Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8520 results about "Thermal resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
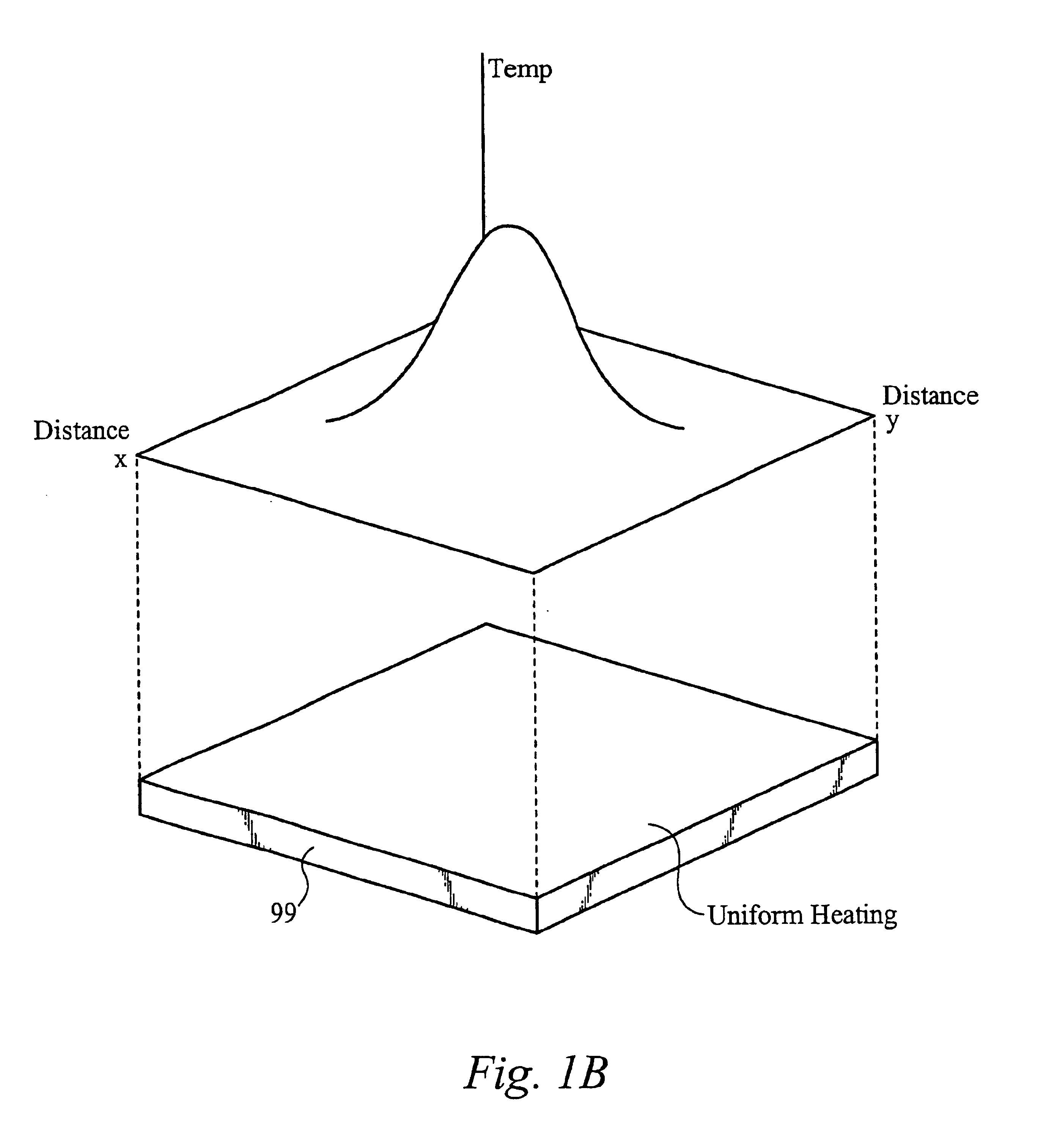
Thermal resistance is a heat property and a measurement of a temperature difference by which an object or material resists a heat flow. Thermal resistance is the reciprocal of thermal conductance.
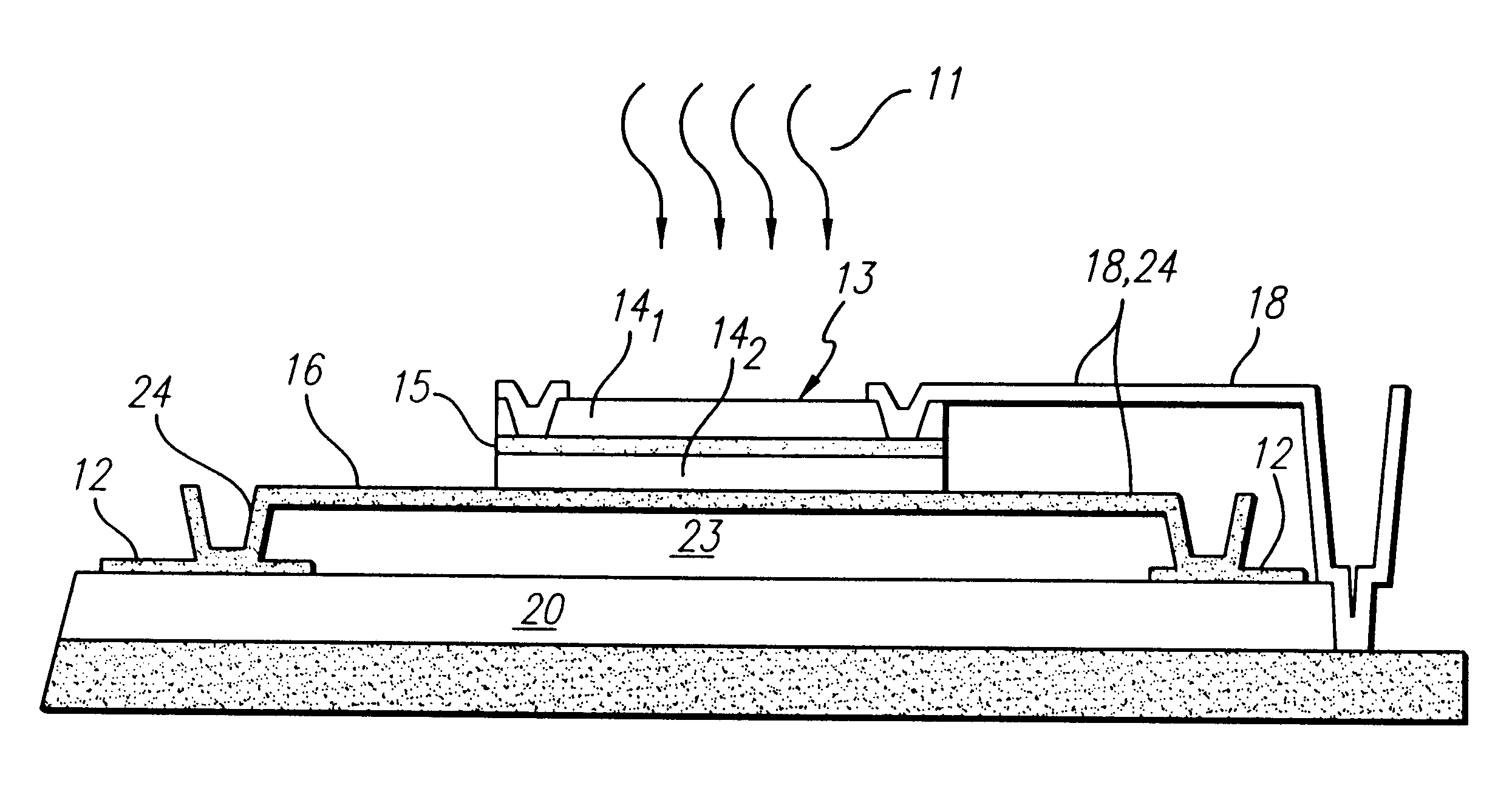
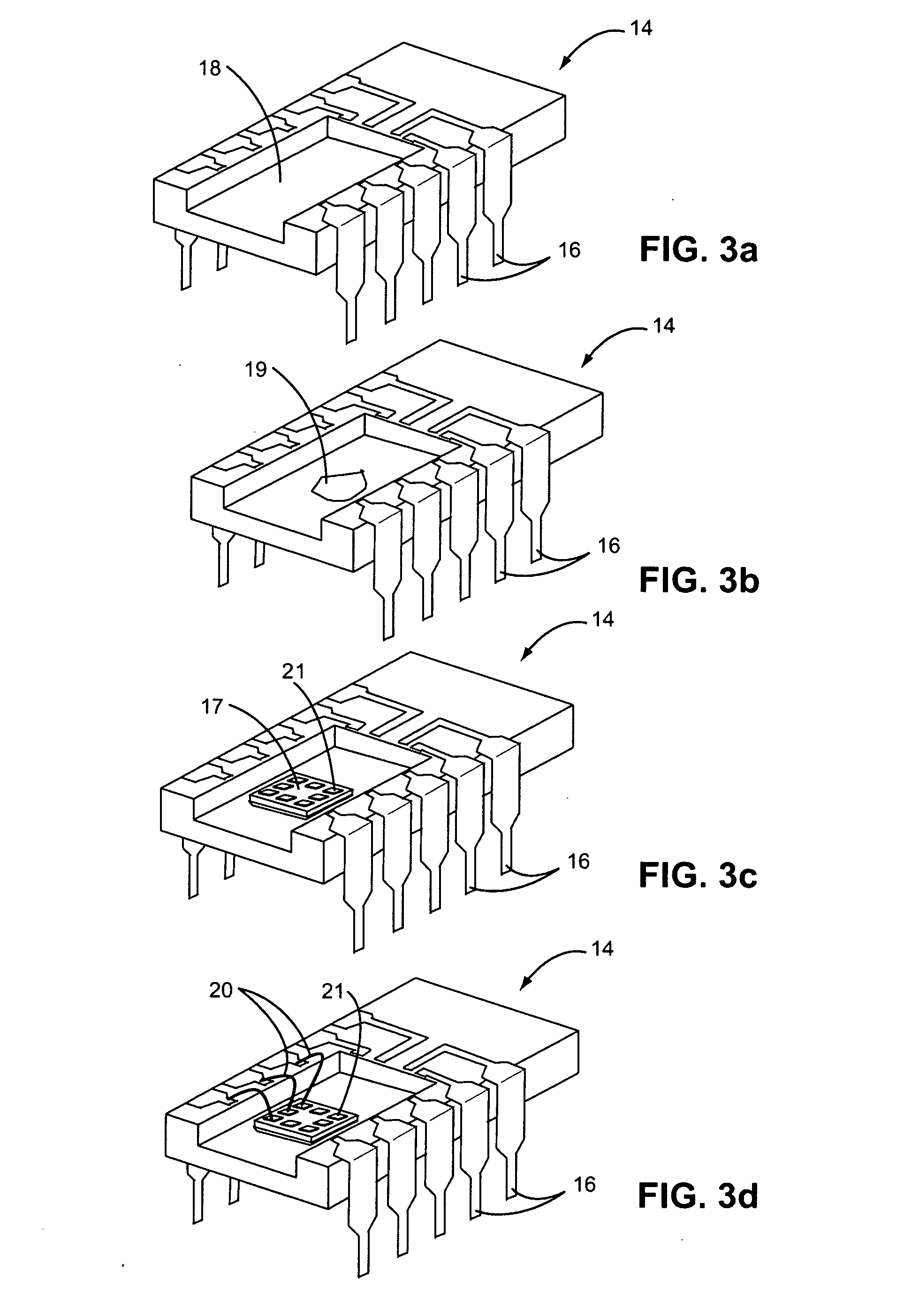
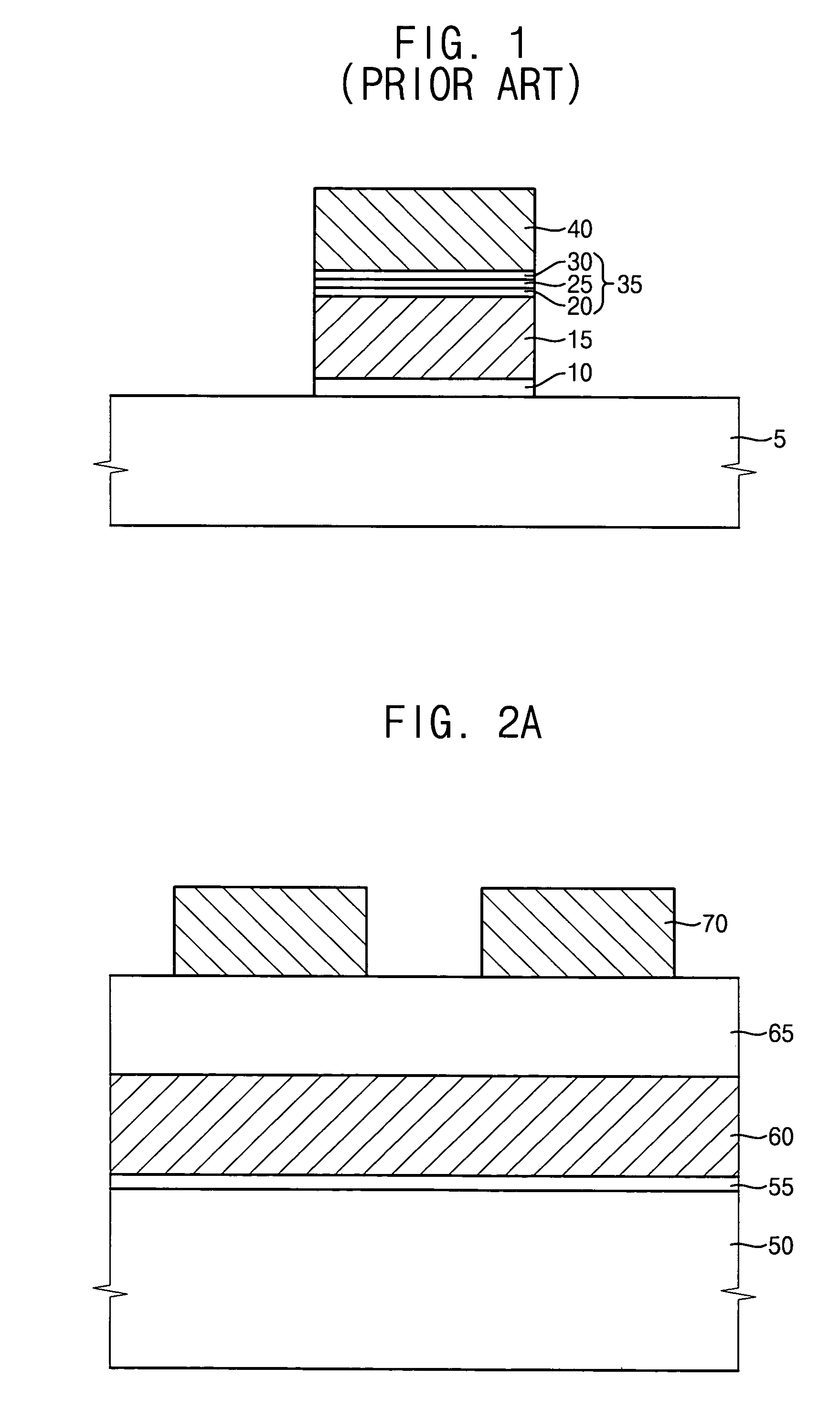
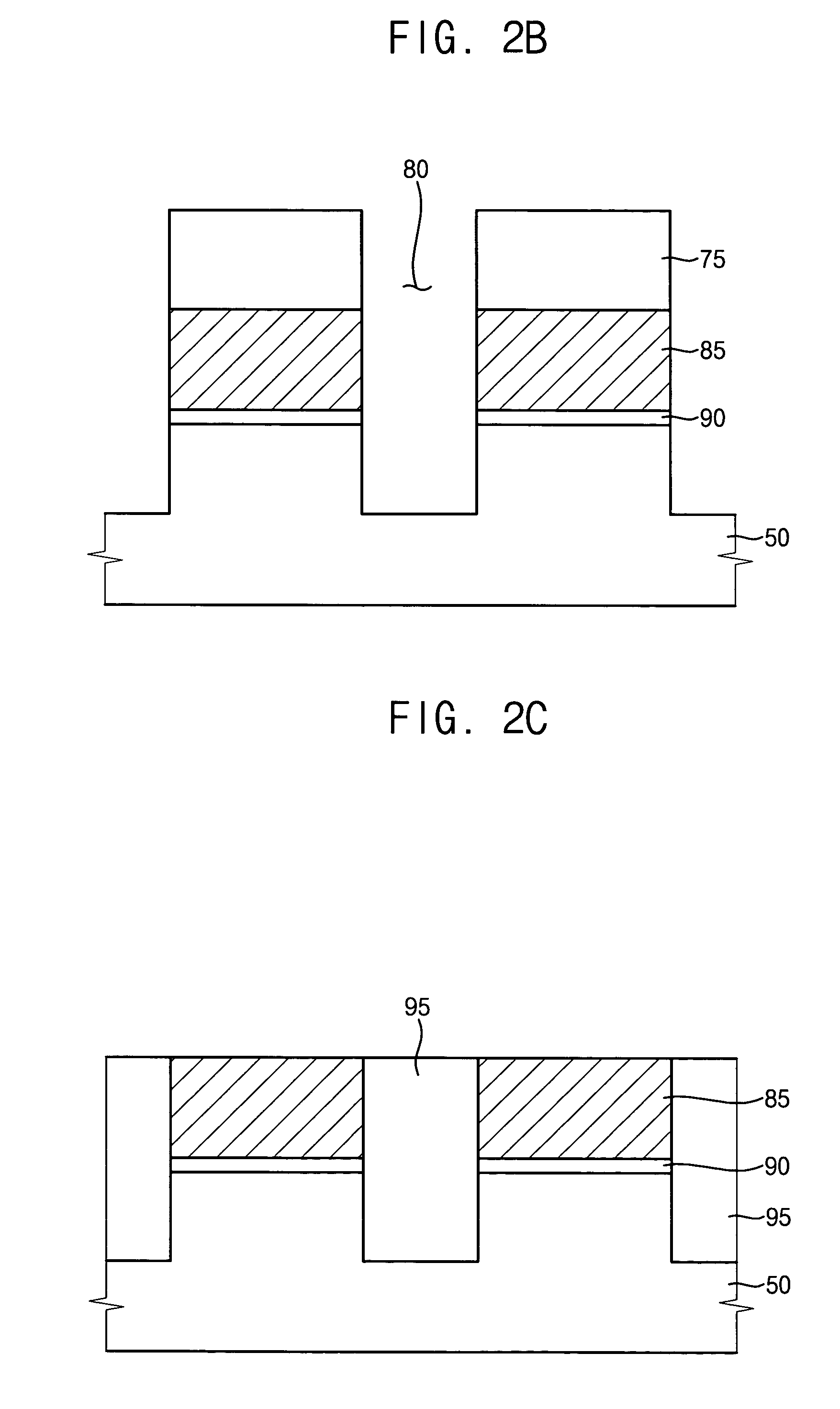
Semiconductor device
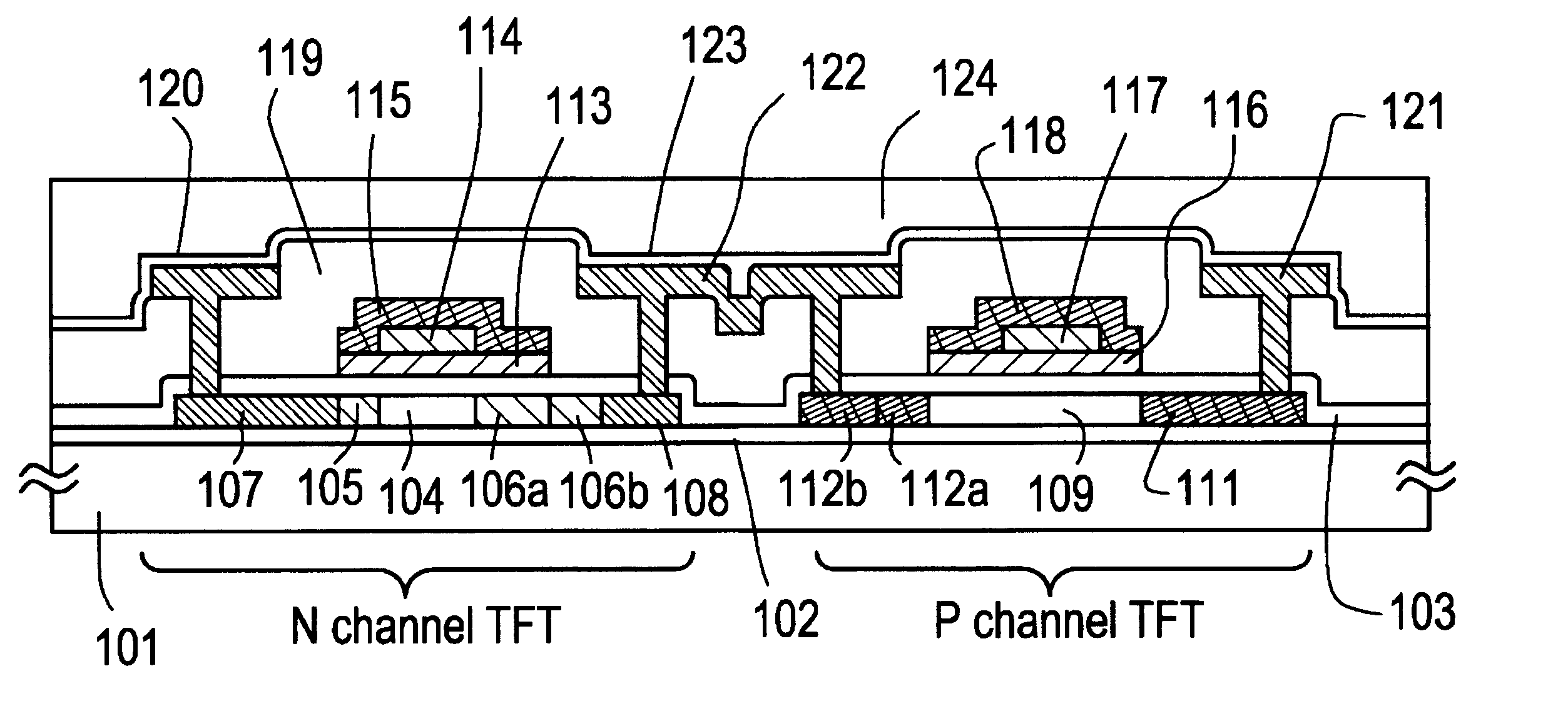
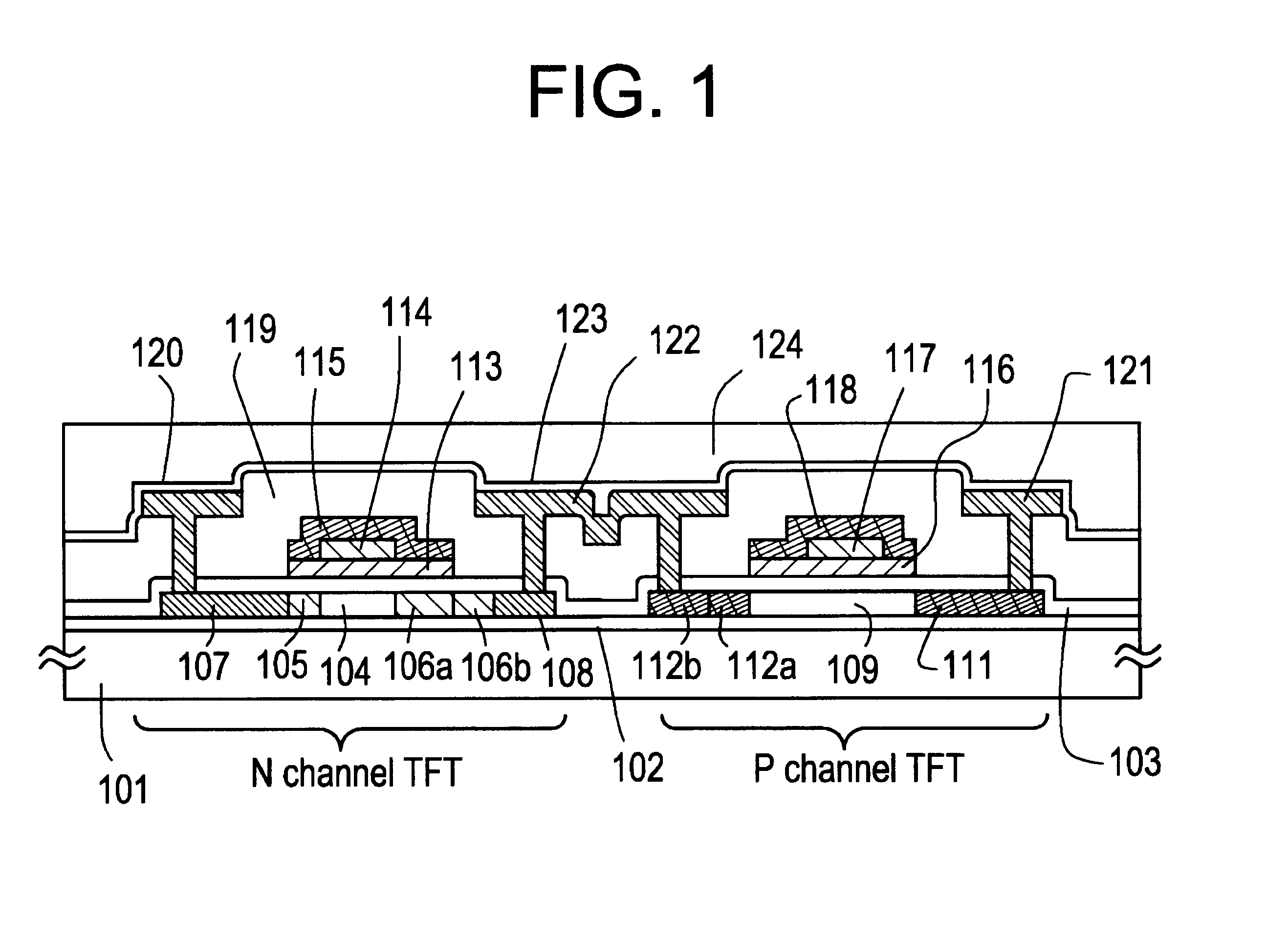
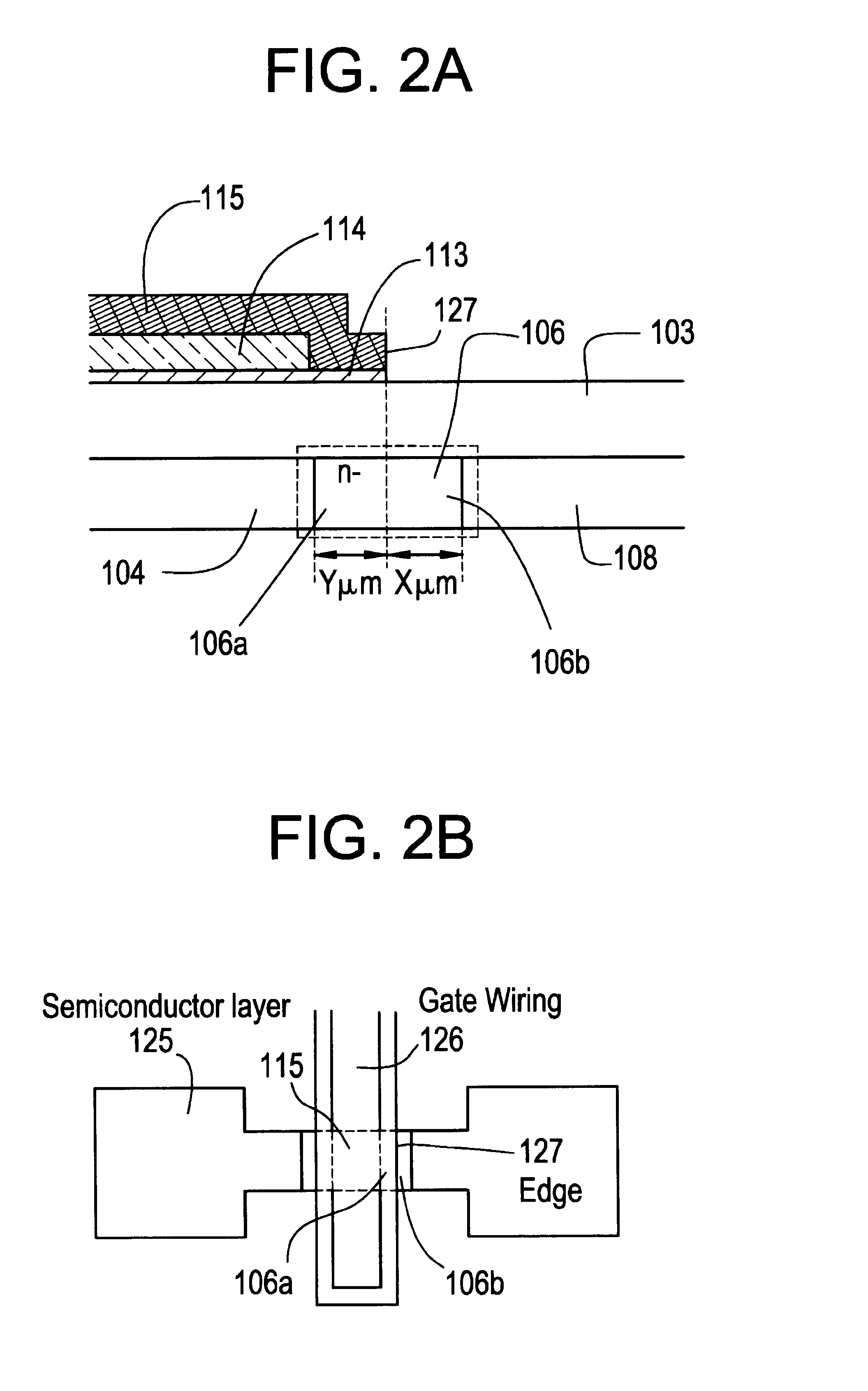
The gate electrode of a crystalline TFT is constructed as a clad structure which consists of a first gate electrode, a second gate electrode and a third gate electrode, thereby to enhance the thermal resistance of the gate electrode. Besides, an n-channel TFT is provided with a low-concentration impurity region which adjoins a channel forming region, and which includes a subregion overlapped by the gate electrode and a subregion not overlapped by the gate electrode, thereby to mitigate a high electric field near the drain of the TFT and to simultaneously prevent the OFF current of the TFT from increasing.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
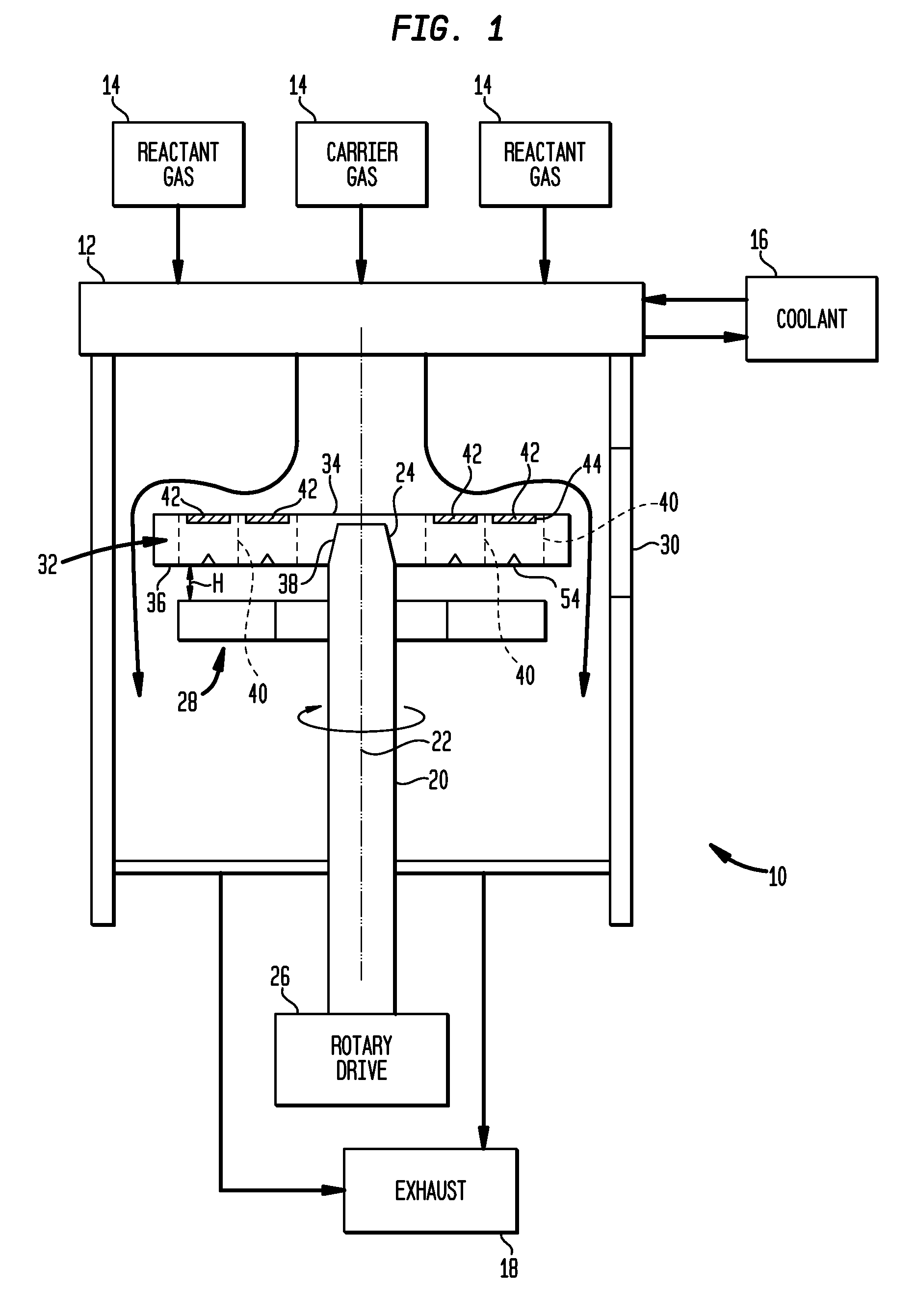
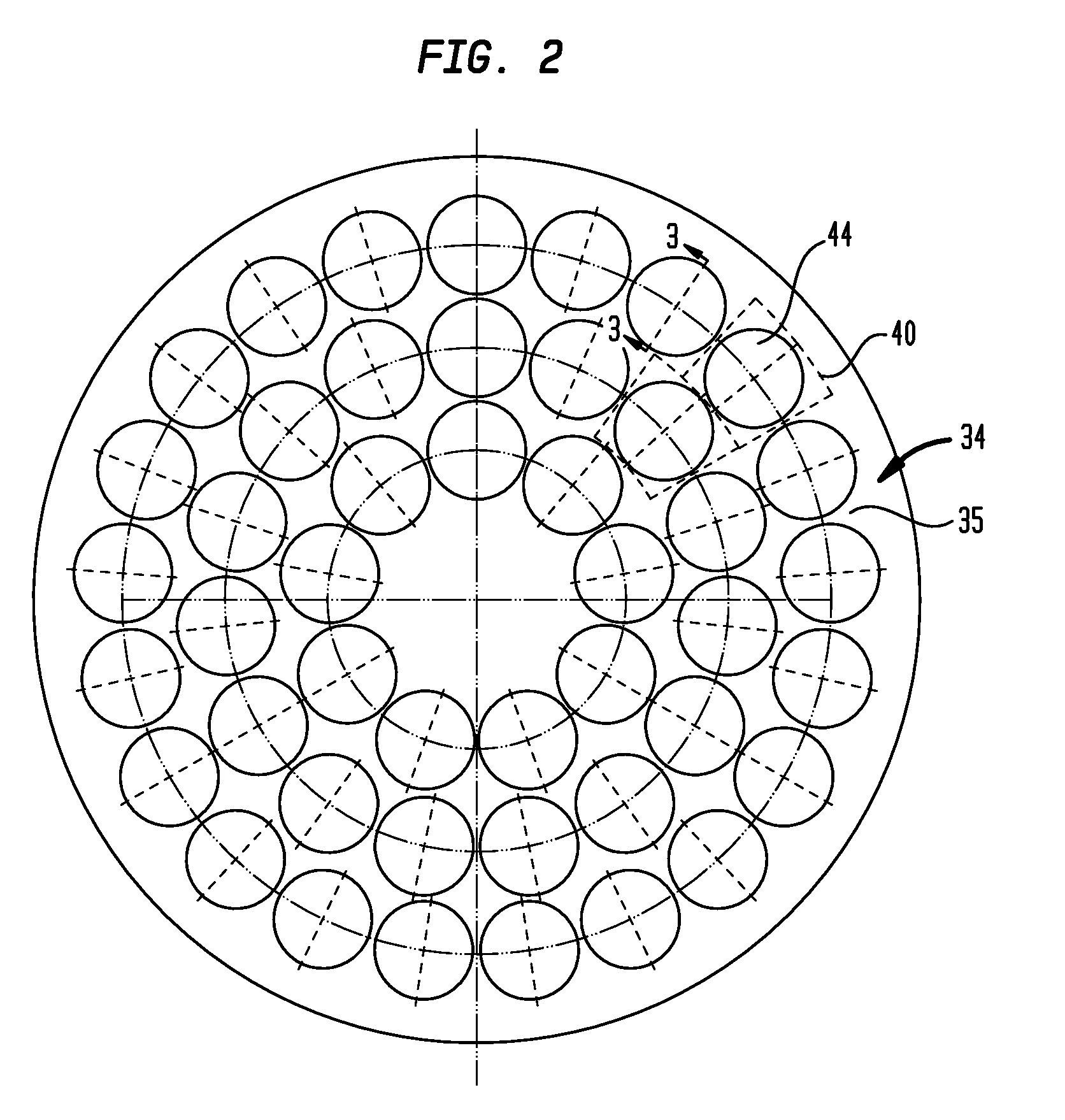
Wafer carrier with varying thermal resistance
InactiveUS20100055318A1Minimize contactImprove temperature uniformityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRadiant heat transfer
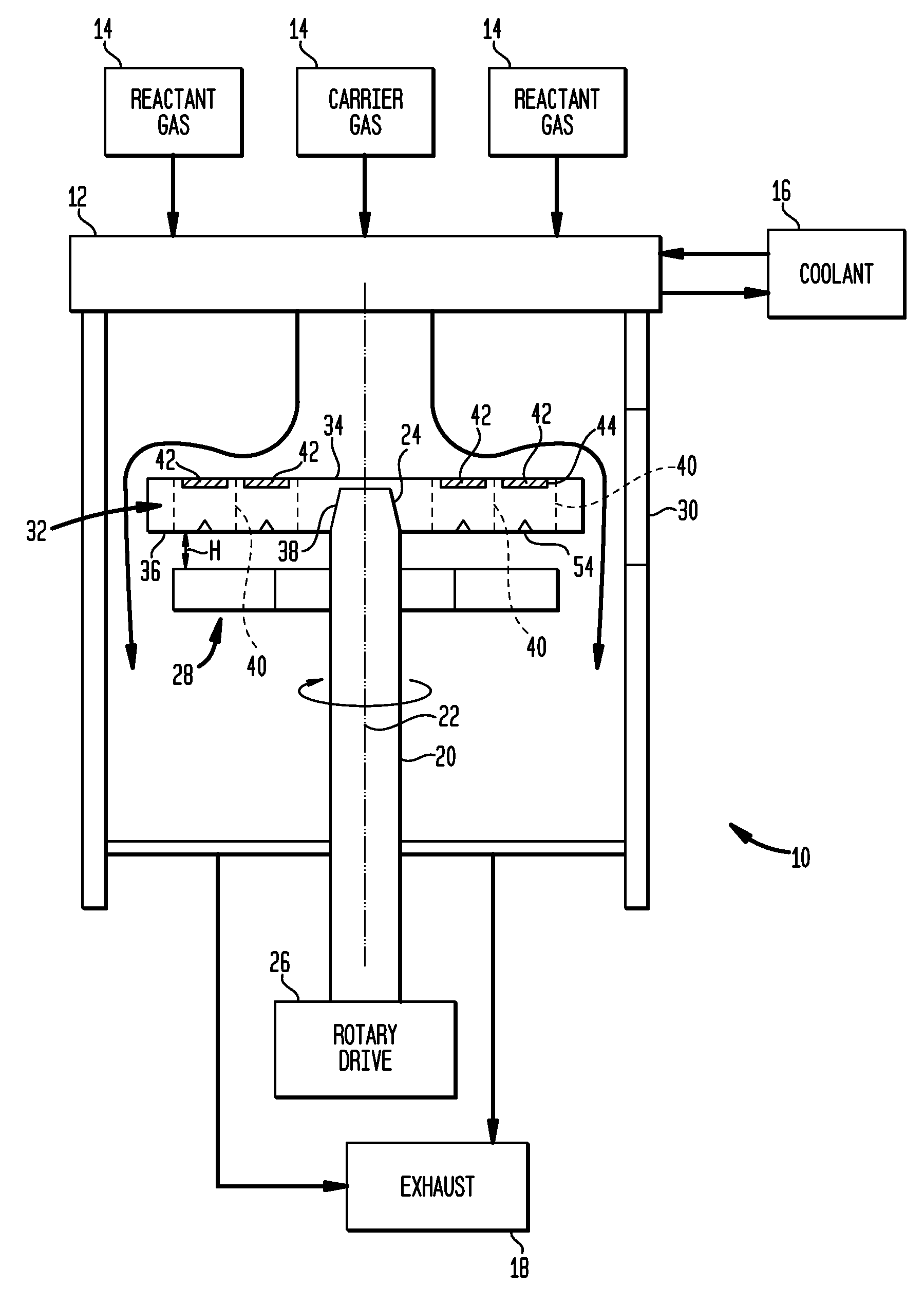
In chemical vapor deposition apparatus, a water carrier (32) has a top surface (34) holding the wafers and a bottom surface (36) heated by radiant heat transfer from a heating element (28). The bottom surface (36) of the wafer carrier is non-planar due to features such as depressions (54) so that the wafer carrier has different thickness at different locations. The thicker portions of the wafer carrier have higher thermal resistance. Differences in thermal resistance at different locations counteract undesired non-uniformities in heat transfer to the wafer. The wafer carrier may have pockets with projections (553, 853) for engaging spaced-apart locations on the edges of the wafer.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
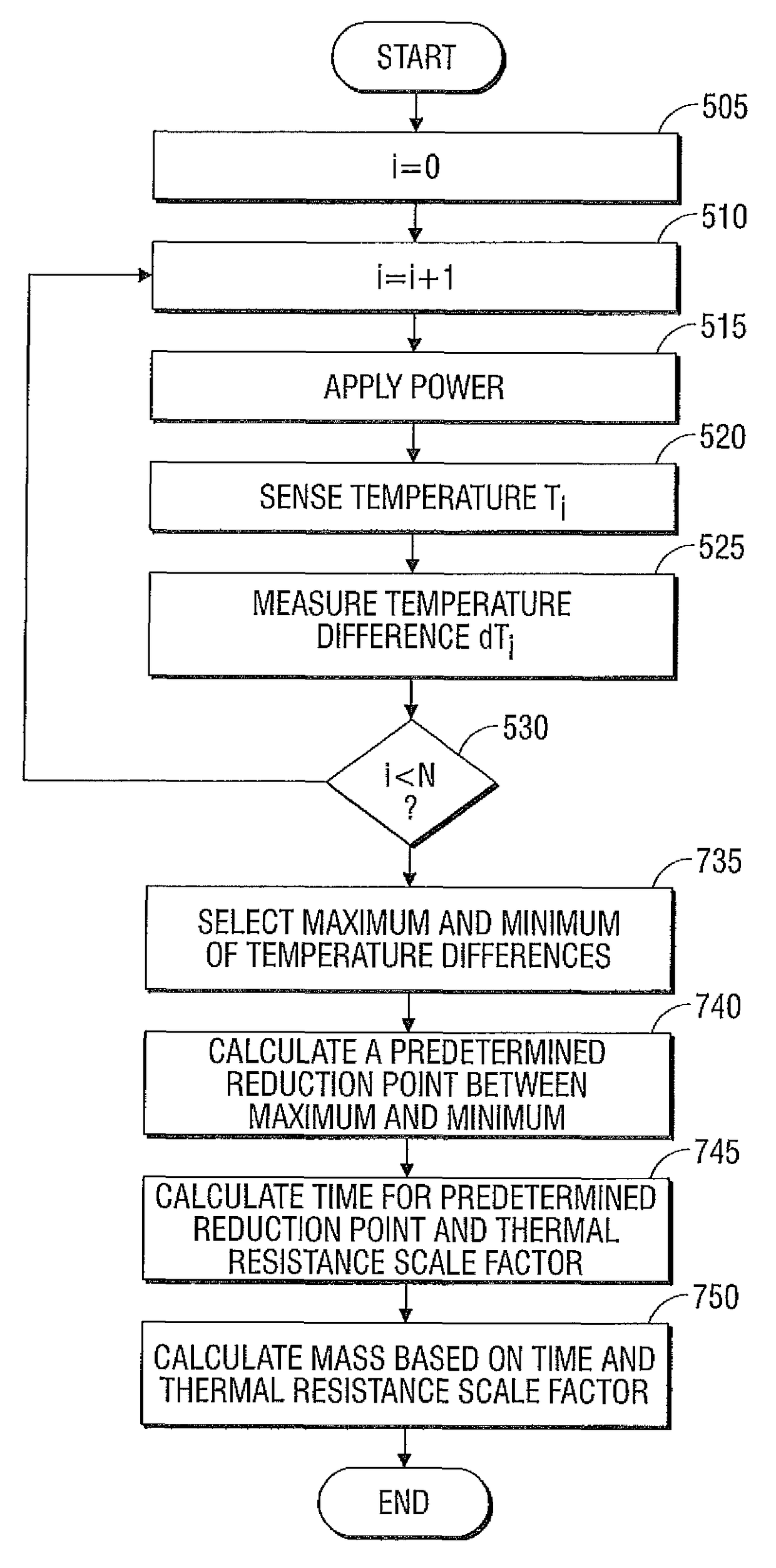
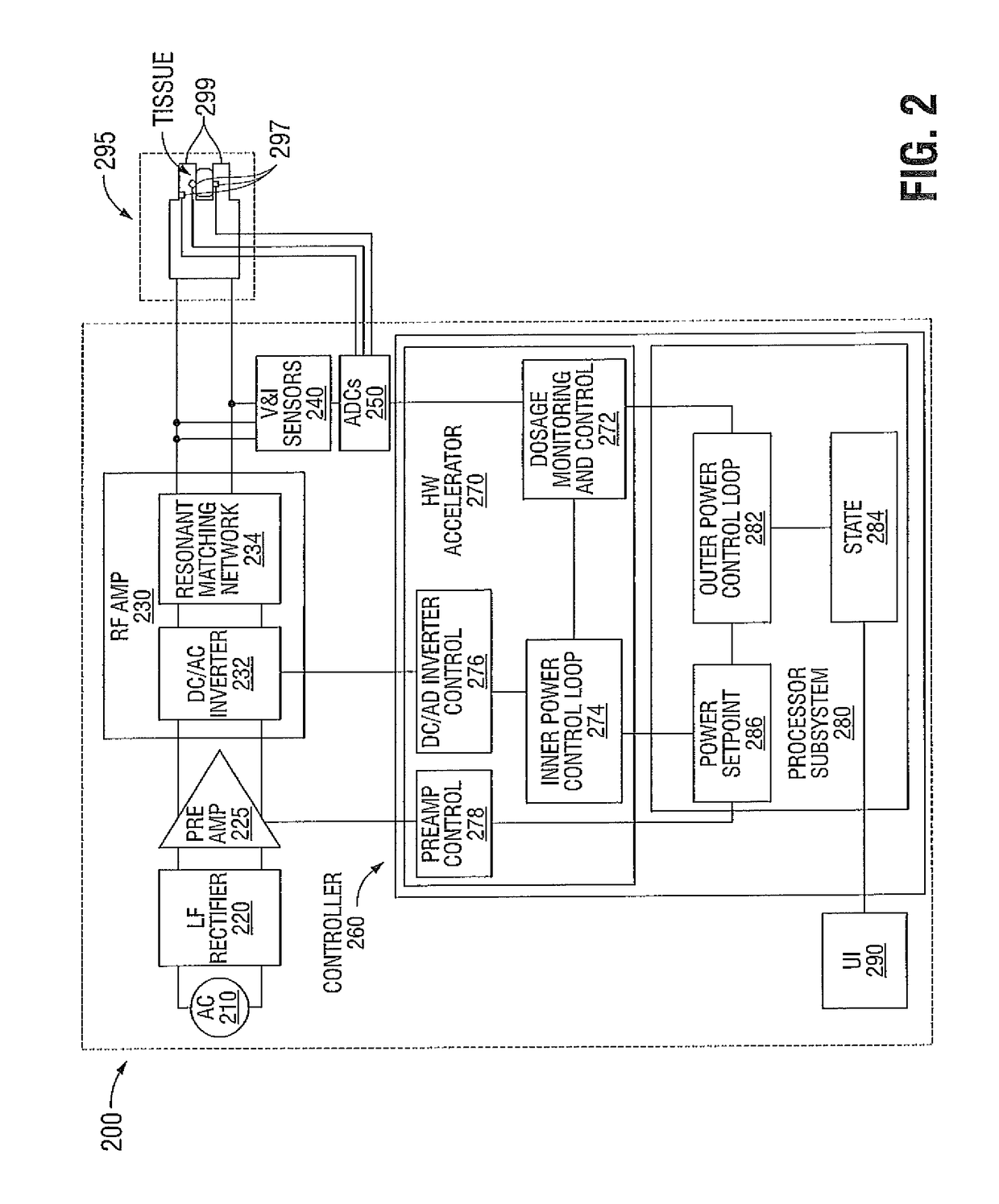
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters using surgical devices
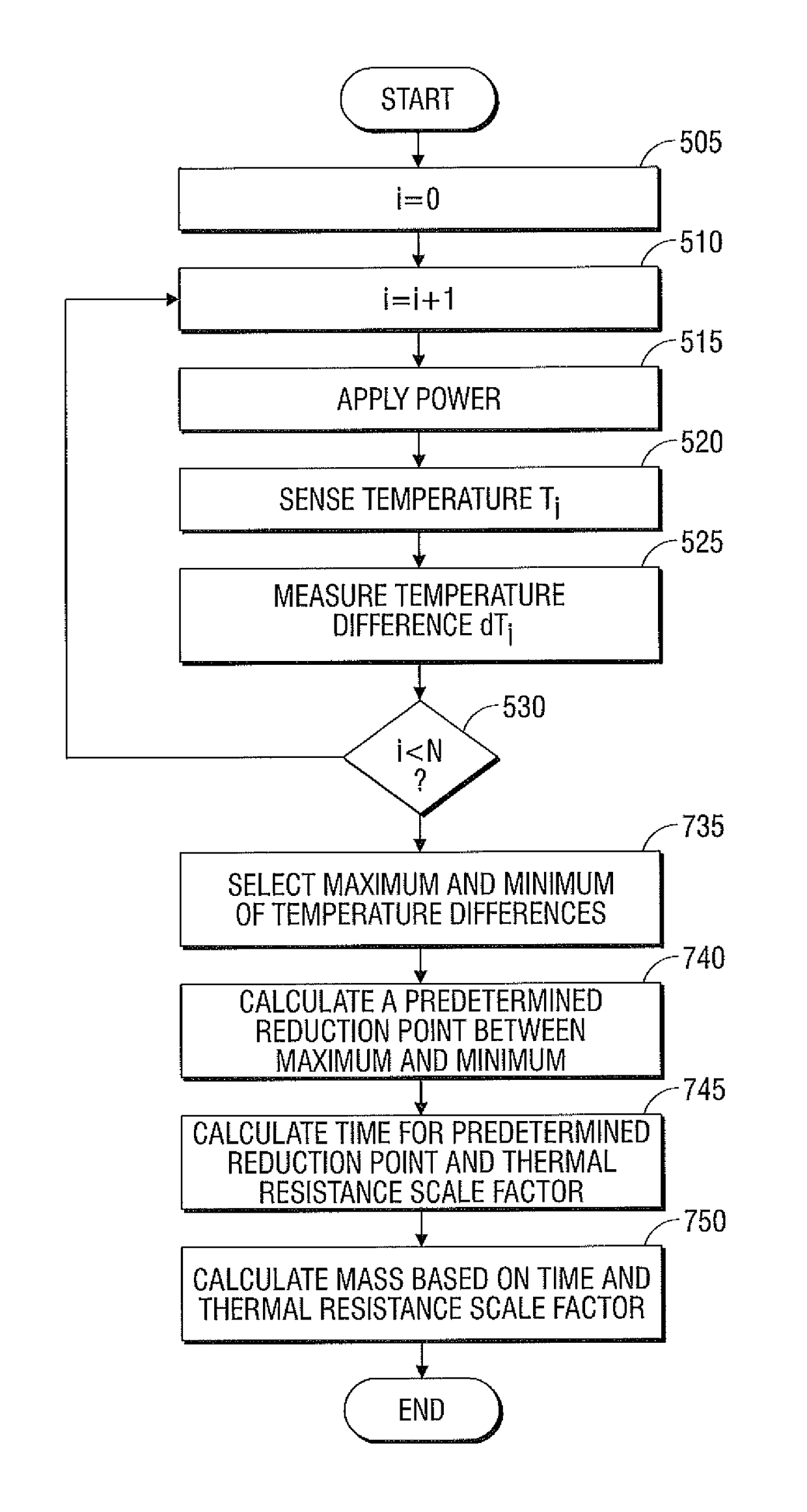
