Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
813results about How to "Thin structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Keypad
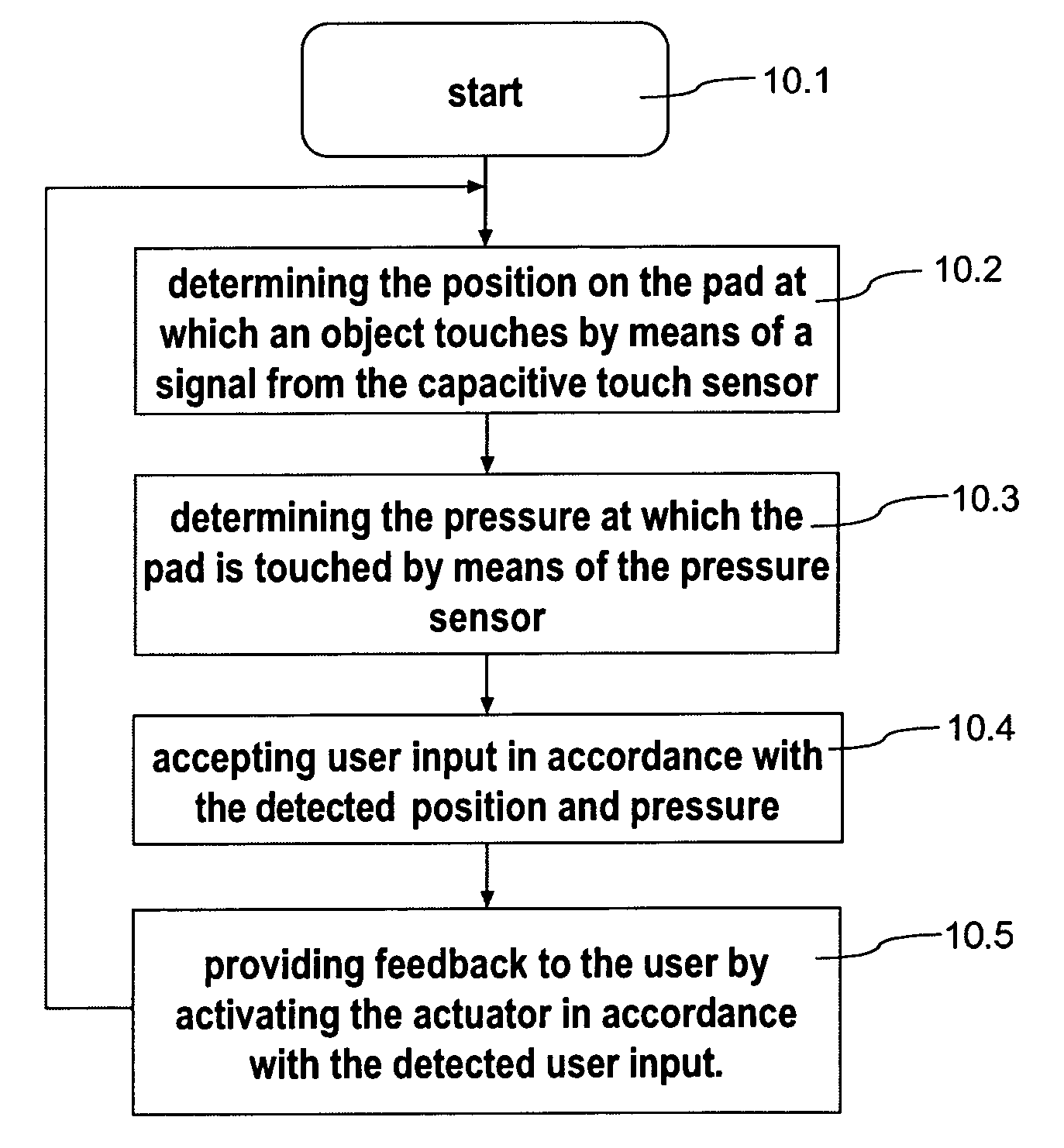
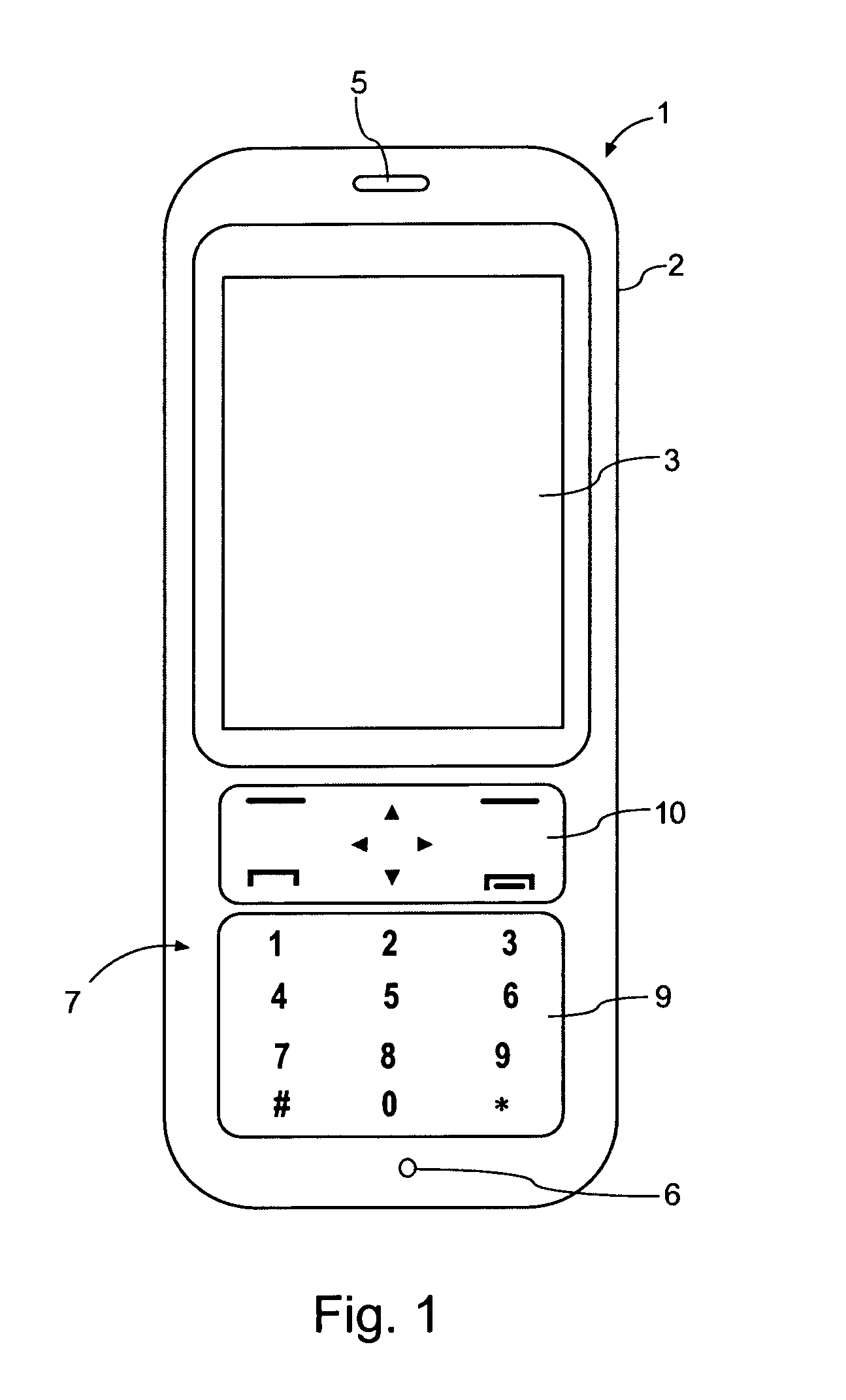
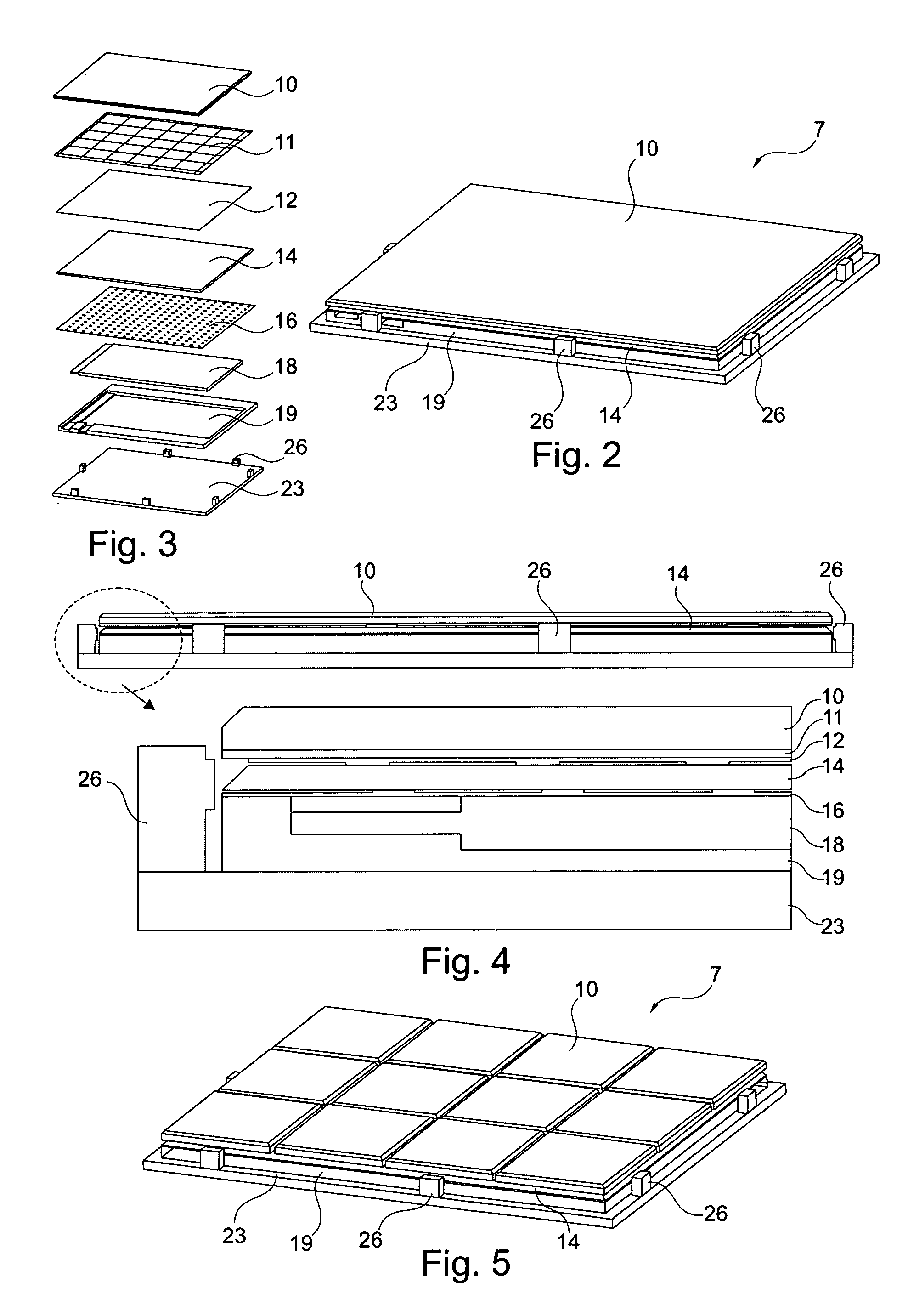
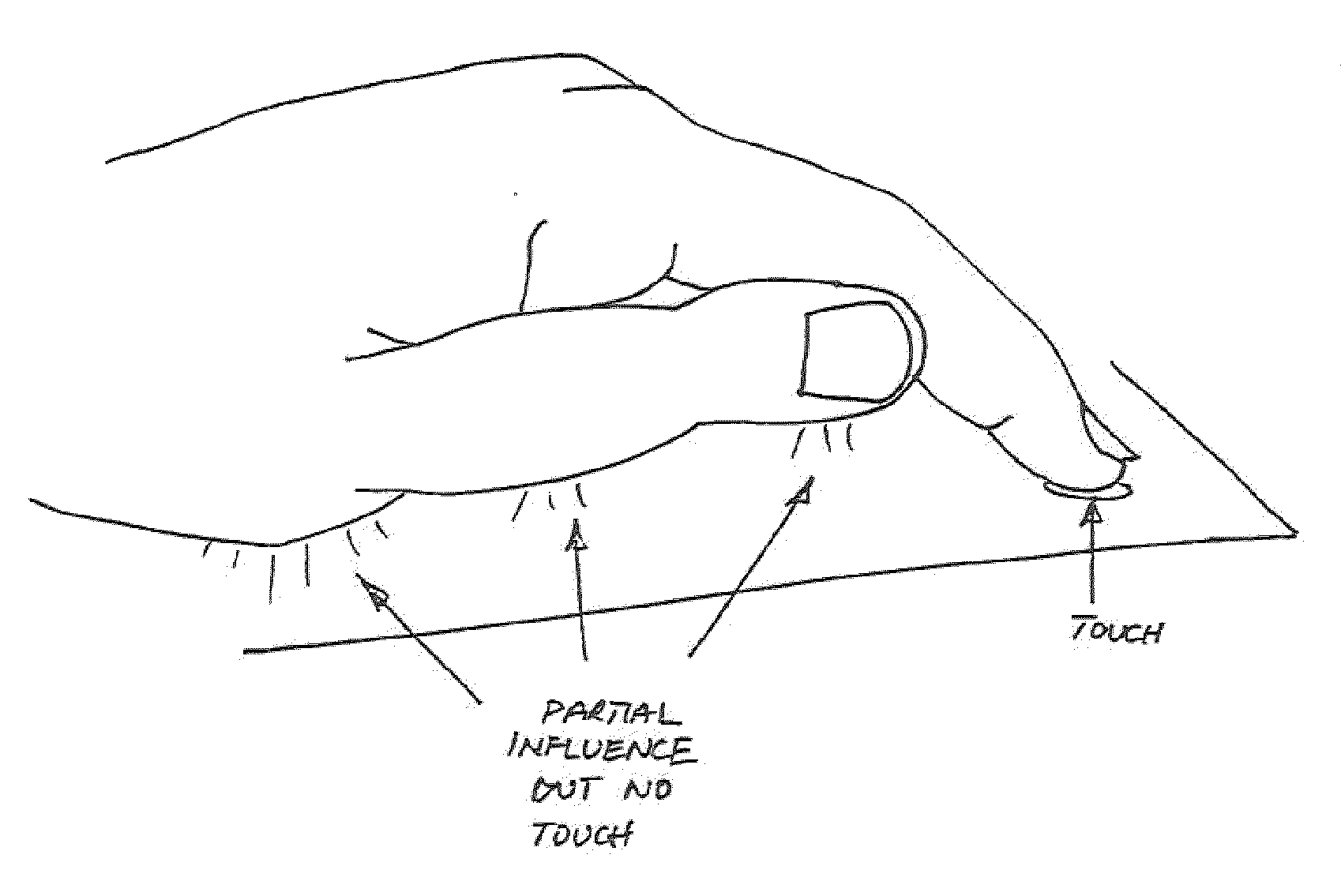
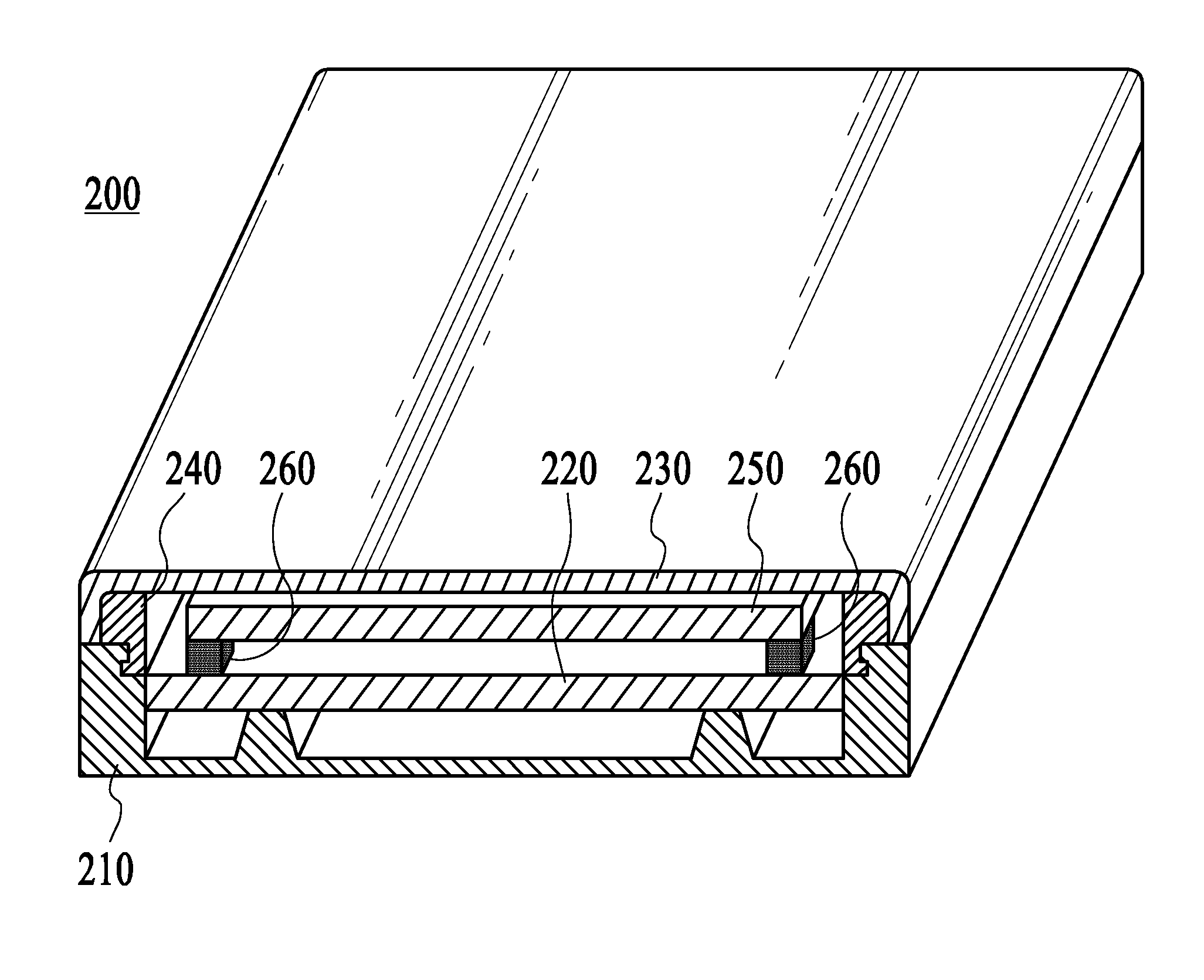
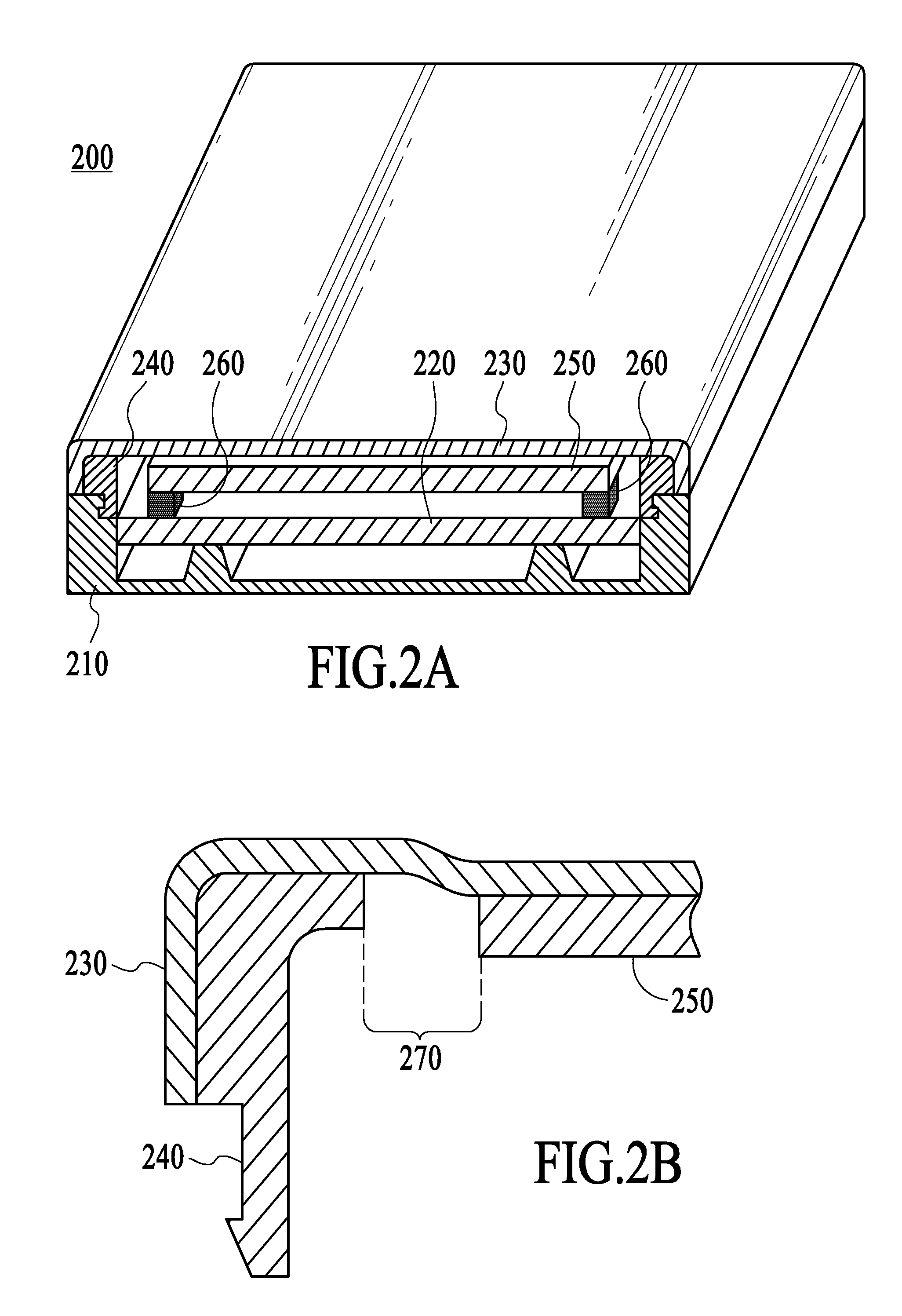
ActiveUS20100052880A1Reduce thicknessImproved determinationInput/output for user-computer interactionRepeater circuitsSurface layerLight guide
A thin keypad including a top surface layer, a light guide layer, a capacitive sensing layer and a piezo layer provides for touch input, pressure input and haptic feedback.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Capacitive Position Sensor
ActiveUS20100045632A1Increase the number ofGood light transmissionTransmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A capacitive position sensor has a two-layer electrode structure. Drive electrodes extending in a first direction on a first plane on one side of a substrate. Sense electrodes extend in a second direction on a second plane on the other side of the substrate so that the sense electrodes cross the drive electrodes at a plurality of intersections which collectively form a position sensing array. The sense electrodes are provided with branches extending in the first direction part of the way towards each adjacent sense electrode so that end portions of the branches of adjacent sense electrodes co-extend with each other in the first direction separated by a distance sufficiently small that capacitive coupling to the drive electrode adjacent to the co-extending portion is reduced. Providing sense electrode branches allow a sensor to be made which has a greater extent in the first direction for a given number of sense channels, since the co-extending portions provide an interpolating effect. The number of sense electrode branches per drive electrode can be increased which allows a sensor to be made which has ever greater extent in the first direction without having to increase the number of sense channels.
