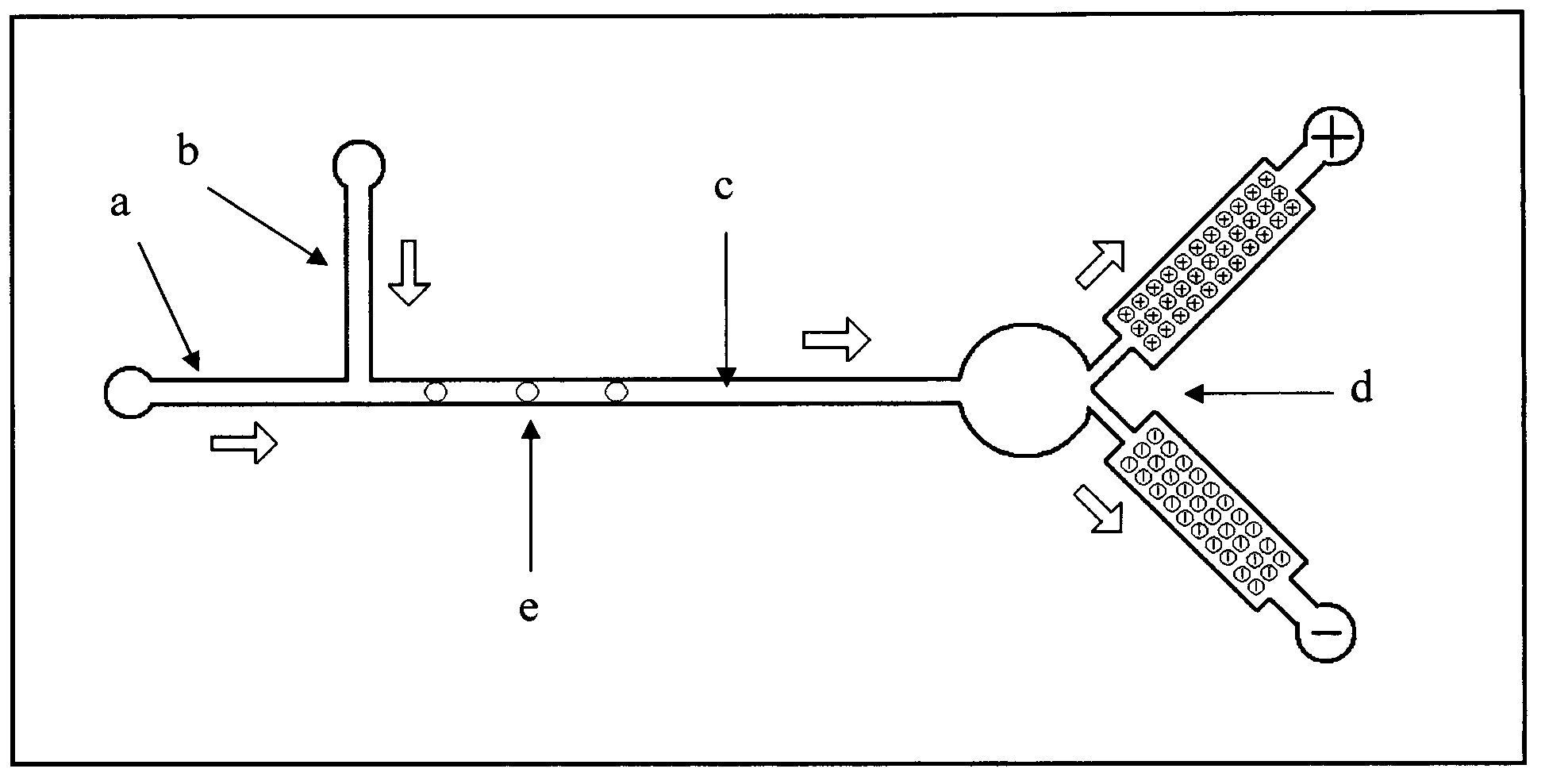
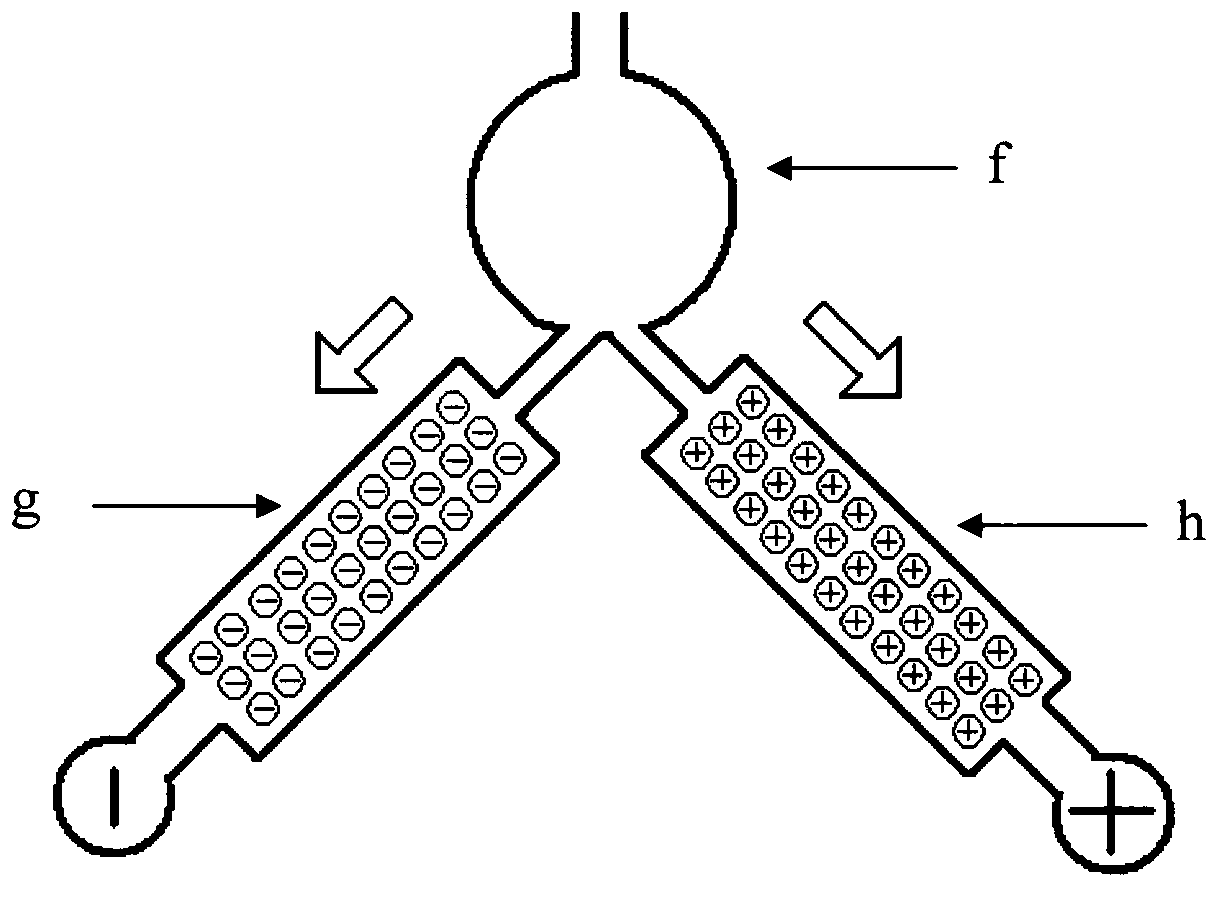
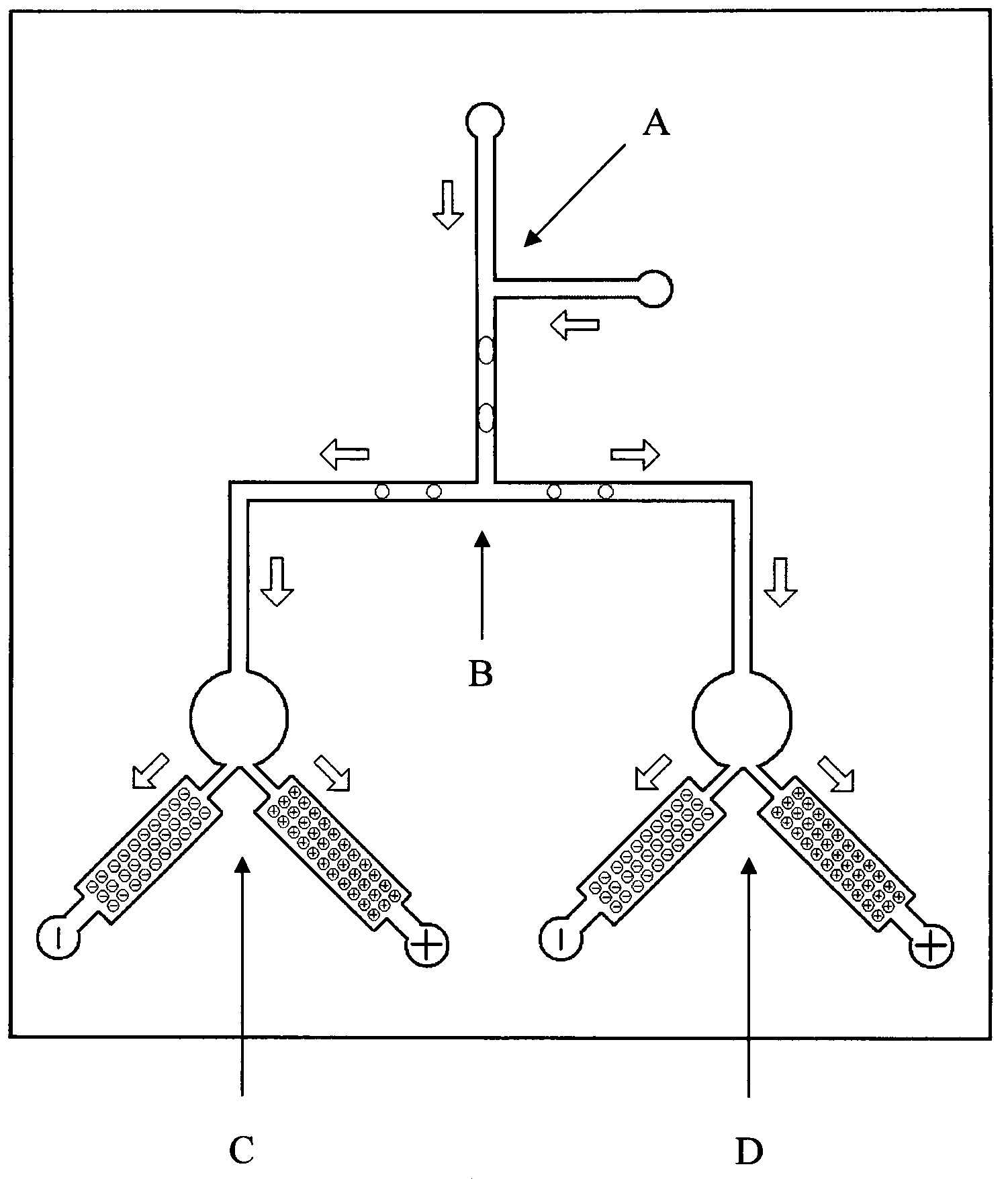
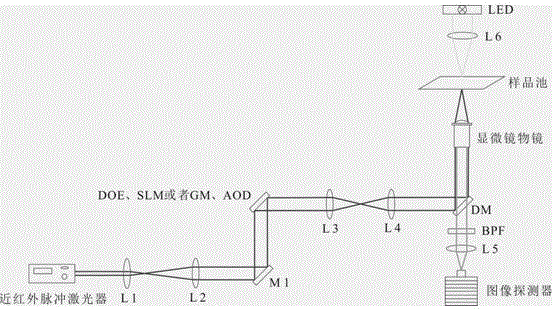
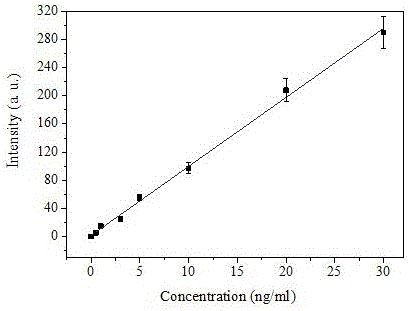
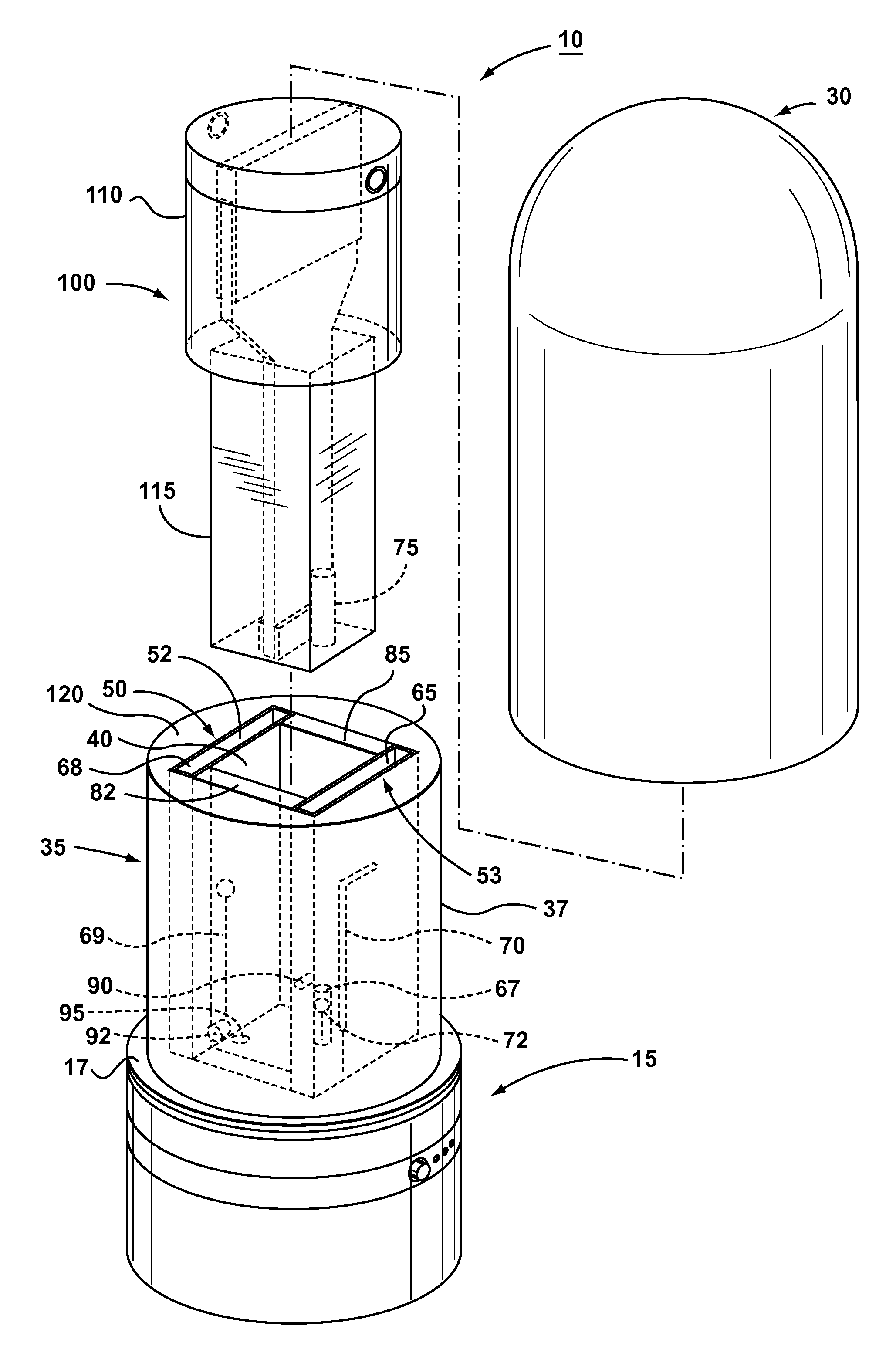
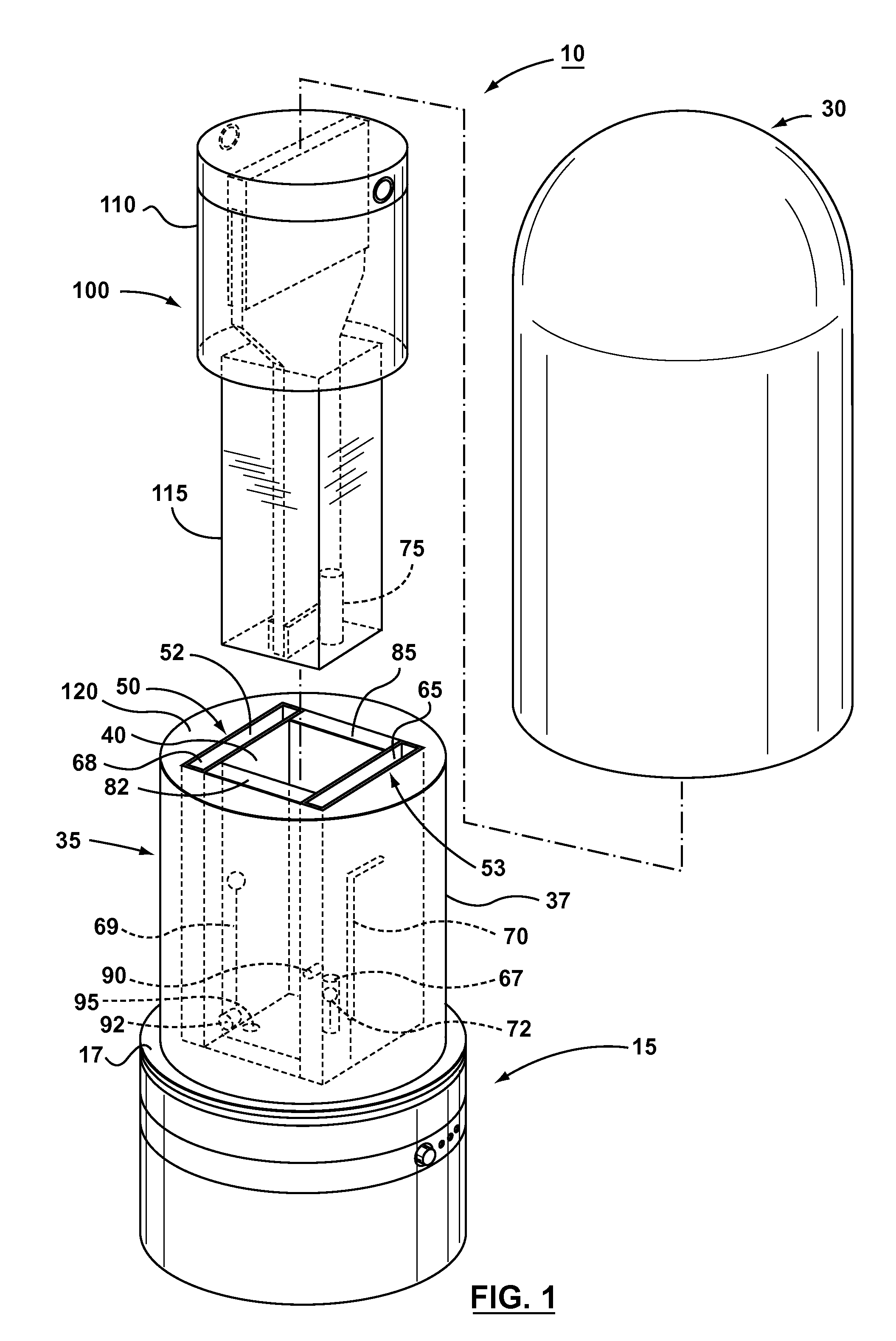
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1236 results about "Sample pool" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
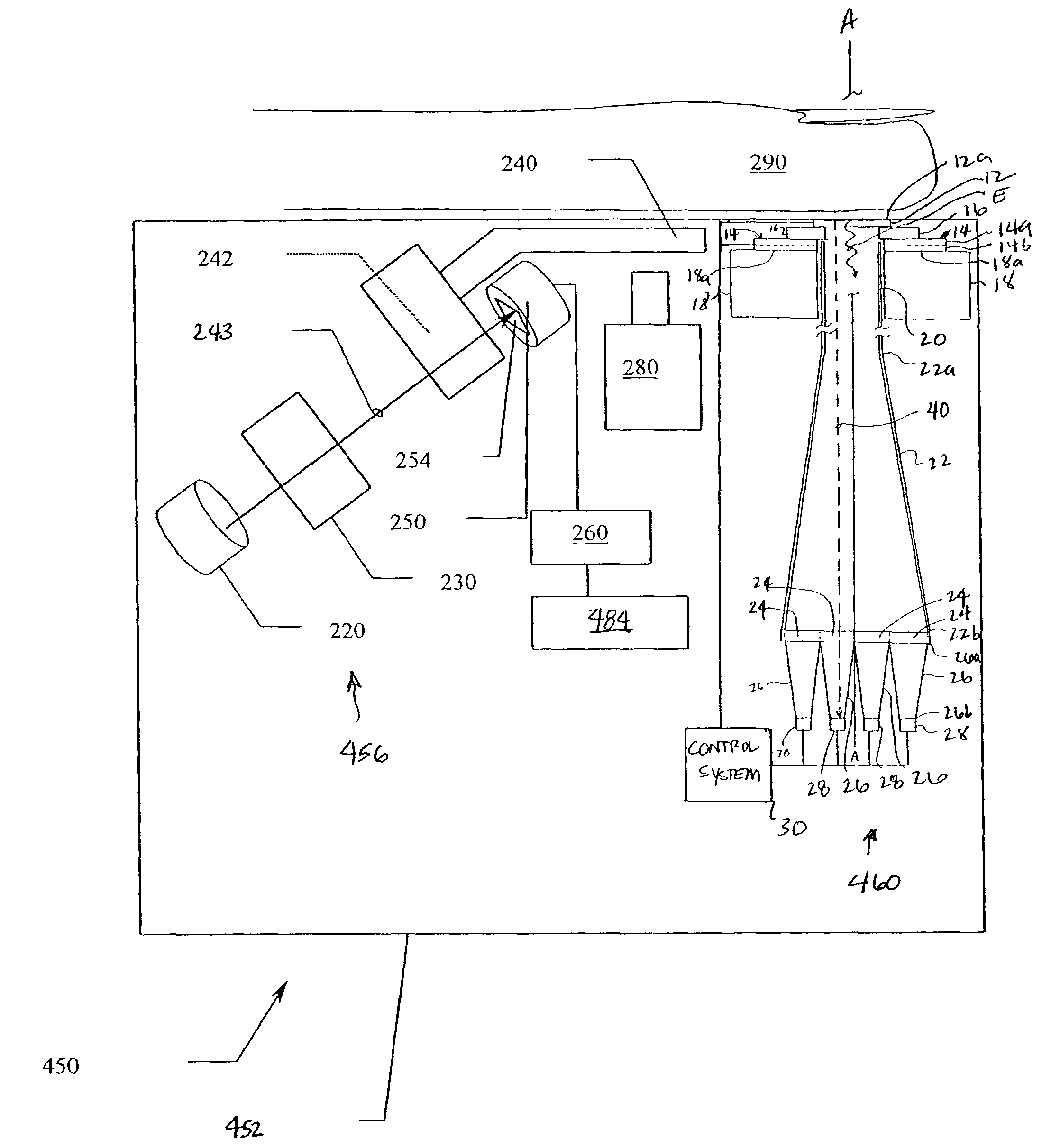
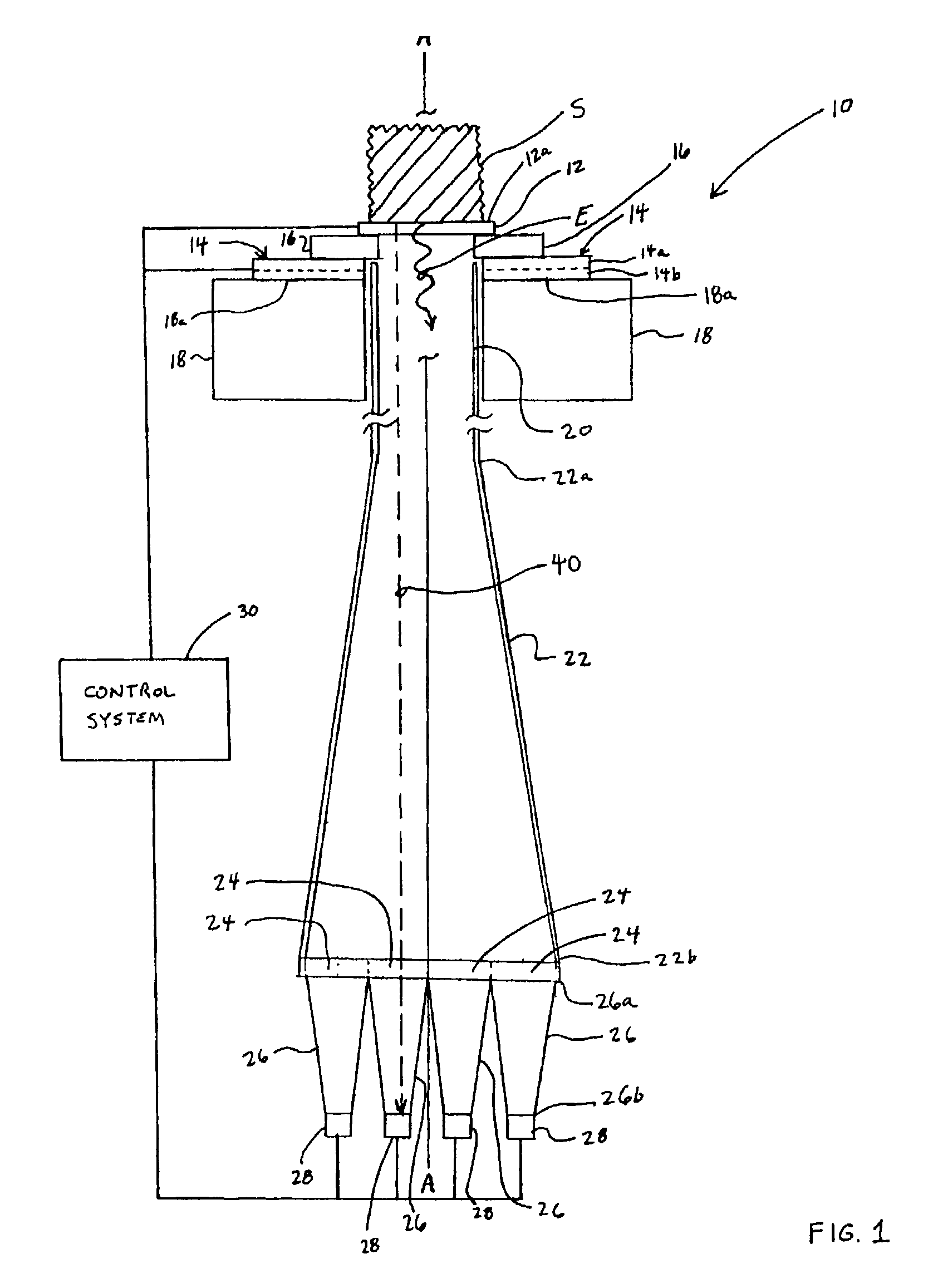
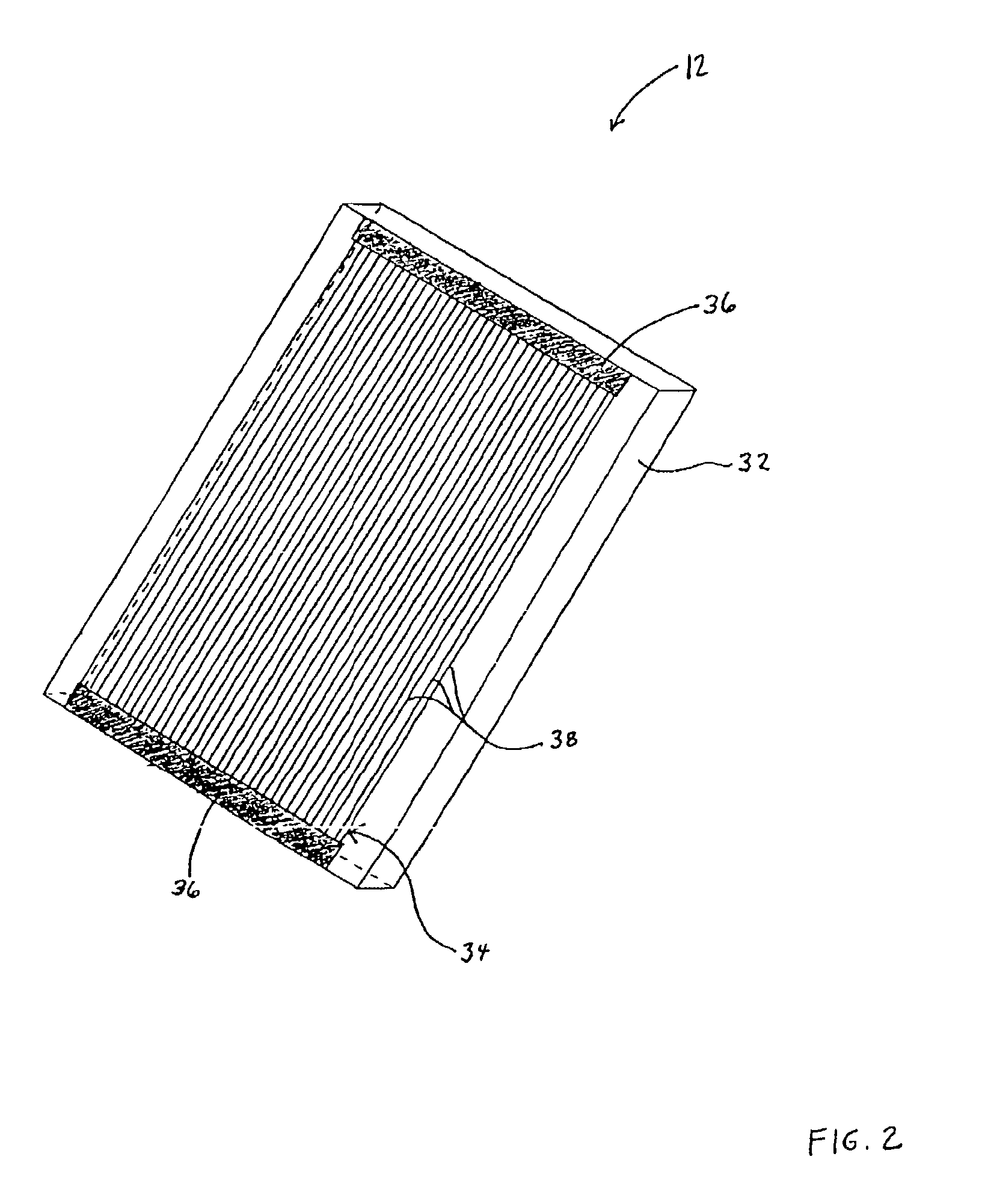
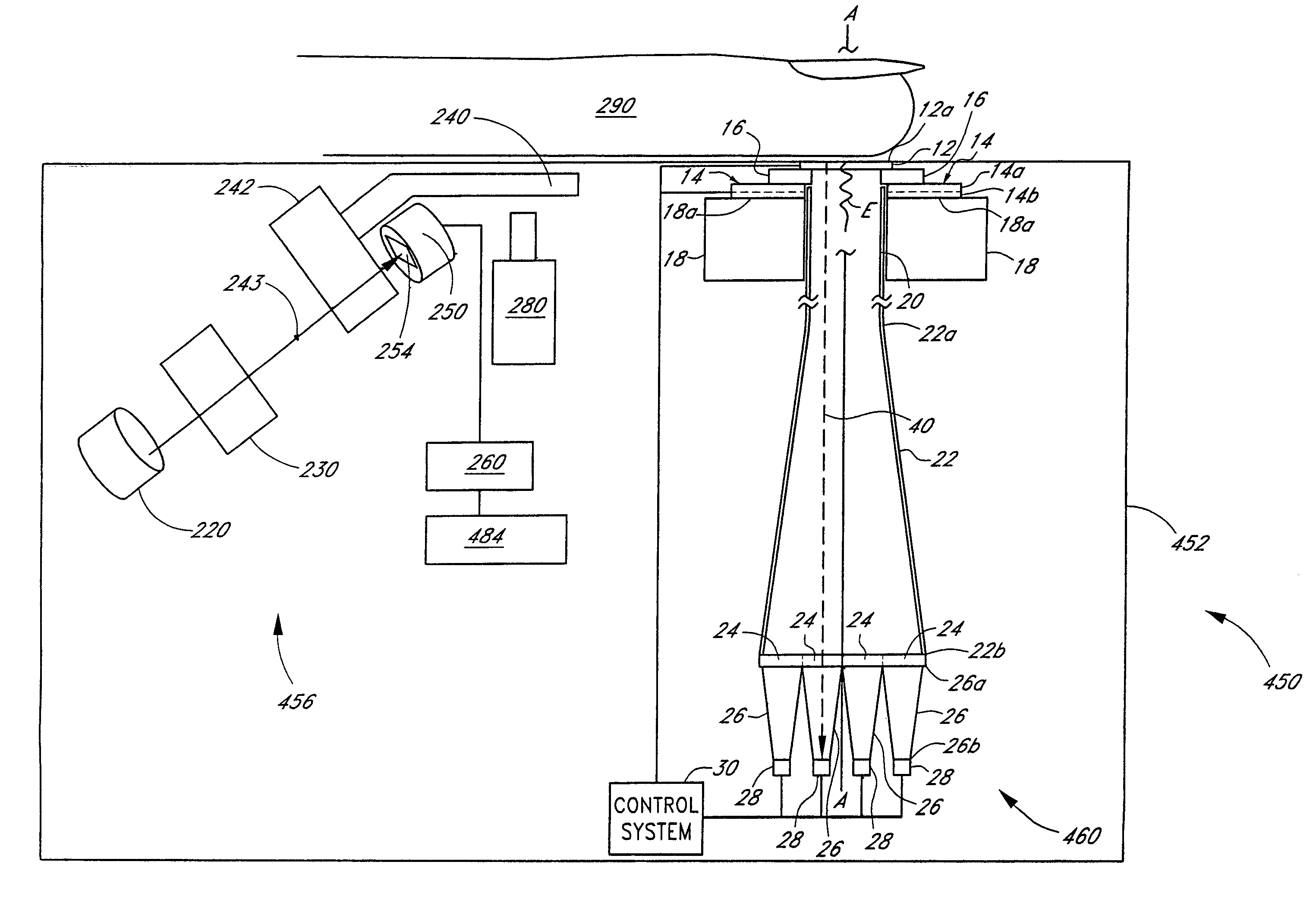
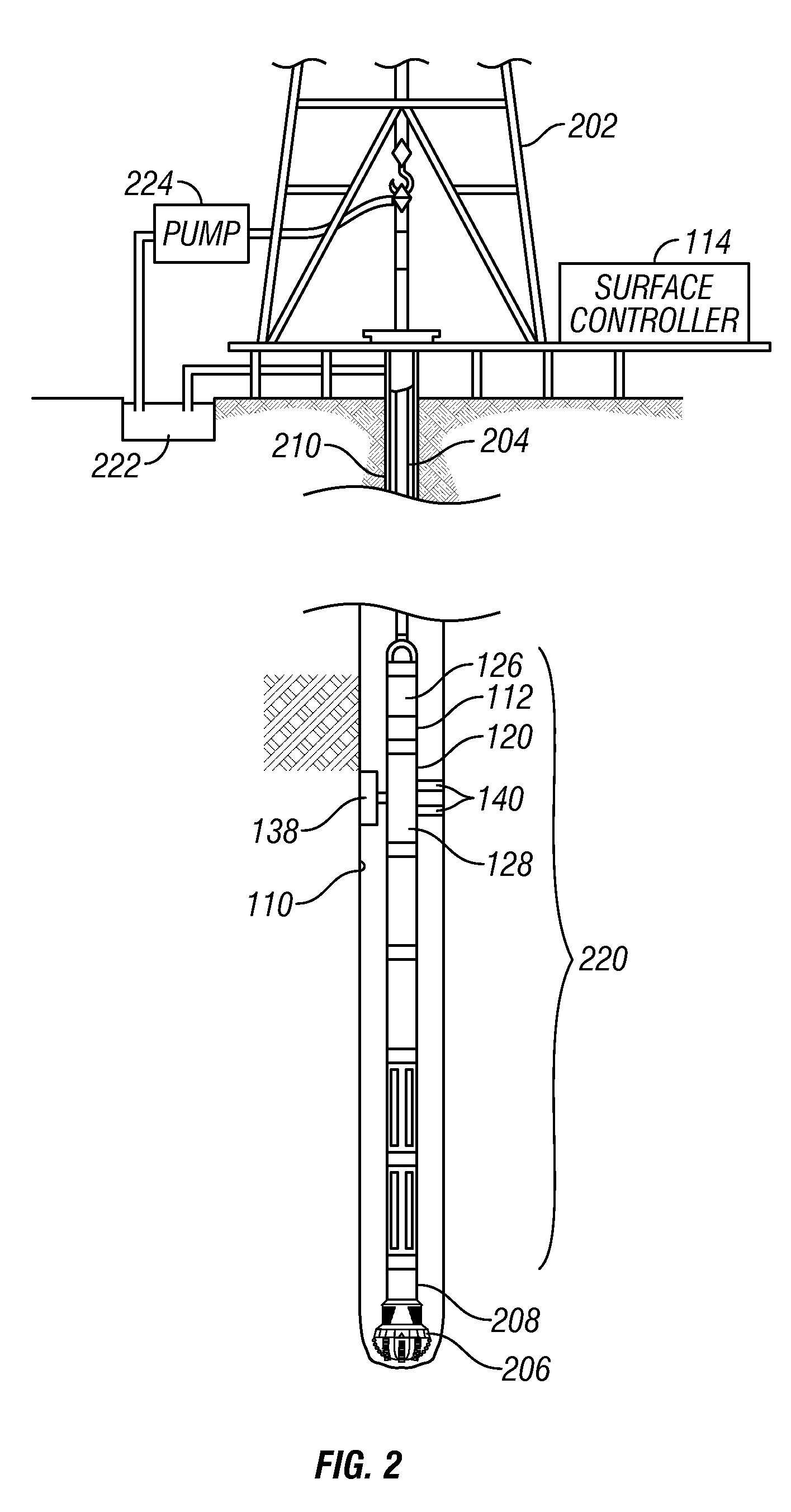
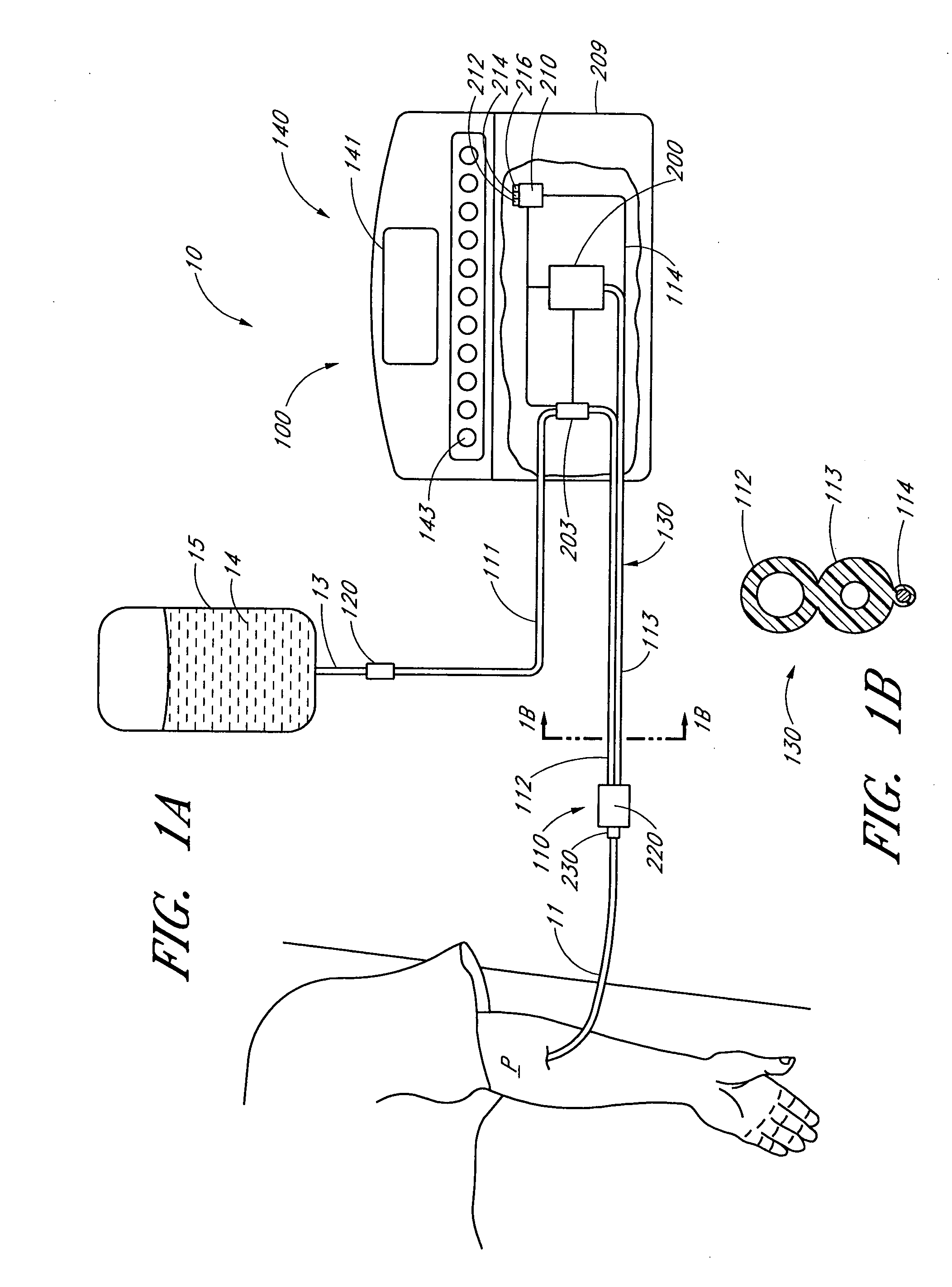
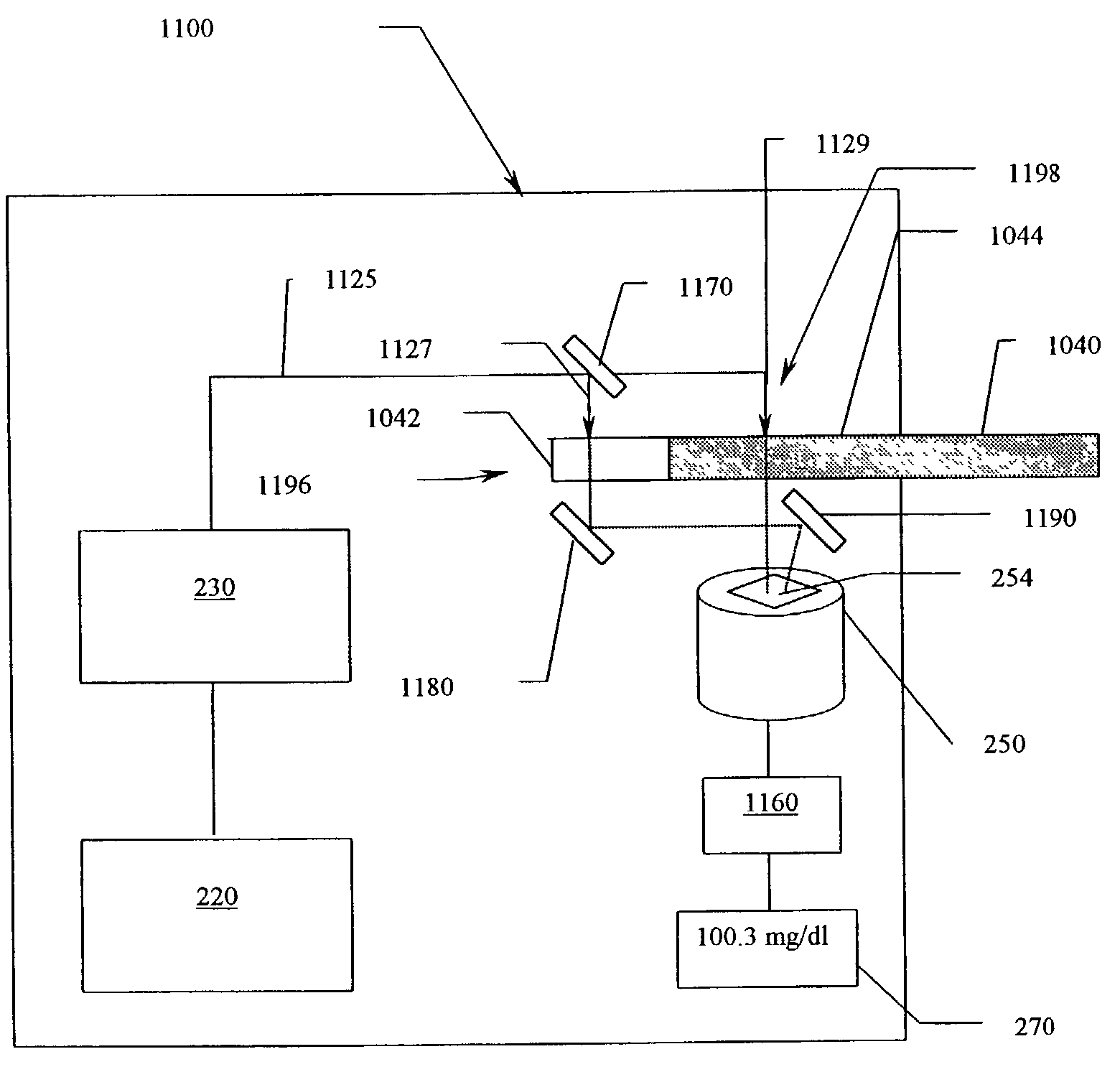
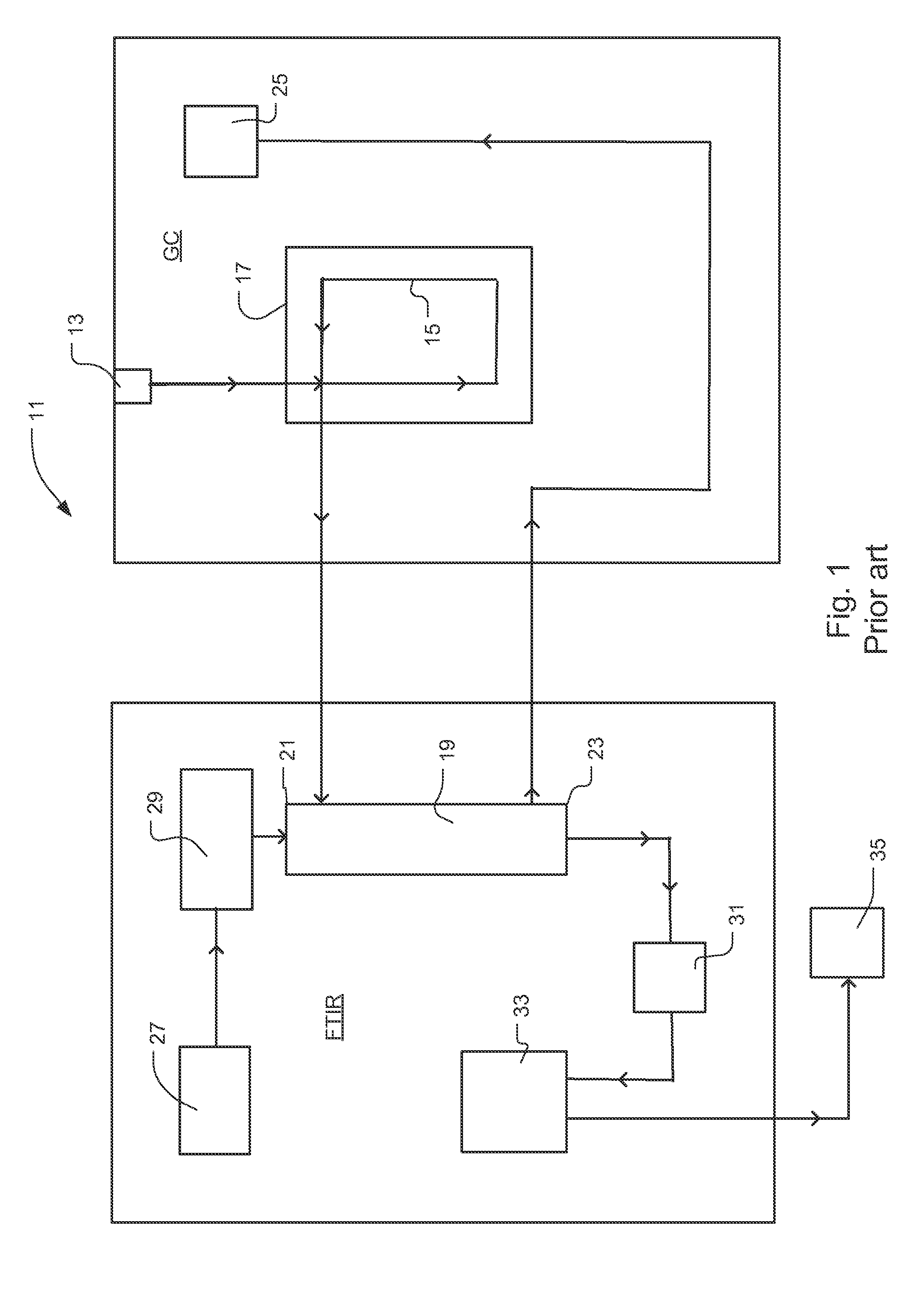
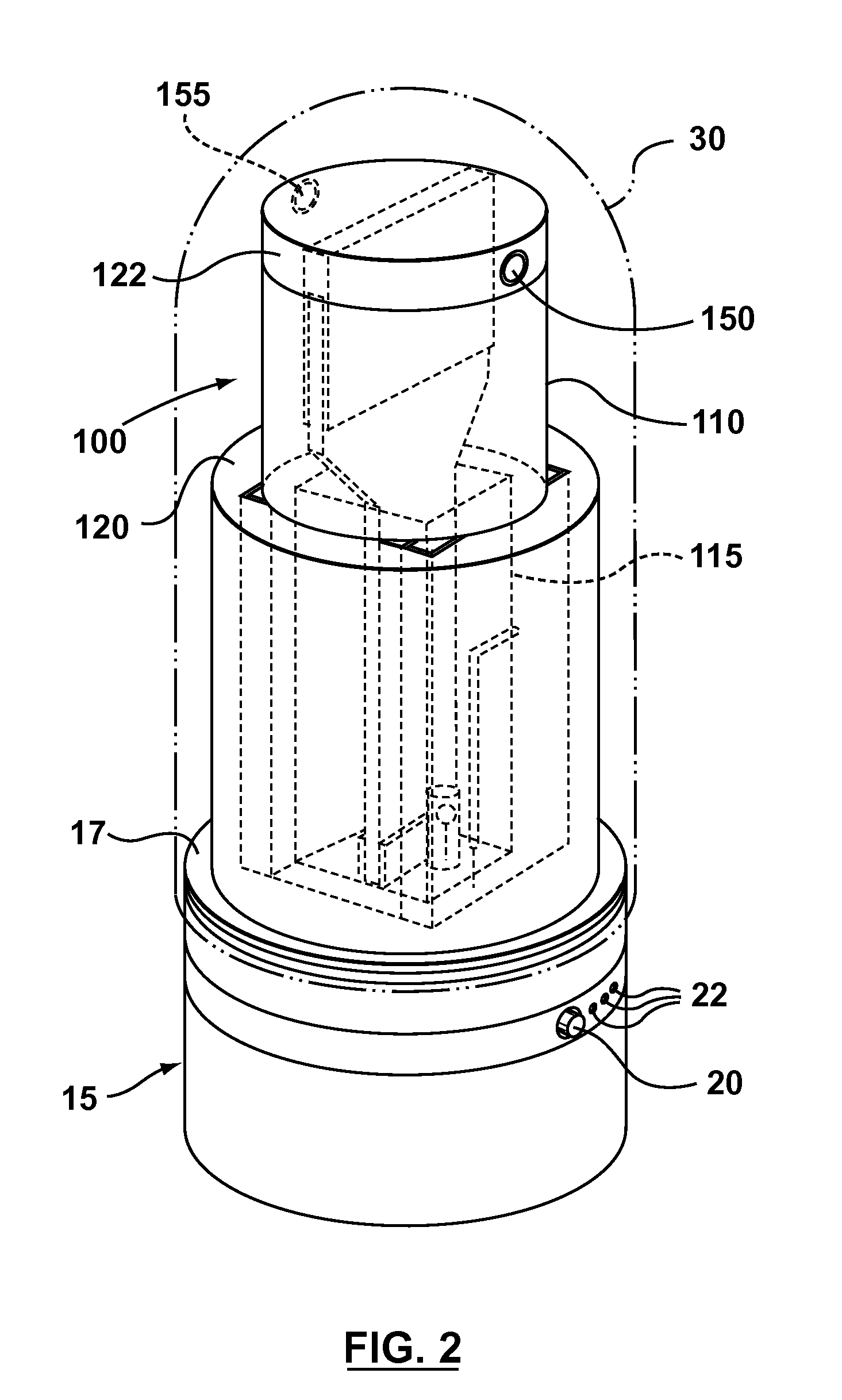
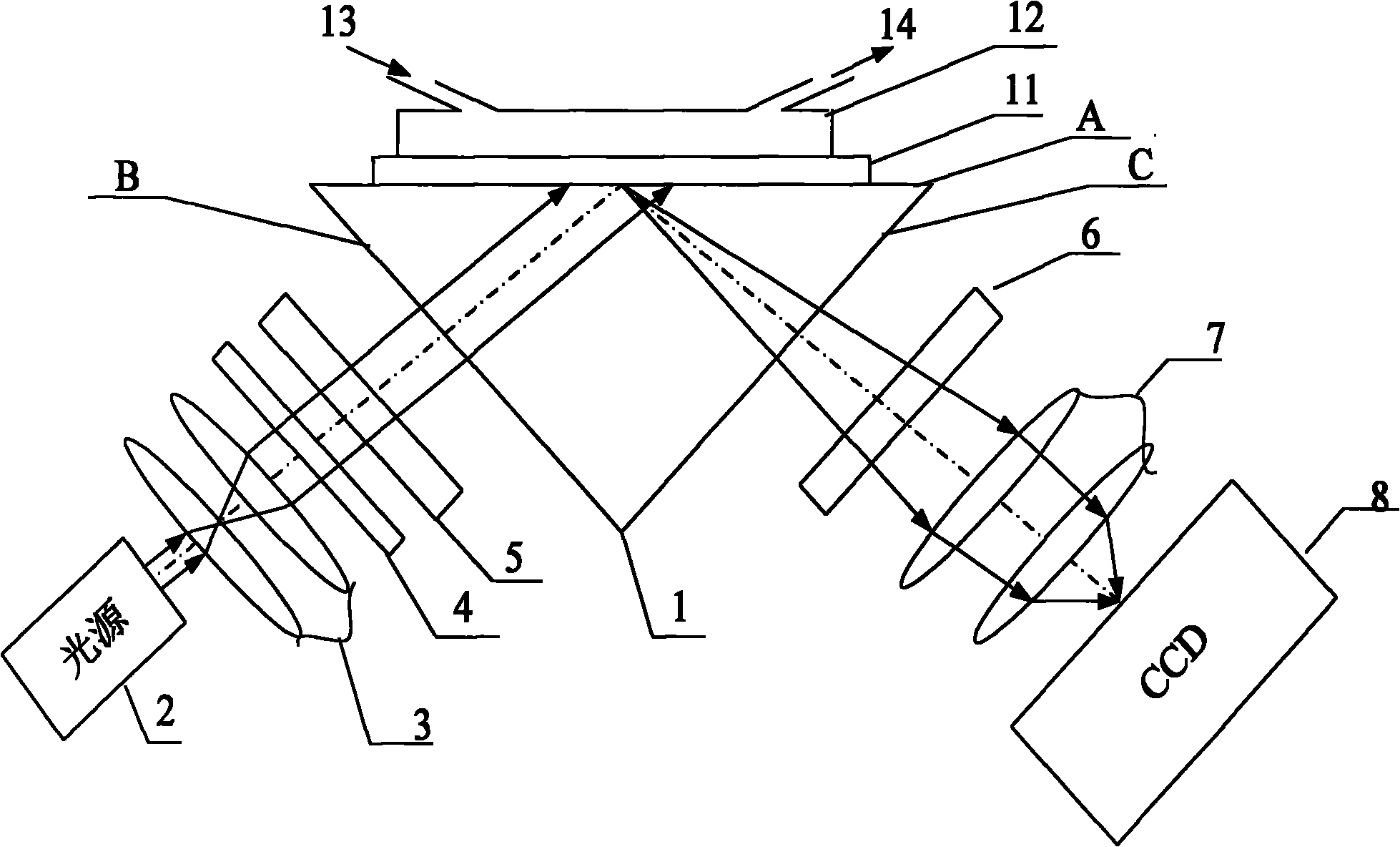
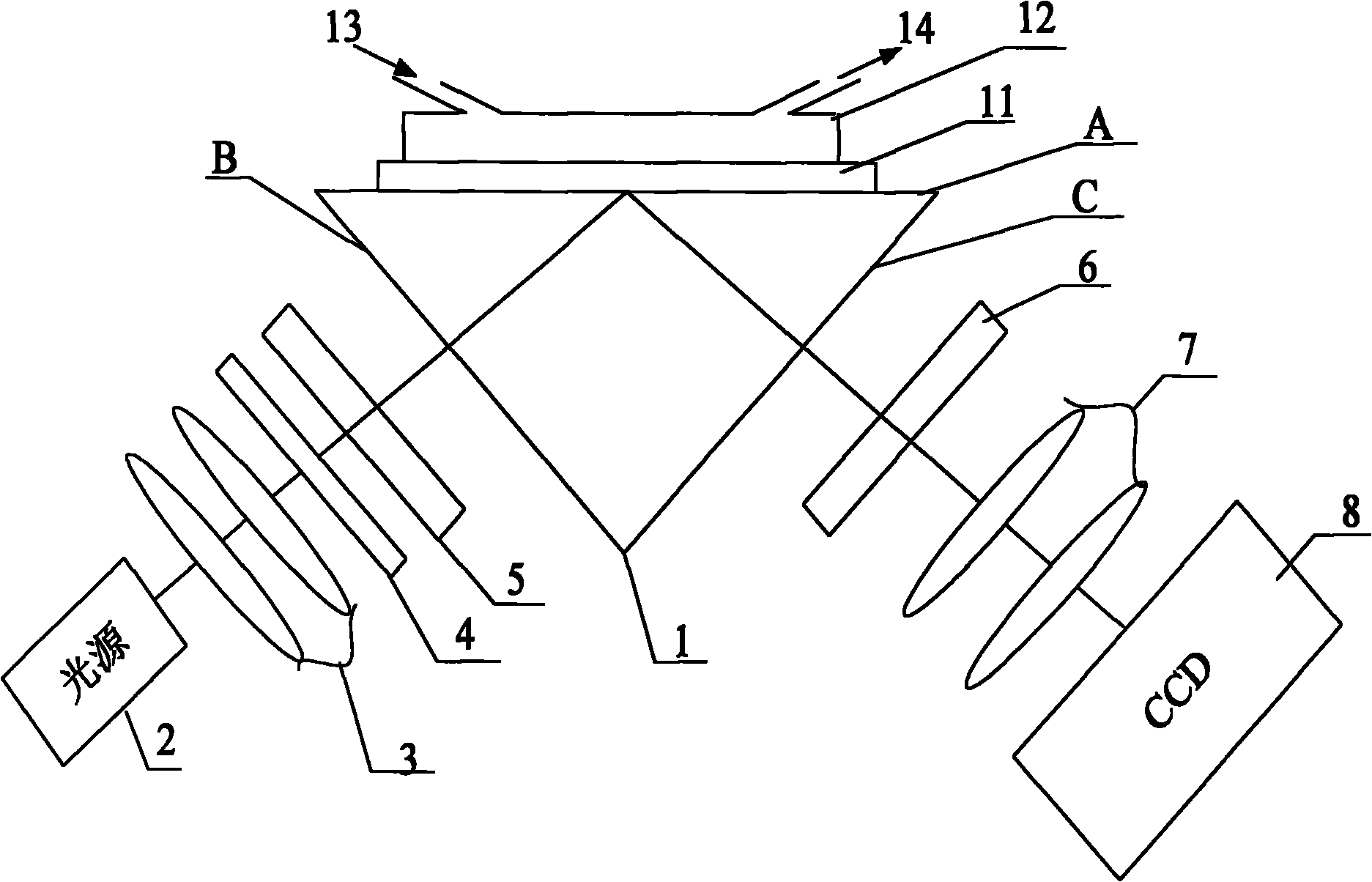
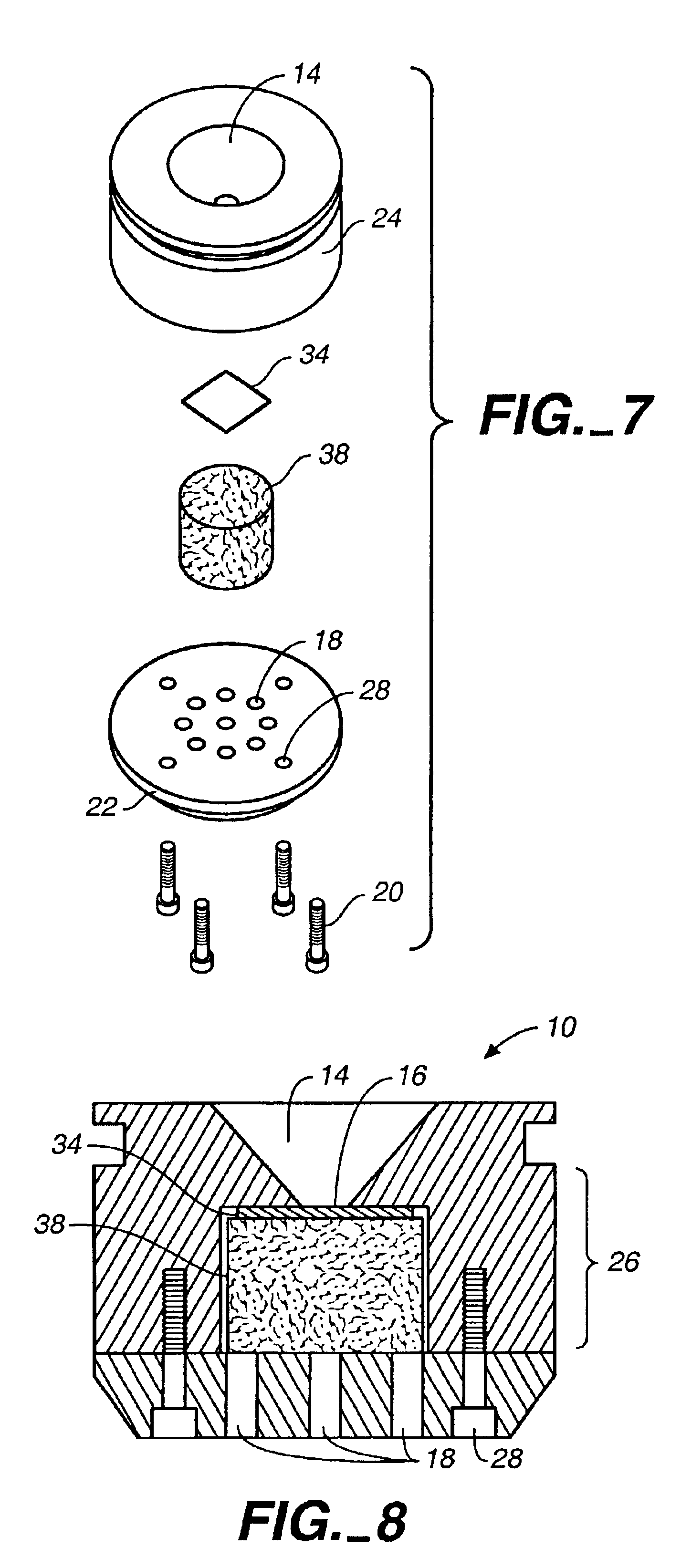
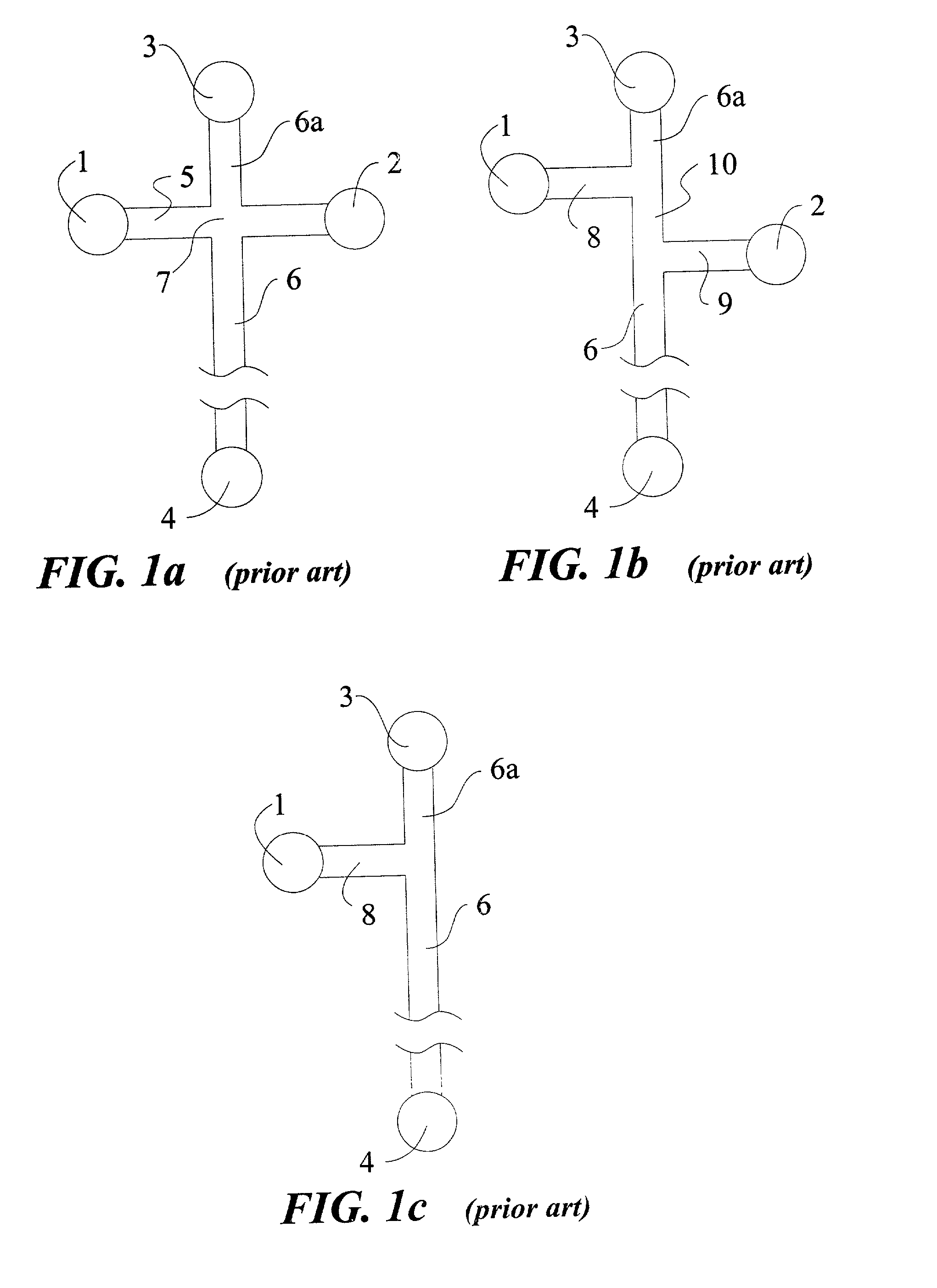
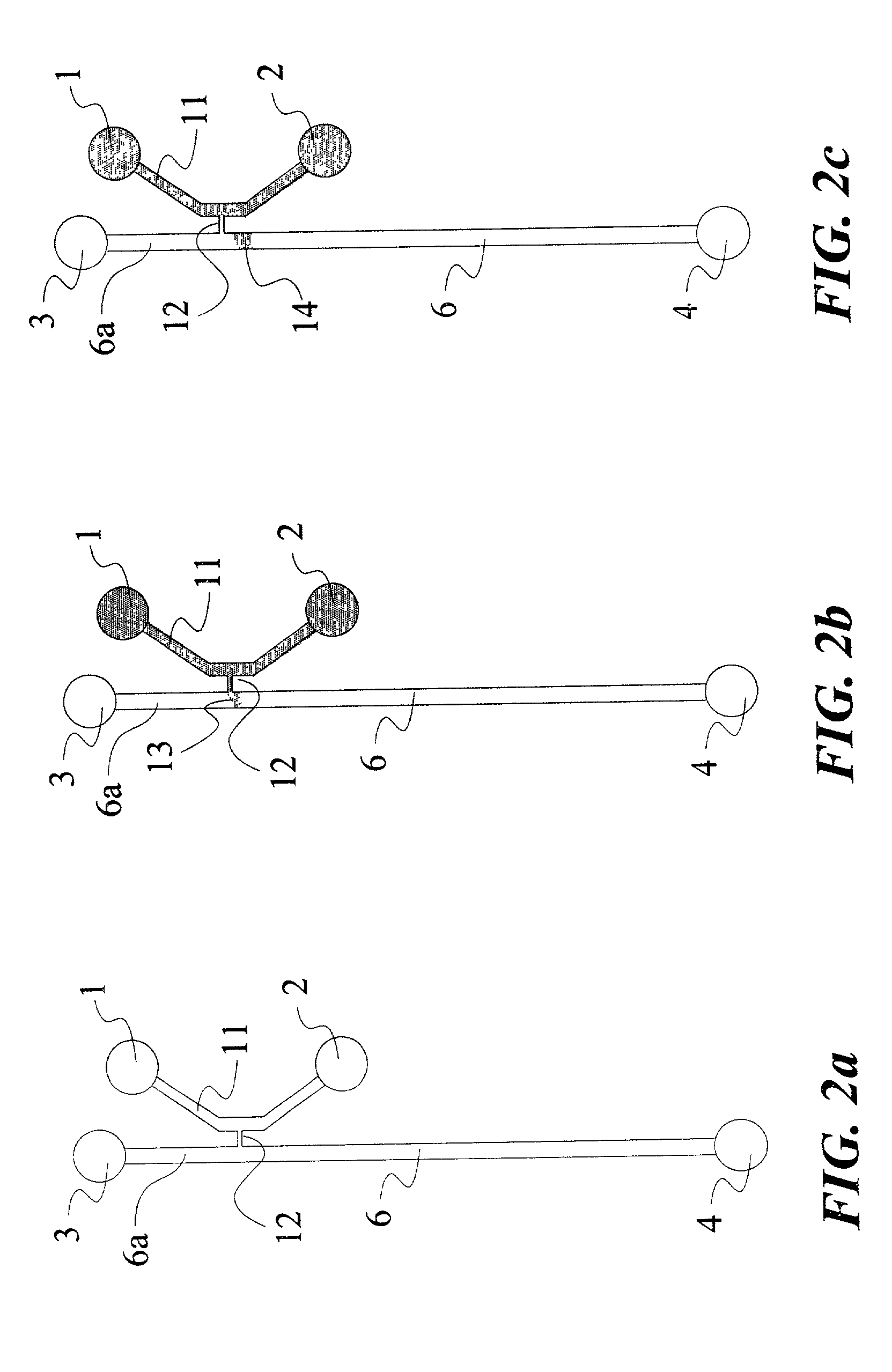
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
InactiveUS6989891B2Withdrawing sample devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpectral bandsCell wall
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
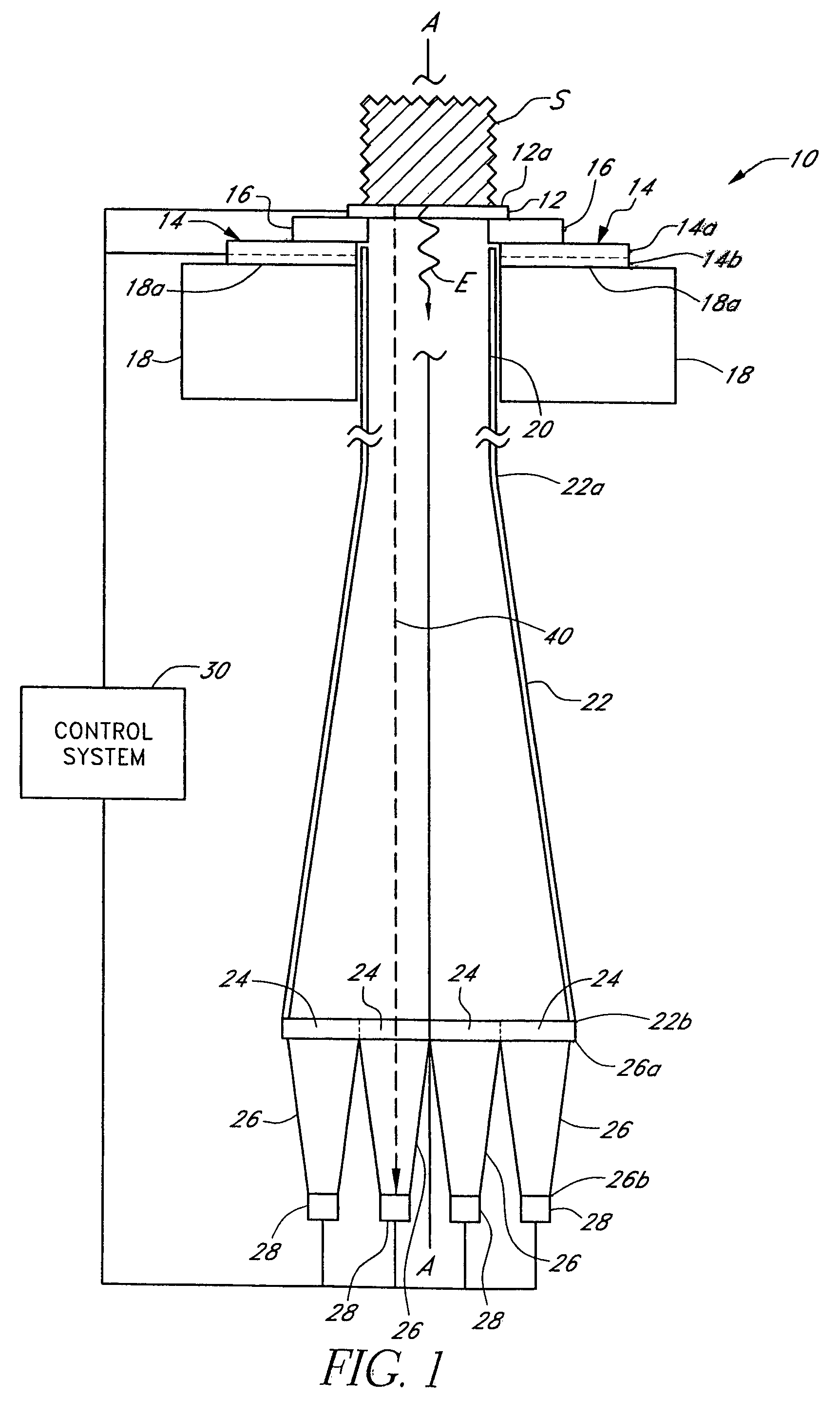
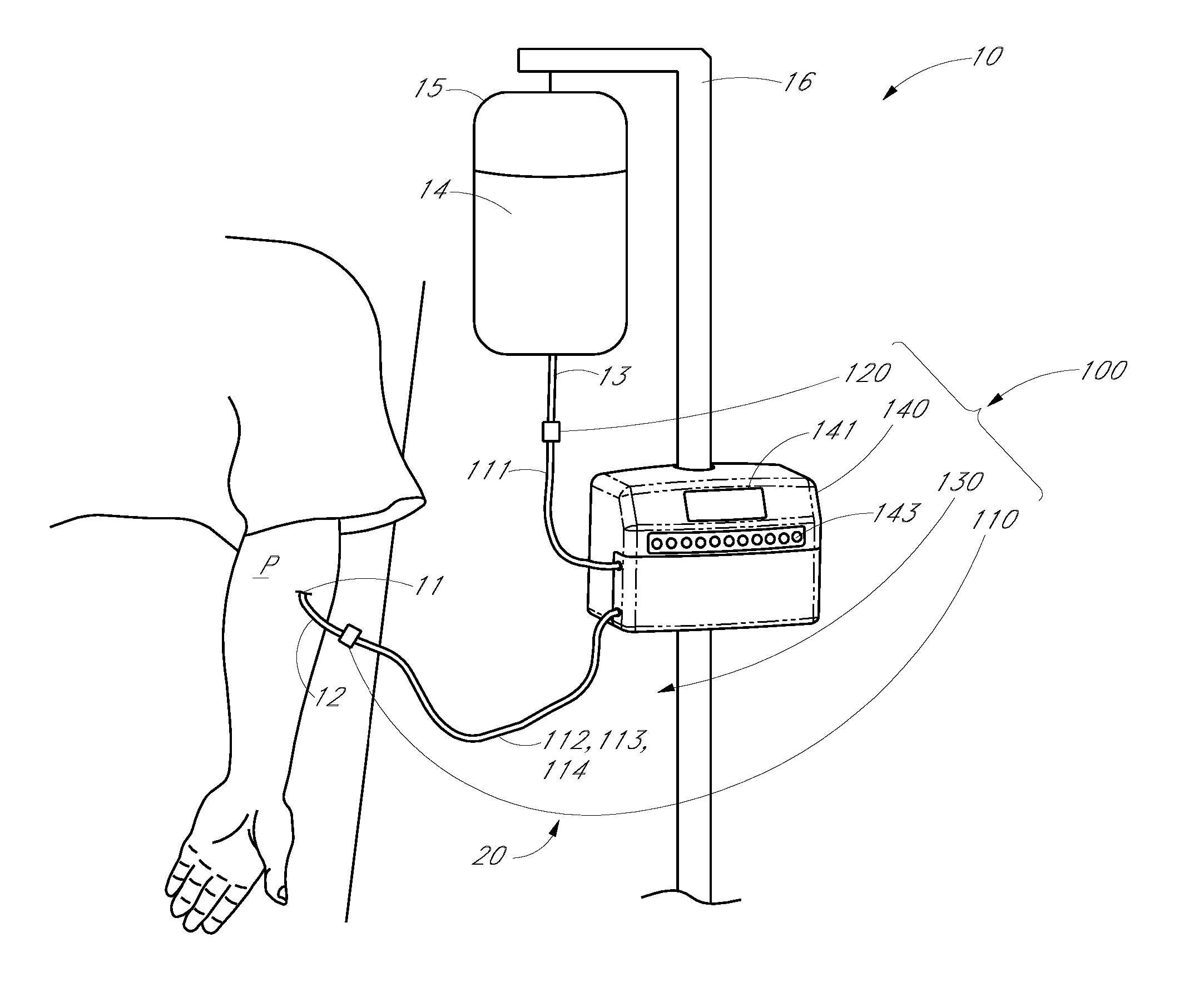
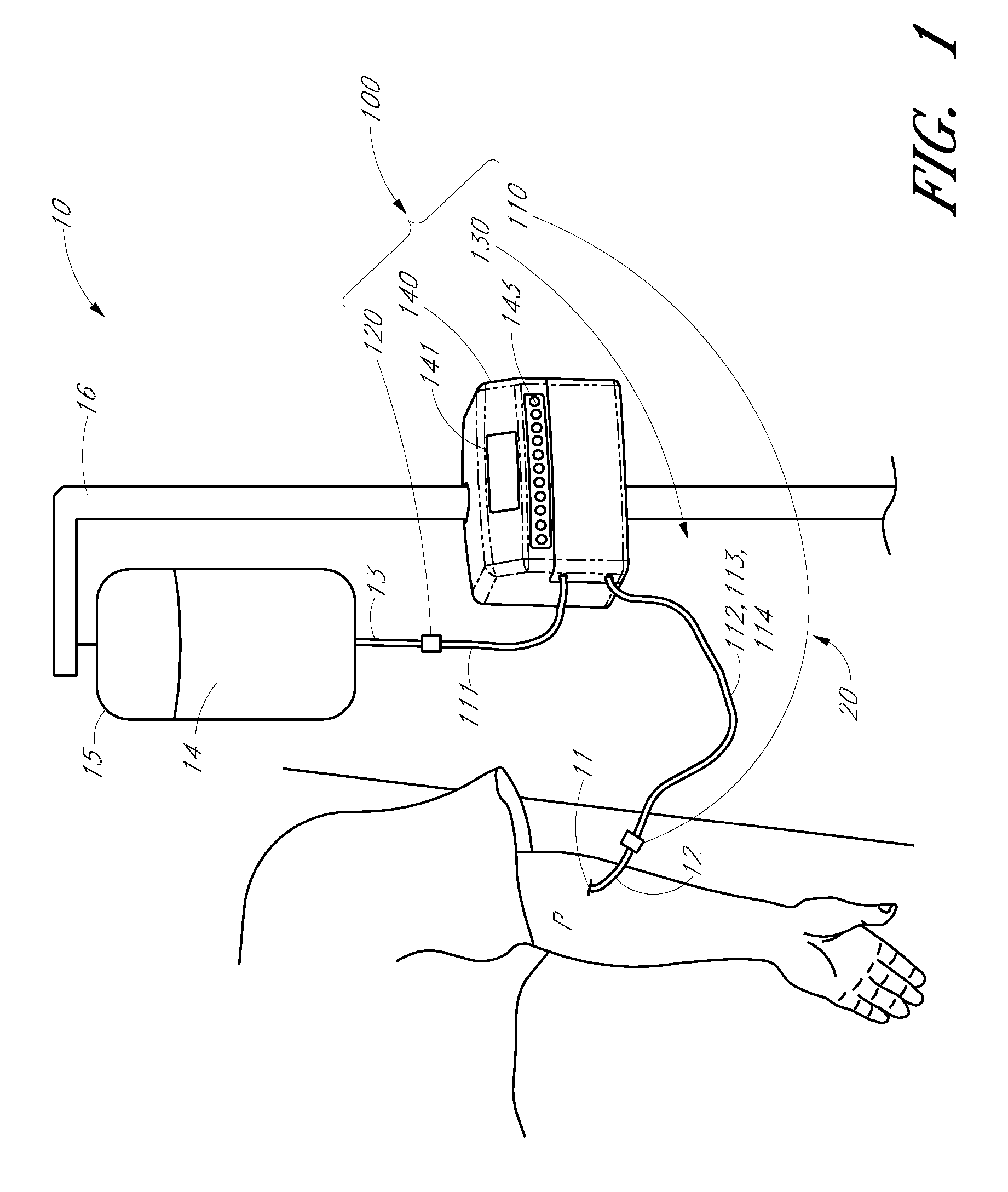
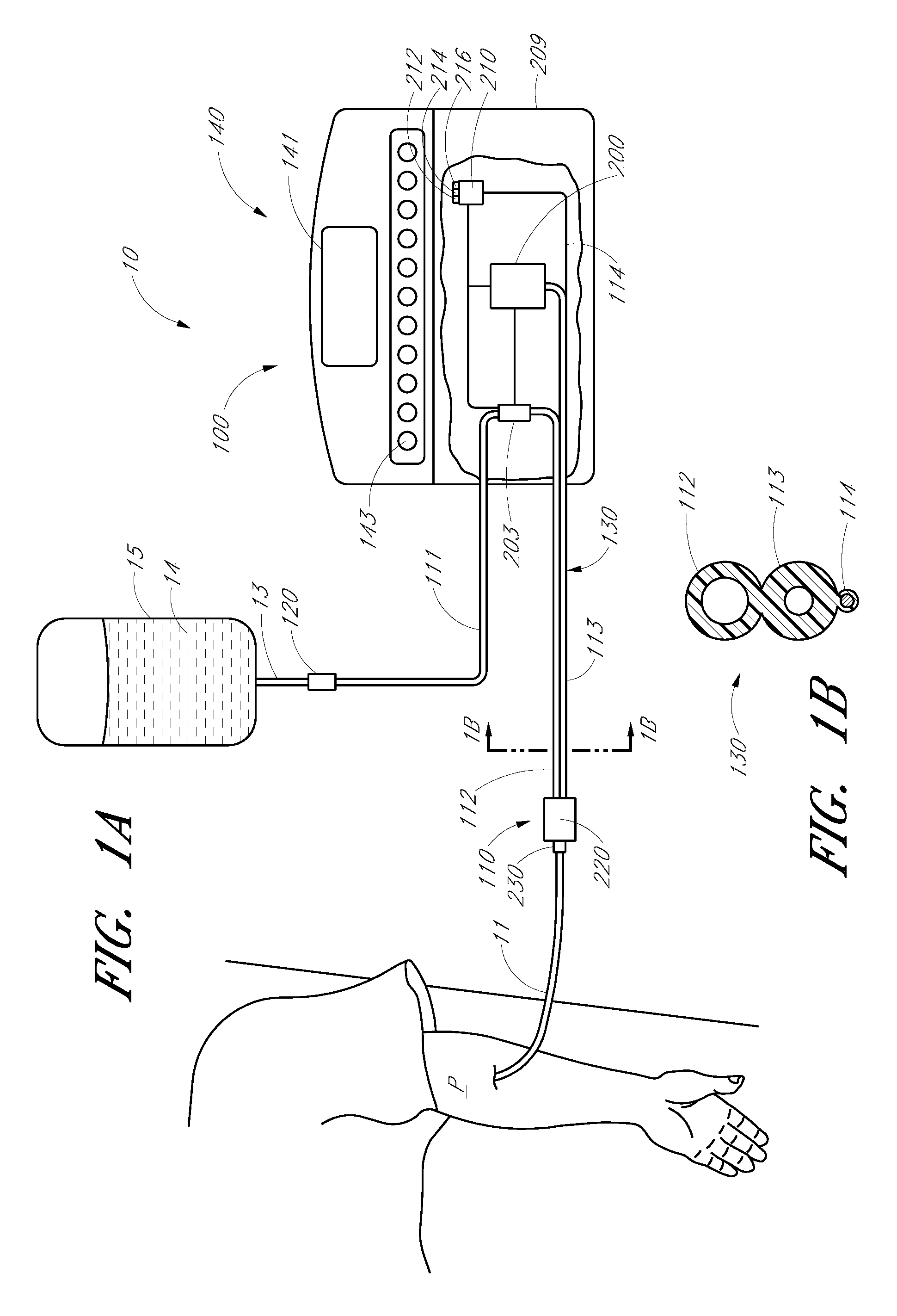
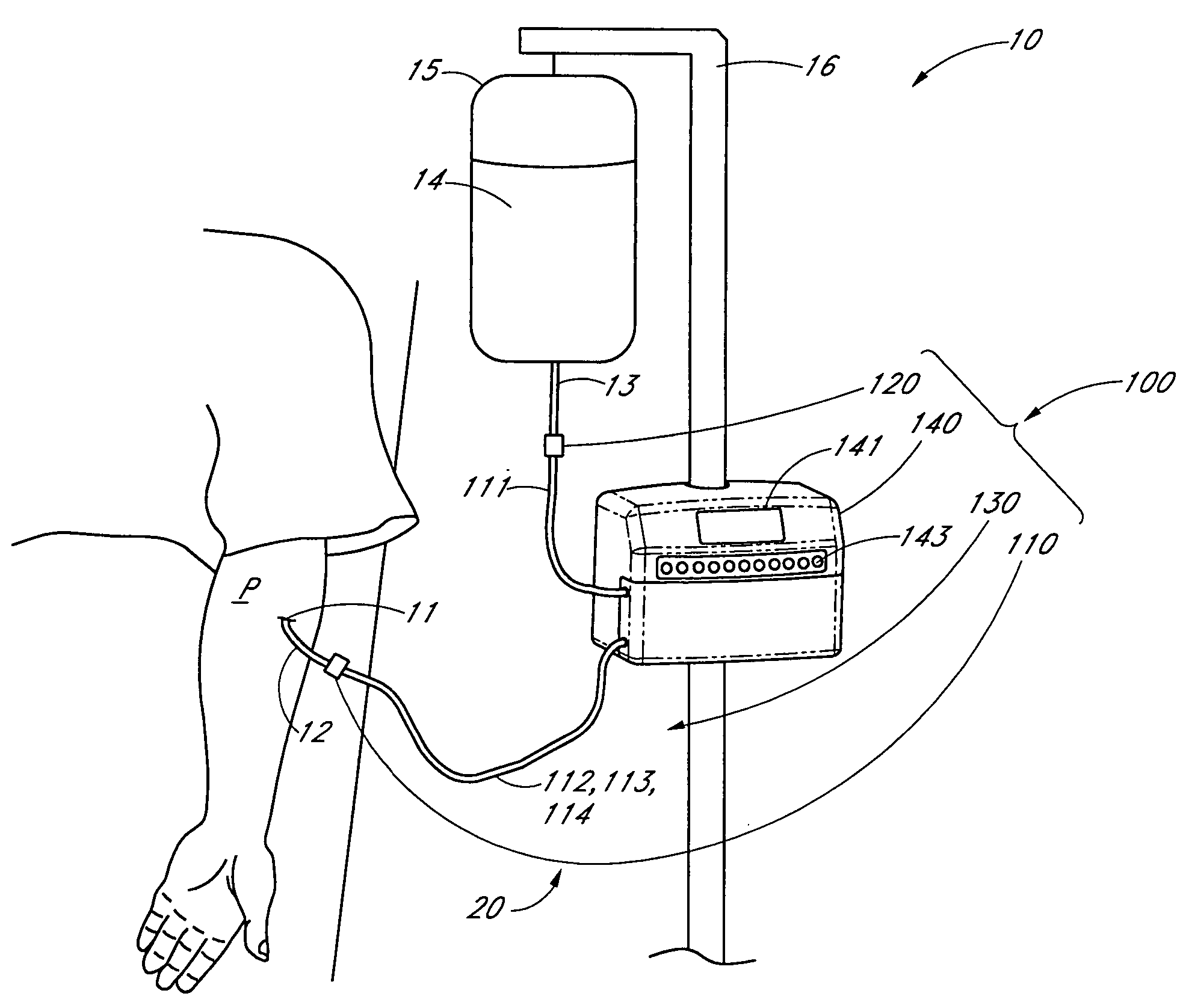
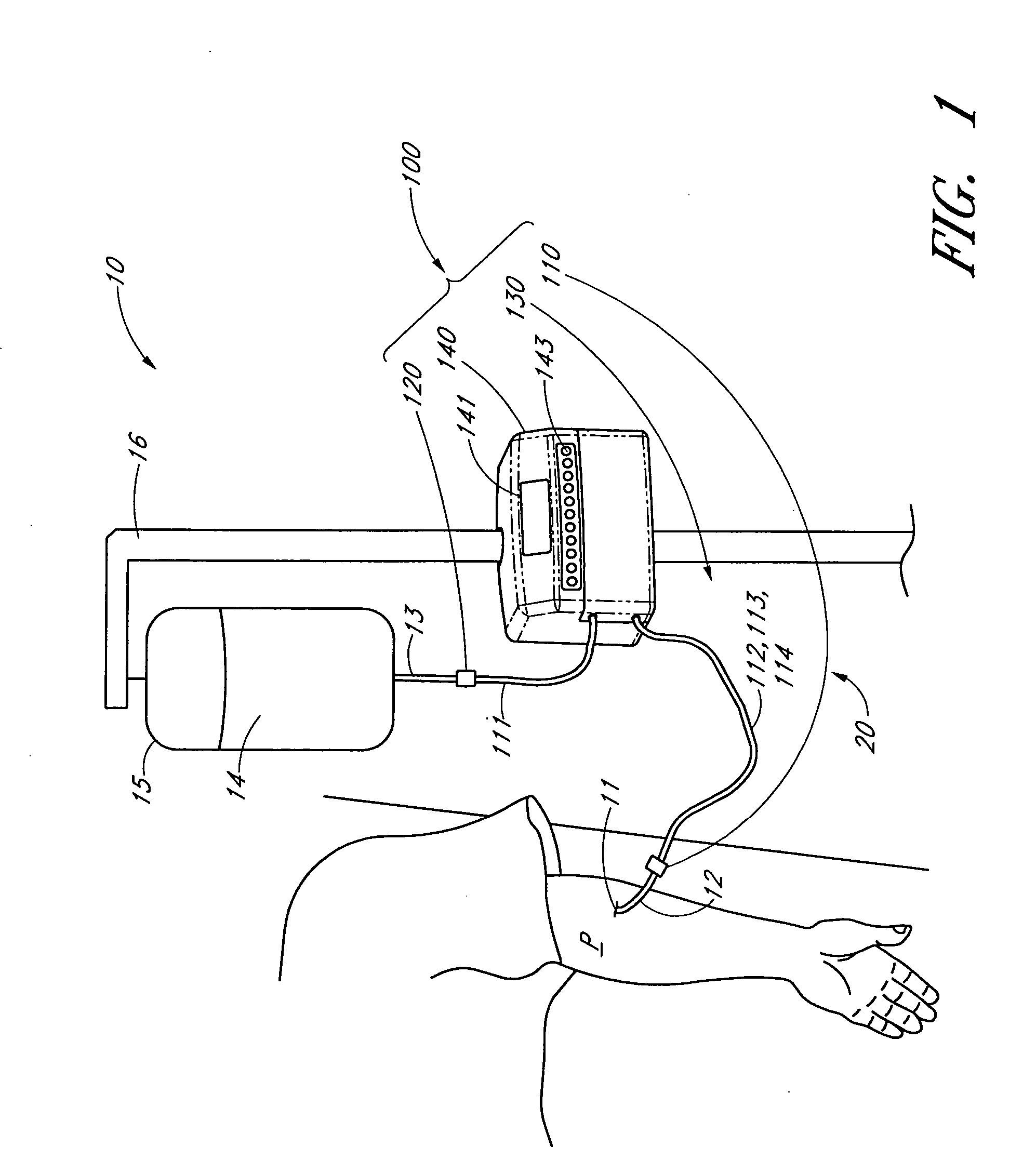
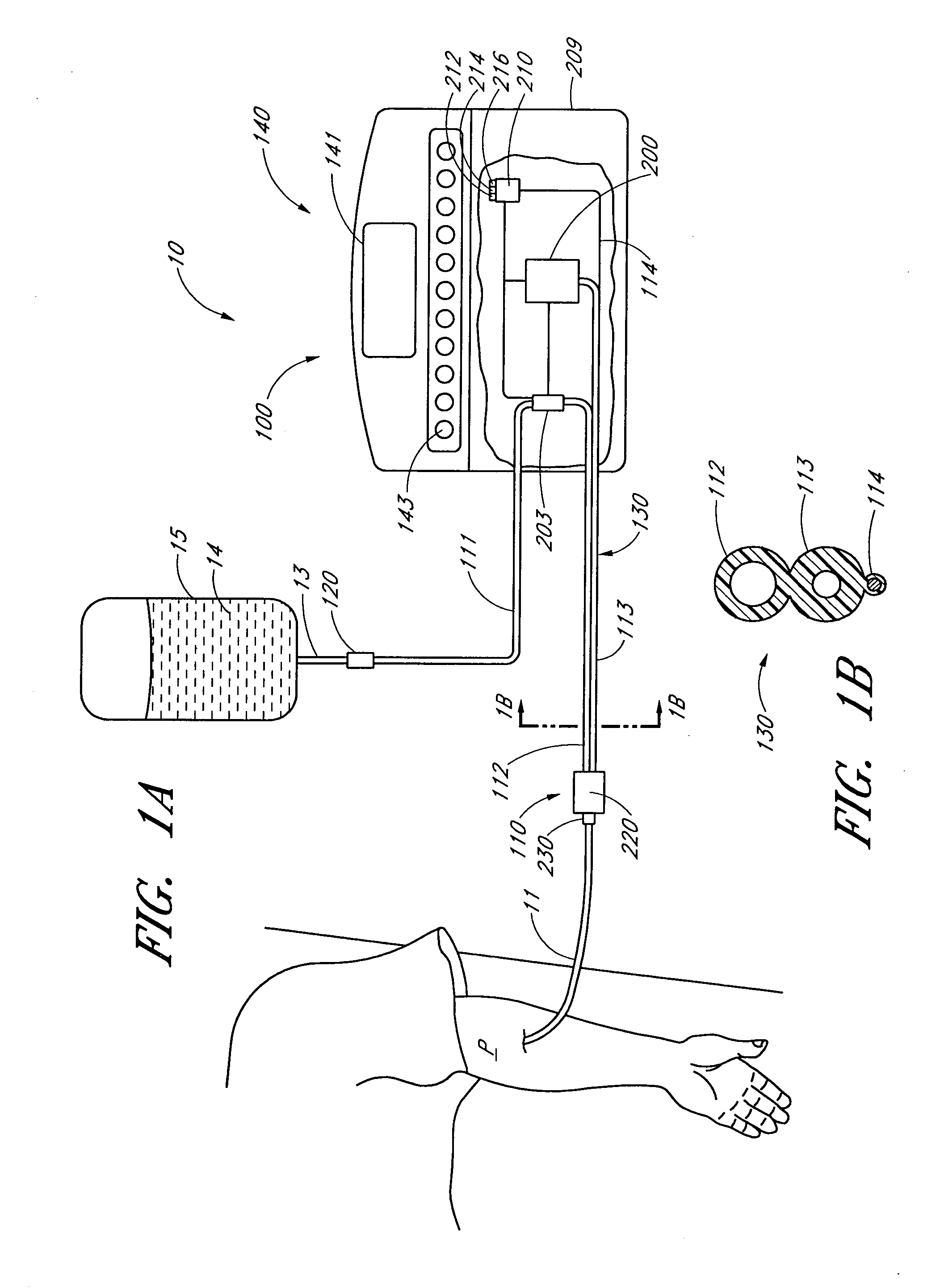
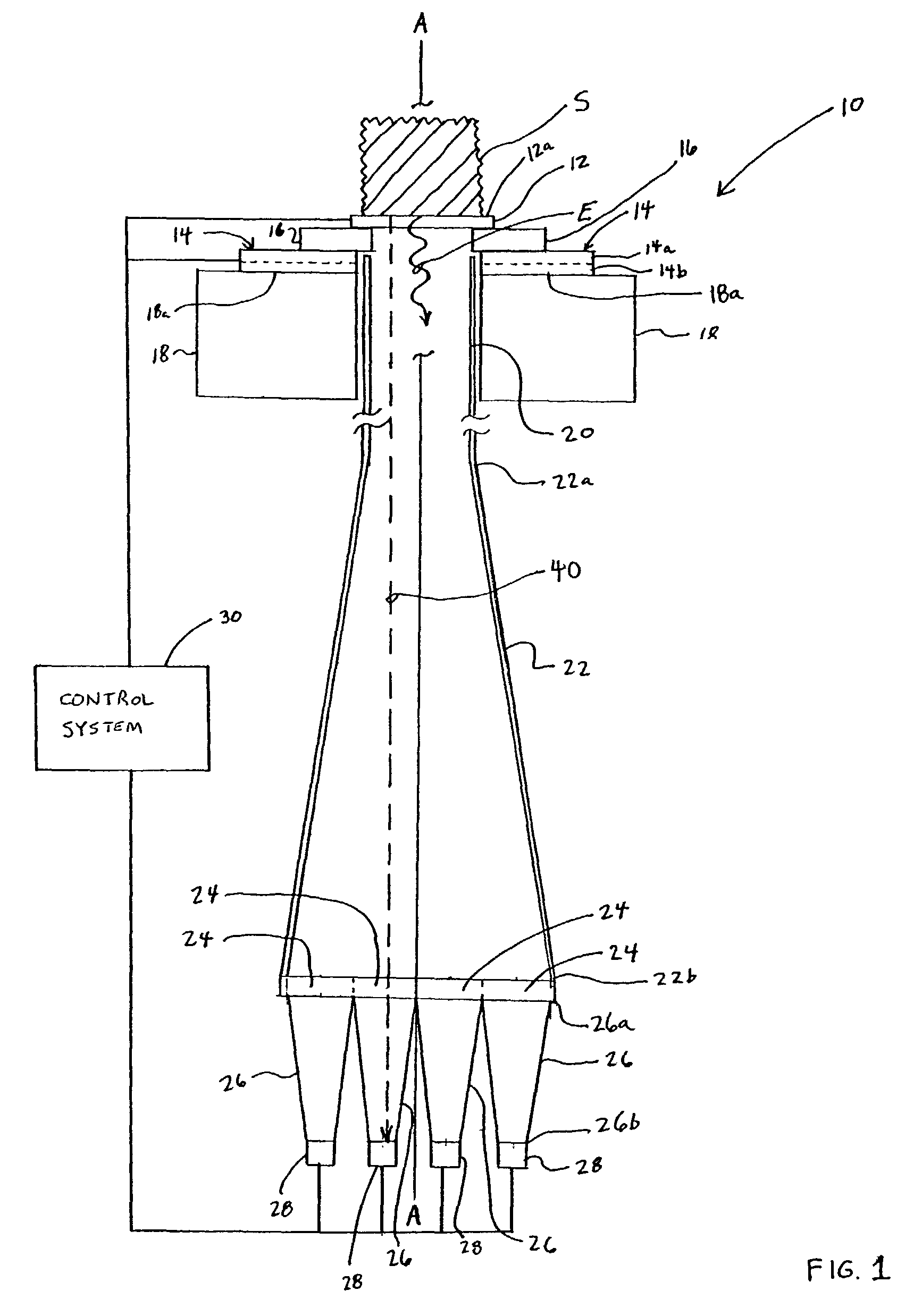
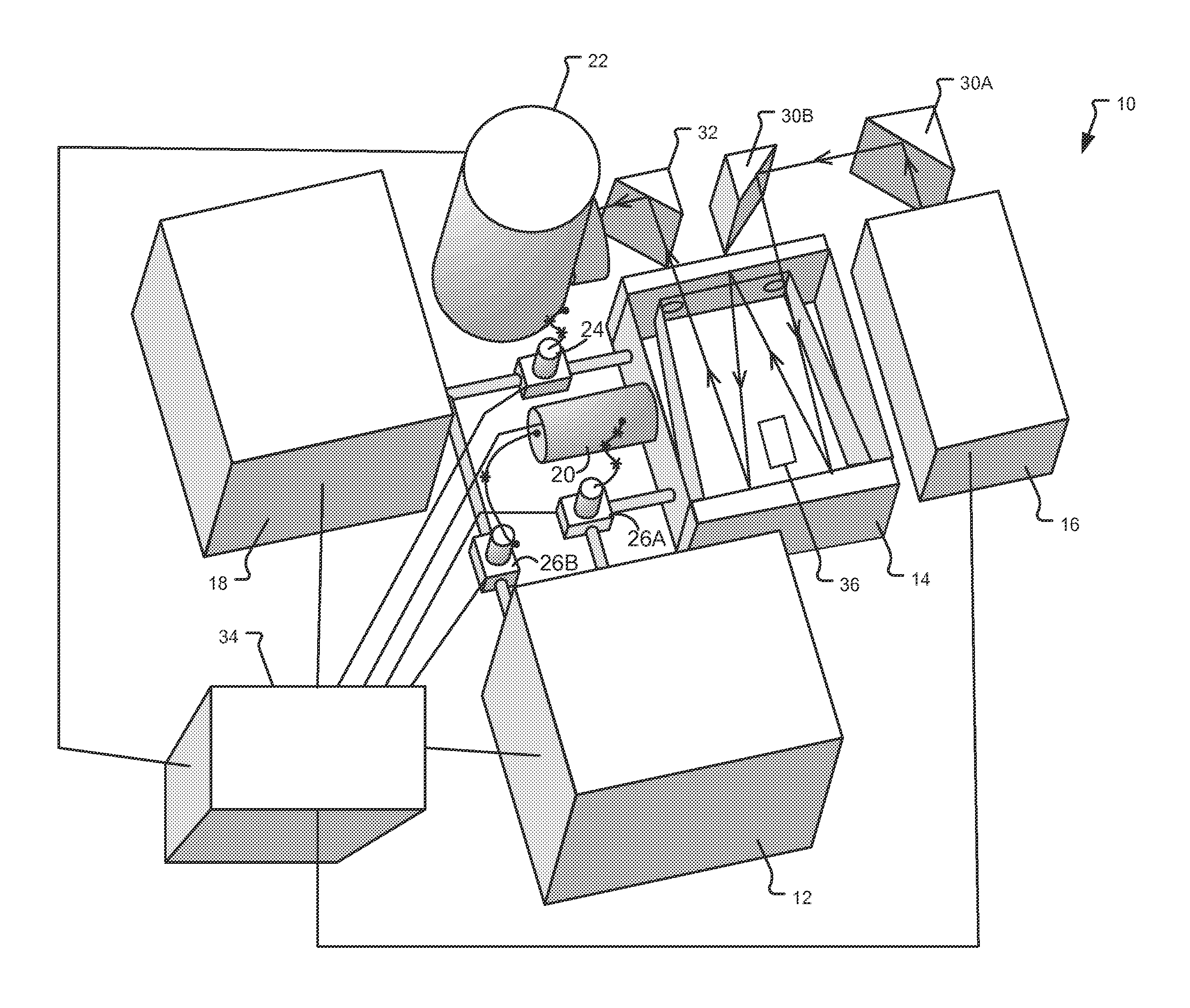
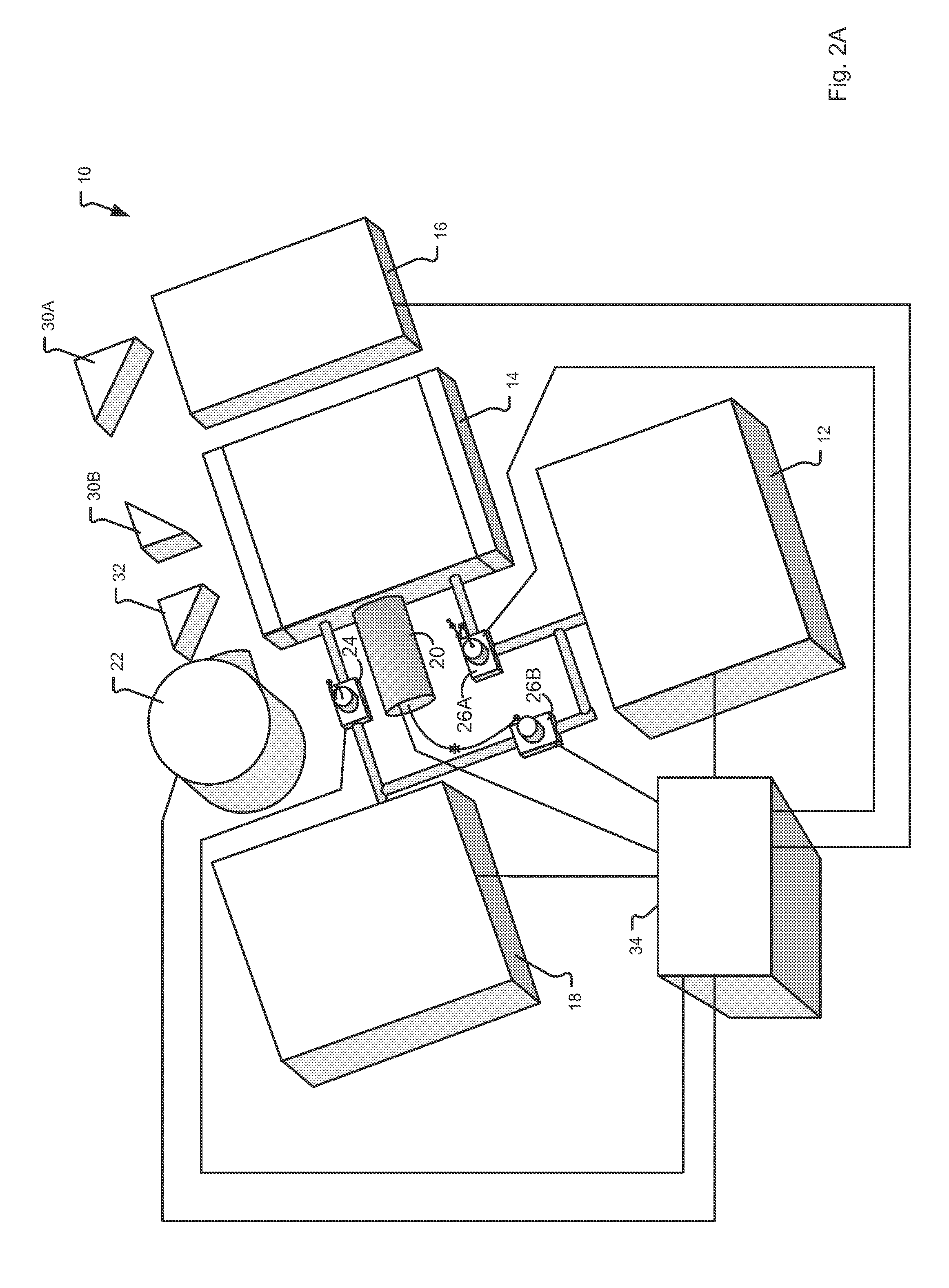
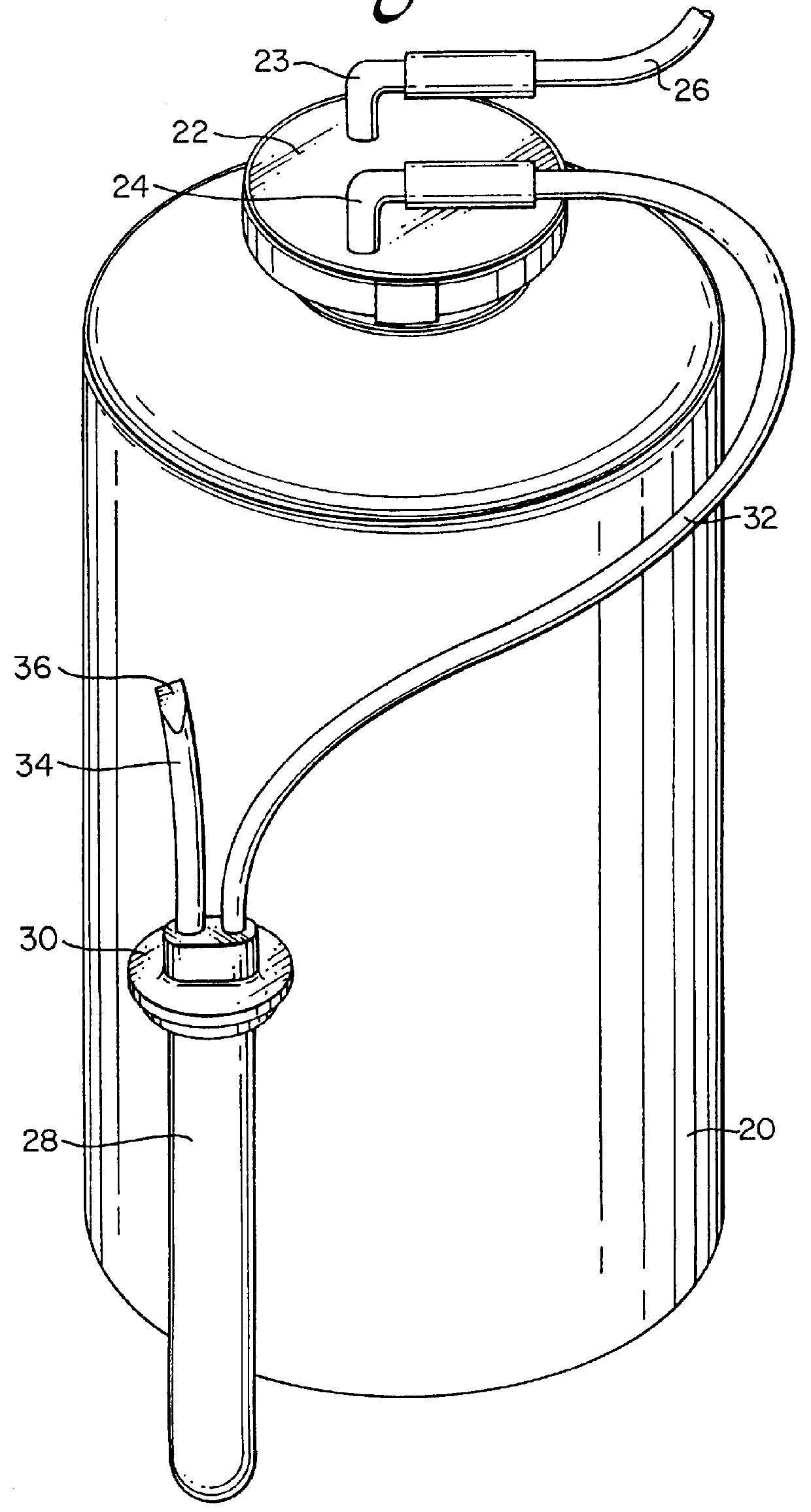
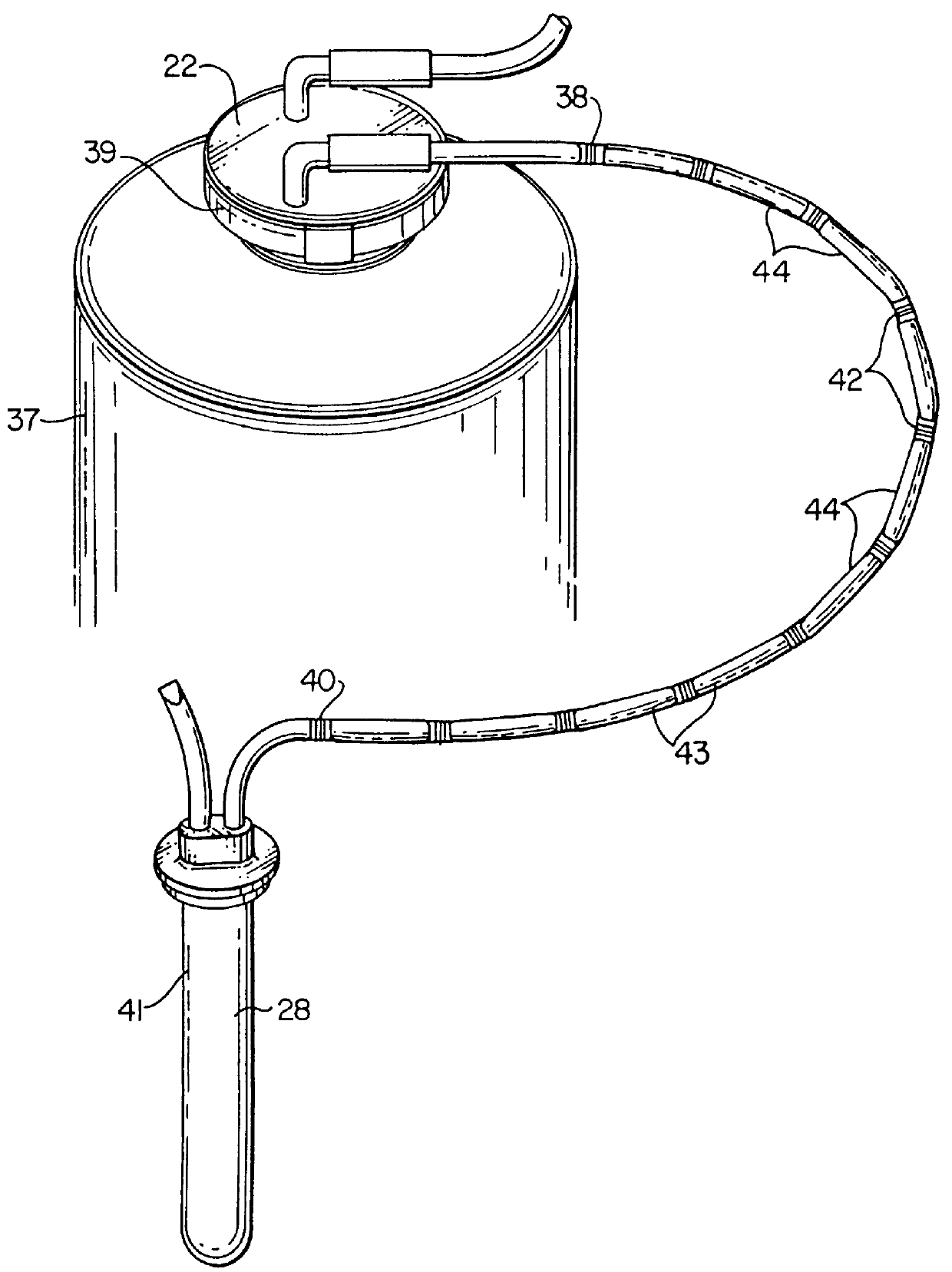
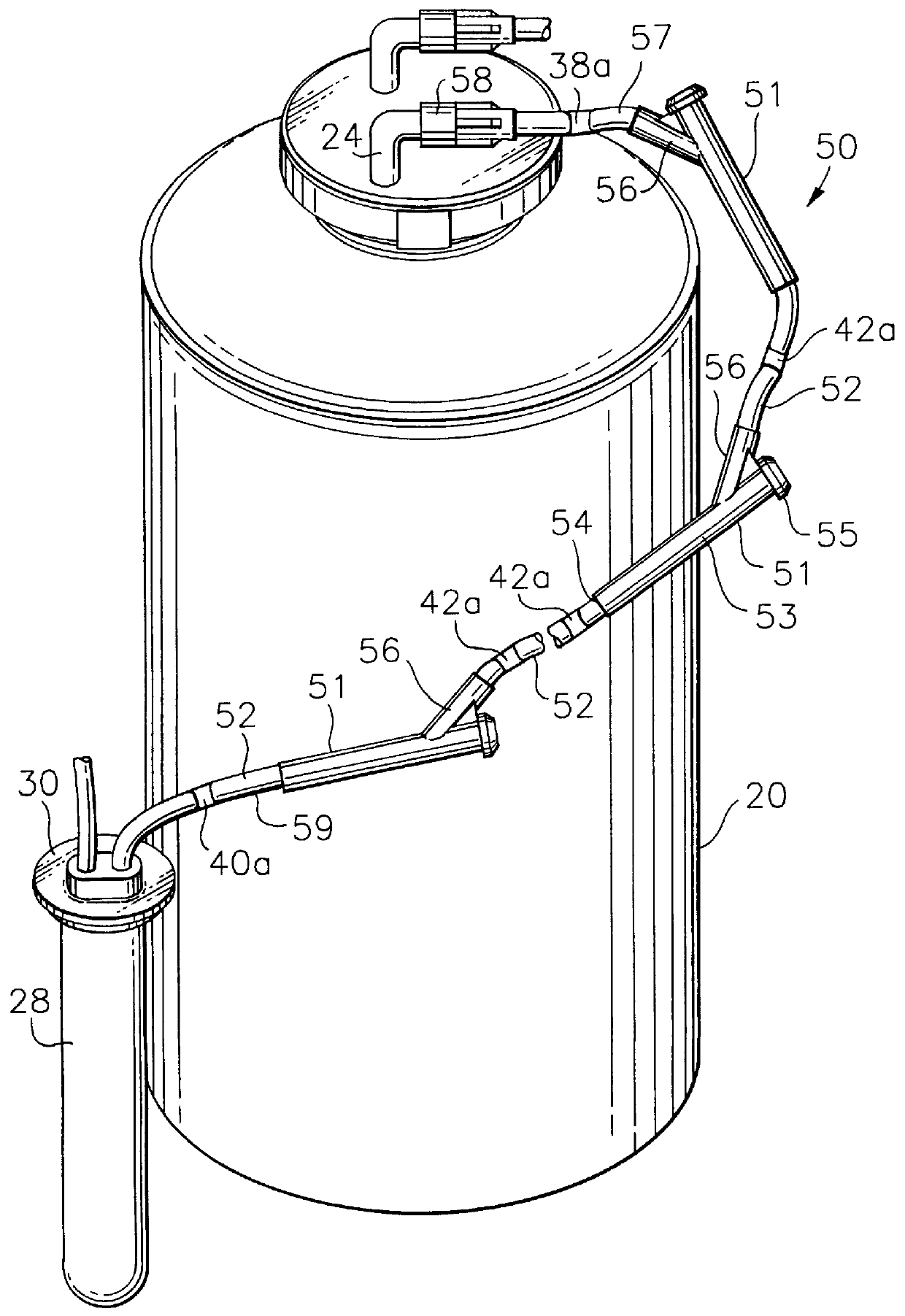
