Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
197results about How to "Much of light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
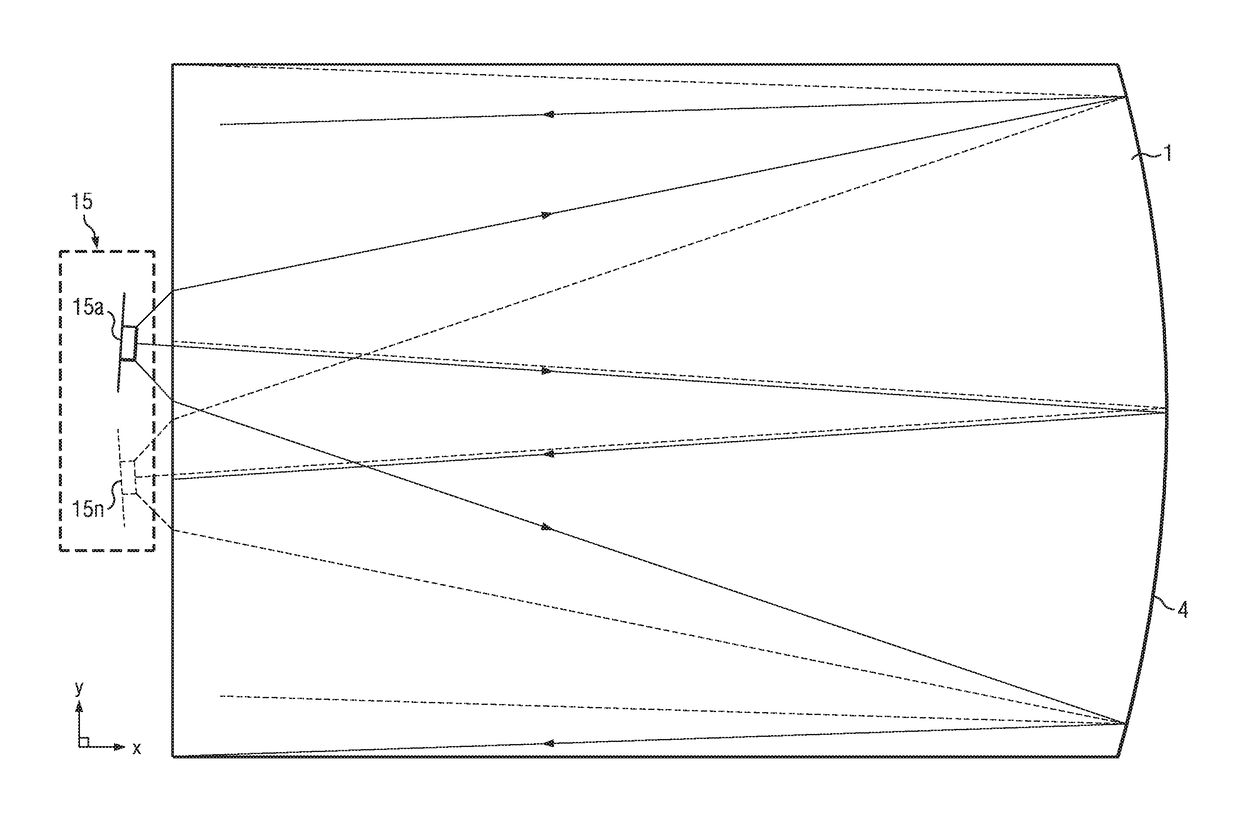
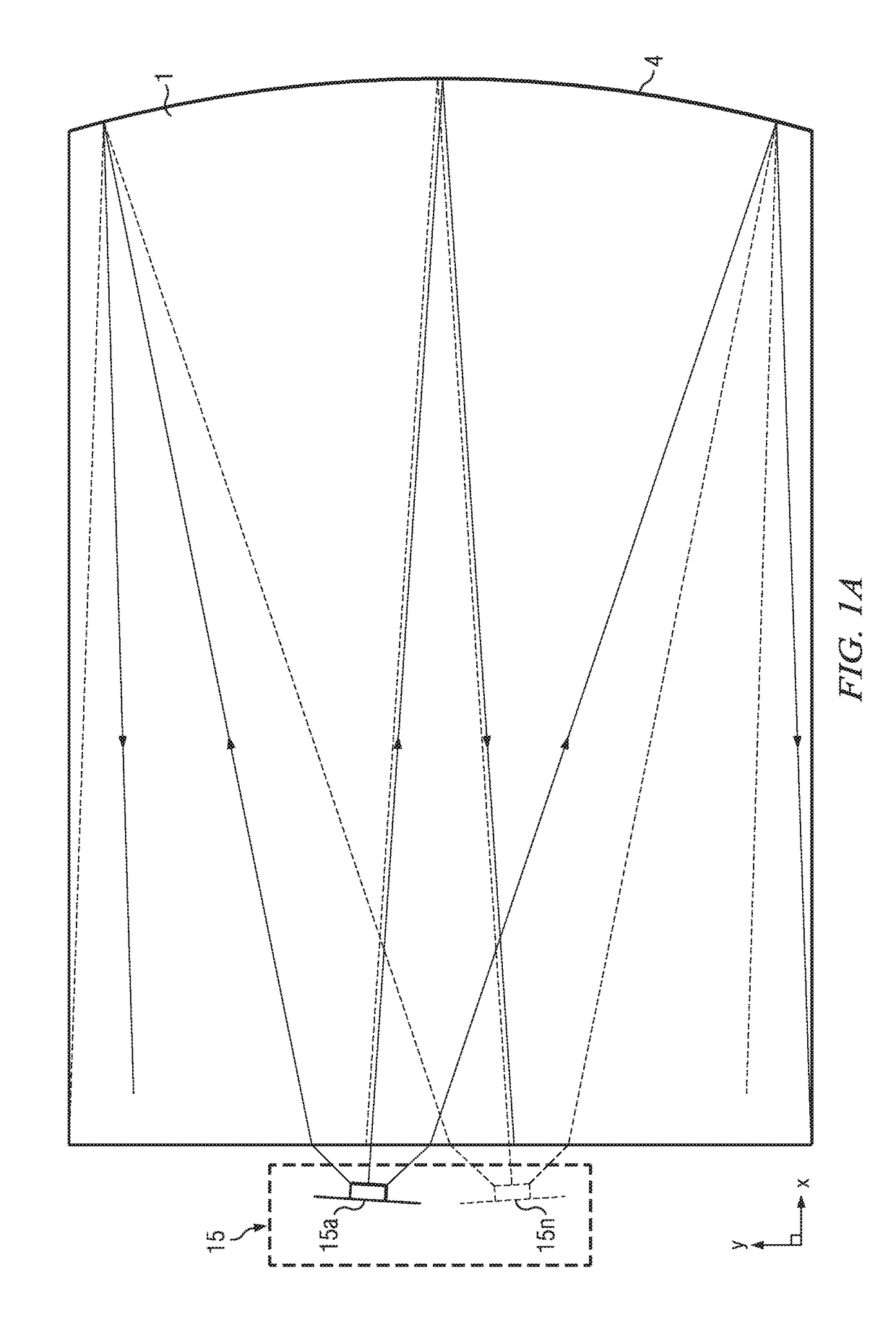
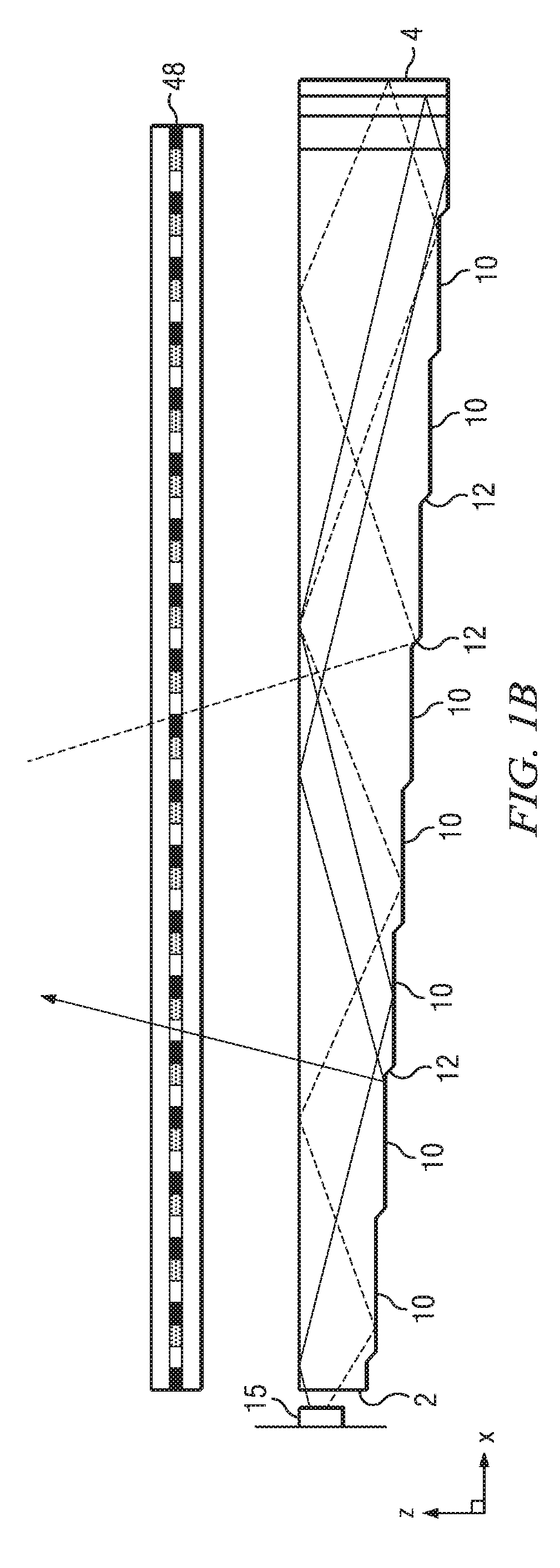
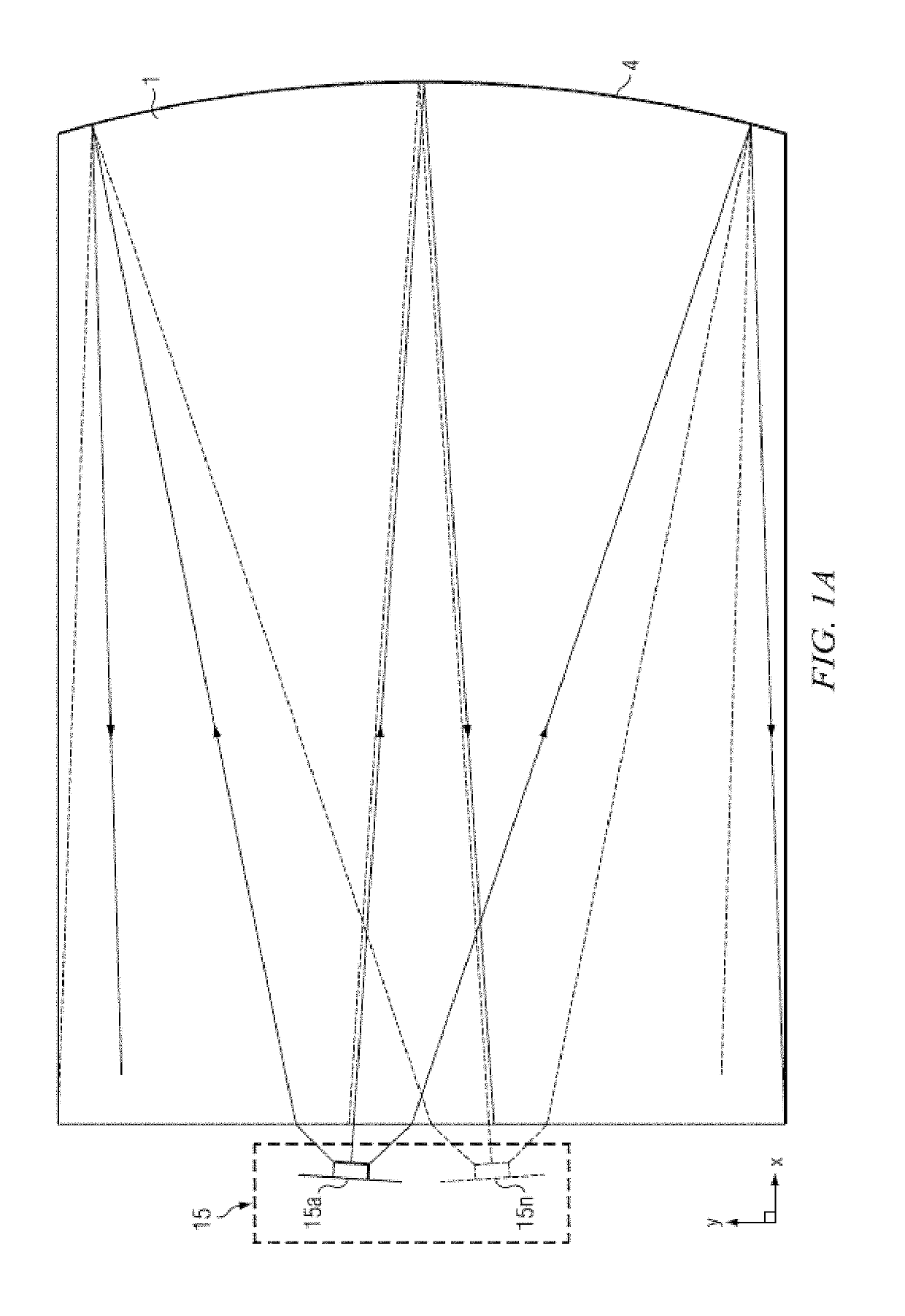
Ambient light rejection for non-imaging contact sensors
ActiveUS20130120760A1Reduce the amount requiredEnhance the imagePerson identificationUsing optical meansLight sensingMagnification
A sensor for capturing images of skin topology is provided having a platen, and a one or two-dimensional array of light sensing pixel elements for receiving light representative of skin topology when skin, such as finger(s), are present upon the platen. Such sensor being improved by structures, layers, or methods for reducing or blocking ambient light which would hinder the light sensing pixel elements from sensing the light representative of skin topology. The sensors are non-imaging contact sensors as they have platen to contact skin to be imaged, and do not require optics, such as lenses for focusing and / or magnification, to enable proper capture of light representative of skin topology on the sensor's light sensing pixel elements.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
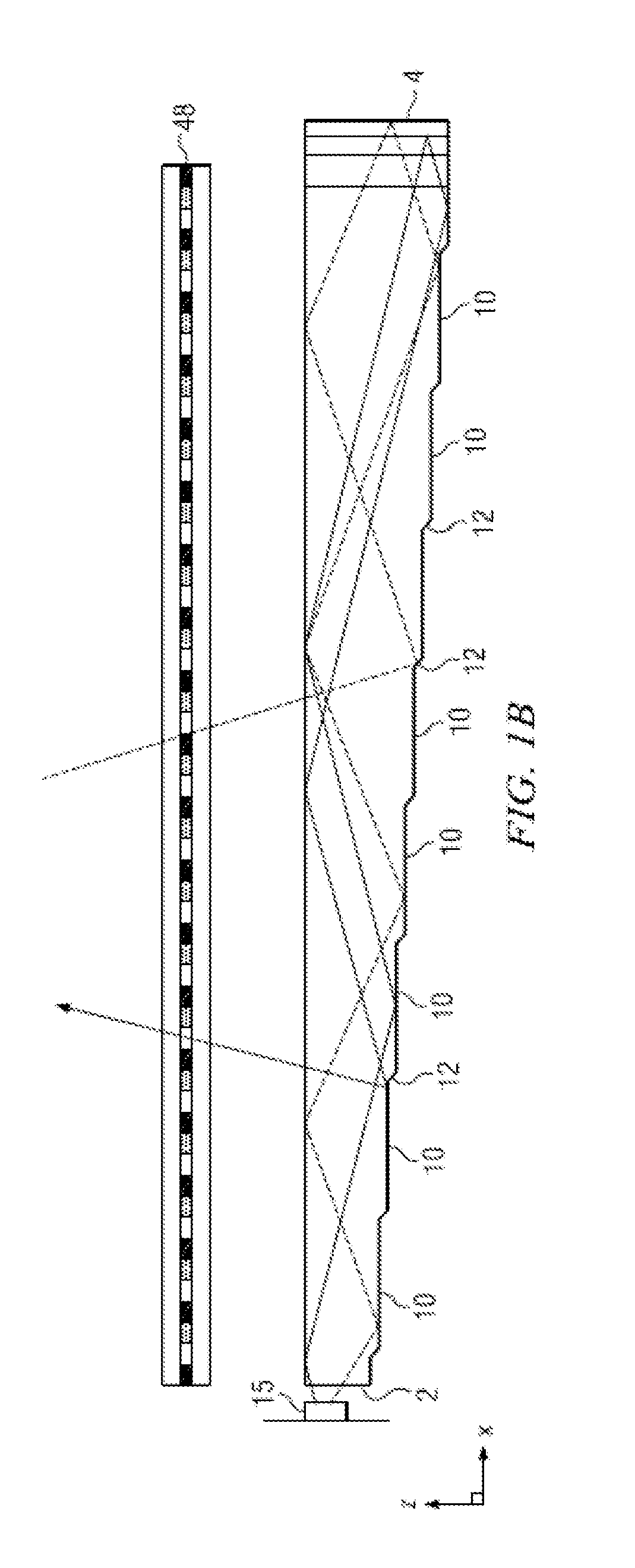
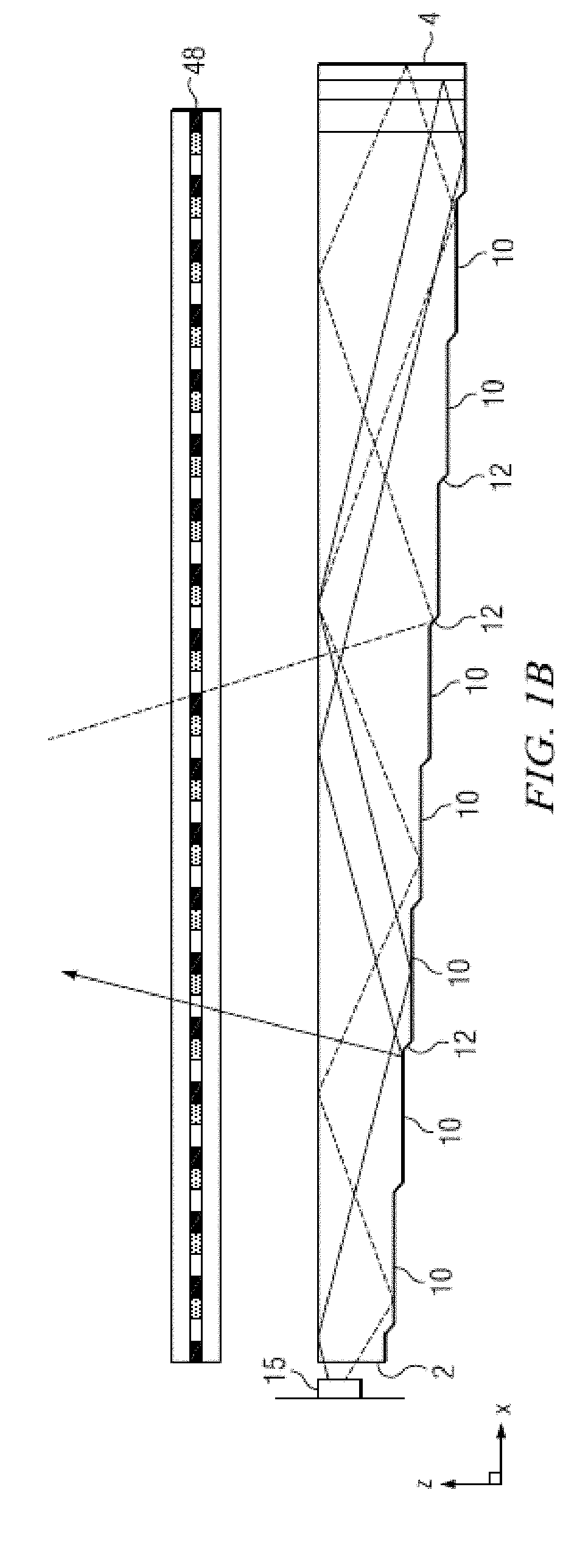
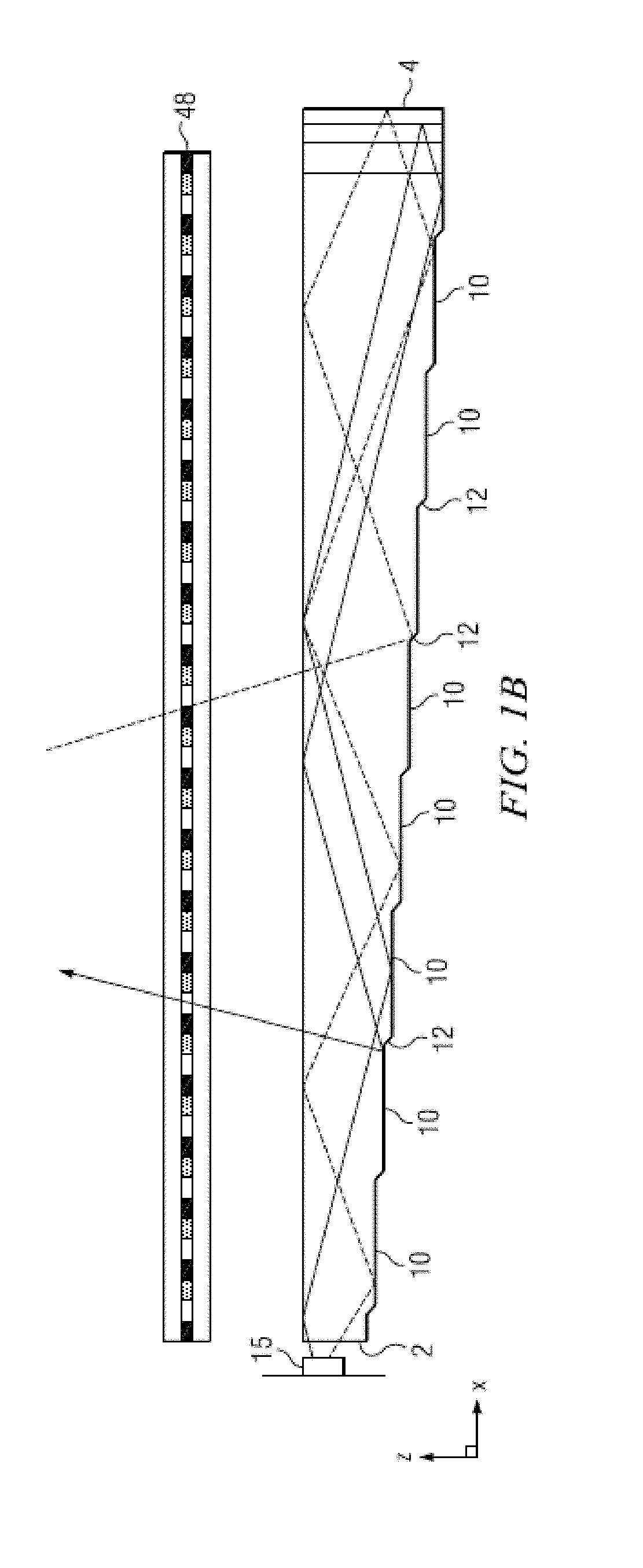
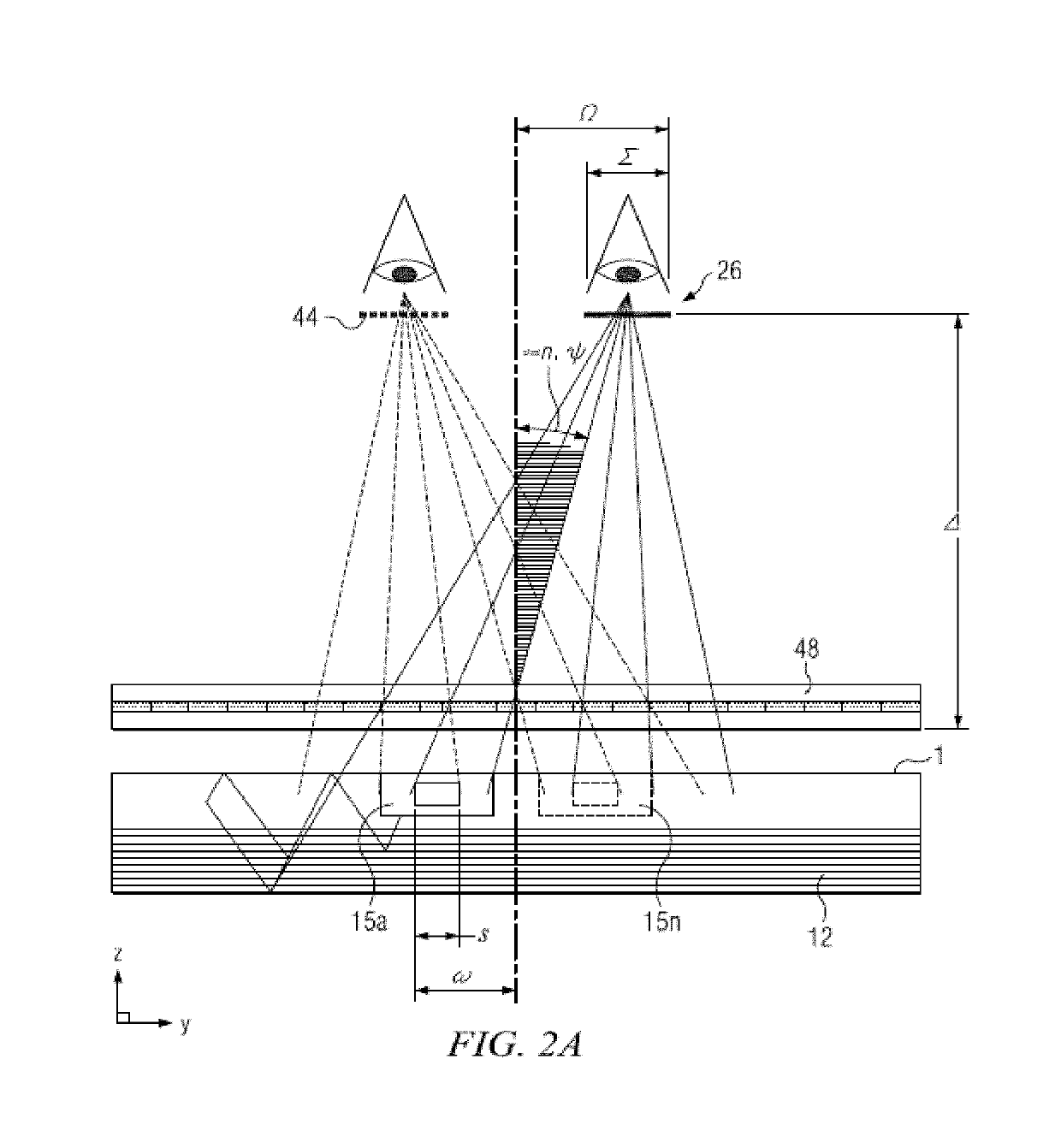
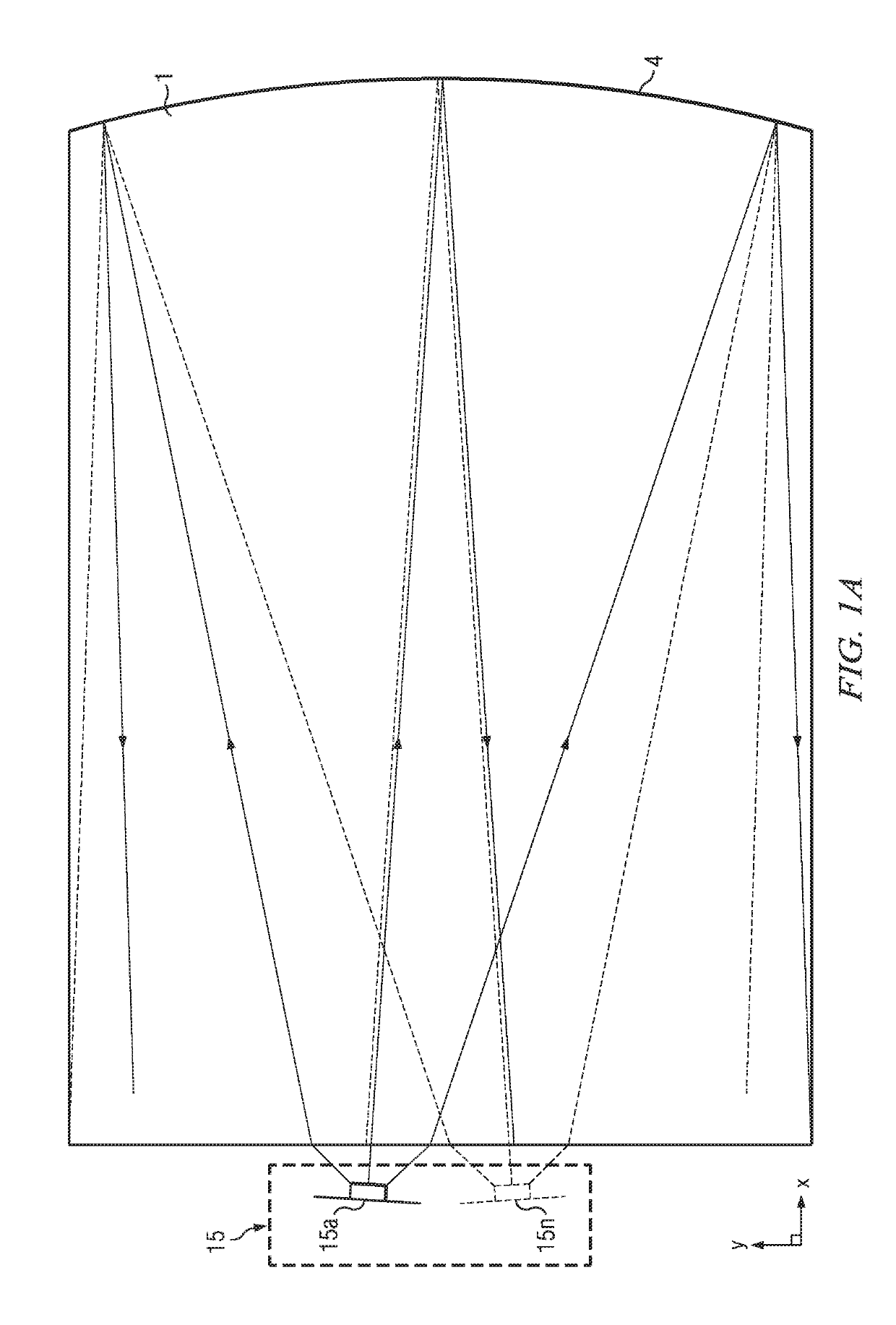
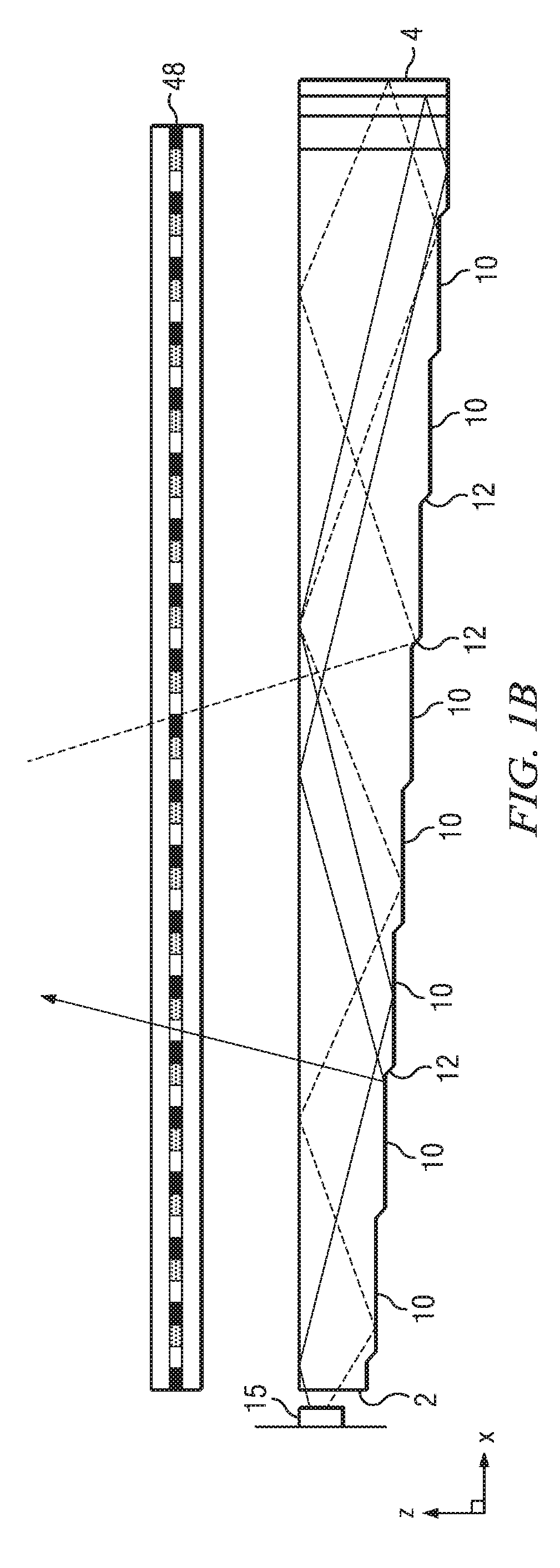
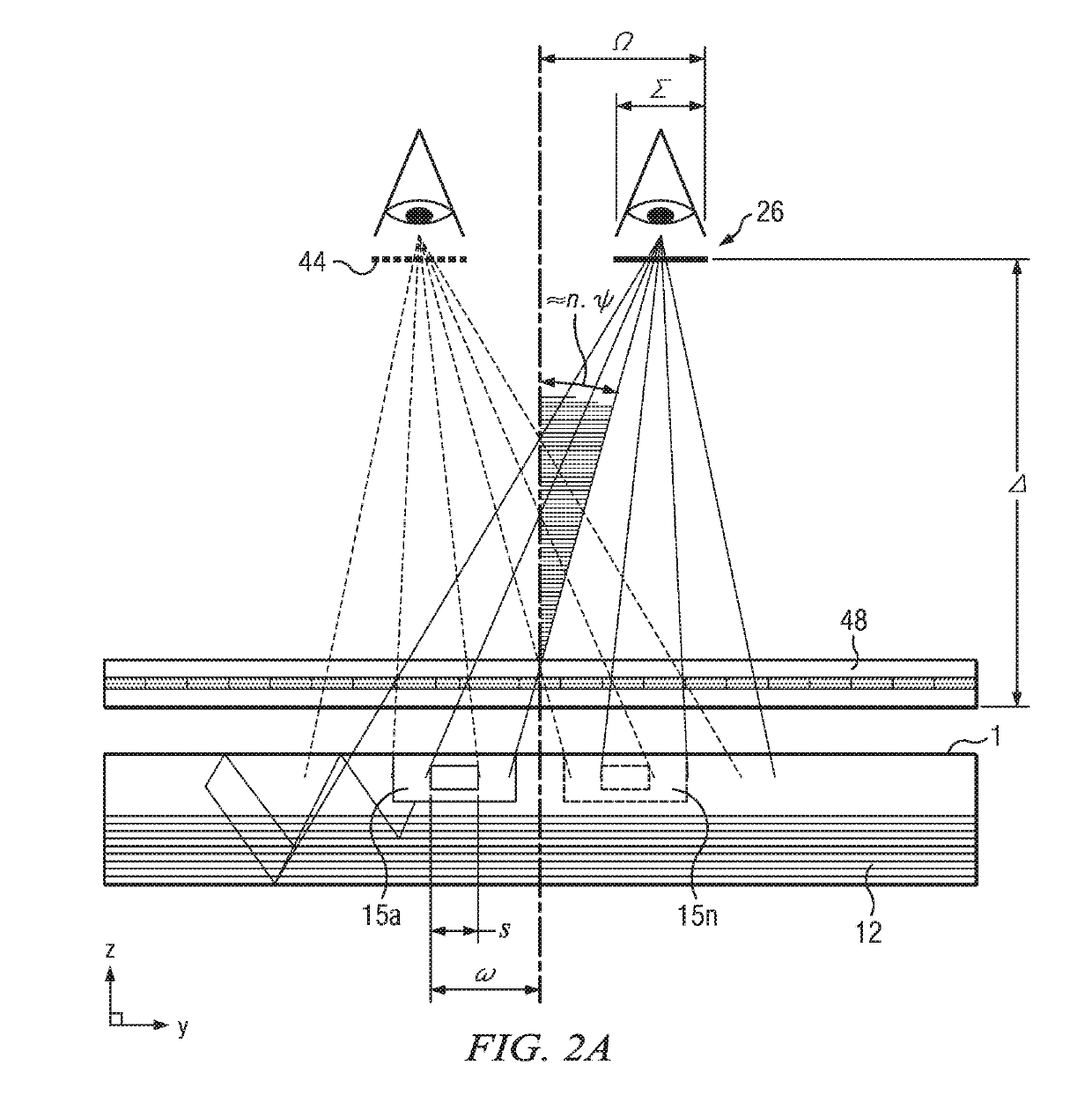
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20130307831A1Improve efficiencyLarge back working distanceMechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. The uncorrected system creates non-illuminated void portions when viewed off-axis preventing uniform wide angle 2D illumination modes. The system may be corrected to remove this non uniformity at wide angles through the introduction of additional sources away from the system's object plane, additional imaging surfaces, and / or by altering ray paths.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Oversampling pulse oximeter
InactiveUS20050020894A1Increased complexityIncrease expensesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDigital signal processingAudio power amplifier
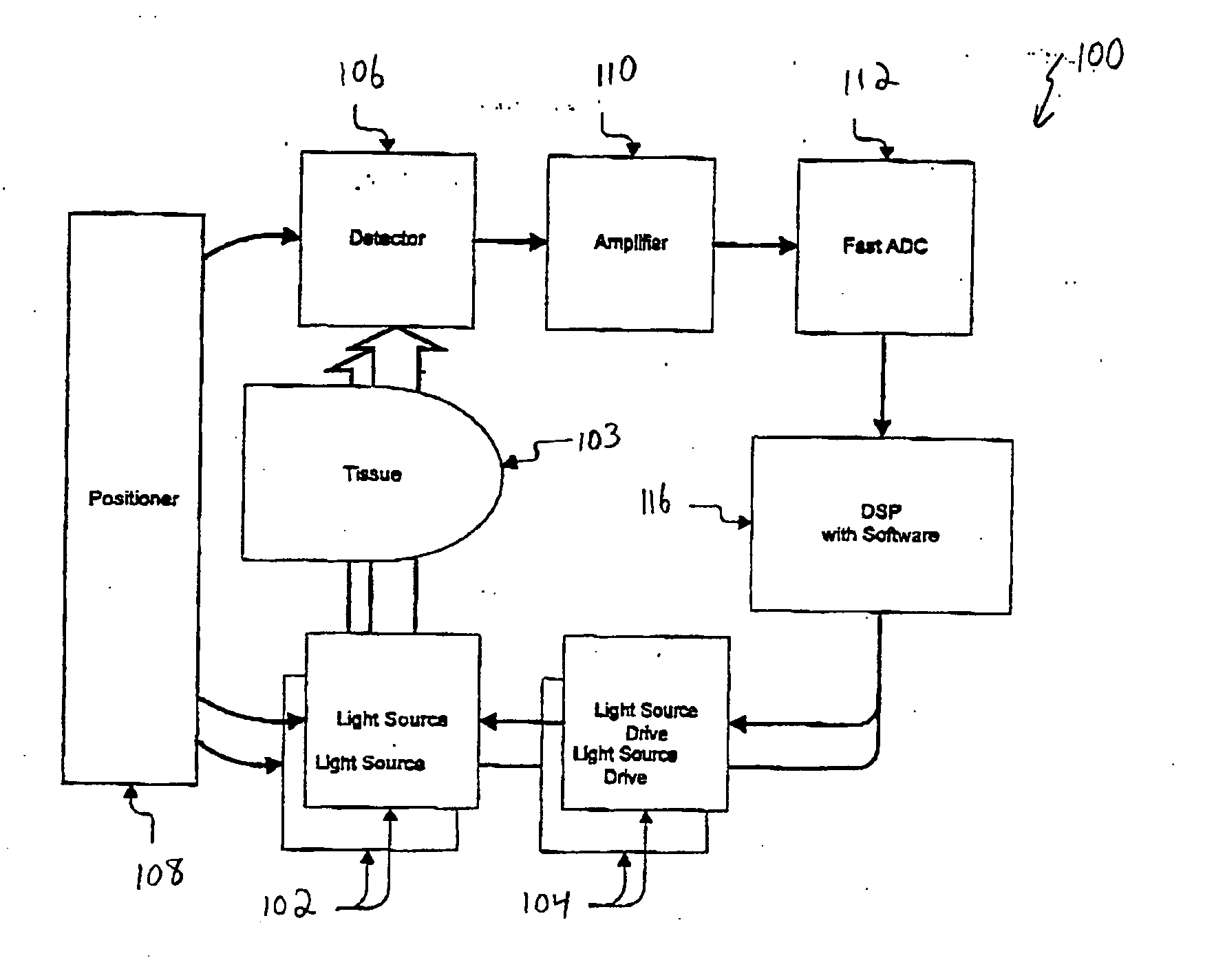
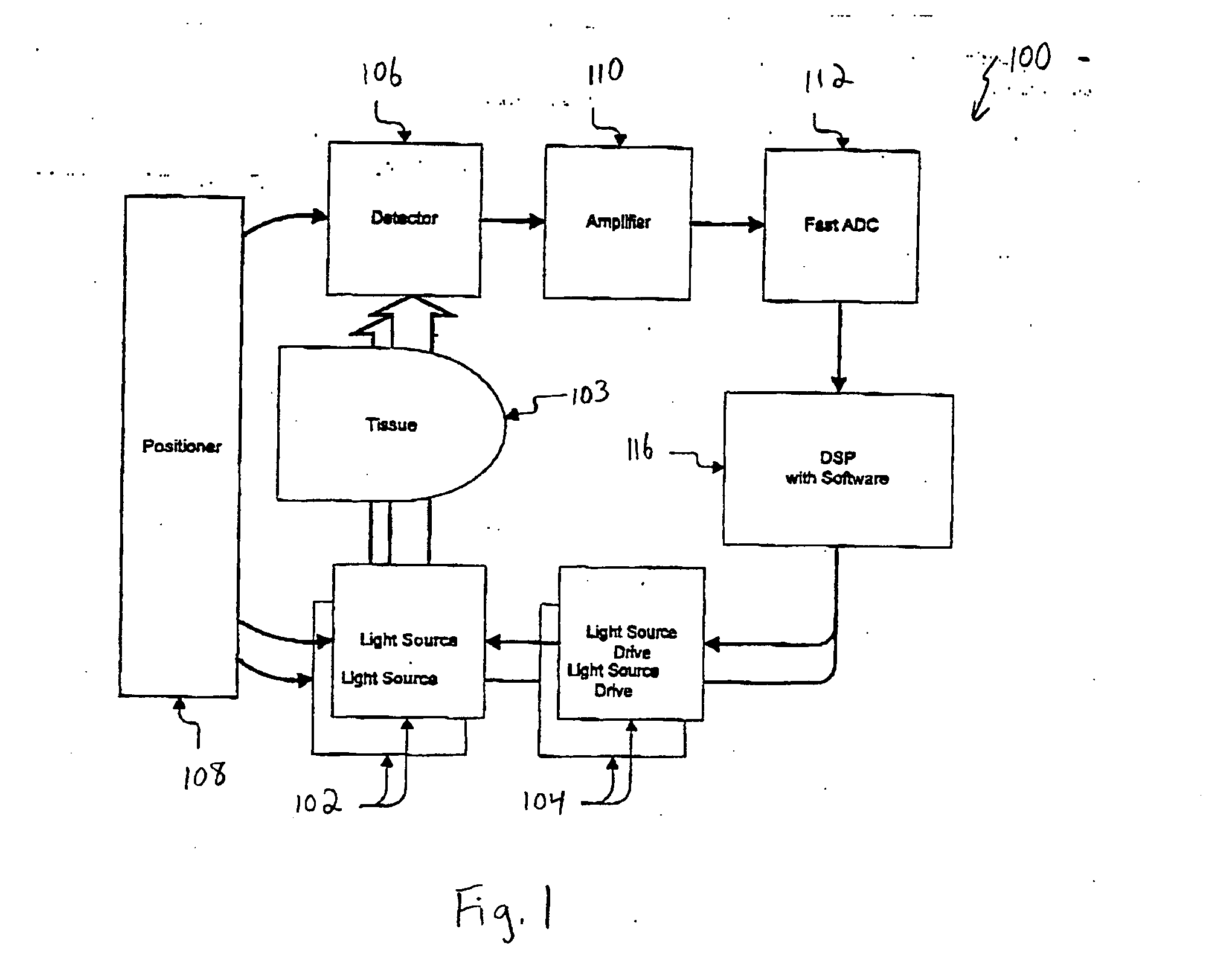
