Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
163results about How to "Reduce disagreement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
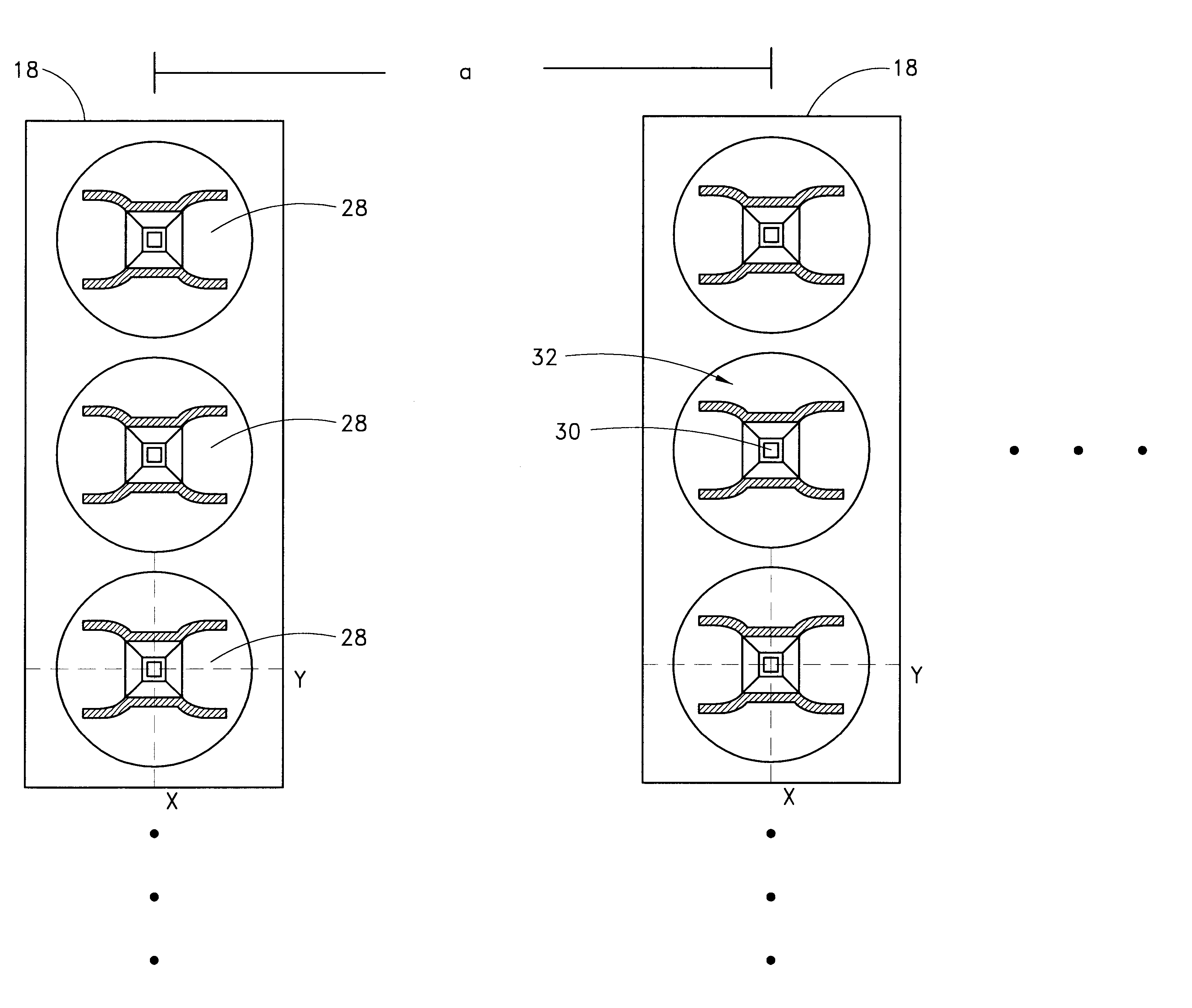
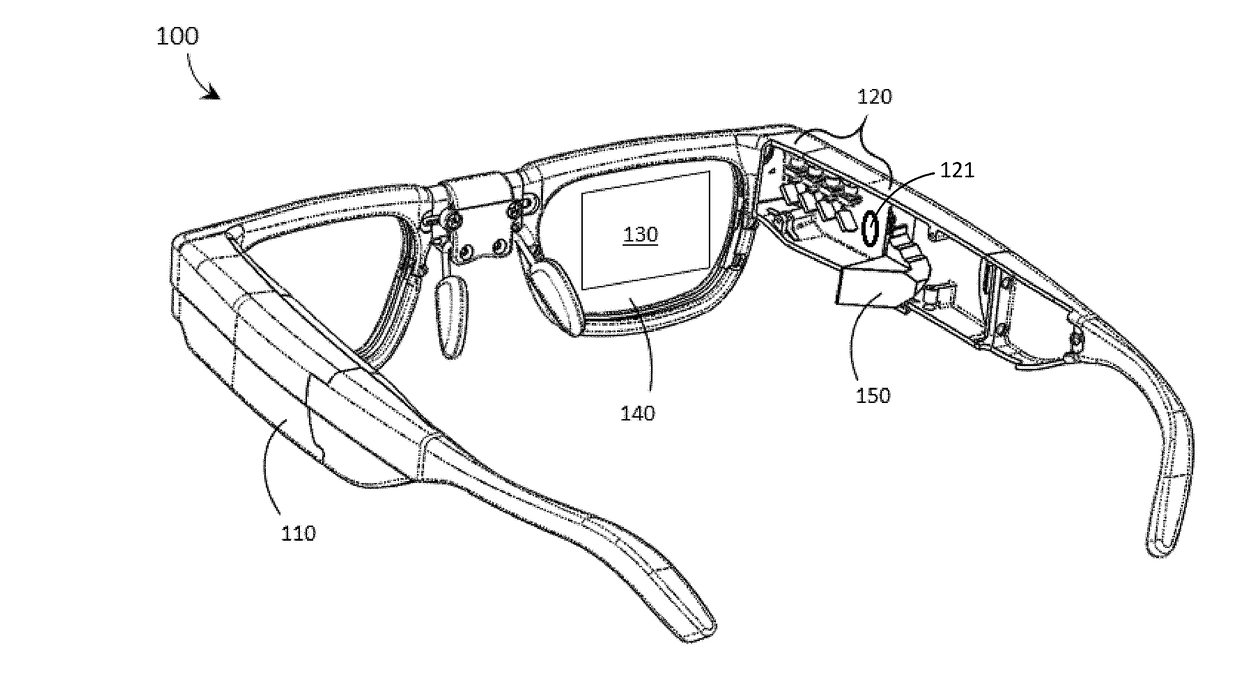
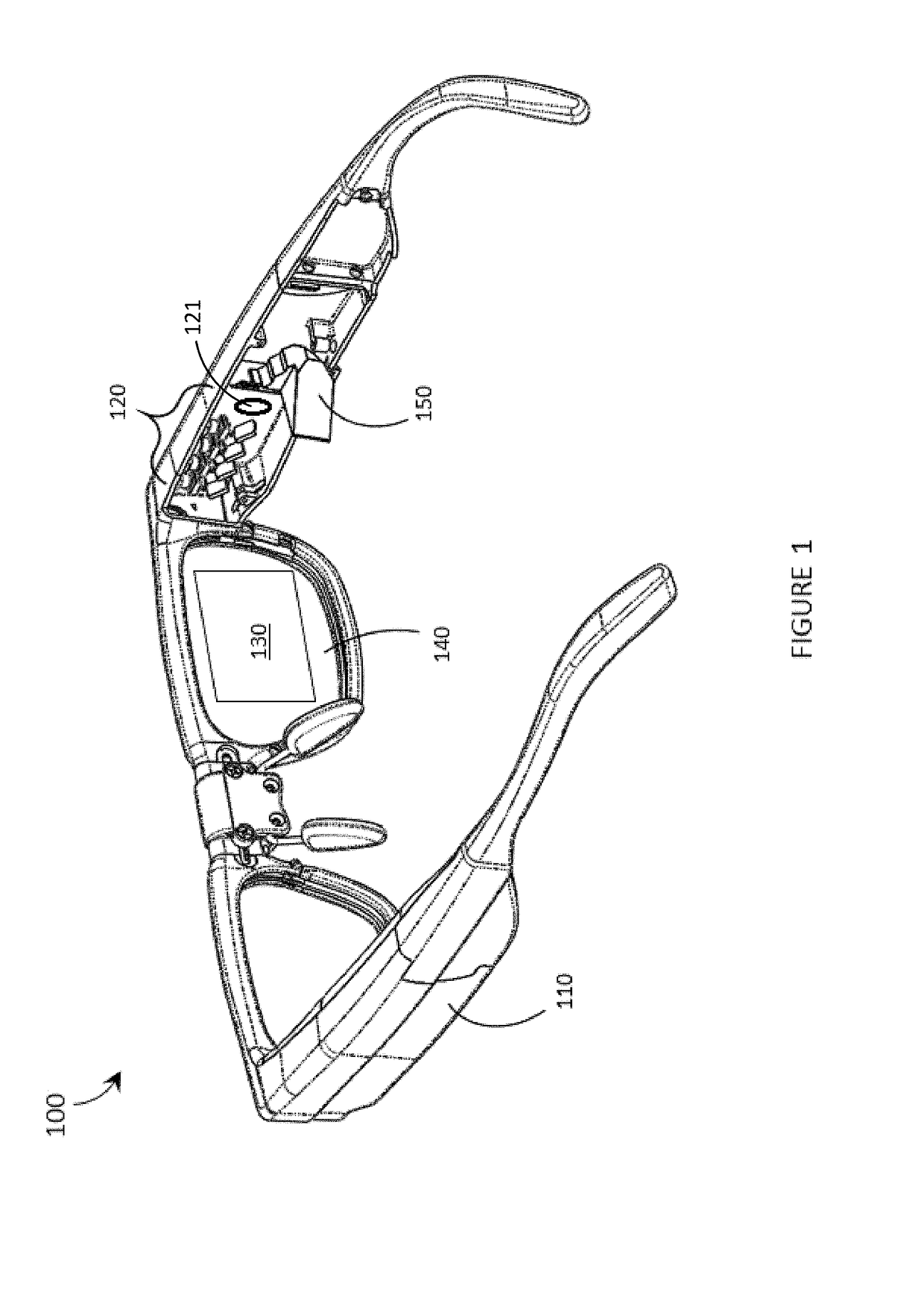
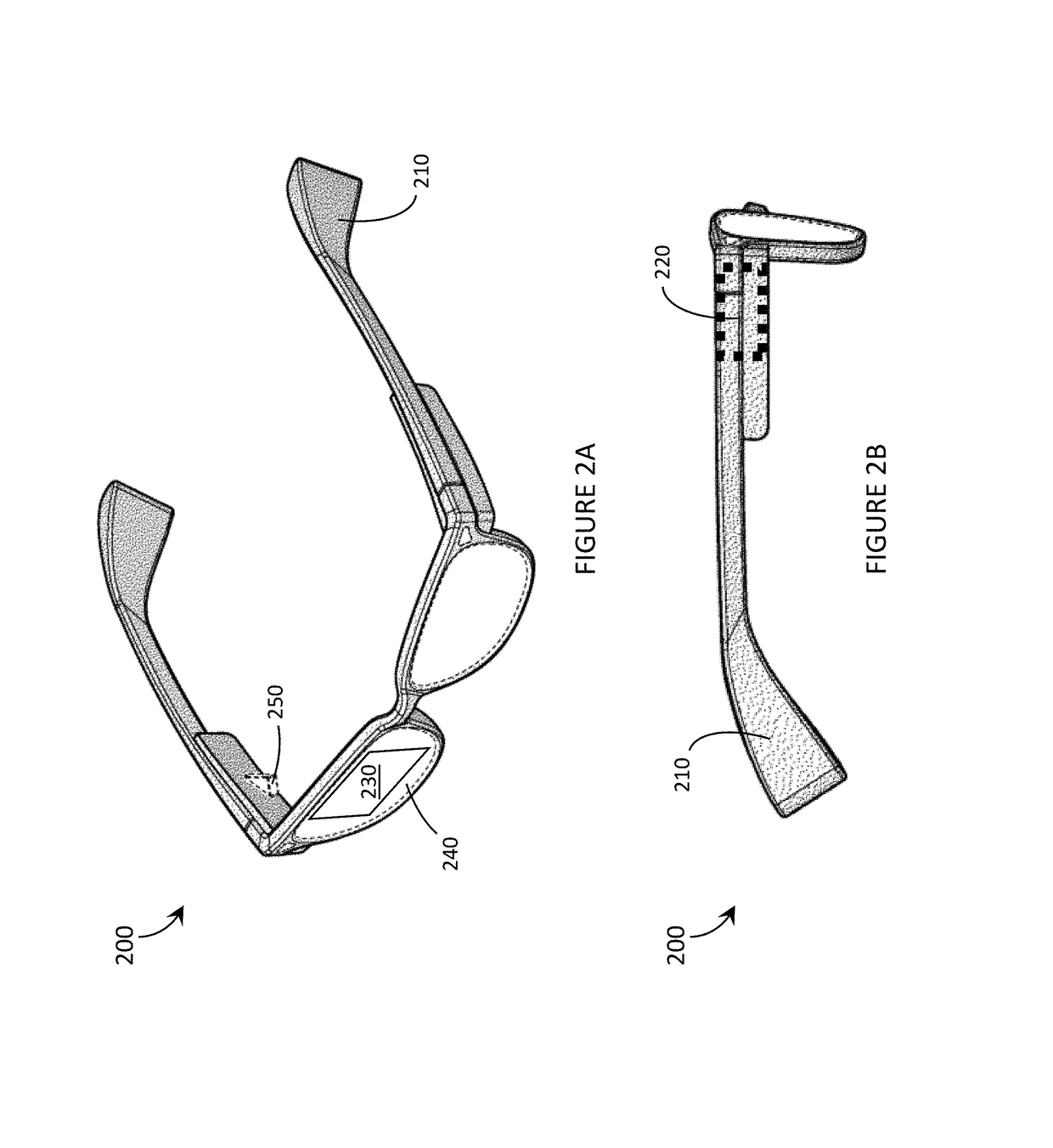
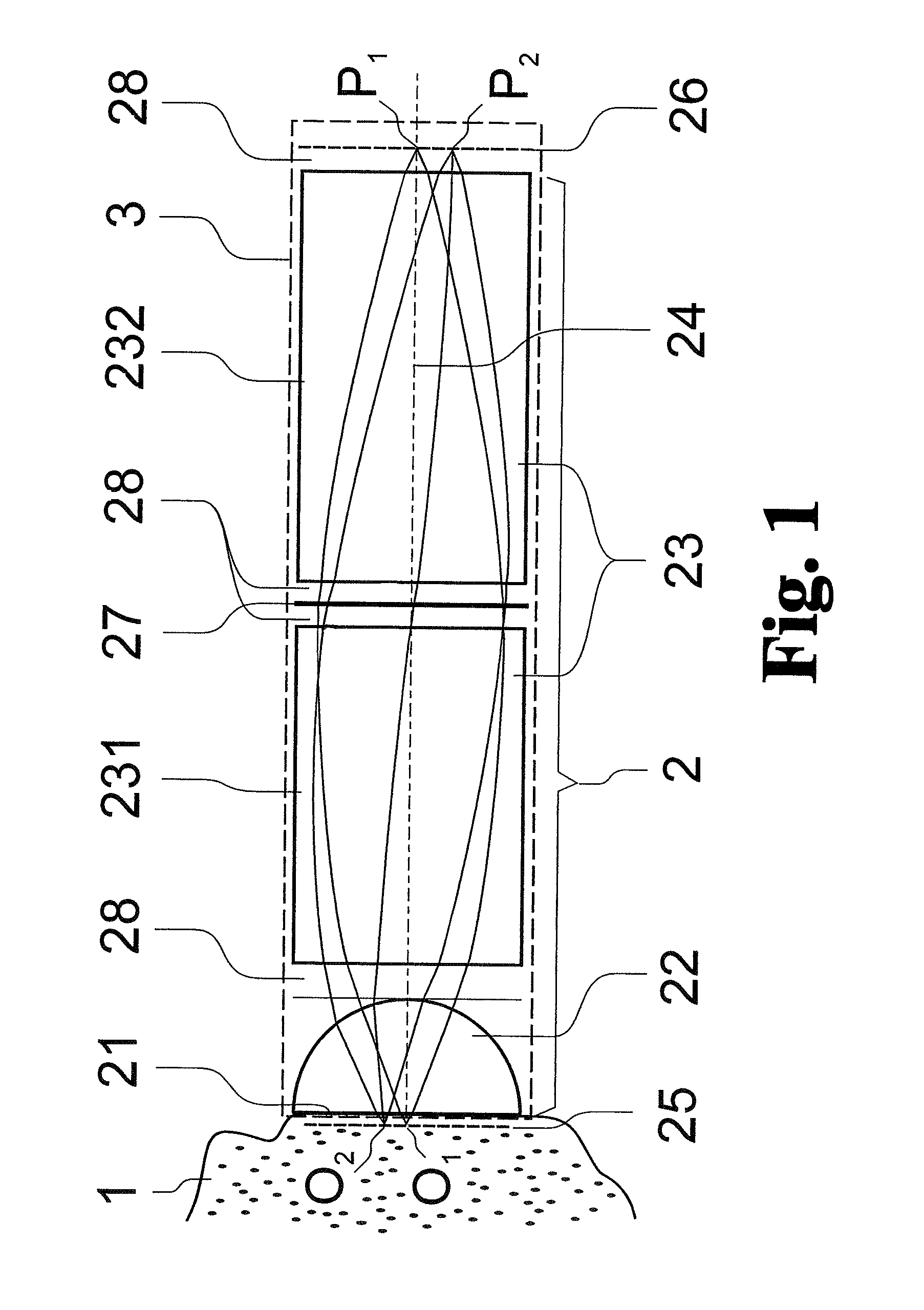
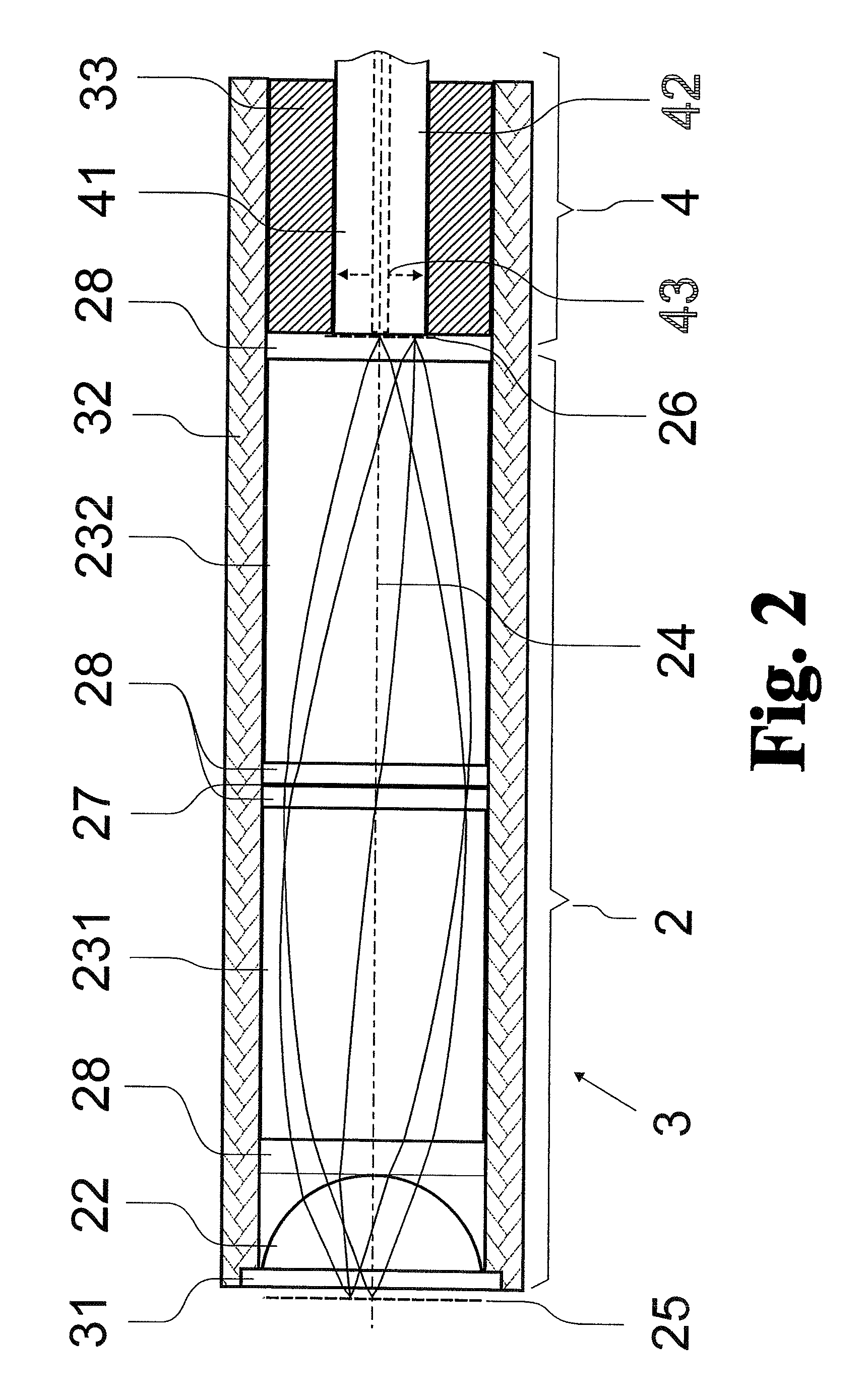
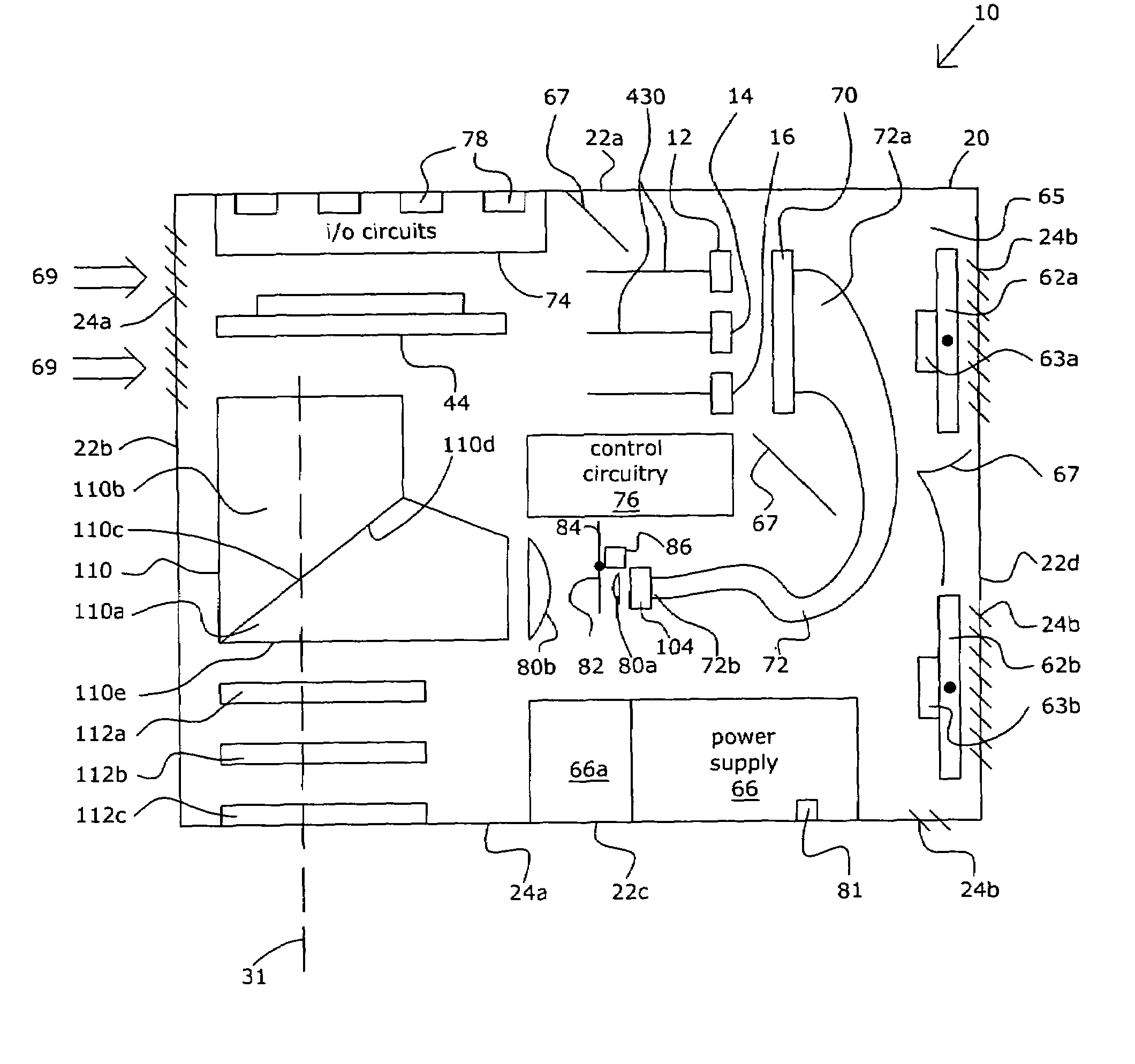
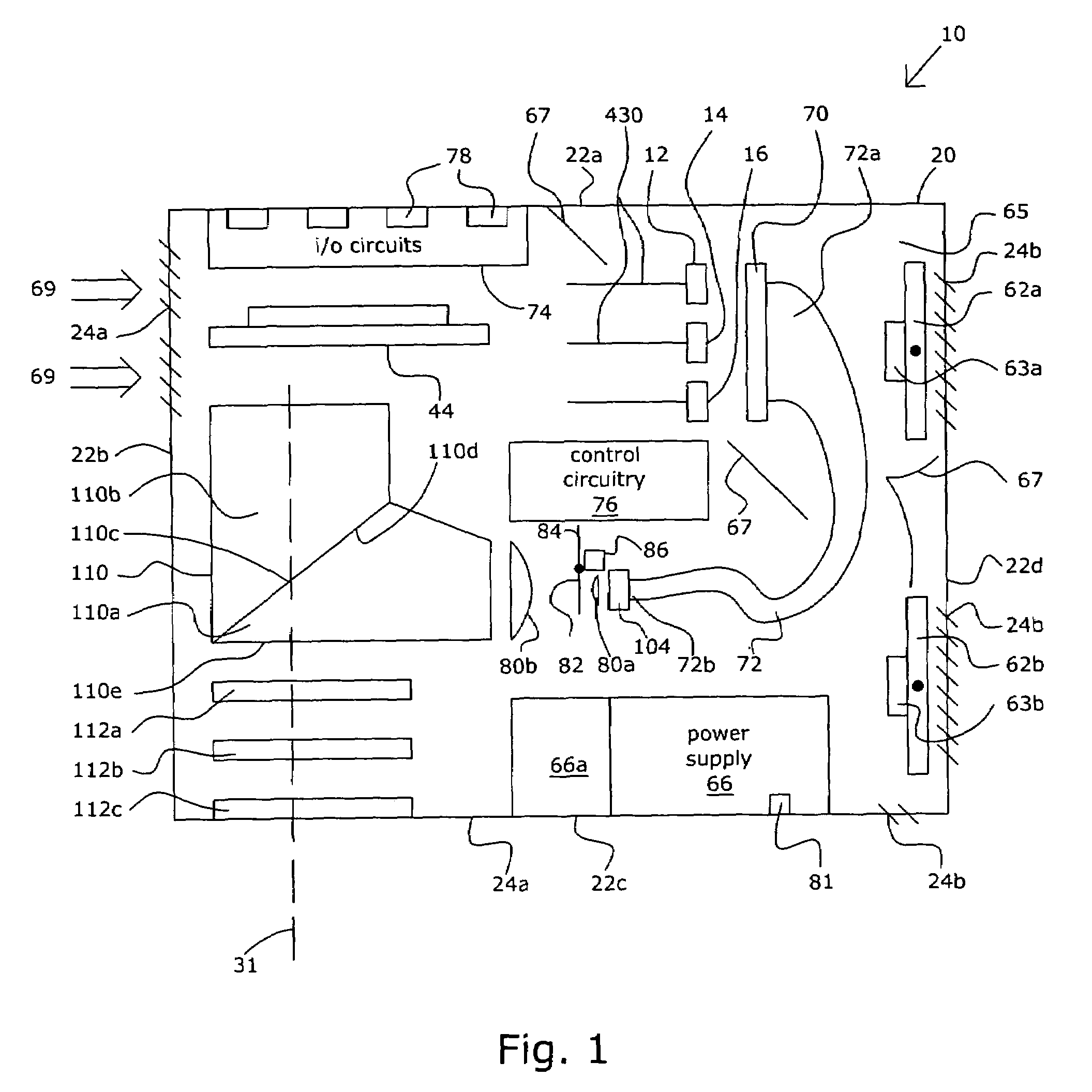
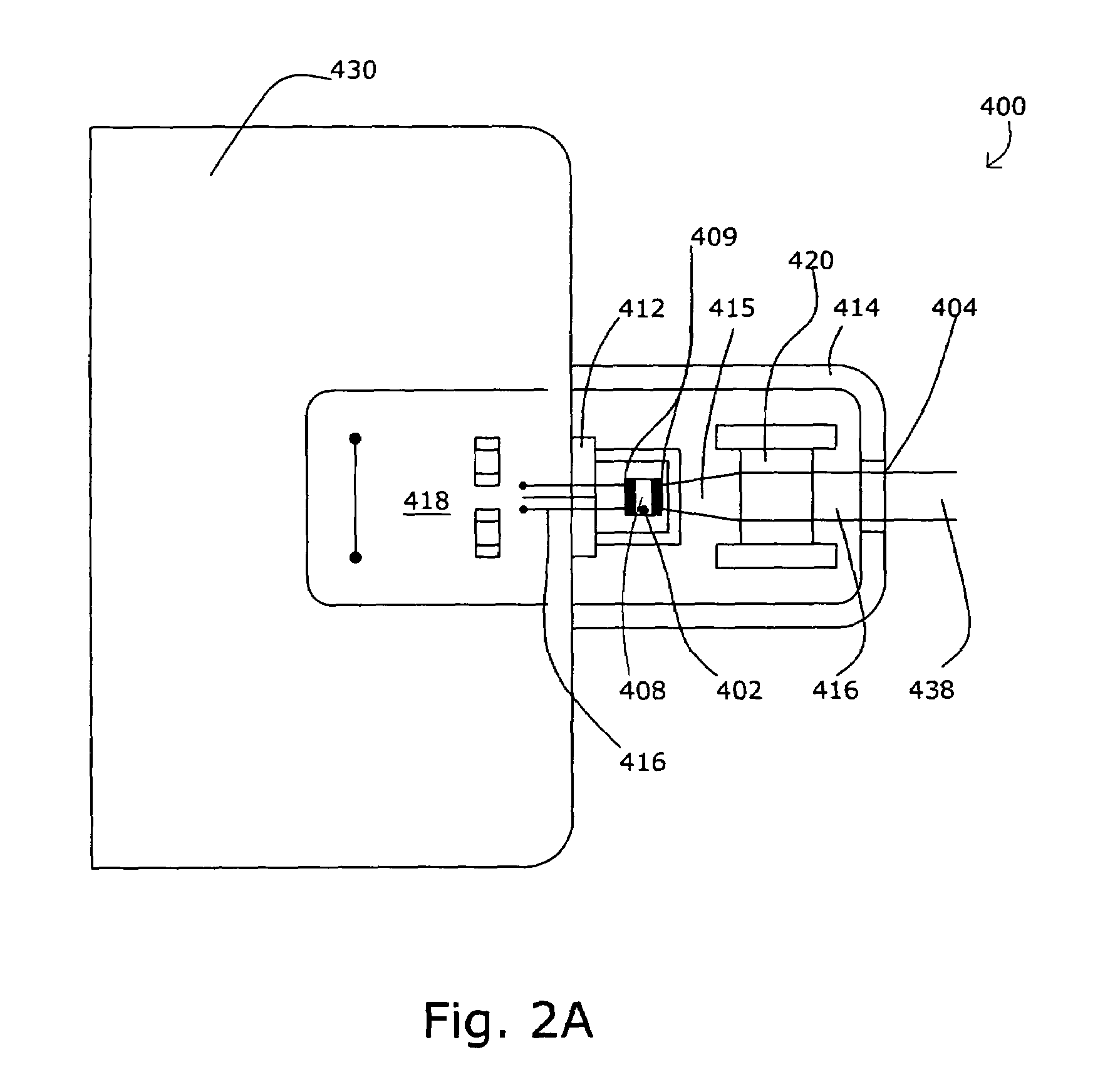
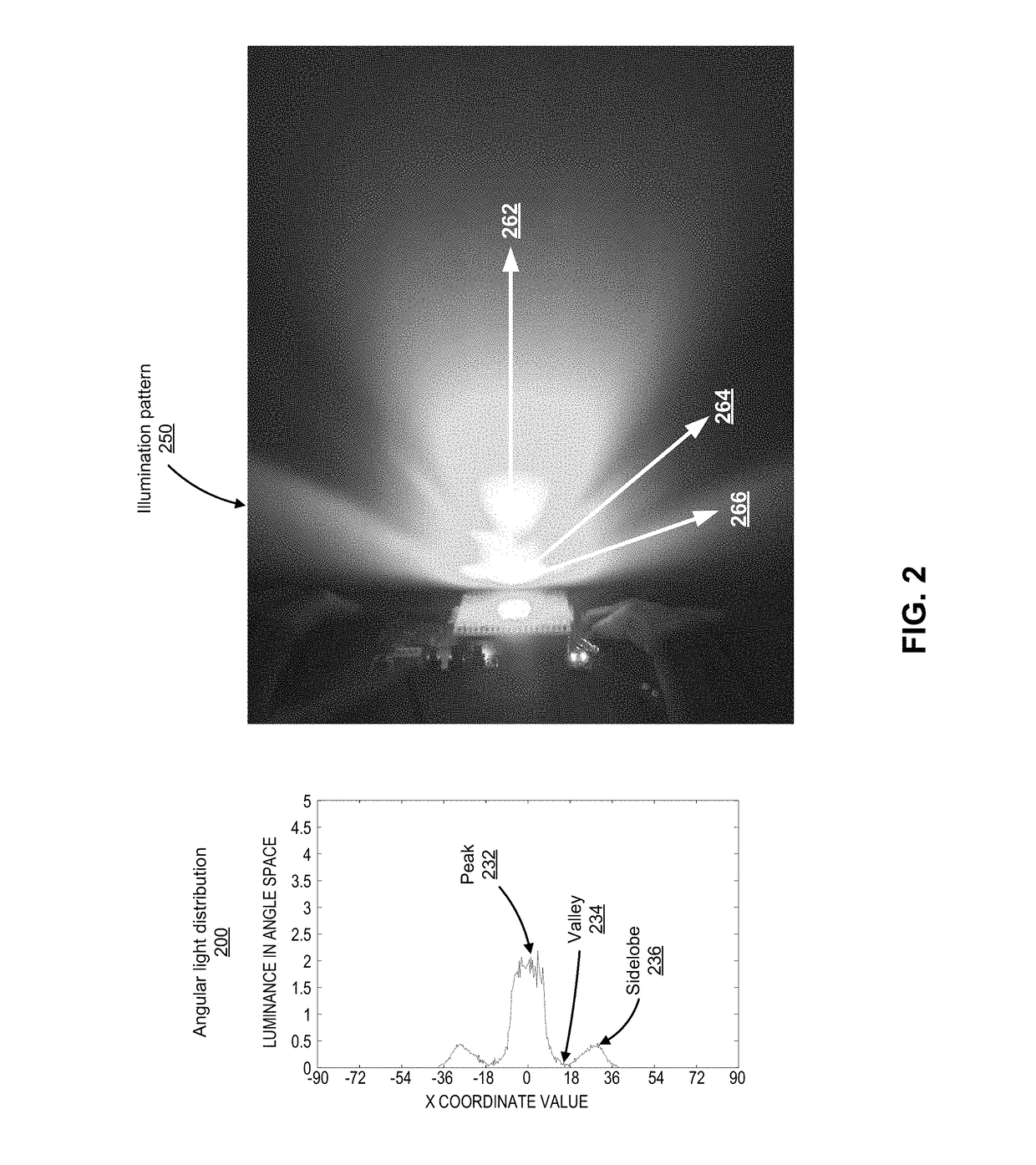
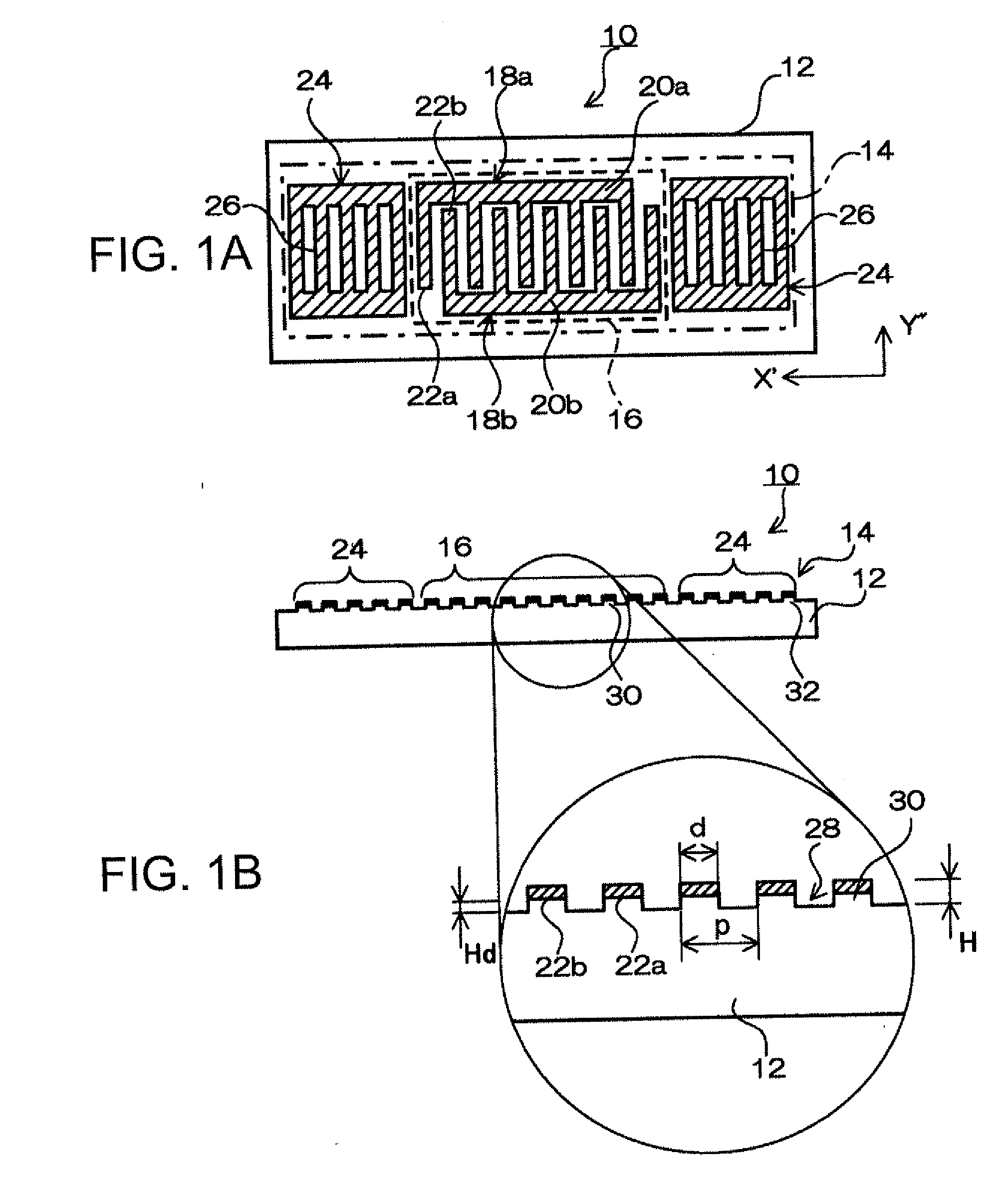
LED light source with field-of-view-controlling optics
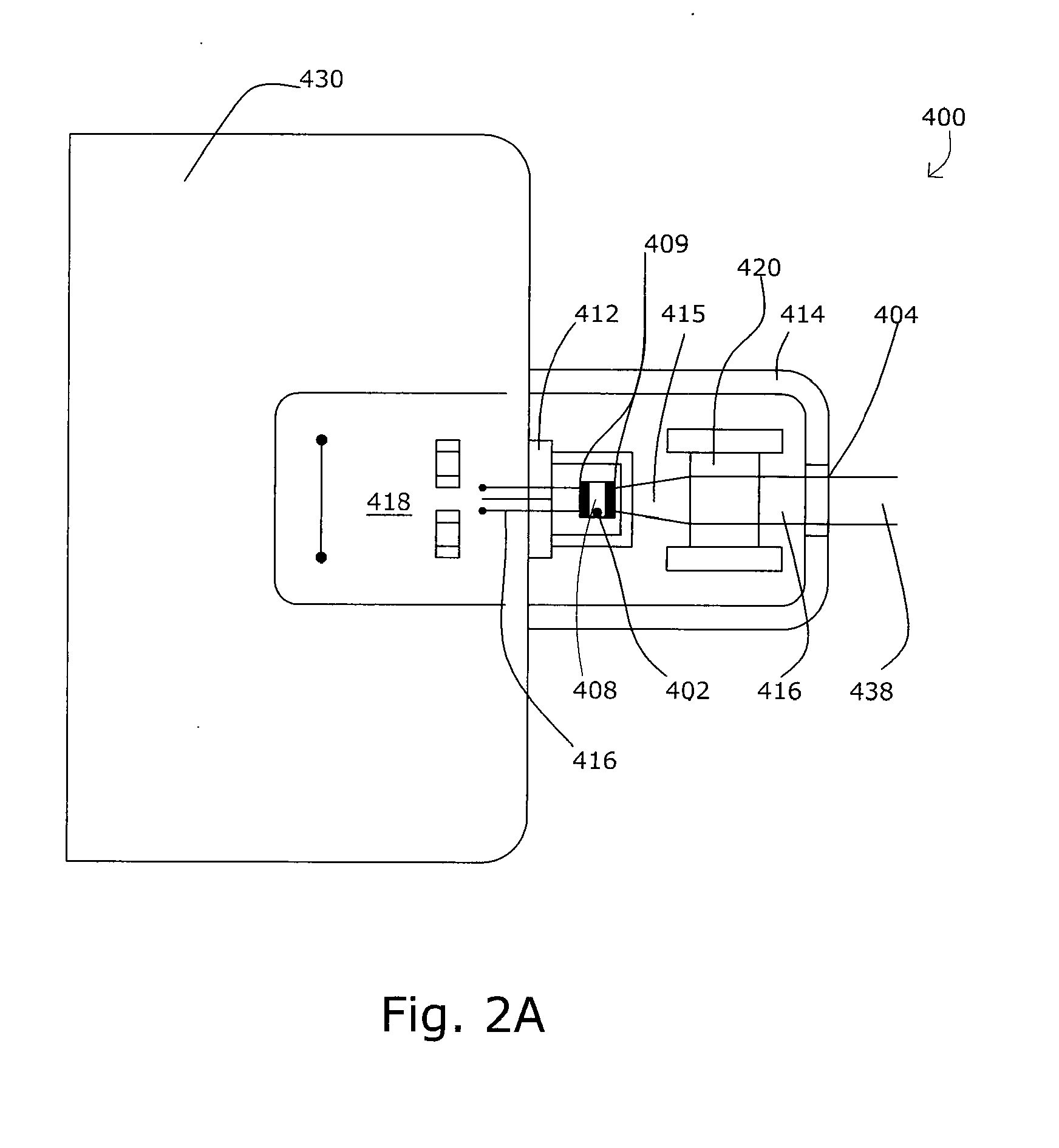
Pixels for a large video display which employs solid-state emitters, such as colored light emitting diodes, as light source are formed by outfitting each colored solid state emitter within the pixel with an individually tailored miniature intensity-enhancing optical system. Each of these miniature optical systems comprises a set of four wide field-of-view Lambertian reflectors 34, a