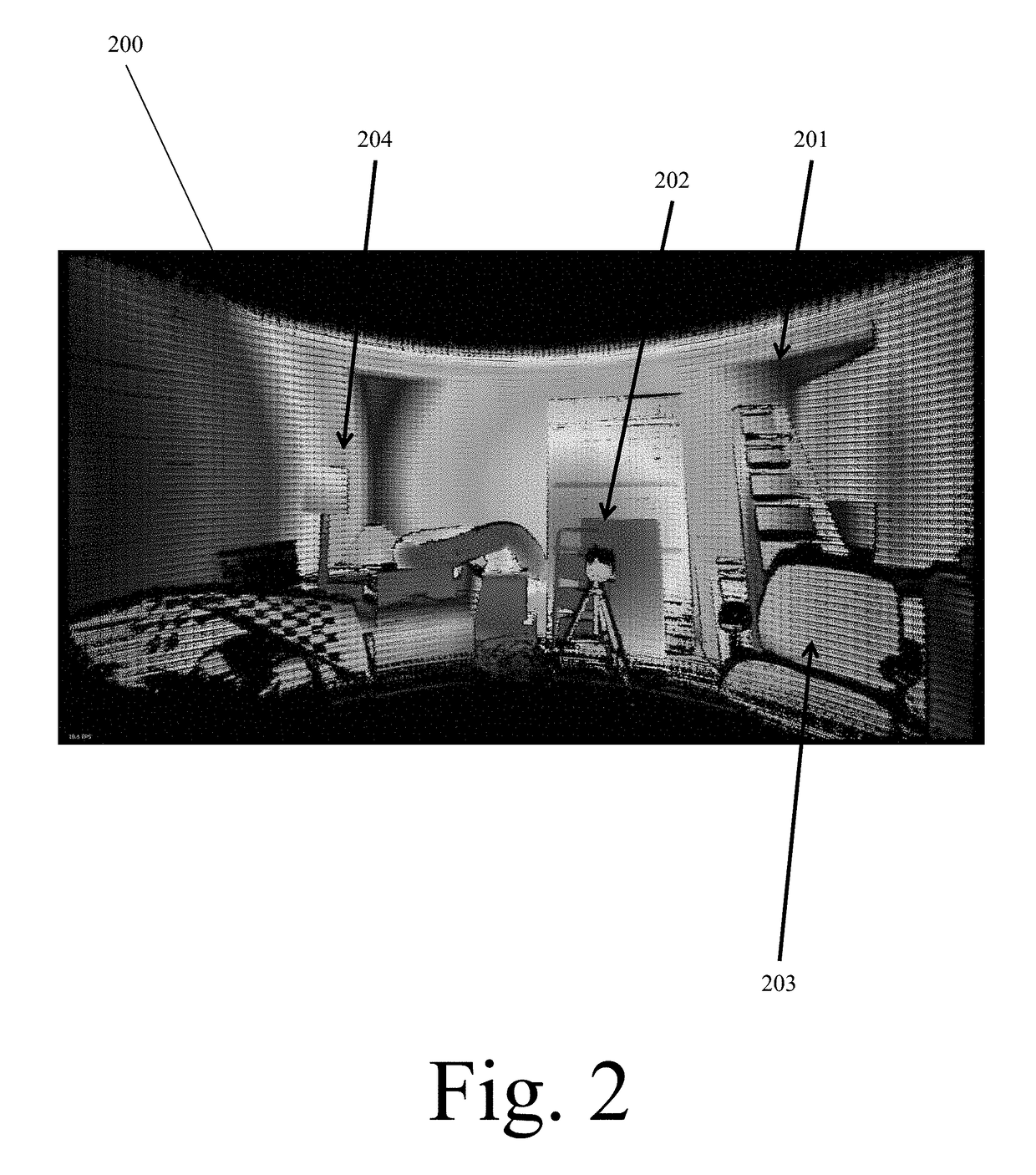
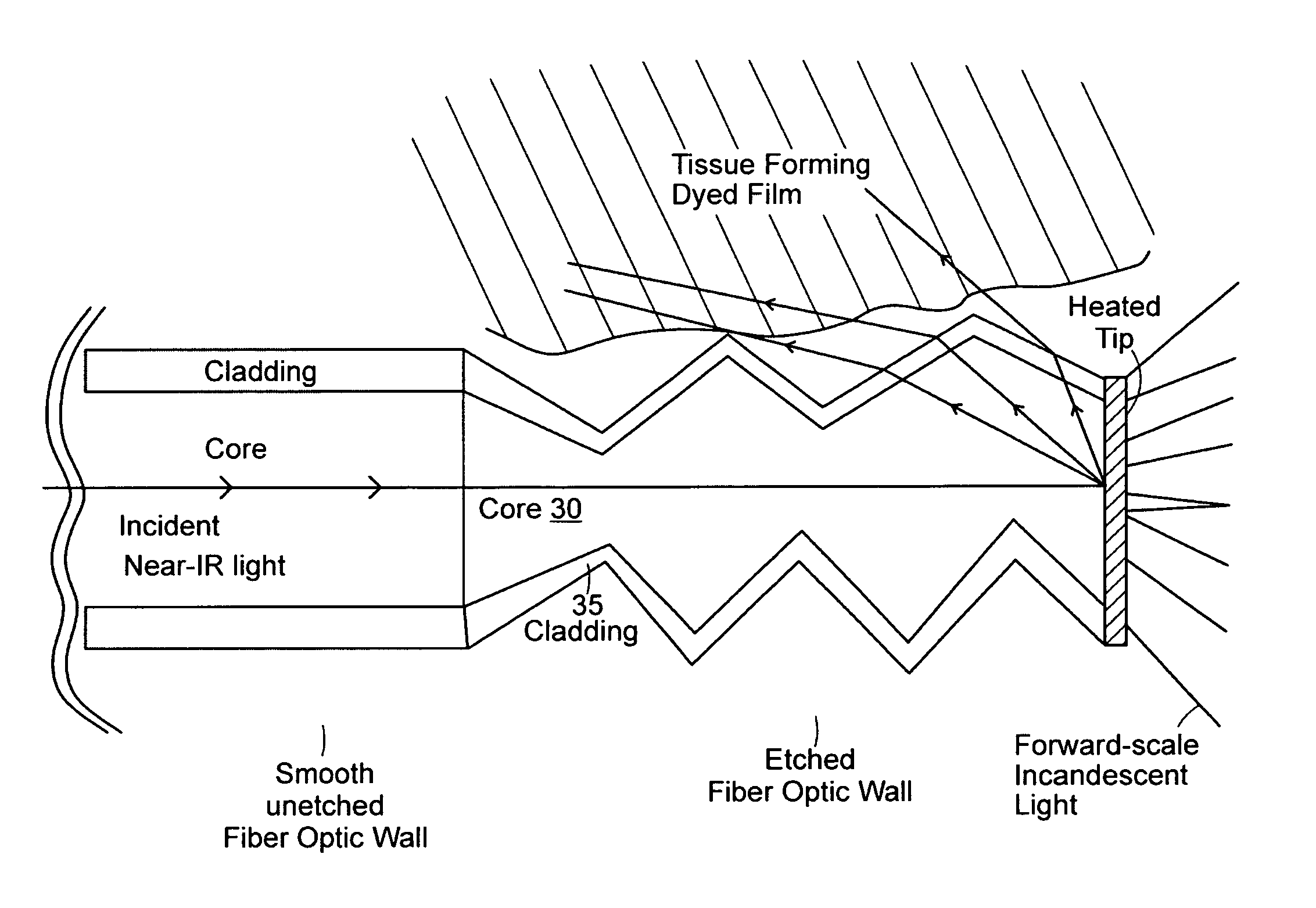
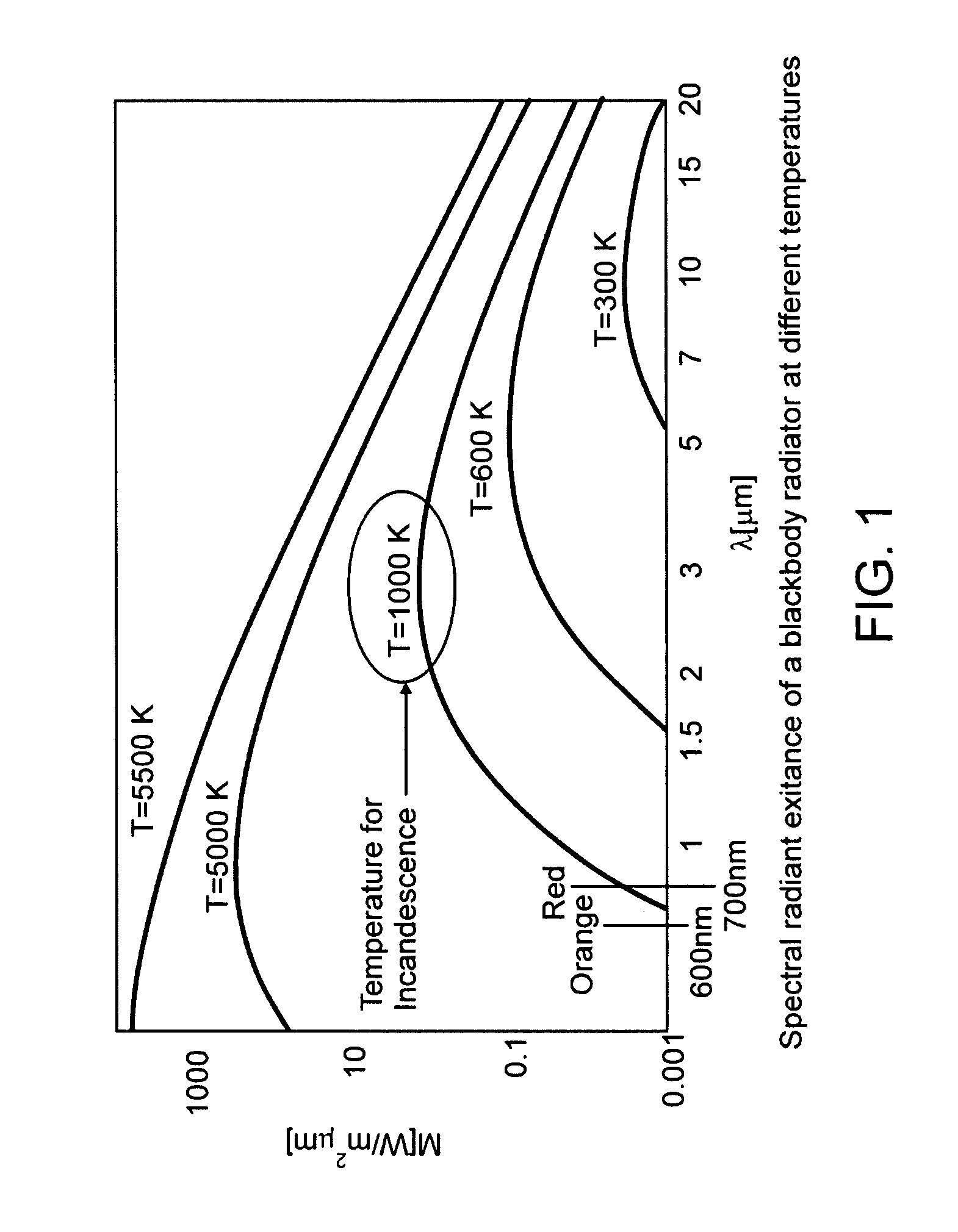
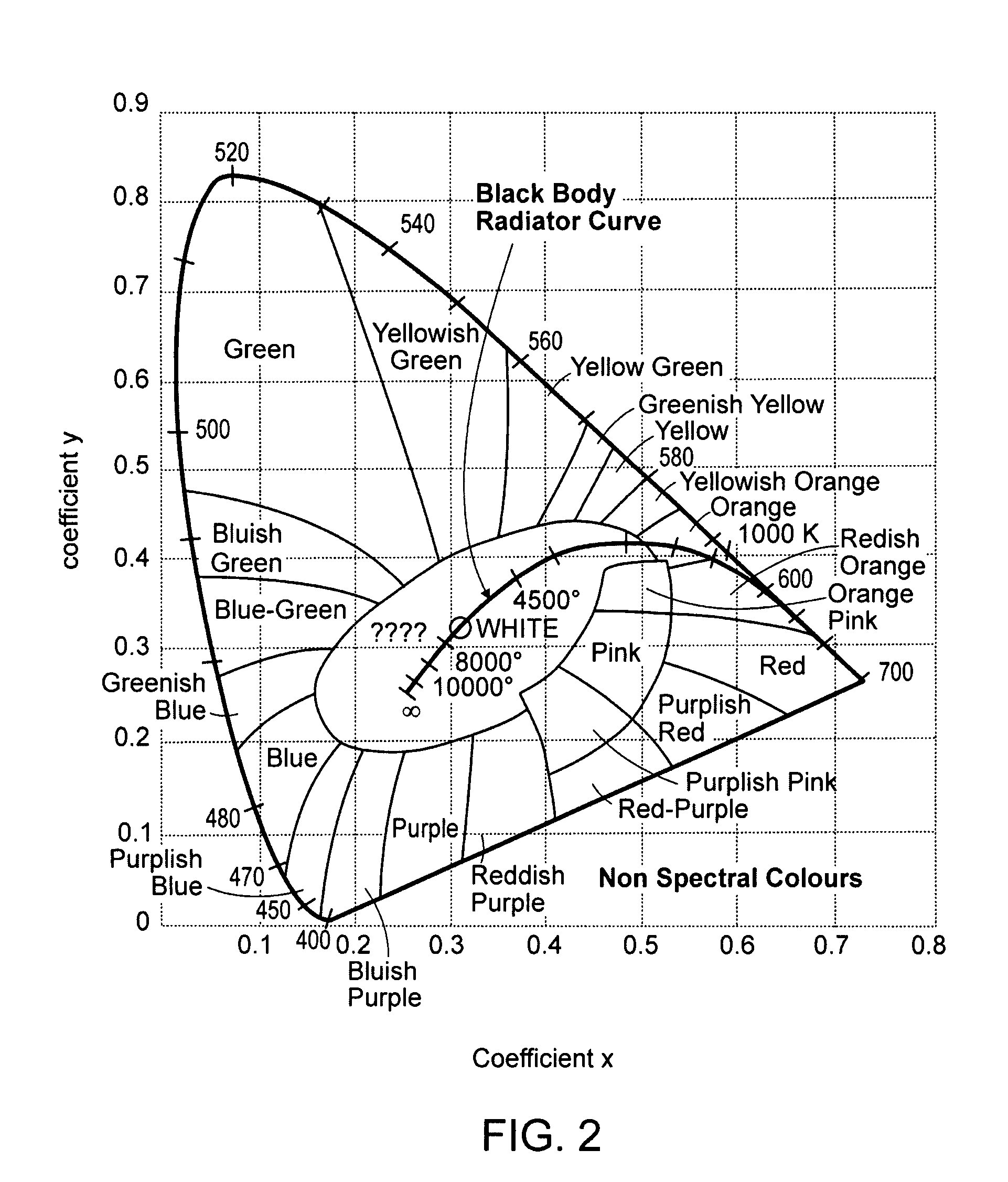
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
606 results about "Near infrared laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
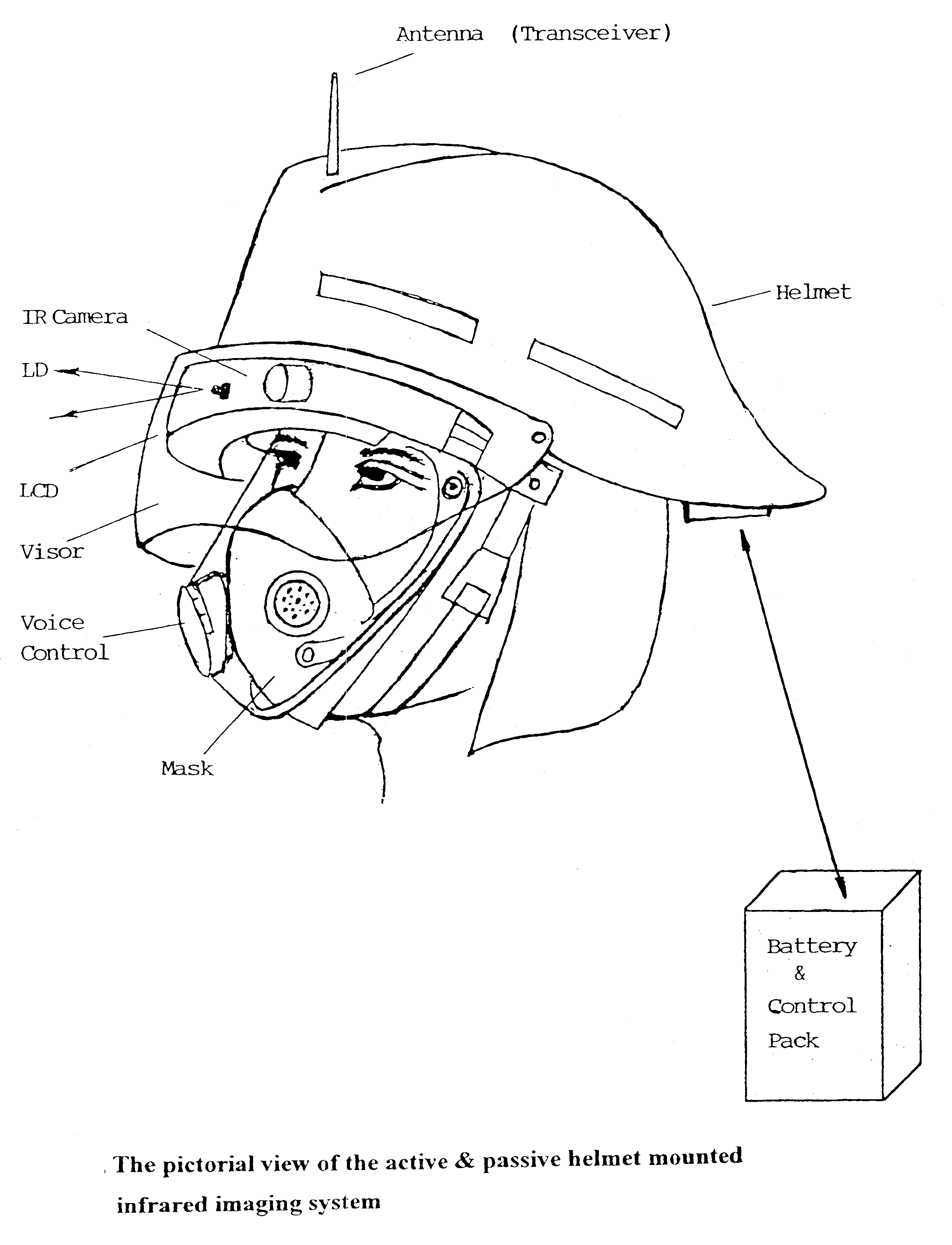
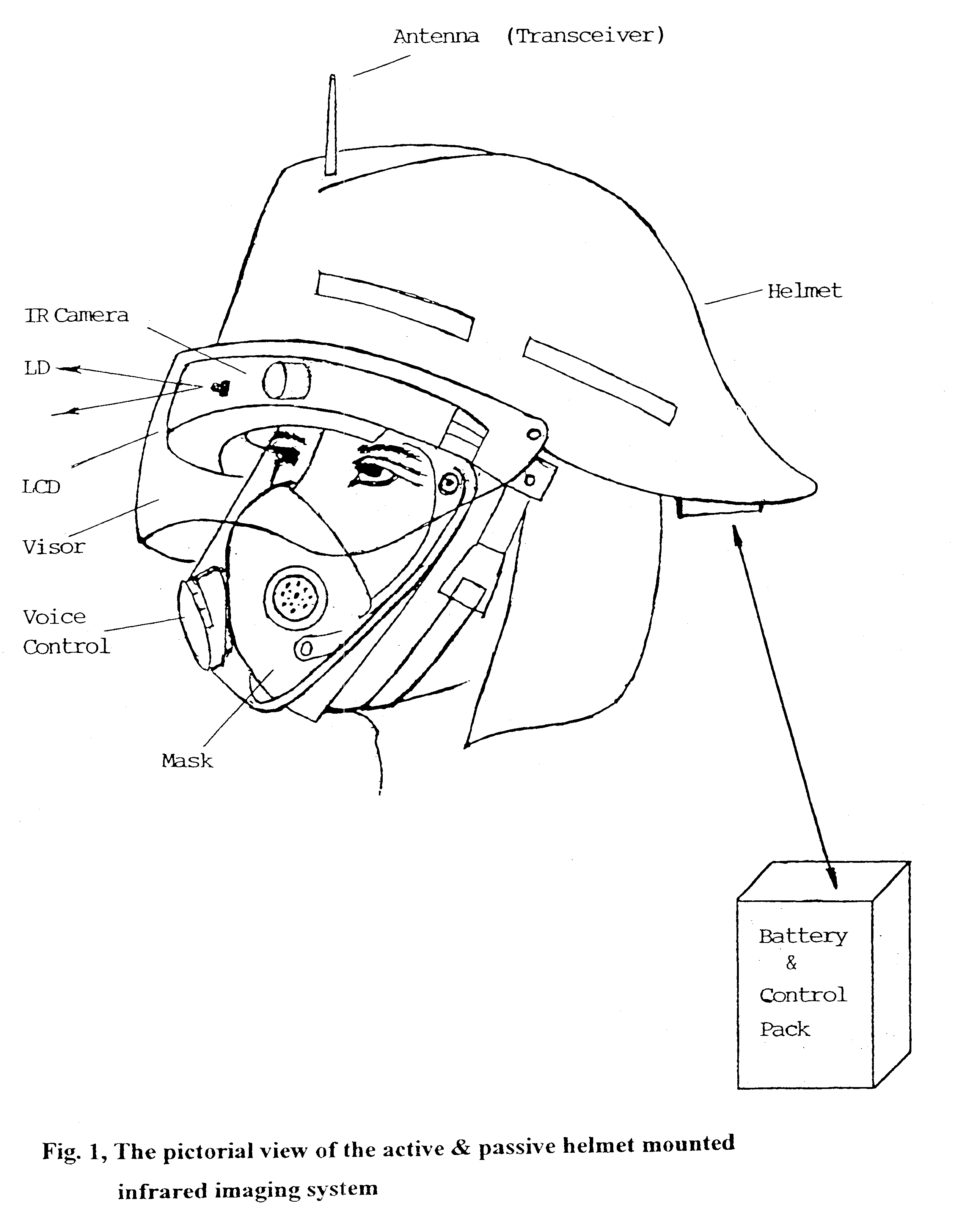
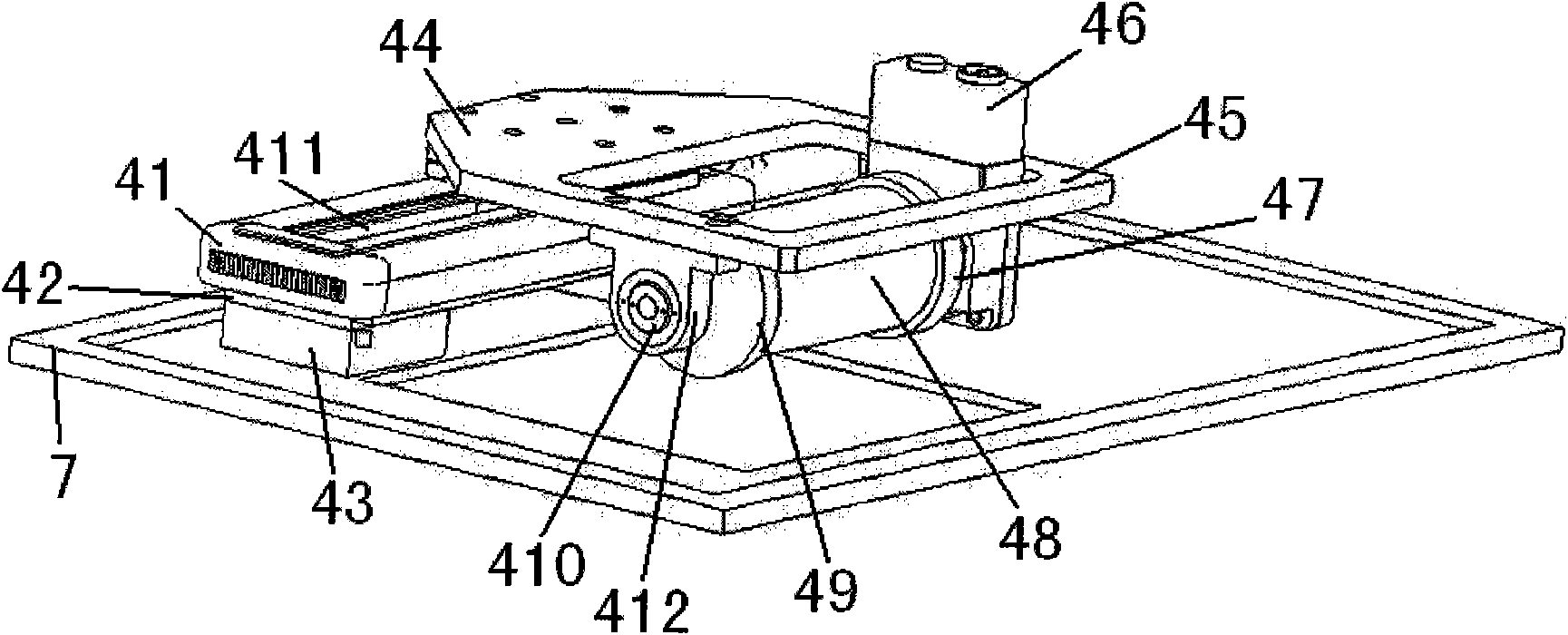
Head/helmet mounted passive and active infrared imaging system with/without parallax
InactiveUS6456261B1Television system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsTransceiverFocal Plane Arrays
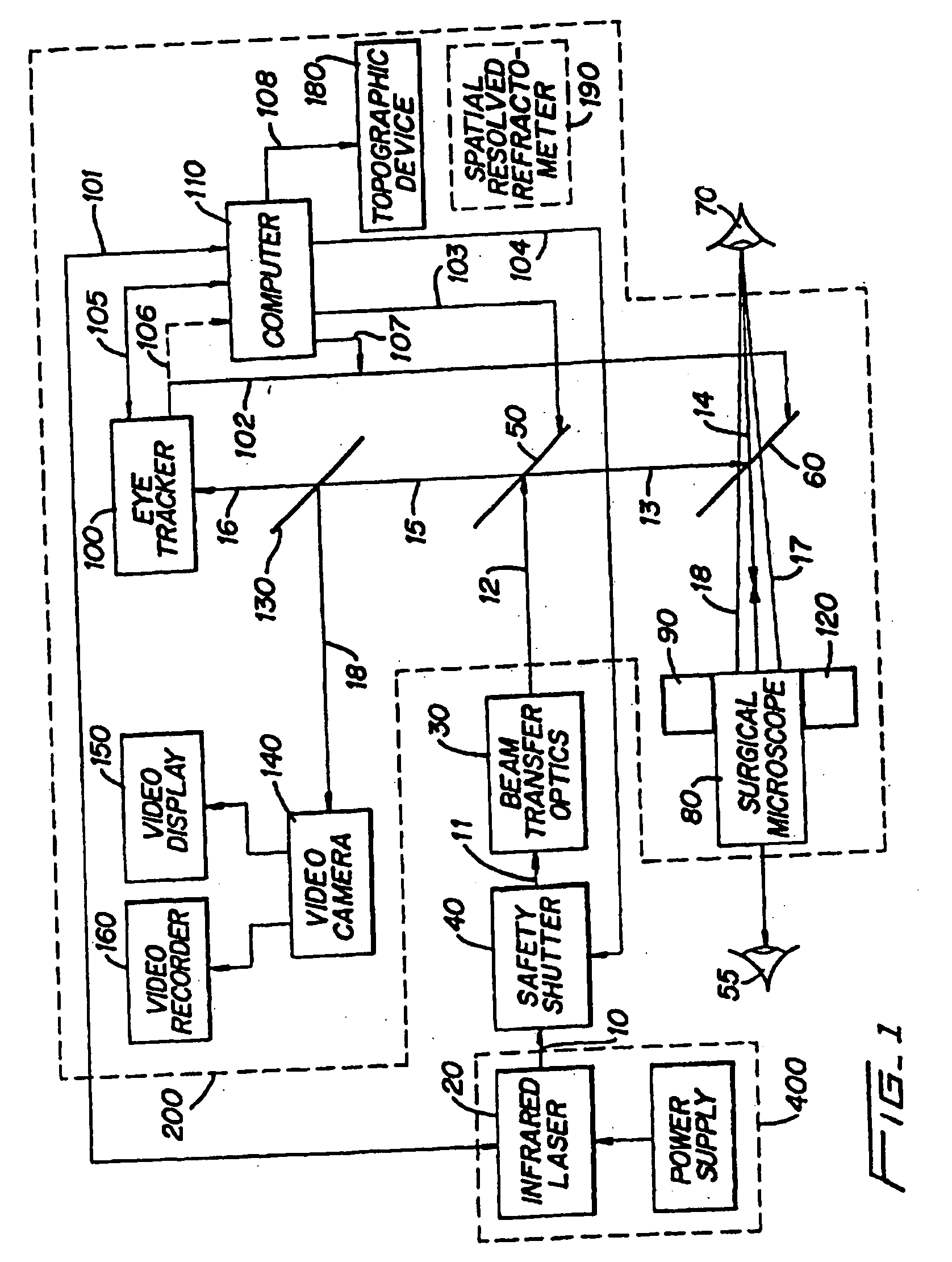
A passive / active infrared imaging system apparatus for mounting on a head / helmet includes a passive infrared camera Head Pack having a removable narrow band filter cover, an objective lens, a beam splitter, an uncooled focal plane array (UFPA) package, an interface board, and a display unit such a liquid crystal display (LCD), with forward / back, up / down, and tilt adjustment functions fitting any mask, mounted in the front of said head / helmet for converting infrared light images into electronic signals. An electronic unit coupled between the UFPA of the infrared camera and the display unit, includes a controller for processing video signals from the infrared camera and supplying them to the display unit. The electronic circuit includes a wireless video & audio transceiver, a piezoelectric microphone, a voice controller, and a neural network pattern recognition chip. The display unit (such as LCD)] is inside the head pack and mounted on the head / helmet for converting electronic signals into visible light images, so that it is in front of eyes of a user, so that the user can directly view an external scene without blocking his normal vision, if the optical axis of the display unit is aligned with the optical axis of the objective lens, the system parallax is eliminated. A Battery Pack having a video controller board and battery is mounted on the rear of the head / helmet so that it gives the video output and power to the infrared system. An eye-safe near infrared laser diode with corresponding optical and electronic attachments mounted on the head / helmet illuminates targets to get images through same passive infrared system.
