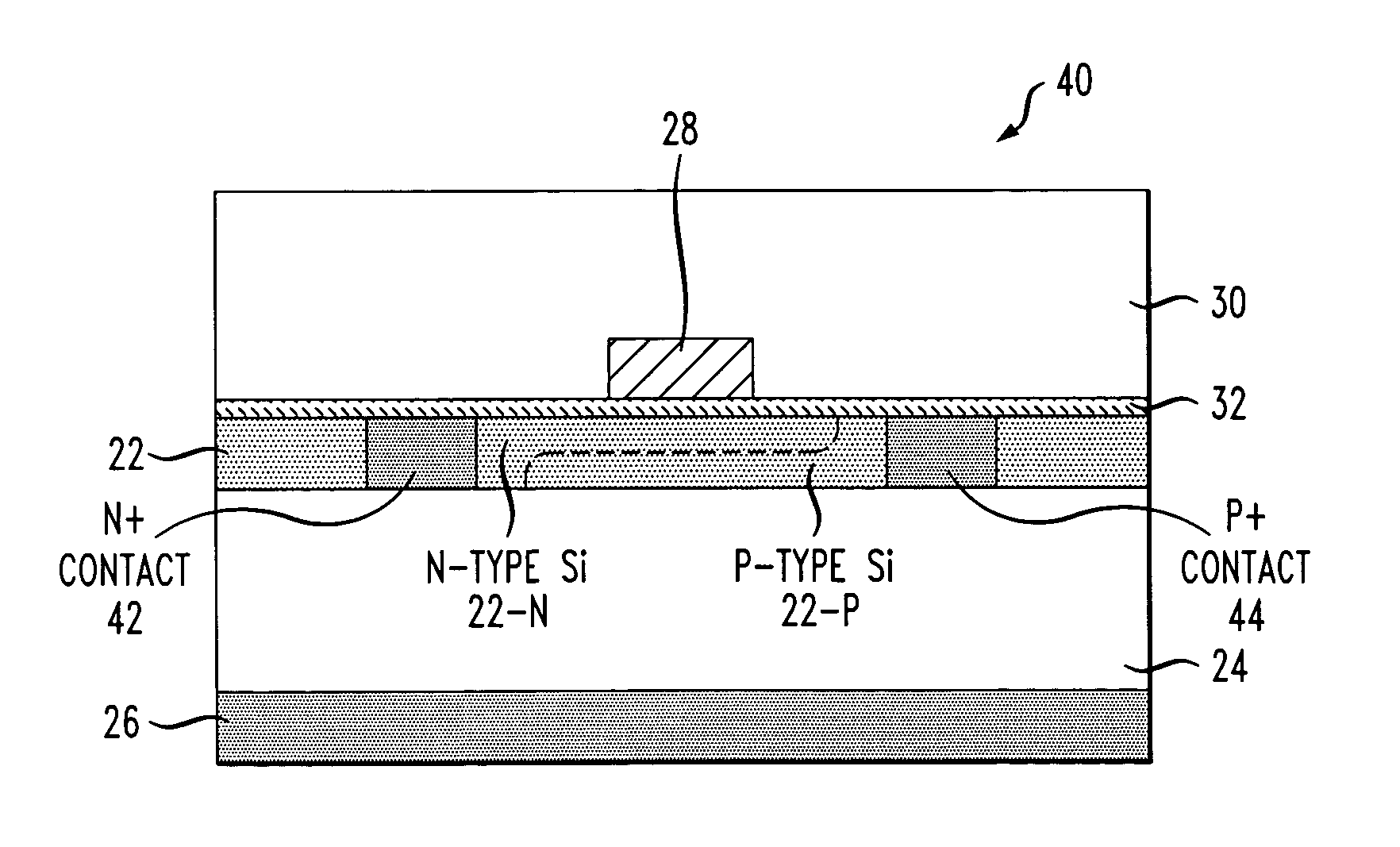
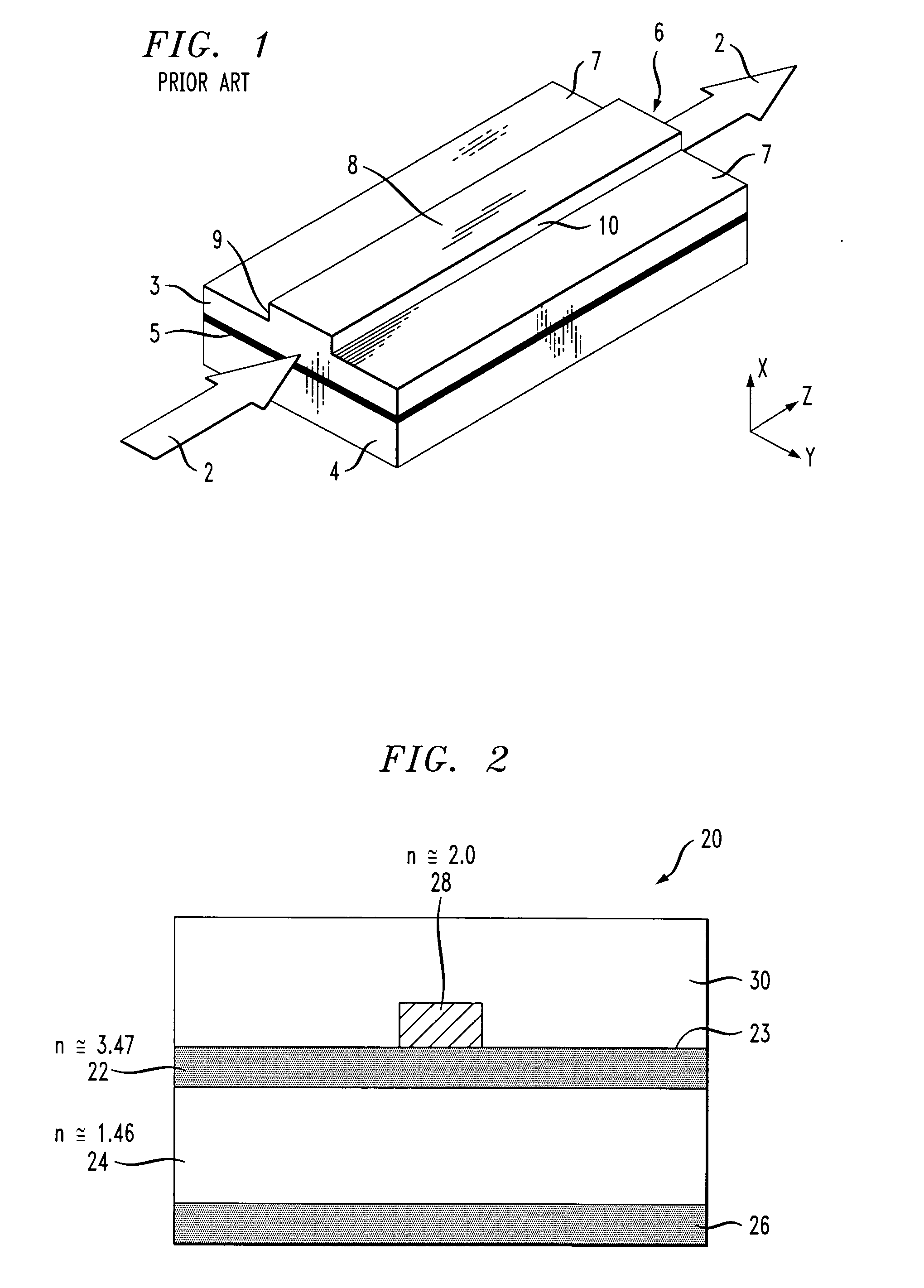
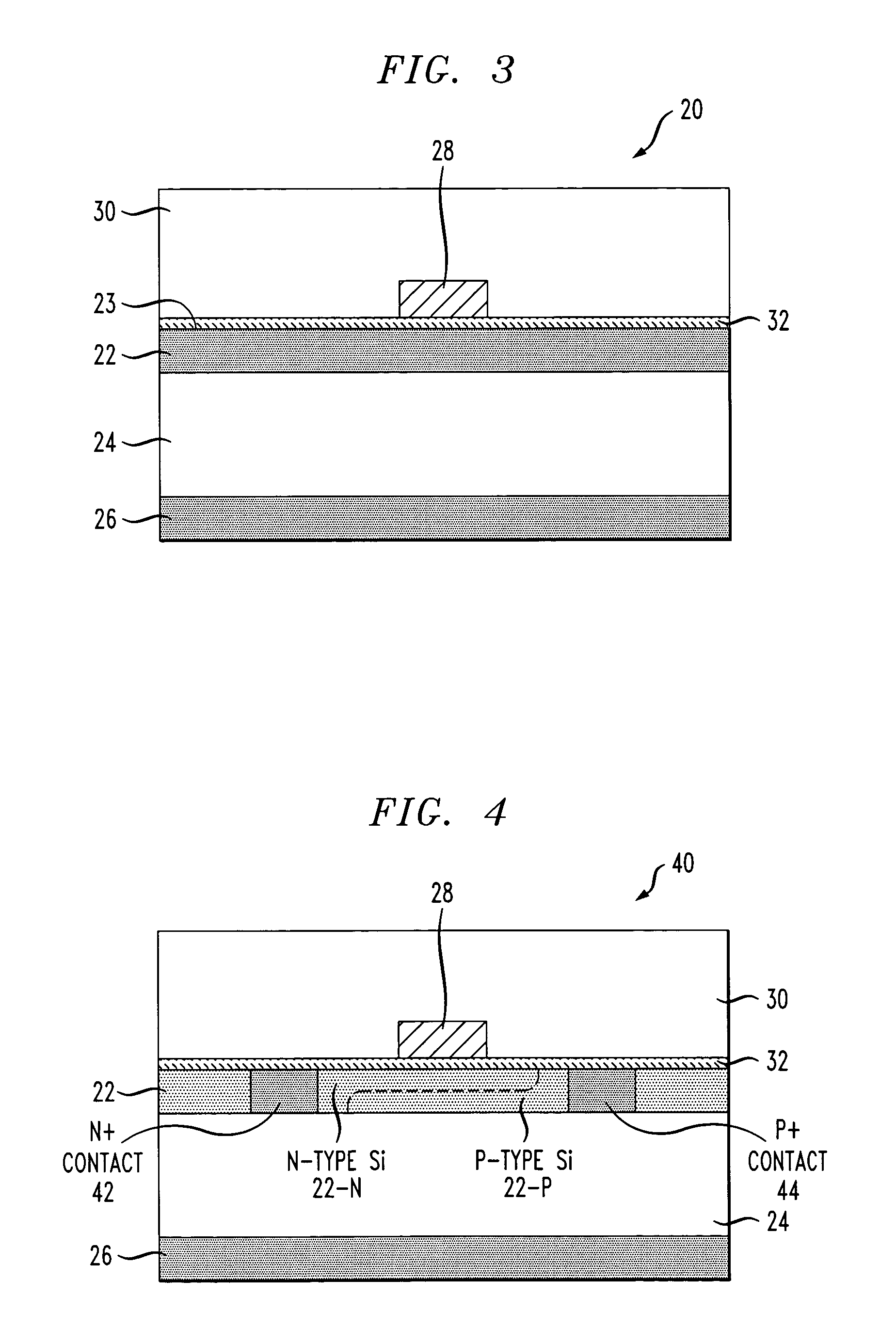
Optical Material and Method for Modifying the Refractive Index
InactiveUS20080001320A1Little and no scattering lossPositive changeSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, which exhibit little or no scattering loss. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, which exhibit little or no scattering loss and are characterized by a positive change in refractive index.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
CT detector array having non pixelated scintillator array
InactiveUS7054408B2Improve efficiencyImprove light outputSolid-state devicesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersImage resolutionScattering loss
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for detecting external cracks from within a metal tube
InactiveUS6271670B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFlaw detection using microwavesRadarScattering loss
A method and tool using a continuous electromagnetic wave from a transverse magnetic-dipole source with a coaxial electric-dipole receiver is described for the detection of external sidewall cracks and other anomalies in boiler tubes and other enclosures. The invention utilizes the concept of radar backscatter rather than eddy-currents or ultrasound, which are sometimes used in prior art crack-detection methods. A numerical study of the distribution of the fields shows that the direct transmission from the source to the receiver is reduced from that in free space. Further, if the diameter of the receiver dipole is made sufficiently small, it should be possible to detect cracks with a scattering loss of up to -40 dB in thin-walled boiler tubes.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Optical material and method for modifying the refractive index
ActiveUS7789910B2Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, wherein the refractive structures are characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Ultra low-loss CMOS compatible silicon waveguides
InactiveUS20060133754A1Reduce lossReduce light lossOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsBand shapeScattering loss
A low loss optical waveguiding structure for silicon-on-insulator (SOI)-based arrangements utilizes a tri-material configuration including a rib / strip waveguide formed of a material with a refractive index less than silicon, but greater than the refractive index of the underlying insulating material. In one arrangement, silicon nitirde may be used. The index mismatch between the silicon surface layer (the SOI layer) and the rib / strip waveguide results in a majority of the optical energy remaining within the SOI layer, thus reducing scattering losses from the rib / strip structure (while the rib / strip allows for guiding along a desired signal path to be followed). Further, since silicon nitirde is an amorphous material without a