Optical Material and Method for Modifying the Refractive Index
a technology applied in the field of optical materials and refractive indexes, can solve the problems that most patients undergoing cataract surgery will not enjoy optimal vision, and achieve the effect of little or no scattering loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Forming Structures in Optical Polymeric Materials
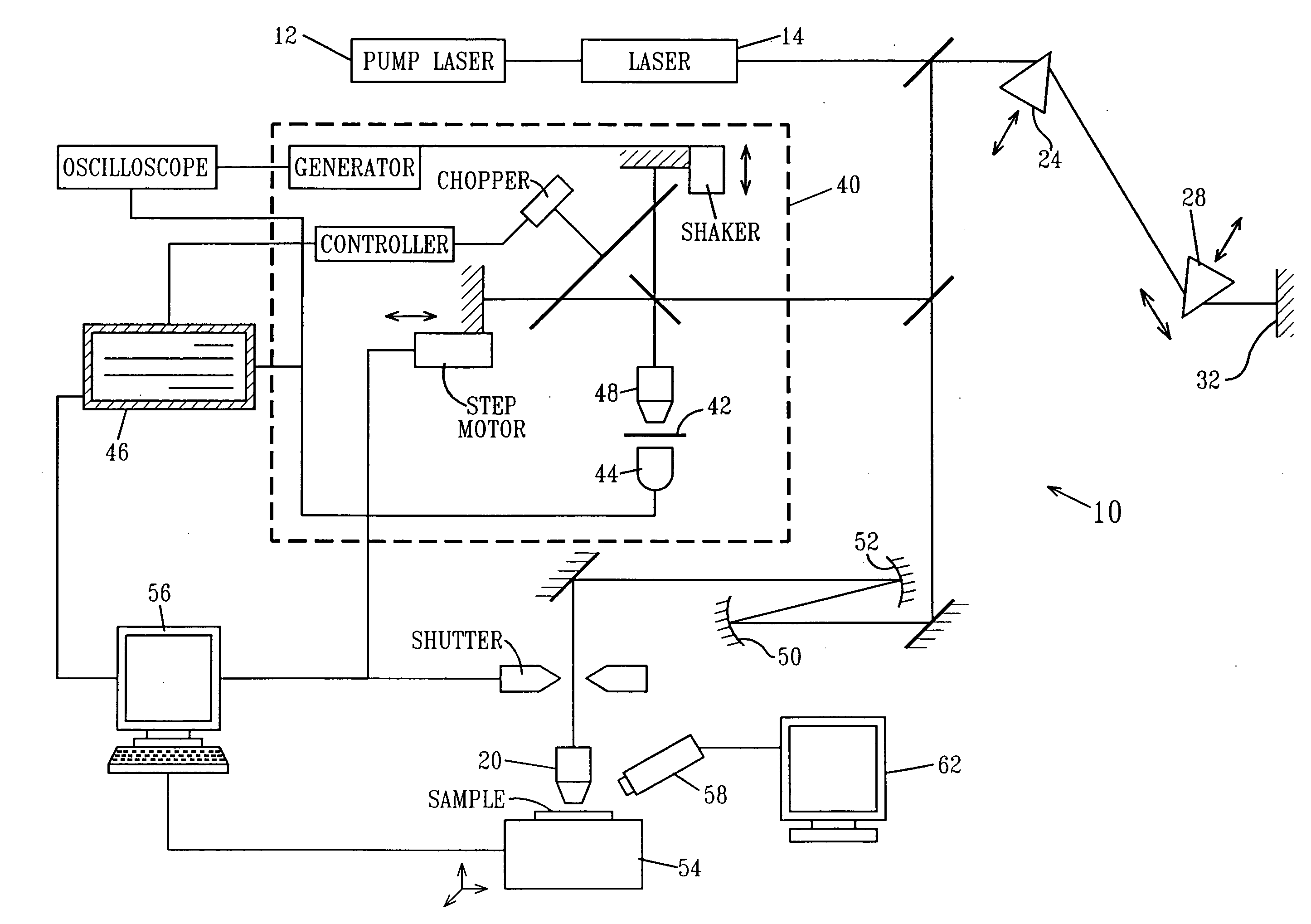
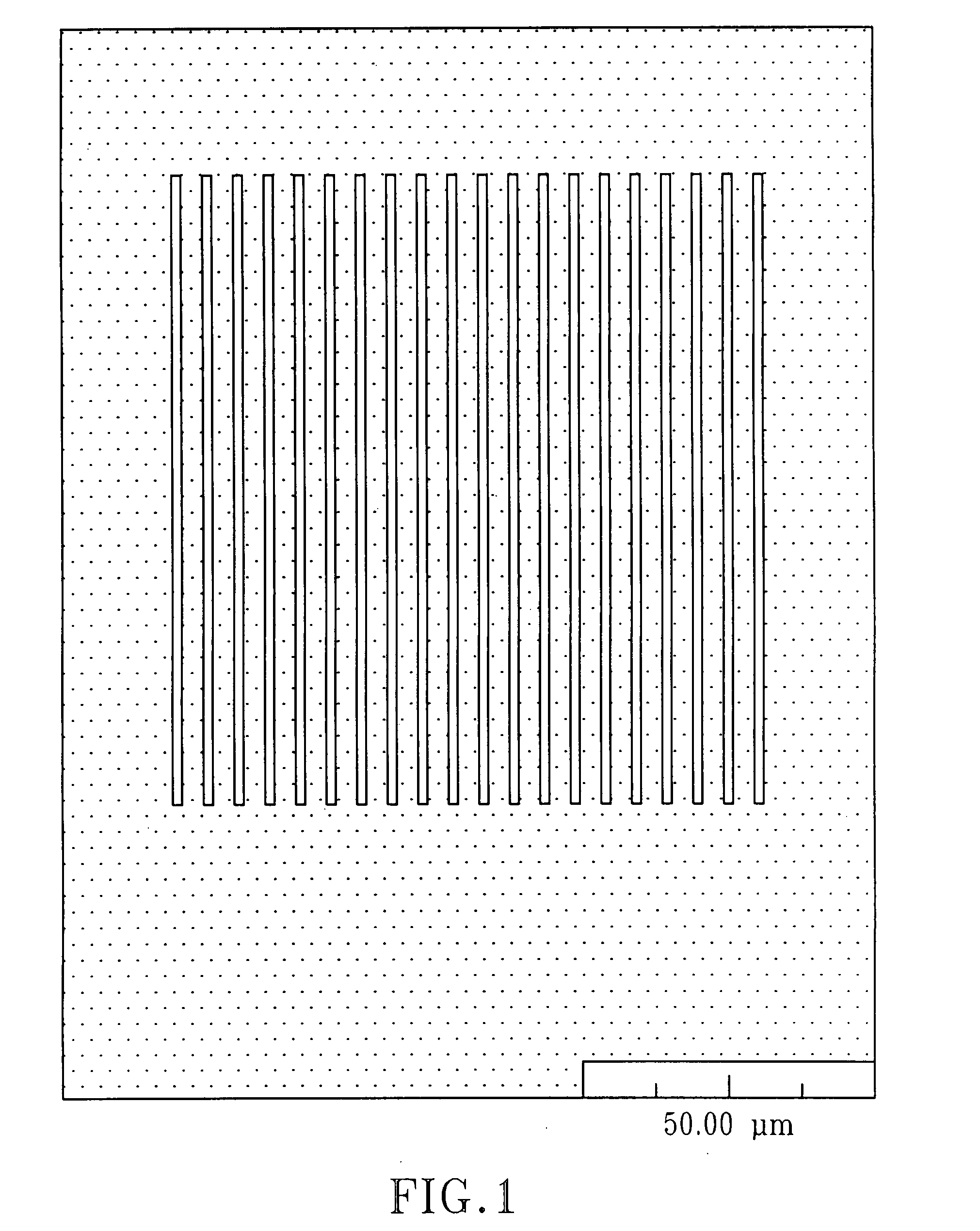
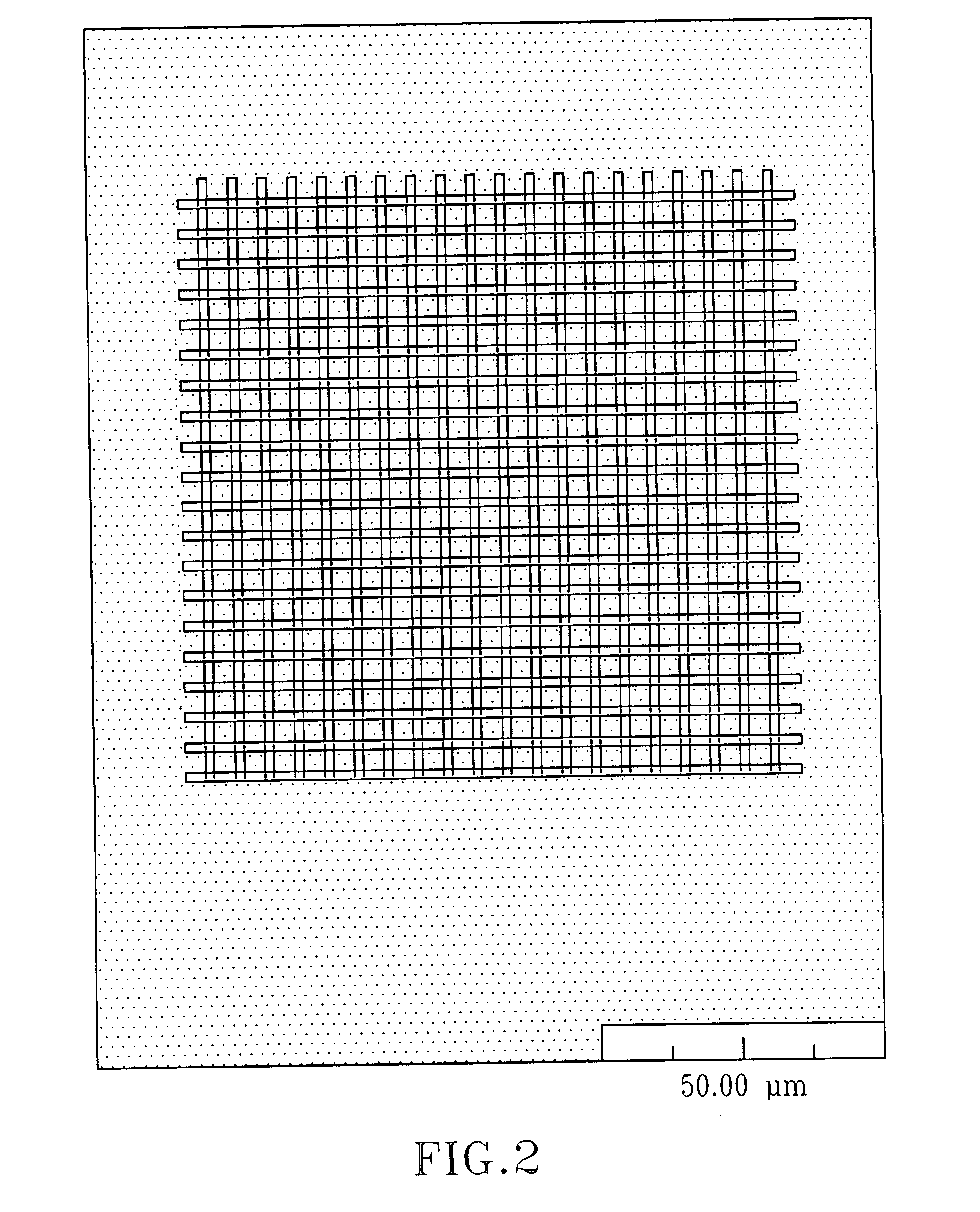
[0089]The optical system described was used to form line structures in select regions of optical materials. Experiments were conducted with three polymeric materials (Bausch & Lomb Incorporated, Rochester, N.Y.): PV2526-164, RD1817, and HEMA B. PV2526-164 is a silicone-containing hydrogel that can absorb about 36% (by total weight). RD1817 is a hydrogel copolymer that comprises about 90% (by weight) N-vinylpyrrolidone (“NVP”) and about 10% (by weight) 4-t-butyl-2-hydroxycyclohexyl methacrylate and that can absorb about 80% (by weight) water. Its refractive index when hydrated is very close to the index of water. HEMA B is poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) cross-linked with about 0.9% (by weight) of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (“EGDMA”), also a hydrogel, which can absorb about 37% (by weight) water. The refractive indices of PV2526-164, RD1817, and HEMA B are 1.422, 1.363, and 1.438, respectively, when they are in the hydrated state...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com