Owner:NEODRON LTD +1
Stereoscopic image displaying device, object proximity detecting device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20100328438A1Improve responsivenessWell formedSteroscopic systemsInput/output processes for data processingParallaxProximity sensor
A stereoscopic image displaying device includes an outer surface that a detection target object approaches; a stereoscopic image generating unit that generates a three-dimensional stereoscopic image based on an input video signal, and a proximity sensor unit that is disposed on a side of the outer surface that is opposite to a side that the detection target object approaches and detects proximity of the detection target object to the outer surface based on a height that is a distance from the outer surface and is set based on parallax information included in the video signal.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Battery electrolytic solution with fluoride-ion-dissociating salt and battery using the same
InactiveUS6306540B1Improve stabilityAvoid conductivitySolid electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsSupporting electrolyteDecomposition
The present invention relates to an electrolytic solution excellent in stability, and also relates to a battery excellent in battery performance and having an outer structure having light weight. The electrolytic solution contains a supporting electrolyte and a gas formation inhibitor in the solvent. The gas formation inhibitor contains a decomposition product of the supporting electrolyte with formation of a gas in the solvent. It functions as controlling to solution equilibrium in the electrolytic solution participating in decomposition reaction of the supporting electrolyte. A battery is obtained by filling the electrolytic solution between a positive electrode and a negative electrode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Drillable drill bit nozzle
InactiveUS6848517B2Thin structureImprove corrosion resistanceDrill bitsDrilling rodsHigh resistanceRubber material
A drill bit nozzle providing a through bore for the passage of drilling fluid through a drill bit. The nozzle is made of a material or materials which can be drilled through by standard well bore drilling equipment. The material(s) are selected to provide a surface to the through bore which has a relatively high resistance to erosion to withstand the abrasive and corrosive impact of jetted drilling fluid. Embodiments are described using a hard chrome / copper combination and a single rubber material.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Steerable distal support system
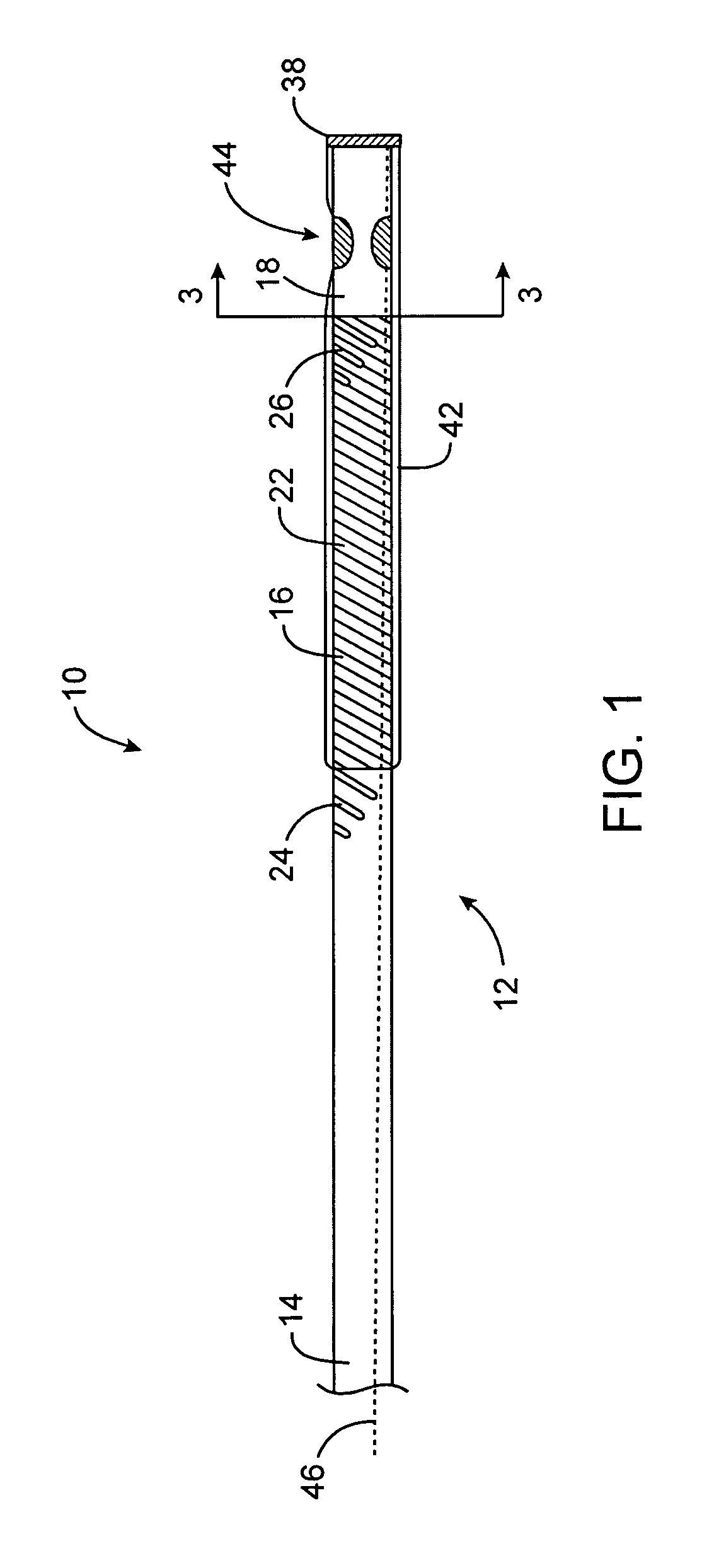
InactiveUS7381198B2Sufficient maneuverabilitySufficient torqueabilitySurgeryMedical devicesSupporting systemMedicine
A steerable distal support system for accessing stenosis, partial occlusions, or complete occlusions within a body lumen. The steerable distal support system generally includes an elongate member that comprises a proximal portion, a more flexible intermediate portion and a deflectable distal tip. The deflectable distal tip is at a distal end of the elongate body to facilitate directionality and positioning of the steerable distal support system to the target site. Optionally, an expandable centering assembly may be disposed on the steerable support assembly to center and anchor the steerable support assembly within the body lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
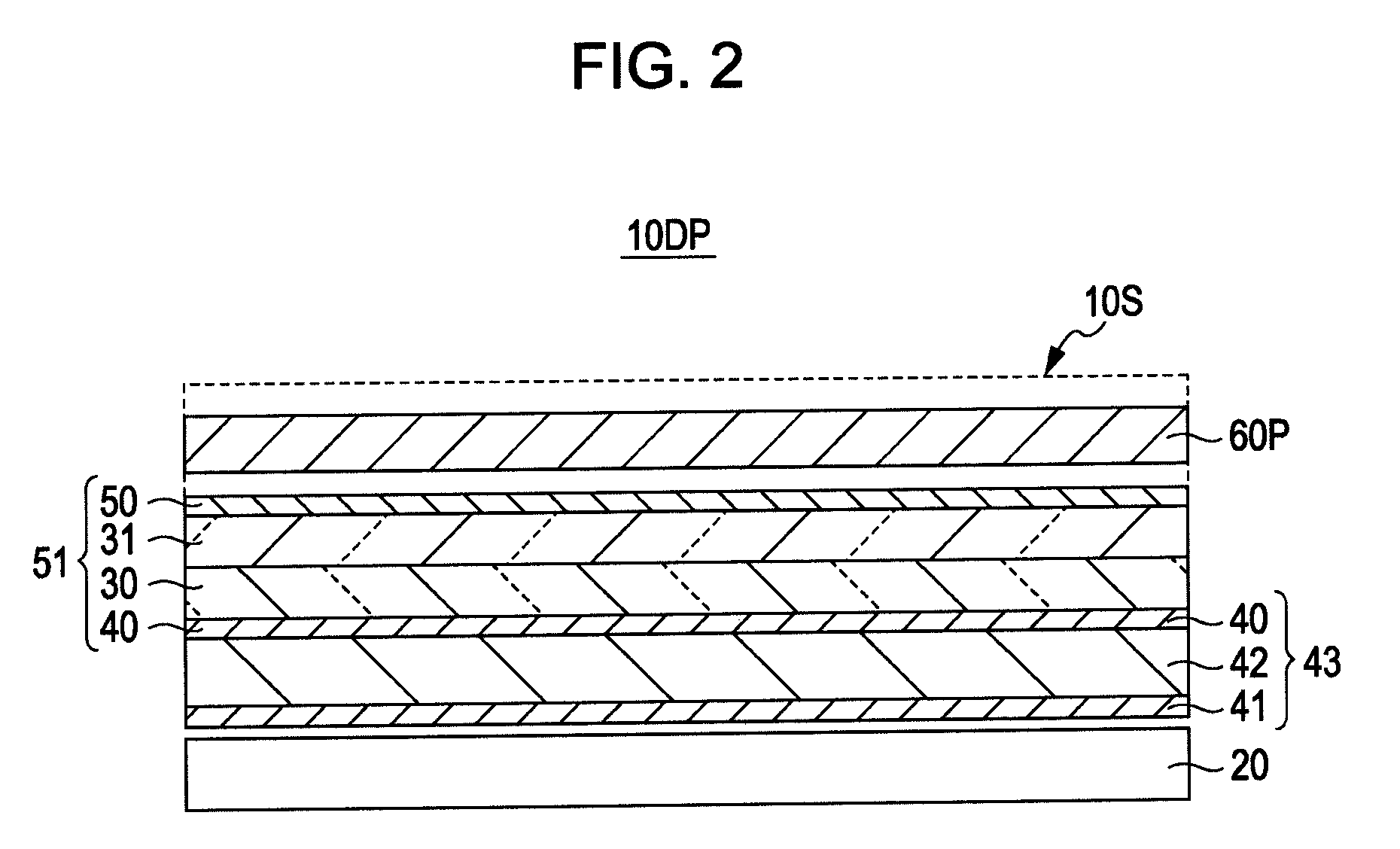
Spatially multiplexed imaging directional backlight displays
InactiveUS20130328866A1Slow responseReduce complexityMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
Disclosed is an imaging directional backlight that cooperates with a spatial light modulator to direct light into a first viewing window for one set of image pixels and into a second viewing window for a second set of image pixels. The waveguide may comprise a stepped structure, where the steps further comprise extraction features hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources and hence defines the relative positions of system elements and ray paths. Such an apparatus may be used to achieve an autostereoscopic display with a flat structure, not requiring fast response speed spatial light modulators.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Efficient polarized directional backlight
ActiveUS20120243204A1Improve electricity efficiencyLow costPolarising elementsOptical light guidesRefractive indexWaveguide
By introducing a stack of alternating high and low index dichroic material layers on the exit surface of a waveguide for a wedge type directional backlight, natural reflectivity differences between polarized components can be increased, effectively reflecting the vast proportion of S-polarized light rays, while at the same time transmitting the P-polarized light rays, of light impacting the exit surface of the waveguide at an angle sufficient to exit the waveguide. This recovers polarization in wedge type backlight systems, increasing illumination exiting the waveguide. Also, on the back reflecting surface of the waveguide, a birefringent material can be added to efficiently transform S-polarized reflected light from the dichroic stack, into returning P-polarized light. Because returning rays that are now P-polarized by the birefringent material have already achieved the critical angle for exiting the waveguide, the rays transformed to P-polarization can now also exit the waveguide, increasing waveguide illumination.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Interconnect module with reduced power distribution impedance