grain structure, this will also reduce scattering losses. Advantageously, the use of silicon nitride allows for conventional CMOS fabrication processes to be used in forming both passive and active devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Accessory ingredient pre-dispersed masterbatch used for refining sizing material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an accessory ingredient pre-dispersed masterbatch and a preparation technology thereof. Powdery or granular accessory ingredient is dispersed into a rubber matrix to form a new evenly-mixed flaky accessory ingredient form which has small possibility of flying. The preparation technology has the beneficial effect that the accessory ingredient is pre-dispersed in the rubber matrix. Compared with the traditional powder or granules, the accessory ingredient pre-dispersed masterbatch is characterized in that the flaky masterbatch does not have flying and scattering loss in the using process to guarantee the accuracy of the formula and improve the quality and the stability of the sizing material; because the accessory ingredient is subjected to the pre-dispersed mixing process, the accessory ingredient masterbatch can be quickly and easily dispersed into the sizing material in the using process, and the dispersibility of the accessory ingredient as well as the uniformity and the production efficiency of the sizing material are improved; the flaky accessory ingredient pre-dispersed masterbatch is more suitable for automatically or semi-automatically weighing, the automation degree of the whole production system is improved, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:特拓(青岛)轮胎技术有限公司
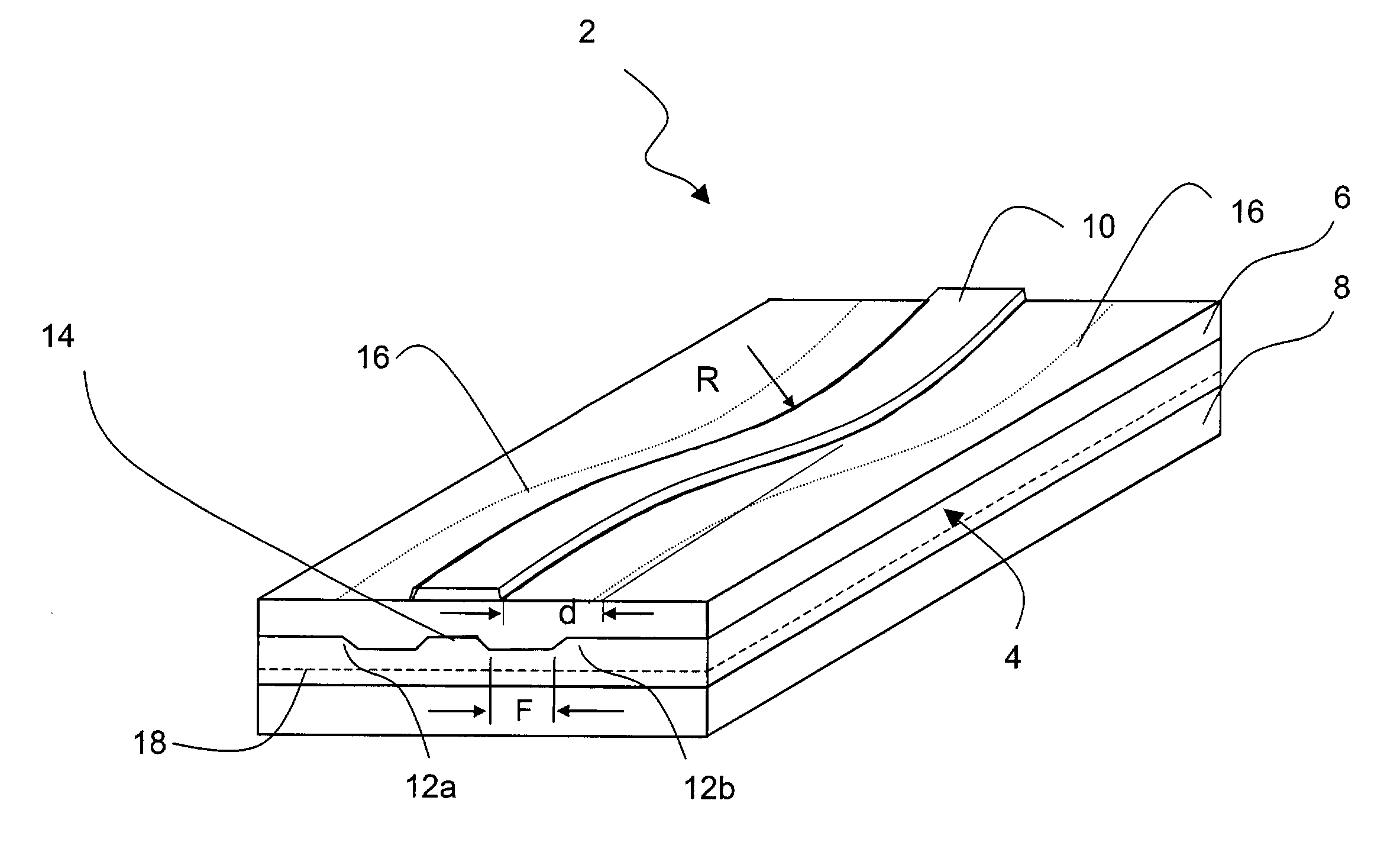
Index guided laser structure
InactiveUS20030219053A1Limit and eliminate oscillationOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionClassical mechanicsLight beam
An index guide laser structure of the invention utilizes the combination of two spatial filter elements to limit or eliminate oscillation of high order lateral modes and beam steering. A preferred structure utilizes a frustrated and curved index guide to induce bend loss in higher order modes, and another preferred structure utilizes frustrating guides to introduce periodic interruptions of the refractive index outside the central guide to induce scattering loss in the higher order modes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Method for extracting images of vascular structure and blood flow from image sequences
InactiveUS7558618B1Unexpected benefitSuppress noiseImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseScattering loss