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters, including mass of tissue to be treated and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode of an energy delivery device, are disclosed. The method includes sensing tissue temperatures, estimating a mass of the tissue and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode, and controlling an electrosurgical generator based on the estimated mass and the estimated thermal resistance scale factor. The method may be performed iteratively and non-iteratively. The iterative method may employ a gradient descent algorithm that iteratively adds a derivative step to the estimates of the mass and thermal resistance scale factor until a condition is met. The non-iterative method includes selecting maximum and minimum temperature differences and estimating the mass and the thermal resistance scale factor based on a predetermined reduction point from the maximum temperature difference to the minimum temperature difference.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
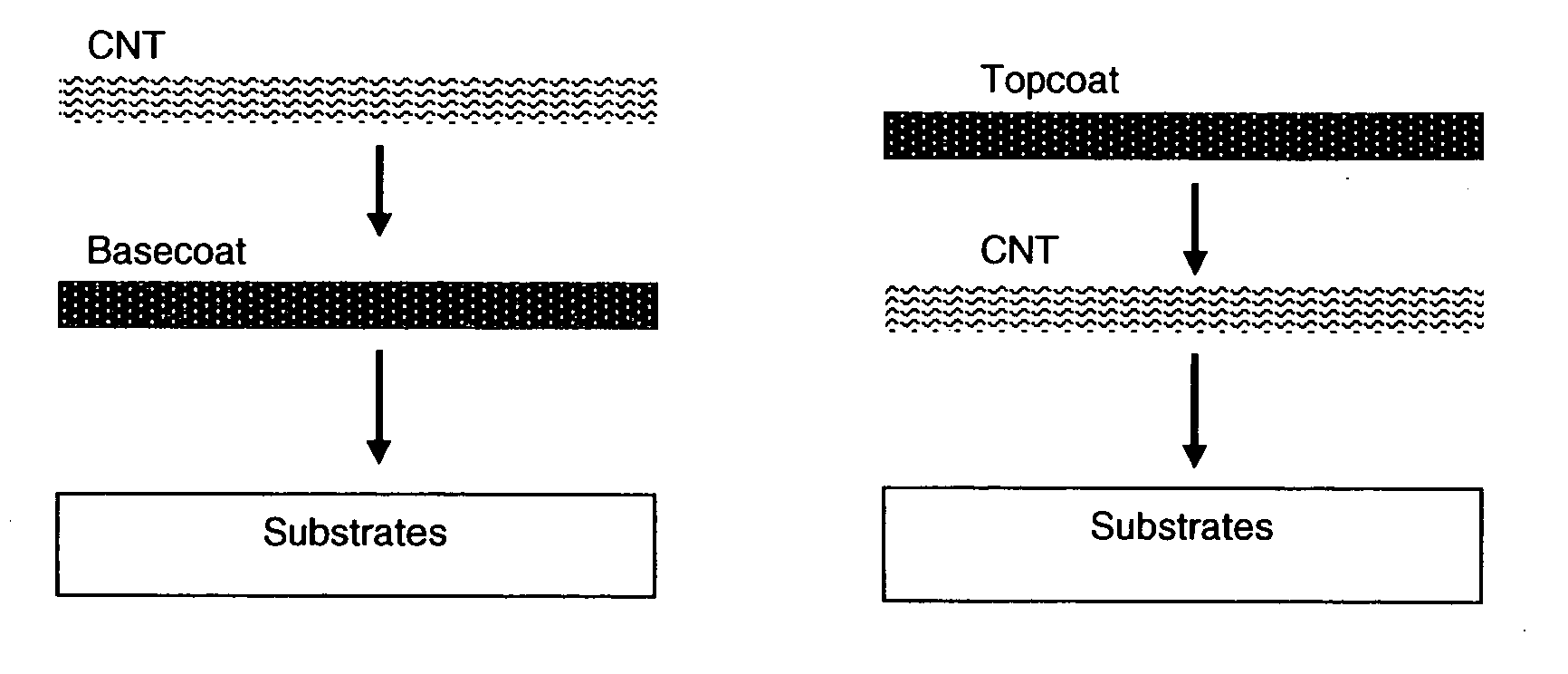
Polymer binders for flexible and transparent conductive coatings containing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050209392A1Decrease in optical transparencyDecrease in surface conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresThermoplasticCarbon nanotube
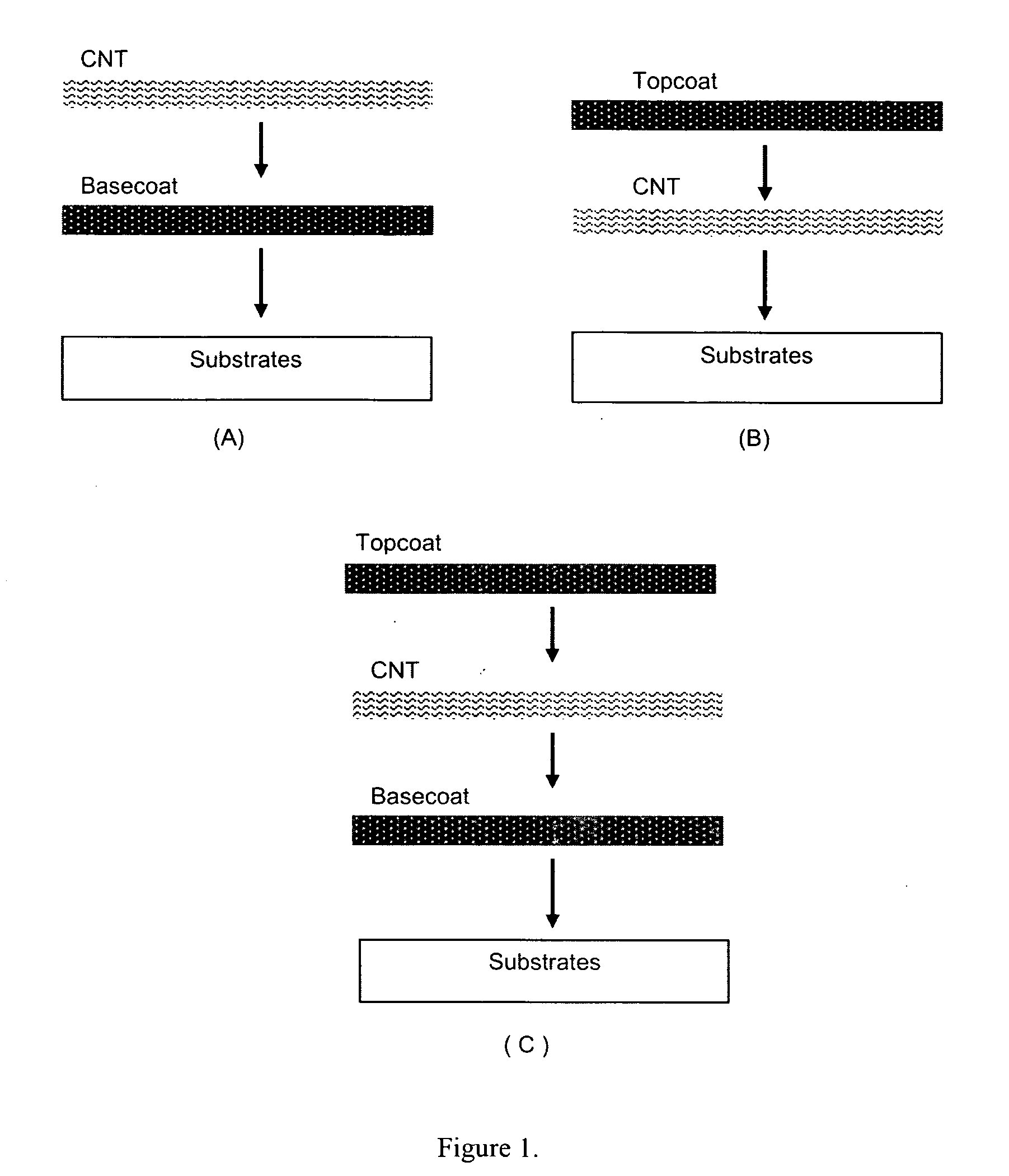
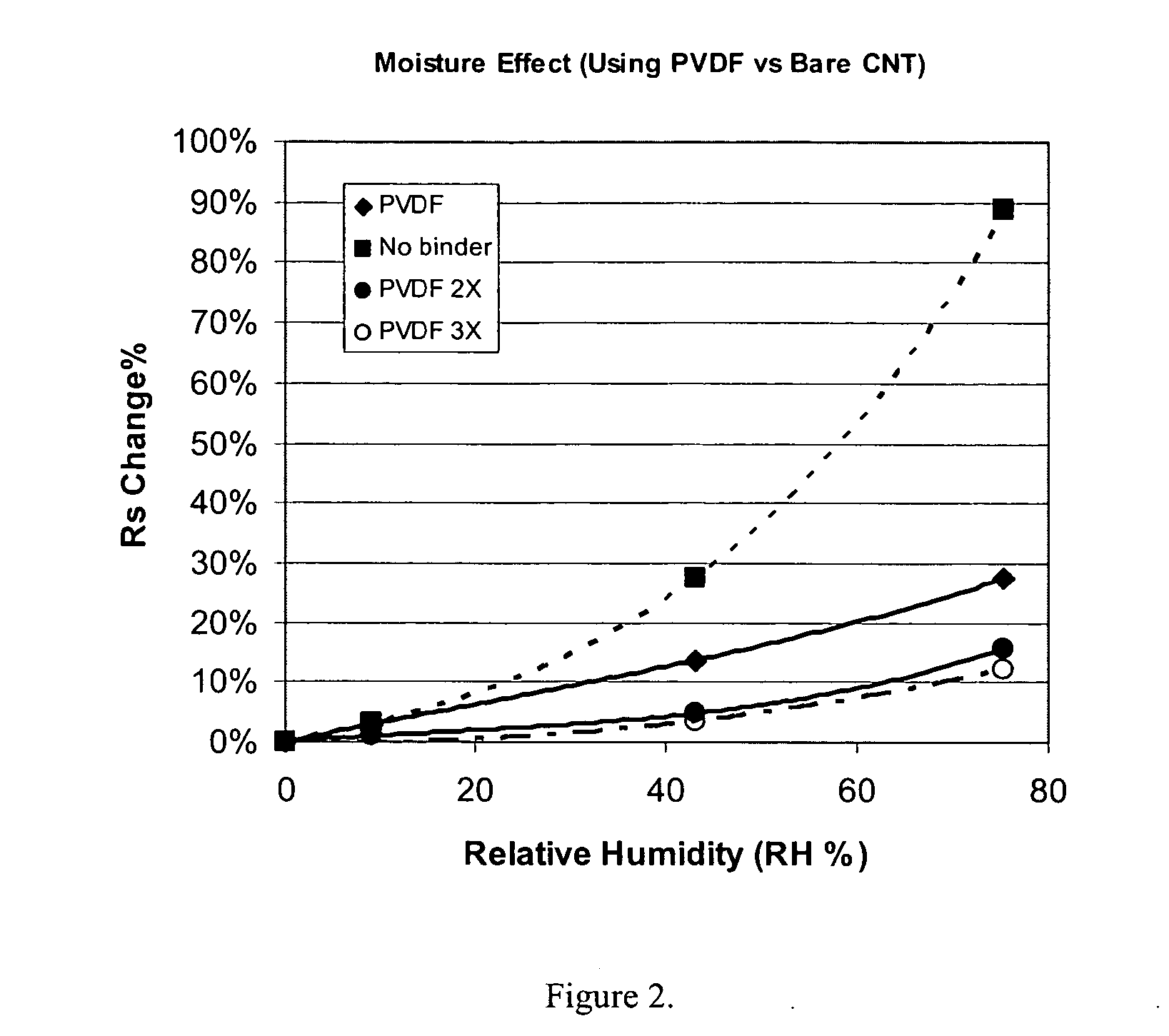
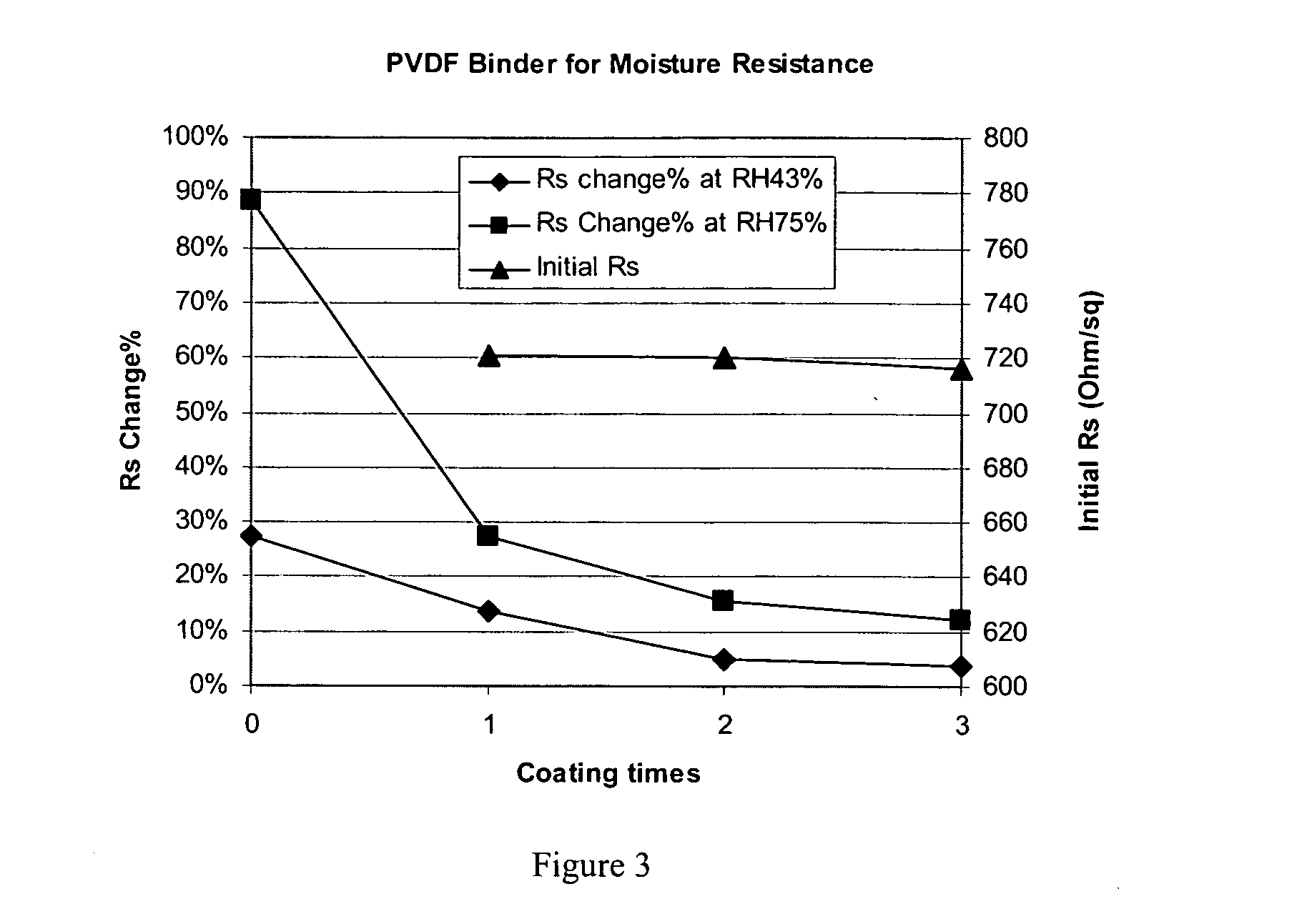
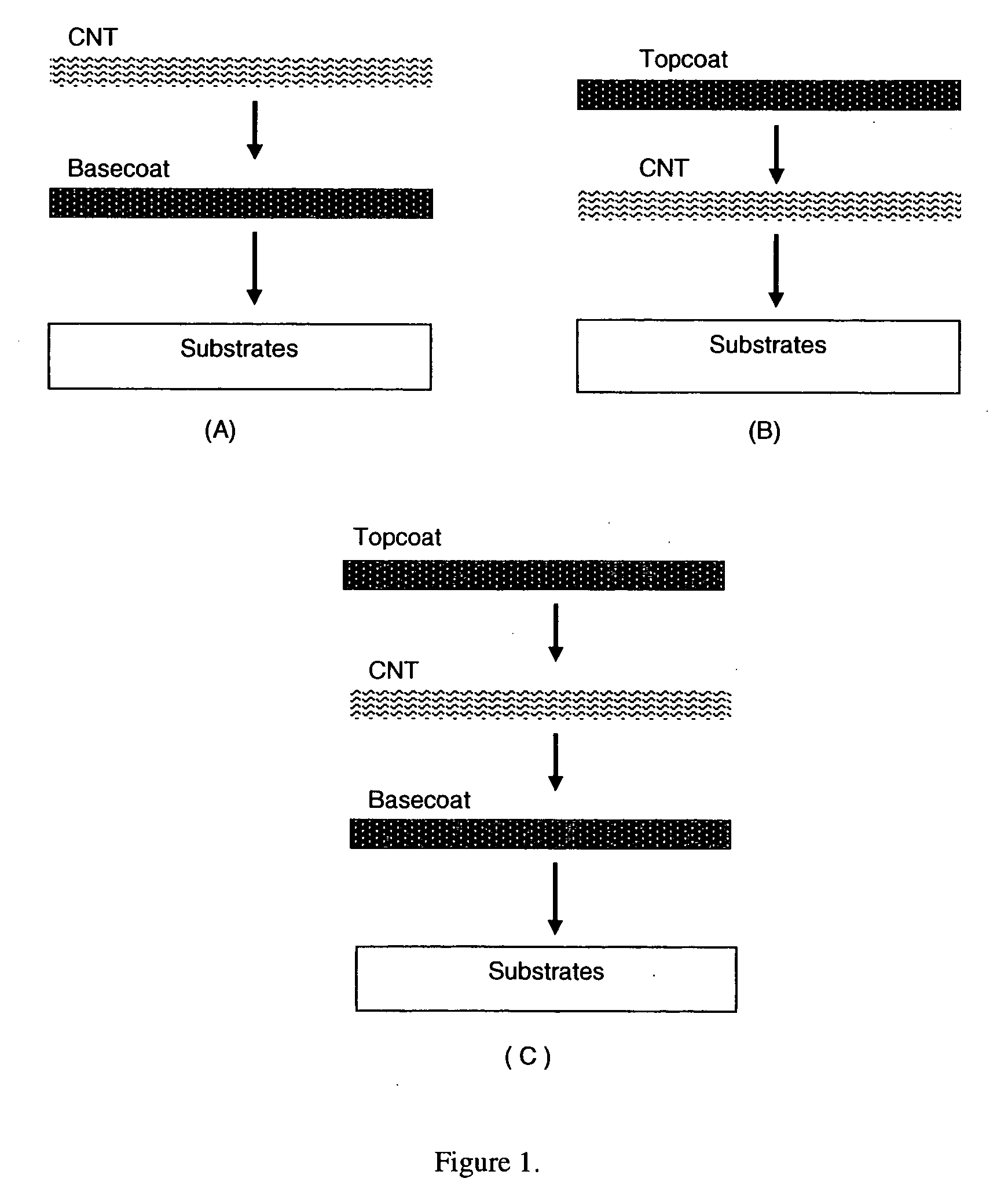
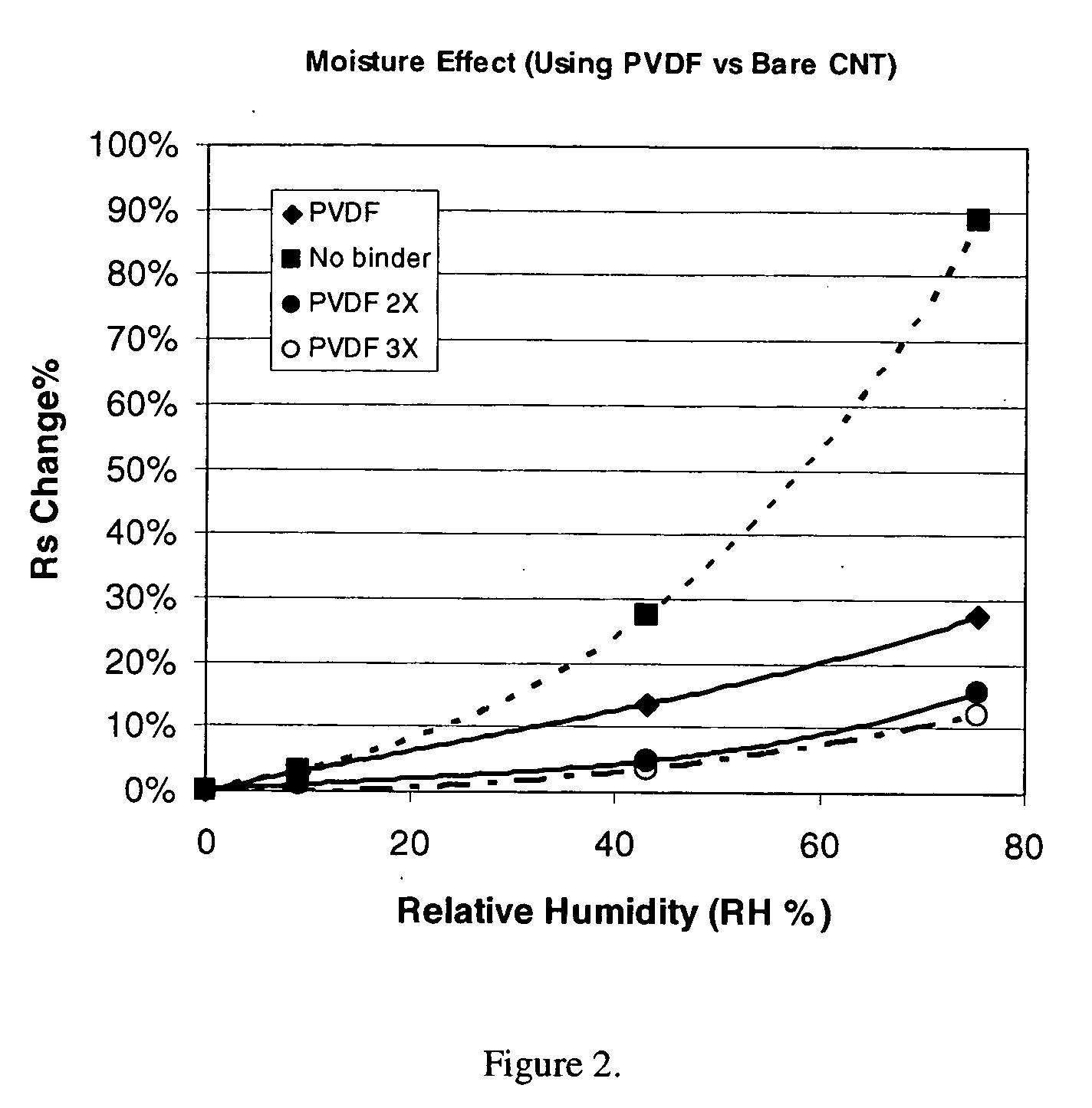
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using single wall carbon nanotubes and polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes (CNT) applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for the enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or any combination of both. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. Resulting films and articles can be used as transparent conductors for flat panel display, touch screen and other electronic devices.
Owner:EIKOS
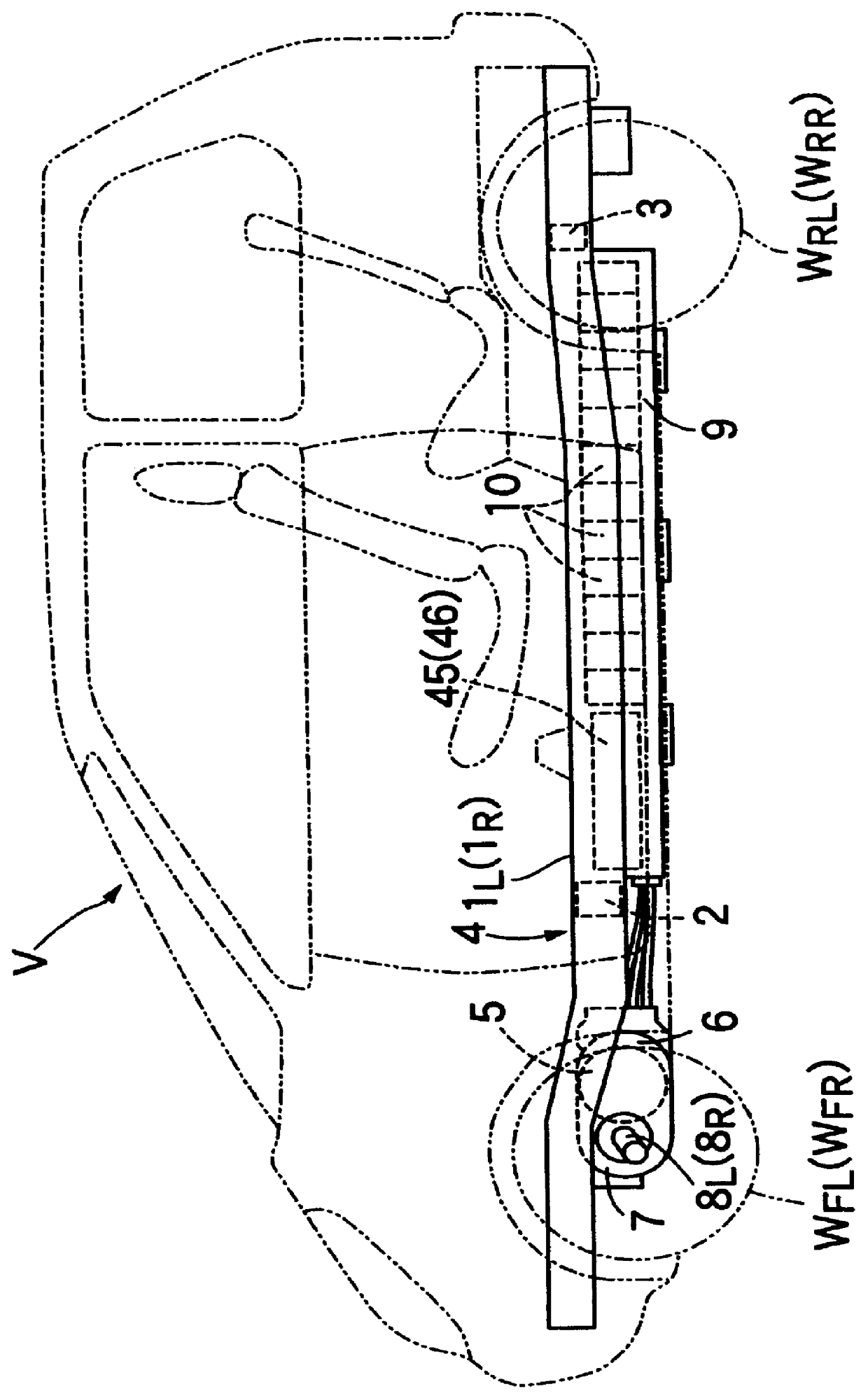
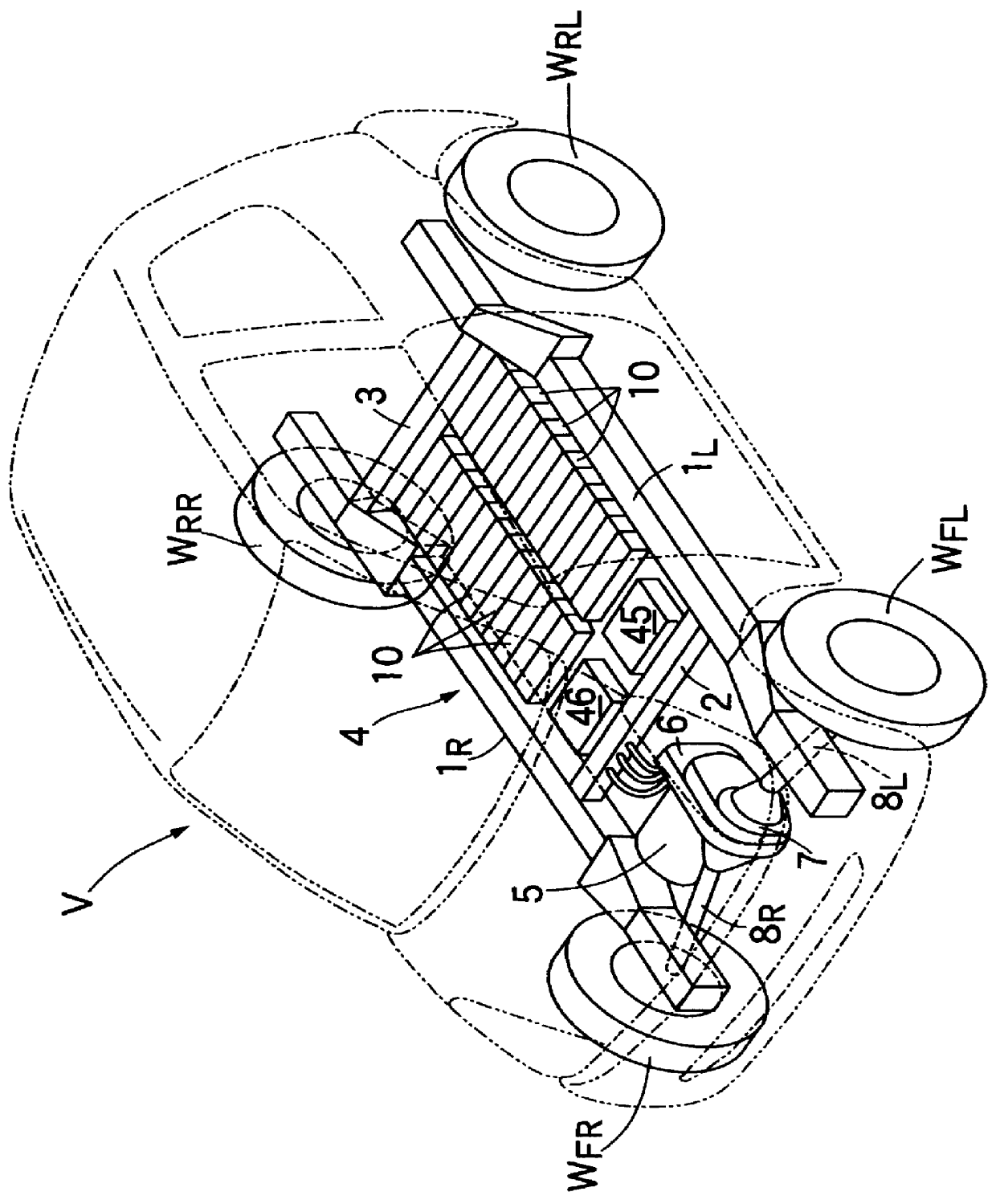
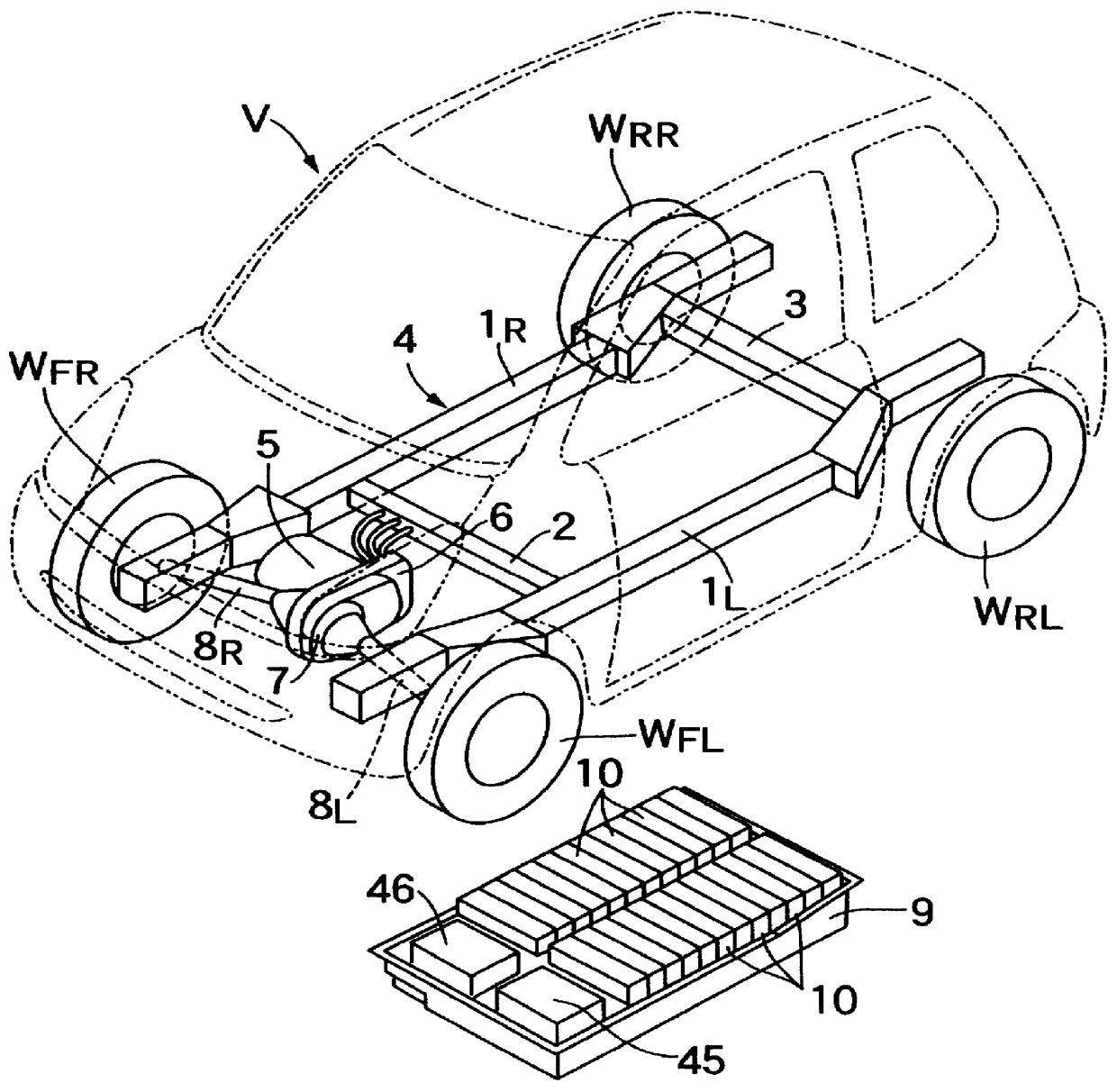
Cooling structure an electric vehicle
InactiveUS6094927AReliable coolingImprove cooling effectDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusAirflowThermal resistance
An electric vehicle includes plurality of batteries accommodated in a rear portion of a battery box, and an electric part is accommodated in an electric part accommodating chamber provided in a front portion of the battery box. Cooling air supplied from a cooling fan to the rear portion of the battery box cools the batteries having a large thermal resistance, while being passed through a first cooling air passage around outer peripheries of the batteries at a low flow rate. A second cooling air passage having a smaller sectional area than that of the first cooling air passage is provided below the electric part accommodating chamber, and cooling fins protruding downwards from the electric part are exposed within the second cooling air passage. The second cooling air passage extends continuously the first cooling air passage in a downstream direction of airflow, so that cooling air which has first cooled the batteries then cools the electric part having a smaller thermal resistance, while being passed through the second cooling air passage at a higher flow rate than that in the first cooling air passage.