Owner:ZHANG EVAN Y W
Optical Material and Method for Modifying the Refractive Index
InactiveUS20080001320A1Little and no scattering lossPositive changeSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, which exhibit little or no scattering loss. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, which exhibit little or no scattering loss and are characterized by a positive change in refractive index.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Ultraviolet, infrared, and near-infrared lidar system and method
Pushbroom and flash lidar operations outside the visible spectrum, most preferably in near-IR but also in IR and UV, are enabled by inserting—ahead of a generally conventional lidar receiver front end—a device that receives light scattered from objects and in response forms corresponding light of a different wavelength from the scattered light. Detailed implementations using arrays of discrete COTS components—most preferably PIN diodes and VCSELs, with intervening semicustom amplifiers—are discussed, as is use of a known monolithic converter. Differential and ratioing multispectral measurements, particularly including UV data, are enabled through either spatial-sharing (e. g. plural-slit) or time-sharing.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Device for optical monitoring of constituent in tissue or body fluid sample using wavelength modulation spectroscopy, such as for blood glucose levels
InactiveUS7356364B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce calculationMedical devicesCatheterConcentrations glucosePhotodetector
A device for monitoring the concentration level of a constituent in tissue or a body fluid sample, such as glucose concentration in blood, has a laser light source which is modulated about a center emission frequency to probe the absorption spectrum of the constituent being monitored, a laser driver circuit for tuning and modulating the laser light, a photodetector for detecting light from the laser light source transmitted through the sample as the modulation frequency of the laser is tuned, and a demodulator for demodulating the transmitted light and detecting variations in magnitude at harmonics of the modulation frequency to assess the concentration level of that constituent. The device utilizes short-wavelength near-infrared laser light to monitor blood glucose levels, and could also be used for drug screening and diagnosis of other medical conditions as well. In one embodiment, the device is used to monitor blood glucose level externally from the body and non-invasively by trans-illumination through a thin layer of skin, without the need for physical penetration of the skin. In another embodiment, the device is used as an intravenous sensor deployed through a catheter, and its output can be used to control an insulin pump to stabilize the patient's blood glucose levels.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
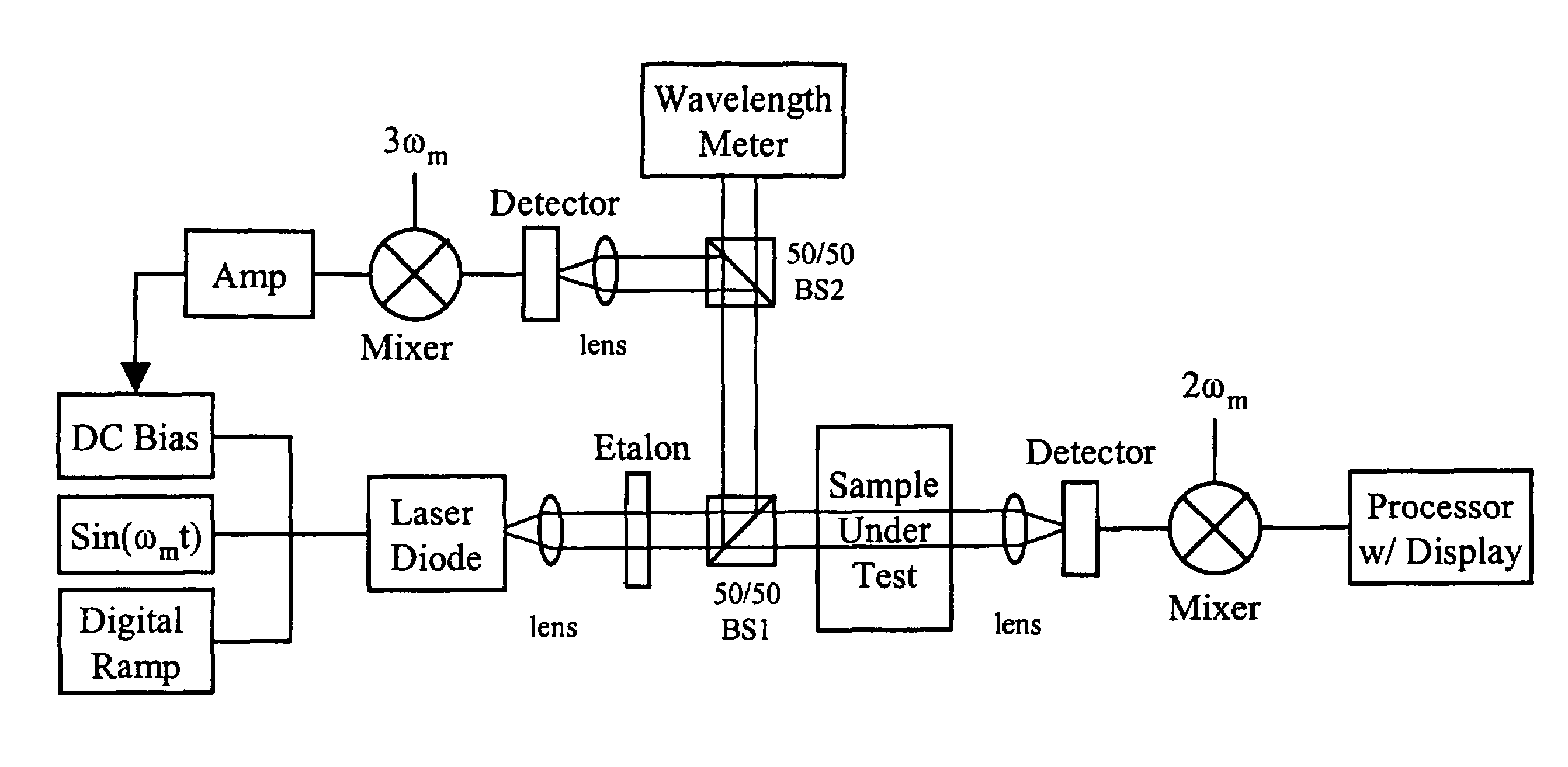
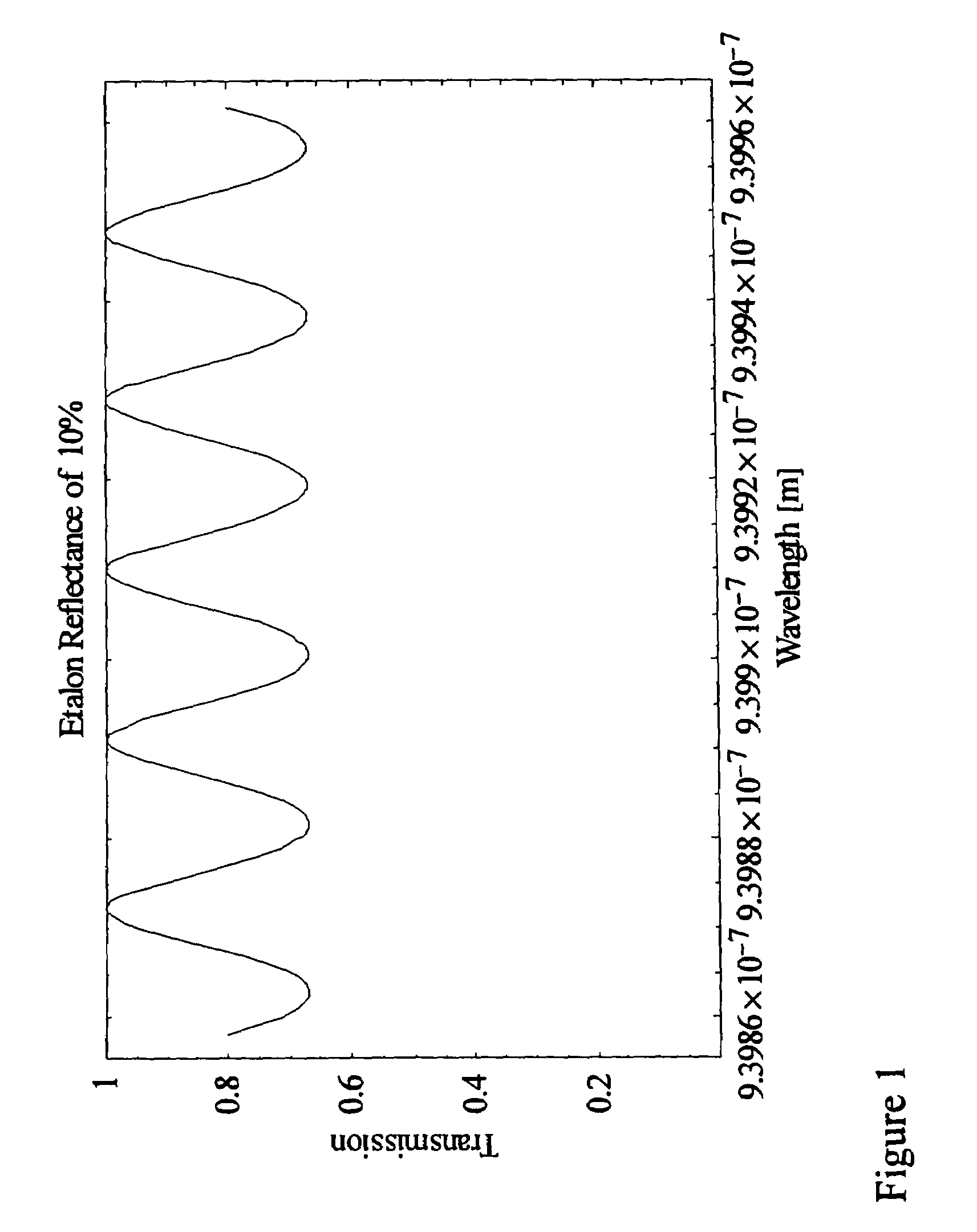
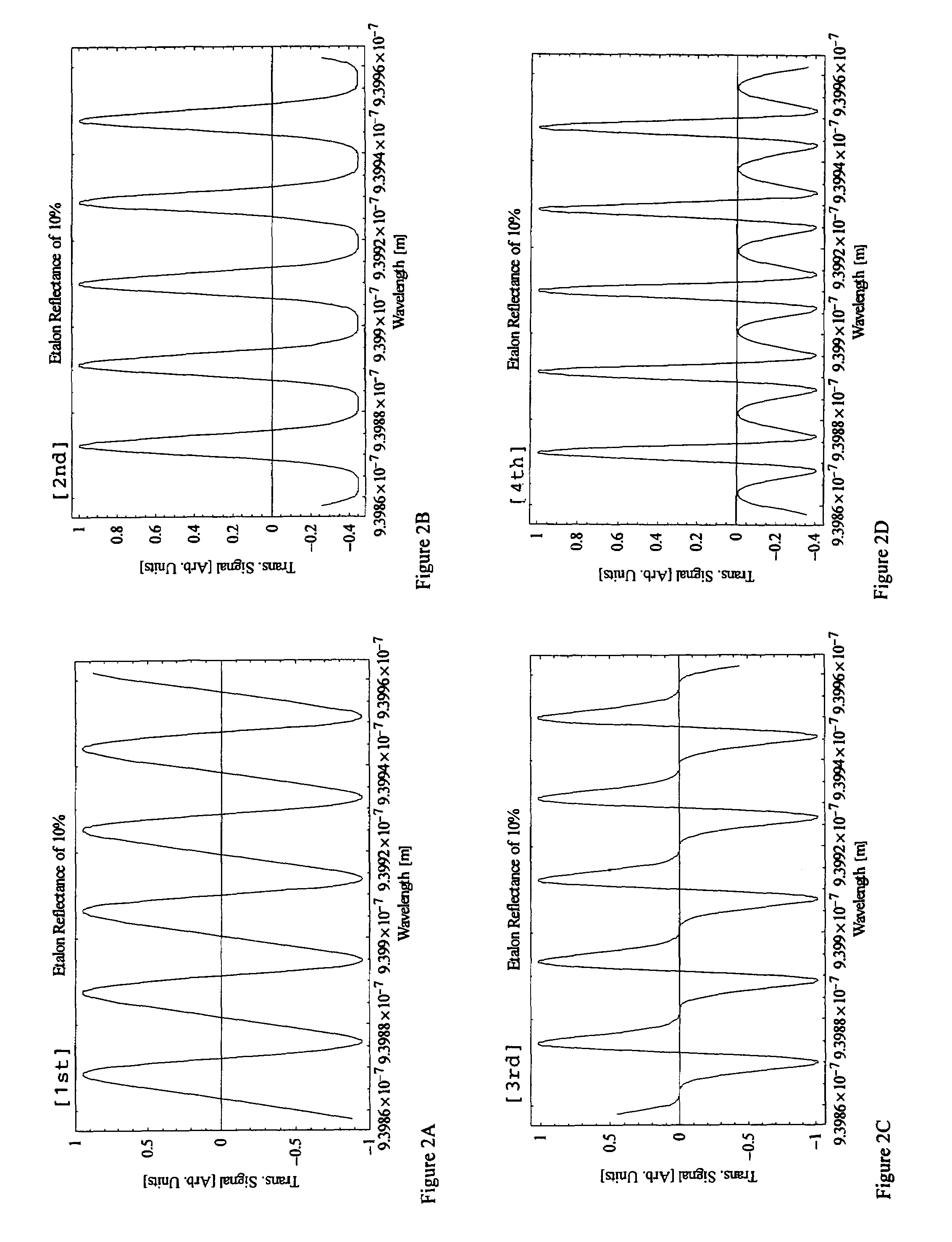
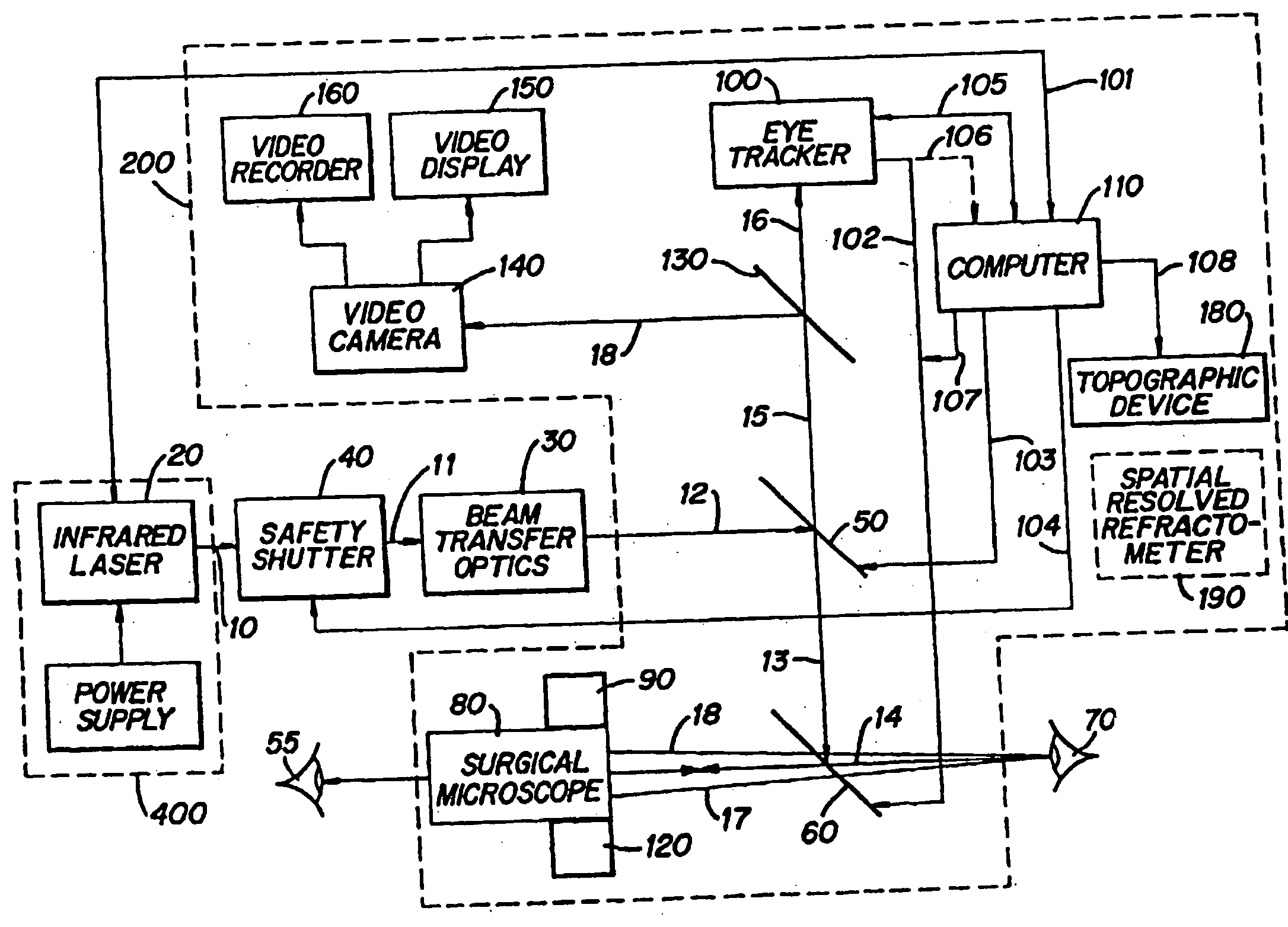
Method and apparatus for removing corneal tissue with infrared laser radiation and short pulse mid-infrared parametric generator for surgery
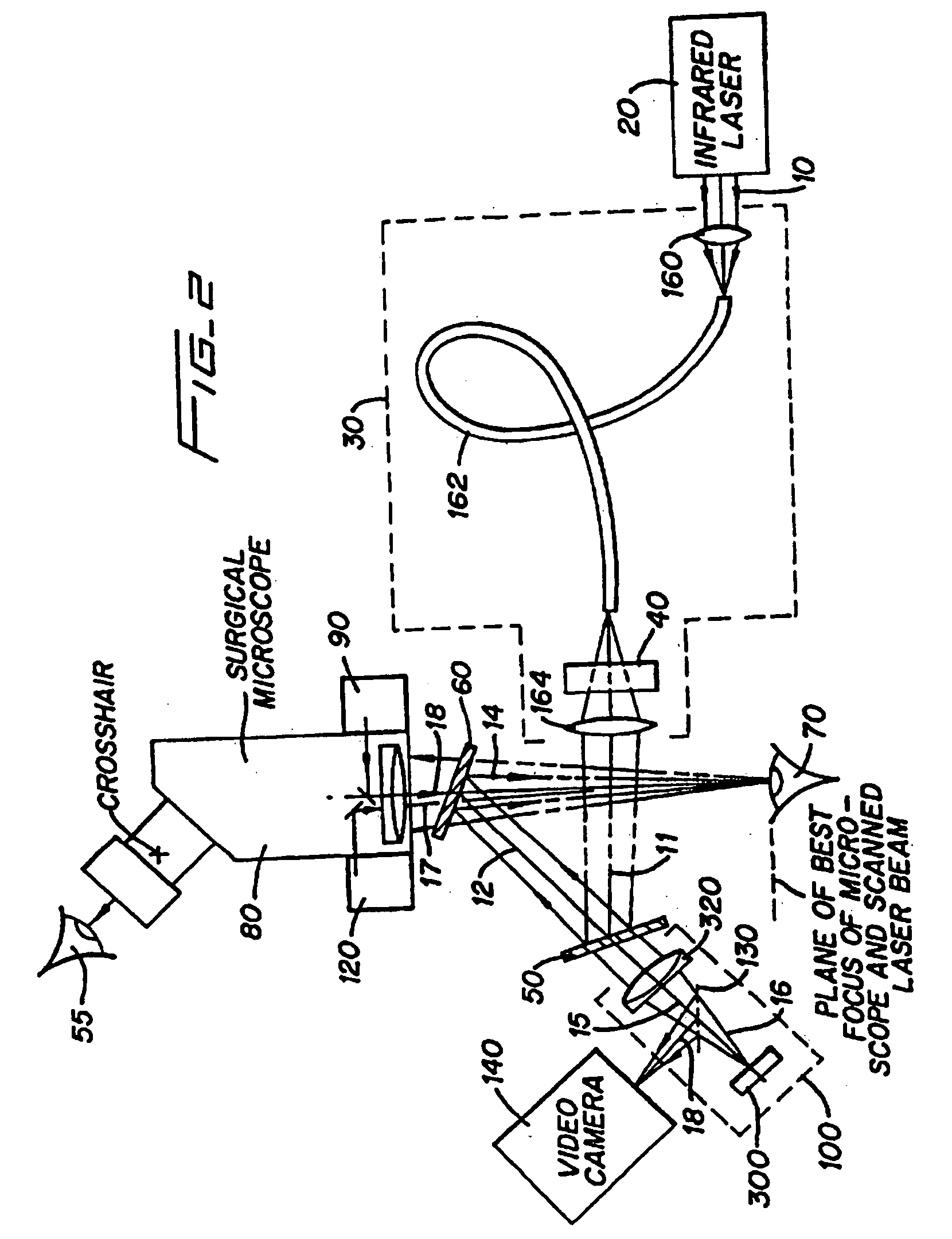
InactiveUS20050197655A1Reduce undesirable thermal damageMaximum flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelMid infrared laser
A surgical technique for removing corneal tissue with scanned infrared radiation is disclosed which utilizes short mid-infrared laser pulses to provide a tissue removal mechanism based on photospallation. Photospallation is a photomechanical ablation mechanism which results from the absorption of incident radiation by the corneal tissue. Since photospallation is a mechanical ablation process, very little heat is generated in the unablated adjacent tissue. The disclosed surgical system includes a scanning beam delivery system which allows uniform irradiation of the treatment region and utilizes low energy outputs to achieve controlled tissue removal. A real-time servo-controlled dynamic eye tracker, based on a multiple-detector arrangement, is also disclosed which senses the motion of the eye and provides signals that are proportional to the errors in the lateral alignment of the eye relative to the axis of the laser beam. Temporal and frequency discrimination are preferably utilized to distinguish the tracking illumination from the ambient illumination and the surgical laser beam. A laser parametric generator for surgical applications is disclosed which utilizes short-pulse, mid-infrared radiation. The mid-infrared radiation may be produced by a pump laser source, such