Periodic biological functions and their related anatomy that cannot be seen in image sequences using typical means, can nonetheless be made visible by demodulating the image sequence according to the timing of that biological function using the described method. In particular, vascular structure and the function of that structure becomes observable when demodulated according to the patient's heart beat. This method suppresses the effects of thermal variations across the anatomy, and of severe scattering loss from buried tissues, that limit current thermographic (heat imaging) methods. It also measures localized changes in the wave front amplitude, shape, and phase, which are expected to prove useful for disease diagnosis and biometry.
Owner:WILLIAMS DARIN S
Wavelength-converting phosphors for enhancing the efficiency of a photovoltaic device
InactiveUS20070295383A1Reducing scattering lossReducing scattering lossesPV power plantsLuminescent compositionsHigh energyScattering loss
The present embodiments are directed to photovoltaic devices that convert sunlight into electrical energy. More specifically, the present embodiments include a phosphor-containing, wavelength-converting material for shifting higher energy light to a lower energy form, the latter being more suitable for the typical solar cell to convert to electricity. The absorption of the phosphor may range from about 280 to 460 nm. Advantageously, the phosphor component of the wavelength converter may be in the form of nano-particles embedded in a transparent matrix for reducing scattering losses.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Optical material and method for modifying the refractive index
ActiveUS20090143858A1Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, wherein the refractive structures are characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Near-infrared super-continuum lasers for early detection of breast and other cancers
InactiveUS20140236021A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh in collagenDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical sensorsConfocalScattering loss
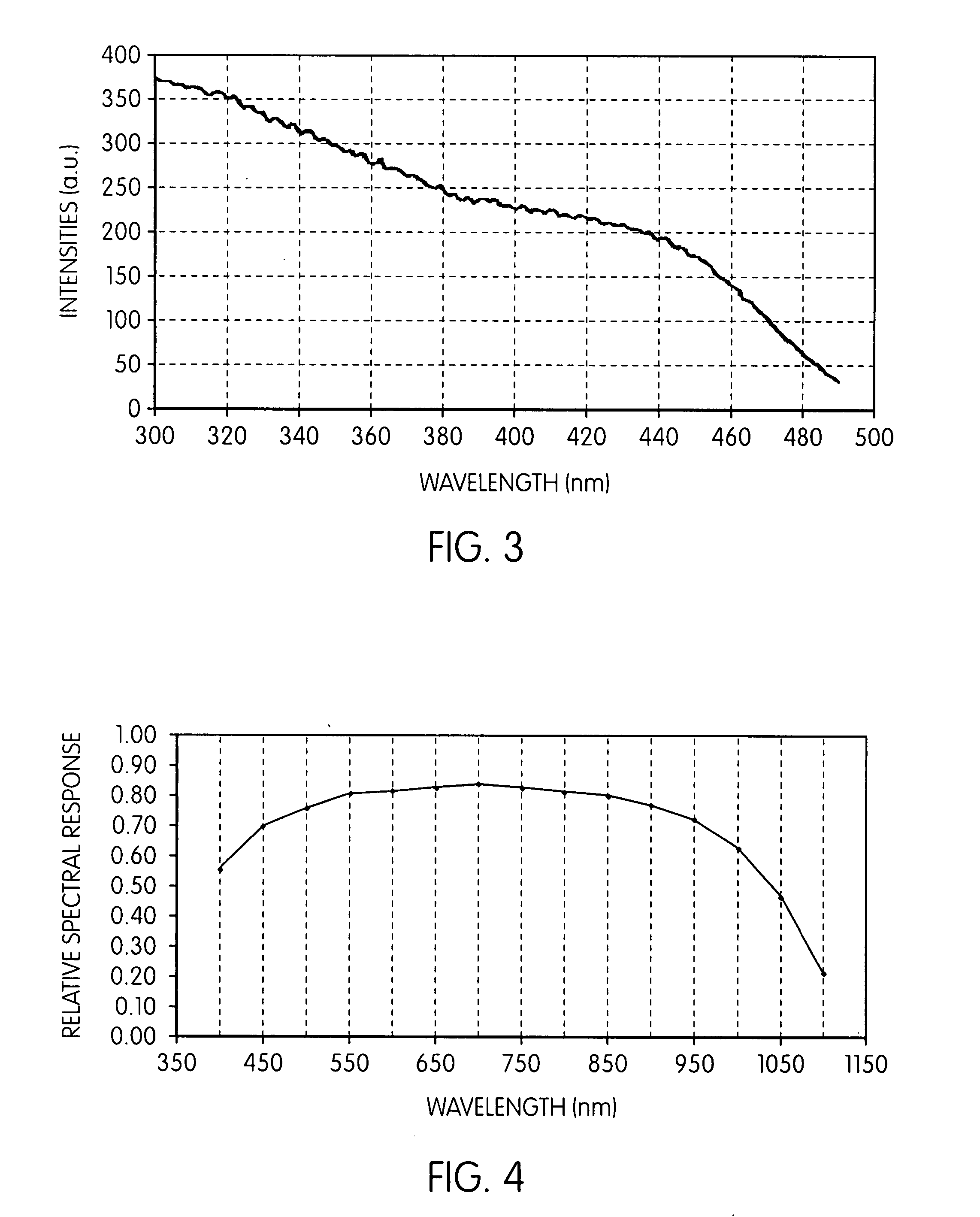
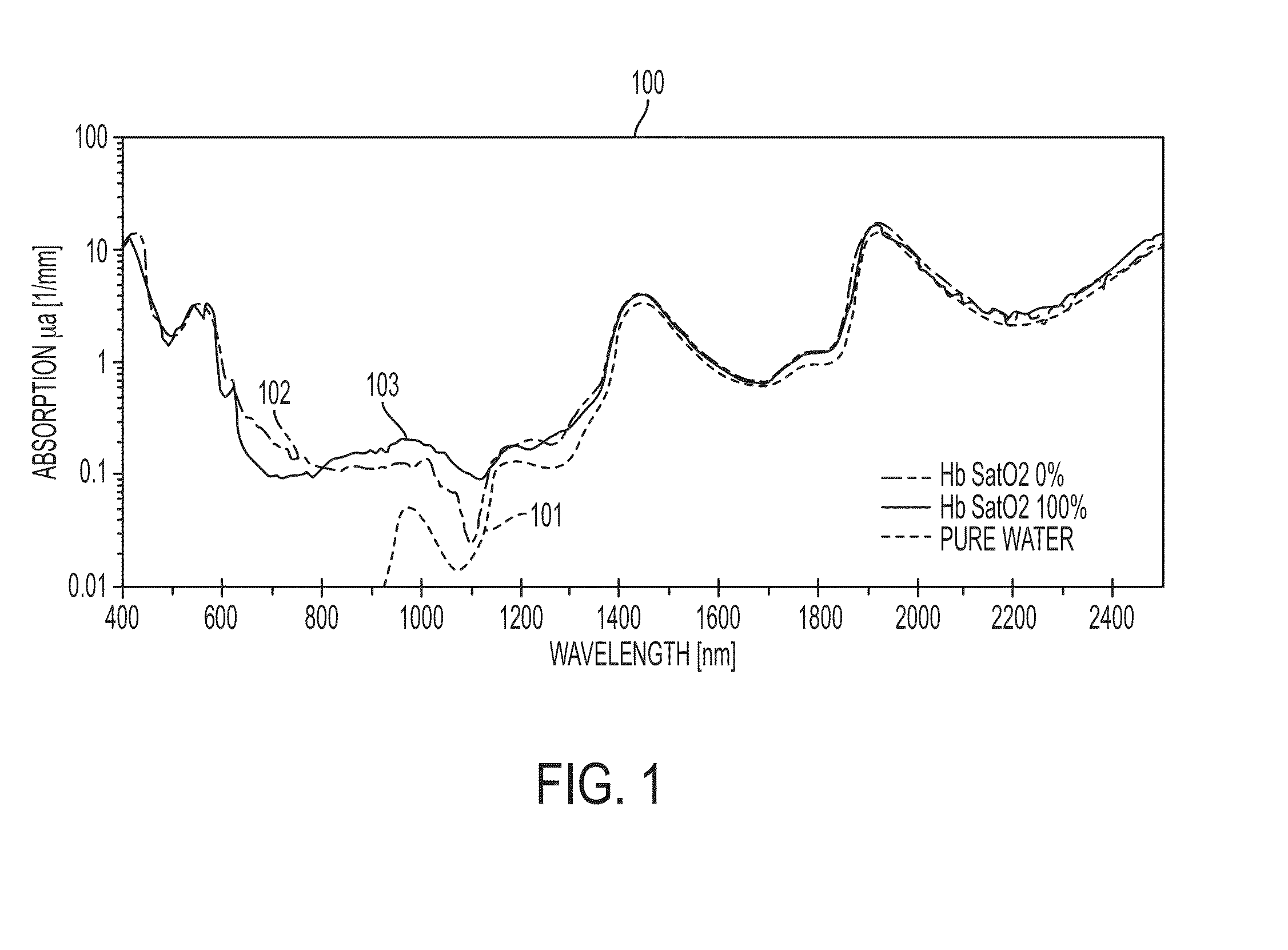
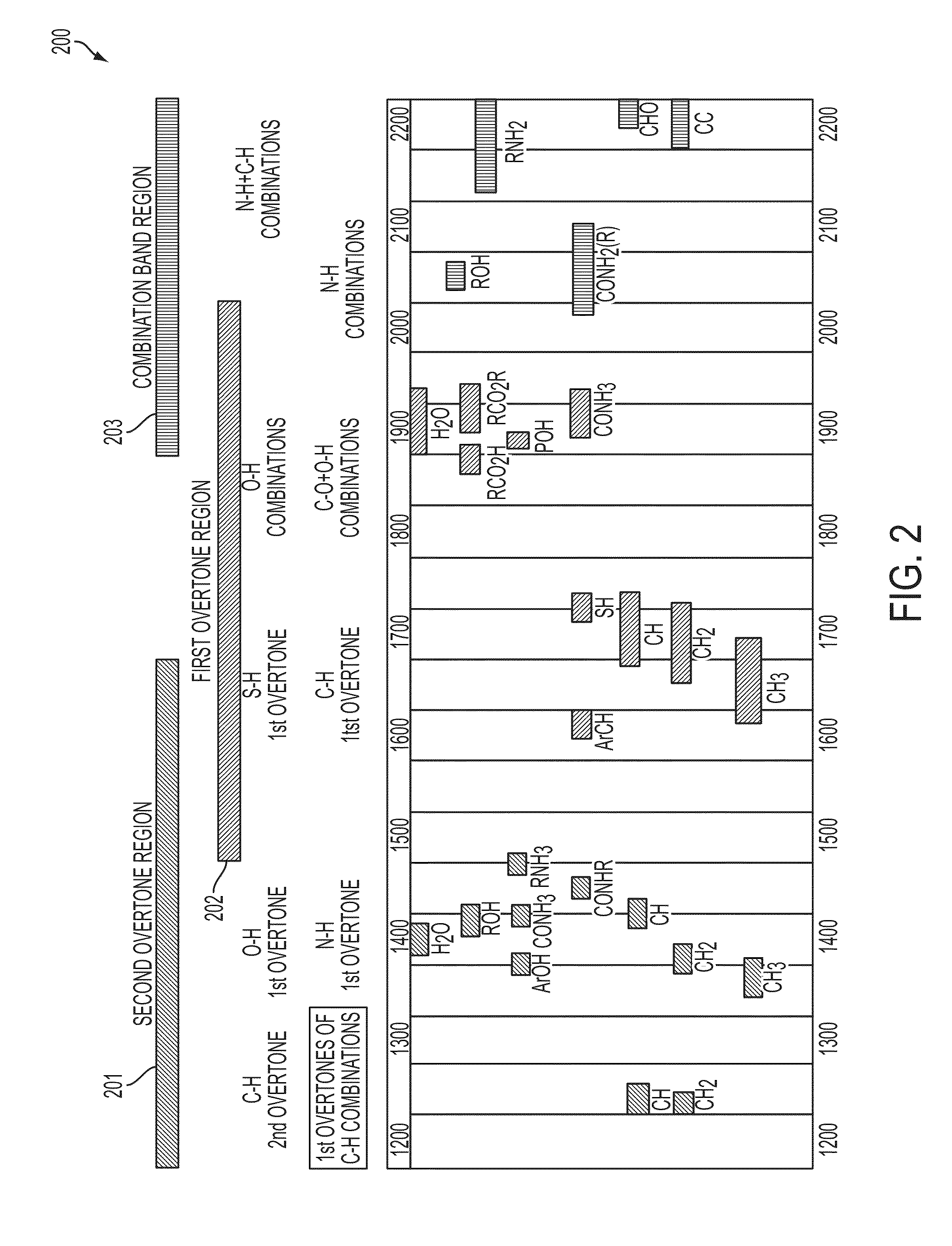
A system and method for using near-infrared or short-wave infrared (SWIR) light sources for early detection and monitoring of breast cancer, as well as other kinds of cancers may detect decreases in lipid content and increases in collagen content, possibly with a shift in the collagen peak wavelengths and changes in spectral features associated with hemoglobin and water content as well. Wavelength ranges between 1000-1400 nm and 1600-1800 nm may permit relatively high penetration depths because they fall within local minima of water absorption, scattering loss decreases with increasing wavelength, and they have characteristic signatures corresponding to overtone and combination bands from chemical bonds of interest, such as hydrocarbons. Broadband light sources and detectors permit spectroscopy in transmission, reflection, and / or diffuse optical tomography. High signal-to-noise ratio may be achieved using a fiber-based super-continuum light source. Risk of pain or skin damage may be mitigated using surface cooling and focused infrared light.
