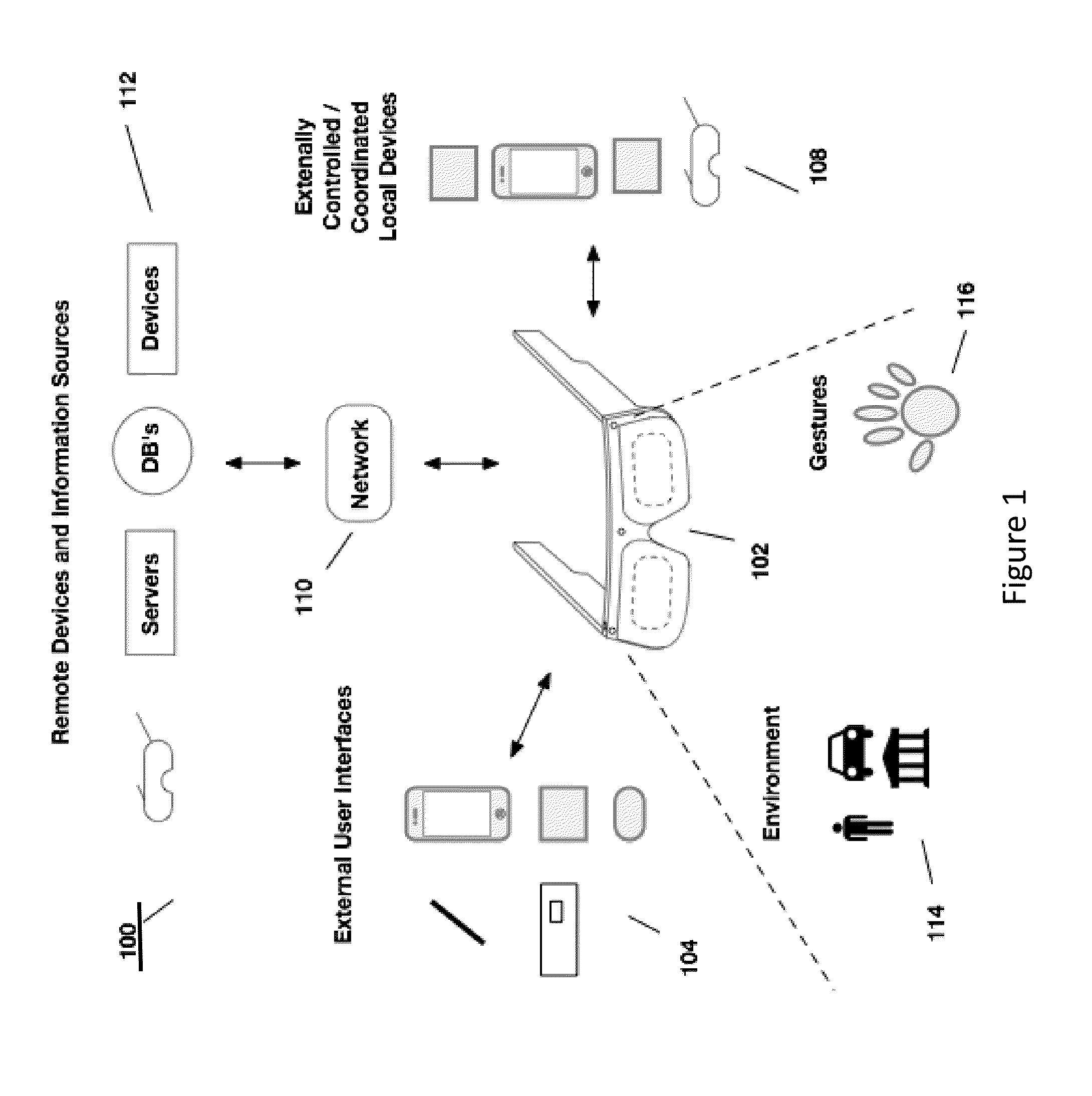
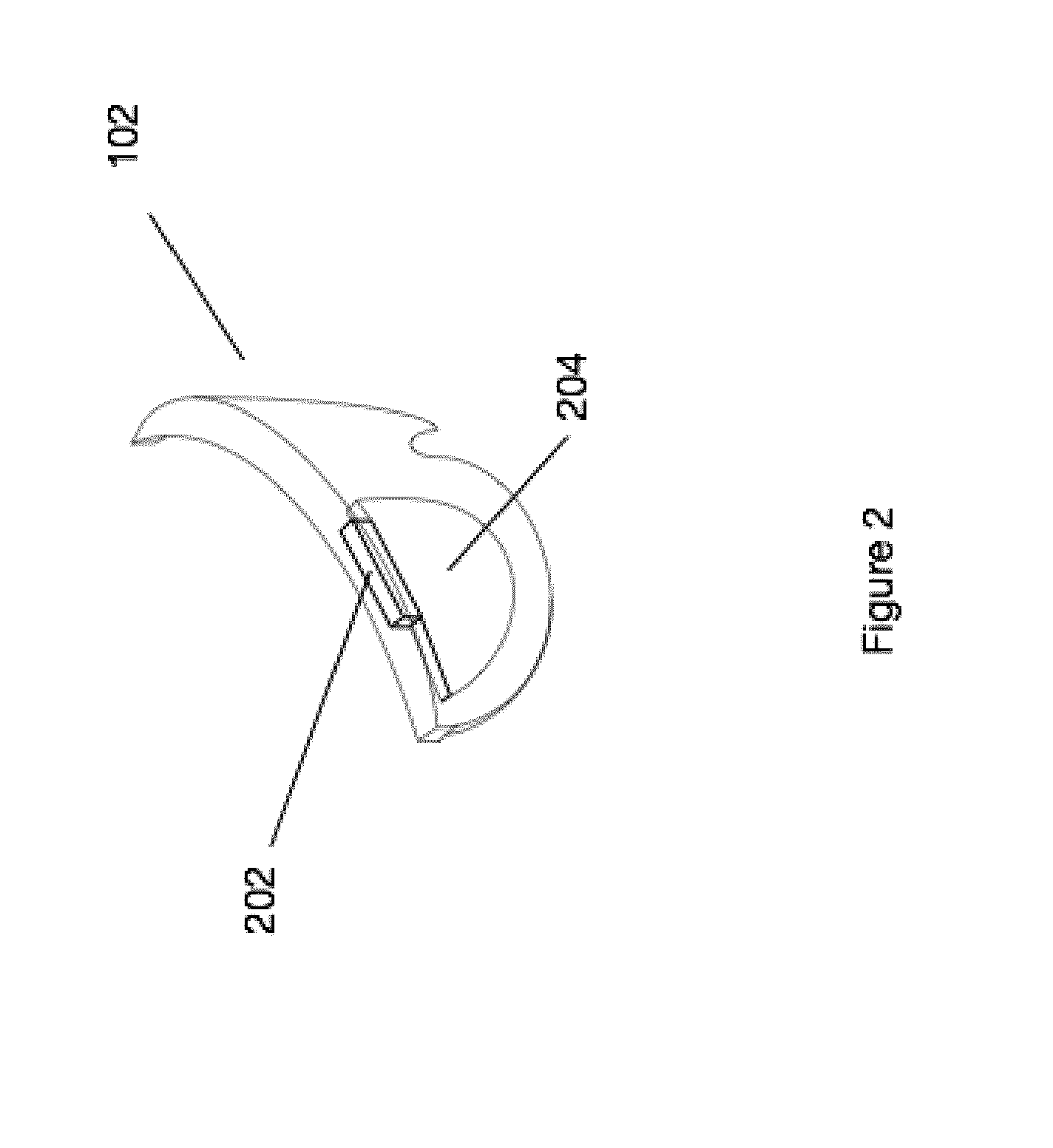
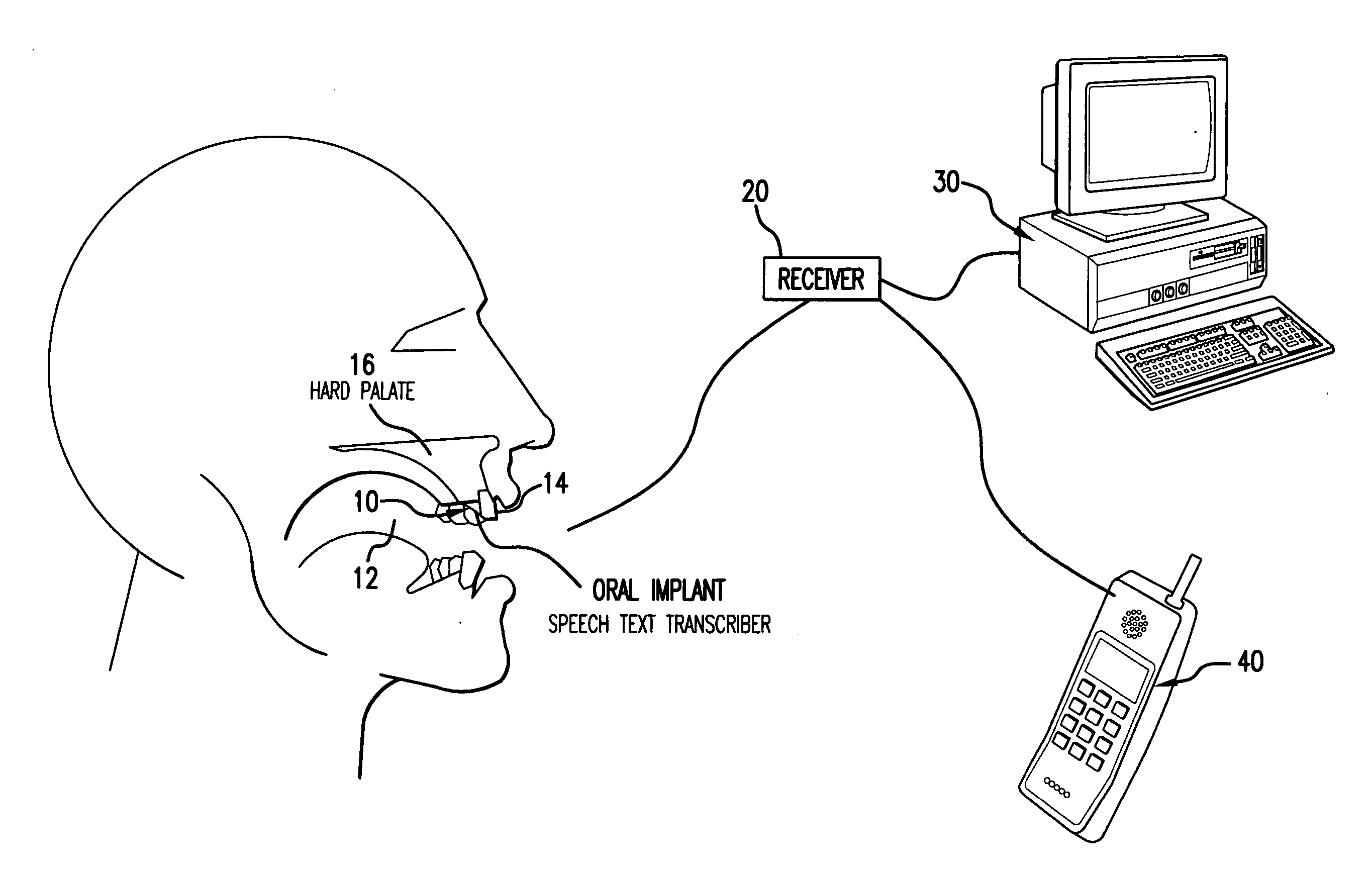
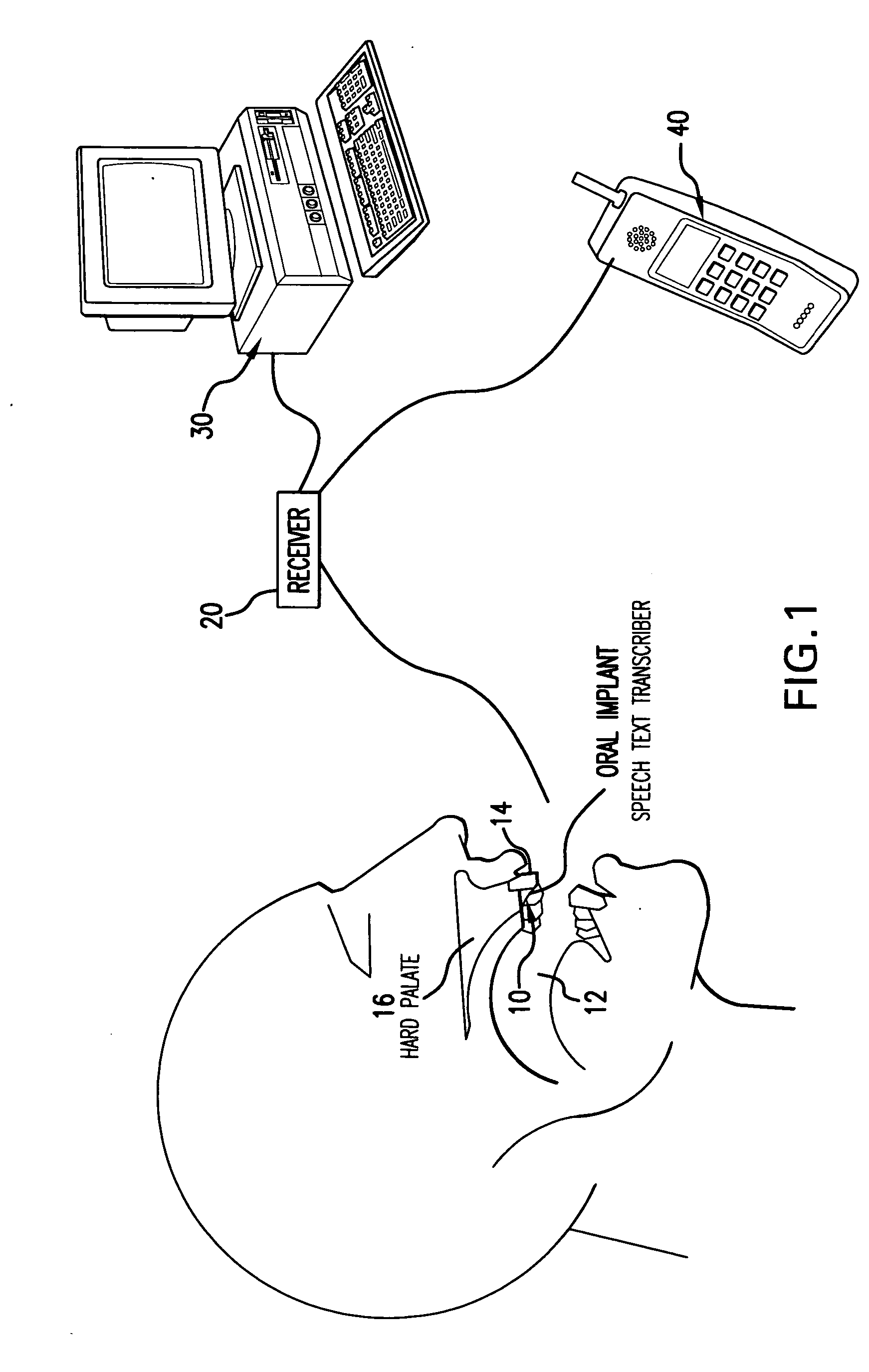
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1159results about "Bone conduction transducer hearing devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
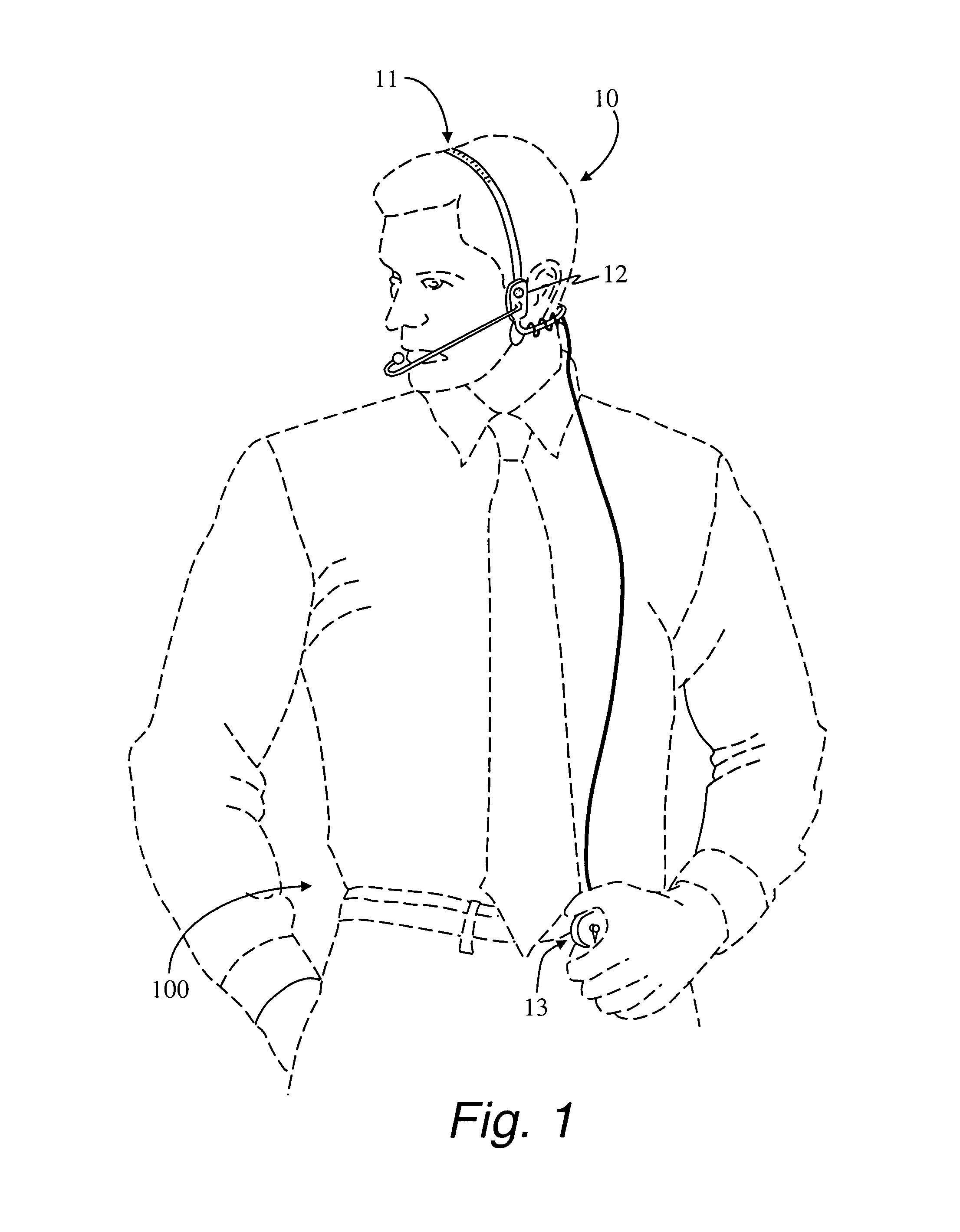
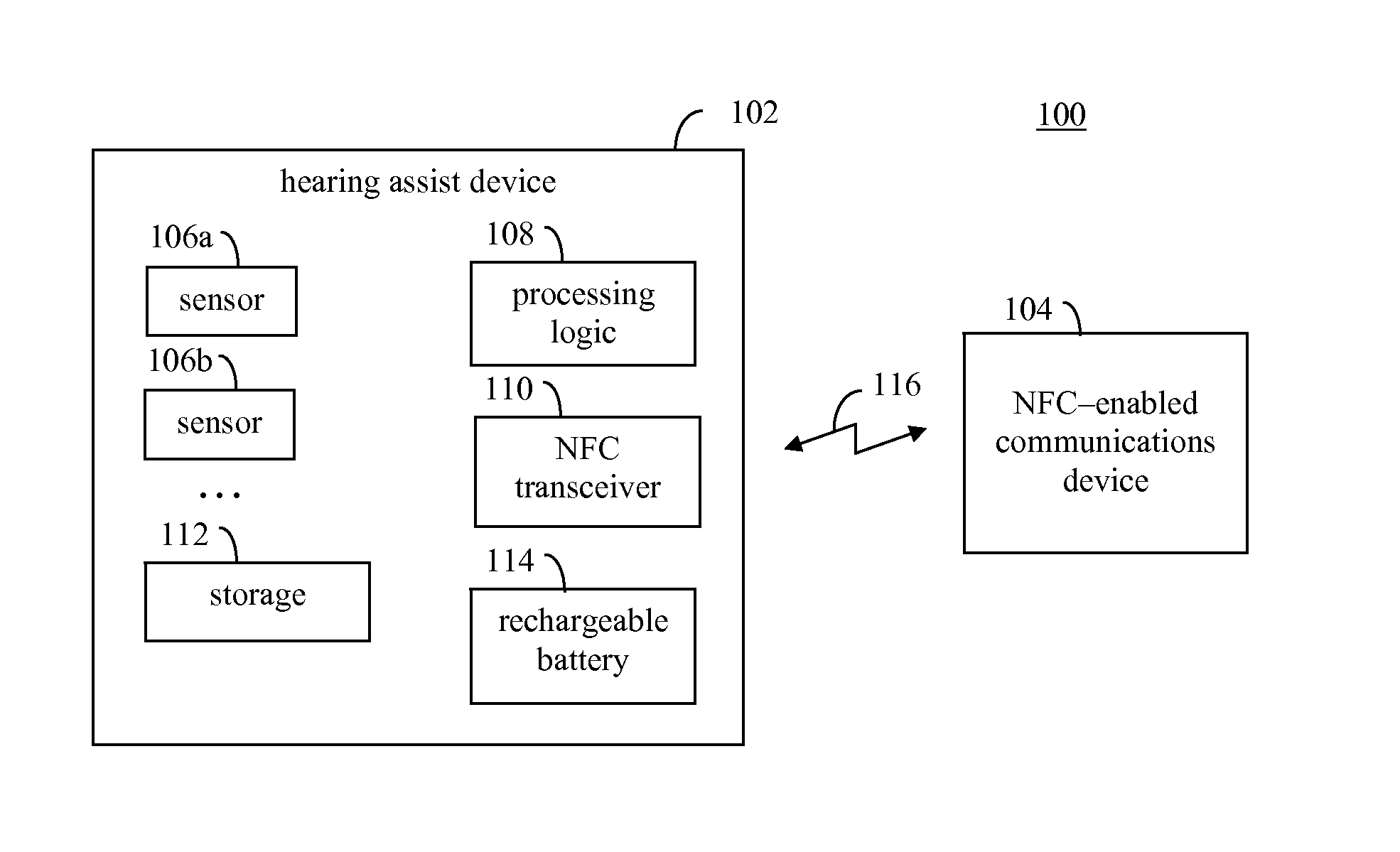
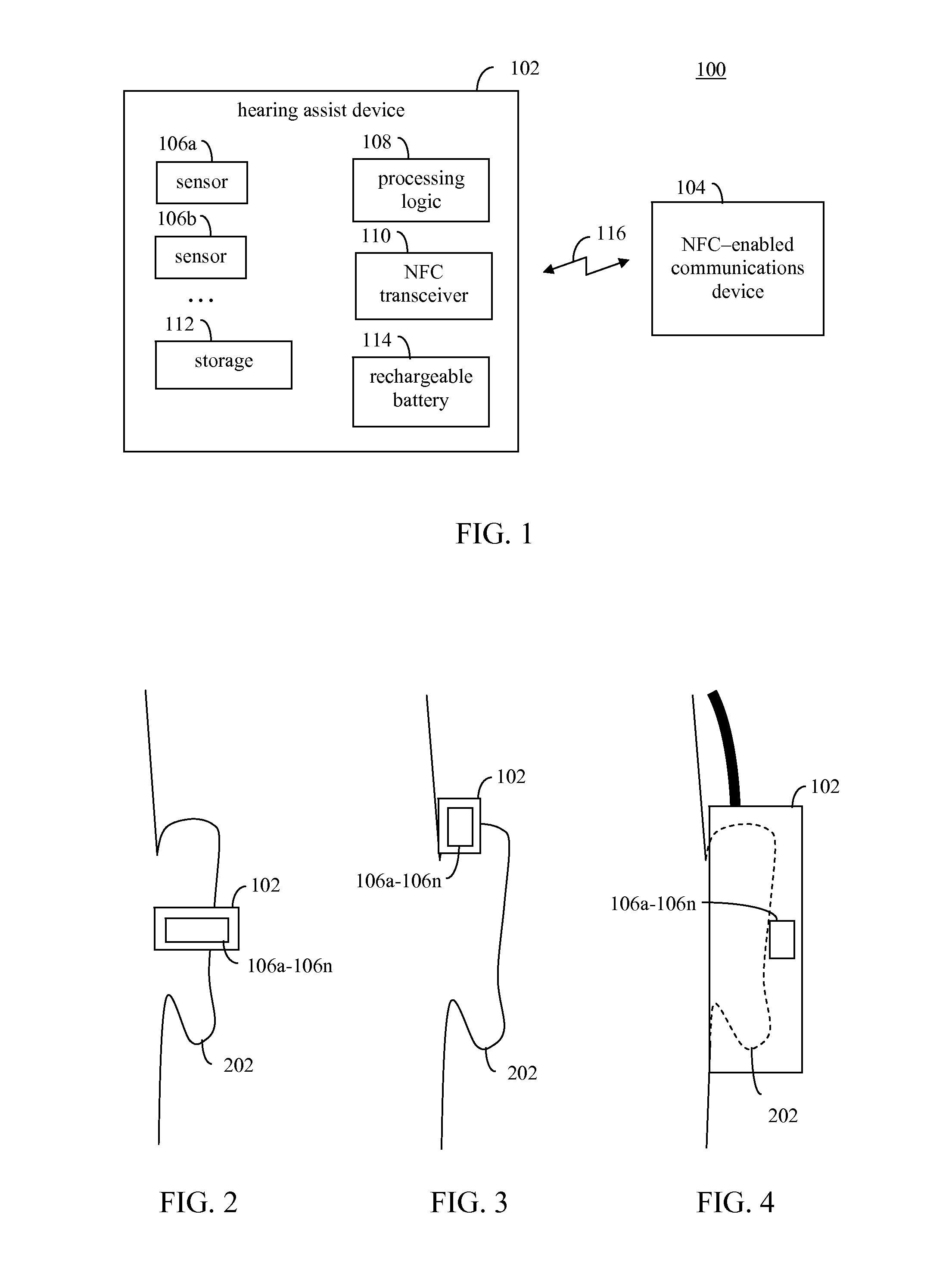
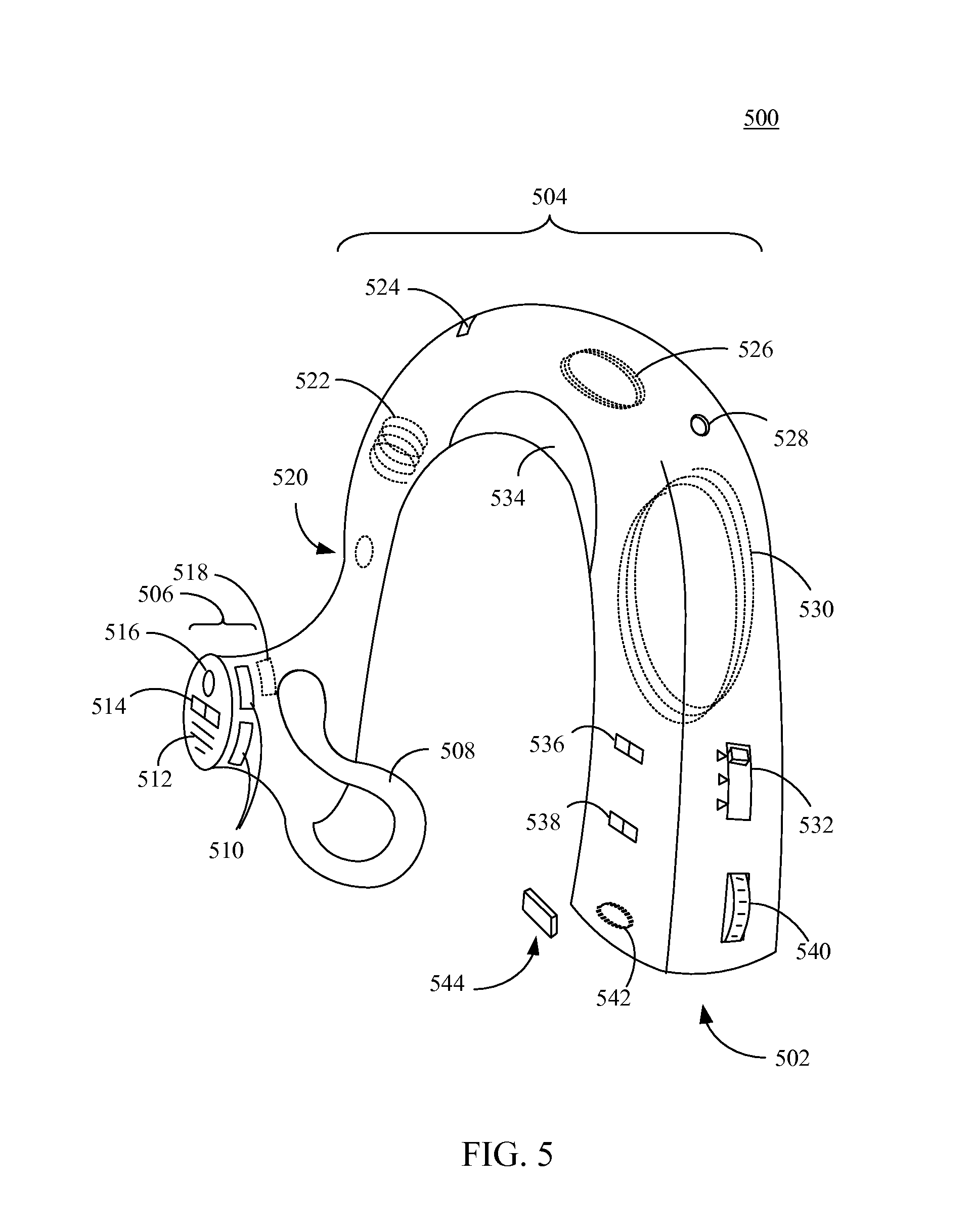
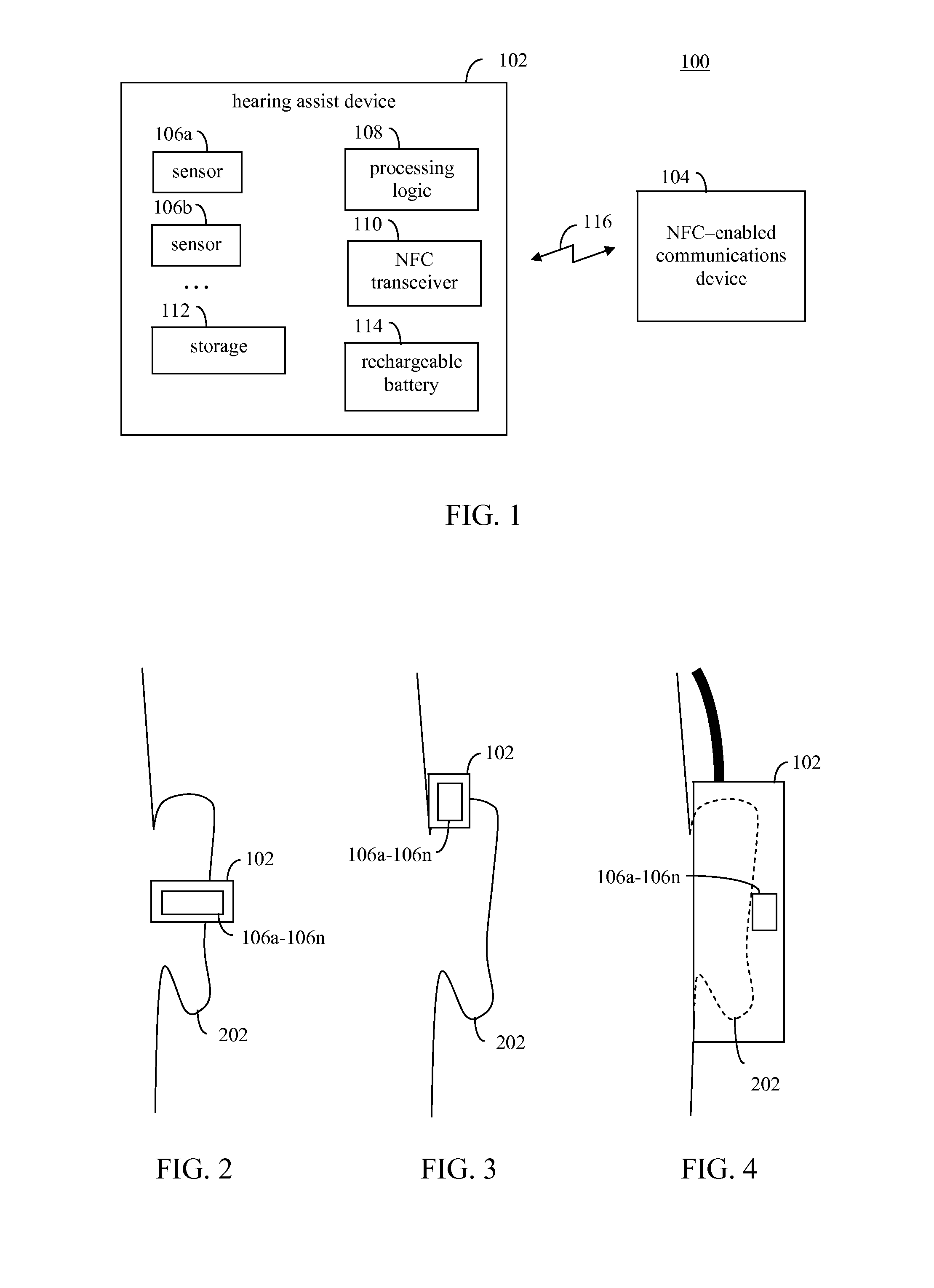
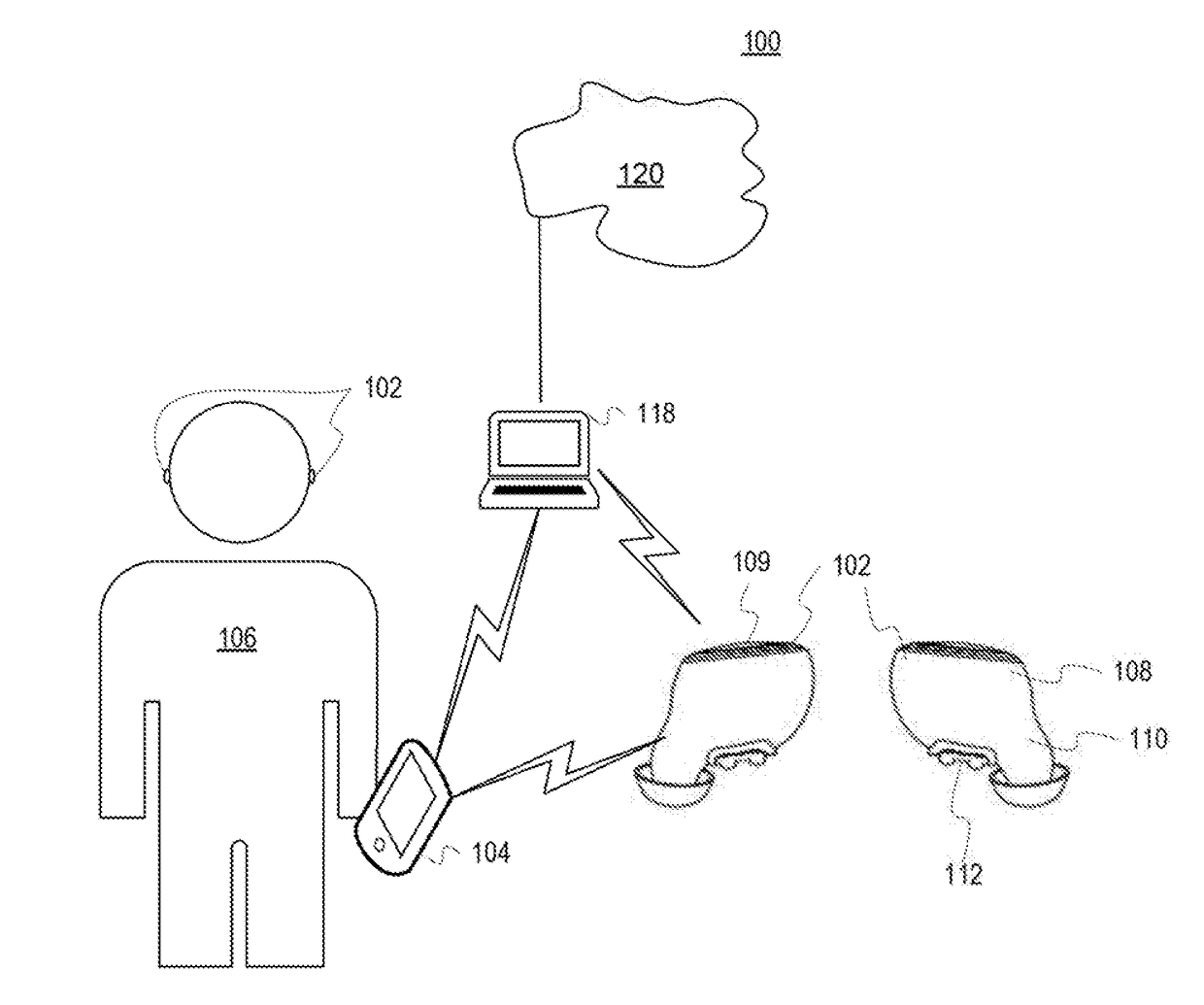
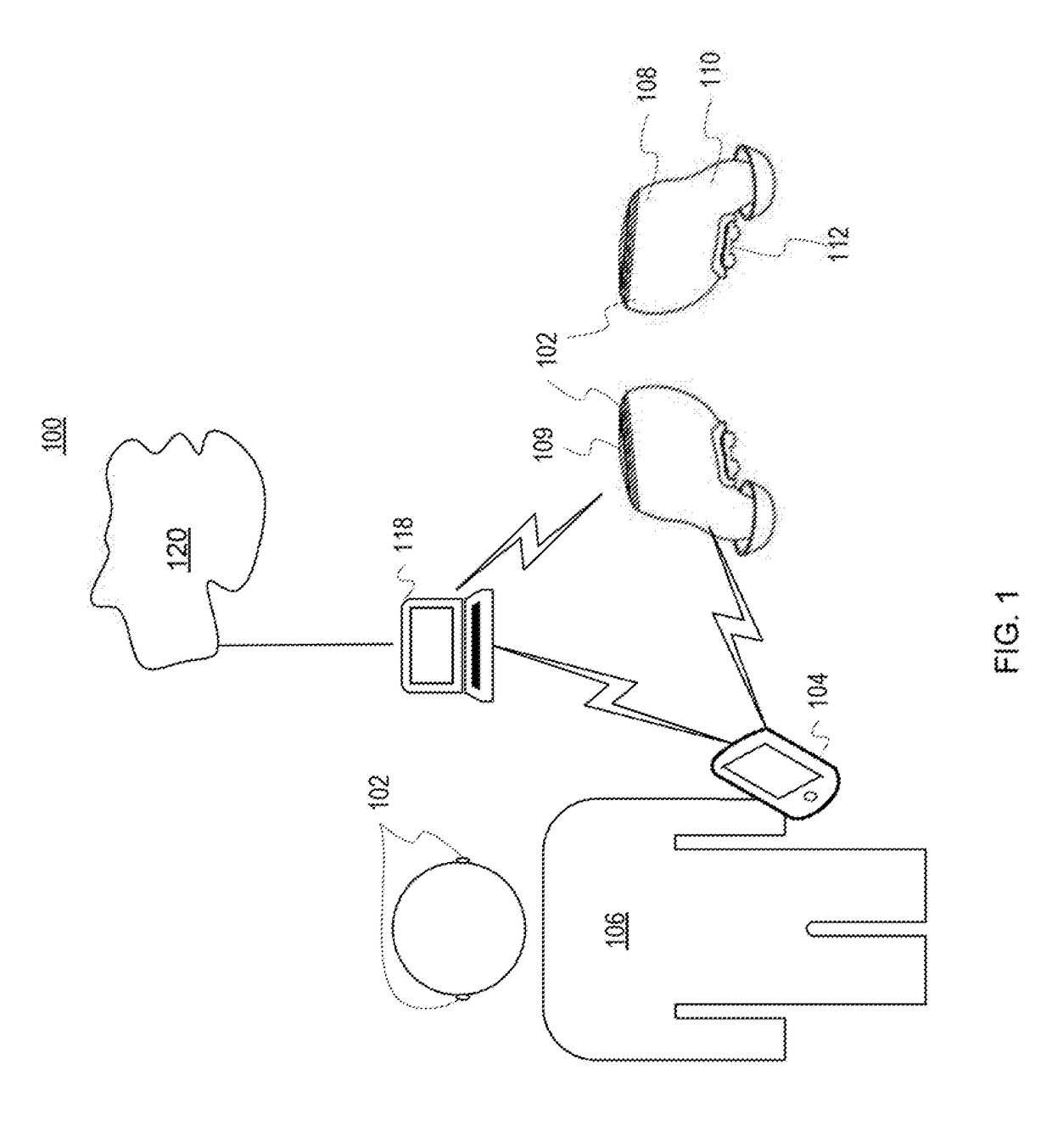
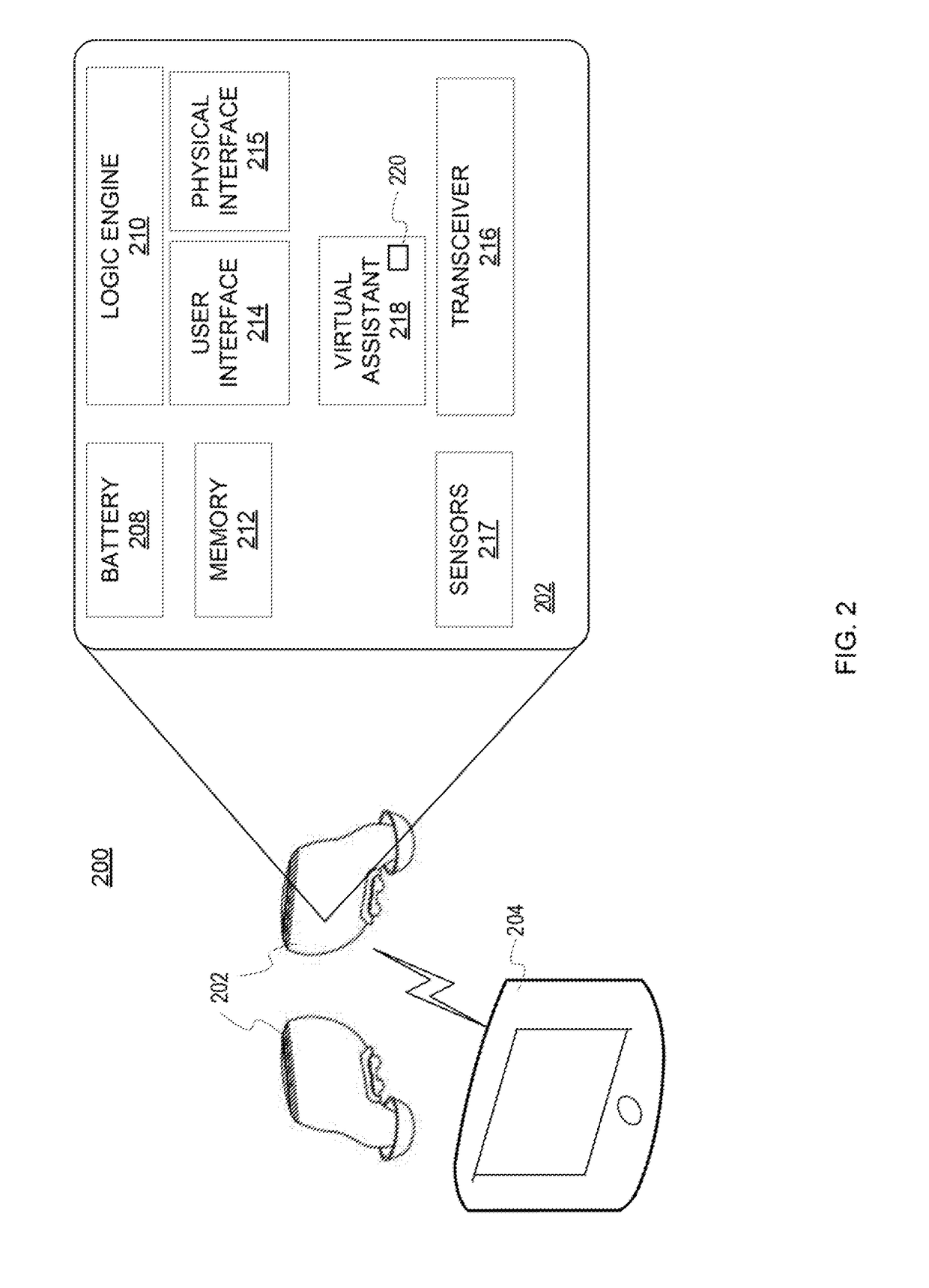
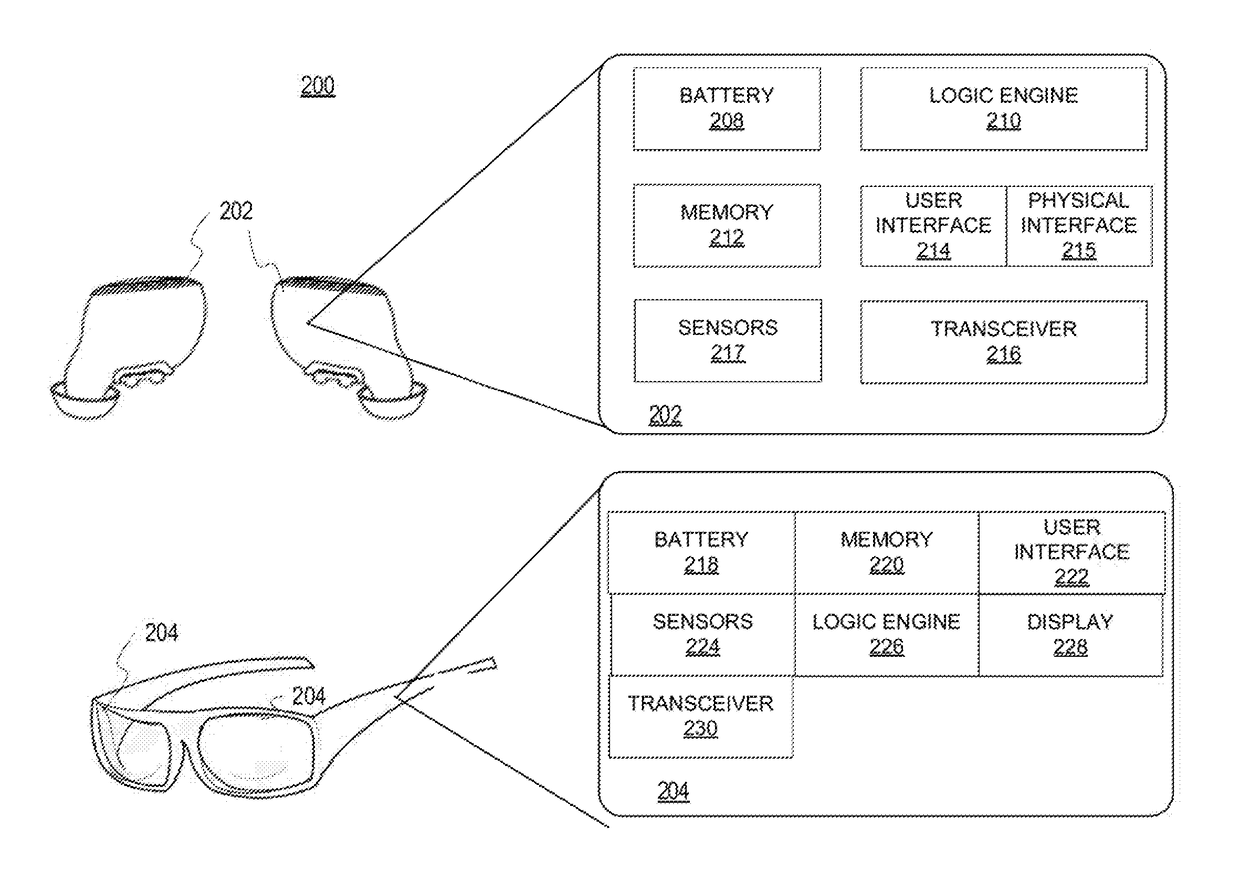
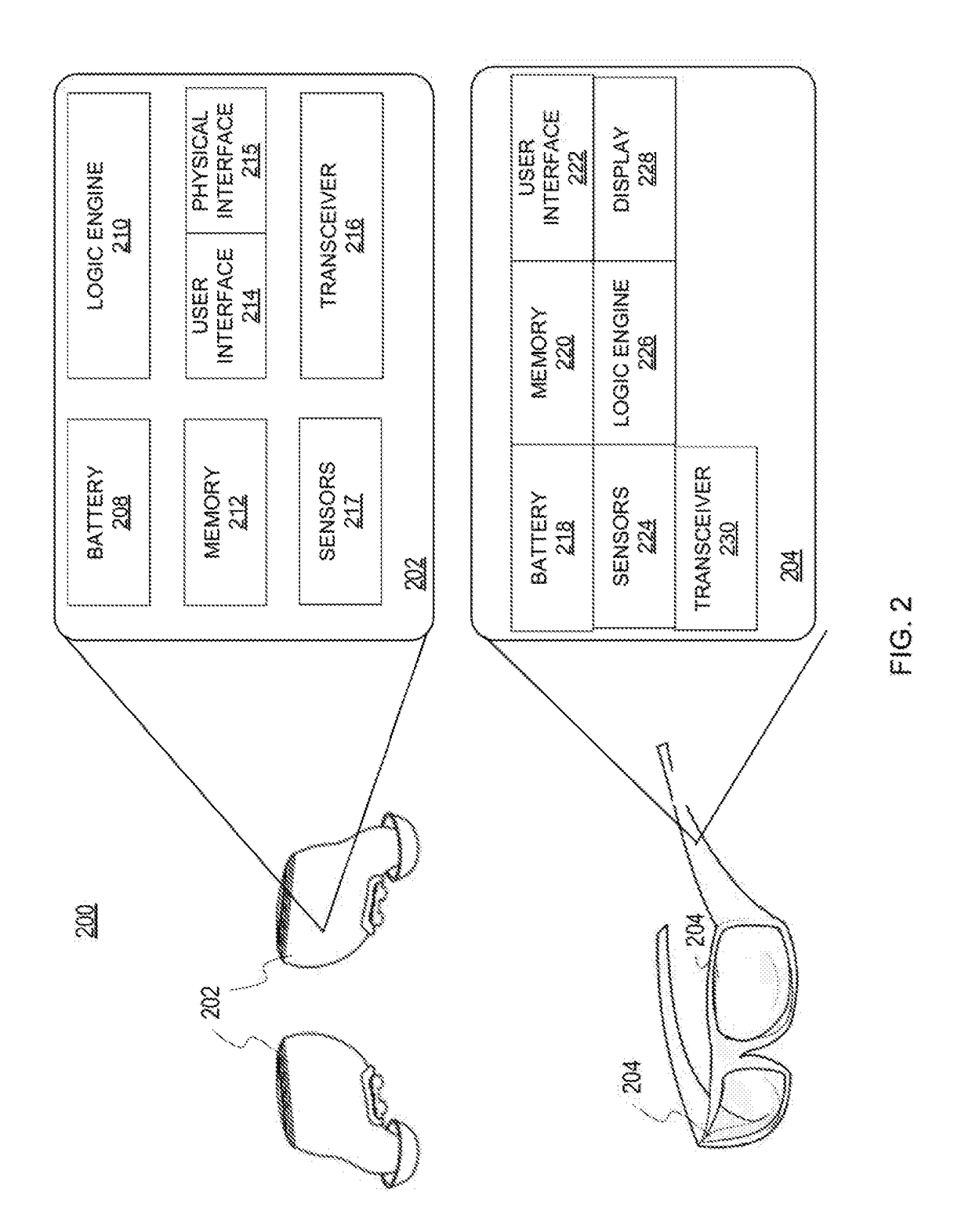
Multisensor hearing assist device for health
InactiveUS20130343585A1Hearing device energy consumption reductionPharmaceutical containersHearing aidRemote analysis
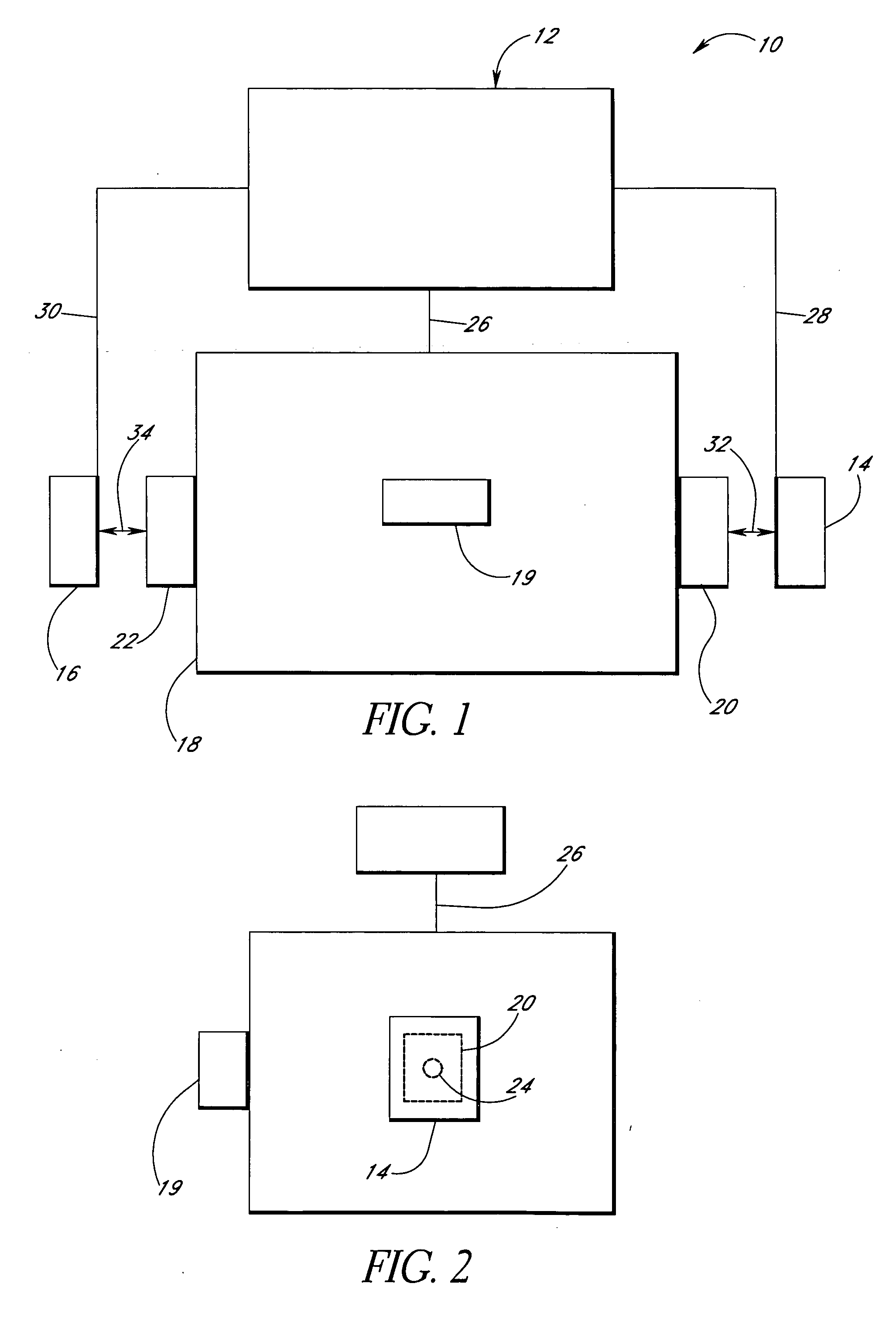
A hearing assist device is associated with an ear of a user. Health characteristics of the user are measured by sensors of the hearing assist device. The measured health characteristics may be analyzed in the hearing assist device, or transmitted from the hearing assist device for remote analysis. Based on the analysis, alerts, instructions, and other information may be displayed to the user in the form of text or graphics, or may be played by the hearing assist device in the form of sound / voice. Medical personnel may be alerted when problems with the user are detected by the hearing assist device. The user may provide verbal commands to the hearing assist device. The hearing assist device may be configured to filter sounds, and may be configured for a personal hearing frequency response of the user. The hearing assist device may be configured for speech recognition to recognize commands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
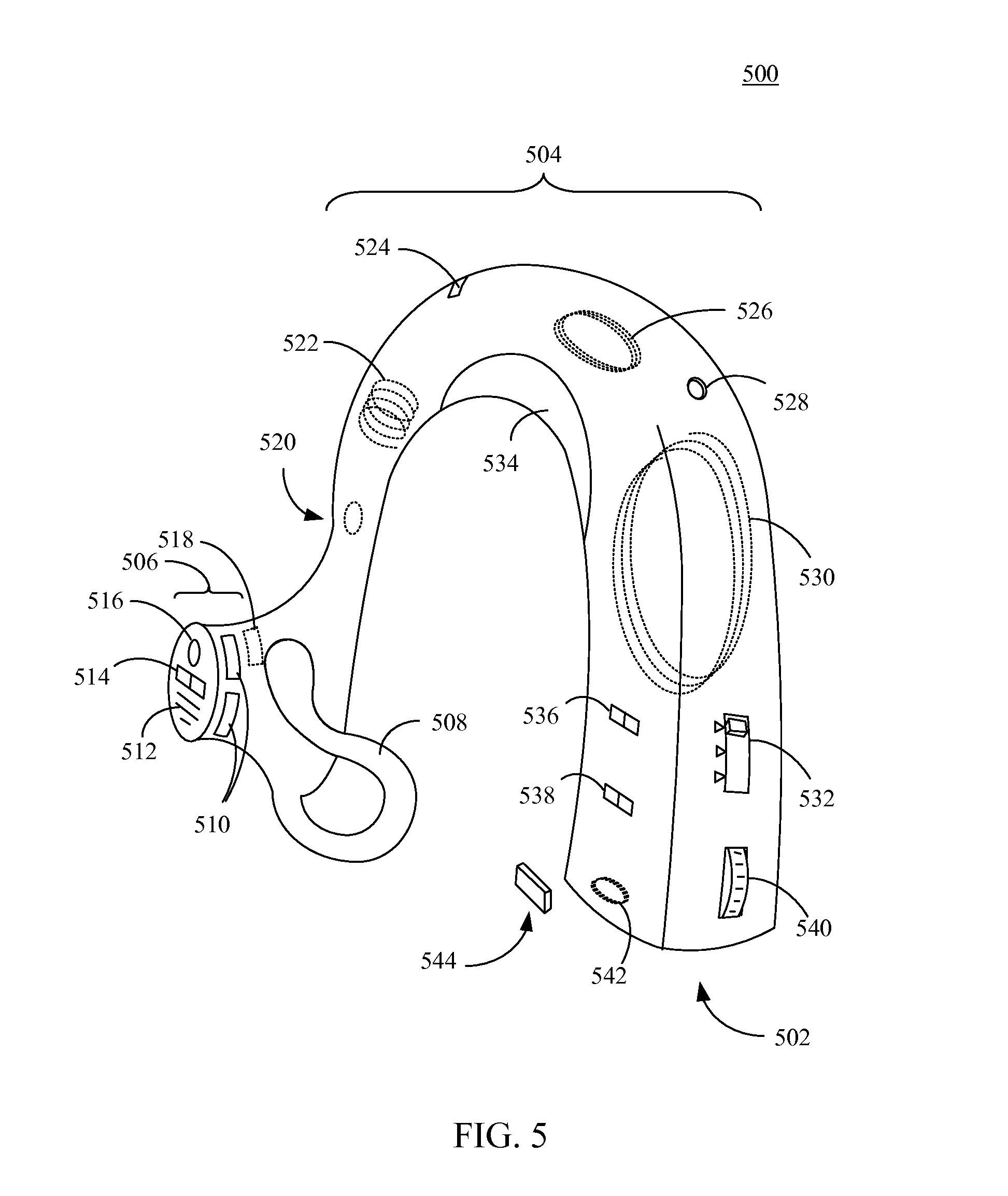
Hearing assist device with external operational support
InactiveUS20130343584A1Hearing device energy consumption reductionPharmaceutical containersHearing aidElectrophonic hearing