An oversampling pulse oximeter includes an analog to digital converter with a sampling rate sufficient to take multiple samples per source cycle. In one embodiment, a pulse oximeter (100) includes two more more light sources (102) driven by light source drives (104) in response to drive signals from a digital signal processing unit (116). The source drives (104) may drive the sources (102) to produce a frequency division multiplex signal. The optical signals transmitted by the light sources (102) are transmitted through a patient's appendage (103) and impinge on a detector (106). The detector (106) provides an analog current signal representative of the received optical signals. An amplifier circuit (110) converts the analog current signal to an analog voltage signal in addition to performing a number of other functions. The amplifier circuit (110) outputs an analog voltage signal which is representative of the optical signals from the sources (102). This analog voltage signal is received by a fast A / D converter (112) which samples the analog voltage signal to generate a digital voltage signal which can be processed by the digital signal processing unit (116). The fast A / D converter (112) operates at a rate sufficient to take multiple samples per source cycle and may have a sampling frequency, for example, of over 41 kHz. The digital signal processing unit (116) implements software for averaging the samples over a source cycle for improved measurement consistency, improved signal to noise ratio and reduced A / D converter word length.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Image creating method and imaging device
InactiveUS20070177004A1Improve dynamic rangeEasy to solveTelevision system detailsSteroscopic systemsImaging qualityImaging equipment
The invention relates to a method of creating an image file in an imaging device and an imaging device comprising at least two image capturing apparatus, each apparatus being arranged to produce an image. The apparatus is configured to utilize at least a portion of the images produced with different image capturing apparatus with each other to produce an image with an enhanced image quality.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Single piece top surface display layer and integrated front cover for an electronic device
InactiveUS20070229475A1Reduce the possibility of damageReduces parallax effectNon-enclosed substationsInput/output for user-computer interactionSurface displayDisplay device
