Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2037 results about "Laser projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
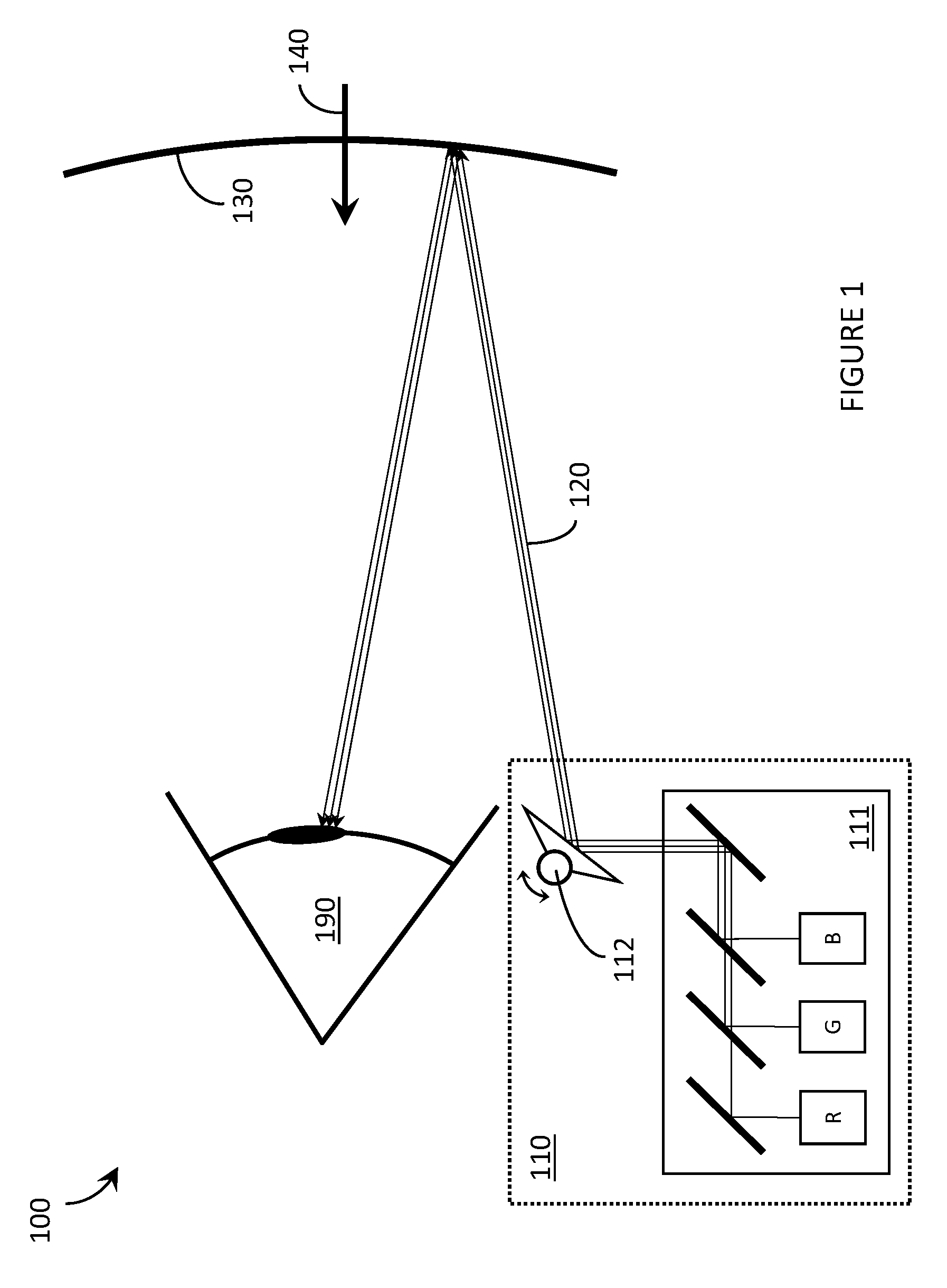
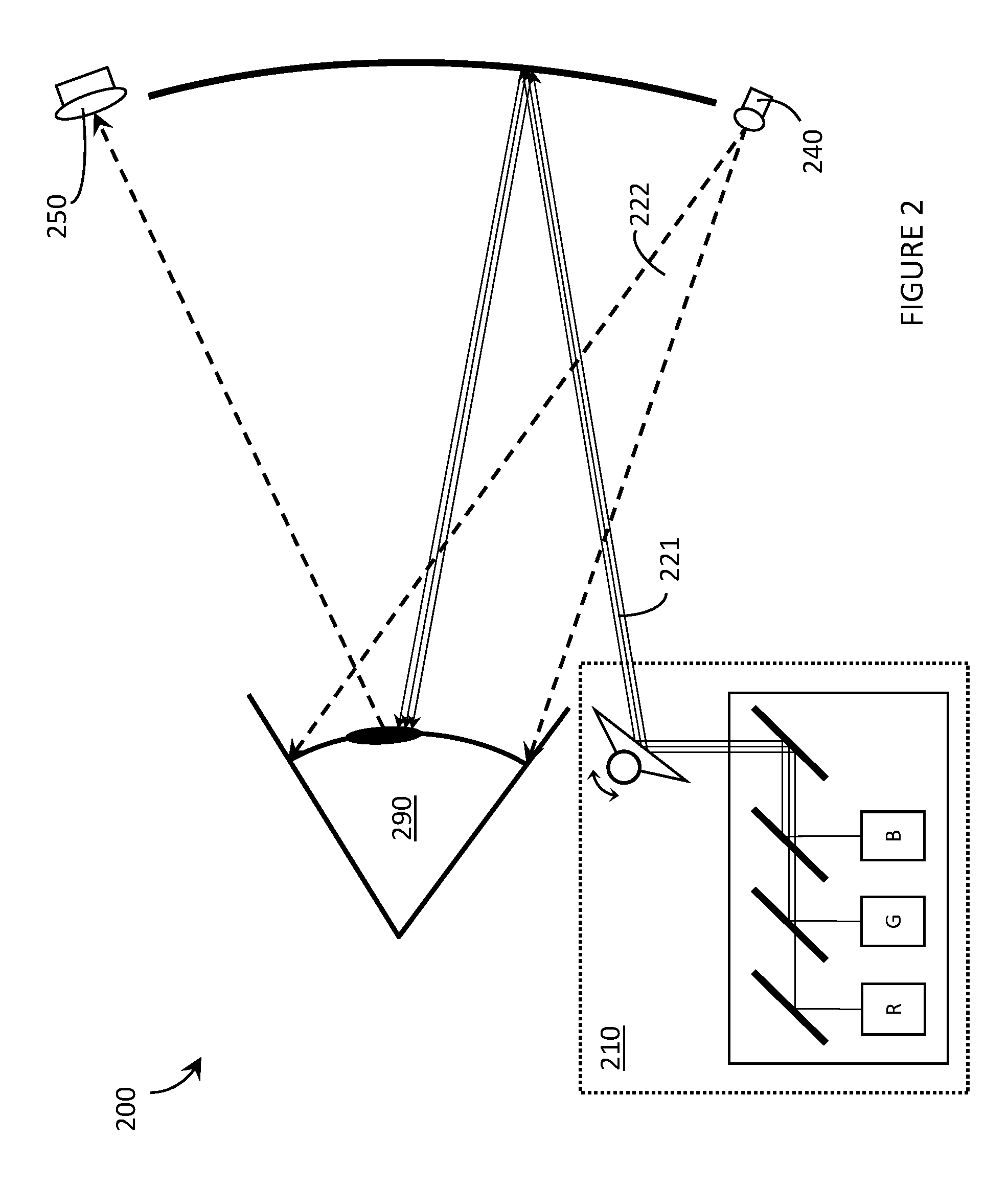
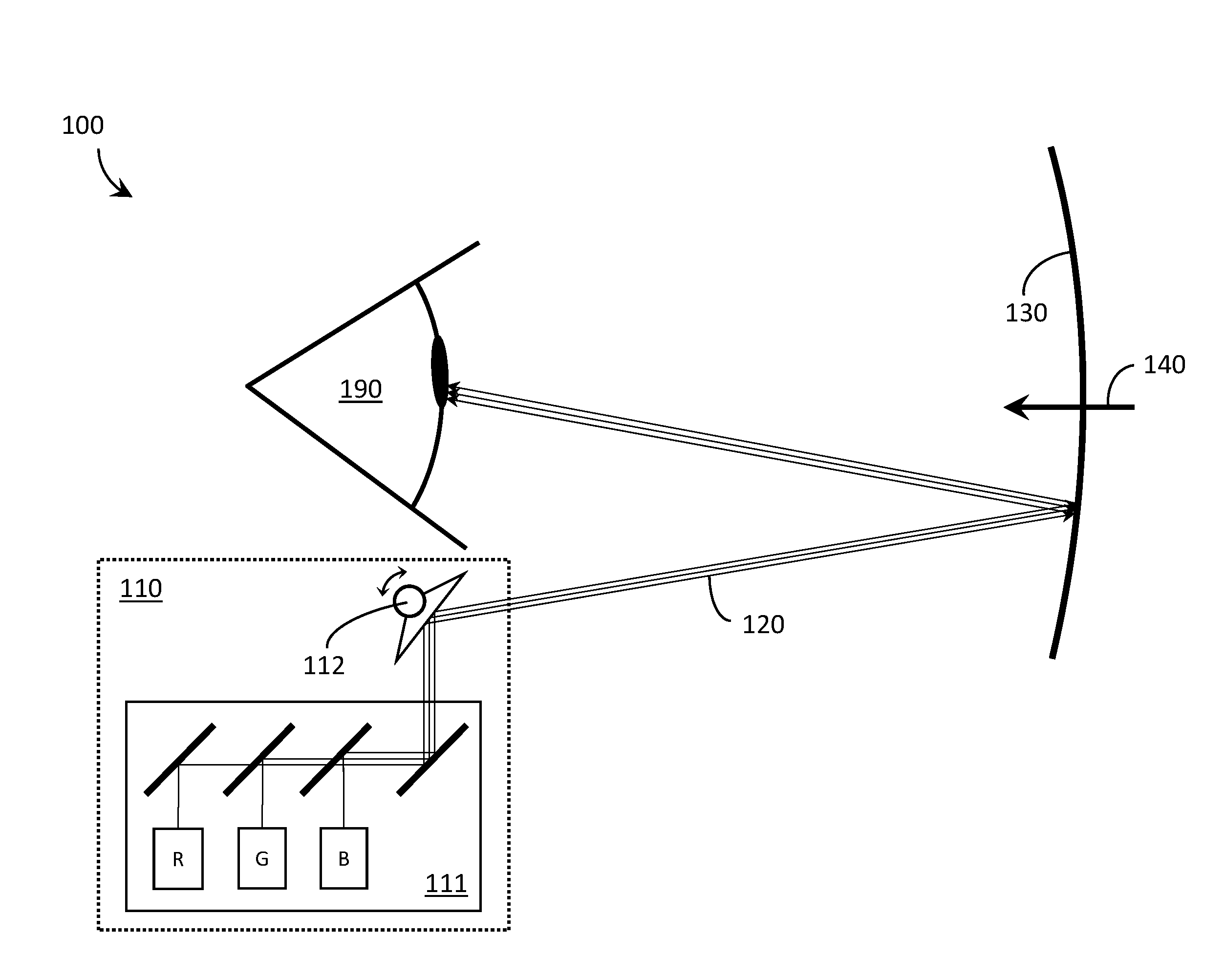
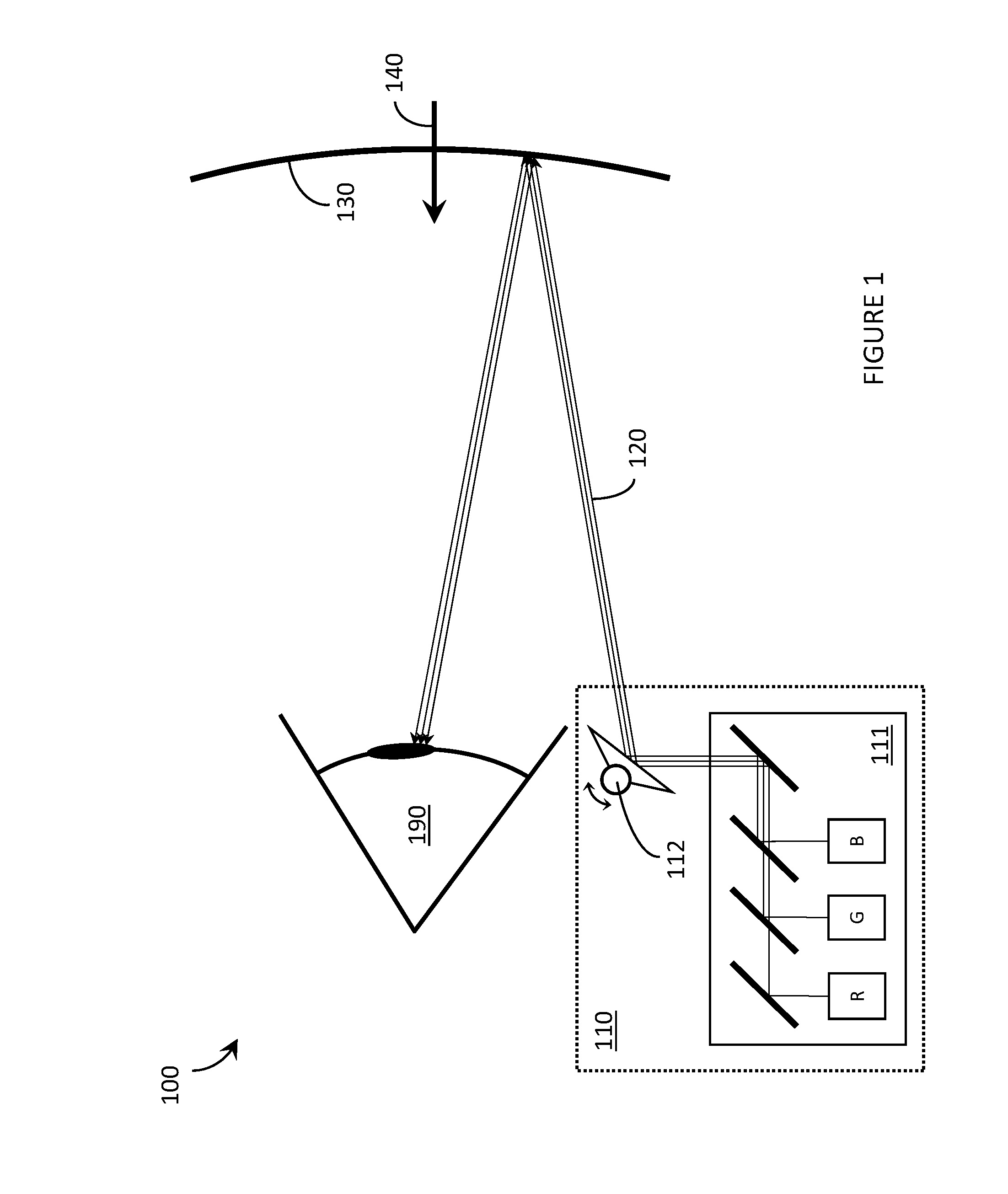
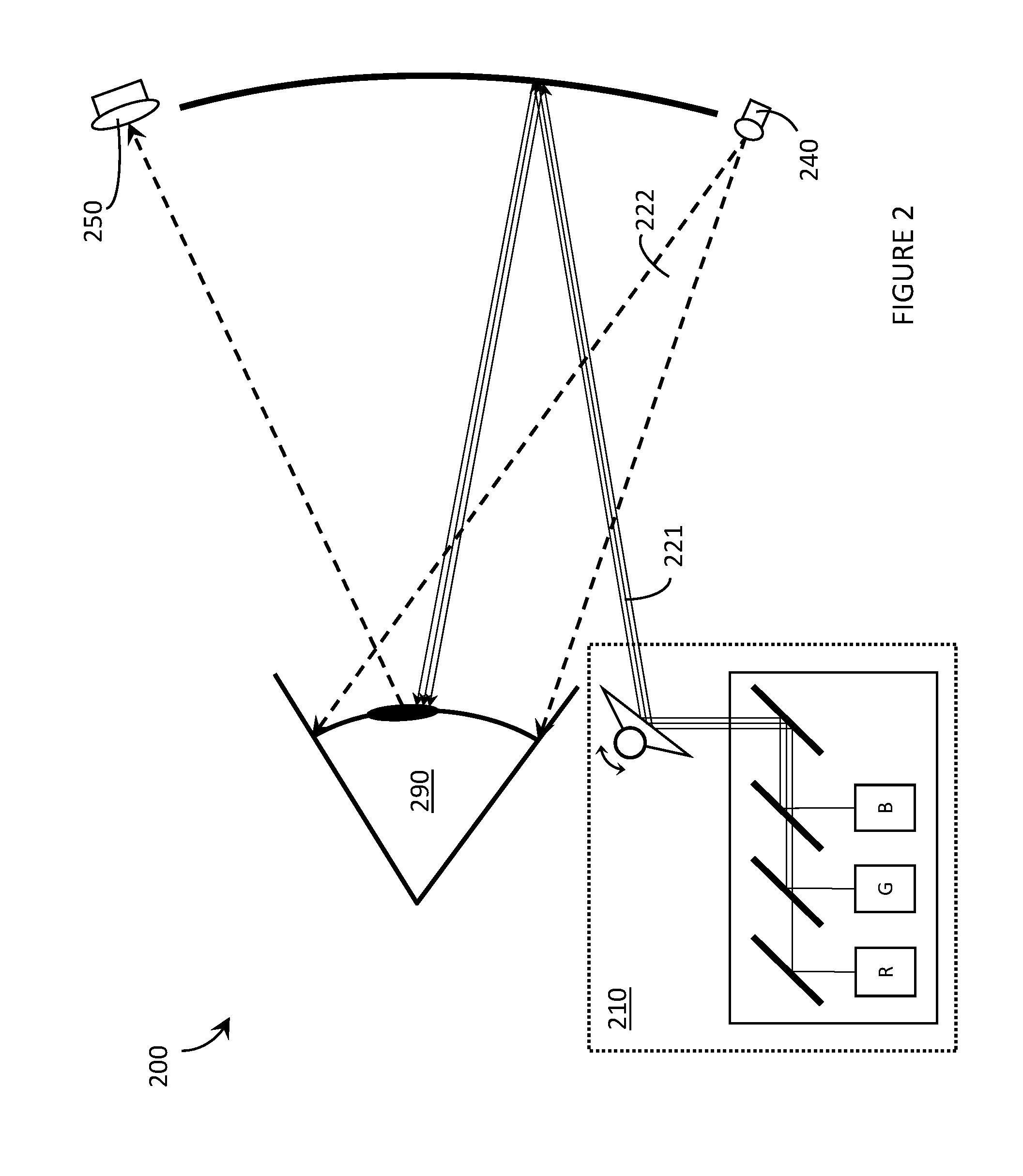
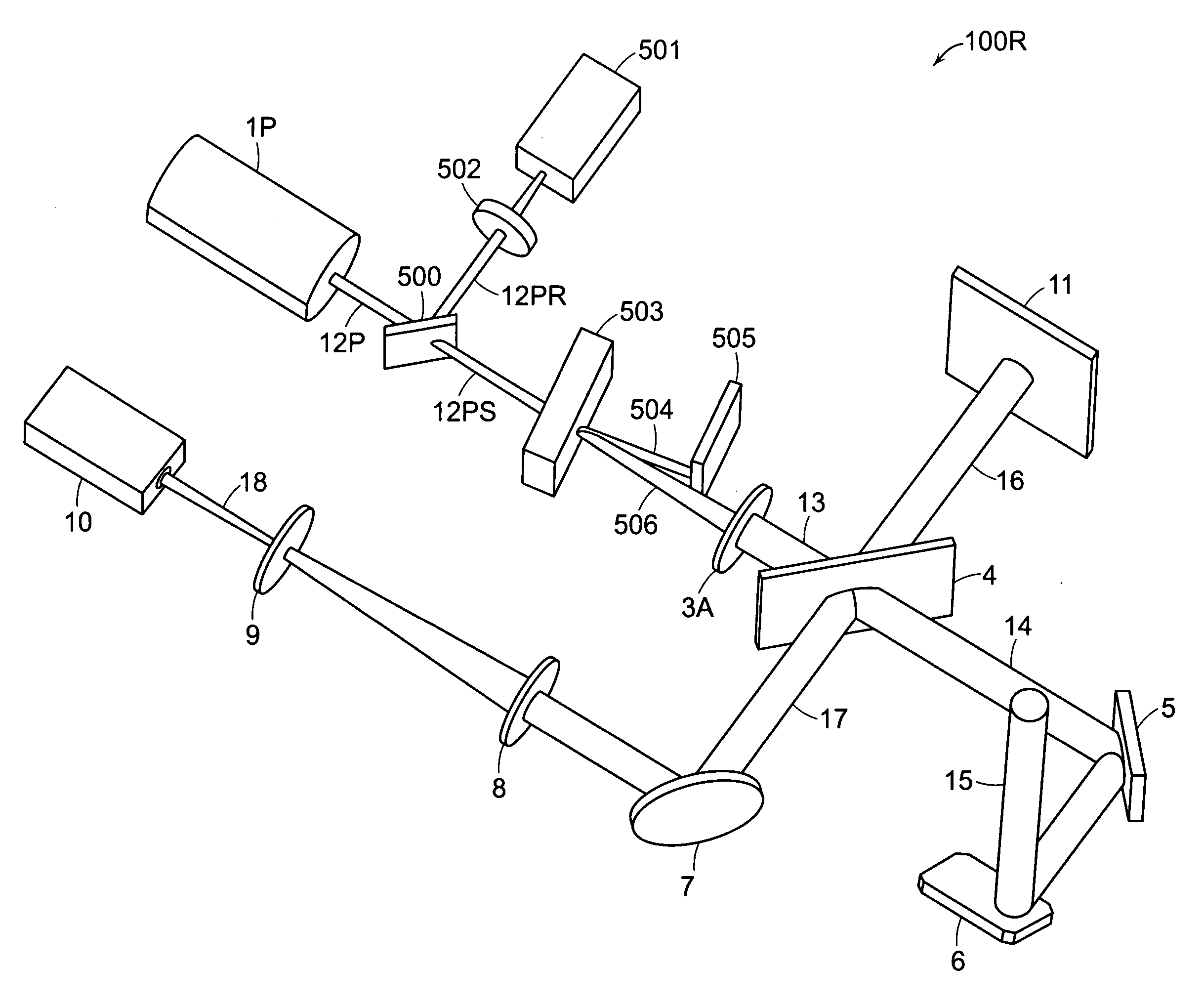
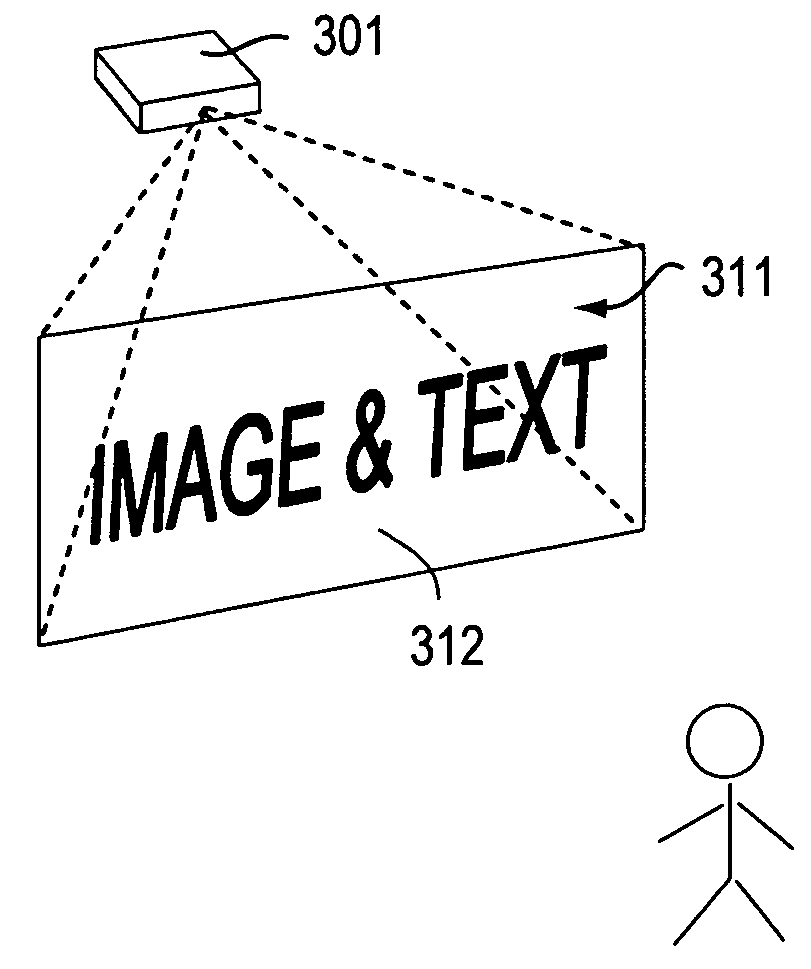
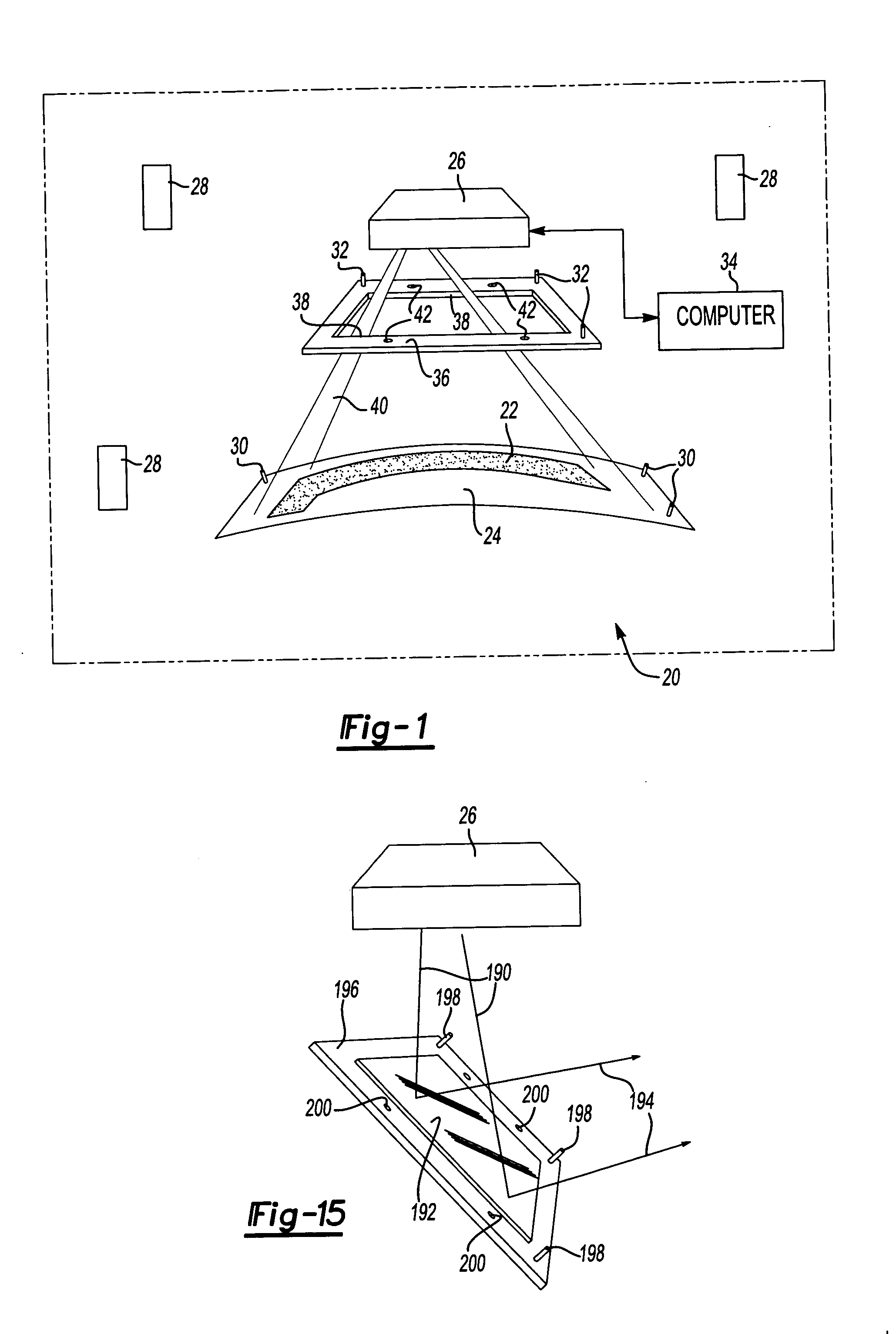
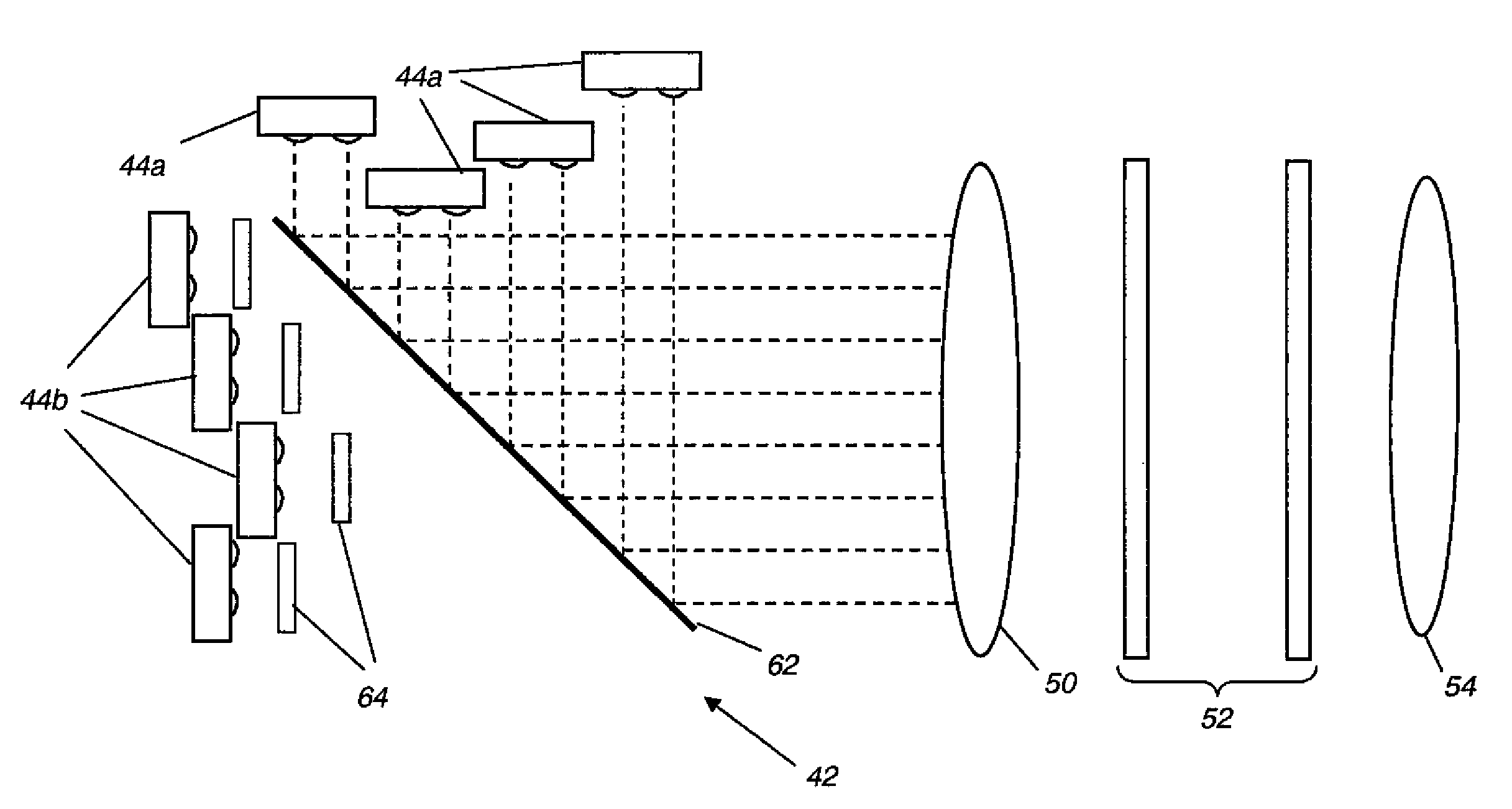
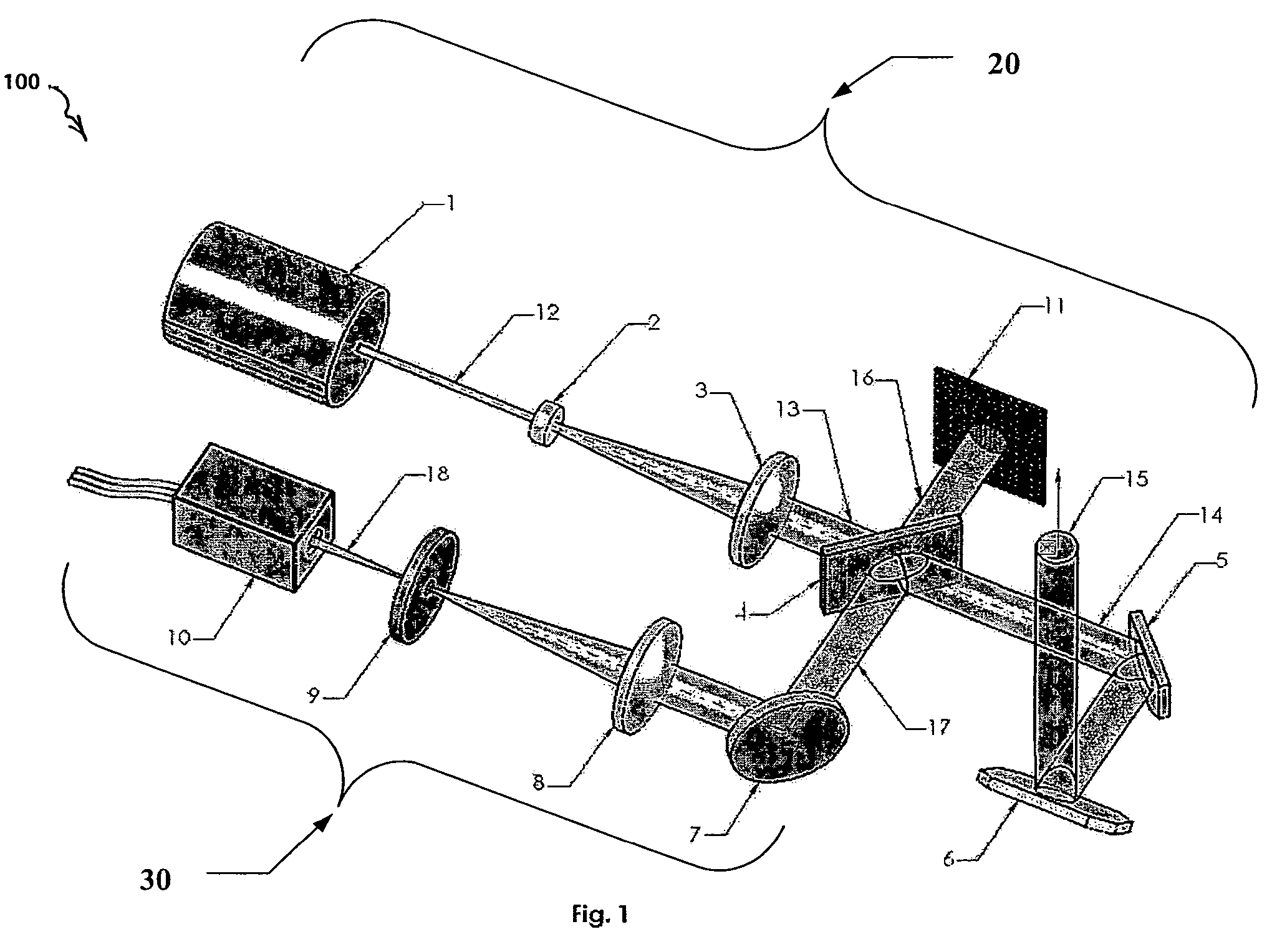
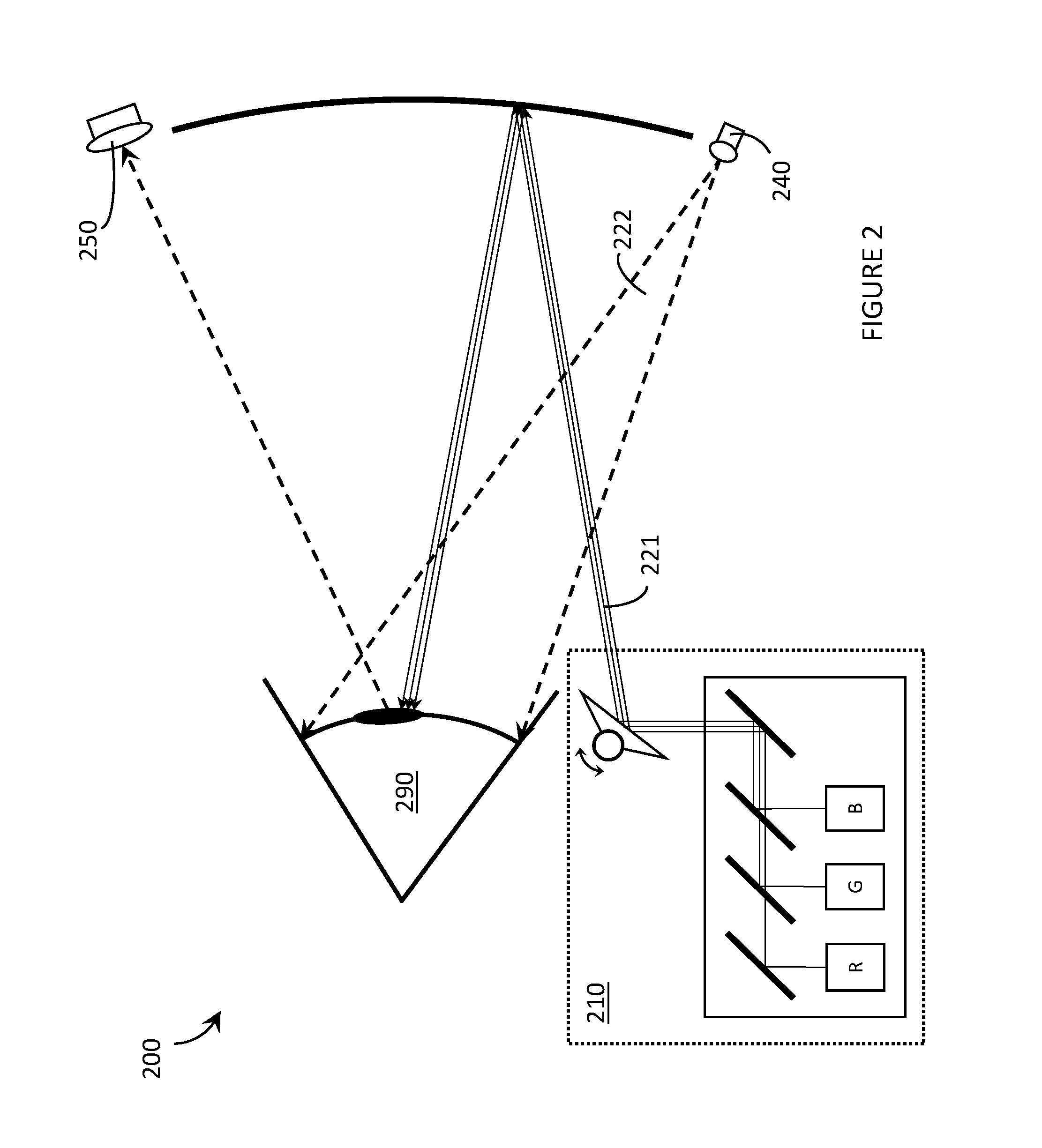
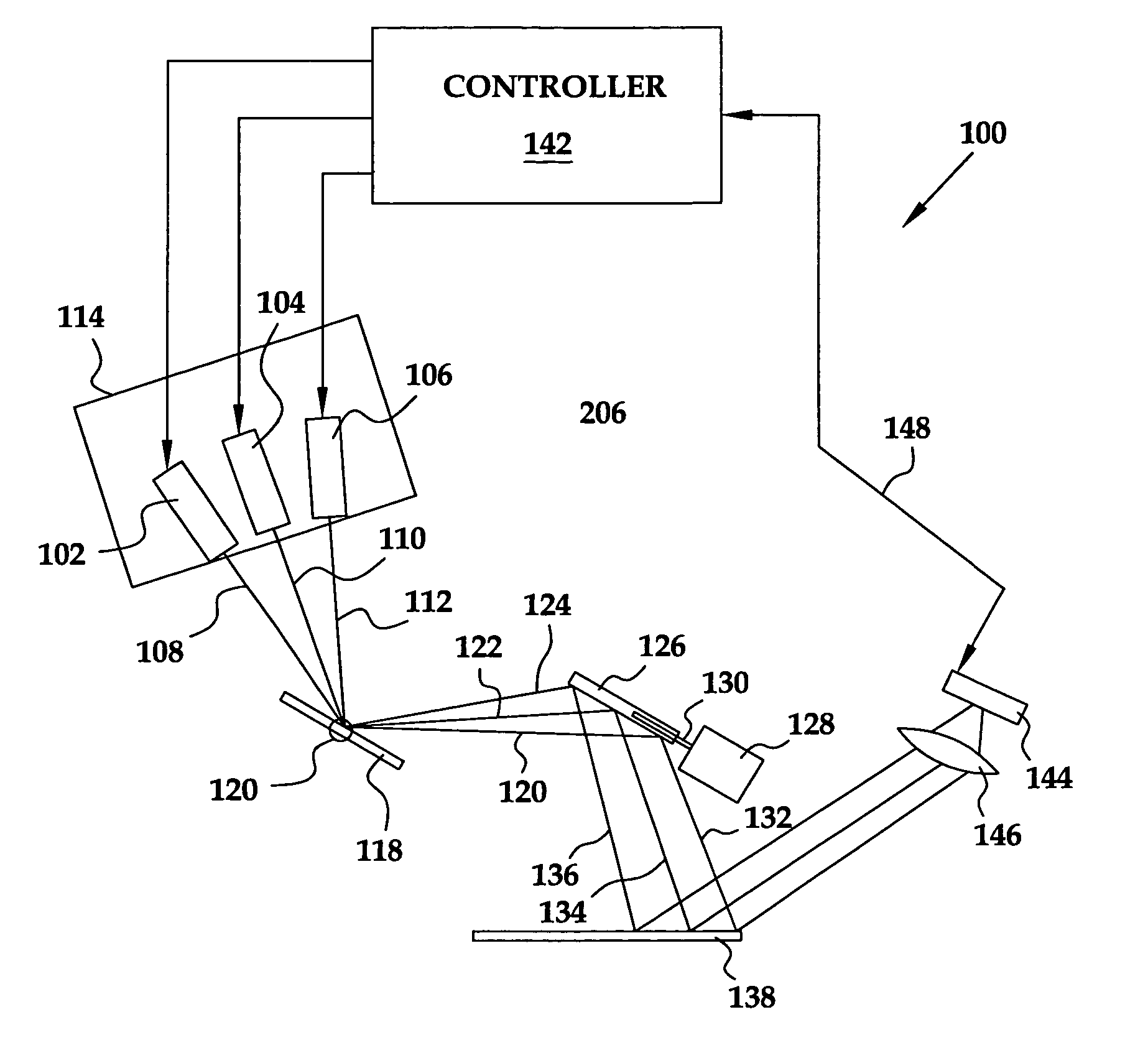
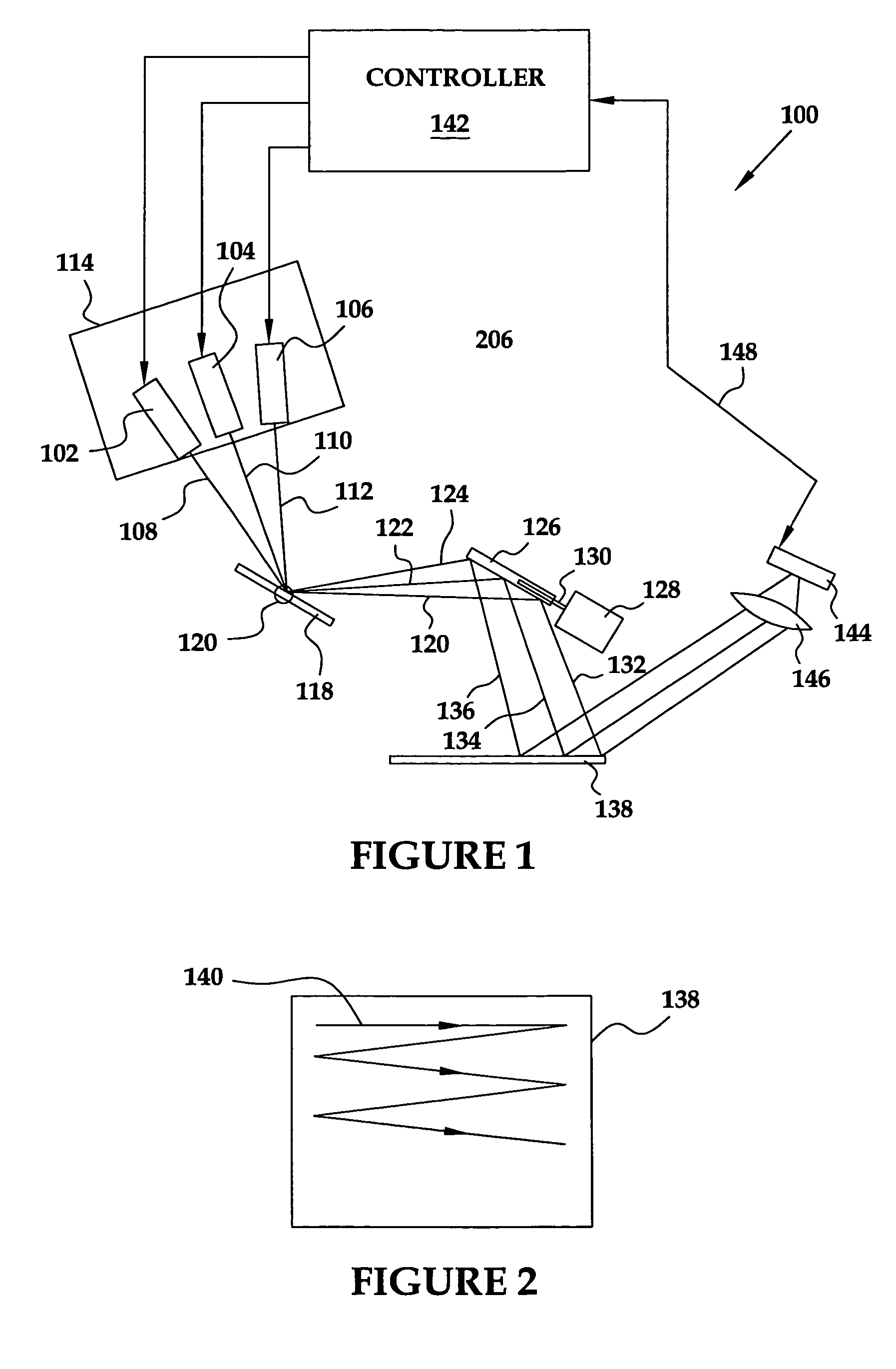