Hearing assist devices and devices and services that are capable of providing external operational support thereto are described. In accordance with various embodiments, the performance of one or more functions by a hearing assist device is assisted or improved in some manner by utilizing resources of an external device and / or service to which the hearing assist device may be communicatively connected. Such performance assistance or improvement may be achieved, for example and without limitation, by utilizing power resources, processing resources, storage resources, sensor resources, and / or user interface resources of an external device or service to which the hearing assist device may be communicatively connected.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
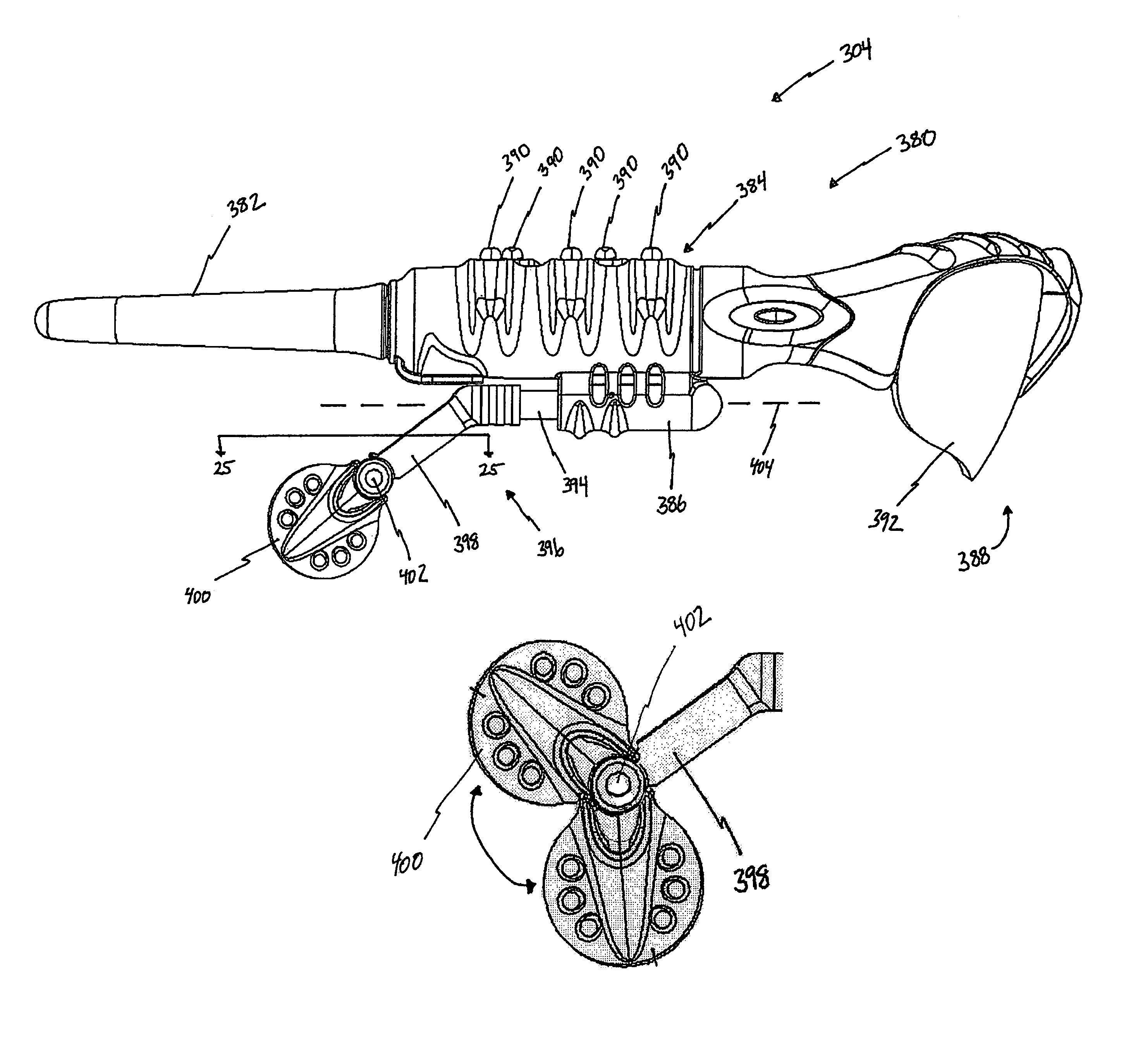
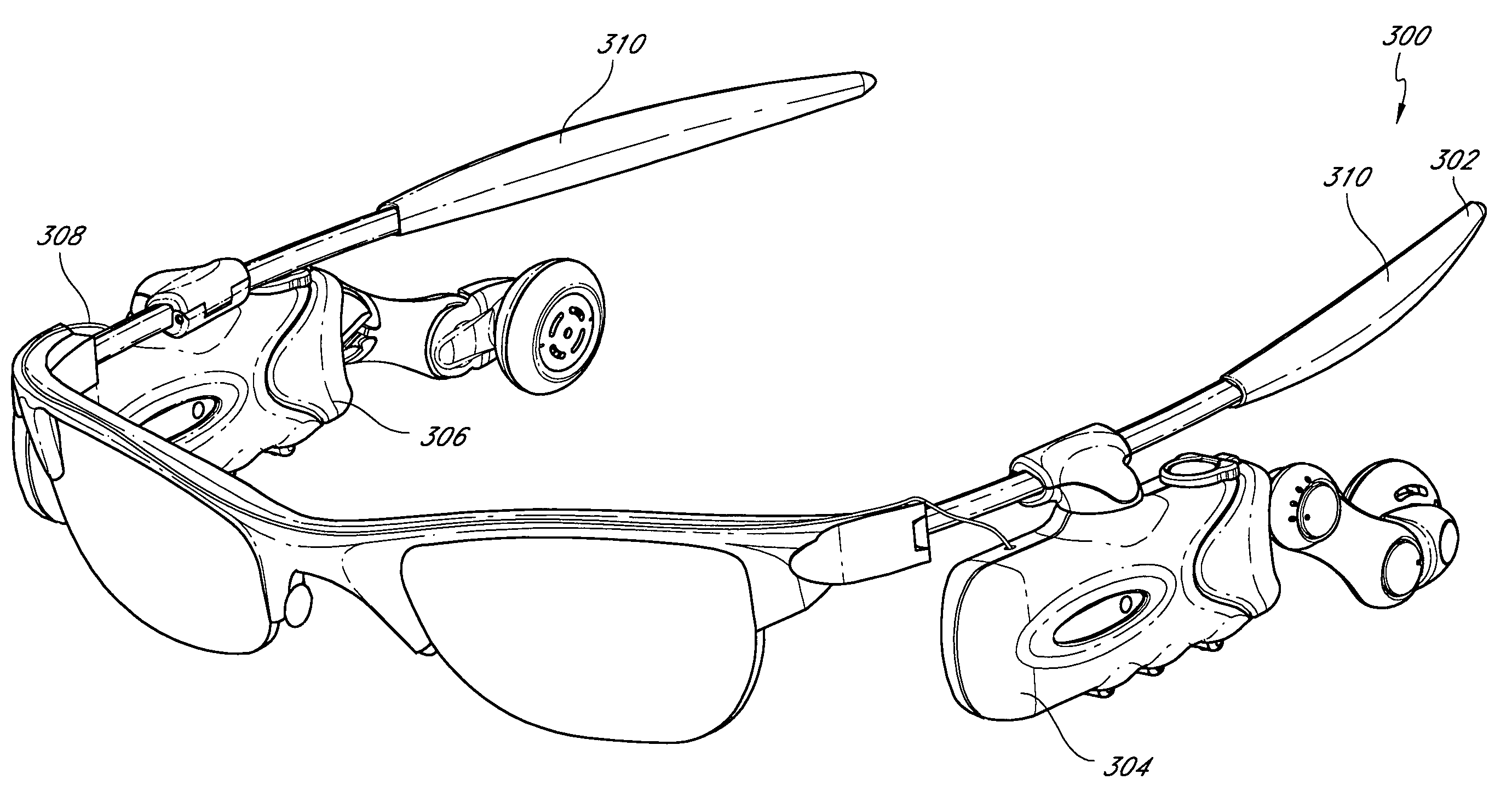
Wireless interactive headset
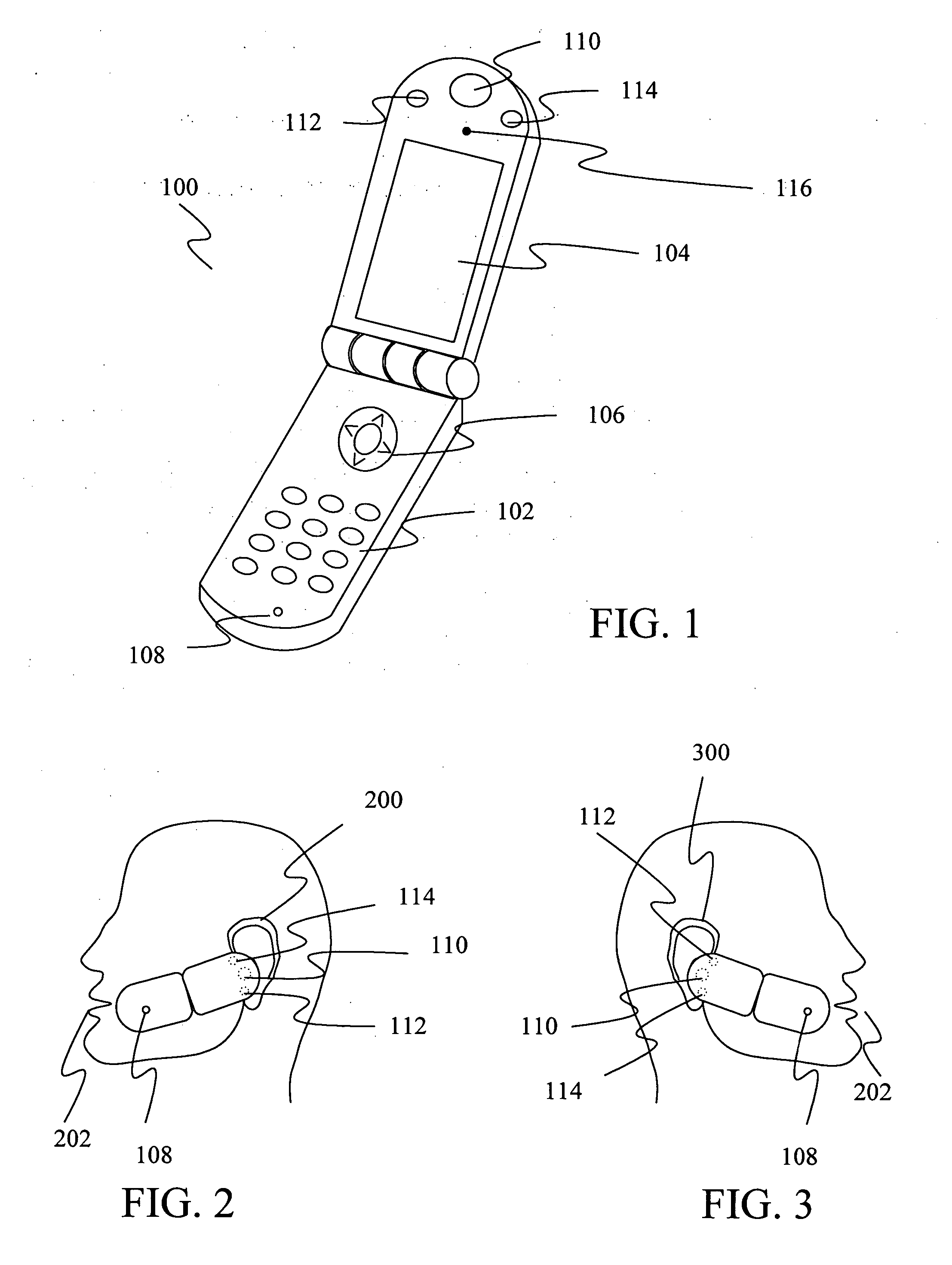
A wearable wireless audio device includes a support, an electronics circuit, and a speaker. The support includes a first ear stem and an orbital, and is configured to support at least one lens in a wearer's field of view. The electronics circuit is supported by the support and is configured to receive at least one digital audio file and generate an audio signal indicative of the at least one digital audio file. The speaker is supported by the support, and is directed toward at least one of the wearer's ears. The speaker is configured to convert the audio signal into sound. The speaker has a speaker face, and the speaker is configured to rotate from a first position in which the speaker face is substantially parallel to a yz-plane to a second position in which the speaker is inclined at an angle with respect to the yz-plane. The speaker is coupled to the support with a speaker pivot, and is configured to rotate about the speaker pivot while maintaining the speaker face substantially parallel to a yz-plane. The speaker is configured to move along an axis substantially parallel to a z-axis with respect to the support.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
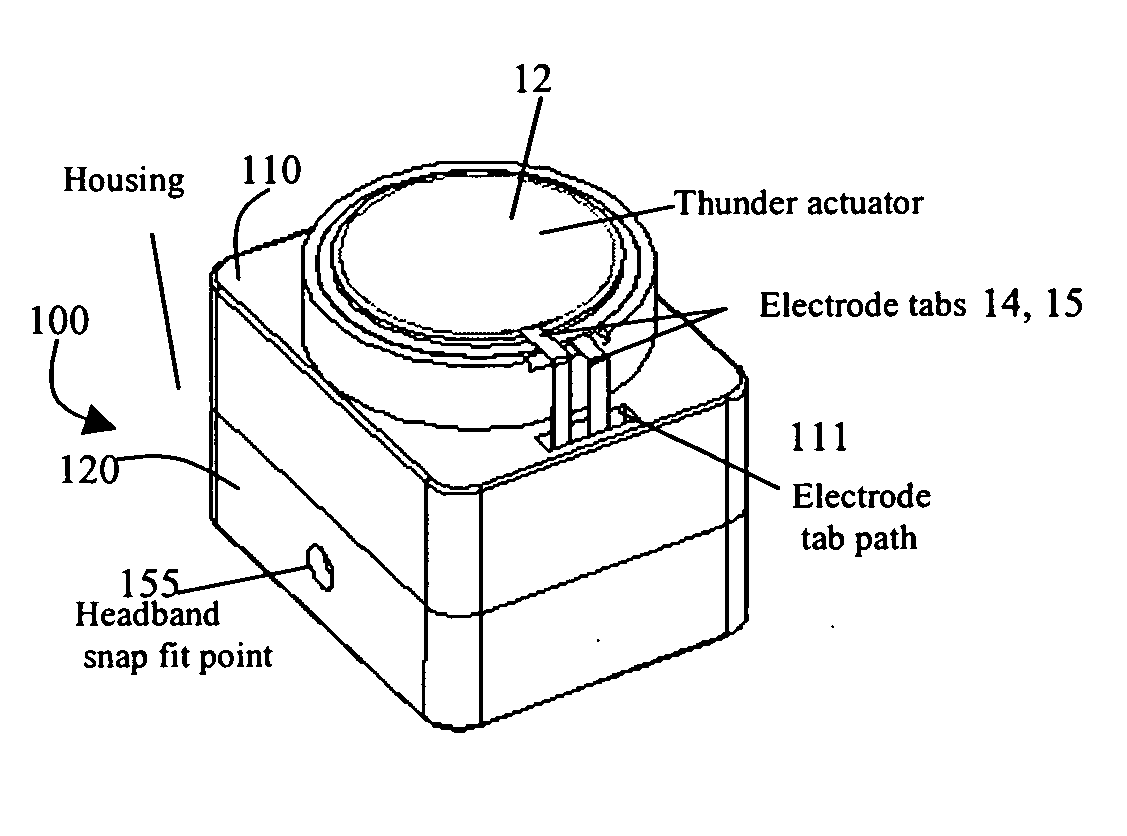
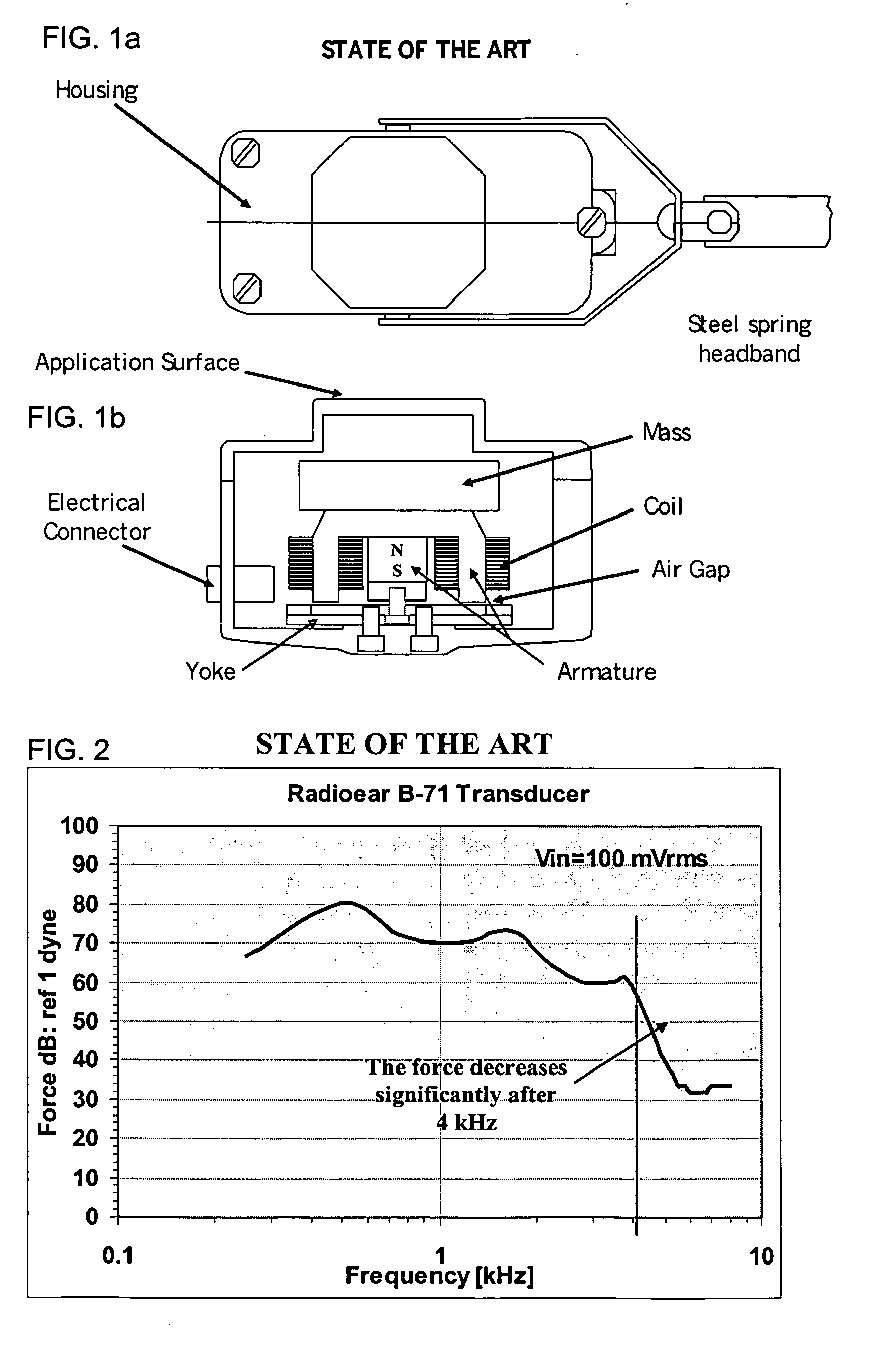
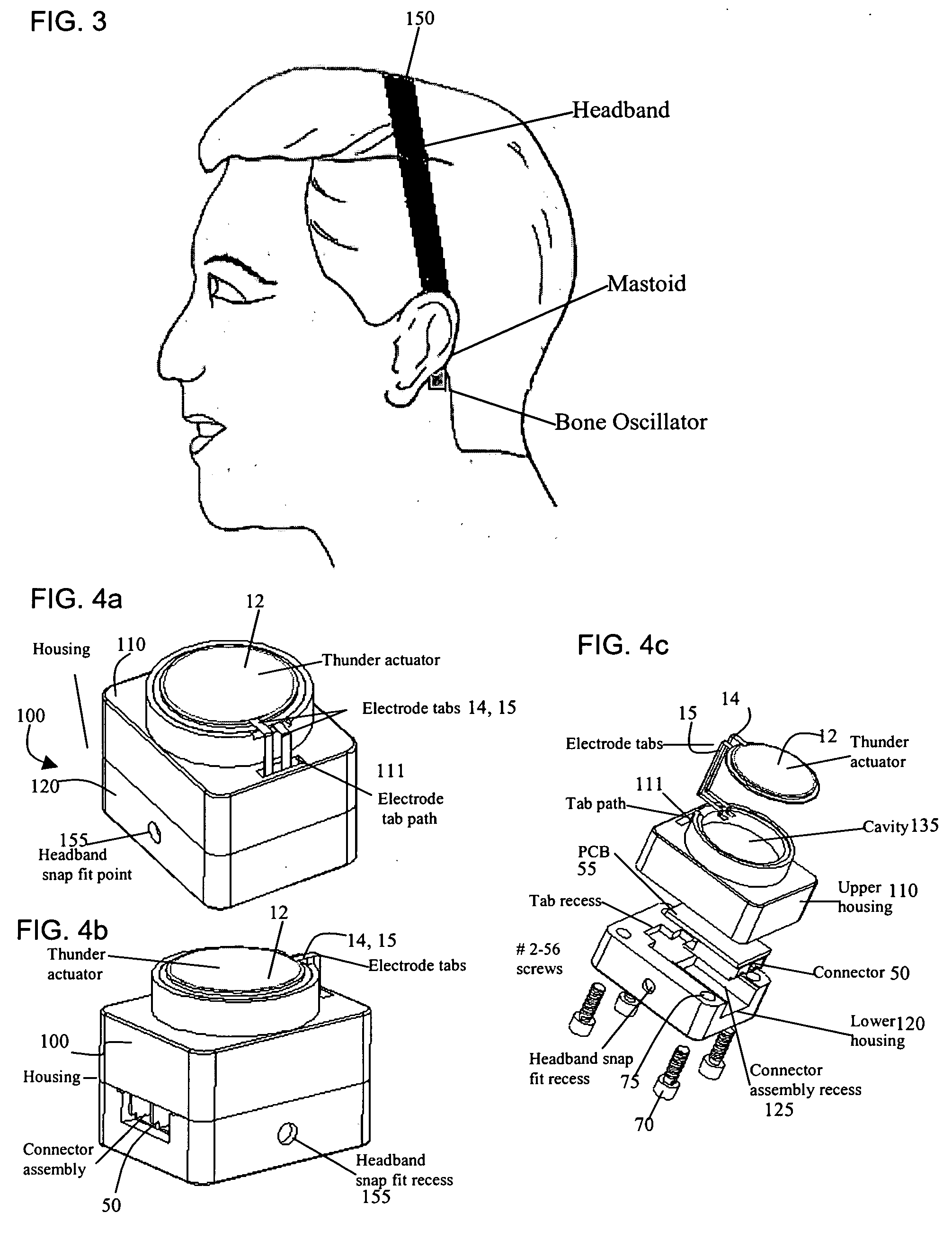
Bone-conduction hearing-aid transducer having improved frequency response
InactiveUS20070041595A1Eliminates soldering wireEliminate useRecord carriersPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFrequency spectrumBone structure