InactiveUS6847527B2Reduced impedance powerReduced ground distributionLight absorption dielectricsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder ballOperating frequency
An interconnect module for an integrated circuit chip incorporates a thin, high dielectric constant embedded capacitor structure to provide reduced power distribution impedance, and thereby promote higher frequency operation. The interconnect module is capable of reliably attaching an integrated circuit chip to a printed wiring board via solder ball connections, while providing reduced power distribution impedance of less than or equal to approximately 0.60 ohms at operating frequencies in excess of 1.0 gigahertz.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
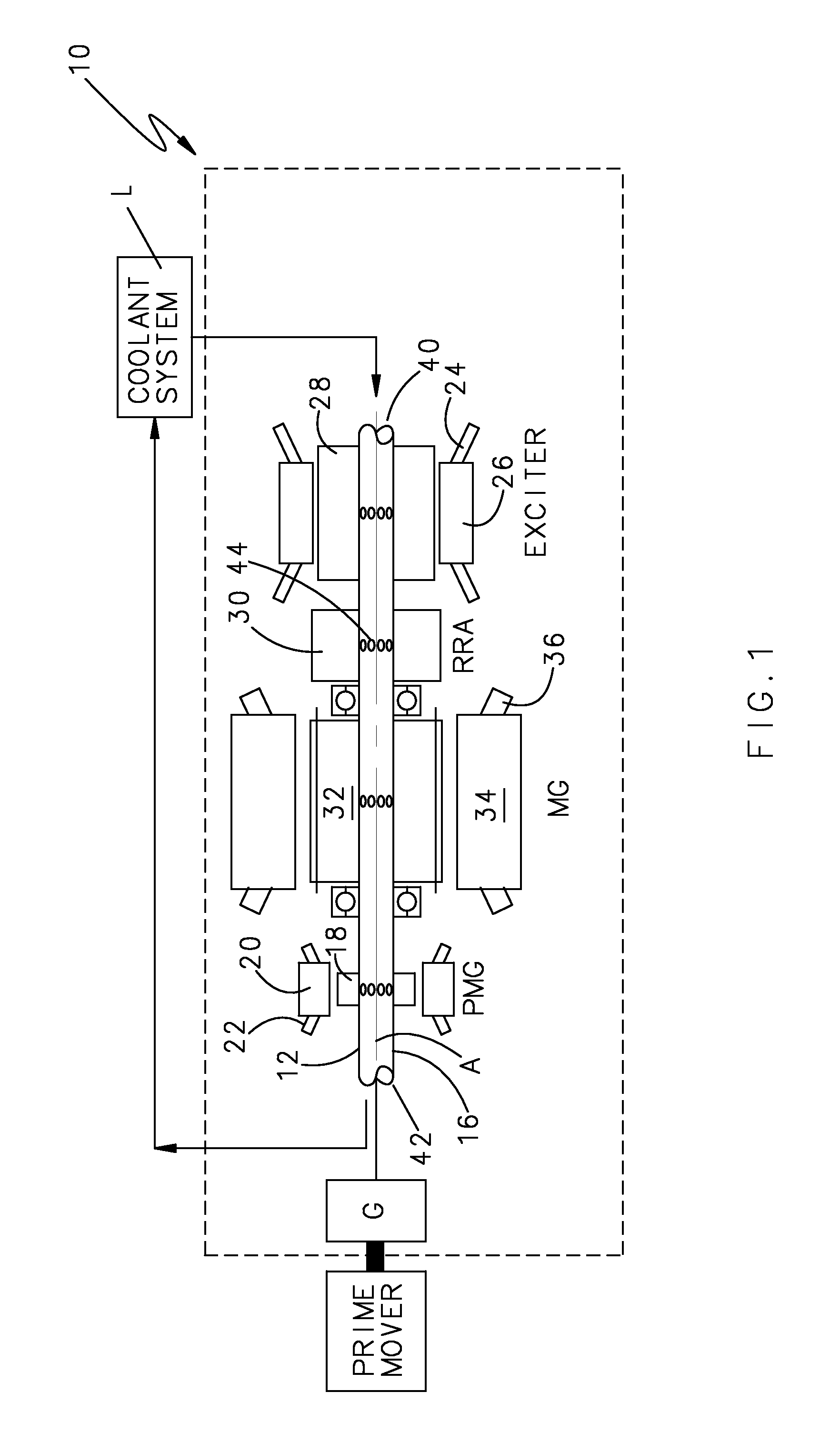
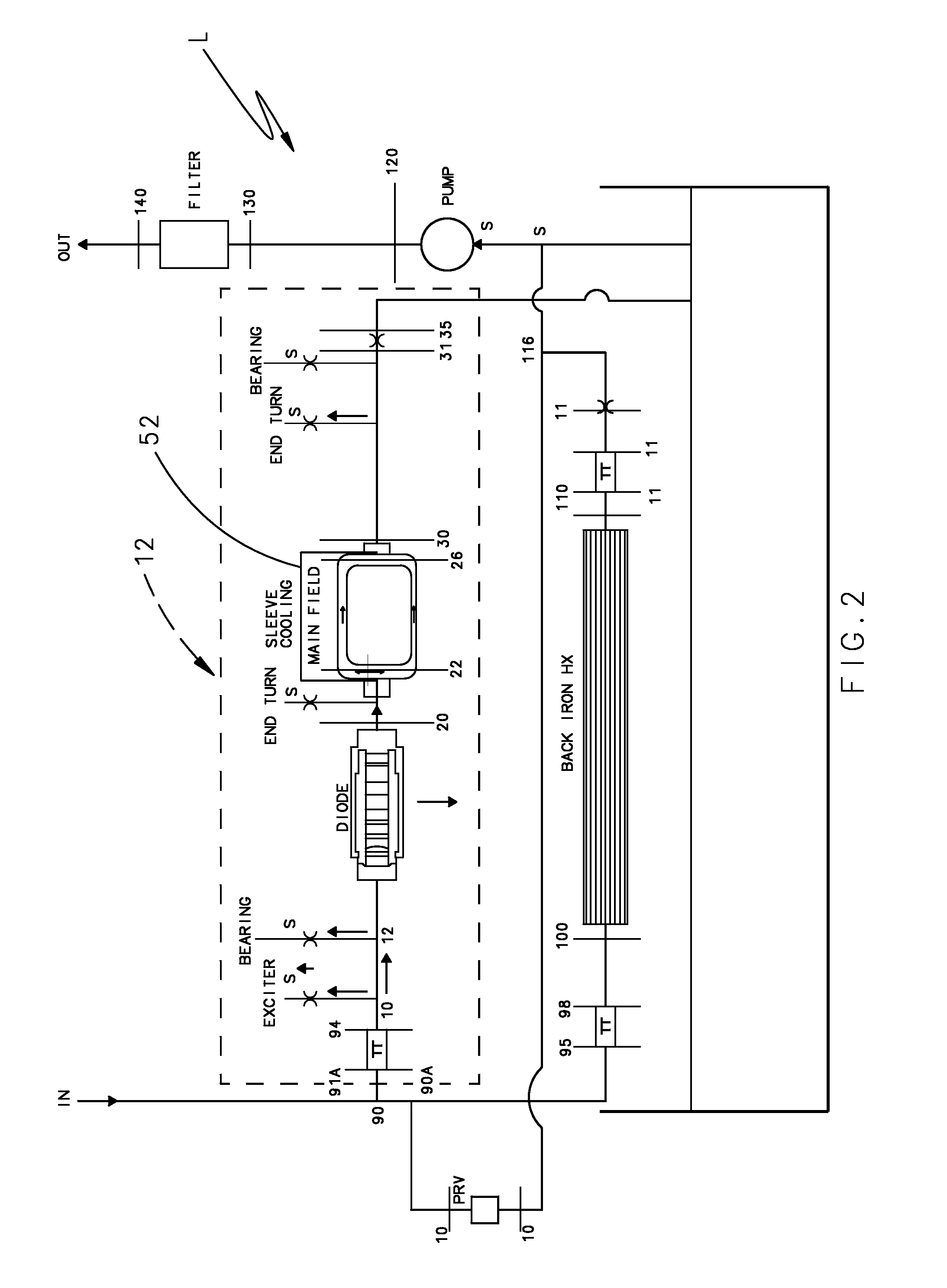
Rotor cooling system for synchronous machines with conductive sleeve
ActiveUS7208854B1Low operating temperatureThin constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsCooling/ventillation arrangementEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A wound field synchronous machine includes direct oil cooling along a conductive sleeve with elongated semi-arcuate shaped channels which alternate with damper bar channels containing tie-rod supports structures. With a reduction in sleeve thickness permitted by the direct cooling, the overall weight of the machine is reduced.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Directionally illuminated waveguide arrangement
ActiveUS20140036361A1Function increaseCompact display structureMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideLight beam
Disclosed is a light guiding valve apparatus comprising an optical valve, a two dimensional light source array and a focusing optic for providing large area collimated illumination from localized light sources. A stepped waveguide may be a stepped structure, in which the steps may be extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A two dimensional array of viewing windows may be produced. Such controlled illumination may provide for efficient, multi-user autostereoscopic displays with wide viewing freedom and low cross talk and near-eye displays that are substantially transparent.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Semiconductor heterostructures and related methods
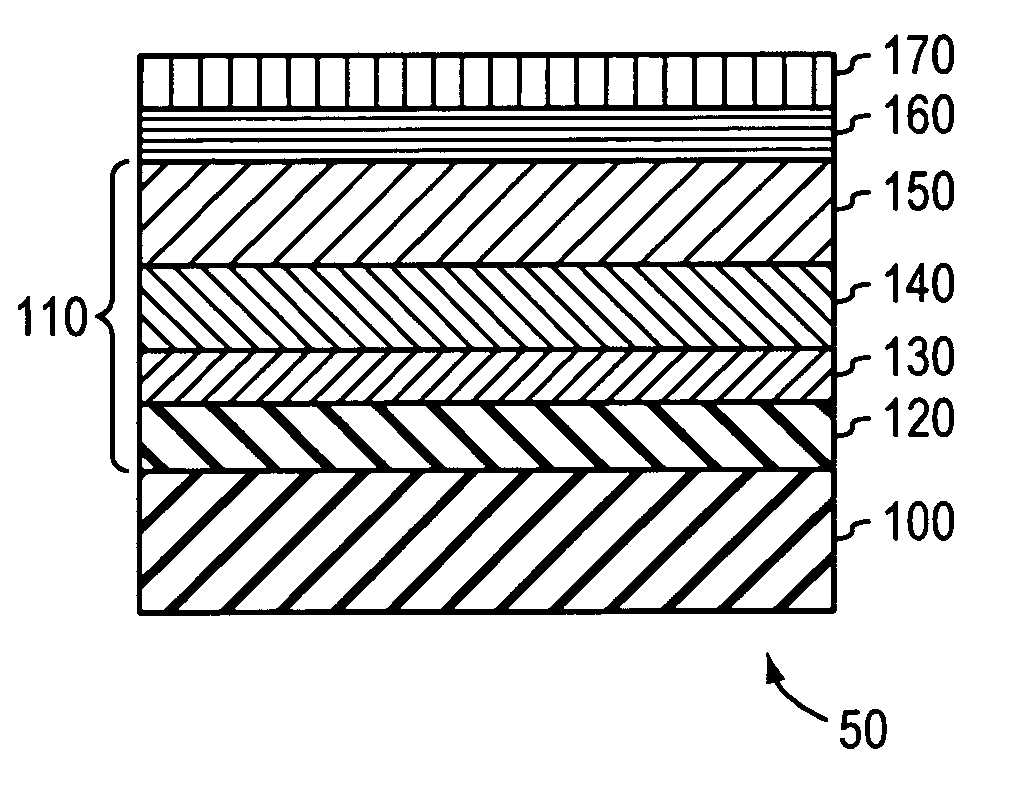
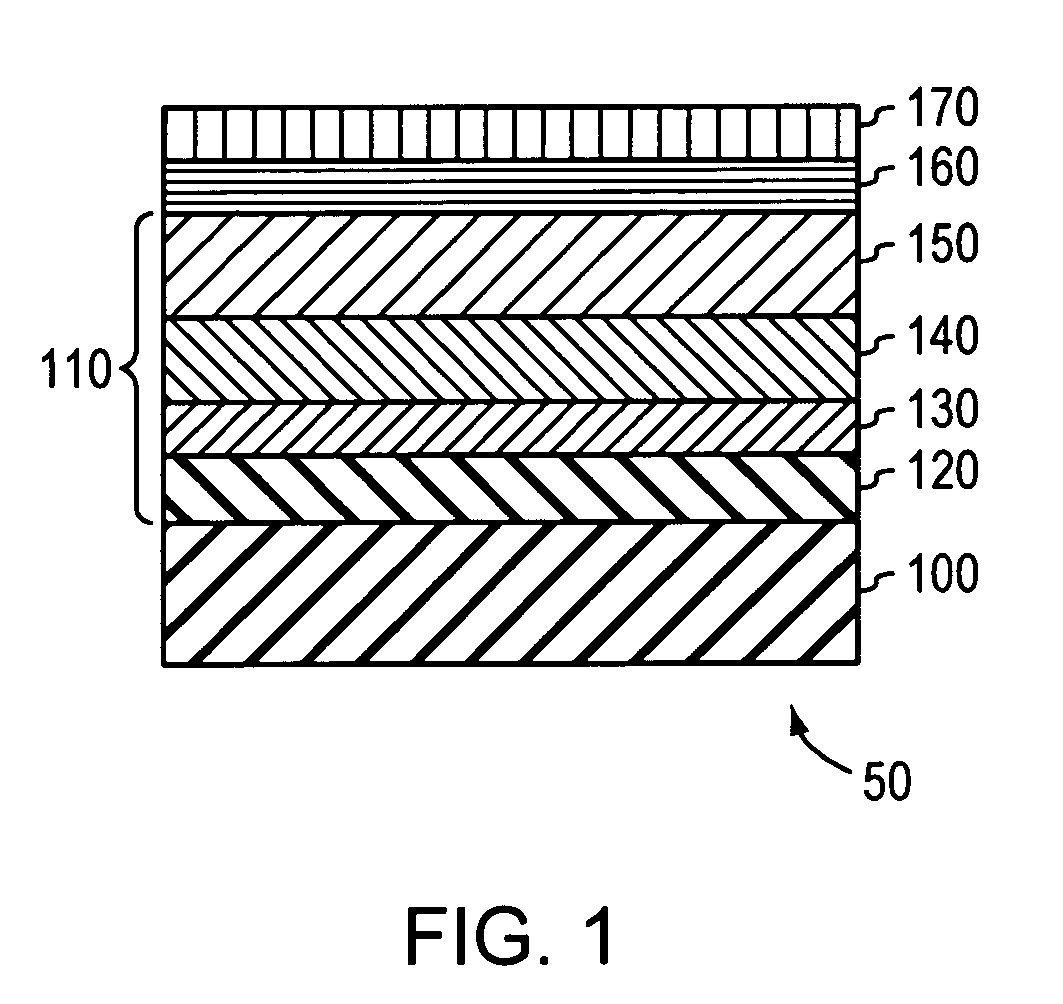
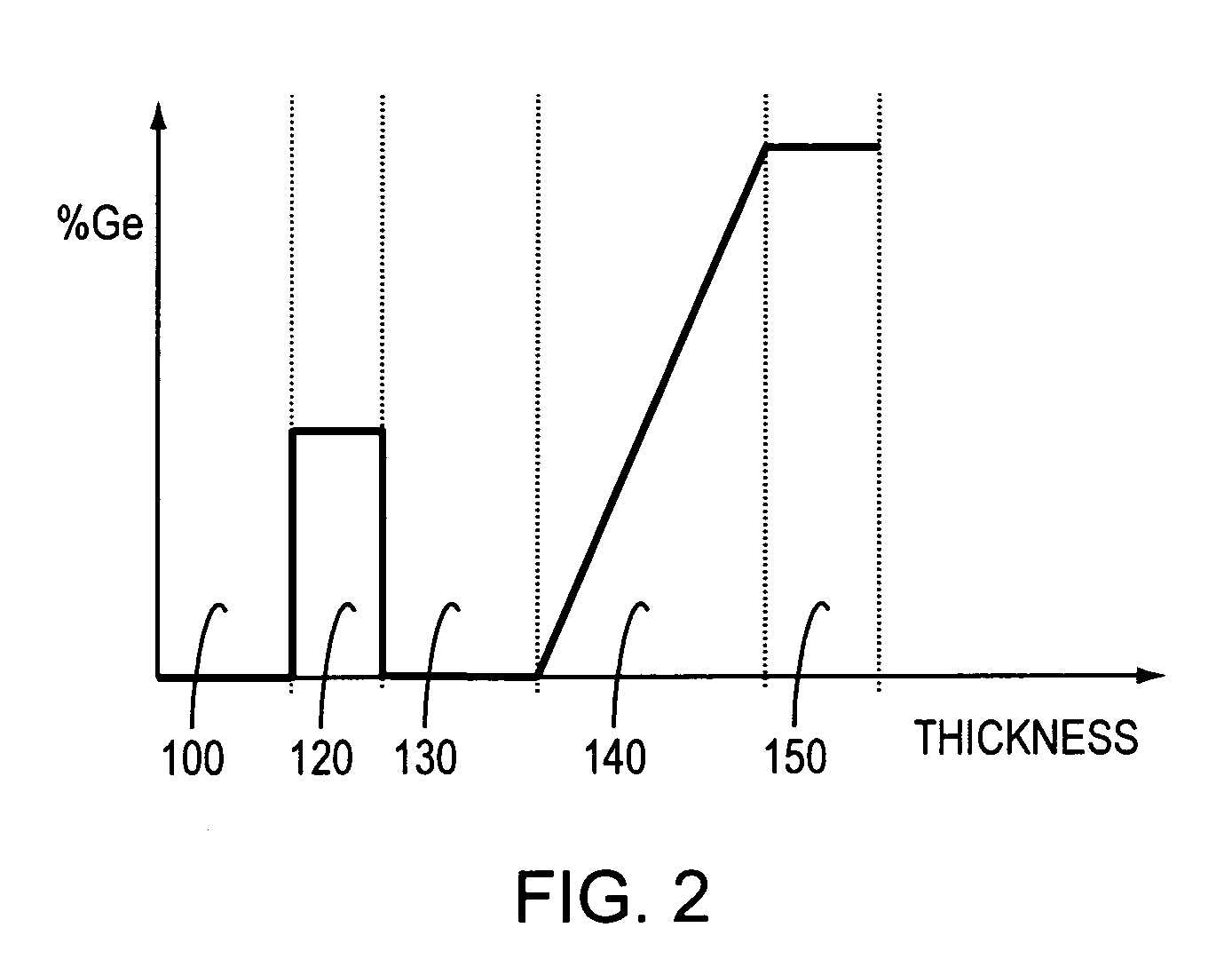
InactiveUS7049627B2Overcome limitationsImprove manufacturabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThreading dislocationsInter layer
Dislocation pile-ups in compositionally graded semiconductor layers are reduced or eliminated, thereby leading to increased semiconductor device yield and manufacturability. This is accomplished by introducing a semiconductor layer having a plurality of threading dislocations distributed substantially uniformly across its surface as a starting layer and / or at least one intermediate layer during growth and relaxation of the compositionally graded layer. The semiconductor layer may include a seed layer disposed proximal to the surface of the semiconductor layer and having the threading dislocations uniformly distributed therein.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
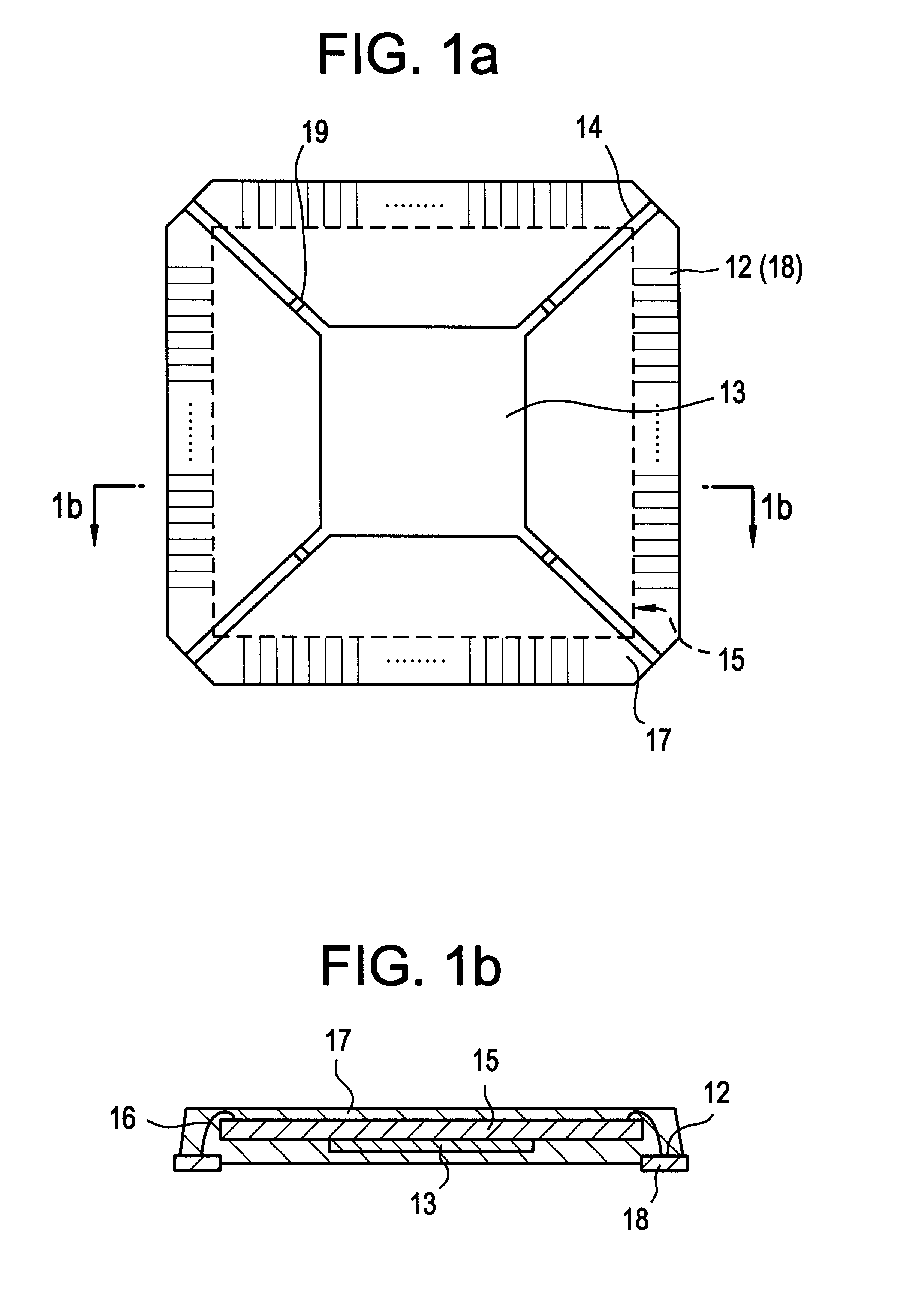
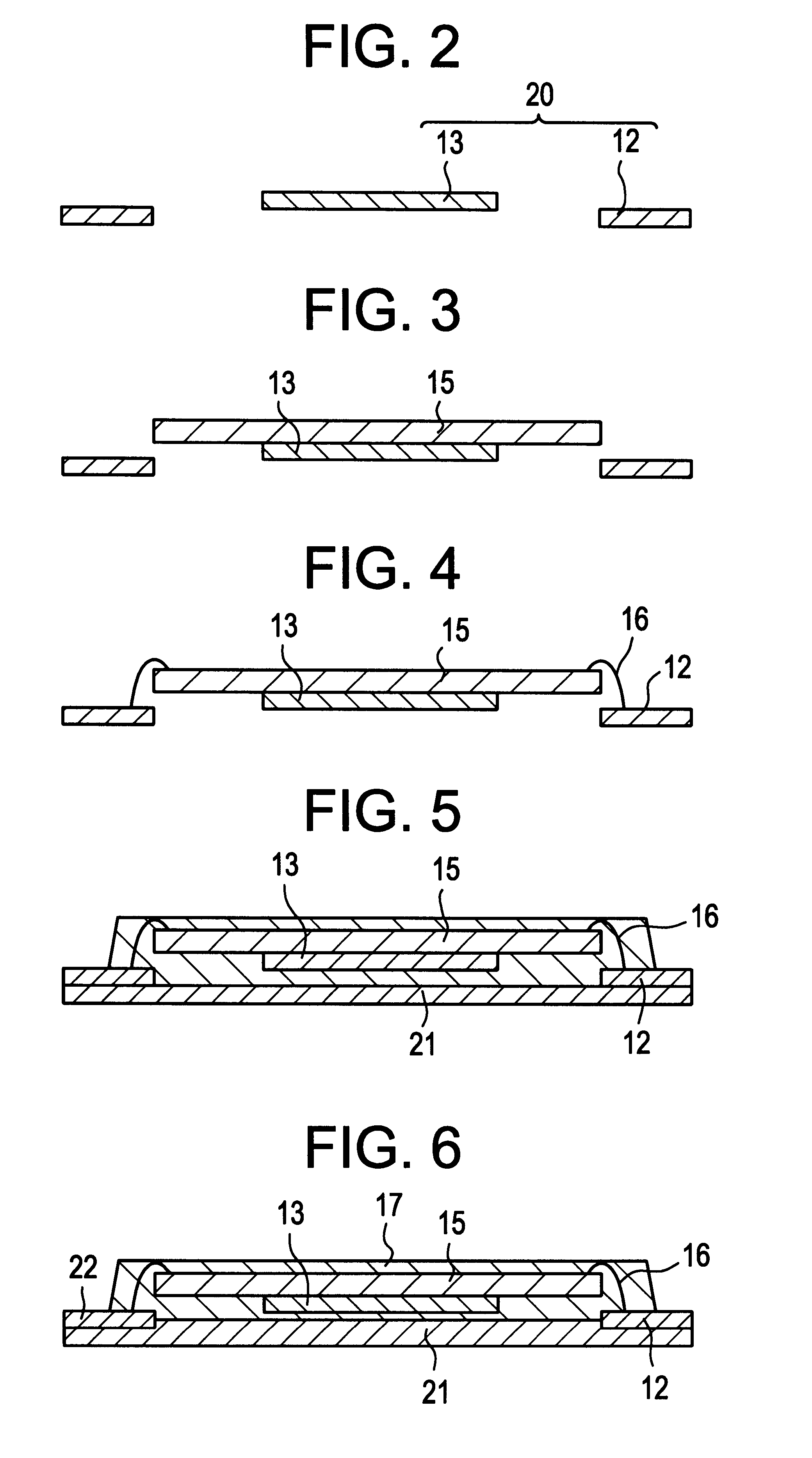
Single piece top surface display layer and integrated front cover for an electronic device
InactiveUS20070229475A1Reduce the possibility of damageReduces parallax effectNon-enclosed substationsInput/output for user-computer interactionSurface displayDisplay device
A single-piece top surface display and integrated front cover for an electronic device. In one embodiment, the cover comprises a thin, flexible, transparent layer coupled with a supporting structure. The flexible layer is supported above a display screen which is coupled with pressure activated sensors located under the display screen. The cover is dust-free, waterproof, and has a flat outer surface that is free of any steps or indentations. Users input data by applying pressure on the cover which causes the display screen to deflect and activate the sensors. The pressure exerted on the sensors is triangulated to register the position of the user input. In another embodiment, the cover is transparent, rigid, and directly contacts the pressure activated sensors which are located in front of the display screen or in the housing behind it. When pressure is applied to the cover, the cover deflects and activates the sensors. In both embodiments, an accelerometer identifies valid input events.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
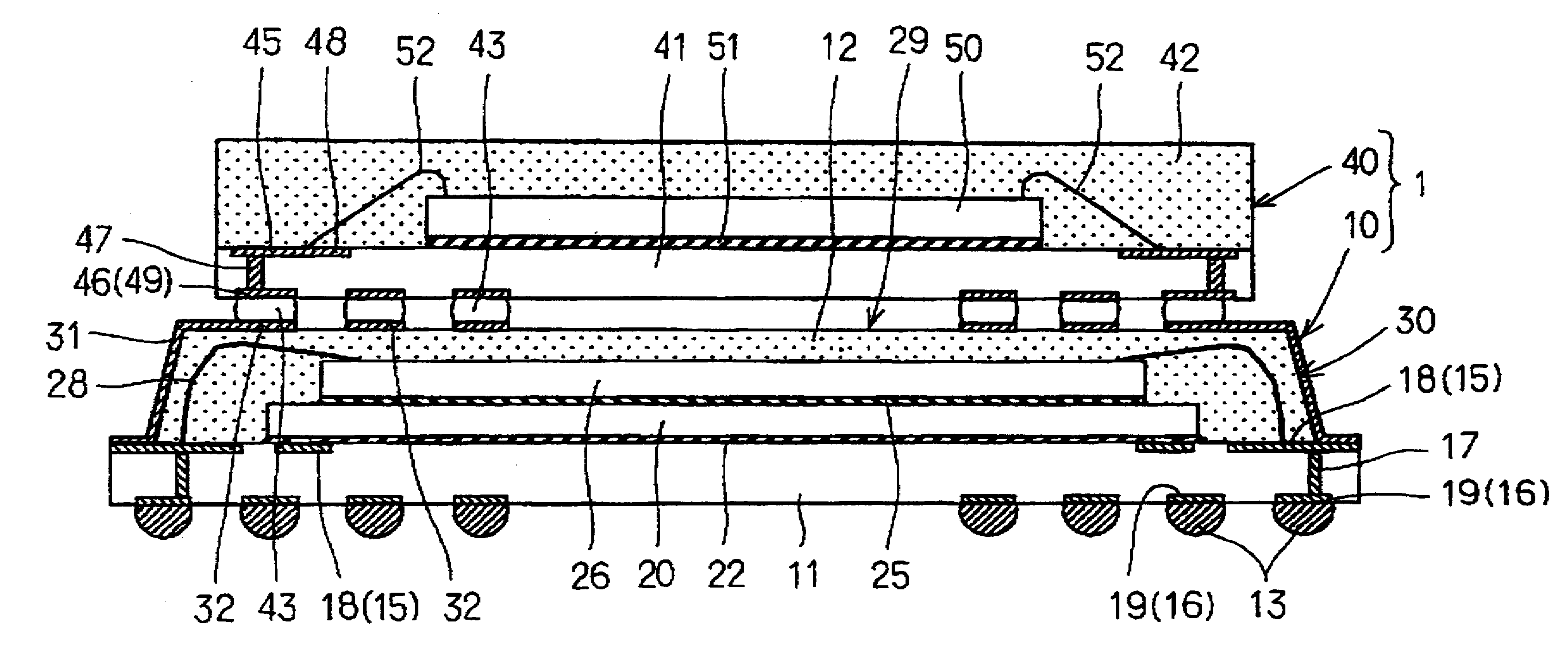
Stacked semiconductor device and fabrication method for same
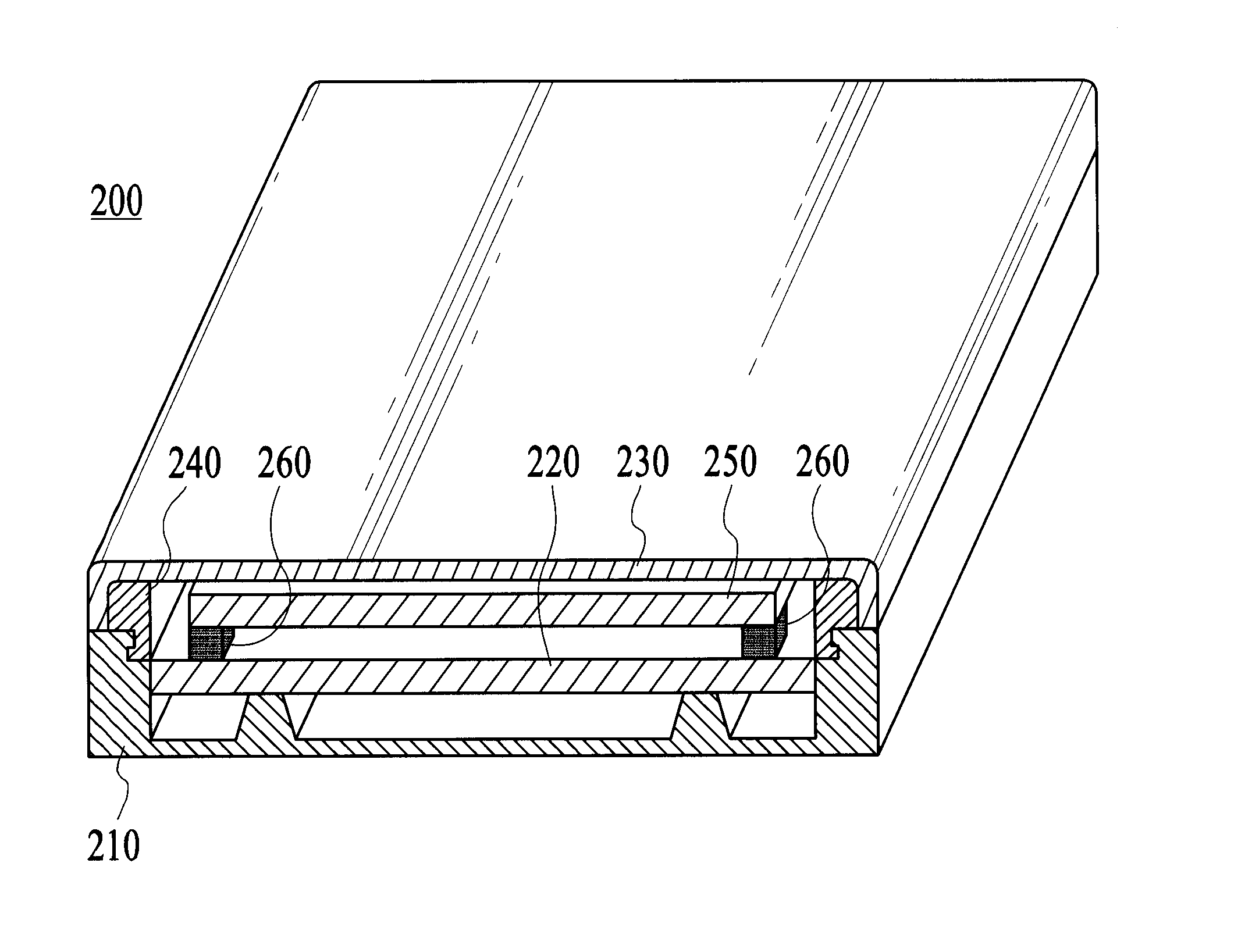
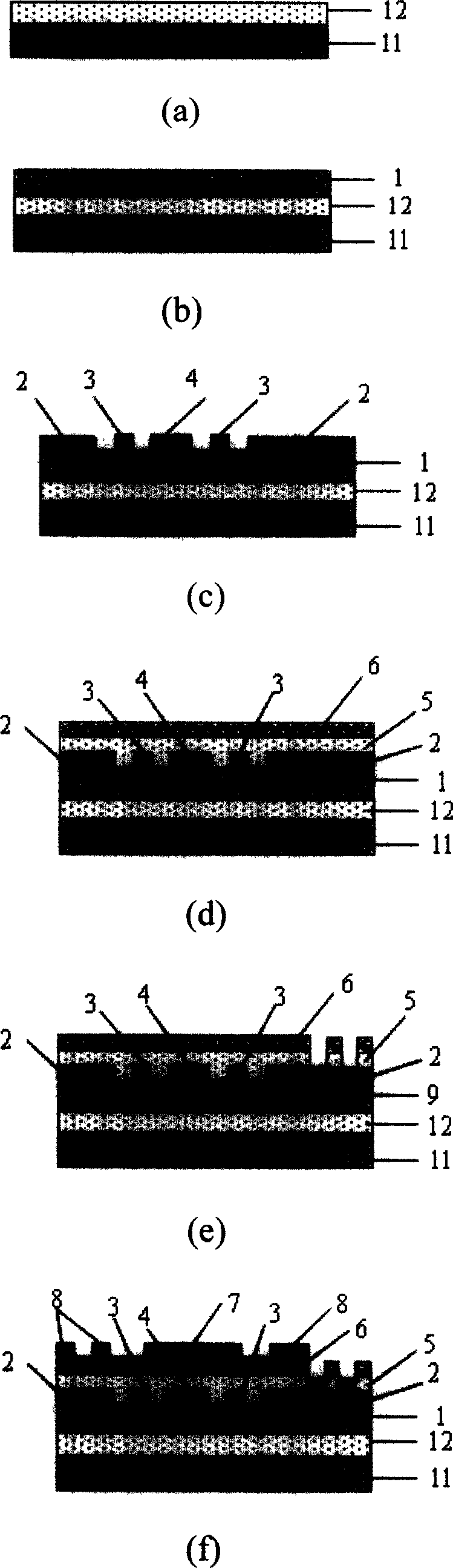
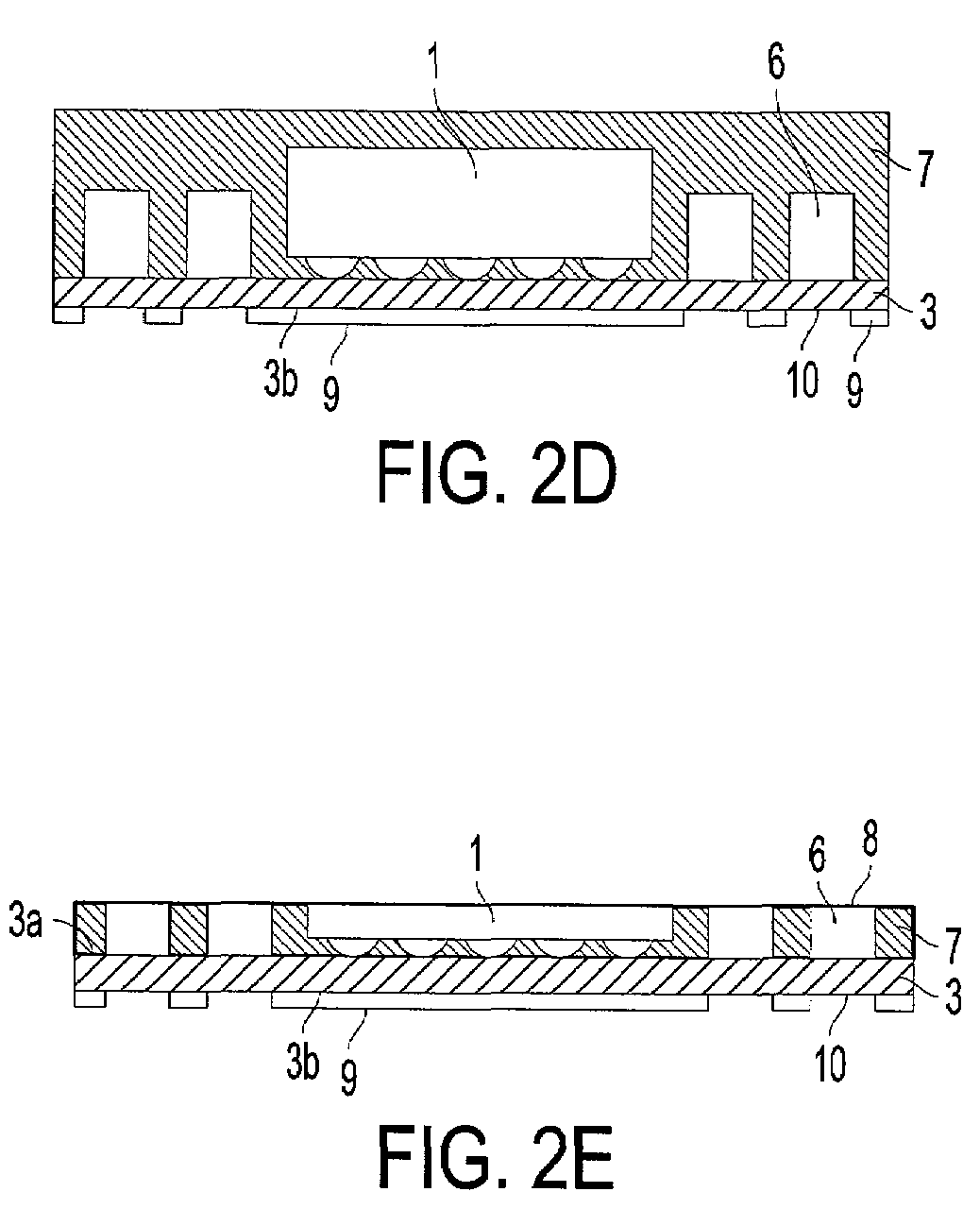
ActiveUS20070241437A1Thin structureReduce the overall heightSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