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS20060113510A1Reduce conductivityFunction increaseNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall carbon nanotubes, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or a combination thereof. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. A fluoropolymer containing binder, which is a solution of one fluoropolymer or a blend of fluoropolymers, which may be formulated with additives, is applied onto a carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate such as PET and glass. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline (with low level of crystallinity) or amorphous, preferably to be amorphous with low refraction index. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. This binder coating significantly improves optical transparency, and also maintain or increases conductivity of the CNT-based coating. With other benefits such as abrasion, thermal and moisture resistance, this binder coating and the resulting products is used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
Method and apparatus for achieving temperature uniformity and hot spot cooling in a heat producing device
ActiveUS7104312B2Minimize temperature differenceTemperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTemperature differenceEngineering
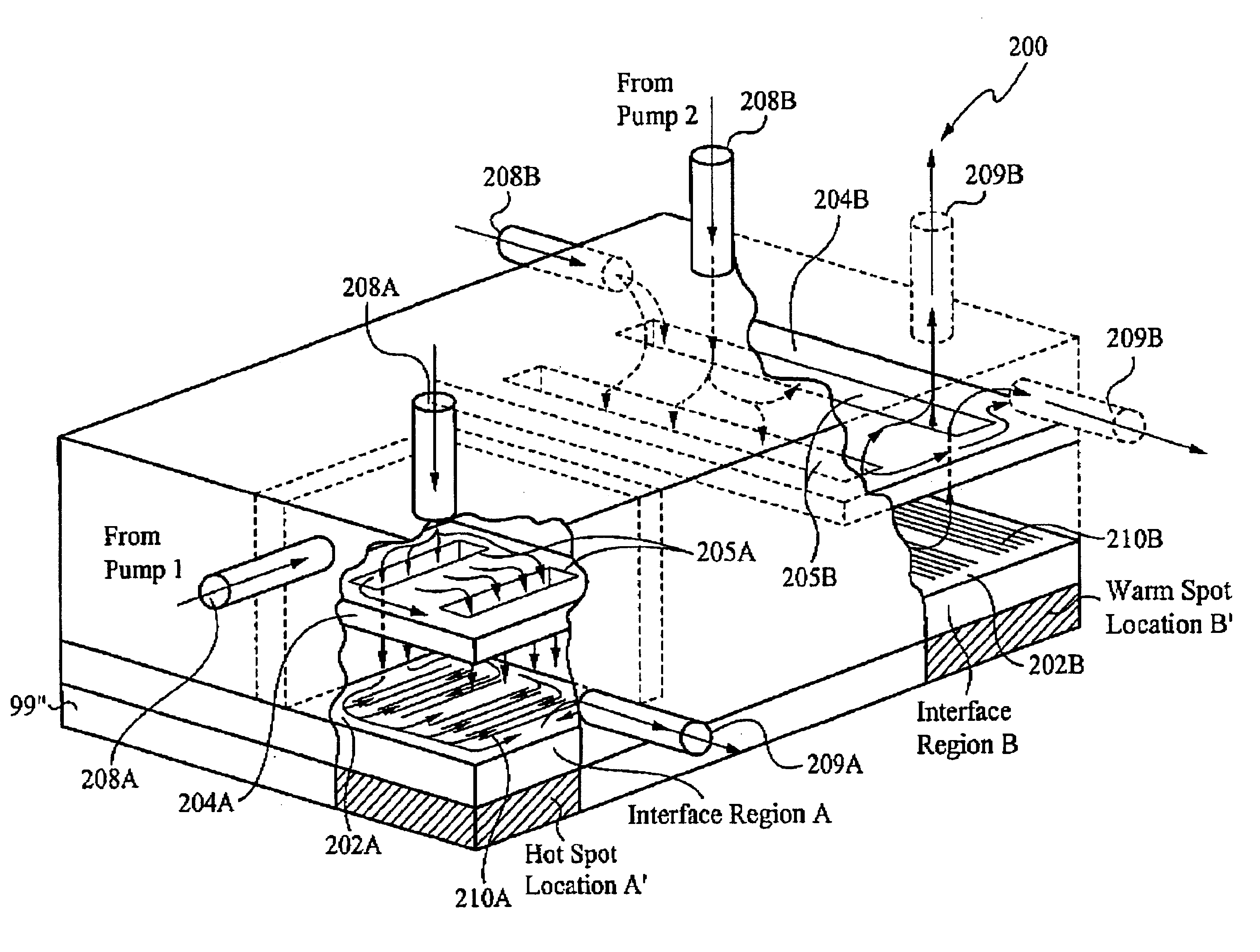
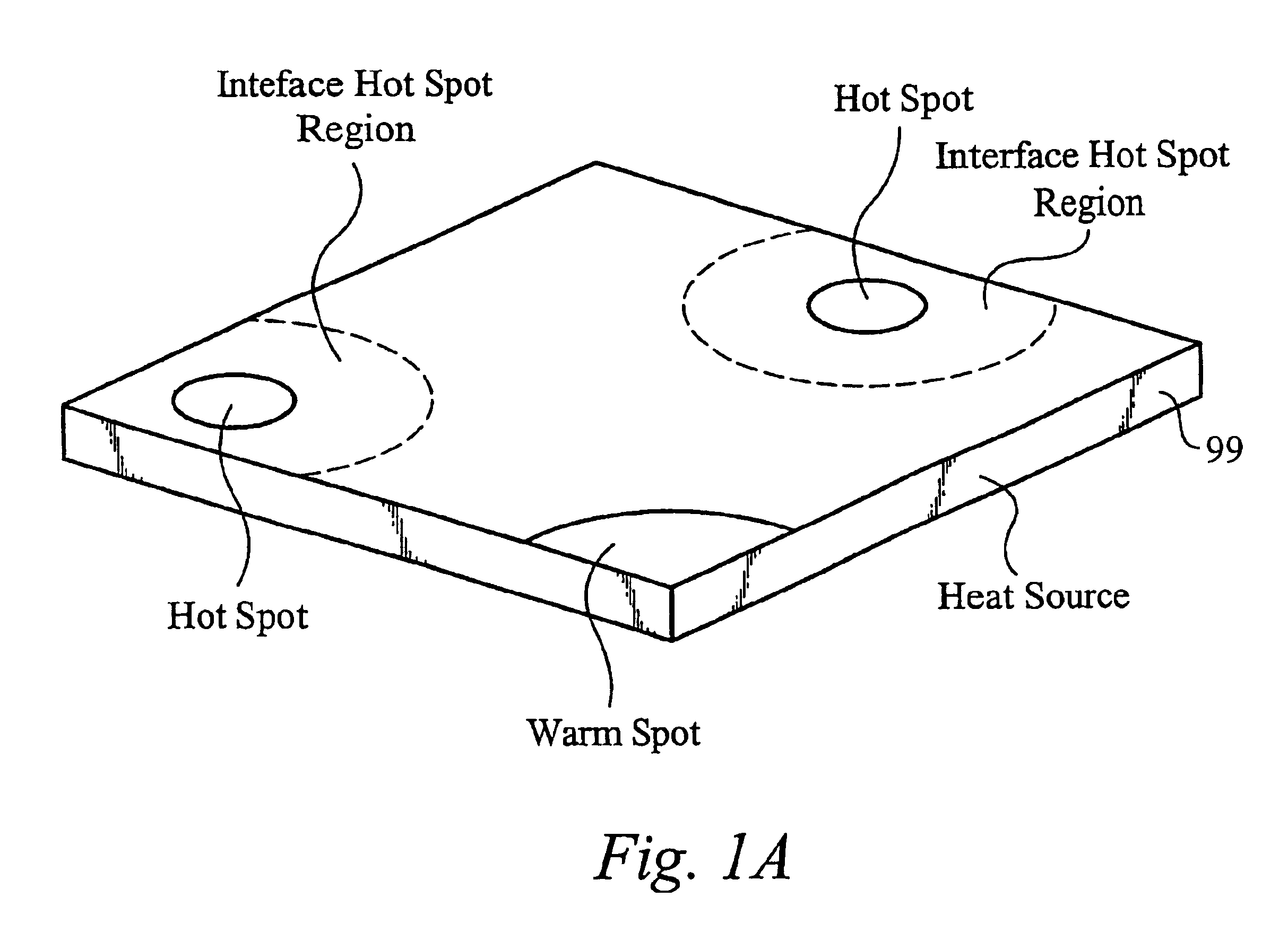
A method of controlling temperature of a heat source in contact with a heat exchanging surface of a heat exchanger, wherein the heat exchanging surface is substantially aligned along a plane. The method comprises channeling a first temperature fluid to the heat exchanging surface, wherein the first temperature fluid undergoes thermal exchange with the heat source along the heat exchanging surface. The method comprises channeling a second temperature fluid from the heat exchange surface, wherein fluid is channeled to minimize temperature differences along the heat source. The temperature differences are minimized by optimizing and controlling the fluidic and thermal resistances in the heat exchanger. The resistances to the fluid are influenced by size, volume and surface area of heat transferring features, multiple pumps, fixed and variable valves and flow impedance elements in the fluid path, pressure and flow rate control of the fluid, and other factors.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Thermal enhancement approach using solder compositions in the liquid state
InactiveUS6281573B1Lower resistanceThermal mismatchPrinted electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal energyThermal coefficient
