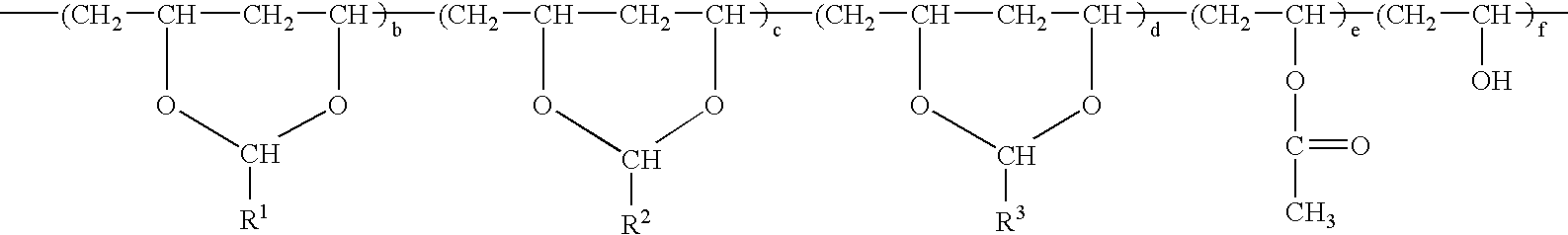
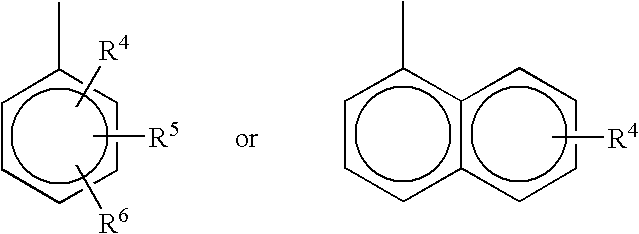
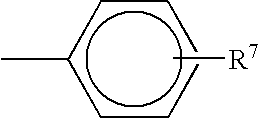
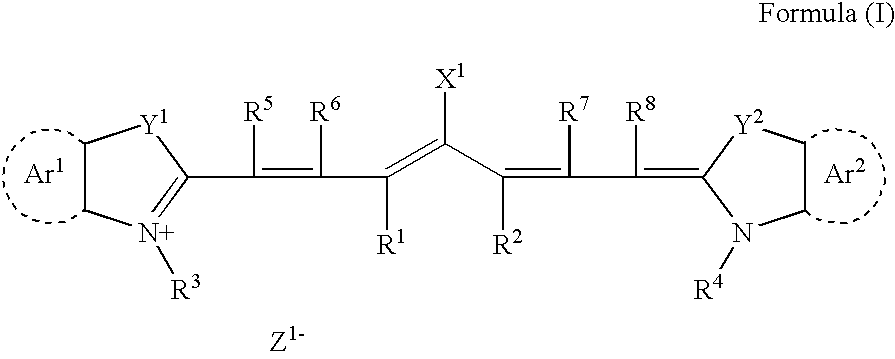
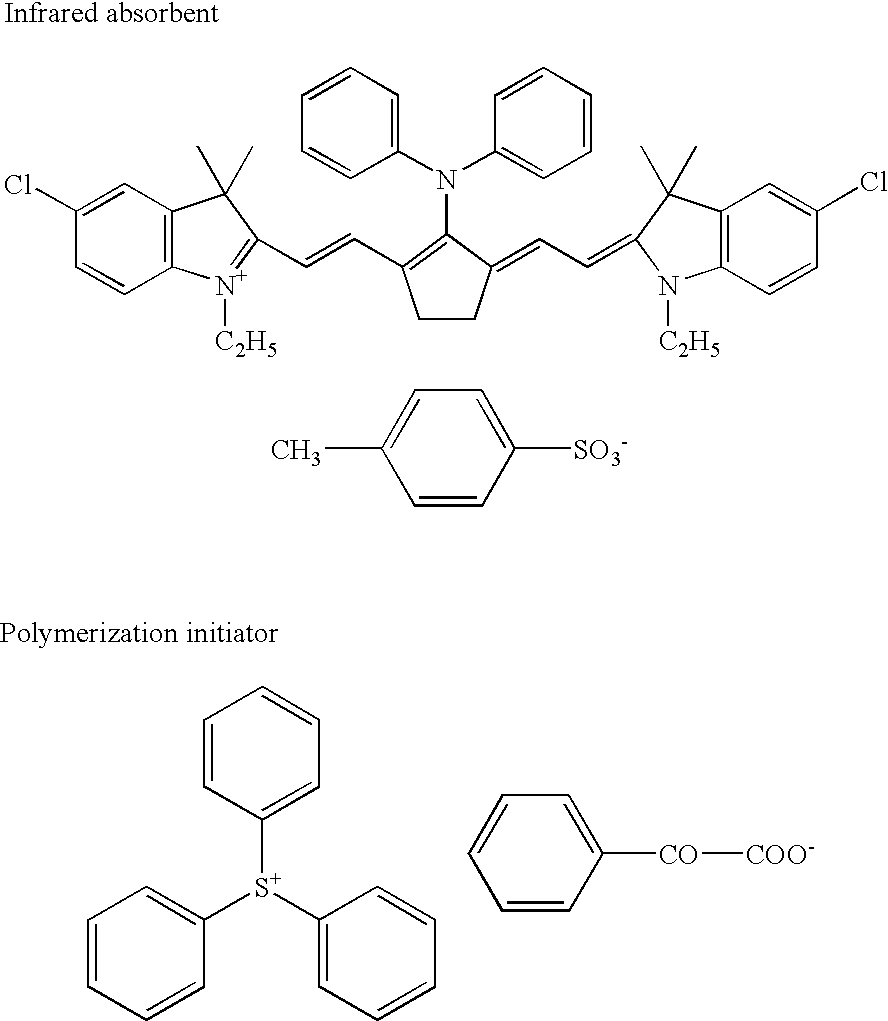
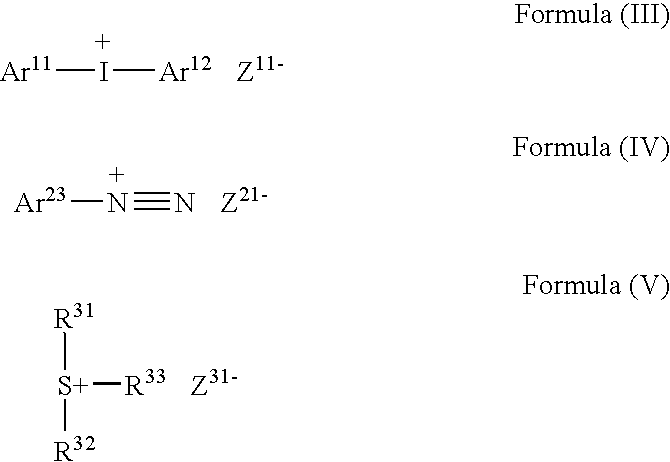Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
812 results about "Ir laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
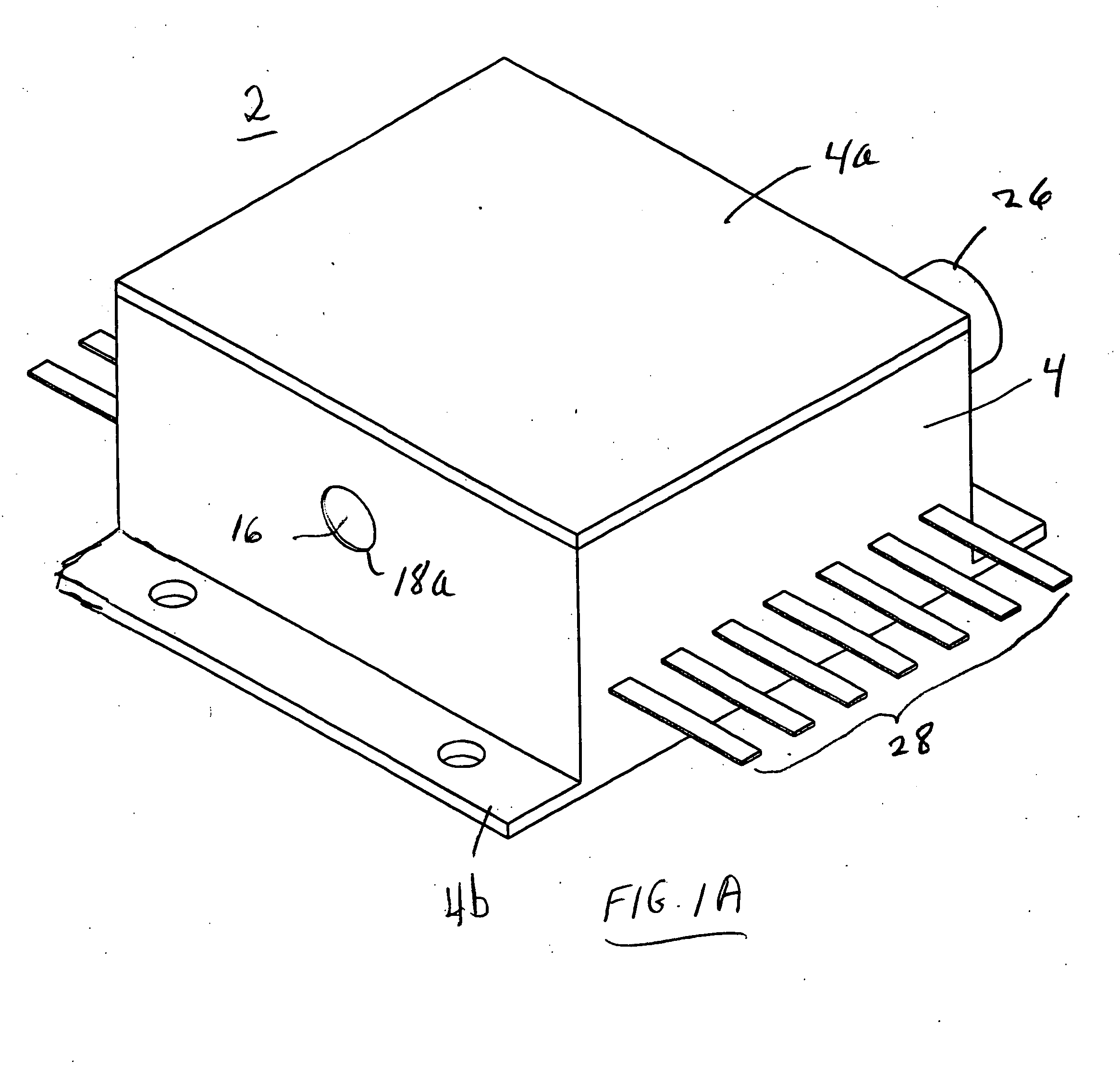
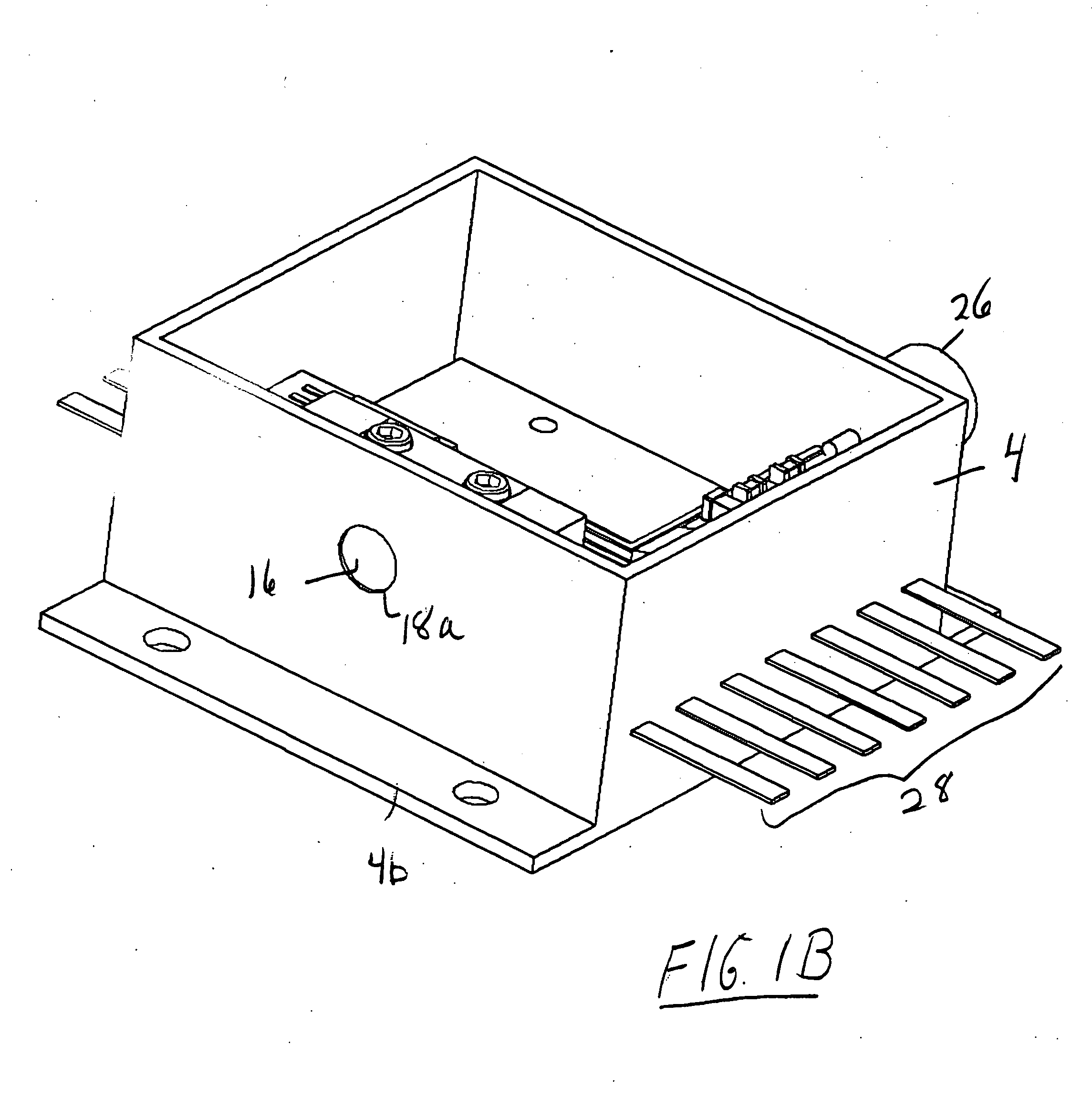
Multi-wavelength laser device
ActiveUS20040196877A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsRed laserLaser light
A multi-wavelength laser device includes at least two of a blue laser diode, a red laser diode, and an infrared laser diode, which are arranged in the same direction on the same base. One laser light emission point is arranged behind another in increasing order of wavelengths of the laser diodes.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
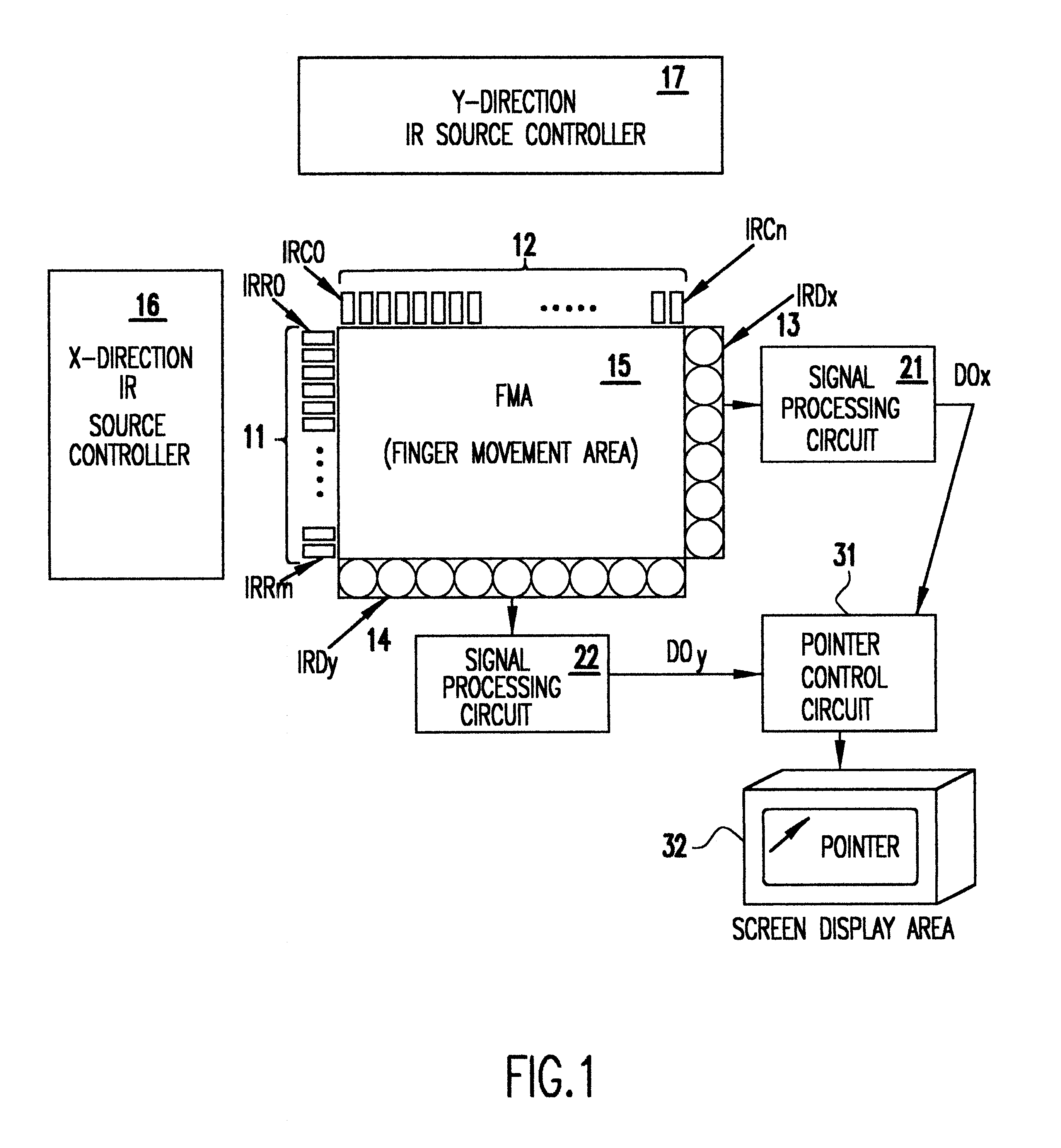
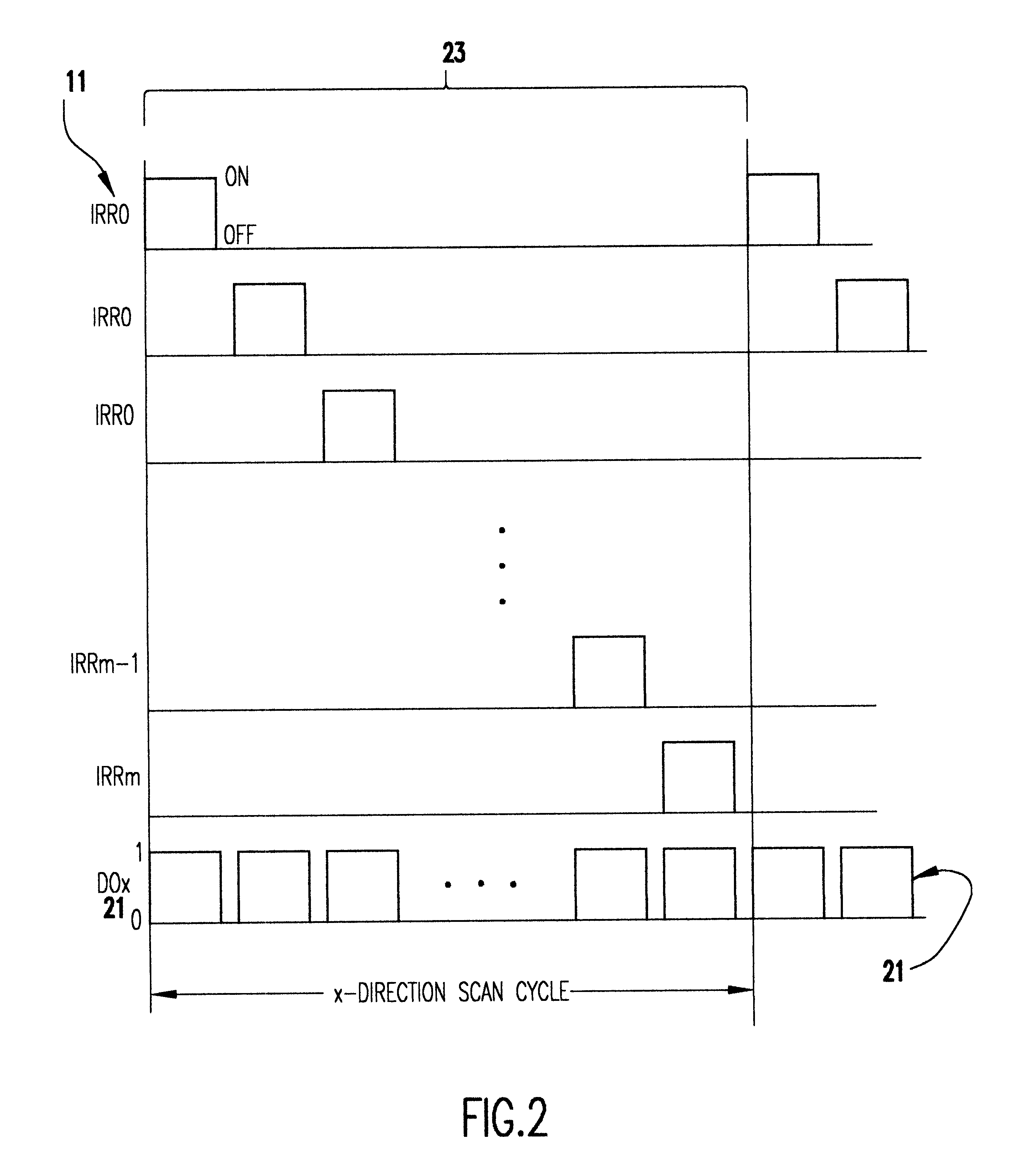
Method and apparatus for mouse positioning device based on infrared light sources and detectors
InactiveUS6333735B1Easy to wearMore robustCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingInfraredLaser beams
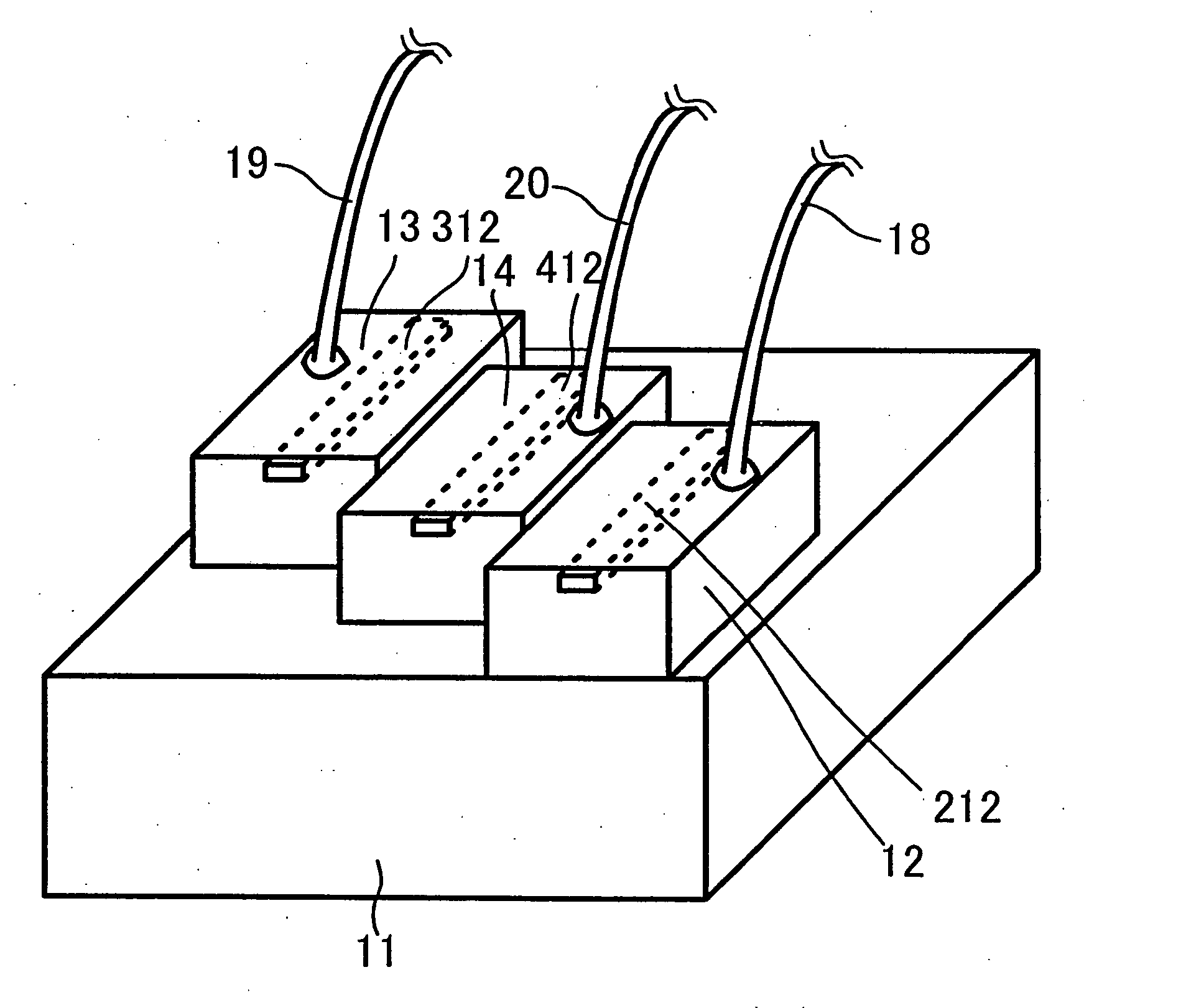
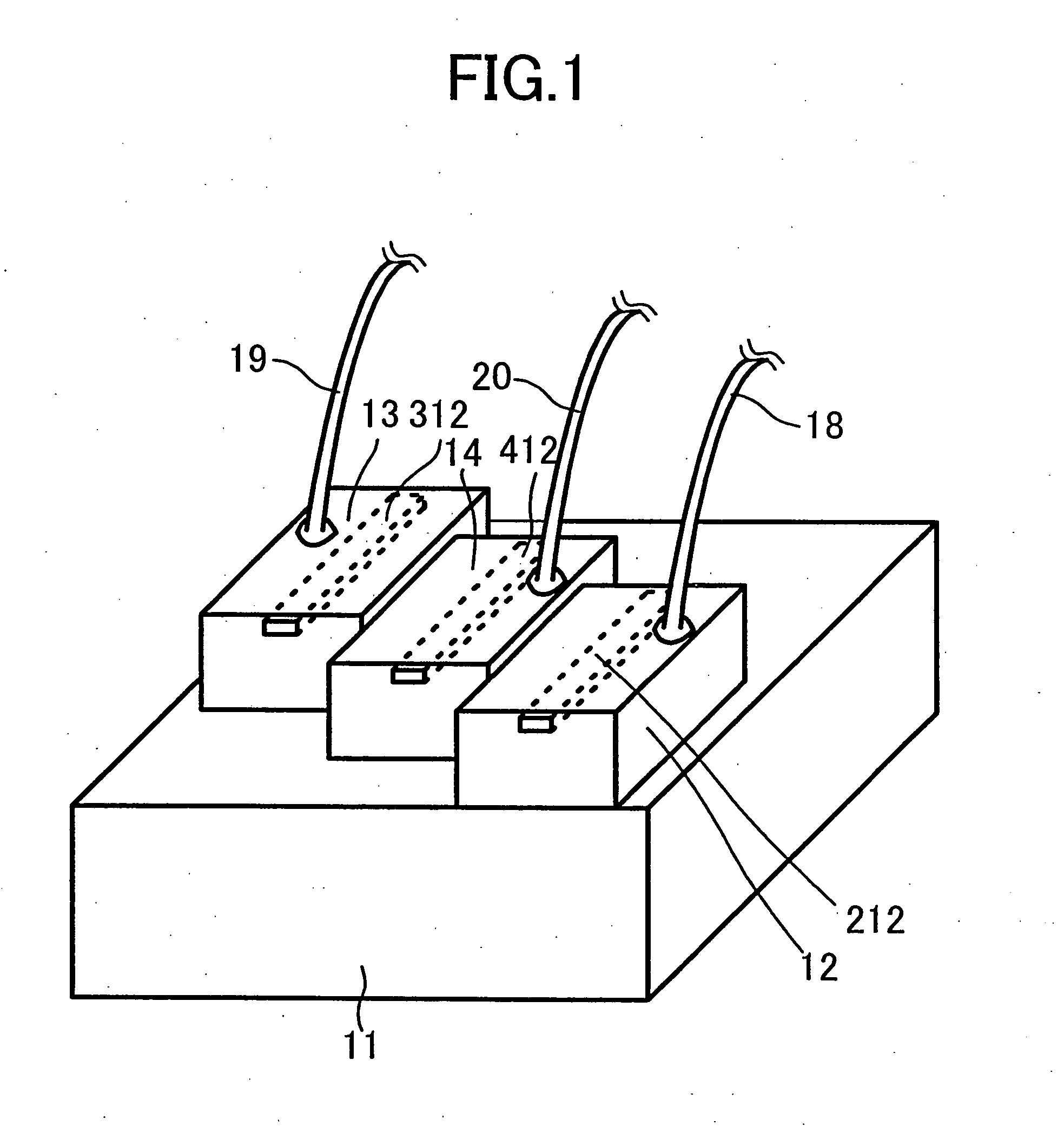
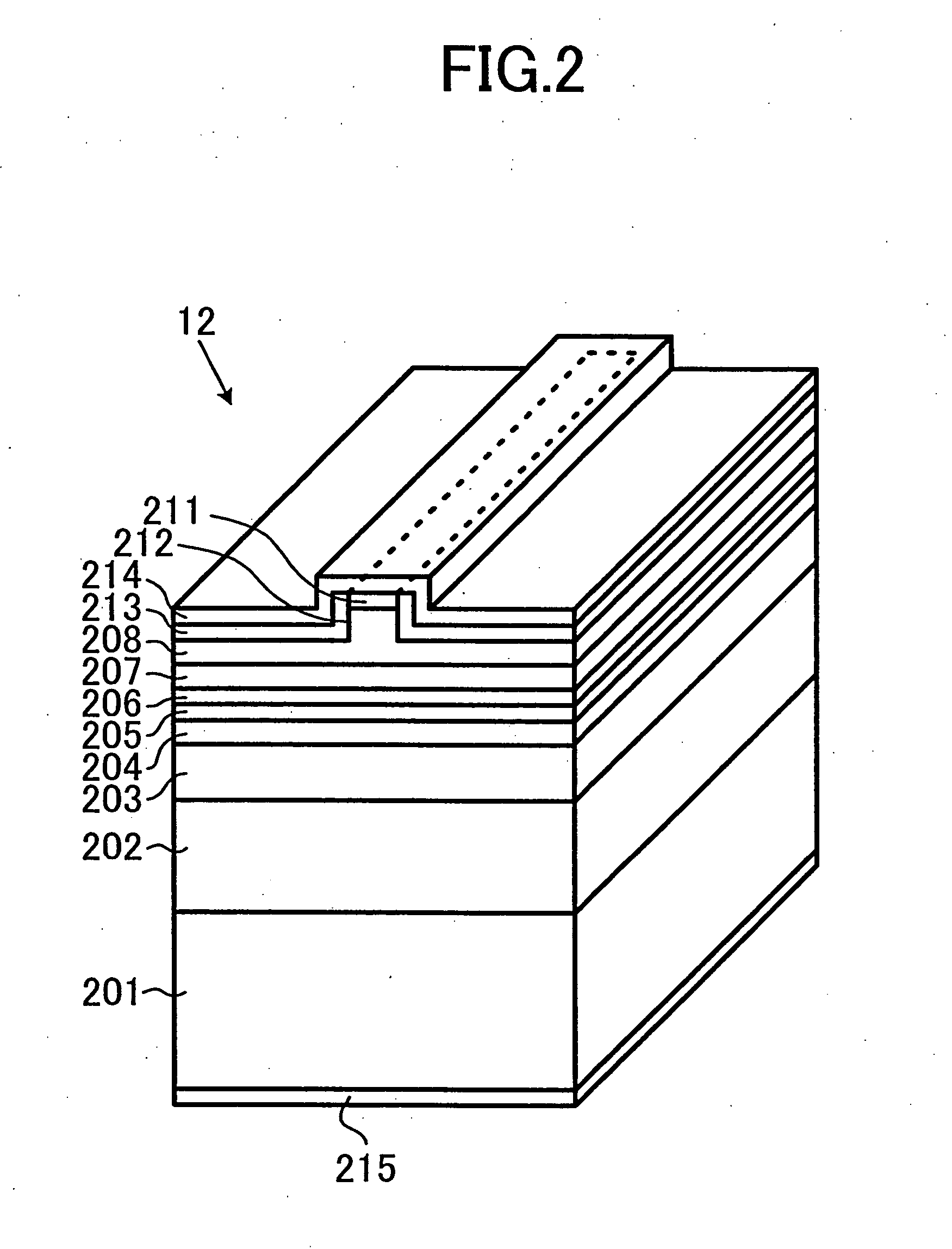
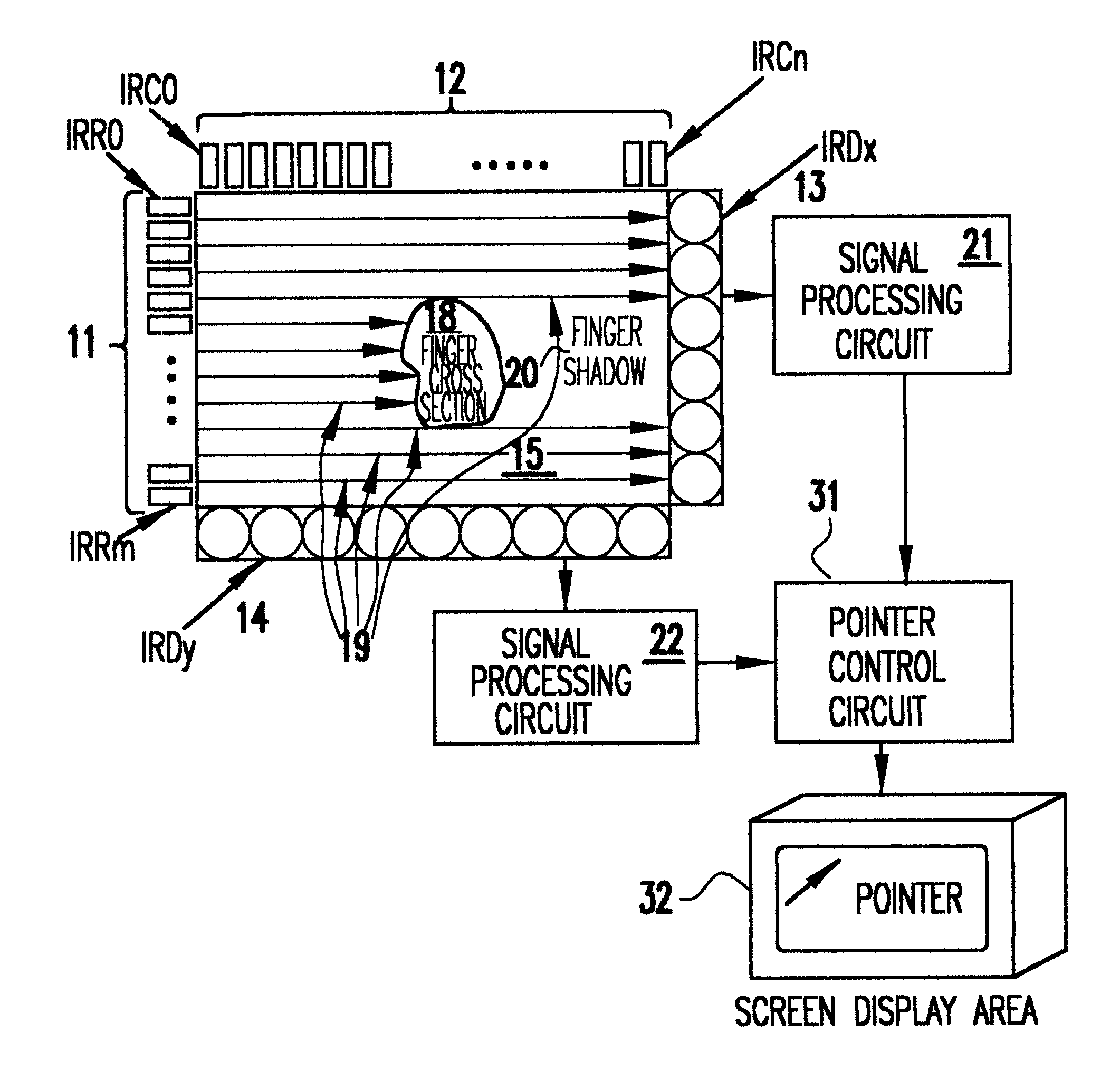
Pointer positioning device based on infrared light sources and detectors that is compact, rugged and ergonomically easy to use such as can be used in laptop computers and similar devices. The pointer positioning device fits in the same area as a conventional touch-pad device in a portable computing device. It detects movement in a movement area by scanning for shadow information with infrared (IR) light sources. To increase the resolution of scanning and to avoid