Owner:OMNI MEDSCI INC
Optical material and method for modifying the refractive index
ActiveUS8337553B2Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryScattering lossRefractive index
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
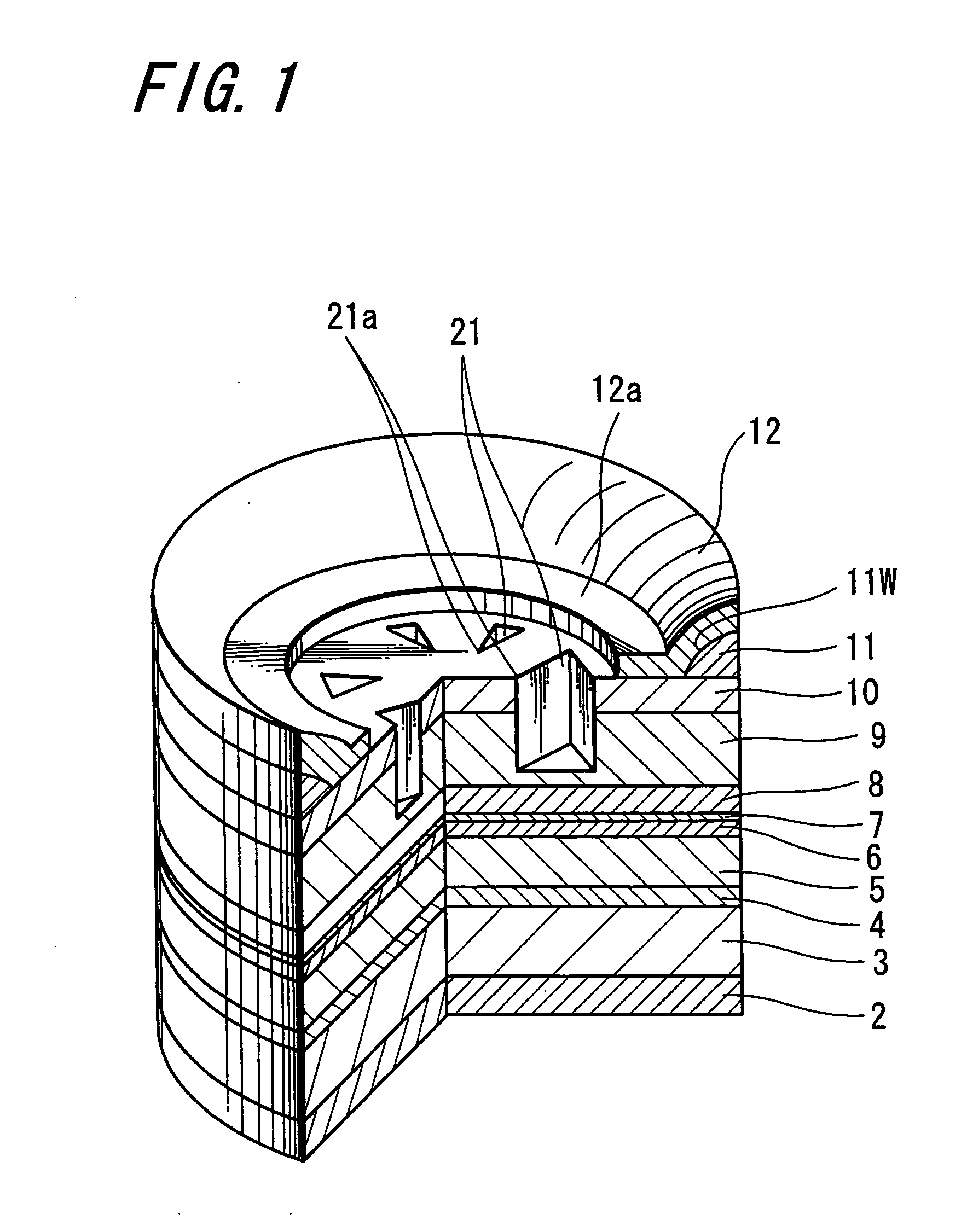
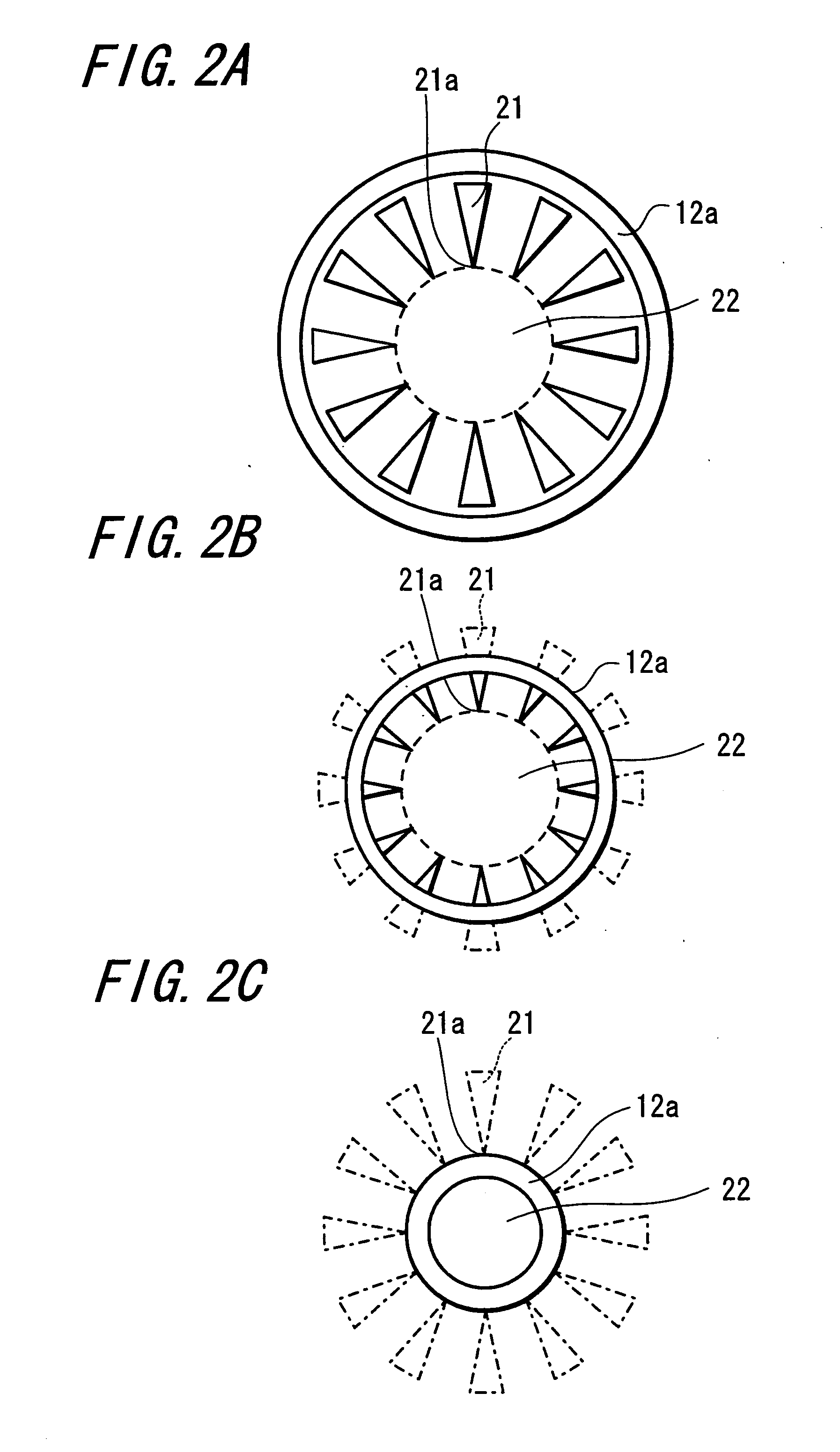
Surface-emitting semiconductor laser and method for manufacturing thereof as well as optical device
ActiveUS20050089075A1Improvement in singularityLower the thresholdLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSingle mode laserAcute angle
A surface-emitting semiconductor laser (VCSEL) having a structure in which the single horizontal mode of high power is stably maintained, and an optical device including a light-source device having this surface-emitting semiconductor laser are provided. A scattering-loss-structure portion composed of a low refractive-index region is disposed around a main current path in a surface-emitting semiconductor laser, namely around a cavity structure portion; the low refractive-index region is disposed at intervals; and the shape of the tip portion opposing to the center portion is set to be a tapered shape, for example, at an acute angle. Accordingly, in the cavity structure portion, the loss of light-emitting laser of a high-order mode localized in the outer circumferential portion becomes large, so that a surface-emitting semiconductor laser that oscillates the single-mode laser with favorable performance is constructed.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
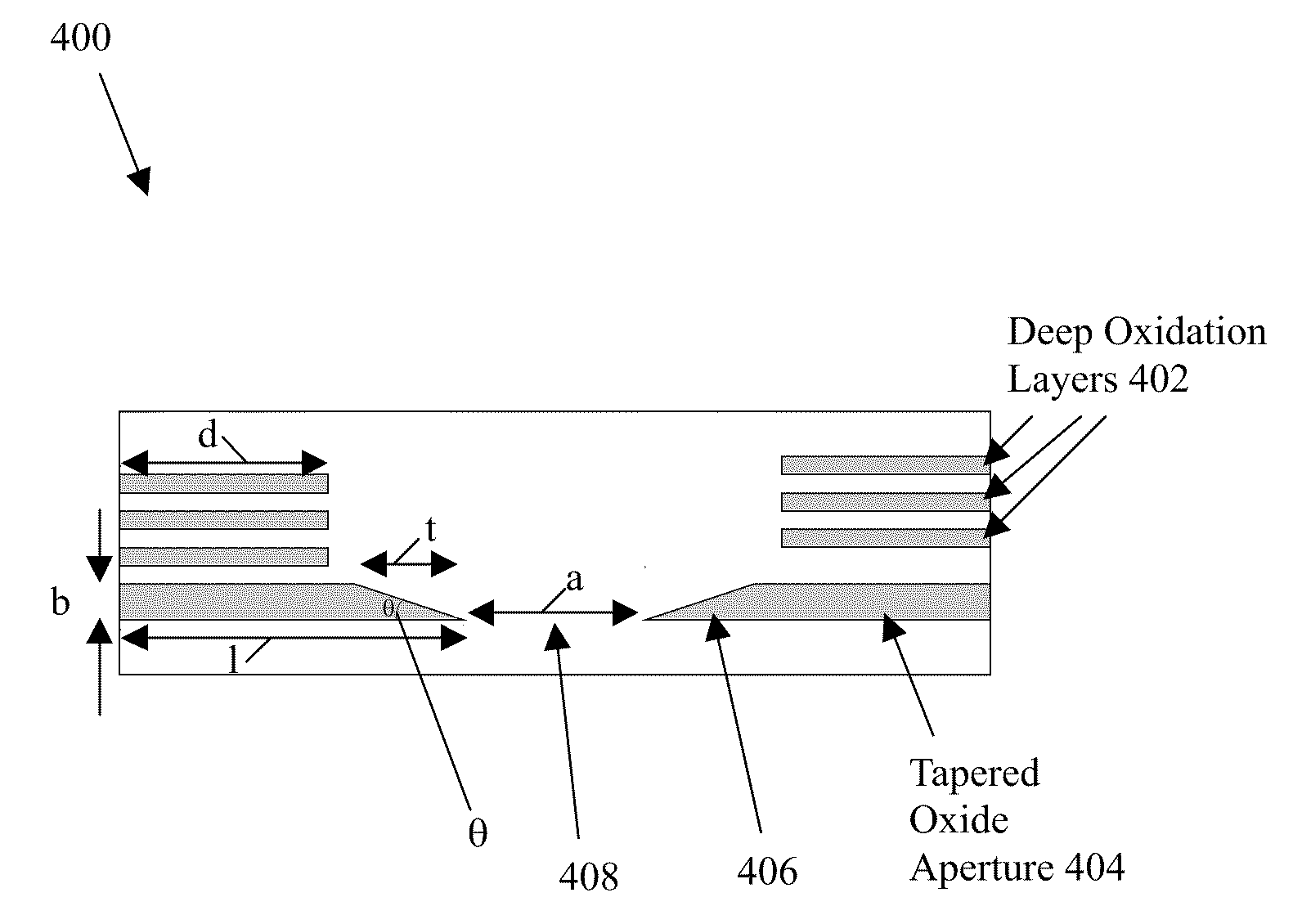
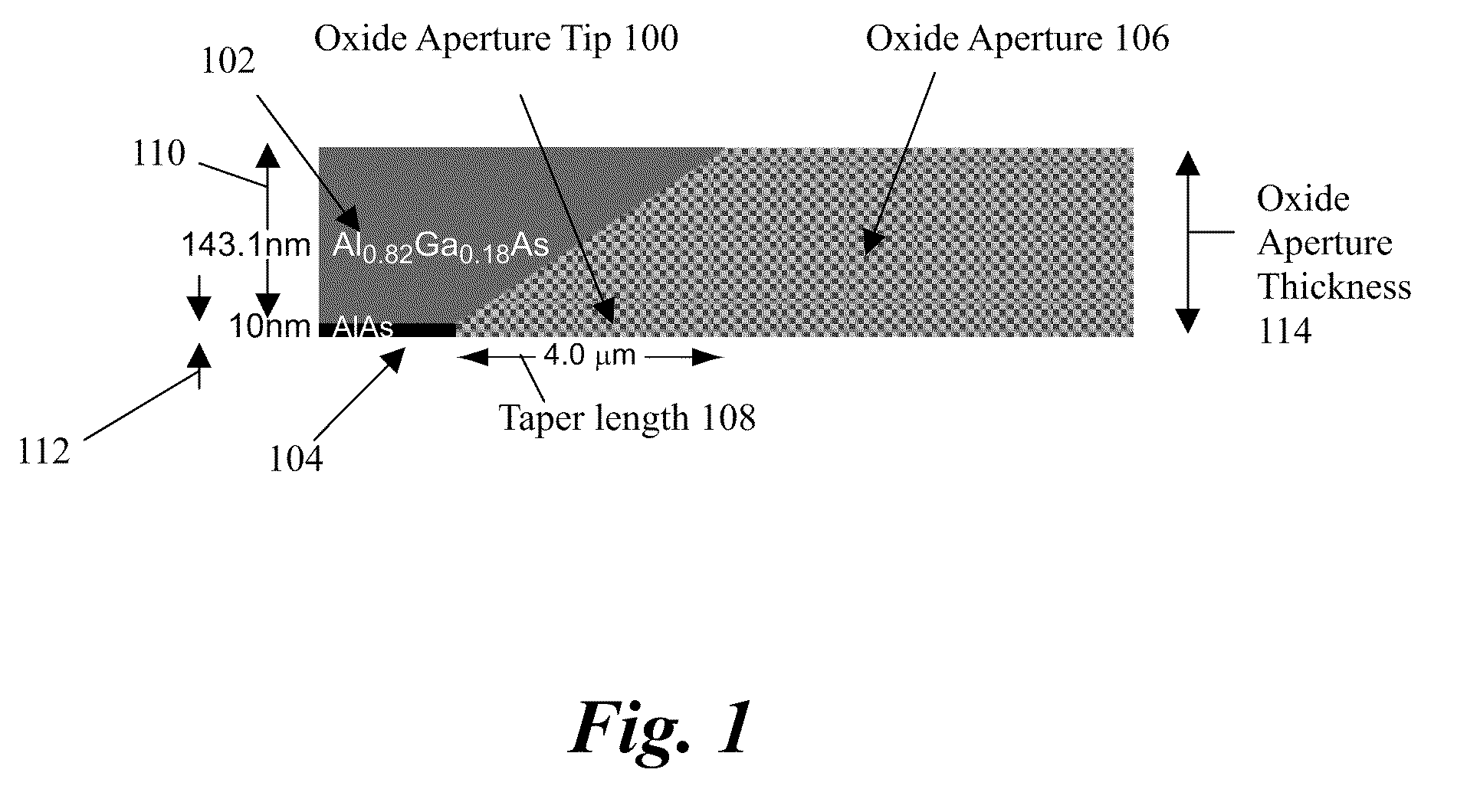
Small dimension high-efficiency high-speed vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
ActiveUS20090262765A1Reduces mode volumeMinimal added lossLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhysicsScattering loss
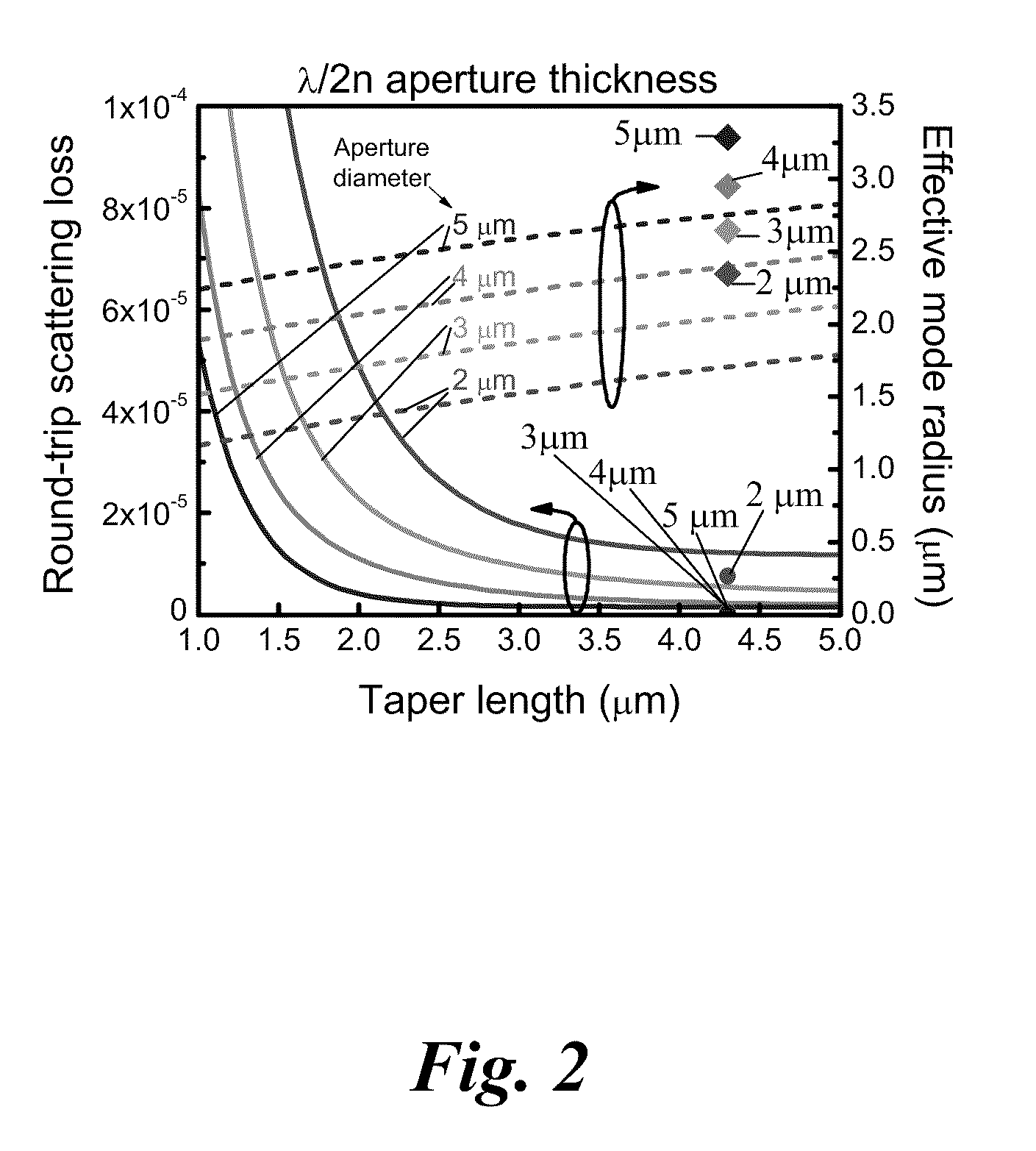
A Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is disclosed, comprising an optical cavity bounded by a top mirror and a bottom mirror, wherein the top mirror has multiple layers of alternating refractive index, of which the bottom three or more layers of the top mirror are deep oxidation layers having an increased oxidation length, a light emitting active region between the top mirror and the bottom mirror, and an aperture with tapered edges between the active region and the top mirror, wherein the aperture has a thickness, a taper length, an oxide aperture length, a taper angle, and an aperture opening diameter designed to reduce an optical mode's diameter without significantly increasing the optical mode's round trip scattering loss.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical Material and Method for Modifying the Refractive Index
ActiveUS20100298933A1Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryComputational physicsScattering loss
The invention is directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, wherein the refractive structures are characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Coupling structure and coupling method of semiconductor laser chip and silicon optical chip
InactiveCN110401101AReduce lossReduce light field scattering lossLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCoupling lossScattering loss
The present invention provides a coupling structure and a coupling method of a semiconductor laser chip and a silicon optical chip. The coupling structure comprises: a laser unit comprising a laser chip; a silicon optical chip provided with a waveguide; and an etching groove arranged at the coupling end of the silicon optical chip and used for connecting with the laser unit and the silicon opticalchip. The coupling structure and the coupling method of the semiconductor laser chip and the silicon optical chip can achieve high-efficiency coupling of the semiconductor laser chip and the siliconoptical chip and facilitates providing of a high-quality light source for the silicon optical hybrid integration, an antireflection film is plated at the coupling end face of the silicon optical chip,the coupling loss and the RIN noise of the laser are reduced, the refractive index matching rubber fills the gap of the laser chip and the silicon optical chip, the scattering loss of the optical field is reduced, and the coupling loss is further reduced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of bio-membrane reactor in sewage treatment, carbon sequestration microalgae harvesting
PendingCN107012072ARealize deep purificationReduced scattering lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsScattering lossDissolution
The invention discloses application of a bio-membrane reactor in sewage treatment, carbon sequestration microalgae harvesting. The bio-membrane reactor comprises a photo-biological reaction system, a gas allocation system and a column-shaped dissolved-gas-gas floating harvesting system. By adopting the reactor, deep sewage purification can be achieved by using microalgae. A vertical space can be very well utilized by using a vertically suspended membrane material; by adopting a membrane component, the gas-liquid transfer efficiency is greatly improved; due to a special arrangement mode of a curtain type membrane component, scattering loss of light can be reduced to the maximum extent, energy loss is avoided, efficient absorption and utilization of the microalgae on a luminous energy envelope are ensured, and the algae cell lighting homogeneity is achieved; low-cost green harvesting of the microalgae on membranes is achieved through simple mechanical scraping. Low-cost green gas dissolution-gas floating harvesting of the suspended microalgae is achieved through the column-shaped dissolved-gas-gas floating harvesting system, meanwhile CO2 dissolved gases are functionally concentrated in a harvesting device, and CO2 enriched microalgae culture is achieved through the gas allocation system and the column-shaped dissolved-gas-gas floating harvesting system in the culture process.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Hollow-core photonic band-gap fiber based on isolated anti-resonance layers