as a neodymium-doped laser, which is parametrically down converted in a suitable nonlinear crystal to the desired mid-infrared range. The short pulses reduce unwanted thermal effects and changes in adjacent tissue to potentially submicron-levels. The parametrically converted radiation source preferably produces pulse durations shorter than 25 ns at or near 3.0 microns but preferably close to the water absorption maximum associated with the tissue. The down-conversion to the desired mid-infrared wavelength is preferably produced by a nonlinear crystal such as KTP or its isomorphs. In one embodiment, a non-critically phased-matched crystal is utilized to shift the wavelength from a near-infrared laser source emitting at or around 880 to 900 nm to the desired 2.9-3.0 microns wavelength range. A fiber, fiber bundle or another waveguide means utilized to separate the pump laser from the optical parametric oscillation (OPO) cavity is also included as part of the invention.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Ultraviolet, infrared, and near-infrared lidar system and method
ActiveUS20070024840A1Eliminate the problemOptical rangefindersCharacter and pattern recognitionInfraredFrequency spectrum
Pushbroom and flash lidar operations outside the visible spectrum, most preferably in near-IR but also in IR and UV, are enabled by inserting—ahead of a generally conventional lidar receiver front end—a device that receives light scattered from objects and in response forms corresponding light of a different wavelength from the scattered light. Detailed implementations using arrays of discrete COTS components—most preferably PIN diodes and VCSELs, with intervening semicustom amplifiers—are discussed, as is use of a known monolithic converter. Differential and ratioing multispectral measurements, particularly including UV data, are enabled through either spatial-sharing (e. g. plural-slit) or time-sharing.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Optical material and method for modifying the refractive index
ActiveUS7789910B2Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, wherein the refractive structures are characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
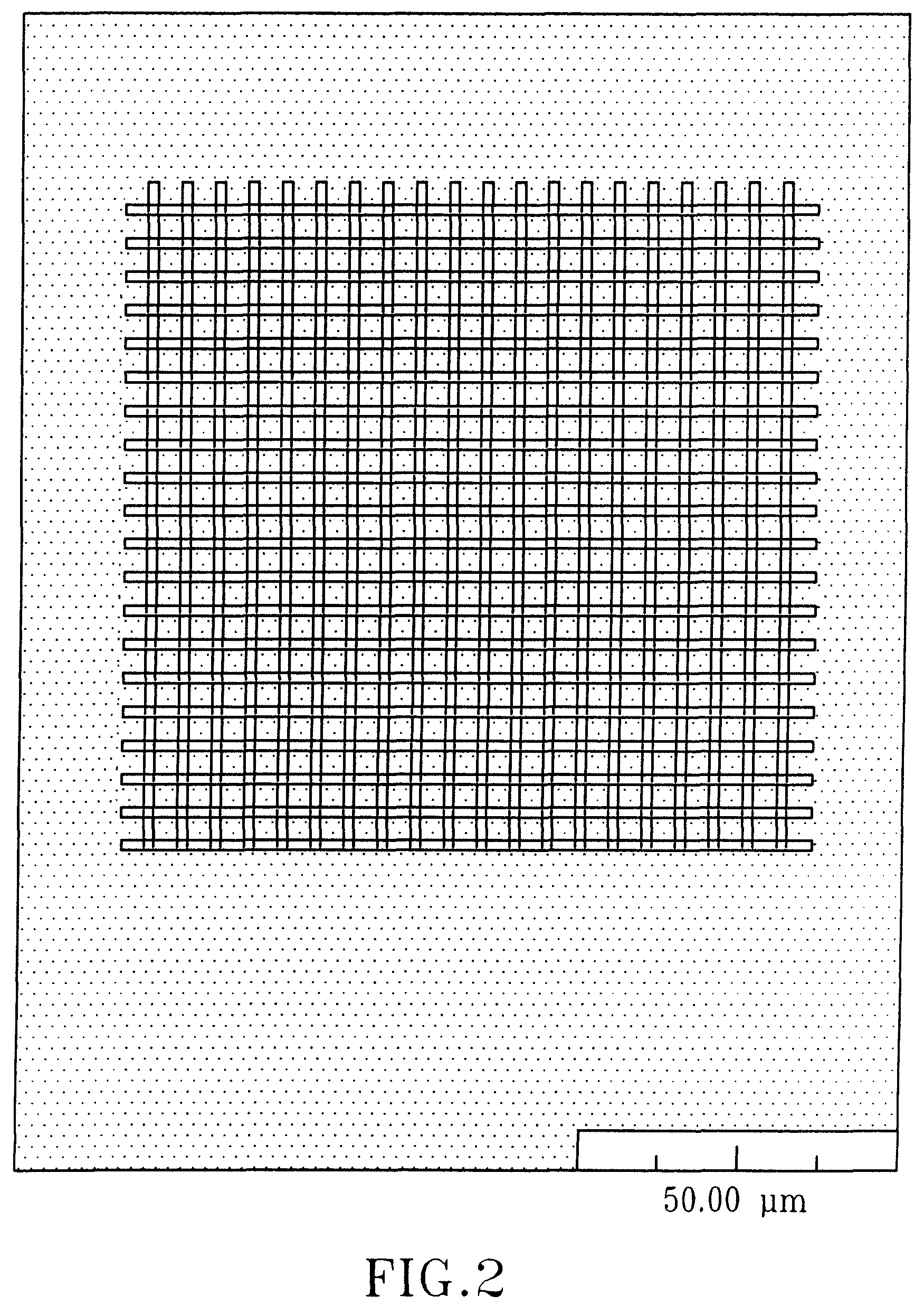
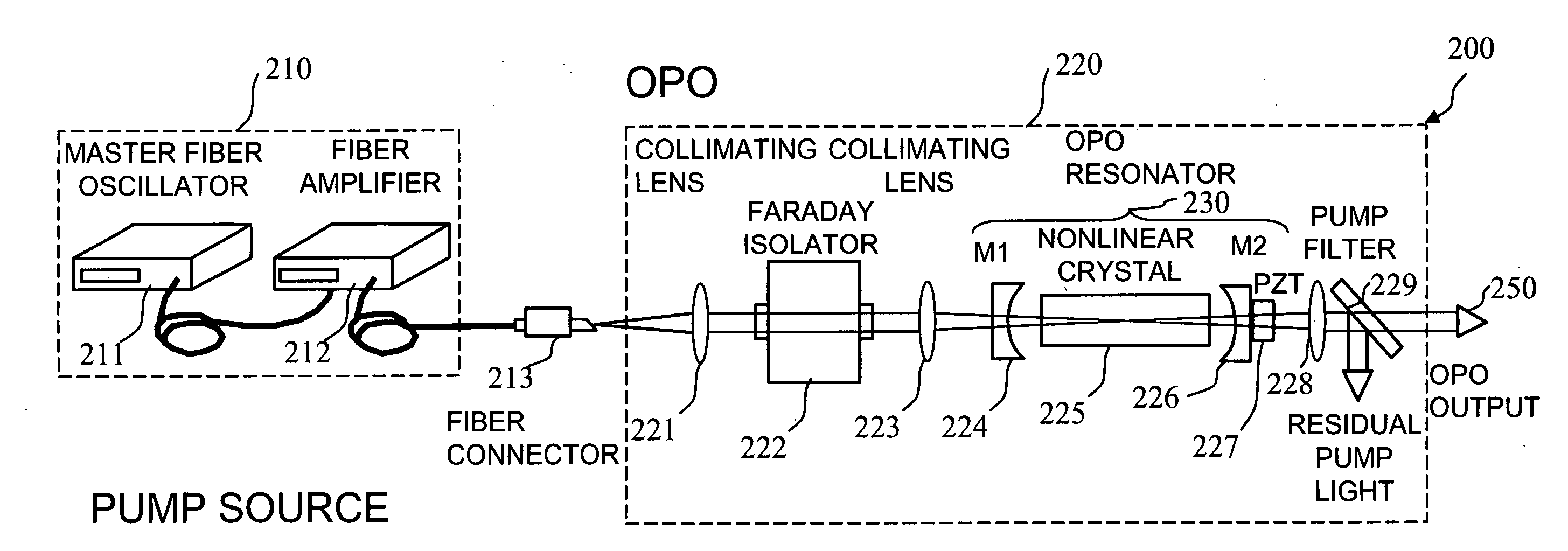
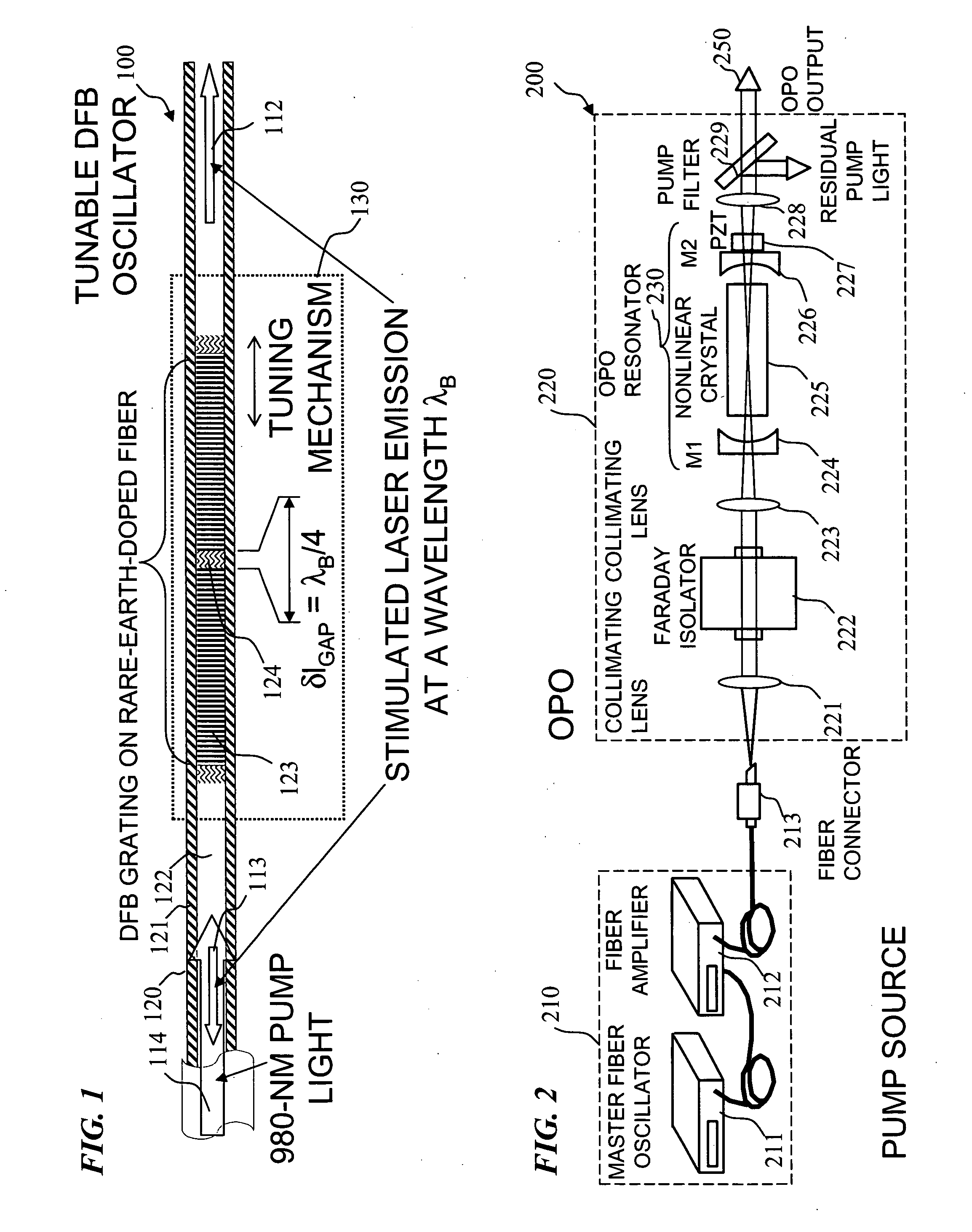
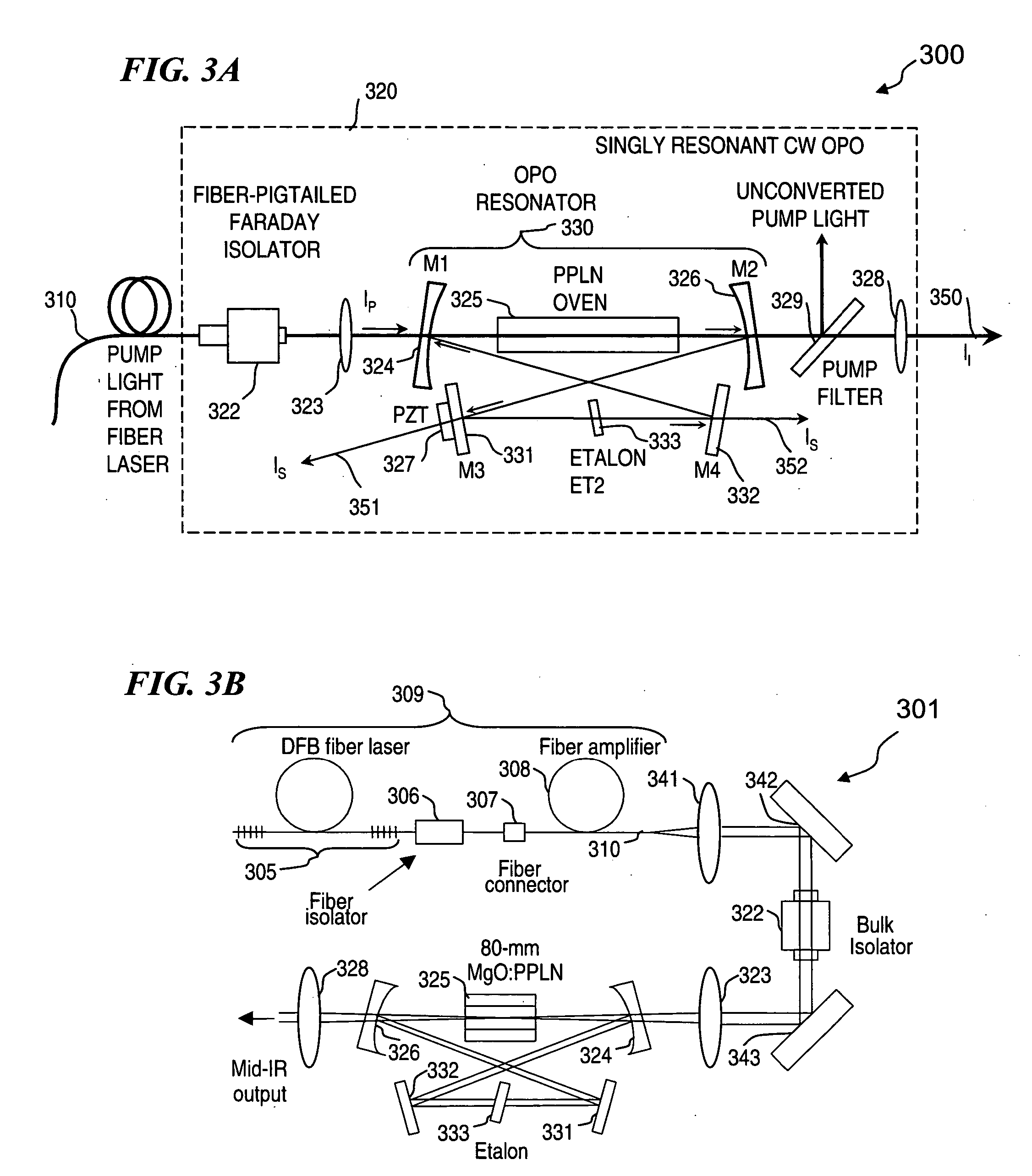
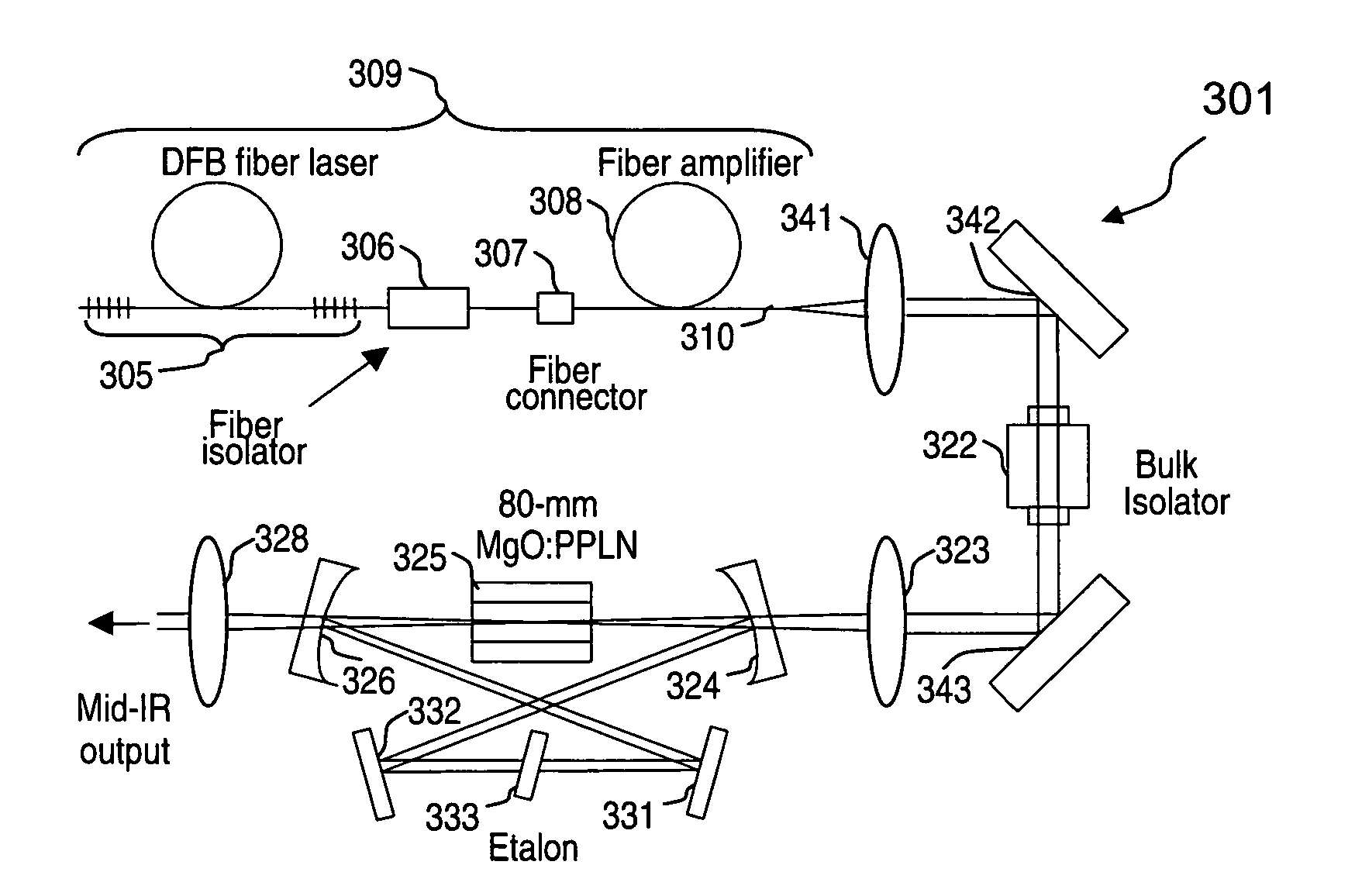
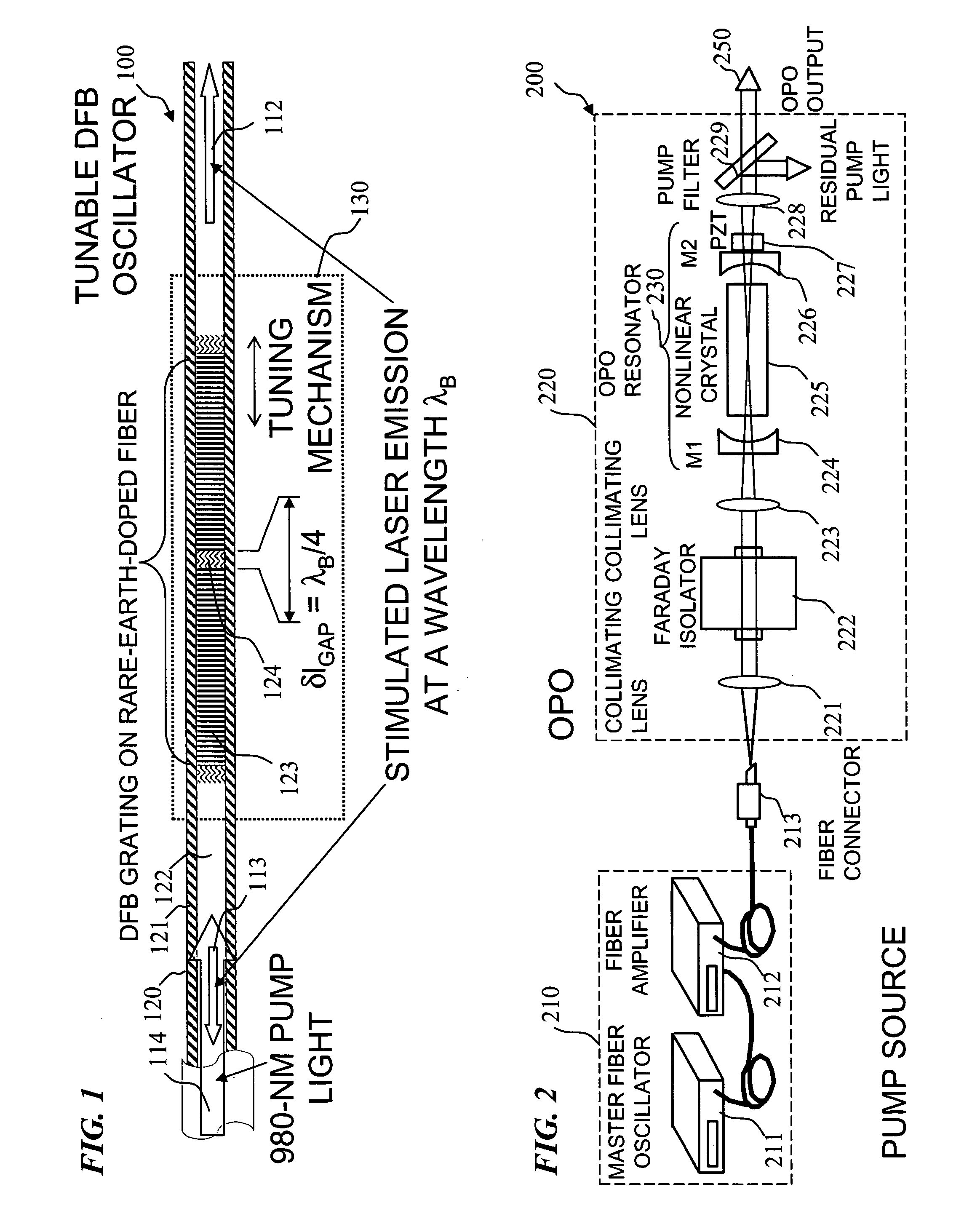
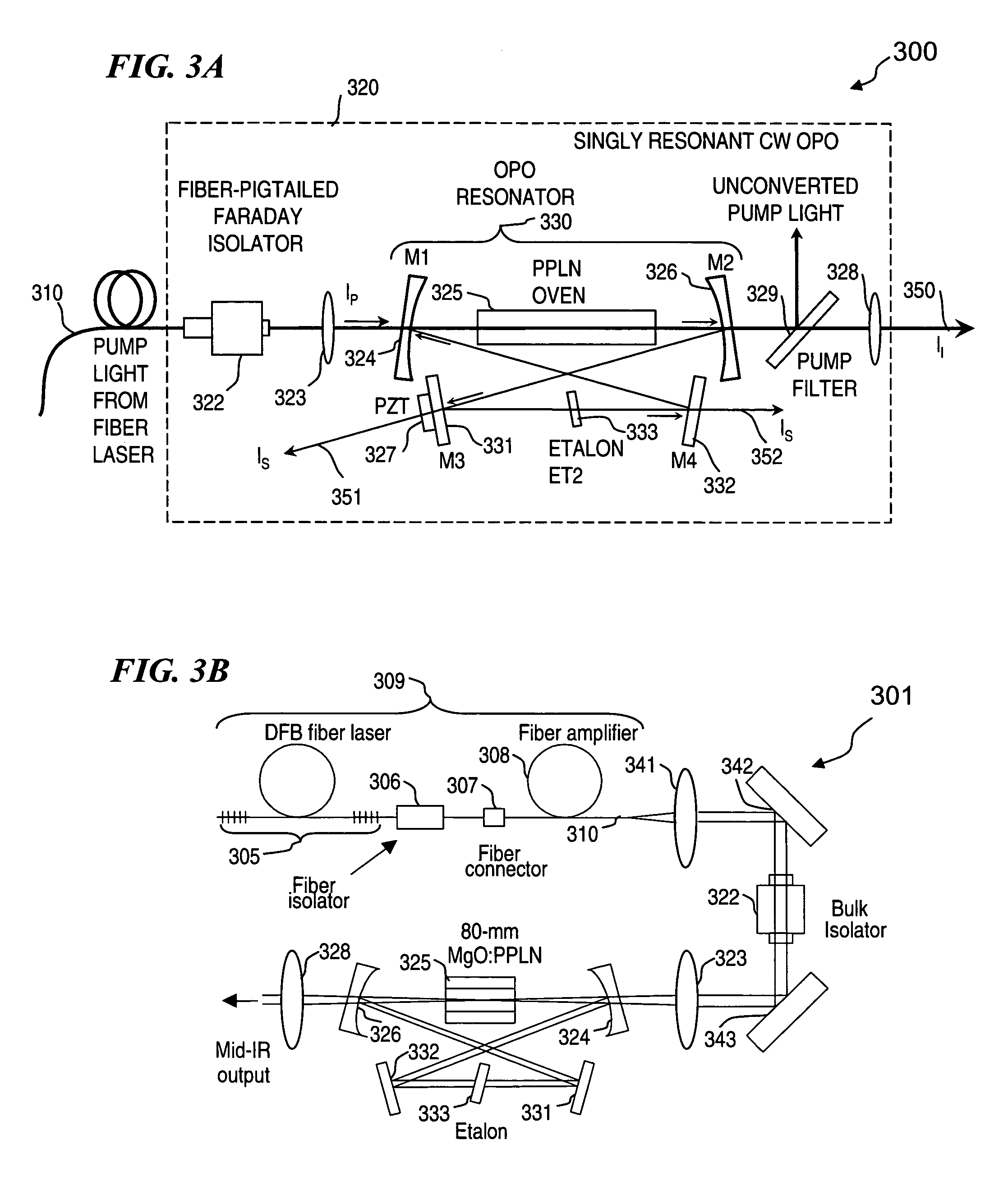
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS20070035810A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
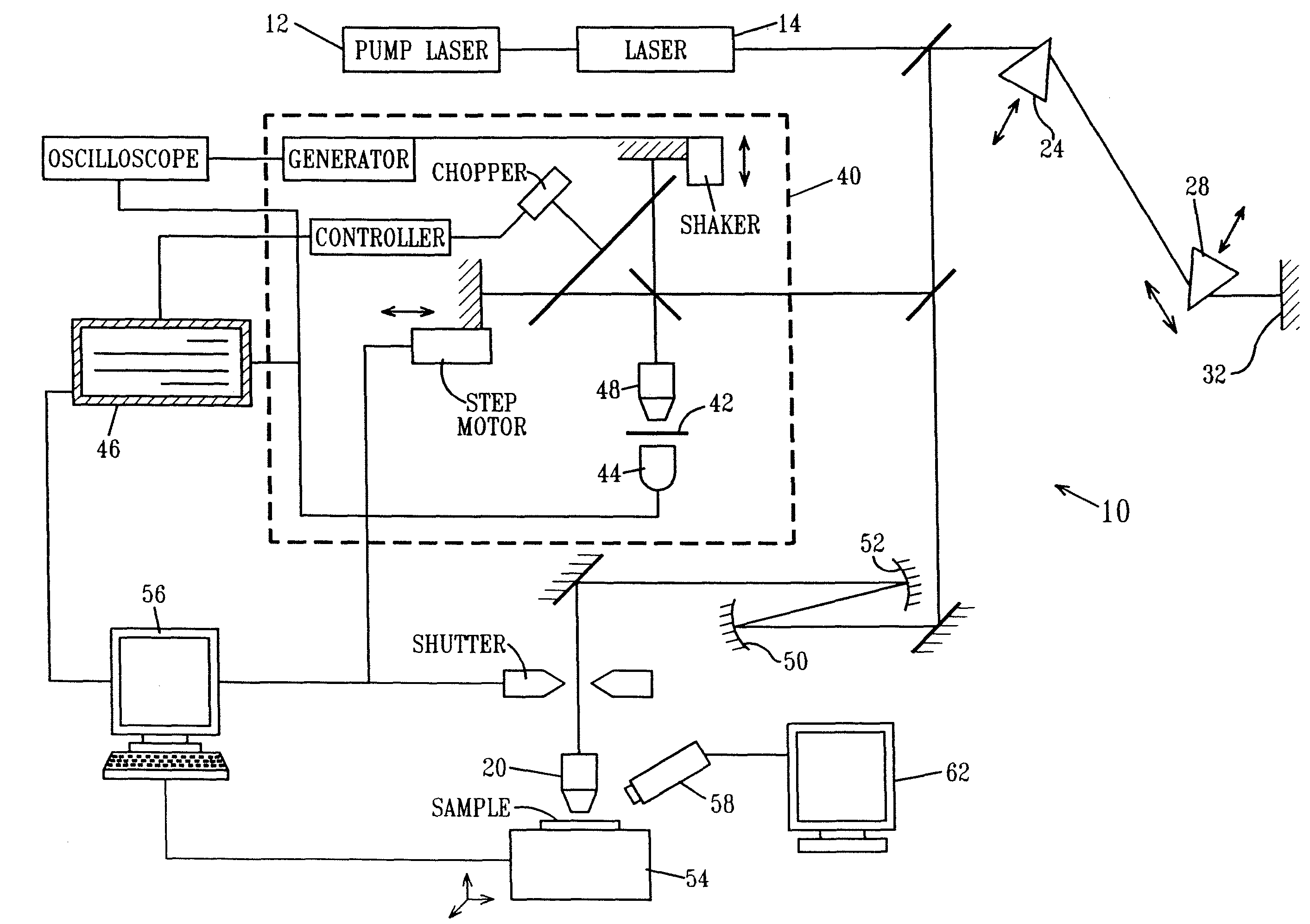
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator). The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
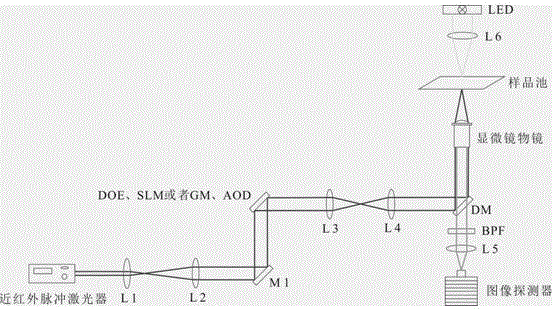
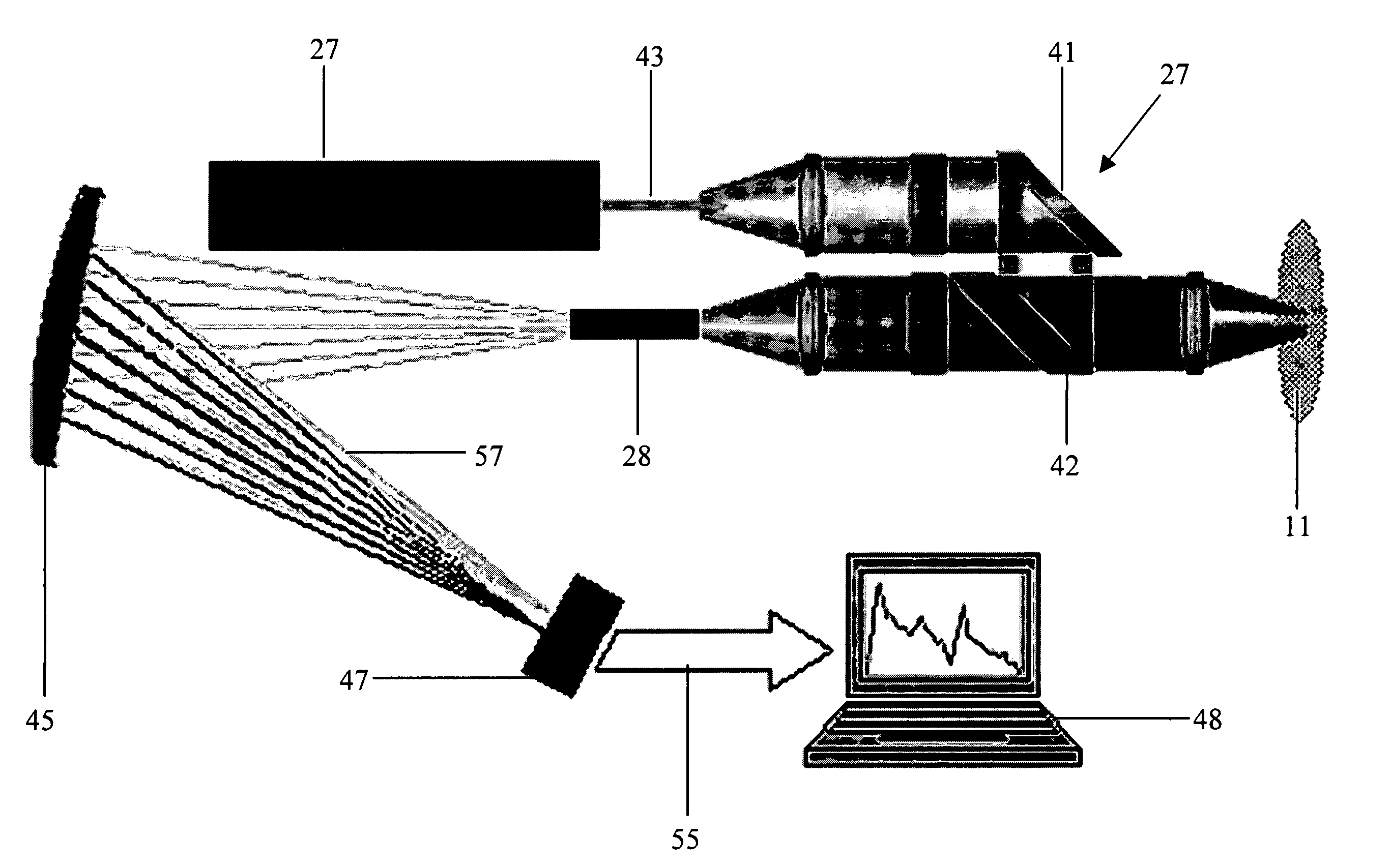
Near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system
ActiveCN102706846AImaging RealizationReduce absorptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention discloses a near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system, which comprises a light path scanning unit and a control unit which adopt a confocal structure, wherein the light path scanning unit comprises a near-infrared laser source, a collimation and extension module, a laser optical filter, a dichroic reflector, a scanning galvanometer, an f-theta lens, a tube lens, an imaging objective lens, a fluorescent optical filter, a convergent lens, a pinhole, a detector and the like, the control unit comprises a motion control module used for controlling the scanning galvanometer, a data acquisition module used for acquiring an output signal of the detector, a data processing module connected with the motion control module and the data acquisition module, and the like. The method matched with the system is characterized in that a sample is marked with near-infrared quantum dots with the fluorescence emission spectrums between 932nm and 1250nm, and then the sample is detected by the near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system. According to the system disclosed by the invention, deep-level imaging of samples such as biological tissues can be accurately and efficiently realized, and the system has a simple structure and is easy to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
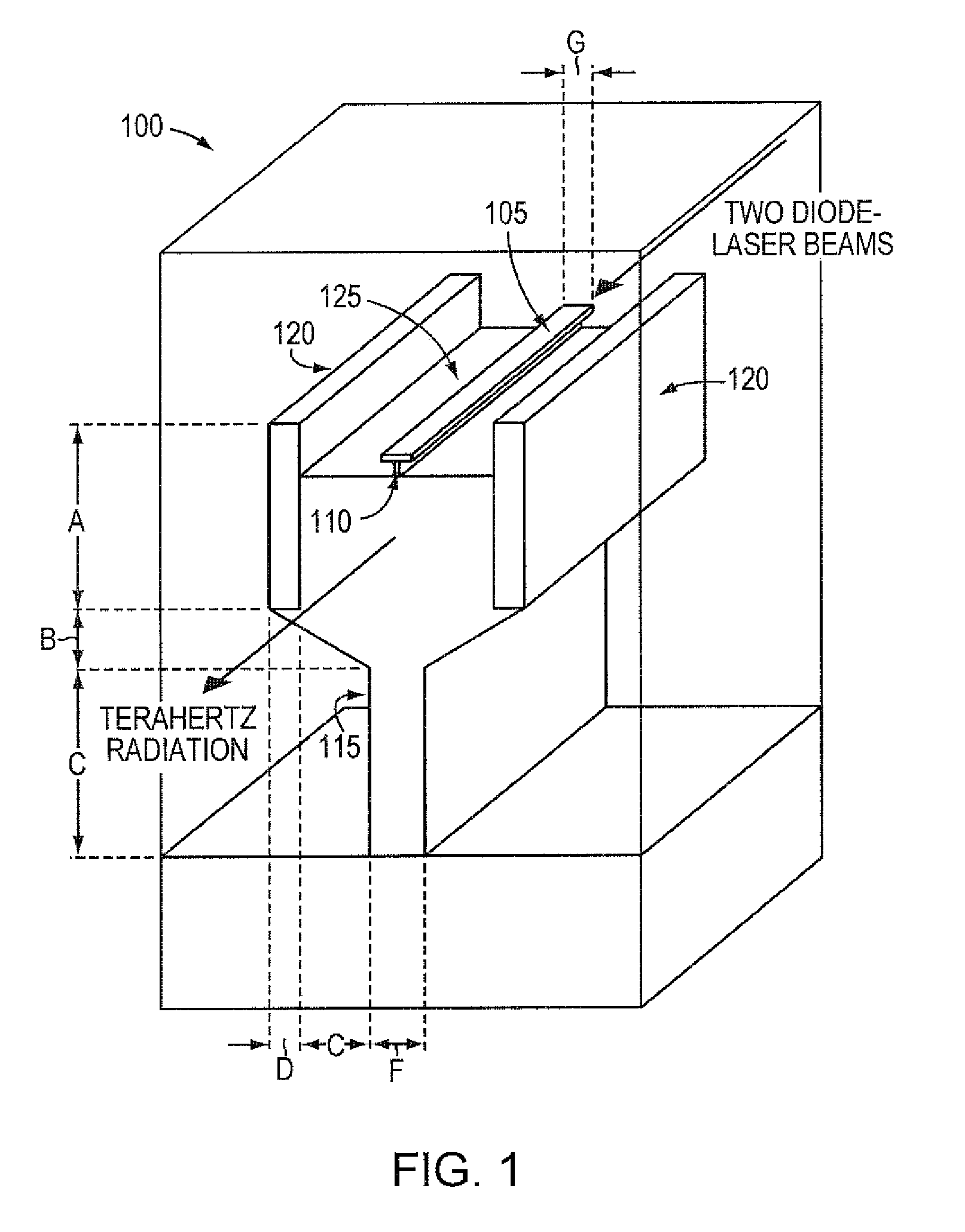
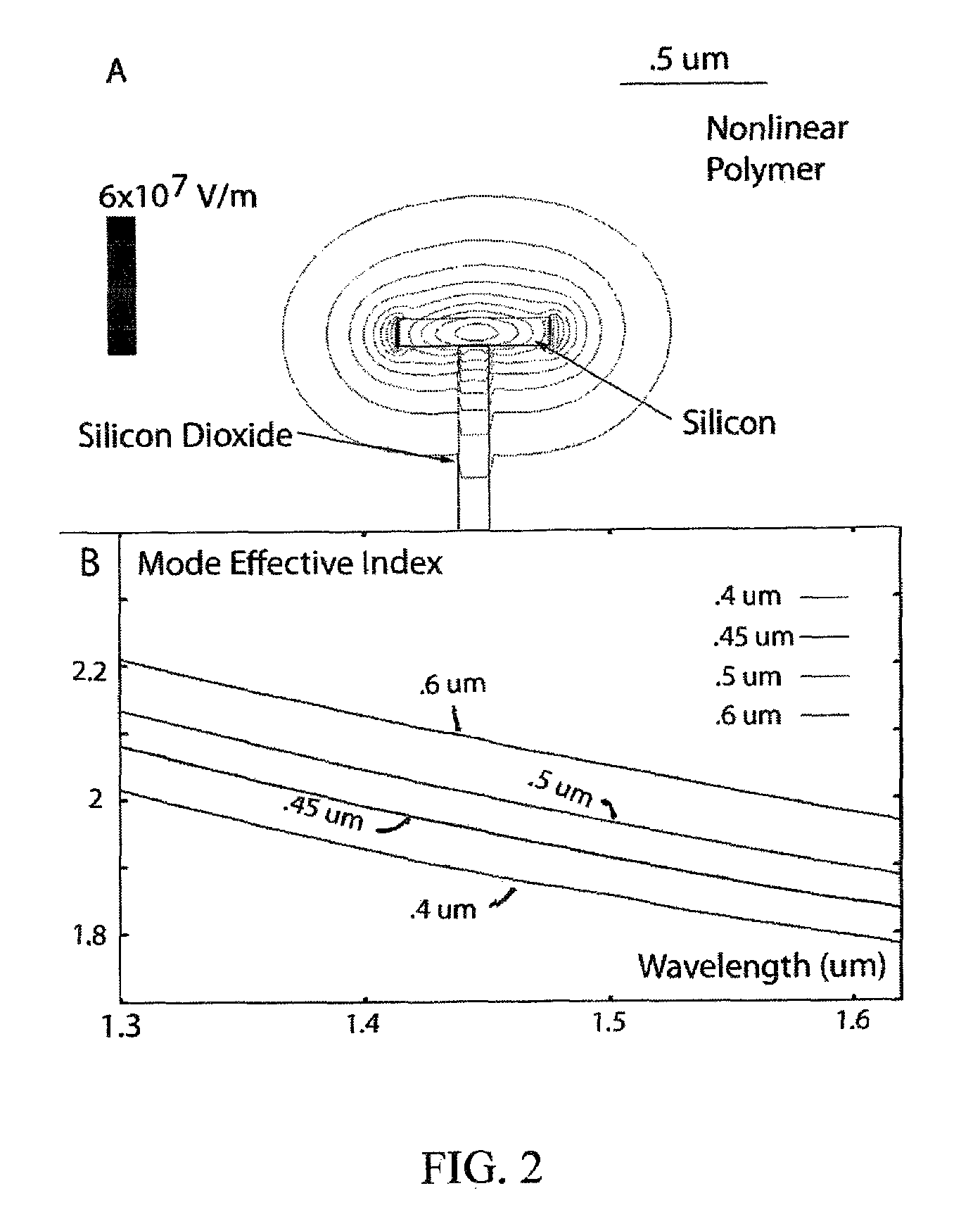
Low loss terahertz waveguides, and terahertz generation with nonlinear optical systems
InactiveUS7480434B2Solid masersOptical waveguide light guideTerahertz radiationNear infrared radiation
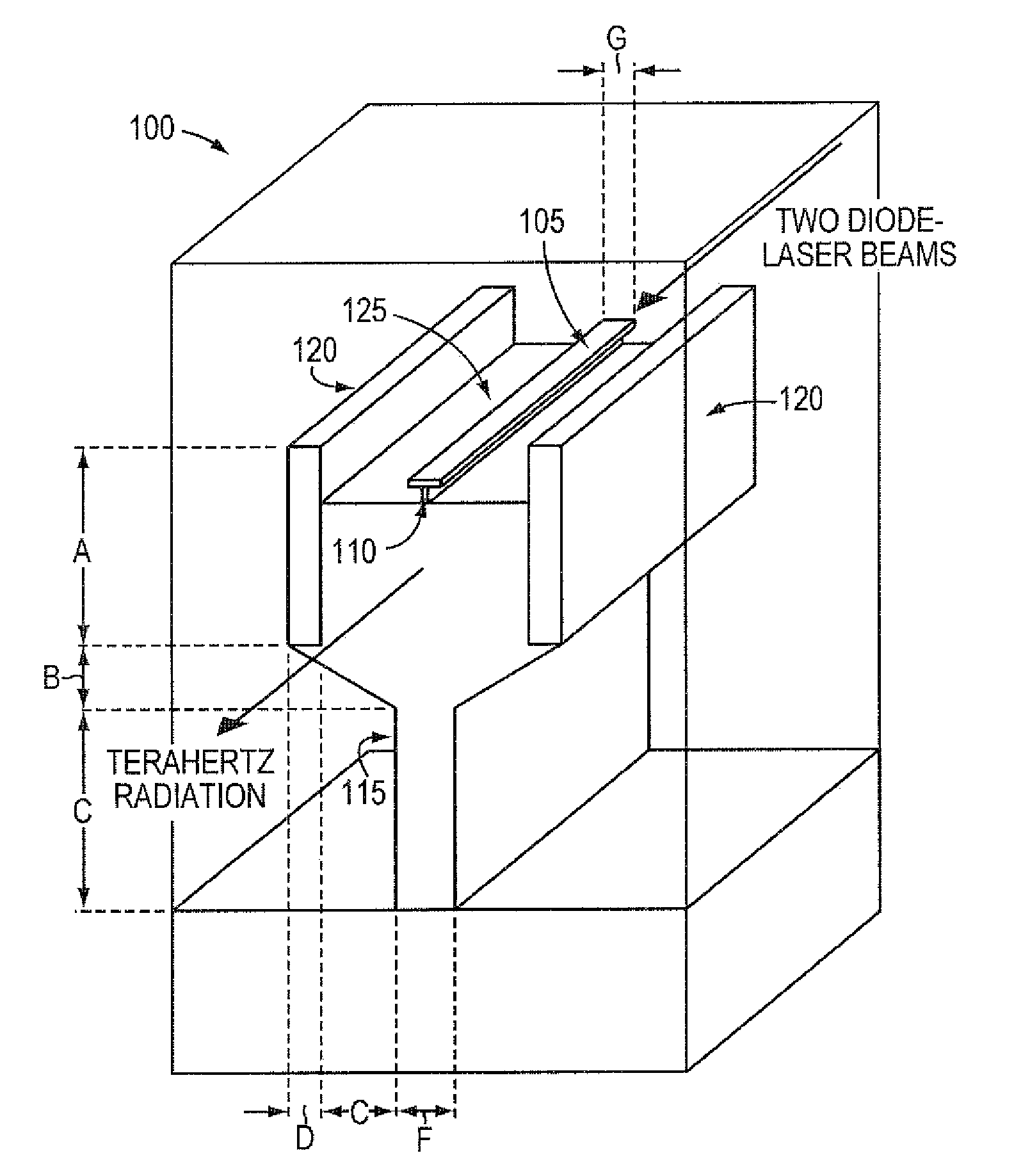