non-uniform beam widths, the scanning of the touchpad area may be carried out by using low power IR laser beams produced by a single IR laser source each for x and y directions and a plurality of optical fibers to transmit the laser beams in the x and y directions. Optionally, this divergency is minimized by positioning IR light sources and light detectors in an alternating pattern around the periphery of a movement area. A mouse device with an opaque plunger depressed with a finger is used as an object to create a well defined shadow in the x and y directions of a movement area.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Ophthalmic surgery method using non-contact scanning laser
InactiveUSRE37504E1Low-powerLow-cost and effectiveLaser surgeryDiagnosticsSystem parametersOphthalmic surgery
A refractive laser surgery process is disclosed for using compact, low-cost ophthalmic laser systems which have computer-controlled scanning with a non-contact delivery device for both photo-ablation and photo-coagulation in corneal reshaping. The basic laser systems may include flash-lamp and diode pumped UV solid state lasers (193-215 nm), compact excimer laser (193 nm), free-running Er:glass (1.54 microns), Ho:YAG (2.1 microns), Q-switched Er:YAG (2.94 microns), and tunable IR lasers, (750-1100) nm and (2.5-3.2) microns. The advantages of the non-contact, scanning device used in the process over other prior art lasers include being safer, reduced cost, more compact and more precise and with greater flexibility. The theory of beam overlap and of ablation rate and coagulation patterns is also disclosed for system parameters. Lasers are selected with energy of (0.01-10) mJ, repetition rate of (1-10,000), pulse duration of 0.01 nanoseconds to a few hundreds of microseconds, and with spot size of (0.05-2) mm for use with refractive laser surgery.