pair of narrow field-of-view Lambertian reflectors 36, and a beam-shaping lens 38. The miniature intensity-enhancing optical system can be specifically designed to restrict emission in the vertical field-of-view, while providing a Lambertian intensity dependence throughout an unrestricted horizontal view. For example, the field-of-view in the vertical direction may be limited to about .+-.30.degree. while the field-of-view is about .+-.90.degree. in the horizontal direction.
Owner:TELEDYNE LIGHTING & DISPLAY PRODS
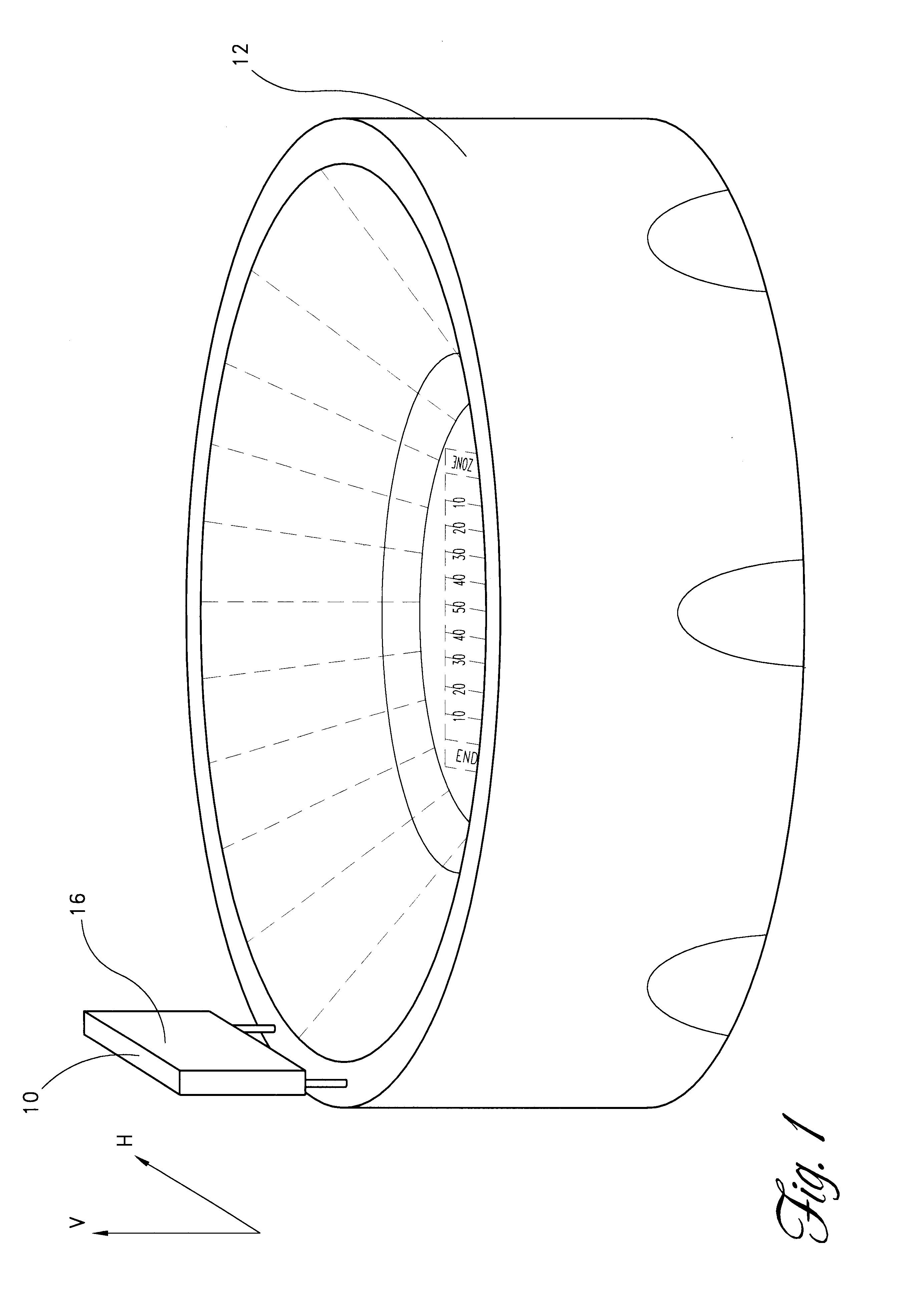
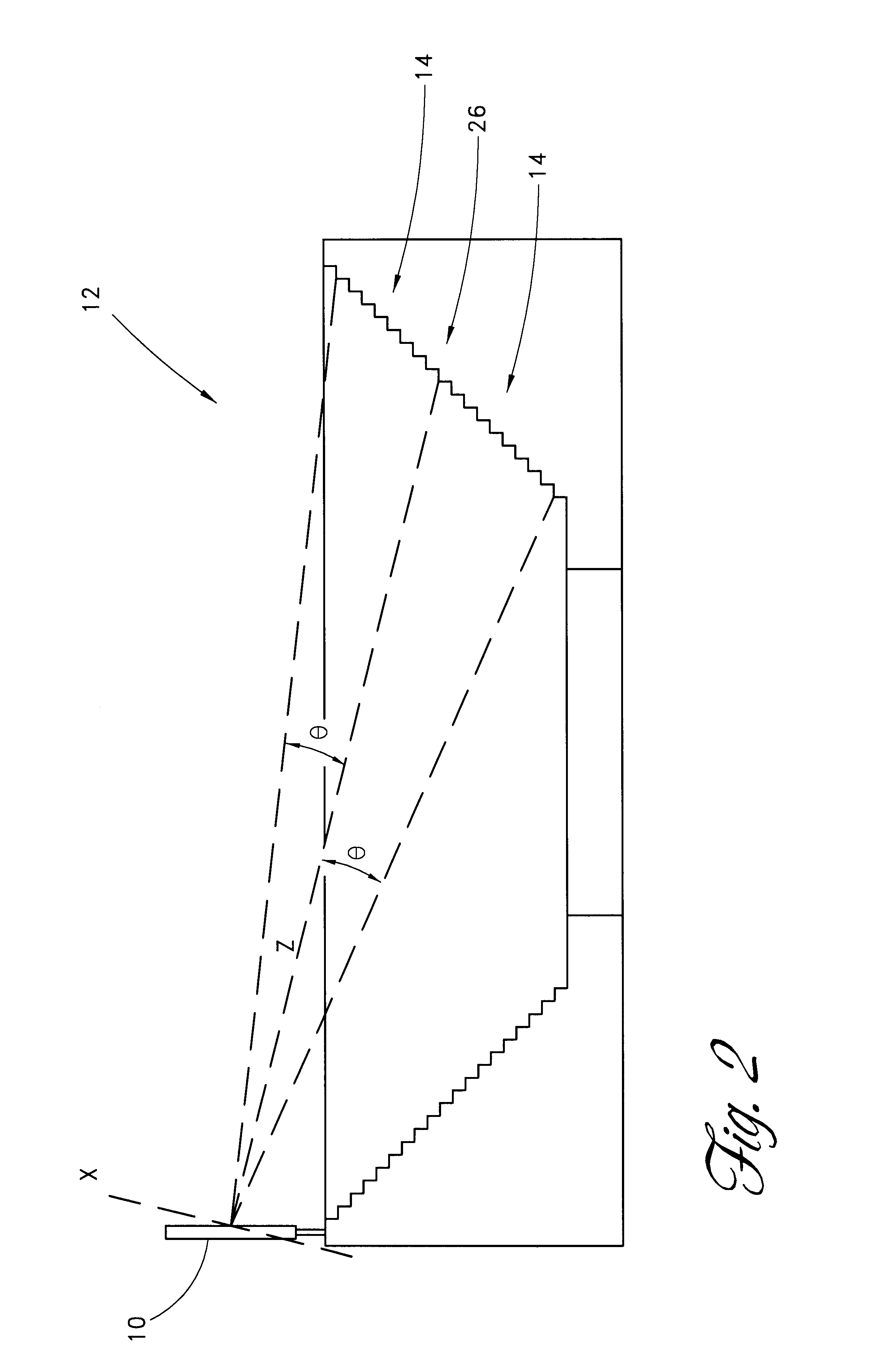
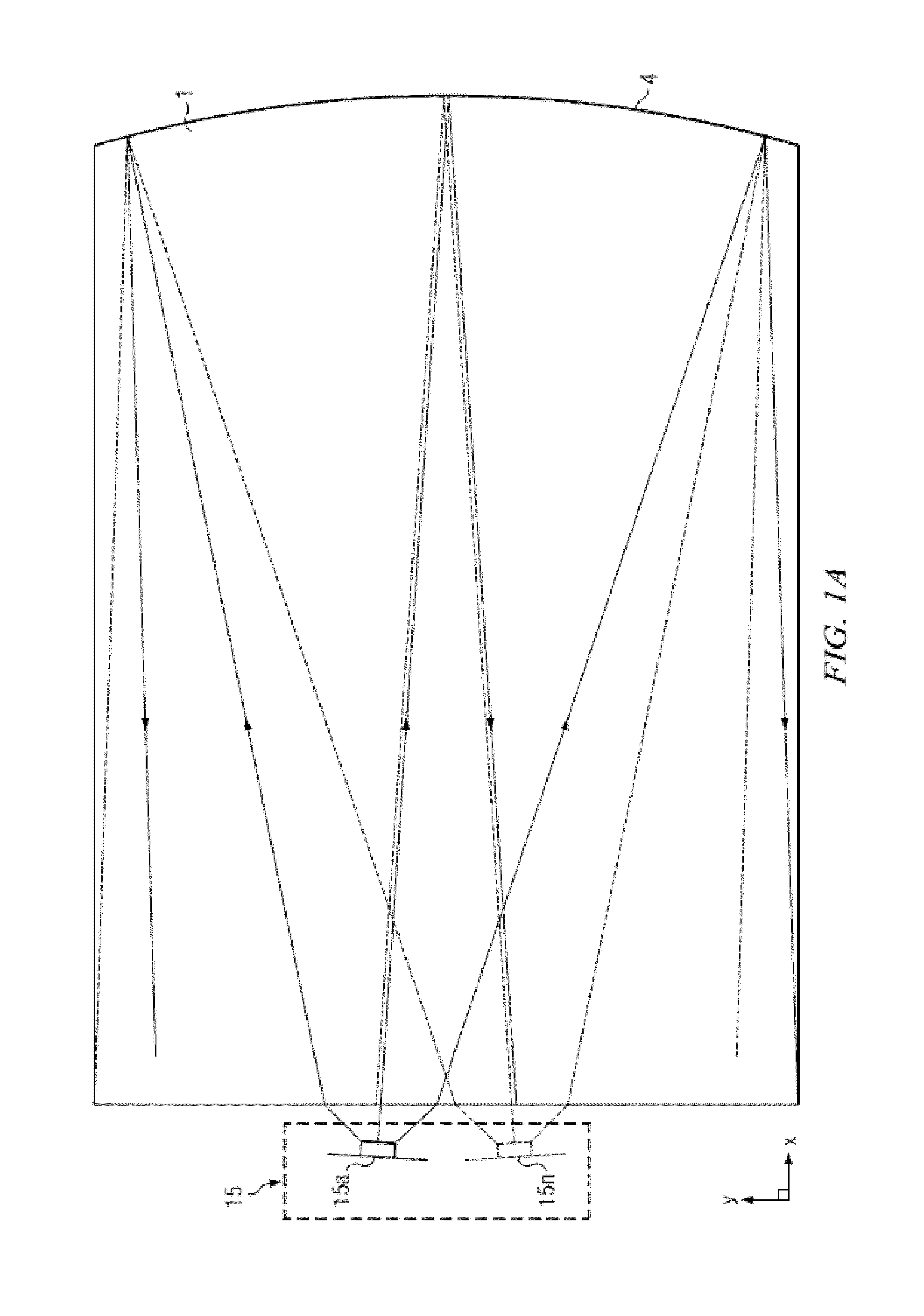
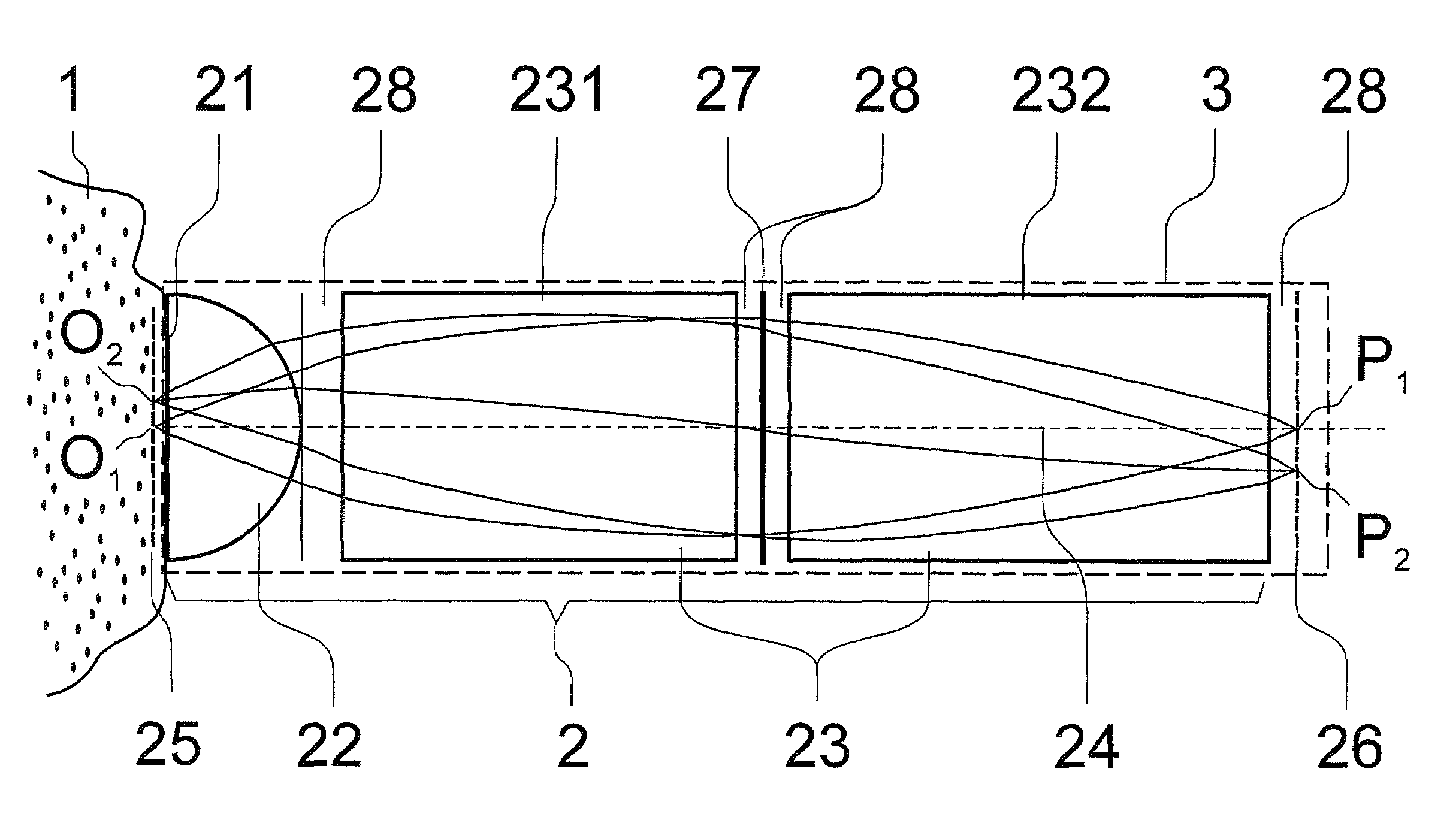
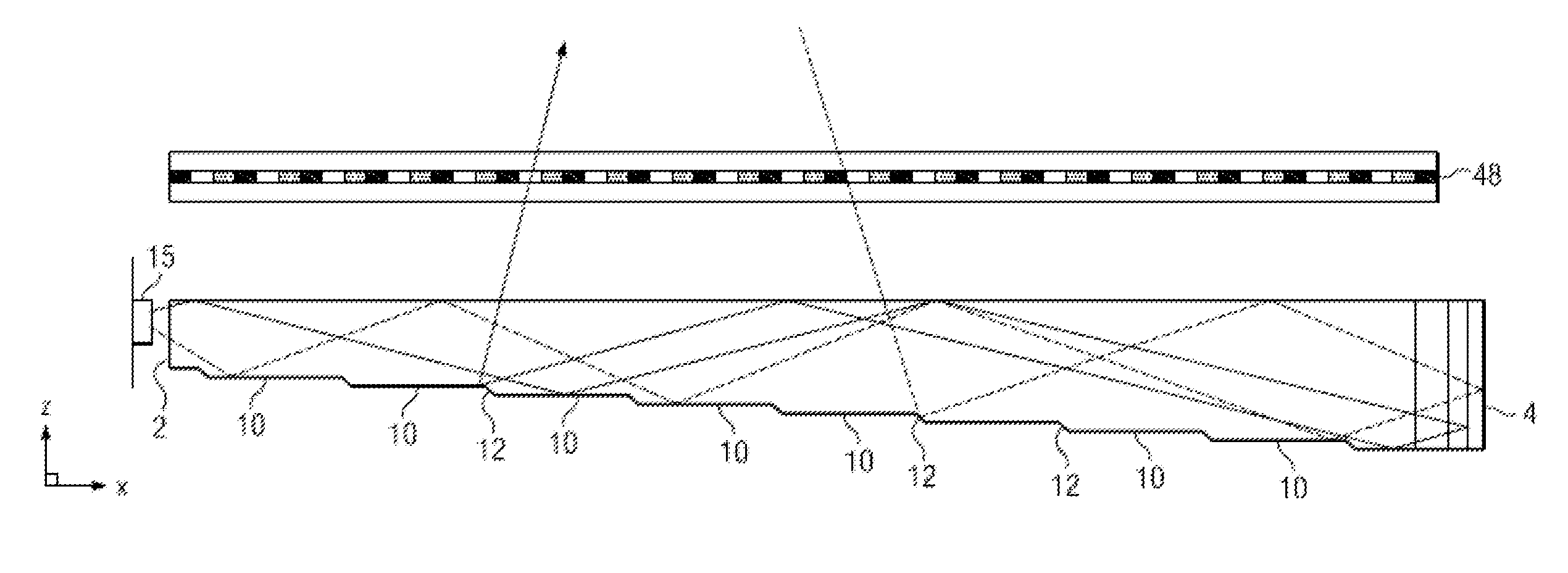
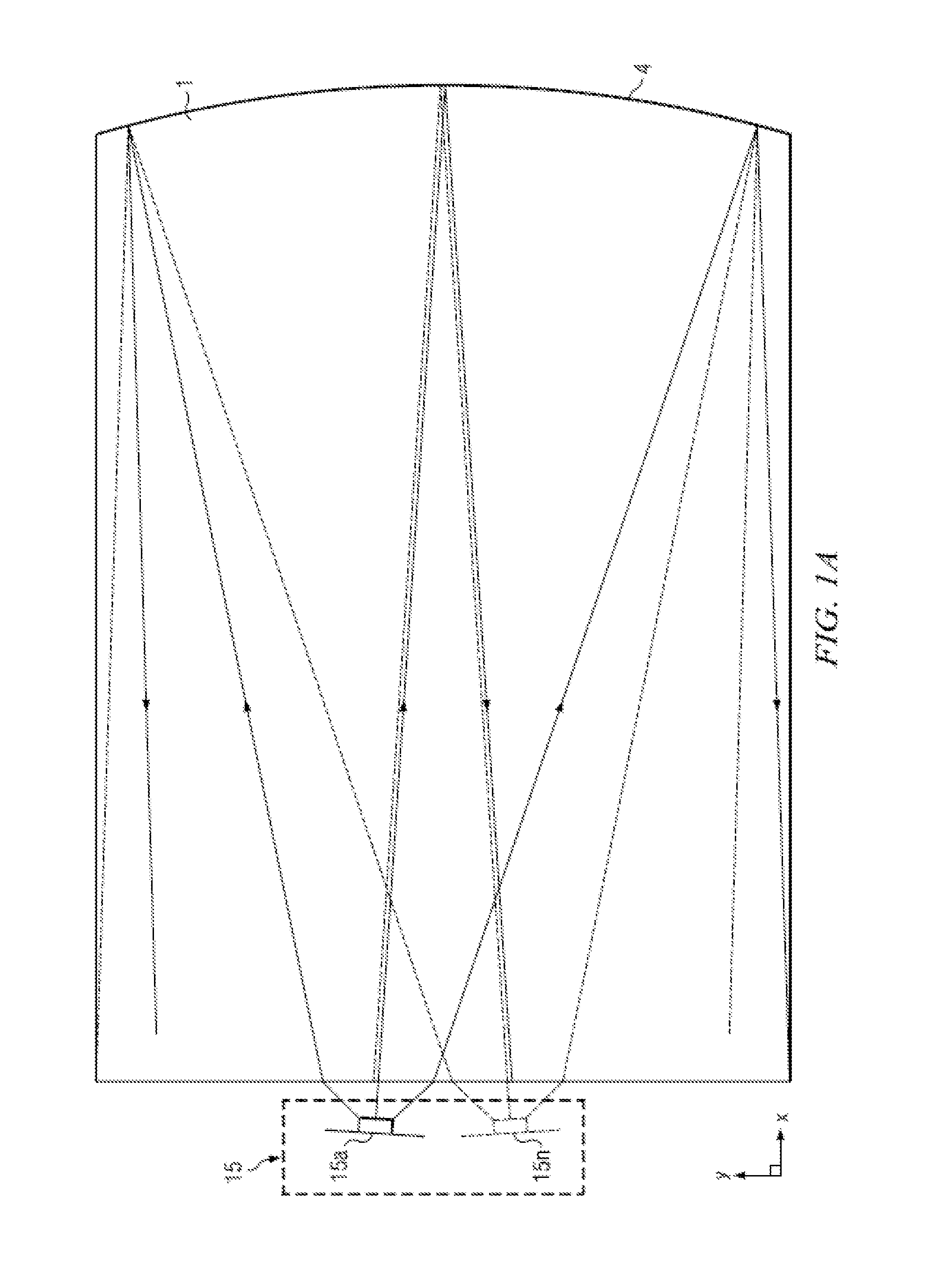
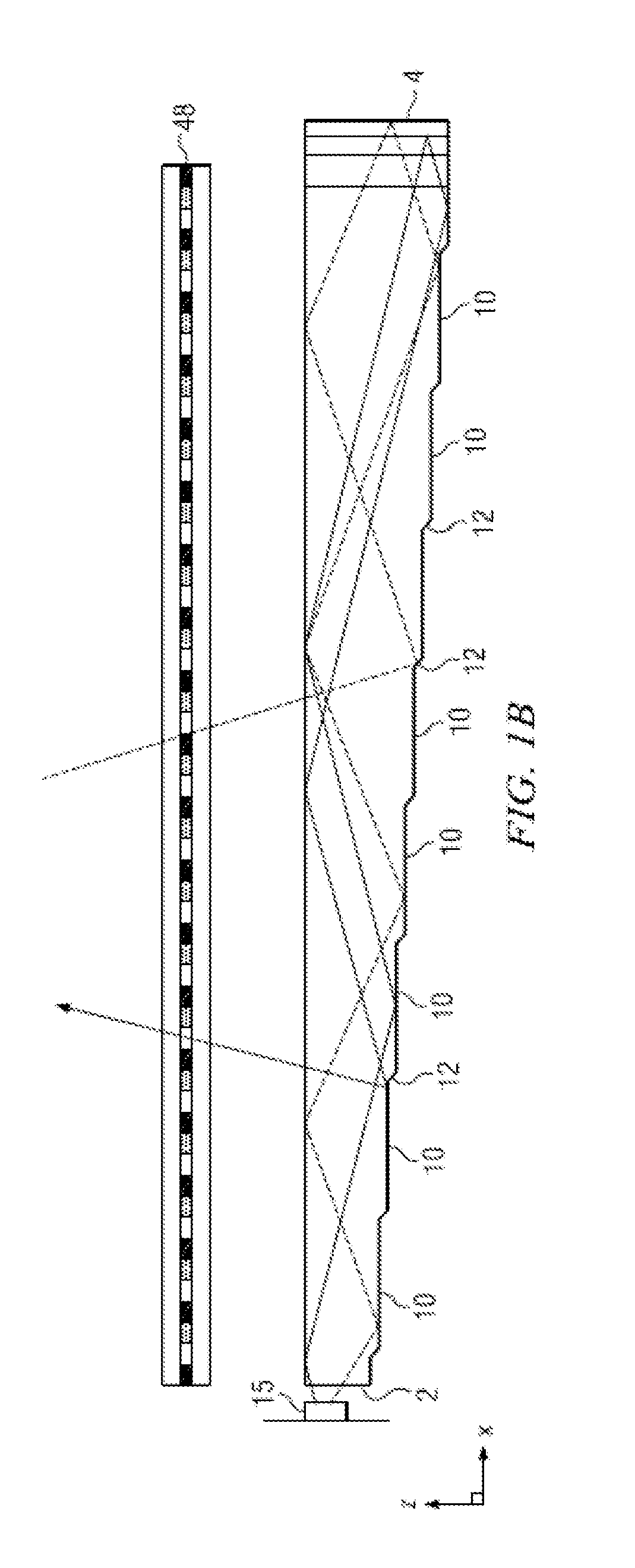
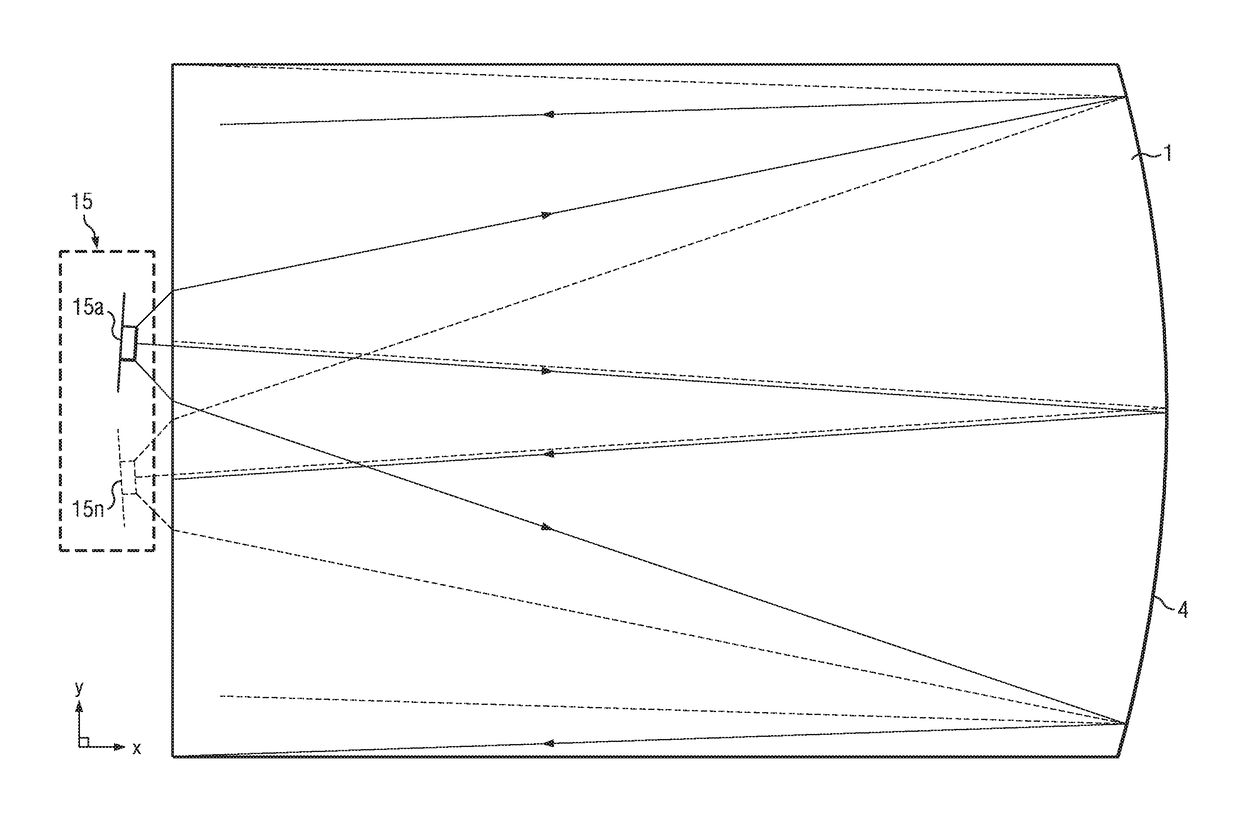
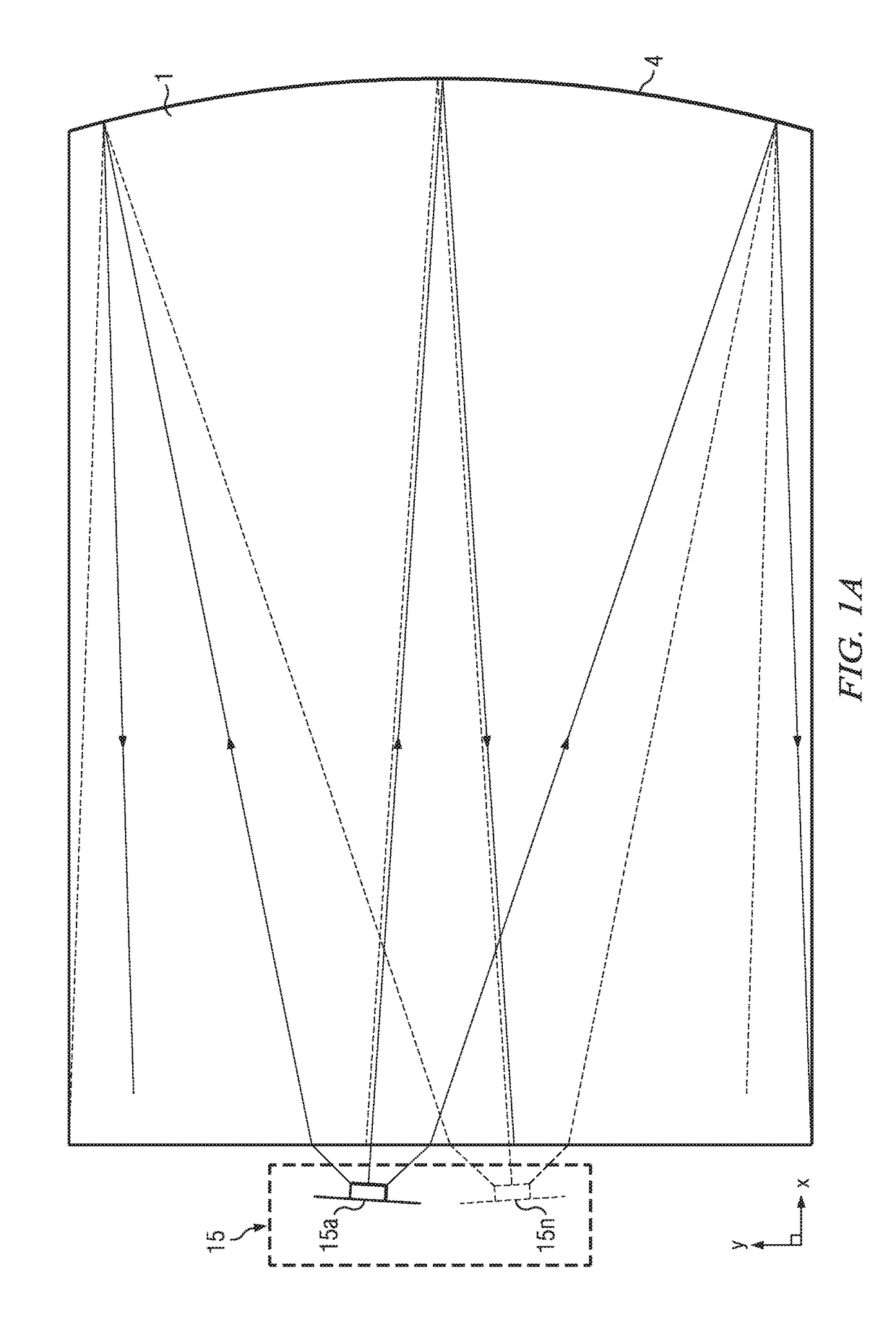
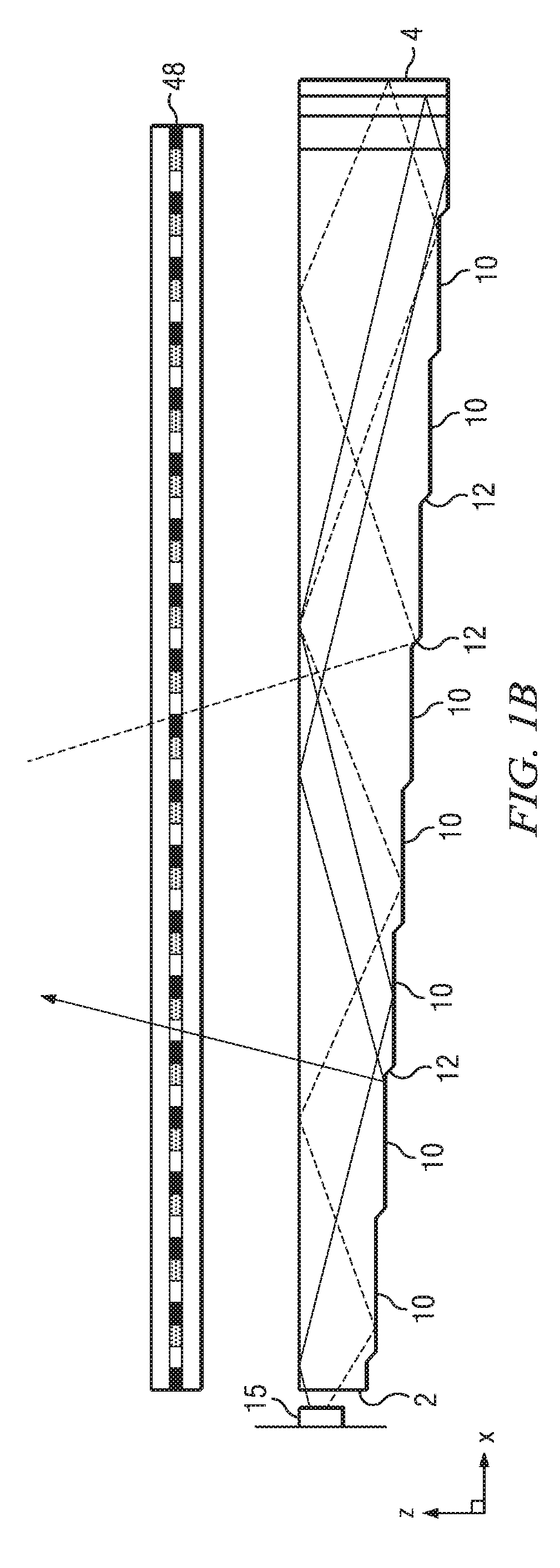
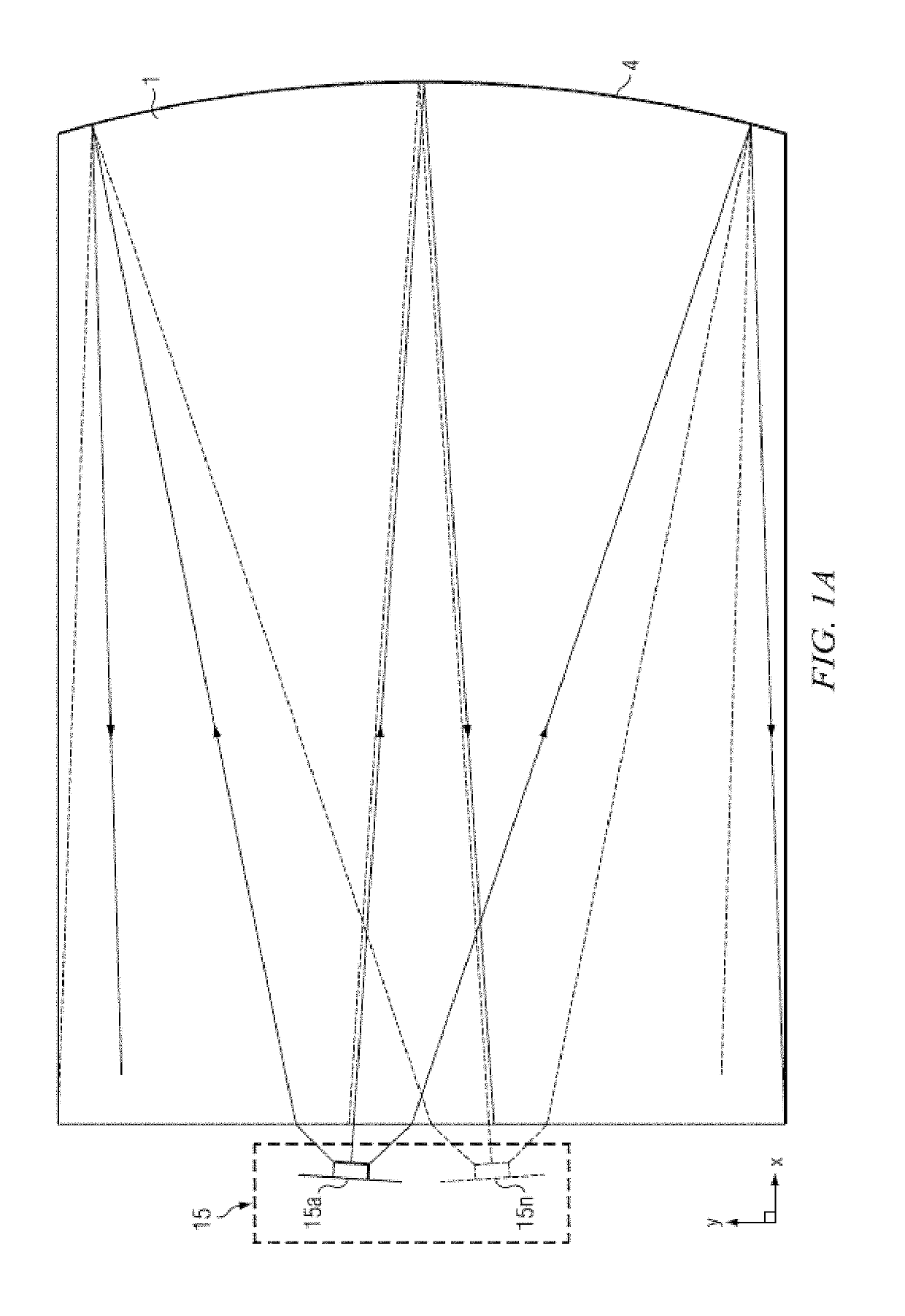
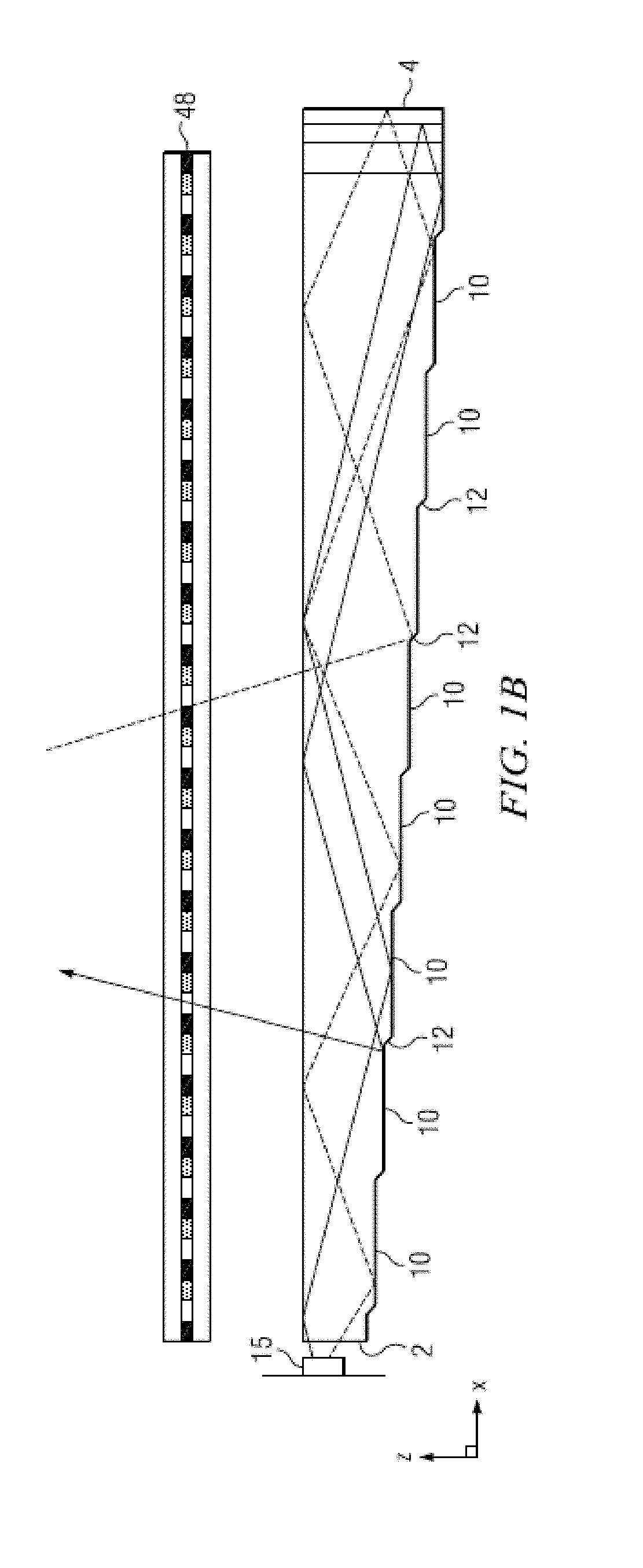
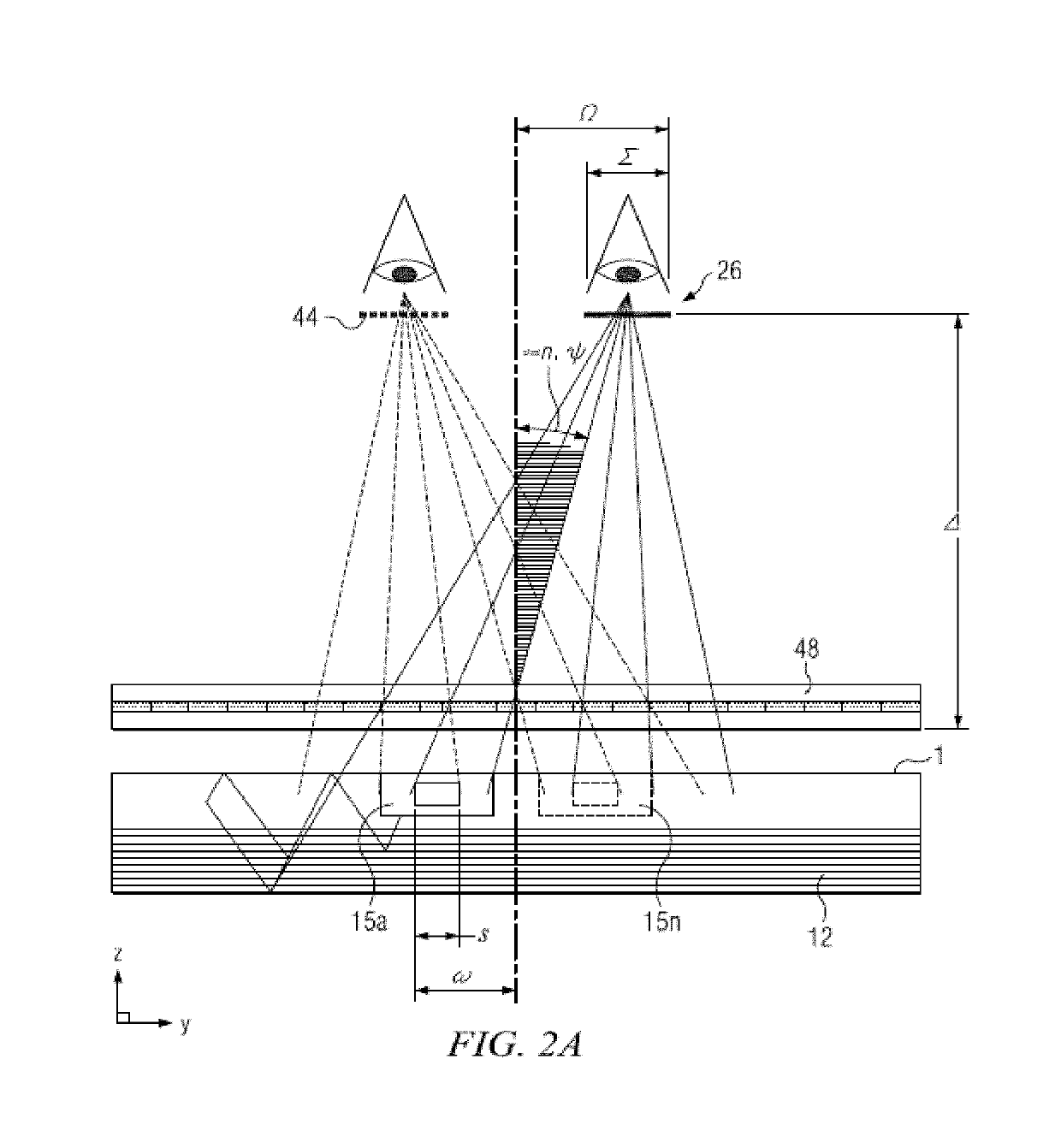
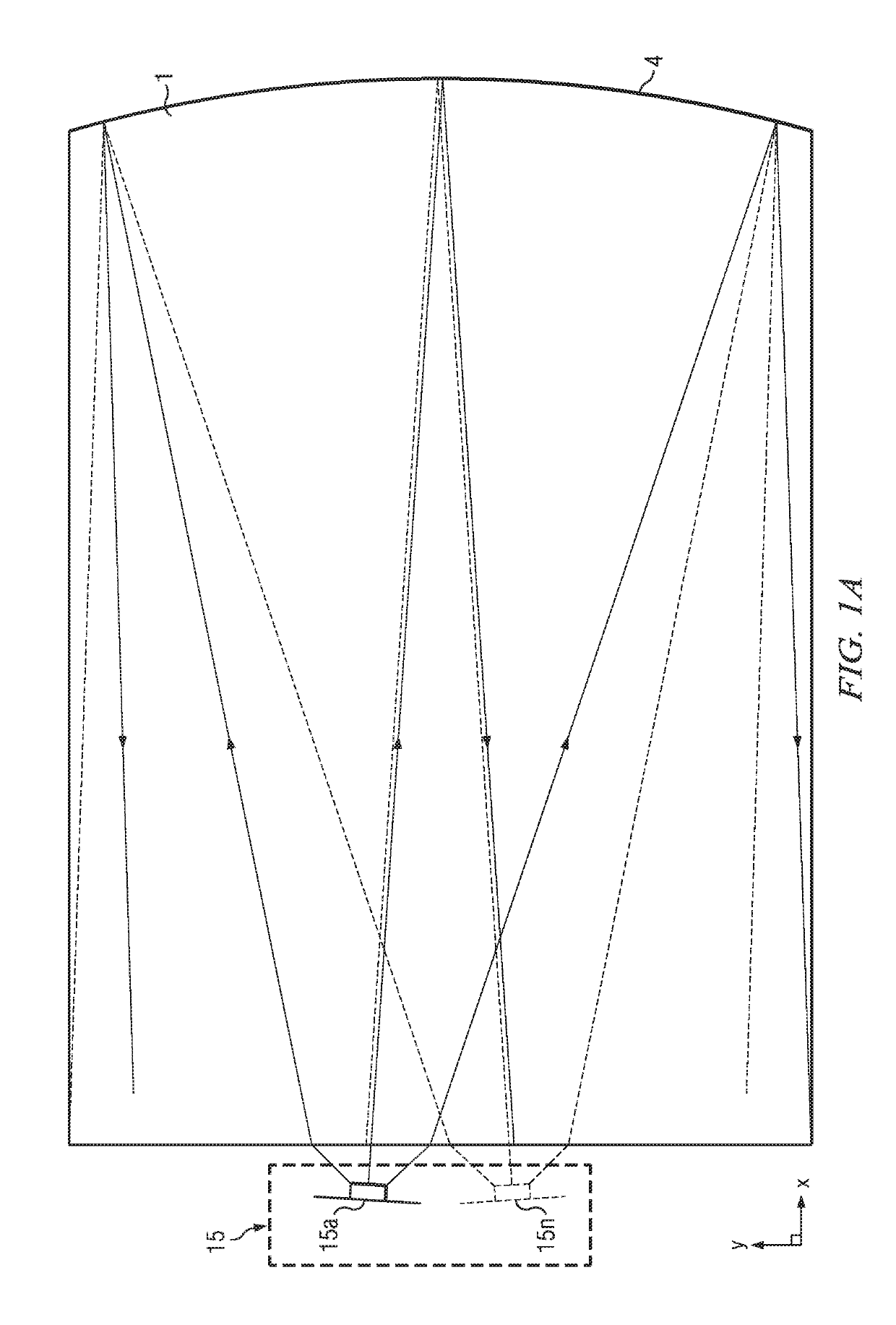