A single-piece top surface display and integrated front cover for an electronic device. In one embodiment, the cover comprises a thin, flexible, transparent layer coupled with a supporting structure. The flexible layer is supported above a display screen which is coupled with pressure activated sensors located under the display screen. The cover is dust-free, waterproof, and has a flat outer surface that is free of any steps or indentations. Users input data by applying pressure on the cover which causes the display screen to deflect and activate the sensors. The pressure exerted on the sensors is triangulated to register the position of the user input. In another embodiment, the cover is transparent, rigid, and directly contacts the pressure activated sensors which are located in front of the display screen or in the housing behind it. When pressure is applied to the cover, the cover deflects and activates the sensors. In both embodiments, an accelerometer identifies valid input events.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
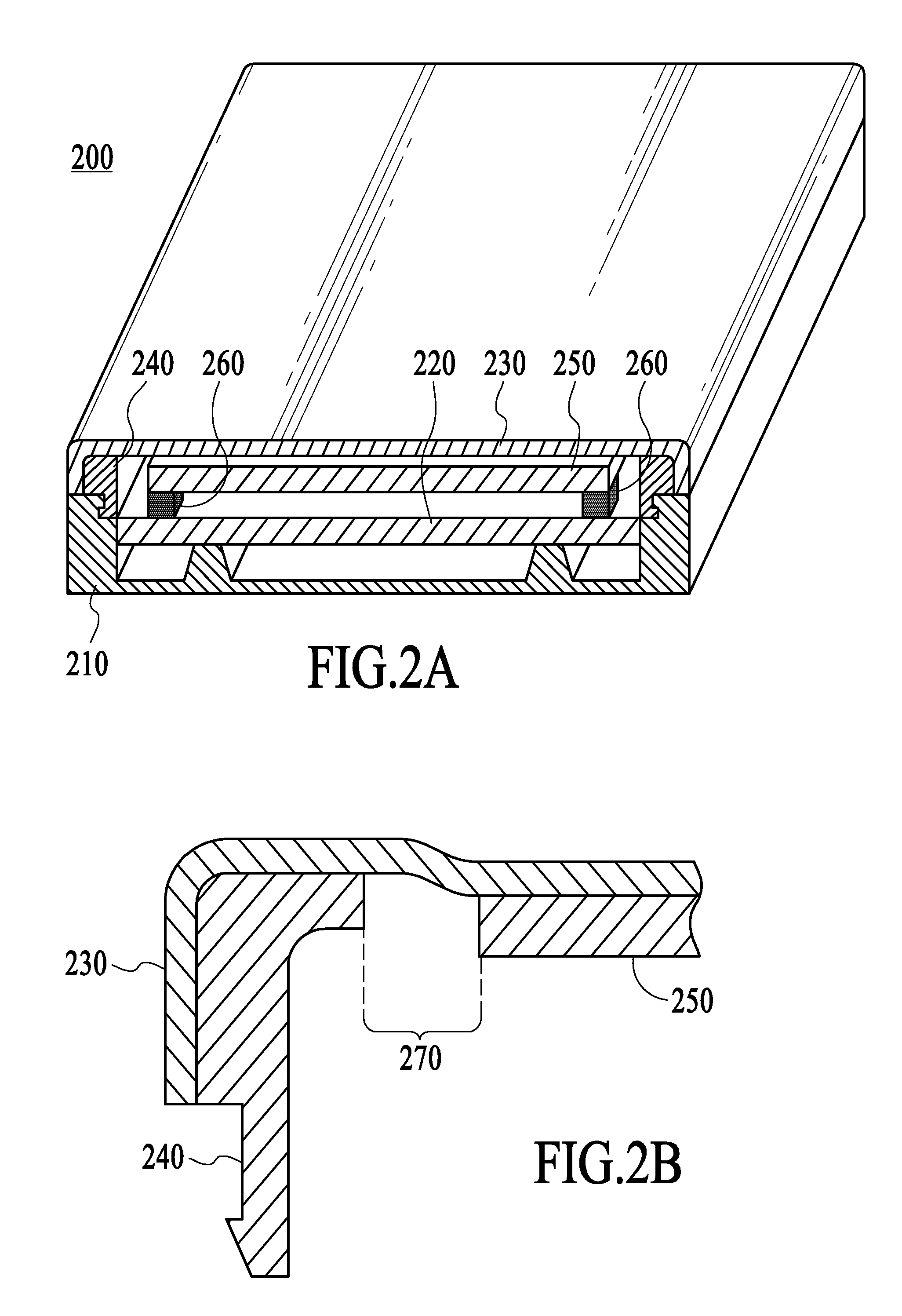
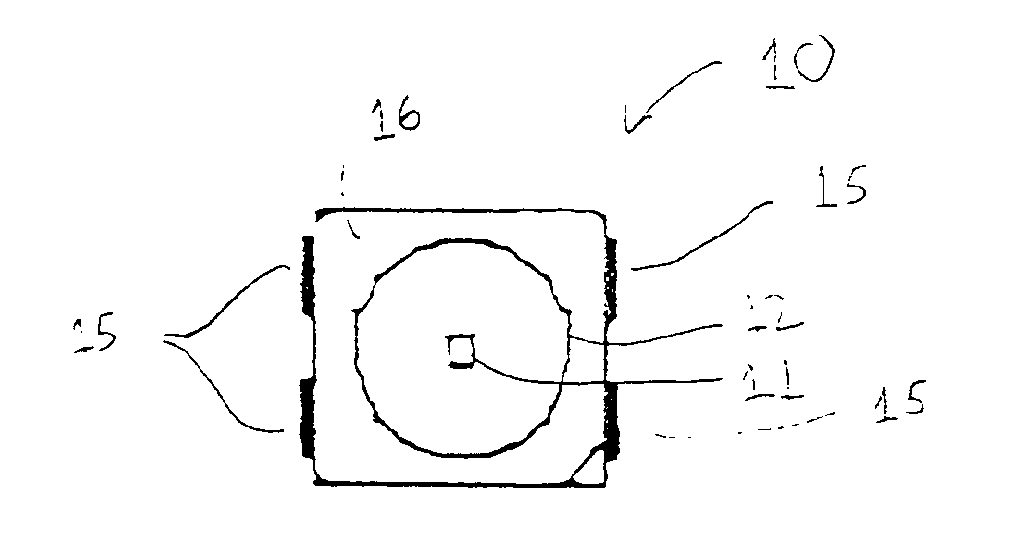
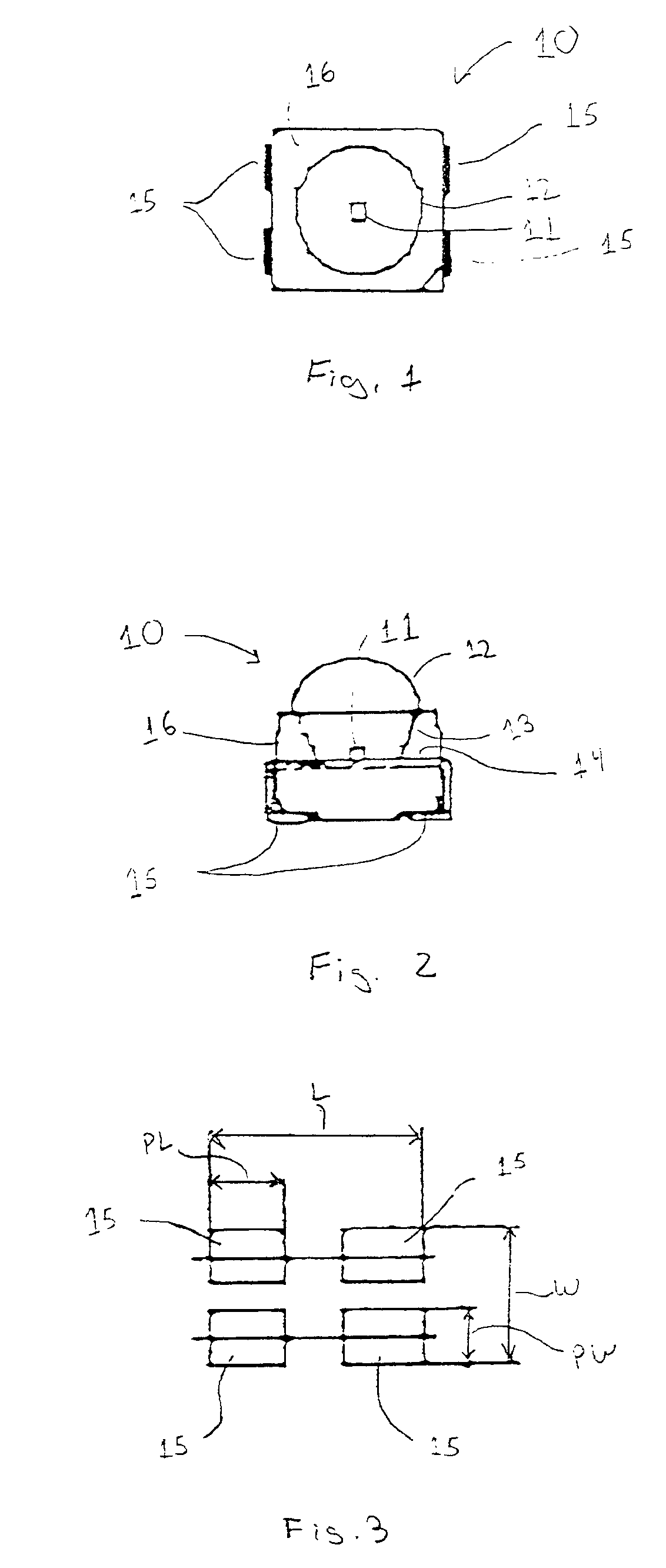
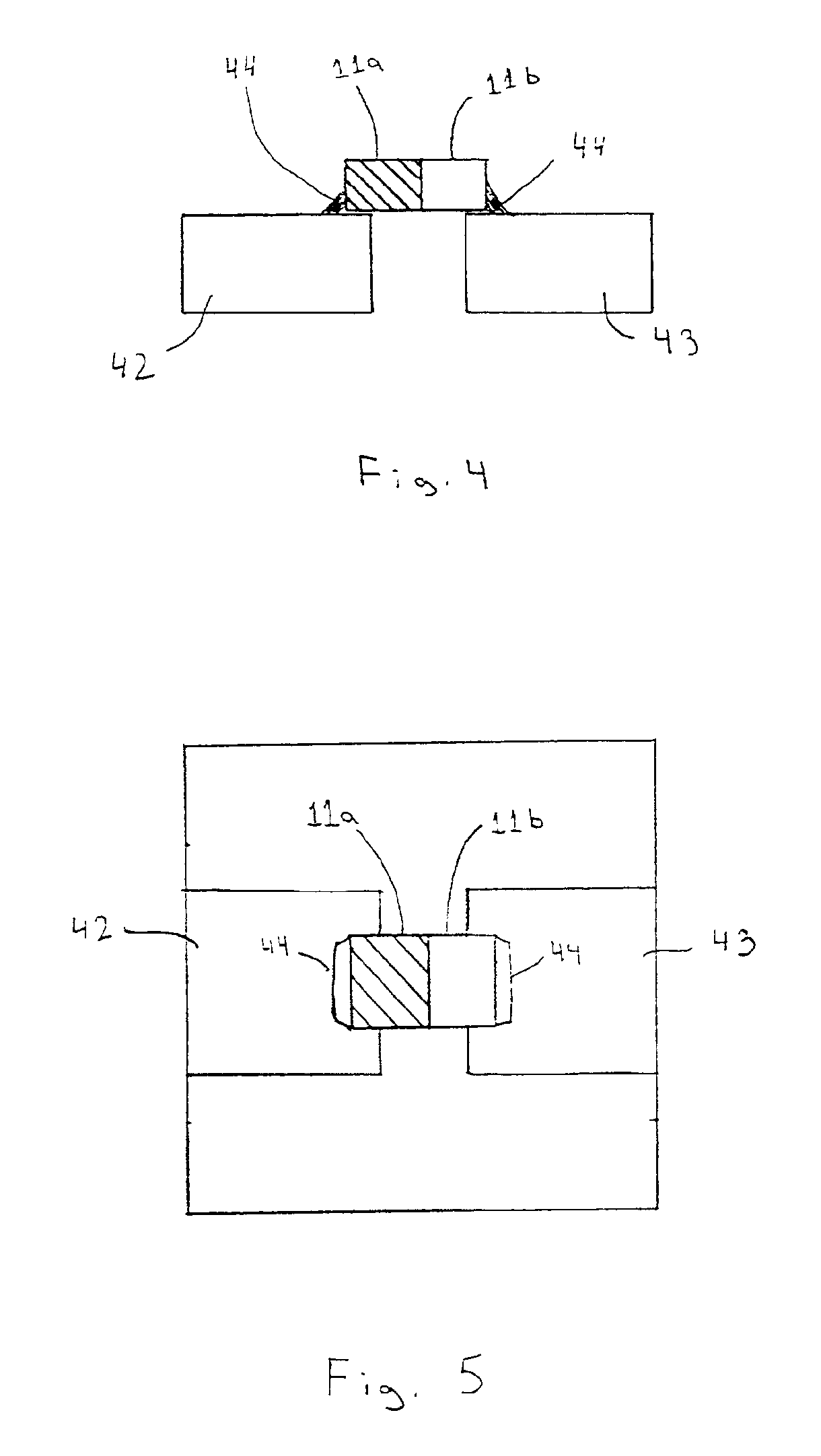
Semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS6940704B2Much of lightGuaranteed uptimeNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceContact padLight-emitting diode
A light emitting diode (LED) including a combination of features that enable the LED to produce a high-brightness predetermined radiation pattern. The combination of features enable the LED to function cooler and more reliably at a higher drive currents and elevated ambient temperatures, and therefore emit light of increased brightness, without overheating, and to have a particular radiation pattern. In particular, a surface mount that is capable of operating at high drive currents and high ambient temperatures is disclosed. The LED comprises a surface mount package having a metal lead frame having mass sufficient to provide low thermal resistance, at least one anode contact pad and at least one cathode contact pad. The LED also includes a reflector positioned within the package, a semiconductor die and an optional focusing dome. The semiconductor die comprises a transparent substrate and a semiconductor component and is positioned within the package so that the semiconductor component and the substrate are arranged side-by-side over the reflector (flop-chip). Alternatively, the die is positioned within the package so that the substrate is on top of the semiconductor component (flip-chip). The optional focusing dome is operative to refract light emitted from the semiconductor die and light reflected from the reflector to create a predetermined radiation pattern.