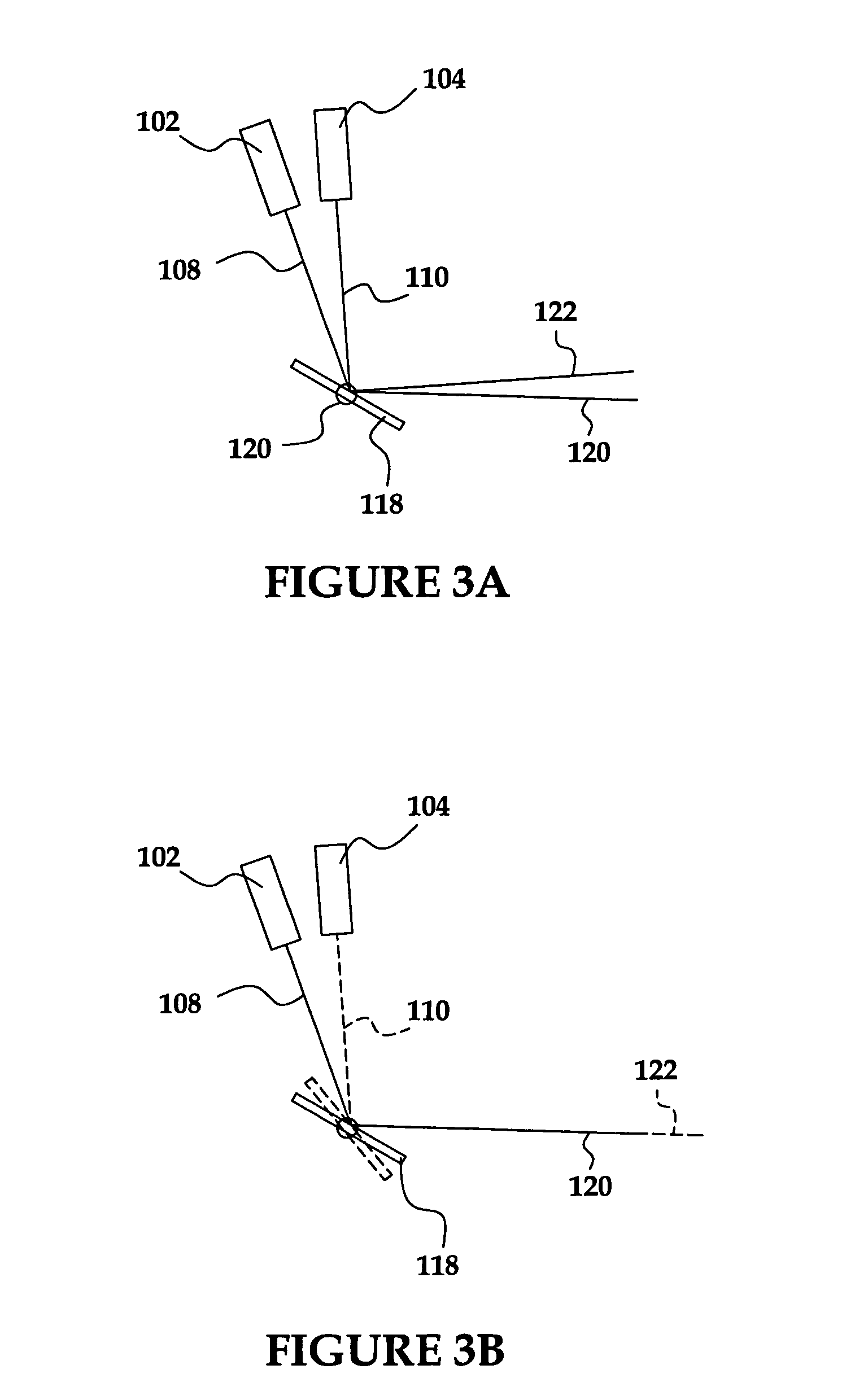
Wide field of view head-up display system
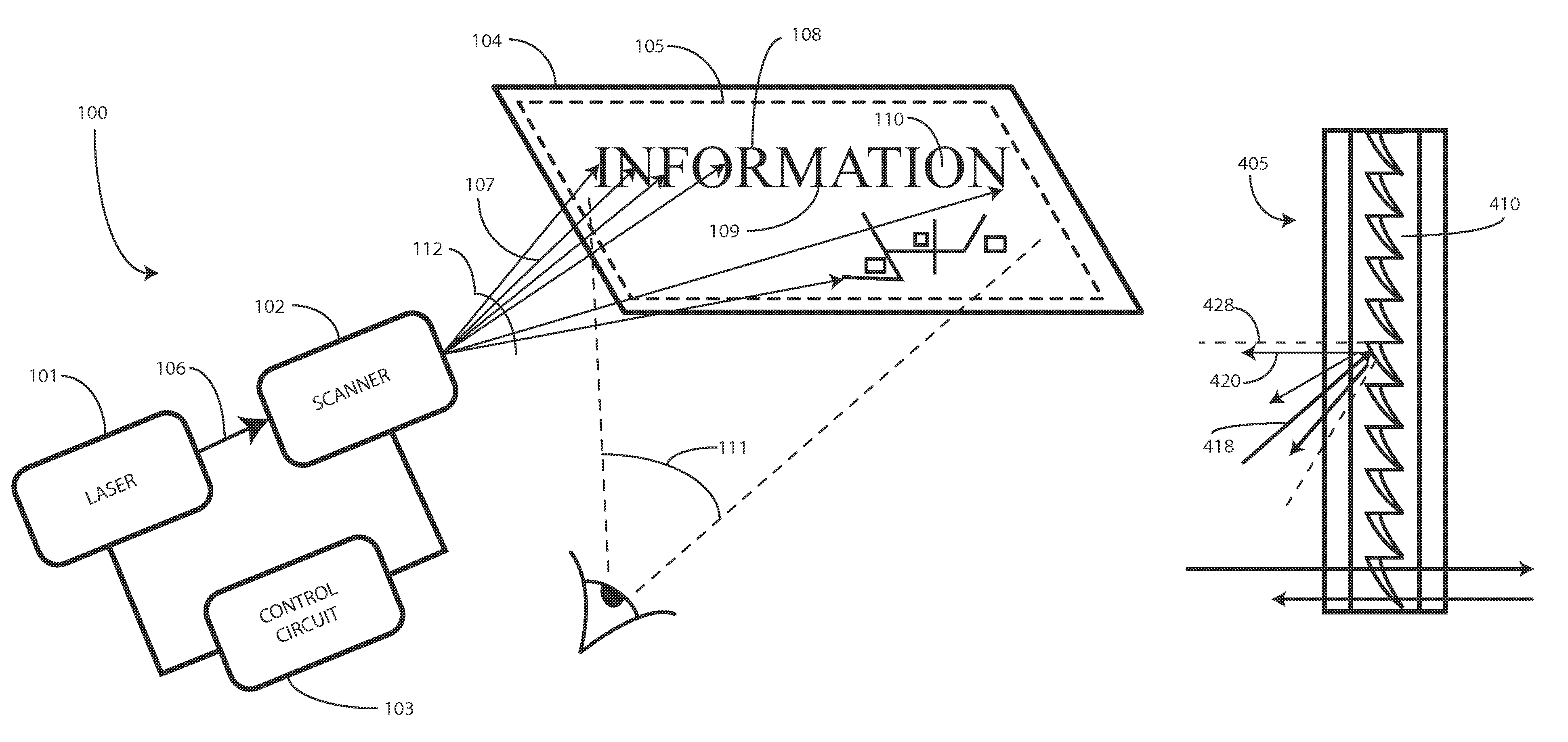
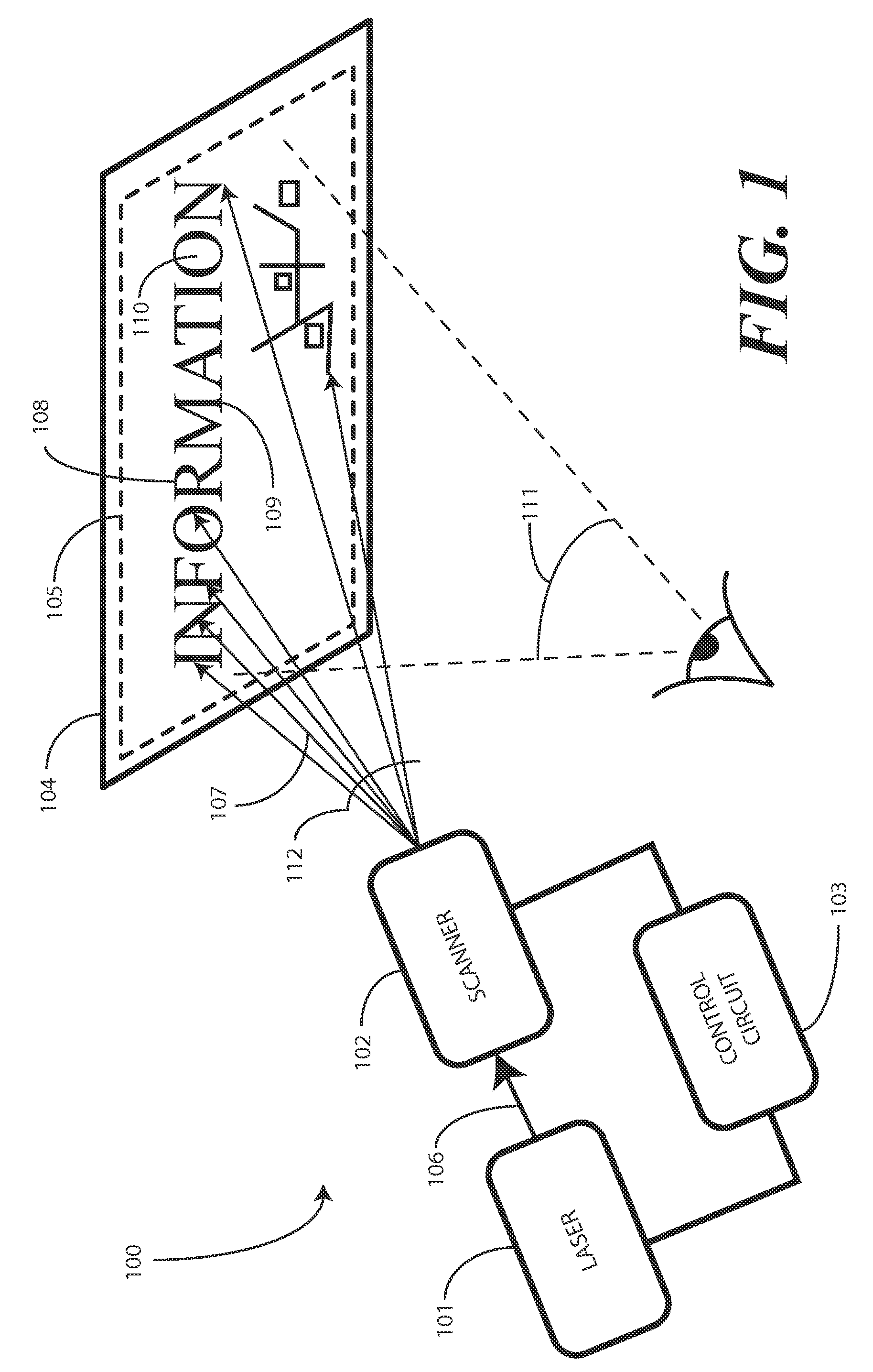
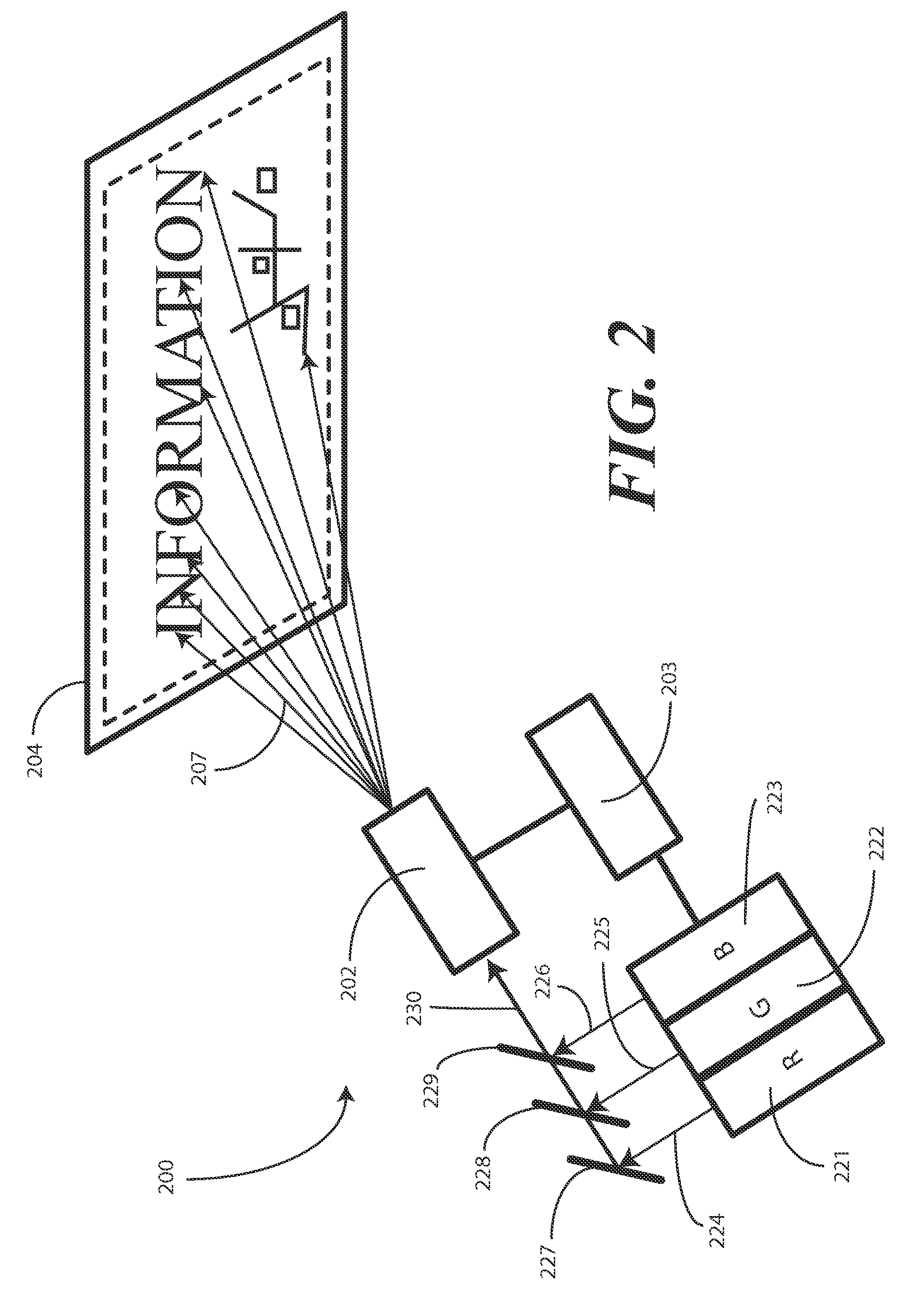
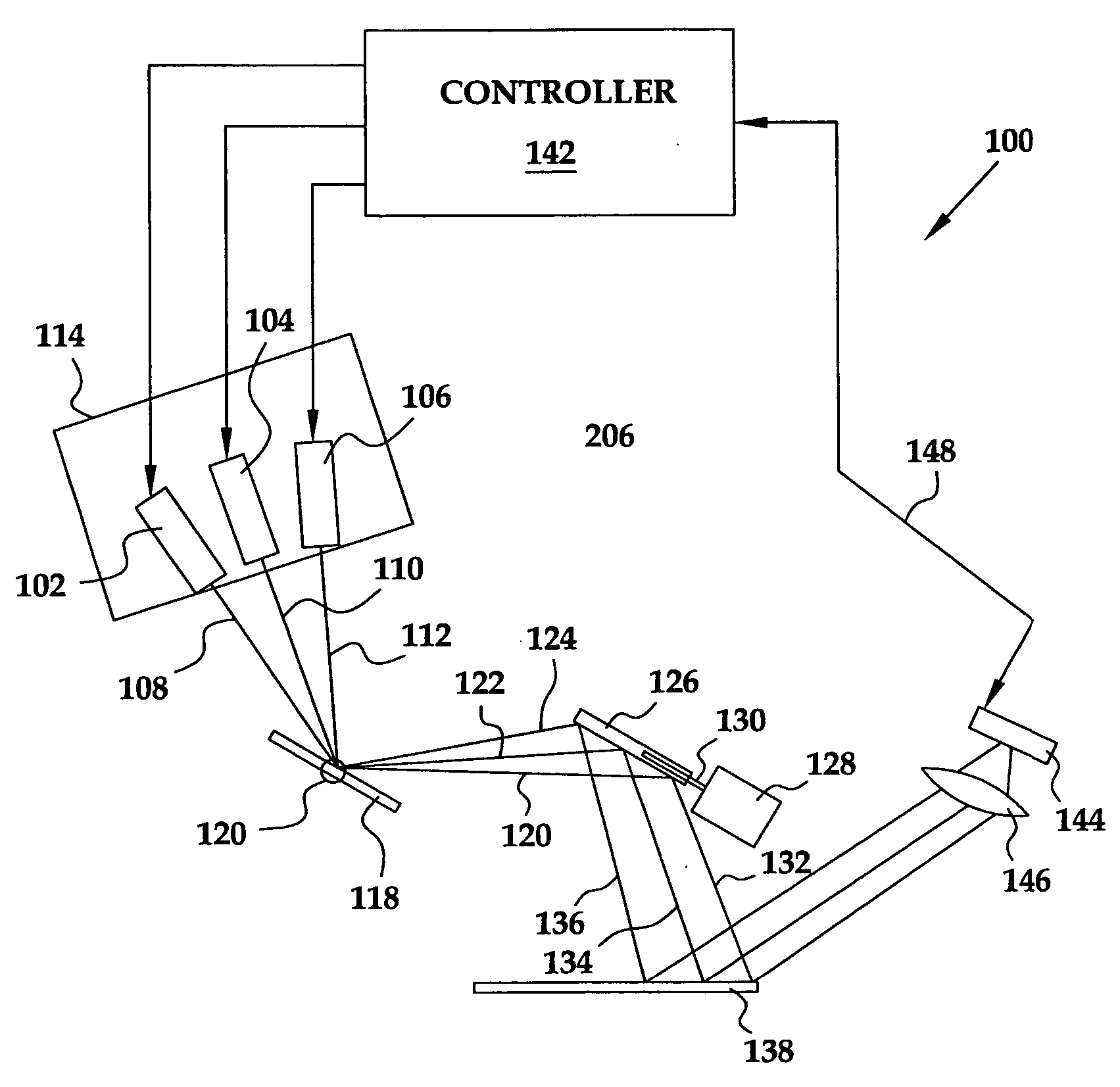
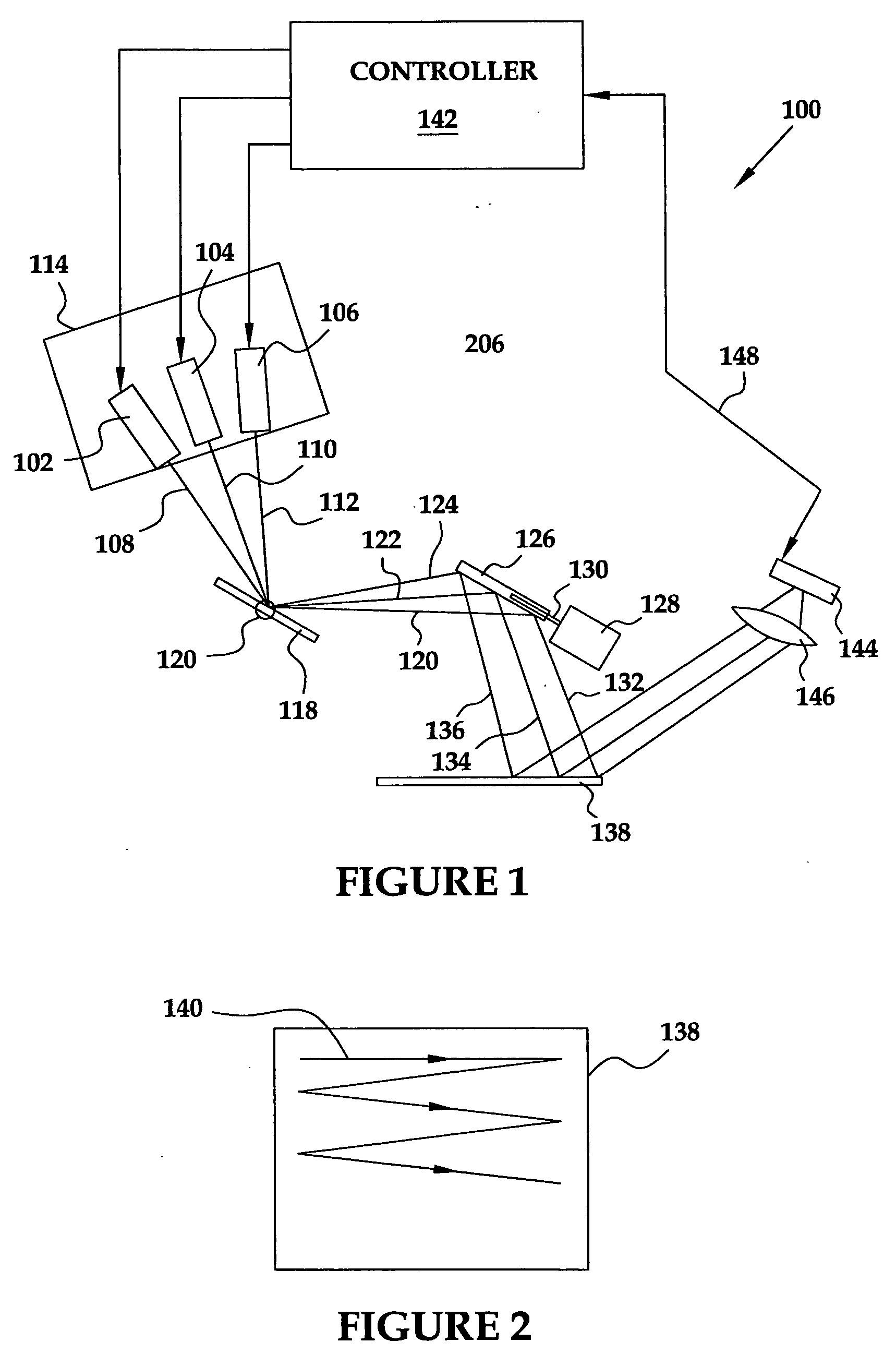
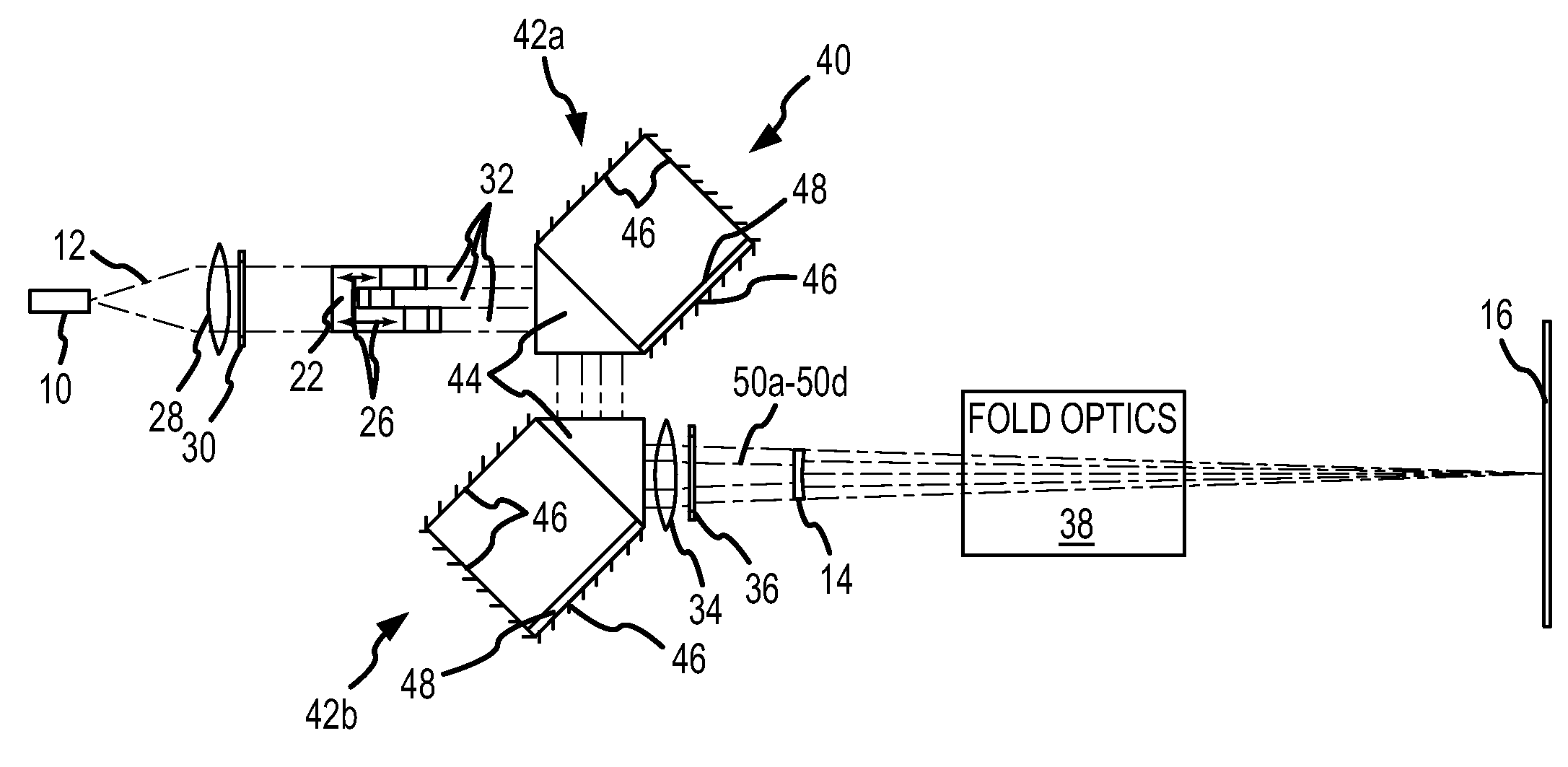
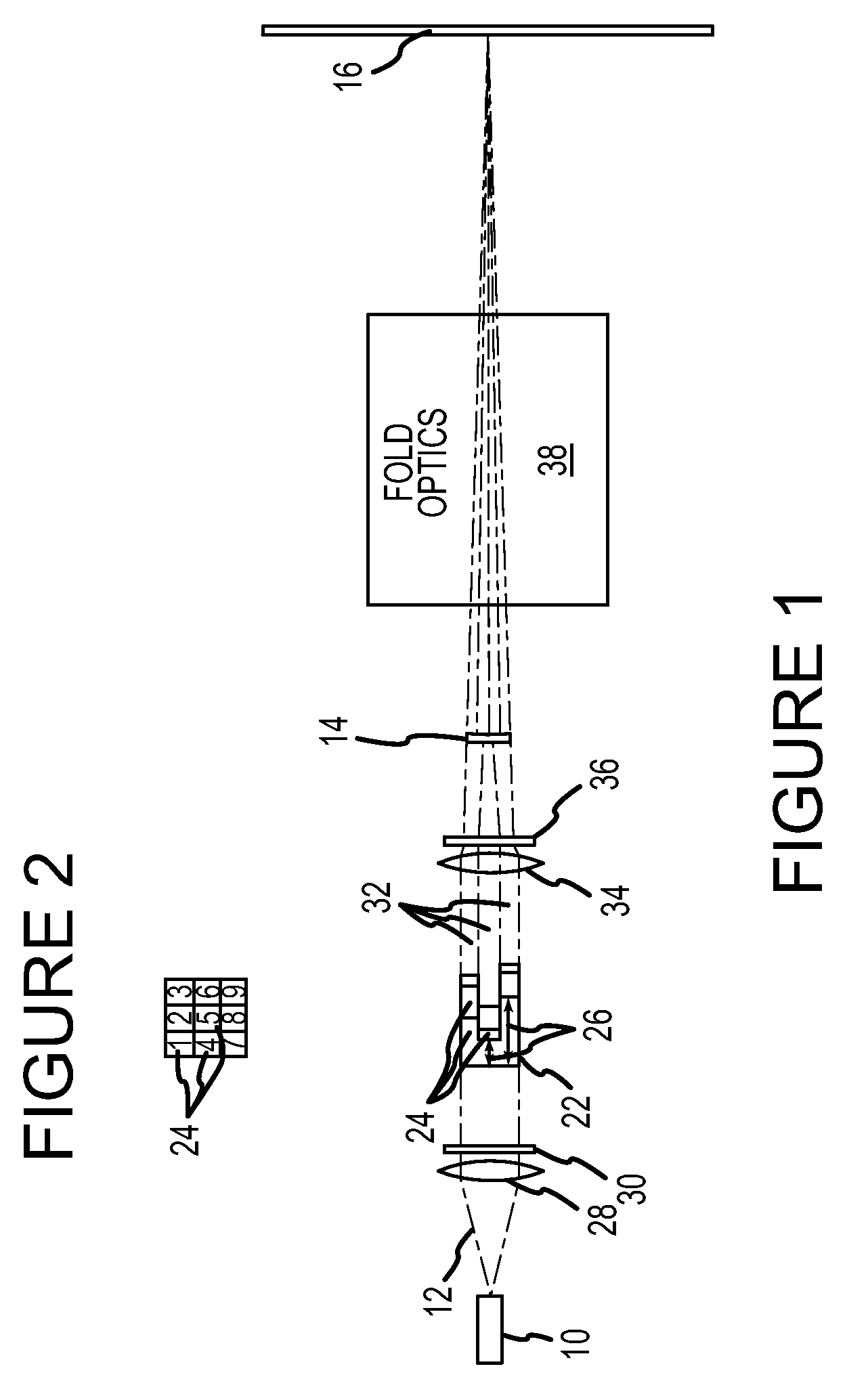
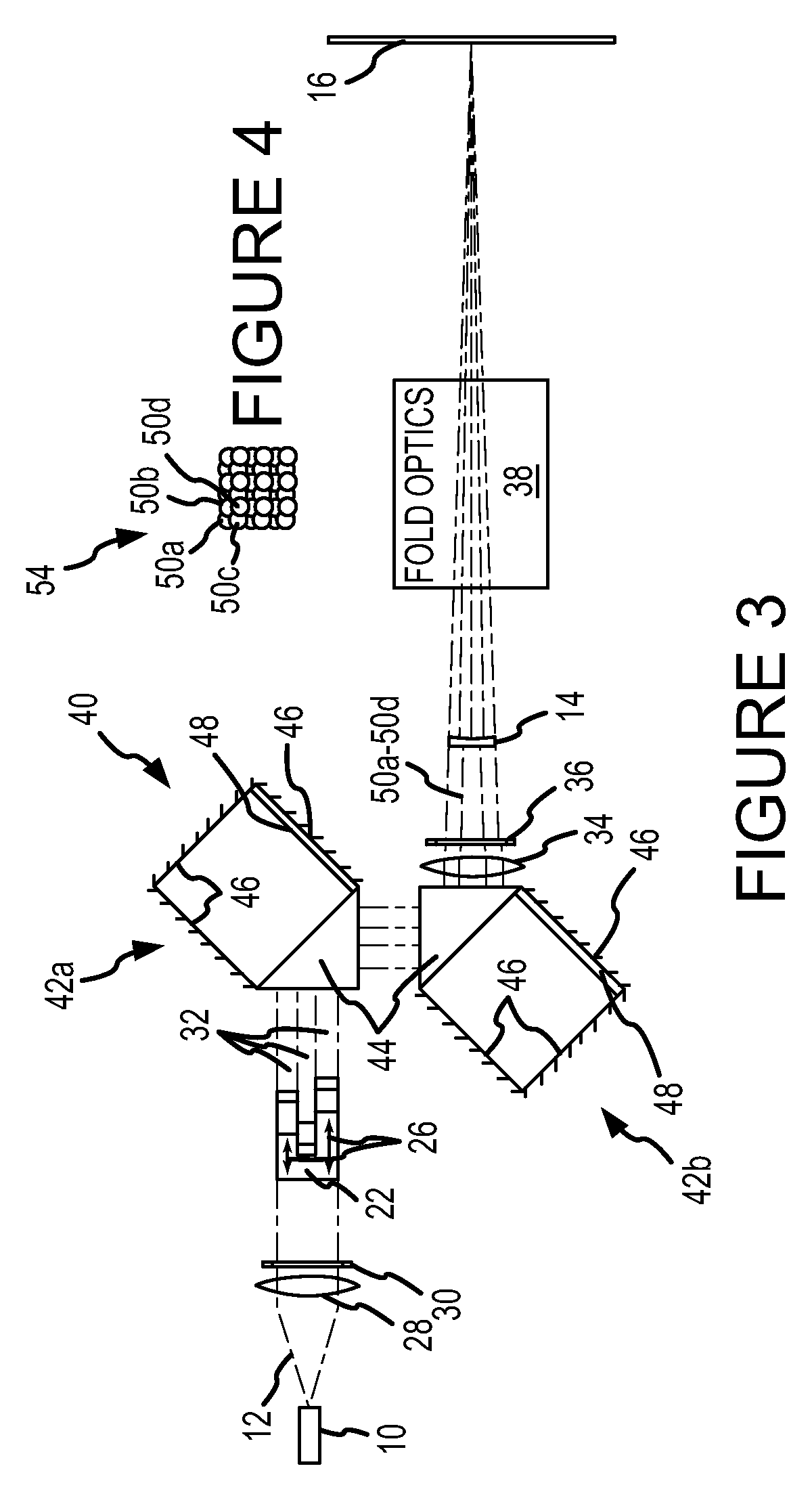
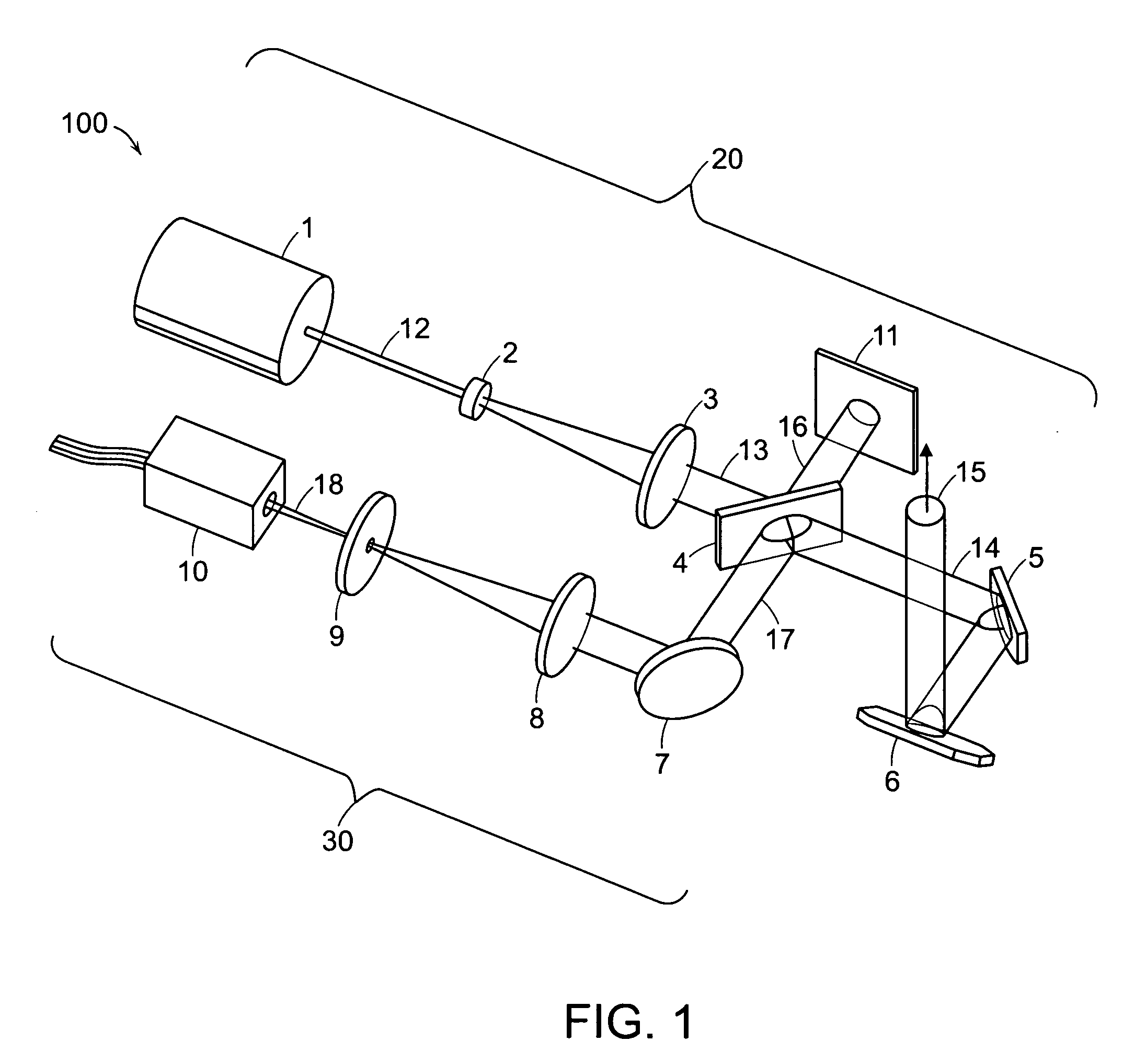
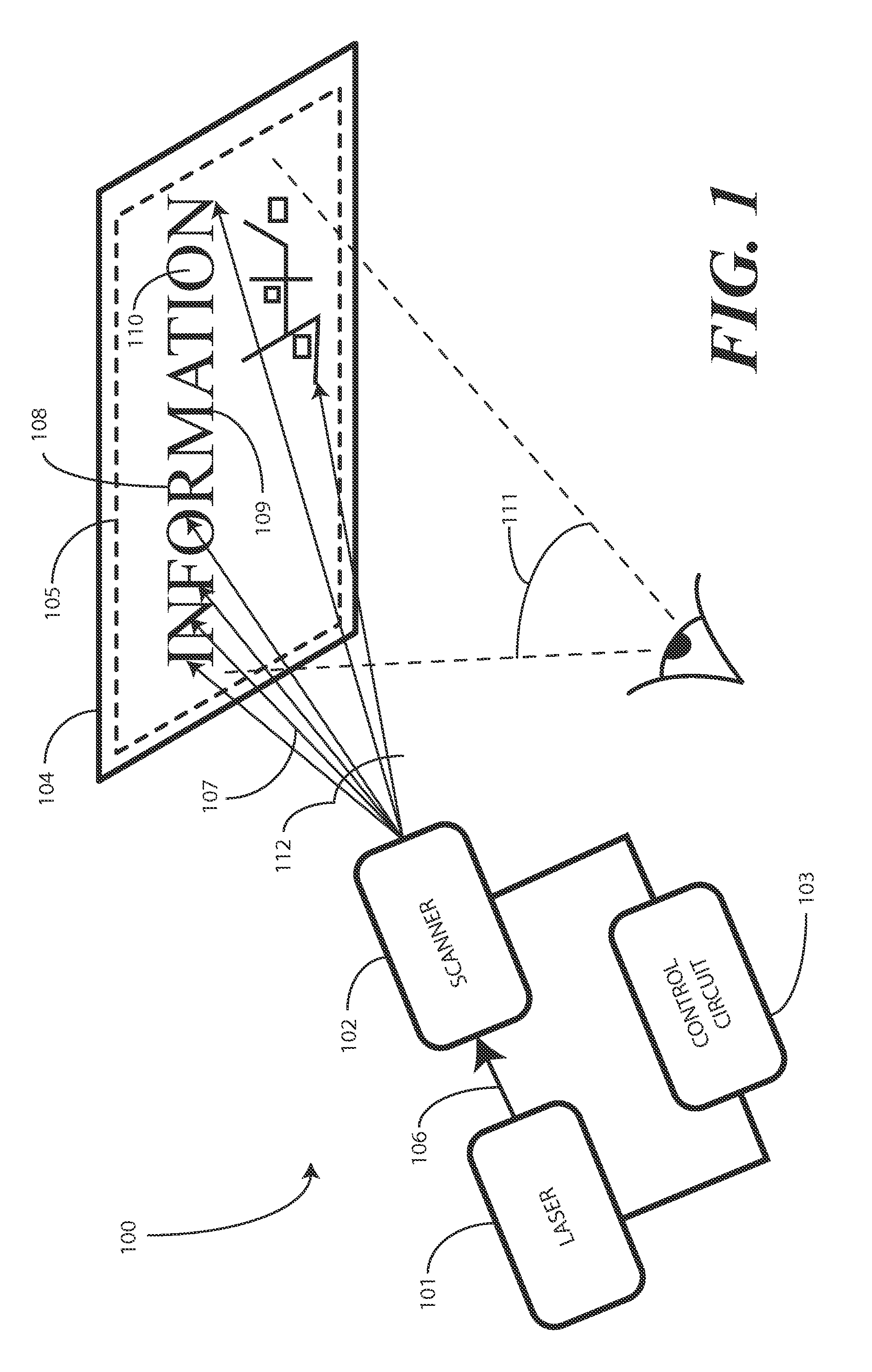
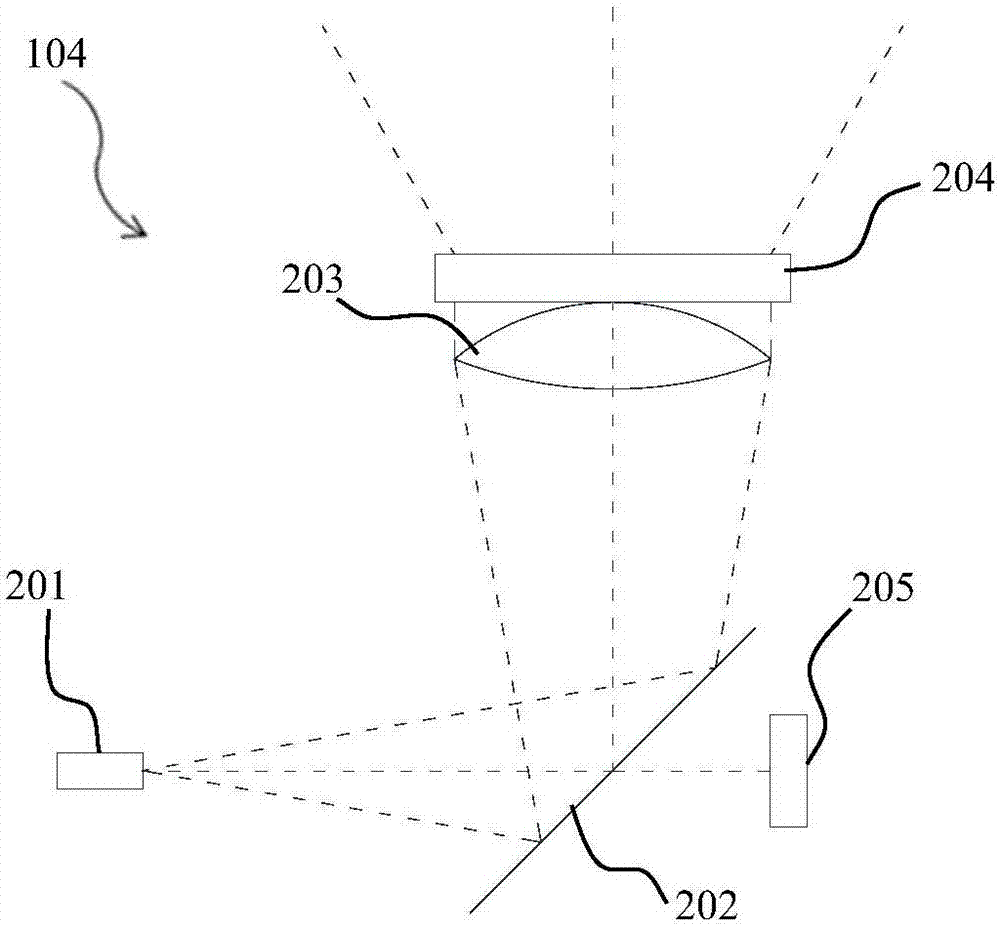
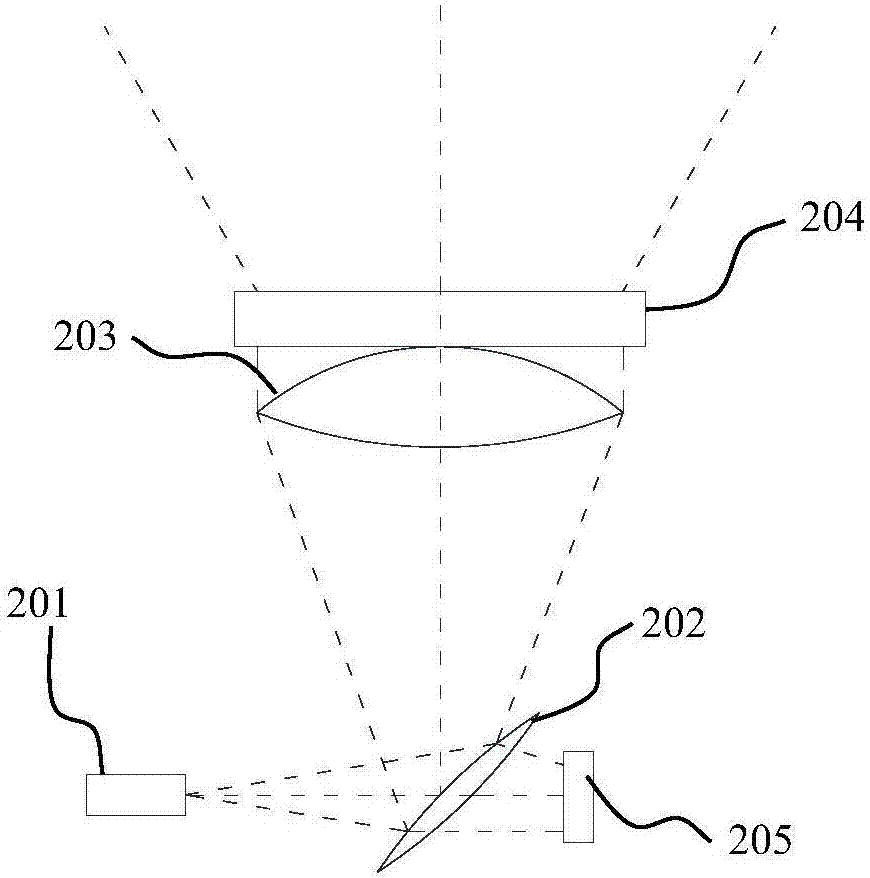
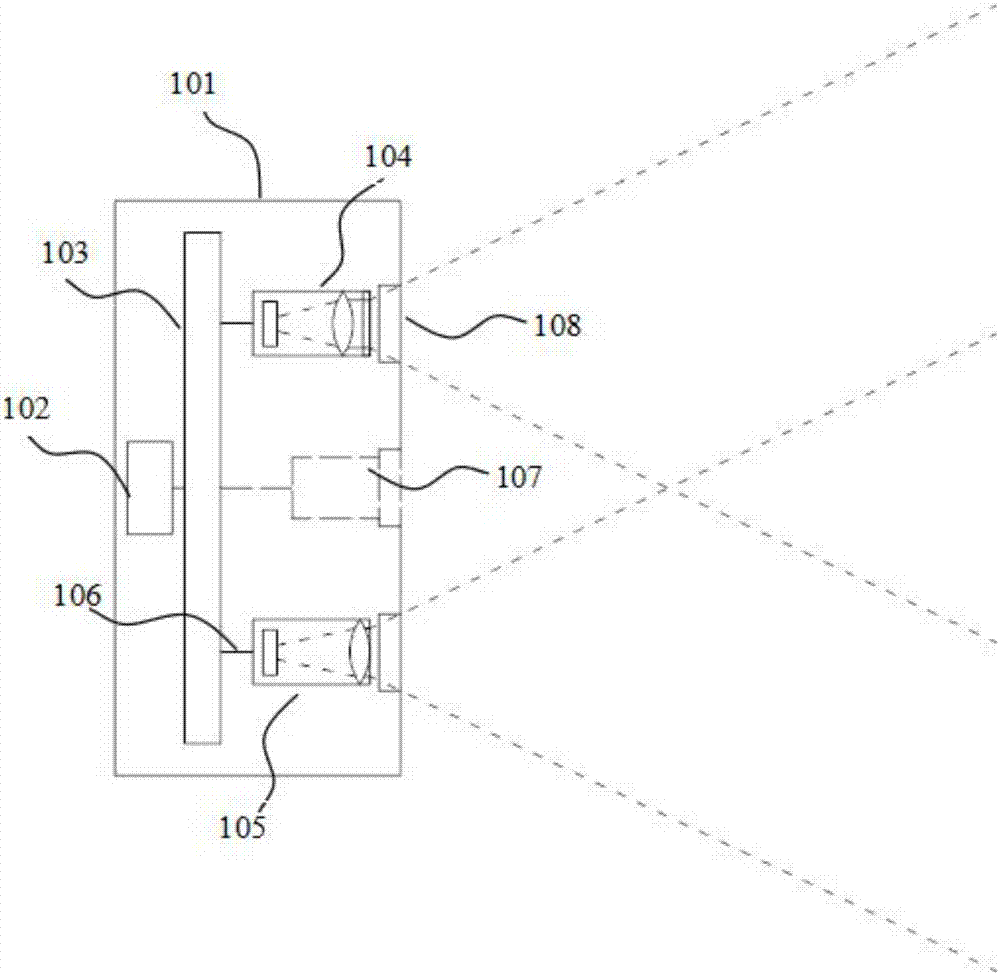