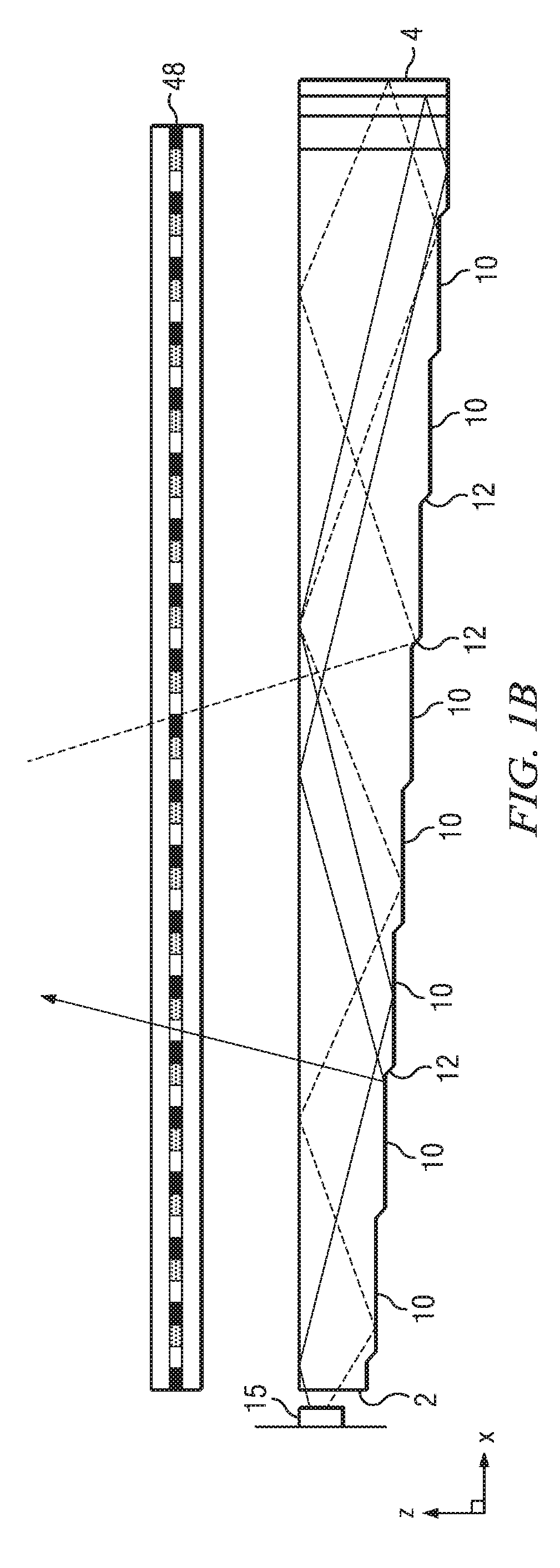
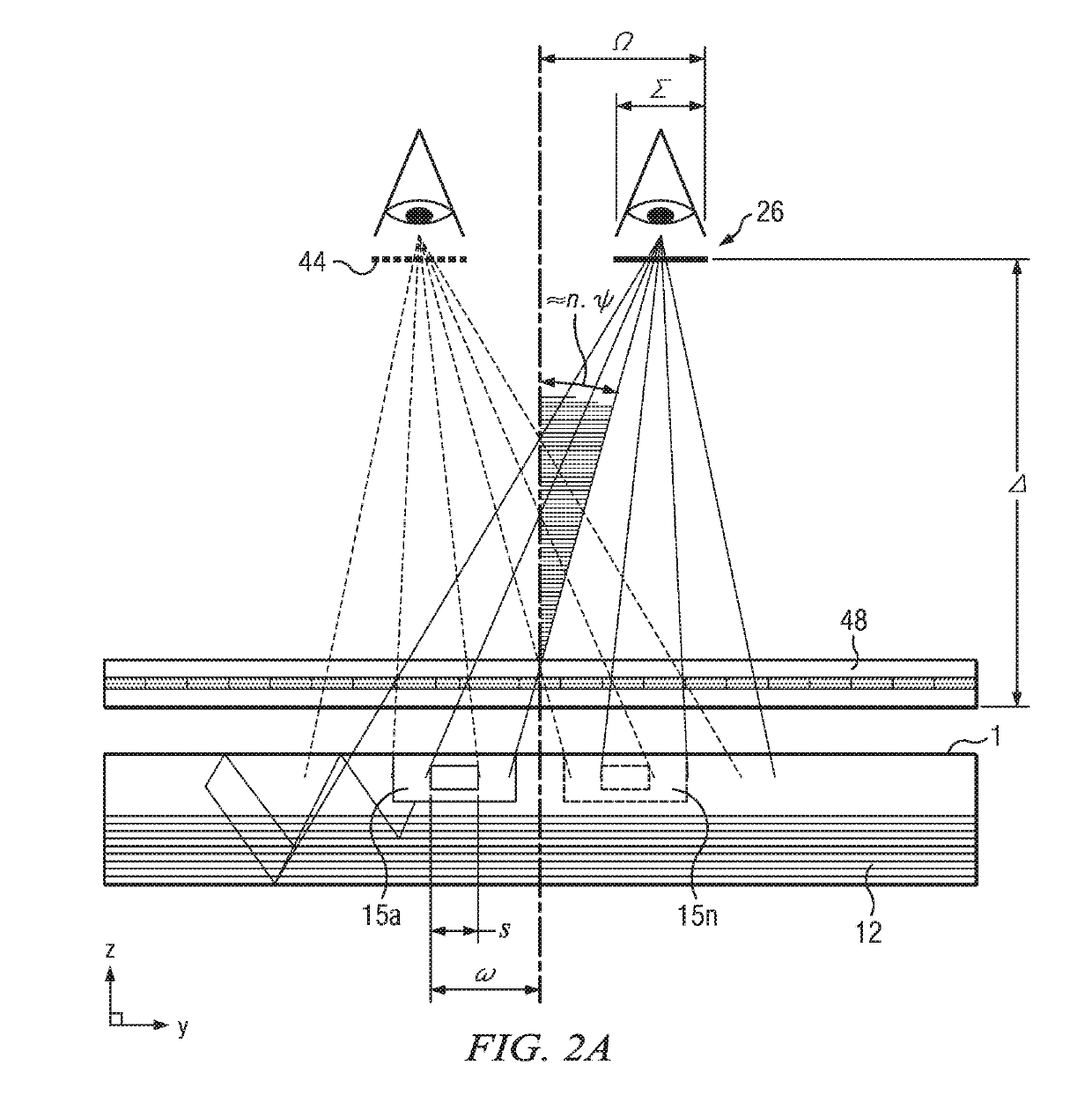
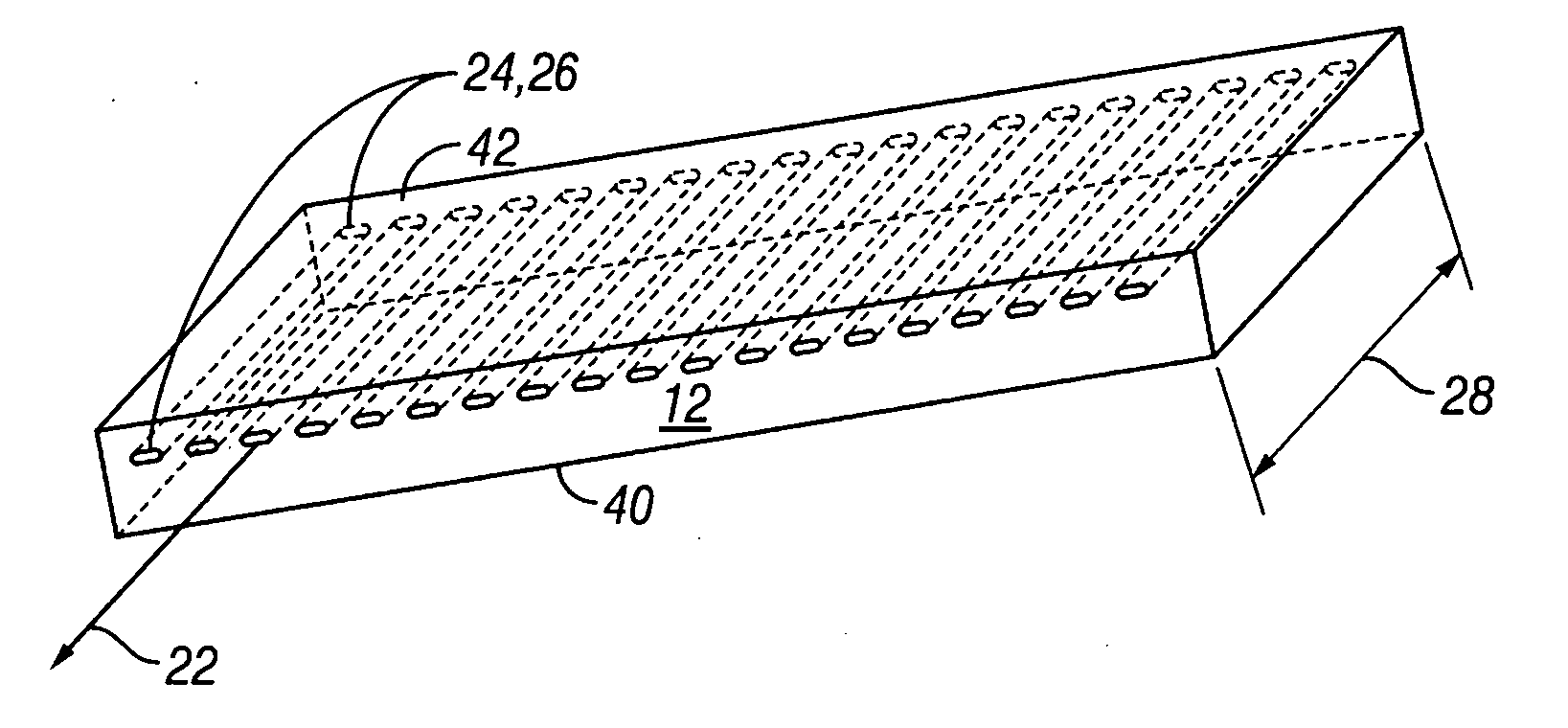
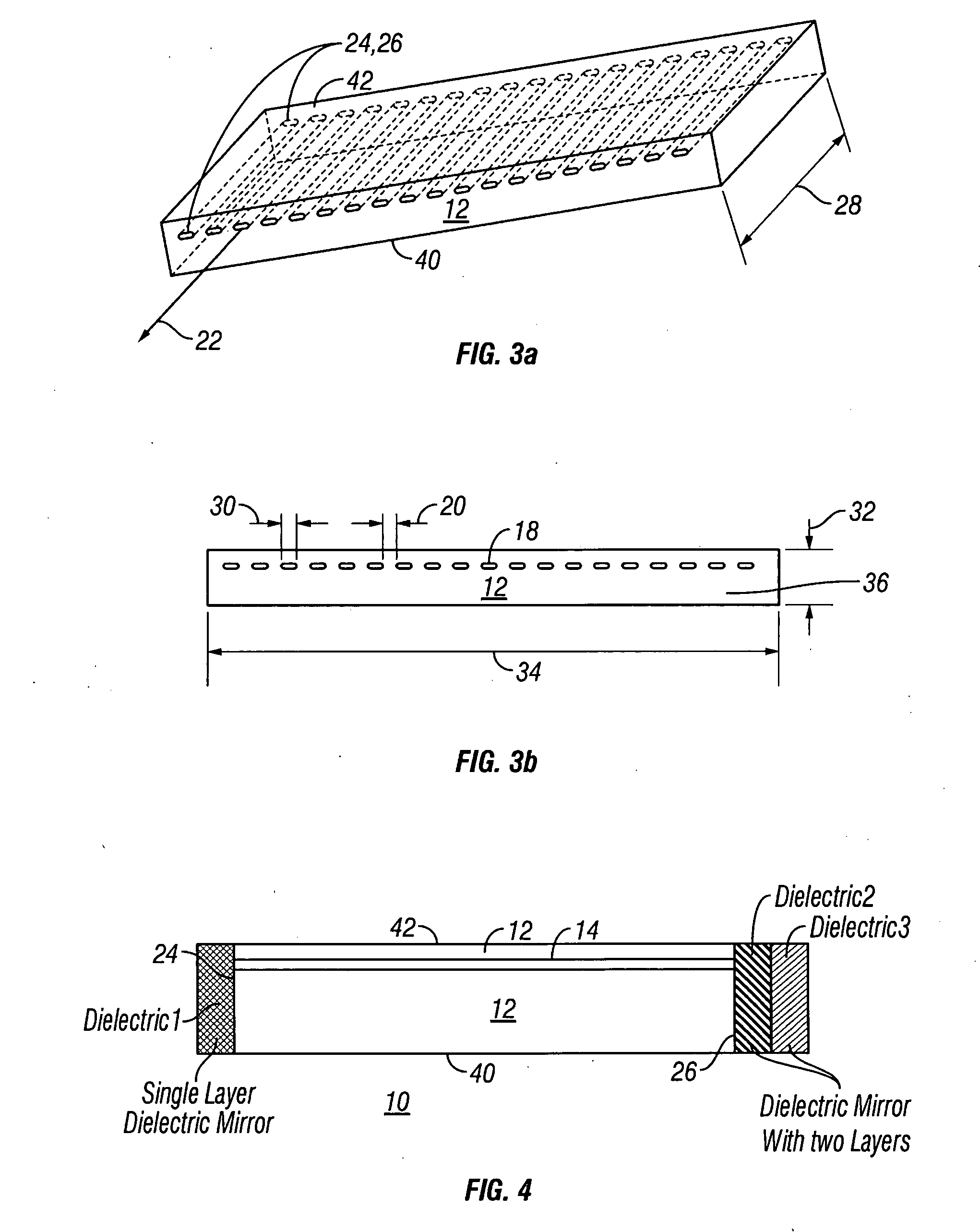
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20130307831A1Improve efficiencyLarge back working distanceMechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsDirect illuminationLight beam
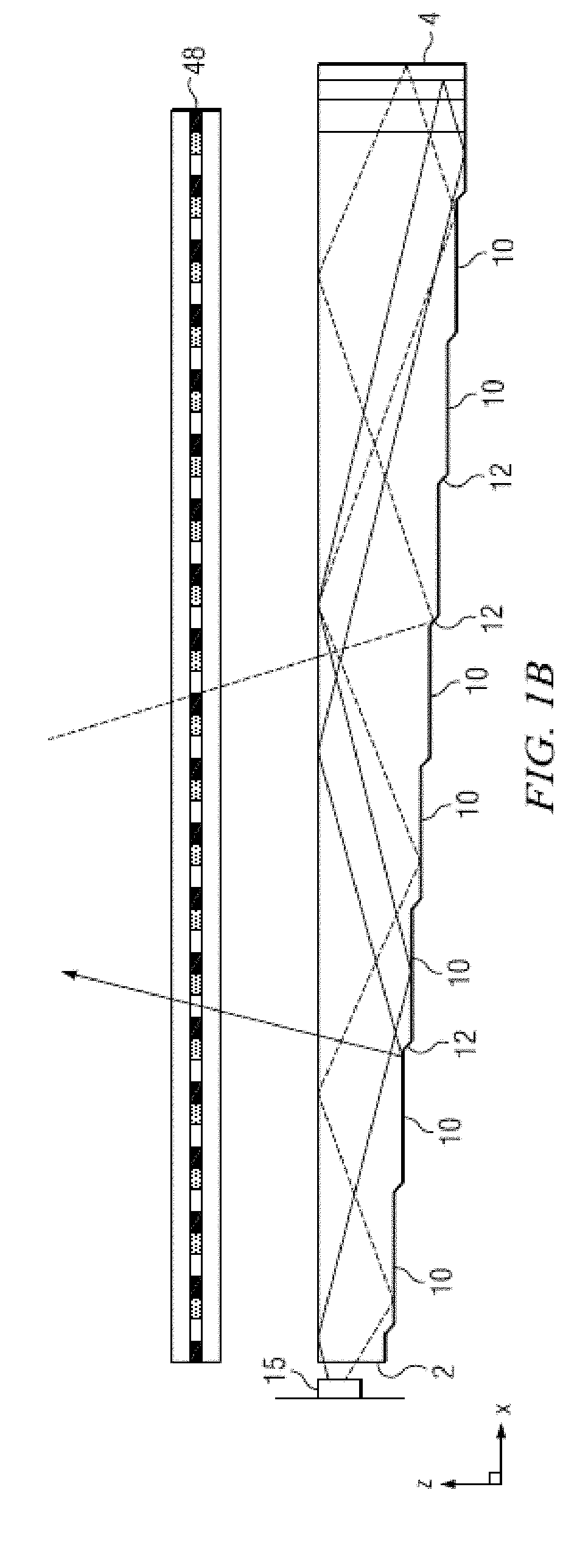
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. The uncorrected system creates non-illuminated void portions when viewed off-axis preventing uniform wide angle 2D illumination modes. The system may be corrected to remove this non uniformity at wide angles through the introduction of additional sources away from the system's object plane, additional imaging surfaces, and / or by altering ray paths.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
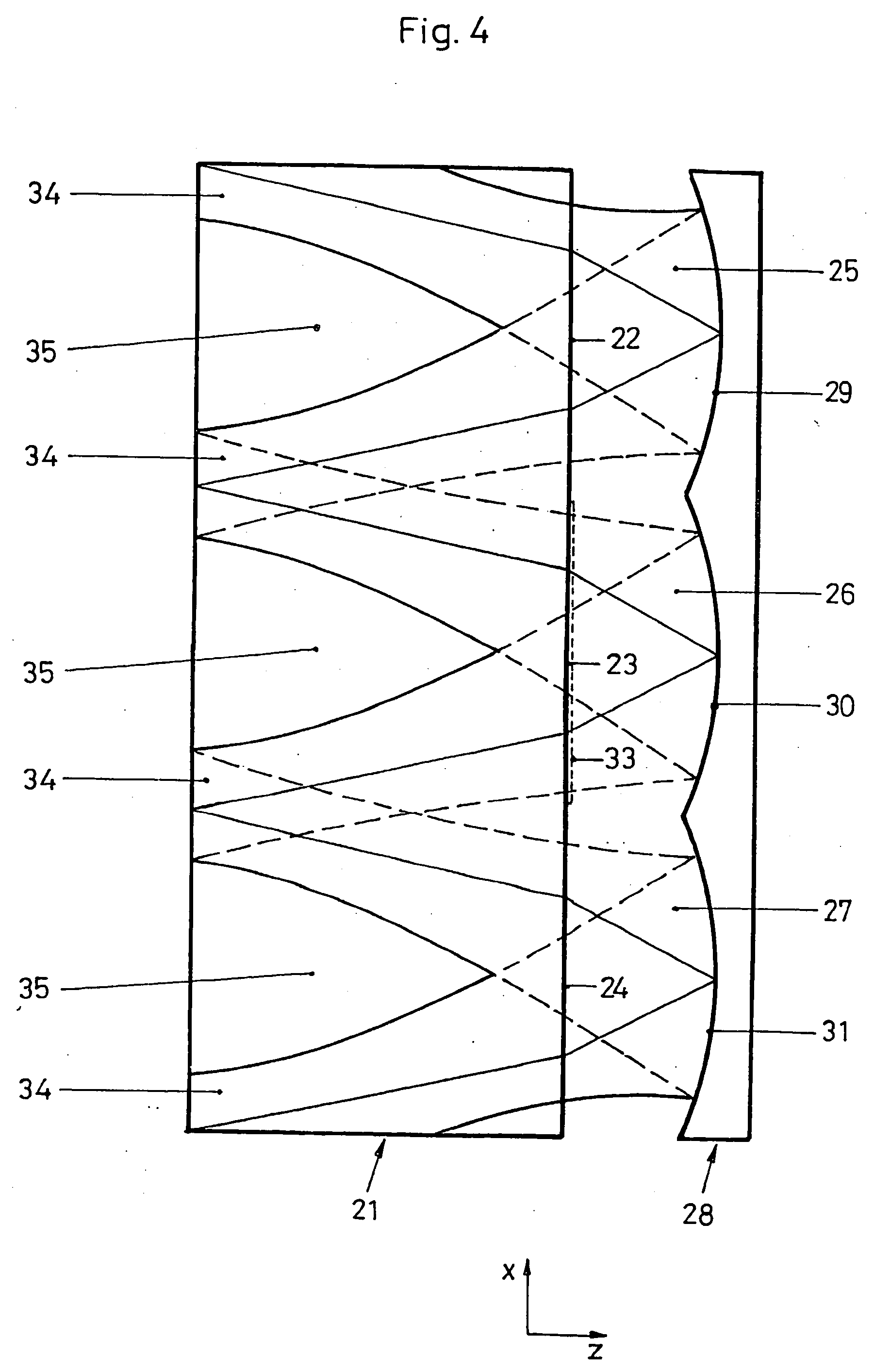
Homogenizing optical sheet, method of manufacture, and illumination system
An optical sheet that accepts light transmitted at or within a specific entrance cone angle that then redirects and transmits the light within an exit cone that is substantially normal to the sheet's plane. The intensity of the light within the exit cone is substantially uniform for any light source entering the sheet within the sheet's acceptance angle. The optical sheet is made of transparent material with microlens arrays formed on its opposite front and back surfaces. The thickness of the optical sheet is sufficient so that the microlens on the opposite surfaces are separated a distance equal to the microlens focal length, with each microlens on the front and back surfaces having substantially similar size and shape, with centers transversely aligned. When used with one or more light sources located on one surface, the transmitted light through the optical sheet is uniform in intensity across a second surface. When used with a second optical sheet, aligned parallel to the first optical sheet, the transmitted light is uniform across and throughout angles within the exit cone at a second surface. An economical method of manufacturing the optical sheet is also provided.
