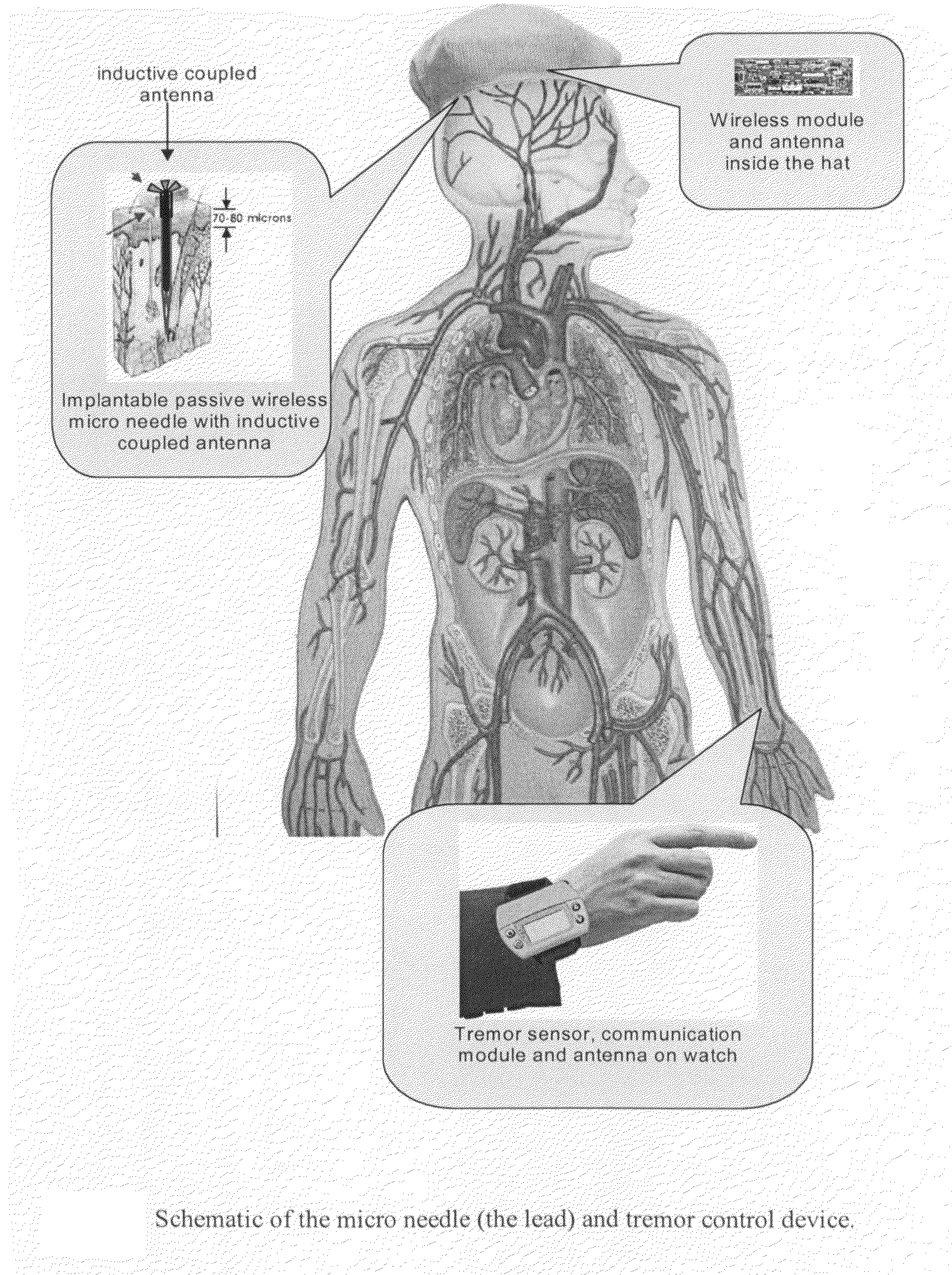Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1277 results about "Force transducer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
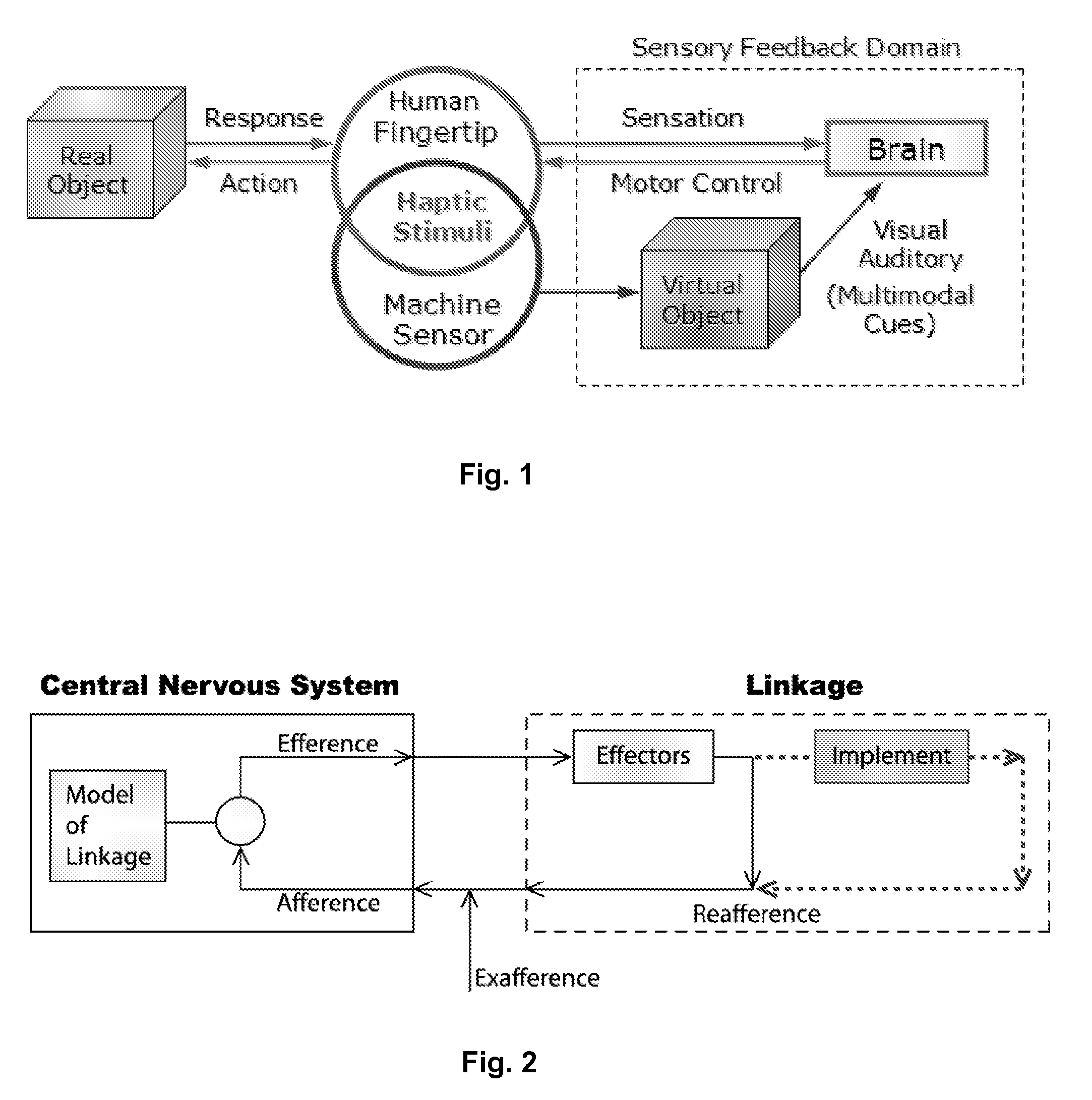
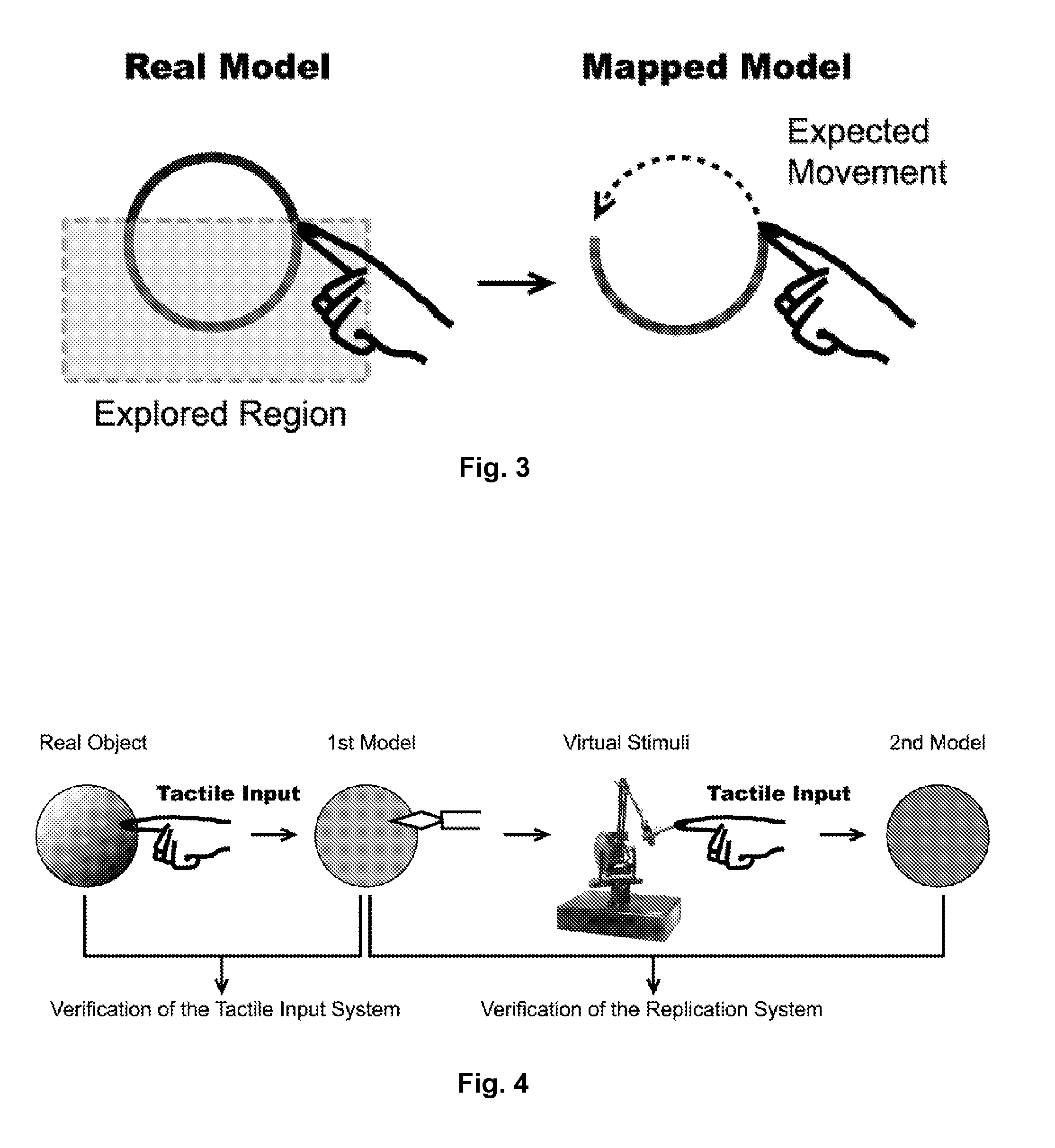
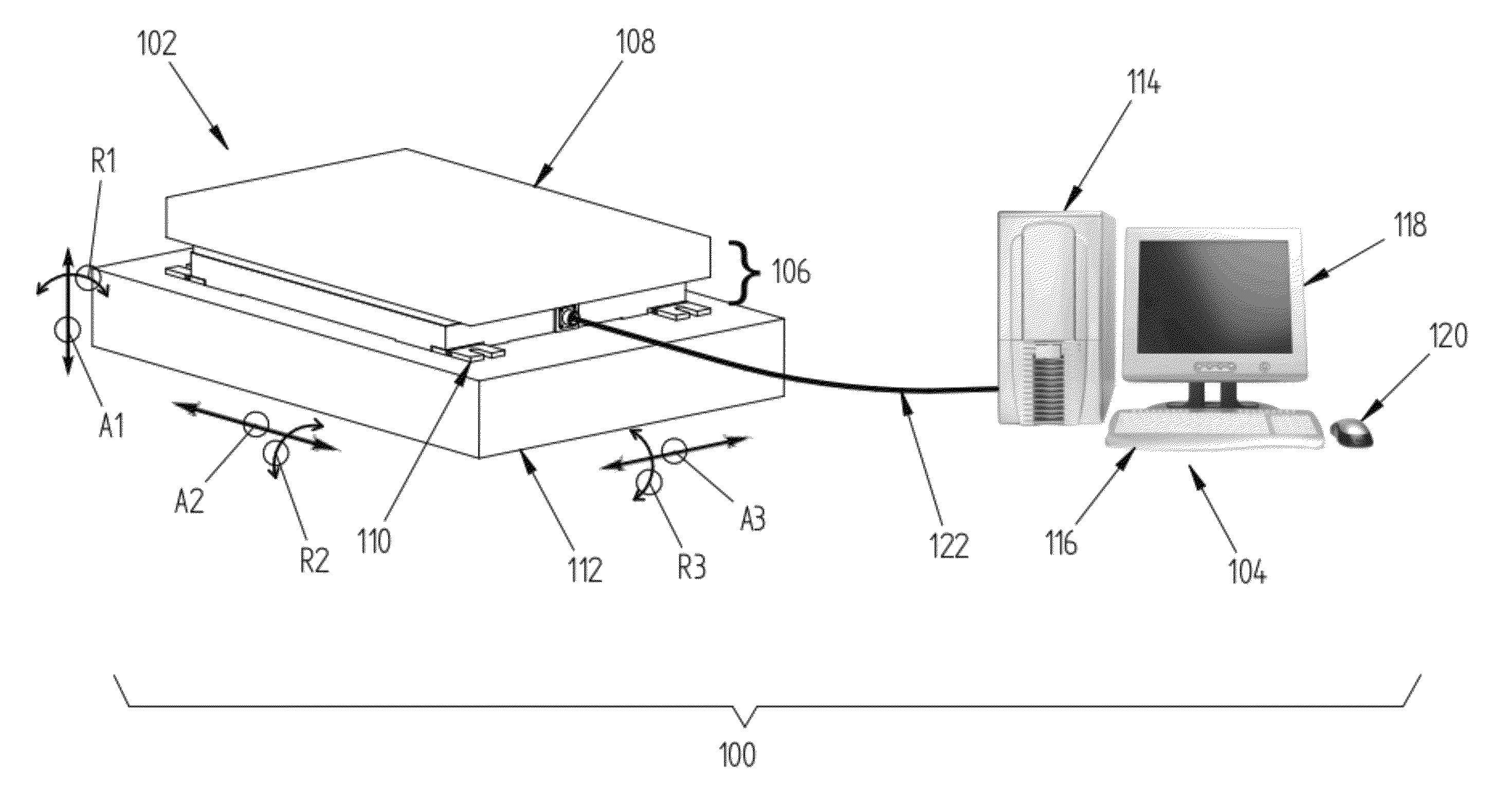
Force Transducer. A force transducer measures the applied force from the proportional deformation of a spring element and converts it into transmitted output signals sent to indicators, controllers, data acquisition systems and computer systems.
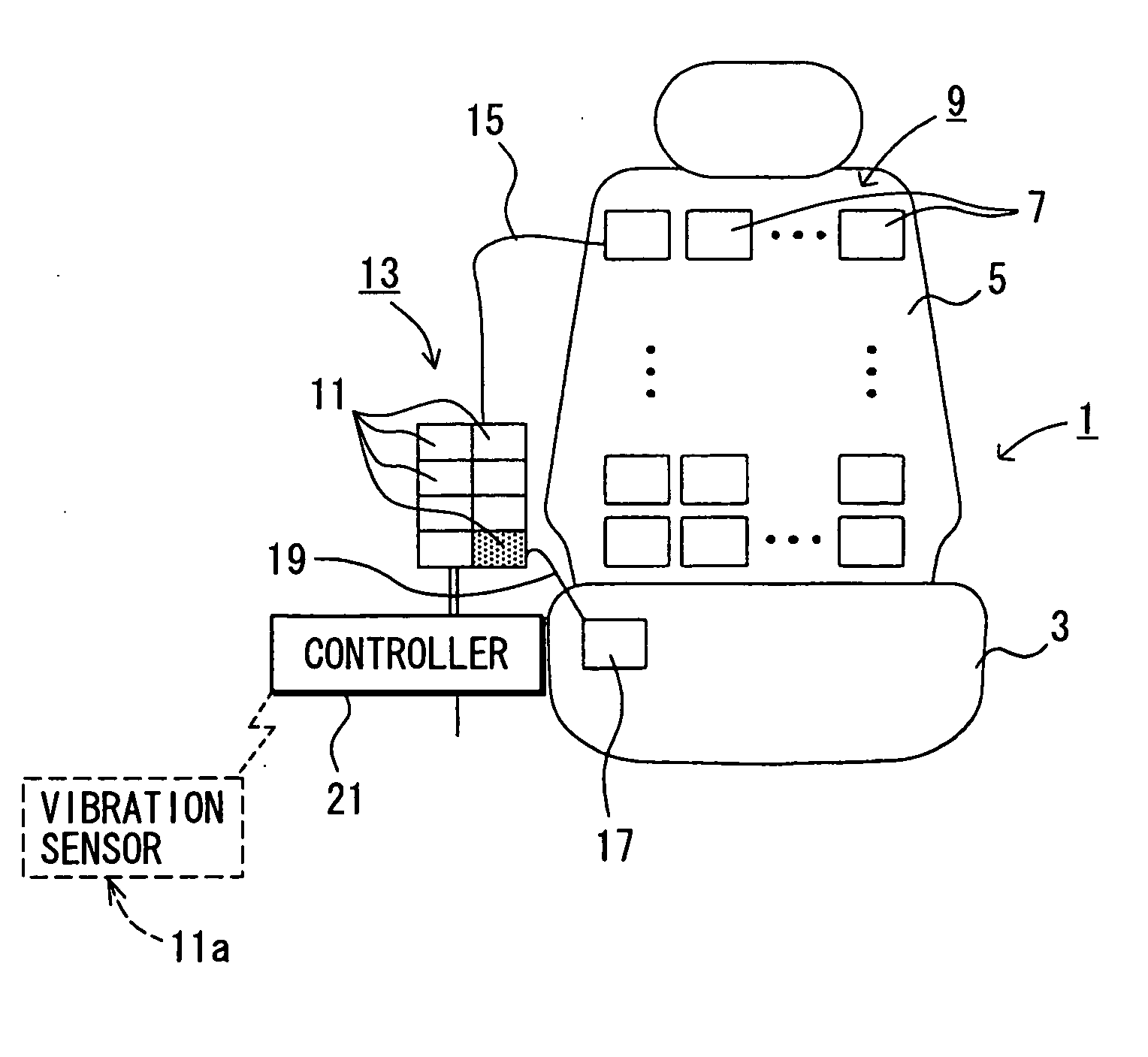
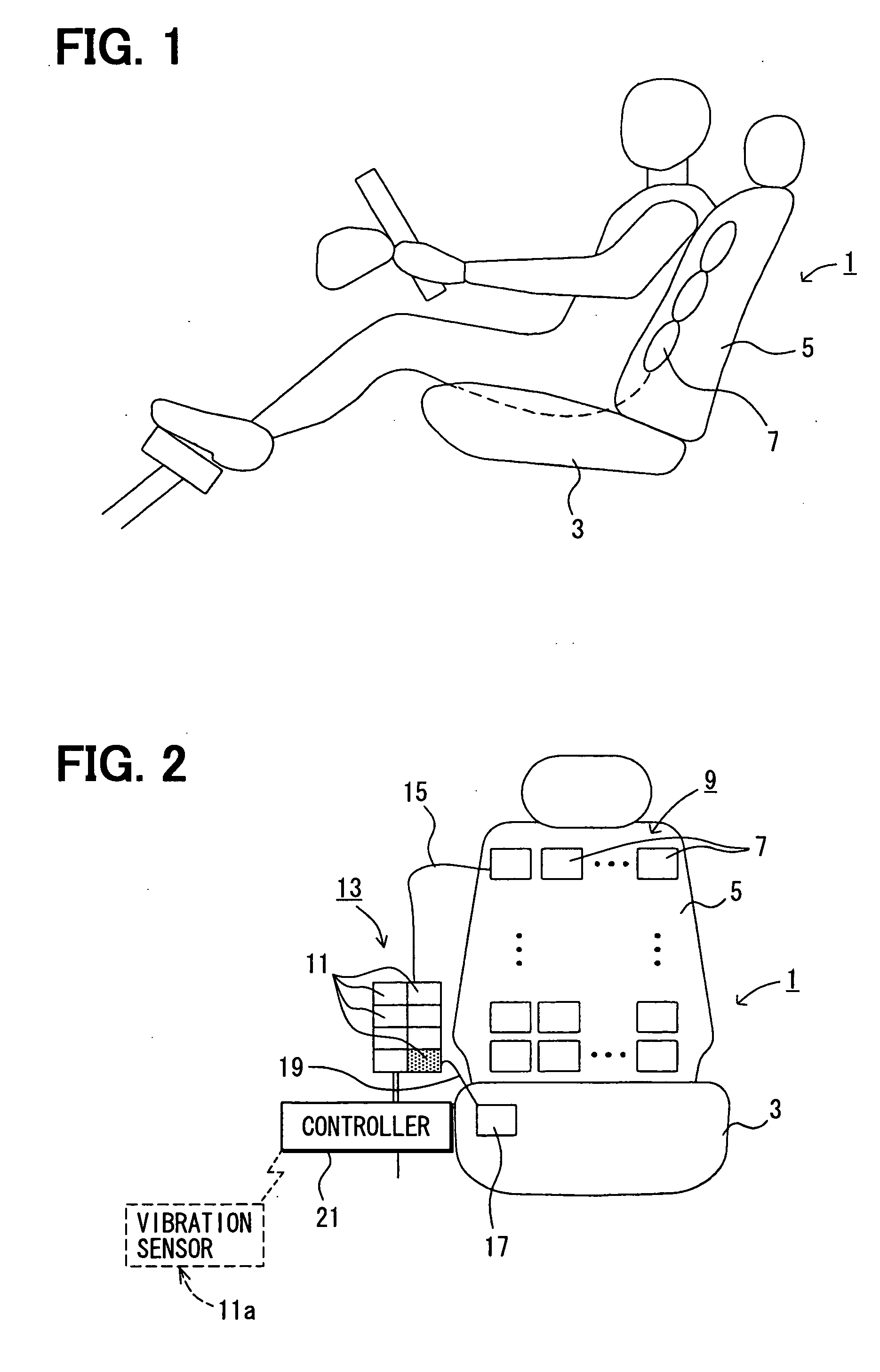
Movement facilitation device
InactiveUS20060094989A1Reliable positioning of handMaximize the benefitsChiropractic devicesForce measurement by measuring optical property variationConductive polymerEngineering
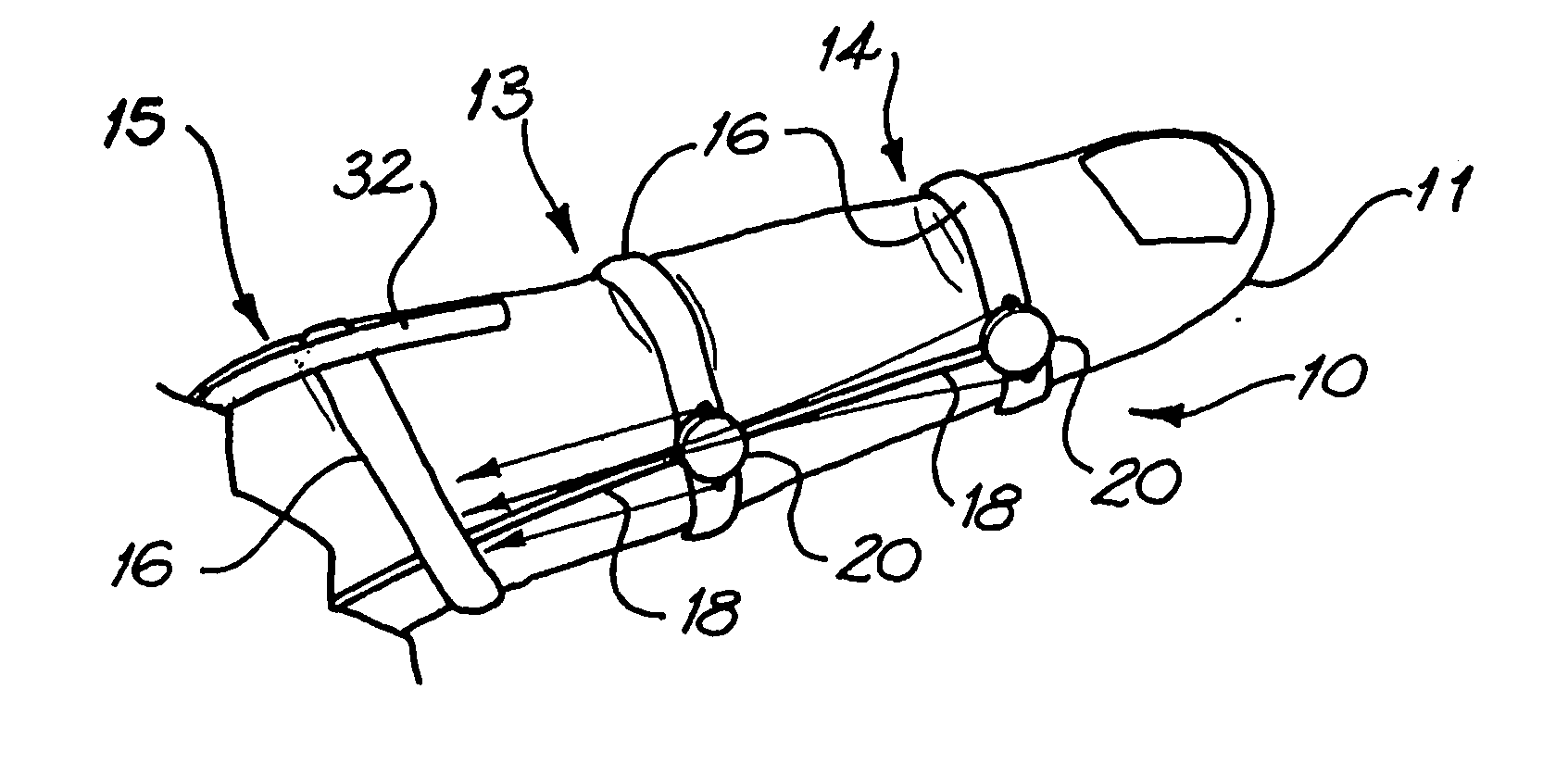
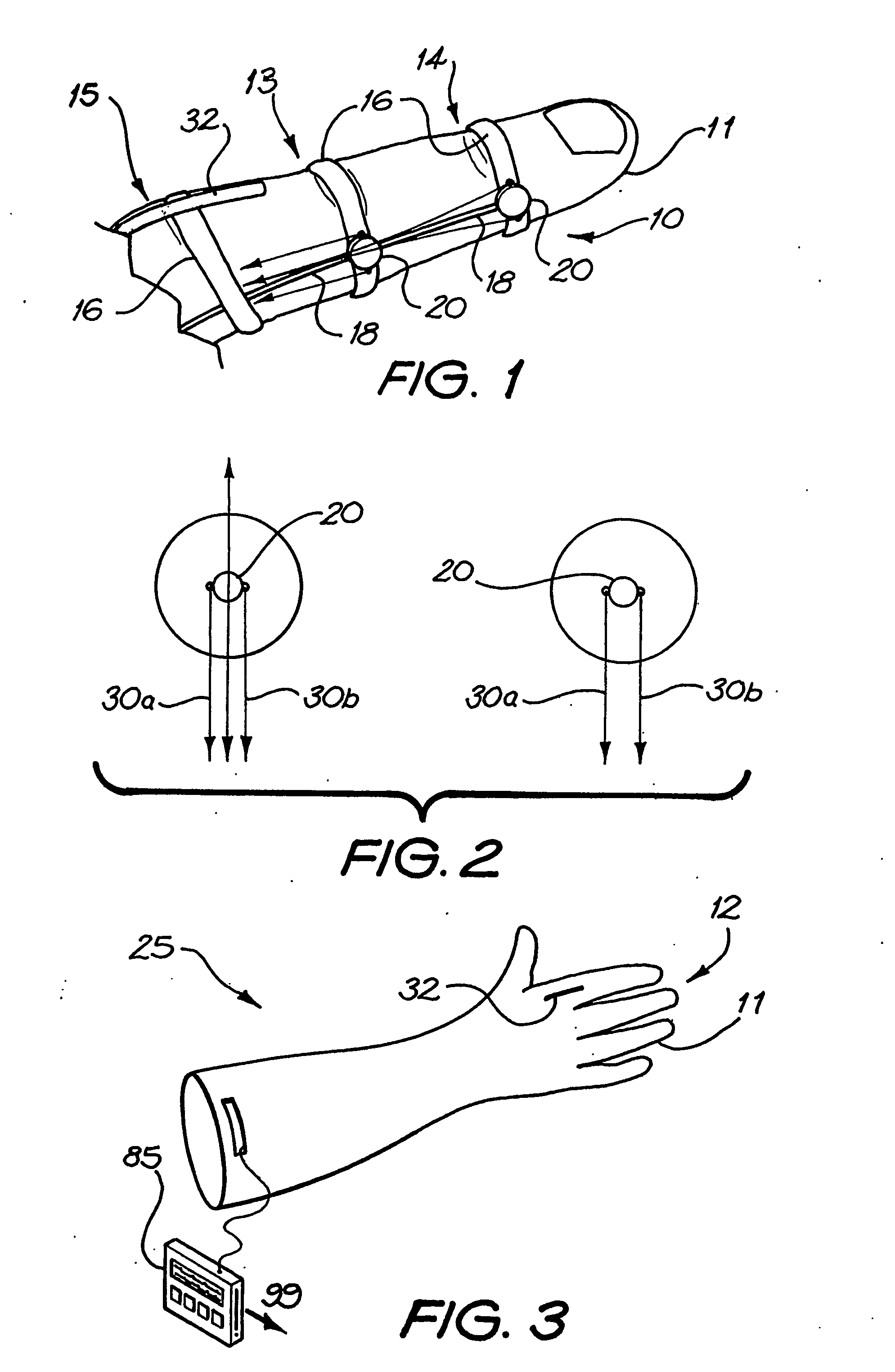
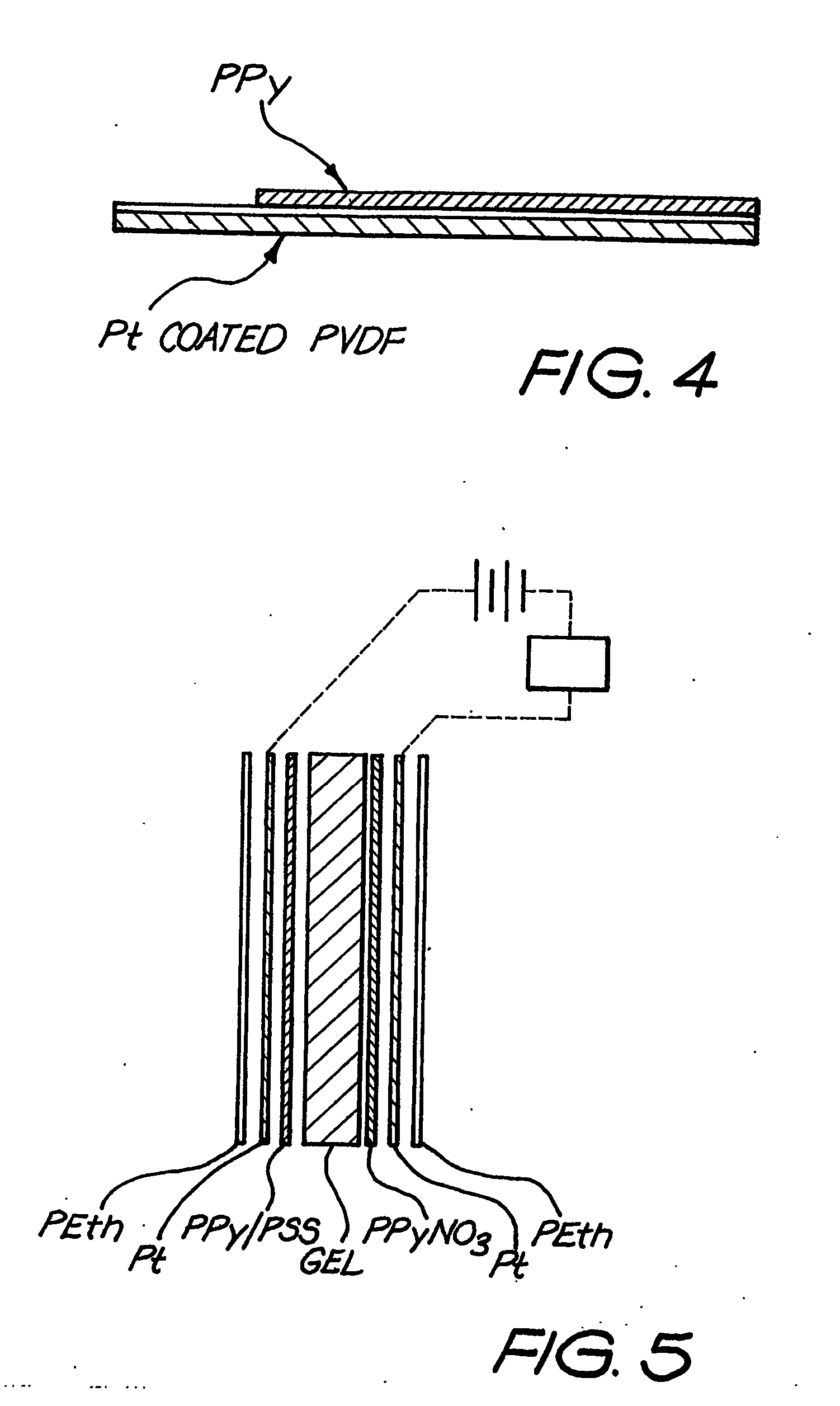