Solder compositions are introduced to interface between an IC chip and its associated heat exchanger cover. The solder compositions have a solidus-liquidus temperature range that encompasses the IC chip operational temperature range. The solder composition has the desired property of absorbing and rejecting heat energy by changing state or phase with each temperature rise and decline that result from temperature fluctuations associated with the thermal cycles of the integrated circuit chips. A path for high thermal conduction (low thermal resistance) from the IC chip to the heat exchanger to the ambient air is provided by an electronic module cover, configured as a cap with a heat exchanger formed or attached as a single construction, and made of the same material as the substrate, or made with materials of compatible thermal coefficients of expansion to mitigate the effects of vertical displacement during thermal cycling. The cap-heat exchanger cover is constructed to be compliant, and to contact both the IC chip and substrate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Light fixture assembly and LED assembly
InactiveUS7866850B2Improve usabilityEasy to remove and replaceWave amplification devicesLighting support devicesEngineeringLight fixture
A removable light fixture assembly is provided. The light fixture assembly includes an LED lighting element and a compression element. Operation of the compression element from a first position to a second position generates a compression force which reduces thermal impedance between the LED assembly and a thermally-conductive housing.
Owner:KORRUS INC
Light fixture assembly and led assembly
InactiveUS20090213595A1Reduce thermal resistanceWave amplification devicesLighting support devicesEffect lightEngineering
A removable light fixture assembly is provided. The light fixture assembly includes an LED lighting element and a compression element. Operation of the compression element from a first position to a second position generates a compression force which reduces thermal impedance between the LED assembly and a thermally-conductive housing.
Owner:KORRUS INC
Differential thermopile heat flux transducer
InactiveUS6278051B1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentHeat flowThermopile
A thin sensor for heat flux and temperature, designed for adhesive attachment to a surface, is manufactured on a flexible insulated metallic substrate. The sensor exhibits a combination of high sensitivity for heat flux and low resistance to the flow of heat. These characteristics enable it to measure heat flux at surface boundaries with improved accuracy over conventional heat flux transducers because the temperature drop produced by the sensor is very small. The response by the sensor to radiation, convection and conduction are equal. As such, the sensor can be calibrated in one mode of heat transfer and used for measurement in other modes. The high sensitivity of the sensor makes it ideal for measuring heat flow through insulating materials, and well adapted to instrumenting heat flow in buildings, detecting fires at an early stage, or remotely measuring the temperature of string and web products in industrial processing.