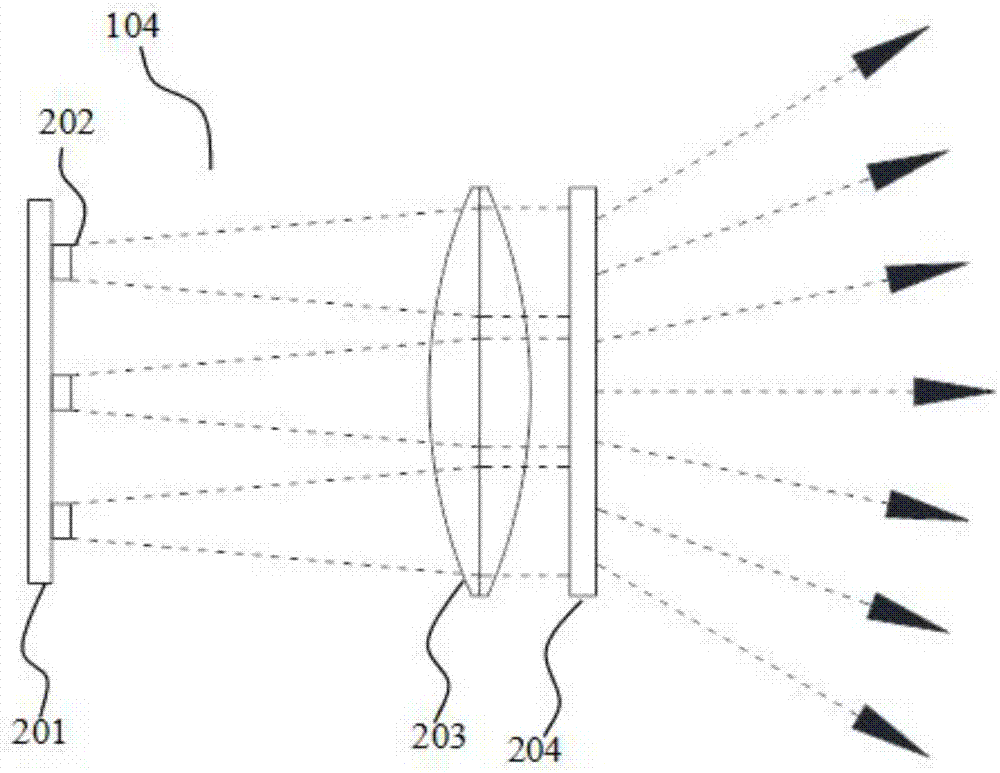
A projection system, such as a system suitable for head-up displays in automobiles, includes a laser projection source (101) and a scanner (102). Light from the laser projection source (101) is scanned across a projection surface (104), which can be a car's windshield. The projection surface (104) includes a buried numerical aperture expander (105) capable of reflecting some light and transmitting other light. The system may also include an image projection source (551) capable of presenting high-resolution images on a sub-region (552) of the projection surface (604) that has a optical relay (650) disposed therein.