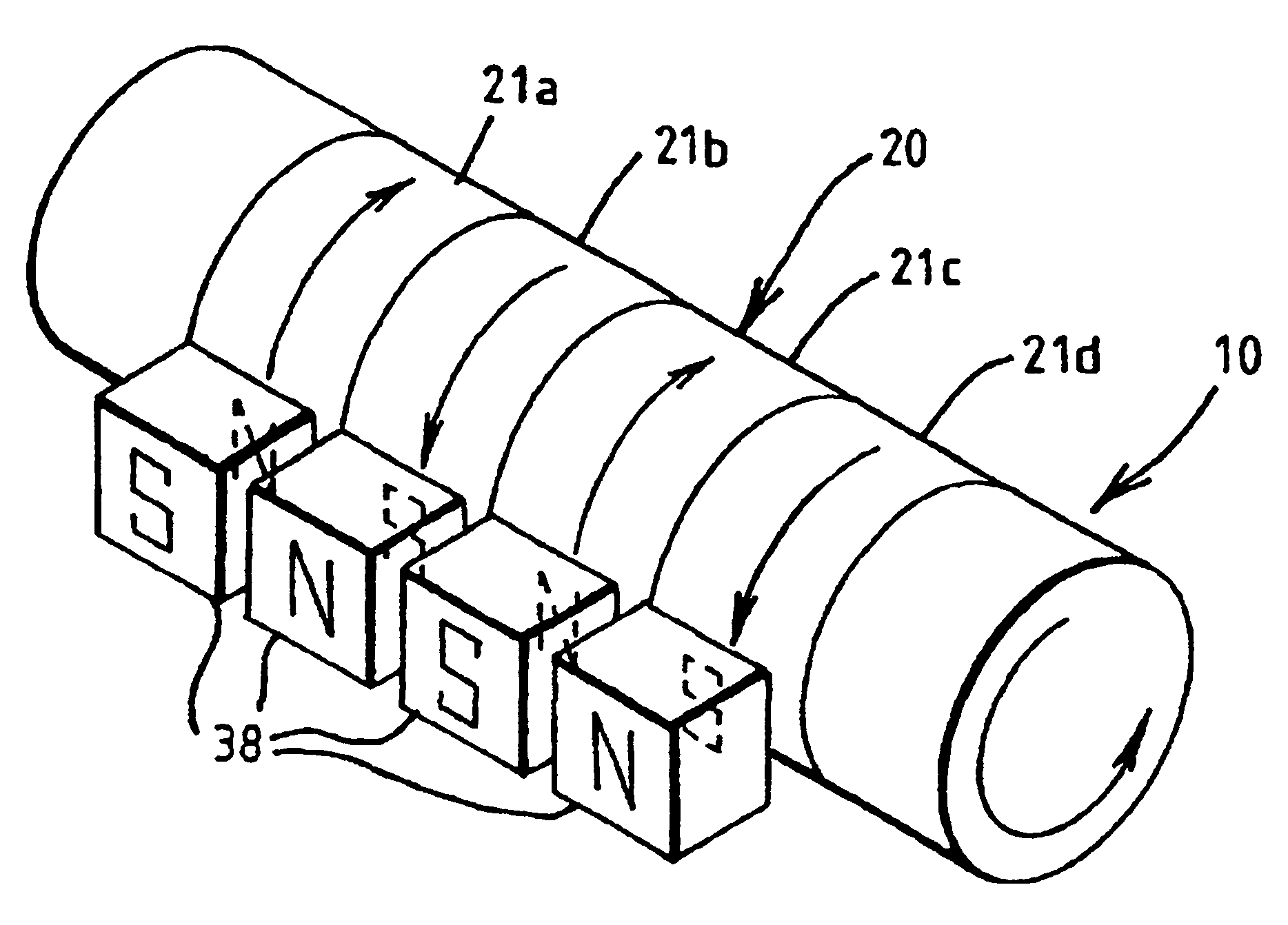
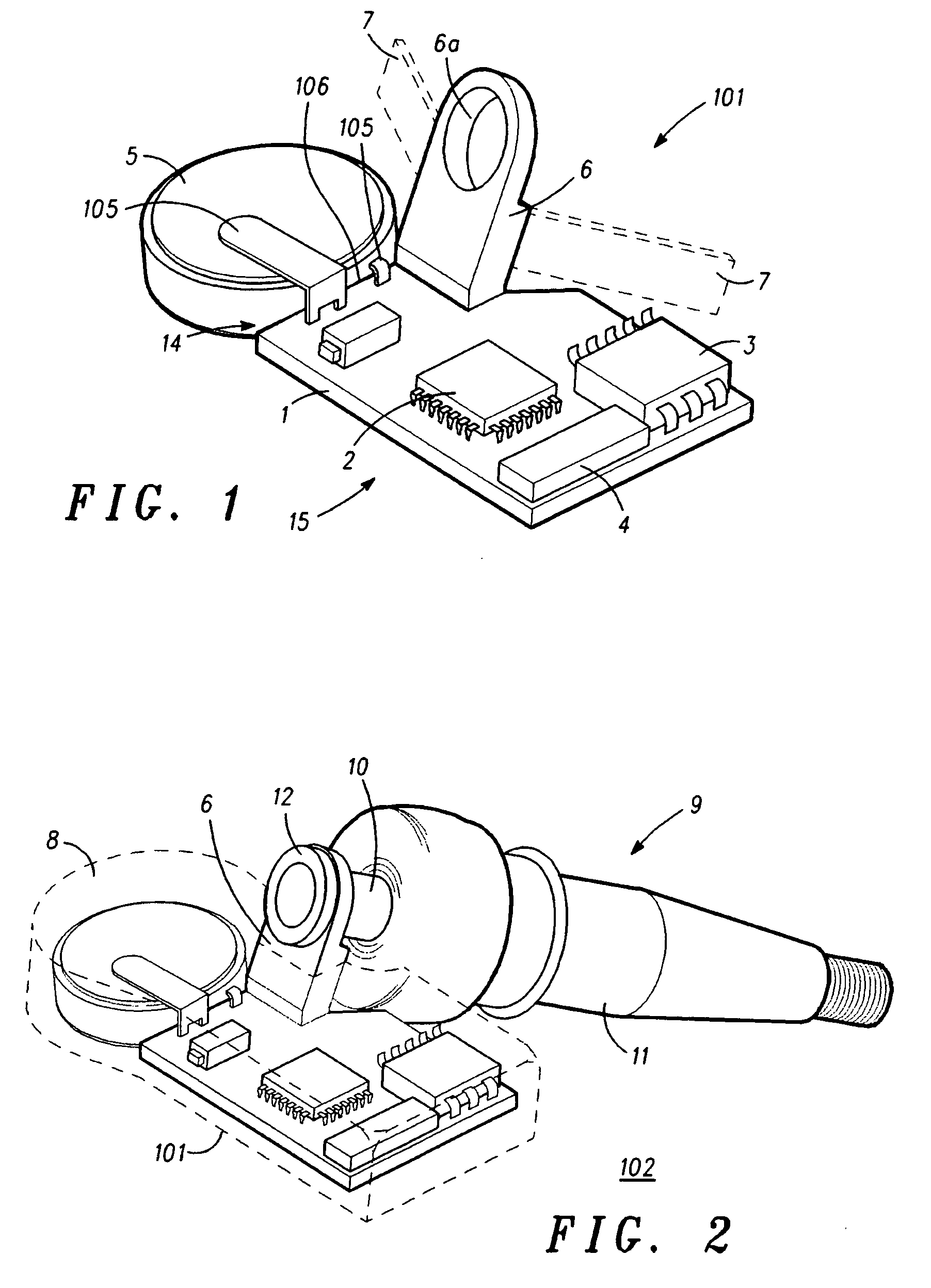
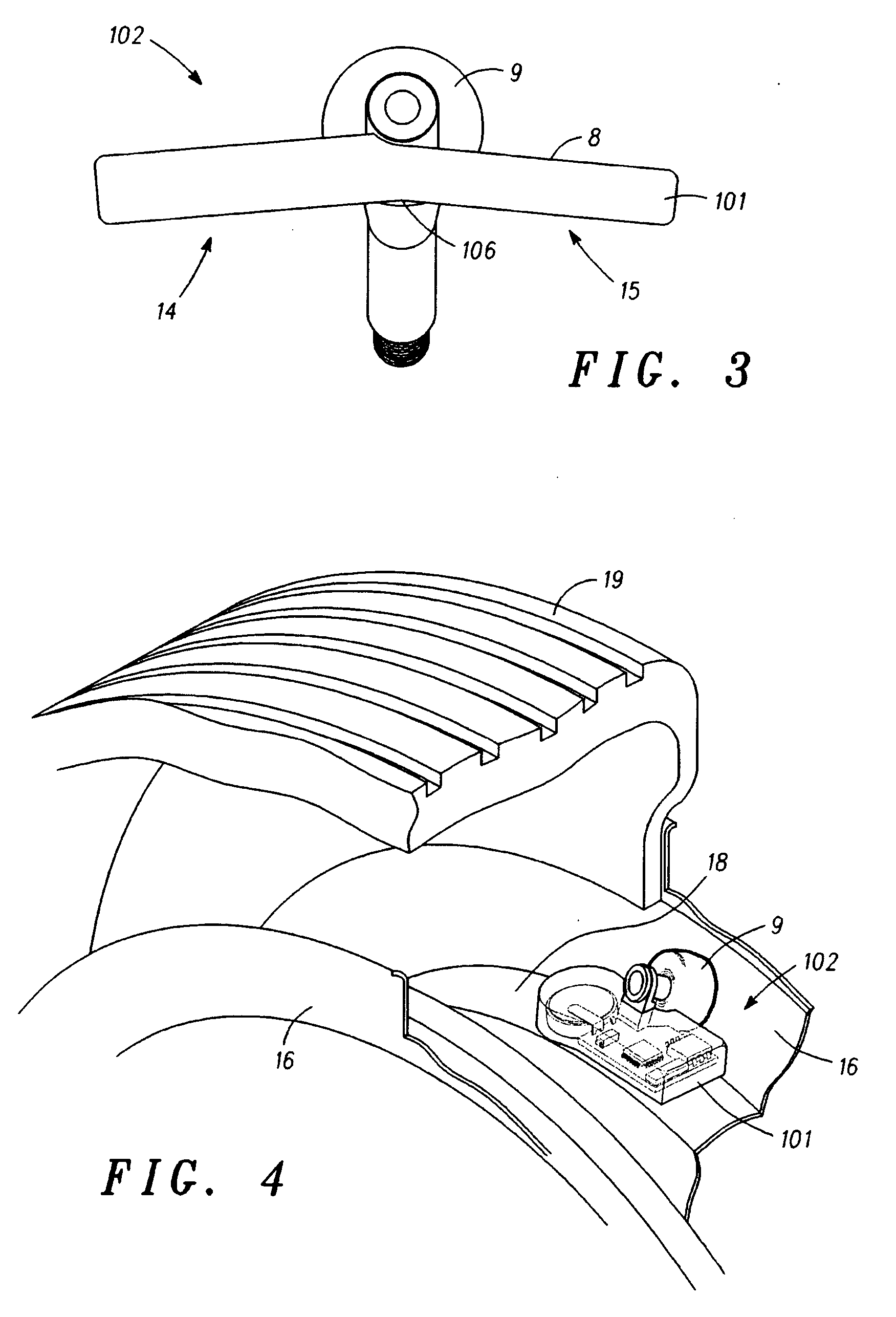
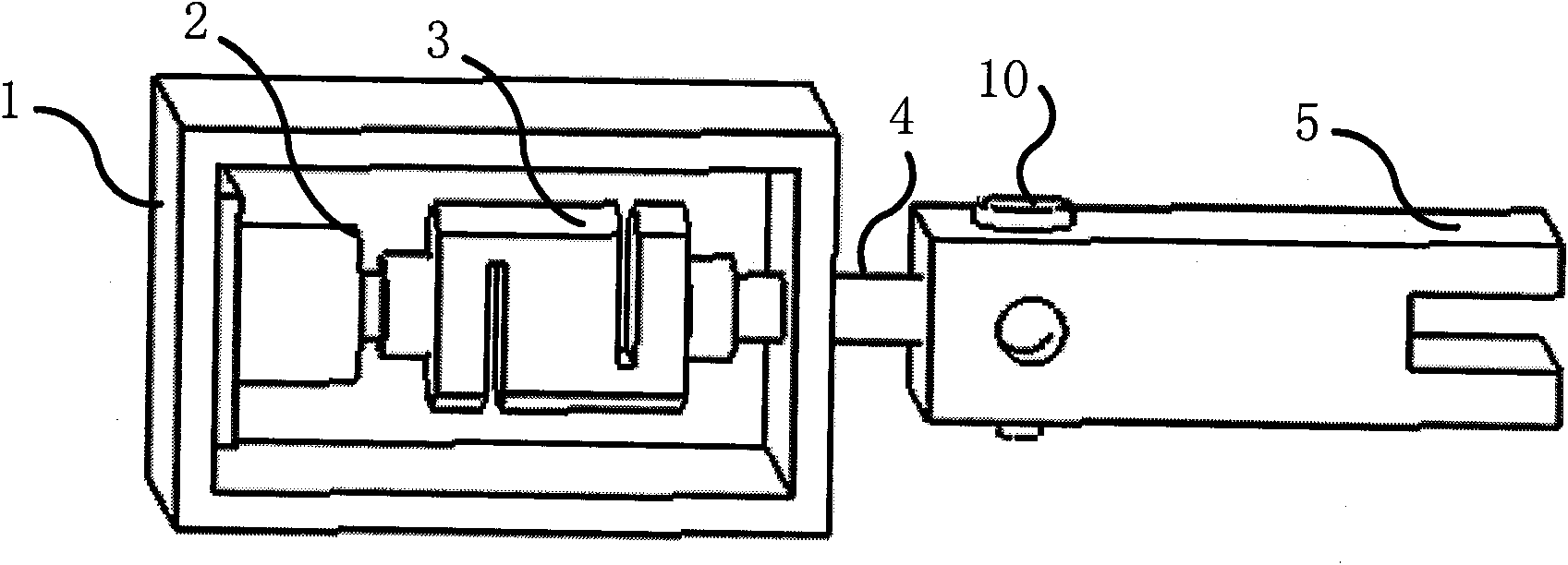
The present invention concerns movement facilitation devices for facilitating movement between a first portion of a first object and a second portion of the first object. One or more of the movement facilitation devices may be combined to form a movement device for facilitating movement of at least one joint or limb of a patient's body. One form of a movement device according to the invention is a glove which at least partially encloses the joint or limb. The invention also encompasses systems for applying Continuous Passive Motion therapy to a joint or limb of a patient using the devices of the invention. The invention also encompasses the use of shape memory materials and of conducting polymers in the devices and systems of the invention, as well as the design of force transducers and actuators that may be used in the devices.