ActiveCN108919417AStrengthen restrictionsSuppress couplingGlass optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideMicrostructure fiberResonance
The invention discloses a hollow-core photonic band-gap fiber based on isolated anti-resonance layers and belongs to the technical field of microstructure fibers. A preparation method of the hollow-core photon band-gap fiber specifically comprises the steps that a complete stacked structure is formed through stacking of capillary tubes; after the capillary tube at the center of the stacked structure is removed, a fiber core glass tube is inserted; the periphery of the complete stacked structure is sleeved with a quartz sleeve to form a fiber preform rod; and the fiber perform rod is drawn through an existing hollow-core photonic band-gap fiber drawing method, a structure with the independent isolated anti-resonance layers is formed at the periphery of a fiber core, and thus the hollow-corephotonic band-gap fiber based on the isolated anti-resonance layers is formed. According to the hollow-core photonic band-gap fiber based on the isolated anti-resonance layers, the fiber core wall atthe fiber core is constituted by the isolated anti-resonance layers, limitation to light is enhanced, the scattering loss is reduced, and coupling between the hollow-core photonic band-gap fiber anda common single-mode fiber is facilitated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ir-activated photoelectric systems
InactiveUS20140076404A1Easy to adaptEasy to integrateLight-sensitive devicesHydroxy compound preparationActivation energyScattering loss
Photoelectric systems combining a semiconductor and a phosphorescent compound with an emission spectrum of photons with energy levels equal to or greater than the activation energy of the semiconductor, wherein the phosphorescent compound is characterized by the emission spec-tram being produced by excitation of the phosphorescent compound with lower energy photons and the separation distance between the semiconductor and the phosphorescent compound is less than the distance at or above which scattering losses predominate. Methods are that embody technological applications of the photoelectric systems are also disclosed, as well as articles that embody technological applications of the photoelectric systems.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Ultra low-loss CMOS compatible silicon waveguides
ActiveUS7941023B2Reduce lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideScattering lossRefractive index
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for simultaneously measuring reflectance, transmittance, scattering loss and absorption loss of high reflection/high transmission optical element
ActiveCN107132029ARealize two-dimensional scanning imaging measurementAmplify laser powerTesting optical propertiesMeasurement testScattering loss
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously measuring the reflection, transmission, scattering and absorption of a high reflection / high transmission optical element. The method is based on the optical cavity ring-down technology, and includes the steps of firstly, measuring the ring-down time [tau]0 of an initial optical resonant cavity, then adding a high reflection / high transmission optical element to be measured, measuring the ring-down time [tau]1 of a test optical resonant cavity, and obtaining the reflectance / transmittance of the high reflection / high transmission optical element through calculation; simultaneously measuring ratios of a transmission / reflection light intensity signal and a scattering light intensity signal of the high reflection / high transmission optical element to a transmitted light intensity signal of an output cavity mirror, and obtaining the transmittance / reflectance and scattering loss of the optical element through calibration; and solving for the absorption loss of the optical element with the reflectance, transmittance and scattering loss. The measuring method can not only measure the reflectance, transmittance, scattering loss and absorption loss of the high reflection / high transmission optical element, but also enable high definition two-dimensional imaging of the distribution thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Array waveguide grating with insensitive temperature
ActiveCN102902011AAchieving temperature insensitivityGood temperature characteristicsOptical waveguide light guideGratingScattering loss
The invention discloses an array waveguide grating with an insensitive temperature. The array waveguide grating comprises an input waveguide zone, an input slab waveguide zone, an array waveguide zone, an output slab waveguide zone and an output waveguide zone which are connected in sequence, wherein the array waveguide zone is embedded with at least two temperature compensation media to realize at least two-order temperature compensation. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the invention, the temperature characteristics of the traditional array waveguide grating can be notably improved, and the temperature insensitiveness of the array waveguide grating can be realized. Meanwhile, as the array waveguide provided by the invention adopts the structural design of a concentric circle, the embedded temperature compensation media are distributed vertically to the array waveguide, thereby effectively reducing scattering loss, realizing symmetry between input and output, and reasonably reducing the overall size of an array waveguide grating device.