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
Optical Material and Method for Modifying the Refractive Index
InactiveUS20080001320A1Little and no scattering lossPositive changeSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryIntraocular lensNear infrared laser
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical, polymeric material. The method comprises irradiating select regions of the optical, polymeric material with a focused, visible or near-IR laser having a pulse energy from 0.05 nJ to 1000 nJ. The irradiation results in the formation of refractive optical structures, which exhibit little or no scattering loss. The method can be used to modify the refractive index of an intraocular lens following the surgical implantation of the intraocular lens in a human eye. The invention is also directed to an optical device comprising refractive optical structures, which exhibit little or no scattering loss and are characterized by a positive change in refractive index.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Dual beam laser module
A dual beam laser aiming module for a firearm has a dual-laser alignment housing with a first IR laser assembly in a first cavity and that provides a first beam axis. A second visible laser assembly is adjustably located in a second cavity to provide a second beam having an axis parallel to the first beam axis. A housing for the dual-laser alignment housing is adapted to be fixed to the firearm. The dual-laser alignment housing has a rounded exterior surface that interfaces with a corresponding rounded surface in the interior of the cavity of the laser housing. The dual-laser alignment housing is adjustably pivoted with respect to the laser housing with a four-point laser alignment mechanism to align the parallel first and second axes further in parallel to a centerline of a barrel of the firearm.
Owner:STEINER EOPTICS INC
Device for optical monitoring of constituent in tissue or body fluid sample using wavelength modulation spectroscopy, such as for blood glucose levels
InactiveUS7356364B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce calculationMedical devicesCatheterConcentrations glucosePhotodetector
A device for monitoring the concentration level of a constituent in tissue or a body fluid sample, such as glucose concentration in blood, has a laser light source which is modulated about a center emission frequency to probe the absorption spectrum of the constituent being monitored, a laser driver circuit for tuning and modulating the laser light, a photodetector for detecting light from the laser light source transmitted through the sample as the modulation frequency of the laser is tuned, and a demodulator for demodulating the transmitted light and detecting variations in magnitude at harmonics of the modulation frequency to assess the concentration level of that constituent. The device utilizes short-wavelength