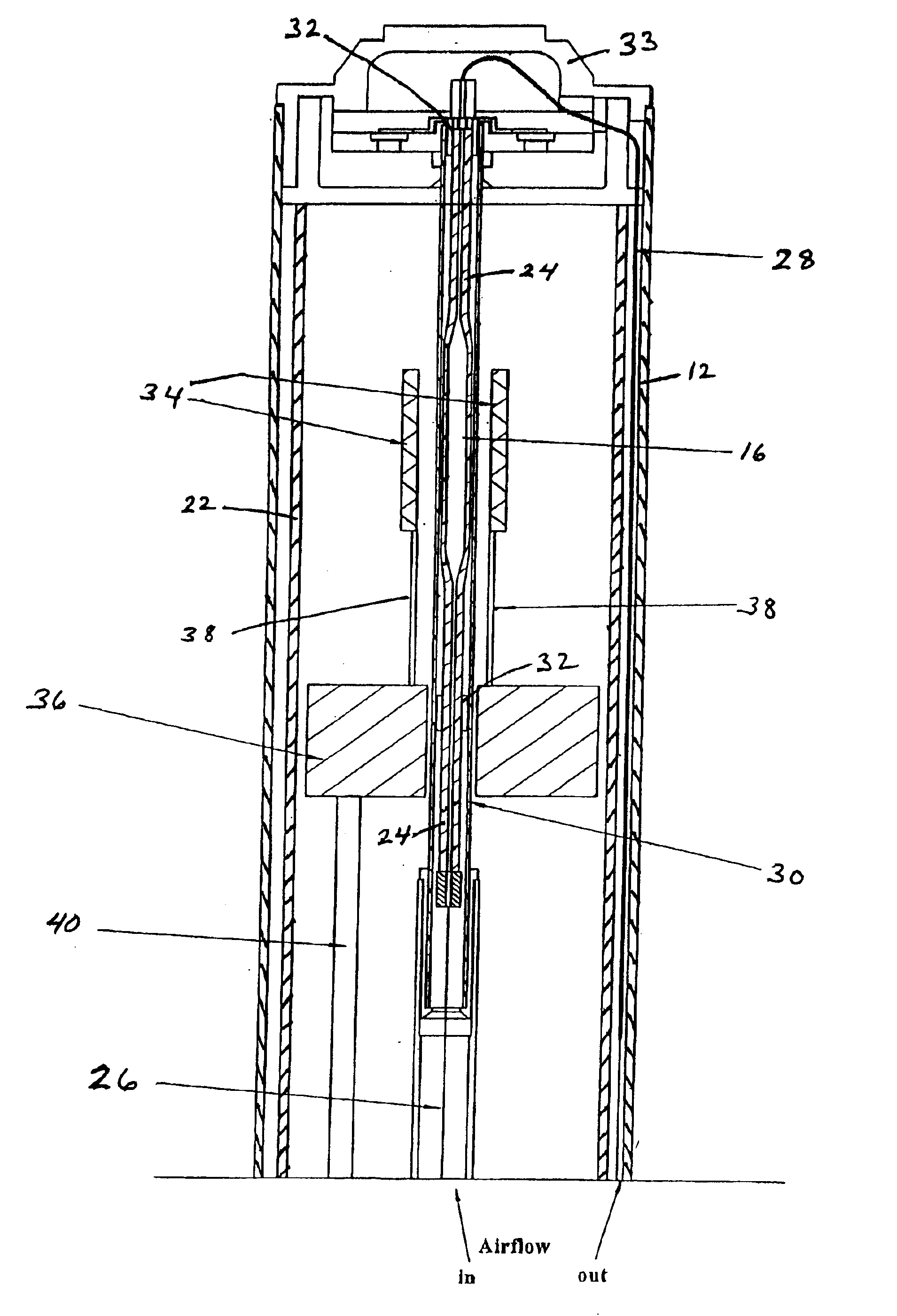
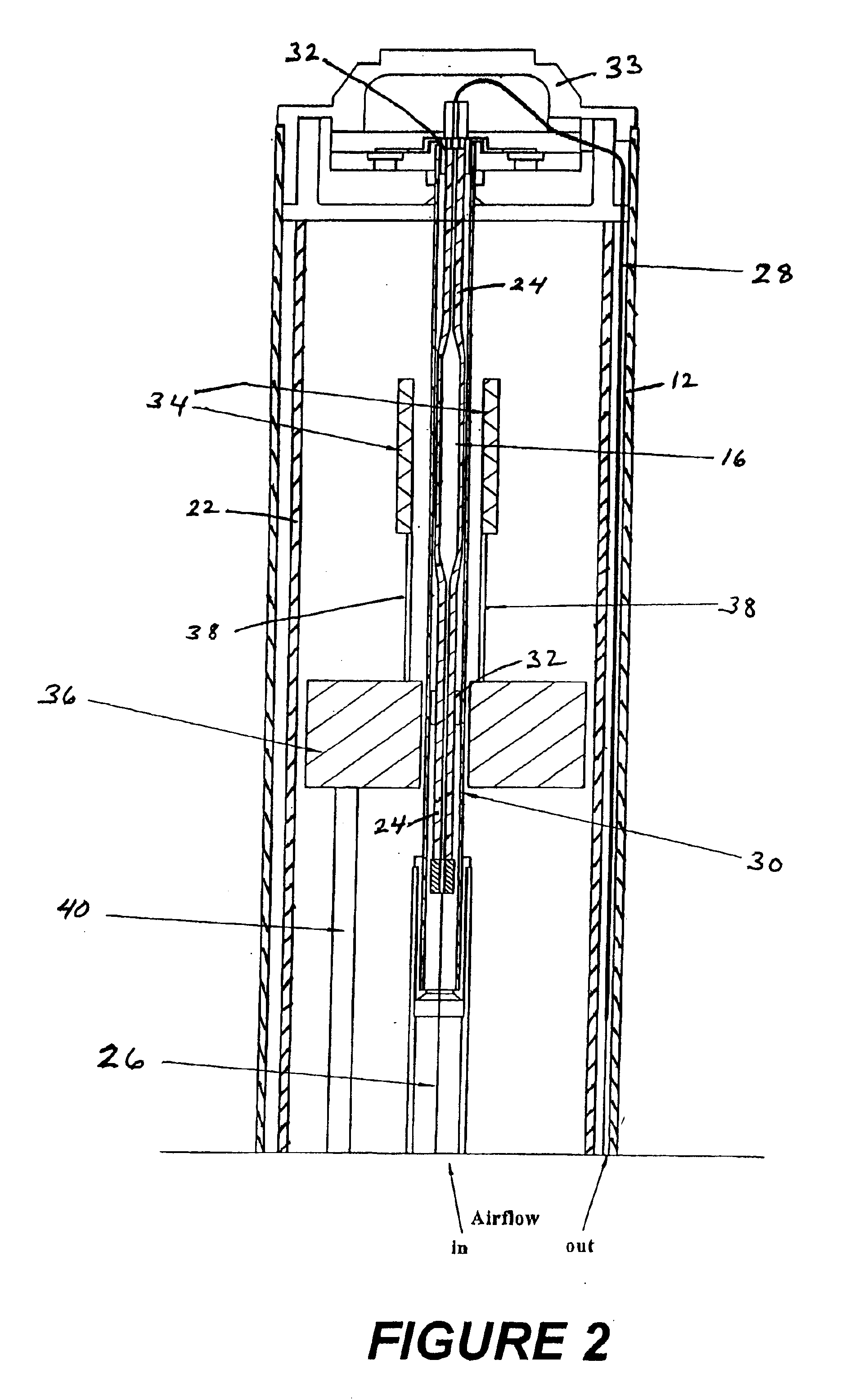
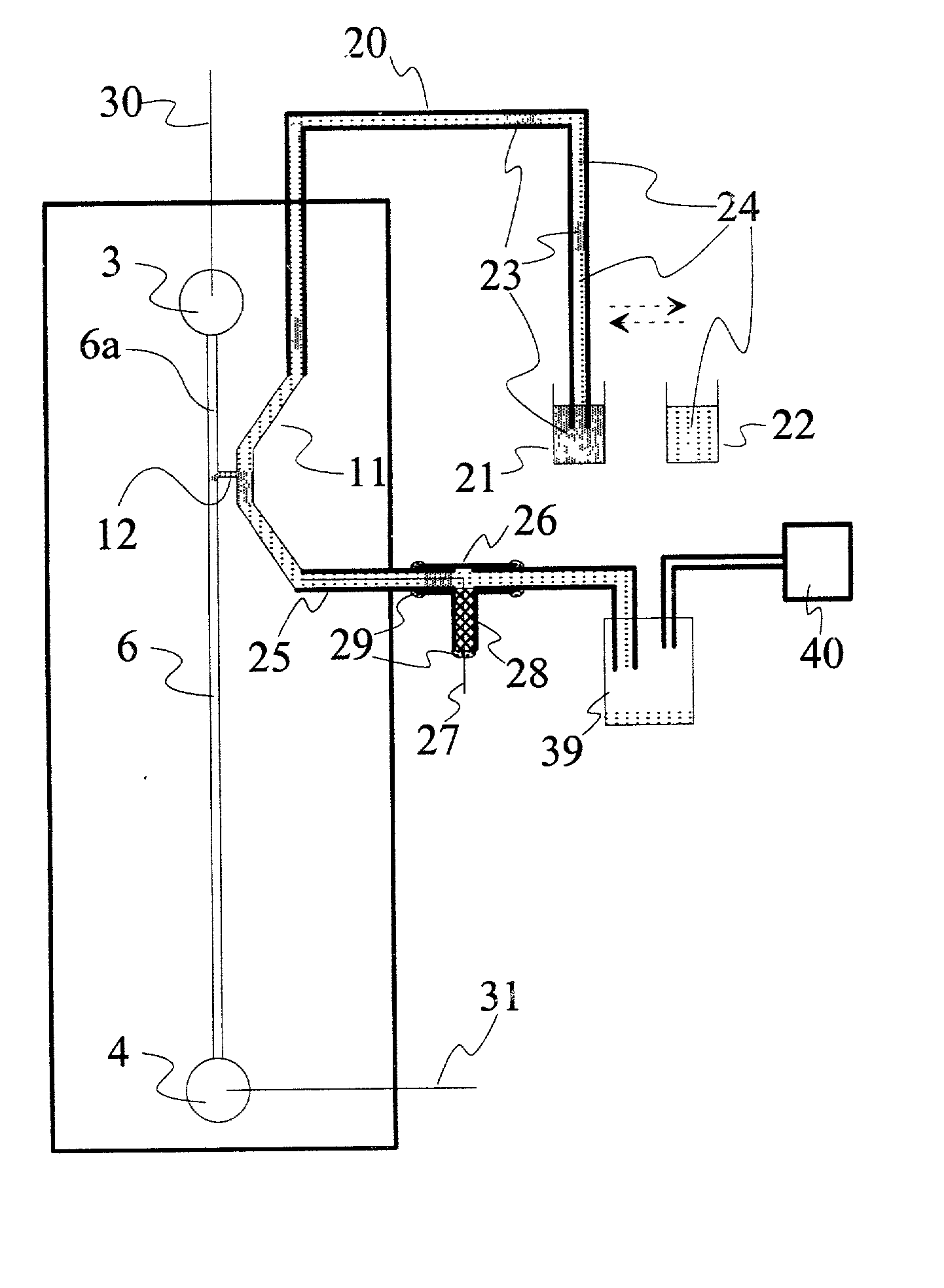
Apparatus and methods for analyzing body fluid samples
An apparatus is provided for monitoring a predetermined parameter of a patient's body fluid while infusing an infusion fluid into the patient. The apparatus comprises an infusion line and a catheter configured for insertion into a blood vessel of the patient, and a reversible infusion pump connected between a source of an infusion fluid and the infusion line and catheter. The apparatus further comprises a body fluid sensor assembly mounted in fluid communication with the infusion line and which includes a first sensor and a sample cell. The first sensor provides a signal indicative of a predetermined parameter of any fluid present in the infusion line. The sample cell is substantially transmissive to light comprising a wavelength λ. The apparatus further comprises a controller that is configured to operate the infusion pump in a forward direction so as to pump the infusion fluid through the infusion line and catheter for infusion into the patient. The controller is configured to intermittently interrupt its operating of the infusion pump in the forward direction to operate the infusion pump in a rearward direction so as to draw a body fluid sample from the patient through the catheter and infusion line. The body fluid sample drawn from the patient is disposed such that a first portion of the body fluid sample is in sensing contact with the first sensor of the body fluid sensor assembly, and a second portion of the body fluid sample is disposed within the sample cell of the body fluid sensor assembly. The controller further is configured to monitor the signal provided