A stacked semiconductor device is constructed by stacking in two levels: a lower semiconductor device having a wiring board, at least one semiconductor chip mounted on a first surface of the wiring board and having electrodes electrically connected to wiring by way of a connection means, an encapsulant composed of insulating plastic that covers the semiconductor chip and the connection means, a plurality of electrodes formed overlying the wiring of a second surface of the wiring board, and a plurality of linking interconnects each having a portion connected to the wiring of the first surface of the wiring board and another portion exposed on the surface of the encapsulant; and an upper semiconductor device in which each electrode overlies and is electrically connected to the exposed portions of each of the linking interconnects of the lower semiconductor device. The linking interconnects extend from the first surface of the wiring board to the side surfaces and upper surface of the encapsulant, and moreover, electrically connect with wiring of the wiring board that projects from the encapsulant.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Methods of fabricating semiconductor heterostructures
InactiveUS20060009012A1Overcome limitationsImprove manufacturabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThreading dislocationsDevice material
Dislocation pile-ups in compositionally graded semiconductor layers are reduced or eliminated, thereby leading to increased semiconductor device yield and manufacturability. This is accomplished by introducing a semiconductor layer having a plurality of threading dislocations distributed substantially uniformly across its surface as a starting layer and / or at least one intermediate layer during growth and relaxation of the compositionally graded layer. The semiconductor layer may include a seed layer disposed proximal to the surface of the semiconductor layer and having the threading dislocations uniformly distributed therein.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Single-piece top surface display layer and integrated front cover for an electronic device
InactiveUS7348964B1Flat bezel-freeReduce the possibility of damageTransmission systemsDigital data processing detailsSurface displayAccelerometer
A single-piece top surface display and integrated front cover for an electronic device. In one embodiment, the cover comprises a thin, flexible, transparent layer coupled with a supporting structure. The flexible layer is supported above a display screen which is coupled with pressure activated sensors located under the display screen. The cover is dust-free, waterproof, and has a flat outer surface that is free of any steps or indentations. Users input data by applying pressure on the cover which causes the display screen to deflect and activate the sensors. The pressure exerted on the sensors is triangulated to register the position of the user input. In another embodiment, the cover is transparent, rigid, and directly contacts the pressure activated sensors which are located in front of the display screen or in the housing behind it. When pressure is applied to the cover, the cover deflects and activates the sensors. In both embodiments, an accelerometer identifies valid input events.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Flexible capacitance type touch sensor production method
InactiveCN101059380ALow costImprove yieldSemi-permeable membranesForce measurementElectricitySensor array
The invention relates to a method for producing flexible capacitor touch sensor, characterized in composed of middle layer preparation of PDMS, preparation of flexible PI substrate, graph metal sensitive electrode and relative electric connection, preparation of a first high-elasticity dielectric layer PDMS and a second flexible dielectric layer PI, graph metal drive electrode and relative electric connection, graph a top flexible insulation protective layer PI, separation of the flexible capacitor touch sensor. The invention optimizes and combines techniques, to realize the compatibility of organic flexible material PDMS, PI and traditional MEMS technique. And the capacitor touch sensor has compact structure, high mechanical strength, and high flexibility, while the product can contact the surface with any curvature to sense the volumes of normal force and tangent force, and be applied for the production of flexile capacitor touch sensor array.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bone conduction speaker with vibration prevention function
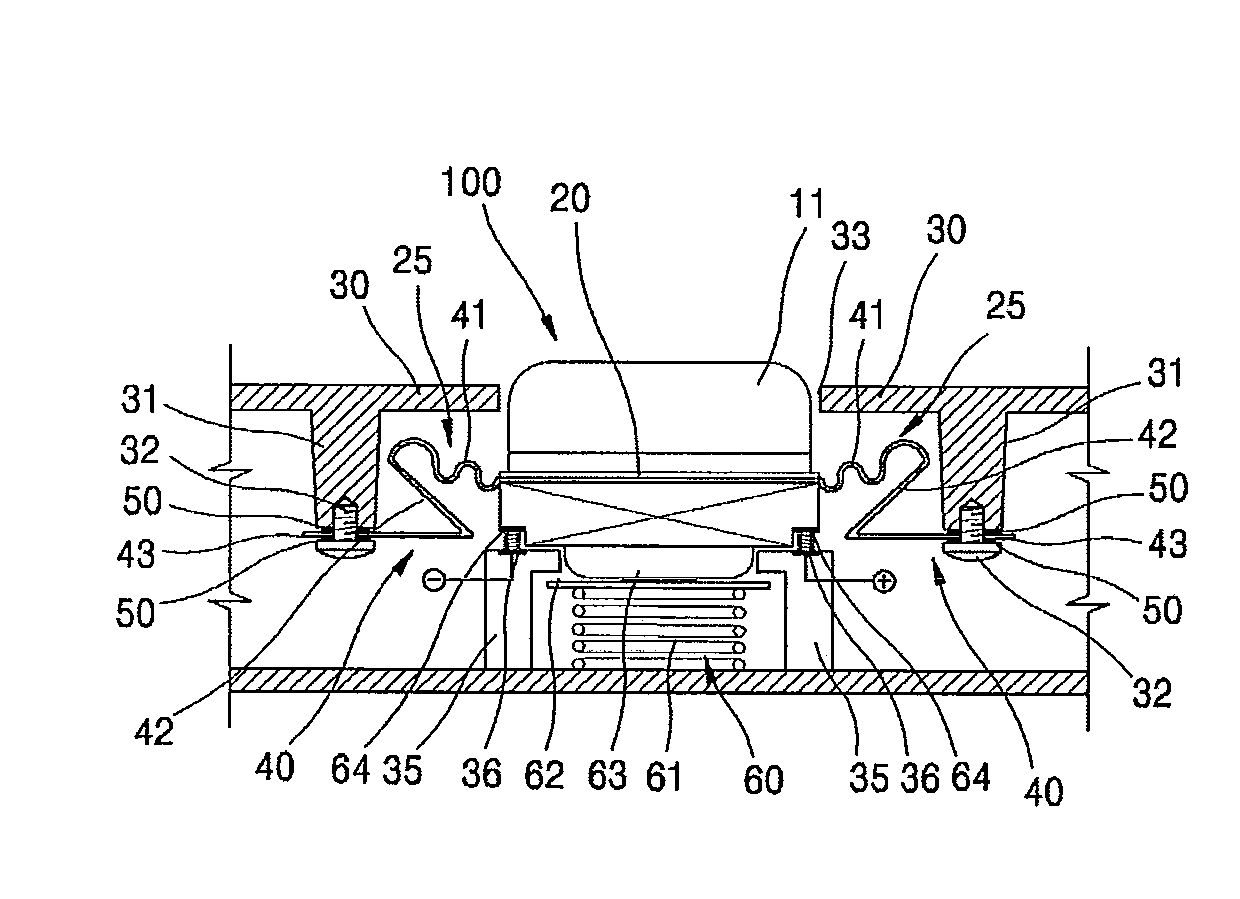
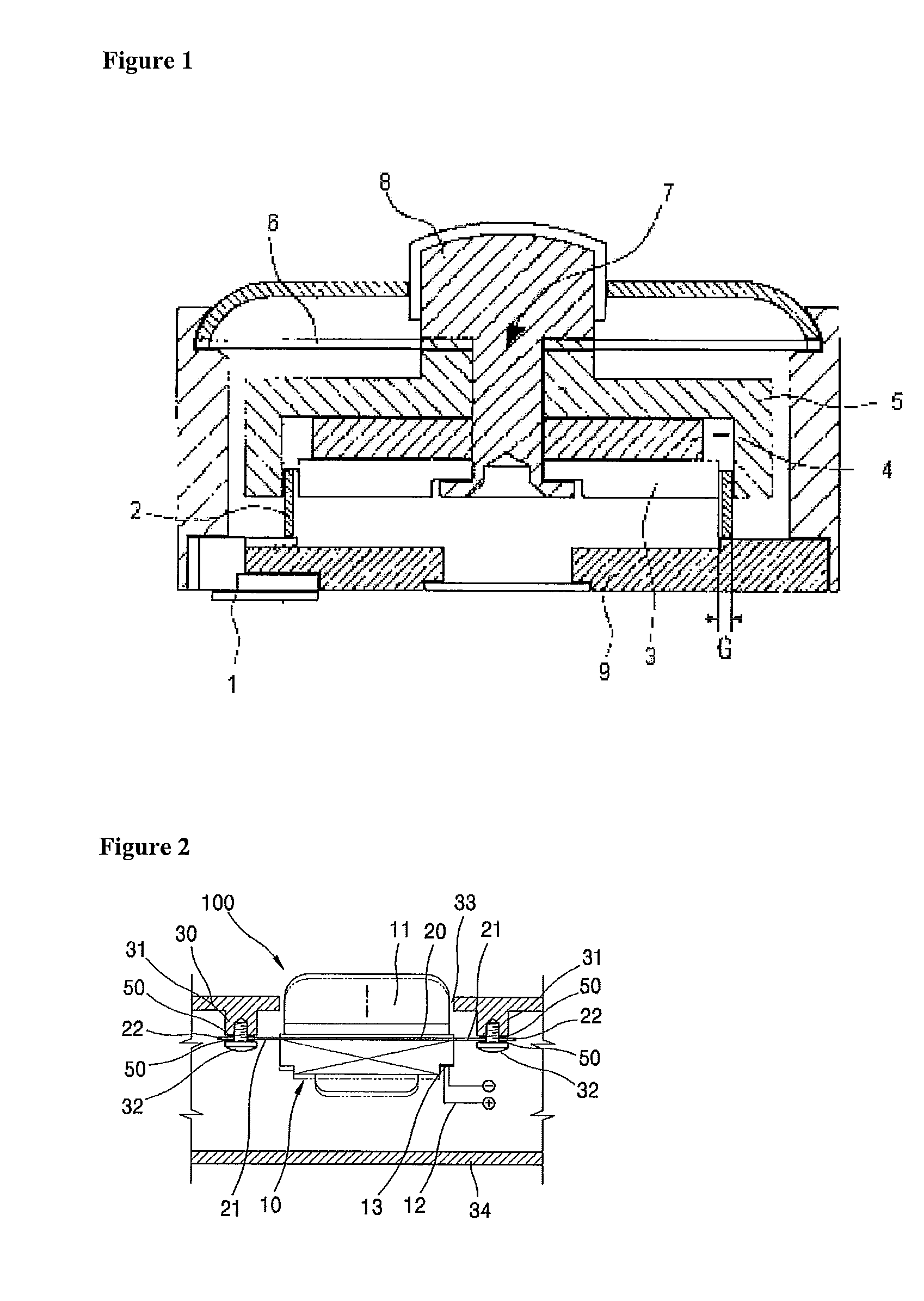
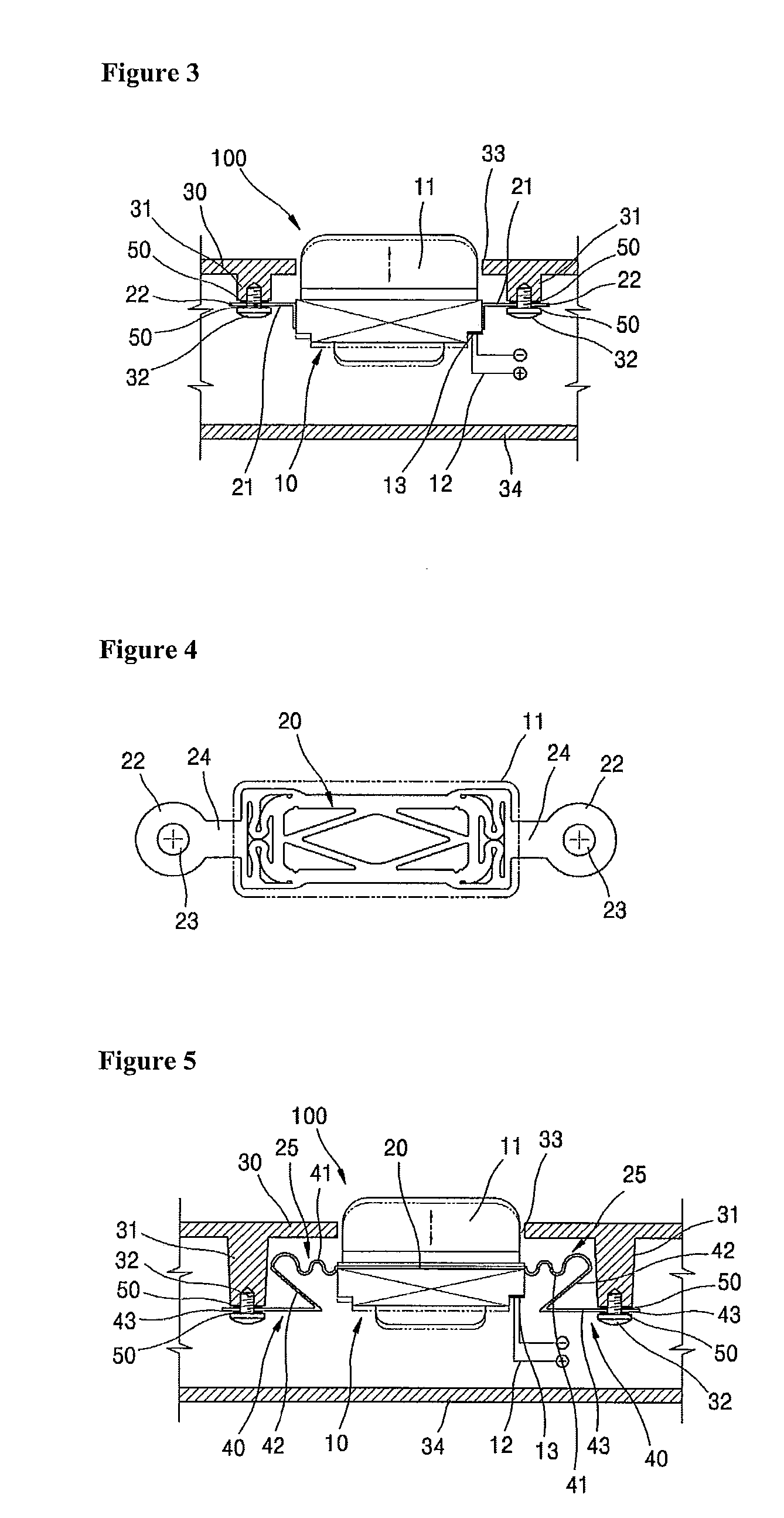
InactiveUS20100316235A1Maximizing output of soundControl spreadLoudspeaker transducer fixingBone conduction transducer hearing devicesEngineeringBone conduction hearing
A bone conduction speaker having a vibration prevention structure is disclosed. In the speaker structure that a magnet and a voice coil are installed in the interior of a housing disposed in an inner side of an external casing of a bone conduction speaker and are engaged with a yoke, and a diaphragm is installed in an outer side of the yoke, there is provided a bone conduction speaker having a vibration prevention structure which comprises one or at least two ribs which are formed as an outer side of the diaphragm is outwardly extended; and an engaging part which is disposed in an end of each rib and is fixedly assembled to the casing.