Owner:VATELL CORP
Polycrystalline diamond cutting elements having improved thermal resistance
InactiveUS20080302579A1Increase thermal resistanceGood adhesionDrill bitsConstructionsHeat resistanceDiamond crystal
Polycrystalline diamond constructions of this invention have a polycrystalline diamond body and a substrate attached thereto, wherein the diamond body has a material microstructure comprising a plurality of bonded-together diamond crystals forming a polycrystalline matrix phase, and second phase formed from different types of materials or sintering aids designed to reduce or eliminate the amount of free Group VIII elements therein. The use of such materials and the reduction and / or elimination of free Group VIII elements, in addition to graphitization, facilitates the sintering the construction at high pressure / high temperature conditions, e.g., greater than about 65 Kbar, to produce a construction having a high degree of thermal stability and / or thermal resistance when compared to conventional PCD materials. Polycrystalline diamond constructions of this invention are preferably configured as cutting elements that are disposed on drill bits used for drilling subterranean earthen formations.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
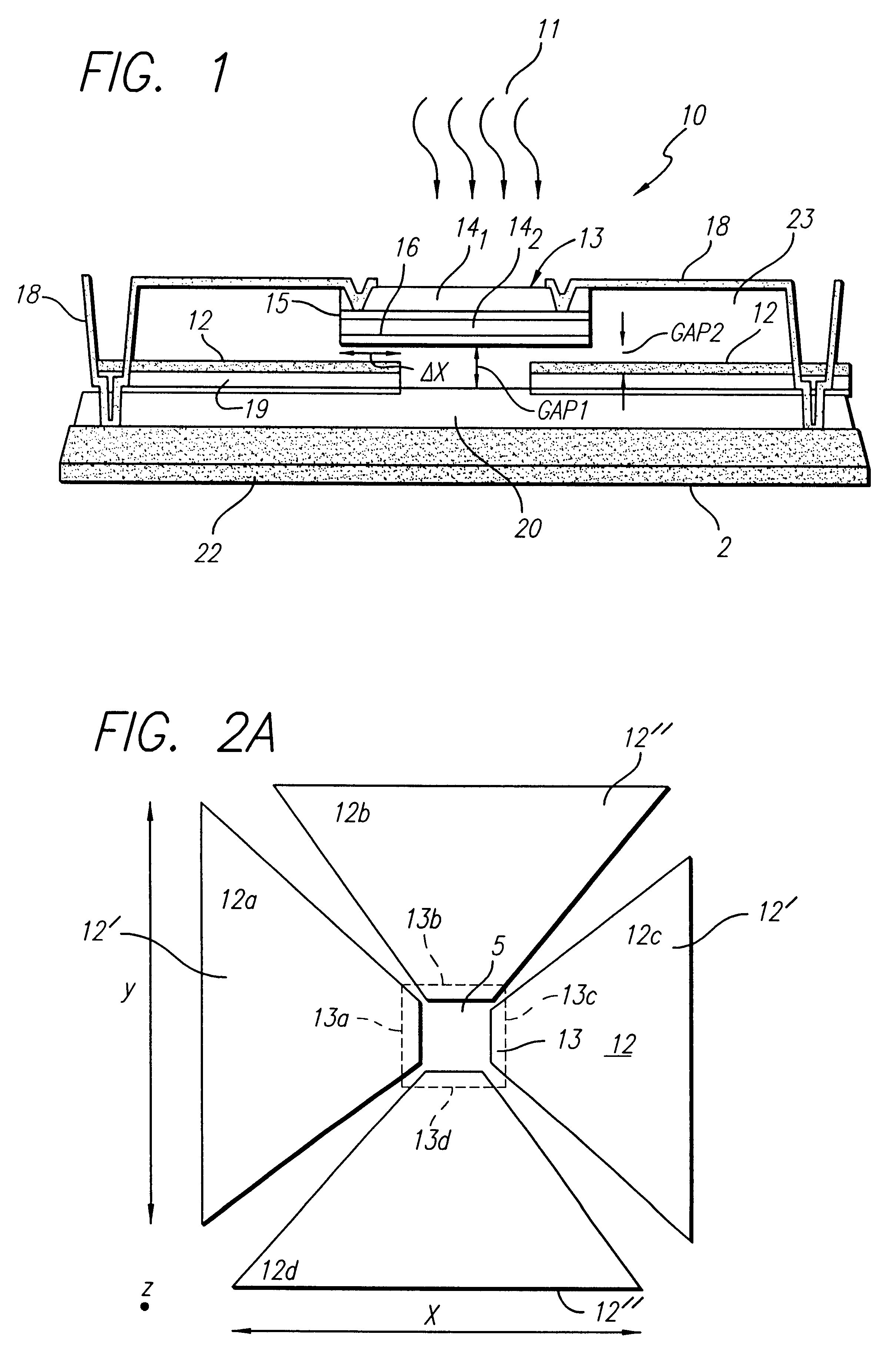
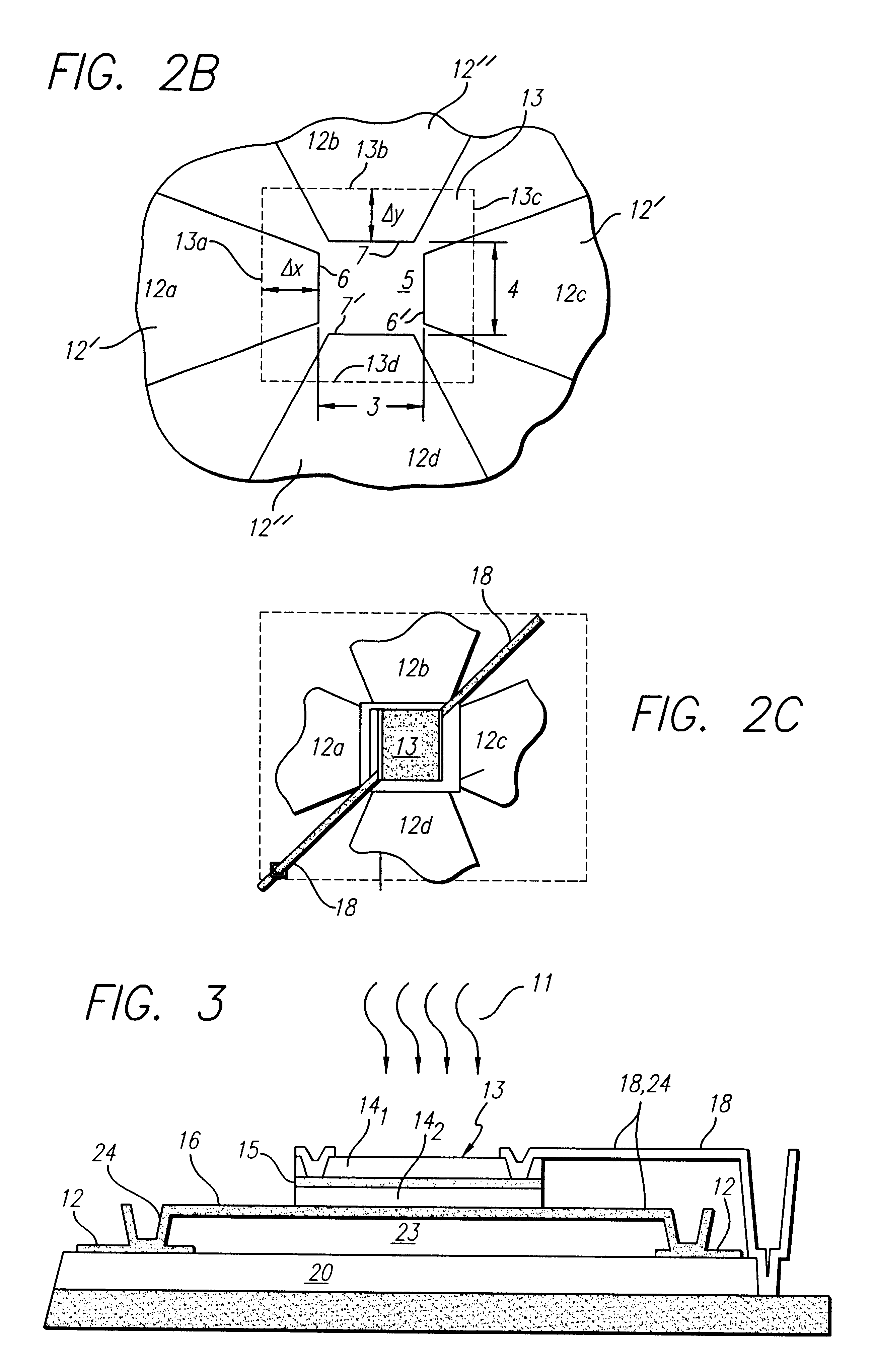
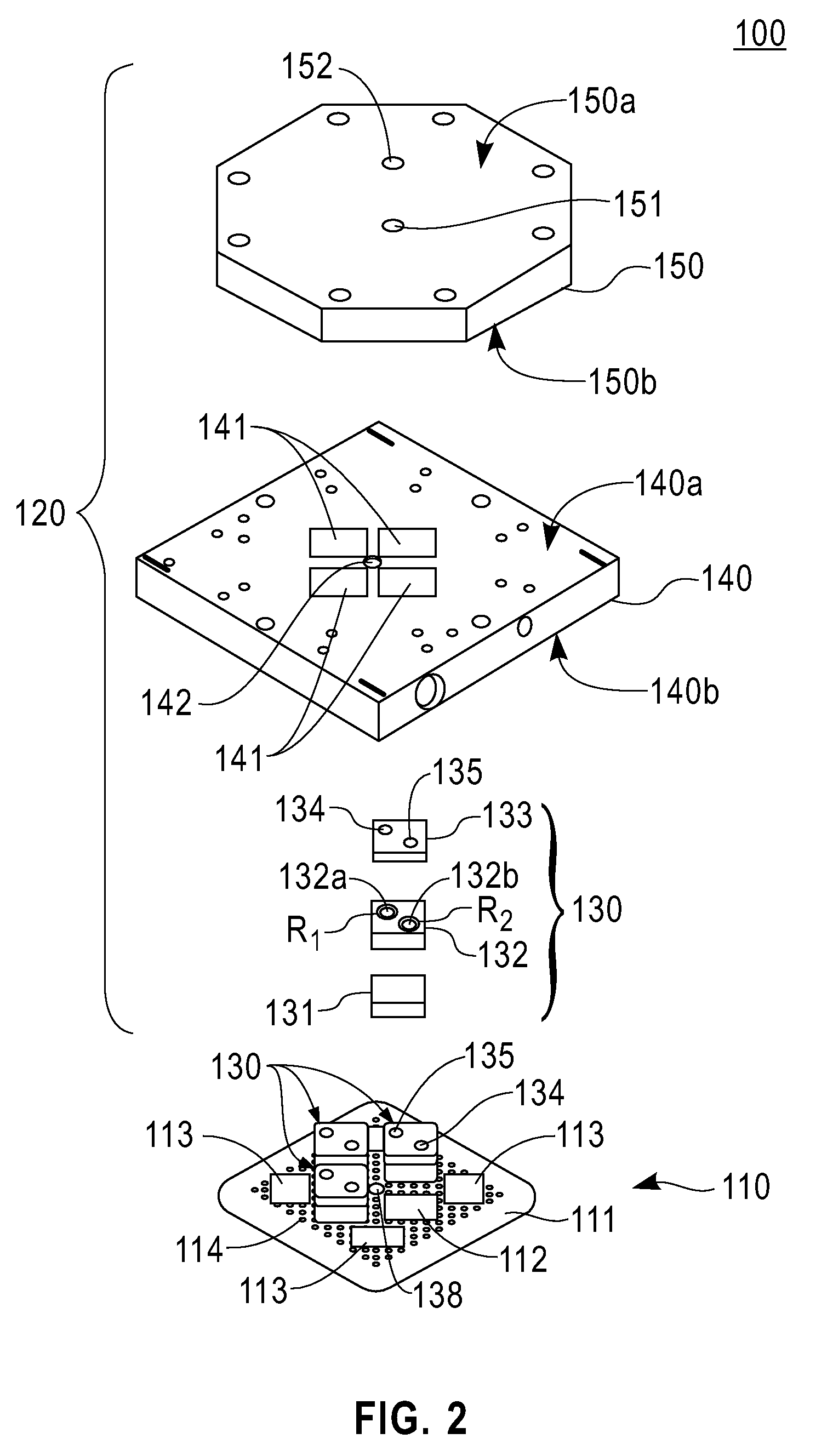
Architecture and method of coupling electromagnetic energy to thermal detectors
InactiveUS6329655B1Antenna supports/mountingsSolid-state devicesSensing applicationsElectromagnetic shielding
A radiation sensor. The inventive sensor has a two-level detector structure formed on a substrate in which a thermal detector element is suspended over the substrate as a microbridge structure. A receiver of electromagnetic radiation is provided on the same side of the substrate in a manner that efficiently couples the radiation field to the thermal detector element. The thermal detector element has a sandwich structure including a heater metal layer, a dielectric layer, and a thin film thermo-resistive material. The thermal detector element is suspended out of physical contact with the receiver. In one embodiment, the receiver is an antenna having a crossed bowtie configuration that efficiently couples the radiation field to the detector element. The inventive radiation sensors are especially useful for mm-wave and microwave sensing applications. The sensor can be used individually or in linear or two-dimensional arrays thereof. The invention also is directed to a method of fabricating such a radiation sensor.