by the first sensor of the body fluid sensor assembly and to detect a change in the signal indicative of the arrival of the body fluid sample at the first sensor. The controller, in response to detecting the arrival of the body fluid sample at the first sensor, is configured to cease its operating of the infusion pump in the rearward direction. The signal produced by the first sensor provides an indication of a predetermined parameter of the patient's body fluid when the body fluid sample is in sensing contact with the first sensor.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Reagent-less whole-blood glucose meter
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
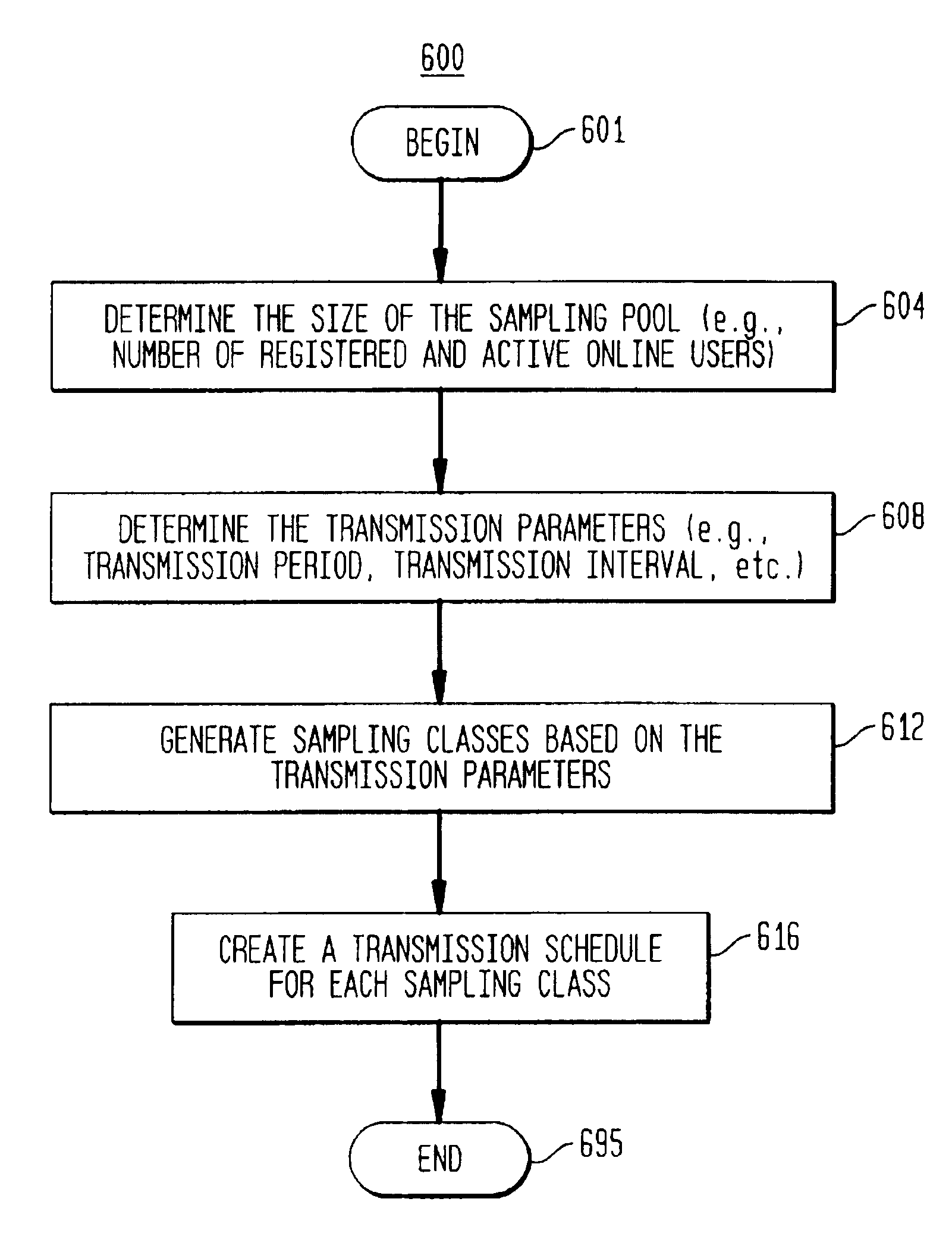
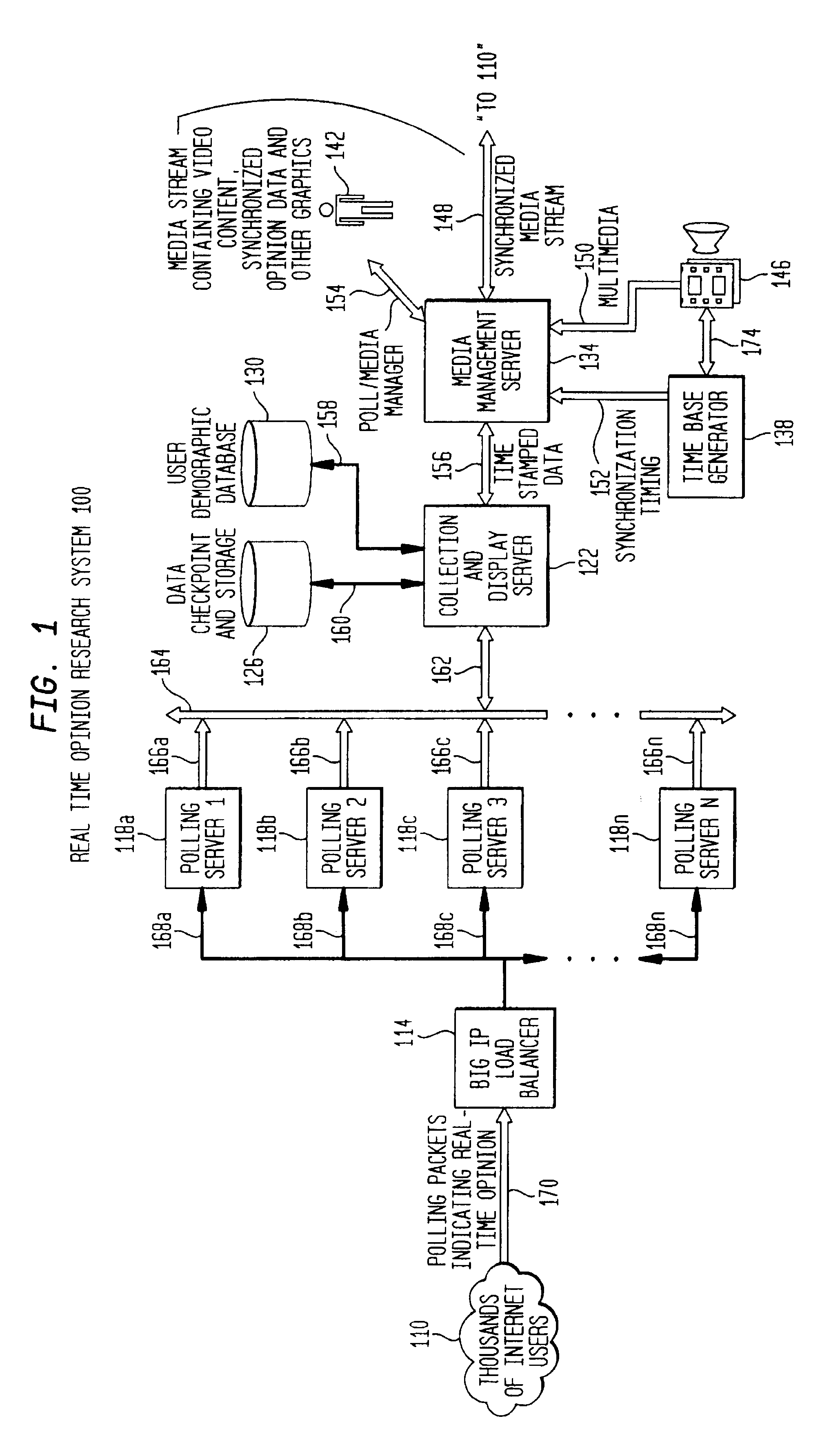
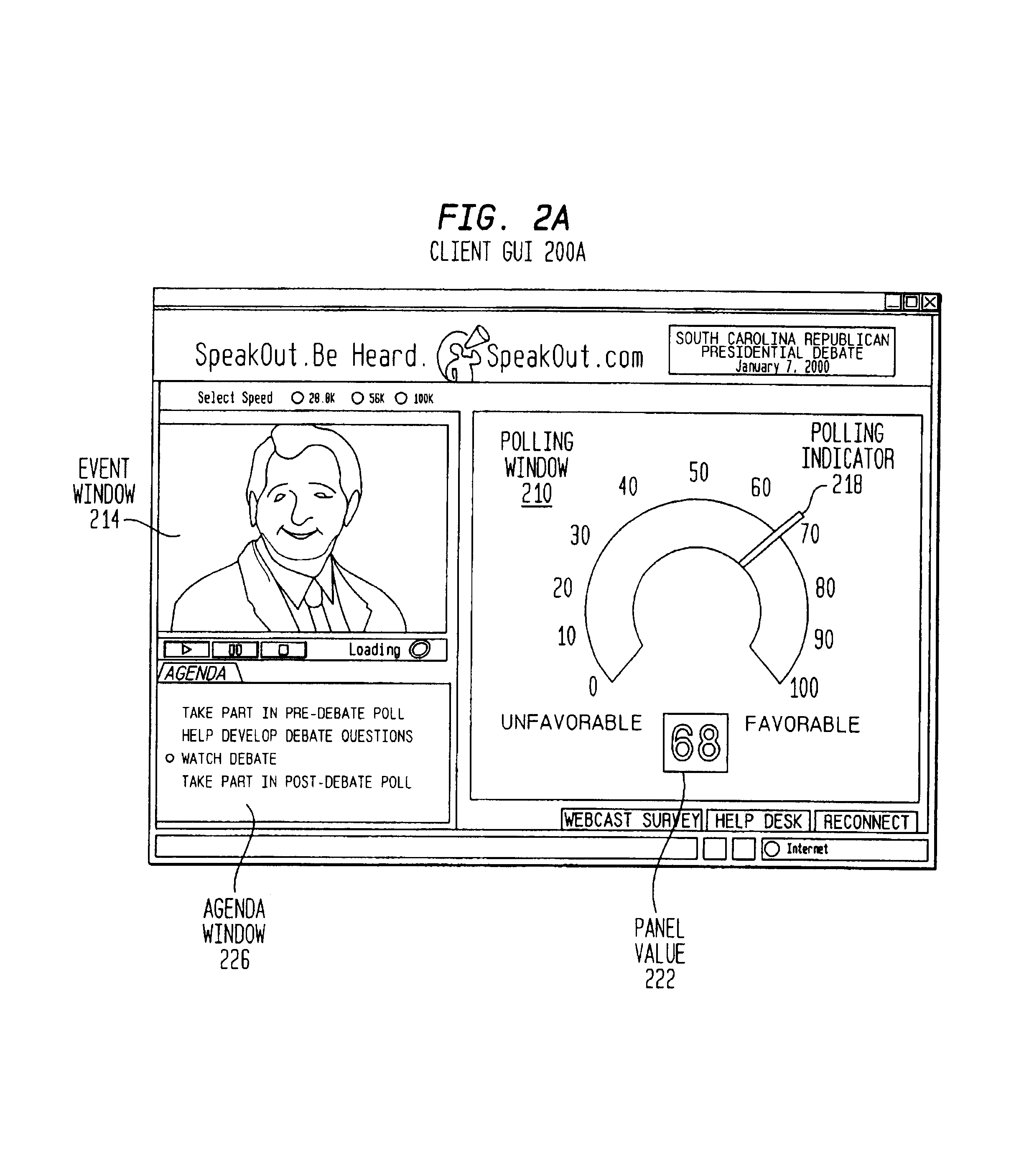
Method of modulating the transmission frequency in a real time opinion research network
ActiveUS7254605B1Increase the number ofVoting apparatusError detection/correctionTTEthernetManagement unit
A computer-implemented transmission scheme is provided to control client-server interchanges within a distributed communications network, such as a real time opinion research system. Interchanges include transmitting media streams between one or more clients to a server over a computer network, including the global Internet. A polling management unit sets and manages the transmission mode that includes event-driven and periodic interchanges. Periodic interchanges can be simultaneously or staggeredly transmitted to a sampling pool of active clients. A transmission mode unit implements the transmission scheme set by the polling management unit. A parameter selector establishes the transmission interval and transmission period which are used to trigger