A hearing-aid device and a method for transmitting sound through bone conduction are disclosed. The hearing-aid device comprises a piezoelectric-type actuator, housing and connector. The piezoelectric actuator is preferably a circular flextensional-type actuator mounted along its peripheral edge in a specifically designed circular structure of the housing. During operation, the bone-conduction transducer is placed against the mastoid area behind the ear of the patient. When the device is energized with an alternating electrical voltage, it flexes back and forth like a circular membrane sustained along its periphery and thus, vibrates as a consequence of the inverse piezoelectric effect. Due to the specific and unique designs proposed, these vibrations are directly transferred trough the human skin to the bone structure (the skull) and provide a means for the sound to be transmitted for patients with hearing malfunctions. The housing acts as a holder for the actuators, as a pre-stress application platform, and as a mass which tailors the frequency spectrum of the device. The apparatus exhibits a performance with a very flat response in the frequency spectrum 200 Hz to 10 kHz, which is a greater spectrum range than any other prior art devices disclosed for bone-conduction transduction which are typically limited to less than 4 kHz.
Owner:FACE INT
Voice transmission apparatus with UWB
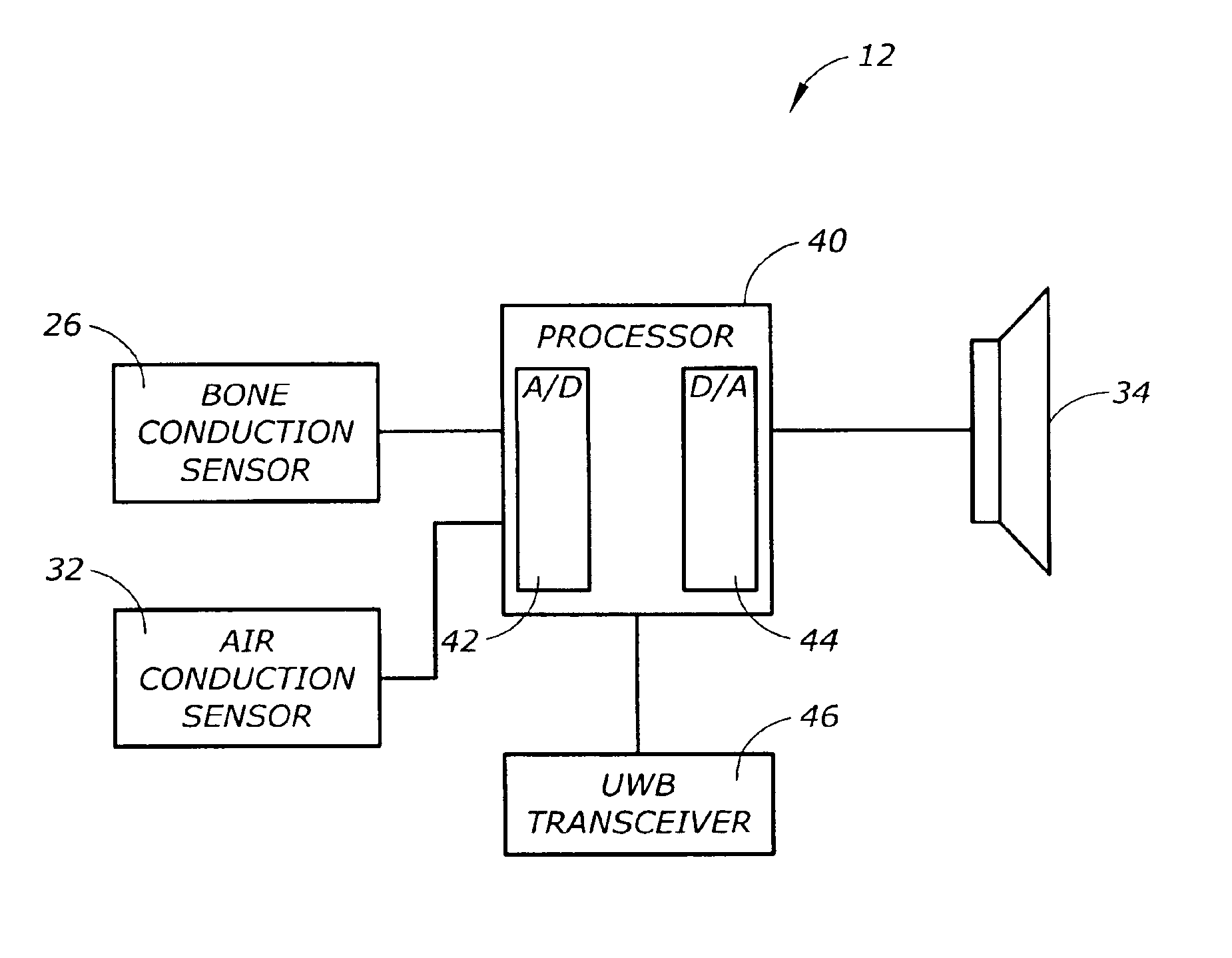
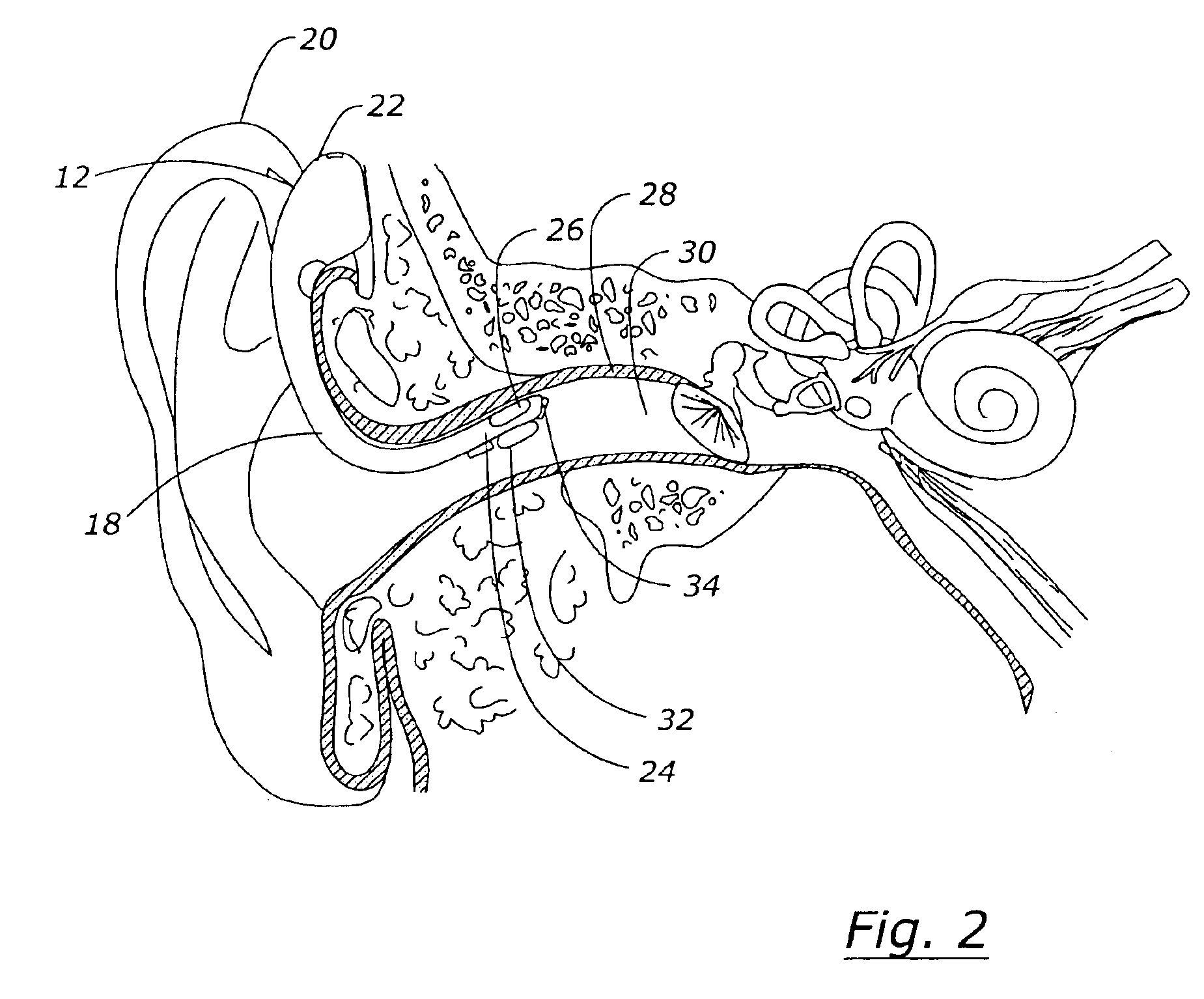
InactiveUS6952483B2Reduce electromagnetic radiationImprove overall senseMicrophonesLoudspeakersTransceiverVoice communication
A voice communication device such as an earpiece that provides for ultra short range transmission of voice sound information using ultra wide band (UWB) radio communications is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a voice communication device includes a speaker, a bone conduction sensor for sensing voice sound vibrations, and an UWB transceiver operatively connected to the speaker and the bone conduction sensor. According to another embodiment of the present invention, a voice communication device is disclosed that includes an earpiece housing, a speaker operatively connected to the earpiece housing for transducing audio, an air conduction sensor operatively connected to the housing for sensing voice sound information, a processor electrically connected to the speaker and the bone conduction sensor and disposed within the earpiece housing, and an UWB transceiver operatively connected to the processor.