A silicon based source for radiation in the 0.5-14 Terahertz regime. This new class of devices will permit continuously tunable, milli-Watt scale, continuous-wave, room temperature operation, a substantial advance over currently available technologies. The Silicon Terahertz Generator (STG) employs a silicon waveguide for near infrared radiation, situated within a metal waveguide for Terahertz radiation. A nonlinear polymer cladding permits two near-infrared lasers to mix, and through difference frequency generation produces Terahertz output. The small dimensions of the design greatly increase the optical fields, enhancing the nonlinear effect. The design can also be used to detect Terahertz radiation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS7620077B2Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Optical material and method for modifying the refractive index
ActiveUS20090143858A1Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, wherein the refractive structures are characterized by a change in refractive index, exhibit little or no scattering loss, and exhibit no significant differences in the Raman spectrum with respect to the non-irradiated optical, polymeric material.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
System and method for detecting CO gas based on quartz tuning fork enhanced photoacoustic spectrometry technology
InactiveCN104237135AHigh quality factorHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansControl signalEngineering
The invention provides a system and a method for detecting CO gas based on a quartz tuning fork enhanced photoacoustic spectrometry technology, relates to a system and a method for detecting the CO gas and aims at solving the problem of low detection accuracy of the existing CO gas photoacoustic spectrometry detection technology. A data processing module transmits a current control signal to a laser device controller via a function generator, and meanwhile, transmits a temperature control parameter to the laser device controller; the laser device controller drives a laser device to emit near infrared laser which is incident into a gas chamber after being collimated and focused; the gas absorbs optical energy so that the optical energy is converted into heat energy and further converted into an acoustic pressure signal; a quartz tuning fork mounted in the gas chamber converts an acoustic signal into an electric signal; the electric signal of the quartz tuning fork is converted and amplified and then input into the measurement channel input end of a phase-locked amplifier; the phase-locked amplifier inverts the concentration of the CO gas to be detected by performing secondary harmonic detection in combination with the reference signal of the function generator. The system and the method for detecting the CO gas based on the quartz tuning fork enhanced photoacoustic spectrometry technology are applicable to CO gas detection.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
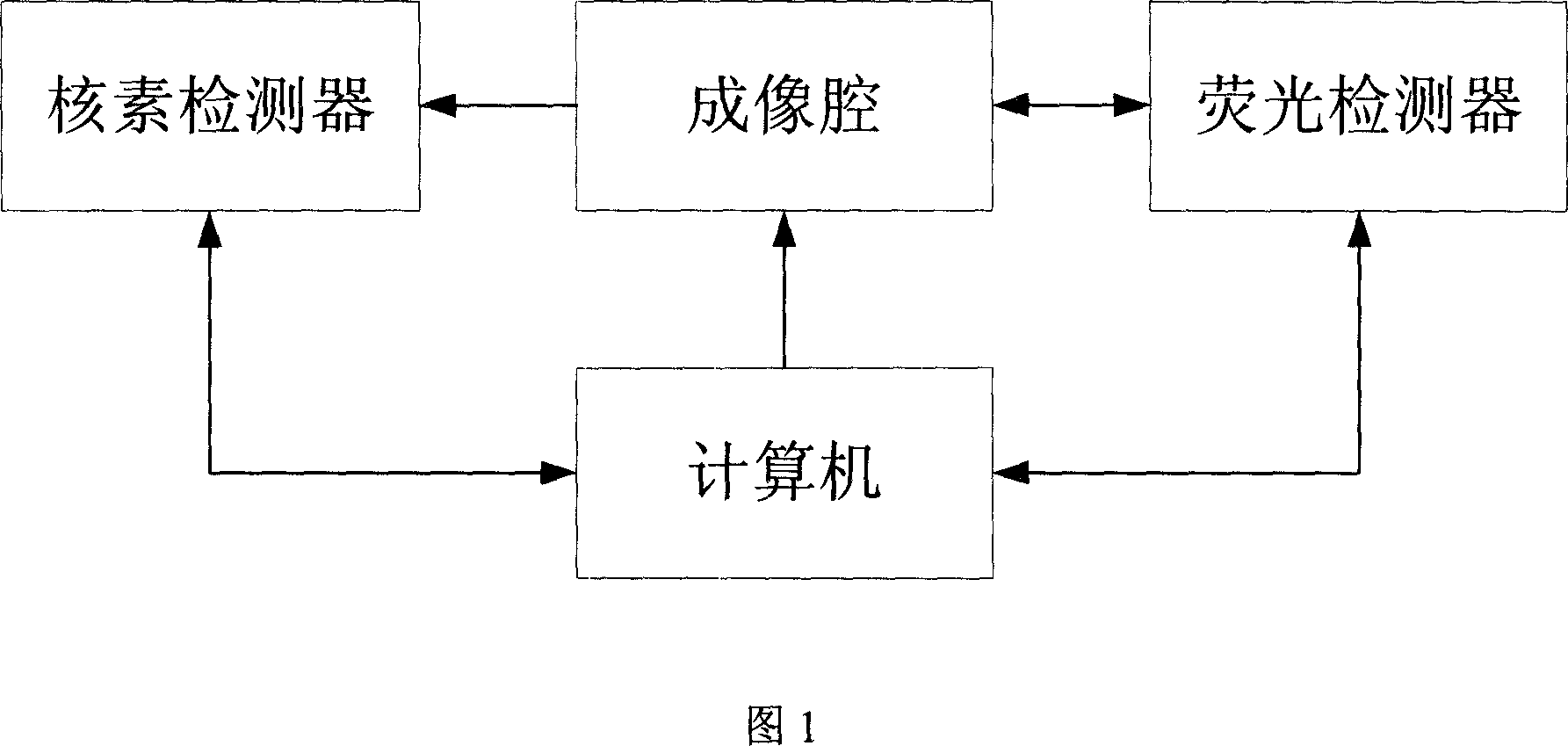
Data acquisition system for nuclein and fluorescent dual module integral small animal molecules imaging
InactiveCN101057788ASmall doseEasy to implementSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsQuantum yieldScintillation crystals
The invention belongs to the field of application of near-infrared laser, nuclear irradiation, electron and image rebuild in systematic biology and medicine. It is characterized in that high-specificity nuclear species and fluorescent probe are implanted in live animal to realize double mark of muscle deep layer or internal organ tumor cell. The emission signal of nuclear species is checked by sensitive electron-multiplier phototube in array copulation position of scintillation crystal; feeble fluorescent signal generated by visible light or infrared agitation is checked by high quantum yield CCD camera. The two checking systems are orthogonally arranged in the same surface, the live nuclear species and fluorescent signal can be checked simultaneously through rotary image cavity, and double module three dimensional tomography image of small animal can be rebuilt with software algorism. The invention is characterized by multi-image forming modules, abundant information and simple operation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Liquid-phase suspension biochip based on multi-optical trap encoding bead array and two-photon fluorescence detection
InactiveCN105784662AReal-time analysisSimplify the enrichment processFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrosphereBand-pass filter