each communication interchange. A client assignor creates one or more sampling classes from the sampling pool by applying a sampling quotient that is generated by the parameter selector. A schedule editor produces a transmission schedule for the active clients. If more than one sampling class has been created, each sampling class would receive a separate transmission schedule for providing staggered transmissions at designated transmission intervals. The transmission schedule can include other data preparation and formatting instructions for compression, aggregation and packetization.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Apparatus and methods for analyzing body fluid samples
An apparatus is provided for monitoring a predetermined parameter of a patient's body fluid while infusing an infusion fluid into the patient. The apparatus comprises an infusion line and a catheter configured for insertion into a blood vessel of the patient, and a reversible infusion pump connected between a source of an infusion fluid and the infusion line and catheter. The apparatus further comprises a body fluid sensor assembly mounted in fluid communication with the infusion line and which includes a first sensor and a sample cell. The first sensor provides a signal indicative of a predetermined parameter of any fluid present in the infusion line. The sample cell is substantially transmissive to light comprising a wavelength B. The apparatus further comprises a controller that is configured to operate the infusion pump in a forward direction so as to pump the infusion fluid through the infusion line and catheter for infusion into the patient. The controller is configured to intermittently interrupt its operating of the infusion pump in the forward direction to operate the infusion pump in a rearward direction so as to draw a body fluid sample from the patient through the catheter and infusion line. The body fluid sample drawn from the patient is disposed such that a first portion of the body fluid sample is in sensing contact with the first sensor of the body fluid sensor assembly, and a second portion of the body fluid sample is disposed within the sample cell of the body fluid sensor assembly. The controller further is configured to monitor the signal provided by the first sensor of the body fluid sensor assembly and to detect a change in the signal indicative of the arrival of the body fluid sample at the first sensor. The controller, in response to detecting the arrival of the body fluid sample at the first sensor, is configured to cease its operating of the infusion pump in the rearward direction. The signal produced by the first sensor provides an indication of a predetermined parameter of the patient's body fluid when the body fluid sample is in sensing contact with the first sensor.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
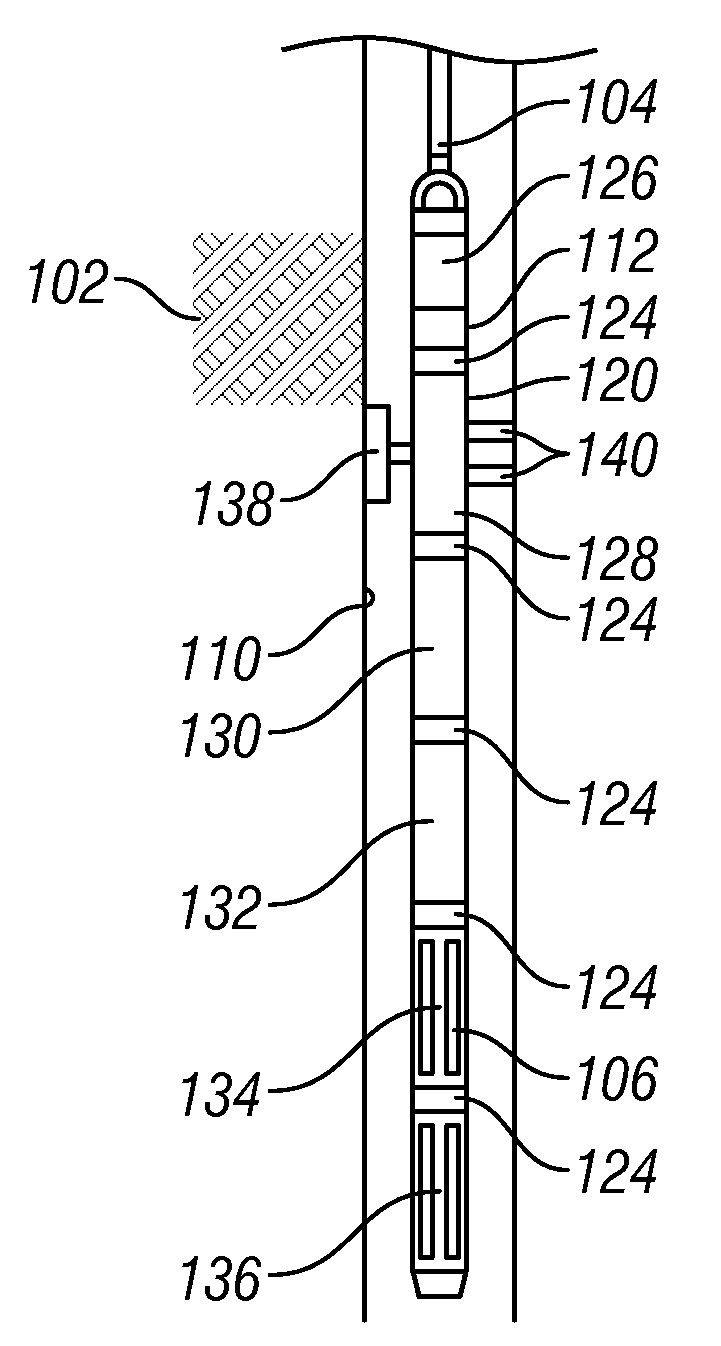
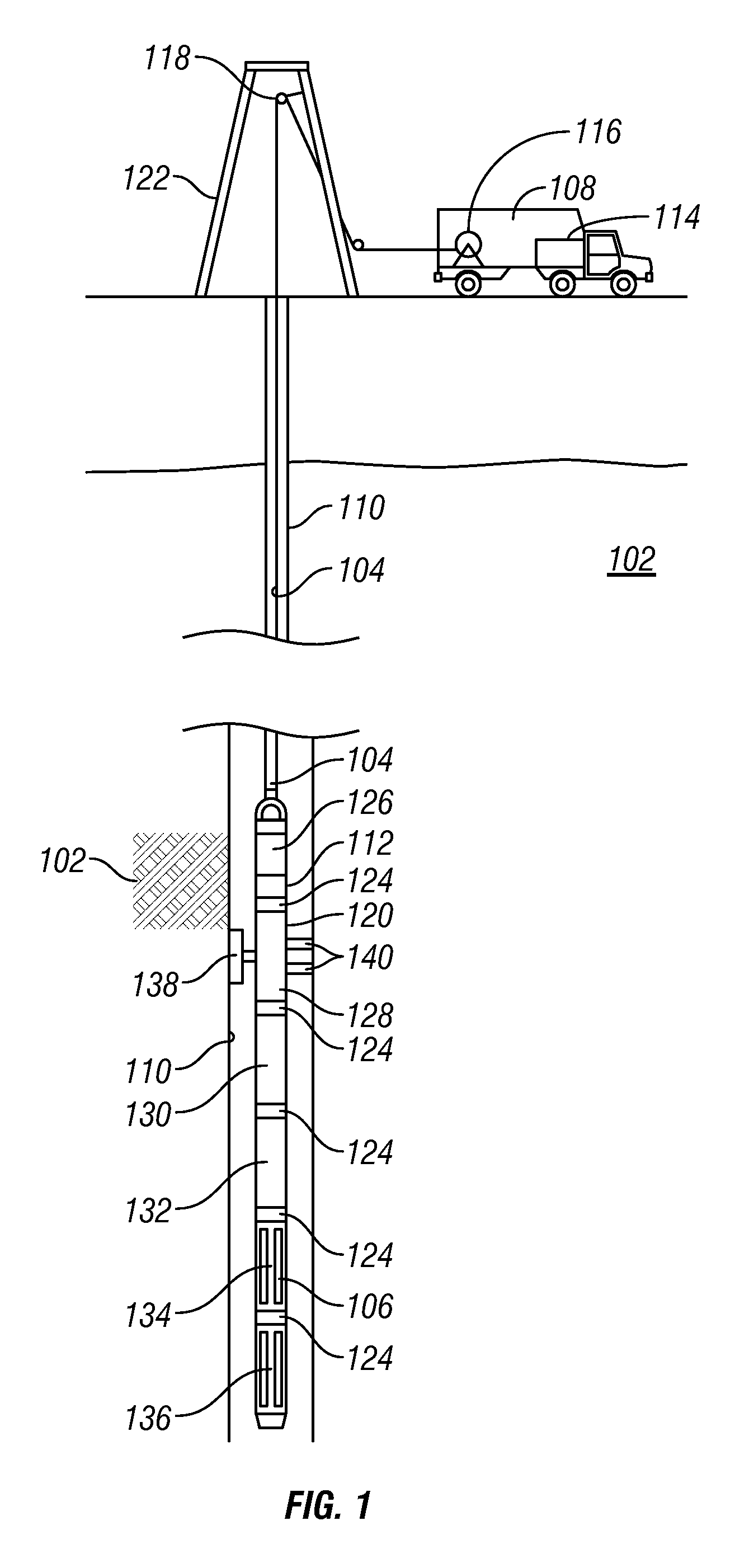
Laser diode array downhole spectrometer
Apparatus and method for downhole formation testing using a spectrometer includes a carrier conveyable into a well borehole that traverses a subterranean formation of interest, a plurality of semiconductor light sources disposed on the carrier, a fluid sample cell that receives light emitted from the plurality of semiconductor light sources, and at least one photodetector that detects light emitted from the plurality of semiconductor light sources and after the light interacts with a fluid in the fluid sample cell.