near-infrared laser light to monitor blood glucose levels, and could also be used for drug screening and diagnosis of other medical conditions as well. In one embodiment, the device is used to monitor blood glucose level externally from the body and non-invasively by trans-illumination through a thin layer of skin, without the need for physical penetration of the skin. In another embodiment, the device is used as an intravenous sensor deployed through a catheter, and its output can be used to control an insulin pump to stabilize the patient's blood glucose levels.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
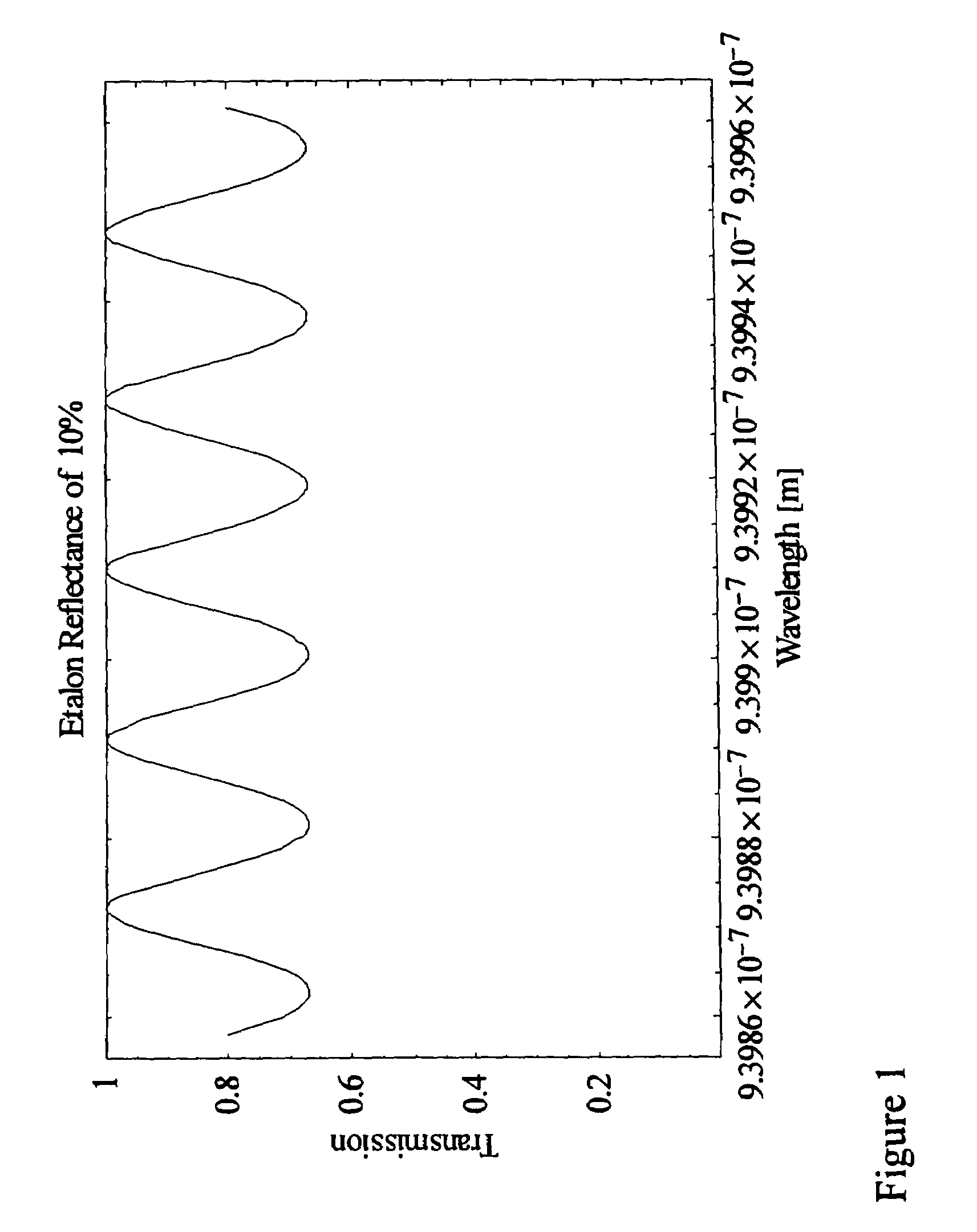
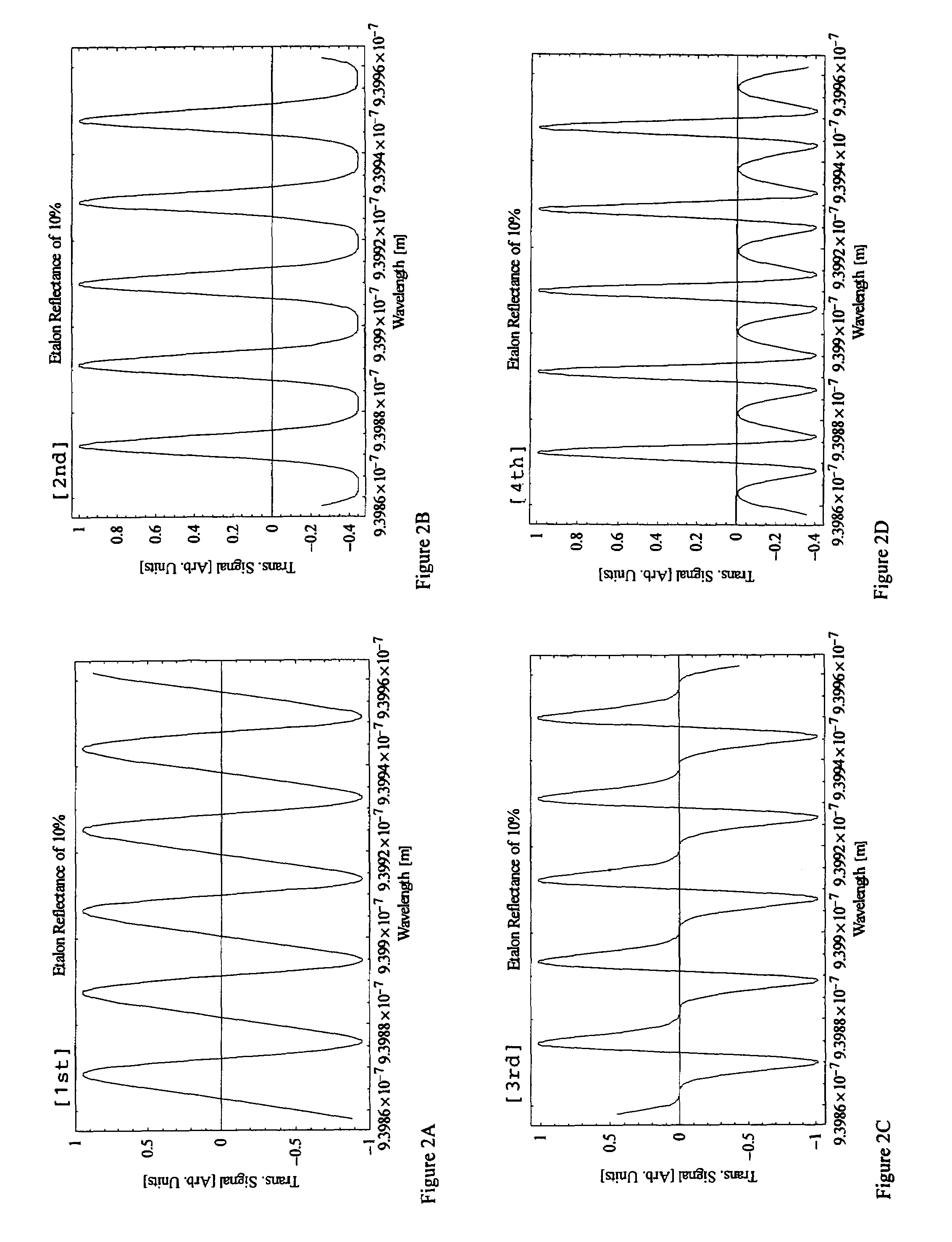
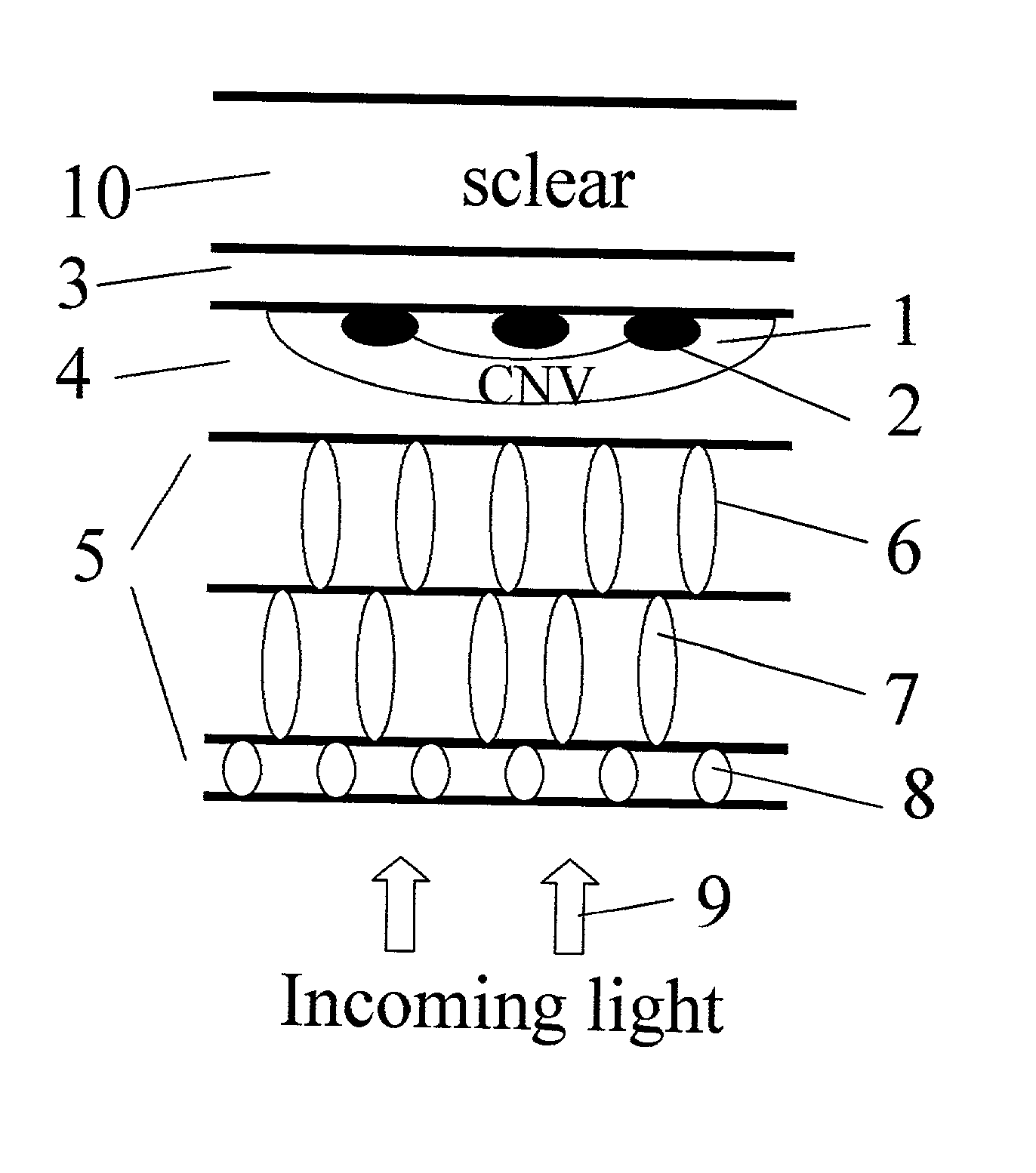
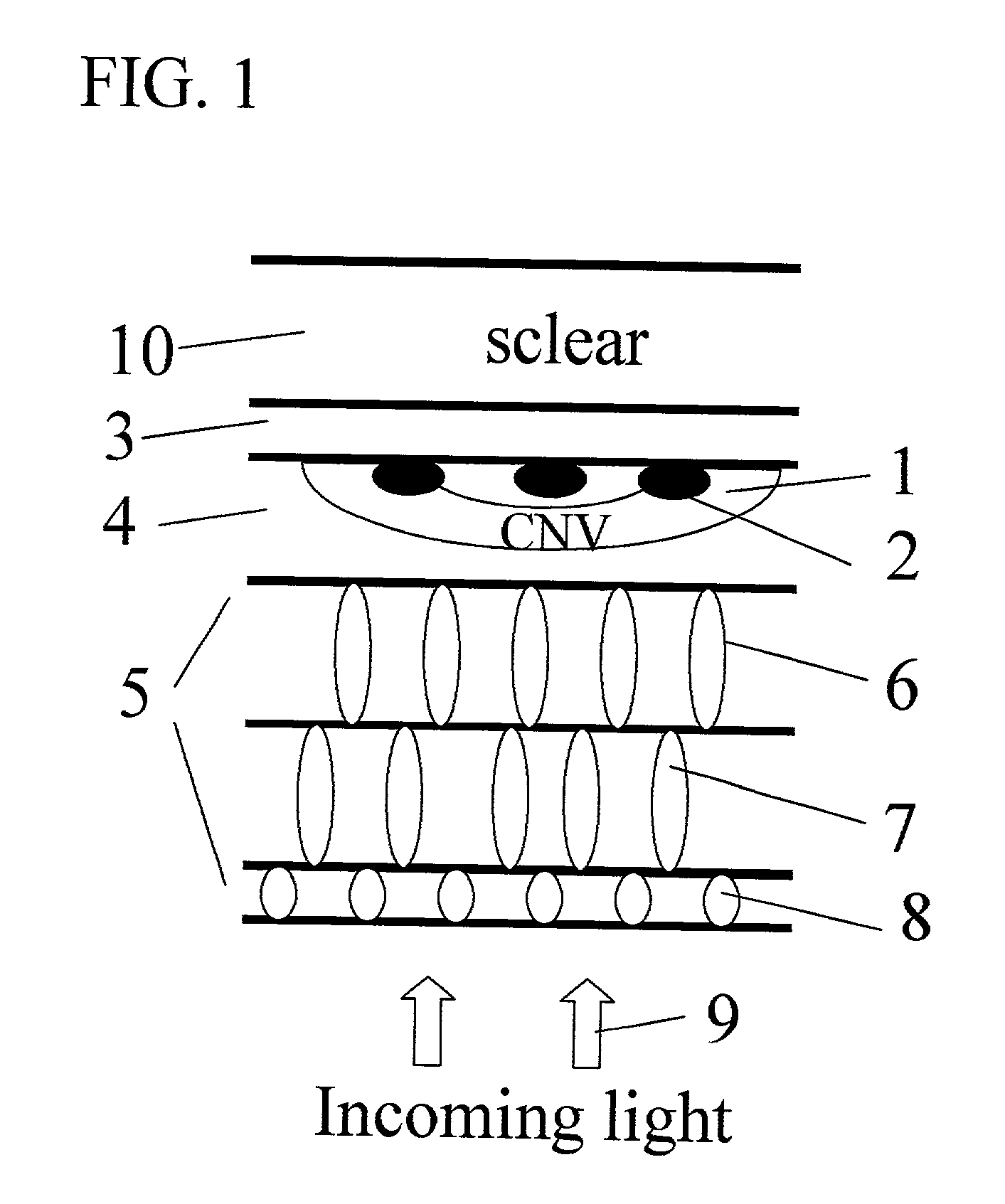
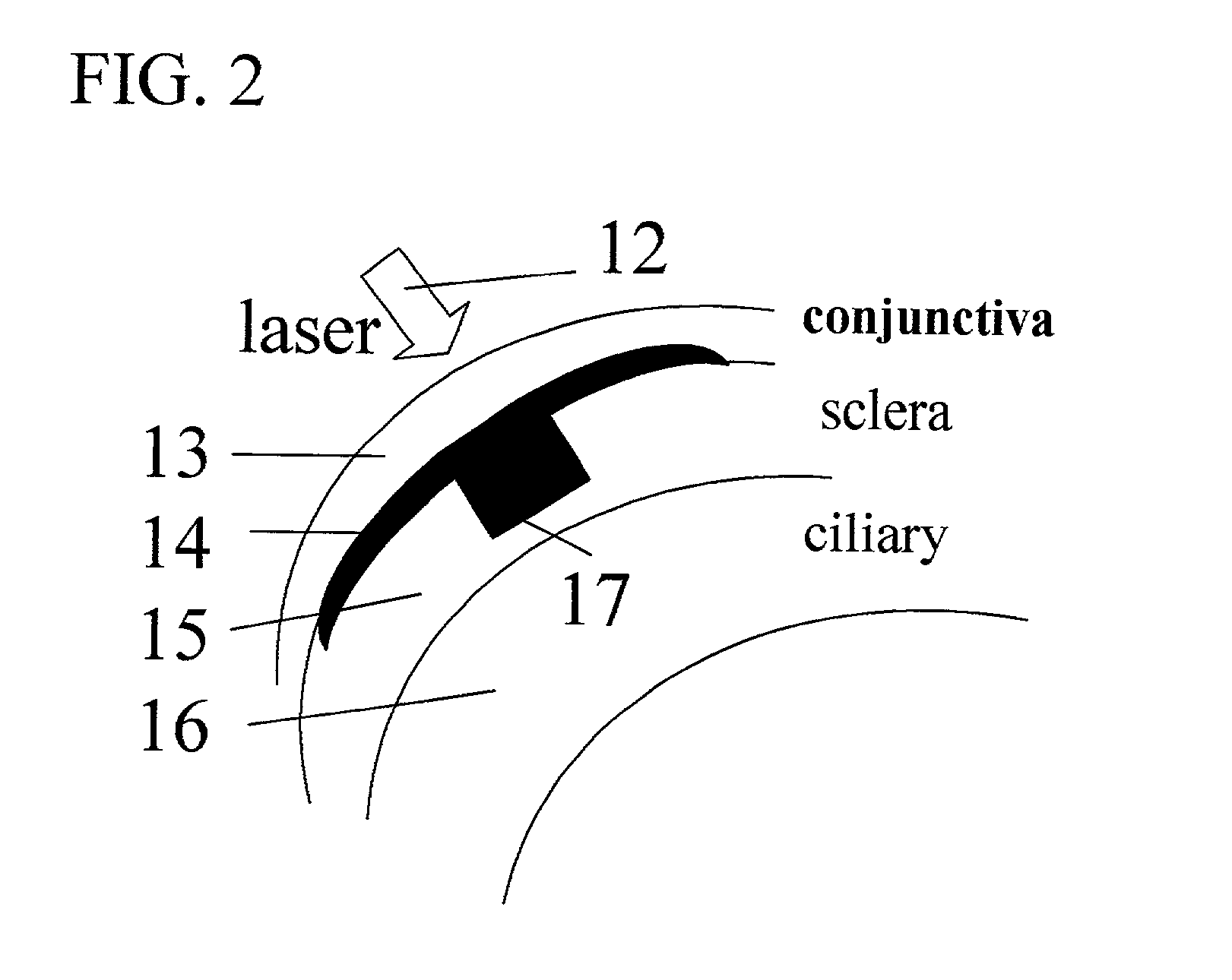
Apparatus and methods for prevention of age-related macular degeneration and other eye diseases
InactiveUS20030105456A1Minor side effectsIncrease flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequencyLaser beams
Surgical apparatus and surgical methods are proposed for the prevention of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and choroidal neovascularization (CNV), and other eye diseases such as glaucoma by removal of the sclera tissue to reduce its rigidity and increase the flood flow and decrease pressure in the choriocapillaris. The disclosed preferred embodiments of the system consists of a tissue ablation means and a control means of ablation patterns and a fiber delivery unit. The basic laser beam includes UV lasers and infrared lasers having wavelength ranges of (0.15-0.36) microns and (0.5-3.2) microns and diode lasers of about 0.98, 1.5 and 1.9 microns. AMD and CNV are prevented, delayed or reversed by using an ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue in a predetermined patterns outside the limbus to increase the elasticity of the sclera tissue surrounding the eye globe The surgery apparatus also includes non-laser device of radio frequency wave, electrode device, bipolar device and plasma assisted device
Owner:LIN J T
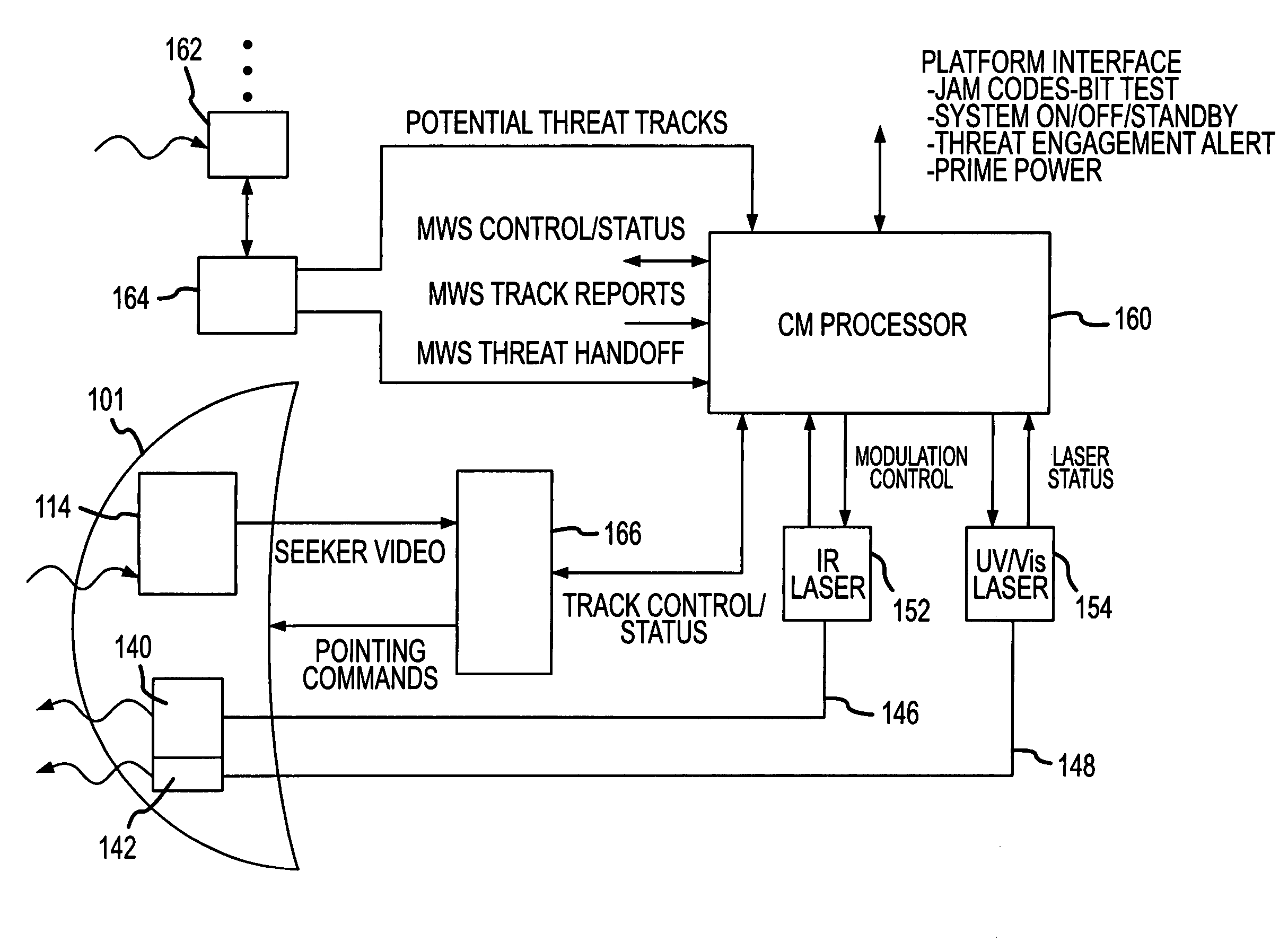
Directed infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) system and method
ActiveUS7378626B2Easy to liftAgile and high-power and reliableWave based measurement systemsDirection controllersMulti bandCountermeasure
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Directed infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) system and method
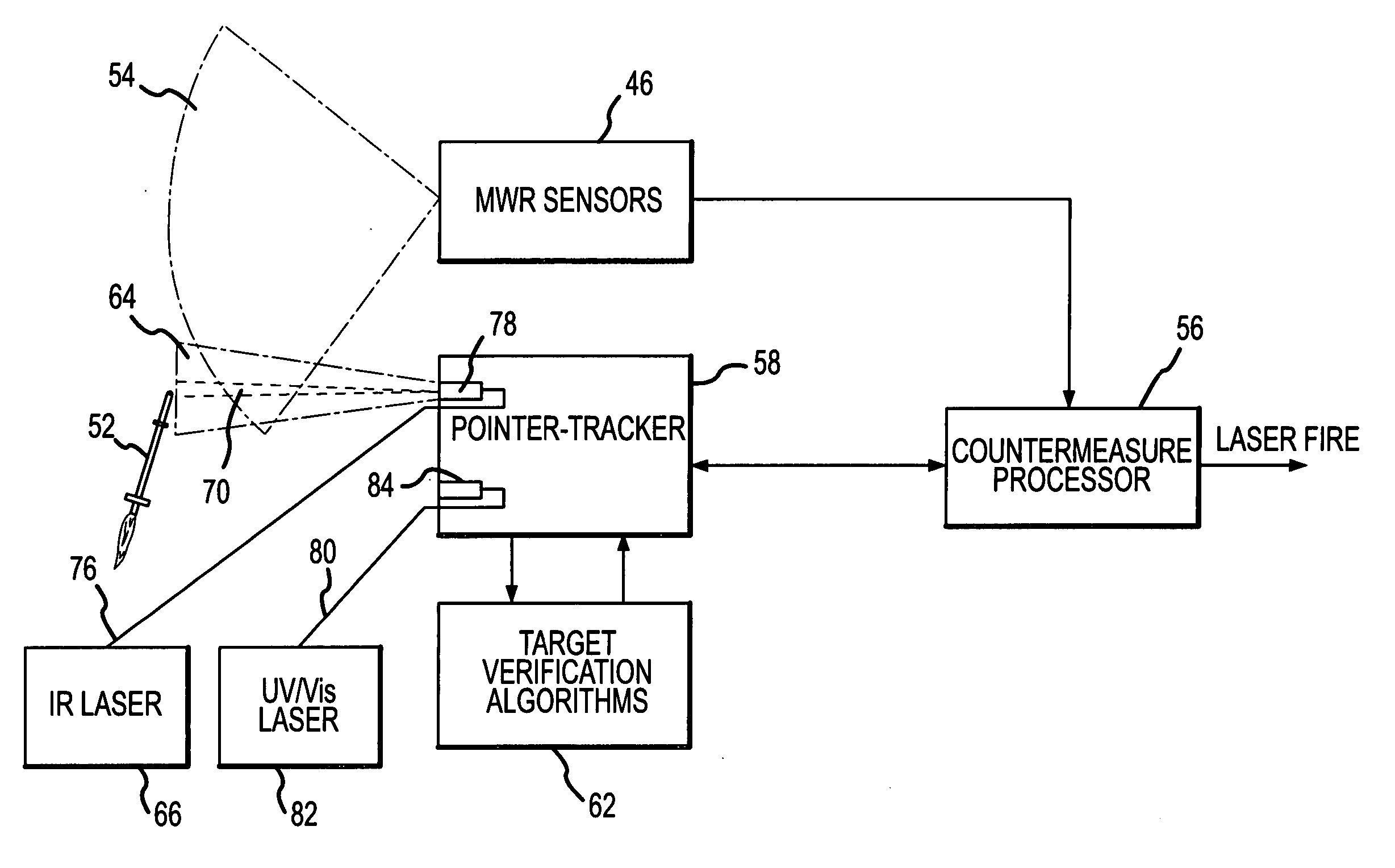
ActiveUS20070075182A1Easy to liftAgile and high-power and reliableWave based measurement systemsDirection controllersMulti bandCountermeasure