Owner:GD TECH
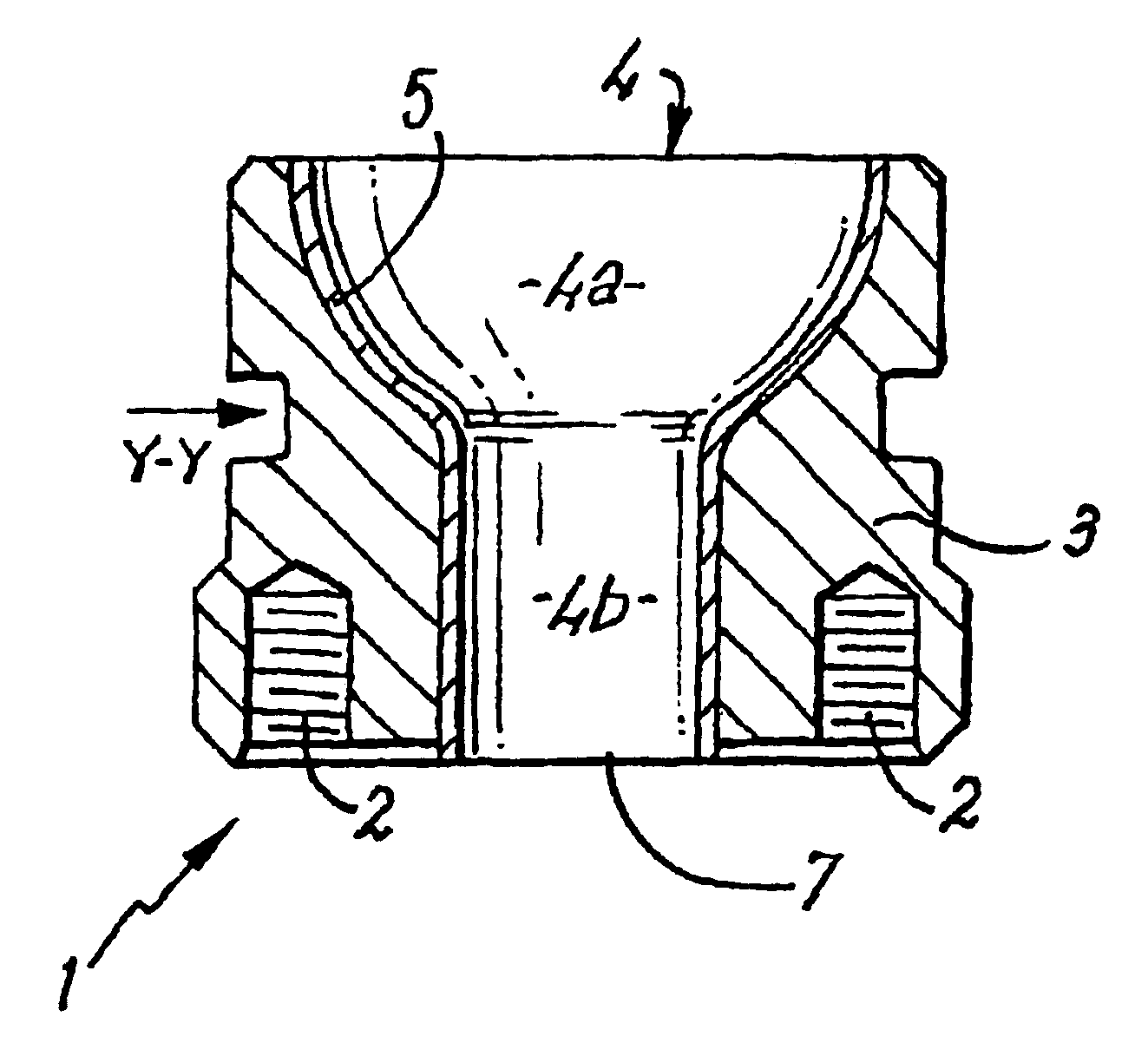
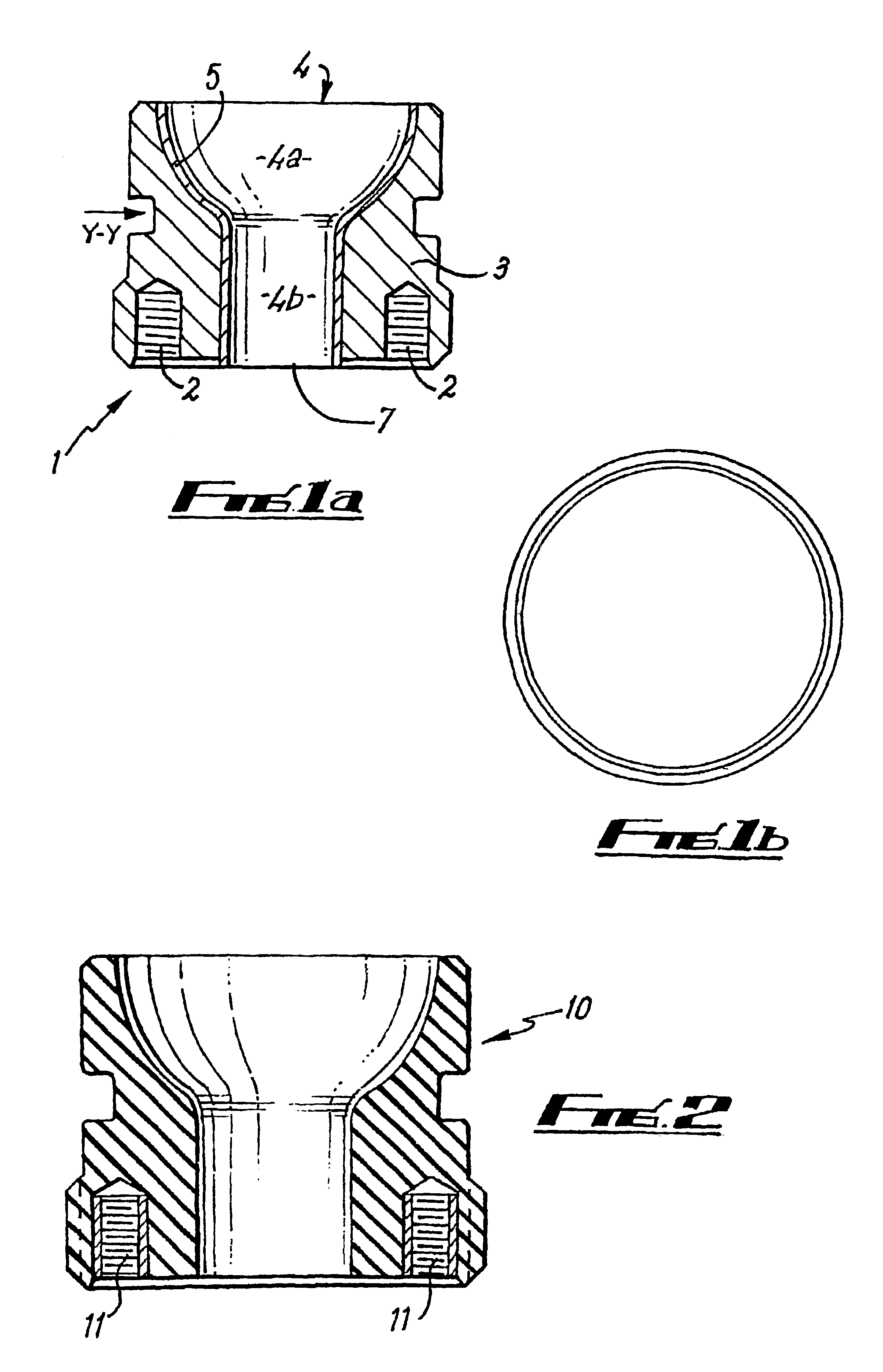
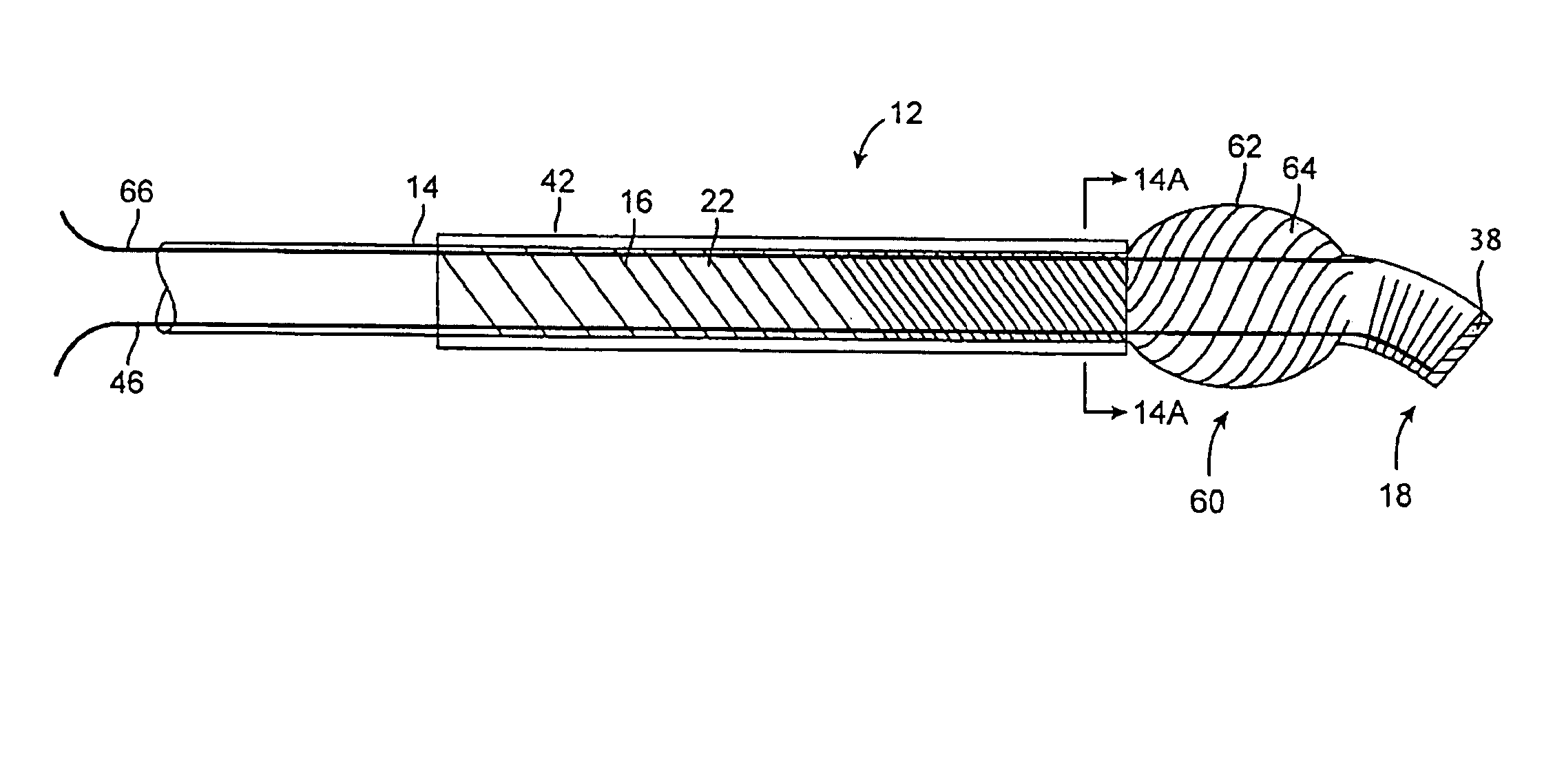
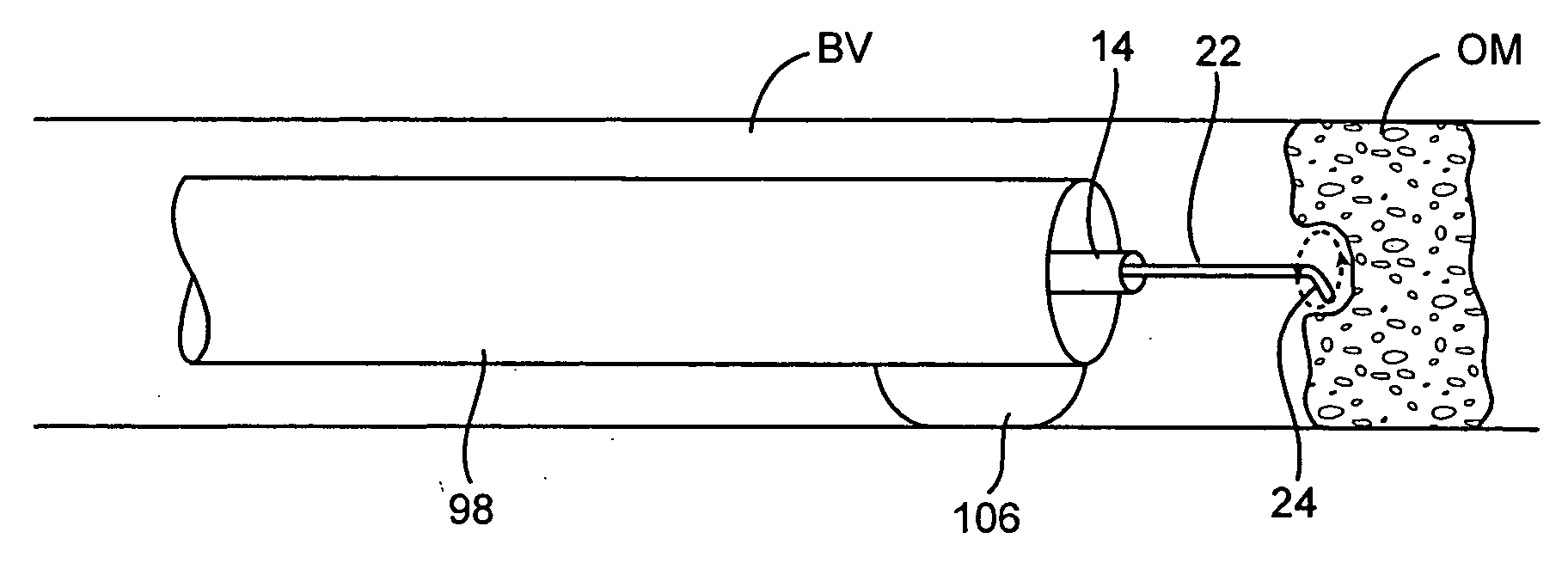
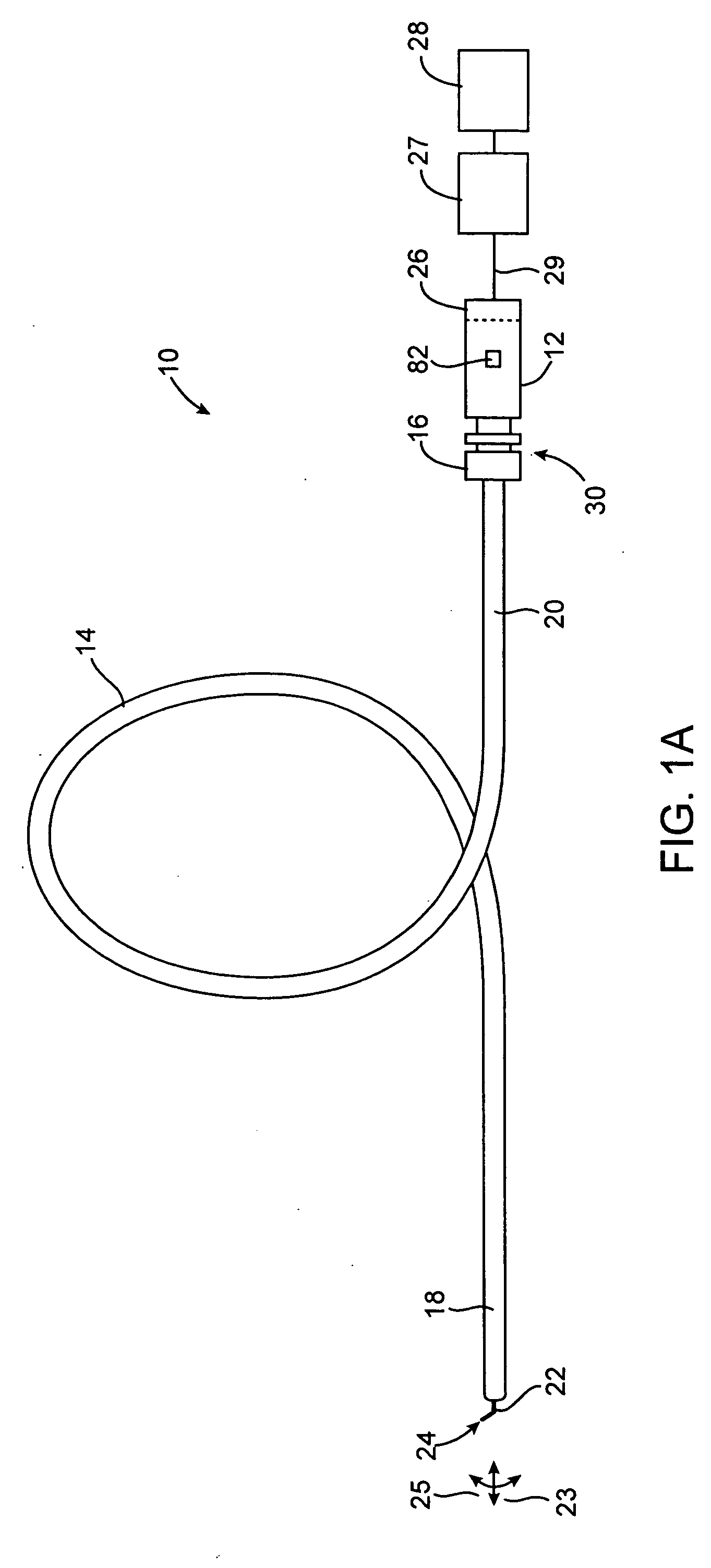
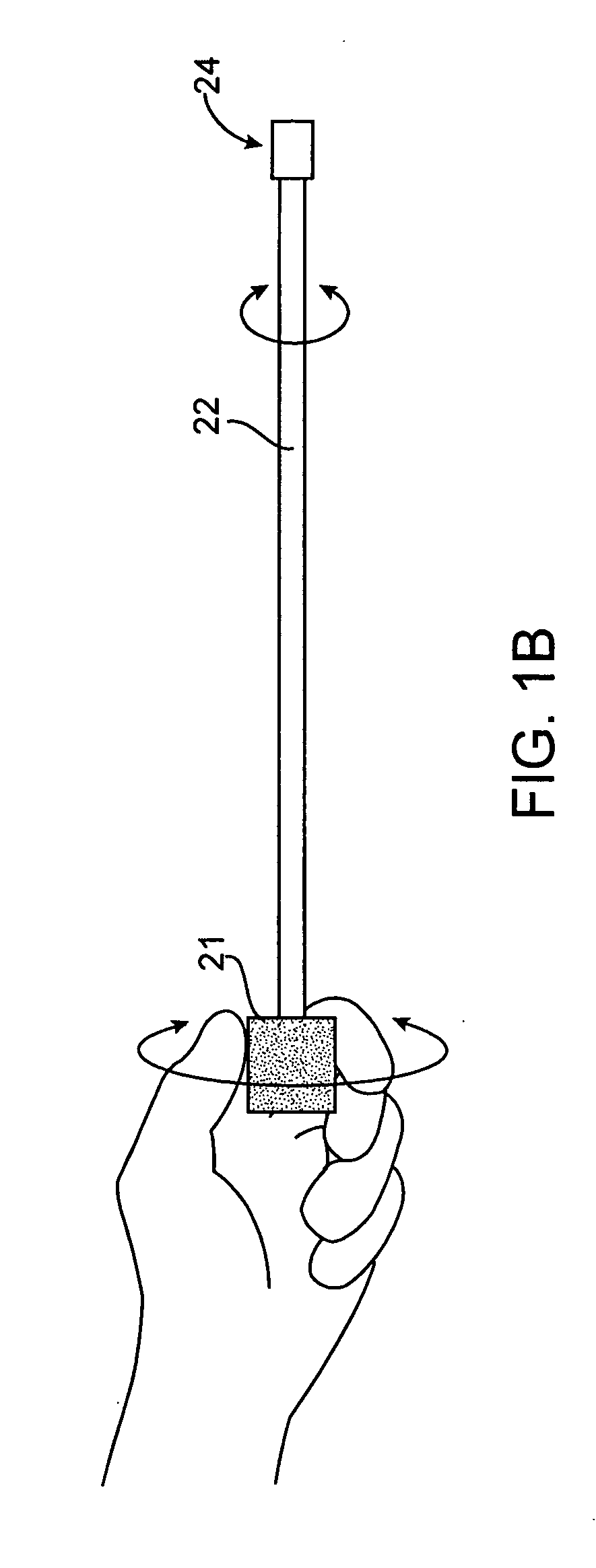
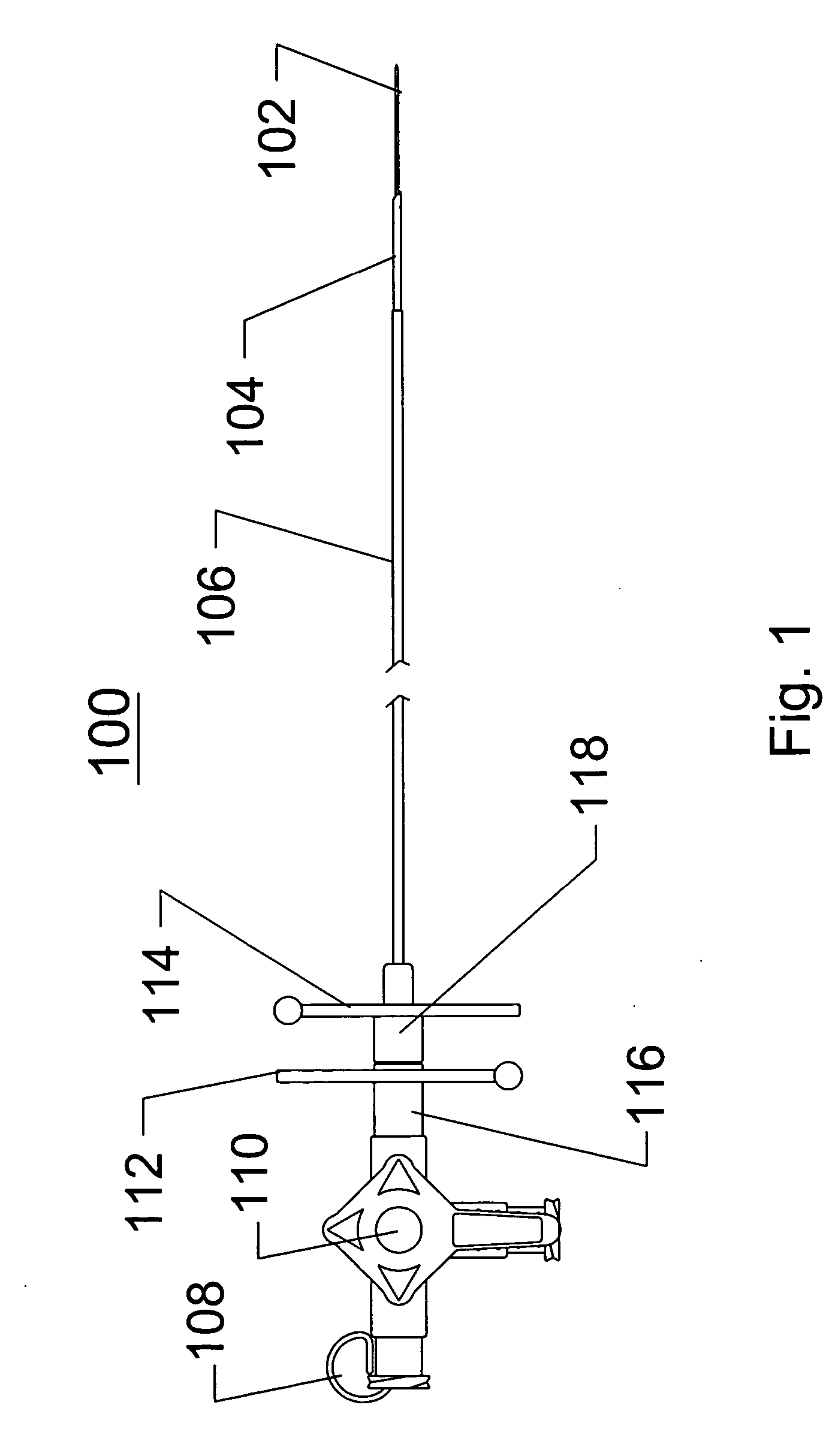
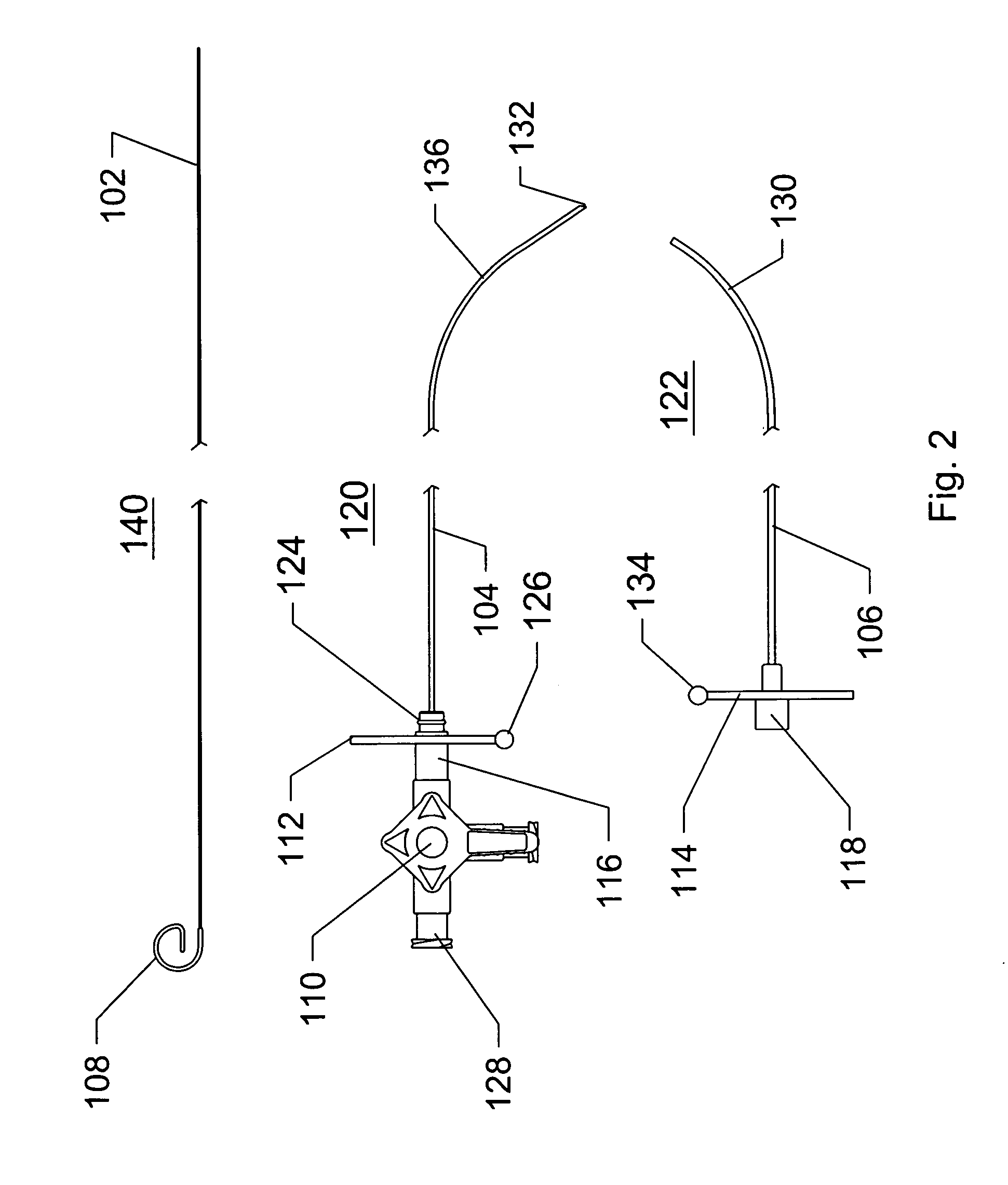
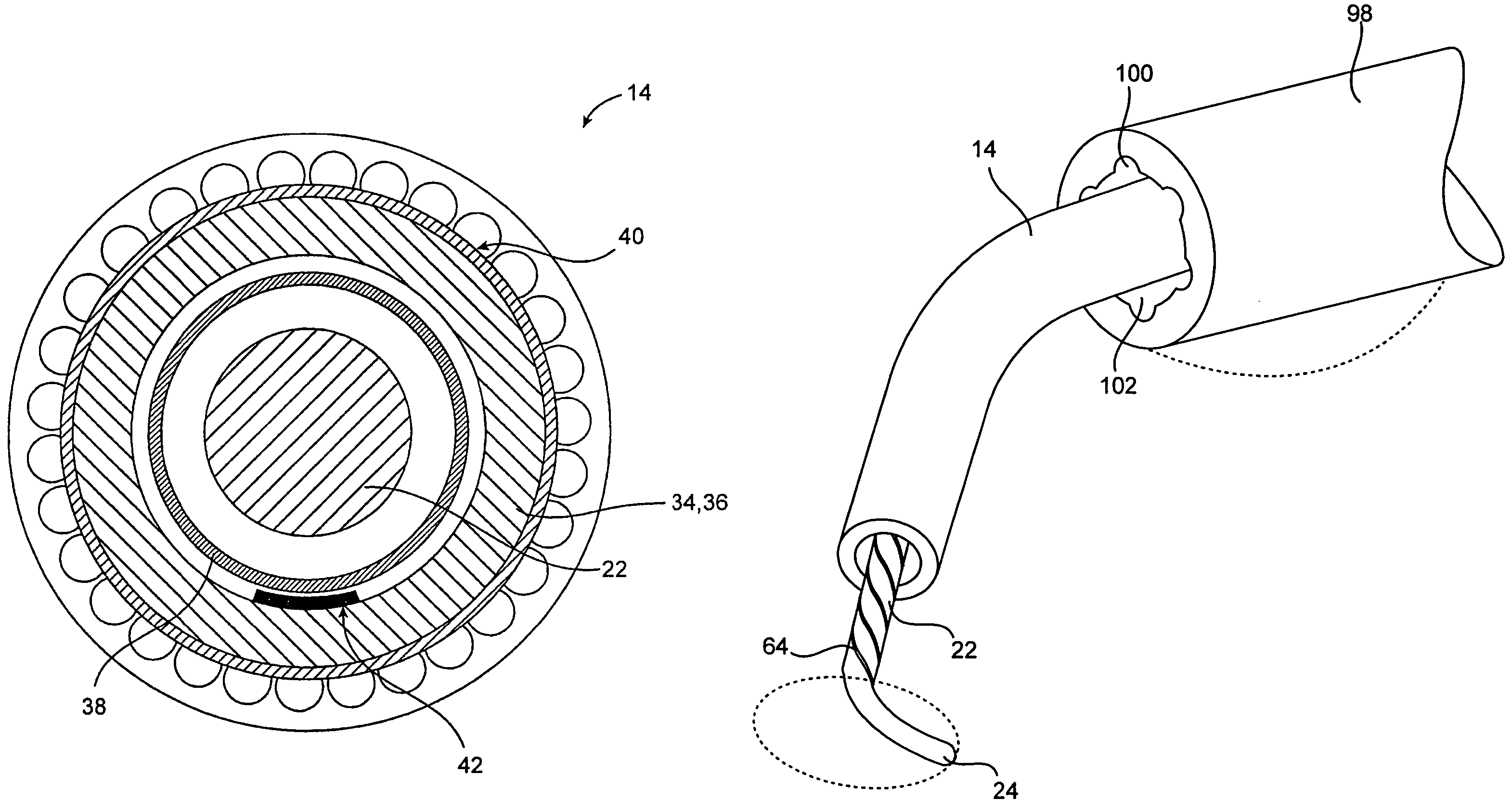
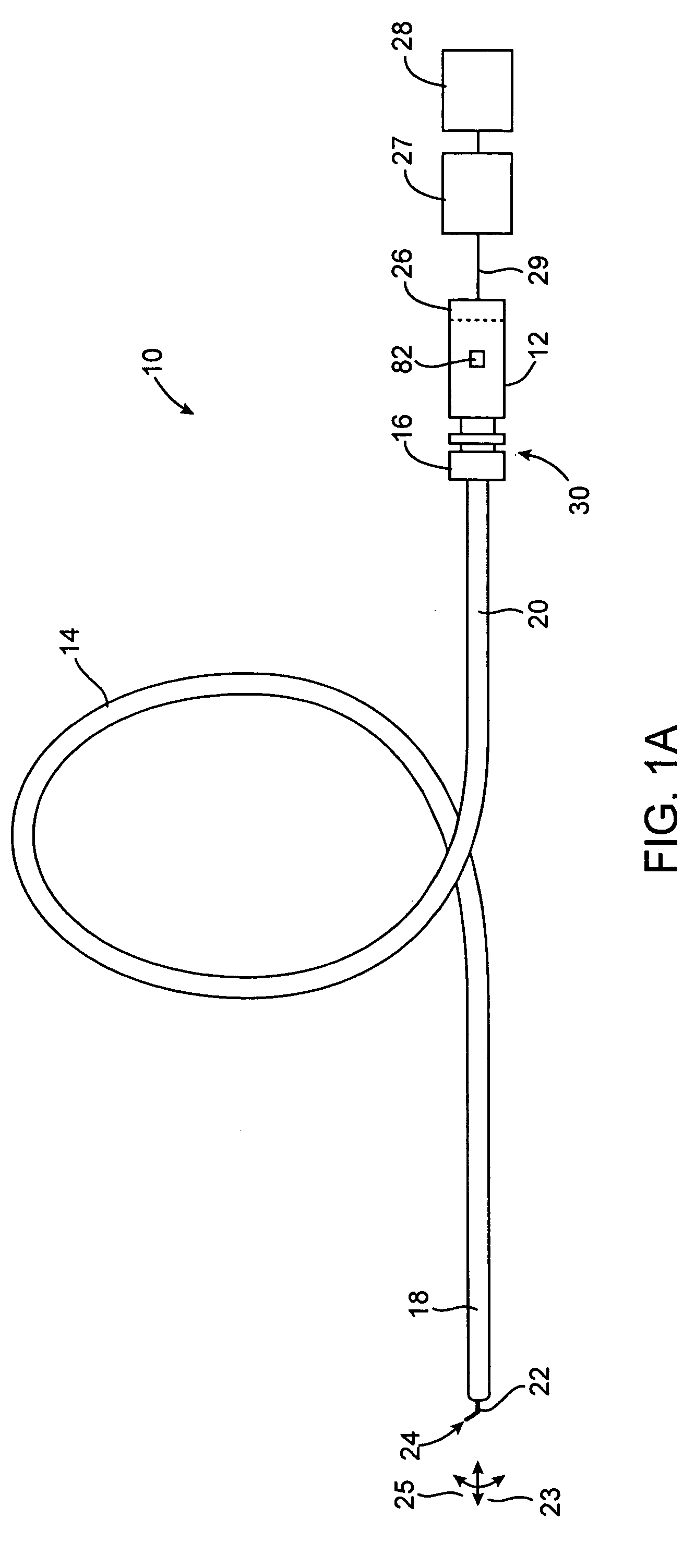
Guidewire for crossing occlusions or stenoses
Systems and methods for crossing stenosis, partial occlusions, or complete occlusions within a body lumen. The systems generally include an elongate member such as a hollow guidewire that houses a rotatable and translatable drive shaft. The drive shaft typically has a distal portion that is advanced to create a path in the occlusive material that is large enough to allow the hollow guidewire to cross the occlusive material.