Owner:HRL LAB +1
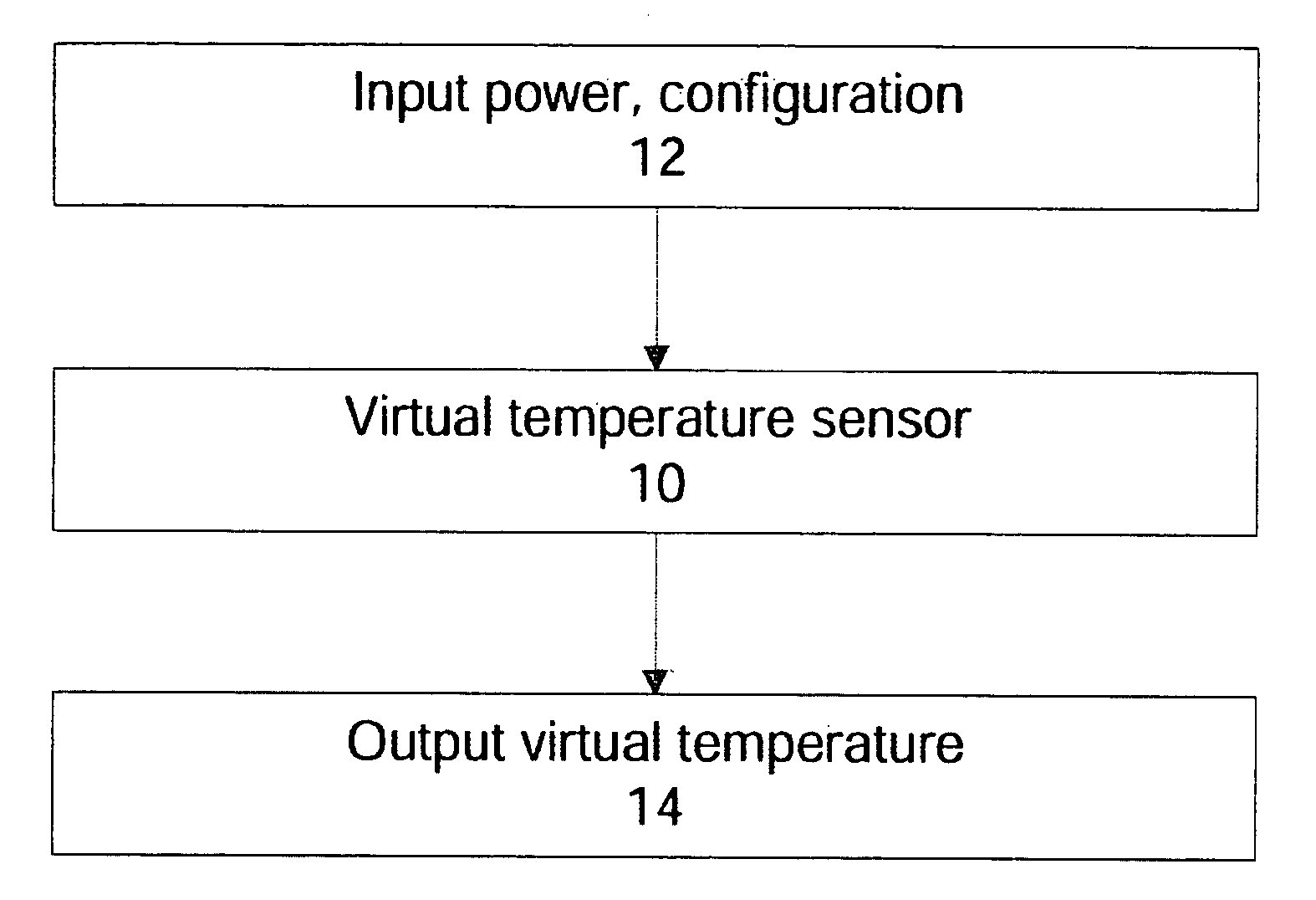
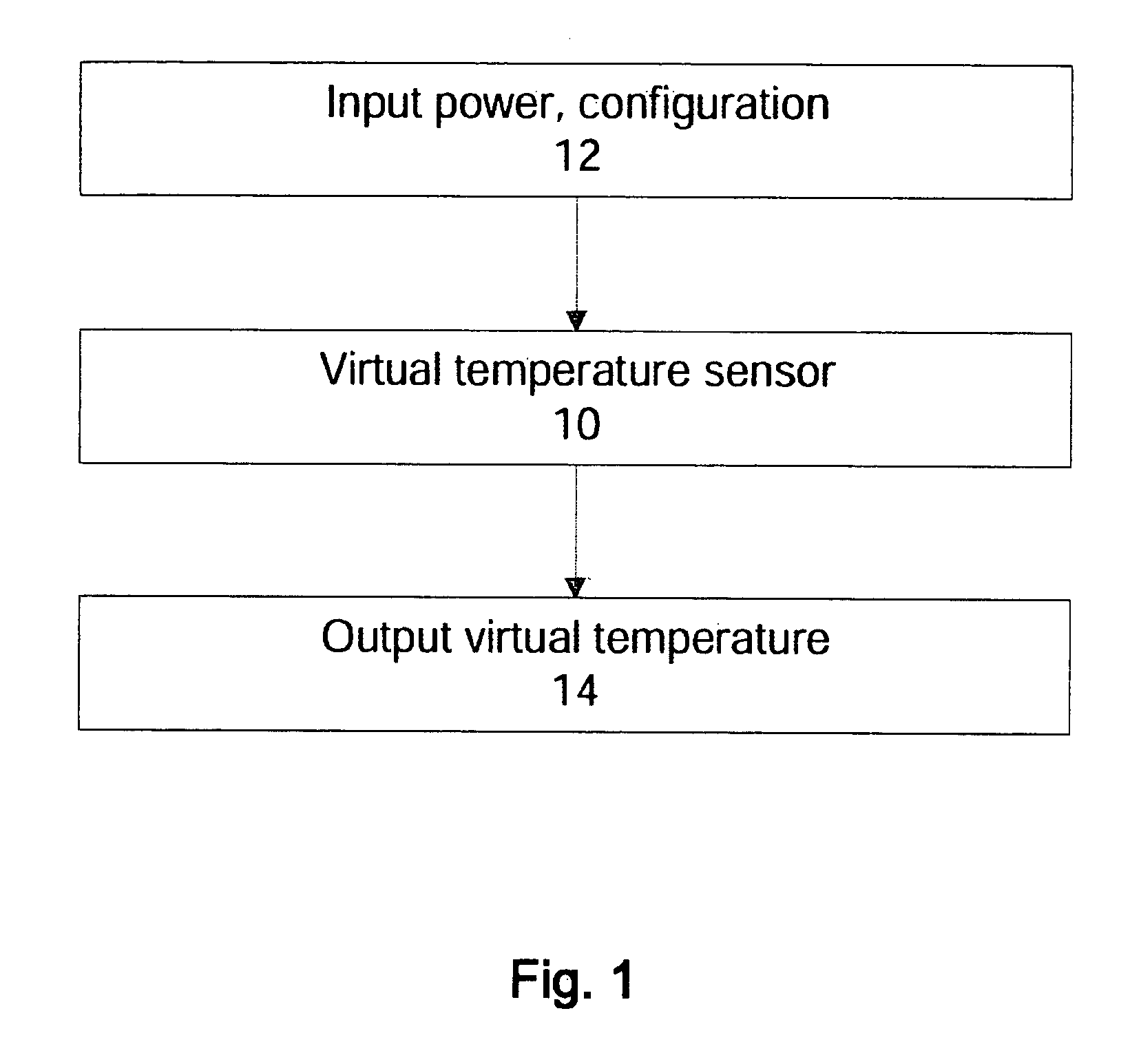
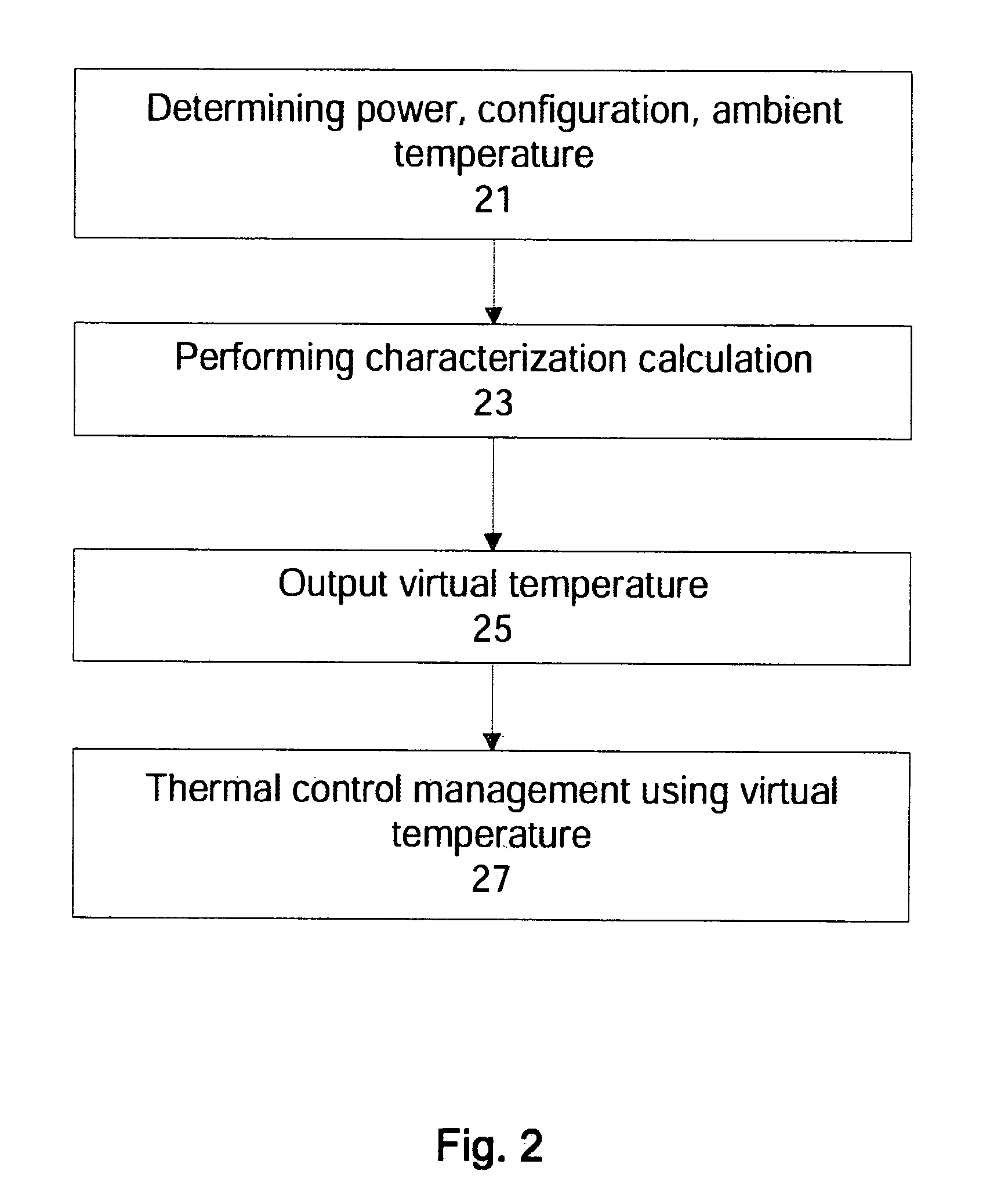
Method and apparatus for a thermal control system based on virtual temperature sensor
ActiveUS20080028778A1Energy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsMathematical modelSystem configuration
Methods and apparatuses for providing virtual temperature sensor to control temperatures in a data processing system. In one aspect, a data processing system includes a virtual temperature sensor to provide system temperature for different system configurations, and a controller coupled to the sensor to control operations of the data processing system according to the virtual temperature. The virtual temperature sensor typically derives the temperature of a particular configuration of the data processing system using mathematical models or one or more operating parameters of the data processing system. In one example, the mathematical models include a characterization table which provides the measured temperature data from various system configurations. These measurements are performed with temperature sensors positioned in ideal locations for different configuration, and are preprocessed to provide the virtual temperature computation. The characterization table also includes thermal characteristics, such as thermal time constant and thermal resistance, of the critical components at multiple thermal control states.
Owner:APPLE INC
Direct chip-cooling through liquid vaporization heat exchange
InactiveUS6085831ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringVaporization
An apparatus for and method of cooling an electronic module comprising a heat sink enclosure placed directly over a chip or substrate in a flip chip package. The heat sink enclosure has a plurality of cooling fins extending from within the cavity of the enclosure. A liquid sealed inside the enclosure is trapped within a thermal transfer means, preferably a metal wick, which sits directly on a chip or substrate. As the chip or substrate heats up, heat is transferred to the thermal transfer means which in turn heats the liquid to its heat of vaporization. The vapors of the liquid rise and condense on the cooling fins and the heat is absorbed by the enclosure and conducted to an outside surface of the enclosure and dissipated. Cooling fins on an exterior surface of the enclosure further reduces the thermal resistance to enhance cooling.
Owner:IBM CORP
Silicone-polyester-polysilicate hybrid compositions for thermal resistance coating
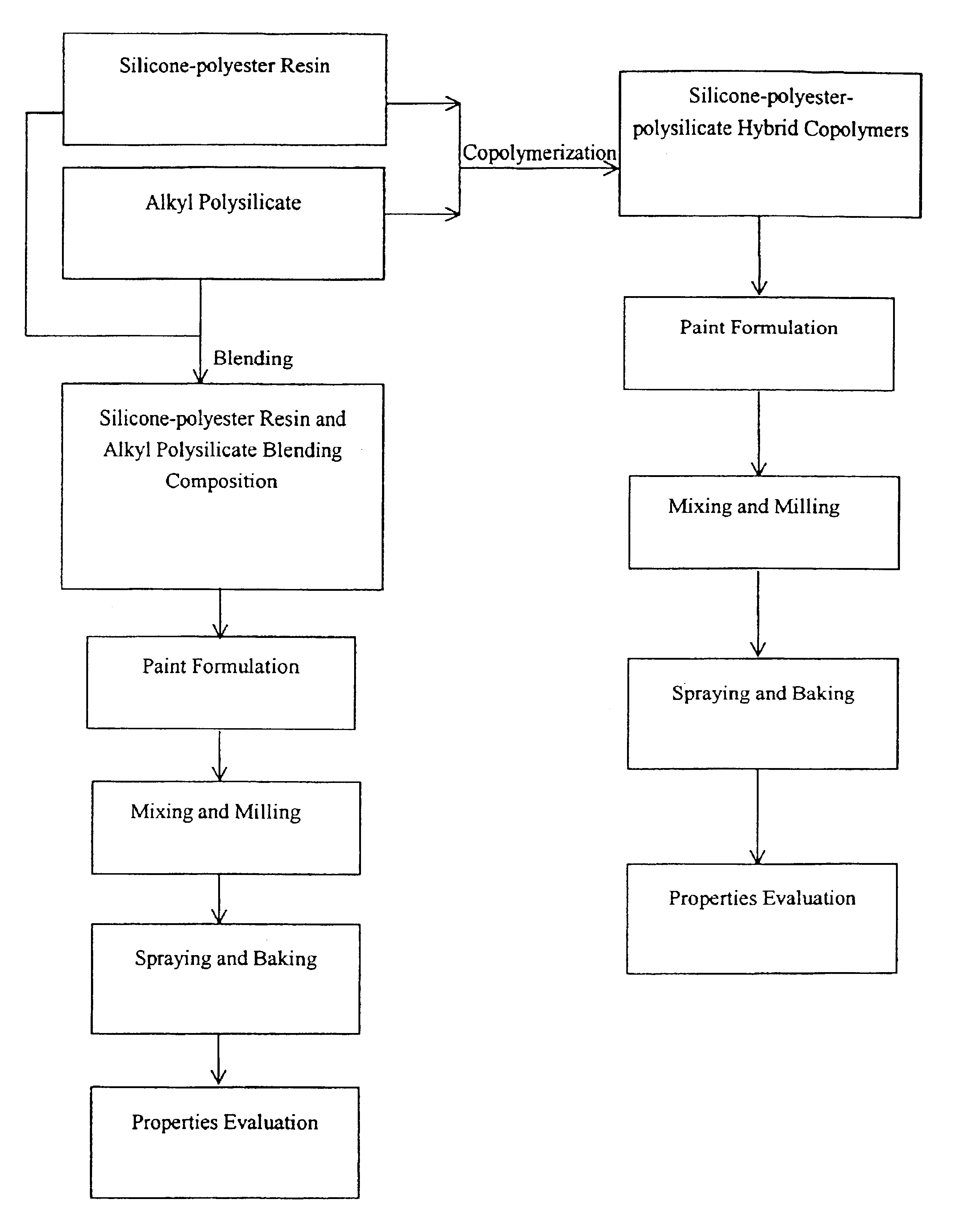
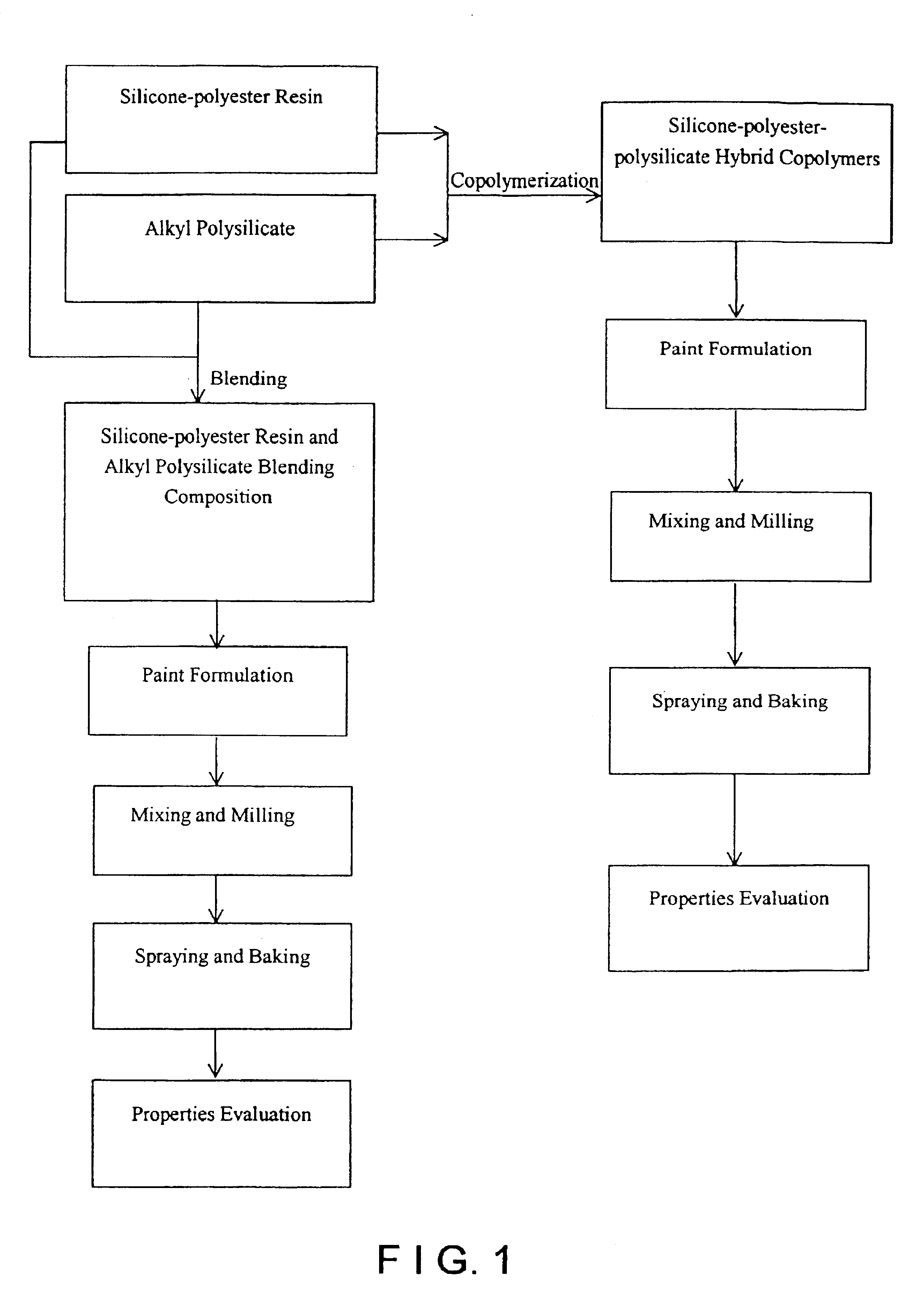
InactiveUS6893724B2Improve heat resistanceExcellent adhesion to metalGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsCopolymerMaterials science
The present invention employs alkyl polysilicate to form silicone-polyester-polysilicate hybrid compositions with an appropriate proportion to modify silicone-polyester resin, or directly adds the alkyl polysilicate at an appropriate proportion into silicone-polyester resin to produce a hybrid composition. The composition in high baking temperature forms a hybrid structure having good thermal resistance, especially, hot-oil resistance and hot hardness, and good adhesion to metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminum. The present invention can be used in the field of the protective coating for heat-resistant metal such as frying pans and electric irons to be a kind of novel heat-resistant composition having hybrid structure. The composition in accordance with the present invention comprises (A)silicone-polyester; (B)alkyl polysilicate and the structure thereof comprises (RO)3—Si—O—(Si(OR)2—O)n—R, where n=0˜20 and R represents —CH3, —C2H5, —C3H7, or —C4H9. The composition mentioned above comprises the compounds of (A) and (B) or the copolymer comprised by (A) and (B).