Owner:GELCORE LLC (US)
Putter head with improved alignment and stability features
InactiveUS6080070APrecise alignmentImpart horizontal stabilityGolf clubsStringed racketsEngineeringTarget line
A putter head includes an aperture through which two rails extending across a bottom of the putter head can be viewed. After establishing a target line, the player first levels the rails flat on the putting surface. Then, the player looks down on the putter head and adjusts his position and aligns the putter head in such a manner that a groove on top of the putter is seen as situated / centered between the rails. A slot running parallel to the putting face of the putter head also is used to ensure that the putter head is in proper alignment. Also, the rails are substantially flat to impart additional horizontal stability and alignment to the putter head during putting.
Owner:AKRIBIS GOLF COMPANY LLC DBA TRAXX PUTTERS
Heat sink and LED cooling system
InactiveUS20120085516A1Improve cooling effectImprove performancePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsEngineeringHeat spreader
A heat sink for cooling LEDs, which includes a heat sink housing which is configured as a finned concentric tube configuration. Also, an LED heat sink assembly and an LED cooling system which include a heat sink housing which is configured as a finned concentric tube configuration. Also, a method for cooling LED modules.
Owner:COOL LUMENS
Wide Angle Imaging Directional Backlights
ActiveUS20160349444A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second deflected direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources from the side of the waveguide and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. A directional backlight with small footprint and low thickness may be provided.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Display apparatus and method for operating a display apparatus
InactiveUS20080238871A1Extension of timeSmall batteryTransmission systemsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsDisplay device
A display apparatus includes a plurality of scanning lines and data lines and, at each intersection of said data lines and scanning lines, an electrochromic pixel element and a sensor element connected to the pixel element. The sensor element is sensitive to a user's graphical input, which changes a charge state of the respective pixel element. The display apparatus also includes a control means, which is configured to allow the pixel element to be selectively set to a first charge state corresponding to a first display state, or to a second charge state corresponding to a second display state. The second display state reflects the user's graphical input. The second charge state of the pixels may be brought about by exposing the sensor elements to light from a light pen or to a magnetic field from a magnetic pen, the pen being drawn across the display screen of the apparatus. Due to the direct action of the sensor elements in modulating the charge on the pixel elements, it is possible to display an image drawn on the screen instantly, without the need to scan the display to determine which pixels have changed their initial charge. This reduces the power consumption of the apparatus.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
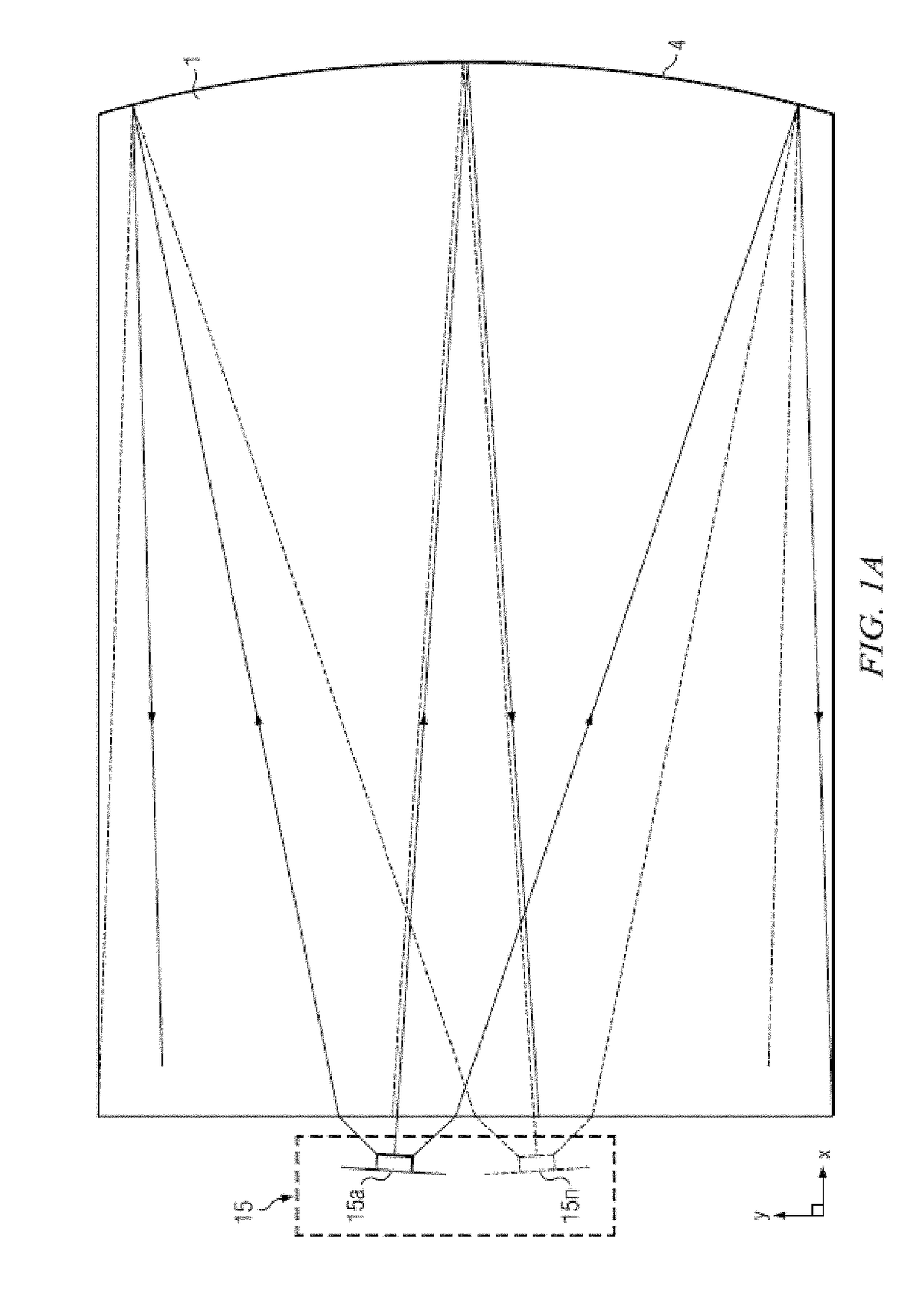
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20170339398A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusStatic indicating devicesWide-angle lensDirect illumination
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources by waveguide facets and rear reflector images in cooperation. Viewing windows may be provided at first and second different window planes to improve uniformity in a lateral direction. Further, stray light may be reduced by inner and outer portions of reflective facets with different inclinations for the rear reflector.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
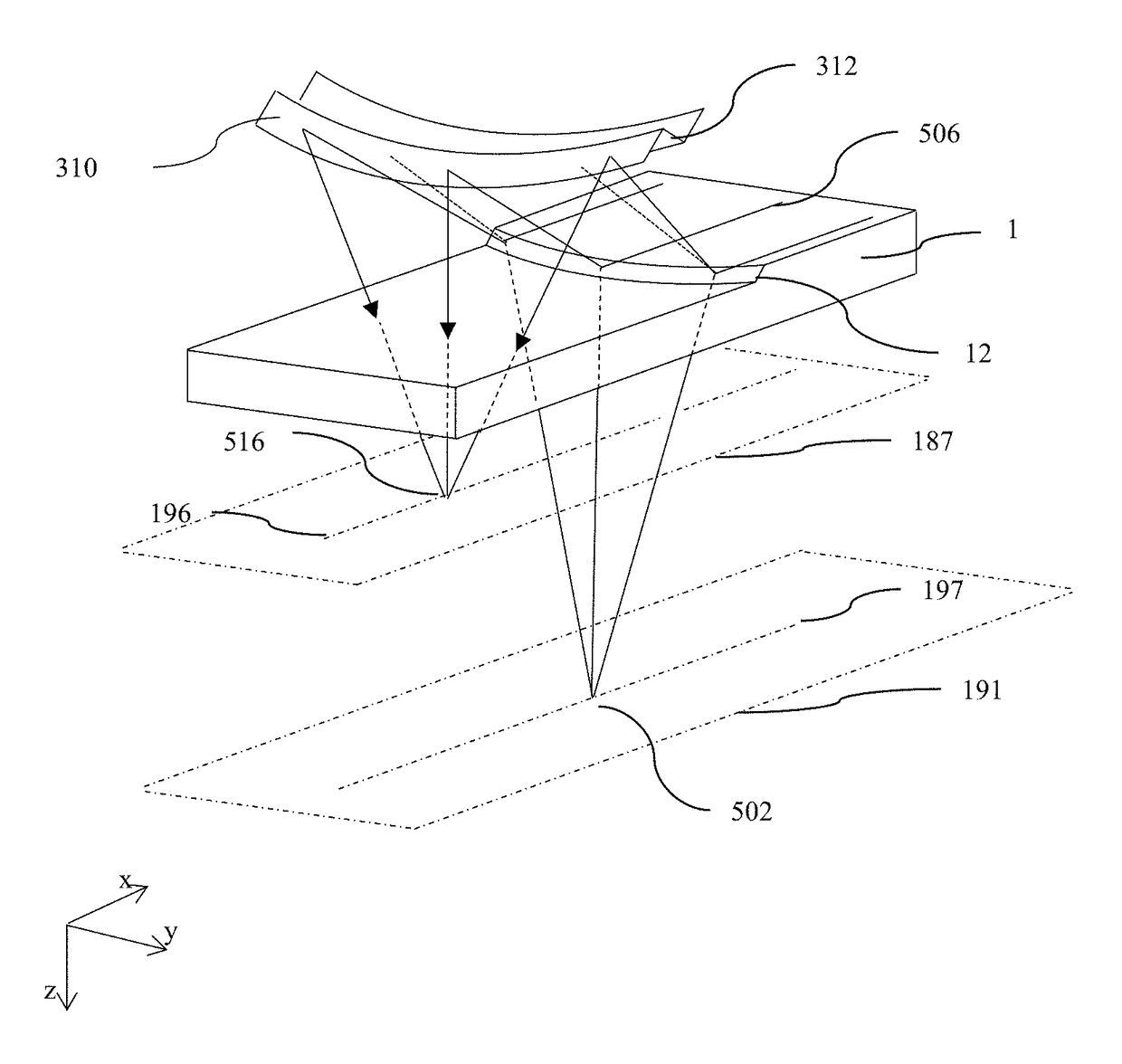
Optical stack for imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20180196275A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsVisibilityDirect illumination
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A rear reflector is arranged to receive light transmitted by the features and to provide polarization recirculation. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Retarder stack arrangements are provided to increase the efficiency of polarization recirculation, reduce the visibility to damage and to reduce color changes with viewing angle.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Privacy display apparatus
ActiveUS20190215509A1Operational savingHigh luminance operationMechanical apparatusDiffusing elementsDirect illuminationLiquid crystal
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. The directional backlight may be arranged to switch between at least a first wide angular luminance profile mode and a second narrow angular luminance profile mode. The directional backlight is arranged to illuminate an LCD with a bias electrode arranged to switch liquid crystal directors in black state pixels between a first wide angular contrast profile mode and a second narrow angular contrast profile mode. Performance of privacy operation for off-axis snoopers is enhanced in comparison to displays with only directional backlights or switchable contrast properties.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20170336661A1High luminance operationSave powerMechanical apparatusImage analysisSystem elementPhysics
An imaging directional backlight apparatus includes a waveguide and a light source array, providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, and the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a forward direction. Returning light propagating in a backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and define the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. The imaging directional backlight apparatus further includes a control system for controlling the light output directional distribution in an automotive or vehicle environment in dependence on the output from sensors mounted on the vehicle. The control system is arranged to control the light output direction distribution of portable directional displays co-located with the vehicle.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Optical stack for imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS10401638B2Reduce disagreementLow costMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsVisibilityDirect illumination