Owner:NORTHERN SYDNEY AREA HEALTH SERVICE +1
Magnetising arrangements for torque/force sensor
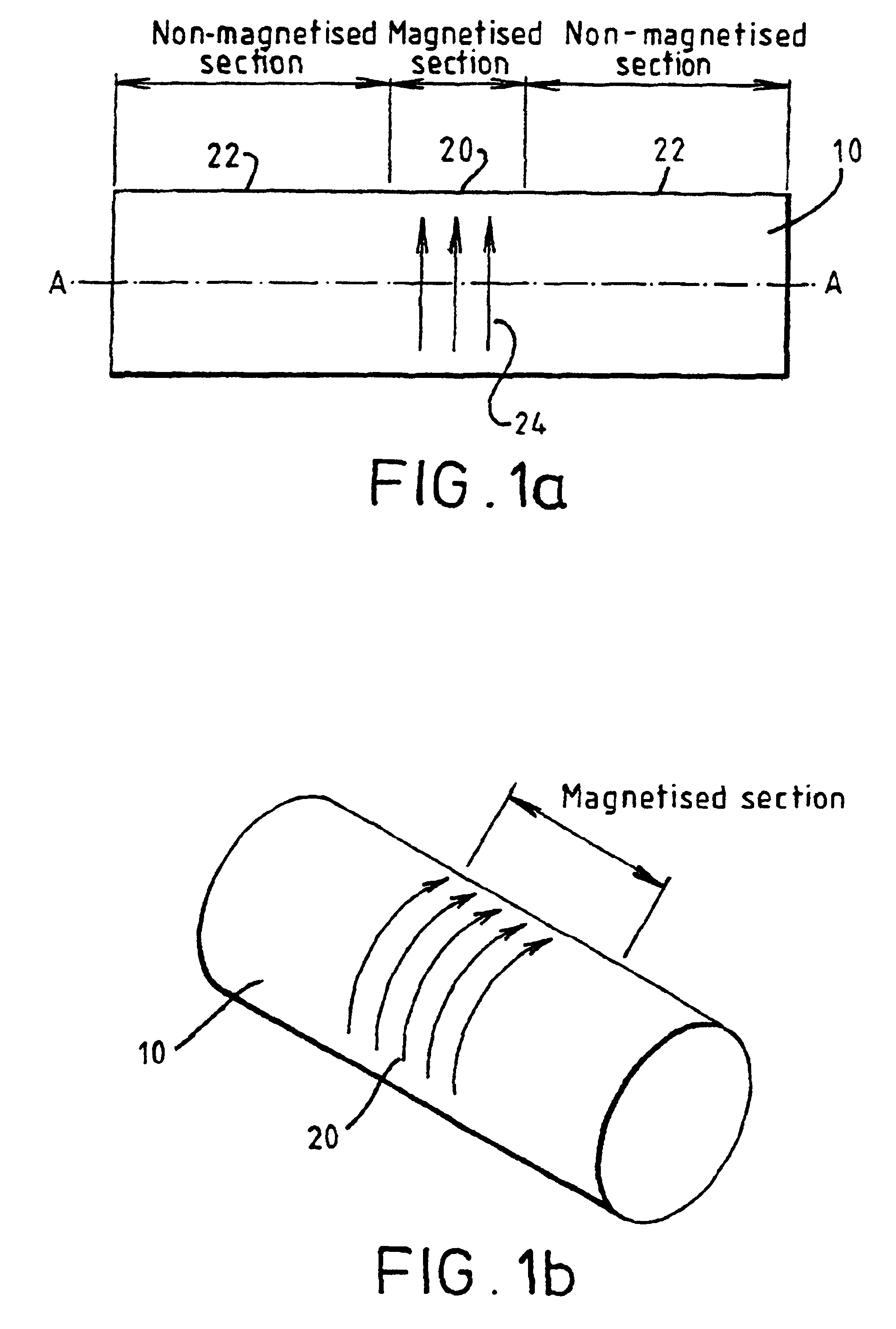
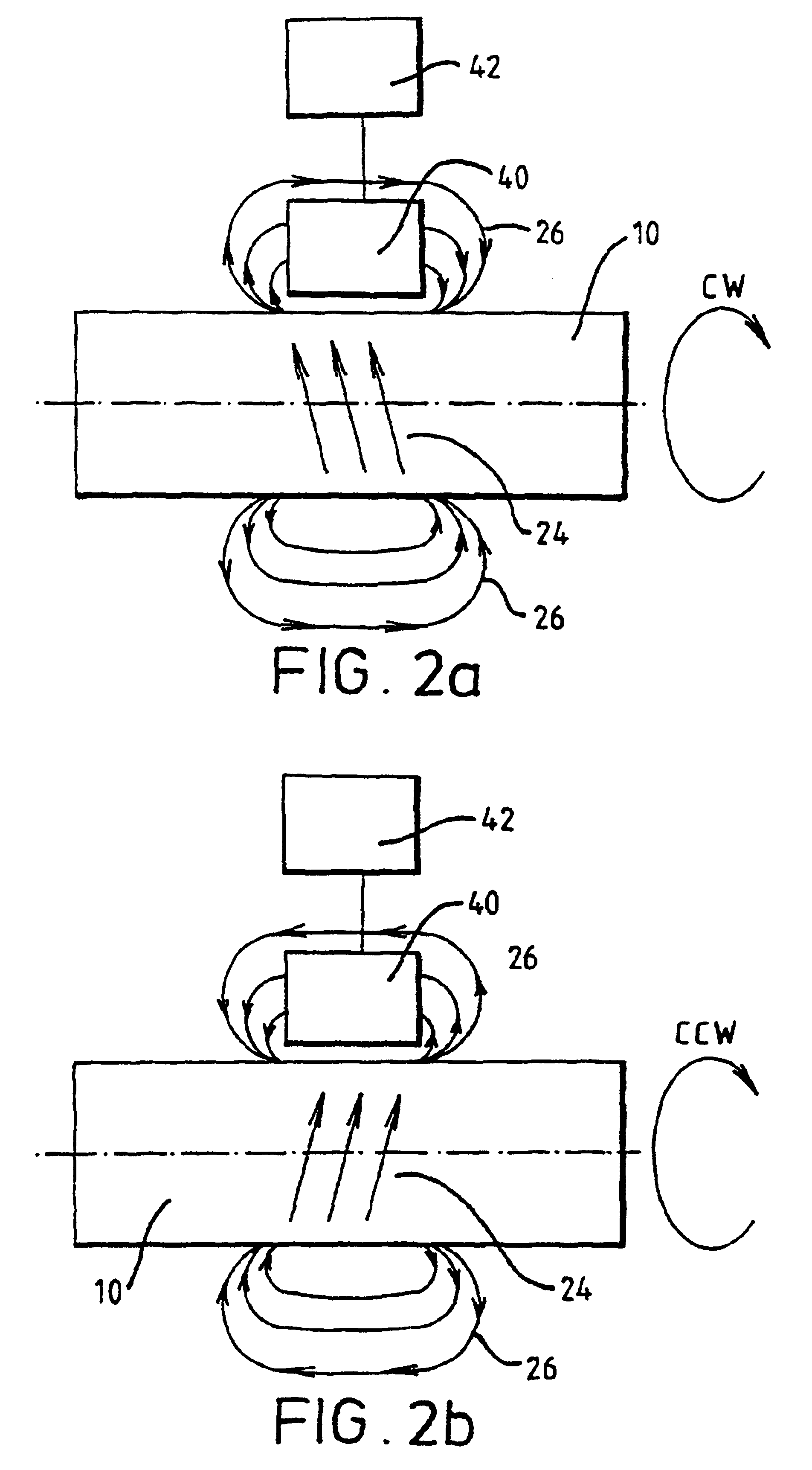
A magnetoclastic transducer for sensing a torque in a shaft (150) is formed by circumferentially magnetising a magnetisable, integral portion (156) of the shaft. To assist in the emanation of a flux-dependent torque, the transducer element portion (156) of the shaft may have further circumferentially magnetised portions (154, 158) to each side. These further portions (154, 158) are of opposite polarity magnetisation to that of the transducer element (156). The external magnetic flux emanated by the transducer (156) is a function of torque and is detectable by a magnetic field sensor (160). An alternative means for the same purpose is to provide the transducer element at a portion (172) of the shaft (170) having an integral annular section of raised profile projecting beyond adjoining portions of the shaft. The shaft may be provided with a series of circumferentially magnetised portions of alternating polarity. A number of ways of achieving circumferential magnetisation are described, together with other directions such as axial. A shaft having the whole or an integral portion of it magnetised can also be used to provide a force transducer sensitive to bending moment induced in the shaft by a force to be measured.
Owner:ABAS
System and method for capturing hand annotations
ActiveUS9092129B2Simplifying the entry of hand annotationsLow costInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsVirtual screen
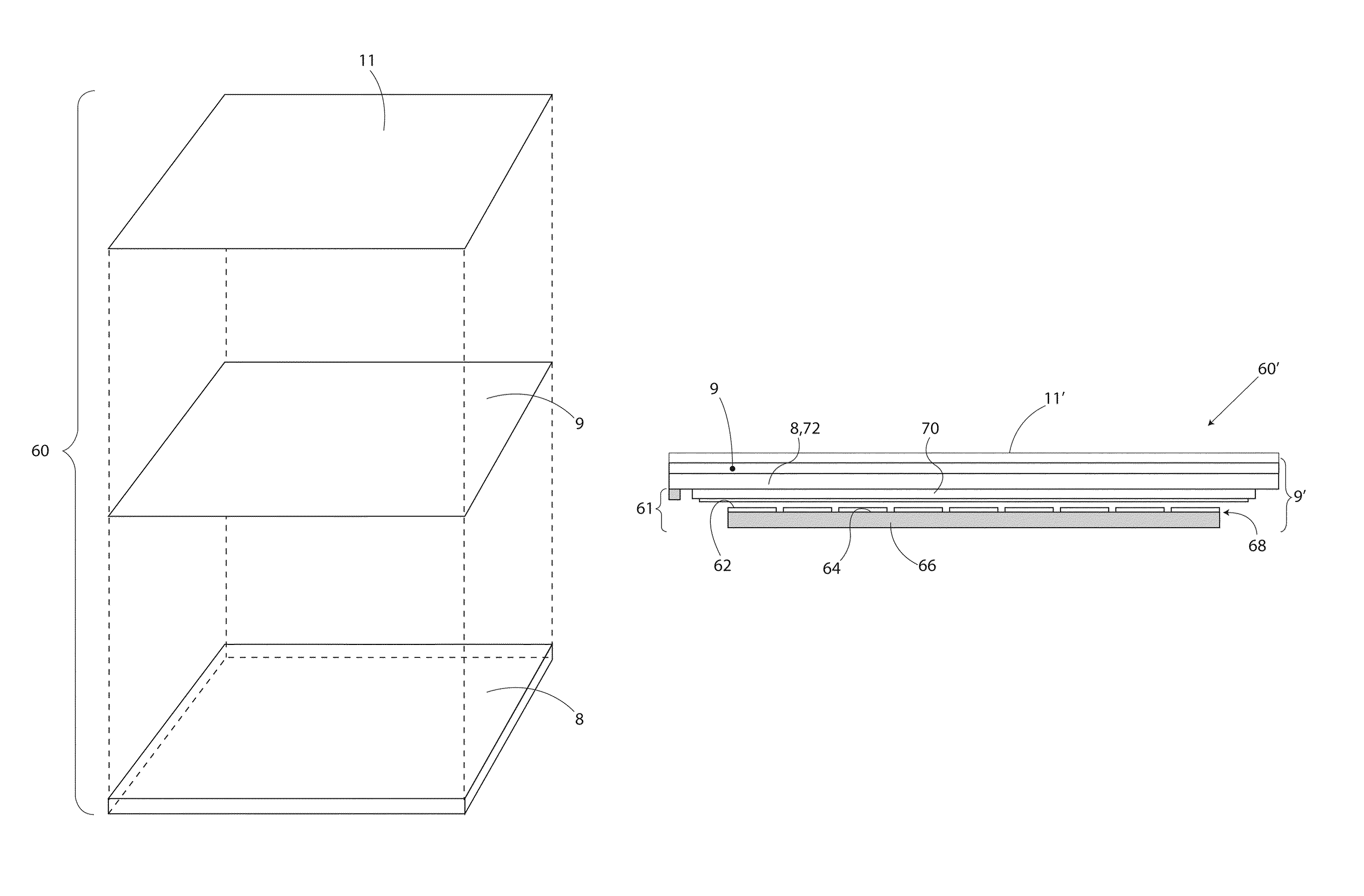
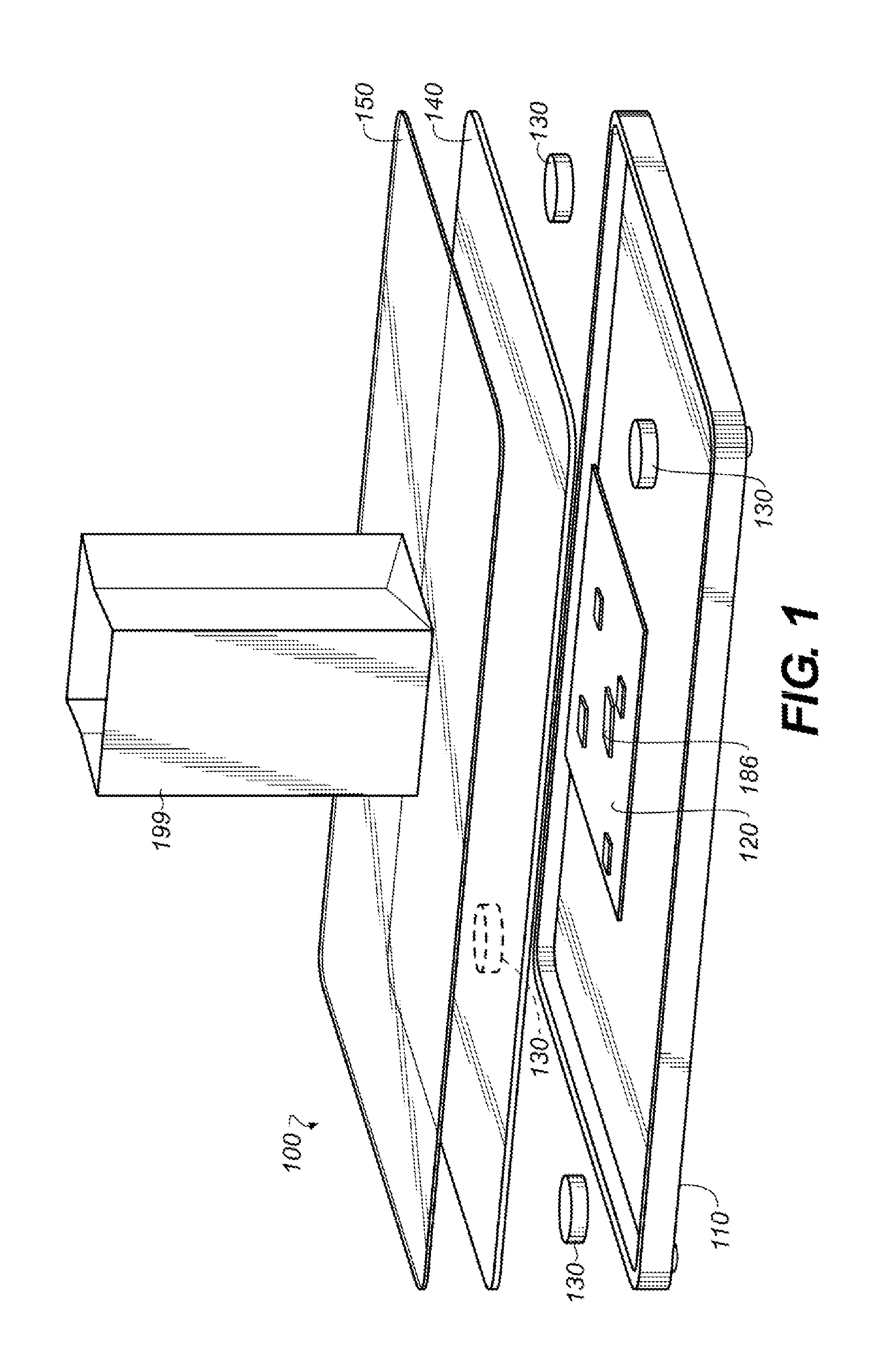
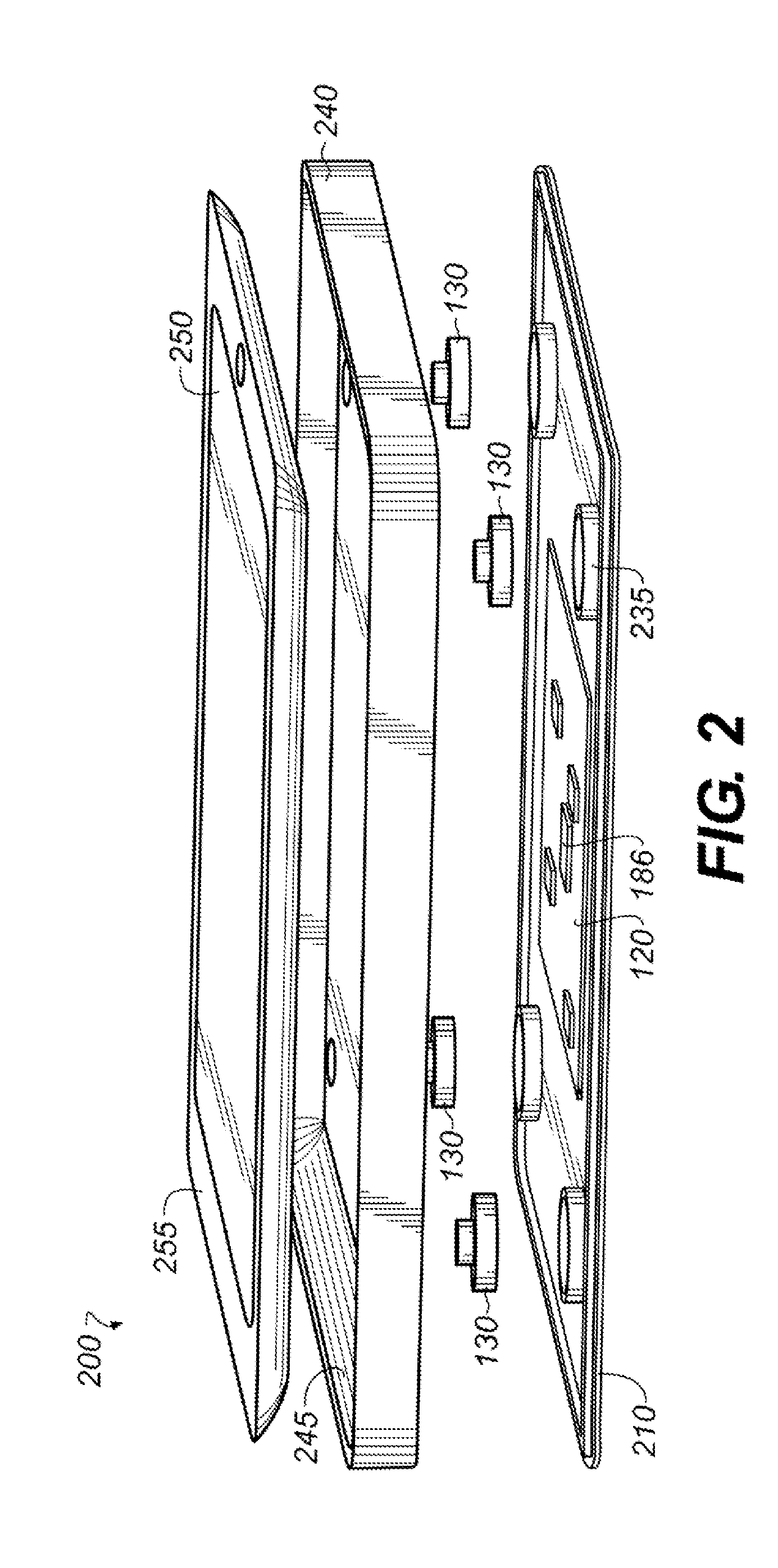
A capture device for remote, virtual on screen data input by hand annotation comprises at least three functional layers including a bottom rigid layer, a middle pressure sensor layer and a top flexible layer. The bottom rigid layer has a surface that provides a mechanical support for writing. The middle pressure sensor layer is adapted to measuring a pressure array or map on the capture active area and to send data representing the measured pressure to a personal computer. The top flexible touch-sensitive passive LCD display layer includes an LCD surface by which whatever is written down on the LCD is impressed graphically due to its liquid crystal physical properties wherein applied pressure changes the crystal particles orientation and light properties, such that when a stylus presses against a writing surface thereof, it leaves a visible trace allowing the user to produce a drawing though no real ink has flown.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Force Measurement System Having Inertial Compensation
ActiveUS20120271565A1Accurate force measurementAccurate compensationForce measurementInertial sensorsAccelerometerAngular velocity
A force measurement system having inertial compensation includes a force measurement assembly with at least one accelerometer configured to measure the acceleration thereof. According to one aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes at least one angular velocity sensor configured to measure the angular velocity of the force measurement assembly. According to another aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes a data processing device with a computer-readable medium loaded thereon that is configured to execute a calibration procedure for determining the inertial parameters of the force measurement assembly by utilizing the measured acceleration of the force measurement assembly while the force measurement assembly is subjected to a plurality of applied linear and / or rotational motion profiles. According to still another aspect of the invention, the at least one accelerometer is disposed on the force transducer.