Owner:BOESEN PETER V M D
Hearing aid system
InactiveUS20070053536A1Easy to changeLittle strengthBone conduction transducer hearing devicesDeaf-aid setsSkin contactEngineering
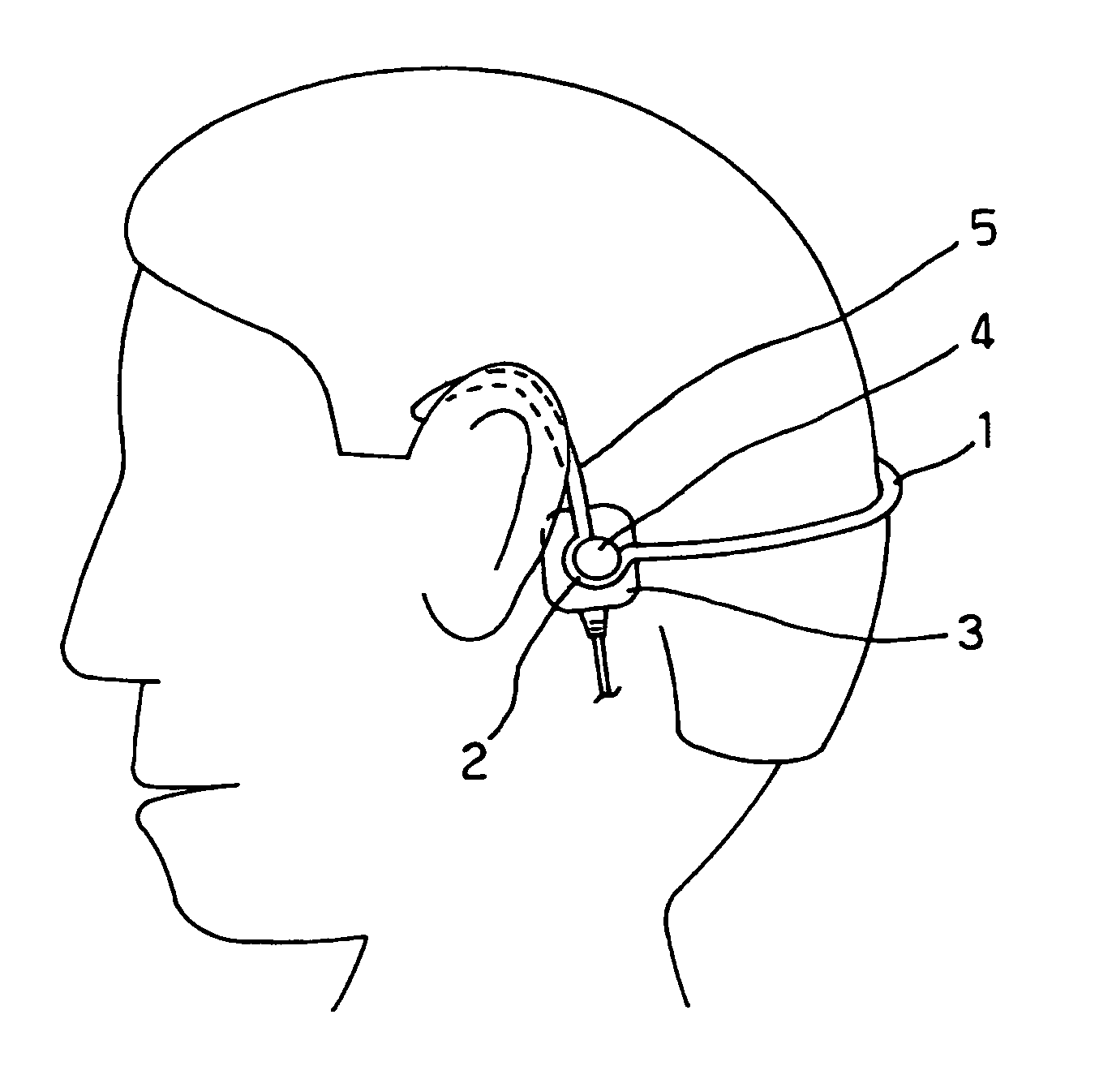
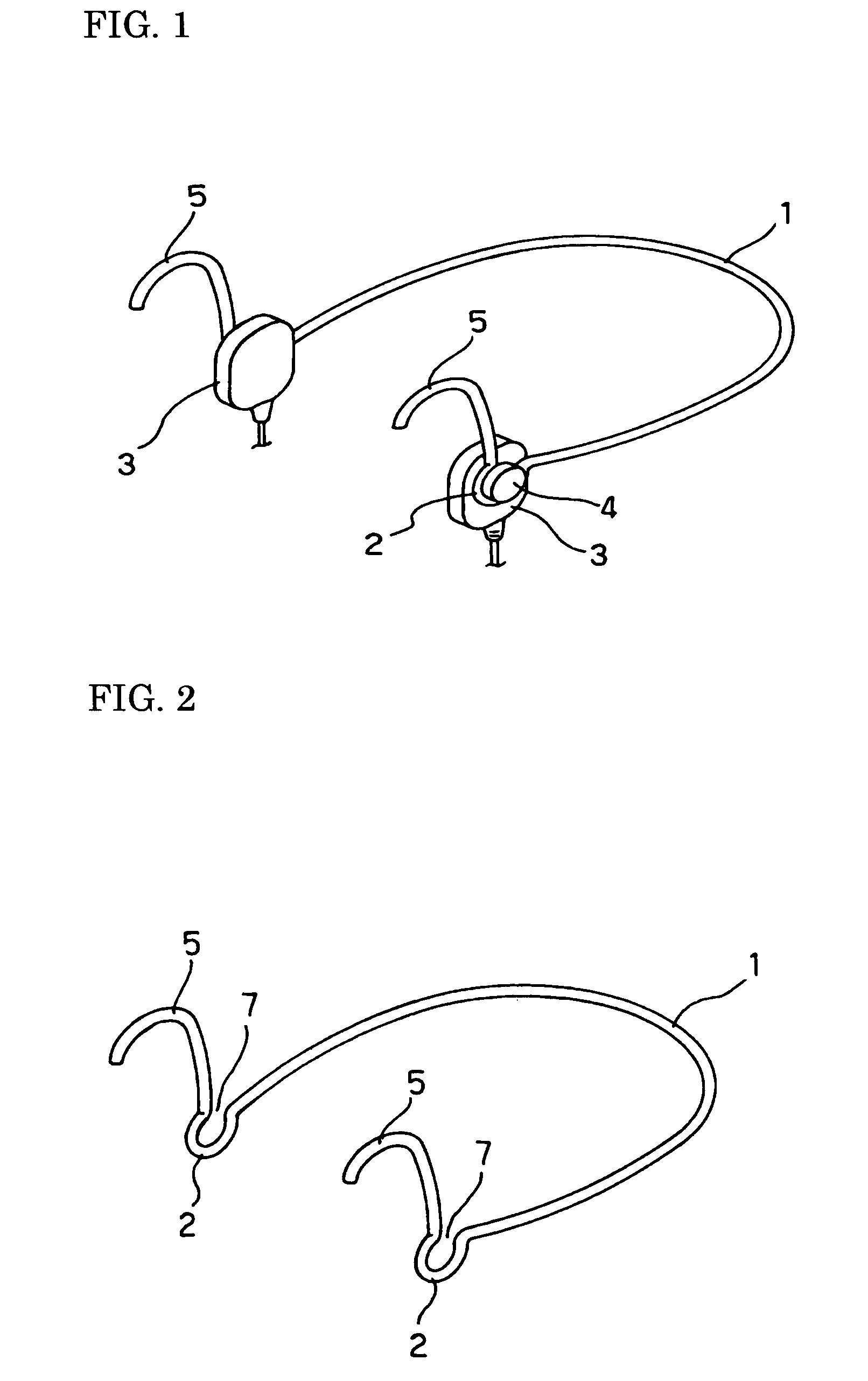
A bone conduction hearing aid system for generating bone conduction vibrations is disclosed. The bone conduction hearing aid system has an external hearing aid unit with a vibrator and a skin contact pressure plate. The skin contact pressure plate is placed on an outside of the external hearing aid unit and the skin contact pressure plate is magnetically attached to an implanted unit anchored to the skull under the skin. The vibrator transforms an electrical signal into mechanical vibrations and the skin contact pressure plate allows transmission of the vibrations from the vibrator to the implanted unit when the external hearing aid unit is magnetically fixed to the implanted unit.
Owner:OTICON
Display Structure with Direct Piezoelectric Actuation
InactiveUS20100225600A1Improve the display effectEasy to useBone conduction transducer hearing devicesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersHand heldEngineering
A user friendly display structure (100) for an electronic device (102), such as a touch screen hand held communications device, is provided with piezoelectric elements (126) bonded or otherwise secured directly to the back of a display module (112) generates effective haptics and sound localized to the display area. Actuation of piezoelectric elements (126) in the display structure (100) generates bending motion of the entire display structure (100) which provides haptics feedback to fingers operating on the display structure (100) as well as generates sound by turning part or the entire display into a speaker.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Wireless interactive headset
A wearable wireless audio device includes a support, an electronics circuit, and a speaker. The support includes a first ear stem and an orbital, and is configured to support at least one lens in a wearer's field of view. The electronics circuit is supported by the support and is configured to receive at least one digital audio file and generate an audio signal indicative of the at least one digital audio file. The speaker is supported by the support, and is directed toward at least one of the wearer's ears. The speaker is configured to convert the audio signal into sound. The speaker has a speaker face, and the speaker is configured to rotate from a first position in which the speaker face is substantially parallel to a yz-plane to a second position in which the speaker is inclined at an angle with respect to the yz-plane. The speaker is coupled to the support with a speaker pivot, and is configured to rotate about the speaker pivot while maintaining the speaker face substantially parallel to a yz-plane. The speaker is configured to move along an axis substantially parallel to a z-axis with respect to the support.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
Speaker assembly for headworn computer
ActiveUS20150346496A1Bone conduction transducer hearing devicesIntra aural earpiecesEngineeringLoudspeaker
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
Orally mounted wireless transcriber device
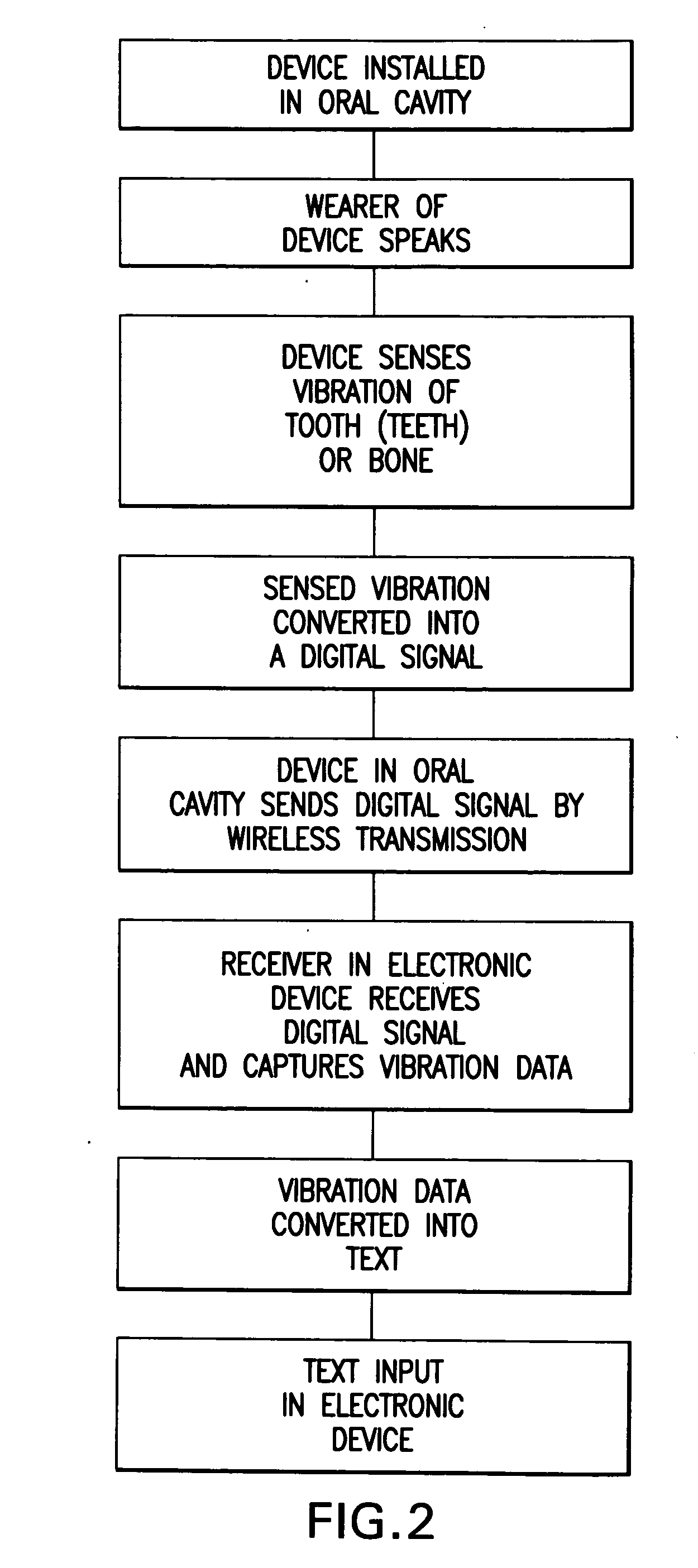
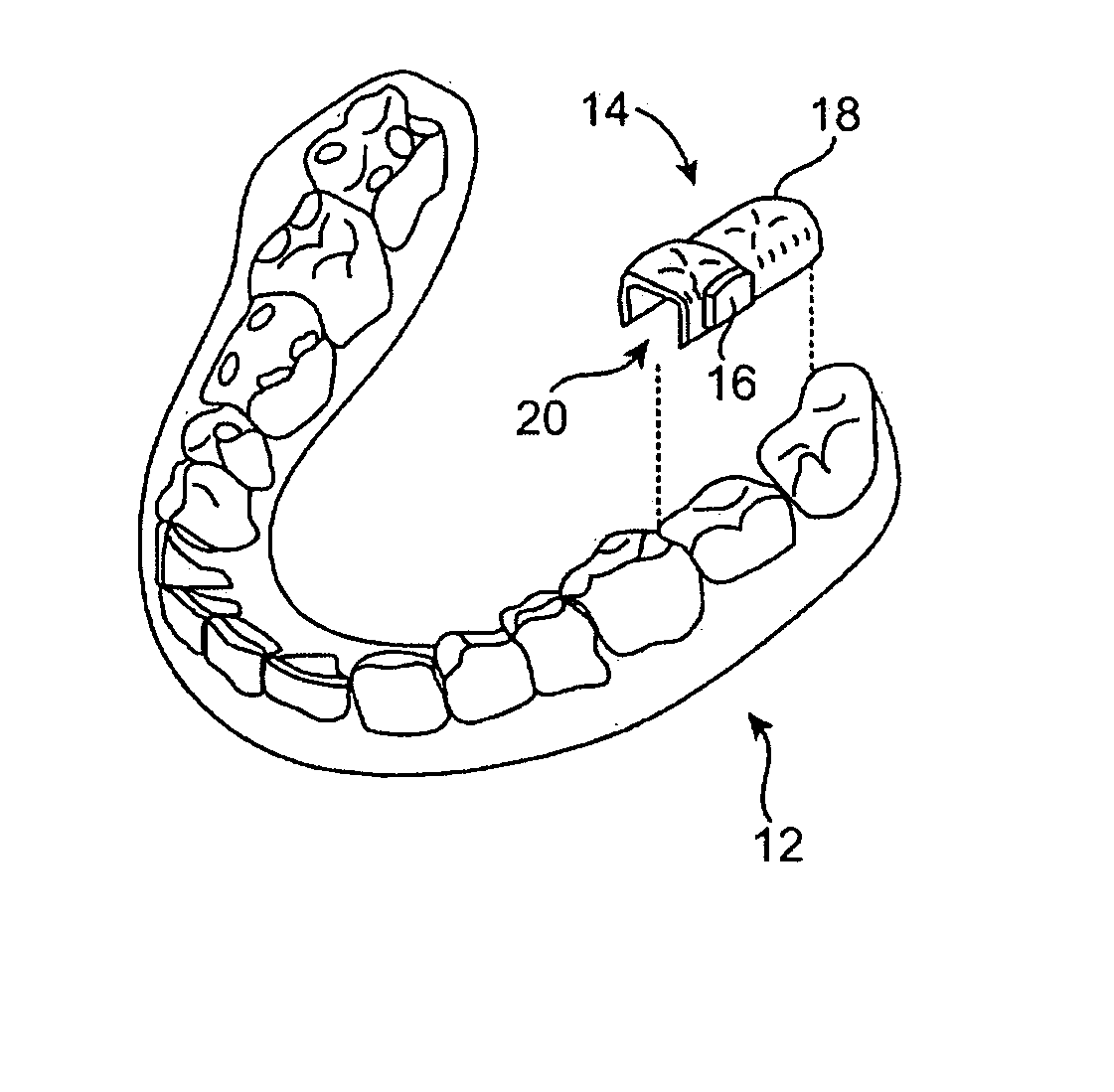
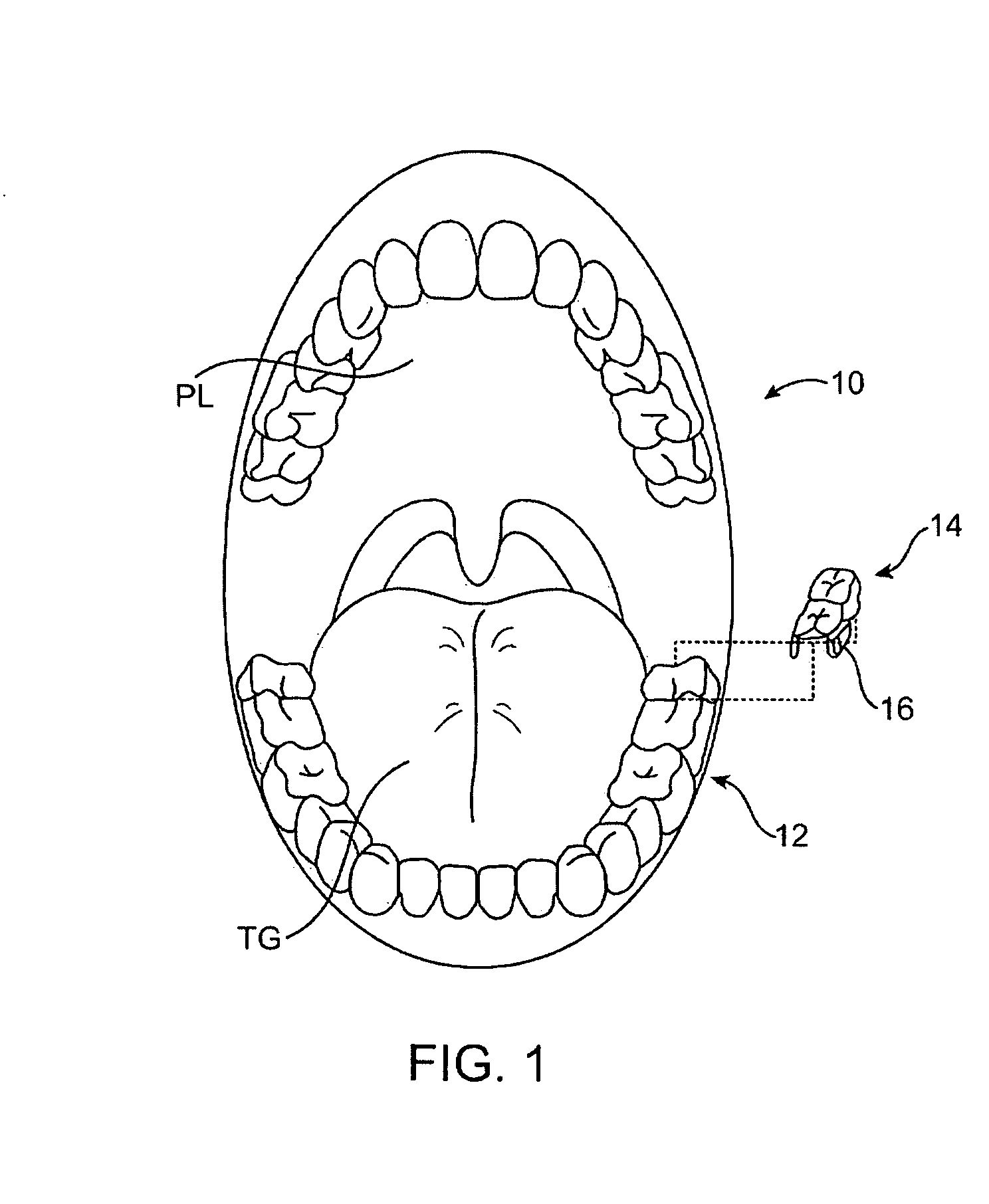
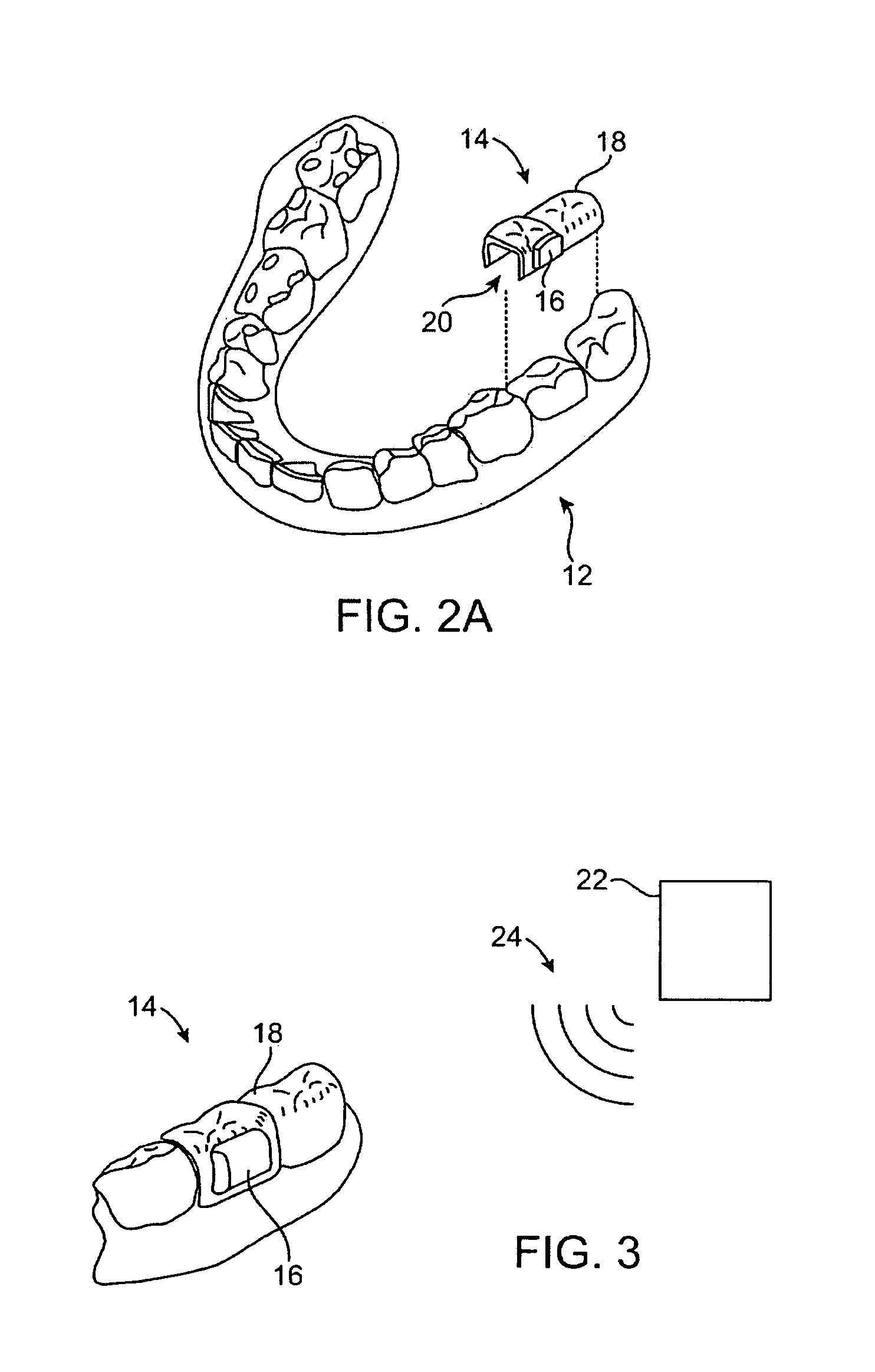
InactiveUS20070105072A1Prevent unauthorized accessTransducer detailsBone conduction transducer hearing devicesDigital dataSpoken language
A wireless electronic device transcribes spoken words into text for input on an electronic device such as, but not limited to, a computer, cell phone, handheld computer, Blackberry or vehicle navigation system. The wireless transcriber device mounts within the oral cavity, preferably to the back side of a tooth, and detects vibration of the tooth and / or palate bone structure as the wearer of the device speaks. The sensed vibrations are converted to digital signals for wireless transmission to the electronic device. The electronic device receives the signals and captures the digital data containing the sensed vibrations. A software program in the electronic device reads the vibration data and converts the vibration data to text for input on the electronic device. The input text can be used for various purposes such as to create a document, fill in a form, send a text message or to give an operational command to the electronic device.
Owner:KOLJONEN REINO
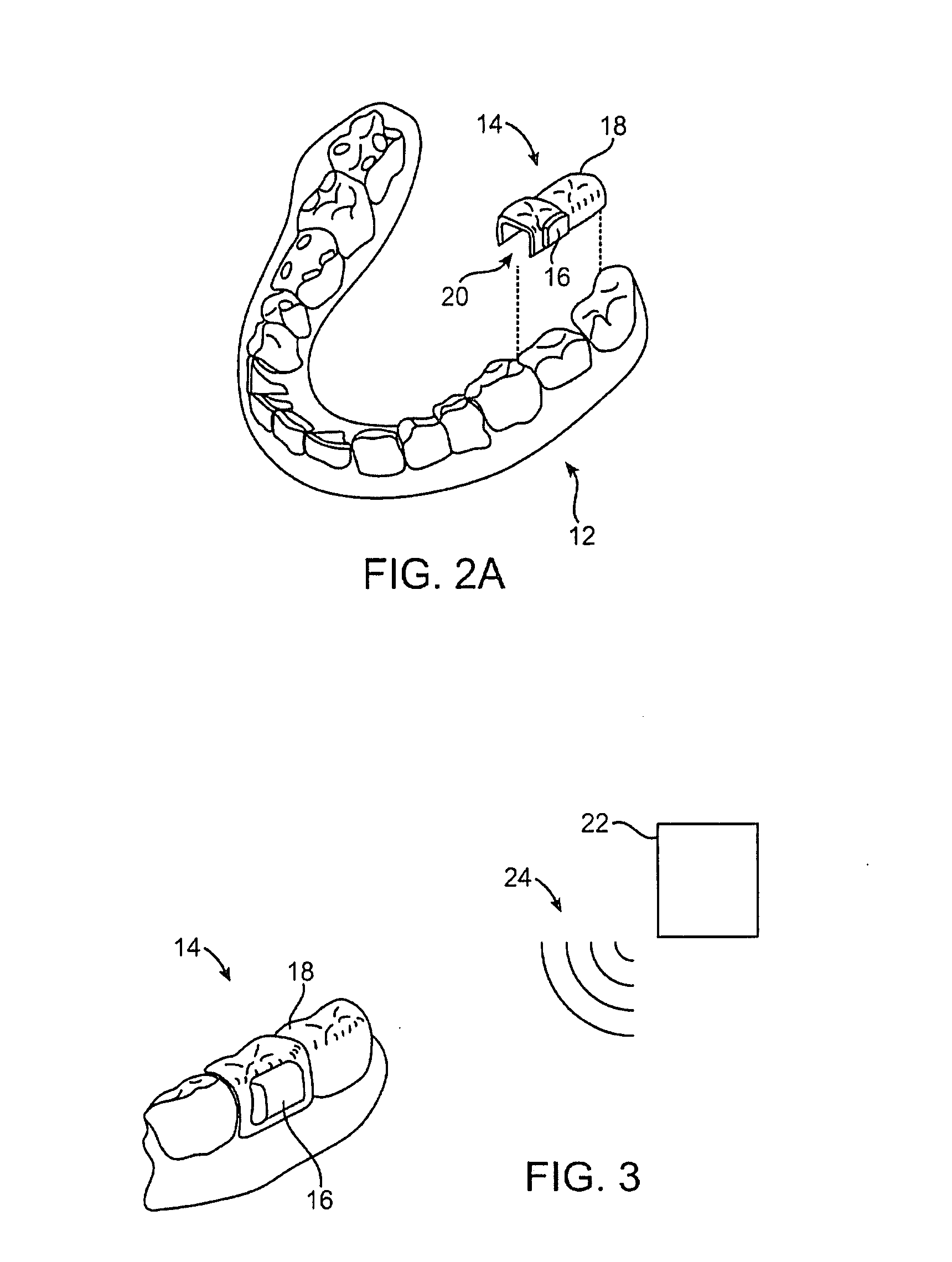
Systems for manufacturing oral-based hearing aid appliances
Systems for manufacturing oral-based hearing aid appliances utilizing various manufacturing methods and apparatus are described herein. The oral appliance may have an electronic and / or transducer assembly for receiving incoming sounds and transmitting processed sounds via a vibrating transducer element coupled to a tooth or teeth. The oral appliance may be formed or fabricated via three-dimensional digital scanning systems or via impression molding to create a housing for the electronics and / or transducer assembly as well as to securely conform the appliance to the user's dentition.
Owner:SHENGTUO MEDICAL TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
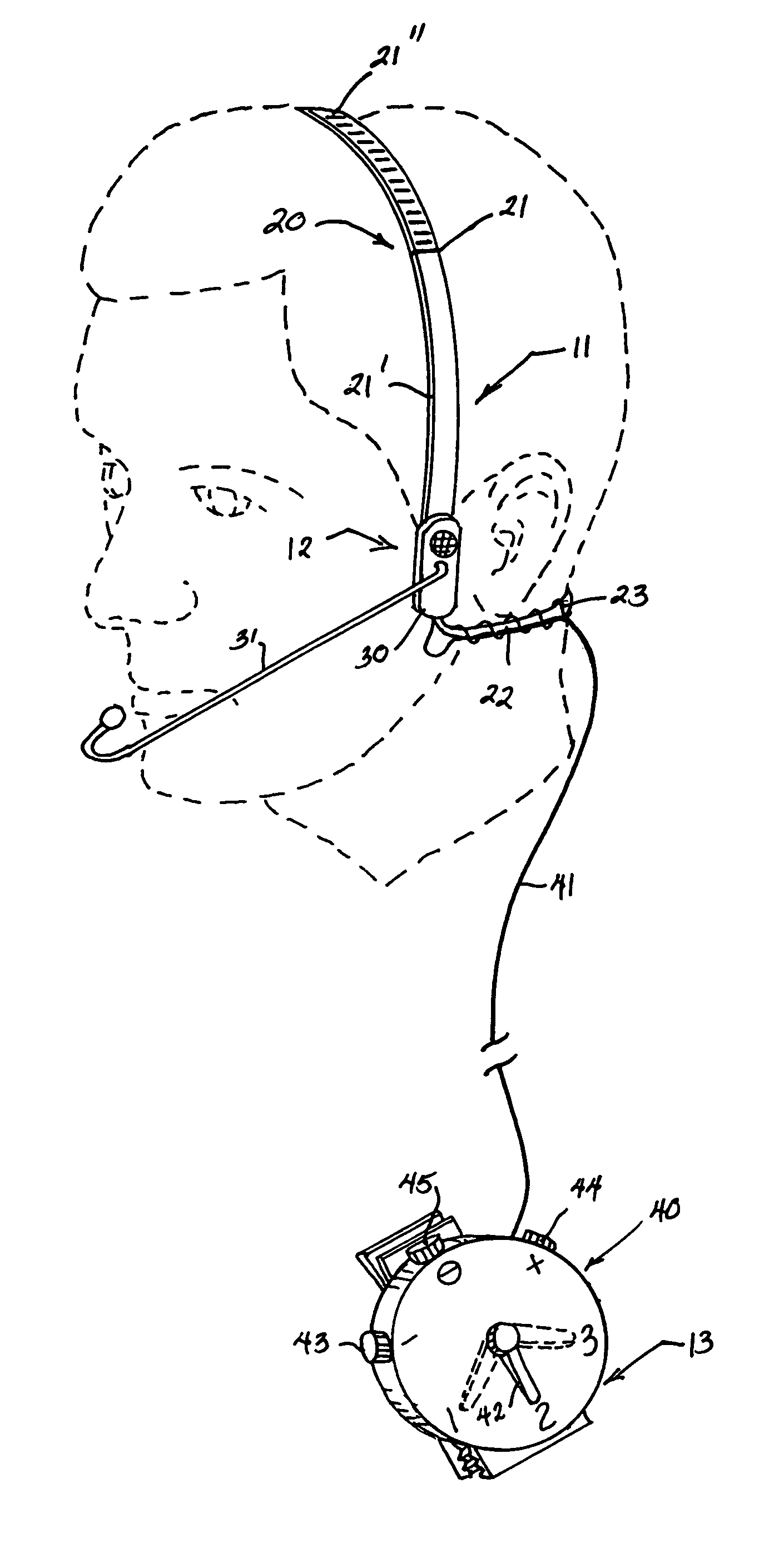
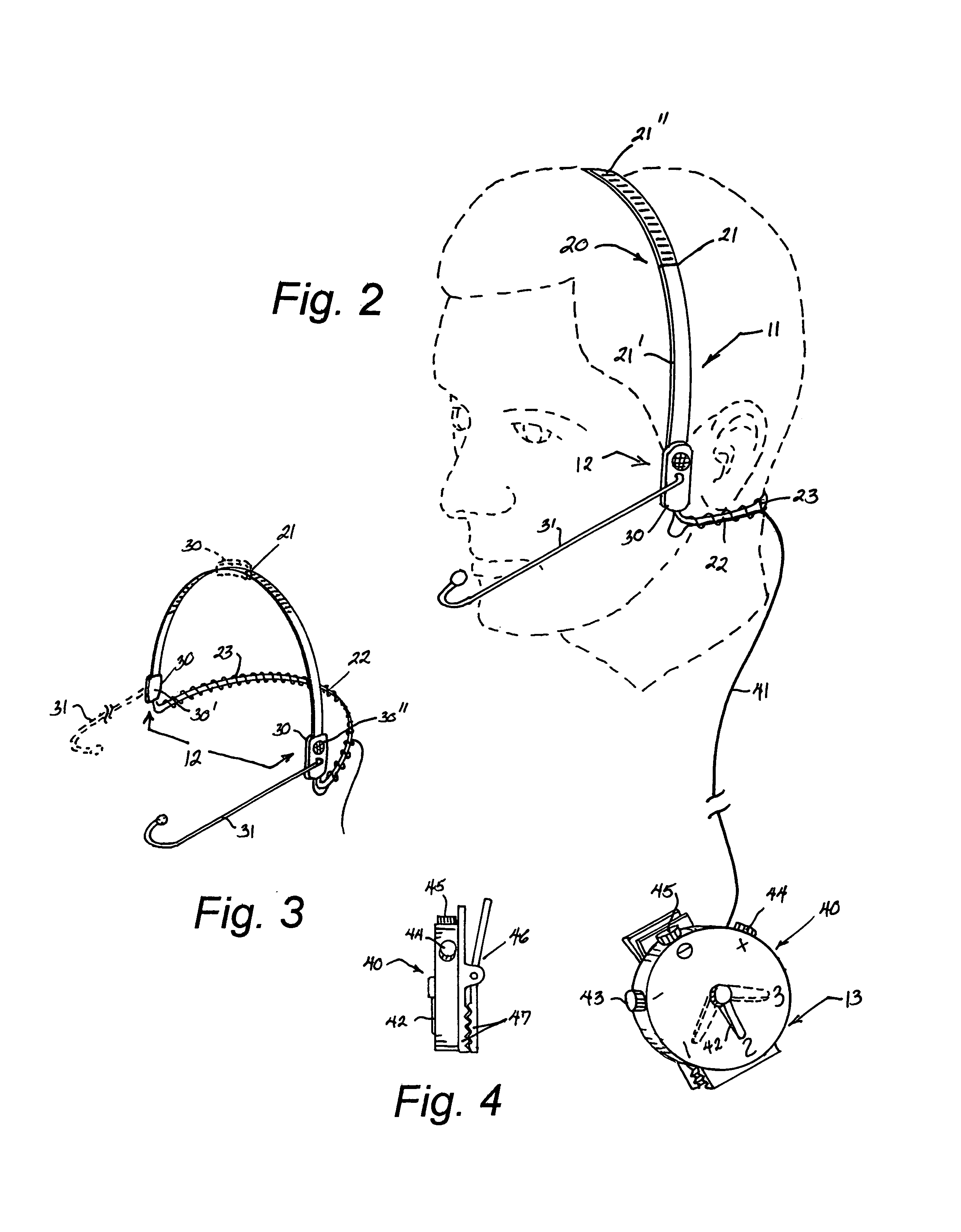
Bone conducting headset apparatus
InactiveUS7010139B1Efficient and effectiveClear communicationMicrophonesLoudspeakersEngineeringDirectional hearing
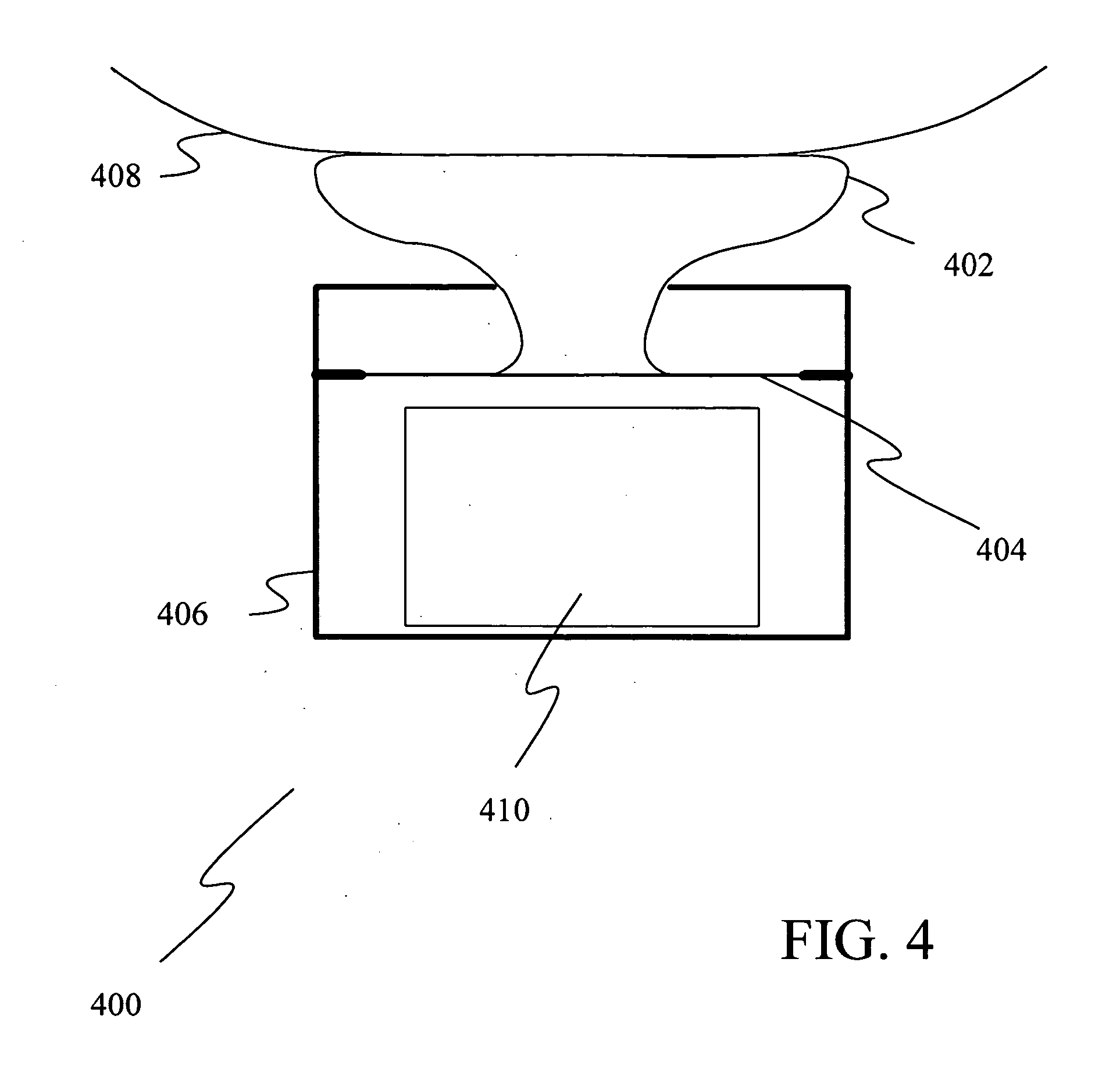
A bone conducting headset apparatus (10) that includes a pair of speaker / microphone members (30) (30) mounted at the juncture of a head strap (21) and a neck strap (22) provided with a spring biasing member (23) wherein, the speaker / microphone members (30) (30) are operatively connected to an electronic control member (40) that is provided with means (46) for selectively attaching the electronic control member (40) to a desired article of the user's clothing wherein, the electronic control member (40) is provided with PTT technology, as well as, high noise cut-off (44) directional hearing (48) (48) and selective communication features (42).