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A rear reflector is arranged to receive light transmitted by the features and to provide polarization recirculation. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Retarder stack arrangements are provided to increase the efficiency of polarization recirculation, reduce the visibility to damage and to reduce color changes with viewing angle.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Streetlight
InactiveUS8353606B2Easy to modifyImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceHeat sinkHigh pressure
A streetlight installed on a street or a sidewalk in order to radiate light includes a base plate detachably fixed to a streetlight body using a clamp and a reflector fixed to one side of the base plate. The reflector has a first slope having a plurality of LEDs mounted thereon, and a second slope having a reflective film mounted thereon, the reflective film arranged opposite the LEDs. The reflector provides illumination by reflecting light, emitted from the LEDs, to the outside. A heat dissipation pad is disposed between the base plate and the reflector. The heat dissipation pad insulates the LEDs from external high-voltage EMS. A cover made of a translucent material has a recess in the central portion thereof to house the reflector therein, and fixes both the reflector and the heat dissipation pad to the base plate. Heat dissipation fins are fixed to the base plate.
Owner:JINSUNG CNC
Wide angle imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20160299281A1Reduce disagreementLow costMechanical apparatusMirrorsDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus including a waveguide, a light source array, for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Lateral non-uniformities of output image are improved by means of adjustment of input aperture shape and reflective aperture shape. Cross talk in autostereoscopic and privacy displays may further be improved by light blocking layers arranged on the input end of the waveguide.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
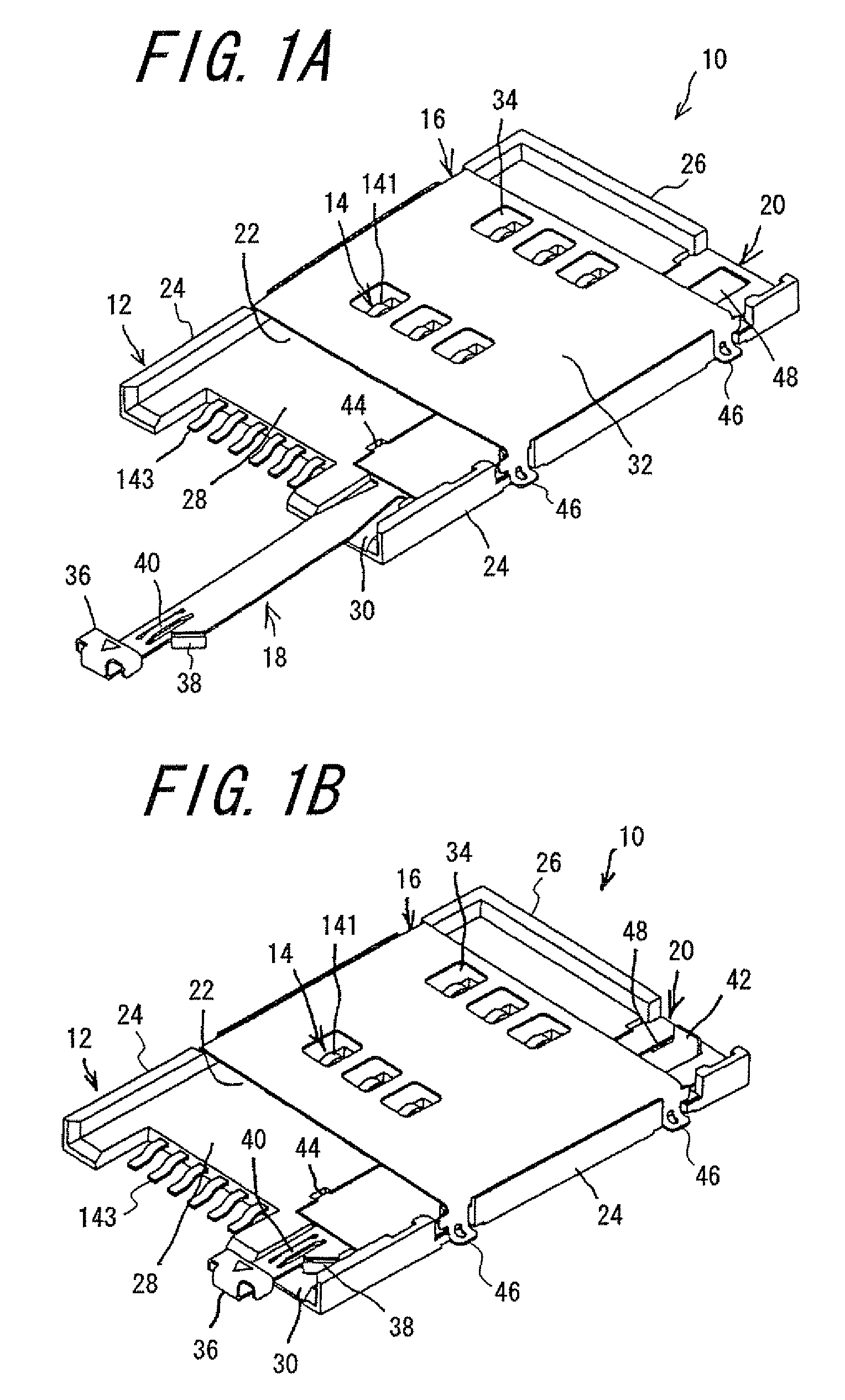
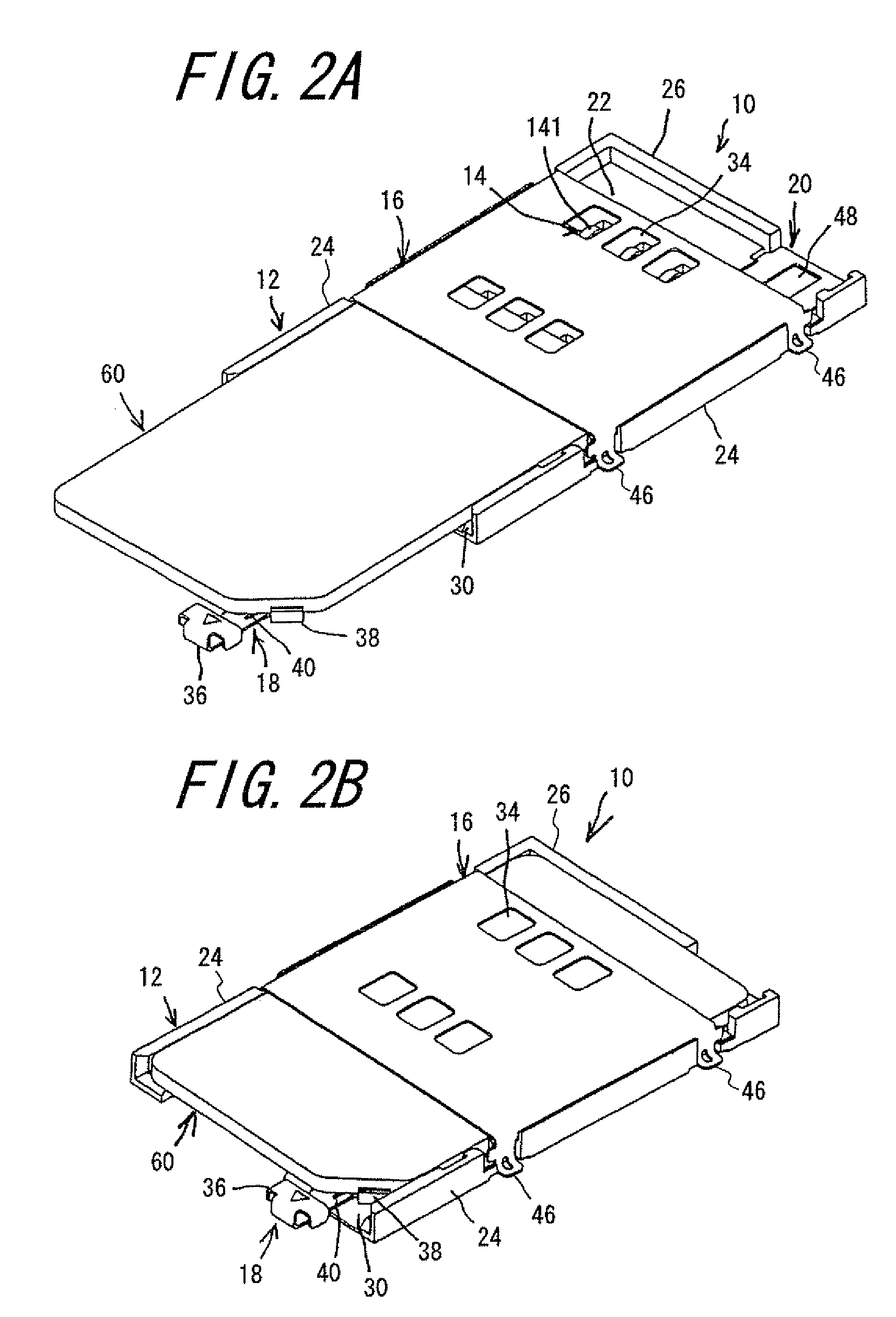
Card connector
InactiveUS7427206B2Easy to disassembleMore compact constructionEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsConveying record carriersEngineeringMemory cards
Owner:DDK LTD
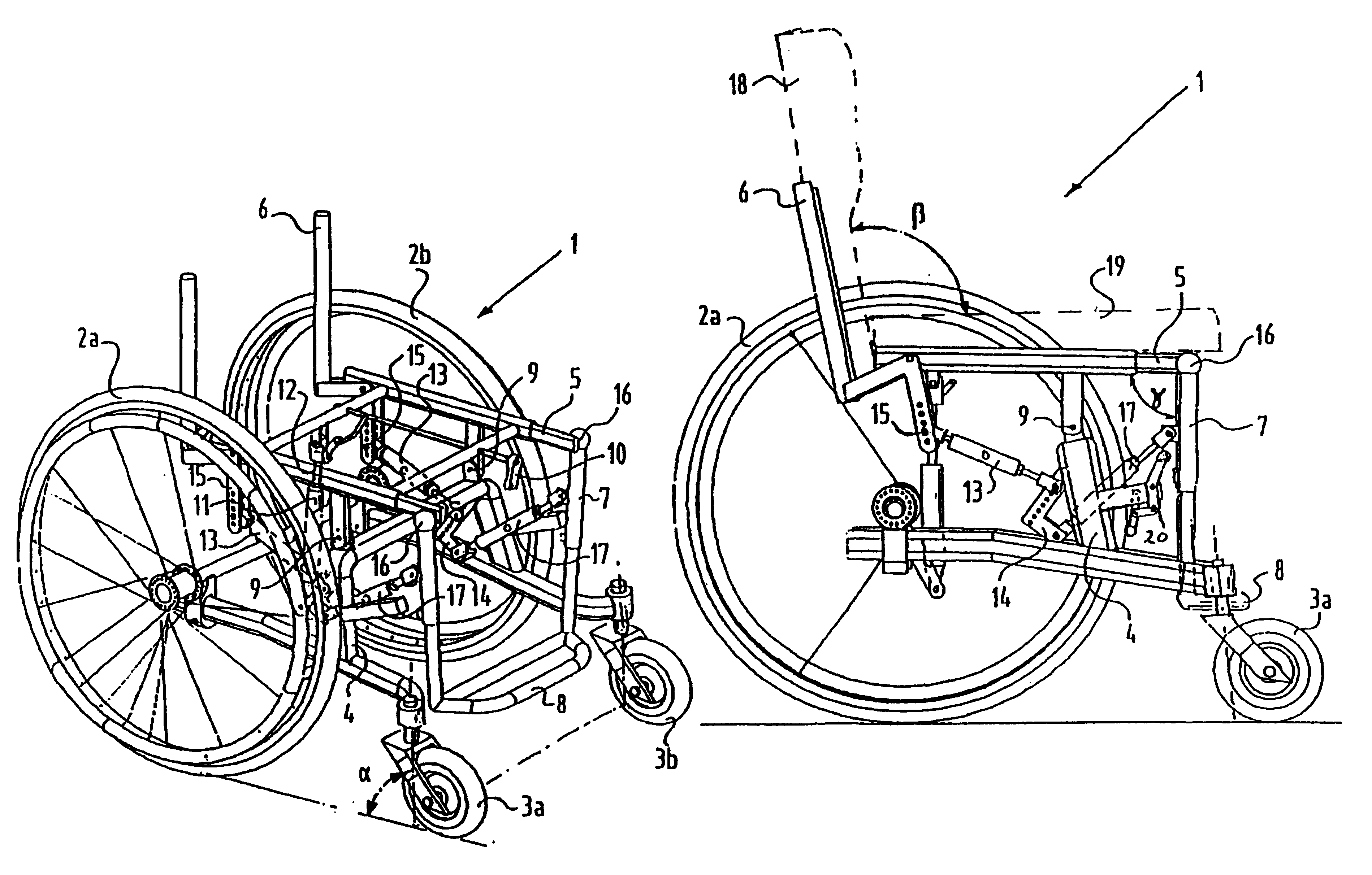
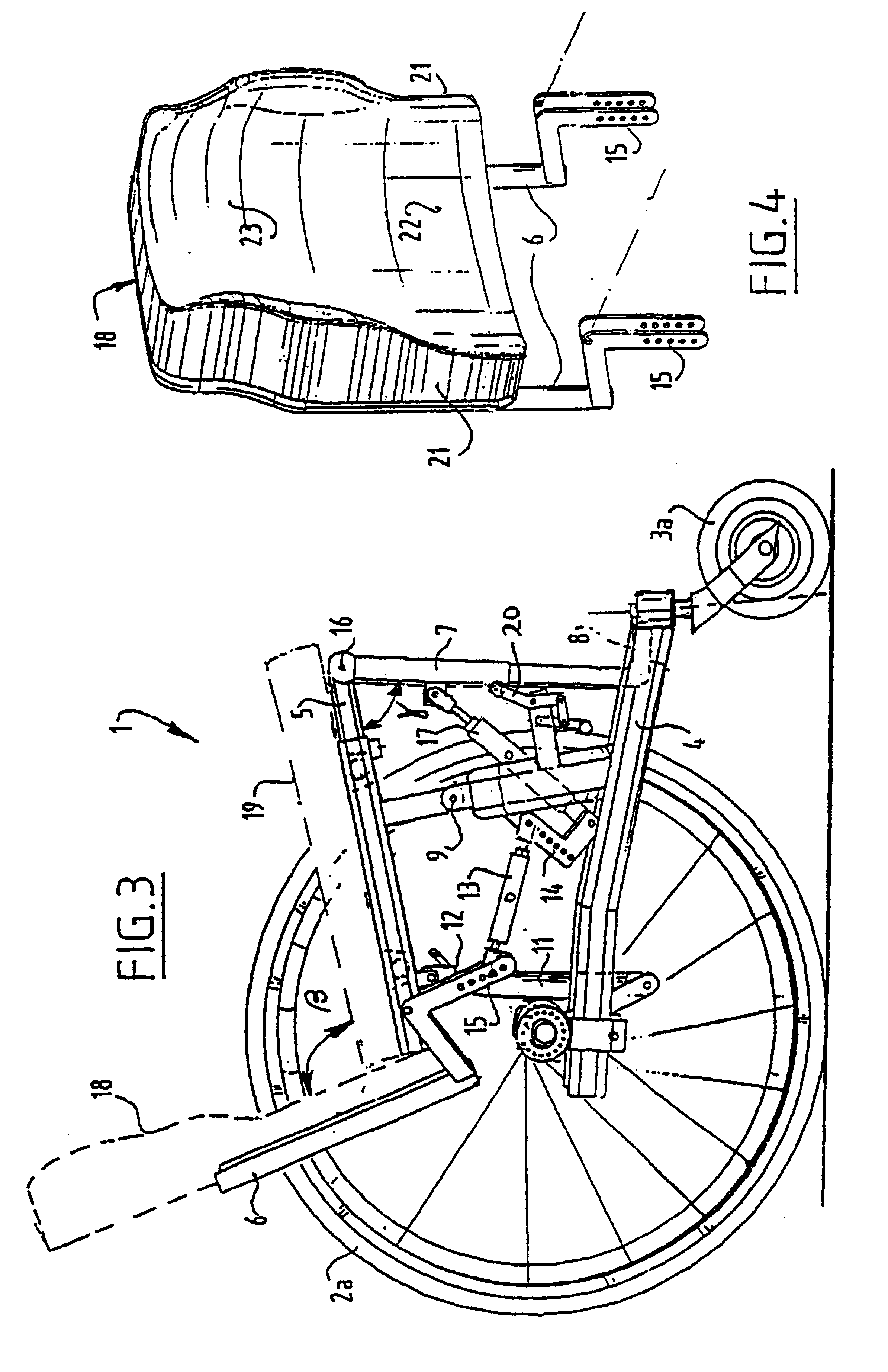
Wheel chair
InactiveUS6705629B2Driving characteristicMuch of lightWheelchairs/patient conveyanceRider propulsionWheelchairEngineering
Owner:HANDICARE HLDG BV
Segmented imaging directional backlights
ActiveUS20180284341A1High luminance operationSave powerMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsDirect illuminationLight beam
An imaging directional backlight apparatus includes a waveguide and a light source array, providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The waveguide may include a stepped structure, and the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a forward direction. Returning light propagating in a backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and define the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. The imaging directional backlight apparatus further includes multiple waveguides with light extraction features arranged to provide uniform output luminance at the seam between the waveguides.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
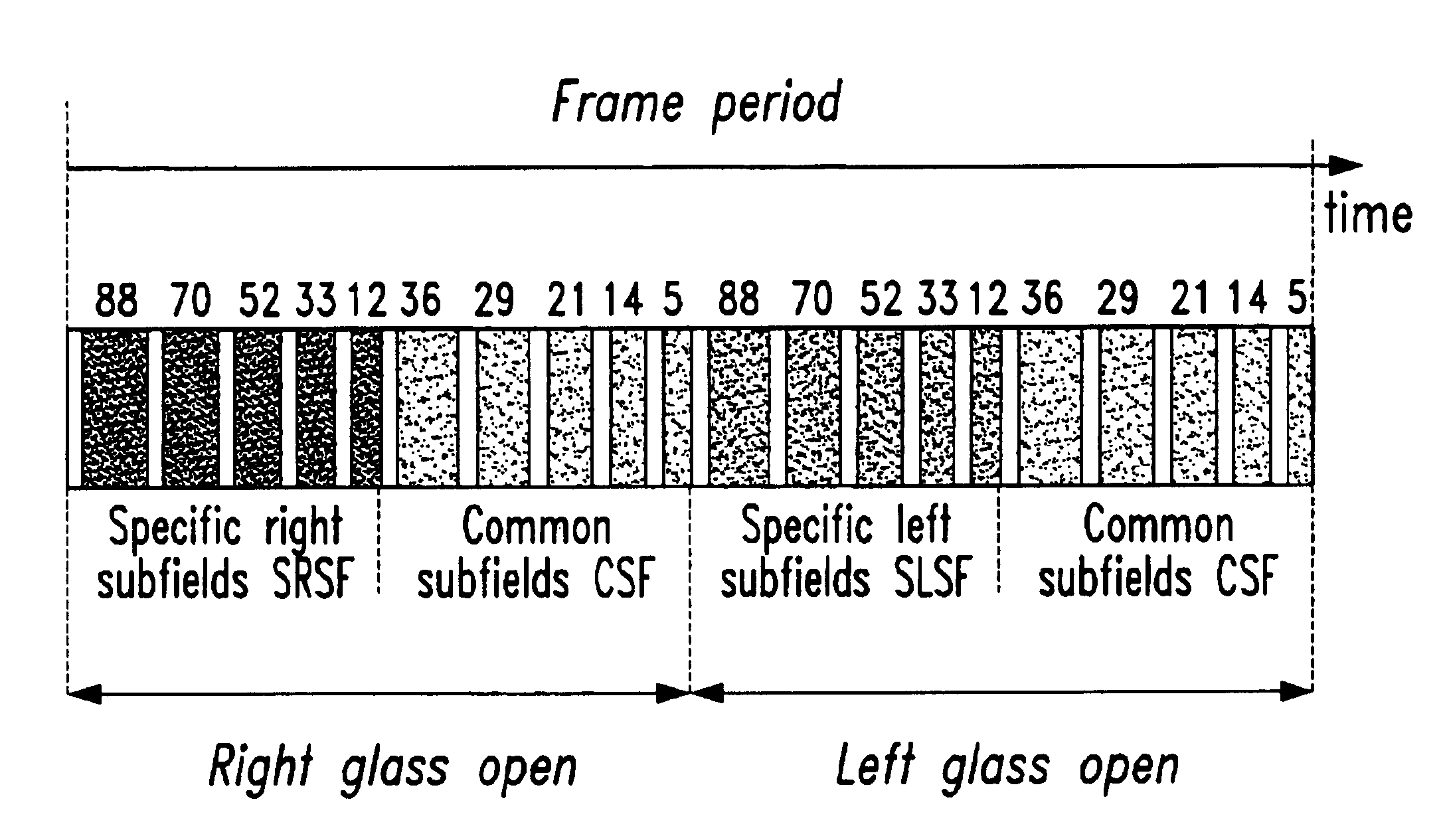
Stereoscopic picture separation for phosphor lag reduction in PDP
InactiveUS6977629B2Reduce decreaseMuch of lightTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Phosphor
For stereoscopic displaying the new plasma display panels are providing promising results. When using shutter glasses that are controlled by the PDP, it is possible to display left and right image in short succession for stereoscopic displaying. However, there is the phosphor lag effect that is really disturbing and can totally impede the stereovision. The frame period of a stereoscopic picture is divided to at least one left period and at least one right period for the left picture and the right picture respectively. According to the invention both pictures are analyzed for similarities and the common part for a pair of corresponding pixels is determined. Sub-field code words for the left / right picture are determined having a part for the specific left / right sub-fields and a part for the common sub-fields. The common sub-fields are positioned at the end of each left / right field for the left / right picture so that the phosphor lag effect is no longer visible.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Ambient light rejection for non-imaging contact sensors
ActiveUS10024655B2Reduce the amount requiredEnhance the imagePerson identificationUsing optical meansLight sensingMagnification
A sensor for capturing images of skin topology is provided having a platen, and a one or two-dimensional array of light sensing pixel elements for receiving light representative of skin topology when skin, such as finger(s), are present upon the platen. Such sensor being improved by structures, layers, or methods for reducing or blocking ambient light which would hinder the light sensing pixel elements from sensing the light representative of skin topology. The sensors are non-imaging contact sensors as they have platen to contact skin to be imaged, and do not require optics, such as lenses for focusing and / or magnification, to enable proper capture of light representative of skin topology on the sensor's light sensing pixel elements.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
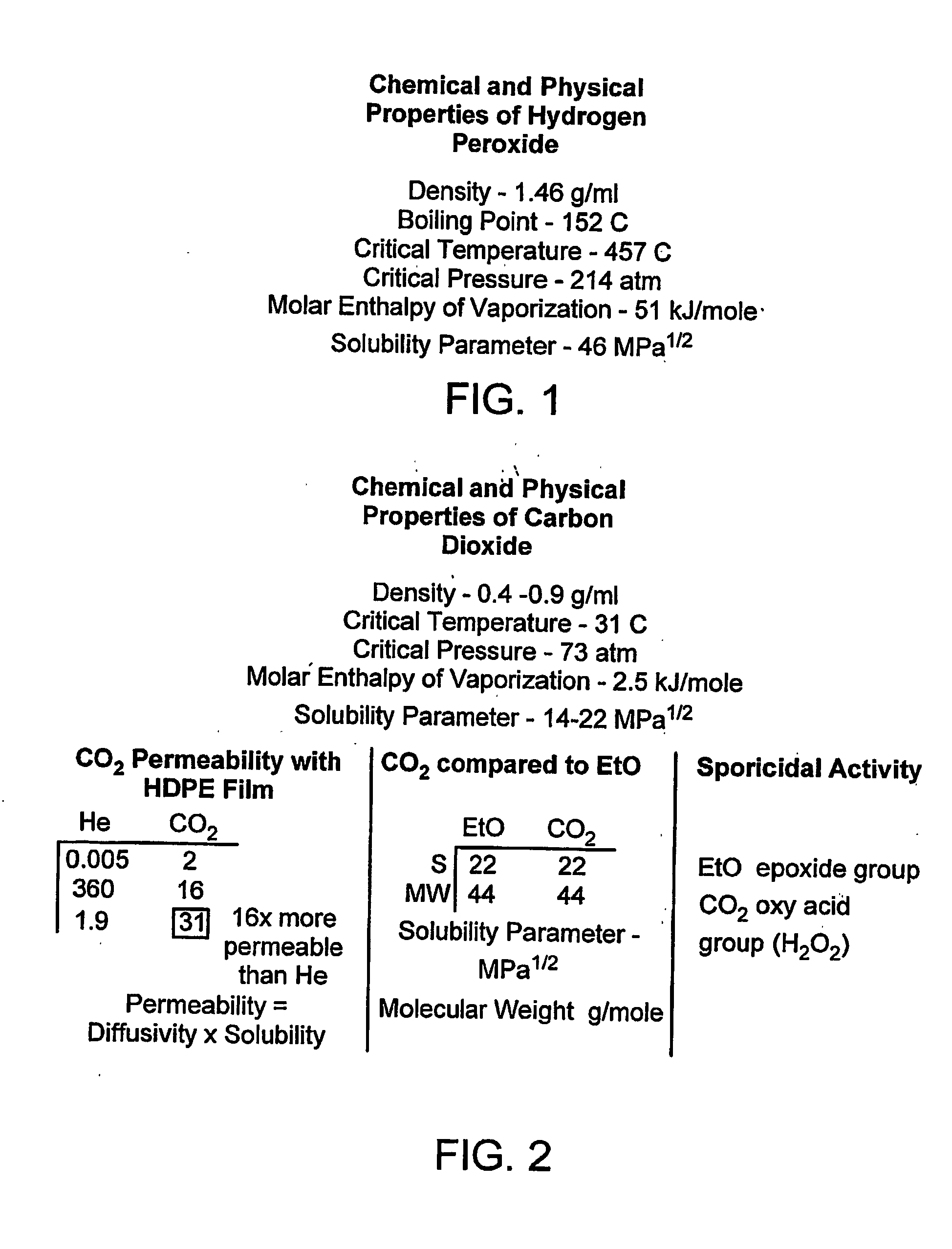
Method, process, chemistry and apparatus for treating a substrate
InactiveUS20050260107A1Much of lightEfficiently usPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesSynthetic resin layered productsCarbon dioxideChemistry
The invention provides new methods for synthesis of percarbonic acid and methods of using percarbonic acid compositions for the treatment of substrates. The invention is particularly useful for cleaning, disinfecting and / or sterilizing a substrate using percarbonic acid or a percarbonic acid-carbon dioxide mixture. The invention further provides an apparatus suitable for use in the substrate treatment methods provided herein. The invention also provides methods and apparatus for the real time monitoring of the treatment processes provided herein.