Owner:BERTEC
Communication device using bone conduction
InactiveUS6885753B2Low costImprove conversion efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersBone conduction transducer hearing devicesCouplingTransducer
A communication device comprising a microphone, a conduction interface and an electromechanical force transducer mounted to the conduction interface to drive the interface to conduct sound to a user by bone conduction, characterised in that the transducer has an intended operative frequency range and comprises a resonant element having a frequency distribution of modes in the operative frequency range and coupling means for mounting the transducer to the interface.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Active Fingertip-Mounted Object Digitizer
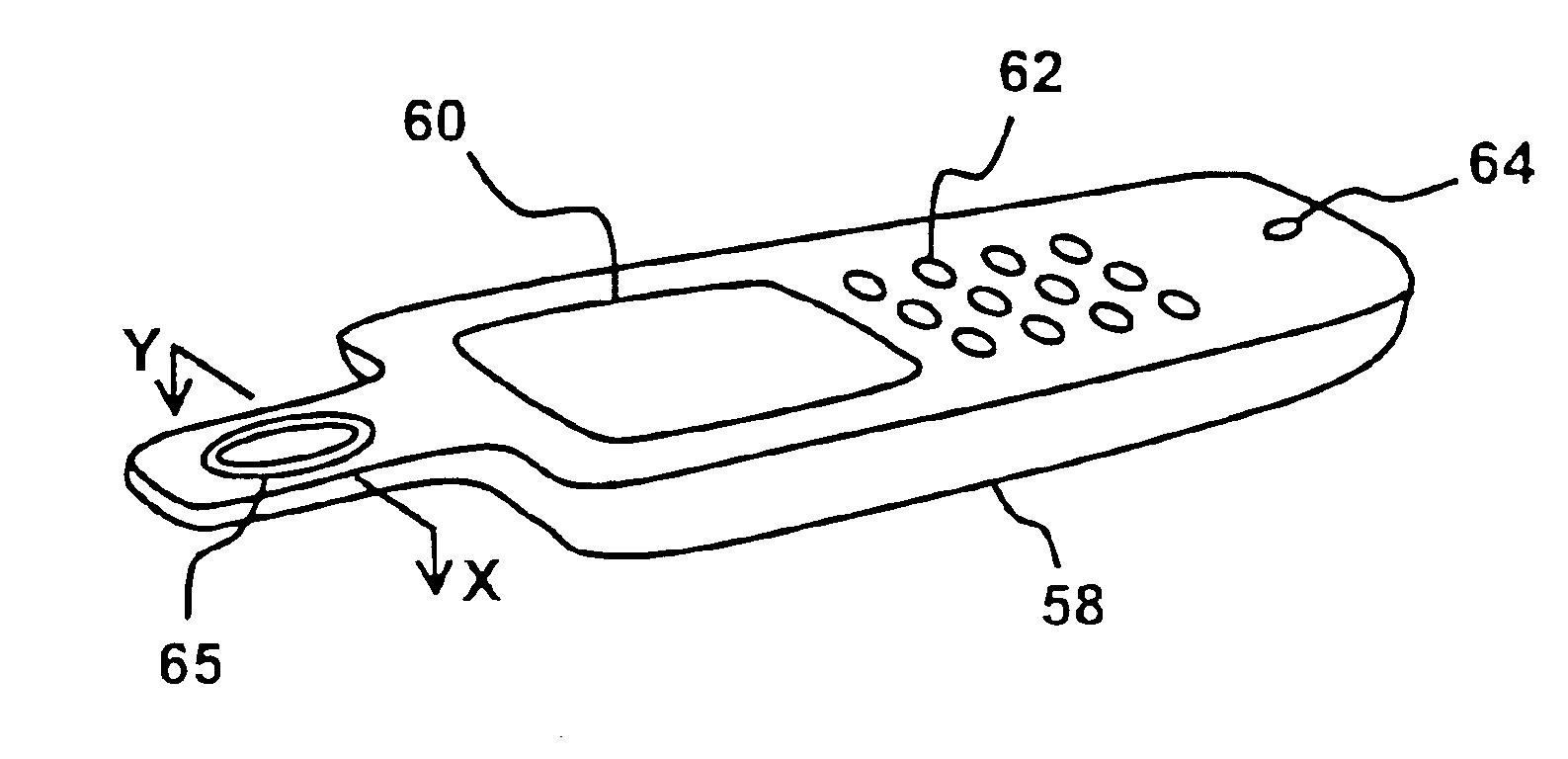
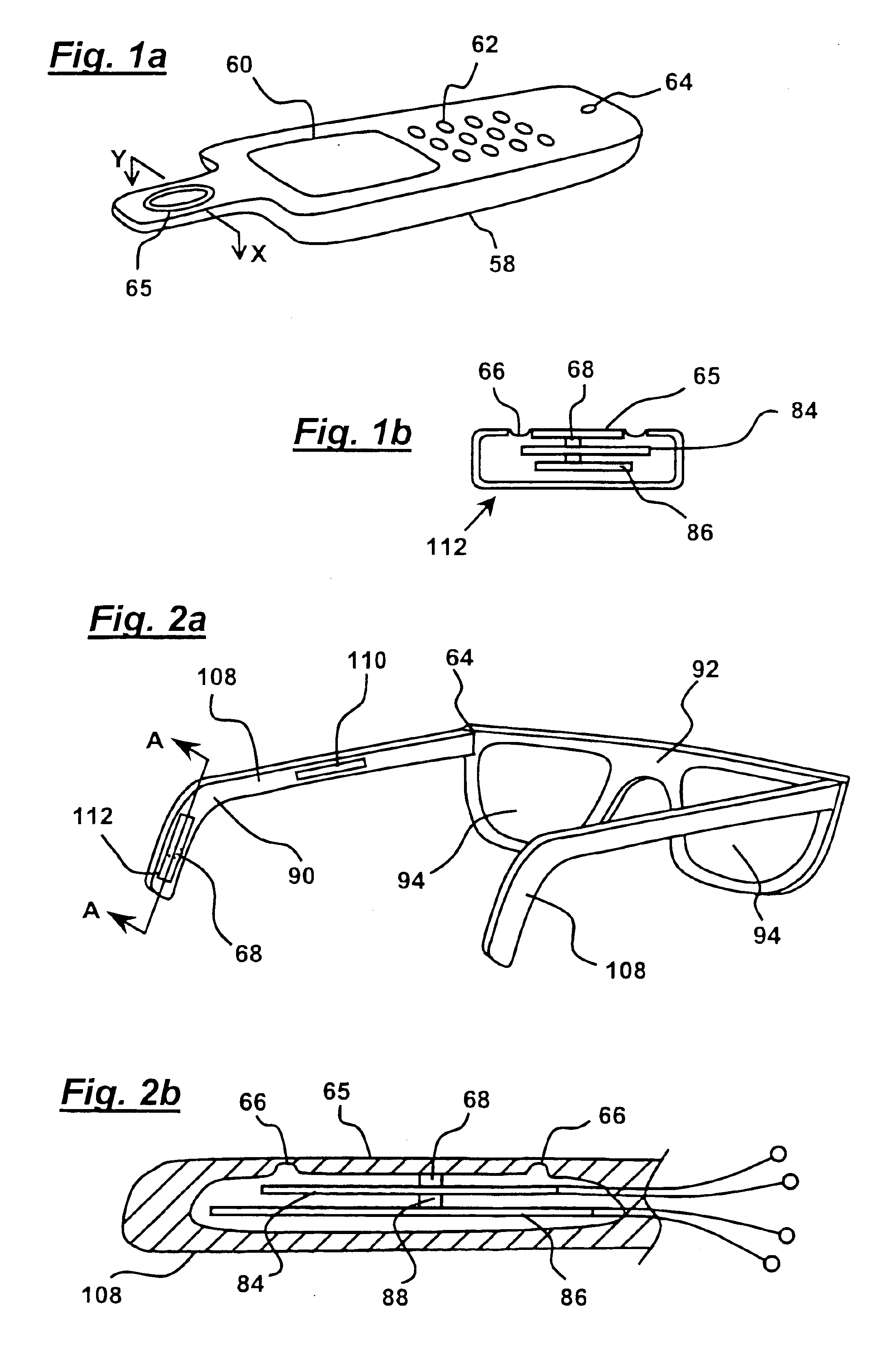
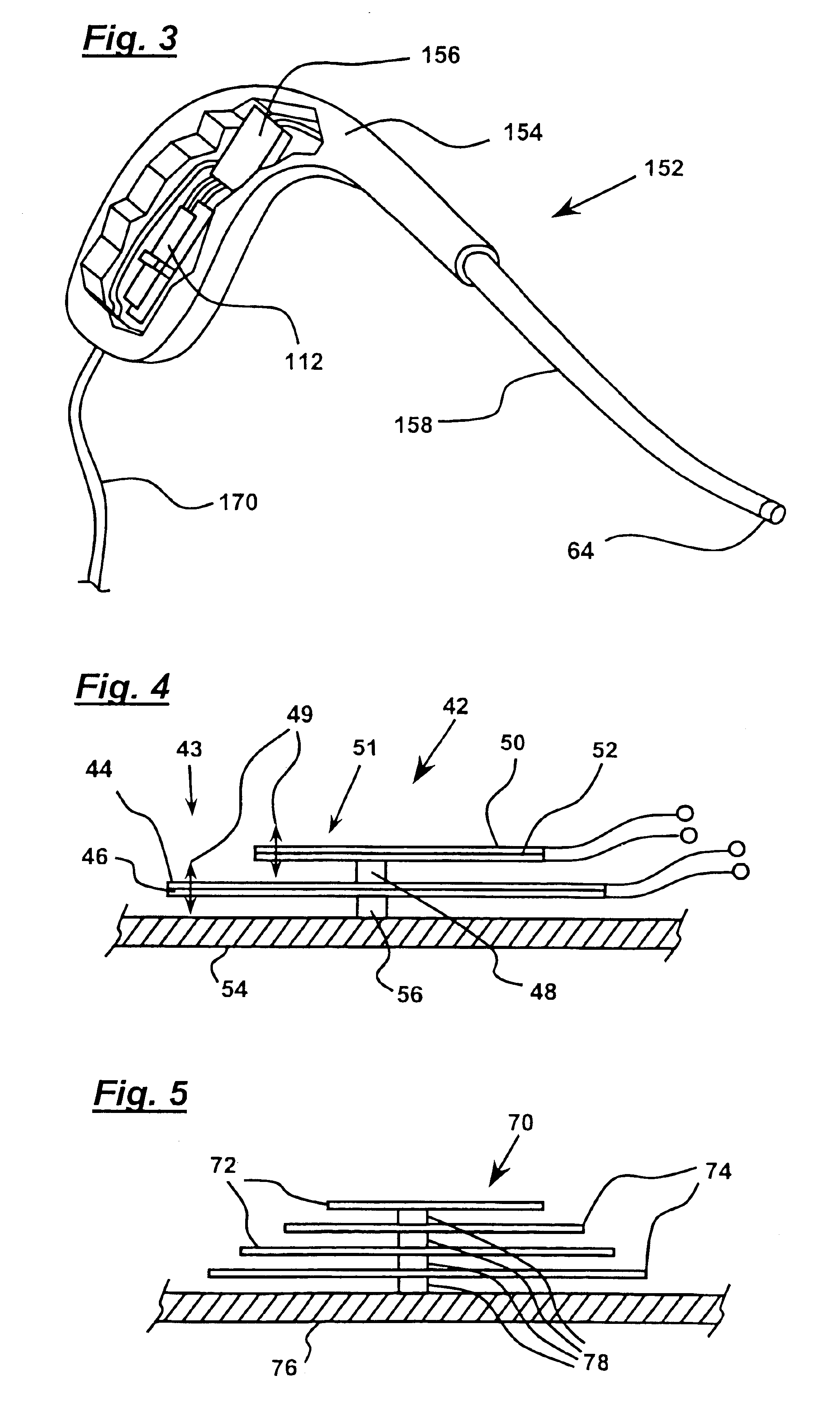
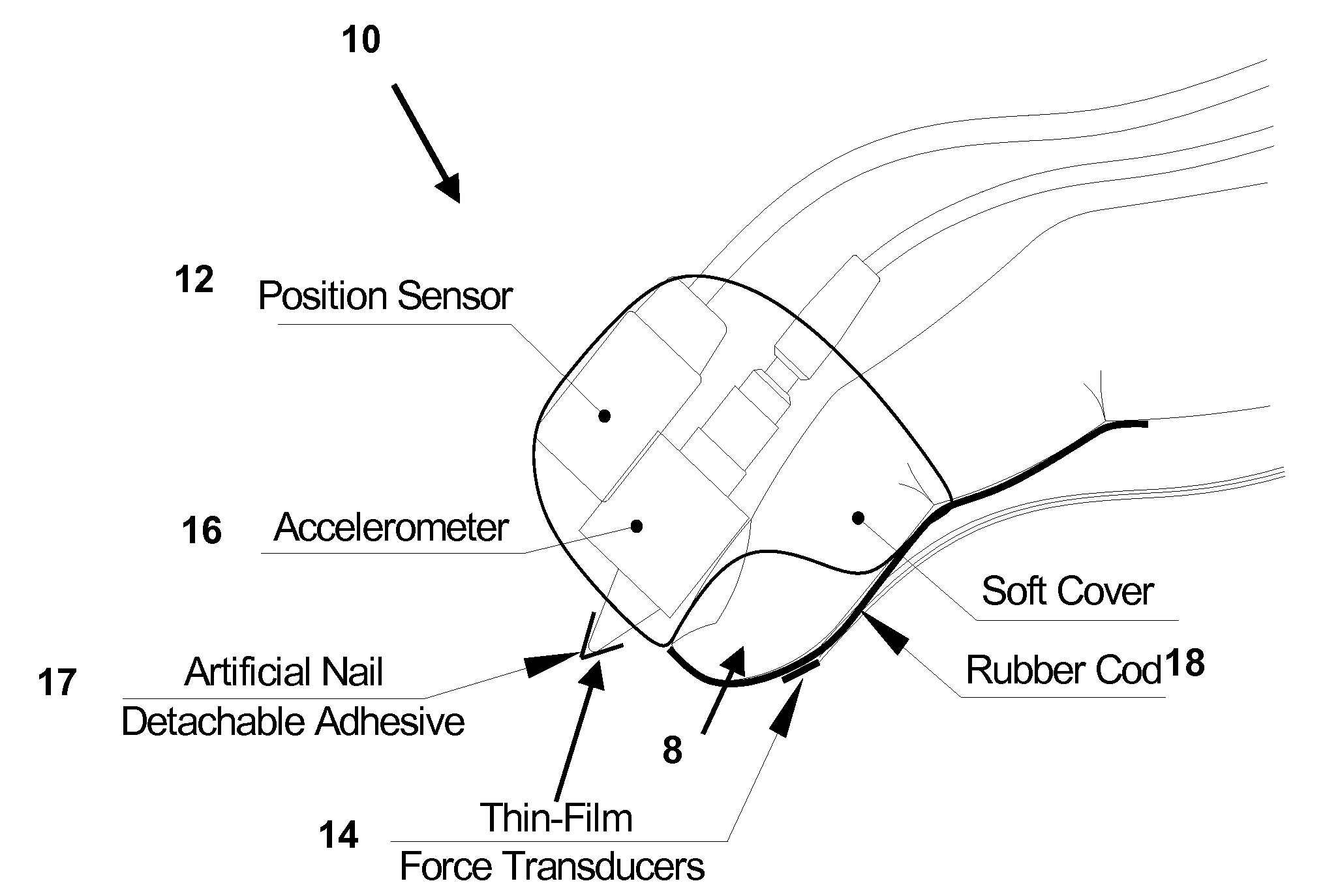
InactiveUS20090278798A1Transmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsMagnetic transducersAccelerometer
A finger-mounted implement including a kinesthetic sensor, at least one tactile sensor, and means for securing the kinesthetic sensor and the at least one tactile sensor to a fingertip. The tactile sensor may be a thin-film force transducer, a piezoelectric accelerometer, or a combination thereof. An artificial fingernail may be connected to the accelerometer. The kinesthetic sensor may include a magnetic transducer and may sense an X-Y-Z position and an angular orientation of a fingertip to which the kinesthetic sensor is secured. The securing means may include at least one means selected from the group consisting of adhesive tape, an elastically deformable cover, and detachable adhesive. The implement can be further connected to a computer processing system for, amongst other things, the virtual representation of sensed objects. The implement can also be used as part of a method of haptic sensing of objects.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Force measurement system having inertial compensation
ActiveUS8315822B2Accurate compensationAccurate force measurementForce measurementInertial sensorsAccelerometerAngular velocity
A force measurement system having inertial compensation includes a force measurement assembly with at least one accelerometer configured to measure the acceleration thereof. According to one aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes at least one angular velocity sensor configured to measure the angular velocity of the force measurement assembly. According to another aspect of the invention, the force measurement system additionally includes a data processing device with a computer-readable medium loaded thereon that is configured to execute a calibration procedure for determining the inertial parameters of the force measurement assembly by utilizing the measured acceleration of the force measurement assembly while the force measurement assembly is subjected to a plurality of applied linear and / or rotational motion profiles. According to still another aspect of the invention, the at least one accelerometer is disposed on the force transducer.