Owner:MICROVISION
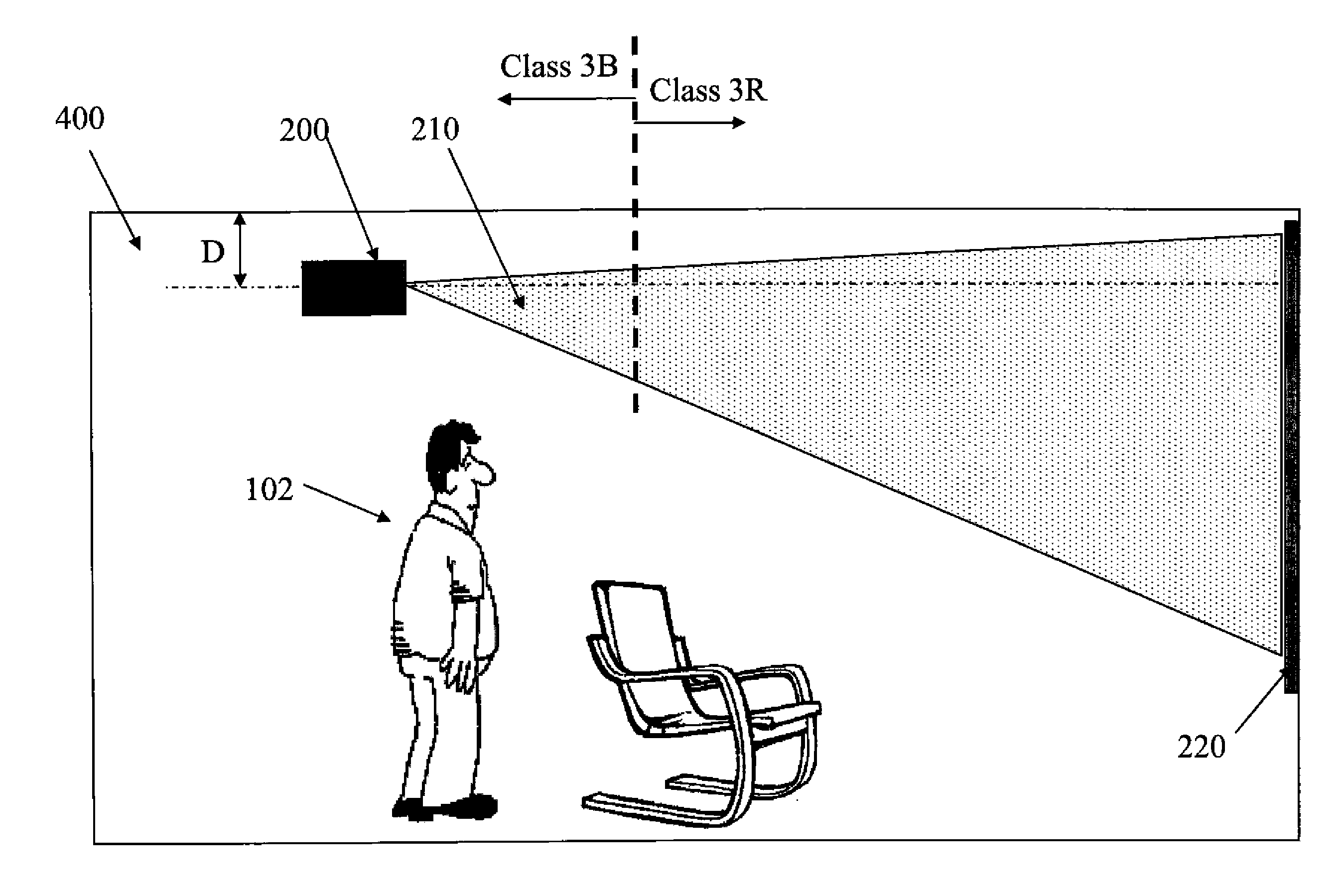
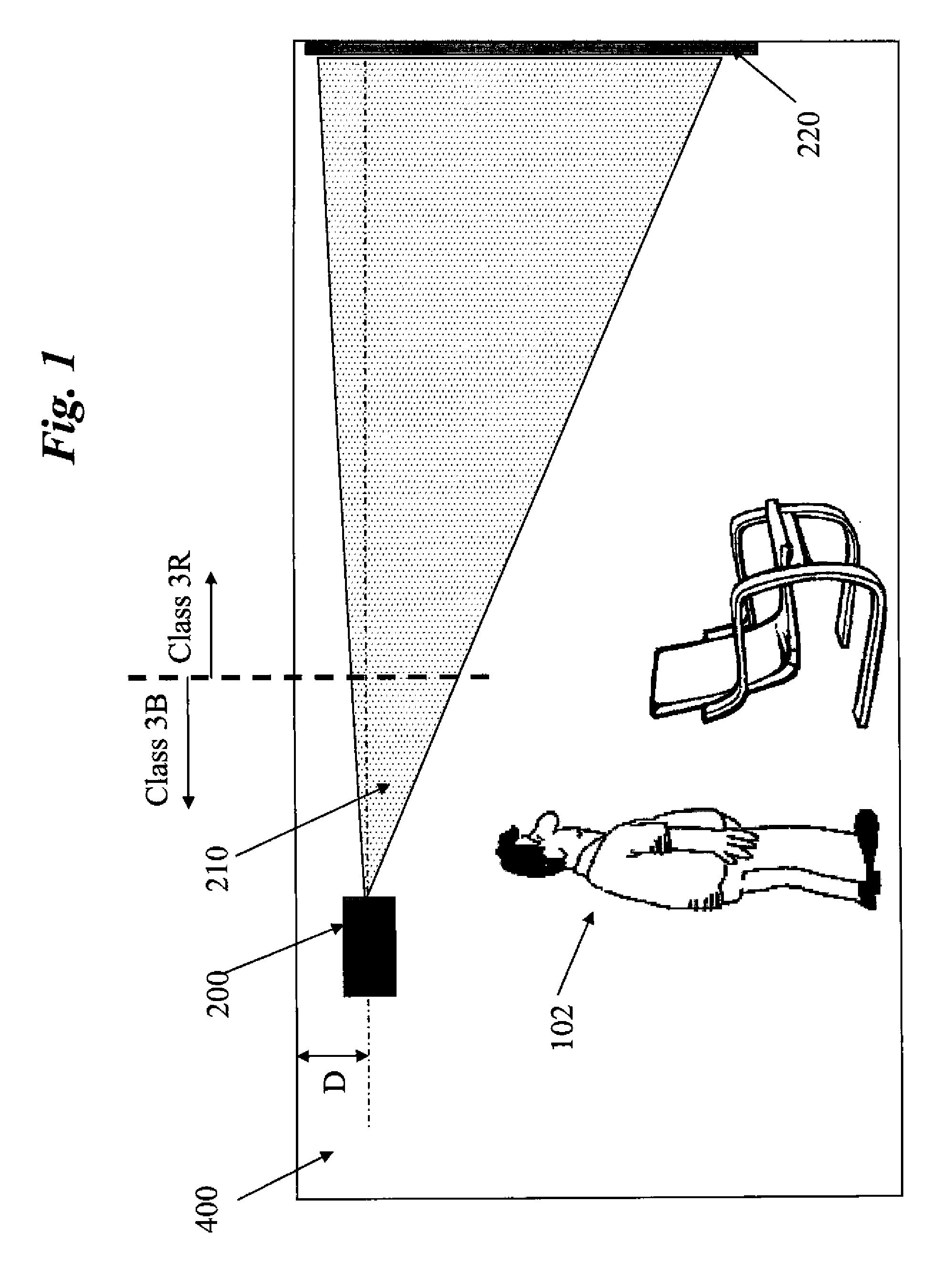
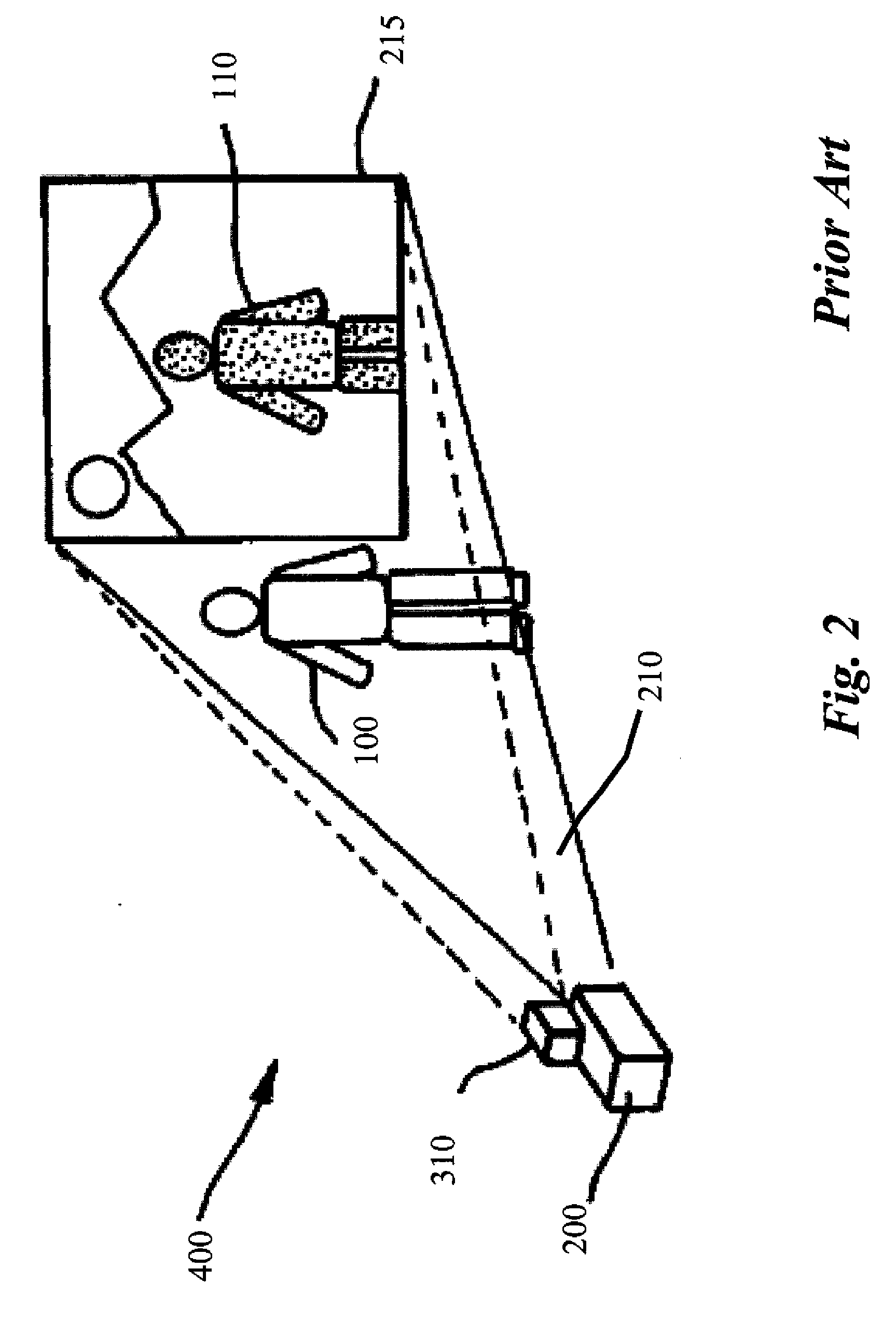
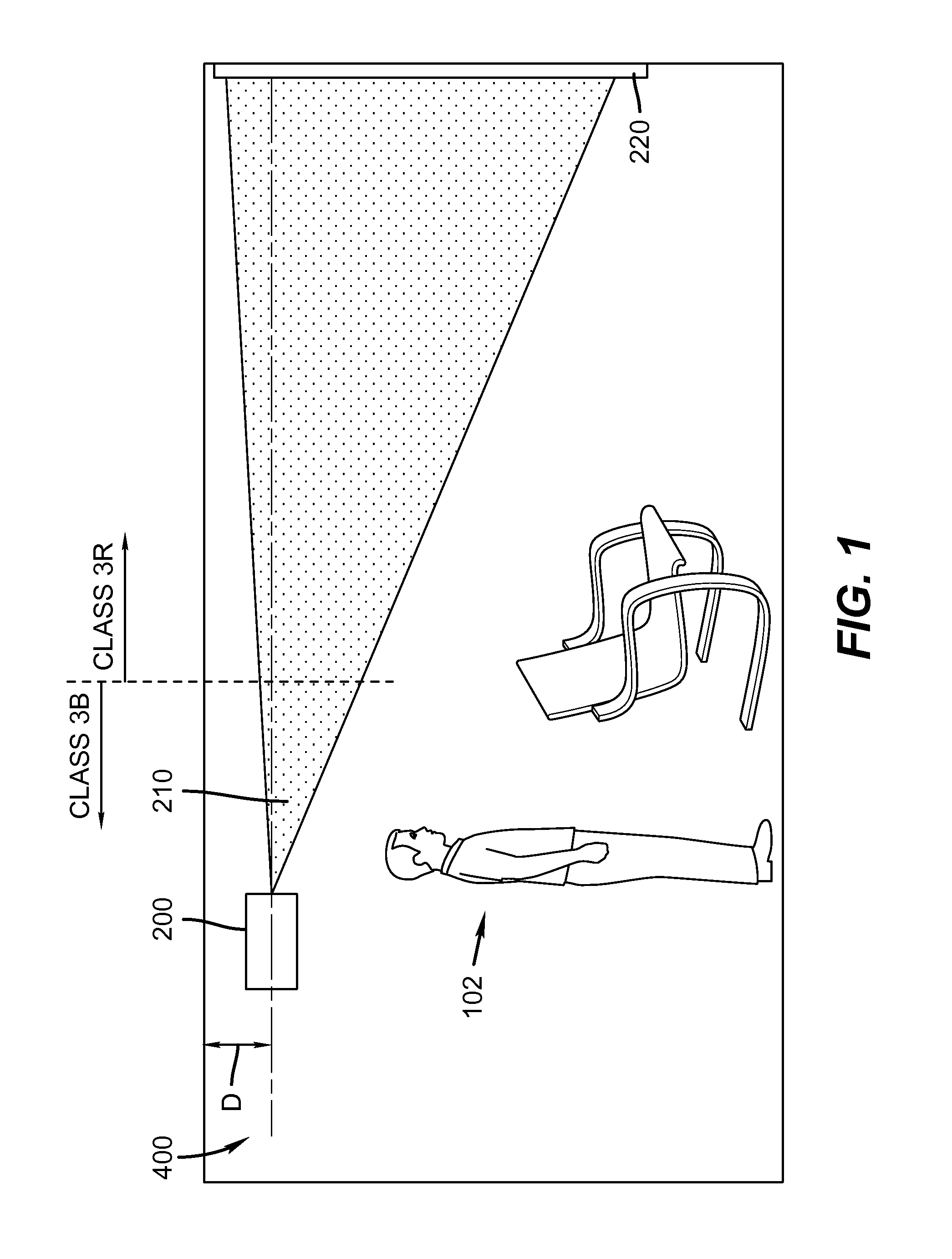
Enhanced safety during laser projection
ActiveUS20100177929A1Improved eye safetyImprove securityColor television detailsBiometric pattern recognitionEngineeringProjection system
The present invention is directed to systems and methods that provide enhanced eye safety for image projection systems. In particular, the instant invention provides enhanced eye safety for long throw laser projection systems.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
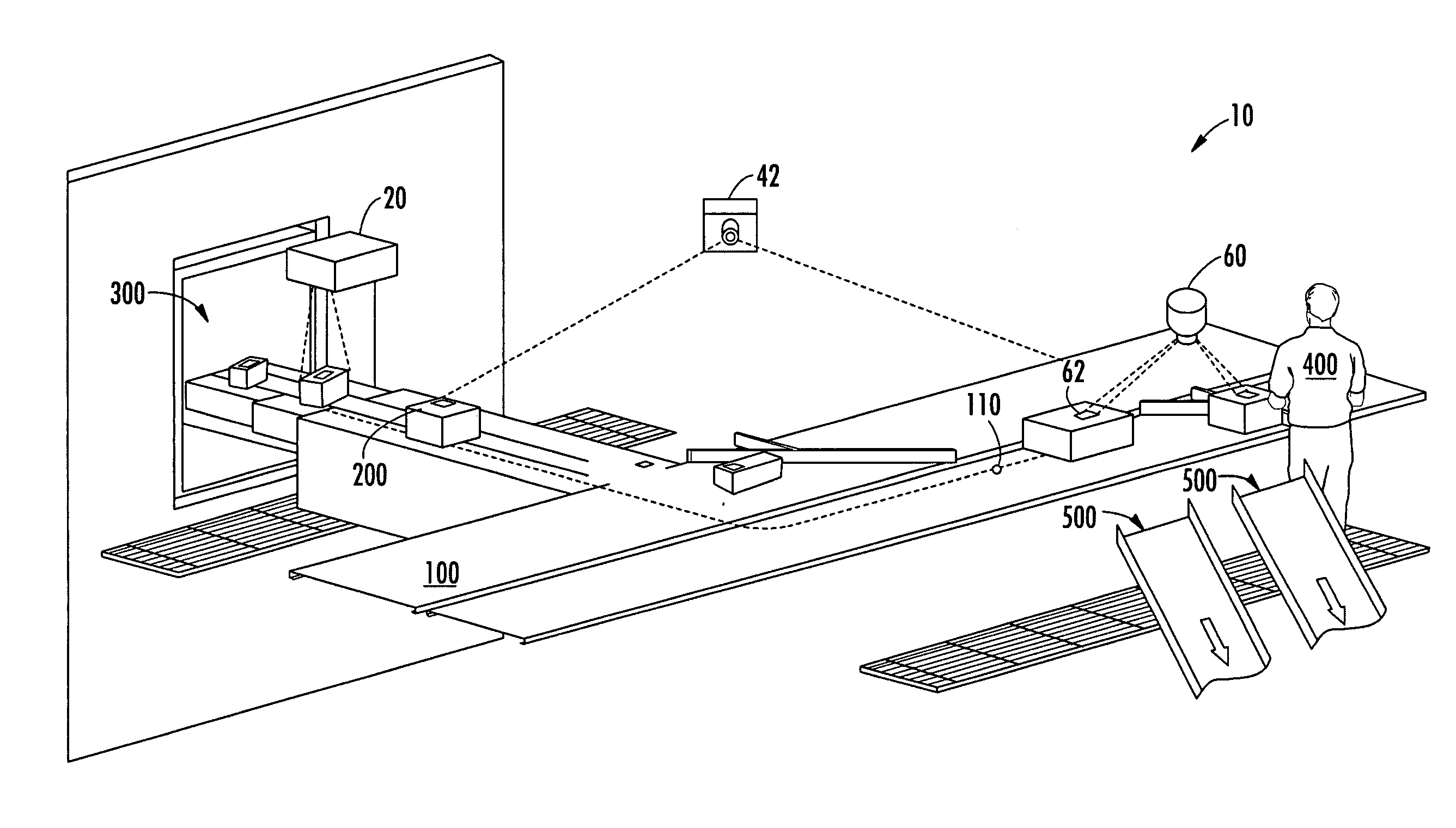
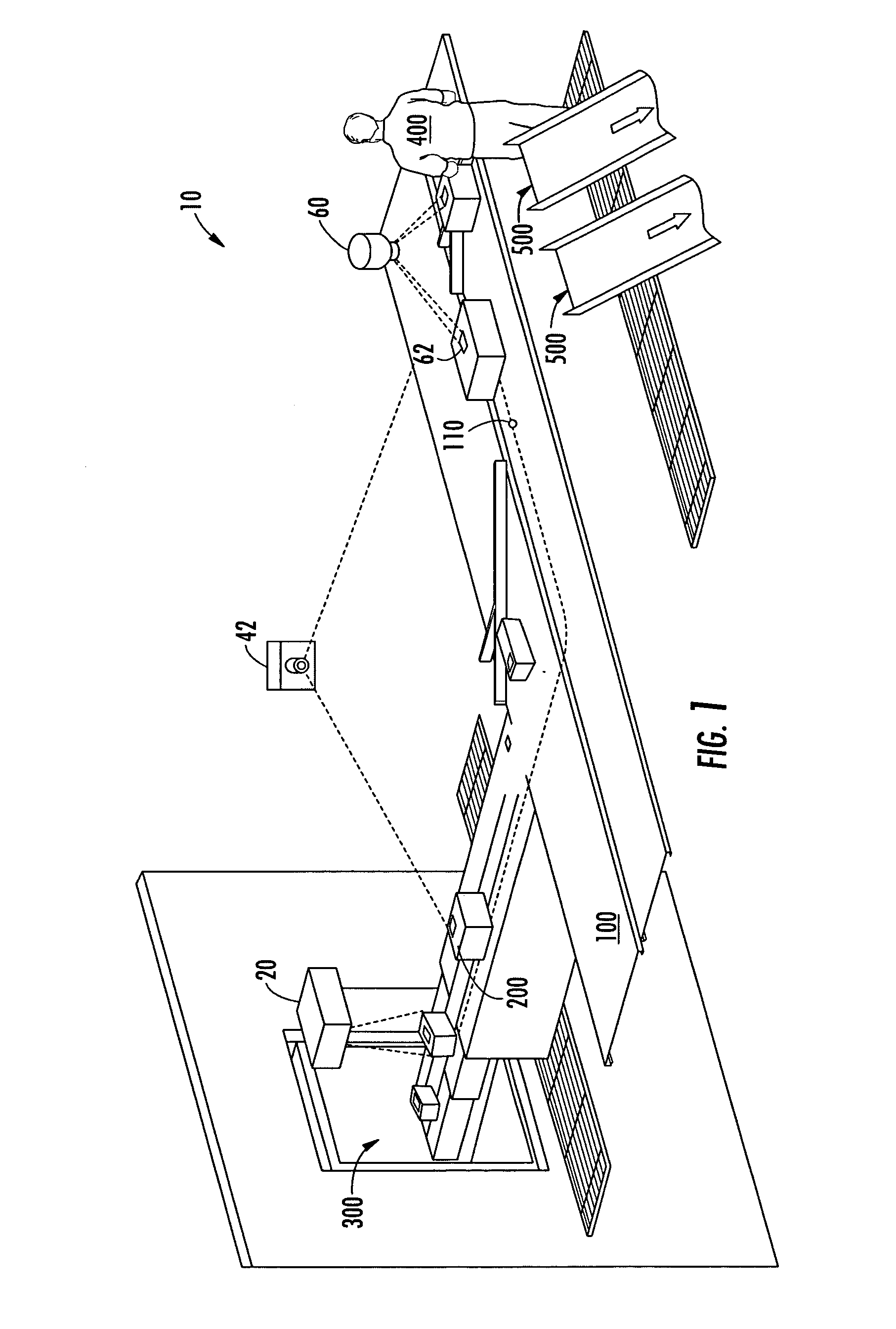
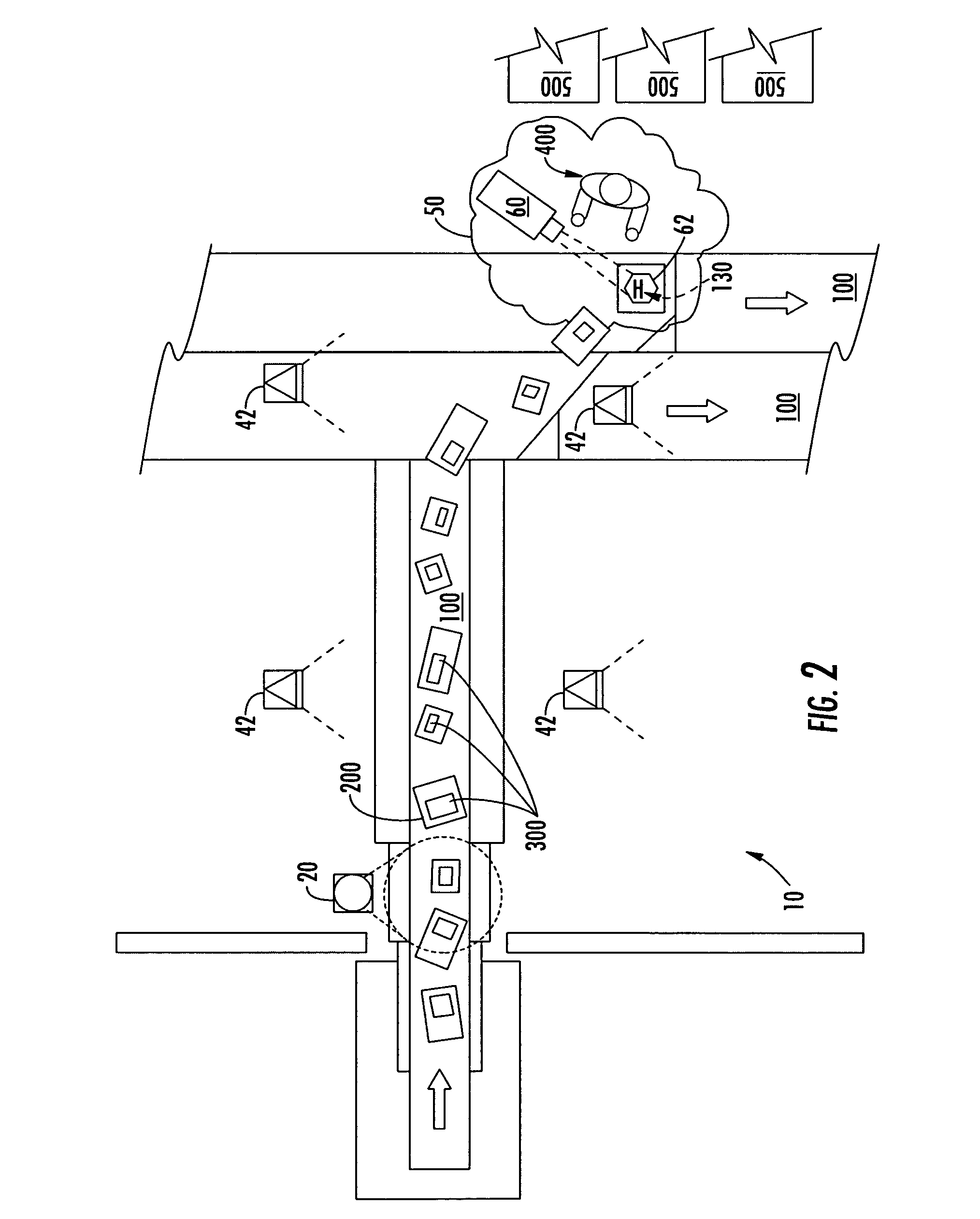
System for projecting a handling instruction onto a moving item or parcel
ActiveUS7090134B2Co-operative working arrangementsVisual presentationProcessing InstructionComputer graphics (images)
The invention includes a system for projecting a display onto an item or parcel using an acquisition device to capture indicia on each parcel, a tracking system, a controller or computer to select the display based on the indicia, and one or more display projectors. In one embodiment the display includes or connotes a handling instruction. The system in one embodiment includes a laser projection system to paint the selected display directly onto a selected exterior surface of the corresponding parcel, for multiple parcels simultaneously. The system may be configured to move each display in order follow each moving parcel so that each display remains legible to a viewer in a display zone where handling takes place.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
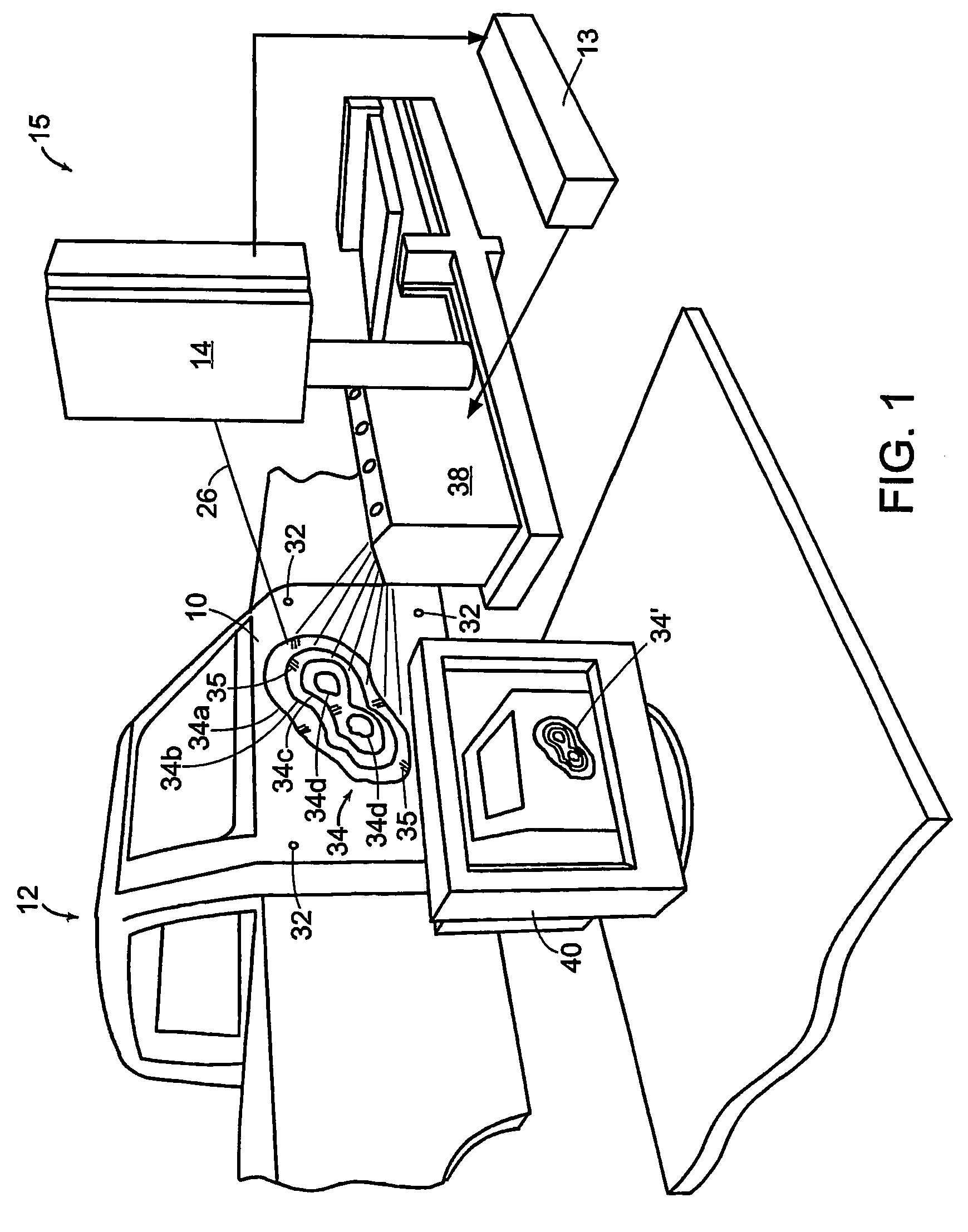
Method and system for visualizing surface errors
ActiveUS7372558B2Shorten the timeProjectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringLaser projection
A method and system for visualizing deviations on an actual surface 10, 30 from a nominal, or designed, surface 28 utilizes a system and method for mapping the spatial (e.g. x, y and z) coordinates of the actual surface 10, 30 into a computer 13, comparing the mapped actual surface to the nominal surface 28 to produce a three-dimensional distribution of deviation values (D), processing this distribution into a topographical pattern 34 of multiple contours or areas 34a . . . 34n, each contour or area having the same, or generally the same, deviation value (D), and optically projecting this topographical pattern 34 onto the actual surface 10, 30 in registry with the initial surface mapping to provide a display of the surface deviations (D) directly on the actual surface 10, 30. The deviations are measured along a direction D normal to the actual surface so that the three-dimensional distribution is given in x, y, D coordinates. The optical projection is preferably a laser projection 38. The mapping and projection onto the actual surface 10, 30 are made, and coordinated with one another, with respect to three reference points 32 on the surface 10, 30.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
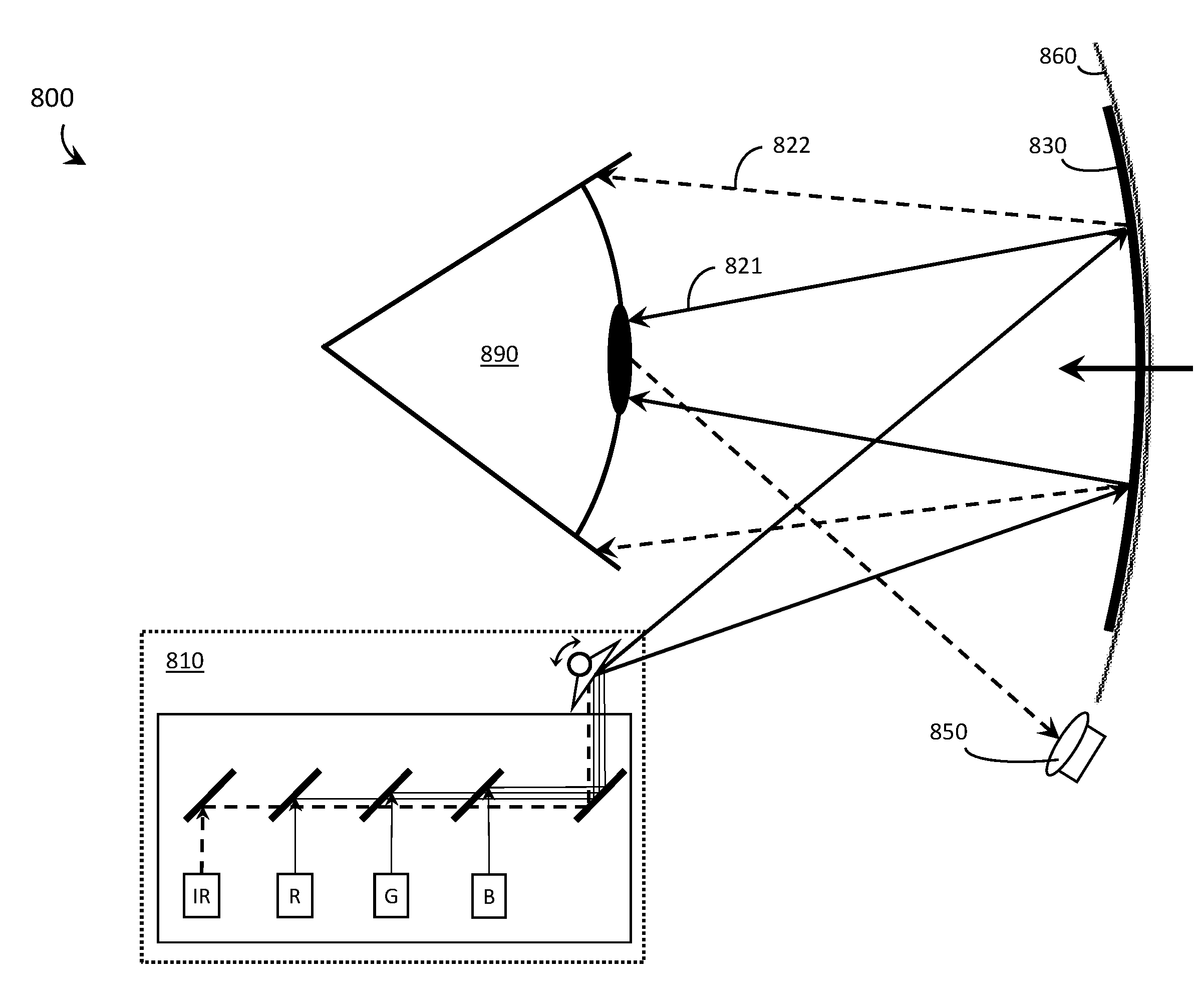
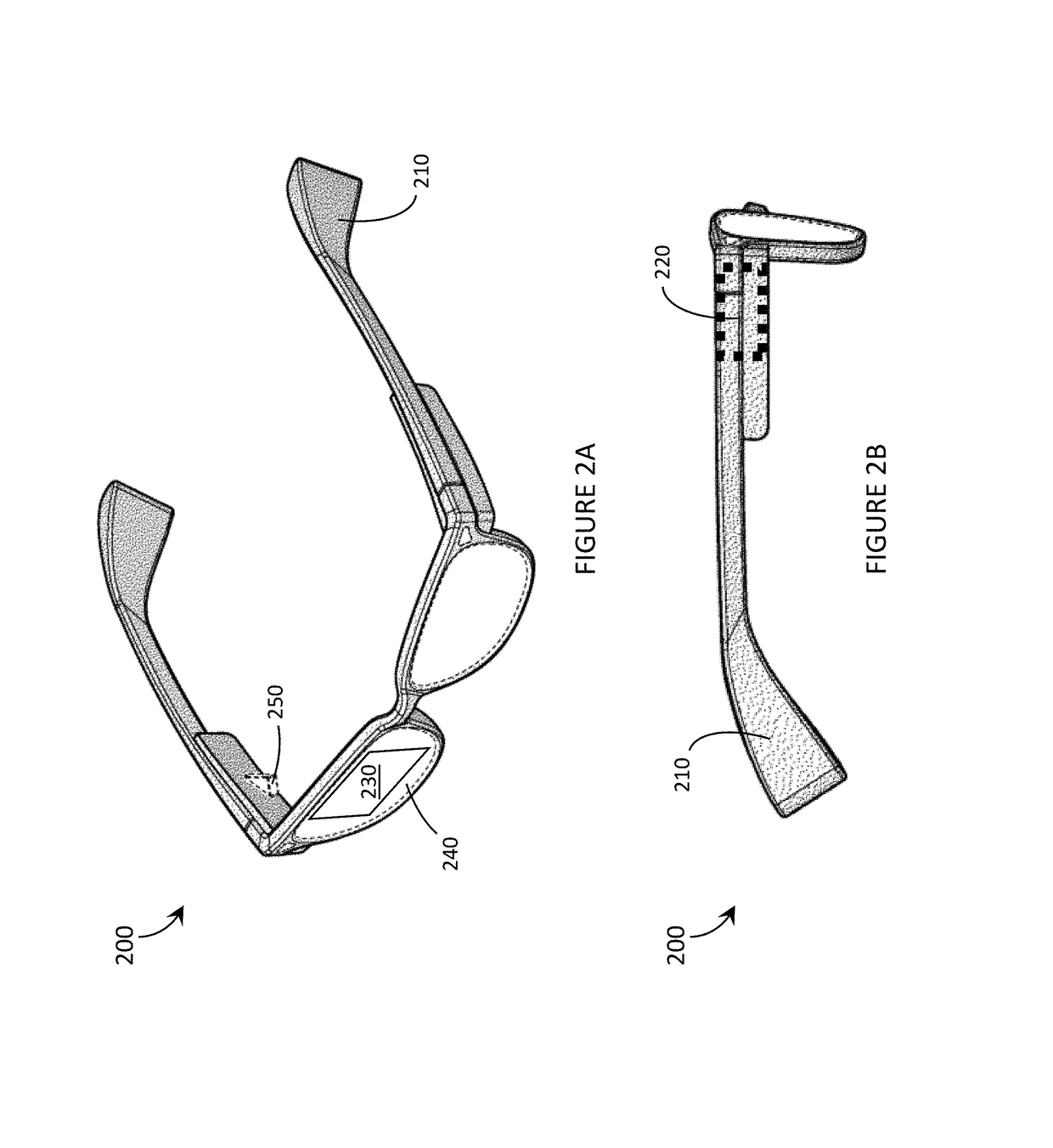
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking and scanning laser projection in wearable heads-up displays
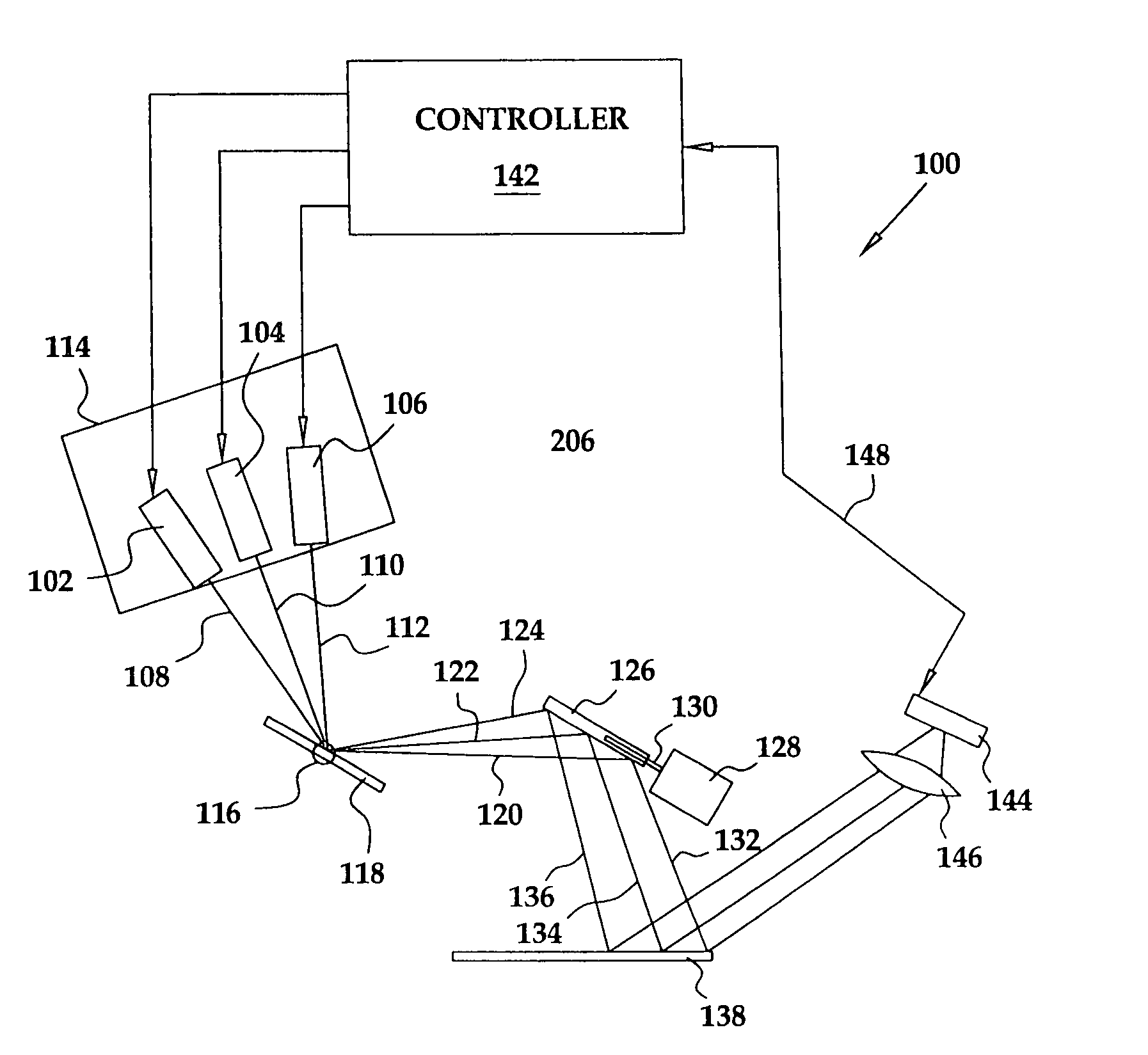
ActiveUS20160349514A1Picture reproducers using projection devicesInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayPhotodetector
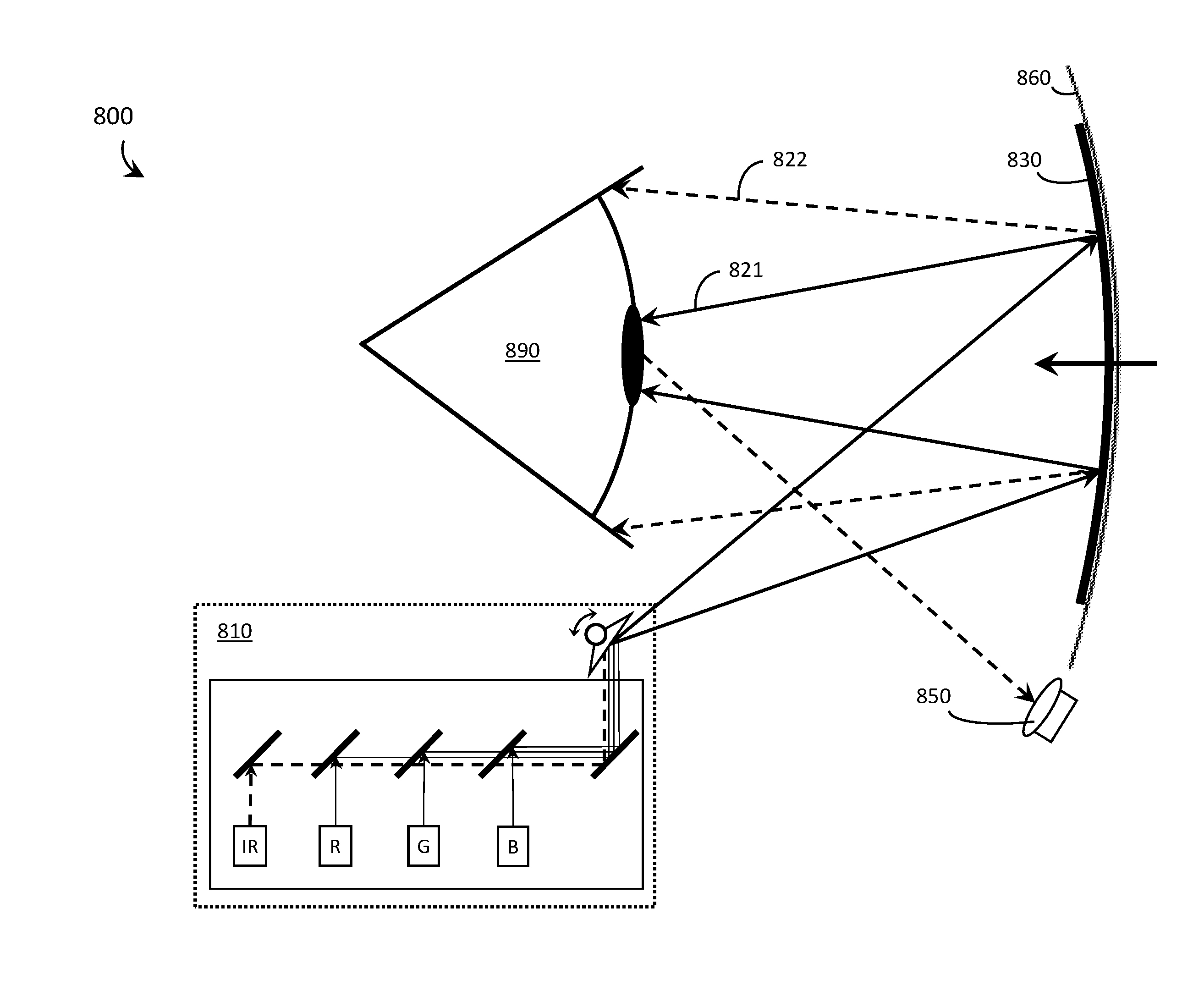
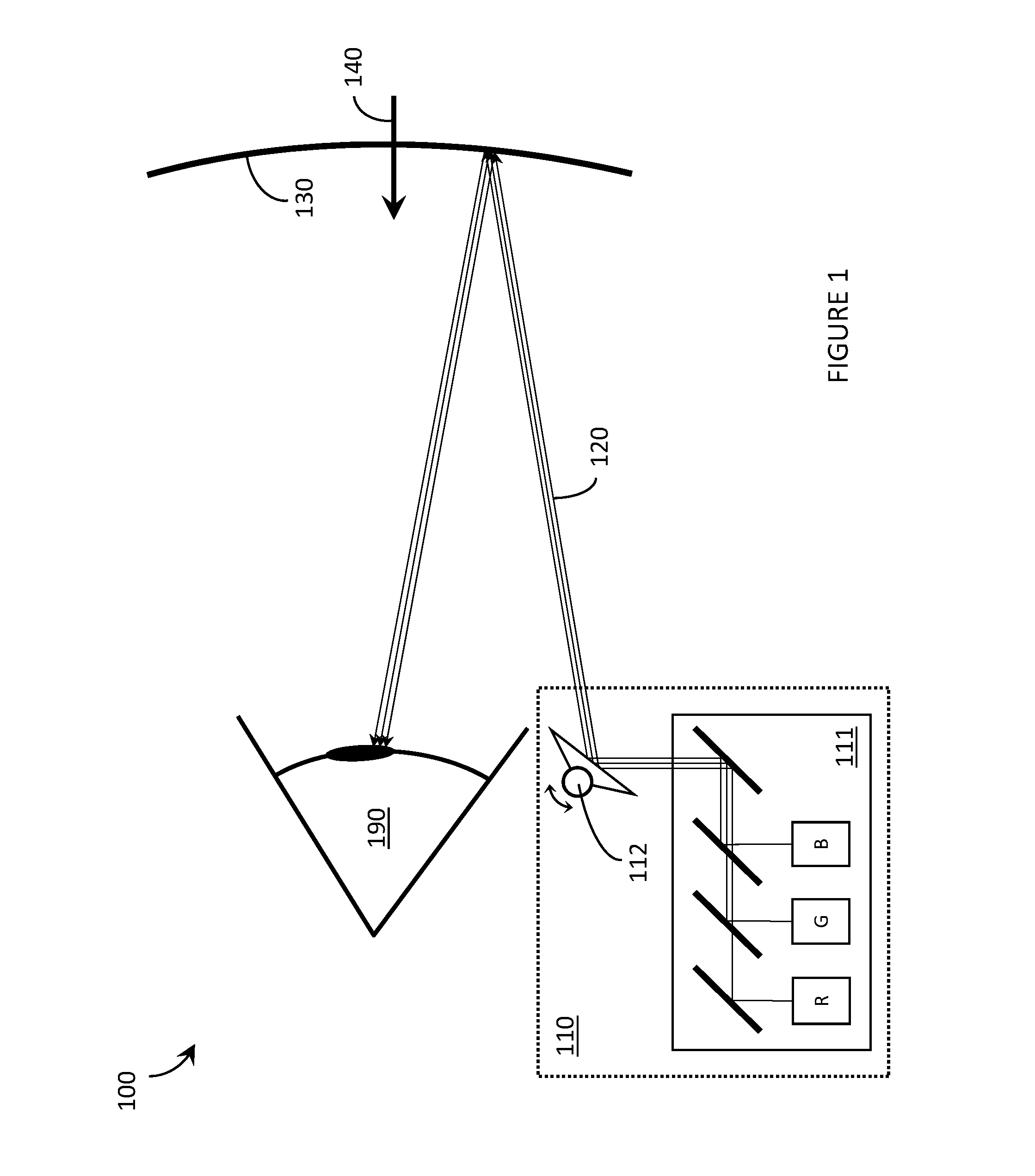