Owner:WILLIAM A YOUNG GASKET CORP
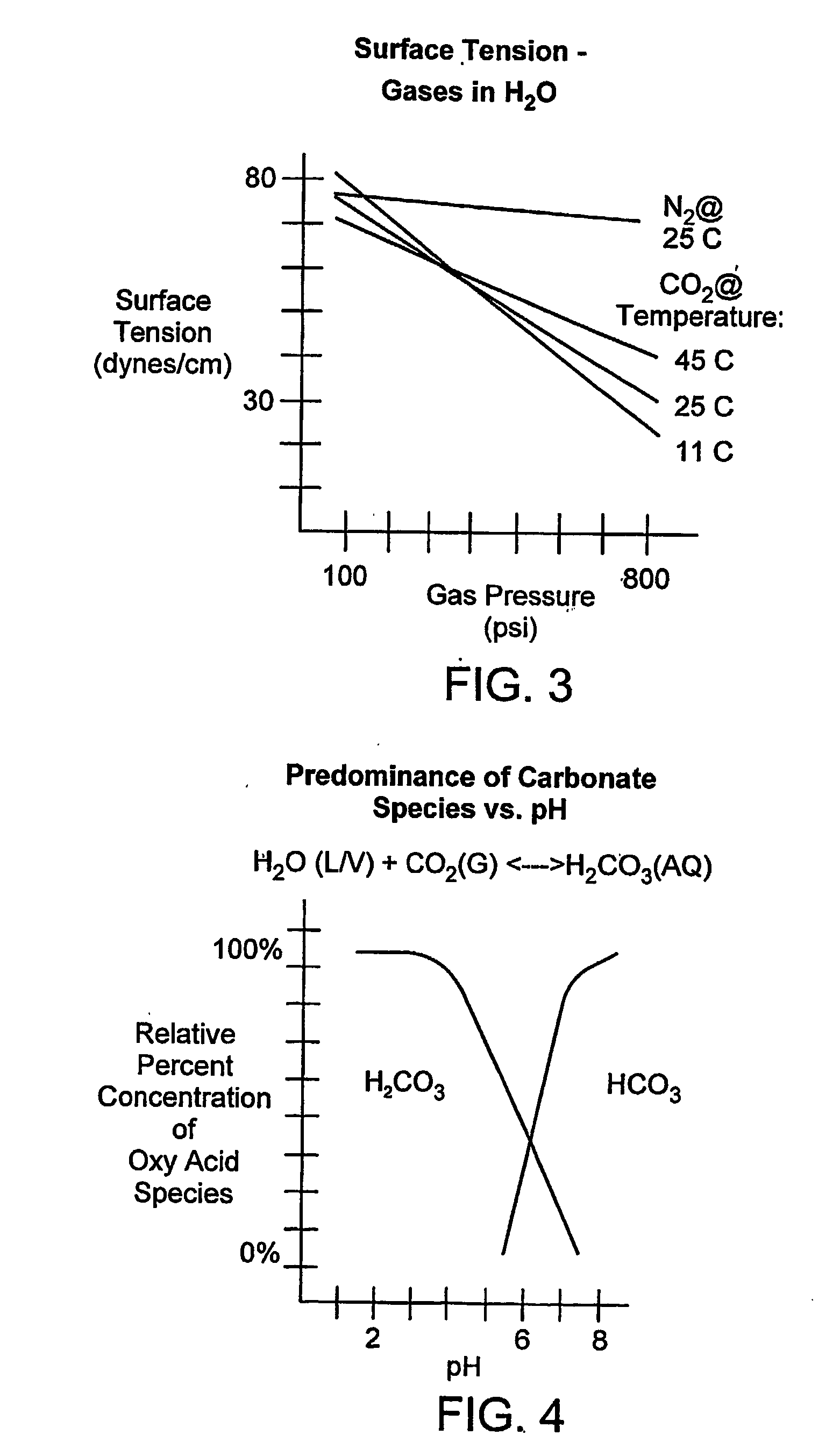
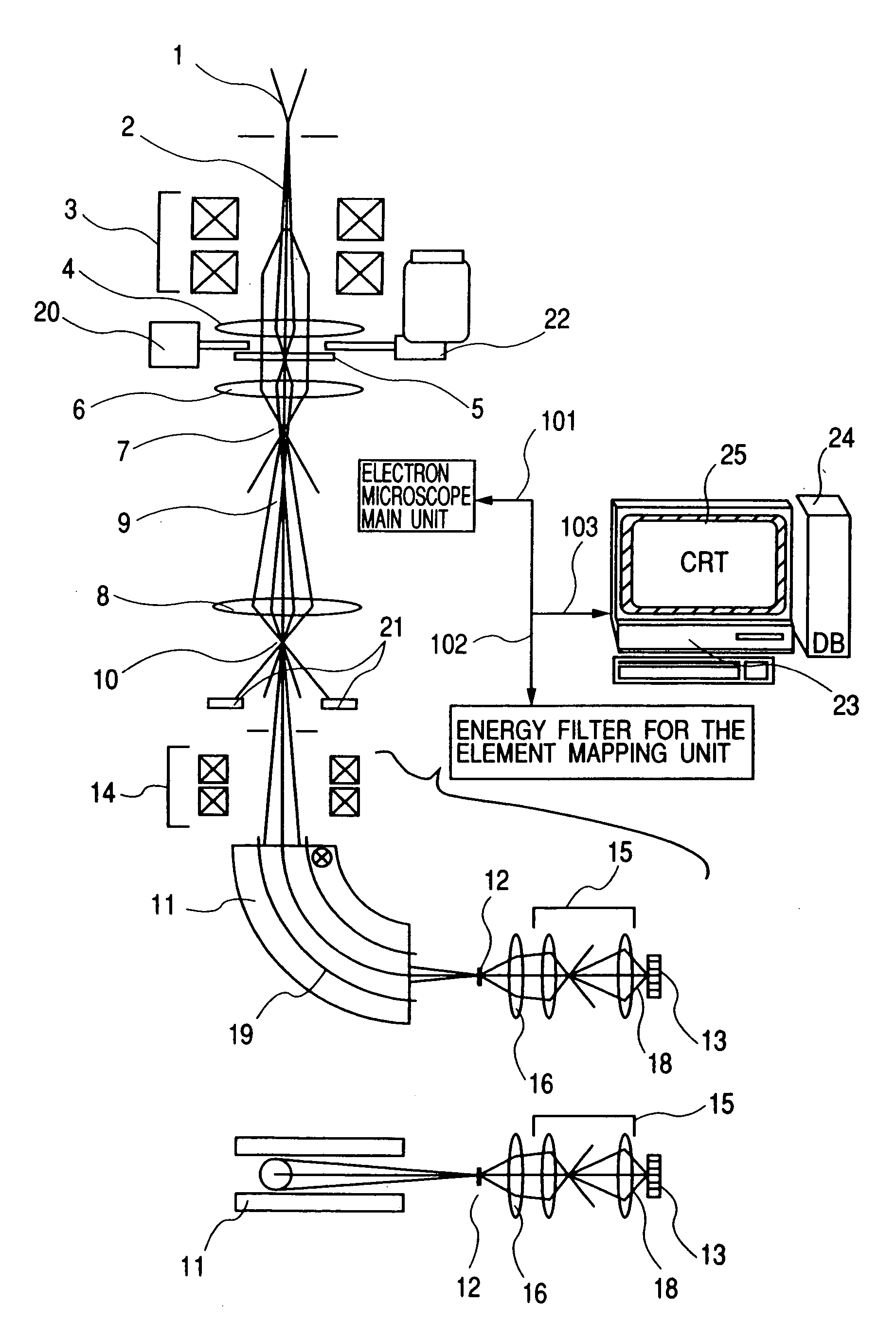
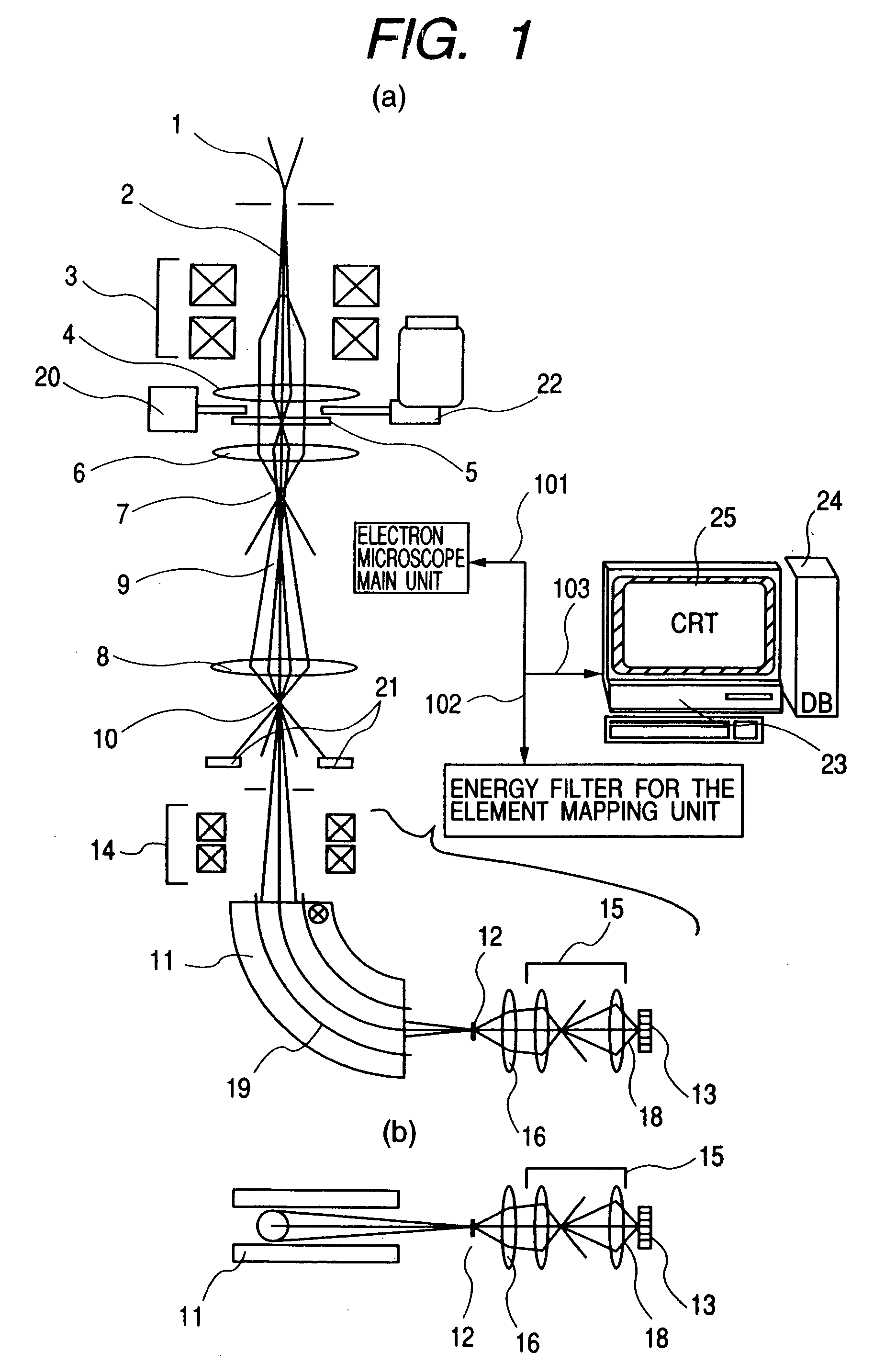
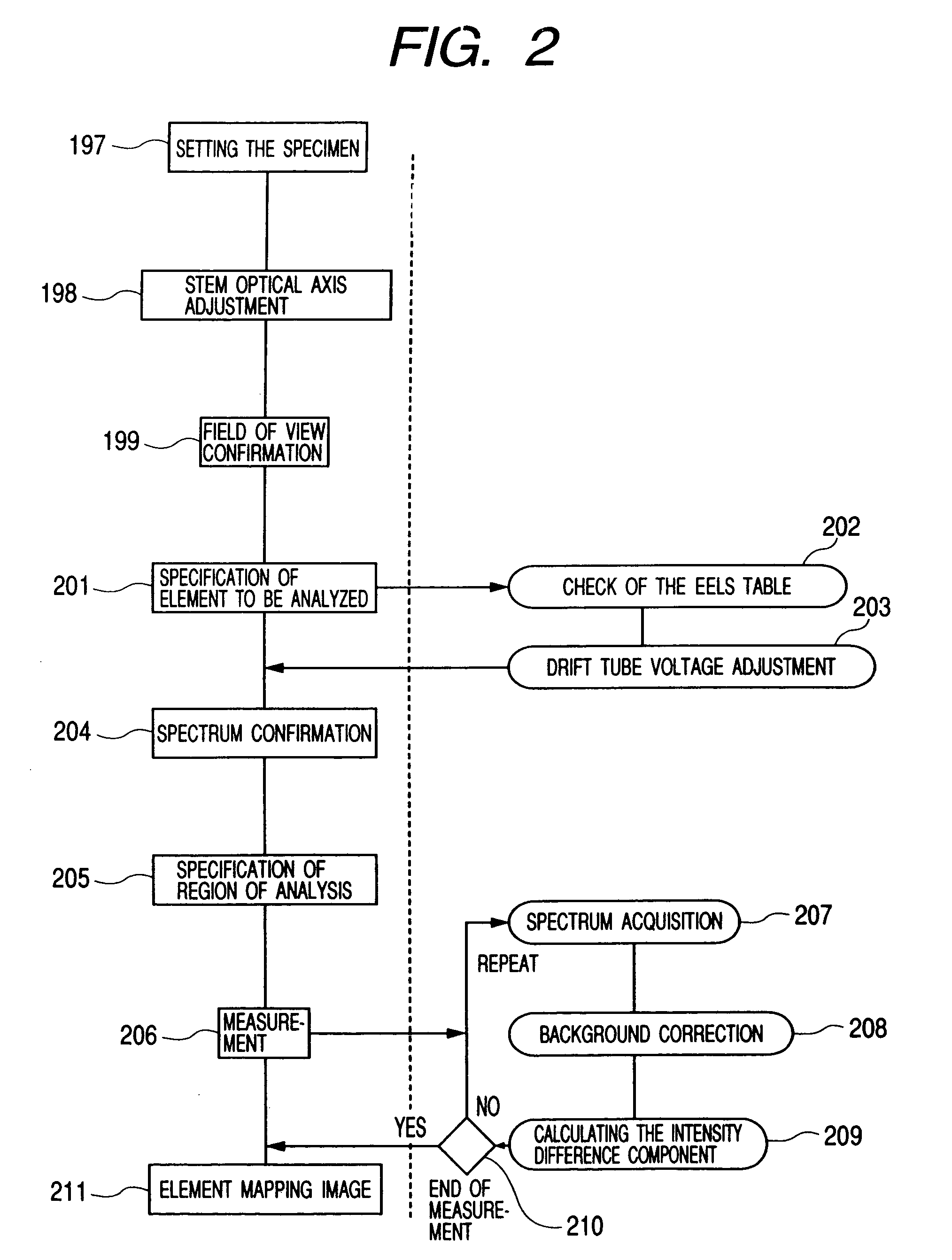
Element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method
InactiveUS20060011836A1Easy to operateHigh EELS spectrum energy stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeFrequency spectrum
There is provided an element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method that enable to acquire an element mapping image very easily. On the scanning transmission electron microscope, the electron beam transmitted through an object to be analyzed enters into the element mapping unit. The electron beam is analyzed of its energy into spectrum by an electron spectrometer and an electron energy loss spectrum is acquired. Because the acceleration voltage data for each element and window data for 2-window method, 3-window method or contrast tuning method are already stored in a database and accordingly the spectrum measurement is carried out immediately even when an element to be analyzed is changed to another, the operator can confirm a two-dimensional element distribution map immediately. Besides, because every electron beam that enters into an energy filter passes through the object point, aberration strain in the electron spectrometer can be minimized and higher energy stability can be achieved. As a result, drift of the electron energy loss spectrum acquired by analyzing the electron beam into spectrum can be minimized and element distribution with higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Lightweight plastic sleds for emergency transport and hauling of loads