Owner:POWELL KARLTON DAVID +1
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors
ActiveUS20170299956A1Reduce disagreementSemiconductor laser arrangementsNon-optical adjunctsHead-up displayLaser light
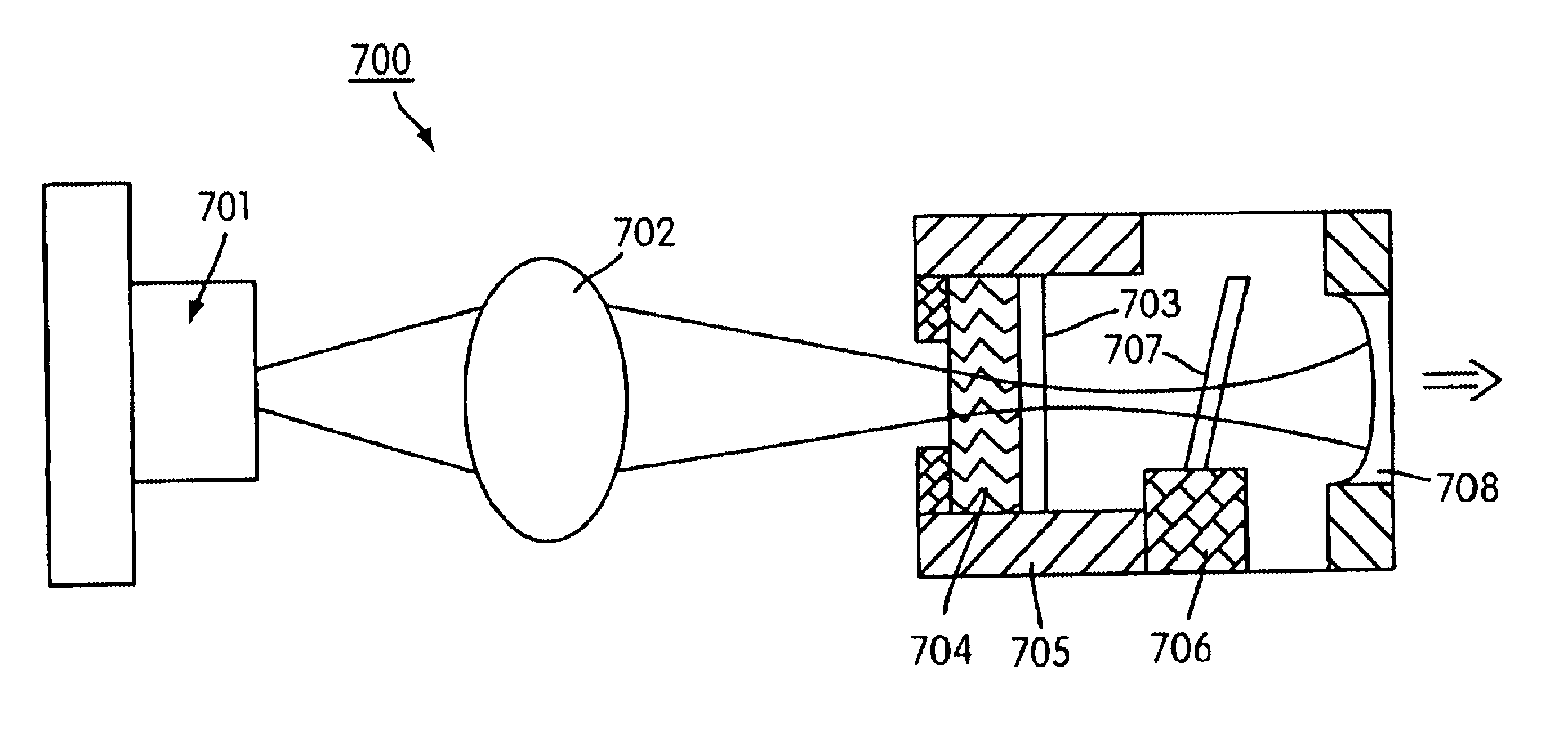
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors are described. A laser projector includes N≧1 laser diodes, each of which emits laser light having a divergence. Each laser diode is paired with a respective primary or collimation lens to at least reduce a divergence of the laser light that the laser diode produces. Downstream from the primary lens(es) in the optical path(s) of the laser light, a single dedicated secondary or convergence lens converges the laser light to a focus. By initiating the convergence of the laser light at the secondary or convergence lens as opposed to at the primary or collimation lens(es), numerous benefits that are particularly advantageous in laser projection-based wearable heads-up displays are realized.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Miniaturized optically imaging system with high lateral and axial resolution
ActiveUS7511891B2Improve efficiencyHigh resolutionPhotometryMicroscopesTransmission systemObject field
The invention is directed to a miniaturized optically imaging system with high lateral and axial resolution for endomicroscopic applications. To provide a miniaturized optical head which permits an appreciable increase in photon efficiency with high lateral and axial spatial resolution compared to conventional GRIN optics the plane side of a refractive, plano-convex, homogeneous lens defines a plane entrance surface of the optical system, and first and second GRIN lenses are arranged along the optical axis orthogonal to the entrance surface, wherein the first GRIN lens being arranged downstream of the refractive lens for reducing the divergence of the highly divergent light bundle transmitted from the object through the refractive lens, and the second GRIN lens being provided for adapting the light bundle transmitted by the first GRIN lens to the aperture and object field size of the downstream transmission system.
Owner:GRINTECH
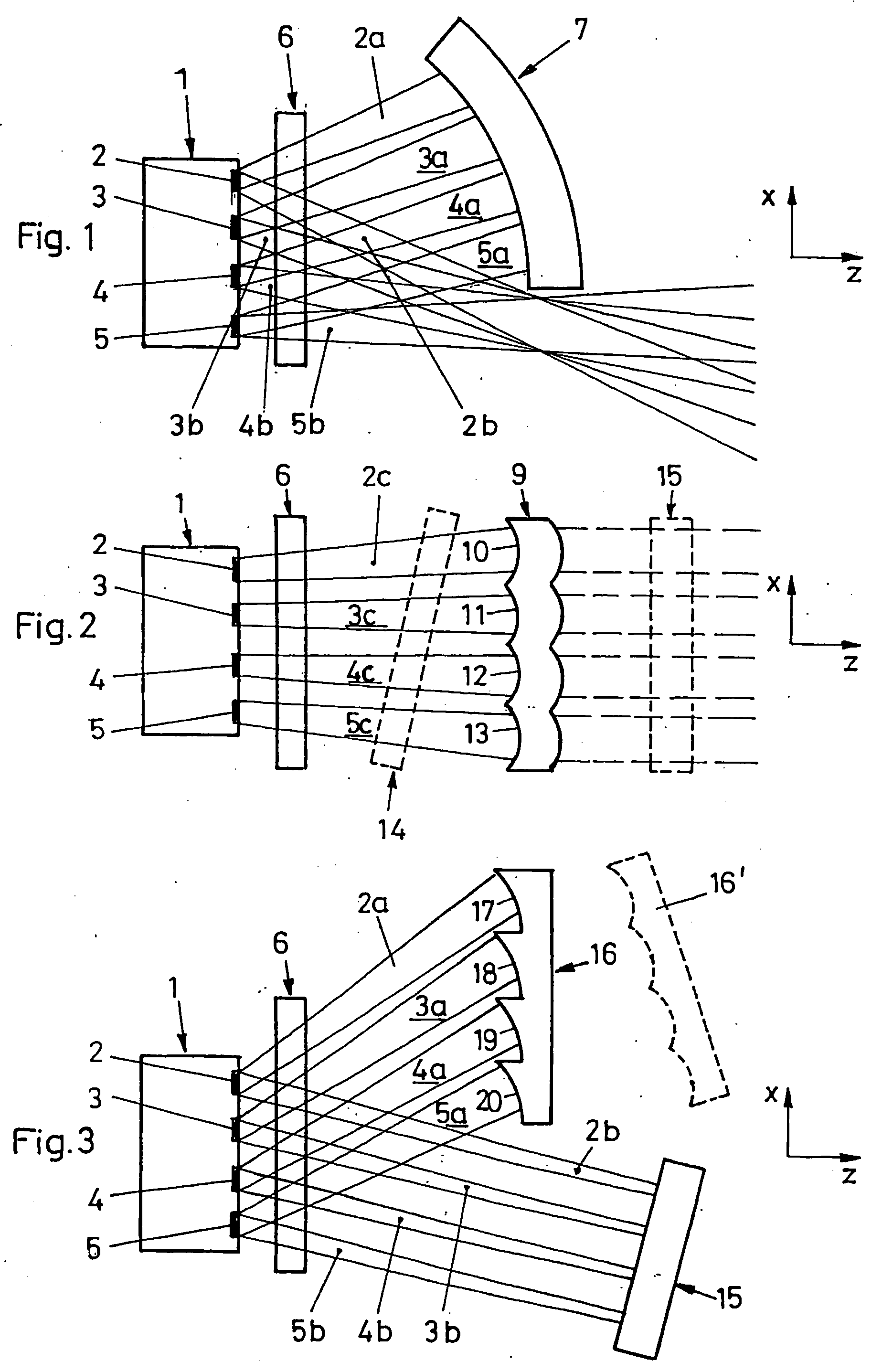
Projection-type display devices with reduced weight and size
ActiveUS20050041000A1Reduce disagreementExtend your lifeStatic indicating devicesProjectorsDisplay deviceLaser light
Described herein are display devices that provide projection-type video output and use diode lasers to generate light. For example, one set of diode lasers may produce red light, while a second set produces blue light. Optics are employed to expand laser light from its small generated or transmitted flux area to a size suitable for transmission onto the optical modulation device. Another aspect of the invention relates to a redundant laser set to generate light. A redundant laser set includes more lasers than that needed to produce the desired amount of light.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IMAGE
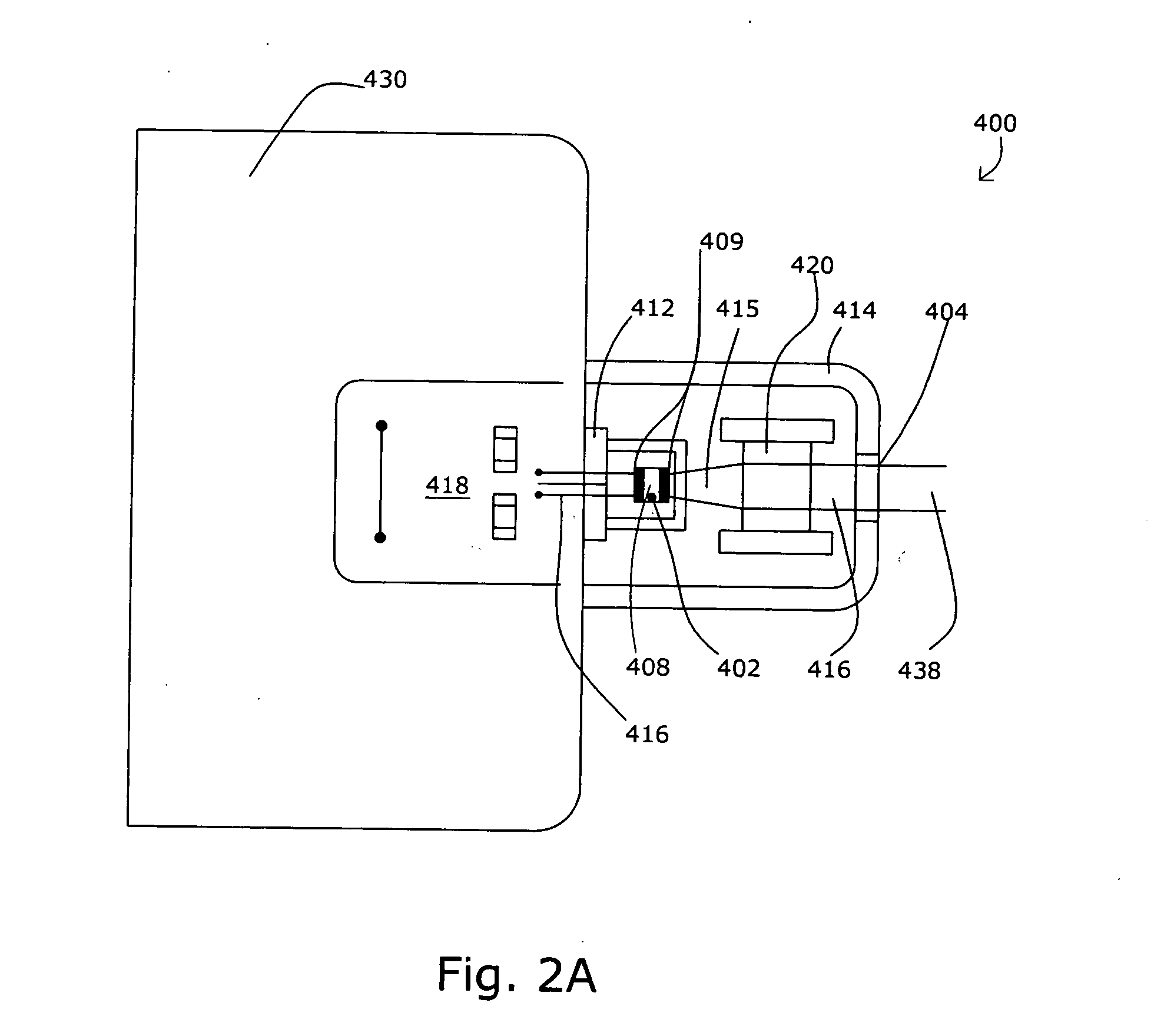
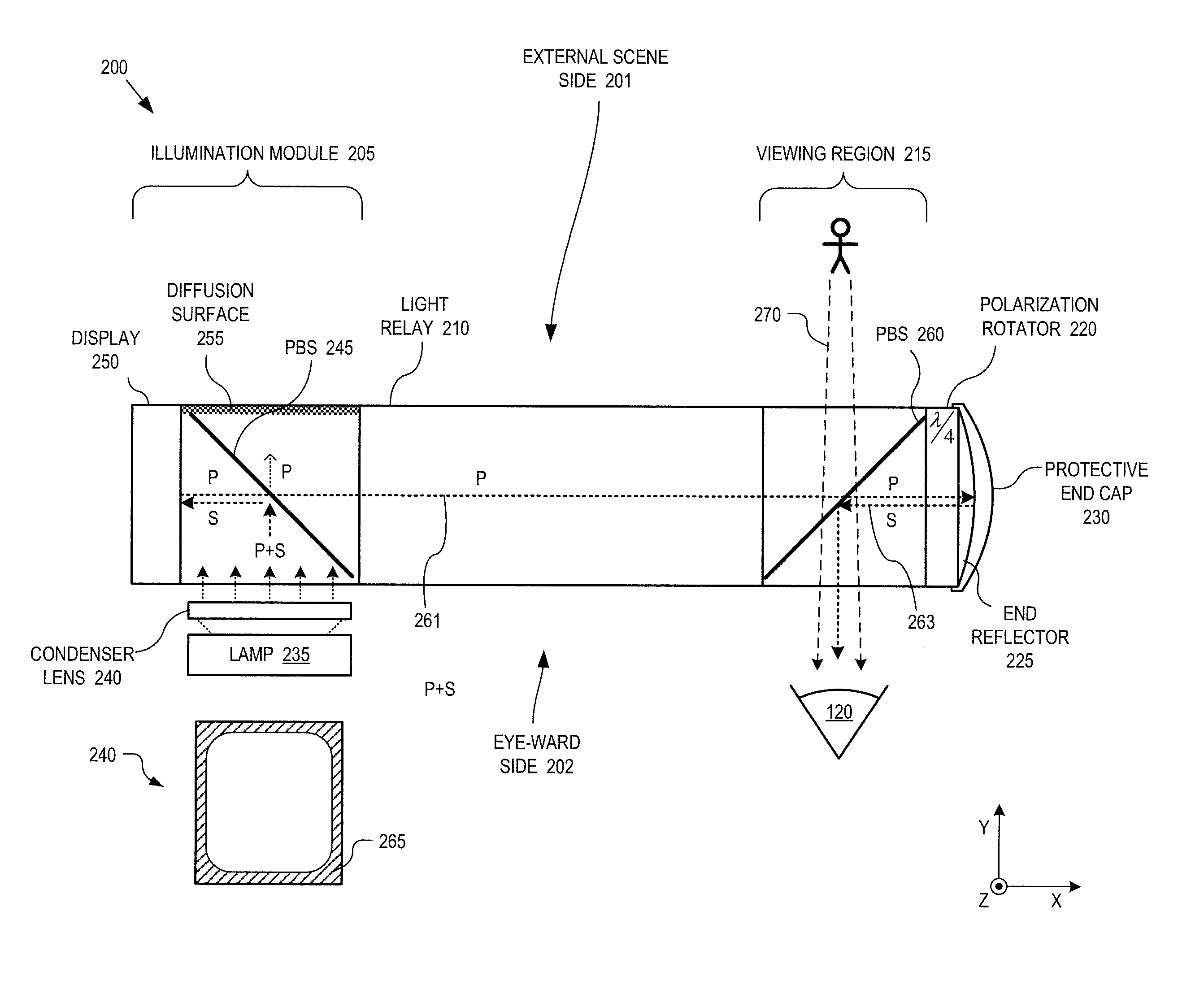
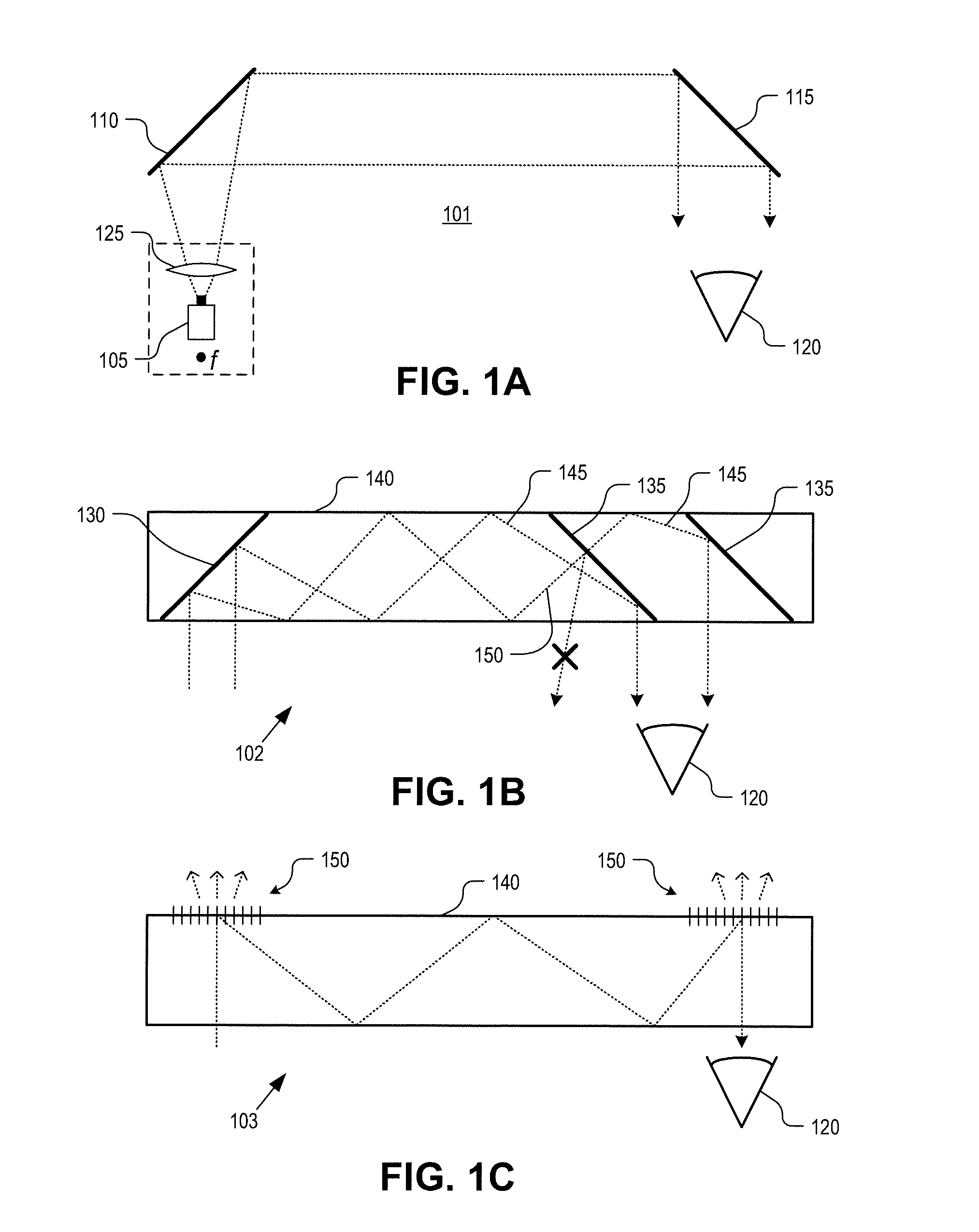
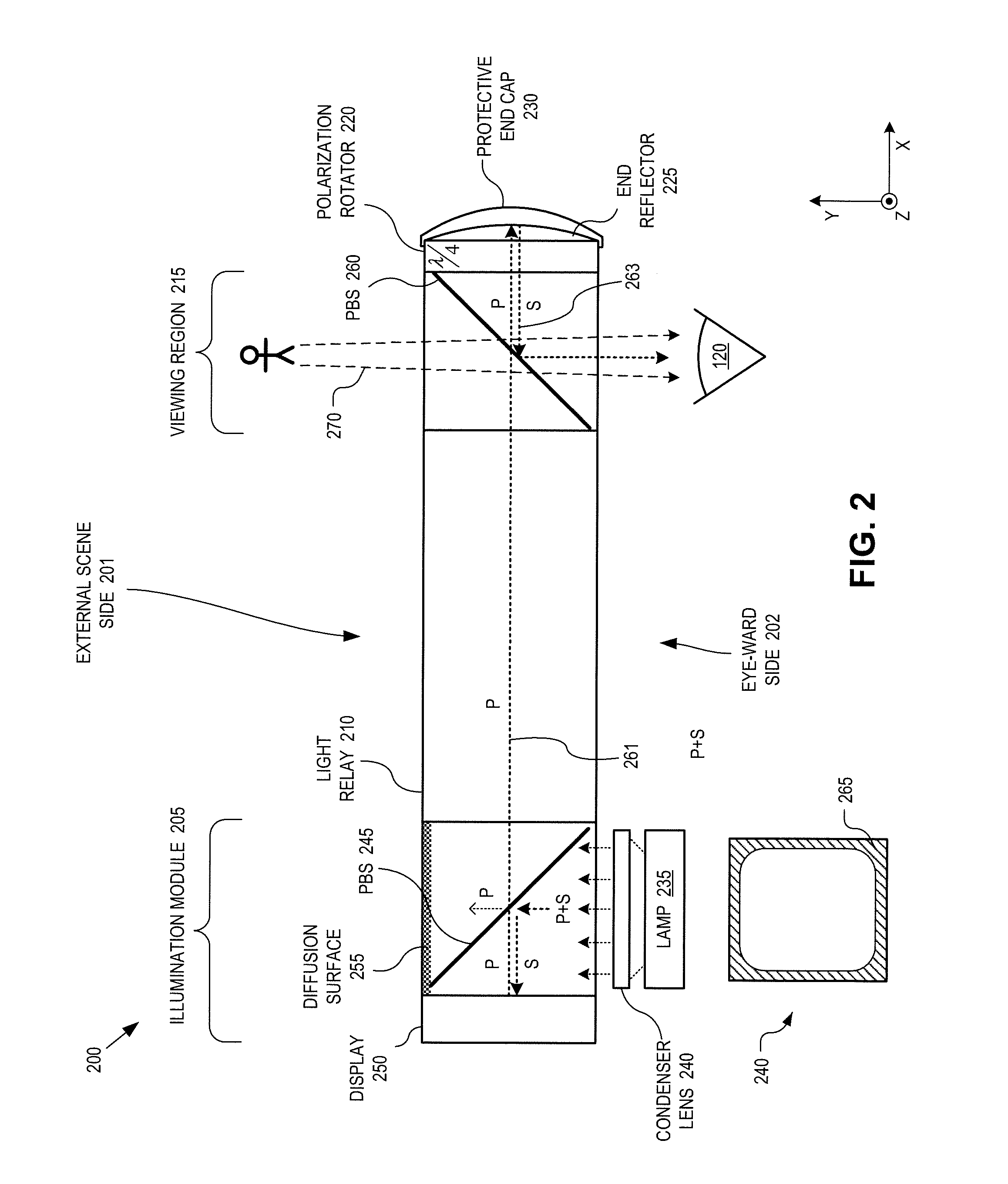
Method and apparatus for a near-to-eye display
InactiveUS20130033756A1Reduce disagreementDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsBeam splitterEyepiece
An eyepiece for a head mounted display includes an illumination module, an end reflector, a viewing region, and a polarization rotator. The illumination module provides CGI light along a forward propagation path within the eyepiece. The end reflector is disposed at an opposite end of the eyepiece from the illumination module to reflect the CGI light back along a reverse propagation path within the eyepiece. The viewing is disposed between the illumination module and the end reflector and includes an out-coupling polarizing beam splitter (“PBS”). The out-coupling PBS passes the CGI light traveling along the forward propagation path and redirects the CGI light traveling along the reverse propagation path out of an eye-ward side of the eyepiece. The polarization rotator is disposed in the forward and reverse propagation paths between the out-coupling PBS and the end reflector.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Wide Angle Imaging Directional Backlights
ActiveUS20160349444A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second deflected direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources from the side of the waveguide and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. A directional backlight with small footprint and low thickness may be provided.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
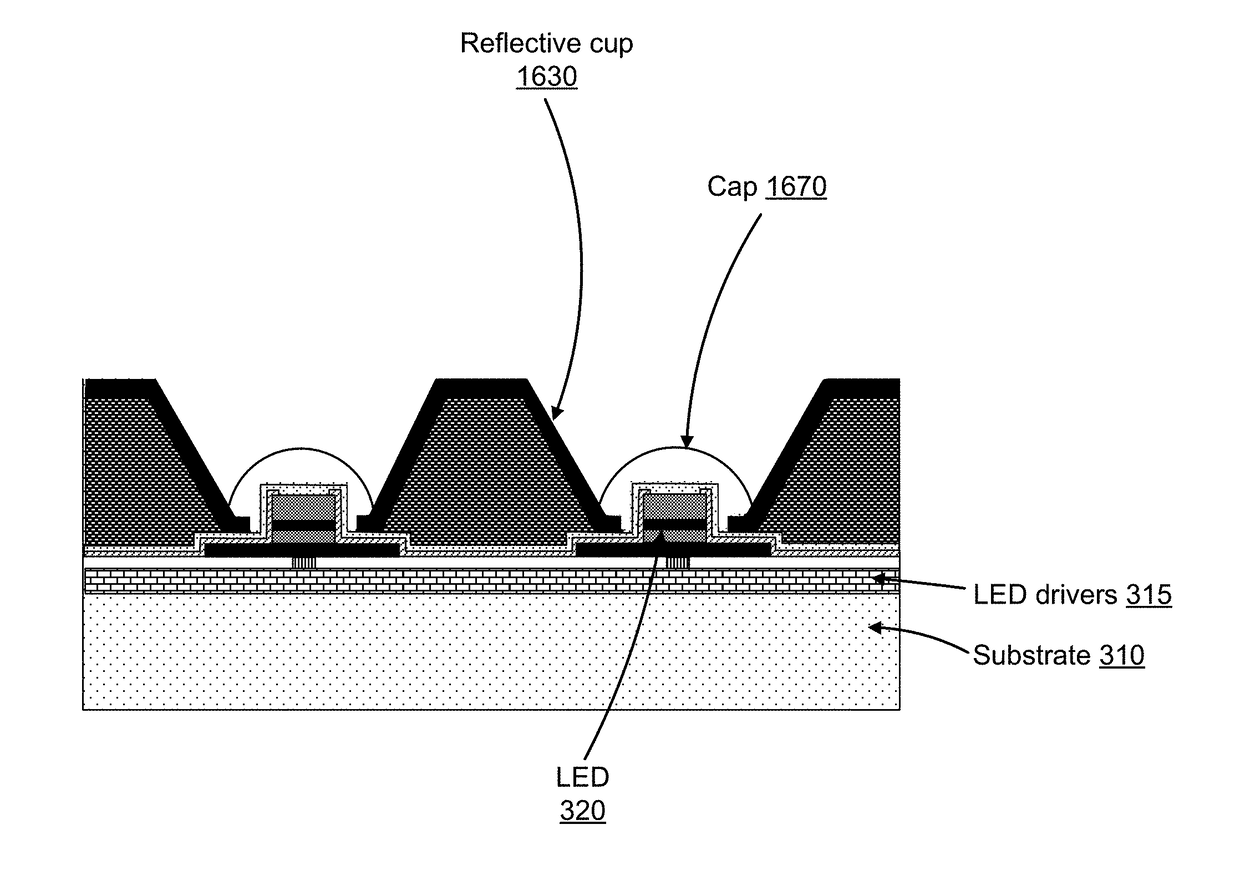
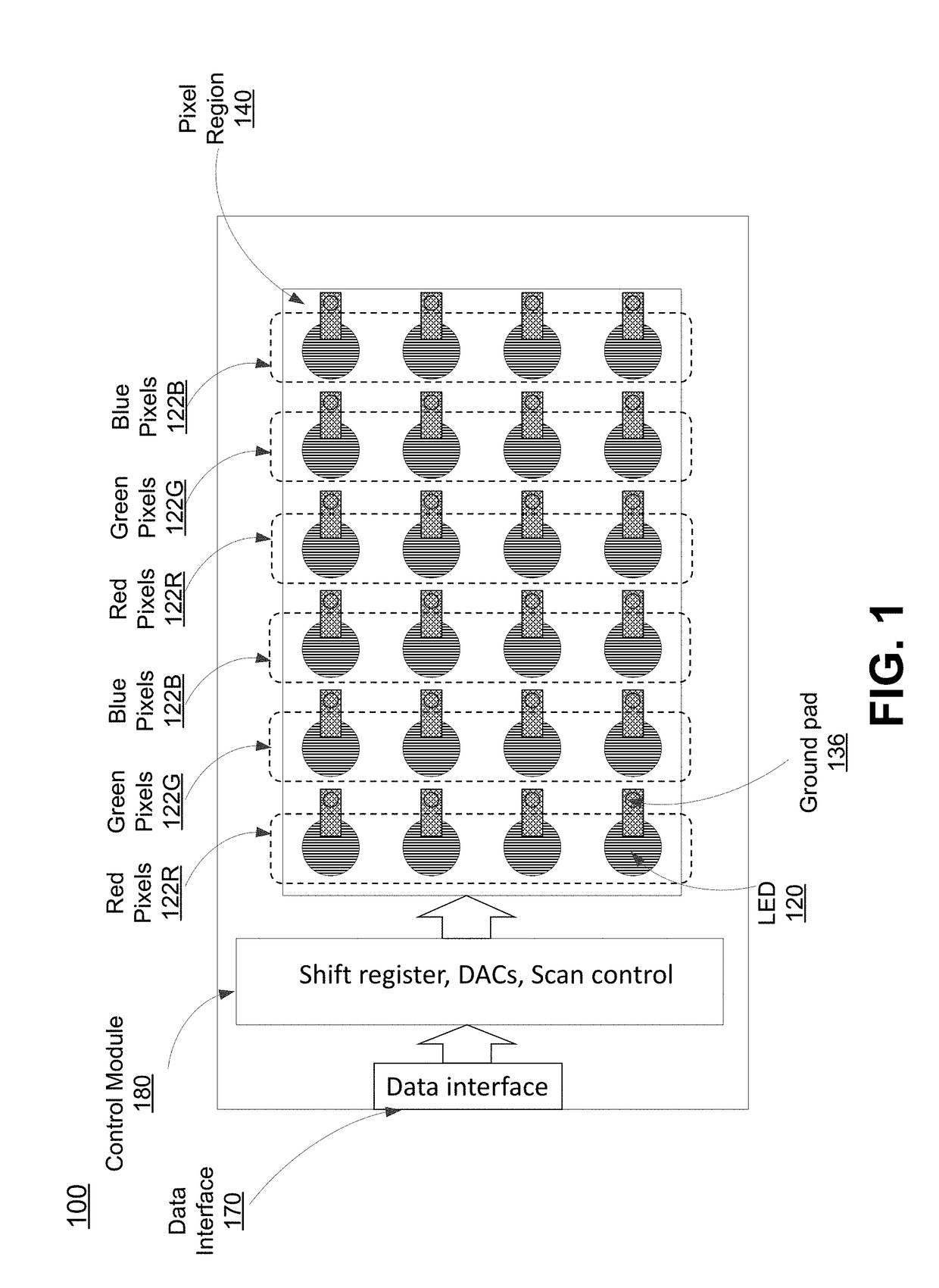
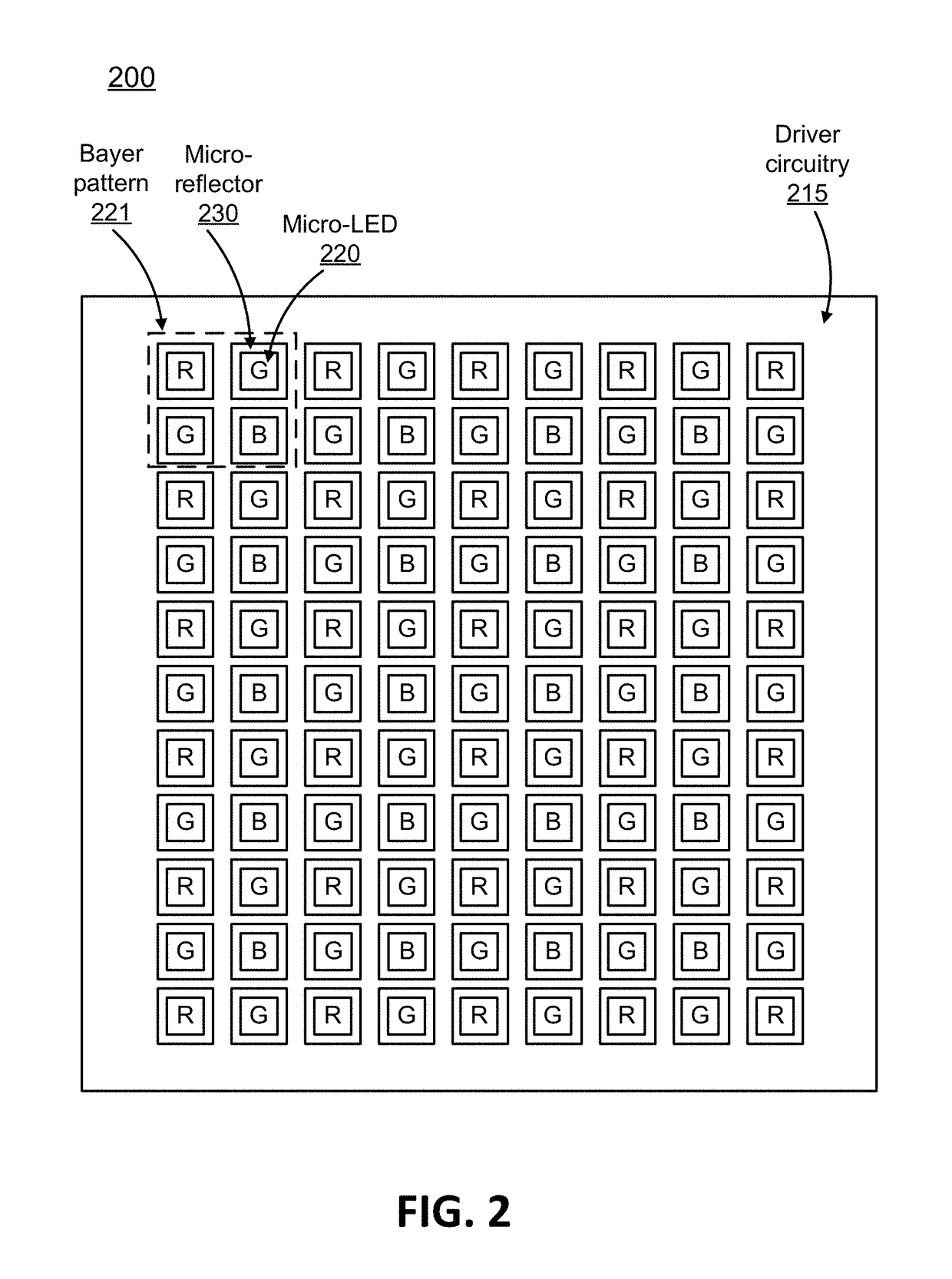
Micro Display Panels With Integrated Micro-Reflectors
ActiveUS20180090058A1Reduce disagreementIncrease projection brightnessStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectricityDriver circuit