An agile, high-power, reliable DIRCM system that is easily extended to address sophisticated UV or UV-visible capable multi-band threats includes a missile warner having missile warning receivers (MWRs), one or two-color suitably in the mid-IR range, that detect likely missile launch and pass the threat coordinates to a pointer-tracker having a Roll / Nod gimbal on which the IR laser transmitter is mounted. The pointer-tracker slews the gimbal to initiate tracking based on the threat coordinates and then uses its detector to continue to track and verify the threat. If the threat is verified, the pointer-tracker engages the laser to fire and jam the missile's IR seeker. By slewing the gimbal based on unverified threat coordinates to initiate tracking the system is highly agile and can respond to short and near simultaneous MANPADS shots.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070291804A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
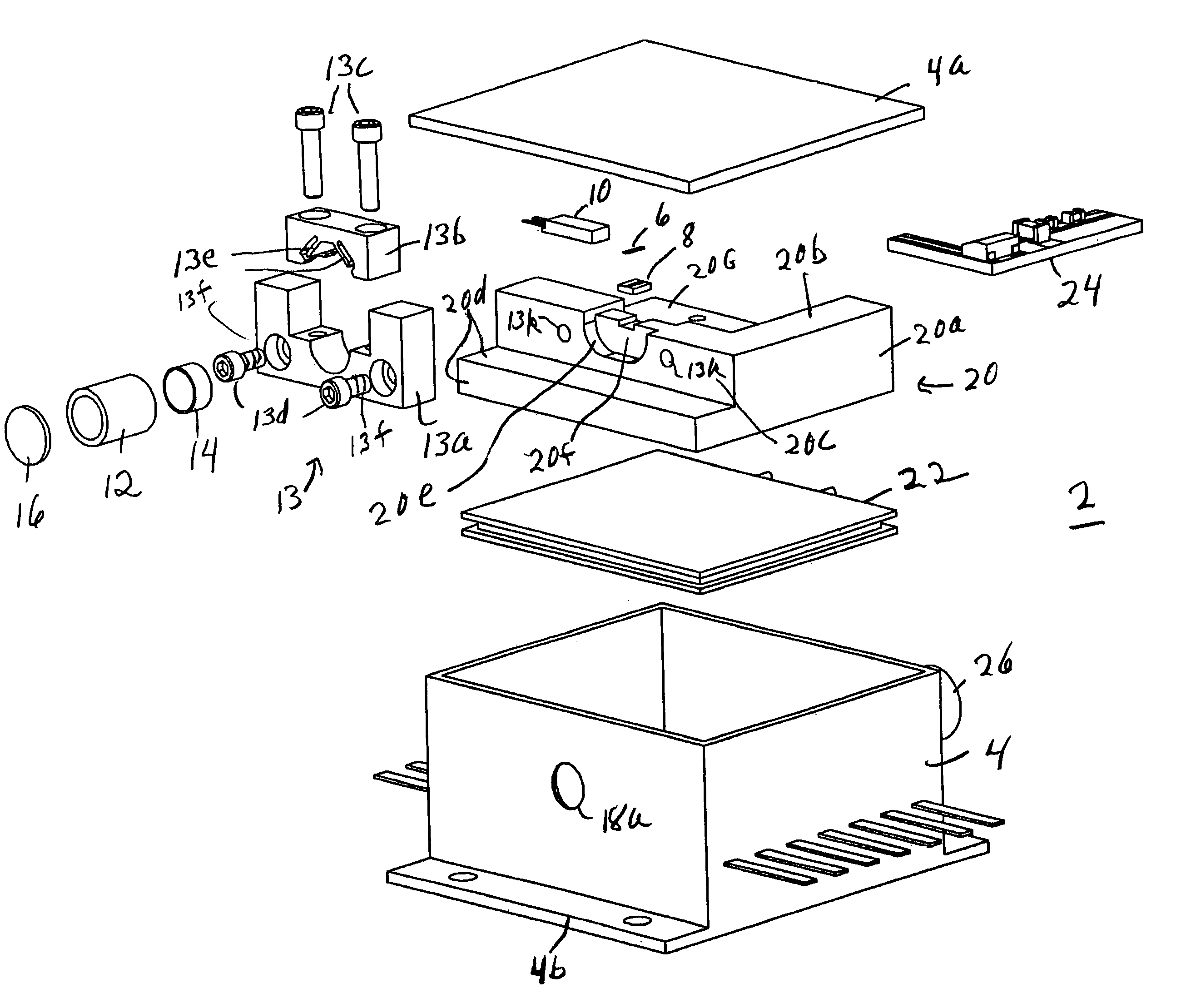
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
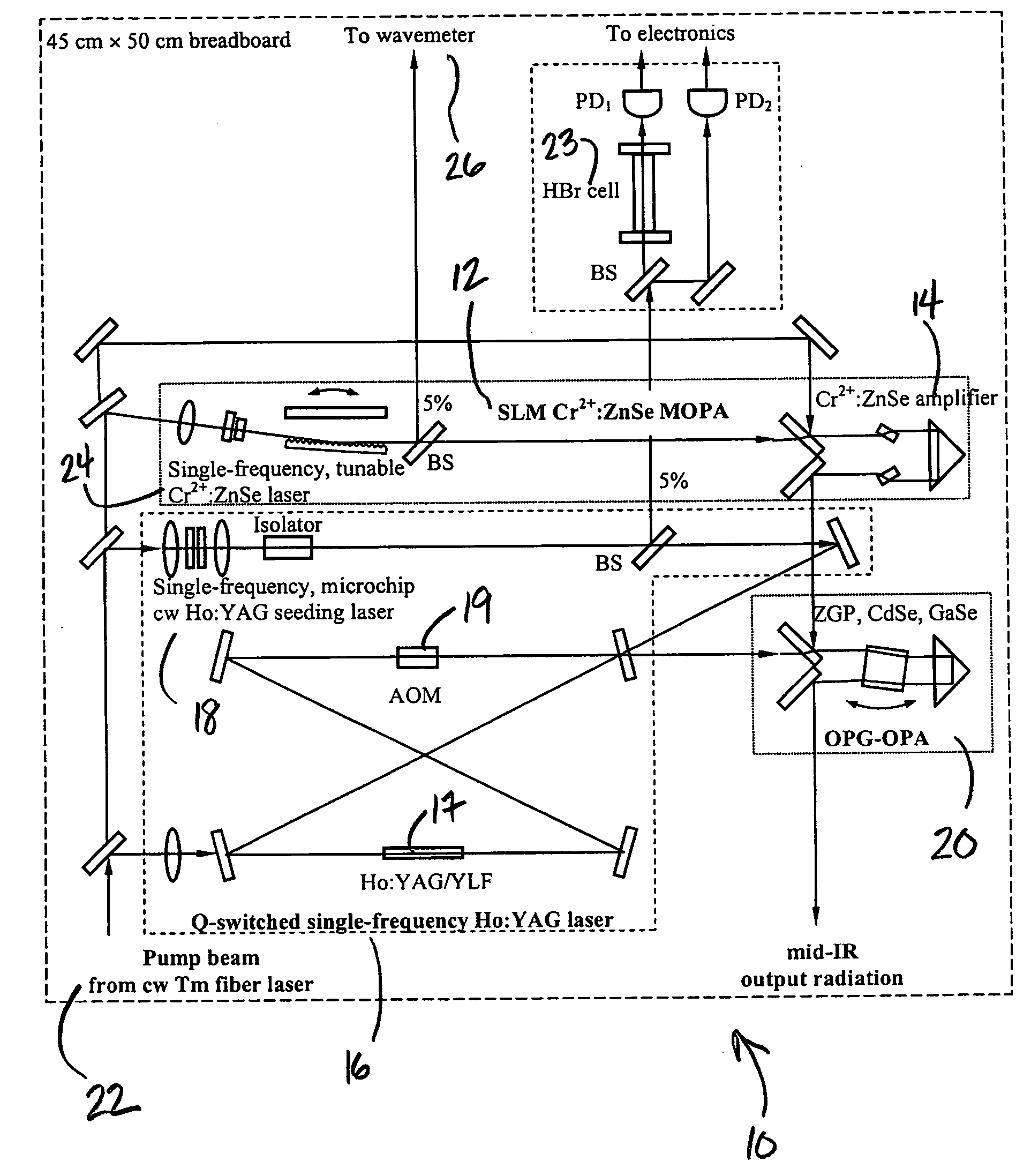
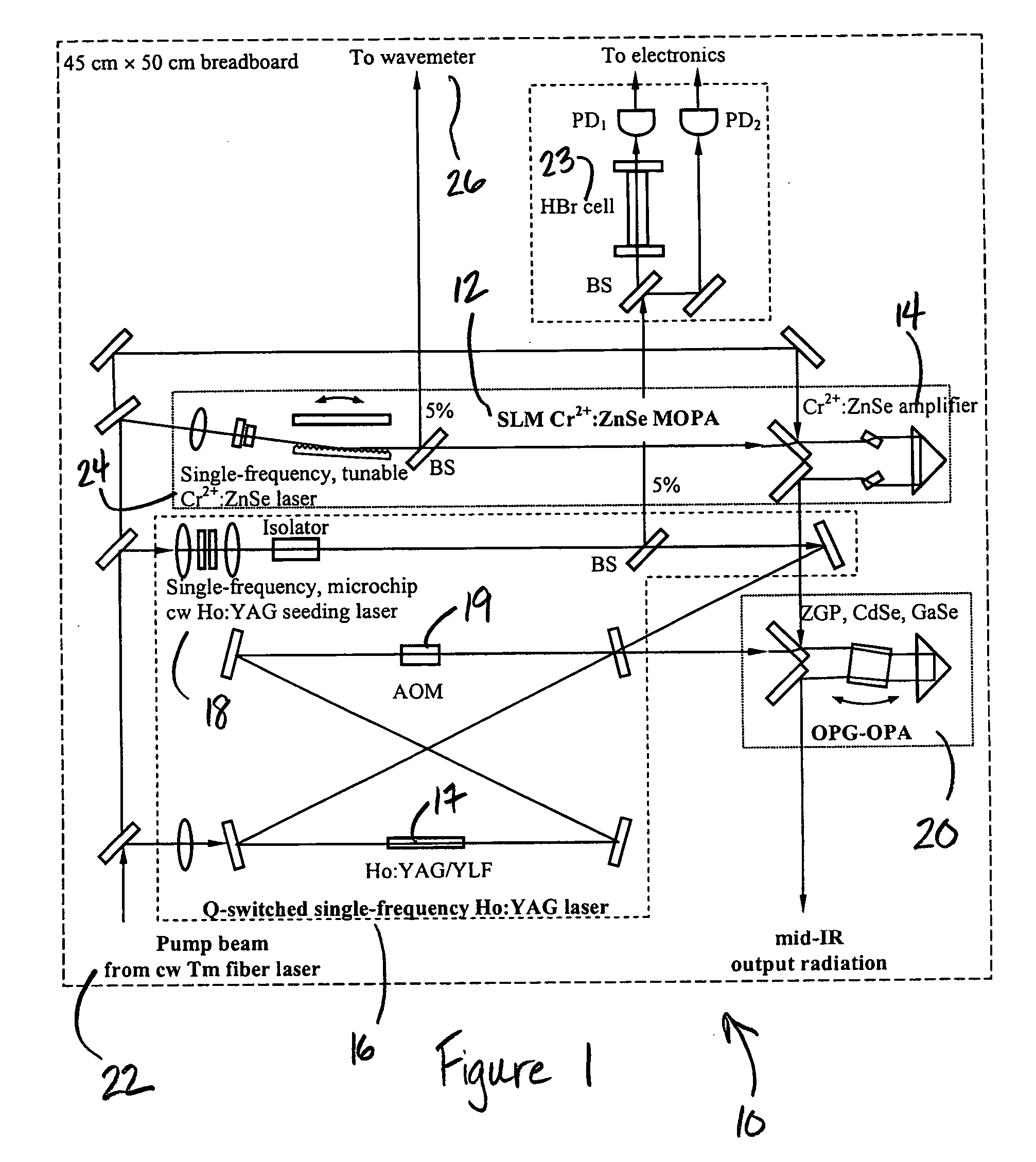
Mid-IR laser instrument for analyzing a gaseous sample and method for using the same
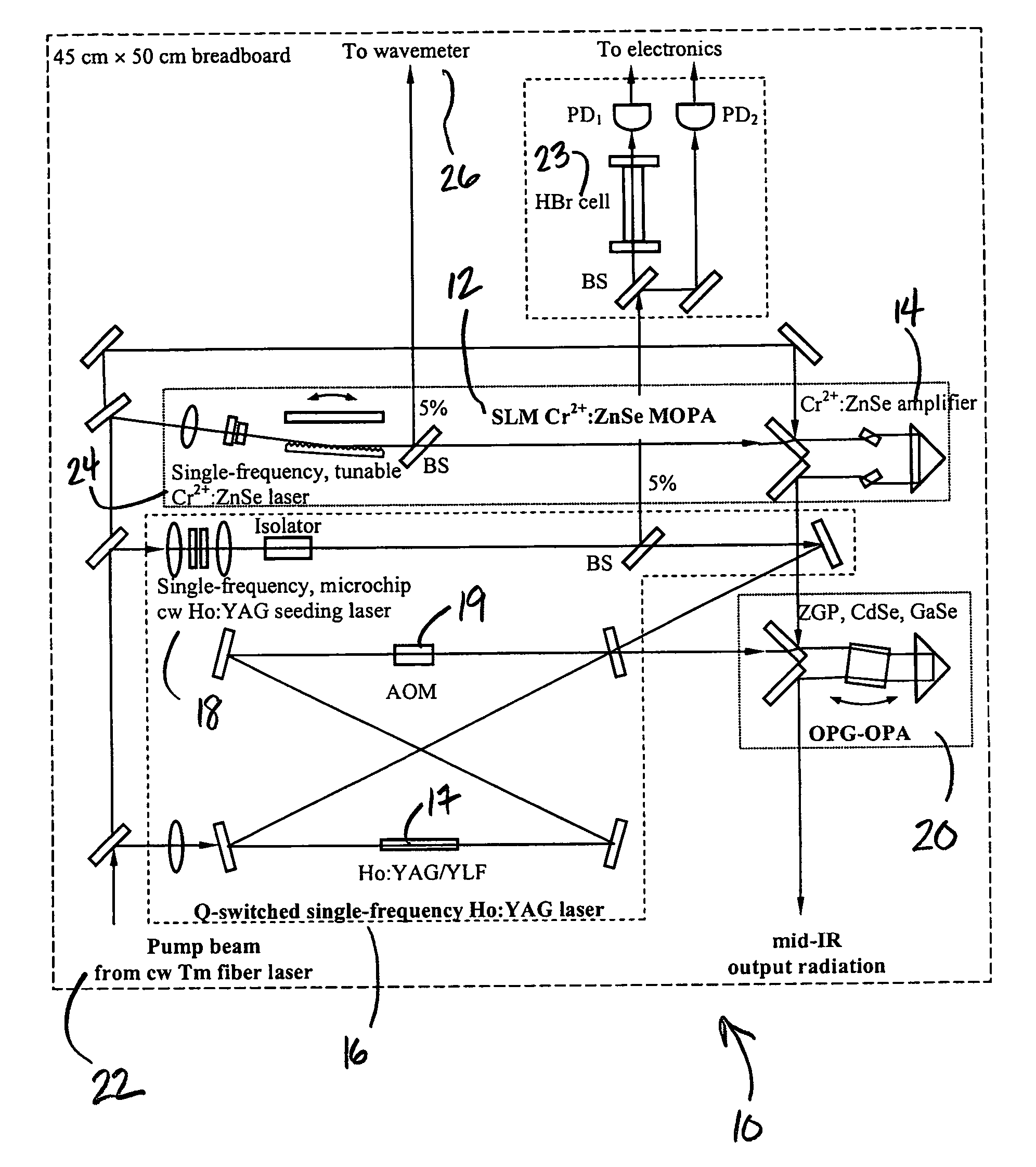
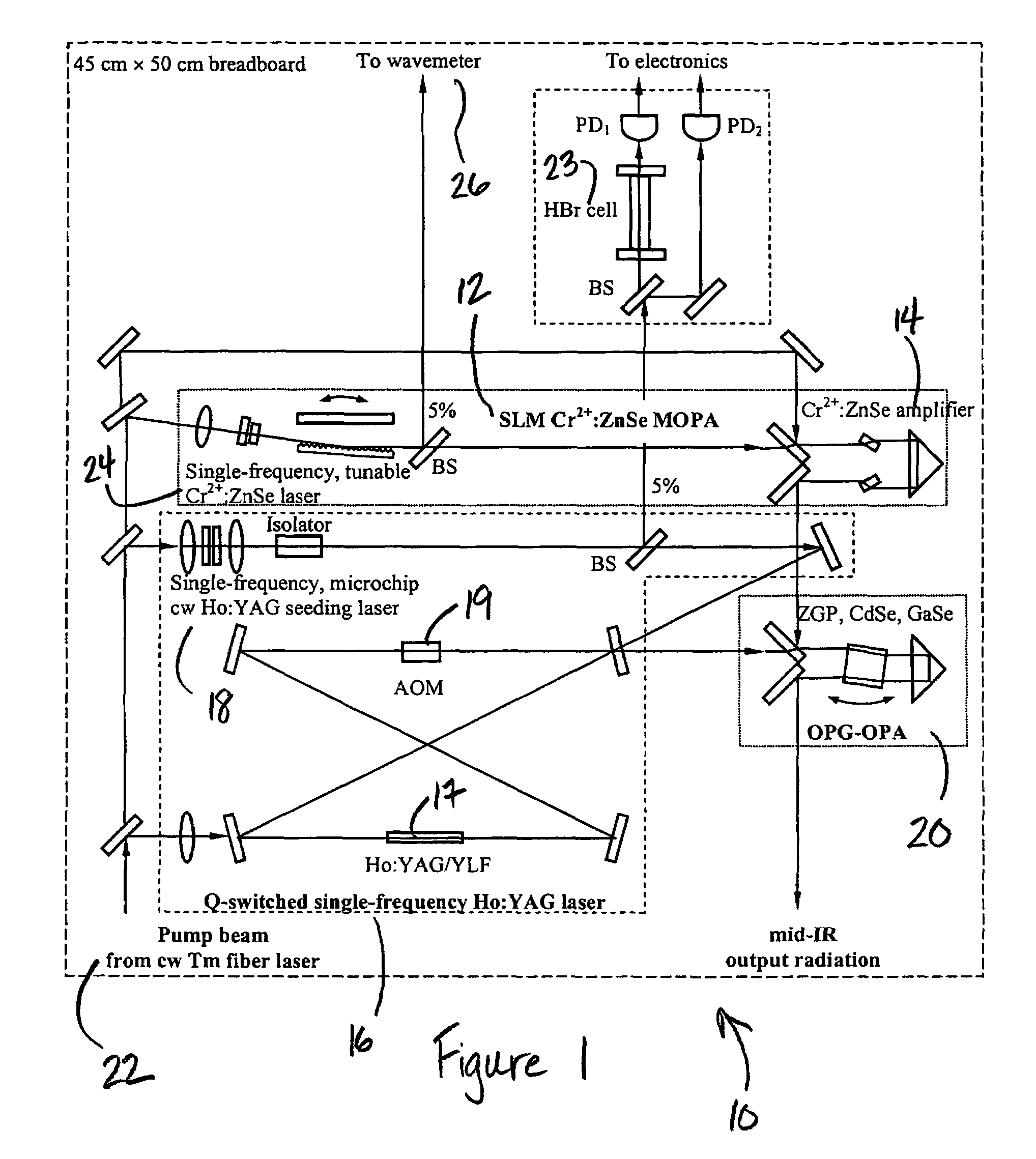
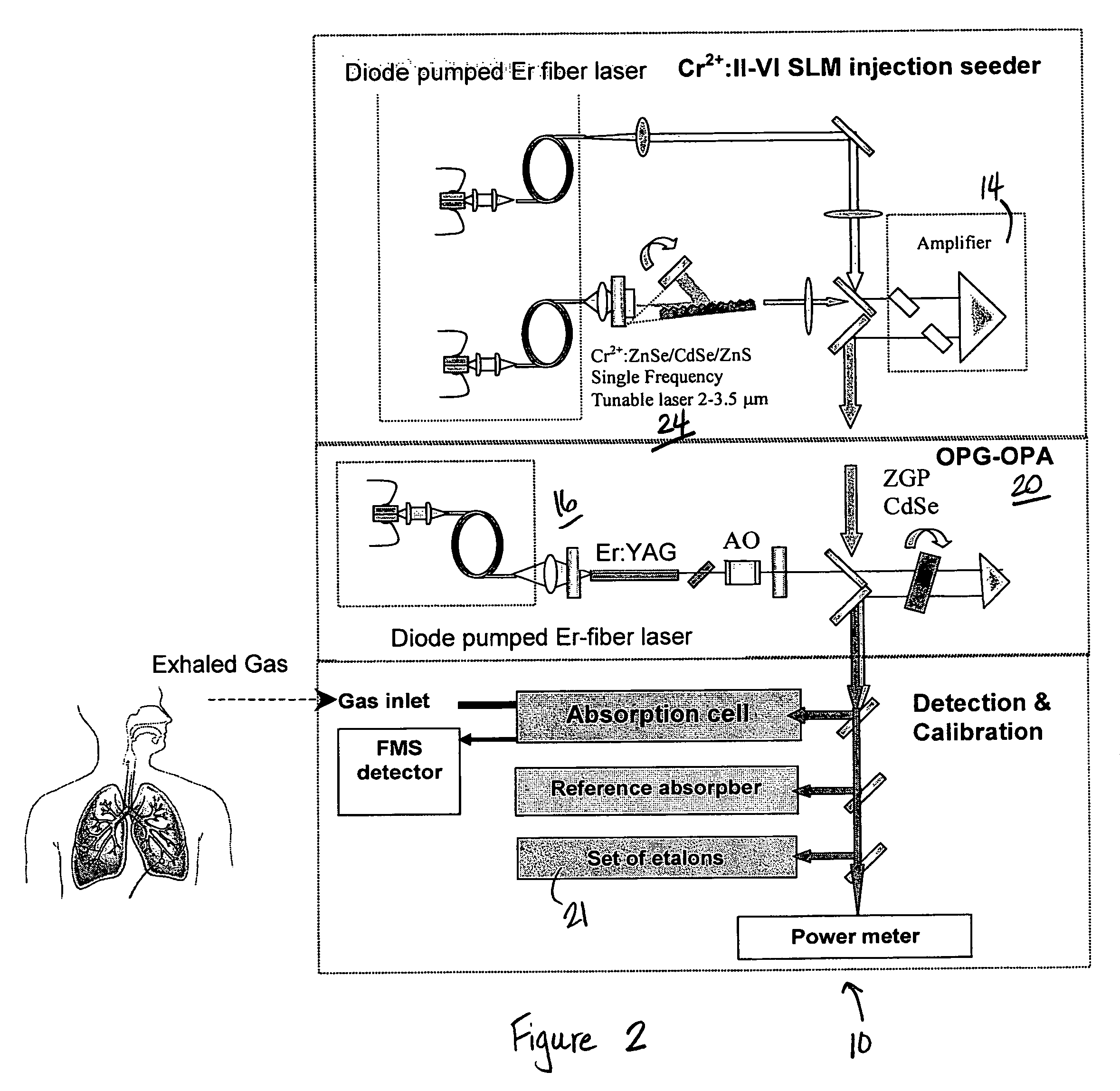
InactiveUS20070064748A1Wide tunabilityRapidly tuned SLM idlerPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingNoseMicrometer
An optical nose for detecting the presence of molecular contaminants in gaseous samples utilizes a tunable seed laser output in conjunction with a pulsed reference laser output to generate a mid-range IR laser output in the 2 to 20 micrometer range for use as a discriminating light source in a photo-acoustic gas analyzer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Laser orthodontic devices
ActiveUS20150164618A1Low profileReinforcement and waterproofingOthrodonticsDental toolsIr laserBite plates
An IR laser bite plate for orthodontic remodeling is disclosed, and the device can be combined with vibrational forces.
Owner:ADVANCED ORTHODONTICS & EDUCATION ASSOC LLC
Diode-laser-pumped ultraviolet and infrared lasers for ablation and coagulation of soft tissue
Method and systems for eye surgery for the treatment of presbyopia, ocular hypertension and glaucoma and other soft tissue surgeries are disclosed. System design parameters of lasing crystals (Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, Er:YAG and Er:YSGG), nonlinear crystals (KTP, BBO, LBO), laser cavity configuration and energy delivery means are disclosed for diode-laser-pumped lasers with output wavelength at UV (263 or 266 nm), green (527 or 523 nm), and mid-IR (2.78 or 2.94 microns). Dual function of ablation and coagulation is proposed by a mode control means. The preferred diode-laser includes a wavelength at about 0.75 to 0.98 microns with power about 15 to 40 W and used in a side-pumping configuration to generate UV or IR having an energy per pulse about 3 to 30 mJ, power of about 0.1 to 1.5 W and operated at free running mode (IR laser) or pulsed mode (UV laser).