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking capability into scanning laser projector (“SLP”)-based wearable heads-up displays are described. An infrared laser diode is added to an RGB SLP and an infrared photodetector is aligned to detect reflections of the infrared light from features of the eye. A holographic optical element (“HOE”) may be used to combine visible light, infrared light, and environmental light into the user's “field of view.” The HOE may be heterogeneous and multiplexed to apply positive optical power to the visible light and zero or negative optical power to the infrared light.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking and scanning laser projection in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160349516A1Color television detailsInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayMultiplexing
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking capability into scanning laser projector (“SLP”)-based wearable heads-up displays are described. An infrared laser diode is added to an RGB SLP and an infrared photodetector is aligned to detect reflections of the infrared light from features of the eye. A holographic optical element (“HOE”) may be used to combine visible light, infrared light, and environmental light into the user's “field of view.” The HOE may be heterogeneous and multiplexed to apply positive optical power to the visible light and zero or negative optical power to the infrared light.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
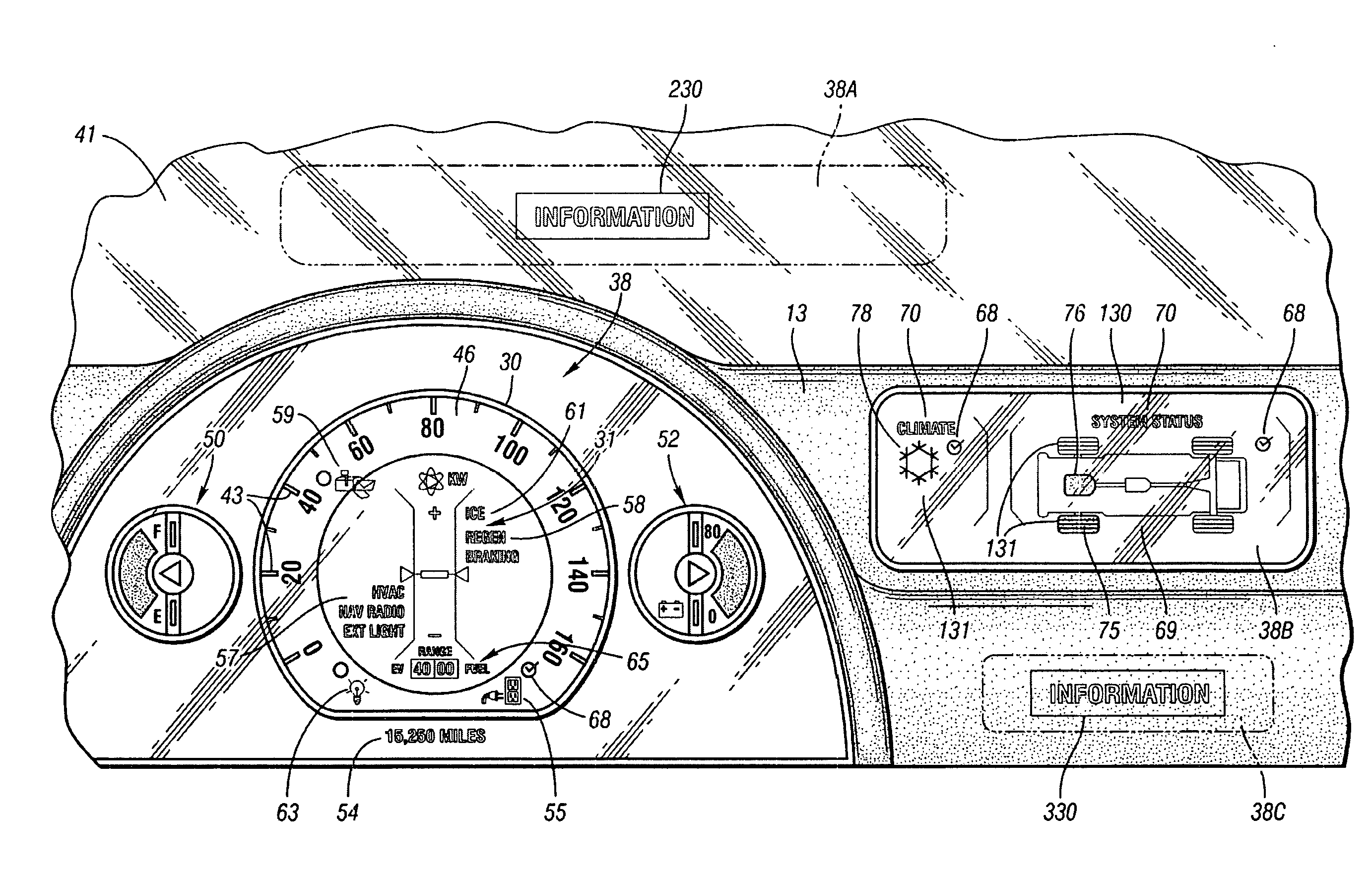
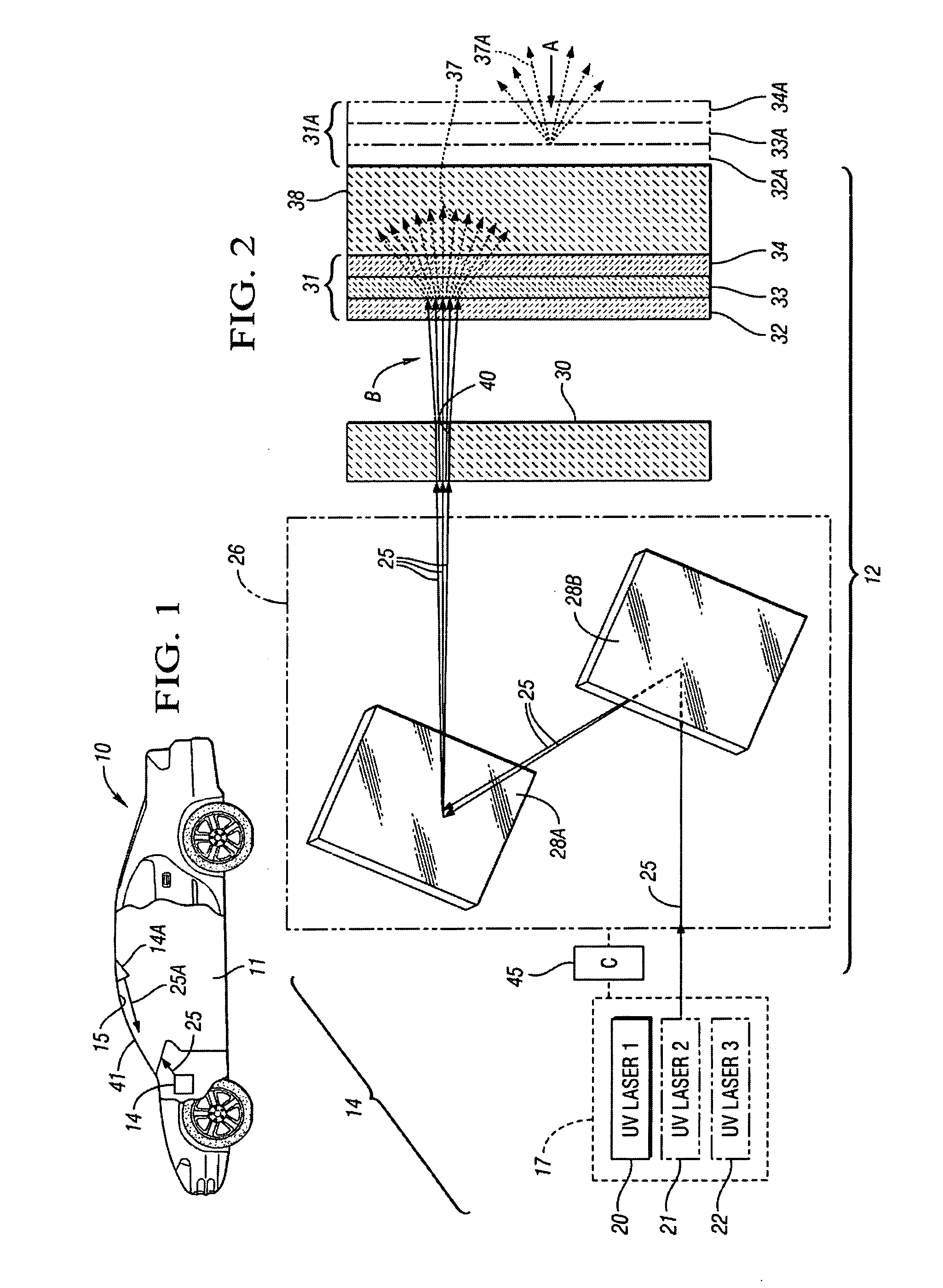
Apparatus And Method For Displaying Information Within A Vehicle Interior
An apparatus for displaying information within a vehicle interior includes a surface having a coating for emitting visible light when excited by an ultraviolet (UV) light beam, and a laser projection device (LPD) for generating and directing the UV light beam onto the coating to display information on the surface. The LPD generates one or more UV laser beams, and the coating has one or more light-emitting layers each excitable by a different UV wavelength. Each layer emits a different color of light when excited. The surface is a transparent windshield or lens, or an opaque surface. A method for displaying information within a vehicle interior includes applying a light-emitting coating to a surface in at least one layer, and generating and projecting a UV light beam onto the coating to present information in at least as many colors as there are layers.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors
ActiveUS20170299956A1Reduce disagreementSemiconductor laser arrangementsNon-optical adjunctsHead-up displayLaser light
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors are described. A laser projector includes N≧1 laser diodes, each of which emits laser light having a divergence. Each laser diode is paired with a respective primary or collimation lens to at least reduce a divergence of the laser light that the laser diode produces. Downstream from the primary lens(es) in the optical path(s) of the laser light, a single dedicated secondary or convergence lens converges the laser light to a focus. By initiating the convergence of the laser light at the secondary or convergence lens as opposed to at the primary or collimation lens(es), numerous benefits that are particularly advantageous in laser projection-based wearable heads-up displays are realized.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for conserving power in a laser projection display
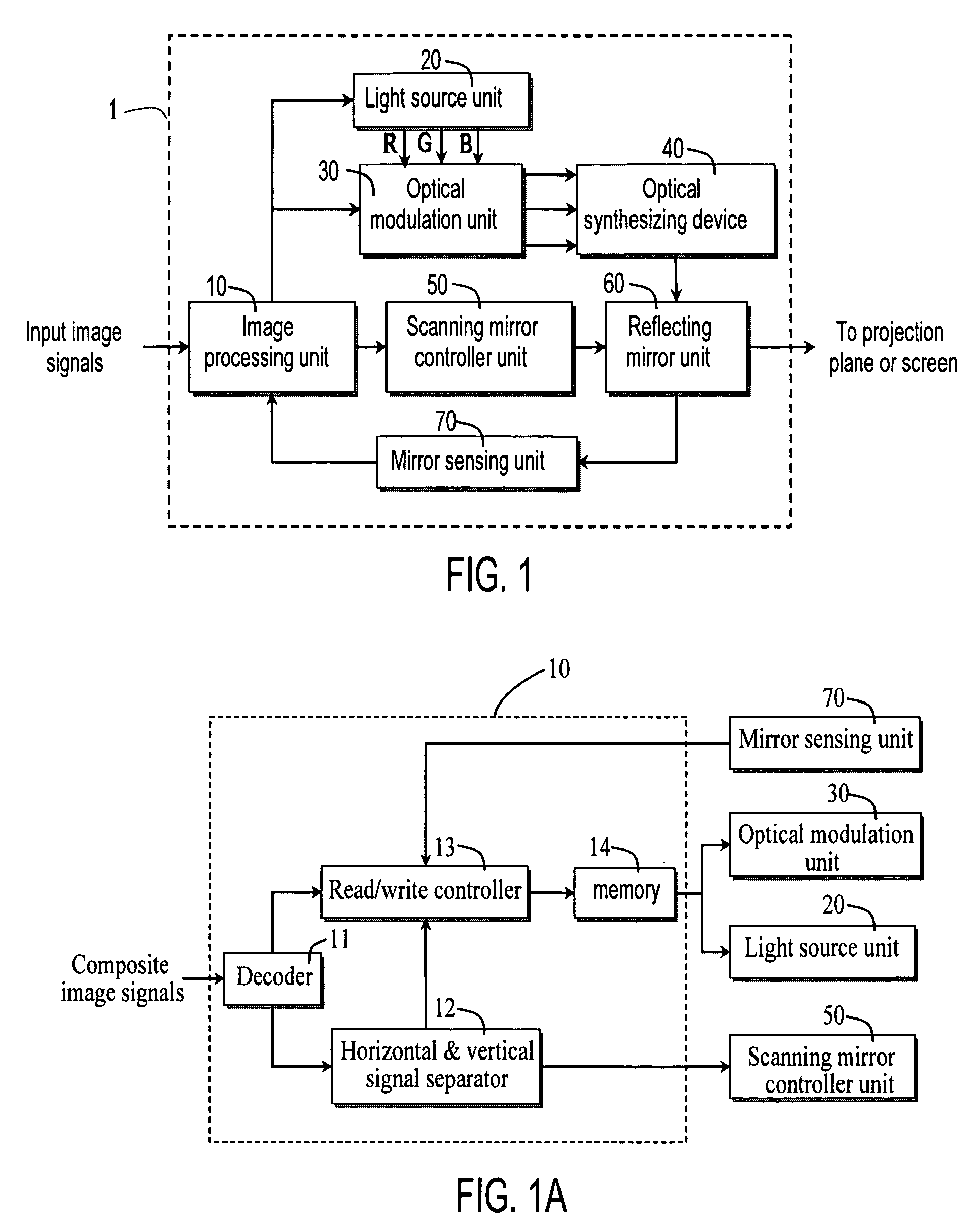
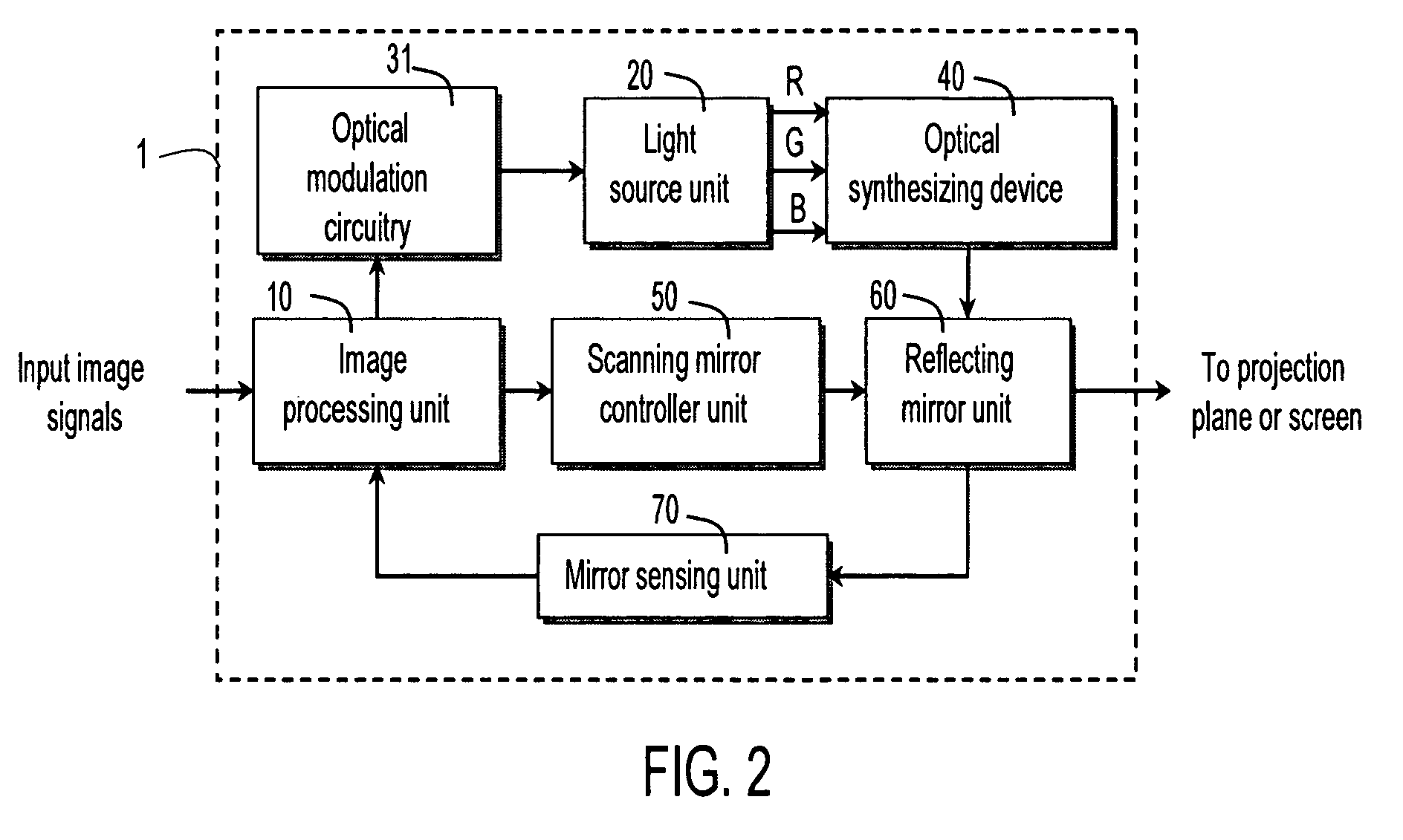
ActiveUS20050141069A1Reduce power consumptionReduce the required powerTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A method and apparatus are provided to controllably reduce power of a laser projection display (LPD). Light is scanned from a laser onto a viewing surface to produce an image thereon, and power used by the laser is reduced used while scanning at least a portion of the viewing surface.