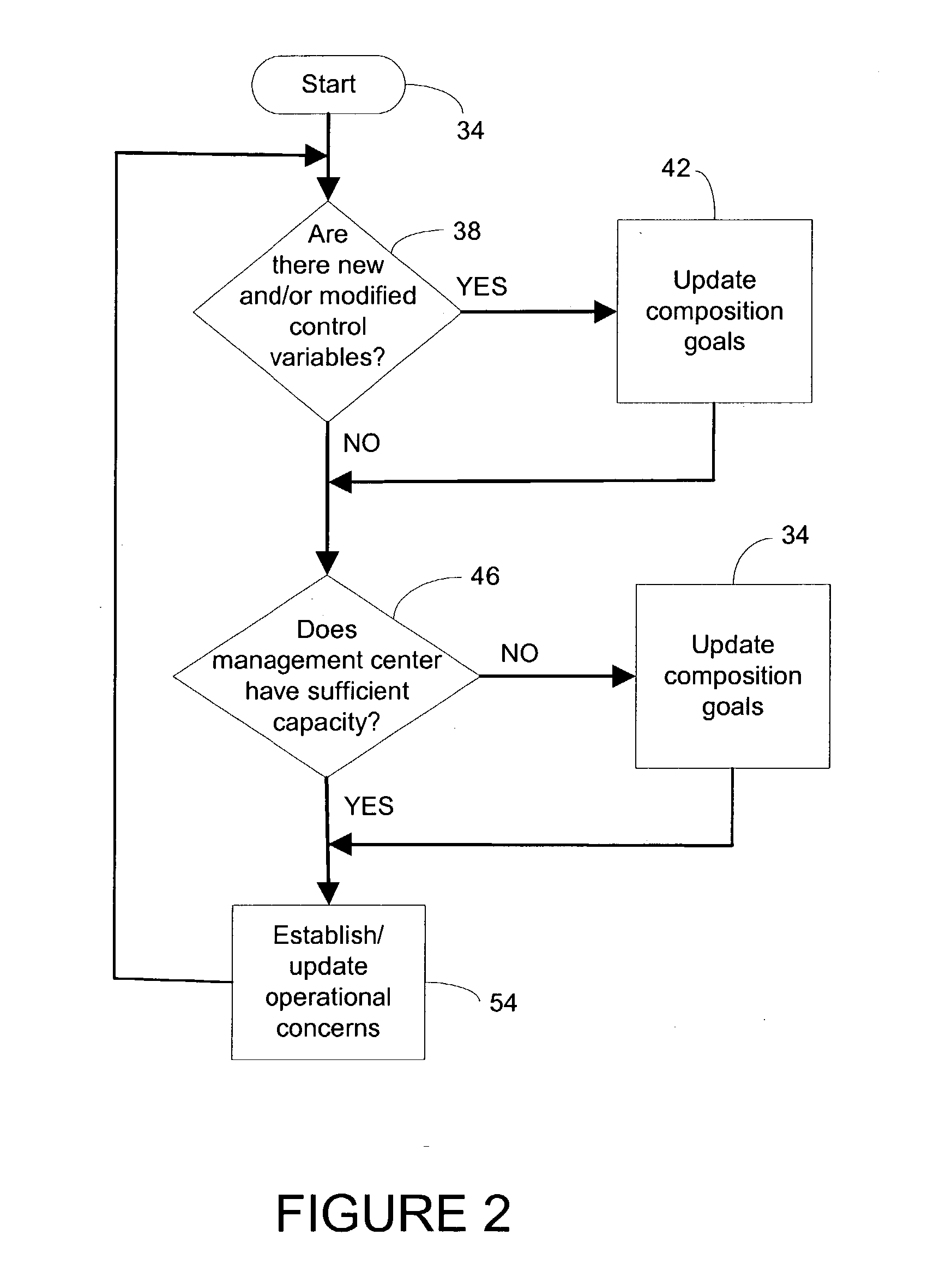
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
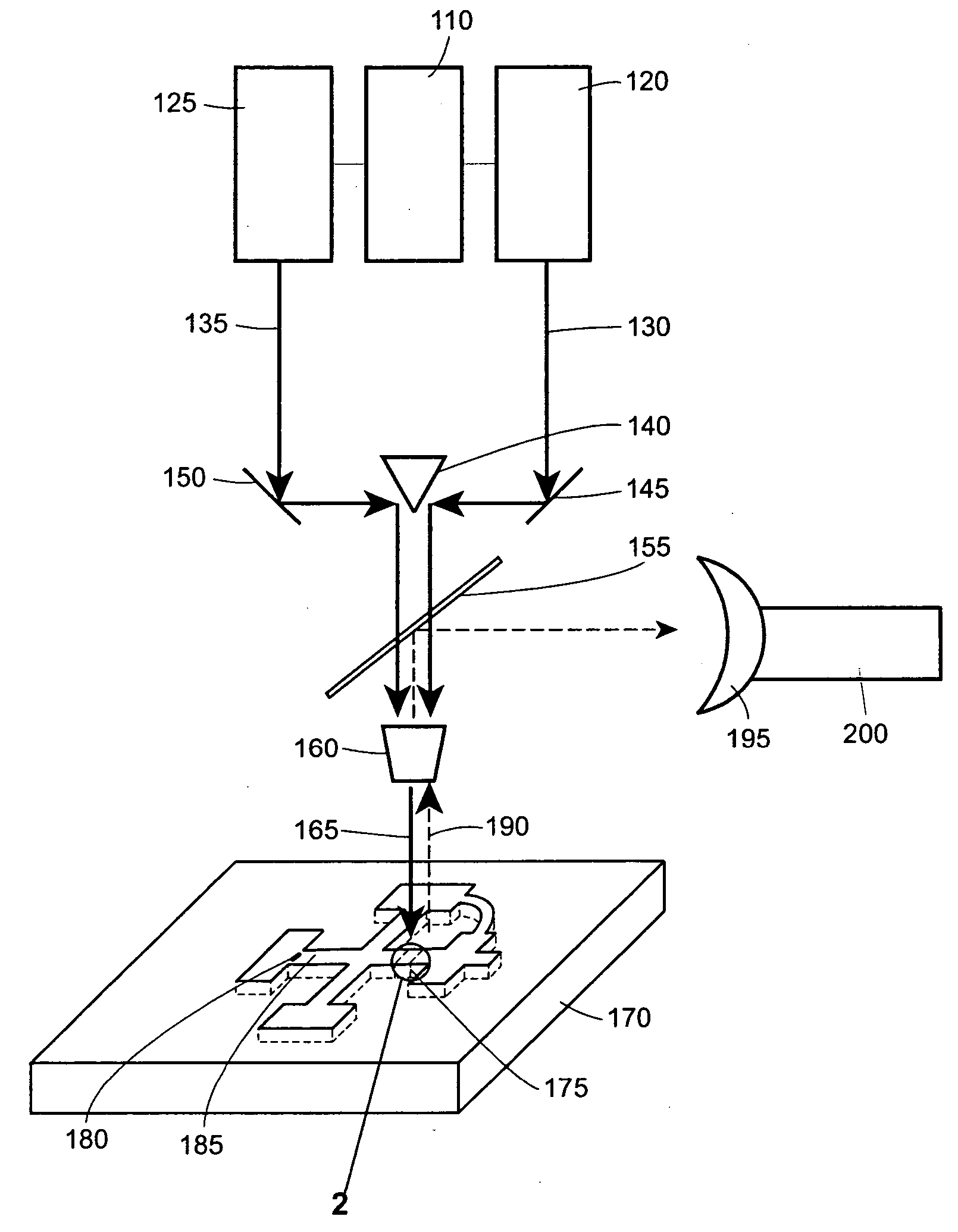
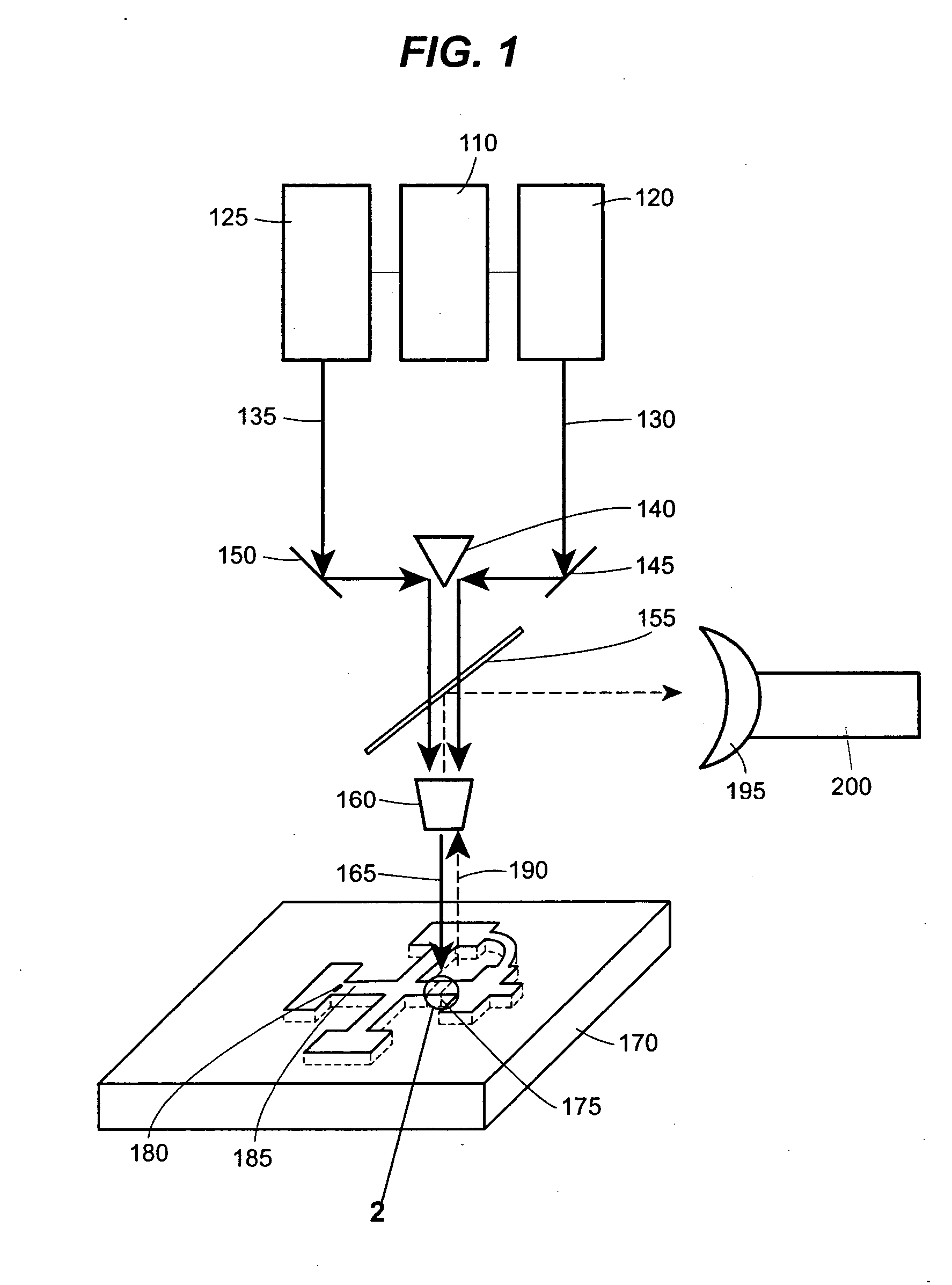
Method and device for detecting a small number of molecules using surface-enhanced coherant anti-stokes raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050084980A1Radiation pyrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsAnalyteCoherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy
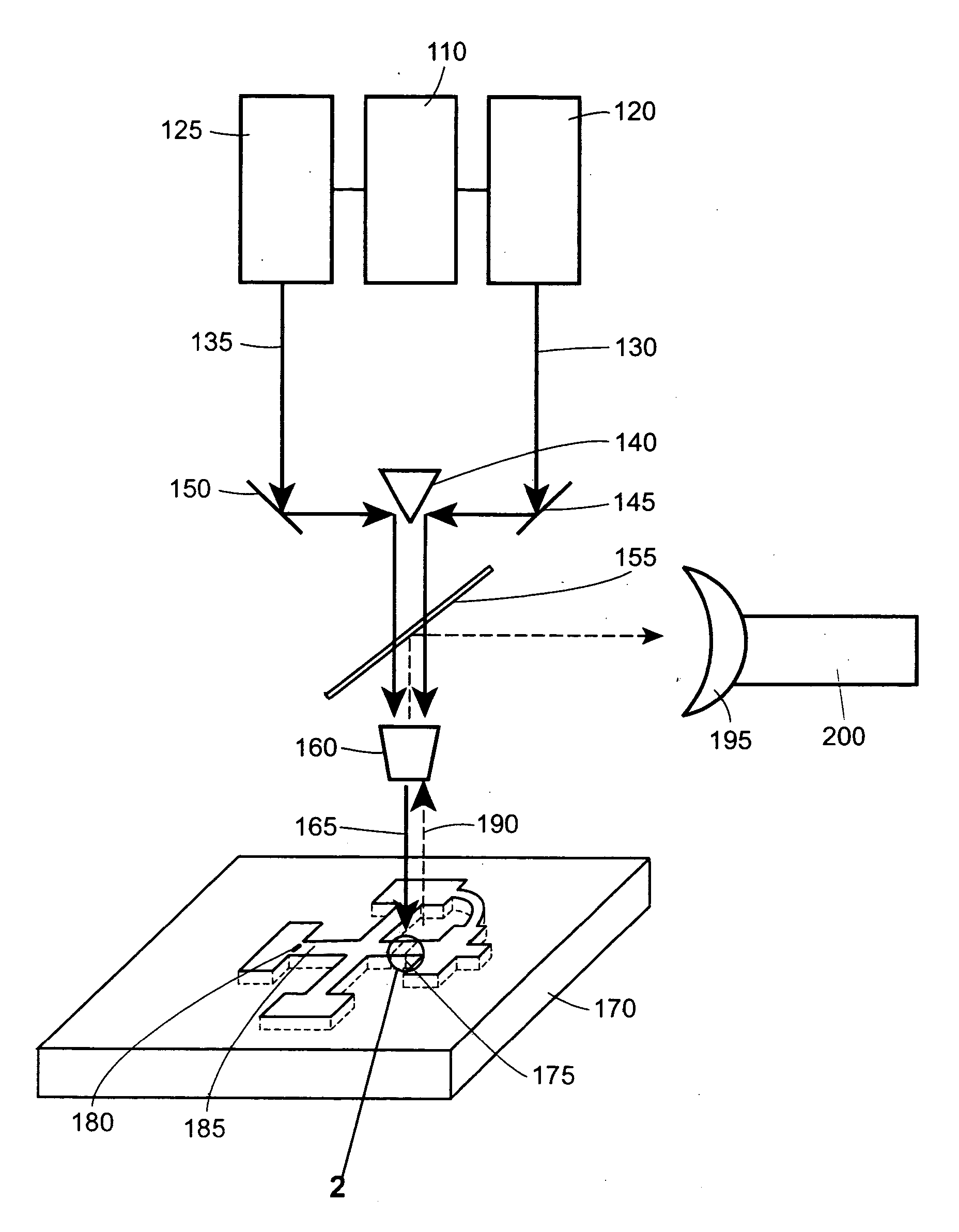
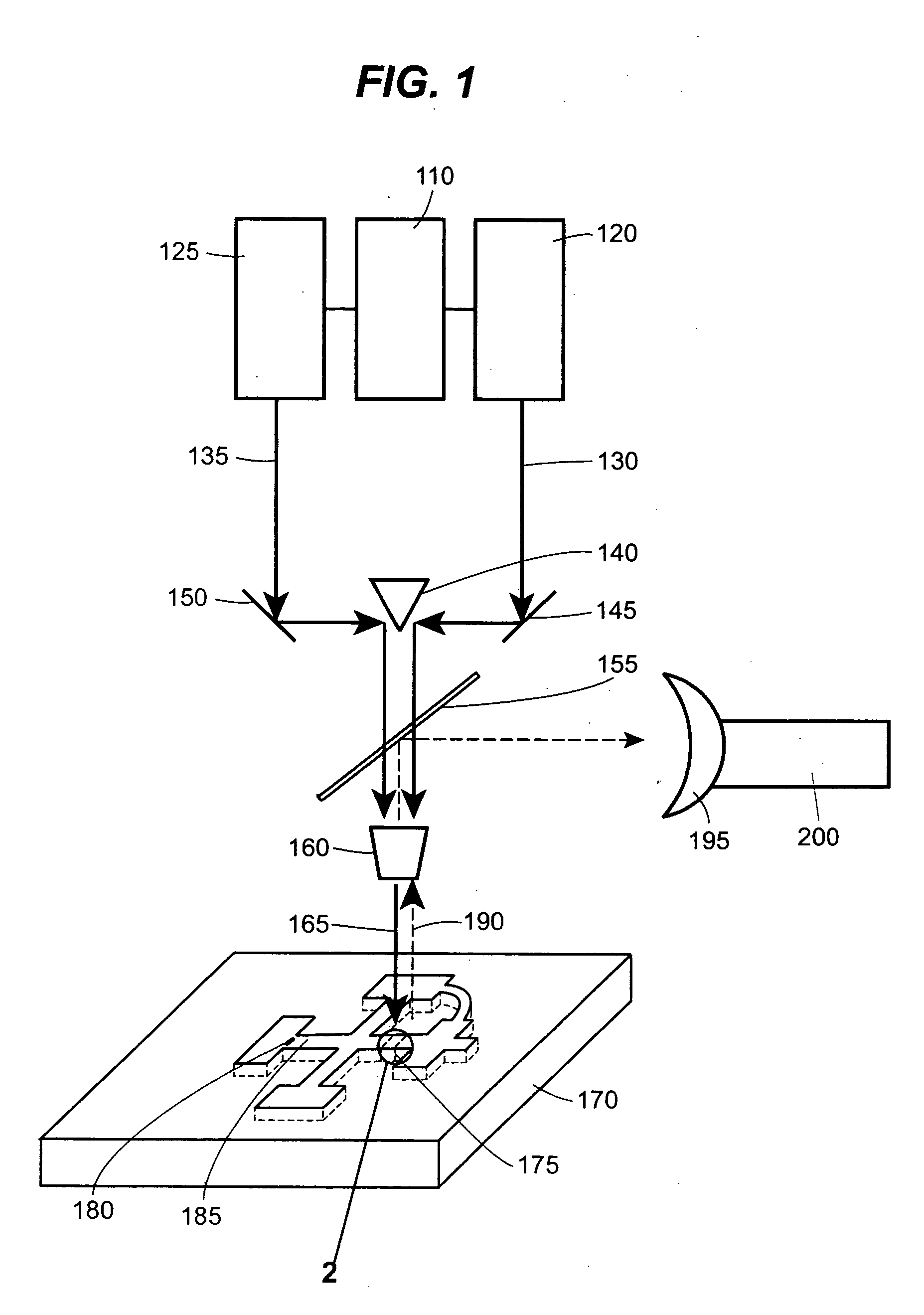
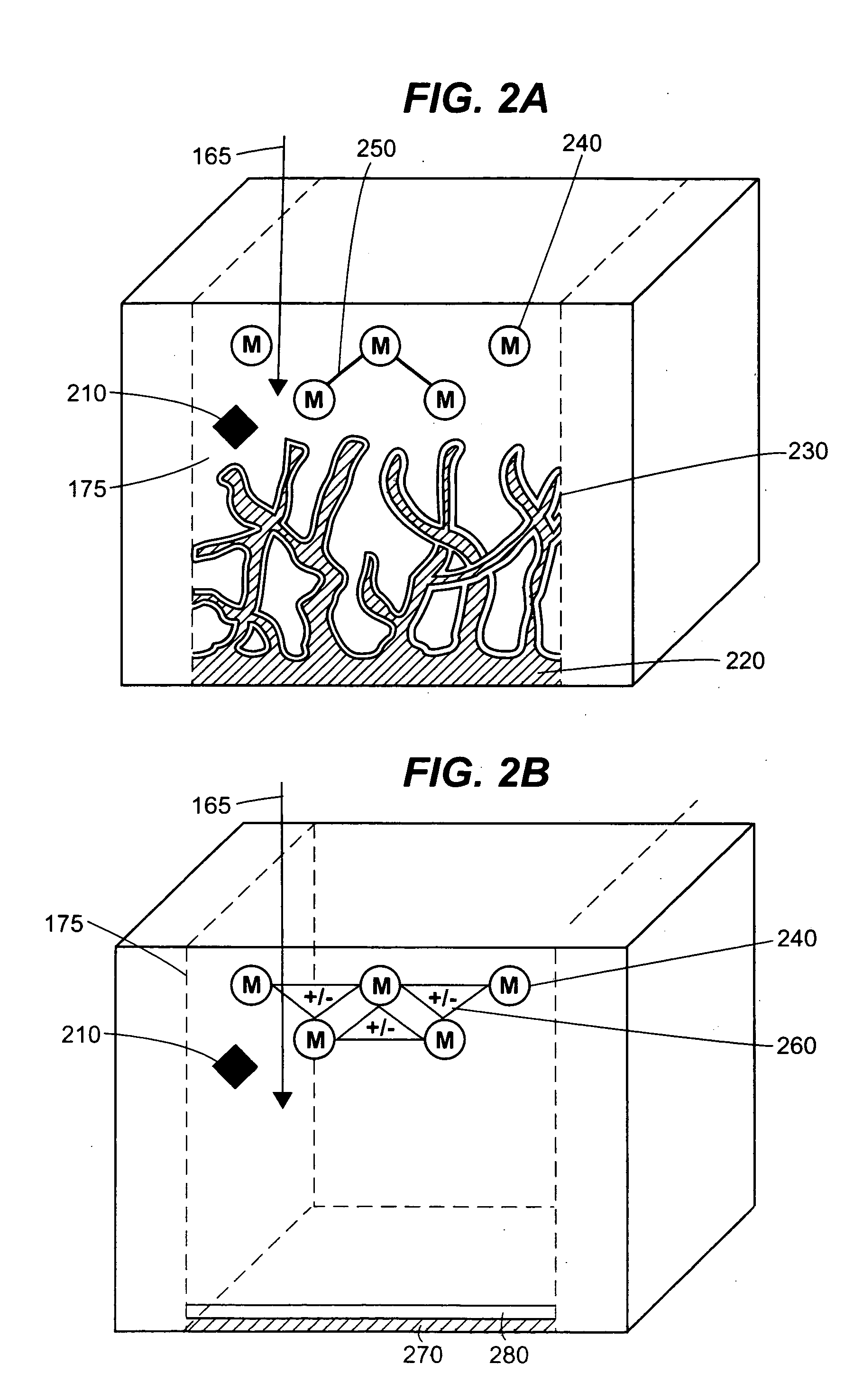
The device and method disclosed herein concern detecting, identifying, and or quantifying analytes, such as nucleic acids, with high resolution and fast response times using surface enhanced coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy. In certain embodiments of the invention, a small number molecular sample of the analyte 210 such as a nucleotide, passes through a microfluidic channel, microchannel, or nanochannel 185 and sample cell 175 that contains Raman-active surfaces, and is detected by surface enhanced, coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy (SECARS). Other embodiments of the invention concern an apparatus for analyte detection.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods and systems for constructing and maintaining sample panels
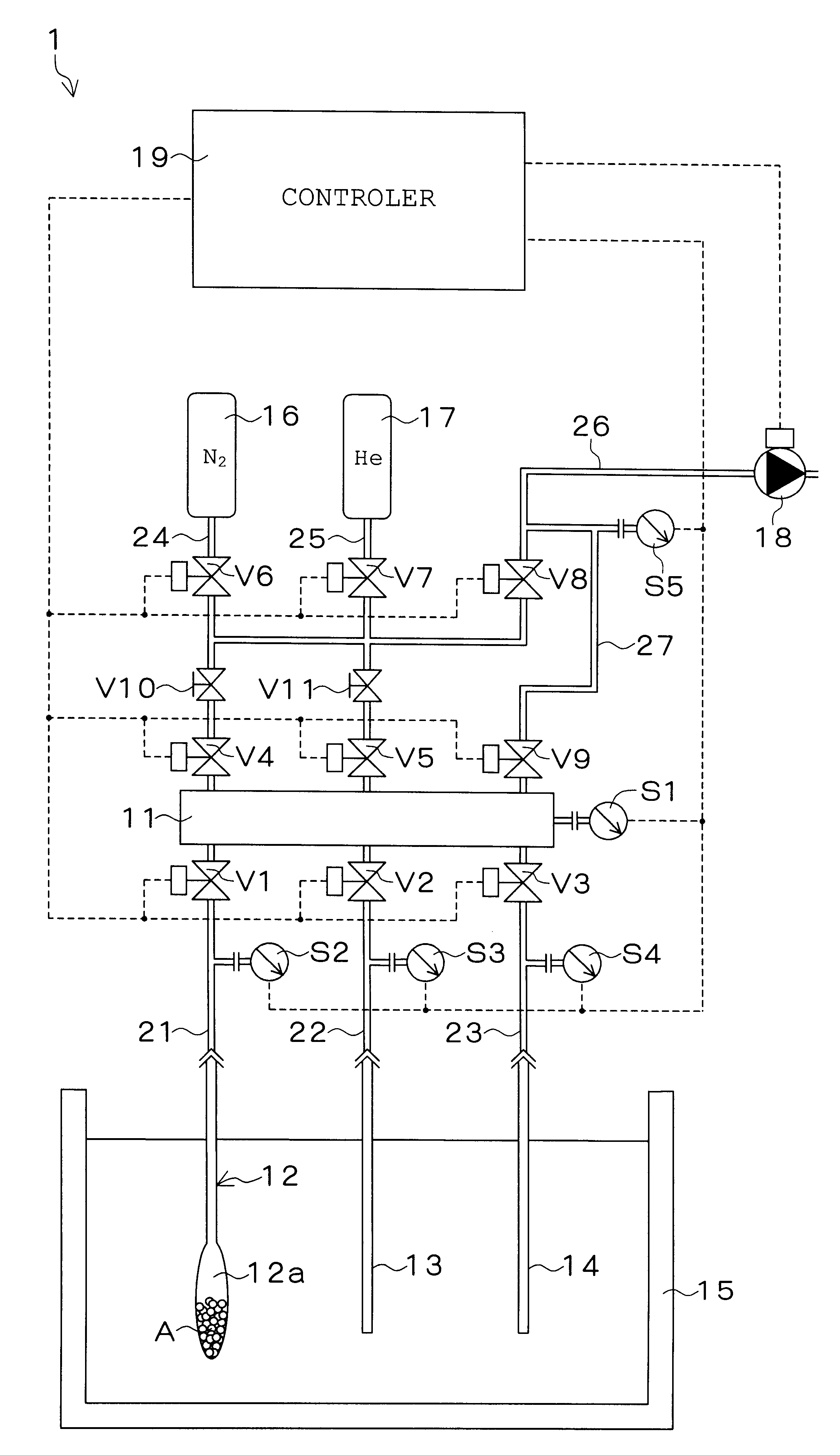
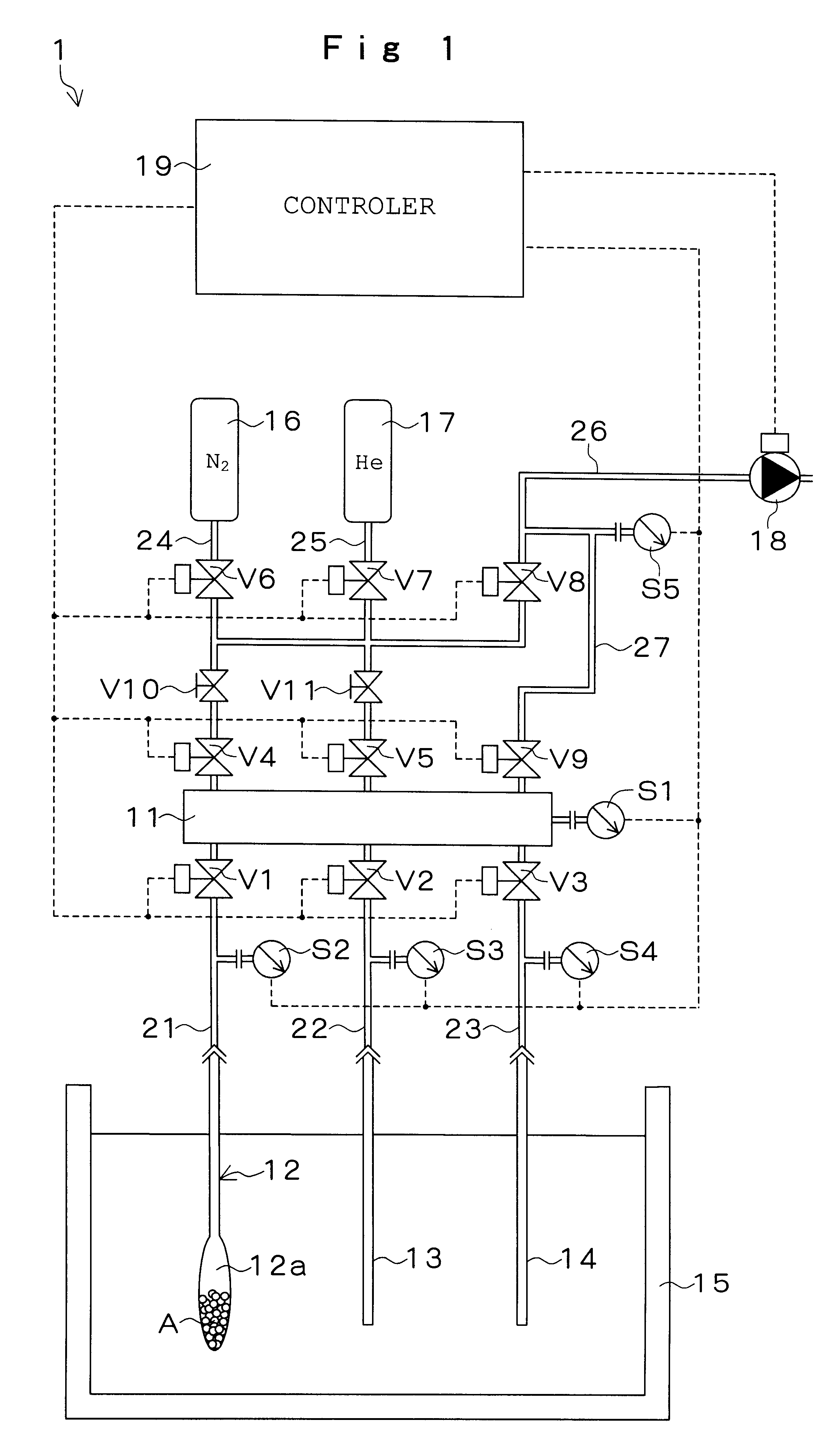
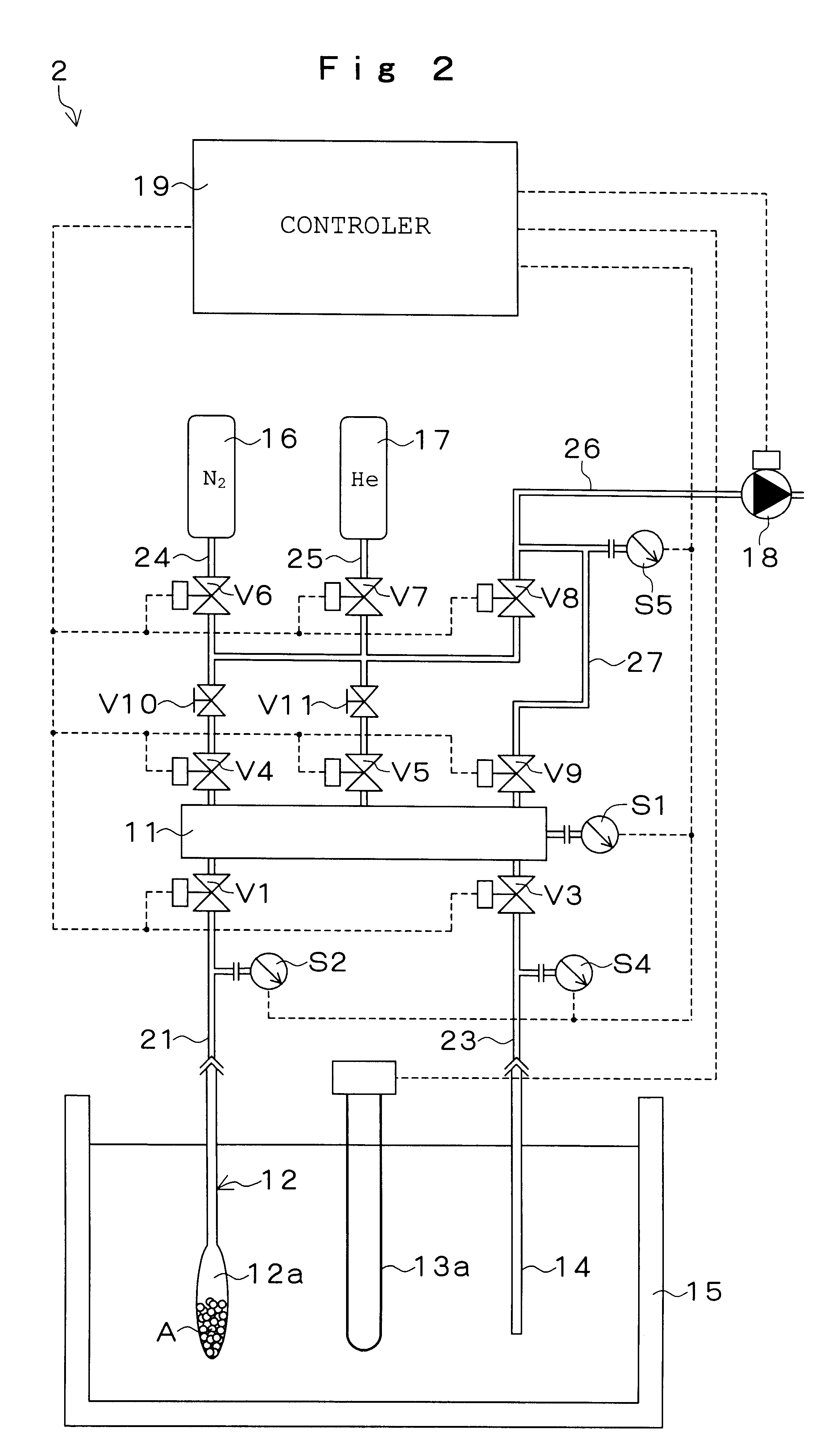
Methods and systems are provided for the dynamic management of a sample panel, the sample panel reflecting an audience population in terms of a geo-demographic composition thereof. Back-out data is provided representing forecasted back-outs of members of the sample panel according to their geo-demographic characteristics. In certain embodiments members are added to and / or removed from the panel based on the back-out data. In other embodiments adjustment data is produced indicating that members should be added to and / or removed from the sample panel based on the back-out data. In still other embodiments, potential panel members are selected from a sample pool for recruitment to the sample panel based on forecasted participation data.
Owner:NIELSEN HLDG NV +1
Method and device for detecting small numbers of molecules using surface-enhanced coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050110990A1Radiation pyrometryRaman scatteringAnalyteCoherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy
The device and method disclosed herein concern detecting, identifying, and or quantifying analytes, such as nucleic acids, with high resolution and fast response times using surface enhanced coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy. In certain embodiments of the invention, a small number molecular sample of the analyte 210 such as a nucleotide, passes through a microfluidic channel, microchannel, or nanochannel 185 and sample cell 175 that contains Raman-active surfaces, and is detected by surface enhanced, coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy (SECARS). Other embodiments of the invention concern an apparatus for analyte detection.