Owner:NEW VISION
Near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system
ActiveCN102706846AImaging RealizationReduce absorptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention discloses a near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system, which comprises a light path scanning unit and a control unit which adopt a confocal structure, wherein the light path scanning unit comprises a near-infrared laser source, a collimation and extension module, a laser optical filter, a dichroic reflector, a scanning galvanometer, an f-theta lens, a tube lens, an imaging objective lens, a fluorescent optical filter, a convergent lens, a pinhole, a detector and the like, the control unit comprises a motion control module used for controlling the scanning galvanometer, a data acquisition module used for acquiring an output signal of the detector, a data processing module connected with the motion control module and the data acquisition module, and the like. The method matched with the system is characterized in that a sample is marked with near-infrared quantum dots with the fluorescence emission spectrums between 932nm and 1250nm, and then the sample is detected by the near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system. According to the system disclosed by the invention, deep-level imaging of samples such as biological tissues can be accurately and efficiently realized, and the system has a simple structure and is easy to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
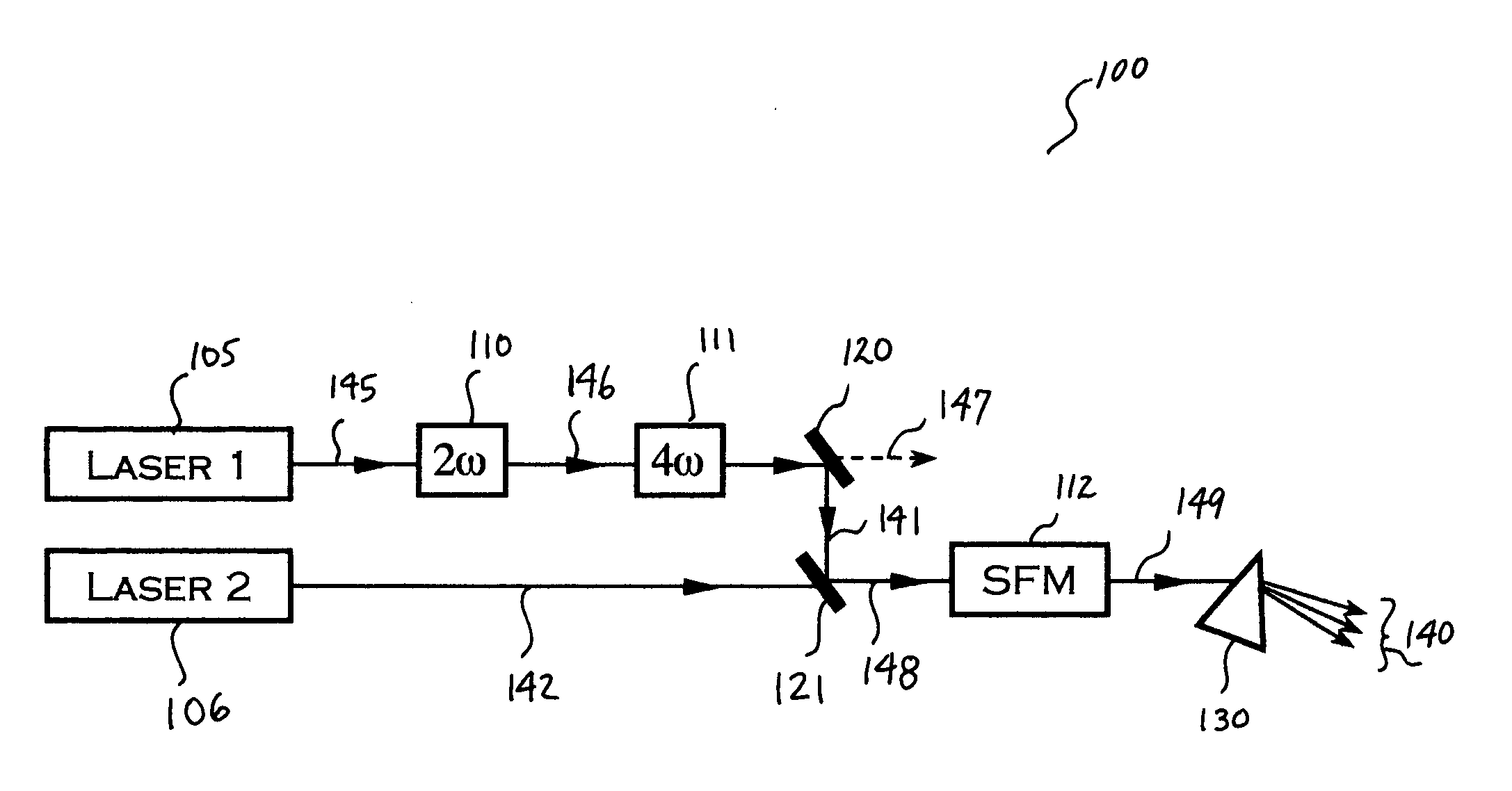
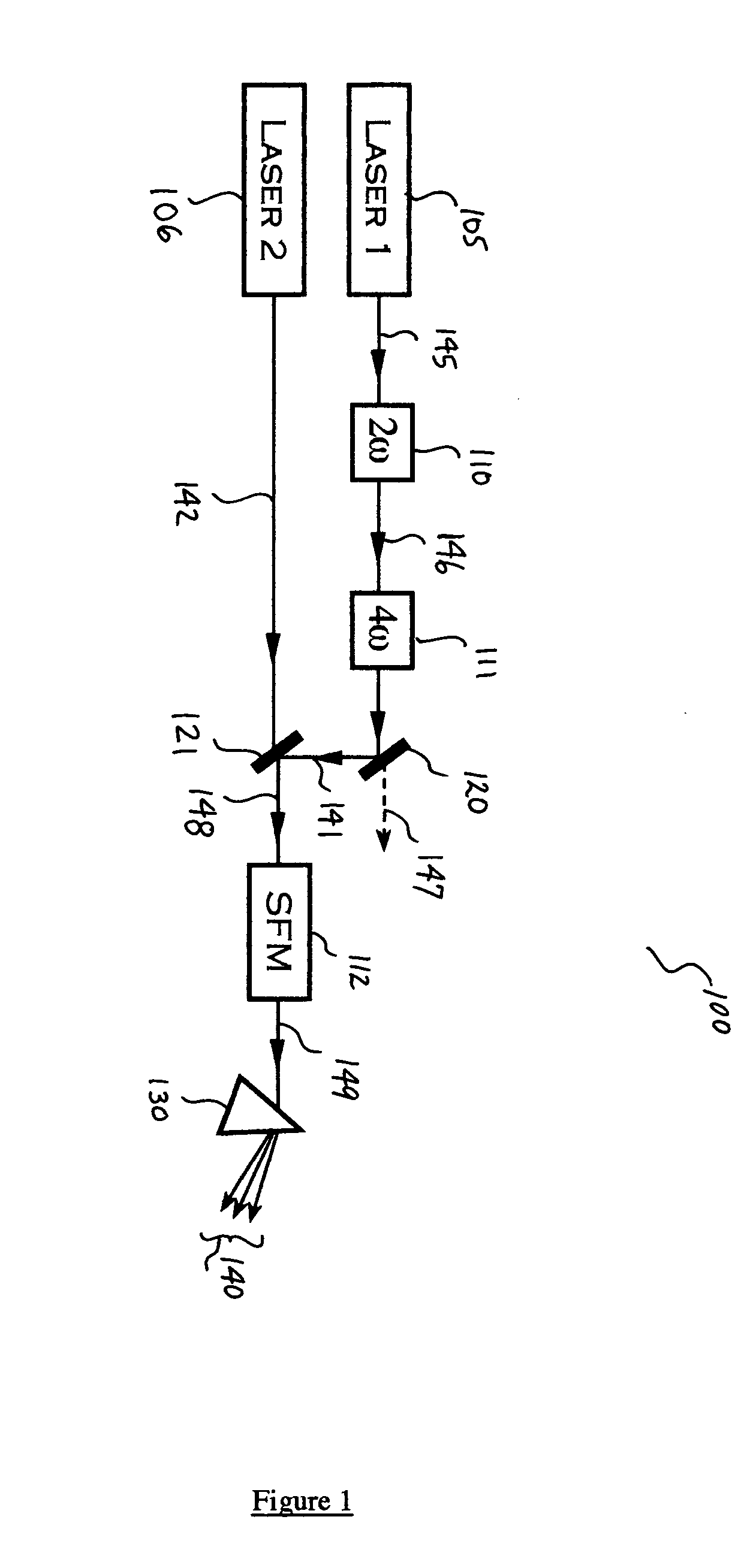
Laser architectures for coherent short-wavelength light generation
InactiveUS20050169326A1Increase power levelMaximize efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsPoynting vectorRare earth
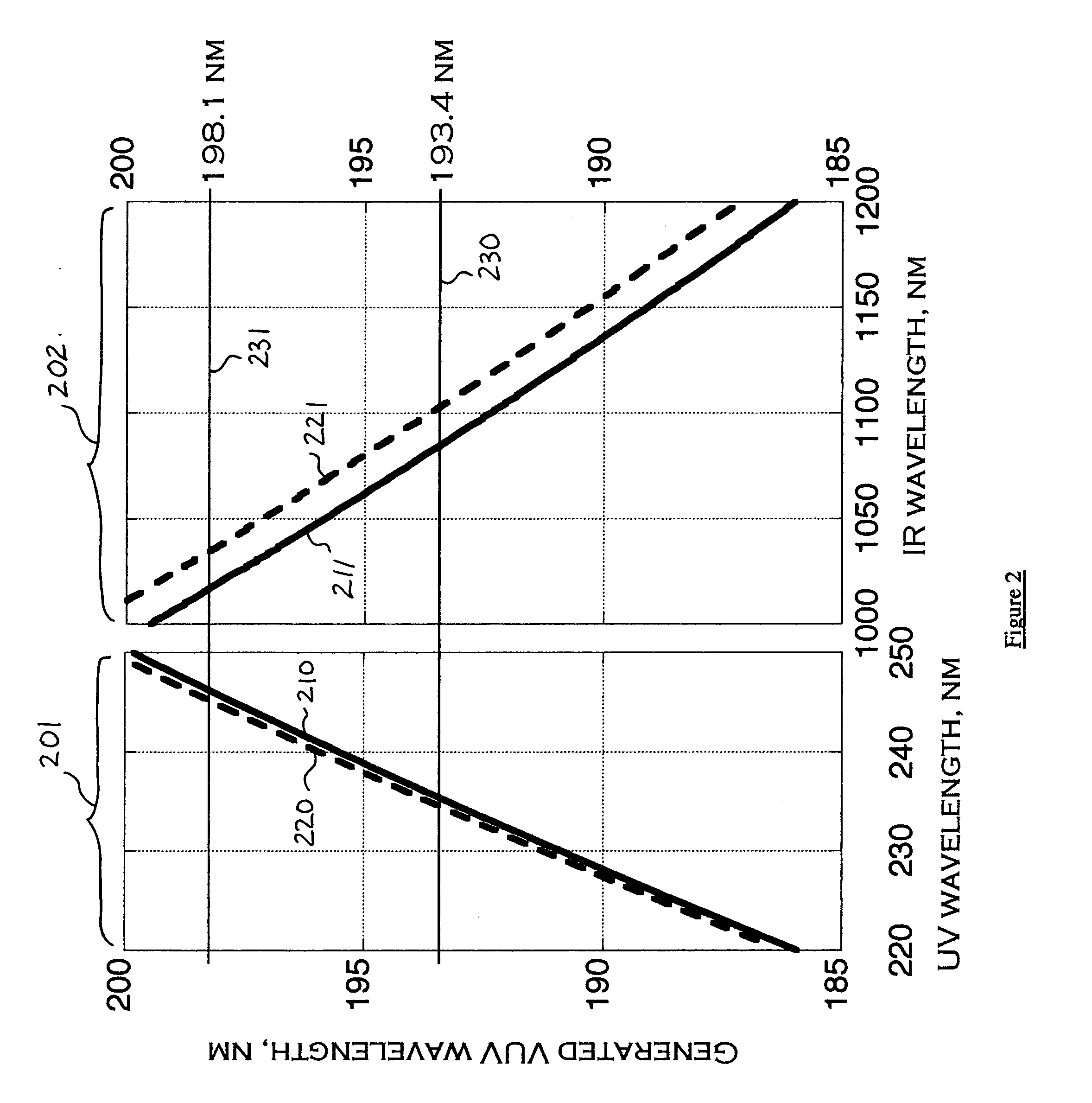
Several methods are disclosed for the generation of coherent short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation through optical nonlinear frequency mixing means. The invention involves several stages of efficient nonlinear frequency conversion to shift the output of high-power infra-red fiber-lasers into the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV). The described laser source architecture is designed around non-critically phase-matched (NCPM) sum-frequency mixing (SFM) interactions in the nonlinear crystal CLBO. The NCPM interaction is an optimum condition for bulk frequency conversion of cw radiation because it allows tight focusing of the input laser radiation without Poynting vector walk-off, thereby increasing the non-linear drive significantly. The sub-200-nm output wave is generated from SFM of a long-wave IR laser field and a short-wave UV laser field. The long-wave laser beam may be derived directly from a rare-earth-doped fiber laser, whereas the short-wavelength UV beam is provided as the fourth frequency harmonic of a second rare-earth-doped fiber laser system.
Owner:JACOB JAMES JEFFREY +1
Mid-IR instrument for analyzing a gaseous sample and method for using the same
InactiveUS7606274B2Wide tunabilityRapidly tuned SLM idlerPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingNoseMicrometer
An optical nose for detecting the presence of molecular contaminants in gaseous samples utilizes a tunable seed laser output in conjunction with a pulsed reference laser output to generate a mid-range IR laser output in the 2 to 20 micrometer range for use as a discriminating light source in a photo-acoustic gas analyzer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
External cavity tunable compact Mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7535936B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
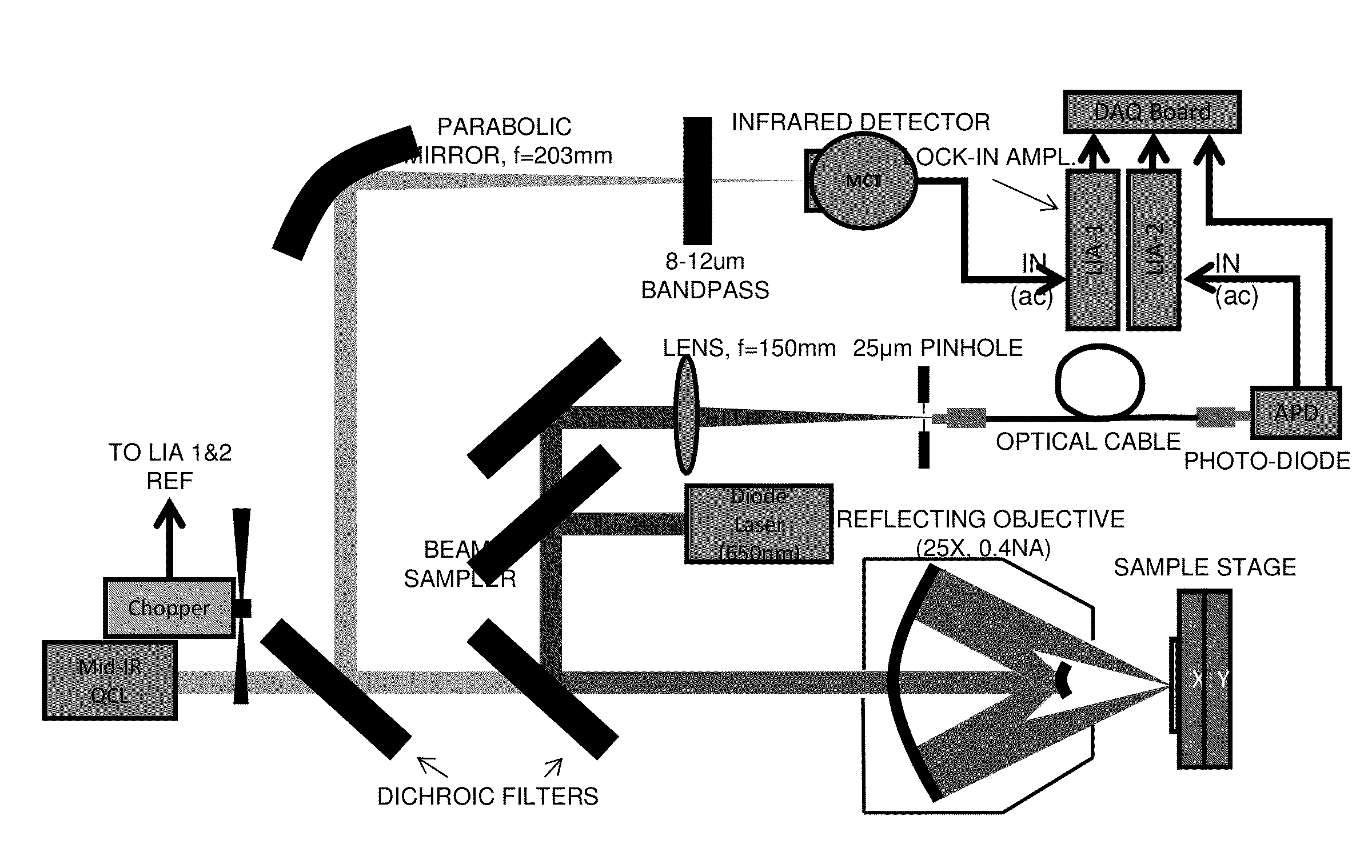
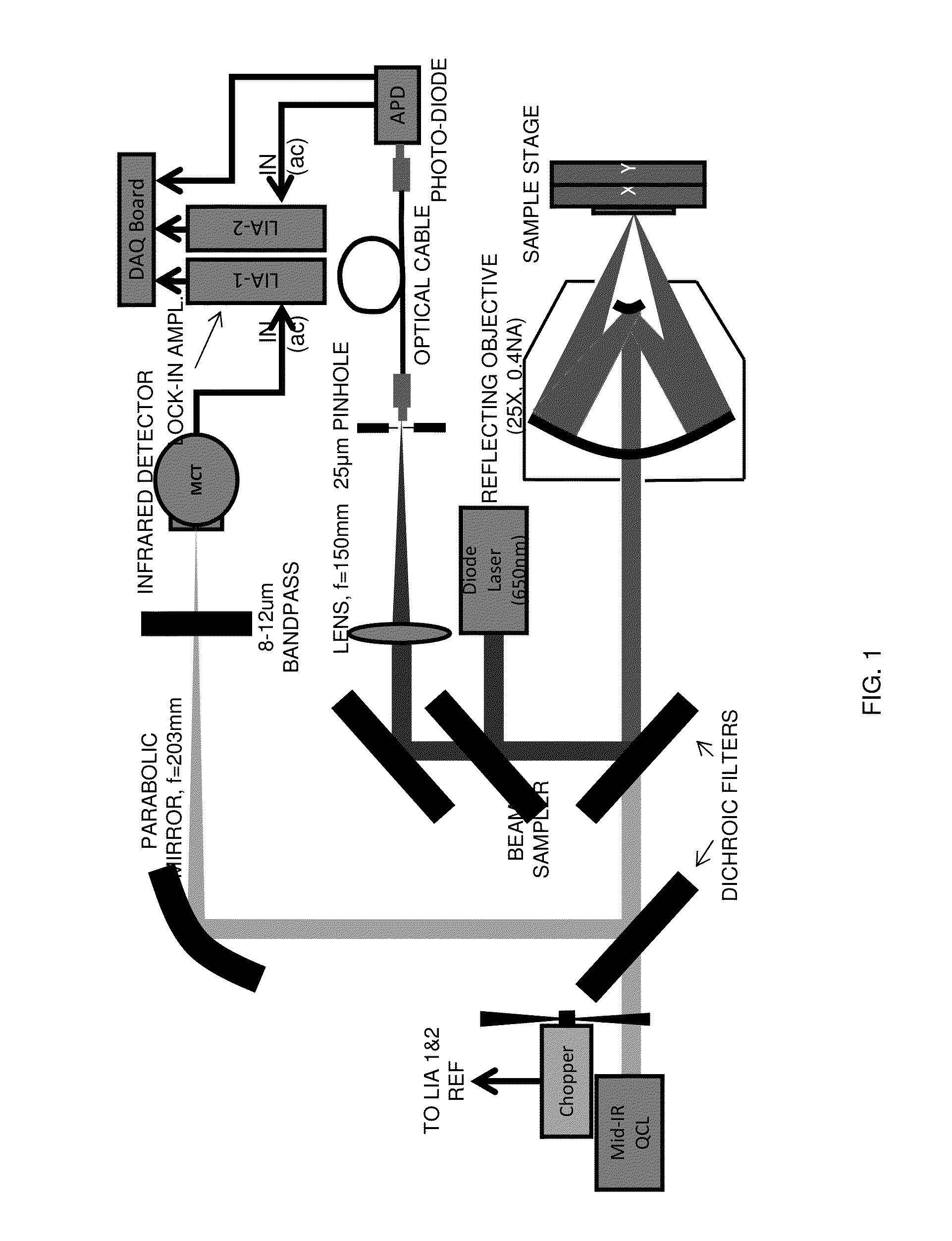
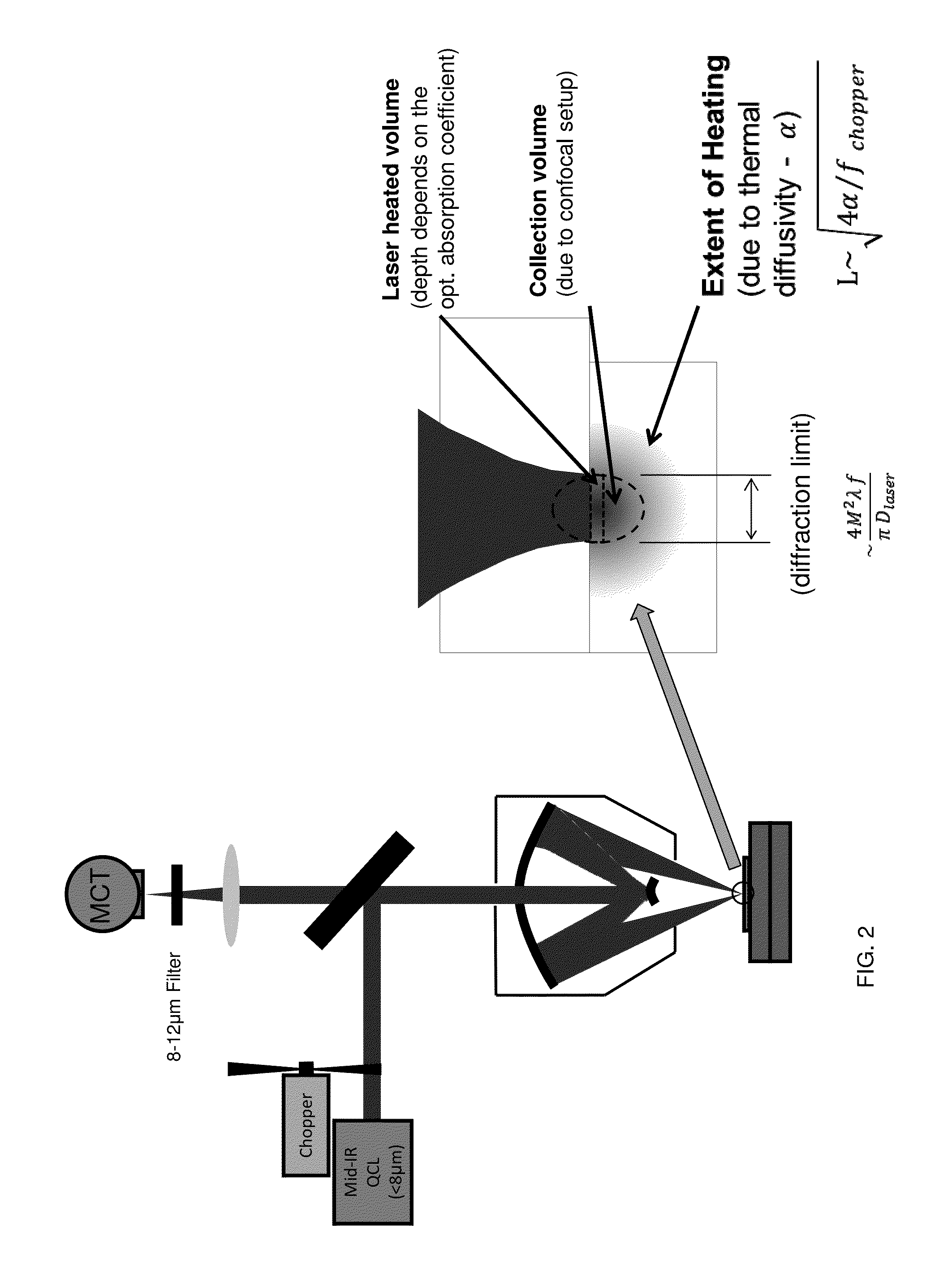
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and NANO scales
ActiveUS20130134310A1Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
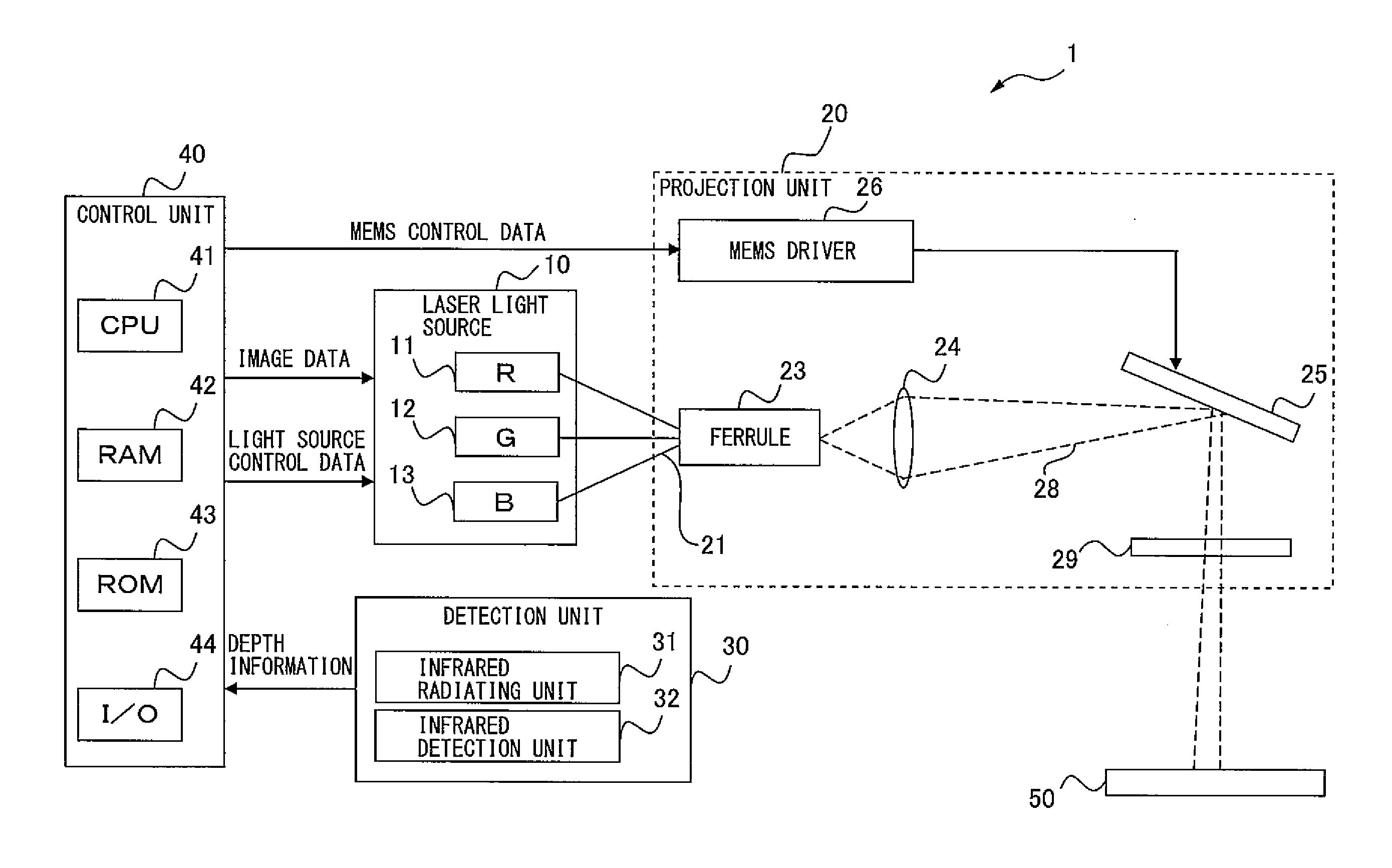
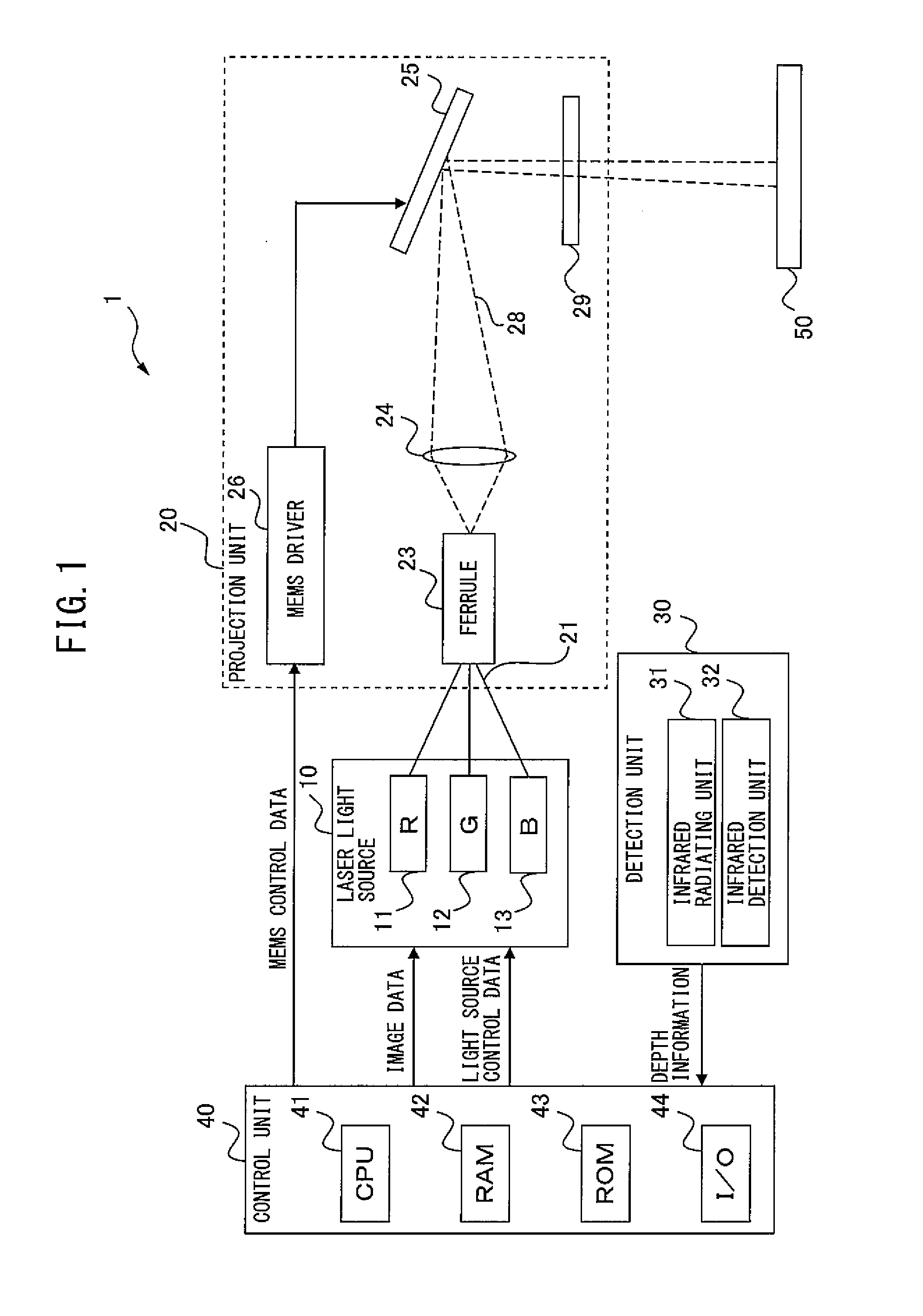
Projection apparatus
ActiveUS20150036105A1Improve utilization efficiencyRemoved positioningTelevision system scanning detailsProjectorsInformation controlProjection image
Provided is a projection apparatus that can enhance the efficiency of utilization of RGB laser lights, eliminate positional displacement in projection point caused by spaced-apart fiber cores emitting the laser lights, and detect additional information while projecting an image with the laser lights. The projection apparatus includes a laser light source emitting infrared and RGB laser lights, a fixing device fixing end portions of an infrared-light fiber and colored-light fibers used to transmit the infrared and RGB laser lights, a scanning unit projecting an image on a projection surface by scanning the projection surface with the RGB laser lights emitted from the end portions of the colored-light fibers, a detection unit detecting reflection of the infrared laser light emitted from the end portion of the infrared-light fiber, and a control unit controlling emission of the RGB laser lights from the light source, based on information detected by the detection unit.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Elevator key and method based on image recognition technology