Owner:BERTEC
Apparatus and method for sensing radial arterial pulses for noninvasive and continuous measurement of blood pressure and arterial elasticity
InactiveUS20100210956A1Improve accuracyEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterContinuous measurementReflected waves
Provided is a radial arterial pulse sensing apparatus for noninvasive and continuous measurement of blood pressure and arterial elasticity. The apparatus includes two pressure sensor for detecting radial arterial pulses, two cuffs that are disposed under the respective pressure sensors and expandable by application of external pressure, a motor unit for providing proper pressure to expandable pouches under the respective pressure sensors in a state where a wrist band having the pressure sensors is put on a wrist, a pulse wave velocity calculating unit that calculates a pulse wave transfer velocity to attain a blood pressure value using an output from the pressure sensors, and an augmentation index calculating unit that estimates the blood pressure value by finding a time point of a reflective wave of the pulses using the outputs from the pressure sensors.
Owner:GRAMPION GRP
Vehicle sobriety interlock device
ActiveUS20050241871A1Accurate readingReduce moistureElectric devicesElectrical apparatusWater filterEngineering
An interlock device for measuring the sobriety of a potential vehicle operator is coupled to the starting mechanism of the vehicle. The interlock device includes a microprocessor controlled handset and base unit. The base unit encloses relays to preclude the starting mechanism from engaging if a predetermined acceptable threshold level of blood alcohol content has been exceeded. The relays receive a signal, through the base unit microprocessor, from the handset microprocessor which has calculated the blood alcohol content of a breath sample introduced into the handset by the vehicle operator. A breath sampling housing is enclosed within the handset in axial alignment with an intake port of the handset. A water filter and valve are positioned upstream from an electrochemical fuel cell. The fuel cell is coupled to the microprocessor. A pressure transducer measures the pressure of the breath sample. The handset microprocessor calculates a pressure offset through an algorithmic equation and applies the offset to the variable reading across the fuel cell to provide a normalized blood alcohol content measurement.
Owner:GUARDIAN INTERLOCK LLC
Tire pressure sensor assembly
The disclosure provides a tire pressure sensor assembly that includes a battery and a printed circuit board (PCB) configured with electronics to measure tire pressure and to transmit an electromagnetic signal related to the measured tire pressure. The PCB and battery are contained in a housing that allows the PCB and the battery to be angularly oriented with respect to each other. Such orientation permits the sensor to conform to the curved surface of the rim. An embodiment of the disclosed tire pressure sensor assembly is adapted to fasten to a valve stem via a metal terminal. The attachment configuration permits the valve stem assembly to deform as the valve stem is installed in a rim and also allows the valve stem to function as a portion of the antenna structure to facilitate transmitting the RF signal to a receiver.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Devices, systems and methods to determine area sensor
ActiveUS20150168205A1Improve accuracyWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersForce measurementTransducerEngineering
A weighing scale includes a platform supporting a load. Force transducers beneath the platform output respective transducer force signals of the load. An area sensor above the platform outputs area force signals of load forces applied to respective spatial areas of the platform. A processor is configured to determine the load's weight and location on the platform based on the transducer force signals and the area force signals. A method of weighing the load is also described. A method of monitoring the load includes measuring first transducer force signal(s) and first area force signal(s) of the load, and then repeatedly measuring second force signal(s) of the load using the transducer(s) or area sensor until the first and second signal(s) indicate a change in a weight or location of the load. A changed weight or changed location of the load is then determined using the measured second force signal(s).
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Biosignal detection device
InactiveUS20060283652A1Detect biological informationEfficient detectionVehicle seatsElectric devicesPhase differenceEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
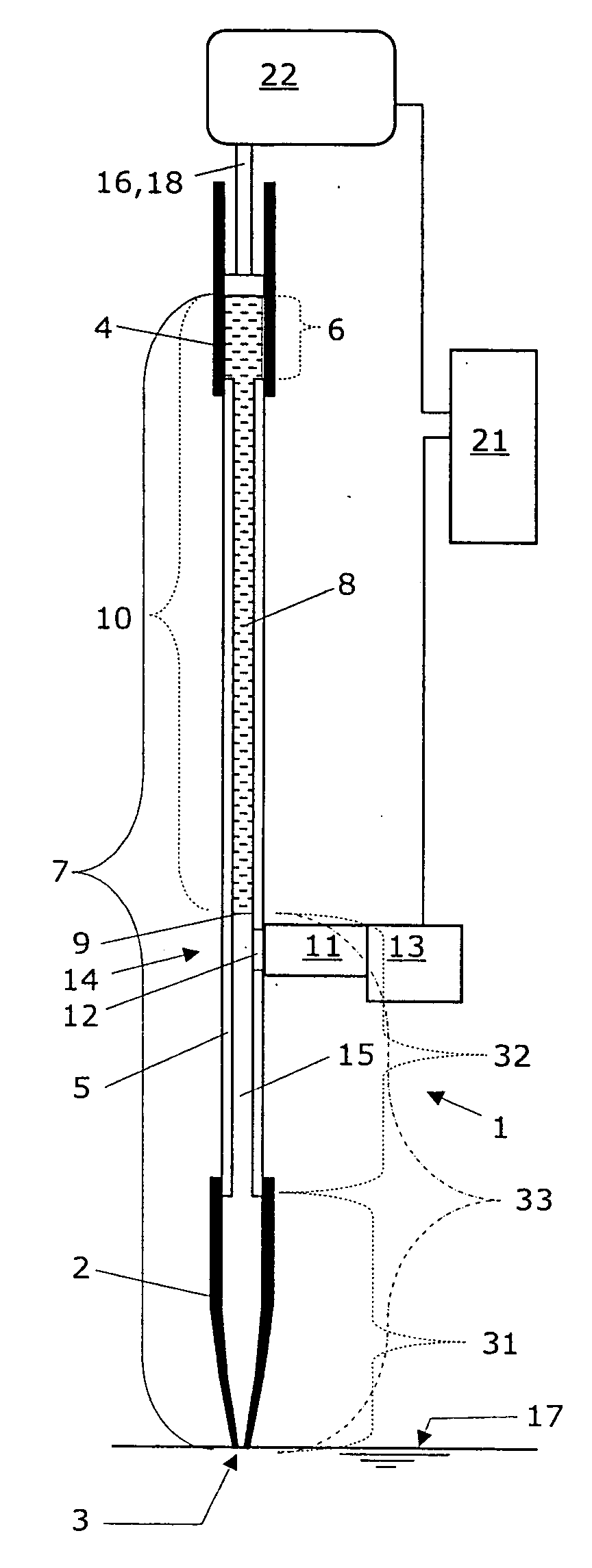
Pipetting apparatus with integrated liquid level and/or gas bubble detection
ActiveUS20060127281A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesVertical motionEngineering
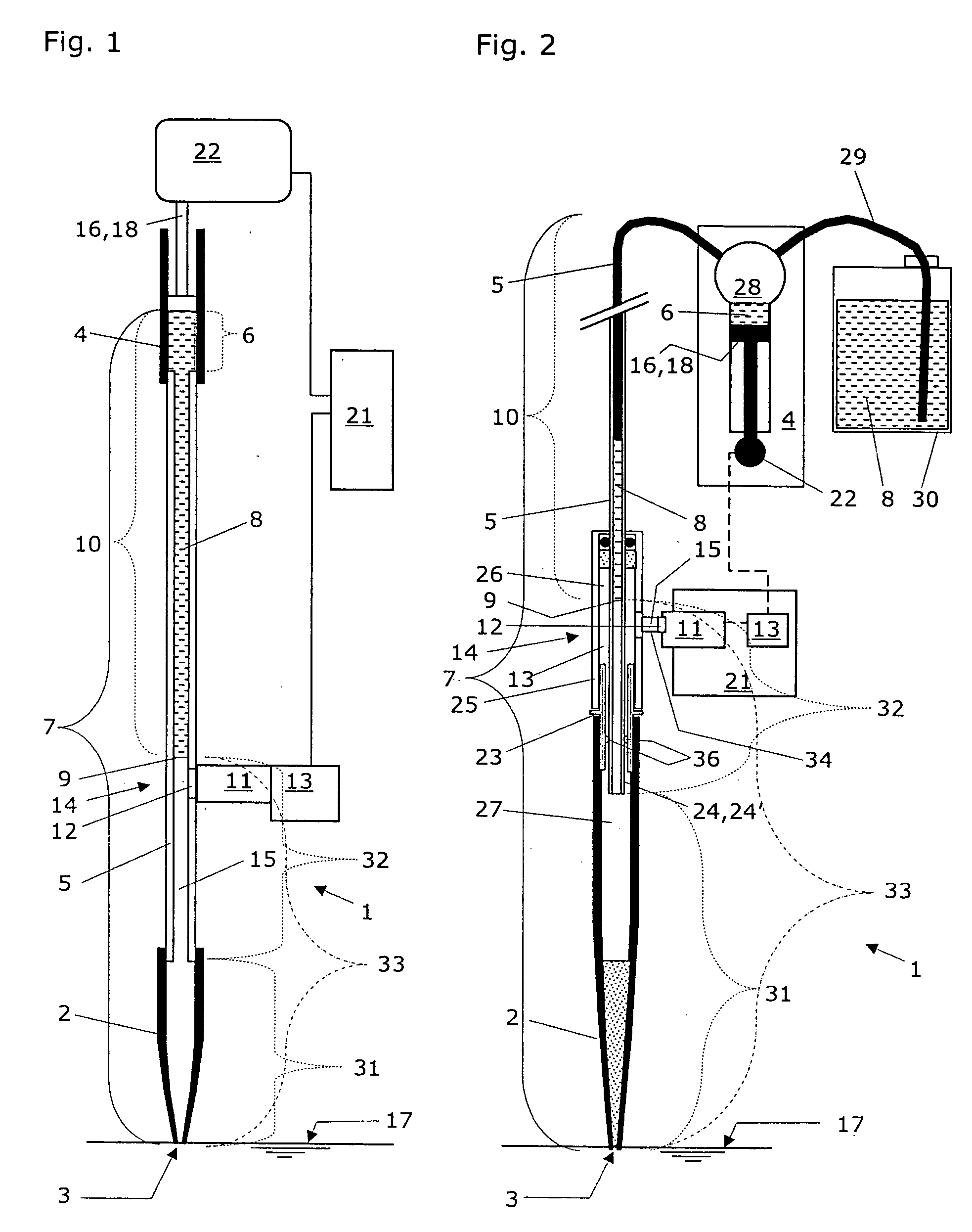
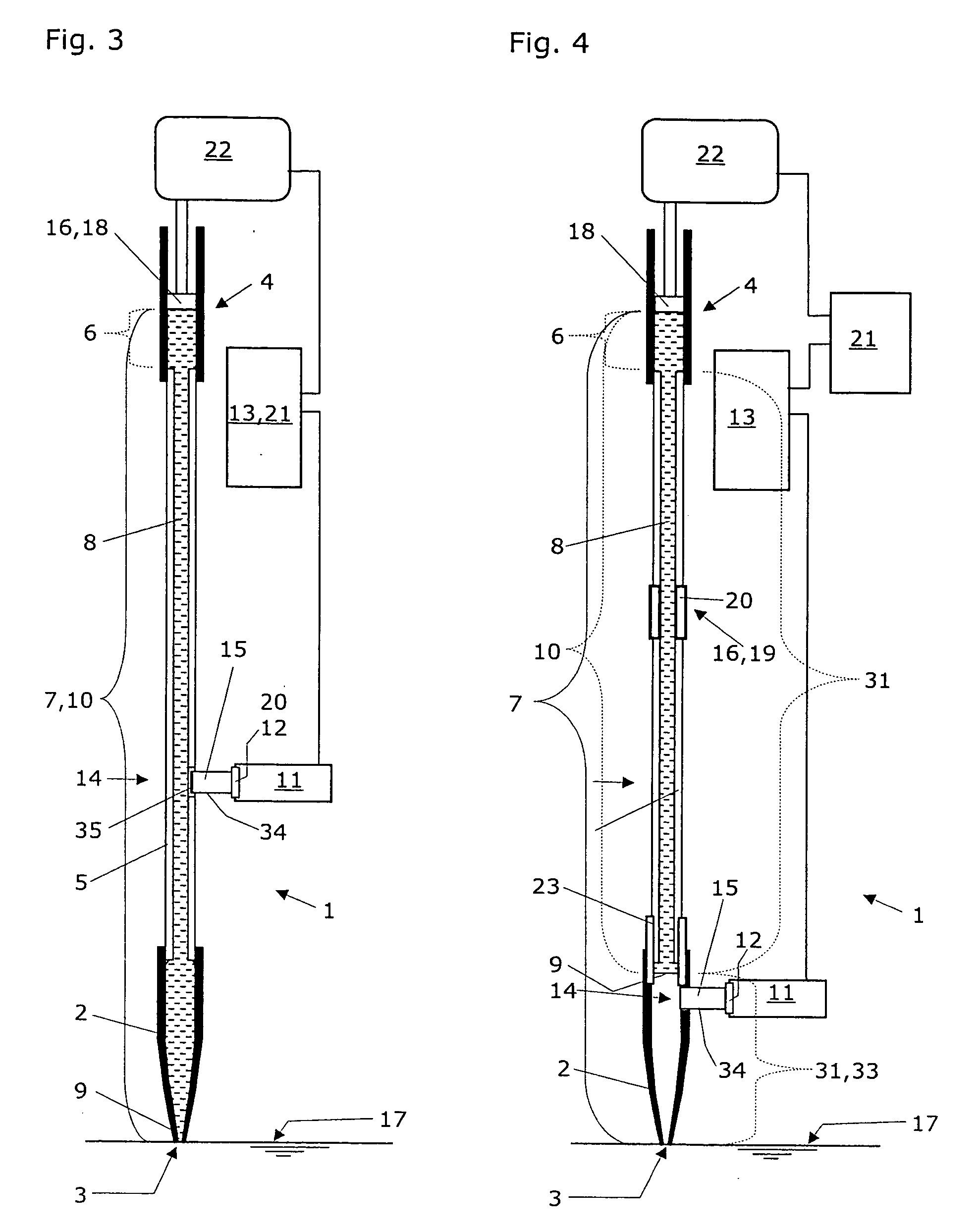
A pipetting apparatus (1) comprises a fluidic space (7), to which a pressure transducer (11) with a pressure sensor (12) is attached with a gas filled space (15). The fluidic space (7) is defined by a pipette tip (2), a first tubing (5) that connects the pipette tip (2) to a pump (4), and an active part (6) of the pump (4). The pipetting apparatus (1) according to the present invention is characterized in that the pipetting apparatus (1) further comprises an impulse generating means (16,18,19) that is in operative contact with a column (10) of system liquid (8) inside the fluidic space (7). The impulse generating means (16,18,19) is designed to induce a vertical movement in this system liquid column (10), which results in a pressure variation in the gas filled space (15) that is pneumatically connected with the fluidic space (7). This pressure variation—as recorded with the pressure transducer (11) and as processed by a first data processing unit (13) during utilization of this pipetting apparatus—is taken as an indicator for the detection of penetration or of quitting of a surface (17) of a liquid, with an orifice (3) of the pipette tip (2), of which liquid an amount is to be aspirated and dispensed. This pressure variation is also taken as an indicator for the detection of the presence or the absence of gas bubbles in the system liquid (8) contained in the fluidic space (7) of this pipetting apparatus.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Force measurement system
A dual force plate system having two independent measurement surfaces is disclosed herein. The dual force plate system includes a first plate component having a first measurement surface for receiving a first portion of a body of a subject, a second plate component having a second measurement surface for receiving a second portion of the body of the subject, a first force transducer element operatively coupled to the first plate component, a second force transducer element operatively coupled to the second plate component, and a third force transducer element operatively coupled to both the first plate component and the second plate component. A force plate system for computing a center of gravity of a subject is also disclosed herein. In addition, a method for determining the center of gravity for a subject disposed on a force measurement assembly is described herein.
Owner:BERTEC
Multifunction flexible composite material impact test apparatus
The invention discloses a falling multifunctional measuring device for an impact test of soft composite materials, comprising an impact test unit. The device is also provided with a transient force and displacement testing unit which comprises a sensor supporting sleeve, a piezoelectric force sensor, a grating bar, a photoelectric sensor, a stabilized voltage supply, a charge amplifier and a signal amplifier. The testing unit can be arranged in the impact test unit in a detachable way; the piezoelectric force transducer is positioned in the sensor supporting sleeve, and the input end thereof is connected with the charge amplifier; the sensor supporting sleeve is arranged at the upper end of a hammer head; the grating bar and the sensor supporting sleeve are positioned at the same horizontal line; the grating bar can move synchronously with the hammer head and a base thereof is provided with the photoelectric sensor; the photoelectric sensor is positioned below the grating bar and the excitation voltage thereof is provided by the stabilized voltage supply; and the signal output end of the photoelectric sensor is connected with the signal amplifier. The device has simple structure, high integration level and low cost, and can provide testing data of composite materials in a small energy test.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Force measurement system
ActiveUS9168420B1Eliminate the problemStatic/dynamic balance measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringInstrumented treadmillEngineering
A force measurement system includes an instrumented treadmill with one or more treadmill belts configured to rotate at a plurality of different speeds, one or more speed adjustment mechanisms coupled to the one or more treadmill belts, and at least one force transducer. The force measurement system further includes a data processing device configured to receive one or more signals that are representative of one or more loads being applied to one or more respective surfaces of the one or more treadmill belts by a subject, and to convert the one or more signals into one or more output load components, the data processing device further configured to determine a position of a body portion of the subject and to control the speed of the one or more treadmill belts using the position determined for the body portion of the subject.