Owner:INTEL CORP
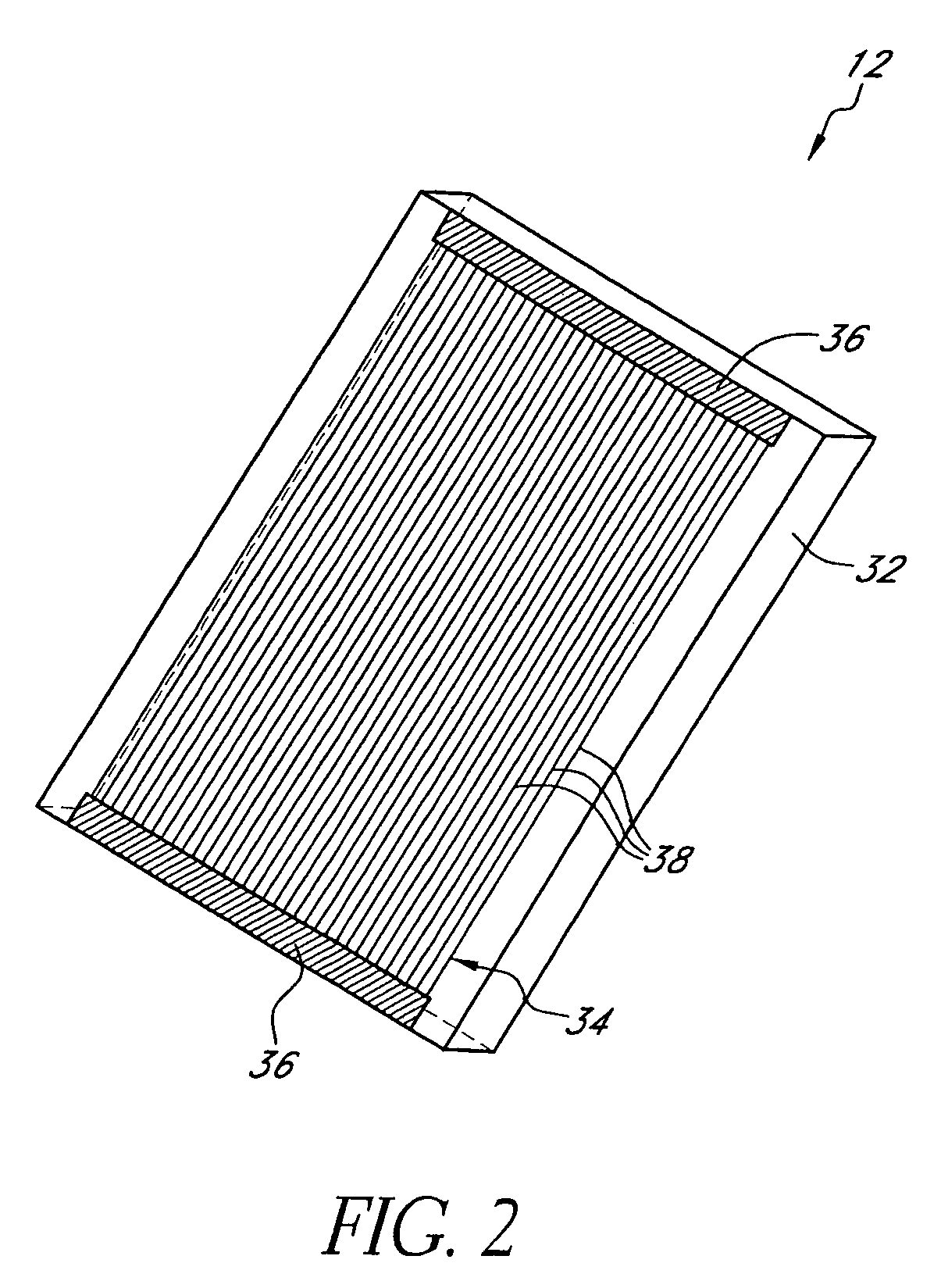
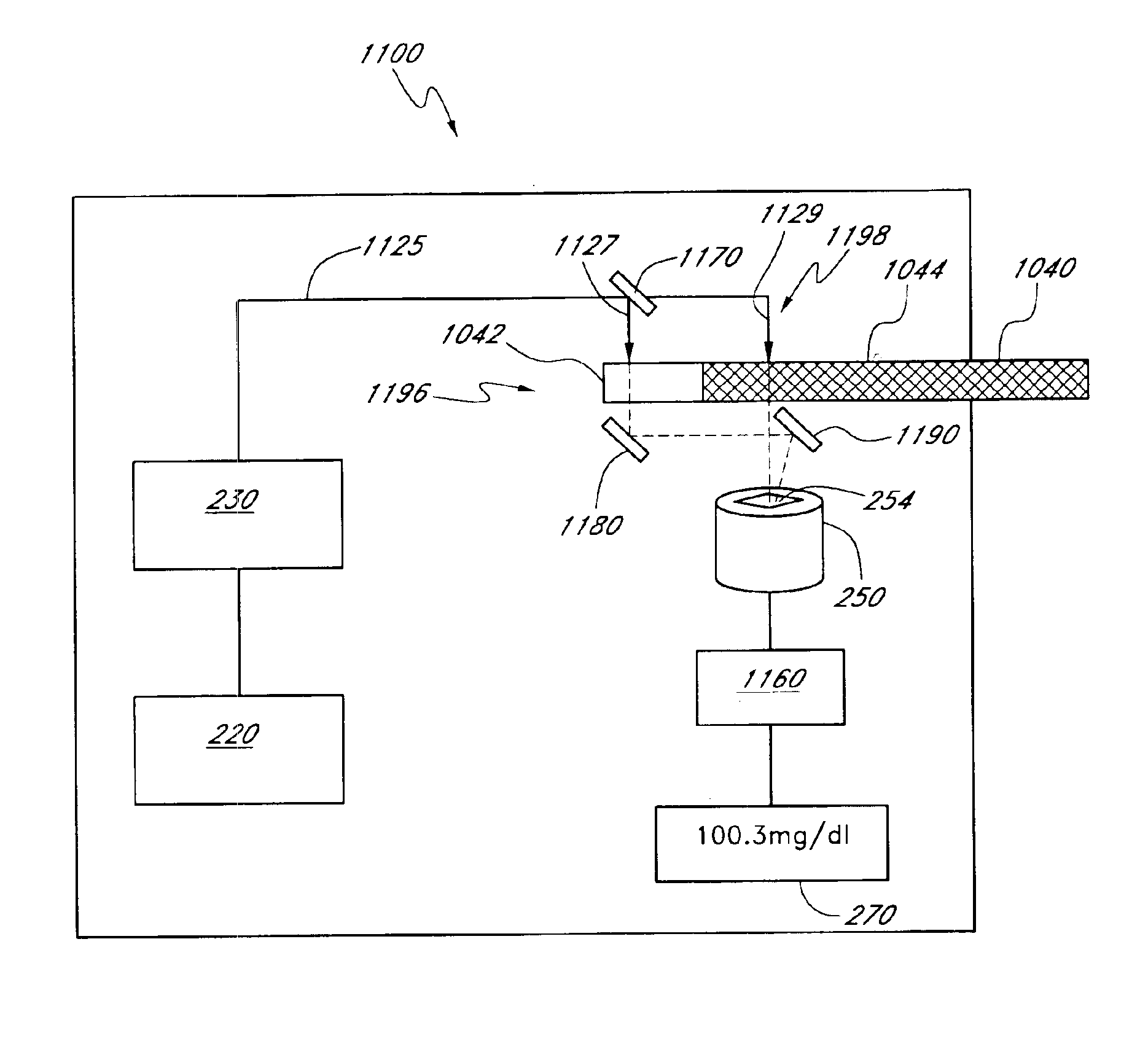
Fluid handling cassette having a spectroscopic sample cell
A fluid handling module is configured for removable engagement with a reusable main fluid handling instrument. The module includes a module housing and a first fluid passageway extending from the module housing. The first fluid passageway has a patient end remote from the housing. The first fluid passageway is configured to provide fluid communication with a bodily fluid in a patient. A fluid component separator is in fluid communication with the first fluid passageway. The fluid component separator is configured to separate at least one component from a portion of the bodily fluid drawn from the patient. A spectroscopic sample cell is configured to hold at least a portion of the first component.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
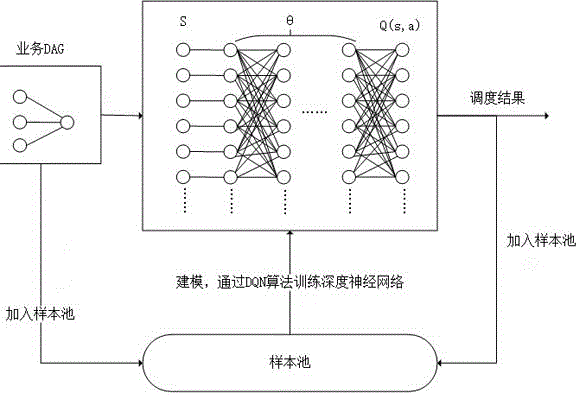
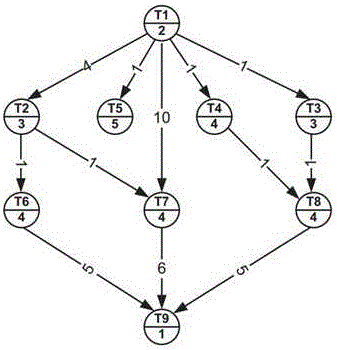
Workflow scheduling method based on depth enhancement learning
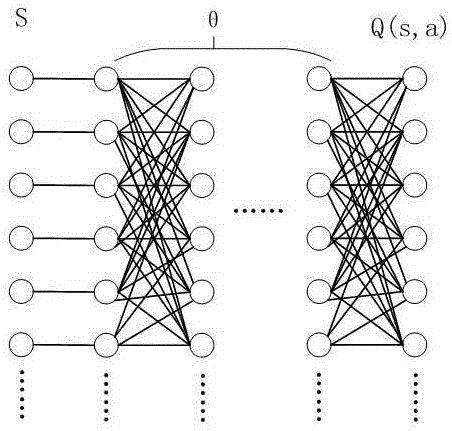
InactiveCN106228314AGuaranteed time and efficiencyImprove generalization abilityResourcesNeural learning methodsDeep neural networksSample pool
The present invention discloses a workflow scheduling method based on depth enhancement learning. The method comprises the following steps of A) collecting M task execution workflow directed acyclic graphs (DAG) in an actual execution environment as a sample pool; B) carrying out the Markov decision process (MDP) modeling on each workflow DAG to generate a task state set S; C) according to a training method DQN of a neural network, using the task state sets S generated by the M workflow DAG and the corresponding known action sets A as the input to substitute into a deep neural network formula, and obtaining the value of a neural network parameter matrix. According to the present invention, and by the above method, the defects that the execution time of the workflow scheduling method is long and the generalization performance is poor under a current distributed environment, are solved, the time efficiency of an algorithm is guaranteed acceleratedly, at the same time, the generalization performance of the algorithm itself is increased, and a scheduling machine can learn a scheduling strategy autonomously according to the actual scene characteristics.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Reagent-less whole-blood glucose meter
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Process and system for rapid sample analysis
ActiveUS20150260695A1Low MDLsLow detection limitRadiation pyrometryComponent separationDistillationElectromagnetic radiation
Components resolved in time by a separator accumulate in a sample cell and are analyzed by electromagnetic radiation-based spectroscopic techniques. The sample cell can be configured for multiple path absorption and can be heated. The separator can be a gas chromatograph or another suitable device, for example a distillation-based separator. The method and system described herein can include other mechanical elements, controls, procedures for handling background and sample data, protocols for species identification and / or quantification, automation, computer interfaces, algorithms, software or other features.
Owner:MLS ACQ INC
Automated method and system for testing blood samples
InactiveUSH1960H1Safely and cost-effectively collectedEfficient and cost-effectiveSamplingLaboratory glasswaresPlasma samplesAutosampler
An automated system and process is provided for pooling samples from a multiplicity of blood or plasma donations for subsequent testing to uniquely identify any such blood or plasma donations which may be infected with a particular virus. The system includes an autosampler needle which is directly inserted into a blood or plasma sample aliquot container in order to withdraw an aliquot portion of the contents for forming a sample pool with aliquot portions of other blood or plasma samples. The autosampler comprises a tubular piercing member having a hollow interior bore and a tubular shroud surrounding the piercing member.
Owner:BAXALTA INC
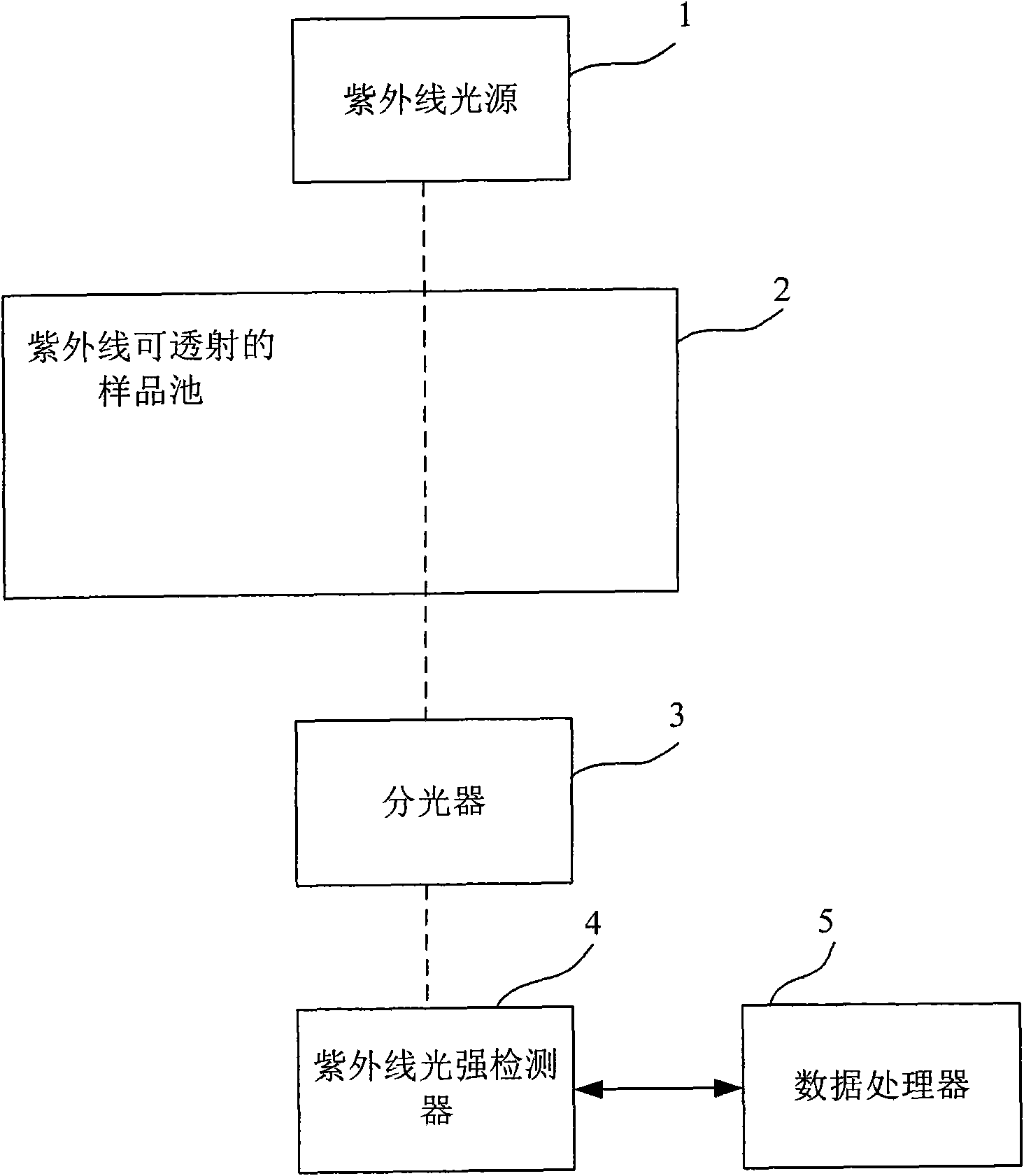
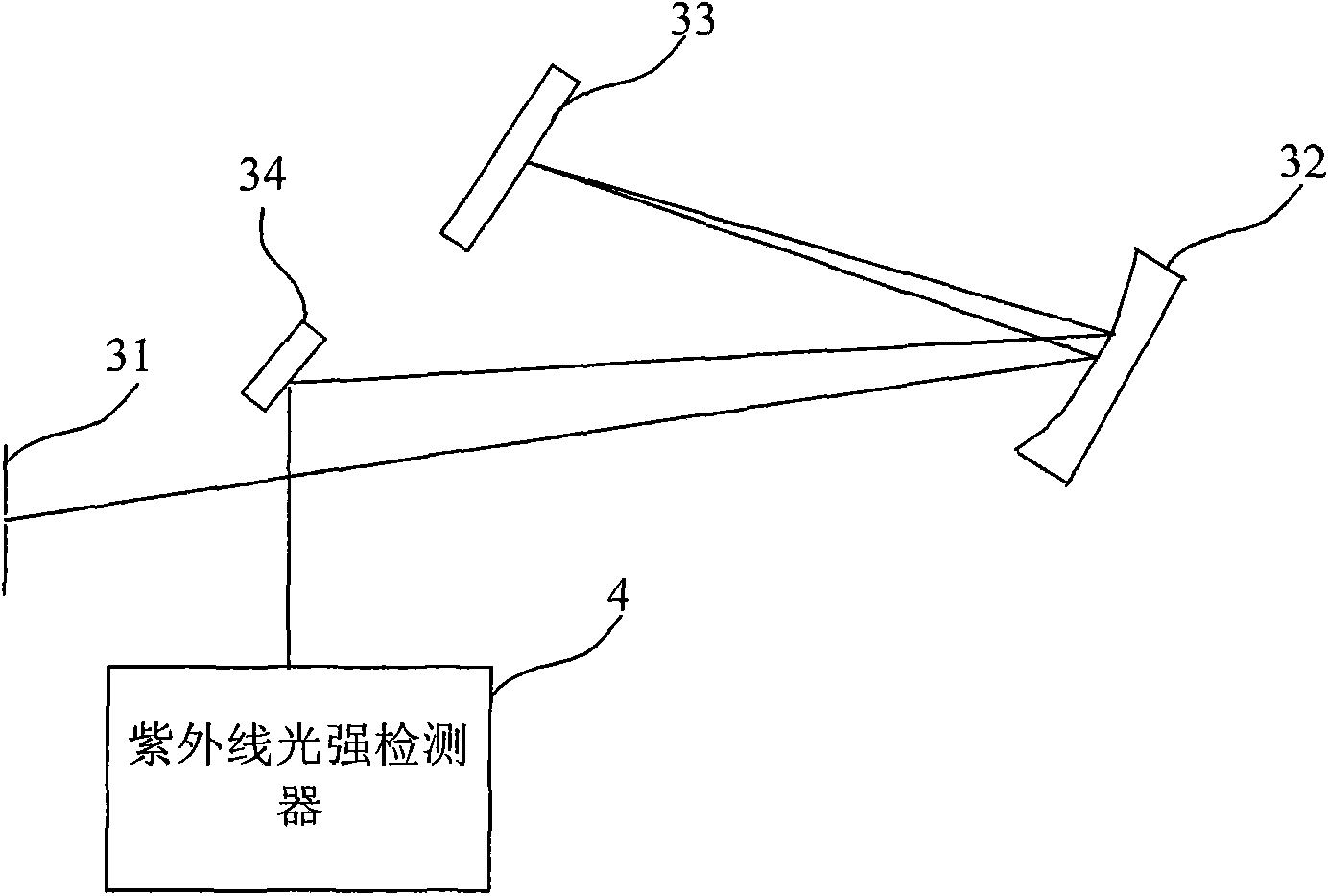
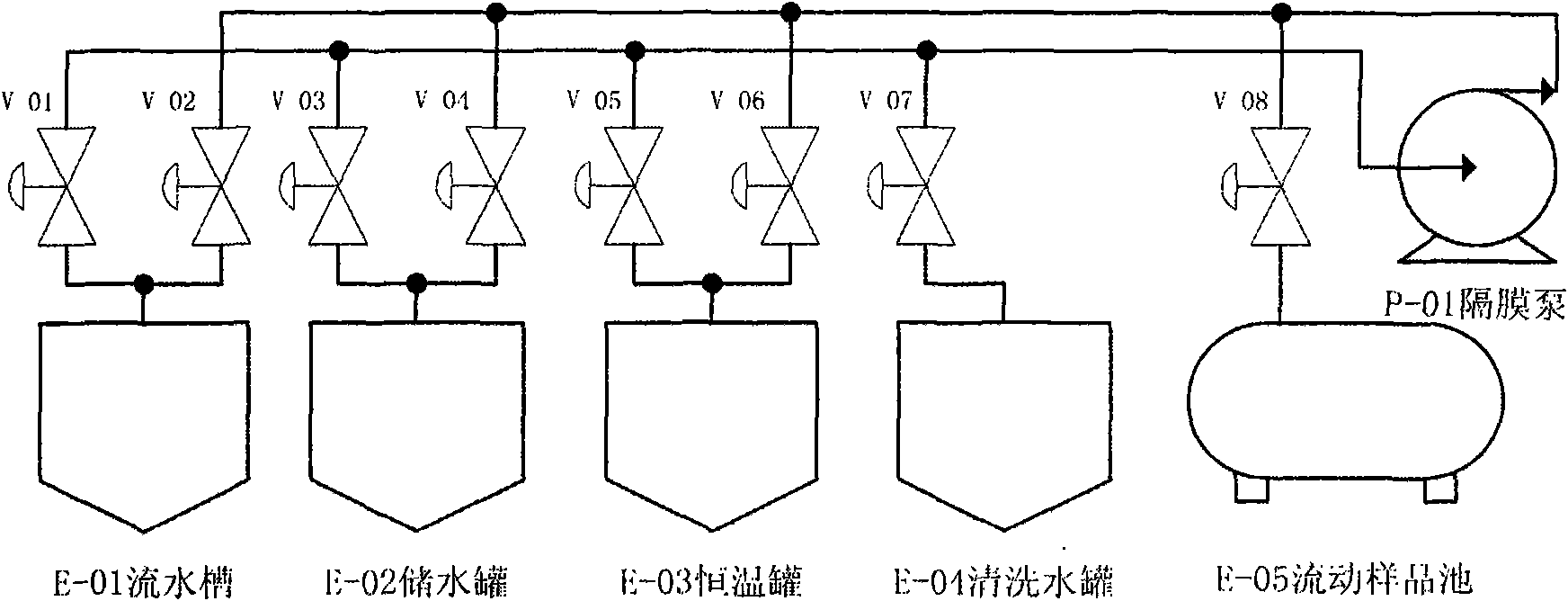
Online detector for detecting total organic carbon (TOC) in sewage with ultraviolet spectrometry method
InactiveCN102042963AAccurately reflectReduce measurement errorColor/spectral properties measurementsGratingUv spectrum
The invention provides a detector for detecting total organic carbon (TOC) in sewage, mainly comprising a sample pool capable of being transmitted by ultraviolet rays, a UV optical splitter and a data processor of the organic carbon. The detector is characterized in that UV can emit 240-450nm of UV beams, and a neon lamp is used as a UV light source; the optical splitter is a UV reflective blazed grating, and the light strength of the light beams at each wavelength is detected by a linear array UV CCD (Charged Coupled Device); and the TOC value is determined according to the relationship between the absorbance at the feature wavelength and the TOC content. As known from the scheme, the detector has low cost and good stability and is capable of fully realizing automation and accurately measuring the TOC value so as to comprehensively reflect the pollution degree of the organic matter in the water. Thus, the detector has important help and realistic significance for monitoring and measuring the sewage discharge and the water pollution on the ground surface.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Detecting method and system for malicious codes
InactiveCN102360408APlatform integrity maintainanceSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseSvm classifier
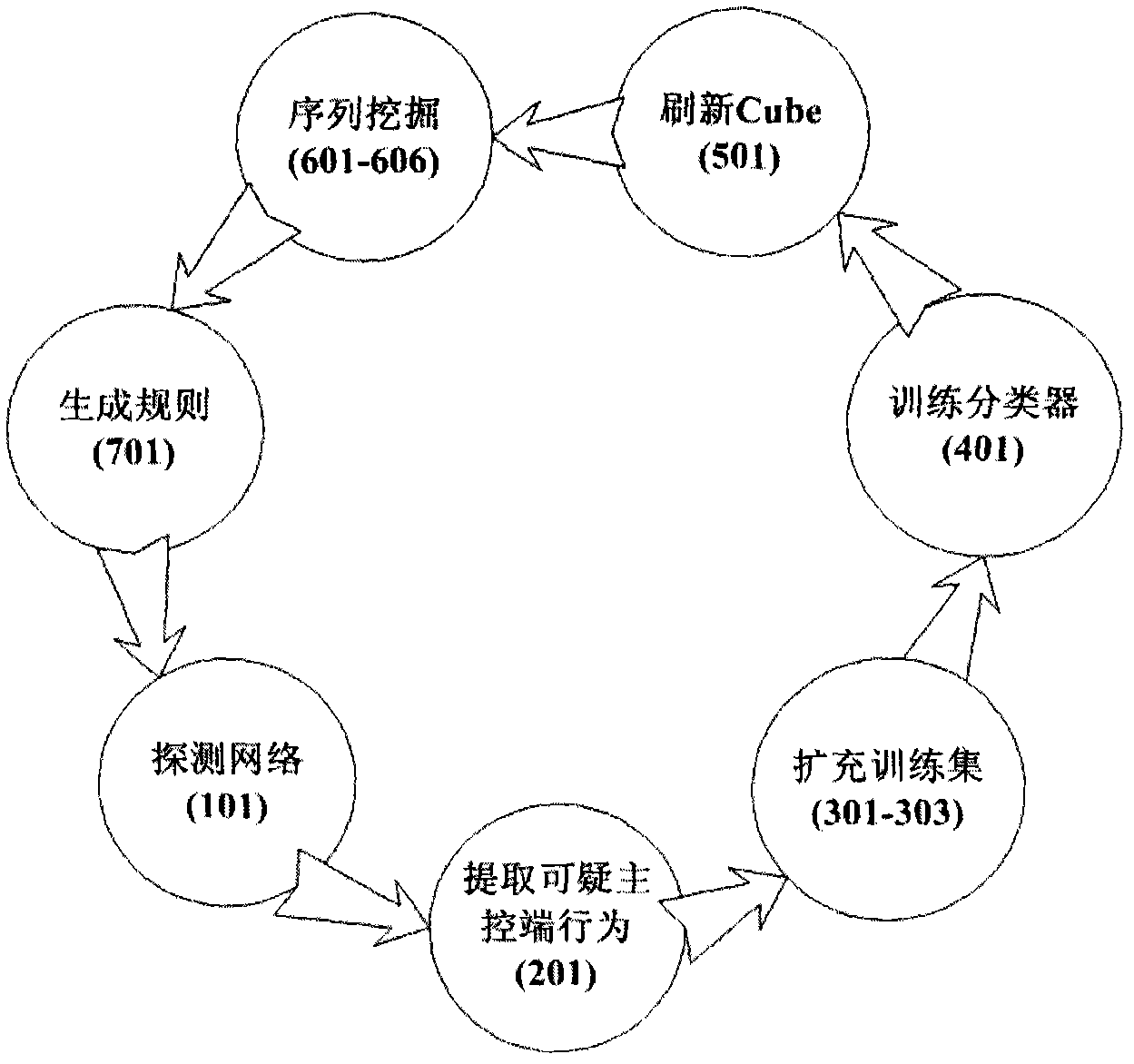
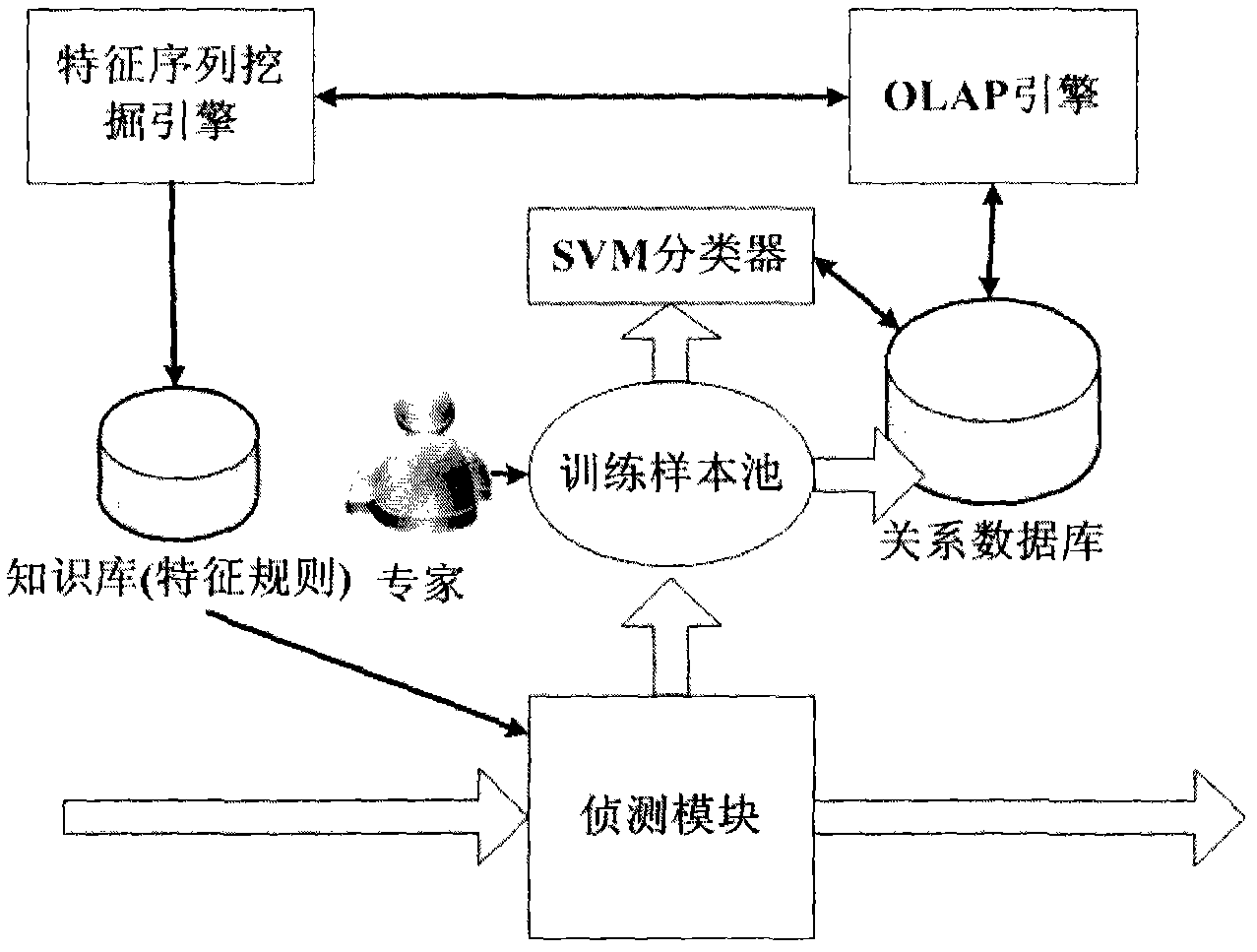
The invention provides a detecting method and a system for malicious codes, which are assisted by an OLAP engine, characterized by interaction behaviors of a main control end and a controlled end of malicious codes and are based on excavation, wherein the detecting method comprises a step 101 of detecting a network; a step 201 of extracting suspicious main control end behaviors; steps 301-303 of expanding a training set; a step 401 of training a classifier; a step of 501 of brushing Cube; steps 601-606 of excavating sequences; and a step 701 of generating a rule. The detecting system comprises a detecting module, a training sample pool, an SVM classifier, a relation database, an OLAP engine, a characteristic sequence excavation engine and a knowledge base.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT +1
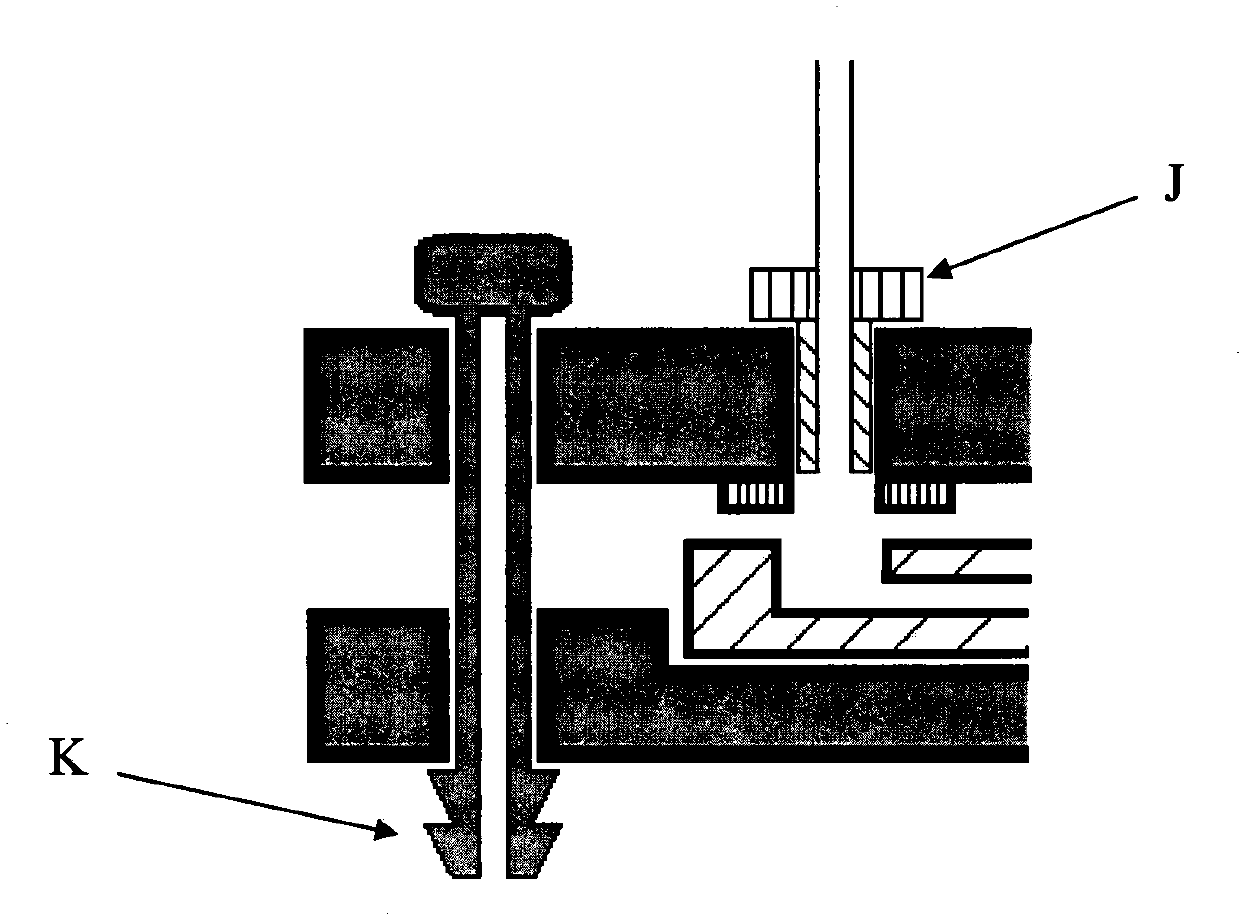
Micro-fluidic chip clamp
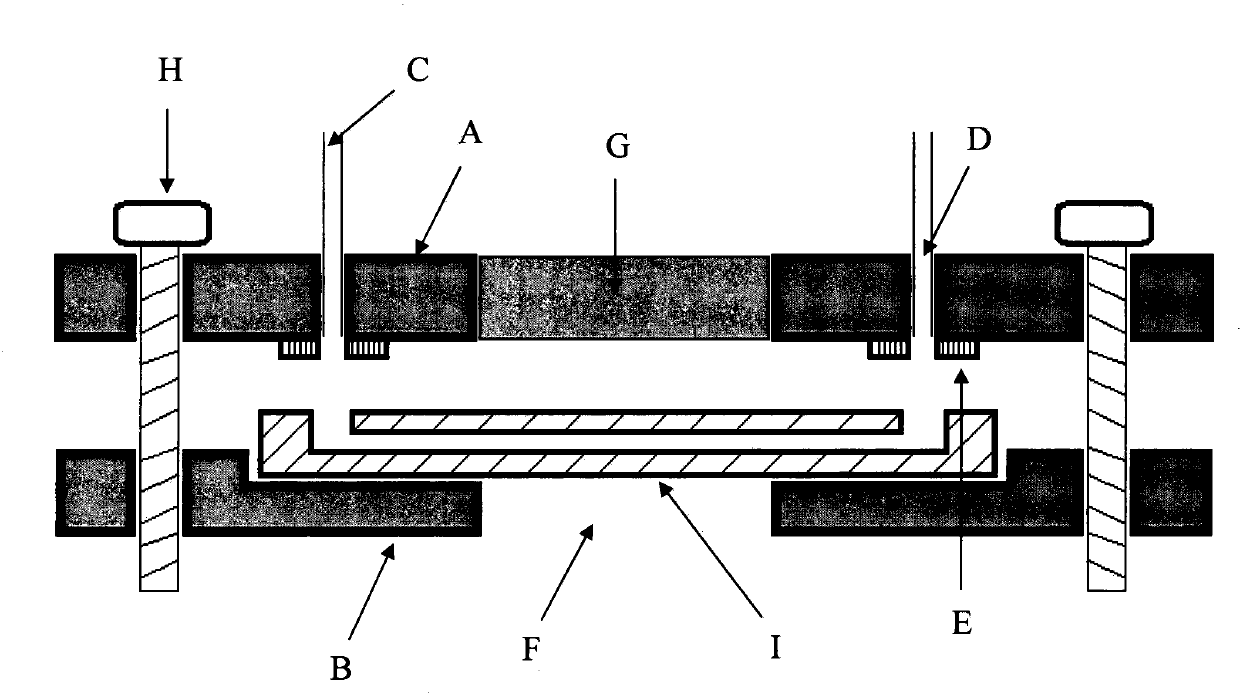
Aiming at the problems, the invention provides a micro-fluidic chip clamp. The micro-fluidic chip clamp is characterized by guaranteeing the immobilization of a micro-fluidic chip in a use process and supplying a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet. The micro-fluidic chip clamp consists of two clamping plates; the micro-fluidic chip is pressed and fixed between the two clamping plates through screws or clamping hook structures; a plurality of conduit connection openings and a plurality of chip sample pool connection openings are formed in the clamping plates and are used for connecting an external fluid control system and the micro-fluidic chip.