Owner:SMEEHUYZEN KEES
Wireless interactive headset
InactiveUS7150526B2Remain highly mobileGain controlSubstation speech amplifiersHeadphonesLoudspeaker
A wearable audio interface includes a support for positioning the plurality of speakers juxtaposed to and spaced from the ears of a wearer. The audio device can include wireless networking electronics so as to allow the device to interact with other wireless network devices.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
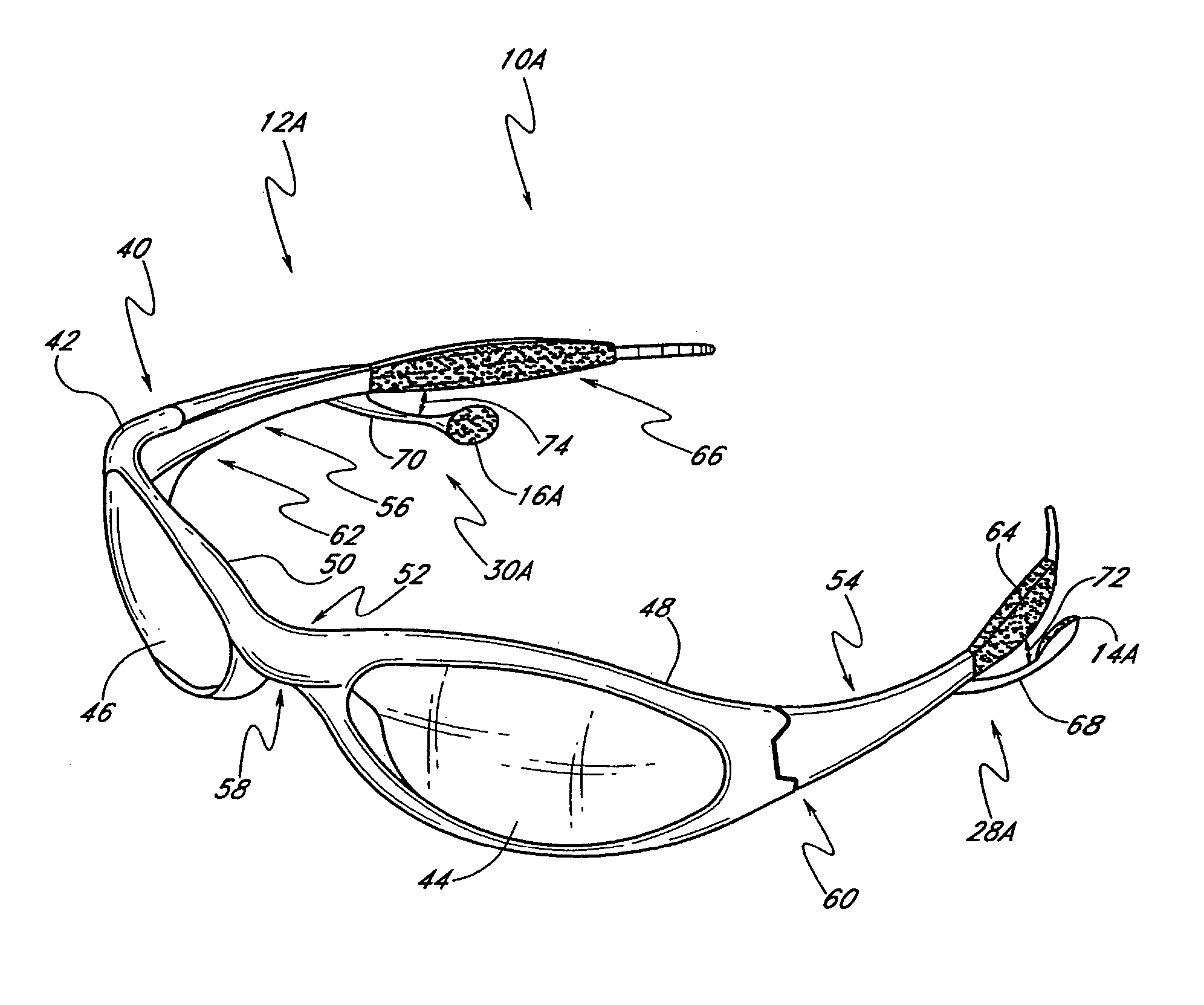
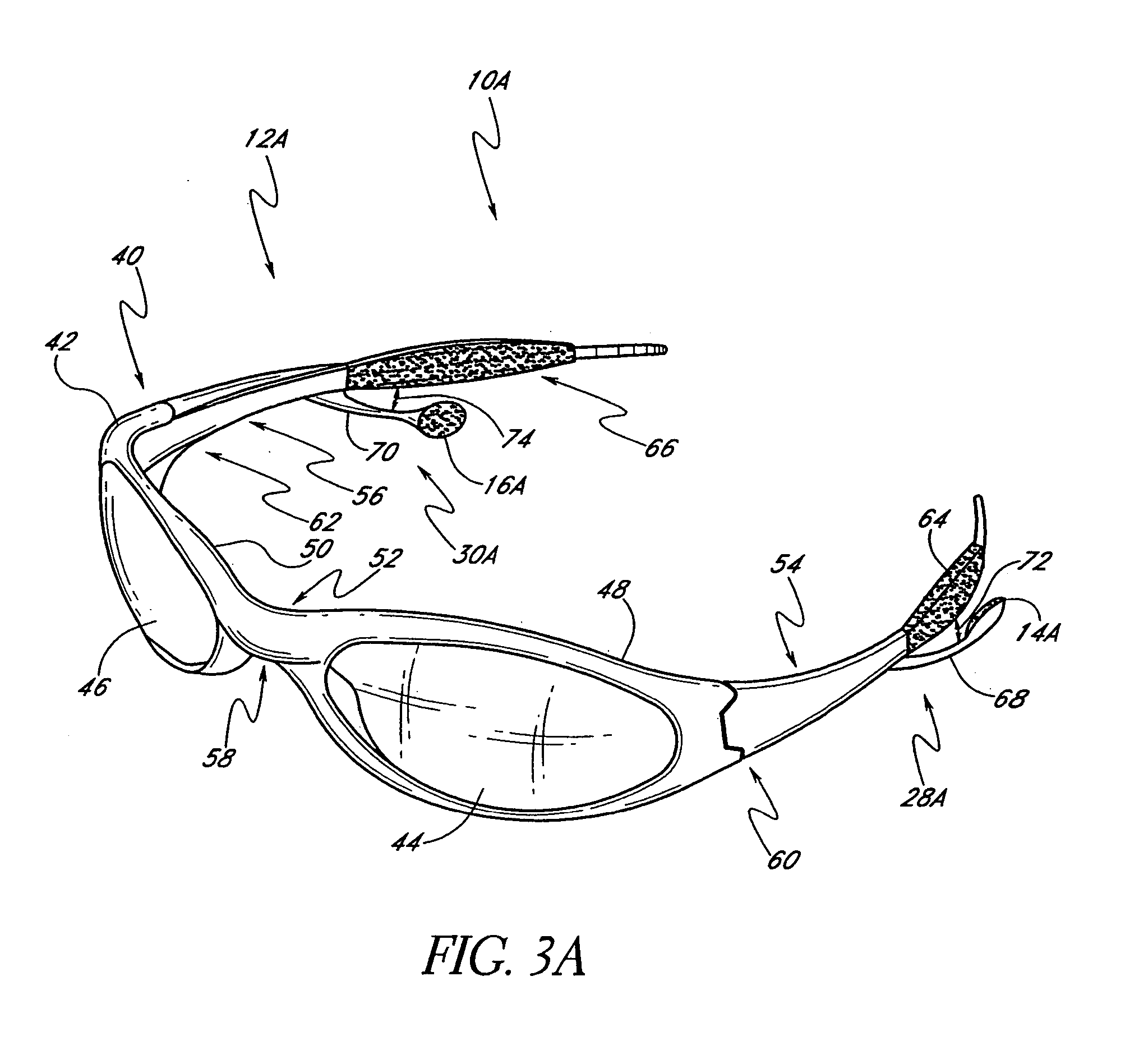
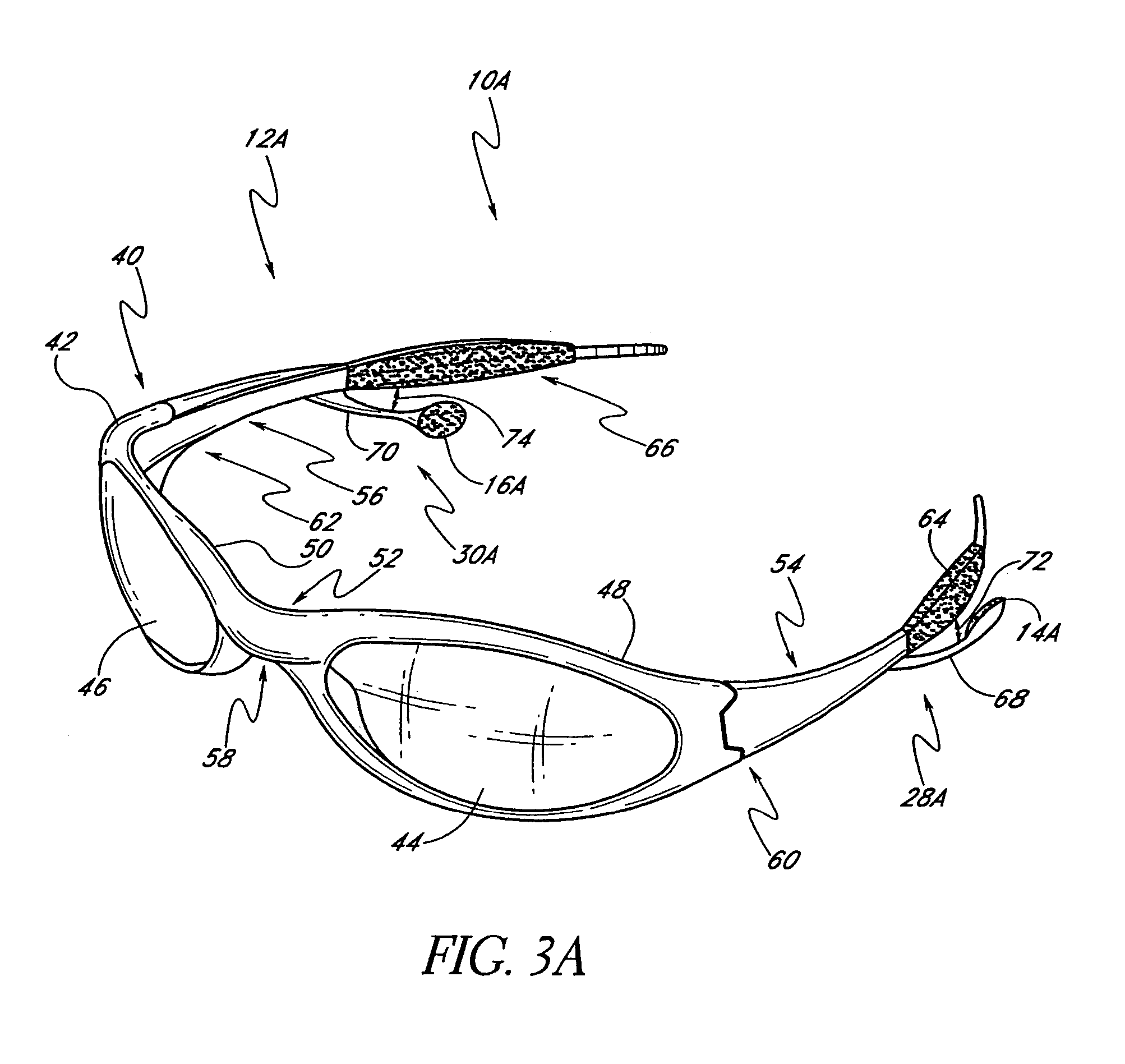
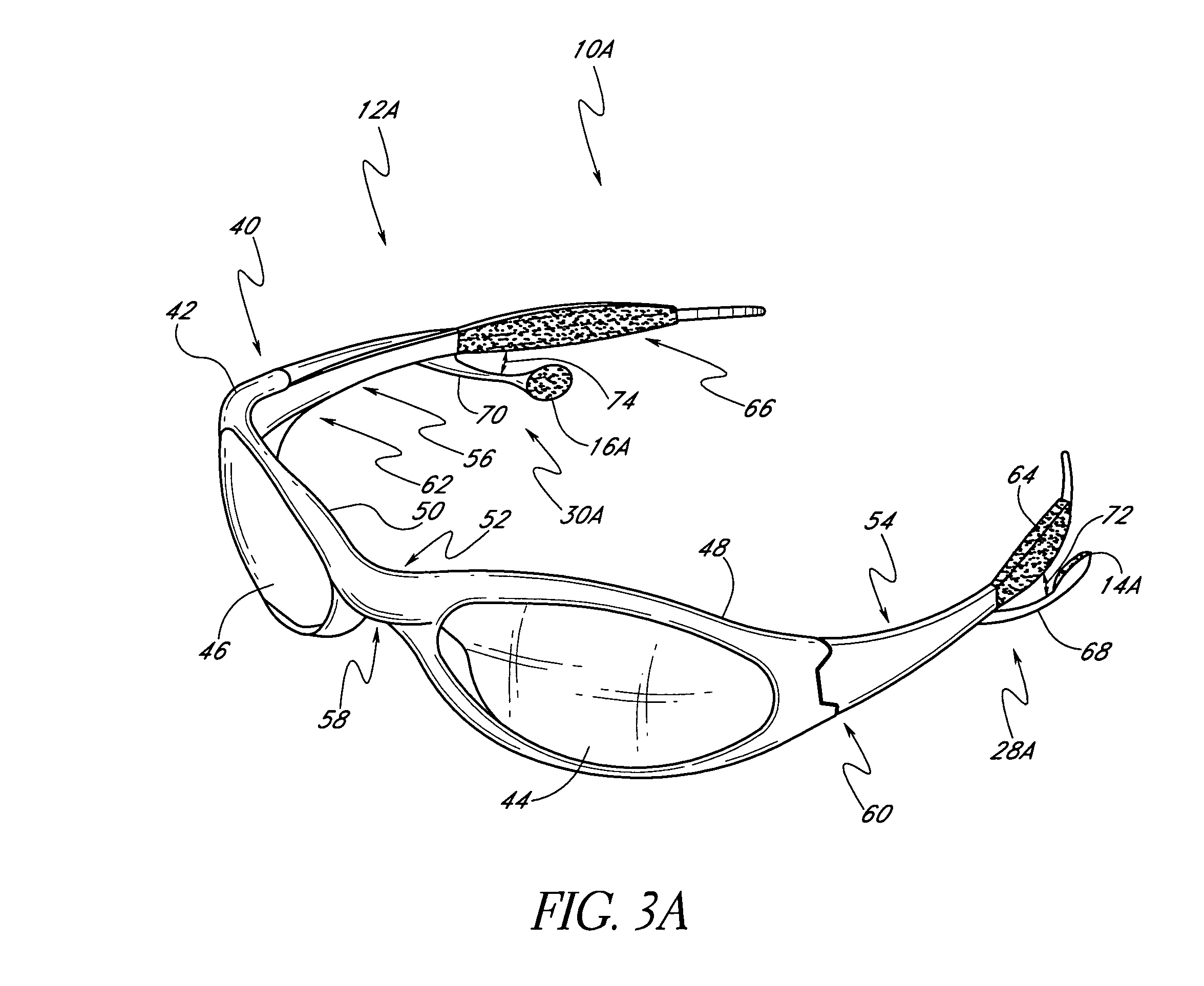
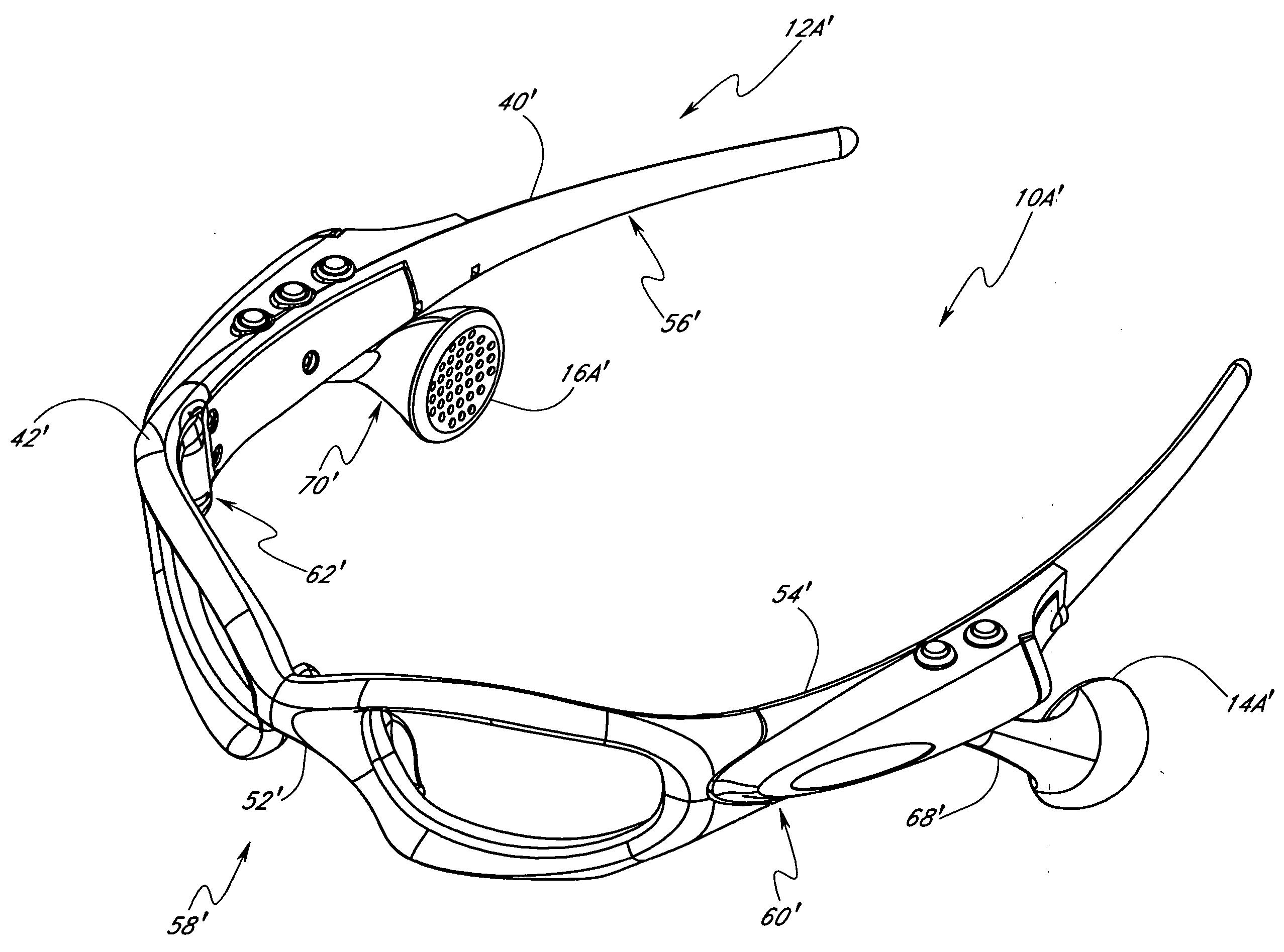
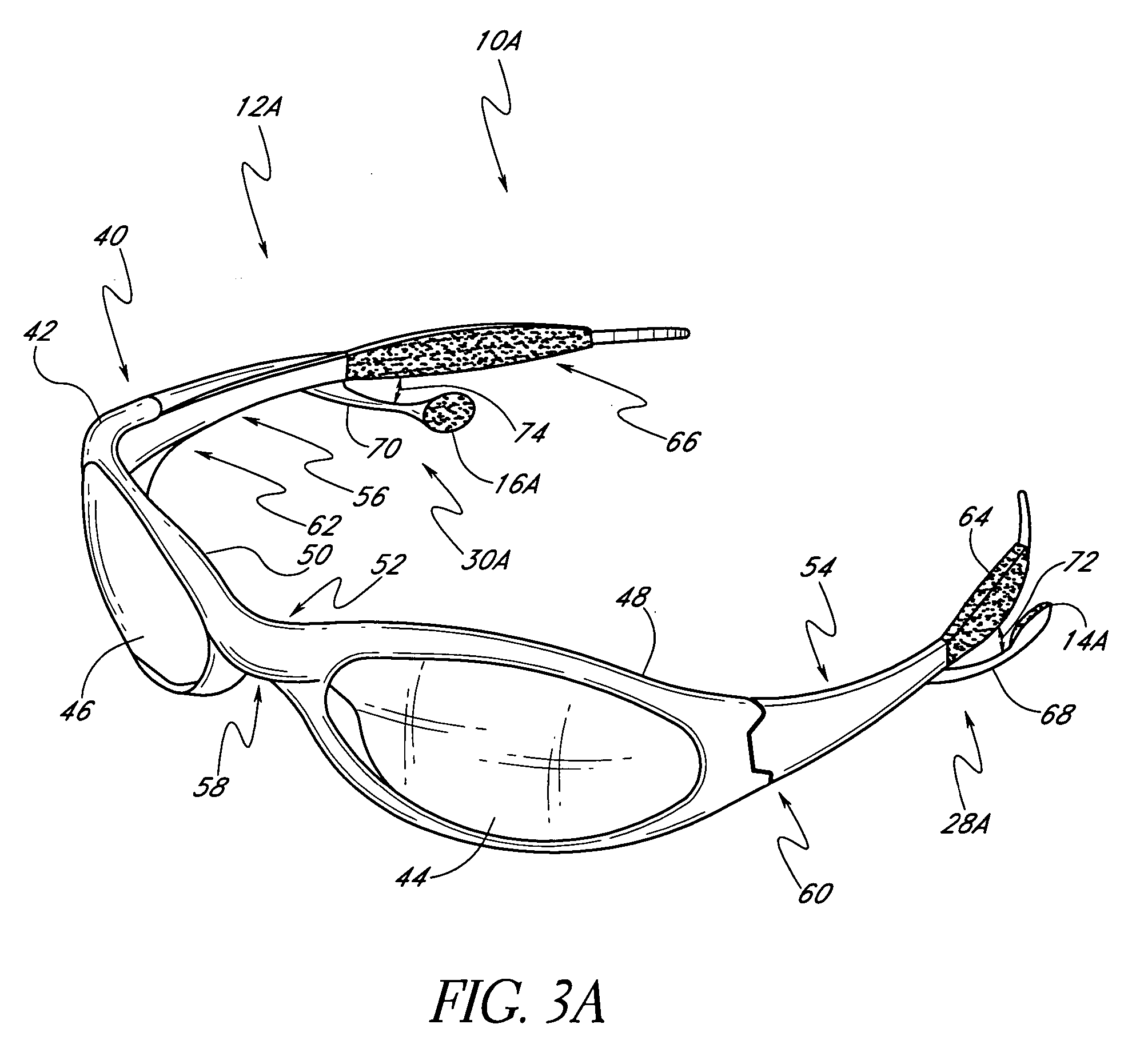
Eyeglasses with detachable adjustable electronics module
A detachable adjustable electronics module may be removably or permanently connected to eyewear. The module may include electronics for processing audio and / or video signals. The module may be provided with an adjustable arm, for adjustably carrying a speaker. The module and / or the speaker may be adjusted relative to the wearer in any of the anterior-posterior direction, the inferior-superior direction and laterally. Rotation adjustments may also be accomplished. Eyewear may be provided with only a single module, on a single side, or with two modules, one on each side, such as to provide stereo audio or dual mono sound.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
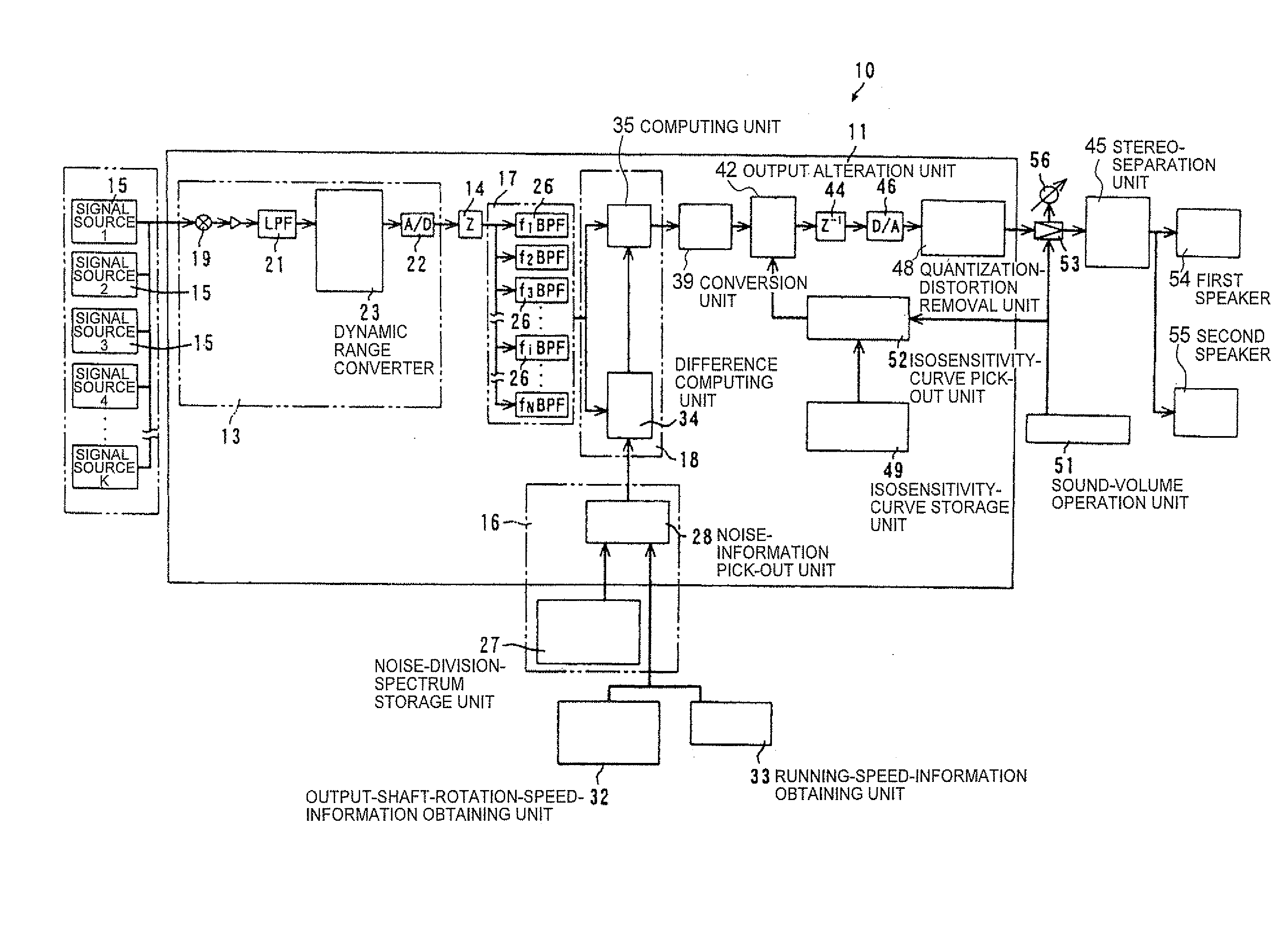
Sound device and sound control device
The sound device includes an audio-information output unit, an analysis unit, an audio-division-spectrum output unit, a noise-division-spectrum output unit and a correction unit. The analysis unit receives audio information from the audio-information output unit, and then outputs sound spectrum information. The noise-division-spectrum output unit outputs sound-volume information for each critical band width of a noise, and the audio-division-spectrum output unit outputs the sound-volume information for each critical band width of the sound-spectrum information. The correction unit corrects the information from the audio-division-spectrum output unit based on the information from the noise-division-spectrum output unit. The audio-signal properties can be well corrected corresponding to the auditory-sense properties of the human, and thus the audio sound, in which an uncomfortable feeling to the auditory sense of the human has been adequately controlled, can be transmitted to a user.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
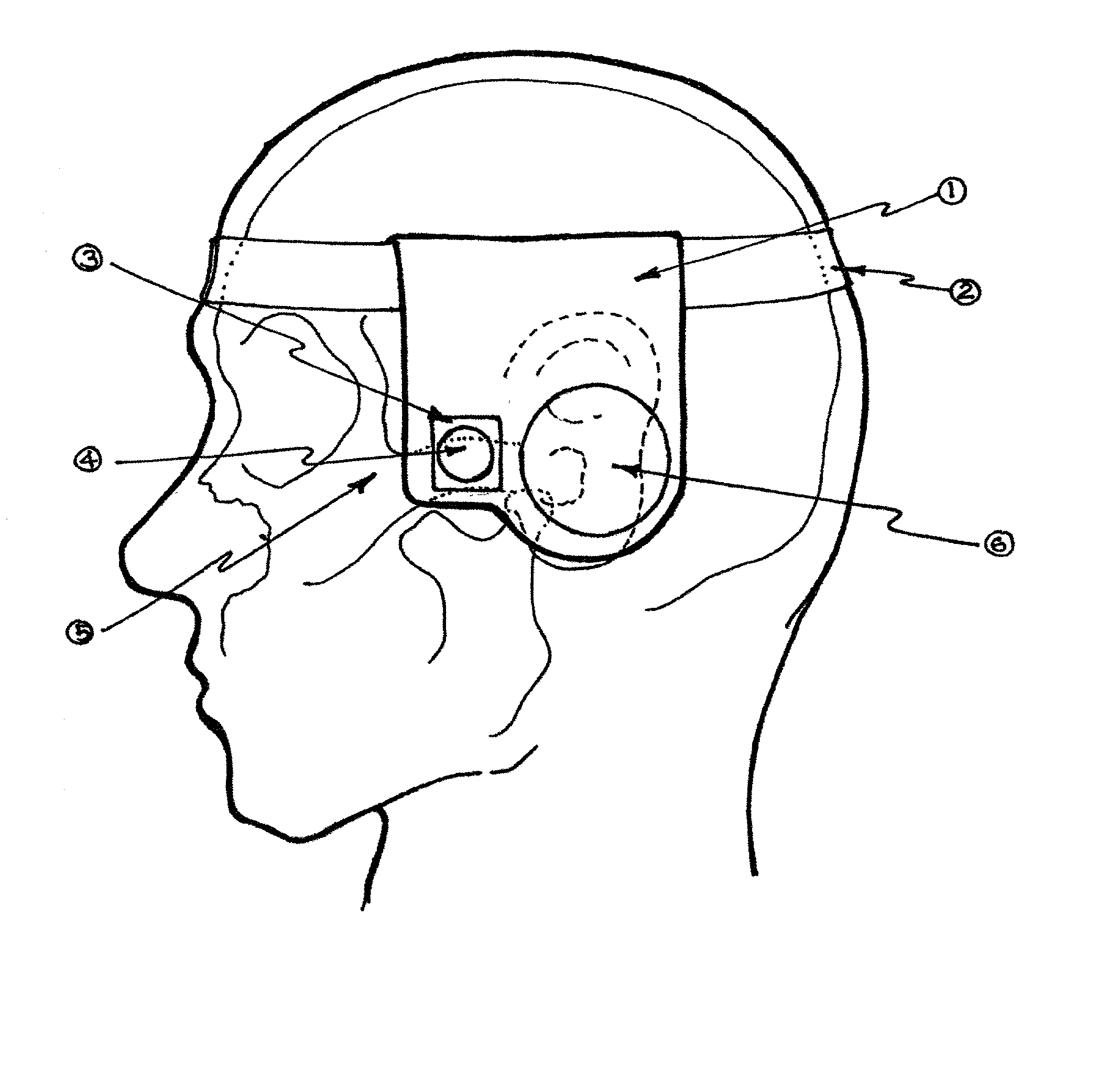
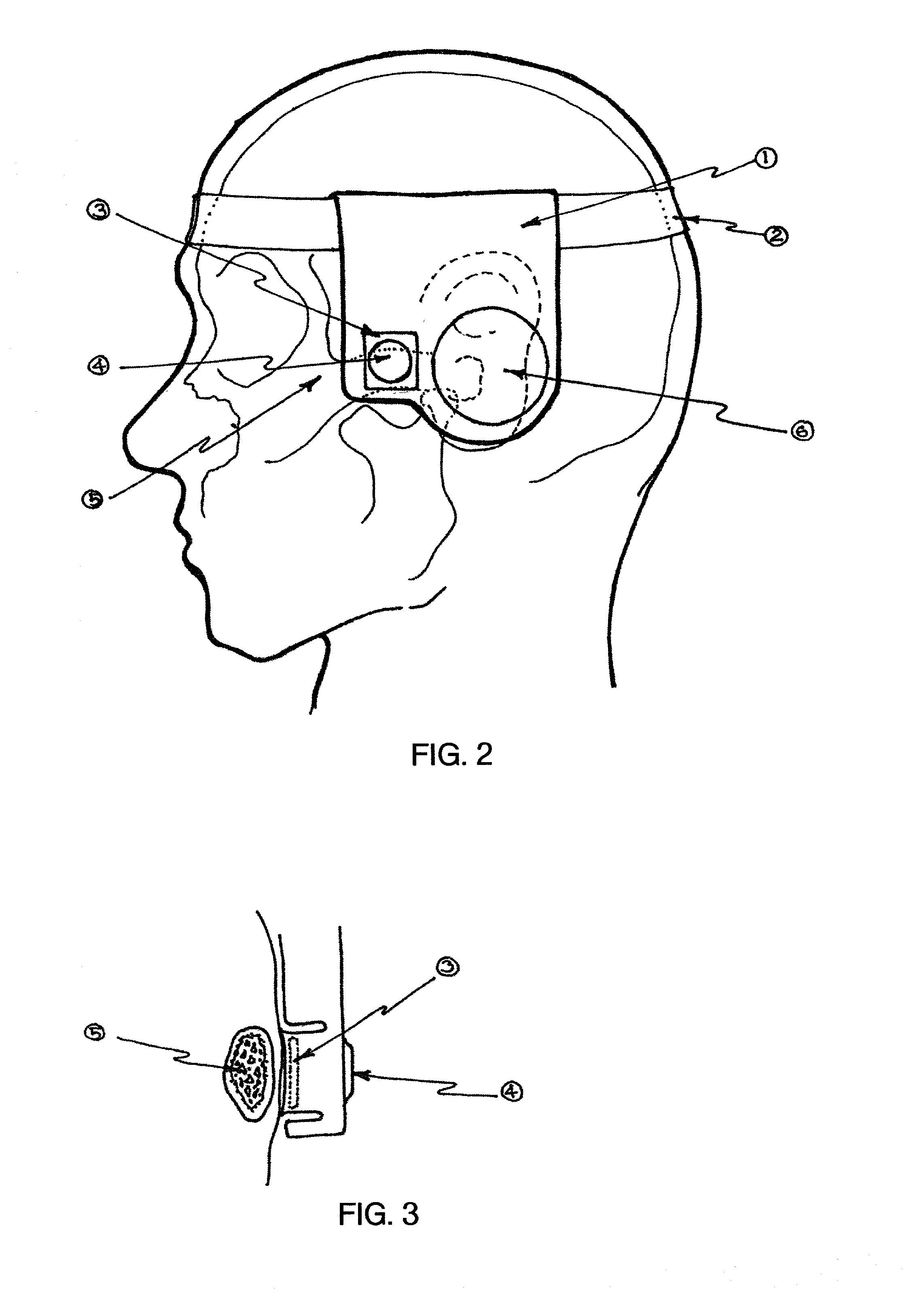
Directional sensors for head-mounted contact microphones
InactiveUS20030059078A1Smooth connectionGuaranteed normal transmissionBone conduction transducer hearing devicesSupra/circum aural earpiecesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Voice communication
Directional piezoelectric devices and methods for their manufacture are provided that improve the quality of piezoelectric device mediated signal detection and provide new thermal imaging devices. The devices can provide over an order of magnitude improved signal to noise ratio compared with previously known devices. The devices may be used along with new head mounted acoustic technologies for improved voice communication systems in inherently noisy environments. The head mounted technologies utilize microphones that are activated by pressure wherein the applied trigger pressure further serves to improve efficiency of the microphones. Also provided are head pieces that include both microphones and speakers that are particularly useful for harsh environments such as those encountered by fire fighters. The head pieces are capable of further functions related to contact with the head of the user, such as reporting physiological variables of the user, along with oral communications.