The invention provides a liquid-phase suspension biochip based on multi-optical trap encoding bead array and two-photon fluorescence detection. The liquid-phase suspension biochip has a configuration as follows: a near-infrared laser beam emitted by a near-infrared laser is expanded by a beam expanding system, is sequentially reflected by a telescope system and a dichroscope by using a holographic technology or a time-share scanning technology, and is focused into a sample pool through a high numerical aperture objective lens, to form multi-optical-trap optical tweezers; the multi-optical-trap optical tweezers capture a plurality of encoding beads enriched with objects to be detected, to form a bead array in the solution; after an infrared laser signal is filtered by a band-pass filter, a two-photon fluorescence signal from each bead is focused to an image detector by a lens and is subjected to imaging detection. The liquid-phase suspension biochip can perform real-time quantitative analysis on nucleic acids, proteins, virus particles and a plurality of objects to be detected, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong anti-interference ability, simultaneous determination of a plurality of components and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
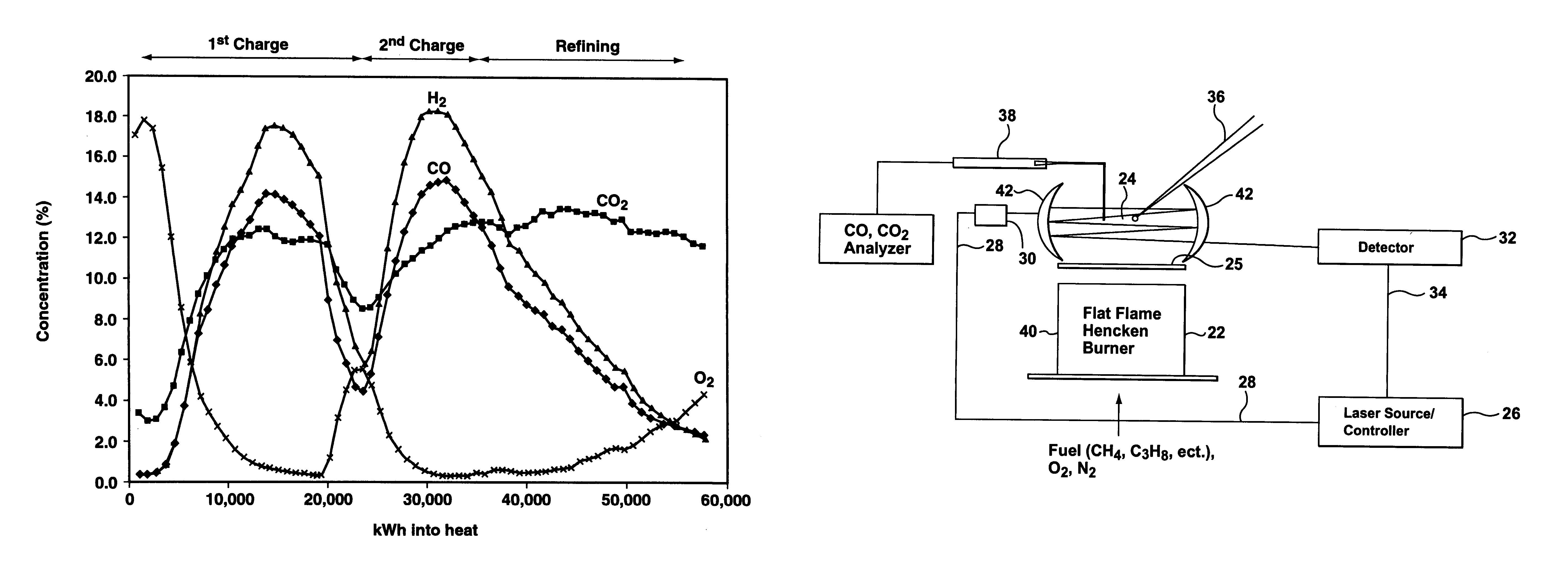
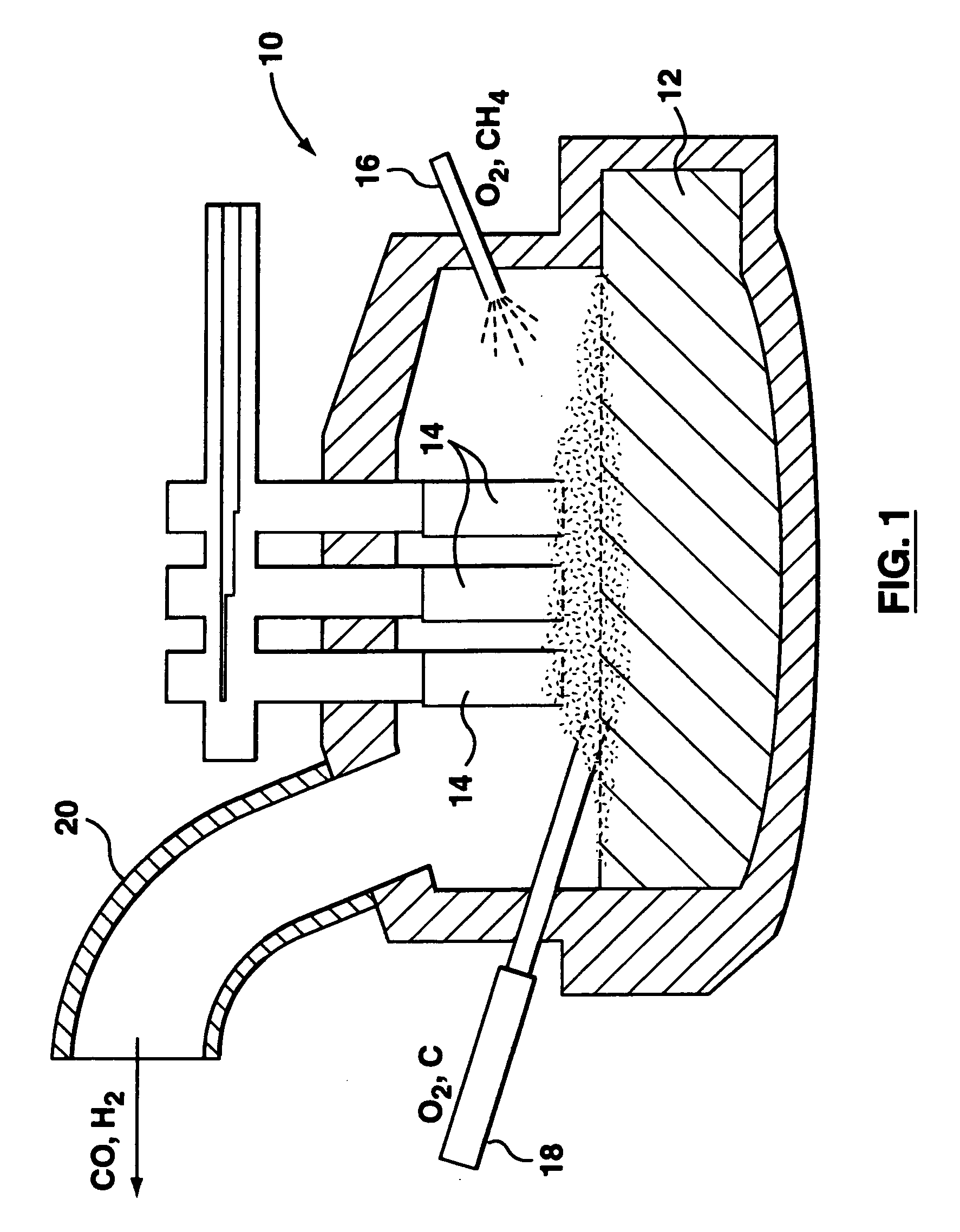
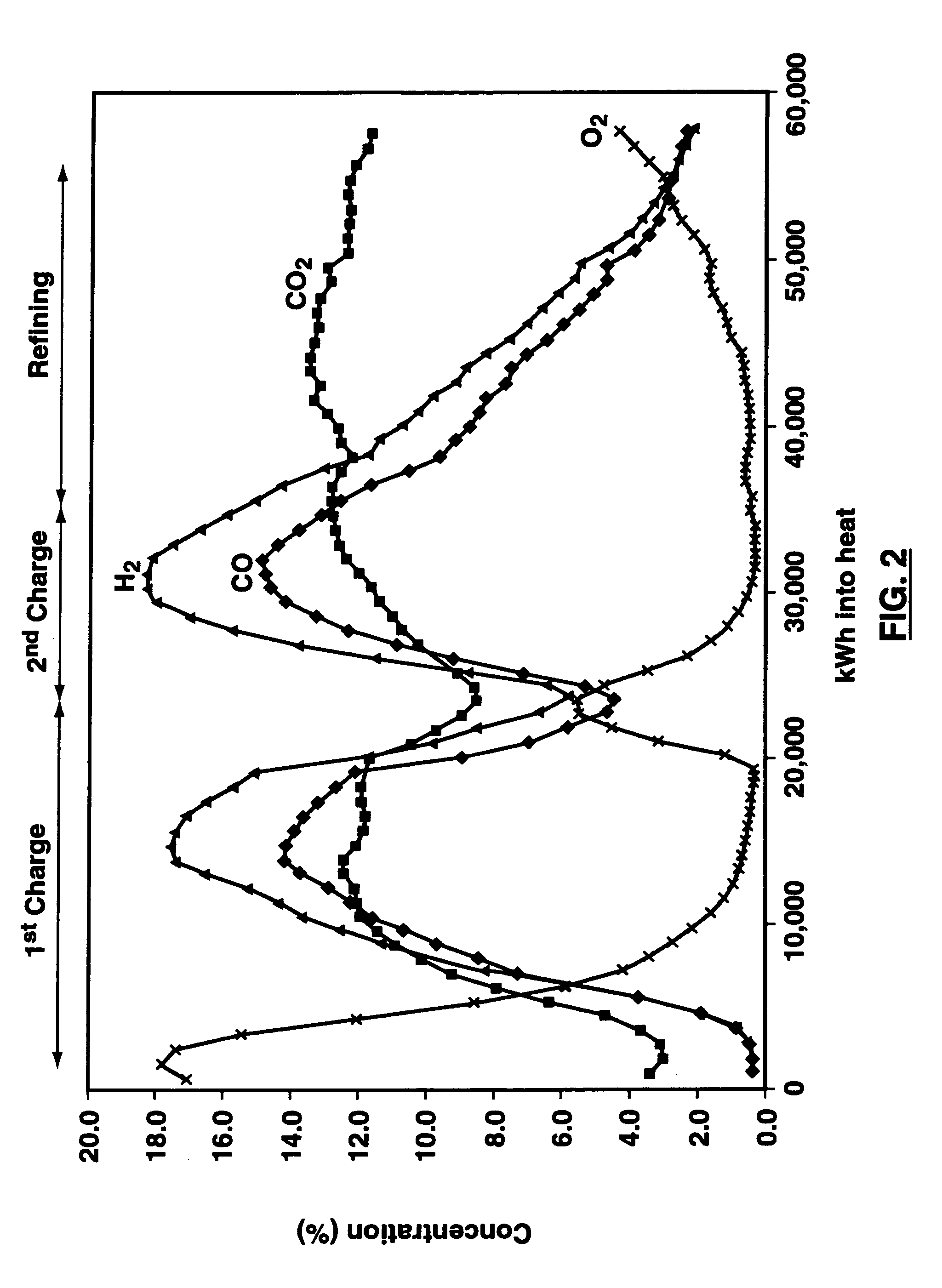
Method and apparatus for improved process control in combustion applications
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for improved process control in combustion applications, and particularly those relating to the steelmaking industry. An apparatus is provided for process control in a combustion application comprising a laser to transmit a near-infrared laser beam through off-gas produced by the combustion application, a detector to detect the transmitted laser beam and convert the detected laser beam to an electrical signal, and a control system for providing adjustment of select inputs to the combustion application in response to the electrical signal from the detector. The method of this invention comprises transmitting a near-infrared laser beam through off-gas produced by the combustion application, detecting the transmitted laser beam, and adjusting select inputs of the combustion application in response to the detected transmitted laser beam.
Owner:THOMSON MURRAY J +3
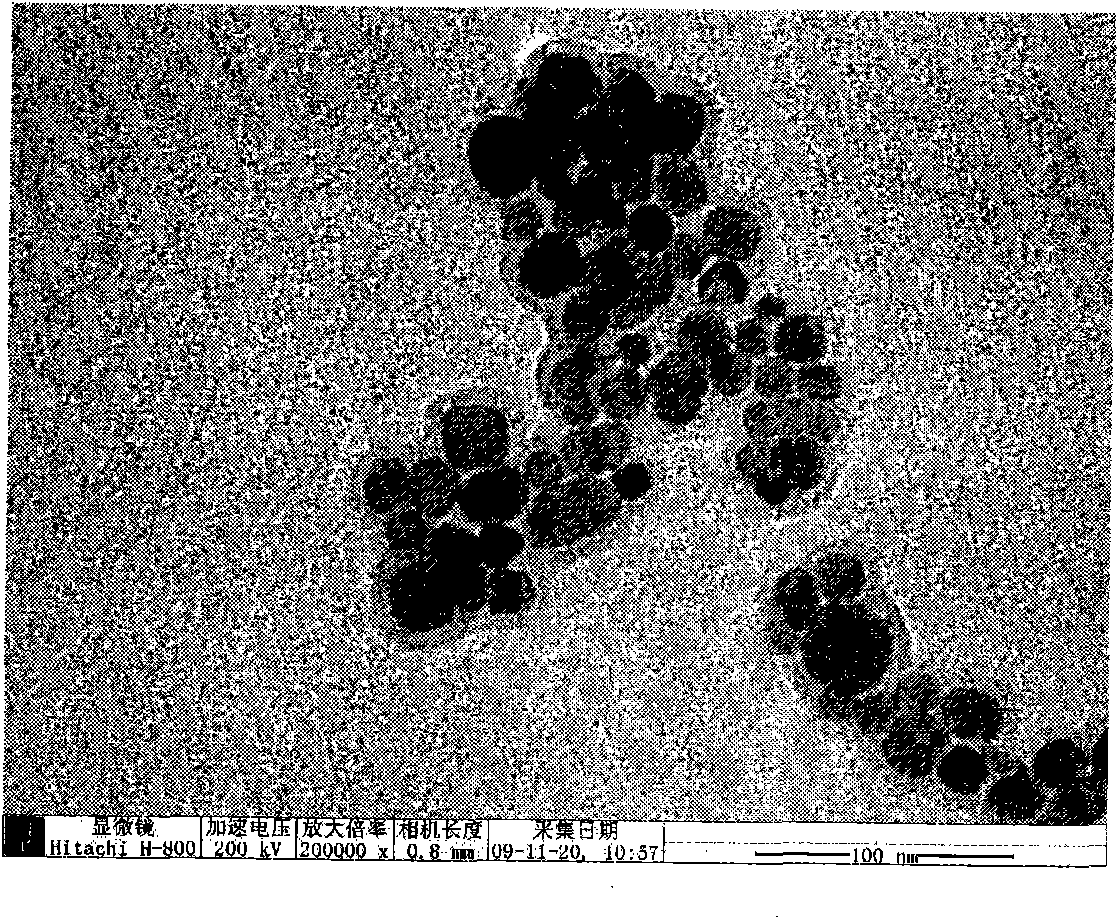
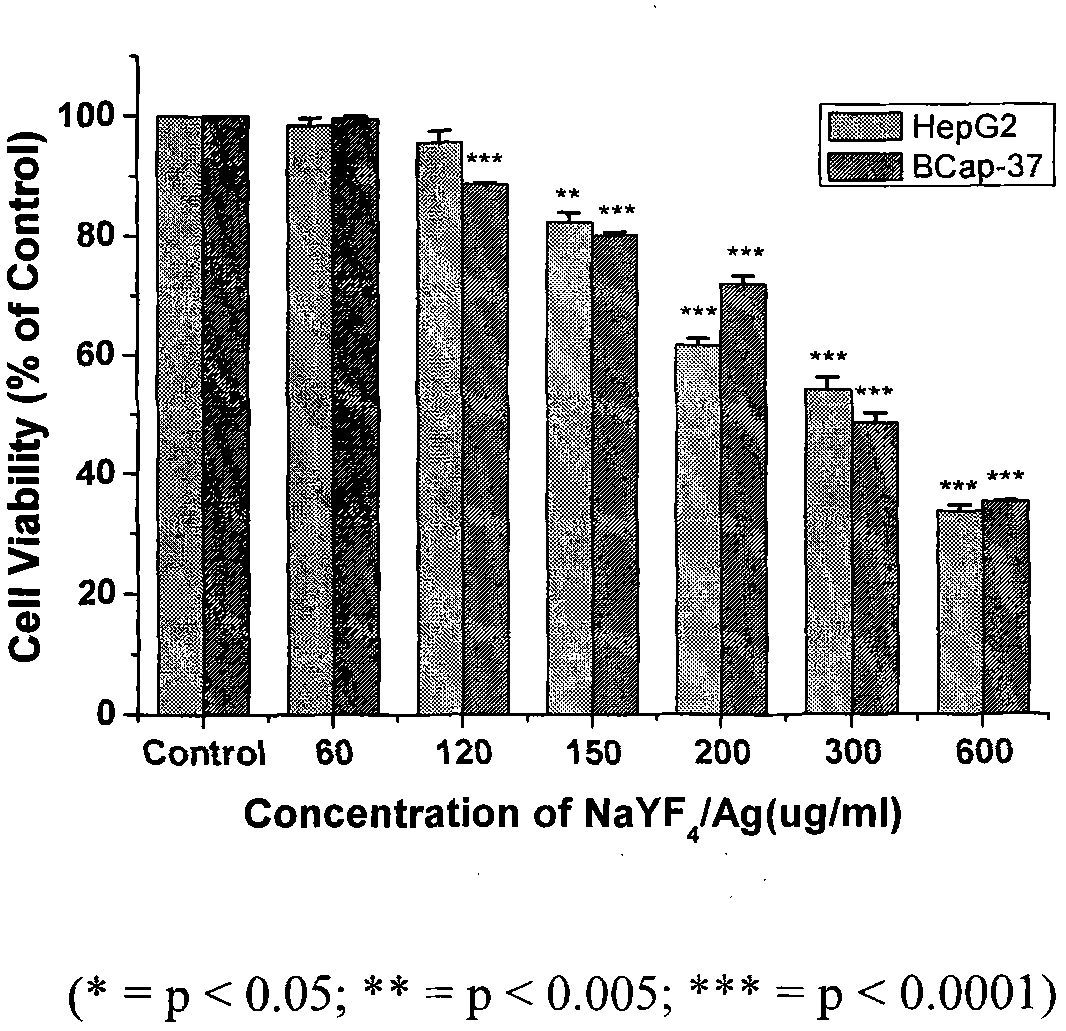
Rare earth upconversion nano crystal/silver difunctional composite nano material, preparation method thereof and application thereof in cancer detection and treatment
InactiveCN101948694ANot easy to decomposeGood light stabilityEnergy modified materialsColor/spectral properties measurementsTumour tissueNear infrared laser
The invention provides a rare earth upconversion nano crystal / silver difunctional composite nano material and a preparation method thereof as well as application thereof in preparation of medicine for treating tumour. The composite nano material can inhibit the growth of tumour tissue and can be used with anti-tumour medicine, thus improving medicine effect and achieving the aim of treatment; thecomposite nano material is difficult to decompose and has good light stability; damage to human body is less, the composite nano material can be taken as heat sensitizing agent and can absorb infrared light, the near infrared region (800-1200nm) is a transmission window of organism tissue, and damage of near infrared laser to human body is far less than that of laser in other wavebands, thus reducing damage to human body, being capable of being used as photothermal conversion agent and being superior when used for diagnosis and treatment on malignant tumour.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
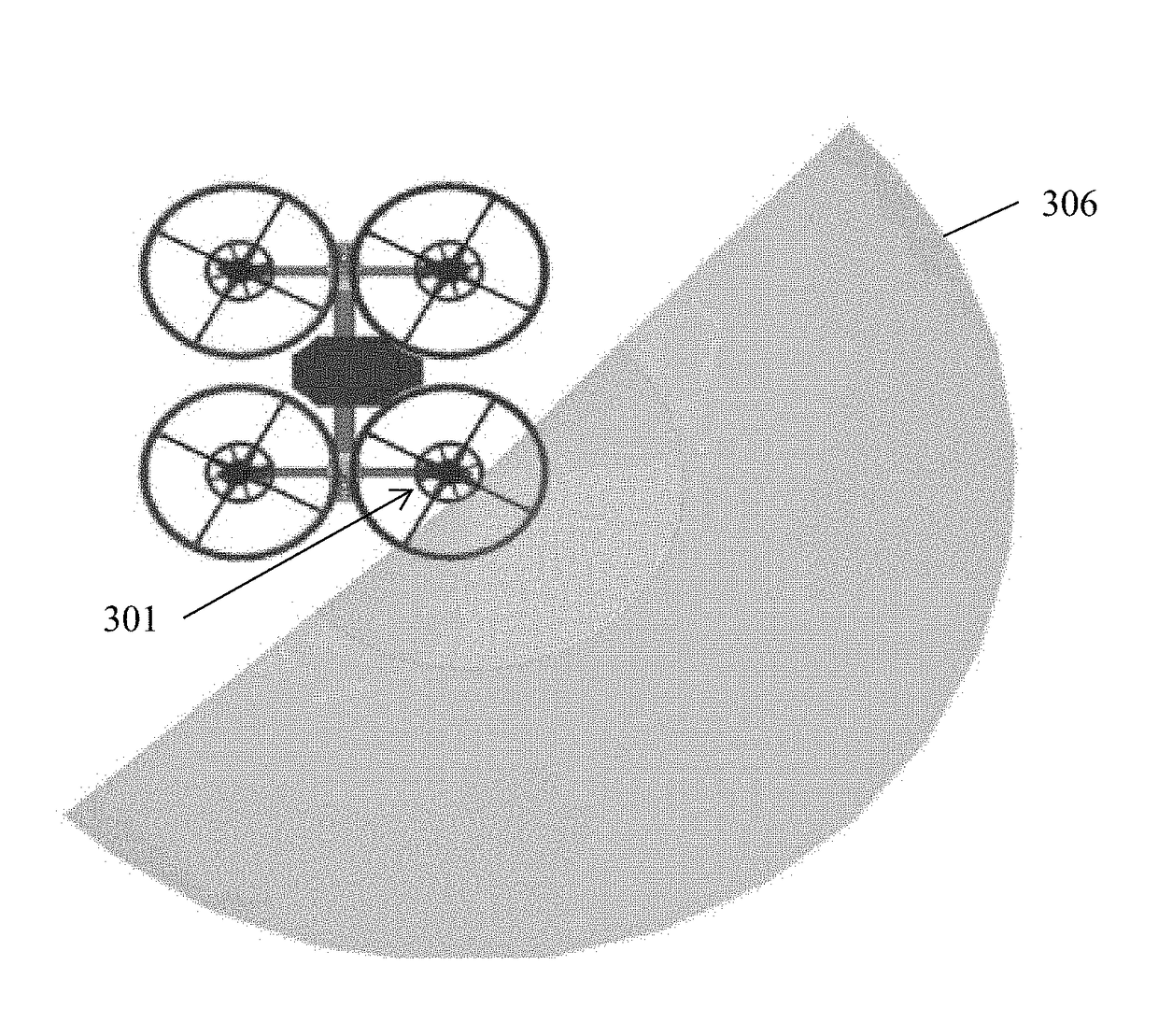
Senising on uavs for mapping and obstacle avoidance
Structured light approaches utilize a laser to project features, which are then captured with a camera. By knowing the disparity between the laser emitter and the camera, the system can triangulate to find the range. Four, 185 degree field-of-view cameras provide overlapping views over nearly the whole unit sphere. The cameras are separated from each other to provide parallax. A near-infrared laser projection unit sends light out into the environment, which is reflected and viewed by the cameras. The laser projection system will create vertical lines, while the cameras will be displaced from each other horizontally. This relative shift of the lines, as viewed by different cameras, enables the lines to be triangulated in 3D space. At each point in time, a vertical stripe of the world will be triangulated. Over time, the laser line will be rotated over all yaw angles to provide full a 360 degree range.