Owner:REVASCULAR THERAPEUTICS
Steerable endoluminal punch
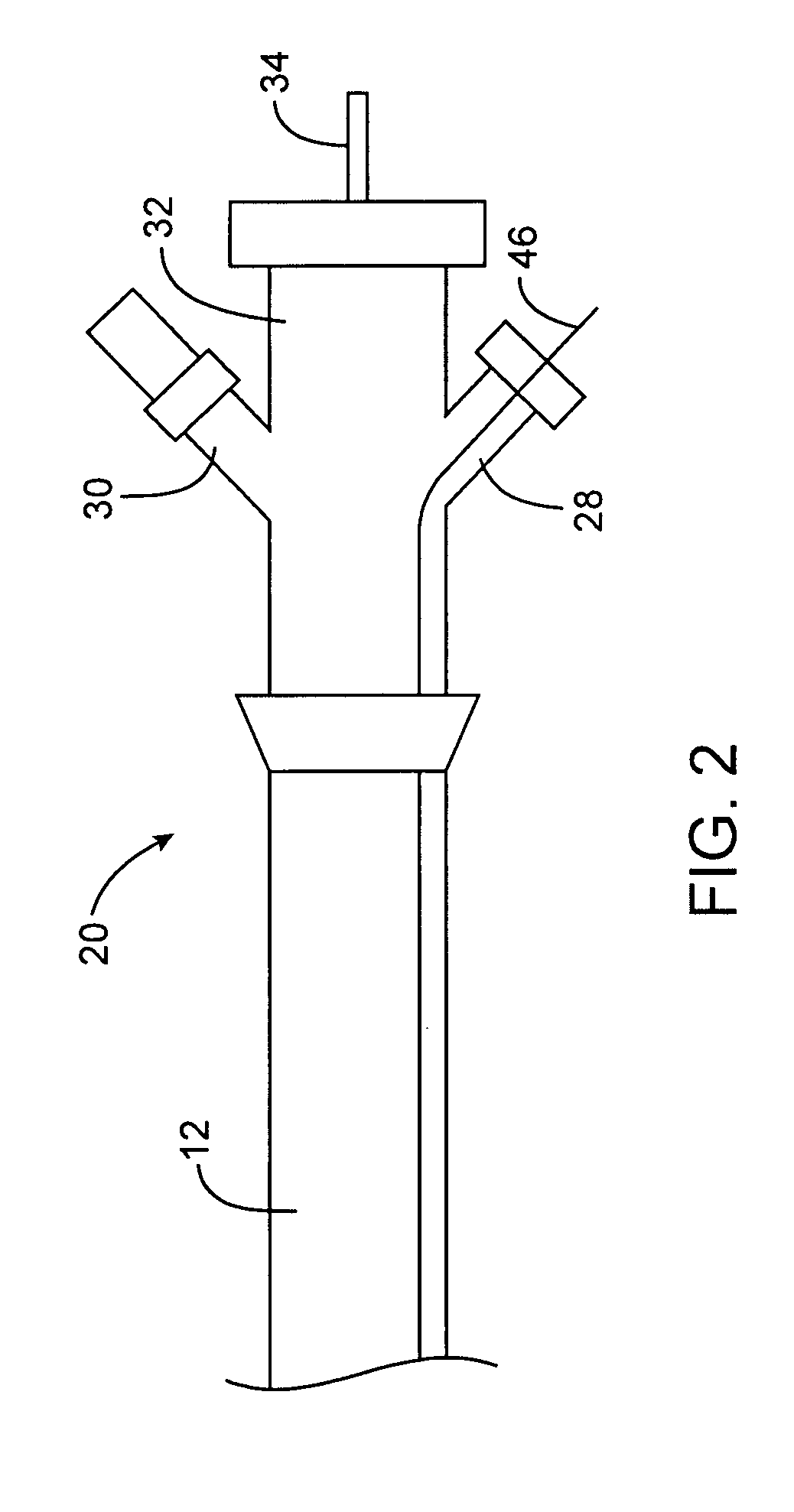
InactiveUS20070021767A1Easy alignmentThin structureSurgical needlesBlunt dissectorsAtrial septumEngineering
This invention is a transvascularly placed punch, further including internal steerability and the ability to articulate in a direction at right angles to its longitudinal axis at or near its distal end. The punch is generally fabricated from stainless steel and includes an outer tube, an intermediate tube, a central stylet, hub structures, and a distal articulating region. The punch can be advanced through a body lumen in its straight configuration and then be selectively articulated or curved to permit negotiation of tortuous curvature or to permit optimal approach or access to a puncture site. The punch is able to create holes in the atrial septum of the heart or other structures and is easier to use than punches that are pre-curved near their distal tip since it is easier to advance through accessory catheters.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M
Thin planar semiconductor device having electrodes on both surfaces and method of fabricating same
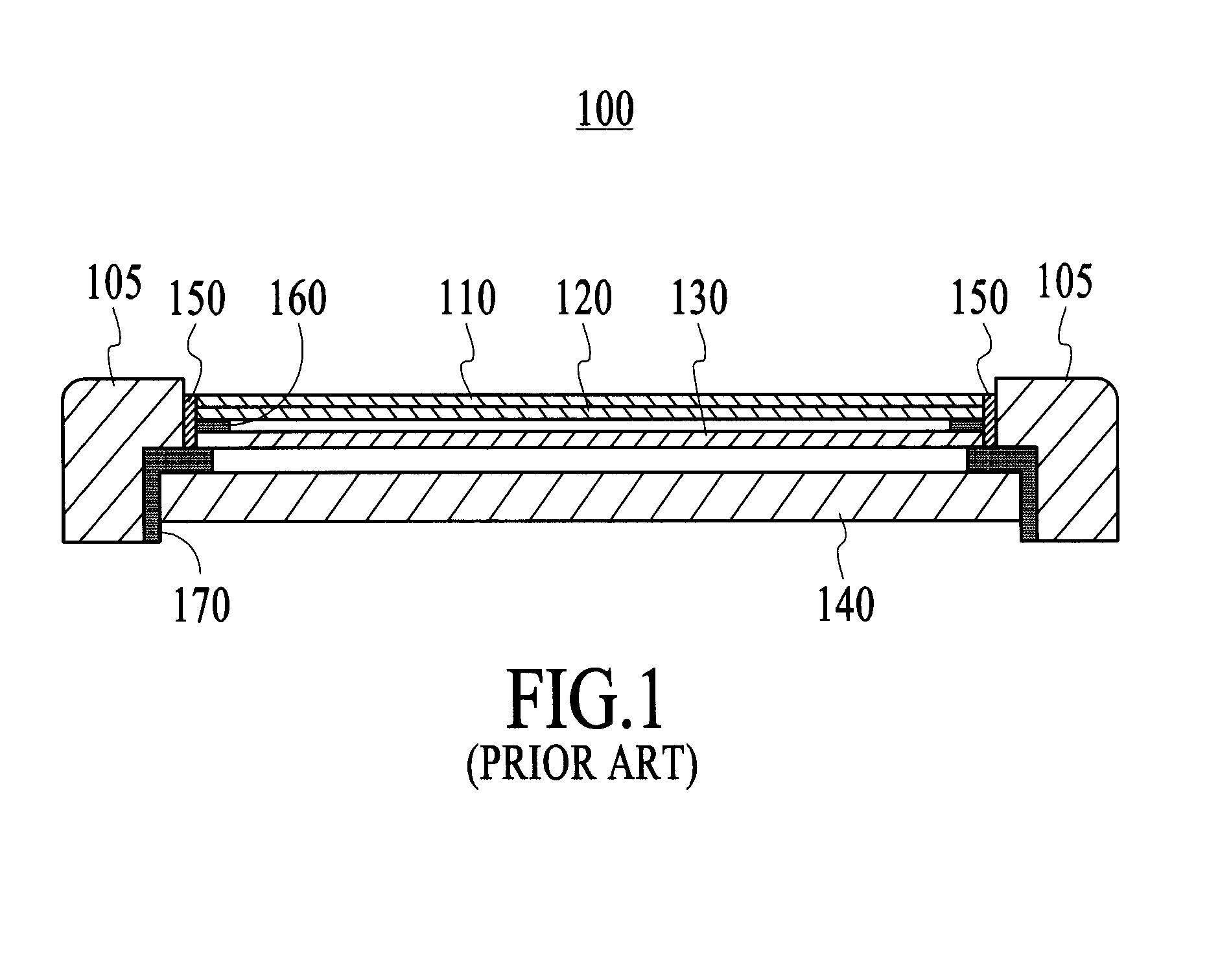
InactiveUS7034386B2Highly integratedThin structureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface electrodeResist
A thin, planar semiconductor device having electrodes on both surfaces is disclosed. This semiconductor device is provided with an IC chip and a wiring layer having one side that is electrically connected to surface electrodes of the IC chip. On this surface of the wiring layer, conductive posts are provided on wiring of the wiring layer, and an insulating resin covers all portions not occupied by the IC chip and conductive posts. The end surfaces of the conductive posts are exposed from the insulating resin and are used as first planar electrodes. In addition, a resist layer is formed on the opposite surface of the wiring layer. Exposed portions are formed in the resist layer to expose desired wiring portions of the wiring layer. These exposed portions are used as second planar electrodes. Stacking semiconductor devices of this construction enables an improvement in the integration of semiconductor integrated circuits.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Guidewire for crossing occlusions or stenoses
Systems and methods for crossing stenosis, partial occlusions, or complete occlusions within a body lumen. The systems generally include an elongate member such as a hollow guidewire that houses a rotatable and translatable drive shaft. The drive shaft typically has a distal portion that is advanced to create a path in the occlusive material that is large enough to allow the hollow guidewire to cross the occlusive material.
Owner:REVASCULAR THERAPEUTICS
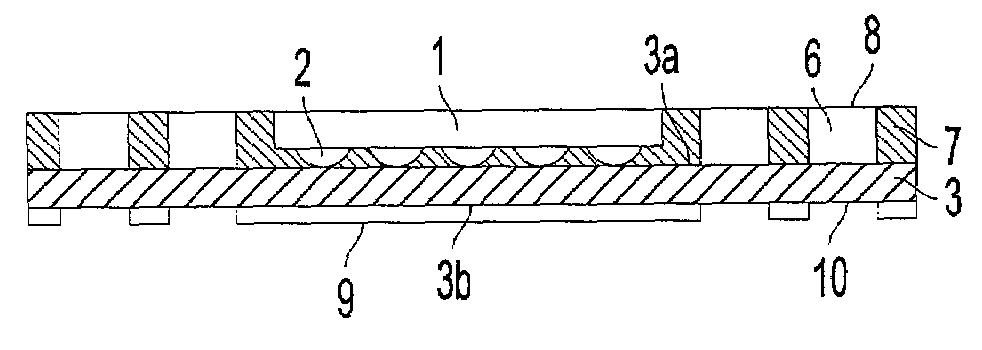
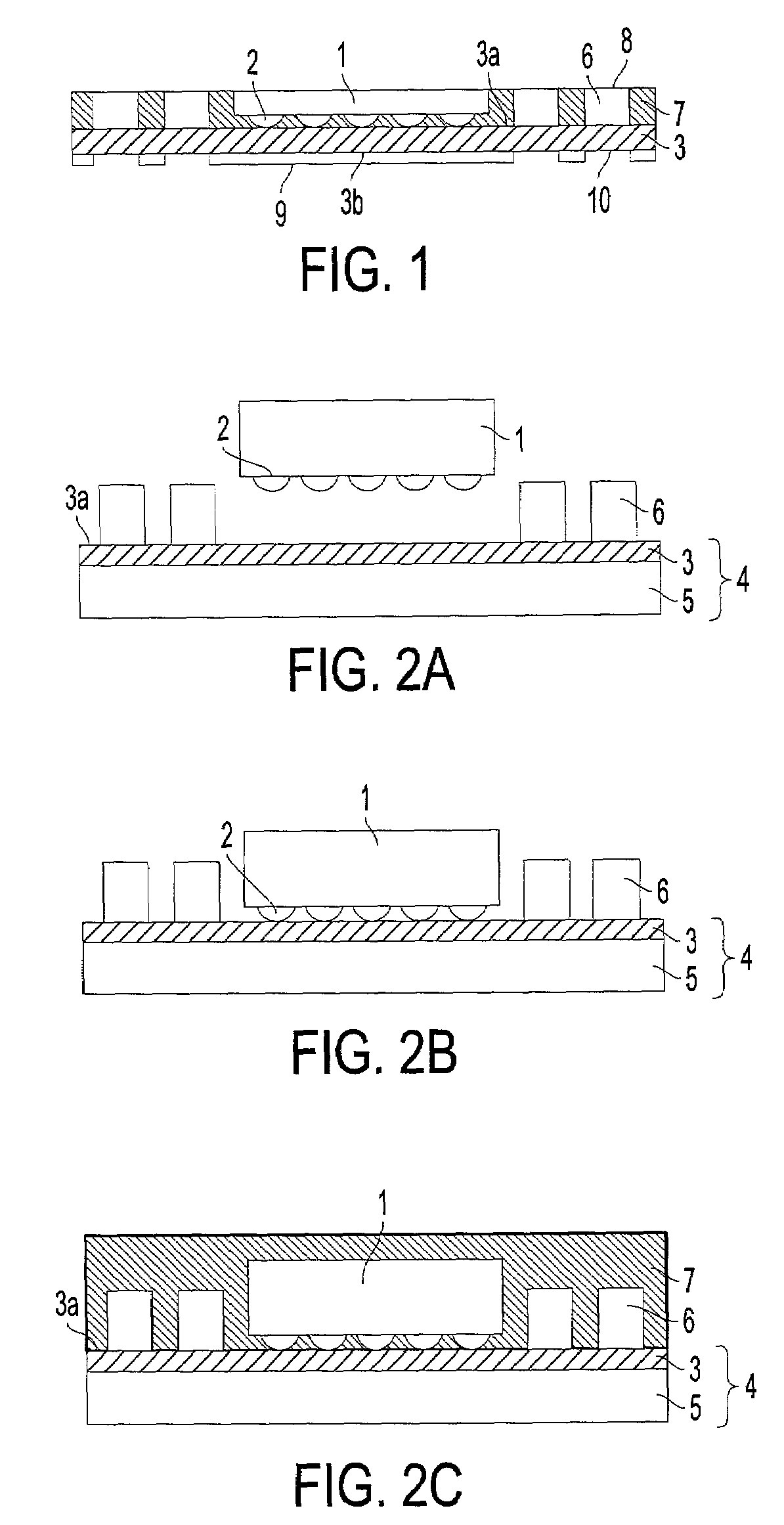
Illumination device and input unit with illumination device
InactiveUS20090273931A1Illumination areaLight utilization efficiency can be improvedMechanical apparatusLegendsLight guideOptoelectronics
A recess portion is formed in a substrate to accommodate a light emitting element so as to be sealed with a sealant. A light guide layer formed of a thin transparent resin film is fixed onto the substrate via an adhesive layer to realize an illuminating device with a thin structure. The light emitted from the light emitting element is irradiated into the light guide layer via the sealant and the adhesive layer. The light fully reflecting on the boundary surfaces between the light guide layer and the adhesive layer, and between the light guide layer and the air layer passes inside the light guide layer. Then the light which has not fully reflected leaks outside from the surface of the transparent resin film which forms the light guide layer. This makes it possible to illuminate the surface of the illumination device 1A entirely with brightness.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
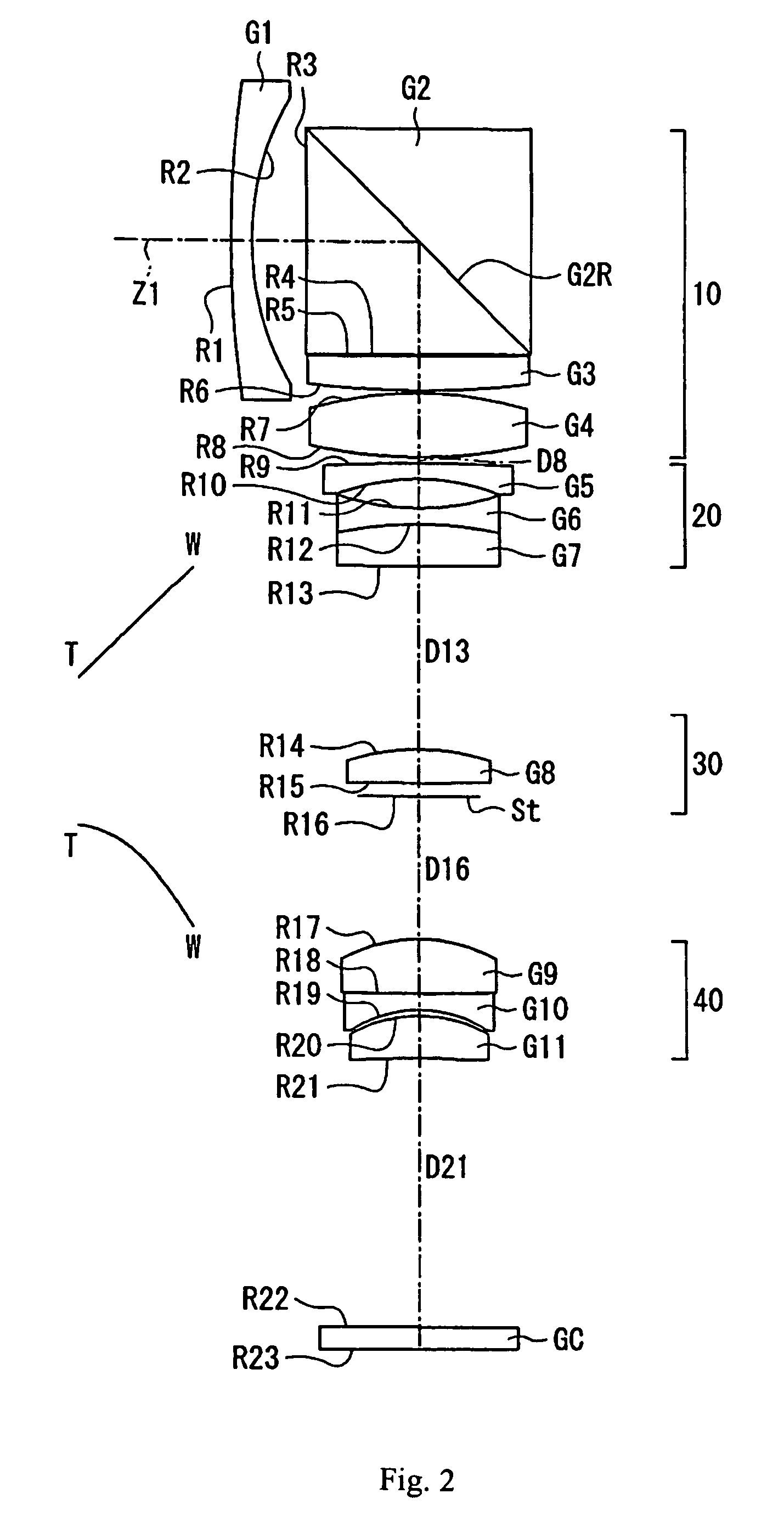
Zoom lens including four lens groups
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
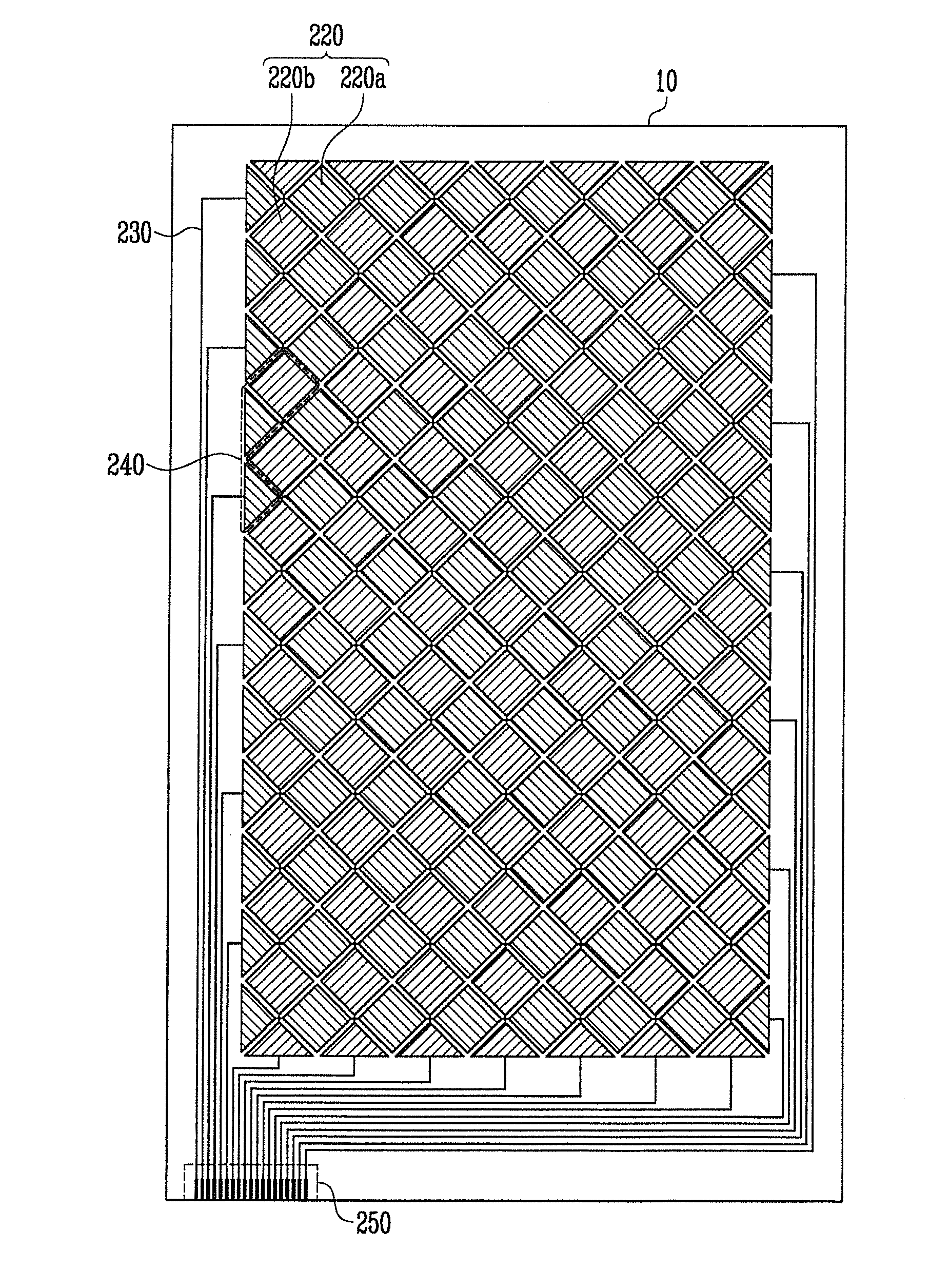
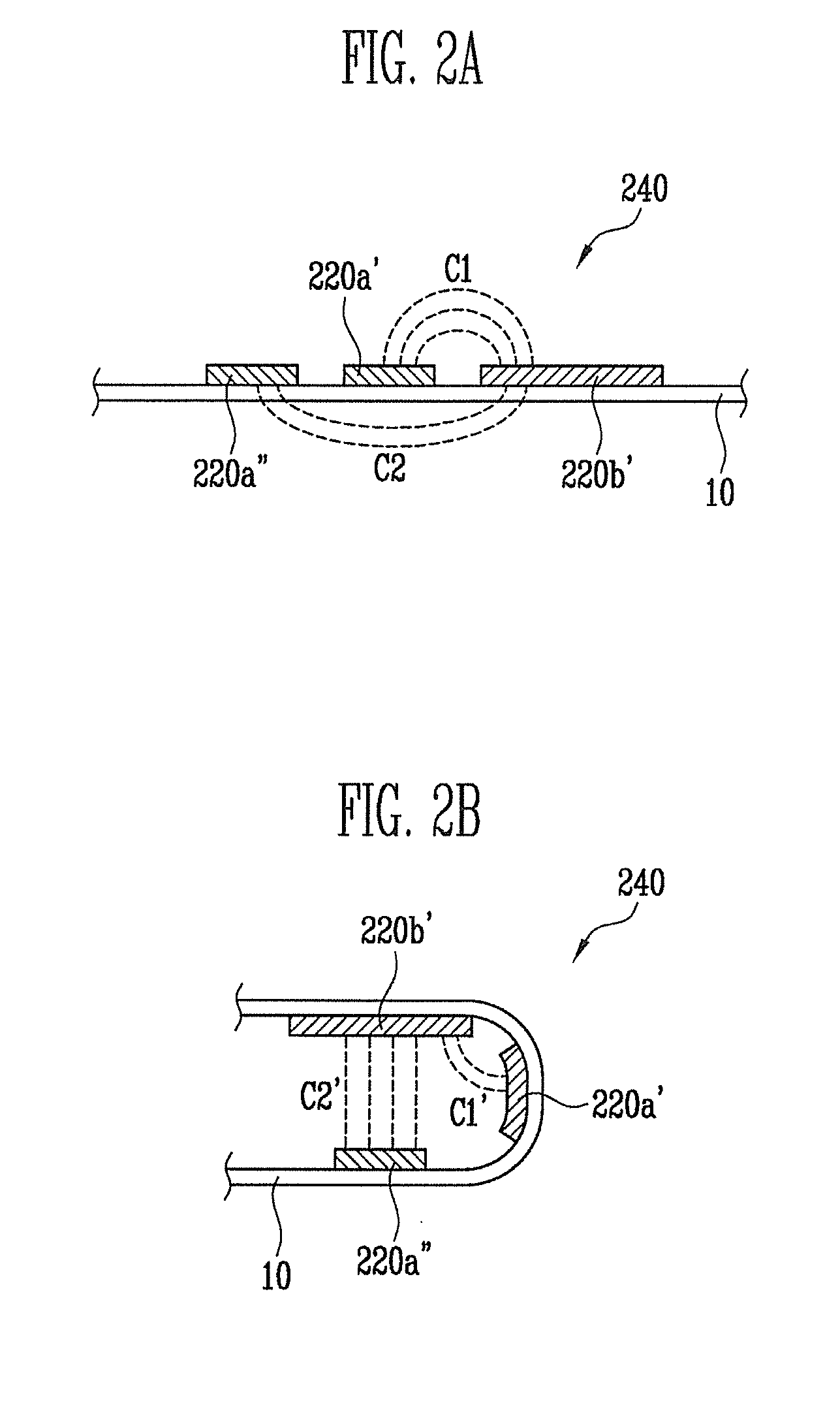
Flexible touch screen panel and flexible display device with the same
ActiveUS20140139447A1Thin structureManufacturing cost can be reduced and minimizedDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringTouchscreen
A flexible touch screen panel includes a substrate, sensing patterns, sensing lines, and at least one bending sensor. The substrate is divided into an active area and a non-active area around the active area. The sensing patterns are on the active area of a first surface of the substrate. The sensing lines are on the non-active area of the first surface of the substrate and connected to the sensing patterns. The at least one bending sensor is implemented with a plurality of sensing patterns at an edge region in the active area. In the flexible touch screen panel, the substrate is configured to be bent along a folding axis in a first direction, and the at least one bending sensor is at a region along the folding axis.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