Owner:HENAN SHIJIA PHOTONS TECH
Method for manufacturing all-polymer plane optical path
InactiveCN103592721ALow costSimple processOptical waveguide light guideMicro structurePolymer adhesive
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing an all-polymer plane optical path. The method comprises the steps of (1) obtaining an initial master mold by means of ultra-violet lithography and deep-etching technologies, duplicating a metallic nickel mold by means of electrochemical sedimentation, and manufacturing a polymer micro-structure part by means of mini molding; (2) conducting segment treatment on the part by means of the thermal annealing technology to reduce the roughness of the lateral wall and reduce scattering loss during optical wave transmission; (3) applying and filling polymer medium materials and obtaining the core structure of the plane optical path after the polymer medium materials are solidified; (4) combining a bondage layer of an element with an optical polymer substrate to achieve the manufacturing of the buried ridge type polymer plane optical path, wherein a polymer adhesive layer serves as the bondage layer of the element. Compared with a traditional method for manufacturing the polymer plane optical path, the method for manufacturing the all-polymer plane optical path has the advantages that cost is reduced and universality of technologies to materials is high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line supporting low-loss fundamental mode transmission
ActiveCN110596813AExtended propagation distanceLow Intermodal CrosstalkCoupling light guidesScattering lossEngineering
The invention discloses a silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line supporting low-loss fundamental mode transmission. A curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide is placed at the centers of curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguides; and two curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguides are annularly and helically arranged,an inner end of one curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguide is connected with one end of the curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide through a bending waveguide, the other end of the curvature gradual change type S bending multimode waveguide is connected with the inner end of the other curvature gradual change type helical bending multimode waveguidethrough another bending waveguide, and the entire silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line is arranged in a central symmetry manner. The silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line disclosed by the invention can effectively avoid mode mismatch loss and inter-mode crosstalk caused by the abrupt curvature change of the traditional structure, and can reduce the scattering loss introduced by a waveguide sidewall, thereby obtaining low-loss fundamental mode transmission in the silicon-based multimode helical waveguide, and the silicon-based multimode helical waveguide delay line has the advantages of low loss and compact structure and the like, and can be applied to optical buffers, optical delay lines and other systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103472525AIncrease the effective areaReduce optical power densityGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingRefractive indexScattering loss