Owner:GRAND TEK ADVANCE MATERIAL SCI
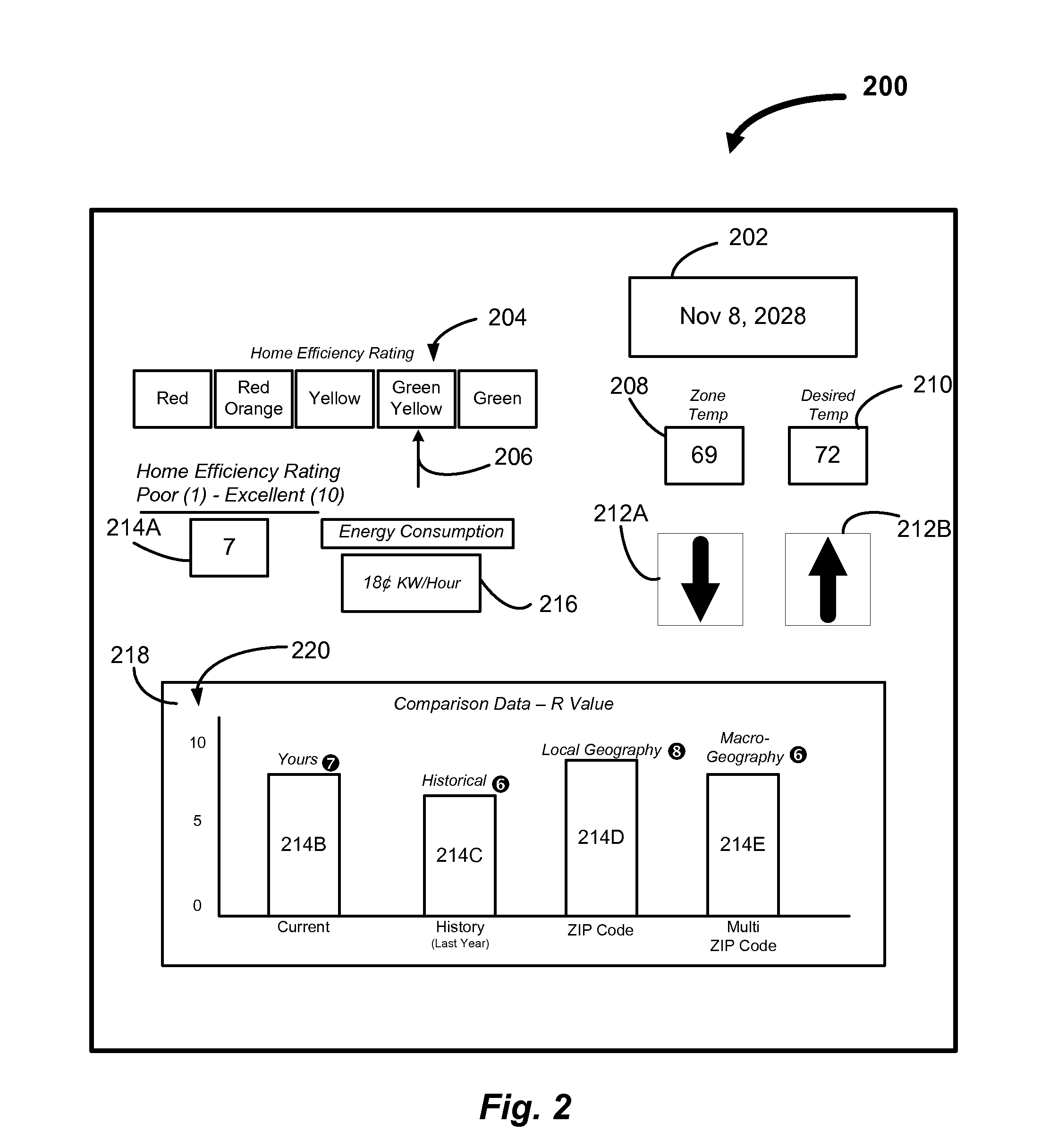
Method and system for calculating energy metrics of a building and one or more zones within the building
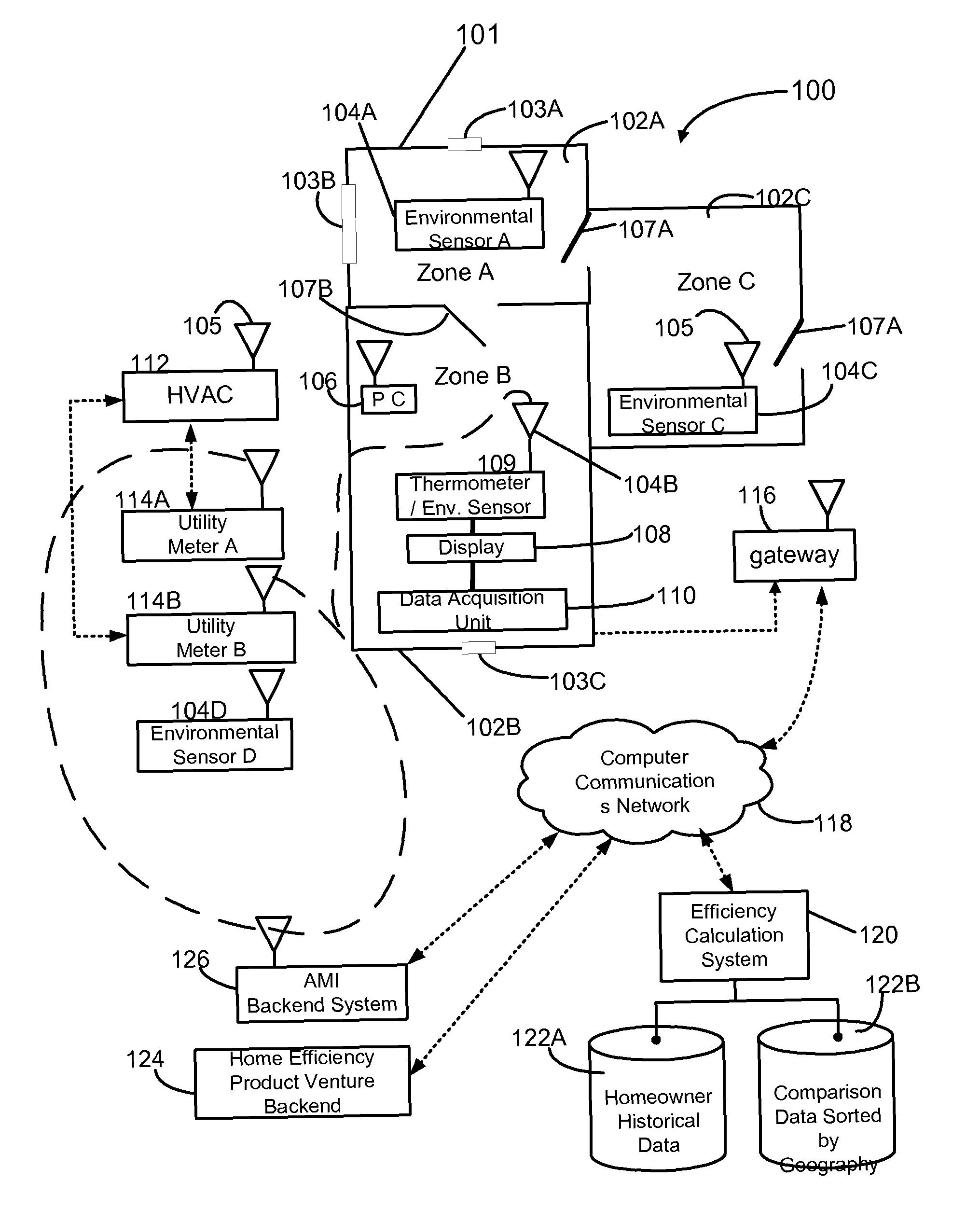
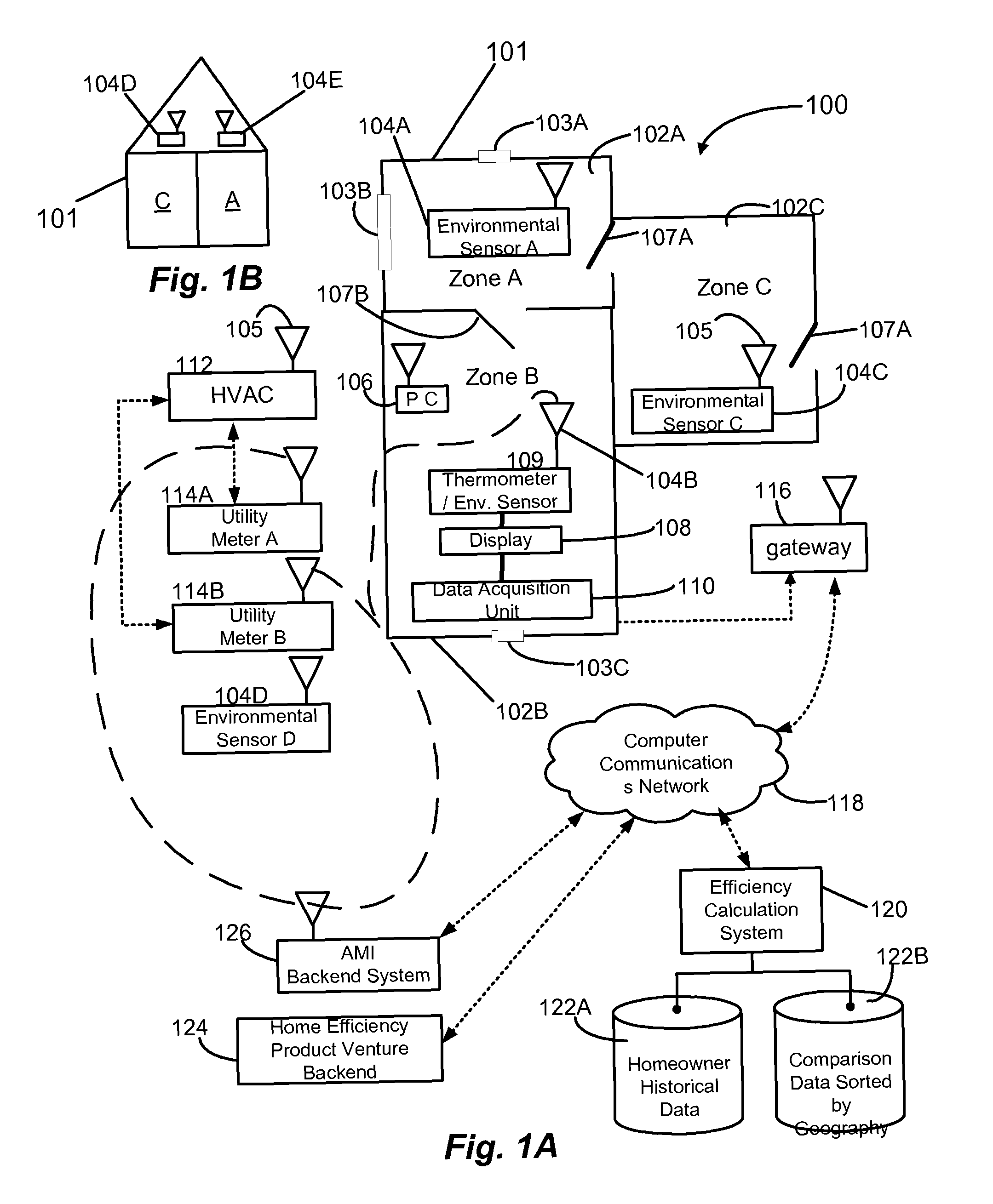
ActiveUS8155900B1Easy to understand visual presentationGeometric CADMechanical apparatusBusiness efficiencyBuilding energy
A method and system can provide building energy performance metrics that can help identify specific zones within a building which may have energy efficiency problems. The method and system can collect data from: indoor temperature sensors and humidity sensors present in each zone of a building; one or more temperature sensors and humidity sensors present outside of the building; one or more utility meters; and one or more HVAC devices. This data from the sensors can be aggregated and formed into a first profile. The energy efficiency calculation system can analyze the first profile to provide various energy performance metrics which can include, but are not limited to, energy efficiency ratios for air conditioners, the R-value or thermal resistance of the building, an amount of heat loss for the building, energy consumption by the building, current HVAC performance parameters, and utility usage comparisons.
Owner:ITRON
Flexible, flame-retardant, aqueous-processable photoimageable composition for coating flexible printed circuits
A flexible, flame-retardant, aqueous processable, photoimageable resin composition for forming a permanent, protective coating film for printed circuitry and a multilayer photoimageable element containing a layer of the photoimageable resin composition in combination with a low tack photoimageable resin sublayer and a temporary support film are disclosed. The photoimageable resin composition has excellent aqueous developability and provides a cured coating film having good flexibility, adhesion, solvent resistance, surface hardness, thermal resistance, electrical insulating properties and flame retardancy.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters using surgical devices
Systems and methods for estimating tissue parameters, including mass of tissue to be treated and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode of an energy delivery device, are disclosed. The method includes sensing tissue temperatures, estimating a mass of the tissue and a thermal resistance scale factor between the tissue and an electrode, and controlling an electrosurgical generator based on the estimated mass and the estimated thermal resistance scale factor. The method may be performed iteratively and non-iteratively. The iterative method may employ a gradient descent algorithm that iteratively adds a derivative step to the estimates of the mass and thermal resistance scale factor until a condition is met. The non-iterative method includes selecting maximum and minimum temperature differences and estimating the mass and the thermal resistance scale factor based on a predetermined reduction point from the maximum temperature difference to the minimum temperature difference.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
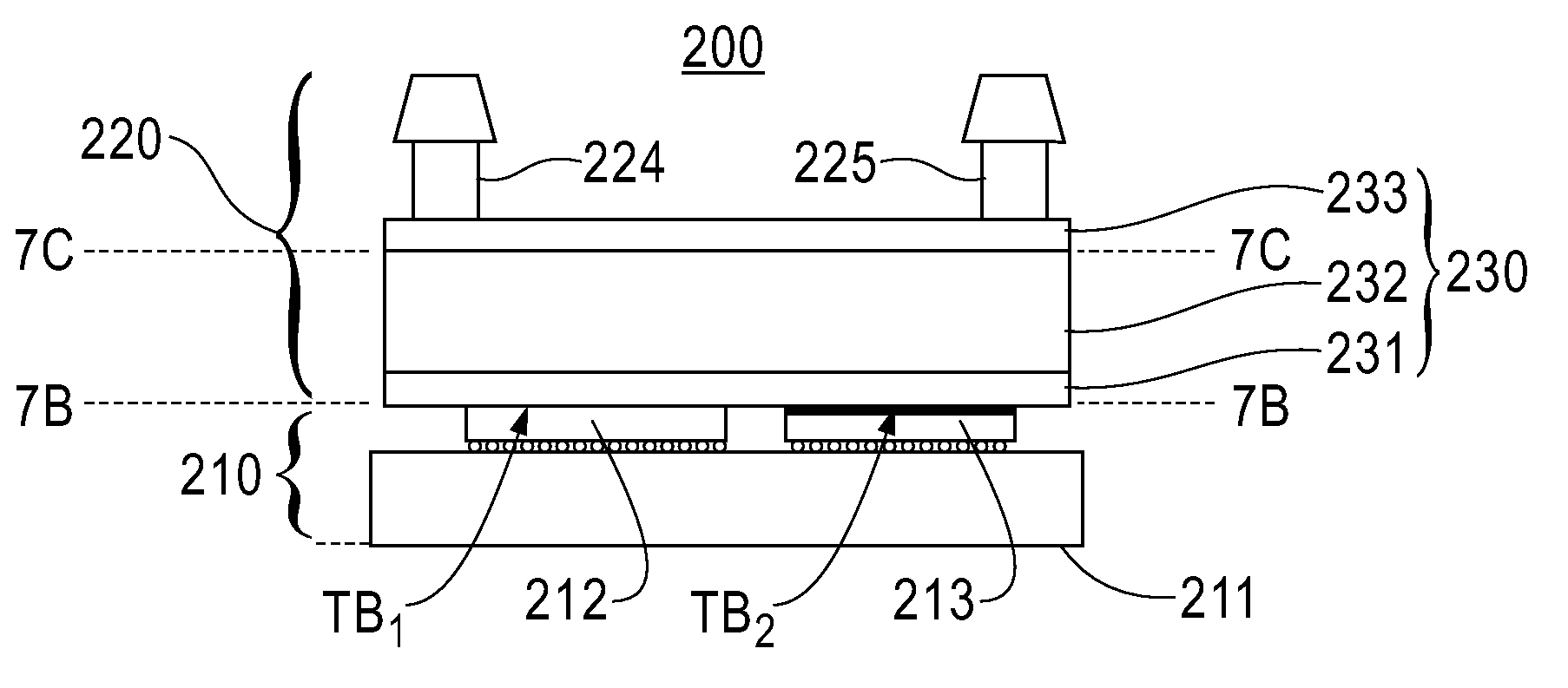
Power Semiconductor Module
InactiveUS20080224303A1Improve cooling effectThermal resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConversion constructional detailsSemiconductor chipEngineering
A power semiconductor module with its thermal resistance and overall size reduced. Insulating substrates with electrode metal layers disposed thereon are joined to both the surfaces of a power semiconductor chip by using, for example, soldering. Metal layers are disposed also on the reverse surfaces of the insulating substrates and the metal layers are joined to the heat spreaders by using brazing. Heat radiating fins are provided on the heat radiating surface of at least one of the heat spreaders. The heat radiating side of each of the heat spreaders is covered by a casing to form a refrigerant chamber through which refrigerant flows to remove heat transmitted from the semiconductor chip to the heat spreader.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS6940704B2Much of lightGuaranteed uptimeNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceContact padLight-emitting diode
A light emitting diode (LED) including a combination of features that enable the LED to produce a high-brightness predetermined radiation pattern. The combination of features enable the LED to function cooler and more reliably at a higher drive currents and elevated ambient temperatures, and therefore emit light of increased brightness, without overheating, and to have a particular radiation pattern. In particular, a surface mount that is capable of operating at high drive currents and high ambient temperatures is disclosed. The LED comprises a surface mount package having a metal lead frame having mass sufficient to provide low thermal resistance, at least one anode contact pad and at least one cathode contact pad. The LED also includes a reflector positioned within the package, a semiconductor die and an optional focusing dome. The semiconductor die comprises a transparent substrate and a semiconductor component and is positioned within the package so that the semiconductor component and the substrate are arranged side-by-side over the reflector (flop-chip). Alternatively, the die is positioned within the package so that the substrate is on top of the semiconductor component (flip-chip). The optional focusing dome is operative to refract light emitted from the semiconductor die and light reflected from the reflector to create a predetermined radiation pattern.