InactiveCN102701033AOvercoming fragileGet dirty easilyCharacter and pattern recognitionElevatorsKey pressingImaging processing
The invention discloses an elevator key and a method based on the image recognition technology. The elevator key comprises a keypad pattern, a linear infrared laser, a camera, a processor and a projection module. Infrared light emitted by the linear infrared laser covers the front face of the keypad pattern in parallel, the back face of the keypad pattern is located in a view finding range of the camera, and the camera and the projection module are respectively connected with the processor. When a finger touches the keypad pattern, the finger can block the infrared light to form a facula, and then an infrared facula can occur in images collected by the camera due to the fact that the keypad pattern is semitransparent. The specific position of the infrared facula is determined according to the image processing technology, and further which key of the keypad pattern is triggered is determined. The processor recognizes the faucla and converts the facula into corresponding instructions for execution, simultaneously key state is displayed by projecting the light at the corresponding position on the keypad pattern through the projection module, and man-machine interaction operation on an elevator can be finished.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multi-modal detection of explosives, narcotics, and other chemical substances
InactiveUS6946300B2Rapidly and accurately discriminates among different substancesAccurate and reliable processWithdrawing sample devicesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCollection systemDesorption
A compact scanning apparatus has an infrared laser adapted to emit light. The light is delivered as a beam by an optical system to illuminate an interrogation area on the surface of an object being scanned to cause selective desorption of molecules of the contraband substance, which are present on the surface, without substantially damaging the surface. A collection system collects at least a portion of the desorbed molecules. At least a portion of the collected molecules is thermally decomposed to form NO2 and transferred to a reaction cell containing an aqueous, alkaline, luminol-containing solution. The NO2 reacts with the luminol to produce light by chemiluminescence. A light detector registers the presence of this light to carry out a rapid screening of the object for the possible presence of the contraband substance. The apparatus further includes a supplemental detector such as a GC / IMS detector that is activated in response to the detection of the chemiluminescent light. The supplemental detector provides confirmation of the detection of contraband substance and activates a signaling device to provide an audible or visible alarm. The rapid pre-screening permits the apparatus to identify suspicious items, while the supplemental detection system can be optimized for more intense, but time-consuming scrutiny of just the suspicious items. Both effective detection and high throughput are thereby achieved in an accurate, reliable manner.
Owner:CONTROL SCREENING
Industrial robot visual servo system and servo method and device
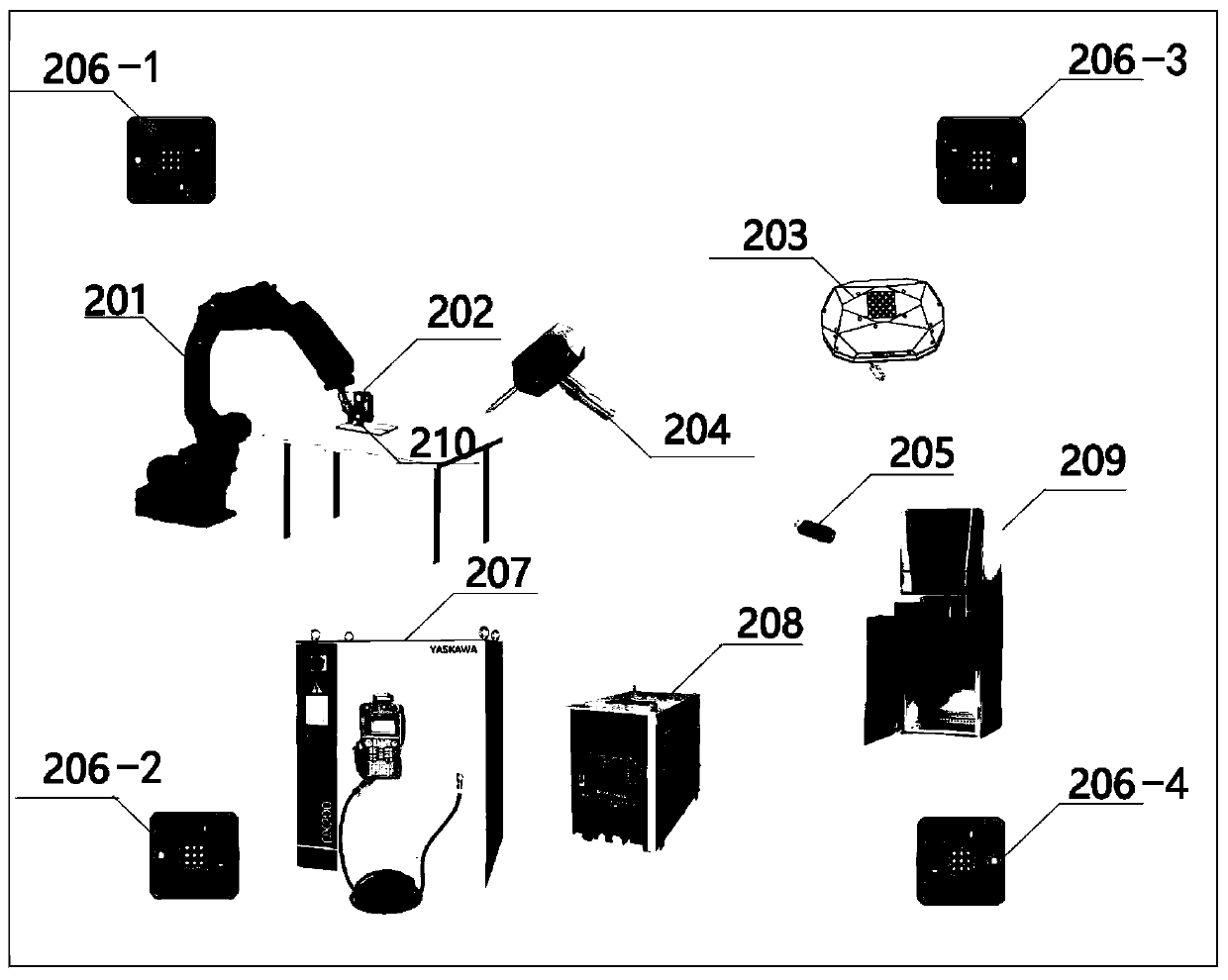
InactiveCN110039523ARealize real-time trackingOptimize workflowProgramme-controlled manipulatorWelding/cutting auxillary devicesRobot controlReal time tracking
The embodiment of the invention discloses an industrial robot visual servo system and a servo method and device. The industrial robot visual servo system comprises a six-axis robot, a weld joint tacker, a calibration object, a wireless handheld demonstrator, a USB wireless receiver, an infrared laser positioning base station, a robot control cabinet, a welding machine power supply control cabinet,an upper computer control cabinet and an automatic wire feeding system. Rapid demonstration without programming is achieved, non-uniform workpiece incoming is avoided, and real-time tracking of welding thermal deformation is achieved; the working process of a traditional welding automatic system is improved, and an operator does not need to use the demonstrator to carry out complex demonstrationprogramming; as the recognition technology based on deep learning is adopted for weld joint tracking, the universality of welding automation is greatly improved; and in addition, welding path planning, demonstration, system calibration and welding real-time tracking are completely integrated in the same upper computer interface, and therefore the process operation and management can be conveniently carried out by the operator.