Owner:DOWNS EDWARD F JR +1
Method and apparatus for tooth bone conduction microphone
ActiveUS7486798B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioOut noisePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesBone conduction transducer hearing devicesEngineeringHeadphones
A two-way communication system particularly valuable for noisy environments where a user has a tooth bone conduction microphone in his mouth normally controlled by a tongue switch that transmits an electrical signal representing speech to a retransmit module usually worn on the user's body or mounted on an earphone or headset where the speech electrical signal is retransmitted to a second user usually by RF. The retransmit module can also receive signals from the second user and transmit them to the earphone or headset thus providing two-way communication.
Owner:MAYUR TECH
Method and apparatus for multi-sensory speech enhancement on a mobile device
A mobile device is provided that includes a digit input that can be manipulated by a user's fingers or thumb, an air conduction microphone and an alternative sensor that provides an alternative sensor signal indicative of speech. Under some embodiments, the mobile device also includes a proximity sensor that provides a proximity signal indicative of the distance from the mobile device to an object. Under some embodiments, the signal from the air conduction microphone, the alternative sensor signal, and the proximity signal are used to form an estimate of a clean speech value. In further embodiments, a sound is produced through a speaker in the mobile device based on the amount of noise in the clean speech value. In other embodiments, the sound produced through the speaker is based on the proximity sensor signal.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Bone conduction headset
InactiveUS7076077B2Easy to useEasy to wearEar treatmentHeadphones for stereophonic communicationEngineeringBone conduction hearing
An object of the invention resides in the provision of a bone conduction headset, which is inconspicuous in appearance during wearing thereof, adapted for use in avoiding absorbing nearby people's attention to the headset thus worn, easy to wear and take off in use, and comprises: a band running around a back part of the user's head; a fastening portion formed in each of opposite end portions of the band; a bone conduction speaker provided with a knob which is engaged with the fastening portion; and, an ear engagement portion, which runs over the bone conduction speaker during wearing of the headset to reach and engage with the user's ear. An extension of either the fastening portion in the band or a casing of the bone conduction speaker may be formed into the ear engagement portion.
Owner:TEMCO JAPAN
Method and apparatus for tooth bone conduction microphone
ActiveUS20050196008A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioFiltering out surrounding noisePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesBone conduction transducer hearing devicesEngineeringBone conduction hearing
A two-way communication system particularly valuable for noisy environments where a user has a tooth bone conduction microphone in his mouth normally controlled by a tongue switch that transmits an electrical signal representing speech to a retransmit module usually worn on the user's body or mounted on an earphone or headset where the speech electrical signal is retransmitted to a second user usually by RF. The retransmit module can also receive signals from the second user and transmit them to the earphone or headset thus providing two-way communication.
Owner:MAYUR TECH
Voice Assistant System for Wireless Earpieces
A system, method, and wireless earpieces for implementing a virtual assistant. A first virtual assistant for a wireless device is activated in response to receiving a request. A second virtual assistant on the wireless earpieces is executed to retrieve information associated with the request. An action is implemented utilizing the wireless device to fulfill the request utilizing the information.
Owner:BRAGI
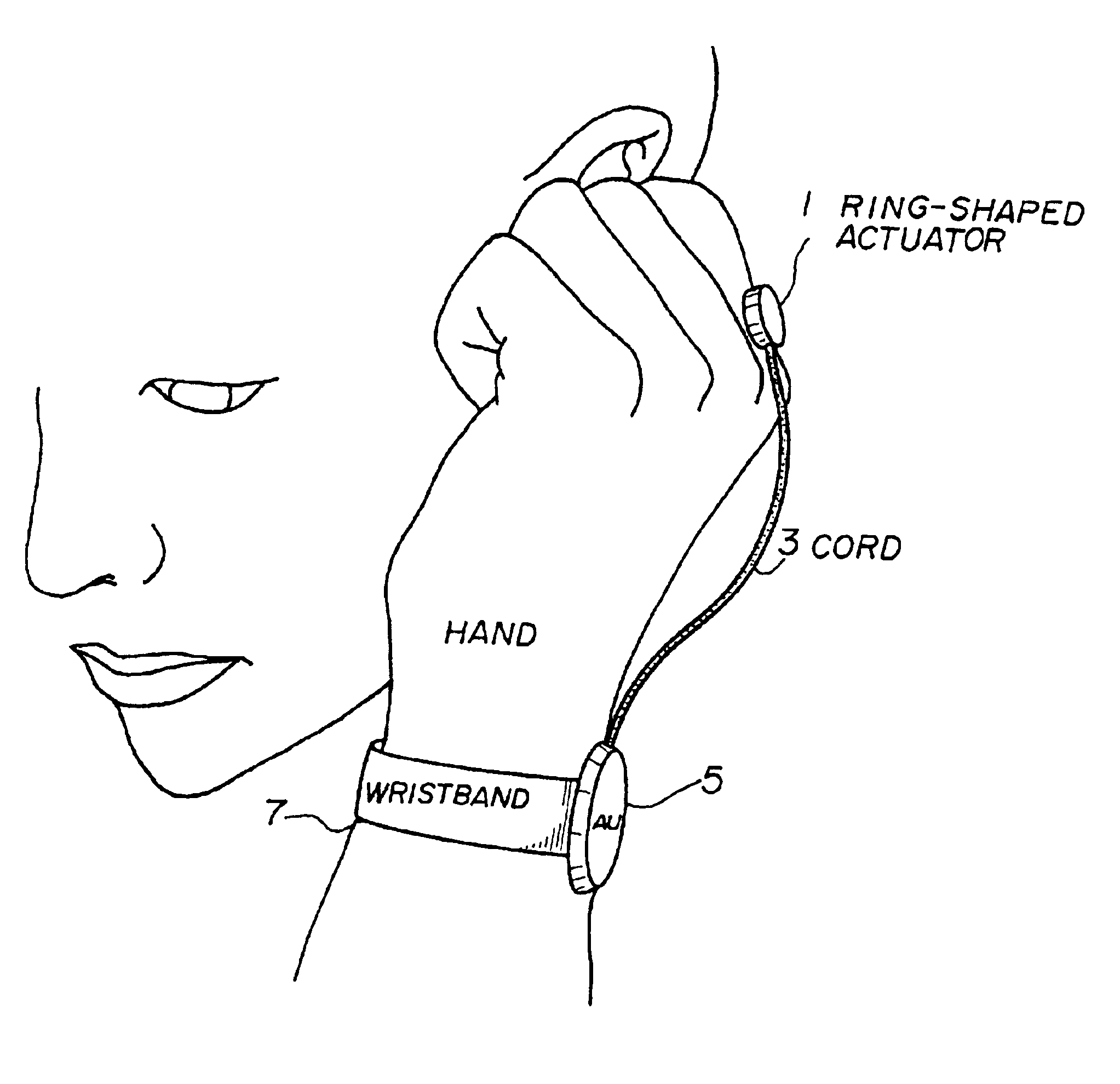
Wearable communication device
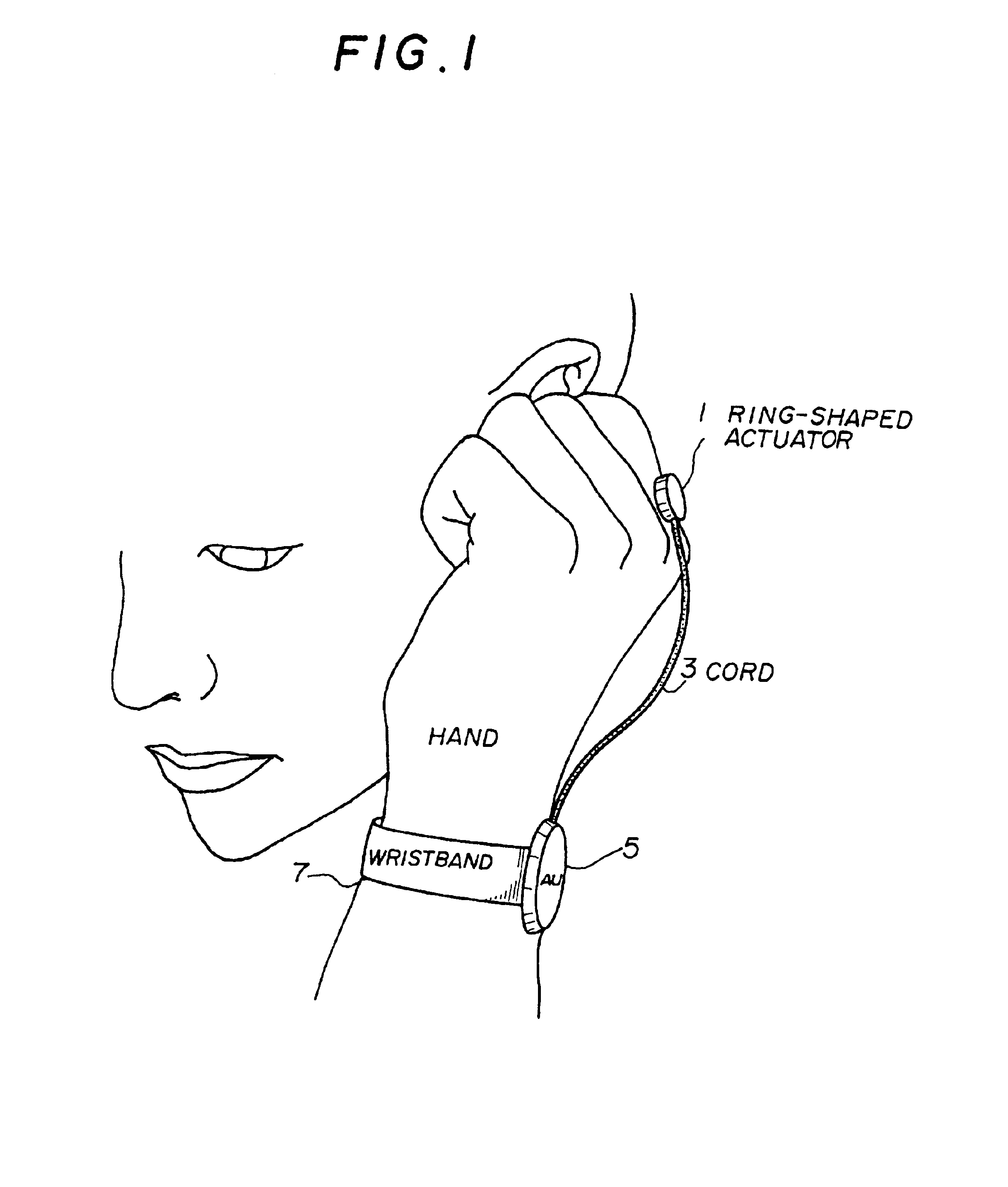
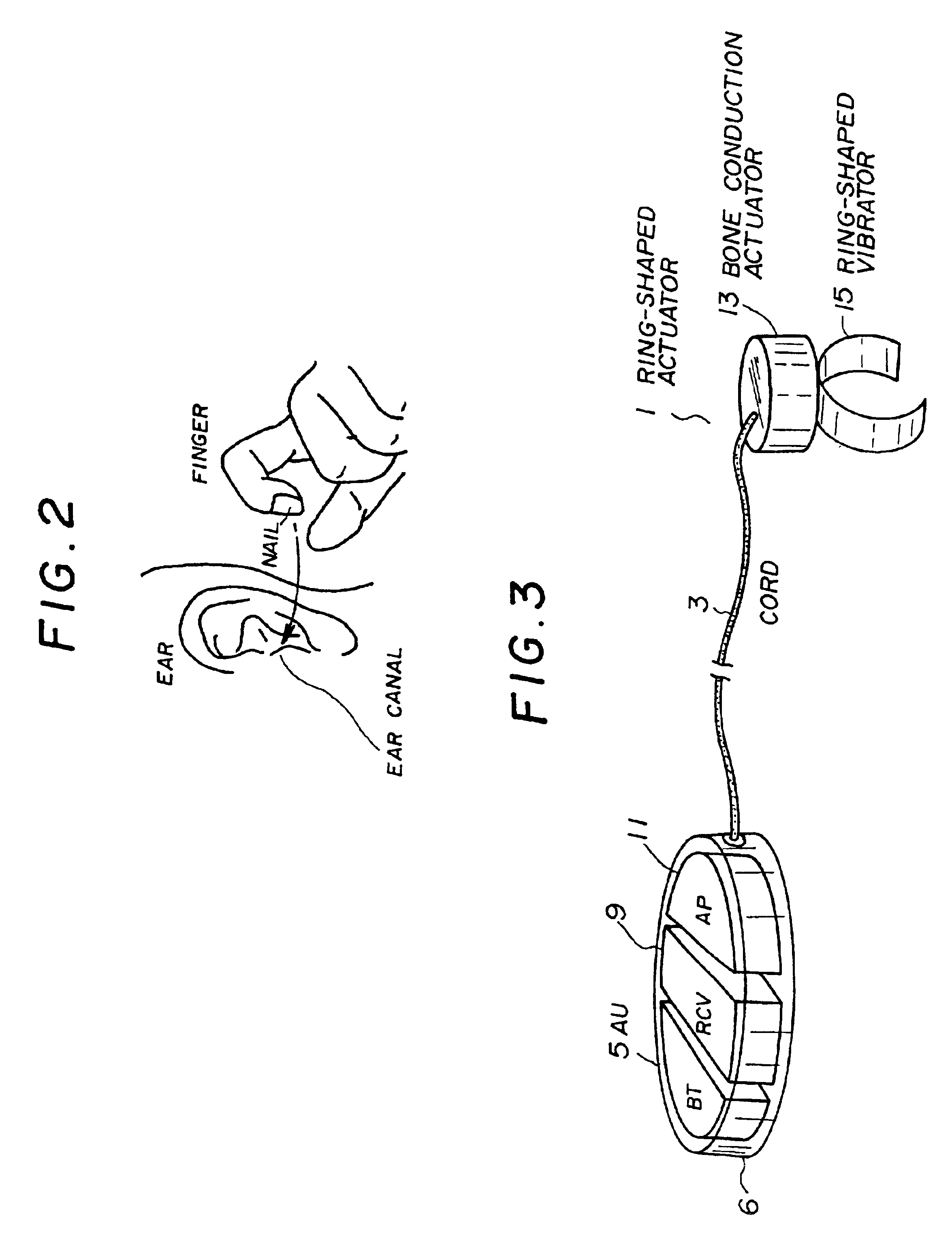
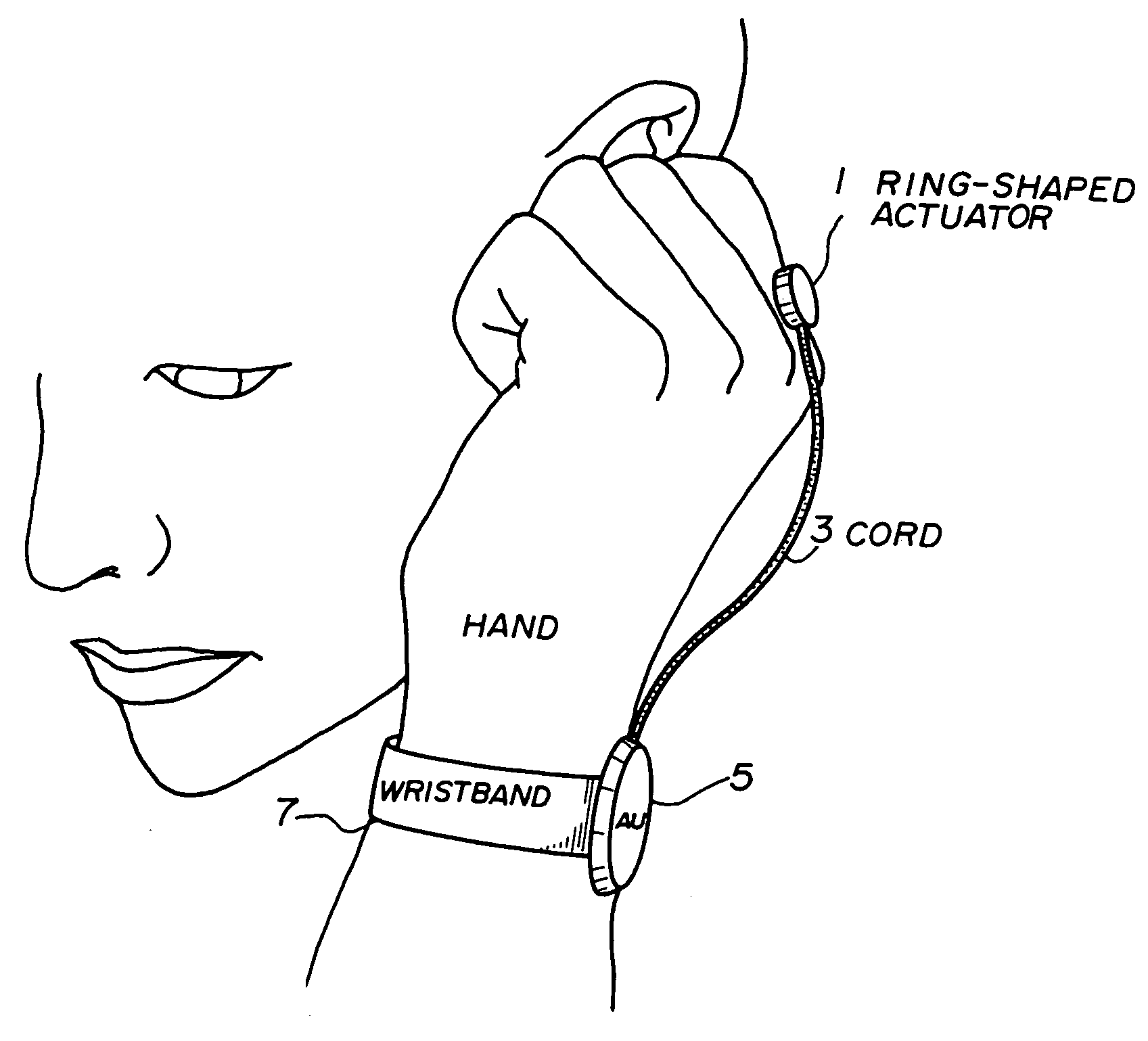
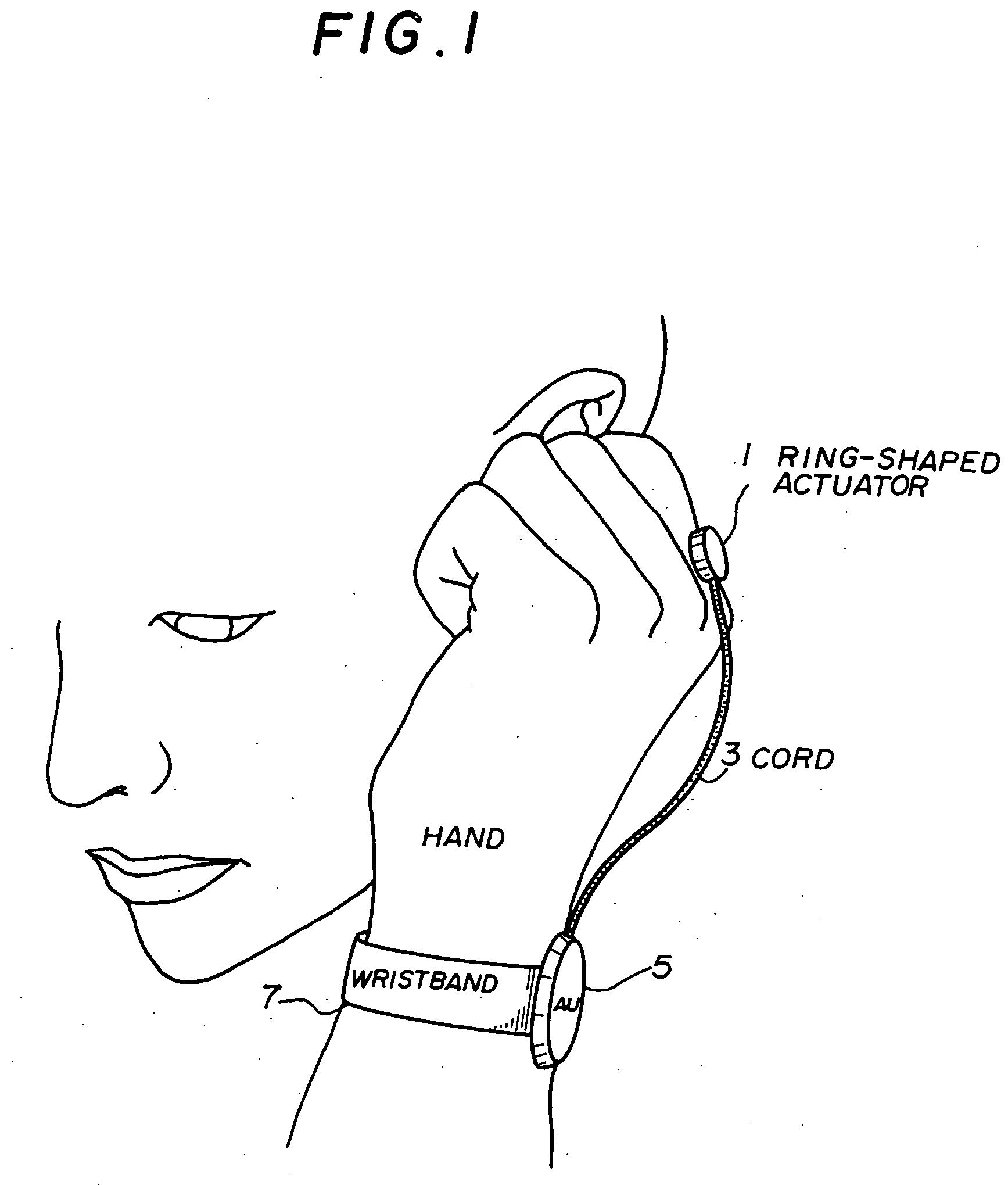
InactiveUS6912287B1Easy to operateImprove usabilityInput/output for user-computer interactionInterconnection arrangementsEngineeringActuator
A wearable communication device includes a bone conduction actuator which is applicable for being in contact with a user's wrist, hand, back of the hand, finger or nail in order to transmit voice signals. The user inserts the user's finger into the user's ear canal, or touches the user's finger to a part near the user's ear, or puts the user's fingertip or nail on the user's ear canal so as to block the user's ear canal when the user uses the wearable communication device. Also, the wearable command input device includes a first part for detecting shock or acceleration which arises when the user taps the user's fingertip on the surface of an object or when the user taps the fingertips mutually and which is transmitted through the user's finger, a second part for detecting specific frequency components which are included in signals from the first part and for detecting the presence or the absence of the tap of the finger of the user, and a part for determining and executing commands based on series of signals output from the second part.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
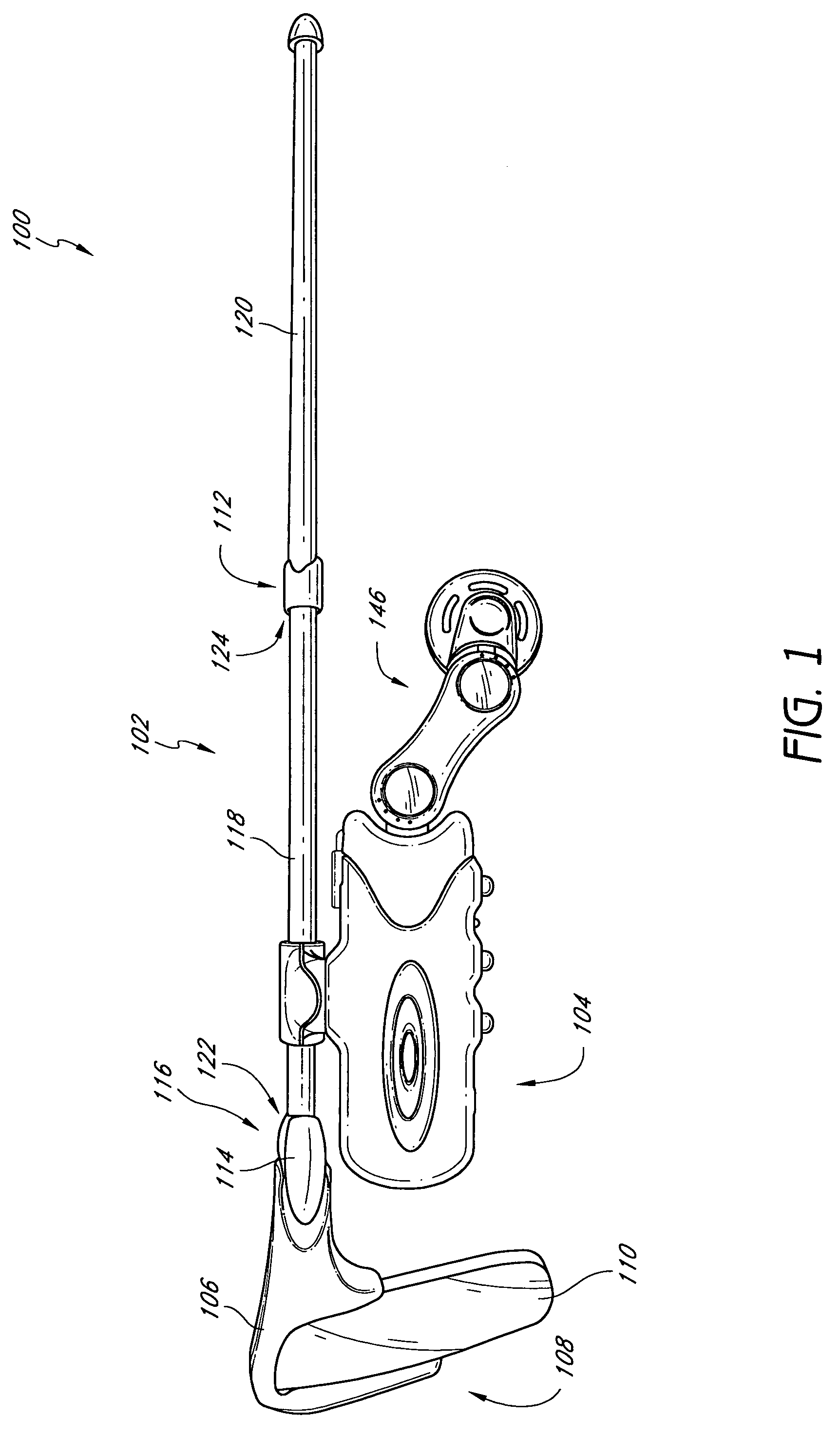
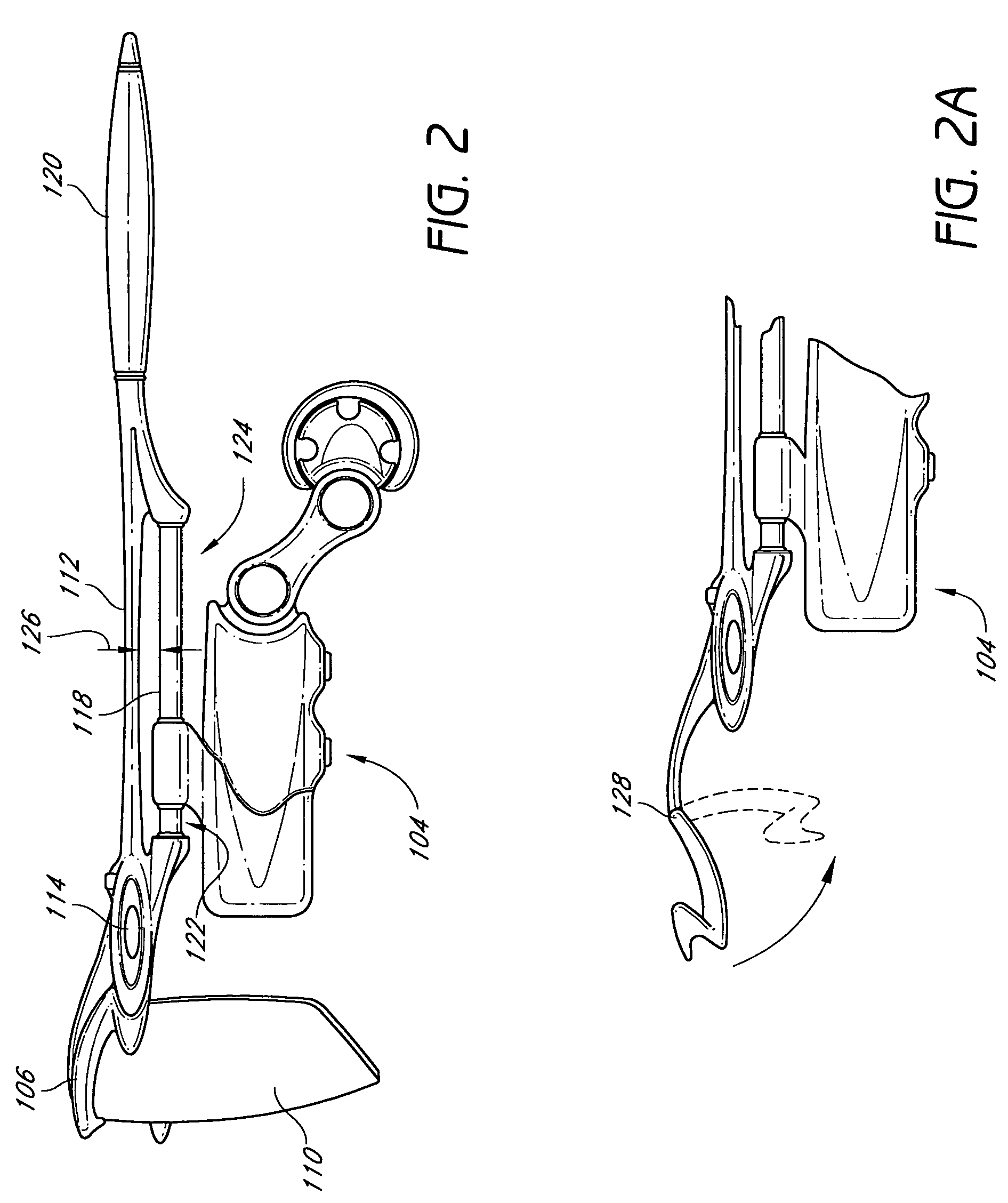
Methods and apparatus for treating tinnitus
InactiveUS20080064993A1Defocus their attention to the tinnitusElectric tinnitus maskersChiropractic devicesSound therapyTransducer
Methods and apparatus for treating tinnitus are described where an oral appliance having an electronic and / or transducer assembly for generating sounds via a vibrating transducer element is coupled to a tooth or teeth. Generally, the transducer may generate one or more frequencies of sound via the actuatable transducer positioned against at least one tooth such that the sound is transmitted via vibratory conductance to an inner ear of the patient, whereby the sound completely or at least partially masks or provides sound therapy for habituation of the tinnitus perceived by the patient. The one or more generated frequencies may be correlated to measured tinnitus frequencies or they may be preset.