Owner:GELCORE LLC (US)
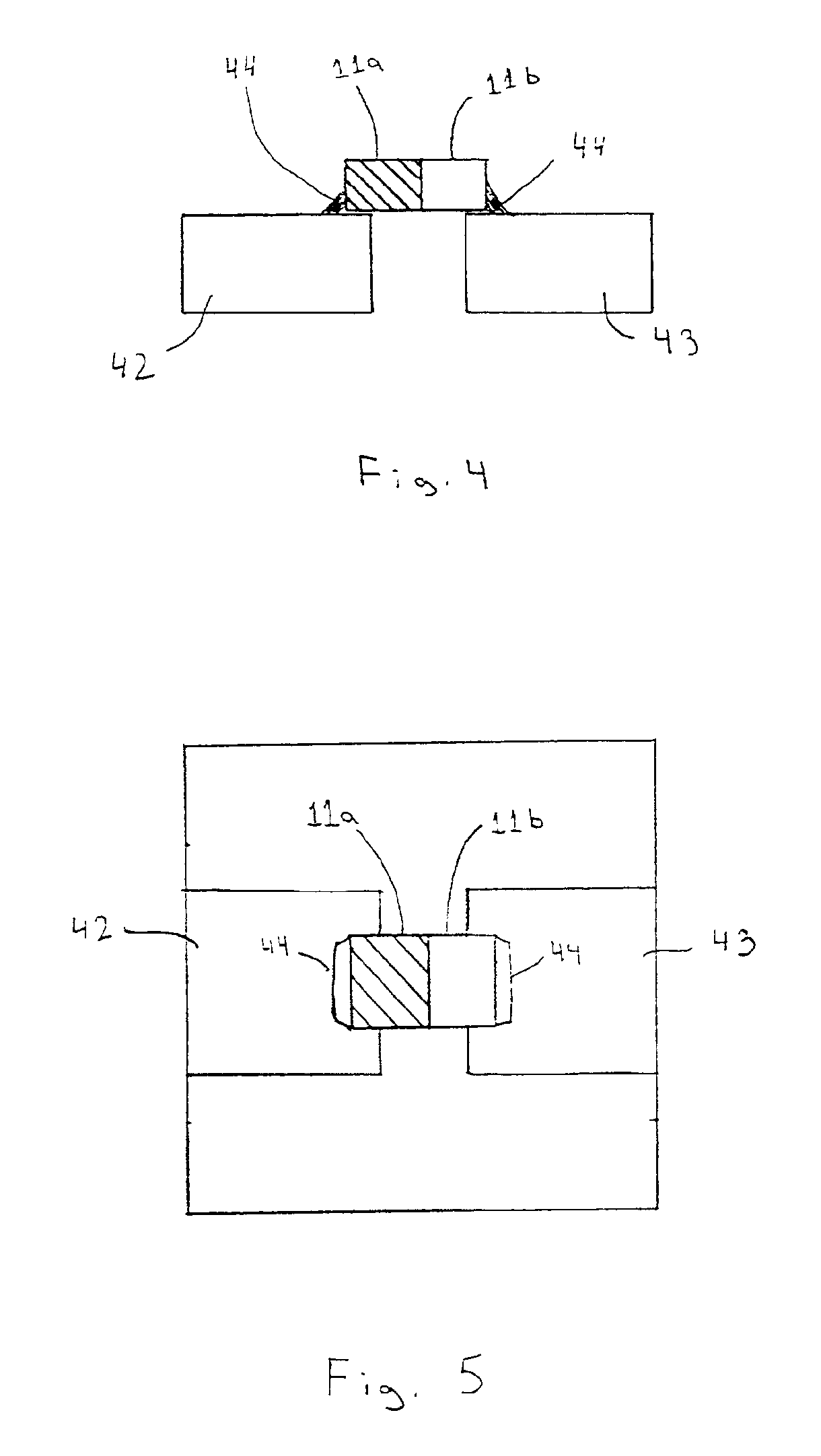
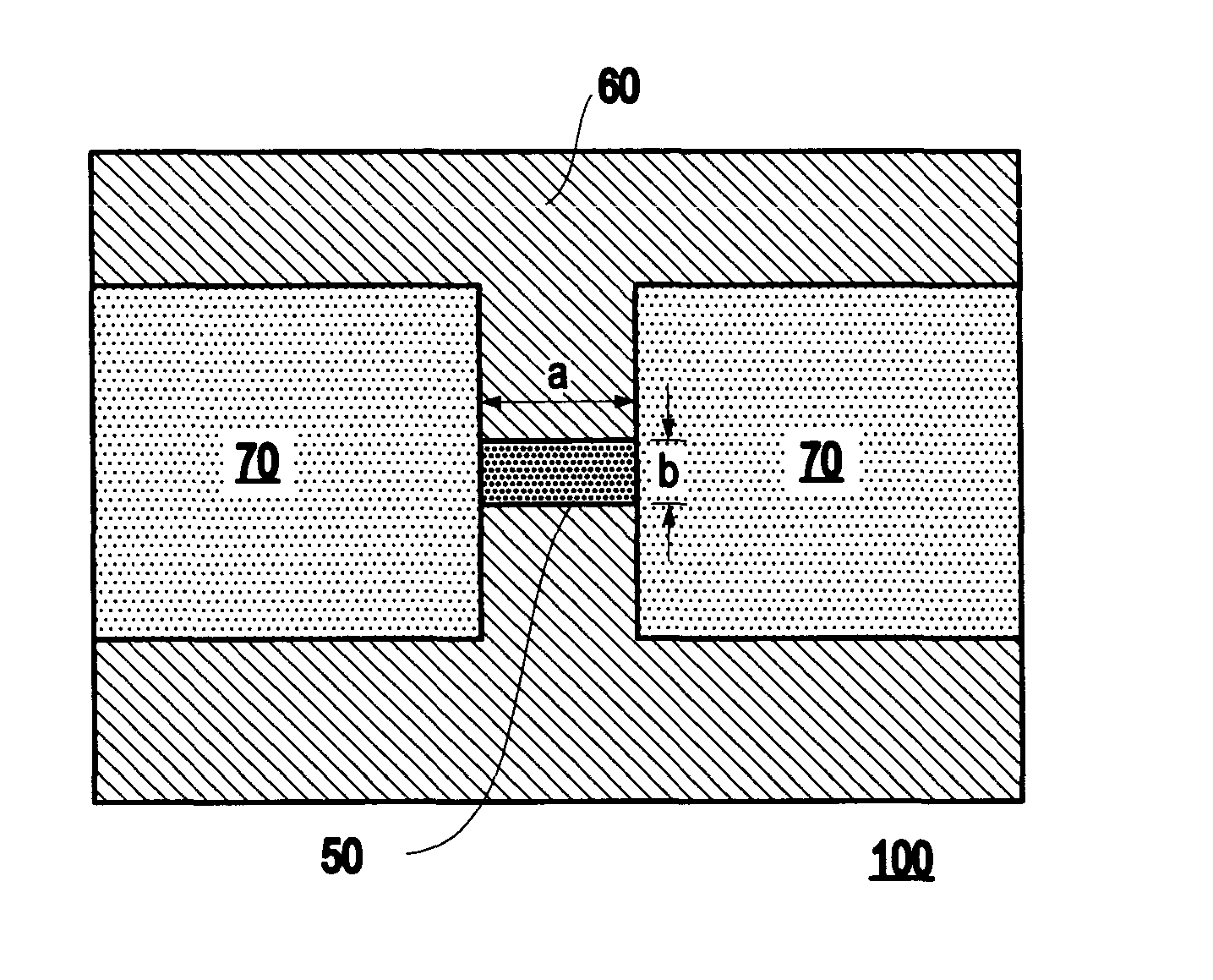
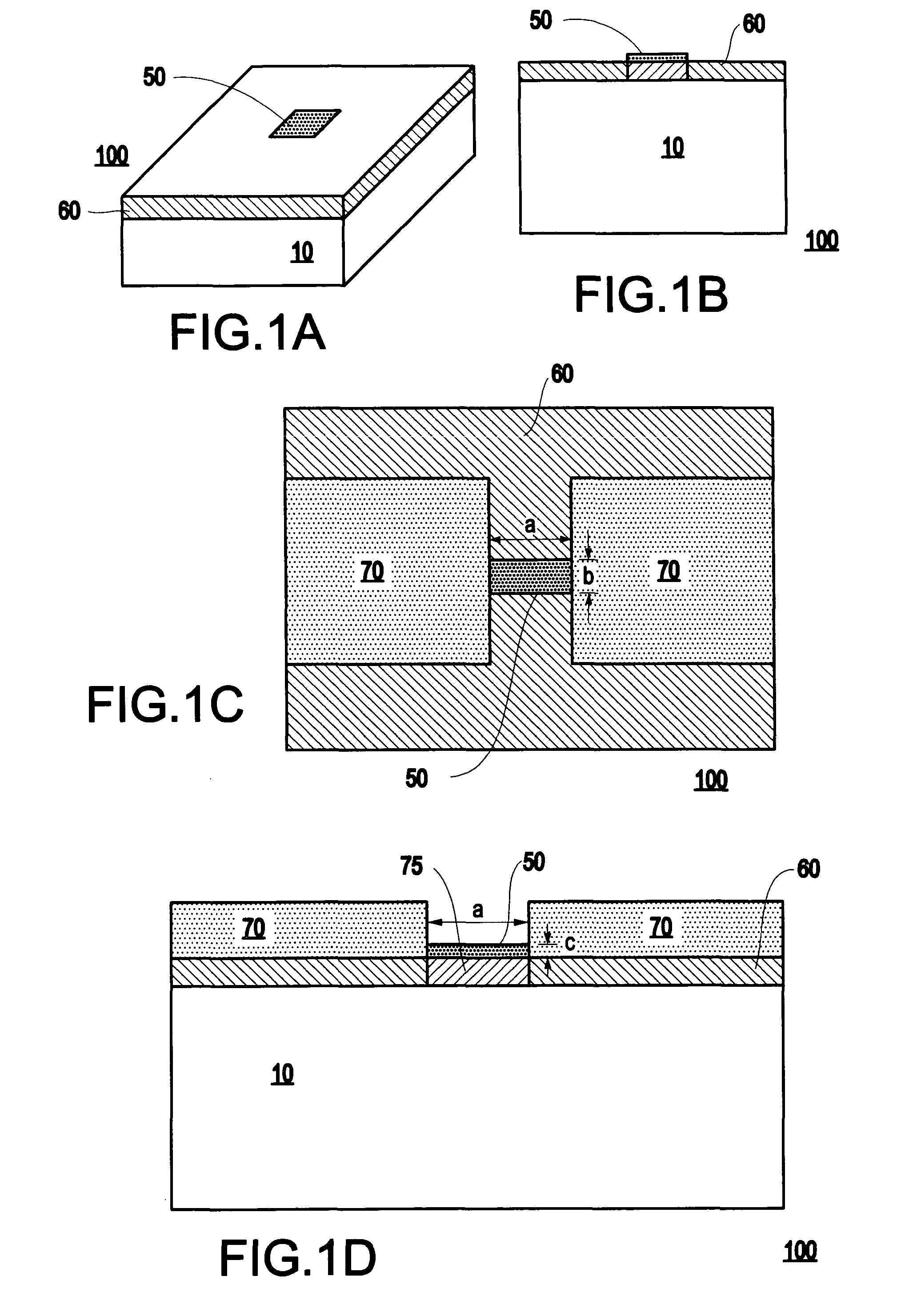
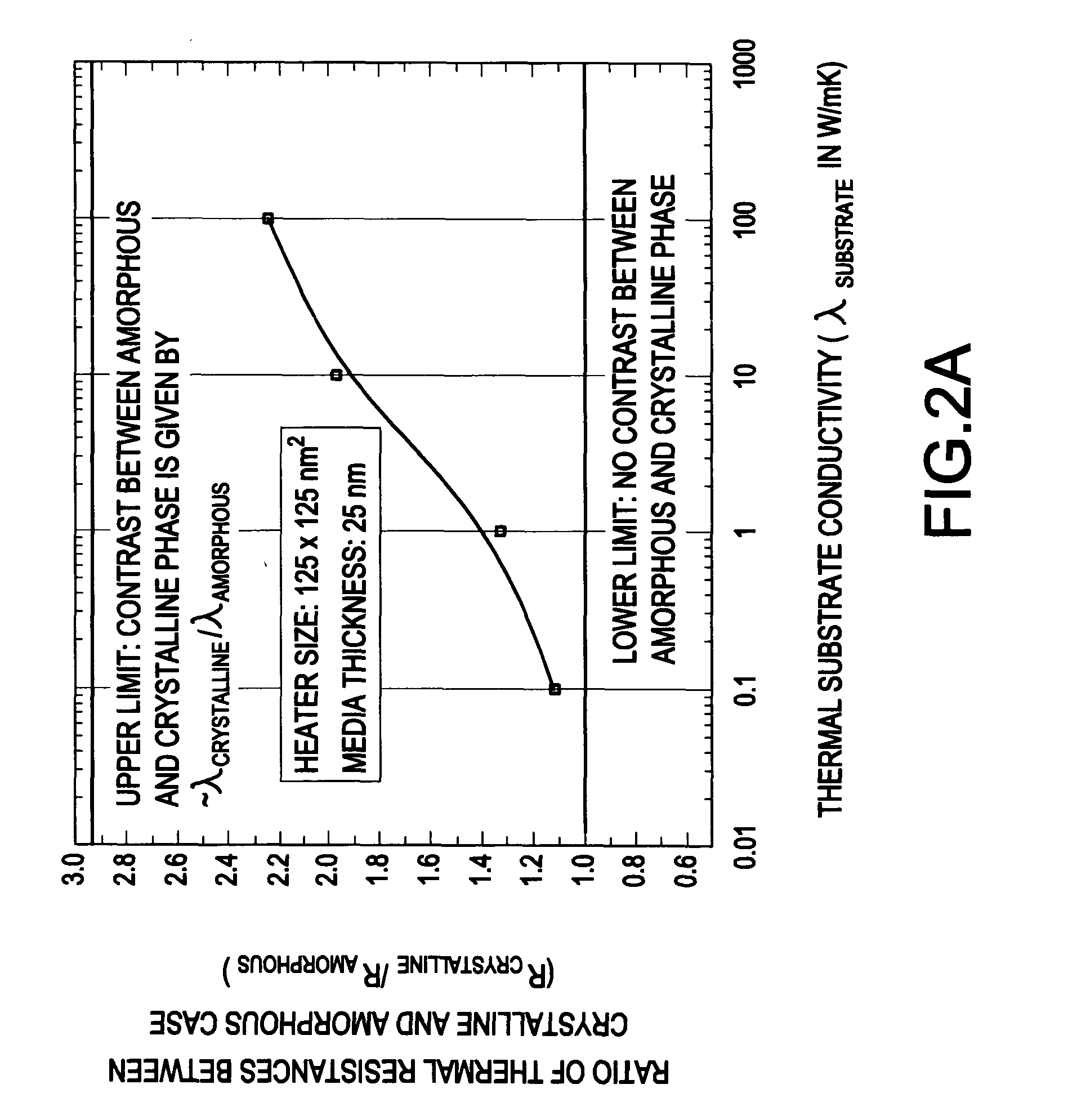
Thermal memory cell and memory device including the thermal memory cell
InactiveUS20040188668A1Facilitate writing informationEasy to readSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical impedance
A memory cell includes a storage medium having a programmable thermal impedance, and a heater in thermal communication with the storage medium for programming the thermal impedance. In another aspect, a memory cell includes a storage medium having a programmable electrical impedance, and a heater in thermal communication with the storage medium for programming the electrical impedance. In a third aspect, a memory device includes a plurality of the memory cells in accordance with the first and / or second aspect of the present invention.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Automated method and apparatus for processor thermal validation
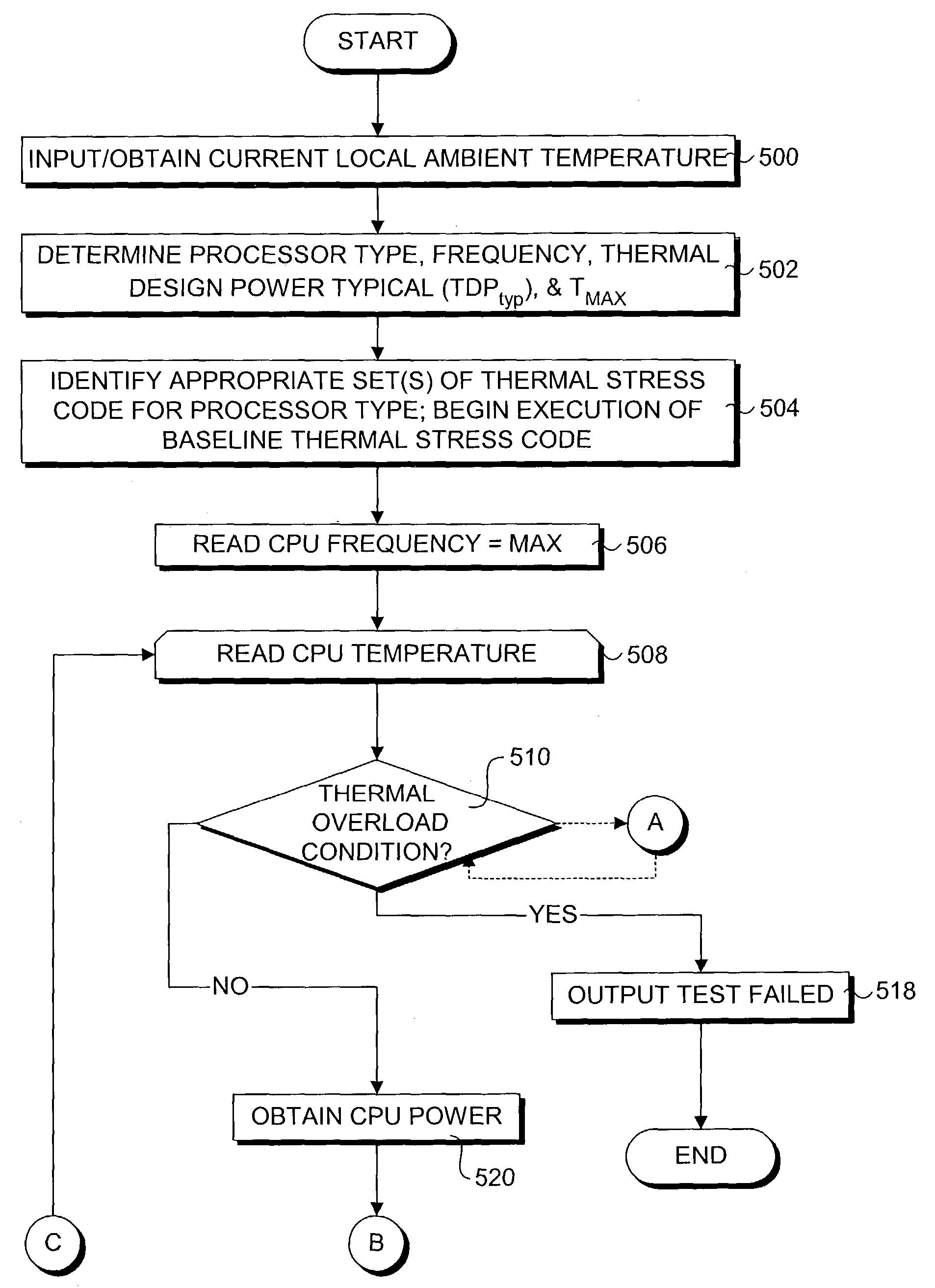
InactiveUS20040128101A1Thermometer detailsDigital data processing detailsThermal solutionAutomated method
A method and corresponding software for automatically validating a computer platform thermal solution. An application program is employed to selectively execute thermal stress code to cause the platform's processor to dissipate an amount of power corresponding to a predetermined value, such as a thermal design power dissipation value specified by the processor's manufacturer. In one embodiment, tests are performed while operating at this power dissipation level to determine if a thermal overload condition exists, which may be determined by the processor's temperature, an indication that the processor is throttled, or a signal provided by the processor indicating the processor has detected a thermal overload condition. In another embodiment, a thermal resistance value is calculated based on the processor power dissipation, the temperature of the processor, and the ambient temperature of the test environment. In one embodiment the entire validation process is automatically performed by the application program without requiring any extraneous test equipment or temperature probes.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dielectric structures having high dielectric constants, methods of forming the dielectric structures, non-volatile semiconductor memory devices having the dielectric structures and methods of manufacturing the non-volatile semiconductor memory devices
ActiveUS20060244147A1High dielectric constantImprove heat resistanceRoofingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceLow leakage
In a method of manufacturing a dielectric structure, after a tunnel oxide layer pattern is formed on a substrate, a floating gate is formed on the tunnel oxide layer. After a first dielectric layer pattern including a metal silicon oxide and a second dielectric layer pattern including a metal silicon oxynitride are formed, a control gate is formed on the dielectric structure. Since the dielectric structure includes at least one metal silicon oxide layer and at least one metal silicon oxynitride layer, the dielectric structure may have a high dielectric constant and a good thermal resistance. A non-volatile semiconductor memory device including the dielectric structure may have good electrical characteristics such as a large capacitance and a low leakage current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low-temperature wafer bonding of semiconductor substrates to metal substrates
ActiveUS20090286382A1Lower resistanceReduce thermal resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceSemiconductor materials
A method of wafer or substrate bonding a substrate made of a semiconductor material with a substrate made from a metallic material is disclosed. The method allows the bonding of the two substrates together without the use of any intermediate joining gluing, or solder layer(s) between the two substrates. The method allows the moderate or low temperature bonding of the metal and semiconductor substrates, combined with methods to modify the materials so as to enable low electrical resistance interfaces to be realized between the bonded substrates, and also combined with methods to obtain a low thermal resistance interface between the bonded substrates, thereby enabling various useful improvements for fabrication, packaging and manufacturing of semiconductor devices and systems.
Owner:FOR NAT RES INITIATIVES
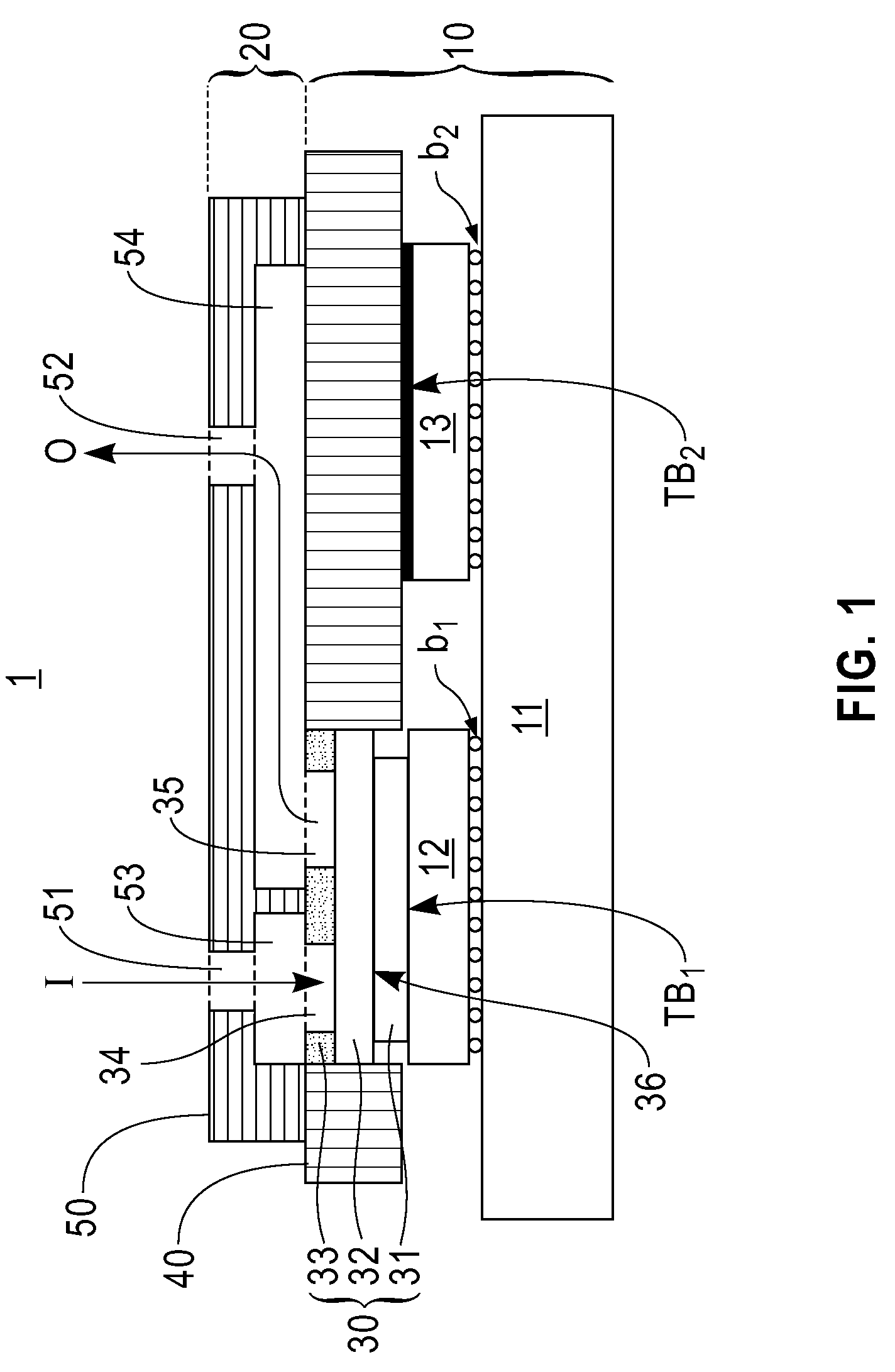
Apparatus and Methods for High-Performance Liquid Cooling of Multiple Chips with Disparate Cooling Requirements
InactiveUS20090284921A1Effective heat conductionMinimizes mechanical stressDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Apparatus and methods are provided for packaging multi-chip modules with liquid cooling modules designed to provide different thermal resistances for effectively conducting heat from various chips with disparate cooling requirements while minimizing mechanical stresses in thermal bonds due to thermal excursions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Heat insulation phase change coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103642364AGood heat reflection performanceImprove heat radiation abilityEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyThermal insulation
The invention discloses a heat insulation phase change coating. The coating comprises the following components in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of double-component epoxy resin, 5-35 parts of heat dissipation filler, 5-30 parts of filler with high heat resistance and 5-25 parts of a phase change material. The heat insulation coating disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high heat reflectivity, high heat radiation, low heat conduction, heat absorption, storage and release in a certain temperature range, multiple effects, good effects of reflecting illumination, realizing heat insulation and reducing temperature, safety, environment-friendly effect, strong adhesion and convenience in construction. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the coating.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light emitting module with optically-transparent thermally-conductive element
ActiveUS20110001157A1Extended service lifeThe process is compact and efficientSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveInorganic materials
A light emitting module with improved optical functionality and reduced thermal resistance is described, which comprises a light emitting device (LED), a wavelength converting (WC) element and an inorganic optically-transmissive thermally-conductive (OTTC) element. The WC element is capable of absorbing light generated from the LED at a specific wavelength and re-emitting light having a different wavelength. The re-emitted light and any unabsorbed light exits through at least one surface of the module. The OTTC is in physical contact with the WC element and at least partially located in the optical path of the light. The OTTC comprises one or more layers of inorganic material having a thermal conductivity greater than that of the WC element. As such, a compact unitary integrated module is provided with excellent thermal characteristics, which may be further enhanced when the OTTC provides a thermal barrier for vertical heat propagation through the module but not lateral propagation.
Owner:LUMILEDS HLDG BV
Dielectric structures having high dielectric constants, and non-volatile semiconductor memory devices having the dielectric structures
ActiveUS7482677B2High dielectric constantImprove heat resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRoofingCapacitanceLow leakage
In a method of manufacturing a dielectric structure, after a tunnel oxide layer pattern is formed on a substrate, a floating gate is formed on the tunnel oxide layer. After a first dielectric layer pattern including a metal silicon oxide and a second dielectric layer pattern including a metal silicon oxynitride are formed, a control gate is formed on the dielectric structure. Since the dielectric structure includes at least one metal silicon oxide layer and at least one metal silicon oxynitride layer, the dielectric structure may have a high dielectric constant and a good thermal resistance. A non-volatile semiconductor memory device including the dielectric structure may have good electrical characteristics such as a large capacitance and a low leakage current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Thermal/environmental barrier coating system for silicon-containing materials
ActiveUS20060280963A1Prolong lifeImprove protectionFireproof paintsBlade accessoriesAluminateCoating system
A coating system for Si-containing materials, particularly those for articles exposed to high temperatures. The coating system exhibits improved resistance to corrosion from sea salt and CMAS as a result of using aluminate compounds to protect silicate-containing layers of the coating system. The coating system includes an environmental barrier coating, a thermal barrier coating overlying the environmental barrier coating and formed of a thermal-insulating material, and a transition layer between the environmental barrier coating and thermal barrier coating, wherein the transition layer contains at least one aluminate compound and / or alumina.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com