Owner:BERTEC
Safe driving monitoring device capable of monitoring physical and psychological states of driver
InactiveCN102490701AReduce intensityReduce riskAcoustic signal devicesAutomatic initiationsDriver/operatorEngineering
A safe driving monitoring device capable of monitoring physical and psychological states of a driver belongs to the field of safe driving of automobiles and solves the problem that an existing safe driving device only detects some single index, does not consider changes of the physical and psychological states of the driver and cannot carry out corresponding reaction movements when the states of the driver change. A neck pulse sensor detects pulse signals, a pressure sensor detects signals indicating whether the driver sits in an automobile, an air bag pressure sensor detects hand gripping signals or foot power signals of the driver, a breathing signal detection circuit detects breathing signals of the driver, a non-contact temperature measuring sensor detects body-temperature signals, an alcohol concentration measuring sensor detects alcohol concentration signals, an ear type sphygmomanometer detects blood pressure signals, and a distance measuring sensor detects relative distance signals. All the signals are analyzed by a control and analysis processor, and the control and analysis processor outputs analysis results to an alarming module so as to give an alarm.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
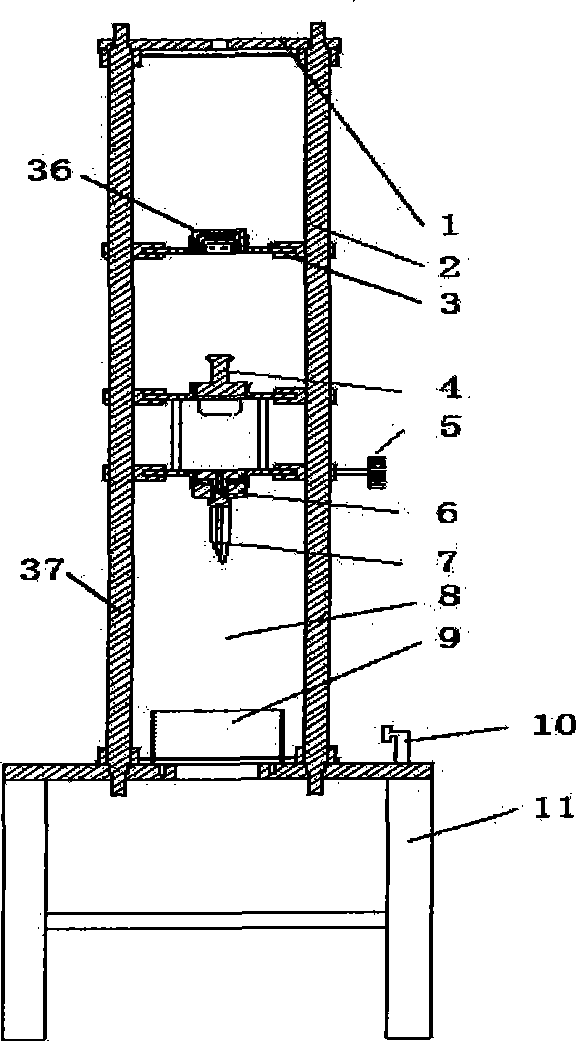
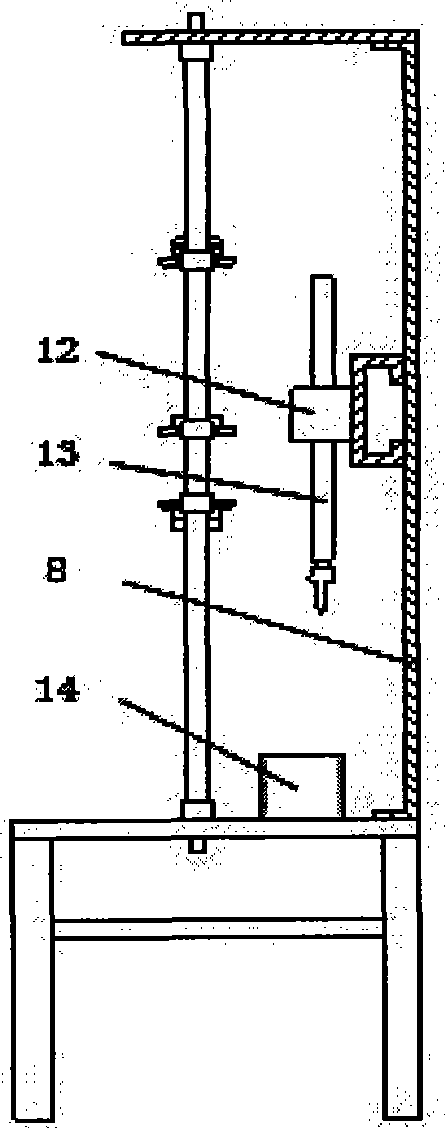
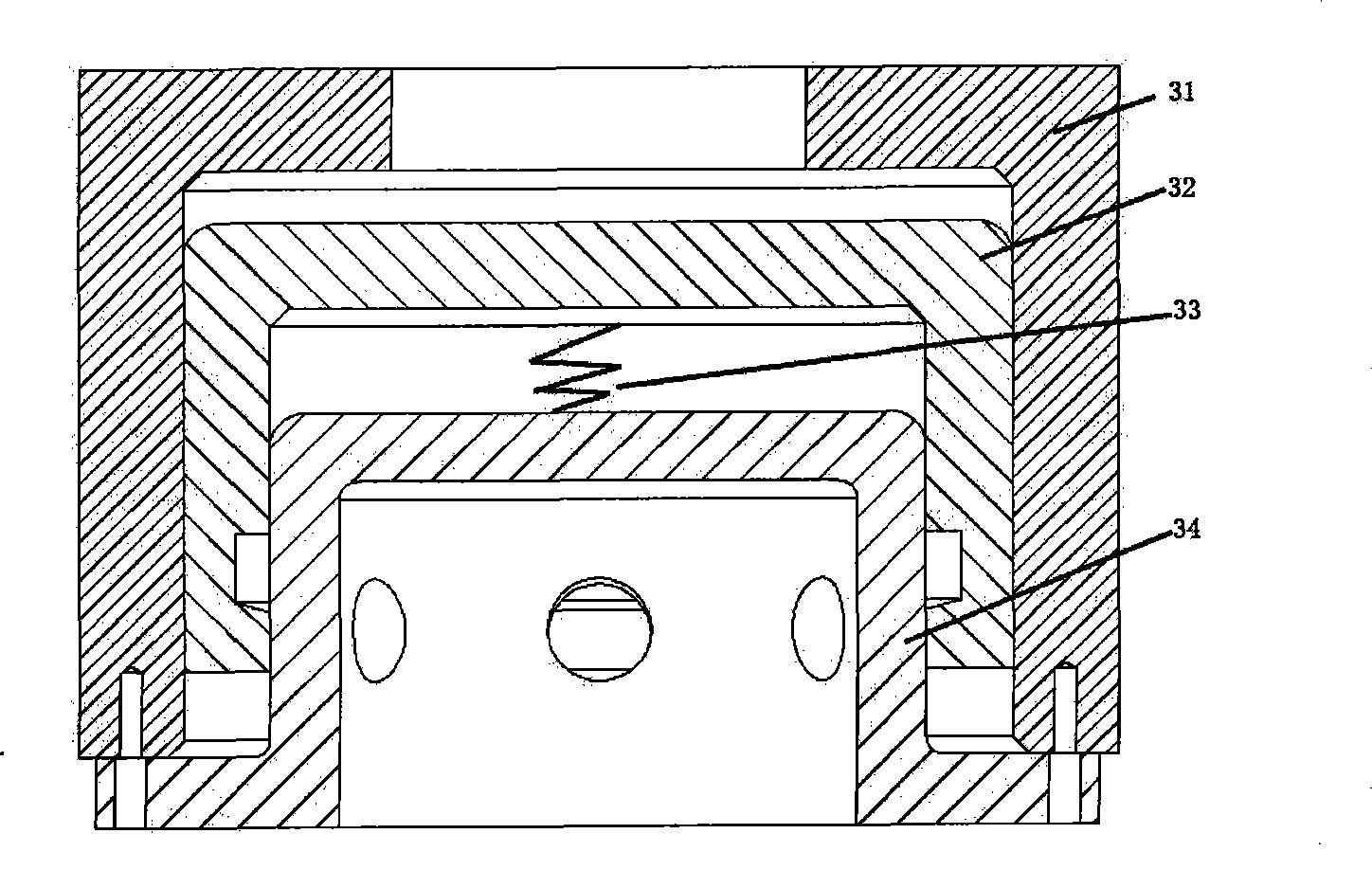
Calibrating and loading bench of large multi-dimensional force transducer
InactiveCN101776506ASimple structureCompact structureForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingHydraulic cylinderTransducer
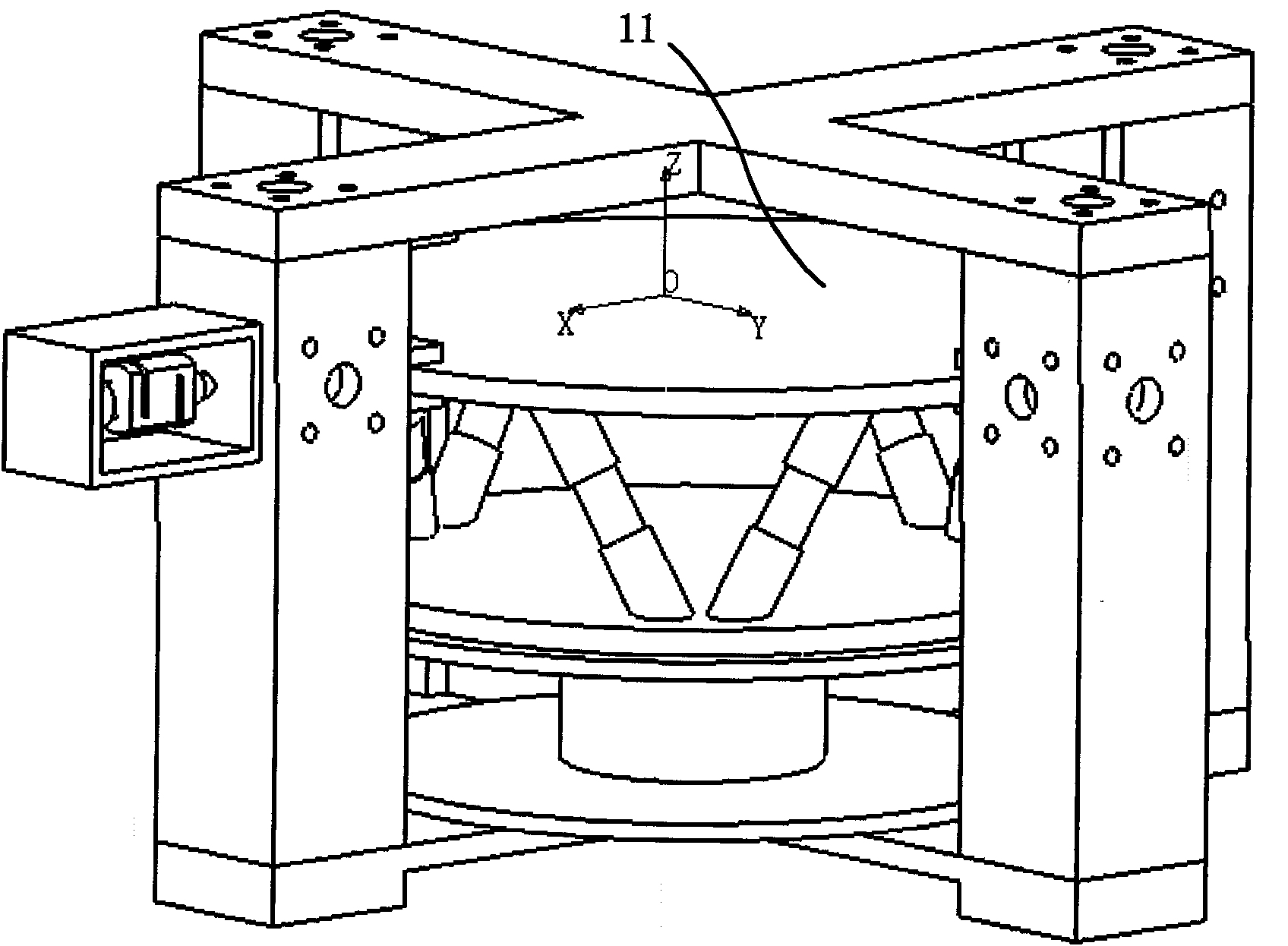
The invention discloses a calibrating and loading bench of a large multi-dimensional force transducer. The loading bench comprises an upper cross frame (6), a loading bench column (7), a lower cross frame (8), a multi-dimensional force transducer fixed support (9), loading units and loading blocks (5), wherein each loading unit comprises a loading frame (1), a loading hydraulic cylinder (2), a one-dimensional tension-pressure transducer (3) and a tension bar (4). By combining the different installation positions of the two loading units and the connection position of the tension bars (4) and the loading blocks (5), the calibration and the loading of the multi-dimensional force transducer can be realized. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of simple and compact structure, large range for calibrating and loading the force and high loading accuracy. Besides, by regulating the pressure of a hydraulic system, the invention can easily realize the continuous adjustment of the loaded force and the automatic and dynamic loading of the calibrated force, thereby being especially applicable to the static and dynamic calibration and loading of the large multi-dimensional force transducer.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Methods and devices for treatment of medical conditions and monitoring physical movements
InactiveUS20090048542A1Accurate monitoringMaterial nanotechnologyElectrotherapyAccelerometerGyroscope
The present systems use nanotechnology, MEMS devices and wireless data transmission to monitor and treat physical activities, and medical and physiological conditions. The MEMS devices and wireless data transmission systems monitor and sense certain patient conditions or reactions, such as changes in pressure, movements, and tremors. These sensor devices include, but are not limited to, MEMS gyroscopes, MEMS accelerometers, and MEMS pressure sensors. Data from the sensor is wirelessly transmitted to a second MEMS device to treat or alter the medical condition being monitored.
Owner:VARADAN VIJAY +1
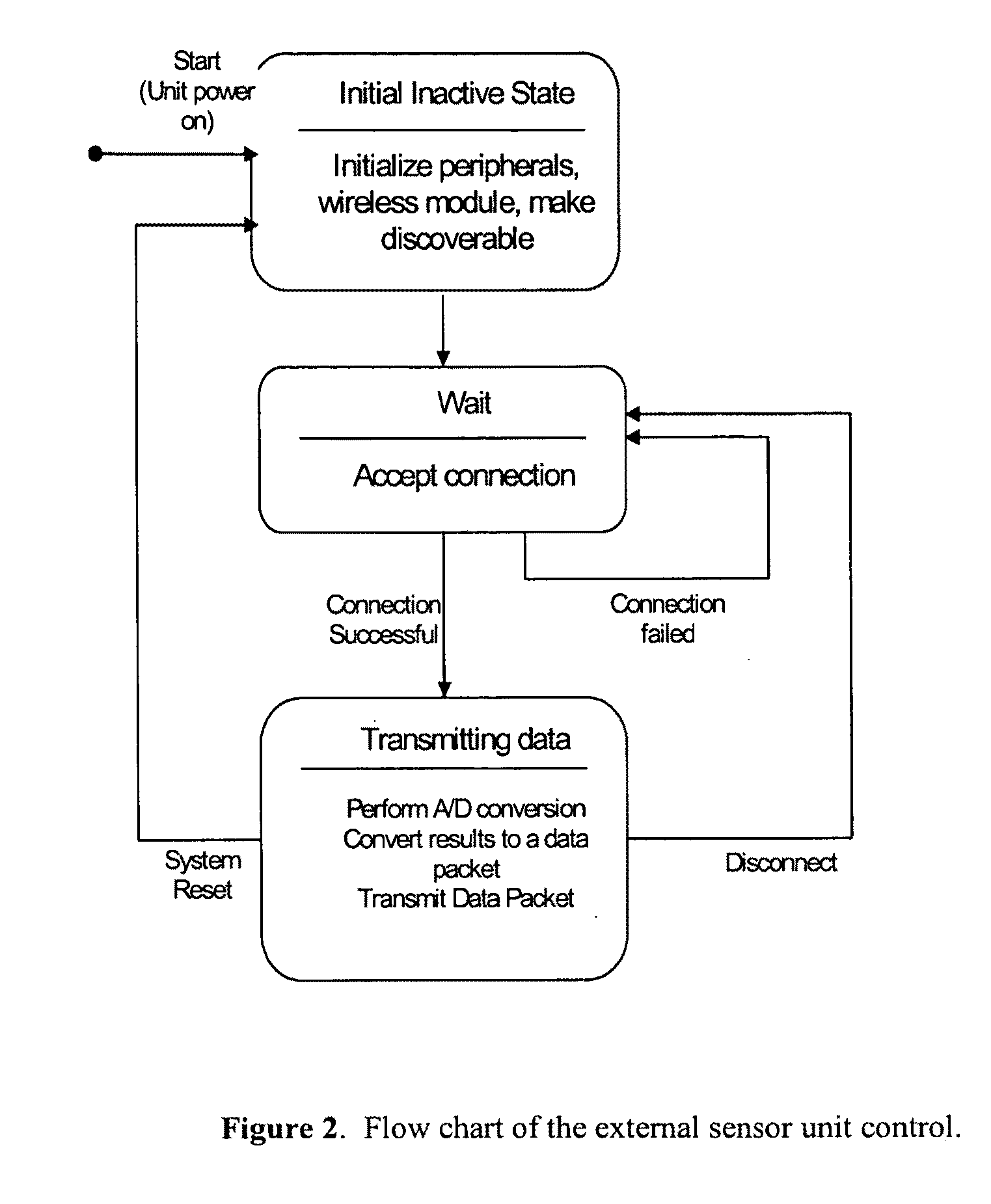
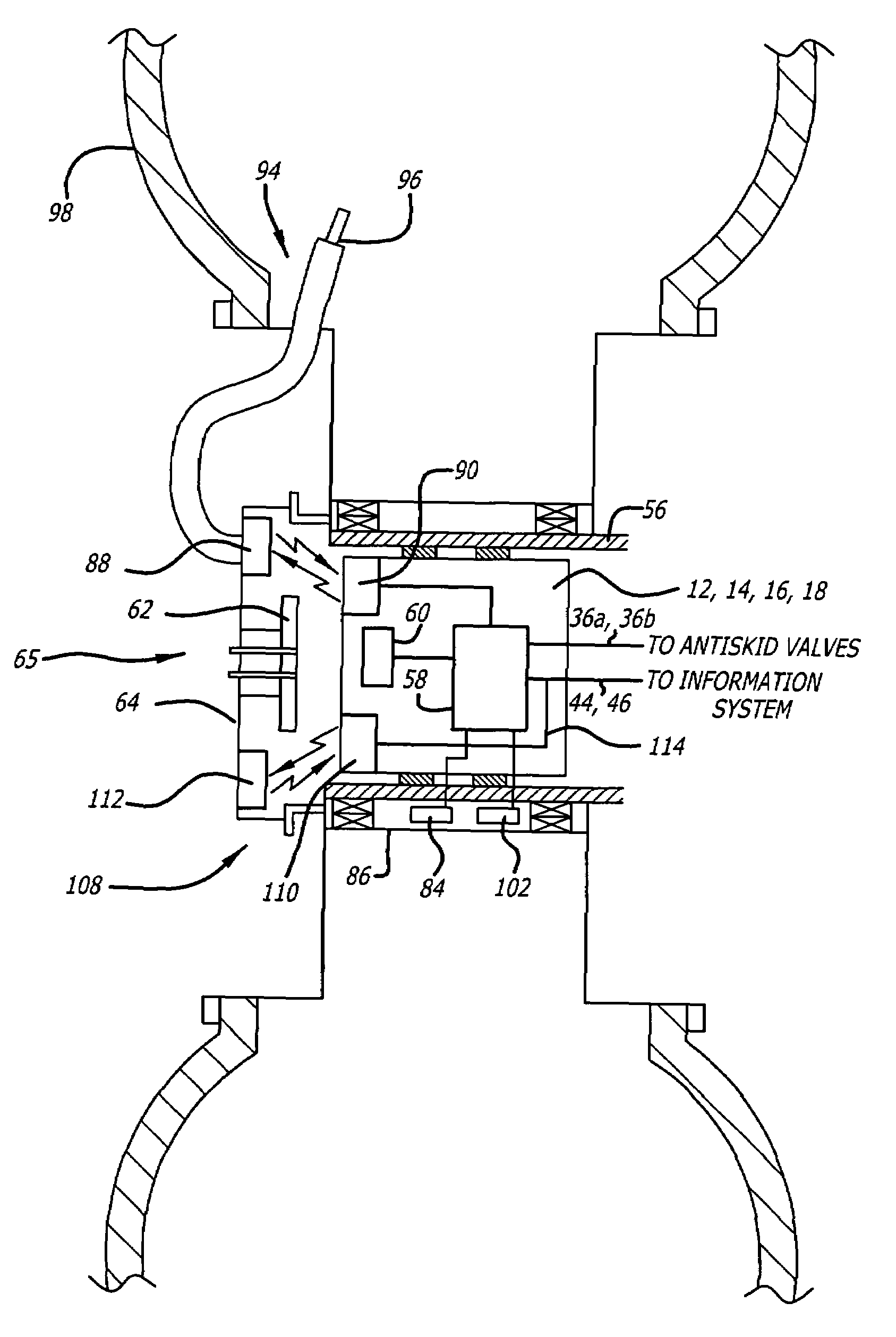
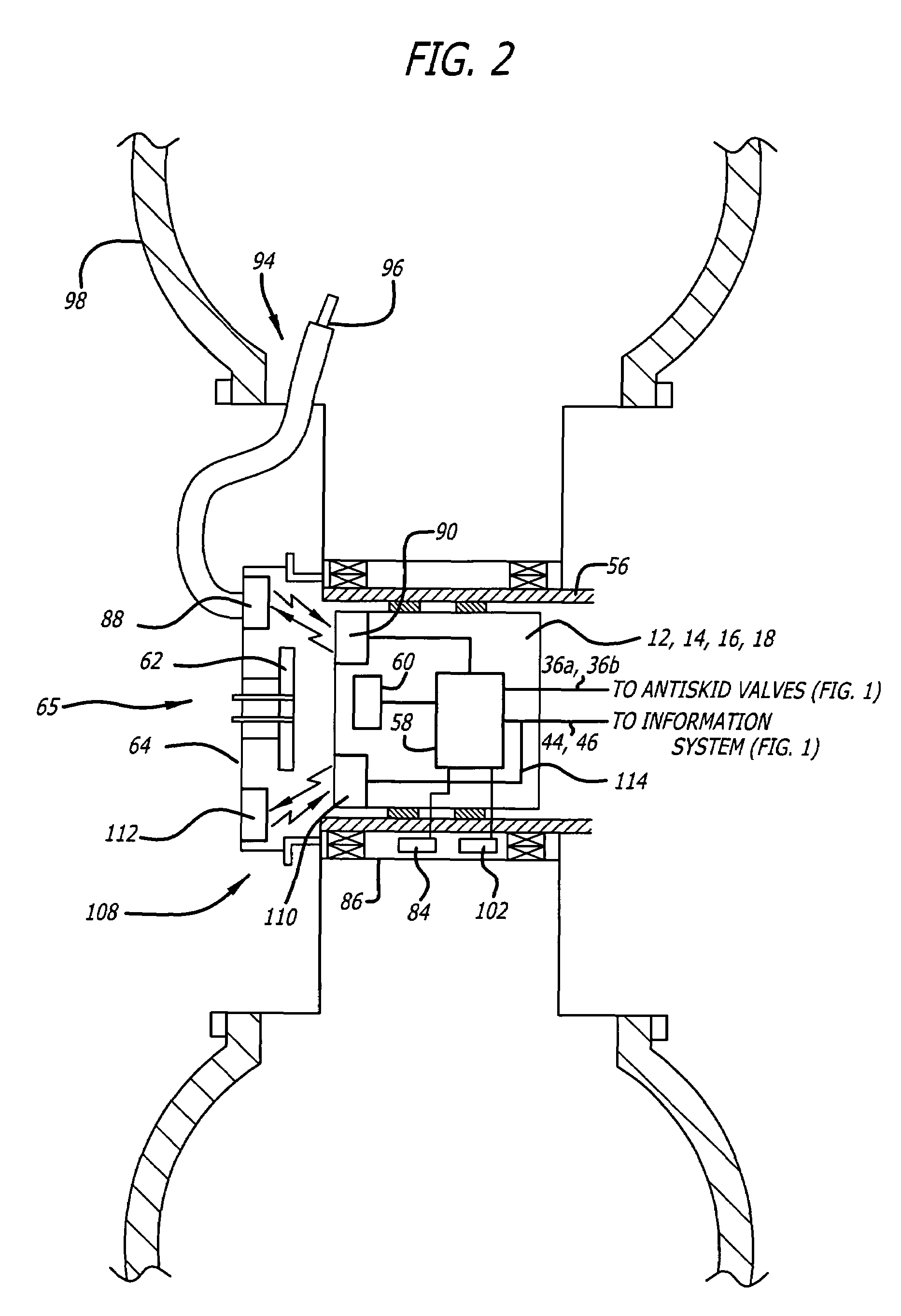
Antiskid control unit and data collection system for vehicle braking system
ActiveUS7489996B2Low costReduce weightRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsWheel speed sensorData acquisition
A wheel speed transducer including a magnetic device associated with a wheel and a sensor device associated with the axle of the wheel provides data indicative of the velocity of the wheel. A processor located at the axle receives the wheel speed data and processes it to perform antiskid control functions. The velocity data is stored in a data concentrator also associated with the axle. A tire pressure sensor, a brake temperature sensor and a brake torque sensor, each associated with the wheel, send data to the processor at the axle, for storage in the data concentrator. A transmitting antenna associated with the axle and in communication with the data concentrator transmits stored data to a receiving antenna associated with the wheel. A data port at the wheel and in communication with the receiving antenna provides an interface to an external device for receiving the data.