Owner:SOUNDMED LLC
Speaker mounts for eyeglass with MP3 player
InactiveUS20050046790A1Reduce weightInhibit transferSubstation speech amplifiersTelephone set constructionsEyewearEngineering
A wearable audio device in the form of eyeglasses speaker mounts supported by the frames of the eyeglass. The speaker mounts are constructed so as to be translatable along the ear stems of the eyeglass. This allows a wearer to move the speakers without changing the shape of the speaker mount, which can occur where the speaker mounts are made from some flexible materials.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
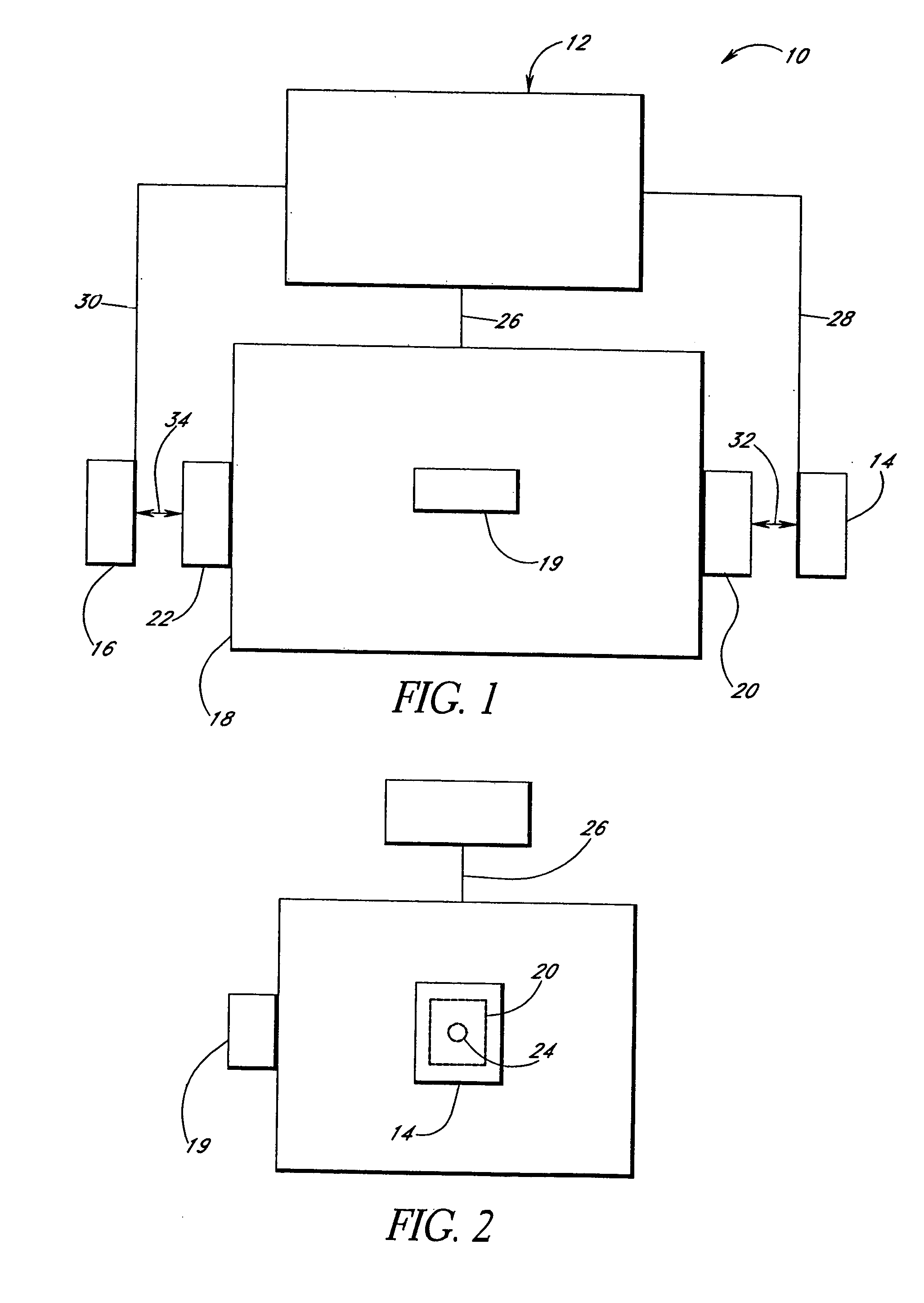
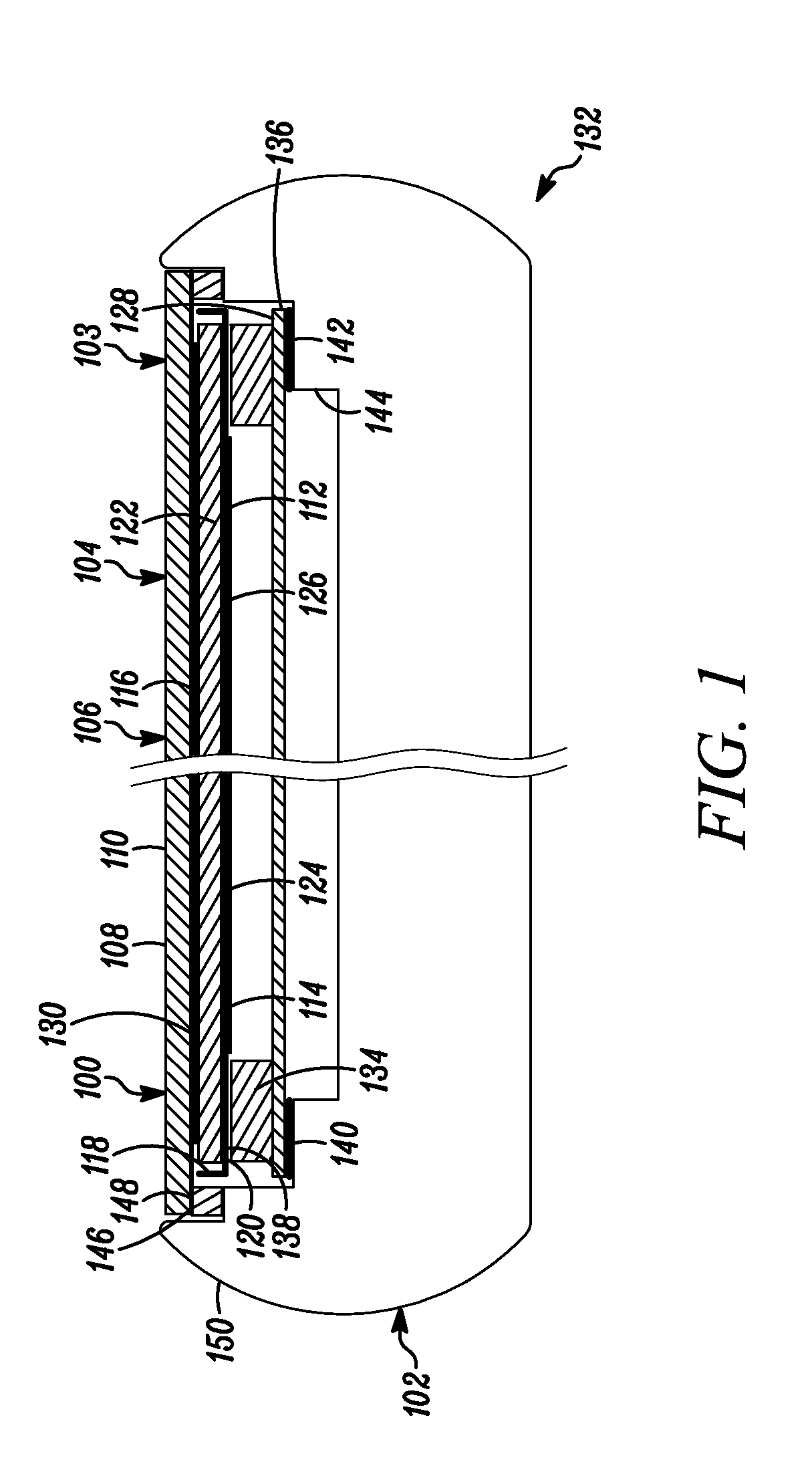
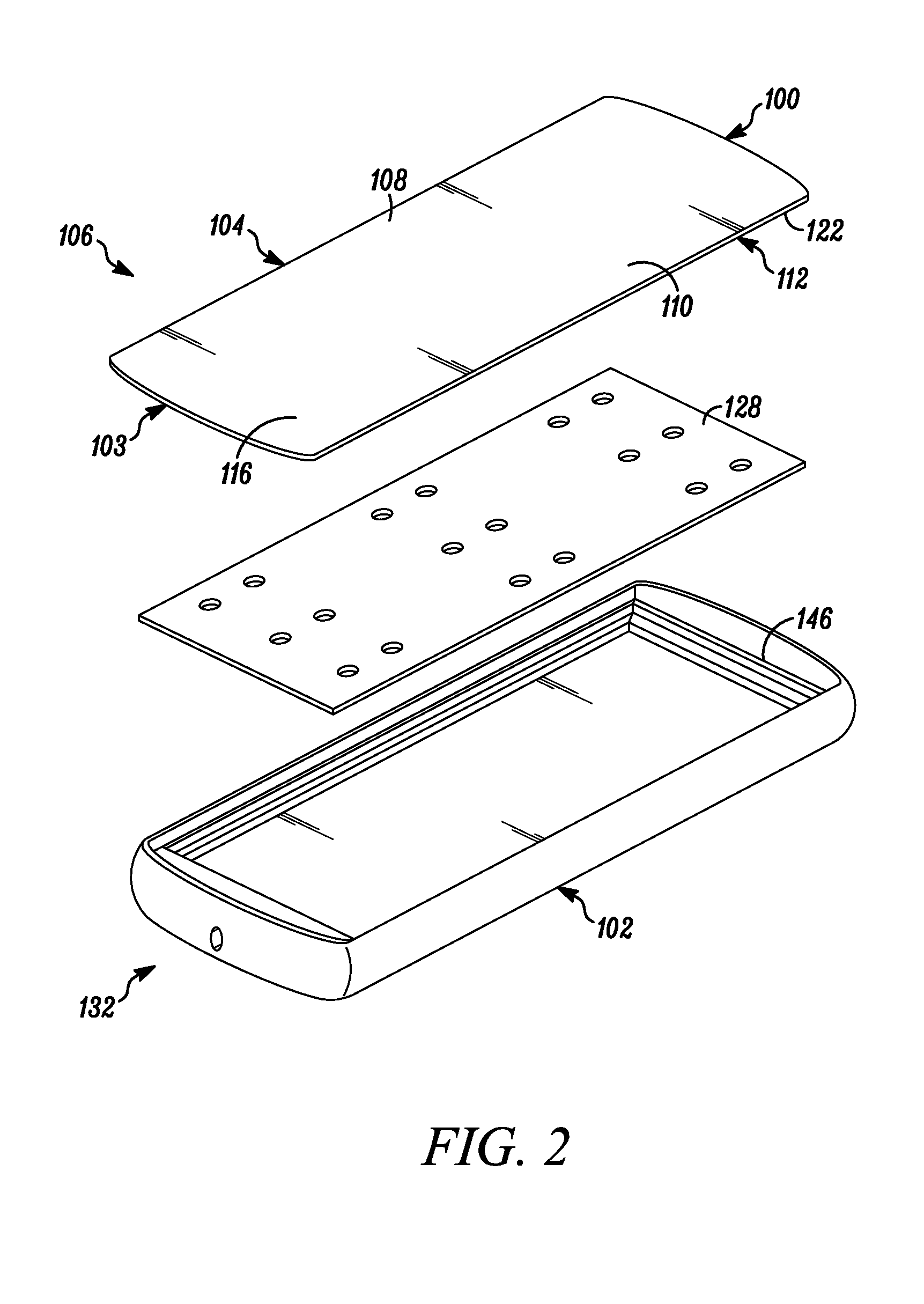
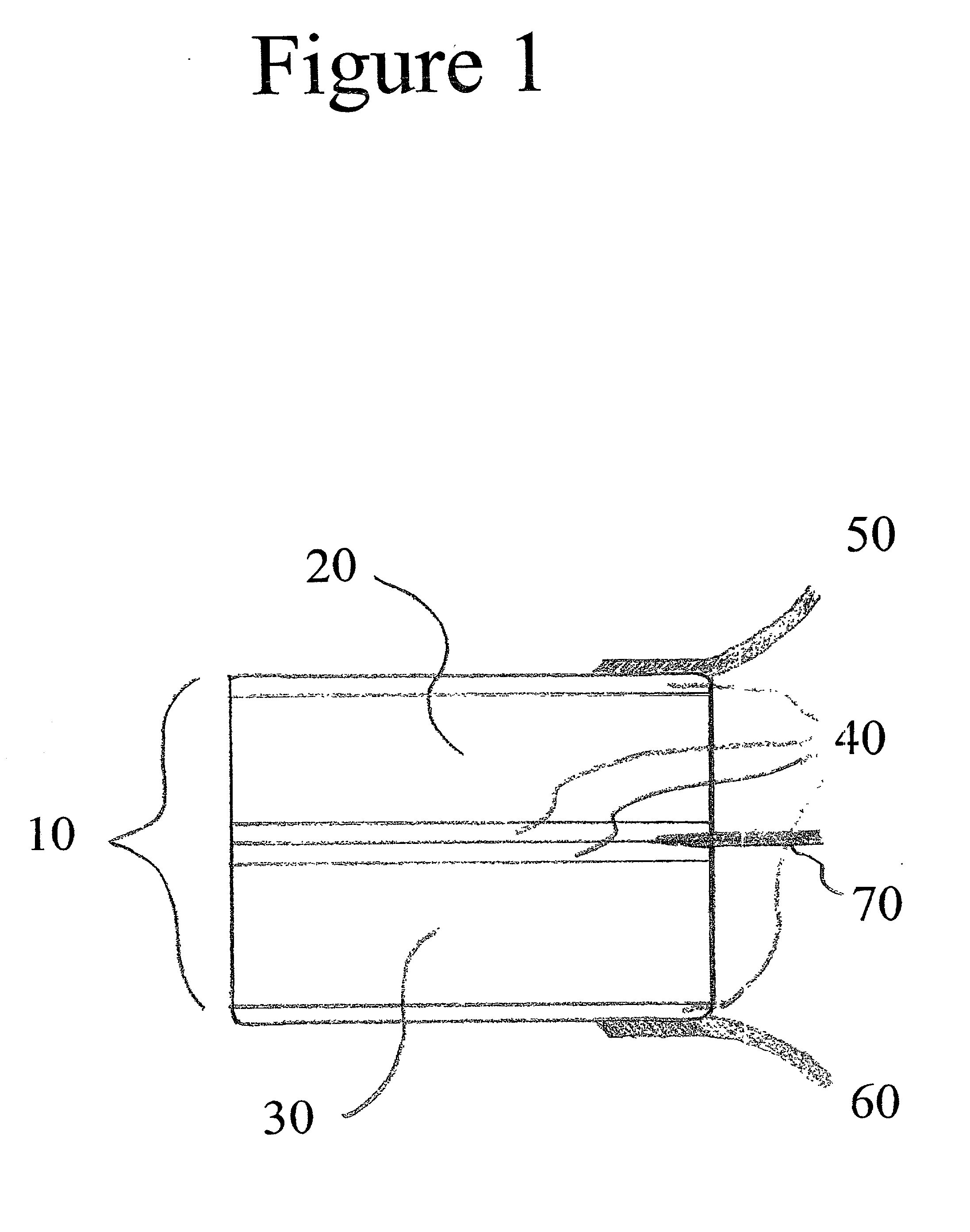
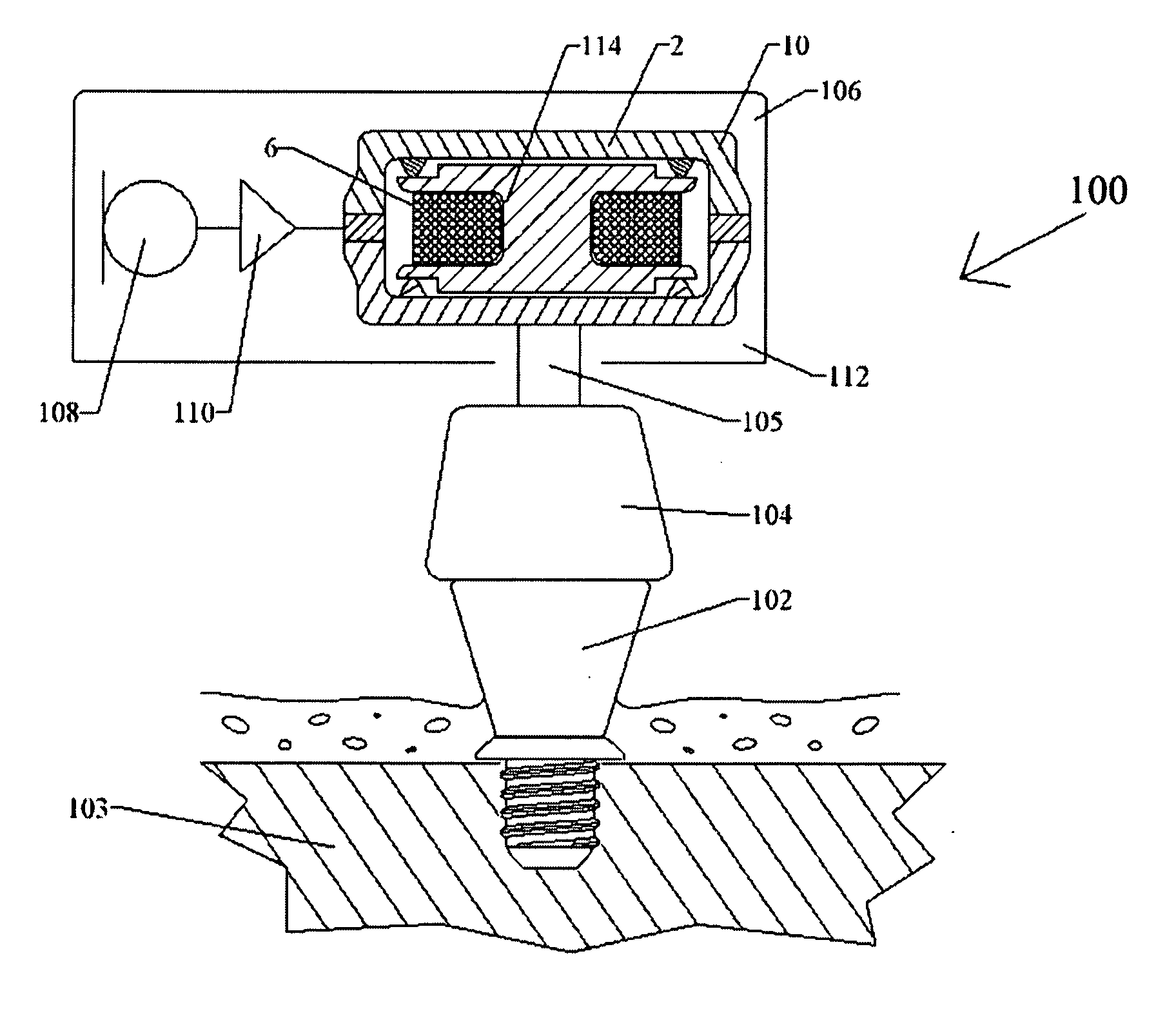
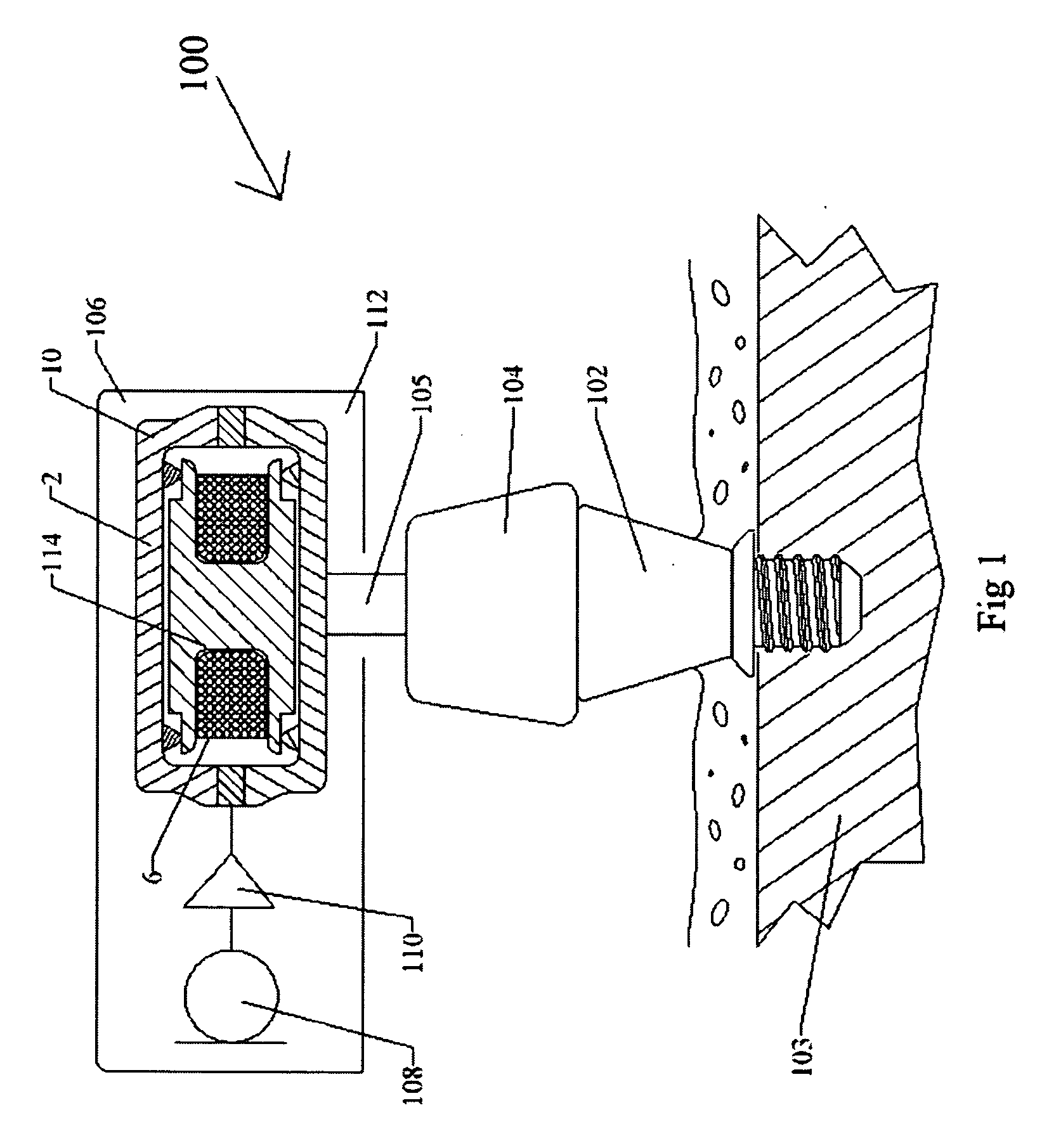
Vibrating earphone with enhanced base sound effect
InactiveUS20080112581A1Good effectMicrophonesHeadphones for stereophonic communicationMedicineBone conduction hearing
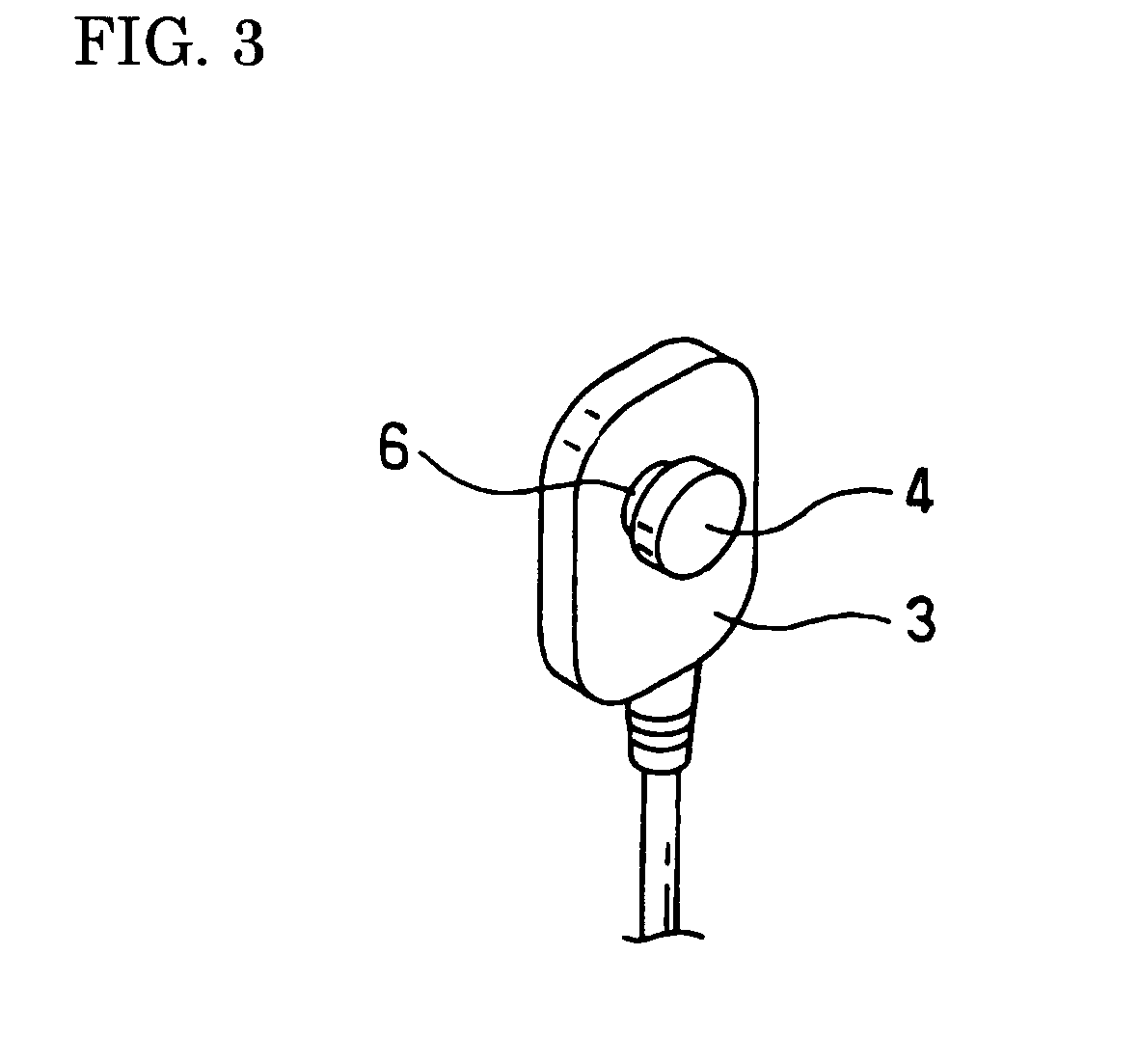
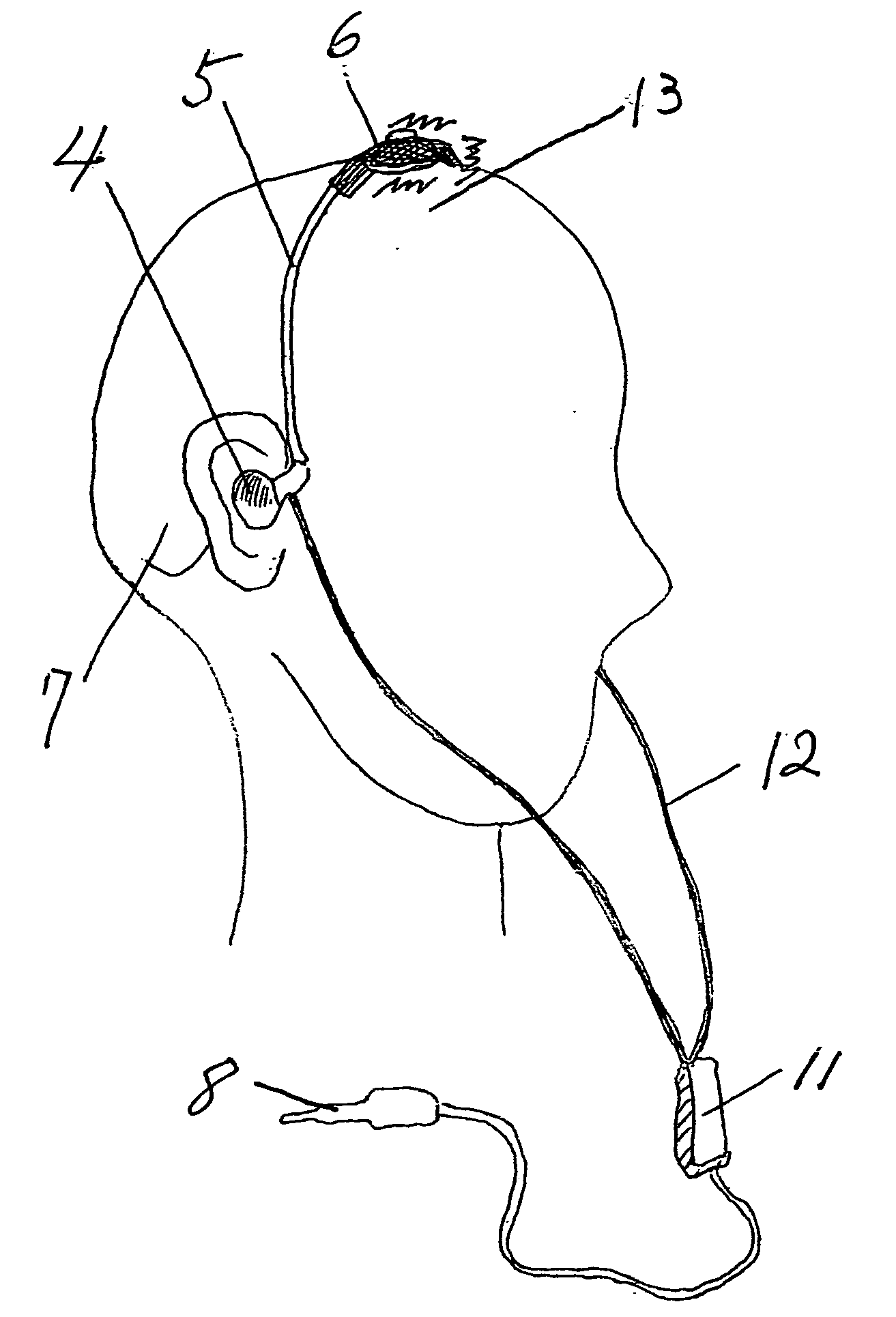
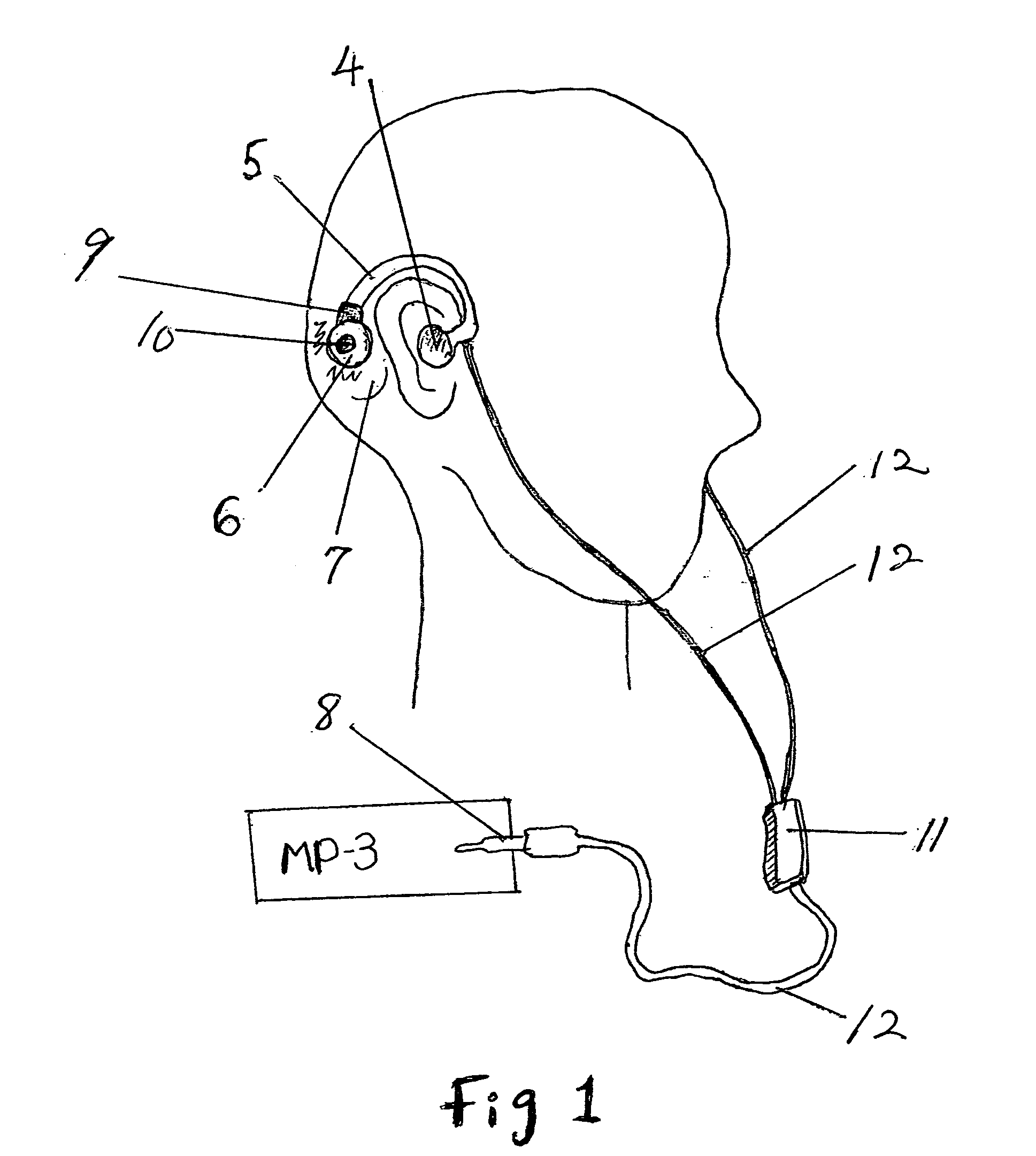
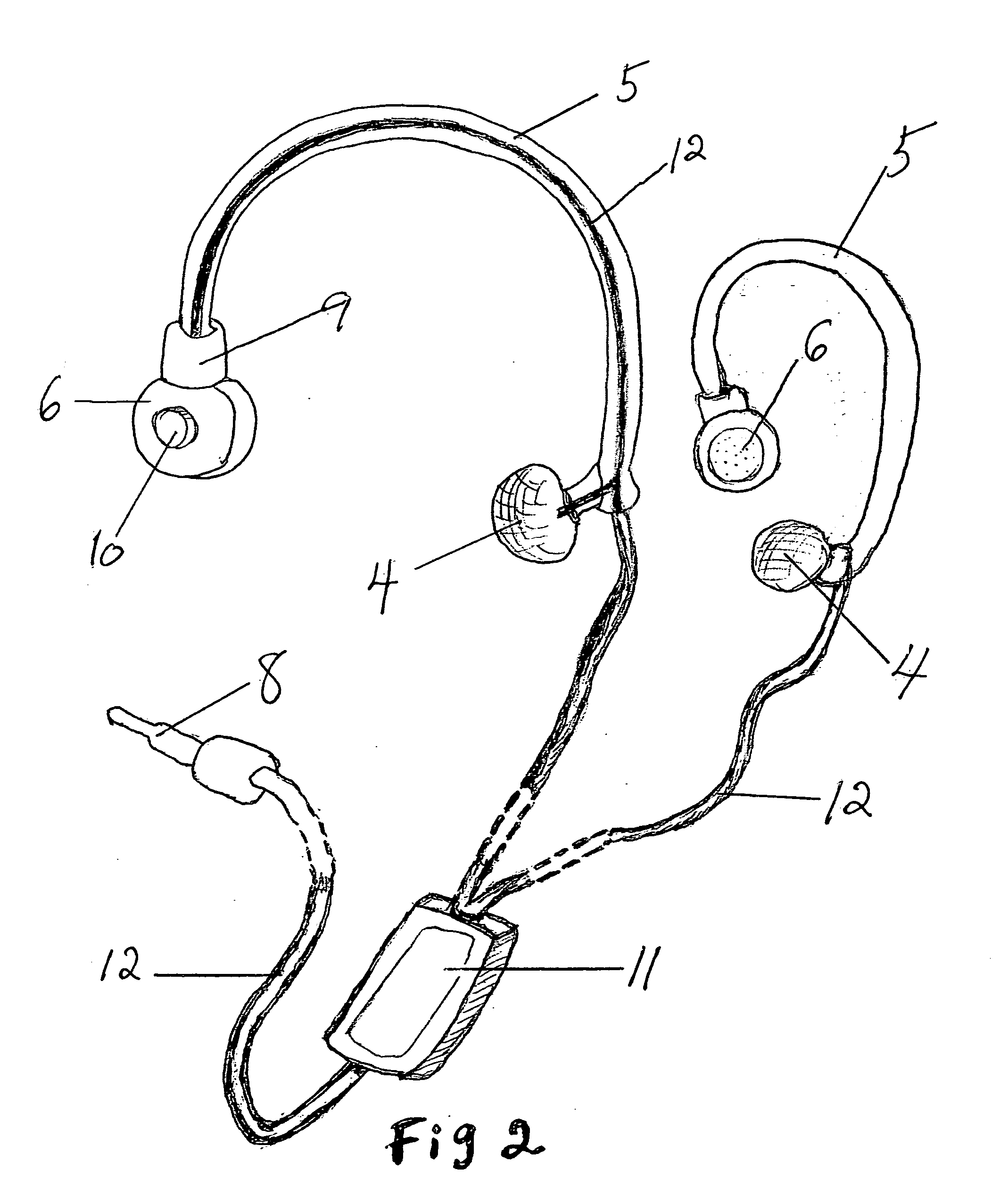
A hearing device (FIG. 1, FIG. 2, FIG. 3) that simultaneously generates both air and bone conduction sounds. The vibrator (6) placed on mastoid bone can effectively produce enhanced bass sound effects.This hearing device can be used for an hearing impaired person.
Owner:KIM STANLEY +1
Wearable communication device
InactiveUS20050207599A1Easy to operateImprove usabilityTime indicationDigital data processing detailsBone conduction hearingActuator
A wearable communication device includes a bone conduction actuator which is applicable for being in contact with a user's wrist, hand, back of the hand, finger or nail in order to transmit voice signals. The user inserts the user's finger into the user's ear canal, or touches the user's finger to a part near the user's ear, or puts the user's fingertip or nail on the user's ear canal so as to block the user's ear canal when the user uses the wearable communication device. Also, the wearable command input device includes a first part for detecting shock or acceleration which arises when the user taps the user's fingertip on the surface of an object or when the user taps the fingertips mutually and which is transmitted through the user's finger, a second part for detecting specific frequency components which are included in signals from the first part and for detecting the presence or the absence of the tap of the finger of the user, and a part for determining and executing commands based on series of signals output from the second part.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Sound outputting device