Owner:北京无远弗届科技有限公司
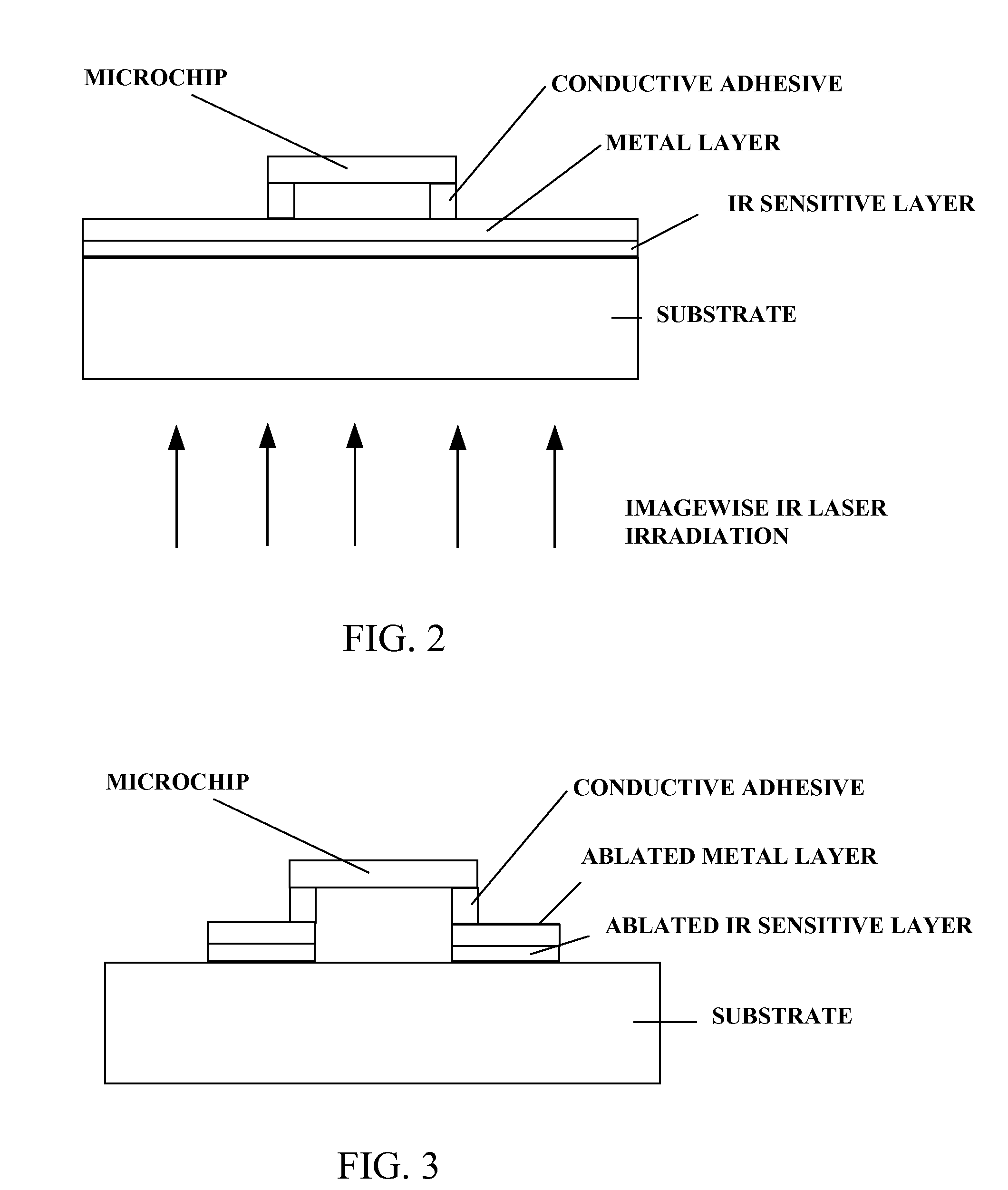
Flexographic element having an infrared ablatable layer
A photosensitive element for use as a photopolymer printing plate comprising a support, a layer of a photopolymerizable material on the support, and an infrared ablation layer which is ablatable by infrared radiation and substantially opaque to actinic radiation on the photopolymerizable material. The infrared ablation layer comprises at least one infrared absorbing material, a radiation opaque material, and at least one binder which is substantially incompatible with low molecular weight materials in the photopolymerizable layer. The infrared ablation layer is tack-free or substantially tack-free on the photopolymerizable layer. The infrared ablation layer is ablatable from the surface of the photopolymerizable layer upon exposure to infrared laser radiation.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method and device for detecting textile structure and dying defect using infrared laser
InactiveCN101187640AConvenient and accurate analysis and identificationInspecting textilesMaterial analysis by optical meansDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a method for detecting textile structures and dyeing defects through infrared laser, which comprises projecting the infrared laser on a textile sample, collecting infrared laser transmitting images of the textile sample, displaying the infrared laser transmitting images of the textile sample on a displaying component. A device for detecting textile structures and dyeing defects through infrared laser is composed of a semiconductor laser and a infrared photography device, wherein the semiconductor laser and the infrared photography device are arranged fixedly on two ends of an optical path, a textile sample holdfast is arranged in the optical path which is between the semiconductor laser and the infrared photography device, a piece of condensing lens is arranged on the optical path which is between the semiconductor laser and the textile sample holdfast, a piece of object lens is arranged on the optical path which is between the textile sample holdfast and the infrared photography device, the infrared photography device is connected with a display. The infrared laser transmitting images of textile materials with grey scale and contrasting chrominance are displayed on the displaying component. The infrared laser transmitting images are provided for technological analysis and identifications.
Owner:上海市纤维检验所
Dual-wavelength positive-working radiation-sensitive elements
InactiveUS7279263B2High sensitivityEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiazo compound compositionsRadiation sensitivityUltraviolet
A positive-working radiation-sensitive composition for use with a radiation source comprises one or more polymers capable of being eluted in an alkaline aqueous solution and a development-enhancing compound. The invention provides a positive-working photosensitive composition of good sensitivity for use with one or both of ultra-violet radiation and an infrared laser radiation source. The composition is stable in its state before exposure and has an excellent handling property. The sensitivity of a radiation-sensitive coating based on the composition of this invention is increased without compromising the handling characteristics. Radiation-sensitive elements based on the composition of the invention have good development latitude. A positive-working lithographic printing precursor is based on the radiation-sensitive composition coated on a hydrophilic surface. The precursor is developable using an alkaline aqueous solution, and may be used with a radiation source in lithographic applications, such as conventional imaging systems, computer-to-plate systems or other direct imaging applications. The precursor is stable in its state before exposure and has an excellent handling property.
Owner:KODAK GRAPHIC COMM CANADA CO
Photopolymerizable composition
InactiveUS6838222B2Harmful effectRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesDouble bondRecording layer
A photopolymerizable composition that is cured with visible light or an infrared laser and is used as a recording layer in a negative planographic printing plate precursor. The photopolymerizable composition is cured by exposure and includes (A) a polymerizable compound that is solid at 25° C. and has at least one radical-polymerizable ethylenically unsaturated double bond in a molecule, (B) a radical polymerization initiator, (C) a binder polymer and, as required, (D) a compound generating heat by infrared exposure.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Non-alkaline aqueous development of thermosensitive lithographic printing plates
InactiveUS6902865B2Excellent developabilityRaise the ratioX-ray/infra-red processesPhotosensitive materialsAqueous solutionPhotochemistry
Negative thermosensitive lithographic printing plates developable with a non-alkaline aqueous developer and method of developing such plates. The plate comprises on a substrate a thermosensitive layer comprising an ethylenically unsaturated monomer, a free radical initiator, and an infrared absorbing dye. The plate can be imagewise exposed with an infrared laser to cause hardening in the exposed areas and then developed with a non-alkaline aqueous developer to remove the non-exposed areas. The non-alkaline aqueous developer can be water or an aqueous solution comprising at least 60% of water and having a pH of 2.0 to 10.0.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
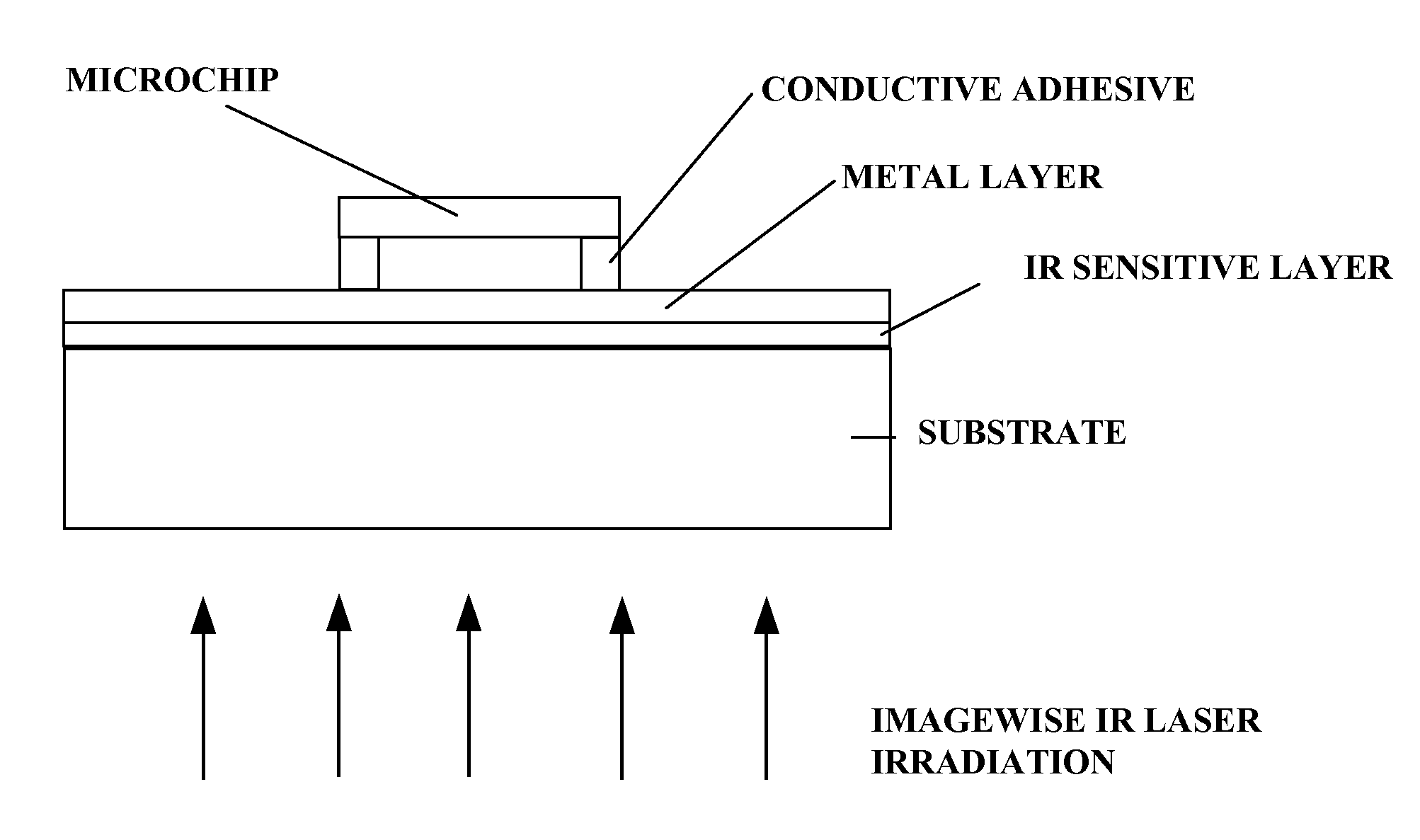
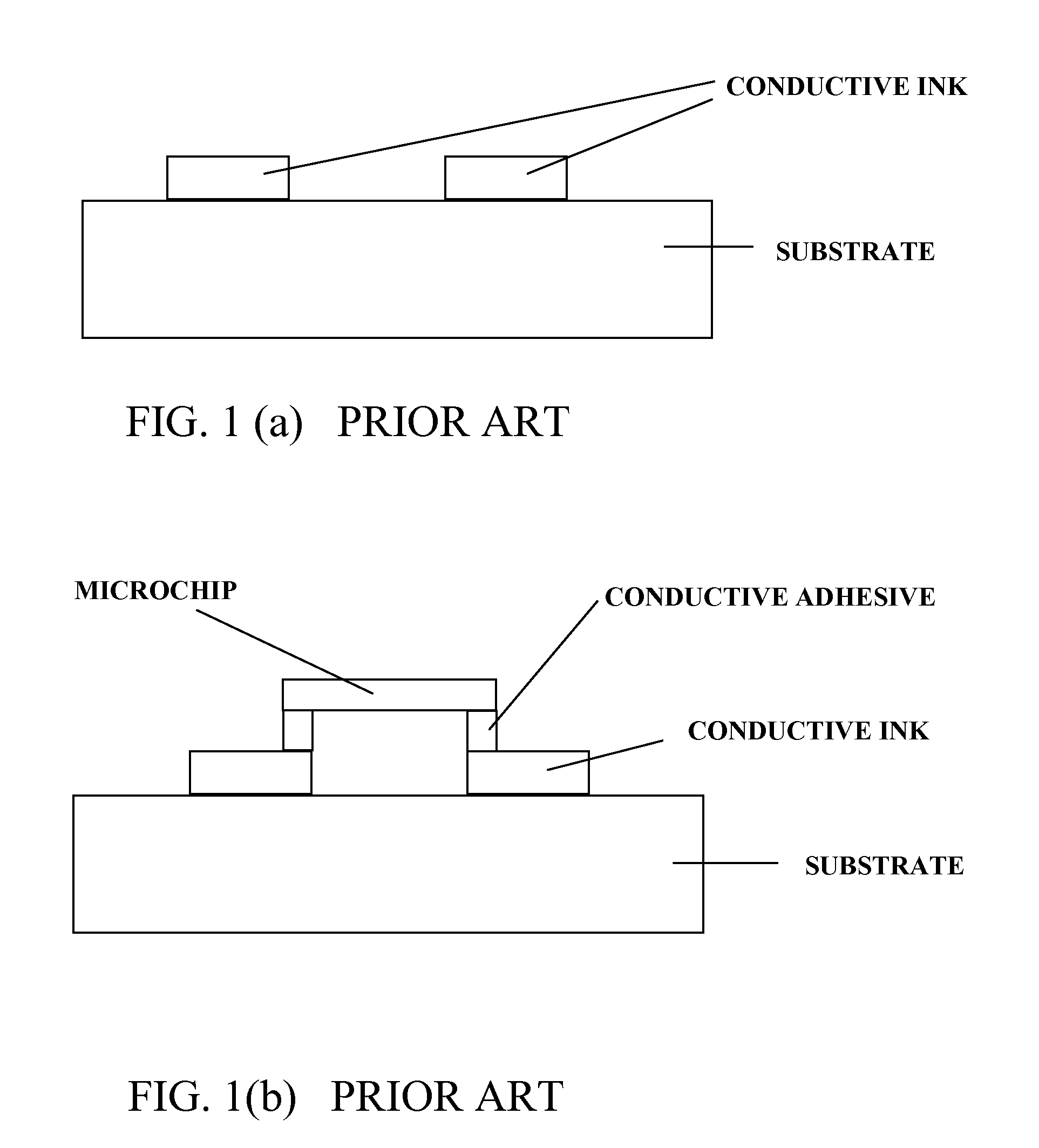
Fabrication method for producing conductive and functional geometric patterns
InactiveUS20080120834A1Printed circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsElectrically conductiveElectronic circuit
The invention provides an article and process for producing electronic devices. More particularly the invention relates to an article and process for fabricating patterns of electrically conductive materials on non-electrically conductive substrates by laser ablation. Such an article and process find use in the production of RDIF devices, antennae, electrical circuits, microwave susceptors, contacts, leads, conductors, interactive displays, electrostatic shielding devices and the like. The process involves first providing an electrically conductive metal layer on an electrically non-conductive substrate. Then an electronic circuit is electrically connected to the electrically conductive metal layer. Thereafter a portion of the electrically conductive metal layer is ablated with infrared laser radiation to form a pattern of electrically conductive areas and electrically non-conductive areas on the substrate, wherein at least a portion of the electrically conductive areas are electrically connected to the electronic circuit.
Owner:IDEON LLC
Low-concentration and multi-component gas detection method based on integration of multiple spectrum technologies
ActiveCN104568836AAccurate measurementEliminate Cross InterferenceColor/spectral properties measurementsDifferential optical absorption spectroscopyLower limit
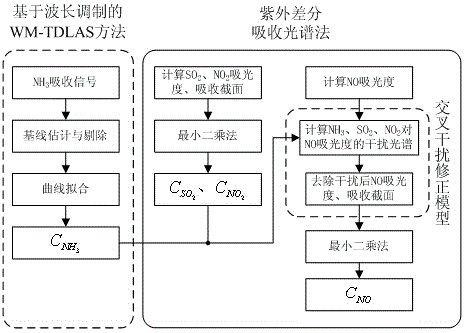
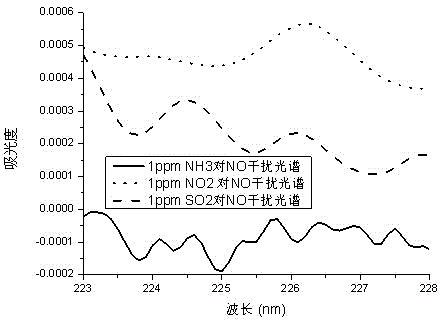
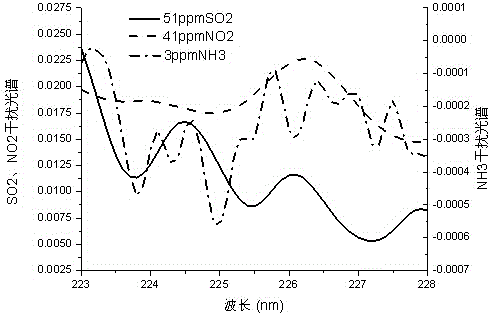
The invention discloses a low-concentration, multi-component and high-sensitivity gas detection method based on integration of multiple spectrum technologies. Advantages of an ultraviolet differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) technology and an infrared tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (IR-TDLAS) technology are integrated, so that information integration and characteristic signal extraction of two kinds of spectrum are realized. The method disclosed by the invention is used for measuring the NH3 concentration in smoke by utilizing a TDLAS method and simultaneously measuring the concentrations of SO2 and NO2 in smoke by utilizing an ultraviolet DOAS method; interference of three components in the NO absorbancy is removed according to the obtained concentrations and an interference spectrum of three kinds of gas to the NO absorbancy, so that the NO concentration without cross interference is solved; and thus, the measurement precision and the detection lower limit are greatly increased.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Three-Dimensional Molecular Imaging By Infrared Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20100012831A1Samples introduction/extractionIsotope separationESI mass spectrometryMolecular imaging
The field of the invention is atmospheric pressure mass spectrometry (MS), and more specifically a process and apparatus which combine infrared laser ablation with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com