The invention discloses a low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and a manufacturing method of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber, and relates to the field of optical fibers. The low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber comprises a quartz glass cladding, an internal coating and an external coating, wherein the quartz glass cladding, the internal coating and the external coating are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; the inside of the quartz glass cladding comprises a first fiber core area, a second fiber core area, a third fiber core area, a fourth fiber core area and a refractive index concave cladding, wherein the first fiber core area, the second fiber core area, the third fiber core area, the fourth fiber core area and the refractive index concave cladding are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; the refractive index concave cladding is subjected to deposition through a PCVD process; the quartz glass cladding is manufactured through an OVD process or a sleeving process. According to the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and the manufacturing method of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber, the scattering loss of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and the additional loss of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber in a bent state can be reduced; due to the fact that the spire distribution of fiber core basic mode electromagnetic field power is adjusted into flattop distribution, optical power density is reduced, the effective area of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is enlarged, the nonlinearity of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is reduced, the incident power of an optical fiber communication system is increased by 0.4-2.6 dB, and the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is suitable for mass production.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
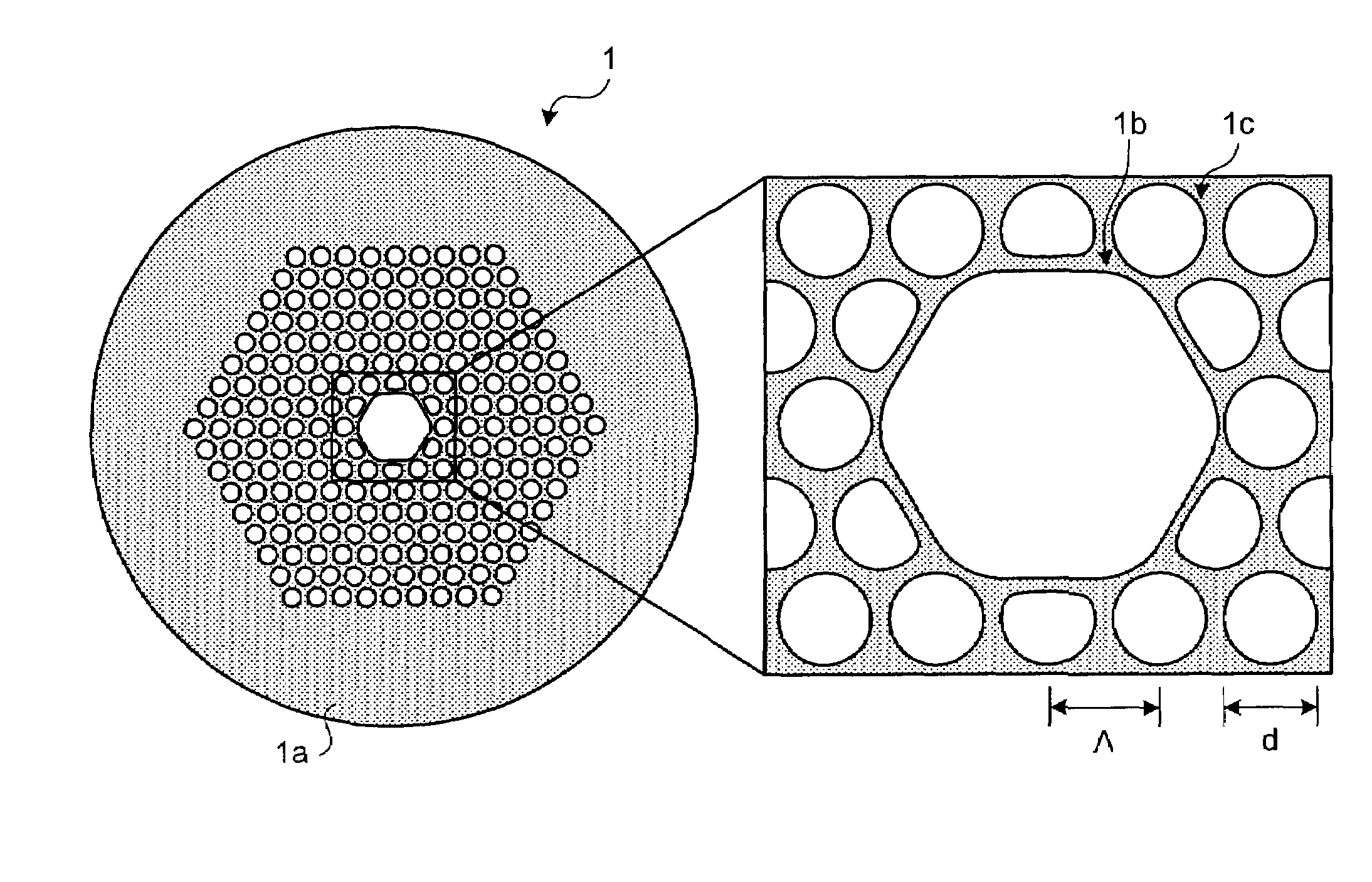
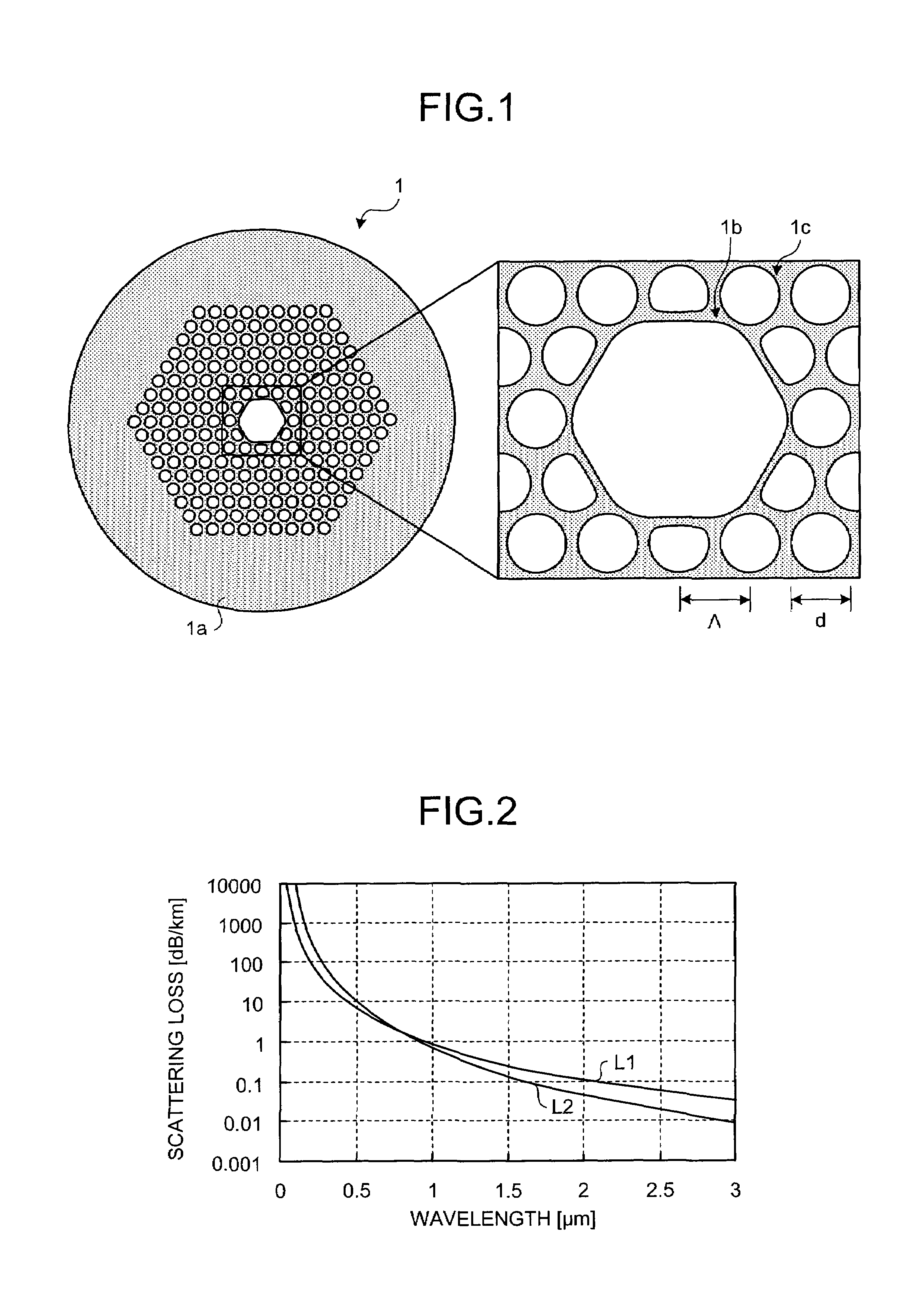
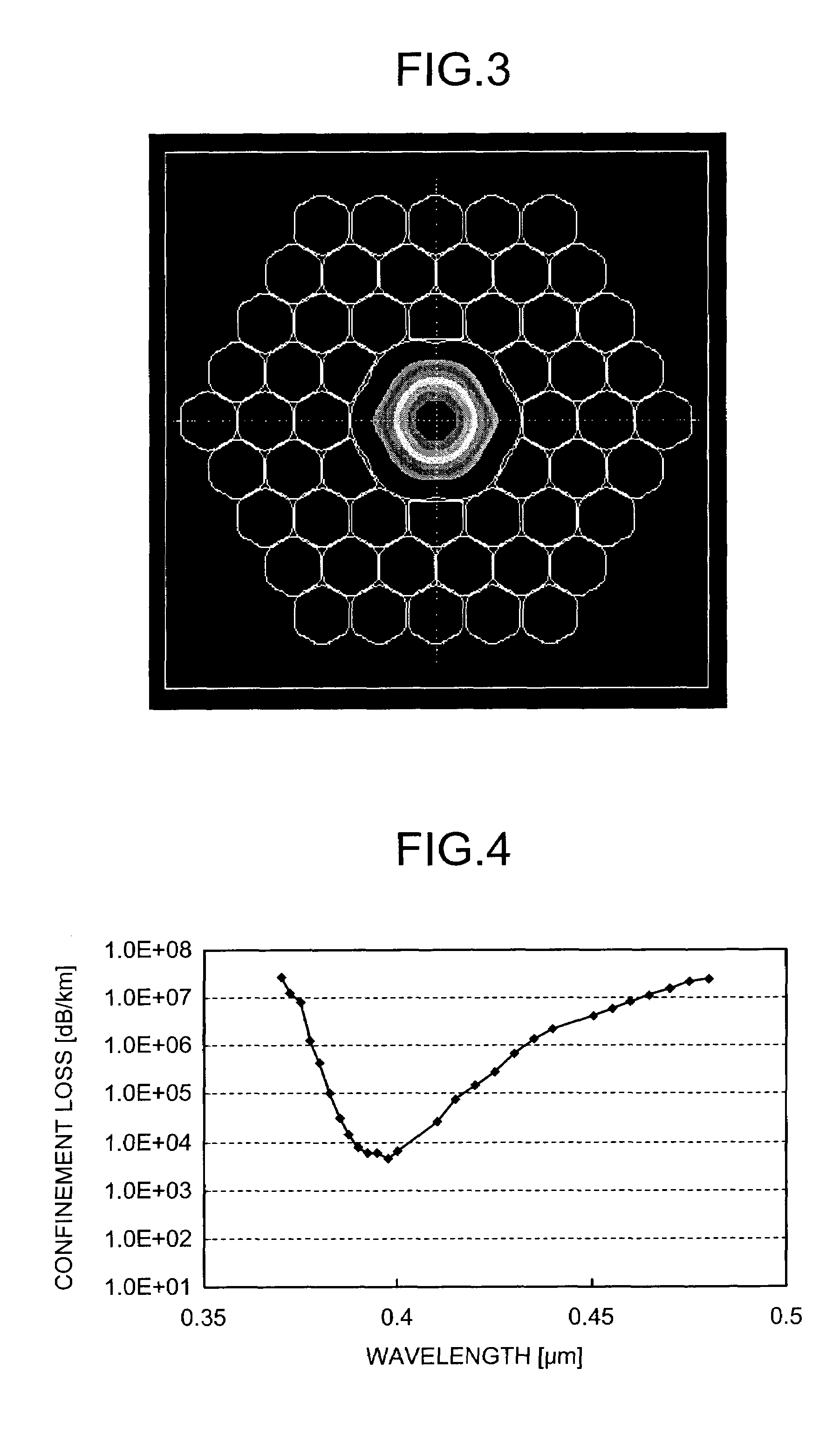
Photonic bandgap fiber
InactiveUS7657141B2Cladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guidePhotonic bandgapScattering loss
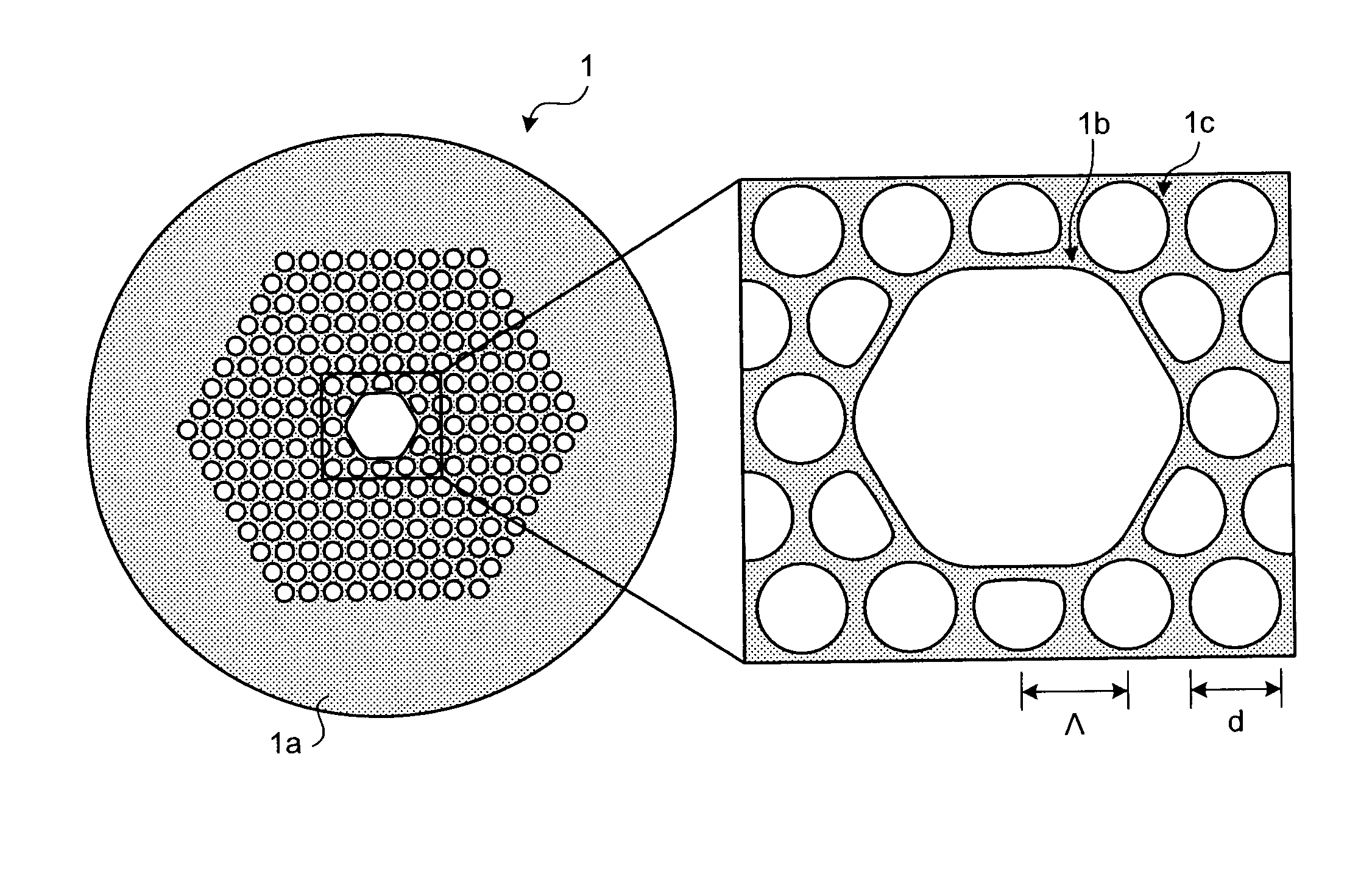
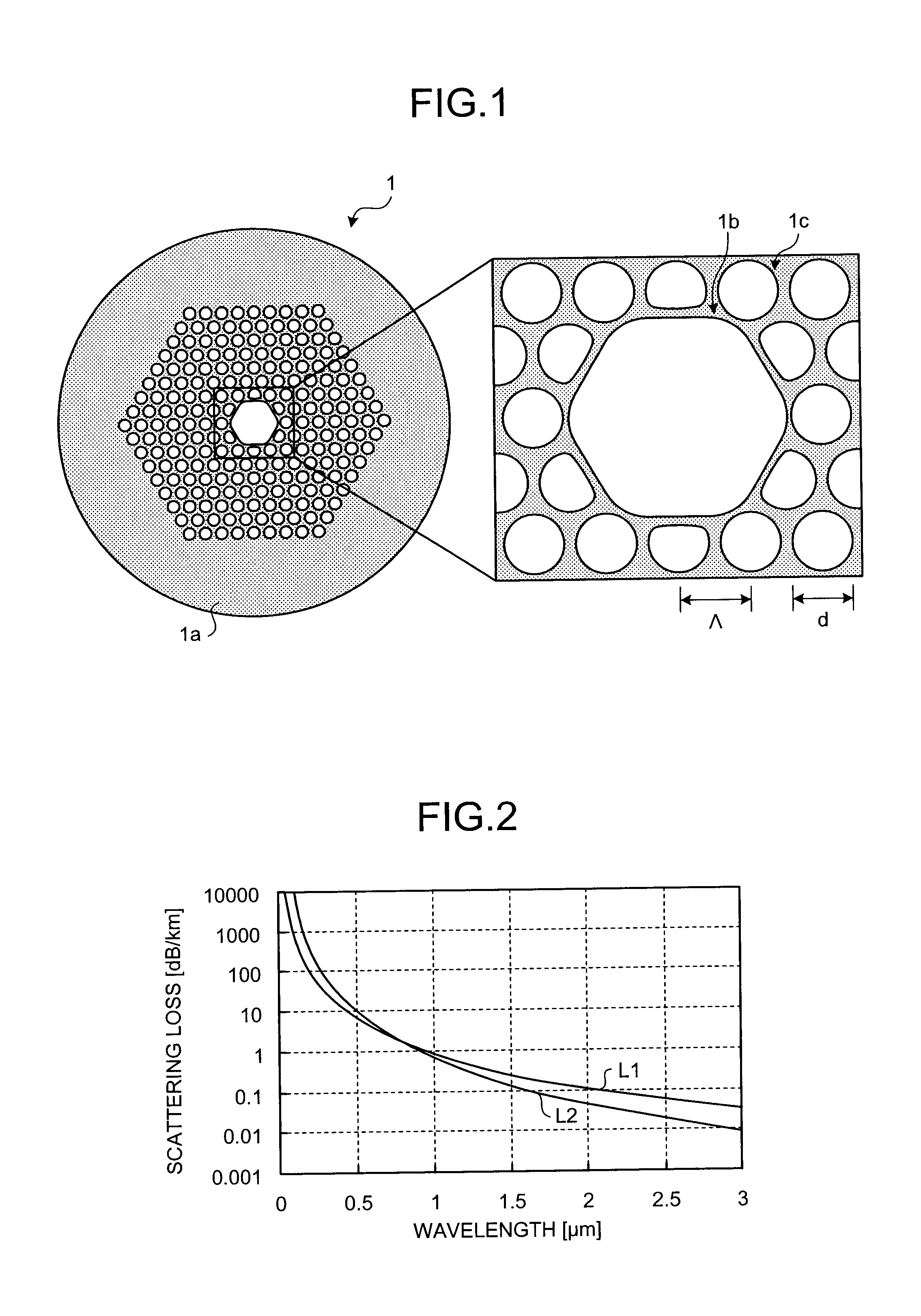
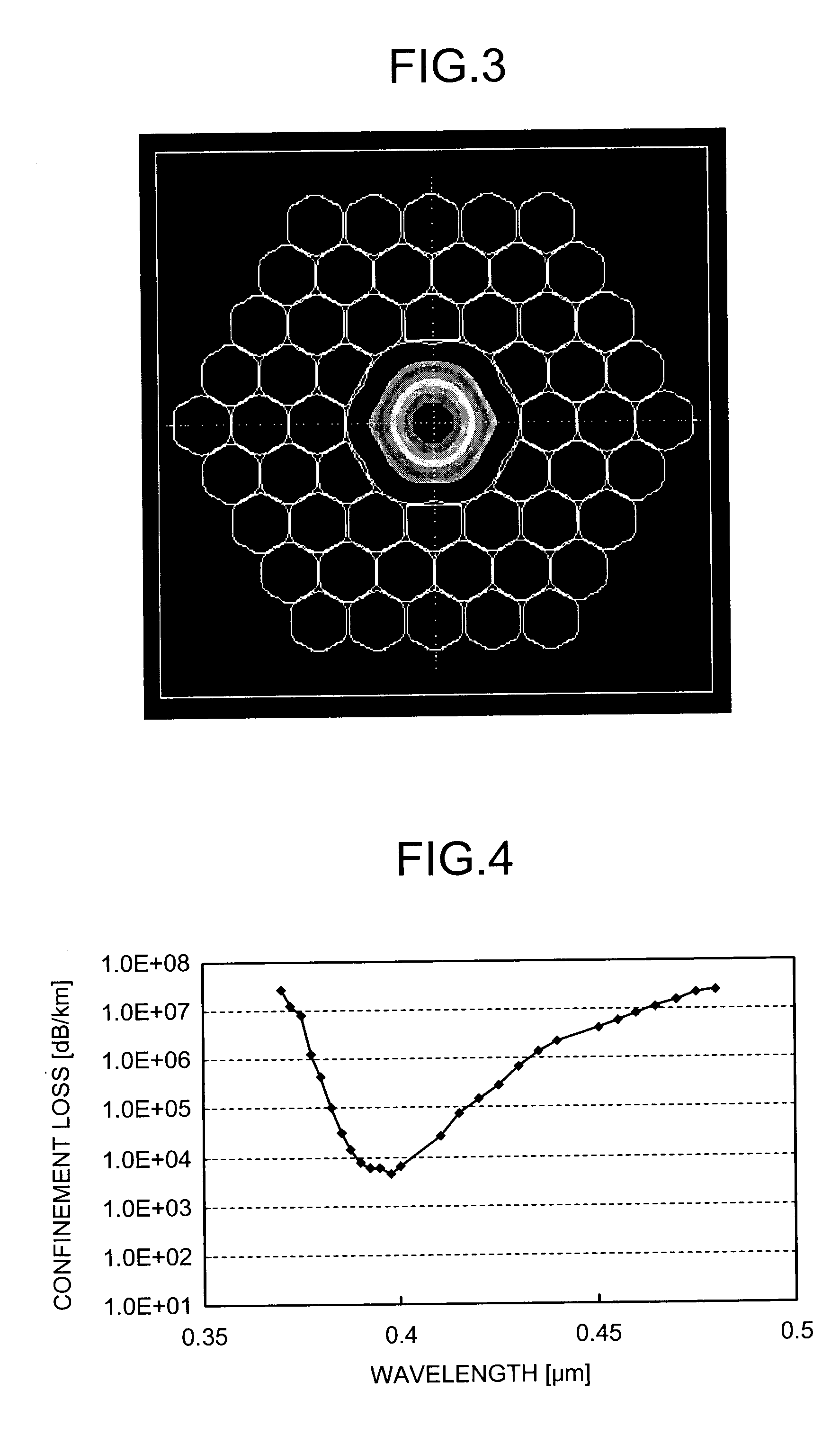
A photonic bandgap fiber includes a hollow core formed along a center axis of the photonic bandgap fiber, through which a light propagates and a cladding region made of silica glass. The cladding region includes air holes forming a triangular lattice arranged around the hollow core. A lattice constant of the triangular lattice of the air holes Λ is equal to or smaller than 2.1 μm. Confinement loss in a predetermined wavelength range including a center wavelength of a photonic bandgap is lower than scattering loss.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
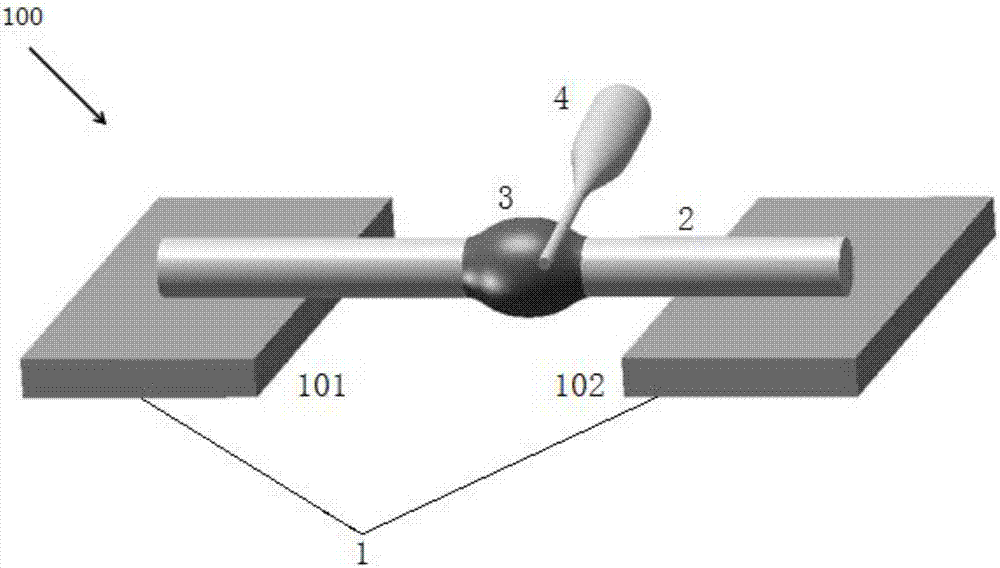
Micro-fiber probe loss modulation-based polymer bottle micro-cavity single-mode laser component
ActiveCN107453196AInhibit outputCompact structureOptical resonator shape and constructionPhotoluminescenceScattering loss
The invention discloses a micro-fiber probe loss modulation-based polymer bottle micro-cavity single-mode laser component. The single-mode laser component comprises a glass slide, a micro-fiber, a polymer bottle micro-cavity and a pumping fiber probe, wherein the glass slide comprises a first glass slide and a second glass slide which are arranged in parallel, two ends of the micro-fiber are respectively arranged on the first glass slide and the second glass slide, the polymer bottle micro-cavity sleeves a middle part of the micro-fiber, the pumping fiber probe is arranged on the polymer bottle micro-cavity and is coupled to the polymer bottle micro-cavity, the polymer bottle micro-cavity is formed by curing a resin solution, and the constituent of the resin solution comprises a laser gain substance, a macromolecule organic solvent, high-viscosity resin and a curing agent. The single-mode laser component is implemented by changing a coupling position of the pumping fiber probe on an axial direction of the polymer bottle micro-cavity; and since great scattering loss is caused by photoluminescence of the pumping light probe at the coupling position, a high-order laser mode is pressured, a base mode in a symmetric center of the cavity is only simulated, so that the output of single-mode laser is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Ultra low-loss CMOS compatible silicon waveguides