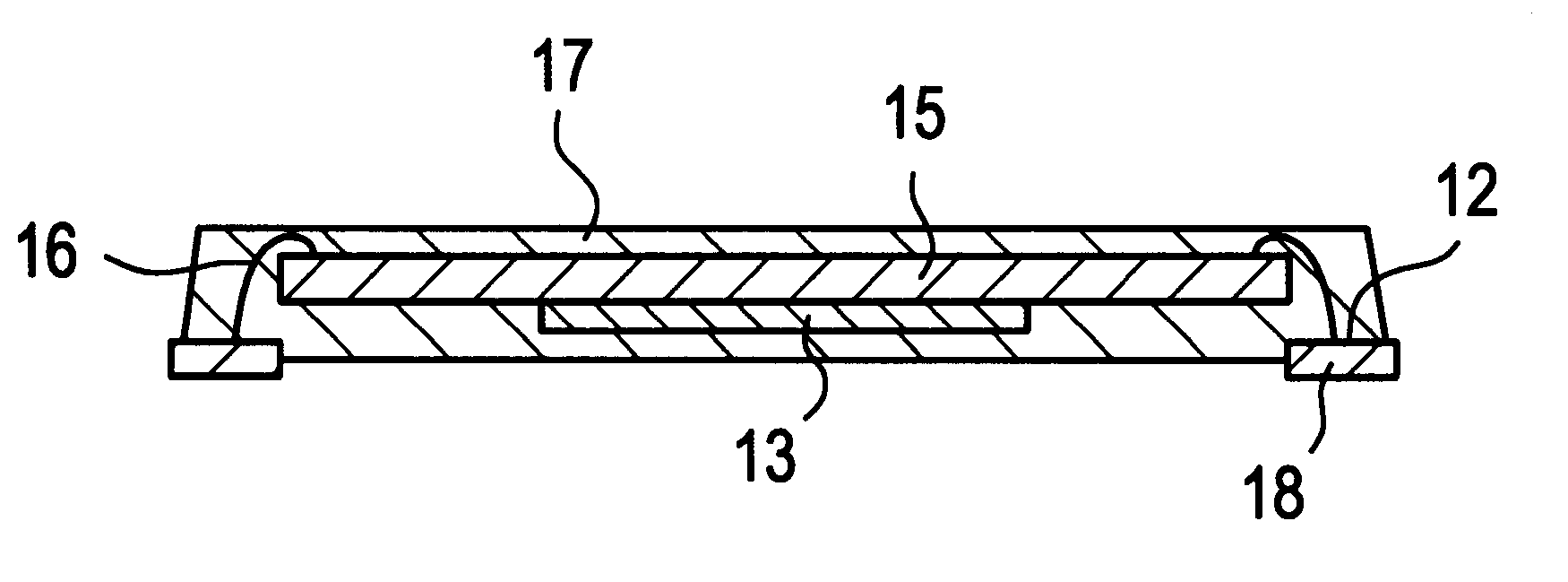
Resin molded semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6291274B1Well formedHigh strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesShell moldingSemiconductor chip
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor chip (15) which is bonded on a die pad (13) of a leadframe, and inner leads (12) are electrically connected to electrode pads of the semiconductor chip (15) with metal fine wires (16). The die pad (13), semiconductor chip (15) and inner leads are molded with a resin encapsulant (17). However, no resin encapsulant (17) exists on the respective back surfaces of the inner leads (12), which protrude downward from the back surface of the resin encapsulant (17) so as to be external electrodes (18).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
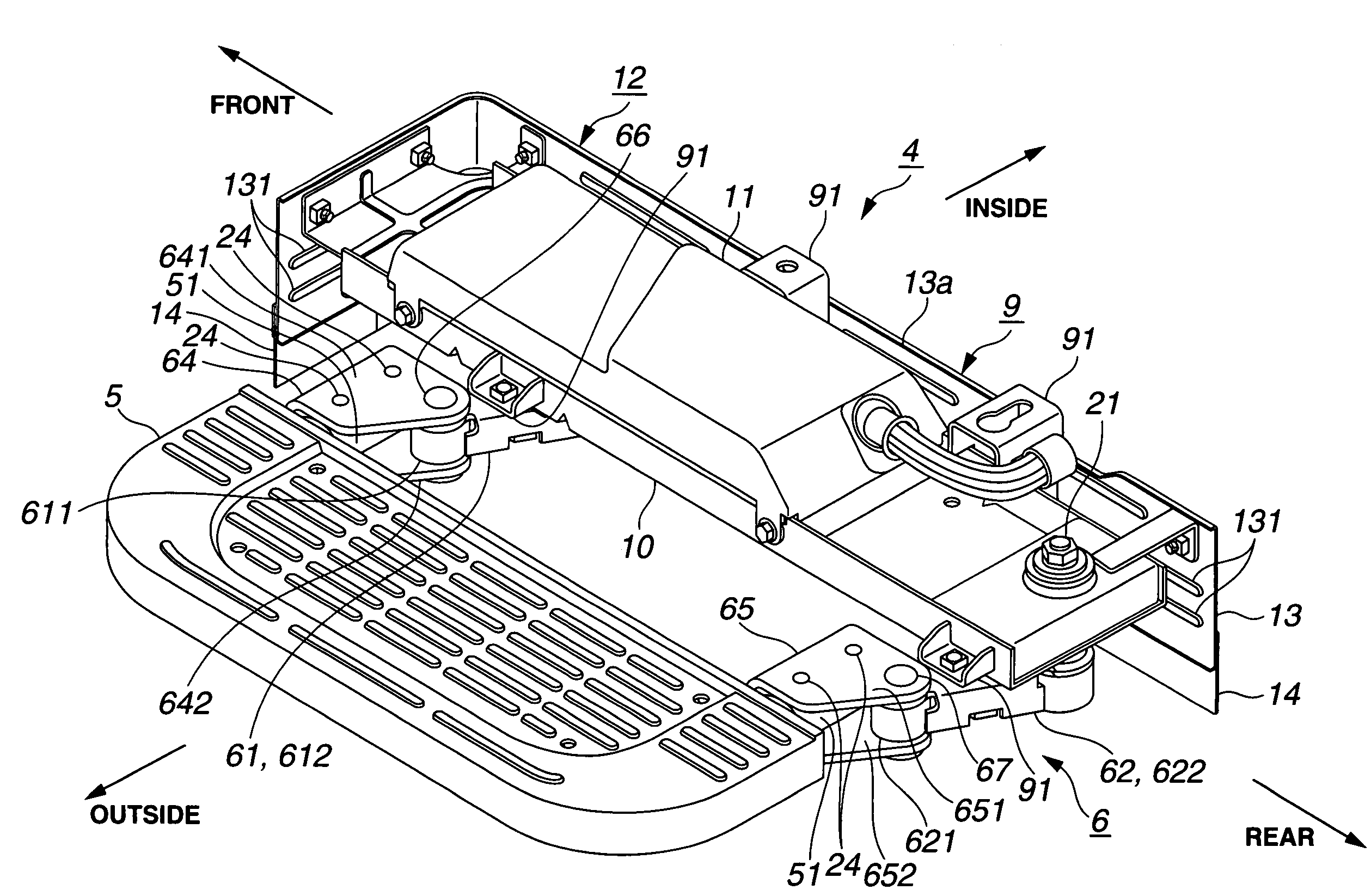
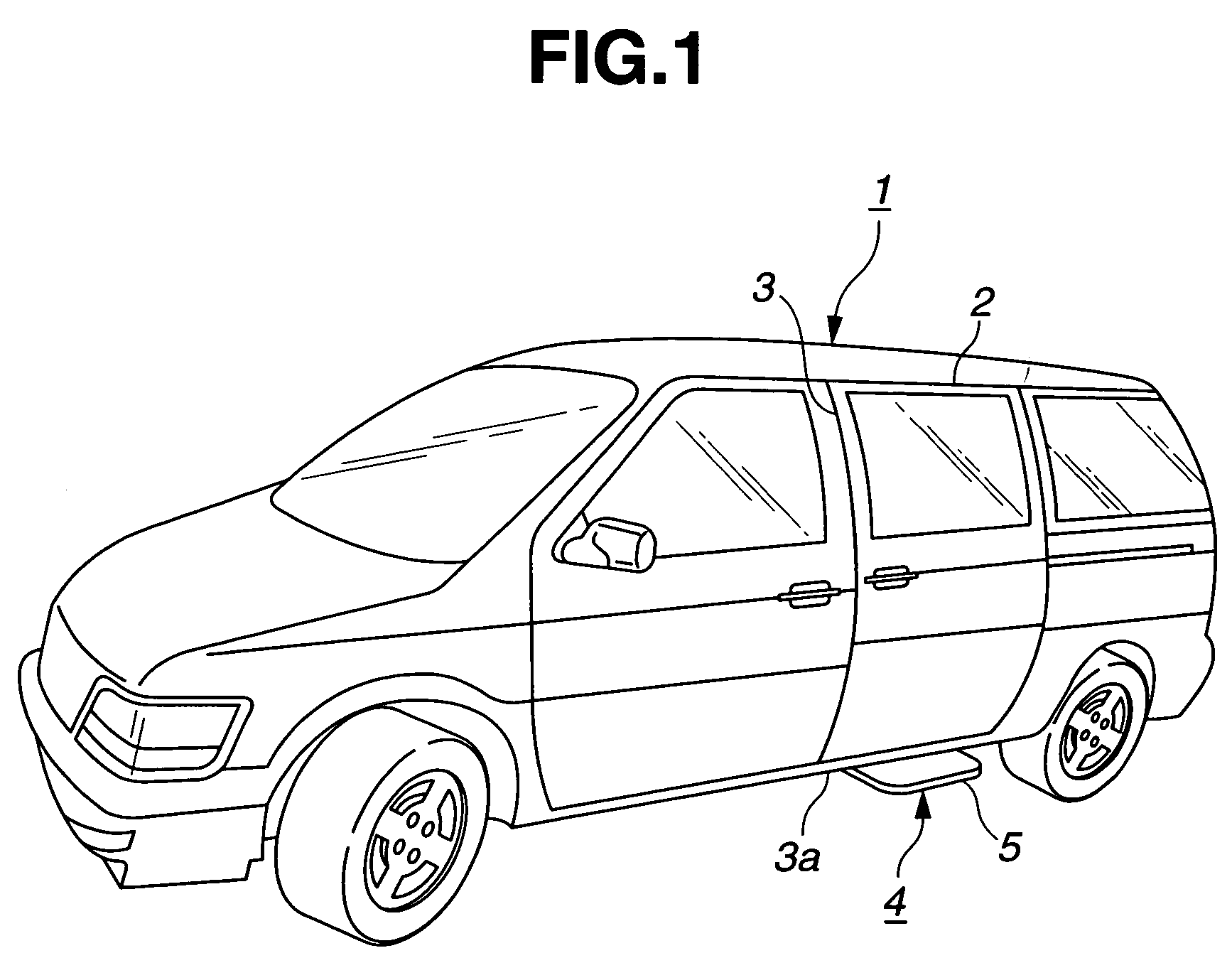
Powered step device of motor vehicle
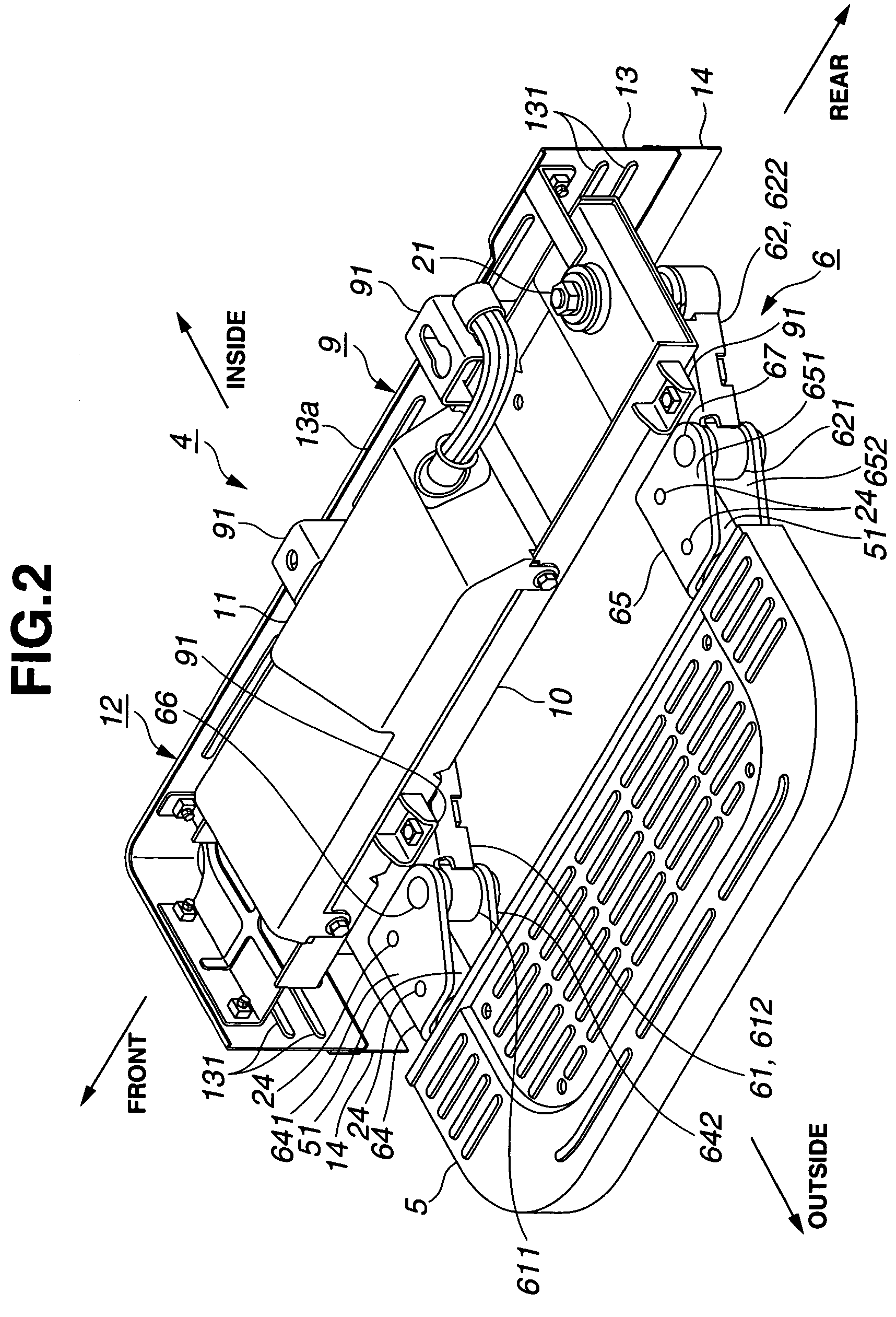
InactiveUS7513520B2Reduce the valueRaise the possibilitySteps arrangementMotor vehicle partEngineering
A powered step device of a vehicle comprises a base member that is adapted to be connected to a vehicle body; a pivoting mechanism held by the base member, the pivoting mechanism being horizontally movable between a first position wherein a given part thereof takes a retracted position relative to the base member and a second position wherein the given part takes a projected position relative to the base member; a step plate connected to the given part of the pivoting mechanism, so that the first and second positions of the pivoting mechanism induce retracted and projected positions of the step plate relative to the base member; and an electric actuator that moves the pivoting mechanism with electric power. The powered step device further comprises a guard member that is fixed to the base member in a manner to cover and protect the pivoting mechanism.
Owner:MITSUI KINZOKU ACT
Slim card reader
ActiveUS7354312B2Easy to carryReduced dimensionTwo-part coupling devicesSensing record carriersEngineeringCard reader
Owner:PING YANG CHUANG +1
Apparatus for and method of forming seals in fuel cells and fuel cell stacks
InactiveUS6852439B2Good chemical resistanceImprove robustnessCellsEngine sealsFuel cellsProbable Case
A sealing technique is provided for forming complex and multiple seal configurations for fuel cells and other electrochemical cells. To provide a seal, for sealing chambers for oxidant, fuel and / or coolant, a groove network is provided extending through the various elements of the fuel cell assembly. A source of seal material is then connected to an external filling port and injected into the groove network, and the seal material is then cured to form the seal. There is thus formed a “seal in place”, that is robust and can accommodate variations in tolerances and dimensions, and that can be bonded, where possible, to individual elements of the fuel cell assembly. This avoids the difficulty, labor intensive cost and complexity of manually assembling many individual gaskets into complex groove shapes and the like. The seal material can be selected to be comparable with a wide variety of gases, liquid coolants and the like.
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Hinge module for a foldable type device
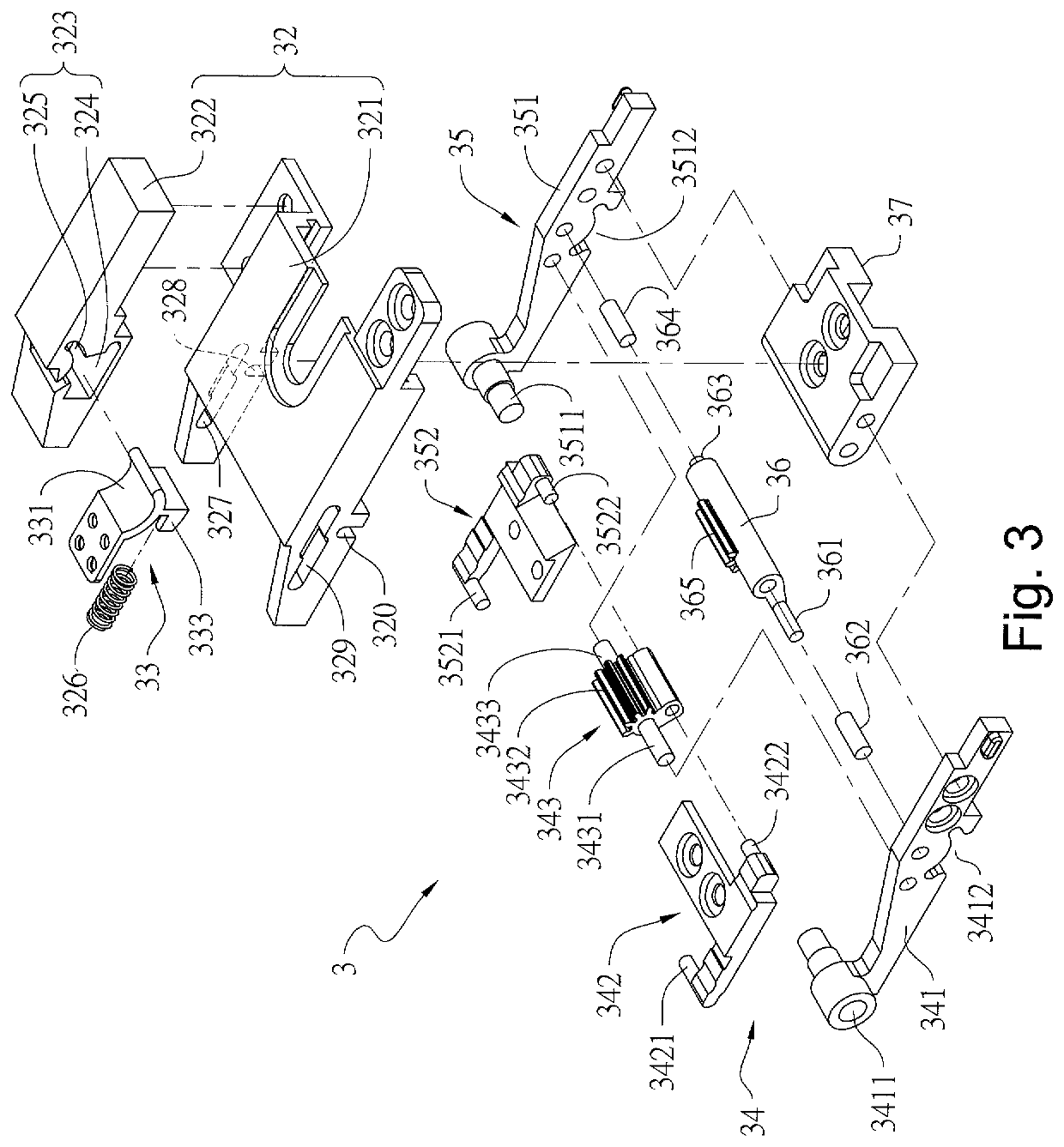
ActiveUS20200103935A1Reduce spacingLower the volumeDetails for portable computersPivotal connectionsDisplay deviceFlexible display
The present invention provides a hinge module for a foldable-type device, one end surface of which is respectively connected to a first housing and a second housing, and another end surface of which is connected to a flexible display so as to have the flexible display folded when the first housing and the second housing is rotated. The hinge module comprises a base and a first sliding mechanism, wherein the base is provided between the first and second housings, and the first sliding mechanism comprises a first sliding cover, a supporting member and a left four-linkage-mechanism and a swinging member. When the first and second housings are rotated to move the left four-linkage-mechanism and the swinging member, the first sliding cover is moved in a linkage way, and one supporting portion of the supporting member is moved by an angle to accommodate the curved part of the flexible display.
Owner:JARLLYTEC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com