Owner:MICROVISION
Enhanced safety during laser projection
ActiveUS8290208B2Improve securityColor television detailsBiometric pattern recognitionEngineeringProjection system
The present invention is directed to systems and methods that provide enhanced eye safety for image projection systems. In particular, the instant invention provides enhanced eye safety for long throw laser projection systems.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Scanning laser projection display devices and methods for projecting one or more images onto a surface with a light-scanning optical fiber
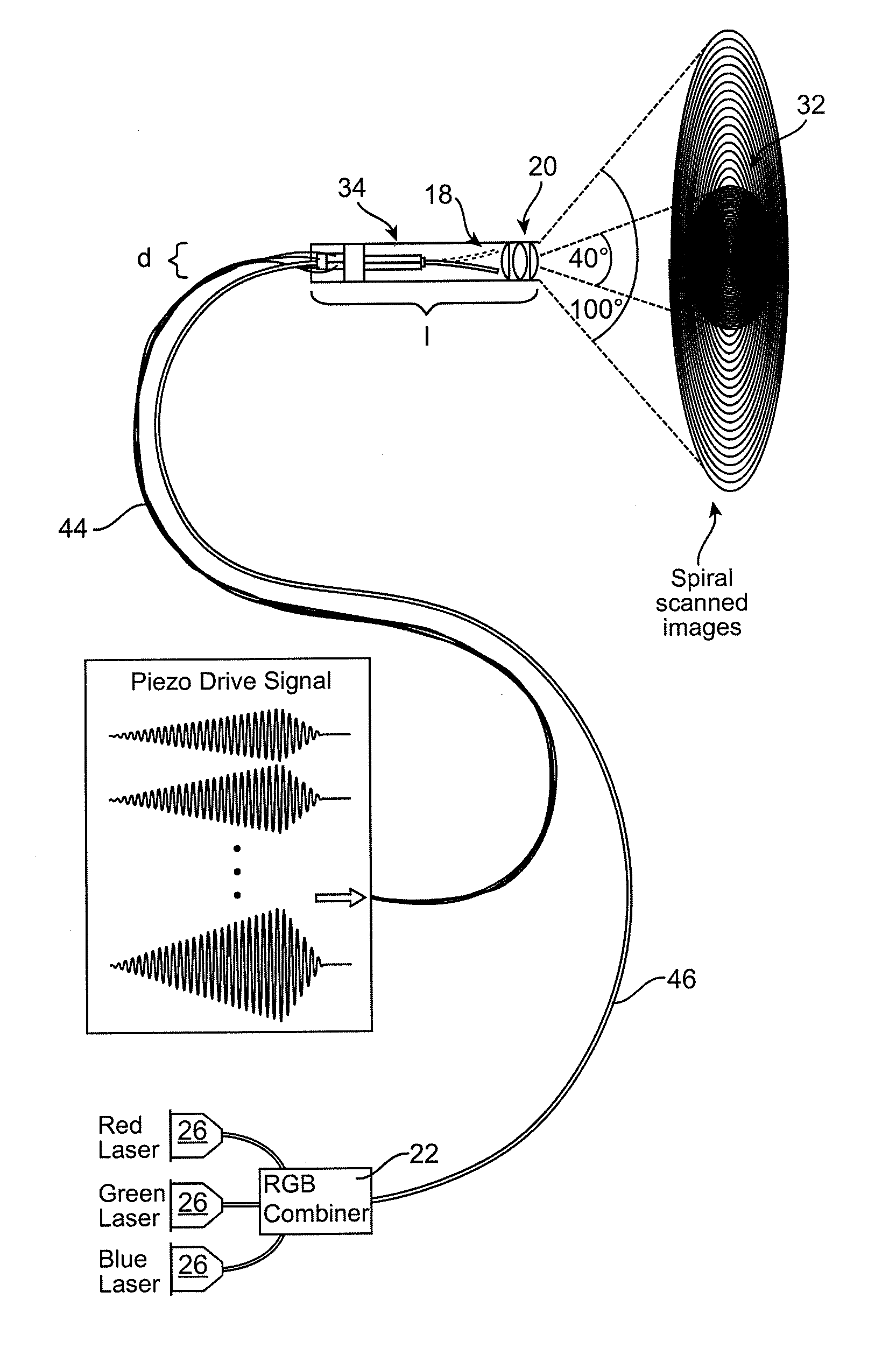
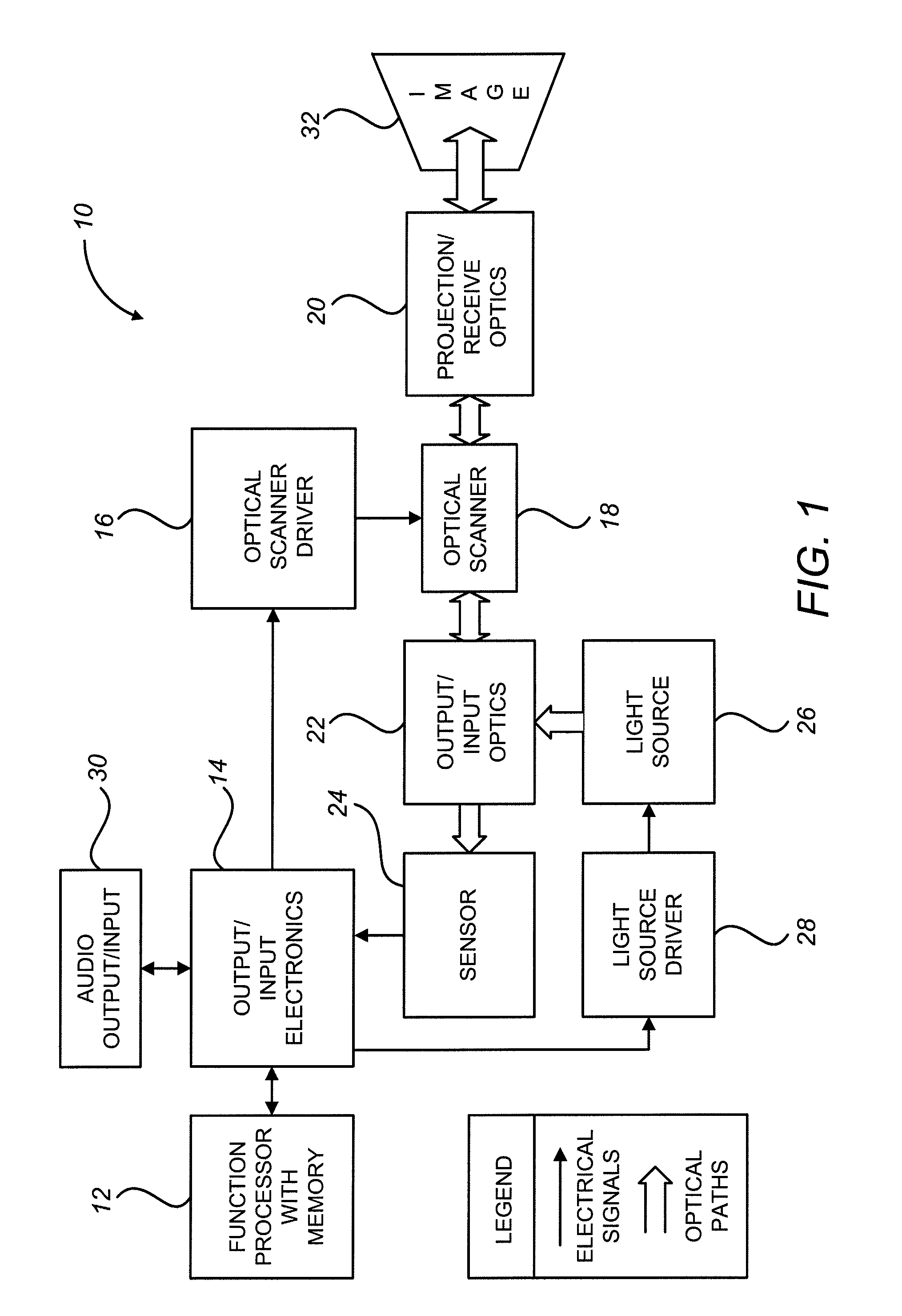
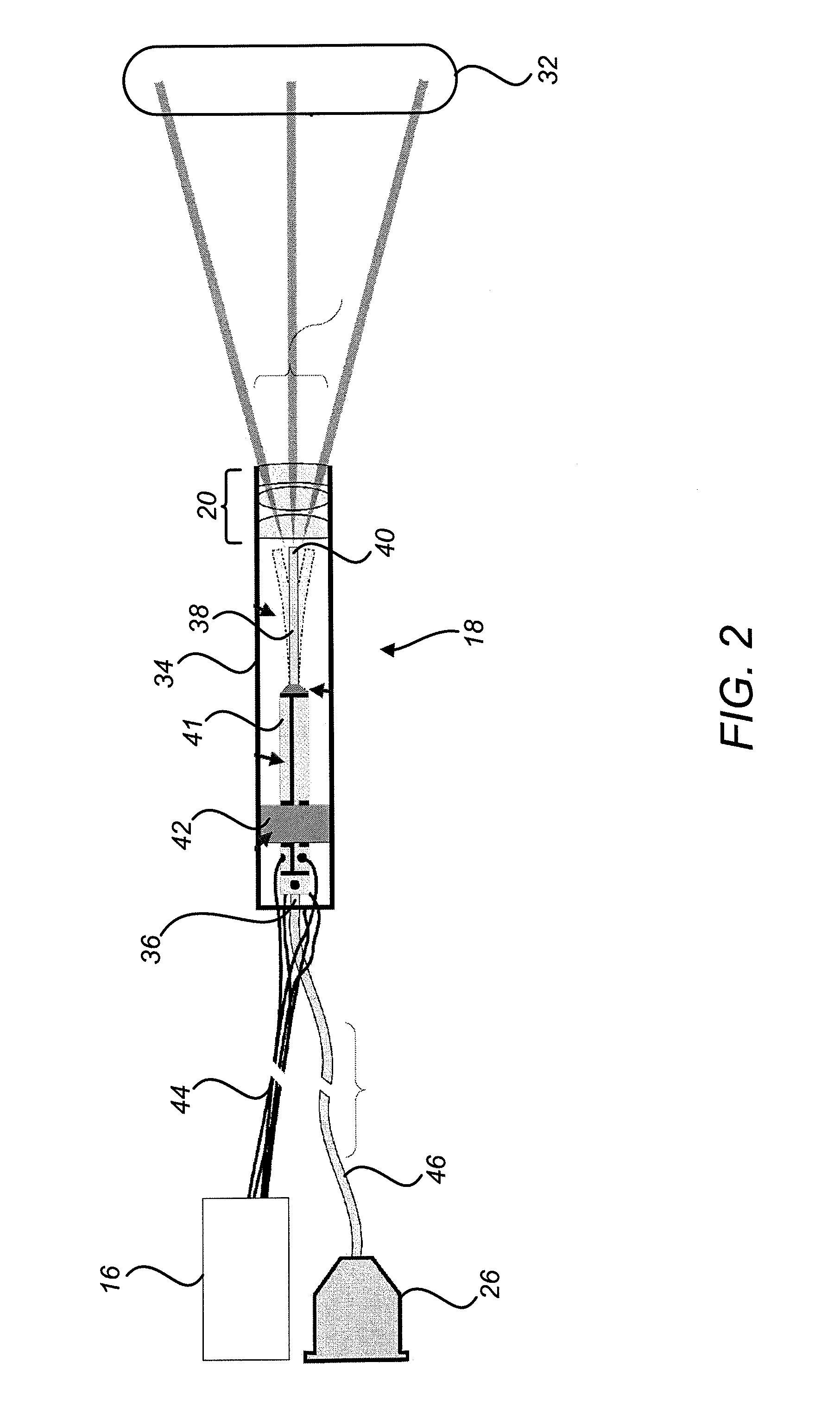
Image projection devices, high-speed fiber scanned displays and related methods for projecting an image onto a surface and interfacing with the projected image are provided. A method for projecting one or more images and obtaining feedback with an optical input-output assembly is provided. The input-output assembly comprising a light-scanning optical fiber and a sensor. The method includes generating a sequence of light in response to one or more image representations and a scan pattern of the optical fiber, articulating the optical fiber in the scan pattern, projecting the sequence of light from the articulated optical fiber, and generating a feedback signal with the sensor in response to reflections of the sequence of light.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Apparent speckle reduction apparatus and method for MEMS laser projection system
A laser projection system is disclosed having reduced apparent speckle. The system includes a laser emitting a first beam on an optical element. The optical element emits a second beam incident on a scanner that scans the beam onto a projection screen. The optical element may be an exit pupil expander, delay plate, or have a locally electrically modulated index of refraction. In other embodiments, the laser has a tunable wavelength distribution that is changed for each frame displayed by the projection system to reduce apparent speckle. In still other embodiments, the angular content of a beam incident on a scanner is modulated to produce a time varying speckle pattern.
Owner:MICROVISION
Laser radar projection with object feature detection and ranging
A 3D pulsed laser projection system scans an object to produce a dense 3D point cloud and projects a laser light beam onto an object as a glowing template. A high-sensitivity optical feedback system receives and detects a feedback beam of the output beam light diffusely reflected from the object. The feedback light and projected beam share the same beam path between steering mirrors and the object. A light suppression component controls stray scattered light, including ambient light, from being detected. A time-of-flight measurement subsystem provides a distance-to-object measurement for projected pulses. An acousto-optical modulator, variable gain detected signal amplification and variable photo-detector power together produce a dynamic range for detected reflected feedback signals of at least 100,000, and up to 500,000. Optical fiber cables spatially filter scattered light and isolate the photo-detectors thermally. The laser is preferably pulsed at least 50 kHz, with sampling of the projected and feedback reflected optical pulse signals at a sampling rate of up to 10 gigasamples per second.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for capturing images using a color laser projection display
A method and apparatus are provided to capture images using a laser projection display (LPD). In a full color LPD camera, three lasers (red, blue, and green) are deployed to scan an image and receive reflected laser light therefrom. The reflected laser light may be analyzed and assembled into a picture. The LPD may also be used to display the picture, to operate as a viewfinder, to print the picture, to operate as a range finder, and the like.
Owner:MICROVISION
Laser projection display and illumination device with MEMS scanning mirror for indoor and outdoor applications
A projection display system includes a light source emitting a light beam, and a reflecting mirror system for scanning the light beam over an image to illuminate the image. The light source can be solid state such as a laser diode. The reflecting mirror system can be one or more MEMS scanning mirrors that rotate to raster scan the light beam over the image. The image can be an advertisement located on a wall, a screen, a sign, or a billboard. The image can also be a semi-transparent image that is projected onto a medium to produce a larger image.
Owner:ADVANCED NUMICRO SYST
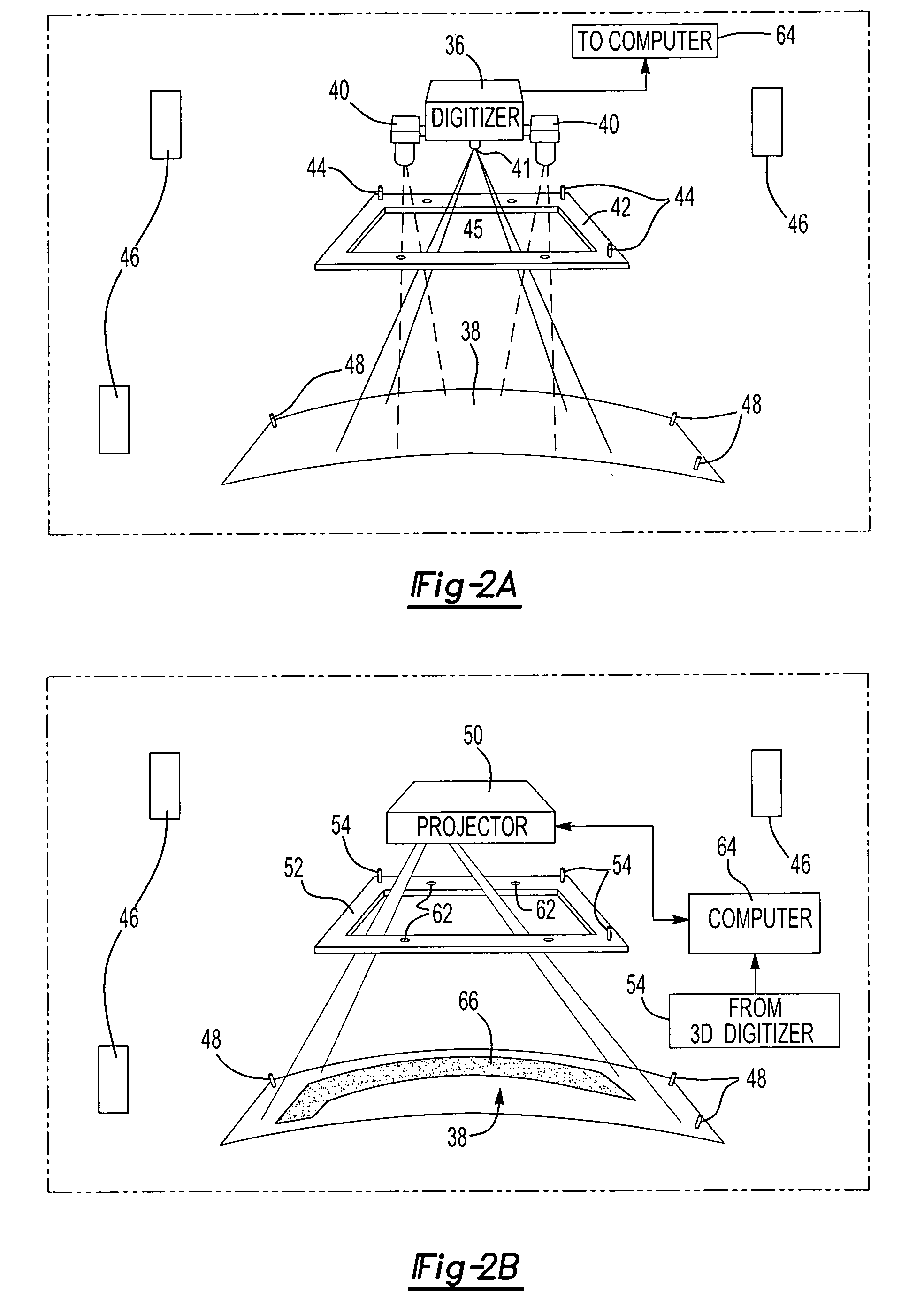
Laser projection systems and methods
ActiveUS20050082262A1Easy to disassemblePrecise positioningProjectorsPosition fixationMetrologyKinematics
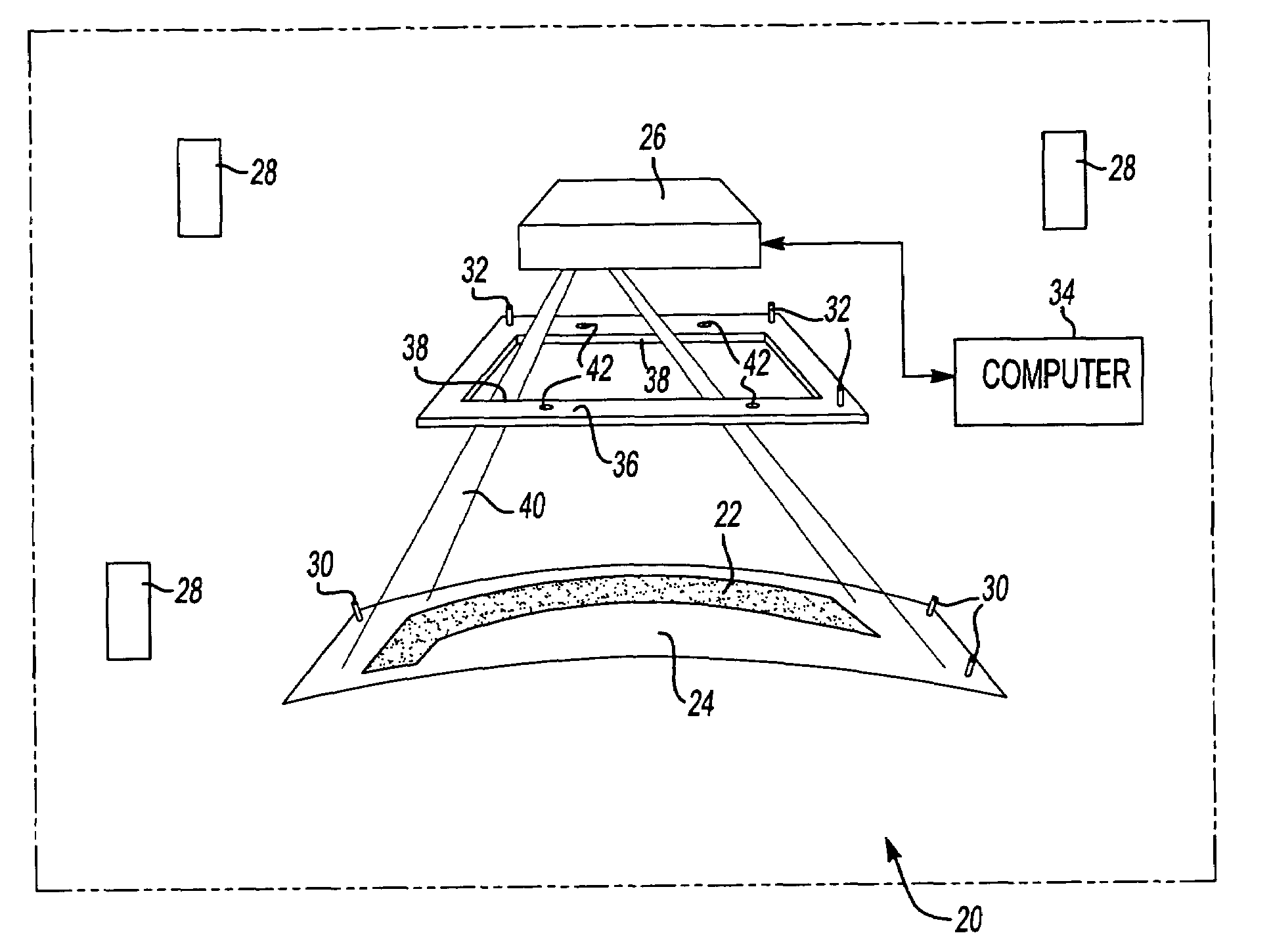
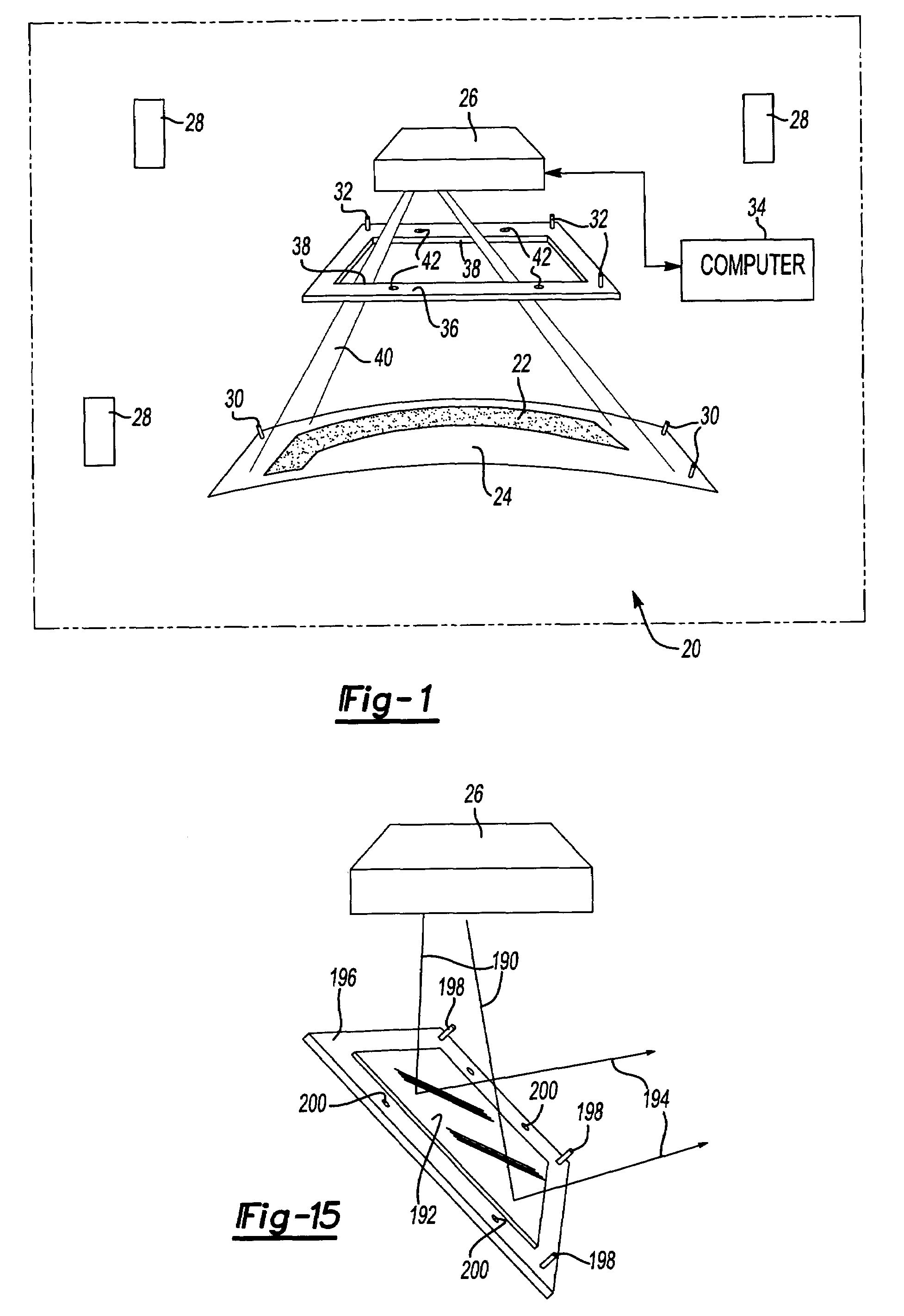
A laser imaging system and method of projecting a laser template on a surface, including independently determining a position and orientation of the surface using an external metrology device, independently determining a position and orientation of a laser projector using the metrology device, generating a signal from the metrology device to a computer and orienting the laser projector relative to the surface to project a laser template. The apparatus includes a plurality of metrology transmitters at fixed locations, a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to the surface and a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to either the laser projector or laser targets within a field of view of the laser projector. A laser projector and frame assembly is also disclosed, wherein the metrology receivers are located on the frame and the frame includes laser targets for correcting laser drift. Kinematic supports for the metrology receivers are disclosed as well as an independent laser tracker.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
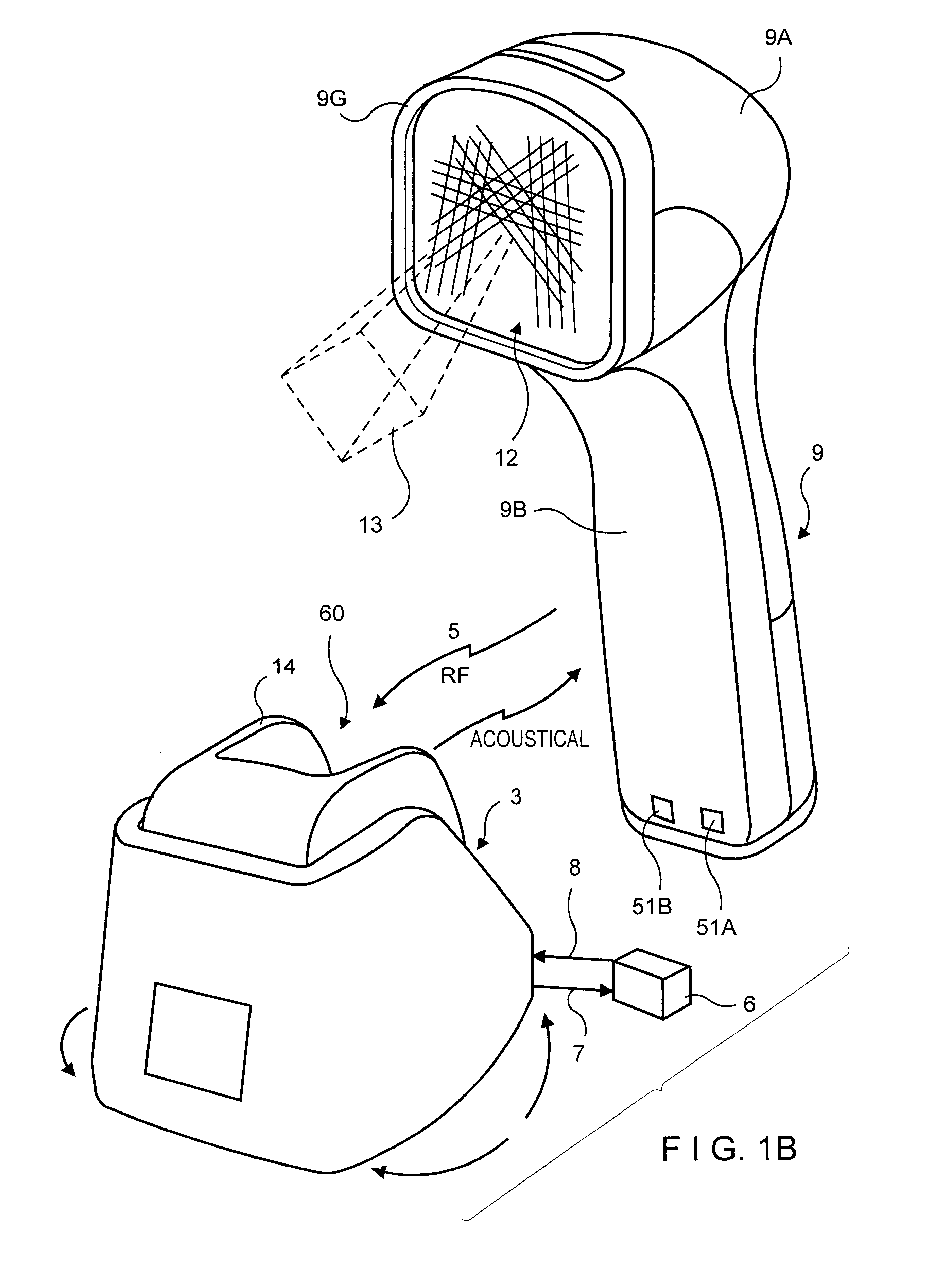
Automatic hand-supportable laser projection scanner for omni-directional reading of bar code symbols within a narrowly confined scanning volume
InactiveUS6286760B1Save power consumptionFacilitate rapid steady-state responseTelevision system scanning detailsCoin-freed apparatus detailsHand heldLaser scanning
A fully automatic bar code symbol reading system comprising an automatic (i.e., triggerless) portable bar code symbol reading device with an omni-directional laser scanning engine mounted within the head portion of its hand-supportable housing, and an associated base unit positioned within the data transmission range thereof without a physical wiring connection thereto.