Owner:苏州扬清芯片科技有限公司
Integrated micro-fluidic chip
ActiveCN107398307AAvoid pollutionReduce air pressureMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTransportation and packagingProcess engineeringPressure balance
The invention relates to an integrated micro-fluidic chip. At least one integrated reaction unit is arranged on a substrate and at least comprises a sample tank, a mixing tank and a reaction tank which are communicated through a liquid channel, and a sample inlet is formed in one end of the sample tank; and the integrated reaction unit further comprises a gas circuit internal cycle system, one end of the gas circuit internal cycle system is connected with the mixing tank, and the other end of the gas circuit internal cycle system at least comprises a first cycle branch connected with one end, far from the sample inlet, of the sample tank. According to the integrated micro-fluidic chip, the air pressure balance in the sample tank and the mixing tank is guaranteed, so that the smooth flow of a sample in a predetermined channel of the micro-fluidic chip is guaranteed, and a reliable foundation is provided for generating a target product from the sample.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP
Droplet micro-fluidic chip and operation method thereof
InactiveCN103285947APrecise handlingGenerate mildLaboratory glasswaresChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesEngineeringDroplet microfluidics
The invention provides a novel droplet micro-fluidic chip and an operation method thereof, and in particular relates to a droplet micro-fluidic chip for integrating an electroosmotic pump. The droplet chip consists of a sample pool, a micro-channel and a micro-electroosmotic pump. One or the combination of micro-droplet generation, splitting or fusion is controlled by regulating negative pressure generated by the micro-electroosmotic pump. Droplet operation is realized in a non-electric field environment. Under the condition, on one hand, droplets can be accurately operated by regulating the pressure of the electroosmotic pump; on the other hand, the droplet generation, splitting and fusion conditions are mild, and interference from an additional electric field is avoided.
Owner:苏州扬清芯片科技有限公司
Liquid-phase suspension biochip based on multi-optical trap encoding bead array and two-photon fluorescence detection
InactiveCN105784662AReal-time analysisSimplify the enrichment processFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrosphereBand-pass filter
The invention provides a liquid-phase suspension biochip based on multi-optical trap encoding bead array and two-photon fluorescence detection. The liquid-phase suspension biochip has a configuration as follows: a near-infrared laser beam emitted by a near-infrared laser is expanded by a beam expanding system, is sequentially reflected by a telescope system and a dichroscope by using a holographic technology or a time-share scanning technology, and is focused into a sample pool through a high numerical aperture objective lens, to form multi-optical-trap optical tweezers; the multi-optical-trap optical tweezers capture a plurality of encoding beads enriched with objects to be detected, to form a bead array in the solution; after an infrared laser signal is filtered by a band-pass filter, a two-photon fluorescence signal from each bead is focused to an image detector by a lens and is subjected to imaging detection. The liquid-phase suspension biochip can perform real-time quantitative analysis on nucleic acids, proteins, virus particles and a plurality of objects to be detected, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong anti-interference ability, simultaneous determination of a plurality of components and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
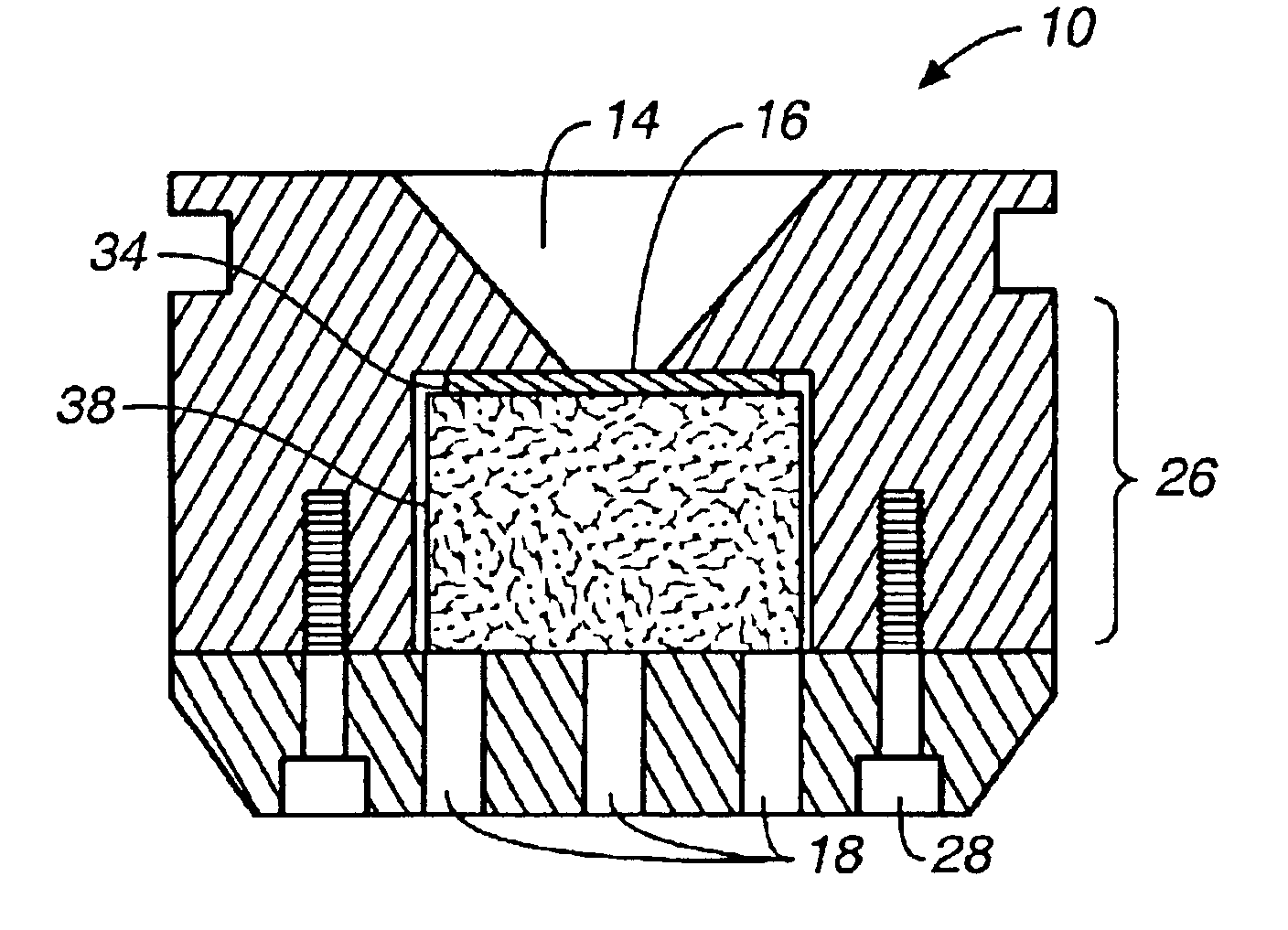
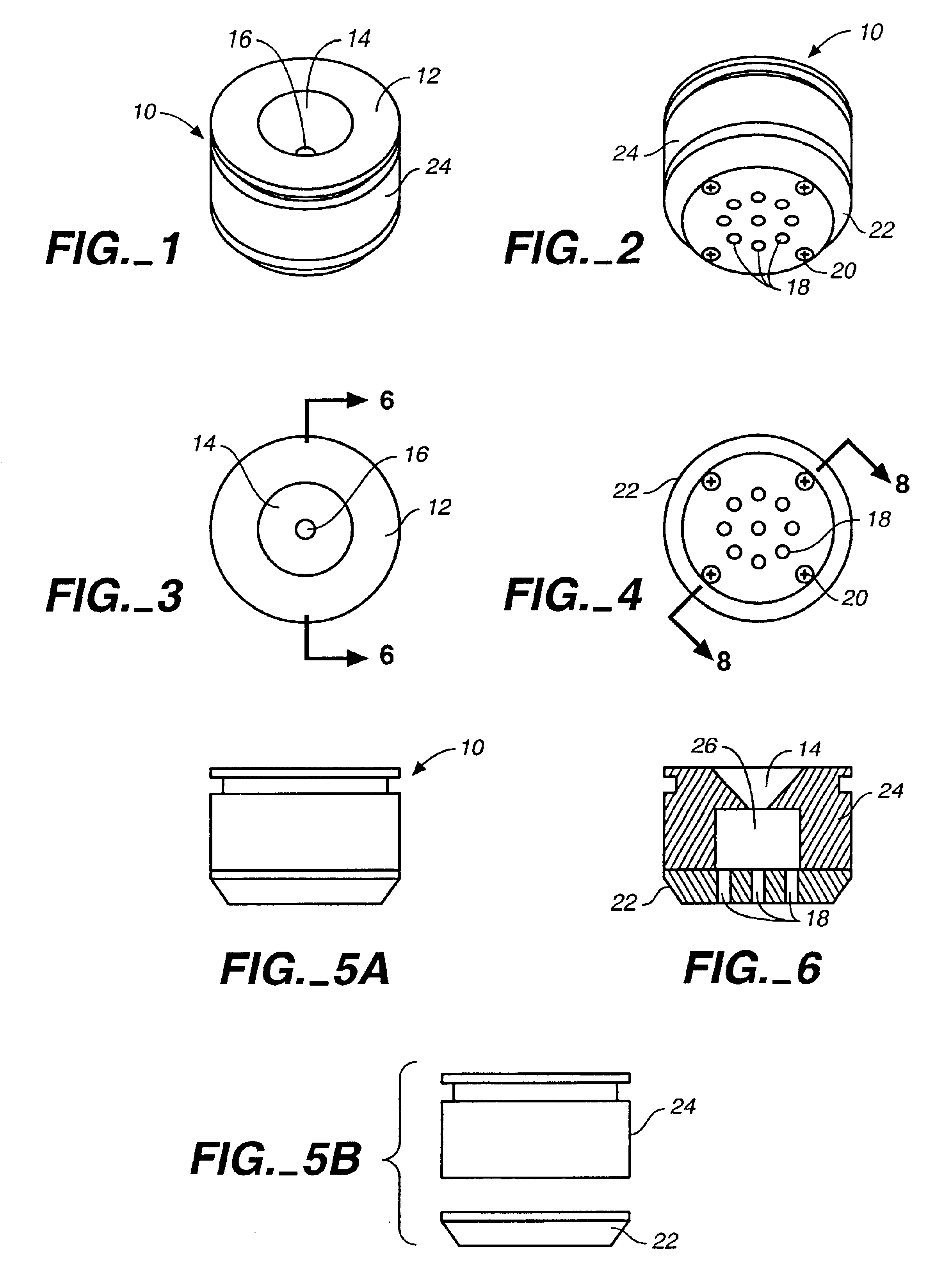
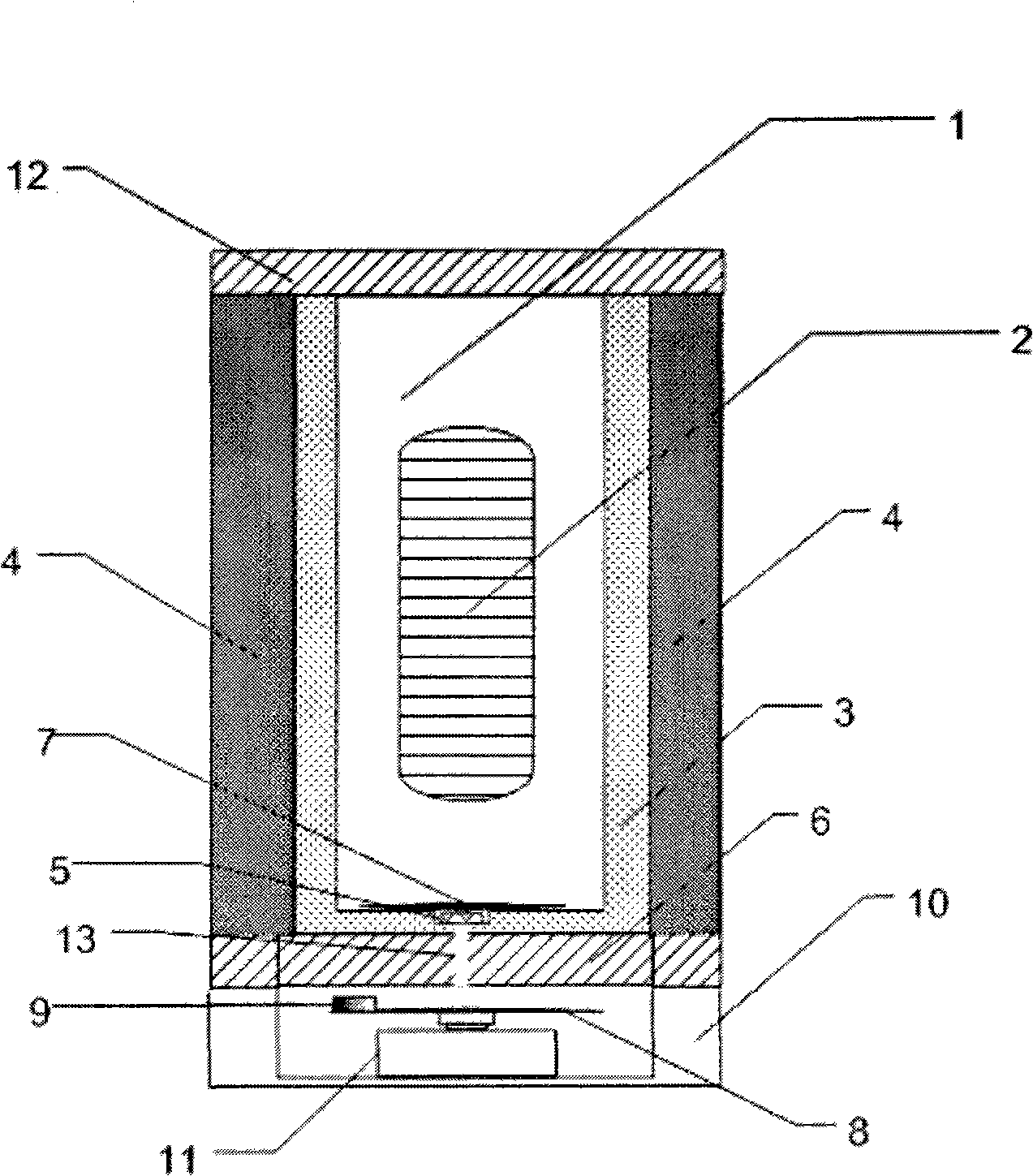
Apparatus and methods for automated diffusion filtration, culturing and photometric detection and enumeration of microbiological parameters in fluid samples
InactiveUS20080293091A1Control directionControl rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteDiffusion
A system providing non-intrusive, automated culturing and photometric detection for analyzing microbiological parameters is described. The system includes a sealed non-intrusive sample cuvette, a housing with an enclosable cover, systems for incubation and photometric detection mounted within the housing. The sample cuvette consists of a clear graduated optically transmitive container with two chambers—a culture chamber and a detection chamber, separated by a permeable membrane wall. The cuvette has an upper part and a lower part of different dimensions. The upper part is bigger in size than the lower part. The sealed top of the cuvette has two fluid inlet / outlet ports for the introduction of the sample into one chamber while when connected to a suitable vacuum device, the second chamber receives the filtered sample through the permeable membrane. The housing has a cuvette holder that is shaped to provide a very snug fit for the cuvette. When placed inside the cuvette holder the bottom of the upper part of the cuvette rests on top of the holder while the bottom part snugly fits inside the holder cavity. The housing with the enclosable cover provides a thermal chamber during simultaneous incubation and photometric enumeration of microbiological parameters. The cuvette holder accommodates a heating element and a temperature sensor. Photometric detection components comprising LEDs and detectors are placed strategically within the holder.
Owner:KANIPAYOR RAVI +1
Method and apparatus for measuring amount of gas adsorption
InactiveUS6595036B1Initial dead volume of the sample cell can easily be correctedEasily and accurately determinedAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFluid-tightness measurement by detecting dimension changeChemical physicsDead volume
In a volumetric gas adsorption measuring method, an initial dead volume of the sample cell and an initial dead volume of a reference cell at the same time point are preliminarily determined. When the gas adsorption on the solid sample is to be measured, a change in the dead volume of the sample cell is calculated on the basis of an internal gas with the sample cell and reference cell immersed in a pressure of the reference cell measured at this time point cryogenic fluid temperature bath, the initial dead volume of the reference cell, and an initial gas pressure of the reference cell measured at a time point of the measurement of the initial dead volume of the reference cell. Then, the initial dead volume of the sample cell preliminarily measured is corrected on the basis of the change in the dead volume of the sample cell for the calculation of the amount of the gas adsorbed on the solid sample.
Owner:BEL JAPAN
Flow-through cryogenic NMR probe
InactiveUS6838880B2Prevent heat lossBig lossElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRoom temperature
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy probe has a sample cell into and out of which a room temperature liquid sample may be directed. The cell is surrounded by a radio frequency coil that is used to perform NMR measurements of the liquid sample, and which is maintained at cryogenic temperatures. The coil is separated from the sample cell by a thermally insulative boundary, such as a vacuum. The sample may enter the cell through an input path, and may exit through an output path. The input path, output path and sample cell may be surrounded by a sheath through which flows room temperature gas. The ends of the sample cell may be tapered to promote thorough flow through the cell, and flow diverters may be included in the sample cell adjacent to the input and output paths to force flow to the outer wall of the sample cell.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
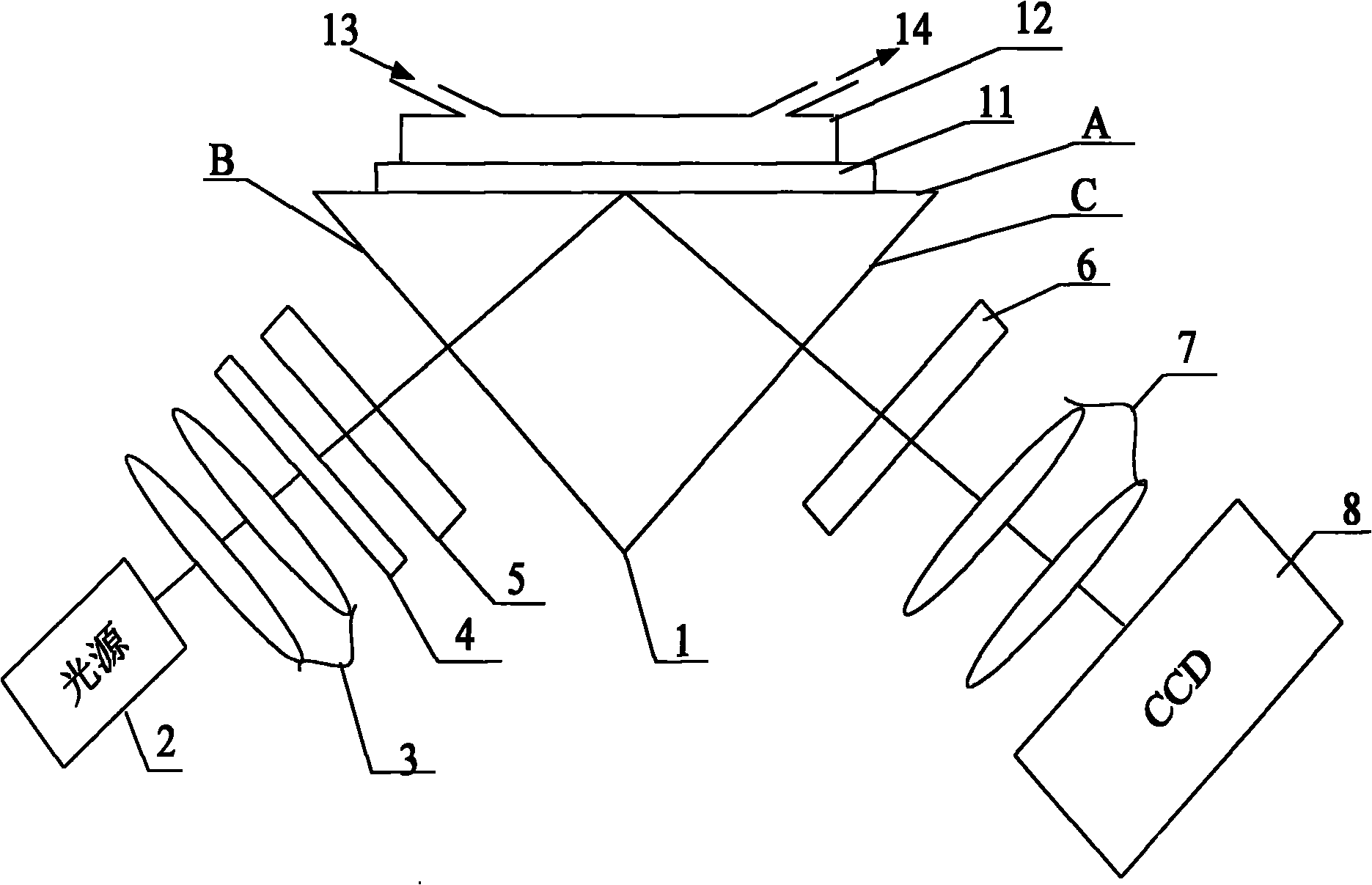
Surface plasmon resonance imaging sensing system
InactiveCN101865840AAvoid speckleEasy to detectPhase-affecting property measurementsPolarizerSurface plasmon resonance imaging
The invention relates to a surface plasmon resonance imaging sensing system, which comprises a plasma resonator with isosceles triangle cross-section, wherein the plane of the bottom side of the isosceles triangle is of a sensing plane, and a layer of metal reflection film is plated on the sensing plane; a sample pool with an inlet and an outlet is arranged on the metal reflection film, and one of the planes of the two sides of equal length is used as an incident plane, and the other thereof is used as an emittance plane; a power source, a beam shaper and a polarizer are sequentially arranged on an incident light path which is vertical to the incident plane to reach the sensing plane, and an analyzer, an imaging lens group and an area array photoelectric sensor are sequentially arranged on a reflection light path generated by the sensing plane; and the area array photoelectric sensor is positioned on a focal plane of the imaging lens group and is connected with an external computer. The surface plasmon resonance imaging sensing system is characterized in that: the light source is a non-coherent light source, and a narrow-band filter is arranged between the polarizer and the incident surface. The invention can be widely used in food safety detection, pesticide residue detection, bio-molecule detection, bio-terrorist detection and other fields.
Owner:SHENZHEN INT TRAVEL HEALTHCARE CENT +1
DSC meter with visualization function
InactiveCN101487806AFunction increaseEasy to assembleMaterial heat developmentMaterial analysis by optical meansReal time analysisHeat flux
The invention discloses a differential scanning calorimeter, which is compatible with visualization and comprises a worktable, a first heat current detection part, a second heat current detection part, temperature control equipment, a temperature-recording instrument, a microscope image pickup system and an image acquisition system; wherein, the worktable is provided with a sample cell and a reference cell. The first heat current detection part is arranged in the sample cell and used for bearing samples and transmitting heat flux with the samples. The second heat current detection part is arranged in the reference cell and is used for bearing reference compound and transmitting heat flux with the reference compound. The temperate control equipment respectively controls the heating up and temperature reduction of the two heat current detection parts. The temperature-recording instrument is respectively connected with the two heat current detection parts by a thermocouple wire. The microscope image pickup system observes the microstructure of the samples by a sample observation window arranged on the sample cell and acquires and records the microstructure variation of the sample by the image acquisition system. The differential scanning calorimeter can monitor and acquires the structure variation information of the sample while measuring the heat flow when the samples change phase, and increases the synchronicity and integrity of real-time analysis detecting of the samples.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Apparatus and method for the measurement of cells in biological samples
InactiveUS6852527B2Improve accuracyReduce risk of exposureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationBiology
An apparatus and method for concentrating and measuring low levels of cells in biological samples. The apparatus, or concentration device, consists of two chambers with an optically level collection membrane intermediating between the chambers. The collection membrane filters the biological sample, trapping cellular elements of interest. A vacuum may be attached to the device to assist in filtration. The surface area of the collection membrane matches the view field of a standard imaging system and the device can be mounted on a standard microscope stage. All the cells in the sample volume are collected onto the membrane. The view field provides a fixed volumetric area for cell counting. Since the volume of sample tested is known, the total number of cells in the original sample may be calculated. The sample reservoir of the concentration device may also be used for sample preparation. The concentration device is fully-contained; therefore, the investigator does not have to handle the sample once it is placed in the sample reservoir.
Owner:INOVX
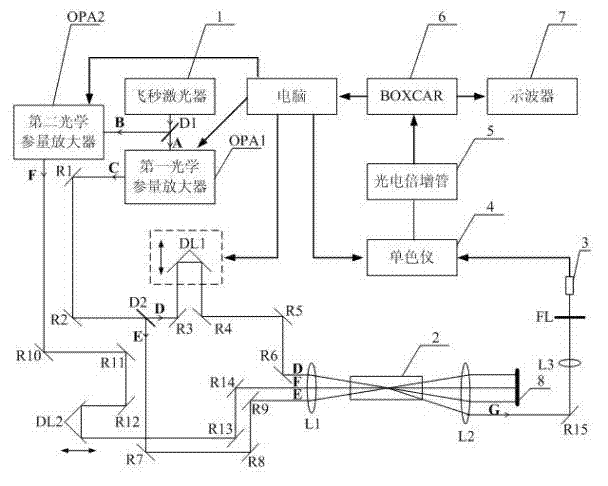
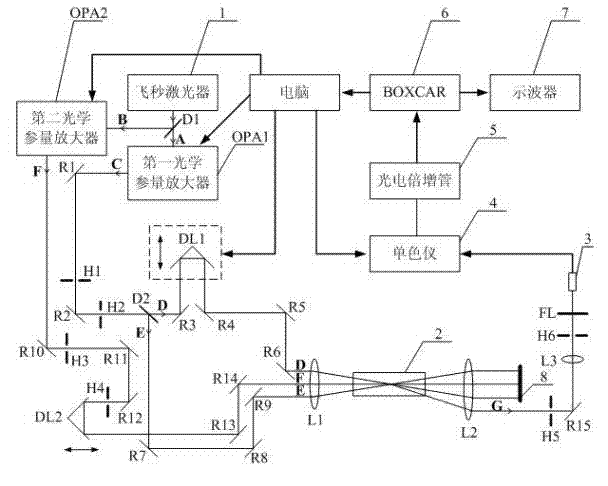
Normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system
InactiveCN101819064ASimple and fast operationImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringNonlinear opticsFemto second laser
The invention relates to a normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system which relates to the technical field of nonlinear optics and solves the problem of multiple limiting factors of traditional femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measuring experiment. Beams output by a femto-second laser are adjusted through a series of reflectors and optical delay lines by the system to form three bundles of beams which have approximate energy and are respectively positioned on three peaks of a square on the vertical direction of the beams, the beams are focused to a sample pool and then emit a new beam along a specific angle, i.e. a CARS signal, the CARS signal is filtered through a filter plate, then received by a probe and input to a monochromator, the data acquisition of an electrical signal converted by a photomultiplier is carried out by utilizing BOCCAR, and the data are input to a computer for data processing. The invention can carry out femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measurement under the experimental conditions of normal temperature and normal pressure and is applicable for the femto-second CARS spectrum measurement of gas samples and liquid samples in a static sample pool.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for sample injection in microfabricated devices
InactiveUS20020168780A1Fixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementSample poolThroughput
An off-column sample injection scheme for introducing samples into micro-reaction channels in microfabricated devices. In one aspect of the present invention, off-column sample injection is effected by introducing sample from a sample reservoir provided on the substrate of the microfabricated device into a reaction channel via a constricted channel or opening interface, e.g., a narrow connection-channel and / or a pinhole. In another embodiment of the present invention, off-column sample injection is effected by introducing sample from a sample reservoir that is provided outside the substrate of the microfabricated device. A through-hole is provided in the substrate to facilitate sample introduction into the reaction channel. In a further aspect of the present invention, the free-end of a capillary tube connected to the sample-channel is moved alternatively to a sample and an auxiliary solution to bring multiple samples in series to the vicinity of a reaction channel for convenient sample introduction and high-throughput assays.
Owner:MICROCHEM SOLUTIONS
Quick changeable temperature small-sized constant temperature sample pool
InactiveCN101281121APrecise and fast temperature controlMeet the requirements of constant temperatureMaterial analysis by optical meansWater/sand/air bathsTemperature controlMetallic materials
The invention relates to a quick variable temperature miniature thermostatic sample cell, which is made of metallic material, an opening is formed in the center of the metallic material and is used as a sample cavity, a light through hole is formed on a metallic shell along the center of the sample cavity, a transparent material is embedded in the light through hole, a Peltier temperature control element is glued on the non-light surface of the metallic material, a groove is arranged on the bottom of the metallic shell for laying aside a temperature sensor, the coat of the metal shell has a heat insulation outer frame, the center of a base connected with the bottom of the heat insulation outer frame is provided with a miniature motor, a small magnet is arranged at the edge of the leaf of a spiral leaf on the shaft of the motor, a stirring magneton is laid aside at the bottom in the sample cavity, the inner wall of the sample cavity and the outer faces of the sensor and the stirring magneton is carried on chemical inertia processing. The invention replaces the water heat conduction with the metal, and changes the system temperature with a thermo-element; the sensor directly observes the temperature of the sample, the heat conduction is speeded up by a miniature electromagnetic stirring system has accelerated; the invention is characterized in having small volume, accurate the temperature measurement, quick variable temperature, and good stability, etc, being able to be placed in analytical instrument such as spectrophotometer, etc., and realizing the quick variable temperature and the accurate thermostatic control of the temperature of the sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com