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
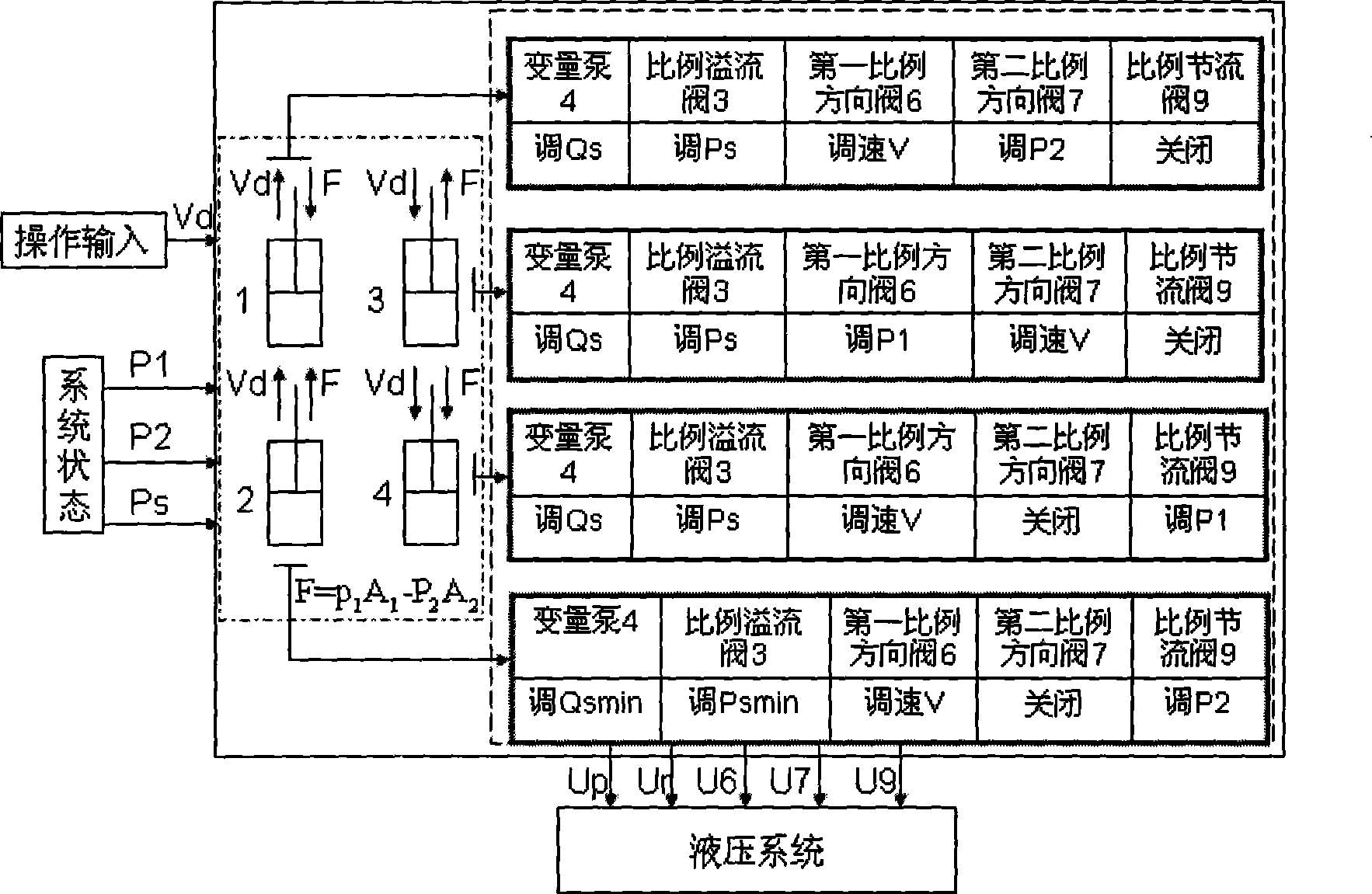
Independent electrohydraulic load sensitive energy regeneration hydraulic system of engineering machinery load port
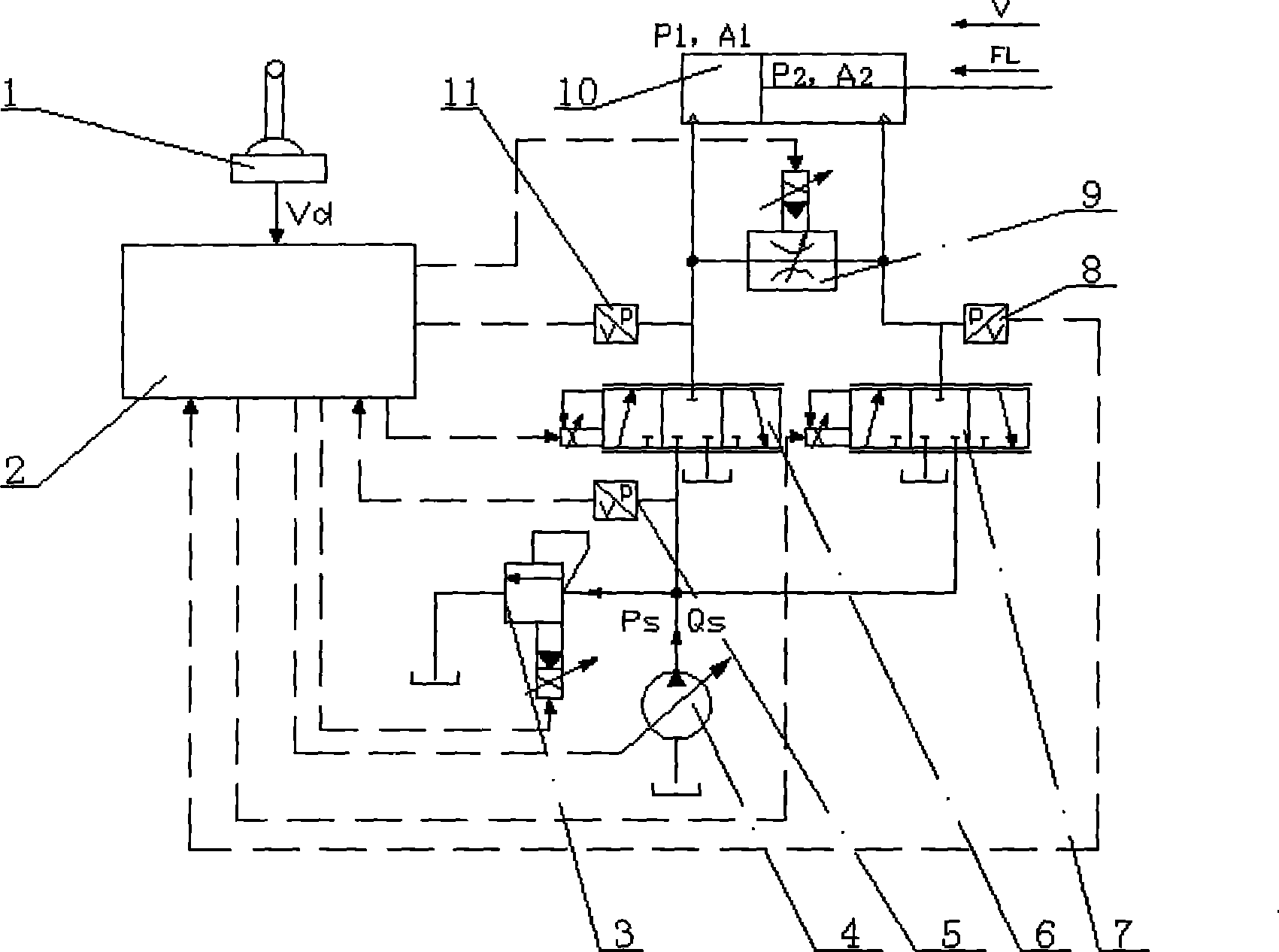
InactiveCN101413522AAchieve regenerationReduce lossFluid-pressure actuator componentsLoad sensingElectrical connection
The invention discloses an independent electrohydraulic load sensing energy regeneration hydraulic system of an actuator port of an engineering machine. An oil outlet of a variable pump is connected with an oil inlet of a proportional relief valve, a first pressure sensor, an oil inlet of a first proportional directional valve, and an oil inlet of a second proportional directional valve respectively. An oil outlet of the first proportional directional valve is connected with a second pressure sensor, the oil inlet of a proportional throttle valve and a rodless cavity of a hydraulic cylinder respectively. An oil outlet of the second proportional directional valve is connected with an oil outlet of the proportional throttle valve, a third pressure sensor and a rod cavity of the hydraulic cylinder. A Controller is in electrical connection with a control handle, the variable pump, the proportional relief valve, two proportional directional valves, the proportional throttle valve and three pressure sensors. The system adopts the pressure sensors to detect working conditions, selects control policies according to the working conditions, reduces energy loss in flow restriction and realizes overload energy regeneration under the control of an actuator. Speed and energy-conservation control is realized through the combination of pump control and valve control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
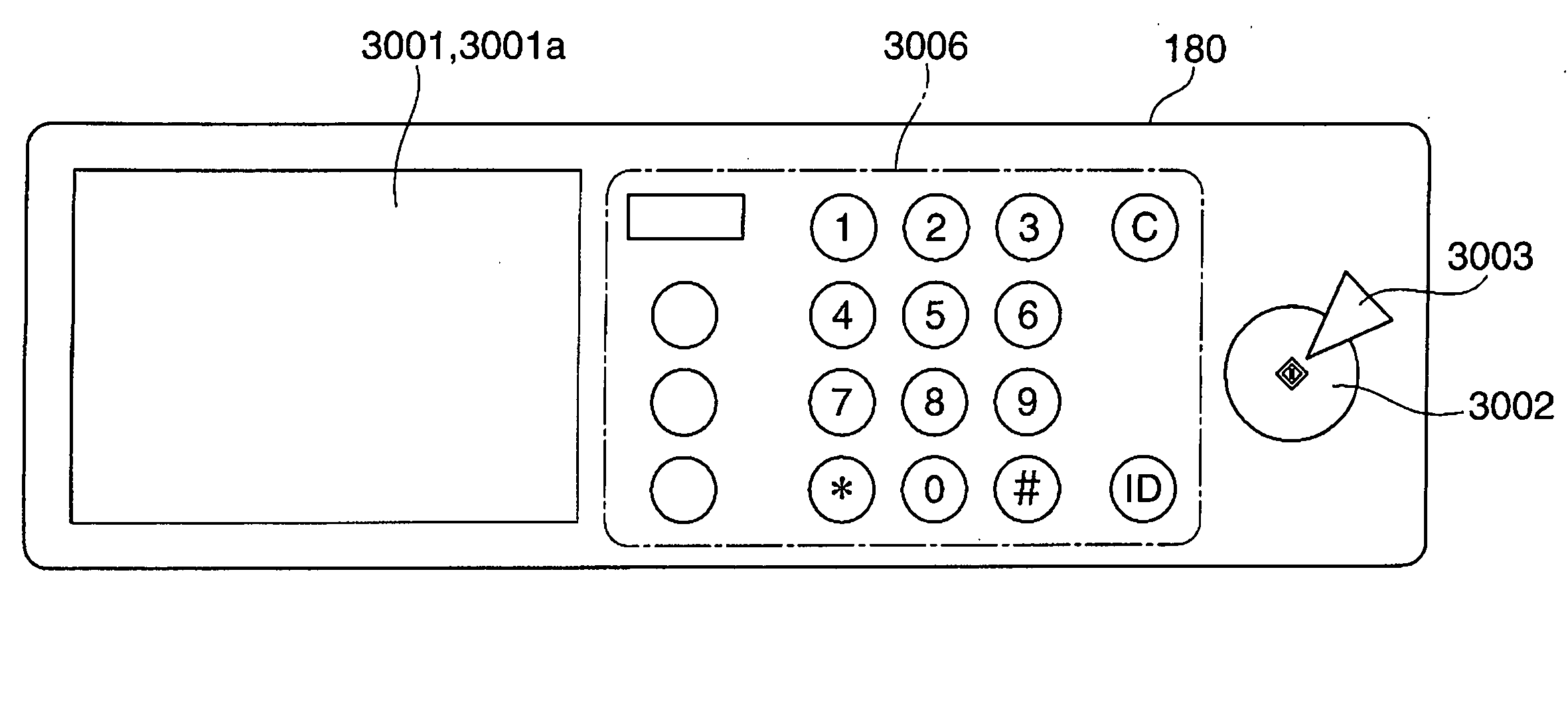
Information input device, information input method, and information input program
InactiveUS20060181520A1Easy to operateCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingOperabilityComputer science
An information input device which enable even a user incapable of seeing an operation panel to identify the respective locations of keys on the operation panel and functions assigned to the keys, thereby enhancing operability of the device. The information input device is provided with a touch panel for inputting coordinate information based on a location thereon touched by a user. A pressure sensor detects the location on the touch panel touched by the user. A CPU determines whether or not there is a key assigned to the location detected by the pressure sensor. When it is determined that there is a key assigned to the location, a vibration generator vibrates the touch panel in a vibration pattern associated with the key. Further, when it is determined that there is a key assigned to the location, a voice output section outputs a voice associated with the key.
Owner:CANON KK
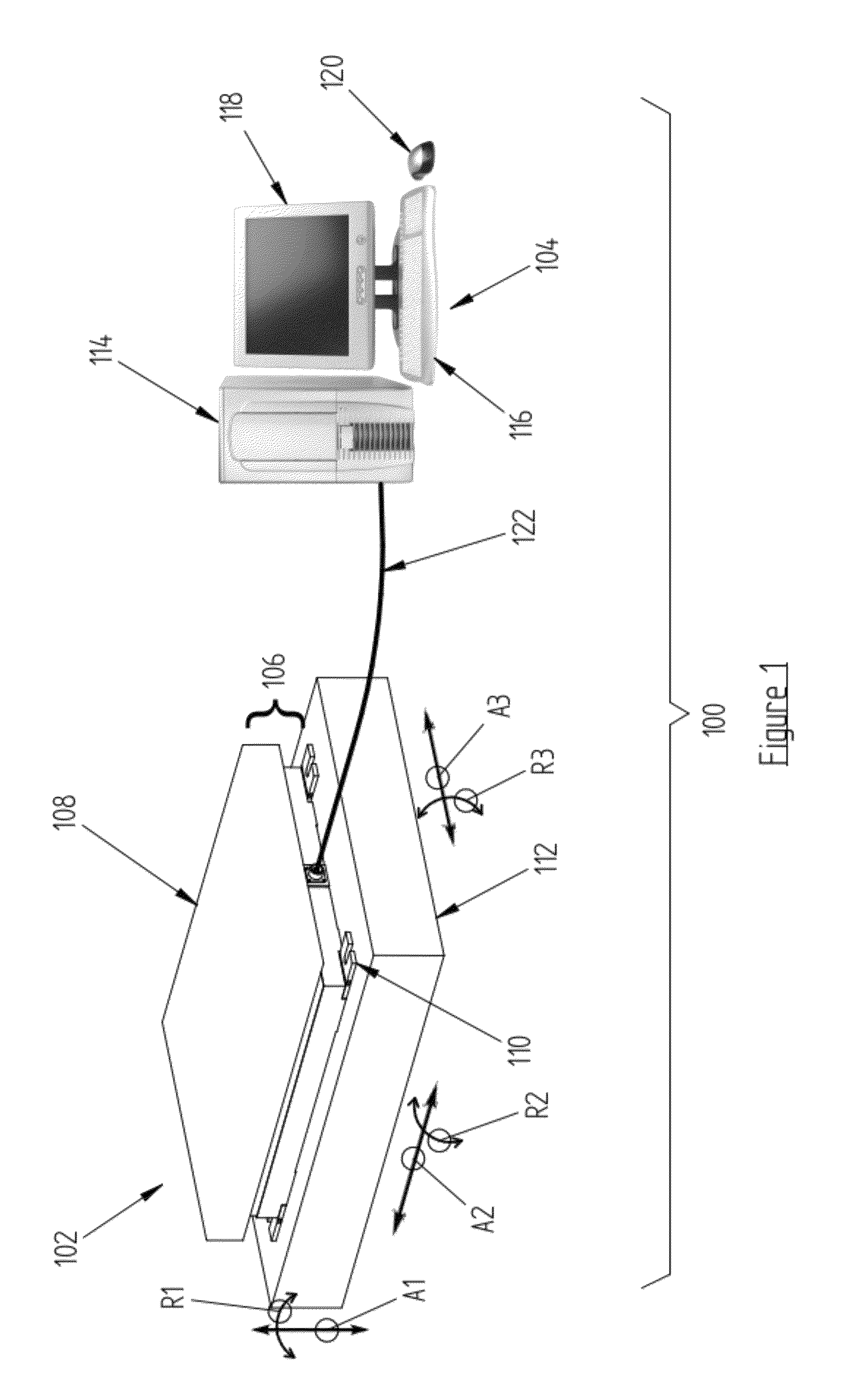
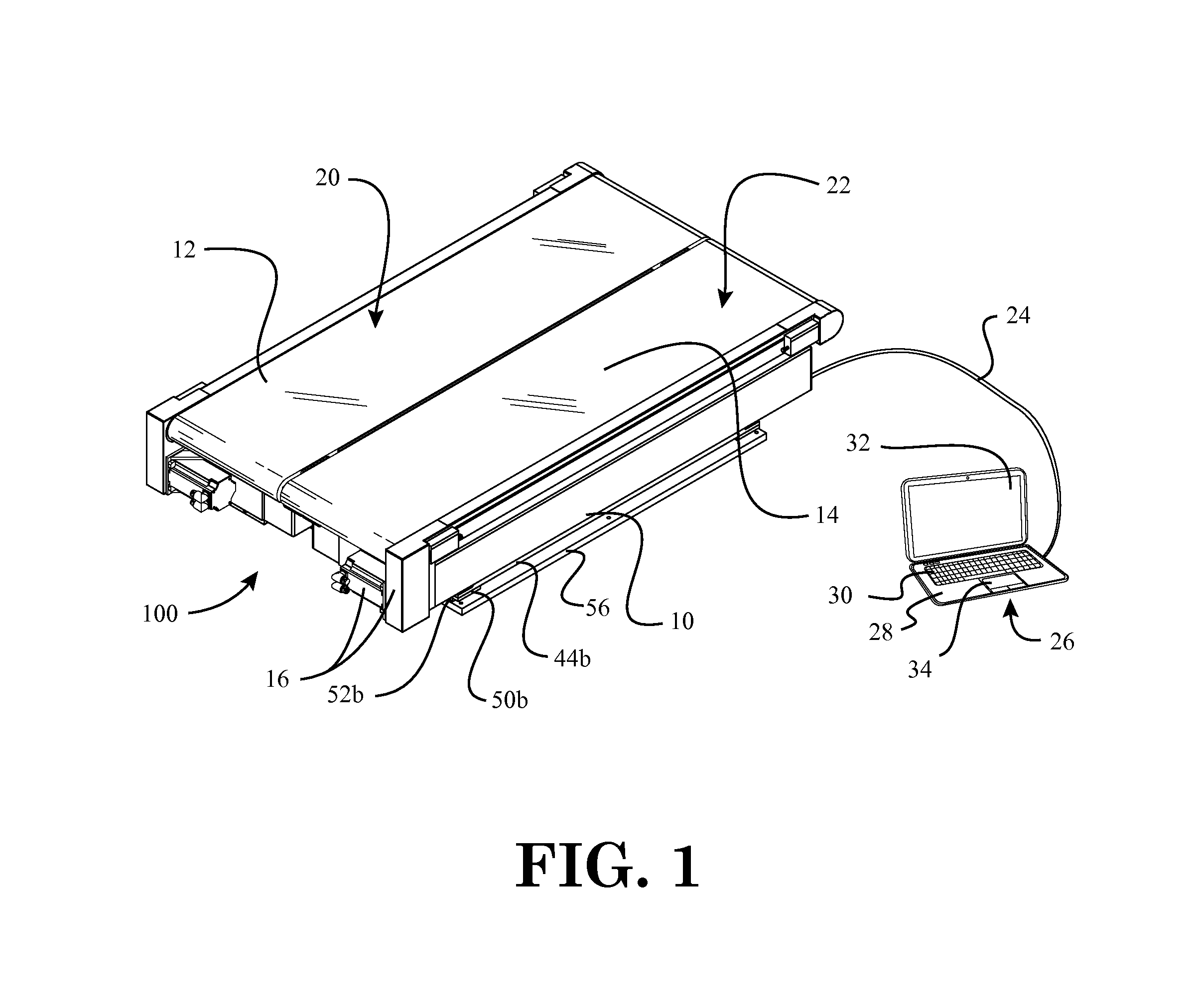
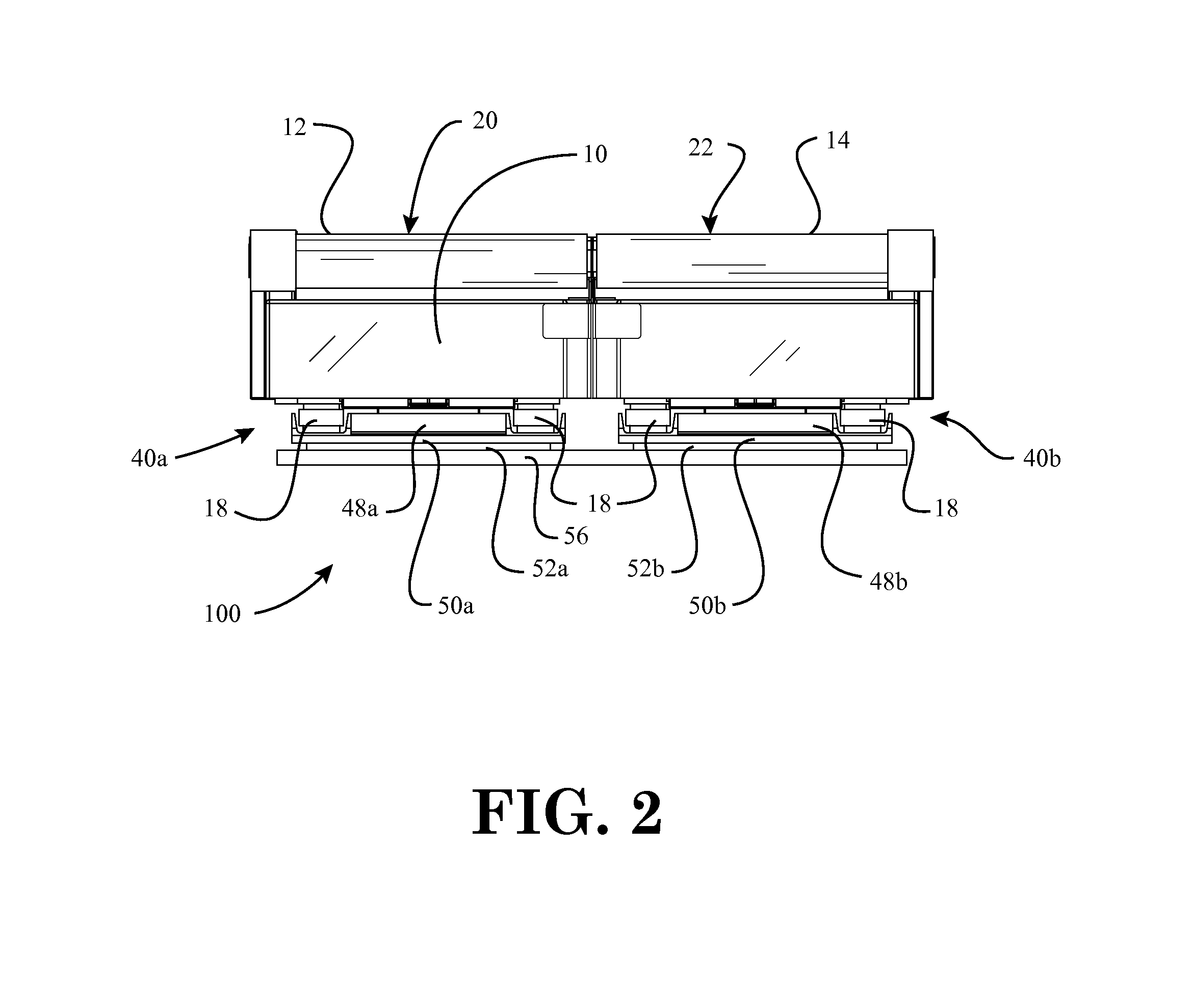
Force measurement system that includes a force measurement assembly, a visual display device, and one or more data processing devices
ActiveUS9916011B1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsInstrumented treadmillDisplay device
A force measurement system includes a force measurement assembly with a top surface configured to receive at least one portion of the body of a subject and at least one force transducer configured to sense forces and / or moments being applied to the top surface; at least one visual display device having an output screen, the output screen comprising an overhanging top portion so that a top edge of the output screen is not readily visible to the subject; and one or more data processing devices operatively coupled to the force measurement assembly and the at least one visual display device. In one or more embodiments, the force measurement assembly may be in the form of an instrumented treadmill. In one or more further embodiments, the force measurement system may additionally comprise a motion capture system configured to detect the motion of one or more body gestures of the subject.