Owner:METROLOTIC INSTR INC
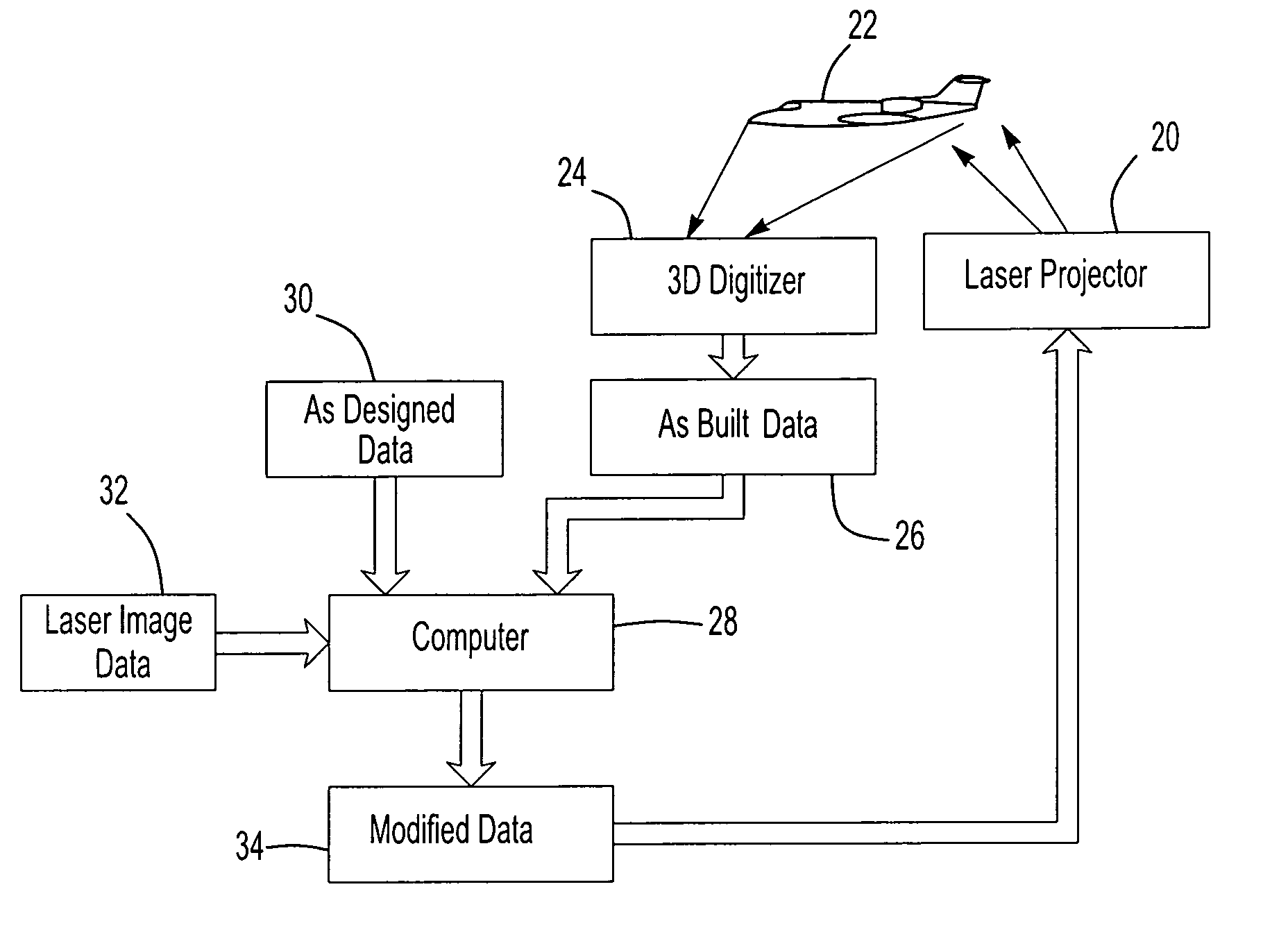
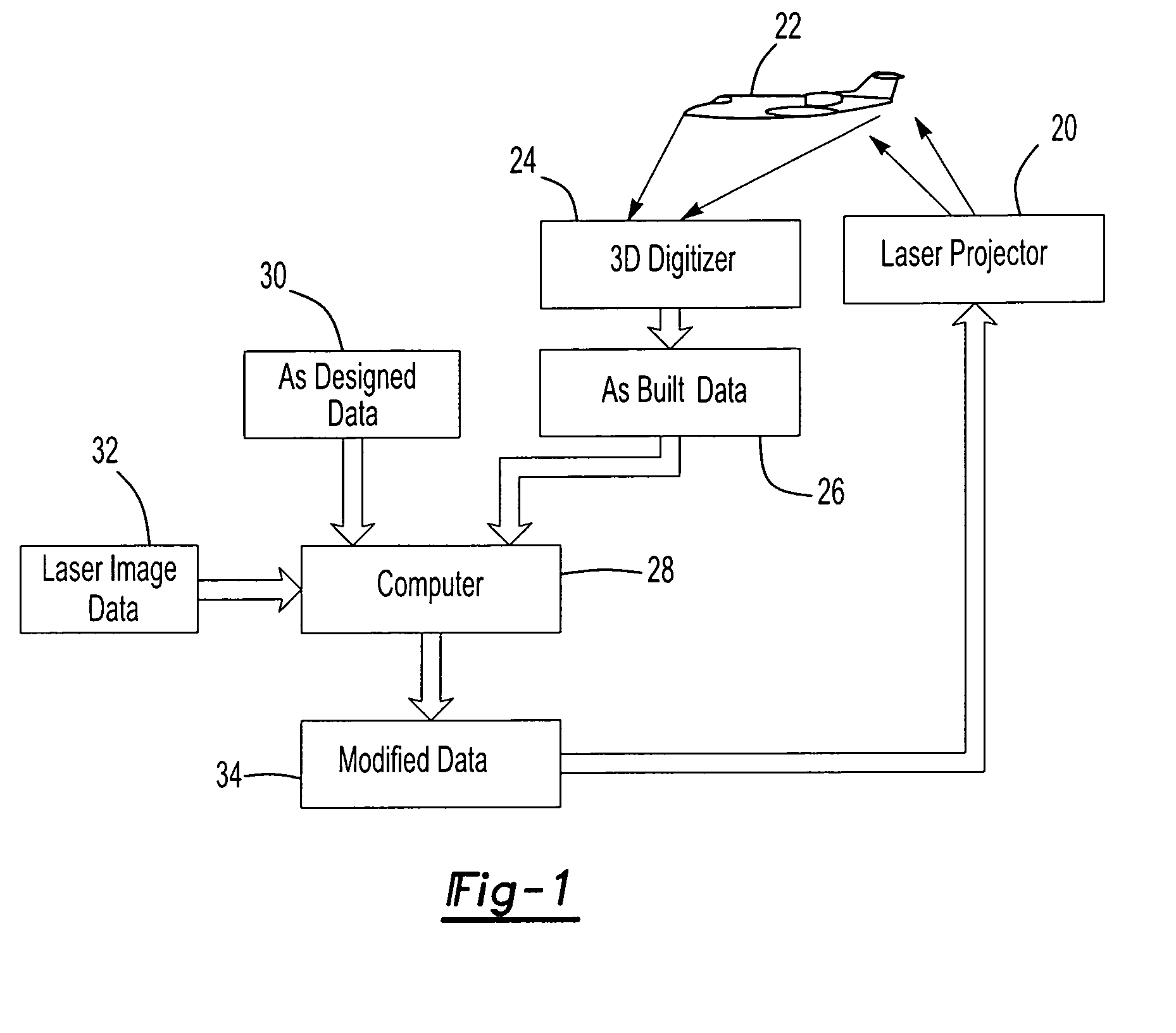
Laser projection system, intelligent data correction system and method
ActiveUS7463368B2Precise positioningAccurate projectionProgramme controlAiming meansMetrologySmart data
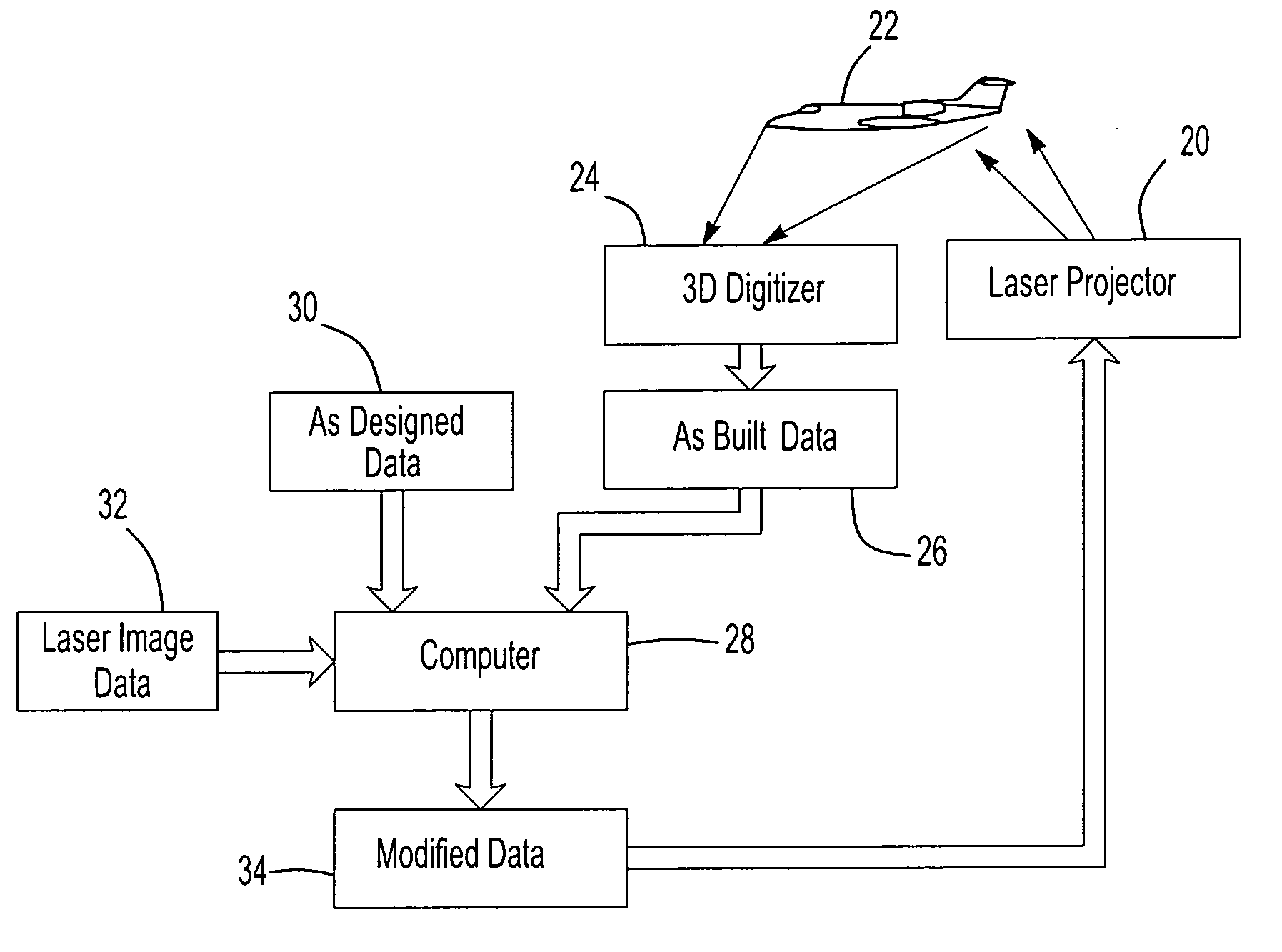
A laser projection system, intelligent data correction system and method which corrects for differences between the as-built condition and the as-designed condition of a workpiece which includes determining the as-built condition of a workpiece with a digitizer scanner and modifying data of the as-built condition or the data of a laser projection based upon the data received from the digitizer scanner of the as-built condition. A preferred intelligent data correction system includes metrology receivers fixed relative to the digitizer scanner and the workpiece and a metrology transmitter to determine the precise location and orientation of the digitizer scanner relative to the workpiece.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
Uniform speckle reduced laser projection using spatial and temporal mixing
ActiveUS20090284713A1Cost optimizationOptimized illumination uniformityProjectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A digital image projector includes a light assembly configured to project light along a light path from at least one laser array light source, the projected light having an overlapping far field illumination in a far field illumination portion of the light path; a temporally varying optical phase shifting device configured to be in the light path; an optical integrator configured to be in the light path; a spatial light modulator located downstream of the temporally varying optical phase shifting device and the optical integrator in the light path, the spatial light modulator configured to be located in the far field illumination portion of the light path; and projection optics located downstream of the spatial light modulator in the light path, the projection optics configured to direct substantially speckle free light from the spatial light modulator toward a display surface.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Laser projection with object feature detection
A laser projection system scans an output laser light beam onto an object to detect features. A high-sensitivity optical feedback system receives and detects a feedback beam of the output beam light diffusely reflected from the object. The feedback light and projected output beam share the same beam path between beam-steering mirrors of the projector and the object. The laser projection system has light suppression components to control stray scattered light, including ambient light, from being detected. A computer of the laser projection system calculates fiducial points on the object from detected features to align the projection system with the object without using targets. This feature detection is used in a process to guide assembly and fabrication on or to the object, and to verify the accurate placement of parts and fabrication steps in place after they are assembled or processed. In one form, the detected feature is a light spot on the object produced by a second light source.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
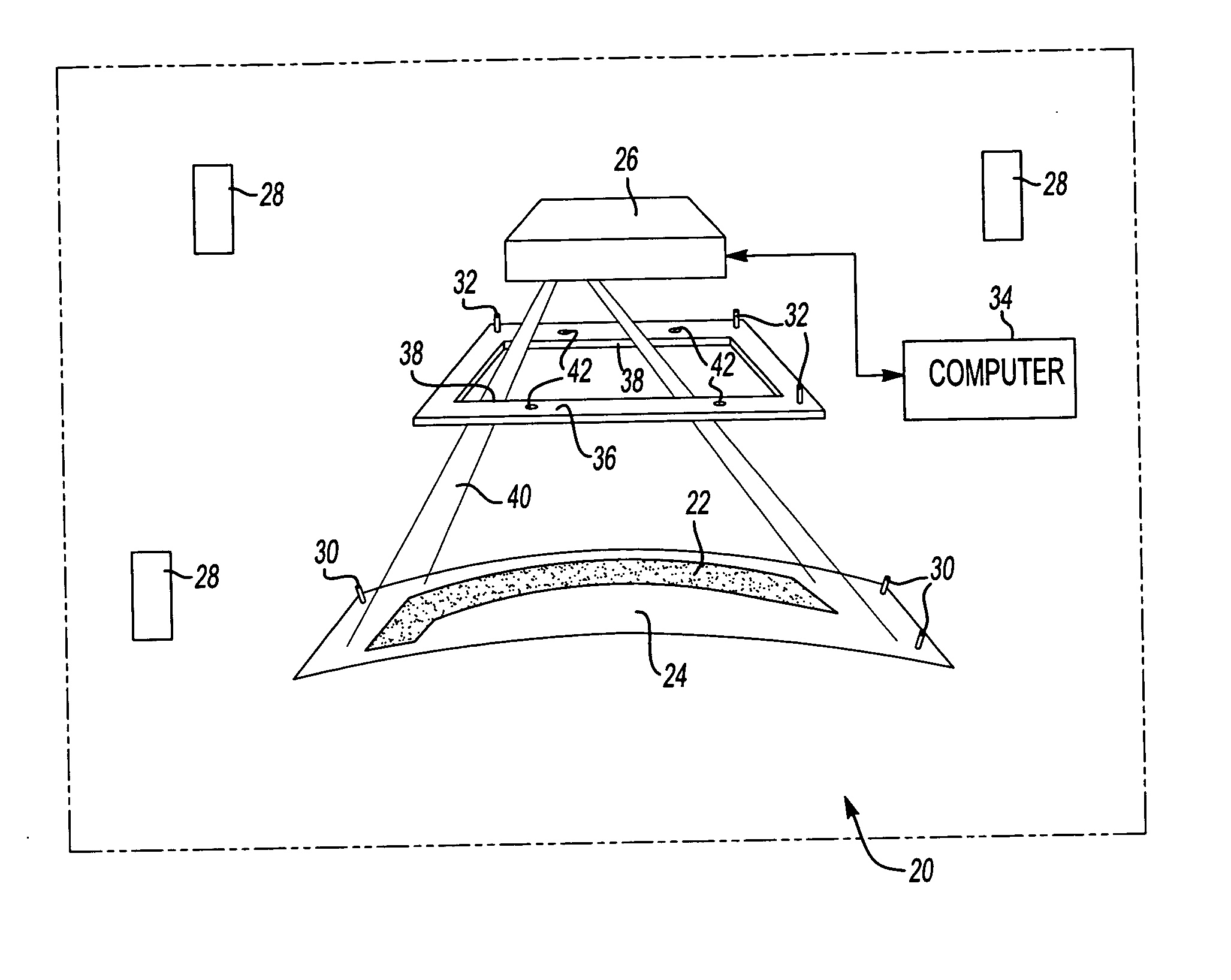
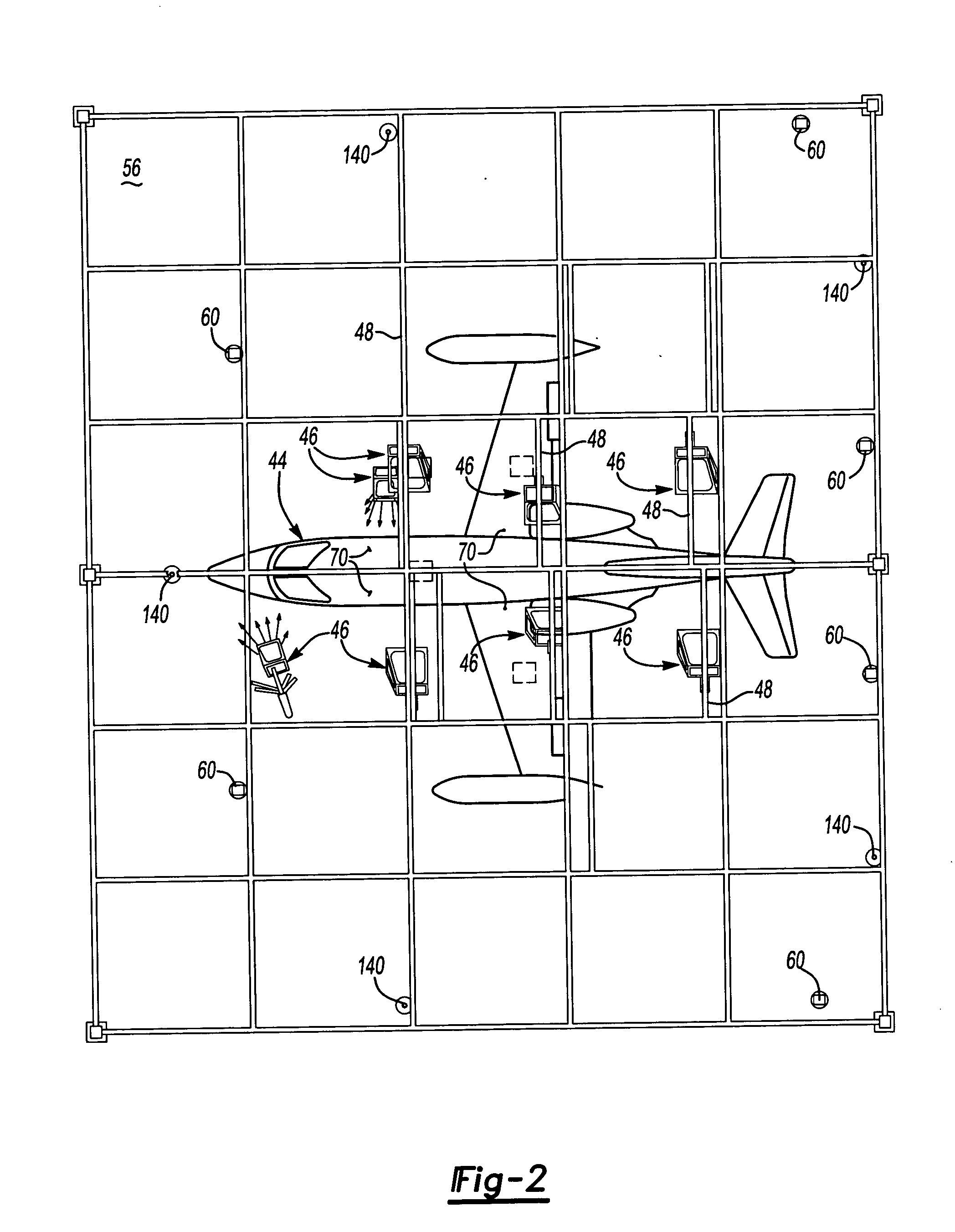
Laser projection system to facilitate layup of complex composite shapes
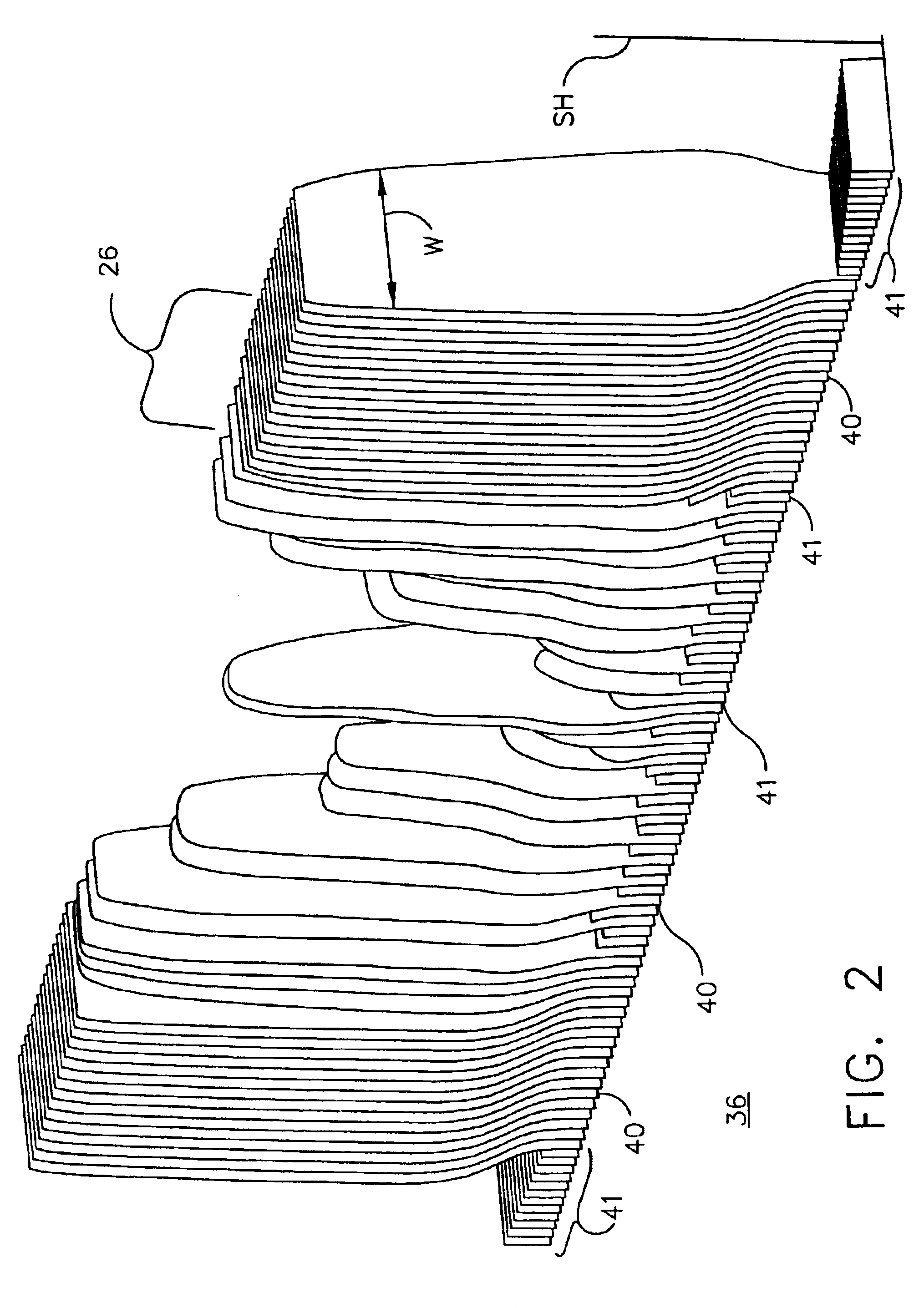
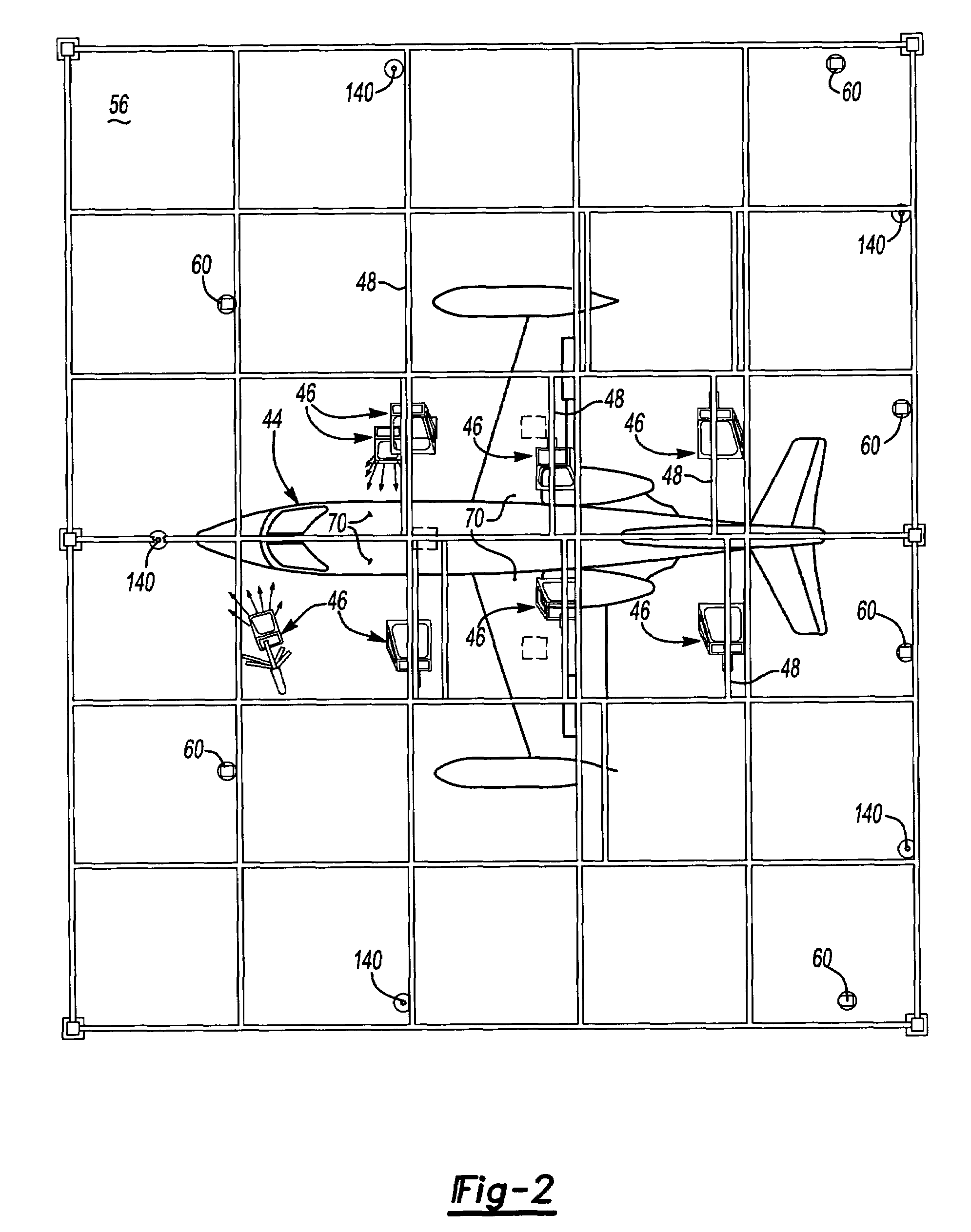
InactiveUS6843565B2Increased ply lay-up speedReduce morbidityBlade accessoriesProjectorsData setComposite laminates
The present invention provides a process for the lay-up of a composite laminate article, the article produced by this process, and the apparatus used to produce the composite laminate article. The composite laminate article may be, for example, an airfoil, particularly useful as a fan blade in a large high bypass ratio turbofan engine, wherein the blade is generally regarded as large and having a high degree of twist. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a process for laying up a composite laminate article comprising a) reading a data set to enable the projection of an image of a ply section onto a work surface, the image indicating a ply section target point; b) laying up a ply section of composite laminating material within the image, wherein the ply section first contacts the work surface at the target point; and c) repeating steps (a)-(b) until the composite laminate article is complete. In a second preferred embodiment, the present invention provides for a lamination apparatus for use in making a composite laminate article comprising a work surface for receiving, in a predetermined sequence, a plurality of ply sections of composite laminating material; a laser projection system using predetermined projection points for outlining an image of a ply section onto the work surface, the image further indicating a ply section target point for making first contact of the ply section with the work surface; and a data set for providing the predetermined projection points to the laser projection system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Laser projection systems and methods
ActiveUS7545517B2Precise positioningEasy to disassembleProjectorsPosition fixationKinematicsLaser target
A laser imaging system and method of projecting a laser template on a surface, including independently determining a position and orientation of the surface using an external metrology device, independently determining a position and orientation of a laser projector using the metrology device, generating a signal from the metrology device to a computer and orienting the laser projector relative to the surface to project a laser template. The apparatus includes a plurality of metrology transmitters at fixed locations, a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to the surface and a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to either the laser projector or laser targets within a field of view of the laser projector. A laser projector and frame assembly is also disclosed, wherein the metrology receivers are located on the frame and the frame includes laser targets for correcting laser drift. Kinematic supports for the metrology receivers are disclosed as well as an independent laser tracker.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
Wide Field of View Head-Up Display System
A projection system, such as a system suitable for head-up displays in automobiles, includes a laser projection source (101) and a scanner (102). Light from the laser projection source (101) is scanned across a projection surface (104), which can be a car's windshield. The projection surface (104) includes a buried numerical aperture expander (105) capable of reflecting some light and transmitting other light. The system may also include an image projection source (551) capable of presenting high-resolution images on a sub-region (552) of the projection surface (604) that has a optical relay (650) disposed therein.