According to an aspect, a sound outputting device includes a front unit, a first side unit, a second side unit, a sound transmitting portion, and a piezoelectric speaker. The first side unit is coupled to one end portion of the front unit. The second side unit is coupled to another end portion of the front unit. The sound transmitting portion is provided in the first side unit for transmitting a sound via cartilage conduction. The piezoelectric speaker vibrates the sound transmitting portion.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Personal Area Network Devices System and Method
InactiveUS20170111723A1Diagnostic recording/measuringDigital data authenticationUser inputSmart glass
A system, method and personal area network for communicating utilizing wireless earpieces. The wireless earpieces are linked with smart glasses. User input is received through the wireless earpieces. A command associated with the user input is determined. The command is sent to the smart glasses from the wireless earpieces and may result in information being displayed with the smart glasses.
Owner:BRAGI
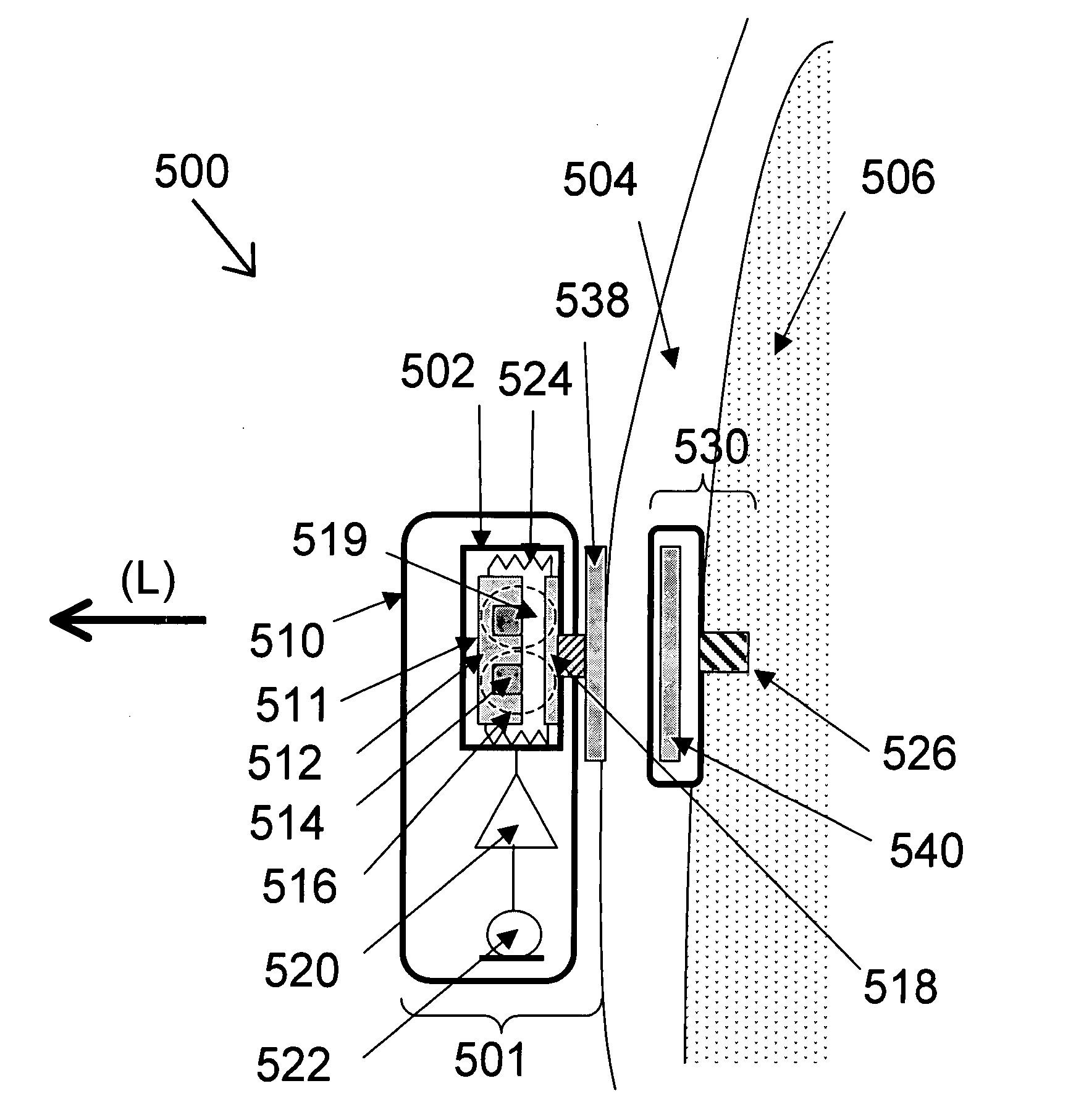
Vibrator for bone-conduction hearing
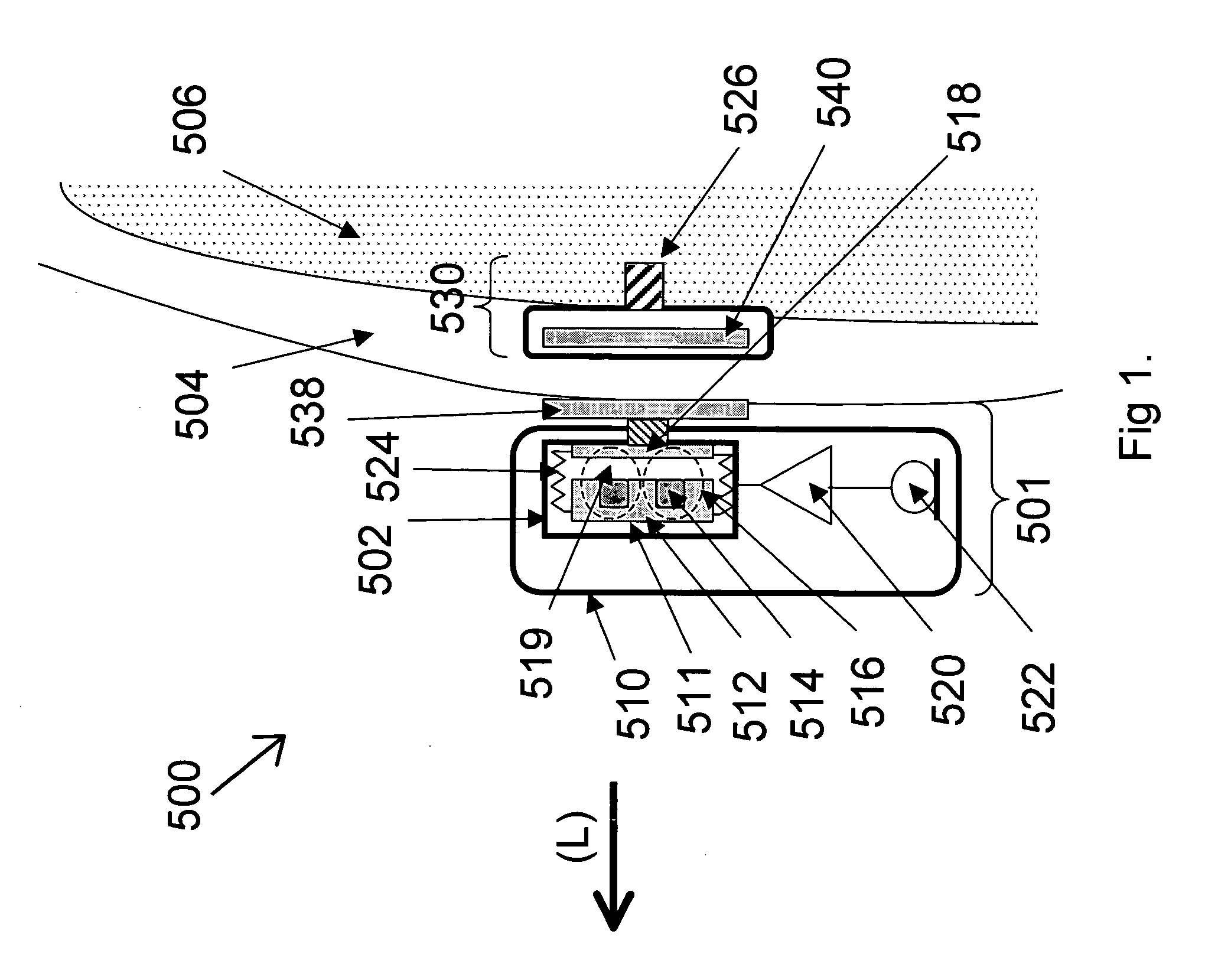
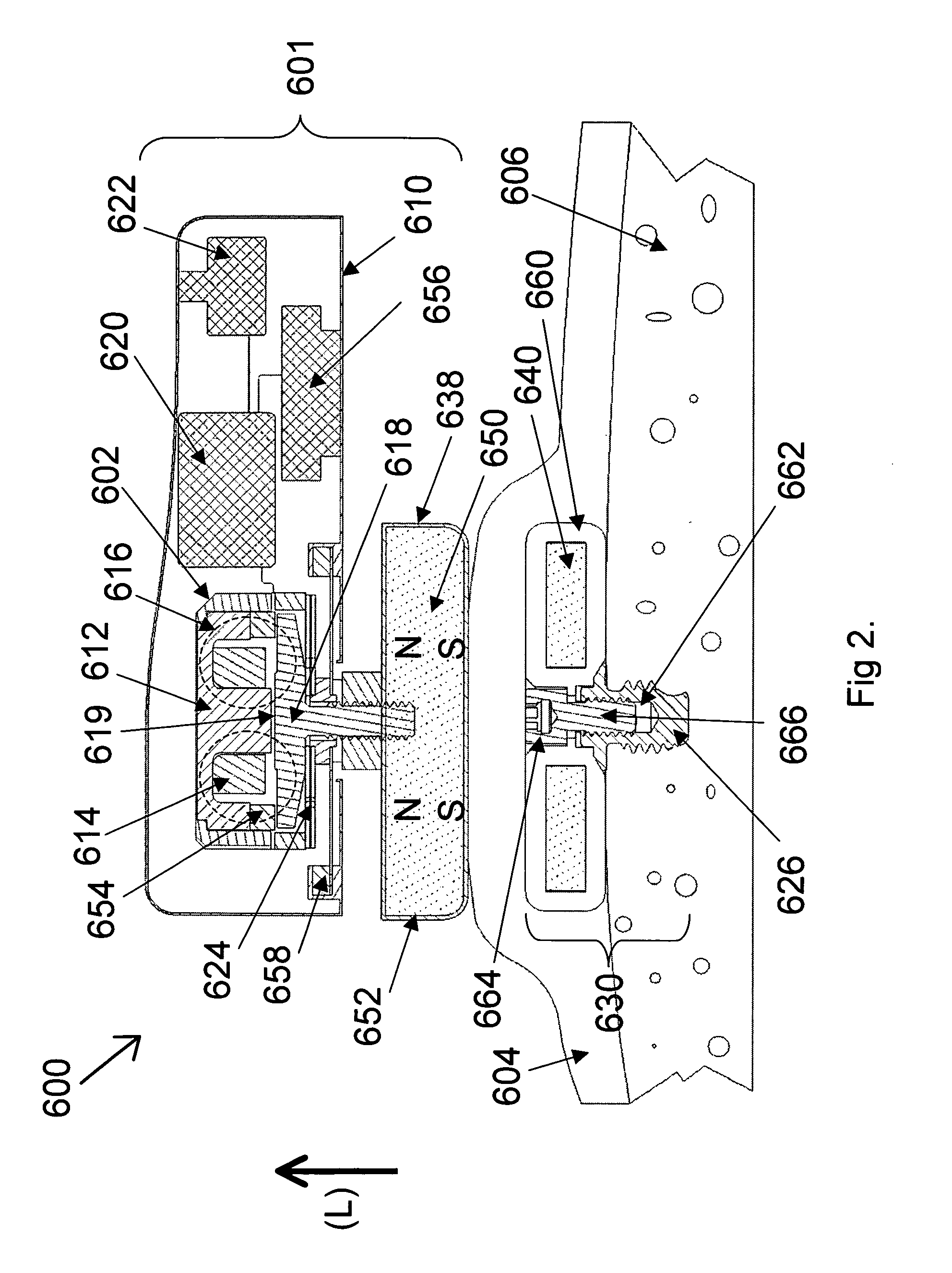
ActiveUS20060045298A1Lower resonance frequencyIncreased durabilityBone conduction transducer hearing devicesMechanical energy handlingBobbinEngineering
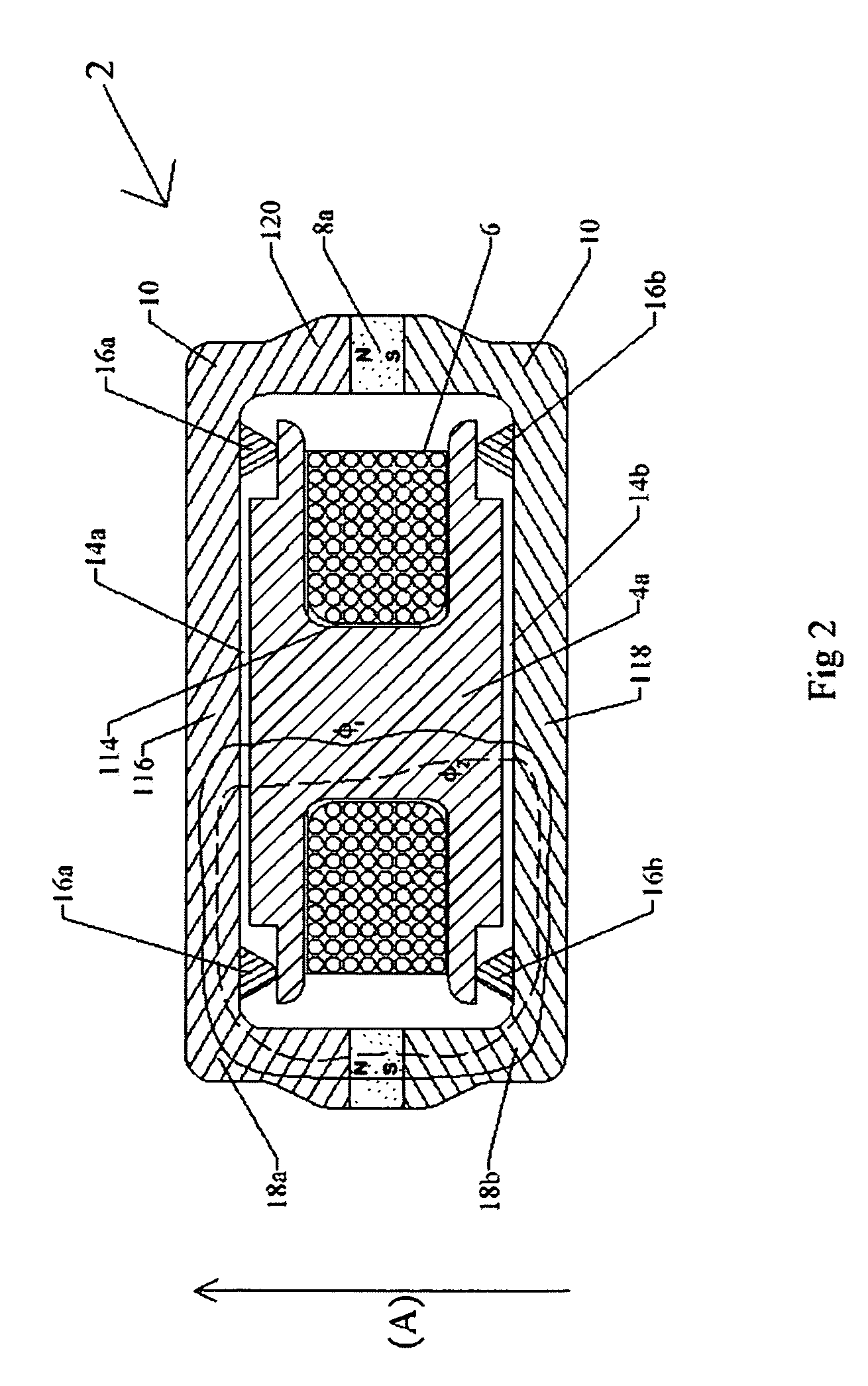
The vibrator system is for generating bone conduction vibrations. A magnet (8a) provides a static magnetic flux (φ1) that follows a first path. A bobbin (4a) is disposed at a center a vibrator (2). A housing (10) encloses the bobbin and has a coil surrounding a center of the bobbin. The coil is powered by an alternating current for providing an alternating dynamic magnetic flux (φ2) following the first path through a magnetic circuit. The housing has an upper end (116). The upper end and the bobbin have a first gap (14a) formed therebetween. The housing has a lower end (118) opposite the upper end. The lower end and the bobbin have a second gap (14b) formed therebetween. The magnet is positioned so that the static magnetic flux (φ1) is passing through the first and second gaps in a direction substantially parallel with an axial direction (A) of the vibrator. Suspension means (16a, 16b) are provided for suspending the bobbin in a center of the housing.
Owner:OTICON
Communication device using bone conduction
InactiveUS6885753B2Low costImprove conversion efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersBone conduction transducer hearing devicesCouplingTransducer
A communication device comprising a microphone, a conduction interface and an electromechanical force transducer mounted to the conduction interface to drive the interface to conduct sound to a user by bone conduction, characterised in that the transducer has an intended operative frequency range and comprises a resonant element having a frequency distribution of modes in the operative frequency range and coupling means for mounting the transducer to the interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com