ActiveUS20070280616A1Reduce lossReduce light lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideSurface layerScattering loss
A low loss optical waveguiding structure for silicon-on-insulator (SOI)-based arrangements utilizes a tri-material configuration including a rib / strip waveguide formed of a material with a refractive index less than silicon, but greater than the refractive index of the underlying insulating material. In one arrangement, silicon nitride may be used. The index mismatch between the silicon surface layer (the SOI layer) and the rib / strip waveguide results in a majority of the optical energy remaining within the SOI layer, thus reducing scattering losses from the rib / strip structure (while the rib / strip allows for guiding along a desired signal path to be followed). Further, since silicon nitride is an amorphous material without a grain structure, this will also reduce scattering losses. Advantageously, the use of silicon nitride allows for conventional CMOS fabrication processes to be used in forming both passive and active devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Photonic bandgap fiber
InactiveUS20090080845A1Cladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guidePhotonic bandgapScattering loss
A photonic bandgap fiber includes a hollow core formed along a center axis of the photonic bandgap fiber, through which a light propagates and a cladding region made of silica glass. The cladding region includes air holes forming a triangular lattice arranged around the hollow core. A lattice constant of the triangular lattice of the air holes Λ is equal to or smaller than 2.1 μm. Confinement loss in a predetermined wavelength range including a center wavelength of a photonic bandgap is lower than scattering loss.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Etching method of silicon chip grooves for optical waveguide
ActiveCN105589131AReduce transmission lossGood resistance to dry etchingOptical light guidesScattering lossSilicon oxide
The invention discloses an etching method of silicon chip grooves for an optical waveguide. The method includes: S1: a dielectric layer and a shielding layer are deposited on the surface of a silicon substrate in sequence, the dielectric layer is a silicon oxide layer or a silicon nitride layer, and the shielding layer is a polysilicon layer or an amorphous silicon layer; S2: shielding patterns of photoresist are formed on the surface of the shielding layer by employing a silicon groove processing photoetching mask; S3: the first etching of the shielding layer is performed by employing a dry method plasma etching process; S4: the polysilicon layer or the amorphous silicon layer after the first etching is regarded as the shielding layer, and the second etching of the dielectric layer is performed; S5: the shielding patterns of the photoresist are formed on the surface of the bare silicon substrate by employing a reverse mask of the silicon groove processing photoetching mask, and the third etching is performed; and S6: the residual dielectric layer is regarded as the shielding layer for silicon etching to obtain the required silicon grooves. According to the method, the roughness of sidewalls of the silicon grooves can be greatly improved, and the scattering loss and the transmission loss of the silicon-based optical waveguide are reduced.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 23 RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com