Owner:MICROVISION
Laser projection system, intelligent data correction system and method
ActiveUS20050121422A1Precise positioningAccurate projectionProgramme controlAiming meansMetrologySmart data
A laser projection system, intelligent data correction system and method which corrects for differences between the as-built condition and the as-designed condition of a workpiece which includes determining the as-built condition of a workpiece with a digitizer scanner and modifying data of the as-built condition or the data of a laser projection based upon the data received from the digitizer scanner of the as-built condition. A preferred intelligent data correction system includes metrology receivers fixed relative to the digitizer scanner and the workpiece and a metrology transmitter to determine the precise location and orientation of the digitizer scanner relative to the workpiece.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking and scanning laser projection in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160349515A1Picture reproducers using projection devicesInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayPhotodetector
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking capability into scanning laser projector (“SLP”)-based wearable heads-up displays are described. At least one narrow waveband laser diode is used in an SLP to define one or more portion(s) of a visible image. At least one corresponding narrow waveband photodetector is aligned to detect reflections of the portion(s) of the image from features of the eye. A holographic optical element (“HOE”) may be used to combine the image and environmental light into the user's “field of view.” Three narrow waveband photodetectors each responsive to a respective one of three narrow wavebands output by the RGB laser diodes of an RGB SLP are aligned to detect reflections of a projected RGB image from features of the eye.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Laser projection display
ActiveUS20050140832A1Control rateLaser detailsTelevision system scanning detailsGratingImage resolution
A method and apparatus are provided for controlling the operation of a Laser Projection Display (LPD). Generally, the LPD is comprised of a laser, an optical system and a controller. The laser is adapted to emit a beam of laser light. The optical system is adapted to scan the beam of laser light on a display surface in a two-dimensional raster pattern. The controller is adapted to control the rate at which the laser beam is scanned to produce regions of varying resolution on the display surface. The controller is also adapted to present laser light onto the display surface within only selected portions of the two-dimensional raster scan pattern so that spaced apart image regions may be created.
Owner:MICROVISION
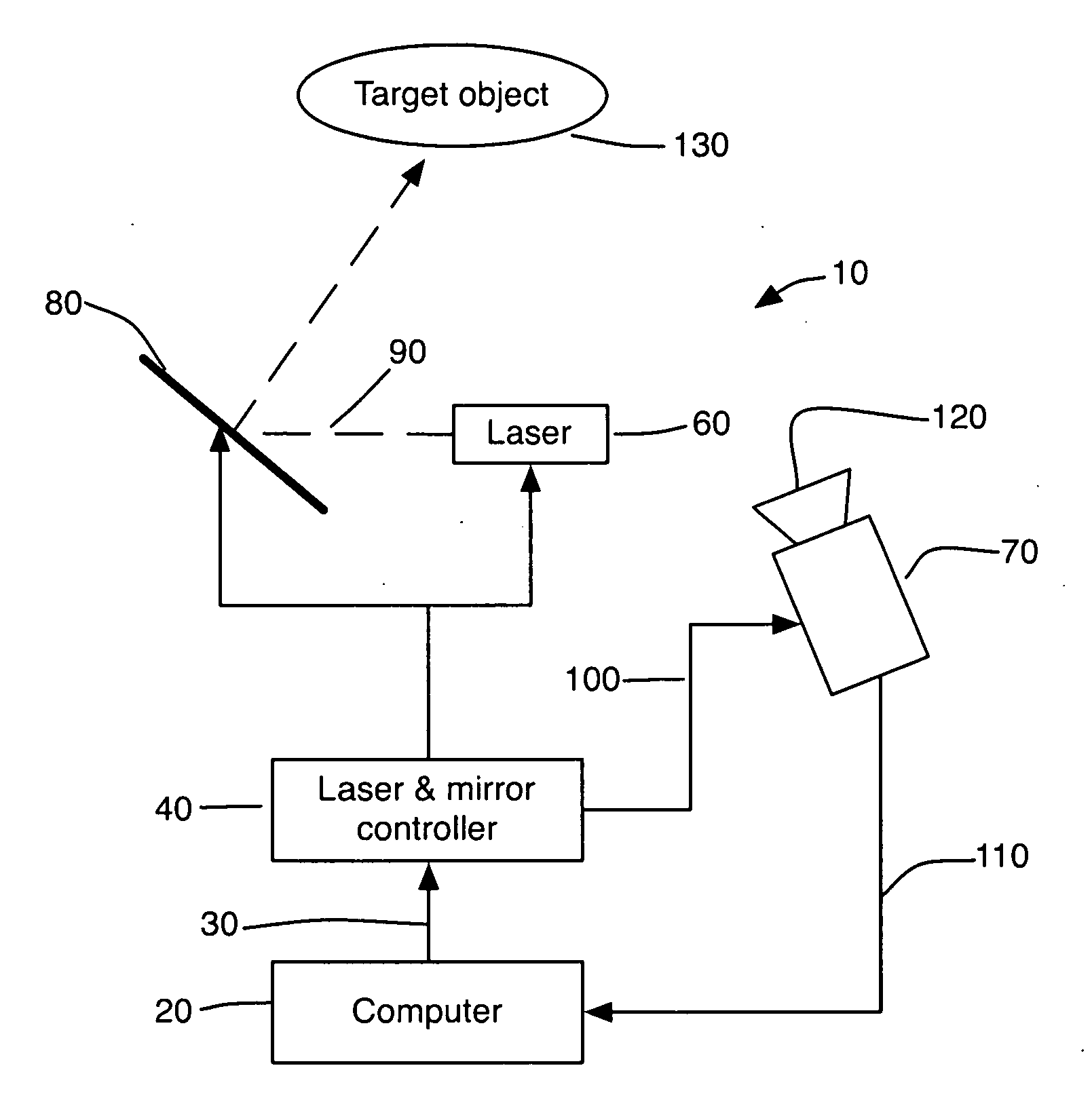
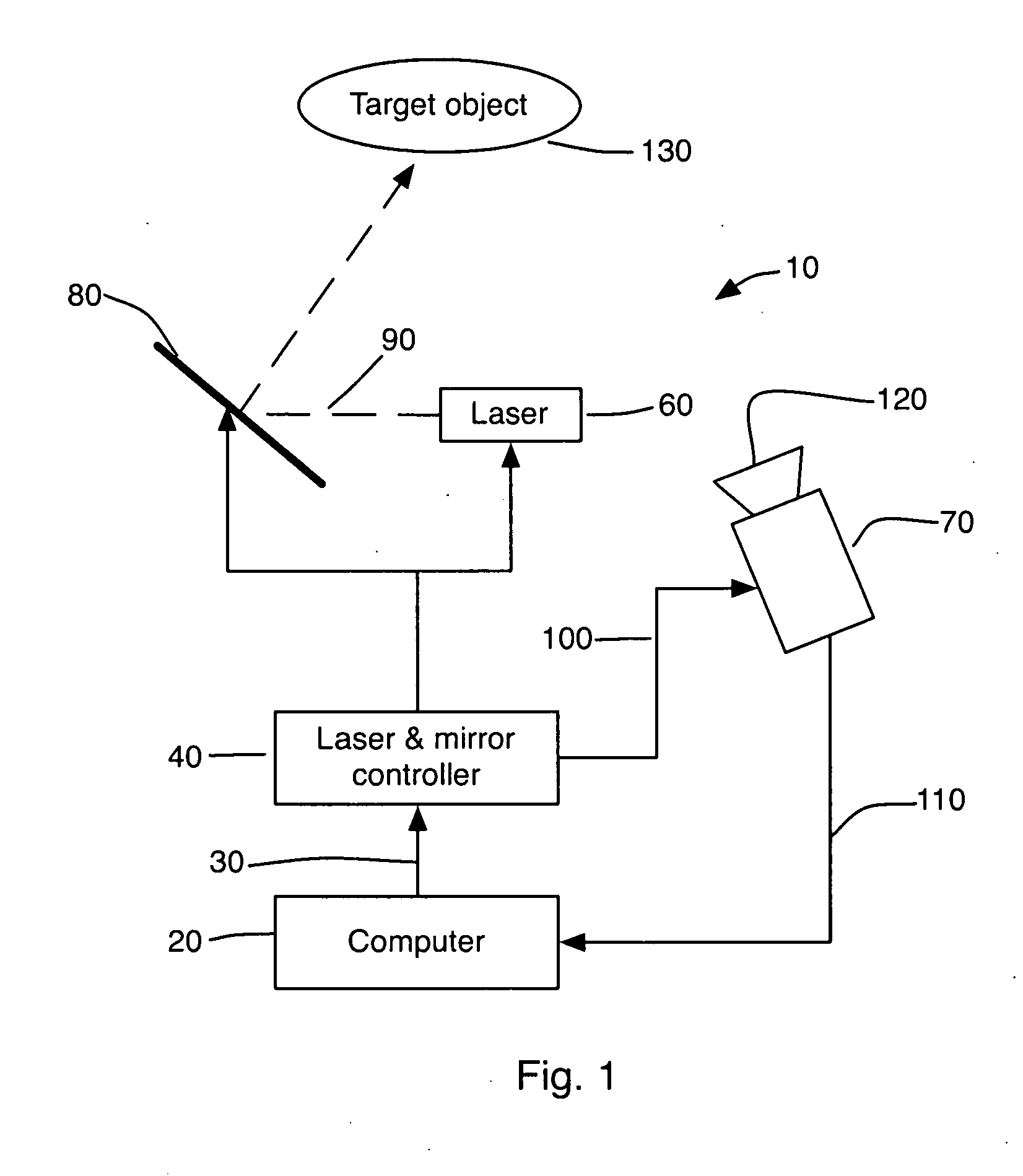
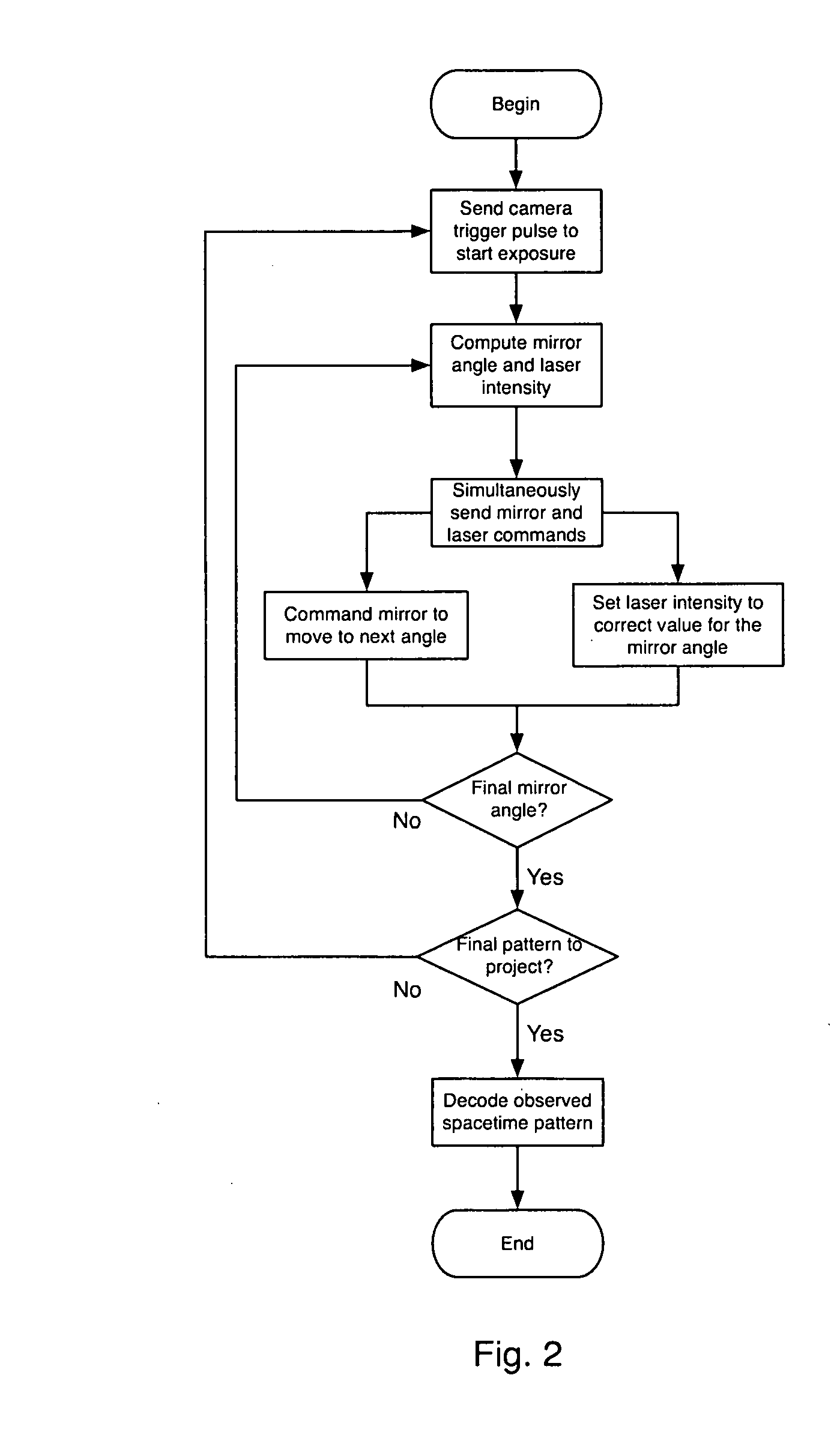
Method and System for 3D Imaging Using a Spacetime Coded Laser Projection System
A desktop three-dimensional imaging system and method projects a modulated plane of light that sweeps across a target object while a camera is set to collect an entire pass of the modulated plane of light over the object in one image to create a line stripe pattern. A spacetime coding scheme is applied to the modulation controller whereby a plurality of images of line stripe patterns can be analyzed and decoded to yield a three-dimensional image of the target object in a reduced scan time and with better accuracy than existing close range scanners.
Owner:THREERIVERS 3D
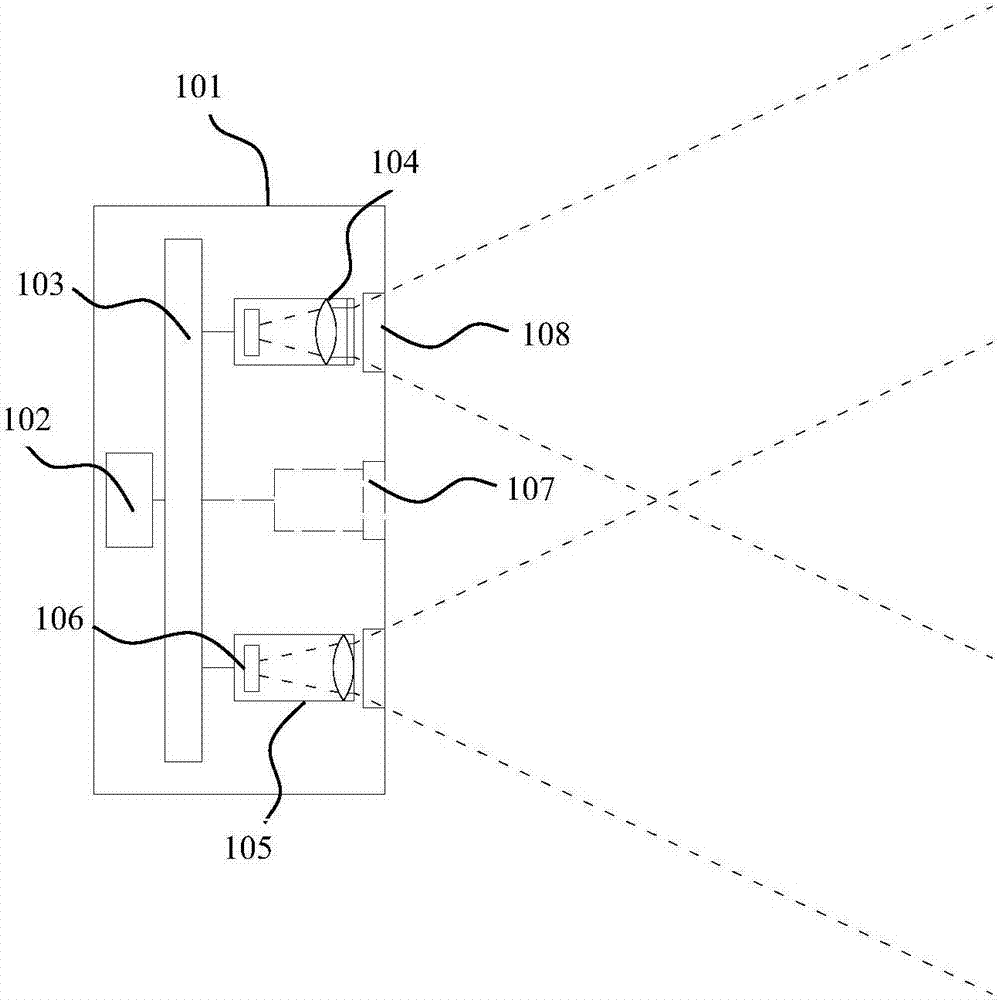
Laser projection module and depth camera
InactiveCN107167997AReduce volumeReduce magnificationProjectorsCamera body detailsLight beamOptoelectronics
The invention provides a laser projection module, which comprises a light source for emitting light beams; a gathering lens used for receiving and gathering the light beams emitted by the light source; a specific optical element, which comprises an optical surface having a reflection function and is used for reflecting at least a part of the light beams; and a pattern generator used for receiving the light beams reflected by the specific optical element and outputting a structured light pattern. The invention also provides a depth camera, which comprises the laser projection module above and is used for projecting a structured light beam image to a target space. According to the laser projection module and the depth camera, by arranging the gathering lens having the gathering function and the specific optical element having the reflection function, the laser projection module and the depth camera are allow to have smaller sizes respectively.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
VCSEL array light source
The invention discloses a VCSEL array light source, a pattern design method of the VCSEL array light source, a laser projection apparatus and 3D imaging equipment. The VCSEL array light source comprises a semiconductor substrate and a plurality of VCSEL light sources which are arranged on the semiconductor substrate in a two-dimensional array form; and the two-dimensional array is generated by at least one sub array through a conversion way. The VCSEL light sources distributed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate have extremely high irrelevance, so that the problem of low irrelevance of the VCSEL light sources in 3D imaging in the prior art can be solved; and the VCSEL array is mainly applied in a depth camera.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
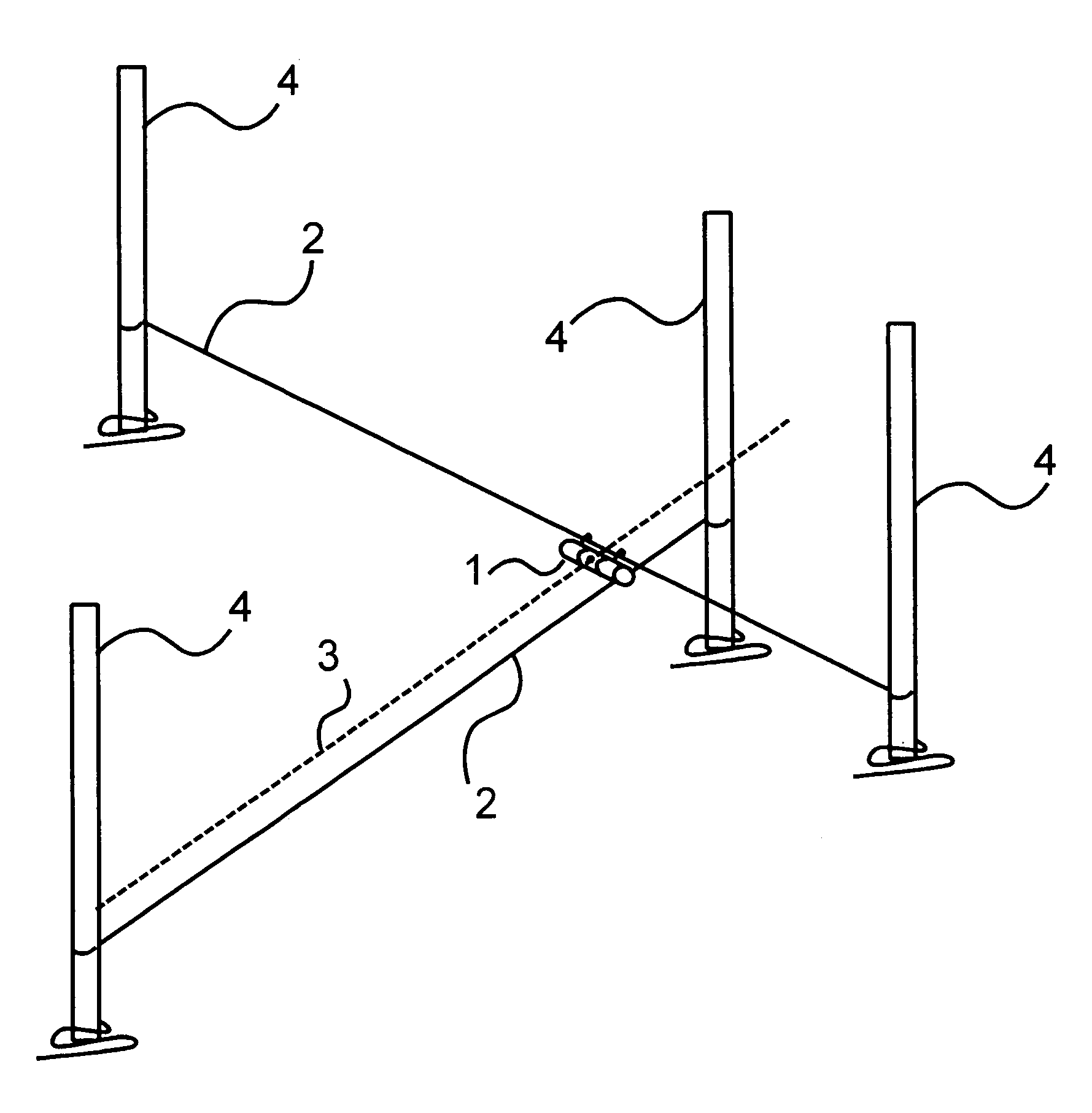
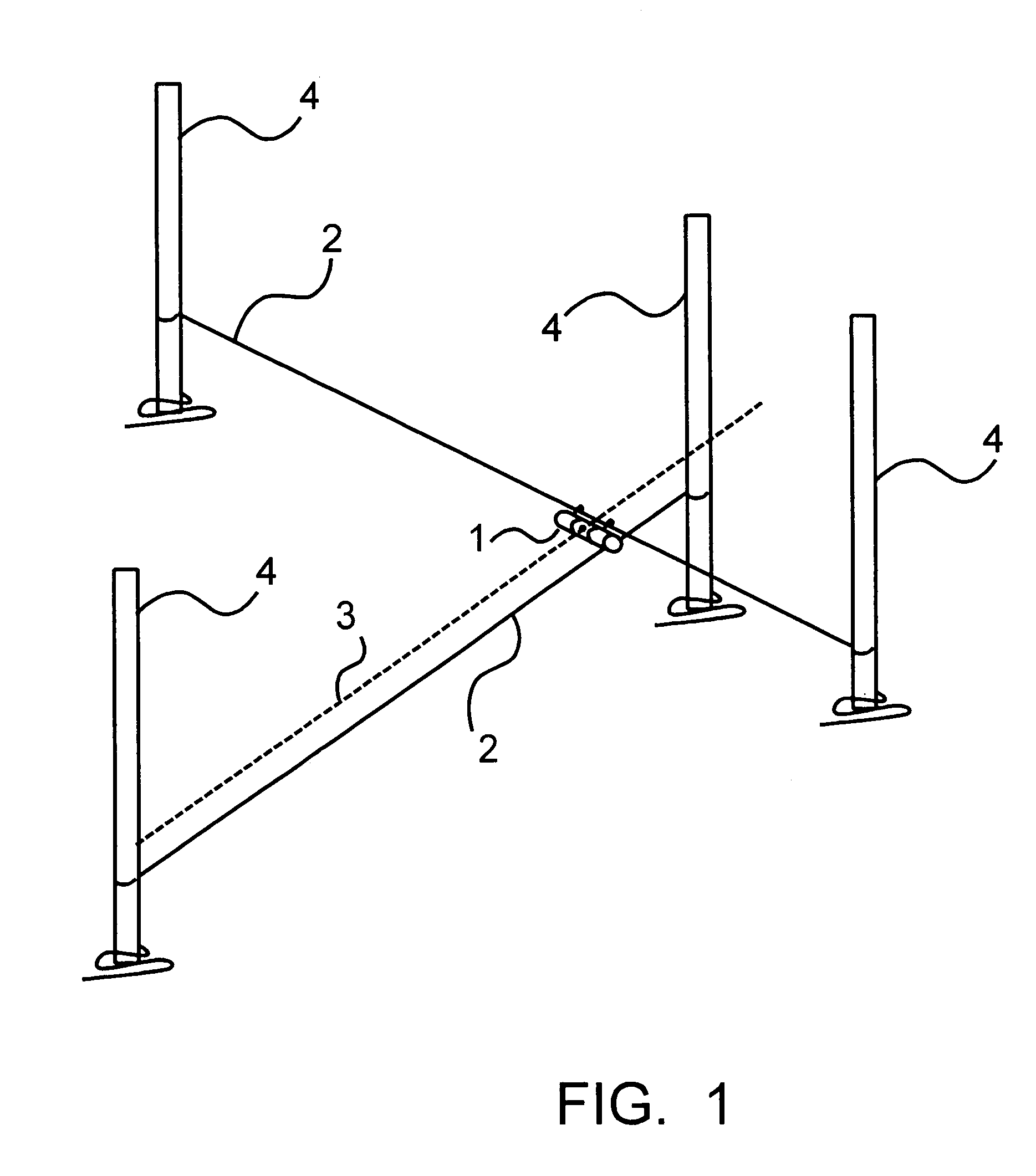
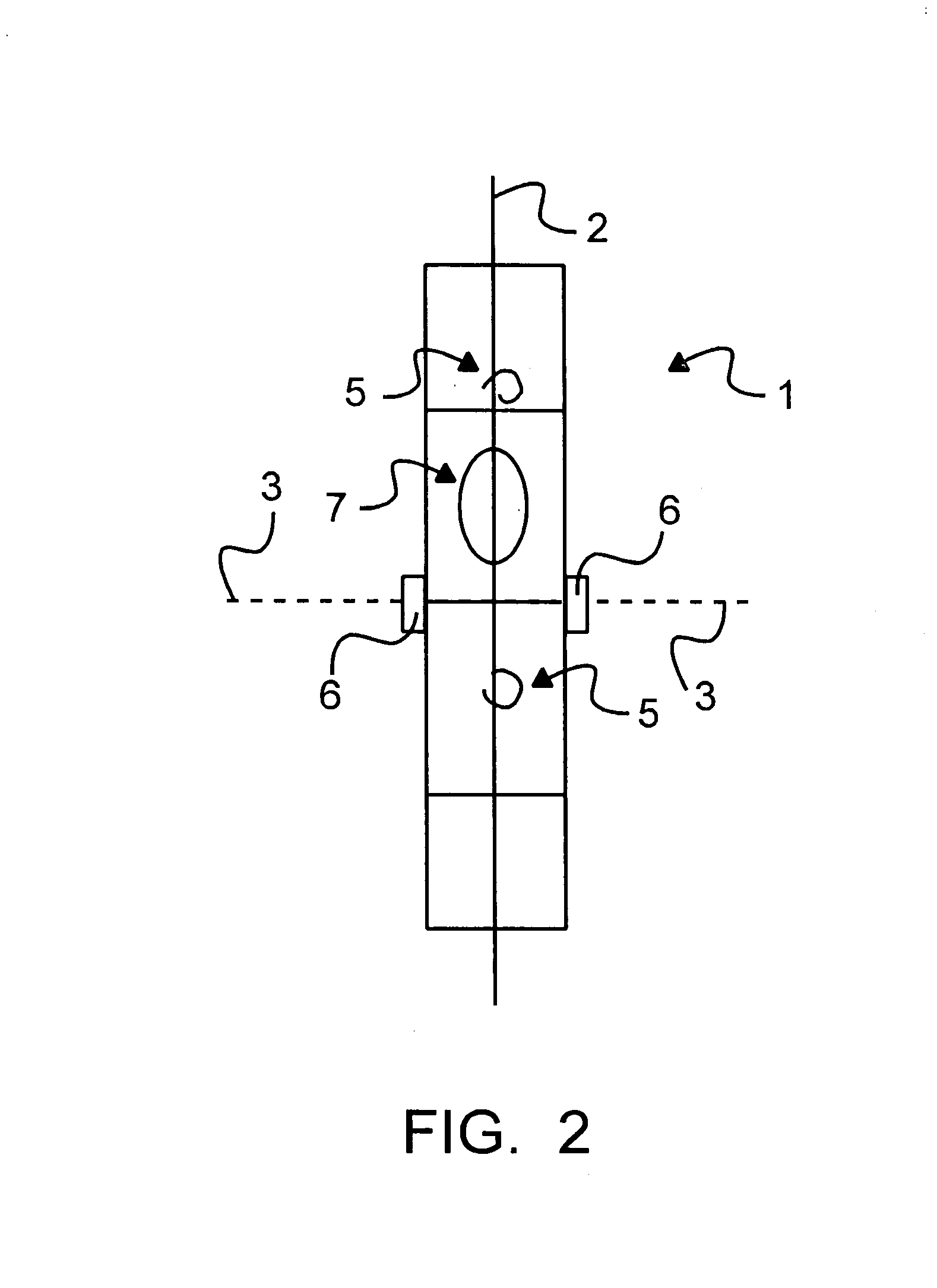
Measuring arrangement to determine location of corners for a building foundation and a wooden base frame, and the use thereof
InactiveUS7137207B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyMeasuring points markingReference line/planes/sectorsEngineeringLaser projection
An arrangement comprising a laser projection device is used in determining the location of corners in constructing a foundation of a building or other structure. The arrangement is also used in positioning wooden beams perpendicular to one another in a floor frame or similar structure.
Owner:ARMSTRONG TIMOTHY D +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com