ActiveUS20060061050A1Avoid tearingReduce weightCarriage/perambulator accessoriesSledgesDead bodyEngineering
Lightweight inexpensive sleds, made of tough plastic or similar material, are disclosed for transporting injured people or inert loads. For ultra-light sleds, a rope or strap is passed through a hole in the sled and affixed directly to a load (e.g., firewood, a deer carcass, etc.). This imposes forces on the load, while merely keeping the sled beneath the load that is being dragged. For rescue sleds, a strong strap is passed through slots around the periphery. This distributes forces in ways that avoid tearing, and it provides secure handholds, allowing people to lift and carry an injured person in a manner comparable to a backboard. A rescue sled including straps weighs only about 6 pounds, and can be carried on foot for miles, affixed to a backpack, making these sleds available immediately when needed.
Owner:ETHOS EVACUATION STRATEGIES LLC
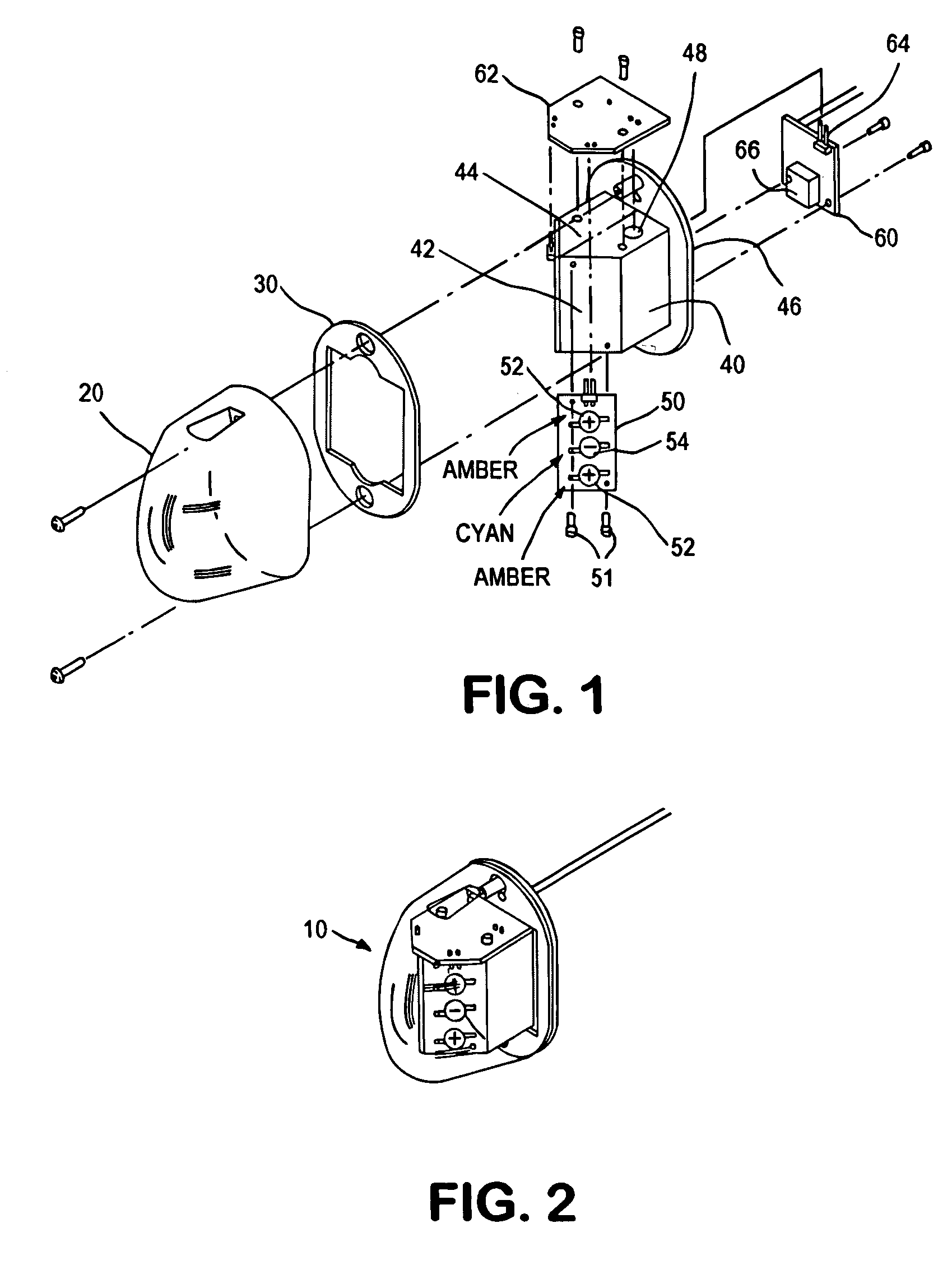
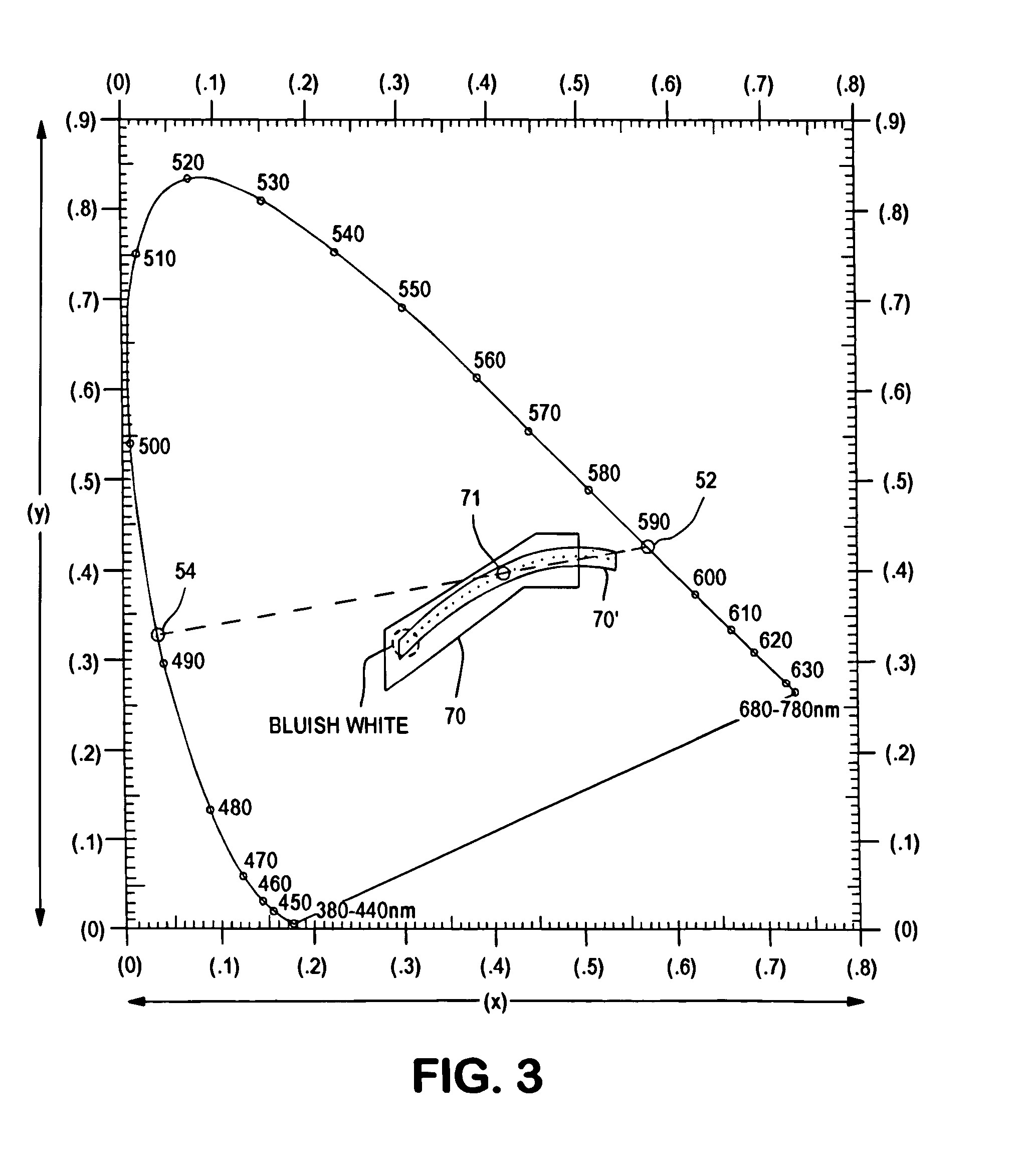
White position taillight for aircraft
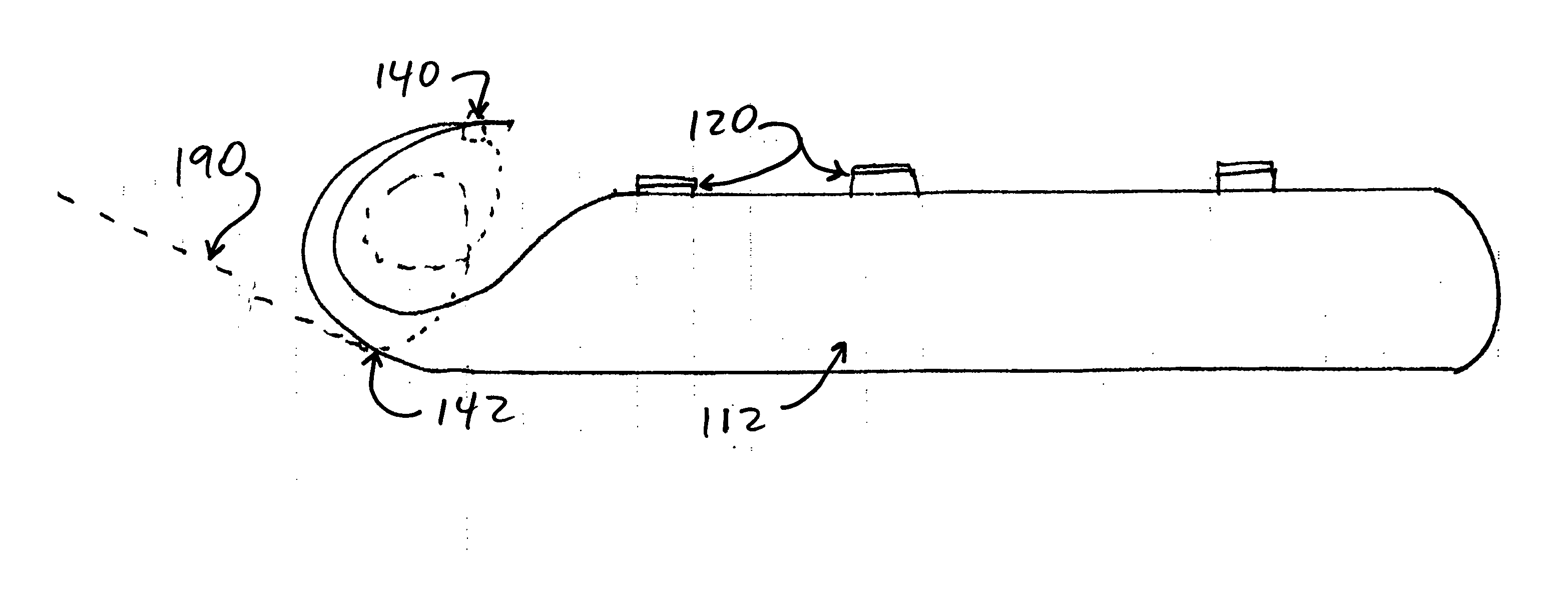
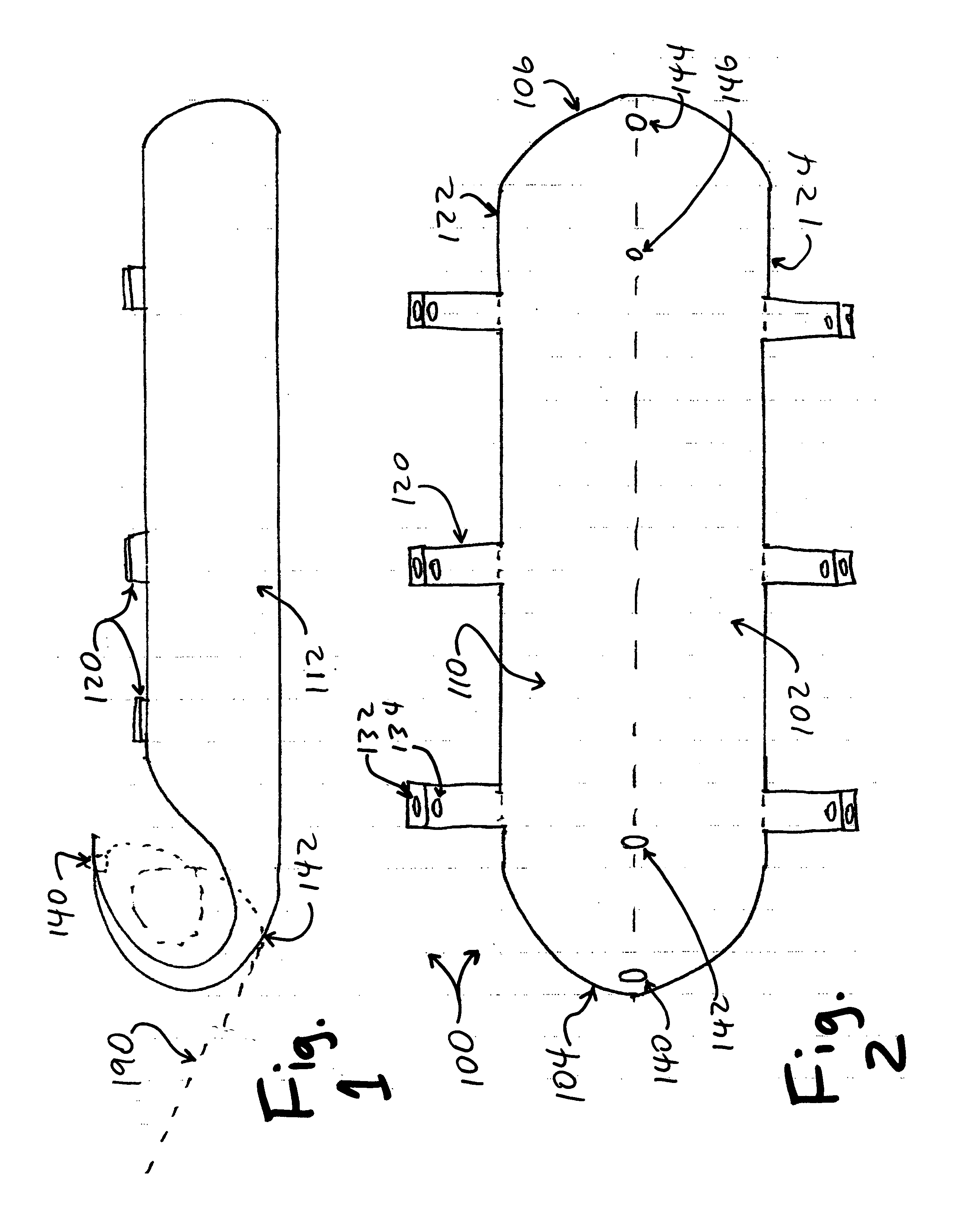
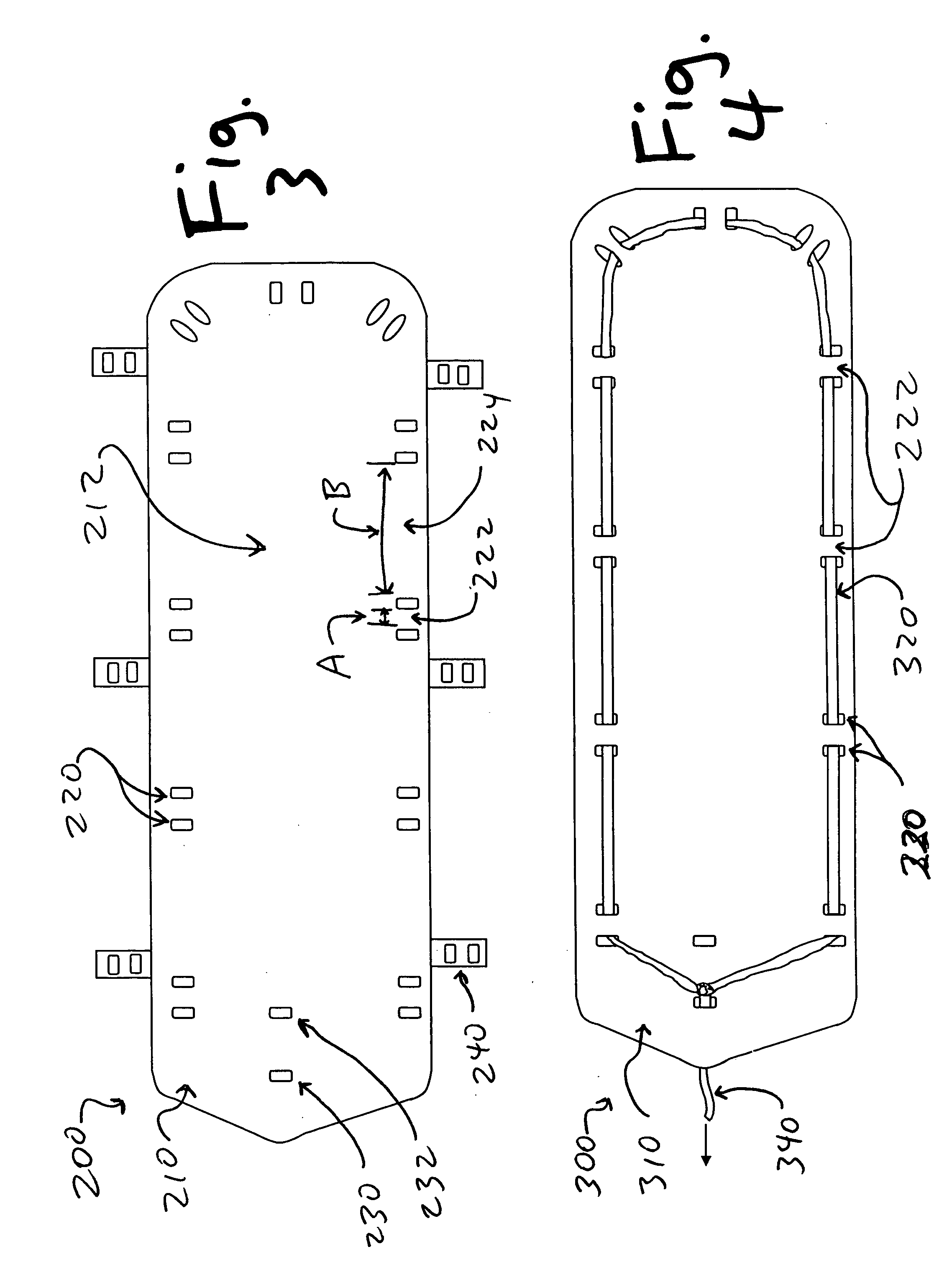
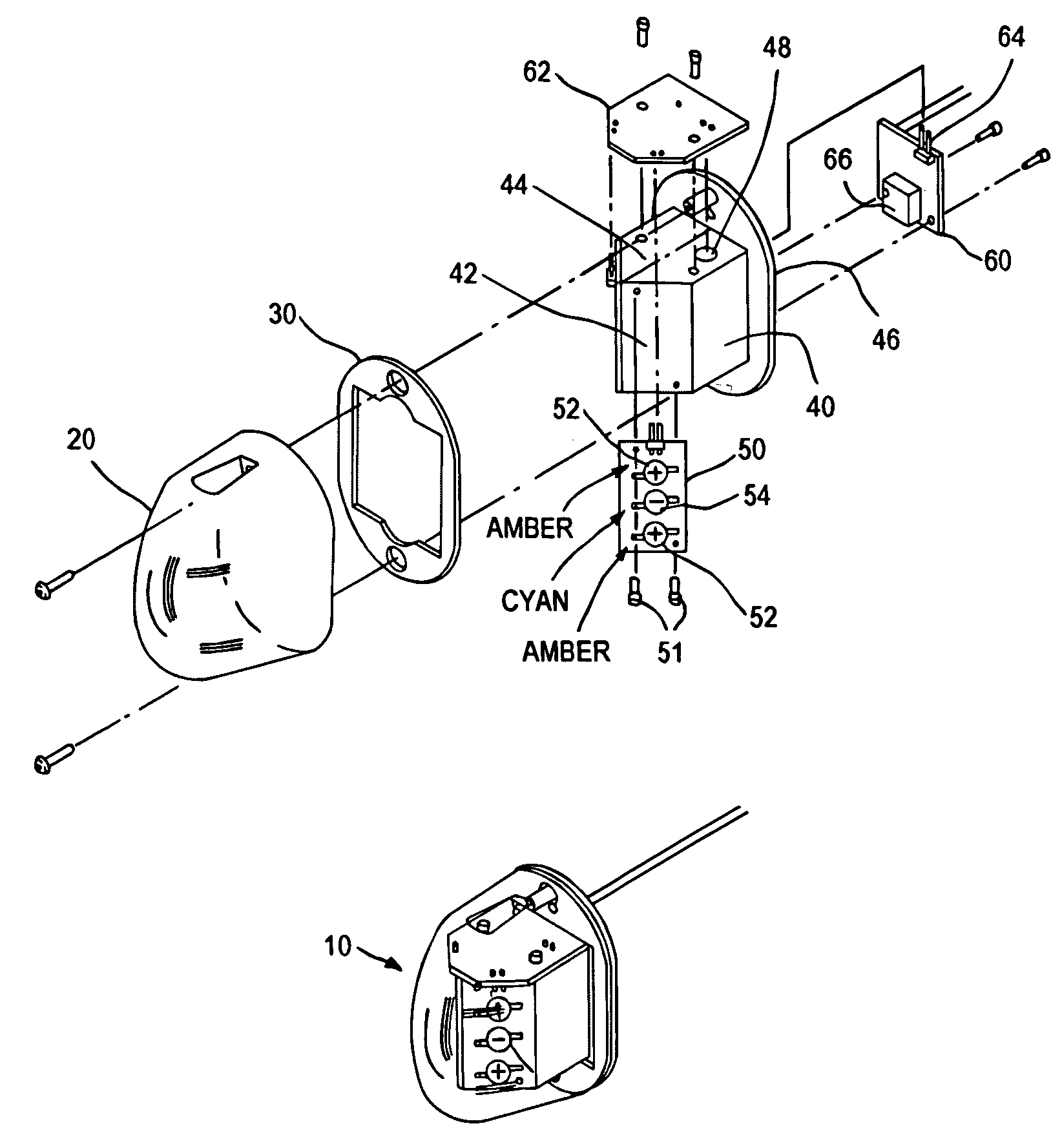
InactiveUS7118261B2Much of lightNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesNight visionLuminous flux
An aircraft position light employs selected colored LEDs to produce a white appearing warning light with a reduced light component in the amplification spectrum of night vision imaging equipment. A combination of amber and cyan LEDs are selected to produce approximately three amber flux units for every cyan flux unit resulting in a white composite light. Both of the selected LEDs have dominant wavelengths of less than 600 nm.