Owner:BERTEC
Force measurement assembly with damping and force measurement system including the same
ActiveUS9568382B1Improve structural rigidityDigital data processing detailsStatic/dynamic balance measurementEngineeringMeasured quantity
A force measurement assembly with damping is disclosed herein. The force measurement assembly includes a force measurement surface for receiving at least one portion of a body of a subject; at least one force transducer, the at least one force transducer configured to sense one or more measured quantities and output one or more signals that are representative of forces and / or moments being applied to the force measurement surface of the force measurement assembly by the subject; at least one base member disposed underneath the at least one force transducer or forming a part of the at least one force transducer; and a damping member disposed between the at least one base member and a mounting surface on which the force measurement assembly is disposed. A force measurement system that includes the force measurement assembly with damping is also disclosed herein.
Owner:BERTEC
Method and device for testing formation and decomposition of gas hydrate
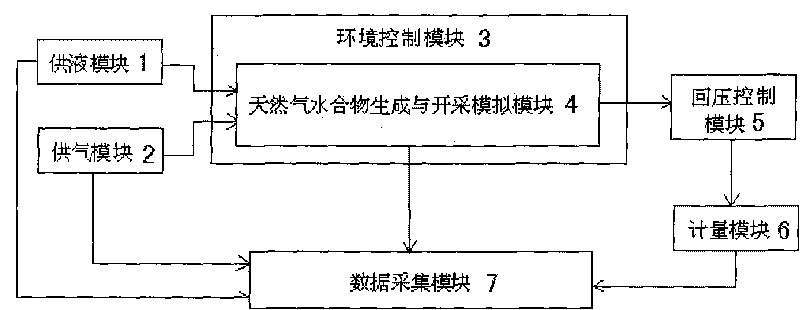
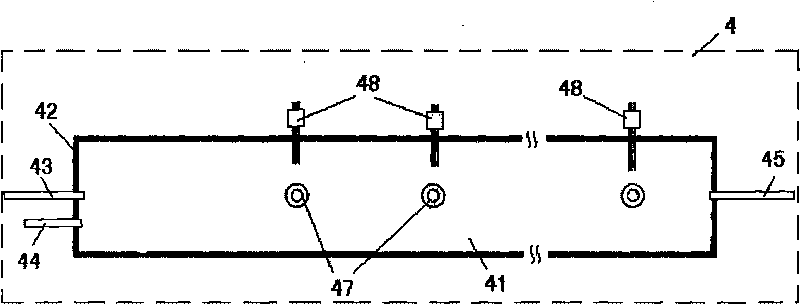
InactiveCN101710088AMonitor the amount of synthesisControl generationMaterial resistanceDecompositionData acquisition
The invention relates to a method and device for testing formation and decomposition of gas hydrate. The method comprises: 1) filling a one-dimensional sand-filling resistivity model tube with sand, closing an end cover, checking leak tightness and putting the model tube into a thermostat; 2) injecting water and methane gas into the model tube, maintaining constant temperature state to gradually generate hydrate, detecting change values of temperature, pressure and resistivity in the tube through a thermocouple, a pressure sensor and an electrode arranged on the wall of the model tube respectively and transmitting the change values to a data acquisition module; 3) reducing pressure after opening the model tube through a back pressure control module during decomposition so as to gradually decompose the hydrate, or injecting hot water into the model tube so as to gradually decompose the hydrate; and 4) passing water and methane gas produced after decomposition through a measurement module, transmitting data to the data acquisition module, detecting the change values of the pressure, the temperature and the resistivity in the tube through the thermocouple, the pressure sensor and the electrode at the same time, transmitting the change values into the data acquisition module, recording and storing the change values. The method and the device can be widely applied in the field of various detection of the formation and decomposition of gas hydrate.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
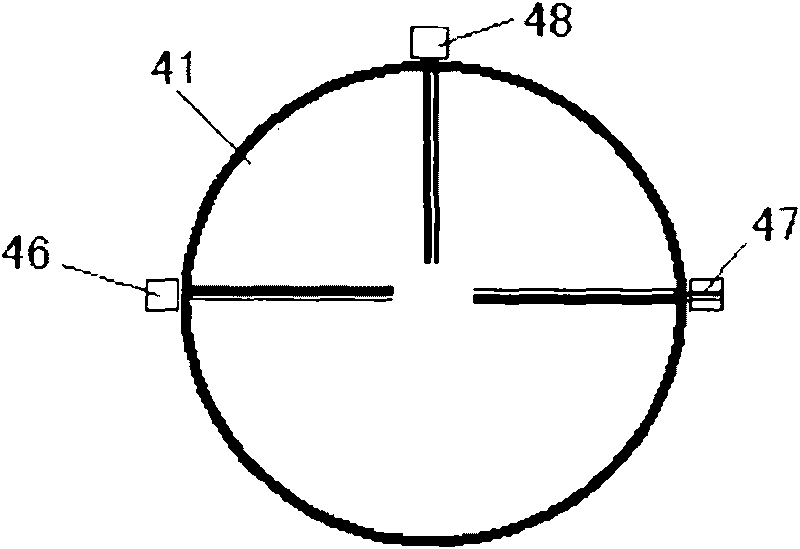
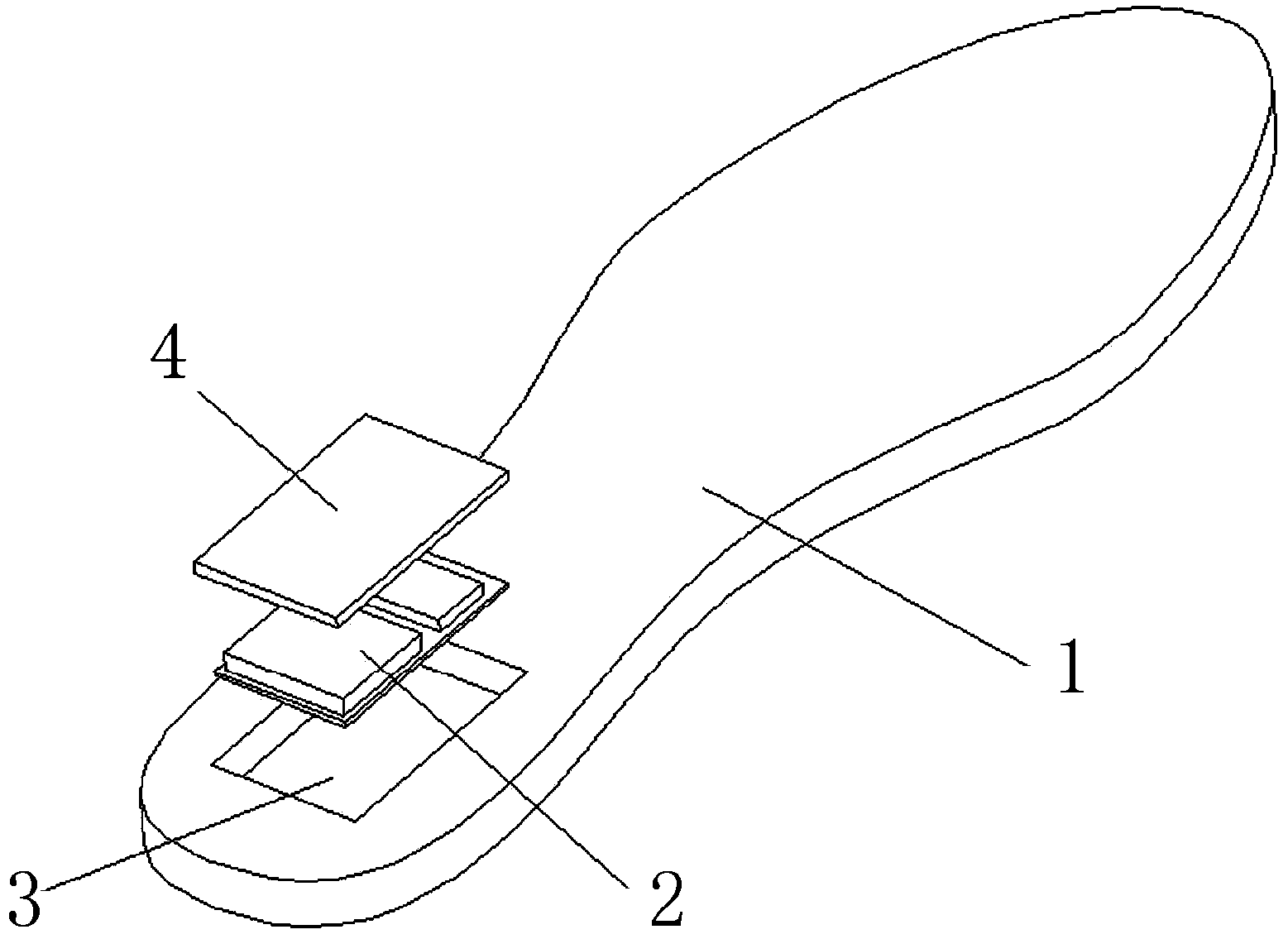
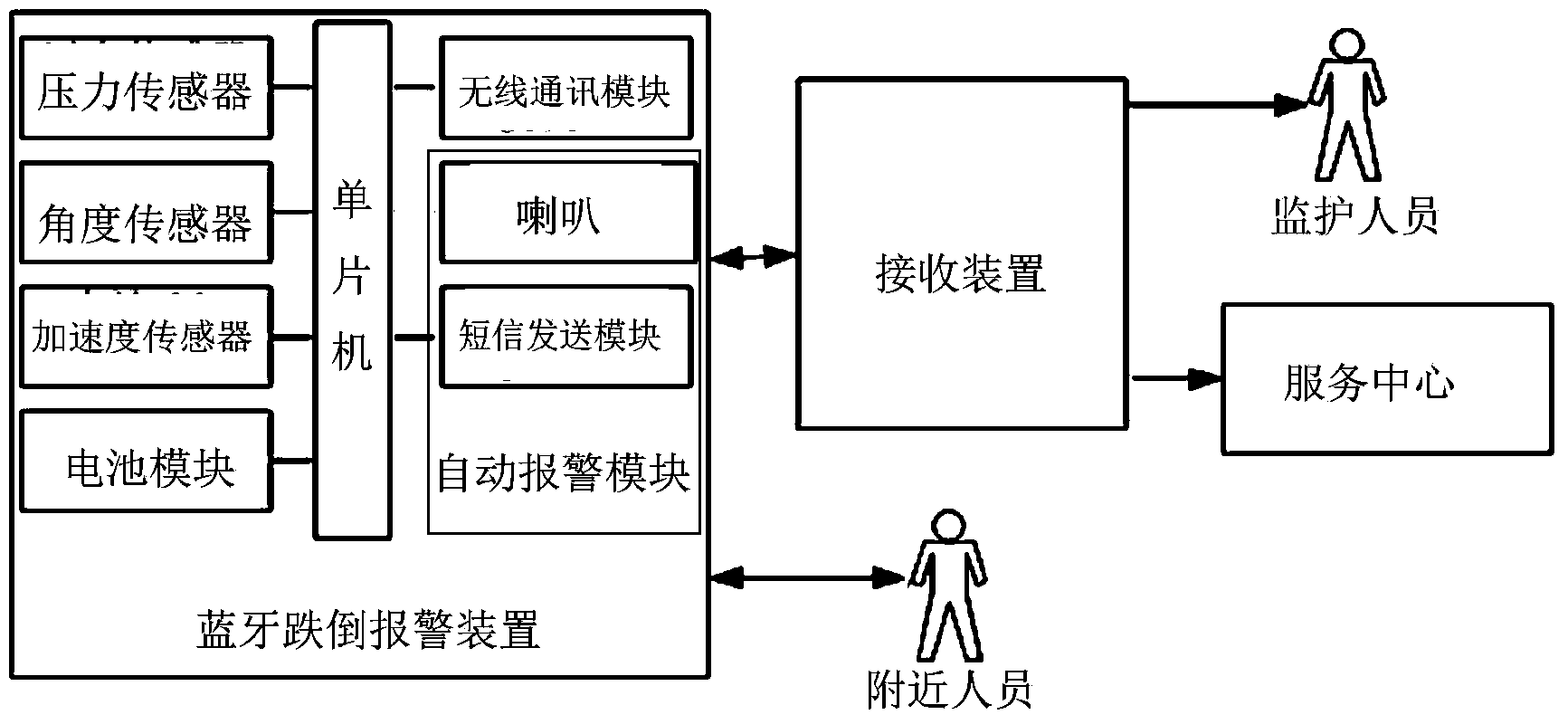
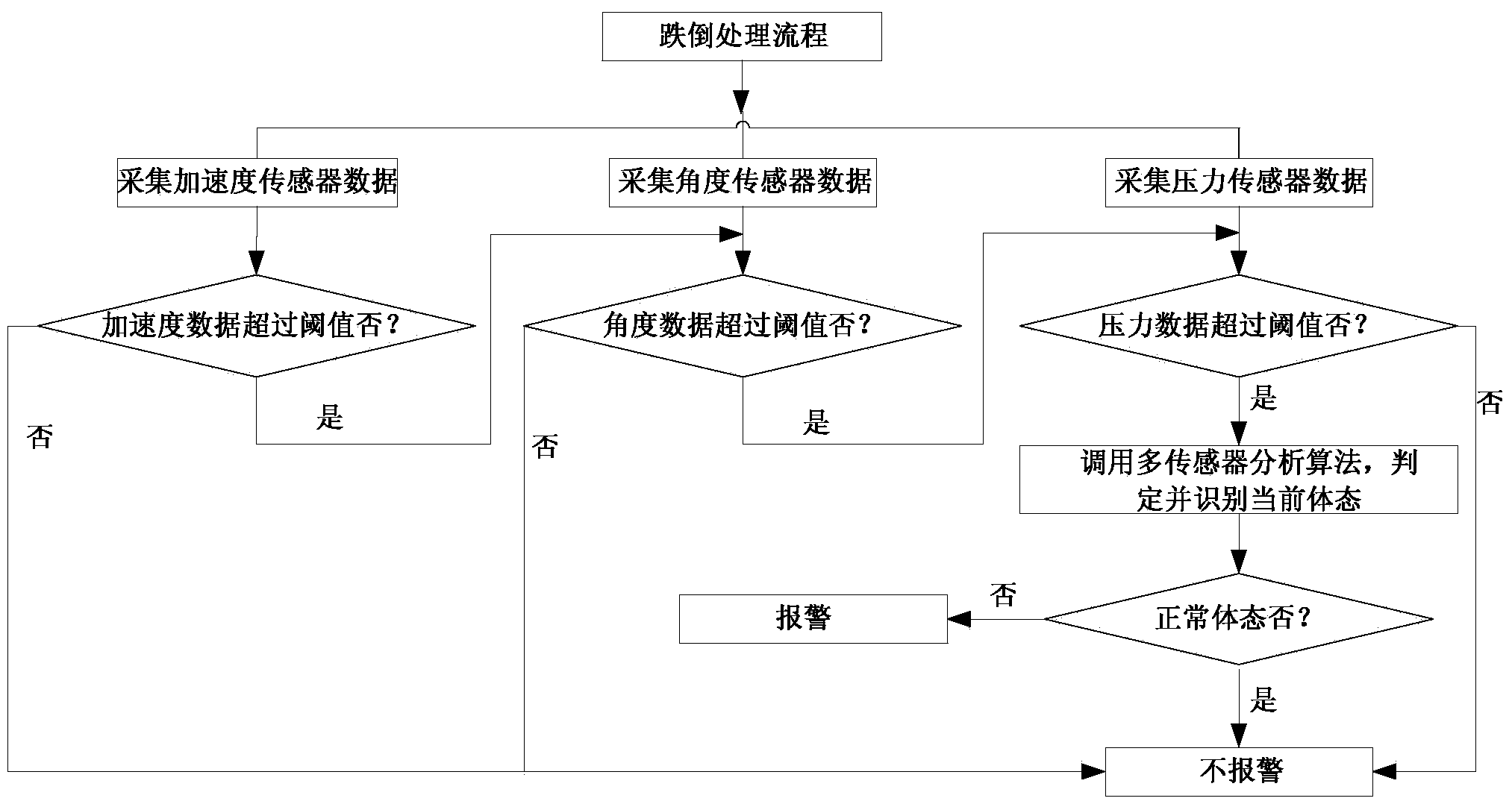
Bluetooth fall-down alarm insoles
ActiveCN103405001AIn line with wearing habitsReduce volumeInsolesInertial sensorsHuman motionEngineering
The invention discloses a pair of Bluetooth fall-down alarm insoles. Each Bluetooth fall-down alarm insole comprises an insole body, wherein a Bluetooth fall-down alarm device for judging whether people fall down and whether to sound the alarm by monitoring motion attitude of people is further arranged in each insole body. The Bluetooth fall-down alarm insoles have the beneficial effects of being small in size and convenient to carry; each bluetooth fall-down alarm insole is integrated and arranged in an insole without any additional feeling, and accords with wearing habit of people; with the combination of information fusion of detection of pressure sensor, angle sensor and acceleration sensor, the judgment accuracy is high, and the accuracy is more than 95%.
Owner:盐城韩资工业园产业发展有限公司
Normal force gradient/shear force sensors and method of measuring internal biological tissue stress
InactiveUS20050241409A1Small sizeEffective friction forceForce measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayElectrical conductor
A normal force gradient / shear force sensor device and measurement method for measuring internal stresses in tissues of a person supported by a chair or bed includes a planar matrix array of peripheral normal force sensors radially spaced from central shear force sensors, comprising an electrically conductive disk located within a circular opening bordered by circumferentially spaced apart electrodes. The disk and electrodes are located between upper and lower cover sheets made of a stretchable material such as polyurethane; one cover sheet is adhered to the disk and the other sheet is adhered to a support sheet for the electrodes. Motion between the cover sheets in response to shear forces exerted on the array causes the disk to press more or less tightly against the electrodes varying electrical conductance between the disk and electrodes proportionally to the magnitude and direction of the shear force. Each normal force sensor includes an electrically conductive film pressed between row and column conductors. Measurements of conductance values of pairs of sensor, which vary proportionally to normal forces exerted on the sensor, are used to calculate a gradient vector of normal forces exerted by a body part on the sensor array, which is combined with the shear force vectors in an algorithm to calculate internal reaction shear forces, e.g., on flesh near a bony prominence.
Owner:VISTA MEDICAL
Force management system that includes a force measurement assembly, a visual display device, and one or more data processing devices
ActiveUS10216262B1Easy for to properly focusInput/output for user-computer interactionStatic indicating devicesMedicineDisplay device
A force measurement system includes a force measurement assembly with a top surface configured to receive at least one portion of the body of a subject and at least one force transducer configured to sense forces and / or moments being applied to the top surface; at least one visual display device having an output screen configured to at least partially circumscribe three sides of a torso of the subject, and one or more data processing devices operatively coupled to the force measurement assembly and the at least one visual display device. In one or more embodiments, the force measurement assembly may be in the form of an instrumented treadmill. In one or more further embodiments, the force measurement system may additionally comprise a motion capture system configured to detect the motion of one or more body gestures of the subject.
Owner:BERTEC
System and method for detecting rotating stall in a centrifugal compressor
ActiveUS6857845B2Simple packagingReduce and eliminate rotating stall noiseEngine manufactureWind motor controlAcoustic energyTransducer
A system and method is provided for detecting and controlling rotating stall in the diffuser region of a centrifugal compressor. The process begins with the detection or sensing of acoustic energy associated with the onset of rotating stall. A pressure transducer is placed in the gas flow path downstream of the impeller, preferably in the compressor discharge passage or the diffuser, to measure the sound or acoustic pressure phenomenon. Next, the signal from the pressure transducer is processed either using analog or digital techniques to determine the presence of rotating stall. Rotating stall is detected by comparing the detected energy amount, which detected energy amount is based on the measured acoustic pressure, with a predetermined threshold amount corresponding to the presence of rotating stall. Finally, an appropriate corrective action is taken to change the operation of the centrifugal compressor in response to the detection of rotating stall.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
Automobile pedal operating mechanism assembly performance test board
ActiveCN102353544AShorten the development and trial production cycleReduce test costsVehicle testingMachine gearing/transmission testingElectricityControl system
Owner:RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV TAIZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com