A display panel with integrated micro-reflectors. The display panel also includes an array of pixel light sources (e.g., micro-LEDs) electrically coupled to corresponding pixel driver circuits (e.g., FETs). The micro-LEDs produce light and the micro-reflectors reduce the divergence of the light produced by the micro-LEDs. Different designs are possible. The micro-reflectors can have different shapes, include the shape of their sidewalls and the shape of their plan cross-section. The array schemes can also vary, including the number of LEDs per micro-reflector. Different fabrication approaches are also possible. In one approach, a support structure is integrated between micro-LEDs. The sides of the support structure are reflective and serve as the reflective sidewalls of the micro-reflector. Alternately, the LED mesa itself can serve as the support structure.
Owner:JADE BIRD DISPLAY SHANG HAI LTD
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20170339398A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusStatic indicating devicesWide-angle lensDirect illumination
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources by waveguide facets and rear reflector images in cooperation. Viewing windows may be provided at first and second different window planes to improve uniformity in a lateral direction. Further, stray light may be reduced by inner and outer portions of reflective facets with different inclinations for the rear reflector.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
VCSEL and VCSEL array having integrated microlenses for use in a semiconductor laser pumped solid state laser system
InactiveUS6888871B1Reduce disagreementHigh power outputSemiconductor laser structural detailsExcitation process/apparatusVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) device with improved power and beam characteristics. The VCSEL device contains one VCSEL or an array of VCSELs. Each VCSEL has a corresponding integrated microlens, and a heat sink is attached to the device side of the VCSEL device. The heat sink allows improved heat dissipation, and therefore provides improved power characteristics of the VCSEL device output laser beam. The microlens or microlens array allows easier and more compact focussing of the VCSEL device output laser beam. The VCSEL device can be used in a variety of optical systems, and its improved power and focusing characteristics provide a compact, low power, low cost laser system.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Optical stack for imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20180196275A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsVisibilityDirect illumination
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A rear reflector is arranged to receive light transmitted by the features and to provide polarization recirculation. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Retarder stack arrangements are provided to increase the efficiency of polarization recirculation, reduce the visibility to damage and to reduce color changes with viewing angle.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Privacy display apparatus
ActiveUS20190215509A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusDiffusing elementsDirect illuminationLiquid crystal
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. The directional backlight may be arranged to switch between at least a first wide angular luminance profile mode and a second narrow angular luminance profile mode. The directional backlight is arranged to illuminate an LCD with a bias electrode arranged to switch liquid crystal directors in black state pixels between a first wide angular contrast profile mode and a second narrow angular contrast profile mode. Performance of privacy operation for off-axis snoopers is enhanced in comparison to displays with only directional backlights or switchable contrast properties.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20170336661A1High luminance operationSave powerMechanical apparatusImage analysisSystem elementPhysics
An imaging directional backlight apparatus includes a waveguide and a light source array, providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, and the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a forward direction. Returning light propagating in a backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and define the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. The imaging directional backlight apparatus further includes a control system for controlling the light output directional distribution in an automotive or vehicle environment in dependence on the output from sensors mounted on the vehicle. The control system is arranged to control the light output direction distribution of portable directional displays co-located with the vehicle.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Optical stack for imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS10401638B2Reduce disagreementLow costMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsVisibilityDirect illumination
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A rear reflector is arranged to receive light transmitted by the features and to provide polarization recirculation. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Retarder stack arrangements are provided to increase the efficiency of polarization recirculation, reduce the visibility to damage and to reduce color changes with viewing angle.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
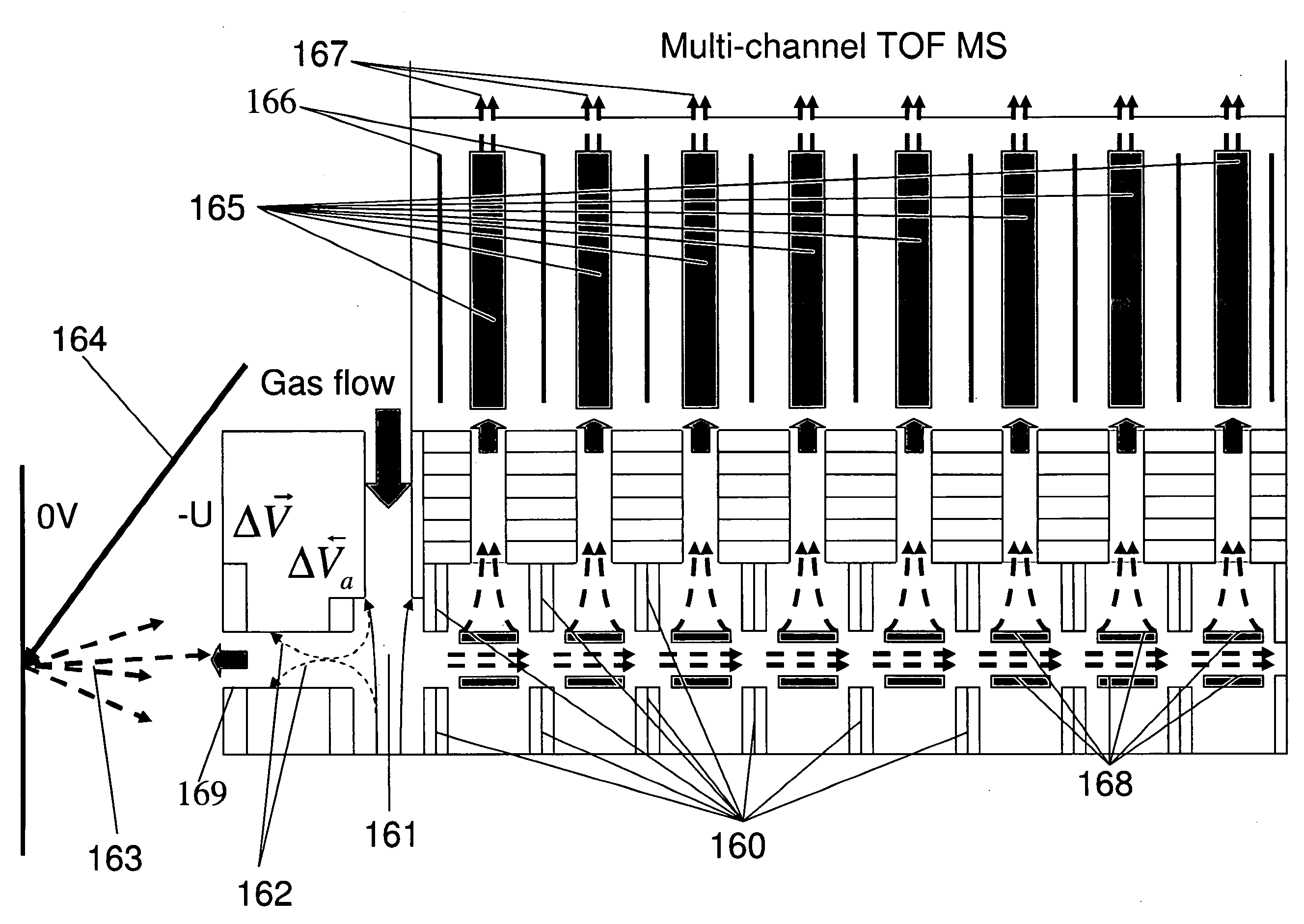
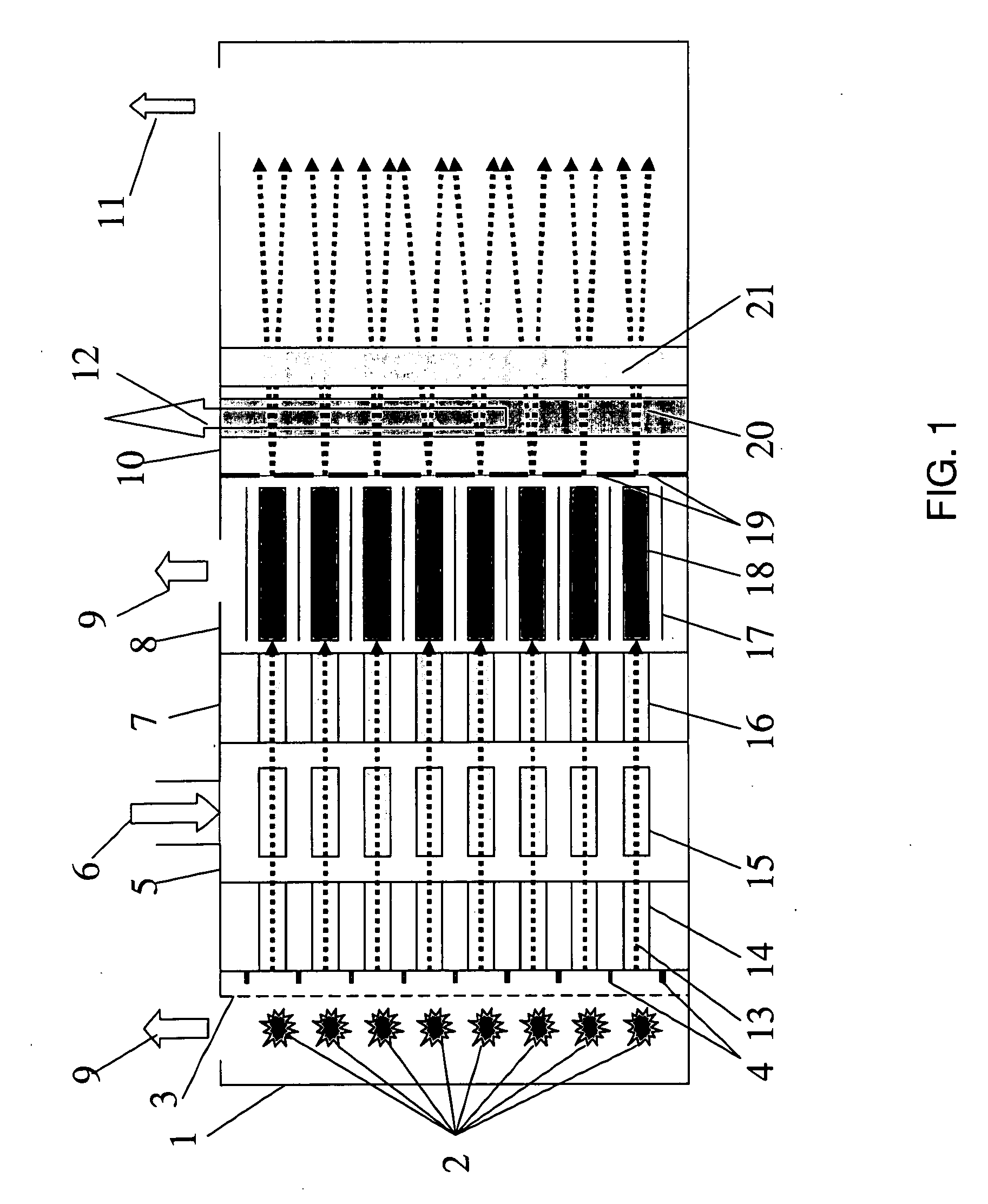
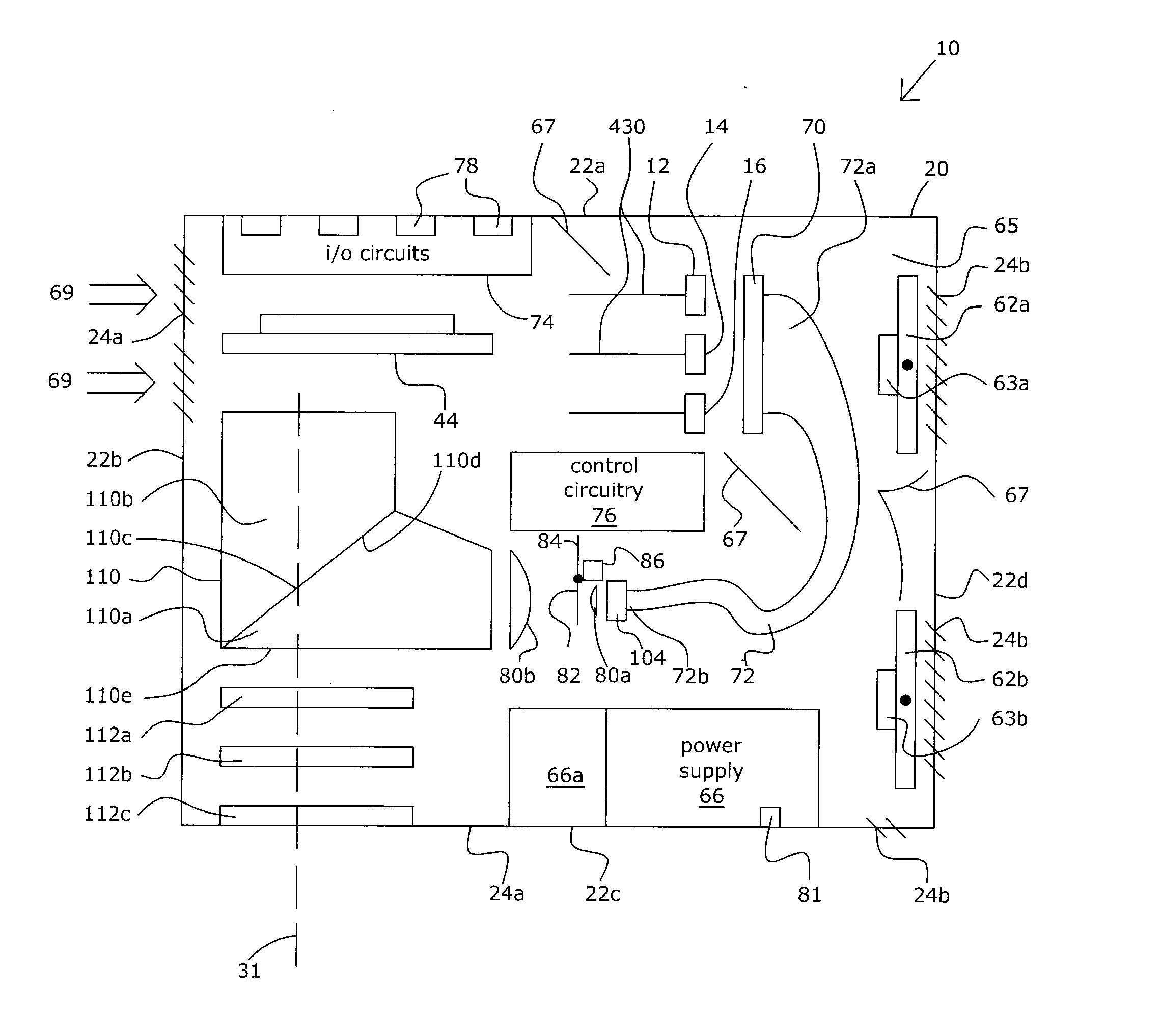
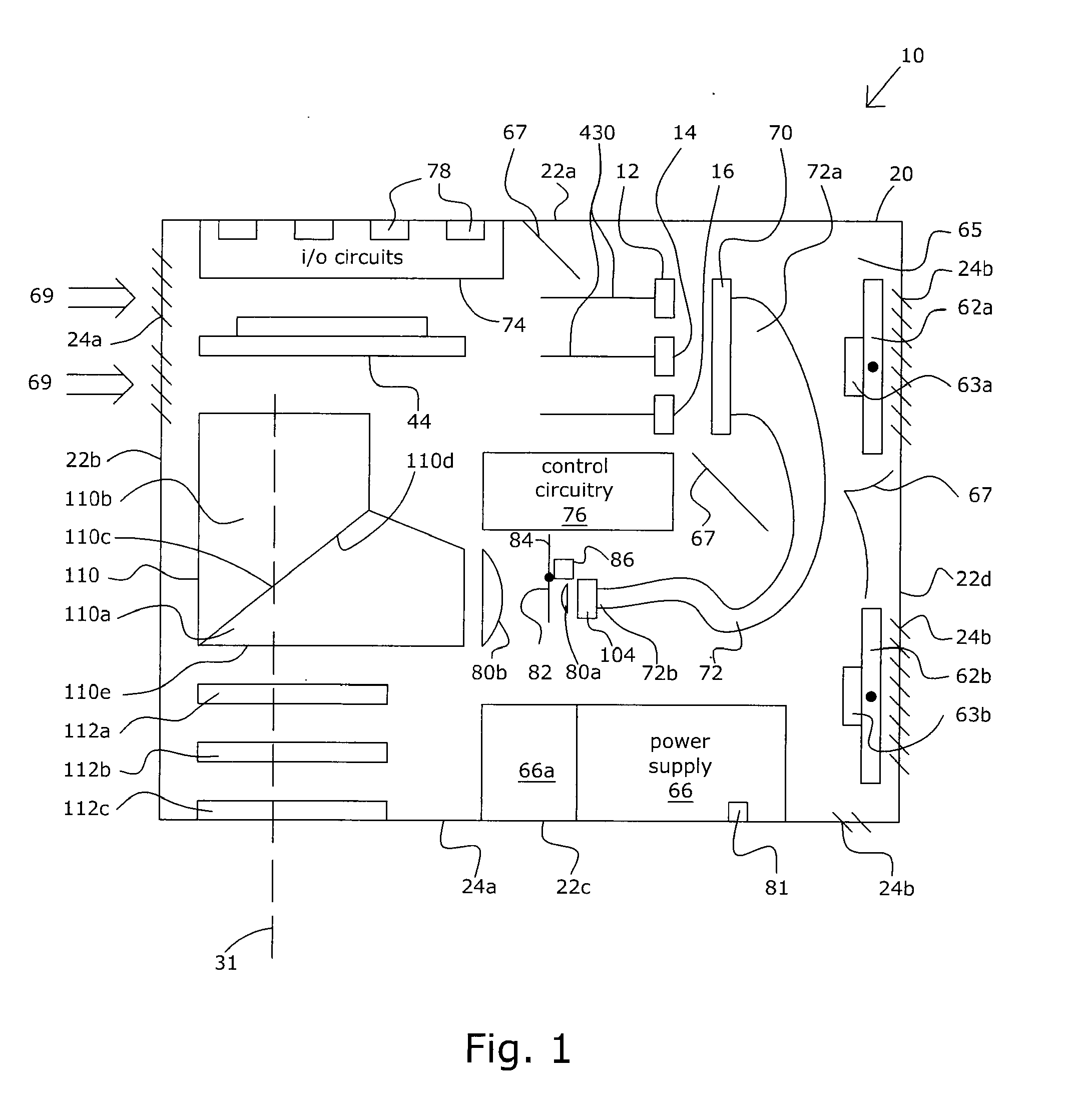
Multi-beam ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry with multi-channel data recording