Owner:ROBOTIC RES OPCO LLC
Use of secondary optical emission as a novel biofilm targeting technology
InactiveUS7621745B2Without harming healthy dental structure and tissueMore processedDental implantsGum massageBiofilmFiber
Owner:NOMIR MEDICAL TECH
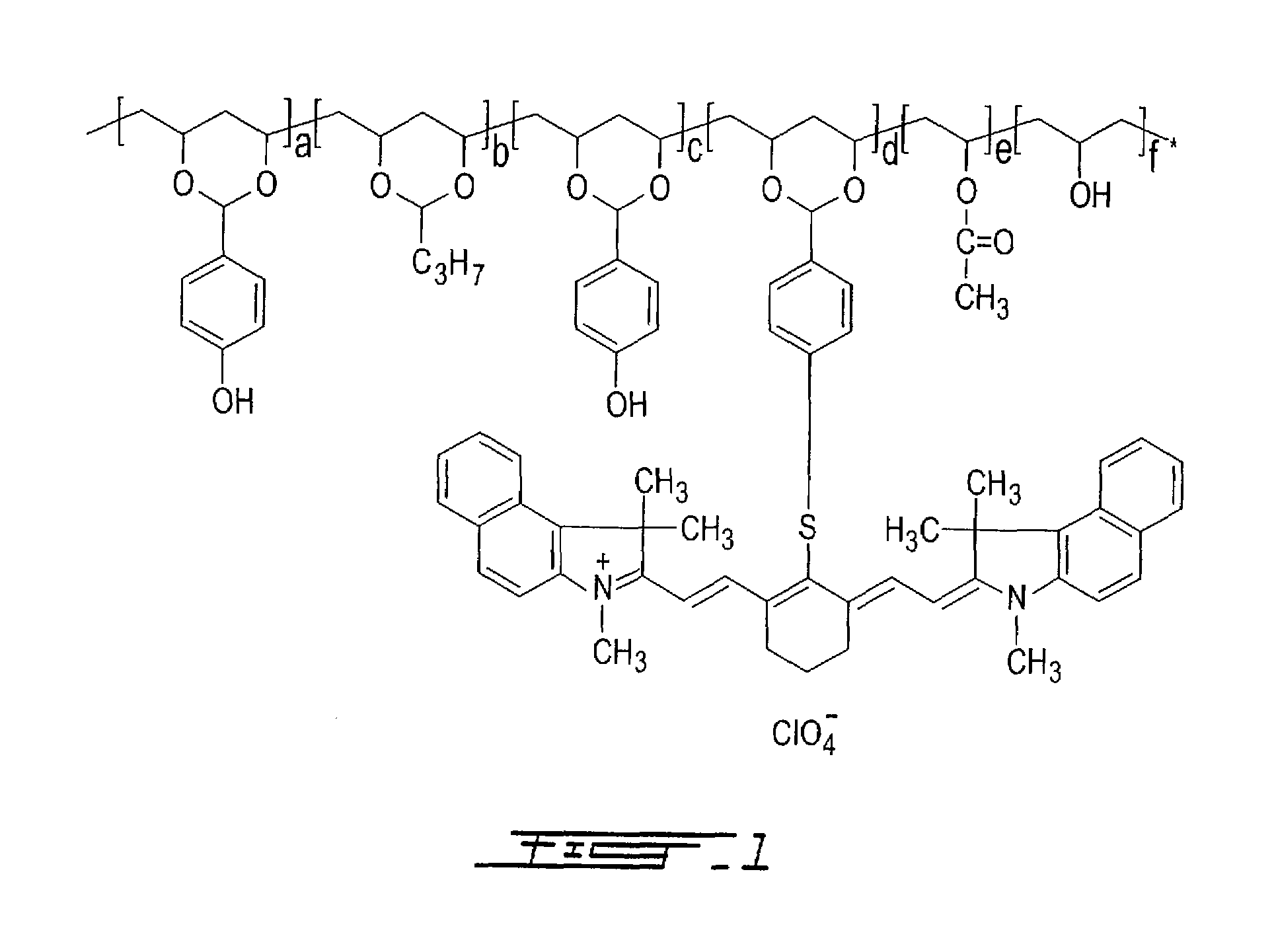
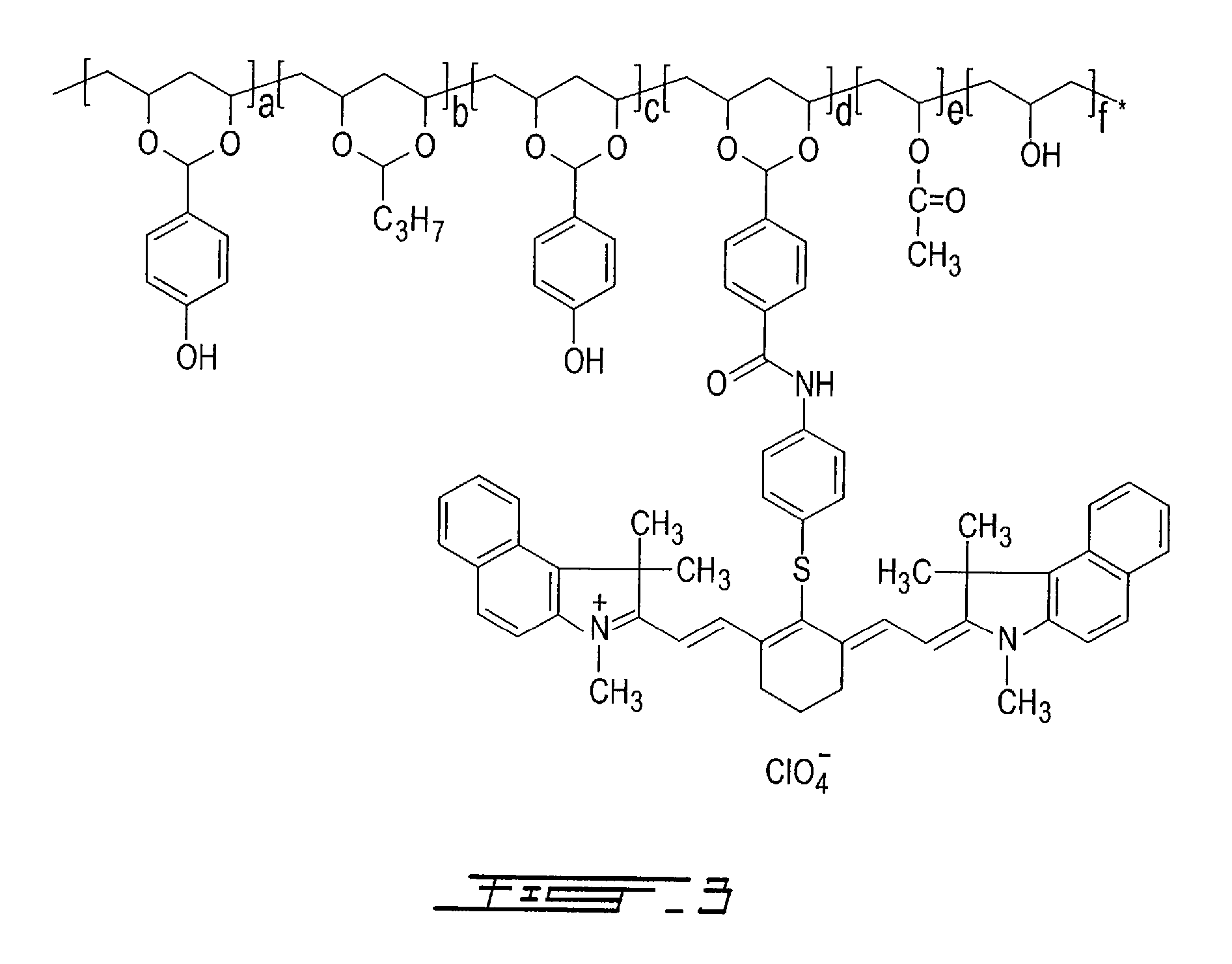
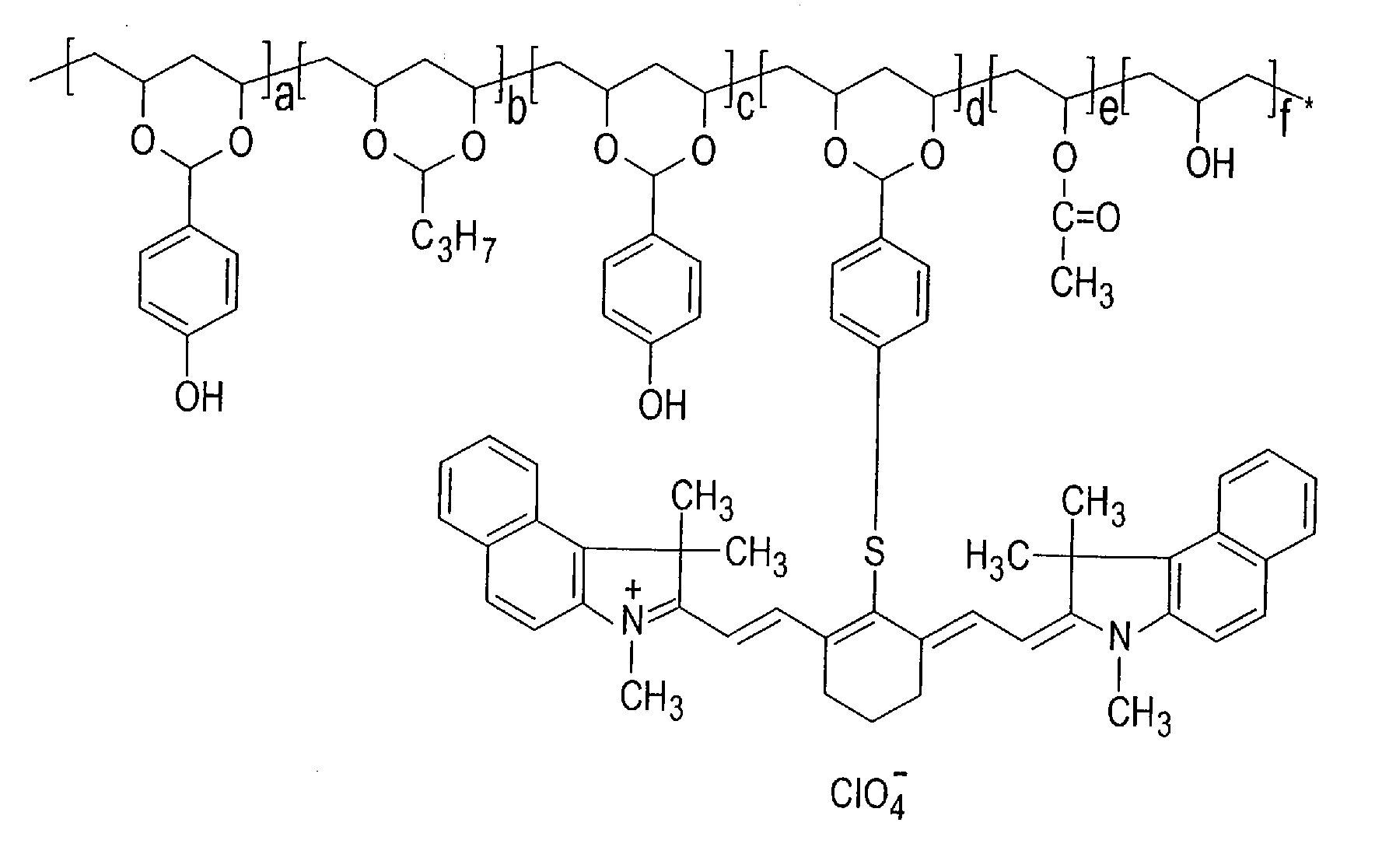
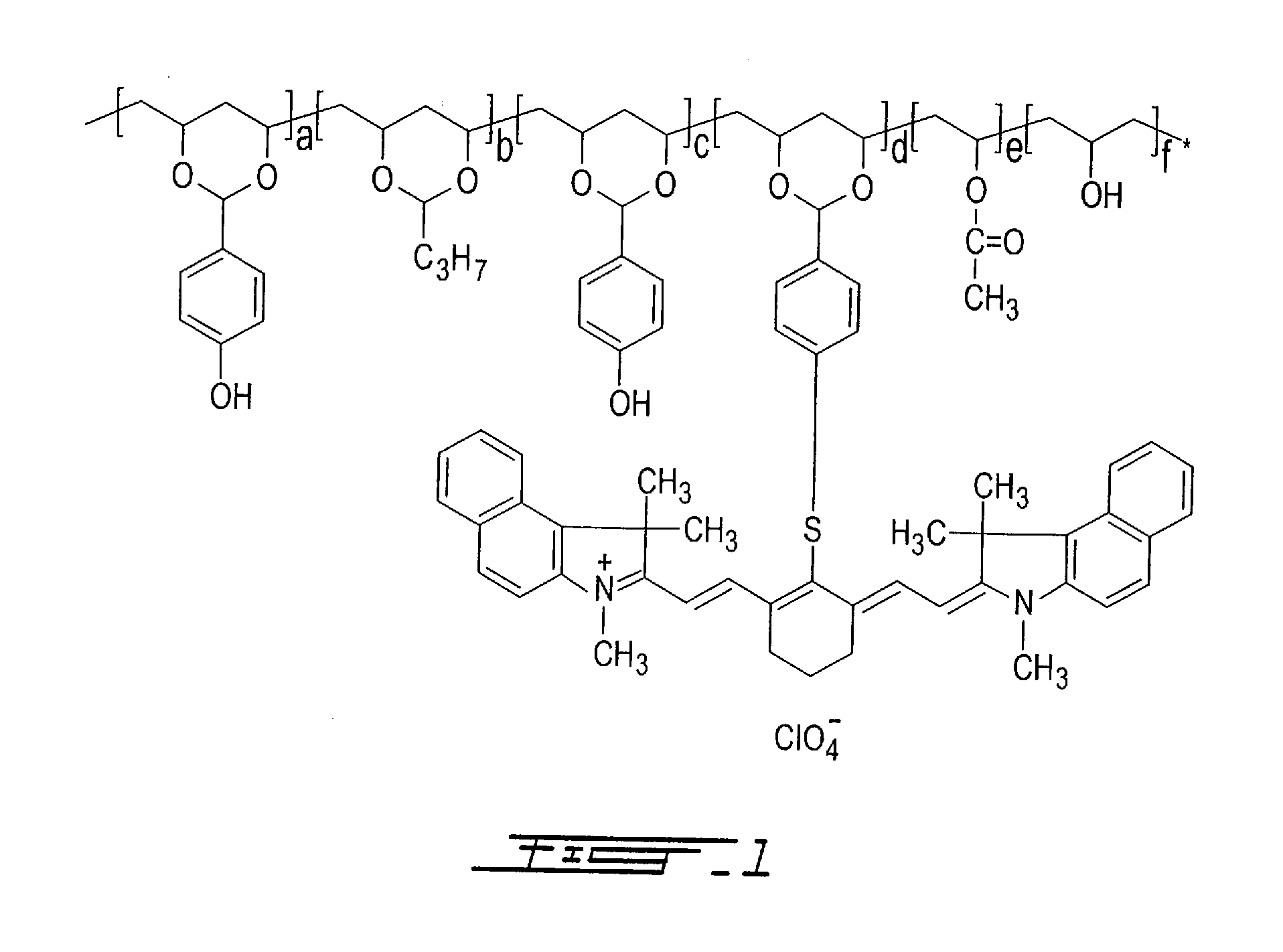
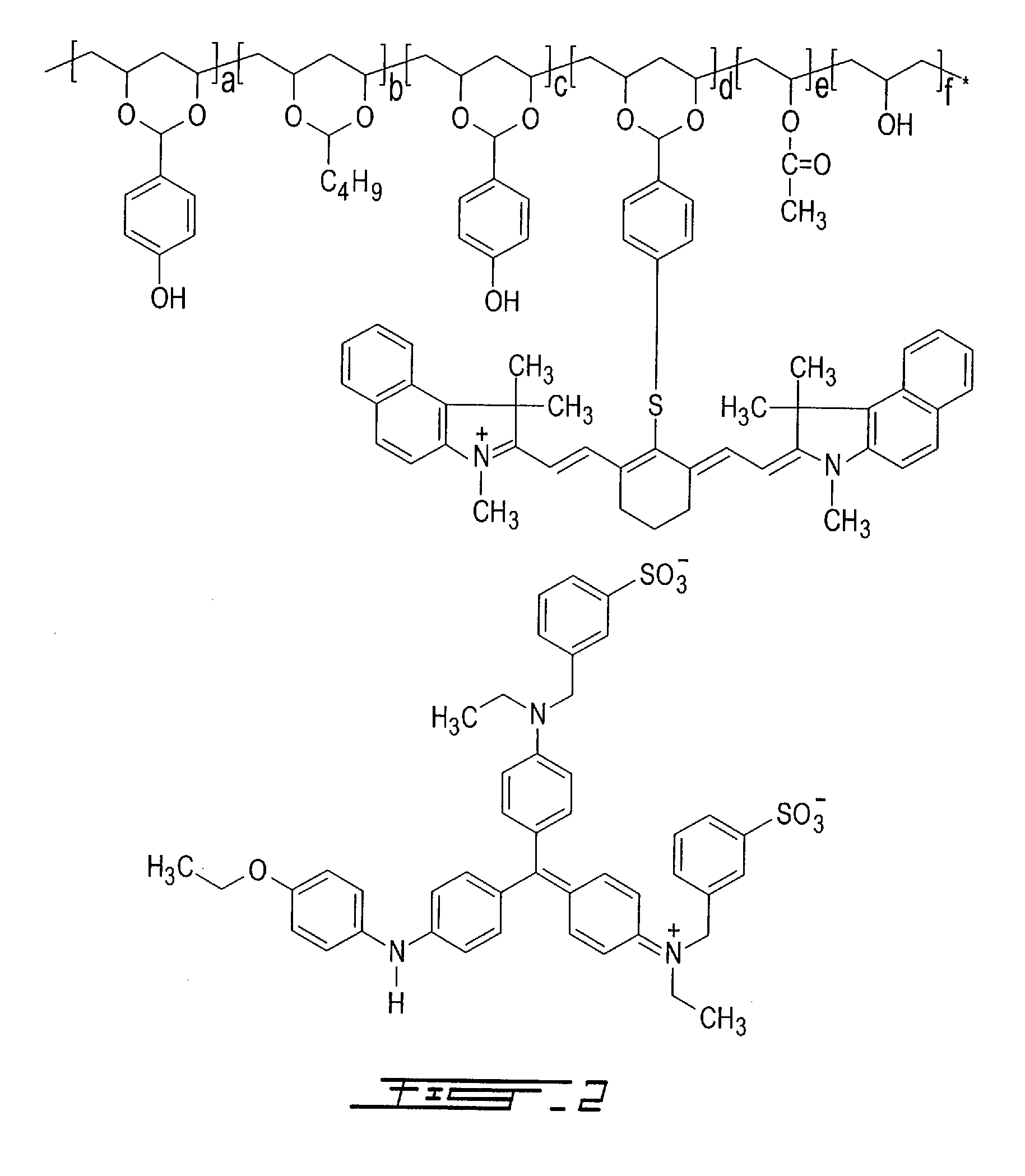
Thermally reactive near-infrared absorbing acetal copolymers, methods of preparation and methods of use
InactiveUS7473515B2Photosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGum printingAcetal copolymer
Described herein are novel thermally reactive near-infrared absorbing acetal copolymers that undergo chemical and physical changes upon exposure to near-infrared radiation. Also described are the methods of preparation of the novel acetal copolymers starting either with vinyl-alcohol polymers or with acetal copolymers. Also described are the methods of use of the new near-infrared absorbing acetal copolymers in coatings used in lithographic offset printing plates that can be directly imaged with near-infrared laser imaging devices in computer-to-plate and digital offset printing technologies. The novel acetal copolymers are also useful in photoresist applications, rapid prototyping of printed circuit boards and chemical sensor development.
Owner:AMERICAN DYE SOURCE
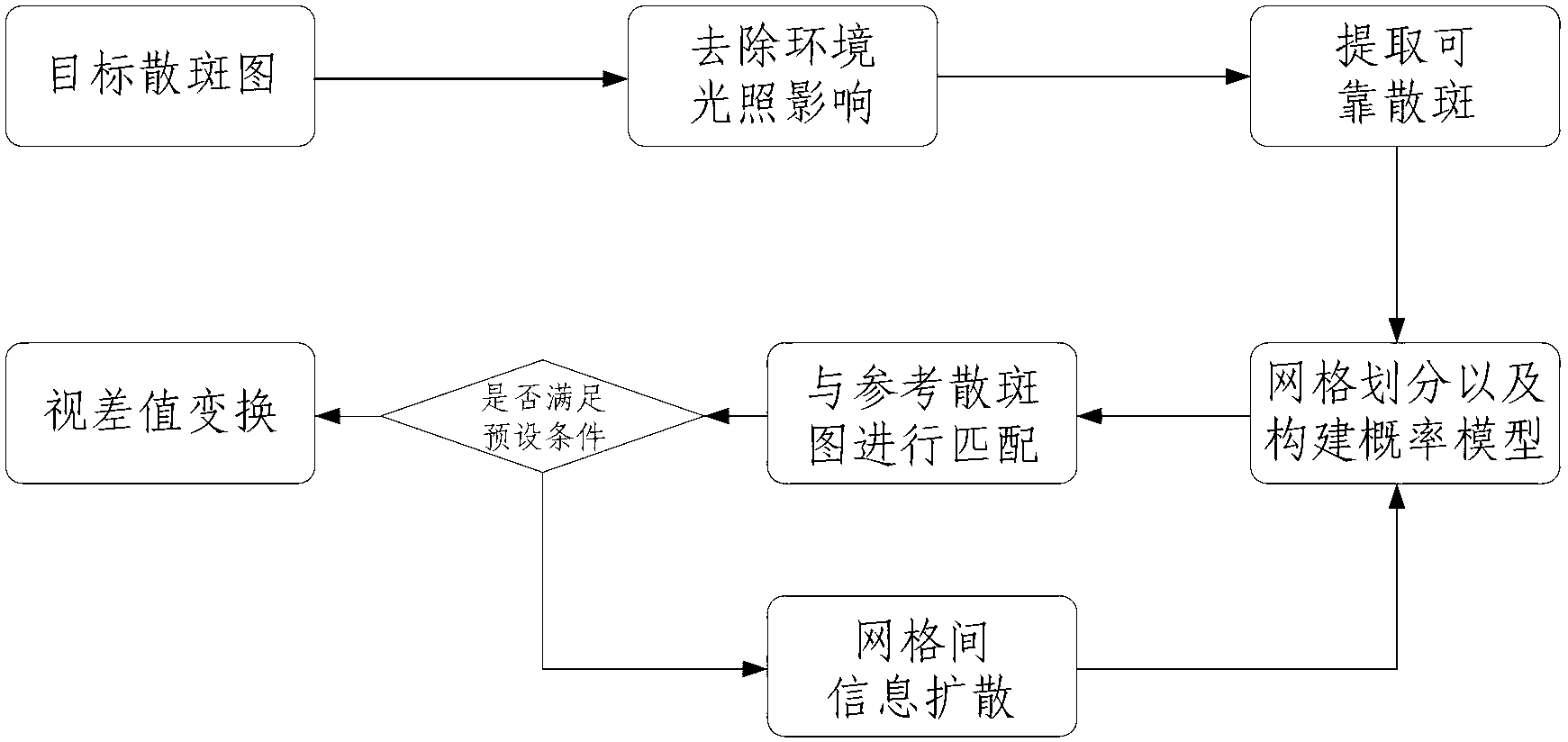
Depth estimation method and device based on near-infrared laser speckles
The invention relates to the technical field of image depth calculation, in particular to a depth estimation method and device based on near-infrared laser speckles. According to the depth estimation method based on the near-infrared laser speckles, through preprocessing conducted on a target speckle image, influences of ambient illumination are eliminated from the target speckle image, and therefore accuracy of depth estimation is improved. Through the fact that speckles are described by the utilization of binary system characteristics, huge difference of brightness and the contrast ratio between the target speckle image and a reference speckle image is effectively offset. Through quick information spread, the depth estimation can be conducted in high efficiency, and meanwhile, due to the fact that parallax error information of an area provided with fewer speckles in the target speckle image is added, the result of the depth estimation can be more comprehensive and more accurate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Photothermal conversion nanometer material as well as preparation method and application method thereof
InactiveCN104017581ARealize micro-zone heatingRealize temperature sensingThermometers using physical/chemical changesLuminescent compositionsUpconversion luminescenceNear infrared laser
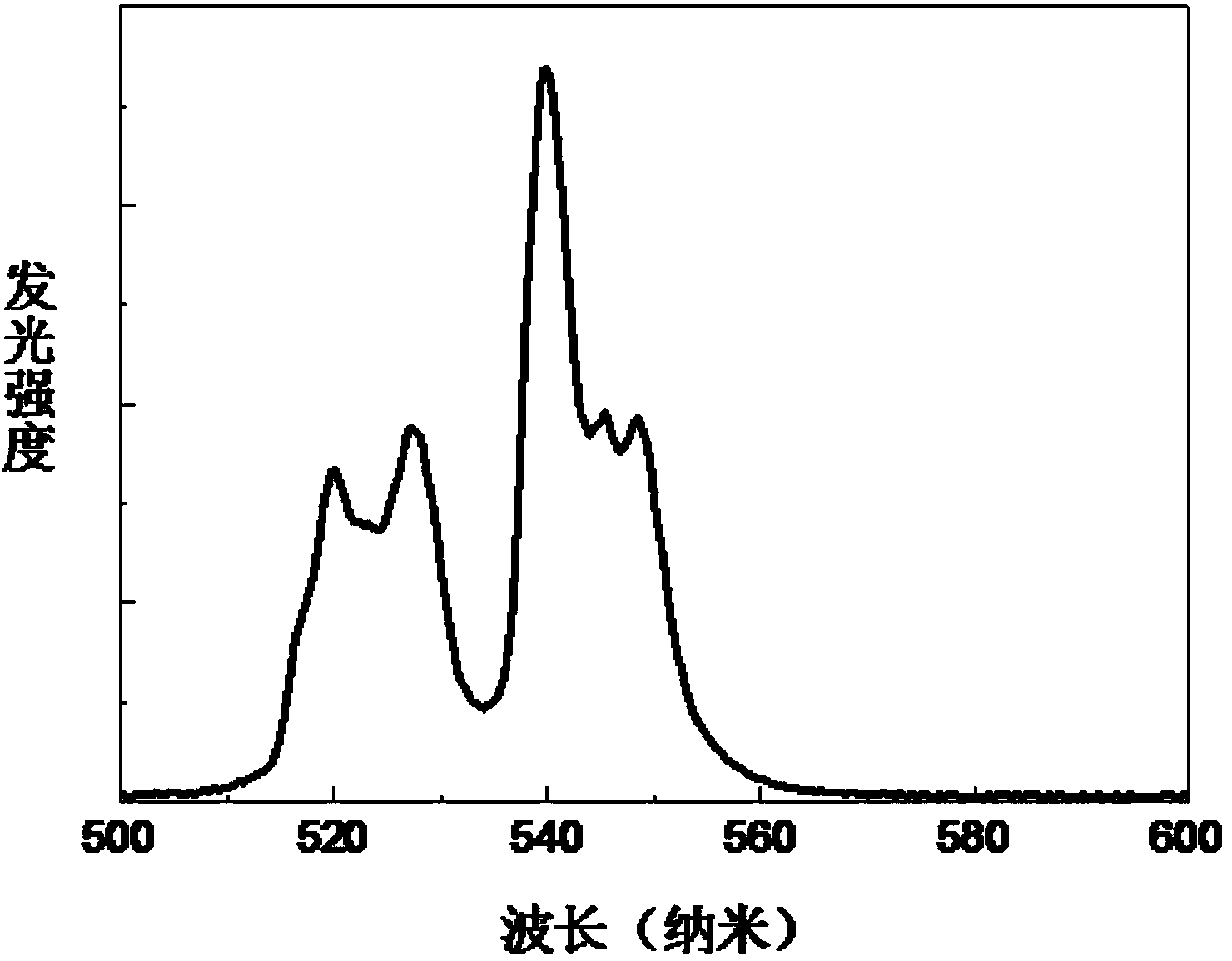
The invention provides a photothermal conversion nanometer material. The chemical formula of the photothermal conversion nanometer material is AR1-x-yF4, wherein Ybx and Ery are doped in the AR1-x-yF4, A is at least one of Li, Na or K, R is at least one of Y, Gd, Lu, or Nd, x is less than or equal to 0.6 and greater than or equal to 0.01, and y is less than or equal to 0.1 and equal to or greater than 0.01; the particle size of the photothermal conversion nanometer material particles is within the wavelength range of 5-40nm. The photothermal conversion nanometer material can emit visible light with the range of 520-660nm under the excitation effect of the near infrared laser with the wavelength range of 750-1100nm, while a temperature rise of about 5-300 DEG C can be achieved, and since the ratio of the emission band with the wavelength of 525nm and emission band with the wavelength of 545nm in the emitted light and the temperature meet a good exponential relationship, the temperature detection function can be realized. The photothermal conversion nanometer material has the significant characteristics that the material can absorb near-infrared laser with the wavelength range of 750-1100nm and the photothermal conversion, upconversion luminescence and temperature detection functions are achieved simultaneously. Another object of the invention is to provide a preparation method and application method of the photothermal conversion nanometer material, and the preparation method is simple, easy to operate, free of pollution and low in cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Use of secondary optical emission as a novel biofilm targeting technology