Owner:WHELEN ENGINEERING COMPANY
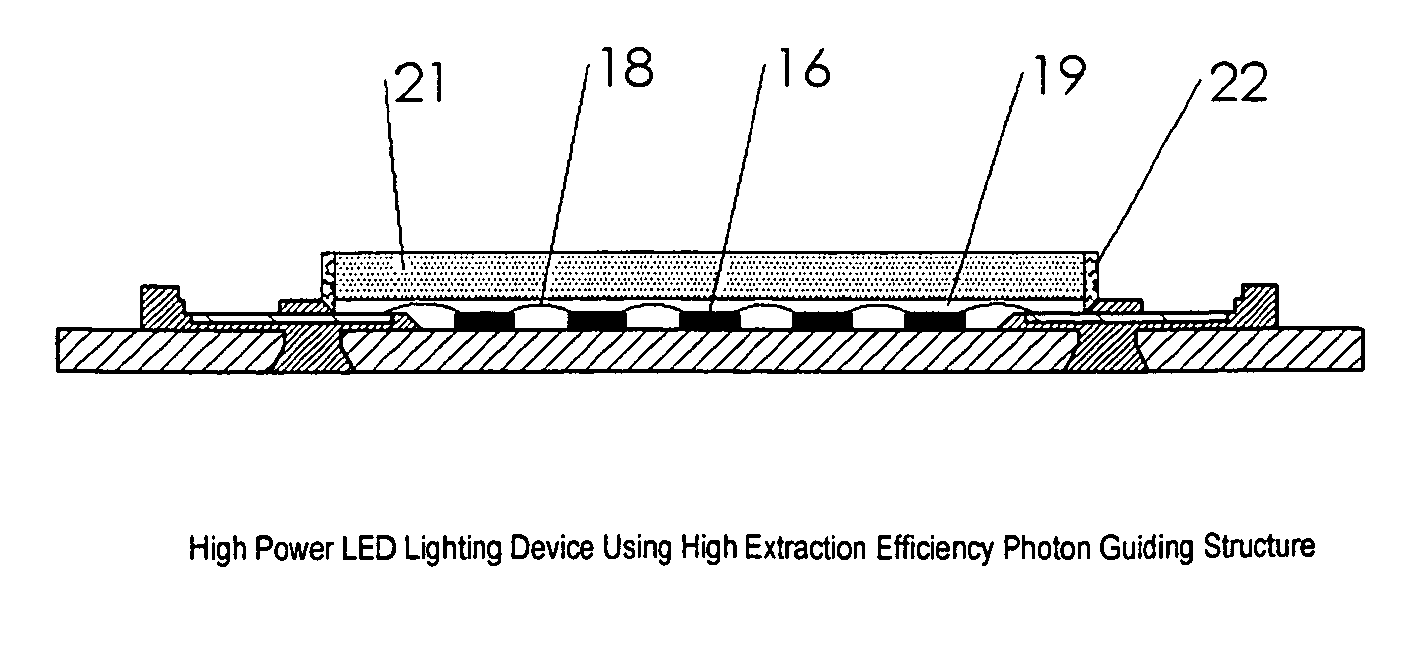
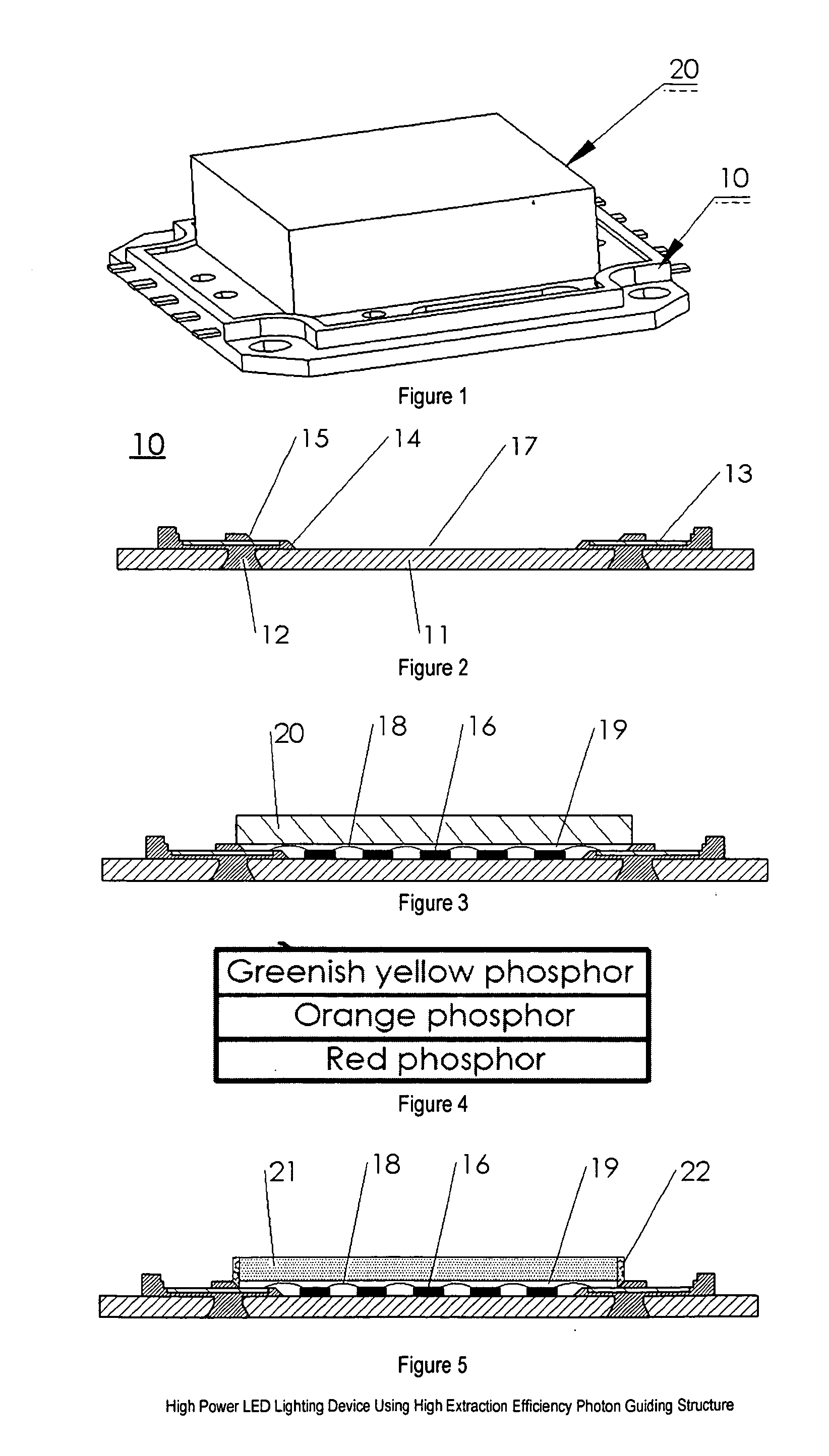
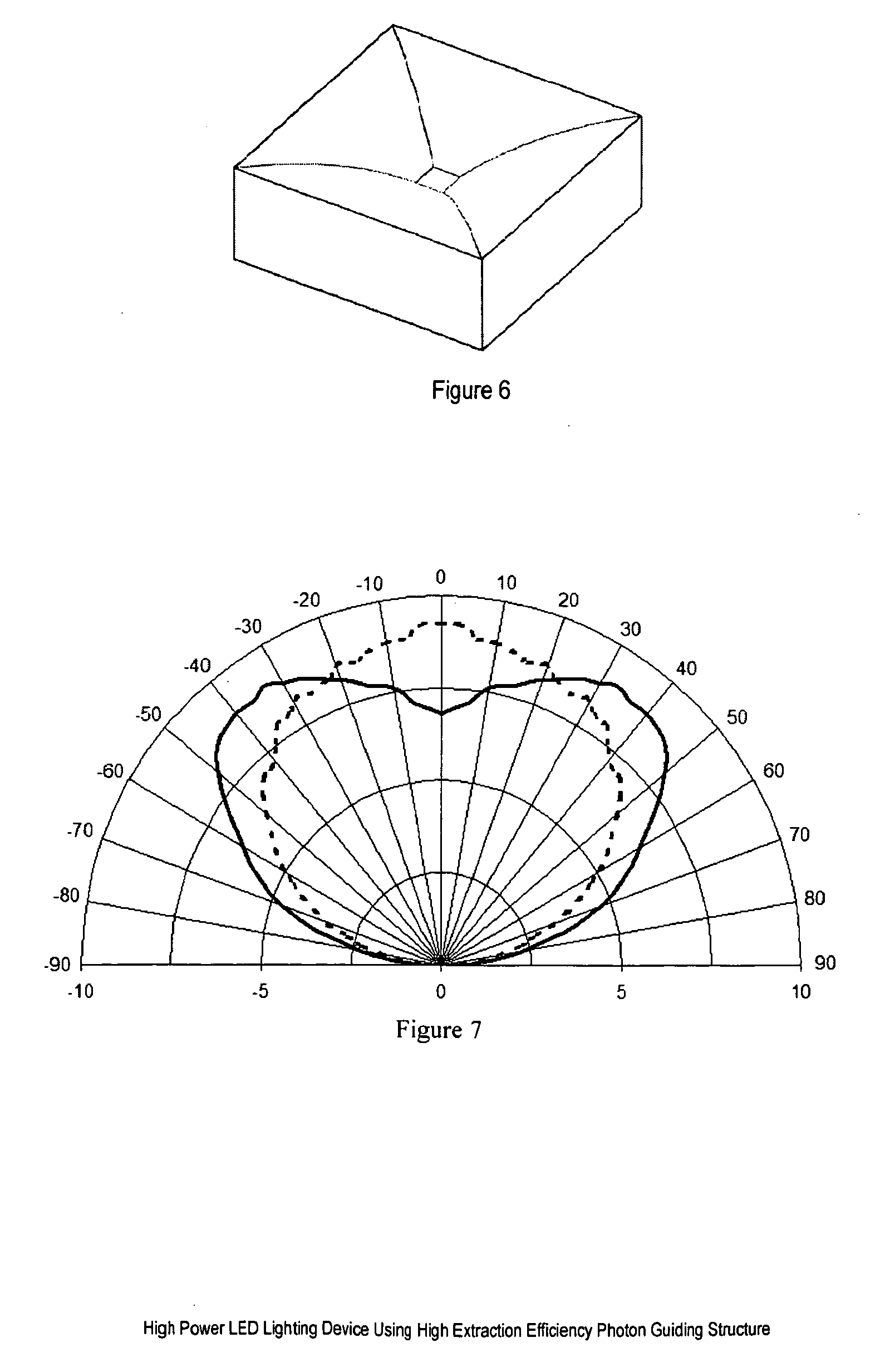
High power LED lighting device using high extraction efficiency photon guiding structure
InactiveUS20110068354A1Improve efficiencyLarge viewing angleMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOn boardPhosphor
The present invention discloses a high power light emitting device using a high extraction efficiency photon-guiding structure for producing high-efficiency white light output with large viewing angle and large amount of light emitted from the side surfaces so that they can provide different light patterns for different applications such as street lighting, parking lighting, tunnel lighting, and etc., as they are used with a reflector. The emitter consists of a leadframe package or chip-on-board substrate, plurality of LED chips, silicone encapsulation material containing phosphor materials to convert short wavelength LED-emanated light to longer wavelength of light, a photon-guiding structure that enhances the efficiency of the LED package and provides light output with large viewing angle.
Owner:SHILED GROUP INT
Reversible, low cost, distributed optical fiber sensor with high spatial resolution
ActiveUS7473906B2Improve spatial resolutionIntenseMaterial analysis by optical meansLuminescent dosimetersHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
A spectroscopic based optical fiber sensor includes a sensitive optical fiber, a probing light source, a power supply, a detector means, a signal processing means, and a display means. The sensitive optical fiber is optically affected by the presence of at least one measurand. The probing light source, adjacent to the sensitive fiber, transversely illuminates the fiber from the outside. The probing light is modified by the sensitive fiber, coupled into the optical fiber core, either as bound modes or leaky modes, as a light signal and guided to a detector means located at the terminus of the optical fiber. The detector means correlates the intensity of the light signal with an electric signal and transmits the electric signal to the signal processing means, wherein the electric signal is correlated to the quantity being measured. The correlated quantity being transmitted and displayed on the display means.
Owner:EGALON CLAUDIO OLIVEIRA
Lenses with graded photochromic, molds and methods of making same
InactiveUS20150231839A1Facilitate outdoor readingEasy to readOptical articlesCoatingsPhotochromic lensOptoelectronics
Certain aspects of the invention are directed to a photochromic lens having a graded or variable tint, methods and molds of making the same. In one embodiment, the photochromic lens includes a lens element having a upper portion and a lower portion; and a UV-absorbing layer formed of a UV-absorbing material on a surface of the lens element, such that the UV-absorbing material is more concentrated at the lower portion of the lens element and less concentrated at the upper portion, thereby allowing more UV light to strike the photochromic at the upper portion of the lens element than at the lower portion. The lens element comprises a photochromic composition.
Owner:QSPEX TECH INC
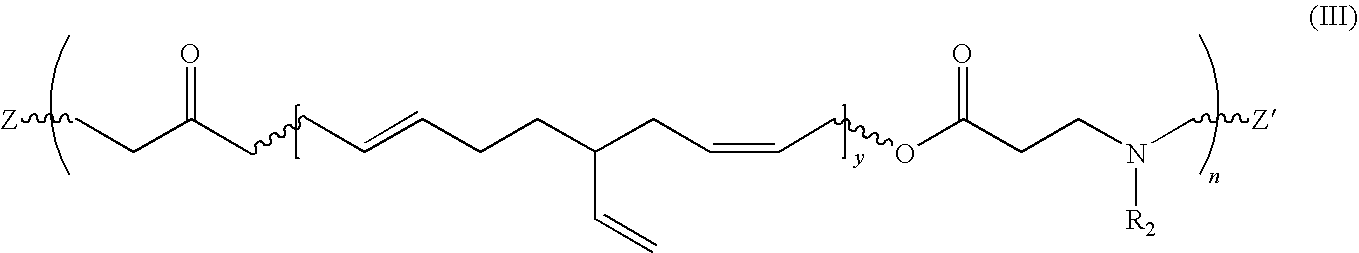
Beta-amino ester compounds and uses thereof
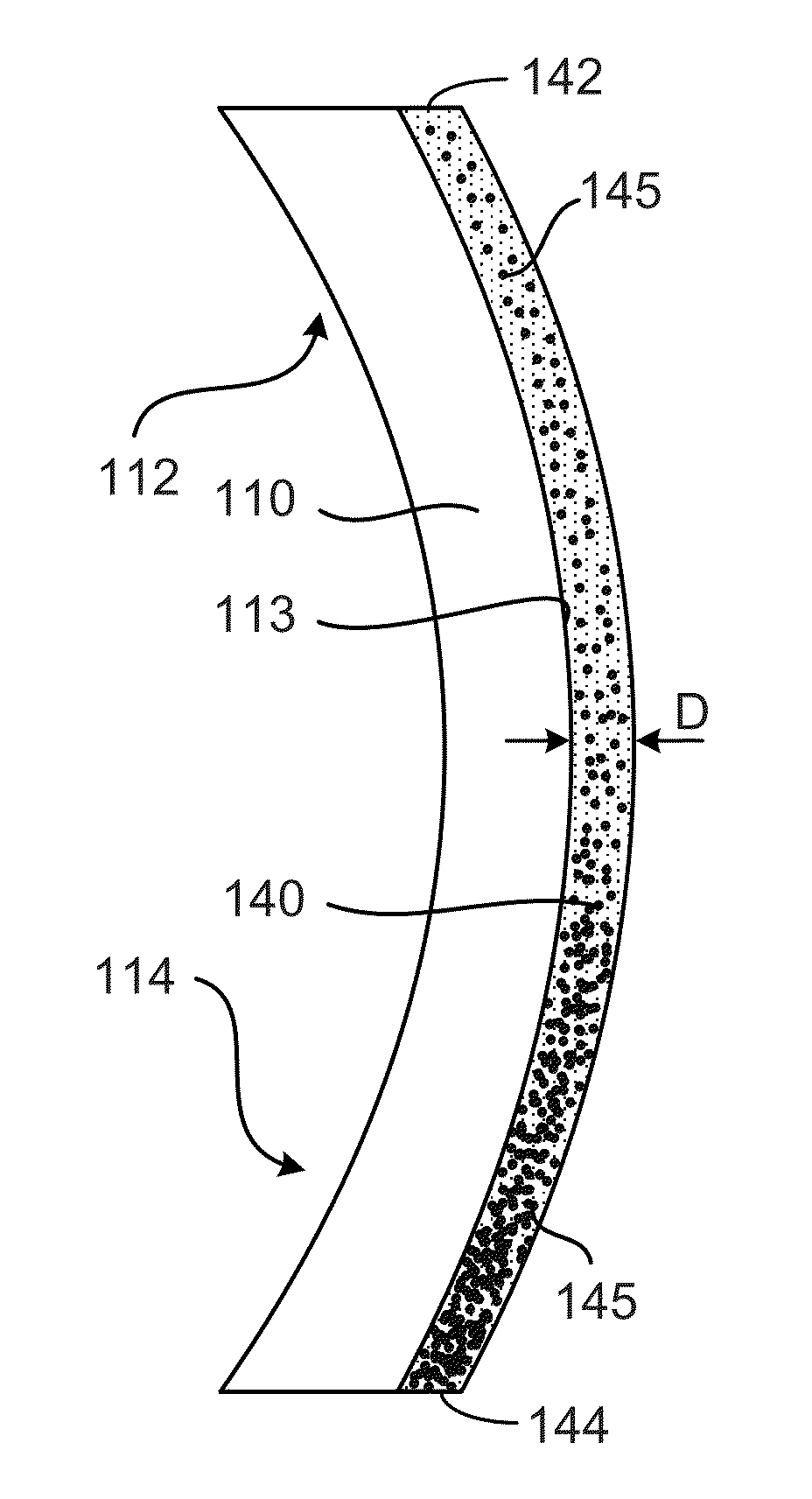
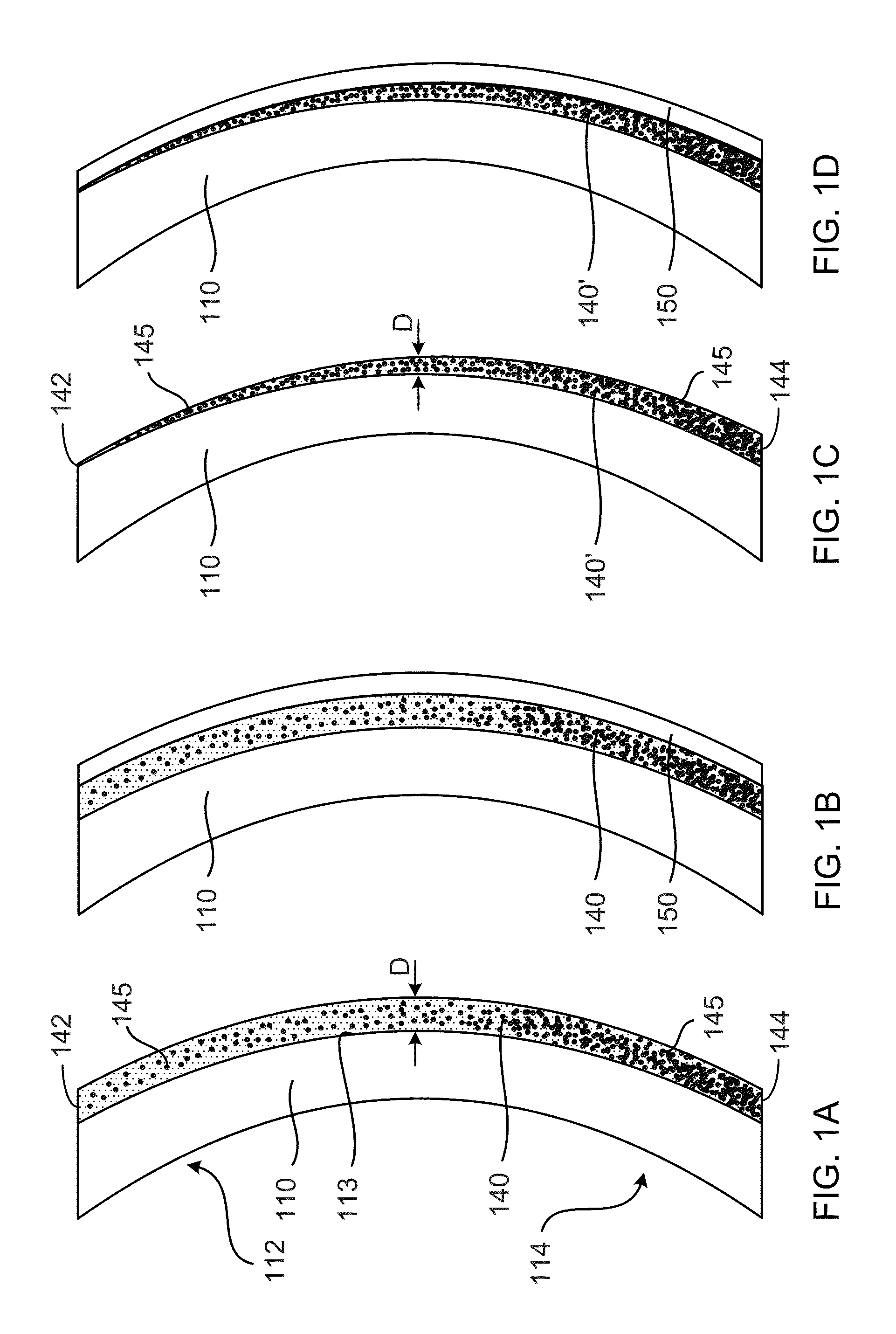
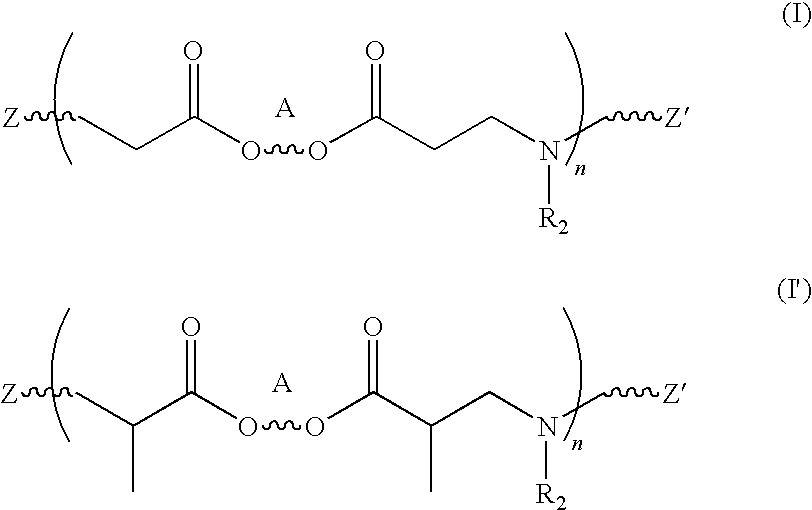
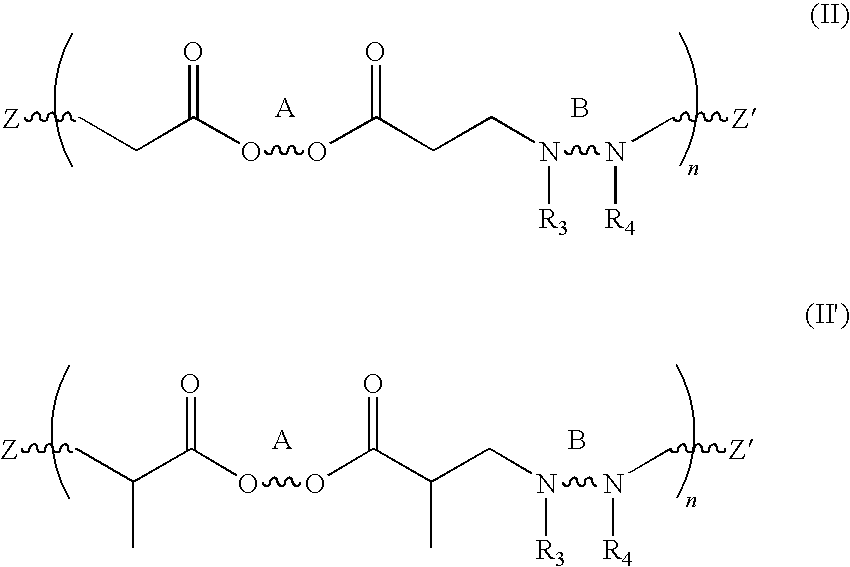
ActiveUS20100178267A1Much of lightIncrease frictionCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsAmino estersMedicine
Hair treatment compositions are disclosed comprising a β-amino ester compound in a cosmetically acceptable vehicle, such as a spray or cream. In embodiments, the compounds include a polybutadiene moiety. Methods of treating hair with the compositions to impart volume, texture and definition are also disclosed.
Owner:LIVING PROOF INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com