InactiveUS20090140140A1Improve efficiencyReduce divergenceTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDense bodyData recording
The content of the invention comprises a concept of multi-beam ion pre-selection from a single sample, coordinated mobility (against the gas flow) separation, cooling ions in supersonic gas flow and mass separation of thus low divergent ions by single or plural compact high-resolution orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometers both linear or reflectron type with controlled collision-induced dissociation (CID) and multi-channel data recording for the optimization of sample use in the analysis, and obtaining as much useful information about the sample as possible in a reasonably short time.
Owner:IONWERKS
Projection-type display devices with reduced weight and size
ActiveUS7156522B2Reduce disagreementExtend your lifeStatic indicating devicesProjectorsDisplay deviceLaser light
Described herein are display devices that provide projection-type video output and use diode lasers to generate light. For example, one set of diode lasers may produce red light, while a second set produces blue light. Optics are employed to expand laser light from its small generated or transmitted flux area to a size suitable for transmission onto the optical modulation device. Another aspect of the invention relates to a redundant laser set to generate light. A redundant laser set includes more lasers than that needed to produce the desired amount of light.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IMAGE
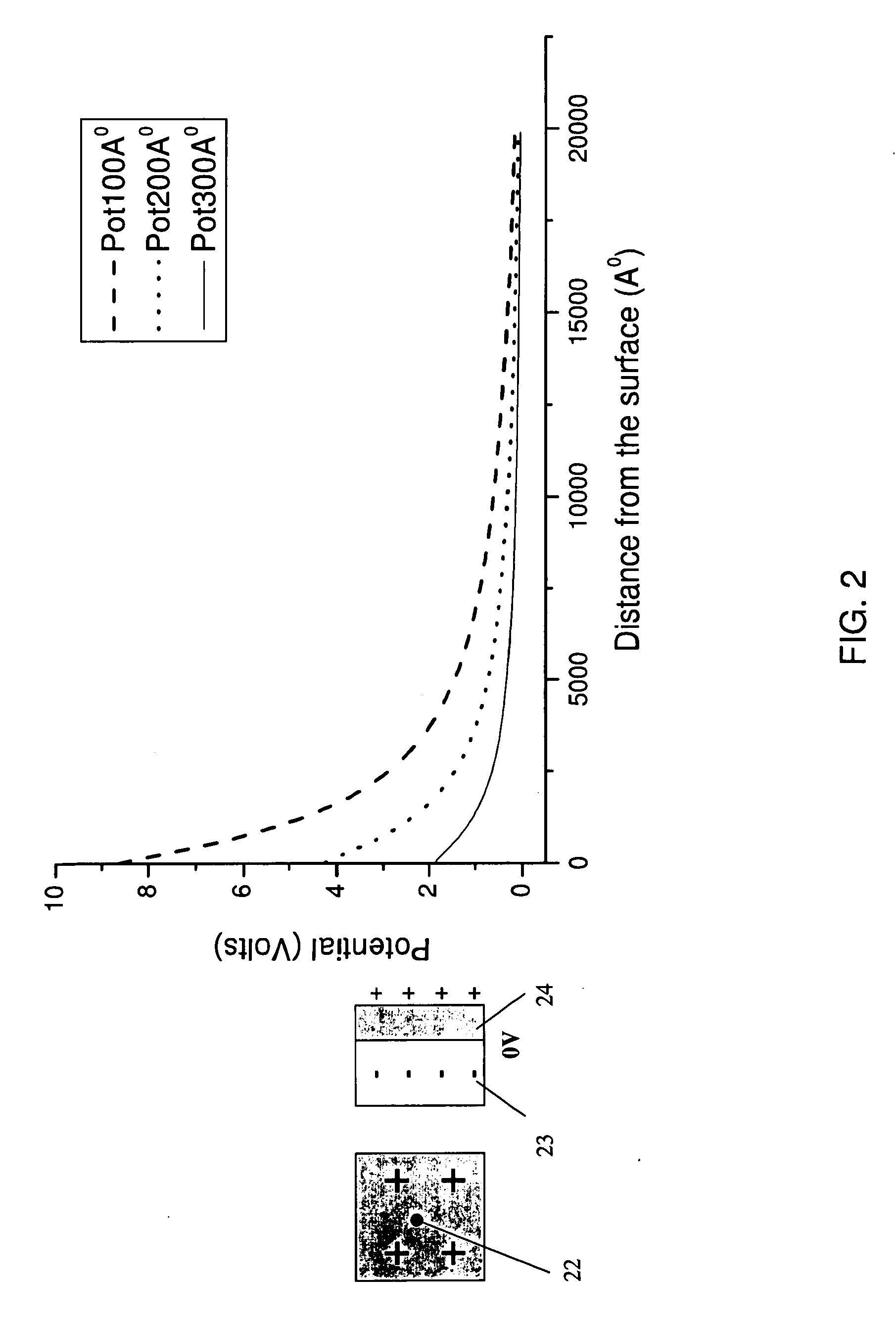
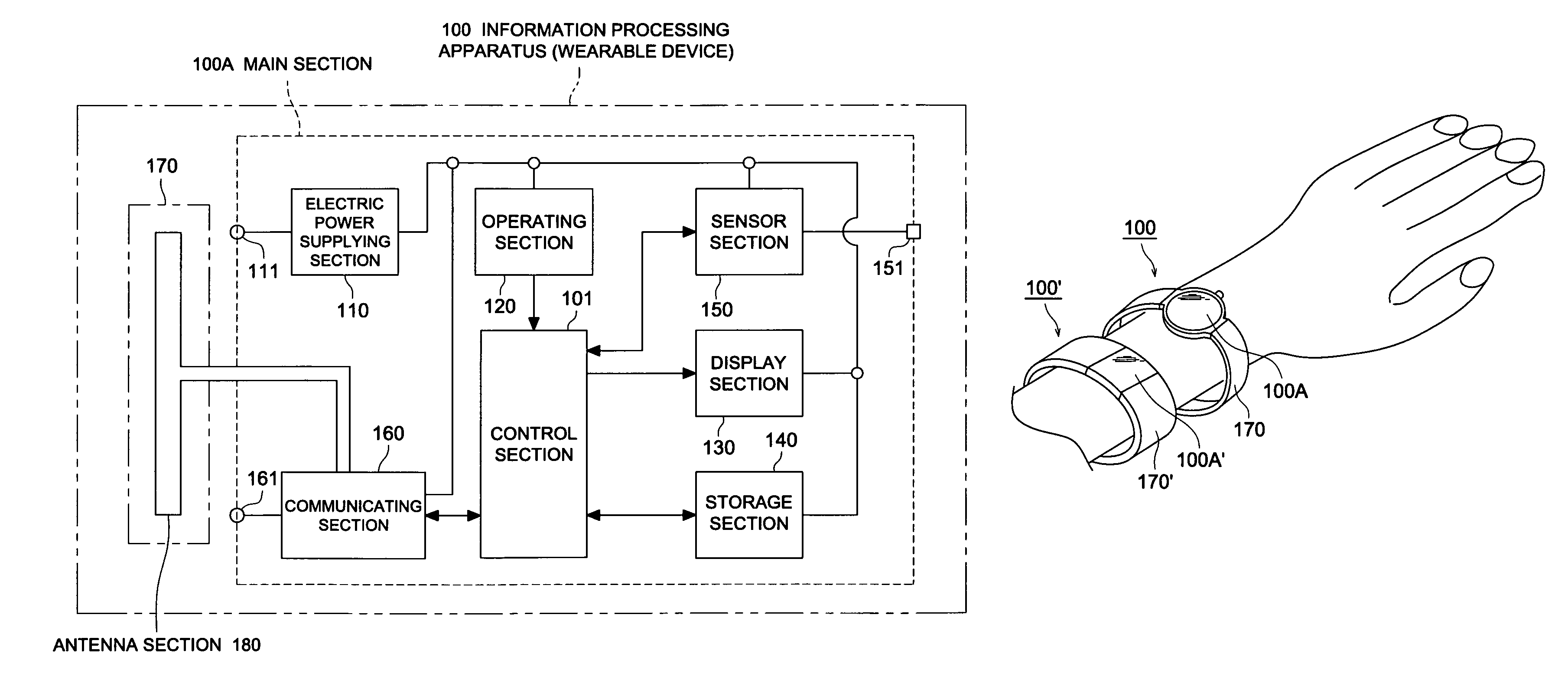
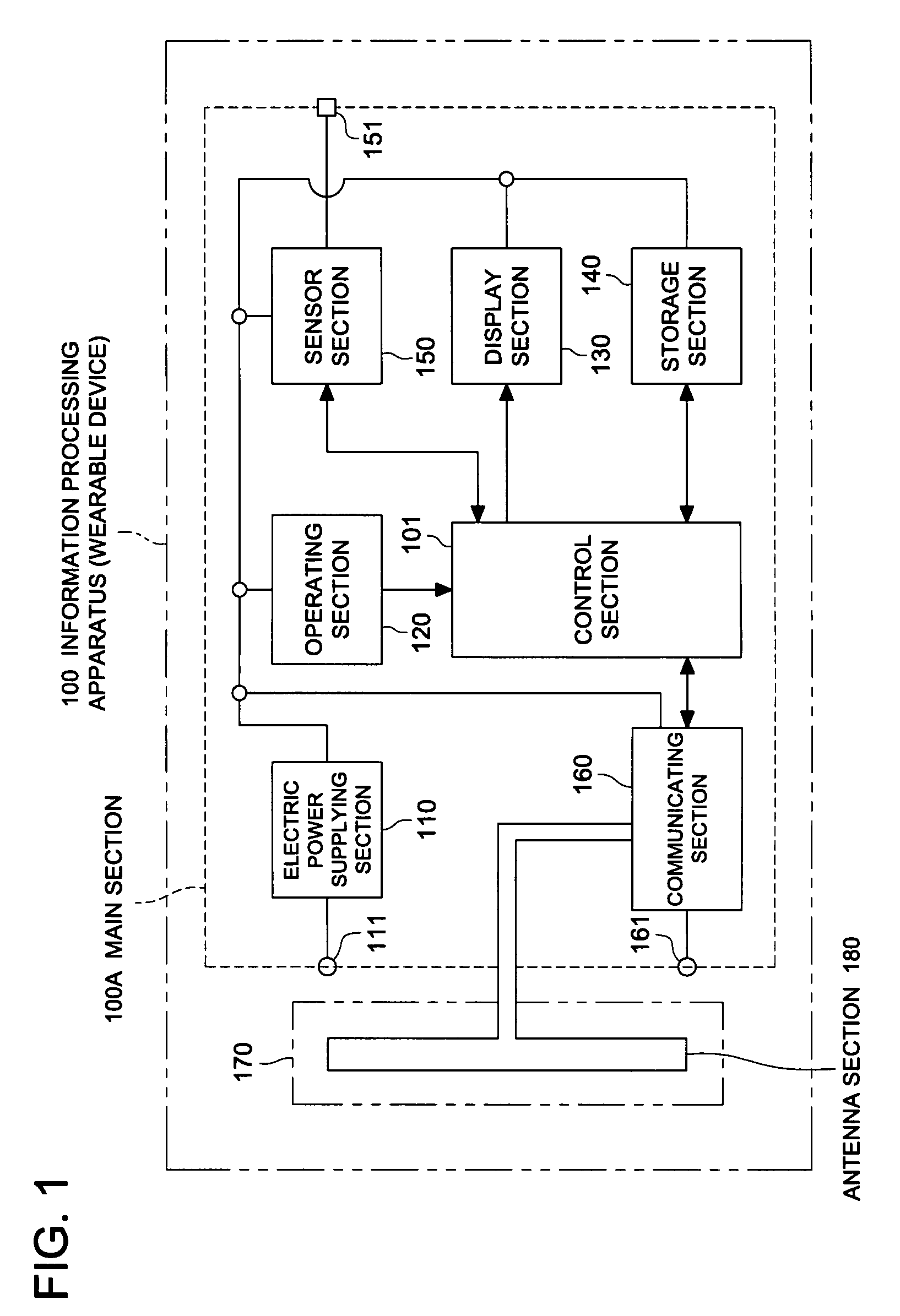
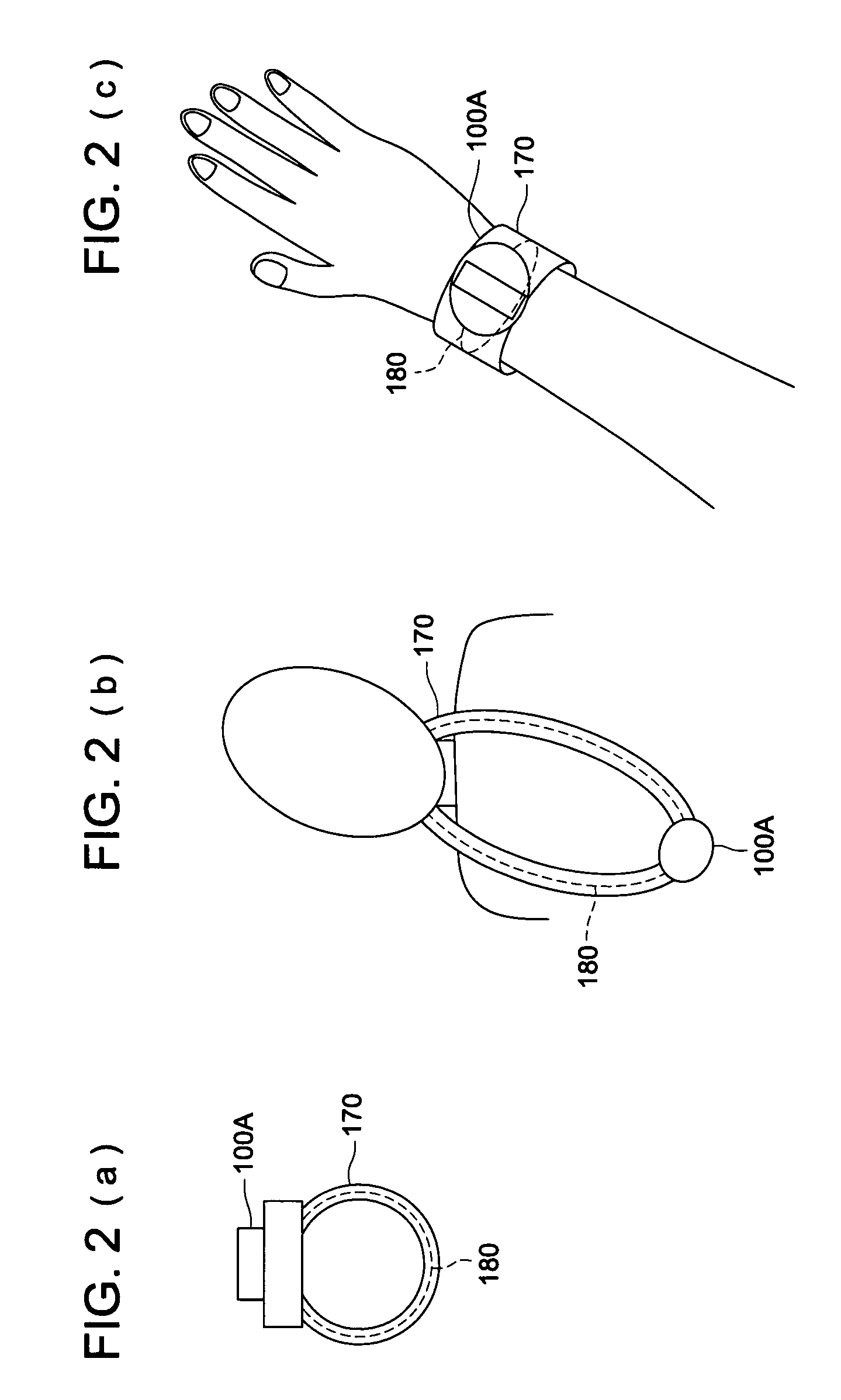
Information processing apparatus
InactiveUS7667657B2Improve securityReduce disagreementResonant long antennasAntenna supports/mountingsInformation processingDipole antenna
The subject is to provide an information processing apparatus serving as a wearable device, which makes it possible not only to reduce the divergence of data toward the peripheral spaces, but also to eliminate the electrode to be contacted to the surface of the living body when wearing it, and further, which is superior in the transmitting efficiency. The information processing apparatus is provided with information processing section 101 to conduct various kinds of information processing; wearing section 170 to make the information processing section wearable onto a living body, by surrounding a part of the living body; antenna section 180 formed in the wearing section and serving as either a loop antenna or a dipole antenna; and communicating section 160 to conduct a wireless communication with an external device by transmitting data, processed by the information processing section, to the external device through the antenna section, or by feeding data, received from the external device through the antenna section, into the information processing section.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Projection-type display devices with reduced speckle
InactiveUS20070195276A1Reduce disagreementExtend your lifeTelevision system detailsProjectorsDisplay deviceLight beam
Described herein are display devices that provide projection-type video output and use lasers to generate light. To reduce any speckle effects for a projected image cast by a projector onto of a non-specular surface, the present invention decreases coherence of the laser-generated light. Coherence reduction is accomplished by introducing a coherence diffuser in a light path of the laser light. Arranging the coherence diffuser in an unfocused light beam reduces both temporal and spatial coherence in the light. Arranging the rotating diffuser at the focus of a beam reduces only the temporal coherence while maintaining the spatial coherence.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IMAGE
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20160299281A1Reduce disagreementLow costMechanical apparatusMirrorsDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Lateral non-uniformities of output image are improved by means of adjustment of input aperture shape and reflective aperture shape. Cross talk in autostereoscopic and privacy displays may further be improved by light blocking layers arranged on the input end of the waveguide.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Graphical systems and methods for human-in-the-loop machine intelligence
InactiveUS20160162458A1Improve accuracyFacilitates annotationNatural language translationData processing applicationsGraphicsHuman-in-the-loop
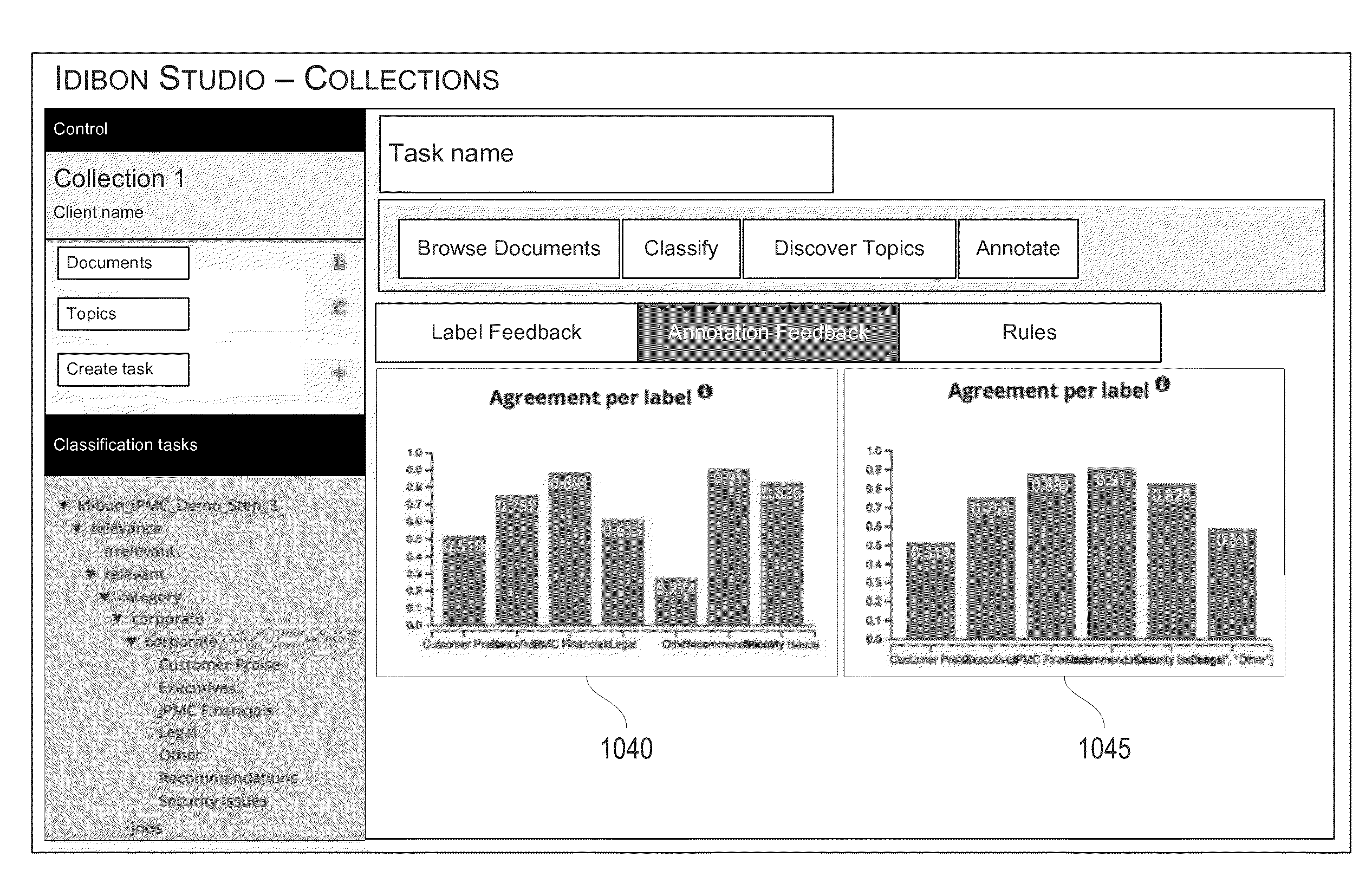
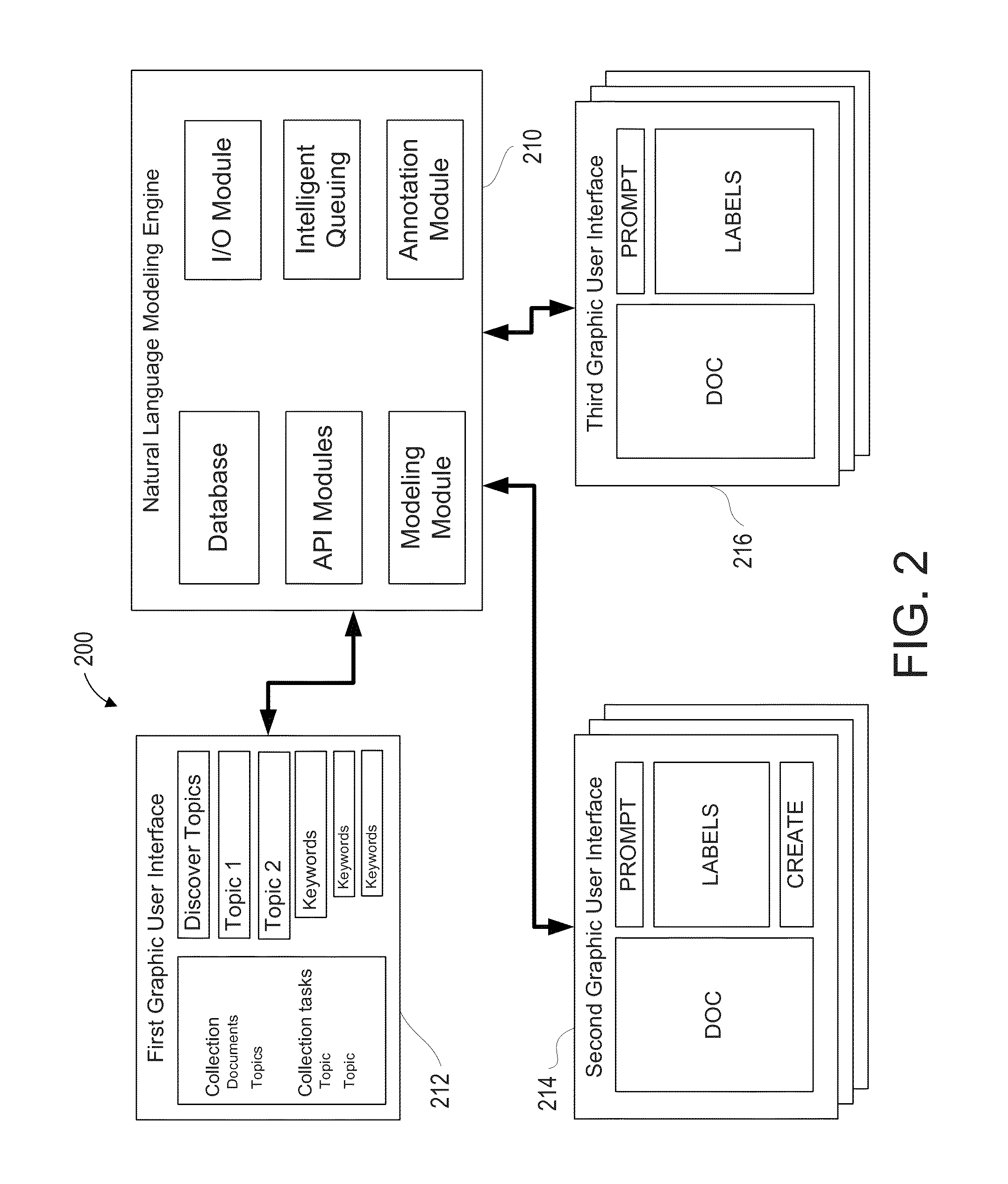
Methods and systems are disclosed for creating and linking a series of interfaces configured to display information and receive confirmation of classifications made by a natural language modeling engine to improve organization of a collection of documents into an hierarchical structure. In some embodiments, the interfaces may display to an annotator a plurality of labels of potential classifications for a document as identified by a natural language modeling engine, collect annotated responses from the annotator, aggregate the annotated responses across other annotators, analyze the accuracy of the natural language modeling engine based on the aggregated annotated responses, and predict accuracies of the natural language modeling engine's classifications of the documents.