InactiveUS20110070552A1Without harming healthy dental structure and tissueMore processedDental implantsTeeth fillingFiberBiofilm
Owner:NOMIR MEDICAL TECH
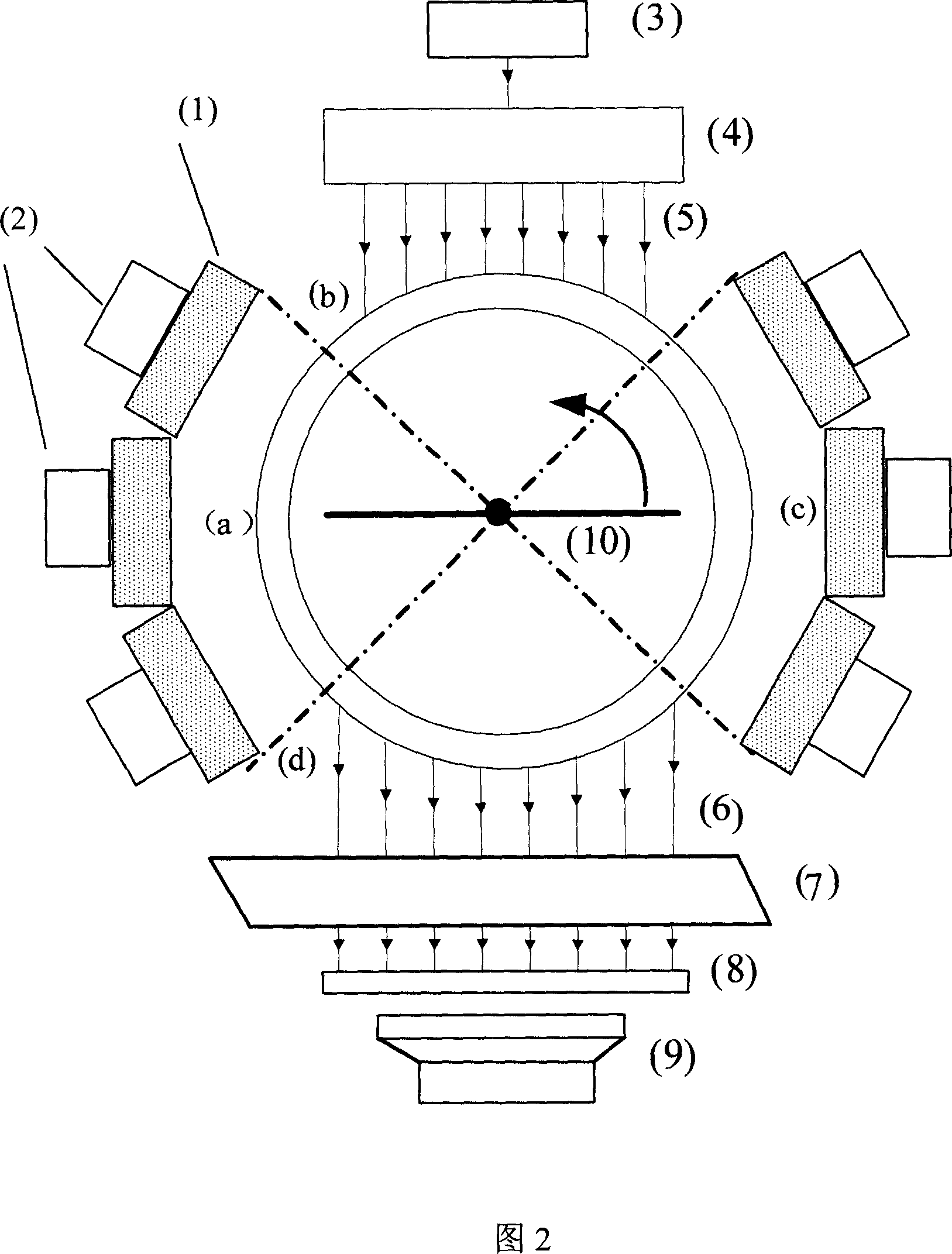
Multi-mode molecular tomography system
InactiveCN101984928ADoes not involve spatial registration issuesConsistent geometric coordinatesSurgeryComputerised tomographsSoft x rayOptical tomography
The invention relates to a multi-mode molecular tomography system which is characterized by comprising one or more light sources of an X-ray source, a near infrared laser light source and a finite spectral width light source for projecting scanning light to an object to be scanned, an electric loading device, an imaging device and a control and processing device, wherein the imaging device is used for obtaining intensity distribution data of x-rays, visible light or near infrared light emerging from the surface of the object to be scanned after scanning, and inputting the intensity distribution data into the control and processing device; the control and processing device is used for controlling the actions of the object to be scanned through the electric loading device; and the control and processing device comprises a tomography module, the tomography module is used for receiving the data of the imaging device, utilizing XCT (X-ray computed tomography) and DOT (diffuse optical tomography) modes to reconstruct an outer boundary and similar information of all internal organizations during marginalization, fusing and reconstructing XCT, DOT, FMT (fluorescence molecular tomography) and BLT (bioluminescence tomography) single-mode or multi-mode tomography image after fusion and outputting. The multi-mode molecular tomography system is applicable to the field of x-ray and optical biomedical imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
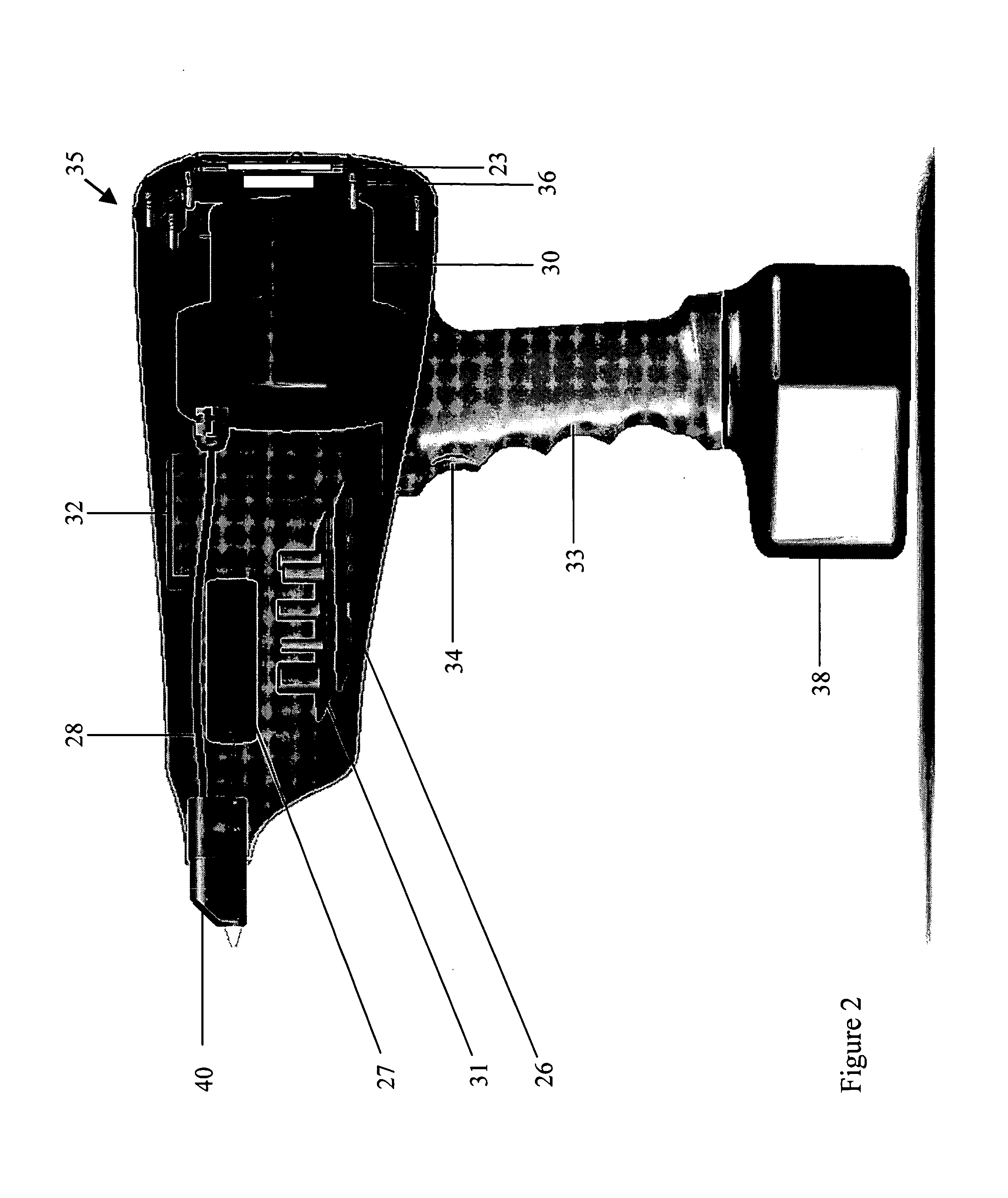
Raman instrumentation
InactiveUS20070279627A1Reduce power consumptionEasy to handleRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSolid state detectorNear infrared laser
A portable Raman spectroscopy instrument capable of discriminating between chemicals in the solid, liquid and vapor states is described. The instrument is in the shape of a gun and uses a solid state detector and an NIR laser. It relies on gating techniques to minimize weight and lower energy needs.
Owner:INTEVAC
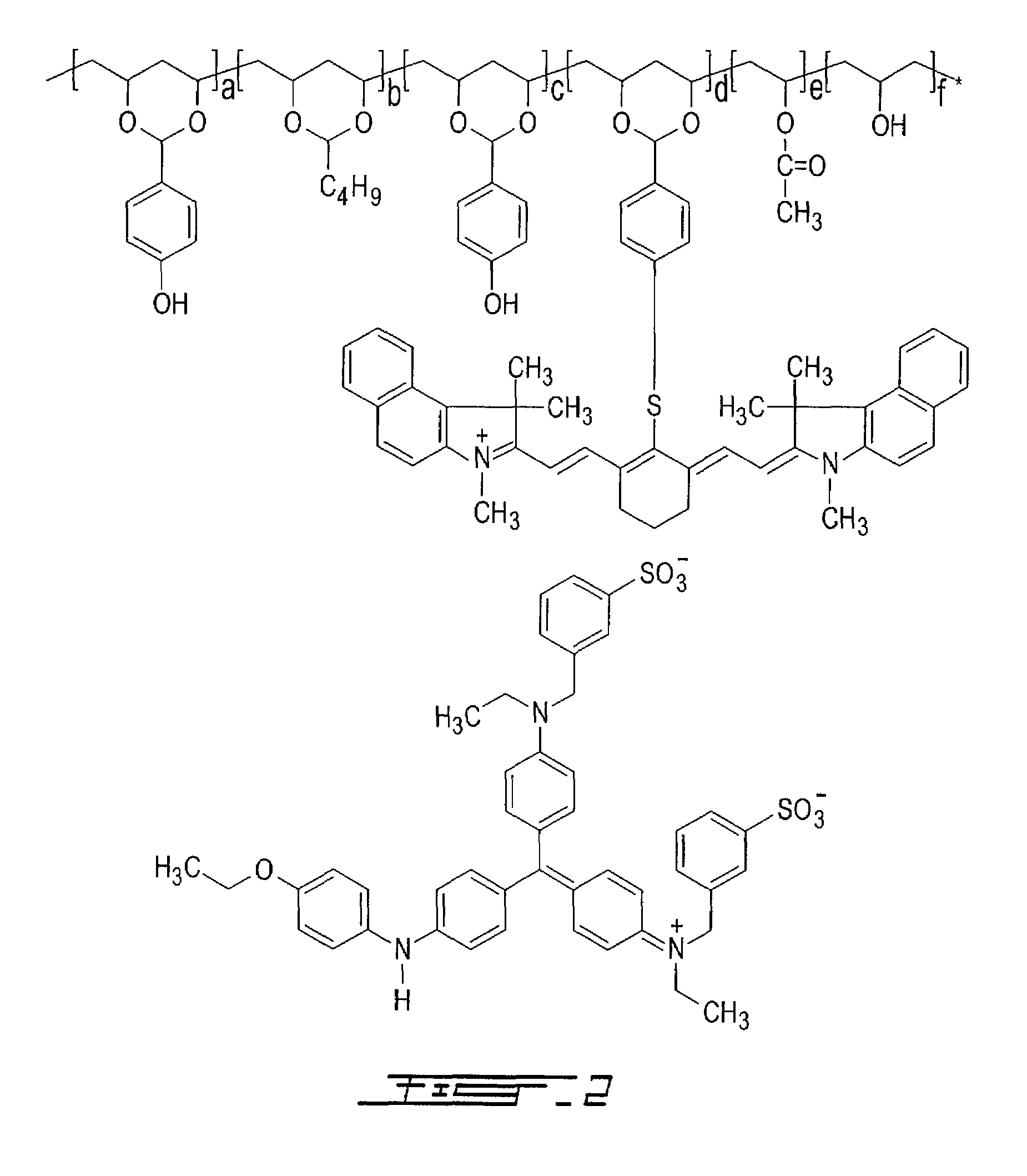
Thermally reactive near-infrared absorbing acetal copolymers, methods of preparation and methods of use
InactiveUS20060275698A1Photosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcetal copolymerNear infrared radiation
Described herein are novel thermally reactive near-infrared absorbing acetal copolymers that undergo chemical and physical changes upon exposure to near-infrared radiation. Also described are the methods of preparation of the novel acetal copolymers starting either with vinyl-alcohol polymers or with acetal copolymers. Also described are the methods of use of the new near-infrared absorbing acetal copolymers in coatings used in lithographic offset printing plates that can be directly imaged with near-infrared laser imaging devices in computer-to-plate and digital offset printing technologies. The novel acetal copolymers are also useful in photoresist applications, rapid prototyping of printed circuit boards and chemical sensor development.
Owner:AMERICAN DYE SOURCE
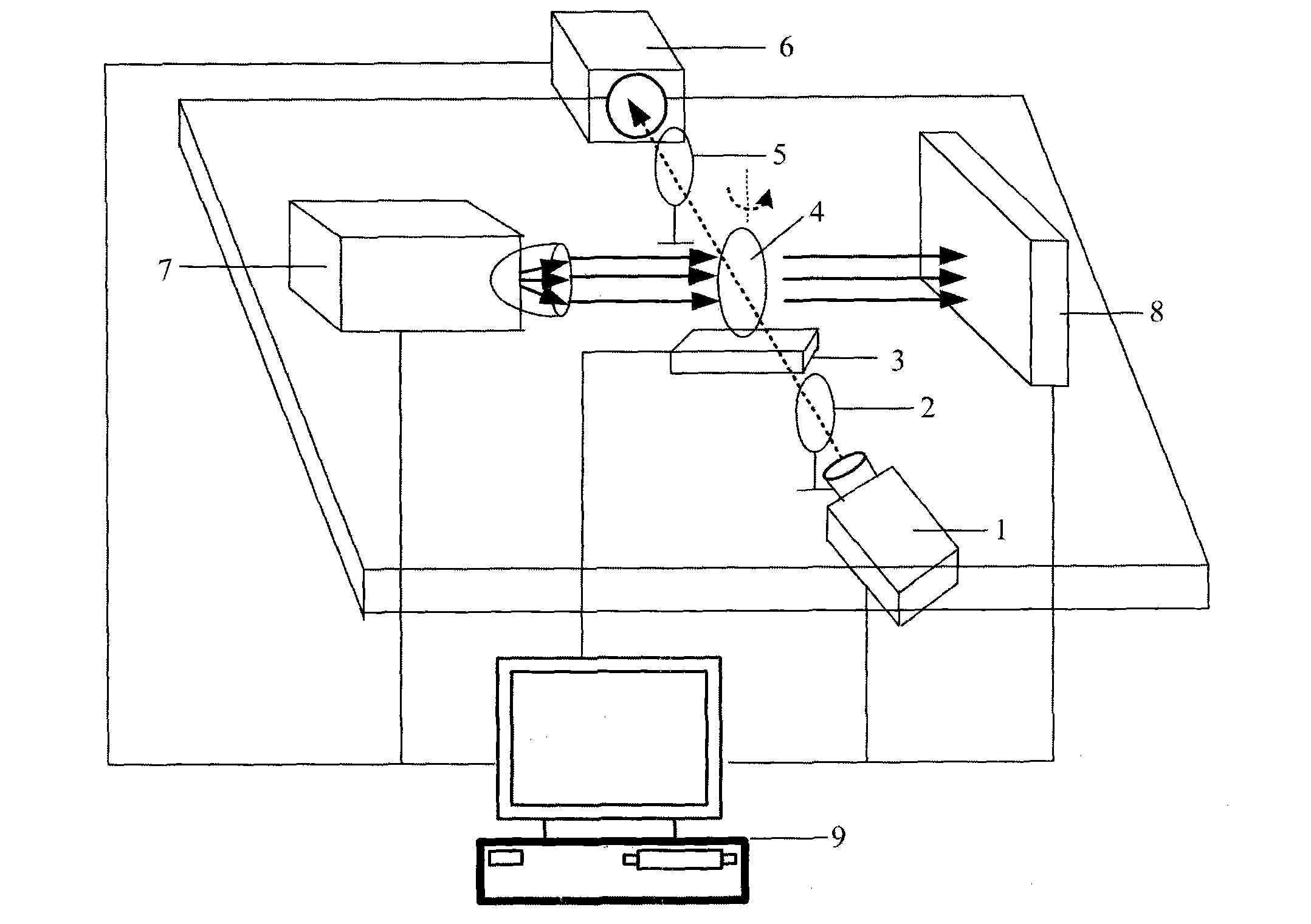
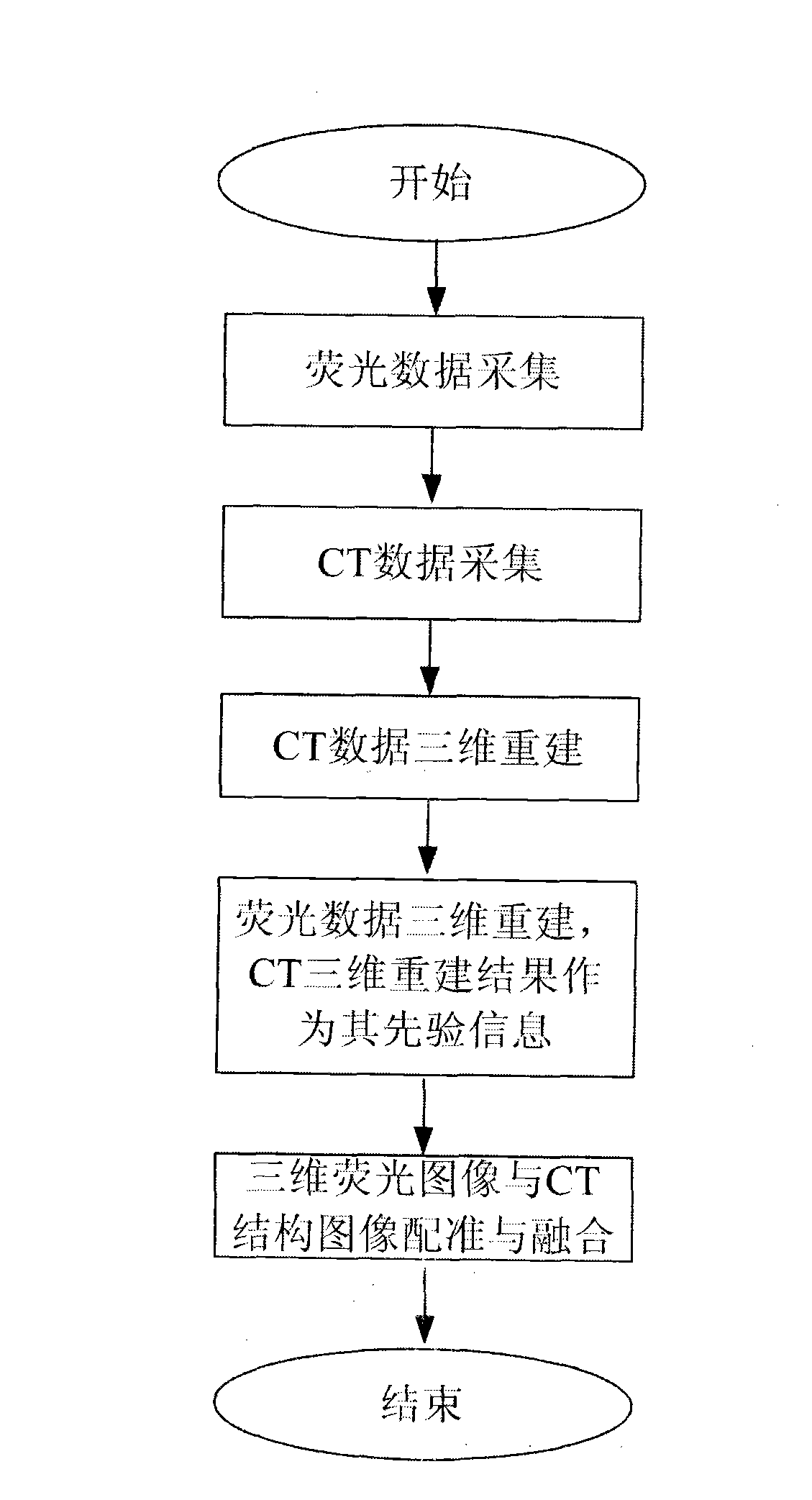
In vivo small animal fluorescent molecular tomography imaging system and method
InactiveCN103070673AImprove signal-to-noise ratioShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRotary stageFluorescence