Owner:100 CO GLOBAL HLDG LLC
Display panels with integrated micro lens array
ActiveUS20170242161A1Reduced divergence angleIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDriver circuitHemt circuits
Various embodiments include a display panel with integrated micro lens array. The display panel typically includes an array of pixel light sources (e.g., LEDs) electrically coupled to corresponding pixel driver circuits (e.g., FETs). The array of micro lenses are aligned to the pixel light sources and positioned to reduce the divergence of light produced by the pixel light sources. The display panel may also include an integrated optical spacer to maintain the positioning between the micro lenses and pixel driver circuits.
Owner:JADE BIRD DISPLAY SHANG HAI LTD
Segmented imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20180284341A1High luminance operationSave powerMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus includes a waveguide and a light source array, providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, and the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a forward direction. Returning light propagating in a backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and define the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. The imaging directional backlight apparatus further includes multiple waveguides with light extraction features arranged to provide uniform output luminance at the seam between the waveguides.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Laser diode arrays with reduced heat induced strain and stress
InactiveUS20060018355A1Improve reliabilityReduce disagreementLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLaser transmitterHeat sink
A laser diode array has a semiconductor layered structure that includes at least one active layer. A heat sink is coupled to semiconductor layered structure. A plurality of laser emitters are formed in the active layer. A majority of the plurality of laser emitters have a spacing between adjacent laser emitters that provides for a more uniform heat distribution.
Owner:COMLASE
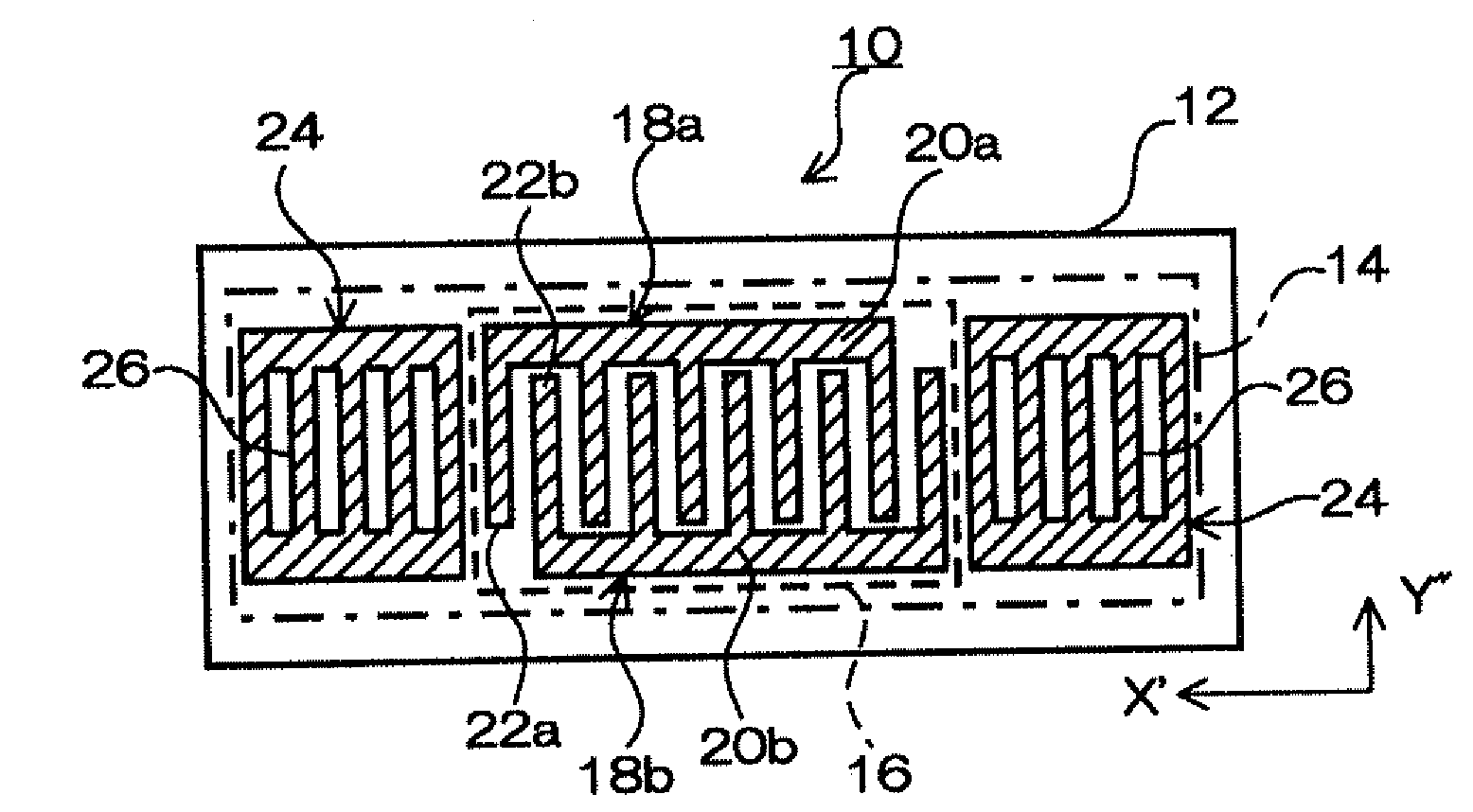
Surface acoustic wave device and surface acoustic wave oscillator
ActiveUS20090206955A1Suitable for mass-productionReduce disagreementImpedence networksInterdigital transducerStopband
A surface acoustic wave device, includes: an interdigital transducer serving as an electrode pattern to excite a Rayleigh surface acoustic wave, the interdigital transducer including a comb-tooth-shaped electrode having a plurality of electrode fingers; a piezoelectric substrate on which the interdigital transducer is formed, the piezoelectric substrate being made of a quartz substrate that is cut out at a cut angle represented by an Euler angle representation (φ, θ, Ψ) of (0°, 95°≦θ≦155°, 33°≦|Ψ|≦46°); electrode finger grooves formed between the electrode fingers of the comb-tooth-shaped electrode; and electrode finger bases being quartz portions sandwiched between the electrode finger grooves and having upper surfaces on which the electrode fingers are positioned The surface acoustic wave device provides an excitation in an upper limit mode of a stop band of the surface acoustic wave.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
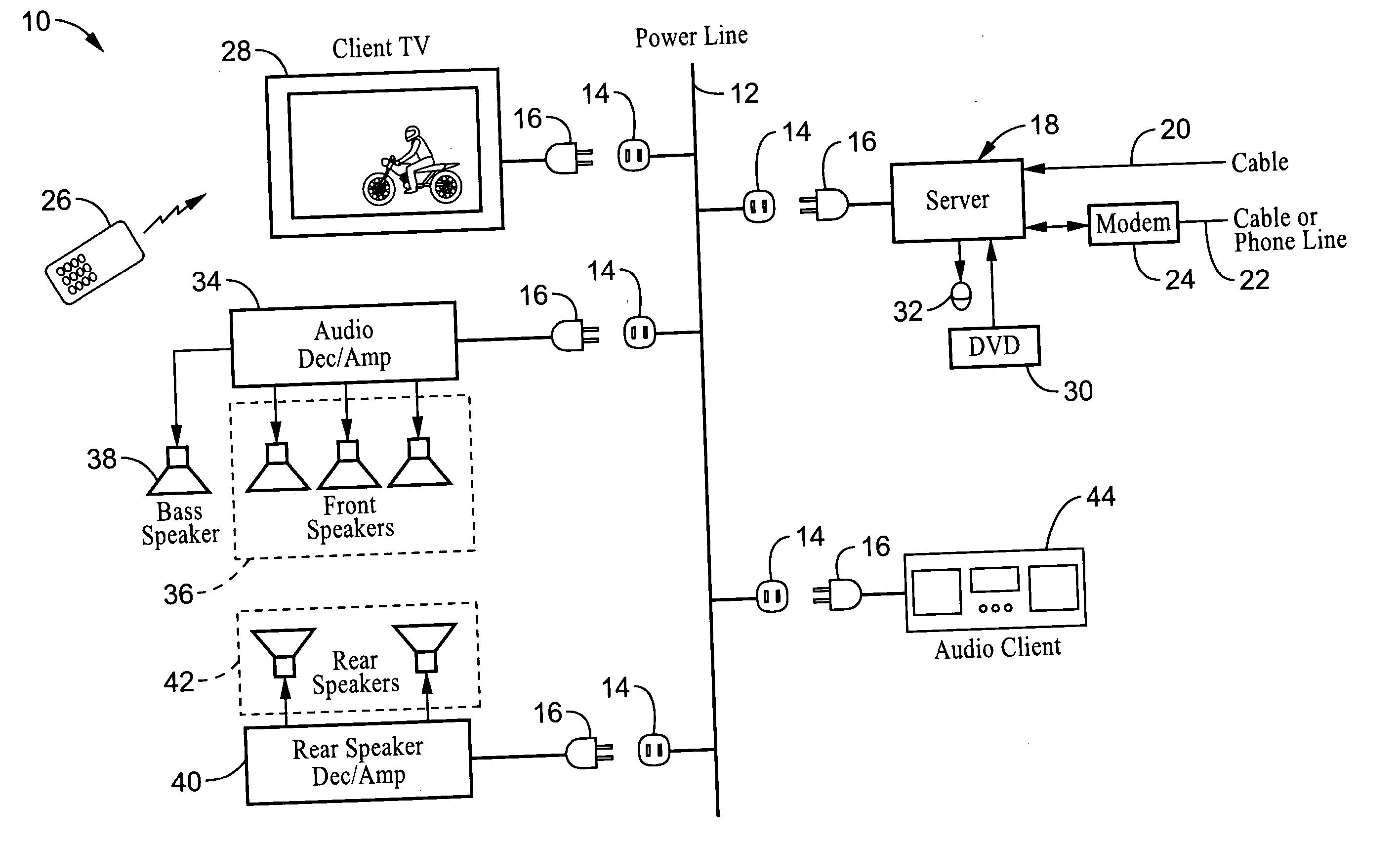
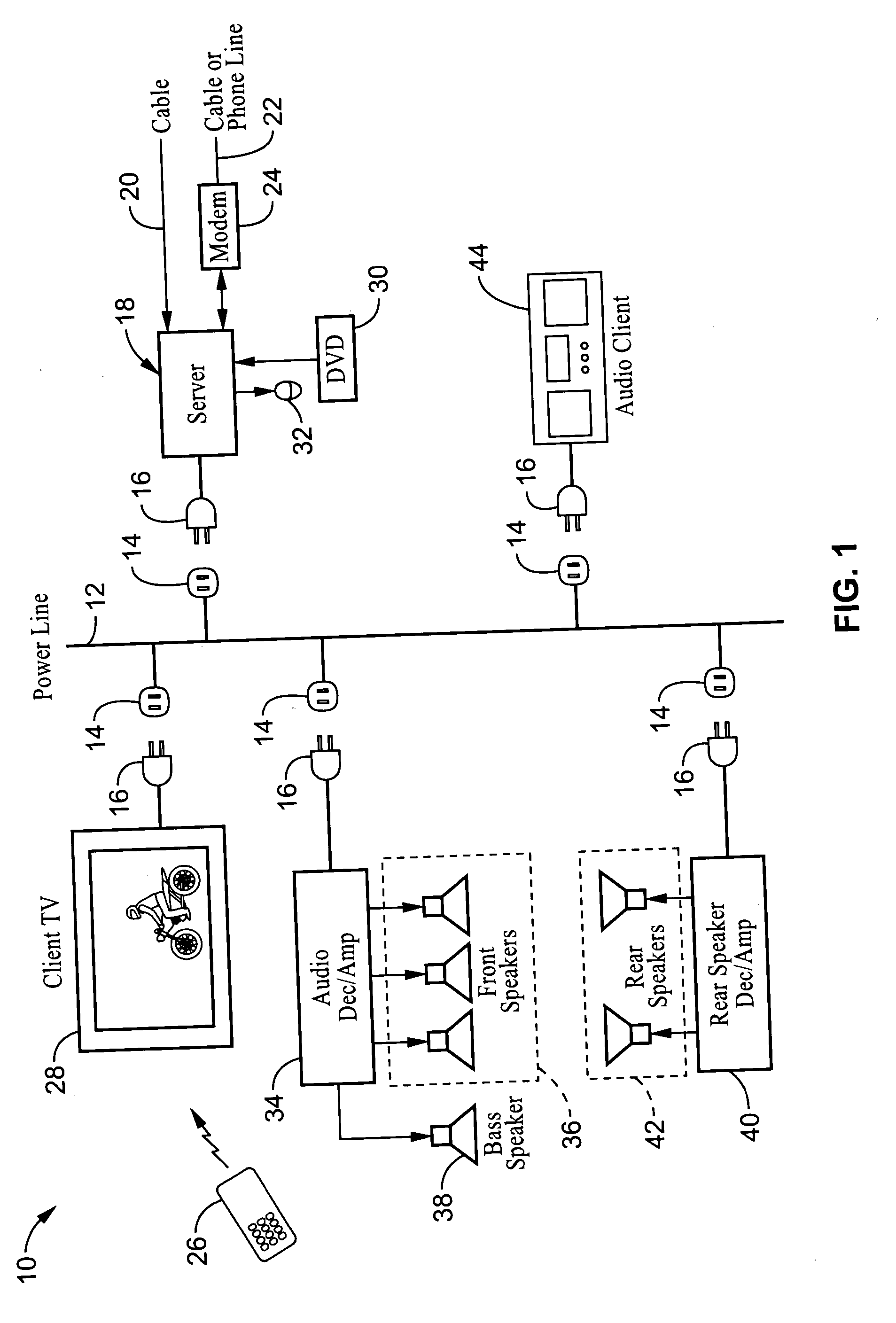
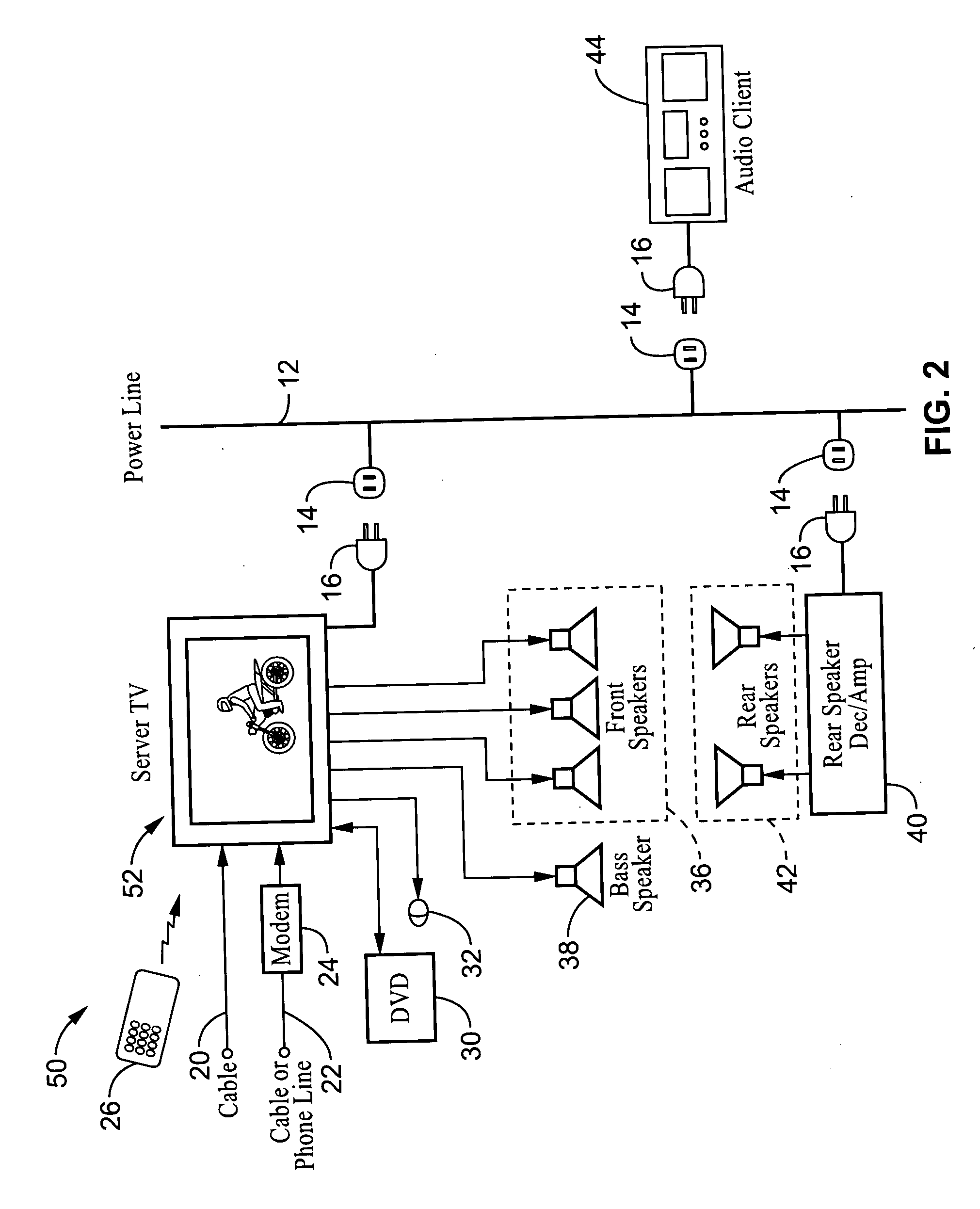
System and method for synchronizing audio-visual devices on a power line communications (PLC) network
ActiveUS20060072695A1Minimum delayMinimize divergenceTime-division multiplexWireless systems/telephoneComputer hardwareClock time
A method and apparatus for synchronizing streaming media devices within a PLC network. Output synchronization errors exceeding ˜30 ms become noticeable when multiple streaming media devices are outputting an audio stream. The present invention provides a system and method for isochronously sending periodic reference clocks from a master device to client devices coupled to the PLC network. The client devices set their clocks based on the reference clock. In addition the clients adjust their system clock time base in response to the average divergence of the system clock with the reference clock, or a count of the number of clocks between beacon frames. In this way the client clock is adjusted to closely track the server clock so that synchronization is maintained between each of the devices. Streaming audio shared between servers and client devices is thus output across the network with high fidelity due to the accurate synchronization.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method and apparatus for unifying light beams
InactiveUS20020051360A1High yieldReduce disagreementPoint-like light sourcePortable electric lightingSquare cross sectionLight energy
A light unifier, which comprises a plurality of light sources, particularly laser diodes, emitting parallel light beams of a rectangular cross-section, for focusing the light energy of all the beams onto a target area through beam-shaping means, which comprises transverse collimators, means for juxtaposing the emitted beams to form a unified beam, a longitudinal collimator for longitudinally collimating the unified beam, and means for focusing it onto the target area. The light beams have a transverse and a longitudinal divergence and the ratio of the transverse divergence to the longitudinal divergence is higher than 1. The transverse collimators are placed at such a distance from the sources that, at the point at which the beams reach them, the sum of the short sides of the beams is equal to the long side of each of them at the point at which they reach the longitudinal collimator. The number of light sources is such as to permit to obtain a unified beam that has a square cross-section and the same divergence on all its sides. Two groups of laser diodes may be arranged in parallel or mutually perpendicular planes and the unified beams produced by them are focused together onto the target area.
Owner:SOLODOVNIKOV VLADIMIR VADIMOVICH +1
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20060165144A1Easy to carryReduce disagreementLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser lightSemiconductor
The invention relates to a semiconductor laser devcie, including a semiconductor laser element, or a number of individual lasers mounted parallel to each other, with a number of output surfaces, from which laser light can escape, having a treater divergence in a first direction (Y) than in a second direction parallel to the above and at least one reflecting means, at a distance from the output surfaces, outside the semiconductor laser element or the individual laser, with at least one reflective surface which reflects at least a part of the laser light escaping from the semiconductor laser element or the individual lasers through the output surfaces back into the semiconductor laser element or the individual lasers, such that the mode spectrum of the semiconductor laser element or the individual lasers is influenced. The at least one reflective surface of the reflecting means has a concave curve.
Owner:LIMO PATENTVERWALTUNG GMBH & CO KG
Specific expression face detection method, and imaging control method, apparatus and program
InactiveUS20070189584A1Reduce the differenceReduce disagreementAcquiring/recognising facial featuresFace detectionRadiology
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Reducing back-reflection in laser micromachining systems
InactiveUS20120152918A1Reduce and prevent back-reflectionsReduce the overall diameterLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusBeam expanderLaser processing
Systems and methods reduce or prevent back-reflections in a laser processing system. A system includes a laser source to generate an incident laser beam, a laser beam output to direct the incident laser beam toward a work surface along a beam path, and a spatial filter. The system further includes a beam expander to expand a diameter of the incident laser beam received through the spatial filter, and a scan lens to focus the expanded incident laser beam at a target location on a work surface. A reflected laser beam from the work surface returns through the scan lens to the beam expander, which reduces a diameter of the reflected beam and increases a divergence angle of the reflected laser beam. The spatial filter blocks a portion of the diverging reflected laser beam from passing through the aperture and returning to the laser beam output.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com