The invention discloses an in vivo small animal fluorescent molecular tomography imaging system and method; the system comprises a near infrared laser, a beam expander, an electric control rotary table, an object to be imaged, a narrowband filter plate, a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera, an X-ray emitter, an X-ray detector and a computer; the CDD camera and the narrowband filter plate are fixedly arranged in a direction which is in parallel with an excitation light source; the excitation light source, the object to be imaged, the CCD camera and the narrowband filter plate are arranged on a same straight line; the X-ray emitter and the detector are arranged on a direction which is vertical to the excitation light source; the X-ray emitter, the object to be imaged and the X-ray detector are arranged on a same straight line; and the computer is connected with the CCD camera, the X-ray emitter and the electric control rotary table. According to the method, the multi-modal information fusion of an in vivo small animal is realized, and the method has the advantages of simple operation process and short data acquisition time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
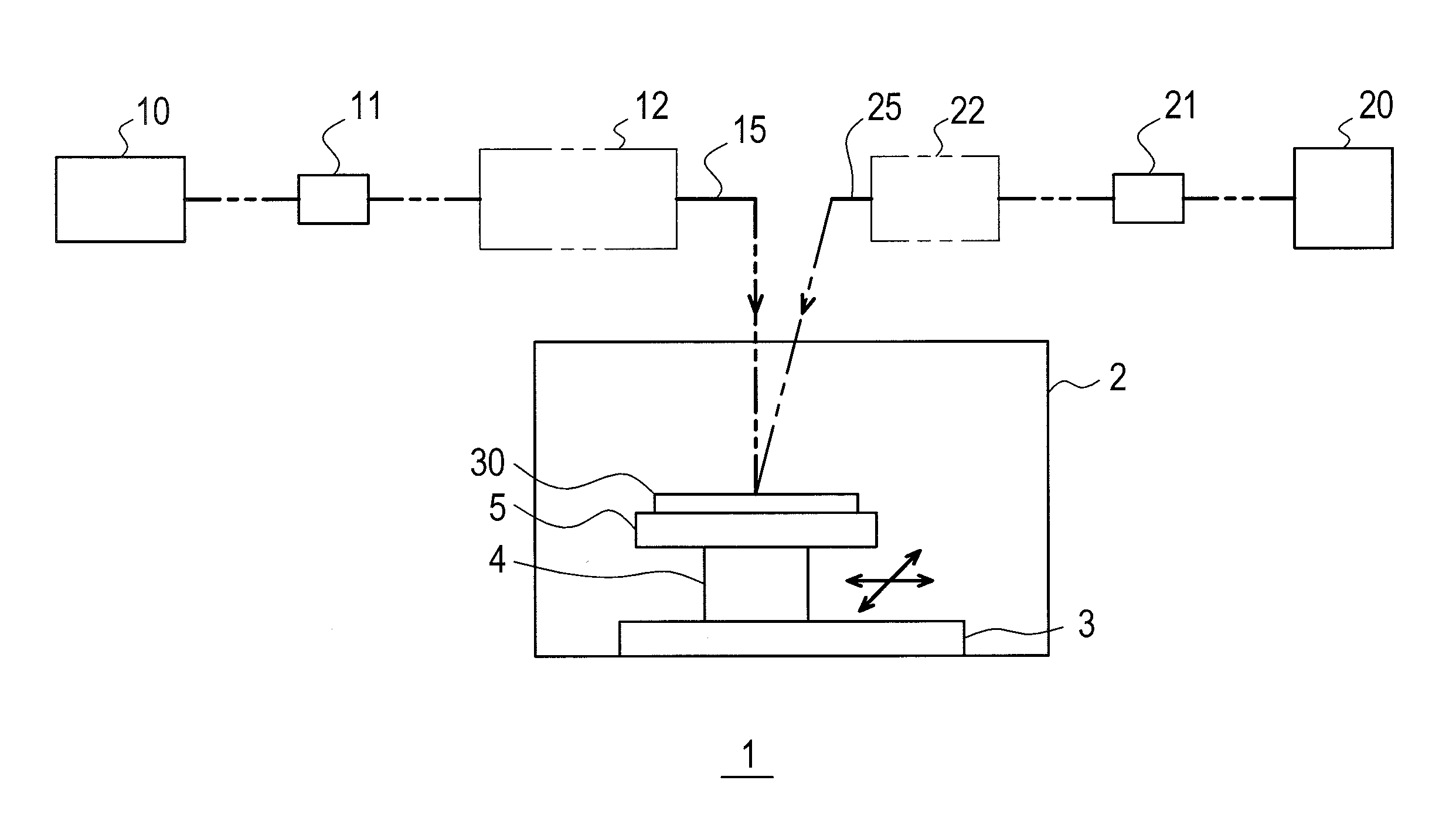
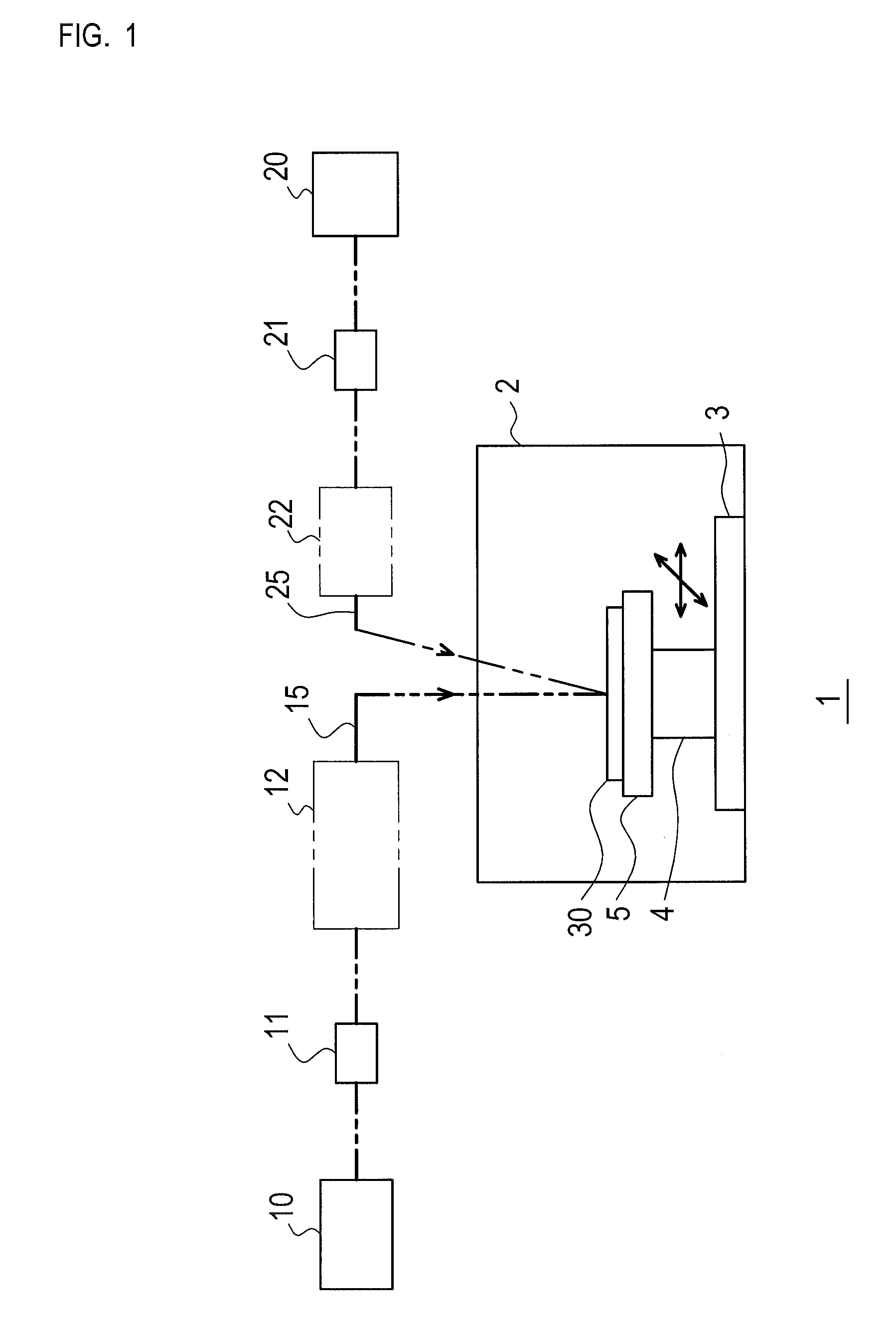
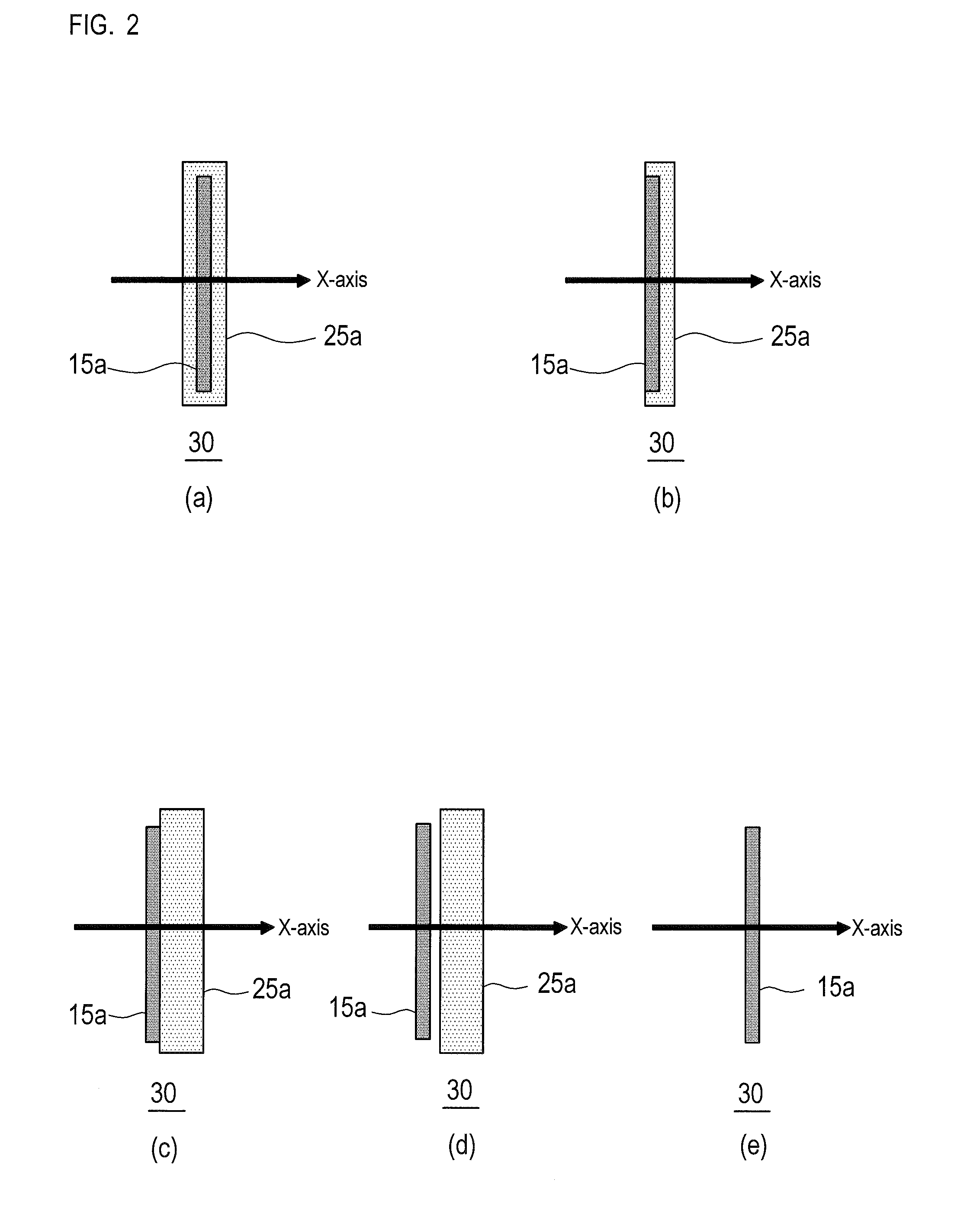
Laser annealing apparatus and laser annealing method
InactiveUS20120234810A1Avoid smallInhibit temperature riseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser sourcePenetration depth
The present invention provides an efficient heat treatment such as activation treatment of impurities on a substrate such as a thick silicon wafer with large heat capacity by laser annealing.Provided is a laser annealing apparatus 1 for heat-treating a surface of a substrate 30 comprising: a pulse oscillation laser source 10 which generates a pulse laser with gentle rise time and long pulse width; a continuous wave laser source 20 which generates a near-infrared laser for assisting annealing; optical systems 12, 22 which shape and guide beams 15, 25 of the two types of lasers respectively so as to irradiate the surface of the substrate 30 therewith; and a moving device 3 which moves the substrate 30 relatively to the laser beams 15, 25 to allow scanning of the combined irradiation of the two types of laser beams. According to this apparatus, deep activation of impurities can be performed in a thick semiconductor substrate with large heat capacity while securing sufficient light penetration depth and thermal diffusion length therefor.
Owner:JAPAN STEEL WORKS LTD
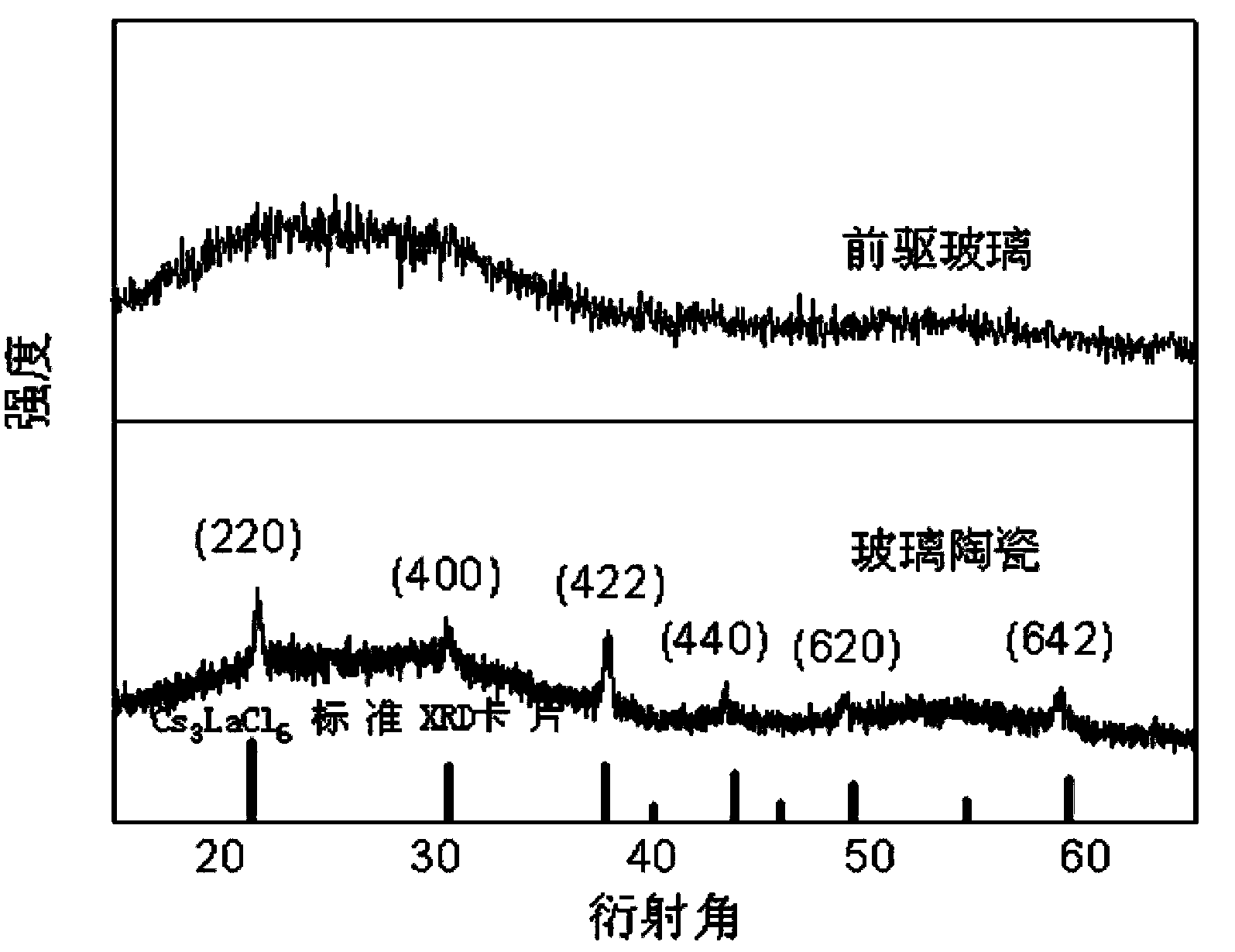
Cs3LaCl6 nanocrystalline-containing transparent chalcohalide glass ceramic and its preparation
The invention discloses a Cs3LaCl6 nanocrystalline-containing transparent chalcohalide glass ceramic and its preparation. The glass ceramic comprises: 40-60 mol% of GeS2; 25-35 mol% of Ga2S3; 2-8 mol% of La2S3; 2-8 mol% of LaCl3; 10-20 mol% of CsCl; and 0.01-0.2 mol% of Re2S3, wherein Re represents a rare earth ion (such as Nd, Er). The preparation process of the glass ceramic consists of melt quenching preparation of precursor glass and subsequent crystallization heat treatment of the precursor glass. By component exploration, the transparent chalcohalide glass ceramic containing the single Cs3LaCl6 nanocrystalline can be prepared. The nanocomposite material has excellent properties of under near-infrared transfer and visible up-conversion luminescence, and has potential application in near infrared lasers, optical fiber amplifiers, three-dimensional solid-state display and other fields.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
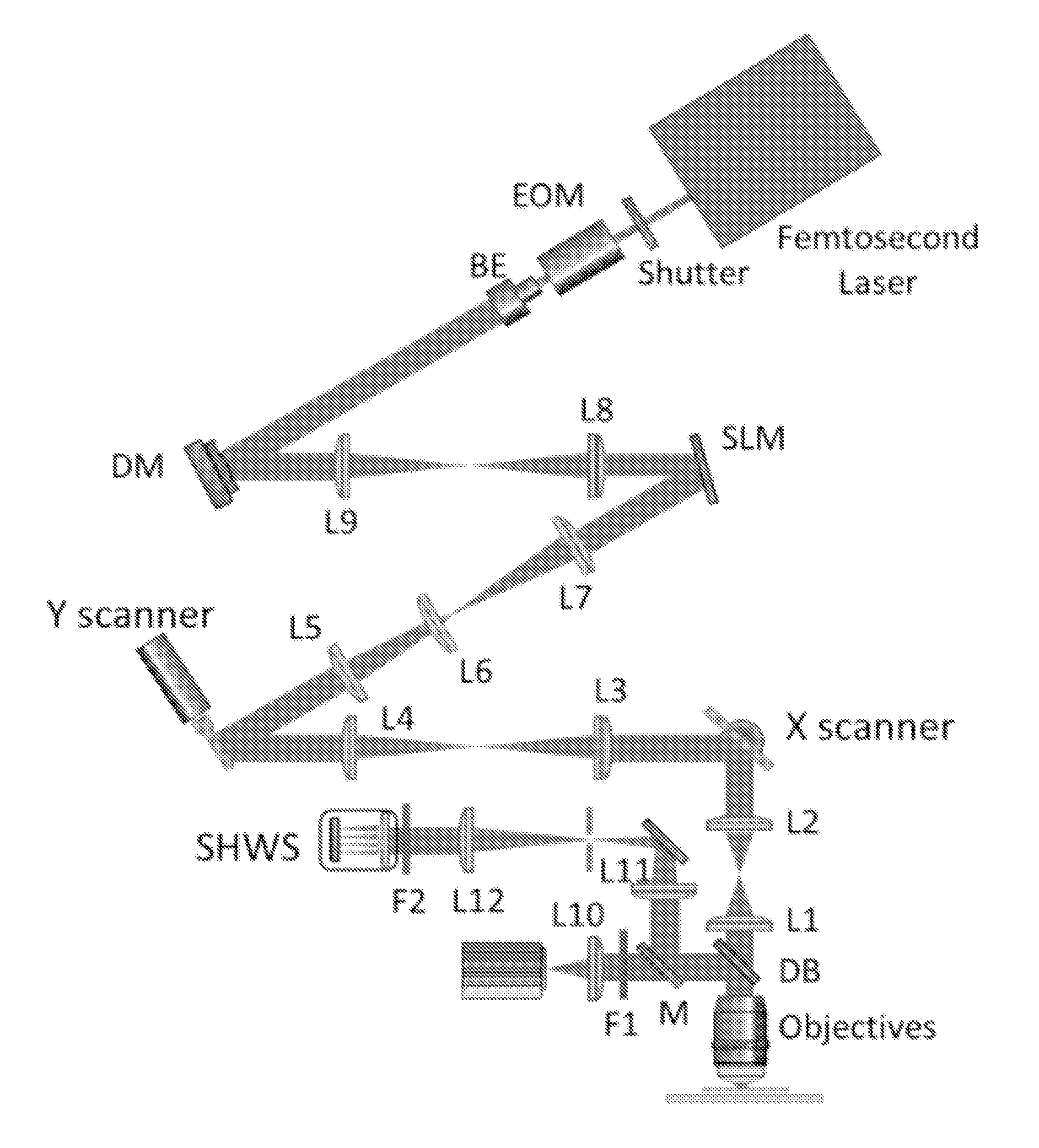
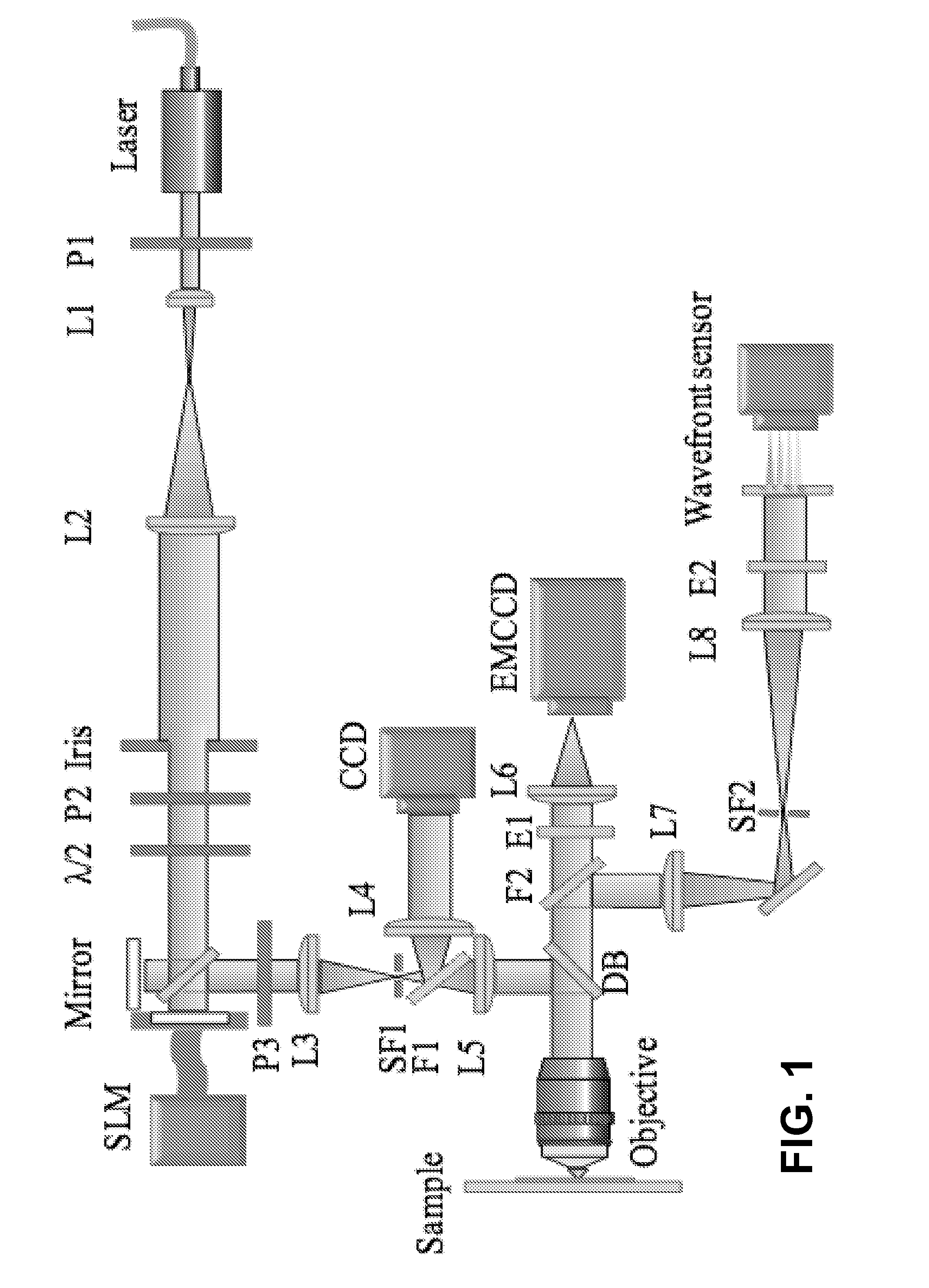
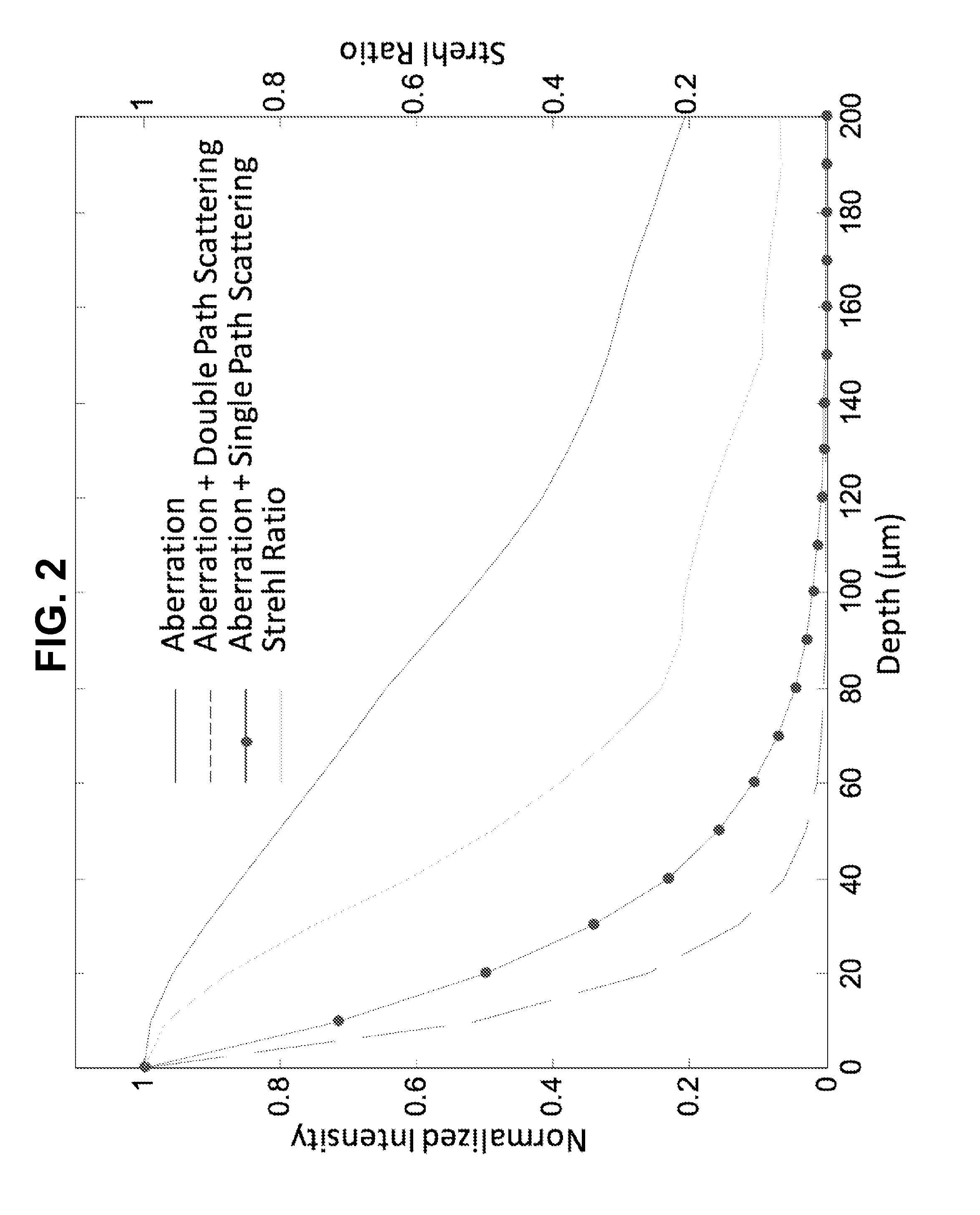
Interferometric focusing of guide-stars for direct wavefront sensing
ActiveUS20160003740A1Limited resolutionReduce penetration depthOptical measurementsPhotometryWavefront sensorNear infrared laser
Interferometric focusing (IF), rather than conventional geometric focusing, of excitation light onto a guide-star that is embedded deeply in tissue, increases its fluorescence intensity. The method can extend the depth of wavefront measurement and improve correction inside of tissues because of its ability to suppress both scattering of diffuse light and aberration of ballistic light. The results showed more than two times improvement in SNR and RMS error of the wavefront measurement. Although only ballistic light in the excitation path is corrected, the intensity after wavefront correction increased by 1.5 times. When applying IF to a two-photon microscope with a near infra-red laser, this method would further extend the measurement depth and achieve high SNR for the wavefront sensor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com